Want to Get your Dissertation Accepted?
Discover how we've helped doctoral students complete their dissertations and advance their academic careers!

Join 200+ Graduated Students

Get Your Dissertation Accepted On Your Next Submission
Get customized coaching for:.
- Crafting your proposal,
- Collecting and analyzing your data, or
- Preparing your defense.
Trapped in dissertation revisions?
How to create a dissertation proposal defense powerpoint (+example), published by steve tippins on june 21, 2022 june 21, 2022.
Last Updated on: 22nd May 2024, 04:14 am
As part of the dissertation process, you will need to create a dissertation proposal defense PowerPoint to present a summary of the plan for your study. You will need to show how important your study is and how it is useful.
When creating the PowerPoint, keep in mind that you need to make sure all of your audience can understand all aspects of your study. The exact content for the defense PowerPoint varies by college, discipline and department, so it is important that you discuss with your committee chair about the requirements. However, we will give some general guidelines that apply to most institutions.

The defense typically takes 20‐30 minutes. You should keep the timeframe in mind as you consider the information you will have in your presentation.
Except for aspects of your presentation, such as the research question(s) or hypothesis(es), do not just read the slides. Instead, explain or expand on what is on the slides. To ensure you keep within the timeframe, practice narrating your PowerPoint presentation.
Although the APA manual does not provide guidelines for creating a PowerPoint presentation, you will need to follow some of the APA style guidelines within your PowerPoint.
For example, provide in-text citations for quotes, paraphrases, images, graphs, and other information that should be cited. Also, you will need to provide a list of pertinent references.
The following are other format requirements for the slides :
- Create 17-20 slides.
- Do not provide a lot of information. Be concise and write a few sentences (approximately 1-7 on each slide).
- Because your slides will contain only a small amount of information, any extra information that you want to touch on should be put in the notes section of the PowerPoint.
- Write the information in your slides for visual appeal and optimum communication, using a legible font size.
- You can use graphics and images to enhance and reinforce the information. However, ensure that they do not distract from your information.
- You can use bullet points but keep them to a minimum of 3-4 for each listing.
Example Dissertation Proposal Defense PowerPoint Template

The dissertation proposal will consist of three chapters, which you will be providing information on in the presentation. Although the contents and order of the contents may vary, there are some basic parts of the proposal that are usually required.
The following is a breakdown of the usual contents that are included in the presentation. Each of these headings below represents the titles of each slide. The information below the headings is the type of content you will need to provide.
Title (1 slide) :
- Dissertation’s Title
- Department of Program of Study/Name of University
- Chair and Committee Members
Statement of the Problem (1 slide):
- Provide the problem that your dissertation will address.
Purpose of the Study (1 slide):
- Provide what the study will do relative to the issue(s) defined in the statement of the problem.
Significance of the Study (1 slide):
- Provide the main argument of why the solution to the problem that you propose is important.
Research Question(s)/Hypothesis(es ) (1 slide):
- Provide the research question(s) or hypothesis(es) relevant to your field of study, written exactly as it is in your dissertation proposal.
The Literature Review (2 slides):
- These slides should consist of a coherent, organized overview of the main literature that frames your study’s problem, and the gap in literature that your study will address. Make sure that you include the sources.
Theoretical/Conceptual Framework (1 slide):
- This slide should consist of the theoretical/conceptual framework that will help you make sense of the phenomenon that you will investigate.
Research Design (1 slide):
- Provide the framework for the methods of data collection and data analysis. Indicate whether the study will be quantitative or qualitative.
Sample and Population (1 slide):
- Provide the population that refers to the entire group that you will draw conclusions about, and the sample that refers to the specific group that you will collect data from.
Data Collection (1 slide):
- Provide the methods by which you will obtain the data. If the research design is quantitative, provide methods such as correlation and regression, mean, mode and median or others. If the design is qualitative, provide methods such as, interviews, questionnaires with open-ended questions, focus groups, observation, game or role-playing, case studies, or others.
Data Analysis (1-2 slides):
- This slide should contain the process you will use to understand, gather, compile, and process the data you will obtain.

Limitations (1 slide):
- In this slide, explain the nature of the limitations and how they will be overcome during your research.
Delimitations (1slide):
- Provide the characteristics that describe the boundaries of your study and limit the scope, such as sample size, geographical location, population traits, or others.
References (1-2 slides):
- Only provide those sources that you referred to in the presentation. Do not provide all the sources that you have in your dissertation proposal.
Thank You/Questions (1 slide):
- Use this final slide to thank your committee and to request questions from them.
Note : For information about citing your references, refer to Chapters 9 and 10 of the APA Manual 7 th edition.
For instructions on how to create a PowerPoint, see How to Create a Powerpoint Presentation .
View this video for “ Tips and Tricks for your Proposal Defense Day Presentation ”
You can find several templates of students’ Dissertation Proposal Defense presentations online by searching for “Dissertation Proposal Defense PowerPoint.” You can also find one at this webpage .
Steve Tippins
Steve Tippins, PhD, has thrived in academia for over thirty years. He continues to love teaching in addition to coaching recent PhD graduates as well as students writing their dissertations. Learn more about his dissertation coaching and career coaching services. Book a Free Consultation with Steve Tippins
Related Posts

Dissertation
Dissertation memes.
Sometimes you can’t dissertate anymore and you just need to meme. Don’t worry, I’ve got you. Here are some of my favorite dissertation memes that I’ve seen lately. My Favorite Dissertation Memes For when you Read more…

Surviving Post Dissertation Stress Disorder
The process of earning a doctorate can be long and stressful – and for some people, it can even be traumatic. This may be hard for those who haven’t been through a doctoral program to Read more…

PhD by Publication
PhD by publication, also known as “PhD by portfolio” or “PhD by published works,” is a relatively new route to completing your dissertation requirements for your doctoral degree. In the traditional dissertation route, you have Read more…

Defending Your Dissertation: A Guide

Written by Luke Wink-Moran | Photo by insta_photos
Dissertation defenses are daunting, and no wonder; it’s not a “dissertation discussion,” or a “dissertation dialogue.” The name alone implies that the dissertation you’ve spent the last x number of years working on is subject to attack. And if you don’t feel trepidation for semantic reasons, you might be nervous because you don’t know what to expect. Our imaginations are great at making The Unknown scarier than reality. The good news is that you’ll find in this newsletter article experts who can shed light on what dissertations defenses are really like, and what you can do to prepare for them.
The first thing you should know is that your defense has already begun. It started the minute you began working on your dissertation— maybe even in some of the classes you took beforehand that helped you formulate your ideas. This, according to Dr. Celeste Atkins, is why it’s so important to identify a good mentor early in graduate school.
“To me,” noted Dr. Atkins, who wrote her dissertation on how sociology faculty from traditionally marginalized backgrounds teach about privilege and inequality, “the most important part of the doctoral journey was finding an advisor who understood and supported what I wanted from my education and who was willing to challenge me and push me, while not delaying me. I would encourage future PhDs to really take the time to get to know the faculty before choosing an advisor and to make sure that the members of their committee work well together.”
Your advisor will be the one who helps you refine arguments and strengthen your work so that by the time it reaches your dissertation committee, it’s ready. Next comes the writing process, which many students have said was the hardest part of their PhD. I’ve included this section on the writing process because this is where you’ll create all the material you’ll present during your defense, so it’s important to navigate it successfully. The writing process is intellectually grueling, it eats time and energy, and it’s where many students find themselves paddling frantically to avoid languishing in the “All-But-Dissertation” doldrums. The writing process is also likely to encroach on other parts of your life. For instance, Dr. Cynthia Trejo wrote her dissertation on college preparation for Latin American students while caring for a twelve-year-old, two adult children, and her aging parents—in the middle of a pandemic. When I asked Dr. Trejo how she did this, she replied:
“I don’t take the privilege of education for granted. My son knew I got up at 4:00 a.m. every morning, even on weekends, even on holidays; and it’s a blessing that he’s seen that work ethic and that dedication and the end result.”
Importantly, Dr. Trejo also exercised regularly and joined several online writing groups at UArizona. She mobilized her support network— her partner, parents, and even friends from high school to help care for her son.
The challenges you face during the writing process can vary by discipline. Jessika Iwanski is an MD/PhD student who in 2022 defended her dissertation on genetic mutations in sarcomeric proteins that lead to severe, neonatal dilated cardiomyopathy. She described her writing experience as “an intricate process of balancing many things at once with a deadline (defense day) that seems to be creeping up faster and faster— finishing up experiments, drafting the dissertation, preparing your presentation, filling out all the necessary documents for your defense and also, for MD/PhD students, beginning to reintegrate into the clinical world (reviewing your clinical knowledge and skill sets)!”
But no matter what your unique challenges are, writing a dissertation can take a toll on your mental health. Almost every student I spoke with said they saw a therapist and found their sessions enormously helpful. They also looked to the people in their lives for support. Dr. Betsy Labiner, who wrote her dissertation on Interiority, Truth, and Violence in Early Modern Drama, recommended, “Keep your loved ones close! This is so hard – the dissertation lends itself to isolation, especially in the final stages. Plus, a huge number of your family and friends simply won’t understand what you’re going through. But they love you and want to help and are great for getting you out of your head and into a space where you can enjoy life even when you feel like your dissertation is a flaming heap of trash.”
While you might sometimes feel like your dissertation is a flaming heap of trash, remember: a) no it’s not, you brilliant scholar, and b) the best dissertations aren’t necessarily perfect dissertations. According to Dr. Trejo, “The best dissertation is a done dissertation.” So don’t get hung up on perfecting every detail of your work. Think of your dissertation as a long-form assignment that you need to finish in order to move onto the next stage of your career. Many students continue revising after graduation and submit their work for publication or other professional objectives.
When you do finish writing your dissertation, it’s time to schedule your defense and invite friends and family to the part of the exam that’s open to the public. When that moment comes, how do you prepare to present your work and field questions about it?
“I reread my dissertation in full in one sitting,” said Dr. Labiner. “During all my time writing it, I’d never read more than one complete chapter at a time! It was a huge confidence boost to read my work in full and realize that I had produced a compelling, engaging, original argument.”
There are many other ways to prepare: create presentation slides and practice presenting them to friends or alone; think of questions you might be asked and answer them; think about what you want to wear or where you might want to sit (if you’re presenting on Zoom) that might give you a confidence boost. Iwanksi practiced presenting with her mentor and reviewed current papers to anticipate what questions her committee might ask. If you want to really get in the zone, you can emulate Dr. Labiner and do a full dress rehearsal on Zoom the day before your defense.
But no matter what you do, you’ll still be nervous:
“I had a sense of the logistics, the timing, and so on, but I didn’t really have clear expectations outside of the structure. It was a sort of nebulous three hours in which I expected to be nauseatingly terrified,” recalled Dr. Labiner.
“I expected it to be terrifying, with lots of difficult questions and constructive criticism/comments given,” agreed Iwanski.
“I expected it to be very scary,” said Dr. Trejo.
“I expected it to be like I was on trial, and I’d have to defend myself and prove I deserved a PhD,” said Dr Atkins.
And, eventually, inexorably, it will be time to present.
“It was actually very enjoyable” said Iwanski. “It was more of a celebration of years of work put into this project—not only by me but by my mentor, colleagues, lab members and collaborators! I felt very supported by all my committee members and, rather than it being a rapid fire of questions, it was more of a scientific discussion amongst colleagues who are passionate about heart disease and muscle biology.”
“I was anxious right when I logged on to the Zoom call for it,” said Dr. Labiner, “but I was blown away by the number of family and friends that showed up to support me. I had invited a lot of people who I didn’t at all think would come, but every single person I invited was there! Having about 40 guests – many of them joining from different states and several from different countries! – made me feel so loved and celebrated that my nerves were steadied very quickly. It also helped me go into ‘teaching mode’ about my work, so it felt like getting to lead a seminar on my most favorite literature.”
“In reality, my dissertation defense was similar to presenting at an academic conference,” said Dr. Atkins. “I went over my research in a practiced and organized way, and I fielded questions from the audience.
“It was a celebration and an important benchmark for me,” said Dr. Trejo. “It was a pretty happy day. Like the punctuation at the end of your sentence: this sentence is done; this journey is done. You can start the next sentence.”
If you want to learn more about dissertations in your own discipline, don’t hesitate to reach out to graduates from your program and ask them about their experiences. If you’d like to avail yourself of some of the resources that helped students in this article while they wrote and defended their dissertations, check out these links:
The Graduate Writing Lab
https://thinktank.arizona.edu/writing-center/graduate-writing-lab
The Writing Skills Improvement Program
https://wsip.arizona.edu
Campus Health Counseling and Psych Services
https://caps.arizona.edu
https://www.scribbr.com/
Preparing For Your Dissertation Defense
13 Key Questions To Expect In The Viva Voce
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) & David Phair (PhD) . Reviewed By: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | June 2021
Preparing for your dissertation or thesis defense (also called a “viva voce”) is a formidable task . All your hard work over the years leads you to this one point, and you’ll need to defend yourself against some of the most experienced researchers you’ve encountered so far.
It’s natural to feel a little nervous.
In this post, we’ll cover some of the most important questions you should be able to answer in your viva voce, whether it’s for a Masters or PhD degree. Naturally, they might not arise in exactly the same form (some may not come up at all), but if you can answer these questions well, it means you’re in a good position to tackle your oral defense.

Viva Voce Prep: 13 Essential Questions
- What is your study about and why did you choose to research this in particular?
- How did your research questions evolve during the research process?
- How did you decide on which sources to include in your literature review?
- How did you design your study and why did you take this approach?
- How generalisable and valid are the findings?
- What were the main shortcomings and limitations created by your research design?
- How did your findings relate to the existing literature?
- What were your key findings in relation to the research questions?
- Were there any findings that surprised you?
- What biases may exist in your research?
- How can your findings be put into practice?
- How has your research contributed to current thinking in the field?
- If you could redo your research, how would you alter your approach?
#1: What is your study about and why did you choose to research this in particular?
This question, a classic party starter, is pretty straightforward.
What the dissertation or thesis committee is assessing here is your ability to clearly articulate your research aims, objectives and research questions in a concise manner. Concise is the keyword here – you need to clearly explain your research topic without rambling on for a half-hour. Don’t feel the need to go into the weeds here – you’ll have many opportunities to unpack the details later on.
In the second half of the question, they’re looking for a brief explanation of the justification of your research. In other words, why was this particular set of research aims, objectives and questions worth addressing? To address this question well in your oral defense, you need to make it clear what gap existed within the research and why that gap was worth filling.
#2: How did your research questions evolve during the research process?
Good research generally follows a long and winding path . It’s seldom a straight line (unless you got really lucky). What they’re assessing here is your ability to follow that path and let the research process unfold.
Specifically, they’ll want to hear about the impact that the literature review process had on you in terms of shaping the research aims, objectives and research questions . For example, you may have started with a certain set of aims, but then as you immersed yourself in the literature, you may have changed direction. Similarly, your initial fieldwork findings may have turned out some unexpected data that drove you to adjust or expand on your initial research questions.
Long story short – a good defense involves clearly describing your research journey , including all the twists and turns. Adjusting your direction based on findings in the literature or the fieldwork shows that you’re responsive , which is essential for high-quality research.

#3: How did you decide on which sources to include in your literature review?
A comprehensive literature review is the foundation of any high-quality piece of research. With this question, your dissertation or thesis committee are trying to assess which quality criteria and approach you used to select the sources for your literature review.
Typically, good research draws on both the seminal work in the respective field and more recent sources . In other words, a combination of the older landmark studies and pivotal work, along with up-to-date sources that build on to those older studies. This combination ensures that the study has a rock-solid foundation but is not out of date.
So, make sure that your study draws on a mix of both the “classics” and new kids on the block, and take note of any major evolutions in the literature that you can use as an example when asked this question in your viva voce.
#4: How did you design your study and why did you take this approach?
This is a classic methodological question that you can almost certainly expect in some or other shape.
What they’re looking for here is a clear articulation of the research design and methodology, as well as a strong justification of each choice . So, you need to be able to walk through each methodological choice and clearly explain both what you did and why you did it. The why is particularly important – you need to be able to justify each choice you made by clearly linking your design back to your research aims, objectives and research questions, while also taking into account practical constraints.
To ensure you cover every base, check out our research methodology vlog post , as well as our post covering the Research Onion .

#5: How generalizable and valid are the findings?
This question is aimed at specifically digging into your understanding of the sample and how that relates to the population, as well as potential validity issues in your methodology.
To answer question this well, you’ll need to critically assess your sample and findings and consider if they truly apply to the entire population, as well as whether they assessed what they set out to. Note that there are two components here – generalizability and validity . Generalizability is about how well the sample represents the population. Validity is about how accurately you’ve measured what you intended to measure .
To ace this part of your dissertation defense, make sure that you’re very familiar with the concepts of generalizability , validity and reliability , and how these apply to your research. Remember, you don’t need to achieve perfection – you just need to be aware of the strengths and weaknesses of your research (and how the weaknesses could be improved upon).
Need a helping hand?
#6: What were the main shortcomings and limitations created by your research design?
This question picks up where the last one left off.
As I mentioned, it’s perfectly natural that your research will have shortcomings and limitations as a result of your chosen design and methodology. No piece of research is flawless. Therefore, a good dissertation defense is not about arguing that your work is perfect, but rather it’s about clearly articulating the strengths and weaknesses of your approach.
To address this question well, you need to think critically about all of the potential weaknesses your design may have, as well as potential responses to these (which could be adopted in future research) to ensure you’re well prepared for this question. For a list of common methodological limitations, check out our video about research limitations here .
#7: How did your findings relate to the existing literature?
This common dissertation defense question links directly to your discussion chapter , where you would have presented and discussed the findings in relation to your literature review.
What your dissertation or thesis committee is assessing here is your ability to compare your study’s findings to the findings of existing research . Specifically, you need to discuss which findings aligned with existing research and which findings did not. For those findings that contrasted against existing research, you should also explain what you believe to be the reasons for this.
As with many questions in a viva voce, it’s both the what and the why that matter here. So, you need to think deeply about what the underlying reasons may be for both the similarities and differences between your findings and those of similar studies.

#8: What were your key findings in relation to the research questions?
This question is similar to the last one in that it too focuses on your research findings. However, here the focus is specifically on the findings that directly relate to your research questions (as opposed to findings in general).
So, a good way to prepare for this question is to step back and revisit your research questions . Ask yourself the following:
- What exactly were you asking in those questions, and what did your research uncover concerning them?
- Which questions were well answered by your study and which ones were lacking?
- Why were they lacking and what more could be done to address this in future research?
Conquering this part dissertation defense requires that you focus squarely on the research questions. Your study will have provided many findings (hopefully!), and not all of these will link directly to the research questions. Therefore, you need to clear your mind of all of the fascinating side paths your study may have lead you down and regain a clear focus on the research questions .
#9: Were there any findings that surprised you?
This question is two-pronged.
First, you should discuss the surprising findings that were directly related to the original research questions . Going into your research, you likely had some expectations in terms of what you would find, so this is your opportunity to discuss the outcomes that emerged as contrary to what you initially expected. You’ll also want to think about what the reasons for these contrasts may be.
Second, you should discuss the findings that weren’t directly related to the research questions, but that emerged from the data set . You may have a few or you may have none – although generally there are a handful of interesting musings that you can glean from the data set. Again, make sure you can articulate why you find these interesting and what it means for future research in the area.
What the committee is looking for in this type of question is your ability to interpret the findings holistically and comprehensively , and to respond to unexpected data. So, take the time to zoom out and reflect on your findings thoroughly.

#10: What biases may exist in your research?
Biases… we all have them.
For this question, you’ll need to think about potential biases in your research , in the data itself but also in your interpretation of the data. With this question, your committee is assessing whether you have considered your own potential biases and the biases inherent in your analysis approach (i.e. your methodology). So, think carefully about these research biases and be ready to explain how these may exist in your study.
In an oral defense, this question is often followed up with a question on how the biases were mitigated or could be mitigated in future research. So, give some thought not just to what biases may exist, but also the mitigation measures (in your own study and for future research).
#11: How can your findings be put into practice?
Another classic question in the typical viva voce.
With this question, your committee is assessing your ability to bring your findings back down to earth and demonstrate their practical value and application. Importantly, this question is not about the contribution to academia or the overall field of research (we’ll get to that next) – it is specifically asking about how this newly created knowledge can be used in the real world.
Naturally, the actionability of your findings will vary depending on the nature of your research topic. Some studies will produce many action points and some won’t. If you’re researching marketing strategies within an industry, for example, you should be able to make some very specific recommendations for marketing practitioners in that industry.
To help you flesh out points for this question, look back at your original justification for the research (i.e. in your introduction and literature review chapters). What were the driving forces that led you to research your specific topic? That justification should help you identify ways in which your findings can be put into practice.
#12: How has your research contributed to current thinking in the field?
While the previous question was aimed at practical contribution, this question is aimed at theoretical contribution . In other words, what is the significance of your study within the current body of research? How does it fit into the existing research and what does it add to it?
This question is often asked by a field specialist and is used to assess whether you’re able to place your findings into the research field to critically convey what your research contributed. This argument needs to be well justified – in other words, you can’t just discuss what your research contributed, you need to also back each proposition up with a strong why .
To answer this question well, you need to humbly consider the quality and impact of your work and to be realistic in your response. You don’t want to come across as arrogant (“my work is groundbreaking”), nor do you want to undersell the impact of your work. So, it’s important to strike the right balance between realistic and pessimistic .
This question also opens the door to questions about potential future research . So, think about what future research opportunities your study has created and which of these you feel are of the highest priority.

#13: If you could redo your research, how would you alter your approach?
This question is often used to wrap up a viva voce as it brings the discussion full circle.
Here, your committee is again assessing your ability to clearly identify and articulate the limitations and shortcomings of your research, both in terms of research design and topic focus . Perhaps, in hindsight, it would have been better to use a different analysis method or data set. Perhaps the research questions should have leaned in a slightly different direction. And so on.
This question intends to assess whether you’re able to look at your work critically , assess where the weaknesses are and make recommendations for the future . This question often sets apart those who did the research purely because it was required, from those that genuinely engaged with their research. So, don’t hold back here – reflect on your entire research journey ask yourself how you’d do things differently if you were starting with a blank canvas today.
Recap: The 13 Key Dissertation Defense Questions
To recap, here are the 13 questions you need to be ready for to ace your dissertation or thesis oral defense:
As I mentioned, this list of dissertation defense questions is certainly not exhaustive – don’t assume that we’ve covered every possible question here. However, these questions are quite likely to come up in some shape or form in a typical dissertation or thesis defense, whether it’s for a Master’s degree, PhD or any other research degree. So, you should take the time to make sure you can answer them well.
If you need assistance preparing for your dissertation defense or viva voce, get in touch with us to discuss 1-on-1 coaching. We can critically review your research and identify potential issues and responses, as well as undertake a mock oral defense to prepare you for the pressures and stresses on the day.

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

12 Comments
Very interesting
Interesting. I appreciate!
Really appreciating
My field is International Trade
Interesting
This is a full course on defence. I was fabulously enlightened and I gained enough confidence for my upcoming Masters Defence.
There are many lessons to learn and the simplicity in presentationmakes thee reader say “YesI can”
This is so helping… it has Enlightened me on how to answer specific questions. I pray to make it through for my upcoming defense
Lovely to hear that 🙂
Really educative and beneficial
Interesting. On-point and elaborate. And comforting too! Thanks.
Thank you very much for the enlightening me, be blessed
Thankyou so much. I am planning to defend my thesis soon and I found this very useful
Very interesting and useful to all masters and PhD students
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

Dissertation Defense | Strategies & Tips

Introduction
The doctoral program, the dissertation stage, what is a dissertation defense, what is the structure of a dissertation defense, preparation for your dissertation defense, what happens after you defend your dissertation.
The dissertation is the centerpiece of a graduate student's career at the doctoral level. It is a demonstration of a doctoral student's ability to conduct and present research with the skills necessary to contribute to scientific knowledge. As a result, the dissertation defense (sometimes called a thesis defense in non-American contexts) is the main opportunity for doctoral students to demonstrate they can contribute to scholarly discussion.
Many graduate students think of the dissertation defense as a final examination or a job interview. It is often a key final step to complete the doctoral degree.

Graduate studies are the venue in which students build expertise in a particular field and focus area. There are different kinds of graduate degrees, but what separates the doctoral journey from all others at this level is one's ability to generate or discover new knowledge through research. Mastery of trivia or encyclopedic knowledge is far less important to doctoral studies than a systematic organization of that knowledge through established research methodologies .
Requirements for a doctoral degree will vary depending on the institution and the program and may include coursework, comprehensive examinations, research experience, and an established record of research publication . In most cases, however, graduate students complete a doctoral degree when they successfully defend their dissertation.
The culmination of a doctoral program is the graduate student's demonstration of their abilities to conduct and present research in academic work. Not only must students show their understanding of theories, methods, and argumentation necessary for contributing to scientific knowledge, they must also navigate the intricacies inherent to academic institutions in a way that shows that they can cohesively work with and engage scholars.
The dissertation represents this understanding and mastery of skills necessary to work in established academic contexts. The research in a dissertation is deemed credible and worthy of being considered scientific knowledge when a university approves it and adds it to its repository, which is made available to all of its members so they can, in turn, conduct research and generate knowledge. However, this approval comes after a lengthy process that involves assembling members of the academic community together to review and develop research.
To be sure, the main objective of dissertation research is to present new knowledge, but the manner in which students conduct that research should also illustrate their understanding of how to generate insights rigorously, ethically, and in collaboration with others. As a result, doctoral programs, while varying with each other on some level, share a number of core characteristics outlining a long-established process of facilitating dissertation research.
Dissertation committee
A dissertation requires an audience of knowledgeable academic scholars who can comment on and critique the research. A committee made up of faculty members internal or external to the student's university fulfills this role by guiding the research, providing feedback, and asking questions about the resulting dissertation. Is the research that the student has produced "state of the art"? Does it meet reasonable standards of research rigor and transparency? Will the research make a valuable contribution to future academic discussions or practical developments outside of the academy?
It's the job of dissertation committee members to help develop and critique the research. Through this process, graduate students can refine their research design and attain guidance on key theories and methodologies . In turn, committee members gain insight from fresh perspectives on the graduate student's research.
The main committee member is your dissertation chair, which might be your supervisor or a committee member who is most knowledgeable about the research you want to conduct for your dissertation. Beyond that, a good committee member is an established scholar who can provide useful insight about the research context, the issues or theories currently being discussed within the research context, and the methods used to further develop those theories.
Oftentimes, students rely on a faculty member whose classes they have taken to serve as committee members. Students might also identify potential external committee members in academic conferences or by asking for recommendations from their professors.
Dissertation proposal
Designing a robust and rigorous study often requires discussion among colleagues within academia so that research methods can be refined before all the data is collected and analyzed.
The proposal stage gives doctoral students a chance to gather preliminary feedback on their prospective research as well as an opportunity to practice their ability to defend their expertise in their chosen field and focus area. At the dissertation level, this aspect of an academic career is represented by the proposal.
The dissertation committee approves the study design as an indication that the dissertation research has potential. Think of the writing and presentation of the dissertation proposal as a practice run for the eventual defense, while the substance of the proposal, in many cases, becomes part of the final dissertation as it details the underlying theories and methodology for the study.
Dissertation research
While the proposal lays out the research design , the study itself is where you will collect and analyze all the data necessary for the findings and discussion sections of your dissertation. Needless to say, the theoretical developments and actionable insights will come from this part of the dissertation process.
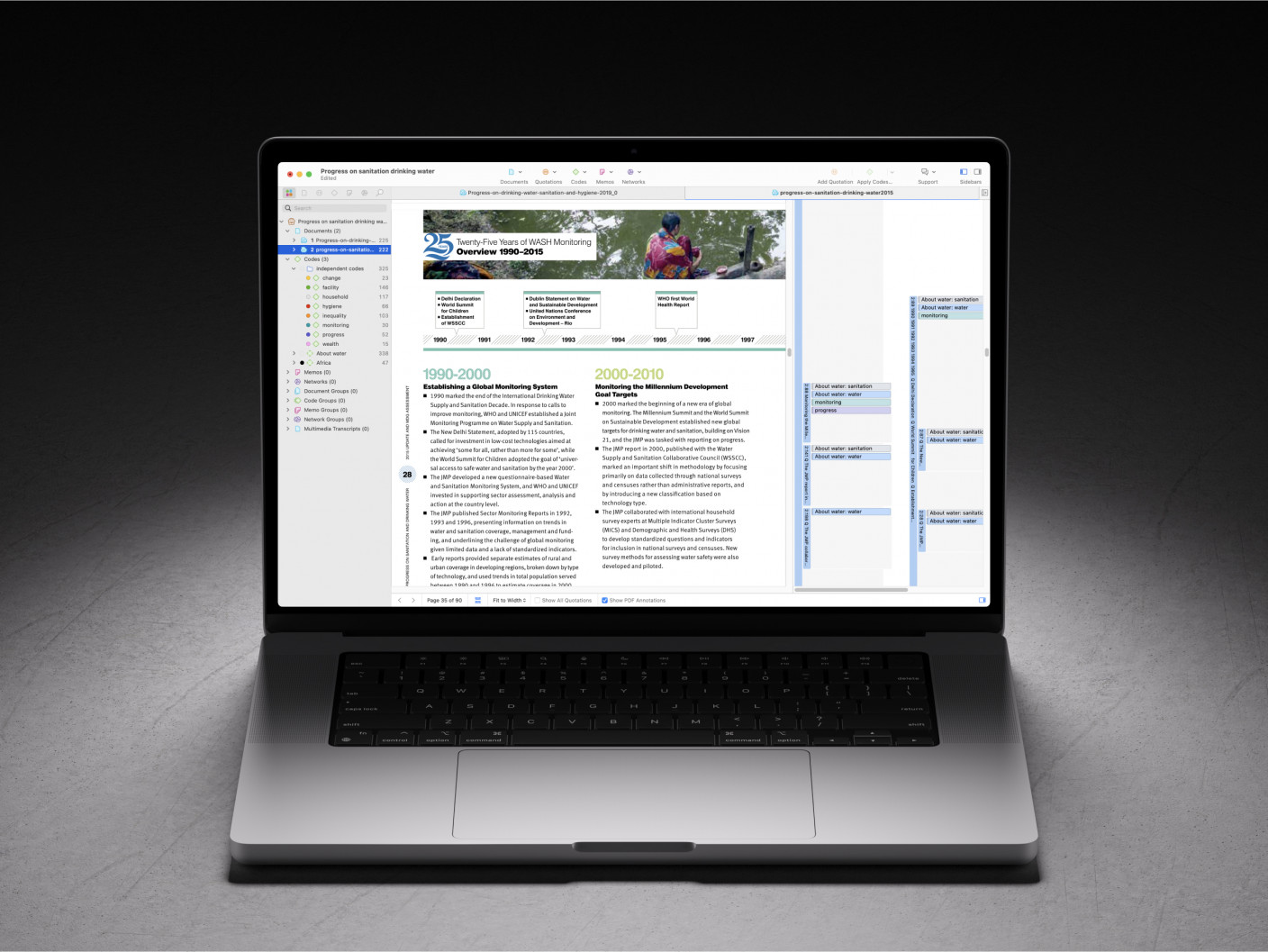
Plan, organize, and develop your research with ATLAS.ti
Powerful tools are there to accompany you at every stage of the research process. See how with a free trial.
The oral defense of your dissertation synthesizes every step of the research process you have undertaken for your research project. It's best to look at it like an opportunity to show off your expertise about the research in your field and, more importantly, your methodological process for developing your original research.
What is the role of a defense?
The defense is the main forum in which you share your research with the larger academic community. Some think of it like a job interview or a test where the committee members assess the worthiness of the research and the student who conducted it. Others consider a defense to be more of a coming out party, a critical event where the student is elevated from a novice scholar to an established expert in their chosen research field.
However it is interpreted, the dissertation defense is a critical event in a graduate student's career. In a successful defense, the doctoral candidate is no longer a newcomer but a scholar who understands the intricacies of academic research and can contribute to it in a substantive manner.
Is a dissertation defense just a formality?
If you are well-prepared and your research is robust and rigorous, you should have no problems passing your oral defense. That said, it is by no means "just" a formality. A graduate student who wants to demonstrate expertise should be prepared enough to anticipate and answer questions from the committee that might otherwise stump or confuse a layperson.
While defenses will differ depending by program and institution, there are a couple of common elements.
First, the doctoral candidate presents their research in a short presentation or lecture. While your committee is already familiar with your research, many defenses are open to the entire academic community who may be interested in your field but may not have the necessary context to understand your research. As a result, this presentation is vital to providing the fundamental knowledge necessary for later discussion.
That discussion, mainly moderated by your dissertation chair and involving all committee members, serves as the central portion of the defense. Committee members will direct questions to you to interrogate your research, but they will also discuss the research amongst themselves to build their own understanding of the key theories and insights.
In some programs, the audience will also have an opportunity to pose questions to the candidate toward the end of the defense. The dissertation committee wants to know if you can engage with outsiders who are less familiar with your research field. This part of the defense is a test of your ability to share scientific knowledge with the greater academic community.
When you get to this stage of the process, most of the preparation for your defense is already complete. That said, the defense is its own event as it is the sole opportunity for the dissertation committee to determine if your research is state of the art and advances scientific knowledge.
In many cases, a dissertation defense can last about two hours and typically follows a set order. It's important to know how to prepare for each part of a defense.
Preparing your dissertation
At this point, the dissertation should be as close to polished as you can make it, but keep in mind you may still receive substantive feedback from your committee members. With the exception of your dissertation chair, members of your committee likely will not deeply engage your research until the oral defense itself. Even so, you still need to present as complete a study as possible during your defense. The key to preparation is to be able to demonstrate a working knowledge of every step of the research process, from research design to how you contribute novel and interesting insights to your field. Successfully defending a dissertation means having a thorough understanding of every major aspect of your study and the surrounding scholarship.
Presenting your dissertation
The dissertation defense typically begins with the student presenting themselves and their research. In many cases, this presentation is similar to those found at conferences or workshops, where the presenter needs to demonstrate that they can showcase their research in a succinct and accessible manner. After all, the audience at a defense will often include members of the academic community who may have a general interest in the research but not a deep familiarity with the specifics of the research.
The presentation itself should be detailed enough to lay out the most important points of the research but within a reasonable amount of time. This presentation lays the groundwork for the ensuing discussion with the rest of the academic community. The dissertation committee or program will often prescribe a set time limit for this presentation; it would be a mistake not to consider this time limit when making your presentation. An overly lengthy presentation or a presenter who meanders with no clear direction will be less persuasive and will not garner the interest of the audience. More importantly, successful time management during the presentation leaves more time for your committee to more thoroughly engage with the research through questions and answers.
Fielding questions asked
Dissertation defense questions make up the primary part of the discussion. This is the main opportunity for members of your committee to point out the novel aspects of your research as well as critique any weak points that should be addressed in revisions to your dissertation.
Ultimately, a successful defense will result in lively discussion among dissertation committee members. A dissertation committee will often look highly on research that engages their thinking and expertise, meaning that novel insights will prove incredibly valuable to a defense.
You may get a question from a committee member to which you may not readily have an answer. After all, it's impossible to anticipate every possible question posed within two hours of scholarly discussion. In the case where a question is truly outside of your knowledge, it's important to acknowledge this and at least explain your thinking about how you would address the question to get a meaningful answer. In other words, it's not always about giving the "correct" answer to all questions asked but demonstrating your ability to reflect and engage in scholarly discussion around your research.
Keep in mind that the defense itself is not the end of the doctoral journey. More often than not, the dissertation committee will accept the dissertation on the condition that revisions will be made based on the committee members' feedback. Even the most successful defense will likely require the doctoral student to make revisions to their dissertation.
In many cases, revisions to the dissertation can be more challenging than the dissertation defense itself. Up until this point, your advisor or dissertation chair was likely the main source of feedback on your dissertation research. After your defense, you will have gained a great deal of rich feedback that you can constructively build on to further hone your dissertation as you move forward in publishing and sharing your research.
ATLAS.ti turns data into critical insights
Download a free trial to see how you can make the most of your qualitative data.

- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Prepare for Your Dissertation Defense

4-minute read
- 1st August 2023
After years of research and study, you’ve finally reached the grand finale of your PhD years: your dissertation defense. Since defending your dissertation is the culmination of all your hard work, it’s essential to do everything you can to prepare for it.
In this post, we’ll take you through how to ready yourself for your dissertation defense so you can focus on your accomplishments and excel during this crucial professional moment.
What is a Dissertation Defense?
The dissertation defense is the crowning moment of years of research – the final examination before a PhD student is awarded their doctoral degree.
During a dissertation defense, the student presents their research, methodology, findings, and conclusions to a committee of faculty members and experts in their field. The committee then engages in a question-and-answer session to assess the student’s understanding of the subject matter, the quality of their research, and their ability to defend their work under scrutiny.
Many PhD students consider it to be the defining moment of their academic career and their chance to prove their expertise in their chosen research field.
If all this sounds overwhelming – don’t worry. If you’re a PhD student, you’ll have plenty of time and opportunity to adequately prepare for your dissertation defense. Below are some strategies to help you get ready for this significant occasion in your career.
1. Know the Requirements
Familiarize yourself with your institution’s guidelines and requirements for the defense process. Understanding the format, time limit, and expectations for the presentation will help you to prepare your material and anticipate any issues.
2. Review Your Dissertation
Even if you think you know it inside and out, review your dissertation from beginning to end. It may have been some time since you’ve last read and considered certain portions of your research and findings. Consider what your committee might ask about your research questions , data analysis, and conclusions.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
3. Work on Starting Strong
To begin your defense on a strong note, work on creating a clear and engaging introduction. You can start by briefly outlining the purpose of your study, research questions, and methodology . Try to stay on topic and don’t veer off track by discussing unrelated or unnecessary information.
4. Practice Presenting
Practice your presentation skills by rehearsing your defense multiple times. Focus on clarity and pacing and try to stay within the allotted time limit. It also helps to record yourself so that you can see yourself from your audience’s point of view.
5. Practice Q&A Sessions
To build your confidence, enlist friends and colleagues to conduct mock question-and-answer sessions. When practicing, remember to pause before answering questions you’re unsure of. It’s better to take your time delivering a response than it is to give an inaccurate or incorrect answer.
6. Seek Feedback
Find out if your institution offers mock defense sessions where peers or mentors play the role of the committee, ask you questions, and give feedback . You can also have colleagues, mentors, or advisors review your presentation and offer practical feedback.
7. Create Visual Aids
Think about any visual aids , such as slides, you may want to use to illustrate your defense and prepare them in advance. Be sure to check that your university allows visuals or images and that they enhance, rather than overwhelm, your presentation.
8. Stay Calm and Confident
It’s natural to feel nervous but try to stay calm and composed during your defense. Take deep breaths and remind yourself of the expertise you’ve gained through the experience of writing your dissertation.
Expert Proofreading Services
The best way to prepare for your dissertation defense is to have your dissertation professionally proofread. Our editing experts have extensive experience with a wide variety of academic subjects and topics and can help ensure your dissertation is ready for presentation. Send in a free sample of 500 words or less and get started today.
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...
How to Ace Slack Messaging for Contractors and Freelancers
Effective professional communication is an important skill for contractors and freelancers navigating remote work environments....
3-minute read
How to Insert a Text Box in a Google Doc
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
- How It Works
- PhD thesis writing
- Master thesis writing
- Bachelor thesis writing
- Dissertation writing service
- Dissertation abstract writing
- Thesis proposal writing
- Thesis editing service
- Thesis proofreading service
- Thesis formatting service
- Coursework writing service
- Research paper writing service
- Architecture thesis writing
- Computer science thesis writing
- Engineering thesis writing
- History thesis writing
- MBA thesis writing
- Nursing dissertation writing
- Psychology dissertation writing
- Sociology thesis writing
- Statistics dissertation writing
- Buy dissertation online
- Write my dissertation
- Cheap thesis
- Cheap dissertation
- Custom dissertation
- Dissertation help
- Pay for thesis
- Pay for dissertation
- Senior thesis
- Write my thesis
Dissertation Defense: Steps To Follow To Succeed

A dissertation defense is arguably one of the most important milestones in every student’s career. While it signals that your tenure as a student is soon about to close, it validates all your efforts towards your thesis.
Being cautious about including all the necessary details is very important to successfully complete your dissertation proposal defense. This article tells you everything that you need to know about writing a defense that can add great credibility to you as a student.

What is A Dissertation Defense?
The first thing that you need to learn is what is a dissertation defense and what is its purpose. In simple terms, it is a presentation made by a student to defend all the ideas and views that are presented in a dissertation.
The presenter must include details like what is the reason for choosing specific research methods, the theory that has been selected for the paper, and other such points. This presentation is made before an audience that comprises of the university committee, professors and even fellow-students. It is met with questions and answers that gives the student an opportunity to provide more clarity on the dissertation in order to convince the committee to approve it.
Stages of a Dissertation Defense
One of the most important dissertation defense tips provided by several professors is to breakdown the process into three steps:
- Preparation : This stage involves collection of all the necessary information that must be included in the defense dissertation and making all the arrangements for the actual meeting.
- The defense meeting : This is where you decide how you will present the defense. The actual meeting is hugely reliant on the performance, body language and the confidence in your oral defense.
- After the defense meeting : This stage, also known as the follow up, requires you to make the necessary revisions suggested by the university committee. You can even provide bound copies of the whole dissertation to distribute among different members of your departments. In the follow up stage, one must also think about expense that are related to publishing the Ph.D. dissertation defense as well as printing additional copies of the manuscript, if required.
How Long is a Dissertation Defense?
The first thing that a student should know is how long does a dissertation defense last? The length has to be carefully calculated to make the impact that you want. One of the most important steps in the dissertation preparation is to understand how much time each department allocates to the closing oral defense. When you plan in the early stages of your dissertation itself, you can write it in a manner that allows you to defend it in the allocated time.
Usually these meetings including the presentation, the oral defense and the question and answer session last for about two hours. In most cases, these two hours also encompass the time needed by members of the committee to deliberate.
How to Prepare for the Dissertation Defense
Now that you know how long is a dissertation defense, the next step is to prepare well enough to make your presentation impressive.
Here are some tips on how to prepare for a dissertation defense:
- Watch other students in action to learn about different presentation styles. You can attend defenses of different colleagues in your department as well as other departments in your university.
- Get all the details about the deadlines and the rules of your college or university about scheduling your defense.
- Scheduling is also a very important part of your preparation. It is important to note that members of the committee and University chairs need to make time for these defences in a very packed schedule. Coordinate the date, venue and time of your defense as early as possible.
- Prepare a manuscript adhering to the necessary formatting rules. Review your manuscript thoroughly before you hand it in. During your PH.D, your faculty will also assist you with the defense. For this, they must have a crisp and polished copy of your manuscript.
- Most colleges have the facility for a pre-defense meeting. This is the best opportunity to sort out any concerns that you may have about the actual meeting. It is a good idea to ask the chairs what types of questions may be put forward and if there are any problems with the defense that need to be resolved. When you prepare for a pre-defense meeting, think of it as the final one and give it your all.
- Put together all the material that you need for the defense. A detailed, yet to-the-point presentation must be prepared.
- The final stage of preparation is practicing your presentation over and over again. It is not just the presentation but also the approach towards the questions that you must practice.
Tips To Nail Your Actual Meeting
With these tips you will be one step closer towards a successful defense that will help your dissertation pass and be approved:
- All meetings should begin by addressing the chair. Make sure you thank all the committee members and the advisors for the efforts that they have put it. This gives you a professional start to the presentation.
- The presentation should cover the following subjects in brief:
- The research topic
- Literature review
- The methods used for analysis
- The primary findings of the research
- Recommendations of additional research on the subject in the focus.
- Do not get rattled by any discussions among the chairs. They will deliberate on any disagreements or topics of interest. This is a part of the process and is not a reflection of the presentation itself.
- There are two questions that are commonly asked that you should be prepared for. This includes the weaknesses of the dissertation and the research plans that you have made post-dissertation.
- Use subtle gestures when you are talking. Do not overuse your hands when doing so. The whole meeting including the question and answer session should have a very formal appeal.
- The tone of your voice must be assertive without making it seem like you are trying to hard. Be clear and enunciate when you speak.
Once the questions have been answered, the committee will leave the room. Then, after the deliberation, you will be informed if your dissertation has passed or not.
For affordable thesis writing assistance , get in touch our team today. The pricing is cheap but students can be assured of top notch quality in all our final products.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Comment * Error message
Name * Error message
Email * Error message
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
As Putin continues killing civilians, bombing kindergartens, and threatening WWIII, Ukraine fights for the world's peaceful future.
Ukraine Live Updates

PhD Dissertation Defense Slides Design: Start
- Tips for designing the slides
- Presentation checklist
- Example slides
- Additional Resources
Purpose of the Guide
This guide was created to help ph.d. students in engineering fields to design dissertation defense presentations. the guide provides 1) tips on how to effectively communicate research, and 2) full presentation examples from ph.d. graduates. the tips on designing effective slides are not restricted to dissertation defense presentations; they can be used in designing other types of presentations such as conference talks, qualification and proposal exams, and technical seminars., the tips and examples are used to help students to design effective presentation. the technical contents in all examples are subject to copyright, please do not replicate. , if you need help in designing your presentation, please contact julie chen ([email protected]) for individual consultation. .
- Example Slides Repository
- Defense slides examples Link to examples dissertation defense slides.
Useful Links
- CIT Thesis and dissertation standards
- Dissertations and Theses @ Carnegie Mellon This link opens in a new window Covers 1920-present. Full text of some dissertations may be available 1997-present. Citations and abstracts of dissertations and theses CMU graduate students have published through UMI Dissertation Publishing. In addition to citations and abstracts, the service provides free access to 24 page previews and the full text in PDF format, when available. In most cases, this will be works published in 1997 forward.
- Communicate your research data Data visualization is very important in communicating your data effectively. Check out these do's and don'ts for designing figures.
Power Point Template and other Resources
- CEE Powerpoint Slide Presentation Template 1
- CEE Powerpoint Slide Presentation Template 2
Source: CEE Department Resources https://www.cmu.edu/cee/resources/index.html
- CMU Powerpoint Slide Template
Source: CMU Marketing and Communications
https://www.cmu.edu/marcom/brand-standards/downloads/index.html
- Use of CMU logos, marks, and Unitmarks
Email me for questions and schedule an appointment

Top 7 tips for your defense presentation
1. show why your study is important, remember, your audience is your committee members, researchers in other fields, and even the general public. you want to convince all of them why you deserve a ph.d. degree. you need to talk about why your study is important to the world. in the engineering field, you also need to talk about how your study is useful. try to discuss why current practice is problematic or not good enough, what needs to be solved, and what the potential benefits will be. , see how dr. posen and dr. malings explained the importance of their studies..
- Carl Malings Defense Slides with Notes
- I. Daniel Posen Defense Slides with Notes
2. Emphasize YOUR contribution
Having a ph.d. means that you have made some novel contributions to the grand field. this is about you and your research. you need to keep emphasizing your contributions throughout your presentation. after talking about what needs to be solved, try to focus on emphasizing the novelty of your work. what problems can be solved using your research outcomes what breakthroughs have you made to the field why are your methods and outcomes outstanding you need to incorporate answers to these questions in your presentation. , be clear what your contributions are in the introduction section; separate what was done by others and what was done by you. , 3. connect your projects into a whole piece of work, you might have been doing multiple projects that are not strongly connected. to figure out how to connect them into a whole piece, use visualizations such as flow charts to convince your audience. the two slides below are two examples. in the first slide, which was presented in the introduction section, the presenter used a flow diagram to show the connection between the three projects. in the second slide, the presenter used key figures and a unique color for each project to show the connection..

- Xiaoju Chen Defense Slides with Notes
4. Tell a good story
The committee members do not necessarily have the same background knowledge as you. plus, there could be researchers from other fields and even the general public in the room. you want to make sure all of your audience can understand as much as possible. focus on the big picture rather than technical details; make sure you use simple language to explain your methods and results. your committee has read your dissertation before your defense, but others have not. , dr. cook and dr. velibeyoglu did a good job explaining their research to everyone. the introduction sessions in their presentations are well designed for this purpose. .
- Laren M. Cook Defense Slides with Notes
- Irem Velibeyoglu Defense with Notes
5. Transition, transition, transition
Use transition slides to connect projects , it's a long presentation with different research projects. you want to use some sort of transition to remind your audience what you have been talking about and what is next. you may use a slide that is designed for this purpose throughout your presentation. , below are two examples. these slides were presented after the introduction section. the presenters used the same slides and highlighted the items for project one to indicate that they were moving on to the first project. throughout the presentation, they used these slides and highlighted different sections to indicate how these projects fit into the whole dissertation. .

You can also use some other indications on your slides, but remember not to make your slides too busy. Below are two examples. In the first example, the presenter used chapter numbers to indicate what he was talking about. In the second example, the presenter used a progress bar with keywords for each chapter as the indicator.

Use transition sentences to connect slides
Remember transition sentences are also important; use them to summarize what you have said and tell your audience what they will expect next. if you keep forgetting the transition sentence, write a note on your presentation. you can either write down a full sentence of what you want to say or some keywords., 6. be brief, put details in backup slides , you won't have time to explain all of the details. if your defense presentation is scheduled for 45 minutes, you can only spend around 10 minutes for each project - that's shorter than a normal research conference presentation focus on the big picture and leave details behind. you can put the details in your backup slides, so you might find them useful when your committee (and other members of the audience) ask questions regarding these details., 7. show your presentation to your advisor and colleagues, make sure to ask your advisor(s) for their comments. they might have a different view on what should be emphasized and what should be elaborated. , you also want to practice at least once in front of your colleagues. they can be your lab mates, people who work in your research group, and/or your friends. they do not have to be experts in your field. ask them to give you some feedback - their comments can be extremely helpful to improve your presentation. , below are some other tips and resources to design your defense presentation. .
- Tips for designing your defense presentation
How important is your presentation, and cookies?

- Next: Tips for designing the slides >>
- Last Updated: Jan 9, 2024 11:18 AM
- URL: https://guides.library.cmu.edu/c.php?g=883178

13 Tips to Prepare for Your PhD Dissertation Defense
How well do you know your project? Years of experiments, analysis of results, and tons of literature study, leads you to how well you know your research study. And, PhD dissertation defense is a finale to your PhD years. Often, researchers question how to excel at their thesis defense and spend countless hours on it. Days, weeks, months, and probably years of practice to complete your doctorate, needs to surpass the dissertation defense hurdle.
In this article, we will discuss details of how to excel at PhD dissertation defense and list down some interesting tips to prepare for your thesis defense.
Table of Contents
What Is Dissertation Defense?
Dissertation defense or Thesis defense is an opportunity to defend your research study amidst the academic professionals who will evaluate of your academic work. While a thesis defense can sometimes be like a cross-examination session, but in reality you need not fear the thesis defense process and be well prepared.
Source: https://www.youtube.com/c/JamesHaytonPhDacademy
What are the expectations of committee members.
Choosing the dissertation committee is one of the most important decision for a research student. However, putting your dissertation committee becomes easier once you understand the expectations of committee members.
The basic function of your dissertation committee is to guide you through the process of proposing, writing, and revising your dissertation. Moreover, the committee members serve as mentors, giving constructive feedback on your writing and research, also guiding your revision efforts.
The dissertation committee is usually formed once the academic coursework is completed. Furthermore, by the time you begin your dissertation research, you get acquainted to the faculty members who will serve on your dissertation committee. Ultimately, who serves on your dissertation committee depends upon you.
Some universities allow an outside expert (a former professor or academic mentor) to serve on your committee. It is advisable to choose a faculty member who knows you and your research work.
How to Choose a Dissertation Committee Member?
- Avoid popular and eminent faculty member
- Choose the one you know very well and can approach whenever you need them
- A faculty member whom you can learn from is apt.
- Members of the committee can be your future mentors, co-authors, and research collaborators. Choose them keeping your future in mind.
How to Prepare for Dissertation Defense?

1. Start Your Preparations Early
Thesis defense is not a 3 or 6 months’ exercise. Don’t wait until you have completed all your research objectives. Start your preparation well in advance, and make sure you know all the intricacies of your thesis and reasons to all the research experiments you conducted.
2. Attend Presentations by Other Candidates
Look out for open dissertation presentations at your university. In fact, you can attend open dissertation presentations at other universities too. Firstly, this will help you realize how thesis defense is not a scary process. Secondly, you will get the tricks and hacks on how other researchers are defending their thesis. Finally, you will understand why dissertation defense is necessary for the university, as well as the scientific community.
3. Take Enough Time to Prepare the Slides
Dissertation defense process harder than submitting your thesis well before the deadline. Ideally, you could start preparing the slides after finalizing your thesis. Spend more time in preparing the slides. Make sure you got the right data on the slides and rephrase your inferences, to create a logical flow to your presentation.
4. Structure the Presentation
Do not be haphazard in designing your presentation. Take time to create a good structured presentation. Furthermore, create high-quality slides which impresses the committee members. Make slides that hold your audience’s attention. Keep the presentation thorough and accurate, and use smart art to create better slides.
5. Practice Breathing Techniques
Watch a few TED talk videos and you will notice that speakers and orators are very fluent at their speech. In fact, you will not notice them taking a breath or falling short of breath. The only reason behind such effortless oratory skill is practice — practice in breathing technique.
Moreover, every speaker knows how to control their breath. Long and steady breaths are crucial. Pay attention to your breathing and slow it down. All you need I some practice prior to this moment.
6. Create an Impactful Introduction
The audience expects a lot from you. So your opening statement should enthrall the audience. Furthermore, your thesis should create an impact on the members; they should be thrilled by your thesis and the way you expose it.
The introduction answers most important questions, and most important of all “Is this presentation worth the time?” Therefore, it is important to make a good first impression , because the first few minutes sets the tone for your entire presentation.
7. Maintain Your Own List of Questions
While preparing for the presentation, make a note of all the questions that you ask yourself. Try to approach all the questions from a reader’s point of view. You could pretend like you do not know the topic and think of questions that could help you know the topic much better.
The list of questions will prepare you for the questions the members may pose while trying to understand your research. Attending other candidates’ open discussion will also help you assume the dissertation defense questions.
8. Practice Speech and Body Language
After successfully preparing your slides and practicing, you could start focusing on how you look while presenting your thesis. This exercise is not for your appearance but to know your body language and relax if need be.
Pay attention to your body language. Stand with your back straight, but relax your shoulders. The correct posture will give you the feel of self-confidence. So, observe yourself in the mirror and pay attention to movements you make.
9. Give Mock Presentation
Giving a trial defense in advance is a good practice. The most important factor for the mock defense is its similarity to your real defense, so that you get the experience that prepares for the actual defense.
10. Learn How to Handle Mistakes
Everyone makes mistakes. However, it is important to carry on. Do not let the mistakes affect your thesis defense. Take a deep breath and move on to the next point.
11. Do Not Run Through the Presentation
If you are nervous, you would want to end the presentation as soon as possible. However, this situation will give rise to anxiety and you will speak too fast, skipping the essential details. Eventually, creating a fiasco of your dissertation defense .
12. Get Plenty of Rest
Out of the dissertation defense preparation points, this one is extremely important. Obviously, sleeping a day before your big event is hard, but you have to focus and go to bed early, with the clear intentions of getting the rest you deserve.
13. Visualize Yourself Defending Your Thesis
This simple exercise creates an immense impact on your self-confidence. All you have to do is visualize yourself giving a successful presentation each evening before going to sleep. Everyday till the day of your thesis defense, see yourself standing in front of the audience and going from one point to another.
This exercise takes a lot of commitment and persistence, but the results in the end are worth it. Visualization makes you see yourself doing the scary thing of defending your thesis.
If you have taken all these points into consideration, you are ready for your big day. You have worked relentlessly for your PhD degree , and you will definitely give your best in this final step.
Have you completed your thesis defense? How did you prepare for it and how was your experience throughout your dissertation defense ? Do write to us or comment below.
The tips are very useful.I will recomend it to our students.
Excellent. As a therapist trying to help a parent of a candidate, I am very impressed and thankful your concise, clear, action-oriented article. Thank you.
Thanks for your sharing. It is so good. I can learn a lot from your ideas. Hope that in my dissertation defense next time I can pass
The tips are effective. Will definitely apply them in my dissertation.
My dissertation defense is coming up in less than two weeks from now, I find this tips quite instructive, I’ll definitely apply them. Thank you so much.
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Reporting Research
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for data interpretation
In research, choosing the right approach to understand data is crucial for deriving meaningful insights.…

Comparing Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Studies: 5 steps for choosing the right approach
The process of choosing the right research design can put ourselves at the crossroads of…

- Career Corner
Unlocking the Power of Networking in Academic Conferences
Embarking on your first academic conference experience? Fear not, we got you covered! Academic conferences…

Research Recommendations – Guiding policy-makers for evidence-based decision making
Research recommendations play a crucial role in guiding scholars and researchers toward fruitful avenues of…

- AI in Academia
Disclosing the Use of Generative AI: Best practices for authors in manuscript preparation
The rapid proliferation of generative and other AI-based tools in research writing has ignited an…
Setting Rationale in Research: Cracking the code for excelling at research
Mitigating Survivorship Bias in Scholarly Research: 10 tips to enhance data integrity
The Power of Proofreading: Taking your academic work to the next level
Facing Difficulty Writing an Academic Essay? — Here is your one-stop solution!

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

As a researcher, what do you consider most when choosing an image manipulation detector?
Reference management. Clean and simple.
How to prepare an excellent thesis defense
What is a thesis defense?
How long is a thesis defense, what happens at a thesis defense, your presentation, questions from the committee, 6 tips to help you prepare for your thesis defense, 1. anticipate questions and prepare for them, 2. dress for success, 3. ask for help, as needed, 4. have a backup plan, 5. prepare for the possibility that you might not know an answer, 6. de-stress before, during, and after, frequently asked questions about preparing an excellent thesis defense, related articles.
If you're about to complete, or have ever completed a graduate degree, you have most likely come across the term "thesis defense." In many countries, to finish a graduate degree, you have to write a thesis .
A thesis is a large paper, or multi-chapter work, based on a topic relating to your field of study.
Once you hand in your thesis, you will be assigned a date to defend your work. Your thesis defense meeting usually consists of you and a committee of two or more professors working in your program. It may also include other people, like professionals from other colleges or those who are working in your field.
During your thesis defense, you will be asked questions about your work. The main purpose of your thesis defense is for the committee to make sure that you actually understand your field and focus area.
The questions are usually open-ended and require the student to think critically about their work. By the time of your thesis defense, your paper has already been evaluated. The questions asked are not designed so that you actually have to aggressively "defend" your work; often, your thesis defense is more of a formality required so that you can get your degree.
- Check with your department about requirements and timing.
- Re-read your thesis.
- Anticipate questions and prepare for them.
- Create a back-up plan to deal with technology hiccups.
- Plan de-stressing activities both before, and after, your defense.
How long your oral thesis defense is depends largely on the institution and requirements of your degree. It is best to consult your department or institution about this. In general, a thesis defense may take only 20 minutes, but it may also take two hours or more. The length also depends on how much time is allocated to the presentation and questioning part.
Tip: Check with your department or institution as soon as possible to determine the approved length for a thesis defense.
First of all, be aware that a thesis defense varies from country to country. This is just a general overview, but a thesis defense can take many different formats. Some are closed, others are public defenses. Some take place with two committee members, some with more examiners.
The same goes for the length of your thesis defense, as mentioned above. The most important first step for you is to clarify with your department what the structure of your thesis defense will look like. In general, your thesis defense will include:
- your presentation of around 20-30 minutes
- questions from the committee
- questions from the audience (if the defense is public and the department allows it)
You might have to give a presentation, often with Powerpoint, Google slides, or Keynote slides. Make sure to prepare an appropriate amount of slides. A general rule is to use about 10 slides for a 20-minute presentation.
But that also depends on your specific topic and the way you present. The good news is that there will be plenty of time ahead of your thesis defense to prepare your slides and practice your presentation alone and in front of friends or family.
Tip: Practice delivering your thesis presentation in front of family, friends, or colleagues.
You can prepare your slides by using information from your thesis' first chapter (the overview of your thesis) as a framework or outline. Substantive information in your thesis should correspond with your slides.
Make sure your slides are of good quality— both in terms of the integrity of the information and the appearance. If you need more help with how to prepare your presentation slides, both the ASQ Higher Education Brief and James Hayton have good guidelines on the topic.
The committee will ask questions about your work after you finish your presentation. The questions will most likely be about the core content of your thesis, such as what you learned from the study you conducted. They may also ask you to summarize certain findings and to discuss how your work will contribute to the existing body of knowledge.
Tip: Read your entire thesis in preparation of the questions, so you have a refreshed perspective on your work.
While you are preparing, you can create a list of possible questions and try to answer them. You can foresee many of the questions you will get by simply spending some time rereading your thesis.
Here are a few tips on how to prepare for your thesis defense:
You can absolutely prepare for most of the questions you will be asked. Read through your thesis and while you're reading it, create a list of possible questions. In addition, since you will know who will be on the committee, look at the academic expertise of the committee members. In what areas would they most likely be focused?
If possible, sit at other thesis defenses with these committee members to get a feel for how they ask and what they ask. As a graduate student, you should generally be adept at anticipating test questions, so use this advantage to gather as much information as possible before your thesis defense meeting.
Your thesis defense is a formal event, often the entire department or university is invited to participate. It signals a critical rite of passage for graduate students and faculty who have supported them throughout a long and challenging process.
While most universities don't have specific rules on how to dress for that event, do regard it with dignity and respect. This one might be a no-brainer, but know that you should dress as if you were on a job interview or delivering a paper at a conference.
It might help you deal with your stress before your thesis defense to entrust someone with the smaller but important responsibilities of your defense well ahead of schedule. This trusted person could be responsible for:
- preparing the room of the day of defense
- setting up equipment for the presentation
- preparing and distributing handouts
Technology is unpredictable. Life is too. There are no guarantees that your Powerpoint presentation will work at all or look the way it is supposed to on the big screen. We've all been there. Make sure to have a plan B for these situations. Handouts can help when technology fails, and an additional clean shirt can save the day if you have a spill.
One of the scariest aspects of the defense is the possibility of being asked a question you can't answer. While you can prepare for some questions, you can never know exactly what the committee will ask.
There will always be gaps in your knowledge. But your thesis defense is not about being perfect and knowing everything, it's about how you deal with challenging situations. You are not expected to know everything.
James Hayton writes on his blog that examiners will sometimes even ask questions they don't know the answer to, out of curiosity, or because they want to see how you think. While it is ok sometimes to just say "I don't know", he advises to try something like "I don't know, but I would think [...] because of x and y, but you would need to do [...] in order to find out.” This shows that you have the ability to think as an academic.
You will be nervous. But your examiners will expect you to be nervous. Being well prepared can help minimize your stress, but do know that your examiners have seen this many times before and are willing to help, by repeating questions, for example. Dora Farkas at finishyourthesis.com notes that it’s a myth that thesis committees are out to get you.
Two common symptoms of being nervous are talking really fast and nervous laughs. Try to slow yourself down and take a deep breath. Remember what feels like hours to you are just a few seconds in real life.
- Try meditational breathing right before your defense.
- Get plenty of exercise and sleep in the weeks prior to your defense.
- Have your clothes or other items you need ready to go the night before.
- During your defense, allow yourself to process each question before answering.
- Go to dinner with friends and family, or to a fun activity like mini-golf, after your defense.
Allow yourself to process each question, respond to it, and stop talking once you have responded. While a smile can often help dissolve a difficult situation, remember that nervous laughs can be irritating for your audience.
We all make mistakes and your thesis defense will not be perfect. However, careful preparation, mindfulness, and confidence can help you feel less stressful both before, and during, your defense.
Finally, consider planning something fun that you can look forward to after your defense.
It is completely normal to be nervous. Being well prepared can help minimize your stress, but do know that your examiners have seen this many times before and are willing to help, by repeating questions for example if needed. Slow yourself down, and take a deep breath.
Your thesis defense is not about being perfect and knowing everything, it's about how you deal with challenging situations. James Hayton writes on his blog that it is ok sometimes to just say "I don't know", but he advises to try something like "I don't know, but I would think [...] because of x and y, you would need to do [...] in order to find out".
Your Powerpoint presentation can get stuck or not look the way it is supposed to do on the big screen. It can happen and your supervisors know it. In general, handouts can always save the day when technology fails.
- Dress for success.
- Ask for help setting up.
- Have a backup plan (in case technology fails you).
- Deal with your nerves.

- Office of the Dean
- Vision, Mission & Values
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Communications Hub
- Our Facilities
- Trailblazers
- Accreditation
- Campus Crime Statistics
- Privacy & Security
- Why William & Mary
- Our Students
- Undergraduate Teacher Education Programs
- Graduate Programs
- International
- Financial Aid, Scholarships, Assistantships
- Non-degree Seeking
- Curriculum & Instruction
- Educational Policy, Planning & Leadership
- School Psychology & Counselor Education
- Online Programs
- Academic Calendar
- Academic Policies
- Course Listing
- Forms & Publications
- Office of Teacher Education
- Registration
- Faculty Listing
- Staff Listing
- Office of Research
- Applying for Grants
- Funding Opportunities
- Faculty Development Resources
- Centers and Projects
- Student Resources
- Research Brown Bags
- Centers, Institutes & Projects
- Request Info
School of Education
- Catalogs & Handbooks
- Doctoral Student Handbook
- Dissertation
- Proposal Defense
Dissertation Proposal Defense
The purpose of the dissertation proposal defense meeting is to assess the merits of the proposed research and the ability of the doctoral candidate to conduct this research in a scholarly manner. The proposal must be defended in a formal meeting to be attended by all members of the committee, in-place or virtually. People other than the committee members and the student proposing the study typically do not attend the proposal defense meeting.
Once the chair deems the proposal ready for the full committee’s review, the candidate will be given permission to schedule a proposal defense. The candidate will contact the committee members to find a date and time acceptable to all members, and will secure a conference room for the defense. The candidate will provide a copy of the proposal to the chair and committee members at least two weeks prior to the scheduled defense of the proposal, either electronically or in hard copy, depending upon the preferences of individual committee members.
At the defense, the candidate will be expected to defend the proposal and answer questions regarding the proposed study. A unanimous vote of the committee members at the time of the proposal defense is required for approval of the proposal. If unanimous approval is not given at this defense, the chair will make recommendations to remedy any deficiencies, and a second proposal defense meeting will be scheduled.
When all committee members are satisfied that a proposal is viable, they will sign a Dissertation Proposal Approval Form . The candidate will submit the signed form to the Office of Academic Programs. In the event that a faculty member resigns from the dissertation committee after the proposal has been formally accepted, the new member appointed to the committee must agree to accept the dissertation proposal as previously approved.
Human Subjects Approval After the dissertation proposal has been approved, the candidate must receive human subjects approval by the School of Education’s Institutional Review Committee (EDIRC) before any data may be generated or analyses begun. The candidate and the dissertation committee chair must submit verification of university required training in research ethics when submitting the online EDIRC proposal form. The candidate is required to designate the dissertation committee chair as a co-principal investigator for this study. More information about this process is available on the Protection of Human Subjects Certification web page.
Williamsburg, VA
- Faculty & Staff
- Community Engagement
- Prospective Students
- Current Students
- Alumni & Friends
404 Not found
Dissertation Defense
- Dissertation Defense: Home
- Preparing for the Defense
Consider These Example Defense Questions
- Student Experience Feedback Buttons
- Attending a Defense
- Sample Defenses
- Zoom Resources
- Dissertation Publishing in ProQuest
- School of Education Educator Dispositions
- What do you see as the main contributions of your research for your discipline, practitioners, and/or policy makers?
- In what ways, if at all, does your study contribute to the existing literature and/or prior research in the field? In what ways does it extend the literature? Contradict the literature? Fill gaps in the literature? Clarify contradictions in the literature?
- In planning and conducting this study, which major theorists influenced your thinking?
- What are the conflicting issues in your field (every field has conflicts—hence, the research problem), and what contributed most to your understanding of these issues?
- In what ways do you expect that your work will clarify the conflicting issues in your field?
- What motivated you to conduct this study? In other words, what brought you to explore this particular topic?
- What new learning about qualitative research have you come away with as a result of conducting this study?
- What, if any, are the unanticipated outcomes of your study? What surprises have you come away with?
- What new learning about yourself have you come away with having conducted this study? What additional insights has the dissertation experience afforded you?
- What were the high and/or low points for you in the dissertation experience?
- If you were to redo this study, how might you conduct this study differently? How might you change your research methodology? Why?
- How could you build on or extend this research in the future?
- What are the major strengths and/or limitations of your research design/methodology?
- What might further strengthen this study?
- Why did you analyze the data in the way that you did? How might you have analyzed your data differently?
- What suggestions might you offer somebody about to conduct a study of this nature?
- How did you arrive at your conceptual framework?
- What are the theoretical components of your framework?
- What informed your conceptual framework?
- How did you decide upon the components that you include in your conceptual framework?
- How did the components of your conceptual framework assist you in visualizing and explaining what you intended to investigate?
- How did you use your conceptual framework to design your research and analyze your findings?
Bloomberg, L. D and Volpe, M: Completing your qualitative dissertation: A Roadmap from Beginning to End (Sage 2016).
Was this resource helpful?
- << Previous: Preparing for the Defense
- Next: Attending a Defense >>
- Last Updated: Sep 12, 2023 2:22 PM
- URL: https://resources.nu.edu/c.php?g=1006027

© Copyright 2024 National University. All Rights Reserved.
Privacy Policy | Consumer Information
University of Washington Information School
Doctorate in information science.
- Advising & Support
- Capstone Projects
- Upcoming Info Sessions
- Videos: Alumni at Work
- Request more information
Proposal Defense Policy & Procedure
The proposal and its purpose.
The Information School encourages and supports the wide range of dissertation topics and methodologies generated from the study of information science. The dissertation proposal represents a formal understanding between the Supervisory Committee and the doctoral Candidate. This agreement outlines the work to be done and the intellectual rigor the Committee expects from the Candidate. The proposal functions as a map guiding the Candidate towards the effective completion of the dissertation project.
The dissertation proposal should substantially advance the doctoral candidate toward completion of the dissertation. It may take the form of the preliminary chapters of the dissertation.
The Elements
The doctoral Candidate works closely with the Chair of the Supervisory Committee and other voting members of the Supervisory Committee in determining the composition of the dissertation proposal and in writing the proposal.
The proposal should contain detail sufficient to describe the significance, background and rationale for the dissertation and the work the Candidate will perform for the dissertation.
The following list of elements is typical for a dissertation proposal in the information field. However, the School recognizes that this list may not fit all dissertation proposals and thus should be considered as illustrative only.
- Statement of the Problem – includes the background, context in the information field and in the broader scheme of academic pursuits, key questions, significance of the problem, and description of chosen methodology.
- Grounding and Rationale – provides a discussion of need in the area of study which may include a comprehensive review of theoretical, conceptual, technological or methodological precedents which directly relate to the dissertation topic. This section may also include a detailed analysis of the precedents that justify the need for the research, or review the literature that relates to the research.
- Research Plan – details the methods that will be used or the processes that will be followed during the course of investigation. This section describes how the questions posed by the dissertation will be addressed.
The Defense
The Candidate, assisted by the Chair as necessary, schedules a date, a time, and a room for the defense. The Candidate submits details regarding the proposal defense, including date, time and location of the defense, members of the Supervisory Committee, proposal defense title, as well as an abstract, to the iSchool web calendar, the Chair of the Ph.D. Program, and Student Services Office.
At least two weeks before the scheduled proposal defense date, the final written proposal must be submitted to all members of the Supervisory Committee. At this time or earlier, the voting members of the Committee, in consultation with the Candidate, determine the length and outline the structure of the defense.
The defense is a scheduled and announced public event. Any person may attend. However, the deliberations of the Supervisory Committee are private.
The Process
Students presents their dissertation proposal orally, with visual accompaniment as desired by the candidate, to the supervisory committee and the public.
The dissertation proposal defense proceeds as outlined below.
Prior to the start of the examination :
- The Candidate must be physically present at the exam.
- The Chair (or at least one Co-Chair), the GSR, and one general committee member must be physically present at the exam.
- If the Chair is not physically present, then the exam must be rescheduled.
- If the GSR is not physically present at the time of the exam, a substitute GSR may be secured subject to Graduate School rules. If no GSR can be found, then the exam must be rescheduled.
- If a general member is not physically present then, the exam should be adjourned and rescheduled to a later time/date.
- A majority of the Supervisory Committee must be physically present at the exam. E.g. a Supervisory Committee with the minimum 4 required members (Chair, GSR, and 2 general members) must have the Chair, the GSR, and at least one general member physically present at the exam. A Supervisory Committee with 5 members (Chair, GSR, and 3 general members) must have the Chair, the GSR, and at least one general member physically present at the exam.
Once the Exam Starts"
- The Supervisory Committee may meet initially in private, with or without the Candidate present.
- The Chair announces when the Candidate and the public may join the Committee for the defense.
- The Candidate presents the key elements of the dissertation proposal.
- The Supervisory Committee and/or the public questions the Candidate.
- The public may question the Candidate as time permits.
- Finally, the Supervisory Committee reconvenes in private for deliberations. The voting members vote for one of the following:
- a. Accept —a PDF version of the proposal will be submitted to Student Services. The proposal will be available to the public for reading.
- b. Accept with minor revisions —the Committee requests minor revisions, which are approved by a process that is established by the Chair. A PDF version of the proposal will be submitted to Student Services. The proposal will be available to the public for reading.
- c. Accept with revisions —revisions require approval by the Chair and selected members or the supervisory Committee. See Process** below.
- d. Reject —the Supervisory Committee may recommend either 1) that a second defense is permitted after a period of additional preparation, or 2) that the student is dropped from the Ph.D. program in Information Science at the University of Washington.
A simple majority vote is required. In the event that a simple majority vote does not occur, the deliberations of the Supervisory Committee are continued and a decision is made within ten days of the proposal defense date.
If after ten days the Supervisory Committee cannot make a decision, then the candidate may reconstitute the Committee, and schedule a new defense.
*Process for 'Accept with Revisions'
The revision process proceeds as follows:
- The committee informs the candidate verbally of the revisions required and the date by which revisions are to be completed.
- The chair, in consultation with the committee prepares a written description of the required revisions. A copy of the letter is provided to Student Services to place in the student's permanent academic file.
- The chair and the candidate determine the date by which the revisions must be completed, normally within 3 months.
- The chair distributes the written description to the candidate and the committee.
- Two weeks after the revisions are submitted by the candidate, the committee informs the candidate whether the revisions are accepted or rejected.
- If accepted, a paper copy and PDF version of the proposal are submitted to Student Services; at least one copy is available to the public for reading.
- If rejected, the committee recommends, as outlined above, to either permit a second defense or to drop the student from the program.
- If the revisions are not completed successfully within the specified time period, the chair may extend the time for revision to up to one year from the date of the proposal defense. After one year, the chair may petition the Ph.D. committee for an extension.
- If the revisions are not completed successfully in the time frame designated, and if the supervisory committee and the Ph.D. committee concur, the proposal is rejected and the student is dropped from the Ph.D. program in Information Science at UW.
Full Results
Customize your experience.
Return to: School of Graduate Engineering and Applied Science: Degree Programs
Ph.D. PROGRAM
The Doctor of Philosophy degree requires 24 graded credits of course work past the bachelor’s degree (including any completed during a Master’s program), plus two Elective Educational Experiences (see below). Students who enter the program already holding a Master’s degree in an engineering discipline from a school other than the University of Virginia must take the core BME courses, completing at least 12 credit hours of graduate level coursework. Students are required to complete an Individual Development Plan (IDP) form annually with their advisors.
Teaching is an integral part of graduate training in Biomedical Engineering. All Ph.D. students must participate 2 BME teaching assistantships in BME undergraduate or graduate courses as part of the academic requirement for the degree, regardless of their source of funding for the stipend or fellowship. MSTP students are required to complete 1 unit of TA. The teaching experience will normally be performed in the second and third years of doctoral study and include one lab-based course and one lecture-based course.
Elective Educational Experiences (EEEs) are intended to encourage students to begin the process of life-long learning essential to a career in Biomedical Engineering. EEEs are intended to cover new material and areas of study that the student has not already covered in previous coursework or research experience or to provide the student with additional depth in a particular area. Two EEEs are required for Ph.D. students, except for MSTP students who require completion of 1. An appropriate EEE is expected to involve roughly the time commitment of a typical graduate course. They must be proposed and approved of by the committee prior to the experience. Possible examples include:
- Taking an additional graduate course beyond the normal course requirements
- Taking an intensive 2-week “short course” to learn a series of specialized techniques
- Completing a summer internship at a biotechnology company.
MSTP (MD/Ph.D.) Students will have medical school physiology courses accepted in lieu of BME 6101. These courses may not have to be replaced with additional credits. MSTP students need to complete at least 18 graded credits, but also need to comply with the SEAS 24 credit requirement for Ph.D. This may be fulfilled with up to 6 graded credits of Independent Research. An EEE with a focus on developing computer programming skills should be completed before the end of the first semester after transitioning to the Ph.D. program if the student does not have sufficient programming experience to succeed in the core graduate BME curriculum. See the graduate program coordinator for details. MSTP students are only required to complete one TAship.
Ph.D. Dissertation Committee
Ph.D. students should begin to arrange for the appointment of a Ph.D. Dissertation Committee in consultation with their Ph.D. advisor and with their Ph.D. advisor’s approval within the first year, and be finalized by July 1st after the second semester in the BME Ph.D. program. Students should consult “Ph.D. Advisory Committee” in the School of Engineering and Applied Science—Academic Rules section of the Record for rules governing thesis committees. All faculty with a primary appointment in BME are considered School of Engineering faculty for this committee. One faculty member from the School of Medicine may substitute for one School of Engineering faculty. Committee chairs must have at least a 25% BME appointment OR have previously served on BME PhD committees of three students through the entirety of the degree process (qualification exam, proposal defense, and dissertation defense). The committee chair may not be the student’s advisor. Two members of the final committee must have 50% or more appointment within BME and may be either faculty or research physicians. One member of the committee must be a UVA faculty or physician who is external to BME with zero percent (0%) appointment in BME. The Dissertation Committee may grow as the student progresses through their Ph.D. career.
Ph.D. Plan of Study
The Ph.D. Plan of Study must be submitted to the Graduate Program Coordinator no later than the end of the summer after second semester of doctoral study and is expected by May 1st of the year the student plans to complete the Ph.D. Qualifying Exam.
Ph.D. Qualifying Exam
The Ph.D. Qualifying Exam is an oral exam lasting approximately three hours, which is administered by the student’s Ph.D. Qualifying Exam Committee. All students should take the Ph.D. Qualifying Examination before the end of the summer after the fourth semester of graduate study (i.e. after their 2nd year). Students may elect to take the Ph.D. Qualifying Exam as early as after the second semester in the Ph.D. program (i.e. after their 1st year). Delayed examination is subject to the approval of the student’s Ph.D. Dissertation Committee. Passage of the Ph.D. Qualifying Exam is required to continue the Ph.D. program. At least three (3) members of the Ph.D. Qualifying Exam Committee must be present for the Ph.D. Qualifying Exam, but may include more than three members.
At least two of the Ph.D. Qualifying Exam Committee members must be primary BME faculty.
Committee chairs must have at least a 25% BME appointment OR have previously served on BME PhD committees of three students through the entirety of the degree process (qualification exam, proposal defense, and dissertation defense). The committee chair may not be the student’s advisor.
If the student’s Ph.D. advisor is BME primary faculty, they may serve as one of the BME faculty members on the Ph.D. Qualifying Exam Committee.
If the Ph.D. advisor is not primary BME faculty, the Ph.D. Qualifying Exam Committee still needs to have at least two primary BME faculty on it.
All members of the Ph.D. Qualifying Exam Committee may be primary BME faculty.
The Chair of the committee will coordinate the preparation of three questions, with input from the entire Exam Committee. The oral examination will consist of a set of integrative questions (typically three) that have been provided to the student one week in advance of the oral examination. The questions will be based upon the student’s program of study and topics relevant to his/her/their anticipated dissertation topic. The questions will:
- Assess the ability to integrate a body of advanced knowledge in biomedical engineering
- Include experimental design and hypothesis testing
- Have a design or a quantitative analysis component.
Successful completion of the Ph.D. Qualifying Examination will be determined by the Ph.D. Qualifying Exam Committee. Ph.D. students must pass the oral examination to continue in the Ph.D. Program. At the discretion of the Ph.D. Qualifying Exam Committee, a student may be allowed at most two attempts to pass the Ph.D. Qualifying Examination.
Ph.D. Dissertation Proposal
The Ph.D. Dissertation Proposal Defense will assess the quality of the student’s research plan (including hypotheses to be tested, experimental design and methodology). The Ph.D. candidate is expected to complete the dissertation proposal no later than 12 months after the Qualifying Examination. Failure to complete and defend a dissertation proposal by the end of the third year of doctoral study may result in a delay in the completion of the program or even dismissal from the program.
The Ph.D. Dissertation Proposal Committee should include a minimum of four (4) members of the UVA faculty, including the student’s faculty advisor. Committee chairs must have at least a 25% BME appointment OR have previously served on BME PhD committees of three students through the entirety of the degree process (qualification exam, proposal defense, and dissertation defense). The committee chair may not be the student’s advisor. Two members of the final committee must have 50% or more appointment within BME and may be either faculty or research physicians. One member of the committee must be a UVA faculty or physician who is external to BME with zero percent (0%) appointment in BME.
Ph.D. Dissertation Defense
The Ph.D. Dissertation Defense is held to demonstrate competence in the field of the dissertation research and to evaluate the quality of the dissertation for publication in scientific journals. The Examining Committee for the dissertation defense is the student’s Ph.D. Dissertation Committee. All five (5) primary members of your committee must be present during the defense. Committee chairs must have at least a 25% BME appointment OR have previously served on BME PhD committees of three students through the entirety of the degree process (qualification exam, proposal defense, and dissertation defense). The committee chair may not be the student’s advisor. Two members of the final committee must have 50% or more appointment within BME and may be either faculty or research physicians. One member of the committee must be a UVA faculty or physician who is external to BME with zero percent (0%) appointment in BME.
The written dissertation will be submitted to the Doctoral Advisory Committee at least two weeks before the final examination. The first 40 minutes is an oral presentation of the thesis which is open to the public. It is followed by a 1-2 hour oral defense before the Doctoral Advisory Committee and interested faculty. In cases of potential failure, possibility for re-examination is determined by the Doctoral Advisory Committee.
Ph.D. Graduate Exit Interview
Following the successful completion of a Ph.D. Dissertation Defense, students will be invited to participate in a 30-minute long Exit Interview with the Graduate Program Director. The purpose of the interview is to obtain feedback from graduates about their experiences in the Ph.D. program in order to inform the Graduate Program Committee about ways to improve the graduate experiences for future students. Graduates will be provided with the interview questions in advance, and invited to edit the documentation of their responses. These will only be shared with the Graduate Program Committee in a de-identified manner.
COURSE REQUIREMENTS
The program requires 24 credits of graded coursework. 12 credits are electives which will be chosen in consideration with the Chair and Committee, and the remaining 12 credits come from the following required courses:
- BME 6001 - Cell and Molecular Physiology for Engineers Credits: 2
- BME 6002 - Organ-Level Physiology for Engineers Credits: 2
- BME 6003 - Biostatistics and Biocomputational Analysis Credits: 2
- BME 6004 - Signals and Systems Analysis for Biomedical Applications Credits: 2
- BME 6005 - Research Fundamentals for Biomedical Engineers Credits: 2
- BME 6006 - Biomedical Data Science and Analytics Credits: 2

COMMENTS
Learn how to prepare and deliver your dissertation proposal defense with confidence and ease. Get advice from a longtime Dissertation Committee Chair and coach on how to anticipate questions, address weaknesses, practice, and more.
Learn how to create a PowerPoint presentation for your dissertation proposal defense, including format, content, and tips. See an example slide and a video tutorial.
Learn from experts how to prepare for your dissertation defense, from choosing an advisor to writing and presenting your work. Find out what to expect, how to cope with challenges, and how to celebrate your achievement.
Learn how to answer 13 key questions in your viva voce, whether it's for a Masters or PhD degree. Find out what the dissertation or thesis committee is assessing and how to prepare for your oral defense.
The oral defense of your dissertation is, in essence, your formal introduction to your new colleagues—you are the expert on your subject. In the defense you'll be expected to cogently and clearly explain your work and how it fits with other research and scholarship in your field. The exact nature of the oral defense varies by discipline and ...
The dissertation is the centerpiece of a graduate student's career at the doctoral level. It is a demonstration of a doctoral student's ability to conduct and present research with the skills necessary to contribute to scientific knowledge. As a result, the dissertation defense (sometimes called a thesis defense in non-American contexts) is the ...
3. Work on Starting Strong. To begin your defense on a strong note, work on creating a clear and engaging introduction. You can start by briefly outlining the purpose of your study, research questions, and methodology. Try to stay on topic and don't veer off track by discussing unrelated or unnecessary information. 4.
Learn what is a dissertation defense, how to prepare for it, and how to present it effectively. Find out the stages, length, tips, and questions to expect in this comprehensive guide by ThesisGeek.
The proposal defense serves two functions. First, the defense allows you to demonstrate your knowledge of the topic and the research process. Second, the defense ensures that you move forward with the dissertation in the strongest possible position. Your chair and committee should make sure you are prepared to complete the study, and that the ...
This Guide was created to help Ph.D. students in engineering fields to design dissertation defense presentations. The Guide provides 1) tips on how to effectively communicate research, and 2) full presentation examples from Ph.D. graduates. The tips on designing effective slides are not restricted to dissertation defense presentations; they can ...
1. Start Your Preparations Early. Thesis defense is not a 3 or 6 months' exercise. Don't wait until you have completed all your research objectives. Start your preparation well in advance, and make sure you know all the intricacies of your thesis and reasons to all the research experiments you conducted. 2.
Writing a proposal or prospectus can be a challenge, but we've compiled some examples for you to get your started. Example #1: "Geographic Representations of the Planet Mars, 1867-1907" by Maria Lane. Example #2: "Individuals and the State in Late Bronze Age Greece: Messenian Perspectives on Mycenaean Society" by Dimitri Nakassis.
Preparing Your PowerPoint. Topic 3: Preparing for Defense. In this activity, you will draft your PowerPoint for your proposal defense. During your defense you will typically have 10-15 minutes for your presentation. There are approximately 9-12 slides. They have read the study, so focus more on findings and implications, less on literature.
Learn what a thesis defense is, how long it lasts, and what happens during it. Get tips on how to create your presentation, anticipate questions, dress for success, and de-stress before and after your defense.
Learn how to prepare and defend your dissertation proposal in a formal meeting with your committee. Find out the requirements, procedures and deadlines for human subjects approval and committee sign-off.
Example Dissertation Proposal Defense Powerful Format. The dissertation proposal willing consist of three chapters, which she wants live providing information on in the demonstration. Although of contents and your of the contents may vary, there are some basis parts of an proposal that are usually required.
Learn how to prepare and defend your dissertation proposal at the University of Washington iSchool. Find out the purpose, process, timeline, and requirements for the proposal defense.
Consider These Example Defense Questions. What do you see as the main contributions of your research for your discipline, practitioners, and/or policy makers? In what ways, if at all, does your study contribute to the existing literature and/or prior research in the field? In what ways does it extend the literature?
A dissertation proposal defense may only take place after the student has completed at least 48 credits of coursework and had their two field statements approved by the Graduate Faculty. At the defense, students should be prepared to discuss their research proposal, to relate their intended research to wider anthropological scholarship, and to ...
of the defense. Copies are also to be distributed widely in and around the Department so all are notified and invited., • All committee members must attend the defense. • Exact procedures at the defense are determined by the committee chair. • At the end of the meeting, student must be told if dissertation proposal defense
Proposal Defense PowerPoint Template. The primary purpose of this defense is to propose methodology for answering your research questions. This document was created for educational purposes. Students are encouraged to discuss the expectations for the defense presentation with the EdD Dissertation Committee. Tips for Creating and Delivering an ...
Phase I: From Start to Proposal Defense. Topic 1: Types of Dissertations. Introduction for Types of Dissertations. Overview of the Dissertation. Self-Assessment Exercise. What is a Dissertation Committee. Different Types of Dissertations. Topic 2: Overview of the Dissertation Process.
The dissertation proposal defense proceeds as outlined below. Prior to the start of the examination: The Candidate must be physically present at the exam. The Chair (or at least one Co-Chair), the GSR, and one general committee member must be physically present at the exam. If the Chair is not physically present, then the exam must be rescheduled.
University Registrar Carruthers Hall, 1001 N. Emmet St. P.O. Box 400203 Charlottesville, VA 22904-4203 Staff Directory
Custom Nursing Dissertation Writing Services: From Proposal to Defense The journey to obtaining a nursing degree often culminates in the development and defense of a dissertation, a rigorous academic task that demands extensive research, critical analysis, and a deep understanding of the chosen subject matter. This complex process can be overwhelming, particularly for students balancing ...