Case Study Questions Class 7 Science Nutrition in Animals
Case study questions class 7 science chapter 8 nutrition in animals, cbse case study questions class 7 science nutrition in animals, case study 1, case study 2.
Que. 2) (d) All of the above

Case study 3
Case study 4.
Que. 3) (c) America
Case study 5
Leave a reply cancel reply, we have a strong team of experienced teachers who are here to solve all your exam preparation doubts, chhattisgarh class 7 math decimal representation of rational numbers and operations solution, up scert solutions class 7 english chapter 6 – a good citizen, dav class 6 english literature book solution chapter 7 bharat desh, dav class 6 english literature book solution chapter 5 today and tomorrow.
NCERT Solutions for Class 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12
Nutrition in Animals Class 7 Extra Questions Science Chapter 2
August 6, 2024 by Bhagya
Nutrition in Animals Class 7 Science Extra Questions Very Short Answer Type
Question 1. What is the total number of teeth in an adult human? Answer: In an adult human, there are total 32 teeth.
Human Digestive System Diagram Class 7
Question 2. Name the parts of the alimentary canal where (a) water gets absorbed from undigested food (b) digested food gets absorbed (c) taste of the food is perceived (d) bile juice is produced [NCERT Exemplar] Answer: (a) large intestine (b) small intestine (c) tongue (d) liver
Question 3. Identify the location of salivary gland. Answer: Salivary gland is present in the buccal cavity and it secretes saliva.
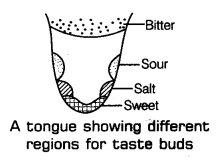
Question 4. You were blindfolded and asked to identify the drinks provided in two different glasses. You could identify drink A as lime juice and B as bitter gourd juice. How could you do it inspite of being blindfolded? [NCERT Exemplar; HOTS] Answer: Inspite of being blindfolded, one could identify two different drinks with the help of taste buds present in the tongue.
Question 5. We should not eat hurriedly. Give reason. Answer: We should not eat hurriedly because if we ingest food in hurry or we talk or laugh while eating we experience hiccups, coughing or choking sensation.
Question 6. Name the secretions of stomach which digest food. Answer: The inner lining of stomach secretes mucous hydrochloric acid and digestive juices.
Question 7. Explain the role of mucus secreted by stomach. Answer: The function of mucus is to protect the lining of stomach from the action of hydrochloric acid secreted by stomach lining.
Question 8. The long structure of small intestine is accommodated in small space within our body. Comment. [HOTS] Answer: The small intestine is about 7.5 metre long It is accommodated in a coiled form inside our body.
Question 9. Suggest the organ of digestive system where the digestive juices from liver and pancreas is poured. Answer: The digestive juices from liver and pancreas is poured into small intestine which helps in complete digestion and absorption of food.
Question 10. From which organ of digestive system, the undigested faecal matter is removed? Answer: The undigested faecal matter is removed through the anus by the process called egestion.
Question 11. Mention the position of the rumen in ruminants. Answer: The rumen is the sac-like structure which is present between small intestine and large intestine in ruminants.
Question 12. What is assimilation? Answer: The process by which absorbed food is taken by body cells and is used for energy, growth and repair is called assimilation.
Question 13. Describe alimentary canal briefly. Answer: Alimentary canal is the tube running from mouth to anus of human and animals here digestion and absorption of food take place.
Question 14. Name the simple forms of carbohydrates, fats and proteins. Answer: The food components and their simple forms are carbohydrates (glucose), fatty (fats) acids and glycerol, proteins (amino acids).
Question 15. Write the shape of stomach. Answer: The shape of stomach is like flattened U-shaped.
Question 16. Discuss the role of hydrochloric acid secreted by gastric glands. Answer: It helps in the breakdown of food particles. It creates an acidic environment which facilitates the action
Nutrition in Animals Class 7 Science Extra Questions Short Answer Type
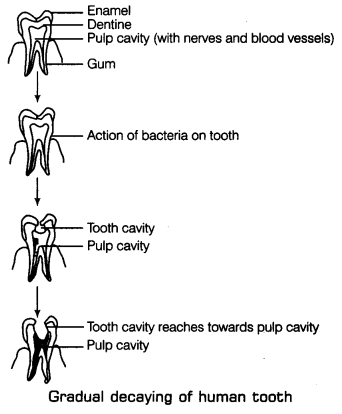
Question 1. With the help of labelled diagram show the gradual decay of tooth. Answer: Sweets and Tooth Decay The tooth is covered by white, hard outer covering of tooth called Enamel enamel below which dentine is present. It is similar to bone which Pulp cavity (with nerves and blood vessels) protects the pulp cavity having nerves and blood vessels. Bacteria are Gum present in our mouth but they are not harmful to us. However, if we do not clean our teeth and mouth after eating, many harmful bacteria also begin to live and grow in it. These bacteria breakdown the sugars present from the leftover food and release acids. The acids gradually damage the tooth. This is called tooth decay.
Question 2. Name the various components of food and their simpler forms. Answer: The various components of food and their simpler forms are
| Components of food | Simpler form |
| Carbohydrate | Glucose |
| Fats | Fatty acids and glycerol |
| Proteins | Amino acids |
| Vitamins | Vitamins |
| Minerals and water | Minerals and water |
Question 3. ‘A’ got her gall bladder removed surgically as she was diagnosed with stones in her gall bladder. After the surgery, she faced problems in digestion of certain food items when consumed in bulk. Can you tell which kind of food items would they be and why? [NCERT Exemplar; HOTS] Answer: After surgical removal of gall bladder, ‘A’ would face problems in digestion of fat and fatty substances when consumed in bulk. This is because the bile juice stored in the gall bladder helps in digestion of fats.
Question 4. Discuss the various associated glands of digestive system and their role in digestion. Answer: The various associated glands of digestive system and their role in digestion are as follows
- Salivary gland digestion of starch in mouth.
- Liver secretes bile juices which help in the digestion of fats.
- Pancreas secretes pancreatic juices which act on carbohydrate, fats and proteins and change them into simpler compounds.
Question 5. Boojho took some grains of boiled rice in test tube ‘A’ and Paheli took boiled and chewed rice in test tube ‘S’. Both of them poured 1-2 drops of iodine solution into the test tube and observed the colour change. What colour change would they have observed? Give reasons for your Answer: [NCERT Exemplar; HOTS] Answer: In test tube A, blue black colour appeared because of presence of starch. In test tube 6, colour of iodine will not change because of digestion of starch into sugars by the action of saliva in our mouth.
Question 6. Mention the different steps of nutrition in animals.
Question 7. List the preventive measures that one should adopt for avoiding tooth decay. Answer: Sweets and Tooth Decay The tooth is covered by white, hard outer covering of tooth called Enamel enamel below which dentine is present. It is similar to bone which Pulp cavity (with nerves and blood vessels) protects the pulp cavity having nerves and blood vessels. Bacteria are Gum present in our mouth but they are not harmful to us. However, if we do not clean our teeth and mouth after eating, many harmful bacteria also begin to live and grow in it. These bacteria breakdown the sugars present from the leftover food and release acids. The acids gradually damage the tooth. This is called tooth decay.
Question 8. Write the difference between milk teeth and permanent teeth. Answer: The difference between milk teeth and permanent teeth are
| Milk teeth | Permanent teeth |
| They grow during infancy, i.e. when one is small baby. | They grow at the age of 6-8 years. |
| They are also called as temporary teeth because these are lost at the age of 6-8 years. | They do not fall till the old age. |
| They can be replaced by permanent teeth. | If these teeth fall down no new teeth arises on its place. |
Question 9. Complete the following table, from the options given below: (Scraping, chewing, siphoning, capturing and swallowing, sponging, sucking, etc.)
| Name of animal | Kind of animal | Mode of feeding |
| Snail | ||
| Ant | ||
| Eagle | ||
| Humming bird | ||
| Lice | ||
| Mosquito | ||
| Butterfly | ||
| Housefly |
Answer: The complete table is
| Name of animal | Kind of food | Mode of feeding | |
| Snail | Leaves and insects | Scraping | |
| Ant | Food particles | Chewing | |
| Eagle | Small animals | Capturing and swallowing | |
| Humming bird | Nectar of flower | Sucking | |
| Lice | Blood | Sucking | |
| Mosquito | Blood | Sucking | |
| Butterfly | Nactar of flower | Siphoning | |
| Housefly | All most everything | Sponging | |
Question 10. Briefly describe the mechanism of producing hiccups while we take food in hurry.
Question 11. Boojho and Paheli were eating their food hurriedly so that they could go out and play during the recess. Suddenly, Boojho started coughing violently. Think of the reasons, why he was coughing and discuss with your friends? [NCERT Exemplar; HOTS] Answer: Sometimes when we eat hurriedly, talks or laughs while eating, the flap-like valve (called epiglottis) which closes the passage of windpipe remains open. Therefore, the food may enter into the windpipe. Coughing helps to clear the passage and returns the food particle back to the foodpipe.
Question 12. Gastric glands in stomach release hydrochloric acid, enzyme pepsin and mucus. What will happen if mucus is not secreted by the gastric glands? Answer: Mucus protects the inner lining of stomach form the action of hydrochloric acid and enzyme pepsin. If mucus is not released, it will lead to erosion of inner lining of stomach leading to acidity and ulcers.
Question 13. Choose the odd one out from each group and give reasons. (a) liver, salivary gland, starch, gall bladder (b) stomach, liver, pancreas, salivary gland (c) tongue, absorption, taste, swallow (d) oesophagus, small intestine, large intestine, rectum [NCERT Exemplar] Answer: (a) Starch, because rest all are glands and starch is a type of carbohydrate. (b) Stomach, because rest all are digestive glands and stomach is a digestive organ. (c) Tongue, because rest all are digestive processes and tongue is a part of digestive system. (d) Small intestine, because it carriers the process of digestion and rest are not involved in digestion.
Question 14. Following statements describe the five steps in animal nutrition. Read each statement and give one word for each statement. Write the terms that describe each process. (a) Transportation of absorbed food to different parts of body and their utilisation. (b) Breaking of complex food substances into simpler and soluble substances. (c) Removal of undigested and unabsorbed solid residues of food from the body. (d) Taking food into the body. (e) Transport of digested and soluble food from the intestine to blood vessels.[NCERT Exemplar] Answer: (a) Assimilation (b) Digestion (c) Egestion (d) Ingestion (e) Absorption
Question 15. Small intestine in herbivores is longer than in carnivores. Do you agree? Support your Answer: Answer: Yes, carnivores animals cannot digest cellulose, hence they have a shorter small intestine. In herbivores, digestion of cellulose takes a longer time. Hence, herbivores need a longer small intestine to allow complete digestion of cellulose.
Amoeba Diagram For Class 7
Question 18. Ruminants such as cows and buffaloes swallow their food hurriedly and then sit restfully and chew their food. Give reason. [NCERT Examplar; HOTS] Answer: Ruminants such as cows and buffaloes swallow their food hurriedly and store it in a part of the stomach called rumen. The cellulose of the food is digested here by the action of certain bacteria which are not present in humans. Later, this partially digested food is returned to the buccal cavity of the animals in small lumps and animal chews it to complete the process of digestion. This process is called rumination.
Question 19. Discuss the position and number of molars in buccal cavity. Answer: Molars are very large teeth which are present behind the premolar, towards the back of our mouth. They are only present in the permanent set of teeth and are 6 in each jaw.
Question 20. Name the three digestive glands in our body. Answer: The three digestive glands are
- Salivary glands
Question 21. The swallowed food moves downwards in the alimentary canal. Explain. Answer: The swallowed food moves downwards in the alimentary canal because of the atternate relaxation contraction movement of muscles in the wall of foodpipe called peristalsis.
Question 22. Explain how assimilation is different from absorption. Answer: The process by which nutrients from the digested food are absorbed by the body is called absorption whereas the process by which the absorbed nutrients are utilised by the body for providing energy is called assimilation.
Question 23. Food moves in the opposite direction during vomiting. How? Answer: The intense pressure is formed in the stomach when the food is not accepted by the stomach. The content in the stomach is then pushed back. This returned content is expelled out from the mouth in the form of vomiting.
Question 24. Briefly explain, why animals like cow cannot chew their food properly at the time they take it in. Answer: Animals like cow cannot chew their food properly due to the presence of cellulose in their diet. At the time they take in food, the food is moistend and is sent for cellulose digestion and softening in rumen.
Question 25. Is there any role of liver in digestion of fats? Explain. Answer: Yes, liver produces bile which has bile salts. These salts break large fat molecules to fine droplets. These fine droplets are further converted into fatty acids and glycerol.
Question 26. Cellulose rich food substances are good source of roughage in human beings. Justify. [HOTS] Answer: Cellulose rich food substances are good source of roughage in human beings. It is because the cellulose digesting bacteria are not present in the body of human beings due to which human beings cannot digest cellulose (present in plant foods).
Question 27. Recall and name the main organs of the digestive system in our body. Answer: The different organs of the alimentary canal are as follows :
- Mouth and mouth cavity
- Small intestine
- Large intestine
Question 28. Alimentary canal is different from digestive system. Comment. Answer: Alimentary canal is a long, muscular coiled tube. It is also known as digestive tract. The alimentary canal with its associated glands constitute the digestive system. These glands are salivary glands, liver and pancreas.
Question 29. Windpipe runs adjacent to the foodpipe. What will happen if food particles enter the windpipe? Explain. Answer: The windpipe carries air from the nostrils to the lungs. It runs adjacent to the foodpipe. If, by chance, food particles enter the windpipe, we feel choked, get hiccups or cough.
Question 30. Explain how is small intestine designed to absorb digested food. Answer: The finger-like projections called villi are present in the inner walls of the small intestine. The villi increase the surface area. The large surface area of small intestine helps in the rapid absorption of the digested food.
Nutrition in Animals Class 7 Science Extra Questions Long Answer Type

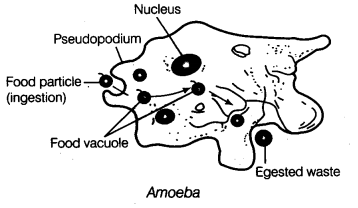
Question 2. Briefly describe the process of digestion in Amoeba with the help of labelled diagram. [NCERT Examplar] Answer: Feeding and Digestion in Amoeba
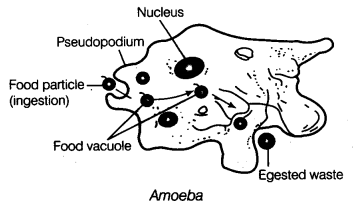
Question 4. Little Rishi (student of class VI) was watching his favourite cartoon serial on television. Suddenly he got hiccups. His elder brother Shubham who was sitting near by him gave him a glass of water and suggested not to eat too fast in a hurry. Little Rishi got confused as he had heard that ‘hicki’ comes when someone remembers. He asked his father. His father smiled and explained him that it is only a myth. He also explained him the proper scientific reason behind it. (a) What is hiccup? (b) Why do we get hiccup? (c) What are the values shown by Rishi? [Value Based Question] Answer: (a) Hiccup is a choking sensation that produces a characteristic gulping sound repeatedly. It is called ‘hicki’ in our local language. (b) Sometimes, when we eat too fast in a hurry or talk too much or laugh while eating, then a little of windpipe remains open due to which food particles may enter the windpipe. It may result in a choking sensation called hiccups. (c) He is sincere and curious to know about the things at an early age.
Question 5. Jaya returned from school and found that grandmother was scolding her maid, Rani as she did not come yesterday. The maid told that his son was passing watery stools frequently that’s why she didn’t come. Jaya’s mother who was listening the discussion came to them and told Rani not to come for coming 3-4 days. She also suggested her to give his son a solution of sugar and salt in clean water, many times a day for fast recovery. Jaya was surprised. She rushed to her mother and asked the scientific reason for it. Her mother smiled and explained her the importance of this solution. (a) Name the term used to describe the condition in which a person passes out watery stools. (b) Name the solution of sugar and salt in water. Why is it given to a person suffering from diarrhoea? (c) What are the values shown by Jaya? [Value Based Question] Answer: (a) Diarrhoea. (b) Oral Rehydration Solution (ORS). It is given to a person suffering from diarrhoea to prevent the dehydration. (c) She is sincere, curious and has interest in science.
Question 6. Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions that follow it. Bile juice is stored in a sac called, gall bladder, located near its organ of secretion, liver. The gall bladder releases the bile juice into the small intestine whenever food reaches there. Though bile juice is devoid of any digestive enzymes, it is required for the digestion of fats. The fats cannot be digested easily because they are insoluble in water and are present as large globules. Bile juice breaks down big fat droplets into smaller droplets. These are then easily digested by the enzymes released from the pancreas (a) Which organ secretes the bile juice? (b) Why is digestion of fats difficult as compared to that of other nutrients? (c) How does bile juice help in digestion of that of other nutrients? (d) Where is the digestion of fat completed? (e) Does bile juice digest fat completely? [NCERT Exemplar] Answer: (a) Bile juice is secreted by liver. (b) Digestion of fats is difficult as compared to that of other nutrients because of insolubility of fat in water. (c) Bile juice helps in digestion of fat by breaking down big fat droplets into smaller droplet. (d) Digestion of fat is completed in small intestine. (e) No, fat is not completely digested by bile juice.
Question 7. Define oral rehydration solution and when it is given to the patient? How can you prepare ORS at home? Answer: Oral rehydration solution is the solution of sugar and salt in a particular ratio in the clean water. When a person passes out watery stools frequently, the disease is called diarrhoea. In this condition there is a loss of water and salt from the body of a person.
This is called dehydration which may be fatal if not cured at proper time. In order to prevent dehydration, the person or patient should be given ORS. ORS makes up the loss of water and salts in the body and sugar provides energy which helps in the recovery of disease. It should be given to a patient suffering from diarrhoea at a regular interval.
At home the ORS can be prepared by dissolving a teaspoonful of sugar and pinch of salt in a glass of clean water. The water used for preparing ORS should be first boiled and then cooled so that all the microorganisms or harmful bacteria may be killed.
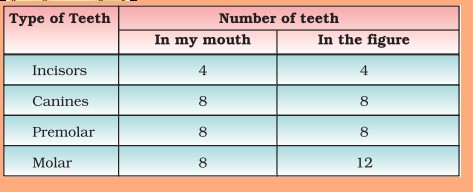
Question 8. Open your mouth, look into a mirror and try to count the different types of teeth of teeth in your mouth. Compare them with figure 2.3 on page 13 of your NCERT textbook. Record your observations in the table below: [NCERT Exemplar]
| Type of teeth | Number of teeth | |
| In my mouth | In the figure | |
| Incisors | ||
| Canines | ||
| Premolars | ||
| Molars | ||
(a) Did you observe any difference in the number of teeth? If yes, could you identify which type of teeth showed the difference? (b) Compare the number and type of teeth in an adult (say your parents or cousins who have reached the age of 25-30 or more). Note your observation. Answer:
| Type of teeth | Number of teeth | |
| In my mouth | In the figure | |
| Incisors | 4 | 4 |
| Canines | 8 | 8 |
| Premolars | 8 | 8 |
| Molars | 8 | 12 |
(a) Yes, the difference has been observed in the number of molars. (b) The number and type of teeth varries in an adult as compared to the child. Children have 28 teeth in their mouth.There are only four molars in each jaw. While, adults have 32 teeth in their mouth which means six molars in each jaw.
Question 9. Explain how the digestion of cellulose occurs in grass eating animals. Answer: Digestion in Grass-Eating Animals
The herbivorous animals such as cow, buffaloes, etc eat grass. These animals quickly swallow the grass and store it in a part of stomach called rumen. The food is not chewed completely. Rumen possess cellulose digesting bacteria which breakdown the food by fermentation. This partially digested food or grass present in the rumen of cow is called cud.
This cud is brought back into the mouth of the cow from the rumen into small lumps and animal chews it again. This process is called rumination and animals are called ruminants. When this cud is thoroughly chewed in the mouth of the cow, it is swallowed again. This time the chewed cud does not go back to rumen but enter into the other compartments of cow’s stomach and then into the small intestine for complete digestion and absorption of food. The cellulose digesting bacteria are not present in the body of human being, therefore human beings and other carnivore cannot digest cellulose present in plant food items.
Nutrition in Animals Class 7 Science Extra Questions Miscellaneous
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1. Hydrochloric acid is secreted by (a) linings of small intestine (b) inner lining of stomach (c) pancreas (d) lining of liver Answer: (b) inner lining of stomach
Question 2. Which of the following pair of teeth differ in structure but are similar in function? [NCERT Exemplar] (a) Canines and incisors (b) Molars and premolars (c) Incisors and molars (d) Premolars and canines Answer: (b) Molars and premolars
Question 3. The swallowed food moves downwards in the alimentary canal because of [NCERT Exemplar] (a) force provided by the muscular tongue (b) the flow of water taken with the food (c) gravitational pull (d) the contraction of muscles in the wall of foodpipe Answer: (d) the contraction of muscles in the wall of foodpipe
Question 4. The acid present in the stomach (a) kills the harmful bacteria that may enter along with the food (b) protects the stomach lining from harmful substances (c) digests starch into simpler sugars (d) makes the medium alkaline Answer: (a) kills the harmful bacteria that may enter along with the food
Question 5. The simplest form of protein is (a) fatty acids (b) glucose (c) glycerol (d) amino acids Answer: (d) amino acids
Question 6. The finger-like outgrowths of Amoeba helps to ingest food. However, the finger-like outgrowths of human intestine helps to [NCERT Exemplar] (a) digest the fatty food substances (b) make the food soluble (c) absorb the digested food (d) absorb the undigested food Answer: (c) absorb the digested food
Question 7. The false feet of Amoeba are used for [NCERT Exemplar] (a) movement only (b) capture of food only (c) capture of food and movement (d) exchange of gases only Answer: (c) capture of food and movement
Question 8. Read the following statements with reference to the villi of small intestine. (i) They have very thin walls. (ii) They have a network of thin and small blood vessels close to the surface. (iii) They have small pores through which food can easily pass. (iv) They are finger-like projections. Identify those statements which enable the villi to absorb digested food. (a) (i), (ii) and (iv) (b) (ii), (iii) and (iv) (c) (iii) and (iv) (d) (i) and (iv) Answer: (c) (iii) and (iv)
Question 9. The absorption of nutrients or food components in its simpler form takes place in (a) blood vessels of small intestine wall (b) large intestine wall (c) gall bladder (d) liver Answer: (a) blood vessels of small intestine wall
Question 10. The enzymes present in the saliva convert [NCERT Exemplar] (a) fats into fatty acids and glycerol (b) starch into simple sugars (c) proteins into amino acids (d) complex sugars into simple sugars Answer: (b) starch into simple sugars
Question 11. Cud is the name given to the food of ruminants which is [NCERT Exemplar] (a) swallowed and undigested (b) swallowed and partially digested (c) properly chewed and partially digested (d) properly chewed and completely digested Answer: (b) swallowed and partially digested
Question 12. Cellulose rich food substances are good sources of roughage in human beings because [NCERT Exemplar] (a) human beings do not have cellulose: digesting enzymes (b) cellulose gets absorbed in the human blood and converts into fibres (c) the cellulose digesting bacteria convert cellulose into fibres (d) cellulose breaks down into smaller components which are egested as roughage Answer: (a) human beings do not have cellulose: digesting enzymes
Question 13. If, by chance, food particles enter the windpipe, we feel (a) hiccups and cough (b) yawning (c) sleep (d) None of these Answer: (a) hiccups and cough
Question 14. The tip or front of tongue taste (a) sour (b) bitter (c) salt and sweet (d) All of these Answer: (c) salt and sweet
Question 15. Dentine protects which part of human teeth? (a) Enamel (b) Pulp cavity (c) Gums (d) Dental cavity Answer: (b) Pulp cavity
Question 16. The finger-like projection presents on the inner lining of small intestine is called (a) villi (b) stomach (c) rumen (d) diarrhoea Answer: (a) villi
Fill in the Blanks
Question 1. ……. is the process of taking food inside the body. Answer: Ingestion
Question 2. ….. is the simplest form of carbohydrate. Answer: Glucose
Question 3. The process of breakdown of complex food material into …… is called ……. Answer: simpler form, digestion
Question 4. Amoeba digests its food inside ……… Answer: food vacuole
Question 5. ……. teeth replaces the milk teeth. Answer: Permanent
Question 6. …… is the long tube-like structure which Answer: Alimentary canal
Question 7. Large intestine absorbs ….. and …… from undigested food. Answer: water, salts
Question 8. Animals are ……. Answer: heterotrophic
Question 9. Cud chewing animals are called …….. Answer: ruminants
Question 10. Four kinds of teeth present in human are ……, …….., …….. and …….. Answer: incisor, cannines, premolar, molar
Question 1. Oesophagus is also called as foodpipe. Answer: True
Question 2. Simplest form of fat is sugars and glucose. Answer: False, simplest form of fat is fatty acid and glycerol.
Question 3. Ruminant can digest cellulose (carbohydrate). Answer: True
Question 4. Canines are used for grinding of food. Answer: False, canines are used for piercing and tearing the food.
Question 5. Amoeba is a microscopic, single celled animal. Answer: True
Question 6. The nutrition in Amoeba takes place by pseudopodia. Answer: True
Question 7. Egestion is the process of removing waste food or undigested food through anus. Answer: True
Question 8. Diarrhoea can be treated by only giving water to the patient. Answer: False, diarrhoea can be treated by giving a solution of sugar and salt in the clean water for several times in a day. This solution is called ORS.
Question 9. Source of energy for living being is food. Answer: True
Question 10. The digestion of starch only takes place in the stomach Answer: False, digestion of starch normally begins in the mouth where it is broken down into smaller sugar molecules, glucose. Additional breakdown of starch occurs in the small intestine.
Match the Columns
Question 1. Match the Column I with Column II. [NCERT Examplar]
| Column 1 | Column II |
| (a) Rectum | (i) Mucus |
| (b) Gallbladder | (ii) Villi |
| (c) Stomach | (iii) Taste buds |
| (d) Tongue | (iv)Faecus |
| (e) Small intestine | (v) Bile juice |
Answers: (a)-(v), (b)-(vi), (c)-(i), (d)-(vii), (e)-(ii), (f)-(iv), (g)-(iii)
Question 2. Match the Column I with Column II.
| Column 1 | Column II |
| (a) Amoeba | (i) ORS |
| (b) Incisors | (ii) Bile juice storage |
| (c) Diarrhoea | (iii) Release of faecus |
| (d) Fat | (iv) Cud chewing animals |
| (e) Gall bladder | (v) Pseudopodia |
| (f) Ruminants | (vi) Cutting and biting |
| (g) Anus | (vi) Fatty Acid and Glycerol |
Answers: (a)-(iii), (b)-(i), (c)-(iv), (d)-(ii)
Extra Questions for Class 7 Science
Free resources.
NCERT Solutions
Quick Resources
- NCERT Exemplar
- NCERT Exemplar Class 7
- Class 7 Science
- Chapter 2 Nutrition In Animals
NCERT Exemplar Solutions Class 7 Science Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals
NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Class 7 Science Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals include answers to all the questions provided in the NCERT Exemplar book. Students are advised to get well acquainted with this NCERT Exemplar as it will guide them in gaining complete knowledge of the concepts covered in Class 7 Science Chapter 2, Nutrition in Animals.
NCERT Exemplar for Class 7 Science will provide you with a variety of questions like MCQs, fill in the blanks, match the following and descriptive type questions on nutrition, types of different organisms, classification of nutrients, etc.
This Exemplar Solution provides answers and explanations to 12 MCQs, 6 very short answer questions, 6 very short answer questions and 6 long answer questions.
Download the PDF of NCERT Exemplar for Class 7 Science Chapter 2 – Nutrition in Animals

Importance of NCERT Exemplar for Class 7 Science Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals
NCERT Class 7 Science Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals covers questions on animal food and nutrition, the mode of food intake, digestion in different animals and protozoans, and a detailed explanation of the mode of nutrition in human beings. This chapter is quite an interesting one, as you can correlate it to many real-life examples.
Topics Covered in NCERT Exemplar for Class 7 Science Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals
2.1 – Different Ways of Taking Food
2.2 – Digestion in Humans
2.3 – Digestion in Grass-Eating Animals
2.4 – Feeding and Digestion in Amoeba.
Access Answers of NCERT Exemplar for Class 7 Science Chapter 2 – Nutrition in Animals
Multiple-choice questions.
1. Given below from (i) to (iv) are some food items.
- Boiled and mashed potato
- Glucose solution
- A slice of bread
- Mustard oil
Which of the above will give a blue-black colour when tested with iodine?
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i) and (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
The answer is (b) (i) and (iii)
Explanation:
Mashed potato and bread are rich in starch. On adding iodine, it reacts with starch to give a blue-black colour.
2. Which of the following pair of teeth differ in structure but are similar in function?
(a) canines and incisors.
(b) molars and premolars.
(c) incisors and molars.
(d) premolars and canines.
The answer is (b) molars and premolars.
Our teeth tear and grind the food before swallowing food. There are four types of teeth.
Incisors: front eight teeth, 4 in the upper jaw and 4 in the lower jaw.
Canines: There are 4 canines, one on each side of each jaw.
Premolars: There are 8 premolars. Two premolars in each of the upper and lower jaws.
Molars: There are 12 molars, three in each half of both upper and lower jaws.
3. Read carefully the terms given below. Which of the following set is the correct combination of organs that do not carry out any digestive functions?
(a) Oesophagus, Large Intestine, Rectum
(b) Buccal cavity, Oesophagus, Rectum
(c) Buccal cavity, Oesophagus, Large Intestine
(d) Small Intestine, Large Intestine, Rectum
The answer is (a) Oesophagus, Large Intestine, Rectum
Oesophagus pushes the food downwards, and it is not involved in any digestive functions.
The large intestine absorbs water and some salts from the undigested food material, and it is not involved in the digestion process.
In the rectum, the remaining waste passes and remains there as semi-solid faeces. It is not involved in any digestive function.
4. The swallowed food moves downwards in the alimentary canal because of
(a) force provided by the muscular tongue.
(b) the flow of water taken with the food.
(c) gravitational pull.
(d) the contraction of muscles in the wall of the food pipe.
The answer is (d) the contraction of muscles in the wall of the food pipe.
Muscles of the Esophagus push food down by the movement of the wall of the food pipe. Actually, this movement takes place throughout the alimentary canal and pushes the food downwards.
5. The acid present in the stomach
(a) kills the harmful bacteria that may enter along with the food.
(b) protects the stomach lining from harmful substances.
(c) digests starch into simpler sugars.
(d) makes the medium alkaline.
The answer is (a) kills the harmful bacteria that may enter along with the food.
The stomach consists of Hydrochloric acid, which kills the bacteria that enter through food. Thus stomach acid is helping in protecting us from harmful bacteria.
6. The finger-like outgrowths of Amoeba help to ingest food. However, the finger-like outgrowths of the human intestine help to
(a) digest the fatty food substances.
(b) make the food soluble.
(c) absorb the digested food.
(d) absorb undigested food.
The answer is (c) absorb the digested food.
Fingerlike projection is present in the small intestine, and they are called Villi. Villi absorb nutrients from digested food by increasing the space of the small intestine.
7. Read the following statements with reference to the villi of the small intestine.
(i) They have very thin walls.
(ii) They have a network of thin and small blood vessels close to the surface.
(iii) They have small pores through which food can easily pass.
(iv) They are finger-like projections. Identify those statements which enable the villi to absorb digested food.
(a) (i), (ii) and (iv)
(b) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
(c) (iii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (iv)
Answer is (a) (i), (ii) and (iv)
The inner walls of the small intestine have thousands of finger-like outgrowths called villi (singular villus). Villi increase the surface area for absorption of the digested food. Each villus has a network of thin and small blood vessels close to its surface. The surface of the villi absorbs the digested food materials. The absorbed substances are transported via the blood vessels to different organs of the body, where they are used to build complex substances such as the proteins required by the body.
8. The false feet of Amoeba are used for
(a) movement only.
(b) the capture of food only.
(c) the capture of food and movement.
(d) exchange of gases only.
The answer is (c) capture of food and movement.
Amoeba constantly changes their shape and position. It pushes out one, or more finger-like projections, called pseudopodia or false feet, for movement and capture of food. Amoeba feeds on some microscopic organisms. When it senses food, it pushes out pseudopodia around the food particle and engulfs it.
9. The enzymes present in the saliva convert
(a) fats into fatty acids and glycerol.
(b) starch into simple sugars.
(c) proteins into amino acids.
(d) complex sugars into simple sugars.
The answer is (b) starch into simple sugars.
Saliva consists of salivary amylase enzyme, which breaks starch into simple sugar, which is further digested by enzymes in the stomach and small intestine.
10. Cud is the name given to the food of ruminants which is
(a) swallowed and undigested.
(b) swallowed and partially digested.
(c) properly chewed and partially digested.
(d) properly chewed and completely digested.
The answer is (b) swallowed and partially digested.
Ruminants quickly swallow the grass and store it in a part of the stomach called the rumen. Here the food gets partially digested and is called cud. But later, the cud returns to the mouth in small lumps, and the animal chews it. This process is called rumination.
11. Choose the correct order of terms that describes the process of nutrition in ruminants.
(a) swallowing → partial digestion → chewing of cud → complete digestion
(b) chewing of cud → swallowing → partial digestion → complete digestion
(c) chewing of cud → swallowing → mixing with digestive juices → digestion
(d) swallowing → chewing and mixing → partial digestion → complete digestion
The answer is (a) swallowing → partial digestion → chewing of cud → complete digestion
12. Cellulose-rich food substances are a good source of roughage in human beings because
(a) human beings do not have cellulose-digesting enzymes.
(b) cellulose gets absorbed in the human blood and converts into fibres.
(c) the cellulose-digesting bacteria convert cellulose into fibres.
(d) cellulose breaks down into smaller components which are egested as roughage.
The answer is (a) human beings do not have cellulose-digesting enzymes.
Very Short Answer Questions
13. Name the parts of the alimentary canal where
(i) water gets absorbed from undigested food.
(ii) digested food gets absorbed.
(iii) taste of the food is perceived.
(iv) bile juice is produced.
(i) Large intestine
(ii) Small intestine
(iii) Tongue
14. Mark the following statements as True or False. If false, write the correct statements.
(a) Tongue is attached to the roof of the mouth cavity at the back.
(b) The large intestine is longer and wider than the small intestine of the human alimentary canal.
(c) Mucus protects the stomach lining from damage.
(d) All heterotrophs have a similar basic process of nutrition.
- False – The tongue is attached to the floor of the mouth cavity at the back.
- False – The large intestine is shorter and wider than the small intestine of the human alimentary canal.
15. Choose the odd one out from each group and give reasons.
(i) liver, salivary gland, starch, gall bladder
(ii) stomach, liver, pancreas, salivary gland
(iii) tongue, absorption, taste, swallow
(iv) oesophagus, small intestine, large intestine, rectum
- The answer is Starch because starch is a carbohydrate, whereas the liver, salivary gland and gall bladder are the glands.
- The answer is the stomach because others are digestive glands
- Absorption is the answer because tongue, swallow and taste are related to the buccal cavity but not absorption.
- The small intestine is the answer because the oesophagus, large intestine and rectum will not take part in digestion, whereas the small intestine plays the main role in the digestion process.
16. You were blindfolded and asked to identify the drinks provided in two different glasses. You could identify drink A as lime juice and B as bitter gourd juice. How could you do it in spite of being blindfolded?
We can identify the juices with the help of different taste buds present in the tongue.
17. Fill in the blanks with suitable words:
(a) The alimentary canal stretches from to.
(b) Teeth are rooted in separate in between the.
(c) Digestion of food starts in and gets completed in.
(d) is the largest gland in the human body.
- The alimentary canal stretches from Mouth to Anus .
- Teeth are rooted in separate Sockets in between the Gums .
- Digestion of food starts in the Buccal cavity and gets completed in Small Intestine .
- The liver is the largest gland in the human body.
18. Following statements describe the five steps in animal nutrition. Read each statement and give one word for each statement. Write the terms that describe each process.
(a) Transportation of absorbed food to different parts of the body and their utilisation.
(b) Breaking of complex food substances into simpler and soluble substances.
(c) Removal of undigested and unabsorbed solid residues of food from the body.
(d) Taking food into the body.
(e) Transport of digested and soluble food from the intestine to blood vessels.
(a) Assimilation
(b) Digestion
(c) Egestion
(d) Ingestion
(e) Absorption
Short Answer Questions
19. Match the animals in Column I with their mode of feeding listed in Column II
| Column I | Column II |
| Animals | Mode of Feeding |
| a) Housefly | iii) Sponging |
| b) Cockroach | i) Biting and chewing |
| c) Mosquitos | iv) Sucking |
| d) Infants | ii) Suckling |
20. Boojho took some grains of boiled rice in a test tube ‘A’, and Paheli took boiled and chewed rice in a test tube ‘B’. Both of them poured 1 – 2 drops of iodine solution into the test tube and observed the colour change. What colour change would they have observed? Give reasons for your answer.
In test-tube A colour of iodine changes to blue-black because of the reaction of iodine with starch. In test-tube B colour will not change because salivary amylase acts on starch while chewing, reducing it to simpler sugars.
21. ‘A’ got her gallbladder removed surgically as she was diagnosed with stones in her gallbladder. After the surgery, she faced problems in the digestion of certain food items when consumed in bulk. Can you tell which kind of food items would they be and why?
Those foods will be fats because of bile juice present in the gall bladder helps in the digestion of fat. Removal of gall bladder makes it hard to digest the fat.
22. Match the organs in Column I with the words listed in Column II.
| a) Rectum | iv) Faeces |
| b) Gall bladder | v) Bile Juices |
| c) Stomach | i) Mucous |
| d) Tongue | iii) Taste Buds |
| e) Small Intestine | ii) Villi |
23. Ruminants such as cows and buffaloes swallow their food hurriedly and then sit restfully and chew their food. Can you reason why?
To digest the food completely, ruminants keep the food as cuds.
24. Boojho and Paheli were eating their food hurriedly so that they could go out and play during the recess. Suddenly, Boojho started coughing violently. Think of the reasons why he was coughing and discuss with your friends.
Sometimes, when one eats hurriedly, talks or laughs while eating, the flap-like valve, epiglottis, closing the passage of the windpipe, remains open. The food may enter the windpipe and coughing helps to clear it.
Long Answer Questions
25. Fill in the blanks using the words listed below.

(a) The digestion of all food components is completed by the ____________ juice.
(b) Large intestine absorbs __________ and some __________ from the undigested food.
(c) Tongue is attached at the _____________ to the floor of the mouth cavity and is free at the _____________.
(d) Amoeba pushes out _____________ around the food and traps it in a food _____________.
(a) The digestion of all food components is completed by the Intestinal juice.
(b) Large intestine absorbs water and some salts from the undigested food.
(c) Tongue is attached at the back to the floor of the mouth cavity and is free at the front .
(d) Amoeba pushes out Pseudopodia around the food and traps it in a food vacuole .
26. Label the below-given Figure 2.1 as directed below in (i) to (iv) and give the name of each type of teeth.

(i) The cutting and biting teeth as ‘A’
(ii) The piercing and tearing teeth as ‘B’
(iii) The grinding and chewing teeth as ‘C’
(iv) The grinding teeth present only in adults as ‘D’
A. Incisors
C. Premolars

27. Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions that follow it. Bile juice is stored in a sac called the gallbladder, located near its organ of secretion, the liver. The gall bladder releases the bile juice into the small intestine whenever food reaches there. Though bile juice is devoid of any digestive enzymes, it is required for the digestion of fats. The fats cannot be digested easily because they are insoluble in water and are present as large globules. Bile juice breaks down big fat droplets into smaller droplets. These are then easily digested by the enzymes released from the pancreas.
(a) Which organ secretes the bile juice?
(b) Why is the digestion of fats difficult as compared to that of other nutrients?
(c) How does bile juice help in the digestion of fat?
(d) Where is the digestion of fat completed?
(e) Does bile juice digest fat completely?
(b) Insolubility of fat in water.
(c) Breaks down big fat droplets into smaller droplets.
(d) Small intestine

Label the following parts in Figure 2.2 and name them.
(a) The largest gland in our body.
(b) The organ where protein digestion starts.
(c) The organ that releases digestive juice into the small
(d) The organ where bile juice gets stored.
(b) Stomach
(c) Pancreas
(d) Gallbladder

29. Open your mouth, look into a mirror and try to count the different types of teeth in your mouth. Compare them with Figure 2.3 on page 13 of your NCERT textbook. Record your observations in the table below:

(a) Did you observe any difference in the number of teeth? If yes, could you identify which type of teeth showed the difference?
(b) Compare the number and type of teeth in an adult (say your parents or cousins who have reached the age of 25–30 or more). Note your observation.

30. Solve the crossword given in Figure 2.3.

1. Cream-coloured digestive gland
3. Undigested excretory solid residues
4. An organ that mixes saliva with the food
5. Point of defecation
7. Stored in the gallbladder
10. Finger-like outgrowth in the small intestine
13. Kind of taste buds
14. Kills bacteria in the stomach
2. Feeds with the help of pseudopodia
6. Total number of molars in one jaw of an adult
8. Largest gland
9. Watery secretion in the mouth
11. A ruminant
12. Form of food chewed by ruminants

The NCERT Exemplar solutions that we provide include relevant exercises that have been solved by our highly qualified subject experts. Detailed explanations are also provided for the students to get a clear understanding and in-depth knowledge of the topic. The NCERT exemplar we provide here is the perfect study material for students to practise and score good marks in the final exam. To get access to all the study material, they can download BYJU’S – The Learning App.
Frequently Asked Questions NCERT Exemplar for Class 7 Science Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals
Ruminants such as cows and buffaloes swallow their food hurriedly and then sit restfully and chew their food. can you reason why, boojho and paheli were eating their food hurriedly so that they could go out and play during recess. suddenly, boojho started coughing violently. think of the reasons why he was coughing and discuss them with your friends..
Sometimes, when one eats hurriedly, talks or laughs while eating, the flap-like valve, epiglottis, closing the passage of the windpipe, remains open. The food may enter the windpipe, and coughing helps to clear it.
‘A’ got her gallbladder removed surgically as she was diagnosed with stones in her gallbladder. After the surgery, she faced problems in the digestion of certain food items when consumed in bulk. Can you tell which kind of food items would they be and why?
The food items would be fat because bile juice present in the gall bladder helps in the digestion of fat. Removal of the gallbladder makes it hard to digest the fat.
| NCERT EXEMPLAR Related Links | |
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
Register here
In case you want to be notified about school in your locality then please register here.
- Are you a Parent or Student?
- Are you a Teacher?
- Are you a School Supplier?

- Our other Domains Olympiad Preparation Math Square Science Square English Square Cyber Square School Square Scholar Square Global Olympiads NCERT Solutions CBSE Sample Papers
- Join WhatsApp Channel
- Apply for CREST Olympiads

Chapter 2: Nutrition in Animals
(www.olympiadsuccess.com)
Chapter 2: Nutrition in Animals
Class: VII
Multiple Choice Questions
Given below from (i) to (iv) are some food items.
(i) Boiled and mashed potato
(ii) Glucose solution
(iii) A slice of bread
(iv) Mustard oil
Which of the above will give blue-black colour when tested with iodine?
(a) (i) and (ii) (b) (i) and (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iii) (d) (iii) and (iv)
Which of the following pair of teeth differ in structure but are similar in function?
(a) canines and incisors.
(b) molars and premolars.
(c) incisors and molars.
(d) premolars and canines.
Read carefully the terms given below. Which of the following set is the correct combination of organs that do not carry out any digestive functions?
(a) Oesophagus, Large Intestine, Rectum
(b) Buccal cavity, Oesophagus, Rectum
(c) Buccal cavity, Oesophagus, Large Intestine
(d) Small Intestine, Large Intestine, Rectum
The swallowed food moves downwards in the alimentary canal because of
(a) force provided by the muscular tongue.
(b) the flow of water taken with the food.
(c) gravitational pull.
(d) the contraction of muscles in the wall of food pipe.
The acid present in the stomach
(a) kills the harmful bacteria that may enter along with the food.
(b) protects the stomach lining from harmful substances.
(c) digests starch into simpler sugars.
(d) makes the medium alkaline.
The finger-like outgrowths of Amoeba helps to ingest food. However, the finger-like outgrowths of human intestine helps to:
(a) digest the fatty food substances.
(b) make the food soluble.
(c) absorb the digested food.
(d) absorb the undigested food.
Read the following statements with reference to the villi of small intestine.
(i) They have very thin walls.
(ii) They have a network of thin and small blood vessels
close to the surface.
(iii) They have small pores through which food can easily
(iv) They are finger-like projections.
Identify those statements which enable the villi to absorb
digested food.
(a) (i), (ii) and (iv) (b) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
(c) (iii) and (iv) (d) (i) and (iv)
The false feet of Amoeba are used for
(a) movement only.
(b) capture of food only.
(c) capture of food and movement.
(d) exchange of gases only.
The enzymes present in the saliva convert
(a) fats into fatty acids and glycerol.
(b) starch into simple sugars.
(c) proteins into amino acids.
(d) complex sugars into simple sugars.
Question 10
Cud is the name given to the food of ruminants which is
(a) swallowed and undigested.
(b) swallowed and partially digested.
(c) properly chewed and partially digested.
(d) properly chewed and completely digested.
Question 11
Choose the correct order of terms that describes the process of nutrition in ruminants.
(a) swallowing → partial digestion → chewing of cud →
complete digestion
(b) chewing of cud → swallowing → partial digestion →
(c) chewing of cud → swallowing → mixing with digestive
juices → digestion
(d) swallowing → chewing and mixing → partial digestion
→ complete digestion
Question 12
Cellulose-rich food substances are good source of roughage in human beings because
(a) human beings do not have cellulose-digesting enzymes.
(b) cellulose gets absorbed in the human blood and converts into fibres.
(c) the cellulose-digesting bacteria convert cellulose into fibres.
(d) cellulose breaks down into smaller components which are egested as roughage.
Very Short Answer Questions
Question 13
Name the parts of the alimentary canal where
(i) water gets absorbed from undigested food.
(ii) digested food gets absorbed.
(iii) taste of the food is perceived.
(iv) bile juice is produced.
(i) Large intestine (ii) Small intestine (iii) Tongue (iv) Liver
Question 14
Mark the following statements as True or False. If false, write the correct statements.
(a) Tongue is attached to the roof of the mouth cavity at the back.
(b) The large intestine is longer and wider than the small intestine of the human alimentary canal.
(c) Mucus protects the stomach lining from damage.
(d) All heterotrophs have a similar basic process of nutrition.
( a) False – Tongue is attached to the floor of the mouth cavity at the back.
(b) False – The large intestine is shorter and wider than the small intestine of the human alimentary canal.
Question 15
Choose the odd one out from each group and give reasons.
(i) liver, salivary gland, starch, gall bladder
(ii) stomach, liver, pancreas, salivary gland
(iii) tongue, absorption, taste, swallow
(iv) oesophagus, small intestine, large intestine, rectum
(i) Starch; gall bladder, liver , salivary glands are all glands.
(ii) Stomach; salivary gland, liver, pancreas are digestive glands.
(iii) Absorption; otaste, tongue, swallow are parts of the mouth.
(iv) Small intestine; no juices are released by other parts/ no digestion in other parts.
Question 16
You were blindfolded and asked to identify the drinks provided in two different glasses. You could identify drink A as lime juice and B as bitter gourd juice. How could you do it inspite of being blindfolded?
Inspite of being blindfolded you were able to identify both the juices distinguishably was because of the different types of taste buds present in the tongue.
Question 17
Fill in the blanks with suitable words:
(a) The alimentary canal stretches from to .
(b) Teeth are rooted in separate in between the .
(c) Digestion of food starts in and gets completed in .
(d) is the largest gland in the human body.
(a) mouth, anus (b) sockets, gums (c) buccal cavity, small intestine (d) liver
Question 18
Following statements describe the five steps in animal nutrition. Read each statement and give one word for each statement. Write the terms that describes each process.
(a) Transportation of absorbed food to different parts of body and their utilisation.
(b) Breaking of complex food substances into simpler and soluble substances.
(c) Removal of undigested and unabsorbed solid residues of food from the body.
(d) Taking food into the body.
(e) Transport of digested and soluble food from the intestine
to blood vessels.
(a) Assimilation (b) Digestion (c) Egestion (d) Ingestion (e) Absorption
Short Answer Questions
Question 19
Match the animals in Column I with their mode of feeding listed in Column II
(a) (iii); (b) (i); (c) (iv); (d) (ii)
Question 20
Boojho took some grains of boiled rice in test tube ‘A’ and Paheli took boiled and chewed rice in test tube ‘B’. Both of them poured 1 – 2 drops of iodine solution into the test tube and observed the colour change. What colour change would they have observed? Give reasons for your answer.
The colour in test tube "A" turned in blue black colour because of the presence of starch.
In test tube ‘B’ – The colour in test tube "B" remain unchanged because of digestion of starch into sugars.
Question 21
‘A’ got her gall bladder removed surgically as she was diagnosed with stones in her gall bladder. After the surgery, she faced problems in digestion of certain food items when consumed in bulk. Can you tell which kind of food items would they be and why?
The kind of food item would have been fat because the bile juice of the gall bladder
helps in the digestion of fat. Removal of gall bladder lead to the difficulty in digestion of fatty substances.
Question 22
Match the organs in Column I with the words listed in Column II.
(a) (iv); (b) (v); (c) (i); (d) (iii); (e) (ii)
Question 23
Ruminants such as cows and buffaloes swallow their food hurriedly and then sit restfully and chew their food. Can you reason why?
Ruminants take time and chew their food properly for complete digestion.
Question 24
Boojho and Paheli were eating their food hurriedly so that they could go out and play during the recess. Suddenly, Boojho started coughing violently. Think of the reasons why he was coughing and discuss with your friends.
Answer: Sometimes, on eating hurriedly, or talking or laughing while eating, the epiglottis (closing the passage of windpipe) remains open. Thus, the food swallowed may enter the wind pipe which will lead to the coughing to help it clear out.
Long Answer Questions
Question 25
Fill in the blanks using the words listed below.
water, front, intestinal, salts, pseudopodia, back, vacuole
(a) The digestion of all food components is completed by
the ____________ juice.
(b) Large intestine absorbs ___________ and some __________
from the undigested food.
(c) Tongue is attached at the _____________ to the floor of
the mouth cavity and is free at the _____________.
(d) Amoeba pushes out _____________ around the food and
traps it in a food _____________.
(a) intestinal (b) water, salts (c) back, front (d) pseudopodia, vacuole
Question 26
Label the below given Figure 2.1 as directed below in (i) to (iv)
and give the name of each type of teeth.
(i) The cutting and biting teeth as ‘A’
(ii) The piercing and tearing teeth as ‘B’
(iii) The grinding and chewing teeth as ‘C’
(iv) The grinding teeth present only in adult as ‘D’
- Incisors B. Canines C. Premolars D. Molars
Question 27
Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions that follows it.
Bile juice is stored in a sac called, gall bladder, located near its organ of secretion, liver. The gall bladder releases the bile juice into the small intestine whenever food reaches there. Though bile juice is devoid of any digestive enzymes, it is required for the digestion of fats. The fats cannot be digested easily because they are insoluble in water and are present as large globules. Bile juice breaks down big fat droplets into smaller droplets. These are then easily digested by the enzymes released from the pancreas.
(a) Which organ secretes the bile juice?
(b) Why is digestion of fats difficult as compared to that of other nutrients?
(c) How does bile juice help in digestion of fat?
(d) Where is the digestion of fat completed?
(e) Does bile juice digest fat completely?
(b) Insolubility of fat in water.
(c) Bile juice helps in breaking down big fat droplets into smaller droplets.
(d) Small intestine
Question 28

Fig. 2.2
Label the following parts in Figure 2.2 and name them.
(a) The largest gland in our body.
(b) The organ where protein digestion starts.
(c) The organ that releases digestive juice into the small intestine.
(d) The organ where bile juice gets stored.
Answer: (a) Liver (b) Stomach (c) Pancreas (d) Gall bladder

Question 29
Open your mouth, look into a mirror and try to count the different types of teeth in your mouth. Compare them with Figure 2.3 on page 13 of your NCERT textbook. Record your observations in the table below:
(a) Did you observe any difference in the number of teeth? If yes, could you identify which type of teeth showed the difference?
(b) Compare the number and type of teeth in an adult (say your parents or cousins who have reached the age of 25–30 or more). Note your observation.
There are 28 teeth in a child’s mouth with only four molars in each jaw and not six unlike in adults who have six molars in each jaw.
Question 30
Solve the crossword given as Figure 2.3.
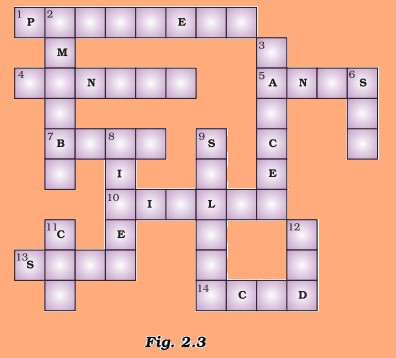
Fig. 2.3
- Cream-coloured digestive gland
- Undigested excretory solid residues
- Organ that mixes saliva with the food
- Point of defecation
- Stored in gall bladder
- Finger-like outgrowth in the small intestine
- Kind of taste buds
- Kills bacteria in the stomach
- Feeds with the help of pseudopodia
- Total number of molars in one jaw of an adult
- Largest gland
- Watery secretion in the mouth
- Form of food chewed by ruminants
Other Chapters
- Chapter 1: Nutrition in Plants
- Chapter 3: Fibre to Fabric
- Chapter 4: Heat
- Chapter 5: Acids, Bases and Salts
- Chapter 6: Physical and Chemical Changes
- Chapter 7: Weather, Climate and Adaptations of Animals to Climate
- Chapter 8: Winds, Storms and Cyclones
- Chapter 9: Soil
- Chapter 10: Respiration in Organisms
- Chapter 11: Respiration in Animals and Plants
- Chapter 12: Reproduction in Plants
- Chapter 13: Motion and time
- Chapter 14: Electric Current and its Effects
- Chapter 15: Light
- Chapter 16: Water - A Precious Resource

Quick Links

SchoolPlus Program
Yearlong program for Olympiads preparation & to build necessary skills for future.

Olympiad Exam Dates
Time to mark your calendar with the upcoming Olympiads exam schedule.

LIVE Classes for Olympiads
Take your Olympiad preparation to next-level by taking LIVE Classes.

Olympiad Test Series
Assess your performance by taking topic-wise and full length mock tests.

India’s First Summer Olympiads
Know your true potential by participating in Unicus Olympiads for classes 1-11.
Asia’s Biggest Winter Olympiads
Give wings to your innovation by appearing in CREST Olympiads for Prep/KG to classes 1-10.
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
Important Questions for CBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 2 - Nutrition in Animals
- Class 7 Important Question
- Chapter 2: Nutrition In Animals

CBSE Class 7 Science Chapter-2 Important Questions - Free PDF Download
Important Questions of Class 7 Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals deals with some important chapter questions that students can expect in exams. Many important terms and facts are covered in the chapter. Subject matter experts develop the important questions on the chapter and its reference notes from Vedantu, and they have provided an in-depth analysis of the chapter in a very unique way. These extra important questions have proved very effective for the students.
The free PDF of the important questions for CBSE Class 7 Chapter 2 is available on the official website of Vedantu, and you can download them on any device.
Following are some important points of Chapter 2 of Class 7 Science that quickly gives you an encapsulation of the chapter.
Important Topics Covered Under CBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 2 - Nutrition in Animals
The important topics which the students will learn from CBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 2 - Nutrition in Animals are as follows:
Process of Nutrition in Animals
Process of Digestion in Grass eating animals
Process of Digestion in Humans
Different Ways of Taking Food
Feeding in Amoeba
Digestion System of Amoeba
Study Important Questions for Class 7 Science Chapter 2 – Nutrition in Animals
Very Short Answer Questions (1 Mark)
1. Match the Following:-
Animal | Mode of Food intake |
Ans: The following is the matched table:
Animal | Mode of Food intake |
c. Suckling | |
a. Sucking | |
d. Siphoning | |
e. Capturing | |
b. Chewing |
2. Fill in the blanks:
a) _______________ is the elimination of unused parts of the food.
Ans: Egestion is the elimination of unused parts of the food.
b) The digestive system in humans consists of ___________________ and_______________.
Ans: The digestive system in humans consists of alimentary canal and digestive glands .
c) The first set of teeth that grow during infancy and fall off between 6-8 years of age is____________.
Ans: The first set of teeth that grow during infancy and fall off between 6-8 years of age is milk teeth .
d) The working of the stomach was discovered by _____________.
Ans: The working of the stomach was discovered by William Beaumont .
Short Answer Questions (2 Mark)
1. Define Nutrition in animals.
Ans: Nutrition in animals is very important. Some of them are plant-eating while others are carnivores. It includes the process of food ingestion, digestion, absorption and assimilation by the cells of their body. It also includes the removal of unused portions of food.
2. Differentiate between absorption and assimilation.
Ans: The difference between absorption and assimilation is as follows:
Absorption | Assimilation |
Absorption is the process of ingestion of the digested food from the alimentary canal into the bloodstream through the intestinal villi. | Assimilation is the process of ingestion of digested food and nutrients and the synthesis of new compounds from the molecules that are absorbed to perform respiration and metabolism. |
3. What is the function of the large intestine in digestion?
Ans: The large intestine reabsorbs all the excess water from unabsorbed and undigested food. Thus, it helps in making the unabsorbed portion of the food as faeces and its elimination by excretion. Thus, returning most of the water to the blood can prevent excess water loss as well as eliminate unabsorbed food from the body.
4. List the different types of teeth present in humans and their functions.
Ans: The different types of teeth present in humans and their functions are:
Incisors: Incisors or the front teeth are the eight visible teeth that are used to bite the food.
Canines: Next to incisors are the canines that are used to tear flesh or other food items. These are very sharp and come in around nine to twelve years of age.
Premolars: Next to canines are the premolars which are typically used for grinding and chewing food.
Molars: Molars are replaced by the eight premolars. They serve the primary function of chewing and grinding food into small particles.
5. What is diarrhoea?
Ans: When excess water from digested food is not reabsorbed, it is passed out through the stool which is loose and watery. Passage of this watery stool frequently is called diarrhoea which is caused by a microbial infection of the alimentary canal. This can lead to severe dehydration that can be controlled by using Oral Rehydration Solutions (ORS).
Long Answer Questions (5 Marks)
1. Explain nutrition in starfish.
Ans: Starfish is an aquatic invertebrate. It has a unique way of obtaining nutrition from other animals.
Ingestion: The mouth of the starfish is on the underside of their body.They wrap themselves around the prey and open the shell of the prey. Then through their mouth they push their stomach out and ingest the soft animal.
Digestion: They digest the animal in the stomach and draw its stomach back into its body.
Absorption and assimilation: This allows them to feed on organisms larger than the ones which can fit into their small mouth.
2. Explain the process of nutrition in amoeba.
Ans: The process of nutrition in amoeba is done through holozoic nutrition and the process is called phagocytosis .
Ingestion: Amoeba moves closer to its food with the help of pseudopodia and encircles it forming a food vacuole to engulf the food.
Digestion: The food is then digested using digestive enzymes present in the lysosomes.
Absorption and assimilation: The digested food is absorbed by the cytoplasm and the energy thus produced from the food is used to perform different life processes.
Egestion: To excrete the undigested food, an amoeba ruptures its cell wall and releases it out of the cell.

3. Explain the process of digestion and absorption in the small intestine.
Ans: The process of digestion as well as absorption in small intestine is as follows:
Digestion: Digestion in the small intestine is accomplished by the action
of digestive juices from the liver, pancreas and small intestine. The bile juice secreted by the liver helps in the digestion of fats, breaking down the big fat droplets into smaller droplets. It does not contain any enzymes. Pancreatic juice secreted by the pancreas contains enzymes for the digestion of carbohydrates, proteins and lipids. Pancreatic amylase helps in the digestion of carbohydrates while trypsin helps in the digestion of proteins. The enzymes of the intestinal juice eventually break down carbohydrates, proteins and lipids into their simplest components such as glucose, amino acids, fatty acids and glycerol etc.
Absorption: Absorption takes place through the walls of the intestine
that are lined with finger-like projections known as villi. These villi improve the surface area available for nutritional absorption. The villi contain blood vessels and hence the digested food is absorbed directly into the bloodstream.
4. Explain the importance of rumen in ruminants.
Ans: Rumen is a part of the stomach in grass-eating animals. It stores the food that the ruminant reproduces, chews again and swallows a second time. Specific bacteria found in the rumen aid in the digestion of cellulose. Ruminants can chew their ruminants for hours every day. The rumen contains many small organisms that aid in the digestion of food such as grass whose cell walls cannot be easily digested by other animals. Cud, or partially digested food, is then reintroduced into the mouth for easier chewing. This process of cud-chewing even when the animal is not eating is called rumination. The rumen ferments this food through the formation of gas, which must be expelled by belching to prevent bloating.
Important Points to Remember Revise the concepts covered in CBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 2 - Nutrition in Animals by solving these important questions. You can also download NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science for all the other chapters to prepare for your exams. All these solutions are available in free PDF format on our website or mobile app.
Nutrition in animals.
Nutrient requirement, mode of intake food and its utilization by the body is the process of animal nutrition.
Ingestion, digestion, absorption, assimilation and egestion are the stages of nutrition in animals.
Ingestion is taking in food. Various animals use different organs for ingestion.
The breakdown of complex components of food into simpler substances is called digestion.
Absorption is the process by which food in soluble form passes into the body fluid like blood and is transported to different parts of the body.
Assimilation involves utilizing the absorbed nutrients for energy, growth and development.
Egestion is the process of removal of undigested waste.
Modes of feeding differ in different organisms. For example, bees and hummingbirds suck the nectar of plants, infants of mammals feed on mother’s milk, python swallows animals they prey upon, few aquatic animals filter tiny particles floating nearby and feed upon them.
Amoeba is a microscopic, single-celled organism found in pond water. It constantly changes its shape and position.
Pseudopodia is a finger-like projection that is pushed out by amoeba.
Amoeba ingests food with the help of pseudopodia (false feet) and ingests it in the food vacuole.
Amoeba feeds on bacteria, microscopic algae and small unicellular organisms.
The food digested by amoeba is used for growth, maintenance and multiplication.
Amoeba releases unwanted waste through its body surface.
Nutrition in Humans
The human digestive system is highly complex.
The human digestive system consists of the buccal cavity, oesophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine ending in rectum and anus.
The human digestive tract is also called an alimentary canal.
The digestive tract and associated glands like salivary glands, liver and pancreas make up the digestive system.
Digestion begins in the mouth and continues in the stomach and the small intestine.
The cavity of the mouth with all its internal parts like cheeks, teeth, tongue and salivary glands is called the buccal cavity.
The alimentary canal begins from the buccal cavity.
Salivary glands, liver and pancreas play a very important role in the process.
Salivary glands present in the human mouth secrete saliva.
Saliva moistens the food and helps in chewing of food by teeth. It also contains an enzyme which breaks down the starch into sugars.
The oesophagus is the food pipe through which the swallowed food passes.
The liver is the largest gland in our body, secretes bile that is stored in the gallbladder.
The stomach is a thick-walled bag, receives food from oesophagus at one end and opens into the small intestine at the other.
Bile plays a vital role in the digestion of fats.
The pancreas is located just below the stomach and secretes pancreatic juice that acts on carbohydrates, fats and proteins and changes them into simpler forms.
Digested food is absorbed in the small intestine.
The small intestine is a coiled structure that receives secretions from the liver and the pancreas.
Villi are thousands of finger-like projections present in the inner walls of the small intestine.
The digested food materials are absorbed by the surface of the villi.
Semi-solid waste in the form of faeces is expelled through the anus.
A fleshy muscular organ inside the human mouth that is attached to the buccal cavity is the tongue.
The tongue is used for speaking, mixing saliva with food, swallowing the food and detecting different tastes of food with the help of taste buds.
The teeth help in chewing the food and breakdown the big pieces of food into small pieces.
All human beings bear two sets of teeth. The first set of teeth called milk teeth appears after the age of six months. Eventually, these milk teeth are replaced by permanent teeth.
An adult human has 32 permanent teeth - incisors, canines, molars and premolars.
Tooth decay is the damage of the teeth due to harmful bacteria breaking down the sugars and releasing acids.
Tooth decay leads to toothache and even loss of teeth.
Nutrition in Ruminating Animals
Ruminants are grass-eating animals.
Ruminants digest their food in two steps.
The rumen is a separate part of the stomach of ruminants where the swallowed food is stored.
Rumination is a process where the ruminants quickly swallow grass and store it in the rumen. In the rumen, the grass is partially digested and forms a cud. Later, the cud returns back to the mouth in small lumps and the animal chews it.
Cellulose is the carbohydrate present in grass.
Ruminants have a large sac-like structure called caecum that is present between the small intestine and the large intestine.
Certain kinds of bacteria present in caecum help in digestion of the cellulose of the food.
The reference notes relating to Important Questions Of Chapter 2 of Science for Class 7 given above will benefit you in understanding the concepts and basic terms of human and animal digestive systems. The important questions and the reference notes related to the chapter created by Vedantu will give a thorough practice and revision for the exams.
Why Must You Choose Vedantu?
Vedantu is the only ed-tech platform that brings an awesome technology that enables learning in a very interactive and engaging manner. It is the only online tutoring platform that connects teachers and students very strongly through their new technology. Vedantu gives utmost priority to teachers because we believe that only good teachers can prepare a child for a better tomorrow. Vedantu has surpassed the traditional methods of teaching with the help of new technology WAVE in order to give a feeling of offline classes to the students.
Students can avail abundant programs and courses available on the Vedantu platform. These programs and courses will give you an insight into what you can do in future and what is the best career for you in this competitive world. Our master teachers are available to give you some quick tips for your exams which will help you boost your confidence.
The USP of Vedantu is the live interactive sessions and innumerable students have been benefited from the courses that Vedantu provides. These live sessions are designed with in-class quizzes which enables master teachers to get real-time feedback on students' understanding. Vedantu also provides advanced classes and courses for IIT-JEE, KVPY and NEET examinations. You can count on Vedantu for a bright and prospective future.
Benefits of CBSE Important Question for Class 7 Chapter 2
CBSE Important Questions for Class 7 Chapter 2 have the following benefits:
Students will get an insight into the pattern of questions and the distribution of marks expected in exams. These patterns of questions will help them solve the questions within time.
Students will learn to manage time properly while solving the questions in exams.
The CBSE Important Questions include some questions that have come in previous year’s exams.
Solving the CBSE Important Questions for Class 7 Chapter 2 will help improve your understanding of the chapter.
Solving CBSE Important Questions will give a thorough revision of the entire chapter.
The collection of important questions for CBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 2 - Nutrition in Animals serves as a valuable resource for students' comprehensive preparation. These questions encompass various aspects of animal nutrition, covering topics such as different modes of feeding, digestive processes, and the significance of essential nutrients. By engaging with these questions, students can enhance their understanding, critical thinking skills, and problem-solving abilities. Moreover, this comprehensive set of questions aids students in building a strong foundation in biological sciences and fosters an appreciation for the intricacies of animal nutrition. Utilising these important questions will undoubtedly contribute to student's academic success and confidence in their scientific knowledge.

FAQs on Important Questions for CBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 2 - Nutrition in Animals
1. How many important questions are there for Chapter 2 of Class 7 Science?
Ans: Vedantu has undertaken the arduous task of listing all the important questions of Class 7 Science Chapter "Nutrition in Animals" in one place. This has been done to make preparation for exams easier for the students. Vedantu has listed two questions of one mark each, five questions of two marks each, and four questions of five marks each for this chapter. The questions have been provided with suitable answers for revision purposes.
2. Why do we eat food?
Ans: We eat food for optimal functioning of our bodily functions. Food contains vital nutrients like fats, proteins, carbohydrates, vitamins, and minerals. These nutrients help in the building, growth, repair, and maintenance of important biological functions in our bodies. Food provides us with energy. Hence, food is essential for our survival.
Chapter 2 "Nutrition in Animals" talks about the various processes of food intake, assimilation, and digestion in various animals and humans.
3. Why is digestion needed for animals?
Ans: All living organisms require some sort of nutrition for survival. Microbes, animals, and human beings require different types of food for optimal performance and survival. This food that we ingest needs to be properly digested so that our body can assimilate the required nutrients from it. The properly digested food then helps our bodies to grow and function well. Without proper digestion, the ingested food will not get absorbed by our bodies.
4. How do different animals digest their food?
Ans: Various animals have varying modes of nutrition. For example, grazing animals like cows, buffalo, etc ingest their grassy and leafy food and store it in a sac-like organ called the rumen. Amoeba on the other hand takes in food with the help of false feet called pseudopodia and then digest it in their food vacuole. Another animal, the starfish, attaches to the hard surface of its prey. It then opens the prey's shell and pops out its own stomach and directly ingests the food through it.
5. What is nutrition?
Ans: Chapter 2 "Nutrition in Animals" talks about various modes of nutrition in human beings and animals. Nutrition is the process by which organisms obtain their food and absorb its nutrients in their bodies. Organisms utilize the food ingested for performing various bodily functions. Nutrition helps in deriving energy from the food. Proper nutrition is an indispensable process for the survival of life on earth. Without proper nutrition, organisms will not be able to survive.
Chapterwise Important Questions for CBSE Class 7 Science
Cbse study materials.
Extra Questions for Class 7 Science Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals
Extra questions for Class 7 Science Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals with answers is given below. Our subject expert prepared these solutions as per the latest NCERT textbook. These questions will be helpful to revise the all topics and concepts. CBSE Class 7 extra questions are the most simple and conceptual questions that are prepared by subject experts for the students to study well for the final exams. By solving these extra questions, students can be very efficient in their exam preparations.
Nutrition in Animals Class 7 Science Extra Questions and Answers
Very short extra questions and answer.
1. Do all animals have the same mode of nutrition?
Answer: No
2. Name the mode of nutrition in which solid whole food particles is ingested.
Answer: Holozoic
3. What is the organ that stores bile?
Answer: Gall bladder
4. Which part of the digestive canal is involved in killing bacteria?
Answer: Stomach
5. Name the part of digestive canal involved in chewing of food.
Answer: Mouth
6. Where are fats digested in the body?
Answer: Fats are mainly digested in the small intestine.
7. Where is the water from undigested food absorbed in the body?
Answer: Water from undigested food is absorbed in the body in large intestine.
8. What kills bacteria that enter along with the juices to act?
Answer: The acid kills many bacteria that enter along with the juices to act.
9. Where food is completely digested?
Answer: The food is completely digested in the small intestine.
10. Where are faeces formed in the human body?
Answer: Faeces are formed in the human body in large intestine.
11. Which glands secrete saliva?
Answer: Salivary glands secrete saliva.
12. Where food is absorbed in our body?
Answer: Absorption of food takes place in small intestine.
13. Which gland in our body secretes bile?
Answer: Bile is a digestive juice that is secreted by the liver.
14. Where faeces are stored?
Answer: Faeces are stored in rectum.
15. What are the end products of carbohydrate?
Answer: The carbohydrates get broken into simple sugars such as glucose.
16. Name the end products of fats.
Answer: Fatty acids and Glycerol
17. Write the end products of proteins.
Answer: Amino acids
18. What causes diarrhoea in human beings?
Answer: It may be caused by an infection, food poisoning or indigestion.
19. Which is the largest gland in the human body?
Answer: Liver is the largest gland in human body.
20. What is ingestion?
Answer: The process of taking food into the body is called ingestion.
21. What are the different types of teeth?
Answer: We have different types of teeth: incisor, canine, premolar and molar.
22. What does saliva do to food in our mouth?
Answer: The saliva breaks down the starch into sugars.
23. How does food pass from the mouth to the stomach?
Answer: Food is pushed down by movement of the wall of the food pipe.
24. What is rumen?
Answer: Ruminants have a large sac-like structure called rumen.
25. How does an amoeba move?
Answer: Amoeba use pseudopodia (false feet) to move.
26. What is the finger like projections present in the inner wall of the small intestine?
Answer: Villi
27. Which organ expelled out the undigested and unabsorbed residues from human body?
Answer: Anus
28. What are permanent teeth?
Answer: The second set that replaces a temporary milk teeth are the permanent teeth.
Short Extra Questions and Answers
1. What does animal nutrition include?
Answer: Animal nutrition includes nutrient requirement, mode of intake of food and its utilisation in the body.
2. What do you mean by animal nutrition?
Answer: Animal nutrition includes nutrient requirement, mode of intake of food and its utilisation in the body.
3. What are the different modes of feeding in animals?
Answer: Scraping, chewing, brewing, capturing and swallowing, sucking etc. are the different mode of feeding in animals.
4. What is digestion?
Answer: The breakdown of complex components of food into simpler substances is called digestion.
5. Name the glands that secrete digestive juices.
Answer: Glands associated such as salivary glands, the liver and the pancreas secrete digestive juices.
6. What is diarrhoea?
Answer: Sometime we may have experienced the need to pass watery stool frequently. This condition is known as diarrhoea.
7. What is ORS?
Answer: Boiled and cooled water with a pinch of salt and sugar dissolved in it is called Oral Rehydration Solution (ORS).
8. Where is the bile produced? Which component of the food does it help to digest?
Answer: Bile is produced in liver. The bile plays an important role in the digestion of fats.
9. What are ruminant animals?
Answer: The grazing animals like cows, buffaloes and deer are known as ruminants.
10. Where is the pancreas located in human body?
Answer: The pancreas is a large cream colored gland located just below the stomach.
11. How does an amoeba capture its food?
Answer: Amoeba captures its food with the help of finger-like projections, called pseudopodia or false feet.
12. What do pancreatic juices digest?
Answer: The pancreatic juice acts on carbohydrates, fats and proteins and changes them into simpler forms.
13. What is absorption in terms of digestion?
Answer: The digested food passes into the blood vessels in the wall of the intestine. This process is called absorption.
14. What do you mean by rumination?
Answer: A process in which partially digested food returns to the mouth in small lumps and the animal chews it is called rumination.
15. What is cud?
Answer: Cud is partly digested food returned from stomach (called rumen) of ruminants to the mouth for further chewing.
16. What are milk teeth?
Answer: The first set of teeth grows during infancy and they fall off at the age between six to eight years. These are termed milk teeth.
17. What are the major culprits of tooth decay?
Answer: Chocolates, sweets, soft drinks and other sugar products are the major culprits of tooth decay.
18. Why do we get instant energy from glucose?
Answer: In the cells, glucose breaks down easily with the help of oxygen into carbon dioxide and water, and energy is released.
19. What are the main parts of the alimentary canal?
Answer: The canal can be divided into various compartments: (1) the buccal cavity, (2) foodpipe or oesophagus, (3) stomach, (4) small intestine, (5) large intestine ending in the rectum and (6) the anus.
20. How is food prevented from entering the windpipe?
Answer: During the act of swallowing a flap-like valve closes the passage of the windpipe and guides the food into the foodpipe. If, by chance, food particles enter the windpipe, we feel choked, get hiccups or cough.
21. What is small intestine?
Answer: The small intestine is highly coiled and is about 7.5 metres long. It receives secretions from the liver and the pancreas. Besides, its wall also secretes juices.
Long Extra Questions and Answers
1. Why we cannot digest cellulose like the cattle do?
Answer: Ruminants have a large sac-like structure called rumen between the oesophagus and the small intestine. The cellulose of the food is digested here by the action of certain bacteria which are not present in humans.
2. Can we survive only on raw, leafy vegetables/grass? Discuss.
Answer: No, human cannot survive only on raw, leafy vegetables, or grass because they are rich in cellulose, which is a type of carbohydrate that humans are not able to digest due to the absence of cellulose-digesting enzymes.
3. Explain the process of digestion in grass eating animals.
Answer: Grass eating animals quickly swallow the grass and store it in a part of the stomach called rumen. Here the food gets partially digested and is called cud. But later the cud returns to the mouth in small lumps and the animal chews it.
4. Write a short note on digestion in starfish.
Answer: Starfish feeds on animals covered by hard shells of calcium carbonate. After opening the shell, the starfish pops out its stomach through its mouth to eat the soft animal inside the shell. The stomach then goes back into the body and the food is slowly digested.
5. Write a short note on large intestine.
Answer: The large intestine is wider and shorter than small intestine. It is about 1.5 metre in length. Its function is to absorb water and some salts from the undigested food material. The remaining waste passes into the rectum and remains there as semi-solid faeces.
6. How can we prevent tooth decay?
Answer: We can prevent tooth decay in the following manner:
- By cleaning the teeth with a brush or datun and dental floss at least twice a day and rinse the mouth after every meal.
- By not putting dirty fingers or any unwashed object in the mouth.
7. What are villi? What is their location and function?
Answer: The inner walls of the small intestine have thousands of finger-like outgrowths. These are called villi (singular villus). These are found in small intestine.
- The villi increase the surface area for absorption of the digested food.
- The surface of the villi absorbs the digested food materials.
8. What are the functions of the tongue in human body?
Answer: Functions of the tongue in human body
- It helps in talking.
- It mixes saliva with the food during chewing and helps in swallowing food.
- It has taste buds that detect different tastes of food.
9. Draw a labeled diagram of amoeba. Answer:
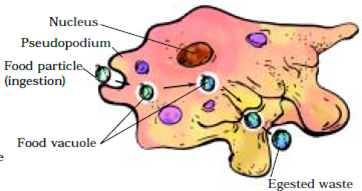
10. Name the type of carbohydrate that can be digested by ruminants but not by humans. Give the reason also.
Answer: Cellulose is a type of carbohydrate that can be digested by ruminants but not by humans. Ruminants have a large sac-like structure called rumen between the oesophagus and the small intestine. The cellulose of the food is digested here by the action of certain bacteria which are not present in humans.
11. What is tooth decay?
Answer: Bacteria are present in our mouth but they are not harmful to us. However, if we do not clean our teeth and mouth after eating, many harmful bacteria also begin to live and grow in it. These bacteria break down the sugars present from the leftover food and release acids. The acids gradually damage the teeth. This is called tooth decay.
12. Explain the process of nutrition in Amoeba.
Answer: Amoeba feeds on some microscopic organisms. When it senses food, it pushes out pseudopodia around the food particle and engulfs it. The food becomes trapped in a food vacuole. Digestive juices are secreted into the food vacuole. They act on the food and break it down into simpler substances. Gradually the digested food is absorbed.
13. What substances are secreted in the stomach?
Answer: The inner lining of the stomach secretes mucous, hydrochloric acid and digestive juices. The mucous protects the lining of the stomach. The acid kills many bacteria that enter along with the food and makes the medium in the stomach acidic and helps the digestive juices to act. The digestive juices break down the proteins into simpler substances.
14. Write one similarity and one difference between the nutrition in amoeba and human beings.
Answer: Similarity In amoeba, digestive juices are secreted into the food vacuole. They act on the food and break it down into simpler substances. Gradually the digested food is absorbed. In human, digestive juices are secreted in buccal cavity, liver and small intestine.
Difference Amoeba captures its food with help of pseudopodia. In human being, food is taken into the body through the mouth.
15. How does the stomach work?
Answer: The stomach is a thick-walled bag. Its shape is like a flattened U and it is the widest part of the alimentary canal. It receives food from the food pipe at one end and opens into the small intestine at the other. The inner lining of the stomach secretes mucous, hydrochloric acid and digestive juices. The mucous protects the lining of the stomach. The acid kills many bacteria that enter along with the food and makes the medium in the stomach acidic and helps the digestive juices to act. The digestive juices break down the proteins into simpler substances.
16. Complete the following table.
| Type of teeth | Number of teeth | Total | |
| Lower jaw | Upper jaw | ||
| Cutting and biting teeth | 4 Incisors | 4 Incisors | 8 Incisors |
| Piercing and tearing teeth | 2 Canines | 2 Canines | 4 Canines |
| Chewing and grinding teeth | 4 Premolars & 6 Molars (Including the wisdom tooth) | 4 Premolars & 6 Molars (Including the wisdom tooth) | 8 Premolars & 12 Molars (Including the wisdom tooth) |
17. Complete the following table.
| Name of animal | Kind of food | Mode of feeding |
| Snail | Leaves and insects | Scraping |
| Ant | Sugar and food particles | Chewing and Scraping |
| Eagle | Small animals | Capturing and Swallowing |
| Humming-bird | Nectar | Sucking |
| Lice | Blood | Sucking |
| Mosquito | Blood | Sucking |
| Butterfly | Nectar | Siphoning |
| House fly | Waste or liquids | Siphoning |
18. Draw a labeled diagram of digestive system of cow. Answer:
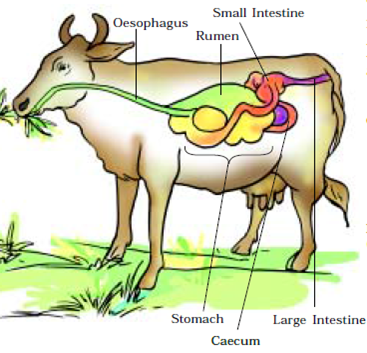
19. Draw a labeled diagram showing arrangement of teeth and different type of teeth. Answer:
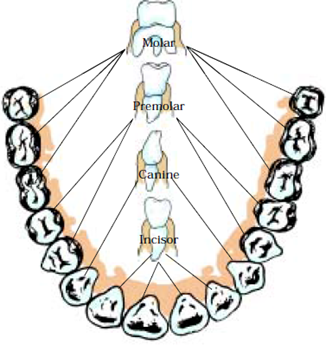
20. Draw a labeled diagram of human digestive system. Answer:
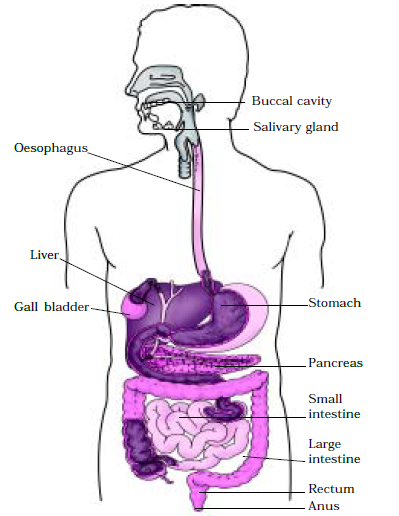
- Nutrition in Plants Class 7 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 1

Last Updated on August 26, 2024 by XAM CONTENT
Hello students, we are providing case study questions for class 7 science. Case study questions are the new question format that is introduced in CBSE board. The resources for case study questions are very less. So, to help students we have created chapterwise case study questions for class 7 science. In this article, you will find case study questions for cbse class 7 science chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants.
| Nutrition in Plants | |
| Case Study Questions | |
| Competency Based Questions | |
| CBSE | |
| 7 | |
| Science | |
| Class 7 Studying Students | |
| Yes | |
| Mentioned | |

Table of Contents
Case Study Questions on Nutrition in Plants
Question 1:
Read the given passage below and answer the question:
Carnivorous plant is especially adapted for capturing and digesting insects and other animals by means of ingenious pitfalls and traps. There are more than 600 known species of carnivorous plants. The apparent trapping mechanism, which is always a modified leaf is a distinctive feature to these plants. The pitcher plant is an example of a carnivorous plant. The leaf of the Pitcher plant is modified into pitcher like structure to trap the insects. The apex of the leaf acts like a lid which can open and close the mouth of the pitcher.
Q.1. Insect eating carnivorous plants are also called ________plant. (a) autotrophic (b) saprophytic (c) insectivorous (d) symbiotic
Difficulty Level: Easy
Ans. Option (c) is correct. Explanation: Carnivorous plants eat insects for their food requirements, so they are called insectivorous plants.
Q.2. One of the most important nutrients a pitcher plant need from insects is: (a) Carbon dioxide (b) Nitrogen (c) Water (d) Oxygen
Ans. Option (b) is correct. Explanation: Pitcher plants grow in soil that is deficient in nitrogen content so they feed on insects to obtain the nitrogen.
Q.3. Consider the following statements about the Pitcher plant: (A) It is a parasite. (B) The leaves are green in colour. (C) The hair present inside the lid is directed downward. (D) Digestive juice is secreted in the apex of the leaf. The correct statements are: (a) (A) and (B) (b) (B) and (C) (c) (C) and (D) (d) (A), (B) and (D)
Difficulty Level: Difficult
Ans. Option (b) is correct. Explanation: Pitcher plant is not a parasite. The plants are grouped under carnivorous plants as they feed upon insects. The digestive juices secreted in the pitcher, the modified part of leaf.
Q.4. What type of mode of nutrition is found in pitcher plants?
Ans. The pitcher plants have chlorophyll so they perform photosynthesis to produce their own food however, they grow in soil that lacks nitrogen content so, they feed on insects to obtain the nitrogen needed for their growth. Hence, they have both autotrophic as well as a partial heterotrophic mode of nutrition.
Q.5. How does a pitcher plant catch insects? (Medium)
Difficulty Level: Medium
Ans. When the insects land in the pitcher its lid closes and the insects are trapped and entangled into the hair. Digestive juices are secreted in the pitcher so the insects get digested and nutrients get absorbed.
- Respiration in Organisms Class 7 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 6
- Physical and Chemical Changes Class 7 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 5
- Acids Bases and Salts Class 7 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 4
Heat Class 7 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 3
Nutrition in animals class 7 case study questions science chapter 2, topics from which case study questions may be asked.
- Define nutrients.
- Discuss the mode of nutrition in plants.
- Describe the process of photosynthesis.
- List the things required for the process of photosynthesis.
- Discuss what are saprotrophs.
- Describe the symbiosis relationship.
- Discuss the nutrients replenishment in soil.
For further practice on case study questions related to Class 7 Science Chapter 1 Nutrition in Plants, we recommend exploring the link given below.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Nutrition in Plants Case Study Questions
Q1: what are case study questions for cbse examinations.
A1: Case study questions in CBSE examinations typically involve scenarios or real-life examples, requiring students to apply their understanding of concepts to solve problems or analyze situations.
Q2: Why are case study questions important for understanding class 7 science chapters?
A2: Case study questions provide a practical context for students to apply theoretical knowledge to real-world situations, fostering deeper understanding and critical thinking skills.
Q3: How should students approach answering case study questions for CBSE?
A3: Students should carefully read the case study, identify the key issues or problems presented, analyze the information provided, apply relevant concepts and principles of plant nutrition, and formulate well-supported solutions or responses.

Q4: Are there any resources available online for students to practice case study questions on class 7 science chapters for CBSE exams?
A4: Yes, several educational websites offer case study questions for CBSE students preparing for science examinations. We also offer a collection of case study questions for all classes and subject on our website. Visit our website to access these questions and enhance your learning experience.
Q5: How can students effectively prepare for case study questions on nutrition in plants for CBSE exams?
A5: Effective preparation strategies include regular revision of concepts, solving practice questions, analyzing case studies from previous exams, seeking clarification on doubts, and consulting with teachers or peers for guidance and support.
Q6: How can teachers incorporate case study questions on nutrition in plants class 7 science into classroom teaching?
A6: Teachers can integrate case studies into lesson plans, group discussions, or interactive activities to engage students in active learning, promote problem-solving skills, and facilitate a deeper understanding of nutrition in plants.

Related Posts


CBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals MCQ with Answers

Explore our comprehensive collection of MCQ on Nutrition in Animals Class 7 designed to enhance your understanding of Chapter 2 from the CBSE syllabus . This chapter delves into the fascinating ways animals, including humans, obtain and digest their food. Our Nutrition in Animals Class 7 MCQ with Answers is tailored to align with the NCERT guidelines and covers key concepts presented in your NCERT textbook .
As a bonus, we’ve also included links to Nutrition in Plants MCQ Class 7 with Answers to help students who are looking to review the entire scope of nutrition covered in their science curriculum. This resource is a great way to prepare for your CBSE exams and ensure you’re on track with the NCERT syllabus.
Fill Out the Form for Expert Academic Guidance!
Please indicate your interest Live Classes Books Test Series Self Learning
Verify OTP Code (required)
I agree to the terms and conditions and privacy policy .
Fill complete details
Target Exam ---
Science Chapter 1 Nutrition in Animals Class 7 MCQ with Answers
Here are the topic wise of various nutrition in animals MCQ with answers:
1. What is the process of breaking down food into simpler substances called?
a) Ingestion
b) Digestion
c) Absorption
d) Assimilation
Answer: b) Digestion
2. Which mode of feeding involves the animal popping out its stomach to eat?
c) Capturing and swallowing
d) Siphoning
Answer: c) Capturing and swallowing
3. What is the main purpose of food for animals?
a) Growth and entertainment
b) Growth, repair, and functioning of the body
c) Growth and sleep
d) Repair and reproduction
Answer: b) Growth, repair, and functioning of the body
4. Where does the digestion of proteins begin in humans?
c) Small intestine
d) Large intestine
Answer: b) Stomach
5. What substance does the liver secrete?
a) Pancreatic juice
d) Gastric juice
Answer: c) Bile
Enroll Now to Foundation Course for Class 7
6. What role does hydrochloric acid play in the stomach?
a) It breaks down fats
b) It kills bacteria
c) It digests proteins
d) It absorbs vitamins
Answer: b) It kills bacteria
7. What are the finger-like projections in the small intestine called?
c) Pseudopodia
Answer: b) Villi
8. What is the function of villi in the small intestine?
a) To secrete digestive juices
b) To increase surface area for absorption
c) To produce bile
d) To chew food
Answer: b) To increase surface area for absorption
9. What does the pancreas secrete?
b) Pancreatic juice
c) Hydrochloric acid
Answer: b) Pancreatic juice
10. How long is the small intestine in humans approximately?
a) 1.5 meters
b) 7.5 meters
c) 5 meters
d) 10 meters
Answer: b) 7.5 meters

11. What type of animals are known as ruminants?
a) Those that chew cud
b) Those that eat meat only
c) Those that eat plants only
d) Those that swallow food whole
Answer: a) Those that chew cud
12. Which animals have a part of the stomach called the rumen?
a) Carnivores
b) Herbivores
c) Omnivores
d) Insectivores
Answer: b) Herbivores
13. What is the purpose of rumination in certain animals?
a) To digest meat more efficiently
b) To break down cellulose
c) To increase food intake
d) To cool down the body
Answer: b) To break down cellulose
14. How does an amoeba ingest food?
a) Through a mouth
b) Using pseudopodia
c) Through gills
d) By absorption through the skin
Answer: b) Using pseudopodia
15. What is the role of digestive juices in the stomach?
a) To make food tastier
b) To break down food into simpler substances
c) To cool down the food
d) To store food for longer periods
Answer: b) To break down food into simpler substances
16. Where is bile stored?
b) Gall bladder
d) Pancreas
Answer: b) Gall bladder
17. What is the primary function of the large intestine?
a) To digest proteins
b) To absorb water and salts
c) To produce digestive enzymes
d) To store undigested food
Answer: b) To absorb water and salts
18. What triggers the production of saliva in the mouth?
a) Seeing food
b) Swallowing food
c) Digesting food
d) Absorbing nutrients
Answer: a) Seeing food
19. What is tooth decay primarily caused by?
a) Acids produced by bacteria
b) Swallowing too quickly
c) Eating too much protein
d) Lack of saliva
Answer: a) Acids produced by bacteria
20. Why should you rinse your mouth after eating?
a) To cool down the mouth
b) To remove food particles and reduce bacteria
c) To taste the food better
d) To prepare for the next meal
Answer: b) To remove food particles and reduce bacteria
What is a common symptom of food poisoning?
a) Coughing
b) Sneezing
c) Diarrhoea
Answer: c) Diarrhoea
22. What should be given to a person suffering from diarrhoea?
a) Cold drinks
b) Oral Rehydration Solution (ORS)
Answer: b) Oral Rehydration Solution (ORS)
23. How do ruminants digest cellulose?
a) Using their own enzymes
b) With the help of bacteria in the rumen
c) By chewing repeatedly
d) Through a long digestive tract
Answer: b) With the help of bacteria in the rumen
24. Why do infants feed on mother’s milk?
a) It is easier to digest
b) It provides necessary nutrients
c) It is a tradition
d) It is more available than other foods
Answer: b) It provides necessary nutrients
Online Courses for Class 7 HOTS
25. What happens in the buccal cavity?
a) Absorption of nutrients
b) Digestion of fats
c) Ingestion and initial digestion of food
d) Storage of food
Answer: c) Ingestion and initial digestion of food
26. What is the role of the tongue in digestion?
a) To push food into the stomach
b) To detect taste and help in mixing food with saliva
c) To digest carbohydrates
d) To store saliva
Answer: b) To detect taste and help in mixing food with saliva
27. What causes the sensation of choking while eating?
a) Food entering the windpipe
b) Food being too hot
c) Allergic reactions to food
d) Overeating
Answer: a) Food entering the windpipe
28. What is the approximate length of the human alimentary canal?
a) 5 meters
b) 10 meters
c) 7 meters
d) 30 meters
Answer: c) 7 meters
29. What is the primary function of the gall bladder?
a) To produce bile
b) To store bile
c) To digest fats
d) To absorb nutrients
Answer: b) To store bile
30. Which part of the digestive system is involved in the absorption of nutrients?
b) Small intestine
c) Large intestine
d) Esophagus
Answer: b) Small intestine
31. What is the role of the stomach in digestion?
a) To absorb nutrients
b) To store undigested food
c) To mix food with digestive juices
d) To secrete bile
Answer: c) To mix food with digestive juices
32. What part of the digestive system has a role in killing bacteria?
a) Small intestine
b) Large intestine
Answer: c) Stomach
33. What are the main steps of nutrition in humans?
a) Ingestion, digestion, absorption, assimilation, egestion
b) Ingestion, respiration, absorption, assimilation, egestion
c) Ingestion, digestion, respiration, assimilation, egestion
d) Ingestion, digestion, absorption, respiration, egestion
Answer: a) Ingestion, digestion, absorption, assimilation, egestion
34. Which gland secretes digestive juices into the small intestine?
a) Salivary glands
c) Gall bladder
Answer: d) Pancreas
35. Where are proteins first digested in the human body?
36. What is the role of the large intestine in the digestive system?
a) To digest carbohydrates
c) To secrete digestive enzymes
d) To produce bile
37. Which teeth are used for tearing food?
c) Incisors
d) Premolars
Answer: b) Canines
38. What is the role of saliva in the digestion of food?
a) It helps in the digestion of proteins
b) It helps in the digestion of fats
c) It helps in the digestion of carbohydrates
d) It does not play a role in digestion
Answer: c) It helps in the digestion of carbohydrates
39. What initiates the digestion of starch?
a) Gastric juices
c) Pancreatic juice
Answer: d) Saliva
40. What is the function of mucus in the stomach?
a) To digest food
b) To protect the stomach lining
c) To absorb nutrients
d) To produce hydrochloric acid
Answer: b) To protect the stomach lining
41. What is the primary function of the teeth?
a) To produce saliva
b) To aid in digestion by breaking down food
d) To protect the tongue
42. Answer: b) To aid in digestion by breaking down food
What does rumination involve?
a) Regurgitating swallowed food to chew it again
b) Swallowing food quickly
c) Digesting cellulose
d) Absorbing nutrients in the stomach
Answer: a) Regurgitating swallowed food to chew it again
43. Why is it advised to brush your teeth after eating sweets?
a) To freshen breath
b) To prevent tooth decay
c) To make teeth whiter
d) To prevent gum diseases
Answer: b) To prevent tooth decay
44. What causes diarrhoea?
a) Virus infection
b) Bacterial infection
c) Overeating
d) Both a and b
Answer: d) Both a and b
45. How does food move through the esophagus?
a) By gravity
b) By peristaltic movements
c) By active transport
d) By passive diffusion
Answer: b) By peristaltic movements
46. What is the first set of teeth called?
a) Permanent teeth
b) Baby teeth
c) Milk teeth
d) Temporary teeth
Answer: c) Milk teeth
47. Which part of the digestive system is the site for complete digestion of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins?
48. What is the role of bile in the digestion of fats?
a) It breaks down fats into fatty acids and glycerol
b) It emulsifies fats
c) It absorbs fats
d) It stores fats
Answer: b) It emulsifies fats
49. What is egestion?
b) Ingestion of food
c) Excretion of undigested food
d) Digestion of food
Answer: c) Excretion of undigested food
50. Which type of carbohydrate can ruminants digest that humans cannot?
c) Cellulose
Answer: c) Cellulose
Related content

Get access to free Mock Test and Master Class
Register to Get Free Mock Test and Study Material
Offer Ends in 5:00
Select your Course
Please select class.
Class 7 Science Chapter 2 HOTS Questions - Nutrition in Animals
| 1 Crore+ students have signed up on EduRev. Have you? |
Q1: The long structure of small intestine is accommodated in small space within our body. Comment.
Ans: The small intestine is about 7.5 metre long It is accommodated in a coiled form inside our body.
Q2: Cellulose rich food substances are good source of roughage in human beings. Justify.
Ans: Cellulose rich food substances are good source of roughage in human beings. It is because the cellulose digesting bacteria are not present in the body of human beings due to which human beings cannot digest cellulose (present in plant foods).
Q3: You were blindfolded and asked to identify the drinks provided in two different glasses. You could identify drink A as lime juice and B as bitter gourd juice. How could you do it inspite of being blindfolded? Ans: Inspite of being blindfolded, one could identify two different drinks with the help of taste buds present in the tongue. Q4: ‘A’ got her gall bladder removed surgically as she was diagnosed with stones in her gall bladder. After the surgery, she faced problems in digestion of certain food items when consumed in bulk. Can you tell which kind of food items would they be and why? Ans: After surgical removal of gall bladder, ‘A’ would face problems in digestion of fat and fatty substances when consumed in bulk. This is because the bile juice stored in the gall bladder helps in digestion of fats. Q5: Boojho took some grains of boiled rice in test tube ‘A’ and Paheli took boiled and chewed rice in test tube ‘S’. Both of them poured 1-2 drops of iodine solution into the test tube and observed the colour change. What colour change would they have observed? Give reasons for your Answer. Ans: In test tube A, blue black colour appeared because of presence of starch. In test tube 6, colour of iodine will not change because of digestion of starch into sugars by the action of saliva in our mouth. Q6: Boojho and Paheli were eating their food hurriedly so that they could go out and play during the recess. Suddenly, Boojho started coughing violently. Think of the reasons, why he was coughing and discuss with your friends? Ans: Sometimes when we eat hurriedly, talks or laughs while eating, the flap-like valve (called epiglottis) which closes the passage of windpipe remains open. Therefore, the food may enter into the windpipe. Coughing helps to clear the passage and returns the food particle back to the foodpipe. Q7: Ruminants such as cows and buffaloes swallow their food hurriedly and then sit restfully and chew their food. Give reason. Ans: Ruminants such as cows and buffaloes swallow their food hurriedly and store it in a part of the stomach called rumen. The cellulose of the food is digested here by the action of certain bacteria which are not present in humans. Later, this partially digested food is returned to the buccal cavity of the animals in small lumps and animal chews it to complete the process of digestion. This process is called rumination. Q8: Name the secretions of stomach which digest food.
Ans: The inner lining of stomach secretes mucous hydrochloric acid and digestive juices.
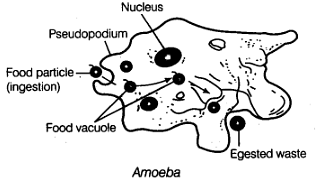
The food of Amoeba are microscopic organisms like tiny plants and animals present in pond water. When Amoeba senses its food, it pushes out pseudopodia around the food particle and engulfs it. The two pseudopodia join around the food particle and trap the food particle with a little water forming vacuole around food, thus the food gets trapped. Digestive juices present inside the vacuole, acts on the food and break it into simpler substances. This digested food is then absorbed and is used for growth, maintenance and multiplication of Amoeba. The undigested food residue is expelled outside by the vacuole. The basic process of digestion of food and release of energy is as similar to the other organisms. Q13: Read the following passage carefully and answer the questions that follow it. Bile juice is stored in a sac called, gall bladder, located near its organ of secretion, liver. The gall bladder releases the bile juice into the small intestine whenever food reaches there. Though bile juice is devoid of any digestive enzymes, it is required for the digestion of fats. The fats cannot be digested easily because they are insoluble in water and are present as large globules. Bile juice breaks down big fat droplets into smaller droplets. These are then easily digested by the enzymes released from the pancreas (a) Which organ secretes the bile juice? (b) Why is digestion of fats difficult as compared to that of other nutrients? (c) How does bile juice help in digestion of that of other nutrients? (d) Where is the digestion of fat completed? (e) Does bile juice digest fat completely? Ans: (a) Bile juice is secreted by liver. (b) Digestion of fats is difficult as compared to that of other nutrients because of insolubility of fat in water. (c) Bile juice helps in digestion of fat by breaking down big fat droplets into smaller droplet. (d) Digestion of fat is completed in small intestine. (e) No, fat is not completely digested by bile juice.
Q14: Discuss the various associated glands of digestive system and their role in digestion.
Ans: The various associated glands of digestive system and their role in digestion are as follows
- Salivary gland digestion of starch in mouth.
- Liver secretes bile juices which help in the digestion of fats.
- Pancreas secretes pancreatic juices which act on carbohydrate, fats and proteins and change them into simpler compounds.
Q15: Windpipe runs adjacent to the foodpipe. What will happen if food particles enter the windpipe? Explain.
Ans: The windpipe carries air from the nostrils to the lungs. It runs adjacent to the foodpipe. If, by chance, food particles enter the windpipe, we feel choked, get hiccups or cough.
Q16: Can we survive only on raw, leafy vegetables/grass? Discuss.
Ans: No, human beings cannot survive only on raw, leafy vegetables or grass for the following reasons:
- Human beings require all essential nutrients like carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, vitamins and minerals for survival.
- Raw, leafy vegetables or grass do not provide the required nutrients to the body, leading to less immunity and risk of catching diseases.
- Sometimes, raw vegetables contain harmful germs and viruses, making them unfit to consume.
Q17: Differentiate between assimilation and egestion.
Ans: Absorbed digested food materials are transported via the blood vessels to different organs of the body where they are used to build complex substances such as the proteins required by the body. This process is called assimilation but the process of removal of waste faecal matter through the anus from time-to-time is called egestion.
Q18: What role does villi performs in the small intestine?
Ans: The villi increase the surface area for absorption of the digested food. The surface of the villi absorbs the digested food materials and passes them into blood. The absorbed substances are transported via the blood vessels to different organs of the body.
| |246 docs|28 tests |
Top Courses for Class 7
FAQs on Class 7 Science Chapter 2 HOTS Questions - Nutrition in Animals
| 1. What is the importance of nutrition in animals? |
| 2. What are the types of nutrition in animals? |
| 3. How do animals obtain nutrients from their food? |
| 4. What are the different modes of feeding in animals? |
| 5. How does nutrition affect the growth and development of animals? |
| Views | |
| Rating | |
| Last updated |
Important questions
Study material, mock tests for examination, sample paper, previous year questions with solutions, video lectures, objective type questions, past year papers, viva questions, semester notes, practice quizzes, extra questions, shortcuts and tricks.

HOTS Questions: Nutrition in Animals Free PDF Download
Importance of hots questions: nutrition in animals, hots questions: nutrition in animals notes, hots questions: nutrition in animals class 7, study hots questions: nutrition in animals on the app.
| cation olution |
| Join the 10M+ students on EduRev |
Welcome Back
Create your account for free.
Forgot Password
Unattempted tests, change country, practice & revise.

- Andhra Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- West Bengal
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Jammu & Kashmir
- NCERT Books 2022-23
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Books
- NCERT Exemplar Solution
- States UT Book
- School Kits & Lab Manual
- NCERT Books 2021-22
- NCERT Books 2020-21
- NCERT Book 2019-2020
- NCERT Book 2015-2016
- RD Sharma Solution
- TS Grewal Solution
- TR Jain Solution
- Selina Solution
- Frank Solution
- Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur Solution
- I.E.Irodov solutions
- ICSE - Goyal Brothers Park
- ICSE - Dorothy M. Noronhe
- Micheal Vaz Solution
- S.S. Krotov Solution
- Evergreen Science
- KC Sinha Solution
- ICSE - ISC Jayanti Sengupta, Oxford
- ICSE Focus on History
- ICSE GeoGraphy Voyage
- ICSE Hindi Solution
- ICSE Treasure Trove Solution
- Thomas & Finney Solution
- SL Loney Solution
- SB Mathur Solution
- P Bahadur Solution
- Narendra Awasthi Solution
- MS Chauhan Solution
- LA Sena Solution
- Integral Calculus Amit Agarwal Solution
- IA Maron Solution
- Hall & Knight Solution
- Errorless Solution
- Pradeep's KL Gogia Solution
- OP Tandon Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Previous Year Question Paper
- Important Question
- Value Based Questions
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE MCQs PDF
- Assertion & Reason
- New Revision Notes
- Revision Notes
- Question Bank
- Marks Wise Question
- Toppers Answer Sheets
- Exam Paper Aalysis
- Concept Map
- CBSE Text Book
- Additional Practice Questions
- Vocational Book
- CBSE - Concept
- KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheets
- Formula Class Wise
- Formula Chapter Wise
- Toppers Notes
- Most Repeated Question
- Diagram Based Question
- Study Planner
- JEE Previous Year Paper
- JEE Mock Test
- JEE Crash Course
- JEE Sample Papers
- Important Info
- SRM-JEEE Previous Year Paper
- SRM-JEEE Mock Test
- VITEEE Previous Year Paper
- VITEEE Mock Test
- BITSAT Previous Year Paper
- BITSAT Mock Test
- Manipal Previous Year Paper
- Manipal Engineering Mock Test
- AP EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- AP EAMCET Mock Test
- COMEDK Previous Year Paper
- COMEDK Mock Test
- GUJCET Previous Year Paper
- GUJCET Mock Test
- KCET Previous Year Paper
- KCET Mock Test
- KEAM Previous Year Paper
- KEAM Mock Test
- MHT CET Previous Year Paper
- MHT CET Mock Test
- TS EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- TS EAMCET Mock Test
- WBJEE Previous Year Paper
- WBJEE Mock Test
- AMU Previous Year Paper
- AMU Mock Test
- CUSAT Previous Year Paper
- CUSAT Mock Test
- AEEE Previous Year Paper
- AEEE Mock Test
- UPSEE Previous Year Paper
- UPSEE Mock Test
- CGPET Previous Year Paper
- BCECE Previous Year Paper
- JCECE Previous Year Paper
- Crash Course
- Previous Year Paper
- NCERT Based Short Notes
- NCERT Based Tests
- NEET Sample Paper
- Previous Year Papers
- Quantitative Aptitude
- Numerical Aptitude Data Interpretation
- General Knowledge
- Mathematics
- Agriculture
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political science
- Enviromental Studies
- Mass Media Communication
- Teaching Aptitude
- Verbal Ability & Reading Comprehension
- Logical Reasoning & Data Interpretation
- CAT Mock Test
- CAT Important Question
- CAT Vocabulary
- CAT English Grammar
- MBA General Knowledge
- CAT Mind Map
- CAT Study Planner
- CMAT Mock Test
- SRCC GBO Mock Test
- SRCC GBO PYQs
- XAT Mock Test
- SNAP Mock Test
- IIFT Mock Test
- MAT Mock Test
- CUET PG Mock Test
- CUET PG PYQs
- MAH CET Mock Test
- MAH CET PYQs
- NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA
- SAINIK SCHOOL (AISSEE)
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Electronics & Communication Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Science Engineering
- CBSE Board News
- Scholarship Olympiad
- School Admissions
- Entrance Exams
- All Board Updates
- Miscellaneous
- State Wise Books
- Engineering Exam
Nutrition in Animals Class 7 MCQ Test (Online Available)
Free mcq test, table of content, nutrition in animals test - 21.
Duration: 10 Mins
Maximum Marks: 10
Read the following instructions carefully.
1. The test contains 10 total questions.
2. Each question has 4 options out of which only one is correct .
3. You have to finish the test in 10 minutes.
4. You will be awarded 1 mark for each correct answer.
5. You can view your Score & Rank after submitting the test.
6. Check detailed Solution with explanation after submitting the test.
7. Rank is calculated on the basis of Marks Scored & Time
Nutrition in Animals Test - 20
Nutrition in animals test - 19, nutrition in animals test - 18, nutrition in animals test - 17, nutrition in animals test - 16, nutrition in animals test - 15, nutrition in animals test - 14, nutrition in animals test - 13, nutrition in animals test - 12, nutrition in animals test - 11, nutrition in animals test - 10, nutrition in animals test - 9, nutrition in animals test - 8, nutrition in animals test - 7, nutrition in animals test - 6, nutrition in animals test - 5, nutrition in animals test - 4, nutrition in animals test - 3, nutrition in animals test - 2, nutrition in animals test - 1.
Objective questions have become the norm now, those students who are studying in class 7 must be well versed with all kinds of MCQ Questions; therefore, the link to access Nutrition in Animals MCQ Class 7 is mentioned here on this page.
Nutrition in Animals Class 7 MCQ questions are curated by subject experts referring to the prescribed NCERT Class 7 Science Book. Those students who have studied the lesson Nutrition in Animals must practise the CBSE Class 7 MCQ Questions as it helps in deepening the understanding of the topics.
Class 7 Nutrition in Animals MCQ with Answers Online
For the ease of students, the subject experts have simplified the practice process of the class 7 Nutrition in Animals MCQ as they have solved each and every question given. The answers are detailed and easy to grasp. Students who want to practise the questions of Class 7 Nutrition in Animals MCQ with Answers online can use the Selfstudys website.
The MCQ Questions of Nutrition in Animals with answers are also given so that students can understand the methods of solving the concepts based questions. As well as, the solutions are helpful to understand where the students are making mistakes and need to improve.
How to Practise MCQ from NCERT Chapter Nutrition in Animals?
There are several ways to practise the MCQ from NCERT Chapter Nutrition in Animals; one is by solving questions from the chapter’s end and another is by using online medium. In this section, we have mentioned the steps to Practise MCQ from NCERT Chapter Nutrition in Animals online.
- First of all open Selfstudys.com on your Smartphone, PC/Laptop
- Navigate to the CBSE by Tapping/clicking on the navigation bar or button
- It will open a new lists where you can find MCQ Test - Click on that
- Then, a new page will load containing the lists of classes; just Tap or click on Class 7. *In Smartphone, you may require to scroll the given classes name towards left.
- Now, after selecting the Class 7, the same page will reload, make sure you select the Science to access the MCQ Questions of Class 7 Nutrition in Animals.
Note: The online MCQ Questions of Nutrition in Animals can’t be downloaded, those who want to access the PDF of Nutrition in Animals MCQ can refer to the CBSE Class 7 MCQ PDF section within the CBSE menu.
What is Nutrition in Animals MCQ and How to Use it?
Since class 7 students are in their early stage of academics they may have questions regarding What is Nutrition in Animals MCQ and How to Use it. So, the answer is MCQ Questions are objective questions which contain questions followed by 4 options where only one is considered the correct answer and remaining as a distraction. Why is it so, because MCQ questions are ideal to assess a student’s conceptual knowledge.
Those who want to use the Nutrition in Animals MCQ can use this website to access the online MCQ questions to practise.
Top 5 Benefits of Nutrition in Animals MCQ Class 7
Nutrition in Animals MCQ Class 7 questions benefit students in several ways; however, here we have mentioned a total of 5 benefits that a student will get if they are using the MCQ from NCERT Chapter Nutrition in Animals.
- Helps in Practising Questions: Sometimes, it's hard to get the questions to practise; therefore, the Selfstudys team has curated various sets of MCQ Questions of Class 7 Nutrition in Animals. Having access to the objective questions of Class 7 Nutrition in Animals helps students practising various questions for free of cost.
- Boosts the Critical Thinking Capability: The MCQs or objective questions must be answered in lesser time; therefore, those who will regularly solve Nutrition in Animals MCQ Class 7 will benefit by having a great boost in the critical thinking capability as the questions are in the objective format which can be answered if one has a good command over the concepts of Nutrition in Animals.
- Assists in Covering the Class 7 Science Syllabus: Nutrition in Animals is a chapter of Class 7 Science and those who are going to solve the MCQs of Class 7 Nutrition in Animals will be able to practise all the questions as per their Science Syllabus.
- Helps in Exam Preparation: If a student solves the objective questions from class 7 Nutrition in Animals, they will be able to be prepared for the annual examination too. It is because the questions that are asked in the online MCQ of Nutrition in Animals are asked in the final exam question papers too.
- A Deeper Understanding of Nutrition in Animals: All the important points that are discussed in Nutrition in Animals must be memorised by students as it helps in deepening the understanding of the Delhi Sultans. One of the great benefits of solving Nutrition in Animals MCQ Class 7 is that one can be thorough with the topics and can develop a deeper understanding of Nutrition in Animals chapter of class 7.
Apply These Techniques To Better Answer the MCQ Questions of Nutrition in Animals
Although, there is no wrong or right method to answer the MCQ Questions, those who are interested in knowing the techniques to better answer the MCQ Questions of Nutrition in Animals can follow the below given methods.
Read the Question Carefully: Questions in Nutrition in Animals MCQ Class 7 can be asked from tricky to hard to understand. In this case, you must read the questions of Nutrition in Animals MCQ carefully. By paying attention to the questions, it will help you connect the dots and assist you recall the studied concepts to answer the MCQs easily.
Eliminate Obviously Wrong Answers: Many questions of Nutrition in Animals MCQ Class 7 will be so familiar that you can be certain for the wrong answer but uncertain for the right answer, in that situation obviously eliminate wrong answers first. By eliminating irrelevant or incorrect answers, it will help you find the one correct answer from all the given four options.
Look for Clues in the Question: As we have discussed the first technique is to read the questions carefully, it is vital for looking for the clues in the questions of Nutrition in Animals MCQ Class 7. Every single question contains some kind of clues that help you answer them easily, but due to running out of time many don’t pay attention to it. In order to solve Nutrition in Animals MCQ Class 7 by using this technique you may have to do a thorough practice of Class 7 MCQ Questions.
Use the Process of Elimination: There is not much difference in the elimination method and eliminating the wrong answer (discussed in point number 2) first, but one difference that makes the elimination process different is you can eliminate the right or wrong answer first.
This means that when you are confused between two options, you can separate them and then you try to focus on only those 2 options to find out the correct answer of Nutrition in Animals MCQ Class 7. This elimination process works best in most of the scenarios.
Don't Spend too Much Time on One Question: It is never a good idea to be rigid on one question and spend most of your time answering them. When you are practising Nutrition in Animals MCQ Class 7 questions, you have limited time and you have to make sure that you use your time smartly to attempt all the questions as asked in the Nutrition in Animals Class 7 MCQ.
Double-check your Answer: Before submitting the Online test of Class 7 Nutrition in Animals MCQ, you should double check your answer if the test time hasn't completed. When you do a double check of your answers, you may find some silly mistakes that you have made due to which you could have lost some marks. Therefore, be conscious and double check your answers before submitting Nutrition in Animals MCQ Class 7.
*As per the Selfstudys Online MCQ Test instructions the time plays a crucial role in calculating your test rank so, be conscious when you use any single minute during your test.
Manage your Time: Having great time management skills doesn’t only help you quickly answer the questions, but gives you the ability to save time to review the questions or in doing a last minute cross-checking. Thus, when you start solving Nutrition in Animals MCQ Class 7 questions, try to manage time and some of your test time to review the answers you have ticked throughout the test.
Apart from this, time management skills give you peace of mind and keep you calm.
Stay Calm to Recall Previously Studied Topics: When you struggle to come up with the correct answer of Nutrition in Animals MCQ Class 7 Questions try to stay calm as it will help you recall previously studied topics. Research says, being calm and relaxed helps in saving energy. Thus, staying calm while solving the MCQ from NCERT Chapter Nutrition in Animals helps you be more focused and answer the questions efficiently. The saved energy can be channelized to increase the focus and concentration to better recall the topics and subtopics of Nutrition in Animals.
There is a high possibility of having more techniques of Nutrition in Animals MCQ Class 7 as mentioned, but these given methods work well in most of the cases.

- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- CBSE Syllabus 2023-24
- Social Media Channels
- Login Customize Your Notification Preferences

- Second click on the toggle icon

Provide prime members with unlimited access to all study materials in PDF format.
Allow prime members to attempt MCQ tests multiple times to enhance their learning and understanding.
Provide prime users with access to exclusive PDF study materials that are not available to regular users.

The Site is down as we are performing important server maintenance, during which time the server will be unavailable for approximately 24 hours. Please hold off on any critical actions until we are finished. As always your feedback is appreciated.

- Study Packages
- NCERT Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Online Test

- Questions Bank
- Nutrition in Animals
- Test Series
- Ncert Solutions
- Solved Papers
- Current Affairs
- JEE Main & Advanced
- Pre-Primary
- MP State Exams
- UP State Exams
- Rajasthan State Exams
- Jharkhand State Exams
- Chhattisgarh State Exams
- Bihar State Exams
- Haryana State Exams
- Gujarat State Exams
- MH State Exams
- Himachal State Exams
- Delhi State Exams
- Uttarakhand State Exams
- Punjab State Exams
- J&K State Exams
7th Class Science Nutrition in Animals Question Bank
Done nutrition in animals total questions - 116.

question_answer 1) An example of heterotrophic organism which can synthesis food. .
A) Paramecium done clear
B) Euglena done clear
C) Amoeba done clear
D) Hydra done clear
question_answer 2) These are blood sucking parasites.
A) Earthworm done clear
B) Hookworm done clear
C) Leeches done clear
D) Bedbugs done clear
question_answer 3) The process in which faucal matter is removed through the anus.
A) Egestion done clear
B) Digestion done clear
C) Absorption done clear
D) Ingestion done clear
question_answer 4) A unicellular protozoan is ________.
A) Paramecium done clear
B) Amoeba done clear
C) Euglena done clear
question_answer 5) Mechanism in which amoeba takes in \[{{O}_{2}}\] and gives out \[C{{O}_{2}}\]is called _______.
A) Respiration done clear
B) Diffusion done clear
C) Assimilation done clear
D) Absorption done clear
question_answer 6) Enzymes which helps in digestion in amoeba
A) Amylase done clear
B) Proteinase done clear
C) None of the above done clear
D) both (a) and (b) done clear
question_answer 7) Nutrients digested by amoeba are
A) Sugar done clear
B) Cellulose done clear
C) Protein done clear
D) all of the above done clear
question_answer 8) Why are nutrition in animals holozoic?
A) because they depend on plants for food done clear
B) because they are heterotrophs done clear
C) because they can shallow food done clear
D) all the above done clear
question_answer 9) The process of breakdown of food particles into small pieces is called _______.
A) Digestion done clear
B) Mastication done clear
C) Peristalsis done clear
D) Diffusion done clear
question_answer 10) Important diet in herbivorous animal?s are-
A) Protein done clear
C) Fat done clear
D) Carbohydrate done clear
question_answer 11) Raccoon is an example of which type of animal-
A) Herbivore done clear
B) Omnivore done clear
C) Carnivore done clear
D) Parasite done clear
question_answer 12) Duodenum, Jejunum, ileum are ______ parts.
A) Small Intestine done clear
B) Large Intestine done clear
C) Esophagus?s done clear
D) Stomach done clear
question_answer 13) Which gland acts as mixed gland?
A) Pancreas done clear
B) Duodenum done clear
C) Hypothalamus gland done clear
D) Digestive gland done clear
question_answer 14) In which part of the human digestive system digestion doesn't take place.
A) Stomach done clear
B) Small Intestine done clear
C) Oesophagus done clear
D) Large Intestine done clear
question_answer 15) Which enzyme helps in transfer of Trypsinogen to trypsin secreted from the walls of the small intestine?
A) Proteinase done clear
B) Enterokinase done clear
C) Amylase done clear
D) Lactase done clear
question_answer 16) Siphoning is the mode of feeding alone in which type of animal.
A) Humming bird done clear
B) Butterfly done clear
C) Ant done clear
D) Housefly done clear
question_answer 17) Bile juice is secreted by which part of digestive system.
A) Small Intestine done clear
B) Liver done clear
C) Pituitary gland done clear
question_answer 18) A locomotory organ found in unicellular animal-
A) Cilia done clear
B) flagella done clear
C) Sessile done clear
D) Pseudopodia done clear
question_answer 19) A fresh water organism which contains cytoplasm.
A) Euglena done clear
B) Paramaecium done clear
C) Hydra done clear
D) Amoeba done clear
question_answer 20) Pulp is a soft material in the tooth and it is rich in
A) Starch and sugar done clear
B) Nerves and blood vessels done clear
C) acids done clear
D) cellulose done clear
question_answer 21) What helps the herbivores to snip off foliage from branches-?
A) Canine teeth done clear
B) Large incisors done clear
C) sharp molars done clear
D) upper jaw done clear
question_answer 22) Which of the following is part of alimentary canal?
A) Stomach done clear
B) Oesophagus done clear
C) Euccal cavity done clear
D) All of these done clear
question_answer 23) Which of the following is part of the digestive tract?
A) Small intestine done clear
B) Large intestine done clear
C) Both of these done clear
D) None of these done clear
question_answer 24) Which of the following secrete digestive juices which convert complex substances of food into simpler substances?
A) Liver done clear
B) Pancreas done clear
C) Both the above done clear
question_answer 25) In digesting which of the following components of food will a person, having liver that does not function properly, feel difficulty?
A) Carbohydrates done clear
B) Fats done clear
C) Proteins done clear
D) Vitamins done clear
question_answer 26) This length of small intestine and large intestine are respectively
A) 7.5 m and 1.5 m done clear
B) 1.5 m and 7.5 m done clear
C) 7.5 m and 1.0 m done clear
D) 1.5 m and 7.0 m done clear
question_answer 27) Digestive system consists of
A) Alimentary Canal and digestive tract done clear
B) Alimentary canal done clear
C) Digestive tract done clear
D) Digestive tract and associated glands done clear
question_answer 28) In human beings the food is taken in by which of the following parts?
A) Mouth done clear
B) Tongue done clear
C) Teeth done clear
question_answer 29) The set of teeth that grows during infancy and fall off at the age of 6-8 years are called
A) milk teeth done clear
B) sweet teeth done clear
C) permanent teeth done clear
D) none of these done clear
question_answer 30) Which one is the widest part of alimentary canal?
A) Food pipe done clear
B) Mouth done clear
C) Stomach done clear
D) Tongue done clear
question_answer 31) Which of the following is incorrect for liver?
A) It is a reddish brown gland done clear
B) It is situated in upper part of abdomen done clear
C) It is the largest gland in the body done clear
D) None of the above is correct done clear
question_answer 32) The pancreatic juice acts on which of the following components of food and change it into simpler substances?
A) Fats done clear
B) Carbohydrates done clear
question_answer 33) The food that reaches the lower part of small intestines is
A) Completely digested done clear
B) Partly digested done clear
C) Can?t say done clear
D) All the above are correct done clear
question_answer 34) The intestinal juice changes fats into
A) Fatty acids done clear
B) glycerol done clear
question_answer 35) The process of change of digested absorbed substances into complex substances and its use is called
A) Absorption done clear
B) assimilation done clear
question_answer 36) When glucose breaks down in the cells with the help of oxygen it results in the formation of
A) Carbon dioxide done clear
B) water done clear
question_answer 37) Select the ruminants from the following
A) Camel done clear
B) Giraffe done clear
C) Deer done clear
question_answer 38) Wisdom teeth normally grow during the age of
A) 17-30 years done clear
B) 12-15 years done clear
C) 34-40 years done clear
D) 40-45 years done clear
question_answer 39) What do all organisms need to survive?
A) Energy done clear
B) blood done clear
C) Carbon dioxide done clear
D) soil done clear
question_answer 40) Which of the following is not correct for small intestine?
A) It is about 1.5m long done clear
B) It is about 7.5m long done clear
C) (c) Its walls secrete juices done clear
D) It receives secretions from liver. done clear
| Column-I | Column-II |
| (A) Small intestine | (p) 7.5 m |
| (B) Large intestine | (q) 1.5 m |
| (C) Buccal cavity | (r) Part of alimentary canal |
| (D) Ingestion | (s) Process of taking food into the body |
A) (A) \[\to \] (p), (B) \[\to \] (q), (C) \[\to \] (r), (D) \[\to \] (s) done clear
B) (A) \[\to \] (q), (B) \[\to \] (p), (C) \[\to \] (r), (D) \[\to \] (s) done clear
C) (A) \[\to \] (p), (B) \[\to \] (q), (C) \[\to \] (s), (D) \[\to \] (r) done clear
D) (A) \[\to \] (q), (B) \[\to \] (p), (C) \[\to \] (s), (D) \[\to \] (r) done clear
| Column - I | Column - II |
| (A) Food Pipe | (p) Digestive tract |
| (B) Alimentary canal | (q) Oesophagus |
| (C) Stomach | (r) Flattened U Shape |
| (D) Widest part of alimentary canal | (s) Stomach |
B) (A) \[\to \] (q), (B) \[\to \] (r), (C) \[\to \] (s), (D) \[\to \] (p) done clear
C) (A) \[\to \] (q), (B) \[\to \] (p), (C) \[\to \] (r), (D) \[\to \] (s) done clear
D) (A) \[\to \] (r), (B) \[\to \] (s), (C) \[\to \] (q), (D) \[\to \] (p) done clear
| Column - I | Column - II |
| (A) Number of molars in a jaw | (p) 4 |
| (B) Number of premolars in a jaw | (q) 2 |
| (C) Number of canine in a jaw | (r) 6 |
| (D) Number of incisor in both jaws | (s) 8 |
B) (A) \[\to \] (r), (B) \[\to \] (p), (C) \[\to \] (q), (D) \[\to \] (s) done clear
D) (A) \[\to \] (s), (B) \[\to \] (r), (C) \[\to \] (q), (D) \[\to \] (p) done clear
question_answer 44) DIRECTIONS: Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow. Passage - 1 The food components gradually get digested as food travels through the various components of alimentary canal. The digested food can pass into the blood vessels in the walls of the small intestine. The digestive system consists of
A) Digestive tract done clear
B) Digestive tract and liver done clear
C) Digestive tract and pancreas done clear
D) Digestive tract and the associated glands done clear
question_answer 45) DIRECTIONS: Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow. Passage - 1 The food components gradually get digested as food travels through the various components of alimentary canal. The digested food can pass into the blood vessels in the walls of the small intestine. The part of our body which contains salivary glands which secrete saliva is
A) Mouth done clear
B) tongue done clear
C) Teeth done clear
D) all of these done clear
question_answer 46) DIRECTIONS: Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow. Passage - 1 The food components gradually get digested as food travels through the various components of alimentary canal. The digested food can pass into the blood vessels in the walls of the small intestine. The saliva breaks down
A) Starch into sugar done clear
B) Sugar into glucose done clear
C) Fats into fatty acids done clear
D) All of the above are correct done clear
question_answer 47) DIRECTIONS: Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow. Passage - 2 We can easily see cows, buffaloes and other grass- eating animals chewing continuously even when they are not eating. In fact, such animals quickly swallow the grass and store it in a part of stomach called rumen. Here the food gets partially digested and is called cud. Later the cud returns to the mouth in small lumps and the animals chew it. How is food ingested by grass-eating animals?
A) by chewing done clear
B) by siphoning done clear
C) by swallowing done clear
D) by sucking done clear
question_answer 48) DIRECTIONS: Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow. Passage - 2 We can easily see cows, buffaloes and other grass- eating animals chewing continuously even when they are not eating. In fact, such animals quickly swallow the grass and store it in a part of stomach called rumen. Here the food gets partially digested and is called cud. Later the cud returns to the mouth in small lumps and the animals chew it. In which of the following is grass rich?
A) Cellulose done clear
B) Starch done clear
question_answer 49) DIRECTIONS: Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow. Passage - 2 We can easily see cows, buffaloes and other grass- eating animals chewing continuously even when they are not eating. In fact, such animals quickly swallow the grass and store it in a part of stomach called rumen. Here the food gets partially digested and is called cud. Later the cud returns to the mouth in small lumps and the animals chew it. Select the part of body of ruminants in which the cellulose of their food is digested.
C) Caecum done clear
question_answer 50) DIRECTIONS: Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow. Passage - 3 Amoeba is a microscopic single-celled organism found in pond water. It has a cell membrane, a rounded, dense nucleus and many small bubble-like vacuoles in its cytoplasm. Amoeba constantly changes it shape and position. It pushes out one or more finger-like projections, called pseudopodia or false feet, for movement or capture of food. A unicellular organism that has contractile vacuoles and in which ingestion of food takes place with the help of cilia is
A) Amoeba done clear
B) Yeast done clear
C) Paramecium done clear
question_answer 51) DIRECTIONS: Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow. Passage - 3 Amoeba is a microscopic single-celled organism found in pond water. It has a cell membrane, a rounded, dense nucleus and many small bubble-like vacuoles in its cytoplasm. Amoeba constantly changes it shape and position. It pushes out one or more finger-like projections, called pseudopodia or false feet, for movement or capture of food. Amoeba
A) is a single-celled organism done clear
B) has a rounded, dense nucleus done clear
C) has many small bubble-like vacuoles in its cytoplasm done clear
D) all the above are correct done clear
question_answer 52) DIRECTIONS: Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow. Passage - 3 Amoeba is a microscopic single-celled organism found in pond water. It has a cell membrane, a rounded, dense nucleus and many small bubble-like vacuoles in its cytoplasm. Amoeba constantly changes it shape and position. It pushes out one or more finger-like projections, called pseudopodia or false feet, for movement or capture of food. For capture of food, Amoeba
A) pushes out one finger-like projection done clear
B) pushes out one or more finger-like projections done clear
C) both the above are correct done clear
D) one of the above is correct done clear
question_answer 53) DIRECTIONS: The questions in this segment consist of two statements, one labeled as "Assertion A" and the other labeled as "Reason R". You are to examine these two statements carefully and decide if the Assertion A and Reason R are individually true and if so, whether the reason is a correct explanation of the assertion. Select your answers to these items using code. Given below. Assertion A: Tongue is a fleshy muscular organ. Reason R: Tongue is used for talking.
A) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A. done clear
B) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A. done clear
C) A is true but R is false. done clear
D) A is false but R is true. done clear
question_answer 54) DIRECTIONS: The questions in this segment consist of two statements, one labeled as "Assertion A" and the other labeled as "Reason R". You are to examine these two statements carefully and decide if the Assertion A and Reason R are individually true and if so, whether the reason is a correct explanation of the assertion. Select your answers to these items using code. Given below. Assertion A: Food pipe runs through neck and chest. Reason R: When food is not accepted by our stomach it is vomited out.
question_answer 55) DIRECTIONS: The questions in this segment consist of two statements, one labeled as "Assertion A" and the other labeled as "Reason R". You are to examine these two statements carefully and decide if the Assertion A and Reason R are individually true and if so, whether the reason is a correct explanation of the assertion. Select your answers to these items using code. Given below. Assertion A: The small intestine is about 7.5m long and highly coiled. Reason R: It is smaller as compared to large intestine.
question_answer 56) DIRECTIONS: The questions in this segment consist of two statements, one labeled as "Assertion A" and the other labeled as "Reason R". You are to examine these two statements carefully and decide if the Assertion A and Reason R are individually true and if so, whether the reason is a correct explanation of the assertion. Select your answers to these items using code. Given below. Assertion A: Liver secretes a juice called bile juice. Reason R: Bile juice is stored in liver.
question_answer 57) DIRECTIONS: Read the following two statements carefully and choose the correct options. (i) Extracellular digestion takes place in small intestine (ii) Digestion does not take place in stomach
A) Statement (i) is correct while statement (ii) is incorrect. done clear
B) Statement (ii) is correct while statement (i) is incorrect. done clear
C) Both statements are correct. done clear
D) Both statements are incorrect. done clear
question_answer 58) DIRECTIONS: Read the following two statements carefully and choose the correct options. (i) Blood vessels and nerves of a tooth are present in pulp (ii) Study of teeth in called dentistry
question_answer 59) DIRECTIONS: Read the following two statements carefully and choose the correct options. (i) Process of taking in food from environment is called digestion (ii) Process by which undigested food is ejected out of the body is called assimilation
A) Small intestine done clear
C) Rectum done clear
D) anus done clear
A) P done clear
B) Q done clear
C) R done clear
D) S done clear
A) Rumen done clear
B) Cud done clear
C) Stomach done clear
question_answer 63) Which statement is correct-?
A) Breakdown of complex substance into simpler substance is called peristalsis. done clear
B) The process of passing of digestive food into blood vessels in the Intestine is called peristalsis. done clear
C) Movement of food through alimentary canal by the wave like movement controlled by involuntary muscles is called Peristalsis. done clear
D) The process of utilization of glucose, amino acid is called peristalsis. done clear
question_answer 64) Which is NOT true for vim?
A) These increase the surface area for absorption of digested food. done clear
B) These are small finger like projections. done clear
C) Villi protects the inner lining of stomach done clear
D) They absorb digested food materials. done clear
question_answer 65) Is this statement correct or in correct Extracellular digestion takes place in small Intestine.
A) Large: Intestine done clear
C) Stomach done clear
question_answer 66) The other name of defecation is _______.
A) Assimilation done clear
B) Absorption done clear
C) Eyestion done clear
A) (i) small intestine (ii) Rumen (iii) Abomgsum (iv) omasum done clear
B) (i) Rumen (ii) Small Intestine (iii) Small Intestine (iv) Abomasum done clear
C) (i) Rumen (ii) Omasum (iii) Small Intestine (iv) Abomasum done clear
D) (i) Abomasum (ii) Omasum (iii) Rumen (iv) small intestine done clear
question_answer 68) The canine of our teeth helps in ______.
A) tearing the food done clear
B) grinding the food done clear
C) biting the food done clear
D) cutting the food done clear
question_answer 69) Which is the largest chamber in the stomach of ruminant?
A) Omasum done clear
B) Rumen done clear
C) Aboniasurn done clear
D) Rsticukim done clear
question_answer 70) The inner lining of stomach secretes
A) Mucous done clear
B) Hydrochloric acid done clear
C) Digestive juices done clear
question_answer 71) What is the function of mucous secreted, by the inner lining of stomach?
A) Kills many bacteria done clear
B) Makes medium in stomach acidic. done clear
C) Protects lining of stomach done clear
D) All the above done clear
question_answer 72) The function of the acid Secreted by inner lining of stomach is
B) Makes the medium in the stomach acidic done clear
C) Helps the digestive juices to act done clear
question_answer 73) Which one is incorrect about liver?
A) It stores proteins and fats done clear
B) It purifies blood done clear
C) It removes and stores iron from dead red blood cells done clear
D) It helps in digestion by producing bile done clear
question_answer 74) Select the one who first discovered one-celled animals
A) Charaka done clear
B) Anton Leeuwenhoek done clear
C) Marcello Malpighi done clear
D) Galen done clear
question_answer 75) As the population of small fish in a lake decreases, the population of large fish that depend on the small fish for food will
A) Reproduce faster done clear
B) Begin to produce their own food done clear
C) Decrease in number done clear
D) Increase in number done clear
question_answer 76) The main function of the human digestive system is to
A) Break down foods for absorption into the blood done clear
B) Exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide in the lungs done clear
C) Release energy from sugars within the cells done clear
D) Carry nutrients to all parts of the body done clear
question_answer 77) It is a carbohydrate and its digestion begins in buccal cavity. It is
A) cellulose done clear
B) starch done clear
C) proteins done clear
D) vitamins done clear
question_answer 78) It is a large cream colored gland and is located just below the stomach. It is
A) liver done clear
B) pancreas done clear
C) heart done clear
question_answer 79) In grass-eating animals, the grass is stored in a part of the stomach where the food gets converted into cud. This part is called
A) stomach done clear
B) rumen done clear
C) rumination done clear
D) ruminant done clear
question_answer 80) It is secreted by salivary glands and its function is to break down starch into sugars. It is
A) Pancreatic juice done clear
B) bile juice done clear
C) Saliva done clear
question_answer 81) Ingestion is
A) the mode of chewing and cutting food in mouth. done clear
B) the process of taking food into the body. done clear
C) both the above are correct. done clear
D) none of these is correct. done clear
question_answer 82) Tongue
A) is a fleshy muscular organ and is attached at the back to the floor of buccal cavity. done clear
B) mixes saliva with food during chewing and helps in swallowing food. done clear
C) helps us to taste food. done clear
D) all the above are correct. done clear
question_answer 83) Absorption
A) is the process by which digested food passes into the blood vessels. done clear
B) is the process by which digested food passes into the blood vessels in the wall of the intestines. done clear
D) none of the above is correct done clear
question_answer 84) Assimilation is
A) the process of change of digested absorbed substances into complex substances and its use. done clear
B) Utilization by living organisms of absorbed food materials in the process of growth, reproduction and repair. done clear
C) Both the above are correct. done clear
question_answer 85) Egestion is
A) The storage of undigested and waste material in rectum done clear
B) Removal of faucal material through anus from time to time done clear
question_answer 86) We vomit out food, because
A) it is not to our taste done clear
B) it is poisonous and should not be allowed to enter our body done clear
C) it is not accepted by our stomach done clear
question_answer 87) From where does saliva come in our mouth?
A) when we see some food of pure liking done clear
B) when we are quite hungry done clear
C) it is secreted by salivary glands situated in our mouth done clear
| Column-I | Column-II |
| (A) Incisors | (p) Grinding teeth |
| (B) Canines | (q) Cracking teeth |
| (C) Premolars | (r) Cutting teeth |
| (D) Molars | (s) Tearing teeth |
A) (A) \[\to \] (p), (B) \[\to \] (s), (C) \[\to \] (q), (D) \[\to \] (r) done clear
B) (A) \[\to \] (q), (B) \[\to \] (p), (C) \[\to \] (s), (D) \[\to \] (r) done clear
C) (A) \[\to \] (r), (B) \[\to \] (s), (C) \[\to \] (q), (D) \[\to \] (p) done clear
D) (A) \[\to \] (r), (B) \[\to \] (q), (C) \[\to \] (s), (D) \[\to \] (p) done clear
| Column-I | Column-II |
| (A) Salivary glands | (p) pepsin |
| (B) Liver | (q) trypoin |
| (C) Small in trstive | (r) amylase |
| (D) Stomach | (s) Bile |
A) (A) \[\to \] (r), (B) \[\to \] (s), (C) \[\to \] (q), (D) \[\to \] (p) done clear
B) (A) \[\to \] (r), (B) \[\to \] (q), (C) \[\to \] (p), (D) \[\to \] (s) done clear
C) (A) \[\to \] (s), (B) \[\to \] (r), (C) \[\to \] (q), (D) \[\to \] (p) done clear
| Column-I | Column-II |
| (A) Unicellular | (p) omnivore |
| (B) Blood sucking | (q) Locomotion |
| (C) Raccoon | (r) amoeba |
| (D) Pseudopodia | (s) leech |
A) (A) \[\to \] (s), (B) \[\to \] (r), (C) \[\to \] (p), (D) \[\to \] (q) done clear
B) (A) \[\to \] (r), (B) \[\to \] (s), (C) \[\to \] (p), (D) \[\to \] (q) done clear
C) (A) \[\to \] (q), (B) \[\to \] (p), (C) \[\to \] (s), (D) \[\to \] (r) done clear
D) (A) \[\to \] (r), (B) \[\to \] (p), (C) \[\to \] (q), (D) \[\to \] (s) done clear
question_answer 91) DIRECTIONS: Read the passage (s) given below and answer the questions that follow. Passage - 1 Our stomach expands when the food entives and contracts when it goes out. Thus the stomach can expand and contract. This is possible because our stomach is made up of
A) Bones done clear
C) Muscles done clear
D) iron done clear
question_answer 92) DIRECTIONS: Read the passage (s) given below and answer the questions that follow. Passage - 1 Our stomach expands when the food entives and contracts when it goes out. Thus the stomach can expand and contract. Our stomach is located
A) In the left side of the body done clear
B) In the right side of the body done clear
C) Below the abdomen done clear
D) In the chest done clear
question_answer 93) DIRECTIONS: Read the passage (s) given below and answer the questions that follow. Passage - 1 Our stomach expands when the food entives and contracts when it goes out. Thus the stomach can expand and contract. The enzyme secreted by the stomach is
A) tripain done clear
B) pepsin done clear
D) laile done clear
question_answer 94) DIRECTIONS: Read the passage (s) given below and answer the questions that follow. Passage - 2 A new born body has no teeth. Teeth begin to appear when the baby is six to seven months old. By the age of three year children have 20 teeth. Which is the layer of the teeth below the enamel?
A) Pulp done clear
B) gum done clear
C) dentive done clear
D) root done clear
question_answer 95) DIRECTIONS: Read the passage (s) given below and answer the questions that follow. Passage - 2 A new born body has no teeth. Teeth begin to appear when the baby is six to seven months old. By the age of three year children have 20 teeth. Which teeth are called grinding teeth
A) Incisors done clear
B) canines done clear
C) Premolars done clear
D) molars done clear
question_answer 96) DIRECTIONS: Read the passage (s) given below and answer the questions that follow. Passage - 2 A new born body has no teeth. Teeth begin to appear when the baby is six to seven months old. By the age of three year children have 20 teeth. An adult has ____ teeth
A) 24 done clear
B) 28 done clear
C) 32 done clear
D) 28 done clear
question_answer 97) DIRECTIONS: Read the passage (s) given below and answer the questions that follow. Passage - 3 The partly digested food reaches the lower part of small intestines and digestion of all components of food is completed here by intestinal juice. What are proteins changed into?
A) Amino acid done clear
B) HCl acid done clear
C) Pepsin done clear
D) starch done clear
question_answer 98) DIRECTIONS: Read the passage (s) given below and answer the questions that follow. Passage - 3 The partly digested food reaches the lower part of small intestines and digestion of all components of food is completed here by intestinal juice. Which gland is called eargest gland in the body?
C) Liver done clear
D) heart done clear
question_answer 99) DIRECTIONS: Read the passage (s) given below and answer the questions that follow. Passage - 3 The partly digested food reaches the lower part of small intestines and digestion of all components of food is completed here by intestinal juice. Which enzyme is secreted by small intestine?
A) Amylase done clear
C) tripsin done clear
D) HCl done clear
question_answer 100) DIRECTIONS: The questions in this segment consist of two statements, one labeled as "Assertion A" and the other labeled as "Reason R". You are to examine these two statements carefully and decide if the Assertion A and Reason R are individually true and if so, whether the reason is a correct explanation of the assertion. Select your answers to these items using codes given below. Assertion (A): Digestion of carbohydrates, like starch, begins in buccal cavity. Reason (R): The digested food is absorbed in the blood vessels from small intestines.
A) Both A and R is true and R is the correct explanation of A. done clear
B) Both A and R is true but R is not the correct explanation of A. done clear
question_answer 101) DIRECTIONS: The questions in this segment consist of two statements, one labeled as "Assertion A" and the other labeled as "Reason R". You are to examine these two statements carefully and decide if the Assertion A and Reason R are individually true and if so, whether the reason is a correct explanation of the assertion. Select your answers to these items using codes given below. Assertion (A): Food is pushed down the food pipe which runs through the neck and chest Reason (R): The peristaltive movement of the wall of the food pipe is a continuous process.
question_answer 102) DIRECTIONS: The questions in this segment consist of two statements, one labeled as "Assertion A" and the other labeled as "Reason R". You are to examine these two statements carefully and decide if the Assertion A and Reason R are individually true and if so, whether the reason is a correct explanation of the assertion. Select your answers to these items using codes given below. Assertion (A): Rumen is the first of four chambers of stomach of ruminants Reason (R): In rumen the food gets partly digested and is called cud.
question_answer 103) DIRECTIONS: The questions in this segment consist of two statements, one labeled as "Assertion A" and the other labeled as "Reason R". You are to examine these two statements carefully and decide if the Assertion A and Reason R are individually true and if so, whether the reason is a correct explanation of the assertion. Select your answers to these items using codes given below. Assertion (A): Digestion in amoeba is intracellular. Reason (R): In the food vacuole the food becomes trapped and is digested by the action of digestive juices secreted into food vacuole
question_answer 104) DIRECTIONS: Read the following two statements carefully and choose the correct options. (i) Permanent teeth lasts throughout life (ii) It is the second set of teeth. (iii) There are 32 milk teeth
A) Statements (i) and (iii) are incorrect but (ii) is correct. done clear
B) Statements (i) and (ii) are incorrect but (iii) is correct. done clear
C) All statements are correct. done clear
D) All statements are incorrect. done clear
question_answer 105) DIRECTIONS: Read the following two statements carefully and choose the correct options. (i) At one end stomach receives food from food pipe (ii) At one end stomach opens into small intensives. (iii) Stomach mall releases HCl acid.
question_answer 106) DIRECTIONS: Read the following two statements carefully and choose the correct options. (i) Length of large intestive in more than small intestive. (ii) Pancreas is the largest gland in human body. (iii) Gall Bladder secretes juice into small intestive
question_answer 107) DIRECTIONS: Read the following two statements carefully and choose the correct options. (i) The mode of taking in food into the body varies for different organisns. (ii) Complex components of food cannot be digested as such. (iii) Digestion of food begins in the mouth.
A) carrot, rabbit, and fox done clear
B) grain, bird, and owl done clear
C) fox, owl, and rabbit done clear
D) bird, mouse, and grasshopper done clear
A) canives done clear
B) incisors done clear
C) premolars done clear
A) I done clear
B) II done clear
C) III done clear
D) IV done clear
A) Tearing teeth done clear
B) canives done clear
C) nolars done clear
D) crocking teeth done clear
A) Molars done clear
B) Premolars done clear
C) Incisors done clear
D) Canines done clear
question_answer 113) Which one of the following degan does not manufacture digestive juices?
A) K done clear
B) d done clear
C) L done clear
D) e done clear
A) Liver done clear
C) Stomach done clear
D) Kidney done clear
A) Gall bladder done clear
C) Stomach done clear
D) Heart done clear
Study Package

Question - Nutrition In animals
Related question.

Reset Password.
OTP has been sent to your mobile number and is valid for one hour
Mobile Number Verified
Your mobile number is verified.

Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download
Assertion Reason Questions for Class 7 Science Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals
- Last modified on: 1 year ago
- Reading Time: 14 Minutes
[Download] Assertion Reason Questions for Class 7 Science Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals
Here we are providing assertion reason questions for Class 7 Science Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals .
Directions:
The question below consists of an assertion and a Reason. Use the following key to choose the appropriate answer. (a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A. (b) Both A and R are true but R is not the correct explanation of A. (c) A is true but R is false. (d) A is false but R is true.
Q1. Assertion (A) : Tongue is fleshy muscular organ. Reason (R) : Tongue is used for talking.
Q2. Assertion (A) : Food pipe runs through neck and chest. Reason (R) : When food is not accepted by our stomach it is vomited out.
Q3. Assertion (A) : The small intestine is about 7.5m long and highly coiled. Reason (R) : It is smaller as compared to large intestine.
Q4. Assertion (A) : Rumen is the first of four chambers of stomach of ruminants Reason (R) : In rumen the food gets partly digested and is called cud.
Q5. Assertion (A) : Liver secretes a juice called bile juice. Reason (R) : Bile juice is stored in liver.
Q6. Assertion (A) : Digestion of carbohydrates, like starch, begins in buccal cavity. Reason (R) : The digested food is absorbed in the blood vessels from small intestines.
Q7. Assertion (A) : Digestion in amoeba is intracellular. Reason (R) : In the food vacuole the food becomes trapped and is digested by the action of digestive juices secreted into food vacuole.
Q8. Assertion (A) : Food is pushed down the food pipe which runs through the neck and chest Reason (R) : The peristaltive movement of the wall of the food pipe is a continuous process.
What is Assertion Reason Questions?
Assertion Reason questions are a specific type of question format commonly used in academic assessments, particularly in science and logical reasoning subjects. These questions consist of two statements: an Assertion and a Reason. The task of the test-taker is to evaluate the relationship between the two statements and determine their combined accuracy.
Here’s a breakdown of the structure of an Assertion Reason question:
- Assertion: The Assertion is a statement presented as a fact or claim. It may be true or false, and it is typically written in a straightforward manner.
- Reason: The Reason is a statement that provides an explanation or justification for the Assertion. It can support or challenge the Assertion, depending on the accuracy of the Reasoning provided.
- Options: Multiple options are typically provided alongside the Assertion Reason pair. The test-taker must choose the correct option that reflects the logical relationship between the Assertion and the Reason.
The possible options typically include:
a) If both the Assertion and the Reason are true, and the Reason is a correct explanation of the Assertion.
b) If both the Assertion and the Reason are true, but the Reason is not a correct explanation of the Assertion.
c) If the Assertion is true, but the Reason is false.
d) If the Assertion is false, but the Reason is true.
e) If both the Assertion and the Reason are false.
To answer Assertion Reason questions correctly, the test-taker needs to analyze the accuracy and logical connection between the two statements. It requires critical thinking, reasoning abilities, and a thorough understanding of the subject matter.
It is important to note that Assertion Reason questions can be challenging, as the test-taker needs to evaluate both statements independently and then determine the relationship between them. Careful reading, logical reasoning, and knowledge of the subject are essential for accurately answering such questions.
Importance of Practicing Assertion Reason Questions for Class 7 Science
Practicing Assertion Reason questions for Class 8 Maths offers several benefits to students. Here are some reasons why it is important:
- Develops critical thinking skills: Assertion Reason questions require students to critically analyze and evaluate the relationship between the Assertion and the Reason. By practicing these types of questions, students develop their critical thinking skills and learn to assess the validity and logical connection between statements.
- Enhances problem-solving abilities: Assertion Reason questions often involve complex problem-solving scenarios. By practicing these questions, students strengthen their problem-solving abilities, as they are required to apply mathematical concepts, reasoning, and logical deduction to determine the accuracy of the statements.
- Encourages deeper understanding: Assertion Reason questions promote a deeper understanding of mathematical concepts. Students need to evaluate the logic and reasoning behind the statements, which helps them grasp the underlying principles and connections between different mathematical ideas.
- Tests conceptual clarity: Assertion Reason questions provide an opportunity to assess students’ conceptual clarity. By encountering these questions, students can identify any gaps in their understanding of specific mathematical concepts. They can then address these gaps and seek clarification to improve their knowledge and comprehension.
- Prepares for competitive exams: Many competitive exams, including scholarship exams, Olympiads, and entrance exams, include Assertion Reason questions in their question papers. By practicing these questions in Class 8, students can develop familiarity with the format and learn how to approach such questions effectively, thus preparing themselves for future exams.
- Enhances logical reasoning skills: Assertion Reason questions require students to evaluate the logical relationship between statements. Through practice, students enhance their logical reasoning skills and become more adept at identifying valid and invalid reasoning.
- Improves exam readiness: Regular practice of Assertion Reason questions prepares students for the format and style of questions they may encounter in exams. It familiarizes them with the task of evaluating statements and choosing the correct option, helping them feel more confident and comfortable during assessments.
- Promotes comprehensive learning: Practicing Assertion Reason questions encourages comprehensive learning. Students are prompted to consider different aspects of a concept, analyze its various components, and evaluate the relationship between them. This holistic approach fosters a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
- Sharpens analytical skills: Assertion Reason questions require students to analyze and evaluate the given statements. By practicing these questions, students develop their analytical skills, including the ability to break down complex problems, identify relevant information, and make logical deductions.
- Reinforces exam time management: Assertion Reason questions often require careful evaluation, which can take time. By practicing these questions, students become better at managing their time during exams, learning to allocate appropriate time to read and analyze the statements, and make informed choices within the given time frame.
Download Books – Exam Special
Sample Papers for CBSE 2025 Exams
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 8 All Subjects (for 2025 Exams)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 9 All Subjects (for 2025 Exams)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 10 All Subjects (for 2025 Exams)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 All Subjects (for 2025 Exams)
CBSE Class 10 Most Downloaded Books
- CBSE Important Numerical Problems Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Practical Based Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important Diagram Based Questions Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Most Repeated Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
CBSE Class 12 Most Downloaded Books
- CBSE Important Diagrams & Graphs Asked in Board Exams Class 12 Physics
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Laws & Principles Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Definitions Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- Master Organic Conversions CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Exams
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Chapterwise Important Questions
CBSE Class 8 Most Downloaded Books
- Worksheets for CBSE Class 8 Maths – Chapterwise
ICSE Class 10
- ICSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (215 Numericals)
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (230 Questions)
- ICSE Mole Concept and Stoichiometry Numericals Class 10 Chemistry (65 Numericals)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
- ICSE Important Functions and Locations Based Questions Class 10 Biology
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Biology BOARD Exams (100 Qs)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Geography BOARD Exams
- ICSE Revision Notes for Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams
- ICSE Revision Notes for Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams
ICSE Class 9
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 9 Physics Exams
- ICSE Important Numerical Problems for Class 9 Physics Exams
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 9 Geography BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
CBSE Chapter-Wise Test Papers
- CBSE Class 9 Science Chapterwise Test Papers
- CBSE Class 10 Science Chapterwise Test Papers
- CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapterwise Test Papers
- CBSE Class 10 Social Science Chapterwise Test Papers
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Chapterwise Test Papers
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapterwise Test papers
✨ Join our Online NEET Test Series for 499/- Only for 1 Year
Leave a Reply Cancel reply

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs
Discover more from Gurukul of Excellence
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
- Sample Paper
- Question Paper
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Books
- NCERT Audio Books
- NCERT Exempler
- Model Papers
- Past Year Question Paper
- Writing Skill Format
- RD Sharma Solutions
- HC Verma Solutions
- CG Board Solutions
- UP Board Solutions
- Careers Opportunities
- Courses & Career
- Courses after 12th
Home » 7th Class » Class 7 Science Notes for Nutrition in Plants (PDF) – Study Material
Class 7 Science Notes for Nutrition in Plants (PDF) – Study Material
Class 7 Science Nutrition in Plants – Get here the Notes, Question & Practice Paper of Class 7 Science for topic Nutrition in Plants Notes. Nutrition in Plants Notes for Class 7 Science are here. You can download the Nutrition in Plants Notes PDF to study all the topics in this chapter. Moreover the Class 7 Science notes include chapter summary, definitions, examples, and key pointers for Nutrition in Plants . Thus if you are studying class Science (विज्ञान), then the Nutrition in Plants notes will help you easily understand the topic and ace it.
Class 7 Science Notes for Nutrition in Plants
Nutrition in Plants is a critical part in the study of Science . In India, it is taught in class. Therefore the Class 7 Notes for Science topic Nutrition in Plants have been compiled by teachers and field experts. They explain the complete chapter of Nutrition in Plants in one-shot .
Nutrition in Plants Notes Download Link – Click Here to Download PDF
Nutrition in Plants Notes for Class 7 Science
Nutrition in Plants Class 7 notes is as follows. You can view the document here and also download it use it anytime for future reference whenever you want to brush up your concepts of Science.
Chapter 1 – Nutrition in Plants
- Nutrition: It is the mode of taking food by an organism and its utilization by the body.
- Nutrients: The components of food that provide nourishment to the body.
- All organisms take food and utilize it to get energy for the growth and maintenance of their bodies.
- Autotrophs- Green plants synthesize their food themselves by the process of photosynthesis. They are autotrophs.
- Photosynthesis: Green plants prepare their own food with the help of carbon dioxide and water taken from the environment in presence of sunlight called chlorophyll (found in green plants) for the manufacture of food. This process is known as photosynthesis.
- Plants use simple chemical substances like carbon dioxide, water and minerals for the synthesis of food.
- Chlorophyll and sunlight are the essential requirements for photosynthesis.
- Complex chemical substances such as carbohydrates are the products of photosynthesis.
- Solar energy is stored in the form of food in the leaves with the help of chlorophyll.
- Oxygen is produced during photosynthesis.
- Oxygen released in photosynthesis is utilized by living organisms for their survival.
- Parasites- Fungi derive nutrition from dead, decaying matter. They are saprotrophs. Plants like Cuscuta are parasites. They take food from the host plant.
- Heterotrophs- A few plants and all animals are dependent on others for their nutrition and are called heterotrophs.
- Parasitic: Organisms that live on the body of other organisms.
- All parasitic plants feed on other plants as either: (i) Partial Parasites: Obtain some of their nutrition from the host, e.g. painted cup. (ii) Total Parasites: dependent completely on the host for nutrition, e.g. mistletoe.
- Saprophytic: Organisms that obtain nutrition from dead and decaying plant and animal matter.
- Mushrooms, moulds and certain types of fungi and bacteria.
- Insectivorous Plants: Green plants which obtain their nourishment partly from soil and atmosphere and partly from small insects. Example: pitcher plant, bladderwort, and venus fly trap.
- Symbiosis: Mode of nutrition in which two different individuals associate with each other to fulfill their requirement of food.
- Lichens found on tree trunks is the association between alga and fugus. Alga obtains water from fungus and it in turn obtains food from alga.

Candidates who are ambitious to qualify the Class 7 with good score can check this article for Notes, Study Material, Practice Paper. Above we provided the link to access the Notes , Important Question and Practice Paper of Class 7 Science for topic Nutrition in Plants.
All Topics Class 7 Science Notes
Chapter wise notes for Science (विज्ञान) are given below.
- Nutrition in Plants
- Nutrition in Animals
- Acids, Bases and Salt
- Physical and Chemical Changes
- Respiration in Organism
- Transportation in Animals and Plants
- Reproduction in Plants
- Motion and Time
- Electric Current and Its Effects
- Forest our Life Line
- Wastewater Story
Class 7 Notes for All Subjects
- Class 7 Maths Notes
- Class 7 Science Notes
NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Nutrition in Plants
The Nutrition in Plants notes here help you solve the questions and answers . Also, you can complete the Class 7 Nutrition in Plants worksheet using the same. In addition you will also tackle CBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions with these Class 7 notes .
However if you still need help, then you can use the NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Nutrition in Plants to get all the answers. Nutrition in Plants solutions contain questions, answers, and steps to solve all questions.
Notes for All Classes
- Class 6 Notes
- Class 7 Notes
- Class 8 Notes
- Class 9 Notes
- Class 10 Notes
- Class 11 Notes
- Class 12 Notes
Nutrition in Plants Notes for Class 7 Science – An Overview
Class 7 Nutrition in Plants Notes for All Boards
You can use the Class 7 Science notes of Nutrition in Plants for all boards.
The education boards in India for which Nutrition in Plants notes are relevant are – CBSE, CISCE, AHSEC, CHSE Odisha, CGBSE, HBSE, HPBOSE, PUE Karnataka, MSBSHSE, PSEB, RBSE, TBSE, UPMSP, UBSE, BIEAP, BSEB, GBSHSE, GSEB, JAC, JKBOSE, KBPE, MBOSE, MBSE, MPBSE, NBSE, DGE TN, TSBIE, COHSEM, WBCHSE .
Therefore you can refer to these notes as CBSE, CISCE, AHSEC, CHSE Odisha, CGBSE, HBSE, HPBOSE, PUE Karnataka, MSBSHSE, PSEB, RBSE, TBSE, UPMSP, UBSE, BIEAP, BSEB, GBSHSE, GSEB, JAC, JKBOSE, KBPE, MBOSE, MBSE, MPBSE, NBSE, DGE TN, TSBIE, COHSEM, WBCHSE notes for class Class 7 / Class / Science for the topic Nutrition in Plants.
To get study material, exam alerts and news, join our Whatsapp Channel .
Class 7 Science Notes for (PDF) – Study Material
Class 7 science notes for nutrition in animals (pdf) – study material, related posts.

Class 7 Sample Paper 2024 PDF | Download for Term 1, Half Yearly, Mid Term, Term 2, Annual Exam Model Papers

TN 7th Quarterly Question Paper 2024 | Download Tamil Nadu Class 7 First Term Summative Assessment September Exam Papers
Tn 7th tamil quarterly exam question paper 2024 pdf | first term tamil exam pyqp.

Class 7 Science Notes for Wastewater Story (PDF) – Study Material
Leave a reply cancel reply, cbse board quick links.
- CBSE Date Sheet
- CBSE Result
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE Sample Papers
- CBSE Question Papers
- CBSE Practice Papers
CISCE Board Quick Links
- CISCE Time Table
- CISCE Results
- CISCE Specimen Papers
- CISCE Syllabus
- CISCE Question Papers
Class Wise Study Material
Board exams 2023.
- Solved Sample Papers
- Revision Notes
- State Board
Study Material
- Class Notes
- Courses After Class 12th
- JEE Main 2024
- Fashion & Design
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
© 2019 aglasem.com
Discover more from AglaSem Schools
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Continue reading

COMMENTS
At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Important Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study. There will various types of marks will given 1 marks, 2 marks, 3 marks, 4 marks. CBSE Case Study Questions Class 7 Science Nutrition in Animals Case study 1
Case Study Questions on Nutrition in Animals. Questions. Question 1: Read the given passage below and answer the question: The small intestine is highly coiled structure. It is about 7.5 metres long. It receives secretions from the liver and the pancreas. The liver is a reddish brown gland located in the upper part of the abdomen on the right side.
[Download] Case Study Questions for Class 7 Science Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals Here we are providing case study or passage-based questions for class 7 science chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals. Case Study/Passage Based Questions Passage-1 Amoeba is a microscopic single-celled organism found in pond water. It has a cell membrane, a rounded, dense nucleus … Continue reading Case Study ...
Find answers to various questions on nutrition in animals, digestion, assimilation and related topics for class 7 science students. Learn about the components of food, the role of digestive glands, the structure of alimentary canal and more.
Find important questions and answers based on NCERT Class 7 Science Book Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals. Learn about digestion, modes of feeding, nutrients, and more with examples and explanations.
Find answers to MCQs, fill in the blanks, match the following and descriptive questions on nutrition in animals. Learn about the different ways of taking food, digestion in humans and grass-eating animals, and feeding and digestion in amoeba.
Access a free question bank for 7th class science students covering the topic of nutrition in animals at StudyAdda.com.
Following statements describe the five steps in animal nutrition. Read each statement and give one word for each statement. Write the terms that describes each process. (a) Transportation of absorbed food to different parts of body and their utilisation. (b) Breaking of complex food substances into simpler and soluble substances.
Learn about the process of nutrition in animals, digestion in humans and grass-eating animals, and different ways of taking food with important questions and answers. Download free PDF of the chapter notes and study materials from Vedantu website.
A collection of extra questions and answers for Class 7 Science students to revise the topics and concepts of nutrition in animals. The questions cover different modes of feeding, digestion, absorption, and teeth in animals.
Case Study Questions on Nutrition in Plants. Questions. Question 1: Read the given passage below and answer the question: Carnivorous plant is especially adapted for capturing and digesting insects and other animals by means of ingenious pitfalls and traps.
Important Questions Class 7 Science Chapter 2 - Nutrition in Animals. Class 7 Science Chapter 2 is about Nutrition in Animals. In Chapter 1, you have learned that in the heterotrophic mode of nutrition, organisms, including herbivorous, carnivores, and a few fungi depend on plants directly or indirectly for the nutrient requirement.
Our Nutrition in Animals Class 7 MCQ with Answers is tailored to align with the NCERT guidelines and covers key concepts presented in your NCERT textbook. As a bonus, we've also included links to Nutrition in Plants MCQ Class 7 with Answers to help students who are looking to review the entire scope of nutrition covered in their science ...
HOTS Questions: Nutrition in Animals Notes offer in-depth insights into the specific topic to help you master it with ease. This comprehensive document covers all aspects related to HOTS Questions: Nutrition in Animals. It includes detailed information about the exam syllabus, recommended books, and study materials for a well-rounded preparation.
Boosts the Critical Thinking Capability: The MCQs or objective questions must be answered in lesser time; therefore, those who will regularly solve Nutrition in Animals MCQ Class 7 will benefit by having a great boost in the critical thinking capability as the questions are in the objective format which can be answered if one has a good command ...
This section on Competency Based Questions has been incorporated in the curriculum in view of the National Education Policy (NEP) 2020. It includes Multiple Choice Questions, Case-based Questions, Assertion-Reasoning Questions, and even Source-Based Questions to help the students undergo an intelligent preparation process.
Learn Nutrition in Animals & get access to important questions, mcq's, videos & revision notes of CBSE Class 7 Science chapter at TopperLearning. Register now!
DIRECTIONS: Read the passage given below and answer the questions that follow. Passage - 2 We can easily see cows, buffaloes and other grass- eating animals chewing continuously even when they are not eating. In fact, such animals quickly swallow the grass and store it in a part of stomach called rumen.
Practice NCERT MCQ Questions for Class 7 Science Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals with Answers Pdf. Test your knowledge on digestion, teeth, food and nutrition with multiple choice questions, fill in the blanks and true or false statements.
CHAPTER-2 (NUTRITION IN ANIMALS) CASE STUDY Pramila and Riya were eating their food hurriedly so that they could go out and play during recess. Suddenly, Pramila started coughing violently. ... CASE STUDY Sannidhya was eating a curry and he wore a white shirt. Suddenly a spoon of gravy fell on his shirt. Now
Free Question Bank for 7th Class Science Nutrition in Animals Nutrition in Animals. Customer Care : 6267349244. ... done Nutrition in Animals Total Questions - 40. question_answer1) ... Study Package. Question - Nutrition in Animals. Buy Now.
[Download] Assertion Reason Questions for Class 7 Science Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals Here we are providing assertion reason questions for Class 7 Science Chapter 2 Nutrition in Animals. Directions: The question below consists of an assertion and a Reason. Use the following key to choose the appropriate answer.(a) Both A and R are true … Continue reading Assertion Reason Questions for ...
In addition you will also tackle CBSE Class 7 Science Important Questions with these Class 7 notes. However if you still need help, then you can use the NCERT Solutions for Class 7 Science Nutrition in Plants to get all the answers. Nutrition in Plants solutions contain questions, answers, and steps to solve all questions. Notes for All Classes