Open Access is an initiative that aims to make scientific research freely available to all. To date our community has made over 100 million downloads. It’s based on principles of collaboration, unobstructed discovery, and, most importantly, scientific progression. As PhD students, we found it difficult to access the research we needed, so we decided to create a new Open Access publisher that levels the playing field for scientists across the world. How? By making research easy to access, and puts the academic needs of the researchers before the business interests of publishers.
We are a community of more than 103,000 authors and editors from 3,291 institutions spanning 160 countries, including Nobel Prize winners and some of the world’s most-cited researchers. Publishing on IntechOpen allows authors to earn citations and find new collaborators, meaning more people see your work not only from your own field of study, but from other related fields too.
Brief introduction to this section that descibes Open Access especially from an IntechOpen perspective
Want to get in touch? Contact our London head office or media team here
Our team is growing all the time, so we’re always on the lookout for smart people who want to help us reshape the world of scientific publishing.
Home > Books > Trade and Global Market

Corruption, Causes and Consequences
Submitted: 12 November 2017 Reviewed: 06 December 2017 Published: 21 February 2018
DOI: 10.5772/intechopen.72953
Cite this chapter
There are two ways to cite this chapter:
From the Edited Volume
Trade and Global Market
Edited by Vito Bobek
To purchase hard copies of this book, please contact the representative in India: CBS Publishers & Distributors Pvt. Ltd. www.cbspd.com | [email protected]
Chapter metrics overview
29,389 Chapter Downloads
Impact of this chapter
Total Chapter Downloads on intechopen.com
Total Chapter Views on intechopen.com
Overall attention for this chapters
Corruption is a constant in the society and occurs in all civilizations; however, it has only been in the past 20 years that this phenomenon has begun being seriously explored. It has many different shapes as well as many various effects, both on the economy and the society at large. Among the most common causes of corruption are the political and economic environment, professional ethics and morality and, of course, habits, customs, tradition and demography. Its effects on the economy (and also on the wider society) are well researched, yet still not completely. Corruption thus inhibits economic growth and affects business operations, employment and investments. It also reduces tax revenue and the effectiveness of various financial assistance programs. The wider society is influenced by a high degree of corruption in terms of lowering of trust in the law and the rule of law, education and consequently the quality of life (access to infrastructure, health care). There also does not exist an unambiguous answer as to how to deal with corruption. Something that works in one country or in one region will not necessarily be successful in another. This chapter tries to answer at least a few questions about corruption and the causes for it, its consequences and how to deal with it successfully.
- economic growth
- rule of law
Author Information
Štefan šumah *.
- FKPV Celje, Slovenia
*Address all correspondence to: [email protected]
1. Introduction
The word corruption is derived from the Latin word “corruptus,” which means “corrupted” and, in legal terms, the abuse of a trusted position in one of the branches of power (executive, legislative and judicial) or in political or other organizations with the intention of obtaining material benefit which is not legally justified for itself or for others.
Corruption was referred to as a great sin already in the Bible: “Do not accept a bribe, for a bribe blinds those who see and twist the words of the innocent.” However, the history of corruption is in fact related to the beginning of the creation of law and the state and was already in the antiquity considered an evil, which negatively affects the public administration and the functioning of the political system. The earliest records of corruption date back to the thirteenth century BC, to the time of the Assyrian civilization. From the found plates, written in cuneiform, the archeologists managed to discern how and who accepted bribes. Under the Roman law, the criminal offense of corruption was defined as giving, receiving or claiming benefits in order to influence an official in connection with his work. Due to the prevalence of corruption in the country, this law was supplemented by a new law, which predicted compensation for damage in double value of the damage, and the loss of political rights for the perpetrator of the corruptive act. However, this did not help alleviate corruption, especially due to the fact that corruption was most practiced by the members of the Senate and senior state officials, both in Rome itself and in the remote Roman provinces. The early Christian faith condemned corruption, yet corruption later also developed greatly in ecclesiastical structures, and achieved its peak with the selling of indulgences in the Middle Ages, all until the condemnation of the latter (as well as of other immoral acts of the clergy, with the Pope at the head) by Martin Luther. Apart from the condemnation of corruption, the Reformation also led to a break with until then dominant Catholic culture and the emergence of Protestant ethics.
As a child (he was a hostage at the Ravenna court), Attila 1 noticed a high level of corruption among the state officials of the Western Roman Empire and how they appropriated the state money (as a consequence, there was less money in the Treasury and therefore the taxes increased). He thus decided that if he would ever to rule, he would do so fairly and by oppressing the corruption in his own country. The early feudalism was familiar with various laws that punished the bribing of courts also with death. Later, when the developed feudalism again turned to the Roman law, a number of laws (Dušan’s Code, Mirror of the Swabians) discussed the abuse of position. Then, in late Feudalism, countries became virtually helpless in the fight against corruption, as illustrated by the case of France, which in 1716 established a special court in which should rule in cases of abuse of royal finances; however, these abuses (embezzlement, extortion, bribery, scams, etc.) were so extensive that the court was abolished and a general amnesty introduced in 1717 made some forms of corruption quite a tradition. The corruption was also widespread during the time of the Spanish Inquisition, where the victim of the accusation could make amends with money, which made the corruption, especially among the inquisitors, extensive.
Throughout the history, many intellectuals dealt with corruption or theorized about it one way or another. Machiavelli 2 had a low opinion on republics, considering them even more corrupt than other regimes, and according to him, corruption leads to moral degradation, bad education and bad faith. On the other hand, however, the great philosopher, diplomat and lawyer Sir Francis Bacon 3 was known both for receiving bribes and taking them. When he reached the highest judicial position in England, he was caught in as many as 28 cases of accepting a bribe and defended himself before the parliament by saying that he usually accepted a bribe from both parties involved and that the dirty money therefore did not affect his decisions. The parliament did not accept these arguments and sent him to the jail where he spent only a few days as he was able to bribe the judge.
Thus, although the corruption has been occurring in society ever since, it has only been given more attention in the recent period—the researches on the phenomenon and its negative impacts have become more common after 1995, when countries and international institutions began to be aware of this problem. The attitude of the public toward corruption was, until then, neutral. In 1998, Kaufmann and Gray [ 1 ] found that:
Bribery is widespread, especially in the developing and transition countries; there are, however, significant differences between and within regions.
Bribery increases transaction costs and creates insecurity in the economy.
Bribery usually leads to ineffective economic results, in the long term impedes foreign and domestic investments, reallocates talents due to income and distorts sectorial priorities and technology choices (for example, it creates incentives for contracting major defense projects or unnecessary infrastructure projects, but does not encourage investments in rural specialist health clinics or in preventive health care). This pushes companies into the “underground” (outside the formal sector), weakens the state’s ability to increase revenue and leads to ever-increasing tax rates (as too little tax is taken), which is levied on less and less taxpayers, consequently diminishing the state’s ability to provide enough public goods, including the rule of law.
Bribery is unfair, as it imposes a regressive tax, which heavily burdens in particular commercial and service activities performed by small businesses.
Corruption destroys the legitimacy of the state.
Many other researchers and institutions (the World Bank Institute—WBI, the European Commission, the United Nations, the EBRD) have investigated corruption and its impact on macroeconomic and microeconomic indicators through various forms of corruption, as well as its connection with local customs and habits, and how it affects the everyday lives of people. Most studies are therefore mainly the analyses of the effects of corruption on various economic indicators, such as GDP growth, investments, employment, tax revenues and foreign investments [ 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 ], or the study of various forms of corruption in relation to politics and the economic environment [ 6 ], the research of its social condition and various manifestations [ 7 , 8 ]. Dobovšek [ 9 ] agrees with the negative effects, i.e. high economic, political and social costs, and adds that corruption is not a weakness of people but of institutions (supervisory and other), as they should be the ones to obstruct the greed and temptation of individuals within them.
2. Causes of corruption
Although corruption differs from country to country, it is possible to identify some of the key common driving forces that generate it. What is common to all countries, which are among the most corrupt, has been identified by Svensson [ 10 ]; all of them are developing countries or countries in transition,
with rare exceptions, low-income countries,
most countries have a closed economy,
the influence of religion is visible (Protestant countries have far the lowest level of corruption),
low media freedom and
a relatively low level of education.
Regardless of the above, corruption cannot be assessed unambiguously, since there is never only one phenomenon that is responsible for the occurrence and the development of it; corruption always arises from an array of several, interrelated factors, which can differ considerably from one another. Among the most commonly mentioned factors that influence the development of corruption are: political and economic environment, professional ethics and legislation, as well as purely ethnological factors, such as customs, habits and traditions.
2.1. Political and economic environment
The phenomenon of corruption is strongly influenced by the political and economic environment. The more is the economic activity in the country regulated and limited, the higher the authority and the power of officials in decision making and the greater the possibility of corruption, since individuals are willing to pay or offer payment in order to avoid restrictions. A great potential for corruption is especially there where the officials are under the regulation given the opportunity to decide on the basis of discretion.
The level of corruption is also affected by the monetary policy. Goel and Nelson [ 11 ] in their research found a strong link between monetary policy and corruptive activity in the States. The States that have a well-regulated financial sector, not a lot of informal economy or black market are also less corrupt than those where the opposite is true. They also find that there is less corruption in the countries with higher economic and political freedom.
Dimant [ 12 ] puts it well in his claim that the level of efficiency of public administration determines the extent to which corruption can find fertile soil and sprout. Such efficiency is determined by the quality of the regulations and permits, since ineffective and unclear regulations help to increase the level of corruption in at least two different ways:
The artificially created monopoly of power that enables civil servants to obtain bribes is based on their superior position and embedded in the system.
On the other hand, however, ineffective and unclear regulations cause inhibition and therefore encourage natural persons to pay bribes in order to speed up the bureaucratic procedure.
Corruption is also strongly influenced by the low salaries of public administration employees (state officials), who are therefore trying to improve their financial position by receiving bribes, and consequently, the socio-economic situation of the government officials also affects the phenomenon of corruption. This is demonstrated also by Allen et al. [ 13 ] in their study where they find that corruption arises because agencies, institutions and the government can no longer control corruption effectively due to underpaid officials, which is a problem especially in the developing countries, where they do not have the sufficient tax revenue to properly reward the local officials. However, low wages are not the only cause of corruption; the poor state of the public administration, which is a consequence of political “overcrowding” 4 of officials, due to which loyalty usually prevails over professional standards, also strongly affects the corruption. As an important factor influencing corruption, some authors also indicate satisfaction with the work done by officials—the more they are dissatisfied with their work or place of work, the higher the degree of corruption, which is confirmed by Sardžoska and Tang [ 14 ] in their studies. The mentioned authors find that the private sector has higher ethical values, in particular those that affect satisfaction with work, than the public sector and is therefore less unethical (especially regarding thefts and corruption). Indirectly, Svenson [ 10 ] also affirms this and states that in principle, the salary level of civil servants affects the receipt of a bribe (the higher it is, the smaller the chance that the person will act corruptly). However, he continues on that a higher salary also strengthens the negotiating power of the official, which leads to higher bribes and he also states that, on the basis of existing research, it is very difficult to determine whether a higher salary causes less corruption, which means that the level of salary is not a decisive factor, but merely one of many.
The economy is unfortunately largely dependent on politics and often reflects the rule of law; various options for eliminating competition are exploited, and bribery is just one of the possible weapons in the struggle to gain a job. At the same time is the mentality of the economy sometimes: “The cost of a bribe is only a substantial business cost, an integral part of the contract,” or “Even if we stop the bribery, our rivals will not, so we must bribe in order to remain competitive, “or” bribery and misleading behaviour are not really crimes, they are just part of the old business practice. They are part of the game and everyone does it.” On the other hand is the point sometimes simply the “lubricating” of the bureaucratic wheel by the private sector to do certain things faster or easier.
The political influence of corruption is also manifested through the proverb: examples are attractive! If the top of the politics (government, parties and leading politicians) is corrupt, then corruption shows at all levels, and this evil at the same time spreads among the ordinary population, as nobody trusts the institutions or the rule of law. Johnston [ 15 ] thus points out useful thinking in terms of two types of equilibrium—the balance between the openness and the autonomy of the institutions and elites it leads and the balance between political and economic power and opportunities for cooperation. Ideally, the institutions should be open to influences and feedback from different sources, yet at the same time sufficiently independent to effectively carry out their work. Where the openness and independence of the institutions are in balance, the officials are accessible, but not excessively exposed to private influences; if they can make authoritative decisions, while not using their power to arbitrate, the corruption is relatively low. But where the official power is poorly institutionalized, too exposed to private influence, and the officials’ independence is reflected in excessive exploitation of their power—they can do as they please—the possibility for extreme corruption is again high.
2.2. Professional ethics and legislation
Lack of professional ethics and deficient laws regulating corruption as a criminal offense, and the prosecution and sanctioning of it are also an important cause for the emergence and spread of corruption. A great influence comes also from the ineffective sanctioning of corruption, which only increases the possibility of continuing the corruptive actions of those involved, creating at the same time a strong likelihood that others will join in the corruption due to this inefficient sanctioning.
The sole lack of professional ethics is a particular issue, as the administration requires different amounts of time to develop or change its ethics and professional standards, which is well known in transition countries (in some, ethics and professional standards changed overnight and approached the equivalents in the developed democracies, and in some, they remained the same as in socialism). It is precisely in the transition countries that the “softer” acts of corruption are often considered to be acceptable and justifiable. Therefore, due to lack of professional ethics in some countries that otherwise manage illegal corruption well, there is nevertheless a widespread form of legal corruption.
Corruption also generates a lack of transparency and a lack of control by supervisory institutions. Therefore, where there is insufficient legal basis or sufficient political will to control, which enables a non-transparent functioning of both politics and the economy, corruption flourishes. Corruption is also affected by the extensive, non-transparent or incomplete legislation, where laws can be interpreted in different ways (for the benefit of the one who pays).
2.3. Habits, customs, tradition and demography
Different countries have different attitudes to corruption. In Europe alone, we can find two extremes; from completely corruption intolerant North to the warm South, where corruption is an almost normal, socially acceptable phenomenon. Or the difference between countries with a democratic past, which traditionally prosecute corruption, and former socialist countries, where the corruption in the state apparatus was a part of folklore tradition. Then, there are also different customs; in some cases, a “thank you” in the form of a gift for a service (for which this person has already been paid with a salary) is an expression of courtesy, and elsewhere it is considered corruption. Everything is only a matter of ethics and morality; however, they can be very different in different areas and different countries.
Some forms of corruption also relate to an informal form of social security, where the family or the immediate community takes care of its members. Such forms of informal social security prevail in less developed countries, where there is no legal regulation of formal social security and in the countries of Southern Europe where the influence of the broader family (patriarchate 5 ) is still very strong, like for example in Italy, Greece, Albania, Bosnia, etc. These countries are known for nepotism, cronyism and patronage, since the family as well as the wider community provide social security. The family or community takes care of their members, who, in return, must be loyal and in a way also repay the benefits they receive from it. The same is true of faith. While the southern, predominantly Catholic, very hierarchically organized part of Europe, encourages the cult of the family (also joint and several community) and several liability, the northern, mainly Protestant part, emphasizes individualism and individual responsibility (which means less forms of corruption). The corruption also prospers better in countries where Islam and Orthodoxy are the main religion. The influence of the dominant religion in the country is thus important.
The influence of majority Protestantism has been tested several times and has proven to be an important factor for the low level of corruption in a country. However, the relationship between Protestantism and good governance is probably rooted more in history than in today’s practice. Today, there are many nominally Protestant countries that are de facto secular, while also many non-Protestant countries fight effectively against corruption. Thus, the influence of Protestantism appears to emerge from its egalitarian ethos, which could indirectly function as a support to the general orientation toward ethical universalism, literacy and the promotion of individualism. Its role is therefore important, as it at certain stages of the development explains why the first countries that were well managed were predominantly Protestant. This does not mean that other religious traditions are incompatible with good governance, but only that they have not succeeded in compiling this particular array of factors at the right moment [ 16 ].
Similarly, the research by North et al. [ 17 ] showed that, according to the authors, the least corrupt countries or those countries where the rule of law is the strongest were predominantly Protestant in 1900 and those who are most corrupt were predominantly Orthodox in the same year. The results of their research have shown that there is a link between religion and corruption on one hand, and respect for the rule of law on the other, but not that the link is causative. The questions therefore arise: Why do some religions respect the rule of law more than others and control corruption? Do the characteristics of a particular religion themselves lead to the results? Are there any differences in religious doctrines, practices or cultures that lead to such results? Are there other links that are not rooted in the religious culture, but are related to religious affiliation?
A study titled Perception of corruption by authors Melgar et al. [ 18 ] tried to find out which groups of people are more likely to pay for corruption. They found that those who think that there is a lot of corruption also perceive it so and are consequently more willing to pay for it (as they think or expect the society to function that way). By using a wide and very heterogeneous set of data and econometrics, it has been shown that the social status and personal characteristics also play an important role in the shaping of corruption perception at the micro level. While divorced women, unemployed persons, persons working in the private sector or the self-employed are considered to be in positive correlation with the perception of corruption (corruption is perceived more and they are more willing to pay bribes), the opposite applies to married persons, full-time employees, people who frequently attend religious ceremonies and people with at least secondary education (they perceive less corruption and are also unwilling to pay). According to the classification of countries, they find that it can be proved that all African and Asian countries are in the upper half of the table, and the same applies to the former socialist countries and most of the East Asian countries. People living in these countries perceive more corruption than others. On the contrary, most European countries and some of the former English colonies show lower perceptions than the average (there are also exceptions) and rank in the lower half, the same as half of the richest countries. They also added that the geographical classification of countries has been strongly correlated with the corruption perception index (CPI), which shows that individual characteristics and social conditions are specific factors that influence the perception of corruption. However, they have also found that better economic results reduce the perception of corruption, while the macroeconomic instability and income inequalities have precisely the opposite effect. With Mahič [ 19 ], we also found a similar influence on the perception of corruption; in the economic crisis (high unemployment and low purchasing power), the perception of corruption is rising.
A very important factor that affects corruption is also demographics. A number of studies have shown that patriarchal society is more prone to corruption. This is confirmed by several researches that actually explore to what extent are men women corrupt. Several earlier, especially econometric contributions to the debate on who is more corrupt, men or women, argued that there is a link between a higher representation of women in government and lower levels of corruption. An influential study of 150 countries in Europe, Africa and Asia by the World Bank [ 20 ] confirmed this and concluded that women are more reliable and less prone to corruption. The subsequent findings were later reinforced by further research. Rivas [ 21 ] also affirms this in his research and notes that, according to the results of the survey, the conclusion could be that women are less corrupt than men and that the increase in the number of women on the labor market and in politics would help fight corruption. Lee and Guven [ 22 ] in the survey: Engaging in corruption—the influence of cultural values and the contagion effects at the micro-level also raised the question of whether men are more corrupt than women. The findings of the research support the thesis that women are less susceptible to corruption than men, especially in cultures that require men to be ambitious, competitive and materially successful, as these factors significantly contribute to unethical behavior. This was surprisingly well shown also in practice [ 23 ] when, due to gender equality, the Peruvian government a decade ago decided to involve more women in the police units. When the 2,500 female police officers were joined as traffic police officers, something unexpected happened; bribery was drastically reduced, and people welcomed the female police officers on the streets.
3. The impact of corruption on the economy
In 1997, Tanzi and Davoodi [ 2 ] conducted a systematic study of the impact of corruption on public finances. Several important findings came to light:
Corruption increases the volume of public investments (at the expense of private investments), as there are many options that allow for public expenditure manipulation and are carried out by high-level officials so as to get bribes (which means that more general government expenditures or a large budget offer more opportunities for corruption).
Corruption redirects the composition of public expenditure from the expenditure necessary for basic functioning and maintenance to expenditure on new equipment.
Corruption tends to pull away the composition of public expenditure from the necessary fixed assets for health and education, as there is less chance of getting commissions than from other, perhaps unnecessary projects.
Corruption reduces the effectiveness of public investments and the infrastructure of a country.
Corruption can reduce tax revenues by compromising the ability of the state administration to collect taxes and fees, although the net effect depends on how the nominal tax and other regulatory burdens were selected by the officials, exposed to corruption.
The influence of corruption on the economy was studied by the same authors [ 3 ] through several factors:
Through the impact of corruption on businesses : The impact of corruption on a business is largely depend on the size of the company. Large companies are better protected in an environment that is prone to corruption, they avoid taxes more easily and their size protects them from petty corruption, while they are often also politically protected, which is why the survival of small (especially start-up companies) and middle-sized companies, regardless of their importance for the growth of the economy and the development, is much more difficult than the survival of large companies.
Through the impact of corruption on investments : Corruption affects (a) total investments, (b) the size and form of investments by foreign direct investors, (c) the size of public investments and (d) the quality of investment decisions and investment projects.
Through the influence of corruption on the allocation of talents : Indirectly, corruption has a negative impact on economic growth through the allocation of talents, since gifted and prospective students are driven, due to the influence of the environment and the situation in the country, for example, to study law rather than engineering, which would add value to the country.
Through the impact of corruption on public spending : Corruption has a negative impact on public spending and has an especially strong impact on education and health. There are also indications of the correlation between corruption and military expenditure, which means that high level of corruption reduces economic growth due to high military expenditure.
Through the impact of corruption on taxes : Because of corruption, less taxes are levied than would otherwise be, as some of the taxes end up in the pockets of corrupt tax officials. There are also frequent tax relieves in the corrupt countries, selective taxes and various progressive taxes; in short, there is much less money than the country could have, and so corruption, through the country’s financial deficit, also affects the economic growth; and conclude the findings on the negative impact (both indirect and direct) of corruption on economic growth.
Smarzynska and Wei [ 5 ] came to similar conclusions regarding the effects of corruption on the size and composition of investments. Corrupt countries are less attractive for investors, and if they do opt for an investment, due to non-transparent bureaucracy, they often enter the market with a joint venture, as they usually understand or control matters of the home country better. The local partner can also help foreign companies with the acquisition of local licenses and permits or can otherwise negotiate with the bureaucratic labyrinths at lower costs. Generally inclined (as investors) to the joint venture in the corrupt countries are especially the US investors; however, even investors from those European countries, which are among the highest ranked on the CPI, quickly adapt to local conditions.
Corruption for various reasons also affects the following:
Employment, because the job does not go to the most suitable or qualified person, but the one who is ready to pay for it or in any other way return the favor.
Also affects total investments [ 24 ].
The size and composition of foreign investments and the size of public investments.
The effectiveness of investment decisions and projects. In the presence of corruption, the investments are smaller, as entrepreneurs are aware that they will have to bribe the officials or even give them a profit share for a successful implementation of a business. Due to these increased costs, the entrepreneurs are not interested in investing.
Wei [ 25 ] even made a projection which predicted that in the case of reduction in corruption in Bangladesh to the level of corruption in Singapore, the growth rate of GDP per capita would increase by 1.8% per year between 1960 and 1985 (assuming that the actual average annual growth rate was 4% per year), and the average per capita income could have been more than 50% higher, whereas the Philippines could, if its level of corruption was reduced to that of Singapore (if everything remained unchanged), have raised their investments in relation to GDP by as much as 6.6%, which means a significant increase in the investments. At the same time, he notes that in order to reduce the corruption to the level of Singapore in the countries that he compared (India, Kenya, Sri Lanka, Turkey, Colombia, Mexico and Ghana), the State should raise the salaries of officials by 400—900%. He therefore asks himself whether this would even be possible. However, he notes that in the event of a large increase in salaries, a new form of corruption would likely arise when everyone would be prepared to pay a bribe for a well-paid official job.
Corruption often reduces the effectiveness of various financial assistance programs (both state and international), as money is “lost somewhere along the way” and does not reach those that need it or for whom it is intended, as the financial benefits, deriving from corruption, are not taxable because they are hidden. The state is thus also losing part of the income from the taxes due to corruption, while the public spending, resulting from corruption (or narrow private interests) leads to negative effects on the budget.
The European Commission in its report found that corruption is costing the European economy about 120 billion a year, and according to the European Commissioner for Home Affairs, Cecilia Malstotröm, the corruption in Europe is most present in public procurement, financing of political parties and health care [ 26 ].
The United Nations estimate that the cost of corruption in Afghanistan amounted to about $ 3.9 billion in 2012. According to Transparency International, the former leader of Indonesia, Suharto, embezzled between $ 15 and $ 35 billion, whereas the embezzlements of Mobutu in Zaire, Ferdinand Marcos in the Philippines and Abacha in Nigeria are estimated to amount to $ 5 billion [ 27 ]. However, the World Bank survey shows that $ 1 billion in bribes, both in rich and developing countries, is paid annually [ 28 ], which means that even the developed countries are not immune to corruption (but in a different form) and that the political corruption is especially present in large infrastructure projects. Bađun [ 29 ] on the example of Croatia gives conclusions, which are valid for all post-communist countries.
Impact on enterprises: A survey conducted by the EBRD and the World Bank shows that bribes paid in smaller companies account for 5% of their annual profits and in medium-sized companies 4% of their annual profits. However, both are, compared to large companies, where bribes comprise less than 3%, in a much worse position, which shows how bribes are causing problems or are putting these smaller companies into a subordinate position compared to the large ones, which in turn leads to the collapse of these.
Also interesting is the study of the Shadow Economy in Highly Developed OECD Countries where Schneider and Buehn [ 30 ] also find the link between the low quality of institutions that are the holders of the rule of law (or degree of corruption) and the shadow economy, and therefore, the weaker the “law” is, the higher the degree of corruption and of shadow economy. In the study Corruption and the Shadow Economy [ 31 ], the same authors explore the relationship between the degree of corruption and the emergence of the shadow economy, and their findings are that the high level of shadow economy and the high degree of corruption are strongly linked to one another. One of the hypotheses in this survey (which has been confirmed) is also: the higher the degree of corruption, the lower the economic development measured by GDP per capita. The authors detected a positive correlation; corruption thus affects the economic development.
However, the extended practice of finding annuity outside the logic of the market and competition can therefore lead to a (neo) liberal conclusion that the root of the existence of corruption is in the very existence of the state—especially in excessive, selective and deforming state interventions and subsidies that create fertile soil for the development of corruption. The truth is that the devastating combination consists of widespread state intervention and subsidies in the simultaneous absence of a strong institutional framework and detailed rules of the game, including the control of public finances and effective anti-trust legislation and legal practices. On the other hand, however, there is no clear evidence that private monopolies are more effective and less corrupt than the public ones and that privatization, especially long-lasting, gradual and non-transparent one (so-called gradualism), reduces positive developmental and social effects, including the reduction of corruption [ 32 ]. Yet market deregulation, legal and judicial reform and transparent management of public procurement would significantly reduce corruption in many developing countries (as well as in transition countries), at which point the government should play an important role in the shaping of the anti-corruption policy. There should be a strong strengthening of the public procurement institution. The law is admittedly strict about the public procurement, but one of the main reasons for public procurement problems is the lack of a skilled workforce, and public procurement is thus still the breeding ground of corruption. There also exists a proverb “poverty is a curse,” which applies largely to all developing countries, as these are the countries that are most affected by poverty. Poverty destroys all ethical and moral values.
One of the important aspects of the damage to the global economy is also the failure to respect copyright and intellectual property. The more corrupt countries are also inclined to lower respect for the aforementioned, and the economic damage amounts to billions of dollars. Cavazos-Cepeda et al. [ 33 ] found that reforms, legal, fiscal and intellectual incentives to respect copyright and intellectual property patents encourage the society to make itself more innovative and economically more effective; however, they underline the importance of human capital and investment in people as one of the most important factors for reducing the level of corruption in the country.
There are also theories that corruption can act as the lubricant of the economic wheel and at least in some cases has a positive impact on the economic growth. The empirical analysis done by Dreher and Gassebner [ 34 ] on a sample of 43 countries between 2003 and 2005 shows that corruption is even useful, but with some reservations. In particular, they investigated the short-term effects of corruption and found, for example, that in countries where corruption is widespread, more new entrepreneurs enter the market (corruption in the public sector is expected to promote private entrepreneurial activity). They are, however, not necessarily to succeed, as there is a high likelihood that they will go bankrupt due to the rigid regulations that block the activity and because of which bribes are needed. They do acknowledge, on the other hand, that most authors who have been doing research for a longer period of time admit the harmfulness of corruption both for society and the economy. Something similar show the data for some Asian countries, where, unlike their findings (short-term benefit), the high degree of corruption coincides with the long-term economic growth.
Svendson [ 10 ] also notes that, in light of the theoretical literature and various research studies, notwithstanding that these show the negative impact of corruption on the economic growth, but this cannot be said for sure, since there are difficulties in measuring corruption, and at the same time, the question arises whether the econometric models that were made are good enough to capture all the important variables. He also states that corruption appears in many forms and that there is no reason to assume that all types of corruption are equally harmful to the economic growth.
Recent empirical researches also attest to that; while many countries have suffered, as a characteristic consequence of corruption, the decline in economic growth, other countries have had economic growth (in some cases a very positive one) despite corruption. The latter is also to be expected, since corruption has many manifestations and it would be surprising if all types of corrupt practices had the same effect on economic performance. Analyses show that one of the reasons for this is the extent to which the perpetrators of corrupt practices—in this case the bureaucrats—coordinate their behavior. In the absence of an organized corruption network, each bureaucrat collects bribes for himself, while ignoring the negative impact of others’ demands for them. In the presence of such a network, the collective bureaucracy reduces the total value of the bribe, which results in lower bribe payments and higher innovation, and the economic growth is consequently higher in the latter case than in the former case. The interesting question is not so much why is the degree of corruption in poor countries higher than in the rich ones, but rather why the nature of corruption differs between countries. The extent to which corruption is organized is just one aspect of this, but there are other aspects. For example, it is common practice in some countries to pay ex post (as a share of profit, for example) instead of ex ante (in advance, as a bribe) to officials or politicians, so it is assumed that the effects on the economy will be different. The precise reason why corruption should take on one form and not the other is an important issue which has been largely ignored and which could have to do with cultural, social and political reasons, as well as economic circumstances [ 35 ].
In the fight against corruption, a remarkable role was also played by the debt crisis. The die Welt newspaper [ 36 ] mentions the study of the Hertie School of Governance, which shows that Italy, Spain and Portugal have made great strides in the fight against bribery and corruption of their civil servants due to lack of money, which enabled a significantly more transparent and “pure” practice for the award of public procurement. The crisis is supposed to dry up monetary resources and thus reduce the chances of corruption. Also, the crisis has changed the perception of the society, and bad business practices, which were acceptable before the crisis, are acceptable no longer. However, the fight against corruption is often similar to the fight against windmills. The case of India shows how corruption is changing, getting new dimensions, not only in scope, but also in methods. Just as the population in India is growing, so is corruption, and there are always new ways how to cheat both the state and the society. The perception of corruption is increasing year after year. Despite all the anti-corruption moves and anti-corruption initiatives, people do not hesitate to offer or accept a bribe. The bribers are becoming innovative, they adapt to the situation and the innovation of companies in paying bribes and hiding them is also visible. However, just as elsewhere in the world, the negative effects of corruption are the same; it reduces foreign direct and domestic investments, increases inequality and poverty, raises the number of freeloaders (renters, free-riders) in the economy, distorts and exploits public investments and reduces public revenues.
4. Discussion
Corruption is, in fact, a multidirectional process. On one hand, the provider benefits, on the other the recipient, and both are aware of the deed that remains hidden. The third link in the chain is everyone else, the victims. Although not every act of corruption is yet a criminal offense, it is, however, unethical and detrimental to the economic and political development of a society. Usually, there are persons involved with political, economic and decision-making power, and as the philosopher Karl Popper wrote in his book, The Open Society and its Enemies , that the greatest problem is not the question of who should give orders, but how to control the one who gives them. How to organize the political and social institutions in order to prevent the weak and incompetent rulers from doing too much harm? However, as there is no general and unmistakable way of preventing the tyranny or corruptions of the heavyweights, the price of freedom is eternal alertness [ 37 ]. Greediness, ambition, rapacity and immorality have been known to the human society ever since the emergence of civilization and use every tool available to them: kinship, common past, school contacts, common interests, friendship and, of course, political as well as religious ties.
In a study by Šumah et al. [ 38 ], we did an analysis of countries, taking into account their ranking on the Corruption Perception Index published every year by Transparency International, and identified the main factors affecting the level of corruption in a particular group of countries, or rather, we tried to find similarities and differences between individual groups of countries in terms of what affects the level of corruption in these groups. We have established a basic model of three factors (risk, benefit and consciousness) that was created on the basis of the merger of several known, scientifically proven factors that cause or reduce corruption or affect its level in the individual country. According to this degree of corruption, we have identified five groups, classified the countries and analyzed their common characteristics. The findings were as follows:
Corruption is linked to the level of GDP (the higher the GDP, the lower the rate of corruption).
Corruption is related to the level of education (the higher the average level of education, the lower the level of corruption).
Corruption is strongly linked to the geographical location. The highest level is in Asia (mainly in Central Asia), Africa (North and Central Africa) and South America (according to the Transparency International map).
Corruption is strongly linked to the country’s prevailing religion.
Corruption is linked to freedom in the country (personal freedom, freedom of speech, economic freedom, etc.), with respect to the rule of law in a country and inefficiency of public administration, which is often also locally limited or is inherently corrupt.
The lower the country is ranked, the more dominant is the patriarchal society.
Many researchers are still involved in corruption. The findings show that there is a link between corruption and its negative effects, but from most of the studies it is not possible to determine what the cause is and what the consequence. Whether is the level of corruption lower due to high GDP, or is it vice versa, cannot be directly identified, since the corruption depends on economic indicators, while at the same time affecting them [ 39 ]. It is also very difficult to claim that the average low level of education is due to corruption or, conversely, that corruption is a result of low education. Similarly goes for the rule of law and (in)efficiency of public administration. This interdependence will surely continue to be the subject of numerous researches in the future, for the only way to be successful in the fight against corruption is if we know the causes and begin to eliminate them.
Nevertheless, there remains something that needs to be emphasized. Almost all of the studies ignore the fact that the top of the most corrupt countries consists of countries with one of the various forms of armed conflict (civil war, intertribal conflicts, inter-religious wars or some other form of aggression), which means that peace in the country is a prerequisite for a successful fight against corruption. The least corrupt countries are countries that have a lasting peace on their territory (most since the Second World War or even longer), which is confirmed by the above fact. Peace is therefore one of the prerequisites for a successful fight against corruption.
The answer to the question of how to deal with corruption is not unambiguous; some countries have achieved great success in dealing with it in a relatively short time (Singapore, Estonia and Georgia) and some have been struggling for a long time (the most famous example is Italy). The first condition is in any case to ensure freedom (personal freedom, economic freedom, freedom of speech, freedom of the press, etc.) and democracy, and then education and awareness of people. However, at this point, it is not about introducing the Western type democracy, as our culture knows it, for it has often proven that, especially with the help of the army, more harm than benefit was caused. It is necessary to start using good practices of countries that are similar to each other (religion, habits, tradition, ethics and morality) and that have common history.
- 1. Kaufmann D, Gray CW. Corruption and development. Finance & Development. 1998; 35 (1):7
- 2. Tanzi V, Davoodi H. Corruption, public investment, and growth. IMF Working Paper 97/139. Washington: International Monetary Fund; 1997
- 3. Tanzi V, Davoodi HR. Corruption, growth, and public finances. IMF Working Paper. 2000. pp. 1-27. Available on: https://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/wp/2000/wp00182.pdf
- 4. Blažek S. Korupcija in gospodarska rast. V: Inovativnost, proizvodnja in management: Zbornik, 8. Koper. 2011. Available on: http://www.fm-kp.si/zalozba/ISBN/978-961-266-123-6/prispevki/046.pdf
- 5. Smarzynska BK, Wei SJ. Corruption and Composition of Foreign Direct Investment: Firm-Level Evidence. Vol. 7969. Cambridge, MA: National Bureau of Economic Research; 2000
- 6. Johnston M. Syndromes of Corruption: Wealth, Power, and Democracy. Cambridge University Press; 2005. Available on: http://www.untag-md.ac.id/files/Perpustakaan_Digital_1/CORRUPTION%20Syndromes%20of%20Corruption.pdf
- 7. Karklins R. Typology of post-communist corruption. Problems of Post Communism. 2002; 49 (4):22-32
- 8. Kasdin M, Nichols PM, Siedel GJ. Corruption as a pan-cultural phenomenon: An empirical study in countries at opposite ends of the former soviet empire. Texas International Law Journal. 2003; 39 :215
- 9. Dobovšek B, Škrbec J. Korupcija, grožnja slovenski (pravni) državi. Revija za kriminalistiko in kriminologijo. 2012; 63 (1):50-59
- 10. Svensson J. Eight questions about corruption. The Journal of Economic Perspectives. 2005; 19 (3):19-42
- 11. Goel RK, Nelson MA. Economic freedom versus political freedom: Cross-country influences on corruption. Australian Economic Papers. 2005; 44 (2):121-133
- 12. Dimant E. The Antecedents and Effects of Corruption – A Reassessment of Current (Empirical) Findings. 2014. Available from: https://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/60947/1/MPRA_60974.pdf [Accessed: Nov 27, 2016]
- 13. Allen F, Qian J, Shen L. Corruption and Competition. 2015. Available from: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=2685219 [Accessed: Jan 9, 2017]
- 14. Sardžoska EG, Tang TLP. Testing a model of behavioral intentions in the republic of Macedonia: Differences between the private and the public sectors. Journal of Business Ethics. 2009; 87 (4):495-517
- 15. Johnston M. Corruption and democratic consolidation. In: Conference on “Democracy and Corruption”. Princeton University; 2000
- 16. Mungiu-Pippidi A. Controlling corruption through collective action. Journal of Democracy. 2013; 24 (1):101-115
- 17. North CM, Orman WH, Gwin CR. Religion, corruption, and the rule of law. Journal of Money, Credit and Banking. 2013; 45 (5):757-779
- 18. Melgar N, Rossi M, Smith TW. The perception of corruption. International Journal of Public Opinion Research. 2010; 22 (1):120-131
- 19. Šumah Š, Mahić E. Impact on the perception of corruption. IOSR Journal of Humanities and Social Science. 2015; 20 (11):21-29. ISSN: 2279-0845
- 20. Dollar D, Fisman R, Gatti R. Are women really the “fairer” sex? Corruption and women in government. Journal of Economic Behavior & Organization. 2001; 46 (4):423-429
- 21. Rivas MF. An experiment on corruption and gender. Bulletin of Economic Research. 2013; 65 (1):10-42
- 22. Lee WS, Guven C. Engaging in corruption: The influence of cultural values and contagion effects at the microlevel. Journal of Economic Psychology. 2013; 39 :287-300
- 23. Karim S. Madame Officer. 2011. Available from: http://www.americasquarterly.org/node/2802 [Accessed: Dec 3, 2015]
- 24. Bucič M. Vrste korupcije v Sloveniji in možnosti za njihovo preprečevanje. Diplomsko delo. Ljubljana: Ekonomska fakulteta; 2004
- 25. Wei SJ. Corruption in Economic Transition and Development: Grease or Sand? Geneva: United Nations Economic Commission for Europe; 2001
- 26. EU Commission. Report from the Commission to the Council and the European Parliament – EU Anti-corruption Report. 2014. Available from: https://ec.europa.eu/home-affairs/sites/homeaffairs/files/e-library/documents/policies/organized-crime-and-human-trafficking/corruption/docs/acr_2014_en.pdf [Accessed: Mar 17, 2016]
- 27. The Guardian. Suharto, Marcos and Mobutu Head Corruption Table with $50 bn Scams. 2004. Available from: http://www.theguardian.com/world/2004/mar/26/indonesia.philippines [Accessed: Apr 23, 2015]
- 28. The World Bank. The Cost of Corruptions. 2004. Available from: http://go.worldbank.org/LJA29GHA80 [Accessed: Jul 1, 2015]
- 29. Bađun M. The relationship between political corruption and public investment-the case of Croatia. Društvena istraživanja. 2011; 20 (2):295-316
- 30. Schneider F, Buehn A. Shadow Economies in Highly Developed OECD Countries: What are the Driving Forces? 2012. Available from: https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=2161228 [Accessed: Dec 9, 2016]
- 31. Buehn A, Schneider F. Corruption and the shadow economy: Like oil and vinegar, like water and fire? International Tax and Public Finance. 2012; 19 (1):172-194
- 32. Stojiljković Z. Karakter i logika korupcije. 2010. Available from: Media.institut – alternativa.org
- 33. Cavazos-Cepeda RH, Lippoldt DC, Senft J. Policy Complements to the Strengthening of IPRs in Developing Countries (No. 104). OECD Publishing; 2010
- 34. Dreher A, Gassebner M. Greasing the wheels? The impact of regulations and corruption on firm entry. Public Choice. 2013; 155 (3-4):413-432
- 35. Blackburn K, Forgues-Puccio GF. Why is corruption less harmful in some countries than in others?. Journal of Economic Behavior & Organization. 2009; 72 (3):797-810
- 36. Die Welt Euro krise bremst Europaweit. 2013. Available from: http://www.welt.de/wirtschaft/article115079570/Euro-Krise-bremst-europaweit-die-Korruption.html [Accessed: Jun 27, 2015]
- 37. Brioschi CA. Kratka povijest korupcije – Od starov vijeka do naših dana. Zagreb: Mate d.o.o; 2003
- 38. Šumah Š, Mahić E. Dejavniki, ki vplivajo na stopnjo korupcije. Revija za kriminalistiko in kriminologijo. 2017; 68 (3):248-257
- 39. Manzin M, Bavec C, Čurin S. Resiliency to corruption-structural model of causalities and consequences. Journal of Criminal Investigation and Criminology/Ljubljana. 2012; 63 :4
- Attila (406–453) was the great ruler of the Huns, who, as the first, united all the Huns and conquered a considerable part of Europe and Asia. He is also known as the Whip of God.
- The Renaissance political theorist (1469–1527) who was for more than a decade engaged in diplomatic and state affairs in Florence. Modern political philosophy and political science consider him the founder of the realistic approach to the theory of politics.
- An English philosopher, writer, judge and politician (1561–1626). He rejected Aristotle’s view and philosophy and sought to gain the reputation of the experimental science.
- Overcrowding in this context implies replenishment of posts in public administration with members of one party.
- Patriarchate is a social arrangement in which all authority is held by male representatives of the families that make up the community. The right to name, social and political status, as well as the possession and authority over family members is automatically transferred from the father to the firstborn or to the nearest male relative.
© 2018 The Author(s). Licensee IntechOpen. This chapter is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Continue reading from the same book
Published: 03 October 2018
By Oguzhan Ozcelebi
1820 downloads
1837 downloads
By Maumita Choudhury
1436 downloads

5 Essays About Corruption
Internationally, there is no legal definition of corruption, but it includes bribery, illegal profit, abuse of power, embezzlement, and more. Corrupt activities are illegal, so they are discreet and done in secrecy. Depending on how deep the corruption goes, there may be many people aware of what’s going on, but they choose to do nothing because they’ve been bribed or they’re afraid of retaliation. Any system can become corrupt. Here are five essays that explore where corruption exists, its effects, and how it can be addressed.
Learn more about anti-corruption in a free course .
Corruption in Global Health: The Open Secret
Dr. Patricia J. Garcia The Lancet (2019)
In this published lecture, Dr. Garcia uses her experience as a researcher, public health worker, and Minister of Health to draw attention to corruption in health systems. She explores the extent of the problem, its origins, and what’s happening in the present day. Additional topics include ideas on how to address the problem and why players like policymakers and researchers need to think about corruption as a disease. Dr. Garcia states that corruption is one of the most significant barriers to global universal health coverage.
Dr. Garcia is the former Minister of Health of Peru and a leader in global health. She also works as a professor and researcher/trainer in global health, STI/HIV, HPV, medical informatics, and reproductive health. She’s the first Peruvian to be appointed as a member to the United States National Academy of Medicine
‘Are women leaders less corrupt? No, but they shake things up”
Stella Dawson Reuters (2012)
This piece takes a closer look at the idea that more women in power will mean less corruption. Reality is more complicated than that. Women are not less vulnerable to corruption in terms of their resistance to greed, but there is a link between more female politicians and less corruption. The reason appears to be that women are simply more likely to achieve more power in democratic, open systems that are less tolerant of corruption. A better gender balance also means more effective problem-solving. This piece goes on to give some examples of lower corruption in systems with more women and the complexities. While this particular essay is old, newer research still supports that more women in power is linked to better ethics and lower corruption levels into systems, though women are not inherently less corrupt.
Stella Dawson left Reuters in 2015, where she worked as a global editor for economics and markets. At the Thomson Reuters Foundation and 100Reporters, she headed a network of reporters focusing on corruption issues. Dawson has been featured as a commentator for BBC, CNB, C-Span, and public radio.
“Transparency isn’t the solution to corruption – here’s why”
David Riverios Garcia One Young World
Many believe that corruption can be solved with transparency, but in this piece, Garcia explains why that isn’t the case. He writes that governments have exploited new technology (like open data platforms and government-monitoring acts) to appear like they care about corruption, but, in Garcia’s words, “transparency means nothing without accountability.” Garcia focuses on corruption in Latin America, including Paraguay where Garcia is originally from. He describes his background as a young anti-corruption activist, what he’s learned, and what he considers the real solution to corruption.
At the time of this essay’s publication, David Riverios Garcia was an Open Young World Ambassador. He ran a large-scale anti-corruption campaign (reAccion Paraguay), stopping corruption among local high school authorities. He’s also worked on poverty relief and education reform. The Ministry of Education recognized him for his achievements and in 2009, he was selected by the US Department of State as one of 10 Paraguayan Youth Ambassadors.
“What the World Could Teach America About Policing”
Yasmeen Serhan The Atlantic (2020)
The American police system has faced significant challenges with public trust for decades. In 2020, those issues have erupted and the country is at a tipping point. Corruption is rampant through the system. What can be done? In this piece, the author gives examples of how other countries have managed reform. These reforms include first dismantling the existing system, then providing better training. Once that system is off the ground, there needs to be oversight. Looking at other places in the world that have successfully made radical changes is essential for real change in the United States.
Atlantic staff writer Yasmeen Serhan is based in London.
“$2.6 Trillion Is Lost to Corruption Every Year — And It Hurts the Poor the Most”
Joe McCarthy Global Citizen (2018)
This short piece is a good introduction to just how significant the effects of corruption are. Schools, hospitals, and other essential services suffer, while the poorest and most vulnerable society carry the heaviest burdens. Because of corruption, these services don’t get the funding they need. Cycles of corruption erode citizens’ trust in systems and powerful government entities. What can be done to end the cycle?
Joe McCarthy is a staff writer for Global Citizen. He writes about global events and environmental issues.
You may also like

15 Political Issues We Must Address

15 Trusted Charities Fighting for LGBTQ+ Rights

16 Inspiring Civil Rights Leaders You Should Know

15 Trusted Charities Fighting for Housing Rights

15 Examples of Gender Inequality in Everyday Life

11 Approaches to Alleviate World Hunger

15 Facts About Malala Yousafzai

12 Ways Poverty Affects Society

15 Great Charities to Donate to in 2024

15 Quotes Exposing Injustice in Society

14 Trusted Charities Helping Civilians in Palestine

The Great Migration: History, Causes and Facts
About the author, emmaline soken-huberty.
Emmaline Soken-Huberty is a freelance writer based in Portland, Oregon. She started to become interested in human rights while attending college, eventually getting a concentration in human rights and humanitarianism. LGBTQ+ rights, women’s rights, and climate change are of special concern to her. In her spare time, she can be found reading or enjoying Oregon’s natural beauty with her husband and dog.
Doha Declaration
Education for justice.
- Agenda Day 1
- Agenda Day 2
- Agenda Day 3
- Agenda Day 4
- Registration
- Breakout Sessions for Primary and Secondary Level
- Breakout Sessions for Tertiary Level
- E4J Youth Competition
- India - Lockdown Learners
- Chuka, Break the Silence
- The Online Zoo
- I would like a community where ...
- Staying safe online
- Let's be respectful online
- We can all be heroes
- Respect for all
- We all have rights
- A mosaic of differences
- The right thing to do
- Solving ethical dilemmas
- UNODC-UNESCO Guide for Policymakers
- UNODC-UNESCO Handbooks for Teachers
- Justice Accelerators
- Introduction
- Organized Crime
- Trafficking in Persons & Smuggling of Migrants
- Crime Prevention & Criminal Justice Reform
- Crime Prevention, Criminal Justice & SDGs
- UN Congress on Crime Prevention & Criminal Justice
- Commission on Crime Prevention & Criminal Justice
- Conference of the Parties to UNTOC
- Conference of the States Parties to UNCAC
- Rules for Simulating Crime Prevention & Criminal Justice Bodies
- Crime Prevention & Criminal Justice
- Engage with Us
- Contact Us about MUN
- Conferences Supporting E4J
- Cyberstrike
- Play for Integrity
- Running out of Time
- Zorbs Reloaded
- Developing a Rationale for Using the Video
- Previewing the Anti-Corruption Video
- Viewing the Video with a Purpose
- Post-viewing Activities
- Previewing the Firearms Video
- Rationale for Using the Video
- Previewing the Human Trafficking Video
- Previewing the Organized Crime Video
- Previewing the Video
- Criminal Justice & Crime Prevention
- Corruption & Integrity
- Human Trafficking & Migrant Smuggling
- Firearms Trafficking
- Terrorism & Violent Extremism
- Introduction & Learning Outcomes
- Corruption - Baseline Definition
- Effects of Corruption
- Deeper Meanings of Corruption
- Measuring Corruption
- Possible Class Structure
- Core Reading
- Advanced Reading
- Student Assessment
- Additional Teaching Tools
- Guidelines for Stand-Alone Course
- Appendix: How Corruption Affects the SDGs
- What is Governance?
- What is Good Governance?
- Corruption and Bad Governance
- Governance Reforms and Anti-Corruption
- Guidelines for Stand-alone Course
- Corruption and Democracy
- Corruption and Authoritarian Systems
- Hybrid Systems and Syndromes of Corruption
- The Deep Democratization Approach
- Political Parties and Political Finance
- Political Institution-building as a Means to Counter Corruption
- Manifestations and Consequences of Public Sector Corruption
- Causes of Public Sector Corruption
- Theories that Explain Corruption
- Corruption in Public Procurement
- Corruption in State-Owned Enterprises
- Responses to Public Sector Corruption
- Preventing Public Sector Corruption
- Forms & Manifestations of Private Sector Corruption
- Consequences of Private Sector Corruption
- Causes of Private Sector Corruption
- Responses to Private Sector Corruption
- Preventing Private Sector Corruption
- Collective Action & Public-Private Partnerships against Corruption
- Transparency as a Precondition
- Detection Mechanisms - Auditing and Reporting
- Whistle-blowing Systems and Protections
- Investigation of Corruption
- Introduction and Learning Outcomes
- Brief background on the human rights system
- Overview of the corruption-human rights nexus
- Impact of corruption on specific human rights
- Approaches to assessing the corruption-human rights nexus
- Human-rights based approach
- Defining sex, gender and gender mainstreaming
- Gender differences in corruption
- Theories explaining the gender–corruption nexus
- Gendered impacts of corruption
- Anti-corruption and gender mainstreaming
- Manifestations of corruption in education
- Costs of corruption in education
- Causes of corruption in education
- Fighting corruption in education
- Core terms and concepts
- The role of citizens in fighting corruption
- The role, risks and challenges of CSOs fighting corruption
- The role of the media in fighting corruption
- Access to information: a condition for citizen participation
- ICT as a tool for citizen participation in anti-corruption efforts
- Government obligations to ensure citizen participation in anti-corruption efforts
- Teaching Guide
- Brief History of Terrorism
- 19th Century Terrorism
- League of Nations & Terrorism
- United Nations & Terrorism
- Terrorist Victimization
- Exercises & Case Studies
- Radicalization & Violent Extremism
- Preventing & Countering Violent Extremism
- Drivers of Violent Extremism
- International Approaches to PVE &CVE
- Regional & Multilateral Approaches
- Defining Rule of Law
- UN Global Counter-Terrorism Strategy
- International Cooperation & UN CT Strategy
- Legal Sources & UN CT Strategy
- Regional & National Approaches
- International Legal Frameworks
- International Human Rights Law
- International Humanitarian Law
- International Refugee Law
- Current Challenges to International Legal Framework
- Defining Terrorism
- Criminal Justice Responses
- Treaty-based Crimes of Terrorism
- Core International Crimes
- International Courts and Tribunals
- African Region
- Inter-American Region
- Asian Region
- European Region
- Middle East & Gulf Regions
- Core Principles of IHL
- Categorization of Armed Conflict
- Classification of Persons
- IHL, Terrorism & Counter-Terrorism
- Relationship between IHL & intern. human rights law
- Limitations Permitted by Human Rights Law
- Derogation during Public Emergency
- Examples of States of Emergency & Derogations
- International Human Rights Instruments
- Regional Human Rights Instruments
- Extra-territorial Application of Right to Life
- Arbitrary Deprivation of Life
- Death Penalty
- Enforced Disappearances
- Armed Conflict Context
- International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights
- Convention against Torture et al.
- International Legal Framework
- Key Contemporary Issues
- Investigative Phase
- Trial & Sentencing Phase
- Armed Conflict
- Case Studies
- Special Investigative Techniques
- Surveillance & Interception of Communications
- Privacy & Intelligence Gathering in Armed Conflict
- Accountability & Oversight of Intelligence Gathering
- Principle of Non-Discrimination
- Freedom of Religion
- Freedom of Expression
- Freedom of Assembly
- Freedom of Association
- Fundamental Freedoms
- Definition of 'Victim'
- Effects of Terrorism
- Access to Justice
- Recognition of the Victim
- Human Rights Instruments
- Criminal Justice Mechanisms
- Instruments for Victims of Terrorism
- National Approaches
- Key Challenges in Securing Reparation
- Topic 1. Contemporary issues relating to conditions conducive both to the spread of terrorism and the rule of law
- Topic 2. Contemporary issues relating to the right to life
- Topic 3. Contemporary issues relating to foreign terrorist fighters
- Topic 4. Contemporary issues relating to non-discrimination and fundamental freedoms
- Module 16: Linkages between Organized Crime and Terrorism
- Thematic Areas
- Content Breakdown
- Module Adaptation & Design Guidelines
- Teaching Methods
- Acknowledgements
- 1. Introducing United Nations Standards & Norms on CPCJ vis-à-vis International Law
- 2. Scope of United Nations Standards & Norms on CPCJ
- 3. United Nations Standards & Norms on CPCJ in Operation
- 1. Definition of Crime Prevention
- 2. Key Crime Prevention Typologies
- 2. (cont.) Tonry & Farrington’s Typology
- 3. Crime Problem-Solving Approaches
- 4. What Works
- United Nations Entities
- Regional Crime Prevention Councils/Institutions
- Key Clearinghouses
- Systematic Reviews
- 1. Introduction to International Standards & Norms
- 2. Identifying the Need for Legal Aid
- 3. Key Components of the Right of Access to Legal Aid
- 4. Access to Legal Aid for Those with Specific Needs
- 5. Models for Governing, Administering and Funding Legal Aid
- 6. Models for Delivering Legal Aid Services
- 7. Roles and Responsibilities of Legal Aid Providers
- 8. Quality Assurance and Legal Aid Services
- 1. Context for Use of Force by Law Enforcement Officials
- 2. Legal Framework
- 3. General Principles of Use of Force in Law Enforcement
- 4. Use of Firearms
- 5. Use of “Less-Lethal” Weapons
- 6. Protection of Especially Vulnerable Groups
- 7. Use of Force during Assemblies
- 1. Policing in democracies & need for accountability, integrity, oversight
- 2. Key mechanisms & actors in police accountability, oversight
- 3. Crosscutting & contemporary issues in police accountability
- 1. Introducing Aims of Punishment, Imprisonment & Prison Reform
- 2. Current Trends, Challenges & Human Rights
- 3. Towards Humane Prisons & Alternative Sanctions
- 1. Aims and Significance of Alternatives to Imprisonment
- 2. Justifying Punishment in the Community
- 3. Pretrial Alternatives
- 4. Post Trial Alternatives
- 5. Evaluating Alternatives
- 1. Concept, Values and Origin of Restorative Justice
- 2. Overview of Restorative Justice Processes
- 3. How Cost Effective is Restorative Justice?
- 4. Issues in Implementing Restorative Justice
- 1. Gender-Based Discrimination & Women in Conflict with the Law
- 2. Vulnerabilities of Girls in Conflict with the Law
- 3. Discrimination and Violence against LGBTI Individuals
- 4. Gender Diversity in Criminal Justice Workforce
- 1. Ending Violence against Women
- 2. Human Rights Approaches to Violence against Women
- 3. Who Has Rights in this Situation?
- 4. What about the Men?
- 5. Local, Regional & Global Solutions to Violence against Women & Girls
- 1. Understanding the Concept of Victims of Crime
- 2. Impact of Crime, including Trauma
- 3. Right of Victims to Adequate Response to their Needs
- 4. Collecting Victim Data
- 5. Victims and their Participation in Criminal Justice Process
- 6. Victim Services: Institutional and Non-Governmental Organizations
- 7. Outlook on Current Developments Regarding Victims
- 8. Victims of Crime and International Law
- 1. The Many Forms of Violence against Children
- 2. The Impact of Violence on Children
- 3. States' Obligations to Prevent VAC and Protect Child Victims
- 4. Improving the Prevention of Violence against Children
- 5. Improving the Criminal Justice Response to VAC
- 6. Addressing Violence against Children within the Justice System
- 1. The Role of the Justice System
- 2. Convention on the Rights of the Child & International Legal Framework on Children's Rights
- 3. Justice for Children
- 4. Justice for Children in Conflict with the Law
- 5. Realizing Justice for Children
- 1a. Judicial Independence as Fundamental Value of Rule of Law & of Constitutionalism
- 1b. Main Factors Aimed at Securing Judicial Independence
- 2a. Public Prosecutors as ‘Gate Keepers’ of Criminal Justice
- 2b. Institutional and Functional Role of Prosecutors
- 2c. Other Factors Affecting the Role of Prosecutors
- Basics of Computing
- Global Connectivity and Technology Usage Trends
- Cybercrime in Brief
- Cybercrime Trends
- Cybercrime Prevention
- Offences against computer data and systems
- Computer-related offences
- Content-related offences
- The Role of Cybercrime Law
- Harmonization of Laws
- International and Regional Instruments
- International Human Rights and Cybercrime Law
- Digital Evidence
- Digital Forensics
- Standards and Best Practices for Digital Forensics
- Reporting Cybercrime
- Who Conducts Cybercrime Investigations?
- Obstacles to Cybercrime Investigations
- Knowledge Management
- Legal and Ethical Obligations
- Handling of Digital Evidence
- Digital Evidence Admissibility
- Sovereignty and Jurisdiction
- Formal International Cooperation Mechanisms
- Informal International Cooperation Mechanisms
- Data Retention, Preservation and Access
- Challenges Relating to Extraterritorial Evidence
- National Capacity and International Cooperation
- Internet Governance
- Cybersecurity Strategies: Basic Features
- National Cybersecurity Strategies
- International Cooperation on Cybersecurity Matters
- Cybersecurity Posture
- Assets, Vulnerabilities and Threats
- Vulnerability Disclosure
- Cybersecurity Measures and Usability
- Situational Crime Prevention
- Incident Detection, Response, Recovery & Preparedness
- Privacy: What it is and Why it is Important
- Privacy and Security
- Cybercrime that Compromises Privacy
- Data Protection Legislation
- Data Breach Notification Laws
- Enforcement of Privacy and Data Protection Laws
- Intellectual Property: What it is
- Types of Intellectual Property
- Causes for Cyber-Enabled Copyright & Trademark Offences
- Protection & Prevention Efforts
- Online Child Sexual Exploitation and Abuse
- Cyberstalking and Cyberharassment
- Cyberbullying
- Gender-Based Interpersonal Cybercrime
- Interpersonal Cybercrime Prevention
- Cyber Organized Crime: What is it?
- Conceptualizing Organized Crime & Defining Actors Involved
- Criminal Groups Engaging in Cyber Organized Crime
- Cyber Organized Crime Activities
- Preventing & Countering Cyber Organized Crime
- Cyberespionage
- Cyberterrorism
- Cyberwarfare
- Information Warfare, Disinformation & Electoral Fraud
- Responses to Cyberinterventions
- Framing the Issue of Firearms
- Direct Impact of Firearms
- Indirect Impacts of Firearms on States or Communities
- International and National Responses
- Typology and Classification of Firearms
- Common Firearms Types
- 'Other' Types of Firearms
- Parts and Components
- History of the Legitimate Arms Market
- Need for a Legitimate Market
- Key Actors in the Legitimate Market
- Authorized & Unauthorized Arms Transfers
- Illegal Firearms in Social, Cultural & Political Context
- Supply, Demand & Criminal Motivations
- Larger Scale Firearms Trafficking Activities
- Smaller Scale Trafficking Activities
- Sources of Illicit Firearms
- Consequences of Illicit Markets
- International Public Law & Transnational Law
- International Instruments with Global Outreach
- Commonalities, Differences & Complementarity between Global Instruments
- Tools to Support Implementation of Global Instruments
- Other United Nations Processes
- The Sustainable Development Goals
- Multilateral & Regional Instruments
- Scope of National Firearms Regulations
- National Firearms Strategies & Action Plans
- Harmonization of National Legislation with International Firearms Instruments
- Assistance for Development of National Firearms Legislation
- Firearms Trafficking as a Cross-Cutting Element
- Organized Crime and Organized Criminal Groups
- Criminal Gangs
- Terrorist Groups
- Interconnections between Organized Criminal Groups & Terrorist Groups
- Gangs - Organized Crime & Terrorism: An Evolving Continuum
- International Response
- International and National Legal Framework
- Firearms Related Offences
- Role of Law Enforcement
- Firearms as Evidence
- Use of Special Investigative Techniques
- International Cooperation and Information Exchange
- Prosecution and Adjudication of Firearms Trafficking
- Teaching Methods & Principles
- Ethical Learning Environments
- Overview of Modules
- Module Adaption & Design Guidelines
- Table of Exercises
- Basic Terms
- Forms of Gender Discrimination
- Ethics of Care
- Case Studies for Professional Ethics
- Case Studies for Role Morality
- Additional Exercises
- Defining Organized Crime
- Definition in Convention
- Similarities & Differences
- Activities, Organization, Composition
- Thinking Critically Through Fiction
- Excerpts of Legislation
- Research & Independent Study Questions
- Legal Definitions of Organized Crimes
- Criminal Association
- Definitions in the Organized Crime Convention
- Criminal Organizations and Enterprise Laws
- Enabling Offence: Obstruction of Justice
- Drug Trafficking
- Wildlife & Forest Crime
- Counterfeit Products Trafficking
- Falsified Medical Products
- Trafficking in Cultural Property
- Trafficking in Persons
- Case Studies & Exercises
- Extortion Racketeering
- Loansharking
- Links to Corruption
- Bribery versus Extortion
- Money-Laundering
- Liability of Legal Persons
- How much Organized Crime is there?
- Alternative Ways for Measuring
- Measuring Product Markets
- Risk Assessment
- Key Concepts of Risk Assessment
- Risk Assessment of Organized Crime Groups
- Risk Assessment of Product Markets
- Risk Assessment in Practice
- Positivism: Environmental Influences
- Classical: Pain-Pleasure Decisions
- Structural Factors
- Ethical Perspective
- Crime Causes & Facilitating Factors
- Models and Structure
- Hierarchical Model
- Local, Cultural Model
- Enterprise or Business Model
- Groups vs Activities
- Networked Structure
- Jurisdiction
- Investigators of Organized Crime
- Controlled Deliveries
- Physical & Electronic Surveillance
- Undercover Operations
- Financial Analysis
- Use of Informants
- Rights of Victims & Witnesses
- Role of Prosecutors
- Adversarial vs Inquisitorial Legal Systems
- Mitigating Punishment
- Granting Immunity from Prosecution
- Witness Protection
- Aggravating & Mitigating Factors
- Sentencing Options
- Alternatives to Imprisonment
- Death Penalty & Organized Crime
- Backgrounds of Convicted Offenders
- Confiscation
- Confiscation in Practice
- Mutual Legal Assistance (MLA)
- Extradition
- Transfer of Criminal Proceedings
- Transfer of Sentenced Persons
- Module 12: Prevention of Organized Crime
- Adoption of Organized Crime Convention
- Historical Context
- Features of the Convention
- Related international instruments
- Conference of the Parties
- Roles of Participants
- Structure and Flow
- Recommended Topics
- Background Materials
- What is Sex / Gender / Intersectionality?
- Knowledge about Gender in Organized Crime
- Gender and Organized Crime
- Gender and Different Types of Organized Crime
- Definitions and Terminology
- Organized crime and Terrorism - International Legal Framework
- International Terrorism-related Conventions
- UNSC Resolutions on Terrorism
- Organized Crime Convention and its Protocols
- Theoretical Frameworks on Linkages between Organized Crime and Terrorism
- Typologies of Criminal Behaviour Associated with Terrorism
- Terrorism and Drug Trafficking
- Terrorism and Trafficking in Weapons
- Terrorism, Crime and Trafficking in Cultural Property
- Trafficking in Persons and Terrorism
- Intellectual Property Crime and Terrorism
- Kidnapping for Ransom and Terrorism
- Exploitation of Natural Resources and Terrorism
- Review and Assessment Questions
- Research and Independent Study Questions
- Criminalization of Smuggling of Migrants
- UNTOC & the Protocol against Smuggling of Migrants
- Offences under the Protocol
- Financial & Other Material Benefits
- Aggravating Circumstances
- Criminal Liability
- Non-Criminalization of Smuggled Migrants
- Scope of the Protocol
- Humanitarian Exemption
- Migrant Smuggling v. Irregular Migration
- Migrant Smuggling vis-a-vis Other Crime Types
- Other Resources
- Assistance and Protection in the Protocol
- International Human Rights and Refugee Law
- Vulnerable groups
- Positive and Negative Obligations of the State
- Identification of Smuggled Migrants
- Participation in Legal Proceedings
- Role of Non-Governmental Organizations
- Smuggled Migrants & Other Categories of Migrants
- Short-, Mid- and Long-Term Measures
- Criminal Justice Reponse: Scope
- Investigative & Prosecutorial Approaches
- Different Relevant Actors & Their Roles
- Testimonial Evidence
- Financial Investigations
- Non-Governmental Organizations
- ‘Outside the Box’ Methodologies
- Intra- and Inter-Agency Coordination
- Admissibility of Evidence
- International Cooperation
- Exchange of Information
- Non-Criminal Law Relevant to Smuggling of Migrants
- Administrative Approach
- Complementary Activities & Role of Non-criminal Justice Actors
- Macro-Perspective in Addressing Smuggling of Migrants
- Human Security
- International Aid and Cooperation
- Migration & Migrant Smuggling
- Mixed Migration Flows
- Social Politics of Migrant Smuggling
- Vulnerability
- Profile of Smugglers
- Role of Organized Criminal Groups
- Humanitarianism, Security and Migrant Smuggling
- Crime of Trafficking in Persons
- The Issue of Consent
- The Purpose of Exploitation
- The abuse of a position of vulnerability
- Indicators of Trafficking in Persons
- Distinction between Trafficking in Persons and Other Crimes
- Misconceptions Regarding Trafficking in Persons
- Root Causes
- Supply Side Prevention Strategies
- Demand Side Prevention Strategies
- Role of the Media
- Safe Migration Channels
- Crime Prevention Strategies
- Monitoring, Evaluating & Reporting on Effectiveness of Prevention
- Trafficked Persons as Victims
- Protection under the Protocol against Trafficking in Persons
- Broader International Framework
- State Responsibility for Trafficking in Persons
- Identification of Victims
- Principle of Non-Criminalization of Victims
- Criminal Justice Duties Imposed on States
- Role of the Criminal Justice System
- Current Low Levels of Prosecutions and Convictions
- Challenges to an Effective Criminal Justice Response
- Rights of Victims to Justice and Protection
- Potential Strategies to “Turn the Tide”
- State Cooperation with Civil Society
- Civil Society Actors
- The Private Sector
- Comparing SOM and TIP
- Differences and Commonalities
- Vulnerability and Continuum between SOM & TIP
- Labour Exploitation
- Forced Marriage
- Other Examples
- Children on the Move
- Protecting Smuggled and Trafficked Children
- Protection in Practice
- Children Alleged as Having Committed Smuggling or Trafficking Offences
- Basic Terms - Gender and Gender Stereotypes
- International Legal Frameworks and Definitions of TIP and SOM
- Global Overview on TIP and SOM
- Gender and Migration
- Key Debates in the Scholarship on TIP and SOM
- Gender and TIP and SOM Offenders
- Responses to TIP and SOM
- Use of Technology to Facilitate TIP and SOM
- Technology Facilitating Trafficking in Persons
- Technology in Smuggling of Migrants
- Using Technology to Prevent and Combat TIP and SOM
- Privacy and Data Concerns
- Emerging Trends
- Demand and Consumption
- Supply and Demand
- Implications of Wildlife Trafficking
- Legal and Illegal Markets
- Perpetrators and their Networks
- Locations and Activities relating to Wildlife Trafficking
- Environmental Protection & Conservation
- CITES & the International Trade in Endangered Species
- Organized Crime & Corruption
- Animal Welfare
- Criminal Justice Actors and Agencies
- Criminalization of Wildlife Trafficking
- Challenges for Law Enforcement
- Investigation Measures and Detection Methods
- Prosecution and Judiciary
- Wild Flora as the Target of Illegal Trafficking
- Purposes for which Wild Flora is Illegally Targeted
- How is it Done and Who is Involved?
- Consequences of Harms to Wild Flora
- Terminology
- Background: Communities and conservation: A history of disenfranchisement
- Incentives for communities to get involved in illegal wildlife trafficking: the cost of conservation
- Incentives to participate in illegal wildlife, logging and fishing economies
- International and regional responses that fight wildlife trafficking while supporting IPLCs
- Mechanisms for incentivizing community conservation and reducing wildlife trafficking
- Critiques of community engagement
- Other challenges posed by wildlife trafficking that affect local populations
- Global Podcast Series
- Apr. 2021: Call for Expressions of Interest: Online training for academics from francophone Africa
- Feb. 2021: Series of Seminars for Universities of Central Asia
- Dec. 2020: UNODC and TISS Conference on Access to Justice to End Violence
- Nov. 2020: Expert Workshop for University Lecturers and Trainers from the Commonwealth of Independent States
- Oct. 2020: E4J Webinar Series: Youth Empowerment through Education for Justice
- Interview: How to use E4J's tool in teaching on TIP and SOM
- E4J-Open University Online Training-of-Trainers Course
- Teaching Integrity and Ethics Modules: Survey Results
- Grants Programmes
- E4J MUN Resource Guide
- Library of Resources
- Anti-Corruption
Module 1: What Is Corruption and Why Should We Care?
- {{item.name}} ({{item.items.length}}) items
- Add new list
University Module Series: Anti-Corruption

This module is a resource for lecturers
Effects of corruption.
The effects of corruption are wide-ranging. Some of these effects are fairly obvious, while others require explanation. They include:
Undermining the Sustainable Development Goals
Corruption hampers the attainment of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) . The SDGs are comprehensive and their susceptibility to be undermined by corruption is unsurprising: it is entirely conceivable that "a better and more sustainable future for all" often runs counter to the interests of a few and can be derailed through many forms of corruption. Under conditions of diminished State capacity, nations fail to eradicate poverty, address hunger, secure good health care and high quality education for their citizens, guarantee gender equality and other human rights, reduce inequality, and so on. Of particular relevance is Goal 16 of the SDGs (or SDG 16), which is titled "Peace, Justice and Strong Institutions" and aims to "Promote peaceful and inclusive societies for sustainable development, provide access to justice for all and build effective, accountable and inclusive institutions at all levels". Given the strong causal link between corruption and institutions that are ineffective, unaccountable and exclusive, three targets of SDG 16 - namely 16.4, 16.5 and 16.6 - specifically call for reducing all forms of corruption, strengthening the recovery and return of stolen assets, and developing transparent institutions. At the same time, corruption limits the realization of all SDGs in many respects, as the vast sums that are lost to corruption could have been used to improve living standards by increasing access to housing, health, education and water. For example, the African Union estimates that 25% of Africa's gross domestic product (GDP) is lost to corruption (UNODC, 2015). Aidt (2010) examines the relationship between corruption and sustainable development and finds that there is a negative correlation between corruption and growth, and that corruption can put a country on an unsustainable path in which its capital base is eroded. In addition, the relationship between corruption and sustainable development has repeatedly been emphasized by resolutions adopted by the Conference of the States Parties to UNCAC. It thus requires the global community to see corruption as an obstacle to the realization of the SDGs and to step up anti-corruption efforts if we truly desire to achieve the SDGs. The appendix includes an SDG table that briefly explains how corruption relates to each of the 17 SDGs. For each SDG, the table also indicates which Modules of the E4J University Module Series on Anti-Corruption address the relationship between corruption and the specific SDG.
Economic loss and inefficiency
Although obtaining exact figures on the economic costs of corruption is difficult, a 2016 report from the International Monetary Fund (IMF) estimated the cost of bribery alone to be between $1.5 to $2 trillion per year. This represents a total economic loss of approximately 2% of global GDP. And yet it does not take into account the economic cost of all other forms of corruption. Regarding fraud, money-laundering and tax evasion, for example, the thousands of leaked documents known as the Mossack Fonseca Papers (commonly referred to as the Panama Papers) exposed the vast economic implications of offshore entities for many nations and for economic inequality in general. Finally, beyond deadweight economic loss, there is economic inefficiency to consider. When jobs (or contracts) are given to people (or companies) who offer bribes or share a personal connection, this occurs to the detriment of competition. The result is that more qualified candidates and firms are turned down. The more widespread such practices are, the more inefficient the economy becomes. Corruption in developing countries may cause underdevelopment. This can occur when international economic and humanitarian initiatives are derailed as funds disbursed from loans and aid are embezzled or handed out to inferior contractors who have won their bids through corrupt means (kickbacks, bribery, nepotism, etc.). Furthermore, investment in physical capital and human capital is reduced as resources are diverted from their most beneficial use.
Poverty and inequality
Corruption is generally not the weapon of the weak. In Nigeria, an (in)famous bribery case, involving the international oil company Shell, deprived Nigerian people of over $1.1 billion as the money went to corrupt officials instead of to the national budget (Global Witness, 2017). Meanwhile, according to the World Bank (2019), more than 50% of the population of the oil-rich country live in extreme poverty. This example shows that as political and economic systems are enlisted in the service of corrupt actors, wealth is redistributed to the least needy sources. Mechanisms such as political representation and economic efficiency are both compromised by self-dealing and secret exchanges. Under conditions of corruption, funding for education, health care, poverty relief, and elections and political parties' operating expenses can become a source of personal enrichment for party officials, bureaucrats and contractors. Social programmes and the redistributive potential of political systems suffer accordingly. A key result of all the instances named above is a state of unequal opportunity in which advantages arise only for those within a corrupt network.
Personal loss, intimidation and inconvenience
When people experience corruption, it is rarely a positive experience. A bribe must be paid to receive medical attention, obtain a building permit, pick up a package, or enjoy phone services. A judge rules against a party, not based on the facts of the case, but because the opponent paid a bribe, knows a power broker, or comes from the same racial or ethnic background. A person is beaten, detained or subject to a higher fine because he or she refuses to pay a bribe solicited by a police officer. Retirement funds are lost to fraudsters or tied up in a money-laundering scheme. While the victims of corruption suffer personal loss, intimidation and inconvenience, those who perpetrate corrupt acts and schemes tend to experience personal gain, a sense of superiority and greater convenience - pending enforcement of the law, that is.
Public and private sector dysfunctionality
The cumulative effect of individual corrupt acts is dysfunctionality. Whether offered by the public or private sectors, the quality of goods and services decrease, and the process of obtaining them becomes more expensive, time consuming and unfair. If bribes can successfully be offered to police, doctors, and civil servants, then those who are most successful at extracting these funds get ahead to the detriment of more honest colleagues and competitors who may perform better on merit. Moreover, corporations lose the incentive to offer better services and products if they can undermine competitors through obtaining political favours. State-owned enterprises and industries are structured to enrich government officials instead of pursuing innovation and efficiencies. This can lead to the loss of intrinsic motivation within organizations. Workers and managers are demoralized. People begin to doubt the value of hard work and innovation.
Failures in infrastructure
When a bridge collapsed in Genoa in August 2018, killing at least 39 people, there were many possible causes to consider (NZHerald, 2018). Corruption was not the most obvious one, but subsequent investigations have found that a Mafia-controlled construction company appears to have used "weakened cement" in the building process. It is widely known that the construction industry is a valuable source of profits and a channel for money-laundering operations by the Mafia (additional information on organized crime can be found in the E4J University Module Series on Organized Crime ). Oversight and competition are both undermined in industries and firms plagued by organized corruption. Relatedly, a 2017 report by Mexicans Against Corruption and Impunity blames corruption for the collapse of over 40 buildings during the September 2017 earthquake in Mexico City. Land-use and permit laws appear to have been bypassed, ostensibly through bribery, cronyism and influence trading, leading to the presence of fundamentally unsafe buildings around the capital.
Rigged economic and political systems
What is described as dysfunctional above is actually functional and profitable for corrupt actors. Whether falling under the label of political cronyism, crony capitalism, political party cartels, oligarchy, plutocracy and even kleptocracy, widespread patterns of private and public corruption construct social systems that are rigged in the private interest. Citizens with strong ethical principles (and citizens who lack significant funds, connections, favours to dispense, "hard power" over others such as guns or private enforcers) lose representation, influence and power.
Impunity and partial justice
When corruption pervades the justice system, people can no longer count on prosecutors and judges to do their jobs. The powerful may escape justice. And citizens, especially those with few resources or few powerful allies, may be unfairly accused of crimes, deprived of due process, and wrongly imprisoned. Resources on preventing corruption and strengthening integrity in the judiciary are available on the website of the UNODC Global Judicial Integrity Network.
Rising illiberal populism
A 2017 TI report and several scholarly publications make the point that increasing authoritarianism is partly fuelled by corruption (see, e.g., this blog post from 2017 by Balisacan as well as the resources referenced in this TI paper ). In a nutshell, corruption increases inequality, decreases popular accountability and political responsiveness, and thus produces rising frustration and hardship among citizens, who are then more likely to accept (or even demand) hard-handed and illiberal tactics. Those tactics shift the blame for economic insecurity and political decline onto immigrants or other minority groups, and onto economic and political elites, who must, the theory goes, be dealt with swiftly and decisively. The rule of law and liberal values of tolerance and human dignity then become obstacles to needed change. For a more general discussion of values, see Module 2 of the E4J University Module Series on Integrity and Ethics.
Organized crime and terrorism
Nefarious elements in society thrive as proceeds can be laundered, funding disguised, and judicial officials and politicians corrupted through bribes (including gifts, favours and other benefits). Levels of violence, illegal drugs, prostitution, sexual slavery, kidnapping and intimidation rise accordingly. The causal arrow goes in both directions. Not only does organized crime cause corruption, but opportunities for corruption left open by a weak, negligent or incapable State can also lead to organized crime. For a further discussion about the corruption-organized crime nexus, see Module 11 of the E4J University Module Series on Anti-Corruption and Module 4 of the E4J University Module Series on Organized Crime.
Diminished state capacity
Even if citizens were to adamantly demand that the problems listed above be addressed, corruption undermines the power of politics. For example, to the extent that bribery, trading in influence and state capture are widespread, political systems become incapable of addressing social problems whose resolution would threaten vested interests. Naturally, this is never acknowledged as such from within - state incapacity may manifest in a great many distracting and misleading ways, such as wedge issues, political party restructuring, the emergence of scandals and overwhelming outside issues that detract from structural problems, and so on. Under conditions of state capture, political arbitrage can be expected to occur in a highly strategic fashion. Issues will be played off against each other in order to frustrate systemic reforms. Moreover, as Della Porta and Vannucci (2005) argue, corruption compromises the ethos of public service and changes political culture so as to render meaningful, public-spirited reforms virtually unthinkable.
Increasing polarization and unrest
When corruption, in particular state capture, becomes the norm, this can lead to polarization among citizens: those in support of corrupt regimes (because of kickbacks and handouts) versus those opposed to them. In the presence of diametrically opposed groups in society, compromise and reasoned discussion diminish. Policy is judged not on the basis of ideology or a project's inherent merits, but on who the policy proponents are and what benefits competing networks can reap.
Climate change and damage to biodiversity
Corruption derails anti-climate change funding and initiatives, defeats forest conservation and sustainable forest management programmes, and fuels wildlife and fishery crimes (for more information, see the E4J University Module Series on Wildlife, Forest and Fisheries Crime). These and other adverse effects of corruption on climate change and the environment are underscored in a TI report from 2011 and additional TI publications . On a broader level, the book This Changes Everything by Naomi Klein (2014) details how state capture by monied interests has derailed legislative efforts to address climate change in the United States. Her analysis applies to many countries around the world, given the power of the fossil fuels and automotive industries over governments - elected and unelected - across the globe. The perilous impact of corruption on the fisheries sector is discussed in detail in the publication Rotten Fish (UNODC, 2019), while the report Authorized to Steal (CIEL, 2019) reveals how corruption enables criminal networks to illegally harvest timber in Peru.
Human rights violations
The observation that corrupt rulers tend to view civil liberties as obstacles to the consolidation of power can be traced back to many historical sources, including the collection of eighteenth century essays on corruption and tyranny known as Cato's Letters . Most recently of all, perhaps, the United Nations Office of the High Commission for Human Rights (OHCHR) has noted significant connections between corruption and human rights violations. Not only do those who report and oppose corruption end up on the receiving end of assassinations and human rights violations of many kinds, but also corruption itself decreases State capacity to address violations of civil and political rights and to make the necessary provisions to guarantee such rights, including socioeconomic rights, which often require complex initiatives on the part of governments. OHCHR calls corruption "a structural obstacle to the enjoyment of human rights" and has detailed many intersections between these two areas. For a further discussion and academic references on the corruption-human rights nexus, see Module 7 of the E4J University Module Series on Anti-Corruption.

Armed conflict and atrocity crimes
The diminished State capacity and development, brought about by corruption, can lead to insecurity and even armed conflict (see, e.g., World Bank, 2011; World Bank, 2017). Indeed, corruption has been recognized as a destabilizing factor and ultimately a "driver of conflict" (USIP, 2010, p. 7). Although the causal link between corruption and atrocity crimes (including genocide, war crimes and crimes against humanity) may be hard to prove, transitional justice mechanisms have identified corruption as a root cause of conflict and atrocity. See, for example the Sierra Leone Truth and Reconciliation Commission Report (2004, chap. 2, para. 13) and the Liberian Truth and Reconciliation Commission Consolidated Final Report (2009, vol. II, pp. 16-17). In post-Arab Spring Tunisia, corruption was recognized as a root cause of the conflict even before the transitional justice mechanism operated. Thus, Tunisia's Law on Transitional Justice from 2013 (see English translation here ) and the Truth and Dignity Commission (Instance vérité et dignité or IVD) that was created by the law were intended to establish accountability for the country's legacy of rampant corruption and human rights violations and to help reform the institutions that engaged in such crimes. Another relevant example is a 2018 report from the Open Society Justice Initiative, which offers evidence linking corruption to crimes against humanity in Mexico. For a further discussion and academic references about the corruption-conflict nexus, see Module 11 of the E4J University Module Series on Anti-Corruption.
Public frustration and cynicism
People lose trust in leaders, in social systems (public institutions) and sometimes even in society and ethics itself when they sense that corruption is widespread and corrupt actors are not being held accountable. When political non-accountability increases, such perceptions persist for protracted periods and political participation diminishes. Moreover, public frustration and the sense that corruption is widespread can in turn pave the way for citizens themselves to take part in corrupt transactions, as discussed in a blog post on the Taxi Driver Paradox . In other words, social norms could encourage corrupt behaviour as people tend to think that "if everybody is doing it, I might as well do it too." (Köbis, 2018). Failure to meet public expectations for zero-tolerance of corruption may have deleterious consequences for the legitimacy of State institutions and the very utility of formal norms that citizens and firms are expected to follow, possibly resulting in higher public tolerance of un-civic and free-riding behaviour.
The effects of corruption mentioned above can be categorized along the following lines: economic, political, moral or psychological, humanitarian, ecological, security-related, and so on. To help us gain a better understanding of corruption, the following section discusses some of the deeper meanings of corruption.
Next: Deeper meanings of corruption
Back to top, supported by the state of qatar, 60 years crime congress.
Corruption as a Social Phenomenon Exploratory Essay
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
The human race has always been accredited with being the most bright and ambitious of living things. One of the defining characteristics of the human civilization is our ambition and drive to excel in all of our endeavors.
As a result of this, human beings often do whatever they can to achieve their goals and objectives using the resources that are at their disposal. This need to further their success is of great importance to their social, economic and political welfare. However, there are obstacles that tend to threaten the process through which these ambitions can be realized.
They include competition, bureaucracies, and in some cases, cultural differences. Consequently, people are sometimes inclined engage in morally unacceptable behaviors or going against the set rules and laws in order to gain an upper hand over other people who are aiming for the same resources. Corruption is one of the concepts that man has adapted to and it has taken its toll in the human society as his desire and greed for material wealth and power increase.
By definition, corruption refers to the use of available resources or designated power for purposes other than the intended ones or for personal gains. It is a very relative concept because it comes in different forms depending on the situation or action taken.
In the current society, this vice has rapidly penetrated the social, political and economic realms and is causing pain and suffering to everyone whom it affects. Corruption comes in various forms and is exhibited at various levels of the society, as such, political analysts and other experts have divided corruption into the various forms that it comes in.
Perhaps the most rampant and damaging form of corruption is political corruption which refers to a dysfunction in a political system whereby government or political officials and employees use their ranks or the resources allocated to them for personal gains. While all manners of corruption are inherently damaging to the society, this particular form of corruption poses the most significant threat since it is the political bodies in our country that are charged with guiding the nation to prosperity and success.
Currently, every nation has some evidence of corruption within its various sectors and institutions. The various forms of corruption have in the recent past manifested themselves at a very alarming rate. Some of these forms of corruption include bribery which refers to a situation where someone is given money or other material things to do something that he is already getting paid to do or a situation where incentives are offered so that a person can go against the set laws or regulations.
Another form of corruption is nepotism which involves the favoring of friends or relatives in regards to getting jobs, promotions or salary increment irrespective of their qualifications. This type of corruption is predominant in almost every country in the world and occurs mostly in family owned businesses or where a particular group of people wants to maintain leadership or control regulations of a particular business or policies.
Another form of corruption that is carried out by people in positions of relative power is the embezzlement of funds. This involves the theft of institutional funds allocated to serve a particular purpose. Embezzlement also includes misappropriation of money and property given to a particular department or sector mainly for personal gains.
A more violent form of corruption which may be exercised by people of relative power is extortion which refers to the use of threats in order to get something from other people. This kind of corruption it also described as the illegal use of state force directed at inflicting harm to others. It is most common with the police force and military agencies.
In order to understand corruption we must look into the possible causes, its effect on the society and at least some of the ways that can be used to curb or prevent it from happening. The most common cause of corruption is presence of low salaries in the economy. As needs increase, the amount of salary may not fully suffice and the people result to using their official capacity to try and get more money or resources to up their social status or even satisfy their greed for material wealth.
In addition to this, there are a lot of loop holes in the regulatory systems which allow people to indulge themselves with this vice. On the same note, the presence of cliques (friendship) and cultural ties have created room for nepotism in all sectors. Poor management and allocation of funds have led to an increase in embezzlement especially in developing countries.
It is a well know fact that corruption leads to the damaging of the very fabric of society. Corruption undermines the value of democracy and the effectiveness of rules, regulation, laws and policies that govern an institution or nation.
As a result, it leads to unequal distribution of political and economical power within the affected society. In addition to this it also causes social and political instabilities leading to war and tribal/cultural clashes. Economically, corruption inhibits development through unfair distribution of resources and funds.
Additionally, it leads to an increase in prices levels brought about by poor price legislation. In social and environmental basis, corruption causes the destruction of natural resources which is brought about by over exploitation of resources, over industrialization which increases pollution. This comes about as a result of bribery which contributes highly to the breaking of protocols and policies put to prevent this from happening.
Whereas corruption seems to be an indestructible vice that is here to stay, this is not the case and there are measures that can be taken to control it from increasing and even reduce its presence in the society. Such measures include the establishment of anticorruption agencies which fight against these vices.
In addition to this, the government should dwell on formulating new and stricter laws that govern the various forms of corruption and pose heavy penalties to those who are guilty of such crimes. There should also be a select committee in every organization that demand at least quarterly accountability of funds accrued towards a particular purpose.
The best preventive measure however should be man’s desire to change the current situation. Everyone has the potential to make a change and as such, people should say no to corruption on a personal level and assist the authorities in fighting this vice if there is hope to make a difference and eventually curb this menace.
It can be irrefutably stated that corruption is by far the worse problem that nations and societies are facing in our contemporary world. It should be noted that the social, economic, political and environmental benefits that may arise from the abolishment of corruption are far much greater than the greed and desire for power and wealth expressed by selected individual. It is therefore prudent that the global community come together in the fight to eradicate corruption for a healthy and prosperous future for all.
- Depiction of White-Collar Crime: Toxic Chemicals and Effects of the Pollutions
- The Corruption Issue in the Education Sector
- Crude World: The Violent Twilight of Oil
- Public Policy Formation
- Poverty in Urban Areas
- Decriminalization of Marijuana
- Deputy Sheriffs Collective Bargaining Issue
- Health Care – Operation & Management in Canada, England and USA
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2018, June 27). Corruption as a Social Phenomenon. https://ivypanda.com/essays/corruption/
"Corruption as a Social Phenomenon." IvyPanda , 27 June 2018, ivypanda.com/essays/corruption/.
IvyPanda . (2018) 'Corruption as a Social Phenomenon'. 27 June.
IvyPanda . 2018. "Corruption as a Social Phenomenon." June 27, 2018. https://ivypanda.com/essays/corruption/.
1. IvyPanda . "Corruption as a Social Phenomenon." June 27, 2018. https://ivypanda.com/essays/corruption/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Corruption as a Social Phenomenon." June 27, 2018. https://ivypanda.com/essays/corruption/.

Essay on Corruption

Updated February 14, 2023
Corruption is the misuse of public or private resources for personal gain. It is a widespread problem affecting governments, businesses, and individuals worldwide. In this essay on corruption you get all the information about corruption and how it was dangerous to our life. Corruption can take many forms, such as bribery, extortion, cronyism, nepotism, fraud, embezzlement, and money laundering. It can lead to economic stagnation, inequality, and political instability and erode trust in institutions.
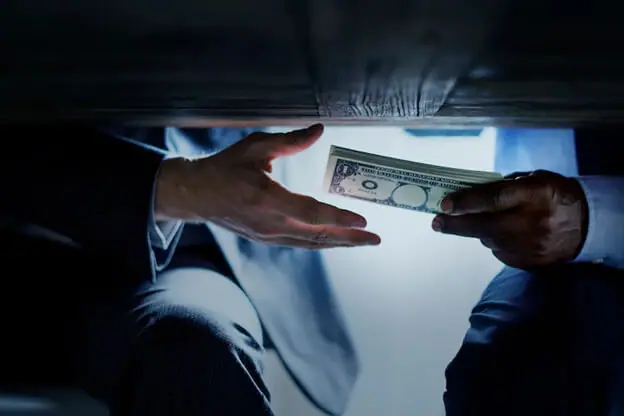

Watch our Demo Courses and Videos
Valuation, Hadoop, Excel, Mobile Apps, Web Development & many more.
The consequences of corruption can be devastating, particularly in developing countries. It can prevent economic growth, entrench poverty, and weaken the rule of law. It can also lead to environmental degradation and human rights abuses.
Combating corruptions requires a comprehensive approach that strengthens the rule of law, improves public sector transparency and accountability, and creates a more equitable society. Governments and institutions can enact legislation and policies to reduce corruption, such as anti-corruption laws, public procurement rules, and whistleblower protections. Civil society and citizens can also play an important role by engaging in advocacy, monitoring public officials, and reporting corruption.
Causes of Corruption
It occurs when individuals or organizations misuse their power or influence for private gain. It can take many forms, from bribery and embezzlement to fraud and extortion. In this essay on corruption or in real life you got opportunity to stop someone from doing it you have to do it for not only yourself but also for others who affected by corruption. It undermines the rule of law, erodes trust in government, and hinders economic growth and development. It can also lead to instability, poverty, and inequality.
Multiple factors cause corruption, but the most common causes are:
- Weak governance systems.
- Political and economic instability.
- Lack of transparency and accountability.
- Lack of access to resources.
Poor governance systems and lack of accountability allow corrupt actors to take advantage of the system and gain access to resources that should be available to everyone. Political and economic instability can also create the conditions for corruption to thrive. In countries where corruption is rampant, citizens lack access to essential services, and political and economic freedoms are limited.
In addition to these factors, the cause of corruption can also be a lack of education and awareness, weak legal frameworks and enforcement, and incentives for corrupt behavior. Failure to enforce laws properly results in corrupt individuals taking advantage of the system and engaging in corrupt behavior without facing significant consequences. Finally, it is also the result of a culture of impunity, where unscrupulous actors are not held accountable for their actions.
It is an illegal practice in which individuals or businesses use their influence to gain an unfair advantage for themselves or others. It can take many forms, such as bribery, extortion, nepotism, cronyism, fraud, money laundering, embezzlement, and misappropriation of funds. It often occurs through the abuse of power and authority involving public and private entities. Bribery is a common form of corruption involving offering money or other forms of incentive in exchange for a particular favor or service. Other forms of it include:
- Extortion is the use of threats or coercion to obtain money or favors.
- Nepotism is the awarding of jobs and promotions based on family relationships.
- Cronyism, which is the favoring of friends and associates.
- Fraud is the intentional misrepresentation of facts.
- Money laundering is the concealment of illegally obtained funds.
- Embezzlement is the misappropriation of funds.
- Misuse of funds, which is the unauthorized use of funds.
In all cases, corruption is a severe violation of the law, and those found guilty of such practices can be subject to criminal penalties.
- It involves a combination of tactics and strategies to reduce the risk of corruption and improve public trust. It includes measures that promote transparency, integrity, and accountability, as well as those that reduce the opportunities for corruption.
- Firstly, corruption prevention requires a strong and effective legal framework. It includes laws, regulations, and policies that are enforced by an independent and impartial judiciary. These laws must strive to address all types of corrupt activities, including bribery, embezzlement, and conflicts of interest. Its legal framework should also create solid sanctions for those who violate it.
- Secondly, corruption prevention also requires strong institutions and systems of checks and balances. It includes establishing independent anti-corruption bodies to monitor and investigate cases of suspected corruption. These bodies must be able to operate independently and have the power to impose sanctions on those found guilty of corruption.
- Thirdly, corruption prevention requires a culture of integrity. It should include promoting values such as honesty, accountability, and transparency. We should incorporate these values in all levels of society, from the highest levels of government to the smallest businesses. Society should develop educational and training programs to help people understand the consequences of engaging in corrupt activities.
- Fourthly, corruption prevention requires robust mechanisms of public oversight and participation. It includes the establishment of whistleblower protection laws and the promotion of public access to information. It will help citizens identify and report any corruptions they may encounter.
- Finally, it requires an effective system of monitoring and enforcement. It should include regular audits and inspections to ensure everyone follows the proper procedure. It also provides for the prosecution of those found guilty of corruption.
- By implementing these measures, governments and organizations can effectively reduce the risk of corruption and maintain public trust.
It is an endemic problem in many countries worldwide, and it can have profound implications for individuals and societies. It can lead to various adverse outcomes, such as economic stagnation, political instability, and social injustice. In this essay on Corruption you got all the useful information about corruption and how to stop it. To combat corruption, governments must take a multi-faceted approach that includes strengthening the rule of law, creating more transparent systems of governance, and increasing public awareness of the issue. Additionally, individuals must take responsibility for their actions and avoid corrupt practices. Only with a concerted effort from both government and citizens can we address the corruption problem.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Essay on Corruption” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information,
- Essay on Globalization
- Essay on Global Warming
- Essay on Climate Change
- Essay on India of My Dreams

*Please provide your correct email id. Login details for this Free course will be emailed to you
By signing up, you agree to our Terms of Use and Privacy Policy .
Valuation, Hadoop, Excel, Web Development & many more.
Forgot Password?
This website or its third-party tools use cookies, which are necessary to its functioning and required to achieve the purposes illustrated in the cookie policy. By closing this banner, scrolling this page, clicking a link or continuing to browse otherwise, you agree to our Privacy Policy

Explore 1000+ varieties of Mock tests View more
Submit Next Question
🚀 Limited Time Offer! - 🎁 ENROLL NOW
Essay on Corruption for Students and Children
500+ words essay on corruption.
Essay on Corruption – Corruption refers to a form of criminal activity or dishonesty. It refers to an evil act by an individual or a group. Most noteworthy, this act compromises the rights and privileges of others. Furthermore, Corruption primarily includes activities like bribery or embezzlement. However, Corruption can take place in many ways. Most probably, people in positions of authority are susceptible to Corruption. Corruption certainly reflects greedy and selfish behavior.

Methods of Corruption
First of all, Bribery is the most common method of Corruption. Bribery involves the improper use of favours and gifts in exchange for personal gain. Furthermore, the types of favours are diverse. Above all, the favours include money, gifts, company shares, sexual favours, employment , entertainment, and political benefits. Also, personal gain can be – giving preferential treatment and overlooking crime.
Embezzlement refers to the act of withholding assets for the purpose of theft. Furthermore, it takes place by one or more individuals who were entrusted with these assets. Above all, embezzlement is a type of financial fraud.
The graft is a global form of Corruption. Most noteworthy, it refers to the illegal use of a politician’s authority for personal gain. Furthermore, a popular way for the graft is misdirecting public funds for the benefit of politicians .
Extortion is another major method of Corruption. It means to obtain property, money or services illegally. Above all, this obtainment takes place by coercing individuals or organizations. Hence, Extortion is quite similar to blackmail.
Favouritism and nepotism is quite an old form of Corruption still in usage. This refers to a person favouring one’s own relatives and friends to jobs. This is certainly a very unfair practice. This is because many deserving candidates fail to get jobs.
Abuse of discretion is another method of Corruption. Here, a person misuses one’s power and authority. An example can be a judge unjustly dismissing a criminal’s case.
Finally, influence peddling is the last method here. This refers to illegally using one’s influence with the government or other authorized individuals. Furthermore, it takes place in order to obtain preferential treatment or favour.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Ways of Stopping Corruption
One important way of preventing Corruption is to give a better salary in a government job. Many government employees receive pretty low salaries. Therefore, they resort to bribery to meet their expenses. So, government employees should receive higher salaries. Consequently, high salaries would reduce their motivation and resolve to engage in bribery.

Tough laws are very important for stopping Corruption. Above all, strict punishments need to be meted out to guilty individuals. Furthermore, there should be an efficient and quick implementation of strict laws.
Applying cameras in workplaces is an excellent way to prevent corruption. Above all, many individuals would refrain from indulging in Corruption due to fear of being caught. Furthermore, these individuals would have otherwise engaged in Corruption.
The government must make sure to keep inflation low. Due to the rise in prices, many people feel their incomes to be too low. Consequently, this increases Corruption among the masses. Businessmen raise prices to sell their stock of goods at higher prices. Furthermore, the politician supports them due to the benefits they receive.
To sum it up, Corruption is a great evil of society. This evil should be quickly eliminated from society. Corruption is the poison that has penetrated the minds of many individuals these days. Hopefully, with consistent political and social efforts, we can get rid of Corruption.
{ “@context”: “https://schema.org”, “@type”: “FAQPage”, “mainEntity”: [{ “@type”: “Question”, “name”: “What is Bribery?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”: “Bribery refers to improper use of favours and gifts in exchange for personal gain.”} }, { “@type”: “Question”, “name”: ” How high salaries help in stopping Corruption?”, “acceptedAnswer”: { “@type”: “Answer”, “text”:”High salaries help in meeting the expenses of individuals. Furthermore, high salaries reduce the motivation and resolve to engage in bribery.”} }] }
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

PovertyCure is an initiative of the Acton Institute
Get the Series

In the context of political economy, corruption refers to an illegal transaction that harms the group the agent is obliged to serve through the transaction. For example, a construction company may offer a kickback to a government official (agent) in return for winning a contract outside the normal bidding process. The official has harmed the government he serves and, by extension, the people it represents because the government probably will pay more for the job than it would have under a competitive process. The issue of corruption in politics and the marketplace is of interest to development economists because it often hamstrings poor countries in their efforts to rise out of poverty through enterprise.
The Cost of Corruption
Besides being immoral, corruption tends to be an inefficient way to bring together buyers and sellers. Because it is by definition illegal—even when it is common and accepted—corruption naturally tends to be private and secretive. In a private arrangement, there is no guarantee that the good or service being bought carries a market price. That is, another buyer may be willing to pay more, or another seller may be willing to sell for less, but it is impossible to know because the market is not public. Further, resources are expended in the effort to maintain the secrecy of the transactions. Finally, corrupt contracts, because they are illegal, must be enforced in extralegal fashion. Thus a corrupt system is an inherently inefficient system.
In some cases corruption might be reasonably viewed as the most expedient option. For example, in a country with excessive bureaucratic hurdles to starting a business, bribery may be a way to speed the process. This is only a stop gap, of course, since it leaves in place a system that serves the corrupt by providing numerous opportunities to demand bribe money and to tilt the playing field to the advantage of friends, family and political patrons.
Corruption as an Obstacle to Development
The monetary cost of corruption is slower economic growth. Studies have shown that decreasing corruption leads to significant gains in foreign direct investment, which is one of the chief spurs to development. Economist Shan-Jin Wei has argued that corruption is proportionately more damaging to economic growth than is taxation of business. In terms of its discouraging effect on investment, Wei found, “An increase in the corruption level from that of Singapore to that of Mexico is equivalent to raising the tax rate on multinationals by over twenty percentage points.”
Turning international business investment away is only one of several ways that corruption stifles growth. “ Corruption and Poverty ,” a review essay commissioned by USAID, summarizes its findings with a long list of negative effects: “Corruption impedes economic growth by discouraging foreign and domestic investment, taxing and dampening entrepreneurship, lowering the quality of public infrastructure, decreasing tax revenues, diverting public talent into rent-seeking, and distorting the composition of public expenditure.” (Rent seeking is an economics term referring to any effort to profit not by adding value but by manipulating a market’s social or political environment in order to gain an artificial advantage.)
The authors of the review also point out that corruption exacerbates income inequality. They find that this link is due to several negative effects of corruption, including distortion of the “legal and policy frameworks allowing some to benefit more than others”; “unfair distribution of government resources and services”; and “lower income households (and businesses) pay[ing] a higher proportion of their income in bribes” than wealthier households.
The Corruption Perception Index
In light of these observations, it is no surprise that nations with high levels of public sector corruption face major development challenges (while nations with relatively low levels of political corruption tend to thrive economically). This is apparent from even a cursory look at Transparency International ’s Corruption Perception Index (CPI), which measures the reputations of national governments with respect to corruption. In 2017, the five worst-scoring countries on the CPI were Yemen, Afghanistan, Syria, South Sudan, and Somalia. The top five were New Zealand, Denmark, Finland, Norway, and Switzerland.
Corruption as an Immoral Choice
Although political reforms may diminish inducements to corruption, it is important to remember that every instance of corruption is an individual decision. Even where corruption is common and widely accepted, people can choose not to engage in it. And even where it is rare and stigmatized, people may initiate a corrupt transaction.
Corruption is a serious violation of justice, because it benefits some at the expense of others without legitimate reason. It erodes the bonds of trust between people within a community, and between people and the government officials who are supposed to represent their interests. Corruption also tends to favor the well-connected while locking out those who are poor and lack high-level connections.
Fighting Corruption
One strategy for combating corruption is simply to limit the extent of state authority. Expansive regulation (such as business licensing) creates ample opportunity and temptation to rig the process in favor of one or another participant. Where government has narrowly defined powers that keep it out of such decision-making, the rule of law is encouraged and corruption discouraged.
Thus, it’s important that government regulatory law curtail the discretion permitted to individual officials. Where gatekeepers in the bureaucracy have wide leeway to interpret and apply the law, the potential for corruption increases. This strategy is no substitute for virtue, of course, since a measure of interpretive leeway is necessary and inevitable in any system of government.
The costs of fighting corruption through government channels also must be realistically assessed. Government anti-corruption initiatives may be costly and may possess some of the same features that promoted corruption in the first place (e.g., layers of bureaucracy and limited resources that force bureaucrats to choose who to focus on and who to ignore).
Thus, while corruption must never be viewed as an acceptable practice, advocates of the rule of law should be realistic about the prospects for its elimination. The inherent weaknesses in political initiatives to limit political corruption also should serve as a spur for cultures to combat corruption by other means, as through the work of civil institutions (e.g., churches, fraternal organizations) in emphasizing the cultivation of personal virtue. When people become convinced that corruption is harmful to society and damaging to their own moral integrity, and when they possess the courage to act accordingly, then a culture is better positioned to make progress in the fight against corruption in politics and the market.

Rethink Poverty
Subtitled in 15 languages, this six part video series that will change absolutely everything about how you approach charity and missions.

Essay on Corruption
Students are often asked to write an essay on Corruption in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Corruption
Understanding corruption.
Corruption is a dishonest behavior by a person in power. It can include bribery or embezzlement. It’s bad because it can hurt society and slow down progress.
Types of Corruption
There are many types of corruption. Bribery is when someone pays to get an unfair advantage. Embezzlement is when someone steals money they’re supposed to look after.
Effects of Corruption
Corruption can lead to inequality and injustice. It can make people lose trust in the government and can cause social unrest.
Fighting Corruption
To fight corruption, we need strong laws and honest leaders. Education can also help people understand why corruption is harmful.
250 Words Essay on Corruption
Introduction.
Corruption, a pervasive and longstanding phenomenon, is a complex issue that undermines social and economic development in all societies. It refers to the misuse of entrusted power for private gain, eroding trust in public institutions and impeding the efficient allocation of resources.
Manifestations and Impacts of Corruption
Corruption manifests in various forms, including bribery, embezzlement, nepotism, and fraud. Its impacts are far-reaching, affecting socio-economic landscapes. Economically, it stifles growth by deterring foreign and domestic investments. Socially, it exacerbates income inequality and hampers the provision of public services.
Anti-Corruption Strategies
Addressing corruption requires a multi-faceted approach. Legislation and law enforcement are critical, but they must be complemented with preventive measures. Transparency, accountability, and good governance practices are key preventive strategies. Technology can also play a significant role, particularly in promoting transparency and reducing opportunities for corrupt practices.
Corruption is a global issue that requires collective action. While governments bear the primary responsibility for curbing corruption, the involvement of civil society, media, and the private sector is indispensable. Thus, the fight against corruption is a shared responsibility, requiring the commitment and efforts of all sectors of society.
500 Words Essay on Corruption
Corruption, an insidious plague with a wide range of corrosive effects on societies, is a multifaceted phenomenon with deep roots in bureaucratic and political institutions. It undermines democracy, hollows out the rule of law, and hampers economic development. This essay explores the concept of corruption, its implications, and potential solutions.
The Nature of Corruption
Implications of corruption.
Corruption poses a significant threat to sustainable development and democracy. It undermines the government’s ability to provide essential services and erodes public trust in institutions. Furthermore, it exacerbates income inequality, as it allows the wealthy and powerful to manipulate economic and political systems to their advantage.
Corruption also hampers economic development by distorting market mechanisms. It discourages foreign and domestic investments, inflates costs, and breeds inefficiency. Additionally, it can lead to misallocation of resources, as corrupt officials may divert public resources for personal gain.
The Root Causes
Combating corruption.
Legal reforms are also essential to strengthen the rule of law and ensure that corrupt practices are adequately punished. Additionally, fostering a culture of ethics and integrity in society can help to change attitudes towards corruption.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.


Essay on Corruption: Causes & its Effects
The term “corruption” can refer to both individual acts of dishonesty or fraud as well as systemic issues like bribery. There are many symptoms of corruption, but it can be difficult to identify its root causes. Corruption thrives on secrecy and the absence of accountability. This essay on corruption will explore the causes of corruption and its overall effect.
What is corruption?
A corrupt act includes an attempted or actual breach of the law, but the crime is committed to further personal advantage or gain for the perpetrator or corruptible person.
Types of corruption
Corruption is the abuse of power, position, or resources to gain an unjust or illegal advantage for oneself or someone else.
Fraud is another form of corruption. It is a corrupt act that includes an attempt to gain an advantage or personal benefit by deception. This is also known as “unlawful gain”.
The causes of corruption
The most obvious way that corruption is detrimental to society is through theft, extortion, and bribery. Every society has some form of crime, but with corruption, the problem is magnified.
However, the most harmful form of corruption is in the sphere of political power. This stems from the fact that corruption can occur in various walks of life, from individuals to corporations. Even the institution of government allows for some level of corruption, but it is not one that is common in government.
The effects of corruption
Corruption distorts the allocation of resources, undermines the rule of law, diminishes civic participation, erodes the quality of public services, and erodes faith in public institutions.
Corrupt practices can take place within any number of activities. For example, tax evasion and tax avoidance. A significant portion of tax revenues is lost to tax avoidance and tax evasion in many countries. Intentional tax avoidance is the concealment of income or expenses that would be reported in tax returns.
Corruption has dire consequences for the economy
Think of bribery to get a construction permit. All the poor need is a building permit to start a business, but they’re more likely to pay off the person who owns the building permit and he’ll be even more likely to give the permit to a business they can’t afford to compete with.
Ways to combat corruption
At the local level, they are implemented by those who maintain public service in government departments or agencies.
Governments can reduce the size of the government and put more resources into programs that benefit the people. They can also increase the salaries of government employees and employees of government-funded agencies. These increases in spending will create incentives for government employees to do their jobs well.
Corruption is an undeniable part of today’s culture. It can be seen every day, in many different forms. However, no matter how big or small a contribution it may be, it’s always going to be a problem.
Corruption is something that can be learned. That’s why the people who dedicate themselves to improving it in their communities are always in demand.
Corruption has been around since the beginning of time. And unfortunately, corruption will continue to exist until people are more conscious about what they’re doing and how they’re living their lives.
Similar Posts
What is a clause different types of clauses with examples | comprehensive guide, past perfect continuous tense worksheet with answers, list of 50+ collective nouns for food and drink, adverb of manner (225 example sentences, list & worksheet), intransitive verbs with examples, starting sentences for essays & tips for opening sentences, leave a reply cancel reply.
Home — Essay Samples — Government & Politics — Political Corruption — The Causes of Political Corruption and Its Negative Effects
The Causes of Political Corruption and Its Negative Effects
- Categories: Political Corruption
About this sample

Words: 971 |
Published: Nov 6, 2018
Words: 971 | Pages: 2 | 5 min read

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Prof. Kifaru
Verified writer
- Expert in: Government & Politics

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
1 pages / 592 words
1 pages / 521 words
1 pages / 643 words
4 pages / 1997 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online

Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Power, in its various forms, has been a subject of fascination and concern throughout human history. Whether it's political, economic, or social power, the question that often arises is whether the acquisition of power leads to [...]
Authoritarianism is a form of government characterized by strong central power and limited political freedoms. It is often associated with a lack of transparency, restrictions on civil liberties, and the absence of democratic [...]
Lincoln Steffens was a political journalist. He became famous when he began to write a series on the corruption of American Cities, called The Shame of Cities. Steffens focused mainly on political corruption of the municipal [...]
In the last presidential election cycle, $1,977,700,000 was independently spent in support of Barrack Obama or Mitt Romney, $828 million of which was raised by political action committees (PACs). This money, enough to send [...]
Topic avoidance and secret keeping have been traditionally been fields of study underexplored in favor of scientific inquiry into self-disclosure, something that only recently started changing in the last few decades. In the [...]
In the wake of Citizens United, the landmark 2010 Supreme Court case that loosened restrictions on political expenditures, campaign financing has gone through the roof. Super PACs and the country’s wealthiest of the wealthy [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
24/7 writing help on your phone
To install StudyMoose App tap and then “Add to Home Screen”
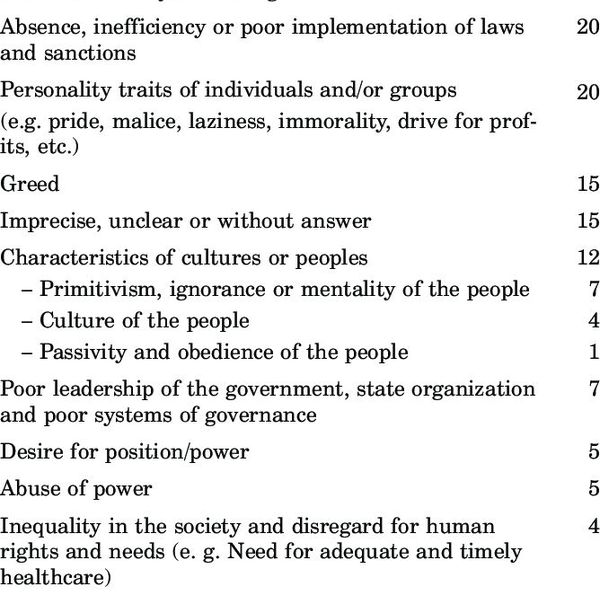
Causes Of Corruption - Free Essay Examples and Topic Ideas
There are several causes of corruption, including weak government institutions, lack of transparency and accountability, poverty, political instability, greed, and impunity. Weak government institutions can create an environment of impunity, where corrupt officials can act without fear of punishment. Lack of transparency and accountability in government processes can encourage corruption, and poverty can lead individuals to engage in corrupt practices in order to meet their basic needs. Political instability can also create opportunities for corruption, as powerful individuals may take advantage of the chaos to further their own interests. Greed is another common cause of corruption, as some individuals may be willing to engage in unethical practices in order to gain personal wealth or power.
- 📘 Free essay examples for your ideas about Causes Of Corruption
- 🏆 Best Essay Topics on Causes Of Corruption
- ⚡ Simple & Causes Of Corruption Easy Topics
- 🎓 Good Research Topics about Causes Of Corruption
Essay examples
Essay topic.
Save to my list
Remove from my list
- Nature and Causes of Police Corruption
- Causes of corruption in developing countries
- Causes of corruption in developed countries
- Causes of corruption in the public sector
- Causes of corruption in the private sector
- Causes of Unemployment
- Causes And Effects Of Poverty Economics
- Causes of Poverty
- Causes of corruption in the judiciary
- Causes and Solutions to World Hunger
- Causes of corruption in the police
- Causes of corruption in the military
- The causes for the failure of White Revolution
- Causes of corruption in the civil service
- Causes and Effects of French Revolution Events
- Global Warming : causes, effects and remedies
- Leading Causes of Morbidity and Mortality in the US
- Causes of corruption in local government
- Causes of corruption in central government
- Causes of high unemployment in Zimbabwe
- Causes of corruption in the European Union
- Causes of corruption in the United Nations
- Causes of corruption in the World Bank
- Causes of corruption in the International Monetary Fund
- Causes of corruption in the World Trade Organization
FAQ about Causes Of Corruption
👋 Hi! I’m your smart assistant Amy!
Don’t know where to start? Type your requirements and I’ll connect you to an academic expert within 3 minutes.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Effects of Corruption. Corruption violates the rights and freedoms of individuals to get basic services from public and private offices. This means that this practice compromises the quality of services offered by employees in the public and private sectors and puts the lives of citizens at risk.
It is this paper's aim to provide a reassessment and a comprehensive state-of-the-art survey of existing literature on corruption and its causes and effects. A particularly strong focus is put on ...
Corruption is a constant in the society and occurs in all civilizations; however, it has only been in the past 20 years that this phenomenon has begun being seriously explored. It has many different shapes as well as many various effects, both on the economy and the society at large. Among the most common causes of corruption are the political and economic environment, professional ethics and ...
According to "15 effects of corruption" (2019), a decrease in foreign investment could occur due to corruption. There are many cases in which foreign investment in developing countries has gone back due to heavy bribery in government bodies. Delay in economic growth and lack of development also cause corruption.
the corruption issue and to try and bring it under control. There is a growing worldwide concern over corruption at the present time. Several factors are responsible for this. First, a consensus has now been reached that corruption is universal. It exists in all countries, both developed and developing, in the public and private sectors,
Corruption has fierce impacts on economic and societal development and is subject to a vast range of institutional, jurisdictional, societal, and economic conditions. It is this paper's aim to provide a reassessment and a comprehensive state-of-the-art survey of existing literature on corruption and its causes and effects. A particularly strong ...
Corruption is a complex social phenomenon and the motivations to engage in corrupt behavior are multifaceted and is the result of interactions at the micro-, meso-, and macrolevel (Bicchieri and Ganegonda, 2016; Dimant and Schulte, 2016). Surprisingly, corruption has rarely been the focus of attention, but rather has been analyzed in a broader ...
5 Essays About Corruption. Internationally, there is no legal definition of corruption, but it includes bribery, illegal profit, abuse of power, embezzlement, and more. Corrupt activities are illegal, so they are discreet and done in secrecy. Depending on how deep the corruption goes, there may be many people aware of what's going on, but ...
policy discourse; 2) the effects of corruption; 3) the deeper meanings of corruption; and 4) different approaches to measuring corruption. Corruption: a baseline definition Despite the many definitions and contextual uses of corruption, most dictionaries and legal systems agree about its basic meaning. The Oxford2
The effects of corruption mentioned above can be categorized along the following lines: economic, political, moral or psychological, humanitarian, ecological, security-related, and so on. To help us gain a better understanding of corruption, the following section discusses some of the deeper meanings of corruption.
accountability, suggesting that some forms of corruption had been curtailed. Both essays suggest that despite substantial corruption in government and fraud in private dealings economic growth was curtailed far less in America than in today's developing economies. The volume then turns to the causes and consequences of reform. Reform and ...
Corruption is one of the concepts that man has adapted to and it has taken its toll in the human society as his desire and greed for material wealth and power increase. By definition, corruption refers to the use of available resources or designated power for purposes other than the intended ones or for personal gains.
aimed at creating the rent and its redistribution via corruption. The second type of corruption is a corruption that violates. the legal rules, or a very biased enforcement of the rules. This is ...
Corruption is the misuse of public or private resources for personal gain. It is a widespread problem affecting governments, businesses, and individuals worldwide. In this essay on corruption you get all the information about corruption and how it was dangerous to our life. Corruption can take many forms, such as bribery, extortion, cronyism ...
Essay Writing Service. Research shows that corruption is more prevalent in underdeveloped or poor countries and contributes to the faster growth of corruption (Myint, 2000). In this type of scenario, some of the members of these nations are even expected to give gifts as seen in Samoa, where leaders are expected to give gifts of sustenance to ...
Essay on Corruption - Corruption refers to a form of criminal activity or dishonesty. It refers to an evil act by an individual or a group. Most noteworthy, this act compromises the rights and privileges of others. Furthermore, Corruption primarily includes activities like bribery or embezzlement. However, Corruption can take place in many ways.
The thesis commences by extensively investigating the causes of corruption. Using the standard economic approach, this study finds that in China regions with more anti-corruption ... demonstrates the pernicious effects of corruption upon, among other things, investment, economic growth, environmental quality and therefore social welfare. In ...
250 Words Essay on Causes of Corruption Introduction. Corruption, a pervasive and long-standing phenomenon, poses a significant threat to social-economic development and political stability. It is a complex issue with roots in a country's institutional and political settings. ... Lack of education and awareness about the detrimental effects ...
"Corruption and Poverty," a review essay commissioned by USAID, summarizes its findings with a long list of negative effects: "Corruption impedes economic growth by discouraging foreign and domestic investment, taxing and dampening entrepreneurship, lowering the quality of public infrastructure, decreasing tax revenues, diverting public ...
Corruption, an insidious plague with a wide range of corrosive effects on societies, is a multifaceted phenomenon with deep roots in bureaucratic and political institutions. It undermines democracy, hollows out the rule of law, and hampers economic development. This essay explores the concept of corruption, its implications, and potential ...
Corruption is the abuse of power, position, or resources to gain an unjust or illegal advantage for oneself or someone else. Corruption can take many forms. It can be thoughts of greed; it can be taking bribes; it can be a misappropriation of public funds; it can be nepotism, and it can even be lying about the true nature of the product.
Get original essay. There are many causes for political corruption on the state and local level including personal greed, lack of efficient punishment, and lack of transparency in affairs. The most significant of those is the lack of transparency of affairs. When state and local governments lack transparency, participation decreases, there is ...
This essay will discuss the sources of corruption carried out at different field and it's several impacts. Firstly, low pay scale and unemployment plays an important role in employee's which in turn results corruption. Secondly, lack of strict punishment caused by absence of transparency leads to corruption.
There are several causes of corruption, including weak government institutions, lack of transparency and accountability, poverty, political instability, greed, and impunity. Weak government institutions can create an environment of impunity, where corrupt officials can act without fear of punishment. Lack of transparency and accountability in ...