What is a Business Plan? Definition, Tips, and Templates
Published: June 07, 2023
In an era where more than 20% of small enterprises fail in their first year, having a clear, defined, and well-thought-out business plan is a crucial first step for setting up a business for long-term success.

Business plans are a required tool for all entrepreneurs, business owners, business acquirers, and even business school students. But … what exactly is a business plan?

In this post, we'll explain what a business plan is, the reasons why you'd need one, identify different types of business plans, and what you should include in yours.

What is a business plan?
A business plan is a documented strategy for a business that highlights its goals and its plans for achieving them. It outlines a company's go-to-market plan, financial projections, market research, business purpose, and mission statement. Key staff who are responsible for achieving the goals may also be included in the business plan along with a timeline.
The business plan is an undeniably critical component to getting any company off the ground. It's key to securing financing, documenting your business model, outlining your financial projections, and turning that nugget of a business idea into a reality.
What is a business plan used for?
The purpose of a business plan is three-fold: It summarizes the organization’s strategy in order to execute it long term, secures financing from investors, and helps forecast future business demands.
Business Plan Template [ Download Now ]

Working on your business plan? Try using our Business Plan Template . Pre-filled with the sections a great business plan needs, the template will give aspiring entrepreneurs a feel for what a business plan is, what should be in it, and how it can be used to establish and grow a business from the ground up.
Purposes of a Business Plan
Chances are, someone drafting a business plan will be doing so for one or more of the following reasons:
1. Securing financing from investors.
Since its contents revolve around how businesses succeed, break even, and turn a profit, a business plan is used as a tool for sourcing capital. This document is an entrepreneur's way of showing potential investors or lenders how their capital will be put to work and how it will help the business thrive.
All banks, investors, and venture capital firms will want to see a business plan before handing over their money, and investors typically expect a 10% ROI or more from the capital they invest in a business.
Therefore, these investors need to know if — and when — they'll be making their money back (and then some). Additionally, they'll want to read about the process and strategy for how the business will reach those financial goals, which is where the context provided by sales, marketing, and operations plans come into play.
2. Documenting a company's strategy and goals.
A business plan should leave no stone unturned.
Business plans can span dozens or even hundreds of pages, affording their drafters the opportunity to explain what a business' goals are and how the business will achieve them.
To show potential investors that they've addressed every question and thought through every possible scenario, entrepreneurs should thoroughly explain their marketing, sales, and operations strategies — from acquiring a physical location for the business to explaining a tactical approach for marketing penetration.
These explanations should ultimately lead to a business' break-even point supported by a sales forecast and financial projections, with the business plan writer being able to speak to the why behind anything outlined in the plan.
.webp)
Free Business Plan Template
The essential document for starting a business -- custom built for your needs.
- Outline your idea.
- Pitch to investors.
- Secure funding.
- Get to work!
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
Free Business Plan [Template]
Fill out the form to access your free business plan., 3. legitimizing a business idea..
Everyone's got a great idea for a company — until they put pen to paper and realize that it's not exactly feasible.
A business plan is an aspiring entrepreneur's way to prove that a business idea is actually worth pursuing.
As entrepreneurs document their go-to-market process, capital needs, and expected return on investment, entrepreneurs likely come across a few hiccups that will make them second guess their strategies and metrics — and that's exactly what the business plan is for.
It ensures an entrepreneur's ducks are in a row before bringing their business idea to the world and reassures the readers that whoever wrote the plan is serious about the idea, having put hours into thinking of the business idea, fleshing out growth tactics, and calculating financial projections.
4. Getting an A in your business class.
Speaking from personal experience, there's a chance you're here to get business plan ideas for your Business 101 class project.
If that's the case, might we suggest checking out this post on How to Write a Business Plan — providing a section-by-section guide on creating your plan?
What does a business plan need to include?
- Business Plan Subtitle
- Executive Summary
- Company Description
- The Business Opportunity
- Competitive Analysis
- Target Market
- Marketing Plan
- Financial Summary
- Funding Requirements
1. Business Plan Subtitle
Every great business plan starts with a captivating title and subtitle. You’ll want to make it clear that the document is, in fact, a business plan, but the subtitle can help tell the story of your business in just a short sentence.
2. Executive Summary
Although this is the last part of the business plan that you’ll write, it’s the first section (and maybe the only section) that stakeholders will read. The executive summary of a business plan sets the stage for the rest of the document. It includes your company’s mission or vision statement, value proposition, and long-term goals.
3. Company Description
This brief part of your business plan will detail your business name, years in operation, key offerings, and positioning statement. You might even add core values or a short history of the company. The company description’s role in a business plan is to introduce your business to the reader in a compelling and concise way.
4. The Business Opportunity
The business opportunity should convince investors that your organization meets the needs of the market in a way that no other company can. This section explains the specific problem your business solves within the marketplace and how it solves them. It will include your value proposition as well as some high-level information about your target market.

5. Competitive Analysis
Just about every industry has more than one player in the market. Even if your business owns the majority of the market share in your industry or your business concept is the first of its kind, you still have competition. In the competitive analysis section, you’ll take an objective look at the industry landscape to determine where your business fits. A SWOT analysis is an organized way to format this section.
6. Target Market
Who are the core customers of your business and why? The target market portion of your business plan outlines this in detail. The target market should explain the demographics, psychographics, behavioristics, and geographics of the ideal customer.
7. Marketing Plan
Marketing is expansive, and it’ll be tempting to cover every type of marketing possible, but a brief overview of how you’ll market your unique value proposition to your target audience, followed by a tactical plan will suffice.
Think broadly and narrow down from there: Will you focus on a slow-and-steady play where you make an upfront investment in organic customer acquisition? Or will you generate lots of quick customers using a pay-to-play advertising strategy? This kind of information should guide the marketing plan section of your business plan.
8. Financial Summary
Money doesn’t grow on trees and even the most digital, sustainable businesses have expenses. Outlining a financial summary of where your business is currently and where you’d like it to be in the future will substantiate this section. Consider including any monetary information that will give potential investors a glimpse into the financial health of your business. Assets, liabilities, expenses, debt, investments, revenue, and more are all useful adds here.
So, you’ve outlined some great goals, the business opportunity is valid, and the industry is ready for what you have to offer. Who’s responsible for turning all this high-level talk into results? The "team" section of your business plan answers that question by providing an overview of the roles responsible for each goal. Don’t worry if you don’t have every team member on board yet, knowing what roles to hire for is helpful as you seek funding from investors.
10. Funding Requirements
Remember that one of the goals of a business plan is to secure funding from investors, so you’ll need to include funding requirements you’d like them to fulfill. The amount your business needs, for what reasons, and for how long will meet the requirement for this section.
Types of Business Plans
- Startup Business Plan
- Feasibility Business Plan
- Internal Business Plan
- Strategic Business Plan
- Business Acquisition Plan
- Business Repositioning Plan
- Expansion or Growth Business Plan
There’s no one size fits all business plan as there are several types of businesses in the market today. From startups with just one founder to historic household names that need to stay competitive, every type of business needs a business plan that’s tailored to its needs. Below are a few of the most common types of business plans.
For even more examples, check out these sample business plans to help you write your own .
1. Startup Business Plan

As one of the most common types of business plans, a startup business plan is for new business ideas. This plan lays the foundation for the eventual success of a business.
The biggest challenge with the startup business plan is that it’s written completely from scratch. Startup business plans often reference existing industry data. They also explain unique business strategies and go-to-market plans.
Because startup business plans expand on an original idea, the contents will vary by the top priority goals.
For example, say a startup is looking for funding. If capital is a priority, this business plan might focus more on financial projections than marketing or company culture.
2. Feasibility Business Plan
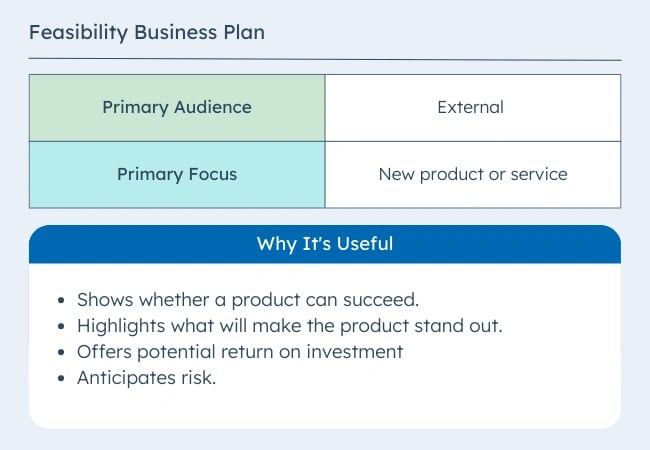
This type of business plan focuses on a single essential aspect of the business — the product or service. It may be part of a startup business plan or a standalone plan for an existing organization. This comprehensive plan may include:
- A detailed product description
- Market analysis
- Technology needs
- Production needs
- Financial sources
- Production operations
According to CBInsights research, 35% of startups fail because of a lack of market need. Another 10% fail because of mistimed products.
Some businesses will complete a feasibility study to explore ideas and narrow product plans to the best choice. They conduct these studies before completing the feasibility business plan. Then the feasibility plan centers on that one product or service.
3. Internal Business Plan

Internal business plans help leaders communicate company goals, strategy, and performance. This helps the business align and work toward objectives more effectively.
Besides the typical elements in a startup business plan, an internal business plan may also include:
- Department-specific budgets
- Target demographic analysis
- Market size and share of voice analysis
- Action plans
- Sustainability plans
Most external-facing business plans focus on raising capital and support for a business. But an internal business plan helps keep the business mission consistent in the face of change.
4. Strategic Business Plan

Strategic business plans focus on long-term objectives for your business. They usually cover the first three to five years of operations. This is different from the typical startup business plan which focuses on the first one to three years. The audience for this plan is also primarily internal stakeholders.
These types of business plans may include:
- Relevant data and analysis
- Assessments of company resources
- Vision and mission statements
It's important to remember that, while many businesses create a strategic plan before launching, some business owners just jump in. So, this business plan can add value by outlining how your business plans to reach specific goals. This type of planning can also help a business anticipate future challenges.
5. Business Acquisition Plan

Investors use business plans to acquire existing businesses, too — not just new businesses.
A business acquisition plan may include costs, schedules, or management requirements. This data will come from an acquisition strategy.
A business plan for an existing company will explain:
- How an acquisition will change its operating model
- What will stay the same under new ownership
- Why things will change or stay the same
- Acquisition planning documentation
- Timelines for acquisition
Additionally, the business plan should speak to the current state of the business and why it's up for sale.
For example, if someone is purchasing a failing business, the business plan should explain why the business is being purchased. It should also include:
- What the new owner will do to turn the business around
- Historic business metrics
- Sales projections after the acquisition
- Justification for those projections
6. Business Repositioning Plan
.webp?width=650&height=450&name=businessplan_6%20(1).webp)
When a business wants to avoid acquisition, reposition its brand, or try something new, CEOs or owners will develop a business repositioning plan.
This plan will:
- Acknowledge the current state of the company.
- State a vision for the future of the company.
- Explain why the business needs to reposition itself.
- Outline a process for how the company will adjust.
Companies planning for a business reposition often do so — proactively or retroactively — due to a shift in market trends and customer needs.
For example, shoe brand AllBirds plans to refocus its brand on core customers and shift its go-to-market strategy. These decisions are a reaction to lackluster sales following product changes and other missteps.
7. Expansion or Growth Business Plan
When your business is ready to expand, a growth business plan creates a useful structure for reaching specific targets.
For example, a successful business expanding into another location can use a growth business plan. This is because it may also mean the business needs to focus on a new target market or generate more capital.
This type of plan usually covers the next year or two of growth. It often references current sales, revenue, and successes. It may also include:
- SWOT analysis
- Growth opportunity studies
- Financial goals and plans
- Marketing plans
- Capability planning
These types of business plans will vary by business, but they can help businesses quickly rally around new priorities to drive growth.
Getting Started With Your Business Plan
At the end of the day, a business plan is simply an explanation of a business idea and why it will be successful. The more detail and thought you put into it, the more successful your plan — and the business it outlines — will be.
When writing your business plan, you’ll benefit from extensive research, feedback from your team or board of directors, and a solid template to organize your thoughts. If you need one of these, download HubSpot's Free Business Plan Template below to get started.
Editor's note: This post was originally published in August 2020 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.
![business planning and entrepreneurship How to Write an Executive Summary Execs Can't Ignore [+ 5 Top Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/executive-summary-example_5.webp)
How to Write an Executive Summary Execs Can't Ignore [+ 5 Top Examples]
20 Free & Paid Small Business Tools for Any Budget

24 of My Favorite Sample Business Plans & Examples For Your Inspiration

Maximizing Your Social Media Strategy: The Top Aggregator Tools to Use

The Content Aggregator Guide for 2024
![business planning and entrepreneurship 7 Gantt Chart Examples You'll Want to Copy [+ 5 Steps to Make One]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/gantt-chart-example.jpg)
7 Gantt Chart Examples You'll Want to Copy [+ 5 Steps to Make One]
![business planning and entrepreneurship The 8 Best Free Flowchart Templates [+ Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/flowchart%20templates.jpg)
The 8 Best Free Flowchart Templates [+ Examples]

16 Best Screen Recorders to Use for Collaboration

The 25 Best Google Chrome Extensions for SEO

Professional Invoice Design: 28 Samples & Templates to Inspire You
2 Essential Templates For Starting Your Business
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform
11.4 The Business Plan
Learning objectives.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Describe the different purposes of a business plan
- Describe and develop the components of a brief business plan
- Describe and develop the components of a full business plan
Unlike the brief or lean formats introduced so far, the business plan is a formal document used for the long-range planning of a company’s operation. It typically includes background information, financial information, and a summary of the business. Investors nearly always request a formal business plan because it is an integral part of their evaluation of whether to invest in a company. Although nothing in business is permanent, a business plan typically has components that are more “set in stone” than a business model canvas , which is more commonly used as a first step in the planning process and throughout the early stages of a nascent business. A business plan is likely to describe the business and industry, market strategies, sales potential, and competitive analysis, as well as the company’s long-term goals and objectives. An in-depth formal business plan would follow at later stages after various iterations to business model canvases. The business plan usually projects financial data over a three-year period and is typically required by banks or other investors to secure funding. The business plan is a roadmap for the company to follow over multiple years.
Some entrepreneurs prefer to use the canvas process instead of the business plan, whereas others use a shorter version of the business plan, submitting it to investors after several iterations. There are also entrepreneurs who use the business plan earlier in the entrepreneurial process, either preceding or concurrently with a canvas. For instance, Chris Guillebeau has a one-page business plan template in his book The $100 Startup . 48 His version is basically an extension of a napkin sketch without the detail of a full business plan. As you progress, you can also consider a brief business plan (about two pages)—if you want to support a rapid business launch—and/or a standard business plan.
As with many aspects of entrepreneurship, there are no clear hard and fast rules to achieving entrepreneurial success. You may encounter different people who want different things (canvas, summary, full business plan), and you also have flexibility in following whatever tool works best for you. Like the canvas, the various versions of the business plan are tools that will aid you in your entrepreneurial endeavor.
Business Plan Overview
Most business plans have several distinct sections ( Figure 11.16 ). The business plan can range from a few pages to twenty-five pages or more, depending on the purpose and the intended audience. For our discussion, we’ll describe a brief business plan and a standard business plan. If you are able to successfully design a business model canvas, then you will have the structure for developing a clear business plan that you can submit for financial consideration.
Both types of business plans aim at providing a picture and roadmap to follow from conception to creation. If you opt for the brief business plan, you will focus primarily on articulating a big-picture overview of your business concept.
The full business plan is aimed at executing the vision concept, dealing with the proverbial devil in the details. Developing a full business plan will assist those of you who need a more detailed and structured roadmap, or those of you with little to no background in business. The business planning process includes the business model, a feasibility analysis, and a full business plan, which we will discuss later in this section. Next, we explore how a business plan can meet several different needs.
Purposes of a Business Plan
A business plan can serve many different purposes—some internal, others external. As we discussed previously, you can use a business plan as an internal early planning device, an extension of a napkin sketch, and as a follow-up to one of the canvas tools. A business plan can be an organizational roadmap , that is, an internal planning tool and working plan that you can apply to your business in order to reach your desired goals over the course of several years. The business plan should be written by the owners of the venture, since it forces a firsthand examination of the business operations and allows them to focus on areas that need improvement.
Refer to the business venture throughout the document. Generally speaking, a business plan should not be written in the first person.
A major external purpose for the business plan is as an investment tool that outlines financial projections, becoming a document designed to attract investors. In many instances, a business plan can complement a formal investor’s pitch. In this context, the business plan is a presentation plan, intended for an outside audience that may or may not be familiar with your industry, your business, and your competitors.
You can also use your business plan as a contingency plan by outlining some “what-if” scenarios and exploring how you might respond if these scenarios unfold. Pretty Young Professional launched in November 2010 as an online resource to guide an emerging generation of female leaders. The site focused on recent female college graduates and current students searching for professional roles and those in their first professional roles. It was founded by four friends who were coworkers at the global consultancy firm McKinsey. But after positions and equity were decided among them, fundamental differences of opinion about the direction of the business emerged between two factions, according to the cofounder and former CEO Kathryn Minshew . “I think, naively, we assumed that if we kicked the can down the road on some of those things, we’d be able to sort them out,” Minshew said. Minshew went on to found a different professional site, The Muse , and took much of the editorial team of Pretty Young Professional with her. 49 Whereas greater planning potentially could have prevented the early demise of Pretty Young Professional, a change in planning led to overnight success for Joshua Esnard and The Cut Buddy team. Esnard invented and patented the plastic hair template that he was selling online out of his Fort Lauderdale garage while working a full-time job at Broward College and running a side business. Esnard had hundreds of boxes of Cut Buddies sitting in his home when he changed his marketing plan to enlist companies specializing in making videos go viral. It worked so well that a promotional video for the product garnered 8 million views in hours. The Cut Buddy sold over 4,000 products in a few hours when Esnard only had hundreds remaining. Demand greatly exceeded his supply, so Esnard had to scramble to increase manufacturing and offered customers two-for-one deals to make up for delays. This led to selling 55,000 units, generating $700,000 in sales in 2017. 50 After appearing on Shark Tank and landing a deal with Daymond John that gave the “shark” a 20-percent equity stake in return for $300,000, The Cut Buddy has added new distribution channels to include retail sales along with online commerce. Changing one aspect of a business plan—the marketing plan—yielded success for The Cut Buddy.
Link to Learning
Watch this video of Cut Buddy’s founder, Joshua Esnard, telling his company’s story to learn more.
If you opt for the brief business plan, you will focus primarily on articulating a big-picture overview of your business concept. This version is used to interest potential investors, employees, and other stakeholders, and will include a financial summary “box,” but it must have a disclaimer, and the founder/entrepreneur may need to have the people who receive it sign a nondisclosure agreement (NDA) . The full business plan is aimed at executing the vision concept, providing supporting details, and would be required by financial institutions and others as they formally become stakeholders in the venture. Both are aimed at providing a picture and roadmap to go from conception to creation.
Types of Business Plans
The brief business plan is similar to an extended executive summary from the full business plan. This concise document provides a broad overview of your entrepreneurial concept, your team members, how and why you will execute on your plans, and why you are the ones to do so. You can think of a brief business plan as a scene setter or—since we began this chapter with a film reference—as a trailer to the full movie. The brief business plan is the commercial equivalent to a trailer for Field of Dreams , whereas the full plan is the full-length movie equivalent.
Brief Business Plan or Executive Summary
As the name implies, the brief business plan or executive summary summarizes key elements of the entire business plan, such as the business concept, financial features, and current business position. The executive summary version of the business plan is your opportunity to broadly articulate the overall concept and vision of the company for yourself, for prospective investors, and for current and future employees.
A typical executive summary is generally no longer than a page, but because the brief business plan is essentially an extended executive summary, the executive summary section is vital. This is the “ask” to an investor. You should begin by clearly stating what you are asking for in the summary.
In the business concept phase, you’ll describe the business, its product, and its markets. Describe the customer segment it serves and why your company will hold a competitive advantage. This section may align roughly with the customer segments and value-proposition segments of a canvas.
Next, highlight the important financial features, including sales, profits, cash flows, and return on investment. Like the financial portion of a feasibility analysis, the financial analysis component of a business plan may typically include items like a twelve-month profit and loss projection, a three- or four-year profit and loss projection, a cash-flow projection, a projected balance sheet, and a breakeven calculation. You can explore a feasibility study and financial projections in more depth in the formal business plan. Here, you want to focus on the big picture of your numbers and what they mean.
The current business position section can furnish relevant information about you and your team members and the company at large. This is your opportunity to tell the story of how you formed the company, to describe its legal status (form of operation), and to list the principal players. In one part of the extended executive summary, you can cover your reasons for starting the business: Here is an opportunity to clearly define the needs you think you can meet and perhaps get into the pains and gains of customers. You also can provide a summary of the overall strategic direction in which you intend to take the company. Describe the company’s mission, vision, goals and objectives, overall business model, and value proposition.
Rice University’s Student Business Plan Competition, one of the largest and overall best-regarded graduate school business-plan competitions (see Telling Your Entrepreneurial Story and Pitching the Idea ), requires an executive summary of up to five pages to apply. 51 , 52 Its suggested sections are shown in Table 11.2 .
Are You Ready?
Create a brief business plan.
Fill out a canvas of your choosing for a well-known startup: Uber, Netflix, Dropbox, Etsy, Airbnb, Bird/Lime, Warby Parker, or any of the companies featured throughout this chapter or one of your choice. Then create a brief business plan for that business. See if you can find a version of the company’s actual executive summary, business plan, or canvas. Compare and contrast your vision with what the company has articulated.
- These companies are well established but is there a component of what you charted that you would advise the company to change to ensure future viability?
- Map out a contingency plan for a “what-if” scenario if one key aspect of the company or the environment it operates in were drastically is altered?
Full Business Plan
Even full business plans can vary in length, scale, and scope. Rice University sets a ten-page cap on business plans submitted for the full competition. The IndUS Entrepreneurs , one of the largest global networks of entrepreneurs, also holds business plan competitions for students through its Tie Young Entrepreneurs program. In contrast, business plans submitted for that competition can usually be up to twenty-five pages. These are just two examples. Some components may differ slightly; common elements are typically found in a formal business plan outline. The next section will provide sample components of a full business plan for a fictional business.
Executive Summary
The executive summary should provide an overview of your business with key points and issues. Because the summary is intended to summarize the entire document, it is most helpful to write this section last, even though it comes first in sequence. The writing in this section should be especially concise. Readers should be able to understand your needs and capabilities at first glance. The section should tell the reader what you want and your “ask” should be explicitly stated in the summary.
Describe your business, its product or service, and the intended customers. Explain what will be sold, who it will be sold to, and what competitive advantages the business has. Table 11.3 shows a sample executive summary for the fictional company La Vida Lola.
Business Description
This section describes the industry, your product, and the business and success factors. It should provide a current outlook as well as future trends and developments. You also should address your company’s mission, vision, goals, and objectives. Summarize your overall strategic direction, your reasons for starting the business, a description of your products and services, your business model, and your company’s value proposition. Consider including the Standard Industrial Classification/North American Industry Classification System (SIC/NAICS) code to specify the industry and insure correct identification. The industry extends beyond where the business is located and operates, and should include national and global dynamics. Table 11.4 shows a sample business description for La Vida Lola.
Industry Analysis and Market Strategies
Here you should define your market in terms of size, structure, growth prospects, trends, and sales potential. You’ll want to include your TAM and forecast the SAM . (Both these terms are discussed in Conducting a Feasibility Analysis .) This is a place to address market segmentation strategies by geography, customer attributes, or product orientation. Describe your positioning relative to your competitors’ in terms of pricing, distribution, promotion plan, and sales potential. Table 11.5 shows an example industry analysis and market strategy for La Vida Lola.
Competitive Analysis
The competitive analysis is a statement of the business strategy as it relates to the competition. You want to be able to identify who are your major competitors and assess what are their market shares, markets served, strategies employed, and expected response to entry? You likely want to conduct a classic SWOT analysis (Strengths Weaknesses Opportunities Threats) and complete a competitive-strength grid or competitive matrix. Outline your company’s competitive strengths relative to those of the competition in regard to product, distribution, pricing, promotion, and advertising. What are your company’s competitive advantages and their likely impacts on its success? The key is to construct it properly for the relevant features/benefits (by weight, according to customers) and how the startup compares to incumbents. The competitive matrix should show clearly how and why the startup has a clear (if not currently measurable) competitive advantage. Some common features in the example include price, benefits, quality, type of features, locations, and distribution/sales. Sample templates are shown in Figure 11.17 and Figure 11.18 . A competitive analysis helps you create a marketing strategy that will identify assets or skills that your competitors are lacking so you can plan to fill those gaps, giving you a distinct competitive advantage. When creating a competitor analysis, it is important to focus on the key features and elements that matter to customers, rather than focusing too heavily on the entrepreneur’s idea and desires.
Operations and Management Plan
In this section, outline how you will manage your company. Describe its organizational structure. Here you can address the form of ownership and, if warranted, include an organizational chart/structure. Highlight the backgrounds, experiences, qualifications, areas of expertise, and roles of members of the management team. This is also the place to mention any other stakeholders, such as a board of directors or advisory board(s), and their relevant relationship to the founder, experience and value to help make the venture successful, and professional service firms providing management support, such as accounting services and legal counsel.
Table 11.6 shows a sample operations and management plan for La Vida Lola.
Marketing Plan
Here you should outline and describe an effective overall marketing strategy for your venture, providing details regarding pricing, promotion, advertising, distribution, media usage, public relations, and a digital presence. Fully describe your sales management plan and the composition of your sales force, along with a comprehensive and detailed budget for the marketing plan. Table 11.7 shows a sample marketing plan for La Vida Lola.
Financial Plan
A financial plan seeks to forecast revenue and expenses; project a financial narrative; and estimate project costs, valuations, and cash flow projections. This section should present an accurate, realistic, and achievable financial plan for your venture (see Entrepreneurial Finance and Accounting for detailed discussions about conducting these projections). Include sales forecasts and income projections, pro forma financial statements ( Building the Entrepreneurial Dream Team , a breakeven analysis, and a capital budget. Identify your possible sources of financing (discussed in Conducting a Feasibility Analysis ). Figure 11.19 shows a template of cash-flow needs for La Vida Lola.
Entrepreneur In Action
Laughing man coffee.
Hugh Jackman ( Figure 11.20 ) may best be known for portraying a comic-book superhero who used his mutant abilities to protect the world from villains. But the Wolverine actor is also working to make the planet a better place for real, not through adamantium claws but through social entrepreneurship.
A love of java jolted Jackman into action in 2009, when he traveled to Ethiopia with a Christian humanitarian group to shoot a documentary about the impact of fair-trade certification on coffee growers there. He decided to launch a business and follow in the footsteps of the late Paul Newman, another famous actor turned philanthropist via food ventures.
Jackman launched Laughing Man Coffee two years later; he sold the line to Keurig in 2015. One Laughing Man Coffee café in New York continues to operate independently, investing its proceeds into charitable programs that support better housing, health, and educational initiatives within fair-trade farming communities. 55 Although the New York location is the only café, the coffee brand is still distributed, with Keurig donating an undisclosed portion of Laughing Man proceeds to those causes (whereas Jackman donates all his profits). The company initially donated its profits to World Vision, the Christian humanitarian group Jackman accompanied in 2009. In 2017, it created the Laughing Man Foundation to be more active with its money management and distribution.
- You be the entrepreneur. If you were Jackman, would you have sold the company to Keurig? Why or why not?
- Would you have started the Laughing Man Foundation?
- What else can Jackman do to aid fair-trade practices for coffee growers?
What Can You Do?
Textbooks for change.
Founded in 2014, Textbooks for Change uses a cross-compensation model, in which one customer segment pays for a product or service, and the profit from that revenue is used to provide the same product or service to another, underserved segment. Textbooks for Change partners with student organizations to collect used college textbooks, some of which are re-sold while others are donated to students in need at underserved universities across the globe. The organization has reused or recycled 250,000 textbooks, providing 220,000 students with access through seven campus partners in East Africa. This B-corp social enterprise tackles a problem and offers a solution that is directly relevant to college students like yourself. Have you observed a problem on your college campus or other campuses that is not being served properly? Could it result in a social enterprise?
Work It Out
Franchisee set out.
A franchisee of East Coast Wings, a chain with dozens of restaurants in the United States, has decided to part ways with the chain. The new store will feature the same basic sports-bar-and-restaurant concept and serve the same basic foods: chicken wings, burgers, sandwiches, and the like. The new restaurant can’t rely on the same distributors and suppliers. A new business plan is needed.
- What steps should the new restaurant take to create a new business plan?
- Should it attempt to serve the same customers? Why or why not?
This New York Times video, “An Unlikely Business Plan,” describes entrepreneurial resurgence in Detroit, Michigan.
- 48 Chris Guillebeau. The $100 Startup: Reinvent the Way You Make a Living, Do What You Love, and Create a New Future . New York: Crown Business/Random House, 2012.
- 49 Jonathan Chan. “What These 4 Startup Case Studies Can Teach You about Failure.” Foundr.com . July 12, 2015. https://foundr.com/4-startup-case-studies-failure/
- 50 Amy Feldman. “Inventor of the Cut Buddy Paid YouTubers to Spark Sales. He Wasn’t Ready for a Video to Go Viral.” Forbes. February 15, 2017. https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbestreptalks/2017/02/15/inventor-of-the-cut-buddy-paid-youtubers-to-spark-sales-he-wasnt-ready-for-a-video-to-go-viral/#3eb540ce798a
- 51 Jennifer Post. “National Business Plan Competitions for Entrepreneurs.” Business News Daily . August 30, 2018. https://www.businessnewsdaily.com/6902-business-plan-competitions-entrepreneurs.html
- 52 “Rice Business Plan Competition, Eligibility Criteria and How to Apply.” Rice Business Plan Competition . March 2020. https://rbpc.rice.edu/sites/g/files/bxs806/f/2020%20RBPC%20Eligibility%20Criteria%20and%20How%20to%20Apply_23Oct19.pdf
- 53 “Rice Business Plan Competition, Eligibility Criteria and How to Apply.” Rice Business Plan Competition. March 2020. https://rbpc.rice.edu/sites/g/files/bxs806/f/2020%20RBPC%20Eligibility%20Criteria%20and%20How%20to%20Apply_23Oct19.pdf; Based on 2019 RBPC Competition Rules and Format April 4–6, 2019. https://rbpc.rice.edu/sites/g/files/bxs806/f/2019-RBPC-Competition-Rules%20-Format.pdf
- 54 Foodstart. http://foodstart.com
- 55 “Hugh Jackman Journey to Starting a Social Enterprise Coffee Company.” Giving Compass. April 8, 2018. https://givingcompass.org/article/hugh-jackman-journey-to-starting-a-social-enterprise-coffee-company/
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Michael Laverty, Chris Littel
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Entrepreneurship
- Publication date: Jan 16, 2020
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/entrepreneurship/pages/11-4-the-business-plan
© Jan 4, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
Learn to Build a Better Business Plan

Sample Business Plan Gallery
Browse our library of over 550 free business plan examples to kickstart your own plan.
Browse our library of over 550 free business plan examples.

How to Write a Business Plan
Step-by-step guide to establish the foundation of your business quickly and efficiently.
Step-by-step guide to establish the foundation of your business.

Business Plan Template
Build your business using the proven planning template designed by the experts at Bplans.
Use the planning template designed by the experts at Bplans.

Subscribe to Bplans business insights
Stay up to date with the latest business planning, management, growth, and funding trends from bplans..
We care about your privacy. See our Privacy Policy .
Popular Downloads

SWOT Analysis
Easily evaluate your competitive position and develop effective growth strategies.
Refine your competitive strategy using a SWOT analysis.

Cash Flow Forecast
Improve the health of your business by easily estimating your business’s financial future.
Estimate and improve the financial health of your business.

Lean Business Plan Template
Fast, simple, and shareable. Start with a one-page plan to grow alongside your business.
Start with a simple one-page plan to grow alongside your business…
Start Your Business

Business Startup Guide
Get everything in order to start your business and write your business plan.
Get everything in order to start your business.

How to start a business with no money
Is it possible to start a business with no money? Check out this proven process to get your business…
Is it possible to start a business with no money? Check out this.…

Startup Checklist
Break down the startup process and check all the necessary boxes.

Estimating Startup Costs
What will it cost to start your business? These are the expenses you will need to consider.
Do you know what it will cost to start your business?

Write Your Business Plan

Business Planning in Under an Hour
Learn how to write your business plan in under an hour.

1-Page Business Plan Template
A faster, more efficient way to develop your business strategy.
Perfect Your Elevator Pitch

Pitch Guide
Learn how to create a winning elevator pitch deck and speech that will impress investors.
Impress investors with a winning pitch deck and elevator pitch.

Elements of the Elevator Pitch
If you're pitching to investors or building a pitch deck, here are the 7 things you need.
Here are the 7 things you need to include in your elevator pitch.

Components of a Pitch Deck
Here are the 11 slides you must have in your pitch deck.

Investor Pitch Template
Start your pitch off right with a proven pitch deck template.

Get Your Business Funded

Funding Guide
Learn how to prepare your business plan and pitch to secure funding for your business.
Prepare your plan and pitch to secure funding for your business.

Ways to Fund Your Business
When it comes to funding, there isn't a one-size-fits-all method. Here are your options.
Find out what funding options are available for your business.
Grow Your Business

How to Grow Your Business
Growing your business can be just as difficult as starting. Here are proven ways to grow.
Try these proven methods to continue growing your business.

Grow Using Your Business Plan
Turn your business plan into a growth-oriented business strategy.

Set Clear and Actionable Goals
Grow your business by setting clear goals and establishing key metrics for success.
Learn to set clear and actionable goals to grow your business.

How to Forecast Cash Flow
Create a cash flow forecast to help keep your business healthy and plan for the future.
Keep your business healthy using a cash flow forecast.

Tim Berry Blog
Learn from renowned business planning expert and founder of Bplans, Tim Berry.

Business Glossary
Definitions for common terminology and acronyms that every small business owner should know.

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Strategy for Start-ups
- Joshua Gans,
- Erin L. Scott,
- Scott Stern

In their haste to get to market first, write Joshua Gans, Erin L. Scott, and Scott Stern, entrepreneurs often run with the first plausible strategy they identify. They can improve their chances of picking the right path by investigating four generic go-to-market strategies and choosing a version that aligns most closely with their founding values and motivations. The authors provide a framework, which they call the entrepreneurial strategy compass, for doing so.
It’s Not About the Framework
The Syracuse University professor Carl Schramm argues that contrary to the teaching at many business schools, entrepreneurs really have no alternative to learning by doing.
“Create Something and Start Selling It”
A conversation with the start-up veterans Niraj Shah, Bijan Sabet, and Jennifer Lum, by Daniel McGinn and Walter Frick
The complete Spotlight package is available in a single reprint.
First answer two questions; then explore four paths.
The Problem
In their haste to get to market, entrepreneurs often run with the first plausible strategy they identify. As a result, they end up losing out to second or even third movers with superior strategies.
Why It Happens
In the innovation space it’s easy to get overwhelmed by the apparent range of opportunities. Entrepreneurs fear that spending too much time weighing the alternatives will delay commercialization. The strategic commitments they make in moving forward limit their ability to pivot.
The Solution
Start-ups can improve their chances of picking the right path by investigating four generic go-to-market strategies, articulating multiple plausible versions of those strategies, and choosing the one that aligns most closely with their founders’ values and motivations.
As a start-up, RapidSOS was an easy sell: It would bring 911 calls into the smartphone age. Emergency-response systems had evolved in a premobile era, which meant that few of them could accurately identify the location of callers who were using mobile phones, compromising response times and medical outcomes. The founders of RapidSOS—Michael Martin, an HBS graduate, and Nick Horelik, an MIT engineer—had developed a way to transmit mobile phone locations to existing 911 systems that would require only minimal adaptation on the part of other players in the emergency-services sector. After attracting early-stage financing at business plan competitions, Martin and Horelik reached a crossroads: How should they take their technology to market?
What many business schools teach has little to do with entrepreneurial success.
- Joshua Gans is the Jeffrey S. Skoll Chair in Technical Innovation and Entrepreneurship at the Rotman School of Management, University of Toronto, and the chief economist at the Creative Destruction Lab. He is a co-author of Power and Prediction: The Disruptive Economics of Artificial Intelligence (Harvard Business Review Press, 2022).
- ES Erin L. Scott is a senior lecturer in the Technological Innovation, Entrepreneurship, and Strategic Management Group at the MIT Sloan School of Management.
- SS Scott Stern is the David Sarnoff Professor of Management at the Sloan School and serves as faculty director of the Martin Trust Center for MIT Entrepreneurship.
Partner Center
Entrepreneurship and Business Planning
- Small Business
- Business Planning & Strategy
- Business Plans
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Pinterest" aria-label="Share on Pinterest">
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Reddit" aria-label="Share on Reddit">
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Flipboard" aria-label="Share on Flipboard">
Methods to Capitalize a Business
Business plans for new inventions, how to write a description for a business plan.
- What Can You Learn by Comparing Successful & Unsuccessful Businesses?
- What Is the Business Planning Process?
Ventures that are thoughtfully planned are more likely to succeed than those based primarily on guesswork and hope. The business planning process in entrepreneurship helps an entrepreneur identify exactly what needs to be accomplished to build the venture, and what human and financial resources are required to implement the plan. It is a planning tool that helps entrepreneur startups get where they are going. The forecast profit and loss statement provides a means to compare actual results to what had been forecast, and make corrections to business strategy if shortfalls in revenue occur.
Aspects of a Business Plan
According to the Small Business Administration, business planning for a start-up venture or an established company does not have to be complicated. You start by describing your products and services in relationship to those of competitors. You describe what you will be doing that is superior to what customers have seen from these other companies. This answers the critical question of why your products solve a significant, current customer need. You then devise strategies for introducing your products and services to the market. You determine the costs of producing the products or delivering the services and the marketing costs required to attract customers. You also plan the managerial and staff resources required to accomplish all of these tasks, when they will be hired, and what their compensation will be.
Know Your Customer
It is vital for entrepreneurs to understand who their target customers are--those who can benefit the most from the company’s products or services. According to Forbes , knowing your customer can help you show that there is significant opportunity and a good market for the goods or services you are trying to provide. Knowing these prime customers’ demographic characteristics allows you to tailor the marketing message so it is most effective. Communicating with teenagers requires a different message and possibly different media than reaching seniors. A depth of understanding about your competition is similarly important. You want to identify their strengths so you don’t attempt to compete with them head-on in a market where they have built an insurmountable advantage. Knowing their weaknesses shows you where you can capture customers from them.
Skills for Success
The ability to envision how you want your company to evolve over the next three to five years is important. These long-range goals help you determine the steps and strategies you need to implement to reach them. A basic knowledge of finance concepts helps you prepare logical financial models and projections using spreadsheet software. Entrepreneurs should also have an understanding of all the functional areas of a business so they can accurately project the costs of running the business.
Planning Versus Writing
Entrepreneurs don’t always understand that the planning process itself is of value. They have been advised they should have a business plan document ready to present to potential investors so they--sometimes reluctantly--devote the time to writing a business plan. Ideally, the document is the final product of a planning process that would be completed whether or not the company was actively seeking capital. The plan is very much like a road map. It helps you choose the best route to get to your destination--creating a successful venture.
Common Financial Miscalculations
Entrepreneurs often underestimate how difficult it will be to launch a company. Gaining the attention and trust of potential customers may take longer than the entrepreneur envisioned. This can result in start-up capital being quickly depleted. In a worst case scenario, the company can go out of business because its funding runs out. Adding five to ten percent more capital to the start-up budget is a prudent way to allow for both lower than planned revenues and higher than anticipated expenses.
- Forbes: Basic Structure of a Business Plan for Beginners
Related Articles
The importance of a business plan, how to plan & grow a business venture, the impact of planning on business growth, advice on business planning, business enterprise planning, why is it important for entrepreneurs to develop financial plans for their companies, key factors to considering business feasibility, how to write a new business pitch, major factors involved in successful entrepreneurship, most popular.
- 1 The Importance of a Business Plan
- 2 How to Plan & Grow a Business Venture
- 3 The Impact of Planning on Business Growth
- 4 Advice on Business Planning
The road to entrepreneurial success: business plans, lean startup, or both?
New England Journal of Entrepreneurship
ISSN : 2574-8904
Article publication date: 19 February 2021
Issue publication date: 18 June 2021
The goal of this research is to investigate the relationship between two different sets of practices, lean startup and business planning, and their relation to entrepreneurial performance.
Design/methodology/approach
The authors collected data from 120 entrepreneurs across the US about a variety of new venture formation activities within the categories of lean startup or business planning. They use hierarchical regression to examine the relationship between these activities and new venture performance using both a subjective and objective measure of performance.
The results show that talking to customers, collecting preorders and pivoting based on customer feedback are lean startup activities correlated with performance; writing a business plan is the sole business planning activity correlated with performance.
Research limitations/implications
This research lays the foundation for understanding the components of both lean startup and business planning. Moreover, these results demonstrate that the separation of lean startup and business planning represents a false dichotomy.
Practical implications
These findings suggest that entrepreneurs should engage in some lean startup activities and still write a business plan.
Originality/value
This article offers the first quantitative, empirical comparison of lean startup activities and business planning. Furthermore, it provides support for the relationship between specific lean startup activities and firm performance.
Business planning
- Entrepreneurship
Lean Startup
Welter, C. , Scrimpshire, A. , Tolonen, D. and Obrimah, E. (2021), "The road to entrepreneurial success: business plans, lean startup, or both?", New England Journal of Entrepreneurship , Vol. 24 No. 1, pp. 21-42. https://doi.org/10.1108/NEJE-08-2020-0031
Emerald Publishing Limited
Copyright © 2021, Chris Welter, Alex Scrimpshire, Dawn Tolonen and Eseoghene Obrimah
Published in New England Journal of Entrepreneurship . Published by Emerald Publishing Limited. This article is published under the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY 4.0) license. Anyone may reproduce, distribute, translate and create derivative works of this article (for both commercial and non-commercial purposes), subject to full attribution to the original publication and authors. The full terms of this license may be seen at http://creativecommons.org/licences/by/4.0/legalcode
Introduction
No business plan survives first contact with a customer – Steve Blank
This quote represents the differing perspectives on the value of business planning relative to the value of lean startup methods proposed by Blank and others ( Blank and Dorf, 2012 ). Much of traditional entrepreneurial training centers on the business plan ( Honig, 2004 ). Collective research on business planning's antecedents ( Brinckmann et al. , 2019 ) and its performance outcomes have found nuanced results ( Brinckmann et al. , 2010 ), but there seem to be at least some instances where business planning reliably increases performance ( Welter and Kim, 2018 ). Studies suggest that the majority of prominent business schools offer business planning courses ( Honig, 2004 ; Katz et al. , 2016 ), and bookstores are filled with books detailing how to write a business plan ( Karlsson and Honig, 2007 ). Nonetheless, the research is fragmented at best, and often results in equivocal findings with regard to its relationship with firm performance ( Brinckmann et al. , 2010 , Delmar and Shane, 2003 ; Gruber, 2007 ). This lack of clear indication from researchers opens the door for critique of business planning from proponents of the lean startup ( Ghezzi et al. , 2015 ).
Lean startup methods have drawn increasing attention in entrepreneurial communities ( Ries, 2011 ). In accelerators, incubators and other spaces within startup ecosystems the wisdom of Eric Ries (2011) and Steve Blank ( Blank and Dorf, 2012 ) can be heard in training sessions and everyday conversations. Some entrepreneurial programs have adopted lean startup methods as well ( Bliemel, 2014 ). On one hand, conceptual articles have described how lean startup fits adjacent to current and past academic conversations ( Contigiani and Levinthal, 2019 ). On the other hand, practitioner articles have discussed the benefits and limitations of the models ( Ladd, 2016 ). In both cases, existing literature describes how these processes aim to avoid the pitfall of launching products that no one actually wants ( Blank, 2013 ).
Despite all the popular attention given to lean startup methods, little empirical research has been completed (see Trimi and Berbegal-Mirabent (2012) , Ghezzi et al. (2015) , and Ghezzi (2019) for exceptions). Some researchers (e.g. Frederickson and Brem, 2017 ) have drawn the parallels between lean startup methods and effectuation ( Sarasvathy, 2001 ), but these parallels do not sufficiently support the use of lean startup methods. While practitioners seem to embrace lean startup methods, academics have offered little in terms of direct investigation into those methods ( Shepherd and Gruber, 2020 ). Most of the research on lean startup methods focuses on cognitive processes ( Yang et al. , 2018 ; York and Danes, 2014 ). Recent critique ( Felin et al. , 2019 ) coupled with the dearth of empirical research calls into question the efficacy of lean startup methods. To that end, more research is needed to see how lean startup methods relate to new venture success especially in comparison to business planning. This is particularly important as new venture formation activities are the practices that can legitimize the firm ( De Clercq and Voronov, 2009 ).
As such, we propose the following question: which individual aspects of business planning and lean startup methods are related to success? We study the components of both business planning and lean startup methods as there is some academic support for aspects of lean startup such as experimentation ( Carmuffo et al. , 2019 ), but limited empirical investigation into lean startup more broadly. We specifically focus on the underlying activities that make up the processes of lean startup and business planning since our initial surveying showed that entrepreneurs often employ aspects of each. To examine this question, we created a survey that captured the various activities – both from lean startup and business planning – that entrepreneurs used in pursuing their new venture and compared those with measures of success.
Our findings suggest that certain lean startup activities and the act of writing a business plan are correlated with success. These findings help to undo a false dichotomy of either lean startup or business planning by suggesting that some activities from each side can lead to success. We contribute to business planning research by offering a possible explanation for the existing equivocal findings. Namely, that the act of writing a business plan may be important, but that the uses of a business plan for feedback or financing are not necessarily associated with success. We contribute to research on lean startup by offering the first quantitative support for specific lean startup activities. Taken together, this research lays the foundation for a more nuanced understanding of the value of business planning and lean startup methods.
Theoretical framework and hypotheses
The literature on business planning is vast focusing on both antecedents to business planning ( Brinckmann et al. , 2019 ) and outcomes of it ( Brinckmann et al. , 2010 ). Honig and colleagues have driven much of the research into business planning since the turn of the century ( Honig, 2004 ; Honig and Karlsson, 2004 ; Honig and Samuelsson, 2012 , 2014 ; Karlsson and Honig, 2009 ). They have challenged prior planning-performance paradigms that suggested planning would naturally increase performance ( Ajzen, 1985 ; Mintzberg and Waters, 1985 ; Ansoff, 1991 ). This debate about the value of planning has underscored the recent research into selection effects associated with business planning ( Burke et al. , 2010 ; Greene and Hopp, 2017 ).
Brinckmann et al. (2010) address this debate directly. Their meta-analytic review of business planning literature suggests that three contingencies need to be considered in terms of the effectiveness of business planning: uncertainty, limited prior information, and the lack of business planning structures. The presence of these three suggest that business planning may be less effective. We look at each of these three contingencies in more depth next.
For uncertainty, planning scholars (e.g. Priem et al. , 1995 ) suggest that unstable and uncertain environments would benefit most from planning as planning can reduce uncertainty through facilitating faster decision-making ( Dean and Sharfman, 1996 ). However, emergent strategies seem to be more effective at controlling uncertainty ( Mintzberg, 1994 ; Sarasvathy, 2001 ). Brinckmann et al. (2010) confirms the latter intuition suggesting that uncertainty makes planning efforts less effective. This logic falls in line with research on effectuation ( Sarasvathy, 2001 ), where planning is described as the appropriate strategy for risky environments and effectuation, in contrast, is appropriate for uncertain environments. Recent work has confirmed this logic depending on how accurate the entrepreneur can be when predicting the future ( Welter and Kim, 2018 ).
Turning to the concept of limited prior information, planning proponents suggest that the shorter feedback cycles in new and small firms combined with the positive motivational effects of planning will make it more effective ( Delmar and Shane, 2003 ). In essence, despite the lack of history for de novo firms, short cycle times create history quickly and planning itself serves to motivate these fledgling organizations. However, Brinckmann et al. (2010) find that these firms lack the information necessary to make such plans effective. As firms pursue novel strategies, planning seems to be less effective or firms abandon plans all together as they move forward ( Karlsson and Honig, 2009 ).
Finally, for plans to be effective firms need to have the structures in place to both plan and make use of those plans ( Brinckmann et al. , 2010 ). New firms tend to lack the organizational structures relevant to create and use plans ( Forbes, 2007 ). While Karlsson and Honig (2009) found that firms typically ignore or abandon plans after they have been made, often due to insufficient support structures, Honig and Samuelsson (2012) show that even when firms change their plans over time there is little impact on firm performance. In general, the literature on business planning suggests that planning has more benefits for established firms with data and history to support both the plan and the planning process.
Business planning activities improve the likelihood of success for new ventures.
Typically, business planning has been analyzed as the single act of writing a business plan (e.g. Honig and Karlsson, 2004 ). However, business planning is made up of a variety of activities ( Gruber, 2007 ), which entrepreneurs may utilize as a whole, or simply choose parts of the business planning process. It is worth noting that these specific activities are not mutually exclusive with lean startup activities that we will detail later. One source of the gap between the prevalence of business planning use and research supporting the efficacy of business plans may be this holistic perspective. The constituent parts of business planning may be executed as a whole, or may be chosen a la carte. Examining the various activities that make up business planning offers insight into which aspects of the process are related to firm performance.
Arguably the first step in the business planning process is the work that precedes the actual writing of a business plan. First, entrepreneurs must collect data – typically external data ( Brinckmann et al. , 2010 ). This data collection process may or may not result in an actual business plan being written and, therefore, can be treated as a separate step itself.
Beyond the data collection and writing, the planning process can play a role in routinizing the initial practices of entrepreneurs. While entrepreneurs may engage in social resourcing ( Keating et al. , 2014 ) and collective sense-making ( Wood and McKinley, 2010 ), the act of codifying the results of these activities can objectify these practices. Entrepreneurs engage socially on a number of dimensions in the pursuit of a venture, but physically writing down a business plan that can be shared externally can serve as a commitment mechanism. Entrepreneurs may share this plan with external stakeholders simply for feedback ( Wood and McKinley, 2010 ) or they may use it to seek funding ( Richbell et al. , 2006 ).
Writing a business plan improves the likelihood of success for new ventures.
Gathering secondary data improves the likelihood of success for new ventures.
Sharing a business plan with potential stakeholders in order to get feedback improves the likelihood of success for new ventures.
Sharing a business plan with potential financiers in order to obtain funding improves the likelihood of success for new ventures.
Lean startup
The concept and the phrase “Lean Startup” stem from Eric Ries (2011) and his popular press book by the same name. The phrase borrows from the idea of lean manufacturing in the sense of eliminating waste and pushing production and supply as late in the process as possible to delay purchasing until the last moment. The book draws primarily on Ries's personal experience in founding a company along with some consulting work. Further development of the ideas around lean startup methods comes from Steve Blank ( Blank and Dorf, 2012 ). Blank (2013) described three principles of lean startup: hypothesis creation, customer development, and agile development. Hypothesis creation represents the belief that founders begin with little more than untested hypotheses. Customer development represents the approach of interviewing and interacting with customers in order to verify or discard the aforementioned hypotheses. Finally, agile development conceptualizes that minimally viable products (MVPs) are deployed quickly to verify the hypotheses that are believed to be true.
These concepts are often practiced by entrepreneurs and taught at incubators and accelerators ( Ladd, 2016 ), but there is little academic research to support these practices. Ghezzi et al. (2015) offer one of the only comparative empirical studies between lean startup and business planning. Their findings from a four-case study suggest that lean startup methods lead to superior outcomes. The majority of other papers are conceptual explorations of lean startup methods focusing on the decision-making of entrepreneurs ( Frederickson and Brem, 2017 ; Yang et al. , 2018 ; York and Danes, 2014 ). These conceptual pieces draw parallels between lean startup and effectuation ( Sarasvathy, 2001 ).
The literature on effectuation is much larger than that of lean startup (see recent reviews and retrospectives by Arend et al. (2015) and Reymen et al. (2015) ). Effectuation has been defined as entrepreneurial expertise that utilizes heuristics to make decisions focused on the means available rather than on desired ends ( Sarasvathy, 2001 ). One heuristic, in particular, has driven the comparison between lean startup and effectuation: experimentation ( Camuffo et al. , 2019 ). However, the comparisons may stem from the lack of clear boundaries in effectuation (see Welter et al. , 2016 ). While some researchers might argue that effectuation is a more robust articulation of lean startup ( Frederickson and Brem, 2017 ), there are significant departures. Effectuation makes no mention of MVPs or agile development, but instead focuses on the means at hand ( Sarasvathy and Dew, 2008 ). These means direct the venture as opposed to a focus on a specific end in mind ( Sarasvathy, 2001 ). This is in contrast to lean startup methods that create specific tests in order to verify a predetermined path ( Blank, 2013 ). Thus, researchers have suggested that lean startup intersects with effectuation, as well as other research streams ( Contigiani and Levinthal, 2019 ; Ghezzi, 2019 ).
Utilizing lean startup methods improves the likelihood of success for new business ventures.
Similar to business planning, lean startup is a process with several component parts from which an entrepreneur may select without needing to accomplish each task. Moreover, these component parts may be used in conjunction with business planning activities. Since lean startup has been developed more by practitioners than academics, there is not a clearly-defined, comprehensive list of activities that constitutes lean startup. Bortolini et al. (2018) review the academic and popular press literature on lean startup and describe the process at a more theoretical level than the work of Blank (2013) and Ries (2011) . Between these two perspectives, a specific list of six lean startup activities can be derived.
The lean startup process begins with customer discovery ( Blank and Dorf, 2012 ). In its most basic sense, the process of customer discovery begins with interviewing potential customers to surface their problems. Blank (2013) describes how lean startups “get out of the building” throughout the process to validate customer assumptions regarding all aspects of a potential business model. This validation process involves a variety of different forms of potential customer interviews.
From there, entrepreneurs craft hypotheses and build experiments as Bortolini et al. (2018) describe. This part of the process can be deconstructed into developing prototypes, showing those prototypes to customers, and running experiments. These sub-processes are discrete steps that may depend on each other, but may also occur independently. For instance, entrepreneurs may develop prototypes in their own quest to improve the product without actually showing a given prototype to potential customers. Alternatively, entrepreneurs may run experiments that do not necessarily involve the use of a prototype. These experiments may include observing customers in their daily routine to better understand customer problems. Each of these processes, however, align with the practitioner perspectives and the theoretical perspectives ( Blank and Dorf, 2012 ; Bortolini et al. , 2018) .
Beyond these specific activities, we examine two other activities within lean startup: collecting preorders and pivoting. Collecting preorders for new products has been suggested by Ries (2011) , but also aligns with research on enrolling external stakeholders ( Burns et al. , 2016 ) and the principles of effectuation ( Sarasvathy, 2001 ). By seeking out early stakeholders to make commitments like preorders or input on prototypes, entrepreneurs seek social resources to enable and direct their progress ( Keating et al. , 2014 ).
Interviewing potential customers improves the likelihood of success for new business ventures.
Developing a prototype improves the likelihood of success for new business ventures.
Showing a prototype to potential customers improves the likelihood of success for new business ventures.
Experimenting to test business model assumptions improves the likelihood of success for new business ventures.
Collecting preorders improves the likelihood of success for new business ventures.
Pivoting based on customer feedback improves the likelihood of success for new business ventures.
We began our study by conducting semi-structured interviews with five entrepreneurs to guide the construction of the survey. These entrepreneurs were selected from the authors' personal networks to represent a variety of perspectives and experiences. The group included two female founders and three male founders; two of the founders created high-tech scalable businesses and three represented small businesses. The interviews lasted 75 min on average.
All interviewees were familiar with business plans. All interviewees had heard of “lean startup” but only one entrepreneur had any education on the subject – they had read Eric Ries's book ( Ries, 2011 ). Nonetheless, none of the entrepreneurs could articulate specific aspects of lean startup or how it would be different from or related to writing a business plan.
The data collected from these interviews was used to develop a survey for distribution to a wider group of entrepreneurs. Within the qualitative data we noted how both business planning and lean startup represented groups of activities to the entrepreneurs. In discussing business planning, all of the entrepreneurs discussed more than simply producing a formal business plan. While four of the five entrepreneurs created formal business plans, each discussed a slightly different process. Some included financial planning while others mentioned secondary research. On the lean startup approach, the entrepreneurs did not specifically state which activities they pursued that were in line with lean startup, but multiple entrepreneurs mentioned each of the aspects of lean startup that we included in the survey.
This qualitative investigation altered our survey design to focus more on the activities that entrepreneurs completed rather than focusing on their understanding of the different approaches. Before distributing the survey, we tested it with two entrepreneurs to obtain feedback on its understandability – one from the original interviewees and one unfamiliar with the research project. Based on these tests, minor modifications to word choice were made.
We reached out to the startup ecosystem in a major Midwestern city. The online survey was emailed to incubators, accelerators, individual entrepreneurs, and organizations that reach outside the Midwest. Participation in the study was voluntary. Participants received a $1 USD donation to a non-profit organization of their choice for completing the survey. A total of 41 entrepreneurs responded to the initial survey request. We excluded seven of these cases because they did not adequately describe their business.
To bolster the sample size, we enlisted the Qualtrics panel development team to collect approximately 100 additional survey responses from entrepreneurs. Qualtrics, in addition to providing online survey tools, is a research panel aggregator with the ability to recruit hard-to-reach demographics. Qualtrics utilizes specialized recruitment campaigns to assemble niche survey panels based on pre-specified criteria. To fit in this group, entrepreneurs must own a business that they have started within the last ten years. Respondents in this group were compensated with $25 USD for their participation and were not offered any donation option. A total of 106 completed surveys were returned from this group. We excluded 20 of these cases because they were unable to adequately describe their business. See the Appendix for the complete survey instrument.
Participants and procedures
The participants completed an online questionnaire with thirty-two questions on the details of how they started their business, the success of the business, activities they conducted while starting the business, and demographic variables. The sample was recruited via a snowball sample method as well as through a Qualtrics panel as described above.
The majority of our sample is comprised of Caucasians (81.7%), followed by Black/African Americans (11.7%), then Hispanics (3.3%), then Asians (1.7%). The median age of our sample was 46.5 years old and the sample was 49.2% female. The majority of our dataset is currently married (61.7%) with 55.8% having at least a bachelor's degree. Table 1 shows the means and standard deviations for each of the variables as well as the correlations between them.
Dependent variables
There are various difficulties in obtaining concrete objective measures of success from entrepreneurs. Reasons stem from factors such as small business owners not always running their businesses to maximize financial performance ( Jacobs et al. , 2016 ) or running a business because it allows for a preferred lifestyle ( Jennings and Beaver, 1997 ; Walker and Brown, 2004 ). Because of this, there are a few ways researchers can gain acceptable insight into the success of an entrepreneurial venture. One approach is to use subjective measures when other types of information are unavailable ( Dawes, 1999 ). Thus, following previous research ( Besser, 1999 ; Jacobs et al. , 2016 ) which has noted that entrepreneurial success may not always mean optimal financial measures and instead may be more along the lines of maintaining an acceptable level of income for themselves and their employees ( Beaver, 2002 ) or sustaining a lifestyle more aimed at being part of a creative output than being financially successful ( Chaston, 2008 ), we first analyzed the entrepreneurs' perceived organizational success. A second approach is to ask about objective success measures. We strengthened our study by asking entrepreneurs about objective measures of their firm's success via focusing on their firm's growth, specifically, asking about objective growth indicators in terms of increased number of employees, increased number of customers, or increased revenue as previous research has used these measures to indicate success ( Walker and Brown, 2004 ). Therefore, we analyzed the full model for both the subjective and objective dependent variables.
Given that entrepreneurial motivations can vary widely ( Shane et al. , 2003 ), defining success can vary based on the individual. To address this, studies have surveyed entrepreneurs for their subjective perception of their venture's success ( Fisher et al. , 2014 ; Keith et al. , 2016 ). Walker and Brown (2004 , p. 585) find that “Personal satisfaction, pride and a flexible lifestyle were the most important considerations for these business owners.” They argue that objective, financial measures that are often used in research offer objectivity and accessibility, but may not capture the true value of success for many entrepreneurs. These alternative motivations make success difficult to quantify objectively, leading researchers to utilize more subjective measures. Therefore, in line with prior research on entrepreneurial success perceptions ( Jacobs et al. , 2016 ; Besser, 1999 ), we asked respondents “How strongly do you agree or disagree with the following statement? My business is a success.” Respondents rated their agreement on a five-point Likert scale (1 = Strongly Agree, 5 = Strongly Disagree).
Firm Growth:
To strengthen the findings from our subjective measure of success we also asked respondents about objective measures of firm growth. By asking respondents about obvious measures of growth we can offer a more objective view on the success of the firm. We asked respondents if their firm had grown by any of the following three metrics: number of employees, number of customers, or total revenue (cf. Jacobs et al. , 2016 ). Given the variety of motivations of entrepreneurs, we chose not to limit the type of growth that would reflect success. In some cases, an entrepreneur may seek to increase the impact of the business by providing services to a greater number of customers, while maintaining a lean staff to control pricing. Alternatively, an entrepreneur may be seeking autonomy, and therefore choose not to hire in order to create greater autonomy. However, it is likely that some firm growth – in revenue, employees, or customers – is likely to occur in successful firms. Therefore, we combined these three types of growth as a dichotomous variable, wherein growth in any one or more of these areas would be coded as a “1” for growth and an answer of no growth in all of these areas would be coded as a “0” for no growth.
Independent variables
Business planning.
We defined business planning using four activities. We asked respondents if they (1) wrote a business plan [ Write BPlan ]; (2) gathered secondary data on industry statistics or trends [ Secondary Data ]; (3) shared your business plan with people outside the company for feedback [ BPlan Feedback ]; and (4) shared your business plan with people outside the company for funding [ BPlan Funding ]. These were not loaded as a factor as these do not represent an underlying factor, but rather are individual activities that all represent a variety of activities pertaining to the use of business plans.
We defined lean startup using six activities. We asked respondents if they (1) interviewed potential customers [ Interview ]; (2) created a prototype [ Prototype ]; (3) showed a prototype to potential customers for feedback [ Show Proto ]; (4) conducted an experiment to better understand some portion of your business [ Experiment ]; (5) used customer feedback to alter the direction of your business (“pivoted”) [ Pivot ]; and (6) accepted money for preorders [ Preorders ]. Similar to business planning activities, these were not loaded as a factor, as these activities do not represent an underlying factor, but rather a collection of potential activities.
For each of the IVs, respondents were first asked which of the above activities they engaged in during their venture startup process. The order of the activities was randomized. For each activity that was selected, respondents were asked to rate “how much did each of those activities positively impact the performance of this venture?” Respondents were given a five-point Likert scale (1 = “Not at all” to 5 = “A great deal”) and if the respondent did not do the activity, the response was coded as a 0. To calculate the IVs, each response was weighted by the level of impact. For example, if the respondent rated Experiment as a 5 for a great deal of impact, then it would be coded 5. If it was rated 3, then it would be coded 3. Any activity not completed was not rated (or effectively coded a 0).
We used the ratings to allow for variance in the impact of any activity. In our preliminary interviews, we heard that entrepreneurs may have performed the same activity, such as interviewing customers, but some placed a greater emphasis on this activity whereas others performed it only cursorily. We also performed a robustness check on the data using non-weighted values for the IVs and found similar results (these are available from the corresponding author upon request).
Control variables
We controlled for the following variables: (1) the firm's age in years [Firm Age] ; (2) the entrepreneur's prior startup experience [Ent XP] ; (3) the entrepreneur's age in years [Age] ; (4) the entrepreneur's education level [Education] ; (5) the case sample [case Sample]; and (6) if the firm was a high-tech growth firm [Hi-tech growth firms] . Firm age is likely related to perceptions of success in the minds of entrepreneurs. If an entrepreneur perceives themselves as unsuccessful, they are likely to quit pursuing their venture. Thus, entrepreneurs with older businesses are more likely to have higher perceptions of their own success. Ent XP, Age , and Education have all been investigated in the past for their relationship to entrepreneurial firm performance (e.g. Hechavarría and Welter, 2015 ). We also control for the case sample since our sample was collected in two different processes. Finally, we control for Hi-tech growth firms since some firms in our sample are oriented toward accelerated growth and others may be content with stable returns, which may impact the use and effectiveness of business planning ( Brinckmann et al. , 2010 ).
Regression results for success DV
We tested our hypotheses using hierarchical regression [ 3 ]. In Step 1, we entered Firm Age (in years), the entrepreneur's prior startup experience, the entrepreneur's age, the entrepreneur's education level, the case source, and whether the firm was a hi-tech growth firm as controls ( Van Dyne and LePine, 1998 ). In Step 2, we entered our independent variables that relate to the business plan approach: writing a business plan, gathering secondary data on the industry, sharing the business plan to receive feedback, and sharing the business plan to obtain funding. We also included the variables related to the lean startup approach: interviewing potential customers, creating prototypes, showing prototypes to potential customers for feedback, conducting an experiment to better understand a portion of the business, pivoting based on customer feedback, and accepting money for preorders.
Table 1 reports descriptive statistics and correlations, whereas Table 2 presents the hierarchical regression results for the success dependent variable. As can be seen in Table 2 , consistent with H1a , writing a business plan was related to success ( β = 0.09, p = 0.09). However, we do not find support for our other hypotheses: gathering secondary data on the industry, sharing the business plan to receive feedback, and sharing the business plan to obtain funding were all not significantly related to success.
When we looked at the activities that contribute to lean startup methods, we found that interviewing potential customers ( β = 0.09, p = 0.08) and accepting money for preorders ( β = 0.15, p = 0.03) supported H2a and H2e respectively, suggesting these are correlated with success. Similar to the business plan approach there was not sufficient support for all our hypotheses: creating prototypes, showing prototypes to potential customers for feedback, conducting an experiment to better understand a portion of the business, and pivoting were not supported. The findings with regard to each hypothesis are summarized in Table 3 .
Regression results for growth DV
Similar to the subjective success dependent variable, we tested our hypotheses using logistic regression for our objective growth dependent variable [ 4 ]. A logistic regression was performed for each of our approaches, the business plan and lean startup since our growth DV is dichotomous ( Mason et al. , 2018 ).
Table 1 reports descriptive statistics and correlations, whereas Table 4 presents the logistic regression results for the effects of writing a business plan, gathering secondary data on the industry, sharing the business plan to receive feedback, and sharing the business plan to obtain funding had on our growth dependent variable. The logistic regression model was statistically significant, χ 2 (10) = 39.16, p < 0.005. The model explained 39.2% (Nagelkerke R 2 ) of the variance in business growth and correctly classified 69.2% of cases. As can be seen in Table 4 , consistent with H1a , writing a business plan was related to success ( β = 0.30, p = 0.036). As before we did not find support for our other hypotheses: gathering secondary data on the industry, sharing the business plan to receive feedback, and sharing the business plan to obtain funding.
Next, we looked at the actions that constitute lean startup, interviewing potential customers, creating prototypes, showing prototypes to potential customers for feedback, conducting an experiment to better understand a portion of the business, and pivoting based on customer feedback had on our growth dependent variable. The logistic regression model was statistically significant, χ 2 (12) = 53.82, p < 0.005. The model explained 51.0% (Nagelkerke R 2 ) of the variance in business growth and correctly classified 85% of cases. Our logistic regression results found that interviewing potential customers ( β = 0.25, p = 0.08), accepting money for preorders ( β = 0.89, p = 0.04), and pivoting based on customer feedback ( β = 0.34, p = 0.03), provided support for H2a , H2e , and H2f respectively, suggesting these are correlated with success in terms of growth. We did not find support for our other hypotheses about lean startup activities. These were, creating prototypes, showing prototypes to potential customers for feedback, conducting an experiment to better understand a portion of the business, and pivoting. The findings with regard to each hypothesis are summarized in Table 5 .
In this paper, we sought to understand the relationship between lean startup activities and success as well as the relationship between business planning activities and success. To answer this question, we began by gathering qualitative data from entrepreneurs to better understand their perspective and language regarding these two approaches. From there, we created a survey and collected responses from 120 entrepreneurs about their activities and their perception of success and the growth of their firms. Controlling for common influencers of success, we found that the act of writing a business plan ( H1a ), interviewing potential customers ( H2a ), and taking preorders ( H2e ) were all correlated with subjective perceptions of success. For the firm growth dependent variable, we found that the act of writing a business plan ( H1a ), taking preorders ( H2e ), and pivoting based on customer feedback ( H2f ) were all correlated with objective measures of firm growth. Interestingly, these results represent a combination of lean startup and business planning activities. What is more, the two activities that are supported by both dependent variables, represent the most well-researched activities. As mentioned, the literature on business planning is well developed ( Honig and Karlsson, 2004 ), and the use of preorders is most directly tied to research on enrolling stakeholders ( Burns et al. , 2016 ) as well as effectuation ( Sarasvathy, 2001 ).
Our results give some understanding to the prior equivocal findings on business planning ( Brinkmann et al. , 2010 ). The qualitative data we gathered suggests that entrepreneurs complete different activities in their business planning process. In the past, there has not been much discussion about separate aspects of business planning or the impact they may have. Our findings suggest that the act of writing a business plan is related to success, but the other business planning activities – gathering secondary data, sharing the business plan for feedback or funding – are not related. This suggests that the planning process itself may mean more than the uses of a business plan. Even if a business plan is not revised or revisited as an entrepreneur pursues their venture ( Karlsson and Honig, 2009 ), the act of writing the plan is still connected with success. Entrepreneurs going through the exercise of planning are likely to gain a better understanding of the entire endeavor of launching a new business. This would give entrepreneurs a better grasp of what the range of possible outcomes would be and likely temper any overly optimistic and unfounded hopes. Therefore, it is likely that simply writing the business plan helps calibrate entrepreneur expectations, which, in turn, helps entrepreneurs achieve success.
Rather than viewing lean startup as a cohesive whole, our qualitative data suggests that entrepreneurs make use of differing combinations of lean startup activities. This discovery informed our survey which offers some of the first direct quantitative evidence of the efficacy of lean startup methods. What we find, however, is that not all activities are linked to success. Perhaps the most straightforward finding is that taking preorders is correlated with both subjective and objective measures of success. If entrepreneurs are able to complete their first sales prior to actually creating their products or services, then success seems much more likely. Venture success, in this case, is agnostic toward the level of innovation in the firm. As such, the critique of lean startup from Felin et al. (2019) as a method that helps orient entrepreneurs to ideas that can be quickly and transparently tested still requires further investigation.
The other relevant activities are those most aligned with customers. Interviewing customers ensures that entrepreneurs design businesses that serve customers rather than building something that no one wants ( Blank and Dorf, 2012 ). However, it is worth noting that interviewing customers must be done with an awareness of the entrepreneur's own cognitive biases ( Chen et al. , 2015 ). Furthermore, pivoting as a result of these discussions with customers also shows a response to customers' desires.
The most interesting aspect of our findings is likely the combination of activities across business planning and lean startup. While lean startup proponents might argue that “no business plan survives its first contact with customers” ( Blank and Dorf, 2012 , p. 53), the act of writing a business plan is correlated with success. It is worth noting that the separation between lean startup and business planning may be a false dichotomy. The underlying activities are not mutually exclusive and do not seem to be detrimental to each other. It is entirely possible, and based on these results advisable, that an entrepreneur would interview customers throughout the process of creating a business plan and use customer feedback to alter both the plan and the business itself. Furthermore, taking customer preorders serves to solidify the relationship between customers and the firm which would only improve that communication.
Limitations
In order to create one of the first quantitative, empirical investigations of business planning and lean startup practices, some tradeoffs needed to be made. We believe that while these limitations may restrict the strength of some of our findings, the direct nature of our approach offers a contribution to the ongoing conversations among scholars and practitioners.
Our sample size is 120. Obviously, a larger sample may lead to more robust and generalizable results. Furthermore, we gathered the sample using two different methods and controlling for the sample method was a significant predictor. We leave it to further research to expand upon our findings and investigate various entrepreneurial samples for differences that may arise.
One of our dependent variables was a subjective measure of success, which may be considered a weakness. We used this measure given the variety of preferred outcomes an entrepreneur may be pursuing – financial objectives, personal objectives, or mission-based objectives. Our other dependent variable was an objective measure of growth across three categories and serves to bolster confidence in the subjective measure.
Another area of concern may be common method variance given that we collected both independent variables and dependent variables from the same instrument. To address this concern, we collected data from individual entrepreneurs that all represented different companies and utilized two different samples so as to minimize the issues that may arise from common method variance ( Chang et al. , 2010 ). Lastly, our independent variables are more objective. For example, writing a business plan is a discrete event as is creating a prototype. For these reasons, we do not believe the common method variance is a major concern for this study.
One other potential weakness is the degree to which entrepreneurs actually utilized the activities of lean startup or business planning. The weighting scheme we employed aims to address this issue by weighting the degree to which entrepreneurs found each activity useful. However, we cannot be sure whether or not an entrepreneur executed the given activity well and this variability goes uncaptured in our study. Quantitative studies like this one will typically suffer from this limitation but case studies may be able to overcome these weaknesses (see Ghezzi et al. , 2015 ).
Finally, our design is cross sectional and does not allow us to make causal inferences. We can only imply the relationship between our independent and dependent variables. Our hope is this is a first step to future research which may be better able to test the causality of the various aspects of business planning and lean startup as they relate to entrepreneurial success.
Implications for research and practice
This manuscript has important implications for research and practice. With respect to research, we have demonstrated that aspects of business planning and lean startup both are associated with success. Furthermore, entrepreneurs seem unlikely to enact either business planning or lean startup wholesale but are likely to pursue individual aspects of these concepts. Future research can investigate how entrepreneurs select between activities as well as how training and education regarding these practices impact the entrepreneurs' choice. The training and education surrounding the entrepreneur represent aspects of the organizing context ( Johannisson, 2011 ), which influence how entrepreneurs construct their firms. Therefore, future research could add further institutional aspects or conduct randomized controlled trials to see the impact of these practices in the organizing context.
In terms of implications for practice, this research highlights the use of a variety of activities when it comes to entrepreneurial success. Some of the activities from both lean startup and business planning are useful for entrepreneurs. This also offers insight for educators as they seek to equip the next generation of entrepreneurs. Educators can offer potential entrepreneurs a wide range of activities without prognosticating one aspect of the false dichotomy between lean startup and business planning.
In this paper, we provide one of the first quantitative empirical studies investigating lean startup methods and business planning. In breaking down these areas, we undermine the false dichotomy between these two startup tools. Our findings demonstrate that truly understanding customers through preorders and interviews can lead to better business plans and better pivots. Ultimately, this results in firms with a greater chance of success. Understanding the variety of activities that entrepreneurs can pursue helps entrepreneurs and educators increase the chances of success for new businesses.
Correlations
Summary regression results for the growth DV
We do not believe that business planning exists as a latent construct necessarily comprised of these activities, but rather each of these activities are potential components of the concept referred to as “business planning” in prior research.
Similar to business planning activities, we believe that lean startup is not a latent construct but rather these activities in some combination is what is meant when practitioners and scholars refer to lean startup. As such we test each of the activities individually rather than as a construct.
Following the extant guidelines on regression assumptions ( Osborne and Waters, 2002 ), we tested our model to ensure the regression assumptions were met. First, to check if our error terms ( Flatt and Jacobs, 2019 ) are normally distributed, the P - P plot suggests normality as the plot is largely linear. Second, to check for a linear relationship between the independent and dependent variable, our residual plot showed a linear relationship. Third, as our variables were not latent, there is no concern for measurement error for this approach. However, we did follow best practices suggested by Flatt and Jacobs (2019) and tested the Durbin–Watson statistic. Our value for this measure is 1.5 and their guidelines are that this statistic should be close to 2. Values between 1.2 and 1.6 represent only a minor violation of the statistical independence of error terms. Finally, to address the assumption of homoscedasticity, inspection of our standardized residuals showed our residuals scattered around the 0 (horizontal line). Therefore, for our dependent variable of success, we can feel comfortable our data meets the assumptions of linear regression.
As this dependent variable was analyzed using logistic regression, we analyzed our data following best practices from Garson (2012) . First, our dependent variable is dichotomous. Second our scatterplot showed no outliers in our data. Third, the correlation table showed no evidence for multicollinearity as no correlations were above 0.9 ( Tabachnick et al. , 2007 ). Hence, we feel our data meets the assumptions for logistic regression.
Appendix Qualtrics Survey
[Business Background]
Started (or am starting it) myself
When you first started pursuing the business, how many people were on the founding team (including yourself)?
High Tech Startup (External/Venture funded)
Steady Growth Business (Internally/Self-funded)
Lifestyle Business
Business Idea
Decision to Start a Business
Occurred Together
Month (1–12)
Year (YYYY)
[Lean Start Up, Business Planning Practices]
Interviewed potential customers
Created a prototype
Showed a prototype to potential customers for feedback
Conducted an experiment to better understand some portion of your business
Wrote a business plan
Accepted money for pre-orders
Used customer feedback to alter the direction of your business ("pivoted")
Gathered secondary data on industry statistics or trends
Shared your business plan with people outside the company for feedback
Shared your business plan with people outside the company for funding
[Demographics]
How old are you? 0.5
Prefer not to answer
Black or African American
American Indian or Alaska Native
Native Hawaiian or Pacific Islander
Living with a partner
Never married
Up to 8th grade
Some High School
High School Diploma
Some College
Associate's Degree
Bachelor's Degree
Some Graduate School
Master's Degree
More than 1
[Success Criteria]
My business is a success
Increased Annual Revenue
Increased Annual Customers
Increased Number of Employees
Thank you for completing the survey!
Ajzen , I. ( 1985 ), “ From intentions to actions: a theory of planned behavior ”, Action Control , Springer , Berlin, Heidelberg , pp. 11 - 39 .
Ansoff , H.I. ( 1991 ), “ Critique of Henry Mintzberg's ‘The design school: reconsidering the basic premises of strategic management’ ”, Strategic Management Journal , Vol. 12 No. 6 , pp. 449 - 461 .
Arend , R. , Sarooghi , H. and Burkemper , A. ( 2015 ), “ Effectuation as ineffectual? Applying the 3E theory-assessment framework to a proposed new theory of entrepreneurship ”, Academy of Management , Vol. 40 No. 4 , pp. 630 - 651 .
Beaver , G. ( 2002 ), Small Business, Entrepreneurship and Enterprise Development , Pearson Education , Harlow .
Besser , T.L. ( 1999 ), “ Community involvement and the perception of success among small business operators in small towns ”, Journal of Small Business Management , Vol. 37 No. 4 , pp. 16 - 29 .
Blank , S. ( 2013 ), “ Why the lean start-up changes everything ”, Harvard Business Review , Vol. 91 No. 5 , pp. 64 - 72 .
Blank , S. and Dorf , B. ( 2012 ), “ The startup owner's manual ”, The Step-by-step Guide for Building a Great Company , Vol. 1 .
Bliemel , M. ( 2014 ), “ Getting entrepreneurship education out of the classroom and into students’ heads ”, Entrepreneurship Research Journal , Vol. 4 No. 2 , pp. 237 - 260 .
Bortolini , R.F. , Nogueira Cortimiglia , M. , Danilevicz , A.D.M.F. and Ghezzi , A. ( 2018 ), “ Lean startup: a comprehensive historical review ”, Management Decision . doi: 10.1108/MD-07-2017-0663 .
Brinckmann , J. , Grichnik , D. and Kapsa , D. ( 2010 ), “ Should entrepreneurs plan or just storm the castle? A meta-analysis on contextual factors impacting the business planning–performance relationship in small firms ”, Journal of Business Venturing , Vol. 25 No. 1 , pp. 24 - 40 .
Brinckmann , J. , Dew , N. , Read , S. , Mayer-Haug , K. and Grichnik , D. ( 2019 ), “ Of those who plan: a meta-analysis of the relationship between human capital and business planning ”, Long Range Planning , Vol. 52 No. 2 , pp. 173 - 188 .
Burke , A. , Fraser , S. and Greene , F. ( 2010 ), “ The multiple effects of business planning on new venture performance ”, Journal of Management Studies , Vol. 47 No. 3 , pp. 391 - 415 .
Burns , B.L. , Barney , J.B. , Angus , R.W. and Herrick , H.N. ( 2016 ), “ Enrolling stakeholders under conditions of risk and uncertainty ”, Strategic Entrepreneurship Journal , Vol. 10 No. 1 , pp. 97 - 106 .
Camuffo , A. , Cordova , A. , Gambardella , A. and Spina , C. ( 2019 ), “ A scientific approach to entrepreneurial decision making: evidence from a randomized control trial ”, Management Science . doi: 10.1287/mnsc.2018.3249 .
Chang , S.J. , Van Witteloostuijn , A. and Eden , L. ( 2010 ), “ From the editors: common method variance in international business research ”, Journal of International Business Studies , Vol. 41 No. 2 , pp. 178 - 184 .
Chaston , I. ( 2008 ), “ Small creative industry firms: a development dilemma? ”, Management Decision , Vol. 46 No. 6 , pp. 819 - 831 .
Chen , T. , Simon , M. , Kim , J. and Poploskie , B. ( 2015 ), “ Out of the building, into the fire: an analysis of cognitive biases during entrepreneurial interviews ”, New England Journal of Entrepreneurship , Vol. 18 No. 1 , pp. 59 - 70 .
Contigiani , A. and Levinthal , D. ( 2019 ), “ Situating the construct of lean startup: adjacent ‘Conversations’ and possible future directions ”, Industrial and Corporate Change , Vol. 28 No. 3 , pp. 551 - 564 .
Dawes , J. ( 1999 ), “ The relationship between subjective and objective company performance measures in market orientation research: further empirical evidence ”, Marketing Bulletin - Department of Marketing Massey University , Vol. 10 , pp. 66 - 75 .
De Clercq , D. and Voronov , M. ( 2009 ), “ Toward a practice perspective of entrepreneurship entrepreneurial legitimacy as habitus ”, International Small Business Journal , Vol. 27 No. 4 , pp. 395 - 419 .
Dean , J. and Sharfman , M. ( 1996 ), “ Does decision process matter? A study of strategic decision-making effectiveness ”, Academy of Management Journal , Vol. 39 No. 2 , pp. 368 - 392 .
Delmar , F. and Shane , S. ( 2003 ), “ Does business planning facilitate the development of new ventures? ”, Strategic Management Journal , Vol. 24 No. 12 , pp. 1165 - 1185 .
Felin , T. , Gambardella , A. , Stern , S. and Zenger , T. ( 2019 ), “ Lean startup and the business model: experimentation revisited ”, Forthcoming in Long Range Planning (Open Access), available at SSRN: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3427084 (accessed 29 June 2019) .
Fisher , R. , Maritz , A. and Lobo , A. ( 2014 ), “ Evaluating entrepreneurs' perception of success: development of a measurement scale ”, International Journal of Entrepreneurial Behavior and Research , Vol. 20 No. 5 , pp. 478 - 492 .
Flatt , C. and Jacobs , R.L. ( 2019 ), “ Principle assumptions of regression analysis: testing, techniques, and statistical reporting of imperfect data sets ”, Advances in Developing Human Resources , Vol. 21 No. 4 , pp. 484 - 502 .
Forbes , D.P. ( 2007 ), “ Reconsidering the strategic implications of decision comprehensiveness ”, Academy of Management Review , Vol. 32 No. 2 , pp. 361 - 376 .
Frederiksen , D. and Brem , A. ( 2017 ), “ How do entrepreneurs think they create value? A scientific reflection of Eric Ries' lean startup approach ”, International Entrepreneurship and Management Journal , Vol. 13 No. 1 , pp. 169 - 189 .
Garson , G.D. ( 2012 ), Logistic Regression: Binomial and Multinomial , Statistical Associates Publishers , Asheboro, NC .
Ghezzi , A. ( 2019 ), “ Digital Startups and the adoption and implementation of Lean Startup approaches: effectuation, bricolage and opportunity creation in practice ”, Technological Forecasting and Social Change , Vol. 146 , pp. 945 - 960 , doi: 10.1016/j.techfore.2018.09.017 .
Ghezzi , A. , Cavallaro , A. , Rangone , A. and Balocco , R. ( 2015 ), “ On business models, resources and exogenous (dis) continuous innovation: evidences from the mobile applications industry ”, International Journal of Technology Management , Vol. 68 Nos 1-2 , pp. 21 - 48 .
Greene , F. and Hopp , C. ( 2017 ), “ Are formal planners more likely to achieve new venture viability? A counterfactual model and analysis ”, Strategic Entrepreneurship Journal , Vol. 11 No. 1 , pp. 36 - 60 .
Gruber , M. ( 2007 ), “ Uncovering the value of planning in new venture creation: a process and contingency perspective ”, Journal of Business Venturing , Vol. 22 No. 6 , pp. 782 - 807 .
Hechavarría , D.M. and Welter , C. ( 2015 ), “ Opportunity types, social entrepreneurship and innovation: evidence from the panel study of entrepreneurial dynamics ”, The International Journal of Entrepreneurship and Innovation , Vol. 16 No. 4 , pp. 237 - 251 .
Honig , B. ( 2004 ), “ Entrepreneurship education: toward a model of contingency-based business planning ”, The Academy of Management Learning and Education , Vol. 3 No. 3 , pp. 258 - 273 .
Honig , B. and Karlsson , T. ( 2004 ), “ Institutional forces and the written business plan ”, Journal of Management , Vol. 30 No. 1 , pp. 29 - 48 .
Honig , B. and Samuelsson , M. ( 2012 ), “ Planning and the entrepreneur: a longitudinal examination of nascent entrepreneurs in Sweden ”, Journal of Small Business Management , Vol. 50 No. 3 , pp. 365 - 388 .
Honig , B. and Samuelsson , M. ( 2014 ), “ Data replication and extension: a study of business planning and venture-level performance ”, Journal of Business Venturing Insights , Vols 1-2 Nos 1-2 , pp. 18 - 25 .
Jacobs , S. , Cambre , B. , Huysentruyt , M. and Schramme , A. ( 2016 ), “ Multiple pathways to success in small creative businesses: the case of Belgian furniture designers ”, Journal of Business Research , Vol. 69 No. 11 , pp. 5461 - 5466 .
Jennings , P. and Beaver , G. ( 1997 ), “ The performance and competitive advantage of small firms: a management perspective ”, International Small Business Journal , Vol. 15 No. 2 , pp. 63 - 75 .
Johannisson , B. ( 2011 ), “ Towards a practice theory of entrepreneuring ”, Small Business Economics , Vol. 36 No. 2 , pp. 135 - 150 .
Karlsson , T. and Honig , B. ( 2007 ), “ Norms surrounding business plans and their effect on entrepreneurial behavior ”, Frontier of Entrepreneurship Research , Vol. 27 No. 22 , pp. 1 - 22 .
Karlsson , T. and Honig , B. ( 2009 ), “ Judging a business by its cover: an institutional perspective on new ventures and the business plan ”, Journal of Business Venturing , Vol. 24 No. 1 , pp. 27 - 45 .
Katz , J.A. , Hanke , R. , Maidment , F. , Weaver , K.M. and Alpi , S. ( 2016 ), “ Proposal for two model undergraduate curricula in entrepreneurship ”, International Entrepreneurship and Management Journal , Vol. 12 No. 2 , pp. 487 - 506 .
Keating , A. , Geiger , S. and McLoughlin , D. ( 2014 ), “ Riding the practice waves: social resourcing practices during new venture development ”, Entrepreneurship: Theory and Practice , Vol. 38 , pp. 1207 - 1235 .
Keith , N. , Unger , J.M. , Rauch , A. and Frese , M. ( 2016 ), “ Informal learning and entrepreneurial success: a longitudinal study of deliberate practice among small business owners ”, Applied Psychology , Vol. 65 No. 3 , pp. 515 - 540 .
Ladd , T. ( 2016 ), “ The limits of the lean startup method ”, Harvard Business Review , Vol. 94 No. 3 , pp. 2 - 3 .
Mason , C. , Twomey , J. , Wright , D. and Whitman , L. ( 2018 ), “ Predicting engineering student attrition risk using a probabilistic neural network and comparing results with a backpropagation neural network and logistic regression ”, Research in Higher Education , Vol. 59 No. 3 , pp. 382 - 400 .
Mintzberg , H. ( 1994 ), “ The fall and rise of strategic planning ”, Harvard Business Review , Vol. 72 No. 1 , pp. 107 - 114 .
Mintzberg , H. and Waters , J.A. ( 1985 ), “ Of strategies, deliberate and emergent ”, Strategic Management Journal , Vol. 6 No. 3 , pp. 257 - 272 .
Osborne , J.W. and Waters , E. ( 2002 ), “ Four assumptions of multiple regression that researchers should always test ”, Practical Assessment, Research, and Evaluation , Vol. 8 No. 1 , pp. 1 - 5, 2 , doi: 10.7275/r222-hv23 .
Priem , R.L. , Rasheed , A.M.A. and Kotulic , A.G. ( 1995 ), “ Rationality in strategic decision processes, environmental dynamism and firm performance ”, Journal of Management , Vol. 21 No. 5 , pp. 913 - 929 .
Reymen , I.M.M.J. , Andries , P. , Berends , H. , Mauer , R. , Stephan , U. and Burg , E. ( 2015 ), “ Understanding dynamics of strategic decision making in venture creation: a process study of effectuation and causation ”, Strategic Entrepreneurship Journal , Vol. 9 No. 4 , pp. 351 - 379 .
Richbell , S.M. , Watts , H.D. and Wardle , P. ( 2006 ), “ Owner-managers and business planning in the small firm ”, International Small Business Journal , Vol. 24 No. 5 , pp. 496 - 514 .
Ries , E. ( 2011 ), The Lean Startup: How Today's Entrepreneurs Use Continuous Innovation to Create Radically Successful Businesses , Crown Business , New York: New York .
Sarasvathy , S.D. ( 2001 ), “ Causation and effectuation: toward a theoretical shift from economic inevitability to entrepreneurial contingency ”, The Academy of Management Review , Vol. 26 No. 2 , pp. 243 - 263 .
Sarasvathy , S.D. and Dew , N. ( 2008 ), “ Effectuation and over-trust: debating goel and karri ”, Entrepreneurship: Theory and Practice , Vol. 32 No. 4 , pp. 727 - 737 .
Shane , S. , Locke , E.A. and Collins , C.J. ( 2003 ), “ Entrepreneurial motivation ”, Human Resource Management Review , Vol. 13 No. 2 , pp. 257 - 279 .
Shepherd , D. and Gruber , M. ( 2020 ), “ The lean startup framework: closing the academic-practitioner divide ”, Entrepreneurship: Theory and Practice . doi: 10.1177/1042258719899415 .
Tabachnick , B.G. , Fidell , L.S. and Ullman , J.B. ( 2007 ), Using Multivariate Statistics , Pearson , Boston, MA , Vol. 5 , pp. 481 - 498 .
Trimi , S. and Berbegal-Mirabent , J. ( 2012 ), “ Business model innovation in entrepreneurship ”, International Entrepreneurship and Management Journal , Vol. 8 No. 4 , pp. 449 - 465 .
Van Dyne , L. and LePine , J.A. ( 1998 ), “ Helping and voice extra-role behaviors: evidence of construct and predictive validity ”, Academy of Management Journal , Vol. 41 No. 1 , pp. 108 - 119 .
Walker , E. and Brown , A. ( 2004 ), “ What success factors are important to small business owners? ”, International Small Business Journal , Vol. 22 No. 6 , pp. 577 - 594 .
Welter , C. and Kim , S. ( 2018 ), “ Effectuation under risk and uncertainty: a simulation model ”, Journal of Business Venturing , Vol. 33 No. 1 , pp. 100 - 116 .
Welter , C. , Mauer , R. and Wuebker , R.J. ( 2016 ), “ Bridging behavioral models and theoretical concepts: effectuation and bricolage in the opportunity creation framework ”, Strategic Entrepreneurship Journal , Vol. 10 No. 1 , pp. 5 - 20 .
Wood , M.S. and McKinley , W. ( 2010 ), “ The production of entrepreneurial opportunity: a constructivist perspective ”, Strategic Entrepreneurship Journal , Vol. 4 No. 1 , pp. 66 - 84 .
Wood , M.S. , Palich , L.E. and Browder , R.E. ( 2018 ), “ Full steam ahead or abandon ship? An empirical investigation of complete pivot decisions ”, Journal of Small Business Management , Vol. 17 No. 4 , pp. 351 - 24 .
Yang , X. , Sun , S.L. and Zhao , X. ( 2018 ), “ Search and execution: examining the entrepreneurial cognitions behind the lean startup model ”, Small Business Economics , pp. 1 - 13 .
York , J. and Danes , J. ( 2014 ), “ Customer development, innovation, and decision-making biases in the lean startup ”, Journal of Small Business Strategy , Vol. 24 No. 2 , pp. 21 - 39 .
Acknowledgements
A portion of this research was funded by the Downing Scholars research grant at Xavier University.
Corresponding author
Related articles, we’re listening — tell us what you think, something didn’t work….
Report bugs here
All feedback is valuable
Please share your general feedback
Join us on our journey
Platform update page.
Visit emeraldpublishing.com/platformupdate to discover the latest news and updates
Questions & More Information
Answers to the most commonly asked questions here

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 5 – Business Planning
Business planning is an important precursor to action in new ventures. By helping firm founders to make decisions, to balance resource supply and demand, and to turn abstract goals into concrete operational steps, business planning reduces the likelihood of venture disbanding and accelerates product development and venture organizing activity. – Delmar and Shane (2003, p. 1165) We always plan too much and always think too little. We resent a call to thinking and hate unfamiliar argument that does not tally with what we already believe or would like to believe. – Joseph Schumpeter Trying to predict the future is like trying to drive down a country road at night with no lights while looking out the back window. – Peter Drucker
Learning Objectives
After completing this chapter you will be able to
- Describe the purposes of business planning
- Describe common business planning principles
- List and explain the elements of the business plan development process outlined in this book
- Explain the purposes of each of the elements of the business plan development process outlined in this book
- Explain how applying the business plan development process outlined in this book can aid in developing a business plan that will meet entrepreneurs’ goals
- Describe general business planning guidelines and format
This chapter describes the purposes of business planning, the general concepts related to business planning, and guidelines and a format for a comprehensive business plan.
Business Planning Purposes
Business plans are developed for both internal and external purposes. Internally, entrepreneurs develop business plans to help put the pieces of their business together. The most common external purpose for a business plan is to raise capital.
Internal Purposes
- defines the vision for the company
- establishes the company’s strategy
- describes how the strategy will be implemented
- provides a framework for analysis of key issues
- provides a plan for the development of the business
- is a measurement and control tool
- helps the entrepreneur to be realistic and to put theories to the test
External Purposes
The business plan is often the main method of describing a company to external audiences such as potential sources for financing and key personnel being recruited. It should assist outside parties to understand the current status of the company, its opportunities, and its needs for resources such as capital and personnel. It also provides the most complete source of information for valuation of the business.
Business Planning Principles
Business plan communication principles.
As Hindle and Mainprize (2006) note, business plan writers must strive to communicate their expectations about the nature of an uncertain future. However, the liabilities of newness make communicating the expected future of new ventures difficult (more so than for existing businesses). They outline five communications principles:
- Translation of your vision of the venture and how it will perform into a format compatible with the expectations of the readers
- you have identified and understood the key success factors and risks
- the projected market is large and you expect good market penetration
- you have a strategy for commercialization, profitability, and market domination
- you can establish and protect a proprietary and competitive position
- Anchoring key events in the plan with specific financial and quantitative values
- your major plan objectives are in the form of financial targets
- you have addressed the dual need for planning and flexibility
- you understand the hazards of neglecting linkages between certain events
- you understand the importance of quantitative values (rather than just chronological dates)
- Nothing lasts forever—things can change to impact the opportunity: tastes, preferences, technological innovation, competitive landscape
- the new combination upon which venture is built
- magnitude of the opportunity or market size
- market growth trends
- venture’s value from the market (% of market share proposed or market share value in dollars)
- Four key aspects describing context within which new venture is intended to function (internal and external environment)
- how the context will help or hinder the proposal
- how the context may change & affect the business & the range of flexibility or response that is built into the venture
- what management can or will do in the event the context turns unfavourable
- what management can do to affect the context in a positive way
- Brief and clear statement of how an idea actually becomes a business that creates value
- Who pays, how much, and how often?
- The activities the company must perform to produce its product, deliver it to its customers and earn revenue
- And be able to defend assertions that the venture is attractive and sustainable and has a competitive edge
Business Plan Credibility Principles
Business plan writers must strive to project credibility (Hindle & Mainprize, 2006), so t here must be a match between what the entrepreneurship team (resource seekers) needs and what the investors (resource providers) expect based on their criteria. A take it or leave it approach (i.e. financial forecasts set in concrete) by the entrepreneurship team has a high likelihood of failure in terms of securing resources. Hindle and Mainprize (2006) outline five principles to help entrepreneurs project credibility:
- Without the right team, nothing else matters.
- What do they know?
- Who do they know?
- How well are they known?
- sub-strategies
- ad-hoc programs
- specific tactical action plans
- Claiming an insuperable lead or a proprietary market position is naïve.
- Anticipate several moves in advance
- View the future as a movie vs. snapshot
- Key assumptions related to market size, penetration rates, and timing issues of market context outlined in the business plan should link directly to the financial statements.
- Income and cash flow statements must be preceded by operational statements setting forth the primary planning assumptions about market sizes, sales, productivity, and basis for the revenue estimate.
- If the main purpose is to enact a harvest, then the business plan must create a value-adding deal structure to attract investors.
- Common things: viability, profit potential, downside risk, likely life-cycle time, potential areas for dispute or improvement
General Business Plan Guidelines
Many businesses must have a business plan to achieve their goals. The following are some basic guidelines for business plan development.
- A standard format helps the reader understand that the entrepreneur has thought everything through, and that the returns justify the risk.
- Binding the document ensures that readers can easily go through it without it falling apart.
- everything is completely integrated: the written part must say exactly the same thing as the financial part
- all financial statements are completely linked and valid (make sure all balance sheets validly balance)
- the document is well formatted (layout makes document easy to read and comprehend—including all diagrams, charts, statements, and other additions)
- everything is correct (there are NO spelling, grammar, sentence structure, referencing, or calculation errors)
- It is usually unnecessary—and even damaging—to state the same thing more than once. To avoid unnecessarily duplicating information, you should combine sections and reduce or eliminate duplication as much as possible.
- all the necessary information is included to enable readers to understand everything in your document
- For example, if your plan says something like “there is a shortage of 100,000 units with competitors currently producing 25,000. We can help fill this huge gap in demand with our capacity to produce 5,000 units,” a reader is left completely confused. Does this mean there is a total shortage of 100,000 units, but competitors are filling this gap by producing 25,000 per year (in which case there will only be a shortage for four years)? Or, is there an annual shortage of 100,000 units with only 25,000 being produced each year, in which case the total shortage is very high and is growing each year? You must always provide the complete perspective by indicating the appropriate time frame, currency, size, or another measurement.
- if you use a percentage figure, you indicate to what it refers, otherwise the figure is completely useless to a reader.
- This can be solved by indicating up-front in the document the currency in which all values will be quoted. Another option is to indicate each time which currency is being used, and sometimes you might want to indicate the value in more than one currency. Of course, you will need to assess the exchange rate risk to which you will be exposed and describe this in your document.
- If a statement is included that presents something as a fact when this fact is not generally known, always indicate the source. Unsupported statements damage credibility
- Be specific. A business plan is simply not of value if it uses vague references to high demand, carefully set prices, and other weak phrasing. It must show hard numbers (properly referenced, of course), actual prices, and real data acquired through proper research. This is the only way to ensure your plan is considered credible.
Developing a High Power Business Plan
The business plan development process described next has been extensively tested with entrepreneurship students and has proven to provide the guidance entrepreneurs need to develop a business plan appropriate for their needs; a high power business plan .
The Stages of Development
There are six stages involved with developing a high power business plan . These stages can be compared to a process for hosting a dinner for a few friends. A host hoping to make a good impression with their anticipated guests might analyze the situation at multiple levels to collect data on new alternatives for healthy ingredients, what ingredients have the best prices and are most readily available at certain times of year, the new trends in party appetizers, what food allergies the expected guests might have, possible party themes to consider, and so on. This analysis is the Essential Initial Research stage.
In the Business Model stage, the host might construct a menu of items to include with the meal along with a list of decorations to order, music to play, and costume themes to suggest to the guests. The mix of these kinds of elements chosen by the host will play a role in the success of the party.
The Initial Business Plan Draft stage is where the host rolls up his or her sleeves and begins to assemble make some of the food items, put up some of the decorations, send invitations, and generally get everything started for the party.
During this stage, the host will begin to realize that some plans are not feasible and that changes are needed. The required changes might be substantial, like the need to postpone the entire party and ultimately start over in a few months, or less drastic, like the need to change the menu when an invited guest indicates that they can’t eat food containing gluten. These changes are incorporated into the plan to make it realistic and feasible in the Making the Business Plan Realistic stage.
Making A Plan to Appeal to Stakeholders stage involves further changes to the party plan to make it more appealing to both the invited guests and to make it a fun experience for the host. For example, the host might learn that some of the single guests would like to bring dates and others might need to be able to bring their children to be able to attend. The host might be able to accommodate those desires or needs in ways that will also make the party more fun for them—maybe by accepting some guests’ offers to bring food or games, or maybe even hiring a babysitter to entertain and look after the children.
The final stage— Finishing the Business Plan— involves the host putting all of the final touches in place for the party in preparation for the arrival of the guests.

Figure 5 – Business Plan Development Process (Illustration by Lee A. Swanson)
Essential Initial Research
A business plan writer should analyze the environment in which they anticipate operating at each of the s ocietal , i ndustry , m arket , and f irm levels of analysis (see pages 51–60). This stage of planning, the e ssential initial research , is a necessary first step to better understand the trends that will affect their business and the decisions they must make to lay the groundwork for, and to improve their potential for success.
In some cases, much of the e ssential initial research should be included in the developing business plan as its own separate section to help build the case for readers that there is a market need for the business being considered and that it stands a good chance of being successful.
In other cases, a business plan will be stronger when the components of the e ssential initial research are distributed throughout the business plan as a way to provide support for the plans and strategies outlined in the business plan. For example, the industry or market part of the e ssential initial research might outline the pricing strategies used by identified competitors and might be best placed in the pricing strategy part of the business plan to support the decision made to employ a particular pricing strategy.
Business Model
Inherent in any business plan is a description of the business model chosen by the entrepreneur as the one that they feel will best ensure success. Based upon their essential initial research of the setting in which they anticipate starting their business (their analysis from stage one) an entrepreneur should determine how each element of their business model—including their revenue streams, cost structure, customer segments, value propositions, key activities, key partners, and so on—might fit together to improve the potential success of their business venture (see Chapter 4 – Business Models ).
For some types of ventures, at this stage an entrepreneur might launch a lean start-up (see page 68) and grow their business by continually pivoting, or constantly adjusting their business model in response to the real-time signals they get from the markets’ reactions to their business operations. In many cases, however, an entrepreneur will require a business plan. In those cases, their initial business model will provide the basis for that plan.
Of course, throughout this and all of the rounds in this process, the entrepreneur should seek to continually gather information and adjust the plans in response to the new knowledge they gather. As shown in Figure 8 by its enclosure in the progressive research box, the business plan developer might need conduct further research before finishing the business model and moving on to the initial business plan draft.
Initial Business Plan Draft
The Business Plan Draft stage involves taking the knowledge and ideas developed during the first two stages and organizing them into a business plan format. An approach preferred by many is to create a full draft of the business plan with all of the sections, including the front part with the business description, vision, mission, values, value proposition statement, preliminary set of goals, and possibly even a table of contents and lists of tables and figures all set up using the software features enabling their automatic generation. Writing all of the operations, human resources, marketing, and financial plans as part of the first draft ensures that all of these parts can be appropriately and necessarily integrated. The business plan will tell the story of a planned business startup in two ways by using primarily words along with some charts and graphs in the operations, human resources, and marketing plans and in a second way through the financial plan. Both ways must tell the same story.
The feedback loop shown in Figure 8 demonstrates that the business developer may need to review the business model. Additionally, as shown by its enclosure in the progressive research box, the business plan developer might need conduct further research before finishing the Initial Business Plan Draft stage and moving on to the Making Business Plan Realisticstage.
Making Business Plan Realistic
The first draft of a business plan will almost never be realistic. As the entrepreneur writes the plan, it will necessarily change as new information is gathered. Another factor that usually renders the first draft unrealistic is the difficulty in making certain that the written part—in the front part of the plan along with the operations, human resources, and marketing plans—tells the exact same story as the financial part does. This stage of work involves making the necessary adjustments to the plan to make it as realistic as possible.
The Making Business Plan Realistic stage has two possible feedback loops. The first goes back to the Initial Business Plan Draft stage in case the initial business plan needs to be significantly changed before it is possible to adjust it so that it is realistic. The second feedback loop circles back to the Business Model stage if the business developer need to rethink the business model. As shown in Figure 8 by its enclosure in the progressive research box, the business plan developer might need conduct further research before finishing the Making Business Plan Realistic stage and moving on to the Making Plan Appeal to Stakeholders stage.
Making Plan Appeal to Stakeholders and Desirable to the Entrepreneur
A business plan can be realistic without appealing to potential investors and other external stakeholders, like employees, suppliers, and needed business partners. It might also be realistic (and possibly appealing to stakeholders) without being desirable to the entrepreneur. During this stage the entrepreneur will keep the business plan realistic as they adjust plans to appeal to potential investors and to themselves.
If, for example, investors will be required to finance the business start, some adjustments might need to be relatively extensive to appeal to potential investors’ needs for an exit strategy from the business, to accommodate the rate of return they expect from their investments, and to convince them that the entrepreneur can accomplish all that is promised in the plan. In this case, and in others, the entrepreneur will also need to get what they want out of the business to make it worthwhile for them to start and run it. So, this stage of adjustments to the developing business plan might be fairly extensive, and they must be informed by a superior knowledge of what targeted investors need from a business proposal before they will invest. They also need to be informed by a clear set of goals that will make the venture worthwhile for the entrepreneur to pursue.
The caution with this stage is to balance the need to make realistic plans with the desire to meet the entrepreneur’s goals while avoiding becoming discouraged enough to drop the idea of pursuing the business idea. If an entrepreneur is convinced that the proposed venture will satisfy a valid market need, there is often a way to assemble the financing required to start and operate the business while also meeting the entrepreneur’s most important goals. To do so, however, might require significant changes to the business model.
One of the feedback loops shown in Figure 8 indicates that the business plan writer might need to adjust the draft business plan while ensuring that it is still realistic before it can be made appealing to the targeted stakeholders and desirable to the entrepreneur. The second feedback loop indicates that it might be necessary to go all the way back to the Business Model stage to re-establish the framework and plans needed to develop a realistic, appealing, and desirable business plan. Additionally, this stage’s enclosure in the progressive research box suggests that the business plan developer might need conduct further research.
Finishing the Business Plan
The final stage involves putting all of the important finishing touches on the business plan so that it will present well to potential investors and others. This involves making sure that the math and links between the written and financial parts are accurate. It also involves ensuring that all the needed corrections are made to the spelling, grammar, and formatting. The final set of goals should be written to appeal to the target readers and to reflect what the business plan says. An executive summary should be written and included as a final step.
General Business Plan Format
Include nice, catchy, professional, appropriate graphics to make it appealing for targeted readers
Executive summary
- Can be longer than normal executive summaries, up to three pages
- Write after remainder of plan is complete
- Includes information relevant to targeted readers as this is the place where they are most likely to form their first impressions of the business idea and decide whether they wish to read the rest of the plan
Table of Con t ents
List of tables.
Each table, figure, and appendix included in the plan must be referenced within the text of the plan so the relevance of each of these elements is clear.
List of Figures
Introduction.
- Describes the business concept
- Indicates the purpose of the plan
- Appeals to targeted readers
Business Idea
- May include description of history behind the idea and the evolution of the business concept if relevant
- Generally outlines what the owner intends for the venture to be
- Should inspire all members of the organization
- Should help stakeholders aspire to achieve greater things through the venture because of the general direction provided through the vision statement
- Should be very brief—a few sentences or a short paragraph
- Indicates what your organization does and why it exists—may describe the business strategy and philosophy
- Indicates the important values that will guide everything the business will do
- Outlines the personal commitments members of the organization must make, and what they should consider to be important
- Defines how people behave and interact with each other.
- Should help the reader understand the type of culture and operating environment this business intends to develop
Major Goals
- Describes the major organizational goals
- Specific, Measurable, Action-Oriented, Realistic, and Timely [SMART]
- Realistic, Understandable, Measurable, Believable, and Achievable [RUMBA]
- Perfectly aligns with everything in plan
Operating Environment
Trend analysis.
- Consider whether this is the right place for this analysis: it may be better positioned in, for example, the Financial Plan section to provide context to the analysis of the critical success factors, or in the Marketing Plan to help the reader understand the basis for the sales projections.
Industry Analysis
- Includes an analysis of the industry in which this business will operate
- consider whether this is the right place for this analysis: it may be better placed in, for example, the Marketing Plan to enhance the competitor analysis, or in the Financial Plan to provide context to the industry standard ratios in the Investment Analysis section
Operations Plan
- expressed as a set physical location
- expressed as a set of requirements and characteristics
- How large will your facility be and why must it be this size?
- How much will it cost to buy or lease your facility?
- What utility, parking, and other costs must you pay for this facility?
- What expansion plans must be factored into the facility requirements?
- What transportation and storage issues must be addressed by facility decisions?
- What zoning and other legal issues must you deal with?
- What will be the layout for your facility and how will this best accommodate customer and employee requirements?
- Given these constraints, what is your operating capacity (in terms of production, sales, etc.)?
- What is the workflow plan for your operation?
- What work will your company do and what work will you outsource?
Operations Timeline
- When will you make the preparations, such as registering the business name and purchasing equipment, to start the venture?
- When will you begin operations and make your first sales?
- When will other milestone events occur such as moving operations to a larger facility, offering a new product line, hiring new key employees, and beginning to sell products internationally?
- May include a graphical timeline showing when these milestone events have occurred and are expected to occur
Business Structure and other Set-up Elements
Somewhere in your business plan you must indicate what legal structure your venture will take. Your financial statements, risk management strategy, and other elements of your plan are affected by the type of legal structure you choose for your business:
- Sole Proprietorship
- Partnership
- Limited Partnership
- Corporation
- Cooperative
As part of your business set-up, you need to determine what kinds of control systems you should have in place, establish necessary relationships with suppliers and prior to your start-up, and generally deal with a list of issues like the following. Many of your decisions related to the following should be described somewhere in your business plan:
- Zoning, equipment prices, suppliers, etc.
- Lease terms, leasehold improvements, signage, pay deposits, etc.
- Getting business license, permits, etc.
- Setting up banking arrangements
- Setting up legal and accounting systems (or professionals)
- Ordering equipment, locks and keys, furniture, etc.
- Recruiting employees, set up payroll system, benefit programs, etc.
- Training employees
- Testing the products/services that will be offered
- Testing the systems for supply, sales, delivery, and other functions
- Deciding on graphics, logos, promotional methods, etc.
- Ordering business cards, letter head, etc.
- Setting up supplier agreements
- Buying inventory, insurance, etc.
- Revising business plan
- And many more things, including, when possible, attracting purchased orders in advance of start-up through personal selling (by the owner, a paid sales force, independent representatives, or by selling through brokers wholesalers, catalog houses, retailers), a promotional campaign, or other means
- What is required to start up your business, including the purchases and activities that must occur before you make your first sale?
- When identifying capital requirements for start-up, a distinction should be made between fixed capital requirements and working capital requirements.
Fixed Capital Requirements
- What fixed assets, including equipment and machinery, must be purchased so your venture can conduct its business?
- This section may include a start-up budget showing the machinery, equipment, furnishings, renovations, and other capital expenditures required prior to operations commencing.
- If relevant you might include information showing the financing required; fixed capital is usually financed using longer-term loans.
Working Capital Requirements
- What money is needed to operate the business (separately from the money needed to purchase fixed assets) including the money needed to purchase inventory and pay initial expenses?
- This section may include a start-up budget showing the cash required to purchase starting inventories, recruit employees, conduct market research, acquire licenses, hire lawyers, and other operating expenditures required prior to starting operations.
- If relevant you might include information showing the financing required … working capital is usually financed with operating loans, trade credit, credit card debt, or other forms of shorter-term loans.

Risk Management Strategies
- enterprise – liability exposure for things like when someone accuses your employees or products you sell of injuring them.
- financial – securing loans when needed and otherwise having the right amount of money when you need it
- operational – securing needed inventories, recruiting needed employees in tight labour markets, customers you counted on not purchasing product as you had anticipated, theft, arson, natural disasters like fires and floods, etc.
- avoid – choose to avoid doing something, outsource, etc.
- reduce – through training, assuming specific operational strategies, etc.
- transfer – insure against, outsource, etc.
- assume – self-insure, accept, etc.
Operating Processes
- What operating processes will you apply?
- How will you ensure your cash is managed effectively?
- How will you schedule your employees?
- How will you manage your inventories?
- If you will have a workforce, how will you manage them?
- How will you bill out your employee time?
- How will you schedule work on your contracts?
- How you will manufacture your product (process flow, job shop, etc.?)
- How will you maintain quality?
- How will you institute and manage effective financial monitoring and control systems that provide needed information in a timely manner?
- How will you manage expansion?
- May include planned layouts for facilities
Organizational Structure
- May include information on Advisory Boards or Board of Directors from which the company will seek advice or guidance or direction
- May include an organizational chart
- Can nicely lead into the Human Resources Plan
Human Resources Plan
- How do you describe your desired corporate culture?
- What are the key positions within your organization?
- How many employees will you have?
- What characteristics define your desired employees?
- What is your recruitment strategy? What processes will you apply to hire the employees you require?
- What is your leadership strategy and why have you chosen this approach?
- What performance appraisal and employee development methods will you use?
- What is your organizational structure and why is this the best way for your company to be organized?
- How will you pay each employee (wage, salary, commission, etc.)? How much will you pay each employee?
- What are your payroll costs, including benefits?
- What work will be outsourced and what work will be completed in-house?
- Have you shown and described an organizational chart?
Recruitment and Retention Strategies
- Includes how many employees are required at what times
- Estimates time required to recruit needed employees
- employment advertisements
- contracts with employment agency or search firms
- travel and accommodations for potential employees to come for interviews
- travel and accommodations for interviewers
- facility, food, lost time, and other interviewing costs
- relocation allowances for those hired including flights, moving companies, housing allowances, spousal employment assistance, etc.
- may include a schedule showing the costs of initial recruitment that then flows into your start-up expense schedules
Leadership and Management Strategies
- What is your leadership philosophy?
- Why is it the most appropriate leadership approach for this venture?
- What training is required because of existing rules and regulations?
- How will you ensure your employees are as capable as required?
- Health and safety (legislation, WHMIS, first aid, defibulators, etc.)
- Initial workplace orientation
- Financial systems
- Product features
Performance Appraisals
- How will you manage your performance appraisal systems?
Health and Safety
- Any legal requirements should be noted in this section (and also legal requirements for other issues that may be included in other parts of the plan)
Compensation
- Always completely justifies your planned employee compensation methods and amounts
- Always includes all components of the compensation (CPP, EI, holiday pay, etc.)
- Outlines how will you ensure both internal and external equity in your pay systems
- Describes any incentive-based pay or profit sharing systems planned
- May include a schedule here that shows the financial implications of your compensation strategy and supports the cash flow and income statements shown later
Key Personnel
- May include brief biographies of the key organizational people
Marketing Plan
- You must show evidence of having done proper research, both primary and secondary. If you make a statement of fact, you must back it up with properly referenced supporting evidence. If you indicate a claim is based on your own assumptions, you must back this up with a description as to how you came to the conclusion.
- It is a given that you must provide some assessment of the economic situation as it relates to your business. For example, you might conclude that the current economic crisis will reduce the potential to export your product and it may make it more difficult to acquire credit with which to operate your business. Of course, conclusions such as these should be matched with your assessment as to how your business will make the necessary adjustments to ensure it will thrive despite these challenges, or how it will take advantage of any opportunities your assessment uncovers.
- If you apply the Five Forces Model, do so in the way in which it was meant to be used to avoid significantly reducing its usefulness while also harming the viability of your industry analysis. This model is meant to be used to consider the entire industry—not a subcomponent of it (and it usually cannot be used to analyze a single organization).
- Your competitor analysis might fit within your assessment of the industry or it might be best as a section within your marketing plan. Usually a fairly detailed description of your competitors is required, including an analysis of their strengths and weaknesses. In some cases, your business may have direct and indirect competitors to consider. Be certain to maintain credibility by demonstrating that you fully understand the competitive environment.
- Assessments of the economic conditions and the state of the industry appear incomplete without accompanying appraisals outlining the strategies the organization can/should employ to take advantage of these economic and industry situations. So, depending upon how you have organized your work, it is usually important to couple your appraisal of the economic and industry conditions with accompanying strategies for your venture. This shows the reader that you not only understand the operating environment, but that you have figured out how best to operate your business within that situation.
- Have you done an effective analysis of your venture? (See the Organizational Analysis section below.)
Market Analysis
- Usually contains customer profiles, constructed through primary and secondary research, for each market targeted
- Contains detailed information on the major product benefits you will deliver to the markets targeted
- Describes the methodology used and the relevant results from the primary market research done
- If there was little primary research completed, justifies why it is acceptable to have done little of this kind of research and/or indicate what will be done and by when
- Includes a complete description of the secondary research conducted and the conclusions reached
- Define your target market in terms of identifiable entities sharing common characteristics. For example, it is not meaningful to indicate you are targeting Canadian universities. It is, however, useful to define your target market as Canadian university students between the ages of 18 and 25, or as information technology managers at Canadian universities, or as student leaders at Canadian universities. Your targeted customer should generally be able to make or significantly influence the buying decision.
- You must usually define your target market prior to describing your marketing mix, including your proposed product line. Sometimes the product descriptions in business plans seem to be at odds with the described target market characteristics. Ensure your defined target market aligns completely with your marketing mix (including product/service description, distribution channels, promotional methods, and pricing). For example, if the target market is defined as Canadian university students between the ages of 18 and 25, the product component of the marketing mix should clearly be something that appeals to this target market.
- Carefully choose how you will target potential customers. Should you target them based on their demographic characteristics, psychographic characteristics, or geographic location?
- You will need to access research to answer this question. Based on what you discover, you will need to figure out the optimum mix of pricing, distribution, promotions, and product decisions to best appeal to how your targeted customers make their buying decisions.
Competition
- However, this information might fit instead under the market analysis section.
- Describes all your direct competitors
- Describes all your indirect competitors
- If you can, includes a competitor positioning map to show where your product will be positioned relative to competitors’ products

Figure 6 – Competitor Positioning Map (Illustration by Lee A. Swanson)
- What distinguishes your business from that of your competitors in a way that will ensure your sales forecasts will be met?
- You must clearly communicate the answers to these questions in your business plan to attract the needed support for your business. One caution is that it may sound appealing to claim you will provide a superior service to the existing competitors, but the only meaningful judge of your success in this regard will be customers. Although it is possible some of your competitors might be complacent in their current way of doing things, it is very unlikely that all your competitors provide an inferior service to that which you will be able to provide.
Marketing Strategy
- Covers all aspects of the marketing mix including the promotional decisions you have made, product decisions, distribution decisions related to how you will deliver your product to the markets targeted, and pricing decisions
- Outlines how you plan to influence your targeted customers to buy from you (what is the optimum marketing mix, and why is this one better than the alternatives)
Organizational Analysis
- Leads in to your marketing strategy or is positioned elsewhere depending upon how your business plan is best structured
- If doing so, always ensure this analysis results in more than a simple list of internal strengths and weaknesses and external opportunities and threats. A SWOT analysis should always prove to the reader that there are organizational strategies in place to address each of the weaknesses and threats identified and to leverage each of the strengths and opportunities identified.
- An effective way to ensure an effective outcome to your SWOT Analysis is to apply a TOWS Matrix approach to develop strategies to take advantage of the identified strengths and opportunities while mitigating the weaknesses and threats. A TOWS Matrix evaluates each of the identified threats along with each of the weaknesses and then each of the strengths. It does the same with each of the identified opportunities. In this way strategies are developed by considering pairs of factors
- The TOWS Matrix is a framework with which to help you organize your thoughts into strategies. Most often you would not label a section of your business plan as a TOWS Matrix. This would not normally add value for the reader. Instead, you should describe the resultant strategies—perhaps while indicating how they were derived from your assessment of the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. For example, you could indicate that certain strategies were developed by considering how internal strengths could be employed toward mitigating external threats faced by the business.
Product Strategy
- If your product or service is standardized, you will need to compete on the basis of something else – like a more appealing price, having a superior location, better branding, or improved service. If you can differentiate your product or service you might be able to compete on the basis of better quality, more features, appealing style, or something else. When describing your product, you should demonstrate that you understand this.
Pricing Strategy
- If you intend to accept payment by credit card (which is probably a necessity for most companies), you should be aware of the fee you are charged as a percentage of the value of each transaction. If you don’t account for this you risk overstating your actual revenues by perhaps one percent or more.
- Sales forecasts must be done on at least a monthly basis if you are using a projected cash flow statement. These must be accompanied by explanations designed to establish their credibility for readers of your business plan. Remember that many readers will initially assume that your planned time frames are too long, your revenues are overstated, and you have underestimated your expenses. Well crafted explanations for all of these numbers will help establish credibility.
Distribution Strategy
- If you plan to use e-commerce, you should include all the costs associated with maintaining a website and accepting payments over the Internet.
Promotions Strategy
- If you are attracting customers away from competitors, how will these rivals respond to the threat you pose to them?
- If you intend to create new customers, how will you convince them to reallocate their dollars toward your product or service (and away from other things they want to purchase)?
- In what ways will you communicate with your targeted customers? When will you communicate with them? What specific messages do you plan to convey to them? How much will this promotions plan cost?
- If your entry into the market will not be a threat to direct competitors, it is likely you must convince potential customers to spend their money with you rather than on what they had previously earmarked those dollars toward. In your business plan you must demonstrate an awareness of these issues.
- Consider listing the promotional methods in rows on a spreadsheet with the columns representing weeks or months over probably about 18 months from the time of your first promotional expenditure. This can end up being a schedule that feeds the costs into your projected cash flow statement and from there into your projected income statements.
- If you phone or visit newspapers, radio stations, or television stations seeking advertising costs, you must go only after you have figured out details like on which days you would like to advertise, at what times on those days, whether you want your print advertisements in color, and what size of print advertisements you want.
- Carefully consider which promotional methods you will use. While using a medium like television may initially sound appealing, it is very expensive unless your ad runs during the non-prime times. If you think this type of medium might work for you, do a serious cost-benefit analysis to be sure.
- Some promotional plans are developed around newspaper ads, promotional pamphlets, printing business cards, and other more obvious mediums of promotion. Be certain to, include the costs of advertising in telephone directories, sponsoring a little league soccer team, producing personalized pens and other promotional client give-always, donating items to charity auctions, printing and mailing client Christmas cards, and doing the many things businesses find they do on-the-fly. Many businesses find it to be useful to join the local chamber of commerce and relevant trade organizations with which to network. Some find that setting a booth up at a trade fair helps launch their business.
- If you are concerned you might have missed some of these promotional expenses, or if you want to have a buffer in place in case you feel some of these opportunities are worthwhile when they arise, you should add some discretionary money to your promotional budget. A problem some companies get into is planning out their promotions in advance only to reallocate some of their newspaper advertisement money, for example, toward some of these other surprise purposes resulting in less newspaper advertising than had been intended.
Financial Plan
- It is nearly certain you will need to make monthly cash flow projections from business inception to possibly three years out. Your projections will show the months in which the activities shown on your fixed capital and working capital schedules will occur. This is nearly the only way to clearly estimate your working capital needs and, specifically, important things like the times when you will need to draw on or can pay down your operating loans and the months when you will need to take out longer-term loans with which to purchase your fixed assets. Without a tool like this you will be severely handicapped when talking with bankers about your expected needs. They will want to know how large of a line of credit you will need and when you anticipate needing to borrow longer-term money. It is only through doing cash flow projections will you be able to answer these questions. This information is also needed to determine things like the changes to your required loan payments and when you can take owner draws or pay dividends.
- Your projected cash flows are also used to develop your projected income statements and balance sheets.
Pro forma Cash Flow Statements
Pro forma income statements, pro forma balance sheets, investment analysis, projected financial ratios and industry standard ratios, critical success factors (sensitivity analysis).
Entrepreneurship and Innovation Toolkit Copyright © 2017 by Lee A. Swanson is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Table of Contents
What is a business plan, the advantages of having a business plan, the types of business plans, the key elements of a business plan, best business plan software, common challenges of writing a business plan, become an expert business planner, business planning: it’s importance, types and key elements.

Every year, thousands of new businesses see the light of the day. One look at the World Bank's Entrepreneurship Survey and database shows the mind-boggling rate of new business registrations. However, sadly, only a tiny percentage of them have a chance of survival.
According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, about 20% of small businesses fail in their first year, about 50% in their fifth year.
Research from the University of Tennessee found that 44% of businesses fail within the first three years. Among those that operate within specific sectors, like information (which includes most tech firms), 63% shut shop within three years.
Several other statistics expose the abysmal rates of business failure. But why are so many businesses bound to fail? Most studies mention "lack of business planning" as one of the reasons.
This isn’t surprising at all.
Running a business without a plan is like riding a motorcycle up a craggy cliff blindfolded. Yet, way too many firms ( a whopping 67%) don't have a formal business plan in place.
It doesn't matter if you're a startup with a great idea or a business with an excellent product. You can only go so far without a roadmap — a business plan. Only, a business plan is so much more than just a roadmap. A solid plan allows a business to weather market challenges and pivot quickly in the face of crisis, like the one global businesses are struggling with right now, in the post-pandemic world.
But before you can go ahead and develop a great business plan, you need to know the basics. In this article, we'll discuss the fundamentals of business planning to help you plan effectively for 2021.
Now before we begin with the details of business planning, let us understand what it is.
No two businesses have an identical business plan, even if they operate within the same industry. So one business plan can look entirely different from another one. Still, for the sake of simplicity, a business plan can be defined as a guide for a company to operate and achieve its goals.
More specifically, it's a document in writing that outlines the goals, objectives, and purpose of a business while laying out the blueprint for its day-to-day operations and key functions such as marketing, finance, and expansion.
A good business plan can be a game-changer for startups that are looking to raise funds to grow and scale. It convinces prospective investors that the venture will be profitable and provides a realistic outlook on how much profit is on the cards and by when it will be attained.
However, it's not only new businesses that greatly benefit from a business plan. Well-established companies and large conglomerates also need to tweak their business plans to adapt to new business environments and unpredictable market changes.
Before getting into learning more about business planning, let us learn the advantages of having one.
Since a detailed business plan offers a birds-eye view of the entire framework of an establishment, it has several benefits that make it an important part of any organization. Here are few ways a business plan can offer significant competitive edge.
- Sets objectives and benchmarks: Proper planning helps a business set realistic objectives and assign stipulated time for those goals to be met. This results in long-term profitability. It also lets a company set benchmarks and Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) necessary to reach its goals.
- Maximizes resource allocation: A good business plan helps to effectively organize and allocate the company’s resources. It provides an understanding of the result of actions, such as, opening new offices, recruiting fresh staff, change in production, and so on. It also helps the business estimate the financial impact of such actions.
- Enhances viability: A plan greatly contributes towards turning concepts into reality. Though business plans vary from company to company, the blueprints of successful companies often serve as an excellent guide for nascent-stage start-ups and new entrepreneurs. It also helps existing firms to market, advertise, and promote new products and services into the market.
- Aids in decision making: Running a business involves a lot of decision making: where to pitch, where to locate, what to sell, what to charge — the list goes on. A well thought-out business plan provides an organization the ability to anticipate the curveballs that the future could throw at them. It allows them to come up with answers and solutions to these issues well in advance.
- Fix past mistakes: When businesses create plans keeping in mind the flaws and failures of the past and what worked for them and what didn’t, it can help them save time, money, and resources. Such plans that reflects the lessons learnt from the past offers businesses an opportunity to avoid future pitfalls.
- Attracts investors: A business plan gives investors an in-depth idea about the objectives, structure, and validity of a firm. It helps to secure their confidence and encourages them to invest.
Now let's look at the various types involved in business planning.
Become a Business and Leadership Professional
- Top 10 skills in demand Business Analysis As A Skill In 2020
- 14% Growth in Jobs Of Business Analysis Profile By 2028
Business Analyst
- Industry-recognized certifications from IBM and Simplilearn
- Masterclasses from IBM experts
Post Graduate Program in Business Analysis
- Certificate from Simplilearn in collaboration with Purdue University
- Become eligible to be part of the Purdue University Alumni Association
Here's what learners are saying regarding our programs:
Assistant Consultant at Tata Consultancy Services , Tata Consultancy Services
My experience with Simplilearn has been great till now. They have good materials to start with, and a wide range of courses. I have signed up for two courses with Simplilearn over the past 6 months, Data Scientist and Agile and Scrum. My experience with both is good. One unique feature I liked about Simplilearn is that they give pre-requisites that you should complete, before a live class, so that you go there fully prepared. Secondly, there support staff is superb. I believe there are two teams, to cater to the Indian and US time zones. Simplilearn gives you the most methodical and easy way to up-skill yourself. Also, when you compare the data analytics courses across the market that offer web-based tutorials, Simplilearn, scores over the rest in my opinion. Great job, Simplilearn!
I was keenly looking for a change in my domain from business consultancy to IT(Business Analytics). This Post Graduate Program in Business Analysis course helped me achieve the same. I am proficient in business analysis now and am looking for job profiles that suit my skill set.
Business plans are formulated according to the needs of a business. It can be a simple one-page document or an elaborate 40-page affair, or anything in between. While there’s no rule set in stone as to what exactly a business plan can or can’t contain, there are a few common types of business plan that nearly all businesses in existence use.
Here’s an overview of a few fundamental types of business plans.
- Start-up plan: As the name suggests, this is a documentation of the plans, structure, and objections of a new business establishments. It describes the products and services that are to be produced by the firm, the staff management, and market analysis of their production. Often, a detailed finance spreadsheet is also attached to this document for investors to determine the viability of the new business set-up.
- Feasibility plan: A feasibility plan evaluates the prospective customers of the products or services that are to be produced by a company. It also estimates the possibility of a profit or a loss of a venture. It helps to forecast how well a product will sell at the market, the duration it will require to yield results, and the profit margin that it will secure on investments.
- Expansion Plan: This kind of plan is primarily framed when a company decided to expand in terms of production or structure. It lays down the fundamental steps and guidelines with regards to internal or external growth. It helps the firm to analyze the activities like resource allocation for increased production, financial investments, employment of extra staff, and much more.
- Operations Plan: An operational plan is also called an annual plan. This details the day-to-day activities and strategies that a business needs to follow in order to materialize its targets. It outlines the roles and responsibilities of the managing body, the various departments, and the company’s employees for the holistic success of the firm.
- Strategic Plan: This document caters to the internal strategies of the company and is a part of the foundational grounds of the establishments. It can be accurately drafted with the help of a SWOT analysis through which the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats can be categorized and evaluated so that to develop means for optimizing profits.
There is some preliminary work that’s required before you actually sit down to write a plan for your business. Knowing what goes into a business plan is one of them.
Here are the key elements of a good business plan:
- Executive Summary: An executive summary gives a clear picture of the strategies and goals of your business right at the outset. Though its value is often understated, it can be extremely helpful in creating the readers’ first impression of your business. As such, it could define the opinions of customers and investors from the get-go.
- Business Description: A thorough business description removes room for any ambiguity from your processes. An excellent business description will explain the size and structure of the firm as well as its position in the market. It also describes the kind of products and services that the company offers. It even states as to whether the company is old and established or new and aspiring. Most importantly, it highlights the USP of the products or services as compared to your competitors in the market.
- Market Analysis: A systematic market analysis helps to determine the current position of a business and analyzes its scope for future expansions. This can help in evaluating investments, promotions, marketing, and distribution of products. In-depth market understanding also helps a business combat competition and make plans for long-term success.
- Operations and Management: Much like a statement of purpose, this allows an enterprise to explain its uniqueness to its readers and customers. It showcases the ways in which the firm can deliver greater and superior products at cheaper rates and in relatively less time.
- Financial Plan: This is the most important element of a business plan and is primarily addressed to investors and sponsors. It requires a firm to reveal its financial policies and market analysis. At times, a 5-year financial report is also required to be included to show past performances and profits. The financial plan draws out the current business strategies, future projections, and the total estimated worth of the firm.
The importance of business planning is it simplifies the planning of your company's finances to present this information to a bank or investors. Here are the best business plan software providers available right now:
- Business Sorter
The importance of business planning cannot be emphasized enough, but it can be challenging to write a business plan. Here are a few issues to consider before you start your business planning:
- Create a business plan to determine your company's direction, obtain financing, and attract investors.
- Identifying financial, demographic, and achievable goals is a common challenge when writing a business plan.
- Some entrepreneurs struggle to write a business plan that is concise, interesting, and informative enough to demonstrate the viability of their business idea.
- You can streamline your business planning process by conducting research, speaking with experts and peers, and working with a business consultant.
Whether you’re running your own business or in-charge of ensuring strategic performance and growth for your employer or clients, knowing the ins and outs of business planning can set you up for success.
Be it the launch of a new and exciting product or an expansion of operations, business planning is the necessity of all large and small companies. Which is why the need for professionals with superior business planning skills will never die out. In fact, their demand is on the rise with global firms putting emphasis on business analysis and planning to cope with cut-throat competition and market uncertainties.
While some are natural-born planners, most people have to work to develop this important skill. Plus, business planning requires you to understand the fundamentals of business management and be familiar with business analysis techniques . It also requires you to have a working knowledge of data visualization, project management, and monitoring tools commonly used by businesses today.
Simpliearn’s Executive Certificate Program in General Management will help you develop and hone the required skills to become an extraordinary business planner. This comprehensive general management program by IIM Indore can serve as a career catalyst, equipping professionals with a competitive edge in the ever-evolving business environment.
What Is Meant by Business Planning?
Business planning is developing a company's mission or goals and defining the strategies you will use to achieve those goals or tasks. The process can be extensive, encompassing all aspects of the operation, or it can be concrete, focusing on specific functions within the overall corporate structure.
What Are the 4 Types of Business Plans?
The following are the four types of business plans:
Operational Planning
This type of planning typically describes the company's day-to-day operations. Single-use plans are developed for events and activities that occur only once (such as a single marketing campaign). Ongoing plans include problem-solving policies, rules for specific regulations, and procedures for a step-by-step process for achieving particular goals.
Strategic Planning
Strategic plans are all about why things must occur. A high-level overview of the entire business is included in strategic planning. It is the organization's foundation and will dictate long-term decisions.
Tactical Planning
Tactical plans are about what will happen. Strategic planning is aided by tactical planning. It outlines the tactics the organization intends to employ to achieve the goals outlined in the strategic plan.
Contingency Planning
When something unexpected occurs or something needs to be changed, contingency plans are created. In situations where a change is required, contingency planning can be beneficial.
What Are the 7 Steps of a Business Plan?
The following are the seven steps required for a business plan:
Conduct Research
If your company is to run a viable business plan and attract investors, your information must be of the highest quality.
Have a Goal
The goal must be unambiguous. You will waste your time if you don't know why you're writing a business plan. Knowing also implies having a target audience for when the plan is expected to get completed.
Create a Company Profile
Some refer to it as a company profile, while others refer to it as a snapshot. It's designed to be mentally quick and digestible because it needs to stick in the reader's mind quickly since more information is provided later in the plan.
Describe the Company in Detail
Explain the company's current situation, both good and bad. Details should also include patents, licenses, copyrights, and unique strengths that no one else has.
Create a marketing plan ahead of time.
A strategic marketing plan is required because it outlines how your product or service will be communicated, delivered, and sold to customers.
Be Willing to Change Your Plan for the Sake of Your Audience
Another standard error is that people only write one business plan. Startups have several versions, just as candidates have numerous resumes for various potential employers.
Incorporate Your Motivation
Your motivation must be a compelling reason for people to believe your company will succeed in all circumstances. A mission should drive a business, not just selling, to make money. That mission is defined by your motivation as specified in your business plan.
What Are the Basic Steps in Business Planning?
These are the basic steps in business planning:
Summary and Objectives
Briefly describe your company, its objectives, and your plan to keep it running.
Services and Products
Add specifics to your detailed description of the product or service you intend to offer. Where, why, and how much you plan to sell your product or service and any special offers.
Conduct research on your industry and the ideal customers to whom you want to sell. Identify the issues you want to solve for your customers.
Operations are the process of running your business, including the people, skills, and experience required to make it successful.
How are you going to reach your target audience? How you intend to sell to them may include positioning, pricing, promotion, and distribution.
Consider funding costs, operating expenses, and projected income. Include your financial objectives and a breakdown of what it takes to make your company profitable. With proper business planning through the help of support, system, and mentorship, it is easy to start a business.
Our Business And Leadership Courses Duration And Fees
Business And Leadership Courses typically range from a few weeks to several months, with fees varying based on program and institution.
Get Free Certifications with free video courses
Business and Leadership
Business Analysis Basics
Data Science & Business Analytics
Business Intelligence Fundamentals
Learn from Industry Experts with free Masterclasses
The Modern Day Business Analyst Role: AI Tools and Techniques for Success
Product Manager Role Breakdown: Skills, Career Paths, and Salaries
Career Information Session: Find Out How to Become a Business Analyst with IIT Roorkee
Recommended Reads
Business Intelligence Career Guide: Your Complete Guide to Becoming a Business Analyst
Corporate Succession Planning: How to Create Leaders According to the Business Need
Top Business Analyst Skills
Business Analytics Basics: A Beginner’s Guide
Financial Planning for Businesses Across the Globe
How to Become a Business Analyst
Get Affiliated Certifications with Live Class programs
- PMP, PMI, PMBOK, CAPM, PgMP, PfMP, ACP, PBA, RMP, SP, and OPM3 are registered marks of the Project Management Institute, Inc.
🎉 Celebrate Small Business Month:
25% Off Annual Plans! SAVE NOW
0 results have been found for “”
Return to blog home
What Is a Business Plan? Definition and Planning Essentials Explained
Posted february 21, 2022 by kody wirth.

What is a business plan? It’s the roadmap for your business. The outline of your goals, objectives, and the steps you’ll take to get there. It describes the structure of your organization, how it operates, as well as the financial expectations and actual performance.
A business plan can help you explore ideas, successfully start a business, manage operations, and pursue growth. In short, a business plan is a lot of different things. It’s more than just a stack of paper and can be one of your most effective tools as a business owner.
Let’s explore the basics of business planning, the structure of a traditional plan, your planning options, and how you can use your plan to succeed.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a document that explains how your business operates. It summarizes your business structure, objectives, milestones, and financial performance. Again, it’s a guide that helps you, and anyone else, better understand how your business will succeed.
Why do you need a business plan?
The primary purpose of a business plan is to help you understand the direction of your business and the steps it will take to get there. Having a solid business plan can help you grow up to 30% faster and according to our own 2021 Small Business research working on a business plan increases confidence regarding business health—even in the midst of a crisis.
These benefits are directly connected to how writing a business plan makes you more informed and better prepares you for entrepreneurship. It helps you reduce risk and avoid pursuing potentially poor ideas. You’ll also be able to more easily uncover your business’s potential. By regularly returning to your plan you can understand what parts of your strategy are working and those that are not.
That just scratches the surface for why having a plan is valuable. Check out our full write-up for fifteen more reasons why you need a business plan .
What can you do with your plan?
So what can you do with a business plan once you’ve created it? It can be all too easy to write a plan and just let it be. Here are just a few ways you can leverage your plan to benefit your business.
Test an idea
Writing a plan isn’t just for those that are ready to start a business. It’s just as valuable for those that have an idea and want to determine if it’s actually possible or not. By writing a plan to explore the validity of an idea, you are working through the process of understanding what it would take to be successful.
The market and competitive research alone can tell you a lot about your idea. Is the marketplace too crowded? Is the solution you have in mind not really needed? Add in the exploration of milestones, potential expenses, and the sales needed to attain profitability and you can paint a pretty clear picture of the potential of your business.
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
Document your strategy and goals
For those starting or managing a business understanding where you’re going and how you’re going to get there are vital. Writing your plan helps you do that. It ensures that you are considering all aspects of your business, know what milestones you need to hit, and can effectively make adjustments if that doesn’t happen.
With a plan in place, you’ll have an idea of where you want your business to go as well as how you’ve performed in the past. This alone better prepares you to take on challenges, review what you’ve done before, and make the right adjustments.
Pursue funding
Even if you do not intend to pursue funding right away, having a business plan will prepare you for it. It will ensure that you have all of the information necessary to submit a loan application and pitch to investors. So, rather than scrambling to gather documentation and write a cohesive plan once it’s relevant, you can instead keep your plan up-to-date and attempt to attain funding. Just add a use of funds report to your financial plan and you’ll be ready to go.
The benefits of having a plan don’t stop there. You can then use your business plan to help you manage the funding you receive. You’ll not only be able to easily track and forecast how you’ll use your funds but easily report on how it’s been used.
Better manage your business
A solid business plan isn’t meant to be something you do once and forget about. Instead, it should be a useful tool that you can regularly use to analyze performance, make strategic decisions, and anticipate future scenarios. It’s a document that you should regularly update and adjust as you go to better fit the actual state of your business.
Doing so makes it easier to understand what’s working and what’s not. It helps you understand if you’re truly reaching your goals or if you need to make further adjustments. Having your plan in place makes that process quicker, more informative, and leaves you with far more time to actually spend running your business.
What should your business plan include?
The content and structure of your business plan should include anything that will help you use it effectively. That being said, there are some key elements that you should cover and that investors will expect to see.
Executive summary
The executive summary is a simple overview of your business and your overall plan. It should serve as a standalone document that provides enough detail for anyone—including yourself, team members, or investors—to fully understand your business strategy. Make sure to cover the problem you’re solving, a description of your product or service, your target market, organizational structure, a financial summary, and any necessary funding requirements.
This will be the first part of your plan but it’s easiest to write it after you’ve created your full plan.
Products & Services
When describing your products or services, you need to start by outlining the problem you’re solving and why what you offer is valuable. This is where you’ll also address current competition in the market and any competitive advantages your products or services bring to the table. Lastly, be sure to outline the steps or milestones that you’ll need to hit to successfully launch your business. If you’ve already hit some initial milestones, like taking pre-orders or early funding, be sure to include it here to further prove the validity of your business.
Market analysis
A market analysis is a qualitative and quantitative assessment of the current market you’re entering or competing in. It helps you understand the overall state and potential of the industry, who your ideal customers are, the positioning of your competition, and how you intend to position your own business. This helps you better explore the long-term trends of the market, what challenges to expect, and how you will need to initially introduce and even price your products or services.
Check out our full guide for how to conduct a market analysis in just four easy steps .
Marketing & sales
Here you detail how you intend to reach your target market. This includes your sales activities, general pricing plan, and the beginnings of your marketing strategy. If you have any branding elements, sample marketing campaigns, or messaging available—this is the place to add it.
Additionally, it may be wise to include a SWOT analysis that demonstrates your business or specific product/service position. This will showcase how you intend to leverage sales and marketing channels to deal with competitive threats and take advantage of any opportunities.
Check out our full write-up to learn how to create a cohesive marketing strategy for your business.
Organization & management
This section addresses the legal structure of your business, your current team, and any gaps that need to be filled. Depending on your business type and longevity, you’ll also need to include your location, ownership information, and business history. Basically, add any information that helps explain your organizational structure and how you operate. This section is particularly important for pitching to investors but should be included even if attempted funding is not in your immediate future.
Financial projections
Possibly the most important piece of your plan, your financials section is vital for showcasing the viability of your business. It also helps you establish a baseline to measure against and makes it easier to make ongoing strategic decisions as your business grows. This may seem complex on the surface, but it can be far easier than you think.
Focus on building solid forecasts, keep your categories simple, and lean on assumptions. You can always return to this section to add more details and refine your financial statements as you operate.
Here are the statements you should include in your financial plan:
- Sales and revenue projections
- Profit and loss statement
- Cash flow statement
- Balance sheet
The appendix is where you add additional detail, documentation, or extended notes that support the other sections of your plan. Don’t worry about adding this section at first and only add documentation that you think will be beneficial for anyone reading your plan.
Types of business plans explained
While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function fully depend on how you intend to use your plan. So, to get the most out of your plan, it’s best to find a format that suits your needs. Here are a few common business plan types worth considering.
Traditional business plan
The tried-and-true traditional business plan is a formal document meant to be used for external purposes. Typically this is the type of plan you’ll need when applying for funding or pitching to investors. It can also be used when training or hiring employees, working with vendors, or any other situation where the full details of your business must be understood by another individual.
This type of business plan follows the outline above and can be anywhere from 10-50 pages depending on the amount of detail included, the complexity of your business, and what you include in your appendix. We recommend only starting with this business plan format if you plan to immediately pursue funding and already have a solid handle on your business information.
Business model canvas
The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea.
The structure ditches a linear structure in favor of a cell-based template. It encourages you to build connections between every element of your business. It’s faster to write out and update, and much easier for you, your team, and anyone else to visualize your business operations. This is really best for those exploring their business idea for the first time, but keep in mind that it can be difficult to actually validate your idea this way as well as adapt it into a full plan.
One-page business plan
The true middle ground between the business model canvas and a traditional business plan is the one-page business plan. This format is a simplified version of the traditional plan that focuses on the core aspects of your business. It basically serves as a beefed-up pitch document and can be finished as quickly as the business model canvas.
By starting with a one-page plan, you give yourself a minimal document to build from. You’ll typically stick with bullet points and single sentences making it much easier to elaborate or expand sections into a longer-form business plan. This plan type is useful for those exploring ideas, needing to validate their business model, or who need an internal plan to help them run and manage their business.
Now, the option that we here at LivePlan recommend is the Lean Plan . This is less of a specific document type and more of a methodology. It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, test, review, refine, and take action based on performance.
It holds all of the benefits of the single-page plan, including the potential to complete it in as little as 27-minutes . However, it’s even easier to convert into a full plan thanks to how heavily it’s tied to your financials. The overall goal of Lean Planning isn’t to just produce documents that you use once and shelve. Instead, the Lean Planning process helps you build a healthier company that thrives in times of growth and stable through times of crisis.
It’s faster, keeps your plan concise, and ensures that your plan is always up-to-date.
Try the LivePlan Method for Lean Business Planning
Now that you know the basics of business planning, it’s time to get started. Again we recommend leveraging a Lean Plan for a faster, easier, and far more useful planning process.
To get familiar with the Lean Plan format, you can download our free Lean Plan template . However, if you want to elevate your ability to create and use your lean plan even further, you may want to explore LivePlan.
It features step-by-step guidance that ensures you cover everything necessary while reducing the time spent on formatting and presenting. You’ll also gain access to financial forecasting tools that propel you through the process. Finally, it will transform your plan into a management tool that will help you easily compare your forecasts to your actual results.
Check out how LivePlan streamlines Lean Planning by downloading our Kickstart Your Business ebook .
Like this post? Share with a friend!
Posted in Business Plan Writing
Join over 1 million entrepreneurs who found success with liveplan, like this content sign up to receive more.
Subscribe for tips and guidance to help you grow a better, smarter business.
You're all set!
Exciting business insights and growth strategies will be coming your way each month.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
Margin Size
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

1.1: Chapter 1 – Introduction to Entrepreneurship
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 21253

- Lee A. Swanson
- University of Saskatchewan
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
Whilst there is no universally accepted definition of entrepreneurship, it is fair to say that it is multi-dimensional. It involves analyzing people and their actions together with the ways in which they interact with their environments, be these social, economic, or political, and the institutional, policy, and legal frameworks that help define and legitimize human activities. – Blackburn (2011, p. xiii)
Entrepreneurship involves such a range of activities and levels of analysis that no single definition is definitive. – Lichtenstein (2011, p. 472)
It is complex, chaotic, and lacks any notion of linearity. As educators, we have the responsibility to develop our students’ discovery, reasoning, and implementation skills so they may excel in highly uncertain environments. – Neck and Greene (2011, p. 55)
Learning Objectives
- Examine the challenges associated with defining the concepts of entrepreneur and entrepreneurship
- Discuss how the evolution of entrepreneurship thought has influenced how we view the concept of entrepreneurship today
- Discuss how the list of basic questions in entrepreneurship research can be expanded to include research inquiries that are important in today’s world
- Discuss how the concepts of entrepreneurial uniqueness, entrepreneurial personality traits, and entrepreneurial cognitions can help society improve its support for entrepreneurship
- Apply the general venturing script to the study of entrepreneurship
This chapter provides you with an overview of entrepreneurship and of the language of entrepreneurship. The challenges associated with defining entrepreneur and entrepreneurship are explored, as is an overview of how entrepreneurship can be studied.
The objective is to enable you to apply current concepts in entrepreneurship to the evaluation of entrepreneurs, their ventures, and the venturing environment. You will develop skills, including the capability to add value in the new venture sector of the economy. You will acquire and practice evaluation skills useful in consulting, advising, and making new venture decisions.
Entrepreneurs and Entrepreneurship
Considerations influencing definitions of entrepreneur and entrepreneurship.
It is necessary to be able to determine exactly who entrepreneurs are before we can, among other things, study them, count them, provide special loans for them, and calculate how and how much they contribute to our economy.
- Does someone need to start a business from scratch to be called an entrepreneur?
- Can we call someone an entrepreneur if they bought an ongoing business from someone else or took over the operations of a family business from their parents?
- If someone starts a small business and never needs to hire employees, can they be called an entrepreneur?
- If someone buys a business but hires professional managers to run it so they don’t have to be involved in the operations, are they an entrepreneur?
- Is someone an entrepreneur if they buy into a franchise so they can follow a well-established formula for running the operation?
- Is someone an entrepreneur because of what they do or because of how they think?
- Can someone be an entrepreneur without owning their own business?
- Can a person be an entrepreneur because of the nature of the work that they do within a large corporation?
It is also necessary to fully understand what we mean by entrepreneurship before we can study the concept.
Gartner (1990) identified 90 attributes that showed up in definitions of entrepreneurs and entrepreneurship provided by entrepreneurs and other experts in the field. The following are a few of these attributes:
- Innovation – Does a person need to be innovative to be considered an entrepreneur? Can an activity be considered to be entrepreneurial if it is not innovative?
- Activities – What activities does a person need to do to be considered an entrepreneur?
- Creation of a new business – Does someone need to start a new business to be considered to be an entrepreneur, or can someone who buys a business, buys into a franchise, or takes over an existing family business be considered an entrepreneur?
- Starts an innovative venture within an established organization – Can someone who works within an existing organization that they don’t own be considered an entrepreneur if they start an innovative venture for their organization?
- Creation of a not-for-profit business – Can a venture be considered to be entrepreneurial if it is a not-for-profit, or should only for-profit businesses be considered entrepreneurial?
After identifying the 90 attributes, Gartner (1990) went back to the entrepreneurs and other experts for help in clustering the attributes into themes that would help summarize what people concerned with entrepreneurship thought about the concept. He ended up with the following eight entrepreneurship themes:
1. The Entrepreneur – The entrepreneur theme is the idea that entrepreneurship involves individuals with unique personality characteristics and abilities (e.g., risk-taking, locus of control, autonomy, perseverance, commitment, vision, creativity). Almost 50% of the respondents rated these characteristics as not important to a definition of entrepreneurship (Gartner, 1990, p. 21, 24).
- “The question that needs to be addressed is: Does entrepreneurship involve entrepreneurs (individuals with unique characteristics)?” (Gartner, 1990, p. 25).
2. Innovation – The innovation theme is characterized as doing something new as an idea, product, service, market, or technology in a new or established organization. The innovation theme suggests that innovation is not limited to new ventures, but recognized as something which older and/or larger organizations may undertake as well (Gartner, 1990, p. 25). Some of the experts Gartner questioned believed that it was important to include innovation in definitions of entrepreneurship and others did not think it was as important.
- “Does entrepreneurship involve innovation?” (Gartner, 1990, p. 25).
3. Organization Creation – The organization creation theme describes the behaviors involved in creating organizations. This theme described acquiring and integrating resource attributes (e.g., Brings resources to bear, integrates opportunities with resources, mobilizes resources, gathers resources) and attributes that described creating organizations (new venture development and the creation of a business that adds value). (Gartner, 1990, p. 25)
- “Does entrepreneurship involve resource acquisition and integration (new venture creation activities)?” (Gartner, 1990, p. 25)
4. Creating Value – This theme articulated the idea that entrepreneurship creates value. The attributes in this factor indicated that value creation might be represented by transforming a business, creating a new business growing a business, creating wealth, or destroying the status quo.
- “Does entrepreneurship involve creating value?” (Gartner, 1990, p. 25).
5. Profit or Nonprofit
- “Does entrepreneurship involve profit-making organizations only” (Gartner, 1990, p. 25)?
- Should a focus on growth be a characteristic of entrepreneurship?
7. Uniqueness – This theme suggested that entrepreneurship must involve uniqueness. Uniqueness was characterized by attributes such as a special way of thinking, a vision of accomplishment, ability to see situations in terms of unmet needs, and creates a unique combination.
- “Does entrepreneurship involve uniqueness?” (Gartner, 1990, p. 26).
8. The Owner-Manager – Some of the respondents questioned by Gartner (1990) did not believe that small mom-and-pop types of businesses should be considered to be entrepreneurial. Some respondents felt that an important element of a definition of entrepreneurship was that a venture be owner-managed.
- To be entrepreneurial, does a venture need to be owner-managed?
Examples of Definitions of Entrepreneur
An entrepreneur can be described as “one who creates a new business in the face of risk and uncertainty for the purpose of achieving profit and growth by identifying significant opportunities and assembling the necessary resources to capitalize on them” (Zimmerer & Scarborough, 2008, p. 5).
An entrepreneur is “one who organizes, manages, and assumes the risks of a business or enterprise” (Entrepreneur, n.d.).
Examples of Definitions of Entrepreneurship
Entrepreneurship can be defined as a field of business that
seeks to understand how opportunities to create something new (e.g., new products or services, new markets, new production processes or raw materials, new ways of organizing existing technologies) arise and are discovered or created by specific persons, who then use various means to exploit or develop them, thus producing a wide range of effects (Baron, Shane, & Reuber, 2008, p. 4)
A concise definition of entrepreneurship “is that it is the process of pursuing opportunities without limitation by resources currently in hand” (Brooks, 2009, p. 3) and “the process of doing something new and something different for the purpose of creating wealth for the individual and adding value to society” (Kao, 1993, p. 70)
The Evolution of Entrepreneurship Thought
This section includes an overview of how entrepreneurship has evolved to the present day.
The following timeline shows some of the most influential entrepreneurship scholars and the schools of thought (French, English, American, German, and Austrian) their perspectives helped influence and from which their ideas evolved. Schools of thought are essentially groups of people who might or might not have personally known each other, but who shared common beliefs or philosophies.

Figure 1 – Historical and Evolutionary Entrepreneurship Thought (Illustration by Lee A. Swanson)
The Earliest Entrepreneurship
The function, if not the name, of the entrepreneur is probably as old as the institutions of barter and exchange. But only after economic markets became an intrusive element of society did the concept take on pivotal importance. Many economists have recognized the pivotal role of the entrepreneur in a market economy. Yet despite his central importance in economic activity, the entrepreneur has been a shadowy and elusive figure in the history of economic theory (Hebert & Link, 2009, p. 1).
Historically those who acted similarly to the ways we associate with modern day entrepreneurs – namely those who strategically assume risks to seek economic (or other) gains – were military leaders, royalty, or merchants. Military leaders planned their campaigns and battles while assuming significant risks, but by doing so they also stood to gain economic benefits if their strategies were successful. Merchants, like Marco Polo who sailed out of Venice in the late 1200s to search for a trade route to the Orient, also assumed substantial risks in the hope of becoming wealthy (Hebert & Link, 2009).
The entrepreneur, who was also called adventurer , projector , and undertaker during the eighteenth century, was not always viewed in a positive light (Hebert & Link, 2009).
Development of Entrepreneurship as a Concept
Risk and uncertainty.
Richard Cantillon (1680-1734) was born in France and belonged to the French School of thought although he was an Irish economist. He appears to be the person who introduced the term entrepreneur to the world. “According to Cantillon, the entrepreneur is a specialist in taking on risk, ‘insuring’ workers by buying their output for resale before consumers have indicated how much they are willing to pay for it” (Casson & Godley, 2005p. 26). The workers’ incomes are mostly stable, but the entrepreneur risks a loss if market prices fluctuate.
Cantillon distinguished entrepreneurs from two other classes of economic agents; landowners, who were financially independent, and hirelings (employees) who did not partake in the decision-making in exchange for relatively stable incomes through employment contracts. He was the first writer to provide a relatively refined meaning for the term entrepreneurship . Cantillon described entrepreneurs as individuals who generated profits through exchanges. In the face of uncertainty, particularly over future prices, they exercise business judgment. They purchase resources at one price and sell their product at a price that is uncertain, with the difference representing their profit (Chell, 2008; Hebert & Link, 2009).
Farmers were the most prominent entrepreneurs during Cantillon’s lifetime, and they interacted with “arbitrageurs” – or middlemen between farmers and the end consumers – who also faced uncertain incomes, and who were also, therefore, entrepreneurs. These intermediaries facilitated the movement of products from the farms to the cities where more than half of the farm output was consumed. Cantillon observed that consumers were willing to pay a higher price per unit to be able to purchase products in the smaller quantities they wanted, which created the opportunities for the intermediaries to make profits. Profits were the rewards for assuming the risks arising from uncertain conditions. The markets in which profits were earned were characterized by incomplete information (Chell, 2008; Hebert & Link, 2009).
Adolph Reidel (1809-1872), form the German School of thought, picked up on Cantillon’s notion of uncertainty and extended it to theorize that entrepreneurs take on uncertainty so others, namely income earners, do not have to be subject to the same uncertainty. Entrepreneurs provide a service to risk-averse income earners by assuming risk on their behalf. In exchange, entrepreneurs are rewarded when they can foresee the impacts of the uncertainty and sell their products at a price that exceeds their input costs (including the fixed costs of the wages they commit to paying) (Hebert & Link, 2009).
Frank Knight (1885-1972) founded the Chicago School of Economics and belonged to the American School of thought. He refined Cantillon’s perspective on entrepreneurs and risk by distinguishing insurable risk as something that is separate from uncertainty, which is not insurable. Some risks can be insurable because they have occurred enough times in the past that the expected loss from such risks can be calculated. Uncertainty, on the other hand, is not subject to probability calculations. According to Knight, entrepreneurs can’t share the risk of loss by insuring themselves against uncertain events, so they bear these kinds of risks themselves, and profit is the reward that entrepreneurs get from assuming uninsurable risks (Casson & Godley, 2005).
Distinction Between Entrepreneur and Manager
Jean-Baptiste Say (1767-1832), also from the French School, advanced Cantillon’s work, but added that entrepreneurship was essentially a form of management. Say “put the entrepreneur at the core of the entire process of production and distribution” (Hebert & Link, 2009, p. 17). Say’s work resulted in something similar to a general theory of entrepreneurship with three distinct functions; “scientific knowledge of the product; entrepreneurial industry – the application of knowledge to useful purpose; and productive industry – the manufacture of the item by manual labour” (Chell, 2008, p. 20).
Frank Knight made several contributions to entrepreneurship theory, but another of note is how he distinguished an entrepreneur from a manager. He suggested that a manager crosses the line to become an entrepreneur “when the exercise of his/her judgment is liable to error and s/he assumes the responsibility for its correctness” (Chell, 2008, p. 33). Knight said that entrepreneurs calculate the risks associated with uncertain business situations and make informed judgments and decisions with the expectation that – if they assessed the situation and made the correct decisions – they would be rewarded by earning a profit. Those who elect to avoid taking these risks choose the relative security of being employees (Chell, 2008).
Alfred Marshall (1842-1924), from the English School of thought, was one of the founders of neoclassical economics. His research involved distinguishing between the terms capitalist, entrepreneur, and manager. Marshall saw capitalists as individuals who “committed themselves to the capacity and honesty of others, when he by himself had incurred the risks for having contributed with the capital” (Zaratiegui & Rabade, 2005, p. 775). An entrepreneur took control of money provided by capitalists in an effort to leverage it to create more money; but would lose less if something went wrong then would the capitalists. An entrepreneur, however, risked his own reputation and the other gains he could have made by pursuing a different opportunity.
Let us suppose that two men are carrying on smaller businesses, the one working with his own, the other chiefly with borrowed capital. There is one set of risks which is common to both; which may be described as the trade risks of the particular business … But there is another set of risks, the burden of which has to be borne by the man working with borrowed capital, and not by the other; and we may call them personal risks (Marshall, 1961, p. 590; Zaratiegui & Rabade, 2005, p. 776).
Marshall recognized that the reward capitalists received for contributing capital was interest income and the reward entrepreneurs earned was profits. Managers received a salary and, according to Marshall, fulfilled a different function than either capitalists or entrepreneurs – although in some cases, particularly in smaller firms, one person might be both an entrepreneur and a manager. Managers “were more inclined to avoid challenges, innovations and what Schumpeter called the ‘perennial torment of creative destruction’ in favour of a more tranquil life” (Zaratiegui & Rabade, 2005, p. 781). The main risks they faced from firm failure were to their reputations or to their employment status. Managers had little incentive to strive to maximize profits (Zaratiegui & Rabade, 2005).
Amasa Walker (1799-1875) and his son Francis Walker (1840-1897) were from the American School of thought, and they helped shape an American perspective of entrepreneurship following the Civil War of 1861-1865. These scholars claimed that entrepreneurs created wealth, and thus played a different role than capitalists. They believed that entrepreneurs had the power of foresight and leadership qualities that enabled them to organize resources and inject energy into activities that create wealth (Chell, 2008).
Entrepreneurship versus Entrepreneur
Adam Smith (1723-1790), from the English School of thought, published An Inquiry into the Nature and Causes of the Wealth of Nations in 1776. In a departure from the previous thought into entrepreneurship and economics, Smith did not dwell on a particular class of individual. He was concerned with studying how all people fit into the economic system. Smith contended that the economy was driven by self-interest in the marketplace (Chell, 2008).
Also from the English School, David Ricardo (1772-1823) was influenced by Smith, Say, and others. His work focused on how the capitalist system worked. He explained how manufacturers must invest their capital in response to the demand for the products they produce. If demand decreases, manufacturers should borrow less and reduce their workforces. When demand is high, they should do the reverse (Chell, 2008).
Carl Menger (1840-1921), from the Austrian School of thought, ranked goods according to their causal connections to human satisfaction. Lower order goods include items like bread that directly satisfy a human want or need like hunger. Higher order goods are those more removed from satisfying a human need. A second order good is the flour that was used to make the bread. The grain used to make the flour is an even higher order good. Entrepreneurs coordinate these factors of production to turn higher order goods into lower order goods that more directly satisfy human wants and needs (Hebert & Link, 2009).
Menger (1950 [1871], p. 160) established that entrepreneurial activity includes: (a) obtaining information about the economic situation, (b) economic calculation – all the various computations that must be made if a production process is to be efficient, (c) the act of will by which goods of higher order are assigned to a particular production process, and (d) supervising the execution of the production plan so that it may be carried through as economically as possible (Hebert & Link, 2009, p. 43).
Entrepreneurship and Innovation
Jeremy Bentham (1748-1832), from the English School of thought, considered entrepreneurs to be innovators. They “depart from routine, discover new markets, find new sources of supply, improve existing products and lower the costs of production” (Chell, 2008).
Joseph Schumpeter’s (1883-1950) parents were Austrian, he studied at the University of Vienna, conducted research at the University of Graz, served as Austria’s Minister of Finance, and was the president of a bank in the country. Because of the rise of Hitler in Europe, he went to the United States and conducted research at Harvard until he retired in 1949. Because of this, he is sometimes associated with the American School of thought on entrepreneurship (Chell, 2008).
Whereas Menger saw entrepreneurship as occurring because of economic progress, Schumpeter took the opposite stance. Schumpeter saw economic activity as leading to economic development (Hebert & Link, 2009). Entrepreneurs play a central role in Schumpeter’s theory of economic development, and economic development can occur when the factors of production are assembled in new combinations .
Schumpeter (1934) viewed innovation as arising from new combinations of materials and forces. He provided the following five cases of new combinations.
- The introduction of a new good – that is one with which consumers are not yet familiar – or of a new quality of good.
- The introduction of a new method of production, that is one not yet tested by experience in the branch of manufacture concerned, which need by no means be founded upon a discovery scientifically new, and can also exist in a new way of handling a commodity commercially.
- The opening of a new market, that is a market into which the particular branch of manufacture of the country in question has not previously entered, whether or not this market has existed before.
- The conquest of a new source of supply of raw materials or half-manufactured goods, again irrespective of whether this source already exists or whether it has first to be created.
- The carrying out of the new organisation of any industry, like the creation of a monopoly position … or the breaking up of a monopoly position (Schumpeter, 1934, p. 66).
Another concept popularized by Schumpeter – in addition to the notion of new combinations – was creative destruction . This was meant to indicate that the existing ways of doing things need to be dismantled – to be destroyed – to enable a transformation through innovation to a new way of doing things. Entrepreneurs use innovation to disrupt how things are done and to establish a better way of doing those things.
Basic Questions in Entrepreneurship Research
According to Baron (2004a), there are three basic questions of interest in the field of entrepreneurship:
- Why do some persons but not others choose to become entrepreneurs?
- Why do some persons but not others recognize opportunities for new products or services that can be profitably exploited?
- Why are some entrepreneurs so much more successful than others (Baron, 2004a, p. 221)?
To understand where these foundational research questions came from and what their relevance is today, it is useful to study what entrepreneurship research has uncovered so far.
Entrepreneurial Uniqueness
Efforts to teach entrepreneurship have included descriptions of entrepreneurial uniqueness based on personality, behavioural, and cognitive traits (Chell, 2008; Duening, 2010).
- Need for achievement
- Internal locus of control (a belief by an individual that they are in control of their own destiny)
- Risk-taking propensity
- Behavioural traits
- Cognitive skills of successful entrepreneurs
Past studies of personality characteristics and behavioural traits have not been overly successful at identifying entrepreneurial uniqueness.
As it turned out, years of painstaking research along this line has not borne significant fruit. It appears that there are simply not any personality characteristics that are either essential to, or defining of, entrepreneurs that differ systematically from non-entrepreneurs…. Again, investigators proposed a number of behavioural candidates as emblematic of entrepreneurs. Unfortunately, this line of research also resulted in a series of dead ends as examples of successful entrepreneurial behaviours had equal counterparts among samples of non-entrepreneurs. As with the personality characteristic school of thought before it, the behavioural trait school of thought became increasingly difficult to support (Duening, 2010, p. 4-5).
This shed doubt on the value of trying to change personality characteristics or implant new entrepreneurial behaviours through educational programs in an effort to promote entrepreneurship.
New research, however, has resurrected the idea that there might be some value in revisiting personality traits as a topic of study. Additionally, Duening (2010) and has suggested that an important approach to teaching and learning about entrepreneurship is to focus on the “cognitive skills that successful entrepreneurs seem uniquely to possess and deploy” (p. 2). In the next sections we consider the new research on entrepreneurial personality traits and on entrepreneurial cognitions.
Entrepreneurial Personality Traits
While acknowledging that research had yet to validate the value of considering personality and behaviour traits as ways to distinguish entrepreneurs from non-entrepreneurs or unsuccessful ones, Chell (2008) suggested that researchers turn their attention to new sets of traits including: “the proactive personality, entrepreneurial self-efficacy, perseverance and intuitive decision-making style. Other traits that require further work include social competence and the need for independence” (p. 140).
In more recent years scholars have considered how the Big Five personality traits – extraversion, agreeableness, conscientiousness, neuroticism (sometimes presented as emotional stability ), and openness to experience (sometimes referred to as intellect) – might be used to better understand entrepreneurs. It appears that the Big Five traits might be of some use in predicting entrepreneurial success. Research is ongoing in this area, but in one example, Caliendo, Fossen, and Kritikos (2014) studied whether personality constructs might “influence entrepreneurial decisions at different points in time” (p. 807), and found that “high values in three factors of the Big Five approach—openness to experience, extraversion, and emotional stability (the latter only when we do not control for further personality characteristics)—increase the probability of entry into self-employment” (p. 807). They also found “that some specific personality characteristics, namely risk tolerance, locus of control, and trust, have strong partial effects on the entry decision” (p. 807). They also found that people who scored higher on agreeableness were more likely to exit their businesses, possibly meaning that people with lower agreeableness scores might prevail longer as entrepreneurs. When it came to specific personality traits, their conclusions indicated that those with an external locus of control were more likely to stop being self-employed after they had run their businesses for a while. There are several implications for research like this, including the potential to better understand why some entrepreneurs behave as they do based upon their personality types and the chance to improve entrepreneurship education and support services.
Entrepreneurial Cognitions
It is only fairly recently that entrepreneurship scholars have focused on cognitive skills as a primary factor that differentiates successful entrepreneurs from non-entrepreneurs and less successful entrepreneurs. This approach deals with how entrepreneurs think differently than non-entrepreneurs (Duening, 2010; Mitchell et al., 2007).
Entrepreneurial cognitions are the knowledge structures that people use to make assessments, judgments or decisions involving opportunity evaluation and venture creation and growth. In other words, research in entrepreneurial cognition is about understanding how entrepreneurs use simplifying mental models to piece together previously unconnected information that helps them to identify and invent new products or services, and to assemble the necessary resources to start and grow businesses (Mitchell, Busenitz, et al., 2002, p. 97).
Mitchell, Smith, et al. (2002) provided the example of how the decision to create a new venture (dependent variable) was influenced by three sets of cognitions (independent variables). They described these cognitions as follows:
Arrangements cognitions are the mental maps about the contacts, relationships, resources, and assets necessary to engage in entrepreneurial activity; willingness cognitions are the mental maps that support commitment to venturing and receptivity to the idea of starting a venture; ability cognitions consist of the knowledge structures or scripts (Glaser, 1984) that individuals have to support the capabilities, skills, norms, and attitudes required to create a venture (Mitchell et al., 2000). These variables draw on the idea that cognitions are structured in the minds of individuals (Read, 1987), and that these knowledge structures act as “scripts” that are the antecedents of decision making (Leddo & Abelson, 1986, p. 121; Mitchell, Smith, et al., 2002, p. 10)
Cognitive Perspective to Understanding Entrepreneurship
According to Baron (2004a), by taking a cognitive perspective, we might better understand entrepreneurs and the role they play in the entrepreneurial process.
The cognitive perspective emphasizes the fact that everything we think, say, or do is influenced by mental processes—the cognitive mechanisms through which we acquire store, transform, and use information. It is suggested here that this perspective can be highly useful to the field of entrepreneurship. Specifically, it can assist the field in answering three basic questions it has long addressed: (1) Why do some persons but not others choose to become entrepreneurs? (2) Why do some persons but not others recognize opportunities for new products or services that can be profitably exploited? And (3) Why are some entrepreneurs so much more successful than others (Baron, 2004a, p. 221-222)?
Baron (2004a), illustrated how cognitive differences between people might explain why some people end up pursuing entrepreneurial pursuits and others do not. For example, prospect theory (Kahneman & Tversky, 1977) and other decision-making or behavioural theories might be useful in this regard. Research into cognitive biases might also help explain why some people become entrepreneurs.
Baron (2004a) also revealed ways in which cognitive concepts like signal detection theory, regulation theory, and entrepreneurial might help explain why some people are better at entrepreneurial opportunity recognition. He also illustrated how some cognitive models and theories – like risk perception, counterfactual thinking, processing style, and susceptibility to cognitive errors – might help explain why some entrepreneurs are more successful than others.
Cognitive Perspective and the Three Questions
- Prospect Theory
- Cognitive Biases
- Signal Detection Theory
- Regulation Theory
- Entrepreneurial Alertness
- Risk Perception
- Counterfactual Thinking
- Processing Style
- Susceptibility to Cognitive Errors
Entrepreneurial Scripts
- “Cognition has emerged as an important theoretical perspective for understanding and explaining human behavior and action” (Dutta & Thornhill, 2008, p. 309).
- Cognitions are all processes by which sensory input is transformed, reduced, elaborated, stored, recovered, and used (Neisser, 1976).
- Cognitions lead to the acquisition of knowledge, and involve human information processing.
- Is a mental model, or information processing short-cut that can give information form and meaning, and enable subsequent interpretation and action.
- The subsequent interpretation and actions can result in expert performance … they can also result in thinking errors.
- the processes that transfer expertise, and
- the actual expertise itself.
- Scripts are generally framed as a linear sequence of steps, usually with feedback loops, that can explain how to achieve a particular task – perhaps like developing a business plan.
- Sometimes scripts can be embedded within other scripts. For example, within a general venturing script that outlines the sequences of activities that can lead to a successful business launch, there will probably be sub-scripts describing how entrepreneurs can search for ideas, screen those ideas until one is selected, plan how to launch a sustainable business based upon that idea and including securing the needed financial resources, setting up the business, starting it, effectively managing its ongoing operations, and managing the venture such that that entrepreneur can extract the value that they desire from the enterprise at the times and in the ways they want it.
- The most effective scripts include an indication of the norms that outline performance standards and indicate how to determine when any step in the sequence has been properly completed.
General Venturing Script
Generally, entrepreneurship is considered to consist of the following elements, or subscripts (Brooks, 2009; Mitchell, 2000).
- Idea Screening
- Planning and Financing
- Ongoing Operations
Searching (also called idea formulation or opportunity recognition)
- This script begins when a person decides they might be a potential entrepreneur (or when an existing entrepreneur decides they need more ideas in their idea pool ).
- This script ends when there are a sufficient number of ideas in the idea pool.
- overcome mental blockages to creativity which might hinder this person’s ability to identify viable ideas;
- implement steps to identify a sufficient number of ideas (most likely 5 or more) which the person is interested in investigating to determine whether they might be viable given general criteria such as this person’s personal interests and capabilities;
Idea Screening (also called concept development)
- This script begins when the person with the idea pool is no longer focusing on adding new ideas to it; but is instead taking steps to choose the best idea for them given a full range of specific criteria .
- This script ends when one idea is chosen from among those in the idea pool.
- Evaluate the political, economic, social, technological, environmental, and legal climates
- Evaluate the degree of competitiveness in the industry, the threat of substitutes emerging, the threat of new entrants to the industry, the degree of bargaining power of buyers, and the degree of bargaining power of suppliers.
- Do a market profile analysis to assess the attractiveness of the position within the industry that the potential venture will occupy.
- Formulate and evaluate potential strategies to leverage organizational strengths, overcome/minimize weaknesses, take advantage of opportunities, and overcome/minimize threats;
- Complete financial projections and analyze them to evaluate financial attractiveness;
- Assess the founder fit with the ideas;
- Evaluate the core competencies of the organization relative to the idea;
- Assess advice solicited from trusted advisers
Planning and Financing (also called resource determination and acquisition)
- This script begins when the idea screening script ends and when the person begins making the plans to implement the single idea chosen from the idea pool, which is done in concert with securing financing to implement the venture idea.
- This script ends when sufficient business planning has been done and when adequate financing has been arranged.
- The scripting process involves a logical flow of steps to develop a business plan and secure adequate financing to start the business.
Set-Up (also called launch)
- This script begins when the planning and financing script ends and when the person begins implementing the plans needed to start the business.
- This script ends when the business is ready to start-up.
- The scripting process involves a logical flow of steps, including purchasing and installing equipment, securing the venture location and finishing all the needed renovations, recruiting and hiring any staff needed for start-up, and the many other steps needed to prepare for start-up.
- Start-Up (also called launch)
- This script begins when the set-up script ends and when the business opens and begins making sales.
- This script ends when the business has moved beyond the point where the entrepreneur must continually fight for the business’s survival and persistence. It ends when the entrepreneur can instead shift emphasis toward business growth or maintaining the venture’s stability.
- The scripting process involves a logical flow of steps needed to establish a new venture.
Ongoing Operations (also called venture growth)
- This script begins when the start-up script ends and when the business has established persistence and is implementing growth (or maintenance) strategies.
- This script ends when the entrepreneur chooses to harvest the value they generated with the venture.
- The scripting process involves a logical flow of steps needed to grow (or maintain) a venture.
Studying Entrepreneurship
The following quotations from two preeminent entrepreneurship and entrepreneurship education researchers indicate the growing interest in studies in this field.
Entrepreneurship has emerged over the last two decades as arguably the most potent economic force the world has ever experienced. With that expansion has come a similar increase in the field of entrepreneurship education. The recent growth and development in the curricula and programs devoted to entrepreneurship and new-venture creation have been remarkable. The number of colleges and universities that offer courses related to entrepreneurship has grown from a handful in the 1970s to over 1,600 in 2005 (Kuratko, 2005, p. 577).
Interest in entrepreneurship has heightened in recent years, especially in business schools. Much of this interest is driven by student demand for courses in entrepreneurship, either because of genuine interest in the subject, or because students see entrepreneurship education as a useful hedge given uncertain corporate careers (Venkataraman, 1997, p. 119).
Approaches to Studying Entrepreneurship
Entrepreneurship is a discipline, which means an individual can learn about it, and about how to be an effective entrepreneur. It is a myth that people are born entrepreneurs and that others cannot learn to become entrepreneurs (Drucker, 1985). Kuratko (2005) asserted that the belief previously held by some that entrepreneurship cannot be taught has been debunked, and the focus has shifted to what topics should be taught and how they should be covered.
Solomon (2007) summarized some of the research on what should be covered in entrepreneurship courses, and how it should be taught. While the initial focus was on actions like developing business plans and being exposed to real entrepreneurs, more recently this approach has been supplemented by an emphasis on technical, industry, and personal experience. “It requires critical thinking and ethical assessment and is based on the premise that successful entrepreneurial activities are a function of human, venture and environmental conditions” (p. 172). Another approach “calls for courses to be structured around a series of strategic development challenges including opportunity identification and feasibility analysis; new venture planning, financing and operating; new market development and expansion strategies; and institutionalizing innovation” (p. 172). This involves having students interact with entrepreneurs by interviewing them, having them act as mentors, and learning about their experiences and approaches through class discussions.
Sources of Information for Studying Entrepreneurship
According to Kuratko (2005), “three major sources of information supply the data related to the entrepreneurial process or perspective” (p. 579).
- Academic journals like Entrepreneurship Theory and Practice , Journal of Business Venturing , and Journal of Small Business Management
- Proceedings of conferences like Proceedings of the Academy of Management and Proceedings of the Administrative Sciences Association of Canada
- Textbooks on entrepreneurship
- Books about entrepreneurship
- Biographies or autobiographies of entrepreneurs
- News periodicals like Canadian Business and Profit
- Trade periodicals like Entrepreneur and Family Business
- Government publications available through sources like the Enterprise Saskatchewan and Canada-Saskatchewan Business Service Centre (CSBSC) websites and through various government resource centers
- Data might be collected from entrepreneurs and about entrepreneurs through surveys, interviews, or other methods applied by researchers.
- Speeches and presentations by practicing entrepreneurs
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
Market Research
Business planning, website development, product or service selection, marketing and promotion, is it a good idea to start an online business, can i start an online business with $100, what are different types of online marketing strategies, the bottom line.
- Small Business
- How to Start a Business
How to Start an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide
Crafting a Winning Business Plan: Setting Goals and Strategies
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/picture-53823-1434118722-5bfc2a8c46e0fb005119858e.jpg)
Katie Miller is a consumer financial services expert. She worked for almost two decades as an executive, leading multi-billion dollar mortgage, credit card, and savings portfolios with operations worldwide and a unique focus on the consumer. Her mortgage expertise was honed post-2008 crisis as she implemented the significant changes resulting from Dodd-Frank required regulations.
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, How To Create One
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons
- Best Startup Business Loans
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros & Cons, and Differences From an LLC
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types
- What is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined
- Corporation: What It Is and How to Form One
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide CURRENT ARTICLE
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide
Oscar Wong / Getty Images
If you want to get into the online business game, it’s a good time to start. The COVID-19 pandemic reshaped online consumer spending, including how people shop online and how they research products.
Today, 76% of Americans buy products online. Furthermore, roughly a third of people purchase items online weekly. From setting up an ecommerce business to offering web design services, there are countless avenues to explore as an entrepreneur.
Below, we’ll walk through each step to building an online business.
Key Takeaways
- When starting an online business, comprehensive market research is critical for identifying your target audience and learning how to resonate with your customers and understand their needs.
- Creating a business plan is an important step for outlining your business goals. It also includes your product description, target market, and financial projections, among other core components.
- Building your website involves setting up a domain name, finding a hosting company, and designing a strong website with consistent branding that allows your customers to navigate it intuitively.
- Choosing the right product or service to sell is essential. It’s important to think about how you’re addressing an unmet need.
- Several digital marketing strategies can be utilized, from content marketing to paid advertising, to help your business grow.
Successful online entrepreneurs study hard in order to have a thorough understanding of their market. This is important for knowing exactly how to reach your target market , because these are the people who will buy your products and drive your business growth.
At its core, market research is about understanding your customers’ needs, pain points, and solutions. It is designed to help your business better meet these needs.
Steps to Conduct Market Research
Market research involves understanding key aspects of your current and future customers. To get a clear sense of your target market, outline the characteristics of your audience—for example, age, location, gender, income, job title, and key pain points.
Once you have identified your target audience, conduct research on the following topics, which will tell you about how they make decisions and how you can better position your business:
- What are the challenges that your target market faces?
- Where do they research a given product or service?
- What are their views on pricing for this product or service?
- What factors influence their decision to make a purchase?
- Who are your competitors?
To put this market research into action, there are a number of different avenues you can take:
- Focus groups
- Competitive analysis
- Brand awareness research
- Market segmentation research
Consider the following questions that may be asked in an interview or focus group to learn more about your audience:
- “How do you search for that product?”
- “How useful was it?”
- “What words do you use when you search on Google?”
When you have completed your market research, identify what you have learned as well as your next steps based on these insights.
Creating a business plan is a key first step for all business owners . It is important for companies looking to secure funding resources. It also serves as a blueprint to summarize your key business objectives and goals.
To write a business plan , incorporate these eight main sections, which are often found in traditional templates:
- Executive summary : This is typically a one-page section that explains your objectives and includes your mission statement, core team, and why your company is positioned for success.
- Company description : This describes what you offer, your competitive advantages, and your business goals.
- Market analysis : This is where you explain your target market, market size, market trends, and competitive landscape.
- Organization and management : Explain who is working on your team and their professional background and experience.
- Service or product line : Describe the product or service you are offering, including any copyright or plans for patenting.
- Marketing and sales : Discuss your marketing and sales strategy. Discuss your pricing, key metrics, and sales plan.
- Funding request : If you are a company looking for funding, here is where you outline the capital you are requesting and where it will be allocated.
- Financial projections : Include projections for your company’s revenue and expenses. Consider including an income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement in this section.
A business plan is important because it helps clarify your action points, who you are, and what you offer, all in a coherent template.
Getting your business online is the next key step. In an ever-changing environment, it is important to know the tools, trends, and strategies for building a strong online presence to allow your business to grow.
Registering Your Domain
The first step is registering your name, or your website address. This can be in the form of your business name “.com.” To purchase your domain name, you can go to sites like GoDaddy or Namecheap . If you decide to build your website using WordPress, you will need to use a site such as these to host your website.
Web Hosting Companies
Alternatively, you can buy your domain name at a hosting company. These are companies like Shopify , Wix , or Amazon Web Services , that may also offer tools to build your website and release content on them.
Website Design
A well-designed website is important for many reasons. Using a website builder, such as Mailchimp or Squarespace , can allow you to choose a theme, customize your pages, create relevant content, and set up a payment page.
Other key aspects of your website design include its functionality, simplicity, and ease of use. Allowing your potential customers to navigate the site intuitively will be key to their experience. Brand consistency—in your logo, colors, and typeface, for example—is also key to creating a unified brand.
Another essential part of website design is its mobile application. You’ll want to ensure that your website runs smoothly on mobile, that images load properly, that the text is legible, and that buttons are intuitive to click.
This step focuses on how to choose the right product or service to sell. At the heart of this choice is the goal of solving a customer’s problem. But there are a number of strategies you can use to identify your product idea.
For example, you might consider analyzing companies with high-profit margins, products that align with your passion, burgeoning trends, items trending on online marketplaces, and/or customer reviews.
With this in mind, analyze how this product will get to your customers. Additionally, you may consider products that are not available in stores in your local market but are offered in communities such as Europe or Japan, for example.
Marketing strategy and promotion is an essential driver of business growth. As the digital landscape evolves, it’s important to have an effective marketing plan that resonates with changing consumer preferences and needs.
Here are questions that companies can consider as they create their marketing strategy, navigating today’s environment:
- Impact, value, and growth : What are the goals and key performance indicators (KPIs) that will measure success for your business? How will you explain the value that the business provides to its customers and/or society? Create an “elevator speech”—a 30-second description of what you offer and why it’s special.
- Customer need and brand promise : How does the brand meet a customer’s need through its products and services?
- Customer experience : How will the business deliver the best experiences at each stage of the customer journey?
- Organizational model : How will the business operate to serve the customer with the most impact?
These will help you understand what types of strategies can have real impact.
Types of Marketing Strategies
Consider the following digital marketing strategies that can be used for your online business:
- Email marketing
- Social media marketing
- Paid advertising
- Search engine optimization (SEO)
- Content marketing
- Influencer marketing
Each of these presents a different way to reach your target audience, drive conversions, or build brand awareness, depending on your marketing goals.
You need to determine that for yourself. But before starting an online business, it’s important to assess the time, investment, and resources you’ll need to get it off the ground. While the barrier to entry can be quite low, it’s worth considering your goals and strategies for making it a reality.
However, compared with starting up a traditional brick-and-mortar business, the risks of launching an online business may be reduced due to lower upfront costs such as rent, staff, and materials, among others.
The short answer: yes. While it depends on the type of business you hope to pursue, there are many ways to set up an online business at very little cost. For example, you could offer your services doing freelance work, photography, bookkeeping, or personal training. The primary costs involved include setting up your business website, which can cost as little as $2 to $20 each year with companies such as GoDaddy.
There are a number of digital marketing strategies that online businesses can use, such as content marketing, email marketing, paid advertising, SEO, and influencer marketing. Each of these strategies can be useful, depending on your product and goals.
Starting an online business can be a powerful way to launch a new product or service while reaching a wider audience. With market research, a solid business plan, a strong website, and a digital marketing strategy, you can get started in growing your company effectively. As customers increasingly make decisions virtually, building an online business is vital to any business owner’s success.
Pew Research Center. “ For Shopping, Phones Are Common and Influencers Have Become a Factor—Especially for Young Adults .”
U.S. Small Business Administration. “ Market Research and Competitive Analysis .”
U.S. Small Business Administration. “ Write Your Business Plan .”
Ogilvy. “ Getting Future Ready with Marketing Transformation ,” Page 15.
GoDaddy. “ How Much Does a Domain Name Cost? Find Out! ”
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/shutterstock_222400081-5bfc47c7c9e77c00587d6bbf.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
- Dr. Tony Nader interviews with prominent philosophers >
- Degrees in the arts, sciences, business & humanities >
- Visit us on campus or virtually >
- Apply Now for an upcoming entry Apply Now for the August 2024 entry >
- MIU launches massive solar arrays >
- Enjoy your own space - single rooms are standard >
- Design your own major >
Home of Consciousness-Based Education Accredited
An accredited non-profit university with on-campus & online degrees >
- Consumer Information
A non-profit university with on-campus and online degree programs
Home of Consciousness-Based Education
Accreditation: Higher Learning Commission
- Degree Programs
- Costs & Aid
- Block System
- Online Learning
- Open Curriculum
- Consciousness-Based Education
- Transcendental Meditation
- Campus Life
- Professors Who Care
- Innovative Sustainability
- Mission & Core Values
- Core Abilities
- Request Info >
- Apply > --> Apply >
Bachelor’s Specialization in Business & Entrepreneurship online or on-campus
- Gain real experience starting your own business
- Develop your product or concept and learn to present it to investors
- Focus on a product or service of real benefit to the world
- Enhance your creativity by practicing the Transcendental Meditation ® technique
- Federal grants and loans typically cover all or most costs for US students
Explore the program
Start your own business
- Identify a viable product or business concept
- Research and evaluate your market’s potential
- Develop a marketing plan
- Create a business plan or feasibility study for your own business
- Design effective advertising for social media
- Start marketing and selling to your customers
Making it easy for transfer students

The TM technique as a tool for better mind performance

This evidence-based technique has been proven to lower stress, enhance mental clarity, and support overall health. It’s kind of like a “brain laser beam.” After meditating regularly, our students often say that they feel more creative, peaceful, and better able to tackle their studies without the stress typical of a college education.
Get started by contacting Pedro

Contact Pedro >
International applicants may connect with us through our international inquiry form .
Next entry: Aug 2024 Apply to MIU > Next entry: Aug 2024 Apply to MIU >
Degree requirements
To graduate with a Specialization in Business & Entrepreneurship, students must complete:
- required courses for the Bachelor of Applied Arts & Sciences or any other bachelor’s degree program you choose.
- 32 additional credits of Business & Entrepreneurship courses
Courses for this specialization may include
- MGT 231 Creative Entrepreneur I
- MGT 316 Principles of Accounting for Decision-Makers I
- MGT 328 Business Law and Ethics
- MGT 378 Marketing Management
- MGT 382 Management and Organization
More courses
- MGT 200 Growing a Business
- MGT 220 Current Topics in Sustainable Economics
- MGT 222 Economics for Entrepreneurs
- MGT 301 Cross-Cultural Communication
- MGT 302 Leadership in the 21st Century
- MGT 329 Human Resource Management
- MGT 336 Social Entrepreneurship
- MGT 346 Career Strategies
- MGT 350 Financial Management
- MGT 384 Mediation and Negotiation
- MGT 481 Internet Marketing
- MGT 498 Internship in Management
- MGT 307 Numerical Methods for Decision-Making
- MGT 432 Entrepreneurship Project
Featured faculty

She holds a PhD in Business, with a particular focus on Social Media Marketing, from Taylor’s University in Malaysia and an MBA with a specialization in Multimedia and Marketing from Multimedia University in Malaysia.
Dr. Naghmeh’s current research focuses on Digital Marketing, Sustainable Marketing, Green Marketing, and Creativity and Innovation in Marketing Strategies through Consciousness-Based Education. She has published her previous research in leading marketing and information technology journals.
Cost & Aid for bachelor’s degree, 2024-25
- US On-Campus Students
US On-Campus Undergraduate
*Applicable only to students living on campus
Additional Financial Aid Information
Personal Expenses and Books
Scholarships and Grants
Federal Student Loans
Education Tax Incentives
Loan Repayment Options
Income-Based
Income Contingent
Income Sensitive
- US Online Students
US Online Undergraduate
Part time online enrollment is available. Tuition is $600 per credit with normal load of 9-11 credits. Federal student loans are available and the federal Pell Grant is proportional to the credit load.
Employer Waiver Program
- $5,500 per year for first-year dependent
- $6,500 per year for second-year dependent
- $7,500 per year for third, fourth, fifth-year dependent
- $9,500 per year for first-year independent
- $10,500 per year for second-year independent
- $12,500 per year for third, fourth, fifth-year independent
Federal Student Loan Repayment
- International On-Campus Students
International On-Campus Undergraduate
Full-time students may apply for up to $6,000 scholarship based on qualifying level of documented family income. Our undergraduate scholarship application form will be available upon application to the university. Tuition, other fees, scholarships, and financial policies are subject to change prior to the entry date.
- International Online Students
International Online Undergraduate

Get your questions answered and download our free booklet.

Sign up for one-on-one virtual visits, Visitors Weekend, or Visitors Saturday.

Our next entries: Aug 2024 and Feb 2025

Related Articles

7 Ways To Stay Motivated At Work During Challenging Times
January 22, 2021.

A Manager’s Guide To Successful Remote Meetings
December 11, 2020.

5 Automation Tools That Every Small Business Should Use
December 10, 2020, do you really need a business plan for a startup, by: andrey zadorozhnyy, published on: july 6, 2018.
Ready to start a business? I'm sure you've been told to start writing a business plan immediately. But do you really have to?
Last week one of my friends who is planning to start his own business came to me to find out if I could help him with writing a business plan. He needs the plan to show it to banks or angel investors in order to get some financial support. From an investors’ perspective, it seems logical to ask an entrepreneur for a plan illustrating some figures. They not only want to see a PowerPoint presentation full of ideas but also to be able to measure the costs and future returns. But is it really worth it to make a business plan for an entrepreneur?
Yes, but…
Some people say “Yes”.
“If you can’t explain it simply, you don’t understand it well enough.” – Albert Einstein’s quote helps to realize why a business plan is necessary for a startup. It helps to figure out and explain your product to others; it is your plan for how you’re going to sell it. This model on paper helps you structure your ideas in a bit more logical, clustered form. According to Jon Westenberg, founder of Creatomic, a business plan has to show :
- What your product is, and what it does;
- Your strategy for bringing that product to market;
- Details about your revenue model;
- Goals and milestones;
- The method you’ll use to know if you’ve failed;
- Your customer personas and target market;
- Your financial needs.
Thus, the key point here is that the plan must be clear and simple not only to the entrepreneur but also to an investor. Otherwise, the product is too complicated.
Also, we can’t overlook the discussions about creating a business plan when we talk about lean startups. Some entrepreneurs, including Tim Berry, suggest making a specific type of business plan – the “lean business plan”. This is a type of a plan which should be used, revised and changed. It should evolve with the development of your startup, it’s continuously cycle-based on three similar repeating phases: plan, review and revise.
According to the research by Francis J. Greene and Christian Hopp in 2017, who studied more than 1000 U.S.-based entrepreneurs, making business plan gives startups more chances for success. “Entrepreneurs who write formal plans are 16% more likely to achieve viability than the otherwise identical non-planning entrepreneurs.” They also concluded that there are two major groups of entrepreneurs who do it: high-growth oriented startup entrepreneurs and entrepreneurs seeking external financial support.
…not all the time.
However, others think differently saying “No” to a business plan.
Brian Hamilton, Chairman of Sageworks, believes that entrepreneurs don’t know how their startups would work in reality . In new business, the areas like product, pricing, marketing, and distribution are unpredictable in the beginning. Entrepreneurs make hypotheses about different aspects of their business and test them in reality. It’s one of the features of a founder, to be flexible and bold, to change the plans that don’t work or work not good enough. At the same time, the business plan can be even harmful; it creates pressure on the entrepreneur, forcing them to follow the wrong path instead of creatively evolving and shaping the future of their business.
Neil Patel says that writing a business plan takes a lot of time and effort which should rather be spent on developing the business itself. Starting a business is an energy- and time-consuming process, so as human beings, entrepreneurs should set priorities. If you prioritize writing a plan, rather than focusing on sales, marketing, development, etc., you lose valuable time.
Our world changes faster and faster every day. Technology is evolving, customer preferences alter, macroeconomic conditions vary. Nowadays, the situation when your business plan will be outdated after a short period of time is very real.
Tony Robbins said : “The most painful mistake I see in first-time entrepreneurs is thinking that just having a business plan or a great concept is enough to guarantee success. It’s not. Business success is 80% psychology and 20% mechanics. And, frankly, most people’s psychology is not meant for building a business.”
Guy Kawasaki said: “I believe that is no longer necessary to write a business plan. You can’t foresee the future five years from now. You know, you’d be lucky if you can foresee one year from now. And even one year from now, you gonna be one year late. Because you just don’t know.”
Find The Golden Mean
The recent study of Greene and Hopp shows that the question is not about whether a business plan should be done or not, but WHEN. According to their research, the most successful entrepreneurs were those who wrote their business plan between 6 and 12 months after deciding to start a business. This increases the probability of venture viability by 8%. They also found that the optimal time to spend on the plan is 3 months, less or more time will have no effect. Writing a business plan during activities such as talking to customers, getting the product ready for market and thinking through promotional and marketing activities, increases a startup’s chances by 27%.
In conclusion, I’d like to say, that if you plan every step of your future venture or rely only on inspiration and creativity, the most important what you should do is to have faith in yourself.
Oh, and what about my friend? I advised him that if he wants to start a business, he should make a simple spreadsheet, a roadmap of his financial costs and revenues. These figures and percentages should reflect the goals of his business. I also told him to keep it close to his garbage bin, because after some months of production, sales and payments; after his enterprise starts running, he will have to throw it away.
And THEN create a real business plan .
____________
Sharing is caring!

As the COVID-19 pandemic puts us in a place we’ve never-seen-before, we need to come up with new approaches to stay healthy and productive. Discover 7 of them in this article!
by FOXYpreneur

This is the essential know-how guide about online meeting types all managers need to know to organize productive and comfortable remote gatherings.

The automation tools described in this article are inexpensive, easy to use, and have been shown to deliver a positive return on investment – both in the short- and long-term!
by Evan Morris

The purpose of informational content is to establish yourself as an authority and to offer a genuine helping hand to your audience. Here’s how to do it:
4 Ways Businesses Can Use Informational Content To Boost Sales
December 9, 2020.

There’s a lot of tools and hacks that promise sales bumps to startup owners. And sure, some may even work. But at the end of the day, increasing sales team productivity will always take more than a single fix. It requires investing in several aspects of their work.
9 Legit Ways To Increase Your Sales Team’s Productivity
October 19, 2020.

Companies that have spent time focusing on upskilling their teams during COVID lockdown are seeing their investments start to pay off as they adapt the new world of working.
Two-Thirds Of Businesses Say Skills Training Is Crucial To Post-COVID Business Recovery
October 1, 2020.

Boosting the performance of your remote team by communicating often, promoting flexibility, and leveraging technology solutions!
4 Productivity Hacks For Bolstering The Overall Performance Of Your Remote Employees
By ben walker, september 15, 2020.

Looking for top tech talent? Because hiring developers can be challenging, we set out to share our top tips to make sure you hire the best fit for your company!
How To Hire Developers & Find Hidden Tech Talent
September 14, 2020.

Looking for a way to increase conversion rates on your website? Take a look at the 6 design tips we share in this article to convince your visitors of your service!
6 Design Elements Startups Should Use To Increase Conversion
September 2, 2020.
- Starting a Business
- Growing a Business
- Small Business Guide
- Business News
- Science & Technology
- Money & Finance
- For Subscribers
- Write for Entrepreneur
- Entrepreneur Store
- United States
- Asia Pacific
- Middle East
- South Africa
Copyright © 2024 Entrepreneur Media, LLC All rights reserved. Entrepreneur® and its related marks are registered trademarks of Entrepreneur Media LLC
Sponsored Content | Brand Spotlight Partner What's This?
Brand Spotlight Partner
Spotlight is brought to you by the Entrepreneur Partner Studio, which creates dynamic and compelling content for our partners. Opinions expressed by Entrepreneur Spotlight partners are their own.
What's the Best Software for Financial Planning and Analysis?
May 29, 2024
Navigating the complex world of financial planning and analysis can be daunting for entrepreneurs, which is why we've gathered insights from CEOs and Founders to share their top software recommendations. From the comprehensive features of Oracle NetSuite to the integrated tools of LivePlan, explore the diverse opinions and top 18 tools that seasoned professionals swear by for effective financial management.
Oracle NetSuite
I would recommend Oracle NetSuite to any entrepreneur looking for software for financial planning and analysis. Although I may be slightly biased, NetSuite has the most comprehensive functionality on the market and has been classified as the best ERP software by G2, Forbes, and Capterra.
In terms of planning, NetSuite has a module called PBCS, which stands for Planning and Budgeting Cloud Service. It uses a company's historical data to predict periods of high demand and allows you to plan for this. The platform's what-if scenario capabilities also enable users to explore and prepare for various business situations, assessing the potential impacts of strategic decisions before they are made. This is vital for making informed decisions on things like regional and product expansion.
In terms of analysis, NetSuite has extensive reporting capabilities. Whether it's mid- or end-of-month, you get real-time access to your financial situation, and this allows for timely decision-making. For businesses that operate across multiple entities, the advanced financial consolidation combined with the reporting means you can see the total picture of your business at any point in time, without having to go through the painful month-end processes.
NetSuite doesn't just provide financial planning and analysis, but it also provides you with a solid CRM function, e-commerce capabilities, supply chain, and inventory management, so you can create the perfect solution for your business.
Karl Threadgold , Managing Director, Threadgold Consulting
Making the transition from software to e-commerce created new challenges on the bookkeeping front. I discovered that most providers were not familiar with the nuances required for physical products. Finaloop proved to be invaluable—a true evolution over the old, stodgy tools like QuickBooks and the agencies that prefer them.
Will Roman , Founder, Chisos Boot Company
Workday Adaptive Planning
I recommend Workday's Adaptive Planning. The key elements here are flexibility, control, and pushing past boundaries. You can customize the dimensions according to your preference, incorporating different levels of analysis and ultimately giving a deeper understanding. Workday has it all in one space. I love the speed at which you can change your budget by taking into consideration different scenarios within one time period. We've reduced our forecasting time significantly.
Ronald Osborne , Founder, Ronald Osborne Business Consultancy and Coaching
I strongly advise aspiring entrepreneurs to adopt cloud-based bookkeeping software such as FreshBooks. These programs come with a user-friendly interface that simplifies financial tasks like recording expenses and generating financial statements through invoices.
What makes them beneficial? Fundera states that a staggering 82% of businesses fail due to poor management of cash flow. Cloud accounting takes care of many procedures, thereby giving you a chance to know how you are faring financially at any given moment. You can track your expenses against specific areas where cuts can be made while at the same time ensuring that enough money is set aside for future use on anticipated costs.
These utilities seamlessly integrate with popular business tools and payment processors, saving valuable time by streamlining financial processes within an organization. It's like having a personal accountant in the palm of your hand but at a fraction of the cost of traditional accounting services.
Arifful Islam , Finance Expert, Sterlinx Global LTD
For the busy entrepreneur, it can be tough trying to shift from the creative nature of running a business to the more methodical task of spreadsheets. It may be tedious, but diligent accounting and financial planning are vital to the success of any business. Utilizing a tool like Wave for bookkeeping and financial planning can help you track transactions, create estimates and invoices, and generate receipts. This suite of apps also allows you to manage payroll. Unlike QuickBooks, Wave is free and well-suited for small businesses that need to better manage day-to-day operations but have not yet scaled to the point of managing hundreds of employees.
Blair Thomas , Co-founder, eMerchantBroker
In 2024, the one technology I recommend entrepreneurs learn and use for financial planning and analysis is Python programming.
It's easier than ever to learn; you do not have to install anything if you use Google Colab, for example. You can use ChatGPT or another LLM to help you learn it and create sample code for you, and if you master Python, it opens a new world for FP&A.
You can do better forecasts, improve your budgets, and overall, your financial analysis capabilities multiply by 10x!
And it is open-source and free to use.
Christian Martinez , Finance Analytics Manager, Kraft Heinz
As an entrepreneur myself, I know how important it is to have a solid handle on your finances. One tool that I always recommend to other business owners is Xero. It's an online accounting software that's really user-friendly and intuitive, even if you don't have a background in finance.
What I love about Xero is that it gives you a real-time view of your cash flow and financial performance. You can easily track your income and expenses, create invoices and purchase orders, and reconcile your bank transactions all in one place. It also has some great reporting features that help you make sense of your numbers and spot trends over time.
Another big selling point for me is that Xero integrates seamlessly with a lot of other business tools that I use, like my CRM and payment processors. This saves me a ton of time and hassle when it comes to data entry and reconciliation.
I think Xero is a fantastic choice for entrepreneurs who want to stay on top of their finances without getting bogged down in complicated spreadsheets or accounting jargon. It's affordable, easy to use, and gives you the insights you need to make smart business decisions.
Sam Kadel , Founder, KBA Web
I recommend Cube as a robust FP&A solution for businesses aiming to enhance the efficiency and precision of their financial forecasting, budgeting, and accounting processes.
It's a platform that integrates seamlessly with spreadsheets, enabling finance teams to make more informed business decisions by automating time-consuming manual tasks and minimizing errors.
With Cube, complex and tedious FP&A and accounting activities, like financial consolidation, are automated, allowing finance teams to concentrate more on strategy, planning, and overall corporate performance. Financial professionals can continue to work within the familiar environment of spreadsheets while benefiting from the advanced features of a contemporary FP&A tool. Since it is based on Excel, it allows for easy adjustments and quick data analysis or changes in forecast drivers. Implementing it required external assistance to become fully operational.
Eric Croak, CFP , President, Croak Capital
One tool I'd recommend for financial planning and analysis is Harvest. It's incredibly user-friendly and effective for tracking time and expenses, helping you maintain control over your project budgets. With Harvest, you can easily determine if your projects are profitable or if they're draining resources. Harvest offers more than just tracking; it integrates time logging, invoicing, and project management in a seamless interface. This can simplify how you handle your financials, allowing you to focus more on growing your business. While Harvest provides the necessary data and tools for making informed financial decisions, leveraging its full potential still depends on you. It streamlines the process, making it easier and more efficient to manage your operations. Give it a try, and see how it can help elevate your business management game.
Travis Schreiber , Director of Operations, Erase Technologies
One tool I highly recommend for financial planning and analysis is eMoney. While it would be nice if this were a paid endorsement, I'm not a representative of the software—but it's still been a valuable asset for my team and clients. It offers a secure website and document vault, making it easy for clients to access their financial information in one place. The platform generates custom reports and analyses tailored to each client's needs, and its integration abilities with other software providers streamline data management for a seamless experience. For entrepreneurial clients, eMoney makes information easily accessible, allowing them to focus on their business while ensuring we have everything needed to plan effectively on their behalf. This streamlined approach enables us to provide informed, personalized guidance that leads to long-term growth.
Delante Greer , Financial Planner, Opulentia LLC
For entrepreneurs who are serious about improving their financial planning and analytical skills, especially in revenue and profit forecasts, PlanGuru is a great tool. As someone who works extensively in the financial industry, I understand how important precise forecasting is to attract investors as well as to guide prudent spending and liquidity management. PlanGuru's strong functionality elevates this process.
The software's ability to integrate revenue and expense modeling into comprehensive forecasts of the balance sheet and cash flow statement is particularly valuable. It also automatically generates key financial ratios and break-even analyses, which are essential for making informed business decisions. These features provide a level of depth and precision that can transform financial planning from a daunting challenge into a manageable and even strategic asset.
While PlanGuru does come with a higher upfront cost, especially if multiple-user access is required, its unique tools and extensive customer support justify the investment for businesses focused on growth and scalability. One big plus is that it offers a free 30-day trial, which lets business owners check out the features and assess how valuable it is for their particular needs without having to commit to anything right away.
In my opinion, a company's capacity to properly plan for the future and react to market dynamics can be significantly impacted by its investment in the appropriate financial management tools. As part of their strategy toolkit, PlanGuru is ideal for individuals who require accurate and comprehensive financial forecasts.
Jocarl Zaide , Chief Financial Officer, SAFC
QuickBooks is my recommended tool for entrepreneurs who need some assistance in financial planning and analysis.
As an entrepreneur, it's important to utilize user-friendly software like QuickBooks to manage finances and make well-informed decisions. Tracking income and expenses, generating financial reports, handling invoices and payments, and simplifying tax preparation are all made easy with QuickBooks. Whether I'm working solo or leading a team, QuickBooks is flexible enough to meet my business requirements, providing scalability and flexibility. The software offers in-depth financial strategies that are crucial for optimizing business operations.
QuickBooks also promotes collaboration by enabling me to share financial information with important stakeholders, such as advisors and team members. This fosters financial literacy and accountability within my organization, empowering individuals to contribute to our financial health and strategic direction.
With QuickBooks integrated into my financial planning and analysis processes, I can confidently navigate business hurdles, ensuring sustainable growth and long-term success.
Heidi Cortez , Founder, Heidi Cortez
Fathom stands out as a particularly powerful tool for financial planning and analysis. It's designed with advanced features for analytics, benchmarking, and tracking key performance indicators. Entrepreneurs can gain deep insights into their business's financial performance, making it easier to identify trends, opportunities, and areas for improvement.
One of Fathom's strengths lies in its ability to simplify complex financial data. It provides clear, visual reports that are easy to understand, even for those who may not have a strong background in finance. This makes it an excellent choice for entrepreneurs who need to make informed decisions quickly.
In addition to its visualization capabilities, Fathom allows for sophisticated benchmarking. Entrepreneurs can compare their business's performance against industry standards or competitors, offering a clear perspective on where they stand and what improvements might be necessary.
Also, Fathom's KPI tracking can be customized to focus on the metrics that matter most to your business. Whether it's profitability, cash flow, or other critical financial indicators, Fathom enables you to monitor these in real-time, ensuring that you stay on top of your financial health.
Mary Tung , Founder & CEO, Lido.app
Microsoft Excel
For entrepreneurs delivering FP&A services, there is no tool more practical for our work than Microsoft Excel. Excel may not be the best software for all planning and data-analysis capabilities at scale, but it's the most universally understood across companies and industries. Nearly all accounting and FP&A software can export to .xlsx or .csv, and Excel can provide a customized blueprint for further analytics and process development.
Carl Seidman , Principal, Seidman Financial
For entrepreneurs who need to integrate payroll, benefits administration, and financial management, Gusto is an excellent choice. This cloud-based platform simplifies payroll processing and automatically handles all tax filings and payments, ensuring compliance and accuracy.
Gusto also offers tools for managing employee benefits and building compensation packages, which can be directly linked to financial forecasting and budgeting within the same tool. The advantage here is the seamless integration of payroll and other HR functions with financial planning, providing a holistic view of the company's financial health.
David Ciccarelli , CEO, Lake
One unique tool that I recommend to entrepreneurs for financial planning and analysis is Float. Float is a cash-flow forecasting software that helps businesses predict their future cash position with accuracy.
What sets Float apart is its intuitive interface and powerful forecasting capabilities. It allows entrepreneurs to create detailed cash-flow projections based on historical data and future expectations. Float also offers scenario planning, which enables entrepreneurs to assess the impact of different business decisions on their cash flow.
One of the unique features of Float is its integration with accounting software like Xero, QuickBooks Online, and FreeAgent. This integration allows entrepreneurs to streamline their financial data and make more informed decisions based on real-time information.
Aqeel Abbas , CEO, WorkStaff360
As an entrepreneur seeking effective financial planning and analysis tools, I recommend Anaplan. This platform dynamically connects financial, strategic, and operational plans in real time. By integrating these aspects, Anaplan empowers businesses to anticipate change, address complexity, and move at market speed. It offers flexibility and allows for quick and structured modeling, which surpasses traditional spreadsheets.
Anaplan's Connected Planning Platform stands out for its ability to view and contextualize current performance while forecasting future outcomes. This functionality helps fuel growth and mitigate risk. For instance, we used Anaplan to optimize our budget allocation, leading to a 15% reduction in operational costs. This streamlined decision-making and improved our strategic initiatives.
However, it's essential to note that Anaplan is not without its challenges. Hosting high volumes of granular data can be problematic. Despite these issues, the platform's benefits outweigh the drawbacks, making it a valuable tool for financial planning and analysis.
Elmo Taddeo , CEO, Parachute
One favorite software program for financial planning and analysis, especially for startups and new businesses, is LivePlan.
I love LivePlan as it makes all the essential first steps for a business easier and faster. You can create a business plan with it (it even has an AI assistant you can try out for this) and then use it to help forecast your business's financials. I think it's a brilliant tool that can really help out new founders who have a great business idea but don't have much experience with the financial side of starting a business.
I find that its integration with QuickBooks (and Xero, if you use that program) is really helpful—this makes getting access to LivePlan's forecasting tools so much easier! It provides very clear and easy-to-understand charts and graphs that help us better visualize our financial situation. Getting revenue forecasts with LivePlan helps companies like ours make better day-to-day decisions. It also allows us to change some of the financial assumptions manually and see what happens to the financial projections as a result.
LivePlan is a very helpful tool for getting new small businesses and startups off the ground! It's also not prohibitively expensive, as it costs $30 a month if you pay yearly.
Ali Azimi , Co-Founder, Cheyn 3D Clothing Design Software, Cheyn
Successfully copied link

Enterprise Organization: Business Law & Entrepreneurship Law
The legal side of operating a business..
Whether it is a large, global corporation or a young start-up, businesses rely on lawyers to provide expert legal assistance with contracts, finances, real estate, employees, investors, mergers, trademarks, acquisitions and a multitude of other areas.
In this program, you will focus on the legal issues that surround the formation, operation and governance of businesses. You will build fundamental lawyering skills and a strong understanding not only of the technical aspects of business law, but also of how businesses generally work.
Listed among the nation's top 50 law schools for public interest and clinical opportunities, the college offers valuable practical experiences representing real clients. Learn business law through externships, a rigorous pro bono program, and clinics, like the Small Business Legal Clinic and the Family Justice Clinic.
Students in this area of emphasis have the option to study in Moscow or Boise.
This program could be a good fit if you:
- Hold an undergraduate degree
- Are interested in business
- Have a strong work ethic
- Have solid skills in negotiation, project management and communication
- Have a strong academic background
- Can think critically and analytically about complex problems
Career Outcomes
With this degree, you could become a:
- Lawyer (J.D.)
- Corporate attorney
- Business leader
- Public administrator
- Entrepreneur
Moscow Boise
Available On-Campus
You may also be interested in:

Gain the legal education, lawyering skills, and professional experiences essential for the successful practice of law.

Accountancy, Master of/J.D. Concurrent Degree, M./J.D.
Prepare to for success in a dynamic global marketplace with an advanced degree in both accounting and law.
More degrees below. Enjoy!
Environmental science.
Build specialized expertise in environmental science concurrently with natural resources and environmental law while earning both a master’s degree and a J.D. degree.
Law: Native Law
Learn how tribal, state and federal law intersect and apply this knowledge to address pressing issues surrounding Native-American law.
Law: Natural Resources & Environmental Law
Develop the specialized expertise to solve legal problems in this highly technical and complex field.
Commercial Law: Business Law & Entrepreneurship Law
Gain the expertise in the laws that govern business and consumer transactions.
Develop the skills to help entrepreneurs and corporate leaders form, operate and govern business.
Accountancy, Master of/J.D. Concurrent Degree
Water resources.
Gain the legal and scientific knowledge required to solve complex water issues.
- Updated Terms of Use
- New Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
- Closed Captioning Policy
Quotes displayed in real-time or delayed by at least 15 minutes. Market data provided by Factset . Powered and implemented by FactSet Digital Solutions . Legal Statement .
This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed. ©2024 FOX News Network, LLC. All rights reserved. FAQ - New Privacy Policy
How to start a candle business in 2024: 5 easy steps to selling candles from the comfort of your home
Starting a candle business can be an excellent source of additional income.

Small business owners fear they won't survive a second Biden term
Katlyn Swaffer and Maher Youssef explain how their small businesses have been affected by inflation and call on President Biden to address the issue.
Americans are rapidly working on side hustles as an additional source of income.
Fifty-four percent of Americans have begun a side hustle in the last twelve months, according to MarketWatch, as a means of making more money in addition to a primary source of income.
All you really need to start a side hustle is an idea and an understanding of how to execute that idea. Taking a creative approach to your entrepreneurship can include a hobby-like business, and one of the more popular ones today is candle making.
Whether you have made a candle before or not, through trial and error, there are simple tricks to producing a product that is unique from what else is on the market.

One side hustle that can bring you extra income is a candle business. You can begin the business at home, selling online and at local craft fairs. (David Crane/MediaNews Group/Los Angeles Daily News via Getty Images / Getty Images)
WANT TO MAKE MONEY OFF YOUR FLOURISHING GARDEN? HERE ARE 4 WAYS TO TURN YOUR CROPS INTO CASH
You can make candles in your own home pretty easily. Here's a guide to get you started on your candle business.
- Learn how to make candles from home
- Come up with a brand name, logo and label for your candles
- Write a business plan
- Register your business
- Decide how you are going to sell and get your business going
1. Learn how to make candles from home
The first step to starting your business is learning how to make candles. You'll need minimal supplies to get you started, including containers for your candles, wax, wicks and fragrance.
It will take trial and error to perfect the look of your candle, the wick placement and the amount of fragrance you need for the perfect scent. If you want to add color to your candle, you'll also need to purchase dye.
At first, the top of your candle may not appear totally smooth, your wick may be crooked, or you may not have enough fragrance for the scent.

Practice makes perfect. The more candles you make, the better you'll get and the quicker you'll be ready to sell. (Creative Touch Imaging Ltd./NurPhoto via Getty Images / Getty Images)
All the candles you make during your trial and error period can be gifts for friends and family because they probably won't be good enough to sell.
You could also buy wax molds to add uniqueness to your candles.
TIPS FOR SELLING EGGS AND TURNING A PROFIT RIGHT FROM YOUR BACKYARD
Once you have made numerous candles with success, you're ready to move to step two.
2. Come up with a brand name, logo and label for your candles
You will need a unique brand name and logo for your business and a label for your candles.
Your brand name should be something unique and memorable. You'll also want to create a logo for your business and a label to put on each of your candles.
On each candle should be your brand name/logo as well as information about the candle itself, like the scent, instructions and safety information.
3. Write a business plan
All businesses start out with a plan.
A business plan is a document that describes the company and also highlights its goals.
In a business plan, you can include elements like the mission statement, the products offered, the target audience of the company, marketing plans and financial information.
HOW TO START A LEMONADE STAND WITH YOUR KIDS THIS SUMMER
Your business plan is by no means set in stone. As your company grows and changes, your plan will, too. You can always make edits to your business plan when needed.
4. Register your business
To run a business, you'll need to register it. The process varies depending on your state, so you'll need to look into the legal requirements where you live to avoid getting fined or having your business shut down.
Once your business is registered, you'll receive an Employer Identification Number (EIN). This number is given to businesses for tax purposes.
Also, make sure you obtain any necessary business licenses or permits in the state to legally operate your business.
You'll want to have all these legal steps taken care of before you start selling candles.

Make sure to have the scent of the candle and the name of your business clearly displayed on each container. (David Crane/MediaNews Group/Los Angeles Daily News via Getty Images / Getty Images)
5. Decide how you are going to sell and get your business going
Now, it's time to officially launch your business.
You will need to determine a price for your candles. According to Forbes, you'll want to aim for a 25% to 50% profit margin, so keep that in mind when you are considering how much to charge.
You should create a website for your business with your contact information for customers to reach out to you. You can also sell your candles through your own website.
Another way to sell is through an online marketplace like Etsy.
GET FOX BUSINESS ON THE GO BY CLICKING HERE
It's also a good idea to start social media channels for your business. Include high-quality pictures of your product on these channels.
Social media is not only a great way to market your business, but another way you can sell your candles.
During the warmer months, consider buying a booth at a local craft fair to sell your products. This is a great way to spend some time outside while also speaking directly with customers.
- Work & Careers
- Life & Arts
Become an FT subscriber
Try unlimited access only $1 for 4 weeks.
Then $75 per month. Complete digital access to quality FT journalism on any device. Cancel anytime during your trial.
- Global news & analysis
- Expert opinion
- Special features
- FirstFT newsletter
- Videos & Podcasts
- Android & iOS app
- FT Edit app
- 10 gift articles per month
Explore more offers.
Standard digital.
- FT Digital Edition
Premium Digital
Print + premium digital, ft professional, weekend print + standard digital, weekend print + premium digital.
Essential digital access to quality FT journalism on any device. Pay a year upfront and save 20%.
- Global news & analysis
- Exclusive FT analysis
- FT App on Android & iOS
- FirstFT: the day's biggest stories
- 20+ curated newsletters
- Follow topics & set alerts with myFT
- FT Videos & Podcasts
- 20 monthly gift articles to share
- Lex: FT's flagship investment column
- 15+ Premium newsletters by leading experts
- FT Digital Edition: our digitised print edition
- Weekday Print Edition
- Videos & Podcasts
- Premium newsletters
- 10 additional gift articles per month
- FT Weekend Print delivery
- Everything in Standard Digital
- Everything in Premium Digital
Complete digital access to quality FT journalism with expert analysis from industry leaders. Pay a year upfront and save 20%.
- 10 monthly gift articles to share
- Everything in Print
- Make and share highlights
- FT Workspace
- Markets data widget
- Subscription Manager
- Workflow integrations
- Occasional readers go free
- Volume discount
Terms & Conditions apply
Explore our full range of subscriptions.
Why the ft.
See why over a million readers pay to read the Financial Times.
International Edition

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A business plan is an aspiring entrepreneur's way to prove that a business idea is actually worth pursuing. As entrepreneurs document their go-to-market process, capital needs, and expected return on investment, entrepreneurs likely come across a few hiccups that will make them second guess their strategies and metrics — and that's exactly ...
If you opt for the brief business plan, you will focus primarily on articulating a big-picture overview of your business concept. This version is used to interest potential investors, employees, and other stakeholders, and will include a financial summary "box," but it must have a disclaimer, and the founder/entrepreneur may need to have the people who receive it sign a nondisclosure ...
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
A business plan lays out a strategic roadmap for any new or growing business. Any entrepreneur with a great idea for a business needs to conduct market research, analyze their competitors, validate their idea by talking to potential customers, and define their unique value proposition.
Traditional business plans use some combination of these nine sections. Executive summary. Briefly tell your reader what your company is and why it will be successful. Include your mission statement, your product or service, and basic information about your company's leadership team, employees, and location.
Add in the company logo and a table of contents that follows the executive summary. 2. Executive summary. Think of the executive summary as the SparkNotes version of your business plan. It should ...
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow. A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It's also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals. After completing your plan, you can ...
Business Glossary. Definitions for common terminology and acronyms that every small business owner should know. Bplans offers free business plan samples and templates, business planning resources, how-to articles, financial calculators, industry reports and entrepreneurship webinars.
A business plan is a written document that defines your business goals and the tactics to achieve those goals. A business plan typically explores the competitive landscape of an industry, analyzes a market and different customer segments within it, describes the products and services, lists business strategies for success, and outlines ...
Read more on Competitive strategy or related topics Disruptive innovation, Entrepreneurial business strategy, Entrepreneurship, Start-ups, Supply chain management and Entrepreneurial exit strategy ...
The business planning process in entrepreneurship helps an entrepreneur identify exactly what needs to be accomplished to build the venture, and what human and financial resources are required to ...
Typically, business planning has been analyzed as the single act of writing a business plan (e.g. Honig and Karlsson, 2004).However, business planning is made up of a variety of activities (Gruber, 2007), which entrepreneurs may utilize as a whole, or simply choose parts of the business planning process.It is worth noting that these specific activities are not mutually exclusive with lean ...
The Importance Of Planning In Entrepreneurship Benjamin Franklin once said, "If you fail to plan, you plan to fail." Planning is an important part of many aspects of our lives, and is especially true in business. Success often doesn't simply happen by chance, but requires a willingness to plan and put in
As the road map for a business's development, the business plan. Defines the vision for the company. Establishes the company's strategy. Describes how the strategy will be implemented. Provides a framework for analysis of key issues. Provides a plan for the development of the business. Helps the entrepreneur develop and measure critical ...
Chapter 5 - Business Planning. Business planning is an important precursor to action in new ventures. By helping firm founders to make decisions, to balance resource supply and demand, and to turn abstract goals into concrete operational steps, business planning reduces the likelihood of venture disbanding and accelerates product development ...
Here are the key elements of a good business plan: Executive Summary: An executive summary gives a clear picture of the strategies and goals of your business right at the outset. Though its value is often understated, it can be extremely helpful in creating the readers' first impression of your business.
It's the roadmap for your business. The outline of your goals, objectives, and the steps you'll take to get there. It describes the structure of your organization, how it operates, as well as the financial expectations and actual performance. A business plan can help you explore ideas, successfully start a business, manage operations, and ...
Examples of Definitions of Entrepreneurship. Entrepreneurship can be defined as a field of business that. seeks to understand how opportunities to create something new (e.g., new products or services, new markets, new production processes or raw materials, new ways of organizing existing technologies) arise and are discovered or created by specific persons, who then use various means to ...
Indeed, research published in the International Small Business Journal demonstrates that engaging in planning activities is associated with better chances of success and greater accuracy. The ...
Creating a business plan is an important step for outlining your business goals. It also includes your product description, target market, and financial projections, among other core components.
4. Pet Care Services. A dog walking business is an excellent opportunity for someone who loves dogs and is good with other people's dogs. You get out every day and enjoy fresh air with grateful ...
Martin et al. (2013) link EE and human capital and confirm that EE has a strong significant relationship with the type of entrepreneurship outcomes, which involves in business planning and financing, new business creation, persistence of running business, and income from established business. In addition, the positive effect of EE on EA can ...
In this capstone course of the BA degree in Creative Entrepreneurship, students integrate and apply the knowledge gained throughout their major to create a business plan. Topics include identifying problems and business opportunities, market analysis, execution plan, and financial projection.
Nowadays, the situation when your business plan will be outdated after a short period of time is very real. Tony Robbins said: "The most painful mistake I see in first-time entrepreneurs is thinking that just having a business plan or a great concept is enough to guarantee success. It's not. Business success is 80% psychology and 20% mechanics.
Float. One unique tool that I recommend to entrepreneurs for financial planning and analysis is Float. Float is a cash-flow forecasting software that helps businesses predict their future cash ...
The legal side of operating a business. Whether it is a large, global corporation or a young start-up, businesses rely on lawyers to provide expert legal assistance with contracts, finances, real estate, employees, investors, mergers, trademarks, acquisitions and a multitude of other areas. In this program, you will focus on the legal issues ...
Okay, so is time management, but you can have two. Start by mapping out your week in advance, noting down your classes, study sessions, business meetings, and any other commitments you might have ...
4. Register your business. To run a business, you'll need to register it. The process varies depending on your state, so you'll need to look into the legal requirements where you live to avoid ...
Six Nato countries are planning to develop a "drone wall" to help defend their borders with Russia after a series of provocations, ranging from forced migration to attempts to amend the frontiers.