

Demonstrative Speech
Demonstrative speech generator.

Your teacher or superior comes up to you and asks to do a demonstrative speech in front of a big audience. For instance, they may ask you how to demonstrate a certain skill such as writing an investigative news article (if in a journalism class) or ask you to teach judo (if in an martial arts class).
- Examples of Persuasive Speech
- Expository Speeches Example
Either way, you might be an expert on this stuff but it’s different if you’re asked to make a demonstrative speech about it. This type of speeches need more clarity and precision for your audiences to understand since they are expecting to learn from you. This might be a difficult task but by following the guidelines below, writing and delivering this kind of speech will be much easier.
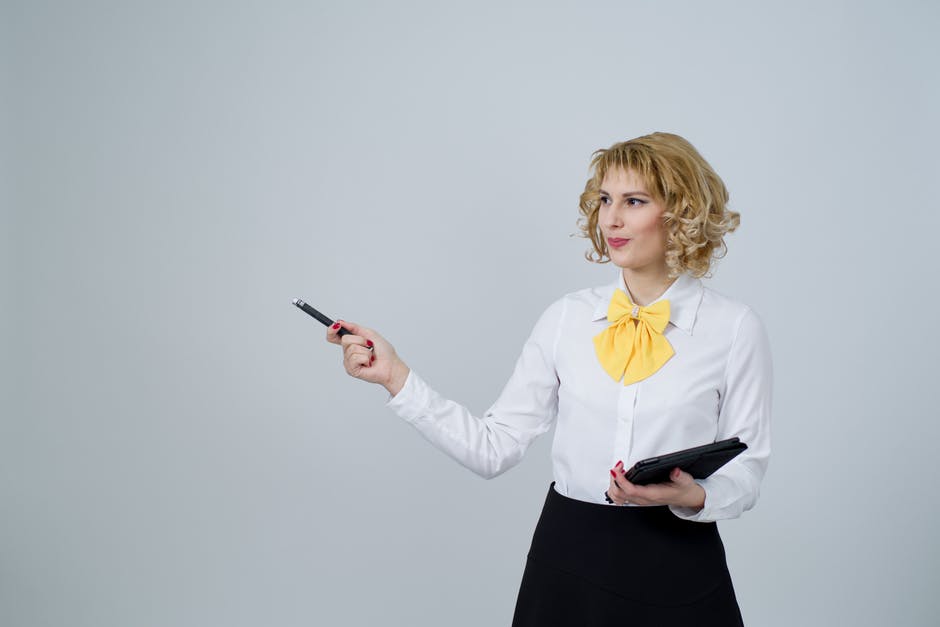

What is a Demonstrative Speech?
Andrew Dlugan described a demonstration speech as a form of informative speech where the speaker’s primary purpose is to teach the audience how to complete a task , and is largely accomplished by demonstrating the task through a series of steps.
Choosing a topic… and how to work it out
There are a wide variety of topics to choose for your demonstrative speech. Choose a hobby, or craft that are not too common. Here are a few examples that can be your main topic in your speech:
- How to be a lumberjack
- How to do pole dancing
- How to be a trainspotter
- How to collect navel fluff
- How to beach comb
- How to do taxidermy
- How to do cosplay
- How to make surveys
- How to read palms
- How to write a limerick
- How to collect stamps
- How to do ice sculpting
Once you’ve figured out what topic you will talk about, assess how long is your speech going to last. If you’re going to teach your audience how to bake a cake, you might need an hour for your presentation since there many different types of cakes. If your presentation is how to bake a lava cake, you may only need a half an hour speech or less. Research on your chosen topic. You can search the internet or your local library for more information. You can also ask experts (if you can) more tidbits or advice about the topic you choose.
If you have too much information on your chosen topic, shorten it by only choosing the essential information vital to your speech. However, if you only found limited information, you can add some fun facts or any related facts in your speech.
Find out who is your audience
Before finalizing your topic for your demonstrative speech, find out first who you will be talking to. If you’re giving a speech to a group of journalists, it’s not the best idea to choose a topic “How to Write News”.You can make your topic more relevant and interesting to them like “How to Battle Fake News in the 21st Century”. The topic “How to Write News” may be more appropriate to students aspiring to become journalists. You also need to determine the age of your audiences. If your audiences are young people, it’s best to give them a mundane and simple topic such as “How to Collect Stamp” or “How to Paint by Numbers”.
Think of how will your audience benefit from your speech
Demonstrating a certain task to your audience is not enough. You need to figure out how will your audience will be motivated to learn from your speech. For example, in networking business, demonstrators usually give speeches on how to earn money by demonstrating certain tasks for the audiences to do such as selling products effectively. The audience are dedicated to learn from the speech because they can benefit to it by knowing how to sell products effectively so they can earn money.
Below are some points you need to consider on how your audiences will benefit greatly by learning the new task you demonstrated in your speech. Will they:
- Earn or save money?
- Get a promotion?
- Improve their skills?
- Make their life easier?
- Provide enjoyment or satisfaction?
- Make them happy?
There are a lot of ways to motivate your audience, but the most effective is to point out how their lives are going to improve with this new knowledge.
Examples of Demonstrative Speech
If you’re not sure how to format your speech, here are some examples on how to write your demonstrative speech:
Sample Demonstration Speech Outline Example

Size: 106 KB
Demonstration Speech Example

Size: 139.8 KB
How to write your speech
Make an outline for your speech. Your outline should only contain three sections: introduction, the body, and the conclusion. Refer to topic outline to familiarize yourself better with writing speeches.
Give a brief overview of the entire process
Before going into specific details about your topic, provide an overview first of what will be the overall task or process in your speech. This will prepare the mindset of your audience as they are going the delve into learning a new skill. This way, your audience can relax since they have an idea of what you are going to demonstrate. You can start your overview along the lines of… “Today, I’m gonna show you how to wrap a wound in three easy steps…”. It’s important to present your outline neatly for your audience to see how the steps will take place later on.
Make the body of your speech
Your body of your speech must contain the actual step processes of performing a certain task. Break each step into manageable ones that can be explained one by one. Explain each step in a sequential order. Try to consider the comprehensiveness of your audience of how they will understand your speech.
It may be helpful to keep the number of steps as low as possible. Having too many steps when doing a demonstration may baffle your audiences and won’t be able to see the point you are trying to make. For every step, you could explain the purpose of the step and how it should be done in a straightforward manner.
If time allows, discuss additional options
When you are doing the demonstration first, you will be explaining the basic and simple way to do the task. If you still have more time in your hands, you can also demonstrate to your audience other variations of doing the task; you can teach them other alternate ways to do it if they don’t like the steps you’ve demonstrated first. Example: If you are explaining how to bake an arctic roll, in this part, you can teach them alternate flavors, ingredients, and other methods of baking the arctic roll.
Allow time for Q&A
If you’ve noticed, many types of speeches are always proceeded by question and answer (Q&A) portion. This part is when the audience can have the privileged to ask clarifications from the speaker if they were confused by certain steps from the speech. Not all Q&A sessions must be at the end of your speech, if you’re feeling confident enough that you can finish your speech on time, you can let the audience ask questions throughout your speech.
Summarize your speech at the conclusion
Once you’re done with your speech and the Q&A session, you can recap your speech by summarizing the process again for further clarifications and mention the benefits the audience can gain from your speech. Now that you’ve written your speech that you think your audience can learn from it, you can add more zing to your speech to make it more engaging.
You may let the audience participate
If you have the time (and funds), you can always provide supplies to your audience so that they can follow the step-by-step demonstration together with you. Audience that are actively engaging in your demonstration will avoid any boredom. They’ll be likely to remember the process the demonstration taught them and it will be also a test for them whether they can achieve the task or not. If you don’t have the opportunity to let all the audience participate, you can ask one to four volunteers to follow the demonstration.
Visuals are excellent in your demonstrative speech
Just to make your speech is memorable. You can add visual props to help you out in your demonstration. Merely speaking is okay, but what if your audience has a hard time catching up? Visuals can be an answer to that issue. You can use:
- Your body. If you’re demonstrating a dance, your body is the best visual. You can’t teach dancing just by standing limply. You need to move in order to demonstrate how to tango. You may invite someone else to do it for you, but it’s best if you also move.
- Use real props. If you’re teaching on how to play the saxophone, you need to bring a real instrument and not just a fake one. This is one way for your audiences to learn effectively from your demonstration.
- Use pictures or diagrams. They can help you go through step by step in your demonstration breezily. Make your visuals eye-catching, neat and organized (if you’re using diagrams or pictures) and visible to your audiences.
Practice Your Speech
Now you’ve prepared your speech and your visuals. Then it’s time for you to practice on delivering your speech. You need to practice before taking the plunge or else your stage fright gets the best of you and leave you stuttering in front of your audience.
Practice delivering your speech alone
Review your speech and notes by standing in front of a mirror and try to speak to it. You can see how will you look while delivering your speech. You can improve the way you talk, move and look while babbling your speech. This way, you can be more aware on how you present your speech and you’ll be able to improve yourself without looking awkward. You can also make some revisions in your speech that may not work while you’re speaking it aloud.
Practice also on how you will handle your visual aides. That way, you can adjust them to make it easier for you to handle once you’ve given your speech. If your props or visuals involves people, let them practice first on how you want them to move during your speech.
Practice delivering your speech with your friends
if you’re satisfied with how you look while you present your speech, invite your family or close friends as your test audience. Choose the people that you trust in giving you constructive criticism when there are things you need to adjust in your speech or give you compliments if you’re feeling too nervous. You need their feedback for you to improve. You can also try asking them specific questions like, do they understand your steps? Or was it too complicated? Once you’ve got their feedback, take note of them. You’re gonna need it to polish your speech.
Demonstrative Speech Outline

Size: 110 KB
Doing a speech, let alone a demonstrative speech is already daunting enough. This guide will help you create a demonstrative speech and give you confidence when you will be doing the demonstration in front of an audience.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Create a Demonstrative Speech on how to bake bread
Generate a Demonstrative Speech on planting a garden
Easy Demonstration Speech Ideas
12 September, 2020
9 minutes read
Author: Mathieu Johnson
If you ever dreamed of becoming an instructor and teach others, you can use an excellent opportunity to act like one while giving a demonstration speech. Believe us: there’ll be no better chance to engage yourself in such an exciting activity. This is probably the most encouraging task professors could ever give you. And you can now use it to share knowledge with others and learn something yourself during the process.

Demonstration speech definition
As the name implies, demonstration speech is a speech devoted to teaching the audience how to do a particular thing. It is a clear, step-by-step practical guide which intends to show people methods of using regular items and even improve someone’s life with it. Demonstration speeches exist in different forms: they can be lengthy and detailed, short and straightforward, or medium and accurate. But either way, the very essence of this task is to teach you how to put thoughts into one, well-structured, and logical sequence of steps. It might seem dubious to take such a specific assignment, but if you take time to explore all the nuances and requirements for this task, it’ll be much easier to handle it eventually. So, what are the processes involved in demonstration speech writing, and what makes trivial persuasive topics sound brilliant?
Follow our guide for more insight.
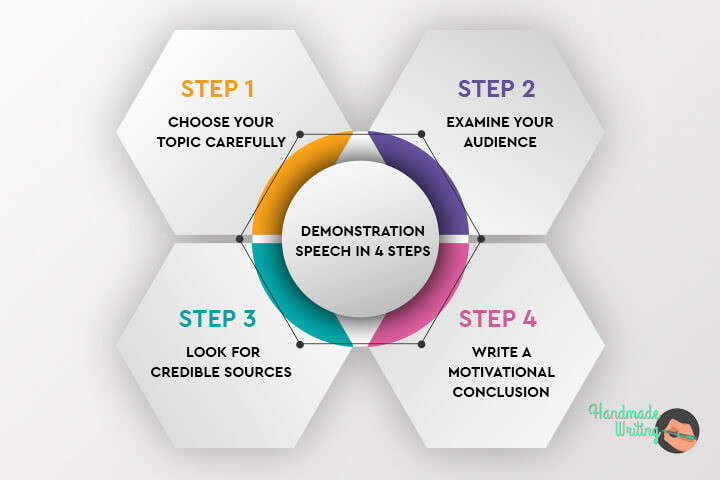
Choose Your Topic Carefully
Like with any other essay type, demonstration speech starts with topic selection. You have a vast field of “how to” speech ideas to talk about, but the ultimate choice is always on you. Also, professors often tend to give a specific topic to their students. In cases like this, it’s even easier. Regardless of what your final topic is, there’s always a need for research. Once the topic is defined, and you’re 100 percent confident that it’s going to fit the timeframe for delivery, go on to the next step, which is the audience analysis.
Examine Your Audience
There are specific criteria which can help you study the audience prior to delivering a speech. These factors include age, occupation, preferences, interests, and so on. So for example, if your listeners are professional gardeners, they’ll probably expect some useful advice on their sphere of interest. Instead of nurturing them with something as banal as “How to grow a plant,” give them real information, like “How to grow and take care of palm Washingtonia.” Likewise, if your audience composes of teenagers, speak about something thought-provoking, yet not too professional and dull. Take, for instance, the topic on how to become successful, or how to deal with depression.
Look for Credible Sources
Before writing the demonstration speech, you’ll first need some assistance to prove the credibility of your sayings. If you don’t want the audience to think like the entire speech is a fly of your imagination, you should arm yourself with relevant evidence to prove the mentioned points. There are many places you can go to, like local libraries. They contain countless books on your topic, so you can use them for your advantage. Alternatively, consider using online resources, but only credible ones if you don’t feel like walking anywhere. Even if such assistance is not enough for you, ask relatives or friends for help. Some of them might be experts in your topic, and more than willing to explain how this or that thing works.
Write a Motivational Conclusion
The best way to finish your demonstration speech is to give your audience a great insight into the process they haven’t experienced themselves. For this, you can call listeners to action and motivate them to follow your practice. Let’s review an example of a proper ending: “Now that you’ve learned about the basics of DIY table creation, you can craft one easily by yourself without costly materials and mountains of time.” Such a prominent calling will make people not only have a positive impression of your speech but also encourage them to make something useful.
Demonstration speech outline
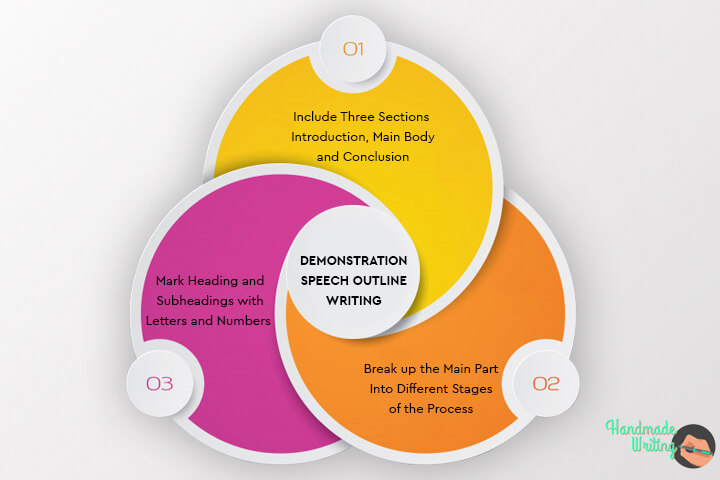
An outline is a way to structure the information that you want to share with your audience. The outline should explicitly showcase the order of steps that you will use in your demonstration speech. Many students seem to neglect the power of creating outlines for their academic writing tasks, but in vain. The key feature that makes outlines as significant as other processes of speech creation is a schematic representation of the main ideas. It means that writing the final variant of your demonstration speech will be much easier as you have an exact plan, and you don’t need to think of the main points on the fly. As for the structure of an outline, it should contain the following elements:
- three sections – introduction, main body, and conclusion.
- the main part should be broken up into different stages of the process.
- headings and subheadings marked with letters and numbers for easier navigation throughout the outline
At the phase of plan creation, it’s also vital to adhere to theses and use them as reference points. These can be either sentences or just keywords. Do as you are accustomed to doing and feel comfortable with making amendments before proceeding with writing the speech text. For each statement, use examples from personal life to validate the adequacy of described steps. Vast reasoning is, of course, excellent, but without specifics, they do not cling. To find the response in the heart of the audience, make your how-to-do instructions more understandable. For example, if you want to explain to your audience how to make and install a wall-mounted folding table, don’t just enumerate the instruments required and tell people how to fold and unfold the table. Rather, give them proper instructions.

5-minute demonstration speech topics
- How to savor wine
- How to make a Spanish salad
- How to clean the house with minimum effort
- How to live the day like it’s the last one
- How to forget the past and move forward
- How to sew clothes
- How to enjoy the moment
- How to practice speed reading
- How to adjust to the realms of massive consumerism
- How to control finances and save money
Funny demonstration speech topics
- How to stop forgetting about turning off the iron
- How to clean up the mess after your “Project X” party
- How to survive in college
- How to master the art of lying with a poker face
- How to get rid of annoying friends
- How to pretend that you’re present in a class
- How to get an A+ for homework while doing nothing at home
- How to stop biting nails and eating hair when you’re nervous
- How to watch horror movies with your eyes open
- How to pretend that you like your birthday present
Demonstration speech ideas for college students
- How to paint using the acrylic pouring technique
- How to find motivation
- How not to burn out in college
- How to find common ground with any professor
- How to understand the subject you hate most of all
- How to decorate a dormitory room for enhanced productivity
- How to force yourself to get out of bed
- How to be a leader in your class
- How to prepare for an exam without psychological suffering
- How to reach new heights in education
Now you have a guide on how to write a demonstration speech, as well as easy speech topics in addition to basic theory. These demonstrative speech topics are a surefire way to give a memorable, informative, and perhaps funny talk, which will undoubtedly crack the audience up. Our essay writers described you the essentials of speech writing, and now it’s your turn. Be patient, take your time, and tailor a blazingly meaningful speech.
Feel free to buy essay tasks if you’re facing some problems with your essay !

A life lesson in Romeo and Juliet taught by death
Due to human nature, we draw conclusions only when life gives us a lesson since the experience of others is not so effective and powerful. Therefore, when analyzing and sorting out common problems we face, we may trace a parallel with well-known book characters or real historical figures. Moreover, we often compare our situations with […]

Ethical Research Paper Topics
Writing a research paper on ethics is not an easy task, especially if you do not possess excellent writing skills and do not like to contemplate controversial questions. But an ethics course is obligatory in all higher education institutions, and students have to look for a way out and be creative. When you find an […]

Art Research Paper Topics
Students obtaining degrees in fine art and art & design programs most commonly need to write a paper on art topics. However, this subject is becoming more popular in educational institutions for expanding students’ horizons. Thus, both groups of receivers of education: those who are into arts and those who only get acquainted with art […]
What Is a Demonstrative Speech? (Topics + Examples)
June 7, 2023

In the realm of public speaking, there are various types of speeches designed to inform, persuade, entertain, and inspire. One captivating form is the demonstrative speech . In this genre, the speaker not only conveys information but also demonstrates how to perform a particular task.
The following comprehensive article dives into the exciting world of demonstrative speeches, providing you with a clear understanding of what they are, their purpose, and some captivating examples. Additionally, we’ll explore how Yoodli, an AI communication coach, can elevate your delivery and transform your speech into a remarkable experience.
Understanding Demonstrative Speeches
A demonstrative speech is a form of speaking where the presenter showcases and explains a process, task, or concept to the audience. The primary objective is to educate and engage the listeners by providing step-by-step instructions, visual aids, and real-time demonstrations.
Demonstrative speech examples are typically found in educational settings, such as workshops and conferences. Today, they are increasingly delivered on online platforms.
The Purpose of Demonstrative Speeches
The purpose of a demonstrative speech is twofold: to inform and to illustrate. By combining verbal explanations with visual aids and live demonstrations, speakers aim to educate the audience on a specific topic or teach them how to perform a particular task.
These speeches are highly effective in both engaging the audience and enhancing their understanding through hands-on learning experiences.
How to Use AI to Practice a Demonstrative Speech
To deliver a remarkable demonstrative speech or any type of presentation, leveraging the power of Yoodli , your AI communication coach, can make a significant difference. Here’s how Yoodli can enhance your public speaking skills and ensure your speech captivates the audience.
Real-time feedback and analysis
Yoodli’s advanced AI algorithms provide real-time feedback on your speech, pace, clarity, and non-verbal cues. By analyzing your delivery, Yoodli helps you identify areas for improvement, ensuring you maintain a captivating presence throughout your speech.
Customized coaching and recommendations
Yoodli tailors its coaching based on your specific needs and goals. By analyzing your strengths and weaknesses, it offers personalized recommendations to enhance your demonstrative speech, including guidance on vocal projection, body language, and slide design.

Interactive practice sessions
Yoodli offers interactive practice sessions where you can rehearse your demonstrative speech in a low-stress, judgement-free environment. It simulates a realistic audience experience, providing follow up questions in real time and boosting your confidence as you refine your delivery.
Accessible anytime, anywhere
With Yoodli, you can practice your demonstrative speech at your convenience. Whether you’re at home, in the office, or on the go, Yoodli’s accessibility allows you to refine your skills and deliver outstanding presentations whenever and wherever you choose.
Embrace the power of Yoodli, and witness the transformation of your speech into an engaging, informative, and memorable experience.
4 Demonstrative Speech Ideas
If you’re ready to write your speech, you’ll need to narrow it down a bit further. To find a demonstrative speech idea, you need to consider a few factors.
How to choose a demonstrative speech topic
Choosing a topic can be difficult at first, but after you consider a few factors, you should be able to nail down exactly what you’d like to talk about.
To start, think about how you’d answer the following questions:
- What types of topics are you genuinely interested in?
- Why do you want to give this speech? What’s the goal of your demonstrative speech?
- Who’s your audience?
Answering these questions can help ease the process of choosing a topic.
Demonstrative speech ideas
To grasp the essence of these speeches, let’s explore a few examples of demonstrative speech topics that highlight the diversity and impact of this speech genre. Here are four demonstrative speech ideas to explore.
1. How to tie a perfect necktie
Imagine a speaker confidently demonstrating various tie knots, sharing tips and tricks to achieve a flawless necktie. Through clear explanations and physical demonstrations, the audience gains valuable knowledge and practical skills they can apply in their everyday lives.
2. The art of origami: Crafting a beautiful paper crane

In this demonstrative speech topic example, the speaker takes the audience on a journey of creativity and craftsmanship by guiding them through the step-by-step process of creating an intricate paper crane. The visual demonstration and hands-on experience make the learning process engaging, enjoyable, and accessible overall as one of the best demonstrative speech ideas.
3. Mastering latte art: Creating stunning coffee designs
With this demonstrative speech idea, the speaker combines their expertise in coffee-making with the art of creating visually stunning latte designs. They walk the audience through both the techniques and secrets of achieving impressive patterns, enabling coffee enthusiasts to elevate their barista skills and create their own coffee masterpieces.
4. The science of baking: perfecting chocolate chip cookies
This demonstrative speech topic example delves into the realm of culinary delights. The speaker shares the science behind baking the perfect chocolate chip cookies, discussing the ingredients, measurements, and techniques that result in delectable treats. The audience not only gains a delicious recipe but also a deeper understanding of the chemistry involved in baking.
Demonstrative Speech Examples
To best illustrate the concept, here are the best demonstrative speech examples to motivate and inspire you.
1. “How to Make a Beautiful Gift Basket”: In this video, speaker Megan Harrell explains how to create a stunning gift basket that people will love.
2. “How to Make Frozen Hot Chocolate”: If you’re in the mood for a cold drink, this explainer will teach you step by step to concoct the perfect frozen hot chocolate.
3. “How to Make a Dalgona Coffee”: In this demonstrative speech example, the speaker guides the audience through the process of making a dalgona coffee, a whipped coffee that only needs a few ingredients to make.
4. “How to Solve a Rubik’s Cube”: Solving a Rubik’s cube can be a little tricky, but following this speaker’s instructions on how to solve one might be exactly what you need to figure out this puzzle.
5. “How to Make Slime”: This demonstrative speech example teaches the audience how to make slime at home. Slime has gone viral on social media apps like TikTok for its versatile appearance and types, so learning how to make it yourself can save you a few bucks.
3 Tips for Giving Your Demonstrative Speech
When giving a speech, it’s important to remember a few key points. Here are three quick tips to ace your speech.
- First, be sure to keep your audience engaged by using engaging visuals and stories that are relevant to the topic.
- Second, keep your speech concise and organized by breaking it down into manageable parts.
- Finally, practice what you’re going to say before the presentation so you don’t get too caught up in details or lose your train of thought during the demonstration.
Demonstrative Speech FAQs
Here are the most common demonstrative speech FAQs that you need to know.
1. What’s the difference between a demonstrative speech and an informative speech?
While both types of speeches aim to educate the audience, a demonstrative speech goes beyond verbal explanations by incorporating live demonstrations and visual aids to showcase a process or task. An informative speech primarily focuses on providing knowledge and understanding through verbal communication.
How long should a demonstrative speech be?
The length of a demonstrative speech can vary depending on the topic and complexity of the demonstration, as well as time constraints set by the event or occasion. Generally, it’s recommended to aim for a duration of 5 to 10 minutes to ensure that you provide sufficient information and engage the audience effectively.
What are some effective visual aids to use in a demonstrative speech?
Visual aids play a crucial role in enhancing the impact of a speech. Some popular visual aids include props, slides or PowerPoint presentations, videos, charts, diagrams, and samples. Choose visual aids that complement your topic and demonstration, ensuring they are easily visible and understandable by the audience.
How can I make my demonstrative speech more engaging?
To make your speech more engaging, consider the following tips:
- Begin with an attention-grabbing introduction to pique the audience’s curiosity.
- Clearly explain the purpose and relevance of the demonstration.
- Use storytelling techniques and real-life examples to connect with the audience.
- Incorporate interactive elements, such as asking questions or involving volunteers from the audience.
- Maintain a conversational tone and avoid excessive jargon.
- Conclude with a concise summary and a call-to-action to encourage the audience to apply what they’ve learned.
Can Yoodli provide assistance with speech organization and structure?
Yes, Yoodli can help with speech organization and structure. Yoodli automatically analyzes the top keywords of your speech or presentation. After practicing with Yoodli, check to make sure your top keywords align with your intended message. If they don’t, then go back to your script and rework the structure and content of your presentation until Yoodli catches the correct top keywords.
How can I incorporate visual aids into my demonstrative speech?
It’s important to use props, slides, videos, or other visual elements to enhance the audience’s understanding and engagement during your demonstration.
Is Yoodli suitable for both beginner and experienced speakers?
Yes, Yoodli is designed to benefit speakers of all levels, from beginners looking to build confidence to experienced speakers seeking to polish their skills. Yoodli’s personalized feedback and tailored recommendations cater to your individual needs, helping you improve and refine your speaking skills regardless of your current proficiency level.
Remember, if you have any specific inquiries or need further assistance, you can always refer to Yoodli’s official website or reach out to their support team for detailed and up-to-date information.
Demonstrative Speeches in Summary
Demonstrative speeches have the power to educate, inspire, and entertain. By combining verbal explanations with visual demonstrations, these speeches create engaging and interactive experiences for the audience.
With the assistance of Yoodli , your AI public speaking coach, you can refine your delivery, boost your confidence overall, and elevate your presentation skills to new heights. Embrace the art of demonstrating, captivate your audience, and unleash your communication power with impactful demonstrative speeches.
Start practicing with Yoodli.
Getting better at speaking is getting easier. Record or upload a speech and let our AI Speech Coach analyze your speaking and give you feedback.
Best Tips To Write An Amazing Demonstrative Speech
6 steps to write a brilliant demonstrative speech + topic ideas.
A demonstrative speech is a form of instruction during which you show your audience how to perform a specific task or complete the process. To make their demonstration easy to understand, speakers rely on visual aids, such as videos or presentations.
In this post, our experts will explain how to develop and deliver an effective demonstration speech even if you don't have much public speaking experience. Below, you will find a step-by-step guide for preparing your speech and some great demonstration speech ideas if you're feeling stuck.
Need your demonstrative speech by tomorrow? Worries aside - the speechwriters of SpeechPath can create a powerful demonstration speech plus visual aids for you in just 12 hours. We will match you with an expert in your area who will work one-on-one with you to develop a persuasive, plagiarism-free speech with your audience in mind. Special student discounts are available!
Choosing a powerful demonstrative speech topic
The purpose of a demonstrative speech is to instruct or educate the listeners about doing something. Thus, you will want to choose an applicable subject and provide your audience with a step-by-step process to complete a specific task (apply makeup, read the stars, play poker, save money, or else).
College students or corporate speakers usually have a specific subject they need to talk about. If you don't have a topic at hand, here's how to choose an efficient subject:
- consider your interests - do you know a specific topic well enough to instruct others? Can you share your knowledge in a way that a wide audience will easily understand? Can you make your topic engaging even if it's technical?
- mind your audience - to whom will you deliver your informative speech? Will your audience be interested in the subject and how will they benefit from your instruction?
- time and location - what is your time limit for delivering a good demonstrative speech? Will you be able to deliver a strong presentation within that limit? How many listeners will be present and what type of the event is it?
By thinking these points through, you'll identify the relevant and helpful subject and evaluate the level of depth and detail for covering your subject. If you are feeling stuck with your demonstrative speeches subject, take a look at some ideas below.
8 examples of a good demonstration speech topic
If you have the freedom to choose your demonstration speech topics, take a look at these options:
- How to swim backstroke: Tips for beginners
- Essential photography composition rules and techniques
- How to manage your email account for better productivity
- Using body language effectively during job interviews
- How to make a paper airplane in five minutes
- How to operate a new content management software
- Tips to quickly change a flat tire
- How to start making money on your blog
6 demonstrative speech topics for students
If you are struggling to choose a demonstrative speech topic you'll deliver in class, consider these ideas:
- How to apply for a scholarship as a college student
- How to find common ground with a demanding instructor
- Planning your diet to stay healthy
- How to apply daily make up
- Choosing and preparing a backpack for a trip to the forest
- How to get excellent grades in college and avoid burnout.
How to create a demonstration speech outline?
Now that you have explored some unique demonstration speech topics and chosen your own, it's time to think through your speech. Since you want to instruct the audience to perform a particular task, you need to deliver your speech in a structured, organized way. Thus, your target audience will grasp your speech better and learn to apply the skills in real life.
A strong outline for demonstrative speeches includes sections as follows:
- Introduction - at the very beginning, you introduce your subject, explaining why you have chosen it, and what your audience will learn. Quickly walk them through the structure of your speech so people knew what to expect.
- Body - in the main part of your speech, you explain the terms and clarify the course of actions to them. Use a simple, step-by-step process, and provide bite-sized information to keep your audience engaged. If the topic allows, show the steps you take in chronological order.
- Conclusion - here, you summarize the key points of your demonstration speech topic for the audience and inspire them to perform a certain action. You might also raise some concerns or share additional information or sources which can be helpful.
Demonstrative speech example
7 tips to create a mind-blowing demonstrative speech
Understand your audience.
To deliver an effective speech, understand who your audience members are. Consider their age, gender, education level, beliefs, interests, and many more. For example, demonstration speeches for corporate professionals or college students will differ from those for the general public.
By understanding your audience, you will be able to use language, examples, and visuals that they will easily comprehend. Thus, you will craft a speech that resonates with your audience and leaves a lasting impression.
Research and gather information
Even if you consider yourself an expert in some area, your speech will only benefit if you do research and look through credible sources. Whether you prepare a speech on mental health, using software, or developing soft skills, this will make your speech more informative and foster deeper understanding.
Gather relevant information and dive deeper into the topic you've chosen by reviewing books, monographs, and articles, or conduct an interview with an expert. Note down the techniques, tips, and interesting examples that might be interesting for your audience. By collecting valuable knowledge, you'll make your speech more engaging and vivid.
Organize and structure your speech
As you gather information, organize it in a logical and structured manner, following the outline presented above. Walk your audience from start to finish of the process, equipping them with valuable insights they need to understand how to perform the task.
Share specific steps with your listeners, followed by a brief explanation of what exactly to do at each stage. Thus, they will stay genuinely interested and follow you, understanding the progression of your speech. Add transitions so that they could see how each step flows smoothly into the next one.
Give the topic overview
When you introduce a completely new topic to the audience, they might be worried that they fail to understand something. Address their concerns by sharing a brief outline of the process with them.
Firstly, define the objective and the core message of your speech, i.e. what people will learn or what skill they will gain at the end of the lecture. After introducing your subject, specify what you'll be talking about, in what order, and what steps you will share with them. Thus, people will know what exactly to expect from your speech and will be more receptive to hearing your thoughts and insights.
Use visual aids and examples
All demonstrative speech topics include showing or telling the audience how to do something. A visual aid can go a long way in this process. By choosing appropriate pictures, videos, charts, and slides, you will explain the topic to the audience more effectively while keeping them engaged and focused throughout your speech.
Make sure that your visual aids are clear, informative, and relevant to your core message. With correct visuals, people will remember more of what you are telling them. Use jokes or memes, if appropriate, to lighten the mood. If you are not creating visual aids yourself, make sure you have the right to use them in your presentation.
Save some time for Q&A
Since you'll be introducing a new topic to the audience, most likely, they will have questions at some point. Reserve some time for a Q&A session at the end of the speech. Anticipate questions that your listeners might have, and prepare answers to them in advance.
If, during your presentation, you notice that the audience looks confused, you might want to repeat the points they find difficult. Thus, you won't have to explain things from scratch during the question-answer session at the end.
Practice delivering the speech
Little people are naturally good at public speaking, so you might want to practice your speech at home. Reading your speech aloud can also help the speech organization, as you'll see if some points of your text need clarification. Plus, rehearsing your speech multiple times builds your confidence and helps perfect your delivery.
You can practice in front of a mirror, watching your body language and facial expressions. Consider delivering your speech to friends or family members to hear their feedback. Time yourself as you speak to make sure that your speech does not exceed the allotted time limit.
Using visual aids in your speech: tips to prepare an engaging presentation
Most demonstrative speeches go with visual aids such as videos, posters, or PowerPoint presentations. Using videos, graphs, and images is of great help to organize your speech and deliver the practical steps to the audience more effectively. Here are some tips to prepare an effective presentation to accompany your speech:
- Avoid transitions and sound effects. They will distract people rather than enhance your ideas and your message. Also, stay away from fancy formatting and bright fonts. Keep your slides simple and professional.
- Do not read from slides. Remember that visual aids are there to enhance your message and show the audience pictures and schemes. Do not use them as your public speaking notes. This can make an impression that you don't know your topic enough or lack confidence.
- Use little text. Use text on slides only to repeat your main points or to list the sequence of actions. Do not put paragraphs or even sentences on slides. The optimal volume of text in your presentation is up to 8 lines per slide.
- Add pictures, graphs, and videos to illustrate your point. Graphics are effective if you want to draw the audience's attention to important steps of the process or share curious facts. Yet, avoid adding pictures for the sake of them - ask yourself "Does this help deliver my message?"
- Use colors properly. Use pastel colors for the background to make the information on your slide easily readable. Opt for complimentary colors so that your slides are easy on the eye, and no more than three colors per slide.
- Be careful with humor. If you deliver your speech in an informal setting, it is okay to add a couple of funny pictures or memes to lighten the mood. However, consider your audience and the event first to avoid putting yourself in an awkward situation.
Using our tips and strategies, you'll manage to craft a great speech even if you haven't written speeches before. Keep your target audience in mind, customizing your message for them, and work on your delivery to make your speech helpful and memorable.
Need a helping hand with your speech?
Our in-house ghostwriters can prepare a unique demonstrative speech for you from scratch, or edit and improve the one you already have. You'll work one-on-one with a dedicated expert who keeps polishing your text until you are satisfied. Chat with us to discuss how we can craft a shiny speech for you at a pocket-friendly price!
Dear visitor, our website has been recently updated. You can contact us if you have any concerns regarding the new version of the website. Your feedback is greatly appreciated.
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Communication Skills
- Public Speaking
- Speechwriting
How to Write a Demonstrative Speech
Last Updated: September 19, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Lynn Kirkham . Lynn Kirkham is a Professional Public Speaker and Founder of Yes You Can Speak, a San Francisco Bay Area-based public speaking educational business empowering thousands of professionals to take command of whatever stage they've been given - from job interviews, boardroom talks to TEDx and large conference platforms. Lynn was chosen as the official TEDx Berkeley speaker coach for the last four years and has worked with executives at Google, Facebook, Intuit, Genentech, Intel, VMware, and others. There are 7 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 270,952 times.
Demonstrative speeches are intended to teach an audience how to do a specific thing. They can be long and detailed, or short and simple. Even if you're an expert at your topic, the process of writing your speech can seem difficult. However, once you sit down to write a great speech, you're likely to get more excited about your topic than ever.
Choosing a Topic

- For example, to give a speech about how to perform general car maintenance, you might need an hour for your presentation. That's because it's a broad topic. If you only have 15 minutes, you should narrow your speech to something like how to change a car's oil.
- If you don't have control over the length of time or the topic, you'll need to adjust your speech accordingly. If you have too much information for a short amount of time, don't go into much detail. If you have a long time for a simple topic, you can expand your speech with some history or related facts.

- For example, if you're giving a speech to professional bakers, it might not be appropriate to choose the topic, “How to Bake a Cake.” You'd probably want to make your topic more interesting to them with something like, “How to Bake Authentic French Style Pastries.”
- The age of your audience matters, too. For example, if your audience is young children, you might choose the topic, “How to Take Care of a Plant” instead of, “How to Grow Perennials.”

- Look up your topic online. Other people may have made instructional videos that you can get tips from.
- If you know any experts on your topic, ask them for advice.
- Visit your local library and checkout books on your topic. Books are excellent sources of information, and are considered reliable sources when doing research.

- You should be able to use useful visual aids via a PowerPoint presentation or manageable props and examples. So a topic like, “How to replace your car's transmission” is probably not a great topic. However, something like, “How to make a spinach salad” would be easy to do.
Writing the Speech

- The outline should contain three sections: the introduction, the body, and the conclusion.
- The body should be broken up into the various steps of the process.

- When writing a speech, you want to simply write notes. You don't need to write out the speech word for word. Write enough to make you comfortable with the material, but not so much that you'll be reading off of your paper.
- Try to remember what it was like when you learned how to do this thing. What steps required more explanation than others?
- Unplug the saw.
- Locate the screw under the blade.
- Turn the screw enough to loosen the blade.
- Remove the blade.
- To keep the audience engaged, think of how you can involve them. Will you include audience participation? Will the demonstration be hands-on? Will you tell jokes or ask the audience questions? These can all be great strategies for keeping people engaged.

- Your call to action could be something like, “By learning to change your own motor oil, you'll be able to save money and feel the empowerment of taking care of your own car!” or, “French style pastries are a welcome addition to any gathering, as you'll see when you bring them to your next party.”
- Avoid introducing new information in the conclusion. That will leave the audience confused and with unanswered questions.

- Writing the introduction last is a good idea, because then you'll have already thought hard about your speech. By now, you know everything you want to say about the speech, so you can determine what is most essential to get people excited about it.
- To get people excited, use inspiring language such as, “You may have never thought you'd be able to change a flat tire yourself, but actually, it's remarkably simple!” or, “French pastries are one of the treasures of European cuisine.”
- Even though you write the introduction last, it is always the beginning of the speech.

- Take note of anything you'll want to add to the speech to explain the visual aids. For example, do you want to say something like, “I'm using unbleached white flour, but you can also used bleached flour if you prefer.”
Practicing Giving the Speech

- Review your notes as you would before giving the speech in front of people.
- Try performing the speech in front of a mirror. You should be able to look yourself in the eye much of the time, instead of always having to look at your notes.
- Go through the complete demonstration, along with your visual aids. If you don't, you might not realize that parts of the demonstration don't work as you've written them.

- Once you've made the changes, practice and try performing the speech for yourself again.
- Always use the visual aids, even if you've already used them once.

- You may want to invite some friends who know nothing about the topic and some who are experts in the topic. That way, you can get different perspectives on how useful your speech was.

- Ask specific questions of your test audience. You can ask them if they understood the different steps, or if there was anything they felt you missed.
- You may want to write down the feedback you get, or ask your friends to write it down so you can look at it later.

- You don't always need to incorporate others' feedback. Sometimes it won't be useful or accurate. However, if you got the same feedback from more than one person, chances are that it would be worthwhile to consider.
Sample Demonstrative Speeches

Expert Q&A

- Writing a speech and giving a speech are related, but are different skills. When it's time to deliver your speech, practice good public speaking. Be warm, upbeat, and clear. Thanks Helpful 1 Not Helpful 0
- Watch videos of other people giving demonstrative speeches. Notice what you appreciate about the good ones, and what doesn't work for you. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 1

You Might Also Like

- ↑ http://www.myspeechclass.com/demonstration-speech-topics.html
- ↑ Lynn Kirkham. Public Speaking Coach. Expert Interview. 20 November 2019.
- ↑ https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/what-is-demonstration-speech
- ↑ https://www.hamilton.edu/academics/centers/oralcommunication/guides/how-to-outline-a-speech
- ↑ https://www.comm.pitt.edu/visual-aids
- ↑ https://www.unr.edu/writing-speaking-center/student-resources/writing-speaking-resources/speech-delivery
- ↑ https://open.lib.umn.edu/publicspeaking/chapter/14-4-practicing-for-successful-speech-delivery/
About This Article

- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Charlene Fowler
Oct 9, 2016
Did this article help you?
John Loid Sumagaysay
Jan 1, 2018
Audrey Mamacita
Apr 5, 2018
Feb 22, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Level up your tech skills and stay ahead of the curve
279 Demonstration Speech Topics and Ideas: A Complete Guide
Before proceeding towards the demonstration speech topic, let us know what it actually does.
Demonstration speech clarifies how to do something or how something works. Here, the objects or physical activity by the presenter is displayed.
It is also considered as one of the basic types of presentation. They are usually assigned to high school and college students.
This type of speech is popular in commercial and other adult training surroundings. They are among the most widespread speech.
A demonstration speech is a kind of informative speech. The primary purpose of the presenter is to teach the audience about the task or the procedures in steps.
Due to its popularity, the presenter must present the demonstration speech decisively. The key purpose of Demonstration speech is to develop skills in expository speaking.
It also helps to present a process or steps using objects or physical activity.
- Argumentative Speech Topics and ideas: A Complete Guide
- Informative Speech Topics and Ideas: The Ultimate Guide
- 100 Easy Persuasive Speech Topics and Guide
Yet, most of you might not know the basics to deliver an effective demonstration speech. If you count on the one, this article is especially dedicated to you.
Through this article, I will present demonstration speech topics along with some effective tips.
When you have selected the demonstration speech topic, make an attractive and effective starting. It is better to start with an introduction.
Follow these steps for better consequence:
- Give short description about the topic you are going to present
- Why you decide to present on the topic
- Why your listeners should understand how to do it. Give them a sneak glance of a few paybacks.
- Tell them that they are going to do it themselves after sometimes. This is the only thing your audience have to do is pursue your directions.
Table of Contents
1. Start with why
4. give a brief summary of the complete process, 3. go through the steps, one-by-one, 4. talk about preferences, extras, or variation, 5. allocate time for queries, 6. summarize briefly, 1. try to get audience members doing it, 2. visuals lead a demonstration speech, 3. expand your demonstration with follow-up resources., some rules for presenting demonstration speech, informative demonstration speech topics:, specific demonstration speech topics:, tech-related demonstration speech topics:, hobby-related demonstration speech topics:, fashion-related demonstration speech topics:, household-related demonstration speech topics:, demonstration speech topics for students:, demonstration speech topics for business:, funny demonstration speech topics:, demonstration speech topics for health/fitness:, conclusions, outline of demonstration speech.
There are different methods to present a demonstration speech. Some of them are listed below:
A demonstration speech deals with training the audience to carry out a task or the whole process. Just as with any instructive task, it can become helpful when your audience is motivated to learn.
It is a must to tell your audience how they get to benefit from the knowledge you are about to present. When your audience knows the reason behind learning a new task, they desire to learn.
There are different ways to encourage your audience. Yet, one of the best ways is to start the speech with a why or some motivational stories. Draw an image of how their life improves with the new knowledge.
Earlier than you dive into the information, give an overview of the general process. An advanced outline of the steps implicated makes audiences understand the benefit of speech.
While learning a new task, some of your audience will fear that it is difficult. An early outline ensures your audience that it is not too difficult.
When you do not provide a brief, it’s complicated for your audience to understand the steps.
The audience won’t have the essential framework. An ideal way to show the outline is a figure explaining the steps of the task at a high level.
Together with the outline, you can list the basic needs of the task, and any assumptions you are making.
For an instance, for a speech on how to format the computer, explain with images. You can also use screenshots here to make them clear.
One of the finest things about a demonstration speech is the core of your overview that is set for you. Here, you only need to endure the steps of the task in order.
Better make the sequence of steps as easy as possible. Break down the process into important steps and make your audience understand clearly.
Now, your audience has noticed the task or procedure presented from start to end. Better provide some extra options or variations.
For an instance, you are presenting on how to cook chicken. Start with the necessary description at first. After that, discuss alternate ingredients, various flavors, and other ways to cook chicken. This makes your speech interesting.
Taking queries from the audience and answering them is compatible for a demonstration speech. This lets the audience look for an explanation on any of the steps which they do not understand. Relevant to the topic and circumstances, you can decide to take questions at the end.
At last, you should summarize the procedure in brief, and review the advantages. This lets your audience know the benefits of performing a similar task.
Best Ways to Elevate Your Demonstration Speech
Below is the list of best tips on how to elevate your demonstration speech:
Your preference for audience participation is often determined by how long your presentation is.
It also includes the setting in which the expression takes place. The accessibility of supplies can be shared by the audiences as well. It will be great if you get the audience to participate in the presentation.
Every demonstration speech gets better with appropriate visuals to follow your demonstration and procedures.
For an instance, for the speech on swimming, keep different relevant images. This gives audiences an idea to swim knowing the procedures.
Find here some options:
- Your body plays a significant role – For physical task speech like playing a football, your body plays a significant role. You can express each of the steps to enhance the demonstration.
- Physical support gives the real experience – There are two different types of support and they are real and models. Real support is the actual objects used while presenting the task. Models are the fake version of the real object and scaled-down version.
- Utilize images as much as possible – When your body and physical support are not enough, use images as much as possible. When you do this, it helps to engross yourself in the images to alive the action that would be implicated.
Any type of images you prefer, make sure your audience can see them with ease. If they cannot see your images they might not understand your speech as well.
A single presentation may not be enough to guarantee your audiences gained the knowledge. To get a better result, provide resources they can use after the demonstration is over.
This covers:
- Internet, books, pamphlets, or other specialist sources. They can ask for deeper information or high-quality training.
- Handout the steps, and diagrams or images to prove key details.
- Give contact information. So that your audience can contact in the future as they try to apply the knowledge you have presented.
- The speech you present should be original by the applicant.
- Objects or physical activity by the presenter should be displayed.
- Presentations will take place in a normal-sized room. A table or desk will be supplied. All visual aids, property, and tools are to be supplied by the presenter.
- This category excludes the use of property or tools. This comprises, but not imperfect too, weapon, sharp knives, unsafe chemicals, and animals.
- Only one person should be used to help out the presenter. They can help as the object of the demonstration. They can also set up or handle the equipment. It is permissible for the assistant to be both an object of expression and to assist with equipment.
- The highest time limit ion of the speech is 10 minutes, counting set up and strikes down. A 30 second is allowed, after which one point will be reduced from the assessment item coping with the rate.
Some Demonstration Speech Topics:

- How to Get the best airfare
- How to Work with a travel agent
- How to become the prime minister
- How to become a pilot
- How to Pack a suitcase
- How to Travel and Leisure
- How to landscape your front yard on a limited budget
- How to read a map
- How to print a digital photo
- How to use oven
- How to set and splint a broken leg (when medical help is not available)
- How to drive a car
- How to prevent injury
- How to calculate a mortgage payment
- How to register for voting
- How to tie a knot
- How to clean running shoes
- Give a baby a bath
- Change a diaper (think about baby safety too)
- Read and understand nutrition labels
- How to avoid identity theft
- How to play poker
- How to make beads
- How to make an ice sculpture
- How to make a bird feeder
- How to attract hummingbirds to your garden
- How to whistle
- How to make your garden full of flowers year round
- How to fix a flat tire
- How to create a Halloween mask
- How to clean your car
- How to cash a blank cheque
- How to Save electricity and save money
- How to Save auto fuel and money
- How to Buying a fuel-efficient car
- How to Save Money
- How to taste wine
- How to organize a surprise party
- How to clean your swimming pool
- How to clean your golf clubs
- How to make a new candle of old ones
- How to organize your wedding
- How to make a water-colour
- How to build a shed
- How to find a public speaking program that works
- How to become a good actress
- How to become a famous film star
- How to write a film script
- How to stop thinking
- How to write a business-like letter
- How to train your brains
- How to greet Japanese people
- How to become a policeman
- How to climb a building
- How to make a dancing show
- How to become the president
- How to be in the chair in a meeting
- How to start Green Commuting
- How to board in sand
- How to ride bicycle
- How to paint a room
- How to swim
- How to draw a house
- How to play chess
- How to clean golf clubs
- How to clean shoes
- How to wash and wax a car
- How to plan a party
- How to arrange flowers
- How to wrap a present
- How to build a sled
- How to Decorate a cake
- How to make a paper aeroplane
- How to juggle
- How to iron a shirt
- How to paint a table
- How to decorate a Christmas tree
- How to Install a dimmer switch for a light (not for fluorescent lights)
- How to Install a car stereo
- How to make garden stepping stones
- How to feed a snake
- How to make a fishing lure
- How to detect if someone is lying
- How to develop the best serve in a tennis game
- How to knot a carpet
- How to make honey
- How to blow a glass
- How to use the cruise control
- How to make a genealogical tree
- How to Make a hydrogen supplemental fuel cell
- How to calculate your golf handicap
- How to make a golf swing
- How to find the best health insurance
- How to find the best car insurance value
- How to calculate wallpaper
- How to build a go-cart
- How to clean silver
- How do bulletproof vests work?
- How do airbags work?
- What can duct tape be used for?
- How to create an animated character
- How to become an empath
- How to format computer
- How to Program your cell phone
- How to Download or upload files on the computer
- How to Build a good website
- How to Build a website
- How to Set up an e-mail account
- How to set up a blog
- How to install a WordPress theme
- How to create an iPhone application
- How to upgrade the memory in your computer
- How to remove scratches from DVD’s
- How to make a foxhole radio
- How to play a computer game
- How to send an email
- How to play an online games
- How to use linkedin
- How to live a more private online life
- How to play clash of clan
- How to use a cell phone
- How to text a message
- How to bottle your own wine
- How make a sweet lassi
- How to make an ice-cream
- How to pick a color and understand the color palette
- How to Grow a herbal garden
- How to dance
- How to do card tricks
- How to make sushi
- How to ride a unicycle
- How to do magic tricks
- How to knit/crochet
- How to decorate a cake
- How to Grow and prune a bonsai tree
- How to throw a ball
- How to Play a video game to win
- How to make your own soap
- How to make candles
- How to play football
- How to use a DSLR camera
- How to create a worm farm
- How to do graffiti
- How to do poi spinning
- How to do origami
- How to take a picture with a digital camera
- How to paint an egg
- How to write a limerick
- How to line dance
- How to compose a photograph
- How to swim the backstroke
- How to pick locks
- How to edit a video
- How to dance a certain dance
- How to solve a Rubik’s cube
- How to make a pop-up card
- How to make animals out of balloons
- How to make paper Mache figures
- How to speak Italian
- How to make stained glass objects
- How to beatbox
- How to raise tadpoles
- How to read music notes
- How to learn playing guitar
- How to use your breath when you sing
- How to make beer
- How to play piano
- How to make a cocktail
- How to bowl
- How to read music
- How to lay a table
- How to waltz
- How to perform a card trick
- How to Apply acrylic fingernails
- How to Manicure your own fingernails
- How to Manicure someone’s fingernails
- How to Polish your shoes
- How to Accessorize with the clothes your wear
- How to Coordinate clothes for any occasion
- How to frost hair
- How to make your own jewellery
- How to apply hair dye to your hair
- How to apply a permanent to someone’s hair
- How to braid cornrows
- How to braid hair (had to do this in nursing school)
- How to dry your hair properly
- How to clean brush your teeth (back it up with scientific research)
- How to put on makeup
- How to trim a bonsai tree
- How to trim your moustache
- How to wrinkle a skirt
- How to do braids
- How to use scarves on your head, neck, body
- How to tie a tie
- How to make your own wedding dress
- How to dress like a princess
- How to become a princess
- How to fold a skirt
- How to apply face paint
- How to Set a formal dinner table
- How to Choose a bottle of wine for dinner
- How to open a can peaches
- How to carve a pumpkin
- How to Plan a vegetarian meal
- How to Frost and decorate a cake
- How to Make a fast summer salad
- How to Make Barbecue sauce
- How to Make a peanut butter and jelly sandwich
- How to make a sweet dessert
- How to make ice
- How to Make a root beer float
- How to Make an omelette
- How to Make pancakes
- How to Make Ice cream
- How to Tenderize meat
- How to Make a subway sandwich
- How to Plan an eight course meal
- How to make peanut butter bars
- How to make chicken chilli
- How to Bake cookies
- How to Make devilled eggs
- How to Bake a cake
- How to Stuff a turkey
- How to Make fudge
- How to bake a pie (or anything else you like / know how to cook)
- How to be a vegetarian
- How to eat oysters
- How to Make your own jelly
- How to Eat with chopsticks
- How to make burgers
- How to make Irish Coffee
- How to make a fast summer salad
- How to Save water at home
- How to Recycle at home
- How to Build Green
- How to Save energy at home
- How to Grow your own garden
- How to change a plug
- How to mend a fuse
- How to Create a PowerPoint presentation
- How to write a resume
- How to be a model student
- How to do well on standardized tests
- How to deliver an informative speech
- How to do proper time management
- How to socialize with more people
- How to balance work and school
- How to find a part-time job
- How to write a college essay
- How to give a presentation
- How to organize an event
- How to start a bed & breakfast
- How to hire the right people
- How to sell yourself
- How to effectively close any client
- How to network well
- How to create a business plan that works
- How to make the most of working from home
- How to do nothing for a living
- How to live an anti-social life
- How to make your ex jealous
- How to get more presents on your birthday
- How to deliver a speech with a handover
- How to scramble together a last-minute presentation
- How to lose your belly fat
- How to do yoga
- How to stretch before working out
- How to kick box
- 5 minute workouts to keep you fit
- How to perform tai chi
- How to plan your diet
- How to snowboard
- How to manage stress
- How to check your blood pressure
- How to check your blood sugar
- How to train for a marathon
The demonstrative speech topics and ideas presented above should help you get started with your demonstrative speech and deliver a powerful speech. Let me know what you think about this article by commenting below.

- Choosing Good Topics
- Controversial
- Demonstration
- Extemporaneous
- Informative
- School/College
- Special Occasion
- Public Speaking Help
- Writing a Speech
- Free Sample Speeches
- Share Your Speech
- Demonstration Speech Outline

A demonstration speech outline is essential when you're writing your presentation, as it helps you logically organize your thoughts. A demonstration speech is a "how to" speech , in which the speaker demonstrates to the audience how to do a particular process or activity.
(If you haven't yet chosen the theme of your presentation, here are some great topic ideas to help you out.)
An outline for this type of speech is easy to prepare since the body of the statement mainly consists of the steps of a process or activity you are demonstrating.
Start your outline by creating a skeleton of the main parts
Sample abbreviated outlines are included below f or the introduction and the conclusion pointing out several important aspects of those sections, such as attention devices, theme, and clinchers. The framework for the main body consists of the main points and sub-points that need to be discussed for the topic.
A typical essay three-two or two-three essay format often works well for a speech. The speech below has three main points: materials/tools, steps, and tips. Fill in the sub-points with details, supporting references, explanations, alternatives, answers to frequently asked questions, or appropriate information necessary to understand the main point.
With a demonstration speech outline, the goal is to construct the content of the speech carefully, so the audience leaves with the targeted degree of understanding. The framework gives you a bird's eye view of the overall presentation and helps the writer to avoid holes in the steps and information provided. While also, the outline helps the writer be concise and organized to avoid giving too much information and causing confusion or overwhelm.
What to put in the introduction and body of the demonstration speech outline?
The outline should start with an introduction that explains to the audience the process you will be demonstrating.
Be sure to include any history or background that is interesting or helpful to the audience.
For example, if you were to demonstrate how to tie-dye clothing, your introduction might touch on the history of tie-dying, showing examples of the types of clothing and accessories that are suitable for the process and a few finished articles!
The body of a demonstration speech can be divided into several sections.
If you are demonstrating how to complete a craft project, for example, you might have a segment on materials, then one containing all the steps, and a final section on how to care for or display the finished product. The sections would be the main points of your speech. For example, if you were to write a demonstration speech outline for a speech about how to make a scrapbook, it might look something like the textual framework below scrapbook image.

Introduction Section - Demonstration Speech Outline
Sample skeleton outline for the introduction on scrapbooking:
A. Attention Device
- ask Q's relate boxes/stacks
- relate pleasure
B. Foreshadowing
- will solve problem
- identify scrapbooking as solution
- pleasurable
C. Transition and overview main points
Detailed Outline of the Scrapbooking Speech Introduction with Draft of the Text:
- How many of you have a box of old photographs? Or maybe a stack of newer ones that keep piling up? How would you like to create something with those photographs that will be fun to make and give people pleasure for years?
- Today I am going to show you some great ideas for preserving your old and new photographs by scrapbooking.
- Scrapbooking has been around for a long time, but lately, it seems to have grown in popularity. This means there are lots of new and fun tools and materials on the market to make scrapbook even more of a pleasurable pastime!
Body Section - Demonstration Speech Outline
1. Materials
- Scrapbook
- Embellishments
- Adhesive
- Stamps
- Scissors
2. Scrapbooking steps
- Select photos
- Choose a theme
- Design page
- Attach pictures, frames, ribbons, etc.
- Add stamps and labels.
OR - use a purchased scrapbooking kit.
OR - freestyle (a more haphazard style of scrapbooking with no 'rules')
3. Tips for preserving scrapbooks
- Use lignin-free paper
- Use acid-free and color safe fabrics
Conclusion Section - Demonstration Speech Outline
Sample Skeleton Outline for the Conclusion:
A. Transition
- clause tying to the body
- begin summary of the main points
B. Tie-in to the theme
C. Clincher
- exhort audience to start scrapbooking
- tie-in to theme of fun
Detailed draft of the text of the scrapbooking speech conclusion:
- Making scrapbooks is a great way to preserve your memories for yourself and others and can last for generations with high quality paper and fabrics.
- So, with the right tools and steps, scrapbooking is also fun and easy.
- Get yourself started and enjoy!
As you can see, the conclusion of a demonstration speech outline generally summarizes the speech and encourages the audience members to try it for themselves. If the presentation was truly effective, the audience should be inspired and feel empowered to give it a try!
I hope that now you can see how easy it is to prepare a demonstration speech outline and feel ready and inspired to try one yourself!
Free email delivery
MASTER INFORMATIVE SPEAKING WITH OUR FREE CHECKLIST!
We are offering you a FREE SpeakFlight Informative Speaking Preparation Checklist. This valuable resource is packed with step-by-step guidance to help you create compelling, memorable, and effective informative speeches.
Share this page
Return to the Top of the Page
Recommended pages:
Another Demonstration Speech Outline to Follow Tips for Writing Demonstration Speeches 100 Demonstrative Speech Topic Ideas "How To" Speech Topics
- Best Speech Topics
- Demonstration Speech Topics

Easily search your speech type
Just check out the sitemap for best-speech-topics.com , which lists all the pages on the site, or use the search box below:
Get to Know Us
- Privacy Policy
Attention Grabbers
- Positive Quotes for Kids
- Quotes for Graduation Speeches
- Poems & Quotes on Death
- Quotes on Retirement
Most Popular Pages
- Free Samples
- Good Speech Topics
- Hypnotize Your Audience
- Welcome Speech
Select a Speech Topic
- Argumentative
- Commemorative
- Inspirational
- Interesting
- Other Topics
Let Us Help You
- How To Write a Speech
- Demonstration Outline
- Informative Outline
- Introductions
- Using a Microphone
- Speech Help
- Speeches Made Easy
- Speech Crafting →
How to Write a Demonstrative Speech (An Instructional Process)

Depending on one’s life and activities, we all have tasks that should be completed every single day, no matter how mundane or difficult they may be. But what if there are tasks that you are required to carry out but have no clue how to? This is where demonstrative speeches come in.
These are basically “how to” speeches that outline and elaborate different ways to complete a particular task. These instructional speeches are very common, especially in high school and college and are also very necessary in environments that require training, such as the corporate world.
Demonstrative speeches usually give a step-by-step process on how to do a specific task, which is then followed up with explanations and any additional information that may be needed to carry out that task. Having some visual aids that help demonstrate the steps required to achieve the task also goes a long way in providing context to your audience.
Process for Writing a Demonstration Speech
First things first, before writing any speech, you need to draw up an outline . This will help you avoid having a jumbled up speech, and will allow you to organize your speech in a way that is easy to follow and understand.
1. Begin your outline by asking yourself "Why"
What new information will an individual gain from your speech? As we have seen above, a demonstrative speech teaches your audience how to carry out a certain task.

People tend to learn easily and understand things better when they are motivated to do so. Therefore, you should tell your audience why they should listen and learn about what you will be teaching them.
People don't buy what you do, they buy WHY you do it."

Simon Sinek
By revealing to them how they will benefit from the information you provide, you motivate your audience to want to learn more about your topic of discussion.
2. Provide an overview
Once you have revealed to your audience your topic of discussion, it is important that you give them a general outline of your entire process. This is because when learning a new task, some people may fear that it will be too complex for them.

Providing an overview helps assure your audience that not only is the topic beneficial but it is also easy to follow.
Additionally, it provides your audience with context on how the steps you highlighted here will fit together as you delve deeper into your demo.
3. Explain the steps involved in your process
This is the most important part of a demonstrative speech.
First, you should ensure that you have arranged your steps in the correct order to avoid any confusion. After this, you will then need to explain each step down to the minute details in a language that is easy to understand .

Here, you will explain what exactly is required in each step, how it will be done and the reason why it must be done. The use of visual aids in this step is crucial as they will assist individuals in your audience to understand better.
Pro-Tip: Ensure that the number of steps you have in your speech are as few as possible, this will help avoid confusion.
Additionally, you should maintain eye contact with your audience as you demonstrate each step.
4 .Talk about variations, other options and instructions
Now that you have demonstrated to your audience how the task should be conducted from start to finish, you can now provide them with variations to the process or additional options.
For instance, if you were explaining how to cook a certain dish, now is the time to reveal to them alternative ingredients that can be used to make the dish.
5. Ensure you allot time for Q&A
Question and answer portions allow a session to be more interactive . Additionally, this time can be used to clarify some steps that had not been well understood by the audience, which in turn, clears up confusion.

Pro-Tip: Monitor your time as you give a demonstration, as this will ensure that you do not rush through the entire process and have to explain everything once more in the Q&A session.
6. Give a brief summary to your instructional speech
You should end your speech by giving a short summary of the whole process, after which you can go through the benefits once more and assure your audience that not only is the entire process easy but it’s also realizable.
You might also like: How to End Your Speech with a Bang
Now that we’re good to go on your speech outline , let’s focus on some extra tips.
How to choose the Best Demonstrative Speech Topic
Your topic is an extremely important part of your presentation, as it should reflect your process as well.
Here are a few tips to guide you on how to choose the best topic for your demonstrative speech.
- Take into consideration the amount of time you have to deliver your speech.
This will make it easy for you to determine how broad or lengthy your topic should be. If you have a significant amount of time, you have the luxury and room to incorporate more ideas into your discussion.
- Your audience
Before deciding on a topic of discussion, you should always ask yourself, “will my audience learn anything?” You should ensure that your topic is not only relevant to your audience but also helpful.
We can now move on to what makes a demonstrative speech good.
How to Improve the Quality of Your Demonstration Speech
I believe it’s common knowledge that everyone can write a speech but not everyone can write a good speech. As we have seen above, demonstrative speeches are all about teaching people, so you first need to be organized to ensure that the process is as easy to understand as it can be.

Here are a few things to bear in mind:
1.Speech Structure
Your speech needs to start with an introduction and end with a summary.
You should ensure that all the parts of your speech are cohesive as this will allow you to get your message across without confusing your audience.
2. Visual Aid
Using visuals such as diagrams and charts in your demonstrative speech will help your audience understand better.
Research has shown that an individual learns better through a visual aid. Scaled-down or real props can also be used during demonstrations.
Pro-Tip: Ensure your visuals can be seen clearly from all angles.

3. Follow-up Resources
Apart from using visuals, you can also provide your audience with follow-up resources that they can use after you have finished up with your demonstration.
This will improve the likelihood that the audience will successfully practice the process or task.
Follow up resources can include:
- Handouts, which summarize the steps in the demonstration and include diagrams that illustrate any important features
- Books, websites or pamphlets that can be used to learn more about a certain process
4. Audience Participation
You could also have a few members of the audience participate in the demonstration.
Actively engaging your audience by having them carry out the steps increases the probability that they will remember the steps and be able to conduct the process or task independently even after the presentation.
However, this is dependent on how much time you have to give your presentation. If you have limited time, then you will have to provide detailed handouts to your audience and if you can, get one or two volunteers from the audience to assist you in your presentation.
Pro-tip: Encouraging participation and engaging your audience allows you to have a healthy discussion where individuals are motivated to learn more.
There you have it! Go ahead and write a demonstrative speech making use of the recommendations above, and see how your audience will follow you all the way to the end!
- Games, topic printables & more
- The 4 main speech types
- Example speeches
- Commemorative
- Declamation
- Demonstration
- Informative
- Introduction
- Student Council
- Speech topics
- Poems to read aloud
- How to write a speech
- Using props/visual aids
- Acute anxiety help
- Breathing exercises
- Letting go - free e-course
- Using self-hypnosis
- Delivery overview
- 4 modes of delivery
- How to make cue cards
- How to read a speech
- 9 vocal aspects
- Vocal variety
- Diction/articulation
- Pronunciation
- Speaking rate
- How to use pauses
- Eye contact
- Body language
- Voice image
- Voice health
- Public speaking activities and games
- About me/contact
- 290 demonstration speech topics
- Demonstration speech topics
290 'how to' demonstration speech ideas
By: Susan Dugdale
What are good topics for demonstration speeches?
The answer is simple, but frustratingly inconclusive. It depends. These are 'how to', 'show and teach' or process speeches with literally squillions of topic possibilities.
You could spend hours, or even days, considering this 'how to' speech idea against that one, or that one, or that one. However, you don't need to.
The easiest way is to use the guidelines below to help you pick a good demo speech idea relatively painlessly and quickly.
What's on this page
- How to choose a good demonstration speech topic - 6 key elements to consider
- 290 good demonstrative speech topics in themed lists
- Links to other pages of ' how to' speech topics and help
- The link to an extremely useful printable - a blank demonstration speech outline form
If you already know how to prepare a good demonstrative speech skip the guidelines and either click the link to go to ALL 290 demonstration speech topics or click on a heading to go a themed list.

Animals/Pets
Gardens/yards, games/sports.
- Food & More
Social/Personal
- And then there's...
Choosing a good demonstration speech topic
What makes a demonstration speech topic a good choice depends on 6 essential elements. You'll want to consider each of them carefully.
1. Your interests
Your choice of demonstrative speech topic needs to be something you are genuinely interested in, and know about or, want to know about.
Without enthusiasm or knowledge, it's incredibly hard to inspire and persuade others that they want to find out more about a subject. And that's your goal!
Ideally when you finish your speech, you'll find yourself on the receiving end of question after question from eager listeners.
2. Who the speech is for
You need to think about your audience before making your final choice.
- What demonstration speech topics would truly interest them?
- If you're considering a 'how to' topic you know they already know well, is there something new you could teach them about it?
- What would be of value, and appropriate, for them to know?
3. The setting of the speech
Where is the speech to be given? In a classroom? In a public hall? In a living room? In the open air?
Does what you're planning to do fit the venue?
4. The time you've got to prepare the speech
Does the topic you're considering need a long time to prepare thoroughly? Are there visual aids you need to make to accompany it? How much research do you need to do before you can begin to prepare the speech?
5. The time you've got to give the speech
There is no point in choosing something complex with a large number of steps to show and teach if you don't have the time to cover them. What you select needs to fit easily into the allotted time limit.
If you really want to tackle a big topic, and it's a good fit with your audience, if it's possible, break it down into smaller, manageable pieces. Then choose one or two aspects (sub-topics) you know you can cover well in the time you have available.
For instance, how to knit has many elements: how to hold the needles, how to cast stitches on, how to choose the right wool, how to read a knitting pattern, how to do a specific stitch... Any one of those could become a speech.
6. The guidelines for assessment ...
... if the speech is part of a public speaking course.
You may find there are restrictions on using varying forms of visual aids: video or power-point presentations for example. Check before you make a final decision.
Return to Top
How to use these demonstration speech ideas
Use the 'how to' topics below to kick-start your own creativity. Think of them as beginnings or starting points.
Rather than pick the first idea that jumps out, build up a short list. Then go through it assessing the positive as well as negative aspects of each idea, keeping the audience members, your interest, setting, time and assessment needs in mind.
290 good demonstration speech topics

- read the clouds
- read the stars
- read the tides
- read tree rings
- recognize differing types of rock
- find fossils
- read and navigate a landscape without a map
- use a topographic map
- water divine
- recognize stars in the night sky
- use the phases of the moon for hunting, fishing, or planting crops
- forage for food safely
- collect wild honey
- take wood for fuel sustainably
- build a fire safely
- recognize the common birds or animals in your area
- identify different types of woods
- ensure water is safe to drink
- use the position of the sun to tell time
- tell if a storm is coming
- track an animal in the wild
- choose a good campsite
- forecast weather
- cross a river safely
- protect yourself from attack by wild animals
- tell if ice is safe to walk on
- tell which way the wind is blowing
- recognize poisonous plants or insects
- survive in the wild without an emergency kit
- prepare a survival kit

- train a puppy
- care for a kitten
- walk a dog on a leash properly
- saddle a horse
- hand milk a cow
- teach a cat to use a litter tray
- tell if your pet dog, cat, rabbit... is happy
- feed a dog, horse, cat...correctly
- carry a dog or cat correctly
- interpret a pet dog's or cat's aggressive behavior
- soothe a frightened dog, cat...
- keep a pet dog or cat in an apartment
- give medicines to your dog, cat...
- care for an injured or sick pet
- teach a child how to care for a pet
- make a cat gym
- dropper feed a fledging that's fallen out of the nest or an injured bird
- groom a cat, dog, cow... for a show
- care for baby chickens
- set up a fish bowl or an aquarium
- choose a pet
- clean an animal's teeth
- pet-proof your home
- re-home a dog safely
- care for an orphaned lamb or calf
- transport a cat, dog, rabbit..., safely
- make healthy treats for dogs
- teach a parrot to talk

- companion plant to protect vegetables from insect pests
- prepare basic landscaping plans
- lay bricks or paving stones
- build a fence
- make a swing
- make a children's play area
- build a compost bin
- make a greenhouse
- make a windbreak
- plant a tree
- build a garden seat
- grow from seed
- graft a plant
- prepare and plant a tub of flowers or vegetables
- plant a window box of herbs
- control garden pests
- mulch a garden
- trim a hedge
- prune a rose bush
- care for garden tools
- choose garden art
- make an ornamental pond
- make a bird feeder
- choose the right plants for the right situations
- plant spring bulbs
- make a no-dig garden
- encourage birds or bees into the garden
- make a patio or deck garden

- design & make a greeting card
- make a scented candle
- make a perfect posy of flowers
- learn to draw, sketch
- learn to paint in water colors
- make paper mache
- work hand or string puppets
- use stencils
- make and use natural dyes
- spin or weave
- create a seasonal center piece for the dining table
- make a Christmas wreath
- press flowers
- design and a friendship bracelet
- up-cycle a piece of clothing
- make attractive face masks
- make your own jewelry from antique buttons
- sew your own clothes
- design your own clothes
- bonsai a plant
- make resin and polymer clay jewelry
- arrange flowers for different uses: for the table, as a corsage...
- make your own soft furnishings
- take a brass rubbing
- make paper flowers
- make and use pom-poms creatively
- make a hand coiled pottery mug
- make a tufted rug or mat
- tie-dye a garment
- carve or whittle wood

- choose the right sport for yourself
- choose the right piece of sporting equipment (bike, surf or skate board, shoes, protective gear...)
- learn to skate board
- learn to surf
- wax a surfboard
- put on, and get off, a wet suit
- score a game of tennis
- serve in tennis
- catch a fish
- make a fishing fly
- cast a fishing line
- prepare and set a fishing net
- tickle a trout
- smoke a fish
- play chess, checkers, dominoes, cards...
- train for a marathon
- use a snorkel correctly
- avoid injury playing football
- learn football skills: pass, block or kick
- improve your golf swing
- care for a set of golf clubs
- set up a pair of ice skates well
- eat well to keep in shape for your sport
- prevent sporting injuries
- stick to a training schedule
- warm up before a game
- do yoga stretches
- be a team player
- hold a baseball bat correctly
- shoot a basketball goal
- practice basketball skills at home: dribble...
- cross country ski
- ski downhill
- set a bike up for yourself: adjust seat height, handle bars...
- fix a flat tire
- learn to ride a bike
Food and More

- make a perfect cup of coffee, tea...
- use chop sticks
- prepare green tea and serve it correctly
- make chocolate
- plan a dinner party
- make a fast summer salad
- store frozen food
- sharpen a knife
- prepare chicken safely
- make your own relish, jam, pastry...
- write a weekly food shopping list
- plan a menu
- organize your pantry
- bake bread, bagels...
- use seasonal vegetables
- dry fruits and vegetables
- make your own wedding cake
- make desserts
- cook economically
- make healthy meals
- carve vegetables
- fold table napkins
- match wine with food
- set a table for a formal dinner
- store fresh fruit and vegetables
- make your own cottage cheese or yoghurt
- make food for a picnic
- make your own baby foods
- use a pressure cooker well
- use an air fryer well
- use a barbecue well
- store and use left over foods safely
- use an oven safely
- select the best fresh fruit and vegetables to buy
- get children to eat vegetables
- train children to try new foods
- serve tasty low calorie meals
- use cutlery (a knife, fork, or spoon) properly
- follow a recipe properly

- read to a child
- use a 24 hour clock
- plan a surprise party
- talk to a deaf person
- buy online safely
- read body language accurately
- understand cultural differences in body language
- travel safely in a foreign country
- play with a small child
- leave a good telephone message
- eat politely
- defend yourself (basic self defense)
- do basic first aid
- take a pulse
- teach a child to read the time
- prepare a baby's bottle
- write a thank you letter
- write a business letter
- read braille
- alter your own clothes...take up a hem etc.
- iron a shirt properly
- take a good photograph
- make a baby sitter's kit
- lift without damaging your back
- apply make-up correctly
- learn French, German, Italian...
- plait or braid hair
- make an effective complaint
- waltz (foxtrot, line dance, dance on point...)
- put on a dancing show
- organize a coffee morning
- run a meeting
- make a presentation
- do a cheap style make-over
- shop at thrift stores
- choose colors that suit you
- choose clothes that suit you
- walk in high heels
- make your own cosmetics, creams, etc.
- start your own business
- recognize sound business deals
- take control of your personal finances
- buy a house
- negotiate a deal
- choose a college
- decide what career you want
- keep mentally alert and fit
- select the right make-up for yourself
- be a good friend
- agree to disagree to maintain a relationship
- say no politely
- do a magic trick
- apologize sincerely
- use the Heimlich maneuver
- handle and store firearms safely
- keep your sense of humor
And then there's these 'how to' ideas...

- fix a blocked sink
- fix a leaking faucet
- replace a cracked tile
- polish wooden furniture
- restore a piece of furniture
- change a car tire
- interpret a modern painting
- read a palm
- burglar proof your home
- use the color wheel
- upcycle old furniture
- break a habit
- build a model airplane
- make and upload a video to YouTube
- become an influencer
- get a baby to go to sleep
- impersonate someone famous
- choose a piece of art
- stack firewood
- to be a good listener

More good demonstration speech ideas & help
How to put an effective demonstration speech together.
Once you've chosen your demonstration speech topic find out more about how good demonstration speeches are structured. This is an easily followed 'how to' prepare your speech guide.
More interesting 'how to' speech topics!

If you're still looking, try this page of 50 how to speech ideas . These are unique demonstration speech topics focusing on teaching the soft skills that are vital for communicating well, living fully and harmoniously in our world. Two examples are: 'how to apologize sincerely' and 'how to accept personal criticism positively'.
100+ 10-minute demonstration speech topics
If you're still looking for inspiration to strike, you may find your perfect topic here: 100+ 10-minute demonstration speech topics . The list has been carefully curated to make sure the suggestions can be covered efficiently and effectively in ten minutes or less.
Here's a couple of examples: how to make a friendship bracelet, and, how to give medicine to your cat without being scratched to bits.

And there is this collection of 188 funny how to speech topics .
Who said a demonstration speech needs to teach something practical and be serious? Many of these speech ideas are neither! Instead, they're pure, unadulterated silliness and fun. ☺
(I've included an example speech outline along with a free printable speech outline for your own use.)

Give your speech structure - use an outline
Would using a printable blank demonstration speech outline help you with your speech?

This outline will take you through an ordered sequence of steps to ensure your speech flows well from beginning to end.

If you'd like to see the outline in use, please check this page: demonstration speech sample outline.
You can follow the text of my speech, 'how to leave an effective voice mail message', through each of the sections in the outline.
I also made a video (audio + slides) so that you can hear, as well as see, how the flow of information from one point to the next works.
I hope both the completed outline and the video help. ☺
How to get top marks!
And if your speech is being formally evaluated why not find out what the judge will be marking you on? Click the link and you'll find a standard speech evaluation form explained and available to download.
- Return to the top of demonstration speech topics
speaking out loud
Subscribe for FREE weekly alerts about what's new For more see speaking out loud

Top 10 popular pages
- Welcome speech
- Impromptu speech topic cards
- Thank you quotes
- Impromptu public speaking topics
- Farewell speeches
- Phrases for welcome speeches
- Student council speeches
- Free sample eulogies
From fear to fun in 28 ways
A complete one stop resource to scuttle fear in the best of all possible ways - with laughter.

Useful pages
- Search this site
- About me & Contact
- Blogging Aloud
- Free e-course
- Privacy policy
©Copyright 2006-24 www.write-out-loud.com
Designed and built by Clickstream Designs
My Speech Class
Public Speaking Tips & Speech Topics
130+ Demonstration Speech Topics

Jim Peterson has over 20 years experience on speech writing. He wrote over 300 free speech topic ideas and how-to guides for any kind of public speaking and speech writing assignments at My Speech Class.

Begin your writing process by selecting some demonstration materials.
Choose a topic you are knowledgeable about, as this will help make your presentation much more effective.
If you cannot come up with good public speaking cases for a presentation, then use any of the subjects listed below for inspiration.
In this article:
How to Choose the Right Demonstration Speech Topic
Our list of good demonstration topics, process demonstration speech topics, health / fitness, technical how to ideas, demonstrate …, your central idea and purpose, how to introduce, your outline, the delivery of your demonstration speech topics.
You likely have plenty of processes and skills that you think would be valuable for others to know how to do, but that doesn’t mean that any topic you pick will be a good idea for your circumstance. You have to consider the complexity of the demo and whether your audience will be able to fully understand the process in the time given. Here are a few things to consider to help you choose a good demonstration speech topic:
Can We Write Your Speech?
Get your audience blown away with help from a professional speechwriter. Free proofreading and copy-editing included.
- Interests – Both you and your audience’s interests are an important factor when deciding on a demonstration speech topic. Your excitement and enthusiasm is needed to inspire the audience to care about what you are teaching. If your speech gains great audience attention, you’ll likely have questions to answer afterword. Make sure to choose a topic you are knowledgeable and confident in.
- Audience demographics – Consider what is appropriate for the group you are addressing. Aim to provide a skill that is of value to them, though be careful not to pick a topic that is either overly simple or complex.
- Setting – Consider what your presentation space is going to be like. Will you be indoors or outdoors? How much room do you have? These details will help you understand which topics will be better suited than others, given the conditions you’re delivering your speech in.
- Time limit – Think about what you can realistically teach in the time you’re given for your speech. While one topic may stand out to you, you may not be able to fully cover it if you’re only given five minutes.
- Visual aids – While your demonstration itself is a visual aid, many how-to speeches can benefit from videos, PowerPoint slideshows, and handouts. Consider what technology or props you’ll have available for your speech.
Speech topics can be broad. To give an effective demonstration speech, it’s a good idea to customize a topic to fit your unique situation. Take a speech topic that interests you and work to hone in on one central idea within that subject.
To discover the main point you want to make in your speech, determine what the specific purpose is of teaching your audience about this topic. What exactly do you want to demonstrate to your audience?
Form a clear thesis statement that answers this question in detail. Describe in one sentence what your demonstration is about and why it’s important that you share it.
Once you’ve determined the central idea of your speech, play with different action verbs to set up your main point. Here are a few phrases and verbs to frame your demonstrative speech topic:
- How to …
- Fix …
- Use …
- … Works
- … is done, produced, or made.
- Structure…
- X Steps to…
Try some of these other verbs too: deal with, draw, handle, execute, create, develop, incorporate, invent, operate, perform, or predict. Those words generate attention and they are in nature describing what your public speaking audience can expect .
These action verbs and phrases help describe to your audience what they can expect from your speech. Your headline will be more of an attention getter with these demonstration-specific words.
Below are lists of demonstration speech topics separated by category. In order to choose an effective demonstration speech topic, remember to consider your interests, audience, and what visual aids are available. Use action verbs to create an attractive headline and better target your audience.
- cook a pie (or anything else you like / know how to cook).
- fix a flat tire.
- create a Halloween mask.
- clean your car.
- play piano.
- change a bank check.
- dress like a princess.
- play a computer game.
- make a cocktail.
- taste wine.
- organize a surprise party.
- print a digital photo.
- eat oysters.
- register for voting.
- make Irish Coffee.
- read music notes.
- learn playing guitar.
- use your breath when you sing.
- open a bottle of wine.
- make your garden full of flowers year around.
- build a web site.
- clean your swimming pool.
- clean your golf clubs.
- make a fast summer salad.
- make a new candle of old ones.
- make your own wedding dress.
- organize your wedding.
- make a water-color.
- build a shed.
- prevent injury.
- knot a carpet.
- stop thinking.
- speak Italian.
- become a good actress.
- become a famous film star.
- write a film script.
- write a business-like letter.
- make honey.
- blow a glass.
- train your brain.
- dry your hair.
- greet Japanese people.
- use the cruise control.
- make a genealogical tree.
- climb a building.
- make a dancing show.
- snow board.
- board on sand.
- make a golf swing.
- draw a cartoon character.
- build a snowman.
- use the content of articles without violating their copyrights.
- put a weave in hair.
- sculpt your eyebrows properly.
- apply nail polish.
- apply makeup.
- find a roommate.
- choose the perfect pet.
- survive in the wilderness.
- make an emergency kit.
- perform a magic trick.
- organize your closet.
- change a baby’s diaper.
- find your ancestors.
- set up an aquarium.
- choose a digital camera.
- use the process of deduction.
- tie various knots.
- use the U.S. Postal Service.
- weave a basket.
- write a resume.
- knit a scarf.
- write a will.
- read a map.
- avoid ID theft.
- make bread crumbs.
- pick a bottle of wine.
- make banana pudding.
- make homemade salsa.
- decorate a cake.
- make pizza.
- make ice cream.
- brush your teeth properly.
- be healthy.
- choose the right running shoe.
- shoot a basketball.
- wax a surfboard.
- play chess.
- play poker.
- weight lift.
- program car keys and remotes.
- backup your DVDs.
- pack a suitcase that passes customs.
- find cheap airline tickets.
- find the best spring break deals.
- use a makeup if you a guy.
- fly an real RC plane (only show this outdoors and only if you are good).
- scribe a good poem.
- be an ninja (PS Joking sorry).
- pot a plant.
- bake a birdhouse.
- build a model.
- make jello Jigglers.
- arrange flowers.
- polish Shoes.
- design wedding cakes.
- stamp greeting cards.
- make ornaments.
- color eggs.
- make a pinata.
- fold napkins in a funny way.
- tie Die shirts.
- get your keys out of a locked car.
- fix a flat tire on a bicycle.
- saddle horse (I did this and tooka video of saddling my horse and narrated it to my audience).
- be a good student
- make jewelrey.
- text effective and clear messages.
- make a paper airplane.
- grow herbs – e.g. chamomile, parsley, catnip – in your own mini greenhouse.
- make the crunchiest marshmallows at a camp fire place.
- care for hamsters or other household pets.
- fold an origami crane.
- prepare invisible ink to write secret messages.
- construct a boomerang that comes back to you.
- prepare a banana chocolate shake to recover from a hangover.
- make twirling confetti eggs for parties and events.
- select the proper running shoes for recreational walks.
- use a sextant for navigation like two centuries ago.
- select and prepare a backpack for travel abroad.
- make up a first aid kit for simple treatment of minor injuries.
- learn break dance tricks and street moves.
- build a rabbit hutch or cages and runs.
- make a real Italian pizza with classic recipes.
- read a barometer and analyze the results.
- get energy from solar cells on your roof.
- identify if a Louis Vuitton bag is authentic.
- practice active listening communication techniques.
- learn fast reading.
- clean and polish golden rings, bracelets, and necklaces.
- pick a color scheme and palette.
- count the calories and make healthier choices.
And so on …
Another way of inventing demonstration speech topics is by association . Look at the general categories and themes below.
Food and Drink, Household Appliances, Sports Equipment, Outdoor Recreation Travel Trips, Health and Beauty Tips, Home Improvement, Home Decoration, Vintage Cars, Government Science, Nature Medicine, College Games, Culture, Tires and Suspension Trademarks, Travel Packing, Acne Curing, Building Treehouses, Vaccines, Vacuum Cleaners, Valentines Day Dating, Vanishing Tricks, Ventilation Systems, Video Game Consoles, Making Home Videos, Volleyball Techniques, Warm Ups and Stretching Training Methods, Water Polo Rules, Wind Turbines, Tasting Wine Vintages, Woodworking, How to Write a Testimonial About Yourself, Sales Elevator Pitches, Yoga for Starters Programs … Et cetera.
Process demonstration speech topics about deciding on an evening dress, roommates, and even personalized rubber stamps for public speaking and on how to do or fabricate something and the working of things and performing their functions.
Here are thirty example topics. You could show and explain how to:
- apply table manners.
- investigate a black box in an airplane.
- choose jewelry for an evening dress.
- choose tasty French champagne.
- deliver an effective speech.
- bake the best doughnuts.
- organize a prom night the whole nine yards.
- find a good dorm roommate.
- get a refund after you bought something you do not like.
- get a satellite tv for free.
- secure your home from burglars.
- lose weight safely and with a lasting effect.
- build a recycle compost bin in your garden.
- build a pyramid of a team cheerleaders.
- prepare for a job interview.
- register or establish a legal valued trademark or patent.
- overcome fear of public speaking before you stand behind a desk.
- get rid of roaches, mice and other pests in the backyard the natural way.
Unique Demonstration Speech Topics
- How asphalt cement is made.
- How batteries and accus work.
- How original Aboriginal boomerangs work.
- How bulletproof vests work.
- How an artificial pacemaker stimulates a heart.
- How perfumes and fragrances are designed.
- How thermometer instruments work.
- How antique barometers work.
- How personalized rubber stamps for hallmark imprinted impresssions are made.
- How topographic maps and globes are fabricated.
- How air bags open.
- How an espresso machine produces your cup of coffee.
- Fireworks and other explosive devices precaution regulation.
- Preparations for a tandem hang glider flight.
- Why hot air balloons fly after the sun is down.
- How lie detectors detect lies. This genre of topics for demonstration speech in education should be prepared with the help of professional officers of course.
- How a cardiac surgeon does a heart bypass operation to relieve pain on the chest and improve blood supply?
- Intelligent high IQ tests of the Mensa foundation for gifted and talented students.
- How metal detectors for treasure hunting work.
- The Academy Awards ceremony of the Motion Picture Arts and Sciences Academy.
- The patent examining procedure of the Trademark Office.
- The organization of political election conventions.
- The ultimate method to remove chocolate stains from your clothes or carpet.
- The UN Security Council explained – start with positioning the permanent
- The smartest and impertinent money laundering conspiracy tricks revealed.
- The sun eclipse – the Moon fully or partially blocks the Sunview on Earth.
- How a radar detector, a speed countermeasure equipment, works.
- The four forms a rainbow can take – primary, secondary and supernumerary rainbows, and glory clouds.
- Why our red blood cell production is important.
- Satellite orbit types – polar, sun synchronous, and geosynchronous.
- Barometers, the instruments used to measure atmospheric pressure.
- The VoIP call process diagram demonstrated for teleconferencing.
- The route of your Short Message Service text from your mobile phone to its destination. Ideal to show the virtual road for passage with a huge map.
- Unique uses for duct tape.
- Catcher hand signals in baseball and how to recognize them.
- How the sun’s ultraviolet rays can damage your eyes.
- How to stake a rose bush to get more flowers.
- Making fake UFO photo’s is not difficult.
- Marinate jumbo-size shrimps for your barbecue.
- Tips for more privacy in a high school or college facebook.
- A step by step guide to write an ebook
- How to close a client
- How to create a business plan
- How to create an awesome finished product
- How to file taxes as a business owner
- How to network
- How to pitch your services
- How to prioritize your time
- How to research a potential product
- How to work from home
- How to ace a test
- How to balance your time as a college student
- How to create the perfect study space
- How to find cheap textbooks
- How to make any professor like you
- How to make friends on campus
- How to make money while going to school
- How to pick your schedule
- How to sign up for classes
- How to deliver an award-winning, persuasive speech
- How to perform well on standardized tests
- How to write a demonstration speech outline
- How to write an informative speech
- How to write in cursive
- How to avoid making eye contact with your ex
- How to breakdance
- How to dress like a princess
- How to prepare a presentation you forgot all about
- The best way to eat a deviled egg without being messy
- How meditation works
- How to check your blood sugar
- How to create a marathon training plan
- How to find the best health insurance
- How to perform an Olympic-style lift
- How to perform a yoga pose
- How to perform tai chi
- How to plan a vegetarian meal
- Incorporate veggies and fruits into your day
- The proper running technique
- The fundamentals of a weight-training routine
- How to bottle your own wine
- How to carve a pumpkin
- How to decorate a cake
- How to fly a kite
- How to grow a vegetable garden
- How to knit a sweater
- How to make peanut butter
- How to perform a simple magic trick
- How to swing a golf club
- Impress friends with an amazing card trick
- Best ways to pack a suitcase
- How to change a baby’s diaper
- How to change a flat tire
- How to organize closet space
- How to organize your email account
- How to save money
- How to tie a tie
- How to wash a car
- The proper way to fold a napkin
- 10 ways to use a curling iron
- How an STM image works
- How to choose the best pattern font for your website
- How to create an email account
- How to create an iPhone app
- How to insert an image placeholder in WordPress
- How to install WordPress
- How to print a digital photo
- Red/green/blue color mixing for website design
- How to apply make-up
- How to apply for college
- How to find a part-time job
- How to French braid hair
Technical how to speech topics to present information and instructional steps in a demo oral. To explain a techie or complicated issue to educate a public speaker must be concrete; do not only talk about abstract theories but describe it, make it vivid with visual aids, common metaphors and comparisons to ordinary live.
International fitting sizes; the different measurements for sizes in the United States and standards used in other countries, all about the yards, feet, inches, meters, centimeters and their history. You can limit these technical how to speech topics to clothing only.
Animation; show how to create a nice short animated movie or funny cartoon from a series of 2 D images. Give the full set of instructions while you are showing what you mean step by step. Start with a simple animated character, an avatar-like puppet that jumps over a wall.
Sunscreen; the working and the urgent need of using a topical product that absorbs and even reflects the ultraviolet sun beams. Everyone like to sit in the sun, although not everyone is aware that sun protection is important to prevent the damaging effects of sunlight on the long term.
Hard Disk Drives; how to recover data for a damaged hard drive, what does the police, government agencies, criminal investigation departments and internationally respected authorities do with modern technology to discover storages media on a computer.
April Fool’s Day; the best speech topics for a funny how to fool someone are from hoaxes and practical jokes on the First of April; give examples – your main points – in a top 3 on notoriety, absurdity and originality of the sense of humor that’s being used.
Tree Climbing Techniques; provide an adequate training in tree climbing for recreational climbers, discuss the gear, ropes and knots. And don’t forget the forest ethics!
Birth control pills; how does the Combined Oral Contraceptive Pill or C O C P, containing the estrogen and progestin hormones, stop an ovulation.
Mosaic Tile Projects; for decorating your kitchen, bedroom, living areas and even the garden wall. Tell your public step by step in this technical topic how to do it.
Room Air Conditioners; how are energy efficient and reliable systmes designed to meet your comfort needs, and which special technology is used?
One advice to help you with making things easier: Most audiences relate to technology issues in general, so again, don’t get to technical and avoid highly complex demonstratives when exploring these nine technic possibilities.
How To Draw
Draw a Bearded Collie dog, an Abyssinian cat, a Swallow Belied Mangalitza pig, a Dwarf Hotot bunny.
To make a picture frame, to do a magic card trick, to draw a cartoon animal, to kick a soccer ball, to do origami, to make flowers out of tissue, to make a ribbon necklace, to make a friendship bracelet, to play indian poker, to play basketball, to hit a volleyball, to make homemade gatorade, throw a baseball the right way, to knit a crochet, to braid hair.
How to Play Baseball You could talk about the rules – show how to swing a bat – also show how to feild – to run the base’s hit homerun’s.
Caps and Hats Describe in speaking instructions lessons how you can tailor made you school sports and collegiate caps and hats with logos in the latest styles and trends. And for affordable prices. Your speech topics could be about the steps you have to take in getting cool caps for your friends. And the call to action could be: let us get those for us all. If you succeed in convincing and persuading them it would be great. Further I will advice you to spice up your demonstration address with some persuasive arguments topics!
Dirt Pudding For the dirt pudding you will need: 4 cups of milk, 2 packages of instant chocolate pudding, 16 ounces of cool whip, You also need: 32 ounces of crushed oreos, 16-20 clear cups.
Horse Riding Saddle a horse, bridle a horse, clean and scrub a hore back, bath a hore tenderly, feed a horse water, feed a goat or sheep, bottle feed a baby goat nice and slow.
Wedding Planning a wedding: all the preps and the day itself.
- riding a unicycle.
- riding a bicycle.
- making a scarf.
- catching a fish.
- sewing something.
- making origami.
- feeding a chicken.
- cooking a meal.
- using a remote.
- eating really fast.
- making someone or yourself faint.
- using pressure points.
- doing self-defence.
Set a table, build a birdhouse, plant a garden, make a scrap book, make friendship bracelets, any type of food, make a duct tape wallet, make a piece of clothing, blow a bubble with gum, make play dough, make paper beads, write a letter, tie your shoe, make soap, any type of mathmatical method, make a snow globe.
These are just a few demos that I have done or thought about. Make sure when conducting your demonstration to make it fun, catchy, and full of personality. This will make the judges or audience. It can also make it memorable to take first place!
Also, it is important to describe why it is important to know how to do what you are demonstrating or how it can be useful. And also warnings or things to look out for as far as safety goes. This generally comes in the conclusion. Also, if there is something that is inexpensive, than include prices of the supplies.
For example: If you choose for a playdough. You could say that in comes in handy for a craft project while babysitting or it makes a great craft project and take home in vacation bible school. Be sure to not let the children eat the any of the supplies or finished product. Children may need parental supervision.
While it is not always necessary, judges often find it impressive if you list and discuss the nutrition facts in a food talk and point out a positive health benefit.
For example: ‘Peanut butter is a sweet treat the contains no cholesterol, but has a lot of protein in it.’
This shows your judges or audience you have complete knowledge of the subject.
Random Things You’ve Never Thought Of Act like a blind sea horse, bring animals back to life using facial hair, create a dinasour out of burnt pop tarts and ashes, use the three unforgivable spells in harry potter, flex a bust out of a steel box, tame a huge dragon after stealing it from its true master, win a cage match against a sea lion and a goat create a weird odd monster using black magic.
How to write a Demonstration Speech
Determine the specific purpose of your matter in hand. State it in one simple sentence. E.g. I want to demonstrate how to ___ .
Determine the central idea of the text. In other words: a clear factual statement. Construe representing features or delineate the stages by using ppt picture and figure slide sheets.
They see at once what your try on is about and why you want to share it. E.g. It is important to preserve family recipes and this project is the best way in which to do that..
Determine the central idea of the text. In other words, produce a clear factual statement. Explain representing features or delineate the stages by using Powerpoint picture and figure slide sheets.
E.g. It is important to preserve family recipes, and this project is the best way in which to do that. .
Once you have decided on a demonstration topic, write an attractive, effective, and interactive attention-getting introduction. Think about these sample elementary preliminary parts:
- Tell them what you are going to teach – (metaphor for “sell”) – them.
- Why you choose to demonstrate this topic.
- Why your listeners should know how to do it. Give them a sneak peek of a few benefits.
- Tell them that they are going to do it themselves in a couple of minutes and that the only thing your audience has to do is follow your instructions.
Lay out in clear terms the procedure – the particular course of actions. You could consider a series of tactical exercises to help them feel what you mean. Design some kind of an approach for acquiring and applying the knowledge you want to share in class.
Arrange the steps. Show the activities or moves you have to make in a logical chronological order. Describe the details. Be clear.
Do not think the audience will understand your demonstration speech topics immediately. Let them ask you questions after each step before you proceed.
Conclude each step in one uncomplicated phrase. Perform these action checks on the main points before you jump to the next step.
Just show them how to do it, step by step. Have you read my checklist? Okay, let’s move forward:
First and for all, remember this ground rule: think about the rules and time limit of the assignment. Plus apply these eight public speaking tips for delivering your demonstration speech topics:
- Visual aids, such as objects, actual items, models, and drawings all can help your presentation. Do bring them in. For a large object, ask your teacher how to incorporate it.
- Include personal stories and examples.
- Provide each audience member the proper materials and ingredients to practice with.
- Ensure everyone is participating – keep eye contact, laugh, and make some funny remarks in between the lines.
- Look around you and see if your audience is following you. If not, repeat some sections. There are always people who will not understand right away, but are too shy to admit it. Assist them to jump over the hump.
- Ask yourself if someone in the audience would assist you with your demonstration. Stay patient and polite, and help if needed. Do not make a fool of that volunteer: praise their efforts in loud and clear supporting terms. You can do it!
- Close with a memorable summary or with a sharply defined call to action.
- Ask if there are any questions. And leave a handout of the explored information for people who want to know more.
274 Speech Topics for Business [Persuasive, Informative]
78 Agriculture Speech Topics
15 thoughts on “130+ Demonstration Speech Topics”
How to be strong
How to put air in your tire
how to fall asleep in class
How to do an ab workout at home
How to get a really bad grade or a F on a speech
How to make teachers hate you.
how to put on a condom
How to gain self confidence
How to play APEX Legends rather than doing your Trigonometry homework…
How to groom a dog
how to draw a cartoon figure how to wash laundry how to decipher someone’s handwriting
how to be happy
how to fail a demonstration speech
How to get out of trouble.
How to bring someone back to life.
example of demonstrative speech about life
Leave a Comment
I accept the Privacy Policy
Reach out to us for sponsorship opportunities
Vivamus integer non suscipit taciti mus etiam at primis tempor sagittis euismod libero facilisi.
© 2024 My Speech Class

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
8 Effective Introductions and Powerful Conclusions
Learning objectives.
- Identify the functions of introductions and conclusions.
- Understand the key parts of an introduction and a conclusion.
- Explore techniques to create your own effective introductions and conclusions.

Introductions and conclusions can be challenging. One of the most common complaints novice public speakers have is that they simply don’t know how to start or end a speech. It may feel natural to start crafting a speech at the beginning, but it can be difficult to craft an introduction for something which doesn’t yet exist. Many times, creative and effective ideas for how to begin a speech will come to speakers as they go through the process of researching and organizing ideas. Similarly, a conclusion needs to be well considered and leave audience members with a sense of satisfaction.
In this chapter, we will explore why introductions and conclusions are important, and we will identify various ways speakers can create impactful beginnings and endings. There is not a “right” way to start or end a speech, but we can provide some helpful guidelines that will make your introductions and conclusions much easier for you as a speaker and more effective for your audience.
The Importance of an Introduction

The introduction of a speech is incredibly important because it needs to establish the topic and purpose, set up the reason your audience should listen to you and set a precedent for the rest of the speech. Imagine the first day of a semester long class. You will have a different perception of the course if the teacher is excited, creative and clear about what is to come then if the teacher recites to you what the class is about and is confused or disorganized about the rest of the semester. The same thing goes for a speech. The introduction is an important opportunity for the speaker to gain the interest and trust of the audience.
Overall, an effective introduction serves five functions. Let’s examine each of these.
Gain Audience Attention and Interest
The first major purpose of an introduction is to gain your audience’s attention and get them interested in what you have to say. While your audience may know you, this is your speeches’ first impression! One common incorrect assumption beginning speakers make that people will naturally listen because the speaker is speaking. While many audiences may be polite and not talk while you’re speaking, actually getting them to listen and care about what you are saying is a completely different challenge. Think to a time when you’ve tuned out a speaker because you were not interested in what they had to say or how they were saying it. However, I’m sure you can also think of a time someone engaged you in a topic you wouldn’t have thought was interesting, but because of how they presented it or their energy about the subject, you were fascinated. As the speaker, you have the ability to engage the audience right away.
State the Purpose of Your Speech
The second major function of an introduction is to reveal the purpose of your speech to your audience. Have you ever sat through a speech wondering what the basic point was? Have you ever come away after a speech and had no idea what the speaker was talking about? An introduction is critical for explaining the topic to the audience and justifying why they should care about it. The speaker needs to have an in-depth understanding of the specific focus of their topic and the goals they have for their speech. Robert Cavett, the founder of the National Speaker’s Association, used the analogy of a preacher giving a sermon when he noted, “When it’s foggy in the pulpit, it’s cloudy in the pews.” The specific purpose is the one idea you want your audience to remember when you are finished with your speech. Your specific purpose is the rudder that guides your research, organization, and development of main points. The more clearly focused your purpose is, the easier it will be both for you to develop your speech and your audience to understand your core point. To make sure you are developing a specific purpose, you should be able to complete the sentence: “I want my audience to understand…” Notice that your specific speech purpose is phrased in terms of expected audience responses, not in terms of your own perspective.
Establish Credibility
One of the most researched areas within the field of communication has been Aristotle’s concept of ethos or credibility. First, and foremost, the idea of credibility relates directly to audience perception. You may be the most competent, caring, and trustworthy speaker in the world on a given topic, but if your audience does not perceive you as credible, then your expertise and passion will not matter to them. As public speakers, we need to communicate to our audiences why we are credible speakers on a given topic. James C. McCroskey and Jason J. Teven have conducted extensive research on credibility and have determined that an individual’s credibility is composed of three factors: competence, trustworthiness, and caring/goodwill (McCroskey & Teven, 1999). Competence is the degree to which a speaker is perceived to be knowledgeable or expert in a given subject by an audience member.
The second factor of credibility noted by McCroskey and Teven is trustworthiness or the degree to which an audience member perceives a speaker as honest. Nothing will turn an audience against a speaker faster than if the audience believes the speaker is lying. When the audience does not perceive a speaker as trustworthy, the information coming out of the speaker’s mouth is automatically perceived as deceitful.
Finally, caring/goodwill is the last factor of credibility noted by McCroskey and Teven. Caring/goodwill refers to the degree to which an audience member perceives a speaker as caring about the audience member. As indicated by Wrench, McCroskey, and Richmond, “If a receiver does not believe that a source has the best intentions in mind for the receiver, the receiver will not see the source as credible. Simply put, we are going to listen to people who we think truly care for us and are looking out for our welfare” (Wrench, McCroskey & Richmond, 2008). As a speaker, then, you need to establish that your information is being presented because you care about your audience and are not just trying to manipulate them. We should note that research has indicated that caring/goodwill is the most important factor of credibility. This understanding means that if an audience believes that a speaker truly cares about the audience’s best interests, the audience may overlook some competence and trust issues.
Credibility relates directly to audience perception. You may be the most competent, caring, and trustworthy speaker in the world on a given topic, but if your audience does not perceive you as credible, then your expertise and passion will not matter to them.
Trustworthiness is the degree to which an audience member perceives a speaker as honest.
Caring/goodwill is the degree to which an audience member perceives a speaker as caring about the audience member.
Provide Reasons to Listen
The fourth major function of an introduction is to establish a connection between the speaker and the audience, and one of the most effective means of establishing a connection with your audience is to provide them with reasons why they should listen to your speech. The idea of establishing a connection is an extension of the notion of caring/goodwill. In the chapters on Language and Speech Delivery, we’ll spend a lot more time talking about how you can establish a good relationship with your audience. This relationship starts the moment you step to the front of the room to start speaking.
Instead of assuming the audience will make their own connections to your material, you should explicitly state how your information might be useful to your audience. Tell them directly how they might use your information themselves. It is not enough for you alone to be interested in your topic. You need to build a bridge to the audience by explicitly connecting your topic to their possible needs.
Preview Main Ideas
The last major function of an introduction is to preview the main ideas that your speech will discuss. A preview establishes the direction your speech will take. We sometimes call this process signposting because you’re establishing signs for audience members to look for while you’re speaking. In the most basic speech format, speakers generally have three to five major points they plan on making. During the preview, a speaker outlines what these points will be, which demonstrates to the audience that the speaker is organized.
A study by Baker found that individuals who were unorganized while speaking were perceived as less credible than those individuals who were organized (Baker, 1965). Having a solid preview of the information contained within one’s speech and then following that preview will help a speaker’s credibility. It also helps your audience keep track of where you are if they momentarily daydream or get distracted.
Putting Together a Strong Introduction

Now that we have an understanding of the functions of an introduction, let’s explore the details of putting one together. As with all aspects of a speech, these may change based on your audience, circumstance, and topic. But this will give you a basic understanding of the important parts of an intro, what they do, and how they work together.
Attention Getting Device
An attention-getter is the device a speaker uses at the beginning of a speech to capture an audience’s interest and make them interested in the speech’s topic. Typically, there are four things to consider in choosing a specific attention-getting device:
- Topic and purpose of the speech
- Appropriateness or relevance to the audience
First, when selecting an attention-getting device is considering your speech topic and purpose. Ideally, your attention-getting device should have a relevant connection to your speech. Imagine if a speaker pulled condoms out of his pocket, yelled “Free sex!” and threw the condoms at the audience. This act might gain everyone’s attention, but would probably not be a great way to begin a speech about the economy. Thinking about your topic because the interest you want to create needs to be specific to your subject. More specifically, you want to consider the basic purpose of your speech. When selecting an attention getter, you want to make sure that you select one that corresponds with your basic purpose. If your goal is to entertain an audience, starting a speech with a quotation about how many people are dying in Africa each day from malnutrition may not be the best way to get your audience’s attention. Remember, one of the goals of an introduction is to prepare your audience for your speech . If your attention-getter differs drastically in tone from the rest of your speech the disjointedness may cause your audience to become confused or tune you out completely.
Possible Attention Getters
These will help you start brainstorming ideas for how to begin your speech. While not a complete list, these are some of the most common forms of attention-getters:
- Reference to Current Events
- Historical Reference
- Startling Fact
- Rhetorical Question
- Hypothetical Situation
- Demonstration
- Personal Reference
- Reference to Audience
- Reference to Occasion
Second, when selecting an attention-getting device, you want to make sure you are being appropriate and relevant to your specific audience. Different audiences will have different backgrounds and knowledge, so you should keep your audience in mind when determining how to get their attention. For example, if you’re giving a speech on family units to a group of individuals over the age of sixty-five, starting your speech with a reference to the television show Gossip Girl may not be the best idea because the television show may not be relevant to that audience.
Finally, the last consideration involves the speech occasion. Different occasions will necessitate different tones or particular styles or manners of speaking. For example, giving a eulogy at a funeral will have a very different feel than a business presentation. This understanding doesn’t mean certain situations are always the same, but rather taking into account the details of your circumstances will help you craft an effective beginning to your speech. When selecting an attention-getter, you want to make sure that the attention-getter sets the tone for the speech and situation.
Tones are particular styles or manners of speaking determined by the speech’s occasion.
Link to Topic
The link to the topic occurs when a speaker demonstrates how an attention-getting device relates to the topic of a speech. This presentation of the relationship works to transition your audience from the attention getter to the larger issue you are discussing. Often the attention-getter and the link to the topic are very clear. But other times, there may need to be a more obvious connection between how you began your attention-getting device and the specific subject you are discussing. You may have an amazing attention-getter, but if you can’t connect it to the main topic and purpose of your speech, it will not be as effective.
Significance
Once you have linked an attention-getter to the topic of your speech, you need to explain to your audience why your topic is important and why they should care about what you have to say. Sometimes you can include the significance of your topic in the same sentence as your link to the topic, but other times you may need to spell out in one or two sentences why your specific topic is important to this audience.
Thesis Statement
A thesis statement is a short, declarative sentence that states the purpose, intent, or main idea of a speech. A strong, clear thesis statement is very valuable within an introduction because it lays out the basic goal of the entire speech. We strongly believe that it is worthwhile to invest some time in framing and writing a good thesis statement. You may even want to write a version of your thesis statement before you even begin conducting research for your speech in order to guide you. While you may end up rewriting your thesis statement later, having a clear idea of your purpose, intent, or main idea before you start searching for research will help you focus on the most appropriate material.
Preview of Speech
The final part of an introduction contains a preview of the major points to be covered by your speech. I’m sure we’ve all seen signs that have three cities listed on them with the mileage to reach each city. This mileage sign is an indication of what is to come. A preview works the same way. A preview foreshadows what the main body points will be in the speech. For example, to preview a speech on bullying in the workplace, one could say, “To understand the nature of bullying in the modern workplace, I will first define what workplace bullying is and the types of bullying, I will then discuss the common characteristics of both workplace bullies and their targets, and lastly, I will explore some possible solutions to workplace bullying.” In this case, each of the phrases mentioned in the preview would be a single distinct point made in the speech itself. In other words, the first major body point in this speech would examine what workplace bullying is and the types of bullying; the second major body point in this speech would discuss the characteristics of both workplace bullies and their targets; and lastly, the third body point in this speech would explore some possible solutions to workplace bullying.
Putting it all together
The importance of introductions often leads speakers to work on them first, attending to every detail. While it is good to have some ideas and notes about the intro, specifically the thesis statement, it is often best to wait until the majority of the speech is crafted before really digging into the crafting of the introduction. This timeline may not seem intuitive, but remember, the intro is meant to introduce your speech and set up what is to come. It is difficult to introduce something that you haven’t made yet. This is why working on your main points first can help lead to an even stronger introduction.
Why Conclusions Matter
Willi Heidelbach – Puzzle2 – CC BY 2.0.
As public speaking professors and authors, we have seen many students give otherwise good speeches that seem to fall apart at the end. We’ve seen students end their three main points by saying things such as “OK, I’m done”; “Thank God that’s over!”; or “Thanks. Now what? Do I just sit down?” It’s understandable to feel relief at the end of a speech, but remember that as a speaker, your conclusion is the last chance you have to drive home your ideas. When a speaker opts to end the speech with an ineffective conclusion, or no conclusion at all, the speech loses the energy that’s been created, and the audience is left confused and disappointed. Instead of falling prey to emotional exhaustion, remind yourself to keep your energy up as you approach the end of your speech, and plan ahead so that your conclusion will be an effective one.
Of course, a good conclusion will not rescue a poorly prepared speech. Thinking again of the chapters in a novel, if one bypasses all the content in the middle, the ending often isn’t very meaningful or helpful. So to take advantage of the advice in this chapter, you need to keep in mind the importance of developing a speech with an effective introduction and an effective body. If you have these elements, you will have the foundation you need to be able to conclude effectively. Just as a good introduction helps bring an audience member into the world of your speech, and a good speech body holds the audience in that world, a good conclusion helps bring that audience member back to the reality outside of your speech.
In this section, we’re going to examine the functions fulfilled by the conclusion of a speech. A strong conclusion serves to signal the end of the speech and helps your listeners remember your speech.
Signals the End
The first thing a good conclusion can do is to signal the end of a speech. You may be thinking that showing an audience that you’re about to stop speaking is a “no brainer,” but many speakers don’t prepare their audience for the end. When a speaker just suddenly stops speaking, the audience is left confused and disappointed. Instead, we want to make sure that audiences are left knowledgeable and satisfied with our speeches. In the next section, we’ll explain in great detail about how to ensure that you signal the end of your speech in a manner that is both effective and powerful.
Aids Audience’s Memory of Your Speech
The second reason for a good conclusion stems out of some research reported by the German psychologist Hermann Ebbinghaus back in 1885 in his book Memory: A Contribution to Experimental Psychology (Ebbinghaus, 1885). Ebbinghaus proposed that humans remember information in a linear fashion, which he called the serial position effect. He found an individual’s ability to remember information in a list (e.g. a grocery list, a chores list, or a to-do list) depends on the location of an item on the list. Specifically, he found that items toward the top of the list and items toward the bottom of the list tended to have the highest recall rates. The serial position effect finds that information at the beginning of a list (primacy) and information at the end of the list (recency) are easier to recall than information in the middle of the list.
So what does this have to do with conclusions? A lot! Ray Ehrensberger wanted to test Ebbinghaus’ serial position effect in public speaking. Ehrensberger created an experiment that rearranged the ordering of a speech to determine the recall of information (Ehrensberger, 1945). Ehrensberger’s study reaffirmed the importance of primacy and recency when listening to speeches. In fact, Ehrensberger found that the information delivered during the conclusion (recency) had the highest level of recall overall.
Steps of a Conclusion

Matthew Culnane – Steps – CC BY-SA 2.0.
In the previous sections, we discussed the importance a conclusion has on a speech. In this section, we’re going to examine the three steps to building an effective conclusion.
Restatement of the Thesis
Restating a thesis statement is the first step to a powerful conclusion. As we explained earlier, a thesis statement is a short, declarative sentence that states the purpose, intent, or main idea of a speech. When we restate the thesis statement at the conclusion of our speech, we’re attempting to reemphasize what the overarching main idea of the speech has been. Suppose your thesis statement was, “I will analyze Barack Obama’s use of lyricism in his July 2008 speech, ‘A World That Stands as One.’” You could restate the thesis in this fashion at the conclusion of your speech: “In the past few minutes, I have analyzed Barack Obama’s use of lyricism in his July 2008 speech, ‘A World That Stands as One.’” Notice the shift in tense. The statement has gone from the future tense (this is what I will speak about) to the past tense (this is what I have spoken about). Restating the thesis in your conclusion reminds the audience of the main purpose or goal of your speech, helping them remember it better.
Review of Main Points
After restating the speech’s thesis, the second step in a powerful conclusion is to review the main points from your speech. One of the biggest differences between written and oral communication is the necessity of repetition in oral communication. When we preview our main points in the introduction, effectively discuss and make transitions to our main points during the body of the speech, and review the main points in the conclusion, we increase the likelihood that the audience will retain our main points after the speech is over.
In the introduction of a speech, we deliver a preview of our main body points, and in the conclusion, we deliver a review . Let’s look at a sample preview:
In order to understand the field of gender and communication, I will first differentiate between the terms biological sex and gender. I will then explain the history of gender research in communication. Lastly, I will examine a series of important findings related to gender and communication.
In this preview, we have three clear main points. Let’s see how we can review them at the conclusion of our speech:
Today, we have differentiated between the terms biological sex and gender, examined the history of gender research in communication, and analyzed a series of research findings on the topic.
In the past few minutes, I have explained the difference between the terms “biological sex” and “gender,” discussed the rise of gender research in the field of communication, and examined a series of groundbreaking studies in the field.
Notice that both of these conclusions review the main points initially set forth. Both variations are equally effective reviews of the main points, but you might like the linguistic turn of one over the other. Remember, while there is a lot of science to help us understand public speaking, there’s also a lot of art as well. You are always encouraged to choose the wording that you think will be most effective for your audience.
Concluding Device
The final part of a powerful conclusion is the concluding device. A concluding device is a final thought you want your audience members to have when you stop speaking. It also provides a definitive sense of closure to your speech. One of the authors of this text often makes an analogy between a gymnastics dismount and the concluding device in a speech. Just as a gymnast dismounting the parallel bars or balance beam wants to stick the landing and avoid taking two or three steps, a speaker wants to “stick” the ending of the presentation by ending with a concluding device instead of with, “Well, umm, I guess I’m done.” Miller observed that speakers tend to use one of ten concluding devices when ending a speech (Miller, 1946). The rest of this section is going to examine these ten concluding devices and one additional device that we have added.
Conclude with a Challenge
The first way that Miller found that some speakers end their speeches is with a challenge. A challenge is a call to engage in some activity that requires a special effort. In a speech on the necessity of fund-raising, a speaker could conclude by challenging the audience to raise 10 percent more than their original projections. In a speech on eating more vegetables, you could challenge your audience to increase their current intake of vegetables by two portions daily. In both of these challenges, audience members are being asked to go out of their way to do something different that involves effort on their part.
Conclude with a Quotation
A second way you can conclude a speech is by reciting a quotation relevant to the speech topic. When using a quotation, you need to think about whether your goal is to end on a persuasive note or an informative note. Some quotations will have a clear call to action, while other quotations summarize or provoke thought. For example, let’s say you are delivering an informative speech about dissident writers in the former Soviet Union. You could end by citing this quotation from Alexander Solzhenitsyn: “A great writer is, so to speak, a second government in his country. And for that reason, no regime has ever loved great writers” (Solzhenitsyn, 1964). Notice that this quotation underscores the idea of writers as dissidents, but it doesn’t ask listeners to put forth the effort to engage in any specific thought process or behavior. If, on the other hand, you were delivering a persuasive speech urging your audience to participate in a very risky political demonstration, you might use this quotation from Martin Luther King Jr.: “If a man hasn’t discovered something that he will die for, he isn’t fit to live” (King, 1963). In this case, the quotation leaves the audience with the message that great risks are worth taking, that they make our lives worthwhile, and that the right thing to do is to go ahead and take that great risk.
Conclude with a Summary
When a speaker ends with a summary, they are simply elongating the review of the main points. While this may not be the most exciting concluding device, it can be useful for information that was highly technical or complex or for speeches lasting longer than thirty minutes. Typically, for short speeches (like those in your class), this summary device should be avoided.
Conclude by Visualizing the Future
The purpose of a conclusion that refers to the future is to help your audience imagine the future you believe can occur. If you are giving a speech on the development of video games for learning, you could conclude by depicting the classroom of the future where video games are perceived as true learning tools and how those tools could be utilized. More often, speakers use visualization of the future to depict how society would be, or how individual listeners’ lives would be different if the speaker’s persuasive attempt worked. For example, if a speaker proposes that a solution to illiteracy is hiring more reading specialists in public schools, the speaker could ask her or his audience to imagine a world without illiteracy. In this use of visualization, the goal is to persuade people to adopt the speaker’s point of view. By showing that the speaker’s vision of the future is a positive one, the conclusion should help to persuade the audience to help create this future.
Conclude with an Appeal for Action
Probably the most common persuasive concluding device is the appeal for action or the call to action. In essence, the appeal for action occurs when a speaker asks their audience to engage in a specific behavior or change in thinking. When a speaker concludes by asking the audience “to do” or “to think” in a specific manner, the speaker wants to see an actual change. Whether the speaker appeals for people to eat more fruit, buy a car, vote for a candidate, oppose the death penalty, or sing more in the shower, the speaker is asking the audience to engage in action.
One specific type of appeal for action is the immediate call to action. Whereas some appeals ask for people to engage in behavior in the future, an immediate call to action asks people to engage in behavior right now. If a speaker wants to see a new traffic light placed at a dangerous intersection, he or she may conclude by asking all the audience members to sign a digital petition right then and there, using a computer the speaker has made available ( http://www.petitiononline.com ). Here are some more examples of immediate calls to action:
- In a speech on eating more vegetables, pass out raw veggies and dip at the conclusion of the speech.
- In a speech on petitioning a lawmaker for a new law, provide audience members with a prewritten e-mail they can send to the lawmaker.
- In a speech on the importance of using hand sanitizer, hand out little bottles of hand sanitizer and show audience members how to correctly apply the sanitizer.
- In a speech asking for donations for a charity, send a box around the room asking for donations.
These are just a handful of different examples we’ve seen students use in our classrooms to elicit an immediate change in behavior. These immediate calls to action may not lead to long-term change, but they can be very effective at increasing the likelihood that an audience will change behavior in the short term.
Conclude by Inspiration
By definition, the word inspire means to affect or connect with someone emotionally. Both affect and arouse have strong emotional connotations. The ultimate goal of an inspiration concluding device is similar to an “appeal for action,” but the ultimate goal is more lofty or ambiguous. The goal is to stir someone’s emotions in a specific manner. Maybe a speaker is giving an informative speech about the prevalence of domestic violence in our society today. That speaker could end the speech by reading Paulette Kelly’s powerful poem “I Got Flowers Today.” “I Got Flowers Today” is a poem that evokes strong emotions because it’s about an abuse victim who received flowers from her abuser every time she was victimized. The poem ends by saying, “I got flowers today… Today was a special day. It was the day of my funeral. Last night he killed me” (Kelly, 1994).
Conclude with Advice
The next concluding device is one that should be used primarily by speakers who are recognized as expert authorities on a given subject. Advice is a speaker’s opinion about what should or should not be done. The problem with opinions is that everyone has one, and one person’s opinion is not necessarily any more correct than another’s. There needs to be a really good reason for your opinion. Your advice should matter to your audience. If, for example, you are an expert in nuclear physics, you might conclude a speech on energy by giving advice about the benefits of nuclear energy.
Conclude by Proposing a Solution
Another way a speaker can conclude a speech powerfully is to offer a solution to the problem discussed within a speech. For example, perhaps a speaker has been discussing the problems associated with the disappearance of art education in the United States. The speaker could then propose a solution for creating more community-based art experiences for school children as a way to fill this gap. Although this can be a compelling conclusion, a speaker must ask themselves whether the solution should be discussed in more depth as a stand-alone main point within the body of the speech so that audience concerns about the proposed solution may be addressed.
Conclude with a Question
Another way you can end a speech is to ask a rhetorical question that forces the audience to ponder an idea. Maybe you are giving a speech on the importance of the environment, so you end the speech by saying, “Think about your children’s future. What kind of world do you want them raised in? A world that is clean, vibrant, and beautiful—or one that is filled with smog, pollution, filth, and disease?” Notice that you aren’t asking the audience to verbally or nonverbally answer the question. The goal of this question is to force the audience into thinking about what kind of world they want for their children.
Conclude with a Reference to Audience
The last concluding device discussed by Miller (1946) was a reference to one’s audience. This concluding device is when a speaker attempts to answer the audience question, “What’s in it for me?” The goal of this concluding device is to spell out the direct benefits a behavior or thought change has for audience members. For example, a speaker talking about stress reduction techniques could conclude by listing all the physical health benefits stress reduction offers (e.g. improved reflexes, improved immune system, improved hearing, reduction in blood pressure). In this case, the speaker is spelling out why audience members should care. They’re telling the audience what’s in it for them!
Connect to your Introduction
Finally, one tactic a speaker often uses is to link the introduction of the speech to the conclusion. For example, if you began your speech with a quotation, your conclusion may refer back to that person’s words in respect to what your audience has learned throughout your speech. While not always necessary, linking back to your introduction can provide a feeling of coming full circle for your audience. The repetitive nature can also help aid in remembering your speech and topic. However, you don’t want to just repeat. Instead, you want to utilize similar aspects of your attention getter to illustrate growth or movement from the beginning of your speech to the end.
A concluding device is a final thought you want your audience members to have when you stop speaking.
A challenge is a call to engage in some activity that requires special effort.
An appeal for action occurs when a speaker asks their audience to engage in a specific behavior or change in thinking.
An immediate call to action asks people to engage in behavior right now.
Inspire means to affect or connect with someone emotionally.
Advice is a speaker’s opinion about what should or should not be done.
Informative versus Persuasive Conclusions
As you read through the ten possible ways to conclude a speech, hopefully, you noticed that some of the methods are more appropriate for persuasive speeches and others are more appropriate for informative speeches. To help you choose appropriate conclusions for informative, persuasive, or entertaining speeches, we’ve created a table to help you quickly identify suitable concluding devices.
Your Speech Purpose and Concluding Devices
Ebbinghaus, H. (1885). Memory: A contribution to experimental psychology [Online version]. Retrieved from http://psychclassics.yorku.ca/Ebbinghaus/index.htm .
Ehrensberger, R. (1945). An experimental study of the relative effectiveness of certain forms of emphasis in public speaking. Speech Monographs, 12 , 94–111. doi: 10.1080/03637754509390108.
Kelly, P. (1994). I got flowers today. In C. J. Palmer & J. Palmer, Fire from within . Painted Post, NY: Creative Arts & Science Enterprises.
King, M. L. (1963, June 23). Speech in Detroit. Cited in Bartlett, J., & Kaplan, J. (Eds.), Bartlett’s familiar quotations (6th ed.). Boston, MA: Little, Brown & Co., p. 760.
Miller, E. (1946). Speech introductions and conclusions. Quarterly Journal of Speech, 32 , 181–183.
Solzhenitsyn, A. (1964). The first circle. New York: Harper & Row. Cited in Bartlett, J., & Kaplan, J. (Eds.), Bartlett’s familiar quotations (6th ed.). Boston, MA: Little, Brown & Co., p. 746.
Stand up, Speak out Copyright © 2017 by Josh Miller; Marnie Lawler-Mcdonough; Megan Orcholski; Kristin Woodward; Lisa Roth; and Emily Mueller is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

50 Speech Closing Lines (& How to Create Your Own) | The Ultimate Guide
Hrideep barot.
- Public Speaking , Speech Writing

While speech openings are definitely one of the most important components of a speech, something that is equally as important is the way you conclude your speech.
There are few worse ways to end your speech than with a terse ‘thank you’–no elaboration or addition whatsoever.
Speech endings are just as crucial to the success of your speech as speech openings, and you must spend just as much time picking the perfect ending as you do to determine your best possible speech opening.
The words you speak at the beginning and end of your speech are words that your audience will pay the most attention to, and remember longer than any other part of your speech.
Speech endings can put even the most experienced speaker in flux, and increase their anxiousness manifold as they sit there attempting to figure out the perfect way to end your speech.
If you’re someone who’s in flux about your speech ending too, don’t worry. We’ve got some amazing ways to conclude your speech with a bang!
1. Circling Back To The Beginning
The idea behind circling back to the beginning of your speech is to reinforce the idea of your speech being a complete whole. By circling back to the beginning and connecting it to your ending, you let the audience understand that the idea of your speech is complete & standalone.
Circling back to the beginning of your speech also acts as an excellent way of reinforcing the central idea of your speech in the audience’s mind, and makes it more likely that they will remember it after the speech ends.
Need more inspiration for speech opening lines? Check out our article on 15 Powerful Speech Opening Lines & Tips To Create Your Own.
How To Circle Back To The Beginning
The easiest way to do this is to set up your beginning for the conclusion of your speech. That is, if you’re saying something like, say, a story or joke in the beginning, then you can leave your audience in a cliffhanger until the ending arrives.
Another great way to circle back to the beginning is by simply restating something you said at the start. The added knowledge from attending the rest of your speech will help the audience see this piece of information in a new–and better–light.
1. Will Stephen
Ending Line: “I’d like you to think about what you heard in the beginning, and I want you to think about what you hear now. Because it was nothing & it’s still nothing.”
2. Canwen Xu
Speech Ending: My name is Canwen, my favorite color is purple and I play the piano but not so much the violin…
Think of a memorable moment from your life, and chances are you’ll realize that it involved a feeling of happiness–something that we can associate with smiling or laughter. And what better way to generate laughter than by incorporating the age-old strategy of good humor.
The happy and lighthearted feeling you associate with good memories is the kind of emotional reaction you want to create in your audience too. That’s what will make your speech stick in their memory.
Done incorrectly, humor can be a disaster. Done right, however, it can entirely transform a speech.
Humor doesn’t only mean slapstick comedy (although there’s nothing wrong with slapstick, either). Humor can come in many forms, including puns, jokes, a funny story…the list is endless.
How To Incorporate Humor In Your Speech Ending
The simplest way to incorporate humor into your speech ending is by telling a plain old joke–something that’s relevant to your topic, of course.
You can also tell them a short, funny anecdote–may be an unexpected conclusion to a story you set up in the beginning.
Another way would be by employing the power of repetition. You can do this by associating something funny with a word, and then repeating the word throughout your speech. During the end, simply say the word or phrase one last time, and it’s likely you’ll leave off your audience with a good chuckle.
1. Woody Roseland
Ending Line: “Why are balloons so expensive? Inflation.”
2. Andras Arato
Ending Line: “There are three rules to becoming famous. Unfortunately, nobody knows what they are.”
3. Hasan Minhaj
Ending Line: “And you want to know the scariest part? Pretty soon every country on the earth is going to have its own TLC show.”
4. Sophie Scott
Speech Ending: In other words, when it comes to laughter, you and me baby, ain’t nothing but mammals.
5. Tim Urban
Speech Ending: We need to stay away from the Instant Gratification Monkey. That’s a job for all of us. And because there’s not that many boxes on there. It’s a job that should probably start today. Well, maybe not today, but, you know, sometime soon.
6. Hasan Minhaj
Speech Ending: Showing my legs on TV is probably the scariest thing I’ve ever done. And keep in mind last week I went after the Prince of Saudi Arabia.
3. Question
The idea behind posing a question at the end of your speech is to get the wheels in your audience’s minds turning and to get them thinking of your speech long after it has ended. A question, if posed correctly, will make your audience re-think about crucial aspects of your speech, and is a great way to prompt discussion after your speech has ended.
How To Add Questions To Your Speech Ending
The best type of questions to add to your speech ending is rhetorical questions. That’s because, unlike a literal question, a rhetorical question will get the audience thinking and make them delve deeper into the topic at hand.
Make sure your question is central to the idea of your speech, and not something frivolous or extra. After all, the point of a question is to reinforce the central idea of your topic.
1. Lexie Alford
Speech Ending: Ask yourself: How uncomfortable are you willing to become in order to reach your fullest potential?
2. Apollo Robbins
Speech Ending: If you could control somebody’s attention, what would you do with it?
Quotes are concise, catchy phrases or sentences that are generally easy to remember and repeat.
Quotes are an age-old way to start–and conclude–a speech. And for good reason.
Quotes can reinforce your own ideas by providing a second voice to back them up. They can also provoke an audience’s mind & get them thinking. So, if you add your quote to the end of your speech, the audience will most likely be thinking about it for long after you have finished speaking.
How To Use Quotes In Your Speech Ending
While adding quotes to your speech ending, make sure that it’s relevant to your topic. Preferably, you want to pick a quote that summarizes your entire idea in a concise & memorable manner.
Make sure that your quote isn’t too long or complicated. Your audience should be able to repeat it as well as feel its impact themselves. They shouldn’t be puzzling over the semantics of your quote, but its intended meaning.
1. Edouard Jacqmin
Speech Ending: “Life is either a daring adventure or nothing at all.”
2. Chris Crowe
Speech Ending: “It’s more certain than death and taxes.”
3. Olivia Remes
Speech Ending: I’d like to leave you with a quote by Martin Luther King: “You don’ have to see the whole staircase. Just take the first step.”
4. Tomislav Perko
Speech Ending: Like that famous quote says, “In twenty years from now on, you’ll be more disappointed by the things you didn’t do than by the things you did do.
5. Diana Nyad
Speech Ending: To paraphrase the poet, Mary Oliver, she says, “So, what is it? What is it you’re doing with this one wild and precious life of yours?”
5. Piece Of Advice
The point of giving a piece of advice at the end of your speech is not to pull your audience down or to make them feel bad/inferior about themselves. Rather, the advice is added to motivate your audience to take steps to do something–something related to the topic at hand.
The key point to remember is that your advice is included to help your audience, not to discourage them.
How To Add Piece Of Advice To Your Speech Ending
To truly make your audience follow the advice you’re sharing, you must make sure it resonates with them. To do so, you need to inject emotions into your advice, and to present it in such a manner that your audience’s emotions are aroused when they hear it.
Your advice shouldn’t be something extra-complicated or seemingly impossible to achieve. This will act as a counter-agent. Remember that you want your audience to follow your advice, not to chuck it away as something impossible.
Our article, 15 Powerful Speech Ending Lines And Tips To Create Your Own , is another great repository for some inspiration.
1. Ricardo Lieuw On
Speech Ending: “Learn something new, or a new way of approaching something old because there are a few skills are valuable as the art of learning.”
2. Tomas Chamorro-Premuzic
Speech Ending: “If we want to improve the competence level of our leaders, then we should first improve our own competence for judging and selecting leaders.”
3. Sharique Samsudheen
Speech Ending: “Some people love money, some people hate money, some people crave money, some people even kill for money. But what they miss is they just need to learn how to manage money well, and that will give them financial freedom.”
4. Kate Simonds
Speech Ending: Teens, you need to believe in your voices and adults, you need to listen.
5. Melissa Butler
Speech Ending: When you go home today, see yourself in the mirror, see all of you, look at all your greatness that you embody, accept it, love it and finally, when you leave the house tomorrow, try to extend that same love and acceptance to someone who doesn’t look like you.
6. Iskra Lawrence
Speech Ending: Speak to your body in a loving way. It’s the only one you got, it’s your home, and it deserves your respect. If you see anyone tearing themselves down, build them back up And watch your life positively grow when you give up the pursuit of perfection.
6. Contemplative Remark
As the name itself suggests, contemplative remarks are intended to make your audience contemplate or mull over something. The ‘something’ in question should be the idea central to your speech, or a key takeaway that you want them to return home with.
The idea is to get your audience thinking and to keep them thinking for a long, long time.
How To Add A Contemplative Remark To Your Speech Ending
To add a contemplative remark to your speech ending, you first need to figure out your key takeaway or main theme. Then, you want to arrange that as a question, and propose it to your audience at the end of your speech.
Remember that your question shouldn’t be something too wordy or complicated to understand. As with the quotes, you don’t want your audience stuck on the semantics. Rather, you want them to focus on the matter at hand.
1. Lisa Penney
Speech Ending: “So I invite you to pay more attention to your thoughts & consider the legacy you leave behind.”
2. Grant Sanderson
Speech Ending: “Some of the most useful math that you can find or teach has its origin in someone who was just looking for a good story.”
3. Greta Thunberg
Speech Ending: “We will not let you get away with this. Right here, right now is where we draw the line. The world is waking up & change is coming whether you like it or not.”
4. Bill Eckstrom
Speech Ending: Now, think about this: it’s not the complexity-triggering individuals or events you should fear the most, but it’s your own willingness to accept or seek discomfort that will dictate the growth of not just you, but our entire world.
5. Robert Hoge
Speech Ending: Choose to accept your face, choose to appreciate your face, don’t look away from the mirror so quickly; understand all the love, and the life, and the pain that is the part of your face, that is the art of your face. Tomorrow when you wake up, what will your choice be?
7. Personal Anecdote
Personal anecdotes, as the name suggests, are anecdotes that are personal to the speaker or instances from their life. Personal anecdotes are a great way to incorporate the magical powers of storytelling in your speech, as well as to make a personal connection with the audience. Using personal anecdotes, you can hit two birds with one stone!
How To Add Personal Anecdotes To Your Speech Ending
To add personal anecdotes to your speech ending, you need to filter through your life experiences to find out ones that directly relate to your topic at hand. You don’t want to include an anecdote, no matter how compelling it is, if it doesn’t relate to your topic.
Remember to not keep your anecdote too long. Your audience will most likely lose their attention if you do so.
1. Sheila Humphries
Speech Ending: “Why do you go work for these people?” My answer to them was, “If I could help one child make it in this world, it’ll be worth it all.”
8. Call To Action
A call-to-action is one of the absolute best ways to conclude a speech with a bang. A well-written speech should aim to alter the audience’s mind or belief system in some way and to make them take an action in that direction. One crucial way to assure your audience does this is by using a call to action.
How To Add A Call To Action To Your Speech Ending
A call to action comes right before the ending of your speech to provide your audience with a clear idea or set of instructions about what they’re supposed to do after your talk ends.
A call to action should provide a roadmap to the audience for their future steps, and to outline clearly what those future steps are going to be.
1. Armin Hamrah
Speech Ending: “So tonight, after you finish your Math homework & before you lay your head down on that fluffy pillow, bring a piece of paper and pen by your bedside…”
2. Graham Shaw
Speech Ending: “So I invite you to get your drawings out there & spread the word that when we draw, we remember more!”
3. Andy Puddicombe
Speech Ending: You don’t have to burn any incense, and you definitely don’t have to sit on the floor. All you need to do is to take out 10 minutes out a day to step back, familiarize yourself with the present moment so that you get to experience a greater sense of focus, calm, and clarity in your life.
4. Amy Cuddy
Speech Ending: Before you go into the next stressful evaluative situation, for two minutes, try doing this in the elevator…
5. Jia Jiang
Speech Ending: When you are facing the next obstacle or the next failure, consider the possibilities. Don’t run! If you just embrace them, they might become your gifts as well.
9. Motivational Remark
As the name clearly explains, a motivational remark motivates your audience to carry out a plan of action. It ruffles the audience’s mind and emotions and has a powerful impact on the steps that your audience will take after you’ve finished speaking.
How To Add A Motivational Remark To Your Speech Ending
The key to a good motivational remark is to inspire your audience. Your motivational remark should act as a ray of hope to your audience and positively inspire them to take a desired course of action.
Your motivational remark should not be negative in any way. You don’t want to guilt or coerce your audience into doing something or feeling a certain way. You want to leave them on a positive note to move forward with their life.
1. Khanh Vy Tran
Speech Ending: “No matter what you’re going through right now & no matter what the future holds for you, please don’t change yourself. Love yourself, accept yourself & then transform yourself.”
2. Mithila Palkar
Speech Ending: “Get a job, leave a job, dance, sing, fall in love. Carve your own niche. But most importantly: learn to love your own randomness.”
3. Andrew Tarvin
Speech Ending: “Anyone can learn to be funnier. And it all starts with a choice. A choice to try to find ways to use humor. A choice to be like my grandmother, to look at the world around you and say WTF–wow, that’s fun.”
4. Laura Vanderkam
Speech Ending: There is time. Even if we are busy, we have time for what matters. And when we focus on what matters, we can build the lives we want in the time we’ve got.
5. Julian Treasure
Speech Ending: Let’s get listening taught in schools, and transform the world in one generation into a conscious listening world, a world of connection, a world of understanding, and a world of peace.
6. Mariana Atencio
Speech Ending: Let’s celebrate those imperfections that make us special. I hope that it teaches you that nobody has a claim on the word ‘normal’. We are all different. We are all quirky and unique and that is what makes us wonderfully human.
10. Challenge
Much like a call to action, the aim of proposing a challenge at the end of your speech is to instigate your audience to take some desired course of action. A challenge should make an appeal to your audience’s emotion, and motivate them to meet it.
How To Add A Challenge To Your Speech Ending
To apply a challenge effectively to your speech ending, you need to make sure that it’s something relevant to your topic. Your challenge should drive the central topic of your speech forward, and make your audience engage in real-life steps to apply your idea in the real world.
While its always a good idea to set a high bar for your challenge, make sure its an achievable one too.
1. Jamak Golshani
Speech Ending: “I challenge you to open your heart to new possibilities, choose a career path that excites you & one that’s aligned to who you truly are.”
2. Ashley Clift-Jennings
Speech Ending: So, my challenge to you today is, “Do you know, would you even know how to recognize your soulmate?” If you are going out in the world right now, would you know what you are looking for?
11. Metaphor
Metaphors are commonly used as a short phrase that draws a comparison between two ideas in a non-literal sense. People use metaphors quite commonly in daily life to explain ideas that might be too difficult or confusing to understand otherwise. Metaphors are also great tools to be used in speech, as they can present your main idea in a simple and memorable way.
How To Add Metaphors To Your Speech Ending
To add a metaphor to your speech ending, you need to first decide on the main idea or takeaway of your speech. Your metaphor should then be organized in such a way that it simplifies your main idea and makes it easier for your audience to understand & remember it.
The key is to not make your metaphor overly complicated or difficult to retain and share. Remember that you’re trying to simplify your idea for the audience–not make them even more confused.
1. Ramona J. Smith
Speech Ending: “Stay in that ring. And even after you take a few hits, use what you learned from those previous fights, and at the end of the round, you’ll still remain standing.”
2. Shi Heng YI
Speech Ending: “If any of you chooses to climb that path to clarity, I will be very happy to meet you at the peak.”
3. Zifang “Sherrie” Su
Speech Ending: “Are you turning your back on your fear? Our life is like this stage, but what scares are now may bring you the most beautiful thing. Give it a chance.”
12. Storytelling
The idea behind using stories to end your speech is to leave your audience with a good memory to take away with them.
Stories are catchy, resonating & memorable ways to end any speech.
Human beings can easily relate to stories. This is because most people have grown up listening to stories of some kind or another, and thus a good story tends to evoke fond feelings in us.
How To Incorporate Stories In Your Speech Ending
A great way to incorporate stories in your speech ending is by setting up a story in the beginning and then concluding it during the end of your speech.
Another great way would be to tell a short & funny anecdote related to a personal experience or simply something related to the topic at hand.
However, remember that it’s the ending of your speech. Your audience is most likely at the end of their attention span. So, keep your story short & sweet.
1. Sameer Al Jaberi
Speech Ending: “I can still see that day when I came back from my honeymoon…”
2. Josephine Lee
Speech Ending: “At the end of dinner, Jenna turned to me and said…”
Facts are another excellent speech ending, and they are used quite often as openings as well. The point of adding a fact as your speech ending is to add shock value to your speech, and to get your audience thinking & discussing the fact even after your speech has ended.
How To Add Facts To Your Speech Ending
The key to adding facts to your speech ending is to pick a fact that thrusts forward your main idea in the most concise form possible. Your fact should also be something that adds shock value to the speech, and it should ideally be something that the audience hasn’t heard before.
Make sure that your fact is relevant to the topic at hand. No matter how interesting, a fact that doesn’t relate to your topic is going to be redundant.
1. David JP Phillips
Speech Ending: 3500 years ago, we started transfering knowledge from generation to generation through text. 28 years ago, PowerPoint was born. Which one do you think our brain is mostly adapted to?
14. Rhethoric Remark
Rhetoric remarks are another excellent way to get the wheels of your audience’s minds turning. Rhetoric remarks make your audience think of an imagined scenario, and to delve deeper into your topic. Rhetoric remarks or questioned don’t necessarily need to have a ‘right’ or one-shot answer, which means you can be as creative with them as possible!
How To Add Rhethoric Remarks To Your Speech Ending
Since rhetorical questions don’t need to have a definite answer, you have much freedom in determining the type of question or statement you wish to make. However, as with all other speech endings, a rhetorical question shouldn’t be asked just for the sake of it.
A rhetorical question should make your audience think about your topic in a new or more creative manner. It should get them thinking about the topic and maybe see it from an angle that they hadn’t before.
Rhetorical questions shouldn’t be too confusing. Use simple language & make sure it’s something that the audience can easily comprehend.
1. Mona Patel
Speech Ending: Pick your problem, ask “What if?” Come up with ideas. Bring them down. Then execute on them. Maybe you’re thinking, “What if we can’t?” I say to you, “What if we don’t?”
2. Lizzie Velasquez
Speech Ending: I want you to leave here and ask yourself what defines you. But remember: Brave starts here.
Another great way to end your speech with a literal bang is by using music! After all, if there’s something that can impact the human mind with just as much force as a few well-placed words, it’s the correct music.
How To Add Music To Your Speech Ending
To add music to your speech ending, you must make sure that the music has something to do with your speech theme. Remember that you’re not playing music in your concert. The piece of music that you choose must be relevant to your topic & work to have a contribution in your overall speech.
1. Tom Thum
Speech Ending: *ends the TED Talk with beat boxing*
16. Reitirate The Title
The title of your speech is its most important component. That’s why you need to pay careful attention to how you pick it, as it is something that your viewers will most likely remember the longest about your speech.
Your title will also act as a guiding hand towards how your audience forms an initial idea about your speech and is what they will associate your entire speech with.
By repeating your title at the end of your speech, you increase the chances that your audience will remember it–and your speech–for a long time.
How To Retierate The Title In Your Speech Ending
Your title is something that your audience associates your entire speech with. However, you don’t want to simply add the title in your speech end for the sake of adding it. Instead, make it flow naturally into your speech ending. This will make it seem less forced, and will also increase the chances of your audience remembering your entire speech ending and not just the title of your speech.
1. Ruairi Robertson
Speech Ending: I feel we can all contribute to this fight worth fighting for our own health, but more importantly, our future generations’ health by restoring the relationship between microbe and man. There is SOME FOOD FOR THOUGHT!
Need more inspiration for speech closing lines? Check out our article on 10 Of The Best Things To Say In Closing Remarks.
Level up your public speaking in 15 minutes!
Get the exclusive Masterclass video delivered to your inbox to see immediate speaking results.
You have successfully joined our subscriber list.
To sum up, speech endings are just as imperative to the success of your speech as speech openings, and you must spend just as much time picking the perfect ending as you do to determine your best possible speech opening. The words you speak at the beginning and end of your speech are words that your audience will pay the most attention to, and remember longer than any other part of your speech.
Still looking for inspiration? Check out this video we made on closing remarks:
Enroll in our transformative 1:1 Coaching Program
Schedule a call with our expert communication coach to know if this program would be the right fit for you

7 Keys to Emcee Like a Pro: Unlock Your Hosting Potential

8 Ways to Rise Above the Noise to Communicate Better

How to Negotiate: The Art of Getting What You Want

- [email protected]
- +91 98203 57888
Get our latest tips and tricks in your inbox always
Copyright © 2023 Frantically Speaking All rights reserved
Kindly drop your contact details so that we can arrange call back
Select Country Afghanistan Albania Algeria AmericanSamoa Andorra Angola Anguilla Antigua and Barbuda Argentina Armenia Aruba Australia Austria Azerbaijan Bahamas Bahrain Bangladesh Barbados Belarus Belgium Belize Benin Bermuda Bhutan Bosnia and Herzegovina Botswana Brazil British Indian Ocean Territory Bulgaria Burkina Faso Burundi Cambodia Cameroon Canada Cape Verde Cayman Islands Central African Republic Chad Chile China Christmas Island Colombia Comoros Congo Cook Islands Costa Rica Croatia Cuba Cyprus Czech Republic Denmark Djibouti Dominica Dominican Republic Ecuador Egypt El Salvador Equatorial Guinea Eritrea Estonia Ethiopia Faroe Islands Fiji Finland France French Guiana French Polynesia Gabon Gambia Georgia Germany Ghana Gibraltar Greece Greenland Grenada Guadeloupe Guam Guatemala Guinea Guinea-Bissau Guyana Haiti Honduras Hungary Iceland India Indonesia Iraq Ireland Israel Italy Jamaica Japan Jordan Kazakhstan Kenya Kiribati Kuwait Kyrgyzstan Latvia Lebanon Lesotho Liberia Liechtenstein Lithuania Luxembourg Madagascar Malawi Malaysia Maldives Mali Malta Marshall Islands Martinique Mauritania Mauritius Mayotte Mexico Monaco Mongolia Montenegro Montserrat Morocco Myanmar Namibia Nauru Nepal Netherlands Netherlands Antilles New Caledonia New Zealand Nicaragua Niger Nigeria Niue Norfolk Island Northern Mariana Islands Norway Oman Pakistan Palau Panama Papua New Guinea Paraguay Peru Philippines Poland Portugal Puerto Rico Qatar Romania Rwanda Samoa San Marino Saudi Arabia Senegal Serbia Seychelles Sierra Leone Singapore Slovakia Slovenia Solomon Islands South Africa South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands Spain Sri Lanka Sudan Suriname Swaziland Sweden Switzerland Tajikistan Thailand Togo Tokelau Tonga Trinidad and Tobago Tunisia Turkey Turkmenistan Turks and Caicos Islands Tuvalu Uganda Ukraine United Arab Emirates United Kingdom United States Uruguay Uzbekistan Vanuatu Wallis and Futuna Yemen Zambia Zimbabwe land Islands Antarctica Bolivia, Plurinational State of Brunei Darussalam Cocos (Keeling) Islands Congo, The Democratic Republic of the Cote d'Ivoire Falkland Islands (Malvinas) Guernsey Holy See (Vatican City State) Hong Kong Iran, Islamic Republic of Isle of Man Jersey Korea, Democratic People's Republic of Korea, Republic of Lao People's Democratic Republic Libyan Arab Jamahiriya Macao Macedonia, The Former Yugoslav Republic of Micronesia, Federated States of Moldova, Republic of Mozambique Palestinian Territory, Occupied Pitcairn Réunion Russia Saint Barthélemy Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan Da Cunha Saint Kitts and Nevis Saint Lucia Saint Martin Saint Pierre and Miquelon Saint Vincent and the Grenadines Sao Tome and Principe Somalia Svalbard and Jan Mayen Syrian Arab Republic Taiwan, Province of China Tanzania, United Republic of Timor-Leste Venezuela, Bolivarian Republic of Viet Nam Virgin Islands, British Virgin Islands, U.S.


Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
11.2 Steps of a Conclusion
Learning objectives.
- Examine the three steps of an effective conclusion: restatement of the thesis, review of the main points, and concluding device.
- Differentiate among Miller’s (1946) ten concluding devices.

Matthew Culnane – Steps – CC BY-SA 2.0.
In Section 11.1 “Why Conclusions Matter” , we discussed the importance a conclusion has on a speech. In this section, we’re going to examine the three steps in building an effective conclusion.
Restatement of the Thesis
Restating a thesis statement is the first step in a powerful conclusion. As we explained in Chapter 9 “Introductions Matter: How to Begin a Speech Effectively” , a thesis statement is a short, declarative sentence that states the purpose, intent, or main idea of a speech. When we restate the thesis statement at the conclusion of our speech, we’re attempting to reemphasize what the overarching main idea of the speech has been. Suppose your thesis statement was, “I will analyze Barack Obama’s use of lyricism in his July 2008 speech, ‘A World That Stands as One.’” You could restate the thesis in this fashion at the conclusion of your speech: “In the past few minutes, I have analyzed Barack Obama’s use of lyricism in his July 2008 speech, ‘A World That Stands as One.’” Notice the shift in tense: the statement has gone from the future tense (this is what I will speak about) to the past tense (this is what I have spoken about). Restating the thesis in your conclusion reminds the audience of the major purpose or goal of your speech, helping them remember it better.
Review of Main Points
After restating the speech’s thesis, the second step in a powerful conclusion is to review the main points from your speech. One of the biggest differences between written and oral communication is the necessity of repetition in oral communication. When we preview our main points in the introduction, effectively discuss and make transitions to our main points during the body of the speech, and finally, review the main points in the conclusion, we increase the likelihood that the audience will retain our main points after the speech is over.
In the introduction of a speech, we deliver a preview of our main body points, and in the conclusion we deliver a review . Let’s look at a sample preview:
In order to understand the field of gender and communication, I will first differentiate between the terms biological sex and gender. I will then explain the history of gender research in communication. Lastly, I will examine a series of important findings related to gender and communication.
In this preview, we have three clear main points. Let’s see how we can review them at the conclusion of our speech:
Today, we have differentiated between the terms biological sex and gender, examined the history of gender research in communication, and analyzed a series of research findings on the topic.
In the past few minutes, I have explained the difference between the terms “biological sex” and “gender,” discussed the rise of gender research in the field of communication, and examined a series of groundbreaking studies in the field.
Notice that both of these conclusions review the main points originally set forth. Both variations are equally effective reviews of the main points, but you might like the linguistic turn of one over the other. Remember, while there is a lot of science to help us understand public speaking, there’s also a lot of art as well, so you are always encouraged to choose the wording that you think will be most effective for your audience.
Concluding Device
The final part of a powerful conclusion is the concluding device. A concluding device is essentially the final thought you want your audience members to have when you stop speaking. It also provides a definitive sense of closure to your speech. One of the authors of this text often makes an analogy between a gymnastics dismount and the concluding device in a speech. Just as a gymnast dismounting the parallel bars or balance beam wants to stick the landing and avoid taking two or three steps, a speaker wants to “stick” the ending of the presentation by ending with a concluding device instead of with, “Well, umm, I guess I’m done.” Miller observed that speakers tend to use one of ten concluding devices when ending a speech (Miller, 1946). The rest of this section is going to examine these ten concluding devices.
Conclude with a Challenge
The first way that Miller found that some speakers end their speeches is with a challenge. A challenge is a call to engage in some kind of activity that requires a contest or special effort. In a speech on the necessity of fund-raising, a speaker could conclude by challenging the audience to raise 10 percent more than their original projections. In a speech on eating more vegetables, you could challenge your audience to increase their current intake of vegetables by two portions daily. In both of these challenges, audience members are being asked to go out of their way to do something different that involves effort on their part.
Conclude with a Quotation
A second way you can conclude a speech is by reciting a quotation relevant to the speech topic. When using a quotation, you need to think about whether your goal is to end on a persuasive note or an informative note. Some quotations will have a clear call to action, while other quotations summarize or provoke thought. For example, let’s say you are delivering an informative speech about dissident writers in the former Soviet Union. You could end by citing this quotation from Alexander Solzhenitsyn: “A great writer is, so to speak, a second government in his country. And for that reason no regime has ever loved great writers” (Solzhenitsyn, 1964). Notice that this quotation underscores the idea of writers as dissidents, but it doesn’t ask listeners to put forth effort to engage in any specific thought process or behavior. If, on the other hand, you were delivering a persuasive speech urging your audience to participate in a very risky political demonstration, you might use this quotation from Martin Luther King Jr.: “If a man hasn’t discovered something that he will die for, he isn’t fit to live” (King, 1963). In this case, the quotation leaves the audience with the message that great risks are worth taking, that they make our lives worthwhile, and that the right thing to do is to go ahead and take that great risk.
Conclude with a Summary
When a speaker ends with a summary, he or she is simply elongating the review of the main points. While this may not be the most exciting concluding device, it can be useful for information that was highly technical or complex or for speeches lasting longer than thirty minutes. Typically, for short speeches (like those in your class), this summary device should be avoided.
Conclude by Visualizing the Future
The purpose of a conclusion that refers to the future is to help your audience imagine the future you believe can occur. If you are giving a speech on the development of video games for learning, you could conclude by depicting the classroom of the future where video games are perceived as true learning tools and how those tools could be utilized. More often, speakers use visualization of the future to depict how society would be, or how individual listeners’ lives would be different, if the speaker’s persuasive attempt worked. For example, if a speaker proposes that a solution to illiteracy is hiring more reading specialists in public schools, the speaker could ask her or his audience to imagine a world without illiteracy. In this use of visualization, the goal is to persuade people to adopt the speaker’s point of view. By showing that the speaker’s vision of the future is a positive one, the conclusion should help to persuade the audience to help create this future.
Conclude with an Appeal for Action
Probably the most common persuasive concluding device is the appeal for action or the call to action. In essence, the appeal for action occurs when a speaker asks her or his audience to engage in a specific behavior or change in thinking. When a speaker concludes by asking the audience “to do” or “to think” in a specific manner, the speaker wants to see an actual change. Whether the speaker appeals for people to eat more fruit, buy a car, vote for a candidate, oppose the death penalty, or sing more in the shower, the speaker is asking the audience to engage in action.
One specific type of appeal for action is the immediate call to action . Whereas some appeals ask for people to engage in behavior in the future, the immediate call to action asks people to engage in behavior right now. If a speaker wants to see a new traffic light placed at a dangerous intersection, he or she may conclude by asking all the audience members to sign a digital petition right then and there, using a computer the speaker has made available ( http://www.petitiononline.com ). Here are some more examples of immediate calls to action:
- In a speech on eating more vegetables, pass out raw veggies and dip at the conclusion of the speech.
- In a speech on petitioning a lawmaker for a new law, provide audience members with a prewritten e-mail they can send to the lawmaker.
- In a speech on the importance of using hand sanitizer, hand out little bottles of hand sanitizer and show audience members how to correctly apply the sanitizer.
- In a speech asking for donations for a charity, send a box around the room asking for donations.
These are just a handful of different examples we’ve actually seen students use in our classrooms to elicit an immediate change in behavior. These immediate calls to action may not lead to long-term change, but they can be very effective at increasing the likelihood that an audience will change behavior in the short term.
Conclude by Inspiration
By definition, the word inspire means to affect or arouse someone. Both affect and arouse have strong emotional connotations. The ultimate goal of an inspiration concluding device is similar to an “appeal for action” but the ultimate goal is more lofty or ambiguous; the goal is to stir someone’s emotions in a specific manner. Maybe a speaker is giving an informative speech on the prevalence of domestic violence in our society today. That speaker could end the speech by reading Paulette Kelly’s powerful poem “I Got Flowers Today.” “I Got Flowers Today” is a poem that evokes strong emotions because it’s about an abuse victim who received flowers from her abuser every time she was victimized. The poem ends by saying, “I got flowers today… / Today was a special day—it was the day of my funeral / Last night he killed me” (Kelly, 1994).
Conclude with Advice
The next concluding device is one that should be used primarily by speakers who are recognized as expert authorities on a given subject. Advice is essentially a speaker’s opinion about what should or should not be done. The problem with opinions is that everyone has one, and one person’s opinion is not necessarily any more correct than another’s. There needs to be a really good reason your opinion—and therefore your advice—should matter to your audience. If, for example, you are an expert in nuclear physics, you might conclude a speech on energy by giving advice about the benefits of nuclear energy.
Conclude by Proposing a Solution
Another way a speaker can conclude a speech powerfully is to offer a solution to the problem discussed within a speech. For example, perhaps a speaker has been discussing the problems associated with the disappearance of art education in the United States. The speaker could then propose a solution of creating more community-based art experiences for school children as a way to fill this gap. Although this can be an effective conclusion, a speaker must ask herself or himself whether the solution should be discussed in more depth as a stand-alone main point within the body of the speech so that audience concerns about the proposed solution may be addressed.
Conclude with a Question
Another way you can end a speech is to ask a rhetorical question that forces the audience to ponder an idea. Maybe you are giving a speech on the importance of the environment, so you end the speech by saying, “Think about your children’s future. What kind of world do you want them raised in? A world that is clean, vibrant, and beautiful—or one that is filled with smog, pollution, filth, and disease?” Notice that you aren’t actually asking the audience to verbally or nonverbally answer the question; the goal of this question is to force the audience into thinking about what kind of world they want for their children.
Conclude with a Reference to Audience
The last concluding device discussed by Miller (1946) was a reference to one’s audience. This concluding device is when a speaker attempts to answer the basic audience question, “What’s in it for me?” The goal of this concluding device is to spell out the direct benefits a behavior or thought change has for audience members. For example, a speaker talking about stress reduction techniques could conclude by clearly listing all the physical health benefits stress reduction offers (e.g., improved reflexes, improved immune system, improved hearing, reduction in blood pressure). In this case, the speaker is clearly spelling out why audience members should care—what’s in it for them!
Informative versus Persuasive Conclusions
As you read through the ten possible ways to conclude a speech, hopefully you noticed that some of the methods are more appropriate for persuasive speeches and others are more appropriate for informative speeches. To help you choose appropriate conclusions for informative, persuasive, or entertaining speeches, we’ve created a table ( Table 11.1 “Your Speech Purpose and Concluding Devices” ) to help you quickly identify appropriate concluding devices.
Table 11.1 Your Speech Purpose and Concluding Devices
Key Takeaways
- An effective conclusion contains three basic parts: a restatement of the speech’s thesis; a review of the main points discussed within the speech; and a concluding device that helps create a lasting image in audiences’ minds.
- Miller (1946) found that speakers tend to use one of ten concluding devices. All of these devices are not appropriate for all speeches, so speakers need to determine which concluding device would have the strongest, most powerful effect for a given audience, purpose, and occasion.
- Take the last speech you gave in class and rework the speech’s conclusion to reflect the three parts of a conclusion. Now do the same thing with the speech you are currently working on for class.
- Think about the speech you are currently working on in class. Write out concluding statements using three of the devices discussed in this chapter. Which of the devices would be most useful for your speech? Why?
Kelly, P. (1994). I got flowers today. In C. J. Palmer & J. Palmer, Fire from within . Painted Post, NY: Creative Arts & Science Enterprises.
King, M. L. (1963, June 23). Speech in Detroit. Cited in Bartlett, J., & Kaplan, J. (Eds.), Bartlett’s familiar quotations (6th ed.). Boston, MA: Little, Brown & Co., p. 760.
Miller, E. (1946). Speech introductions and conclusions. Quarterly Journal of Speech, 32 , 181–183.
Solzhenitsyn, A. (1964). The first circle. New York: Harper & Row. Cited in Bartlett, J., & Kaplan, J. (Eds.), Bartlett’s familiar quotations (6th ed.). Boston, MA: Little, Brown & Co., p. 746.
Stand up, Speak out Copyright © 2016 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

- Essay Writing
- Research Writing
- Business Papers & Classes
- Nursing Papers
- Presentations & Design
- Free Q&A
- Analytical Essays
- AP Lang Essays
- Argumentative Essays
- Cause and Effect Essays
- Classification & Division Essays
- Compare & Contrast Essays
- Definition Essays
- Descriptive Essays
- Expository Essays
- Illustrative Essays
- Literary Analysis Essays
- Narrative Essays
- Persuasive Essays
- Problem-Solution Essays
- Process Analysis Essays
- Reflective Essays
- Response Essays
- Rhetorical Analysis Essays
- Synthesis Essays
- Research Papers
- Thesis Papers
- Term Papers
- Position Papers
- Case Study Analysis
- Capstone Projects
- Project Proposals
- SWOT Analysis
- PESTLE Analysis
- Porter's 5 Forces
- Competitor Analysis
- Stakeholder Analysis
- Financial Analysis
- Strategy Analysis & Dev
- Business Plans
- Business Proposals
- Marketing Plans
- Grant Proposals
- Business Reports
- Nursing Personal Statements
- Nursing Philosophy Essays
- Application to Practice Essays
- Nursing Article Critiques
- Nursing Case Analysis
- Model-Based Reflections
- Nursing Care Plans (NCPs)
- Progress Notes
- Nursing Research Papers
- PICOT Papers
- Essay Writing Lab
- Speech Writing
- Annotated Bibliographies
How to Write a Demonstrative Speech (+ Example Essays)
- January 23, 2023 April 1, 2024
- What You Should Know
- Sample Persuasive Speech: Dangers of Racism in U.S
- Sample Persuasive Speech: Art of Procrastination
- Sample Demonstrative Speech: Making A Natural Face Mask At Home
- Sample Demonstrative Speech: How to Tie a Tie
- Sample Entertaining Speech: Online Dating
- Sample Informative Speech: Rastafarianism
- Sample Informative Speech: African American Culture
- Sample Motivational Speech
- Sample Commencement/ Graduation Speech
A demonstrative speech is a type of informative speech in which the speaker demonstrates or shows the audience how to do something. The main goal of a demonstrative speech is to teach the audience a specific skill or process by providing clear, step-by-step instructions and using visual aids or props to enhance understanding.
Here are sample demonstrative speech essays:
How to Tie a Tie
Making A Natural Face Mask At Home
- Specific Purpose: To demonstrate how to make homemade pasta from scratch.
- Thesis Statement: Homemade pasta is not only delicious but also surprisingly easy to make at home with just a few simple ingredients and the right technique.
- Pattern: Chronological (step-by-step demonstration from preparing the dough to cooking the pasta).
- Specific Purpose: To show how to create a vertical garden for small spaces.
- Thesis Statement: Vertical gardens are a creative and space-saving solution for urban dwellers to enjoy gardening and greenery at home.
- Pattern: Spatial (demonstration involves building the structure, planting, and maintaining the vertical garden).
- Specific Purpose: To teach a beginner-friendly yoga sequence for relaxation and flexibility.
- Thesis Statement: Regular practice of yoga can improve physical and mental well-being by reducing stress and increasing flexibility.
- Pattern: Topical (divided into segments focusing on warm-up, basic poses, and cool-down).
- Specific Purpose: To guide users on setting up a secure password manager for digital security.
- Thesis Statement: Password managers are essential tools for managing and securing online passwords, enhancing digital privacy and security.
- Pattern: Problem-Solution (identifying the need for password security and providing a solution through the setup process).
- Specific Purpose: To demonstrate the art of paper quilling to create decorative designs.
- Thesis Statement: Paper quilling is a versatile and artistic craft that allows individuals to create intricate designs using rolled paper strips.
- Pattern: Comparative (contrasting different quilling techniques and showcasing their application in creating unique designs).
- Specific Purpose: To demonstrate how to install a basic smart home security system.
- Thesis Statement: Smart home security systems offer convenience and peace of mind by integrating technology to monitor and protect homes.
- Pattern: Sequential (step-by-step guide from choosing the system to installation and setup).
- Specific Purpose: To illustrate the concept of water purification through a simple DIY filtration experiment.
- Thesis Statement: Understanding water purification methods is crucial for ensuring access to clean and safe drinking water.
- Pattern: Cause and Effect (demonstrating how contaminants are removed through filtration and the resulting clean water).
- Specific Purpose: To teach a basic self-defense move for escaping a wrist grab.
- Thesis Statement: Learning self-defense techniques empowers individuals to protect themselves and improve personal safety.
- Pattern: Problem-Solution (identifying the threat of a wrist grab and providing a solution through the escape technique).
- Specific Purpose: To demonstrate how to play a beginner-level song on the guitar.
- Thesis Statement: Playing musical instruments like the guitar can be a fulfilling and enjoyable hobby that enhances creativity and relaxation.
- Pattern: Chronological (step-by-step guide to learning and playing the song).
- Specific Purpose: To show how to practice mindfulness meditation for stress reduction.
- Thesis Statement: Mindfulness meditation promotes mental well-being by cultivating present-moment awareness and reducing stress levels.
- Pattern: Topical (covering the benefits of mindfulness, meditation techniques, and practical tips for beginners).
- Specific Purpose: To demonstrate an effective method for memorizing vocabulary in a foreign language.
- Thesis Statement: Using mnemonic devices and spaced repetition can significantly improve vocabulary retention and language learning.
- Pattern: Problem-Solution (addressing the challenge of vocabulary retention and providing a solution through the demonstrated technique).
- Specific Purpose: To show how to compost organic waste at home to reduce environmental impact.
- Thesis Statement: Composting is a sustainable practice that helps reduce waste and enrich soil for healthier plants.
- Pattern: Chronological (step-by-step guide from collecting organic waste to maintaining the compost pile).
- Specific Purpose: To teach effective strategies for creating and delivering a compelling PowerPoint presentation.
- Thesis Statement: Mastering presentation skills is essential for effectively communicating ideas and engaging audiences in professional settings.
- Pattern: Topical (divided into segments focusing on slide design, content organization, delivery techniques, and audience interaction).
- Specific Purpose: To demonstrate how to capture stunning landscape photographs using basic camera settings.
- Thesis Statement: Learning photography fundamentals can help individuals take captivating photos and unleash their creativity.
- Pattern: Spatial (demonstration involves setting up the camera, adjusting settings, composing the shot, and capturing the image).
- Specific Purpose: To explain the concept of budgeting and demonstrate how to create a personal budget plan.
- Thesis Statement: Effective budgeting is key to achieving financial goals, managing expenses, and building financial stability.
- Pattern: Comparative (contrasting budgeting methods and providing a step-by-step guide to creating a budget plan).
How to Write
In summary, the key to a successful demonstrative speech is thorough preparation, clear organization, engaging delivery, and audience interaction. Choose a relevant topic, conduct thorough research, and organize your speech effectively with a clear structure. Engage the audience with visual aids, clear communication, and eye contact. Practice delivery to build confidence and be prepared to address audience questions. By focusing on these elements, you can deliver a compelling and informative demonstrative speech.
Demonstrative Speech Topics 2020: A Complete Guide with Examples, Ideas, Outlines
I like building and growing simple yet powerful products for the world and the worldwide web.
Published Date : February 15, 2024
Reading Time :
We have all learned a lot from demonstrative speeches. Teachers have resorted to demonstrative speeches to pass on their knowledge since the inception of formal education. Listening and learning from a teacher’s Demonstration Speech <!-- wp:paragraph --> <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:274">A type of informative speech where the speaker <strong>demonstrates</strong> how to do something, showcasing a process, skill, or product clearly and engagingly. It combines elements of explanation, instruction, and visual aids to educate and entertain the audience.</p> <h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:12"><strong>Purpose:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-11:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:121"><strong>Teach a new skill:</strong> Guide the audience through a process step-by-step, providing clear instructions and visual cues.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:124"><strong>Increase understanding:</strong> Explain complex concepts through practical demonstrations, making them relatable and engaging.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-9:115"><strong>Persuade the audience:</strong> Showcase a product's or service's benefits and features through live demonstration.</li> <li data-sourcepos="10:1-11:0"><strong>Entertain and inform:</strong> Combine clear instruction with an engaging presentation to keep the audience interested and learning.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="12:1-12:17"><strong>Key Elements:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="14:1-19:0"> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:113"><strong>Clear explanation:</strong> Break down the process into manageable steps, using simple language and avoiding jargon.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:133"><strong>Engaging delivery:</strong> Maintain a dynamic and enthusiastic tone, utilizing vocal variety and gestures to keep the audience focused.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-16:117"><strong>Visual aids:</strong> Employ effective visuals like diagrams, props, or live demonstrations to support your explanation.</li> <li data-sourcepos="17:1-17:118"><strong>Audience interaction:</strong> Invite participation through questions, hands-on activities, or audience engagement tools.</li> <li data-sourcepos="18:1-19:0"><strong>Smooth transitions:</strong> Guide the audience seamlessly between explanation, demonstration, and key takeaways.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="20:1-20:15"><strong>Challenges:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="22:1-26:0"> <li data-sourcepos="22:1-22:110"><strong>Balancing depth and clarity:</strong> Providing enough detail without overwhelming the audience with information.</li> <li data-sourcepos="23:1-23:95"><strong>Managing time effectively:</strong> Ensuring the demonstration fits within the allotted timeframe.</li> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:126"><strong>Troubleshooting unexpected issues:</strong> Adapting to technical difficulties or unforeseen challenges during the demonstration.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-26:0"><strong>Engaging different learning styles:</strong> Catering to diverse learning preferences through multiple modalities (visual, auditory, kinesthetic).</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="27:1-27:26"><strong>Overcoming Challenges:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="29:1-34:0"> <li data-sourcepos="29:1-29:128"><strong>Practice and rehearse:</strong> Thoroughly practice the explanation and demonstration, ensuring smooth transitions and timing.</li> <li data-sourcepos="30:1-30:131"><strong>Seek feedback:</strong> Share your draft speech and demonstration with trusted individuals for constructive criticism and suggestions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:177">Consider <strong>speech coaching</strong>: A coach can guide you in tailoring your explanation, refining your delivery, and managing potential challenges during the demonstration.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:106"><strong>Anticipate problems:</strong> Practice handling potential technical issues or unexpected situations smoothly.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-34:0"><strong>Utilize diverse visuals:</strong> Combine different types of visuals, such as diagrams, pictures, or live demonstrations, to cater to various learning styles.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="35:1-35:277"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="35:1-35:277">A well-prepared and engaging <strong>demonstration speech</strong> can be highly informative and impactful. By focusing on clarity, visual aids, audience engagement, and effective preparation, you can deliver a speech that teaches, entertains, and leaves a lasting impression.</p> <!-- /wp:list --> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/demonstration-speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">demonstration speech topics has always been easy.
However, things may take a different turn when you are in charge of passing on knowledge, and Demonstration Speech <!-- wp:paragraph --> <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:274">A type of informative speech where the speaker <strong>demonstrates</strong> how to do something, showcasing a process, skill, or product clearly and engagingly. It combines elements of explanation, instruction, and visual aids to educate and entertain the audience.</p> <h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:12"><strong>Purpose:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-11:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:121"><strong>Teach a new skill:</strong> Guide the audience through a process step-by-step, providing clear instructions and visual cues.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:124"><strong>Increase understanding:</strong> Explain complex concepts through practical demonstrations, making them relatable and engaging.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-9:115"><strong>Persuade the audience:</strong> Showcase a product's or service's benefits and features through live demonstration.</li> <li data-sourcepos="10:1-11:0"><strong>Entertain and inform:</strong> Combine clear instruction with an engaging presentation to keep the audience interested and learning.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="12:1-12:17"><strong>Key Elements:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="14:1-19:0"> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:113"><strong>Clear explanation:</strong> Break down the process into manageable steps, using simple language and avoiding jargon.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:133"><strong>Engaging delivery:</strong> Maintain a dynamic and enthusiastic tone, utilizing vocal variety and gestures to keep the audience focused.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-16:117"><strong>Visual aids:</strong> Employ effective visuals like diagrams, props, or live demonstrations to support your explanation.</li> <li data-sourcepos="17:1-17:118"><strong>Audience interaction:</strong> Invite participation through questions, hands-on activities, or audience engagement tools.</li> <li data-sourcepos="18:1-19:0"><strong>Smooth transitions:</strong> Guide the audience seamlessly between explanation, demonstration, and key takeaways.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="20:1-20:15"><strong>Challenges:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="22:1-26:0"> <li data-sourcepos="22:1-22:110"><strong>Balancing depth and clarity:</strong> Providing enough detail without overwhelming the audience with information.</li> <li data-sourcepos="23:1-23:95"><strong>Managing time effectively:</strong> Ensuring the demonstration fits within the allotted timeframe.</li> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:126"><strong>Troubleshooting unexpected issues:</strong> Adapting to technical difficulties or unforeseen challenges during the demonstration.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-26:0"><strong>Engaging different learning styles:</strong> Catering to diverse learning preferences through multiple modalities (visual, auditory, kinesthetic).</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="27:1-27:26"><strong>Overcoming Challenges:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="29:1-34:0"> <li data-sourcepos="29:1-29:128"><strong>Practice and rehearse:</strong> Thoroughly practice the explanation and demonstration, ensuring smooth transitions and timing.</li> <li data-sourcepos="30:1-30:131"><strong>Seek feedback:</strong> Share your draft speech and demonstration with trusted individuals for constructive criticism and suggestions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:177">Consider <strong>speech coaching</strong>: A coach can guide you in tailoring your explanation, refining your delivery, and managing potential challenges during the demonstration.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:106"><strong>Anticipate problems:</strong> Practice handling potential technical issues or unexpected situations smoothly.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-34:0"><strong>Utilize diverse visuals:</strong> Combine different types of visuals, such as diagrams, pictures, or live demonstrations, to cater to various learning styles.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="35:1-35:277"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="35:1-35:277">A well-prepared and engaging <strong>demonstration speech</strong> can be highly informative and impactful. By focusing on clarity, visual aids, audience engagement, and effective preparation, you can deliver a speech that teaches, entertains, and leaves a lasting impression.</p> <!-- /wp:list --> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/demonstration-speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">demonstration speech ideas somehow vanish in those moments. As we all know, the ability to teach is an especially vital leadership skill, and it makes understanding demonstrative speaking a thousand times more crucial.
Presenting and coming up with demonstrative Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech topics may be exhausting, but you can do it like a pro, too. And that is what I’ll “demonstrate” in this post.
If you aren’t interested in learning the intricacies of Demonstration Speech <!-- wp:paragraph --> <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:274">A type of informative speech where the speaker <strong>demonstrates</strong> how to do something, showcasing a process, skill, or product clearly and engagingly. It combines elements of explanation, instruction, and visual aids to educate and entertain the audience.</p> <h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:12"><strong>Purpose:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-11:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:121"><strong>Teach a new skill:</strong> Guide the audience through a process step-by-step, providing clear instructions and visual cues.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:124"><strong>Increase understanding:</strong> Explain complex concepts through practical demonstrations, making them relatable and engaging.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-9:115"><strong>Persuade the audience:</strong> Showcase a product's or service's benefits and features through live demonstration.</li> <li data-sourcepos="10:1-11:0"><strong>Entertain and inform:</strong> Combine clear instruction with an engaging presentation to keep the audience interested and learning.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="12:1-12:17"><strong>Key Elements:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="14:1-19:0"> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:113"><strong>Clear explanation:</strong> Break down the process into manageable steps, using simple language and avoiding jargon.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:133"><strong>Engaging delivery:</strong> Maintain a dynamic and enthusiastic tone, utilizing vocal variety and gestures to keep the audience focused.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-16:117"><strong>Visual aids:</strong> Employ effective visuals like diagrams, props, or live demonstrations to support your explanation.</li> <li data-sourcepos="17:1-17:118"><strong>Audience interaction:</strong> Invite participation through questions, hands-on activities, or audience engagement tools.</li> <li data-sourcepos="18:1-19:0"><strong>Smooth transitions:</strong> Guide the audience seamlessly between explanation, demonstration, and key takeaways.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="20:1-20:15"><strong>Challenges:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="22:1-26:0"> <li data-sourcepos="22:1-22:110"><strong>Balancing depth and clarity:</strong> Providing enough detail without overwhelming the audience with information.</li> <li data-sourcepos="23:1-23:95"><strong>Managing time effectively:</strong> Ensuring the demonstration fits within the allotted timeframe.</li> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:126"><strong>Troubleshooting unexpected issues:</strong> Adapting to technical difficulties or unforeseen challenges during the demonstration.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-26:0"><strong>Engaging different learning styles:</strong> Catering to diverse learning preferences through multiple modalities (visual, auditory, kinesthetic).</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="27:1-27:26"><strong>Overcoming Challenges:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="29:1-34:0"> <li data-sourcepos="29:1-29:128"><strong>Practice and rehearse:</strong> Thoroughly practice the explanation and demonstration, ensuring smooth transitions and timing.</li> <li data-sourcepos="30:1-30:131"><strong>Seek feedback:</strong> Share your draft speech and demonstration with trusted individuals for constructive criticism and suggestions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:177">Consider <strong>speech coaching</strong>: A coach can guide you in tailoring your explanation, refining your delivery, and managing potential challenges during the demonstration.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:106"><strong>Anticipate problems:</strong> Practice handling potential technical issues or unexpected situations smoothly.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-34:0"><strong>Utilize diverse visuals:</strong> Combine different types of visuals, such as diagrams, pictures, or live demonstrations, to cater to various learning styles.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="35:1-35:277"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="35:1-35:277">A well-prepared and engaging <strong>demonstration speech</strong> can be highly informative and impactful. By focusing on clarity, visual aids, audience engagement, and effective preparation, you can deliver a speech that teaches, entertains, and leaves a lasting impression.</p> <!-- /wp:list --> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/demonstration-speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">demonstration speech , skip to the end, where I share final tips and conclude. But that’s if you are fine with missing examples of demonstrative Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech topics and elements, how to write an outline, and other details in the body.
What is Demonstrative Speech?
Firstly, a Demonstrative Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech will teach the receiving audience how to do a specific task or process. Even experts may struggle with Speech Writing <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:400"><strong>Speech writing</strong> is crafting a message to be delivered orally to an audience. It involves structuring thoughts, arguments, and language to effectively engage listeners, inform, persuade, or inspire action. While <strong>improving public speaking</strong> skills can enhance delivery, effective <strong>speech writing</strong> lays the foundation for a powerful and impactful presentation.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:17"><strong>Key Elements:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-13:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:138"><strong>Clear message and purpose:</strong> Define your intention – to inform, persuade, entertain, or inspire – and tailor your message accordingly.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:109"><strong>Strong opening:</strong> Capture attention with a compelling anecdote, question, or quote to hook your audience.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-9:144"><strong>Logical structure:</strong> Organize your speech with a clear introduction, body points, and conclusion to guide the audience through your message.</li> <li data-sourcepos="10:1-10:151"><strong>Compelling arguments and evidence:</strong> Support your claims with facts, statistics, stories, or personal anecdotes to build credibility and resonance.</li> <li data-sourcepos="11:1-11:136"><strong>Strong language and imagery:</strong> Use clear, concise, and vivid imagery to engage your audience and leave a lasting impression.</li> <li data-sourcepos="12:1-13:0"><strong>Call to action:</strong> Clearly state your desired outcome, whether it's prompting applause, encouraging further discussion, or motivating specific action.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="14:1-14:41"><strong>Benefits of Effective Speech Writing:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="16:1-21:0"> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-16:108"><strong>Clarity and organization:</strong> Ensures your message is well-structured and easy for the audience to follow.</li> <li data-sourcepos="17:1-17:108"><strong>Increased impact:</strong> Helps you deliver your message with maximum impact and achieve your desired outcome.</li> <li data-sourcepos="18:1-18:108"><strong>Enhanced confidence:</strong> A well-written speech boosts your confidence and allows you to focus on delivery.</li> <li data-sourcepos="19:1-19:109"><strong>Memorable message:</strong> Creates a lasting impression on your audience with a clear and well-crafted message.</li> <li data-sourcepos="20:1-21:0"><strong>Time management:</strong> Allows you to stay within your allotted time and avoid rushed or incomplete delivery.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:31"><strong>Crafting a Powerful Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-29:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:111"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Research their interests, needs, and expectations to tailor your message accordingly.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:124"><strong>Focus on storytelling:</strong> Use personal anecdotes, relatable examples, or inspiring stories to connect with your audience.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:126"><strong>Consider tone and style:</strong> Adapt your language and approach to fit the formality of the occasion and your target audience.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-27:107"><strong>Practice and rehearse:</strong> Deliver your speech aloud to refine your timing, pacing, and overall delivery.</li> <li data-sourcepos="28:1-29:0"><strong>Seek feedback:</strong> Share your speech with a trusted friend, colleague, or <strong>speech coach</strong> for constructive feedback.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="30:1-30:39"><strong>Speech Writing vs. Public Speaking:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="32:1-32:308">While both are crucial for success, <strong>speech writing</strong> focuses on crafting the content of the message, while <strong>public speaking</strong> focuses on delivering it effectively. Effective <strong>speech writing</strong> forms the foundation for powerful <strong>public speaking</strong>, ensuring your message is clear, organized, and impactful.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="34:1-34:357"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="34:1-34:357">Mastering the art of <strong>speech writing</strong> is a valuable skill that can empower you to communicate effectively in various situations. By understanding the key elements, employing strategic approaches, and considering resources like <strong>speech coaching</strong>, you can craft speeches that resonate with your audience and achieve your communication goals.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech-writing/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech writing despite having all the knowledge on the proposed topic.
Writing a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech that ensures your audience learns something new can be challenging. In this case, the reason is that a demonstrative speaker is like a guide that takes the audience through an engaging step-by-step”‘ how-to” process.
This type of Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech is also known as an explanation Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech or a demonstrative presentation.
The essence of Demonstration Speech <!-- wp:paragraph --> <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:274">A type of informative speech where the speaker <strong>demonstrates</strong> how to do something, showcasing a process, skill, or product clearly and engagingly. It combines elements of explanation, instruction, and visual aids to educate and entertain the audience.</p> <h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:12"><strong>Purpose:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-11:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:121"><strong>Teach a new skill:</strong> Guide the audience through a process step-by-step, providing clear instructions and visual cues.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:124"><strong>Increase understanding:</strong> Explain complex concepts through practical demonstrations, making them relatable and engaging.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-9:115"><strong>Persuade the audience:</strong> Showcase a product's or service's benefits and features through live demonstration.</li> <li data-sourcepos="10:1-11:0"><strong>Entertain and inform:</strong> Combine clear instruction with an engaging presentation to keep the audience interested and learning.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="12:1-12:17"><strong>Key Elements:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="14:1-19:0"> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:113"><strong>Clear explanation:</strong> Break down the process into manageable steps, using simple language and avoiding jargon.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:133"><strong>Engaging delivery:</strong> Maintain a dynamic and enthusiastic tone, utilizing vocal variety and gestures to keep the audience focused.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-16:117"><strong>Visual aids:</strong> Employ effective visuals like diagrams, props, or live demonstrations to support your explanation.</li> <li data-sourcepos="17:1-17:118"><strong>Audience interaction:</strong> Invite participation through questions, hands-on activities, or audience engagement tools.</li> <li data-sourcepos="18:1-19:0"><strong>Smooth transitions:</strong> Guide the audience seamlessly between explanation, demonstration, and key takeaways.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="20:1-20:15"><strong>Challenges:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="22:1-26:0"> <li data-sourcepos="22:1-22:110"><strong>Balancing depth and clarity:</strong> Providing enough detail without overwhelming the audience with information.</li> <li data-sourcepos="23:1-23:95"><strong>Managing time effectively:</strong> Ensuring the demonstration fits within the allotted timeframe.</li> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:126"><strong>Troubleshooting unexpected issues:</strong> Adapting to technical difficulties or unforeseen challenges during the demonstration.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-26:0"><strong>Engaging different learning styles:</strong> Catering to diverse learning preferences through multiple modalities (visual, auditory, kinesthetic).</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="27:1-27:26"><strong>Overcoming Challenges:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="29:1-34:0"> <li data-sourcepos="29:1-29:128"><strong>Practice and rehearse:</strong> Thoroughly practice the explanation and demonstration, ensuring smooth transitions and timing.</li> <li data-sourcepos="30:1-30:131"><strong>Seek feedback:</strong> Share your draft speech and demonstration with trusted individuals for constructive criticism and suggestions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:177">Consider <strong>speech coaching</strong>: A coach can guide you in tailoring your explanation, refining your delivery, and managing potential challenges during the demonstration.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:106"><strong>Anticipate problems:</strong> Practice handling potential technical issues or unexpected situations smoothly.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-34:0"><strong>Utilize diverse visuals:</strong> Combine different types of visuals, such as diagrams, pictures, or live demonstrations, to cater to various learning styles.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="35:1-35:277"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="35:1-35:277">A well-prepared and engaging <strong>demonstration speech</strong> can be highly informative and impactful. By focusing on clarity, visual aids, audience engagement, and effective preparation, you can deliver a speech that teaches, entertains, and leaves a lasting impression.</p> <!-- /wp:list --> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/demonstration-speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">demonstration speech ideas and topics is in conveying logical information. However, to captivate one’s audience, a bit of emotion becomes necessary, which leads to my point on the elements of Demonstration Speech <!-- wp:paragraph --> <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:274">A type of informative speech where the speaker <strong>demonstrates</strong> how to do something, showcasing a process, skill, or product clearly and engagingly. It combines elements of explanation, instruction, and visual aids to educate and entertain the audience.</p> <h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:12"><strong>Purpose:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-11:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:121"><strong>Teach a new skill:</strong> Guide the audience through a process step-by-step, providing clear instructions and visual cues.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:124"><strong>Increase understanding:</strong> Explain complex concepts through practical demonstrations, making them relatable and engaging.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-9:115"><strong>Persuade the audience:</strong> Showcase a product's or service's benefits and features through live demonstration.</li> <li data-sourcepos="10:1-11:0"><strong>Entertain and inform:</strong> Combine clear instruction with an engaging presentation to keep the audience interested and learning.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="12:1-12:17"><strong>Key Elements:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="14:1-19:0"> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:113"><strong>Clear explanation:</strong> Break down the process into manageable steps, using simple language and avoiding jargon.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:133"><strong>Engaging delivery:</strong> Maintain a dynamic and enthusiastic tone, utilizing vocal variety and gestures to keep the audience focused.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-16:117"><strong>Visual aids:</strong> Employ effective visuals like diagrams, props, or live demonstrations to support your explanation.</li> <li data-sourcepos="17:1-17:118"><strong>Audience interaction:</strong> Invite participation through questions, hands-on activities, or audience engagement tools.</li> <li data-sourcepos="18:1-19:0"><strong>Smooth transitions:</strong> Guide the audience seamlessly between explanation, demonstration, and key takeaways.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="20:1-20:15"><strong>Challenges:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="22:1-26:0"> <li data-sourcepos="22:1-22:110"><strong>Balancing depth and clarity:</strong> Providing enough detail without overwhelming the audience with information.</li> <li data-sourcepos="23:1-23:95"><strong>Managing time effectively:</strong> Ensuring the demonstration fits within the allotted timeframe.</li> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:126"><strong>Troubleshooting unexpected issues:</strong> Adapting to technical difficulties or unforeseen challenges during the demonstration.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-26:0"><strong>Engaging different learning styles:</strong> Catering to diverse learning preferences through multiple modalities (visual, auditory, kinesthetic).</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="27:1-27:26"><strong>Overcoming Challenges:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="29:1-34:0"> <li data-sourcepos="29:1-29:128"><strong>Practice and rehearse:</strong> Thoroughly practice the explanation and demonstration, ensuring smooth transitions and timing.</li> <li data-sourcepos="30:1-30:131"><strong>Seek feedback:</strong> Share your draft speech and demonstration with trusted individuals for constructive criticism and suggestions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:177">Consider <strong>speech coaching</strong>: A coach can guide you in tailoring your explanation, refining your delivery, and managing potential challenges during the demonstration.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:106"><strong>Anticipate problems:</strong> Practice handling potential technical issues or unexpected situations smoothly.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-34:0"><strong>Utilize diverse visuals:</strong> Combine different types of visuals, such as diagrams, pictures, or live demonstrations, to cater to various learning styles.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="35:1-35:277"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="35:1-35:277">A well-prepared and engaging <strong>demonstration speech</strong> can be highly informative and impactful. By focusing on clarity, visual aids, audience engagement, and effective preparation, you can deliver a speech that teaches, entertains, and leaves a lasting impression.</p> <!-- /wp:list --> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/demonstration-speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">demonstration speech .
What Are the Main Elements of a Demonstrative Speech?
As you’ll see later, Demonstration Speech <!-- wp:paragraph --> <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:274">A type of informative speech where the speaker <strong>demonstrates</strong> how to do something, showcasing a process, skill, or product clearly and engagingly. It combines elements of explanation, instruction, and visual aids to educate and entertain the audience.</p> <h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:12"><strong>Purpose:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-11:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:121"><strong>Teach a new skill:</strong> Guide the audience through a process step-by-step, providing clear instructions and visual cues.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:124"><strong>Increase understanding:</strong> Explain complex concepts through practical demonstrations, making them relatable and engaging.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-9:115"><strong>Persuade the audience:</strong> Showcase a product's or service's benefits and features through live demonstration.</li> <li data-sourcepos="10:1-11:0"><strong>Entertain and inform:</strong> Combine clear instruction with an engaging presentation to keep the audience interested and learning.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="12:1-12:17"><strong>Key Elements:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="14:1-19:0"> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:113"><strong>Clear explanation:</strong> Break down the process into manageable steps, using simple language and avoiding jargon.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:133"><strong>Engaging delivery:</strong> Maintain a dynamic and enthusiastic tone, utilizing vocal variety and gestures to keep the audience focused.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-16:117"><strong>Visual aids:</strong> Employ effective visuals like diagrams, props, or live demonstrations to support your explanation.</li> <li data-sourcepos="17:1-17:118"><strong>Audience interaction:</strong> Invite participation through questions, hands-on activities, or audience engagement tools.</li> <li data-sourcepos="18:1-19:0"><strong>Smooth transitions:</strong> Guide the audience seamlessly between explanation, demonstration, and key takeaways.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="20:1-20:15"><strong>Challenges:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="22:1-26:0"> <li data-sourcepos="22:1-22:110"><strong>Balancing depth and clarity:</strong> Providing enough detail without overwhelming the audience with information.</li> <li data-sourcepos="23:1-23:95"><strong>Managing time effectively:</strong> Ensuring the demonstration fits within the allotted timeframe.</li> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:126"><strong>Troubleshooting unexpected issues:</strong> Adapting to technical difficulties or unforeseen challenges during the demonstration.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-26:0"><strong>Engaging different learning styles:</strong> Catering to diverse learning preferences through multiple modalities (visual, auditory, kinesthetic).</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="27:1-27:26"><strong>Overcoming Challenges:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="29:1-34:0"> <li data-sourcepos="29:1-29:128"><strong>Practice and rehearse:</strong> Thoroughly practice the explanation and demonstration, ensuring smooth transitions and timing.</li> <li data-sourcepos="30:1-30:131"><strong>Seek feedback:</strong> Share your draft speech and demonstration with trusted individuals for constructive criticism and suggestions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:177">Consider <strong>speech coaching</strong>: A coach can guide you in tailoring your explanation, refining your delivery, and managing potential challenges during the demonstration.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:106"><strong>Anticipate problems:</strong> Practice handling potential technical issues or unexpected situations smoothly.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-34:0"><strong>Utilize diverse visuals:</strong> Combine different types of visuals, such as diagrams, pictures, or live demonstrations, to cater to various learning styles.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="35:1-35:277"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="35:1-35:277">A well-prepared and engaging <strong>demonstration speech</strong> can be highly informative and impactful. By focusing on clarity, visual aids, audience engagement, and effective preparation, you can deliver a speech that teaches, entertains, and leaves a lasting impression.</p> <!-- /wp:list --> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/demonstration-speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">demonstration speech ideas and content vary per field. However, the significant elements that make a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech demonstrative are somewhat similar.
So, what are these elements?
The Nature of Demonstration Speech
One way people refer to demonstrative Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech topics or demonstrative Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech itself is “How-to.” because they show:
- How to prepare (or make) something
- How to perform (or complete) a process
- How something works
The Demonstrative Speech Topic
As I earlier stated, demonstrative Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech topics will usually answer a question of how to do something. However, some questions you will have to ask yourself when picking a title are:
- Do I know this topic sufficiently? If yes,
- Will my audience learn anything from my Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech ?
- Can I deliver my point within the allotted time for my Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech ?
- Is my topic technical? And does it require a lot of steps to make my listeners understand?
- Can I easily share this knowledge with a large group of people?
If your topic meets all the above criteria, you can move to my next point. Otherwise, you may want to reanalyze your title and find more practical Demonstration Speech <!-- wp:paragraph --> <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:274">A type of informative speech where the speaker <strong>demonstrates</strong> how to do something, showcasing a process, skill, or product clearly and engagingly. It combines elements of explanation, instruction, and visual aids to educate and entertain the audience.</p> <h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:12"><strong>Purpose:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-11:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:121"><strong>Teach a new skill:</strong> Guide the audience through a process step-by-step, providing clear instructions and visual cues.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:124"><strong>Increase understanding:</strong> Explain complex concepts through practical demonstrations, making them relatable and engaging.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-9:115"><strong>Persuade the audience:</strong> Showcase a product's or service's benefits and features through live demonstration.</li> <li data-sourcepos="10:1-11:0"><strong>Entertain and inform:</strong> Combine clear instruction with an engaging presentation to keep the audience interested and learning.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="12:1-12:17"><strong>Key Elements:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="14:1-19:0"> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:113"><strong>Clear explanation:</strong> Break down the process into manageable steps, using simple language and avoiding jargon.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:133"><strong>Engaging delivery:</strong> Maintain a dynamic and enthusiastic tone, utilizing vocal variety and gestures to keep the audience focused.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-16:117"><strong>Visual aids:</strong> Employ effective visuals like diagrams, props, or live demonstrations to support your explanation.</li> <li data-sourcepos="17:1-17:118"><strong>Audience interaction:</strong> Invite participation through questions, hands-on activities, or audience engagement tools.</li> <li data-sourcepos="18:1-19:0"><strong>Smooth transitions:</strong> Guide the audience seamlessly between explanation, demonstration, and key takeaways.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="20:1-20:15"><strong>Challenges:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="22:1-26:0"> <li data-sourcepos="22:1-22:110"><strong>Balancing depth and clarity:</strong> Providing enough detail without overwhelming the audience with information.</li> <li data-sourcepos="23:1-23:95"><strong>Managing time effectively:</strong> Ensuring the demonstration fits within the allotted timeframe.</li> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:126"><strong>Troubleshooting unexpected issues:</strong> Adapting to technical difficulties or unforeseen challenges during the demonstration.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-26:0"><strong>Engaging different learning styles:</strong> Catering to diverse learning preferences through multiple modalities (visual, auditory, kinesthetic).</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="27:1-27:26"><strong>Overcoming Challenges:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="29:1-34:0"> <li data-sourcepos="29:1-29:128"><strong>Practice and rehearse:</strong> Thoroughly practice the explanation and demonstration, ensuring smooth transitions and timing.</li> <li data-sourcepos="30:1-30:131"><strong>Seek feedback:</strong> Share your draft speech and demonstration with trusted individuals for constructive criticism and suggestions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:177">Consider <strong>speech coaching</strong>: A coach can guide you in tailoring your explanation, refining your delivery, and managing potential challenges during the demonstration.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:106"><strong>Anticipate problems:</strong> Practice handling potential technical issues or unexpected situations smoothly.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-34:0"><strong>Utilize diverse visuals:</strong> Combine different types of visuals, such as diagrams, pictures, or live demonstrations, to cater to various learning styles.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="35:1-35:277"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="35:1-35:277">A well-prepared and engaging <strong>demonstration speech</strong> can be highly informative and impactful. By focusing on clarity, visual aids, audience engagement, and effective preparation, you can deliver a speech that teaches, entertains, and leaves a lasting impression.</p> <!-- /wp:list --> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/demonstration-speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">demonstration speech ideas.
More information here:
Speech Organization
Additionally, with the organization, you should aim for Conciseness <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:326">In the realm of <strong>public speaking</strong>, <strong>conciseness</strong> refers to the ability to express your message clearly and effectively using the fewest possible words. It's about conveying your ideas precisely, avoiding unnecessary details and rambling while maintaining your message's essence and impact.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:33"><strong>Benefits for Public Speakers:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-11:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:137"><strong>Engaged audience:</strong> A concise speech keeps your audience focused and prevents them from losing interest due to excessive information.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:117"><strong>Increased clarity:</strong> By removing unnecessary clutter, your core message becomes clearer and easier to understand.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-9:137"><strong>Enhanced credibility:</strong> Concise communication projects professionalism and efficiency, making you appear more confident and prepared.</li> <li data-sourcepos="10:1-11:0"><strong>Reduced anxiety:</strong> Knowing you have a clear and concise message can help manage <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong> by minimizing the pressure to fill time.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="12:1-12:35"><strong>Challenges for Public Speakers:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="14:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:126"><strong>Striking a balance:</strong> Knowing where to draw the line between conciseness and omitting important information can be tricky.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:115"><strong>Avoiding oversimplification:</strong> Complex topics may require elaboration to ensure clarity and understanding.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Overcoming natural tendencies:</strong> Some speakers naturally use more words than others, requiring a conscious effort to be concise.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:41"><strong>Strategies for Achieving Conciseness:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="20:1-25:0"> <li data-sourcepos="20:1-20:92"><strong>Identify your core message:</strong> What is your audience's main point to remember?</li> <li data-sourcepos="21:1-21:128"><strong>Prioritize and eliminate:</strong> Analyze your content and remove any information not directly supporting your core message.</li> <li data-sourcepos="22:1-22:133"><strong>Use strong verbs and active voice:</strong> This makes your sentences more impactful and avoids passive constructions that can be wordy.</li> <li data-sourcepos="23:1-23:109"><strong>Simplify your language:</strong> Avoid jargon and technical terms unless they are essential and clearly defined.</li> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-25:0"><strong>Practice and refine:</strong> Rehearse your speech aloud and identify areas where you can tighten your wording or eliminate redundancies.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="26:1-26:20"><strong>Additional Tips:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="28:1-31:0"> <li data-sourcepos="28:1-28:93"><strong>Use storytelling:</strong> Engaging narratives can convey complex ideas concisely and memorably.</li> <li data-sourcepos="29:1-29:110"><strong>Focus on the visuals:</strong> Powerful visuals can support your message without extensive explanation.</li> <li data-sourcepos="30:1-31:0"><strong>Embrace silence:</strong> Pausing deliberately can emphasize key points and give your audience time to absorb your message.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="32:1-32:404"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="32:1-32:404"><strong>Conciseness</strong> is a powerful tool for <strong>public speakers</strong>. By eliminating unnecessary words and focusing on your core message, you can create a more engaging, impactful, and memorable presentation for your audience. This can also help manage <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong> by reducing the pressure to fill time and enabling you to focus on delivering your message with clarity and confidence.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/conciseness/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">conciseness in your Demonstration Speech <!-- wp:paragraph --> <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:274">A type of informative speech where the speaker <strong>demonstrates</strong> how to do something, showcasing a process, skill, or product clearly and engagingly. It combines elements of explanation, instruction, and visual aids to educate and entertain the audience.</p> <h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:12"><strong>Purpose:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-11:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:121"><strong>Teach a new skill:</strong> Guide the audience through a process step-by-step, providing clear instructions and visual cues.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:124"><strong>Increase understanding:</strong> Explain complex concepts through practical demonstrations, making them relatable and engaging.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-9:115"><strong>Persuade the audience:</strong> Showcase a product's or service's benefits and features through live demonstration.</li> <li data-sourcepos="10:1-11:0"><strong>Entertain and inform:</strong> Combine clear instruction with an engaging presentation to keep the audience interested and learning.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="12:1-12:17"><strong>Key Elements:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="14:1-19:0"> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:113"><strong>Clear explanation:</strong> Break down the process into manageable steps, using simple language and avoiding jargon.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:133"><strong>Engaging delivery:</strong> Maintain a dynamic and enthusiastic tone, utilizing vocal variety and gestures to keep the audience focused.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-16:117"><strong>Visual aids:</strong> Employ effective visuals like diagrams, props, or live demonstrations to support your explanation.</li> <li data-sourcepos="17:1-17:118"><strong>Audience interaction:</strong> Invite participation through questions, hands-on activities, or audience engagement tools.</li> <li data-sourcepos="18:1-19:0"><strong>Smooth transitions:</strong> Guide the audience seamlessly between explanation, demonstration, and key takeaways.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="20:1-20:15"><strong>Challenges:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="22:1-26:0"> <li data-sourcepos="22:1-22:110"><strong>Balancing depth and clarity:</strong> Providing enough detail without overwhelming the audience with information.</li> <li data-sourcepos="23:1-23:95"><strong>Managing time effectively:</strong> Ensuring the demonstration fits within the allotted timeframe.</li> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:126"><strong>Troubleshooting unexpected issues:</strong> Adapting to technical difficulties or unforeseen challenges during the demonstration.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-26:0"><strong>Engaging different learning styles:</strong> Catering to diverse learning preferences through multiple modalities (visual, auditory, kinesthetic).</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="27:1-27:26"><strong>Overcoming Challenges:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="29:1-34:0"> <li data-sourcepos="29:1-29:128"><strong>Practice and rehearse:</strong> Thoroughly practice the explanation and demonstration, ensuring smooth transitions and timing.</li> <li data-sourcepos="30:1-30:131"><strong>Seek feedback:</strong> Share your draft speech and demonstration with trusted individuals for constructive criticism and suggestions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:177">Consider <strong>speech coaching</strong>: A coach can guide you in tailoring your explanation, refining your delivery, and managing potential challenges during the demonstration.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:106"><strong>Anticipate problems:</strong> Practice handling potential technical issues or unexpected situations smoothly.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-34:0"><strong>Utilize diverse visuals:</strong> Combine different types of visuals, such as diagrams, pictures, or live demonstrations, to cater to various learning styles.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="35:1-35:277"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="35:1-35:277">A well-prepared and engaging <strong>demonstration speech</strong> can be highly informative and impactful. By focusing on clarity, visual aids, audience engagement, and effective preparation, you can deliver a speech that teaches, entertains, and leaves a lasting impression.</p> <!-- /wp:list --> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/demonstration-speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">demonstration speech outline.
Instead of writing out a long step-by-step process, try categorizing those steps into a series of main points or headings. This process will help listeners classify your information and make things less ambiguous.
Preparation
Furthermore, the next part of the organization is your preparation. One helpful facet or enhancer of any Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech process is visual aids .
When preparing, organize potential audiovisual aids and test them to avoid surprises. Next, practice your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech and organize your work area before time.
You must present during the main presentation, knowing that your audience may be learning new stuff. So, some critical aspects you may want to work on are:
- Your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech pace
- Eye contact (avoid speaking to your visual aids)
- Language (use simple, easy-to-understand words)
- Demonstration
- Avoid passing handouts during your presentation to avoid distractions, except when necessary to make a point in your presentation. If you need to give them, do it before or after you start.
- If you will need a volunteer, it is best to inform them on time.
- People may have questions, so prepare to answer them.
- Try not to be disorganized (clear your items up quickly) since you may not be the last speaker.
Prepare and practice your demonstrative Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech with Orai. Download the App now.
Demonstrative Speech Topics
Is the topic significant or necessary in Demonstration Speech <!-- wp:paragraph --> <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:274">A type of informative speech where the speaker <strong>demonstrates</strong> how to do something, showcasing a process, skill, or product clearly and engagingly. It combines elements of explanation, instruction, and visual aids to educate and entertain the audience.</p> <h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:12"><strong>Purpose:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-11:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:121"><strong>Teach a new skill:</strong> Guide the audience through a process step-by-step, providing clear instructions and visual cues.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:124"><strong>Increase understanding:</strong> Explain complex concepts through practical demonstrations, making them relatable and engaging.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-9:115"><strong>Persuade the audience:</strong> Showcase a product's or service's benefits and features through live demonstration.</li> <li data-sourcepos="10:1-11:0"><strong>Entertain and inform:</strong> Combine clear instruction with an engaging presentation to keep the audience interested and learning.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="12:1-12:17"><strong>Key Elements:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="14:1-19:0"> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:113"><strong>Clear explanation:</strong> Break down the process into manageable steps, using simple language and avoiding jargon.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:133"><strong>Engaging delivery:</strong> Maintain a dynamic and enthusiastic tone, utilizing vocal variety and gestures to keep the audience focused.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-16:117"><strong>Visual aids:</strong> Employ effective visuals like diagrams, props, or live demonstrations to support your explanation.</li> <li data-sourcepos="17:1-17:118"><strong>Audience interaction:</strong> Invite participation through questions, hands-on activities, or audience engagement tools.</li> <li data-sourcepos="18:1-19:0"><strong>Smooth transitions:</strong> Guide the audience seamlessly between explanation, demonstration, and key takeaways.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="20:1-20:15"><strong>Challenges:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="22:1-26:0"> <li data-sourcepos="22:1-22:110"><strong>Balancing depth and clarity:</strong> Providing enough detail without overwhelming the audience with information.</li> <li data-sourcepos="23:1-23:95"><strong>Managing time effectively:</strong> Ensuring the demonstration fits within the allotted timeframe.</li> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:126"><strong>Troubleshooting unexpected issues:</strong> Adapting to technical difficulties or unforeseen challenges during the demonstration.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-26:0"><strong>Engaging different learning styles:</strong> Catering to diverse learning preferences through multiple modalities (visual, auditory, kinesthetic).</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="27:1-27:26"><strong>Overcoming Challenges:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="29:1-34:0"> <li data-sourcepos="29:1-29:128"><strong>Practice and rehearse:</strong> Thoroughly practice the explanation and demonstration, ensuring smooth transitions and timing.</li> <li data-sourcepos="30:1-30:131"><strong>Seek feedback:</strong> Share your draft speech and demonstration with trusted individuals for constructive criticism and suggestions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:177">Consider <strong>speech coaching</strong>: A coach can guide you in tailoring your explanation, refining your delivery, and managing potential challenges during the demonstration.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:106"><strong>Anticipate problems:</strong> Practice handling potential technical issues or unexpected situations smoothly.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-34:0"><strong>Utilize diverse visuals:</strong> Combine different types of visuals, such as diagrams, pictures, or live demonstrations, to cater to various learning styles.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="35:1-35:277"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="35:1-35:277">A well-prepared and engaging <strong>demonstration speech</strong> can be highly informative and impactful. By focusing on clarity, visual aids, audience engagement, and effective preparation, you can deliver a speech that teaches, entertains, and leaves a lasting impression.</p> <!-- /wp:list --> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/demonstration-speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">demonstration speech ideas? Absolutely!
As I stated earlier, your title is essential when we look at the demonstrative Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech elements. Your demonstrative Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech topics should reflect the semantic meaning of your chosen process.
The significance of your title in this type of Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech brings me to my next point. How can you choose the best demonstrative Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech topic?
How to Choose the Best Demonstrative Speech Topic
Your topic is vital to your presentation , and this knowledge could make you nervous. So, if you are unsure of the right demonstrative Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech topics, here are three tips to guide your choice.
The Allotted Time For Speech Delivery
So, How much time do you have to deliver the demonstrative Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech ?
Sometimes, you could have just six minutes to present your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech . Other times, you could get as much as two hours.
When you look at the time you have to present, it will be easier to determine how broad your topic should be. For example, let’s look at these two topics:
- How to make Egg fried rice
- Four easy Egg fried rice recipes for a college student
Which of these demonstrative Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech topics will be better for a 6-minute Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech ? Option one, because it requires one recipe.
Therefore , with more time allowance, your topic will have room to accommodate more ideas .
Your Audience
If you remember the questions to ask when picking a topic, one of them has to do with your audience: “Will they learn anything?”
You can be a passionate professional and deliver your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech while hitting all the right notes. But will they learn from it, or does it relate to your audience?
For instance, you must give a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech to senior citizens without internet exposure. Of course, talking about “How to build your brand on Instagram” will only bore them.
Apart from the complex terms you may need to use, they have no reason to remember your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech .
For another example, suppose you are talking to a group of sophomores. A Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech on “How to navigate college applications” may be in a similar domain, but it isn’t relevant.
So, your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech demonstrative Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech topics should be relevant and helpful .
Is Your Demonstration Speech Idea Speech-Worthy?
Moreover, some topics are not worthy of a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech . For example, “How to tie a knot” is more like a YouTube video than an oration.
A better type of Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech topic would be “How to set realistic goals.” And this leads to the next subheading— Demonstration Speech <!-- wp:paragraph --> <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:274">A type of informative speech where the speaker <strong>demonstrates</strong> how to do something, showcasing a process, skill, or product clearly and engagingly. It combines elements of explanation, instruction, and visual aids to educate and entertain the audience.</p> <h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:12"><strong>Purpose:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-11:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:121"><strong>Teach a new skill:</strong> Guide the audience through a process step-by-step, providing clear instructions and visual cues.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:124"><strong>Increase understanding:</strong> Explain complex concepts through practical demonstrations, making them relatable and engaging.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-9:115"><strong>Persuade the audience:</strong> Showcase a product's or service's benefits and features through live demonstration.</li> <li data-sourcepos="10:1-11:0"><strong>Entertain and inform:</strong> Combine clear instruction with an engaging presentation to keep the audience interested and learning.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="12:1-12:17"><strong>Key Elements:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="14:1-19:0"> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:113"><strong>Clear explanation:</strong> Break down the process into manageable steps, using simple language and avoiding jargon.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:133"><strong>Engaging delivery:</strong> Maintain a dynamic and enthusiastic tone, utilizing vocal variety and gestures to keep the audience focused.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-16:117"><strong>Visual aids:</strong> Employ effective visuals like diagrams, props, or live demonstrations to support your explanation.</li> <li data-sourcepos="17:1-17:118"><strong>Audience interaction:</strong> Invite participation through questions, hands-on activities, or audience engagement tools.</li> <li data-sourcepos="18:1-19:0"><strong>Smooth transitions:</strong> Guide the audience seamlessly between explanation, demonstration, and key takeaways.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="20:1-20:15"><strong>Challenges:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="22:1-26:0"> <li data-sourcepos="22:1-22:110"><strong>Balancing depth and clarity:</strong> Providing enough detail without overwhelming the audience with information.</li> <li data-sourcepos="23:1-23:95"><strong>Managing time effectively:</strong> Ensuring the demonstration fits within the allotted timeframe.</li> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:126"><strong>Troubleshooting unexpected issues:</strong> Adapting to technical difficulties or unforeseen challenges during the demonstration.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-26:0"><strong>Engaging different learning styles:</strong> Catering to diverse learning preferences through multiple modalities (visual, auditory, kinesthetic).</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="27:1-27:26"><strong>Overcoming Challenges:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="29:1-34:0"> <li data-sourcepos="29:1-29:128"><strong>Practice and rehearse:</strong> Thoroughly practice the explanation and demonstration, ensuring smooth transitions and timing.</li> <li data-sourcepos="30:1-30:131"><strong>Seek feedback:</strong> Share your draft speech and demonstration with trusted individuals for constructive criticism and suggestions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:177">Consider <strong>speech coaching</strong>: A coach can guide you in tailoring your explanation, refining your delivery, and managing potential challenges during the demonstration.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:106"><strong>Anticipate problems:</strong> Practice handling potential technical issues or unexpected situations smoothly.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-34:0"><strong>Utilize diverse visuals:</strong> Combine different types of visuals, such as diagrams, pictures, or live demonstrations, to cater to various learning styles.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="35:1-35:277"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="35:1-35:277">A well-prepared and engaging <strong>demonstration speech</strong> can be highly informative and impactful. By focusing on clarity, visual aids, audience engagement, and effective preparation, you can deliver a speech that teaches, entertains, and leaves a lasting impression.</p> <!-- /wp:list --> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/demonstration-speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">demonstration speech examples.
Watch this video for more:
Examples of Excellent Topic Choices
You can look at Demonstration Speech <!-- wp:paragraph --> <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:274">A type of informative speech where the speaker <strong>demonstrates</strong> how to do something, showcasing a process, skill, or product clearly and engagingly. It combines elements of explanation, instruction, and visual aids to educate and entertain the audience.</p> <h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:12"><strong>Purpose:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-11:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:121"><strong>Teach a new skill:</strong> Guide the audience through a process step-by-step, providing clear instructions and visual cues.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:124"><strong>Increase understanding:</strong> Explain complex concepts through practical demonstrations, making them relatable and engaging.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-9:115"><strong>Persuade the audience:</strong> Showcase a product's or service's benefits and features through live demonstration.</li> <li data-sourcepos="10:1-11:0"><strong>Entertain and inform:</strong> Combine clear instruction with an engaging presentation to keep the audience interested and learning.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="12:1-12:17"><strong>Key Elements:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="14:1-19:0"> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:113"><strong>Clear explanation:</strong> Break down the process into manageable steps, using simple language and avoiding jargon.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:133"><strong>Engaging delivery:</strong> Maintain a dynamic and enthusiastic tone, utilizing vocal variety and gestures to keep the audience focused.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-16:117"><strong>Visual aids:</strong> Employ effective visuals like diagrams, props, or live demonstrations to support your explanation.</li> <li data-sourcepos="17:1-17:118"><strong>Audience interaction:</strong> Invite participation through questions, hands-on activities, or audience engagement tools.</li> <li data-sourcepos="18:1-19:0"><strong>Smooth transitions:</strong> Guide the audience seamlessly between explanation, demonstration, and key takeaways.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="20:1-20:15"><strong>Challenges:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="22:1-26:0"> <li data-sourcepos="22:1-22:110"><strong>Balancing depth and clarity:</strong> Providing enough detail without overwhelming the audience with information.</li> <li data-sourcepos="23:1-23:95"><strong>Managing time effectively:</strong> Ensuring the demonstration fits within the allotted timeframe.</li> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:126"><strong>Troubleshooting unexpected issues:</strong> Adapting to technical difficulties or unforeseen challenges during the demonstration.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-26:0"><strong>Engaging different learning styles:</strong> Catering to diverse learning preferences through multiple modalities (visual, auditory, kinesthetic).</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="27:1-27:26"><strong>Overcoming Challenges:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="29:1-34:0"> <li data-sourcepos="29:1-29:128"><strong>Practice and rehearse:</strong> Thoroughly practice the explanation and demonstration, ensuring smooth transitions and timing.</li> <li data-sourcepos="30:1-30:131"><strong>Seek feedback:</strong> Share your draft speech and demonstration with trusted individuals for constructive criticism and suggestions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:177">Consider <strong>speech coaching</strong>: A coach can guide you in tailoring your explanation, refining your delivery, and managing potential challenges during the demonstration.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:106"><strong>Anticipate problems:</strong> Practice handling potential technical issues or unexpected situations smoothly.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-34:0"><strong>Utilize diverse visuals:</strong> Combine different types of visuals, such as diagrams, pictures, or live demonstrations, to cater to various learning styles.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="35:1-35:277"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="35:1-35:277">A well-prepared and engaging <strong>demonstration speech</strong> can be highly informative and impactful. By focusing on clarity, visual aids, audience engagement, and effective preparation, you can deliver a speech that teaches, entertains, and leaves a lasting impression.</p> <!-- /wp:list --> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/demonstration-speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">demonstration speech ideas if you struggle to develop a topic for your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech . However, before that, let’s look at verbs and phrases to help you when you come up with your title.
- N Steps to__ (where n is a number)
- How __ is made, produced, or done
- How __ works
- The procedure of __
- Tips for __
- A step-by-step guide to __
Do you get the idea?
Likewise, let us see 25 sentences’ examples of demonstrative Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech topics.
25 Demonstrative Speech Topic Examples
Additionally, let’s test your understanding by comparing five potential Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech topics.
5 Potential Demonstrative Speech Topics
There are many topic ideas for a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech . For example, you could do something funny like “How to ensure you make eye contact with your crush.”
If you have a friend or relative similar to your target audience, try to run your topic by them. They can help you pick a helpful title, or you can use a virtual assistant.
I hope you have new Demonstration Speech <!-- wp:paragraph --> <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:274">A type of informative speech where the speaker <strong>demonstrates</strong> how to do something, showcasing a process, skill, or product clearly and engagingly. It combines elements of explanation, instruction, and visual aids to educate and entertain the audience.</p> <h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:12"><strong>Purpose:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-11:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:121"><strong>Teach a new skill:</strong> Guide the audience through a process step-by-step, providing clear instructions and visual cues.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:124"><strong>Increase understanding:</strong> Explain complex concepts through practical demonstrations, making them relatable and engaging.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-9:115"><strong>Persuade the audience:</strong> Showcase a product's or service's benefits and features through live demonstration.</li> <li data-sourcepos="10:1-11:0"><strong>Entertain and inform:</strong> Combine clear instruction with an engaging presentation to keep the audience interested and learning.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="12:1-12:17"><strong>Key Elements:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="14:1-19:0"> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:113"><strong>Clear explanation:</strong> Break down the process into manageable steps, using simple language and avoiding jargon.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:133"><strong>Engaging delivery:</strong> Maintain a dynamic and enthusiastic tone, utilizing vocal variety and gestures to keep the audience focused.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-16:117"><strong>Visual aids:</strong> Employ effective visuals like diagrams, props, or live demonstrations to support your explanation.</li> <li data-sourcepos="17:1-17:118"><strong>Audience interaction:</strong> Invite participation through questions, hands-on activities, or audience engagement tools.</li> <li data-sourcepos="18:1-19:0"><strong>Smooth transitions:</strong> Guide the audience seamlessly between explanation, demonstration, and key takeaways.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="20:1-20:15"><strong>Challenges:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="22:1-26:0"> <li data-sourcepos="22:1-22:110"><strong>Balancing depth and clarity:</strong> Providing enough detail without overwhelming the audience with information.</li> <li data-sourcepos="23:1-23:95"><strong>Managing time effectively:</strong> Ensuring the demonstration fits within the allotted timeframe.</li> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:126"><strong>Troubleshooting unexpected issues:</strong> Adapting to technical difficulties or unforeseen challenges during the demonstration.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-26:0"><strong>Engaging different learning styles:</strong> Catering to diverse learning preferences through multiple modalities (visual, auditory, kinesthetic).</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="27:1-27:26"><strong>Overcoming Challenges:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="29:1-34:0"> <li data-sourcepos="29:1-29:128"><strong>Practice and rehearse:</strong> Thoroughly practice the explanation and demonstration, ensuring smooth transitions and timing.</li> <li data-sourcepos="30:1-30:131"><strong>Seek feedback:</strong> Share your draft speech and demonstration with trusted individuals for constructive criticism and suggestions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:177">Consider <strong>speech coaching</strong>: A coach can guide you in tailoring your explanation, refining your delivery, and managing potential challenges during the demonstration.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:106"><strong>Anticipate problems:</strong> Practice handling potential technical issues or unexpected situations smoothly.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-34:0"><strong>Utilize diverse visuals:</strong> Combine different types of visuals, such as diagrams, pictures, or live demonstrations, to cater to various learning styles.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="35:1-35:277"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="35:1-35:277">A well-prepared and engaging <strong>demonstration speech</strong> can be highly informative and impactful. By focusing on clarity, visual aids, audience engagement, and effective preparation, you can deliver a speech that teaches, entertains, and leaves a lasting impression.</p> <!-- /wp:list --> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/demonstration-speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">demonstration speech ideas now. Once you select the perfect topic, you must move on to the next phase. Additionally, here’s a link to 500+ demonstrative Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech ideas.
Tips on Creating Your Demonstration Speech Outline
Why do you need a Demonstration Speech <!-- wp:paragraph --> <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:274">A type of informative speech where the speaker <strong>demonstrates</strong> how to do something, showcasing a process, skill, or product clearly and engagingly. It combines elements of explanation, instruction, and visual aids to educate and entertain the audience.</p> <h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:12"><strong>Purpose:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-11:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:121"><strong>Teach a new skill:</strong> Guide the audience through a process step-by-step, providing clear instructions and visual cues.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:124"><strong>Increase understanding:</strong> Explain complex concepts through practical demonstrations, making them relatable and engaging.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-9:115"><strong>Persuade the audience:</strong> Showcase a product's or service's benefits and features through live demonstration.</li> <li data-sourcepos="10:1-11:0"><strong>Entertain and inform:</strong> Combine clear instruction with an engaging presentation to keep the audience interested and learning.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="12:1-12:17"><strong>Key Elements:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="14:1-19:0"> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:113"><strong>Clear explanation:</strong> Break down the process into manageable steps, using simple language and avoiding jargon.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:133"><strong>Engaging delivery:</strong> Maintain a dynamic and enthusiastic tone, utilizing vocal variety and gestures to keep the audience focused.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-16:117"><strong>Visual aids:</strong> Employ effective visuals like diagrams, props, or live demonstrations to support your explanation.</li> <li data-sourcepos="17:1-17:118"><strong>Audience interaction:</strong> Invite participation through questions, hands-on activities, or audience engagement tools.</li> <li data-sourcepos="18:1-19:0"><strong>Smooth transitions:</strong> Guide the audience seamlessly between explanation, demonstration, and key takeaways.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="20:1-20:15"><strong>Challenges:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="22:1-26:0"> <li data-sourcepos="22:1-22:110"><strong>Balancing depth and clarity:</strong> Providing enough detail without overwhelming the audience with information.</li> <li data-sourcepos="23:1-23:95"><strong>Managing time effectively:</strong> Ensuring the demonstration fits within the allotted timeframe.</li> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:126"><strong>Troubleshooting unexpected issues:</strong> Adapting to technical difficulties or unforeseen challenges during the demonstration.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-26:0"><strong>Engaging different learning styles:</strong> Catering to diverse learning preferences through multiple modalities (visual, auditory, kinesthetic).</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="27:1-27:26"><strong>Overcoming Challenges:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="29:1-34:0"> <li data-sourcepos="29:1-29:128"><strong>Practice and rehearse:</strong> Thoroughly practice the explanation and demonstration, ensuring smooth transitions and timing.</li> <li data-sourcepos="30:1-30:131"><strong>Seek feedback:</strong> Share your draft speech and demonstration with trusted individuals for constructive criticism and suggestions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:177">Consider <strong>speech coaching</strong>: A coach can guide you in tailoring your explanation, refining your delivery, and managing potential challenges during the demonstration.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:106"><strong>Anticipate problems:</strong> Practice handling potential technical issues or unexpected situations smoothly.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-34:0"><strong>Utilize diverse visuals:</strong> Combine different types of visuals, such as diagrams, pictures, or live demonstrations, to cater to various learning styles.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="35:1-35:277"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="35:1-35:277">A well-prepared and engaging <strong>demonstration speech</strong> can be highly informative and impactful. By focusing on clarity, visual aids, audience engagement, and effective preparation, you can deliver a speech that teaches, entertains, and leaves a lasting impression.</p> <!-- /wp:list --> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/demonstration-speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">demonstration speech outline? An outline will help you stay on track during your presentation.
An essential outline creation tip is allocating time to different segments based on the duration of your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech .
- Introduction: This shouldn’t take too long. If you can do it in less than 2 minutes, it gives you more time to talk. However, it should ideally not exceed 5 minutes.
- Body: It is the central part of your article, and the time allocation will depend on your topic and Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech time. So it could run from 5 minutes to 30 minutes or more.
- Conclusion: Make a summary that you can present in 5 minutes or less. Your finale doesn’t need to run too long.
- Question and Answer: The time you give needs to be at your discretion. The best thing to do is set a time limit, preferably less than 10 minutes, and inform your audience of the number of questions you can take during the section at the beginning. So, you can answer 2-5, depending on brevity.
So, how do you prepare your demonstration speech outline?
- The first step is to pick a topic we discussed extensively above.
- Next, you must make an introduction – Your introduction will keep your audience listening to you. So try to grab the attention of your listeners with your introduction.
- Outline the step-by-step process of what you describe or the points you give as tips.
- Next, add more details to the step-by-step process.
- List and gather additional tools that you will need to help your audience understand. Here, you gather visual tools like dummies, drawings, videos, or even human models.
- Since you have a better picture of your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech , include your outline in your introduction. It gives your audience an overall idea of what you are talking about
- Write your conclusion -Try to go over the crucial points you made. Add something memorable so your audience has a takeaway from your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech .
Writing the Demonstrative Speech Proper
In addition to the outline, here are tips for writing the main Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech .
What is your purpose?
- Why should your audience listen to you?
The body of your story
Question and answer segment, variations of your topic.
This is the ideal place to add an emotional element to your Demonstration Speech <!-- wp:paragraph --> <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:274">A type of informative speech where the speaker <strong>demonstrates</strong> how to do something, showcasing a process, skill, or product clearly and engagingly. It combines elements of explanation, instruction, and visual aids to educate and entertain the audience.</p> <h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:12"><strong>Purpose:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-11:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:121"><strong>Teach a new skill:</strong> Guide the audience through a process step-by-step, providing clear instructions and visual cues.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:124"><strong>Increase understanding:</strong> Explain complex concepts through practical demonstrations, making them relatable and engaging.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-9:115"><strong>Persuade the audience:</strong> Showcase a product's or service's benefits and features through live demonstration.</li> <li data-sourcepos="10:1-11:0"><strong>Entertain and inform:</strong> Combine clear instruction with an engaging presentation to keep the audience interested and learning.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="12:1-12:17"><strong>Key Elements:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="14:1-19:0"> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:113"><strong>Clear explanation:</strong> Break down the process into manageable steps, using simple language and avoiding jargon.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:133"><strong>Engaging delivery:</strong> Maintain a dynamic and enthusiastic tone, utilizing vocal variety and gestures to keep the audience focused.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-16:117"><strong>Visual aids:</strong> Employ effective visuals like diagrams, props, or live demonstrations to support your explanation.</li> <li data-sourcepos="17:1-17:118"><strong>Audience interaction:</strong> Invite participation through questions, hands-on activities, or audience engagement tools.</li> <li data-sourcepos="18:1-19:0"><strong>Smooth transitions:</strong> Guide the audience seamlessly between explanation, demonstration, and key takeaways.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="20:1-20:15"><strong>Challenges:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="22:1-26:0"> <li data-sourcepos="22:1-22:110"><strong>Balancing depth and clarity:</strong> Providing enough detail without overwhelming the audience with information.</li> <li data-sourcepos="23:1-23:95"><strong>Managing time effectively:</strong> Ensuring the demonstration fits within the allotted timeframe.</li> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:126"><strong>Troubleshooting unexpected issues:</strong> Adapting to technical difficulties or unforeseen challenges during the demonstration.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-26:0"><strong>Engaging different learning styles:</strong> Catering to diverse learning preferences through multiple modalities (visual, auditory, kinesthetic).</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="27:1-27:26"><strong>Overcoming Challenges:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="29:1-34:0"> <li data-sourcepos="29:1-29:128"><strong>Practice and rehearse:</strong> Thoroughly practice the explanation and demonstration, ensuring smooth transitions and timing.</li> <li data-sourcepos="30:1-30:131"><strong>Seek feedback:</strong> Share your draft speech and demonstration with trusted individuals for constructive criticism and suggestions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:177">Consider <strong>speech coaching</strong>: A coach can guide you in tailoring your explanation, refining your delivery, and managing potential challenges during the demonstration.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:106"><strong>Anticipate problems:</strong> Practice handling potential technical issues or unexpected situations smoothly.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-34:0"><strong>Utilize diverse visuals:</strong> Combine different types of visuals, such as diagrams, pictures, or live demonstrations, to cater to various learning styles.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="35:1-35:277"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="35:1-35:277">A well-prepared and engaging <strong>demonstration speech</strong> can be highly informative and impactful. By focusing on clarity, visual aids, audience engagement, and effective preparation, you can deliver a speech that teaches, entertains, and leaves a lasting impression.</p> <!-- /wp:list --> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/demonstration-speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">demonstration speech idea.
Why? When stating your purpose, you can tell your audience why you care about the topic and why they should.
When you start your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech by passionately discussing your purpose, you can keep your audience intrigued.
Why Should your audience listen to you?
Before, we established that a demonstrative Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech topic makes your audience expect to learn from you from the onset. So, your next goal is to tell your listeners why you are the best presenter to teach them.
This section can serve as your introduction and take storytelling’s direction.
For example, let’s say you want to discuss “how to maintain your blood sugar as a diabetic.” Now will be a perfect time to tell a story about how you are diabetic or a doctor who treats them.
After you establish credibility and intrigue, it is time to start talking. This part should be a walkover since you picked a demonstrative Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech topic you understand well.
Key points to remember here are:
- Try to make your point easy for your audience to understand
- Although your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech is functional, don’t forget to keep your audience engaged using visual aids or interactions . More on that later.
- You can take two approaches to present your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech and both work. You could summarize all the points then start explaining them or introduce each one as you go.
Everyone in your audience is unique and may have questions you did not cover in your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech . As a result, it would be best if you remembered that this could happen irrespective of how excellent your presentation was.
So, set some time aside for questions and answers. But this is only if your time is enough to make a Q and A session. Otherwise, you can be generous to give them the means to contact you with their questions.
Furthermore, if you want to add details to your topic, you can include a segment or a branch of the subject.
For example, when you talk about “How college students can manage their time,” A great addition can be “How medical students can manage their time.”
As I stated in the Demonstration Speech <!-- wp:paragraph --> <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:274">A type of informative speech where the speaker <strong>demonstrates</strong> how to do something, showcasing a process, skill, or product clearly and engagingly. It combines elements of explanation, instruction, and visual aids to educate and entertain the audience.</p> <h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:12"><strong>Purpose:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-11:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:121"><strong>Teach a new skill:</strong> Guide the audience through a process step-by-step, providing clear instructions and visual cues.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:124"><strong>Increase understanding:</strong> Explain complex concepts through practical demonstrations, making them relatable and engaging.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-9:115"><strong>Persuade the audience:</strong> Showcase a product's or service's benefits and features through live demonstration.</li> <li data-sourcepos="10:1-11:0"><strong>Entertain and inform:</strong> Combine clear instruction with an engaging presentation to keep the audience interested and learning.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="12:1-12:17"><strong>Key Elements:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="14:1-19:0"> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:113"><strong>Clear explanation:</strong> Break down the process into manageable steps, using simple language and avoiding jargon.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:133"><strong>Engaging delivery:</strong> Maintain a dynamic and enthusiastic tone, utilizing vocal variety and gestures to keep the audience focused.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-16:117"><strong>Visual aids:</strong> Employ effective visuals like diagrams, props, or live demonstrations to support your explanation.</li> <li data-sourcepos="17:1-17:118"><strong>Audience interaction:</strong> Invite participation through questions, hands-on activities, or audience engagement tools.</li> <li data-sourcepos="18:1-19:0"><strong>Smooth transitions:</strong> Guide the audience seamlessly between explanation, demonstration, and key takeaways.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="20:1-20:15"><strong>Challenges:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="22:1-26:0"> <li data-sourcepos="22:1-22:110"><strong>Balancing depth and clarity:</strong> Providing enough detail without overwhelming the audience with information.</li> <li data-sourcepos="23:1-23:95"><strong>Managing time effectively:</strong> Ensuring the demonstration fits within the allotted timeframe.</li> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:126"><strong>Troubleshooting unexpected issues:</strong> Adapting to technical difficulties or unforeseen challenges during the demonstration.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-26:0"><strong>Engaging different learning styles:</strong> Catering to diverse learning preferences through multiple modalities (visual, auditory, kinesthetic).</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="27:1-27:26"><strong>Overcoming Challenges:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="29:1-34:0"> <li data-sourcepos="29:1-29:128"><strong>Practice and rehearse:</strong> Thoroughly practice the explanation and demonstration, ensuring smooth transitions and timing.</li> <li data-sourcepos="30:1-30:131"><strong>Seek feedback:</strong> Share your draft speech and demonstration with trusted individuals for constructive criticism and suggestions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:177">Consider <strong>speech coaching</strong>: A coach can guide you in tailoring your explanation, refining your delivery, and managing potential challenges during the demonstration.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:106"><strong>Anticipate problems:</strong> Practice handling potential technical issues or unexpected situations smoothly.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-34:0"><strong>Utilize diverse visuals:</strong> Combine different types of visuals, such as diagrams, pictures, or live demonstrations, to cater to various learning styles.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="35:1-35:277"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="35:1-35:277">A well-prepared and engaging <strong>demonstration speech</strong> can be highly informative and impactful. By focusing on clarity, visual aids, audience engagement, and effective preparation, you can deliver a speech that teaches, entertains, and leaves a lasting impression.</p> <!-- /wp:list --> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/demonstration-speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">demonstration speech ideas for an outline, your summary or conclusion is essential. Since you taught them a lot, you can do an overview so they have your key takeaways.
Final Helpful Tips For Your Speech Writing
As promised, if you skipped until the end, you can start with the concluding tips here. Let’s continue with some final points to remember when preparing your Demonstration Speech <!-- wp:paragraph --> <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:274">A type of informative speech where the speaker <strong>demonstrates</strong> how to do something, showcasing a process, skill, or product clearly and engagingly. It combines elements of explanation, instruction, and visual aids to educate and entertain the audience.</p> <h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:12"><strong>Purpose:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-11:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:121"><strong>Teach a new skill:</strong> Guide the audience through a process step-by-step, providing clear instructions and visual cues.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:124"><strong>Increase understanding:</strong> Explain complex concepts through practical demonstrations, making them relatable and engaging.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-9:115"><strong>Persuade the audience:</strong> Showcase a product's or service's benefits and features through live demonstration.</li> <li data-sourcepos="10:1-11:0"><strong>Entertain and inform:</strong> Combine clear instruction with an engaging presentation to keep the audience interested and learning.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="12:1-12:17"><strong>Key Elements:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="14:1-19:0"> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:113"><strong>Clear explanation:</strong> Break down the process into manageable steps, using simple language and avoiding jargon.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:133"><strong>Engaging delivery:</strong> Maintain a dynamic and enthusiastic tone, utilizing vocal variety and gestures to keep the audience focused.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-16:117"><strong>Visual aids:</strong> Employ effective visuals like diagrams, props, or live demonstrations to support your explanation.</li> <li data-sourcepos="17:1-17:118"><strong>Audience interaction:</strong> Invite participation through questions, hands-on activities, or audience engagement tools.</li> <li data-sourcepos="18:1-19:0"><strong>Smooth transitions:</strong> Guide the audience seamlessly between explanation, demonstration, and key takeaways.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="20:1-20:15"><strong>Challenges:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="22:1-26:0"> <li data-sourcepos="22:1-22:110"><strong>Balancing depth and clarity:</strong> Providing enough detail without overwhelming the audience with information.</li> <li data-sourcepos="23:1-23:95"><strong>Managing time effectively:</strong> Ensuring the demonstration fits within the allotted timeframe.</li> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:126"><strong>Troubleshooting unexpected issues:</strong> Adapting to technical difficulties or unforeseen challenges during the demonstration.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-26:0"><strong>Engaging different learning styles:</strong> Catering to diverse learning preferences through multiple modalities (visual, auditory, kinesthetic).</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="27:1-27:26"><strong>Overcoming Challenges:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="29:1-34:0"> <li data-sourcepos="29:1-29:128"><strong>Practice and rehearse:</strong> Thoroughly practice the explanation and demonstration, ensuring smooth transitions and timing.</li> <li data-sourcepos="30:1-30:131"><strong>Seek feedback:</strong> Share your draft speech and demonstration with trusted individuals for constructive criticism and suggestions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:177">Consider <strong>speech coaching</strong>: A coach can guide you in tailoring your explanation, refining your delivery, and managing potential challenges during the demonstration.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:106"><strong>Anticipate problems:</strong> Practice handling potential technical issues or unexpected situations smoothly.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-34:0"><strong>Utilize diverse visuals:</strong> Combine different types of visuals, such as diagrams, pictures, or live demonstrations, to cater to various learning styles.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="35:1-35:277"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="35:1-35:277">A well-prepared and engaging <strong>demonstration speech</strong> can be highly informative and impactful. By focusing on clarity, visual aids, audience engagement, and effective preparation, you can deliver a speech that teaches, entertains, and leaves a lasting impression.</p> <!-- /wp:list --> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/demonstration-speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">demonstration speech ideas for those who kept reading.
Keep things Simple
You do not need a bogus presentation. Unless you are making a list of one or two-word items, keeping your points between 3-7 is best.
Using big words is unnecessary, except if your audience knows it or the term has no synonym.
Engagement is Key
Engagement is vital regardless of the type of Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech or demonstrative Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech topic. Not only do you want your audience to remember your lesson, but you also want your listeners to be involved.
If your topic allows you to call up volunteers, try that or involve them in active participation.
Visual Aids is Your Best Friend
Also, using visual aids makes a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech more useful. The easiest way to add visuals to your oration is by utilizing PowerPoint presentations.
Instead of using many words in your presentation, let it contain more pictures while you talk. You can also add props to make the presentation even better.
Give Your Audience Reason to Remember You
Finally, not every audience member will instantly grasp what you say. So, try to give them the means to contact you, a website to check, or a pamphlet to read after your presentation.
These factors help them remember your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech and keep your points in their minds.
Practice your memorable Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech with Orai. Perfect it with feedback on your tone, tempo, and many more!
How can I make my demonstrative speech more engaging?
Captivate your audience in your next demonstrative Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech by following this recipe: hook them with a thought-provoking intro, clearly explain the “why” and connect through relatable stories, actively engage them with questions and participation, enhance visuals with props and charts, speak conversationally with touches of humor, summarize key points and empower them with a call to action. This dynamic recipe will ensure your audience remembers and applies your valuable message!
What are some effective visual aids to use in a demonstrative speech?
To truly engage your audience in your demonstrative Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech , choose visual aids that are both relevant and impactful. Consider using props for tangible connections, slides or presentations for organized information, videos for dynamic demonstrations, charts or diagrams to simplify complex data, and even samples for hands-on experiences. Remember, the key is to select visuals that enrich understanding and keep your audience engaged, leaving them captivated by your topic.
What is the difference between a demonstrative speech and an informative speech?
Though both demonstrative and informative speeches educate, they do so in distinct ways. While informative speeches rely on storytelling and facts to convey knowledge verbally, demonstrative speeches prioritize hands-on learning through live demonstrations and engaging visual aids, showcasing processes, and tasks for deeper understanding. Imagine baking a cake: a demonstrative Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech would present each step visually, while an informative one would share the history and cultural significance of the cake through captivating narratives. The type of Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech you choose hinges on whether you want your audience to know or actively do simply.
How can AI be used to practice a demonstrative speech?
Forget the practice mirror! AI Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech coaches are here to elevate your demonstrative Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech game. Get real-time feedback on everything from pace to non-verbal cues, receive personalized tips on storytelling and slide design, and practice interactively in a stress-free zone. Plus, enjoy the flexibility to polish your skills on the go, anytime, anywhere. With AI-powered coaching, you’ll refine your delivery, boost your Confidence <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:305">In the context of <strong>public speaking</strong>, <strong>confidence</strong> refers to the belief in one's ability to communicate effectively and deliver one's message with clarity and impact. It encompasses various elements, including self-belief, composure, and the ability to manage one's <strong>fear of public speaking</strong>.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:16"><strong>Key Aspects:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-12:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:108"><strong>Self-belief:</strong> A strong conviction in your knowledge, skills, and ability to connect with your audience.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:95"><strong>Composure:</strong> Maintaining calmness and poise under pressure, even in challenging situations.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-9:100"><strong>Assertiveness:</strong> Expressing your ideas clearly and concisely, avoiding hesitation or self-doubt.</li> <li data-sourcepos="10:1-10:104"><strong>Positive self-talk:</strong> Countering negative thoughts with affirmations and focusing on your strengths.</li> <li data-sourcepos="11:1-12:0"><strong>Strong body language:</strong> Using gestures, posture, and eye contact that project confidence and professionalism.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="13:1-13:27"><strong>Benefits of Confidence:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="15:1-19:0"> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:99"><strong>Reduced anxiety:</strong> Feeling confident helps manage <strong>fear of public speaking</strong> and stage fright.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-16:133"><strong>Engaging delivery:</strong> Confident speakers project their voices, hold eye contact, and connect with their audience more effectively.</li> <li data-sourcepos="17:1-17:137"><strong>Increased persuasiveness:</strong> A confident presentation inspires belief and motivates your audience to listen and remember your message.</li> <li data-sourcepos="18:1-19:0"><strong>Greater impact:</strong> Confidently delivered speeches leave a lasting impression and achieve desired outcomes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="20:1-20:15"><strong>Challenges:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="22:1-26:0"> <li data-sourcepos="22:1-22:112">Overcoming <strong>fear of public speaking</strong>: Many people experience some level of anxiety when speaking publicly.</li> <li data-sourcepos="23:1-23:101"><strong>Imposter syndrome:</strong> Doubting your abilities and qualifications, even when objectively qualified.</li> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:92"><strong>Negative self-talk:</strong> Internalized criticism and limiting beliefs can hamper confidence.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-26:0"><strong>Past negative experiences:</strong> Unsuccessful presentations or negative feedback can erode confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="27:1-27:24"><strong>Building Confidence:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="29:1-36:0"> <li data-sourcepos="29:1-29:102"><strong>Practice and preparation:</strong> Thoroughly rehearse your speech to feel comfortable with the material.</li> <li data-sourcepos="30:1-30:101"><strong>Visualization:</strong> Imagine yourself delivering a successful presentation with confidence and poise.</li> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:100"><strong>Positive self-talk:</strong> Actively replace negative thoughts with affirmations about your abilities.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:106"><strong>Seek feedback:</strong> Ask trusted individuals for constructive criticism and use it to improve your skills.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:157">Consider a <strong>speaking coach</strong>: Working with a coach can provide personalized guidance and support to address specific challenges and confidence barriers.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-34:114"><strong>Start small:</strong> Gradually increase the size and complexity of your speaking engagements as you gain experience.</li> <li data-sourcepos="35:1-36:0"><strong>Focus on progress:</strong> Celebrate small successes and acknowledge your improvement over time.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="37:1-37:282"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="37:1-37:282"><strong>Confidence</strong> in public speaking is a journey, not a destination. By actively practicing, embracing feedback, and focusing on your strengths, you can overcome <strong>fear of public speaking</strong> and develop the <strong>confidence</strong> to deliver impactful and memorable presentations.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/confidence/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">confidence , and captivate your audience with polished, impactful presentations. It’s like having a personal Speech Coach <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:411">A <strong>speech coach</strong> is a trained professional who provides personalized guidance and support to individuals seeking to improve their <strong>public speaking</strong> skills. Whether you aim to <strong>master public speaking</strong> for professional presentations, overcome stage fright, or simply hone your everyday communication, a <strong>speech coach</strong> can tailor their expertise to meet your needs and goals.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:32"><strong>What Does a Speech Coach Do?</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-13:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:124"><strong>Conduct assessments:</strong> Analyze your strengths, weaknesses, and communication style through evaluations and observations.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:149"><strong>Develop personalized plans:</strong> Create a customized roadmap with exercises, techniques, and feedback to address your specific areas of improvement.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-9:167"><strong>Offer expert instruction:</strong> We will guide you through various aspects of public speaking, including vocal control, body language, content delivery, and overcoming anxiety.</li> <li data-sourcepos="10:1-10:168"><strong>Provide practice opportunities:</strong> Facilitate mock presentations, simulations, and role-playing scenarios to refine your skills in a safe and supportive environment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="11:1-11:114"><strong>Offer constructive feedback:</strong> Identify areas for improvement and suggest strategies for achieving your goals.</li> <li data-sourcepos="12:1-13:0"><strong>Boost confidence and motivation:</strong> Encourage and support you throughout your journey, empowering you to become a confident and impactful communicator.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="14:1-14:40"><strong>Who Can Benefit from a Speech Coach?</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="16:1-20:0"> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-16:174"><strong>Professionals:</strong> Refining public speaking skills can benefit executives, entrepreneurs, salespeople, leaders, and anyone who presents in professional settings.</li> <li data-sourcepos="17:1-17:160"><strong>Students:</strong> Teachers, public speakers, debaters, and students wanting to excel in presentations or classroom settings can gain valuable skills with a coach.</li> <li data-sourcepos="18:1-18:176"><strong>Individuals who fear public speaking:</strong> Coaching can help those who experience anxiety or nervousness when speaking in public develop strategies and gain confidence.</li> <li data-sourcepos="19:1-20:0"><strong>Anyone seeking to improve communication:</strong> A coach can provide guidance to individuals seeking to enhance their communication skills for personal or professional development.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="21:1-21:28"><strong>Types of Speech Coaches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="23:1-26:0"> <li data-sourcepos="23:1-23:110"><strong>Private coaches:</strong> Work one-on-one with individuals to provide highly personalized attention and feedback.</li> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:130"><strong>Group coaches:</strong> Offer workshops or classes in group settings, often at a lower cost but with less individualized attention.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-26:0"><strong>Specialization coaches:</strong> Some coaches specialize in executive communication, storytelling, or presentation design.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="27:1-27:35"><strong>Finding the Right Speech Coach:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="29:1-33:0"> <li data-sourcepos="29:1-29:91"><strong>Identify your goals:</strong> What areas do you want to improve? What are your specific needs?</li> <li data-sourcepos="30:1-30:109"><strong>Research credentials and experience:</strong> Look for qualified coaches with relevant experience and expertise.</li> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:122"><strong>Consider availability and budget:</strong> Set a budget and explore options that fit your schedule and financial constraints.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-33:0"><strong>Schedule consultations:</strong> Talk to potential coaches to assess their personality, approach, and compatibility with your needs.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="34:1-34:418"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="34:1-34:418">Investing in a <strong>speech coach</strong> can be a transformative experience, enhancing your communication skills, boosting your confidence, and empowering you to achieve your communication goals. Whether you're a seasoned professional or just starting your journey, consider exploring the potential of working with a <strong>speech coach</strong> to unlock your full potential as a communicator and <strong>master public speaking</strong>.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech-coach/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech coach in your pocket, ready to help you deliver stand-out speeches!
What is the purpose of a demonstrative speech?
Craft a demonstrative Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech that truly connects with your audience! Infuse your purpose with passion, establishing yourself as the ideal guide, and remember, it’s about informing and engaging. Combine clear explanations with captivating visuals and live demos, drawing inspiration from both articles: yours highlights the power of emotional connection and expertise, and theirs emphasizes the effectiveness of hands-on learning experiences. This winning formula ensures your audience is informed, engaged, and ready to implement their newfound knowledge!
Conclusion
If this were a demonstrative Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech , we would have needed a break since it is quite long. I hope you learned something new and ace your next presentation like a pro.
Just like this post helped you learn all about demonstrative speaking, it will make me happy to know you are applying everything you learned. So, let’s recap the essential points.
- How do you choose the right topic?
- What are the critical elements of demonstrative speaking ideas?
- How do you write a demonstrative Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech ?
- What were our final tips?
Always remember the role of visual aids and engage your listeners! Thank you.
You might also like
Father of the groom speech – wedding tips & rehearsal dinner ..., public speaking practice: complete guide to nailing your next speaking o..., quick links.
- Presentation Topics
Useful Links
- Start free trial
- The art of public speaking
- improve public speaking
- mastering public speaking
- public speaking coach
- professional speaking
- public speaking classes - Courses
- public speaking anxiety
- © Orai 2023
Automated page speed optimizations for fast site performance
150 Interesting and Unique Demonstration Speech ideas

A demonstration speech aims to teach an audience how to complete a task. It’s a type of presentation where you demonstrate a process or teach a skill to an audience. Students are often assigned demonstration speeches to improve their communication and presentation skills.
Need help to find a good idea for your demonstration speech? We’ve got plenty of them here in this blog post. Ensure you read it all the way through to get the most out of it.
Table of Contents
How to Choose a Demonstration Speech Idea?
The important stage of choosing a good demonstration speech idea is considering your audience. Think about what may intrigue them and ensure it’s something relevant. Here are some tips from professional paper help providers to get you started:
Brainstorm ideas
Write down anything that pops into your head. It could be sports, arts, life skills, or anything else. Then pick a few that you have the most knowledge in.
Narrow Down Your Options
Go over your list and take out any topics that might be too hard. Stick with the topics you can show in a reasonable amount of time.
Research Your Options
Once you’ve whittled down the topics, do some digging to get the facts. Get your hands on some dependable sources, like books, articles, or websites, so that you can give a thorough presentation.
Engage your Audience
Pick a topic that your audience will find both captivating and exciting. Think of fun, unexpected elements you could add, like humor or something interactive, that can make your speech stand out.
Consider the Educational Value
Your presentation should have something valuable to offer your audience. Ensure it’s an informative topic that teaches a skill and has practical applications they can use in real life.
Practice and Refine
Once you’ve picked your idea for a demonstration speech, practice it many times so you’re confident with the material and the demo. Tweak your speech and make changes if you need to make it clearer and smoother.
Now. Let’s explore the list of amazing demonstration speech ideas.
Unique Demonstration Speech Ideas
- How to create a personalized gratitude jar
- The art of making homemade scented candles
- Quick and easy meal prep for busy weekdays
- DIY natural skincare products using kitchen ingredients
- The art of flower arranging for special occasions
- How to master basic calligraphy techniques
- Creating your mini herb garden indoors
- Simple steps to make your eco-friendly cleaning products
- The Secrets of brewing the perfect cup of coffee
- Creating a stylish and organized capsule wardrobe
- Mastering the art of basic origami folds
- How to create a stunning floral centerpiece
- Quick and healthy smoothie recipes for a busy lifestyle
- The art of making homemade bath bombs
- Creating your custom-designed T-shirts
- The basics of self-defense techniques for personal safety
- How to properly apply natural makeup for a fresh look
- Essential tips for effective time management
- Creating a budget-friendly home office setup
- The art of making homemade pizza from scratch
Demonstration Speech Ideas High School
- How to tie a basic necktie knot
- The art of folding a paper airplane
- Creating a simple fruit salad
- How to make a classic grilled cheese sandwich
- Quick and easy steps to make a paper crane
- The basics of juggling with three balls
- How to do a basic card trick
- Creating a DIY face mask using household ingredients
- The art of making a basic origami fortune teller
- How to make a refreshing lemonade from scratch
- Quick and easy steps to wrap a gift elegantly
- Creating a simple and stylish flower arrangement
- The art of creating a basic pencil sketch
- How to make a DIY bookmark using decorative paper
- Quick and easy steps to fold a paper napkin into a fancy shape
- The basics of solving a Rubik’s Cube
- How to make a delicious chocolate mug cake in minutes
- Creating a DIY terrarium with succulent plants
Good Demonstration Speech Topics
- The art of creating a mesmerizing acrylic pour painting
- How to make homemade organic soap with unique scents
- Creating a DIY mini-indoor garden using recycled materials
- The process of creating a captivating stop-motion animation
- How to create a stunning layered dessert parfait
- The art of creating a beautiful hand-lettered quote on canvas
- DIY techniques for transforming old clothes into trendy fashion pieces
- How to make a personalized photo album using scrapbooking techniques
- Creating a homemade natural facial mask with exotic ingredients
- The process of making artisanal bread from scratch
- How to design and assemble a custom-built computer
- Creating a unique and stylish terrazzo-inspired resin art piece
- The art of creating a custom-designed website using website builders
- DIY techniques for upcycling glass bottles into decorative vases
- How to create a delicious and visually appealing charcuterie board
- The process of making homemade gourmet chocolates with various fillings
- Creating a mesmerizing light painting using long-exposure photography
- How to design and sew your eco-friendly tote bag
- The art of creating intricate paper quilling designs
- DIY techniques for transforming a plain room into a vibrant and stylish space
Captivating How to Demonstrative Speech Ideas
- How to effectively manage your time and increase productivity
- How to write a cover letter for seeking job
- How to prepare and deliver a persuasive speech
- How to perform basic car maintenance and troubleshooting
- How to start your own successful online business
- How to apply professional makeup for special occasions
- How to create a budget and manage personal finances
- How to develop effective study habits for academic success
- How to navigate and utilize social media for personal branding
- How to make homemade pasta from scratch
- How to meditate for relaxation and stress relief
- How to grow your own organic vegetable garden
- How to play basic guitar chords and strumming patterns
- How to perform basic first aid techniques for common injuries
- How to cook a nutritious and delicious meal in under 30 minutes
- How to change a flat tire on a car
- How to write a narrative essay
- How to effectively negotiate and communicate in a professional setting
- How to develop and maintain a healthy exercise routine
- How to create a visually appealing presentation using PowerPoint
- How to plan and execute a successful event or party
Easy Demonstration Speech Ideas on Food
- How to make a classic peanut butter and jelly sandwich
- The art of brewing the perfect cup of coffee
- How to make fluffy scrambled eggs in minutes
- Creating a refreshing and colorful fruit salad
- How to prepare a simple and delicious guacamole dip
- The process of making a crispy homemade pizza
- How to cook a mouthwatering steak on a stovetop
- Creating a flavorful and nutritious green smoothie
- How to make a creamy and comforting bowl of mashed potatoes
- The art of creating a homemade salsa with fresh ingredients
- How to bake soft and chewy chocolate chip cookies
- Creating a refreshing and tangy lemonade from scratch
- How to make a flavorful homemade tomato sauce for pasta
- The process of making a fluffy and light pancake stack
- How to cook a perfect and juicy grilled chicken breast
- Creating a creamy and indulgent chocolate mousse dessert
- How to assemble a delicious and colorful veggie wrap
- The art of making a flavorful and aromatic cup of tea
- How to prepare a crunchy and satisfying homemade Caesar salad
- Creating a mouthwatering and cheesy baked macaroni and cheese dish
Demonstration Speech Examples (Topics) on Marketing
- How to create an effective social media marketing strategy
- The process of conducting market research for a new product
- How to optimize a website for search engine optimization (SEO)
- Creating engaging content for a successful content marketing campaign
- How to develop a compelling brand identity and logo design
- The art of creating persuasive advertising copywriting
- How to implement email marketing campaigns for customer engagement
- Creating a successful influencer marketing campaign
- How to use data analytics to track and optimize marketing performance
- The process of designing and launching a mobile app for marketing purposes
- How to leverage video marketing to engage and captivate your audience
- Creating an effective customer loyalty program to drive repeat business
- How to implement effective affiliate marketing strategies
- The art of creating visually appealing and impactful marketing materials
- How to plan and execute a successful product launch event
- Creating an engaging and interactive user experience (UX) on a website
- How to utilize storytelling techniques in marketing campaigns
- The process of setting up and managing a successful Google Ads campaign
- How to develop and implement a successful influencer partnership program
- Creating an effective lead generation strategy to grow your customer base
Funny Ideas for Demonstration Speech
- How to make a gourmet sandwich that looks incredible but tastes terrible
- The art of creating a perfectly imperfect DIY hairstyle
- How to fold a fitted bed sheet into an unrecognizable mess
- The process of attempting to walk in high heels like a pro
- How to prepare a “culinary masterpiece” using only microwaveable meals
- Creating a DIY craft project that ends up looking like a kindergarten art project
- How to attempt a yoga pose that looks graceful but ends up in a hilarious fail
- The art of imitating celebrity impressions (with humorous outcomes)
- How to make a healthy smoothie that tastes absolutely awful
- Attempting to break a world record for the most failed attempts at a simple task
- The process of attempting to dance like a professional without any coordination
- How to create a DIY fashion trend that is intentionally bizarre and unconventional
- The art of creating a failed magic trick with predictable and comedic outcomes
- How to organize a cluttered room most messily and chaotically possible
- Attempting to learn a new language in a ridiculously short amount of time (with humorous mistakes)
- The process of attempting to bake a cake without any baking skills or knowledge
- How to give yourself a “professional” haircut that ends up looking hilariously uneven
- Creating a “gourmet” dish using unconventional and strange food combinations
- How to attempt extreme sports or activities with amusing and clumsy results
- The art of telling funny and cheesy jokes that elicit groans instead of laughter
Hopefully, you have now shortlisted a topic or two for your demonstration speech. Be it the food, marketing, or crafts you are in, our lists of demonstrative speech topics have many ideas to get you started. Remember, it’s not about choosing a topic only, but it’s more about captivating your audience.
Moreover, if you still need help with demonstration speech ideas, order now so our experts can be at your service right away.
Order Original Papers & Essays
Your First Custom Paper Sample is on Us!
Timely Deliveries
No Plagiarism & AI
100% Refund
Try Our Free Paper Writing Service
Related blogs.

Connections with Writers and support
Privacy and Confidentiality Guarantee
Average Quality Score

15 Informative Speech Examples to Inspire Your Next Talk
- The Speaker Lab
- May 13, 2024
Table of Contents
A good informative speech is one of the most effective tools in a speaker’s arsenal. But with so many potential topics out there, it can be tough to know where to start. That’s why we’ve compiled 15 informative speech examples to help you find your perfect subject. Whether you’re unearthing secrets from history for your listeners or delving into future technologies, informative speeches can prove to be the recipe for the perfect talk.
But crafting an effective informative speech is about more than just picking a topic. You have to research topics, put your thoughts in order, and speak up clearly and confidently. In this post, we’ll explore strategies for each step of the process, so you can create a speech that informs, engages, and makes a lasting impact on your listeners. Let’s get started.
15 Informative Speech Examples
If you’re looking for some inspiration for your next informative speech, look no further. Below are 15 examples of informative speech topics that are sure to engage and educate your audience.
- The history and evolution of social media platforms
- The benefits and drawbacks of renewable energy sources
- The impact of sleep deprivation on mental and physical health
- The role of emotional intelligence in personal and professional success
- The science behind climate change and its potential consequences
- The importance of financial literacy for young adults
- The influence of artificial intelligence on various industries
- The benefits of regular exercise and a balanced diet
- The history and cultural significance of a specific art form or genre
- The impact of technology on interpersonal communication
- The psychology behind procrastination and effective strategies to overcome it
- The role of diversity and inclusion in fostering innovation and creativity
- The importance of mental health awareness and resources for students
- The future of space exploration and its potential benefits for humanity
- The impact of globalization on local economies and cultures
These topics cover a wide range of subjects, from technology and science to psychology and culture. By choosing one of these informative speech examples, you’ll have plenty of material to work with to create an engaging and educational presentation.
Remember, the key to a successful informative speech is to choose a topic that you’re passionate about and that will resonate with your audience. Do your research, organize your thoughts, and practice your delivery to ensure that your message comes across loud and clear.
What Is an Informative Speech?
If you’ve ever been to a conference or seminar, chances are you’ve heard an informative speech. But what exactly is an informative speech? Simply put, it’s a type of speech designed to educate the audience on a particular topic. The goal is to provide interesting and useful information, ensuring the audience walks away with new knowledge or insights. Unlike persuasive speeches that aim to convince the audience of a viewpoint, informative speeches focus on explaining a subject clearly and objectively.
Types of Informative Speeches
Informative speeches come in various forms, each with its own purpose. The most common types are definition, explanation, description, and demonstration speeches. Depending on the objective, an informative speech can take on different structures and styles.
For example, a definition speech aims to explain a concept or term, while a demonstration speech shows the audience how to perform a task or process. An explanatory speech, on the other hand, provides a detailed account of a complex subject, breaking it down into digestible parts.
Purpose of Informative Speeches
At its core, the purpose of an informative speech is to share knowledge with the audience. These speeches are characterized by their fact-based, non-persuasive nature. The focus is on delivering information in an engaging and accessible way.
A well-crafted informative speech not only educates but also sparks curiosity and encourages further learning. By dedicating yourself to providing valuable information and appealing to your audience’s interests, you can succeed as an informative speaker.
Strategies for Selecting an Informative Speech Topic
Choosing the right topic is crucial for an effective informative speech. You want a subject that is not only interesting to you but also relevant and engaging for your audience. Consider their knowledge level, background, and expectations when selecting your topic.
One strategy is to focus on a subject you’re passionate about or have expertise in. This allows you to speak with authority and enthusiasm, making your speech more compelling. Another approach is to address current events or trending topics that are on people’s minds.
When brainstorming potential topics, consider your speech’s purpose and the type of informative speech you want to deliver. Is your goal to define a concept, explain a process, describe an event, or demonstrate a skill? Answering these questions will help guide your topic selection.
Find Out Exactly How Much You Could Make As a Paid Speaker
Use The Official Speaker Fee Calculator to tell you what you should charge for your first (or next) speaking gig — virtual or in-person!
How to Write an Informative Speech
Now that you’ve selected your topic, it’s time to start writing your informative speech. The key to a successful speech is thorough preparation and a clear, organized structure. Let’s break down the steps involved in crafting an engaging and informative presentation.
Researching Your Topic
Before you start writing, it’s essential to conduct thorough research on your topic. Gather facts, statistics, examples, and other supporting information for your informative speech. These things will help you explain and clarify the subject matter to your audience.
As you research, use reliable sources such as academic journals, reputable websites, and expert opinions to ensure the accuracy and credibility of your information. Take notes and organize your findings in a way that makes sense for your speech’s structure.
Structuring Your Speech
A typical informative speech structure includes three main parts, namely, an introduction, body, and conclusion. The introduction should grab the audience’s attention, establish your credibility , and preview the main points you’ll cover.
The body of your speech is where you’ll present your main points and supporting evidence. Use clear transitions between each point to maintain a logical flow. The conclusion should summarize your key takeaways and leave a lasting impression on your audience.
Outlining Your Speech
Creating an outline is a crucial step in organizing your thoughts and ensuring a coherent flow of information. Start by listing your main points and then add subpoints and supporting details for each section.
A well-structured outline will serve as a roadmap for your speech, keeping you on track and helping you stay focused on your key messages. It also makes the writing process more efficient and less overwhelming.
Writing Your Draft
With your outline in hand, it’s time to start writing your draft. Focus on presenting information clearly and concisely, using simple language and avoiding jargon. Provide examples and analogies throughout your informative speech in order to illustrate complex ideas and make them more relatable to your audience.
As you write, keep your audience in mind and tailor your language and examples to their level of understanding. Use transitions to link your ideas and maintain a smooth flow throughout the speech.
Editing and Revising
Once you’ve completed your draft, take the time to edit and revise your speech. First, check for clarity, accuracy, and logical organization. Then, eliminate unnecessary details, repetition, and filler words.
Read your speech aloud to identify any awkward phrasing or unclear passages. Lastly, seek feedback from others and be open to making changes based on their suggestions. Remember, the goal is to create a polished and effective informative speech.
Delivering an Informative Speech
You’ve written a fantastic informative speech, but now comes the real challenge: delivering it effectively. The way you present your speech can make all the difference in engaging your audience and ensuring they retain the information you’re sharing.
Practicing Your Speech
Practice makes perfect, and this couldn’t be more true when it comes to public speaking. Rehearse your speech multiple times to build confidence and familiarity with the content. Practice in front of a mirror, family members, or friends to get comfortable with your delivery.
As you practice, focus on your pacing, intonation, and body language. Aim for a conversational tone and maintain eye contact with your audience. The more you practice, the more natural and engaging your delivery will become.
Using Visual Aids
Visual aids such as slides, charts, or props can enhance your informative speech by making complex information more accessible and engaging. When utilized in your informative speech, they can help illustrate key points, provide visual examples, and break up the monotony of a purely verbal presentation.
Of course, it’s important to ensure your visuals are clear, relevant, and easy to understand. Otherwise, they may end up obscuring your points instead of clarifying them. In light of this, avoid cluttering your slides with too much text or overwhelming your audience with too many visuals. Use them strategically to support your message, not distract from it.
Engaging Your Audience
Engaging your audience is crucial for a successful informative speech. Use rhetorical questions, anecdotes, or interactive elements to keep them involved and attentive. Encourage participation, if appropriate, and maintain a conversational tone to create a connection with your listeners.
Pay attention to your audience’s reactions and adapt your delivery accordingly. If you sense confusion or disinterest, try rephrasing your points or providing additional examples to clarify your message. Remember, your goal is to educate and inspire your audience, so keep them at the forefront of your mind throughout your speech.
Handling Nerves
It’s normal to feel nervous before and during a speech, but there are strategies to help you manage those nerves . Take deep breaths, visualize success, and focus on your message rather than your anxiety. Remember, your audience wants you to succeed, and a little nervousness can actually enhance your performance by showing enthusiasm and authenticity.
If you find yourself getting overwhelmed, take a moment to pause, collect your thoughts, and regain your composure. Smile, make eye contact, and remind yourself that you’ve prepared thoroughly and have valuable information to share.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
To deliver an effective informative speech, it’s important to be aware of common pitfalls and mistakes. One of the biggest errors is overloading your audience with too much information. Remember, less is often more when it comes to public speaking.
Another mistake is failing to organize your content logically or using complex jargon without explanation. Make sure your speech has a clear structure and that you’re explaining any technical terms or concepts in a way that your audience can understand.
Finally, don’t neglect the importance of practice and preparation. Winging it or relying too heavily on notes can lead to a disjointed and unengaging speech. Take the time to rehearse, refine your delivery, and internalize your key points.
By avoiding these common mistakes and focusing on the strategies we’ve discussed, you’ll be well on your way to delivering an informative speech that educates, engages, and inspires your audience.
Tips for Delivering a Compelling Informative Speech
Once you’ve chosen your topic and done your research, it’s time to focus on delivering a compelling speech. Here are a few tips to keep in mind:
- Start with a strong attention-grabbing opening that draws your audience in and sets the tone for your speech.
- Use clear, concise language and avoid jargon or technical terms that your audience may not understand.
- Incorporate storytelling, examples, and anecdotes to make your points more relatable and memorable.
- Use visual aids , such as slides or props, to enhance your message and keep your audience engaged.
- Practice your delivery and timing to ensure that you stay within your allotted time and maintain a natural, conversational tone.
By following these tips and choosing a topic that you’re passionate about, you’ll be well on your way to delivering an informative speech that educates and inspires your audience.
Free Download: 6 Proven Steps to Book More Paid Speaking Gigs in 2024
Download our 18-page guide and start booking more paid speaking gigs today!
20 Bonus Topics for Informative Speeches
In case the informative speech examples above didn’t pique your interest, we have several more for you to consider. Ranging from topics like science and technology to history and education, these 20 topics are perfect for your next presentation.
- The history and development of virtual reality technology
- The benefits and challenges of remote work
- The science behind the formation of hurricanes and tornadoes
- The impact of social media on political campaigns and elections
- The importance of sustainable fashion and its environmental benefits
- The role of emotional support animals in mental health treatment
- The history and cultural significance of a specific cuisine or dish
- The impact of plastic pollution on marine ecosystems
- The benefits and risks of gene editing technology
- The psychology behind conspiracy theories and their spread online
- The importance of digital privacy and data security in the modern age
- The role of music therapy in healthcare and wellness
- The impact of deforestation on biodiversity and climate change
- The history and evolution of a specific sport or athletic event
- The benefits and challenges of alternative education models
- The science behind the human immune system and how vaccines work
- The impact of mass incarceration on communities and families
- The role of storytelling in preserving cultural heritage and traditions
- The importance of financial planning for retirement and old age
- The impact of urban agriculture on food security and community development
Choosing a Topic That Resonates With Your Audience
When selecting a topic for your informative speech, it’s important to consider your audience and what will resonate with them. Think about their interests, backgrounds, and knowledge levels, and choose a topic that will be both informative and engaging.
For example, if you’re speaking to a group of high school students, you may want to choose a topic that relates to their experiences or concerns, such as the impact of social media on mental health or the importance of financial literacy for young adults. If you’re speaking to a group of business professionals, you may want to focus on topics related to industry trends, leadership strategies, or emerging technologies.
By choosing a topic that resonates with your audience, you’ll be more likely to capture their attention and keep them engaged throughout your speech. And remember, even if you’re not an expert on the topic, you can still deliver an informative and engaging speech by doing your research and presenting the information in a clear and accessible way.
FAQs on Informative Speech Examples
What is an example of informative speech.
An example includes breaking down the impacts of climate change, detailing causes, effects, and potential solutions.
What are the 3 types of informative speeches?
The three main types are explanatory (breaks down complex topics), descriptive (paints a picture with words), and demonstrative (shows how to do something).
What are the 5 useful topics of an informative speech?
Top picks include technology advances, mental health awareness, environmental conservation efforts, cultural diversity appreciation, and breakthroughs in medical research.
What is an effective informative speech?
An effective one delivers clear info on a specific topic that educates listeners without overwhelming them. It’s well-researched and engaging.
Informative speech examples are everywhere, if you know where to look. From TED Talks to classroom lectures, there’s no shortage of inspiration for your next presentation. All you have to do is find a topic that lights your fire while engaging your audience.
Remember, a great informative speech is all about clarity, organization, and engagement. By following the tips and examples we’ve covered, you’ll be well on your way to delivering an informative speech that educates, enlightens, and leaves a lasting impression. So go ahead, pick your topic, and start crafting your own informative speech today!
- Last Updated: May 9, 2024

Explore Related Resources
Learn How You Could Get Your First (Or Next) Paid Speaking Gig In 90 Days or Less
We receive thousands of applications every day, but we only work with the top 5% of speakers .
Book a call with our team to get started — you’ll learn why the vast majority of our students get a paid speaking gig within 90 days of finishing our program .
If you’re ready to control your schedule, grow your income, and make an impact in the world – it’s time to take the first step. Book a FREE consulting call and let’s get you Booked and Paid to Speak ® .
About The Speaker Lab
We teach speakers how to consistently get booked and paid to speak. Since 2015, we’ve helped thousands of speakers find clarity, confidence, and a clear path to make an impact.
Get Started
Let's connect.
Copyright ©2023 The Speaker Lab. All rights reserved.
Advertisement
Supported by
Antiwar Protest Camp in Dublin Is Dismantled After College Agrees to Divest
Students against the war in Gaza began taking down the camp after Trinity College Dublin said it would divest from three Israeli companies.
- Share full article

By Ed O’Loughlin
Reporting from Dublin
Students who oppose the war in Gaza began dismantling their protest camp at Trinity College Dublin in Ireland on Wednesday evening, after the institution agreed to divest from three Israeli companies listed by the United Nations for their links to settlements in the occupied Palestinian territories.
Trinity said that it would move to divest as soon as next month, and that its endowment fund would also seek to divest from investments in other Israeli companies in the future.
“We fully understand the driving force behind the encampment on our campus, and we are in solidarity with the students in our horror of what is happening in Gaza,” the college said in a statement released on Wednesday evening.
“We abhor and condemn all violence and war, including the atrocities of October 7th, the taking of hostages and the continuing ferocious and disproportionate onslaught in Gaza,” it added. “The humanitarian crisis in Gaza and the dehumanisation of its people is obscene.”
The statement was approved by the college’s board.
Trinity’s protest, which began five days ago and had remained peaceful, was organized by the student union and its branch of the Boycott, Divestment and Sanctions, or B.D.S., movement. The demonstration emerged as students across Europe staged pro-Palestinian sit-ins and protests against antisemitism at other universities on the continent, taking a similar approach to their counterparts in the United States.
Jenny Maguire, the incoming president of Trinity’s student union, contrasted the calm atmosphere in the college’s Fellow’s Square, where students were already taking down flags and tents in anticipation of the statement’s release, to the violence at some U.S. universities, where police were deployed to clear some occupied buildings amid antiwar protests.
“The college was determined that it would be an example going forward,” Ms. Maguire said on Wednesday evening. “It refused to follow the U.S. example of bringing police in and made it clear that it would not pursue anything like that here.”
Prof. Eoin O’Sullivan, who led the college’s negotiation team, said, “I think the negotiations were very productive and very fruitful, and I’d compliment the students for their part in it.”
Support for the Palestinian cause is strong in Ireland, where many people compare Israel’s military occupation of Palestinian territories to centuries of British colonialism in their own country.
Ireland is also, along with Spain, one of the strongest supporters of the Palestinian cause in the European Union. Last month, the prime ministers of both governments, Simon Harris and Pedro Sánchez, said they would recognize a state of Palestine “when the time is right.”
Protesting students at Trinity said they were pleased that the college had met their demands, which included the establishment of a special working group to consider its future involvement with Israeli companies, academic institutions and student exchanges. The college has also undertaken a plan to fund tuition and accommodation for eight students from Gaza.
This week’s protest had forced the college to shut down the world-famous Book of Kells exhibition, where some of Ireland’s most ancient and valuable books are stored — one of the college’s main sources of outside revenue — along with college libraries and other facilities. About one million tourists pay to visit the Kells exhibition every year.
Professor O’Sullivan said the review of Trinity’s ties with Israel and the larger Middle East would most likely follow the model of a recent working group on the college’s own colonial legacy.
One main recommendation was to rename a college library formerly named after the philosopher Bishop George Berkeley, a renowned Trinity graduate who was a slave owner during his years in the American colonies. It’s now known on-campus as the X library.
Our Coverage of the U.S. Campus Protests
News and Analysis
Pomona College: At least one person was arrested after scuffles broke out among pro-Palestinian protesters , private security officers and police officers outside Pomona College’s commencement in Los Angeles.
U.W. Milwaukee: Protesters at the University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee will take down a pro-Palestinian encampment that had stood for two weeks under an agreement reached with the school , university officials said.
Duke: Dozens of students walked out of Duke University’s commencement ceremony as Jerry Seinfeld, who has been vocal about his support for Israel, received an honorary degree.
Turning to Al Jazeera : Students active in campus protests value the Arab news network’s on-the-ground coverage and its perspective on the Israel-Hamas war. They draw distinctions between it and major American outlets.
Black Colleges : The White House appears anxious about President Biden’s speech at Morehouse College, a historically Black institution. But for complex reasons, such campuses have had far less visible Gaza tensions .
A Different Approach : University leaders in Britain have so far adopted a more permissive attitude to pro-Palestinian encampments than their U.S. counterparts. Here’s why .

COMMENTS
Demonstrative Speech. Your teacher or superior comes up to you and asks to do a demonstrative speech in front of a big audience. For instance, they may ask you how to demonstrate a certain skill such as writing an investigative news article (if in a journalism class) or ask you to teach judo (if in an martial arts class). Examples of Persuasive ...
Demonstration speech outline. An outline is a way to structure the information that you want to share with your audience. The outline should explicitly showcase the order of steps that you will use in your demonstration speech. Many students seem to neglect the power of creating outlines for their academic writing tasks, but in vain.
Here are some examples of Demonstrative Speech Topics. ... Anything that will help them after you are done with your speech and leave the venue would be a great addition to your demonstrative speech. Conclusion. In closing, a demonstrative speech is a great way of teaching an audience a lesson or skill. We've used to before (knowingly or ...
The body of demonstration speeches. In your planning concentrate on the outcome you want and then focus on the logical steps needed to achieve it. This will form the body of your speech. The easiest way to get this part right is by doing it yourself. As you go through the process, (of making a friendship bracelet, tying a tie, fixing a flat ...
Get a printable blank demonstration speech outline. The outline template I've used is available for your use too. I've made a printable blank version of it for you download. You'll find the link at the foot of the page, along with a video of the speech. The voice you'll hear, when you play that, is me, Susan.
The art of origami: Crafting a beautiful paper crane. "How to fold a paper crane" is a great example of a demonstrative speech topic. In this demonstrative speech topic example, the speaker takes the audience on a journey of creativity and craftsmanship by guiding them through the step-by-step process of creating an intricate paper crane.
A demonstration speech outline should include the following elements: 1. Introduction: Start off the speech with an attention-grabbing statement or anecdote to draw in the audience's interest. 2. Objectives: Explain the purpose of your speech, what you will be demonstrating, and what outcomes you hope to achieve.
Conclusion - here, you summarize the key points of your demonstration speech topic for the audience and inspire them to perform a certain action. You might also raise some concerns or share additional information or sources which can be helpful. Demonstrative speech example. 7 tips to create a mind-blowing demonstrative speech Understand your ...
1. Create an outline for your speech. An outline is a way to organize the information that you want to convey. The outline should mirror the order of steps that you will use in your speech. [6] The outline should contain three sections: the introduction, the body, and the conclusion.
This demonstrative speech outline will help you organize your steps and make writing your demonstration speech easier. Just fill in the blanks above the examples given. Choose from our demonstration speech topics if you still need an idea then return here to get started on your draft. This outline example below on "how to groom your dog" is ...
1. Start with why. A demonstration speech deals with training the audience to carry out a task or the whole process. Just as with any instructive task, it can become helpful when your audience is motivated to learn. It is a must to tell your audience how they get to benefit from the knowledge you are about to present.
For example, if you were to write a demonstration speech outline for a speech about how to make a scrapbook, it might look something like the textual framework below scrapbook image. ... As you can see, the conclusion of a demonstration speech outline generally summarizes the speech and encourages the audience members to try it for themselves ...
A demonstration speech is a type of presentation in which the speaker's goal is to teach the audience how to complete a task. Students often give demonstration speeches when doing class projects, while professionals may give demonstration speeches to teach colleagues how to perform a task, highlight a new product, showcase service to potential ...
2. Provide an overview. 3. Explain the steps involved in your process. 4 .Talk about variations, other options and instructions. 5. Ensure you allot time for Q&A. 6. Give a brief summary to your instructional speech.
recognize the common birds or animals in your area. identify different types of woods. ensure water is safe to drink. use the position of the sun to tell time. tell if a storm is coming. track an animal in the wild. choose a good campsite. forecast weather. cross a river safely.
130+ Demonstration Speech Topics. Jim Peterson has over 20 years experience on speech writing. He wrote over 300 free speech topic ideas and how-to guides for any kind of public speaking and speech writing assignments at My Speech Class. Demonstration speech topics and methods to develop hundred demonstratives for good public speaking, step by ...
Demonstration; Personal Reference; ... Finally, one tactic a speaker often uses is to link the introduction of the speech to the conclusion. For example, if you began your speech with a quotation, your conclusion may refer back to that person's words in respect to what your audience has learned throughout your speech.
5. Piece Of Advice. The point of giving a piece of advice at the end of your speech is not to pull your audience down or to make them feel bad/inferior about themselves. Rather, the advice is added to motivate your audience to take steps to do something-something related to the topic at hand.
Examine the three steps of an effective conclusion: restatement of the thesis, review of the main points, and concluding device. Differentiate among Miller's (1946) ten concluding devices. Matthew Culnane - Steps - CC BY-SA 2.0. In Section 11.1 "Why Conclusions Matter", we discussed the importance a conclusion has on a speech.
Tips. Introduction. - Briefly introduce yourself and the topic of your speech. - Clearly state the purpose and objective of the speech. - Grab the audience's attention with a hook or interesting fact related to the topic. - Keep the introduction concise and to the point.
Here, you gather visual toolslike dummies, drawings, videos, or even human models. Since you have a better picture of your speech, include your outline in your introduction. It gives your audience an overall idea of what you are talking about. Write your conclusion -Try to go over the crucial points you made.
Good Demonstration Speech Topics. The art of creating a mesmerizing acrylic pour painting. How to make homemade organic soap with unique scents. Creating a DIY mini-indoor garden using recycled materials. The process of creating a captivating stop-motion animation. How to create a stunning layered dessert parfait.
For example, a definition speech aims to explain a concept or term, while a demonstration speech shows the audience how to perform a task or process. An explanatory speech, on the other hand, provides a detailed account of a complex subject, breaking it down into digestible parts. ... Conclusion. Informative speech examples are everywhere, if ...
The statement was approved by the college's board. Trinity's protest, which began five days ago and had remained peaceful, was organized by the student union and its branch of the Boycott ...