
How To Write The Results/Findings Chapter
For quantitative studies (dissertations & theses).
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewed By: Kerryn Warren (PhD) | July 2021
So, you’ve completed your quantitative data analysis and it’s time to report on your findings. But where do you start? In this post, we’ll walk you through the results chapter (also called the findings or analysis chapter), step by step, so that you can craft this section of your dissertation or thesis with confidence. If you’re looking for information regarding the results chapter for qualitative studies, you can find that here .
Overview: Quantitative Results Chapter
- What exactly the results chapter is
- What you need to include in your chapter
- How to structure the chapter
- Tips and tricks for writing a top-notch chapter
- Free results chapter template
What exactly is the results chapter?
The results chapter (also referred to as the findings or analysis chapter) is one of the most important chapters of your dissertation or thesis because it shows the reader what you’ve found in terms of the quantitative data you’ve collected. It presents the data using a clear text narrative, supported by tables, graphs and charts. In doing so, it also highlights any potential issues (such as outliers or unusual findings) you’ve come across.
But how’s that different from the discussion chapter?
Well, in the results chapter, you only present your statistical findings. Only the numbers, so to speak – no more, no less. Contrasted to this, in the discussion chapter , you interpret your findings and link them to prior research (i.e. your literature review), as well as your research objectives and research questions . In other words, the results chapter presents and describes the data, while the discussion chapter interprets the data.
Let’s look at an example.
In your results chapter, you may have a plot that shows how respondents to a survey responded: the numbers of respondents per category, for instance. You may also state whether this supports a hypothesis by using a p-value from a statistical test. But it is only in the discussion chapter where you will say why this is relevant or how it compares with the literature or the broader picture. So, in your results chapter, make sure that you don’t present anything other than the hard facts – this is not the place for subjectivity.
It’s worth mentioning that some universities prefer you to combine the results and discussion chapters. Even so, it is good practice to separate the results and discussion elements within the chapter, as this ensures your findings are fully described. Typically, though, the results and discussion chapters are split up in quantitative studies. If you’re unsure, chat with your research supervisor or chair to find out what their preference is.

What should you include in the results chapter?
Following your analysis, it’s likely you’ll have far more data than are necessary to include in your chapter. In all likelihood, you’ll have a mountain of SPSS or R output data, and it’s your job to decide what’s most relevant. You’ll need to cut through the noise and focus on the data that matters.
This doesn’t mean that those analyses were a waste of time – on the contrary, those analyses ensure that you have a good understanding of your dataset and how to interpret it. However, that doesn’t mean your reader or examiner needs to see the 165 histograms you created! Relevance is key.
How do I decide what’s relevant?
At this point, it can be difficult to strike a balance between what is and isn’t important. But the most important thing is to ensure your results reflect and align with the purpose of your study . So, you need to revisit your research aims, objectives and research questions and use these as a litmus test for relevance. Make sure that you refer back to these constantly when writing up your chapter so that you stay on track.

As a general guide, your results chapter will typically include the following:
- Some demographic data about your sample
- Reliability tests (if you used measurement scales)
- Descriptive statistics
- Inferential statistics (if your research objectives and questions require these)
- Hypothesis tests (again, if your research objectives and questions require these)
We’ll discuss each of these points in more detail in the next section.
Importantly, your results chapter needs to lay the foundation for your discussion chapter . This means that, in your results chapter, you need to include all the data that you will use as the basis for your interpretation in the discussion chapter.
For example, if you plan to highlight the strong relationship between Variable X and Variable Y in your discussion chapter, you need to present the respective analysis in your results chapter – perhaps a correlation or regression analysis.
Need a helping hand?
How do I write the results chapter?
There are multiple steps involved in writing up the results chapter for your quantitative research. The exact number of steps applicable to you will vary from study to study and will depend on the nature of the research aims, objectives and research questions . However, we’ll outline the generic steps below.
Step 1 – Revisit your research questions
The first step in writing your results chapter is to revisit your research objectives and research questions . These will be (or at least, should be!) the driving force behind your results and discussion chapters, so you need to review them and then ask yourself which statistical analyses and tests (from your mountain of data) would specifically help you address these . For each research objective and research question, list the specific piece (or pieces) of analysis that address it.
At this stage, it’s also useful to think about the key points that you want to raise in your discussion chapter and note these down so that you have a clear reminder of which data points and analyses you want to highlight in the results chapter. Again, list your points and then list the specific piece of analysis that addresses each point.
Next, you should draw up a rough outline of how you plan to structure your chapter . Which analyses and statistical tests will you present and in what order? We’ll discuss the “standard structure” in more detail later, but it’s worth mentioning now that it’s always useful to draw up a rough outline before you start writing (this advice applies to any chapter).
Step 2 – Craft an overview introduction
As with all chapters in your dissertation or thesis, you should start your quantitative results chapter by providing a brief overview of what you’ll do in the chapter and why . For example, you’d explain that you will start by presenting demographic data to understand the representativeness of the sample, before moving onto X, Y and Z.
This section shouldn’t be lengthy – a paragraph or two maximum. Also, it’s a good idea to weave the research questions into this section so that there’s a golden thread that runs through the document.

Step 3 – Present the sample demographic data
The first set of data that you’ll present is an overview of the sample demographics – in other words, the demographics of your respondents.
For example:
- What age range are they?
- How is gender distributed?
- How is ethnicity distributed?
- What areas do the participants live in?
The purpose of this is to assess how representative the sample is of the broader population. This is important for the sake of the generalisability of the results. If your sample is not representative of the population, you will not be able to generalise your findings. This is not necessarily the end of the world, but it is a limitation you’ll need to acknowledge.
Of course, to make this representativeness assessment, you’ll need to have a clear view of the demographics of the population. So, make sure that you design your survey to capture the correct demographic information that you will compare your sample to.
But what if I’m not interested in generalisability?
Well, even if your purpose is not necessarily to extrapolate your findings to the broader population, understanding your sample will allow you to interpret your findings appropriately, considering who responded. In other words, it will help you contextualise your findings . For example, if 80% of your sample was aged over 65, this may be a significant contextual factor to consider when interpreting the data. Therefore, it’s important to understand and present the demographic data.
Step 4 – Review composite measures and the data “shape”.
Before you undertake any statistical analysis, you’ll need to do some checks to ensure that your data are suitable for the analysis methods and techniques you plan to use. If you try to analyse data that doesn’t meet the assumptions of a specific statistical technique, your results will be largely meaningless. Therefore, you may need to show that the methods and techniques you’ll use are “allowed”.
Most commonly, there are two areas you need to pay attention to:
#1: Composite measures
The first is when you have multiple scale-based measures that combine to capture one construct – this is called a composite measure . For example, you may have four Likert scale-based measures that (should) all measure the same thing, but in different ways. In other words, in a survey, these four scales should all receive similar ratings. This is called “ internal consistency ”.
Internal consistency is not guaranteed though (especially if you developed the measures yourself), so you need to assess the reliability of each composite measure using a test. Typically, Cronbach’s Alpha is a common test used to assess internal consistency – i.e., to show that the items you’re combining are more or less saying the same thing. A high alpha score means that your measure is internally consistent. A low alpha score means you may need to consider scrapping one or more of the measures.
#2: Data shape
The second matter that you should address early on in your results chapter is data shape. In other words, you need to assess whether the data in your set are symmetrical (i.e. normally distributed) or not, as this will directly impact what type of analyses you can use. For many common inferential tests such as T-tests or ANOVAs (we’ll discuss these a bit later), your data needs to be normally distributed. If it’s not, you’ll need to adjust your strategy and use alternative tests.
To assess the shape of the data, you’ll usually assess a variety of descriptive statistics (such as the mean, median and skewness), which is what we’ll look at next.

Step 5 – Present the descriptive statistics
Now that you’ve laid the foundation by discussing the representativeness of your sample, as well as the reliability of your measures and the shape of your data, you can get started with the actual statistical analysis. The first step is to present the descriptive statistics for your variables.
For scaled data, this usually includes statistics such as:
- The mean – this is simply the mathematical average of a range of numbers.
- The median – this is the midpoint in a range of numbers when the numbers are arranged in order.
- The mode – this is the most commonly repeated number in the data set.
- Standard deviation – this metric indicates how dispersed a range of numbers is. In other words, how close all the numbers are to the mean (the average).
- Skewness – this indicates how symmetrical a range of numbers is. In other words, do they tend to cluster into a smooth bell curve shape in the middle of the graph (this is called a normal or parametric distribution), or do they lean to the left or right (this is called a non-normal or non-parametric distribution).
- Kurtosis – this metric indicates whether the data are heavily or lightly-tailed, relative to the normal distribution. In other words, how peaked or flat the distribution is.
A large table that indicates all the above for multiple variables can be a very effective way to present your data economically. You can also use colour coding to help make the data more easily digestible.
For categorical data, where you show the percentage of people who chose or fit into a category, for instance, you can either just plain describe the percentages or numbers of people who responded to something or use graphs and charts (such as bar graphs and pie charts) to present your data in this section of the chapter.
When using figures, make sure that you label them simply and clearly , so that your reader can easily understand them. There’s nothing more frustrating than a graph that’s missing axis labels! Keep in mind that although you’ll be presenting charts and graphs, your text content needs to present a clear narrative that can stand on its own. In other words, don’t rely purely on your figures and tables to convey your key points: highlight the crucial trends and values in the text. Figures and tables should complement the writing, not carry it .
Depending on your research aims, objectives and research questions, you may stop your analysis at this point (i.e. descriptive statistics). However, if your study requires inferential statistics, then it’s time to deep dive into those .

Step 6 – Present the inferential statistics
Inferential statistics are used to make generalisations about a population , whereas descriptive statistics focus purely on the sample . Inferential statistical techniques, broadly speaking, can be broken down into two groups .
First, there are those that compare measurements between groups , such as t-tests (which measure differences between two groups) and ANOVAs (which measure differences between multiple groups). Second, there are techniques that assess the relationships between variables , such as correlation analysis and regression analysis. Within each of these, some tests can be used for normally distributed (parametric) data and some tests are designed specifically for use on non-parametric data.
There are a seemingly endless number of tests that you can use to crunch your data, so it’s easy to run down a rabbit hole and end up with piles of test data. Ultimately, the most important thing is to make sure that you adopt the tests and techniques that allow you to achieve your research objectives and answer your research questions .
In this section of the results chapter, you should try to make use of figures and visual components as effectively as possible. For example, if you present a correlation table, use colour coding to highlight the significance of the correlation values, or scatterplots to visually demonstrate what the trend is. The easier you make it for your reader to digest your findings, the more effectively you’ll be able to make your arguments in the next chapter.

Step 7 – Test your hypotheses
If your study requires it, the next stage is hypothesis testing. A hypothesis is a statement , often indicating a difference between groups or relationship between variables, that can be supported or rejected by a statistical test. However, not all studies will involve hypotheses (again, it depends on the research objectives), so don’t feel like you “must” present and test hypotheses just because you’re undertaking quantitative research.
The basic process for hypothesis testing is as follows:
- Specify your null hypothesis (for example, “The chemical psilocybin has no effect on time perception).
- Specify your alternative hypothesis (e.g., “The chemical psilocybin has an effect on time perception)
- Set your significance level (this is usually 0.05)
- Calculate your statistics and find your p-value (e.g., p=0.01)
- Draw your conclusions (e.g., “The chemical psilocybin does have an effect on time perception”)
Finally, if the aim of your study is to develop and test a conceptual framework , this is the time to present it, following the testing of your hypotheses. While you don’t need to develop or discuss these findings further in the results chapter, indicating whether the tests (and their p-values) support or reject the hypotheses is crucial.
Step 8 – Provide a chapter summary
To wrap up your results chapter and transition to the discussion chapter, you should provide a brief summary of the key findings . “Brief” is the keyword here – much like the chapter introduction, this shouldn’t be lengthy – a paragraph or two maximum. Highlight the findings most relevant to your research objectives and research questions, and wrap it up.
Some final thoughts, tips and tricks
Now that you’ve got the essentials down, here are a few tips and tricks to make your quantitative results chapter shine:
- When writing your results chapter, report your findings in the past tense . You’re talking about what you’ve found in your data, not what you are currently looking for or trying to find.
- Structure your results chapter systematically and sequentially . If you had two experiments where findings from the one generated inputs into the other, report on them in order.
- Make your own tables and graphs rather than copying and pasting them from statistical analysis programmes like SPSS. Check out the DataIsBeautiful reddit for some inspiration.
- Once you’re done writing, review your work to make sure that you have provided enough information to answer your research questions , but also that you didn’t include superfluous information.
If you’ve got any questions about writing up the quantitative results chapter, please leave a comment below. If you’d like 1-on-1 assistance with your quantitative analysis and discussion, check out our hands-on coaching service , or book a free consultation with a friendly coach.

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

Thank you. I will try my best to write my results.
Awesome content 👏🏾
this was great explaination
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
When you choose to publish with PLOS, your research makes an impact. Make your work accessible to all, without restrictions, and accelerate scientific discovery with options like preprints and published peer review that make your work more Open.
- PLOS Biology
- PLOS Climate
- PLOS Complex Systems
- PLOS Computational Biology
- PLOS Digital Health
- PLOS Genetics
- PLOS Global Public Health
- PLOS Medicine
- PLOS Mental Health
- PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases
- PLOS Pathogens
- PLOS Sustainability and Transformation
- PLOS Collections
- How to Write Discussions and Conclusions

The discussion section contains the results and outcomes of a study. An effective discussion informs readers what can be learned from your experiment and provides context for the results.
What makes an effective discussion?
When you’re ready to write your discussion, you’ve already introduced the purpose of your study and provided an in-depth description of the methodology. The discussion informs readers about the larger implications of your study based on the results. Highlighting these implications while not overstating the findings can be challenging, especially when you’re submitting to a journal that selects articles based on novelty or potential impact. Regardless of what journal you are submitting to, the discussion section always serves the same purpose: concluding what your study results actually mean.
A successful discussion section puts your findings in context. It should include:
- the results of your research,
- a discussion of related research, and
- a comparison between your results and initial hypothesis.
Tip: Not all journals share the same naming conventions.
You can apply the advice in this article to the conclusion, results or discussion sections of your manuscript.
Our Early Career Researcher community tells us that the conclusion is often considered the most difficult aspect of a manuscript to write. To help, this guide provides questions to ask yourself, a basic structure to model your discussion off of and examples from published manuscripts.
Questions to ask yourself:
- Was my hypothesis correct?
- If my hypothesis is partially correct or entirely different, what can be learned from the results?
- How do the conclusions reshape or add onto the existing knowledge in the field? What does previous research say about the topic?
- Why are the results important or relevant to your audience? Do they add further evidence to a scientific consensus or disprove prior studies?
- How can future research build on these observations? What are the key experiments that must be done?
- What is the “take-home” message you want your reader to leave with?
How to structure a discussion
Trying to fit a complete discussion into a single paragraph can add unnecessary stress to the writing process. If possible, you’ll want to give yourself two or three paragraphs to give the reader a comprehensive understanding of your study as a whole. Here’s one way to structure an effective discussion:
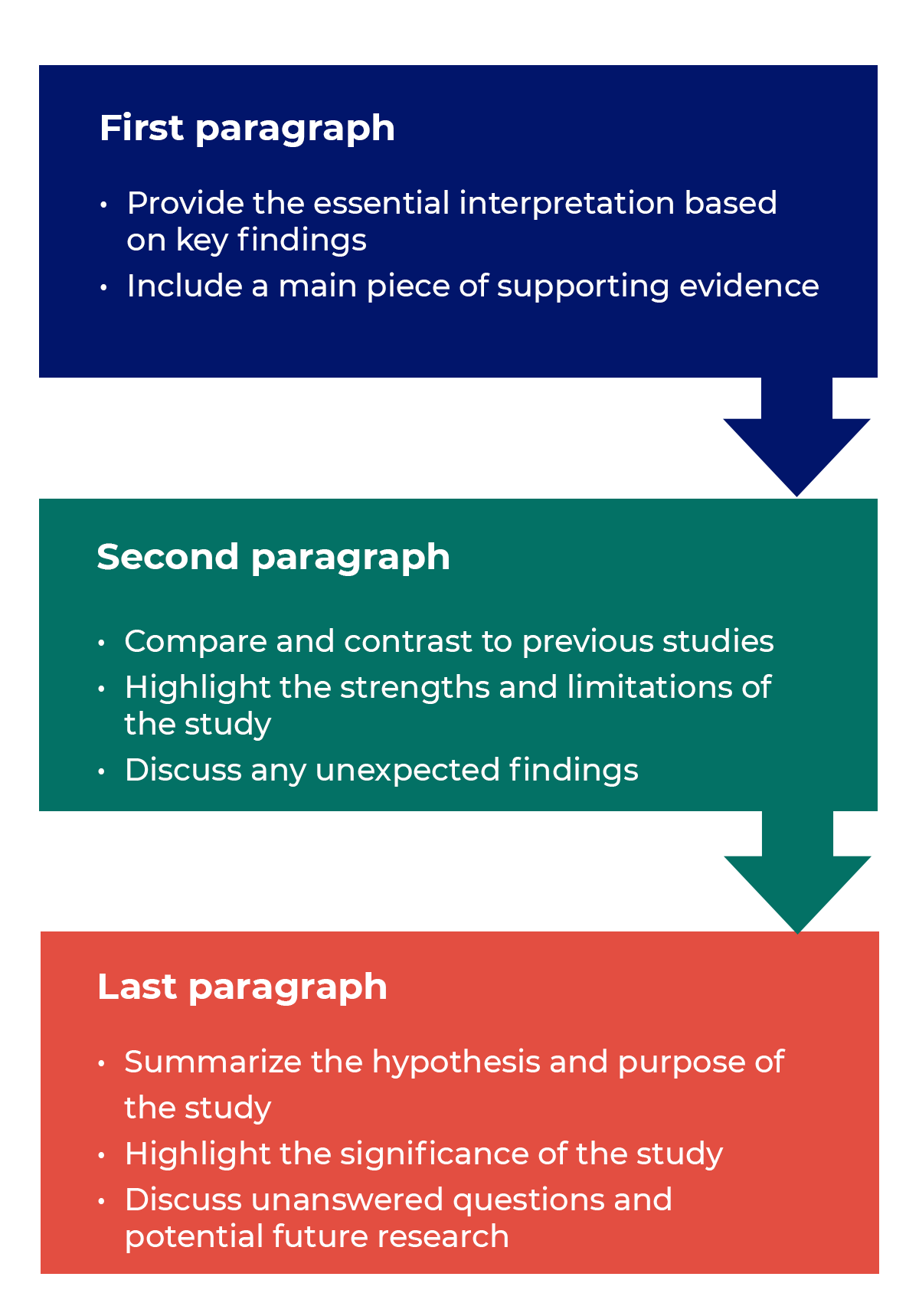
Writing Tips
While the above sections can help you brainstorm and structure your discussion, there are many common mistakes that writers revert to when having difficulties with their paper. Writing a discussion can be a delicate balance between summarizing your results, providing proper context for your research and avoiding introducing new information. Remember that your paper should be both confident and honest about the results!

- Read the journal’s guidelines on the discussion and conclusion sections. If possible, learn about the guidelines before writing the discussion to ensure you’re writing to meet their expectations.
- Begin with a clear statement of the principal findings. This will reinforce the main take-away for the reader and set up the rest of the discussion.
- Explain why the outcomes of your study are important to the reader. Discuss the implications of your findings realistically based on previous literature, highlighting both the strengths and limitations of the research.
- State whether the results prove or disprove your hypothesis. If your hypothesis was disproved, what might be the reasons?
- Introduce new or expanded ways to think about the research question. Indicate what next steps can be taken to further pursue any unresolved questions.
- If dealing with a contemporary or ongoing problem, such as climate change, discuss possible consequences if the problem is avoided.
- Be concise. Adding unnecessary detail can distract from the main findings.

Don’t
- Rewrite your abstract. Statements with “we investigated” or “we studied” generally do not belong in the discussion.
- Include new arguments or evidence not previously discussed. Necessary information and evidence should be introduced in the main body of the paper.
- Apologize. Even if your research contains significant limitations, don’t undermine your authority by including statements that doubt your methodology or execution.
- Shy away from speaking on limitations or negative results. Including limitations and negative results will give readers a complete understanding of the presented research. Potential limitations include sources of potential bias, threats to internal or external validity, barriers to implementing an intervention and other issues inherent to the study design.
- Overstate the importance of your findings. Making grand statements about how a study will fully resolve large questions can lead readers to doubt the success of the research.
Snippets of Effective Discussions:
Consumer-based actions to reduce plastic pollution in rivers: A multi-criteria decision analysis approach
Identifying reliable indicators of fitness in polar bears
- How to Write a Great Title
- How to Write an Abstract
- How to Write Your Methods
- How to Report Statistics
- How to Edit Your Work
The contents of the Peer Review Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
The contents of the Writing Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
There’s a lot to consider when deciding where to submit your work. Learn how to choose a journal that will help your study reach its audience, while reflecting your values as a researcher…
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- How to Write a Results Section | Tips & Examples
How to Write a Results Section | Tips & Examples
Published on 27 October 2016 by Bas Swaen . Revised on 25 October 2022 by Tegan George.
A results section is where you report the main findings of the data collection and analysis you conducted for your thesis or dissertation . You should report all relevant results concisely and objectively, in a logical order. Don’t include subjective interpretations of why you found these results or what they mean – any evaluation should be saved for the discussion section .
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
How to write a results section, reporting quantitative research results, reporting qualitative research results, results vs discussion vs conclusion, checklist: research results, frequently asked questions about results sections.
When conducting research, it’s important to report the results of your study prior to discussing your interpretations of it. This gives your reader a clear idea of exactly what you found and keeps the data itself separate from your subjective analysis.
Here are a few best practices:
- Your results should always be written in the past tense.
- While the length of this section depends on how much data you collected and analysed, it should be written as concisely as possible.
- Only include results that are directly relevant to answering your research questions . Avoid speculative or interpretative words like ‘appears’ or ‘implies’.
- If you have other results you’d like to include, consider adding them to an appendix or footnotes.
- Always start out with your broadest results first, and then flow into your more granular (but still relevant) ones. Think of it like a shoe shop: first discuss the shoes as a whole, then the trainers, boots, sandals, etc.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
If you conducted quantitative research , you’ll likely be working with the results of some sort of statistical analysis .
Your results section should report the results of any statistical tests you used to compare groups or assess relationships between variables . It should also state whether or not each hypothesis was supported.
The most logical way to structure quantitative results is to frame them around your research questions or hypotheses. For each question or hypothesis, share:
- A reminder of the type of analysis you used (e.g., a two-sample t test or simple linear regression ). A more detailed description of your analysis should go in your methodology section.
- A concise summary of each relevant result, both positive and negative. This can include any relevant descriptive statistics (e.g., means and standard deviations ) as well as inferential statistics (e.g., t scores, degrees of freedom , and p values ). Remember, these numbers are often placed in parentheses.
- A brief statement of how each result relates to the question, or whether the hypothesis was supported. You can briefly mention any results that didn’t fit with your expectations and assumptions, but save any speculation on their meaning or consequences for your discussion and conclusion.
A note on tables and figures
In quantitative research, it’s often helpful to include visual elements such as graphs, charts, and tables , but only if they are directly relevant to your results. Give these elements clear, descriptive titles and labels so that your reader can easily understand what is being shown. If you want to include any other visual elements that are more tangential in nature, consider adding a figure and table list .
As a rule of thumb:
- Tables are used to communicate exact values, giving a concise overview of various results
- Graphs and charts are used to visualise trends and relationships, giving an at-a-glance illustration of key findings
Don’t forget to also mention any tables and figures you used within the text of your results section. Summarise or elaborate on specific aspects you think your reader should know about rather than merely restating the same numbers already shown.
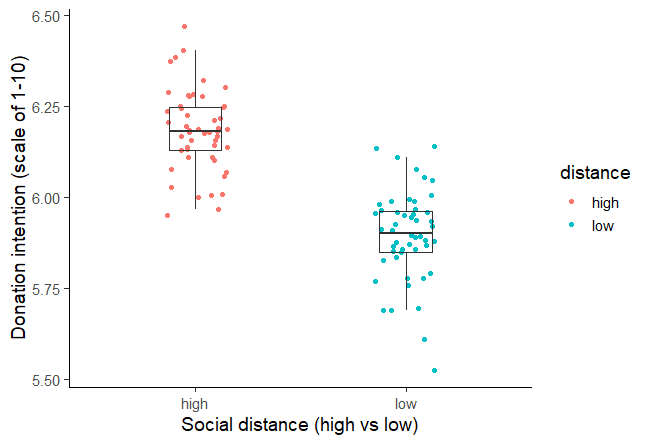
Figure 1: Intention to donate to environmental organisations based on social distance from impact of environmental damage.
In qualitative research , your results might not all be directly related to specific hypotheses. In this case, you can structure your results section around key themes or topics that emerged from your analysis of the data.
For each theme, start with general observations about what the data showed. You can mention:
- Recurring points of agreement or disagreement
- Patterns and trends
- Particularly significant snippets from individual responses
Next, clarify and support these points with direct quotations. Be sure to report any relevant demographic information about participants. Further information (such as full transcripts , if appropriate) can be included in an appendix .
‘I think that in role-playing games, there’s more attention to character design, to world design, because the whole story is important and more attention is paid to certain game elements […] so that perhaps you do need bigger teams of creative experts than in an average shooter or something.’
Responses suggest that video game consumers consider some types of games to have more artistic potential than others.
Your results section should objectively report your findings, presenting only brief observations in relation to each question, hypothesis, or theme.
It should not speculate about the meaning of the results or attempt to answer your main research question . Detailed interpretation of your results is more suitable for your discussion section , while synthesis of your results into an overall answer to your main research question is best left for your conclusion .
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
I have completed my data collection and analyzed the results.
I have included all results that are relevant to my research questions.
I have concisely and objectively reported each result, including relevant descriptive statistics and inferential statistics .
I have stated whether each hypothesis was supported or refuted.
I have used tables and figures to illustrate my results where appropriate.
All tables and figures are correctly labelled and referred to in the text.
There is no subjective interpretation or speculation on the meaning of the results.
You've finished writing up your results! Use the other checklists to further improve your thesis.
The results chapter of a thesis or dissertation presents your research results concisely and objectively.
In quantitative research , for each question or hypothesis , state:
- The type of analysis used
- Relevant results in the form of descriptive and inferential statistics
- Whether or not the alternative hypothesis was supported
In qualitative research , for each question or theme, describe:
- Recurring patterns
- Significant or representative individual responses
- Relevant quotations from the data
Don’t interpret or speculate in the results chapter.
Results are usually written in the past tense , because they are describing the outcome of completed actions.
The results chapter or section simply and objectively reports what you found, without speculating on why you found these results. The discussion interprets the meaning of the results, puts them in context, and explains why they matter.
In qualitative research , results and discussion are sometimes combined. But in quantitative research , it’s considered important to separate the objective results from your interpretation of them.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Swaen, B. (2022, October 25). How to Write a Results Section | Tips & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 14 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/results-section/
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked
What is a research methodology | steps & tips, how to write a discussion section | tips & examples, how to write a thesis or dissertation conclusion.
Writing Quantitative Research Studies
- Reference work entry
- First Online: 13 January 2019
- Cite this reference work entry

- Ankur Singh 2 ,
- Adyya Gupta 3 &
- Karen G. Peres 4
1273 Accesses
1 Citations
Summarizing quantitative data and its effective presentation and discussion can be challenging for students and researchers. This chapter provides a framework for adequately reporting findings from quantitative analysis in a research study for those contemplating to write a research paper. The rationale underpinning the reporting methods to maintain the credibility and integrity of quantitative studies is outlined. Commonly used terminologies in empirical studies are defined and discussed with suitable examples. Key elements that build consistency between different sections (background, methods, results, and the discussion) of a research study using quantitative methods in a journal article are explicated. Specifically, recommended standard guidelines for randomized controlled trials and observational studies for reporting and discussion of findings from quantitative studies are elaborated. Key aspects of methodology that include describing the study population, sampling strategy, data collection methods, measurements/variables, and statistical analysis which informs the quality of a study from the reviewer’s perspective are described. Effective use of references in the methods section to strengthen the rationale behind specific statistical techniques and choice of measures has been highlighted with examples. Identifying ways in which data can be most succinctly and effectively summarized in tables and graphs according to their suitability and purpose of information is also detailed in this chapter. Strategies to present and discuss the quantitative findings in a structured discussion section are also provided. Overall, the chapter provides the readers with a comprehensive set of tools to identify key strategies to be considered when reporting quantitative research.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Bhaumik S, Arora M, Singh A, Sargent JD. Impact of entertainment media smoking on adolescent smoking behaviours. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015;6:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD011720 .
Article Google Scholar
Dickersin K, Manheimer E, Wieland S, Robinson KA, Lefebvre C, McDonald S. Development of the Cochrane Collaboration’s CENTRAL register of controlled clinical trials. Eval Health Prof. 2002;25(1):38–64.
Google Scholar
Docherty M, Smith R. The case for structuring the discussion of scientific papers: much the same as that for structuring abstracts. Br Med J. 1999;318(7193):1224–5.
Greenland S, Pearl J, Robins JM. Causal diagrams for epidemiologic research. Epidemiology. 1999;10(1):37–48.
Horton R. The rhetoric of research. Br Med J. 1995;310(6985):985–7.
Kool B, Ziersch A, Robinson P, Wolfenden L, Lowe JB. The ‘Seven deadly sins’ of rejected papers. Aust N Z J Public Health. 2016;40(1):3–4.
Mannocci A, Saulle R, Colamesta V, D’Aguanno S, Giraldi G, Maffongelli E, et al. What is the impact of reporting guidelines on public health journals in Europe? The case of STROBE, CONSORT and PRISMA. J Public Health. 2015;37(4):737–40.
Rothwell PM. External validity of randomised controlled trials: “to whom do the results of this trial apply?”. Lancet. 2005;365(9453):82–93.
Schulz KF, Altman DG, Moher D. CONSORT 2010 statement: updated guidelines for reporting parallel group randomised trials. PLoS Med. 2010;7(3):e1000251.
Szklo M. Quality of scientific articles. Rev Saude Publica. 2006;40 Spec no:30–5.
Vandenbroucke JP, von Elm E, Altman DG, Gotzsche PC, Mulrow CD, Pocock SJ, et al. Strengthening the reporting of observational studies in epidemiology (STROBE): explanation and elaboration. PLoS Med. 2007;4(10):e297.
Weiss NS, Koepsell TD, Psaty BM. Generalizability of the results of randomized trials. Arch Intern Med. 2008;168(2):133–5.
Singh A, Gupta A, Peres MA, Watt RG, Tsakos G, Mathur MR. Association between tooth loss and hypertension among a primarily rural middle aged and older Indian adult population. J Public Health Dent. 2016;76:198–205.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Centre for Health Equity, Melbourne School of Population and Global Health, The University of Melbourne, Melbourne, VIC, Australia
Ankur Singh
School of Public Health, The University of Adelaide, Adelaide, SA, Australia
Adyya Gupta
Australian Research Centre for Population Oral Health (ARCPOH), Adelaide Dental School, The University of Adelaide, Adelaide, SA, Australia
Karen G. Peres
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Ankur Singh .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
School of Science and Health, Western Sydney University, Penrith, NSW, Australia
Pranee Liamputtong
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this entry
Cite this entry.
Singh, A., Gupta, A., Peres, K.G. (2019). Writing Quantitative Research Studies. In: Liamputtong, P. (eds) Handbook of Research Methods in Health Social Sciences. Springer, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-5251-4_117
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-5251-4_117
Published : 13 January 2019
Publisher Name : Springer, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-10-5250-7
Online ISBN : 978-981-10-5251-4
eBook Packages : Social Sciences Reference Module Humanities and Social Sciences Reference Module Business, Economics and Social Sciences
Share this entry
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Results Section – Writing Guide and Examples
Research Results Section – Writing Guide and Examples
Table of Contents

Research Results
Research results refer to the findings and conclusions derived from a systematic investigation or study conducted to answer a specific question or hypothesis. These results are typically presented in a written report or paper and can include various forms of data such as numerical data, qualitative data, statistics, charts, graphs, and visual aids.
Results Section in Research
The results section of the research paper presents the findings of the study. It is the part of the paper where the researcher reports the data collected during the study and analyzes it to draw conclusions.
In the results section, the researcher should describe the data that was collected, the statistical analysis performed, and the findings of the study. It is important to be objective and not interpret the data in this section. Instead, the researcher should report the data as accurately and objectively as possible.
Structure of Research Results Section
The structure of the research results section can vary depending on the type of research conducted, but in general, it should contain the following components:
- Introduction: The introduction should provide an overview of the study, its aims, and its research questions. It should also briefly explain the methodology used to conduct the study.
- Data presentation : This section presents the data collected during the study. It may include tables, graphs, or other visual aids to help readers better understand the data. The data presented should be organized in a logical and coherent way, with headings and subheadings used to help guide the reader.
- Data analysis: In this section, the data presented in the previous section are analyzed and interpreted. The statistical tests used to analyze the data should be clearly explained, and the results of the tests should be presented in a way that is easy to understand.
- Discussion of results : This section should provide an interpretation of the results of the study, including a discussion of any unexpected findings. The discussion should also address the study’s research questions and explain how the results contribute to the field of study.
- Limitations: This section should acknowledge any limitations of the study, such as sample size, data collection methods, or other factors that may have influenced the results.
- Conclusions: The conclusions should summarize the main findings of the study and provide a final interpretation of the results. The conclusions should also address the study’s research questions and explain how the results contribute to the field of study.
- Recommendations : This section may provide recommendations for future research based on the study’s findings. It may also suggest practical applications for the study’s results in real-world settings.
Outline of Research Results Section
The following is an outline of the key components typically included in the Results section:
I. Introduction
- A brief overview of the research objectives and hypotheses
- A statement of the research question
II. Descriptive statistics
- Summary statistics (e.g., mean, standard deviation) for each variable analyzed
- Frequencies and percentages for categorical variables
III. Inferential statistics
- Results of statistical analyses, including tests of hypotheses
- Tables or figures to display statistical results
IV. Effect sizes and confidence intervals
- Effect sizes (e.g., Cohen’s d, odds ratio) to quantify the strength of the relationship between variables
- Confidence intervals to estimate the range of plausible values for the effect size
V. Subgroup analyses
- Results of analyses that examined differences between subgroups (e.g., by gender, age, treatment group)
VI. Limitations and assumptions
- Discussion of any limitations of the study and potential sources of bias
- Assumptions made in the statistical analyses
VII. Conclusions
- A summary of the key findings and their implications
- A statement of whether the hypotheses were supported or not
- Suggestions for future research
Example of Research Results Section
An Example of a Research Results Section could be:
- This study sought to examine the relationship between sleep quality and academic performance in college students.
- Hypothesis : College students who report better sleep quality will have higher GPAs than those who report poor sleep quality.
- Methodology : Participants completed a survey about their sleep habits and academic performance.
II. Participants
- Participants were college students (N=200) from a mid-sized public university in the United States.
- The sample was evenly split by gender (50% female, 50% male) and predominantly white (85%).
- Participants were recruited through flyers and online advertisements.
III. Results
- Participants who reported better sleep quality had significantly higher GPAs (M=3.5, SD=0.5) than those who reported poor sleep quality (M=2.9, SD=0.6).
- See Table 1 for a summary of the results.
- Participants who reported consistent sleep schedules had higher GPAs than those with irregular sleep schedules.
IV. Discussion
- The results support the hypothesis that better sleep quality is associated with higher academic performance in college students.
- These findings have implications for college students, as prioritizing sleep could lead to better academic outcomes.
- Limitations of the study include self-reported data and the lack of control for other variables that could impact academic performance.
V. Conclusion
- College students who prioritize sleep may see a positive impact on their academic performance.
- These findings highlight the importance of sleep in academic success.
- Future research could explore interventions to improve sleep quality in college students.
Example of Research Results in Research Paper :
Our study aimed to compare the performance of three different machine learning algorithms (Random Forest, Support Vector Machine, and Neural Network) in predicting customer churn in a telecommunications company. We collected a dataset of 10,000 customer records, with 20 predictor variables and a binary churn outcome variable.
Our analysis revealed that all three algorithms performed well in predicting customer churn, with an overall accuracy of 85%. However, the Random Forest algorithm showed the highest accuracy (88%), followed by the Support Vector Machine (86%) and the Neural Network (84%).
Furthermore, we found that the most important predictor variables for customer churn were monthly charges, contract type, and tenure. Random Forest identified monthly charges as the most important variable, while Support Vector Machine and Neural Network identified contract type as the most important.
Overall, our results suggest that machine learning algorithms can be effective in predicting customer churn in a telecommunications company, and that Random Forest is the most accurate algorithm for this task.
Example 3 :
Title : The Impact of Social Media on Body Image and Self-Esteem
Abstract : This study aimed to investigate the relationship between social media use, body image, and self-esteem among young adults. A total of 200 participants were recruited from a university and completed self-report measures of social media use, body image satisfaction, and self-esteem.
Results: The results showed that social media use was significantly associated with body image dissatisfaction and lower self-esteem. Specifically, participants who reported spending more time on social media platforms had lower levels of body image satisfaction and self-esteem compared to those who reported less social media use. Moreover, the study found that comparing oneself to others on social media was a significant predictor of body image dissatisfaction and lower self-esteem.
Conclusion : These results suggest that social media use can have negative effects on body image satisfaction and self-esteem among young adults. It is important for individuals to be mindful of their social media use and to recognize the potential negative impact it can have on their mental health. Furthermore, interventions aimed at promoting positive body image and self-esteem should take into account the role of social media in shaping these attitudes and behaviors.
Importance of Research Results
Research results are important for several reasons, including:
- Advancing knowledge: Research results can contribute to the advancement of knowledge in a particular field, whether it be in science, technology, medicine, social sciences, or humanities.
- Developing theories: Research results can help to develop or modify existing theories and create new ones.
- Improving practices: Research results can inform and improve practices in various fields, such as education, healthcare, business, and public policy.
- Identifying problems and solutions: Research results can identify problems and provide solutions to complex issues in society, including issues related to health, environment, social justice, and economics.
- Validating claims : Research results can validate or refute claims made by individuals or groups in society, such as politicians, corporations, or activists.
- Providing evidence: Research results can provide evidence to support decision-making, policy-making, and resource allocation in various fields.
How to Write Results in A Research Paper
Here are some general guidelines on how to write results in a research paper:
- Organize the results section: Start by organizing the results section in a logical and coherent manner. Divide the section into subsections if necessary, based on the research questions or hypotheses.
- Present the findings: Present the findings in a clear and concise manner. Use tables, graphs, and figures to illustrate the data and make the presentation more engaging.
- Describe the data: Describe the data in detail, including the sample size, response rate, and any missing data. Provide relevant descriptive statistics such as means, standard deviations, and ranges.
- Interpret the findings: Interpret the findings in light of the research questions or hypotheses. Discuss the implications of the findings and the extent to which they support or contradict existing theories or previous research.
- Discuss the limitations : Discuss the limitations of the study, including any potential sources of bias or confounding factors that may have affected the results.
- Compare the results : Compare the results with those of previous studies or theoretical predictions. Discuss any similarities, differences, or inconsistencies.
- Avoid redundancy: Avoid repeating information that has already been presented in the introduction or methods sections. Instead, focus on presenting new and relevant information.
- Be objective: Be objective in presenting the results, avoiding any personal biases or interpretations.
When to Write Research Results
Here are situations When to Write Research Results”
- After conducting research on the chosen topic and obtaining relevant data, organize the findings in a structured format that accurately represents the information gathered.
- Once the data has been analyzed and interpreted, and conclusions have been drawn, begin the writing process.
- Before starting to write, ensure that the research results adhere to the guidelines and requirements of the intended audience, such as a scientific journal or academic conference.
- Begin by writing an abstract that briefly summarizes the research question, methodology, findings, and conclusions.
- Follow the abstract with an introduction that provides context for the research, explains its significance, and outlines the research question and objectives.
- The next section should be a literature review that provides an overview of existing research on the topic and highlights the gaps in knowledge that the current research seeks to address.
- The methodology section should provide a detailed explanation of the research design, including the sample size, data collection methods, and analytical techniques used.
- Present the research results in a clear and concise manner, using graphs, tables, and figures to illustrate the findings.
- Discuss the implications of the research results, including how they contribute to the existing body of knowledge on the topic and what further research is needed.
- Conclude the paper by summarizing the main findings, reiterating the significance of the research, and offering suggestions for future research.
Purpose of Research Results
The purposes of Research Results are as follows:
- Informing policy and practice: Research results can provide evidence-based information to inform policy decisions, such as in the fields of healthcare, education, and environmental regulation. They can also inform best practices in fields such as business, engineering, and social work.
- Addressing societal problems : Research results can be used to help address societal problems, such as reducing poverty, improving public health, and promoting social justice.
- Generating economic benefits : Research results can lead to the development of new products, services, and technologies that can create economic value and improve quality of life.
- Supporting academic and professional development : Research results can be used to support academic and professional development by providing opportunities for students, researchers, and practitioners to learn about new findings and methodologies in their field.
- Enhancing public understanding: Research results can help to educate the public about important issues and promote scientific literacy, leading to more informed decision-making and better public policy.
- Evaluating interventions: Research results can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of interventions, such as treatments, educational programs, and social policies. This can help to identify areas where improvements are needed and guide future interventions.
- Contributing to scientific progress: Research results can contribute to the advancement of science by providing new insights and discoveries that can lead to new theories, methods, and techniques.
- Informing decision-making : Research results can provide decision-makers with the information they need to make informed decisions. This can include decision-making at the individual, organizational, or governmental levels.
- Fostering collaboration : Research results can facilitate collaboration between researchers and practitioners, leading to new partnerships, interdisciplinary approaches, and innovative solutions to complex problems.
Advantages of Research Results
Some Advantages of Research Results are as follows:
- Improved decision-making: Research results can help inform decision-making in various fields, including medicine, business, and government. For example, research on the effectiveness of different treatments for a particular disease can help doctors make informed decisions about the best course of treatment for their patients.
- Innovation : Research results can lead to the development of new technologies, products, and services. For example, research on renewable energy sources can lead to the development of new and more efficient ways to harness renewable energy.
- Economic benefits: Research results can stimulate economic growth by providing new opportunities for businesses and entrepreneurs. For example, research on new materials or manufacturing techniques can lead to the development of new products and processes that can create new jobs and boost economic activity.
- Improved quality of life: Research results can contribute to improving the quality of life for individuals and society as a whole. For example, research on the causes of a particular disease can lead to the development of new treatments and cures, improving the health and well-being of millions of people.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Korean Med Sci
- v.37(16); 2022 Apr 25

A Practical Guide to Writing Quantitative and Qualitative Research Questions and Hypotheses in Scholarly Articles
Edward barroga.
1 Department of General Education, Graduate School of Nursing Science, St. Luke’s International University, Tokyo, Japan.
Glafera Janet Matanguihan
2 Department of Biological Sciences, Messiah University, Mechanicsburg, PA, USA.
The development of research questions and the subsequent hypotheses are prerequisites to defining the main research purpose and specific objectives of a study. Consequently, these objectives determine the study design and research outcome. The development of research questions is a process based on knowledge of current trends, cutting-edge studies, and technological advances in the research field. Excellent research questions are focused and require a comprehensive literature search and in-depth understanding of the problem being investigated. Initially, research questions may be written as descriptive questions which could be developed into inferential questions. These questions must be specific and concise to provide a clear foundation for developing hypotheses. Hypotheses are more formal predictions about the research outcomes. These specify the possible results that may or may not be expected regarding the relationship between groups. Thus, research questions and hypotheses clarify the main purpose and specific objectives of the study, which in turn dictate the design of the study, its direction, and outcome. Studies developed from good research questions and hypotheses will have trustworthy outcomes with wide-ranging social and health implications.
INTRODUCTION
Scientific research is usually initiated by posing evidenced-based research questions which are then explicitly restated as hypotheses. 1 , 2 The hypotheses provide directions to guide the study, solutions, explanations, and expected results. 3 , 4 Both research questions and hypotheses are essentially formulated based on conventional theories and real-world processes, which allow the inception of novel studies and the ethical testing of ideas. 5 , 6
It is crucial to have knowledge of both quantitative and qualitative research 2 as both types of research involve writing research questions and hypotheses. 7 However, these crucial elements of research are sometimes overlooked; if not overlooked, then framed without the forethought and meticulous attention it needs. Planning and careful consideration are needed when developing quantitative or qualitative research, particularly when conceptualizing research questions and hypotheses. 4
There is a continuing need to support researchers in the creation of innovative research questions and hypotheses, as well as for journal articles that carefully review these elements. 1 When research questions and hypotheses are not carefully thought of, unethical studies and poor outcomes usually ensue. Carefully formulated research questions and hypotheses define well-founded objectives, which in turn determine the appropriate design, course, and outcome of the study. This article then aims to discuss in detail the various aspects of crafting research questions and hypotheses, with the goal of guiding researchers as they develop their own. Examples from the authors and peer-reviewed scientific articles in the healthcare field are provided to illustrate key points.
DEFINITIONS AND RELATIONSHIP OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
A research question is what a study aims to answer after data analysis and interpretation. The answer is written in length in the discussion section of the paper. Thus, the research question gives a preview of the different parts and variables of the study meant to address the problem posed in the research question. 1 An excellent research question clarifies the research writing while facilitating understanding of the research topic, objective, scope, and limitations of the study. 5
On the other hand, a research hypothesis is an educated statement of an expected outcome. This statement is based on background research and current knowledge. 8 , 9 The research hypothesis makes a specific prediction about a new phenomenon 10 or a formal statement on the expected relationship between an independent variable and a dependent variable. 3 , 11 It provides a tentative answer to the research question to be tested or explored. 4
Hypotheses employ reasoning to predict a theory-based outcome. 10 These can also be developed from theories by focusing on components of theories that have not yet been observed. 10 The validity of hypotheses is often based on the testability of the prediction made in a reproducible experiment. 8
Conversely, hypotheses can also be rephrased as research questions. Several hypotheses based on existing theories and knowledge may be needed to answer a research question. Developing ethical research questions and hypotheses creates a research design that has logical relationships among variables. These relationships serve as a solid foundation for the conduct of the study. 4 , 11 Haphazardly constructed research questions can result in poorly formulated hypotheses and improper study designs, leading to unreliable results. Thus, the formulations of relevant research questions and verifiable hypotheses are crucial when beginning research. 12
CHARACTERISTICS OF GOOD RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Excellent research questions are specific and focused. These integrate collective data and observations to confirm or refute the subsequent hypotheses. Well-constructed hypotheses are based on previous reports and verify the research context. These are realistic, in-depth, sufficiently complex, and reproducible. More importantly, these hypotheses can be addressed and tested. 13
There are several characteristics of well-developed hypotheses. Good hypotheses are 1) empirically testable 7 , 10 , 11 , 13 ; 2) backed by preliminary evidence 9 ; 3) testable by ethical research 7 , 9 ; 4) based on original ideas 9 ; 5) have evidenced-based logical reasoning 10 ; and 6) can be predicted. 11 Good hypotheses can infer ethical and positive implications, indicating the presence of a relationship or effect relevant to the research theme. 7 , 11 These are initially developed from a general theory and branch into specific hypotheses by deductive reasoning. In the absence of a theory to base the hypotheses, inductive reasoning based on specific observations or findings form more general hypotheses. 10
TYPES OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Research questions and hypotheses are developed according to the type of research, which can be broadly classified into quantitative and qualitative research. We provide a summary of the types of research questions and hypotheses under quantitative and qualitative research categories in Table 1 .

Research questions in quantitative research
In quantitative research, research questions inquire about the relationships among variables being investigated and are usually framed at the start of the study. These are precise and typically linked to the subject population, dependent and independent variables, and research design. 1 Research questions may also attempt to describe the behavior of a population in relation to one or more variables, or describe the characteristics of variables to be measured ( descriptive research questions ). 1 , 5 , 14 These questions may also aim to discover differences between groups within the context of an outcome variable ( comparative research questions ), 1 , 5 , 14 or elucidate trends and interactions among variables ( relationship research questions ). 1 , 5 We provide examples of descriptive, comparative, and relationship research questions in quantitative research in Table 2 .
Hypotheses in quantitative research
In quantitative research, hypotheses predict the expected relationships among variables. 15 Relationships among variables that can be predicted include 1) between a single dependent variable and a single independent variable ( simple hypothesis ) or 2) between two or more independent and dependent variables ( complex hypothesis ). 4 , 11 Hypotheses may also specify the expected direction to be followed and imply an intellectual commitment to a particular outcome ( directional hypothesis ) 4 . On the other hand, hypotheses may not predict the exact direction and are used in the absence of a theory, or when findings contradict previous studies ( non-directional hypothesis ). 4 In addition, hypotheses can 1) define interdependency between variables ( associative hypothesis ), 4 2) propose an effect on the dependent variable from manipulation of the independent variable ( causal hypothesis ), 4 3) state a negative relationship between two variables ( null hypothesis ), 4 , 11 , 15 4) replace the working hypothesis if rejected ( alternative hypothesis ), 15 explain the relationship of phenomena to possibly generate a theory ( working hypothesis ), 11 5) involve quantifiable variables that can be tested statistically ( statistical hypothesis ), 11 6) or express a relationship whose interlinks can be verified logically ( logical hypothesis ). 11 We provide examples of simple, complex, directional, non-directional, associative, causal, null, alternative, working, statistical, and logical hypotheses in quantitative research, as well as the definition of quantitative hypothesis-testing research in Table 3 .
Research questions in qualitative research
Unlike research questions in quantitative research, research questions in qualitative research are usually continuously reviewed and reformulated. The central question and associated subquestions are stated more than the hypotheses. 15 The central question broadly explores a complex set of factors surrounding the central phenomenon, aiming to present the varied perspectives of participants. 15
There are varied goals for which qualitative research questions are developed. These questions can function in several ways, such as to 1) identify and describe existing conditions ( contextual research question s); 2) describe a phenomenon ( descriptive research questions ); 3) assess the effectiveness of existing methods, protocols, theories, or procedures ( evaluation research questions ); 4) examine a phenomenon or analyze the reasons or relationships between subjects or phenomena ( explanatory research questions ); or 5) focus on unknown aspects of a particular topic ( exploratory research questions ). 5 In addition, some qualitative research questions provide new ideas for the development of theories and actions ( generative research questions ) or advance specific ideologies of a position ( ideological research questions ). 1 Other qualitative research questions may build on a body of existing literature and become working guidelines ( ethnographic research questions ). Research questions may also be broadly stated without specific reference to the existing literature or a typology of questions ( phenomenological research questions ), may be directed towards generating a theory of some process ( grounded theory questions ), or may address a description of the case and the emerging themes ( qualitative case study questions ). 15 We provide examples of contextual, descriptive, evaluation, explanatory, exploratory, generative, ideological, ethnographic, phenomenological, grounded theory, and qualitative case study research questions in qualitative research in Table 4 , and the definition of qualitative hypothesis-generating research in Table 5 .
Qualitative studies usually pose at least one central research question and several subquestions starting with How or What . These research questions use exploratory verbs such as explore or describe . These also focus on one central phenomenon of interest, and may mention the participants and research site. 15
Hypotheses in qualitative research
Hypotheses in qualitative research are stated in the form of a clear statement concerning the problem to be investigated. Unlike in quantitative research where hypotheses are usually developed to be tested, qualitative research can lead to both hypothesis-testing and hypothesis-generating outcomes. 2 When studies require both quantitative and qualitative research questions, this suggests an integrative process between both research methods wherein a single mixed-methods research question can be developed. 1
FRAMEWORKS FOR DEVELOPING RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
Research questions followed by hypotheses should be developed before the start of the study. 1 , 12 , 14 It is crucial to develop feasible research questions on a topic that is interesting to both the researcher and the scientific community. This can be achieved by a meticulous review of previous and current studies to establish a novel topic. Specific areas are subsequently focused on to generate ethical research questions. The relevance of the research questions is evaluated in terms of clarity of the resulting data, specificity of the methodology, objectivity of the outcome, depth of the research, and impact of the study. 1 , 5 These aspects constitute the FINER criteria (i.e., Feasible, Interesting, Novel, Ethical, and Relevant). 1 Clarity and effectiveness are achieved if research questions meet the FINER criteria. In addition to the FINER criteria, Ratan et al. described focus, complexity, novelty, feasibility, and measurability for evaluating the effectiveness of research questions. 14
The PICOT and PEO frameworks are also used when developing research questions. 1 The following elements are addressed in these frameworks, PICOT: P-population/patients/problem, I-intervention or indicator being studied, C-comparison group, O-outcome of interest, and T-timeframe of the study; PEO: P-population being studied, E-exposure to preexisting conditions, and O-outcome of interest. 1 Research questions are also considered good if these meet the “FINERMAPS” framework: Feasible, Interesting, Novel, Ethical, Relevant, Manageable, Appropriate, Potential value/publishable, and Systematic. 14
As we indicated earlier, research questions and hypotheses that are not carefully formulated result in unethical studies or poor outcomes. To illustrate this, we provide some examples of ambiguous research question and hypotheses that result in unclear and weak research objectives in quantitative research ( Table 6 ) 16 and qualitative research ( Table 7 ) 17 , and how to transform these ambiguous research question(s) and hypothesis(es) into clear and good statements.
a These statements were composed for comparison and illustrative purposes only.
b These statements are direct quotes from Higashihara and Horiuchi. 16
a This statement is a direct quote from Shimoda et al. 17
The other statements were composed for comparison and illustrative purposes only.
CONSTRUCTING RESEARCH QUESTIONS AND HYPOTHESES
To construct effective research questions and hypotheses, it is very important to 1) clarify the background and 2) identify the research problem at the outset of the research, within a specific timeframe. 9 Then, 3) review or conduct preliminary research to collect all available knowledge about the possible research questions by studying theories and previous studies. 18 Afterwards, 4) construct research questions to investigate the research problem. Identify variables to be accessed from the research questions 4 and make operational definitions of constructs from the research problem and questions. Thereafter, 5) construct specific deductive or inductive predictions in the form of hypotheses. 4 Finally, 6) state the study aims . This general flow for constructing effective research questions and hypotheses prior to conducting research is shown in Fig. 1 .

Research questions are used more frequently in qualitative research than objectives or hypotheses. 3 These questions seek to discover, understand, explore or describe experiences by asking “What” or “How.” The questions are open-ended to elicit a description rather than to relate variables or compare groups. The questions are continually reviewed, reformulated, and changed during the qualitative study. 3 Research questions are also used more frequently in survey projects than hypotheses in experiments in quantitative research to compare variables and their relationships.
Hypotheses are constructed based on the variables identified and as an if-then statement, following the template, ‘If a specific action is taken, then a certain outcome is expected.’ At this stage, some ideas regarding expectations from the research to be conducted must be drawn. 18 Then, the variables to be manipulated (independent) and influenced (dependent) are defined. 4 Thereafter, the hypothesis is stated and refined, and reproducible data tailored to the hypothesis are identified, collected, and analyzed. 4 The hypotheses must be testable and specific, 18 and should describe the variables and their relationships, the specific group being studied, and the predicted research outcome. 18 Hypotheses construction involves a testable proposition to be deduced from theory, and independent and dependent variables to be separated and measured separately. 3 Therefore, good hypotheses must be based on good research questions constructed at the start of a study or trial. 12
In summary, research questions are constructed after establishing the background of the study. Hypotheses are then developed based on the research questions. Thus, it is crucial to have excellent research questions to generate superior hypotheses. In turn, these would determine the research objectives and the design of the study, and ultimately, the outcome of the research. 12 Algorithms for building research questions and hypotheses are shown in Fig. 2 for quantitative research and in Fig. 3 for qualitative research.

EXAMPLES OF RESEARCH QUESTIONS FROM PUBLISHED ARTICLES
- EXAMPLE 1. Descriptive research question (quantitative research)
- - Presents research variables to be assessed (distinct phenotypes and subphenotypes)
- “BACKGROUND: Since COVID-19 was identified, its clinical and biological heterogeneity has been recognized. Identifying COVID-19 phenotypes might help guide basic, clinical, and translational research efforts.
- RESEARCH QUESTION: Does the clinical spectrum of patients with COVID-19 contain distinct phenotypes and subphenotypes? ” 19
- EXAMPLE 2. Relationship research question (quantitative research)
- - Shows interactions between dependent variable (static postural control) and independent variable (peripheral visual field loss)
- “Background: Integration of visual, vestibular, and proprioceptive sensations contributes to postural control. People with peripheral visual field loss have serious postural instability. However, the directional specificity of postural stability and sensory reweighting caused by gradual peripheral visual field loss remain unclear.
- Research question: What are the effects of peripheral visual field loss on static postural control ?” 20
- EXAMPLE 3. Comparative research question (quantitative research)
- - Clarifies the difference among groups with an outcome variable (patients enrolled in COMPERA with moderate PH or severe PH in COPD) and another group without the outcome variable (patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH))
- “BACKGROUND: Pulmonary hypertension (PH) in COPD is a poorly investigated clinical condition.
- RESEARCH QUESTION: Which factors determine the outcome of PH in COPD?
- STUDY DESIGN AND METHODS: We analyzed the characteristics and outcome of patients enrolled in the Comparative, Prospective Registry of Newly Initiated Therapies for Pulmonary Hypertension (COMPERA) with moderate or severe PH in COPD as defined during the 6th PH World Symposium who received medical therapy for PH and compared them with patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH) .” 21
- EXAMPLE 4. Exploratory research question (qualitative research)
- - Explores areas that have not been fully investigated (perspectives of families and children who receive care in clinic-based child obesity treatment) to have a deeper understanding of the research problem
- “Problem: Interventions for children with obesity lead to only modest improvements in BMI and long-term outcomes, and data are limited on the perspectives of families of children with obesity in clinic-based treatment. This scoping review seeks to answer the question: What is known about the perspectives of families and children who receive care in clinic-based child obesity treatment? This review aims to explore the scope of perspectives reported by families of children with obesity who have received individualized outpatient clinic-based obesity treatment.” 22
- EXAMPLE 5. Relationship research question (quantitative research)
- - Defines interactions between dependent variable (use of ankle strategies) and independent variable (changes in muscle tone)
- “Background: To maintain an upright standing posture against external disturbances, the human body mainly employs two types of postural control strategies: “ankle strategy” and “hip strategy.” While it has been reported that the magnitude of the disturbance alters the use of postural control strategies, it has not been elucidated how the level of muscle tone, one of the crucial parameters of bodily function, determines the use of each strategy. We have previously confirmed using forward dynamics simulations of human musculoskeletal models that an increased muscle tone promotes the use of ankle strategies. The objective of the present study was to experimentally evaluate a hypothesis: an increased muscle tone promotes the use of ankle strategies. Research question: Do changes in the muscle tone affect the use of ankle strategies ?” 23
EXAMPLES OF HYPOTHESES IN PUBLISHED ARTICLES
- EXAMPLE 1. Working hypothesis (quantitative research)
- - A hypothesis that is initially accepted for further research to produce a feasible theory
- “As fever may have benefit in shortening the duration of viral illness, it is plausible to hypothesize that the antipyretic efficacy of ibuprofen may be hindering the benefits of a fever response when taken during the early stages of COVID-19 illness .” 24
- “In conclusion, it is plausible to hypothesize that the antipyretic efficacy of ibuprofen may be hindering the benefits of a fever response . The difference in perceived safety of these agents in COVID-19 illness could be related to the more potent efficacy to reduce fever with ibuprofen compared to acetaminophen. Compelling data on the benefit of fever warrant further research and review to determine when to treat or withhold ibuprofen for early stage fever for COVID-19 and other related viral illnesses .” 24
- EXAMPLE 2. Exploratory hypothesis (qualitative research)
- - Explores particular areas deeper to clarify subjective experience and develop a formal hypothesis potentially testable in a future quantitative approach
- “We hypothesized that when thinking about a past experience of help-seeking, a self distancing prompt would cause increased help-seeking intentions and more favorable help-seeking outcome expectations .” 25
- “Conclusion
- Although a priori hypotheses were not supported, further research is warranted as results indicate the potential for using self-distancing approaches to increasing help-seeking among some people with depressive symptomatology.” 25
- EXAMPLE 3. Hypothesis-generating research to establish a framework for hypothesis testing (qualitative research)
- “We hypothesize that compassionate care is beneficial for patients (better outcomes), healthcare systems and payers (lower costs), and healthcare providers (lower burnout). ” 26
- Compassionomics is the branch of knowledge and scientific study of the effects of compassionate healthcare. Our main hypotheses are that compassionate healthcare is beneficial for (1) patients, by improving clinical outcomes, (2) healthcare systems and payers, by supporting financial sustainability, and (3) HCPs, by lowering burnout and promoting resilience and well-being. The purpose of this paper is to establish a scientific framework for testing the hypotheses above . If these hypotheses are confirmed through rigorous research, compassionomics will belong in the science of evidence-based medicine, with major implications for all healthcare domains.” 26
- EXAMPLE 4. Statistical hypothesis (quantitative research)
- - An assumption is made about the relationship among several population characteristics ( gender differences in sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of adults with ADHD ). Validity is tested by statistical experiment or analysis ( chi-square test, Students t-test, and logistic regression analysis)
- “Our research investigated gender differences in sociodemographic and clinical characteristics of adults with ADHD in a Japanese clinical sample. Due to unique Japanese cultural ideals and expectations of women's behavior that are in opposition to ADHD symptoms, we hypothesized that women with ADHD experience more difficulties and present more dysfunctions than men . We tested the following hypotheses: first, women with ADHD have more comorbidities than men with ADHD; second, women with ADHD experience more social hardships than men, such as having less full-time employment and being more likely to be divorced.” 27
- “Statistical Analysis
- ( text omitted ) Between-gender comparisons were made using the chi-squared test for categorical variables and Students t-test for continuous variables…( text omitted ). A logistic regression analysis was performed for employment status, marital status, and comorbidity to evaluate the independent effects of gender on these dependent variables.” 27
EXAMPLES OF HYPOTHESIS AS WRITTEN IN PUBLISHED ARTICLES IN RELATION TO OTHER PARTS
- EXAMPLE 1. Background, hypotheses, and aims are provided
- “Pregnant women need skilled care during pregnancy and childbirth, but that skilled care is often delayed in some countries …( text omitted ). The focused antenatal care (FANC) model of WHO recommends that nurses provide information or counseling to all pregnant women …( text omitted ). Job aids are visual support materials that provide the right kind of information using graphics and words in a simple and yet effective manner. When nurses are not highly trained or have many work details to attend to, these job aids can serve as a content reminder for the nurses and can be used for educating their patients (Jennings, Yebadokpo, Affo, & Agbogbe, 2010) ( text omitted ). Importantly, additional evidence is needed to confirm how job aids can further improve the quality of ANC counseling by health workers in maternal care …( text omitted )” 28
- “ This has led us to hypothesize that the quality of ANC counseling would be better if supported by job aids. Consequently, a better quality of ANC counseling is expected to produce higher levels of awareness concerning the danger signs of pregnancy and a more favorable impression of the caring behavior of nurses .” 28
- “This study aimed to examine the differences in the responses of pregnant women to a job aid-supported intervention during ANC visit in terms of 1) their understanding of the danger signs of pregnancy and 2) their impression of the caring behaviors of nurses to pregnant women in rural Tanzania.” 28
- EXAMPLE 2. Background, hypotheses, and aims are provided
- “We conducted a two-arm randomized controlled trial (RCT) to evaluate and compare changes in salivary cortisol and oxytocin levels of first-time pregnant women between experimental and control groups. The women in the experimental group touched and held an infant for 30 min (experimental intervention protocol), whereas those in the control group watched a DVD movie of an infant (control intervention protocol). The primary outcome was salivary cortisol level and the secondary outcome was salivary oxytocin level.” 29
- “ We hypothesize that at 30 min after touching and holding an infant, the salivary cortisol level will significantly decrease and the salivary oxytocin level will increase in the experimental group compared with the control group .” 29
- EXAMPLE 3. Background, aim, and hypothesis are provided
- “In countries where the maternal mortality ratio remains high, antenatal education to increase Birth Preparedness and Complication Readiness (BPCR) is considered one of the top priorities [1]. BPCR includes birth plans during the antenatal period, such as the birthplace, birth attendant, transportation, health facility for complications, expenses, and birth materials, as well as family coordination to achieve such birth plans. In Tanzania, although increasing, only about half of all pregnant women attend an antenatal clinic more than four times [4]. Moreover, the information provided during antenatal care (ANC) is insufficient. In the resource-poor settings, antenatal group education is a potential approach because of the limited time for individual counseling at antenatal clinics.” 30
- “This study aimed to evaluate an antenatal group education program among pregnant women and their families with respect to birth-preparedness and maternal and infant outcomes in rural villages of Tanzania.” 30
- “ The study hypothesis was if Tanzanian pregnant women and their families received a family-oriented antenatal group education, they would (1) have a higher level of BPCR, (2) attend antenatal clinic four or more times, (3) give birth in a health facility, (4) have less complications of women at birth, and (5) have less complications and deaths of infants than those who did not receive the education .” 30
Research questions and hypotheses are crucial components to any type of research, whether quantitative or qualitative. These questions should be developed at the very beginning of the study. Excellent research questions lead to superior hypotheses, which, like a compass, set the direction of research, and can often determine the successful conduct of the study. Many research studies have floundered because the development of research questions and subsequent hypotheses was not given the thought and meticulous attention needed. The development of research questions and hypotheses is an iterative process based on extensive knowledge of the literature and insightful grasp of the knowledge gap. Focused, concise, and specific research questions provide a strong foundation for constructing hypotheses which serve as formal predictions about the research outcomes. Research questions and hypotheses are crucial elements of research that should not be overlooked. They should be carefully thought of and constructed when planning research. This avoids unethical studies and poor outcomes by defining well-founded objectives that determine the design, course, and outcome of the study.
Disclosure: The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author Contributions:
- Conceptualization: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Methodology: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Writing - original draft: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.
- Writing - review & editing: Barroga E, Matanguihan GJ.

Writing the Dissertation - Guides for Success: The Results and Discussion
- Writing the Dissertation Homepage
- Overview and Planning
- The Literature Review
- The Methodology
- The Results and Discussion
- The Conclusion
- The Abstract
- The Difference
- What to Avoid
Overview of writing the results and discussion
The results and discussion follow on from the methods or methodology chapter of the dissertation. This creates a natural transition from how you designed your study, to what your study reveals, highlighting your own contribution to the research area.
Disciplinary differences
Please note: this guide is not specific to any one discipline. The results and discussion can vary depending on the nature of the research and the expectations of the school or department, so please adapt the following advice to meet the demands of your project and department. Consult your supervisor for further guidance; you can also peruse our Writing Across Subjects guide .
Guide contents
As part of the Writing the Dissertation series, this guide covers the most common conventions of the results and discussion chapters, giving you the necessary knowledge, tips and guidance needed to impress your markers! The sections are organised as follows:
- The Difference - Breaks down the distinctions between the results and discussion chapters.
- Results - Provides a walk-through of common characteristics of the results chapter.
- Discussion - Provides a walk-through of how to approach writing your discussion chapter, including structure.
- What to Avoid - Covers a few frequent mistakes you'll want to...avoid!
- FAQs - Guidance on first- vs. third-person, limitations and more.
- Checklist - Includes a summary of key points and a self-evaluation checklist.
Training and tools
- The Academic Skills team has recorded a Writing the Dissertation workshop series to help you with each section of a standard dissertation, including a video on writing the results and discussion (embedded below).
- The dissertation planner tool can help you think through the timeline for planning, research, drafting and editing.
- iSolutions offers training and a Word template to help you digitally format and structure your dissertation.
Introduction
The results of your study are often followed by a separate chapter of discussion. This is certainly the case with scientific writing. Some dissertations, however, might incorporate both the results and discussion in one chapter. This depends on the nature of your dissertation and the conventions within your school or department. Always follow the guidelines given to you and ask your supervisor for further guidance.
As part of the Writing the Dissertation series, this guide covers the essentials of writing your results and discussion, giving you the necesary knowledge, tips and guidance needed to leave a positive impression on your markers! This guide covers the results and discussion as separate – although interrelated – chapters, as you'll see in the next two tabs. However, you can easily adapt the guidance to suit one single chapter – keep an eye out for some hints on how to do this throughout the guide.
Results or discussion - what's the difference?
To understand what the results and discussion sections are about, we need to clearly define the difference between the two.
The results should provide a clear account of the findings . This is written in a dry and direct manner, simply highlighting the findings as they appear once processed. It’s expected to have tables and graphics, where relevant, to contextualise and illustrate the data.
Rather than simply stating the findings of the study, the discussion interprets the findings to offer a more nuanced understanding of the research. The discussion is similar to the second half of the conclusion because it’s where you consider and formulate a response to the question, ‘what do we now know that we didn’t before?’ (see our Writing the Conclusion guide for more). The discussion achieves this by answering the research questions and responding to any hypotheses proposed. With this in mind, the discussion should be the most insightful chapter or section of your dissertation because it provides the most original insight.
Across the next two tabs of this guide, we will look at the results and discussion chapters separately in more detail.
Writing the results
The results chapter should provide a direct and factual account of the data collected without any interpretation or interrogation of the findings. As this might suggest, the results chapter can be slightly monotonous, particularly for quantitative data. Nevertheless, it’s crucial that you present your results in a clear and direct manner as it provides the necessary detail for your subsequent discussion.
Note: If you’re writing your results and discussion as one chapter, then you can either:
1) write them as distinctly separate sections in the same chapter, with the discussion following on from the results, or...
2) integrate the two throughout by presenting a subset of the results and then discussing that subset in further detail.
Next, we'll explore some of the most important factors to consider when writing your results chapter.
How you structure your results chapter depends on the design and purpose of your study. Here are some possible options for structuring your results chapter (adapted from Glatthorn and Joyner, 2005):
- Chronological – depending on the nature of the study, it might be important to present your results in order of how you collected the data, such as a pretest-posttest design.
- Research method – if you’ve used a mixed-methods approach, you could isolate each research method and instrument employed in the study.
- Research question and/or hypotheses – you could structure your results around your research questions and/or hypotheses, providing you have more than one. However, keep in mind that the results on their own don’t necessarily answer the questions or respond to the hypotheses in a definitive manner. You need to interpret the findings in the discussion chapter to gain a more rounded understanding.
- Variable – you could isolate each variable in your study (where relevant) and specify how and whether the results changed.
Tables and figures
For your results, you are expected to convert your data into tables and figures, particularly when dealing with quantitative data. Making use of tables and figures is a way of contextualising your results within the study. It also helps to visually reinforce your written account of the data. However, make sure you’re only using tables and figures to supplement , rather than replace, your written account of the results (see the 'What to avoid' tab for more on this).
Figures and tables need to be numbered in order of when they appear in the dissertation, and they should be capitalised. You also need to make direct reference to them in the text, which you can do (with some variation) in one of the following ways:
Figure 1 shows…
The results of the test (see Figure 1) demonstrate…
The actual figures and tables themselves also need to be accompanied by a caption that briefly outlines what is displayed. For example:
Table 1. Variables of the regression model
Table captions normally appear above the table, whilst figures or other such graphical forms appear below, although it’s worth confirming this with your supervisor as the formatting can change depending on the school or discipline. The style guide used for writing in your subject area (e.g., Harvard, MLA, APA, OSCOLA) often dictates correct formatting of tables, graphs and figures, so have a look at your style guide for additional support.
Using quotations
If your qualitative data comes from interviews and focus groups, your data will largely consist of quotations from participants. When presenting this data, you should identify and group the most common and interesting responses and then quote two or three relevant examples to illustrate this point. Here’s a brief example from a qualitative study on the habits of online food shoppers:
Regardless of whether or not participants regularly engage in online food shopping, all but two respondents commented, in some form, on the convenience of online food shopping:
"It’s about convenience for me. I’m at work all week and the weekend doesn’t allow much time for food shopping, so knowing it can be ordered and then delivered in 24 hours is great for me” (Participant A).
"It fits around my schedule, which is important for me and my family” (Participant D).
"In the past, I’ve always gone food shopping after work, which has always been a hassle. Online food shopping, however, frees up some of my time” (Participant E).
As shown in this example, each quotation is attributed to a particular participant, although their anonymity is protected. The details used to identify participants can depend on the relevance of certain factors to the research. For instance, age or gender could be included.
Writing the discussion
The discussion chapter is where “you critically examine your own results in the light of the previous state of the subject as outlined in the background, and make judgments as to what has been learnt in your work” (Evans et al., 2014: 12). Whilst the results chapter is strictly factual, reporting on the data on a surface level, the discussion is rooted in analysis and interpretation , allowing you and your reader to delve beneath the surface.
Next, we will review some of the most important factors to consider when writing your discussion chapter.
Like the results, there is no single way to structure your discussion chapter. As always, it depends on the nature of your dissertation and whether you’re dealing with qualitative, quantitative or mixed-methods research. It’s good to be consistent with the results chapter, so you could structure your discussion chapter, where possible, in the same way as your results.
When it comes to structure, it’s particularly important that you guide your reader through the various points, subtopics or themes of your discussion. You should do this by structuring sections of your discussion, which might incorporate three or four paragraphs around the same theme or issue, in a three-part way that mirrors the typical three-part essay structure of introduction, main body and conclusion.

Figure 1: The three-part cycle that embodies a typical essay structure and reflects how you structure themes or subtopics in your discussion.
This is your topic sentence where you clearly state the focus of this paragraph/section. It’s often a fairly short, declarative statement in order to grab the reader’s attention, and it should be clearly related to your research purpose, such as responding to a research question.
This constitutes your analysis where you explore the theme or focus, outlined in the topic sentence, in further detail by interrogating why this particular theme or finding emerged and the significance of this data. This is also where you bring in the relevant secondary literature.
This is the evaluative stage of the cycle where you explicitly return back to the topic sentence and tell the reader what this means in terms of answering the relevant research question and establishing new knowledge. It could be a single sentence, or a short paragraph, and it doesn’t strictly need to appear at the end of every section or theme. Instead, some prefer to bring the main themes together towards the end of the discussion in a single paragraph or two. Either way, it’s imperative that you evaluate the significance of your discussion and tell the reader what this means.
A note on the three-part structure
This is often how you’re taught to construct a paragraph, but the themes and ideas you engage with at dissertation level are going to extend beyond the confines of a short paragraph. Therefore, this is a structure to guide how you write about particular themes or patterns in your discussion. Think of this structure like a cycle that you can engage in its smallest form to shape a paragraph; in a slightly larger form to shape a subsection of a chapter; and in its largest form to shape the entire chapter. You can 'level up' the same basic structure to accommodate a deeper breadth of thinking and critical engagement.
Using secondary literature
Your discussion chapter should return to the relevant literature (previously identified in your literature review ) in order to contextualise and deepen your reader’s understanding of the findings. This might help to strengthen your findings, or you might find contradictory evidence that serves to counter your results. In the case of the latter, it’s important that you consider why this might be and the implications for this. It’s through your incorporation of secondary literature that you can consider the question, ‘What do we now know that we didn’t before?’
Limitations
You may have included a limitations section in your methodology chapter (see our Writing the Methodology guide ), but it’s also common to have one in your discussion chapter. The difference here is that your limitations are directly associated with your results and the capacity to interpret and analyse those results.
Think of it this way: the limitations in your methodology refer to the issues identified before conducting the research, whilst the limitations in your discussion refer to the issues that emerged after conducting the research. For example, you might only be able to identify a limitation about the external validity or generalisability of your research once you have processed and analysed the data. Try not to overstress the limitations of your work – doing so can undermine the work you’ve done – and try to contextualise them, perhaps by relating them to certain limitations of other studies.
Recommendations
It’s often good to follow your limitations with some recommendations for future research. This creates a neat linearity from what didn’t work, or what could be improved, to how other researchers could address these issues in the future. This helps to reposition your limitations in a positive way by offering an action-oriented response. Try to limit the amount of recommendations you discuss – too many can bring the end of your discussion to a rather negative end as you’re ultimately focusing on what should be done, rather than what you have done. You also don’t need to repeat the recommendations in your conclusion if you’ve included them here.
What to avoid
This portion of the guide will cover some common missteps you should try to avoid in writing your results and discussion.
Over-reliance on tables and figures
It’s very common to produce visual representations of data, such as graphs and tables, and to use these representations in your results chapter. However, the use of these figures should not entirely replace your written account of the data. You don’t need to specify every detail in the data set, but you should provide some written account of what the data shows, drawing your reader’s attention to the most important elements of the data. The figures should support your account and help to contextualise your results. Simply stating, ‘look at Table 1’, without any further detail is not sufficient. Writers often try to do this as a way of saving words, but your markers will know!
Ignoring unexpected or contradictory data
Research can be a complex process with ups and downs, surprises and anomalies. Don’t be tempted to ignore any data that doesn’t meet your expectations, or that perhaps you’re struggling to explain. Failing to report on data for these, and other such reasons, is a problem because it undermines your credibility as a researcher, which inevitably undermines your research in the process. You have to do your best to provide some reason to such data. For instance, there might be some methodological reason behind a particular trend in the data.
Including raw data
You don’t need to include any raw data in your results chapter – raw data meaning unprocessed data that hasn’t undergone any calculations or other such refinement. This can overwhelm your reader and obscure the clarity of the research. You can include raw data in an appendix, providing you feel it’s necessary.
Presenting new results in the discussion
You shouldn’t be stating original findings for the first time in the discussion chapter. The findings of your study should first appear in your results before elaborating on them in the discussion.
Overstressing the significance of your research
It’s important that you clarify what your research demonstrates so you can highlight your own contribution to the research field. However, don’t overstress or inflate the significance of your results. It’s always difficult to provide definitive answers in academic research, especially with qualitative data. You should be confident and authoritative where possible, but don’t claim to reach the absolute truth when perhaps other conclusions could be reached. Where necessary, you should use hedging (see definition) to slightly soften the tone and register of your language.
Definition: Hedging refers to 'the act of expressing your attitude or ideas in tentative or cautious ways' (Singh and Lukkarila, 2017: 101). It’s mostly achieved through a number of verbs or adverbs, such as ‘suggest’ or ‘seemingly.’
Q: What’s the difference between the results and discussion?
A: The results chapter is a factual account of the data collected, whilst the discussion considers the implications of these findings by relating them to relevant literature and answering your research question(s). See the tab 'The Differences' in this guide for more detail.
Q: Should the discussion include recommendations for future research?
A: Your dissertation should include some recommendations for future research, but it can vary where it appears. Recommendations are often featured towards the end of the discussion chapter, but they also regularly appear in the conclusion chapter (see our Writing the Conclusion guide for more). It simply depends on your dissertation and the conventions of your school or department. It’s worth consulting any specific guidance that you’ve been given, or asking your supervisor directly.
Q: Should the discussion include the limitations of the study?
A: Like the answer above, you should engage with the limitations of your study, but it might appear in the discussion of some dissertations, or the conclusion of others. Consider the narrative flow and whether it makes sense to include the limitations in your discussion chapter, or your conclusion. You should also consult any discipline-specific guidance you’ve been given, or ask your supervisor for more. Be mindful that this is slightly different to the limitations outlined in the methodology or methods chapter (see our Writing the Methodology guide vs. the 'Discussion' tab of this guide).
Q: Should the results and discussion be in the first-person or third?
A: It’s important to be consistent , so you should use whatever you’ve been using throughout your dissertation. Third-person is more commonly accepted, but certain disciplines are happy with the use of first-person. Just remember that the first-person pronoun can be a distracting, but powerful device, so use it sparingly. Consult your lecturer for discipline-specific guidance.
Q: Is there a difference between the discussion and the conclusion of a dissertation?
A: Yes, there is a difference. The discussion chapter is a detailed consideration of how your findings answer your research questions. This includes the use of secondary literature to help contextualise your discussion. Rather than considering the findings in detail, the conclusion briefly summarises and synthesises the main findings of your study before bringing the dissertation to a close. Both are similar, particularly in the way they ‘broaden out’ to consider the wider implications of the research. They are, however, their own distinct chapters, unless otherwise stated by your supervisor.
The results and discussion chapters (or chapter) constitute a large part of your dissertation as it’s here where your original contribution is foregrounded and discussed in detail. Remember, the results chapter simply reports on the data collected, whilst the discussion is where you consider your research questions and/or hypothesis in more detail by interpreting and interrogating the data. You can integrate both into a single chapter and weave the interpretation of your findings throughout the chapter, although it’s common for both the results and discussion to appear as separate chapters. Consult your supervisor for further guidance.
Here’s a final checklist for writing your results and discussion. Remember that not all of these points will be relevant for you, so make sure you cover whatever’s appropriate for your dissertation. The asterisk (*) indicates any content that might not be relevant for your dissertation. To download a copy of the checklist to save and edit, please use the Word document, below.
- Results and discussion self-evaluation checklist

- << Previous: The Methodology
- Next: The Conclusion >>
- Last Updated: Apr 19, 2024 12:38 PM
- URL: https://library.soton.ac.uk/writing_the_dissertation
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Systematic Review
- Open access
- Published: 17 May 2024
Risk factors and incidence of central venous access device-related thrombosis in hospitalized children: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Maoling Fu 1 , 2 ,
- Quan Yuan 2 ,
- Qiaoyue Yang 1 , 2 ,
- Yaqi Yu 1 , 2 ,
- Wenshuai Song 1 , 2 ,
- Xiuli Qin 1 ,
- Ying Luo 1 ,
- Xiaoju Xiong 1 &
- Genzhen Yu 1
Pediatric Research ( 2024 ) Cite this article
66 Accesses
Metrics details
The risk factors for central venous access device-related thrombosis (CRT) in children are not fully understood. We used evidence-based medicine to find the risk factors for CRT by pooling current studies reporting risk factors of CRT, aiming to guide clinical diagnosis and treatment.
A systematic search of PubMed, Web of Science, Embase, Cochrane Library, Scopus, CNKI, Sinomed, and Wanfang databases was conducted. RevMan 5.4 was employed for data analysis.
The review included 47 studies evaluating 262,587 children with CVAD placement. Qualitative synthesis and quantitative meta-analysis identified D-dimer, location of insertion, type of catheter, number of lumens, catheter indwelling time, and central line-associated bloodstream infection as the most critical risk factors for CRT. Primarily due to observational design, the quality of evidence was regarded as low certainty for these risk factors according to the GRADE approach.
Because fewer high-quality studies are available, larger sample sizes and well-designed prospective studies are still needed to clarify the risk factors affecting CRT. In the future, developing pediatric-specific CRT risk assessment tools is important. Appropriate stratified preventive strategies for CRT according to risk assessment level will help improve clinical efficiency, avoid the occurrence of CRT, and alleviate unnecessary suffering of children.
This is the latest systematic review of risk factors and incidence of CRT in children.
A total of 47 studies involving 262,587 patients were included in our meta-analysis, according to which the pooled prevalence of CRT was 9.1%.
This study identified several of the most critical risk factors affecting CRT in children, including D-dimer, insertion location, type of catheter, number of lumens, catheter indwelling time, and central line-associated bloodstream infection (CLABSI).
Similar content being viewed by others
Acute kidney injury

Using National Early Warning Score (NEWS) 2 to help manage medical emergencies in the dental practice

Management of hypertensive crisis: British and Irish Hypertension Society Position document
Introduction.
Central venous access device (CVAD) is an infusion device inserted through different parts to make the tip of the catheter to the vena cava. In the clinic, CVAD is mainly divided into the following four categories: tunneled central venous catheter (CVC), nontunneled CVC, peripherally inserted central catheter (PICC), and totally implantable venous access port (TIVAP). 1 Pediatric patients often require stable, multifunctional, and comfortable long-term vascular access due to factors such as poor puncture cooperation, small vessel diameter, poor peripheral venous visibility and tolerance, high water content in the body leading to easy dehydration, and easy changes in condition after diseases. 2 The application of CVAD can significantly reduce the frequency of venipuncture, relieve the stimulation of drugs on the venous blood vessels, alleviate the pain and fear of the children, improve their medication compliance, ensure the effectiveness of intravenous infusion, and improve the quality of disease treatment. 3 , 4 , 5 Therefore, CVAD is widely used in pediatric clinics and has become an indispensable aspect of complex medical care for children with severe and chronic diseases.
Although CVAD has become an important tool in the pediatric treatment and nursing process, there are also risks of complications related to it, including CVAD-related thrombosis (CRT), phlebitis, fluid and blood leakage at the puncture point, catheter displacement, catheter obstruction, central line-associated bloodstream infection (CLABSI) and so on. 6 , 7 Among these, CRT is one of the most common and serious complications. The prevalence of CRT in children varies significantly by country, age, disease, and medical institution, ranging from 2 to 81%, 4 , 8 , 9 , 10 while in Chinese children without prophylactic treatment ranges from 20 to 66%. 11 , 12 CRT has no obvious clinical symptoms in the early stage, but it may still cause serious side effects, not only increasing the patient pain and medical costs but also delaying treatment timing, affecting prognosis and quality of life, and in severe cases, may even lead to thromboembolism, endangering life. 13 , 14 , 15
Identifying risk factors and incidence of CRT facilitates clinical practitioners in the early identification of high-risk patients, designing specific preventive strategies, treatment regimens, and management plans, thereby effectively reducing the incidence of CRT in hospitalized children and alleviating unnecessary patient suffering. However, most current research on CRT involves only small-scale groups in isolated nursing units or specific disease types. To date, no up-to-date systematic review provides pooled estimates of the risk factors and prevalence of CRT in children. Therefore, this study had a dual purpose: 1. to explore potential risk factors for CRT in children and to determine a pooled level of CRT prevalence; and 2. to provide evidence-based recommendations to improve the recognition, control, and treatment of CRT in children, as well as better nursing management for CRT.
This review was conducted following the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines. 16 The detailed research protocol can be accessed on the PROSPERO website (registration number: CRD42023421353).
Search strategy
Eight electronic databases were utilized to conduct a thorough literature search: PubMed, Web of Science, Embase, Cochrane Library, Scopus, China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), Sinomed, and Wanfang. The search in these databases was conducted from the earliest records available up to January 31st, 2024. The search strategy used a combination of Mesh terms and free words. The following Mesh terms and free words were mainly used: “child,” “children,” “adolescent,” “infant,” “pediatrics,” “central venous access device-related thrombosis,” “CRT,” “catheter-related thrombosis,” “catheter-related venous thrombosis,” “CVC-related thrombosis,” “risk factors,” “protective factors,” “predictors,” “causality,” “influencing factors”. The full search strategy for each database is available in the Supplementary Materials. In addition, we screened the reference lists of all included studies for relevant studies that met the criteria. Grey literature was searched as well. Some authors were contacted through email to gather more information or clarify any uncertainties.
Inclusion criteria
The study population was hospitalized children aged ≤18 years.
The primary research objective was to explore the risk factors for CRT.
The study results have at least one statistically significant predictor.
Case-control studies or cohort studies.
Published in English or Chinese.
Exclusion criteria
Catheter-related infection, catheter dysfunction, or other catheter complications as the primary outcome indicators.
Repeated published research.
Case reports, study designs, or clinical trials.
Reviews, editorials, letters, and conference abstracts.
In vitro or animal research.
Data were incomplete and could not be extracted.
Unable to find the original article.
Data extraction
Data from each eligible study were independently extracted by two reviewers using a pre-designed data collection form. Any disagreements were resolved by discussions among all authors. Data on the following characteristics were obtained from all included studies (see Supplementary Table S 1 for details):
Basic information: first author, country, year of publication, study duration, and study design.
Demographic characteristics: study population, sample size, number of CRT, and CRT rate.
Catheter-related features: catheter type, CRT type, and diagnostic method.
Potential risk factors for CRT: odds ratios (OR) or relative risks (RR) values and 95% confidence interval (CI) were extracted for each risk factor. If the study did not provide specific values, it was calculated by constructing a 2 × 2 contingency table.
Quality assessment
Two reviewers evaluated the quality of each study independently using the Risk of Bias Assessment for Nonrandomized Studies tool, 17 with any differences settled via group discussion. The tool assessed six domains of risk of bias: participant selection, confounding variables, exposure measurement, blinding of outcome assessment, incomplete outcome data, and selective outcome reporting. If all six domains were rated as low risk, the overall risk of bias for the study was low. The overall risk of bias was moderate if at least one domain was rated as unclear risk, and no domain was rated as high risk, and high if one or more domains were rated as high risk.
To ensure the accuracy of the assessment results, a third reviewer randomly selected five studies to check the data extraction and quality assessment.
Qualitative synthesis and quantitative meta-analysis
Qualitatively classify each risk factor as definite, likely, unclear, or not a risk factor based on the total number of studies with low and moderate bias risks and the proportion of studies demonstrating positive association (Box 1 in the supplementary material). If a risk factor was reported by more than two studies with low or moderate risk of bias, and the definition and reference range were sufficiently consistent, a quantitative meta-analysis was performed to estimate the combined OR.
Data were analyzed using Revman 5.4 software. In the meta-analysis of risk factors and CRT rate, the generic inverse variance method was applied, which only required effect estimate and standard error (SE). 18 The SE was obtained by inverse transforming the 95% CI applying the standard normal distribution. Heterogeneity tests were performed on the studies included in the Meta-analysis to examine for the combinability of the results of each independent study. P ≥ 0.05 and I-squared ( I 2 ) < 50% considered less heterogeneity between studies and therefore a fixed-effects model was chosen for the analysis, conversely, P < 0.05 or I 2 ≥ 50% considered greater heterogeneity, and a random-effects model was chosen.
Certainty of the evidence
The Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation (GRADE) method was used to assess the certainty of the evidence. In this method, observational studies were initially classified as low-quality evidence and then downgraded and upgraded according to five downgrading and three upgrading principles. The 5 downgrading factors included risk of bias, inconsistency, indirectness, imprecision, and publication bias, and the 3 upgrading factors included the magnitude of an effect, dose-response gradient, and effect of plausible residual confounding. Based on these considerations, the overall certainty of each piece of evidence was rated as one of four levels: high, moderate, low, or very low.
The initial search of the databases extracted a total of 4193 articles, of which 1656 were duplicates and removed. The titles and abstracts of the remaining 2537 articles were screened according to the inclusion criteria and 142 were selected for full-text search. After a rigorous eligibility review, 45 articles met the inclusion criteria. In addition, two articles were found to meet the eligibility criteria in a search of the reference lists of the selected articles and grey literature. In the end, a total of 47 articles were included in this review, of which 43 contributed to the qualitative synthesis and quantitative meta-analysis (Fig. 1 ).
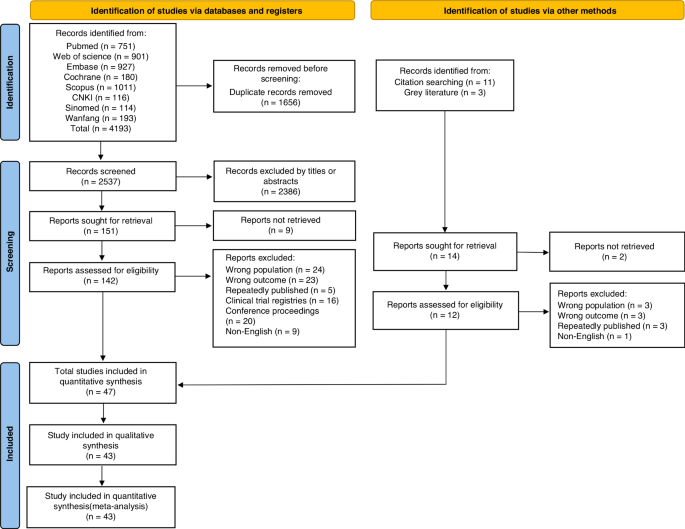
Demonstrate the screening and inclusion process for systematic literature search.
Of the 47 studies, 19 were prospective 4 , 13 , 19 , 20 , 21 , 22 , 23 , 24 , 25 , 26 , 27 , 28 , 29 , 30 , 31 , 32 , 33 , 34 , 35 and the rest were retrospective, 9 , 12 , 36 , 37 , 38 , 39 , 40 , 41 , 42 , 43 , 44 , 45 , 46 , 47 , 48 , 49 , 50 , 51 , 52 , 53 , 54 , 55 , 56 , 57 , 58 , 59 , 60 , 61 of which 10 were multicenter 4 , 9 , 13 , 21 , 23 , 26 , 27 , 28 , 49 , 59 and 37 were single-center. 12 , 19 , 20 , 22 , 24 , 25 , 29 , 30 , 31 , 32 , 33 , 34 , 35 , 36 , 37 , 38 , 39 , 40 , 41 , 42 , 43 , 44 , 45 , 46 , 47 , 48 , 50 , 51 , 52 , 53 , 54 , 55 , 56 , 57 , 58 , 60 , 61 The sample sizes ranged from 47 to 158,299, with the two largest being 71,782 13 and 158,299, 59 respectively. In addition, three studies constructed clinical prediction models. 22 , 28 , 47 Table 1 lists the summary characteristics of the included studies.
Study populations and CRT rates in included studies
These studies investigated a series of hospitalized children of different ages and departments, of which 12 studies with all hospitalized children as the study population, 12 studies with PICU hospitalized children as the study population, six studies with NICU hospitalized children as the study population, one study with all ICU hospitalized children as the study population, four studies with leukemia children as the study population, two studies with infants under 1-year-old as the study population, and the other ten studies with children with a specific disease as the study population.
The combined CRT rate was 9.1% (95% CI : 5.7–14.5%) with a high degree of heterogeneity ( I 2 = 100%). The combined CRT rate was 11.5% (95% CI : 5.7–23.1%; I 2 = 99%) in both male and female children. The frequency of CRT in PICU and NICU was available from 13 articles with 234,464 children and 7 articles with 6093 infants, which combined CRT rates were 10.7% (95% CI : 3.8–23.7%; I 2 = 100%), 2.9% (95% CI : 1.0–6.5%; I 2 = 96%), respectively. The combined CRT rate of children with leukemia was 13.0% (95% CI : 2.9–38.3%; I 2 = 98%) (Supplementary Material Figs. S 1 – 6 )
Quality of the CRT studies
The methodological quality of the included studies varied (Fig. 2 and Supplementary Material Fig. S 7 ). Nine studies had a low overall risk of bias, as all six domains were categorized as low risk. Four studies had a high overall risk of bias, three of which were associated with confounding variables and one to participant selection. The remaining 34 studies had a moderate overall risk of bias, with at least one of the six domains having an unclear risk.
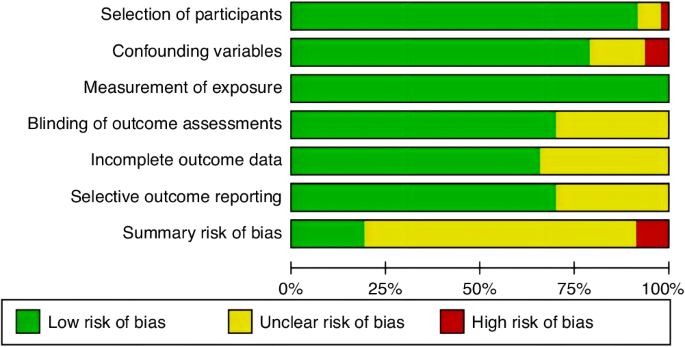
A summary presentation of the assessment results of risk of bias for the 47 studies.
Risk factors of CRT in included studies
The 47 included studies reported 61 statistically significant risk factors for CRT (Table 1 ). These factors were classified into three categories: patient-related risk factors (37.7%, 23/61); CVAD-related risk factors (34.4%, 21/61), and treatment-related risk factors (27.9%, 17/61).
Based on the qualitative synthesis, six variables were considered to be definite risk factors for CRT, including D-dimer, location of insertion, type of catheter, number of lumens, catheter indwelling time, and CLABSI. Eleven variables were considered likely associated with CRT, including gastrointestinal diseases, history of catheterization, thrombophilia, geographic location of line placement, catheter dysfunction, number of catheters, insertion length (cm), catheter to vein ratio, dialysis, hypertonic liquid, and cardiac catheterization. For 42 variables, the relationship with CRT was deemed unclear due to conflicting results from studies assessed as having low and moderate risk of bias, or because they were positively associated in only one study. Additionally, birth weight and gestational age were considered non-risk factors (Table 2 ).
Meta-analyses were implemented for risk factors that were reported by at least two low or moderate risk of bias studies with a consistent definition and reference range (Table 3 and Figs. 3 – 6 ).
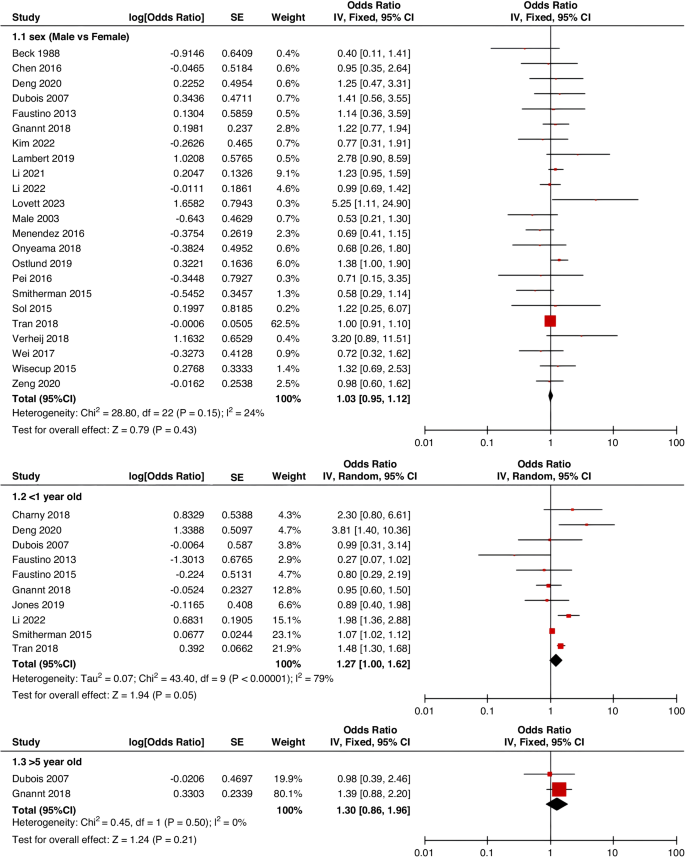
Forest plots of odds ratios (OR) that were included in the quantitative meta-analysis and the associated overall OR. For each OR, the size of the red square region is proportional to the corresponding study weight. Diamond shape intervals represent the overall OR. I 2 represents the fraction of variability among the individual OR that cannot be explained by sampling variability.
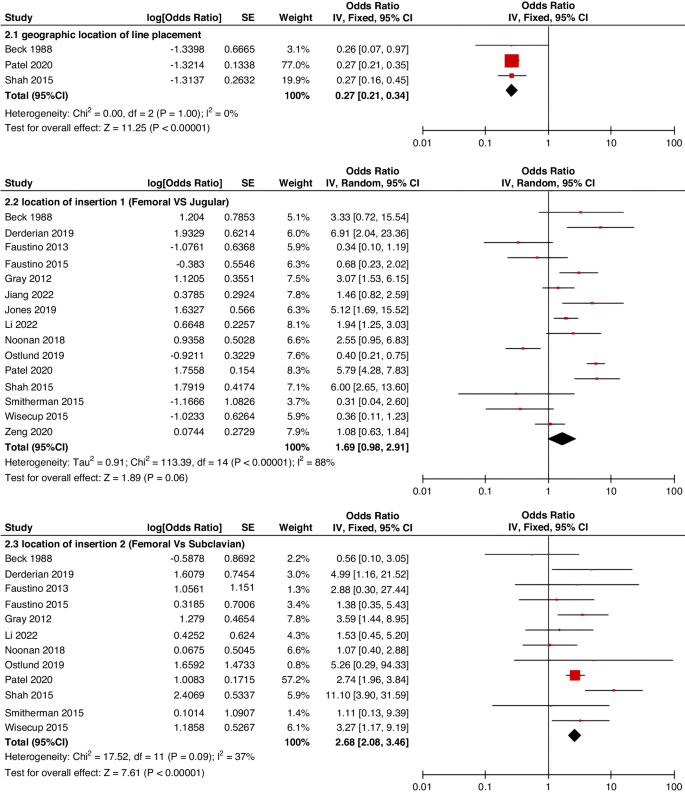
Forest plots of odds ratios (OR) that were included in the quantitative meta-analysis and the associated overall OR. For each OR, the size of the red square region is proportional to the corresponding study weight. Diamond shape intervals represent the overall OR. I 2 represents the fraction of variability among the individual OR that cannot be explained by sampling variability.
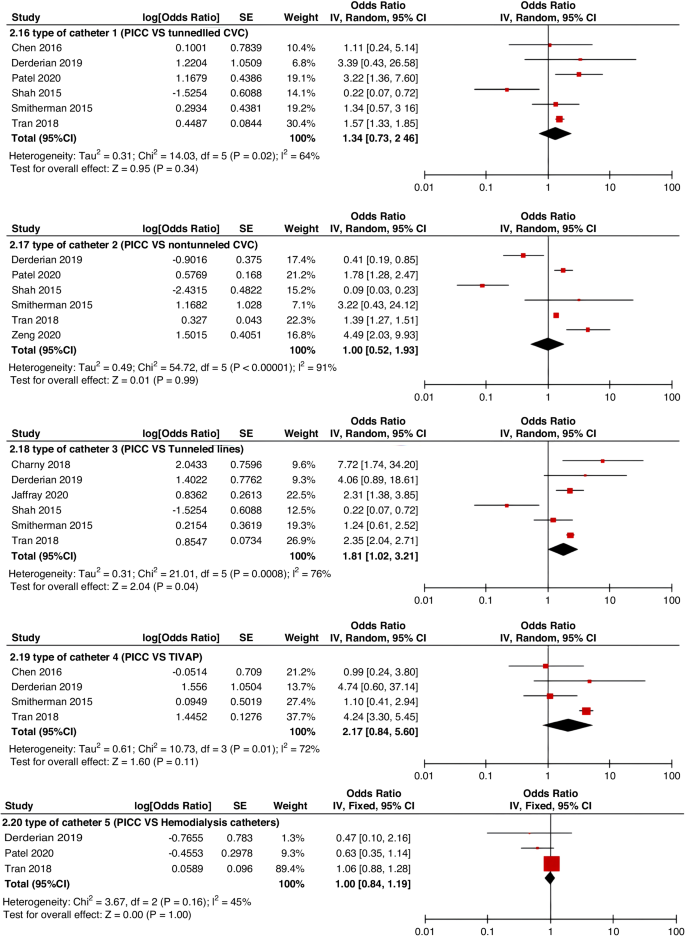
GRADE assessment of evidence
Supplementary Table S 2 shows GRADE assessments for the certainty of evidence. Due to the design of the observational studies, all evidence was initially rated as low certainty. Based on five downgrading and three upgrading principles, 17 pieces of evidence were still rated as low certainty, and the remaining 44 pieces of evidence were downgraded to very low certainty for serious inconsistency and imprecision.
Our study is the latest systematic review of risk factors and the incidence of CRT in hospitalized children. Based on 47 studies included in the current meta-analysis, which involved a total of 262,587 patients, the pooled prevalence of CRT is 9.1%. We conducted a qualitative synthesis analysis of 61 predictive factors and a quantitative meta-analysis of 38 factors, identifying six definite factors, 11 likely factors, and 42 unclear factors associated with CRT. Definite predictors included being of D-dimer, location of insertion, type of catheter, number of lumens, catheter indwelling time and CLABSI. The findings of our systematic review provide the latest comprehensive evidence summary that can inform the early identification of children at risk for CRT and the development of intervention measures to prevent and reduce CRT.
Implantable and temporary medical devices such as CVAD are exposed to blood for weeks to years depending on the type of CVAD in place. Since CVAD is an artificial surface and lacks an endothelial layer that inhibits platelet coagulation and adhesion, it is thought to potentially activate the contact pathways, ultimately leading to thrombosis. Assembly of artificial surface contact systems might be part of the host defense mechanism against foreign substances, but it can lead to kinin and thrombin generation, and complement activation. 62 This eventually promotes thrombosis and inflammation. The presence of CVAD is the most common risk factor for venous thromboembolism (VTE). CRT accounts for 10% of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) in adults and 50–80% in children. 10 , 55 , 63 The incidence of CRT in hospitalized children has increased significantly by 30–70% over the past 20 years, 64 , 65 which may cause serious medical complications besides increasing healthcare expenditures and length of stay.
We discover that a higher level of D-dimer is an independent risk factor for CRT in hospitalized children, consistent with the results of adult studies. 66 D-dimer is a soluble fibrin degradation product deriving from the plasmin-mediated degradation of cross-linked fibrin that is increased or positive in secondary hyperfibrinolysis, such as hypercoagulable states, disseminated intravascular coagulation, and thrombolytic therapy. 67 , 68 Increased D-dimer suggests an association with thrombotic disorders in the body of various origins and an increase in fibrinolytic activity. D-dimer has been extensively investigated for excluding the diagnosis of VTE and is used routinely for this indication. 67 , 69 Therefore, for early recognition and to reduce the incidence of CRT, D-dimer levels should be closely monitored before and after catheterization. However, the elevated D-dimer test results cannot fully explain the cause and location of CRT formation and must be analyzed in conjunction with clinical and other test results. Inherited thrombophilia, caused by genetic defects leading to a deficiency or abnormality in associated proteins, including protein C, protein S, antithrombin, the coagulation factor V Leiden mutation, and factor II mutation G20210A, 70 is considered a potential risk factor for CRT. The prevalence of thrombophilia varies widely among different populations, with a reported prevalence of 10% to 59% in pediatric VTE patients. 71 Children with gastrointestinal diseases like short bowel syndrome (SBS) and inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) have an increased risk of developing CRT during hospitalization. The precise mechanism behind this association is still uncertain according to current research. It may be attributed to the heightened inflammation levels during catheterization, particularly in patients with active IBD episodes or admissions during surgery, which leads to a period of increased inactivity. 55 This suggests that delaying placement during the most active period of inflammation may reduce the rate of thrombosis.
A narrative review pointed out that age is one of the most significant risk factors for VTE. In children, CRT shows a bimodal distribution, with the highest incidence rate in infancy and adolescence. 10 The higher incidence in infancy may be due in part to the smaller diameter of the vein, making insertion difficult and requiring multiple attempts. However, whether age is a risk factor for CRT is still highly controversial. The study by Chojnacka et al. did not find a statistically significant difference, 39 although a trend toward a similar bimodal distribution was found in the study population. Cancer, cardiovascular disease, sepsis, asphyxia, and neurological diseases are also considered unclear factors for CRT. Pediatric patients diagnosed with leukemia have multiple risk factors for VTE formation, such as the presence of hypercoagulable blast cells, the pro-thrombotic nature of the cancer itself, and treatment with steroids and L-asparaginase. Chen et al. 38 and Jaffray et al. 4 concluded that children with leukemia are more likely to develop CRT. Sepsis causes the coagulation mechanism to become fragile, which in turn activates the coagulation system and creates thrombosis. 72 However, a study by Onyeama et al. 52 showed that sepsis was significantly associated with a reduced incidence of CRT, and the exact mechanism is currently unknown.
The location of insertion and type of catheter are critical risk factors for CRT. The incidence of CRT is higher in femoral vein catheterizations compared to subclavian and jugular vein catheterizations in children, which is contrary to findings in adult patients. 73 The femoral location is a larger vessel and allows placement of a larger size catheter. Femoral CVAD is prioritized in urgent and emergency situations. In such cases, the patients tend to be more critically ill and often immobilized, further exacerbating the low-flow state. In addition, there may be vein compression and kinking beneath the inguinal ligament with leg movement, which may increase the risk of CRT. 27 PICC catheters provide a reliable medium to long-term route to intravenous therapy for children, but compared with other types of catheters, the risk of CRT is higher. We speculate that the long tunnel length and relatively large lumen size of the PICC, compared to the diameter of the vessel at the insertion site, may lead to increased blood flow obstruction. 52 Additionally, patients with PICC may be more likely to be diagnosed with symptomatic VTE than tunneled lines (TLs) because PICC is often placed in smaller vessels and journeys through the arm or leg causing limb pain and swelling, whereas TLs are located in the chest.
The risk of CRT increases with the number of lumens. A possible explanation for this finding is that multilumen catheters tend to have larger catheter sizes and thus occupy more area within the vessel lumen, leading to obstruction of normal blood flow within the veins. The relationship between CRT and CLABSI is bidirectional. Following catheter insertion, a fibrin sheath forms around the catheter. Microorganisms, especially staphylococcus aureus, easily adhere to the fibrin sheaths, and may lead to CLABSI. 74 Conversely, CLABSI can trigger inflammatory reactions, leading to further progression of thrombosis. CVAD duration is positively associated with the risk of CRT. Catheter placement may cause mechanical injury to the vein. As the indwelling duration increases, many damaged smooth muscle and endothelial cells become embedded within the fibrin, resulting in thrombus formation. In addition, prolonged indwelling increases the chance of platelet contact with the vessel lining, activating coagulation factors and thrombin, increasing the risk of thrombosis. 22 Therefore, nurses should perform routine maintenance of the catheter in children who require long-term CVAD indwelling. The duration of CVAD should be monitored, the necessity of its indwelling should be assessed daily, and the catheter should be removed as early as possible while ensuring treatment.
As obstruction of venous blood flow from the CVAD is considered an essential causative mechanism for the development of VTE, a high ratio between catheter size and vein diameter could be a risk factor for CRT. The 2012 international guidelines on pediatric CVC insertion recommend that the ratio between the catheter’s external diameter and the cannulated vein’s diameter should not exceed 0.33. 75 However, this suggestion is only based on expert opinions and currently lacks relevant clinical data support. Therefore, further research is still needed to verify it. Catheter dysfunction is mainly caused by small clots or fibrous sheaths wrapping around the tip of the catheter. Prolonged accumulation may lead to incomplete or complete blockage of blood vessels, becoming a gathering point for thrombosis. 74 Journeycake et al. observed that the risk of VTE was highest in pediatric cancer patients with multiple episodes of catheter dysfunction. 76 A study of pediatric brain tumor patients reported that VTE was more common in patients with catheter dysfunction. 77 Thus, these studies and the current data support the need to consider catheter dysfunction as a possible risk factor for CRT and to design further screening and intervention studies for early identification and prevention of catheter dysfunction.
The rationale for studying the relationship between the insertion side of CVAD and the risk of CRT is based on the anatomy of the upper body venous system. The left brachiocephalic vein is longer and courses more horizontally than the right side, thus entering the superior vena cava at a sharper angle. The right jugular vein is the most direct and shortest route for the CVAD to enter the heart. By contrast, the CVAD located in the left jugular vein has a greater distance to the heart and passes through 2 angles in the venous system, which may cause endothelial damage and increase the likelihood of blood flow obstruction and venous wall adhesion. 26 However, our meta-analysis did not find a statistically significant increase in the risk of CRT with left-sided placement compared to right-sided placement. The ideal location for the catheter tip is the junction of the superior vena cava and the right atrium. This location is preferred because of the higher blood flow rate, which may be protective against thrombosis. 43 Currently, the pediatric literature on the effect of optimal tip position on CRT is scarce and inconclusive. In addition, catheter tips do not always remain in that position after initial placement. Therefore, tip movement should be a significant concern in pediatric patients, especially active, growing, and requiring long-term catheter use.
Providing renal replacement therapy is a lifelong task for pediatric end-stage renal disease (ESRD) patients. Although successful transplantation can be achieved even in young patients, the lifespan of the graft is limited. Consequently, many transplant recipients may be put back on dialysis as part of their ESRD treatment. 78 CVC remains the main vascular access for hemodialysis in children. Long-term reliance on CVC is related to a high incidence of catheter dysfunction and failure. The frequent need for recurrent CVC placement in such patients leads to an elevated risk of central vein stenosis and CRT. Cardiac catheterization is also a possible risk factor for CRT. Appropriate anticoagulation is required during catheterization, without which the risk of thrombosis is up to 40%. However, the use of unfractionated heparin in pediatric patients is challenging because the coagulation system and heparin response are different from that of adults. 79 There’s a need for further research to determine if children are receiving adequate doses of heparin during cardiac catheterization to prevent thrombosis without increasing the risk of bleeding complications. The incidence of VTE in adult patients who are chronically bedridden and braked is 3.59 times higher than in patients with normal activity levels. 80 In critically ill or surgical children, mechanical ventilation is often performed in the early stages, requiring continuous use of multiple sedative or inotropic drugs to reduce cardiac load and protect pulmonary function. During sedation, the child is in a braked state, limb activity is reduced or even inactive, blood flow slows down, and blood stagnates in the veins, increasing the chance of platelet adhesion to the endothelium, which may increase the risk of CRT. Therefore, passive movements such as limb abduction, internal rotation, elbow flexion and elbow extension should be performed appropriately when the child’s condition permits.
Nutritional support is an important part of critical illness treatment, including enteral and parenteral nutrition (PN). CVAD is the supply channel for total parenteral nutrition (TPN), and some children may even need this method to provide calories for a long time. High glucose and calcium concentrations in PN are both possible triggers of CRT, and PN has been shown to upregulate the extrinsic coagulation cascade, especially with long-term use. 60 Diamanti et al. reported that the incidence rate of TPN complicated with CRT was 20%. 81 Mannitol or glycerol fructose are widely used as hypertonic drugs in clinical practice, which can increase plasma osmolality to dehydrate tissues after entering the body. At the same time, it may cause a cellular stress response, induce apoptosis, and can activate inflammatory cytokines and coagulation pathways to induce thrombosis. Jiang et al. 22 found vasoactive drugs to be a risk factor for CRT. The possible reason is that vasoactive drugs can cause strong vasoconstriction, endothelial function damage or impairment, and promote fibrinogen synthesis. However, this is contrary to the findings of Marquez et al. 28 and Faustino et al. 21 Therefore, larger prospective studies are still needed to assess this risk factor more precisely.
The strengths of this study include the systematic identification of all relevant studies of risk factors for CRT in hospitalized children and the classification of risk factors into three categories, patient-related risk factors, CVAD-related risk factors, and treatment-related risk factors, to offer a logical progression of the possible causes of CRT in children. However, several limitations of this systematic review should be stated. Firstly, as most of the studies originate from Western countries, extrapolating these results to Eastern populations is questionable. Second, significant heterogeneity was encountered in our analysis, potentially stemming from variations in regimen, duration, population enrolled, and center setting, among other factors. This diversity necessitates a cautious interpretation of the results. In addition, only a few high-quality studies with a low risk of bias, and many of the studies suffer from significant sources of bias. Furthermore, the effect in many occasions was assessed by very few studies. Therefore, the evidence to support it is low, which needs to be validated in future studies. Finally, risk factors for CRT could not be made causal assertions since the majority of studies were retrospective.
Conclusions
In conclusion, we have identified several critical factors that affect CRT, including D-dimer, location of insertion, type of catheter, number of lumens, catheter indwelling time, and CLABSI. Nevertheless, none of the included studies considered the impact of socio-demographic factors on CRT, such as parental education level, occupation, and family economic status. Therefore, larger sample sizes and well-designed prospective studies are still needed to clarify the predictors affecting CRT in the future. In addition, there is a lack of pediatric-specific CRT risk assessment tools, which need to be further developed and validated. Machine learning (ML), as a method for designing risk assessment models that help to efficiently explore and mine useful information, has been widely used in recent years to solve a variety of challenging medical problems. Likewise, the application of ML in CRT risk diagnosis may contribute to a more precise assessment. In clinical practice, it is necessary to take appropriate stratified preventive measures according to the level of CRT risk assessment of children, to improve the efficiency of clinical work, reduce the burden of clinical work, and minimize the occurrence of CRT under the premise of ensuring the safety of children.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Yeow, M. et al. A systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials on choice of central venous access device for delivery of chemotherapy. J. Vasc. Surg. Venous Lymphat. Disord. 10 , 1184–91.e8 (2022).
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Cellini, M. et al. Guidelines of the Italian Association of Pediatric Hematology and Oncology for the management of the central venous access devices in pediatric patients with onco-hematological disease. J. Vasc. Access 23 , 3–17 (2022).
Ares, G. & Hunter, C. J. Central venous access in children: indications, devices, and risks. Curr. Opin. Pediatr. 29 , 340–346 (2017).
Jaffray, J. et al. Peripherally inserted central catheters lead to a high risk of venous thromboembolism in children. Blood 135 , 220–226 (2020).
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Zhang, J. J. et al. Factors affecting mechanical complications of central venous access devices in children. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 38 , 1067–1073 (2022).
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Akhtar, N. & Lee, L. Utilization and Complications of Central Venous Access Devices in Oncology Patients. Curr. Oncol. 28 , 367–377 (2021).
Ullman, A. J., Marsh, N., Mihala, G., Cooke, M. & Rickard, C. M. Complications of Central Venous Access Devices: A Systematic Review. Pediatrics 136 , e1331–e1344 (2015).
Östlund, Å. et al. Erratum to ‘Incidence of and risk factors for venous thrombosis in children with percutaneous non-tunnelled central venous catheters’ (Br J Anaesth 2019; 123: 316-24). Br. J. Anaesth. 123 , 918 (2019).
McLaughlin, C. M. et al. Symptomatic catheter-associated thrombosis in pediatric trauma patients: Choose your access wisely. Surgery 166 , 1117–1121 (2019).
Citla Sridhar, D., Abou-Ismail, M. Y. & Ahuja, S. P. Central venous catheter-related thrombosis in children and adults. Thromb. Res. 187 , 103–112 (2020).
Zhou, X. et al. A retrospective analysis of risk factors associated with catheter-related thrombosis: a single-center study. Perfusion 35 , 806–813 (2020).
Li, S. et al. Risk factors for central venous catheter-related thrombosis in hospitalized children: a single-center a retrospective cohort study. Transl. Pediatr. 11 , 1840–1851 (2022).
Patel, N., Petersen, T. L., Simpson, P. M., Feng, M. & Hanson, S. J. Rates of Venous Thromboembolism and Central Line-Associated Bloodstream Infections Among Types of Central Venous Access Devices in Critically Ill Children. Crit. Care Med. 48 , 1340–1348 (2020).
Timsit, J. F. et al. A state of the art review on optimal practices to prevent, recognize, and manage complications associated with intravascular devices in the critically ill. Intensive Care Med. 44 , 742–759 (2018).
Ullman, A. J. et al. Pediatric central venous access devices: practice, performance, and costs. Pediatr. Res. 92 , 1381–1390 (2022).
Hutton, B. et al. The PRISMA extension statement for reporting of systematic reviews incorporating network meta-analyses of health care interventions: checklist and explanations. Ann. Intern Med. 162 , 777–784 (2015).
Kim, S. Y. et al. Testing a tool for assessing the risk of bias for nonrandomized studies showed moderate reliability and promising validity. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 66 , 408–414 (2013).
Borenstein, M., Hedges, L. V., Higgins, J. P. & Rothstein, H. R. A basic introduction to fixed-effect and random-effects models for meta-analysis. Res. Synth. Methods 1 , 97–111 (2010).
Beck, C., Dubois, J., Grignon, A., Lacroix, J. & David, M. Incidence and risk factors of catheter-related deep vein thrombosis in a pediatric intensive care unit: a prospective study. J. Pediatr. 133 , 237–241 (1998).
Dubois, J. et al. Incidence of deep vein thrombosis related to peripherally inserted central catheters in children and adolescents. Cmaj 177 , 1185–1190 (2007).
Faustino, E. V. et al. Incidence and acute complications of asymptomatic central venous catheter-related deep venous thrombosis in critically ill children. J. Pediatr. 162 , 387–391 (2013).
Jiang, W. et al. Construction and validation of a risk prediction model for central venous catheter-associated deep venous thromboses in children with congenital heart disease after surgery. Chin. J. Nurs. 57 , 2217–2224 (2022).
Google Scholar
Faustino, E. V. et al. Factor VIII May Predict Catheter-Related Thrombosis in Critically Ill Children: A Preliminary Study. Pediatr. Crit. Care Med. 16 , 497–504 (2015).
Jones, S., Butt, W., Monagle, P., Cain, T. & Newall, F. The natural history of asymptomatic central venous catheter-related thrombosis in critically ill children. Blood 133 , 857–866 (2019).
Kim, E. H. et al. Central venous catheter-related thrombosis in pediatric surgical patients: A prospective observational study. Paediatr. Anaesth. 32 , 563–571 (2022).
Male, C. et al. Central venous line-related thrombosis in children: association with central venous line location and insertion technique. Blood 101 , 4273–4278 (2003).
Male, C., Julian, J. A., Massicotte, P., Gent, M. & Mitchell, L. Significant association with location of central venous line placement and risk of venous thrombosis in children. Thromb. Haemost. 94 , 516–521 (2005).
Marquez, A., Shabanova, V. & Faustino, E. V. Prediction of Catheter-Associated Thrombosis in Critically Ill Children. Pediatr. Crit. Care Med. 17 , e521–e528 (2016).
Menéndez, J. J. et al. Incidence and risk factors of superficial and deep vein thrombosis associated with peripherally inserted central catheters in children. J. Thromb. Haemost. 14 , 2158–2168 (2016).
Rubio Longo, M. C. et al. Catheter-related deep vein thrombosis in newborn infants. Arch. Argent. Pediatr. 119 , 32–38 (2021).
PubMed Google Scholar
Östlund, Å. et al. Incidence of and risk factors for venous thrombosis in children with percutaneous non-tunnelled central venous catheters. Br. J. Anaesth. 123 , 316–324 (2019).
Sol, J. J. et al. Chronic Complications After Femoral Central Venous Catheter-related Thrombosis in Critically Ill Children. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 37 , 462–467 (2015).
van Rooden, C. J. et al. Infectious complications of central venous catheters increase the risk of catheter-related thrombosis in hematology patients: a prospective study. J. Clin. Oncol. 23 , 2655–2660 (2005).
Zeng, X., Zhang, C. & Shi, Y. Analysis of risk factors for complicated catheter-related thrombosis in children. Chin. J. Emerg. Med. 29 , 719–723 (2020).
Wei, Y. et al. The incidence and risk factors of catheter-related-thrombosis during induction chemotherapy in acute lymphocytic leukemia children. Chin. J. Hematol. 38 , 313–317 (2017).
CAS Google Scholar
Deng, G. & Liao, Q. Analysis of risk factors for venous thrombosis after PICC placement in critically ill children. Int. I Nurs. 39 , 775–777 (2020).
Badheka, A. V. et al. Catheter related thrombosis in hospitalized infants: A neural network approach to predict risk factors. Thromb. Res. 200 , 34–40 (2021).
Chen, K. et al. Risk factors for central venous catheter-related thrombosis in children: a retrospective analysis. Blood Coagul. Fibrinol. 27 , 384–388 (2016).
Article Google Scholar
Chojnacka, K., Krasiński, Z., Wróblewska-Seniuk, K. & Mazela, J. Catheter-related venous thrombosis in NICU: A case-control retrospective study. J. Vasc. Access 23 , 88–93 (2022).
Derderian, S. C., Good, R., Vuille-Dit-Bille, R. N., Carpenter, T. & Bensard, D. D. Central venous lines in critically ill children: Thrombosis but not infection is site dependent. J. Pediatr. Surg. 54 , 1740–1743 (2019).
Diamond, C. E. et al. Catheter-Related Venous Thrombosis in Hospitalized Pediatric Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Incidence, Characteristics, and Role of Anticoagulant Thromboprophylaxis with Enoxaparin. J. Pediatr. 198 , 53–59 (2018).
Noailly Charny, P. A. et al. Increased Risk of Thrombosis Associated with Peripherally Inserted Central Catheters Compared with Conventional Central Venous Catheters in Children with Leukemia. J. Pediatr. 198 , 46–52 (2018).
Gnannt, R. et al. Increased risk of symptomatic upper-extremity venous thrombosis with multiple peripherally inserted central catheter insertions in pediatric patients. Pediatr. Radio. 48 , 1013–1020 (2018).
Gray, B. W. et al. Characterization of central venous catheter-associated deep venous thrombosis in infants. J. Pediatr. Surg. 47 , 1159–1166 (2012).
Haddad, H. et al. Routine surveillance ultrasound for the management of central venous catheters in neonates. J. Pediatr. 164 , 118–122 (2014).
Lambert, I., Tarima, S., Uhing, M. & Cohen, S. S. Risk Factors Linked to Central Catheter-Associated Thrombosis in Critically Ill Infants in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit. Am. J. Perinatol. 36 , 291–295 (2019).
Li, H. et al. Prediction of central venous catheter-associated deep venous thrombosis in pediatric critical care settings. BMC Med. Inf. Decis. Mak. 21 , 332 (2021).
Article CAS Google Scholar
Lovett, M. E. et al. Catheter-associated deep vein thrombosis in children with severe traumatic brain injury: A single-center experience. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 70 , e30044 (2023).
MacLean, J. et al. Need for tissue plasminogen activator for central venous catheter dysfunction is significantly associated with thrombosis in pediatric cancer patients. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 65 , e27015 (2018).
Noonan, P. J., Hanson, S. J., Simpson, P. M., Dasgupta, M. & Petersen, T. L. Comparison of Complication Rates of Central Venous Catheters Versus Peripherally Inserted Central Venous Catheters in Pediatric Patients. Pediatr. Crit. Care Med. 19 , 1097–1105 (2018).
Pei, L. et al. Clinical characteristics and risk factors of symptomatic central venous catheter-related deep vein thrombosis in children. Chin. Pediatr. Emerg. Med. 23 , 450–454 (2016).
Onyeama, S. N. et al. Central Venous Catheter-associated Venous Thromboembolism in Children With Hematologic Malignancy. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 40 , e519–e524 (2018).
Shah, S. H. et al. Clinical risk factors for central line-associated venous thrombosis in children. Front. Pediatr. 3 , 35 (2015).
Shin, H. S., Towbin, A. J., Zhang, B., Johnson, N. D. & Goldstein, S. L. Venous thrombosis and stenosis after peripherally inserted central catheter placement in children. Pediatr. Radio. 47 , 1670–1675 (2017).
Smitherman, A. B. et al. The incidence of catheter-associated venous thrombosis in noncritically ill children. Hosp. Pediatr. 5 , 59–66 (2015).
Steen, E. H. et al. Central Venous Catheter-Related Deep Vein Thrombosis in the Pediatric Cardiac Intensive Care Unit. J. Surg. Res 241 , 149–159 (2019).
Wang, J. & Ren, G. Peripherally inserted central catheter related venous thromboembolism in children with acute leukemia: a factorial analysis. Chin. J. Biomed. Eng. 27 , 288–293 (2021).
Dubbink-Verheij, G. H. et al. Femoral Vein Catheter is an Important Risk Factor for Catheter-related Thrombosis in (Near-)term Neonates. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 40 , e64–e68 (2018).
Tran, M., Shein, S. L., Ji, X. & Ahuja, S. P. Identification of a “VTE-rich” population in pediatrics - Critically ill children with central venous catheters. Thromb. Res 161 , 73–77 (2018).
Wisecup, S., Eades, S. & Turiy, Y. Characterizing the Risk Factors Associated With Venous Thromboembolism in Pediatric Patients After Central Venous Line Placement. J. Pediatr. Pharm. Ther. 20 , 358–366 (2015).
Zhu, W., Zhang, H., Xing, Y. Clinical Characteristics of Venous Thrombosis Associated with Peripherally Inserted Central Venous Catheter in Premature Infants. Children 9 , https://doi.org/10.3390/children9081126 (2022).
Ekdahl, K. N. et al. Innate immunity activation on biomaterial surfaces: a mechanistic model and coping strategies. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 63 , 1042–1050 (2011).
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Takemoto, C. M. et al. Hospital-associated venous thromboembolism in children: incidence and clinical characteristics. J. Pediatr. 164 , 332–338 (2014).
Boulet, S. L. et al. Trends in venous thromboembolism-related hospitalizations, 1994-2009. Pediatrics 130 , e812–e820 (2012).
Raffini, L., Huang, Y. S., Witmer, C. & Feudtner, C. Dramatic increase in venous thromboembolism in children’s hospitals in the United States from 2001 to 2007. Pediatrics 124 , 1001–1008 (2009).
Lin, S., Zhu, N., YihanZhang, Du, L. & Zhang, S. Development and validation of a prediction model of catheter-related thrombosis in patients with cancer undergoing chemotherapy based on ultrasonography results and clinical information. J. Thromb. Thrombolysis 54 , 480–491 (2022).
Johnson, E. D., Schell, J. C. & Rodgers, G. M. The D-dimer assay. Am. J. Hematol. 94 , 833–839 (2019).
Favresse, J. et al. D-dimer: Preanalytical, analytical, postanalytical variables, and clinical applications. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab Sci. 55 , 548–577 (2018).
Weitz, J. I., Fredenburgh, J. C. & Eikelboom, J. W. A Test in Context: D-Dimer. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 70 , 2411–2420 (2017).
Darlow, J. & Mould, H. Thrombophilia testing in the era of direct oral anticoagulants. Clin. Med. 21 , e487–e491 (2021).
Monagle, P. et al. American Society of Hematology 2018 Guidelines for management of venous thromboembolism: treatment of pediatric venous thromboembolism. Blood Adv. 2 , 3292–3316 (2018).
Meziani, F., Gando, S. & Vincent, J. L. Should all patients with sepsis receive anticoagulation? Yes. Intensive Care Med 43 , 452–454 (2017).
Saber, W. et al. Risk factors for catheter-related thrombosis (CRT) in cancer patients: a patient-level data (IPD) meta-analysis of clinical trials and prospective studies. J. Thromb. Haemost. 9 , 312–319 (2011).
Journeycake, J. M. & Buchanan, G. R. Thrombotic complications of central venous catheters in children. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 10 , 369–374 (2003).
Lamperti, M. et al. International evidence-based recommendations on ultrasound-guided vascular access. Intensive Care Med 38 , 1105–1117 (2012).
Journeycake, J. M. & Buchanan, G. R. Catheter-related deep venous thrombosis and other catheter complications in children with cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 24 , 4575–4580 (2006).
Deitcher, S. R., Gajjar, A., Kun, L. & Heideman, R. L. Clinically evident venous thromboembolic events in children with brain tumors. J. Pediatr. 145 , 848–850 (2004).
Mandel-Shorer, N., Tzvi-Behr, S., Harvey, E. & Revel-Vilk, S. Central venous catheter-related venous thrombosis in children with end-stage renal disease undergoing hemodialysis. Thromb. Res 172 , 150–157 (2018).
Chen, D., Långström, S., Petäjä, J., Heikinheimo, M. & Pihkala, J. Thrombin formation and effect of unfractionated heparin during pediatric cardiac catheterization. Catheter Cardiovasc Inter. 81 , 1174–1179 (2013).
Reynolds, P. M. et al. Evaluation of Prophylactic Heparin Dosage Strategies and Risk Factors for Venous Thromboembolism in the Critically Ill Patient. Pharmacotherapy 39 , 232–241 (2019).
Diamanti, A. et al. Prevalence of life-threatening complications in pediatric patients affected by intestinal failure. Transpl. Proc. 39 , 1632–1633 (2007).
Download references
This study was supported by the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities [grant numbers YCJJ20230244] and Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology Research Fund [grant numbers 2022C09].
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Nursing, Tongji Hospital, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China
Maoling Fu, Qiaoyue Yang, Yaqi Yu, Wenshuai Song, Xiuli Qin, Ying Luo, Xiaoju Xiong & Genzhen Yu
School of Nursing, Tongji Medical College, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China
Maoling Fu, Quan Yuan, Qiaoyue Yang, Yaqi Yu & Wenshuai Song
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
GY and YL framed the review questions on the basis of input from MF and QY. YY and XQ conducted the literature search. MF, WS, and QY screened and evaluated the identified papers. GY and YY performed data extraction and analysis. MF, WS, XQ and QY prepared the initial manuscript with revisions and comments from GY, YL, and XX. All authors approved the final manuscript as submitted and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Genzhen Yu .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary checklist, supplemental digital tables1, supplemental digital tables2, supplemental digital, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Fu, M., Yuan, Q., Yang, Q. et al. Risk factors and incidence of central venous access device-related thrombosis in hospitalized children: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pediatr Res (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41390-024-03225-0
Download citation
Received : 06 October 2023
Revised : 18 March 2024
Accepted : 25 March 2024
Published : 17 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1038/s41390-024-03225-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies

Fully automated hematoma expansion prediction from non-contrast computed tomography in spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage patients
- Find this author on Google Scholar
- Find this author on PubMed
- Search for this author on this site
- ORCID record for Natasha Ironside
- For correspondence: [email protected]
- ORCID record for Kareem El Naamani
- ORCID record for Tanvir Rizvi
- ORCID record for Ching-Jen Chen
- ORCID record for Stephan Mayer
- Info/History
- Preview PDF
Background Hematoma expansion is an independent predictor of poor neurological outcome after spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH), and a promising quantifiable and modifiable therapeutic target. Practical tools to identify patients at risk of hematoma expansion are lacking, limiting early preventative intervention. We hypothesized that three-dimensional transport-based morphometry (3D-TBM), could automatically predict future hematoma expansion from non-contrast computed tomography (NCCT) images at the time of hospital presentation.
Methods One hundred and seventy spontaneous ICH patients enrolled in the multi-center international Virtual International Trials of Stroke Archive (VISTA-ICH), were separated into training (60%) and testing (40%) cohorts for model derivation and validation, respectively. A unique transport-based representation was produced from each presentation NCCT hematoma image for statistical analysis. The 3D-TBM model was interrogated to visualize the physical hematoma characteristics predictive of future expansion.
Results 3D-TBM outperformed each of the existing clinician-based BAT, Brain, Heavn, NAG and 10-point NCCT hematoma expansion prediction scores in the testing dataset. 3D-TBM adjusted for location and clinical information predicted hematoma expansion in the testing dataset with an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) of 0.698 (95% CI 0.695-0.702), while the AUROC for the best performing clinician method, the Heavn score, was 0.663 (95% CI 0.660–0.666). The predominant hematoma characteristics predicting future expansion were larger size, textural heterogeneity, shape irregularity and peripheral intensity distribution.
Discussion We present a quantitative method that outperformed clinicians and permitted visualization of the morphometric features for predicting hematoma expansion from NCCT in ICH patients. Our study contributes insight into the underlying mechanisms driving hematoma expansion and suggests that it can be identified at a reversible stage.
Competing Interest Statement
The authors have declared no competing interest.
Funding Statement
No external funding was received
Author Declarations
I confirm all relevant ethical guidelines have been followed, and any necessary IRB and/or ethics committee approvals have been obtained.
The details of the IRB/oversight body that provided approval or exemption for the research described are given below:
Not applicable. This study uses data that were not collected specifically for this study and no one on our study team had access to the subject identifiers linked to the specimens or data. Therefore, this study is not considered human subjects research. Because it is not considered human subjects research, an IRB exemption was not required to conduct this study. T
I confirm that all necessary patient/participant consent has been obtained and the appropriate institutional forms have been archived, and that any patient/participant/sample identifiers included were not known to anyone (e.g., hospital staff, patients or participants themselves) outside the research group so cannot be used to identify individuals.
I understand that all clinical trials and any other prospective interventional studies must be registered with an ICMJE-approved registry, such as ClinicalTrials.gov. I confirm that any such study reported in the manuscript has been registered and the trial registration ID is provided (note: if posting a prospective study registered retrospectively, please provide a statement in the trial ID field explaining why the study was not registered in advance).
I have followed all appropriate research reporting guidelines, such as any relevant EQUATOR Network research reporting checklist(s) and other pertinent material, if applicable.
Data Availability
Data used for his manuscript is available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
View the discussion thread.
Thank you for your interest in spreading the word about medRxiv.
NOTE: Your email address is requested solely to identify you as the sender of this article.

Citation Manager Formats
- EndNote (tagged)
- EndNote 8 (xml)
- RefWorks Tagged
- Ref Manager
- Tweet Widget
- Facebook Like
- Google Plus One
Subject Area
- Addiction Medicine (324)
- Allergy and Immunology (628)
- Anesthesia (165)
- Cardiovascular Medicine (2381)
- Dentistry and Oral Medicine (289)
- Dermatology (207)
- Emergency Medicine (380)
- Endocrinology (including Diabetes Mellitus and Metabolic Disease) (838)
- Epidemiology (11777)
- Forensic Medicine (10)
- Gastroenterology (703)
- Genetic and Genomic Medicine (3751)
- Geriatric Medicine (350)
- Health Economics (635)
- Health Informatics (2401)
- Health Policy (933)
- Health Systems and Quality Improvement (899)
- Hematology (341)
- HIV/AIDS (782)
- Infectious Diseases (except HIV/AIDS) (13320)
- Intensive Care and Critical Care Medicine (768)
- Medical Education (366)
- Medical Ethics (105)
- Nephrology (398)
- Neurology (3510)
- Nursing (198)
- Nutrition (528)
- Obstetrics and Gynecology (675)
- Occupational and Environmental Health (665)
- Oncology (1825)
- Ophthalmology (538)
- Orthopedics (219)
- Otolaryngology (287)
- Pain Medicine (233)
- Palliative Medicine (66)
- Pathology (446)
- Pediatrics (1035)
- Pharmacology and Therapeutics (426)
- Primary Care Research (420)
- Psychiatry and Clinical Psychology (3180)
- Public and Global Health (6149)
- Radiology and Imaging (1280)
- Rehabilitation Medicine and Physical Therapy (749)
- Respiratory Medicine (828)
- Rheumatology (379)
- Sexual and Reproductive Health (372)
- Sports Medicine (323)
- Surgery (402)
- Toxicology (50)
- Transplantation (172)
- Urology (146)

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The results chapter (also referred to as the findings or analysis chapter) is one of the most important chapters of your dissertation or thesis because it shows the reader what you've found in terms of the quantitative data you've collected. It presents the data using a clear text narrative, supported by tables, graphs and charts.
Reporting quantitative research results. If you conducted quantitative research, you'll likely be working with the results of some sort of statistical analysis.. Your results section should report the results of any statistical tests you used to compare groups or assess relationships between variables.It should also state whether or not each hypothesis was supported.
Tips to Write the Results Section. Direct the reader to the research data and explain the meaning of the data. Avoid using a repetitive sentence structure to explain a new set of data. Write and highlight important findings in your results. Use the same order as the subheadings of the methods section.
Begin with a clear statement of the principal findings. This will reinforce the main take-away for the reader and set up the rest of the discussion. Explain why the outcomes of your study are important to the reader. Discuss the implications of your findings realistically based on previous literature, highlighting both the strengths and ...
Reporting Research Results in APA Style | Tips & Examples. Published on December 21, 2020 by Pritha Bhandari.Revised on January 17, 2024. The results section of a quantitative research paper is where you summarize your data and report the findings of any relevant statistical analyses.. The APA manual provides rigorous guidelines for what to report in quantitative research papers in the fields ...
Table of contents. What not to include in your discussion section. Step 1: Summarize your key findings. Step 2: Give your interpretations. Step 3: Discuss the implications. Step 4: Acknowledge the limitations. Step 5: Share your recommendations. Discussion section example. Other interesting articles.
Reporting quantitative research results. If you conducted quantitative research, you'll likely be working with the results of some sort of statistical analysis. ... Tips & Examples In the discussion, you interpret the meaning of the results and show why they matter. You can also note limitations and make recommendations.
After a research article has presented the substantive background, the methods and the results, the discussion section assesses the validity of results and draws conclusions by interpreting them. The discussion puts the results into a broader context and reflects their implications for theoretical (e.g. etiological) and practical (e.g ...
IMRaD Results Discussion. Results and Discussion Sections in Scientific Research Reports (IMRaD) After introducing the study and describing its methodology, an IMRaD* report presents and discusses the main findings of the study. In the results section, writers systematically report their findings, and in discussion, they interpret these findings.
Summarizing quantitative data and its effective presentation and discussion can be challenging for students and researchers. This chapter provides a framework for adequately reporting findings from quantitative analysis in a research study for those contemplating to write a research paper. The rationale underpinning the reporting methods to ...
Research results refer to the findings and conclusions derived from a systematic investigation or study conducted to answer a specific question or hypothesis. These results are typically presented in a written report or paper and can include various forms of data such as numerical data, qualitative data, statistics, charts, graphs, and visual aids.
Do you want to learn how to write effective results and discussion chapters for quantitative research? This pdf document from Massey University provides clear guidelines and examples for structuring and presenting your findings and implications. You will also find useful tips on how to avoid common pitfalls and errors in your writing.
Introduction to discussion chapter The following sections will focus on the general outcomes, results, conclusions and implications of the experiments of this thesis. Identified limitations and weaknesses of the research will also be discussed, followed by recommendations for future research. Finally, the main conclusions of this
The results section of a research paper tells the reader what you found, while the discussion section tells the reader what your findings mean. The results section should present the facts in an academic and unbiased manner, avoiding any attempt at analyzing or interpreting the data. Think of the results section as setting the stage for the ...
INTRODUCTION. Scientific research is usually initiated by posing evidenced-based research questions which are then explicitly restated as hypotheses.1,2 The hypotheses provide directions to guide the study, solutions, explanations, and expected results.3,4 Both research questions and hypotheses are essentially formulated based on conventional theories and real-world processes, which allow the ...
International Journal of Engineering Research and Applications (IJERA) is an open access online peer reviewed international journal that publishes research and review articles in the fields of Computer Science, Neural Networks, Electrical Engineering, Software Engineering, Information Technology, Mechanical Engineering, Chemical Engineering, Plastic Engineering, Food Technology, Textile ...
Overview of writing the results and discussion. The results and discussion follow on from the methods or methodology chapter of the dissertation. This creates a natural transition from how you designed your study, to what your study reveals, highlighting your own contribution to the research area. Disciplinary differences
Chapter 4-Quantitative Results and Discussion 4.1. Introduction In the previous chapter, the research design used in this study was described in detail. This included both the quantitative data collection involving the two questionnaires: BALLI and PELLEM, and the qualitative data collection which entailed a semistructured interview.
The analysis and interpretation of data is carried out in two phases. The. first part, which is based on the results of the questionnaire, deals with a quantitative. analysis of data. The second, which is based on the results of the interview and focus group. discussions, is a qualitative interpretation.
This chapter 5 presents the results of the study. First, an outline of the informants included in the study and an overview of the statistical techniques employed in the data analyses are given ...
Chapter 3 Results and Discussion This Chapter - Free download as Word Doc (.doc / .docx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. This chapter discusses the results of a study examining stereotype threat, self-efficacy, and academic performance among female engineering students. It presents five key findings: 1. Most respondents were aged 17-19, in their second year of study ...
Chapter III RESULTS AND DISCUSSION. The presentation, analysis, and interpretation of the data acquired for this study are all included in this chapter. According to the methodology, statistical tools are utilized to determine the student's perceptions towards the preservation and improvement of Central Luzon State University's landmark.
The results chapter or section simply and objectively reports what you found, without speculating on why you found these results. The discussion interprets the meaning of the results, puts them in context, and explains why they matter. In qualitative research, results and discussion are sometimes combined. But in quantitative research, it's ...
The risk factors for central venous access device-related thrombosis (CRT) in children are not fully understood. We used evidence-based medicine to find the risk factors for CRT by pooling current ...
Discussion We present a quantitative method that outperformed clinicians and permitted visualization of the morphometric features for predicting hematoma expansion from NCCT in ICH patients. Our study contributes insight into the underlying mechanisms driving hematoma expansion and suggests that it can be identified at a reversible stage.