

6 Steps to Evaluate the Effectiveness of Statistical Hypothesis Testing
You know what is tragic? Having the potential to complete the research study but not doing the correct hypothesis testing. Quite often, researchers think the most challenging aspect of research is standardization of experiments, data analysis or writing the thesis! But in all honesty, creating an effective research hypothesis is the most crucial step in designing and executing a research study. An effective research hypothesis will provide researchers the correct basic structure for building the research question and objectives.
In this article, we will discuss how to formulate and identify an effective research hypothesis testing to benefit researchers in designing their research work.
Table of Contents
What Is Research Hypothesis Testing?
Hypothesis testing is a systematic procedure derived from the research question and decides if the results of a research study support a certain theory which can be applicable to the population. Moreover, it is a statistical test used to determine whether the hypothesis assumed by the sample data stands true to the entire population.
The purpose of testing the hypothesis is to make an inference about the population of interest on the basis of random sample taken from that population. Furthermore, it is the assumption which is tested to determine the relationship between two data sets.
Types of Statistical Hypothesis Testing
Source: https://www.youtube.com/c/365DataScience
1. there are two types of hypothesis in statistics, a. null hypothesis.
This is the assumption that the event will not occur or there is no relation between the compared variables. A null hypothesis has no relation with the study’s outcome unless it is rejected. Null hypothesis uses H0 as its symbol.
b. Alternate Hypothesis
The alternate hypothesis is the logical opposite of the null hypothesis. Furthermore, the acceptance of the alternative hypothesis follows the rejection of the null hypothesis. It uses H1 or Ha as its symbol
Hypothesis Testing Example: A sanitizer manufacturer company claims that its product kills 98% of germs on average. To put this company’s claim to test, create null and alternate hypothesis H0 (Null Hypothesis): Average = 98% H1/Ha (Alternate Hypothesis): The average is less than 98%
2. Depending on the population distribution, you can categorize the statistical hypothesis into two types.
A. simple hypothesis.
A simple hypothesis specifies an exact value for the parameter.
b. Composite Hypothesis
A composite hypothesis specifies a range of values.
Hypothesis Testing Example: A company claims to have achieved 1000 units as their average sales for this quarter. (Simple Hypothesis) The company claims to achieve the sales in the range of 900 to 100o units. (Composite Hypothesis).
3. Based on the type of statistical testing, the hypothesis in statistics is of two types.
A. one-tailed.
One-Tailed test or directional test considers a critical region of data which would result in rejection of the null hypothesis if the test sample falls in that data region. Therefore, accepting the alternate hypothesis. Furthermore, the critical distribution area in this test is one-sided which means the test sample is either greater or lesser than a specific value.

b. Two-Tailed
Two-Tailed test or nondirectional test is designed to show if the sample mean is significantly greater than and significantly less than the mean population. Here, the critical distribution area is two-sided. If the sample falls within the range, the alternate hypothesis is accepted and the null hypothesis is rejected.
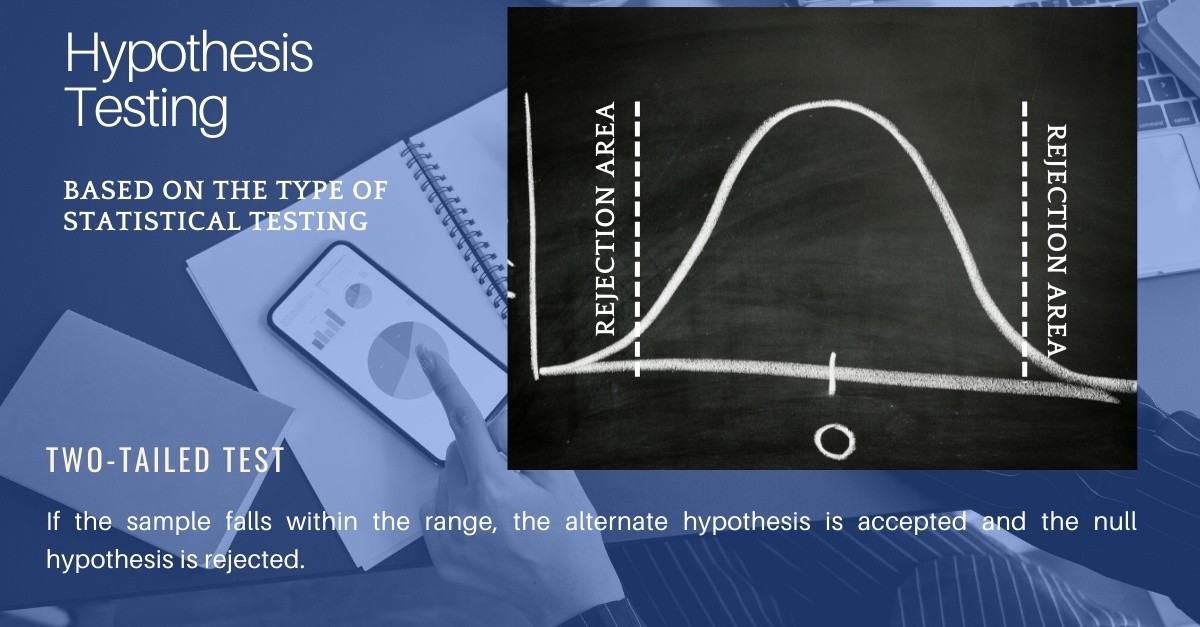
Statistical Hypothesis Testing Example: Suppose H0: mean = 100 and H1: mean is not equal to 100 According to the H1, the mean can be greater than or less than 100. (Two-Tailed test) Similarly, if H0: mean >= 100, then H1: mean < 100 Here the mean is less than 100. (One-Tailed test)
Steps in Statistical Hypothesis Testing
Step 1: develop initial research hypothesis.
Research hypothesis is developed from research question. It is the prediction that you want to investigate. Moreover, an initial research hypothesis is important for restating the null and alternate hypothesis, to test the research question mathematically.
Step 2: State the null and alternate hypothesis based on your research hypothesis
Usually, the alternate hypothesis is your initial hypothesis that predicts relationship between variables. However, the null hypothesis is a prediction of no relationship between the variables you are interested in.
Step 3: Perform sampling and collection of data for statistical testing
It is important to perform sampling and collect data in way that assists the formulated research hypothesis. You will have to perform a statistical testing to validate your data and make statistical inferences about the population of your interest.
Step 4: Perform statistical testing based on the type of data you collected
There are various statistical tests available. Based on the comparison of within group variance and between group variance, you can carry out the statistical tests for the research study. If the between group variance is large enough and there is little or no overlap between groups, then the statistical test will show low p-value. (Difference between the groups is not a chance event).
Alternatively, if the within group variance is high compared to between group variance, then the statistical test shows a high p-value. (Difference between the groups is a chance event).
Step 5: Based on the statistical outcome, reject or fail to reject your null hypothesis
In most cases, you will use p-value generated from your statistical test to guide your decision. You will consider a predetermined level of significance of 0.05 for rejecting your null hypothesis , i.e. there is less than 5% chance of getting the results wherein the null hypothesis is true.
Step 6: Present your final results of hypothesis testing
You will present the results of your hypothesis in the results and discussion section of the research paper . In results section, you provide a brief summary of the data and a summary of the results of your statistical test. Meanwhile, in discussion, you can mention whether your results support your initial hypothesis.
Note that we never reject or fail to reject the alternate hypothesis. This is because the testing of hypothesis is not designed to prove or disprove anything. However, it is designed to test if a result is spuriously occurred, or by chance. Thus, statistical hypothesis testing becomes a crucial statistical tool to mathematically define the outcome of a research question.
Have you ever used hypothesis testing as a means of statistically analyzing your research data? How was your experience? Do write to us or comment below.
Well written and informative article.
good article
Nicely explained!
Its amazing & really helpful.
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Reporting Research
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for data interpretation
In research, choosing the right approach to understand data is crucial for deriving meaningful insights.…

Demystifying the Role of Confounding Variables in Research
In the realm of scientific research, the pursuit of knowledge often involves complex investigations, meticulous…

Research Interviews: An effective and insightful way of data collection
Research interviews play a pivotal role in collecting data for various academic, scientific, and professional…

Planning Your Data Collection: Designing methods for effective research
Planning your research is very important to obtain desirable results. In research, the relevance of…

- Manuscripts & Grants
- Trending Now
Unraveling Research Population and Sample: Understanding their role in statistical inference
Research population and sample serve as the cornerstones of any scientific inquiry. They hold the…
Qualitative Vs. Quantitative Research — A step-wise guide to conduct research
How to Use Creative Data Visualization Techniques for Easy Comprehension of…

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is Hypothesis Testing?
- How It Works
4 Step Process
The bottom line.
- Fundamental Analysis
Hypothesis Testing: 4 Steps and Example
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/ChristinaMajaski-5c9433ea46e0fb0001d880b1.jpeg)
Hypothesis testing, sometimes called significance testing, is an act in statistics whereby an analyst tests an assumption regarding a population parameter. The methodology employed by the analyst depends on the nature of the data used and the reason for the analysis.
Hypothesis testing is used to assess the plausibility of a hypothesis by using sample data. Such data may come from a larger population or a data-generating process. The word "population" will be used for both of these cases in the following descriptions.
Key Takeaways
- Hypothesis testing is used to assess the plausibility of a hypothesis by using sample data.
- The test provides evidence concerning the plausibility of the hypothesis, given the data.
- Statistical analysts test a hypothesis by measuring and examining a random sample of the population being analyzed.
- The four steps of hypothesis testing include stating the hypotheses, formulating an analysis plan, analyzing the sample data, and analyzing the result.
How Hypothesis Testing Works
In hypothesis testing, an analyst tests a statistical sample, intending to provide evidence on the plausibility of the null hypothesis. Statistical analysts measure and examine a random sample of the population being analyzed. All analysts use a random population sample to test two different hypotheses: the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis.
The null hypothesis is usually a hypothesis of equality between population parameters; e.g., a null hypothesis may state that the population mean return is equal to zero. The alternative hypothesis is effectively the opposite of a null hypothesis. Thus, they are mutually exclusive , and only one can be true. However, one of the two hypotheses will always be true.
The null hypothesis is a statement about a population parameter, such as the population mean, that is assumed to be true.
- State the hypotheses.
- Formulate an analysis plan, which outlines how the data will be evaluated.
- Carry out the plan and analyze the sample data.
- Analyze the results and either reject the null hypothesis, or state that the null hypothesis is plausible, given the data.
Example of Hypothesis Testing
If an individual wants to test that a penny has exactly a 50% chance of landing on heads, the null hypothesis would be that 50% is correct, and the alternative hypothesis would be that 50% is not correct. Mathematically, the null hypothesis is represented as Ho: P = 0.5. The alternative hypothesis is shown as "Ha" and is identical to the null hypothesis, except with the equal sign struck-through, meaning that it does not equal 50%.
A random sample of 100 coin flips is taken, and the null hypothesis is tested. If it is found that the 100 coin flips were distributed as 40 heads and 60 tails, the analyst would assume that a penny does not have a 50% chance of landing on heads and would reject the null hypothesis and accept the alternative hypothesis.
If there were 48 heads and 52 tails, then it is plausible that the coin could be fair and still produce such a result. In cases such as this where the null hypothesis is "accepted," the analyst states that the difference between the expected results (50 heads and 50 tails) and the observed results (48 heads and 52 tails) is "explainable by chance alone."
When Did Hypothesis Testing Begin?
Some statisticians attribute the first hypothesis tests to satirical writer John Arbuthnot in 1710, who studied male and female births in England after observing that in nearly every year, male births exceeded female births by a slight proportion. Arbuthnot calculated that the probability of this happening by chance was small, and therefore it was due to “divine providence.”
What are the Benefits of Hypothesis Testing?
Hypothesis testing helps assess the accuracy of new ideas or theories by testing them against data. This allows researchers to determine whether the evidence supports their hypothesis, helping to avoid false claims and conclusions. Hypothesis testing also provides a framework for decision-making based on data rather than personal opinions or biases. By relying on statistical analysis, hypothesis testing helps to reduce the effects of chance and confounding variables, providing a robust framework for making informed conclusions.
What are the Limitations of Hypothesis Testing?
Hypothesis testing relies exclusively on data and doesn’t provide a comprehensive understanding of the subject being studied. Additionally, the accuracy of the results depends on the quality of the available data and the statistical methods used. Inaccurate data or inappropriate hypothesis formulation may lead to incorrect conclusions or failed tests. Hypothesis testing can also lead to errors, such as analysts either accepting or rejecting a null hypothesis when they shouldn’t have. These errors may result in false conclusions or missed opportunities to identify significant patterns or relationships in the data.
Hypothesis testing refers to a statistical process that helps researchers determine the reliability of a study. By using a well-formulated hypothesis and set of statistical tests, individuals or businesses can make inferences about the population that they are studying and draw conclusions based on the data presented. All hypothesis testing methods have the same four-step process, which includes stating the hypotheses, formulating an analysis plan, analyzing the sample data, and analyzing the result.
Sage. " Introduction to Hypothesis Testing ," Page 4.
Elder Research. " Who Invented the Null Hypothesis? "
Formplus. " Hypothesis Testing: Definition, Uses, Limitations and Examples ."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/z-test.asp-final-81378e9e20704163ba30aad511c16e5d.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices

- > Machine Learning
- > Statistics
What is Hypothesis Testing? Types and Methods
- Soumyaa Rawat
- Jul 23, 2021

Hypothesis Testing
Hypothesis testing is the act of testing a hypothesis or a supposition in relation to a statistical parameter. Analysts implement hypothesis testing in order to test if a hypothesis is plausible or not.
In data science and statistics , hypothesis testing is an important step as it involves the verification of an assumption that could help develop a statistical parameter. For instance, a researcher establishes a hypothesis assuming that the average of all odd numbers is an even number.
In order to find the plausibility of this hypothesis, the researcher will have to test the hypothesis using hypothesis testing methods. Unlike a hypothesis that is ‘supposed’ to stand true on the basis of little or no evidence, hypothesis testing is required to have plausible evidence in order to establish that a statistical hypothesis is true.
Perhaps this is where statistics play an important role. A number of components are involved in this process. But before understanding the process involved in hypothesis testing in research methodology, we shall first understand the types of hypotheses that are involved in the process. Let us get started!
Types of Hypotheses
In data sampling, different types of hypothesis are involved in finding whether the tested samples test positive for a hypothesis or not. In this segment, we shall discover the different types of hypotheses and understand the role they play in hypothesis testing.
Alternative Hypothesis
Alternative Hypothesis (H1) or the research hypothesis states that there is a relationship between two variables (where one variable affects the other). The alternative hypothesis is the main driving force for hypothesis testing.
It implies that the two variables are related to each other and the relationship that exists between them is not due to chance or coincidence.
When the process of hypothesis testing is carried out, the alternative hypothesis is the main subject of the testing process. The analyst intends to test the alternative hypothesis and verifies its plausibility.
Null Hypothesis
The Null Hypothesis (H0) aims to nullify the alternative hypothesis by implying that there exists no relation between two variables in statistics. It states that the effect of one variable on the other is solely due to chance and no empirical cause lies behind it.
The null hypothesis is established alongside the alternative hypothesis and is recognized as important as the latter. In hypothesis testing, the null hypothesis has a major role to play as it influences the testing against the alternative hypothesis.
(Must read: What is ANOVA test? )
Non-Directional Hypothesis
The Non-directional hypothesis states that the relation between two variables has no direction.
Simply put, it asserts that there exists a relation between two variables, but does not recognize the direction of effect, whether variable A affects variable B or vice versa.
Directional Hypothesis
The Directional hypothesis, on the other hand, asserts the direction of effect of the relationship that exists between two variables.
Herein, the hypothesis clearly states that variable A affects variable B, or vice versa.
Statistical Hypothesis
A statistical hypothesis is a hypothesis that can be verified to be plausible on the basis of statistics.
By using data sampling and statistical knowledge, one can determine the plausibility of a statistical hypothesis and find out if it stands true or not.
(Related blog: z-test vs t-test )
Performing Hypothesis Testing
Now that we have understood the types of hypotheses and the role they play in hypothesis testing, let us now move on to understand the process in a better manner.
In hypothesis testing, a researcher is first required to establish two hypotheses - alternative hypothesis and null hypothesis in order to begin with the procedure.
To establish these two hypotheses, one is required to study data samples, find a plausible pattern among the samples, and pen down a statistical hypothesis that they wish to test.
A random population of samples can be drawn, to begin with hypothesis testing. Among the two hypotheses, alternative and null, only one can be verified to be true. Perhaps the presence of both hypotheses is required to make the process successful.
At the end of the hypothesis testing procedure, either of the hypotheses will be rejected and the other one will be supported. Even though one of the two hypotheses turns out to be true, no hypothesis can ever be verified 100%.
(Read also: Types of data sampling techniques )
Therefore, a hypothesis can only be supported based on the statistical samples and verified data. Here is a step-by-step guide for hypothesis testing.
Establish the hypotheses
First things first, one is required to establish two hypotheses - alternative and null, that will set the foundation for hypothesis testing.
These hypotheses initiate the testing process that involves the researcher working on data samples in order to either support the alternative hypothesis or the null hypothesis.
Generate a testing plan
Once the hypotheses have been formulated, it is now time to generate a testing plan. A testing plan or an analysis plan involves the accumulation of data samples, determining which statistic is to be considered and laying out the sample size.
All these factors are very important while one is working on hypothesis testing.
Analyze data samples
As soon as a testing plan is ready, it is time to move on to the analysis part. Analysis of data samples involves configuring statistical values of samples, drawing them together, and deriving a pattern out of these samples.
While analyzing the data samples, a researcher needs to determine a set of things -
Significance Level - The level of significance in hypothesis testing indicates if a statistical result could have significance if the null hypothesis stands to be true.
Testing Method - The testing method involves a type of sampling-distribution and a test statistic that leads to hypothesis testing. There are a number of testing methods that can assist in the analysis of data samples.
Test statistic - Test statistic is a numerical summary of a data set that can be used to perform hypothesis testing.
P-value - The P-value interpretation is the probability of finding a sample statistic to be as extreme as the test statistic, indicating the plausibility of the null hypothesis.
Infer the results
The analysis of data samples leads to the inference of results that establishes whether the alternative hypothesis stands true or not. When the P-value is less than the significance level, the null hypothesis is rejected and the alternative hypothesis turns out to be plausible.
Methods of Hypothesis Testing
As we have already looked into different aspects of hypothesis testing, we shall now look into the different methods of hypothesis testing. All in all, there are 2 most common types of hypothesis testing methods. They are as follows -
Frequentist Hypothesis Testing
The frequentist hypothesis or the traditional approach to hypothesis testing is a hypothesis testing method that aims on making assumptions by considering current data.
The supposed truths and assumptions are based on the current data and a set of 2 hypotheses are formulated. A very popular subtype of the frequentist approach is the Null Hypothesis Significance Testing (NHST).
The NHST approach (involving the null and alternative hypothesis) has been one of the most sought-after methods of hypothesis testing in the field of statistics ever since its inception in the mid-1950s.
Bayesian Hypothesis Testing
A much unconventional and modern method of hypothesis testing, the Bayesian Hypothesis Testing claims to test a particular hypothesis in accordance with the past data samples, known as prior probability, and current data that lead to the plausibility of a hypothesis.
The result obtained indicates the posterior probability of the hypothesis. In this method, the researcher relies on ‘prior probability and posterior probability’ to conduct hypothesis testing on hand.
On the basis of this prior probability, the Bayesian approach tests a hypothesis to be true or false. The Bayes factor, a major component of this method, indicates the likelihood ratio among the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis.
The Bayes factor is the indicator of the plausibility of either of the two hypotheses that are established for hypothesis testing.
(Also read - Introduction to Bayesian Statistics )
To conclude, hypothesis testing, a way to verify the plausibility of a supposed assumption can be done through different methods - the Bayesian approach or the Frequentist approach.
Although the Bayesian approach relies on the prior probability of data samples, the frequentist approach assumes without a probability. A number of elements involved in hypothesis testing are - significance level, p-level, test statistic, and method of hypothesis testing.
(Also read: Introduction to probability distributions )
A significant way to determine whether a hypothesis stands true or not is to verify the data samples and identify the plausible hypothesis among the null hypothesis and alternative hypothesis.
Share Blog :
Be a part of our Instagram community
Trending blogs
5 Factors Influencing Consumer Behavior
Elasticity of Demand and its Types
What is PESTLE Analysis? Everything you need to know about it
An Overview of Descriptive Analysis
What is Managerial Economics? Definition, Types, Nature, Principles, and Scope
5 Factors Affecting the Price Elasticity of Demand (PED)
6 Major Branches of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
Scope of Managerial Economics
Dijkstra’s Algorithm: The Shortest Path Algorithm
Different Types of Research Methods
Latest Comments
- School Guide
- Mathematics
- Number System and Arithmetic
- Trigonometry
- Probability
- Mensuration
- Maths Formulas
- Class 8 Maths Notes
- Class 9 Maths Notes
- Class 10 Maths Notes
- Class 11 Maths Notes
- Class 12 Maths Notes
- Data Analysis with Python
Introduction to Data Analysis
- What is Data Analysis?
- Data Analytics and its type
- How to Install Numpy on Windows?
- How to Install Pandas in Python?
- How to Install Matplotlib on python?
- How to Install Python Tensorflow in Windows?
Data Analysis Libraries
- Pandas Tutorial
- NumPy Tutorial - Python Library
- Data Analysis with SciPy
- Introduction to TensorFlow
Data Visulization Libraries
- Matplotlib Tutorial
- Python Seaborn Tutorial
- Plotly tutorial
- Introduction to Bokeh in Python
Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA)
- Univariate, Bivariate and Multivariate data and its analysis
- Measures of Central Tendency in Statistics
- Measures of spread - Range, Variance, and Standard Deviation
- Interquartile Range and Quartile Deviation using NumPy and SciPy
- Anova Formula
- Skewness of Statistical Data
- How to Calculate Skewness and Kurtosis in Python?
- Difference Between Skewness and Kurtosis
- Histogram | Meaning, Example, Types and Steps to Draw
- Interpretations of Histogram
- Quantile Quantile plots
- What is Univariate, Bivariate & Multivariate Analysis in Data Visualisation?
- Using pandas crosstab to create a bar plot
- Exploring Correlation in Python
- Mathematics | Covariance and Correlation
- Factor Analysis | Data Analysis
- Data Mining - Cluster Analysis
- MANOVA Test in R Programming
- Python - Central Limit Theorem
- Probability Distribution Function
- Probability Density Estimation & Maximum Likelihood Estimation
- Exponential Distribution in R Programming - dexp(), pexp(), qexp(), and rexp() Functions
- Mathematics | Probability Distributions Set 4 (Binomial Distribution)
- Poisson Distribution - Definition, Formula, Table and Examples
- P-Value: Comprehensive Guide to Understand, Apply, and Interpret
- Z-Score in Statistics
- How to Calculate Point Estimates in R?
- Confidence Interval
- Chi-square test in Machine Learning
Understanding Hypothesis Testing
Data preprocessing.
- ML | Data Preprocessing in Python
- ML | Overview of Data Cleaning
- ML | Handling Missing Values
- Detect and Remove the Outliers using Python
Data Transformation
- Data Normalization Machine Learning
- Sampling distribution Using Python
Time Series Data Analysis
- Data Mining - Time-Series, Symbolic and Biological Sequences Data
- Basic DateTime Operations in Python
- Time Series Analysis & Visualization in Python
- How to deal with missing values in a Timeseries in Python?
- How to calculate MOVING AVERAGE in a Pandas DataFrame?
- What is a trend in time series?
- How to Perform an Augmented Dickey-Fuller Test in R
- AutoCorrelation
Case Studies and Projects
- Top 8 Free Dataset Sources to Use for Data Science Projects
- Step by Step Predictive Analysis - Machine Learning
- 6 Tips for Creating Effective Data Visualizations
Hypothesis testing involves formulating assumptions about population parameters based on sample statistics and rigorously evaluating these assumptions against empirical evidence. This article sheds light on the significance of hypothesis testing and the critical steps involved in the process.
What is Hypothesis Testing?
Hypothesis testing is a statistical method that is used to make a statistical decision using experimental data. Hypothesis testing is basically an assumption that we make about a population parameter. It evaluates two mutually exclusive statements about a population to determine which statement is best supported by the sample data.
Example: You say an average height in the class is 30 or a boy is taller than a girl. All of these is an assumption that we are assuming, and we need some statistical way to prove these. We need some mathematical conclusion whatever we are assuming is true.

Defining Hypotheses
Key Terms of Hypothesis Testing
- P-value: The P value , or calculated probability, is the probability of finding the observed/extreme results when the null hypothesis(H0) of a study-given problem is true. If your P-value is less than the chosen significance level then you reject the null hypothesis i.e. accept that your sample claims to support the alternative hypothesis.
- Test Statistic: The test statistic is a numerical value calculated from sample data during a hypothesis test, used to determine whether to reject the null hypothesis. It is compared to a critical value or p-value to make decisions about the statistical significance of the observed results.
- Critical value : The critical value in statistics is a threshold or cutoff point used to determine whether to reject the null hypothesis in a hypothesis test.
- Degrees of freedom: Degrees of freedom are associated with the variability or freedom one has in estimating a parameter. The degrees of freedom are related to the sample size and determine the shape.
Why do we use Hypothesis Testing?
Hypothesis testing is an important procedure in statistics. Hypothesis testing evaluates two mutually exclusive population statements to determine which statement is most supported by sample data. When we say that the findings are statistically significant, thanks to hypothesis testing.
One-Tailed and Two-Tailed Test
One tailed test focuses on one direction, either greater than or less than a specified value. We use a one-tailed test when there is a clear directional expectation based on prior knowledge or theory. The critical region is located on only one side of the distribution curve. If the sample falls into this critical region, the null hypothesis is rejected in favor of the alternative hypothesis.
One-Tailed Test
There are two types of one-tailed test:
Two-Tailed Test
A two-tailed test considers both directions, greater than and less than a specified value.We use a two-tailed test when there is no specific directional expectation, and want to detect any significant difference.
What are Type 1 and Type 2 errors in Hypothesis Testing?
In hypothesis testing, Type I and Type II errors are two possible errors that researchers can make when drawing conclusions about a population based on a sample of data. These errors are associated with the decisions made regarding the null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis.
How does Hypothesis Testing work?
Step 1: define null and alternative hypothesis.
We first identify the problem about which we want to make an assumption keeping in mind that our assumption should be contradictory to one another, assuming Normally distributed data.
Step 2 – Choose significance level
Step 3 – Collect and Analyze data.
Gather relevant data through observation or experimentation. Analyze the data using appropriate statistical methods to obtain a test statistic.
Step 4-Calculate Test Statistic
The data for the tests are evaluated in this step we look for various scores based on the characteristics of data. The choice of the test statistic depends on the type of hypothesis test being conducted.
There are various hypothesis tests, each appropriate for various goal to calculate our test. This could be a Z-test , Chi-square , T-test , and so on.
- Z-test : If population means and standard deviations are known. Z-statistic is commonly used.
- t-test : If population standard deviations are unknown. and sample size is small than t-test statistic is more appropriate.
- Chi-square test : Chi-square test is used for categorical data or for testing independence in contingency tables
- F-test : F-test is often used in analysis of variance (ANOVA) to compare variances or test the equality of means across multiple groups.
We have a smaller dataset, So, T-test is more appropriate to test our hypothesis.
T-statistic is a measure of the difference between the means of two groups relative to the variability within each group. It is calculated as the difference between the sample means divided by the standard error of the difference. It is also known as the t-value or t-score.
Step 5 – Comparing Test Statistic:
In this stage, we decide where we should accept the null hypothesis or reject the null hypothesis. There are two ways to decide where we should accept or reject the null hypothesis.
Method A: Using Crtical values
Comparing the test statistic and tabulated critical value we have,
- If Test Statistic>Critical Value: Reject the null hypothesis.
- If Test Statistic≤Critical Value: Fail to reject the null hypothesis.
Note: Critical values are predetermined threshold values that are used to make a decision in hypothesis testing. To determine critical values for hypothesis testing, we typically refer to a statistical distribution table , such as the normal distribution or t-distribution tables based on.
Method B: Using P-values
We can also come to an conclusion using the p-value,
Note : The p-value is the probability of obtaining a test statistic as extreme as, or more extreme than, the one observed in the sample, assuming the null hypothesis is true. To determine p-value for hypothesis testing, we typically refer to a statistical distribution table , such as the normal distribution or t-distribution tables based on.
Step 7- Interpret the Results
At last, we can conclude our experiment using method A or B.
Calculating test statistic
To validate our hypothesis about a population parameter we use statistical functions . We use the z-score, p-value, and level of significance(alpha) to make evidence for our hypothesis for normally distributed data .
1. Z-statistics:
When population means and standard deviations are known.
- μ represents the population mean,
- σ is the standard deviation
- and n is the size of the sample.
2. T-Statistics
T test is used when n<30,
t-statistic calculation is given by:
- t = t-score,
- x̄ = sample mean
- μ = population mean,
- s = standard deviation of the sample,
- n = sample size
3. Chi-Square Test
Chi-Square Test for Independence categorical Data (Non-normally distributed) using:
- i,j are the rows and columns index respectively.
Real life Hypothesis Testing example
Let’s examine hypothesis testing using two real life situations,
Case A: D oes a New Drug Affect Blood Pressure?
Imagine a pharmaceutical company has developed a new drug that they believe can effectively lower blood pressure in patients with hypertension. Before bringing the drug to market, they need to conduct a study to assess its impact on blood pressure.
- Before Treatment: 120, 122, 118, 130, 125, 128, 115, 121, 123, 119
- After Treatment: 115, 120, 112, 128, 122, 125, 110, 117, 119, 114
Step 1 : Define the Hypothesis
- Null Hypothesis : (H 0 )The new drug has no effect on blood pressure.
- Alternate Hypothesis : (H 1 )The new drug has an effect on blood pressure.
Step 2: Define the Significance level
Let’s consider the Significance level at 0.05, indicating rejection of the null hypothesis.
If the evidence suggests less than a 5% chance of observing the results due to random variation.
Step 3 : Compute the test statistic
Using paired T-test analyze the data to obtain a test statistic and a p-value.
The test statistic (e.g., T-statistic) is calculated based on the differences between blood pressure measurements before and after treatment.
t = m/(s/√n)
- m = mean of the difference i.e X after, X before
- s = standard deviation of the difference (d) i.e d i = X after, i − X before,
- n = sample size,
then, m= -3.9, s= 1.8 and n= 10
we, calculate the , T-statistic = -9 based on the formula for paired t test
Step 4: Find the p-value
The calculated t-statistic is -9 and degrees of freedom df = 9, you can find the p-value using statistical software or a t-distribution table.
thus, p-value = 8.538051223166285e-06
Step 5: Result
- If the p-value is less than or equal to 0.05, the researchers reject the null hypothesis.
- If the p-value is greater than 0.05, they fail to reject the null hypothesis.
Conclusion: Since the p-value (8.538051223166285e-06) is less than the significance level (0.05), the researchers reject the null hypothesis. There is statistically significant evidence that the average blood pressure before and after treatment with the new drug is different.
Python Implementation of Hypothesis Testing
Let’s create hypothesis testing with python, where we are testing whether a new drug affects blood pressure. For this example, we will use a paired T-test. We’ll use the scipy.stats library for the T-test.
Scipy is a mathematical library in Python that is mostly used for mathematical equations and computations.
We will implement our first real life problem via python,
In the above example, given the T-statistic of approximately -9 and an extremely small p-value, the results indicate a strong case to reject the null hypothesis at a significance level of 0.05.
- The results suggest that the new drug, treatment, or intervention has a significant effect on lowering blood pressure.
- The negative T-statistic indicates that the mean blood pressure after treatment is significantly lower than the assumed population mean before treatment.
Case B : Cholesterol level in a population
Data: A sample of 25 individuals is taken, and their cholesterol levels are measured.
Cholesterol Levels (mg/dL): 205, 198, 210, 190, 215, 205, 200, 192, 198, 205, 198, 202, 208, 200, 205, 198, 205, 210, 192, 205, 198, 205, 210, 192, 205.
Populations Mean = 200
Population Standard Deviation (σ): 5 mg/dL(given for this problem)
Step 1: Define the Hypothesis
- Null Hypothesis (H 0 ): The average cholesterol level in a population is 200 mg/dL.
- Alternate Hypothesis (H 1 ): The average cholesterol level in a population is different from 200 mg/dL.
As the direction of deviation is not given , we assume a two-tailed test, and based on a normal distribution table, the critical values for a significance level of 0.05 (two-tailed) can be calculated through the z-table and are approximately -1.96 and 1.96.
Step 4: Result
Since the absolute value of the test statistic (2.04) is greater than the critical value (1.96), we reject the null hypothesis. And conclude that, there is statistically significant evidence that the average cholesterol level in the population is different from 200 mg/dL
Limitations of Hypothesis Testing
- Although a useful technique, hypothesis testing does not offer a comprehensive grasp of the topic being studied. Without fully reflecting the intricacy or whole context of the phenomena, it concentrates on certain hypotheses and statistical significance.
- The accuracy of hypothesis testing results is contingent on the quality of available data and the appropriateness of statistical methods used. Inaccurate data or poorly formulated hypotheses can lead to incorrect conclusions.
- Relying solely on hypothesis testing may cause analysts to overlook significant patterns or relationships in the data that are not captured by the specific hypotheses being tested. This limitation underscores the importance of complimenting hypothesis testing with other analytical approaches.
Hypothesis testing stands as a cornerstone in statistical analysis, enabling data scientists to navigate uncertainties and draw credible inferences from sample data. By systematically defining null and alternative hypotheses, choosing significance levels, and leveraging statistical tests, researchers can assess the validity of their assumptions. The article also elucidates the critical distinction between Type I and Type II errors, providing a comprehensive understanding of the nuanced decision-making process inherent in hypothesis testing. The real-life example of testing a new drug’s effect on blood pressure using a paired T-test showcases the practical application of these principles, underscoring the importance of statistical rigor in data-driven decision-making.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. what are the 3 types of hypothesis test.
There are three types of hypothesis tests: right-tailed, left-tailed, and two-tailed. Right-tailed tests assess if a parameter is greater, left-tailed if lesser. Two-tailed tests check for non-directional differences, greater or lesser.
2.What are the 4 components of hypothesis testing?
Null Hypothesis ( ): No effect or difference exists. Alternative Hypothesis ( ): An effect or difference exists. Significance Level ( ): Risk of rejecting null hypothesis when it’s true (Type I error). Test Statistic: Numerical value representing observed evidence against null hypothesis.
3.What is hypothesis testing in ML?
Statistical method to evaluate the performance and validity of machine learning models. Tests specific hypotheses about model behavior, like whether features influence predictions or if a model generalizes well to unseen data.
4.What is the difference between Pytest and hypothesis in Python?
Pytest purposes general testing framework for Python code while Hypothesis is a Property-based testing framework for Python, focusing on generating test cases based on specified properties of the code.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- data-science
- Data Science
- Machine Learning
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
A lock ( ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Signs and Symptoms
- Living with Autism Spectrum Disorder
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- Data and Statistics on Autism Spectrum Disorder
- Autism Materials and Resources
- Diagnosis ASD
- Information on ASD for Healthcare Providers
- Acceptance Month Partner Toolkit
- 2023 Community Report on Autism
- Autism Data Visualization Tool
Screening for Autism Spectrum Disorder
- Diagnosing autism spectrum disorder (ASD) can be difficult because there is no medical test, such as a blood test, to diagnose the disorder. Doctors look at the child's developmental history and behavior to make a diagnosis.
- Diagnosing ASD involves several steps.
- Some people with ASD are not diagnosed until they are adolescents or adults. This delay means that they might not get the early help they need.

Developmental monitoring
Developmental monitoring is an active, ongoing process of watching a child grow and encouraging conversations between parents and providers about a child's skills and abilities. Developmental monitoring involves observing how your child grows and whether your child meets the typical developmental milestones, or skills that most children reach by a certain age, in playing, learning, speaking, behaving, and moving.
Parents, grandparents, early childhood education providers, and other caregivers can participate in developmental monitoring. CDC's Learn the Signs. Act Early. program has developed free materials, including CDC's Milestone Tracker app, to help parents and providers work together to monitor your child's development and know when there might be a concern and if more screening is needed. You can use a brief checklist of milestones to see how your child is developing. If you notice that your child is not meeting milestones, talk with your doctor or nurse about your concerns and ask about developmental screening. Learn more about CDC's Milestone Tracker app, milestone checklists, and other parent materials.
When you take your child to a well visit, your child's doctor or nurse will also do developmental monitoring. The doctor or nurse might ask you questions about your child's development or will talk and play with your child to see if they are developing and meeting milestones.
Your child's doctor or nurse may also ask about your child's family history. Be sure to let the doctor or nurse know about any conditions that your child's family members have, including ASD, learning disorders, intellectual disability, or attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD).
Developmental screening
Developmental screening takes a closer look at how your child is developing.
Developmental screening is more formal than developmental monitoring. It is a regular part of some well-child visits even if there is not a known concern.
The American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP) recommends developmental and behavioral screening for all children during regular well-child visits at these ages:
In addition, AAP recommends that all children be screened specifically for ASD during regular well-child visits at these ages:
Did you know?
Screening questionnaires and checklists are based on research that compares your child with other children of the same age. Questions may ask about language, movement, and thinking skills, as a well as behaviors and emotions.
Developmental screening can be done by a doctor or nurse, or other professionals in healthcare, community, or school settings. Your doctor may ask you to complete a questionnaire as part of the screening process. Screening at times other than the recommended ages should be done if you or your doctor have a concern. Additional screening should also be done if a child is at high risk for ASD (for example, having a sibling or other family member with ASD) or if behaviors sometimes associated with ASD are present.
If your child’s healthcare provider does not periodically check your child with a developmental screening test, you can ask that it be done.
Developmental diagnosis
Diagnosing children with ASD as early as possible is important to make sure children receive the services and supports they need to reach their full potential. 2 There are several steps in this process.
A brief test using a screening tool does not provide a diagnosis, but it can indicate whether a child is on the right development track or if a specialist should take a closer look. If the screening tool identifies an area of concern, a formal developmental evaluation may be needed.
This formal evaluation is a more in-depth look at a child's development and is usually done by a trained specialist such as a developmental pediatrician, child psychologist, speech-language pathologist, or occupational therapist. The results of a formal developmental evaluation can also show whether your child needs early intervention services. In some cases, the specialist might recommend genetic counseling and testing for your child.
The specialist may observe the child and give the child a structured test, ask the parents or caregivers questions, or ask the parents or caregivers to fill out questionnaires. The results of this formal evaluation highlight your child's strengths and challenges and can inform whether they meet criteria for a developmental diagnosis.

- Learn More About Your Child's Development: Fact Sheet on Developmental Monitoring and Screening [English and Spanish versions]
- CDC's Developmental Milestones
- CDC's Milestone Tracker App
- Lord C, Risi S, DiLavore PS, Shulman C, Thurm A, Pickles A. Autism from 2 to 9 years of age . Arch Gen Psychiatry . 2006;63(6):694-701.
- Hyman SL, Levy SE, Myers SM; COUNCIL ON CHILDREN WITH DISABILITIES, SECTION ON DEVELOPMENTAL AND BEHAVIORAL PEDIATRICS. Identification, Evaluation, and Management of Children With Autism Spectrum Disorder. Pediatrics . 2020;145(1):e20193447.
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a developmental disability that can cause significant social, communication and behavioral challenges. CDC is committed to continuing to provide essential data on ASD and develop resources that help identify children with ASD as early as possible.
For Everyone
Health care providers, public health.

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

11.7: Steps in Hypothesis Testing
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 2424

- Rice University
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
Learning Objectives
- Be able to state the null hypothesis for both one-tailed and two-tailed tests
- Differentiate between a significance level and a probability level
- State the four steps involved in significance testing
- The first step is to specify the null hypothesis. For a two-tailed test, the null hypothesis is typically that a parameter equals zero although there are exceptions. A typical null hypothesis is \(\mu _1-\mu _2=0\) which is equivalent to \(\mu _1=\mu _2\). For a one-tailed test, the null hypothesis is either that a parameter is greater than or equal to zero or that a parameter is less than or equal to zero. If the prediction is that \(\mu _1\) is larger than \(\mu _2\), then the null hypothesis (the reverse of the prediction) is \(\mu _1-\mu _2\geq 0\). This is equivalent to \(\mu _1\leq \mu _2\).
- The second step is to specify the \(\alpha\) level which is also known as the significance level. Typical values are \(0.05\) and \(0.01\).
- The third step is to compute the probability value (also known as the \(p\) value). This is the probability of obtaining a sample statistic as different or more different from the parameter specified in the null hypothesis given that the null hypothesis is true.
- Finally, compare the probability value with the \(\alpha\) level. If the probability value is lower then you reject the null hypothesis. Keep in mind that rejecting the null hypothesis is not an all-or-none decision. The lower the probability value, the more confidence you can have that the null hypothesis is false. However, if your probability value is higher than the conventional \(\alpha\) level of \(0.05\), most scientists will consider your findings inconclusive. Failure to reject the null hypothesis does not constitute support for the null hypothesis. It just means you do not have sufficiently strong data to reject it.
User Preferences
Content preview.
Arcu felis bibendum ut tristique et egestas quis:
- Ut enim ad minim veniam, quis nostrud exercitation ullamco laboris
- Duis aute irure dolor in reprehenderit in voluptate
- Excepteur sint occaecat cupidatat non proident
Keyboard Shortcuts
10.2 - steps used in a hypothesis test.
Regardless of the type of hypothesis being considered, the process of carrying out a significance test is the same and relies on four basic steps:
State the null and alternative hypotheses (see section 10.1 ) Also think about the type 1 error (rejecting a true null) and type 2 error (declaring the plausibility of a false null) possibilities at this time and how serious each mistake would be in terms of the problem.
Collect and summarize the data so that a test statistic can be calculated. A test statistic is a summary of the data that measures the difference between what is seen in the data and what would be expected if the null hypothesis were true. It is typically standardized so that a p -value can be obtained from a reference distribution like the normal curve.
Use the test statistic to find the p -value. The p -value represents the likelihood of getting our test statistic or any test statistic more extreme if, in fact, the null hypothesis is true.
- For a one-sided "greater than" alternative hypothesis, the "more extreme" part of the interpretation refers to test statistic values larger than the test statistic given.
- For a one-sided "less than" alternative hypothesis, the "more extreme" part of the interpretation refers to test statistic values smaller than the test statistic given.
- For a two-sided "not equal to" alternative hypothesis, the "more extreme" part of the interpretation refers to test statistic values that are farther away from the null hypothesis that the test statistic given at either the upper end or lower end of the reference distribution (both "tails").
Interpret what the p -value is telling you and make a decision using the p -value. Does the null hypothesis provide a reasonable explanation of the data or not? If not it is statistically significant and we have evidence favoring the alternative. State a conclusion in terms of the problem.
Common Decision Rules seen in the literature
- If the p -value ≤ .05 , we often see scientists declare their data to be "significant."
- If the p -value ≤ .01 , we often see scientists declare their data to be "highly significant".
- If the p -value > .05 , we often see scientists declare their data to be "not significant".
Example 10.9: Left Handed Artists: (continuation of example 10.2) Section
About 10% of the human population is left-handed. A researcher at Penn State speculates that students in the College of Arts and Architecture are more likely to be left-handed that people in the general population. A random sample of 100 students in the College of Arts and Architecture is obtained and 18 of these students were found to be left-handed.
Research Question : Are artists more likely to be left-handed than people in the general population?
- Null Hypothesis : Population proportion of left-handed students in the College of Art and Architecture = 0.10 ( p = 0.10).
- Alternative Hypothesis : Population proportion of left-handed students in the College of Art and Architecture > 0.10 ( p > 0.10).
Now that you know the null and alternative hypothesis, did you think about what the type 1 and type 2 errors are? It is important to note that Step 1 is before we even collect data. Identifying these errors helps to improve the design of your research study. Let's write them out:
- Type 1 error : Claim artists are more likely to be left-handed than people in the general population when in truth they are not more likely.
- Type 2 error : Fail to claim artists are more likely to be left-handed than people in the general population when they are in fact more likely.
In this case, the consequences of these two errors are fairly similar (e.g. installing more or fewer left-handed desks in classrooms that are needed).
In the sample of 100 students listed above, the sample proportion is 18 / 100 = 0.18. The hypothesis test will determine whether or not the null hypothesis that p = 0.1 provides a plausible explanation for the data. If not we will see this as evidence that the proportion of left-handed Art & Architecture students is greater than 0.10.
If the null hypothesis is true then the standard error of the sample proportion would be \(\sqrt{\frac{0.1(1-0.1)}{100}} = 0.03\) and the sample proportion would follow the normal curve. Thus, we can use the standard score z = (0.18-0.10) / 0.03 = 2.67 as our test statistic.
Using the normal curve table for the Z -value of 2.67 we find the p -value to be about 0.004. Notice that the one-sided alternative hypothesis says to watch out for large values so we look at the percentage of the normal curve above 2.67 to get the p -value.
Interpretation of the p -value. The likelihood of getting our test statistic of 2.67 or any higher value, if in fact, the null hypothesis is true, is 0.004.
Since the p -value of 0.004 is so small, the null hypothesis provides a very poor explanation of the data. We find good evidence that the population proportion of left-handed students in the College of Art and Architecture exceeds 0.10.
Now that we have made our decision, we are only at risk of making a type 1 error. It is not possible at this point to make a type 2 error because we rejected the null hypothesis.
Example 10.10: The Weight of McDonald's French Fries in Japan Section

After receiving complaints from McDonald's customers in Japan about the amount of french fries being served, the online news magazine "Rocket News" decided to test the actual of the fries served at a particular Japanese McDonald's restaurant. According to the Rocket News article, the official weight standard set by McDonald's of Japan is for a medium-sized fries to weigh 135 grams. The publication weighed the fries from ten different medium fries they purchased and found the average weight of the fries in their sample to be 130 grams with a standard deviation of 9 grams.
Research Question : Does the data suggest that the medium fries from this McDonald's in Japan are underpacked?
- Null Hypothesis : Population mean weight of medium fries = 135 grams
- Alternative Hypothesis : Population mean weight of medium fries < 135 grams
The sample mean weight was 130 grams. Also, the sample standard deviation was 9 grams so the standard error of the mean is found to be \(\frac{9}{\sqrt{10}} = 2.85\) grams. The test statistic would be the standardized value (130-135) / 2.85 = -1.76.
Since the sample size is only 10, the sample standard deviation would be an unreliable estimate of the population standard deviation so the normal curve would not be appropriate to use as the reference distribution to find the p -value. In this case, the t curve would be used instead and it turns out that the percentage of a t -curve below -1.76 when you have a sample size of 10 is about 6%.
Interpretation of the p -value. The likelihood of getting our test statistic of -1.76 or any smaller value, if in fact, the null hypothesis is true, is about 6%.
Since the p -value is around 6% we are near the border of what people often use as a cutoff for declaring a significant result. Given the amount of variability from one package of fries to the next, there is a reasonable chance that we would see a sample average like this even if the restaurant met the official standard weight on average.
It is important to remember in carrying out the mechanics of a significance test that you are only doing a probability calculation assuming the null hypothesis is true . Because the calculation is done under that assumption, it cannot say anything about the chances that the null hypothesis or the alternative hypothesis are true.
BREAKING: A second case of bird flu is confirmed in a Michigan worker who had contact with dairy cows, the state’s health department says
Justice Department takes 'major step' toward rescheduling marijuana
WASHINGTON — The Justice Department took a significant step toward rescheduling marijuana Thursday, formalizing its process to reclassify the drug as lower-risk and remove it from a category in which it has been treated as more dangerous than fentanyl and meth.
President Joe Biden announced the “major” move in a direct-to-camera video posted to his official account on X. “This is monumental,” Biden said in the message. “It’s an important move towards reversing long-standing inequities. … Far too many lives have been upended because of a failed approach to marijuana, and I’m committed to righting those wrongs. You have my word on it.”
The Biden administration has been signaling that it would move to reschedule the drug from Schedule I — a strict classification including drugs like heroin — to the less-stringent Schedule III, which would for the first time acknowledge the drug’s medical benefits at the federal level. The Drug Enforcement Administration submitted a notice of proposed rulemaking in the Federal Register on Thursday afternoon, triggering a 60-day comment period that will allow members of the public to submit remarks regarding the rescheduling proposal before it is finalized.
Biden first directed federal agencies to review how marijuana is scheduled in October 2022, weeks before that year’s midterm elections. The process was led by the DOJ and the Department of Health and Human Services.
“Look folks, no one should be in jail for merely using or possessing marijuana. Period,” Biden said in Thursday’s video, his third time speaking extensively on the topic since his directive two years ago.
The second time Biden addressed the issue was during this year’s State of the Union address, making history by referring to marijuana from the dais in the House chamber. “No one should be jailed for using or possessing marijuana,” he said at the time.
Vice President Kamala Harris also released a video Thursday, hailing the progress.
“Currently marijuana is classified on the same level as heroin and more dangerous than fentanyl. We are finally changing that,” Harris said. “We are on the road to getting it done.”
During the first 30 days of the comment period, interested parties could request a hearing regarding the rescheduling proposal. Under the statute, the DEA would be required to hold a hearing before an administrative law judge.
After the DEA reviews and considers the public comments, and at the conclusion of any requested hearing, the DEA will issue a final order to reschedule marijuana. (The DEA could decline to reschedule the drug but that’s unlikely given the administration’s strong support).
The entire process can take anywhere from a few months to up to a year.
Once completed, federal scientists will be able to research and study the potential medical benefits of the drug for the first time since the Controlled Substances Act was enacted in 1971. It could also open the door for pharmaceutical companies to get involved with the sale and distribution of medical marijuana in states where it is legal.
For the $34 billion cannabis industry, the move would also eliminate significant tax burdens for businesses in states where the drug is legal, notably removing it from the IRS code’s Section 280E, which prohibits legal cannabis companies from deducting what would otherwise be ordinary business expenses.

The Justice Department’s rescheduling decision could also help shrink the black market, which has thrived despite legalization in states like New York and California, and has undercut legal markets, which are fiercely regulated and highly taxed.
Dr. Kevin Sabet, president of the anti-marijuana legalization group Smart Approaches to Marijuana, blasted the decision. “It’s become undeniable that politics, not science, is driving this decision and has been since the very beginning. This decision won’t legalize marijuana, and it won’t release anyone from prison or jail,” Sabet said. “This is setting the stage to create the Big Tobacco of our time.”
During his time in office, Biden issued pardons for prior federal offenses of simple possession of marijuana and issued a proclamation granting additional pardons for simple possession, attempted simple possession and use of the drug.
The White House has also urged governors to do the same in their states and some have heeded the call, including in Oregon and Massachusetts.
Democrats in Congress are pursuing a partisan effort to remove cannabis entirely from the Controlled Substances Act, empowering states to create their own cannabis laws and prioritize restorative and economic justice for those affected by the “war on drugs.”
“Congress must do everything we can to end the federal prohibition on cannabis and address long-standing harms caused by the War on Drugs,” Senate Majority Leader Chuck Schumer, D-N.Y., said earlier this month.
Julie Tsirkin is a correspondent covering Capitol Hill.
Monica Alba is a White House correspondent for NBC News.
TYRE PARTNER

ASSOCIATE PARTNER

Symbiosis SET, SLAT and SITEEE 2024 Result Released; How to Download
Published By : Suramya Sunilraj
Trending Desk
Last Updated: May 22, 2024, 14:52 IST
New Delhi, India

The next step of the selection procedure consists of SET counselling and a personal interview round (Representational/ File Photo)
The SET 2024 Phase 1 and Phase 2 exams were held on May 5 and May 11, respectively. Candidates must have their SET ID and password to check the results
The Symbiosis Entrance Test (SET), Symbiosis Law Admission Test (SLAT) and the SIT Engineering Entrance Exam (SITEEE)
2024 results have been announced by Symbiosis International (Deemed) University today, May 22. Scorecards for the university’s undergraduate entrance exams for law and engineering have also been issued, according to information posted on the official website. The SET 2024 result can be downloaded at set-test.org by candidates who took the Symbiosis entrance exam 2024. To get the Symbiosis result 2024, candidates must have their SET ID and password.
SET Result 2024: Steps to check
To download the Symbiosis entrance test result 2024, candidates need to follow the below-given steps:
Step 1. Visit the Symbiosis official website set-test.org.
Step 2. Now click on the link ‘Download SET result 2024’.
Step 3. From the homepage log in using your SET username and password.
Step 4. After submitting, the result will be shown on your screen.
Step 5. Check the details properly.
Step 6. Now, you can download your SET result and take the printout.
SET Scorecard 2024: Details Mentioned
Every SET scorecard will have the following information on it:
-Name of the candidate.
-Roll number and SET registration.
-Candidate’s subject scores.
-Candidate’s overall score.
It is recommended that candidates verify all information included in the scorecard and notify the appropriate authorities if they find any inaccuracies. Candidates need to download their scorecards within the allotted time frame, as the institute will not process any request for scorecards after the given time frame.
The next step of the selection procedure, which consists of SET counselling and a personal interview round, will be open to applicants who pass the entrance exam. The cost for seat confirmation must be paid by candidates who make the cut during the counselling process.
SET Exam Result 2024: Exam Process
After the SET 2024 results are revealed, the following steps are followed:
1. A merit list of chosen applicants who qualify for the next level of selection, which entails personal interviews (PI), will be made public by each participating institute following the SET cut-off marks.
2. Candidates’ performance in the SET 2024 exam and the WAT/PI/ST rounds will determine their final admission status.
3. The institutes that will call candidates for the PI round are those that they applied to before the payment deadline. The call letters will be distributed to the candidates four to five days before the personal interview session.
The SET 2024 Phase 1 and Phase 2 exams were held on May 5 and May 11, respectively. The SET admission exam is conducted to choose students to be considered for Symbiosis International University’s undergraduate programmes in engineering, economics, computer studies, mass communication, liberal arts, law and management.
Stay ahead with all the exam results updates on News18 Website .
- college admissions
- Symbiosis International University

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Present the findings in your results and discussion section. Though the specific details might vary, the procedure you will use when testing a hypothesis will always follow some version of these steps. Table of contents. Step 1: State your null and alternate hypothesis. Step 2: Collect data. Step 3: Perform a statistical test.
In hypothesis testing, there are certain steps one must follow. Below these are summarized into six such steps to conducting a test of a hypothesis. Set up the hypotheses and check conditions: Each hypothesis test includes two hypotheses about the population. One is the null hypothesis, notated as \(H_0 \), which is a statement of a particular ...
Step 7: Based on steps 5 and 6, draw a conclusion about H0. If the F\calculated from the data is larger than the Fα, then you are in the rejection region and you can reject the null hypothesis with (1 − α) level of confidence. Note that modern statistical software condenses steps 6 and 7 by providing a p -value.
A hypothesis test consists of five steps: 1. State the hypotheses. State the null and alternative hypotheses. These two hypotheses need to be mutually exclusive, so if one is true then the other must be false. 2. Determine a significance level to use for the hypothesis. Decide on a significance level.
Figure 8.1.1 8.1. 1: You can use a hypothesis test to decide if a dog breeder's claim that every Dalmatian has 35 spots is statistically sound. (Credit: Robert Neff) A statistician will make a decision about these claims. This process is called "hypothesis testing." A hypothesis test involves collecting data from a sample and evaluating the data.
The process of testing hypotheses follows a simple four-step procedure. This process will be what we use for the remained of the textbook and course, and though the hypothesis and statistics we use will change, this process will not. Step 1: State the Hypotheses Your hypotheses are the first thing you need to lay out.
The general idea of hypothesis testing involves: Making an initial assumption. Collecting evidence (data). Based on the available evidence (data), deciding whether to reject or not reject the initial assumption. Every hypothesis test — regardless of the population parameter involved — requires the above three steps.
Photo from StepUp Analytics. Hypothesis testing is a method of statistical inference that considers the null hypothesis H₀ vs. the alternative hypothesis Ha, where we are typically looking to assess evidence against H₀. Such a test is used to compare data sets against one another, or compare a data set against some external standard. The former being a two sample test (independent or ...
Step 6: Find the. test statistic. using this formula: For this set of data: z= (112.5 - 100) / (15/√30) = 4.56. Step 6: If Step 6 is greater than Step 5, reject the null hypothesis. If it's less than Step 5, you cannot reject the null hypothesis. In this case, it is more (4.56 > 1.645), so you can reject the null.
The curse of hypothesis testing is that we will never know if we are dealing with a True or a False Positive (Negative). All we can do is fill the confusion matrix with probabilities that are acceptable given our application. To be able to do that, we must start from a hypothesis. Step 1. Defining the hypothesis
State the four steps involved in significance testing. The first step is to specify the null hypothesis. For a two-tailed test, the null hypothesis is typically that a parameter equals zero although there are exceptions. A typical null hypothesis is μ 1 - μ 2 = 0 which is equivalent to μ 1 = μ 2. For a one-tailed test, the null hypothesis ...
Steps in Statistical Hypothesis Testing Step 1: Develop initial research hypothesis. Research hypothesis is developed from research question. It is the prediction that you want to investigate. Moreover, an initial research hypothesis is important for restating the null and alternate hypothesis, to test the research question mathematically.
Hypothesis testing is an act in statistics whereby an analyst tests an assumption regarding a population parameter. The methodology employed by the analyst depends on the nature of the data used ...
Steps to Hypothesis Testing 1. Identify Population and Sample ... These are the conditions that need to be met in order for the hypothesis test to be performed. If the conditions are not met, then the results of the test are not valid. 4. Calculate the Test Statistic The test statistic varies depending on the test performed, see statistical ...
Step 7: Based on Steps 5 and 6, draw a conclusion about H 0. If F calculated is larger than F α, then you are in the rejection region and you can reject the null hypothesis with ( 1 − α) level of confidence. Note that modern statistical software condenses Steps 6 and 7 by providing a p -value. The p -value here is the probability of getting ...
Hypothesis testing is the process of using statistics to determine the probability that a specific hypothesis is true. ... The process of hypothesis testing consists of four main steps: Step 1 ...
Hypothesis Testing. Hypothesis testing is the act of testing a hypothesis or a supposition in relation to a statistical parameter. Analysts implement hypothesis testing in order to test if a hypothesis is plausible or not. In data science and statistics, hypothesis testing is an important step as it involves the verification of an assumption ...
The process of testing hypotheses follows a simple four-step procedure. This process will be what we use for the remainder of the textbook and course, and though the hypothesis and statistics we use will change, this process will not. Step 1: State the Hypotheses. Your hypotheses are the first thing you need to lay out.
Step 3: Compute the test statistic. The test statistic is calculated by using the z formula Z= and we get accordingly , Z=2.039999999999992. Step 4: Result. Since the absolute value of the test statistic (2.04) is greater than the critical value (1.96), we reject the null hypothesis.
Calculation Example: There are six steps you would follow in hypothesis testing: Formulate the null and alternative hypotheses in three different ways: H0: θ = θ0 versus H1: θ ≠ θ0. H0: θ ≤ θ0 versus H1: θ > θ0. H0: θ ≥ θ0 versus H1: θ < θ0.
Step 1: Check assumptions and write hypotheses. When conducting a chi-square goodness-of-fit test, it makes the most sense to write the hypotheses first. The hypotheses will depend on the research question. The null hypothesis will always contain the equalities and the alternative hypothesis will be that at least one population proportion is ...
1. Define Hypothesis. Be the first to add your personal experience. 2. Choose Test. Be the first to add your personal experience. 3. Set Significance. Be the first to add your personal experience.
After running the T-Test, you'll get a test statistic and a p-value. Our test statistic reflects the difference between our sample means, normalized by the variability of our data, telling us the magnitude of the effect. The p-value, on the other hand, gives us the probability of seeing such results if the null hypothesis (no difference) is true.
Diagnosing children with ASD as early as possible is important to make sure children receive the services and supports they need to reach their full potential. 2 There are several steps in this process. A brief test using a screening tool does not provide a diagnosis, but it can indicate whether a child is on the right development track or if a ...
As reported by the World Health Organization (WHO), about 10-20% of people have experienced mid- to long-term effects following SARS-CoV-2 infection, collectively referred to as post-COVID-19 condition or long-COVID, including some neurovegetative symptoms. Numerous findings have suggested that the onset of these neurovegetative symptoms upon viral infection may be caused by the production ...
The first step is to specify the null hypothesis. For a two-tailed test, the null hypothesis is typically that a parameter equals zero although there are exceptions. A typical null hypothesis is \(\mu _1-\mu _2=0\) which is equivalent to \(\mu _1=\mu _2\).
The Maryland board this week voted to advance cost reviews for six out of the eight drugs it considered, including Novo Nordisk's Ozempic, Eli Lilly's Trulicity, Boehringer Ingelheim's ...
Step 1: State Null and Alternative Hypotheses. Null Hypothesis: Population mean weight of medium fries = 135 grams. Alternative Hypothesis: Population mean weight of medium fries < 135 grams. Step 2: Collect and summarize the data so that a test statistic can be calculated. The sample mean weight was 130 grams.
By Julie Tsirkin and Monica Alba. WASHINGTON — The Justice Department took a significant step toward rescheduling marijuana Thursday, formalizing its process to reclassify the drug as lower-risk ...
The SET 2024 result can be downloaded at set-test.org by candidates who took the Symbiosis entrance exam 2024. To get the Symbiosis result 2024, candidates must have their SET ID and password. SET Result 2024: Steps to check. To download the Symbiosis entrance test result 2024, candidates need to follow the below-given steps: Step 1.