Loading metrics
Open Access
Peer-reviewed
Research Article

Assessing the impact of healthcare research: A systematic review of methodological frameworks
Roles Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing
Affiliation Centre for Patient Reported Outcomes Research, Institute of Applied Health Research, College of Medical and Dental Sciences, University of Birmingham, Birmingham, United Kingdom
Roles Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing
* E-mail: [email protected]
Roles Data curation, Formal analysis, Methodology, Validation, Writing – review & editing
Roles Formal analysis, Methodology, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing
- Samantha Cruz Rivera,
- Derek G. Kyte,
- Olalekan Lee Aiyegbusi,
- Thomas J. Keeley,
- Melanie J. Calvert

- Published: August 9, 2017
- https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1002370
- Reader Comments
Increasingly, researchers need to demonstrate the impact of their research to their sponsors, funders, and fellow academics. However, the most appropriate way of measuring the impact of healthcare research is subject to debate. We aimed to identify the existing methodological frameworks used to measure healthcare research impact and to summarise the common themes and metrics in an impact matrix.
Methods and findings
Two independent investigators systematically searched the Medical Literature Analysis and Retrieval System Online (MEDLINE), the Excerpta Medica Database (EMBASE), the Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature (CINAHL+), the Health Management Information Consortium, and the Journal of Research Evaluation from inception until May 2017 for publications that presented a methodological framework for research impact. We then summarised the common concepts and themes across methodological frameworks and identified the metrics used to evaluate differing forms of impact. Twenty-four unique methodological frameworks were identified, addressing 5 broad categories of impact: (1) ‘primary research-related impact’, (2) ‘influence on policy making’, (3) ‘health and health systems impact’, (4) ‘health-related and societal impact’, and (5) ‘broader economic impact’. These categories were subdivided into 16 common impact subgroups. Authors of the included publications proposed 80 different metrics aimed at measuring impact in these areas. The main limitation of the study was the potential exclusion of relevant articles, as a consequence of the poor indexing of the databases searched.
Conclusions
The measurement of research impact is an essential exercise to help direct the allocation of limited research resources, to maximise research benefit, and to help minimise research waste. This review provides a collective summary of existing methodological frameworks for research impact, which funders may use to inform the measurement of research impact and researchers may use to inform study design decisions aimed at maximising the short-, medium-, and long-term impact of their research.
Author summary
Why was this study done.
- There is a growing interest in demonstrating the impact of research in order to minimise research waste, allocate resources efficiently, and maximise the benefit of research. However, there is no consensus on which is the most appropriate tool to measure the impact of research.
- To our knowledge, this review is the first to synthesise existing methodological frameworks for healthcare research impact, and the associated impact metrics by which various authors have proposed impact should be measured, into a unified matrix.
What did the researchers do and find?
- We conducted a systematic review identifying 24 existing methodological research impact frameworks.
- We scrutinised the sample, identifying and summarising 5 proposed impact categories, 16 impact subcategories, and over 80 metrics into an impact matrix and methodological framework.
What do these findings mean?
- This simplified consolidated methodological framework will help researchers to understand how a research study may give rise to differing forms of impact, as well as in what ways and at which time points these potential impacts might be measured.
- Incorporating these insights into the design of a study could enhance impact, optimizing the use of research resources.
Citation: Cruz Rivera S, Kyte DG, Aiyegbusi OL, Keeley TJ, Calvert MJ (2017) Assessing the impact of healthcare research: A systematic review of methodological frameworks. PLoS Med 14(8): e1002370. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1002370
Academic Editor: Mike Clarke, Queens University Belfast, UNITED KINGDOM
Received: February 28, 2017; Accepted: July 7, 2017; Published: August 9, 2017
Copyright: © 2017 Cruz Rivera et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Data Availability: All relevant data are within the paper and supporting files.
Funding: Funding was received from Consejo Nacional de Ciencia y Tecnología (CONACYT). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript ( http://www.conacyt.mx/ ).
Competing interests: I have read the journal's policy and the authors of this manuscript have the following competing interests: MJC has received consultancy fees from Astellas and Ferring pharma and travel fees from the European Society of Cardiology outside the submitted work. TJK is in full-time paid employment for PAREXEL International.
Abbreviations: AIHS, Alberta Innovates—Health Solutions; CAHS, Canadian Academy of Health Sciences; CIHR, Canadian Institutes of Health Research; CINAHL+, Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature; EMBASE, Excerpta Medica Database; ERA, Excellence in Research for Australia; HEFCE, Higher Education Funding Council for England; HMIC, Health Management Information Consortium; HTA, Health Technology Assessment; IOM, Impact Oriented Monitoring; MDG, Millennium Development Goal; NHS, National Health Service; MEDLINE, Medical Literature Analysis and Retrieval System Online; PHC RIS, Primary Health Care Research & Information Service; PRISMA, Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses; PROM, patient-reported outcome measures; QALY, quality-adjusted life year; R&D, research and development; RAE, Research Assessment Exercise; REF, Research Excellence Framework; RIF, Research Impact Framework; RQF, Research Quality Framework; SDG, Sustainable Development Goal; SIAMPI, Social Impact Assessment Methods for research and funding instruments through the study of Productive Interactions between science and society
Introduction
In 2010, approximately US$240 billion was invested in healthcare research worldwide [ 1 ]. Such research is utilised by policy makers, healthcare providers, and clinicians to make important evidence-based decisions aimed at maximising patient benefit, whilst ensuring that limited healthcare resources are used as efficiently as possible to facilitate effective and sustainable service delivery. It is therefore essential that this research is of high quality and that it is impactful—i.e., it delivers demonstrable benefits to society and the wider economy whilst minimising research waste [ 1 , 2 ]. Research impact can be defined as ‘any identifiable ‘benefit to, or positive influence on the economy, society, public policy or services, health, the environment, quality of life or academia’ (p. 26) [ 3 ].
There are many purported benefits associated with the measurement of research impact, including the ability to (1) assess the quality of the research and its subsequent benefits to society; (2) inform and influence optimal policy and funding allocation; (3) demonstrate accountability, the value of research in terms of efficiency and effectiveness to the government, stakeholders, and society; and (4) maximise impact through better understanding the concept and pathways to impact [ 4 – 7 ].
Measuring and monitoring the impact of healthcare research has become increasingly common in the United Kingdom [ 5 ], Australia [ 5 ], and Canada [ 8 ], as governments, organisations, and higher education institutions seek a framework to allocate funds to projects that are more likely to bring the most benefit to society and the economy [ 5 ]. For example, in the UK, the 2014 Research Excellence Framework (REF) has recently been used to assess the quality and impact of research in higher education institutions, through the assessment of impact cases studies and selected qualitative impact metrics [ 9 ]. This is the first initiative to allocate research funding based on the economic, societal, and cultural impact of research, although it should be noted that research impact only drives a proportion of this allocation (approximately 20%) [ 9 ].
In the UK REF, the measurement of research impact is seen as increasingly important. However, the impact element of the REF has been criticised in some quarters [ 10 , 11 ]. Critics deride the fact that REF impact is determined in a relatively simplistic way, utilising researcher-generated case studies, which commonly attempt to link a particular research outcome to an associated policy or health improvement despite the fact that the wider literature highlights great diversity in the way research impact may be demonstrated [ 12 , 13 ]. This led to the current debate about the optimal method of measuring impact in the future REF [ 10 , 14 ]. The Stern review suggested that research impact should not only focus on socioeconomic impact but should also include impact on government policy, public engagement, academic impacts outside the field, and teaching to showcase interdisciplinary collaborative impact [ 10 , 11 ]. The Higher Education Funding Council for England (HEFCE) has recently set out the proposals for the REF 2021 exercise, confirming that the measurement of such impact will continue to form an important part of the process [ 15 ].
With increasing pressure for healthcare research to lead to demonstrable health, economic, and societal impact, there is a need for researchers to understand existing methodological impact frameworks and the means by which impact may be quantified (i.e., impact metrics; see Box 1 , 'Definitions’) to better inform research activities and funding decisions. From a researcher’s perspective, understanding the optimal pathways to impact can help inform study design aimed at maximising the impact of the project. At the same time, funders need to understand which aspects of impact they should focus on when allocating awards so they can make the most of their investment and bring the greatest benefit to patients and society [ 2 , 4 , 5 , 16 , 17 ].
Box 1. Definitions
- Research impact: ‘any identifiable benefit to, or positive influence on, the economy, society, public policy or services, health, the environment, quality of life, or academia’ (p. 26) [ 3 ].
- Methodological framework: ‘a body of methods, rules and postulates employed by a particular procedure or set of procedures (i.e., framework characteristics and development)’ [ 18 ].
- Pathway: ‘a way of achieving a specified result; a course of action’ [ 19 ].
- Quantitative metrics: ‘a system or standard of [quantitative] measurement’ [ 20 ].
- Narrative metrics: ‘a spoken or written account of connected events; a story’ [ 21 ].
Whilst previous researchers have summarised existing methodological frameworks and impact case studies [ 4 , 22 – 27 ], they have not summarised the metrics for use by researchers, funders, and policy makers. The aim of this review was therefore to (1) identify the methodological frameworks used to measure healthcare research impact using systematic methods, (2) summarise common impact themes and metrics in an impact matrix, and (3) provide a simplified consolidated resource for use by funders, researchers, and policy makers.
Search strategy and selection criteria
Initially, a search strategy was developed to identify the available literature regarding the different methods to measure research impact. The following keywords: ‘Impact’, ‘Framework’, and ‘Research’, and their synonyms, were used during the search of the Medical Literature Analysis and Retrieval System Online (MEDLINE; Ovid) database, the Excerpta Medica Database (EMBASE), the Health Management Information Consortium (HMIC) database, and the Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature (CINAHL+) database (inception to May 2017; see S1 Appendix for the full search strategy). Additionally, the nonindexed Journal of Research Evaluation was hand searched during the same timeframe using the keyword ‘Impact’. Other relevant articles were identified through 3 Internet search engines (Google, Google Scholar, and Google Images) using the keywords ‘Impact’, ‘Framework’, and ‘Research’, with the first 50 results screened. Google Images was searched because different methodological frameworks are summarised in a single image and can easily be identified through this search engine. Finally, additional publications were sought through communication with experts.
Following Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines (see S1 PRISMA Checklist ), 2 independent investigators systematically screened for publications describing, evaluating, or utilising a methodological research impact framework within the context of healthcare research [ 28 ]. Papers were eligible if they included full or partial methodological frameworks or pathways to research impact; both primary research and systematic reviews fitting these criteria were included. We included any methodological framework identified (original or modified versions) at the point of first occurrence. In addition, methodological frameworks were included if they were applicable to the healthcare discipline with no need of modification within their structure. We defined ‘methodological framework’ as ‘a body of methods, rules and postulates employed by a particular procedure or set of procedures (i.e., framework characteristics and development)’ [ 18 ], whereas we defined ‘pathway’ as ‘a way of achieving a specified result; a course of action’ [ 19 ]. Studies were excluded if they presented an existing (unmodified) methodological framework previously available elsewhere, did not explicitly describe a methodological framework but rather focused on a single metric (e.g., bibliometric analysis), focused on the impact or effectiveness of interventions rather than that of the research, or presented case study data only. There were no language restrictions.
Data screening
Records were downloaded into Endnote (version X7.3.1), and duplicates were removed. Two independent investigators (SCR and OLA) conducted all screening following a pilot aimed at refining the process. The records were screened by title and abstract before full-text articles of potentially eligible publications were retrieved for evaluation. A full-text screening identified the publications included for data extraction. Discrepancies were resolved through discussion, with the involvement of a third reviewer (MJC, DGK, and TJK) when necessary.
Data extraction and analysis
Data extraction occurred after the final selection of included articles. SCR and OLA independently extracted details of impact methodological frameworks, the country of origin, and the year of publication, as well as the source, the framework description, and the methodology used to develop the framework. Information regarding the methodology used to develop each methodological framework was also extracted from framework webpages where available. Investigators also extracted details regarding each framework’s impact categories and subgroups, along with their proposed time to impact (‘short-term’, ‘mid-term’, or ‘long-term’) and the details of any metrics that had been proposed to measure impact, which are depicted in an impact matrix. The structure of the matrix was informed by the work of M. Buxton and S. Hanney [ 2 ], P. Buykx et al. [ 5 ], S. Kuruvila et al. [ 29 ], and A. Weiss [ 30 ], with the intention of mapping metrics presented in previous methodological frameworks in a concise way. A consensus meeting with MJC, DGK, and TJK was held to solve disagreements and finalise the data extraction process.
Included studies
Our original search strategy identified 359 citations from MEDLINE (Ovid), EMBASE, CINAHL+, HMIC, and the Journal of Research Evaluation, and 101 citations were returned using other sources (Google, Google Images, Google Scholar, and expert communication) (see Fig 1 ) [ 28 ]. In total, we retrieved 54 full-text articles for review. At this stage, 39 articles were excluded, as they did not propose new or modified methodological frameworks. An additional 15 articles were included following the backward and forward citation method. A total of 31 relevant articles were included in the final analysis, of which 24 were articles presenting unique frameworks and the remaining 7 were systematic reviews [ 4 , 22 – 27 ]. The search strategy was rerun on 15 May 2017. A further 19 publications were screened, and 2 were taken forward to full-text screening but were ineligible for inclusion.
- PPT PowerPoint slide
- PNG larger image
- TIFF original image
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1002370.g001
Methodological framework characteristics
The characteristics of the 24 included methodological frameworks are summarised in Table 1 , 'Methodological framework characteristics’. Fourteen publications proposed academic-orientated frameworks, which focused on measuring academic, societal, economic, and cultural impact using narrative and quantitative metrics [ 2 , 3 , 5 , 8 , 29 , 31 – 39 ]. Five publications focused on assessing the impact of research by focusing on the interaction process between stakeholders and researchers (‘productive interactions’), which is a requirement to achieve research impact. This approach tries to address the issue of attributing research impact to metrics [ 7 , 40 – 43 ]. Two frameworks focused on the importance of partnerships between researchers and policy makers, as a core element to accomplish research impact [ 44 , 45 ]. An additional 2 frameworks focused on evaluating the pathways to impact, i.e., linking processes between research and impact [ 30 , 46 ]. One framework assessed the ability of health technology to influence efficiency of healthcare systems [ 47 ]. Eight frameworks were developed in the UK [ 2 , 3 , 29 , 37 , 39 , 42 , 43 , 45 ], 6 in Canada [ 8 , 33 , 34 , 44 , 46 , 47 ], 4 in Australia [ 5 , 31 , 35 , 38 ], 3 in the Netherlands [ 7 , 40 , 41 ], and 2 in the United States [ 30 , 36 ], with 1 model developed with input from various countries [ 32 ].
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1002370.t001
Methodological framework development
The included methodological frameworks varied in their development process, but there were some common approaches employed. Most included a literature review [ 2 , 5 , 7 , 8 , 31 , 33 , 36 , 37 , 40 – 46 ], although none of them used a recognised systematic method. Most also consulted with various stakeholders [ 3 , 8 , 29 , 31 , 33 , 35 – 38 , 43 , 44 , 46 , 47 ] but used differing methods to incorporate their views, including quantitative surveys [ 32 , 35 , 43 , 46 ], face-to-face interviews [ 7 , 29 , 33 , 35 , 37 , 42 , 43 ], telephone interviews [ 31 , 46 ], consultation [ 3 , 7 , 36 ], and focus groups [ 39 , 43 ]. A range of stakeholder groups were approached across the sample, including principal investigators [ 7 , 29 , 43 ], research end users [ 7 , 42 , 43 ], academics [ 3 , 8 , 39 , 40 , 43 , 46 ], award holders [ 43 ], experts [ 33 , 38 , 39 ], sponsors [ 33 , 39 ], project coordinators [ 32 , 42 ], and chief investigators [ 31 , 35 ]. However, some authors failed to identify the stakeholders involved in the development of their frameworks [ 2 , 5 , 34 , 41 , 45 ], making it difficult to assess their appropriateness. In addition, only 4 of the included papers reported using formal analytic methods to interpret stakeholder responses. These included the Canadian Academy of Health Sciences framework, which used conceptual cluster analysis [ 33 ]. The Research Contribution [ 42 ], Research Impact [ 29 ], and Primary Health Care & Information Service [ 31 ] used a thematic analysis approach. Finally, some authors went on to pilot their framework, which shaped refinements on the methodological frameworks until approval. Methods used to pilot the frameworks included a case study approach [ 2 , 3 , 30 , 32 , 33 , 36 , 40 , 42 , 44 , 45 ], contrasting results against available literature [ 29 ], the use of stakeholders’ feedback [ 7 ], and assessment tools [ 35 , 46 ].
Major impact categories
1. primary research-related impact..
A number of methodological frameworks advocated the evaluation of ‘research-related impact’. This encompassed content related to the generation of new knowledge, knowledge dissemination, capacity building, training, leadership, and the development of research networks. These outcomes were considered the direct or primary impacts of a research project, as these are often the first evidenced returns [ 30 , 62 ].
A number of subgroups were identified within this category, with frameworks supporting the collection of impact data across the following constructs: ‘research and innovation outcomes’; ‘dissemination and knowledge transfer’; ‘capacity building, training, and leadership’; and ‘academic collaborations, research networks, and data sharing’.
1 . 1 . Research and innovation outcomes . Twenty of the 24 frameworks advocated the evaluation of ‘research and innovation outcomes’ [ 2 , 3 , 5 , 7 , 8 , 29 – 39 , 41 , 43 , 44 , 46 ]. This subgroup included the following metrics: number of publications; number of peer-reviewed articles (including journal impact factor); citation rates; requests for reprints, number of reviews, and meta-analysis; and new or changes in existing products (interventions or technology), patents, and research. Additionally, some frameworks also sought to gather information regarding ‘methods/methodological contributions’. These advocated the collection of systematic reviews and appraisals in order to identify gaps in knowledge and determine whether the knowledge generated had been assessed before being put into practice [ 29 ].
1 . 2 . Dissemination and knowledge transfer . Nineteen of the 24 frameworks advocated the assessment of ‘dissemination and knowledge transfer’ [ 2 , 3 , 5 , 7 , 29 – 32 , 34 – 43 , 46 ]. This comprised collection of the following information: number of conferences, seminars, workshops, and presentations; teaching output (i.e., number of lectures given to disseminate the research findings); number of reads for published articles; article download rate and number of journal webpage visits; and citations rates in nonjournal media such as newspapers and mass and social media (i.e., Twitter and blogs). Furthermore, this impact subgroup considered the measurement of research uptake and translatability and the adoption of research findings in technological and clinical applications and by different fields. These can be measured through patents, clinical trials, and partnerships between industry and business, government and nongovernmental organisations, and university research units and researchers [ 29 ].
1 . 3 . Capacity building , training , and leadership . Fourteen of 24 frameworks suggested the evaluation of ‘capacity building, training, and leadership’ [ 2 , 3 , 5 , 8 , 29 , 31 – 35 , 39 – 41 , 43 ]. This involved collecting information regarding the number of doctoral and postdoctoral studentships (including those generated as a result of the research findings and those appointed to conduct the research), as well as the number of researchers and research-related staff involved in the research projects. In addition, authors advocated the collection of ‘leadership’ metrics, including the number of research projects managed and coordinated and the membership of boards and funding bodies, journal editorial boards, and advisory committees [ 29 ]. Additional metrics in this category included public recognition (number of fellowships and awards for significant research achievements), academic career advancement, and subsequent grants received. Lastly, the impact metric ‘research system management’ comprised the collection of information that can lead to preserving the health of the population, such as modifying research priorities, resource allocation strategies, and linking health research to other disciplines to maximise benefits [ 29 ].
1 . 4 . Academic collaborations , research networks , and data sharing . Lastly, 10 of the 24 frameworks advocated the collection of impact data regarding ‘academic collaborations (internal and external collaborations to complete a research project), research networks, and data sharing’ [ 2 , 3 , 5 , 7 , 29 , 34 , 37 , 39 , 41 , 43 ].
2. Influence on policy making.
Methodological frameworks addressing this major impact category focused on measurable improvements within a given knowledge base and on interactions between academics and policy makers, which may influence policy-making development and implementation. The returns generated in this impact category are generally considered as intermediate or midterm (1 to 3 years). These represent an important interim stage in the process towards the final expected impacts, such as quantifiable health improvements and economic benefits, without which policy change may not occur [ 30 , 62 ]. The following impact subgroups were identified within this category: ‘type and nature of policy impact’, ‘level of policy making’, and ‘policy networks’.
2 . 1 . Type and nature of policy impact . The most common impact subgroup, mentioned in 18 of the 24 frameworks, was ‘type and nature of policy impact’ [ 2 , 7 , 29 – 38 , 41 – 43 , 45 – 47 ]. Methodological frameworks addressing this subgroup stressed the importance of collecting information regarding the influence of research on policy (i.e., changes in practice or terminology). For instance, a project looking at trafficked adolescents and women (2003) influenced the WHO guidelines (2003) on ethics regarding this particular group [ 17 , 21 , 63 ].
2 . 2 . Level of policy impact . Thirteen of 24 frameworks addressed aspects surrounding the need to record the ‘level of policy impact’ (international, national, or local) and the organisations within a level that were influenced (local policy makers, clinical commissioning groups, and health and wellbeing trusts) [ 2 , 5 , 8 , 29 , 31 , 34 , 38 , 41 , 43 – 47 ]. Authors considered it important to measure the ‘level of policy impact’ to provide evidence of collaboration, coordination, and efficiency within health organisations and between researchers and health organisations [ 29 , 31 ].
2 . 3 . Policy networks . Five methodological frameworks highlighted the need to collect information regarding collaborative research with industry and staff movement between academia and industry [ 5 , 7 , 29 , 41 , 43 ]. A policy network emphasises the relationship between policy communities, researchers, and policy makers. This relationship can influence and lead to incremental changes in policy processes [ 62 ].
3. Health and health systems impact.
A number of methodological frameworks advocated the measurement of impacts on health and healthcare systems across the following impact subgroups: ‘quality of care and service delivering’, ‘evidence-based practice’, ‘improved information and health information management’, ‘cost containment and effectiveness’, ‘resource allocation’, and ‘health workforce’.
3 . 1 . Quality of care and service delivery . Twelve of the 24 frameworks highlighted the importance of evaluating ‘quality of care and service delivery’ [ 2 , 5 , 8 , 29 – 31 , 33 – 36 , 41 , 47 ]. There were a number of suggested metrics that could be potentially used for this purpose, including health outcomes such as quality-adjusted life years (QALYs), patient-reported outcome measures (PROMs), patient satisfaction and experience surveys, and qualitative data on waiting times and service accessibility.
3 . 2 . Evidence-based practice . ‘Evidence-based practice’, mentioned in 5 of the 24 frameworks, refers to making changes in clinical diagnosis, clinical practice, treatment decisions, or decision making based on research evidence [ 5 , 8 , 29 , 31 , 33 ]. The suggested metrics to demonstrate evidence-based practice were adoption of health technologies and research outcomes to improve the healthcare systems and inform policies and guidelines [ 29 ].
3 . 3 . Improved information and health information management . This impact subcategory, mentioned in 5 of the 24 frameworks, refers to the influence of research on the provision of health services and management of the health system to prevent additional costs [ 5 , 29 , 33 , 34 , 38 ]. Methodological frameworks advocated the collection of health system financial, nonfinancial (i.e., transport and sociopolitical implications), and insurance information in order to determine constraints within a health system.
3 . 4 . Cost containment and cost-effectiveness . Six of the 24 frameworks advocated the subcategory ‘cost containment and cost-effectiveness’ [ 2 , 5 , 8 , 17 , 33 , 36 ]. ‘Cost containment’ comprised the collection of information regarding how research has influenced the provision and management of health services and its implication in healthcare resource allocation and use [ 29 ]. ‘Cost-effectiveness’ refers to information concerning economic evaluations to assess improvements in effectiveness and health outcomes—for instance, the cost-effectiveness (cost and health outcome benefits) assessment of introducing a new health technology to replace an older one [ 29 , 31 , 64 ].
3 . 5 . Resource allocation . ‘Resource allocation’, mentioned in 6frameworks, can be measured through 2 impact metrics: new funding attributed to the intervention in question and equity while allocating resources, such as improved allocation of resources at an area level; better targeting, accessibility, and utilisation; and coverage of health services [ 2 , 5 , 29 , 31 , 45 , 47 ]. The allocation of resources and targeting can be measured through health services research reports, with the utilisation of health services measured by the probability of providing an intervention when needed, the probability of requiring it again in the future, and the probability of receiving an intervention based on previous experience [ 29 , 31 ].
3 . 6 . Health workforce . Lastly, ‘health workforce’, present in 3 methodological frameworks, refers to the reduction in the days of work lost because of a particular illness [ 2 , 5 , 31 ].
4. Health-related and societal impact.
Three subgroups were included in this category: ‘health literacy’; ‘health knowledge, attitudes, and behaviours’; and ‘improved social equity, inclusion, or cohesion’.
4 . 1 . Health knowledge , attitudes , and behaviours . Eight of the 24 frameworks suggested the assessment of ‘health knowledge, attitudes, behaviours, and outcomes’, which could be measured through the evaluation of levels of public engagement with science and research (e.g., National Health Service (NHS) Choices end-user visit rate) or by using focus groups to analyse changes in knowledge, attitudes, and behaviour among society [ 2 , 5 , 29 , 33 – 35 , 38 , 43 ].
4 . 2 . Improved equity , inclusion , or cohesion and human rights . Other methodological frameworks, 4 of the 24, suggested capturing improvements in equity, inclusion, or cohesion and human rights. Authors suggested these could be using a resource like the United Nations Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) (superseded by Sustainable Development Goals [SDGs] in 2015) and human rights [ 29 , 33 , 34 , 38 ]. For instance, a cluster-randomised controlled trial in Nepal, which had female participants, has demonstrated the reduction of neonatal mortality through the introduction of maternity health care, distribution of delivery kits, and home visits. This illustrates how research can target vulnerable and disadvantaged groups. Additionally, this research has been introduced by the World Health Organisation to achieve the MDG ‘improve maternal health’ [ 16 , 29 , 65 ].
4 . 3 . Health literacy . Some methodological frameworks, 3 of the 24, focused on tracking changes in the ability of patients to make informed healthcare decisions, reduce health risks, and improve quality of life, which were demonstrably linked to a particular programme of research [ 5 , 29 , 43 ]. For example, a systematic review showed that when HIV health literacy/knowledge is spread among people living with the condition, antiretroviral adherence and quality of life improve [ 66 ].
5. Broader economic impacts.
Some methodological frameworks, 9 of 24, included aspects related to the broader economic impacts of health research—for example, the economic benefits emerging from the commercialisation of research outputs [ 2 , 5 , 29 , 31 , 33 , 35 , 36 , 38 , 67 ]. Suggested metrics included the amount of funding for research and development (R&D) that was competitively awarded by the NHS, medical charities, and overseas companies. Additional metrics were income from intellectual property, spillover effects (any secondary benefit gained as a repercussion of investing directly in a primary activity, i.e., the social and economic returns of investing on R&D) [ 33 ], patents granted, licences awarded and brought to the market, the development and sales of spinout companies, research contracts, and income from industry.
The benefits contained within the categories ‘health and health systems impact’, ‘health-related and societal impact’, and ‘broader economic impacts’ are considered the expected and final returns of the resources allocated in healthcare research [ 30 , 62 ]. These benefits commonly arise in the long term, beyond 5 years according to some authors, but there was a recognition that this could differ depending on the project and its associated research area [ 4 ].
Data synthesis
Five major impact categories were identified across the 24 included methodological frameworks: (1) ‘primary research-related impact’, (2) ‘influence on policy making’, (3) ‘health and health systems impact’, (4) ‘health-related and societal impact’, and (5) ‘broader economic impact’. These major impact categories were further subdivided into 16 impact subgroups. The included publications proposed 80 different metrics to measure research impact. This impact typology synthesis is depicted in ‘the impact matrix’ ( Fig 2 and Fig 3 ).
CIHR, Canadian Institutes of Health Research; HTA, Health Technology Assessment; PHC RIS, Primary Health Care Research & Information Service; RAE, Research Assessment Exercise; RQF, Research Quality Framework.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1002370.g002
AIHS, Alberta Innovates—Health Solutions; CAHS, Canadian Institutes of Health Research; IOM, Impact Oriented Monitoring; REF, Research Excellence Framework; SIAMPI, Social Impact Assessment Methods for research and funding instruments through the study of Productive Interactions between science and society.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1002370.g003
Commonality and differences across frameworks
The ‘Research Impact Framework’ and the ‘Health Services Research Impact Framework’ were the models that encompassed the largest number of the metrics extracted. The most dominant methodological framework was the Payback Framework; 7 other methodological framework models used the Payback Framework as a starting point for development [ 8 , 29 , 31 – 35 ]. Additional methodological frameworks that were commonly incorporated into other tools included the CIHR framework, the CAHS model, the AIHS framework, and the Exchange model [ 8 , 33 , 34 , 44 ]. The capture of ‘research-related impact’ was the most widely advocated concept across methodological frameworks, illustrating the importance with which primary short-term impact outcomes were viewed by the included papers. Thus, measurement of impact via number of publications, citations, and peer-reviewed articles was the most common. ‘Influence on policy making’ was the predominant midterm impact category, specifically the subgroup ‘type and nature of policy impact’, in which frameworks advocated the measurement of (i) changes to legislation, regulations, and government policy; (ii) influence and involvement in decision-making processes; and (iii) changes to clinical or healthcare training, practice, or guidelines. Within more long-term impact measurement, the evaluations of changes in the ‘quality of care and service delivery’ were commonly advocated.
In light of the commonalities and differences among the methodological frameworks, the ‘pathways to research impact’ diagram ( Fig 4 ) was developed to provide researchers, funders, and policy makers a more comprehensive and exhaustive way to measure healthcare research impact. The diagram has the advantage of assorting all the impact metrics proposed by previous frameworks and grouping them into different impact subgroups and categories. Prospectively, this global picture will help researchers, funders, and policy makers plan strategies to achieve multiple pathways to impact before carrying the research out. The analysis of the data extraction and construction of the impact matrix led to the development of the ‘pathways to research impact’ diagram ( Fig 4 ). The diagram aims to provide an exhaustive and comprehensive way of tracing research impact by combining all the impact metrics presented by the different 24 frameworks, grouping those metrics into different impact subgroups, and grouping these into broader impact categories.
NHS, National Health Service; PROM, patient-reported outcome measure; QALY, quality-adjusted life year; R&D, research and development.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1002370.g004
This review has summarised existing methodological impact frameworks together for the first time using systematic methods ( Fig 4 ). It allows researchers and funders to consider pathways to impact at the design stage of a study and to understand the elements and metrics that need to be considered to facilitate prospective assessment of impact. Users do not necessarily need to cover all the aspects of the methodological framework, as every research project can impact on different categories and subgroups. This review provides information that can assist researchers to better demonstrate impact, potentially increasing the likelihood of conducting impactful research and reducing research waste. Existing reviews have not presented a methodological framework that includes different pathways to impact, health impact categories, subgroups, and metrics in a single methodological framework.
Academic-orientated frameworks included in this review advocated the measurement of impact predominantly using so-called ‘quantitative’ metrics—for example, the number of peer-reviewed articles, journal impact factor, and citation rates. This may be because they are well-established measures, relatively easy to capture and objective, and are supported by research funding systems. However, these metrics primarily measure the dissemination of research finding rather than its impact [ 30 , 68 ]. Whilst it is true that wider dissemination, especially when delivered via world-leading international journals, may well lead eventually to changes in healthcare, this is by no means certain. For instance, case studies evaluated by Flinders University of Australia demonstrated that some research projects with non-peer-reviewed publications led to significant changes in health policy, whilst the studies with peer-reviewed publications did not result in any type of impact [ 68 ]. As a result, contemporary literature has tended to advocate the collection of information regarding a variety of different potential forms of impact alongside publication/citations metrics [ 2 , 3 , 5 , 7 , 8 , 29 – 47 ], as outlined in this review.
The 2014 REF exercise adjusted UK university research funding allocation based on evidence of the wider impact of research (through case narrative studies and quantitative metrics), rather than simply according to the quality of research [ 12 ]. The intention was to ensure funds were directed to high-quality research that could demonstrate actual realised benefit. The inclusion of a mixed-method approach to the measurement of impact in the REF (narrative and quantitative metrics) reflects a widespread belief—expressed by the majority of authors of the included methodological frameworks in the review—that individual quantitative impact metrics (e.g., number of citations and publications) do not necessary capture the complexity of the relationships involved in a research project and may exclude measurement of specific aspects of the research pathway [ 10 , 12 ].
Many of the frameworks included in this review advocated the collection of a range of academic, societal, economic, and cultural impact metrics; this is consistent with recent recommendations from the Stern review [ 10 ]. However, a number of these metrics encounter research ‘lag’: i.e., the time between the point at which the research is conducted and when the actual benefits arise [ 69 ]. For instance, some cardiovascular research has taken up to 25 years to generate impact [ 70 ]. Likewise, the impact may not arise exclusively from a single piece of research. Different processes (such as networking interactions and knowledge and research translation) and multiple individuals and organisations are often involved [ 4 , 71 ]. Therefore, attributing the contribution made by each of the different actors involved in the process can be a challenge [ 4 ]. An additional problem associated to attribution is the lack of evidence to link research and impact. The outcomes of research may emerge slowly and be absorbed gradually. Consequently, it is difficult to determine the influence of research in the development of a new policy, practice, or guidelines [ 4 , 23 ].
A further problem is that impact evaluation is conducted ‘ex post’, after the research has concluded. Collecting information retrospectively can be an issue, as the data required might not be available. ‘ex ante’ assessment is vital for funding allocation, as it is necessary to determine the potential forthcoming impact before research is carried out [ 69 ]. Additionally, ex ante evaluation of potential benefit can overcome the issues regarding identifying and capturing evidence, which can be used in the future [ 4 ]. In order to conduct ex ante evaluation of potential benefit, some authors suggest the early involvement of policy makers in a research project coupled with a well-designed strategy of dissemination [ 40 , 69 ].
Providing an alternate view, the authors of methodological frameworks such as the SIAMPI, Contribution Mapping, Research Contribution, and the Exchange model suggest that the problems of attribution are a consequence of assigning the impact of research to a particular impact metric [ 7 , 40 , 42 , 44 ]. To address these issues, these authors propose focusing on the contribution of research through assessing the processes and interactions between stakeholders and researchers, which arguably take into consideration all the processes and actors involved in a research project [ 7 , 40 , 42 , 43 ]. Additionally, contributions highlight the importance of the interactions between stakeholders and researchers from an early stage in the research process, leading to a successful ex ante and ex post evaluation by setting expected impacts and determining how the research outcomes have been utilised, respectively [ 7 , 40 , 42 , 43 ]. However, contribution metrics are generally harder to measure in comparison to academic-orientated indicators [ 72 ].
Currently, there is a debate surrounding the optimal methodological impact framework, and no tool has proven superior to another. The most appropriate methodological framework for a given study will likely depend on stakeholder needs, as each employs different methodologies to assess research impact [ 4 , 37 , 41 ]. This review allows researchers to select individual existing methodological framework components to create a bespoke tool with which to facilitate optimal study design and maximise the potential for impact depending on the characteristic of their study ( Fig 2 and Fig 3 ). For instance, if researchers are interested in assessing how influential their research is on policy making, perhaps considering a suite of the appropriate metrics drawn from multiple methodological frameworks may provide a more comprehensive method than adopting a single methodological framework. In addition, research teams may wish to use a multidimensional approach to methodological framework development, adopting existing narratives and quantitative metrics, as well as elements from contribution frameworks. This approach would arguably present a more comprehensive method of impact assessment; however, further research is warranted to determine its effectiveness [ 4 , 69 , 72 , 73 ].
Finally, it became clear during this review that the included methodological frameworks had been constructed using varied methodological processes. At present, there are no guidelines or consensus around the optimal pathway that should be followed to develop a robust methodological framework. The authors believe this is an area that should be addressed by the research community, to ensure future frameworks are developed using best-practice methodology.
For instance, the Payback Framework drew upon a literature review and was refined through a case study approach. Arguably, this approach could be considered inferior to other methods that involved extensive stakeholder involvement, such as the CIHR framework [ 8 ]. Nonetheless, 7 methodological frameworks were developed based upon the Payback Framework [ 8 , 29 , 31 – 35 ].
Limitations
The present review is the first to summarise systematically existing impact methodological frameworks and metrics. The main limitation is that 50% of the included publications were found through methods other than bibliographic databases searching, indicating poor indexing. Therefore, some relevant articles may not have been included in this review if they failed to indicate the inclusion of a methodological impact framework in their title/abstract. We did, however, make every effort to try to find these potentially hard-to-reach publications, e.g., through forwards/backwards citation searching, hand searching reference lists, and expert communication. Additionally, this review only extracted information regarding the methodology followed to develop each framework from the main publication source or framework webpage. Therefore, further evaluations may not have been included, as they are beyond the scope of the current paper. A further limitation was that although our search strategy did not include language restrictions, we did not specifically search non-English language databases. Thus, we may have failed to identify potentially relevant methodological frameworks that were developed in a non-English language setting.
In conclusion, the measurement of research impact is an essential exercise to help direct the allocation of limited research resources, to maximise benefit, and to help minimise research waste. This review provides a collective summary of existing methodological impact frameworks and metrics, which funders may use to inform the measurement of research impact and researchers may use to inform study design decisions aimed at maximising the short-, medium-, and long-term impact of their research.
Supporting information
S1 appendix. search strategy..
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1002370.s001
S1 PRISMA Checklist. Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) checklist.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1002370.s002
Acknowledgments
We would also like to thank Mrs Susan Bayliss, Information Specialist, University of Birmingham, and Mrs Karen Biddle, Research Secretary, University of Birmingham.
- View Article
- PubMed/NCBI
- Google Scholar
- 3. HEFCE. REF 2014: Assessment framework and guidance on submissions 2011 [cited 2016 15 Feb]. Available from: http://www.ref.ac.uk/media/ref/content/pub/assessmentframeworkandguidanceonsubmissions/GOS%20including%20addendum.pdf .
- 8. Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Developing a CIHR framework to measure the impact of health research 2005 [cited 2016 26 Feb]. Available from: http://publications.gc.ca/collections/Collection/MR21-65-2005E.pdf .
- 9. HEFCE. HEFCE allocates £3.97 billion to universities and colleges in England for 2015–1 2015. Available from: http://www.hefce.ac.uk/news/newsarchive/2015/Name,103785,en.html .
- 10. Stern N. Building on Success and Learning from Experience—An Independent Review of the Research Excellence Framework 2016 [cited 2016 05 Aug]. Available from: https://www.gov.uk/government/uploads/system/uploads/attachment_data/file/541338/ind-16-9-ref-stern-review.pdf .
- 11. Matthews D. REF sceptic to lead review into research assessment: Times Higher Education; 2015 [cited 2016 21 Apr]. Available from: https://www.timeshighereducation.com/news/ref-sceptic-lead-review-research-assessment .
- 12. HEFCE. The Metric Tide—Report of the Independent Review of the Role of Metrics in Research Assessment and Management 2015 [cited 2016 11 Aug]. Available from: http://www.hefce.ac.uk/media/HEFCE,2014/Content/Pubs/Independentresearch/2015/The,Metric,Tide/2015_metric_tide.pdf .
- 14. LSE Public Policy Group. Maximizing the impacts of your research: A handbook for social scientists. http://www.lse.ac.uk/government/research/resgroups/LSEPublicPolicy/Docs/LSE_Impact_Handbook_April_2011.pdf . London: LSE; 2011.
- 15. HEFCE. Consultation on the second Research Excellence Framework. 2016.
- 18. Merriam-Webster Dictionary 2017. Available from: https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/methodology .
- 19. Oxford Dictionaries—pathway 2016 [cited 2016 19 June]. Available from: http://www.oxforddictionaries.com/definition/english/pathway .
- 20. Oxford Dictionaries—metric 2016 [cited 2016 15 Sep]. Available from: https://en.oxforddictionaries.com/definition/metric .
- 21. WHO. WHO Ethical and Safety Guidelines for Interviewing Trafficked Women 2003 [cited 2016 29 July]. Available from: http://www.who.int/mip/2003/other_documents/en/Ethical_Safety-GWH.pdf .
- 31. Kalucy L, et al. Primary Health Care Research Impact Project: Final Report Stage 1 Adelaide: Primary Health Care Research & Information Service; 2007 [cited 2016 26 Feb]. Available from: http://www.phcris.org.au/phplib/filedownload.php?file=/elib/lib/downloaded_files/publications/pdfs/phcris_pub_3338.pdf .
- 33. Canadian Academy of Health Sciences. Making an impact—A preferred framework and indicators to measure returns on investment in health research 2009 [cited 2016 26 Feb]. Available from: http://www.cahs-acss.ca/wp-content/uploads/2011/09/ROI_FullReport.pdf .
- 39. HEFCE. RAE 2008—Guidance in submissions 2005 [cited 2016 15 Feb]. Available from: http://www.rae.ac.uk/pubs/2005/03/rae0305.pdf .
- 41. Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences. The societal impact of applied health research—Towards a quality assessment system 2002 [cited 2016 29 Feb]. Available from: https://www.knaw.nl/en/news/publications/the-societal-impact-of-applied-health-research/@@download/pdf_file/20021098.pdf .
- 48. Weiss CH. Using social research in public policy making: Lexington Books; 1977.
- 50. Kogan M, Henkel M. Government and research: the Rothschild experiment in a government department: Heinemann Educational Books; 1983.
- 51. Thomas P. The Aims and Outcomes of Social Policy Research. Croom Helm; 1985.
- 52. Bulmer M. Social Science Research and Government: Comparative Essays on Britain and the United States: Cambridge University Press; 2010.
- 53. Booth T. Developing Policy Research. Aldershot, Gower1988.
- 55. Kalucy L, et al Exploring the impact of primary health care research Stage 2 Primary Health Care Research Impact Project Adelaide: Primary Health Care Research & Information Service (PHCRIS); 2009 [cited 2016 26 Feb]. Available from: http://www.phcris.org.au/phplib/filedownload.php?file=/elib/lib/downloaded_files/publications/pdfs/phcris_pub_8108.pdf .
- 56. CHSRF. Canadian Health Services Research Foundation 2000. Health Services Research and Evidence-based Decision Making [cited 2016 February]. Available from: http://www.cfhi-fcass.ca/migrated/pdf/mythbusters/EBDM_e.pdf .
- 58. W.K. Kellogg Foundation. Logic Model Development Guide 2004 [cited 2016 19 July]. Available from: http://www.smartgivers.org/uploads/logicmodelguidepdf.pdf .
- 59. United Way of America. Measuring Program Outcomes: A Practical Approach 1996 [cited 2016 19 July]. Available from: https://www.bttop.org/sites/default/files/public/W.K.%20Kellogg%20LogicModel.pdf .
- 60. Nutley S, Percy-Smith J and Solesbury W. Models of research impact: a cross sector review of literature and practice. London: Learning and Skills Research Centre 2003.
- 61. Spaapen J, van Drooge L. SIAMPI final report [cited 2017 Jan]. Available from: http://www.siampi.eu/Content/SIAMPI_Final%20report.pdf .
- 63. LSHTM. The Health Risks and Consequences of Trafficking in Women and Adolescents—Findings from a European Study 2003 [cited 2016 29 July]. Available from: http://www.oas.org/atip/global%20reports/zimmerman%20tip%20health.pdf .
- 70. Russell G. Response to second HEFCE consultation on the Research Excellence Framework 2009 [cited 2016 04 Apr]. Available from: http://russellgroup.ac.uk/media/5262/ref-consultation-response-final-dec09.pdf .
- Research article
- Open access
- Published: 22 August 2019
Empirical research in clinical supervision: a systematic review and suggestions for future studies
- Franziska Kühne ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-9636-5247 1 ,
- Jana Maas 1 ,
- Sophia Wiesenthal 1 &
- Florian Weck 1
BMC Psychology volume 7 , Article number: 54 ( 2019 ) Cite this article
21k Accesses
36 Citations
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
Although clinical supervision is considered to be a major component of the development and maintenance of psychotherapeutic competencies, and despite an increase in supervision research, the empirical evidence on the topic remains sparse.
Because most previous reviews lack methodological rigor, we aimed to review the status and quality of the empirical literature on clinical supervision, and to provide suggestions for future research. MEDLINE, PsycInfo and the Web of Science Core Collection were searched and the review was conducted according to current guidelines. From the review results, we derived suggestions for future research on clinical supervision.
The systematic literature search identified 19 publications from 15 empirical studies. Taking into account the review results, the following suggestions for further research emerged: Supervision research would benefit from proper descriptions of how studies are conducted according to current guidelines, more methodologically rigorous empirical studies, the investigation of active supervision interventions, from taking diverse outcome domains into account, and from investigating supervision from a meta-theoretical perspective.
Conclusions
In all, the systematic review supported the notion that supervision research often lags behind psychotherapy research in general. Still, the results offer detailed starting points for further supervision research.
Trial registration
PROSPERO; CRD42017072606 , registered on June 20, 2017.
Peer Review reports
Although in psychotherapy training and in profession-long learning, clinical supervision is regarded as one of the major components for change in psychotherapeutic competencies and expertise, its evidence base is still considered weak [ 1 , 2 , 3 ]. Clinical supervision is currently considered a distinct competency in need of professional training and systematic evaluation; however, theoretical developments and experience-driven practice still seem to diverge, and “significant gaps in the research base” are evident ([ 1 ], p. 88).
Definitions of supervision underline different aspects, whereas a lack of consensus seems to impede research [ 1 ]. Falender and Shafranske [ 4 , 5 ] stress the development of testable psychotherapeutic competencies in the learners, i.e., their knowledge, skills and values/attitudes, through supervision; on the other hand, supervisors need to develop competence to deliver supervision. Milne and Watkins [ 6 ] describe clinical supervision as “the formal provision, by approved supervisors, of a relationship-based education and training that is work-focused and which manages, supports, develops and evaluates the work of colleague/s” (p. 4). In contrast, Bernard and Goodyear [ 7 ] emphasize supervision’s hierarchical approach, in as much as it is provided by more senior to more junior members of a profession. The goals of supervision may thus range between the poles of being normative (i.e., ensuring quality and case management), restorative (i.e., providing emotional and coping support) and formative (i.e., promoting therapeutic competence), and, thus, may ultimately lead to effective and safe psychotherapy [ 6 ]. Hence, it is pivotal for supervisors to reflect upon their own knowledge or skills gaps, and to engage in further qualification [ 8 ]. Clinical supervision may involve different therapeutic approaches and thus addresses therapists from varying mental health backgrounds [ 8 ], which is the stance taken in the current review.
Besides providing a definition of clinical supervision, it is relevant to delineate related terms. One is feedback , a supervision technique that “refers to the ‘timely and specific’ process of explicitly communicating information about performance” ([ 8 ], p. 28). Contrary to supervision, coaching strives to enhance well-being and performance in personal and work domains [ 9 ], and is therefore clearly distinct from supervision and psychotherapy with mental health patients provided by licensed therapists.
In the supervision literature, there is no paucity of narrative reviews, commentaries or concept papers. Previous reviews have revealed positive effects of supervision, for example on supervisee’s satisfaction, autonomy, awareness or self-efficacy [ 10 , 11 , 12 , 13 ]. Still, results on the impact of supervision on patient outcomes are still considered mixed [ 10 ]. Importantly, there is a knowledge gap regarding the active components of supervision, i.e., the effects of supervision or supervisor interventions on supervisees and their patients [ 10 ].
Past reviews, however, suffer from several limitations (for details, see [ 14 ]). First of all, strategies used for literature search and screening have not always been described or implemented rigorously, that is, implemented in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA [ 15 ]) reporting guidelines (e.g. [ 10 , 11 , 12 , 16 , 17 , 18 , 19 ]). Further, several reviews focus specifically on the positive effects of supervision [ 19 ] or specifically on learning disabilities [ 11 ], emphasize the authors’ point of view [ 20 , 21 ], or concentrate on the supervisory relationship only [ 14 ]. While the majority of the above-mentioned reviews are narrative, Alfonsson and colleagues conducted a systematic review [ 14 ], pre-registered and published a review protocol [ 22 ] and implemented a thorough literature search and methodological appraisal. However, since they focused exclusively on cognitive behavioral supervision and on experimental designs, only five studies fit their inclusion criteria. Additionally, interrater agreement was only moderate during screening. Likewise, in our previous scoping review [ 23 ], we concentrated on cognitive behavioral supervision. Furthermore, like other supervision reviews [ 20 , 21 ], it was published in German only, limiting its scope.
Thus, the current systematic review aimed to complement previous reviews by using a comprehensive methodology and concise reporting. First, we aimed to review the current status of supervision interventions (e.g., setting, session frequency, therapeutic background) and of the methodological quality of the empirical literature on clinical supervision. Second, we aimed to provide suggestions for future supervision research.
Materials and methods
We conducted a systematic review by referring to the PRISMA reporting guidelines [ 15 ]. The review protocol was registered and published with the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO; CRD42017072606).
Inclusion and exclusion criteria
We included studies referring to clinical supervision as defined above by Milne and Watkins [ 6 ] above. Both, supervision conducted on its own or as part of a larger intervention (as in psychotherapy training) were included. Treatment studies in which supervision was conducted solely to foster treatment delivery were excluded because they mainly address study adherence and are still covered in other reviews [ 24 , 25 ]. Furthermore, clinical supervision had to refer to psychotherapy, whereas supportive interventions accompanying other treatments (e.g., clinical management) were excluded. Thus, we included studies referring to mental health patients, and studies with patients with physical diseases were considered only if the reason for treatment was patients’ mental health. Studies with another population (e.g., simulated patients or pseudo-clients) were excluded. In order to focus the review in the heterogeneous field of clinical supervision, we limited it to adult patients. Studies on family therapy were included if they focused on adults. Studies with mixed adult and child/adolescent populations were included if the results were reported for the adult population separately. No prerequisites were predefined for supervisor qualification. Any empirical study published within a peer-reviewed process (i.e., without commentaries or reviews) and any outcome measures were included. As such, any supervision outcome (e.g., supervisees’ satisfaction or competence), including negative or unexpected outcomes (e.g., non-disclosure), were allowed. In line with Hill & Knox [ 10 ], we did not focus on studies exclusively examining the supervision process because firstly, it does not provide knowledge on the effectiveness of supervision, and secondly, relationship variables are already covered by other reviews [ 11 ]. Thus, the review focused on supervision interventions, and studies exclusively focusing on the effects of relationship variables or attitudes between the supervisee and supervisor (i.e., as independent variables) were excluded. However, relationship variables were considered if they were considered as dependent variables in the primary studies.
Study search
The bibliographic database search was conducted during February and March 2017 in key electronic mental health databases (Fig. 1 ). To include the current evidence, we focused our search on studies published from 1996 onwards. There were no language restrictions. The following search strategy was used: supervis* AND (psychotherap* OR cognitive-behav* OR behav* therapy OR CBT OR psychodynamic OR psychoanaly* OR occupational therapy OR family therapy OR marital therapy) NOT (management OR employ* OR child* OR adolesc*). Then, we inspected the reference lists of the included studies (backward search) and conducted a cited reference search (forward search). We finished our search in July 2017.
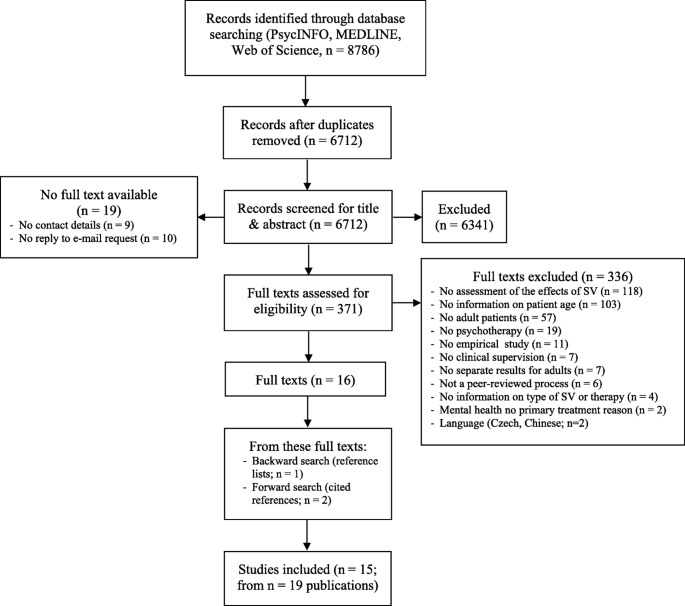
Flowchart on study selection. Adapted from Moher and colleagues (15); SV: supervision
Screening and extraction
Referring to Perepletchikova, Treat and Kazdin [ 26 ], one reviewer (FK) introduced two Master’s psychology students (JM, SW) to the review methods, and the group discussed the review process in weekly one-hour sessions. First, titles and abstracts were screened for inclusion (JM, SW). The first 10% ( n = 671) of all titles and abstracts were screened by both raters independently. Inter-rater agreement regarding title/abstract screening amounted to κ = .83 [CI = .73–.93], which is considered high [ 27 ].
Next, full texts of eligible and unclear studies were retrieved and then screened again independently by both raters (JM, SW). Disagreements were resolved through discussion or through the inclusion of a third reviewer (FK). If publications were not available through inter-library loans, a copy was requested from the corresponding author. For nine authors, contact details were not retrievable, and out of the 15 authors that were contacted, five replied. Inter-rater agreement concerning full text screenings for inclusion/exclusion was κ = .87 [CI = .77–.97].
For data extraction, we used a structured form that was piloted by three reviewers (FK, JM, SW) on five studies. It comprised information on supervision characteristics (e.g., setting, implementation and competence) and study characteristics (e.g., design, main outcome). Data were extracted independently by two raters, the results were then compared, and disagreements resolved again by mutual inspection of the original data.
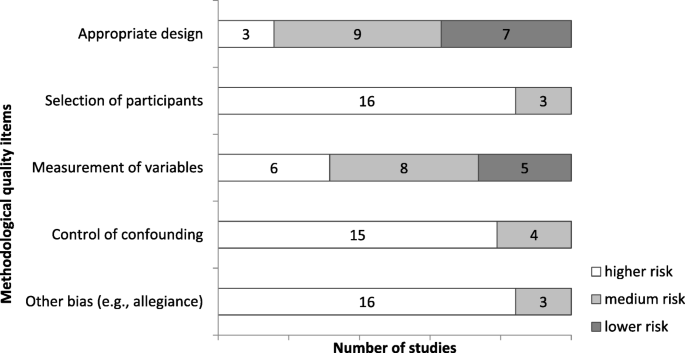
Methodological quality
Since we included various study designs, we could not refer to one common tool for the assessment of methodological quality. We therefore developed a comprehensive tool applicable to various study designs to allow for comparability between studies. For the development, we followed prominent recommendations [ 27 , 28 , 29 ]. The items were as follows: a) an appropriate design regarding the study question; b) the selection of participants; c) measurement of variables/data collection; d) control/consideration of confounding variables; and e) other sources of bias (such as allegiance bias or conflicts of interest). Every item was rated on whether low (1), medium (2) or high (3) threats to the methodological quality were supposed. The resulting sum score ranges from 5 to 15, with higher values indicating the possibility of greater threats to the methodological quality. The methodological quality was rated by two review authors independently (JM or SW and FK). Inter-rater reliability for the sum scores reached ICC (1, 2) = .88 [CI = .70–.95], which is considered high [ 30 ]. Disagreements in ratings were again resolved through discussion within the review group.
Due to the heterogeneity of the study designs and outcomes, we will present the review results narratively and in clearly arranged evidence tables.
Current status of supervision
Psychotherapies.
Overall, 15 empirical studies allocated to 19 publications were included (Fig. 1 ). Information on the supervision characteristics is reported on the study level (Table 1 ). Most of the supervisees used cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) as the active intervention [ 35 , 37 , 39 , 40 , 43 , 44 , 45 ], in four studies, specific interventions such as Motivational Interviewing (MI [ 38 , 42 ]), Dialectical Behavioral Therapy (DBT [ 41 ];) or Problem Solving Treatment (PST [ 32 ]) were used, and one study referred to psychodynamic therapy [ 31 ] (recommendation to “Conduct supervision from a meta-theoretical perspective”).
Supervisions
Only a minority of studies described any form of supervision manual used or any prior training of supervisors [ 32 , 37 , 38 , 39 , 42 , 43 ]. In most cases, supervisees were postgraduates or had a PhD degree. Regarding the frequency of supervision sessions, most studies reported weekly sessions [ 31 , 32 , 34 , 35 , 37 , 41 , 42 ], and the total number varied considerably from 3 [ 35 ] to 78 sessions [ 31 ]. Three studies did not describe the supervision frequency [ 33 , 36 , 45 ], and one singled out one supervision session only [ 44 ] (recommendation to “Describe how the study is conducted”).
Interventions
Whereas different forms of feedback or multiple-component supervision interventions were commonly studied, active interventions such as role play were seldom used [ 37 , 39 , 40 ]. Three studies did not describe the interventions used within supervision [ 35 , 44 , 45 ] (recommendation to “Investigate active supervision methods”). Four supervisions used a form of live intervention [ 36 , 41 , 42 , 43 ], and the remainder conducted supervision face-to-face. All but five studies [ 32 , 33 , 34 , 44 , 45 ] investigated some form of technological support.
The following sections describe the methodologies used in the studies, which is why all 19 publications are now referred to (Table 2 ). Five were randomized controlled trials (RCTs [ 32 , 34 , 38 , 42 , 43 ];), and one was a cluster-RCT [ 34 ]. In addition to cohort designs [ 31 , 44 ], cross-sectional designs were common [ 35 , 36 , 37 , 45 , 48 , 49 ]. Only in three publications was follow-up data collected [ 33 , 38 , 42 ]. Most studies covering satisfaction with supervision included one assessment time, usually post-intervention [ 34 , 35 , 37 , 39 , 48 , 49 ].
The assessments of the methodological quality are presented in Table 2 . The total methodological quality score was between 9 and 11 in six publications [ 32 , 38 , 41 , 42 , 43 , 46 , 49 ], between 12 and 13 in eight publications (score of 12–12 [ 31 , 33 , 34 , 35 , 36 , 45 , 49 ];), and between 14 and 15 in five of the 19 publications [ 37 , 39 , 40 , 44 , 47 ], with a lower score indicating a lower risk of a threat to the methodological quality. On an item level, most problems referred to the selection of participants, the control of confounders, and other bias such as allegiance bias (Fig. 2 ; recommendation to “Conduct methodologically stringent empirical studies”).
Methodological quality of the included studies. Lower risk … lower possible threats to methodological quality , sum score of 9–11 (range 5–15); medium risk … 12–13; higher risk … 14–15; e.g., 16 studies with higher risk of threats regarding selection of participant issues
Effects of clinical supervision
The most consistent result refers to the high acceptance, satisfaction and the perceived helpfulness of supervision by supervisees [ 34 , 35 , 36 , 37 , 39 , 41 , 44 , 48 , 49 ]. Further, the therapeutic relationship [ 31 , 32 , 43 , 44 , 45 ], and therapeutic competence seem to benefit from supervision [ 37 , 38 , 40 , 42 , 43 ]. On the other hand, non-significant findings [ 34 , 38 ], small effects [ 31 , 44 , 45 ] and relevant alternative explanations [ 32 , 33 , 43 , 46 ] hamper proper conclusions (see Fig. 3 ).
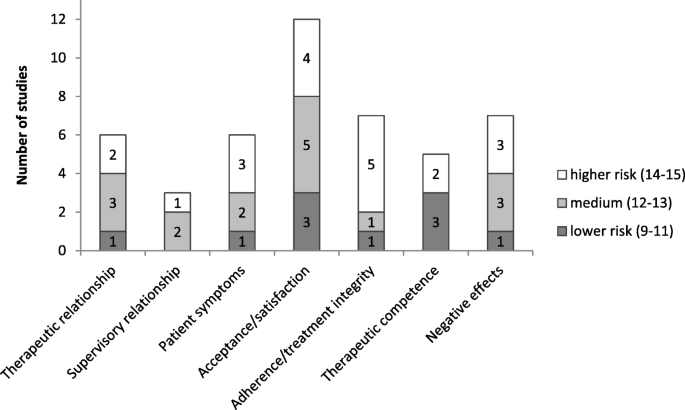
Supervision outcomes and methodological quality of the respective studies. In relation to the methodological quality; e.g., 2 studies with medium and 1 study with higher risk of possible threats to methodological quality investigated the supervisory relationship
Whereas most publications did not describe negative or unexpected effects of supervision, two mentioned them without further specification [ 31 , 42 ], two referred to unwanted effects as being unrelated to the outcome [ 33 , 38 ], and three described limits to therapists’ cognitive capacity and perceived anxiety or stress during supervision [ 39 , 48 , 49 ] (recommendation to “Investigate diverse positive and negative supervision outcomes aside from acceptance”).
The aim of the present study was to systematically review the status and quality of the current empirical literature on clinical supervision and, based on the review findings, to draw conclusions for future studies. The current review identified 19 publications referring to 15 empirical studies on the status of clinical supervision. Despite using wide inclusion criteria, it is remarkable that only such a small number of studies could be included. In contrast to former reviews, our study was conducted systematically according to current guidelines, using a reproducible methodology and concise reporting. Compared to previous reviews, it was not limited to psychotherapeutic approaches or study designs.
Regarding the psychotherapeutic approaches of the supervisees, most interventions had a CBT background, which still documents a research gap in studies on clinical supervision between CBT and other therapeutic approaches.
Aside from psychotherapy approaches, the meta-theoretical perspective of competency-based supervision, as proposed by the American Psychological Association [ 8 ], provides a more integrative and broader view. Their supervision guidelines involve seven key domains central to good-quality supervision, from supervisor competencies to diversity or ethical issues. Importantly, they describe supervision to be science-informed, which again underlines the importance of supervisors and supervisees to keep their evidence-based knowledge and skills up-to-date during profession-long learning.
Considering the conduction of supervision, face-to-face supervision was prevalent, but technological support was common as well, at least in published empirical studies. A variety of interventions was used, including less active ones such as case discussions and coaching, as well as more active ones such as feedback on patient outcomes or supervisee performance. It is clearly positive that active interventions (such as coaching and feedback) were implemented and evaluated because they have proven useful in active learning and therapist training [ 50 ]. Nevertheless, even more active methods, such as exercise or role play, were an exception [ 23 ]. Furthermore, it remains unclear which interventions are helpful in profession-long learning and maintenance of expertise [ 21 , 23 ]. We found that central supervision characteristics, such as the training of supervisors or the manual used for supervision, were not described consistently. Although a detailed description of how studies were conducted seems intuitive, it is surprising that reporting guidelines are not referred to consistently.
Concerning design characteristics, most studies were uncontrolled or used small samples. Further constraints were associated with the lack of follow-up data and major inconsistencies in the evaluation of negative effects. Although external observers, which were only sometimes independent, were used, almost half of the studies relied exclusively on self-reported questionnaires. Another problem was that the heterogeneity in the designs and instruments hampered the quantitative summary of results. Methodological quality has been criticized in supervision research for years (e.g. [ 16 , 17 ],), and inconclusive findings or relevant alternative explanations additionally impeded firm conclusions on supervision effects. Regarding the effects of clinical supervision, the review documents that supervision research clearly lags behind psychotherapy research in general; that is, we still have limited evidence on supervision effects, especially those regarding patient benefits [ 10 ], and we continue to search for active supervision ingredients [ 51 ].
Acceptance and satisfaction are crucial prerequisites for supervision effects, and they were the variables most frequently investigated. Although positive results in these domains may be considered stable [ 13 ], satisfaction may not be confused with effectiveness. Taken from health care-related conceptualizations [ 52 ], subjective satisfaction may depend on a number of variables, such as mutual expectations, communication, the supervisory relationship, the access to supervision or financial strains. In this sense, satisfaction is distinct from learning and competence development. Other important outcomes of supervision, such as the therapeutic relationship and competencies, treatment integrity, patient symptoms or unwanted effects, clearly need further investigation [ 10 , 21 ]. Other ideas include considering not only the supervisory relationship but also supervisory expectations as important process variables across psychotherapeutic approaches [ 13 ].
Limitations
We constructed a short tool for rating methodological quality, which enabled comparisons between the diverse designs of the studies included. Although inter-rater reliability was high, it lacks comparability with other reviews. Due to a stricter operationalization of the inclusion criteria, six studies were included in our previous scoping review [ 23 ], and three were included in another current review [ 14 ] that were not part of the current systematic review. More specifically, one study was not located via our search strategy, and the other publications did not describe explicitly if the patients were adults. As the excluded publications were mainly referring to CBT supervision, it generally reflects the stronger evidence-base of CBT that has its roots in basic research. Since the review aimed to illustrate the status and quality of supervision research, we did not restrict it to specific designs, but mapped the status quo. This necessarily increased heterogeneity, and especially regarding supervision effects, it limited the possibility to draw clear-cut conclusions or to combine the results statistically. Differences in the results of reviews may result not only from methodological aspects but also from diversity in the primary studies, which may be addressed only by better supervision research [ 14 ].
The review provides a variety of starting points for future research. The recommendations derived mainly refer to the replicability of research (i.e., to conduct methodologically stringent empirical studies, and to include positive and negative supervision outcomes). Taking a competency-based view, the following are examples of significant foci of both future practice and supervision research [ 23 , 53 , 54 ]:
Define, review and continuously develop supervisor competencies.
Include active methods, live feedback and video-based supervision.
Enhance the deliberate commitment to ethical standards to protect patients.
Positively value and include scientific knowledge and progress.
Foster profession-long learning of supervisees and supervisors.
Logistics may be an important issue in supervision research. Therefore, if large-scale quantitative studies are difficult to conduct or fund, methodologically sound pragmatic trials [ 3 ] and experimental studies may be feasible alternatives. Most of the results still speak to the lack of scientific rigor in supervision research. Thus, we consider competency-based supervision and research investigating the essential components of supervision as the major goals for future supervision research and practice.
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in the published article.
Abbreviations
Cognitive-behavioral therapy
Dialectical behavioral therapy
Motivational interviewing
Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses
International prospective register of systematic reviews
Problem solving treatment
Randomized controlled trial
- Supervision
Falender CA, Shafranske EP. Supervision essentials for the practice of competency-based supervision. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association; 2017.
Book Google Scholar
Goodyear RK, Lichtenberg J, Hutman H, Overland E, Bedi R, Christiani K, et al. A global portrait of counselling psychologists’ characteristics, perspectives, and professional behaviors. Couns Psychol Q. 2016;29(2):115–38.
Article Google Scholar
Owen J. Supervisory processes in the training of psychotherapists: introduction to the special section. Psychotherapy. 2015;52(2):151–2.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Falender CA, Shafranske EP. Competence in competency-based supervision practice: construct and application. Prof Psychol Res Pract. 2007;38(3):232–40.
Falender CA, Cornish JAE, Goodyear R, Hatcher R, Kaslow NJ, Leventhal G, et al. Defining competencies in psychology supervision: a consensus statement. J Clin Psychol. 2004;60(7):771–85.
Milne DL, Watkins CE. Defining and understanding clinical supervision: a functional approach. In: Watkins CE, Milne DL, editors. The Wiley international handbook of clinical supervision. Chichester: Wiley; 2014. p. 3–19.
Google Scholar
Bernard JM, Goodyear RK. Fundamentals of clinical supervision., 3rd ed. Needham Heights: Allyn & Bacon; 2004.
American Psychological Association. Guidelines for clinical supervision in health service psychology. Am Psychol. 2015;70(1):33–46.
International Society for Coaching Psychology. https://www.isfcp.info/what-is-coaching-psychology/ . Accessed 19 June 2019.
Hill CE, Knox S. Training and supervision in psychotherapy. In: Lambert MJ, editor. Bergin and Garfield’s handbook of psychotherapy and behavior change. 6. Hoboken: Wiley; 2013. p. 775–812.
Milne DL, James I. A systematic review of effective cognitive-behavioral supervision. Br J Clin Psychol. 2000;39(2):111–27.
Wheeler S, Richards K. The impact of clinical supervision on counsellors and therapists, their practice and their clients. A systematic review of the literature. Couns Psychother Res. 2007;7(1):54–65.
Watkins CE. How does psychotherapy supervision work? Contributions of connection, conception, allegiance, alignment, and action. J Psychother Integr. 2017;27(2):201.
Alfonsson S, Parling T, Spännargård Å, Andersson G, Lundgren T. The effects of clinical supervision on supervisees and patients in cognitive behavioral therapy: a systematic review. Cogn Behav Ther. 2017;47(3):1–23.
Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG. Prisma Group. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009;6(7):e1000097.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Ellis MV, Krengel M, Ladany N, Schult D. Clinical supervision research from 1981 to 1993: a methodological critique. J Couns Psychol. 1996;43(1):35–50.
Freitas GJ. The impact of psychotherapy supervision on client outcome: a critical examination of 2 decades of research. Psychotherapy. 2002;39(4):354–67.
Rakovshik SG, McManus F. Establishing evidence-based training in cognitive behavioral therapy: a review of current empirical findings and theoretical guidance. Clin Psychol Rev. 2010;30(5):496–516.
Reiser RP, Milne DL. A systematic review and reformulation of outcome evaluation in clinical supervision: applying the fidelity framework. Train Educ Prof Psychol. 2014;8(3):149–57.
Auckenthaler A. Supervision of psychotherapy: claims, facts, trends. [supervision von Psychotherapie: Behauptungen-Fakten-trends.]. Psychotherapeut. 1999;44(3):139–52.
Strauß B, Wheeler S, Nodop S. Clinical supervision. Review of the state of research. [Klinische supervision: Überblick Über den stand der Forschung.]. Psychotherapeut. 2010;55(6):455–64.
Alfonsson S, Spännargård Å, Parling T, Andersson G, Lundgren T. The effects of clinical supervision on supervisees and patients in cognitive-behavioral therapy: a study protocol for a systematic review. Syst Rev. 2017;6(1):1–6.
Kühne F, Maas J, Wiesenthal S, Weck F. Supervision in behavioral therapy. A scoping review for identification of research objectives. [Supervision in der Verhaltenstherapie. Ein Scoping Review zur Identifikation von Forschungszielen.]. Zeitschrift für Klinische Psychologie und Psychotherapie. 2017;46(2):73–82.
Muse K, McManus F. A systematic review of methods for assessing competence in cognitive–behavioural therapy. Clin Psychol Rev. 2013;33(3):484–99.
Roth AD, Pilling S, Turner J. Therapist training and supervision in clinical trials: implications for clinical practice. Behav Cogn Psychother. 2010;38(3):291–302.
Perepletchikova F, Treat TA, Kazdin AE. Treatment integrity in psychotherapy research: analysis of the studies and examination of the associated factors. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2007;75(6):829–41.
Higgins JP, Green S. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 5.1. 0 (updated March 2011). Cochrane Collab; 2011.
CASP Checklist. http://www.casp-uk.net/checklists . Accessed 08 Jan 2018.
Sanderson S, Tatt ID, Higgins J. Tools for assessing quality and susceptibility to bias in observational studies in epidemiology: a systematic review and annotated bibliography. Int J Epidemiol. 2007;36(3):666–76.
Wirtz MA, Caspar F. Beurteilerübereinstimmung und Beurteilerreliabilität: Methoden zur Bestimmung und Verbesserung der Zuverlässigkeit von Einschätzungen mittels Kategoriensystemen und Ratingskalen. Göttingen: Hogrefe; 2002.
Anderson T, Crowley MEJ, Patterson CL, Heckman BD. The influence of supervision on manual adherence and therapeutic processes. J Clin Psychol. 2012;68(9):972–88.
Bambling M, King R, Raue P, Schweitzer R, Lambert W. Clinical supervision: its influence on client-rated working alliance and client symptom reduction in the brief treatment of major depression. Psychother Res. 2006;16(3):317–31.
Davidson KM, Rankin ML, Begley A, Lloyd S, Barry SJE, McSkimming P, et al. Assessing patient progress in psychological therapy through feedback in supervision: the memos randomized controlled trial (measuring and monitoring clinical outcomes in supervision: memos). Behav Cogn Psychother. 2017;45(3):209–24.
Grossl AB, Reese RJ, Norsworthy LA, Hopkins NB. Client feedback data in supervision: effects on supervision and outcome. Train Educ Prof Psychol. 2014;8(3):182–8.
Hiltunen AJ, Kocys E, Perrin-Wallqvist R. Effectiveness of cognitive behavioral therapy: an evaluation of therapies provided by trainees at a university psychotherapy training center. Psych J. 2013;2(2):101–12.
Locke LD, McCollum EE. Clients’ views of live supervision and satisfaction with therapy. J Marital Fam Ther. 2001;27(1):129–33.
Lu W, Yanos PT, Gottlieb JD, Duva SM, Silverstein SM, Xie H, et al. Use of fidelity assessments to train clinicians in the CBT for PTSD program for clients with serious mental illness. Psychiatr Serv. 2012;63(8):785–92.
Martino S, Paris M, Anez L, Nich C, Canning-Ball M, Hunkele K, et al. The effectiveness and cost of clinical supervision for motivational interviewing: a randomized controlled trial. J Subst Abus Treat. 2016;68:11–23.
Milne DL, Reiser RP, Cliffe T, Breese L, Boon A, Raine R, et al. A qualitative comparison of cognitive-behavioural and evidence-based clinical supervision. Cogn Behav Ther. 2011;4(4):152–66.
Ng RMK, Cheung MSM. Supervision of cognitive behavioural therapy for psychosis: a Hong Kong experience. Hong Kong J Psychiatry. 2007;17(4):124–30.
Rizvi SL, Yu J, Geisser S, Finnegan D. The use of “bug-in-the-eye” live supervision for training in dialectical behavior therapy: a case study. Clin Case Stud. 2016;15(3):243–58.
Smith JL, Carpenter KM, Amrhein PC, Brooks AC, Levin D, Schreiber EA, et al. Training substance abuse clinicians in motivational interviewing using live supervision via teleconferencing. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2012;80(3):450–64.
Weck F, Jakob M, Neng JMB, Hofling V, Grikscheit F, Bohus M. The effects of bug-in-the-eye supervision on therapeutic alliance and therapist competence in cognitive-behavioural therapy: a randomized controlled trial. Clin Psychol Psychother. 2016;23(5):386–96.
Willutzki U, Tönnies B, Meyer F. Psychotherapy supervision and the therapeutic alliance-A process study. [Psychotherapiesupervision und die therapeutische Beziehung-Eine Prozessstudie.]. Verhaltenstherapie & Psychosoziale Praxis. 2005;37(3):507–16.
Zarbock G, Drews M, Bodansky A, Dahme B. The evaluation of supervision: construction of brief questionnaires for the supervisor and the supervisee. Psychother Res. 2009;19(2):194–204.
Anderson T, Crowley MEJ, Binder JL, Heckman BD, Patterson CL. Does the supervisor's teaching style influence the supervisee's learning prescribed techniques? Psychother Res. 2017;27(5):549–57.
Milne DL, Reiser RP, Cliffe T. An N=1 evaluation of enhanced CBT supervision. Behav Cogn Psychother. 2013;41(2):210–20.
Jakob M, Weck F, Bohus M. Live supervision: From the one-way mirror to video-based online-supervision. [Live-Supervision: Vom Einwegspiegel zur videobasierten Online-Supervision.]. Verhaltenstherapie. 2013;23(3):170–80.
Jakob M, Weck F, Schornick M, Krause T, Bohus M. When the supervisor is watching. Qualitative analysis of the acceptance of live supervision. [Wenn der supervisor zuschaut: qualitative analyse der Akzeptanz von live-supervision.]. Psychotherapeut. 2015;60(3):210–5.
Beidas RS, Kendall PC. Training therapists in evidence-based practice: a critical review of studies from a systems-contextual perspective. Clin Psychol Sci Pract. 2010;17(1):1–30.
Rakovshik SG, McManus F, Vazquez-Montes M, Muse K, Ougrin D. Is supervision necessary? Examining the effects of internet-based CBT training with and without supervision. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2016;84(3):191–9.
Brettschneider C, Lühmann D, Raspe H-H. Der Stellenwert von patient-reported outcomes (PRO) im Kontext von health technology assessment (HTA): DIMDI; 2010.
Gonsalvez CJ, Calvert FL. Competency-based models of supervision: principles and applications. Promises Chall Aust Psychologist. 2014;49(4):200–8.
Falender CA. Clinical supervision-the missing ingredient. Am Psychol. 2018;73(9):1240.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the two reviewers for their valuable and important contributions to a former version of the manuscript.
We greatfully acknowledge the support of the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG) and the Open Access Publishing Fund of the University of Potsdam.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Psychology, Clinical Psychology and Psychotherapy, University of Potsdam, Karl-Liebknecht-Str. 24-25, 14476, Potsdam, Germany
Franziska Kühne, Jana Maas, Sophia Wiesenthal & Florian Weck
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
FK conceptualized the research goal, developed the design and the methodology, provided the resources needed for the study, supervised and managed the research, collected the data/evidence, analyzed, synthesized and visualized the study data and wrote the initial draft of the paper. JM and SW aided in collecting the data, in analyzing, synthesizing and visualizing the data and revised the work. FW took part in the conceptualization process, the coordination of the responsibilities, the validation and reviewing process and supervised the research activity. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Franziska Kühne .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ ), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Kühne, F., Maas, J., Wiesenthal, S. et al. Empirical research in clinical supervision: a systematic review and suggestions for future studies. BMC Psychol 7 , 54 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-019-0327-7
Download citation
Received : 04 March 2019
Accepted : 18 July 2019
Published : 22 August 2019
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-019-0327-7
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Clinical supervision
- Systematic review
- Evidence-based psychotherapy
BMC Psychology
ISSN: 2050-7283
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 24 February 2022
Systematic literature review of schizophrenia clinical practice guidelines on acute and maintenance management with antipsychotics
- Christoph U. Correll ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-7254-5646 1 , 2 , 3 ,
- Amber Martin 4 ,
- Charmi Patel 5 ,
- Carmela Benson 5 ,
- Rebecca Goulding 6 ,
- Jennifer Kern-Sliwa 5 ,
- Kruti Joshi 5 ,
- Emma Schiller 4 &
- Edward Kim ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-8247-6675 7
Schizophrenia volume 8 , Article number: 5 ( 2022 ) Cite this article
14k Accesses
51 Citations
14 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Schizophrenia
Clinical practice guidelines (CPGs) translate evidence into recommendations to improve patient care and outcomes. To provide an overview of schizophrenia CPGs, we conducted a systematic literature review of English-language CPGs and synthesized current recommendations for the acute and maintenance management with antipsychotics. Searches for schizophrenia CPGs were conducted in MEDLINE/Embase from 1/1/2004–12/19/2019 and in guideline websites until 06/01/2020. Of 19 CPGs, 17 (89.5%) commented on first-episode schizophrenia (FES), with all recommending antipsychotic monotherapy, but without agreement on preferred antipsychotic. Of 18 CPGs commenting on maintenance therapy, 10 (55.6%) made no recommendations on the appropriate maximum duration of maintenance therapy, noting instead individualization of care. Eighteen (94.7%) CPGs commented on long-acting injectable antipsychotics (LAIs), mainly in cases of nonadherence (77.8%), maintenance care (72.2%), or patient preference (66.7%), with 5 (27.8%) CPGs recommending LAIs for FES. For treatment-resistant schizophrenia, 15/15 CPGs recommended clozapine. Only 7/19 (38.8%) CPGs included a treatment algorithm.
Similar content being viewed by others
Adults who microdose psychedelics report health related motivations and lower levels of anxiety and depression compared to non-microdosers
Psilocybin microdosers demonstrate greater observed improvements in mood and mental health at one month relative to non-microdosing controls

The serotonin theory of depression: a systematic umbrella review of the evidence
Introduction.
Schizophrenia is an often debilitating, chronic, and relapsing mental disorder with complex symptomology that manifests as a combination of positive, negative, and/or cognitive features 1 , 2 , 3 . Standard management of schizophrenia includes the use of antipsychotic medications to help control acute psychotic episodes 4 and prevent relapses 5 , 6 , whereas maintenance therapy is used in the long term after patients have been stabilized 7 , 8 , 9 . Two main classes of drugs—first- and second-generation antipsychotics (FGA and SGA)—are used to treat schizophrenia 10 . SGAs are favored due to the lower rates of adverse effects, such as extrapyramidal effects, tardive dyskinesia, and relapse 11 . However, pharmacologic treatment for schizophrenia is complicated because nonadherence is prevalent, and is a major risk factor for relapse 9 and poor overall outcomes 12 . The use of long-acting injectable (LAI) versions of antipsychotics aims to limit nonadherence-related relapses and poor outcomes 13 .
Patient treatment pathways and treatment choices are determined based on illness acuity/severity, past treatment response and tolerability, as well as balancing medication efficacy and adverse effect profiles in the context of patient preferences and adherence patterns 14 , 15 . Clinical practice guidelines (CPG) serve to inform clinicians with recommendations that reflect current evidence from meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials (RCTs), individual RCTs and, less so, epidemiologic studies, as well as clinical experience, with the goal of providing a framework and road-map for treatment decisions that will improve quality of care and achieve better patients outcomes. The use of clinical algorithms or other decision trees in CPGs may improve the ease of implementation of the evidence in clinical practice 16 . While CPGs are an important tool for mental health professionals, they have not been updated on a regular basis like they have been in other areas of medicine, such as in oncology. In the absence of current information, other governing bodies, healthcare systems, and hospitals have developed their own CPGs regarding the treatment of schizophrenia, and many of these have been recently updated 17 , 18 , 19 . As such, it is important to assess the latest guidelines to be aware of the changes resulting from consideration of updated evidence that informed the treatment recommendations. Since CPGs are comprehensive and include the diagnosis as well as the pharmacological and non-pharmacological management of individuals with schizophrenia, a detailed comparative review of all aspects of CPGs for schizophrenia would have been too broad a review topic. Further, despite ongoing efforts to broaden the pharmacologic tools for the treatment of schizophrenia 20 , antipsychotics remain the cornerstone of schizophrenia management 8 , 21 . Therefore, a focused review of guideline recommendations for the management of schizophrenia with antipsychotics would serve to provide clinicians with relevant information for treatment decisions.
To provide an updated overview of United States (US) national and English language international guidelines for the management of schizophrenia, we conducted a systematic literature review (SLR) to identify CPGs and synthesize current recommendations for pharmacological management with antipsychotics in the acute and maintenance phases of schizophrenia.
Systematic searches for the SLR yielded 1253 hits from the electronic literature databases. After removal of duplicate references, 1127 individual articles were screened at the title and abstract level. Of these, 58 publications were deemed eligible for screening at the full-text level, from which 19 were ultimately included in the SLR. Website searches of relevant organizations yielded 10 additional records, and an additional three records were identified by the state-by-state searches. Altogether, this process resulted in 32 records identified for inclusion in the SLR. Of the 32 sources, 19 primary CPGs, published/issued between 2004 and 2020, were selected for extraction, as illustrated in the PRISMA diagram (Fig. 1 ). While the most recent APA guideline was identified and available for download in 2020, the reference to cite in the document indicates a publication date of 2021.
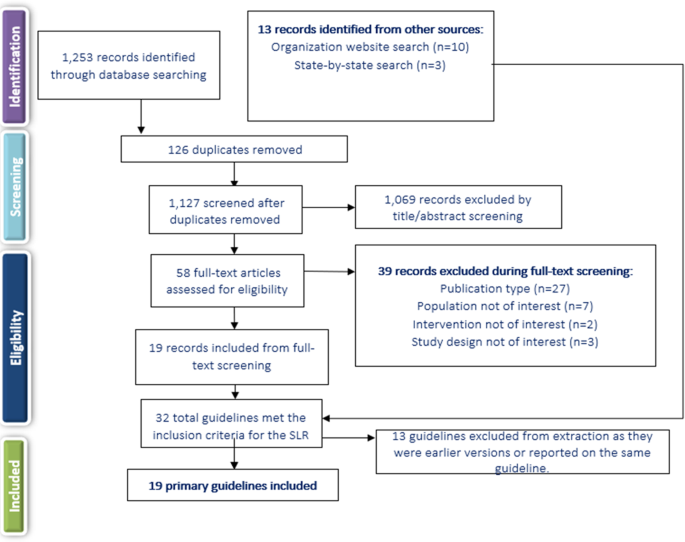
SLR systematic literature review.
Of the 19 included CPGs (Table 1 ), three had an international focus (from the following organizations: International College of Neuropsychopharmacology [CINP] 22 , United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees [UNHCR] 23 , and World Federation of Societies of Biological Psychiatry [WFSBP] 24 , 25 , 26 ); seven originated from the US; 17 , 18 , 19 , 27 , 28 , 29 , 30 , 31 , 32 three were from the United Kingdom (British Association for Psychopharmacology [BAP] 33 , the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence [NICE] 34 , and the Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network [SIGN] 35 ); and one guideline each was from Singapore 36 , the Polish Psychiatric Association (PPA) 37 , 38 , the Canadian Psychiatric Association (CPA) 14 , the Royal Australia/New Zealand College of Psychiatrists (RANZCP) 39 , the Association Française de Psychiatrie Biologique et de Neuropsychopharmacologie (AFPBN) from France 40 , and Italy 41 . Fourteen CPGs (74%) recommended treatment with specific antipsychotics and 18 (95%) included recommendations for the use of LAIs, while just seven included a treatment algorithm Table 2 ). The AGREE II assessment resulted in the highest score across the CPGs domains for NICE 34 followed by the American Psychiatric Association (APA) guidelines 17 . The CPA 14 , BAP 33 , and SIGN 35 CPGs also scored well across domains.

Acute therapy
Seventeen CPGs (89.5%) provided treatment recommendations for patients experiencing a first schizophrenia episode 14 , 17 , 18 , 19 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 28 , 30 , 31 , 32 , 33 , 34 , 35 , 36 , 39 , 40 , 41 , but the depth and focus of the information varied greatly (Supplementary Table 1 ). In some CPGs, information on treatment of a first schizophrenia episode was limited or grouped with information on treating any acute episode, such as in the CPGs from CINP 22 , AFPBN 40 , New Jersey Division of Mental Health Services (NJDMHS) 32 , the APA 17 , and the PPA 37 , 38 , while the others provided more detailed information specific to patients experiencing a first schizophrenia episode 14 , 18 , 19 , 23 , 24 , 28 , 33 , 34 , 35 , 36 , 39 , 41 . The American Association of Community Psychiatrists (AACP) Clinical Tips did not provide any information on the treatment of schizophrenia patients with a first episode 29 .
There was little agreement among CPGs regarding the preferred antipsychotic for a first schizophrenia episode. However, there was strong consensus on antipsychotic monotherapy and that lower doses are generally recommended due to better treatment response and greater adverse effect sensitivity. Some guidelines recommended SGAs over FGAs when treating a first-episode schizophrenia patient (RANZCP 39 , Texas Medication Algorithm Project [TMAP] 28 , Oregon Health Authority 19 ), one recommended starting patients on an FGA (UNHCR 23 ), and others stated specifically that there was no evidence of any difference in efficacy between FGAs and SGAs (WFSBP 24 , CPA 14 , SIGN 35 , APA 17 , Singapore guidelines 36 ), or did not make any recommendation (CINP 22 , Italian guidelines 41 , NICE 34 , NJDMHS 32 , Schizophrenia Patient Outcomes Research Team [PORT] 30 , 31 ). The BAP 33 and WFBSP 24 noted that while there was probably no difference between FGAs and SGAs in efficacy, some SGAs (olanzapine, amisulpride, and risperidone) may perform better than some FGAs. The Schizophrenia PORT recommendations noted that while there seemed to be no differences between SGAs and FGAs in short-term studies (≤12 weeks), longer studies (one to two years) suggested that SGAs may provide benefits in terms of longer times to relapse and discontinuation rates 30 , 31 . The AFPBN guidelines 40 and Florida Medicaid Program guidelines 18 , which both focus on use of LAI antipsychotics, both recommended an SGA-LAI for patients experiencing a first schizophrenia episode. A caveat in most CPGs was that physicians and their patients should discuss decisions about the choice of antipsychotic and that the choice should consider individual patient factors/preferences, risk of adverse and metabolic effects, and symptom patterns 17 , 18 , 19 , 22 , 24 , 28 , 30 , 31 , 32 , 33 , 34 , 35 , 36 , 39 , 41 .
Most CPGs recommended switching to a different monotherapy if the initial antipsychotic was not effective or not well tolerated after an adequate antipsychotic trial at an appropriate dose 14 , 17 , 18 , 19 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 28 , 32 , 33 , 35 , 36 , 39 . For patients initially treated with an FGA, the UNHCR recommended switching to an SGA (olanzapine or risperidone) 23 . Guidance on response to treatment varied in the measures used but typically required at least a 20% improvement in symptoms (i.e. reduction in Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale or Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale scores) from pre-treatment levels.
Several CPGs contained recommendations on the duration of antipsychotic therapy after a first schizophrenia episode. The NJDMHS guidelines 32 recommended nine to 12 months; CINP 22 recommended at least one year; CPA 14 recommended at least 18 months; WFSBP 25 , the Italian guidelines 41 , and NICE 34 recommended 1 to 2 years; and the RANZCP 39 , BAP 33 , and SIGN 35 recommended at least 2 years. The APA 17 and TMAP 28 recommended continuing antipsychotic treatment after resolution of first-episode symptoms but did not recommend a specific length of therapy.
Twelve guidelines 14 , 18 , 22 , 24 , 28 , 30 , 31 , 33 , 34 , 35 , 36 , 39 , 40 (63.2%) discussed the treatment of subsequent/multiple episodes of schizophrenia (i.e., following relapse). These CPGs noted that the considerations guiding the choice of antipsychotic for subsequent/multiple episodes were similar to those for a first episode, factoring in prior patient treatment response, adverse effect patterns and adherence. The CPGs also noted that response to treatment may be lower and require higher doses to achieve a response than for first-episode schizophrenia, that a different antipsychotic than used to treat the first episode may be needed, and that a switch to an LAI is an option.
Several CPGs provided recommendations for patients with specific clinical features (Supplementary Table 1 ). The most frequently discussed group of clinical features was negative symptoms, with recommendations provided in the CINP 22 , UNHCR 23 , WFSBP 24 , AFPBN 40 , SIGN 35 , BAP 33 , APA 17 , and NJDMHS guidelines; 32 negative symptoms were the sole focus of the guidelines from the PPA 37 , 38 . The guidelines noted that due to limited evidence in patients with predominantly negative symptoms, there was no clear benefit for any strategy, but that options included SGAs (especially amisulpride) rather than FGAs (WFSBP 24 , CINP 22 , AFPBN 40 , SIGN 35 , NJDMHS 32 , PPA 37 , 38 ), and addition of an antidepressant (WFSBP 24 , UNHCR 23 , SIGN 35 , NJDMHS 32 ) or lamotrigine (SIGN 35 ), or switching to another SGA (NJDMHS 32 ) or clozapine (NJDMHS 32 ). The PPA guidelines 37 , 38 stated that the use of clozapine or adding an antidepressant or other medication class was not supported by evidence, but recommended the SGA cariprazine for patients with predominant and persistent negative symptoms, and other SGAs for those with full-spectrum negative symptoms. However, the BAP 33 stated that no recommendations can be made for any of these strategies because of the quality and paucity of the available evidence.
Some of the CPGs also discussed treatment of other clinical features to a limited degree, including depressive symptoms (CINP 22 , UNHCR 23 , CPA 14 , APA 17 , and NJDMHS 32 ), cognitive dysfunction (CINP 22 , UNHCR 23 , WFSBP 24 , AFPBN 40 , SIGN 35 , BAP 33 , and NJDMHS 32 ), persistent aggression (CINP 22 , WFSBP 24 , CPA 14 , AFPBN 40 , NICE 34 , SIGN 35 , BAP 33 , and NJDMHS 32 ), and comorbid psychiatric diagnoses (CINP 22 , RANZCP 39 , BAP 33 , APA 17 , and NJDMHS 32 ).
Fifteen CPGs (78.9%) discussed treatment-resistant schizophrenia (TRS); all defined it as persistent, predominantly positive symptoms after two adequate antipsychotic trials; clozapine was the unanimous first choice 14 , 17 , 18 , 19 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 28 , 30 , 31 , 32 , 33 , 34 , 35 , 36 , 39 . However, the UNHCR guidelines 23 , which included recommendations for treatment of refugees, noted that clozapine is only a reasonable choice in regions where white blood cell monitoring and specialist supervision are available, otherwise, risperidone or olanzapine are alternatives if they had not been used in the previous treatment regimen.
There were few options for patients who are resistant to clozapine therapy, and evidence supporting these options was limited. The CPA guidelines 14 therefore stated that no recommendation can be given due to inadequate evidence. Other CPGs discussed options (but noted there was limited supporting evidence), such as switching to olanzapine or risperidone (WFSBP 24 , TMAP 28 ), adding a second antipsychotic to clozapine (CINP 22 , NICE 34 , TMAP 28 , BAP 33 , Florida Medicaid Program 18 , Oregon Health Authority 19 , RANZCP 39 ), adding lamotrigine or topiramate to clozapine (CINP 22 , Florida Medicaid Program 18 ), combination therapy with two non-clozapine antipsychotics (Florida Medicaid Program 18 , NJDMHS 32 ), and high-dose non-clozapine antipsychotic therapy (BAP 33 , SIGN 35 ). Electroconvulsive therapy was noted as a last resort for patients who did not respond to any pharmacologic therapy, including clozapine, by 10 CPGs 17 , 18 , 19 , 22 , 24 , 28 , 32 , 35 , 36 , 39 .
Maintenance therapy
Fifteen CPGs (78.9%) discussed maintenance therapy to various degrees via dedicated sections or statements, while three others referred only to maintenance doses by antipsychotic agent 18 , 23 , 29 without accompanying recommendations (Supplementary Table 2 ). Only the Italian guideline provided no reference or comments on maintenance treatment. The CINP 22 , WFSBP 25 , RANZCP 39 , and Schizophrenia PORT 30 , 31 recommended keeping patients on the same antipsychotic and at the same dose on which they had achieved remission. Several CPGs recommended maintenance therapy at the lowest effective dose (NJDMHS 32 , APA 17 , Singapore guidelines 36 , and TMAP 28 ). The CPA 14 and SIGN 35 defined the lower dose as 300–400 mg chlorpromazine equivalents or 4–6 mg risperidone equivalents, and the Singapore guidelines 36 stated that the lower dose should not be less than half the original dose. TMAP 28 stated that given the relapsing nature of schizophrenia, the maintenance dose should often be close to the original dose. While SIGN 35 recommended that patients remain on the same antipsychotic that provided remission, these guidelines also stated that maintenance with amisulpride, olanzapine, or risperidone was preferred, and that chlorpromazine and other low-potency FGAs were also suitable. The BAP 33 recommended that the current regimen be optimized before any dose reduction or switch to another antipsychotic occurs. Several CPGs recommended LAIs as an option for maintenance therapy (see next section).
Altogether, 10/18 (55.5%) CPGs made no recommendations on the appropriate duration of maintenance therapy, noting instead that each patient should be considered individually. Other CPGs made specific recommendations: Both the Both BAP 33 and SIGN 35 guidelines suggested a minimum of 2 years, the NJDMHS guidelines 32 recommended 2–3 years; the WFSBP 25 recommended 2–5 years for patients who have had one relapse and more than 5 years for those who have had multiple relapses; the RANZCP 39 and the CPA 14 recommended 2–5 years; and the CINP 22 recommended that maintenance therapy last at least 6 years for patients who have had multiple episodes. The TMAP was the only CPG to recommend that maintenance therapy be continued indefinitely 28 .
Recommendations on the use of LAIs
All CPGs except the one from Italy (94.7%) discussed the use of LAIs for patients with schizophrenia to some extent. As shown in Table 3 , among the 18 CPGs, LAIs were primarily recommended in 14 CPGs (77.8%) for patients who are non-adherent to other antipsychotic administration routes (CINP 22 , UNHCR 23 , RANZCP 39 , PPA 37 , 38 , Singapore guidelines 36 , NICE 34 , SIGN 35 , BAP 33 , APA 17 , TMAP 28 , NJDMHS 32 , AACP 29 , Oregon Health Authority 19 , Florida Medicaid Program 18 ). Twelve CPGs (66.7%) also noted that LAIs should be prescribed based on patient preference (RANZCP 39 , CPA 14 , AFPBN 40 , Singapore guidelines 36 , NICE 34 , SIGN 35 , BAP 33 , APA 17 , Schizophrenia PORT 30 , 31 , AACP 29 , Oregon Health Authority 19 , Florida Medicaid Program 18 ).
Thirteen CPGs (72.2%) recommended LAIs as maintenance therapy 18 , 19 , 24 , 28 , 29 , 30 , 31 , 32 , 33 , 34 , 35 , 36 , 39 , 40 . While five CPGs (27.8%), i.e., AFPBN 40 , RANZCP 39 , TMAP 28 , NJDMHS 32 , and the Florida Medicaid Program 18 recommended LAIs specifically for patients experiencing a first episode. While the CPA 14 did not make any recommendations regarding when LAIs should be used, they discussed recent evidence supporting their use earlier in treatment. Five guidelines (27.8%, i.e., Singapore 36 , NICE 34 , SIGN 35 , BAP 33 , and Schizophrenia PORT 30 , 31 ) noted that evidence around LAIs was not sufficient to support recommending their use for first-episode patients. The AFPBN guidelines 40 also stated that LAIs (SGAs as first-line and FGAs as second-line treatment) should be more frequently considered for maintenance treatment of schizophrenia. Four CPGs (22.2%, i.e., CINP 22 , UNHCR 23 , Italian guidelines 41 , PPA guidelines 37 , 38 ) did not specify when LAIs should be used. The AACP guidelines 29 , which evaluated only LAIs, recommended expanding their use beyond treatment for nonadherence, suggesting that LAIs may offer a more convenient mode of administration or potentially address other clinical and social challenges, as well as provide more consistent plasma levels.
Treatment algorithms
Only Seven CPGs (36.8%) included an algorithm as part of the treatment recommendations. These included decision trees or flow diagrams that map out initial therapy, durations for assessing response, and treatment options in cases of non-response. However, none of these guidelines defined how to measure response, a theme that also extended to guidelines that did not include treatment algorithms. Four of the seven guidelines with algorithms recommended specific antipsychotic agents, while the remaining three referred only to the antipsychotic class.
LAIs were not consistently incorporated in treatment algorithms and in six CPGs were treated as a separate category of medicine reserved for patients with adherence issues or a preference for the route of administration. The only exception was the Florida Medicaid Program 18 , which recommended offering LAIs after oral antipsychotic stabilization even to patients who are at that point adherent to oral antipsychotics.
Benefits and harms
The need to balance the efficacy and safety of antipsychotics was mentioned by all CPGs as a basic treatment paradigm.
Ten CPGs provided conclusions on benefits of antipsychotic therapy. The APA 17 and the BAP 33 guidelines stated that antipsychotic treatment can improve the positive and negative symptoms of psychosis and leads to remission of symptoms. These CPGs 17 , 33 as well as those from NICE 34 and CPA 14 stated that these treatment effects can also lead to improvements in quality of life (including quality-adjusted life years), improved functioning, and reduction in disability. The CPA 14 and APA 17 guidelines noted decreases in hospitalizations with antipsychotic therapy, and the APA guidelines 17 stated that long-term antipsychotic treatment can also reduce mortality. The UNHCR 23 and the Italian 41 guidelines noted that early intervention increased positive outcomes. The WFSBP 24 , AFPBN 40 , CPA 14 , BAP 33 , APA 17 , and NJDMHS 32 affirmed that relapse prevention is a benefit of continued/maintenance treatment.
Some CPGs (WFSBP 24 , Italian 41 , CPA 14 , and SIGN 35 ) noted that reduced risk for extrapyramidal adverse effects and treatment discontinuation were potential benefits of SGAs vs. FGAs.
The risk of adverse effects (e.g., extrapyramidal, metabolic, cardiovascular, and hormonal adverse effects, sedation, and neuroleptic malignant syndrome) was noted by all CPGs as the major potential harm of antipsychotic therapy 14 , 17 , 18 , 19 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 28 , 29 , 30 , 31 , 32 , 34 , 35 , 36 , 37 , 39 , 40 , 41 , 42 . These adverse effects are known to limit long-term treatment and adherence 24 .
This SLR of CPGs for the treatment of schizophrenia yielded 19 most updated versions of individual CPGs, published/issued between 2004 and 2020. Structuring our comparative review according to illness phase, antipsychotic type and formulation, response to antipsychotic treatment as well as benefits and harms, several areas of consistent recommendations emerged from this review (e.g., balancing risk and benefits of antipsychotics, preferring antipsychotic monotherapy; using clozapine for treatment-resistant schizophrenia). On the other hand, other recommendations regarding other areas of antipsychotic treatment were mostly consistent (e.g., maintenance antipsychotic treatment for some time), somewhat inconsistent (e.g., differences in the management of first- vs multi-episode patients, type of antipsychotic, dose of antipsychotic maintenance treatment), or even contradictory (e.g., role of LAIs in first-episode schizophrenia patients).
Consistent with RCT evidence 43 , 44 , antipsychotic monotherapy was the treatment of choice for patients with first-episode schizophrenia in all CPGs, and all guidelines stated that a different single antipsychotic should be tried if the first is ineffective or intolerable. Recommendations were similar for multi-episode patients, but factored in prior patient treatment response, adverse effect patterns, and adherence. There was also broad consensus that the side-effect profile of antipsychotics is the most important consideration when making a decision on pharmacologic treatment, also reflecting meta-analytic evidence 4 , 5 , 10 . The risk of extrapyramidal symptoms (especially with FGAs) and metabolic effects (especially with SGAs) were noted as key considerations, which are also reflected in the literature as relevant concerns 4 , 45 , 46 , including for quality of life and treatment nonadherence 47 , 48 , 49 , 50 .
Largely consistent with the comparative meta-analytic evidence regarding the acute 4 , 51 , 52 and maintenance antipsychotic treatment 5 effects of schizophrenia, the majority of CPGs stated there was no difference in efficacy between SGAs and FGAs (WFSBP 24 , CPA 14 , SIGN 35 , APA 17 , and Singapore guidelines 36 ), or did not make any recommendations (CINP 22 , Italian guidelines 41 , NICE 34 , NJDMHS 32 , and Schizophrenia PORT 30 , 31 ); three CPGs (BAP 33 , WFBSP 24 , and Schizophrenia PORT 30 , 31 ) noted that SGAs may perform better than FGAs over the long term, consistent with a meta-analysis on this topic 53 .
The 12 CPGs that discussed treatment of subsequent/multiple episodes generally agreed on the factors guiding the choices of an antipsychotic, including that the decision may be more complicated and response may be lower than with a first episode, as described before 7 , 54 , 55 , 56 .
There was little consensus regarding maintenance therapy. Some CPGs recommended the same antipsychotic and dose that achieved remission (CINP 22 , WFSBP 25 , RANZCP 39 , and Schizophrenia PORT 30 , 31 ) and others recommended the lowest effective dose (NJDMHS 32 , APA 17 , Singapore guidelines 36 , TMAP 28 , CPA 14 , and SIGN 35 ). This inconsistency is likely based on insufficient data as well as conflicting results in existing meta-analyses on this topic 57 , 58 , 59 .
The 15 CPGs that discussed TRS all used the same definition for this condition, consistent with recent commendations 60 , and agreed that clozapine is the primary evidence-based treatment choice 14 , 17 , 18 , 19 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 28 , 30 , 31 , 32 , 33 , 34 , 35 , 36 , 39 , reflecting the evidence base 61 , 62 , 63 . These CPGs also agreed that there are few options well supported by evidence for patients who do not respond to clozapine, with a recent meta-analysis of RCTs showing that electroconvulsive therapy augmentation may be the most evidence-based treatment option 64 .
One key gap in the treatment recommendations was how long patients should remain on antipsychotic therapy after a first episode or during maintenance therapy. While nine of the 17 CPGs discussing treatment of a first episode provided a recommended timeframe (varying from 1 to 2 years) 14 , 22 , 24 , 32 , 33 , 34 , 35 , 39 , 41 , the APA 17 and TMAP 28 recommended continuing antipsychotic treatment after resolution of first-episode symptoms but did not recommend a specific length of therapy. Similarly, six of the 18 CPGs discussing maintenance treatment recommended a specific duration of therapy (ranging from two to six years) 14 , 22 , 25 , 32 , 39 , while as many as 10 CPGs did not point to a firm end of the maintenance treatment, instead recommending individualized decisions. The CPGs not stating a definite endpoint or period of maintenance treatment after repeated schizophrenia episodes or even after a first episode of schizophrenia, reflects the different evidence types on which the recommendation is based. The RCT evidence ends after several years of maintenance treatment vs. discontinuation supporting ongoing antipsychotic treatment; however, naturalistic database studies do not indicate any time period after which one can safely discontinue maintenance antipsychotic care, even after a first schizophrenia episode 8 , 65 . In fact, stopping antipsychotics is associated not only with a substantially increased risk of hospitalization but also mortality 65 , 66 , 67 . In this sense, not stating an endpoint for antipsychotic maintenance therapy should not be taken as an implicit statement that antipsychotics should be discontinued at any time; data suggest the contrary.
A further gap exists regarding the most appropriate treatment of negative symptoms, such as anhedonia, amotivation, asociality, affective flattening, and alogia 1 , a long-standing challenge in the management of patients with schizophrenia. Negative symptoms often persist in patients after positive symptoms have resolved, or are the presenting feature in a substantial minority of patients 22 , 35 . Negative symptoms can also be secondary to pharmacotherapy 22 , 68 . Antipsychotics have been most successful in treating positive symptoms, and while eight of the CPGs provided some information on treatment of negative symptoms, the recommendations were generally limited 17 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 32 , 33 , 35 , 40 . Negative symptom management was a focus of the PPA guidelines, but the guidelines acknowledged that supporting evidence was limited, often due to the low number of patients with predominantly negative symptoms in clinical trials 37 , 38 . The Polish guidelines are also one of the more recently developed and included the newer antipsychotic cariprazine as a first-line option, which although being a point of differentiation from the other guidelines, this recommendation was based on RCT data 69 .
Another area in which more direction is needed is on the use of LAIs. While all but one of the 19 CPGs discussed this topic, the extent of information and recommendations for LAI use varied considerably. All CPGs categorized LAIs as an option to improve adherence to therapy or based on patient preference. However, 5/18 CPGs (27.8%) recommended the use of LAI early in treatment (at first episode: AFPBN 40 , RANZCP 39 , TMAP 28 , NJDMHS 32 , and Florida Medicaid Program 18 ) or across the entire illness course, while five others stated there was not sufficient evidence to recommend LAIs for these patients (Singapore 36 , NICE 34 , SIGN 35 , BAP 33 , and Schizophrenia PORT 30 , 31 ). The role of LAIs in first-episode schizophrenia was the only point where opposing recommendations were found across CPGs. This contradictory stance was not due to the incorporation of newer data suggesting benefits of LAIs in first episode and early-phase patients with schizophrenia 70 , 71 , 72 , 73 , 74 in the CPGs recommending LAI use in first-episode patients, as CPGs recommending LAI use were published between 2005 and 2020, while those opposing LAI use were published between 2011 and 2020. Only the Florida Medicaid CPG recommended LAIs as a first step equivalent to oral antipsychotics (OAP) after initial OAP response and tolerability, independent of nonadherence or other clinical variables. This guideline was also the only CPG to fully integrate LAI use in their clinical algorithm. The remaining six CPGs that included decision tress or treatment algorithms regarded LAIs as a separate paradigm of treatment reserved for nonadherence or patients preference rather than a routine treatment option to consider. While some CPGs provided fairly detailed information on the use of LAIs (AFPBN 40 , AACP 29 , Oregon Health Authority 19 , and Florida Medicaid Program 18 ), others mentioned them only in the context of adherence issues or patient preference. Notably, definitions of and means to determine nonadherence were not reported. One reason for this wide range of recommendations regarding the placement of LAIs in the treatment algorithm and clinical situations that prompt LAI use might be due to the fact that CPGs generally favor RCT evidence over evidence from other study designs. In the case of LAIs, there was a notable dissociation between consistent meta-analytic evidence of statistically significant superiority of LAIs vs OAPs in mirror-image 75 and cohort study designs 76 and non-significant advantages in RCTs 77 . Although patients in RCTs comparing LAIs vs OAPs were less severely ill and more adherent to OAPs 77 than in clinical care and although mirror-image and cohort studies arguably have greater external validity than RCTs 78 , CPGs generally disregard evidence from other study designs when RCT evidence exits. This narrow focus can lead to disregarding important additional data. Nevertheless, a most updated meta-analysis of all 3 study designs comparing LAIs with OAPs demonstrated consistent superiority of LAIs vs OAPs for hospitalization or relapse across all 3 designs 79 , which should lead to more uniform recommendations across CPGs in the future.
Only seven CPGs included treatment algorithms or flow charts to guide LAI treatment selection for patients with schizophrenia 17 , 18 , 19 , 24 , 29 , 35 , 40 . However, there was little commonality across algorithms beyond the guidance on LAIs mentioned above, as some listed specific treatments and conditions for antipsychotic switches, while others indicated that medication choice should be based on a patient’s preferences and responses, side effects, and in some cases, cost effectiveness. Since algorithms and flow charts facilitate the reception, adoption and implementation of guidelines, future CPGs should include them as dissemination tools, but they need to reflect the data and detailed text and be sufficiently specific to be actionable.
The systematic nature in the identification, summarization, and assessment of the CPGs is a strength of this review. This process removed any potential bias associated with subjective selection of evidence, which is not reproducible. However, only CPGs published in English were included and regardless of their quality and differing timeframes of development and publication, complicating a direct comparison of consensus and disagreement. Finally, based on the focus of this SLR, we only reviewed pharmacologic management with antipsychotics. Clearly, the assessment, other pharmacologic and, especially, psychosocial interventions are important in the management of individuals with schizophrenia, but these topics that were covered to varying degrees by the evaluated CPGs were outside of the scope of this review.
Numerous guidelines have recently updated their recommendations on the pharmacological treatment of patients with schizophrenia, which we have summarized in this review. Consistent recommendations were observed across CPGs in the areas of balancing risk and benefits of antipsychotics when selecting treatment, a preference for antipsychotic monotherapy, especially for patients with a first episode of schizophrenia, and the use of clozapine for treatment-resistant schizophrenia. By contrast, there were inconsistencies with regards to recommendations on maintenance antipsychotic treatment, with differences existing on type and dose of antipsychotic, as well as the duration of therapy. However, LAIs were consistently recommended, but mainly suggested in cases of nonadherence or patient preference, despite their established efficacy in broader patient populations and clinical scenarios in clinical trials. Guidelines were sometimes contradictory, with some recommending LAI use earlier in the disease course (e.g., first episode) and others suggesting they only be reserved for later in the disease. This inconsistency was not due to lack of evidence on the efficacy of LAIs in first-episode schizophrenia or the timing of the CPG, so that other reasons might be responsible, including possibly bias and stigma associated with this route of treatment administration. Lastly, gaps existed in the guidelines for recommendations on the duration of maintenance treatment, treatment of negative symptoms, and the development/use of treatment algorithms whenever evidence is sufficient to provide a simplified summary of the data and indicate their relevance for clinical decision making, all of which should be considered in future guideline development/revisions.
The SLR followed established best methods used in systematic review research to identify and assess the available CPGs for pharmacologic treatment of schizophrenia with antipsychotics in the acute and maintenance phases 80 , 81 . The SLR was conducted in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines, including use of a prespecified protocol to outline methods for conducting the review. The protocol for this review was approved by all authors prior to implementation but was not submitted to an external registry.
Data sources and search algorithms
Searches were conducted by two independent investigators in the MEDLINE and Embase databases via OvidSP to identify CPGs published in English. Articles were identified using search algorithms that paired terms for schizophrenia with keywords for CPGs. Articles indexed as case reports, reviews, letters, or news were excluded from the searches. The database search was limited to CPGs published from January 1, 2004, through December 19, 2019, without limit to geographic location. In addition to the database sources, guideline body websites and state-level health departments from the US were also searched for relevant CPGs published through June 2020. A manual check of the references of recent (i.e., published in the past three years), relevant SLRs and relevant practice CPGs was conducted to supplement the above searches and ensure and the most complete CPG retrieval.
This study did not involve human subjects as only published evidence was included in the review; ethical approval from an institution was therefore not required.
Selection of CPGs for inclusion
Each title and abstract identified from the database searches was screened and selected for inclusion or exclusion in the SLR by two independent investigators based on the populations, interventions/comparators, outcomes, study design, time period, language, and geographic criteria shown in Table 4 . During both rounds of the screening process, discrepancies between the two independent reviewers were resolved through discussion, and a third investigator resolved any disagreement. Articles/documents identified by the manual search of organizational websites were screened using the same criteria. All accepted studies were required to meet all inclusion criteria and none of the exclusion criteria. Only the most recent version of organizational CPGs was included for data extraction.
Data extraction and synthesis
Information on the recommendations regarding the antipsychotic management in the acute and maintenance phases of schizophrenia and related benefits and harms was captured from the included CPGs. Each guideline was reviewed and extracted by a single researcher and the data were validated by a senior team member to ensure accuracy and completeness. Additionally, each included CPG was assessed using the Appraisal of Guidelines for Research and Evaluation II (AGREE II) tool. Following extraction and validation, results were qualitatively summarized across CPGs.
Reporting summary
Further information on research design is available in the Nature Research Reporting Summary linked to this article.
Data availability
The data that support the findings of the SLR are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Correll, C. U. & Schooler, N. R. Negative symptoms in schizophrenia: a review and clinical guide for recognition, assessment, and treatment. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 16 , 519–534 (2020).
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Kahn, R. S. et al. Schizophrenia. Nat. Rev. Dis. Prim. 1 , 15067 (2015).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Millan, M. J. et al. Altering the course of schizophrenia: progress and perspectives. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 15 , 485–515 (2016).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Huhn, M. et al. Comparative efficacy and tolerability of 32 oral antipsychotics for the acute treatment of adults with multi-episode schizophrenia: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Lancet 394 , 939–951 (2019).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Kishimoto, T., Hagi, K., Nitta, M., Kane, J. M. & Correll, C. U. Long-term effectiveness of oral second-generation antipsychotics in patients with schizophrenia and related disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis of direct head-to-head comparisons. World Psychiatry 18 , 208–224 (2019).
Leucht, S. et al. Antipsychotic drugs versus placebo for relapse prevention in schizophrenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 379 , 2063–2071 (2012).
Carbon, M. & Correll, C. U. Clinical predictors of therapeutic response to antipsychotics in schizophrenia. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 16 , 505–524 (2014).
Correll, C. U., Rubio, J. M. & Kane, J. M. What is the risk-benefit ratio of long-term antipsychotic treatment in people with schizophrenia? World Psychiatry 17 , 149–160 (2018).
Emsley, R., Chiliza, B., Asmal, L. & Harvey, B. H. The nature of relapse in schizophrenia. BMC Psychiatry 13 , 50 (2013).
Correll, C. U. & Kane, J. M. Ranking antipsychotics for efficacy and safety in schizophrenia. JAMA Psychiatry 77 , 225–226 (2020).
Kane, J. M. & Correll, C. U. Pharmacologic treatment of schizophrenia. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 12 , 345–357 (2010).
Kane, J. M., Kishimoto, T. & Correll, C. U. Non-adherence to medication in patients with psychotic disorders: epidemiology, contributing factors and management strategies. World Psychiatry 12 , 216–226 (2013).
Correll, C. U. et al. The use of long-acting injectable antipsychotics in schizophrenia: evaluating the evidence. J. Clin. Psychiatry 77 , 1–24 (2016).
Remington, G. et al. Guidelines for the pharmacotherapy of schizophrenia in adults. Can. J. Psychiatry 62 , 604–616 (2017).
American Psychiatric Association. Treatment recommendations for patients with schizophrenia. Am. J. Psychiatry 161 , 1–56 (2004).
Institute of Medicine (US) Committee to Advise the Public Health Service on Clinical Practice Guidelines, Field, M. J., & Lohr, K. N. (Eds.). Clinical Practice Guidelines: Directions for a New Program. (National Academies Press (US), 1990).
American Psychiatric Association. Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Patients With Schizophrenia , 3rd edn. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1176/appi.books.9780890424841 .
Florida Medicaid Drug Therapy Management Program. 2019–2020 Florida Best Practice Psychotherapeutic Medication Guidelines for Adults . (2020). Available at: https://floridabhcenter.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/04/2019-Psychotherapeutic-Medication-Guidelines-for-Adults-with-References_06-04-20.pdf .
Mental Health Clinical Advisory Group, Oregon Health Authority. Mental Health Care Guide for Licensed Practitioners and Mental Health Professionals. (2019). Available at: https://sharedsystems.dhsoha.state.or.us/DHSForms/Served/le7548.pdf .
Krogmann, A. et al. Keeping up with the therapeutic advances in schizophrenia: a review of novel and emerging pharmacological entities. CNS Spectr. 24 , 38–69 (2019).
Fountoulakis, K. N. et al. The report of the joint WPA/CINP workgroup on the use and usefulness of antipsychotic medication in the treatment of schizophrenia. CNS Spectr . https://doi.org/10.1017/S1092852920001546 (2020).
Leucht, S. et al. CINP Schizophrenia Guidelines . (CINP, 2013). Available at: https://www.cinp.org/resources/Documents/CINP-schizophrenia-guideline-24.5.2013-A-C-method.pdf .
Ostuzzi, G. et al. Mapping the evidence on pharmacological interventions for non-affective psychosis in humanitarian non-specialised settings: A UNHCR clinical guidance. BMC Med. 15 , 197 (2017).
Hasan, A. et al. World Federation of Societies of Biological Psychiatry (WFSBP) Guidelines for Biological Treatment of Schizophrenia, Part 1: Update 2012 on the acute treatment of schizophrenia and the management of treatment resistance. World J. Biol. Psychiatry 13 , 318–378 (2012).
Hasan, A. et al. World Federation of Societies of Biological Psychiatry (WFSBP) Guidelines for Biological Treatment of Schizophrenia, Part 2: Update 2012 on the long-term treatment of schizophrenia and management of antipsychotic-induced side effects. World J. Biol. Psychiatry 14 , 2–44 (2013).
Hasan, A. et al. World Federation of Societies of Biological Psychiatry (WFSBP) guidelines for biological treatment of schizophrenia - a short version for primary care. Int. J. Psychiatry Clin. Pract. 21 , 82–90 (2017).
Moore, T. A. et al. The Texas Medication Algorithm Project antipsychotic algorithm for schizophrenia: 2006 update. J. Clin. Psychiatry 68 , 1751–1762 (2007).
Texas Medication Algorithm Project (TMAP). Texas Medication Algorithm Project (TMAP) Procedural Manual . (2008). Available at: https://jpshealthnet.org/sites/default/files/inline-files/tmapalgorithmforschizophrenia.pdf .
American Association of Community Psychiatrists (AACP). Clinical Tips Series, Long Acting Antipsychotic Medications. (2017). Accessed at: https://drive.google.com/file/d/1unigjmjFJkqZMbaZ_ftdj8oqog49awZs/view .
Buchanan, R. W. et al. The 2009 schizophrenia PORT psychopharmacological treatment recommendations and summary statements. Schizophr. Bull. 36 , 71–93 (2010).
Kreyenbuhl, J. et al. The Schizophrenia Patient Outcomes Research Team (PORT): updated treatment recommendations 2009. Schizophr. Bull. 36 , 94–103 (2010).
New Jersey Division of Mental Health Services. Pharmacological Practice Guidelines for the Treatment of Schizophrenia . (2005). Available at: https://www.state.nj.us/humanservices/dmhs_delete/consumer/NJDMHS_Pharmacological_Practice_Guidelines762005.pdf .
Barnes, T. R. et al. Evidence-based guidelines for the pharmacological treatment of schizophrenia: updated recommendations from the British Association for Psychopharmacology. J. Psychopharmacol. 34 , 3–78 (2020).
National Institute for Health and Care Excellence (NICE). Psychosis and schizophrenia in adults: prevention and management. (2014). Available at: http://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg178 .
Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network (SIGN). Management of Schizophrenia: A National Clinical Guideline . (2013). Available at: https://www.sign.ac.uk/assets/sign131.pdf .
Verma, S. et al. Ministry of Health Clinical Practice Guidelines: Schizophrenia. Singap. Med. J. 52 , 521–526 (2011).
CAS Google Scholar
Szulc, A. et al. Recommendations for the treatment of schizophrenia with negative symptoms. Standards of pharmacotherapy by the Polish Psychiatric Association (Polskie Towarzystwo Psychiatryczne), part 1. Rekomendacje dotyczace leczenia schizofrenii z. objawami negatywnymi. Stand. farmakoterapii Polskiego Tow. Psychiatrycznego, czesc 1. 53 , 497–524 (2019).
Google Scholar
Szulc, A. et al. Recommendations for the treatment of schizophrenia with negative symptoms. Standards of pharmacotherapy by the Polish Psychiatric Association (Polskie Towarzystwo Psychiatryczne), part 2. Rekomendacje dotyczace leczenia schizofrenii z. objawami negatywnymi. Stand. farmakoterapii Polskiego Tow. Psychiatrycznego, czesc 2. 53 , 525–540 (2019).
Galletly, C. et al. Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Psychiatrists clinical practice guidelines for the management of schizophrenia and related disorders. Aust. N. Z. J. Psychiatry 50 , 410–472 (2016).
Llorca, P. M. et al. Guidelines for the use and management of long-acting injectable antipsychotics in serious mental illness. BMC Psychiatry 13 , 340 (2013).
De Masi, S. et al. The Italian guidelines for early intervention in schizophrenia: development and conclusions. Early Intervention Psychiatry 2 , 291–302 (2008).
Article Google Scholar
Barnes, T. R. Evidence-based guidelines for the pharmacological treatment of schizophrenia: recommendations from the British Association for Psychopharmacology. J. Psychopharmacol. 25 , 567–620 (2011).
Correll, C. U. et al. Efficacy of 42 pharmacologic cotreatment strategies added to antipsychotic monotherapy in schizophrenia: systematic overview and quality appraisal of the meta-analytic evidence. JAMA Psychiatry 74 , 675–684 (2017).
Galling, B. et al. Antipsychotic augmentation vs. monotherapy in schizophrenia: systematic review, meta-analysis and meta-regression analysis. World Psychiatry 16 , 77–89 (2017).
Pillinger, T. et al. Comparative effects of 18 antipsychotics on metabolic function in patients with schizophrenia, predictors of metabolic dysregulation, and association with psychopathology: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Lancet Psychiatry 7 , 64–77 (2020).
Rummel-Kluge, C. et al. Second-generation antipsychotic drugs and extrapyramidal side effects: a systematic review and meta-analysis of head-to-head comparisons. Schizophr. Bull. 38 , 167–177 (2012).
Angermeyer, M. C. & Matschinger, H. Attitude of family to neuroleptics. Psychiatr. Prax. 26 , 171–174 (1999).
CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Dibonaventura, M., Gabriel, S., Dupclay, L., Gupta, S. & Kim, E. A patient perspective of the impact of medication side effects on adherence: results of a cross-sectional nationwide survey of patients with schizophrenia. BMC Psychiatry 12 , 20 (2012).
McIntyre, R. S. Understanding needs, interactions, treatment, and expectations among individuals affected by bipolar disorder or schizophrenia: the UNITE global survey. J. Clin. Psychiatry 70 (Suppl 3), 5–11 (2009).
Tandon, R. et al. The impact on functioning of second-generation antipsychotic medication side effects for patients with schizophrenia: a worldwide, cross-sectional, web-based survey. Ann. Gen. Psychiatry 19 , 42 (2020).
Zhang, J. P. et al. Efficacy and safety of individual second-generation vs. first-generation antipsychotics in first-episode psychosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 16 , 1205–1218 (2013).
Zhu, Y. et al. Antipsychotic drugs for the acute treatment of patients with a first episode of schizophrenia: a systematic review with pairwise and network meta-analyses. Lancet Psychiatry 4 , 694–705 (2017).
Kishimoto, T. et al. Relapse prevention in schizophrenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of second-generation antipsychotics versus first-generation antipsychotics. Mol. Psychiatry 18 , 53–66 (2013).
Leucht, S. et al. Sixty years of placebo-controlled antipsychotic drug trials in acute schizophrenia: systematic review, Bayesian meta-analysis, and meta-regression of efficacy predictors. Am. J. Psychiatry 174 , 927–942 (2017).
Samara, M. T., Nikolakopoulou, A., Salanti, G. & Leucht, S. How many patients with schizophrenia do not respond to antipsychotic drugs in the short term? An analysis based on individual patient data from randomized controlled trials. Schizophr. Bull. 45 , 639–646 (2019).
Zhu, Y. et al. How well do patients with a first episode of schizophrenia respond to antipsychotics: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 27 , 835–844 (2017).
Bogers, J. P. A. M., Hambarian, G., Michiels, M., Vermeulen, J. & de Haan, L. Risk factors for psychotic relapse after dose reduction or discontinuation of antipsychotics in patients with chronic schizophrenia. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Schizophr. Bull. Open 46 , Suppl 1 S326 (2020).
Tani, H. et al. Factors associated with successful antipsychotic dose reduction in schizophrenia: a systematic review of prospective clinical trials and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Neuropsychopharmacology 45 , 887–901 (2020).
Uchida, H., Suzuki, T., Takeuchi, H., Arenovich, T. & Mamo, D. C. Low dose vs standard dose of antipsychotics for relapse prevention in schizophrenia: meta-analysis. Schizophr. Bull. 37 , 788–799 (2011).
Howes, O. D. et al. Treatment-resistant schizophrenia: treatment response and resistance in psychosis (TRRIP) working group consensus guidelines on diagnosis and terminology. Am. J. Psychiatry 174 , 216–229 (2017).
Masuda, T., Misawa, F., Takase, M., Kane, J. M. & Correll, C. U. Association with hospitalization and all-cause discontinuation among patients with schizophrenia on clozapine vs other oral second-generation antipsychotics: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. JAMA Psychiatry 76 , 1052–1062 (2019).
Siskind, D., McCartney, L., Goldschlager, R. & Kisely, S. Clozapine v. first- and second-generation antipsychotics in treatment-refractory schizophrenia: systematic review and meta-analysis. Br. J. Psychiatry 209 , 385–392 (2016).
Siskind, D., Siskind, V. & Kisely, S. Clozapine response rates among people with treatment-resistant schizophrenia: data from a systematic review and meta-analysis. Can. J. Psychiatry 62 , 772–777 (2017).
Wang, G. et al. ECT augmentation of clozapine for clozapine-resistant schizophrenia: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Psychiatr. Res. 105 , 23–32 (2018).
Tiihonen, J., Tanskanen, A. & Taipale, H. 20-year nationwide follow-up study on discontinuation of antipsychotic treatment in first-episode schizophrenia. Am. J. Psychiatry 175 , 765–773 (2018).
Taipale, H. et al. Antipsychotics and mortality in a nationwide cohort of 29,823 patients with schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res . 197 , 274–280 (2018).
Taipale, H. et al. 20-year follow-up study of physical morbidity and mortality in relationship to antipsychotic treatment in a nationwide cohort of 62,250 patients with schizophrenia (FIN20). World Psychiatry 19 , 61–68 (2020).
Carbon, M. & Correll, C. U. Thinking and acting beyond the positive: the role of the cognitive and negative symptoms in schizophrenia. CNS Spectr. 19 (Suppl 1), 38–52 (2014).
PubMed Google Scholar
Krause, M. et al. Antipsychotic drugs for patients with schizophrenia and predominant or prominent negative symptoms: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 268 , 625–639 (2018).
Kane, J. M. et al. Effect of long-acting injectable antipsychotics vs usual care on time to first hospitalization in early-phase schizophrenia: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry 77 , 1217–1224 (2020).
Schreiner, A. et al. Paliperidone palmitate versus oral antipsychotics in recently diagnosed schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 169 , 393–399 (2015).
Subotnik, K. L. et al. Long-acting injectable risperidone for relapse prevention and control of breakthrough symptoms after a recent first episode of schizophrenia. A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Psychiatry 72 , 822–829 (2015).
Tiihonen, J. et al. A nationwide cohort study of oral and depot antipsychotics after first hospitalization for schizophrenia. Am. J. Psychiatry 168 , 603–609 (2011).
Zhang, F. et al. Efficacy, safety, and impact on hospitalizations of paliperidone palmitate in recent-onset schizophrenia. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 11 , 657–668 (2015).
Kishimoto, T., Nitta, M., Borenstein, M., Kane, J. M. & Correll, C. U. Long-acting injectable versus oral antipsychotics in schizophrenia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of mirror-image studies. J. Clin. Psychiatry 74 , 957–965 (2013).
Kishimoto, T. et al. Effectiveness of long-acting injectable vs oral antipsychotics in patients with schizophrenia: a meta-analysis of prospective and retrospective cohort studies. Schizophr. Bull. 44 , 603–619 (2018).
Kishimoto, T. et al. Long-acting injectable vs oral antipsychotics for relapse prevention in schizophrenia: a meta-analysis of randomized trials. Schizophr. Bull. 40 , 192–213 (2014).
Kane, J. M., Kishimoto, T. & Correll, C. U. Assessing the comparative effectiveness of long-acting injectable vs. oral antipsychotic medications in the prevention of relapse provides a case study in comparative effectiveness research in psychiatry. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 66 , S37–41 (2013).
Kishimoto, T., Hagi, K., Kurokawa, S., Kane, J. M. & Correll, C. U. Long-acting injectable versus oral antipsychotics for the maintenance treatment of schizophrenia: a systematic review and comparative meta-analysis of randomised, cohort, and pre-post studies. Lancet Psychiatry 8 , 387–404 (2021).
Cook, D. J., Mulrow, C. D. & Haynes, R. B. Systematic reviews: synthesis of best evidence for clinical decisions. Ann. Intern. Med. 126 , 376–380 (1997).
Higgins, J. P. T. & Green, S. Cochrane Collaboration Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions . (The Cochrane Collaboration and John Wiley & Sons, Ltd, 2008).
Download references
Acknowledgements
This study received financial funding from Janssen Scientific Affairs.
Open Access funding enabled and organized by Projekt DEAL.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
The Zucker Hillside Hospital, Department of Psychiatry, Northwell Health, Glen Oaks, NY, USA
- Christoph U. Correll
Donald and Barbara Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell, Department of Psychiatry and Molecular Medicine, Hempstead, NY, USA
Charité Universitätsmedizin Berlin, Department of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, Berlin, Germany
Evidera, Waltham, MA, USA
Amber Martin & Emma Schiller
Janssen Scientific Affairs, LLC, Titusville, NJ, USA
Charmi Patel, Carmela Benson, Jennifer Kern-Sliwa & Kruti Joshi
Goulding HEOR Consulting Inc., Vancouver, BC, Canada
Rebecca Goulding
Biohaven Pharmaceuticals, New Haven, CT, USA
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
C.C., A.M., R.G., C.P., C.B., K.J., J.K.S., E.S. and E.K. contributed to the conception and the design of the study. A.M., R.G. and E.S. conducted the literature review, including screening, and extraction of the included guidelines. All authors contributed to the interpretations of the results for the review; A.M. and C.C. drafted the manuscript and all authors revised it critically for intellectual content. All authors gave their final approval of the completed manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Christoph U. Correll .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
C.C. has received personal fees from Alkermes plc, Allergan plc, Angelini Pharma, Gedeon Richter, Gerson Lehrman Group, Intra-Cellular Therapies, Inc, Janssen Pharmaceutica/Johnson & Johnson, LB Pharma International BV, H Lundbeck A/S, MedAvante-ProPhase, Medscape, Neurocrine Biosciences, Noven Pharmaceuticals, Inc, Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co, Inc, Pfizer, Inc, Recordati, Rovi, Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma, Sunovion Pharmaceuticals, Inc, Supernus Pharmaceuticals, Inc, Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited, Teva Pharmaceuticals, Acadia Pharmaceuticals, Inc, Axsome Therapeutics, Inc, Indivior, Merck & Co, Mylan NV, MedInCell, and Karuna Therapeutics and grants from Janssen Pharmaceutica, Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited, Berlin Institute of Health, the National Institute of Mental Health, Patient Centered Outcomes Research Institute, and the Thrasher Foundation outside the submitted work; receiving royalties from UpToDate; and holding stock options in LB Pharma. A.M., R.G., and E.S. were all employees of Evidera at the time the study was conducted on which the manuscript was based. C.P., C.B., K.J., J.K.S., and E.K. were all employees of Janssen Scientific Affairs, who hold stock/shares, at the time the study was conducted.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary information, reporting summary, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Correll, C.U., Martin, A., Patel, C. et al. Systematic literature review of schizophrenia clinical practice guidelines on acute and maintenance management with antipsychotics. Schizophr 8 , 5 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41537-021-00192-x
Download citation
Received : 26 February 2021
Accepted : 02 November 2021
Published : 24 February 2022
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41537-021-00192-x
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
This article is cited by
Psychosis superspectrum ii: neurobiology, treatment, and implications.
- Roman Kotov
- William T. Carpenter
- Katherine G. Jonas
Molecular Psychiatry (2024)
Sex Differences Between Female and Male Individuals in Antipsychotic Efficacy and Adverse Effects in the Treatment of Schizophrenia
- Megan Galbally
- Karen Wynter
- Susanna Every-Palmer
CNS Drugs (2024)
Antipsychotic Discontinuation through the Lens of Epistemic Injustice
- Helene Speyer
- Lene Falgaard Eplov
Community Mental Health Journal (2024)
Delphi panel to obtain clinical consensus about using long-acting injectable antipsychotics to treat first-episode and early-phase schizophrenia: treatment goals and approaches to functional recovery
- Celso Arango
- Andrea Fagiolini
BMC Psychiatry (2023)
Machine learning methods to predict outcomes of pharmacological treatment in psychosis
- Lorenzo Del Fabro
- Elena Bondi
- Paolo Brambilla
Translational Psychiatry (2023)
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
See More About
Sign up for emails based on your interests, select your interests.
Customize your JAMA Network experience by selecting one or more topics from the list below.
- Academic Medicine
- Acid Base, Electrolytes, Fluids
- Allergy and Clinical Immunology
- American Indian or Alaska Natives
- Anesthesiology
- Anticoagulation
- Art and Images in Psychiatry
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assisted Reproduction
- Bleeding and Transfusion
- Caring for the Critically Ill Patient
- Challenges in Clinical Electrocardiography
- Climate and Health
- Climate Change
- Clinical Challenge
- Clinical Decision Support
- Clinical Implications of Basic Neuroscience
- Clinical Pharmacy and Pharmacology
- Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Consensus Statements
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Critical Care Medicine
- Cultural Competency
- Dental Medicine
- Dermatology
- Diabetes and Endocrinology
- Diagnostic Test Interpretation
- Drug Development
- Electronic Health Records
- Emergency Medicine
- End of Life, Hospice, Palliative Care
- Environmental Health
- Equity, Diversity, and Inclusion
- Facial Plastic Surgery
- Gastroenterology and Hepatology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Genomics and Precision Health
- Global Health
- Guide to Statistics and Methods
- Hair Disorders
- Health Care Delivery Models
- Health Care Economics, Insurance, Payment
- Health Care Quality
- Health Care Reform
- Health Care Safety
- Health Care Workforce
- Health Disparities
- Health Inequities
- Health Policy
- Health Systems Science
- History of Medicine
- Hypertension
- Images in Neurology
- Implementation Science
- Infectious Diseases
- Innovations in Health Care Delivery
- JAMA Infographic
- Law and Medicine
- Leading Change
- Less is More
- LGBTQIA Medicine
- Lifestyle Behaviors
- Medical Coding
- Medical Devices and Equipment
- Medical Education
- Medical Education and Training
- Medical Journals and Publishing
- Mobile Health and Telemedicine
- Narrative Medicine
- Neuroscience and Psychiatry
- Notable Notes
- Nutrition, Obesity, Exercise
- Obstetrics and Gynecology
- Occupational Health
- Ophthalmology
- Orthopedics
- Otolaryngology
- Pain Medicine
- Palliative Care
- Pathology and Laboratory Medicine
- Patient Care
- Patient Information
- Performance Improvement
- Performance Measures
- Perioperative Care and Consultation
- Pharmacoeconomics
- Pharmacoepidemiology
- Pharmacogenetics
- Pharmacy and Clinical Pharmacology
- Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation
- Physical Therapy
- Physician Leadership
- Population Health
- Primary Care
- Professional Well-being
- Professionalism
- Psychiatry and Behavioral Health
- Public Health
- Pulmonary Medicine
- Regulatory Agencies
- Reproductive Health
- Research, Methods, Statistics
- Resuscitation
- Rheumatology
- Risk Management
- Scientific Discovery and the Future of Medicine
- Shared Decision Making and Communication
- Sleep Medicine
- Sports Medicine
- Stem Cell Transplantation
- Substance Use and Addiction Medicine
- Surgical Innovation
- Surgical Pearls
- Teachable Moment
- Technology and Finance
- The Art of JAMA
- The Arts and Medicine
- The Rational Clinical Examination
- Tobacco and e-Cigarettes
- Translational Medicine
- Trauma and Injury
- Treatment Adherence
- Ultrasonography
- Users' Guide to the Medical Literature
- Vaccination
- Venous Thromboembolism
- Veterans Health
- Women's Health
- Workflow and Process
- Wound Care, Infection, Healing
Get the latest research based on your areas of interest.
Others also liked.
- Download PDF
- X Facebook More LinkedIn
Giustini AJ , Schroeder AR , Axelrod DM. Trends in Views of Articles Published in 3 Leading Medical Journals During the COVID-19 Pandemic. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4(4):e216459. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.6459
Manage citations:
© 2024
- Permissions
Trends in Views of Articles Published in 3 Leading Medical Journals During the COVID-19 Pandemic
- 1 Department of Anesthesiology, Stanford University School of Medicine, Stanford, California
- 2 Department of Pediatrics, Stanford University School of Medicine, Stanford, California
The COVID-19 pandemic is changing the peer review, publication, and readership of scientific articles. 1 - 3 The scientific community has voiced concern that the focus on COVID-19 adversely affects dissemination of research into other diseases. 4 , 5 Recently, the number of article views has been recognized as a metric for article impact. 6 In this study, we sought to assess the trends in views of articles published in 3 leading medical journals during the pandemic.
Because no patients were involved in this study (only analysis of journal article reads), we did not obtain institutional review board approval or informed consent. To assess changes in views of medical scientific articles, in this cross-sectional study we examined full and PDF views of articles published by 3 widely read, English-language, general medical journals— JAMA , The New England Journal of Medicine ( NEJM ), and BMJ —from January to July of 2019 and 2020. All articles other than journal mastheads were included in data collection. Article types included research articles, educational articles, opinion, reviews, letters, erratum, and scientific news.
Views data were acquired by inspecting the metrics information for each article provided by the journal websites with the Scrapy web scraping and website parsing package version 2.3.0 (Scrapy) for Python statistical software version 3.8.3 (Python Software Foundation) with the Spyder open-source interface version 4.1.4. We first determined whether articles were COVID-19 focused and original research (yes or no). COVID-19–focused articles were defined as those that referenced COVID-19 (or a synonymous term) in the title, or whose content was judged by the primary author (A.J.G.) to be primarily pandemic related. Unclear article categorization was decided in consensus by all 3 authors. Articles were categorized as original research if they were original research articles, including meta-analyses.
We compared the views of non–COVID-19 original research articles from March 2020 (when COVID-19 attention began to mount) to July 2020 with the same period in 2019. Because of journal variation in metric reporting methods, we standardized view accrual time by summing views through the end of the month following the date of issue. Differences in median views of the 457 relevant articles were assessed with the Wilcoxon rank-sum test using R statistical software version 4.0.2 with the RStudio version 1.3.1073 interface (both from R Project for Statistical Computing). We then performed subgroup analyses on the 3 journals with a Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons, with significance set at 2-tailed P = .017. Data analysis was performed from October to December 2020.
In total, the number of views for 7528 articles were collected: 4059 articles from BMJ , 2079 from JAMA , and 1390 from NEJM . In March to July of 2020, the median (interquartile range) number of views of COVID-19 original research articles was 117 341.5 (51 114-294 8595.5) views, and the median (interquartile range) number of views of non–COVID-19 original research articles was 10 171 (5848-20 406) views. In March to July 2019, there were 258 non–COVID-19 research articles published (68 in BMJ , 97 in JAMA , and 93 in NEJM ), compared with 199 non–COVID-19 original research articles published in March to July 2020 (49 in BMJ , 70 in JAMA , and 80 in NEJM ), a decrease of 23%. Overall readership of articles between March to July 2019 and March to July 2020 increased by 557%, whereas the total number of articles published per month remained constant ( Figure 1 ). Although the total number of non–COVID-19 original research articles decreased from 2019 to 2020 ( Figure 1 B and 1 D), the median number of views of each article was not substantially different between March to July of 2019 and March to July 2020 ( Figure 2 ).
The COVID-19 pandemic has increased overall article views for major medical journals in 2020, with unprecedented views per article for COVID-19–related publications. Although the total number of published original non–COVID-19 research articles decreased during the pandemic in these 3 journals, the number of views per article has remained constant, implying that individual non–COVID-19 original research articles are receiving similar attention as before the pandemic. The pandemic may detrimentally affect the broader evidence base because fewer non–COVID-19 research articles have been published in the 3 journals studied. This work begins to address the question of how the COVID-19 pandemic has affected attention to other diseases in the medical literature. These findings may be limited by different approaches to page view reporting and variable numbers of articles published between the studied journals.
Accepted for Publication: February 26, 2021.
Published: April 1, 2021. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.6459
Open Access: This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the CC-BY License . © 2021 Giustini AJ et al. JAMA Network Open .
Corresponding Author: Andrew J. Giustini, MD, PhD, Department of Anesthesiology, Stanford University School of Medicine, 300 Pasteur Dr, Rm H3580, MC 5640, Stanford, CA 94305 ( [email protected] ).
Author Contributions: Dr Giustini had full access to all of the data in the study and takes responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis.
Concept and design: All authors.
Acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data: Giustini, Axelrod.
Drafting of the manuscript: Giustini, Axelrod.
Critical revision of the manuscript for important intellectual content: All authors.
Statistical analysis: Giustini.
Administrative, technical, or material support: Axelrod.
Supervision: Axelrod.
Conflict of Interest Disclosures: None reported.
- Register for email alerts with links to free full-text articles
- Access PDFs of free articles
- Manage your interests
- Save searches and receive search alerts
“Lord Knows What’s Being Done with My Blood!”: Black Women’s Perceptions of Biospecimen Donation for Clinical Research in the United States
- Published: 07 May 2024
Cite this article

- Kyrah K. Brown ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-7028-6791 1 ,
- Shameka Poetry Thomas ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-5225-0090 2 ,
- R. Mathew Brothers ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-3281-5277 1 &
- Yue Liao ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-9384-336X 1
59 Accesses
Explore all metrics
Black women are underrepresented in clinical research and clinical trials. Knowledge gaps lead to biased clinical practice and care. There is a small but growing body of literature on Black women’s perceptions about participation when biospecimen donation is sought by researchers. This is the first known study to investigate willingness to participate in clinical research involving biospecimen donation among Black women of reproductive age in the United States.
This cross-sectional study recruited 496 Black women (ages 18–49) from a research crowdsourcing platform. Participants completed a 46-item online survey which asked about their willingness to provide blood samples for clinical health research and reasons for their willingness or for any unwillingness. Descriptive statistics and thematic analysis method were used to analyze the data.
Less than half (44%) of participants reported willingness to provide blood samples for clinical research. The most common concerns of those expressing unwillingness to provide samples were “fear of blood sample being misused” and “distrust with the health researchers handling the samples.” We identified six qualitative themes from the analysis of participants’ open-ended responses. The most important factors include a desire for integrity and transparency in research, institutional racism contributing to mistrust, and adequate compensation and clearly defined benefits to participation.
Conclusions
The recruitment and engagement of Black women in clinical biospecimen research should involve transparent, trustworthy, and anti-racist practices and informed respect for Black women’s autonomy. There is a need to address Black women’s concerns about exploitative profits and mistrust of academic and medical institutions.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
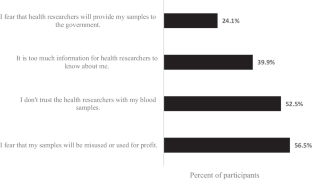
Similar content being viewed by others

Differences in preferences for models of consent for biobanks between Black and White women
Promoting inclusive recruitment: a qualitative study of black adults’ decision to participate in genetic research, biobanking in israel 2016–17; expressed perceptions versus real life enrollment, data availability.
The data presented in this study are available on reasonable request from the corresponding author.
Powell-Wiley TM, Baumer Y, Baah FO, Baez AS, Farmer N, Mahlobo CT, et al. Social determinants of cardiovascular disease. Circul Res. 2022;130:782–99.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Forrester S, Jacobs D, Zmora R, Schreiner P, Roger V, Kiefe CI. Racial differences in weathering and its associations with psychosocial stress: the CARDIA study. SSM - Popul Health. 2019;7:100319.
Article Google Scholar
Geronimus AT, Hicken M, Keene D, Bound J. Weathering and age patterns of allostatic load scores among Blacks and Whites in the United States. Am J Public Health. 2006;96:826–33.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Akins JD, Martin ZT, Patik JC, Curtis BM, Campbell JC, Olvera G, et al. Young, non-hispanic black men and women exhibit divergent peripheral and cerebral vascular reactivity. Exp Physiol. 2022;107:450–61.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Allen AM, Wang Y, Chae DH, Price MM, Powell W, Steed TC, et al. Racial discrimination, the superwoman schema, and allostatic load: exploring an integrative stress-coping model among African American women. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2019;1457:104–27.
Martin ZT, Al-daas IO, Cardenas N, Vu J, Brown KK, Brothers R. Conduit artery and forearm microvascular reactivity in Black and White females: examining the role of Greater Superwoman Schema endorsement. FASEB J. https://faseb.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1096/fasebj.2022.36.S1.R4850 .
National Cancer Institute, Division of Cancer Treatment and Diagnosis. Frequently asked questions (FAQs) [Internet]. [cited 2023 Oct 8]. https://biospecimens.cancer.gov/patientcorner/faq.asp#q2 .
Bowen DJ, Penchaszadeh VB. Special issue: enhancing minority recruitment into genetics research. Community Genet. 2008;11:189–190.
Branson RD, Davis K, Butler KL. African Americans’ participation in clinical research: importance, barriers, and solutions. Am J Surg. 2007;193:32–9. discussion 40.
Compadre AJ, Simonson ME, Gray K, Runnells G, Kadlubar S, Zorn KK. Challenges in recruiting African-American women for a breast cancer genetics study. Hered Cancer Clin Pract. 2018;16:8.
Gorelick PB, Harris Y, Burnett B, Bonecutter FJ. The recruitment triangle: reasons why African Americans enroll, refuse to enroll, or voluntarily withdraw from a clinical trial. An interim report from the African-American Antiplatelet Stroke Prevention Study (AAASPS). J Natl Med Assoc. 1998;90:141–5.
CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Hughes C, Peterson SK, Ramirez A, Gallion KJ, McDonald PG, Skinner CS, et al. Minority recruitment in hereditary breast cancer research. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2004;13:1146–55.
Spruill IJ. Enhancing recruitment of African-American families into genetic research: lessons learned from Project SuGar. J Community Genet. 2010;1:125–32.
Wujcik D, Wolff SN. Recruitment of African Americans to National Oncology Clinical Trials through a clinical trial shared resource. J Health Care Poor Underserved. 2010;21:38–50.
Ambrosone CB, Zirpoli G, Ruszczyk M, Shankar J, Hong C-C, McIlwain D, et al. Parity and breastfeeding among African-American women: differential effects on breast cancer risk by estrogen receptor status in the women’s Circle of Health Study. Cancer Causes Control. 2014;25:259–65.
Bekash A, Saini J, Fan X, Hooke J, Mural R, Shriver C, et al. Differential benign breast disease co-occurrence with cancer in Caucasian and African American women. Cancer Res. 2009;69:3066.
Conti DV, Darst BF, Moss LC, Saunders EJ, Sheng X, Chou A, et al. Trans-ancestry genome-wide association meta-analysis of prostate cancer identifies new susceptibility loci and informs genetic risk prediction. Nat Genet. 2021;53:65–75.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Manrai AK, Funke BH, Rehm HL, Olesen MS, Maron BA, Szolovits P, et al. Genetic misdiagnoses and the potential for health disparities. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:655–65.
Rebbeck TR, Bridges JFP, Mack JW, Gray SW, Trent JM, George S, et al. A framework for promoting diversity, equity, and inclusion in genetics and genomics research. JAMA Health Forum. 2022;3:e220603.
Adams-Campbell LL, Dash C, Palmer JR, Wiedemeier MV, Russell CW, Rosenberg L, et al. Predictors of biospecimen donation in the Black women’s Health Study. Cancer Causes Control. 2016;27:797–803.
Barber LE, Palmer JR, Bertrand KA, Wang C. Abstract C040: predictors of blood biospecimen provision among African American women. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2020;29:C040–040.
Radecki Breitkopf C, Williams KP, Ridgeway JL, Parker MW, Strong-Simmons A, Hayes SN, et al. Linking education to action: a program to increase research participation among African American Women. J Women’s Health. 2018;27:1242–1249.
Ridley-Merriweather KE, Head KJ. African American women’s perspectives on donating healthy breast tissue for research: implications for recruitment. Health Commun. 2017;32:1571–1580.
Smith YR, Johnson AM, Newman LA, Greene A, Johnson TRB, Rogers JL. Perceptions of clinical research participation among African American women. J Womens Health (Larchmt). 2007;16:423–8.
Sheppard VB, Hurtado-de-Mendoza A, Zheng Y-L, Wang Y, Graves KD, Lobo T, et al. Biospecimen donation among Black and White breast cancer survivors: opportunities to promote precision medicine. J Cancer Surviv. 2018;12:74–81.
Yen GP, Davey A, Ma GX. Factors that affect willingness to donate blood for the purpose of biospecimen research in the Korean American community. Biopreserv Biobank. 2015;13:107–13.
Scherr CL, Ramesh S, Marshall-Fricker C, Perera MA. A review of African Americans’ beliefs and attitudes about genomic studies: opportunities for message design. Front Genet. 2019 [cited 2021 May 30];10. https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/ https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2019.00548/full .
Liao Y, Brown KK. Usage of digital health tools and perception of mHealth intervention for physical activity and sleep in Black women. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022;19:1557.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. About chronic health diseases [Internet]. [Cited 9 September 2023]. National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion. 2022. https://www.cdc.gov/chronicdisease/about/index.htm .
Braun V, Clarke V. Thematic analysis. In: Cooper H, Camic PM, Long DL, Panter AT, Rindskopf D, Sher KJ, editors. APA handbook of research methods in psychology, vol 2: research designs: quantitative, qualitative, neuropsychological, and biological. Washington, DC, US: American Psychological Association; 2012. p. 57–71.
Chapter Google Scholar
Royal C, Baffoe-Bonnie A, Kittles R, Powell I, Bennett J, Hoke G, et al. Recruitment experience in the first phase of the African American Hereditary Prostate Cancer (AAHPC) study. Ann Epidemiol. 2000;10:S68–77.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Shavers VL, Lynch CF, Burmeister LF. Racial differences in factors that influence the willingness to participate in medical research studies. Ann Epidemiol. 2002;12:248–56.
Shavers-Hornaday VL, Lynch CF, Burmeister LF, Torner JC. Why are African Americans under-represented in medical research studies? Impediments to participation. Ethn Health. 1997;2:31–45.
Tong EK, Fung L-C, Stewart SL, Paterniti DA, Dang JHT, Chen MS Jr. Impact of a biospecimen collection seminar on willingness to donate biospecimens among Chinese Americans: results from a randomized, controlled community-based trial. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2014;23:392–401.
Raines-Milenkov A, Felini M, Baker E, Acharya R, Diese EL, Onsa S et al. Willingness of a multiethnic immigrant population to donate biospecimens for research purposes. J Immigrant Minority Health [Internet]. 2021 [cited 2022 Jan 23]; https://doi.org/10.1007/s10903-021-01241-4 .
Scott EA, Schlumpf KS, Mathew SM, Mast AE, Busch MP, Gottschall JL, et al. Biospecimen repositories: are blood donors willing to participate? Transfusion. 2010;50:1943–1950.
Dash C, Wallington SF, Muthra S, Dodson E, Mandelblatt J, Adams-Campbell LL. Disparities in knowledge and willingness to donate research biospecimens: a mixed-methods study in an underserved urban community. J Community Genet. 2014;5:329–336.
Hagiwara N, Berry-Bobovski L, Francis C, Ramsey L, Chapman RA, Albrecht TL. Unexpected findings in the exploration of African American underrepresentation in biospecimen collection and biobanks. J Canc Educ. 2014;29:580–7.
Hinton EC. Black American millennials coping with the myth of a post-racist society. Dissertation [Internet]. Minnesota, United States: Walden University; 2020 [cited 2024 Apr 3]. https://www.proquest.com/docview/2386924967/abstract/F3D47F93F35B442CPQ/1 .
Jones-Eversley S, Adedoyin AC, Robinson MA, Moore SE. Protesting Black inequality: a commentary on the Civil Rights Movement and Black Lives Matter. J Community Pract. 2017;25:309–24.
Luckerson V. Why millenials can’t afford to be colorblind. Time [Internet]. 2015 Jul 6 [cited 2024 Apr 3]; https://time.com/3944697/millennials-race-confederate-flag/ .
Merdad L, Aldakhil L, Gadi R, Assidi M, Saddick SY, Abuzenadah A, et al. Assessment of knowledge about biobanking among healthcare students and their willingness to donate biospecimens. BMC Med Ethics. 2017;18:32.
Henderson C, Scott T, Schinder B, Hager E, Friedman FS, Miller E, et al. Shifting the paradigm from participant mistrust to researcher and institutional trustworthiness: a qualitative study of researchers’ perspectives on building trustworthiness with Black communities. Community Health Equity Res Policy. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1177/0272684X221117710 .
Thomas SP. Trust also means centering Black women’s reproductive health narratives. Hastings Cent Rep. 2022;52:S18–21.
Wilson Y. Is trust enough? Anti-Black racism and the perception of Black vaccine “hesitancy.” Hastings Cent Rep. 2022;52(Suppl 1):S12–7.
PubMed Google Scholar
Dang JHT, Rodriguez EM, Luque JS, Erwin DO, Meade CD, Chen MS. Engaging diverse populations about biospecimen donation for cancer research. J Community Genet. 2014;5:313–327.
Griffith DM, Jaeger EC, Bergner EM, Stallings S, Wilkins CH. Determinants of trustworthiness to conduct medical research: findings from focus groups conducted with racially and ethnically diverse adults. J Gen Intern Med. 2020;35:2969–75.
Association of American Medical Colleges. The principles of trustworthiness [Internet]. Center For Health Justice. 2022 [cited 2022 Jun 22]. https://www.aamchealthjustice.org/resources/trustworthiness-toolkit .
Thomas SP, Amini K, Floyd KJ, Willard R, Wossenseged F, Keller M, et al. Cultivating diversity as an ethos with an anti-racism approach in the scientific enterprise. HGG Adv. 2021;2:100052.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Ford CL, Airhihenbuwa CO. The public health critical race methodology: praxis for antiracism research. Soc Sci Med. 2010;71:1390–8.
Goings TC, Belgrave FZ, Mosavel M, Evans CBR. An antiracist research framework: principles, challenges, and recommendations for dismantling racism through research. J Soc Social Work Res. 2023;14:101–28.
Ross LJ. Reproductive justice as intersectional feminist activism. Souls. 2017;19:286–314.
ten Have H. Patrão Neves M do C. Respect for autonomy. In: ten Have H, Patrão Neves M do C, editors. Dictionary of global bioethics [Internet]. Cham: Springer International Publishing; 2021 [cited 2023 Aug 2]. pp. 913–913. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-54161-3_450 .
Davis D-A. Obstetric racism: the racial politics of pregnancy, Labor, and Birthing. Med Anthropol. 2019;38:560–73.
Roberts D. Killing the Black body: race, reproduction, and the meaning of liberty. Knopf Doubleday Publishing Group; 2014.
Google Scholar
Wilson WD, Jackson FH, Harrell JR. Framework for ethical community engagement (ECE) with underserved populations in the rural south: a help for bioethics and healthcare promotion. J Health Care Poor Underserved. 2019;30:91–104.
Erwin DO, Moysich K, Kiviniemi MT, Saad-Harfouche FG, Davis W, Clark-Hargrave N, et al. Community-based partnership to identify keys to biospecimen research participation. J Canc Educ. 2013;28:43–51.
Veseli B, Sandner S, Studte S, Clement M. The impact of COVID-19 on blood donations. PLoS ONE. 2022;17:e0265171.
Behar-Horenstein L, Warren R, Setiawan VW, Perkins C, Schmittgen TD. Enhancing African American participation in biospecimens: a case in point for pancreatic cancer. CHD [Internet]. 2020 [cited 2021 May 30]; Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8294622/ .
Beskow LM. Lessons from HeLa cells: the ethics and policy of biospecimens. Annu Rev Genom Hum Genet. 2016;17:395–417.
Beskow LM, Friedman JY, Hardy NC, Lin L, Weinfurt KP. Developing a simplified consent form for biobanking. PLoS ONE. 2010;5:e13302.
Clark US, Hurd YL. Addressing racism and disparities in the biomedical sciences. Nat Hum Behav. 2020;4:774–7.
Flory J, Emanuel E. Interventions to improve research participants’ understanding in informed consent for research: a systematic review. JAMA. 2004;292:1593–601.
Kim EJ, Kim SH. Simplification improves understanding of informed consent information in clinical trials regardless of health literacy level. Clin Trails. 2015;12:232–6.
Page SA, Manhas KP, Muruve DA. A survey of patient perspectives on the research use of health information and biospecimens. BMC Med Ethics. 2016;17:48.
Spector-Bagdady K. Hospitals should act now to notify patients about research use of their data and biospecimens. Nat Med. 2020;26:306–308.
Rodriguez EM, Saad-Harfouche FG, Miller A, Mahoney MC, Ambrosone CB, Morrison CD, et al. Engaging diverse populations in biospecimen donation: results from the Hoy Y Mañana study. J Community Genet. 2016;7:271–277.
Download references
This research study was supported by startup funds awarded to Dr. Yue Liao from the University of Texas at Arlington.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Kinesiology, University of Texas at Arlington, 500 W. Nedderman Drive, Arlington, TX, 76019, USA
Kyrah K. Brown, R. Mathew Brothers & Yue Liao
School of Public Health, Harvard University, Boston, MA, USA
Shameka Poetry Thomas
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Conceptualization, K.K.B and Y.L.; methodology, Y.L. and K.K.B.; formal analysis, K.K.B and Y.L.; writing—original draft preparation, K.K.B.; writing—review and editing, Y.L., S.P.T., R.M.B; funding acquisition, Y.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Kyrah K. Brown .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics Approval
This study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Review Board of the University of Texas at Arlington (protocol number 2021−0207) on 1 February 2021.
Consent to Participate
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Brown, K.K., Thomas, S.P., Brothers, R.M. et al. “Lord Knows What’s Being Done with My Blood!”: Black Women’s Perceptions of Biospecimen Donation for Clinical Research in the United States. J. Racial and Ethnic Health Disparities (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40615-024-02015-y
Download citation
Received : 05 November 2023
Revised : 06 April 2024
Accepted : 28 April 2024
Published : 07 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s40615-024-02015-y
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Biospecimen
- Patient preference
- Black or African American
- Health inequities
- Women’s health
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
- Search Menu
- Advance articles
- Digital Collections
- Author Guidelines
- Submission Site
- Open Access Policy
- Self-Archiving Policy
- About the ASBMR
- Editorial Board
- Journals on Oxford Academic
- Books on Oxford Academic
Article Contents
Lay summary, effect of abdominal tissue thickness on trabecular bone score and fracture risk in adults with diabetes: the manitoba bmd registry.
- Article contents
- Figures & tables
- Supplementary Data
William D Leslie, Neil Binkley, John T Schousboe, Barbara C Silva, Didier Hans, Effect of Abdominal Tissue Thickness on Trabecular Bone Score and Fracture Risk in Adults With Diabetes: The Manitoba BMD Registry, Journal of Bone and Mineral Research , 2024;, zjae073, https://doi.org/10.1093/jbmr/zjae073
- Permissions Icon Permissions
Individuals with type 2 diabetes have lower trabecular bone score (TBS) and increased fracture risk despite higher bone mineral density (BMD). However, measures of trabecular microarchitecture from high resolution peripheral computed tomography (HRpQCT) are not lower in type 2 diabetes. We hypothesized that confounding effects of abdominal tissue thickness may explain this discrepancy, since central obesity is a risk factor for diabetes and also artifactually lowers TBS. This hypothesis was tested in individuals aged 40 years and older from a large DXA registry, stratified by sex and diabetes status. When DXA-measured abdominal tissue thickness was not included as a covariate, men without diabetes had lower TBS than women without diabetes (mean difference -0.074, p<0.001). TBS was lower in women with versus without diabetes (mean difference -0.037, p<0.001), and men with versus without diabetes (mean difference -0.007, p=0.042). When adjusted for tissue thickness these findings reversed, and TBS became greater in men versus women without diabetes (mean difference +0.053, p<0.001), in women with versus without diabetes (mean difference +0.008, p<0.001) and in men with versus without diabetes (mean difference +0.014, p<0.001). During mean 8.7 years observation, incident major osteoporotic fractures were seen in 7048 (9.6%). Adjusted for multiple covariates except tissue thickness, TBS predicted fracture in all subgroups with no significant diabetes interaction. When further adjusted for tissue thickness, HR per SD lower TBS remained significant and even increased slightly. In conclusion, TBS predicts fractures independent of other clinical risk factors in both women and men, with and without diabetes. Excess abdominal tissue thickness in men and individuals with type 2 diabetes may artifactually lower TBS using the current algorithm, which reverses after accounting for tissue thickness. This supports ongoing efforts to update the TBS algorithm to directly account for the effects of abdominal tissue thickness for improved fracture risk prediction.
Individuals with type 2 diabetes are at increased fracture risk despite having higher bone mineral density (BMD). Previous studies suggest that trabecular bone score (TBS), a measure of bone derived from spine DXA images that can be used to assess fracture risk in addition to BMD, may be lower in individuals with type 2 diabetes. However, TBS is artificially lowered by greater abdominal obesity. We showed that abdominal obesity explained the lower TBS measurements that were seen in individuals with type 2 diabetes. However, even when we considered the effect of abdominal obesity, TBS was still able to predict major fractures in both women and men, with and without diabetes.
Supplementary data
Email alerts, related articles in.
- Google Scholar
Citing articles via
- Recommend to your Library
- Advertising & Corporate Services
- Journals Career Network
Affiliations
- Online ISSN 1523-4681
- Print ISSN 0884-0431
- Copyright © 2024 American Society for Bone and Mineral Research
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.

Artificial Intelligence Uncertainty Quantification in Radiotherapy Applications - A Scoping Review
- Find this author on Google Scholar
- Find this author on PubMed
- Search for this author on this site
- ORCID record for Kareem A. Wahid
- For correspondence: [email protected]
- ORCID record for Amy C Moreno
- ORCID record for Clifton David Fuller
- Info/History
- Preview PDF
Background/purpose: The use of artificial intelligence (AI) in radiotherapy (RT) is expanding rapidly. However, there exists a notable lack of clinician trust in AI models, underscoring the need for effective uncertainty quantification (UQ) methods. The purpose of this study was to scope existing literature related to UQ in RT, identify areas of improvement, and determine future directions. Methods: We followed the PRISMA-ScR scoping review reporting guidelines. We utilized the population (human cancer patients), concept (utilization of AI UQ), context (radiotherapy applications) framework to structure our search and screening process. We conducted a systematic search spanning seven databases, supplemented by manual curation, up to January 2024. Our search yielded a total of 8980 articles for initial review. Manuscript screening and data extraction was performed in Covidence. Data extraction categories included general study characteristics, RT characteristics, AI characteristics, and UQ characteristics. Results: We identified 56 articles published from 2015-2024. 10 domains of RT applications were represented; most studies evaluated auto-contouring (50%), followed by image-synthesis (13%), and multiple applications simultaneously (11%). 12 disease sites were represented, with head and neck cancer being the most common disease site independent of application space (32%). Imaging data was used in 91% of studies, while only 13% incorporated RT dose information. Most studies focused on failure detection as the main application of UQ (60%), with Monte Carlo dropout being the most commonly implemented UQ method (32%) followed by ensembling (16%). 55% of studies did not share code or datasets. Conclusion: Our review revealed a lack of diversity in UQ for RT applications beyond auto-contouring. Moreover, there was a clear need to study additional UQ methods, such as conformal prediction. Our results may incentivize the development of guidelines for reporting and implementation of UQ in RT.
Competing Interest Statement
KAW serves as an Editorial Board Member for Physics and Imaging in Radiation Oncology. CDF has received travel, speaker honoraria and/or registration fee waiver unrelated to this project from: The American Association for Physicists in Medicine; the University of Alabama-Birmingham; The American Society for Clinical Oncology; The Royal Australian and New Zealand College of Radiologists; The American Society for Radiation Oncology; The Radiological Society of North America; and The European Society for Radiation Oncology.
Funding Statement
KAW was supported by an Image Guided Cancer Therapy (IGCT) T32 Training Program Fellowship from T32CA261856. ZYKs time was supported by a doctoral fellowship from the Cancer Prevention Research Institute of Texas grant #RP210042. MAN receives funding from NIH National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research (NIDCR) Grant (R03DE033550). CDF received/receives unrelated funding and salary support from: NIH National Institute of Dental and Craniofacial Research (NIDCR) Academic Industrial Partnership Grant (R01DE028290) and the Administrative Supplement to Support Collaborations to Improve AIML-Readiness of NIH-Supported Data (R01DE028290-04S2); NIDCR Establishing Outcome Measures for Clinical Studies of Oral and Craniofacial Diseases and Conditions award (R01DE025248); NSF/NIH Interagency Smart and Connected Health (SCH) Program (R01CA257814); NIH National Institute of Biomedical Imaging and Bioengineering (NIBIB) Research Education Programs for Residents and Clinical Fellows Grant (R25EB025787); NIH NIDCR Exploratory/Developmental Research Grant Program (R21DE031082); NIH/NCI Cancer Center Support Grant (CCSG) Pilot Research Program Award from the UT MD Anderson CCSG Radiation Oncology and Cancer Imaging Program (P30CA016672); Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCS-1609-36195) sub-award from Princess Margaret Hospital; National Science Foundation (NSF) Division of Civil, Mechanical, and Manufacturing Innovation (CMMI) grant (NSF 1933369). CDF receives grant and infrastructure support from MD Anderson Cancer Center via: the Charles and Daneen Stiefel Center for Head and Neck Cancer Oropharyngeal Cancer Research Program; the Program in Image-guided Cancer Therapy; and the NIH/NCI Cancer Center Support Grant (CCSG) Radiation Oncology and Cancer Imaging Program (P30CA016672). ACM received/receives funding and salary support from: NIDCR (K01DE030524, R21DE031082), the NIH National Cancer Institute (K12CA088084), and the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center Charles and Daneen Stiefel Center for Head and Neck Cancer Oropharyngeal Cancer Research Program. DF was supported by R01CA195524 and NSF-2111147. Disclaimer: The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the funders.
Author Declarations
I confirm all relevant ethical guidelines have been followed, and any necessary IRB and/or ethics committee approvals have been obtained.
I confirm that all necessary patient/participant consent has been obtained and the appropriate institutional forms have been archived, and that any patient/participant/sample identifiers included were not known to anyone (e.g., hospital staff, patients or participants themselves) outside the research group so cannot be used to identify individuals.
I understand that all clinical trials and any other prospective interventional studies must be registered with an ICMJE-approved registry, such as ClinicalTrials.gov. I confirm that any such study reported in the manuscript has been registered and the trial registration ID is provided (note: if posting a prospective study registered retrospectively, please provide a statement in the trial ID field explaining why the study was not registered in advance).
I have followed all appropriate research reporting guidelines, such as any relevant EQUATOR Network research reporting checklist(s) and other pertinent material, if applicable.
Data Availability
A CSV file containing the final studies and corresponding extracted data for this scoping review are made publicly available through Figshare (doi: 10.6084/m9.figshare.25535017). All Python code used in the analysis can be found on Github (URL: https://github.com/kwahid/RT_UQ_scoping_review/tree/main). Data will be private until formal manuscript acceptance in journal.
View the discussion thread.
Thank you for your interest in spreading the word about medRxiv.
NOTE: Your email address is requested solely to identify you as the sender of this article.

Citation Manager Formats
- EndNote (tagged)
- EndNote 8 (xml)
- RefWorks Tagged
- Ref Manager
- Tweet Widget
- Facebook Like
- Google Plus One
- Addiction Medicine (323)
- Allergy and Immunology (627)
- Anesthesia (163)
- Cardiovascular Medicine (2363)
- Dentistry and Oral Medicine (287)
- Dermatology (206)
- Emergency Medicine (378)
- Endocrinology (including Diabetes Mellitus and Metabolic Disease) (833)
- Epidemiology (11755)
- Forensic Medicine (10)
- Gastroenterology (701)
- Genetic and Genomic Medicine (3720)
- Geriatric Medicine (348)
- Health Economics (632)
- Health Informatics (2387)
- Health Policy (929)
- Health Systems and Quality Improvement (894)
- Hematology (340)
- HIV/AIDS (780)
- Infectious Diseases (except HIV/AIDS) (13298)
- Intensive Care and Critical Care Medicine (767)
- Medical Education (365)
- Medical Ethics (104)
- Nephrology (398)
- Neurology (3481)
- Nursing (197)
- Nutrition (522)
- Obstetrics and Gynecology (672)
- Occupational and Environmental Health (661)
- Oncology (1817)
- Ophthalmology (535)
- Orthopedics (218)
- Otolaryngology (286)
- Pain Medicine (232)
- Palliative Medicine (66)
- Pathology (445)
- Pediatrics (1030)
- Pharmacology and Therapeutics (426)
- Primary Care Research (418)
- Psychiatry and Clinical Psychology (3167)
- Public and Global Health (6128)
- Radiology and Imaging (1274)
- Rehabilitation Medicine and Physical Therapy (743)
- Respiratory Medicine (825)
- Rheumatology (379)
- Sexual and Reproductive Health (372)
- Sports Medicine (322)
- Surgery (400)
- Toxicology (50)
- Transplantation (171)
- Urology (145)

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Clinical research is an alternative terminology used to describe medical research. Clinical research involves people, and it is generally carried out to evaluate the efficacy of a therapeutic drug, a medical/surgical procedure, or a device as a part of treatment and patient management. ... [Google Scholar] 7. Bayesian adaptive clinical trial ...
Clinical Trials is dedicated to advancing knowledge on the design and conduct of clinical trials related research methodologies. Covering the design, conduct, analysis, synthesis and evaluation of key methodologies, the journal remains on … | View full journal description. This journal is a member of the Committee on Publication Ethics (COPE).
The New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM) is a weekly general medical journal that publishes new medical research and review articles, and editorial opinion on a wide variety of topics of ...
European network established to promote evidence based clinical research, particularly the need to use systematic reviews when planning new studies and when placing new results in context. ... Researchers' declaration of interests should be required by all academic institutions, funders and journals. The Open Research and Contributor ID ...
We are rapidly moving toward a world in which broad sharing of participant-level clinical trial data is the norm. 1-4 The European Medicines Agency has implemented a policy to expand public access ...
The COVID-19 pandemic made "clinical trials" a household phrase, highlighting the critical value of clinical research in creating vaccines and treatments and demonstrating the need for large-scale, well-designed, and rapidly deployed clinical trials to address the public health emergency.
COVID-19 has had negative repercussions on the entire global population. Despite there being a common goal that should have unified resources and efforts, there have been an overwhelmingly large number of clinical trials that have been registered that are of questionable methodological quality. As the final paper of this Series, we discuss how the medical research community has responded to ...
Assessing research impact in academic clinical medicine: a study using Research Excellence Framework pilot impact indicators. BMC Health Serv Res. 2012;12. pmid:23259467 . View Article PubMed/NCBI Google Scholar 17. Kuruvilla S, Mays N, Walt G. Describing the impact of health services and policy research. ...
Although clinical supervision is considered to be a major component of the development and maintenance of psychotherapeutic competencies, and despite an increase in supervision research, the empirical evidence on the topic remains sparse. Because most previous reviews lack methodological rigor, we aimed to review the status and quality of the empirical literature on clinical supervision, and ...
Reports commissioned by a government agency can have more influence than scholarly articles because the agency can often enact the recommendations into policy. ... biomedical research, clinical ...
August 3, 2023. It is time for a measurement-based care professional practice guideline in psychology. from Psychotherapy. July 31, 2023. Methodological and quantitative issues in the study of personality pathology. from Personality Disorders: Theory, Research, and Treatment. April 26, 2023.
Clinical practice guidelines (CPGs) translate evidence into recommendations to improve patient care and outcomes. To provide an overview of schizophrenia CPGs, we conducted a systematic literature ...
Clinical Nursing Research (CNR) is a leading international nursing journal, published eight times a year.CNR aims to publish the best available evidence from multidisciplinary teams, with the goal of reporting clinically applicable nursing science and phenomena of interest to nursing. Part of CNR's mission is to bring to light clinically applicable solutions to some of the most complex ...
Google Scholar provides a simple way to broadly search for scholarly literature. Search across a wide variety of disciplines and sources: articles, theses, books, abstracts and court opinions. Advanced search. Find articles. with all of the words. with the exact phrase. with at least one of the words. without the ...
Further offsetting clinical workload relative to dedicated research time remains a challenge. The experience and success at this academic medical center suggest it is feasible to develop a robust, sustainable clinical pharmacy department research program.
Abstract Objective: Based on a single intake interview, mental health clinicians must distill their assessment to brief statements reflecting essential information. We explored how clinicians organize and prioritize the clinical information they collect during the initial assessment of their clients. Method: We conducted in-depth semistructured interviews with a convenience sample of 38 ...
In total, the number of views for 7528 articles were collected: 4059 articles from BMJ, 2079 from JAMA, and 1390 from NEJM.In March to July of 2020, the median (interquartile range) number of views of COVID-19 original research articles was 117 341.5 (51 114-294 8595.5) views, and the median (interquartile range) number of views of non-COVID-19 original research articles was 10 171 (5848-20 ...
Purpose Black women are underrepresented in clinical research and clinical trials. Knowledge gaps lead to biased clinical practice and care. There is a small but growing body of literature on Black women's perceptions about participation when biospecimen donation is sought by researchers. This is the first known study to investigate willingness to participate in clinical research involving ...
In conclusion, TBS predicts fractures independent of other clinical risk factors in both women and men, with and without diabetes. Excess abdominal tissue thickness in men and individuals with type 2 diabetes may artifactually lower TBS using the current algorithm, which reverses after accounting for tissue thickness.
Background/purpose: The use of artificial intelligence (AI) in radiotherapy (RT) is expanding rapidly. However, there exists a notable lack of clinician trust in AI models, underscoring the need for effective uncertainty quantification (UQ) methods. The purpose of this study was to scope existing literature related to UQ in RT, identify areas of improvement, and determine future directions.
Deidre Grant MSN, RN AHN-BC worked on Maimonides' widely-recognized care partner program that helps patients during treatment and post-discharge. Arshia Sandozi, DO, MPH studied whether vaginal ...