Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts

Annotated Bibliography Samples

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Below you will find sample annotations from annotated bibliographies, each with a different research project. Remember that the annotations you include in your own bibliography should reflect your research project and/or the guidelines of your assignment.
As mentioned elsewhere in this resource, depending on the purpose of your bibliography, some annotations may summarize, some may assess or evaluate a source, and some may reflect on the source’s possible uses for the project at hand. Some annotations may address all three of these steps. Consider the purpose of your annotated bibliography and/or your instructor’s directions when deciding how much information to include in your annotations.
Please keep in mind that all your text, including the write-up beneath the citation, must be indented so that the author's last name is the only text that is flush left.
Sample MLA Annotation
Lamott, Anne. Bird by Bird: Some Instructions on Writing and Life . Anchor Books, 1995.
Lamott's book offers honest advice on the nature of a writing life, complete with its insecurities and failures. Taking a humorous approach to the realities of being a writer, the chapters in Lamott's book are wry and anecdotal and offer advice on everything from plot development to jealousy, from perfectionism to struggling with one's own internal critic.
In the process, Lamott includes writing exercises designed to be both productive and fun. Lamott offers sane advice for those struggling with the anxieties of writing, but her main project seems to be offering the reader a reality check regarding writing, publishing, and struggling with one's own imperfect humanity in the process. Rather than a practical handbook to producing and/or publishing, this text is indispensable because of its honest perspective, its down-to-earth humor, and its encouraging approach.
Chapters in this text could easily be included in the curriculum for a writing class. Several of the chapters in Part 1 address the writing process and would serve to generate discussion on students' own drafting and revising processes. Some of the writing exercises would also be appropriate for generating classroom writing exercises. Students should find Lamott's style both engaging and enjoyable.
In the sample annotation above, the writer includes three paragraphs: a summary, an evaluation of the text, and a reflection on its applicability to his/her own research, respectively.
For information on formatting MLA citations, see our MLA 9th Edition (2021) Formatting and Style Guide .
Sample APA Annotation
Ehrenreich, B. (2001). Nickel and dimed: On (not) getting by in America . Henry Holt and Company.
In this book of nonfiction based on the journalist's experiential research, Ehrenreich attempts to ascertain whether it is currently possible for an individual to live on a minimum-wage in America. Taking jobs as a waitress, a maid in a cleaning service, and a Walmart sales employee, the author summarizes and reflects on her work, her relationships with fellow workers, and her financial struggles in each situation.
An experienced journalist, Ehrenreich is aware of the limitations of her experiment and the ethical implications of her experiential research tactics and reflects on these issues in the text. The author is forthcoming about her methods and supplements her experiences with scholarly research on her places of employment, the economy, and the rising cost of living in America. Ehrenreich’s project is timely, descriptive, and well-researched.
The annotation above both summarizes and assesses the book in the citation. The first paragraph provides a brief summary of the author's project in the book, covering the main points of the work. The second paragraph points out the project’s strengths and evaluates its methods and presentation. This particular annotation does not reflect on the source’s potential importance or usefulness for this person’s own research.
For information on formatting APA citations, see our APA Formatting and Style Guide .
Sample Chicago Manual of Style Annotation
Davidson, Hilda Ellis. Roles of the Northern Goddess . London: Routledge, 1998.
Davidson's book provides a thorough examination of the major roles filled by the numerous pagan goddesses of Northern Europe in everyday life, including their roles in hunting, agriculture, domestic arts like weaving, the household, and death. The author discusses relevant archaeological evidence, patterns of symbol and ritual, and previous research. The book includes a number of black and white photographs of relevant artifacts.
This annotation includes only one paragraph, a summary of the book. It provides a concise description of the project and the book's project and its major features.
For information on formatting Chicago Style citations, see our Chicago Manual of Style resources.
How to Write an Annotated Bibliography - APA Style (7th Edition)
What is an annotation, how is an annotation different from an abstract, what is an annotated bibliography, types of annotated bibliographies, descriptive or informative, analytical or critical, to get started.
An annotation is more than just a brief summary of an article, book, website, or other type of publication. An annotation should give enough information to make a reader decide whether to read the complete work. In other words, if the reader were exploring the same topic as you, is this material useful and if so, why?
While an abstract also summarizes an article, book, website, or other type of publication, it is purely descriptive. Although annotations can be descriptive, they also include distinctive features about an item. Annotations can be evaluative and critical as we will see when we look at the two major types of annotations.
An annotated bibliography is an organized list of sources (like a reference list). It differs from a straightforward bibliography in that each reference is followed by a paragraph length annotation, usually 100–200 words in length.
Depending on the assignment, an annotated bibliography might have different purposes:
- Provide a literature review on a particular subject
- Help to formulate a thesis on a subject
- Demonstrate the research you have performed on a particular subject
- Provide examples of major sources of information available on a topic
- Describe items that other researchers may find of interest on a topic
There are two major types of annotated bibliographies:
A descriptive or informative annotated bibliography describes or summarizes a source as does an abstract; it describes why the source is useful for researching a particular topic or question and its distinctive features. In addition, it describes the author's main arguments and conclusions without evaluating what the author says or concludes.
For example:
McKinnon, A. (2019). Lessons learned in year one of business. Journal of Legal Nurse Consulting , 30 (4), 26–28. This article describes some of the difficulties many nurses experience when transitioning from nursing to a legal nurse consulting business. Pointing out issues of work-life balance, as well as the differences of working for someone else versus working for yourself, the author offers their personal experience as a learning tool. The process of becoming an entrepreneur is not often discussed in relation to nursing, and rarely delves into only the first year of starting a new business. Time management, maintaining an existing job, decision-making, and knowing yourself in order to market yourself are discussed with some detail. The author goes on to describe how important both the nursing professional community will be to a new business, and the importance of mentorship as both the mentee and mentor in individual success that can be found through professional connections. The article’s focus on practical advice for nurses seeking to start their own business does not detract from the advice about universal struggles of entrepreneurship makes this an article of interest to a wide-ranging audience.
An analytical or critical annotation not only summarizes the material, it analyzes what is being said. It examines the strengths and weaknesses of what is presented as well as describing the applicability of the author's conclusions to the research being conducted.
Analytical or critical annotations will most likely be required when writing for a college-level course.
McKinnon, A. (2019). Lessons learned in year one of business. Journal of Legal Nurse Consulting , 30 (4), 26–28. This article describes some of the difficulty many nurses experience when transitioning from nursing to a nurse consulting business. While the article focuses on issues of work-life balance, the differences of working for someone else versus working for yourself, marketing, and other business issues the author’s offer of only their personal experience is brief with few or no alternative solutions provided. There is no mention throughout the article of making use of other research about starting a new business and being successful. While relying on the anecdotal advice for their list of issues, the author does reference other business resources such as the Small Business Administration to help with business planning and professional organizations that can help with mentorships. The article is a good resource for those wanting to start their own legal nurse consulting business, a good first advice article even. However, entrepreneurs should also use more business research studies focused on starting a new business, with strategies against known or expected pitfalls and issues new businesses face, and for help on topics the author did not touch in this abbreviated list of lessons learned.
Now you are ready to begin writing your own annotated bibliography.
- Choose your sources - Before writing your annotated bibliography, you must choose your sources. This involves doing research much like for any other project. Locate records to materials that may apply to your topic.
- Review the items - Then review the actual items and choose those that provide a wide variety of perspectives on your topic. Article abstracts are helpful in this process.
- The purpose of the work
- A summary of its content
- Information about the author(s)
- For what type of audience the work is written
- Its relevance to the topic
- Any special or unique features about the material
- Research methodology
- The strengths, weaknesses or biases in the material
Annotated bibliographies may be arranged alphabetically or chronologically, check with your instructor to see what he or she prefers.
Please see the APA Examples page for more information on citing in APA style.
- Last Updated: Aug 8, 2023 11:27 AM
- URL: https://libguides.umgc.edu/annotated-bibliography-apa
How to Prepare an Annotated Bibliography: The Annotated Bibliography
- The Annotated Bibliography
- Fair Use of this Guide
Explanation, Process, Directions, and Examples
What is an annotated bibliography.
An annotated bibliography is a list of citations to books, articles, and documents. Each citation is followed by a brief (usually about 150 words) descriptive and evaluative paragraph, the annotation. The purpose of the annotation is to inform the reader of the relevance, accuracy, and quality of the sources cited.
Annotations vs. Abstracts
Abstracts are the purely descriptive summaries often found at the beginning of scholarly journal articles or in periodical indexes. Annotations are descriptive and critical; they may describe the author's point of view, authority, or clarity and appropriateness of expression.
The Process
Creating an annotated bibliography calls for the application of a variety of intellectual skills: concise exposition, succinct analysis, and informed library research.
First, locate and record citations to books, periodicals, and documents that may contain useful information and ideas on your topic. Briefly examine and review the actual items. Then choose those works that provide a variety of perspectives on your topic.
Cite the book, article, or document using the appropriate style.
Write a concise annotation that summarizes the central theme and scope of the book or article. Include one or more sentences that (a) evaluate the authority or background of the author, (b) comment on the intended audience, (c) compare or contrast this work with another you have cited, or (d) explain how this work illuminates your bibliography topic.
Critically Appraising the Book, Article, or Document
For guidance in critically appraising and analyzing the sources for your bibliography, see How to Critically Analyze Information Sources . For information on the author's background and views, ask at the reference desk for help finding appropriate biographical reference materials and book review sources.
Choosing the Correct Citation Style
Check with your instructor to find out which style is preferred for your class. Online citation guides for both the Modern Language Association (MLA) and the American Psychological Association (APA) styles are linked from the Library's Citation Management page .
Sample Annotated Bibliography Entries
The following example uses APA style ( Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association , 7th edition, 2019) for the journal citation:
Waite, L., Goldschneider, F., & Witsberger, C. (1986). Nonfamily living and the erosion of traditional family orientations among young adults. American Sociological Review, 51 (4), 541-554. The authors, researchers at the Rand Corporation and Brown University, use data from the National Longitudinal Surveys of Young Women and Young Men to test their hypothesis that nonfamily living by young adults alters their attitudes, values, plans, and expectations, moving them away from their belief in traditional sex roles. They find their hypothesis strongly supported in young females, while the effects were fewer in studies of young males. Increasing the time away from parents before marrying increased individualism, self-sufficiency, and changes in attitudes about families. In contrast, an earlier study by Williams cited below shows no significant gender differences in sex role attitudes as a result of nonfamily living.
This example uses MLA style ( MLA Handbook , 9th edition, 2021) for the journal citation. For additional annotation guidance from MLA, see 5.132: Annotated Bibliographies .
Waite, Linda J., et al. "Nonfamily Living and the Erosion of Traditional Family Orientations Among Young Adults." American Sociological Review, vol. 51, no. 4, 1986, pp. 541-554. The authors, researchers at the Rand Corporation and Brown University, use data from the National Longitudinal Surveys of Young Women and Young Men to test their hypothesis that nonfamily living by young adults alters their attitudes, values, plans, and expectations, moving them away from their belief in traditional sex roles. They find their hypothesis strongly supported in young females, while the effects were fewer in studies of young males. Increasing the time away from parents before marrying increased individualism, self-sufficiency, and changes in attitudes about families. In contrast, an earlier study by Williams cited below shows no significant gender differences in sex role attitudes as a result of nonfamily living.
Versión española
Tambíen disponible en español: Cómo Preparar una Bibliografía Anotada
Content Permissions
If you wish to use any or all of the content of this Guide please visit our Research Guides Use Conditions page for details on our Terms of Use and our Creative Commons license.
Reference Help

- Next: Fair Use of this Guide >>
- Last Updated: Sep 29, 2022 11:09 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.cornell.edu/annotatedbibliography
- ENC Learning Commons
Annotated Bibliography
- Sample APA Annotation
- URL: https://libguides.enc.edu/writing_basics/annotatedbib
- Definition and Descriptions
- Evaluation Tools
- Parts of an Annotation
- Sample ASA Annotation
- Sample Chicago Annotation
- Sample MLA Annotation
Research Tools
American Psychological Association (APA) Annotations
Creating an annotated bibliography in APA style
The Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association 7th edition (APA Manual) is kept behind the iDesk on the First Floor.
This example is based on the APA style guide, but your instructor might give you other formatting instructions .
General guidelines
Some annotations are merely descriptive , summarizing the authors' qualifications, research methods, and arguments.
Many annotations evaluate the quality of scholarship in a book or article. You might want to consider the logic of authors' arguments, and the quality of their evidence. Your findings can be positive, negative, or mixed.
Your professor might also want you to explain why the source is relevant to your assignment.
Sample Page: APA-formatted annotated bibliography
|
(pp. 21-44). Waterloo, ON: Wilfrid Laurier University Press. Ken Battle draws on his research as an extensively-published policy analyst, and a close study of some government documents, to explain child benefits in Canada. He outlines some fundamental assumptions supporting the belief that all society members should contribute to the upbringing of children. His comparison of Canadian child poverty rates to those in other countries provides a useful wake-up to anyone assuming Canadian society is doing a good job of protecting children from want. He pays particular attention to the National Child Benefit (NCB), arguing that it did not deserve the criticism it received from politicians and journalists. He outlines the NCB’s development, costs, and benefits, including its dollar contribution to a typical recipient’s income. He laments that the Conservative government scaled back the program in favour of the Universal Child Care Benefit (UCCB), and clearly explains why it is inferior. However, Battle relies too heavily on his own work; he is the sole or primary author of almost half the sources in his bibliography. He could make this work stronger by drawing from the perspectives of others' analyses. However, Battle does offer a valuable source for this essay, because the chapter provides a concise overview of government-funded assistance currently available to parents. This offers context for analyzing the scope and financial reality of child poverty in Canada. , (3), 321-335. Sociology professors Kerr and Beaujot analyze the demographics of impoverished families. Drawing on data from Canada’s annual Survey of Consumer Finances, the authors consider whether each family had one or two parents, the age of single parents, and the number of children in each household. They analyze child poverty rates in light of these demographic factors, as well as larger |
Rules! rules! rules!
The Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (7th ed.) states the following formatting rules:
- The text and the reference list should be double-spaced.
- Numbering starts on the title page, at the top right of the page.
- Reference list entries must have a hanging indent (to do this in Microsoft Word 2003, click Format, then Paragraph, then Special, and choose Hanging).
- There should be 1 inch (2.54 cm) margins all around (top, bottom, left, and right) on each page.
- Use Times Roman font, or a similar serif font.
- Each paragraph should be indented.
More Sample Annotations
Cornell University Library offers these instructions on preparing an annotated bibliography.
- << Previous: Sample Annotations
- Next: Sample ASA Annotation >>
- Last Updated: Nov 7, 2023 8:23 AM

Annotated Bibliographies
What this handout is about.
This handout will explain why annotated bibliographies are useful for researchers, provide an explanation of what constitutes an annotation, describe various types of annotations and styles for writing them, and offer multiple examples of annotated bibliographies in the MLA, APA, and CBE/CSE styles of citation.
Introduction
Welcome to the wonderful world of annotated bibliographies! You’re probably already familiar with the need to provide bibliographies, reference pages, and works cited lists to credit your sources when you do a research paper. An annotated bibliography includes descriptions and explanations of your listed sources beyond the basic citation information you usually provide.
Why do an annotated bibliography?
One of the reasons behind citing sources and compiling a general bibliography is so that you can prove you have done some valid research to back up your argument and claims. Readers can refer to a citation in your bibliography and then go look up the material themselves. When inspired by your text or your argument, interested researchers can access your resources. They may wish to double check a claim or interpretation you’ve made, or they may simply wish to continue researching according to their interests. But think about it: even though a bibliography provides a list of research sources of all types that includes publishing information, how much does that really tell a researcher or reader about the sources themselves?
An annotated bibliography provides specific information about each source you have used. As a researcher, you have become an expert on your topic: you have the ability to explain the content of your sources, assess their usefulness, and share this information with others who may be less familiar with them. Think of your paper as part of a conversation with people interested in the same things you are; the annotated bibliography allows you to tell readers what to check out, what might be worth checking out in some situations, and what might not be worth spending the time on. It’s kind of like providing a list of good movies for your classmates to watch and then going over the list with them, telling them why this movie is better than that one or why one student in your class might like a particular movie better than another student would. You want to give your audience enough information to understand basically what the movies are about and to make an informed decision about where to spend their money based on their interests.
What does an annotated bibliography do?
A good annotated bibliography:
- encourages you to think critically about the content of the works you are using, their place within a field of study, and their relation to your own research and ideas.
- proves you have read and understand your sources.
- establishes your work as a valid source and you as a competent researcher.
- situates your study and topic in a continuing professional conversation.
- provides a way for others to decide whether a source will be helpful to their research if they read it.
- could help interested researchers determine whether they are interested in a topic by providing background information and an idea of the kind of work going on in a field.
What elements might an annotation include?
- Bibliography according to the appropriate citation style (MLA, APA, CBE/CSE, etc.).
- Explanation of main points and/or purpose of the work—basically, its thesis—which shows among other things that you have read and thoroughly understand the source.
- Verification or critique of the authority or qualifications of the author.
- Comments on the worth, effectiveness, and usefulness of the work in terms of both the topic being researched and/or your own research project.
- The point of view or perspective from which the work was written. For instance, you may note whether the author seemed to have particular biases or was trying to reach a particular audience.
- Relevant links to other work done in the area, like related sources, possibly including a comparison with some of those already on your list. You may want to establish connections to other aspects of the same argument or opposing views.
The first four elements above are usually a necessary part of the annotated bibliography. Points 5 and 6 may involve a little more analysis of the source, but you may include them in other kinds of annotations besides evaluative ones. Depending on the type of annotation you use, which this handout will address in the next section, there may be additional kinds of information that you will need to include.
For more extensive research papers (probably ten pages or more), you often see resource materials grouped into sub-headed sections based on content, but this probably will not be necessary for the kinds of assignments you’ll be working on. For longer papers, ask your instructor about their preferences concerning annotated bibliographies.
Did you know that annotations have categories and styles?
Decisions, decisions.
As you go through this handout, you’ll see that, before you start, you’ll need to make several decisions about your annotations: citation format, type of annotation, and writing style for the annotation.
First of all, you’ll need to decide which kind of citation format is appropriate to the paper and its sources, for instance, MLA or APA. This may influence the format of the annotations and bibliography. Typically, bibliographies should be double-spaced and use normal margins (you may want to check with your instructor, since they may have a different style they want you to follow).
MLA (Modern Language Association)
See the UNC Libraries citation tutorial for basic MLA bibliography formatting and rules.
- MLA documentation is generally used for disciplines in the humanities, such as English, languages, film, and cultural studies or other theoretical studies. These annotations are often summary or analytical annotations.
- Title your annotated bibliography “Annotated Bibliography” or “Annotated List of Works Cited.”
- Following MLA format, use a hanging indent for your bibliographic information. This means the first line is not indented and all the other lines are indented four spaces (you may ask your instructor if it’s okay to tab over instead of using four spaces).
- Begin your annotation immediately after the bibliographic information of the source ends; don’t skip a line down unless you have been told to do so by your instructor.
APA (American Psychological Association)
See the UNC Libraries citation tutorial for basic APA bibliography formatting and rules.
- Natural and social sciences, such as psychology, nursing, sociology, and social work, use APA documentation. It is also used in economics, business, and criminology. These annotations are often succinct summaries.
- Annotated bibliographies for APA format do not require a special title. Use the usual “References” designation.
- Like MLA, APA uses a hanging indent: the first line is set flush with the left margin, and all other lines are indented four spaces (you may ask your instructor if it’s okay to tab over instead of using four spaces).
- After the bibliographic citation, drop down to the next line to begin the annotation, but don’t skip an extra line.
- The entire annotation is indented an additional two spaces, so that means each of its lines will be six spaces from the margin (if your instructor has said that it’s okay to tab over instead of using the four spaces rule, indent the annotation two more spaces in from that point).
CBE (Council of Biology Editors)/CSE (Council of Science Editors)
See the UNC Libraries citation tutorial for basic CBE/CSE bibliography formatting and rules.
- CBE/CSE documentation is used by the plant sciences, zoology, microbiology, and many of the medical sciences.
- Annotated bibliographies for CBE/CSE format do not require a special title. Use the usual “References,” “Cited References,” or “Literature Cited,” and set it flush with the left margin.
- Bibliographies for CSE in general are in a slightly smaller font than the rest of the paper.
- When using the name-year system, as in MLA and APA, the first line of each entry is set flush with the left margin, and all subsequent lines, including the annotation, are indented three or four spaces.
- When using the citation-sequence method, each entry begins two spaces after the number, and every line, including the annotation, will be indented to match the beginning of the entry, or may be slightly further indented, as in the case of journals.
- After the bibliographic citation, drop down to the next line to begin the annotation, but don’t skip an extra line. The entire annotation follows the indentation of the bibliographic entry, whether it’s N-Y or C-S format.
- Annotations in CBE/CSE are generally a smaller font size than the rest of the bibliographic information.
After choosing a documentation format, you’ll choose from a variety of annotation categories presented in the following section. Each type of annotation highlights a particular approach to presenting a source to a reader. For instance, an annotation could provide a summary of the source only, or it could also provide some additional evaluation of that material.
In addition to making choices related to the content of the annotation, you’ll also need to choose a style of writing—for instance, telescopic versus paragraph form. Your writing style isn’t dictated by the content of your annotation. Writing style simply refers to the way you’ve chosen to convey written information. A discussion of writing style follows the section on annotation types.
Types of annotations
As you now know, one annotation does not fit all purposes! There are different kinds of annotations, depending on what might be most important for your reader to learn about a source. Your assignments will usually make it clear which citation format you need to use, but they may not always specify which type of annotation to employ. In that case, you’ll either need to pick your instructor’s brain a little to see what they want or use clue words from the assignment itself to make a decision. For instance, the assignment may tell you that your annotative bibliography should give evidence proving an analytical understanding of the sources you’ve used. The word analytical clues you in to the idea that you must evaluate the sources you’re working with and provide some kind of critique.
Summary annotations
There are two kinds of summarizing annotations, informative and indicative.
Summarizing annotations in general have a couple of defining features:
- They sum up the content of the source, as a book report might.
- They give an overview of the arguments and proofs/evidence addressed in the work and note the resulting conclusion.
- They do not judge the work they are discussing. Leave that to the critical/evaluative annotations.
- When appropriate, they describe the author’s methodology or approach to material. For instance, you might mention if the source is an ethnography or if the author employs a particular kind of theory.
Informative annotation
Informative annotations sometimes read like straight summaries of the source material, but they often spend a little more time summarizing relevant information about the author or the work itself.
Indicative annotation
Indicative annotation is the second type of summary annotation, but it does not attempt to include actual information from the argument itself. Instead, it gives general information about what kinds of questions or issues are addressed by the work. This sometimes includes the use of chapter titles.
Critical/evaluative
Evaluative annotations don’t just summarize. In addition to tackling the points addressed in summary annotations, evaluative annotations:
- evaluate the source or author critically (biases, lack of evidence, objective, etc.).
- show how the work may or may not be useful for a particular field of study or audience.
- explain how researching this material assisted your own project.
Combination
An annotated bibliography may combine elements of all the types. In fact, most of them fall into this category: a little summarizing and describing, a little evaluation.
Writing style
Ok, next! So what does it mean to use different writing styles as opposed to different kinds of content? Content is what belongs in the annotation, and style is the way you write it up. First, choose which content type you need to compose, and then choose the style you’re going to use to write it
This kind of annotated bibliography is a study in succinctness. It uses a minimalist treatment of both information and sentence structure, without sacrificing clarity. Warning: this kind of writing can be harder than you might think.
Don’t skimp on this kind of annotated bibliography. If your instructor has asked for paragraph form, it likely means that you’ll need to include several elements in the annotation, or that they expect a more in-depth description or evaluation, for instance. Make sure to provide a full paragraph of discussion for each work.
As you can see now, bibliographies and annotations are really a series of organized steps. They require meticulous attention, but in the end, you’ve got an entire testimony to all the research and work you’ve done. At the end of this handout you’ll find examples of informative, indicative, evaluative, combination, telescopic, and paragraph annotated bibliography entries in MLA, APA, and CBE formats. Use these examples as your guide to creating an annotated bibliography that makes you look like the expert you are!
MLA Example
APA Example
CBE Example
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
American Psychological Association. 2010. Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association . 6th ed. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Bell, I. F., and J. Gallup. 1971. A Reference Guide to English, American, and Canadian Literature . Vancouver: University of British Columbia Press.
Bizzell, Patricia, and Bruce Herzburg. 1991. Bedford Bibliography for Teachers of Writing , 3rd ed. Boston: Bedford Books.
Center for Information on Language Teaching, and The English Teaching Information Center of the British Council. 1968. Language-Teaching Bibliography . Cambridge: Cambridge University.
Engle, Michael, Amy Blumenthal, and Tony Cosgrave. 2012. “How to Prepare an Annotated Bibliography.” Olin & Uris Libraries. Cornell University. Last updated September 25, 2012. https://olinuris.library.cornell.edu/content/how-prepare-annotated-bibliography.
Gibaldi, Joseph. 2009. MLA Handbook for Writers of Research Papers , 7th ed. New York: The Modern Language Association of America.
Huth, Edward. 1994. Scientific Style and Format: The CBE Manual for Authors, Editors, and Publishers . New York: University of Cambridge.
Kilborn, Judith. 2004. “MLA Documentation.” LEO: Literacy Education Online. Last updated March 16, 2004. https://leo.stcloudstate.edu/research/mla.html.
Spatt, Brenda. 1991. Writing from Sources , 3rd ed. New York: St. Martin’s.
University of Kansas. 2018. “Bibliographies.” KU Writing Center. Last updated April 2018. http://writing.ku.edu/bibliographies .
University of Wisconsin-Madison. 2019. “Annotated Bibliography.” The Writing Center. Accessed June 14, 2019. https://writing.wisc.edu/handbook/assignments/annotatedbibliography/ .
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
Generate accurate Chicago citations for free
- Knowledge Base
- Chicago Style
How to Write an Annotated Bibliography in Chicago/Turabian Style
Published on October 15, 2019 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on April 9, 2024.
While a standard Chicago style bibliography provides publication details of your sources, an annotated bibliography also provides a summary (and often an evaluation) of each source.
Turabian style , a version of Chicago style specifically designed for students and researchers, provides formatting guidelines for an annotated bibliography. A typical entry might look like this:
Kenny, Anthony. A New History of Western Philosophy: In Four Parts . Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2010.
Chicago Citation Generator
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
How to write annotations, how to format an annotated bibliography.
The purpose of annotations is to give the reader relevant information about each source you have consulted. There are two main types of annotation.
Descriptive annotations simply describe your sources, briefly summarizing their arguments and ideas . They are useful for keeping a record of your reading and giving a quick overview of sources related to your topic.
Evaluative annotations go into more detail and provide your own perspective on each source. For example, you may evaluate your sources by:
- assessing the strength of the author’s arguments.
- describing the ways in which the source is helpful or unhelpful to your own research.
- evaluating the evidence presented in the source, discussing the credibility .
Check the requirements of your assignment to find out whether you need to write descriptive or evaluative annotations.
How long should annotations be?
Annotations can vary in length according to the approach taken and the length of the source. You may write a couple of sentences describing the argument of an essay, or several paragraphs summarizing and evaluating a book .
A good guideline is to aim for 50 to 200 words for each source. Consult your instructor to check how long your annotated bibliography should be and how many sources you need to include.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Each entry starts with a Chicago style citation , which gives full publication details of the source. The citation is formatted the same as a normal bibliography entry:
- Single-spaced
- Each line after the first indented ( hanging indent )
- Organized in alphabetical order by author last name
The annotation appears on a new line directly after the source citation. The whole annotation is indented, to make it clear when the annotation ends and a new source appears.
According to Turabian guidelines, annotations should be formatted the same as the main text of any paper:
- Double-spaced
- Left-aligned
- Indent the first line of each new paragraph

Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2024, April 09). How to Write an Annotated Bibliography in Chicago/Turabian Style. Scribbr. Retrieved June 24, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/chicago-style/chicago-annotated-bibliography/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, what is an annotated bibliography | examples & format, creating a chicago style bibliography | format & examples, chicago style format for papers | requirements & examples, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
Home / Guides / Citation Guides / Citation Basics / Annotated Bibliography Format & Examples
Annotated Bibliography Format & Examples
A complete guide to the mla & apa annotated bibliography.
If you’ve just received an assignment that requires an MLA or APA annotated bibliography, you may be wondering where to start. This guide will help answer all of your questions and includes step-by-step instructions on how to do an annotated bibliography in MLA style, as well as an APA annotated bibliography. You will also find sample annotated bibliographies, real-life examples, and opportunities to practice what you have learned.
The MLA ( Modern Language Association ) and APA (American Psychological Association) are not associated with this guide. All of the information provided here, however, offers direction for students and researchers who use these citation styles in their work.
The structures and annotated bibliography templates on this page were created by the in-house librarians at EasyBib.com.
If you’re simply looking for an example of an annotated bibliography (both in MLA format and APA format), scroll down toward the bottom of the page. We’ve included links to visuals for those of you who need help with the structure and styling of an annotated bibliography. If you’re looking for a variety of annotated bibliography topics, and you’re truly searching for the answer to, “What is an annotated bibliography?” then continue reading!
Here’s a run-through of everything this page includes:
Table of contents
What is an annotated bibliography, annotations vs. abstract, why include annotations.
- Step 1: Analyze your sources
Step 2: Write the descriptions
- Step 3a: Formatting an MLA style annotated bibliography
- Step 3b: Formatting an APA style annotated bibliography
Annotated Bibliography Templates
Using the easybib annotation tool.
A bibliography is a complete list of the sources that were used to complete a research paper or project.
Depending on the style guide you follow, you may also see this called a Works Cited (also called an MLA bibliography) or Reference List (APA format). Each listed source, or citation , shares information about the author, title, publishing year, and other details that serve to credit the original authors whose work informed your research. These details also help other students and researchers find and read the source materials.
When your research is related to a scholastic assignment, you should always verify your instructor’s requirements for the types and number of sources to include, as well as the style you should adhere to when formatting your paper and bibliography.
An MLA annotated bibliography and an APA format annotated bibliography are bibliographies that include a concise explanation, or annotation , of each listed source. Depending on the assignment, this annotation may be solely descriptive, or analytical.
An abstract and annotation should not be confused; they differ in both their substance as well as their placement in a paper.
Annotations:
- Usually found in bibliographies at the end of a paper
- Are subjective
- Purpose is to summarize and evaluate . It should briefly communicate the work’s main point, but also discuss the background of the author or study, and the strengths/weaknesses of the work.
Abstracts:
- Usually found in journal databases or the beginning of a paper
- Are objective
- Purpose is to summarize . It should provide a short overview of the article and communicate the main points and themes.
If you would like to learn more , this link further explores the difference between an abstract and an annotation.
This resource provides additional information on how to write a bibliography with annotations in other formats. You can also take advantage of the plagiarism checker and bibliography tools that come with EasyBib Plus to help you create your reference lists.
Before you learn how to make an annotated bibliography, you may be wondering why you need to.
Sometimes instructors want you to create and include annotations in your bibliography, either as part of an assignment or as an assignment unto itself. Understanding the purpose of this approach to your reference list can help to ensure that you gain all of the benefits that the annotated bibliography process provides.
As a student, this method will help you develop or hone your research skills, providing you with practice not only in locating sources but also in analyzing and evaluating them for relevance and quality.
Your instructor will gain insight into your research abilities, as well, allowing them to assess your work more thoroughly. If you plan to publish your research, this comprehensive approach to detailing your sources will provide readers and other researchers with a substantial directory of resources to evaluate for their own work.
Whether you’re publishing or submitting your annotated bibliography, make sure your spelling and wording is correct! If you need to brush up on any parts of speech topics, check out our interjection , determiner , and adverb pages!
Step 1: Analyze your sources
Each annotation should be a summarization or analysis of your source. If you have been tasked with writing annotations as part of a research paper or project, begin to create both the citation and notes on the source while you identify and analyze your sources.
Not only will this approach help you to hone your research skills and identify sources that are relevant and useful for your topic, but you will also save time. When done in this manner, both your citations and annotations will be nearly complete before you begin to write the body of your paper.
Analyzing your potential sources requires a two-pronged approach that first evaluates the author, publication, and date, and then examines the content.
When conducting your initial assessment of the source, consider some of the following questions to guide your appraisal:
- What qualifies the author to write on this subject?
- Is the author affiliated with a reputable institution in this field?
- Is the author credentialed or otherwise considered an expert in this field?
- Is this source current?
- Is this the most recent edition?
- Is the publisher reputable?
- Is the journal reputable?
Once your primary evaluation is complete, you will move on the assessing the content itself. Consider some of these elements as you review each source:
- Who is the intended audience?
- Is the author presenting her opinion or interpretation as the truth, or stating facts?
- What supporting evidence does the author provide?
- Did the author perform the research, or curate and present the research of others?
- If the author used the research of others, are the sources the author cites credible?
- Are there errors or omissions of fact?
- Is the author writing objectively and without bias?
Also, consider the value each source provides to you:
- Is the information helpful for your particular assignment?
- Does it help answer your research question(s)?
- Is this source different from your other sources, or does it repeat information you already have?
- Is the source providing you with a different perspective on your topic, or changing your beliefs or thinking about your subject?
To make it easier for you to create your reference page, write your notes in the format you will be using when you construct this part of the assignment (for instance, as short phrases or complete sentences). Once you have identified all of the sources you wish to include, you will merely need to insert what you have already written on the page and write your citation, which is explained in the next section.
Click here for additional information and a supplementary annotated bibliography sample. For an MLA bibliography example (with annotations), check out our visual example of an MLA annotated bibliography .
An annotated bibliography entry may be written either as short phrases or complete sentences. Your instructor will advise you of which approach you are required to take.
Annotations should include either:
- The main points from the source, as well as the topics covered, the approach used, and any findings.
- Or your critical evaluation.
- A standard annotation is approximately one paragraph.
- Take care not to include any unnecessary details, as the goal is to summarize each source as succinctly as possible and, in some cases, evaluate them.
- Your field of study or instructor will determine what format your annotated bibliography will use. In this guide, you’ll find examples of an MLA and an APA annotated bibliography.
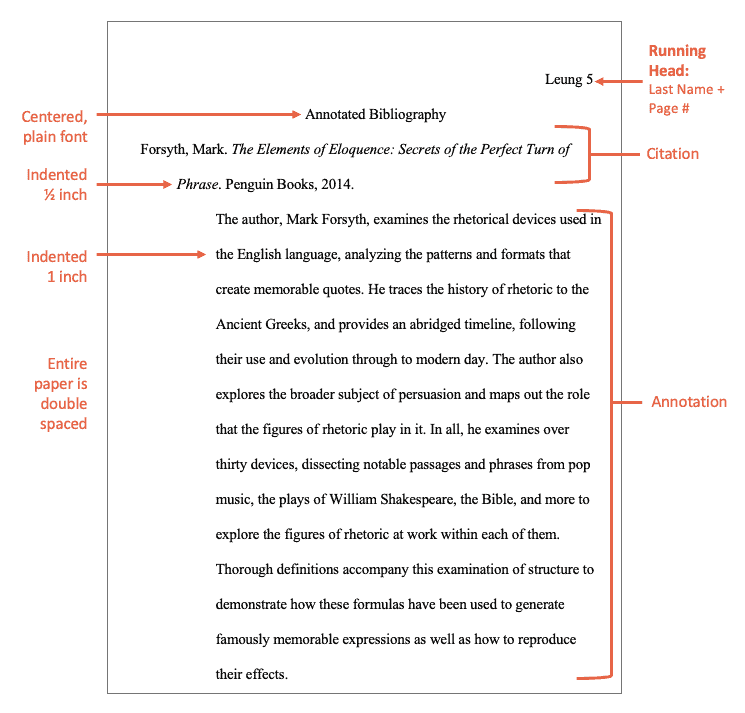
Here is an annotated bibliography example MLA annotation for the book The Elements of Eloquence: Secrets of the Perfect Turn of Phrase by UK author and blogger Mark Forsyth:
The author, Mark Forsyth, examines the rhetorical devices used in the English language, analyzing the patterns and formats that create memorable quotes. He traces the history of rhetoric to the Ancient Greeks, and provides an abridged timeline, following their use and evolution through to modern day. The author also explores the broader subject of persuasion and maps out the role that the figures of rhetoric play in it. In all, he examines over thirty devices, dissecting notable passages and phrases from pop music, the plays of William Shakespeare, the Bible, and more to explore the figures of rhetoric at work within each of them. Thorough definitions accompany this examination of structure to demonstrate how these formulas have been used to generate famously memorable expressions as well as how to reproduce their effects.
Notice how the annotated bibliography MLA entry above is descriptive enough so the reader has an idea of what the source is about with just a single paragraph. For more information on annotations, check out this informative site . If you’re looking to strengthen your writing in general, reading these grammar guides could be a good start.
For guidance on creating entries in MLA format , APA format , and more styles , check out the EasyBib library of resources or try the EasyBib annotation tool—we talk about it below!
Step 3a: MLA annotated bibliography format
The MLA Style Center and the current edition of the MLA Handbook provide the following guidance for formatting an MLA annotated bibliography:
- Title your reference page as “Annotated Bibliography” or “Annotated List of Works Cited.”
- Place each annotation after its reference.
- Annotations should typically not exceed a single paragraph.
- Annotations should be indented one inch from the start of your citation.
- Double-space all text on the page.
- 1-inch margins around the page.
Sources in an annotated bibliography can be organized alphabetically by the first word in each reference (as with a normal Works Cited page), by publication date, or by subject.
For a visual example of an annotated bibliography, as well as specific annotation examples, visit the MLA annotated bibliography guide .
If you are required to share your references in a manner other than in MLA bibliography format, the EasyBib style guides can help you with many common styles. While you’re at it, check out their conjunction , preposition , and pronoun pages to help keep your paper in mint condition!
Step 3b: APA annotated bibliography format
The American Psychological Association states that your instructor should set the guidelines for your annotated bibliography, but asks that the bibliography be formatted according to their standard reference page rules (see Section 9.51 of the Publication Manual ). If your teacher has requested an APA formatted annotated bibliography, first ask them for guidelines. Otherwise, here are some quick rules for you to follow:
- Double space all text on the page.
- Title your page “Annotated Bibliogra phy”. Bold and center the title.
- Organize references alphabetically by the first word of each reference.
- Only the first line of a ref erence is flush with the left margin. Any other lines after the first line should be indented ½ inch from the left.
- Add annotations on the next line after their paired reference.
- Fully indent annotations by a ½ inch from the left.
- Keep annotations short. No more than one paragraph.
For examples of a properly formatted APA annotation, visit this guide on APA annotated bibliographies .
In comparison to the sample annotated bibliography MLA, the APA sample formats its page elements and references differently.

Students and researchers who type their research notes can save time by using an annotated bibliography template in MLA format while reviewing and analyzing sources. By adding the relevant information into a pre-formatted template, you’ll create a resource that helps you when you begin writing your paper in addition to saving time by completing your references and summaries alongside your research.
Students who prefer to take notes by hand can employ a modified version of this approach, with an additional step required to transfer your handwritten and formatted references from your notebook to populate your reference page.
Bibliography Template for MLA
To create an annotated bibliography MLA template, copy the following details into the program in which you will take notes or hand write it on the top margin of a page in your notebook. For each source, use this template to guide you as you identify the necessary details and insert them into your notes:
- Author (Last name, First name).
- Title of source.
- Title of the container ,
- Other contributors (names and roles),
- Publication Date,
- Location of the source (such as URL or page range).
- Summary or Analysis.
The MLA 9 model for MLA works cited entries offers a single format for all source type, and a great deal of flexibility to include the information most relevant to your topic and omit that which isn’t.
Hopefully our visual annotated bibliography example in MLA above has helped. If you still have lingering questions, visit the MLA Style Center online ( linked here ). Also, here’s a guide if you’re looking for more on the related topic of MLA in-text & parenthetical citations .
Bibliography Template for APA
Students and researchers who are still asking themselves how to piece together an annotated bibliography, or still questioning what is an annotated bibliography, could probably benefit from a template, similar to the one above. This one, however, is for those of you who are tasked with creating an annotated bibliography in the style created by the American Psychological Association.
The tricky thing about this specific style though, is that every reference is styled differently. Books, websites, journal articles, newspaper articles, and many others each have their own reference structure.
For most sources though, you should look for the following, basic information:
- Type of source
- Author (last name, first name)
- Title of source/article/web page, etc.
- Title of where source was found (e.g., database name, website name, etc.)
- Other contributors (names and roles)
- Location of the source (such as URL, DOI, or page range)
- Summary or Analysis
We understand it can get tricky, and it’s very different from the Modern Language Association’s structure for references. Take a moment to either use the other handy guides on EasyBib.com or use our automatic generator to form your references in just a few clicks. Our tools help take the pain away from having to rack your brain to form references properly. Capitals, lowercase letters, italics, quotation marks, punctuation in the appropriate places, it can all be quite overwhelming. Do yourself a favor, and use the EasyBib automatic citation generator.
Even though there are a lot of different variations, here’s a commonly used structure for sources:
Author’s Last Name, First initial, Middle initial. (Year the source was published). Title of the source . Retrieved from (insert the website address here)
Underneath the reference, include your summary or analysis paragraph.
Hopefully, this page helped answer all of your “What is an annotated bibliography?” questions. If you’re seeking out an annotated bibliography generator, follow the steps above the annotated bibliography examples.
Looking for additional help with other related topics? Don’t forget about the various beneficial guides on EasyBib.com! Our APA in-text citation guide and our APA parenthetical citation guide are two of our most popular pages. Learn the ins and outs of referencing your work in the body of your paper with our thorough, complete, and reader-friendly guides.
If you are creating a bibliography in MLA format, the EasyBib MLA bibliography generator can help save you time formatting your citations and annotations correctly. You can create entries for websites, books, videos, databases, dictionary articles, and many other types of sources.
In addition to forming the citations, you can also enter your annotation text to produce the complete entry for each source. The process for this is simple. You can follow along below to practice creating one:
- First, select your source type from among the 50+ available options. For this example, we will use the acting career of Keanu Reeves as our research topic and use the movie Point Break from 1991 as our first source. To cite this film, you would select the option for “Film/Online Video.” As you follow along, pick the option that is suitable for your source if you are using a different example.
- Enter the title of your source or, if you are citing a website, you may enter the URL. (Now would be a great time to peek at how to cite websites in MLA ). After you enter the title or URL for your reference, the EasyBib citation tool will scan for titles that match it and provide you with a list of results. Select “Cite this” next to the listing that matches your source.
- You will see a citation form. This gives you the option to add additional relevant or necessary information. For our sample topic, we will specifically cite Keanu Reeves as the performer and Kathryn Bigelow as the director.
- After entering any additional details, you have the option to expand your entry and include an annotation. To do so, select “Add annotation” at the bottom of the page, and a text box will open up.
Then, type your summary or analysis into the text box. If you took notes during the research stage using the format of your paper, this might be as simple as copying and pasting your already written summary or critique. Once you have entered all of the necessary information, select “Create citation” to generate the complete entry. You can then copy and paste this into your MLA bibliography.
Here’s what it’ll look like:
Point Break . Directed by Kathryn Bigelow, performance by Keanu Reeves, 20th Century Fox, 1991.
Reeves’ role as rookie FBI Agent Johnny Utah in Point Break marks the turning point in his Hollywood film career. While he’d risen to fame due to the success of the Bill and Ted franchise, his status today as an action star began when Point Break provided him with the material to establish himself as capable of portraying more than the lovable but unserious characters of his previous starring roles. In a parallel arc, director Kathryn Bigelow’s career also sees a shift beginning with Point Break , establishing her within the traditional action genre as a serious director capable of creating high-action and visually memorable films. While Point Break leaves plenty to be desired in terms of dialogue, it afforded Bigelow and Reeves the opportunities to showcase themselves and their talent in new ways that still echo in their work today.
- Works Cited
Harner, James L. On Compiling an Annotated Bibliography . 2nd ed., Modern Language Association of America, 2000.
MLA Handbook . 9th ed., Modern Language Association of America, 2021.
Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association . 7th ed., American Psychological Association, 2020.
“What Guidance Should I Give My Students for Preparing an Annotated Bibliography?” The MLA Style Center , The Modern Language Association, 4 Nov. 2016, style.mla.org/annotated-bibliographies/.
Visit our EasyBib Twitter feed to discover more citing tips, fun grammar facts, and the latest product updates.
Published October 18, 2015. Updated July 25, 2021.
Written and edited by Michele Kirschenbaum and Elise Barbeau. Michele Kirschenbaum is a school library media specialist and is the in-house librarian at EasyBib.com. Elise Barbeau is the Citation Specialist at Chegg. She has worked in digital marketing, libraries, and publishing.
Citation Guides
- Annotated Bibliography
- Block Quotes
- Citation Examples
- et al Usage
- In-text Citations
- Page Numbers
- Reference Page
- Sample Paper
- APA 7 Updates
- View APA Guide
- Bibliography
- MLA 8 Updates
- View MLA Guide
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
An annotated bibliography is a list containing complete information of sources, such as journals, books, and reports, cited in the text. In addition, it provides a brief description of each source in about 100–150 words. The annotation can explain the topics covered in the source or evaluate the source. The main objective of giving the annotation is to provide the reader the importance, accuracy, and value of the source.
An example of an annotated bibliography in APA style is given below.
Lim, L. (2014). Ideology, rationality and reproduction in education: A critical discourse analysis. Discourse: Studies in the Cultural Politics of Education, 35 (1), 61–76. https://doi:10.1080/01596306.2012.739467
Lim (2014) focuses on issues of power and ideology dominant in curricular discourses of rationality to study a discourse analysis of the goals of one of the most important curricula in the teaching of thinking. He proves that political and class commitments are reproduced in the forms of thinking that are valued in societies. Through his research, Lim asserts that such curricula engage in making our understanding of what thinking and rationality are. It must facilitate the social reproduction of a specific proportion of the middle class.
If you want to evaluate or provide a description of a source you are citing, you can create an annotated bibliography. Write your annotation in 100–150 words and add it below the source for which you are providing your annotation. Remember, your annotation should provide the reader the importance, accuracy, and value of the source. Below are the guidelines and rules to be followed while writing an annotated bibliography for APA style:
Order your reference entries in alphabetical order, similar to how you would order entries in the reference list.
If you want to add an annotation to an entry, add it as a fresh paragraph below the reference entry. The annotation is indented 0.5 inches from the left margin. However, the first line of the annotation is not indented.
To format the annotated bibliography, follow the recommendations given below:
Set the left, right, top, and bottom margins to 1 inch.
Give double-line spacing.
Title the page “Annotated Bibliography.” Set it in bold.
The title should be aligned to the center of the page.
As you format reference entries, left-align all references in the annotated bibliography section. If any entry runs over more than a line, indent the subsequent lines 0.5 inch from the left margin.
Arrange all reference entries alphabetically according to the surname of the authors.
Provide your annotations below the reference entry for which you want to give your annotation. Indent annotations 0.5 inches from the left margin.
Citation Basics
Harvard Referencing
Plagiarism Basics
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started

- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
Common Assignments: Annotated Bibliographies
Basics of annotated bibliographies.
An annotated bibliography is a combination of the words "annotation" and "bibliography." An annotation is a set of notes, comments, or critiques. A bibliography is list of references that helps a reader identify sources of information. An annotated bibliography is a list of references that not only identifies the sources of information but also includes information such as a summary, a critique or analysis, and an application of those sources' information.
Review our resources on the following pages for more information about each component of an annotated bibliography. As always, read the instructions and any examples in your assignment carefully; some of what follows might not be required in your particular course.
Components of an Annotated Entry
Download the following sample to see the components of an annotated bibliography. Follow the links to more information on formatting, summary, critique/analysis, application, and example in the left sidebar menu. Note that citations are not necessary in the annotations since the notes are understood to be about the listed source.
- Annotated Bibliography Sample Document A sample of an annotated bibliography illustrating its various components. Updated to APA 7 guidelines.
Related Multimedia Resources
Didn't find what you need? Email us at [email protected] .
- Previous Page: Other Tips
- Next Page: Formatting
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.

Creating an Annotated Bibliography in APA Style
Definitions.
A bibliography is a list of source material, cited in whatever citation style you're required to use in a specific course.
An annotation is a summary and/or evaluation.
Put the two together and you have an Annotated Bibliography !
An annotated bibliography is an organizational tool . an annotated bibliography....
- Is an alphabetical list of all of your source material
- Includes sources you may or may not use in your research
- Summarizes each resource so you can remember what it's about
- Can include any type of resource unless specified in the assignment instructions (For an overview of the types of resources you can find through our library, view our description of resource types on our Evaluating Sources guide .)
Why must you do an Annotated Bibliography?
- If you're utilizing print resources through the library, you may not be able to renew items. How will you remember what the resource was about if you have to send it back?
- If you're utilizing electronic resources, nothing online is permanent. How will you find the resource again if it disappears?
- In larger projects, every resource starts to look the same. An Annotated Bibliography can save you time by reminding you of what you've already found.
What types of resources are used?
An Annotated Bibliography can include any type of resource unless otherwise specified by the assignment. This can include (but is not limited to):
- Scholarly materials
- Government documents
Annotated Bibliographies can be a great resource for students before they write other types of assignments, like literature reviews .
There are TWO PARTS to each entry in an Annotated Bibliography. They are:
- The citation of the resource , in whatever citation style you're required to use.
- The annotation describing the contents of the resource and how it may or may not contribute to your research.
Be sure to carefully read over the assignment instructions when you're asked to compose an Annotated Bibliography, and reach out to your professor with any questions!
Citation Help
Consult your course style guide to confirm the accuracy of your citation.
You can also...
- View our guide for APA Style Help .
- Consult resources like Academic Writer or Grammarly .
Skimming Sources
Focus on key areas of a text to learn enough so that you can write a strong annotation. This includes:
- Abstracts, prefaces, and summaries
- Paragraph headings
- Charts/graphs/images and their captions
- Introduction paragraph(s)
- Conclusion paragraph(s)
- Sources/References/Bibliography
These areas will provide you with enough information to determine the topic, arguments, and conclusions drawn from any research presented.
Writing Annotations
A strong annotation will have three main parts:
Length requirements can vary from a few sentences to a single paragraph or a full page. Be sure to verify length requirements with your professor and/or through the assignment instructions.
When writing the summary, ask yourself:
- What topics are covered in the resource?
- What are the main arguments?
- What are the main conclusions drawn from the resource?
When writing the assessment, ask yourself:
- Is the source useful?
- How does it compare to your other resources?
- Is there bias present?
- Is the source reliable?
Our guide for Evaluating Your Sources can help you assess your research material.
When writing the reflection, ask yourself:
- How does the source fit into your research?
- How might the source support your argument?
- Did the source change your mind about the topic?
Sample APA Style citation with annotation:
Bell, C., & Holder, M. (2019, January/February). The Interrelationship between Race, Social Norms, and Dietary Behaviors among College-attending
Women. American Journal of Health Behavior , 43 (1), 23-36.
This article examines a study conducted to compare racial identity and dietary habits of women on college campuses. The findings of the
study found that women with perceived differences and social/family norms were more likely to develop unhealthy dietary habits in college,
most specifically related to fruit and vegetable consumption. This resource is useful because it examines self-perception of race and how that
can impact behavior in ways that influence one's health in the future.
View a full example in APA Style:
- Annotated Bibliography Example- APA Style A full Annotated Bibliography formatted in APA Style. Users, please verify that formatting matches your course style guide's requirements.
- << Previous: Welcome
- Next: Tutorials >>
- Last Updated: May 22, 2023 10:46 AM
- URL: https://library.tiffin.edu/annotatedbibliography

APA Style & Citation 7th edition
- What's new with the 7th edition
Annotated Bibliography
- PowerPoint and APA
- Citations: References
- Citations: In-Text
- Library Databases
- Books and Ebooks
- Media (includes videos)
- Other types of sources
- Numbers, Capitalization, Italics
- Additional Resources
Information on Annotated Bibliographies can be found in Section 9.51 of the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (7th ed.)
- Title page, page numbers, font style and size, etc. See Format basics
- Alphabetical with hanging indents etc. See Citations: references
- The annotation - the notes you have about the source - appear in a new paragraph below its reference entry, indented 0.5 inches from the left margin
- << Previous: Format Basics
- Next: PowerPoint and APA >>
- Last Updated: Apr 18, 2023 5:31 PM
- URL: https://guides.centralpenn.edu/APA7th
Annotated Bibliography
An annotated bibliography is an organized list of sources, each of which is followed by a brief note or “annotation.”
These annotations do one or more of the following:
- describe the content and focus of the book or article
- suggest the source’s usefulness to your research
- evaluate its method, conclusions, or reliability
- record your reactions to the source.
How do I format the bibliographic citations?
Check with your instructor to determine which documentation style is required for your class: APA, MLA, Chicago/Turabian, CBE, Numbered References, APSA, etc.
Then, remember that the bibliography is an organized list of sources used. The annotation may immediately follow the bibliographic information on the same line, or it may begin on a new line, two lines below the publication information.
But, since style manuals differ, check with your instructor about which one to use concerning form, spacing, and consistency.
If you are using APA documentation, the Writing Center offers a short workshop called “APA Documentation”.
What goes into the content of the annotations?
Below are some of the most common forms of annotated bibliographies. Click on the links to see examples of each.
This form of annotation defines the scope of the source, lists the significant topics included, and tells what the source is about.
This type is different from the informative entry in that the informative entry gives actual information about its source.
In the indicative entry there is no attempt to give actual data such as hypotheses, proofs, etc. Generally, only topics or chapter titles are included.
Indicative (descriptive–tell us what is included in the source) Griffin, C. Williams, ed. (1982). Teaching writing in all disciplines. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass. Ten essays on writing-across-the-curriculum programs, teaching writing in disciplines other than English, and teaching techniques for using writing as learning. Essays include Toby Fulwiler, “Writing: An Act of Cognition”; Barbara King, “Using Writing in the Mathematics Class: Theory and Pratice”; Dean Drenk, “Teaching Finance Through Writing”; Elaine P. Maimon, “Writing Across the Curriculum: Past, Present, and Future.” (Bizzell and Herzberg, 1991, p. 47)
Informative
Simply put, this form of annotation is a summary of the source.
To write it, begin by writing the thesis; then develop it with the argument or hypothesis, list the proofs, and state the conclusion.
Informative (summary–tell us what the main findings or arguments are in the source) Voeltz, L.M. (1980). Children’s attitudes toward handicapped peers. American Journal of Mental Deficiency, 84, 455-464. As services for severely handicapped children become increasingly available within neighborhood public schools, children’s attitudes toward handicapped peers in integrated settings warrant attention. Factor analysis of attitude survey responses of 2,392 children revealed four factors underlying attitudes toward handicapped peers: social-contact willingness, deviance consequation, and two actual contact dimensions. Upper elementary-age children, girls, and children in schools with most contact with severely handicapped peers expressed the most accepting attitudes. Results of this study suggest the modifiability of children’s attitudes and the need to develop interventions to facilitate social acceptance of individual differences in integrated school settings. (Sternlicht and Windholz, 1984, p. 79)
In this form of annotation you need to assess the source’s strengths and weaknesses.
You get to say why the source is interesting or helpful to you, or why it is not. In doing this you should list what kind of and how much information is given; in short, evaluate the source’s usefulness.
Evaluative (tell us what you think of the source) Gurko, Leo. (1968). Ernest Hemingway and the pursuit of heroism. New York: Crowell. This book is part of a series called “Twentieth Century American Writers”: a brief introduction to the man and his work. After fifty pages of straight biography, Gurko discussed Hemingway’s writing, novel by novel. There’s an index and a short bibliography, but no notes. The biographical part is clear and easy to read, but it sounds too much like a summary. (Spatt, 1991, p. 322) Hingley, Ronald. (1950). Chekhov: A biographical and critical study. London: George Allen & Unwin. A very good biography. A unique feature of this book is the appendix, which has a chronological listing of all English translations of Chekhov’s short stories. (Spatt, 1991, p. 411)
Combination
Most annotated bibliographies are of this type.
They contain one or two sentences summarizing or describing content and one or two sentences providing an evaluation.
Combination Morris, Joyce M. (1959). Reading in the primary school: An investigation into standards of reading and their association with primary school characteristics. London: Newnes, for National Foundation for Educational Research. Report of a large-scale investigation into English children’s reading standards, and their relation to conditions such as size of classes, types of organisation and methods of teaching. Based on enquiries in sixty schools in Kent and covering 8,000 children learning to read English as their mother tongue. Notable for thoroughness of research techniques.
Which writing style should I use in the annotations?
The most important thing to understand is that entries should be brief.
Only directly significant details will be mentioned and any information apparent in the title can be omitted from the annotation.
In addition, background materials and references to previous work by the same author usually are not included.
Listed below are three writing styles used in annotated bibliographies. Click on a link to see examples of each.
Telegraphic
(phrases, non-sentences)
Get the information out, quickly and concisely. Be clear, but complete and grammatically correct sentences are unnecessary.
Telegraphic (phrases, non-sentences) Vowles, Richard B. (1962). Psychology and drama: A selected checklist. Wisconsin Studies in Contemporary Literature, 3,(1), 35-48. Divided by individual authors. Reviews the research between 1920 and 1961. (Bell and Gallup, 1971, p. 68)
Complete sentences
In this style you must always use complete sentences.
The length of the sentences varies. Subjects and conjunctions are not eliminated even though the tone may be terse. Avoid long and complex sentences.
Complete sentences Kinter, W. R., and R L. Pfaltzgraff. (1972). Assessing the Moscow SALT agreements. Orbis, 16, 34l-360. The authors hold the conservative view that SALT can not halt the slipping nuclear advantage of the United States. They conclude that the United States needs a national reassessment of defense policy. They further conclude that the only utility of SALT is in developing a dialogue with the Soviets. This is a good conservative critique of SALT I. (Strenski and Manfred, 1981, p. 165)
When using this form of annotation, you must write a full, coherent paragraph.
Sometimes this can be similar to the form of a bibliographic essay. It goes without saying that you need to use complete sentences.
Paragraph (a little more formal) Voeltz, L.M. (1980). Children’s attitudes toward handicapped peers. American Journal of Mental Deficiency, 84, 455-464. As services for severely handicapped children become increasingly available within neighborhood public schools, children’s attitudes toward handicapped peers in integrated settings warrant attention. Factor analysis of attitude survey responses of 2,392 children revealed four factors underlying attitudes toward handicapped peers: social- contact willingness, deviance consequation, and two actual contact dimensions. Upper elementary-age children, girls, and children in schools with most contact with severely handicapped peers expressed the most accepting attitudes. Results of this study suggest the modifiability of children’s attitudes and the need to develop interventions to facilitate social acceptance of individual differences in integrated school settings. (Sternlicht and Windholz, 1984, p. 79)
Additional information
If you have additional questions, ask your course instructor or consider scheduling an appointment with a Writing Center instructor.
The Writing Center also has information on different documentation systems, such as MLA, APA, Chicago/Turabian, CBE, Numbered References, and APSA styles of citation.
If you are using APA documentation, you are in luck! The Writing Center offers a short class called “The Basics of APA Documentation”!
References for examples used
Bell, Inglis F., and Jennifer Gallup. (1971). A reference guide to English, American, and Canadian literature . Vancouver: University of British Columbia Press.
Bizzell, Patricia, and Bruce Herzberg. (1991). Bedford bibliography for teachers of writing . 3rd ed. Boston: Bedford Books of St. Martin’s Press.
Center for Information on Language Teaching and The English Teaching Information Center of the British Council. (1968). A Language-teaching bibliography . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Spatt, Brenda. (1991). Writing from sources . 3rd ed. New York: St. Martin’s Press.
Sternlicht, Manny, and George Windholz. (1984). Social behavior of the mentally retarded. New York and London: Garland Press.
Strenski, Ellen, and Madge Manfred. (1981). The research paper workbook . 2nd ed. New York and London: Longman.

Academic and Professional Writing
This is an accordion element with a series of buttons that open and close related content panels.
Analysis Papers
Reading Poetry
A Short Guide to Close Reading for Literary Analysis
Using Literary Quotations
Play Reviews
Writing a Rhetorical Précis to Analyze Nonfiction Texts
Incorporating Interview Data
Grant Proposals
Planning and Writing a Grant Proposal: The Basics
Additional Resources for Grants and Proposal Writing
Job Materials and Application Essays
Writing Personal Statements for Ph.D. Programs
- Before you begin: useful tips for writing your essay
- Guided brainstorming exercises
- Get more help with your essay
- Frequently Asked Questions
Resume Writing Tips
CV Writing Tips
Cover Letters
Business Letters
Proposals and Dissertations
Resources for Proposal Writers
Resources for Dissertators

Research Papers
Planning and Writing Research Papers
Quoting and Paraphrasing
Writing Annotated Bibliographies
Creating Poster Presentations
Writing an Abstract for Your Research Paper
Thank-You Notes
Advice for Students Writing Thank-You Notes to Donors
Reading for a Review
Critical Reviews
Writing a Review of Literature
Scientific Reports
Scientific Report Format
Sample Lab Assignment
Writing for the Web
Writing an Effective Blog Post
Writing for Social Media: A Guide for Academics

- Writing Center
- Current Students
- Online Only Students
- Faculty & Staff
- Parents & Family
- Alumni & Friends
- Community & Business
- Student Life
- Video Introduction
- Become a Writing Assistant
- All Writers
- Graduate Students
- ELL Students
- Campus and Community
- Testimonials
- Encouraging Writing Center Use
- Incentives and Requirements
- Open Educational Resources
- How We Help
- Get to Know Us
- Conversation Partners Program
- Workshop Series
- Professors Talk Writing
- Computer Lab
- Starting a Writing Center
- A Note to Instructors
- Annotated Bibliography
- Literature Review
- Research Proposal
- Argument Essay
- Rhetorical Analysis
Annotated Bibliography Assignment

Note to instructors: This annotated bibliography assignment may be used as a stand-alone project, or it may be used as part of an ongoing research project. You are encouraged to adopt, adapt, or remix these guidelines to suit your goals for your class.
Due dates
Rough Draft: Peer Review: Final Draft:
This assignment will help you become aware of how writers and researchers review and become familiar with previous work on a topic before they begin additional research.
- Skills : This assignment will help you practice skills essential to success in and beyond this course: Locate a variety of scholarly print and digital sources that represent multiple perspectives on a topic. Analyze sources by critically reading, annotating, engaging, comparing, and drawing implications.
- Methods for conducting research
- Analytical reading and writing strategies
An annotated bibliography is an alphabetized list of source citations that includes an annotation underneath each entry. In your annotated bibliography, each of your source citations will include an annotation summarizing the source and describing the aim, purpose, and relevance to your research project.
You will develop an annotated bibliography containing five academic sources as well as a discussion of what you learned from your research. Your annotated bibliography should have three parts: an introduction, a discussion of sources, and a conclusion.
Introduction, 150-200 words
In the introduction, present your research topic. Consider the following: Why does this topic interest you personally? (Finding a topic that interests you leads to a better paper.) Why should others care about this topic? Why is your topic worth researching? What were your research questions?
Discussion of Sources, 150-200 words per source
Gather at least five sources on your topic. Two of these sources must come from academic journals (peer-reviewed, scholarly, found using GALILEO), but the others may come from credible newspapers and magazines. One of the sources may be chosen from a website, but this site should be from a reliable organization like The Associated Press or the Centers for Disease Control (CDC). Articles from GALILEO databases are not considered internet sources. Read and reread each source carefully. Once you have selected your sources and read them carefully, write annotations for each. Each annotation should . . .
- Include a brief summary of the source.
- Evaluate the source and its use in your research.
- Discuss relation of the source to your other sources. Consider whether sources agree or disagree with/contradict each other.
- Comment on the source’s reliability.
Write citations in MLA, 9th edition, format. Summarize the articles using your own words. List your entries alphabetically and check them carefully for mistakes in MLA documentation. Here are two sample annotations: link.
Conclusion, 150-200 words
In the conclusion, detail the most important contributions your sources make to your research topic; you may also point out commonalities, conflicts, or problems. Include a discussion of what your review of your sources has demonstrated about the topic. Consider the following: What is your preliminary thesis? Did your research create new questions for you? What sources (in addition to those listed in your discussion) do you need to find? What possible conclusions to your questions do you foresee?
Final Directions
Remember to properly cite any information from your sources that you use in your introduction and conclusion. Be sure that your summaries are very different from the abstracts of the articles you have read.
Formatting requirements
Follow MLA format. Use black Calibri or Times New Roman font in size 12. Double-space the entire document. Use 1-inch margins on all sides.
Criteria for Success
general criteria: .
- The writing is clear and coherent/makes sense.
- The tone and language are appropriate for the audience.
- The writer has gone through the entire writing process, revising substantially and thoughtfully.
- The writing adheres to grammar and punctuation rules.
In the introduction, you should . . .
- Present your research topic.
- Clarify why this topic matters and is worth researching.
- Ensure your introduction is 150-200 words.
In the source discussion section, you should . . .
- Include at least five scholarly sources from reliable sources.
- Alphabetize your entries.
- Ensure each annotation includes complete and accurate works cited information following MLA format.
- Briefly summarize each source.
- Ensure each annotation contains an explanation of how the source will be used in your research project.
- Note difference of opinions among sources.
- Comment on the reliability of each source.
- Ensure annotations are in your own words, not copied from abstracts or the source itself.
- Ensure each annotation is 150-200 words.
In the conclusion, you should . . .
- Detail the most important contributions your sources make to your research topic.
- Include a discussion of what your review of your sources has demonstrated about your research topic.
- Identify your preliminary thesis.
- Identify new questions that have arisen as a result of your research.
- Discuss sources (in addition to those listed in your discussion) you still need to find.
- Identify any possible conclusions to your questions that you foresee.
The annotated bibliography should adhere to all formatting criteria:
- Follow MLA format for all citations.
- The entire document should be double-spaced.
- The font should be Calibri or Times New Roman in size 12.
- The margins should be one inch on all sides.

This material was developed by the COMPSS team and is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License . All materials created by the COMPSS team are free to use and can be adopted, adapted, and/or shared at will as long as the materials are attributed. Please keep this information on COMPSS materials you adapt, adopt, and/or share.
Contact Info
Kennesaw Campus 1000 Chastain Road Kennesaw, GA 30144
Marietta Campus 1100 South Marietta Pkwy Marietta, GA 30060
Campus Maps
Phone 470-KSU-INFO (470-578-4636)
kennesaw.edu/info
Media Resources
Resources For
Related Links
- Financial Aid
- Degrees, Majors & Programs
- Job Opportunities
- Campus Security
- Global Education
- Sustainability
- Accessibility
470-KSU-INFO (470-578-4636)
© 2024 Kennesaw State University. All Rights Reserved.
- Privacy Statement
- Accreditation
- Emergency Information
- Report a Concern
- Open Records
- Human Trafficking Notice
Writing an Annotated Bibliography
- Annotated Bibliography Home
- Types of Resources
- Find Sources
- Evaluate Sources
- Citing Sources This link opens in a new window
- Need Help? Ask a Librarian This link opens in a new window
Here's an example of an entry from an annotated bibliography, with the citation of the book in Chicago style and a brief description of the book:
Garrow, David J. Protest at Selma: Martin Luther King and the Voting Rights Act of 1965 . New Haven: Yale University Press, 1978.
Garrow describes how the strategy of protest employed by Martin Luther King, Jr., and SCLC at Selma influenced the emergence of the Voting Rights Act of 1965. He contends that the choice of Selma as a site for civil rights protests and the specific tactics that SCLC adopted in Selma were part of a plan to force the introduction and passage of national voting rights legislation. The foremost consideration in this campaign was the need to elicit "unprovoked white violence aimed at peaceful and unresisting civil rights demonstrators." Garrow argues that at Selma "a strategy that bordered on nonviolent provocation supplanted the earlier belief in nonviolent persuasion." SCLC correctly assumed that police violence would generate national media coverage and this, in turn, would stimulate reactions "throughout the country, and especially Washington," leading to pressure for federal voting rights legislation.
(Example from: The Civil Rights Movement: References and Resources , by Paul T. Murray. New York: G.K. Hall & Co., 1993.)
Dunnow, I. "Predictors of Young Adult Voting Behavior; the Beavis and Butthead' Experience." Annals of Antipathy 30.1 (1995): 57-98. I.
Dunnow's humorous satire of young voters also includes considerable research. Included are results of four surveys of first time voters conducted during the 1990s. Dunnow's tongue-in-cheek approach to developing his article entertains but doesn't distract the reader from the issues covered in the article.
(Example from: UNF LibGuide Creating an Annotated Bibliography )
- Annotated bibliographies in the library collection
- Purdue OWL Writing Center Examples
- UNF LibGiuide - Creating an Annotated Bibliography
- << Previous: Annotated Bibliography Home
- Next: Types of Resources >>
- Last Updated: Apr 11, 2024 12:25 PM
- URL: https://library.mcla.edu/annotatedbib
- Jump to menu
- Student Home
- Accept your offer
- How to enrol
- Student ID card
- Set up your IT
- Orientation Week
- Fees & payment
- Academic calendar
- Special consideration
- Transcripts
- The Nucleus: Student Hub
- Referencing
- Essay writing
- Learning abroad & exchange
- Professional development & UNSW Advantage
- Employability
- Financial assistance
- International students
- Equitable learning
- Postgraduate research
- Health Service
- Events & activities
- Emergencies
- Volunteering
- Clubs and societies
- Accommodation
- Health services
- Sport and gym
- Arc student organisation
- Security on campus
- Maps of campus
- Careers portal
- Change password
Annotated Bibliography
What is an annotated bibliography.
An annotated bibliography provides an overview or a brief account of the available research on a given topic. It is a list of research sources that takes the form of a citation for each source, followed by an annotation - a short paragraph sumarising and evaluating the source. An annotated bibliography may be a stand-alone assignment or a component of a larger assignment.
Purpose of an annotated bibliography
When set as an assignment, an annotated bibliography allows you to get acquainted with the material available on a particular topic.
Depending on your specific assignment, an annotated bibliography might:
- review the literature of a particular subject;
- demonstrate the quality and depth of reading that you have done;
- exemplify the scope of sources available—such as journals, books, web sites and magazine articles;
- highlight sources that may be of interest to other readers and researchers;
- explore and organise sources for further research.
What does an annotated bibliography look like?
Each entry in an annotated biliography has two components:
- a bibliographic citation followed by
- a short paragraph (an annotation) that includes concise descriptions and evaluations of each source.
The annotation usually contains a brief summary of content and a short analysis or evaluation. Depending on your assignment you may be asked to summarise, reflect on, critique, evaluate or analyse each source. While an annotation can be as brief as one sentence, a paragraph is more usual. An example is provided below.
As with a normal reference list or bibliography, an annotated bibliography is usually arranged alphabetically according to the author’s last name.
An annotated bibliography summary should be about 100 - 200 words per citation—check with your lecturer/tutor as this may vary between faculties and assessments. Please also check with your lecturer about the elements each annotation should include.
Steps to writing an annotated bibliography
- Choose your sources - locate and record citations to sources of research that may contain useful information and ideas on your topic.
- Review the items that you’ve collected in your search.
- Write the citation using the correct style.
- Write the annotation.
Questions to consider when selecting sources
The sources for your annotated bibliography should be carefully selected. Start by reading abstracts or skimming to help you identify and select relevant sources. Also keep in mind that, while annotated bibliographies are often ‘stand alone’ assignments, they can also be preliminary research about a particular topic or issue, and further research or a longer literature review may follow. Try to choose sources which together will present a comprehensive review of the topic.
Keep the following questions in mind to help clarify your choices
- What topic/ problem am I investigating?
- What question(s) am I exploring? (Identify the aim of your literature research).
- What kind of material am I looking at and why? Am I looking for journal articles, reports, policies or primary data?
- Am I being judicious in my selection of sources? Does each one relate to my research topic and assignment requirements?
- Have I selected a range of sources? Choose those sources that provide a variety of perspectives on your topic
- What are the essential or key works about my topic? Am I finding them? Are the sources valuable or often referred to in other sources?
Surveying the sources
Take notes on your selected texts as you read. Pay attention to:
- the author’s theoretical approach.
- which parts of the topic are covered.
- main points or findings on the topic.
- the author’s position or argument.
Evaluate and ask questions as you read
Record evaluations in your notes and consider:
- How, and how effectively, does this source address the topic?
- Does it cover the topic thoroughly or only one aspect of it?
- Do the research methods seem appropriate?
- Does the argument seem reasonable?
- Where does it stand in relation to other studies? Agree with or contradict?
How should I write the annotations?
- Each annotation should be concise. Do not write too much—annotations should not extend beyond one paragraph (unless assignment guidelines say otherwise).
- The summary should be a brief outline of argument(s) and main ideas. Only mention details that are significant or relevant, and only when necessary.
- Any information apparent in the title of thesourcel can be omitted from the annotation.
- Background materials and references to previous work by the same author usually are not included. As you are addressing one text at a time, there is no need to cross reference or use in-text citations to support your annotation.
- Find out what referencing style you need to use for the bibliographic citations, and use it consistently.
- In-text citations would usually only be necessary for quotations or to draw attention to information from specific pages.
- Unless otherwise stipulated, you should write in full sentences using academic vocabulary.
Contents of an annotated bibliography
An annotation may contain all or part of the following elements depending on the word limit and the content of the sources you are examining.
- Provide the full bibliographic citation.
- Indicate the background of the author(s).
- Indicate the content or scope of the text.
- Outline the main argument.
- Indicate the intended audience.
- Identify the research methods if applicable.
- Identify any conclusions made by the author/s.
- Discuss the reliability of the text.
- Highlight any special features of the text that were unique or helpful e.g. charts, graphs etc.
- Discuss the relevance or usefulness of the text for your research.
- Point out in what way the text relates to themes or concepts in your course.
- State the strengths and limitations of the text.
- Present your view or reaction to the text.
Sample annotation
The citation goes first and is followed by the annotation. Make sure that you follow your faculty’s preferred citation style. The summary needs to be concise. Please note the following example is entirely fictitious.
In the sample annotation below, each element is numbered (see Key).
| (1) Trevor, C.O., Lansford, B. and Black, J.W., 2004, ‘Employee turnover and job performance: monitoring the influences of salary growth and promotion’, Journal of Armchair Psychology, vol 113, no.1, pp. 56-64. (2) In this article Trevor et al. review the influences of pay and job opportunities in respect to job performance, turnover rates and employee motivation.(3) The authors use data gained through organisational surveys of blue-chip companies in Vancouver, Canada to try to identify the main causes of employee turnover and whether it is linked to salary growth.(4) Their research focuses on assessing a range of pay structures such as pay for performance and organisational reward schemes.(5) The article is useful to my research topic, as Trevor et al. suggest that there are numerous reasons for employee turnover and variances in employee motivation and performance.(6) The main limitation of the article is that the survey sample was restricted to mid-level management,(7) thus the authors indicate that further, more extensive, research needs to be undertaken to develop a more in-depth understanding of employee turnover and job performance.(8) This article will not form the basis of my research; however it will be useful supplementary information for my research on pay structures. |
(1) Citation (2) Introduction (3) Aims & Research methods (4) Scope (5) Usefulness (to your research/ to a particular topic) (6) Limitations (7) Conclusions (8) Reflection (explain how this work illuminates your topic or how it will fit in with your research) |
Essay and assignment writing guide
- Essay writing basics
- Essay and assignment planning
- Answering assignment questions
- Editing checklist
- Writing a critical review
- Annotated bibliography
- Reflective writing
- ^ More support
Study Hacks Workshops | All the hacks you need! 28 May – 25 Jul 2024
Types of Assignment
- Starting an assignment
- Academic poster
- Annotated bibliography
- Project Proposal
- Dissertation or final year project
- Literature review
- Critical Assessment - Assessing Academic Journal Articles
- Systematic Review (Postgraduate resource)
- Presentation
- Reports in Microsoft Word
| n | |
Annotated bibliography: Things you need to know...
An annotated bibliography provides the following details to illustrate the quality and appropriateness of your text :
- Concise summary of the resources used for the academic work.
- Comments about why and how you have used the information.
- A list and a brief critical analysis (annotation) of the research you have used, often presented in a tabular format.
- Full bibliographic details in the referencing style of your subject should be used (Havard, APA, Oscola).
I nclude specific information such as:
- Author - who wrote the text? why? what experience have they?
- Brief summary of text - what are the aims and conclusions made?
- Why did you use this information - mention: reliability of the research; who was the intended audience? why did you like this text? what were the limitations of the text?
- Annotated bibliography What is an annotated bibliography, what information to include and how to present one.

Look at Staffordshire University Library's RefZone .
- << Previous: Academic poster
- Next: Essay >>
- Last Updated: May 20, 2024 10:59 AM
- URL: https://libguides.staffs.ac.uk/assignments
- Library and Learning Services, Staffordshire University, College Road, Stoke-on-Trent, ST4 2DE
- Accessibility
- Library Regulations
- Appointments
- Library Search


Annotated Bibliography
Ai generator.

You may have gone through this once in your life or even daily, depending on the work you do. But looking for sources to support the research you are doing for a topic is also necessary. Bibliographies come in different forms, they could be enumerative, analytical, or even annotated.
What Is an Annotated Bibliography?
An annotated bibliography is simply a list of sources, such as book , articles , and documents, that typically comes with a brief description of each item. This could be to describe, gives an evaluation, or explain a given item. An annotated bibliography can be selective or comprehensive in nature.
Annotated Bibliography Format
An annotated bibliography is a list of citations to books, articles, and documents. Each citation is followed by a brief (usually about 150 words) descriptive and evaluative paragraph, the annotation . The purpose of the annotation is to inform the reader of the relevance, accuracy, and quality of the sources cited.
The title should be concise and descriptive. For example, “Annotated Bibliography on Climate Change.”
2. Citations
Citations should be formatted according to the style guide you are following (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.). Below are examples for APA and MLA styles.
Format: Author(s). (Year). Title of the book. Publisher.
Example: Smith, J. (2020). Understanding Climate Change. Green Earth Publishers.
Format: Author(s). Title of the Book. Publisher, Year.
Example: Smith, John. Understanding Climate Change. Green Earth Publishers, 2020.
3. Annotations
Annotations should provide a summary of the source and evaluate its relevance, accuracy, and quality. Below are examples of annotations in APA and MLA styles.
Format: Author(s). (Year). Title of the book. Publisher. Summary: A brief summary of the source’s content. Evaluation: An assessment of the source’s reliability and relevance. Reflection: How the source fits into your research.
Example: Smith, J. (2020). Understanding Climate Change. Green Earth Publishers. Summary : This book provides an overview of climate change, including its causes, effects, and potential solutions. Evaluation: The author is a renowned environmental scientist with numerous publications on the topic, making this a reliable source. Reflection: This source will be useful for understanding the basic concepts of climate change and its global impact.
Format: Author(s). Title of the Book. Publisher, Year. Summary: A brief summary of the source’s content. Evaluation: An assessment of the source’s reliability and relevance. Reflection: How the source fits into your research.
Example: Smith, John. Understanding Climate Change. Green Earth Publishers, 2020. Summary: This book provides an overview of climate change, including its causes, effects, and potential solutions. Evaluation: The author is a renowned environmental scientist with numerous publications on the topic, making this a reliable source. Reflection: This source will be useful for understanding the basic concepts of climate change and its global impact.
Types of Annotated Bibliography
Annotated bibliographies can serve various purposes depending on the needs of the researcher or the requirements of the assignment. They can be categorized based on the content of the annotations. Here are the main types:
1. Descriptive or Informative Annotated Bibliography
A descriptive or informative annotated bibliography provides a summary of the source. It describes the main points and arguments of the work without offering an evaluation.
Purpose: The purpose of a descriptive annotation is to inform the reader about the content of the source. It focuses on the main ideas and key points.
Smith, J. (2020). Understanding Climate Change . Green Earth Publishers. Summary: This book provides an overview of climate change, including its causes, effects, and potential solutions. The author discusses various scientific studies and offers predictions for future climate patterns.
2. Evaluative or Critical Annotated Bibliography
An evaluative or critical annotated bibliography not only summarizes the source but also evaluates its quality, accuracy, and relevance. It provides a critical assessment of the source’s strengths and weaknesses.
Purpose: The purpose of an evaluative annotation is to provide an analysis of the source’s credibility and its contribution to the topic. It helps the reader understand the source’s value in relation to other research.
Doe, A. (2019). Climate Change: A Comprehensive Study . Blue Ocean Press. Summary: This study examines the impact of climate change on various ecosystems. Evaluation: The research is thorough and well-documented, making it a credible source. However, the author’s strong bias towards policy advocacy might influence the interpretation of the data.
3. Summative Annotated Bibliography
A summative annotated bibliography combines elements of both descriptive and evaluative annotations. It provides a summary of the source along with a brief evaluation.
Purpose : The purpose of a summative annotation is to give a comprehensive overview of the source, covering both its content and its usefulness.
Brown, C. (2018). The Economics of Climate Change . Eco Press. Summary: This book explores the economic impacts of climate change, discussing both the costs and potential benefits. Evaluation: The author’s analysis is balanced and well-supported by empirical data, making it a valuable resource for understanding the economic implications of environmental policies.
4. Indicative Annotated Bibliography
An indicative annotated bibliography provides a general overview of the source. It outlines the main topics or themes covered without delving into specific details or evaluations.
Purpose: The purpose of an indicative annotation is to give the reader an idea of what the source covers, allowing them to decide if it is relevant to their research.
Williams, L. (2017). Environmental Policy and Climate Change . Green Leaf Publications. Summary: This book discusses various environmental policies related to climate change, including international agreements and national regulations.
Annotated bibliography Examples for Students
Citation: Smith, J. (2020). The Art of Effective Study . Academic Press. Annotation: This book provides comprehensive strategies for effective study habits, including time management, note-taking, and test preparation. Smith emphasizes the importance of discipline and organization in achieving academic success. The book is well-researched and includes practical examples, making it a valuable resource for students. Evaluation: The book is thorough and covers a wide range of topics related to study techniques. Smith’s writing is clear and accessible, and the strategies provided are backed by research. However, some sections could benefit from more detailed explanations. Reflection: This source will be useful in the section of my project discussing effective study techniques. It provides practical advice that can be directly applied to improve academic performance.
2. Journal Article
Citation: Johnson, L. & Lee, M. (2021). The impact of social media on student productivity. Journal of Educational Psychology, 33 (4), 456-469. https://doi.org/10.1234/jep.2021.0456 Annotation: Johnson and Lee explore the effects of social media on students’ productivity through a series of controlled experiments. The study finds a significant negative correlation between social media usage and academic performance. The article is peer-reviewed and provides strong empirical evidence. Evaluation: The study is well-designed and offers valuable insights into the impact of social media on student productivity. The findings are significant and supported by robust data analysis. However, the sample size is relatively small, which may limit the generalizability of the results. Reflection: This source will help illustrate the negative aspects of social media in my research on student productivity. Its empirical evidence will support my argument on the detrimental effects of excessive social media use.
Citation: National Institute of Mental Health. (2022, January 15). Tips for managing stress. NIMH . https://www.nimh.nih.gov/tips-for-managing-stress Annotation: This webpage offers practical tips for managing stress, including relaxation techniques and lifestyle changes. The information is reliable and up-to-date, making it a valuable resource for those seeking to improve their mental health. Evaluation: The tips provided are practical and easy to implement. The website is credible, being an official health institute, and the information is presented in a clear and concise manner. However, it lacks in-depth explanations of some techniques. Reflection: This source will be used to provide stress management strategies in my project on student well-being. Its practical advice will help support the section on coping mechanisms for academic stress.
4. Book Chapter
Citation: Brown, R. (2019). Cognitive development in early childhood. In S. Green & P. White (Eds.), Foundations of Child Psychology (pp. 45-68). Springer. Annotation: Brown discusses the stages of cognitive development in early childhood, providing insights from various psychological theories. The chapter is thorough and includes references to key studies in the field. Evaluation: The analysis is well-structured and accessible, making it a valuable resource for understanding early cognitive development. Brown effectively integrates different theoretical perspectives. However, the chapter could benefit from more recent studies. Reflection: This source will be used to support the theoretical framework of my research on child psychology. It provides a foundation for discussing developmental stages and will help contextualize my findings.
5. Magazine Article
Citation: Martinez, L. (2023, June 10). The future of educational technology. Education Today , 45(6), 22-25. Annotation: Martinez explores emerging trends in educational technology, including AI and virtual reality. The article is well-researched and provides insights into the potential future of education. Evaluation: The article is informative and offers a comprehensive overview of potential technological advancements in education. However, it lacks empirical data to support some of its claims. Despite this, it is a valuable resource for understanding future trends. Reflection: This source will be used to discuss technological advancements in my project on education. It will provide a contemporary perspective on how technology can enhance learning experiences.
Annotated Bibliography Examples for College Students
1. scholarly book.
Citation: Smith, J. (2020). The Art of Effective Study . Academic Press. Annotation: Smith provides comprehensive strategies for effective study habits, including time management, note-taking, and test preparation. Emphasizing the importance of discipline and organization, the book is well-researched and includes practical examples. Evaluation: The book is thorough and covers a wide range of topics related to study techniques. Smith’s writing is clear and accessible, making the strategies easy to understand and implement. However, more detailed explanations in some sections would enhance its usefulness. Reflection: This source will be particularly useful for the section of my project that discusses effective study techniques. It offers practical advice that I can apply directly to improve my academic performance.
Citation: Johnson, L. & Lee, M. (2021). The impact of social media on student productivity. Journal of Educational Psychology, 33 (4), 456-469. https://doi.org/10.1234/jep.2021.0456 Annotation: Johnson and Lee explore the effects of social media on students’ productivity through controlled experiments. The study finds a significant negative correlation between social media usage and academic performance. Evaluation: The study is well-designed and offers valuable insights into the impact of social media on student productivity. The findings are significant and supported by robust data analysis, though the relatively small sample size may limit the generalizability of the results. Reflection: This source will help illustrate the negative aspects of social media in my research on student productivity, providing empirical evidence to support my argument on the detrimental effects of excessive social media use.
3. Government Website
Citation: National Institute of Mental Health. (2022, January 15). Tips for managing stress. NIMH . https://www.nimh.nih.gov/tips-for-managing-stress Annotation: This webpage from the National Institute of Mental Health offers practical tips for managing stress, including relaxation techniques and lifestyle changes. Evaluation: The tips are practical and easy to implement. The website is credible and the information is presented in a clear and concise manner. However, it lacks in-depth explanations of some techniques. Reflection: This source will be used to provide stress management strategies in my project on student well-being, offering practical advice for coping with academic stress.
Citation: Brown, R. (2019). Cognitive development in early childhood. In S. Green & P. White (Eds.), Foundations of Child Psychology (pp. 45-68). Springer. Annotation: Brown discusses the stages of cognitive development in early childhood, providing insights from various psychological theories. The chapter includes references to key studies in the field. Evaluation: The chapter is well-structured and accessible, making it a valuable resource for understanding early cognitive development. Brown effectively integrates different theoretical perspectives, though more recent studies would enhance the chapter. Reflection: This source will support the theoretical framework of my research on child psychology, providing a foundation for discussing developmental stages and contextualizing my findings.
Citation: Martinez, L. (2023, June 10). The future of educational technology. Education Today , 45(6), 22-25. Annotation: Martinez explores emerging trends in educational technology, including AI and virtual reality. The article provides insights into the potential future of education. Evaluation: The article is informative and offers a comprehensive overview of potential technological advancements in education. However, it lacks empirical data to support some of its claims. Despite this, it is a valuable resource for understanding future trends. Reflection: This source will be used to discuss technological advancements in my project on education, providing a contemporary perspective on how technology can enhance learning experiences.
Examples of Annotated Bibliography in APA Format
1. research report.
Citation: Pew Research Center. (2023). The state of online learning: A comprehensive study . Pew Research Center. https://www.pewresearch.org/online-learning Annotation: The report provides an in-depth analysis of the current trends in online learning, including demographic data, student performance metrics, and user satisfaction. The study highlights the rapid growth of online education and its impact on traditional learning environments. Evaluation: This report is highly detailed and utilizes a wide range of data sources, making it a credible and comprehensive resource. However, it is primarily descriptive and lacks a critical analysis of the data presented. Reflection: This source will be instrumental in providing current data and trends in the online education section of my project, offering a broad overview of the state of online learning today.
2. Documentary Film
Citation: Morris, T. (Director). (2020). The digital classroom: Technology in education [Film]. Educational Media Productions. Annotation: The documentary explores the integration of technology in modern classrooms, featuring interviews with educators, students, and technology experts. It examines both the benefits and challenges of digital tools in education. Evaluation: The film is well-produced and offers diverse perspectives on the subject. The visual and anecdotal evidence provided is compelling, though it could benefit from more empirical data to support its claims. Reflection: This documentary will be useful in illustrating real-world applications and challenges of educational technology, complementing the more data-driven sources in my research.
3. Encyclopedia Entry
Citation: Encyclopedia Britannica. (2021). Mindfulness. In Encyclopedia Britannica online . https://www.britannica.com/topic/mindfulness Annotation: The entry provides a concise overview of mindfulness, its origins, and its applications in various fields such as psychology, education, and healthcare. It also includes references to key studies and practitioners in the field. Evaluation: As a tertiary source, the entry is a reliable and accessible summary of the topic. However, it lacks the depth and detailed analysis found in primary and secondary sources. Reflection: This entry will serve as a foundational overview of mindfulness, helping to frame the broader context for the more detailed studies and articles I will use in my project.
4. Blog Post
Citation: Walker, K. (2022, September 14). How to balance work and study: Tips from successful students. College Life Blog . https://www.collegelifeblog.com/balance-work-study Annotation: Walker shares practical advice from successful students on how to balance work and study commitments. The post includes time management strategies, personal anecdotes, and links to additional resources. Evaluation: The blog post is engaging and practical, written in an accessible style that resonates with its target audience. However, it is anecdotal and lacks the empirical support found in academic sources. Reflection: This source will provide practical tips and real-life examples for the section of my project on time management, offering a relatable perspective to complement academic research.
5. Newspaper Article
Citation: Green, A. (2023, March 5). Schools adopt new technologies to enhance learning. The New York Times . https://www.nytimes.com/2023/03/05/education/schools-new-technologies.html Annotation: Green discusses the latest technological innovations being adopted by schools to enhance learning, including virtual reality, AI, and personalized learning platforms. The article includes interviews with educators and students. Evaluation: The article is current and provides firsthand accounts of the impact of new technologies in education. However, it is relatively short and lacks the depth of academic journal articles. Reflection: This source will be valuable for providing contemporary examples of technological advancements in education, helping to illustrate the practical applications of the concepts discussed in my research.
Examples of Annotated Bibliography in MLA Format
Citation: Smith, John. The Art of Effective Study . Academic Press, 2020. Annotation: Smith provides comprehensive strategies for effective study habits, including time management, note-taking, and test preparation. Emphasizing the importance of discipline and organization, the book is well-researched and includes practical examples. Evaluation: The book is thorough and covers a wide range of topics related to study techniques. Smith’s writing is clear and accessible, making the strategies easy to understand and implement. However, more detailed explanations in some sections would enhance its usefulness. Reflection: This source will be particularly useful for the section of my project that discusses effective study techniques. It offers practical advice that I can apply directly to improve my academic performance.
Citation: Johnson, Linda, and Mark Lee. “The Impact of Social Media on Student Productivity.” Journal of Educational Psychology , vol. 33, no. 4, 2021, pp. 456-469. Annotation: Johnson and Lee explore the effects of social media on students’ productivity through controlled experiments. The study finds a significant negative correlation between social media usage and academic performance. Evaluation: The study is well-designed and offers valuable insights into the impact of social media on student productivity. The findings are significant and supported by robust data analysis, though the relatively small sample size may limit the generalizability of the results. Reflection: This source will help illustrate the negative aspects of social media in my research on student productivity, providing empirical evidence to support my argument on the detrimental effects of excessive social media use.
Citation: National Institute of Mental Health. “Tips for Managing Stress.” NIMH , 15 Jan. 2022, www.nimh.nih.gov/tips-for-managing-stress . Annotation: This webpage from the National Institute of Mental Health offers practical tips for managing stress, including relaxation techniques and lifestyle changes. Evaluation: The tips are practical and easy to implement. The website is credible and the information is presented in a clear and concise manner. However, it lacks in-depth explanations of some techniques. Reflection: This source will be used to provide stress management strategies in my project on student well-being, offering practical advice for coping with academic stress.
Citation: Brown, Rebecca. “Cognitive Development in Early Childhood.” Foundations of Child Psychology , edited by Susan Green and Peter White, Springer, 2019, pp. 45-68. Annotation: Brown discusses the stages of cognitive development in early childhood, providing insights from various psychological theories. The chapter includes references to key studies in the field. Evaluation: The chapter is well-structured and accessible, making it a valuable resource for understanding early cognitive development. Brown effectively integrates different theoretical perspectives, though more recent studies would enhance the chapter. Reflection: This source will support the theoretical framework of my research on child psychology, providing a foundation for discussing developmental stages and contextualizing my findings.
Citation: Martinez, Laura. “The Future of Educational Technology.” Education Today , vol. 45, no. 6, 10 June 2023, pp. 22-25. Annotation: Martinez explores emerging trends in educational technology, including AI and virtual reality. The article provides insights into the potential future of education. Evaluation: The article is informative and offers a comprehensive overview of potential technological advancements in education. However, it lacks empirical data to support some of its claims. Despite this, it is a valuable resource for understanding future trends. Reflection: This source will be used to discuss technological advancements in my project on education, providing a contemporary perspective on how technology can enhance learning experiences.
More Annotated Bibliography Examples & Samples in PDF
1. free annotated bibliography example.

2. Simple Annotated Bibliography

3. MLA Annotated Bibliography

4. APA Annotated Bibliography

5. Visual Annotated Bibliography

6. Annotated Bibliography Format in PDF

7. Annotated Bibliography Examples

8. Annotated Bibliography Document

9. Short Annotated Bibliography Examples

10. English Annotated Bibliography

Purpose of an Annotated Bibliography
An annotated bibliography serves several important purposes in academic research and writing. Below are the key purposes it fulfills:
1. Provide a Summary of Sources
An annotated bibliography summarizes the main ideas and arguments of each source. This helps the reader understand the content and scope of the sources without having to read them in full.
Smith, J. (2021). The Future of Renewable Energy. Green Energy Publishers. Summary: This book provides an overview of the current state of renewable energy, including solar, wind, and hydroelectric power. The author discusses the benefits and challenges associated with each type of renewable energy.
2. Evaluate the Quality and Credibility of Sources
Annotations often include an evaluation of the source’s reliability, accuracy, and relevance to the research topic. This helps determine the usefulness and scholarly value of the sources.
Evaluation: The author is a recognized expert in the field, making this a reliable source. However, some data might be outdated due to rapid technological advancements.
3. Reflect on the Source’s Relevance to Your Research
Annotations allow the researcher to reflect on how each source contributes to their research. This includes how it supports or contradicts their thesis, what new insights it offers, and how it fits into the broader context of their study.
Reflection: This source is useful for understanding the basic concepts and the potential of renewable energy, making it a good starting point for my research on sustainable energy solutions.
4. Assist in the Organization of Research
Creating an annotated bibliography helps in organizing and managing sources. It allows researchers to keep track of what they have read and ensures they can easily reference sources in their writing.
- Keeping a detailed annotated bibliography can prevent duplication of effort and help in identifying gaps in the existing research.
5. Facilitate a Deeper Understanding of the Topic
Writing annotations requires critical thinking and a deep engagement with the source material. This process enhances the researcher’s understanding of the topic and the existing literature.
- By summarizing and evaluating sources, researchers gain a comprehensive view of the scholarly conversation on their topic, which can inform their own analysis and arguments.
6. Support the Development of a Thesis or Research Question
Annotated bibliographies help in refining and focusing a research question or thesis. By reviewing various sources, researchers can better understand the scope of their topic and identify key issues and debates.
- Reviewing annotated sources may reveal patterns, trends, and gaps that can shape the direction of the research.
7. Provide a Resource for Other Researchers
Annotated bibliographies serve as valuable resources for other researchers interested in the same topic. They provide an overview of the existing literature and can guide others in their own research efforts.
- A well-constructed annotated bibliography on renewable energy can serve as a reference point for future studies in the field.
How to Write an Annotated Bibliography

An annotated bibliography is a valuable research tool that includes citations to books, articles, and other sources, each accompanied by a brief descriptive and evaluative paragraph. This guide will walk you through the process of writing an annotated bibliography, ensuring that your work is well-organized, informative, and relevant.
Step 1: Select Your Sources
Start by choosing sources that are relevant to your research topic. These can include books, journal articles, websites, and other types of publications. Ensure that you select credible and authoritative sources to support your research.
Step 2: Cite the Sources
List your sources in alphabetical order according to the citation style required by your instructor or field of study (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago). Each citation should include the author, title, publication date, and other pertinent information.
Example (APA Style):
Smith, J. (2020). Understanding Annotated Bibliographies . Academic Press.
Step 3: Write the Annotations
Each annotation typically consists of three parts: a summary, an evaluation, and a reflection.
- Summary: Briefly describe the main points and arguments of the source.
- Evaluation: Assess the source’s credibility, reliability, and relevance to your research.
- Reflection: Explain how this source fits into your research, how it will help you, and any insights you gained from it.
Example Annotation:
Smith, J. (2020). Understanding Annotated Bibliographies . Academic Press. This book provides a comprehensive overview of how to compile annotated bibliographies, including the purpose, structure, and examples from various disciplines. Smith emphasizes the importance of critical thinking and offers practical tips for evaluating sources. This source is highly credible, as it is written by an expert in academic writing. It is particularly useful for my research on academic writing techniques as it provides clear guidelines and strategies that I can apply.
Step 4: Format Your Annotated Bibliography
Ensure that your annotated bibliography is formatted correctly according to the citation style you are using. Pay attention to details such as indentation, spacing, and order of entries.
Step 5: Review and Revise
Carefully review your annotated bibliography for accuracy, clarity, and completeness. Make sure each annotation is concise and informative, and that all sources are properly cited.
How do you format an annotated bibliography?
Format according to your citation style (APA, MLA, etc.), list sources alphabetically, and include a summary, evaluation, and reflection for each source.
How long should an annotation be?
An annotation is typically 100-200 words, including a summary, evaluation, and reflection on the source’s relevance to your research.
Can you include websites in an annotated bibliography?
Yes, websites can be included if they are credible and relevant to your research topic, and properly cited in your chosen citation style.
Do annotations replace the need for a bibliography?
No, an annotated bibliography includes both the citation and a descriptive/evaluative paragraph. It supplements a regular bibliography, providing more detail.
Should annotations be written in first or third person?
Annotations are usually written in third person to maintain an objective and formal tone, but check with your instructor for specific preferences.
How do I evaluate a source for an annotation?
Assess the source’s credibility, relevance, and quality. Consider the author’s expertise, the publication’s reputation, and the source’s contribution to your research.
Can I use annotations from abstracts?
No, annotations should be written by you, providing a summary, evaluation, and reflection tailored to your research needs, not just the abstract provided by the source.
Is there a specific order for elements in an annotation?
Yes, typically start with a summary of the source, followed by an evaluation of its credibility and usefulness, and conclude with a reflection on its relevance to your research.
How many sources should be in an annotated bibliography?
The number of sources depends on your assignment requirements. Typically, an annotated bibliography includes 5-20 sources, but check your guidelines.
Can annotated bibliographies include primary and secondary sources?
Yes, both primary and secondary sources can be included as long as they are relevant and credible for your research topic.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
Pardon Our Interruption
As you were browsing something about your browser made us think you were a bot. There are a few reasons this might happen:
- You've disabled JavaScript in your web browser.
- You're a power user moving through this website with super-human speed.
- You've disabled cookies in your web browser.
- A third-party browser plugin, such as Ghostery or NoScript, is preventing JavaScript from running. Additional information is available in this support article .
To regain access, please make sure that cookies and JavaScript are enabled before reloading the page.
- Newsletters
IE 11 Not Supported
Istelive 24: how to counter misuse of ai writing in grades 7-12, for all the opportunities generative ai brings to middle and high school students, it could also undermine their proficiency at reading and writing. experienced teachers have some suggestions for how to make it work..

WHY STUDENTS USE AI
What teachers can do.
- Frame instructions as questions, or give students a question-based outline to work from, because they like questions and naturally try to answer them. For example, rather than telling students to summarize a quote, ask them what the quote is basically saying.
- To build student confidence and encourage discourse, use “mini Socratics,” or scaled-down versions of Socratic seminars, in which groups of three to five students collaborate to share ideas on each other’s essay topics.
- During the peer-review processes, offer students a choice in how they want to receive feedback. “The student who really loves red-line editing, maybe that’s what they’re choosing, that they’re going to go through and help with some sentence structure,” Miller said. “But maybe another student just wants to look and see whether or not they understand the content and whether or not it’s clear and concise.” A teacher in the audience also recommended floopedu.com as a useful free website for anonymous peer review and feedback.
- To encourage critical thinking, have students do targeted annotations so they can work their way through difficult material and actively engage with the text.
- During the research phase of an essay, have students do an annotated bibliography. This can provide evidence of critical reading, a summary of main points, and justifications for using those sources. “Have them turn (an annotated bibliography) in, and then if they’re comfortable with that source, they’re going to be more likely to actually use it in their writing, because they understand it,” Miller said.
- Use AI only in small doses and when needed. Don’t have students put their entire essay into an AI for feedback.
- Use AI-resistant prompts. Ask students for subjective explanations, evaluative critical thinking, personal experiences, or reflections on their own writing or thinking.
HOW TO HANDLE CHEATING


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Below you will find sample annotations from annotated bibliographies, each with a different research project. Remember that the annotations you include in your own bibliography should reflect your research project and/or the guidelines of your assignment. As mentioned elsewhere in this resource, depending on the purpose of your bibliography ...
Published on March 9, 2021 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on August 23, 2022. An annotated bibliography is a list of source references that includes a short descriptive text (an annotation) for each source. It may be assigned as part of the research process for a paper, or as an individual assignment to gather and read relevant sources on a topic.
MLA Style Annotated Bibliography | Format & Examples. Published on July 13, 2021 by Jack Caulfield.Revised on March 5, 2024. An annotated bibliography is a special assignment that lists sources in a way similar to the MLA Works Cited list, but providing an annotation for each source giving extra information.. You might be assigned an annotated bibliography as part of the research process for a ...
An annotated bibliography is an organized list of sources (like a reference list). It differs from a straightforward bibliography in that each reference is followed by a paragraph length annotation, usually 100-200 words in length. Depending on the assignment, an annotated bibliography might have different purposes:
All annotated bibliographies have a title, annotation, and citation. While the annotation is the same for all, the way you create your title and citation varies based on your style. The three main bibliography styles used include MLA, APA, and Chicago. Annotated Bibliography Examples. Get examples of an annotated bibliography in each different ...
What Is an Annotated Bibliography? An annotated bibliography is a list of citations to books, articles, and documents. Each citation is followed by a brief (usually about 150 words) descriptive and evaluative paragraph, the annotation. The purpose of the annotation is to inform the reader of the relevance, accuracy, and quality of the sources ...
You might want to consider the logic of authors' arguments, and the quality of their evidence. Your findings can be positive, negative, or mixed. Your professor might also want you to explain why the source is relevant to your assignment. Sample Page: APA-formatted annotated bibliography. Child Poverty in Canada 2. Battle, K. (2007).
What this handout is about. This handout will explain why annotated bibliographies are useful for researchers, provide an explanation of what constitutes an annotation, describe various types of annotations and styles for writing them, and offer multiple examples of annotated bibliographies in the MLA, APA, and CBE/CSE styles of citation.
The annotation appears on a new line directly after the source citation. The whole annotation is indented, to make it clear when the annotation ends and a new source appears. According to Turabian guidelines, annotations should be formatted the same as the main text of any paper: Double-spaced. Left-aligned.
Step 3a: MLA annotated bibliography format. The MLA Style Center and the current edition of the MLA Handbook provide the following guidance for formatting an MLA annotated bibliography: Title your reference page as "Annotated Bibliography" or "Annotated List of Works Cited.". Place each annotation after its reference.
An annotated bibliography is a combination of the words "annotation" and "bibliography." An annotation is a set of notes, comments, or critiques. A bibliography is list of references that helps a reader identify sources of information. An annotated bibliography is a list of references that not only identifies the sources of information but also ...
After your APA annotated bibliography is formatted, you create a citation for each entry. The composition of your citation varies based on the type of source you are using. For example, a book citation in APA is different than a journal citation. Therefore, when creating your citation, use the format APA has designated for that specific source.
Annotated Bibliographies can be a great resource for students before they write other types of assignments, like literature reviews . There are TWO PARTS to each entry in an Annotated Bibliography. They are: The citation of the resource, in whatever citation style you're required to use. The annotation describing the contents of the resource ...
Information on Annotated Bibliographies can be found in Section 9.51 of the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (7th ed.) The format of your annotated bibliography follow the same format as any APA paper. Title page, page numbers, font style and size, etc. See Format basics. Alphabetical with hanging indents etc.
Annotated Bibliography. An annotated bibliography is an organized list of sources, each of which is followed by a brief note or "annotation.". These annotations do one or more of the following: describe the content and focus of the book or article. suggest the source's usefulness to your research. evaluate its method, conclusions, or ...
Title of Your Assignment: Annotated Bibliography Your Name Institution Name Course Number: Title Instructor's Name Month Day, Year . APA SAMPLE: ANNOTATED BIBLIOGRAPHY Handout Provided by U of A Title of Your Assignment: Annotated Bibliography Author, A. (Year Published). Article title.
MLA Annotated Bibliography Examples. Cook, Sybilla. Instruction Design. New York: Garland, 1986. This book provides an annotated. bibliography of sources concerning instructional patterns for research libraries. Written for an. academic audience, the author provides information on how such a bibliography can be used.
Purpose. This assignment will help you become aware of how writers and researchers review and become familiar with previous work on a topic before they begin additional research. Locate a variety of scholarly print and digital sources that represent multiple perspectives on a topic. Analyze sources by critically reading, annotating, engaging ...
Here's an example of an entry from an annotated bibliography, with the citation of the book in Chicago style and a brief description of the book: Garrow, David J. Protest at Selma: Martin Luther King and the Voting Rights Act of 1965. New Haven: Yale University Press, 1978.
An annotated bibliography provides an overview or a brief account of the available research on a given topic. It is a list of research sources that takes the form of a citation for each source, followed by an annotation - a short paragraph sumarising and evaluating the source. An annotated bibliography may be a stand-alone assignment or a ...
There are two parts to every entry in an annotated bibliography: the citation and the annotation. The Citation. The citation includes the bibliographic information of the source. OHS uses the MLA documentation style for all citations. Follow the instructions for the assignment, and the guidelines in the appropriate documentation style.
An annotated bibliography provides the following details to illustrate the quality and appropriateness of your text: Concise summary of the resources used for the academic work. Comments about why and how you have used the information. A list and a brief critical analysis (annotation) of the research you have used, often presented in a tabular ...
An annotated bibliography serves several important purposes in academic research and writing. Below are the key purposes it fulfills: 1. Provide a Summary of Sources. An annotated bibliography summarizes the main ideas and arguments of each source. This helps the reader understand the content and scope of the sources without having to read them ...
Management document from American Public University, 9 pages, LEADERSHIP TRAITS - THESIS STATEMENT AND ANNOTATED BIBLIOGRAPHY Leadership Skills - Thesis Statement and Annotated Bibliography Assignment Saliou Aboudou Liberty University PADM 712 01/04/2024 1 LEADERSHIP TRAITS - THESIS STATEMENT AND ANNOTATED BIBLIOGR
During the research phase of an essay, have students do an annotated bibliography. This can provide evidence of critical reading, a summary of main points, and justifications for using those sources.