- Trending Now
- Foundational Courses
- Data Science
- Practice Problem
- Machine Learning
- System Design
- DevOps Tutorial
- Cloud Computing Tutorial

Basics Of Cloud Computing
What is cloud computing .
- History of Cloud Computing
- Evolution of Cloud Computing
- Characteristics of Cloud Computing
- Top 7 Advantages of Cloud Computing
- Architecture of Cloud Computing
- Cloud Computing Infrastructure
- Cloud Management in Cloud Computing
- What is Cloud Storage?
- How Cloud Storage Actually Works !!
- Real World Applications of Cloud Computing
- Cloud Deployment Models
- Types of Cloud Computing
- Difference Between Public Cloud and Private Cloud
- Public Cloud vs Private Cloud vs Hybrid Cloud
Cloud Service Models
- Cloud Based Services
- Platform As A Service (PaaS) and its Types
- Software As A Service (SaaS)
- Difference between IAAS, PAAS and SAAS
Cloud Virtualization
- Virtualization in Cloud Computing and Types
- Difference between Cloud Computing and Virtualization
- Pros and Cons of Virtualization in Cloud Computing
- Data Virtualization
- Hardware Based Virtualization
- Server Virtualization
- Types of Server Virtualization in Computer Network
- Network Virtualization in Cloud Computing
- Operating system based Virtualization
Cloud Service Provider
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) Tutorial
- Microsoft Azure Tutorial
- Google Cloud Platform Tutorial
Advanced Concepts of Cloud
- On Premises VS On Cloud
- Differences between Cloud Servers and Dedicated Servers
- Cloud Networking
- Server Consolidation in Cloud Computing
- Hypervisor Security in Cloud Computing
- Cloud Computing Security
- Security Issues in Cloud Computing
- 7 Privacy Challenges in Cloud Computing
- Security Threats in Implementing SaaS of Cloud Computing
- Multitenancy in Cloud computing
- Middleware in Grid Computing
- Difference between Cloud Computing and Grid Computing
- Scalability and Elasticity in Cloud Computing
- Cloud Bursting vs Cloud Scaling
- Automated Scaling Listener in Cloud Computing
- Difference Between Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Cloud
- Difference Between Cloud Computing and Fog Computing
- Overview of Multi Cloud
- Service level agreements in Cloud computing
- Overview of Everything as a Service (XaaS)
- Resource Pooling Architecture in Cloud Computing
- Load balancing in Cloud Computing
- Overview of Desktop as a Service (DaaS)
- IoT and Cloud Computing
- Container as a Service (CaaS)
- Principles of Cloud Computing
- Resiliency in Cloud Computing
- Serverless Computing
Nowadays, Cloud computing is adopted by every company, whether it is an MNC or a startup many are still migrating towards it because of the cost-cutting, lesser maintenance, and the increased capacity of the data with the help of servers maintained by the cloud providers.
One more reason for this drastic change from the On-premises servers of the companies to the Cloud providers is the ‘Pay as you go ’ principle-based services provided by them i.e., you only have to pay for the service which you are using. The disadvantage On-premises server holds is that if the server is not in use the company still has to pay for it.
Table of Content
What Is Cloud Computing?
Understanding how cloud computing works, origins of cloud computing, what is virtualization in cloud computing, architecture of cloud computing, what are the types of cloud computing services, what are cloud deployment models, what is cloud hosting, characteristics of cloud computing, top reasons to switch from on-premise to cloud computing, top leading cloud computing companies, advantages of cloud computing, disadvantages of cloud computing, cloud sustainability, cloud security, use cases of cloud computing, cloud computing – faqs.
Cloud Computing means storing and accessing the data and programs on remote servers that are hosted on the internet instead of the computer’s hard drive or local server. Cloud computing is also referred to as Internet-based computing, it is a technology where the resource is provided as a service through the Internet to the user. The data that is stored can be files, images, documents, or any other storable document.
The following are some of the Operations that can be performed with Cloud Computing
- Storage, backup, and recovery of data
- Delivery of software on demand
- Development of new applications and services
- Streaming videos and audio
Cloud computing helps users in easily accessing computing resources like storage, and processing over internet rather than local hardwares. Here we discussing how it works in nutshell:
- Infrastructure: Cloud computing depends on remote network servers hosted on internet for store, manage, and process the data.
- On-Demand Acess: Users can access cloud services and resources based on-demand they can scale up or down the without having to invest for physical hardware.
- Types of Services: Cloud computing offers various benefits such as cost saving, scalability, reliability and acessibility it reduces capital expenditures, improves efficiency.
Mainframe computing in the 1950s and the internet explosion in the 1990s came together to give rise to cloud computing. Since businesses like Amazon, Google, and Salesforce started providing web-based services in the early 2000s. The term “cloud computing” has gained popularity. Scalability, adaptability, and cost-effectiveness are to be facilitated by the concept’s on-demand internet-based access to computational resources.
These days, cloud computing is pervasive, driving a wide range of services across markets and transforming the processing, storage, and retrieval of data
Virtualization is the software technology that helps in providing the logical isolation of physical resources. Creating logical isolation of physical resources such as RAM, CPU, and Storage.. over the cloud is known as Virtualization in Cloud Computing. In simple we can say creating types of Virtual Instances of computing resources over the cloud. It provides better management and utilization of hardware resources with logical isolation making the applications independent of others. It facilitates streamlining the resource allocation and enhancing scalability for multiple virtual computers within a single physical source offering cost-effectiveness and better optimization of resources.
To know about this refer this Article – Virtualization in Cloud Computing and Types
Cloud computing architecture refers to the components and sub-components required for cloud computing. These components typically refer to:
- Front end ( Fat client, Thin client)
- Back-end platforms ( Servers, Storage )
- Cloud-based delivery and a network ( Internet, Intranet, Intercloud )
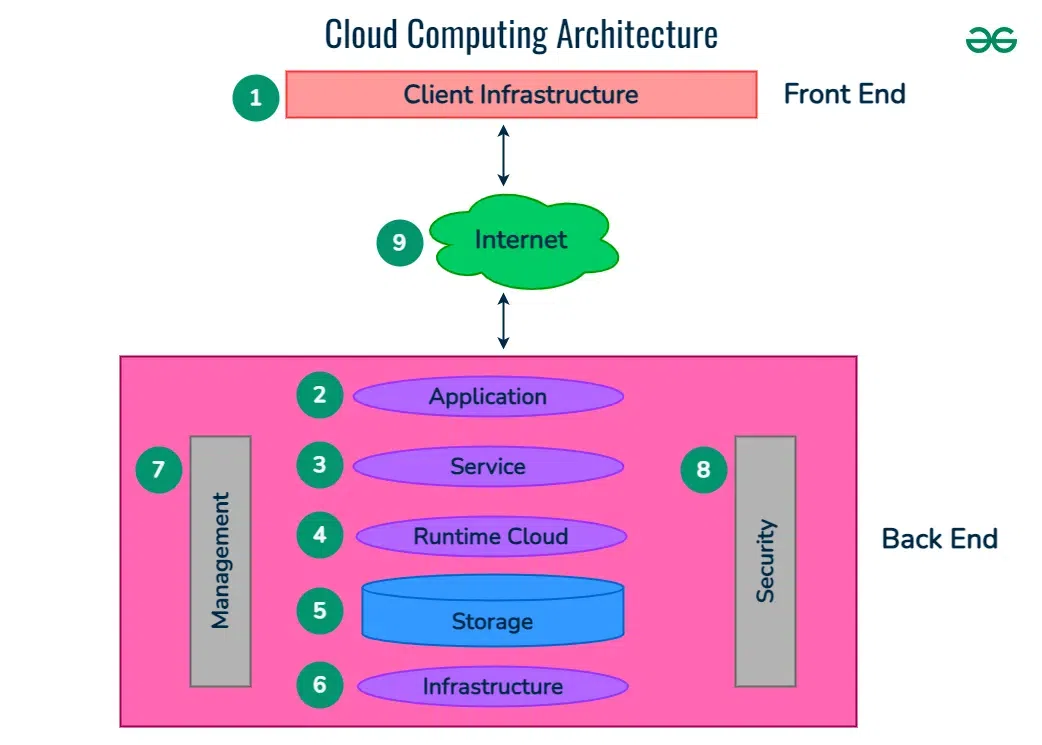
1. Front End ( User Interaction Enhancement )
The User Interface of Cloud Computing consists of 2 sections of clients. The Thin clients are the ones that use web browsers facilitating portable and lightweight accessibilities and others are known as Fat Clients that use many functionalities for offering a strong user experience.
2. Back-end Platforms ( Cloud Computing Engine )
The core of cloud computing is made at back-end platforms with several servers for storage and processing computing. Management of Applications logic is managed through servers and effective data handling is provided by storage. The combination of these platforms at the backend offers the processing power, and capacity to manage and store data behind the cloud.
3. Cloud-Based Delivery and Network
On-demand access to the computer and resources is provided over the Internet, Intranet, and Intercloud. The Internet comes with global accessibility, the Intranet helps in internal communications of the services within the organization and the Intercloud enables interoperability across various cloud services. This dynamic network connectivity ensures an essential component of cloud computing architecture on guaranteeing easy access and data transfer.
The following are the types of Cloud Computing:
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
- Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- Software as a Service (SaaS)
- Function as as Service (FaaS)
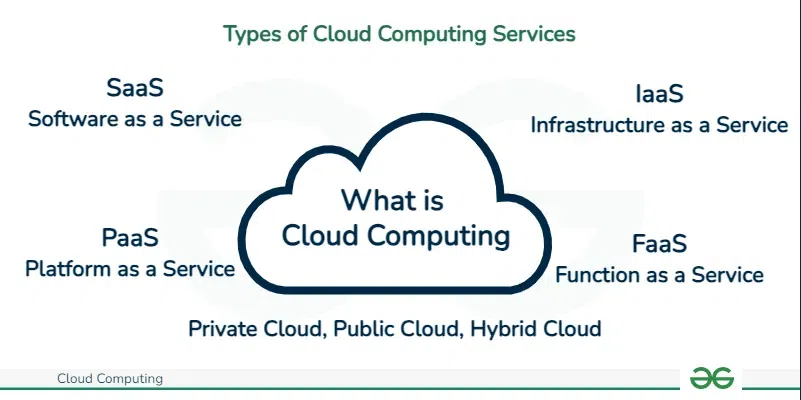
1. Infrastructure as a Service ( IaaS )
- Flexibility and Control: IaaS comes up with providing virtualized computing resources such as VMs, Storage, and networks facilitating users with control over the Operating system and applications.
- Reducing Expenses of Hardware : IaaS provides business cost savings with the elimination of physical infrastructure investments making it cost-effective.
- Scalability of Resources: The cloud provides in scaling of hardware resources up or down as per demand facilitating optimal performance with cost efficiency.
2. Platform as a Service ( PaaS )
- Simplifying the Development: Platform as a Service offers application development by keeping the underlying Infrastructure as an Abstraction. It helps the developers to completely focus on application logic ( Code ) and background operations are completely managed by the AWS platform.
- Enhancing Efficiency and Productivity: PaaS lowers the Management of Infrastructure complexity, speeding up the Execution time and bringing the updates quickly to market by streamlining the development process.
- Automation of Scaling: Management of resource scaling, guaranteeing the program’s workload efficiency is ensured by PaaS.
3. SaaS (software as a service)
- Collaboration And Accessibility: Software as a Service (SaaS) helps users to easily access applications without having the requirement of local installations. It is fully managed by the AWS Software working as a service over the internet encouraging effortless cooperation and ease of access.
- Automation of Updates: SaaS providers manage the handling of software maintenance with automatic latest updates ensuring users gain experience with the latest features and security patches.
- Cost Efficiency: SaaS acts as a cost-effective solution by reducing the overhead of IT support by eliminating the need for individual software licenses.
4. Function as a Service (FaaS)
- Event-Driven Execution: FaaS helps in the maintenance of servers and infrastructure making users worry about it. FaaS facilitates the developers to run code as a response to the events.
- Cost Efficiency: FaaS facilitates cost efficiency by coming up with the principle “Pay as per you Run” for the computing resources used.
- Scalability and Agility: Serverless Architectures scale effortlessly in handing the workloads promoting agility in development and deployment.
To know more about the Types of Cloud Computing Difference please read this article – IaaS vs PaaS vs SaaS
The following are the Cloud Deployment Models:
1. Private Deployment Model
- It provides an enhancement in protection and customization by cloud resource utilization as per particular specified requirements. It is perfect for companies which looking for security and compliance needs.
2. Public Deployment Model
- It comes with offering a pay-as-you-go principle for scalability and accessibility of cloud resources for numerous users. it ensures cost-effectiveness by providing enterprise-needed services.
3. Hybrid Deployment Model
It comes up with a combination of elements of both private and public clouds providing seamless data and application processing in between environments. It offers flexibility in optimizing resources such as sensitive data in private clouds and important scalable applications in the public cloud.
To know more about the Cloud Deployment Models, read this Articles
- Differences of Cloud Deployment Models
The Infrastructure is where the people start and begin to build from the scratch. This is the layer where the cloud hosting lives. Let’s say you have a company and a website and the website has a lot of communications that are exchanged between members. You start with a few members talking with each other and then gradually the number of members increases. As time passes, as the number of members increases, there would be more traffic on the network and your server will get slow down. This would cause a problem.
A few years ago, the websites are put on the server somewhere, in this way you have to run around or buy and set the number of servers. It costs a lot of money and takes a lot of time. You pay for these servers when you are using them and as well as when you are not using them. This is called hosting. This problem is overcome by cloud hosting. With Cloud Computing, you have access to computing power when you needed. Now, your website is put in the cloud server as you put it on a dedicated server. People start visiting your website and if you suddenly need more computing power, you would scale up according to the need.
The following are the characterisitics of Cloud Computing:
- Scalability: With Cloud hosting, it is easy to grow and shrink the number and size of servers based on the need. This is done by either increasing or decreasing the resources in the cloud. This ability to alter plans due to fluctuations in business size and needs is a superb benefit of cloud computing, especially when experiencing a sudden growth in demand.
- Save Money: An advantage of cloud computing is the reduction in hardware costs. Instead of purchasing in-house equipment, hardware needs are left to the vendor. For companies that are growing rapidly, new hardware can be large, expensive, and inconvenient. Cloud computing alleviates these issues because resources can be acquired quickly and easily. Even better, the cost of repairing or replacing equipment is passed to the vendors. Along with purchase costs, off-site hardware cuts internal power costs and saves space. Large data centers can take up precious office space and produce a large amount of heat. Moving to cloud applications or storage can help maximize space and significantly cut energy expenditures.
- Reliability: Rather than being hosted on one single instance of a physical server, hosting is delivered on a virtual partition that draws its resource, such as disk space, from an extensive network of underlying physical servers. If one server goes offline it will have no effect on availability, as the virtual servers will continue to pull resources from the remaining network of servers.
- Physical Security: The underlying physical servers are still housed within data centers and so benefit from the security measures that those facilities implement to prevent people from accessing or disrupting them on-site.
- Outsource Management: When you are managing the business, Someone else manages your computing infrastructure. You do not need to worry about management as well as degradation.
The following are the Top reasons to switch from on-premise to cloud computing:
- Reduces cost: The cost-cutting ability of businesses that utilize cloud computing over time is one of the main advantages of this technology. On average 15% of the total cost can be saved by companies if they migrate to the cloud. By the use of cloud servers businesses will save and reduce costs with no need to employ a staff of technical support personnel to address server issues. There are many great business modules regarding the cost-cutting benefits of cloud servers such as the Coca-Cola and Pinterest case studies.
- More storage: For software and applications to execute as quickly and efficiently as possible, it provides more servers, storage space, and computing power. Many tools are available for cloud storage such as Dropbox, Onedrive, Google Drive, iCloud Drive, etc.
- Employees Better Work Life Balance: Direct connections between cloud computing benefits, and the work and personal lives of an enterprise’s workers can both improve because of cloud computing. Even on holidays, the employees have to work with the server for its security, maintenance, and proper functionality. But with cloud storage the thing is not the same, employees get ample of time for their personal life and the workload is even less comparatively.
1. Amazon Web Services(AWS)
One of the most successful cloud-based businesses is Amazon Web Services(AWS), which is an Infrastructure as a Service(Iaas) offering that pays rent for virtual computers on Amazon’s infrastructure.
2. Microsoft Azure Cloud Platform
Microsoft is creating the Azure platform which enables the .NET Framework Application to run over the internet as an alternative platform for Microsoft developers. This is the classic Platform as a Service(PaaS).
3. Google Cloud Platform ( GCP )
- Google has built a worldwide network of data centers to service its search engine. From this service, Google has captured the world’s advertising revenue. By using that revenue, Google offers free software to users based on infrastructure. This is called Software as a Service(SaaS).
The following are main advantages of Cloud Computing:
- Cost Efficiency: Cloud Computing provides flexible pricing to the users with the principal pay-as-you-go model. It helps in lessening capital expenditures of Infrastructure, particularly for small and medium-sized businesses companies.
- Flexibility and Scalability: Cloud services facilitate the scaling of resources based on demand. It ensures the efficiency of businesses in handling various workloads without the need for large amounts of investments in hardware during the periods of low demand.
- Collaboration and Accessibility: Cloud computing provides easy access to data and applications from anywhere over the internet. This encourages collaborative team participation from different locations through shared documents and projects in real-time resulting in quality and productive outputs.
- Automatic Maintenance and Updates: AWS Cloud takes care of the infrastructure management and keeping with the latest software automatically making updates they is new versions. Through this, AWS guarantee the companies always having access to the newest technologies to focus completely on business operations and innvoations.
The following are the main disadvantages of Cloud Computing:
- Security Concerns: Storing of sensitive data on external servers raised more security concerns which is one of the main drawbacks of cloud computing.
- Downtime and Reliability: Even though cloud services are usually dependable, they may also have unexpected interruptions and downtimes. These might be raised because of server problems, Network issues or maintenance disruptions in Cloud providers which negative effect on business operations, creating issues for users accessing their apps.
- Dependency on Internet Connectivity: Cloud computing services heavily rely on Internet connectivity. For accessing the cloud resources the users should have a stable and high-speed internet connection for accessing and using cloud resources. In regions with limited internet connectivity, users may face challenges in accessing their data and applications.
- Cost Management Complexity: The main benefit of cloud services is their pricing model that coming with Pay as you go but it also leads to cost management complexities. On without proper careful monitoring and utilization of resources optimization, Organizations may end up with unexpected costs as per their use scale. Understanding and Controlled usage of cloud services requires ongoing attention.
The following are the some of the key points of Cloud sustainability:
- Enery Efficiency: Cloud Providers supports the optimization of data center operations for minimizing energy consumption and improve efficiency.
- Renewable Energy: On increasing the adoption of renewable energy sources like solar and wind power to data centers and reduce carbon emissions.
- Virtualization: Server virtualization facilitates better utilization of hardware resources, reducing the need for physical servers and lowering the energy consumptions.
Cloud security recommended to measures and practices designed to protect data, applications, and infrastructure in cloud computing environments. The following are some of the best practices of cloud security:
- Data Encryption: Encryption is essential for securing data stored in the cloud. It ensures that data remains unreadable to unauthorized users even if it is intercepted.
- Access Control: Implementing strict access controls and authentication mechanisms helps ensure that only authorized users can access sensitive data and resources in the cloud.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of verification, such as passwords, biometrics, or security tokens, before gaining access to cloud services.
Cloud computing provides many use cases across industries and various applications:
- Scalable Infrastructure : Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) enables organizations to scale computing resources based on demand without investing in physical hardware.
- Efficient Application Development : Platform as a Service (PaaS) simplifies application development, offering tools and environments for building, deploying, and managing applications.
- Streamlined Software Access : Software as a Service (SaaS) provides subscription-based access to software applications over the internet, reducing the need for local installation and maintenance.
- Data Analytics : Cloud-based platforms facilitate big data analytics, allowing organizations to process and derive insights from large datasets efficiently.
- Disaster Recovery : Cloud-based disaster recovery solutions offer cost-effective data replication and backup, ensuring quick recovery in case of system failures or disasters.
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud Computing is a technology that facilitates the users in accessing and utilizing the computing resources over the internet offering scalability and flexibility.
How does Cloud Security work?
It involves encryption, maintenance of data confidentiality guarding from unauthorized, unwanted access with features Authentication and authorization .
What are the benefits of Cloud Deployment?
Cloud Deployment offers accessibility, scalability, and cost savings features facilitating the organizations to focus on Innovation rather than managing the physical infrastructure.
What is the difference between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS?
IaaS provides virtualized resources, PaaS comes up with features for the deployment of applications, and finally, SaaS facilitates fully managed functional software as a service over the Internet.
How can organizations ensure data compliance in the cloud?
Organizations choose cloud providers with strong security features and measures for ensuring data compliance. Organizations use cloud providers for implementing encryption, maintaining security measures, and supporting industry-specific regulations.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- C++-Misc C++
- Cloud-Computing
- TCS-coding-questions
- Volkswagen IT Services
- Cloud Computing
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
BloomTech’s Downfall: A Long Time Coming

Coursera’s 2023 Annual Report: Big 5 Domination, Layoffs, Lawsuit, and Patents
Coursera sees headcount decrease and faces lawsuit in 2023, invests in proprietary content while relying on Big 5 partners.
- [2024] 1300+ Free SWAYAM + NPTEL Courses
- 6 Best Crystal Programming Courses for 2024
- 10 Best Pandas Courses for 2024
- 10 Best React Native Courses for 2024
- Revolutionizing Web Animation: Best Ways to Learn GSAP in 2024
600 Free Google Certifications
Most common
- computer science
Popular subjects
Web Development
Communication Skills
Social Media Marketing
Popular courses
Understanding Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
Mechanical Ventilation for COVID-19
Tsinghua Chinese: Start Talking with 1.3 Billion People
Organize and share your learning with Class Central Lists.
View our Lists Showcase
Class Central is learner-supported. When you buy through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission.
Introduction to Cloud Computing
IBM via Coursera Help
Limited-Time Offer: Up to 75% Off Coursera Plus!
- Overview of Cloud Computing
- In Module 1, in the first lesson, you will learn the definition of cloud computing and its five essential characteristics. In the next topic, you will learn about the history and evolution of cloud computing and the benefits of the pay-as-you-go feature of cloud computing. The third topic will describe the key considerations, benefits, and challenges of cloud computing. You will next discuss some common cloud service providers. In the second lesson, you will learn the need for cloud adoption by businesses. You will then discuss some case studies of businesses that benefitted from cloud adoption. In the third lesson, you will learn about emerging technologies like IoT, AI, Blockchain, and so on that leverage cloud’s scalability and processing power to provide value to individuals and businesses alike, supported by some case studies.
- Cloud Computing Models
- In Module 2, you will learn about the different types of service and deployment models of cloud computing. The first lesson covers the three main service models available on the cloud—Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS), and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS). You will learn the differences between each model, the advantages of each, and the key components of cloud infrastructure. The second lesson goes over the four main deployment models available on the cloud—public, private, hybrid, and community. You will learn what deployment models are and the differences and advantages of each model. At the end of the module, you will create an account on IBM Cloud.
- Components of Cloud Computing
- In Module 3, you will learn about the various components of a cloud computing architecture, such as the virtualization of virtual machines and bare metal servers, and the difference between virtual machines and bare metal servers. You will learn the different types of virtual machines, how to build a secure cloud networking presence, how container-based technologies work, and the benefits of a Content Delivery Network. In the second lesson, we will also familiarize you with the four main types of cloud storage—Direct Attached, File, Block, and Object Storage. You will learn the differences in how they can be accessed, the capacity they offer, how much they cost, the types of data they are best suited to store, and their read-write speed.
- Emergent Trends and Practices
- In Module 4, you will learn about the use cases and challenges of emergent trends in cloud computing, such as hybrid multi-cloud, serverless computing, and microservices. Additionally, this module will teach you about the core concepts and benefits of cloud native applications, the role of DevOps in addressing some of the complexities of cloud computing, and how organizations can benefit from modernizing their applications.
- Cloud Security, Monitoring, Case Studies, Jobs
- In Module 5, you will learn about elements of cloud security, including Identity and Access Management and cloud encryption. This module will cover how organizations leverage cloud monitoring solutions to optimize business benefits. It will familiarize you with cloud adoption case studies in different industry verticals, and the various career opportunities and job roles available in the field of cloud computing today.
- Final Project and Assignment
- In this module, you will complete a final project to deploy a containerized application on the cloud using a serverless technology (no programming experience needed). You can also demonstrate your knowledge of cloud computing by completing an optional assessment based on a cloud architecture design case study.
- united states
Related Courses
Introduction to cloud, cloud application development foundations, intro to cloud computing, foundation to multi-cloud, cloud computing primer: infrastructure as a service (iaas), related articles, 9 best microservices courses, 1700 coursera courses that are still completely free, 250 top free coursera courses of all time, massive list of mooc-based microcredentials.
4.0 rating, based on 1 Class Central review
4.6 rating at Coursera based on 5912 ratings
Select rating
Start your review of Introduction to Cloud Computing
- AW Allison W 2 years ago Very happy to take this course. Gives a broad overview of where computing is today, rather than focus on any one, particular language or technology. Helpful
Never Stop Learning.
Get personalized course recommendations, track subjects and courses with reminders, and more.


Cloud computing
| Course Status : | Completed | |||
| Course Type : | Elective | |||
| Duration : | 8 weeks | |||
| Category : | ||||
| Credit Points : | 2 | Undergraduate | ||
| Start Date : | 15 Feb 2021 | |||
| End Date : | 09 Apr 2021 | |||
| Enrollment Ends : | 15 Feb 2021 | |||
| Exam Date : | 25 Apr 2021 IST | |||
| Name | Download | Download Size |
|---|---|---|
| Lecture Note | 38M |
| Module Name | Download |
|---|---|
| noc20_cs20_assigment_1 | |
| noc20_cs20_assigment_2 | |
| noc20_cs20_assigment_3 | |
| noc20_cs20_assigment_4 | |
| noc20_cs20_assigment_5 | |
| noc20_cs20_assigment_6 | |
| noc20_cs20_assigment_7 | |
| noc20_cs20_assigment_8 | |
| noc20_cs20_assigment_9 |
| Sl.No | Chapter Name | MP4 Download |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Lecture 1: | |
| 2 | Lecture 2: | |
| 3 | Lecture 3: | |
| 4 | Lecture 4: | |
| 5 | Lecture 5: | |
| 6 | Lecture 6 | |
| 7 | Lecture 7 | |
| 8 | Lecture 8 | |
| 9 | Lecture 9 | |
| 10 | Lecture 10 | |
| 11 | Lecture 11: | |
| 12 | Lecture 12: | |
| 13 | Lecture 13 : | |
| 14 | lecture 14 : | |
| 15 | Lecture 15 : | |
| 16 | Lecture 16 | |
| 17 | Lecture 17: | |
| 18 | Lecture 18: | |
| 19 | Lecture 19: | |
| 20 | Lecture 20: | |
| 21 | Lecture 21 : SLA-Tutorial | |
| 22 | Lecture 22 : Cloudonomics-Tutorial | |
| 23 | Lecture 23 : MapReduce-Tutorial | |
| 24 | Lecture 24 : ResourceMgmt-I | |
| 25 | Lecture 25 : ResourceMgmt-II | |
| 26 | Lecture 26: Cloud Computing: Security I | |
| 27 | Lecture 27: Cloud Computing: Security II | |
| 28 | Lecture 28: Cloud Computing: Security III | |
| 29 | Lecture 29: Cloud Computing: Security Issues in Collaborative SaaS Cloud | |
| 30 | Lecture 30; Cloud Computing: Broker for Cloud Marketplace | |
| 31 | Lecture 31: Mobile Cloud Computing -I | |
| 32 | Lecture 32: Mobile Cloud Computing -II | |
| 33 | Lecture 33: Fog Computing-I | |
| 34 | Lecture 34: Fog Computing-II | |
| 35 | Lecture 35:Use Case-Geo-spatial Cloud | |
| 36 | Lecture 36 : Introduction to DOCKER Container | |
| 37 | Lecture 37 : Green Cloud | |
| 38 | Lecture 38 : Sensor Cloud Computing | |
| 39 | Lecture 39 : IoT Cloud | |
| 40 | Lecture 40 : Course Summary and Research Areas | |
| 41 | Lecture - 41 Cloudââ¬âFog Computing - Overview | |
| 42 | Lecture - 42 Resource Management - I | |
| 43 | Lecture 43 Resource Management - II | |
| 44 | Lecture 44 Cloud Federation | |
| 45 | Lecture 45 "VM Migration - Basics Migration strategies" | |
| 46 | Lecture 46 "VM Migration - Basics Migration strategies" | |
| 47 | Lecture 47 "Containers Container based Virtualization Kubernetes Docker Container " | |
| 48 | Lecture 48 "Docker Container ââ¬â Overview Docker ââ¬â Components Docker ââ¬â Architecture" | |
| 49 | Lecture 49 Docker Container - Demo | |
| 50 | Lecture 50 Docker Container - Demo | |
| 51 | Lecture 51 Dew Computing | |
| 52 | Lecture 52 Serverless Computing - I | |
| 53 | Lecture 53 Serverless Computing - II | |
| 54 | Lecture 54 Sustainable Cloud Computing - I | |
| 55 | Lecture 55 Sustainable Cloud Computing - II |
| Sl.No | Chapter Name | English |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Lecture 1: | |
| 2 | Lecture 2: | |
| 3 | Lecture 3: | |
| 4 | Lecture 4: | |
| 5 | Lecture 5: | |
| 6 | Lecture 6 | |
| 7 | Lecture 7 | |
| 8 | Lecture 8 | |
| 9 | Lecture 9 | |
| 10 | Lecture 10 | |
| 11 | Lecture 11: | |
| 12 | Lecture 12: | |
| 13 | Lecture 13 : | |
| 14 | lecture 14 : | |
| 15 | Lecture 15 : | |
| 16 | Lecture 16 | |
| 17 | Lecture 17: | |
| 18 | Lecture 18: | |
| 19 | Lecture 19: | |
| 20 | Lecture 20: | |
| 21 | Lecture 21 : SLA-Tutorial | |
| 22 | Lecture 22 : Cloudonomics-Tutorial | |
| 23 | Lecture 23 : MapReduce-Tutorial | |
| 24 | Lecture 24 : ResourceMgmt-I | |
| 25 | Lecture 25 : ResourceMgmt-II | |
| 26 | Lecture 26: Cloud Computing: Security I | |
| 27 | Lecture 27: Cloud Computing: Security II | |
| 28 | Lecture 28: Cloud Computing: Security III | |
| 29 | Lecture 29: Cloud Computing: Security Issues in Collaborative SaaS Cloud | |
| 30 | Lecture 30; Cloud Computing: Broker for Cloud Marketplace | |
| 31 | Lecture 31: Mobile Cloud Computing -I | |
| 32 | Lecture 32: Mobile Cloud Computing -II | |
| 33 | Lecture 33: Fog Computing-I | |
| 34 | Lecture 34: Fog Computing-II | |
| 35 | Lecture 35:Use Case-Geo-spatial Cloud | |
| 36 | Lecture 36 : Introduction to DOCKER Container | |
| 37 | Lecture 37 : Green Cloud | |
| 38 | Lecture 38 : Sensor Cloud Computing | |
| 39 | Lecture 39 : IoT Cloud | |
| 40 | Lecture 40 : Course Summary and Research Areas | |
| 41 | Lecture - 41 Cloudââ¬âFog Computing - Overview | PDF unavailable |
| 42 | Lecture - 42 Resource Management - I | PDF unavailable |
| 43 | Lecture 43 Resource Management - II | PDF unavailable |
| 44 | Lecture 44 Cloud Federation | PDF unavailable |
| 45 | Lecture 45 "VM Migration - Basics Migration strategies" | PDF unavailable |
| 46 | Lecture 46 "VM Migration - Basics Migration strategies" | PDF unavailable |
| 47 | Lecture 47 "Containers Container based Virtualization Kubernetes Docker Container " | PDF unavailable |
| 48 | Lecture 48 "Docker Container ââ¬â Overview Docker ââ¬â Components Docker ââ¬â Architecture" | PDF unavailable |
| 49 | Lecture 49 Docker Container - Demo | PDF unavailable |
| 50 | Lecture 50 Docker Container - Demo | PDF unavailable |
| 51 | Lecture 51 Dew Computing | PDF unavailable |
| 52 | Lecture 52 Serverless Computing - I | PDF unavailable |
| 53 | Lecture 53 Serverless Computing - II | PDF unavailable |
| 54 | Lecture 54 Sustainable Cloud Computing - I | PDF unavailable |
| 55 | Lecture 55 Sustainable Cloud Computing - II | PDF unavailable |
| Sl.No | Chapter Name | Bengali |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Lecture 1: | |
| 2 | Lecture 2: | |
| 3 | Lecture 3: | |
| 4 | Lecture 4: | |
| 5 | Lecture 5: | |
| 6 | Lecture 6 | |
| 7 | Lecture 7 | |
| 8 | Lecture 8 | |
| 9 | Lecture 9 | |
| 10 | Lecture 10 | |
| 11 | Lecture 11: | |
| 12 | Lecture 12: | |
| 13 | Lecture 13 : | |
| 14 | lecture 14 : | |
| 15 | Lecture 15 : | |
| 16 | Lecture 16 | |
| 17 | Lecture 17: | |
| 18 | Lecture 18: | |
| 19 | Lecture 19: | |
| 20 | Lecture 20: | |
| 21 | Lecture 21 : SLA-Tutorial | |
| 22 | Lecture 22 : Cloudonomics-Tutorial | |
| 23 | Lecture 23 : MapReduce-Tutorial | |
| 24 | Lecture 24 : ResourceMgmt-I | |
| 25 | Lecture 25 : ResourceMgmt-II | |
| 26 | Lecture 26: Cloud Computing: Security I | |
| 27 | Lecture 27: Cloud Computing: Security II | |
| 28 | Lecture 28: Cloud Computing: Security III | |
| 29 | Lecture 29: Cloud Computing: Security Issues in Collaborative SaaS Cloud | |
| 30 | Lecture 30; Cloud Computing: Broker for Cloud Marketplace | |
| 31 | Lecture 31: Mobile Cloud Computing -I | |
| 32 | Lecture 32: Mobile Cloud Computing -II | |
| 33 | Lecture 33: Fog Computing-I | |
| 34 | Lecture 34: Fog Computing-II | |
| 35 | Lecture 35:Use Case-Geo-spatial Cloud | |
| 36 | Lecture 36 : Introduction to DOCKER Container | |
| 37 | Lecture 37 : Green Cloud | |
| 38 | Lecture 38 : Sensor Cloud Computing | |
| 39 | Lecture 39 : IoT Cloud | |
| 40 | Lecture 40 : Course Summary and Research Areas | |
| 41 | Lecture - 41 Cloudââ¬âFog Computing - Overview | Not Available |
| 42 | Lecture - 42 Resource Management - I | Not Available |
| 43 | Lecture 43 Resource Management - II | Not Available |
| 44 | Lecture 44 Cloud Federation | Not Available |
| 45 | Lecture 45 "VM Migration - Basics Migration strategies" | Not Available |
| 46 | Lecture 46 "VM Migration - Basics Migration strategies" | Not Available |
| 47 | Lecture 47 "Containers Container based Virtualization Kubernetes Docker Container " | Not Available |
| 48 | Lecture 48 "Docker Container ââ¬â Overview Docker ââ¬â Components Docker ââ¬â Architecture" | Not Available |
| 49 | Lecture 49 Docker Container - Demo | Not Available |
| 50 | Lecture 50 Docker Container - Demo | Not Available |
| 51 | Lecture 51 Dew Computing | Not Available |
| 52 | Lecture 52 Serverless Computing - I | Not Available |
| 53 | Lecture 53 Serverless Computing - II | Not Available |
| 54 | Lecture 54 Sustainable Cloud Computing - I | Not Available |
| 55 | Lecture 55 Sustainable Cloud Computing - II | Not Available |
| Sl.No | Chapter Name | Gujarati |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Lecture 1: | |
| 2 | Lecture 2: | |
| 3 | Lecture 3: | |
| 4 | Lecture 4: | |
| 5 | Lecture 5: | |
| 6 | Lecture 6 | |
| 7 | Lecture 7 | |
| 8 | Lecture 8 | |
| 9 | Lecture 9 | |
| 10 | Lecture 10 | |
| 11 | Lecture 11: | |
| 12 | Lecture 12: | |
| 13 | Lecture 13 : | |
| 14 | lecture 14 : | |
| 15 | Lecture 15 : | |
| 16 | Lecture 16 | |
| 17 | Lecture 17: | |
| 18 | Lecture 18: | |
| 19 | Lecture 19: | |
| 20 | Lecture 20: | |
| 21 | Lecture 21 : SLA-Tutorial | |
| 22 | Lecture 22 : Cloudonomics-Tutorial | |
| 23 | Lecture 23 : MapReduce-Tutorial | |
| 24 | Lecture 24 : ResourceMgmt-I | |
| 25 | Lecture 25 : ResourceMgmt-II | |
| 26 | Lecture 26: Cloud Computing: Security I | |
| 27 | Lecture 27: Cloud Computing: Security II | |
| 28 | Lecture 28: Cloud Computing: Security III | |
| 29 | Lecture 29: Cloud Computing: Security Issues in Collaborative SaaS Cloud | |
| 30 | Lecture 30; Cloud Computing: Broker for Cloud Marketplace | |
| 31 | Lecture 31: Mobile Cloud Computing -I | |
| 32 | Lecture 32: Mobile Cloud Computing -II | |
| 33 | Lecture 33: Fog Computing-I | |
| 34 | Lecture 34: Fog Computing-II | |
| 35 | Lecture 35:Use Case-Geo-spatial Cloud | |
| 36 | Lecture 36 : Introduction to DOCKER Container | |
| 37 | Lecture 37 : Green Cloud | |
| 38 | Lecture 38 : Sensor Cloud Computing | |
| 39 | Lecture 39 : IoT Cloud | |
| 40 | Lecture 40 : Course Summary and Research Areas | |
| 41 | Lecture - 41 Cloudââ¬âFog Computing - Overview | Not Available |
| 42 | Lecture - 42 Resource Management - I | Not Available |
| 43 | Lecture 43 Resource Management - II | Not Available |
| 44 | Lecture 44 Cloud Federation | Not Available |
| 45 | Lecture 45 "VM Migration - Basics Migration strategies" | Not Available |
| 46 | Lecture 46 "VM Migration - Basics Migration strategies" | Not Available |
| 47 | Lecture 47 "Containers Container based Virtualization Kubernetes Docker Container " | Not Available |
| 48 | Lecture 48 "Docker Container ââ¬â Overview Docker ââ¬â Components Docker ââ¬â Architecture" | Not Available |
| 49 | Lecture 49 Docker Container - Demo | Not Available |
| 50 | Lecture 50 Docker Container - Demo | Not Available |
| 51 | Lecture 51 Dew Computing | Not Available |
| 52 | Lecture 52 Serverless Computing - I | Not Available |
| 53 | Lecture 53 Serverless Computing - II | Not Available |
| 54 | Lecture 54 Sustainable Cloud Computing - I | Not Available |
| 55 | Lecture 55 Sustainable Cloud Computing - II | Not Available |
| Sl.No | Chapter Name | Hindi |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Lecture 1: | |
| 2 | Lecture 2: | |
| 3 | Lecture 3: | |
| 4 | Lecture 4: | |
| 5 | Lecture 5: | |
| 6 | Lecture 6 | |
| 7 | Lecture 7 | |
| 8 | Lecture 8 | |
| 9 | Lecture 9 | |
| 10 | Lecture 10 | |
| 11 | Lecture 11: | |
| 12 | Lecture 12: | |
| 13 | Lecture 13 : | |
| 14 | lecture 14 : | |
| 15 | Lecture 15 : | |
| 16 | Lecture 16 | |
| 17 | Lecture 17: | |
| 18 | Lecture 18: | |
| 19 | Lecture 19: | |
| 20 | Lecture 20: | |
| 21 | Lecture 21 : SLA-Tutorial | |
| 22 | Lecture 22 : Cloudonomics-Tutorial | |
| 23 | Lecture 23 : MapReduce-Tutorial | |
| 24 | Lecture 24 : ResourceMgmt-I | |
| 25 | Lecture 25 : ResourceMgmt-II | |
| 26 | Lecture 26: Cloud Computing: Security I | |
| 27 | Lecture 27: Cloud Computing: Security II | |
| 28 | Lecture 28: Cloud Computing: Security III | |
| 29 | Lecture 29: Cloud Computing: Security Issues in Collaborative SaaS Cloud | |
| 30 | Lecture 30; Cloud Computing: Broker for Cloud Marketplace | |
| 31 | Lecture 31: Mobile Cloud Computing -I | |
| 32 | Lecture 32: Mobile Cloud Computing -II | |
| 33 | Lecture 33: Fog Computing-I | |
| 34 | Lecture 34: Fog Computing-II | |
| 35 | Lecture 35:Use Case-Geo-spatial Cloud | |
| 36 | Lecture 36 : Introduction to DOCKER Container | |
| 37 | Lecture 37 : Green Cloud | |
| 38 | Lecture 38 : Sensor Cloud Computing | |
| 39 | Lecture 39 : IoT Cloud | |
| 40 | Lecture 40 : Course Summary and Research Areas | |
| 41 | Lecture - 41 Cloudââ¬âFog Computing - Overview | Not Available |
| 42 | Lecture - 42 Resource Management - I | Not Available |
| 43 | Lecture 43 Resource Management - II | Not Available |
| 44 | Lecture 44 Cloud Federation | Not Available |
| 45 | Lecture 45 "VM Migration - Basics Migration strategies" | Not Available |
| 46 | Lecture 46 "VM Migration - Basics Migration strategies" | Not Available |
| 47 | Lecture 47 "Containers Container based Virtualization Kubernetes Docker Container " | Not Available |
| 48 | Lecture 48 "Docker Container ââ¬â Overview Docker ââ¬â Components Docker ââ¬â Architecture" | Not Available |
| 49 | Lecture 49 Docker Container - Demo | Not Available |
| 50 | Lecture 50 Docker Container - Demo | Not Available |
| 51 | Lecture 51 Dew Computing | Not Available |
| 52 | Lecture 52 Serverless Computing - I | Not Available |
| 53 | Lecture 53 Serverless Computing - II | Not Available |
| 54 | Lecture 54 Sustainable Cloud Computing - I | Not Available |
| 55 | Lecture 55 Sustainable Cloud Computing - II | Not Available |
| Sl.No | Chapter Name | Kannada |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Lecture 1: | |
| 2 | Lecture 2: | |
| 3 | Lecture 3: | |
| 4 | Lecture 4: | |
| 5 | Lecture 5: | |
| 6 | Lecture 6 | |
| 7 | Lecture 7 | |
| 8 | Lecture 8 | |
| 9 | Lecture 9 | |
| 10 | Lecture 10 | |
| 11 | Lecture 11: | |
| 12 | Lecture 12: | |
| 13 | Lecture 13 : | |
| 14 | lecture 14 : | |
| 15 | Lecture 15 : | |
| 16 | Lecture 16 | |
| 17 | Lecture 17: | |
| 18 | Lecture 18: | |
| 19 | Lecture 19: | |
| 20 | Lecture 20: | |
| 21 | Lecture 21 : SLA-Tutorial | |
| 22 | Lecture 22 : Cloudonomics-Tutorial | |
| 23 | Lecture 23 : MapReduce-Tutorial | |
| 24 | Lecture 24 : ResourceMgmt-I | |
| 25 | Lecture 25 : ResourceMgmt-II | |
| 26 | Lecture 26: Cloud Computing: Security I | |
| 27 | Lecture 27: Cloud Computing: Security II | |
| 28 | Lecture 28: Cloud Computing: Security III | |
| 29 | Lecture 29: Cloud Computing: Security Issues in Collaborative SaaS Cloud | |
| 30 | Lecture 30; Cloud Computing: Broker for Cloud Marketplace | |
| 31 | Lecture 31: Mobile Cloud Computing -I | |
| 32 | Lecture 32: Mobile Cloud Computing -II | |
| 33 | Lecture 33: Fog Computing-I | |
| 34 | Lecture 34: Fog Computing-II | |
| 35 | Lecture 35:Use Case-Geo-spatial Cloud | |
| 36 | Lecture 36 : Introduction to DOCKER Container | |
| 37 | Lecture 37 : Green Cloud | |
| 38 | Lecture 38 : Sensor Cloud Computing | |
| 39 | Lecture 39 : IoT Cloud | |
| 40 | Lecture 40 : Course Summary and Research Areas | |
| 41 | Lecture - 41 Cloudââ¬âFog Computing - Overview | Not Available |
| 42 | Lecture - 42 Resource Management - I | Not Available |
| 43 | Lecture 43 Resource Management - II | Not Available |
| 44 | Lecture 44 Cloud Federation | Not Available |
| 45 | Lecture 45 "VM Migration - Basics Migration strategies" | Not Available |
| 46 | Lecture 46 "VM Migration - Basics Migration strategies" | Not Available |
| 47 | Lecture 47 "Containers Container based Virtualization Kubernetes Docker Container " | Not Available |
| 48 | Lecture 48 "Docker Container ââ¬â Overview Docker ââ¬â Components Docker ââ¬â Architecture" | Not Available |
| 49 | Lecture 49 Docker Container - Demo | Not Available |
| 50 | Lecture 50 Docker Container - Demo | Not Available |
| 51 | Lecture 51 Dew Computing | Not Available |
| 52 | Lecture 52 Serverless Computing - I | Not Available |
| 53 | Lecture 53 Serverless Computing - II | Not Available |
| 54 | Lecture 54 Sustainable Cloud Computing - I | Not Available |
| 55 | Lecture 55 Sustainable Cloud Computing - II | Not Available |
| Sl.No | Chapter Name | Malayalam |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Lecture 1: | |
| 2 | Lecture 2: | |
| 3 | Lecture 3: | |
| 4 | Lecture 4: | |
| 5 | Lecture 5: | |
| 6 | Lecture 6 | |
| 7 | Lecture 7 | |
| 8 | Lecture 8 | |
| 9 | Lecture 9 | |
| 10 | Lecture 10 | |
| 11 | Lecture 11: | |
| 12 | Lecture 12: | |
| 13 | Lecture 13 : | |
| 14 | lecture 14 : | |
| 15 | Lecture 15 : | |
| 16 | Lecture 16 | |
| 17 | Lecture 17: | |
| 18 | Lecture 18: | |
| 19 | Lecture 19: | |
| 20 | Lecture 20: | |
| 21 | Lecture 21 : SLA-Tutorial | |
| 22 | Lecture 22 : Cloudonomics-Tutorial | |
| 23 | Lecture 23 : MapReduce-Tutorial | |
| 24 | Lecture 24 : ResourceMgmt-I | |
| 25 | Lecture 25 : ResourceMgmt-II | |
| 26 | Lecture 26: Cloud Computing: Security I | |
| 27 | Lecture 27: Cloud Computing: Security II | |
| 28 | Lecture 28: Cloud Computing: Security III | |
| 29 | Lecture 29: Cloud Computing: Security Issues in Collaborative SaaS Cloud | |
| 30 | Lecture 30; Cloud Computing: Broker for Cloud Marketplace | |
| 31 | Lecture 31: Mobile Cloud Computing -I | |
| 32 | Lecture 32: Mobile Cloud Computing -II | |
| 33 | Lecture 33: Fog Computing-I | |
| 34 | Lecture 34: Fog Computing-II | |
| 35 | Lecture 35:Use Case-Geo-spatial Cloud | |
| 36 | Lecture 36 : Introduction to DOCKER Container | |
| 37 | Lecture 37 : Green Cloud | |
| 38 | Lecture 38 : Sensor Cloud Computing | |
| 39 | Lecture 39 : IoT Cloud | |
| 40 | Lecture 40 : Course Summary and Research Areas | |
| 41 | Lecture - 41 Cloudââ¬âFog Computing - Overview | Not Available |
| 42 | Lecture - 42 Resource Management - I | Not Available |
| 43 | Lecture 43 Resource Management - II | Not Available |
| 44 | Lecture 44 Cloud Federation | Not Available |
| 45 | Lecture 45 "VM Migration - Basics Migration strategies" | Not Available |
| 46 | Lecture 46 "VM Migration - Basics Migration strategies" | Not Available |
| 47 | Lecture 47 "Containers Container based Virtualization Kubernetes Docker Container " | Not Available |
| 48 | Lecture 48 "Docker Container ââ¬â Overview Docker ââ¬â Components Docker ââ¬â Architecture" | Not Available |
| 49 | Lecture 49 Docker Container - Demo | Not Available |
| 50 | Lecture 50 Docker Container - Demo | Not Available |
| 51 | Lecture 51 Dew Computing | Not Available |
| 52 | Lecture 52 Serverless Computing - I | Not Available |
| 53 | Lecture 53 Serverless Computing - II | Not Available |
| 54 | Lecture 54 Sustainable Cloud Computing - I | Not Available |
| 55 | Lecture 55 Sustainable Cloud Computing - II | Not Available |
| Sl.No | Chapter Name | Marathi |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Lecture 1: | |
| 2 | Lecture 2: | |
| 3 | Lecture 3: | |
| 4 | Lecture 4: | |
| 5 | Lecture 5: | |
| 6 | Lecture 6 | |
| 7 | Lecture 7 | |
| 8 | Lecture 8 | |
| 9 | Lecture 9 | |
| 10 | Lecture 10 | |
| 11 | Lecture 11: | |
| 12 | Lecture 12: | |
| 13 | Lecture 13 : | |
| 14 | lecture 14 : | |
| 15 | Lecture 15 : | |
| 16 | Lecture 16 | |
| 17 | Lecture 17: | |
| 18 | Lecture 18: | |
| 19 | Lecture 19: | |
| 20 | Lecture 20: | |
| 21 | Lecture 21 : SLA-Tutorial | |
| 22 | Lecture 22 : Cloudonomics-Tutorial | |
| 23 | Lecture 23 : MapReduce-Tutorial | |
| 24 | Lecture 24 : ResourceMgmt-I | |
| 25 | Lecture 25 : ResourceMgmt-II | |
| 26 | Lecture 26: Cloud Computing: Security I | |
| 27 | Lecture 27: Cloud Computing: Security II | |
| 28 | Lecture 28: Cloud Computing: Security III | |
| 29 | Lecture 29: Cloud Computing: Security Issues in Collaborative SaaS Cloud | |
| 30 | Lecture 30; Cloud Computing: Broker for Cloud Marketplace | |
| 31 | Lecture 31: Mobile Cloud Computing -I | |
| 32 | Lecture 32: Mobile Cloud Computing -II | |
| 33 | Lecture 33: Fog Computing-I | |
| 34 | Lecture 34: Fog Computing-II | |
| 35 | Lecture 35:Use Case-Geo-spatial Cloud | |
| 36 | Lecture 36 : Introduction to DOCKER Container | |
| 37 | Lecture 37 : Green Cloud | |
| 38 | Lecture 38 : Sensor Cloud Computing | |
| 39 | Lecture 39 : IoT Cloud | |
| 40 | Lecture 40 : Course Summary and Research Areas | |
| 41 | Lecture - 41 Cloudââ¬âFog Computing - Overview | Not Available |
| 42 | Lecture - 42 Resource Management - I | Not Available |
| 43 | Lecture 43 Resource Management - II | Not Available |
| 44 | Lecture 44 Cloud Federation | Not Available |
| 45 | Lecture 45 "VM Migration - Basics Migration strategies" | Not Available |
| 46 | Lecture 46 "VM Migration - Basics Migration strategies" | Not Available |
| 47 | Lecture 47 "Containers Container based Virtualization Kubernetes Docker Container " | Not Available |
| 48 | Lecture 48 "Docker Container ââ¬â Overview Docker ââ¬â Components Docker ââ¬â Architecture" | Not Available |
| 49 | Lecture 49 Docker Container - Demo | Not Available |
| 50 | Lecture 50 Docker Container - Demo | Not Available |
| 51 | Lecture 51 Dew Computing | Not Available |
| 52 | Lecture 52 Serverless Computing - I | Not Available |
| 53 | Lecture 53 Serverless Computing - II | Not Available |
| 54 | Lecture 54 Sustainable Cloud Computing - I | Not Available |
| 55 | Lecture 55 Sustainable Cloud Computing - II | Not Available |
| Sl.No | Chapter Name | Tamil |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Lecture 1: | |
| 2 | Lecture 2: | |
| 3 | Lecture 3: | |
| 4 | Lecture 4: | |
| 5 | Lecture 5: | |
| 6 | Lecture 6 | |
| 7 | Lecture 7 | |
| 8 | Lecture 8 | |
| 9 | Lecture 9 | |
| 10 | Lecture 10 | |
| 11 | Lecture 11: | |
| 12 | Lecture 12: | |
| 13 | Lecture 13 : | |
| 14 | lecture 14 : | |
| 15 | Lecture 15 : | |
| 16 | Lecture 16 | |
| 17 | Lecture 17: | |
| 18 | Lecture 18: | |
| 19 | Lecture 19: | |
| 20 | Lecture 20: | |
| 21 | Lecture 21 : SLA-Tutorial | |
| 22 | Lecture 22 : Cloudonomics-Tutorial | |
| 23 | Lecture 23 : MapReduce-Tutorial | |
| 24 | Lecture 24 : ResourceMgmt-I | |
| 25 | Lecture 25 : ResourceMgmt-II | |
| 26 | Lecture 26: Cloud Computing: Security I | |
| 27 | Lecture 27: Cloud Computing: Security II | |
| 28 | Lecture 28: Cloud Computing: Security III | |
| 29 | Lecture 29: Cloud Computing: Security Issues in Collaborative SaaS Cloud | |
| 30 | Lecture 30; Cloud Computing: Broker for Cloud Marketplace | |
| 31 | Lecture 31: Mobile Cloud Computing -I | |
| 32 | Lecture 32: Mobile Cloud Computing -II | |
| 33 | Lecture 33: Fog Computing-I | |
| 34 | Lecture 34: Fog Computing-II | |
| 35 | Lecture 35:Use Case-Geo-spatial Cloud | |
| 36 | Lecture 36 : Introduction to DOCKER Container | |
| 37 | Lecture 37 : Green Cloud | |
| 38 | Lecture 38 : Sensor Cloud Computing | |
| 39 | Lecture 39 : IoT Cloud | |
| 40 | Lecture 40 : Course Summary and Research Areas | |
| 41 | Lecture - 41 Cloudââ¬âFog Computing - Overview | Not Available |
| 42 | Lecture - 42 Resource Management - I | Not Available |
| 43 | Lecture 43 Resource Management - II | Not Available |
| 44 | Lecture 44 Cloud Federation | Not Available |
| 45 | Lecture 45 "VM Migration - Basics Migration strategies" | Not Available |
| 46 | Lecture 46 "VM Migration - Basics Migration strategies" | Not Available |
| 47 | Lecture 47 "Containers Container based Virtualization Kubernetes Docker Container " | Not Available |
| 48 | Lecture 48 "Docker Container ââ¬â Overview Docker ââ¬â Components Docker ââ¬â Architecture" | Not Available |
| 49 | Lecture 49 Docker Container - Demo | Not Available |
| 50 | Lecture 50 Docker Container - Demo | Not Available |
| 51 | Lecture 51 Dew Computing | Not Available |
| 52 | Lecture 52 Serverless Computing - I | Not Available |
| 53 | Lecture 53 Serverless Computing - II | Not Available |
| 54 | Lecture 54 Sustainable Cloud Computing - I | Not Available |
| 55 | Lecture 55 Sustainable Cloud Computing - II | Not Available |
| Sl.No | Chapter Name | Telugu |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Lecture 1: | |
| 2 | Lecture 2: | |
| 3 | Lecture 3: | |
| 4 | Lecture 4: | |
| 5 | Lecture 5: | |
| 6 | Lecture 6 | |
| 7 | Lecture 7 | |
| 8 | Lecture 8 | |
| 9 | Lecture 9 | |
| 10 | Lecture 10 | |
| 11 | Lecture 11: | |
| 12 | Lecture 12: | |
| 13 | Lecture 13 : | |
| 14 | lecture 14 : | |
| 15 | Lecture 15 : | |
| 16 | Lecture 16 | |
| 17 | Lecture 17: | |
| 18 | Lecture 18: | |
| 19 | Lecture 19: | |
| 20 | Lecture 20: | |
| 21 | Lecture 21 : SLA-Tutorial | |
| 22 | Lecture 22 : Cloudonomics-Tutorial | |
| 23 | Lecture 23 : MapReduce-Tutorial | |
| 24 | Lecture 24 : ResourceMgmt-I | |
| 25 | Lecture 25 : ResourceMgmt-II | |
| 26 | Lecture 26: Cloud Computing: Security I | |
| 27 | Lecture 27: Cloud Computing: Security II | |
| 28 | Lecture 28: Cloud Computing: Security III | |
| 29 | Lecture 29: Cloud Computing: Security Issues in Collaborative SaaS Cloud | |
| 30 | Lecture 30; Cloud Computing: Broker for Cloud Marketplace | |
| 31 | Lecture 31: Mobile Cloud Computing -I | |
| 32 | Lecture 32: Mobile Cloud Computing -II | |
| 33 | Lecture 33: Fog Computing-I | |
| 34 | Lecture 34: Fog Computing-II | |
| 35 | Lecture 35:Use Case-Geo-spatial Cloud | |
| 36 | Lecture 36 : Introduction to DOCKER Container | |
| 37 | Lecture 37 : Green Cloud | |
| 38 | Lecture 38 : Sensor Cloud Computing | |
| 39 | Lecture 39 : IoT Cloud | |
| 40 | Lecture 40 : Course Summary and Research Areas | |
| 41 | Lecture - 41 Cloudââ¬âFog Computing - Overview | Not Available |
| 42 | Lecture - 42 Resource Management - I | Not Available |
| 43 | Lecture 43 Resource Management - II | Not Available |
| 44 | Lecture 44 Cloud Federation | Not Available |
| 45 | Lecture 45 "VM Migration - Basics Migration strategies" | Not Available |
| 46 | Lecture 46 "VM Migration - Basics Migration strategies" | Not Available |
| 47 | Lecture 47 "Containers Container based Virtualization Kubernetes Docker Container " | Not Available |
| 48 | Lecture 48 "Docker Container ââ¬â Overview Docker ââ¬â Components Docker ââ¬â Architecture" | Not Available |
| 49 | Lecture 49 Docker Container - Demo | Not Available |
| 50 | Lecture 50 Docker Container - Demo | Not Available |
| 51 | Lecture 51 Dew Computing | Not Available |
| 52 | Lecture 52 Serverless Computing - I | Not Available |
| 53 | Lecture 53 Serverless Computing - II | Not Available |
| 54 | Lecture 54 Sustainable Cloud Computing - I | Not Available |
| 55 | Lecture 55 Sustainable Cloud Computing - II | Not Available |
| Sl.No | Language | Book link |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | English | |
| 2 | Bengali | |
| 3 | Gujarati | Not Available |
| 4 | Hindi | |
| 5 | Kannada | |
| 6 | Malayalam | |
| 7 | Marathi | |
| 8 | Tamil | |
| 9 | Telugu |

- Microsoft Azure
Computer Network
Control System
- Interview Q
Microsoft Azure Tutorial
Azure storage service, network services, compute services, app services, database service, azure devops.
Interview Questions
| Cloud Computing is the delivery of computing services such as servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, intelligence, and more, over the Cloud (Internet). But if we choose Cloud Computing, a cloud vendor is responsible for the hardware purchase and maintenance. They also provide a wide variety of software and platform as a service. We can take any required services on rent. The cloud computing services will be charged based on usage. It reduces the huge capital costs of buying hardware and software. Resources can be accessed in minutes, typically within a few clicks. We can increase or decrease the requirement of resources according to the business requirements. While using cloud computing, we put less operational effort. We do not need to apply patching, as well as no need to maintain hardware and software. So, in this way, the IT team can be more productive and focus on achieving business goals. Backup and recovery of data are less expensive and very fast for business continuity. Many cloud vendors offer a broad set of policies, technologies, and controls that strengthen our data security. The cloud resources that are owned and operated by a third-party cloud service provider are termed as public clouds. It delivers computing resources such as servers, software, and storage over the internet The cloud computing resources that are exclusively used inside a single business or organization are termed as a private cloud. A private cloud may physically be located on the company’s on-site datacentre or hosted by a third-party service provider. It is the combination of public and private clouds, which is bounded together by technology that allows data applications to be shared between them. Hybrid cloud provides flexibility and more deployment options to the business. In IaaS, we can rent IT infrastructures like servers and virtual machines (VMs), storage, networks, operating systems from a cloud service vendor. We can create VM running Windows or Linux and install anything we want on it. Using IaaS, we don’t need to care about the hardware or virtualization software, but other than that, we do have to manage everything else. Using IaaS, we get maximum flexibility, but still, we need to put more effort into maintenance. This service provides an on-demand environment for developing, testing, delivering, and managing software applications. The developer is responsible for the application, and the PaaS vendor provides the ability to deploy and run it. Using PaaS, the flexibility gets reduce, but the management of the environment is taken care of by the cloud vendors. It provides a centrally hosted and managed software services to the end-users. It delivers software over the internet, on-demand, and typically on a subscription basis. E.g., Microsoft One Drive, Dropbox, WordPress, Office 365, and Amazon Kindle. SaaS is used to minimize the operational cost to the maximum extent. |

- Send your Feedback to [email protected]
Help Others, Please Share

Learn Latest Tutorials
Transact-SQL
Reinforcement Learning
R Programming
React Native
Python Design Patterns
Python Pillow
Python Turtle
Preparation

Verbal Ability

Company Questions
Trending Technologies
Artificial Intelligence
Cloud Computing
Data Science
Machine Learning
B.Tech / MCA
Data Structures
Operating System
Compiler Design
Computer Organization
Discrete Mathematics
Ethical Hacking
Computer Graphics
Software Engineering
Web Technology
Cyber Security
C Programming
Data Mining
Data Warehouse

Navigation Menu
Search code, repositories, users, issues, pull requests..., provide feedback.
We read every piece of feedback, and take your input very seriously.
Saved searches
Use saved searches to filter your results more quickly.
To see all available qualifiers, see our documentation .
- Notifications You must be signed in to change notification settings
Introduction to Cloud
365kim/IBM_Clouders
Folders and files.
| Name | Name | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 18 Commits | ||||
Repository files navigation
Free Course : IBM Cloud Core Free Cloud Service : IBM Cloud Object Storage
☁️ Course Syllabus
- Module 1: Overview of Cloud Computing
- Module 2: Cloud Adoption and Emerging Technologies on the Cloud
- Module 3: Cloud Computing Service and Deployment Models
- Module 4: Components of Cloud Computing
- Module 5: Cloud Computing Storage and Content Delivery Networks
- Module 6: Emergent Trends, Cloud Native, DevOps, and Application Modernization
☁️ Course Overview
- Definition and essential characteristics of cloud computing, its history, emerging trends, and the business case for cloud computing.
- Various cloud service models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS) and deployment models (Public Cloud, Private Cloud, Hybrid Cloud) and the key components of cloud architecture (Virtualization, VMs, Storage, Networking, Containers)
- Emerging trends associated with cloud including, Hybrid Multicloud, Microservices, Serverless, Cloud Native, DevOps, and Application modernization
☁️ Grading Scheme
- Graded Quiz(50%, no time limit) + Final Exam(50%, 1-hour time limit)
☁️ Badge & Certificate
This course is not yet live; some links might not yet work. Coming July 1, 2024.
We offer many courses. For each, we offer verified certificates for a fee and a free certificate. Verified certificates involve a verification process through edX and, therefore, may be regarded by others as more authentic. Free certificates are issued using a unique URL.
Some of our courses are geared toward those who want to learn more about programming and data science:
- CS50x is our flagship course. This course teaches students how to think algorithmically and solve problems efficiently. Topics include abstraction, algorithms, data structures, encapsulation, resource management, security, software engineering, and web programming. Languages include C, Python, and SQL, plus HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
- CS50 AI is a follow-up to CS50x . The course explores the concepts and algorithms at the foundation of modern artificial intelligence, diving into the ideas that give rise to technologies like game-playing engines, handwriting recognition, and machine translation. Through hands-on projects, students gain exposure to the theory behind graph search algorithms, classification, optimization, reinforcement learning, and other topics in artificial intelligence and machine learning as they incorporate them into their own Python programs. By the course’s end, students emerge with experience in libraries for machine learning as well as knowledge of artificial intelligence principles that enable them to design intelligent systems of their own.
- CS50 Games picks up where CS50x leaves off, focusing on the development of 2D and 3D interactive games. Students explore the design of such childhood games as Super Mario Bros., Legend of Zelda, and Portal in a quest to understand how video games themselves are implemented. Via lectures and hands-on projects, the course explores principles of 2D and 3D graphics, animation, sound, and collision detection using frameworks like Unity and LÖVE 2D, as well as languages like Lua and C#. By class’s end, students will have programmed several of their own games and gained a thorough understanding of the basics of game design and development.
- CS50 Web picks up where CS50x leaves off, diving more deeply into the design and implementation of web apps with Python, JavaScript, and SQL using frameworks like Django, React, and Bootstrap. Topics include database design, scalability, security, and user experience. Through hands-on projects, students learn to write and use APIs, create interactive UIs, and leverage cloud services like GitHub and Heroku. By the course’s end, students emerge with knowledge and experience in principles, languages, and tools that empower them to design and deploy applications on the Internet.
- CS50 Python is an introduction to programming using a language called Python. Learn how to read and write code as well as how to test and “debug” it. This course is designed for students with or without prior programming experience who’d like to learn Python specifically. Learn about functions, arguments, and return values (oh my!); variables and types; conditionals and Boolean expressions; and loops. Learn how to handle exceptions, find and fix bugs, and write unit tests; use third-party libraries; validate and extract data with regular expressions; model real-world entities with classes, objects, methods, and properties; and read and write files. Hands-on opportunities for lots of practice. Exercises inspired by real-world programming problems. No software is required except for a web browser, or you can write code on your own PC or Mac. Whereas CS50x itself focuses on computer science more generally, as well as programming with C, Python, SQL, and JavaScript, this course, aka CS50 Python , is entirely focused on programming with Python. You can take CS50 Python before CS50x , during CS50x , or after CS50x . But for an introduction to computer science itself, you should still take CS50x !
- CS50 R is an introduction to programming using a language called R, a popular language for statistical computing and graphics in data science and other domains. Learn to use RStudio, a popular integrated development environment (IDE). Learn to represent real-world data with vectors, matrices, arrays, lists, and data frames. Filter data with conditions, via which you can analyze subsets of data. Apply functions and loops, via which you can manipulate and summarize data sets. Write functions to modularize code and raise exceptions when something goes wrong. Tidy data with R’s tidyverse and create colorful visualizations with R’s grammar of graphics. By course’s end, learn to package, test, and share R code for others to use. Assignments inspired by real-world data sets.
- CS50 Scratch is an introduction to programming using Scratch, a visual programming language via which aspiring programmers can write code by dragging and dropping graphical blocks (that resemble puzzle pieces) instead of typing out text. Used at the start of Harvard College’s introductory course in computer science, CS50x , Scratch was designed at MIT’s Media Lab, empowering students with no prior programming experience to design their own animations, games, interactive art, and stories. Using Scratch, this course introduces students to fundamentals of programming, found not only in Scratch itself but in traditional text-based languages (like Java and Python) as well. Topics include: functions, which are instructions that perform tasks; return values, which are results that functions provide; conditions, via which programs can decide whether or not to perform some action; loops, via which programs can take action again and again; variables, via which programs can remember information; and more. Ultimately, this course prepares students for subsequent courses in programming.
- CS50 SQL is an introduction to databases using a language called SQL. Learn how to create, read, update, and delete data with relational databases, which store data in rows and columns. Learn how to model real-world entities and relationships among them using tables with appropriate types, triggers, and constraints. Learn how to normalize data to eliminate redundancies and reduce the potential for errors. Learn how to join tables together using primary and foreign keys. Learn how to automate searches with views and expedite searches with indexes. Learn how to connect SQL with other languages like Python and Java. The course begins with SQLite for portability’s sake and ends with introductions to PostgreSQL and MySQL for scalability’s sake as well. Assignments inspired by real-world datasets. Whereas CS50x itself focuses on computer science more generally, as well as programming with C, Python, SQL, and JavaScript, this course, aka CS50 SQL , is entirely focused on SQL. You can take CS50 SQL before CS50x , during CS50x , or after CS50x . But for an introduction to computer science itself, you should still take CS50x !
Some of our courses are geared toward professionals who do not want to jump into programming right away:
- CS50 Business is a variant of CS50x designed especially for business professionals. Whereas CS50x takes a bottom-up approach, emphasizing mastery of low-level concepts and implementation details thereof, this course takes a top-down approach, emphasizing mastery of high-level concepts and design decisions related thereto. Ultimately, this course empowers students to make technological decisions even if not technologists themselves. Topics include cloud computing, networking, privacy, scalability, security, and more, with an emphasis on web and mobile technologies. Students emerge from this course with a first-hand appreciation of how it all works and all the more confident in the factors that should guide their decision-making. This course is designed for managers, product managers, founders, and decision-makers more generally.
- CS50 Cybersecurity is an introduction to cybersecurity for technical and non-technical audiences alike. Learn how to secure your accounts, data, systems, and software against today’s threats and how to recognize and evaluate tomorrow’s as well, both at home and at work. Learn how to preserve your own privacy. Learn to view cybersecurity not in absolute terms but relative, a function of risks and rewards (for an adversary) and costs and benefits (for you). Learn to recognize cybersecurity as a trade-off with usability itself. This course presents both high-level and low-level examples of threats, providing students with all they need to know technically to understand both. Assignments inspired by real-world events.
- CS50 for Lawyers is a variant of CS50x designed especially for lawyers (and law students). Whereas CS50x itself takes a bottom-up approach, emphasizing mastery of low-level concepts and implementation details thereof, this course takes a top-down approach, emphasizing mastery of high-level concepts and design decisions related thereto. Ultimately, it equips students with a deeper understanding of the legal implications of technological decisions made by clients.
- CS50 Technology is for students who don’t (yet) consider themselves computer persons. Designed for students who work with technology every day but don’t necessarily understand how it all works underneath the hood or how to solve problems when something goes wrong, this course fills in the gaps, empowering students to use and troubleshoot technology more effectively. Through lectures on hardware, the Internet, multimedia, security, programming, and web development, as well as through readings on current events, this course equips students for today’s technology and prepares them for tomorrow’s as well.
Information
- Author Services
Initiatives
You are accessing a machine-readable page. In order to be human-readable, please install an RSS reader.
All articles published by MDPI are made immediately available worldwide under an open access license. No special permission is required to reuse all or part of the article published by MDPI, including figures and tables. For articles published under an open access Creative Common CC BY license, any part of the article may be reused without permission provided that the original article is clearly cited. For more information, please refer to https://www.mdpi.com/openaccess .
Feature papers represent the most advanced research with significant potential for high impact in the field. A Feature Paper should be a substantial original Article that involves several techniques or approaches, provides an outlook for future research directions and describes possible research applications.
Feature papers are submitted upon individual invitation or recommendation by the scientific editors and must receive positive feedback from the reviewers.
Editor’s Choice articles are based on recommendations by the scientific editors of MDPI journals from around the world. Editors select a small number of articles recently published in the journal that they believe will be particularly interesting to readers, or important in the respective research area. The aim is to provide a snapshot of some of the most exciting work published in the various research areas of the journal.
Original Submission Date Received: .
- Active Journals
- Find a Journal
- Proceedings Series
- For Authors
- For Reviewers
- For Editors
- For Librarians
- For Publishers
- For Societies
- For Conference Organizers
- Open Access Policy
- Institutional Open Access Program
- Special Issues Guidelines
- Editorial Process
- Research and Publication Ethics
- Article Processing Charges
- Testimonials
- Preprints.org
- SciProfiles
- Encyclopedia

Article Menu

- Subscribe SciFeed
- Recommended Articles
- Google Scholar
- on Google Scholar
- Table of Contents
Find support for a specific problem in the support section of our website.
Please let us know what you think of our products and services.
Visit our dedicated information section to learn more about MDPI.
JSmol Viewer
Towards sustainable cloud computing: load balancing with nature-inspired meta-heuristic algorithms.

1. Introduction
- Nature-inspired meta-heuristic focus: Unlike other research primarily examining traditional load-balancing solutions, this study delves further into nature-inspired meta-heuristic algorithms. This study examines the benefits, distinctive characteristics, and present use of cloud computing, providing a fresh viewpoint.
- Comparative performance evaluation: Our approach involves surveying current meta-heuristic algorithms, conducting a thorough study, and comparing their performance using actual data obtained from case studies and experiments. This technique allows us to determine which algorithms are most suited for certain cloud resource load-balancing situations we have established.
- Integration of heuristic initial solutions: Our study emphasizes the significance of using typical heuristic methods to provide initial solutions for meta-heuristics to enhance the overall optimization process. This hybrid technique has received little attention in the existing literature and represents a novel addition to the discipline.
2. Background
2.1. cloud computing characteristics, 2.2. role of load balancing in cloud computing, 2.3. load-balancing challenges, 2.4. load-balancing policies, 2.5. meta-heuristic algorithms, 2.6. classification of load-balancing algorithms, 3. meta-heuristic algorithms for cloud load balancing, 3.1. ant colony optimization algorithm, 3.2. artificial bee colony algorithm, 3.3. genetic algorithm, 3.4. particle swarm optimization algorithm, 3.5. bat algorithm, 3.6. whale optimization algorithm, 3.7. simulated annealing algorithm, 3.8. biogeography-based optimization algorithm, 3.9. firefly algorithm, 3.10. grey wolf optimizer, 4. discussion.
- Complex optimization: Load balancing in cloud computing involves distributing tasks and workloads across multiple servers or VMs to ensure efficient resource utilization and reduced response times. This task is often a complex optimization problem that requires finding optimal or near-optimal solutions. Nature-inspired algorithms provide powerful optimization techniques to tackle these challenges.
- Global search: Cloud environments can have numerous variables and constraints, making it challenging to find the best solution. Nature-inspired algorithms, such as genetic algorithms, particle swarm optimization, and ant colony optimization, are designed to perform global searches in the solution space, helping to find solutions that traditional algorithms might miss.
- Flexibility and adaptability: Nature-inspired algorithms are often designed to adapt and evolve, mimicking the ability of natural systems to adapt to changing environments. In cloud computing, workloads and resource availability can vary dynamically. These algorithms can help adapt load-balancing strategies to changing conditions effectively.
- Parallelism and scalability: Cloud environments are inherently parallel and scalable. Many nature-inspired algorithms can be easily parallelized, allowing them to leverage the distributed nature of cloud computing resources. This makes them well-suited for addressing load-balancing challenges in large-scale cloud environments.
- Multi-objective optimization: Load balancing often involves optimizing multiple objectives simultaneously, such as minimizing response time, maximizing resource utilization, and minimizing energy consumption. Nature-inspired algorithms can handle multi-objective optimization, allowing cloud administrators to find trade-offs among different goals.
- Dynamic nature: Some nature-inspired algorithms, like particle swarm optimization, mimic the behavior of particles moving through a solution space. This dynamic nature aligns well with the dynamic nature of load balancing in cloud computing, where workloads and resources change over time.
- Exploration and exploitation: Nature-inspired algorithms strike a balance between exploration (searching for new and unexplored areas of the solution space) and exploitation (refining solutions in promising regions). This is vital for finding optimal or near-optimal solutions to load-balancing problems.
- Heuristic solutions: Load-balancing problems are often NP-hard, meaning that finding an optimal solution in a reasonable amount of time is practically impossible. Nature-inspired algorithms provide heuristic solutions that can efficiently find good solutions even for highly complex and large-scale load-balancing instances.
- Domain-agnostic: Nature-inspired algorithms are generally domain-agnostic and can be applied to various problems, including load balancing in cloud computing. They can adapt to different system architectures and characteristics.
- Earliest Deadline First (EDF): Tasks are prioritized according to their deadlines, with the tasks with the earliest dates given more priority. This strategy is efficient in time-sensitive situations where fulfilling deadlines is essential.
- Least Laxity First (LLF): Similar to EDF, LLF arranges jobs according to the amount of time available before their deadlines, known as slack time or laxity. Tasks with the lowest amount of flexibility are assigned more importance, guaranteeing prompt completion.
- First-Fit Decreasing (FFD): The tasks are arranged in descending order based on their size, then assigned to the first available resource to accommodate them. This strategy optimally allocates jobs within restricted resources, minimizes fragmentation, and enhances resource use.
- Best-Fit Decreasing (BFD): Like FFD, tasks are assigned to the resource that has the lowest remaining capacity following the assignment. The objective of this strategy is to reduce the amount of unused space and enhance the efficiency of packing.
- Greedy algorithms: These algorithms use local, optimal decisions at each stage in the expectation of discovering a global optimum. For instance, a greedy load balancer may allocate each incoming job to the server with the lowest current load, with the objective of gradually achieving load balance.
- Dynamic policy selection: The scheduler assesses many policies in real time and selects the one that most effectively aligns with the present workload and system condition. This flexibility improves efficiency and the usage of resources.
- Policy portfolio: The portfolio comprises a varied range of scheduling policies, including round-robin, least-connection, and FCFS. This enables the scheduler to seamlessly transition between policies as required in order to optimize performance.
5. Open Issues and Future Directions
6. conclusions, author contributions, data availability statement, conflicts of interest.
- Pourghebleh, B.; Anvigh, A.A.; Ramtin, A.R.; Mohammadi, B. The importance of nature-inspired meta-heuristic algorithms for solving virtual machine consolidation problem in cloud environments. Clust. Comput. 2021 , 24 , 2673–2696. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Hayyolalam, V.; Pourghebleh, B.; Chehrehzad, M.R.; Kazem, A.A.P. Single-objective service composition methods in cloud manufacturing systems: Recent techniques, classification, and future trends. Concurr. Comput. Pract. Exp. 2022 , 34 , e6698. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Pourghebleh, B.; Hayyolalam, V. A comprehensive and systematic review of the load balancing mechanisms in the Internet of Things. Clust. Comput. 2019 , 23 , 641–661. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Afzal, S.; Kavitha, G. Load balancing in cloud computing—A hierarchical taxonomical classification. J. Cloud Comput. 2019 , 8 , 22. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Kumar, P.; Kumar, R. Issues and challenges of load balancing techniques in cloud computing: A survey. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 2019 , 51 , 1–35. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Shafiq, D.A.; Jhanjhi, N.Z.; Abdullah, A.; Alzain, M.A. A load balancing algorithm for the data centres to optimize cloud computing applications. IEEE Access 2021 , 9 , 41731–41744. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Agrawal, N.; Tapaswi, S. Defense mechanisms against DDoS attacks in a cloud computing environment: State-of-the-art and research challenges. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2019 , 21 , 3769–3795. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Zhang, W.-Z.; Elgendy, I.A.; Hammad, M.; Iliyasu, A.M.; Du, X.; Guizani, M.; El-Latif, A.A.A. Secure and optimized load balancing for multitier IoT and edge-cloud computing systems. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020 , 8 , 8119–8132. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Mazumder, A.M.R.; Uddin, K.A.; Arbe, N.; Jahan, L.; Whaiduzzaman, M. Dynamic task scheduling algorithms in cloud computing. In Proceedings of the 2019 3rd International conference on Electronics, Communication and Aerospace Technology (ICECA), Coimbatore, India, 12–14 June 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA; pp. 1280–1286. [ Google Scholar ]
- Saeik, F.; Avgeris, M.; Spatharakis, D.; Santi, N.; Dechouniotis, D.; Violos, J.; Leivadeas, A.; Athanasopoulos, N.; Mitton, N.; Papavassiliou, S. Task offloading in Edge and Cloud Computing: A survey on mathematical, artificial intelligence and control theory solutions. Comput. Netw. 2021 , 195 , 108177. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Hayyolalam, V.; Pourghebleh, B.; Kazem, A.A.P. Trust management of services (TMoS): Investigating the current mechanisms. Trans. Emerg. Telecommun. Technol. 2020 , 31 , e4063. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, L.; Luo, J.; Liu, J. A two-stage container management in the cloud for optimizing the load balancing and migration cost. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2022 , 135 , 303–314. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Tawfeeg, T.M.; Yousif, A.; Hassan, A.; Alqhtani, S.M.; Hamza, R.; Bashir, M.B.; Ali, A. Cloud Dynamic Load Balancing and Reactive Fault Tolerance Techniques: A Systematic Literature Review (SLR). IEEE Access 2022 , 10 , 71853–71873. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Kong, L.; Mapetu, J.P.B.; Chen, Z. Heuristic load balancing based zero imbalance mechanism in cloud computing. J. Grid Comput. 2020 , 18 , 123–148. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Kumar, K. P2BED-C: A novel peer to peer load balancing and energy efficient technique for data-centers over cloud. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2022 , 123 , 311–324. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Liang, B.; Dong, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X. A low-power task scheduling algorithm for heterogeneous cloud computing. J. Supercomput. 2020 , 76 , 7290–7314. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Raza, M.S.; Wei, J.; Muslam, M.M.A. A Succinct Review of Intelligent Computational Techniques in Green Cloud Computing. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Communications, Signal Processing, and their Applications (ICCSPA, Sharjah, United Arab Emirates, 16–18 March 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 1–4. [ Google Scholar ]
- Li, C.; Sun, H.; Tang, H.; Luo, Y. Adaptive resource allocation based on the billing granularity in edge-cloud architecture. Comput. Commun. 2019 , 145 , 29–42. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Ebrahim, M.; Hafid, A. Resilience and load balancing in Fog networks: A Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis approach. Microprocess. Microsyst. 2023 , 101 , 104893. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Kumar, Y.; Kaul, S.; Hu, Y.-C. Machine learning for energy-resource allocation, workflow scheduling and live migration in cloud computing: State-of-the-art survey. Sustain. Comput. Inform. Syst. 2022 , 36 , 100780. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Motlagh, A.A.; Movaghar, A.; Rahmani, A.M. Task scheduling mechanisms in cloud computing: A systematic review. Int. J. Commun. Syst. 2020 , 33 , e4302. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Neelakantan, P.; Yadav, N.S. An Optimized Load Balancing Strategy for an Enhancement of Cloud Computing Environment. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2023 , 131 , 1745–1765. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Li, K.; Chang, C.; Yun, K.; Zhang, J. Research on Container Migration Mechanism of Power Edge Computing on Load Balancing. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 6th International Conference on Cloud Computing and Big Data Analytics (ICCCBDA), Chengdu, China, 24–26 April 2021; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA; pp. 386–390. [ Google Scholar ]
- Guo, X.-Q.; Chen, W.-N.; Wei, F.-F.; Mao, W.-T.; Hu, X.-M.; Zhang, J. Edge–Cloud Co-Evolutionary Algorithms for Distributed Data-Driven Optimization Problems. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2022 , 53 , 6598–6611. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Kannan, K.; Sunitha, G.; Deepa, S.; Babu, D.V.; Avanija, J. A multi-objective load balancing and power minimization in cloud using bio-inspired algorithms. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2022 , 102 , 108225. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Qawqzeh, Y.; Alharbi, M.T.; Jaradat, A.; Sattar, K.N.A. A review of swarm intelligence algorithms deployment for scheduling and optimization in cloud computing environments. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2021 , 7 , e696. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Sridharan, S.; Subramanian, R.K.; Srirangan, A.K. Physics based meta heuristics in manufacturing. Mater. Today Proc. 2021 , 39 , 805–811. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Camacho-Villalón, C.L.; Dorigo, M.; Stützle, T. Exposing the grey wolf, moth-flame, whale, firefly, bat, and antlion algorithms: Six misleading optimization techniques inspired by bestial metaphors. Int. Trans. Oper. Res. 2023 , 30 , 2945–2971. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Gao, R.; Wu, J. Dynamic load balancing strategy for cloud computing with ant colony optimization. Future Internet 2015 , 7 , 465–483. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Muteeh, A.; Sardaraz, M.; Tahir, M. MrLBA: Multi-resource load balancing algorithm for cloud computing using ant colony optimization. Clust. Comput. 2021 , 24 , 3135–3145. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Xu, P.; He, G.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Z. An efficient load balancing algorithm for virtual machine allocation based on ant colony optimization. Int. J. Distrib. Sens. Netw. 2018 , 14 , 1550147718793799. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Gabhane, J.P.; Pathak, S.; Thakare, N.M. A novel hybrid multi-resource load balancing approach using ant colony optimization with Tabu search for cloud computing. Innov. Syst. Softw. Eng. 2023 , 19 , 81–90. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Bui, K.T.; Pham, T.V.; Tran, H.C. A load balancing game approach for VM provision cloud computing based on ant colony optimization. In Proceedings of the Context-Aware Systems and Applications: 5th International Conference, ICCASA 2016, Thu Dau Mot, Vietnam, 24–25 November 2016; Proceedings 5. Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 52–63. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ragmani, A.; Elomri, A.; Abghour, N.; Moussaid, K.; Rida, M. An improved hybrid fuzzy-ant colony algorithm applied to load balancing in cloud computing environment. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2019 , 151 , 519–526. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Mohammadian, V.; Navimipour, N.J.; Hosseinzadeh, M.; Darwesh, A. LBAA: A novel load balancing mechanism in cloud environments using ant colony optimization and artificial bee colony algorithms. Int. J. Commun. Syst. 2023 , 36 , e5481. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Raghav, Y.Y.; Vyas, V. ACBSO: A hybrid solution for load balancing using ant colony and bird swarm optimization algorithms. Int. J. Inf. Technol. 2023 , 15 , 2847–2857. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Minarolli, D. A Distributed Task Scheduling Approach for Cloud Computing Based on Ant Colony Optimization and Queue Load Information. In Proceedings of the International Conference on P2P, Parallel, Grid, Cloud and Internet Computing, Tirana, Albania, 27–29 October 2022; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; pp. 13–24. [ Google Scholar ]
- Amer, D.A.; Attiya, G.; Ziedan, I. An efficient multi-objective scheduling algorithm based on spider monkey and ant colony optimization in cloud computing. Clust. Comput. 2023 , 27 , 1799–1819. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Kruekaew, B.; Kimpan, W. Multi-objective task scheduling optimization for load balancing in cloud computing environment using hybrid artificial bee colony algorithm with reinforcement learning. IEEE Access 2022 , 10 , 17803–17818. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Kruekaew, B.; Kimpan, W. Enhancing of artificial bee colony algorithm for virtual machine scheduling and load balancing problem in cloud computing. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Syst. 2020 , 13 , 496–510. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Kumar, R.; Chaturvedi, A. Improved cuckoo search with artificial bee colony for efficient load balancing in cloud computing environment. In Proceedings of the Smart Innovations in Communication and Computational Sciences: Proceedings of ICSICCS 2020, Dallas, TX, USA; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021; pp. 123–131. [ Google Scholar ]
- Janakiraman, S.; Priya, M.D. Improved artificial bee colony using monarchy butterfly optimization algorithm for load balancing (IABC-MBOA-LB) in cloud environments. J. Netw. Syst. Manag. 2021 , 29 , 39. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Milan, S.T.; Navimipour, N.J.; Bavil, H.L.; Yalcin, S. A QoS-based technique for load balancing in green cloud computing using an artificial bee colony algorithm. J. Exp. Theor. Artif. Intell. 2023 , 1–36. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Sefati, S.S.; Halunga, S. A hybrid service selection and composition for cloud computing using the adaptive penalty function in genetic and artificial bee colony algorithm. Sensors 2022 , 22 , 4873. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Makasarwala, H.A.; Hazari, P. Using genetic algorithm for load balancing in cloud computing. In Proceedings of the 2016 8th International Conference on Electronics, Computers and Artificial Intelligence (ECAI), Ploiesti, Romania, 30 June–2 July 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 1–6. [ Google Scholar ]
- Saadat, A.; Masehian, E. Load balancing in cloud computing using genetic algorithm and fuzzy logic. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Computational Science and Computational Intelligence (CSCI), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 5–7 December 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1435–1440. [ Google Scholar ]
- Gulbaz, R.; Siddiqui, A.B.; Anjum, N.; Alotaibi, A.A.; Althobaiti, T.; Ramzan, N. Balancer genetic algorithm—A novel task scheduling optimization approach in cloud computing. Appl. Sci. 2021 , 11 , 6244. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Pradhan, A.; Bisoy, S.K. A novel load balancing technique for cloud computing platform based on PSO. J. King Saud Univ.-Comput. Inf. Sci. 2022 , 34 , 3988–3995. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Alguliyev, R.M.; Imamverdiyev, Y.N.; Abdullayeva, F.J. PSO-based load balancing method in cloud computing. Autom. Control Comput. Sci. 2019 , 53 , 45–55. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Mapetu, J.P.B.; Chen, Z.; Kong, L. Low-time complexity and low-cost binary particle swarm optimization algorithm for task scheduling and load balancing in cloud computing. Appl. Intell. 2019 , 49 , 3308–3330. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Malik, M.; Suman. Lateral Wolf Based Particle Swarm Optimization (LW-PSO) for Load Balancing on Cloud Computing. Wirel. Pers. Commun. 2022 , 125 , 1125–1144. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Sharma, S.; Luhach, A.K.; Sinha, S. An optimal load balancing technique for cloud computing environment using bat algorithm. Indian J. Sci. Technol. 2016 , 9 , 1–4. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Ullah, A.; Chakir, A. Improvement for tasks allocation system in VM for cloud datacenter using modified bat algorithm. Multimed. Tools Appl. 2022 , 81 , 29443–29457. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Zheng, J.; Wang, Y. A hybrid multi-objective bat algorithm for solving cloud computing resource scheduling problems. Sustainability 2021 , 13 , 7933. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Ramya, K.; Ayothi, S. Hybrid dingo and whale optimization algorithm-based optimal load balancing for cloud computing environment. Trans. Emerg. Telecommun. Technol. 2023 , 34 , e4760. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Strumberger, I.; Bacanin, N.; Tuba, M.; Tuba, E. Resource scheduling in cloud computing based on a hybridized whale optimization algorithm. Appl. Sci. 2019 , 9 , 4893. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Ni, L.; Sun, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, J. GCWOAS2: Multiobjective task scheduling strategy based on Gaussian cloud-whale optimization in cloud computing. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2021 , 2021 , 5546758. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Sabar, N.R.; Song, A. Grammatical evolution enhancing simulated annealing for the load balancing problem in cloud computing. in Proc. Genet. Evol. Comput. Conf. 2016 , 2016 , 997–1003. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hanine, M.; Benlahmar, E.-H. A load-balancing approach using an improved simulated annealing algorithm. J. Inf. Process. Syst. 2020 , 16 , 132–144. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kumar, S.; Singh, G.; Prakash, S. A Performance Improvement Model for Cloud Computing Using Simulated Annealing Algorithm. Int. J. Softw. Innov. (IJSI) 2022 , 10 , 1–17. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ghobaei-Arani, M. A workload clustering based resource provisioning mechanism using Biogeography based optimization technique in the cloud based systems. Soft Comput. 2021 , 25 , 3813–3830. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Bouhank, A.; Daoudi, M. Non-dominated ranking biogeography based optimization algorithm for virtual machine placement in cloud Computing. In Intelligent Computing: Proceedings of the 2021 Computing Conference ; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2022; Volume 1, pp. 423–438. [ Google Scholar ]
- Devaraj, A.F.S.; Elhoseny, M.; Dhanasekaran, S.; Lydia, E.L.; Shankar, K. Hybridization of firefly and improved multi-objective particle swarm optimization algorithm for energy efficient load balancing in cloud computing environments. J. Parallel Distrib. Comput. 2020 , 142 , 36–45. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- RM, S.P.; Bhattacharya, S.; Maddikunta, P.K.R.; Somayaji, S.R.K.; Lakshmanna, K.; Kaluri, R.; Hussien, A.; Gadekallu, T.R. Load balancing of energy cloud using wind driven and firefly algorithms in internet of everything. J. Parallel Distrib. Comput. 2020 , 142 , 16–26. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Sekaran, K.; Khan, M.S.; Patan, R.; Gandomi, A.H.; Krishna, P.V.; Kallam, S. Improving the response time of m-learning and cloud computing environments using a dominant firefly approach. IEEE Access 2019 , 7 , 30203–30212. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Gohil, B.N.; Patel, D.R. A hybrid GWO-PSO algorithm for load balancing in cloud computing environment. In Proceedings of the 2018 Second International Conference on Green Computing and Internet of Things (ICGCIoT), Bangalore, India, 16–18 August 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 185–191. [ Google Scholar ]
- Sefati, S.; Mousavinasab, M.; Farkhady, R.Z. Load balancing in cloud computing environment using the Grey wolf optimization algorithm based on the reliability: Performance evaluation. J. Supercomput. 2022 , 78 , 18–42. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Sekaran, R.; Munnangi, A.K.; Rajeyyagari, S.; Ramachandran, M.; Al-Turjman, F. Ant colony resource optimization for Industrial IoT and CPS. Int. J. Intell. Syst. 2021 , 37 , 10513–10532. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Karaboga, D.; Akay, B. A comparative study of artificial bee colony algorithm. Appl. Math. Comput. 2009 , 214 , 108–132. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Zhao, F.; Zeng, X. Simulated annealing–genetic algorithm for transit network optimization. J. Comput. Civ. Eng. 2006 , 20 , 57–68. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Shami, T.M.; El-Saleh, A.A.; Alswaitti, M.; Al-Tashi, Q.; Summakieh, M.A.; Mirjalili, S. Particle swarm optimization: A comprehensive survey. IEEE Access 2022 , 10 , 10031–10061. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Yang, X.S.; Gandomi, A.H. Bat algorithm: A novel approach for global engineering optimization. Eng. Comput. 2012 , 29 , 464–483. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Mirjalili, S.; Lewis, A. The whale optimization algorithm. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2016 , 95 , 51–67. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Amine, K. Multiobjective simulated annealing: Principles and algorithm variants. Adv. Oper. Res. 2019 , 2019 , 8134674. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Simon, D. Biogeography-based optimization. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2008 , 12 , 702–713. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Yang, X.-S.; He, X. Firefly algorithm: Recent advances and applications. Int. J. Swarm Intell. 2013 , 1 , 36–50. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Mirjalili, S.; Mirjalili, S.M.; Lewis, A. Grey wolf optimizer. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2014 , 69 , 46–61. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
Click here to enlarge figure
| Reference | Main Objective | Targeted Issue | Key Contributions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gao and Wu [ ] | Optimal resource utilization and load avoidance | Task distribution and coordination in cloud computing | Efficient load balancing in cloud computing using ACO with improved network performance. |
| Muteeh et al. [ ] | Efficient resource utilization and load balancing | Load balancing in cloud computing | Significant reduction in execution time and cost in cloud resource utilization. |
| Xu et al. [ ] | Achieving load balancing and enhancing resource utilization | Multidimensional resource load balancing across physical machines | Improved resource utilization and load balancing in cloud computing through ACO-based VM allocation. |
| Gabhane et al. [ ] | Enhancing multi-resource load balancing | Multi-resource load balancing | Outperformance of existing optimization methods in terms of data delivery and processing. |
| Bui et al. [ ] | Balancing the interests of service providers and customers | VM provisioning and load balancing | Use of coefficients for achieving load balancing in VM provisioning. |
| Ragmani et al. [ ] | Enhancing load balancing and response time | Load balancing in the cloud | Superior load balancing and response time using Fuzzy-ACO. |
| Mohammadian et al. [ ] | Evenly distributing the workload across systems | Load balancing in data centers | Improved response time, imbalance degree, makespan, and resource utilization. |
| Raghav and Vyas [ ] | Hybrid approach for load balancing | Load balancing in cloud computing | Improved performance compared to standalone ACO and bird swarm optimization. |
| Minarolli [ ] | Distributed task scheduling using swarm intelligence | Task allocation during high-load conditions | Superior outcomes compared to distributed scheduling based solely on ACO or queue load information. |
| Amer et al. [ ] | Efficient resource allocation and cloud performance enhancement | Multi-objective scheduling challenges | Efficient resource allocation, cloud performance enhancement, and increased profits. |
| Reference | Main Objective | Targeted Issue | Key Contributions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Kruekaew and Kimpan [ ] | Optimizing task scheduling and resource utilization | Scheduling optimization and load balancing in cloud computing | Improved makespan, cost reduction, load balancing, increased throughput, and resource utilization. |
| Kruekaew and Kimpan [ ] | Enhanced VM scheduling | VM scheduling in cloud computing | Superior VM scheduling in both homogeneous and heterogeneous environments. |
| Kumar and Chaturvedi [ ] | Load balancing for efficient VM scheduling | Load distribution across VMs in cloud computing | Superior average VM load distribution, high accuracy, and low complexity compared to existing methods. |
| Janakiraman and Priya [ ] | Optimizing resource allocation in cloud environments | Resource allocation challenges in cloud computing | Minimizing load variance, makespan, connection deviations, imbalance degree, and maximizing throughput. |
| Tabagchi Milan et al. [ ] | Improving QoS and reducing energy consumption | QoS and energy efficiency in green computing | Enhanced QoS, reduced makespan, and minimized energy usage compared to alternatives. |
| Sefati and Halunga [ ] | Optimized service selection in cloud computing | Service selection and allocation optimization in cloud computing | Improvements in reliability, availability, and cost-effectiveness in service selection and allocation. |
| Reference | Main Objective | Targeted Issue | Key Contributions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Makasarwala and Hazari [ ] | Enhancing real-world applicability of load balancing | Cloud computing load balancing | Incorporation of time-based request priority for improved real-world relevance and superior performance. |
| Saadat and Masehian [ ] | Swift optimization and user satisfaction improvement | Load balancing in cloud computing | Achieving superior solutions faster, enhancing user satisfaction, and elevating cloud computing load balancing. |
| Gulbaz et al. [ ] | Simultaneous improvement in makespan and load balancing | Load balancing in computing systems | An effective load-balancing mechanism considers the actual VM load and significantly improves makespan, throughput, and load balancing. |
| Reference | Main Objective | Targeted Issue | Key Contributions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pradhan and Bisoy [ ] | Optimizing task scheduling in cloud environments | Task scheduling and resource utilization in the cloud | Superior performance in minimizing makespan and maximizing resource utilization. |
| Alguliyev et al. [ ] | Task-based load balancing in the cloud | Load balancing and task migration in cloud computing | Achieves optimal task scheduling, equitable task distribution, and reduced time consumption for task-to-VM assignments. |
| Mapetu et al. [ ] | Efficient task scheduling and load balancing in cloud computing | Task scheduling and load balancing | Outperforms existing heuristic and meta-heuristic algorithms in enhancing task scheduling and load distribution. |
| Malik and Suman [ ] | Optimal load distribution and task scheduling in cloud computing | Task scheduling and VM load balancing | Balanced VM loads, reduced response times, and superior performance over existing systems in task scheduling and load distribution. |
| Reference | Main Objective | Targeted Issue | Key Contributions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sharma et al. [ ] | Fulfilling load balancer objectives using the bat algorithm | Load balancing and its impact on response time | Acknowledged the impact of load balancing on response time and aims for future work on job migration algorithm development. |
| Ullah and Chakir [ ] | Enhancing task distribution within cloud computing’s VMs | Task distribution and load balancing in cloud computing | Outperforms standard techniques, significantly boosting the accuracy and efficiency of cloud data centers. |
| Zheng and Wang [ ] | Enhancing cloud computing service quality through a hybrid multi-objective bat algorithm | Service quality improvement in cloud computing | Superior performance over multiple optimization algorithms, particularly regarding makespan, imbalance degree, throughput, and cost. |
| Reference | Main Objective | Targeted Issue | Key Contributions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ramya and Ayothi [ ] | Enhancing cloud performance through load balancing | Cloud performance optimization | Improved throughput, reliability, makespan, and resource allocation in CloudSim experiments. |
| Strumberger et al. [ ] | Tackling cloud resource scheduling challenges | Cloud resource scheduling | Consistently outperforms the original whale optimization algorithm and other heuristics and meta-heuristics in enhancing cloud resource scheduling. |
| Ni et al. [ ] | Multi-objective task scheduling in cloud computing | Task scheduling, resource utilization, and load balancing | Improved task completion time, VM load balance, and resource utilization compared to other meta-heuristic algorithms. |
| Reference | Main Objective | Targeted Issue | Key Contributions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sabar and Song [ ] | Novel load-balancing technique combining simulated annealing (SA) with grammatical evolution (GE) | Load balancing and parameter tuning in SA | Superiority over state-of-the-art algorithms in achieving load balancing, particularly for the Google machine reassignment problem. |
| Hanine and Benlahmar [ ] | Achieving workload balance among VMs | Workload balance among VMs | Improved task allocation with fewer iterations compared to standard SA. |
| Kumar et al. [ ] | Minimizing execution time and ensuring load balance in job scheduling | Job scheduling and load balancing | Optimal solutions outperform various algorithms and significantly reduce job schedule execution times. |
| Reference | Main Objective | Targeted Issue | Key Contributions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ghobaei-Arani [ ] | Optimizing cloud application execution through workload clustering and resource provisioning | Workload clustering and QoS-aware resource provisioning | Reduction in delay, SLA violations, cost, and energy consumption compared to alternatives, confirming superiority in optimizing cloud application execution. |
| Bouhank and Daoudi [ ] | Minimizing resource wastage and power consumption during VM placement | Resource optimization in VM placement | Improved efficiency, convergence, and solution coverage compared to other multi-objective approaches for VM placement. |
| Reference | Main Objective | Targeted Issue | Key Contributions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Devaraj et al. [ ] | Balancing load distribution, enhancing resource utilization, and reducing task response times | Load balancing in cloud computing | Achieves balanced load distribution, enhanced resource utilization, and reduced task response times, outperforming alternatives in simulations. |
| RM et al. [ ] | Integrating domains for energy-efficient Internet of Everything (IoE) services | Energy efficiency and traffic reduction in IoT networks | Superiority in extending IoT network lifetimes and significantly reducing traffic burdens compared to state-of-the-art techniques. |
| Sekaran et al. [ ] | Optimizing task distribution for improved mobile learning system accuracy | Load balancing in cloud servers for m-learning | Potential to boost throughput and response times in mobile and cloud environments by addressing load imbalance in cloud servers for m-learning. |
| Reference | Main Objective | Targeted Issue | Key Contributions |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gohil and Patel [ ] | Enhancing system performance and resource utilization equity in cloud computing | Load balancing in cloud computing | Enhanced convergence rates and implementation simplicity compared to other optimization techniques, promising potential for advancing cloud load balancing. |
| Sefati et al. [ ] | Achieving effective load balancing with resource reliability consideration | Load balancing and resource allocation in cloud computing | Superior performance over alternatives, with reduced costs, response times, and optimal solutions in CloudSim-based simulations, addressing cloud-based load-balancing challenges effectively. |
| The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
Share and Cite
Li, P.; Wang, H.; Tian, G.; Fan, Z. Towards Sustainable Cloud Computing: Load Balancing with Nature-Inspired Meta-Heuristic Algorithms. Electronics 2024 , 13 , 2578. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13132578
Li P, Wang H, Tian G, Fan Z. Towards Sustainable Cloud Computing: Load Balancing with Nature-Inspired Meta-Heuristic Algorithms. Electronics . 2024; 13(13):2578. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13132578
Li, Peiyu, Hui Wang, Guo Tian, and Zhihui Fan. 2024. "Towards Sustainable Cloud Computing: Load Balancing with Nature-Inspired Meta-Heuristic Algorithms" Electronics 13, no. 13: 2578. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13132578
Article Metrics
Article access statistics, further information, mdpi initiatives, follow mdpi.

Subscribe to receive issue release notifications and newsletters from MDPI journals
Materials Horizons
Recent advances in flexible memristors for advanced computing and sensing.

* Corresponding authors
a School of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Nanyang Technological University, 50 Nanyang Avenue, Singapore, Singapore E-mail: [email protected] , [email protected]
Conventional computing systems based on von Neumann architecture face challenges such as high power consumption and limited data processing capability. Improving device performance via scaling guided by Moore's Law becomes increasingly difficult. Emerging memristors can provide a promising solution for achieving high-performance computing systems with low power consumption. In particular, the development of flexible memristors is an important topic for wearable electronics, which can lead to intelligent systems in daily life with high computing capacity and efficiency. Here, recent advances in flexible memristors are reviewed, from operating mechanisms and typical materials to representative applications. Potential directions and challenges for future study in this area are also discussed.

- This article is part of the themed collection: Recent Review Articles
Article information
Download Citation
Permissions.
J. Xu, Z. Luo, L. Chen, X. Zhou, H. Zhang, Y. Zheng and L. Wei, Mater. Horiz. , 2024, Advance Article , DOI: 10.1039/D4MH00291A
This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported Licence . You can use material from this article in other publications without requesting further permissions from the RSC, provided that the correct acknowledgement is given.
Read more about how to correctly acknowledge RSC content .
Social activity
Search articles by author.
This article has not yet been cited.
Advertisements




IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Course Syllabus • 1 minute. Lesson 1 Summary: Introduction to Cloud Computing • 1 minute. Lesson 2 Summary: Business Case for Cloud Computing • 1 minute. Lesson 3 Summary: Emerging Technologies Accelerated by Cloud • 1 minute. Module 1 Glossary: Overview of Cloud Computing • 2 minutes. 4 assignments • Total 48 minutes.
Nowadays, Cloud computing is adopted by every company, whether it is an MNC or a startup many are still migrating towards it because of the cost-cutting, lesser maintenance, and the increased capacity of the data with the help of servers maintained by the cloud providers. One more reason for this drastic change from the On-premises servers of the companies to the Cloud providers is the 'Pay ...
Offered by IBM. Start your cloud computing journey with this self-paced introductory course! Whether you need general cloud computing ... Enroll for free.
edX
7000+ certificate courses from Google, Microsoft, IBM, and many more. India: 75% Off World: 40% Off. Start your cloud computing journey with this self-paced introductory course! Whether you need general cloud computing knowledge for school or business, or you are considering a career change, this beginner-friendly course is right for you.
About This Course. Cloud computing is one of the hottest technical topics today, with broad-. rchitecture, Business, Softwar. Engineering, and Data Storage. This cou. se serves as an introduction tocloud computing fo. nd organizations.PrerequisitesNo previous programming or arch. e is necessary.Time Commitmen.
Introduction to Cloud Computing | Coursera | IBM | Week 1 to 5 | Complete Quiz Answers + Assignment.. Course Link to Enroll:https://www.coursera.org/learn/in...
Data Storage. This course serves as an introduction to cloud computing for individuals and organizations. Prerequisites No previous programming or architecture knowledge is necessary Time Commitment Approximately six hours total, self-paced Deadlines All coursework, assignments, and tests must be complete by 10 November, 23:30 UTC What you'll learn
a Storage:6.Data is stored:in the "cloud", in certain cases closer. the site where it is used.appears to the users as if stored in a. ocation-independent manner.7.The data storage strategy can increase reliability, as well as security, and c. unication costs.Management:8.The maintenance and security are o.
Week 1: Introduction to Cloud Computing. Week 2: Cloud Computing Architecture. Week 3: Service Management in Cloud Computing. Week 4: Data Management in Cloud Computing. Week 5: Resource Management in Cloud. Week 6: Cloud Security. Week 7: Open Source and Commercial Clouds, Cloud Simulator. Week 8: Research trend in Cloud Computing, Fog Computing.
Course Syllabus • 1 minute. Lesson 1 Summary: Introduction to Cloud Computing • 1 minute. Lesson 2 Summary: Business Case for Cloud Computing • 1 minute. Lesson 3 Summary: Emerging Technologies Accelerated by Cloud • 1 minute. Module 1 Glossary: Overview of Cloud Computing • 2 minutes. 4 assignments • Total 48 minutes.
In this assignment, you can either choose a research publication that is relevant to your proposed work in Project 4, or you may choose to read the paper "Cloud computing and emerging IT platforms : Vision, Hype and reality for delivering computing as a 5th utility" by R. Buyya et. al. This paper can be downloaded using the following URL ...
Welcome to Cloud Computing Basics (Cloud 101). Over the next few weeks, we will discuss the basics of Cloud computing: what it is, what it supports, and how it is delivered. We will delve into storage services, Cloud economics, levels of managed infrastructure, and Azure services. We will also explore different deployment models of Cloud ...
Introduction To Cloud Computing (CBD-2234) 33 33 documents. 0 0 questions 3 3 students. Follow this course. Introduction To Cloud Computing (CBD-2234) Follow. ... Assignment 1 - It is a research paper regarding Istio. 11 pages 2023/2024 None. 2023/2024 None. Save. Evaluation Timetable-2021S CSD 2214 00. 1 page 2016/2017 None.
New Assignments. Module Name Download; noc20_cs20_assigment_1: noc20_cs20_assigment_1: ... Lecture 29: Cloud Computing: Security Issues in Collaborative SaaS Cloud: Download ... Lecture 36 : Introduction to DOCKER Container : Download Verified; 37: Lecture 37 : Green Cloud: Download
Join us on a journey through the fundamentals of cloud computing as we tackle all 10 assignments in this playlist from NPTEL. Whether you're just starting ou...
Introduction to Cloud Computing. Cloud Computing is the delivery of computing services such as servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, intelligence, and more, over the Cloud (Internet). Cloud Computing provides an alternative to the on-premises datacentre. With an on-premises datacentre, we have to manage everything, such ...
Cloud computing is accessing on demand computing resources via the internet, such as software, storage and even infrastructure. Cloud computing has existed in concept for nearly 50 years, however only recently has technology progressed to where it has become a multi-billion dollar annual industry.
Module 2: Cloud Adoption and Emerging Technologies on the Cloud. Module 3: Cloud Computing Service and Deployment Models. Module 4: Components of Cloud Computing. Module 5: Cloud Computing Storage and Content Delivery Networks. Module 6: Emergent Trends, Cloud Native, DevOps, and Application Modernization. Final Exam.
1, Heroku: it is a famous cloud computing platform that also provides mobile cloud services. The developers can develop and manage the applications on a scalable cloud computing platform with Heroku. It also offers a powerful set of features for mobile cloud computing which has become the reason for its brilliance.
CS50 Python is an introduction to programming using a language called Python. Learn how to read and write code as well as how to test and "debug" it. ... Assignments inspired by real-world datasets. ... Topics include cloud computing, networking, privacy, scalability, security, and more, with an emphasis on web and mobile technologies ...
Cloud computing is considered suitable for organizations thanks to its flexibility and the provision of digital services via the Internet. The cloud provides nearly limitless computing resources on demand without any upfront costs or long-term contracts, enabling organizations to meet their computing needs more economically. Furthermore, cloud computing provides higher security, scalability ...
Emerging memristors can provide a promising solution for achieving high-performance computing systems with low power consumption. In particular, the development of flexible memristors is an important topic for wearable electronics, which can lead to intelligent systems in daily life with high computing capacity and efficiency. Here, recent ...
The history of cloud computing • 10 minutes; Introduction to artificial intelligence ... Access to lectures and assignments depends on your type of enrollment. If you take a course in audit mode, you will be able to see most course materials for free. To access graded assignments and to earn a Certificate, you will need to purchase the ...
Overview of Cloud Computing. Module 1 • 1 hour to complete. In Module 1, in the first lesson, you will learn the definition of cloud computing and its five essential characteristics. In the next topic, you will learn about the history and evolution of cloud computing and the benefits of the pay-as-you-go feature of cloud computing.