
Theory vs. Thesis: What's the Difference?
Key Differences
Comparison chart, theory and thesis definitions, can theories be proven, what is an example of a theory, what does "theory" mean, is a theory just a guess, how is a theory different from a hypothesis, can a theory change, is "theory" a scientific term only, is a theory the same as a law, how long is a typical thesis, what is the origin of the word "theory", can a thesis be a question, is a thesis always based on original research, how is a thesis structured, what is a thesis defense, how do you develop a theory, what is a thesis statement, is a thesis always for academic purposes, what does "thesis" mean, what's the difference between a thesis and a dissertation, what's the origin of the word "thesis".

Trending Comparisons

Popular Comparisons

New Comparisons

- Have your assignments done by seasoned writers. 24/7
- Contact us:
- +1 (213) 221-0069
- [email protected]

Thesis vs Hypothesis vs Theory: the Differences and examples

thesis hypothesis and theory
Many students may have a hard time understanding the differences between a thesis, a hypothesis, and a theory. It is important to understand their differences. Such an understanding will be instrumental.
More so, when writing complex research papers that require a thesis that has a hypothesis and utilizes theories. We have gathered from responses of our college writing service that the difference between the three is confusing.

That being said, this article is meant to explain the differences between a thesis, a hypothesis, and a theory.
Difference between Hypothesis and Thesis
There are major differences between hypothesis and thesis. While they seem to be related on the face, their differences are huge both in concept and practice.
A hypothesis is a proposed explanation of something or a phenomenon. A scientific hypothesis uses a scientific method that requires any hypothesis to be tested. As such, scientists and researchers base their hypothesis on observations that have been previously made and that which cannot be explained by the available or prevailing scientific theories.
From the definition of a hypothesis, you can see that theories must be included in any scientific method. This is the reason why this article tries to differentiate a thesis, a hypothesis, and a theory.
Moving forward, a thesis can be defined as a written piece of academic work that is submitted by students to attain a university degree. However, on a smaller scale, there is something that is referred to as a thesis statement.
This is written at the introduction of a research paper or essay that is supported by a credible argument. The link between a hypothesis and thesis is that a thesis is a distinction or an affirmation of the hypothesis.
What this means is that whenever a research paper contains a hypothesis, there should be a thesis that validates it.
People Also Read: Is using an Essay Writing Service Cheating? Is it Ethical?
What is a Hypothesis?
A hypothesis can be defined as the proposed or suggested explanation for an occurrence, something, or a phenomenon. It should be testable through scientific methods. The reason why scholarly works should have a hypothesis is that the observed phenomena could not be explained using the prevailing scientific theories hence the reason why it should be tested.
Testing the hypothesis may result in the development of new or improved scientific theories that are beneficial to the discipline and society in general.
What is a Thesis?
A thesis is a written piece of academic work that is submitted by students to attain a university degree. When a thesis is used as a stand-alone word, it denotes academic papers written by university students. It is mostly written by those pursuing postgraduate degrees, at the end of their courses. They demonstrate their proficiency in their disciplines and the topics they have selected for research.
However, when a thesis is used to refer to a statement, it denotes the statement that is written at the introduction of a research paper or essay. A thesis is supported by a credible argument.
Every research paper must have a thesis statement that acts as a guide to what the research will be all about. It is possible to receive very poor grades or even score a zero if your research paper lacks the thesis statement.
What is a Theory?
A theory can be defined as a rational form of abstract perspectives or thinking concerning the results of such thinking or a phenomenon. The process of rational and contemplative thinking is mostly associated with processes such as research or observational study.
As such, a theory can be considered to belong to both scientific and non-scientific disciplines. Theories can also belong to no discipline.
From a modernistic scientific approach, a theory can mean scientific theories that have been well confirmed to explain nature and that are created in such a way that they are consistent with the standard scientific method. A theory should fulfill all the criteria required by modern-day science.
A theory should be described in a way that scientific tests that have been conducted can provide empirical support or contradiction to the theory.
Because of the nature by which scientific theories are developed, they tend to be the most rigorous, reliable, and comprehensive when it comes to describing and supporting scientific knowledge.
The connection between a theory and a hypothesis is that when a theory has not yet been proven, it can be referred to as a hypothesis.
The thing about theories is that they are not meant to help the scientist or researcher reach a particular goal. Rather, a theory is meant to guide the process of finding facts about a phenomenon or an observation.
People Also Read: How to Use Personal Experience in Research Paper or Essay
Difference between a Theory and Thesis
A theory is a rational form of abstract perspectives or thinking concerning the results of such thinking or a phenomenon. The process of rational and contemplative thinking is mostly associated with processes such as research or observational study. On the other hand, a thesis is a written piece of academic work that is submitted by students to attain a university degree.
It denotes academic papers that are written by students in the university, especially those pursuing postgraduate degrees, at the end of their courses to demonstrate their proficiency in their disciplines and the topics they have selected for research.
To understand the application of these, read our guide on the difference between a research paper and a thesis proposal to get a wider view.
How to write a Good Hypothesis
1. asking a question.
Asking a question is the first step in the scientific method and the question should be based on who, what, where, when, why, and how . The question should be focused, specific, and researchable.
2. Gathering preliminary research
This is the process of collecting relevant data. It can be done by researching academic journals, conducting case studies, observing phenomena, and conducting experiments.
3. Formulating an answer
When the research is completed, you should think of how best to answer the question and defend your position. The answer to your question should be objective.
4. Writing the hypothesis
When your answer is ready, you can move to the next step of formulating the hypothesis. A good hypothesis should contain relevant variables, predicted outcomes, and a study group that can include non-human things. The hypothesis should not be a question but a complete statement.
5. Refining the hypothesis
Though you may skip this step, it is advisable to include it because your study may involve two groups or be a correlational study. Refining the hypothesis will ensure that you have stated the difference or relationship you expect to find.
6. Creating a null and alternative hypotheses
A null hypothesis (H0) will postulate that there is no evidence to support the difference. On the other hand, an alternative hypothesis (H1) posits that there is evidence in support of the difference.
People Also Read: Research Paper Graph: How to insert Graphs, Tables & Figures
Frequently Asked Questions
Difference between thesis and hypothesis example.
Thesis: High levels of alcohol consumption have detrimental effects on your health, such as weight gain, heart disease, and liver complications.
Hypothesis: The people who consume high levels of alcohol experience detrimental effects on their health such as weight gain, heart disease, and liver complications.
What is the difference between a summary and a thesis statement?
A summary is a brief account or statement of the main points from the researches. A thesis statement is a statement that is written at the end of the introduction of a research paper or essay that summarizes the main claims of the paper.
Difference between hypothesis and statement of the problem
A hypothesis can be defined as the proposed or suggested explanation for an occurrence, something, or a phenomenon. The same should be testable through scientific methods. Conversely, a statement of a problem is a concise description of the issue to be addressed on how it can be improved.

When not handling complex essays and academic writing tasks, Josh is busy advising students on how to pass assignments. In spare time, he loves playing football or walking with his dog around the park.
Related posts

Titles for Essay about Yourself
Good Titles for Essays about yourself: 31 Personal Essay Topics

How to Write a Diagnostic Essay
How to Write a Diagnostic Essay: Meaning and Topics Example

How Scantron Detects Cheating
Scantron Cheating: How it Detects Cheating and Tricks Students Use

Theory vs. Thesis — What's the Difference?
Difference Between Theory and Thesis
Table of contents, key differences, comparison chart, contribution, compare with definitions, common curiosities, can a thesis become a theory, what is the main difference between a theory and a thesis, what makes a strong thesis, how does one develop a theory, can theories be applied outside of science, what is the purpose of a thesis, is a theory always true, do all academic fields use the concept of theories, what is the difference in scope between a theory and a thesis, how do theories influence everyday life, can anyone propose a theory, how do theories evolve, why is peer review important for a thesis, how are theories tested, what role do theses play in professional qualifications, share your discovery.

Author Spotlight
Popular Comparisons

Trending Comparisons

New Comparisons

Trending Terms

The Real Differences Between Thesis and Hypothesis (With table)
A thesis and a hypothesis are two very different things, but they are often confused with one another. In this blog post, we will explain the differences between these two terms, and help you understand when to use which one in a research project.
As a whole, the main difference between a thesis and a hypothesis is that a thesis is an assertion that can be proven or disproven, while a hypothesis is a statement that can be tested by scientific research.
We probably need to expand a bit on this topic to make things clearer for you, let’s start with definitions and examples.
Definitions
A thesis is a statement or theory that is put forward as a premise to be maintained or proved. A thesis statement is usually one sentence, and it states your position on the topic at hand.
You may also like:
The best way to understand the slight difference between those terms, is to give you an example for each of them.
If your hypothesis is correct, then further research should be able to confirm it. However, if your hypothesis is incorrect, research will disprove it. Either way, a hypothesis is an important part of the scientific process.
The word “hypothesis” comes from the Greek words “hupo,” meaning “under”, and “thesis” that we just explained.
Argumentation vs idea
A thesis is usually the result of extensive research and contemplation, and seeks to prove a point or theory.
5 mains differences between thesis and hypothesis
So, in short, a thesis is an argument, while a hypothesis is a prediction. A thesis is more detailed and longer than a hypothesis, and it is based on research. Finally, a thesis must be proven, while a hypothesis does not need to be proven.
| Thesis | Hypothesis | |
|---|---|---|
| Can be argued | Cannot be argued, and don’t need to | |
| Generally longer | Generally shorter | |
| Generally more detailed | Generally more general | |
| Based on real research | Often just an opinion, not (yet) backed by science | |
| Must be proven | Don’t need to be proven |
Is there a difference between a thesis and a claim?
Is a hypothesis a prediction, what’s the difference between thesis and dissertation.
A thesis is usually shorter and more focused than a dissertation, and it is typically achieved in order to earn a bachelor’s degree. A dissertation is usually longer and more comprehensive, and it is typically completed in order to earn a master’s or doctorate degree.
What is a good thesis statement?
I am very curious and I love to learn about all types of subjects. Thanks to my experience on the web, I share my discoveries with you on this site :)
Similar Posts
Centaurs vs satyrs: what’s the real difference, 5 key distinctions between centaurs and minotaurs, what’s the difference between talent and skill, wales vs ireland: 7 key differences explained, 7 differences between greek and roman gods you don’t know, comedy vs. tragedy: what’s the difference (with table).
Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
Theory, Thesis, Hypothesis and the mysterious Theorem
lately I have been thinking about the terms theory, thesis, hypothesis and theorem. I am quite sure about the differences between a thesis and a hypothesis, but I did not really get what a theorem is. I would like to ask you to confirm my definition of each term or don' t. If you disagree with my definition, please explain why and give - if possible - a good example.
As an example I will use the axiom "Nothing is faster than light" of the Theory of Relativity.
Thesis : As far as I have figured out, a thesis is an assertion which a controversy is immanent to. So it needs a argumentative reasoning.
My first question, in reference to my example, is if every axiom is implicitly a thesis or not.
I am not sure about it, because if I took the axiom from the example, I would not know if there is any controversy about this assertion or if it is just an undisputed assertion, although there could be a controversy, because nobody can know if there is not something faster than light. On the other hand, if I have the assertion "There is a God", its clear to me that there will be a controversy. So it must be a thesis.
Further on I will assume the example axiom to be a thesis for further illustration.
Hypothesis : A hypothesis is a derived form of a thesis. It asserts a correlation between - at least - two factors (where a thesis is simply an assertion).
So in reference to the example I could derive the hypothesis "If there was something faster than light, then there would be a God" from my thesis "Nothing is faster than light". It asserts a correlation between the factors "speed of light" and "existence of a God" (although there is no causal relationship).
Theory: A theory is an abstract concept which tries to explain a discipline of reality. It consists of axioms/theses.
Theorem: This is something that I was not really able to figure out. I found a pattern in theoremes: It always seems to be based on some theory and tries to solve some paradoxon or other problem the theory has, but it does not change the theory at all. It is some lego that is put on the theory to fill a hole.
I don' t know if there is any truth in what I have written about the theoreme.
So I hope you can help me understanding :)
- terminology
- The words have different meaning in difference contexts, i.e. you don't prove theorems in physics you prove theories but a theory in physics is more like a conjecture in mathematics. A theorem is something that is proved deductively using logical reasoning or inference (think about what you do in a formal logical system like propositional logic). Mathematical theorems, like the fundamental theorem of arithmetic, are theorems because they can be proved in a completely deductive way. Physical laws are not proved deductively, they are proved inductively through observation and experiment. – Not_Here Commented Jul 29, 2017 at 10:42
- From wikipedia's article on theorem: "In light of the requirement that theorems be proved, the concept of a theorem is fundamentally deductive, in contrast to the notion of a scientific law, which is experimental." In mathematics, conjectures are a lot more like scientific laws than theorems because they are things that we do not have a deductive proof for yet, but every test we've ever done to the conjecture came up positive. Consider Goldbach's conjecture, it is a conjecture because it doesn't have a proof yet, but we have yet to find a single counterexample, despite massive testing. – Not_Here Commented Jul 29, 2017 at 10:44
- The biggest issue you're having, I think, is that you're mixing how the words are used in science and how they're used in math. Obviously there is over lap but the words have different meanings when they're used very strictly in those two contexts. For example, your definition of theory (besides the use of the term axioms because those also have different meanings in different contexts) is correct when applied to science but theory has a different definition in mathematical logic where it's a set of axioms and theorems in some formal language. – Not_Here Commented Jul 29, 2017 at 10:51
- See if any of these definitions help you theorem , axiom , scientific hypotheses and scientific theories , mathematical conjecture , general statement of hypothesis that also touches on how its specifically used in mathematics . – Not_Here Commented Jul 29, 2017 at 10:55
The biggest trouble that you will face when thinking about these ideas is that you are mixing terminology from two distinct fields into one. Some of those words are used very differently in science than they are in mathematics. It can become even more confusing when you consider how much math is used in science, but an explanation of how the words are used in their specific contexts will help illuminate the delineating line.
In mathematics, "thesis", "hypothesis", and "conjecture" are all used synonymously. From Wolfram's Mathworld:
Hypothesis: "A hypothesis is a proposition that is consistent with known data, but has been neither verified nor shown to be false." "In general mathematical usage, 'hypothesis' is roughly synonymous with 'conjecture.'" Conjecture: "A proposition which is consistent with known data, but has neither been verified nor shown to be false. It is synonymous with hypothesis."
Additionally, if you go to the disambiguation of the word "thesis" on wikipedia you see that in the subjects of mathematics and logic it links to "hypothesis" and "conjecture" as well. An example of a mathematical thesis is the Church-Turing thesis which, as you can see, is also sometimes called the Church-Turing conjecture and is described in that article as being a hypothesis. The reason that the Church-Turing thesis is a thesis is because it tries to take an informal idea (the idea of an algorithm) and give it a precise mathematical statement. Due to the fact that it starts with an informal idea, there isn't a purely deductive way to prove that the idea is true, therefore it's left open as a hypothesis and would be proven untrue if a counter example is shown.
As such, mathematical conjectures, theses, and hypotheses are statements in mathematics that seem probable and no counter example has yet been shown. This means that conjectures have yet to be proven , which delineates them from theorems.
A theorem is something that is not a conjecture, it is something that has been proven true. From Mathworld:
Theorem: "A theorem is a statement that can be demonstrated to be true by accepted mathematical operations and arguments. In general, a theorem is an embodiment of some general principle that makes it part of a larger theory. The process of showing a theorem to be correct is called a proof."
Examples of theorems are proven mathematical statements, things like the fundamental theorems of arithmetic , algebra , and calculus . Other, much simpler theorems, are things like the Pythagorean theorem . The picture of a theorem as something that solves a paradox or other problem is incorrect, a theorem is just a provably true statement. The Pythagorean theorem doesn't resolve a paradox in geometry, it is just a statement that has to be true, is provable, given the initial rules of geometry (the axioms).
Those are how the words are used in mathematics alone and in science they are sometimes used very differently. One important thing to understand is that science does not deal with theorems, scientific theories don't prove theorems. This is because science relies on inductive and abductive reasoning to learn about the world through empirical observation. A scientific theory is a general description of the world that is testable and has withstood repeated testing. In this way, they're usually made up out of scientific laws .
Scott Aaronson , a quantum information scientist who works on both fields, has highlighted the differences in the terminology on multiple occasions:
"I've learned from working in quantum information that there's a difference in terminology between fields. What mathematicians and computer scientists call a conjecture is typically what physicists would call a law." "I think my word is 'theorem'. It's something that you say is true and then you explain why it's true and then you put a box."
The context for the second quote is that Leonard Susskind asked Aaronson to explain a word from his mathematical background that people with a physics background might not understand or use in the same way. The reason everyone laughed is because the other physicists and computer scientists in the room understood how tongue in cheek Aaronson's pick for the word was: physics doesn't deal with theorems, in a mathematical sense, it deals with conjectures. That's why Susskind sarcastically says "A theorem, what's that?" And of course the "box" comment is a reference to what's put at the end of a proof of a theorem .
Ultimately, theorems are things that are deductively proven and as such exist in mathematics and logic. Theorems are used in science as well, you can use the Pythagorean theorem to help you solve a mechanics problem, but science doesn't prove theorems. Science tries to create theoretical models that help explain physical phenomena and those models can always be revised via new information. So if you are trying to apply the word theorem to a physical theory you are going to fail, the only parts of the physical theory that are theorems are the purely mathematical parts.
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you're looking for browse other questions tagged terminology ..
- Featured on Meta
- User activation: Learnings and opportunities
- Site maintenance - Mon, Sept 16 2024, 21:00 UTC to Tue, Sept 17 2024, 2:00...
- 2024 Community Moderator Election Results
Hot Network Questions
- How many minutes the Apollo astronauts had to wait from splashdown until the first frogmen touched the CM?
- For a bike with "Forged alloy crank with 44T compact disc chainring", can the chainring be removed?
- Сhanging borders of shared polygon shapefile features in QGIS
- Is it safe to use the dnd 3.5 skill system in pathfinder 1e?
- How to decrease by 1 integers in an expl3's clist?
- How can I analyze the anatomy of a humanoid species to create sounds for their language?
- Is it a correct rendering of Acts 1,24 when the New World Translation puts in „Jehovah“ instead of Lord?
- What is the oldest open math problem outside of number theory?
- What factors cause differences between dried herb/spice brands?
- Is it feasible to create an online platform to effectively teach college-level math (abstract algebra, real analysis, etc.)?
- What would a planet need for rain drops to trigger explosions upon making contact with the ground?
- How did NASA figure out when and where the Apollo capsule would touch down on the ocean?
- Rocky Mountains Elevation Cutout
- Does Rom.8.11 teach sanctification, or glorification?
- Was Willy Wonka correct when he accused Charlie of stealing Fizzy Lifting Drinks?
- What would be an appropriate translation of Solitude?
- Why did early ASCII have ← and ↑ but not ↓ or →?
- Why was Esther included in the canon?
- Why does Sfas Emes start his commentary on Parshat Noach by saying he doesn't know it? Is the translation faulty?
- Strange behavior of Polygon with a hole
- Custom PCB with Esp32-S3 isn't recognised by Device Manager for every board ordered
- Will "universal" SMPS work at any voltage in the range, even DC?
- In Photoshop, when saving as PNG, why is the size of my output file bigger when I have more invisible layers in the original file?
- Is a thing just a class with only one member?
- Home »
- Advice »
What is the Difference Between a Dissertation and a Thesis?
Find your perfect postgrad program search our database of 30,000 courses.
And to make it even more confusing, some institutions or departments will even use the terms differently!
But what are we all really talking about when we refer to a dissertation or a thesis? And does the term you use actually impact on what you actually end up writing?
This article covers the main differences between a dissertation and thesis, and how the terms may differ depending on the course, university and location.
What is a dissertation?
A dissertation is a piece of academic writing centred around original research. In their dissertations, students review existing research but also build on this with unique hypotheses and approaches.
A dissertation can be used to disprove a previous theory or take existing theories and research in a new direction. It is a large research project that is usually completed at the end of the academic year.
Usually, a dissertation starts with a dissertation proposal , which is approved by a study supervisor. The student then completes the research and writes up the methodology , findings, evaluations and conclusions from the research.
Dissertations can be undertaken by both undergraduate and postgraduate students. At undergraduate level the word count is around 5,000 to 8,000 and at postgraduate level it is usually 10,000 to 15,000.
What is a thesis?
A thesis is an academic paper covering an in-depth review of existing research in a particular discipline. It will involve an academic argument, although it doesn’t usually require original research from the student. The existing research is used to support and evaluate the proposed argument.
A thesis is not usually required at undergraduate level and is more common at postgraduate level.
This large piece of written-up research is usually completed at the end of a masters degree. Some masters courses require a thesis to graduate.
Differences between a dissertation vs thesis
The main purpose of a writing a dissertation is to add new findings to the existing literature in that field with original research. Whereas theses tend to evaluate existing findings, as their purpose is to demonstrate knowledge and skills within the course’s subject matter.
In terms of how long it takes to complete a thesis or dissertation project, a thesis is typically shorter than a dissertation since there are fewer original research aspects involved. This means that it will probably take less time. However, this can differ depending on the university and the course.
Dissertations sometimes require an oral presentation, known as a viva , where findings are showcased to academics who ask questions about the research. Theses usually do not require this.
The root of the words
The word ‘dissertation’ originates from the Latin word ‘dissertare’, meaning to continue to discuss and the Latin word ‘disserere’ which means to examine and discuss .
The word ‘thesis’ originally comes from the Greek word ‘tithenai’, which means to place or position. This later evolved into the Latin ‘thesis’, which had two meanings: an abstract question and to put something forward .
Similarities between a dissertation vs thesis
Although there are some key differences between a dissertation and a thesis, there are also similarities.
- Both are generally long pieces of academic writing, much longer than a typical essay.
- Both explore a topic in depth, whether you are conducting totally unique research or structuring an argument based on existing research.
- Both are considered a final project and usually required to graduate from a degree, masters or PhD. Students can graduate without a thesis or dissertation if they choose to complete a postgraduate diploma or postgraduate certificate instead.
- Excellent academic writing skills are highly important for both types of research project.
Is a dissertation harder than a thesis?
Though, the difficulty of a thesis or dissertation depends on your personal skill set. For instance, students that learn better by developing their own research ideas may find a dissertation easier than a thesis.
Difficulty can also depend on the level of the course. For instance, a thesis completed at doctorate level is likely to require more advanced knowledge than a thesis at undergraduate level.
The difficulty of either type of research project can also vary depending on the subject matter and the resources available to you.
Both dissertations and theses can be challenging, but don’t be put off by the thought of having to produce a larger body of work. Your supervisor will be there to support you.
Definitions depend on where you are
The terms ‘dissertation’ and ‘thesis’ are sometimes used interchangeably, and the meanings can differ depending on the country and university.
There are plenty of differences between the variant forms of English, such as British English and American English. Around the world, different English-speaking countries use the words ‘dissertation’ and ‘thesis’ differently.
Generally, nations with British-based academic systems of university education use dissertation to refer to the body of work at the end of an undergraduate or masters level degree . British-based institutions generally use thesis to refer to the body of work produced at the end of a PhD .
In countries and institutions that are based on the American system of education, the words tend to be used in reverse. However, institutions and even different departments in the same university can use the words differently.
If you're in doubt, then stick with the way the university and department you're currently attending use the terms.
Definitions can depend on the subject
In the UK, the terms ‘dissertation’ and ‘thesis’ are generally applied equally across institutions and subjects.
However, in the US the meanings can differ between different subject areas. The term ‘thesis’ can be used to describe a piece of original research in US academia, whereas original research is usually referred to as a dissertation in the UK.
If you’re studying in the US , you may complete a thesis at masters level in another subject area that involves wide-ranging reading and understanding rather than original research and still call it a thesis.
With so much interchangeability between the two terms, it’s understandable that there is often confusion in the debate between a dissertation vs thesis, as there is no clear answer.
Always read specific course details to understand exactly what’s involved in the research project that you are required to produce.
Examples from US and UK universities
Georgetown University in the US refers to a dissertation and a thesis as both adding to your 'field of knowledge' . The University of Edinburgh recommends that you refer to your individual course handbook for guides to dissertations, so each department will have their own guidelines to using the word dissertation and thesis. At University College London they refer to a thesis as the piece of work at the end of an EngD, MPhil, MD(Res) or PhD, which are all research degrees.
In conclusion
Ultimately, it doesn't really matter which word you use as both refer to a serious and lengthy piece of work where you can show what you have researched and understood as part of your postgraduate studies.
As long as you are referring to the piece of work that you are compiling in the same way as those in your department then you will avoid confusion.
It is important to check whether the research piece involves original research or expects you to build upon existing research.
Writing a dissertation or a thesis requires a substantial amount of planning and work and you don't want to let yourself down at the last hurdle with poor presentation of your work, so always keep an eye on your course or department guidelines.
Related articles
Top Tips On Writing Your Postgraduate Dissertation Or Thesis
How To Write A Thesis
Writing A Dissertation Proposal
Top Thesis Writing Tools
Postgrad Solutions Study Bursaries

Exclusive bursaries Open day alerts Funding advice Application tips Latest PG news
Complete Our Destination Survey

Take 2 minutes to complete our Destination Survey for the chance to win a Postgrad Study Bursary worth £2,000.
All we need to know is:
- Your university
- Your PG course
While Sandel argues that pursuing perfection through genetic engineering would decrease our sense of humility, he claims that the sense of solidarity we would lose is also important.
This thesis summarizes several points in Sandel’s argument, but it does not make a claim about how we should understand his argument. A reader who read Sandel’s argument would not also need to read an essay based on this descriptive thesis.
Broad thesis (arguable, but difficult to support with evidence)
Michael Sandel’s arguments about genetic engineering do not take into consideration all the relevant issues.
This is an arguable claim because it would be possible to argue against it by saying that Michael Sandel’s arguments do take all of the relevant issues into consideration. But the claim is too broad. Because the thesis does not specify which “issues” it is focused on—or why it matters if they are considered—readers won’t know what the rest of the essay will argue, and the writer won’t know what to focus on. If there is a particular issue that Sandel does not address, then a more specific version of the thesis would include that issue—hand an explanation of why it is important.
Arguable thesis with analytical claim
While Sandel argues persuasively that our instinct to “remake” (54) ourselves into something ever more perfect is a problem, his belief that we can always draw a line between what is medically necessary and what makes us simply “better than well” (51) is less convincing.
This is an arguable analytical claim. To argue for this claim, the essay writer will need to show how evidence from the article itself points to this interpretation. It’s also a reasonable scope for a thesis because it can be supported with evidence available in the text and is neither too broad nor too narrow.
Arguable thesis with normative claim
Given Sandel’s argument against genetic enhancement, we should not allow parents to decide on using Human Growth Hormone for their children.
This thesis tells us what we should do about a particular issue discussed in Sandel’s article, but it does not tell us how we should understand Sandel’s argument.
Questions to ask about your thesis
- Is the thesis truly arguable? Does it speak to a genuine dilemma in the source, or would most readers automatically agree with it?
- Is the thesis too obvious? Again, would most or all readers agree with it without needing to see your argument?
- Is the thesis complex enough to require a whole essay's worth of argument?
- Is the thesis supportable with evidence from the text rather than with generalizations or outside research?
- Would anyone want to read a paper in which this thesis was developed? That is, can you explain what this paper is adding to our understanding of a problem, question, or topic?
- picture_as_pdf Thesis
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

What is a thesis | A Complete Guide with Examples

Table of Contents
A thesis is a comprehensive academic paper based on your original research that presents new findings, arguments, and ideas of your study. It’s typically submitted at the end of your master’s degree or as a capstone of your bachelor’s degree.
However, writing a thesis can be laborious, especially for beginners. From the initial challenge of pinpointing a compelling research topic to organizing and presenting findings, the process is filled with potential pitfalls.
Therefore, to help you, this guide talks about what is a thesis. Additionally, it offers revelations and methodologies to transform it from an overwhelming task to a manageable and rewarding academic milestone.
What is a thesis?
A thesis is an in-depth research study that identifies a particular topic of inquiry and presents a clear argument or perspective about that topic using evidence and logic.
Writing a thesis showcases your ability of critical thinking, gathering evidence, and making a compelling argument. Integral to these competencies is thorough research, which not only fortifies your propositions but also confers credibility to your entire study.
Furthermore, there's another phenomenon you might often confuse with the thesis: the ' working thesis .' However, they aren't similar and shouldn't be used interchangeably.
A working thesis, often referred to as a preliminary or tentative thesis, is an initial version of your thesis statement. It serves as a draft or a starting point that guides your research in its early stages.
As you research more and gather more evidence, your initial thesis (aka working thesis) might change. It's like a starting point that can be adjusted as you learn more. It's normal for your main topic to change a few times before you finalize it.
While a thesis identifies and provides an overarching argument, the key to clearly communicating the central point of that argument lies in writing a strong thesis statement.
What is a thesis statement?
A strong thesis statement (aka thesis sentence) is a concise summary of the main argument or claim of the paper. It serves as a critical anchor in any academic work, succinctly encapsulating the primary argument or main idea of the entire paper.
Typically found within the introductory section, a strong thesis statement acts as a roadmap of your thesis, directing readers through your arguments and findings. By delineating the core focus of your investigation, it offers readers an immediate understanding of the context and the gravity of your study.
Furthermore, an effectively crafted thesis statement can set forth the boundaries of your research, helping readers anticipate the specific areas of inquiry you are addressing.
Different types of thesis statements
A good thesis statement is clear, specific, and arguable. Therefore, it is necessary for you to choose the right type of thesis statement for your academic papers.
Thesis statements can be classified based on their purpose and structure. Here are the primary types of thesis statements:
Argumentative (or Persuasive) thesis statement
Purpose : To convince the reader of a particular stance or point of view by presenting evidence and formulating a compelling argument.
Example : Reducing plastic use in daily life is essential for environmental health.
Analytical thesis statement
Purpose : To break down an idea or issue into its components and evaluate it.
Example : By examining the long-term effects, social implications, and economic impact of climate change, it becomes evident that immediate global action is necessary.
Expository (or Descriptive) thesis statement
Purpose : To explain a topic or subject to the reader.
Example : The Great Depression, spanning the 1930s, was a severe worldwide economic downturn triggered by a stock market crash, bank failures, and reduced consumer spending.
Cause and effect thesis statement
Purpose : To demonstrate a cause and its resulting effect.
Example : Overuse of smartphones can lead to impaired sleep patterns, reduced face-to-face social interactions, and increased levels of anxiety.
Compare and contrast thesis statement
Purpose : To highlight similarities and differences between two subjects.
Example : "While both novels '1984' and 'Brave New World' delve into dystopian futures, they differ in their portrayal of individual freedom, societal control, and the role of technology."
When you write a thesis statement , it's important to ensure clarity and precision, so the reader immediately understands the central focus of your work.
What is the difference between a thesis and a thesis statement?
While both terms are frequently used interchangeably, they have distinct meanings.
A thesis refers to the entire research document, encompassing all its chapters and sections. In contrast, a thesis statement is a brief assertion that encapsulates the central argument of the research.
Here’s an in-depth differentiation table of a thesis and a thesis statement.
Aspect | Thesis | Thesis Statement |
Definition | An extensive document presenting the author's research and findings, typically for a degree or professional qualification. | A concise sentence or two in an essay or research paper that outlines the main idea or argument. |
Position | It’s the entire document on its own. | Typically found at the end of the introduction of an essay, research paper, or thesis. |
Components | Introduction, methodology, results, conclusions, and bibliography or references. | Doesn't include any specific components |
Purpose | Provides detailed research, presents findings, and contributes to a field of study. | To guide the reader about the main point or argument of the paper or essay. |
Now, to craft a compelling thesis, it's crucial to adhere to a specific structure. Let’s break down these essential components that make up a thesis structure
15 components of a thesis structure
Navigating a thesis can be daunting. However, understanding its structure can make the process more manageable.
Here are the key components or different sections of a thesis structure:
Your thesis begins with the title page. It's not just a formality but the gateway to your research.

Here, you'll prominently display the necessary information about you (the author) and your institutional details.
- Title of your thesis
- Your full name
- Your department
- Your institution and degree program
- Your submission date
- Your Supervisor's name (in some cases)
- Your Department or faculty (in some cases)
- Your University's logo (in some cases)
- Your Student ID (in some cases)
In a concise manner, you'll have to summarize the critical aspects of your research in typically no more than 200-300 words.

This includes the problem statement, methodology, key findings, and conclusions. For many, the abstract will determine if they delve deeper into your work, so ensure it's clear and compelling.
Acknowledgments
Research is rarely a solitary endeavor. In the acknowledgments section, you have the chance to express gratitude to those who've supported your journey.

This might include advisors, peers, institutions, or even personal sources of inspiration and support. It's a personal touch, reflecting the humanity behind the academic rigor.
Table of contents
A roadmap for your readers, the table of contents lists the chapters, sections, and subsections of your thesis.

By providing page numbers, you allow readers to navigate your work easily, jumping to sections that pique their interest.
List of figures and tables
Research often involves data, and presenting this data visually can enhance understanding. This section provides an organized listing of all figures and tables in your thesis.

It's a visual index, ensuring that readers can quickly locate and reference your graphical data.
Introduction
Here's where you introduce your research topic, articulate the research question or objective, and outline the significance of your study.

- Present the research topic : Clearly articulate the central theme or subject of your research.
- Background information : Ground your research topic, providing any necessary context or background information your readers might need to understand the significance of your study.
- Define the scope : Clearly delineate the boundaries of your research, indicating what will and won't be covered.
- Literature review : Introduce any relevant existing research on your topic, situating your work within the broader academic conversation and highlighting where your research fits in.
- State the research Question(s) or objective(s) : Clearly articulate the primary questions or objectives your research aims to address.
- Outline the study's structure : Give a brief overview of how the subsequent sections of your work will unfold, guiding your readers through the journey ahead.
The introduction should captivate your readers, making them eager to delve deeper into your research journey.
Literature review section
Your study correlates with existing research. Therefore, in the literature review section, you'll engage in a dialogue with existing knowledge, highlighting relevant studies, theories, and findings.

It's here that you identify gaps in the current knowledge, positioning your research as a bridge to new insights.
To streamline this process, consider leveraging AI tools. For example, the SciSpace literature review tool enables you to efficiently explore and delve into research papers, simplifying your literature review journey.
Methodology
In the research methodology section, you’ll detail the tools, techniques, and processes you employed to gather and analyze data. This section will inform the readers about how you approached your research questions and ensures the reproducibility of your study.

Here's a breakdown of what it should encompass:
- Research Design : Describe the overall structure and approach of your research. Are you conducting a qualitative study with in-depth interviews? Or is it a quantitative study using statistical analysis? Perhaps it's a mixed-methods approach?
- Data Collection : Detail the methods you used to gather data. This could include surveys, experiments, observations, interviews, archival research, etc. Mention where you sourced your data, the duration of data collection, and any tools or instruments used.
- Sampling : If applicable, explain how you selected participants or data sources for your study. Discuss the size of your sample and the rationale behind choosing it.
- Data Analysis : Describe the techniques and tools you used to process and analyze the data. This could range from statistical tests in quantitative research to thematic analysis in qualitative research.
- Validity and Reliability : Address the steps you took to ensure the validity and reliability of your findings to ensure that your results are both accurate and consistent.
- Ethical Considerations : Highlight any ethical issues related to your research and the measures you took to address them, including — informed consent, confidentiality, and data storage and protection measures.
Moreover, different research questions necessitate different types of methodologies. For instance:
- Experimental methodology : Often used in sciences, this involves a controlled experiment to discern causality.
- Qualitative methodology : Employed when exploring patterns or phenomena without numerical data. Methods can include interviews, focus groups, or content analysis.
- Quantitative methodology : Concerned with measurable data and often involves statistical analysis. Surveys and structured observations are common tools here.
- Mixed methods : As the name implies, this combines both qualitative and quantitative methodologies.
The Methodology section isn’t just about detailing the methods but also justifying why they were chosen. The appropriateness of the methods in addressing your research question can significantly impact the credibility of your findings.
Results (or Findings)
This section presents the outcomes of your research. It's crucial to note that the nature of your results may vary; they could be quantitative, qualitative, or a mix of both.

Quantitative results often present statistical data, showcasing measurable outcomes, and they benefit from tables, graphs, and figures to depict these data points.
Qualitative results , on the other hand, might delve into patterns, themes, or narratives derived from non-numerical data, such as interviews or observations.
Regardless of the nature of your results, clarity is essential. This section is purely about presenting the data without offering interpretations — that comes later in the discussion.
In the discussion section, the raw data transforms into valuable insights.
Start by revisiting your research question and contrast it with the findings. How do your results expand, constrict, or challenge current academic conversations?
Dive into the intricacies of the data, guiding the reader through its implications. Detail potential limitations transparently, signaling your awareness of the research's boundaries. This is where your academic voice should be resonant and confident.
Practical implications (Recommendation) section
Based on the insights derived from your research, this section provides actionable suggestions or proposed solutions.
Whether aimed at industry professionals or the general public, recommendations translate your academic findings into potential real-world actions. They help readers understand the practical implications of your work and how it can be applied to effect change or improvement in a given field.
When crafting recommendations, it's essential to ensure they're feasible and rooted in the evidence provided by your research. They shouldn't merely be aspirational but should offer a clear path forward, grounded in your findings.
The conclusion provides closure to your research narrative.
It's not merely a recap but a synthesis of your main findings and their broader implications. Reconnect with the research questions or hypotheses posited at the beginning, offering clear answers based on your findings.

Reflect on the broader contributions of your study, considering its impact on the academic community and potential real-world applications.
Lastly, the conclusion should leave your readers with a clear understanding of the value and impact of your study.
References (or Bibliography)
Every theory you've expounded upon, every data point you've cited, and every methodological precedent you've followed finds its acknowledgment here.

In references, it's crucial to ensure meticulous consistency in formatting, mirroring the specific guidelines of the chosen citation style .
Proper referencing helps to avoid plagiarism , gives credit to original ideas, and allows readers to explore topics of interest. Moreover, it situates your work within the continuum of academic knowledge.
To properly cite the sources used in the study, you can rely on online citation generator tools to generate accurate citations!
Here’s more on how you can cite your sources.
Often, the depth of research produces a wealth of material that, while crucial, can make the core content of the thesis cumbersome. The appendix is where you mention extra information that supports your research but isn't central to the main text.

Whether it's raw datasets, detailed procedural methodologies, extended case studies, or any other ancillary material, the appendices ensure that these elements are archived for reference without breaking the main narrative's flow.
For thorough researchers and readers keen on meticulous details, the appendices provide a treasure trove of insights.
Glossary (optional)
In academics, specialized terminologies, and jargon are inevitable. However, not every reader is versed in every term.
The glossary, while optional, is a critical tool for accessibility. It's a bridge ensuring that even readers from outside the discipline can access, understand, and appreciate your work.

By defining complex terms and providing context, you're inviting a wider audience to engage with your research, enhancing its reach and impact.
Remember, while these components provide a structured framework, the essence of your thesis lies in the originality of your ideas, the rigor of your research, and the clarity of your presentation.
As you craft each section, keep your readers in mind, ensuring that your passion and dedication shine through every page.
Thesis examples
To further elucidate the concept of a thesis, here are illustrative examples from various fields:
Example 1 (History): Abolition, Africans, and Abstraction: the Influence of the ‘Noble Savage’ on British and French Antislavery Thought, 1787-1807 by Suchait Kahlon.
Example 2 (Climate Dynamics): Influence of external forcings on abrupt millennial-scale climate changes: a statistical modelling study by Takahito Mitsui · Michel Crucifix
Checklist for your thesis evaluation
Evaluating your thesis ensures that your research meets the standards of academia. Here's an elaborate checklist to guide you through this critical process.
Content and structure
- Is the thesis statement clear, concise, and debatable?
- Does the introduction provide sufficient background and context?
- Is the literature review comprehensive, relevant, and well-organized?
- Does the methodology section clearly describe and justify the research methods?
- Are the results/findings presented clearly and logically?
- Does the discussion interpret the results in light of the research question and existing literature?
- Is the conclusion summarizing the research and suggesting future directions or implications?
Clarity and coherence
- Is the writing clear and free of jargon?
- Are ideas and sections logically connected and flowing?
- Is there a clear narrative or argument throughout the thesis?
Research quality
- Is the research question significant and relevant?
- Are the research methods appropriate for the question?
- Is the sample size (if applicable) adequate?
- Are the data analysis techniques appropriate and correctly applied?
- Are potential biases or limitations addressed?
Originality and significance
- Does the thesis contribute new knowledge or insights to the field?
- Is the research grounded in existing literature while offering fresh perspectives?
Formatting and presentation
- Is the thesis formatted according to institutional guidelines?
- Are figures, tables, and charts clear, labeled, and referenced in the text?
- Is the bibliography or reference list complete and consistently formatted?
- Are appendices relevant and appropriately referenced in the main text?
Grammar and language
- Is the thesis free of grammatical and spelling errors?
- Is the language professional, consistent, and appropriate for an academic audience?
- Are quotations and paraphrased material correctly cited?
Feedback and revision
- Have you sought feedback from peers, advisors, or experts in the field?
- Have you addressed the feedback and made the necessary revisions?
Overall assessment
- Does the thesis as a whole feel cohesive and comprehensive?
- Would the thesis be understandable and valuable to someone in your field?
Ensure to use this checklist to leave no ground for doubt or missed information in your thesis.
After writing your thesis, the next step is to discuss and defend your findings verbally in front of a knowledgeable panel. You’ve to be well prepared as your professors may grade your presentation abilities.
Preparing your thesis defense
A thesis defense, also known as "defending the thesis," is the culmination of a scholar's research journey. It's the final frontier, where you’ll present their findings and face scrutiny from a panel of experts.
Typically, the defense involves a public presentation where you’ll have to outline your study, followed by a question-and-answer session with a committee of experts. This committee assesses the validity, originality, and significance of the research.
The defense serves as a rite of passage for scholars. It's an opportunity to showcase expertise, address criticisms, and refine arguments. A successful defense not only validates the research but also establishes your authority as a researcher in your field.
Here’s how you can effectively prepare for your thesis defense .
Now, having touched upon the process of defending a thesis, it's worth noting that scholarly work can take various forms, depending on academic and regional practices.
One such form, often paralleled with the thesis, is the 'dissertation.' But what differentiates the two?
Dissertation vs. Thesis
Often used interchangeably in casual discourse, they refer to distinct research projects undertaken at different levels of higher education.
To the uninitiated, understanding their meaning might be elusive. So, let's demystify these terms and delve into their core differences.
Here's a table differentiating between the two.
Aspect | Thesis | Dissertation |
Purpose | Often for a master's degree, showcasing a grasp of existing research | Primarily for a doctoral degree, contributing new knowledge to the field |
Length | 100 pages, focusing on a specific topic or question. | 400-500 pages, involving deep research and comprehensive findings |
Research Depth | Builds upon existing research | Involves original and groundbreaking research |
Advisor's Role | Guides the research process | Acts more as a consultant, allowing the student to take the lead |
Outcome | Demonstrates understanding of the subject | Proves capability to conduct independent and original research |
Wrapping up
From understanding the foundational concept of a thesis to navigating its various components, differentiating it from a dissertation, and recognizing the importance of proper citation — this guide covers it all.
As scholars and readers, understanding these nuances not only aids in academic pursuits but also fosters a deeper appreciation for the relentless quest for knowledge that drives academia.
It’s important to remember that every thesis is a testament to curiosity, dedication, and the indomitable spirit of discovery.
Good luck with your thesis writing!
Frequently Asked Questions
A thesis typically ranges between 40-80 pages, but its length can vary based on the research topic, institution guidelines, and level of study.
A PhD thesis usually spans 200-300 pages, though this can vary based on the discipline, complexity of the research, and institutional requirements.
To identify a thesis topic, consider current trends in your field, gaps in existing literature, personal interests, and discussions with advisors or mentors. Additionally, reviewing related journals and conference proceedings can provide insights into potential areas of exploration.
The conceptual framework is often situated in the literature review or theoretical framework section of a thesis. It helps set the stage by providing the context, defining key concepts, and explaining the relationships between variables.
A thesis statement should be concise, clear, and specific. It should state the main argument or point of your research. Start by pinpointing the central question or issue your research addresses, then condense that into a single statement, ensuring it reflects the essence of your paper.
You might also like

Chat PDF Tools Compared: SciSpace ChatPDF and Sider AI

This ChatGPT Alternative Will Change How You Read PDFs Forever!

Smallpdf vs SciSpace: Which ChatPDF is Right for You?
This is the Difference Between a Hypothesis and a Theory
What to Know A hypothesis is an assumption made before any research has been done. It is formed so that it can be tested to see if it might be true. A theory is a principle formed to explain the things already shown in data. Because of the rigors of experiment and control, it is much more likely that a theory will be true than a hypothesis.
As anyone who has worked in a laboratory or out in the field can tell you, science is about process: that of observing, making inferences about those observations, and then performing tests to see if the truth value of those inferences holds up. The scientific method is designed to be a rigorous procedure for acquiring knowledge about the world around us.

In scientific reasoning, a hypothesis is constructed before any applicable research has been done. A theory, on the other hand, is supported by evidence: it's a principle formed as an attempt to explain things that have already been substantiated by data.
Toward that end, science employs a particular vocabulary for describing how ideas are proposed, tested, and supported or disproven. And that's where we see the difference between a hypothesis and a theory .
A hypothesis is an assumption, something proposed for the sake of argument so that it can be tested to see if it might be true.
In the scientific method, the hypothesis is constructed before any applicable research has been done, apart from a basic background review. You ask a question, read up on what has been studied before, and then form a hypothesis.
What is a Hypothesis?
A hypothesis is usually tentative, an assumption or suggestion made strictly for the objective of being tested.
When a character which has been lost in a breed, reappears after a great number of generations, the most probable hypothesis is, not that the offspring suddenly takes after an ancestor some hundred generations distant, but that in each successive generation there has been a tendency to reproduce the character in question, which at last, under unknown favourable conditions, gains an ascendancy. Charles Darwin, On the Origin of Species , 1859 According to one widely reported hypothesis , cell-phone transmissions were disrupting the bees' navigational abilities. (Few experts took the cell-phone conjecture seriously; as one scientist said to me, "If that were the case, Dave Hackenberg's hives would have been dead a long time ago.") Elizabeth Kolbert, The New Yorker , 6 Aug. 2007
What is a Theory?
A theory , in contrast, is a principle that has been formed as an attempt to explain things that have already been substantiated by data. It is used in the names of a number of principles accepted in the scientific community, such as the Big Bang Theory . Because of the rigors of experimentation and control, its likelihood as truth is much higher than that of a hypothesis.
It is evident, on our theory , that coasts merely fringed by reefs cannot have subsided to any perceptible amount; and therefore they must, since the growth of their corals, either have remained stationary or have been upheaved. Now, it is remarkable how generally it can be shown, by the presence of upraised organic remains, that the fringed islands have been elevated: and so far, this is indirect evidence in favour of our theory . Charles Darwin, The Voyage of the Beagle , 1839 An example of a fundamental principle in physics, first proposed by Galileo in 1632 and extended by Einstein in 1905, is the following: All observers traveling at constant velocity relative to one another, should witness identical laws of nature. From this principle, Einstein derived his theory of special relativity. Alan Lightman, Harper's , December 2011
Non-Scientific Use
In non-scientific use, however, hypothesis and theory are often used interchangeably to mean simply an idea, speculation, or hunch (though theory is more common in this regard):
The theory of the teacher with all these immigrant kids was that if you spoke English loudly enough they would eventually understand. E. L. Doctorow, Loon Lake , 1979 Chicago is famous for asking questions for which there can be no boilerplate answers. Example: given the probability that the federal tax code, nondairy creamer, Dennis Rodman and the art of mime all came from outer space, name something else that has extraterrestrial origins and defend your hypothesis . John McCormick, Newsweek , 5 Apr. 1999 In his mind's eye, Miller saw his case suddenly taking form: Richard Bailey had Helen Brach killed because she was threatening to sue him over the horses she had purchased. It was, he realized, only a theory , but it was one he felt certain he could, in time, prove. Full of urgency, a man with a mission now that he had a hypothesis to guide him, he issued new orders to his troops: Find out everything you can about Richard Bailey and his crowd. Howard Blum, Vanity Fair , January 1995
And sometimes one term is used as a genus, or a means for defining the other:
Laplace's popular version of his astronomy, the Système du monde , was famous for introducing what came to be known as the nebular hypothesis , the theory that the solar system was formed by the condensation, through gradual cooling, of the gaseous atmosphere (the nebulae) surrounding the sun. Louis Menand, The Metaphysical Club , 2001 Researchers use this information to support the gateway drug theory — the hypothesis that using one intoxicating substance leads to future use of another. Jordy Byrd, The Pacific Northwest Inlander , 6 May 2015 Fox, the business and economics columnist for Time magazine, tells the story of the professors who enabled those abuses under the banner of the financial theory known as the efficient market hypothesis . Paul Krugman, The New York Times Book Review , 9 Aug. 2009
Incorrect Interpretations of "Theory"
Since this casual use does away with the distinctions upheld by the scientific community, hypothesis and theory are prone to being wrongly interpreted even when they are encountered in scientific contexts—or at least, contexts that allude to scientific study without making the critical distinction that scientists employ when weighing hypotheses and theories.
The most common occurrence is when theory is interpreted—and sometimes even gleefully seized upon—to mean something having less truth value than other scientific principles. (The word law applies to principles so firmly established that they are almost never questioned, such as the law of gravity.)
This mistake is one of projection: since we use theory in general use to mean something lightly speculated, then it's implied that scientists must be talking about the same level of uncertainty when they use theory to refer to their well-tested and reasoned principles.
The distinction has come to the forefront particularly on occasions when the content of science curricula in schools has been challenged—notably, when a school board in Georgia put stickers on textbooks stating that evolution was "a theory, not a fact, regarding the origin of living things." As Kenneth R. Miller, a cell biologist at Brown University, has said , a theory "doesn’t mean a hunch or a guess. A theory is a system of explanations that ties together a whole bunch of facts. It not only explains those facts, but predicts what you ought to find from other observations and experiments.”
While theories are never completely infallible, they form the basis of scientific reasoning because, as Miller said "to the best of our ability, we’ve tested them, and they’ve held up."
More Differences Explained
- Epidemic vs. Pandemic
- Diagnosis vs. Prognosis
- Treatment vs. Cure
Word of the Day
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Games & Quizzes


Commonly Confused
'canceled' or 'cancelled', is it 'home in' or 'hone in', the difference between 'race' and 'ethnicity', homophones, homographs, and homonyms, on 'biweekly' and 'bimonthly', grammar & usage, every letter is silent, sometimes: a-z list of examples, how to use em dashes (—), en dashes (–) , and hyphens (-), the difference between 'i.e.' and 'e.g.', plural and possessive names: a guide, 31 useful rhetorical devices, pilfer: how to play and win, 8 words with fascinating histories, flower etymologies for your spring garden, 8 words for lesser-known musical instruments, it's a scorcher words for the summer heat.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
Theoretical Framework Example for a Thesis or Dissertation
Published on October 14, 2015 by Sarah Vinz . Revised on July 18, 2023 by Tegan George.
Your theoretical framework defines the key concepts in your research, suggests relationships between them, and discusses relevant theories based on your literature review .
A strong theoretical framework gives your research direction. It allows you to convincingly interpret, explain, and generalize from your findings and show the relevance of your thesis or dissertation topic in your field.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Sample problem statement and research questions, sample theoretical framework, your theoretical framework, other interesting articles.
Your theoretical framework is based on:
- Your problem statement
- Your research questions
- Your literature review
A new boutique downtown is struggling with the fact that many of their online customers do not return to make subsequent purchases. This is a big issue for the otherwise fast-growing store.Management wants to increase customer loyalty. They believe that improved customer satisfaction will play a major role in achieving their goal of increased return customers.
To investigate this problem, you have zeroed in on the following problem statement, objective, and research questions:
- Problem : Many online customers do not return to make subsequent purchases.
- Objective : To increase the quantity of return customers.
- Research question : How can the satisfaction of the boutique’s online customers be improved in order to increase the quantity of return customers?
The concepts of “customer loyalty” and “customer satisfaction” are clearly central to this study, along with their relationship to the likelihood that a customer will return. Your theoretical framework should define these concepts and discuss theories about the relationship between these variables.
Some sub-questions could include:
- What is the relationship between customer loyalty and customer satisfaction?
- How satisfied and loyal are the boutique’s online customers currently?
- What factors affect the satisfaction and loyalty of the boutique’s online customers?
As the concepts of “loyalty” and “customer satisfaction” play a major role in the investigation and will later be measured, they are essential concepts to define within your theoretical framework .
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Below is a simplified example showing how you can describe and compare theories in your thesis or dissertation . In this example, we focus on the concept of customer satisfaction introduced above.
Customer satisfaction
Thomassen (2003, p. 69) defines customer satisfaction as “the perception of the customer as a result of consciously or unconsciously comparing their experiences with their expectations.” Kotler & Keller (2008, p. 80) build on this definition, stating that customer satisfaction is determined by “the degree to which someone is happy or disappointed with the observed performance of a product in relation to his or her expectations.”
Performance that is below expectations leads to a dissatisfied customer, while performance that satisfies expectations produces satisfied customers (Kotler & Keller, 2003, p. 80).
The definition of Zeithaml and Bitner (2003, p. 86) is slightly different from that of Thomassen. They posit that “satisfaction is the consumer fulfillment response. It is a judgement that a product or service feature, or the product of service itself, provides a pleasurable level of consumption-related fulfillment.” Zeithaml and Bitner’s emphasis is thus on obtaining a certain satisfaction in relation to purchasing.
Thomassen’s definition is the most relevant to the aims of this study, given the emphasis it places on unconscious perception. Although Zeithaml and Bitner, like Thomassen, say that customer satisfaction is a reaction to the experience gained, there is no distinction between conscious and unconscious comparisons in their definition.
The boutique claims in its mission statement that it wants to sell not only a product, but also a feeling. As a result, unconscious comparison will play an important role in the satisfaction of its customers. Thomassen’s definition is therefore more relevant.
Thomassen’s Customer Satisfaction Model
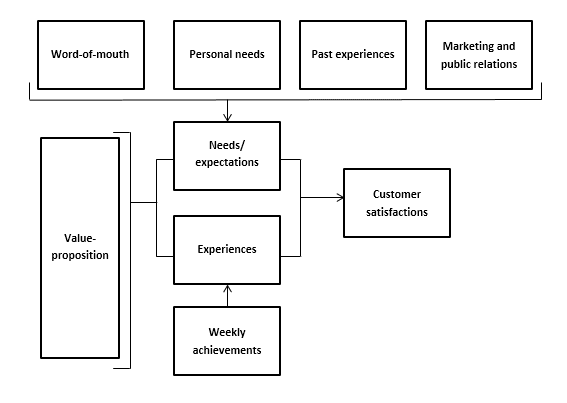
According to Thomassen, both the so-called “value proposition” and other influences have an impact on final customer satisfaction. In his satisfaction model (Fig. 1), Thomassen shows that word-of-mouth, personal needs, past experiences, and marketing and public relations determine customers’ needs and expectations.
These factors are compared to their experiences, with the interplay between expectations and experiences determining a customer’s satisfaction level. Thomassen’s model is important for this study as it allows us to determine both the extent to which the boutique’s customers are satisfied, as well as where improvements can be made.
Figure 1 Customer satisfaction creation
Of course, you could analyze the concepts more thoroughly and compare additional definitions to each other. You could also discuss the theories and ideas of key authors in greater detail and provide several models to illustrate different concepts.
If you want to know more about AI for academic writing, AI tools, or research bias, make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
Research bias
- Anchoring bias
- Halo effect
- The Baader–Meinhof phenomenon
- The placebo effect
- Nonresponse bias
- Deep learning
- Generative AI
- Machine learning
- Reinforcement learning
- Supervised vs. unsupervised learning
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Vinz, S. (2023, July 18). Theoretical Framework Example for a Thesis or Dissertation. Scribbr. Retrieved September 13, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/theoretical-framework-example/
Is this article helpful?
Sarah's academic background includes a Master of Arts in English, a Master of International Affairs degree, and a Bachelor of Arts in Political Science. She loves the challenge of finding the perfect formulation or wording and derives much satisfaction from helping students take their academic writing up a notch.
Other students also liked
What is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, how to write a literature review | guide, examples, & templates, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, what is your plagiarism score.
“Theory” vs. “Hypothesis”: What Is The Difference?
Chances are you’ve heard of the TV show The Big Bang Theory . Lots of people love this lighthearted sitcom for its quirky characters and their relationships, but others haven’t even given the series a chance for one reason: they don’t like science and assume the show is boring.
However, it only takes a few seconds with Sheldon and Penny to disprove this assumption and realize that this theory ab0ut The Big Bang Theory is wrong—it isn’t a scientific snoozefest.
But wait: is it a theory or a hypothesis about the show that leads people astray? And would the actual big bang theory— the one that refers to the beginning of the universe—mean the same thing as a big bang hypothesis ?
Let’s take a closer look at theory and hypothesis to nail down what they mean.
What does theory mean?
As a noun, a theory is a group of tested general propositions “commonly regarded as correct, that can be used as principles of explanation and prediction for a class of phenomena .” This is what is known as a scientific theory , which by definition is “an understanding that is based on already tested data or results .” Einstein’s theory of relativity and the theory of evolution are both examples of such tested propositions .
Theory is also defined as a proposed explanation you might make about your own life and observations, and it’s one “whose status is still conjectural and subject to experimentation .” For example: I’ve got my own theories about why he’s missing his deadlines all the time. This example refers to an idea that has not yet been proven.
There are other uses of the word theory as well.
- In this example, theory is “a body of principles or theorems belonging to one subject.” It can be a branch of science or art that deals with its principles or methods .
- For example: when she started to follow a new parenting theory based on a trendy book, it caused a conflict with her mother, who kept offering differing opinions .
First recorded in 1590–1600, theory originates from the Late Latin theōria , which stems from the Greek theōría. Synonyms for theory include approach , assumption , doctrine , ideology , method , philosophy , speculation , thesis , and understanding .
What does hypothesis mean?
Hypothesis is a noun that means “a proposition , or set of propositions, set forth as an explanation” that describe “some specified group of phenomena.” Sounds familiar to theory , no?
But, unlike a theory , a scientific hypothesis is made before testing is done and isn’t based on results. Instead, it is the basis for further investigation . For example: her working hypothesis is that this new drug also has an unintended effect on the heart, and she is curious what the clinical trials will show .
Hypothesis also refers to “a proposition assumed as a premise in an argument,” or “mere assumption or guess.” For example:
- She decided to drink more water for a week to test out her hypothesis that dehydration was causing her terrible headaches.
- After a night of her spouse’s maddening snoring, she came up with the hypothesis that sleeping on his back was exacerbating the problem.
Hypothesis was first recorded around 1590–1600 and originates from the Greek word hypóthesis (“basis, supposition”). Synonyms for hypothesis include: assumption , conclusion , conjecture , guess , inference , premise , theorem , and thesis .
How to use each
Although theory in terms of science is used to express something based on extensive research and experimentation, typically in everyday life, theory is used more casually to express an educated guess.
So in casual language, theory and hypothesis are more likely to be used interchangeably to express an idea or speculation .
In most everyday uses, theory and hypothesis convey the same meaning. For example:
- Her opinion is just a theory , of course. She’s just guessing.
- Her opinion is just a hypothesis , of course. She’s just guessing.
It’s important to remember that a scientific theory is different. It is based on tested results that support or substantiate it, whereas a hypothesis is formed before the research.
For example:
- His hypothesis for the class science project is that this brand of plant food is better than the rest for helping grass grow.
- After testing his hypothesis , he developed a new theory based on the experiment results: plant food B is actually more effective than plant food A in helping grass grow.
In these examples, theory “doesn’t mean a hunch or a guess,” according to Kenneth R. Miller, a cell biologist at Brown University. “A theory is a system of explanations that ties together a whole bunch of facts. It not only explains those facts, but predicts what you ought to find from other observations and experiments.”
So if you have a concept that is based on substantiated research, it’s a theory .
But if you’re working off of an assumption that you still need to test, it’s a hypothesis .
So remember, first comes a hypothesis , then comes theory . Now who’s ready for a Big Bang Theory marathon?
Now that you’ve theorized and hypothesized through this whole article … keep testing your judgment (Or is it judgement?). Find out the correct spelling here!
Or find out the difference between these two common issues below!
WATCH: "Lethologica" vs. "Lethonomia": What's The Difference?
Go Behind The Words!
- By clicking "Sign Up", you are accepting Dictionary.com Terms & Conditions and Privacy policies.
- Name This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Commonly Confused

Hobbies & Passions
Word Origins
Current Events
[ rip - snawr -ter ]

- Majors & Careers
- Online Grad School
- Preparing For Grad School
- Student Life
Dissertation vs Thesis: Your 2024 Guide

If you’ve been thinking about going to graduate school, you may be familiar with the application requirements, rigorous academic schedule, and thesis or dissertation you’ll be expected to complete. So, what exactly is the difference between a thesis and a dissertation? While there are similarities, there’s a clear difference between the two. In our guide, we compare dissertation vs thesis. Discover more about both – and what you can expect during your graduate program. Let’s get started!
- Table of Contents
What Is a Thesis?
A thesis is an academic paper or project that’s completed towards the end of a master’s degree program . It is typically completed as the capstone project , meaning it’s the final project required for a student to graduate.
Students need to select a narrow, specific topic within – or relating to – their field of study. Once they’ve selected a topic, students must conduct an in-depth review of existing research on their chosen subjects. The next step is to formulate an academic argument, an assertion they’ll need to support or prove with said research.
Therefore, a thesis is akin to an in-depth research paper. It’s comprised of research that essentially proves what a student has learned during their program.
What Is a Typical Thesis Structure?
A thesis generally follows a rigid structure that’s decided by the program, department, or university. Here is an example of a thesis structure:
- The Title Page
- Summary of Thesis Abstract
- Table of Maps and Figures
- The Thesis Body (Sometimes divided into chapters)
- The Results or Conclusion
Who Needs to Complete a Thesis?
Most master’s degree programs require students to complete a thesis. While some undergraduate programs may also require a thesis, these are generally shorter and narrower in scope.
Some programs will also require a master’s student to defend their thesis in front of a panel or committee.
What Is a Dissertation?
What is “the PhD paper” called? Some people refer to it as a PhD thesis, but it’s most commonly known as a dissertation in the US. Dissertations are the capstone project required at the tail end of a PhD program . It is almost always required, except for a select few one-year PhD programs .
Much like a thesis, dissertations are also academic papers that aim to prove a student’s expertise – while adding to the current body of knowledge – in their field. Thus, a student must look at existing research and conduct their own research .

Basically, it’s the magnum opus of a doctoral journey in the United States. A dissertation isn’t just a long research paper; it’s a beast of a project. It demands extensive research, originality, and the ability to make a meaningful contribution to your chosen field. Think of it as a research odyssey guided by a seasoned mentor. Once you’ve conquered this scholarly quest and defended your findings, you’ll proudly emerge with your hard-earned doctoral degree, a testament to your dedication and scholarly prowess.
A dissertation typically comes after a PhD student completes their required courses and passes their qualifying exams. In some programs, the dissertation process is embedded into the coursework. In such cases, students receive a jump start on their work, allowing them to potentially finish their program earlier.
What Does a Dissertation Do?
PhD candidates must present a new theory or hypothesis. Alternatively, they must present their research to question (or disprove) the existing accepted theory on their chosen subject. Students may choose to tackle their topic from a new angle or take their research in a different direction.
Most programs will require students to defend their dissertations. During the defense, candidates must be able to justify the methodology of their research and the results and interpretation of their findings. Defenses are typically oral presentations in front of a dissertation committee , where the students are asked questions or presented with challenges.
Although the defense may seem daunting, PhD students work closely with their advisors to prepare for their dissertations. Students receive feedback and advice to guide their dissertations in their chosen direction.
What Is the Typical Dissertation Structure?
Dissertations follow a rigid structure typically set by the program, department, or university. Here is an example format:
- The Acknowledgments Page
- The Abstract
- Introduction
- The Literature Review & Theoretical Framework
- The Methodology
- Findings/Results
- Discussions of the Findings, including analysis, interpretation, and applications
- The Conclusion
- List of References
- Any Appendices
What Is a Doctoral Thesis?
A doctoral thesis is a substantial piece of scholarly work that marks the pinnacle of a doctoral degree program, such as a PhD. Think of it as the academic grand finale. Its primary mission? To showcase the candidate’s mastery in their chosen field and their knack for delving deep into research.

In a nutshell, a doctoral thesis is a mammoth project that calls for originality. You’ve got to dig, investigate, gather data, crunch numbers, and present real data-supported findings. All this hard work usually happens under the watchful eye of a knowledgeable mentor. Once you’ve conquered this scholarly mountain and defended your thesis successfully, you’ll be proudly awarded your well-deserved doctoral degree. It’s the hallmark of your expertise and contribution to your field.
And how does a doctoral thesis differ from a dissertation? That’s mainly a geographic explanation. While they’re largely similar in scope and purpose, when comparing a doctoral thesis vs. a dissertation:
- A dissertation is the PhD capstone requirement in the US .
- A doctoral thesis is the PhD capstone requirement in Europe .
Related Reading: The Easiest PhDs
Dissertation vs. Thesis: The Similarities
In the master’s thesis vs dissertation discussion, there are plenty of similarities. Both are lengthy academic papers that require intense research and original writing. They’re also capstone projects which are completed at the tail end of their respective programs.
Students must work closely with their respective committees (e.g., faculty members, advisors, professionals) who provide feedback and guidance on their research, writing, and academic arguments. Both thesis and dissertation committees have a committee chair with whom the students work closely.
In some ways, the requirements for theses and dissertations are quite similar. They require a skillful defense of a student’s academic arguments. What’s more, both papers require critical thinking and good analytical reasoning, as well as in-depth expertise in the chosen field of study.
Students must also invest a significant amount of time into both projects while also being able to accept and action feedback on their work.
Dissertation vs. Thesis: The Differences
What are the differences between a PhD dissertation vs. thesis? The first and most distinct difference is the degree program requiring a PhD dissertation or thesis. A dissertation is typically the capstone project for a doctorate, while a thesis is the capstone project for a master’s degree program (or undergraduate program).
Candidates will have to defend their dissertation during an oral presentation in front of their committee. Only some master’s theses require this.
During a thesis, students typically conduct research by reviewing existing literature and knowledge on their chosen subject. During a dissertation, students must do their own research and prove their theory, concept, or hypothesis. They should also expect to develop a unique concept and defend it based on the practical and theoretical results achieved from their rigorous research.
Theses are also typically shorter (around 40 to 80 pages). Dissertations, however, are much longer (between 100 and 300 pages). Of course, the actual length of the paper may depend on the topic, program, department, or university.
Related Reading : PhD Candidate vs Student: What’s the Difference?
Dissertations and Theses: US vs. Europe
Whether you’re in the US or Europe, dissertations and theses are similar. However, European requirements and conventions differ slightly:
Doctoral Thesis
To ensure your PhD graduation, a dissertation is generally required. Doctoral theses in Europe are much like a PhD dissertation in the US : You must complete your own research and add to the existing body of knowledge in your field.
Master’s Dissertation
It may seem odd to require a dissertation for master’s degree programs, but in Europe, this is exactly what you’ll need. A master’s dissertation is a broader post-graduate program research project , though it’s most typically required for master’s programs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are a few of the most common questions we hear about the meaning of thesis vs. dissertation.
Is a Thesis and a Dissertation the Same?
Yes and no. In some ways, a dissertation and a thesis are the same. For example, both require original writing, critical skills, analytical thinking, plenty of research, and lots of academic effort. However, a thesis is more commonly reserved for master’s – and some undergraduate – programs. Dissertations are generally required by PhD programs in the United States.
Additionally, a thesis typically calls for heavy research and compilation of existing knowledge and literature on a subject. A dissertation requires candidates to conduct their own research to prove their own theory, concept, or hypothesis – adding to the existing body of knowledge in their chosen field of study.
How Long Is a Thesis vs. a Dissertation?
One of the primary differences between thesis and dissertation papers is their length. While a thesis might be anywhere from 40 to 80 pages long, a dissertation can easily run from 100 to 300. It’s important to note that these numbers depend on the specific program and university.
Does a PhD Require a Thesis or a Dissertation?
It all depends on where you are! While a US-based PhD requires you to complete a dissertation, a thesis (or “doctoral thesis”) is more commonly required for PhD candidates in Europe. In the US, a thesis is more commonly reserved for master’s degree programs and occasionally undergraduate programs. In Europe, a “master’s dissertation” is typically required for the completion of a master’s degree.
So, there you have it: an in-depth comparison of the dissertation vs. thesis academic requirements. Now that you know the primary similarities and differences between the two, it might become easier to decide your academic path. Just remember, you may be able to find a master’s program without a thesis or a doctorate without a dissertation requirement if you prefer. Good luck!
Are you ready to jump into your doctorate? Find out if you need a master’s degree to get a PhD .

Chriselle Sy
Chriselle has been a passionate professional content writer for over 10 years. She writes educational content for The Grad Cafe, Productivity Spot, The College Monk, and other digital publications. When she isn't busy writing, she spends her time streaming video games and learning new skills.
- Chriselle Sy https://blog.thegradcafe.com/author/chriselle-sy/ When to Apply for Grad School: Easy Monthly Timeline [2025-2026]
- Chriselle Sy https://blog.thegradcafe.com/author/chriselle-sy/ Best Laptop for Programming Students in 2024
- Chriselle Sy https://blog.thegradcafe.com/author/chriselle-sy/ The Best Academic Planners for 2024/2025
- Chriselle Sy https://blog.thegradcafe.com/author/chriselle-sy/ Graduate Certificate vs Degree: What’s the Difference? [2024 Guide]
This Week’s Top 5 Graduate Opportunities
These are the best states to start your tech career, related posts.

- How Many Grad Schools Should I Apply To?
![difference between thesis and theory When to Apply for Grad School: The Simple Guide [2026/2027]](https://blog.thegradcafe.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/When-to-Apply-to-Grad-School-350x250.png)
- When to Apply for Grad School: Easy Monthly Timeline [2025-2026]

- 30+ Best Dorm Room Essentials for Guys in 2024

- Best Laptop for Programming Students in 2024

The Sassy Digital Assistant Revolutionizing Student Budgeting

The Best Academic Planners for 2024/2025

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Recent Posts
- Last Mile Education Fund Paves the Way for Tech Students, Offers Lifeline Grants

© 2024 TheGradCafe.com All rights reserved
- Partner With Us
- Results Search
- Submit Your Results
- Write For Us

PSC 352: Introduction to Comparative Politics
- Getting Started
- Comparative Politics Overview
- Current World/Political News Feeds
- Choose a country
What is the difference between a thesis & a hypothesis?
- Find Books/eBooks
- Find Articles, Reports & Documents
- Find Statistics
- Find Poll & Survey Results
- Evaluate Your Sources
- Cite Your Sources
B oth the hypothesis statement and the thesis statement answer the research question of the study. When the statement is one that can be proved or disproved, it is an hypothesis statement. If, instead, the statement specifically shows the intentions/objectives/position of the researcher, it is a thesis statement.
A hypothesis is a statement that can be proved or disproved. It is typically used in quantitative research and predicts the relationship between variables.
A thesis statement is a short, direct sentence that summarizes the main point or claim of an essay or research paper. It is seen in quantitative, qualitative, and mixed methods research. A thesis statement is developed, supported, and explained in the body of the essay or research report by means of examples and evidence.
Every research study should contain a concise and well-written thesis statement. If the intent of the study is to prove/disprove something, that research report will also contain an hypothesis statement.
Jablonski , Judith. What is the difference between a thesis statement and an hypothesis statement? Online Library. American Public University System. Jun 16, 2014. Web. http://apus.libanswers.com/faq/2374
Let’s say you are interested in the conflict in Darfur, and you conclude that the issues you wish to address include the nature, causes, and effects of the conflict, and the international response. While you could address the issue of international response first, it makes the most sense to start with a description of the conflict, followed by an exploration of the causes, effects, and then to discuss the international response and what more could/should be done.
This hypothetical example may lead to the following title, introduction, and statement of questions:
Conflict in Darfur: Causes, Consequences, and International Response This paper examines the conflict in Darfur, Sudan. It is organized around the following questions: (1) What is the nature of the conflict in Darfur? (2) What are the causes and effects of the conflict? (3) What has the international community done to address it, and what more could/should it do?
Following the section that presents your questions and background, you will offer a set of responses/answers/(hypo)theses. They should follow the order of the questions. This might look something like this, “The paper argues/contends/ maintains/seeks to develop the position that...etc.” The most important thing you can do in this section is to present as clearly as possible your best thinking on the subject matter guided by course material and research. As you proceed through the research process, your thinking about the issues/questions will become more nuanced, complex, and refined. The statement of your theses will reflect this as you move forward in the research process.
So, looking to our hypothetical example on Darfur:
The current conflict in Darfur goes back more than a decade and consists of fighting between government-supported troops and residents of Darfur. The causes of the conflict include x, y, and z. The effects of the conflict have been a, b, and c. The international community has done 0, and it should do 1, 2, and 3.
Once you have setup your thesis you will be ready to begin amassing supporting evidence for you claims. This is a very important part of the research paper, as you will provide the substance to defend your thesis.
- << Previous: Choose a country
- Next: Find Books/eBooks >>
- Last Updated: Sep 13, 2024 2:35 PM
- URL: https://libguides.mssu.edu/PSC352
This site is maintained by the librarians of George A. Spiva Library . If you have a question or comment about the Library's LibGuides, please contact the site administrator .

Home » Education » Difference Between Thesis and Hypothesis
Difference Between Thesis and Hypothesis
Main difference – thesis vs hypothesis .
Thesis and hypothesis are two common terms that are often found in research studies. Hypothesis is a logical proposition that is based on existing knowledge that serves as the starting point of an investigation. A thesis is a statement that is put forward as a premise to be maintained or proved. The main difference between thesis and hypothesis is that thesis is found in all research studies whereas a hypothesis is mainly found in experimental quantitative research studies.
This article explains,
1. What is a Thesis? – Definition, Features, Function
2. What is a Hypothesis? – Definition, Features, Function

What is a Thesis
The word thesis has two meanings in a research study. Thesis can either refer to a dissertation or a thesis statement. Thesis or dissertation is the long essay or document that consists of the research study. Thesis can also refer to a theory or statement that is used as a premise to be maintained or proved.
The thesis statement in a research article is a sentence found at the beginning of the paper that presents the main argument of the paper. The rest of the document will gather, organize and present evidence to support this argument. The thesis statement will basically present the topic of the paper and indicate what position the researcher is going to take in relation to this topic. A thesis statement can generally be found at the end of the first paragraph (introductory paragraph) of the paper.

What is a Hypothesis
A hypothesis is a logical assumption based on available evidence. Hypothesis is defined as “a supposition or proposed explanation made on the basis of limited evidence as a starting point for further investigation” in the Oxford dictionary and as “an idea or theory that is not proven but that leads to further study or discussion” in the Merriam-Webster dictionary. In simple words, it is an educated guess that is not proven with concrete scientific evidence. Once it is scientifically tested and proven, it becomes a theory. However, it is important to note that a hypothesis can be accurate or inaccurate.
Hypotheses are mostly used in experiments and research studies. However, hypotheses are not used in every research study. They are mostly used in quantitative research studies that deal with experiments. Hypotheses are often used to test a specific model or theory . They can be used only when the researcher has sufficient knowledge about the subject since hypothesis are always based on the existing knowledge. Once the hypothesis is built, the researcher can find and analyze data and use them to prove or disprove the hypothesis.

Thesis: A thesis is a “statement or theory that is put forward as a premise to be maintained or proved” or a “long essay or dissertation involving personal research, written by a candidate for a university degree” (Oxford dictionary).
Hypothesis: A hypothesis is “a supposition or proposed explanation made on the basis of limited evidence as a starting point for further investigation” (Oxford dictionary).
Thesis: Thesis statement can be found in all research papers.
Hypothesis: Hypotheses are usually found in experimental quantitative research studies.
Thesis: Thesis statement may explain the hypothesis and how the researcher intends to support it.
Hypothesis: Hypothesis is an educated guess based on the existing knowledge.
Image Courtesy:
“Master’s Thesis” by Henri Sivonen (CC BY 2.0) via Flickr
“Colonial Flagellate Hypothesis” By Katelynp1 – Own work (CC BY-SA 3.0) via Commons Wikimedia
About the Author: Hasa
Hasanthi is a seasoned content writer and editor with over 8 years of experience. Armed with a BA degree in English and a knack for digital marketing, she explores her passions for literature, history, culture, and food through her engaging and informative writing.
You May Also Like These
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
What is the difference between hypothesis, thesis statement and research goal?
Can someone explain the difference between hypothesis, thesis statement and research goal based on an example?
- terminology
- 1 You should mention which subject you are in. 'Hypothesis' has opposite meanings in maths and physics. – Jessica B Commented May 31, 2018 at 11:22
2 Answers 2
I had this same question recently and did some research on it. The definitions I found weren't consistent, but from them I derived the following.
Thesis statement -- A definitive statement about the way the world (or your system of interest) works, especially what is most important in causing or influencing the behavior of the system.
"Family expectations has primary significance on the performance in college for Latino girls in the Western US" is an example of a thesis statement.
Research goal -- Expresses what you hope to learn or shed light on in your research. Specifically, the goal should specify what type of results you are hoping to achieve. It contextualizes your work in relation to other research, especially theory. It also feeds into your choice of method.
"My research goal is to develop a theoretical model of cultural influence on college performance, contextualized by gender and ethnicity" is an example of a research goal.
Hypotheses -- What specific conditions or relations do you aim to test or evaluate in your research. Any research that does not include a method for hypothesis testing should not claim to test hypotheses. A hypothesis statement must be specific enough that it is testable by the methods you choose, and also it should be falsifiable -- i.e. it is clear what evidence might prove the hypothesis false, and such evidence should be plausible and possible.
"Low family expectations has a detrimental effect on the college completion rate and time-to-complete for high-achieving Latino girls" is an example of a hypothesis statement.
Notice how there are specific, testable conditions and metrics -- "college completion rates" and "time-to-complete". These conditions should appear as metrics in your research methods -- i.e. instruments and analysis methods.
A thesis statement usually helps guide the research paper. It is a short sentence or summary containing the central idea of the research paper. It helps a reader have a clear glimpse of what the paper is about.
The Hypothesis statement comes in different format but with the intent to help prove or disprove a phenomenon. The hypothesis can help defend, support, explain or disprove, argue against the thesis statement.Usually the hypothesis measures specific issues or variables-two or more and therefore should be testable. The thesis statement creates a background while the hypothesis creates a means to measure the interrelationship.
The research goal takes a look into the future of your study or research paper. |It tries to help you state what the outcomes you seek to achieve by the research work. With a research goal you can set specific milestones to accomplish at the end of the research work.
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you're looking for browse other questions tagged thesis terminology ..
- Featured on Meta
- Site maintenance - Mon, Sept 16 2024, 21:00 UTC to Tue, Sept 17 2024, 2:00...
- User activation: Learnings and opportunities
- Join Stack Overflow’s CEO and me for the first Stack IRL Community Event in...
Hot Network Questions
- Why was Esther included in the canon?
- How to avoid bringing paper silverfish home from a vacation place?
- Will "universal" SMPS work at any voltage in the range, even DC?
- Mounting network afp volume from command line
- What are the pros and cons of the classic portfolio by Wealthfront?
- Custom PCB with Esp32-S3 isn't recognised by Device Manager for every board ordered
- siunitx dollar per hour broken going from SI to qty
- Should I change advisors because mine doesn't object to publishing at MDPI?
- security concerns of executing mariadb-dump with password over ssh
- What would a planet need for rain drops to trigger explosions upon making contact with the ground?
- C++ std::function-like queue
- Are there something like standard documents for 8.3 filename which explicitly mention about the folder names?
- "There is a bra for every ket, but there is not a ket for every bra"
- Concerns with newly installed floor tile
- Is "my death" a/the telos of human life?
- Subject verb agreement - I as well as he is/am the culprit
- In Photoshop, when saving as PNG, why is the size of my output file bigger when I have more invisible layers in the original file?
- What is the book in a world with no metal, where a librarian builds a "computer" from kidnapped people?
- Is it true that before European modernity, there were no "nations"?
- Color nested bonds
- Place with signs in Chinese & Arabic
- Do carbon fiber wings need a wing spar?
- How to decrease by 1 integers in an expl3's clist?
- If Act A repeals another Act B, and Act A is repealed, what happens to the Act B?
Best 9 Differences Between Thesis And Dissertation

You’ve probably heard people mention a “thesis” and a “dissertation” when talking about advanced studies, but what do these terms actually mean? While they are both involved in doing research and writing, they are not the same thing. A thesis is commonly written for a master’s degree, but a dissertation is required for a doctorate. Knowing the differences between them can help you understand what each one is all about and what’s expected of you.
In this article, we’ll explain what makes a thesis different from a dissertation. We’ll look at their main purposes, how they are structured, and what kind of work they involve. Whether you’re thinking about graduate school or already studying, this guide will help you understand what each of these research projects entails so you can plan your academic path more confidently. Thesis and Dissertation and different according to the country. For example, In the Philippines, the terms “dissertation” and “thesis” are used to describe different types of academic research projects required for various degrees.
What is a Thesis?
Table of Contents
A thesis is a detailed study document that students write to complete their master’s degree. It involves studying a specific topic in detail within their field, showing they can gather, analyze, and present information clearly and logically. A thesis is a chance for students to prove their knowledge, research skills, and ability to contribute meaningfully to their subject area.
Purpose of a Thesis in a Master’s Degree Program
The main goal of a thesis in a master’s program is to let students dive deep into a particular topic and add something valuable to their field of study. By writing a thesis, students develop important skills like critical thinking, thorough research, and academic writing. It serves as a final project that demonstrates their understanding of the subject and prepares them for the next steps, whether that’s further study or starting a career.
Writing a thesis also shows that a student can conduct independent research. It involves coming up with a research question, designing a study to answer it, analyzing the results, and drawing conclusions. Completing a thesis successfully can open doors to further education, like pursuing a Ph.D., or help in building a strong professional profile by showing a high level of expertise and commitment.
What is a Dissertation?
A dissertation is a big research project that you need to complete to get a Ph.D. Unlike regular papers, a dissertation is much more detailed and involves years of work. It’s all about exploring a unique question or problem that hasn’t been fully studied before and adding new knowledge to your field. Doing a dissertation shows that you can handle complex research, analyze your findings, and explain them clearly. It’s the final test of your expertise and research skills.
Role of a Dissertation in a Doctoral Program
In a Ph.D. program, your dissertation is very important for several reasons:
- Showing Original Research : The main goal of your dissertation is to prove that you can do original research on your own. This means picking a unique question, designing and carrying out a study, and figuring out what the results mean. Your dissertation should offer something new to your field and help expand what’s known about your topic.
- Becoming an Expert : Completing a dissertation shows that you are an expert in your field. It demands a deep understanding of your subject, great research skills, and the ability to think critically about existing knowledge. Successfully defending your dissertation in front of a panel of experts confirms your expertise and knowledge.
- Developing Important Skills : Writing a dissertation helps you develop valuable skills that are useful in both academic and professional settings. These abilities include critical thinking, problem-solving, data analysis , and effective communication. Finishing your dissertation can open up more opportunities for further research or advanced roles in various fields.
- Fulfilling Graduation Requirements : The dissertation is a key part of earning your Ph.D. It’s the final requirement you need to complete your doctoral studies and graduate. Successfully finishing and defending your dissertation is necessary to receive your degree.
The Difference Between Thesis and Dissertation
| Needed for a master’s degree. | Required for a Ph.D. or doctoral degree. | |
| Shows your ability to research a specific topic and understand it. Usually involves looking at existing ideas and solving a particular problem. | Aims to make a new and important contribution to your field. Focuses on a new research question or problem that hasn’t been studied before. | |
| Usually 50-100 pages; less detailed. It covers a topic more narrowly. | Often over 200 pages, very detailed and complex. It involves a lot of research and deep analysis. | |
| Uses existing knowledge to explore a new issue. Shows you can apply theories, but it doesn’t have to be revolutionary. | Requires original research that adds new knowledge or insights. Your work should provide significant new findings or ideas. | |
| Often involves looking at and analyzing existing studies. Applies known theories to new situations. | Involves collecting and analyzing new data. Your research should explore new areas and produce original results. | |
| Guided by a faculty advisor who helps and supports you throughout. The process is generally more structured. | Supervised by a committee of experts who offer advice, but you work more independently. Requires a high level of self-direction. | |
| Includes a title page, abstract, introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, conclusion, references, and sometimes appendices. | Also includes a title page, abstract, introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, conclusion, references, and detailed appendices. It’s more extensive. | |
| It may include a final presentation or defense, but it’s usually less formal. | Requires a formal defense where you present and explain your research findings in detail to a committee. | |
| In some places, “thesis” might be used for both master’s and doctoral research, or it might be used like a “dissertation.” | In many places, “dissertation” is specifically for doctoral research, while “thesis” is used for master’s research. |
Dissertation vs Thesis: What’s the Difference in the USA?
In the U.S., “dissertation” and “thesis” refer to different research projects needed for various degrees. Here’s a straightforward comparison:
1. Degree Level
- Thesis : Required for a master’s degree. It’s a big research project that shows you understand your field and can work on your own.
- Dissertation : Needed for a Ph.D. or other doctoral degrees. It’s a more detailed and original research project that should make a significant impact in your field.
2. Purpose and Scope
- Thesis : You need to research and apply what you’ve learned to a specific topic. This usually means looking at existing studies and answering a focused question.
- Dissertation : You must create new knowledge or insights. This involves original research that brings new findings or challenges current ideas. It’s more extensive and detailed.
3. Length and Complexity
- Thesis : Usually 50 to 100 pages long. It’s detailed but not as complex, focusing on a narrower topic.
- Dissertation : Often over 200 pages long. It’s more complex and covers a broader and deeper topic.
4. Research Contribution
- Thesis : This involves analyzing existing research or theories. It doesn’t need to be groundbreaking but should demonstrate strong research skills.
- Dissertation : Requires original research that adds new knowledge. This might mean collecting new data or developing new theories.
5. Supervision and Guidance
- Thesis : You work closely with an advisor who provides regular feedback and helps you stay on track. The process is more structured and involves frequent check-ins.
- Dissertation : You’re guided by a committee of experts. You work more independently, with less frequent but more intensive feedback.
- Thesis : Include a simpler presentation or review. It’s generally less formal compared to a dissertation defense.
- Dissertation : Requires a formal defense where you present your research in detail and answer questions from a committee.
7. Approval Process
- Thesis : Needs to be reviewed and approved by your advisor and sometimes a committee, depending on your school’s rules.
- Dissertation : Must be approved by a committee of faculty members and undergo a more thorough review process before you get your doctoral degree.
In short, a thesis is a major project for a master’s degree, showing your ability to research a specific topic. A dissertation is a larger, original research project for a doctoral degree aimed at contributing new knowledge to your field.
Misconceptions About Thesis and Dissertation
There are several common myths about theses and dissertations that need to be clarified. Here’s a simple explanation of what’s true and what’s not:
1. Thesis and Dissertation Are the Same
Truth : A thesis and a dissertation are different. A thesis is for a master’s degree and involves research on a specific topic. A dissertation is for a Ph.D. and requires original research that should make a big impact in your field.
2. A Thesis Is Less Important Than a Dissertation
Truth : Both are important but for different reasons. A thesis shows you can do research at the master’s level, while a dissertation shows you can make a significant contribution at the doctoral level. Each is valuable in its way.
3. A Thesis Is Easier Than a Dissertation
Truth : A thesis might be shorter and less complex, but it still requires a lot of work. A dissertation is longer and involves more original research, but both need a lot of effort and dedication.
4. A Thesis Cannot Be Published
Truth : You can publish a thesis. Many students turn their thesis into journal articles or books. The length doesn’t limit its potential; what matters is the quality of the research.
5. Thesis and Dissertation Defenses Are the Same
Truth : Defending a thesis is usually less formal than defending a dissertation. A thesis defense might be a presentation to your advisor or a small committee. In contrast, a dissertation defense is more formal, with a detailed presentation and lots of questions from a committee.
6. Writing a Thesis or Dissertation Is a Solo Job
Truth : You don’t do it alone. Advisors or committees provide guidance and feedback. Their input is crucial for producing good research.
7. Only Writing Matters
Truth : Writing is just one part. You also need to do thorough research, analyze data, and review existing studies. The quality of your research is what really counts.
8. Approval Processes Are the Same
Truth : Getting approval for a thesis and a dissertation can be different. A thesis might need approval from your advisor and a small committee, while a dissertation usually requires a more detailed review and a formal defense.
9. Work Is Only Relevant to Academia
Truth : Research from both theses and dissertations can have real-world uses. It can affect industry practices, help with public policy, or solve practical problems, making a difference beyond just academic circles.
Understanding these differences helps you know what to expect and how to approach each type of project. In the Philippines, understanding these distinctions helps students navigate their academic requirements effectively and prepares them for the expectations of their respective degree programs.
Final words
Grasping the difference between a thesis and a dissertation is key to navigating your academic journey, especially in the Philippines. Here’s a straightforward look at each:
A thesis is something you typically write for a master’s degree. It involves researching a specific topic and showing that you can dive deep into it and understand it well. A dissertation, on the other hand, is for a doctoral degree. It’s a much larger project that requires original research and aims to add something new to your field.
Both a thesis and a dissertation require thorough research, lots of writing, and a formal defense. However, a thesis is usually more focused, while a dissertation covers a broader range and aims to make a bigger impact.
Understanding these differences helps you prepare better for either project. Both represent important milestones in your academic and professional growth in the Philippines.
There are lots of students who are searching for the best business dissertation help in the Philippines and many other countries; if you are one of them, feel free to contact our experts now.
FAQs About Thesis and Dissertation
How long are theses compared to dissertations.
A thesis is usually shorter, often between 80 and 120 pages, depending on your field and school requirements. A dissertation is generally much longer, frequently more than 200 pages, because it covers a broader scope and involves deeper research.
Do you need to defend both a thesis and a dissertation?
Yes, both require a defense, but they are different. A thesis defense is usually less formal, where you present your work to a small committee or your advisor. A dissertation defense is more formal and involves a detailed presentation and lots of questions from a committee of experts.
Who helps you with a thesis or dissertation?
For a thesis, you usually work with an advisor or mentor. For a dissertation, you work with a committee of faculty members. Both will guide you, provide feedback, and make sure your research meets academic standards .
Related Posts

Step by Step Guide on The Best Way to Finance Car

The Best Way on How to Get Fund For Business to Grow it Efficiently
Leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Thesis and Purpose Statements
Use the guidelines below to learn the differences between thesis and purpose statements.
In the first stages of writing, thesis or purpose statements are usually rough or ill-formed and are useful primarily as planning tools.
A thesis statement or purpose statement will emerge as you think and write about a topic. The statement can be restricted or clarified and eventually worked into an introduction.
As you revise your paper, try to phrase your thesis or purpose statement in a precise way so that it matches the content and organization of your paper.
Thesis statements
A thesis statement is a sentence that makes an assertion about a topic and predicts how the topic will be developed. It does not simply announce a topic: it says something about the topic.
Good: X has made a significant impact on the teenage population due to its . . . Bad: In this paper, I will discuss X.
A thesis statement makes a promise to the reader about the scope, purpose, and direction of the paper. It summarizes the conclusions that the writer has reached about the topic.
A thesis statement is generally located near the end of the introduction. Sometimes in a long paper, the thesis will be expressed in several sentences or an entire paragraph.
A thesis statement is focused and specific enough to be proven within the boundaries of the paper. Key words (nouns and verbs) should be specific, accurate, and indicative of the range of research, thrust of the argument or analysis, and the organization of supporting information.
Purpose statements
A purpose statement announces the purpose, scope, and direction of the paper. It tells the reader what to expect in a paper and what the specific focus will be.
Common beginnings include:
“This paper examines . . .,” “The aim of this paper is to . . .,” and “The purpose of this essay is to . . .”
A purpose statement makes a promise to the reader about the development of the argument but does not preview the particular conclusions that the writer has drawn.
A purpose statement usually appears toward the end of the introduction. The purpose statement may be expressed in several sentences or even an entire paragraph.
A purpose statement is specific enough to satisfy the requirements of the assignment. Purpose statements are common in research papers in some academic disciplines, while in other disciplines they are considered too blunt or direct. If you are unsure about using a purpose statement, ask your instructor.
This paper will examine the ecological destruction of the Sahel preceding the drought and the causes of this disintegration of the land. The focus will be on the economic, political, and social relationships which brought about the environmental problems in the Sahel.
Sample purpose and thesis statements
The following example combines a purpose statement and a thesis statement (bold).
The goal of this paper is to examine the effects of Chile’s agrarian reform on the lives of rural peasants. The nature of the topic dictates the use of both a chronological and a comparative analysis of peasant lives at various points during the reform period. . . The Chilean reform example provides evidence that land distribution is an essential component of both the improvement of peasant conditions and the development of a democratic society. More extensive and enduring reforms would likely have allowed Chile the opportunity to further expand these horizons.
For more tips about writing thesis statements, take a look at our new handout on Developing a Thesis Statement.

Writing Process and Structure
This is an accordion element with a series of buttons that open and close related content panels.
Getting Started with Your Paper
Interpreting Writing Assignments from Your Courses
Generating Ideas for Your Paper
Creating an Argument
Thesis vs. Purpose Statements
Developing a Thesis Statement
Architecture of Arguments
Working with Sources
Quoting and Paraphrasing Sources
Using Literary Quotations
Citing Sources in Your Paper
Drafting Your Paper
Introductions
Paragraphing
Developing Strategic Transitions
Conclusions
Revising Your Paper
Peer Reviews
Reverse Outlines
Revising an Argumentative Paper
Revision Strategies for Longer Projects
Finishing Your Paper
Twelve Common Errors: An Editing Checklist
How to Proofread your Paper
Writing Collaboratively
Collaborative and Group Writing

Hypothesis vs. Theory: Understanding the Differences
“Hypothesis” and “theory” are two terms often used in science, but they have different meanings. Understanding the distinction between these two words can help us make sense of scientific explanations. In this article, we will explore the differences between “hypothesis” and “theory” in a way that is easy to understand. By the end, you’ll have a clearer grasp of these concepts and be able to use them confidently in scientific discussions.
Hypothesis vs. Theory
- A hypothesis is a preliminary assumption to be tested.
- A theory is a well-supported explanation for a broad range of phenomena.

Hypothesis vs. Theory: The Definition
What does hypothesis mean.
A hypothesis is a proposed explanation for a phenomenon or a scientific question that can be tested through experimentation or observation. It is an essential part of the scientific method, which involves formulating a hypothesis, conducting experiments to test it, and analyzing the results to draw conclusions.
In scientific research, a hypothesis serves as a tentative solution to a problem or a preliminary explanation for an observed phenomenon. It is based on existing knowledge and is formulated to be tested and potentially refuted through empirical evidence. A well-constructed hypothesis is specific, testable, and falsifiable, meaning that it can be proven false through experimentation or observation.
- Example of a hypothesis : “If a person consumes more vitamin C, then their immune system will be stronger and they will have a lower likelihood of catching a cold.”
What Does Theory Mean?
A theory is a well-substantiated explanation of some aspect of the natural world that is based on a body of evidence, observations, and experimentation. In the scientific context, a theory is more than just a guess or a hypothesis; it is a comprehensive framework that has been rigorously tested and supported by a substantial amount of empirical data.
Scientific theories are developed through the scientific method, which involves formulating hypotheses, conducting experiments, and analyzing the results. As evidence accumulates and supports a particular explanation, it may be elevated to the status of a theory. Importantly, scientific theories are not static or unchangeable; they are subject to modification or even rejection in light of new evidence or more comprehensive explanations.
- Example of a theory: The theory of evolution, which explains how species change over time through the process of natural selection.
Hypothesis vs. Theory: Usage
You employ hypotheses during the early stages of research to develop experiments. For instance, you might hypothesize that a plant given more sunlight will grow faster.
A theory , like the Theory of Evolution, summarizes a group of tested hypotheses and facts to explain a complex set of patterns and behaviors.
For a better understanding of the differences between the two terms, let’s take a look at the table below:
| Feature | Hypothesis | Theory |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A proposed explanation for a phenomenon | Well-substantiated explanation of some aspect |
| Basis | Based on limited evidence and observations | Based on extensive research and evidence |
| Testability | Can be tested through experiments and research | Has been extensively tested and supported |
| Scope | Narrow in scope, specific to a particular phenomenon | Broader in scope, applicable to multiple phenomena |
| Status | Preliminary and subject to change | Established and widely accepted in the scientific community |
Tips to Remember the Differences
- Think of a hypothesis as a “hunch” to be tested.
- View a theory as a “tapestry” of well-tested ideas.
- Use the phrase “hypothesis for testing” and “theory for explaining” to keep them distinct in your mind.
Hypothesis vs. Theory: Examples
Example sentences using hypothesis.
- She formulated a hypothesis to explain the observed pattern in the data.
- The researchers tested their hypothesis through a series of carefully controlled experiments.
- The hypothesis proposed by the scientist led to a new understanding of the chemical reaction.
- It is essential to develop a clear and testable hypothesis before conducting the research.
- The hypothesis was supported by the experimental results, providing valuable insights into the phenomenon.
Example Sentences Using Theory
- Einstein ‘s theory of relativity has fundamentally altered our understanding of space and time.
- Darwin’s theory of natural selection provides a framework for understanding the evolution of species.
- The germ theory of disease is fundamental in developing medical hygiene practices.
- The Big Bang theory is widely accepted as the leading explanation for the origin of the universe.
- The kinetic molecular theory explains the behavior of gases, including their volume and temperature relationships.
Related Confused Words
Hypothesis vs thesis.
A hypothesis is a specific, testable prediction that is proposed before conducting a research study, while a thesis is a statement or theory put forward to be maintained or proved. In essence, a hypothesis is a tentative assumption made in order to draw out and test its logical or empirical consequences, while a thesis is a proposition that is maintained by argument.
Both play distinct roles in the scientific and academic realms, with hypotheses guiding research and theses forming the central point of an argument or discussion.
Theory vs. Law
The primary difference between a scientific theory and a scientific law lies in their scope and function. A scientific theory is a well-substantiated explanation of some aspect of the natural world that is based on a body of evidence and has undergone rigorous testing and validation. In contrast, a scientific law describes a concise statement or mathematical equation that summarizes a wide variety of observations and experiments, often expressing a fundamental principle of nature.
While a theory provides an overarching framework for understanding a phenomenon, a law describes a specific, observable relationship. Both theory and law are vital components of scientific understanding, with theories offering explanations and laws providing concise descriptions of natural phenomena.
- Ethics vs. Morals
- Latest Posts
- Skillset or Skill Set: Which Is Correct? - March 9, 2024
- Vender or Vendor: What Is The Difference? - February 5, 2024
- Take Effect vs. Take Affect: Which Is Correct? - February 3, 2024

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Key Differences. A theory is a coherent group of tested general propositions, commonly regarded as correct, that can explain phenomena in the natural world. In contrast, a thesis is a long essay or dissertation involving personal research, written by a candidate for a college degree. 10. Theories are often used to predict future occurrences ...
Difference between a Theory and Thesis. A theory is a rational form of abstract perspectives or thinking concerning the results of such thinking or a phenomenon. The process of rational and contemplative thinking is mostly associated with processes such as research or observational study. On the other hand, a thesis is a written piece of ...
Theories are more general and abstract, aiming to provide a framework that can explain a wide range of phenomena within a certain domain. In contrast, a thesis is usually more specific, targeting a particular question or problem and is typically confined to the academic or professional context in which it is presented.
5 mains differences between thesis and hypothesis. Thesis and hypothesis are different in several ways, here are the 5 keys differences between those terms: A thesis is a statement that can be argued, while a hypothesis cannot be argued. A thesis is usually longer than a hypothesis. A thesis is more detailed than a hypothesis.
Revised on April 16, 2024. A thesis is a type of research paper based on your original research. It is usually submitted as the final step of a master's program or a capstone to a bachelor's degree. Writing a thesis can be a daunting experience. Other than a dissertation, it is one of the longest pieces of writing students typically complete.
The primary difference between a dissertation vs thesis is the degree programs that require these projects. Students in a master's degree program will write a thesis, whereas students in a doctoral degree program will complete a dissertation. Another difference between the two projects is that a dissertation usually requires an oral defense ...
From Mathworld: Theorem: "A theorem is a statement that can be demonstrated to be true by accepted mathematical operations and arguments. In general, a theorem is an embodiment of some general principle that makes it part of a larger theory. The process of showing a theorem to be correct is called a proof."
Differences between a dissertation vs thesis. The main difference between a dissertation and thesis is the scope of the research. A dissertation develops unique and original concepts in a particular field of research, whereas a thesis is usually a culmination of existing research. The main purpose of a writing a dissertation is to add new ...
Thesis. Your thesis is the central claim in your essay—your main insight or idea about your source or topic. Your thesis should appear early in an academic essay, followed by a logically constructed argument that supports this central claim. A strong thesis is arguable, which means a thoughtful reader could disagree with it and therefore ...
A thesis is an in-depth research study that identifies a particular topic of inquiry and presents a clear argument or perspective about that topic using evidence and logic. Writing a thesis showcases your ability of critical thinking, gathering evidence, and making a compelling argument. Integral to these competencies is thorough research ...
A hypothesis is an assumption made before any research has been done. It is formed so that it can be tested to see if it might be true. A theory is a principle formed to explain the things already shown in data. Because of the rigors of experiment and control, it is much more likely that a theory will be true than a hypothesis.
Theoretical Framework Example for a Thesis or Dissertation. Published on October 14, 2015 by Sarah Vinz. Revised on July 18, 2023 by Tegan George. Your theoretical framework defines the key concepts in your research, suggests relationships between them, and discusses relevant theories based on your literature review.
Dissertations and theses (the plural of thesis) are often confused because they're both lengthy research papers written for higher education. In American English, a dissertation is written to earn a doctorate whereas a thesis is written to earn a master's (or sometimes a bachelor's). In many informal situations, however, the terms ...
Level Up Your Team. See why leading organizations rely on MasterClass for learning & development. Though you may hear the terms "theory" and "hypothesis" used interchangeably, these two scientific terms have drastically different meanings in the world of science.
How to use each. Although theory in terms of science is used to express something based on extensive research and experimentation, typically in everyday life, theory is used more casually to express an educated guess. So in casual language, theory and hypothesis are more likely to be used interchangeably to express an idea or speculation.
PhD candidates must present a new theory or hypothesis. Alternatively, they must present their research to question (or disprove) the existing accepted theory on their chosen subject. ... One of the primary differences between thesis and dissertation papers is their length. While a thesis might be anywhere from 40 to 80 pages long, a ...
What is the difference between a thesis & a hypothesis? B oth the hypothesis statement and the thesis statement answer the research question of the study. When the statement is one that can be proved or disproved, it is an hypothesis statement. If, instead, the statement specifically shows the intentions/objectives/position of the researcher ...
A thesis is a statement that is put forward as a premise to be maintained or proved. The main difference between thesis and hypothesis is that thesis is found in all research studies whereas a hypothesis is mainly found in experimental quantitative research studies. This article explains, 1. What is a Thesis? - Definition, Features, Function. 2.
The hypothesis can help defend, support, explain or disprove, argue against the thesis statement.Usually the hypothesis measures specific issues or variables-two or more and therefore should be testable. The thesis statement creates a background while the hypothesis creates a means to measure the interrelationship.
In science a 'thesis' is a proposition for a theory, which may turn out true or false. A 'theory' is the system of knowledge, laws, and evidence in a particular field or about the question under consideration. For example, in the field of inheritance and evolution, Jean-Baptiste Lamarck's thesis was that adults pass traits to their offspring ...
1. Degree Level. Thesis: Required for a master's degree.It's a big research project that shows you understand your field and can work on your own. Dissertation: Needed for a Ph.D. or other doctoral degrees.It's a more detailed and original research project that should make a significant impact in your field.
A thesis statement or purpose statement will emerge as you think and write about a topic. The statement can be… Use the guidelines below to learn the differences between thesis and purpose statements In the first stages of writing, thesis or purpose statements are usually rough or ill-formed and are useful primarily as planning tools.
Hypothesis vs Thesis. A hypothesis is a specific, testable prediction that is proposed before conducting a research study, while a thesis is a statement or theory put forward to be maintained or proved. ... Theory vs. Law. The primary difference between a scientific theory and a scientific law lies in their scope and function. A scientific ...
Reply. Award. themaskedugly. • 7 yr. ago. The lay difference between hypothesis and theory is the amount of evidence supporting them; a hypothesis requires limited or no evidence, and is effectively a 'guess'. A theory is a broad framework that ties together a range of evidence. 2.