

What Is a Prompt in Writing? (Ultimate Guide + 200 Examples)
Ever stumbled upon a blank page and didn’t know where to start?
That’s where a writing prompt steps in, kicking your creativity into gear and guiding your pen (or cursor) in the right direction.
What is a prompt in writing?
A prompt in writing is a starting point designed to ignite creativity, guiding writers to explore themes, genres, or emotions. It can be a word, question, image, or scenario, aiding in overcoming writer’s block.
Keep reading to learn everything you need to know about prompts in writing.
What Is a Prompt in Writing (Long Description)?

Table of Contents
A writing prompt is essentially a starting point.
Think of it as a spark designed to ignite your creativity and guide your thoughts in a specific direction.
This little nudge can come in various forms – a word, a sentence, a question, or even a picture – and serves the purpose of inspiring you to write.
Whether you’re drafting a story, an essay, or just jotting down your thoughts, prompts help overcome the intimidation of a blank page.
It sets a predefined theme or direction for your writing.
They’re not just about what you write, but how you think and approach writing, encouraging you to explore new ideas, genres, and perspectives.
Here is a good video that explains prompts in writing:
Types of Prompts in Writing
Now let’s go over different types of prompts in writing.
Common prompt types include:
The Story Starter
The question quest, picture this, the first line frenzy.
The Story Starter is your classic nudge towards narrative creativity.
It’s a sentence or scenario meant to kick off your storytelling journey, helping you dive straight into the plot, characters, or setting.
This type of prompt is great for fiction writers looking for a jumping-off point to explore various themes or genres.
It can be as detailed or as open-ended as you like, providing just enough information to spark an idea without dictating the direction of your story.
- “When the clock struck midnight, she realized…”
- “Lost in the forest, he stumbled upon a hidden village…”
- “The last person on Earth sat alone in a room. Suddenly, there was a knock at the door…”
- “In a world where magic is real, a young apprentice discovers…”
- “The photograph in the old book revealed a secret that would change everything…”
- “Stranded on a desert island, they found a message in a bottle…”
- “On her hundredth birthday, she received a letter that took her back to her youth…”
- “The map led them to a place that wasn’t supposed to exist…”
- “In the midst of war, a forbidden love blossomed…”
- “He inherited an old mansion, not knowing the ancestors would still be around…”
The Question Quest prompt type uses intriguing questions to push your thinking boundaries and explore ideas in depth.
It’s perfect for essays, reflective writing, or exploring complex themes and issues.
These prompts challenge you to consider different perspectives, analyze situations, and develop reasoned arguments or narratives based on the question posed.
- “What would you do if you could travel back in time?”
- “How would society change if humans lived to be 300 years old?”
- “Is it possible to live a completely ethical life in today’s world?”
- “What does true bravery look like?”
- “How would the discovery of extraterrestrial life impact humanity?”
- “What is the true cost of progress?”
- “Can happiness be measured?”
- “What role does fate play in our lives?”
- “Is technology bringing us closer together or driving us apart?”
- “What would you change if you were the leader of your country for a day?”
Picture This prompts use images as the springboard for writing.
A photograph, painting, or even a random doodle can unlock a flood of creativity.
Which makes it an excellent tool for both fiction and non-fiction writers.
This visual cue encourages you to dive into descriptive writing, storytelling, or even analytical essays, exploring the emotions, stories, or ideas evoked by the image.
- A deserted street at dawn, with an old bicycle leaning against a lamppost.
- A vintage suitcase, open and filled with letters and photographs.
- A bustling market scene in a foreign country.
- A child gazing out of a rain-spattered window.
- A majestic mountain range under the stars.
- An abandoned house, its rooms still furnished but covered in dust.
- A close-up of a spider web with dewdrops.
- A lively street festival, with people dancing and musicians playing.
- An old, faded map with several places marked in red.
- A serene lake at sunset, with a lone boat tied to a wooden dock.
The First Line Frenzy is a thrilling way to dive into a story.
These prompts provide the opening sentence of your narrative, setting the tone and direction for everything that follows.
It’s a fantastic method for overcoming writer’s block and sparking your imagination, as the initial line can lead to unexpected and exciting story developments.
- “The day began with a mysterious package on my doorstep.”
- “I never believed in ghosts until I moved into the old Henderson house.”
- “The moment I heard the news, I knew my life would never be the same.”
- “Under the light of a full moon, the city revealed its true secrets.”
- “It was the kind of café you’d stumble upon once and never find again.”
- “With a deep breath, I stepped into the unknown.”
- “The letter, sealed with a wax emblem, contained a proposition I couldn’t refuse.”
- “As the train pulled away, she realized her mistake.”
- “In the heart of the ancient forest, a hidden path led to unexpected wonders.”
- “The discovery promised to rewrite history, but at what cost?”
Dialogue Driven
Dialogue Driven prompts center around a snippet of conversation, offering a dynamic entry point into your writing.
This approach is particularly effective for character development and exploring relationships through direct speech.
It can set the scene, reveal personalities, and drive the plot forward, all through the power of dialogue.
- “Did you really think I wouldn’t find out?” “I was hoping.”
- “Why is this door always locked?” “You’re not ready to know what’s behind it.”
- “Just because you can, doesn’t mean you should.” “That’s where you’re wrong.”
- “The stars look different here.” “Everything does.”
- “I wish I could stay.” “Then why are you leaving?”
- “It’s not about what I want anymore.” “Then what’s it about?”
- “I’ve never seen anything like it.” “And you never will again.”
- “Can you keep a secret?” “Depends on the secret.”
- “We’re not in Kansas anymore.” “We’re not even on the same planet.”
- “It was supposed to be a simple plan.” “Since when does anything go according to plan?”
The Sensory Dive
The Sensory Dive prompts are designed to immerse you and your reader in vivid, sensory-rich experiences.
These prompts encourage descriptive writing that appeals to the senses, painting a scene so tangible that readers feel they can touch, taste, hear, see, and smell it.
It’s a powerful tool for creating immersive worlds and experiences.
- Describe the cacophony of a bustling city market at noon.
- The taste of the first snowflake of winter.
- The scent of old books in a forgotten library.
- The feeling of sand between your toes as waves crash on the shore.
- The sight of a landscape transformed by autumn’s touch.
- The sound of a distant thunderstorm approaching.
- The warmth of a crackling fire on a cold night.
- The chill of walking through a foggy graveyard at dusk.
- The texture of an ancient, carved stone.
- The silence of a snow-covered forest.
The What-If Wonder
The What-If Wonder prompts take you on a journey of imagination, exploring alternate realities and scenarios.
These prompts ask you to consider how different choices, events, or conditions might alter the world, characters, or story.
It’s an excellent way to delve into speculative fiction, science fiction, and fantasy, pushing the boundaries of reality.
- What if humans had the ability to communicate telepathically?
- What if gravity suddenly became a variable force on Earth?
- What if you woke up 100 years in the past with your current memories intact?
- What if plants were the dominant intelligent species on the planet?
- What if you could see the future but only 24 hours ahead?
- What if water was as rare as gold?
- What if everyone had their lifespan displayed above their heads?
- What if you found a door that could take you to parallel universes?
- What if animals could petition for their rights?
- What if dreams were actually glimpses into alternate realities?
The Emotional Rollercoaster
The Emotional Rollercoaster prompt is all about exploring the depths of human emotion, challenging you to convey complex feelings and reactions.
These prompts are perfect for delving into character development, interpersonal relationships, and personal reflection.
By focusing on the emotional landscape, writers can create compelling narratives that resonate with readers on a deeply personal level.
- The moment you realized you were in love.
- Feeling utterly lost in a place you once called home.
- The bitter sweetness of a farewell.
- Overcoming a fear that once held you back.
- The complex emotions of reuniting with someone after many years.
- The guilt of a lie that spiraled out of control.
- The rush of achieving something you thought was impossible.
- The profound sadness of losing a cherished memory to time.
- The unexpected joy found in a simple act of kindness.
- The peace of accepting things you cannot change.
The Genre Blender
The Genre Blender prompts encourage you to mix elements from different genres, creating unique and innovative narratives.
These prompts are excellent for writers looking to break the mold and experiment with their storytelling.
Whether it’s combining science fiction with historical fiction or fantasy with mystery, the possibilities are endless.
- A detective in a dystopian future solving a crime that could change the course of history.
- A romance blossoming in the midst of a zombie apocalypse.
- A fantasy world where magic is dying, and technology is on the rise.
- A historical drama set in ancient Rome, but with a twist of time travel.
- A horror story set in space, aboard a ship with a mysterious alien artifact.
- A western where the frontier towns are protected by wizards instead of gunslingers.
- A cyberpunk thriller featuring a heist in a virtual reality world.
- A mystery set in a magical school where the students must uncover a dark secret.
- A superhero story grounded in the real-world challenges of modern society.
- An adventure tale that blends deep-sea exploration with ancient mythology.
The Time Traveler’s Gateway
The Time Traveler’s Gateway prompts explore the intricacies of time travel, its implications, and its paradoxes.
This type of prompt is perfect for science fiction and speculative fiction writers, offering a playground for the imagination that challenges our understanding of time, history, and causality.
- Discovering a time machine in your backyard and deciding where to go first.
- A message from the future warning of an impending disaster.
- The consequences of changing a small event in the past.
- A society where time travel is common, but strictly regulated.
- An ancient civilization that had advanced time travel technology.
- Meeting your ancestors and learning their secrets.
- The ethical dilemmas of using time travel for personal gain.
- A love story that transcends time barriers.
- The discovery that history is a construct, shaped by time travelers.
- A time loop where the protagonist must solve a puzzle to escape.
The World Builder’s Dream
The World Builder’s Dream prompts invite you to create entire worlds from scratch.
This type of prompt is a boon for fantasy and science fiction writers, offering the freedom to craft unique settings, cultures, laws of nature, and societies.
It’s an opportunity to let your imagination run wild and establish the groundwork for epic tales.
- A planet where the seasons last for decades.
- A city built entirely on the back of a giant, wandering creature.
- A society where people’s roles are determined by their innate magical abilities.
- An underwater civilization that has never seen the surface.
- A world where dreams can be entered and manipulated.
- A floating island nation that travels the skies.
- A dystopian future where memories can be bought and sold.
- A kingdom where music is the source of all magic.
- A realm where the night lasts half the year.
- An alternate Earth where the continents never split apart.
The Unseen Perspective
The Unseen Perspective prompts challenge you to write from the viewpoint of non-human characters or entities.
This approach forces you to step outside the human experience and consider the world from a completely different angle.
It’s a fantastic way to explore themes of consciousness, nature, and the interconnectedness of life.
- The life of a tree over centuries, witnessing the changes in the world.
- A day in the life of a household pet during a major family event.
- The thoughts of a spaceship AI as it travels through the cosmos.
- The experiences of a ghost haunting an old mansion.
- A story told from the perspective of a river, from source to sea.
- The journey of a single leaf from sprout to falling to the ground.
- The collective consciousness of a hive of bees facing environmental challenges.
- The ancient spirit of a mountain overseeing its surroundings.
- The adventures of a book as it passes from reader to reader, experiencing different interpretations and emotions.
- The perspective of a city as it grows and evolves over centuries, through peace and conflict.
The Emotional Journey
The Emotional Journey prompts focus on the internal growth and transformation of characters.
It invites writers to delve into personal development, self-discovery, and the overcoming of obstacles.
This type of prompt is ideal for character-driven narratives, where the emphasis is on emotional depth and the evolution of the protagonist’s inner self.
- A character grappling with the loss of a loved one and finding a way to move forward.
- The journey of self-acceptance for someone who feels out of place in their world.
- A hero facing their darkest fears in order to save what they cherish most.
- A villain’s realization of the impact of their actions and their quest for redemption.
- A young adult’s transition into independence and the challenges they face along the way.
- The transformation of a skeptic into a believer through a series of unexplainable events.
- The struggle of a character to forgive themselves and others for past mistakes.
- The process of rebuilding one’s life after a catastrophic event.
- A character’s journey from indifference to passionate advocacy for a cause.
- The evolving relationship between two characters who start as rivals and become allies.
The Moral Dilemma
The Moral Dilemma prompts put characters in situations where they must make difficult choices, often between two equally undesirable options.
These prompts are great for exploring ethical questions, character morality, and the complexity of human nature.
They challenge writers to think deeply about what it means to make a “right” decision.
- Choosing between saving a loved one or a group of strangers from danger.
- Deciding whether to expose a painful truth that could destroy a friend’s happiness.
- The choice of upholding the law or doing what is morally right in a corrupt society.
- A character must decide whether to seek revenge or forgive an unforgivable act.
- The dilemma of sacrificing personal dreams for the greater good.
- Deciding whether to keep a secret that protects one person but harms others.
- A leader’s choice between peace at the cost of justice or war for the sake of freedom.
- The ethical implications of using advanced technology to alter human nature.
- A scientist faces a moral conflict over a discovery that could change the world but has dangerous implications.
- The struggle of a character who finds out that their entire life is based on a lie and must choose how to react.
The Creative Challenge
The Creative Challenge prompts are designed to push the boundaries of conventional storytelling.
It encourages experimentation with narrative structure, style, and content.
These prompts invite writers to play with unconventional formats, such as a story told in reverse, a narrative composed entirely of dialogue, or a tale that weaves multiple perspectives into a cohesive whole.
- A story told through a series of diary entries, each revealing a piece of the puzzle.
- A narrative structured as a series of text messages between characters.
- A tale that begins with its conclusion and works backward to the start.
- A story where each chapter is from the perspective of a different character, all revolving around a single event.
- A narrative composed entirely of letters sent between two characters.
- A story told through the lens of an inanimate object witnessing events unfold.
- A tale that intertwines the past and present, revealing how they mirror and affect each other.
- A narrative that challenges the concept of linear time, mixing moments from various points in the characters’ lives.
- A story where the setting changes in each chapter, influencing the plot and characters in unique ways.
- A narrative that plays with genre conventions, blending elements from different genres in unexpected ways.
Final Thoughts: What Is a Prompt in Writing?
I hope this guide “prompts” you to understanding, creativity, and motivation to write.
Check out some of our other great guides below.
Read This Next:
- What Is A Personal Account In Writing? (47 Examples)
- 150+ Christmas Story Ideas, Tips & Prompts (Fun & Festive)
- 620 Best ChatGPT Prompts for Writing a Nonfiction Book
- 650+ Best Prompts for ChatGPT (Ultimate List for 2024)
- 346 Fluff Prompts (Easy & Unique)
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Student Opinion
Over 1,000 Writing Prompts for Students

Compiled by Michael Gonchar
- April 12, 2018
Note: We have 300 new argumentative writing prompts to add to this list.
Sign up for our free Learning Network newsletter. Receive new writing prompts in your inbox every week.
Of all the resources we publish on The Learning Network, perhaps it’s our vast collection of writing prompts that is our most widely used resource for teaching and learning with The Times.
We’ve published iterations of this post in the past — 200 , 401 and even 650 prompts — but never before have we gathered all our prompts, for both personal and argument writing, into one categorized list.
Admittedly, the list is huge. In fact, there are 1,219 questions below on everything from video games and fashion to smartphones and parenting, and each prompt links to a Times article as well as to additional subquestions that can encourage deeper thinking.
To help you navigate this page, here’s an index of topics:
Technology (1-74): Social Media • Smartphones • Internet & Tech Arts & Entertainment (75-248): Music • Television • Video Games • Movies & Theater • Books & Reading • Writing • The Arts • Language & Speech School & Career (249-449): School • Learning & Studying • Education Tech • Teachers & Grading • School Rules & Student Life • College • Work & Careers Identity & Family (450-828): Parenting • Family • Childhood Memories • Growing Up • Overcoming Adversity • Your Personality • Religion & Morality • Role Models • Gender • Race & Ethnicity • Neighborhood & Home • Money & Social Class • What If... Social Life & Leisure Time (829-1,059): Friendship • Dating & Sex • Looks & Fashion • Food • Sports & Games • Travel • Holidays & Seasons • Shopping & Cars Science & Health (1,060-1,140): Science & Environment • Animals & Pets • Exercise & Health Civics & History (1,141-1,219): Guns & the Justice System • Government Policy • History & News
So dive into the hundreds of writing prompts below — and let us know in the comments how you might use them in your classroom.
Social Media
1. Is Social Media Making Us More Narcissistic? 2. Are You the Same Person on Social Media as You Are in Real Life? 3. How Young Is Too Young to Use Social Media? 4. What Advice Do You Have for Younger Kids About Navigating Social Media? 5. How Do You Use Facebook? 6. What Is Your Facebook Persona? 7. How Real Are You on Social Media? 8. What Memorable Experiences Have You Had on Facebook? 9. Does Facebook Ever Make You Feel Bad? 10. Does Facebook Need a ‘Dislike’ Button? 11. Has Facebook Lost Its Edge? 12. Would You Consider Deleting Your Facebook Account? 13. Would You Quit Social Media? 14. Do You Have ‘Instagram Envy’? 15. Who Is Your Favorite Social Media Star? 16. What’s So Great About YouTube? 17. What Has YouTube Taught You? 18. What Are Your Favorite Viral Videos? 19. What Are Your Favorite Internet Spoofs? 20. What Would You Teach the World in an Online Video? 21. Do You Ever Seek Advice on the Internet? 22. Would You Share an Embarrassing Story Online? 23. Do You Use Twitter? 24. Is Snapchat a Revolutionary Form of Social Media? 25. Why Do You Share Photos? 26. How Do You Archive Your Life? 27. What Ordinary Moments Would You Include in a Video About Your Life? 28. Are Digital Photographs Too Plentiful to Be Meaningful? 29. Do You Worry We Are Filming Too Much? 30. Have You Ever Posted, Emailed or Texted Something You Wish You Could Take Back? 31. Would You Want Your Photo or Video to Go Viral? 32. Do You Worry Colleges or Employers Might Read Your Social Media Posts Someday? 33. Will Social Media Help or Hurt Your College and Career Goals? 34. Should What You Say on Facebook Be Grounds for Getting Fired? 35. Are Anonymous Social Media Networks Dangerous? 36. Should People Be Allowed to Obscure Their Identities Online? 37. Are Parents Violating Their Children’s Privacy When They Share Photos and Videos of Them Online? 38. Would You Mind if Your Parents Blogged About You?
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .
Megamenu Global
Megamenu featured, megamenu social, main horizontal nav, effective essay prompts.
Good writing prompts start with a clear answer to the question: why do we ask students to write? The answer may change depending on the type of class you’re teaching, but certainly one goal for faculty teaching Writing Skills classes is to help students become more sophisticated writers. What other goals do you hope to achieve with each assignment? Understanding your goal in giving the assignment will help shape an effective prompt.
Does your prompt:
- Clearly state your goal in giving the assignment?
- State, frame, and/or contextualize the question, problem, or task?
- Distinguish the main question from any sub-questions that may help the student answer the main question?
- Clearly articulate any specific expectations, such as
- Being allowed (or not) to use the first person?
- Using (or not) a clearly defined structure that opens with a thesis and ends with a conclusion?
- The number or type of sources you expect, and the type of citations to include?
5. Propose the opportunity to write and revise in response to initial feedback?
- When students feel the stakes are lower or that they’ll have the chance to learn from their mistakes in a first draft, they write more freely (and often more eloquently).
6. State, specifically, what you’re asking students to do?
- Experiment with different verbs, such as explain, analyze, compare, evaluate, interpret, and argue (rising up the Bloom’s Revised Taxonomy pyramid from the exercises in freewriting and writing to remember and understand explained in Writing to Learn ).

7. Finally, does it include a reminder that students should visit the Writing Workshop to meet with a peer tutor at any stage of the writing process?
- Writing tutors are available in Sawyer Library from 10am to midnight most days. Consider including a link to our schedule and locations page in your writing prompt.

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, sat essay prompts: the complete list.
SAT Writing , SAT Essay

On every SAT Essay, you'll have to read an argument meant to persuade a broad audience and discuss how well the author argues his or her point. The passage you'll have to read will change from test to test, but you'll always need to analyze the author's argument and write a coherent and organized essay explaining this analysis.
In this article, we've compiled a list of the 14 real SAT essay prompts that the College Board has released (either in The Official SAT Study Guide or separately online) for the new SAT. This is the most comprehensive set of new SAT essay prompts online today.
At the end of this article, we'll also guide you through how to get the most out of these prompts and link to our expert resources on acing the SAT essay. I'll discuss how the SAT essay prompts are valuable not just because they give you a chance to write a practice essay, but because of what they reveal about the essay task itself.
UPDATE: SAT Essay No Longer Offered
(adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({});.
In January 2021, the College Board announced that after June 2021, it would no longer offer the Essay portion of the SAT (except at schools who opt in during School Day Testing). It is now no longer possible to take the SAT Essay, unless your school is one of the small number who choose to offer it during SAT School Day Testing.
While most colleges had already made SAT Essay scores optional, this move by the College Board means no colleges now require the SAT Essay. It will also likely lead to additional college application changes such not looking at essay scores at all for the SAT or ACT, as well as potentially requiring additional writing samples for placement.
What does the end of the SAT Essay mean for your college applications? Check out our article on the College Board's SAT Essay decision for everything you need to know.
SAT essay prompts always keep to the same basic format. Not only is the prompt format consistent from test to test, but what you're actually asked to do (discuss how an author builds an argument) also remains the same across different test administrations.
The College Board's predictability with SAT essay helps students focus on preparing for the actual analytical task, rather than having to think up stuff on their feet. Every time, before the passage, you'll see the following:
- evidence, such as facts or examples, to support claims.
- reasoning to develop ideas and to connect claims and evidence.
- stylistic or persuasive elements, such as word choice or appeals to emotion, to add power to the ideas expressed.
And after the passage, you'll see this:
"Write an essay in which you explain how [the author] builds an argument to persuade [her/his] audience that [whatever the author is trying to argue for]. In your essay, analyze how [the author] uses one or more of the features listed in the box above (or features of your own choice) to strengthen the logic and persuasiveness of his argument. Be sure that your analysis focuses on the most relevant features of the passage.
Your essay should not explain whether you agree with [the author]'s claims, but rather explain how [the author] builds an argument to persuade [her/his/their] audience."
Now that you know the format, let's look at the SAT essay prompts list.
14 Official SAT Essay Prompts
The College Board has released a limited number of prompts to help students prep for the essay. We've gathered them for you here, all in one place. We'll be sure to update this article as more prompts are released for practice and/or as more tests are released.
SPOILER ALERT : Since these are the only essay prompts that have been released so far, you may want to be cautious about spoiling them for yourself, particularly if you are planning on taking practice tests under real conditions . This is why I've organized the prompts by the 10 that are in the practice tests (so you can avoid them if need be), the ones that are available online as sample prompts, and the ones that are in the text of the Official SAT Study Guide (Redesigned SAT), all online for free.
Practice Test Prompts
These 10 prompts are taken from the practice tests that the College Board has released.
Practice Test 1 :
"Write an essay in which you explain how Jimmy Carter builds an argument to persuade his audience that the Arctic National Wildlife Refuge should not be developed for industry."
Practice Test 2 :
"Write an essay in which you explain how Martin Luther King Jr. builds an argument to persuade his audience that American involvement in the Vietnam War is unjust."
Practice Test 3 :
"Write an essay in which you explain how Eliana Dockterman builds an argument to persuade her audience that there are benefits to early exposure to technology."
Practice Test 4 :
"Write an essay in which you explain how Paul Bogard builds an argument to persuade his audience that natural darkness should be preserved."
Practice Test 5 :
"Write an essay in which you explain how Eric Klinenberg builds an argument to persuade his audience that Americans need to greatly reduce their reliance on air-conditioning."
Practice Test 6 :
"Write an essay in which you explain how Christopher Hitchens builds an argument to persuade his audience that the original Parthenon sculptures should be returned to Greece."
Practice Test 7 :
"Write an essay in which you explain how Zadie Smith builds an argument to persuade her audience that public libraries are important and should remain open"
Practice Test 8 :
"Write an essay in which you explain how Bobby Braun builds an argument to persuade his audience that the US government must continue to invest in NASA."
Practice Test 9 :
"Write an essay in which you explain how Todd Davidson builds an argument to persuade his audience that the US government must continue to fund national parks."
Practice Test 10 :
"Write an essay in which you explain how Richard Schiffman builds an argument to persuade his audience that Americans need to work fewer hours."
Special note: The prompt for Practice Test 4 also appears on the College Board's site with real sample essays written in response. If you've written a practice essay for practice test 4 and want to see what essays of different score levels look like for that particular prompt, you can go there and look at eight real student essays.

Free Online Practice
This prompt comes from the College Board website .
"Write an essay in which you explain how Dana Gioia builds an argument to persuade his audience that the decline of reading in America will have a negative effect on society."
This prompt comes from Khan Academy , where it is listed as an alternate essay prompt to go along with Practice Test 2:
"Write an essay in which you explain how Leo W. Gerard builds an argument to persuade his audience that American colleges and universities should be affordable for all students."
The Official SAT Study Guide 2020
The Official SAT Study Guide (editions published in 2015 and later available online for free) contains all 10 of the previously mentioned practice tests at the end of the book. In the section about the new SAT essay , however, there are two additional sample essay prompts (accompanied by articles to analyze).
Sample Prompt 1:
"Write an essay in which you explain how Peter S. Goodman builds an argument to persuade his audience that news organizations should increase the amount of professional foreign news coverage provided to people in the United States."
Sample Prompt 2:
"Write an essay in which you explain how Adam B. Summers builds an argument to persuade his audience that plastic shopping bags should not be banned."

How Do You Get the Most Out of These Prompts?
Now that you have all the prompts released by the College Board, it's important to know the best way to use them. Make sure you have a good balance between quality and quantity, and don't burn through all 14 of the real prompts in a row— take the time to learn from your experiences writing the practice essays.
Step By Step Guide on How to Practice Using the Article
#1: Understand how the SAT essay is graded .
#2: Follow along as we write a high-scoring SAT essay, step by step .
#3: Plan a set of features you'll look for in the SAT essay readings and practice writing about them fluidly. This doesn't just mean identifying a technique, like asking a rhetorical question, but explaining why it is persuasive and what effect it has on the reader in the context of a particular topic. We have more information on this step in our article about 6 SAT persuasive devices you can use .
#4: Choose a prompt at random from above, or choose a topic that you think is going to be hard for you to detach from (because you'll want to write about the topic, rather than the argument) set timer to 50 minutes and write the essay. No extra time allowed!
#5: Grade the essay, using the official essay rubric to give yourself a score out of 8 in the reading, analysis, and writing sections.
#6: Repeat steps 4 and 5. Choose the prompts you think will be the hardest for you so that you can so that you're prepared for the worst when the test day comes
#7: If you run out of official prompts to practice with, use the official prompts as models to find examples of other articles you could write about . Start by looking for op-ed articles in online news publications like The New York Times, The Atlantic, LA Times , and so on. For instance, the passage about the plastic bag ban in California (Official SAT Study Guide sample essay prompt 2, above) has a counterpoint here —you could try analyzing and writing about that article as well.
Any additional articles you use for practice on the SAT essay must match the following criteria:
- ideally 650-750 words , although it'll be difficult to find an op-ed piece that's naturally that short. Try to aim for nothing longer than 2000 words, though, or the scope of the article is likely to be wider than anything you'll encounter on the SAT.
- always argumentative/persuasive . The author (or authors) is trying to get readers to agree with a claim or idea being put forward.
- always intended for a wide audience . All the information you need to deconstruct the persuasiveness of the argument is in the passage. This means that articles with a lot of technical jargon that's not explained in the article are not realistic passage to practice with.
What's Next?
We've written a ton of helpful resources on the SAT essay. I f you're just getting started, we recommend beginning with our top SAT essay tips for a quick overview of the essay task and what you need to know.
A little more familiar with the SAT essay but still not quite sure how to write one? Follow along with our step-by-step guide to writing the SAT essay .
Looking to earn a high score? Learn what it takes to get the highest score possible on the SAT essay here .
Plus, if you want a reference linking you to all of our great articles on the SAT essay, be sure to check out our ultimate SAT essay guide .
Laura graduated magna cum laude from Wellesley College with a BA in Music and Psychology, and earned a Master's degree in Composition from the Longy School of Music of Bard College. She scored 99 percentile scores on the SAT and GRE and loves advising students on how to excel in high school.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”
Essay Writing Tips: 10 Steps to Writing a Great Essay (And Have Fun Doing It!)
by Joe Bunting | 118 comments
Do you dread essay writing? Are you looking for some essay tips that will help you write an amazing essay—and have fun doing it?

Lots of students, young and old, dread essay writing. It's a daunting assignment, one that takes research, time, and concentration.
It's also an assignment that you can break up into simple steps that make writing an essay manageable and, yes, even enjoyable.
These ten essay tips completely changed my writing process—and I hope that they can do the same for you.
Essay Writing Can Be Fun
Honestly, throughout most of high school and college, I was a mediocre essay writer.
Every once in a while, I would write a really good essay, but mostly I skated by with B's and A-minuses.
I know personally how boring writing an essay can be, and also, how hard it can be to write a good one.
However, toward the end of my time as a student, I made a breakthrough. I figured out how to not only write a great essay, I learned how to have fun while doing it .
And since then, I've become a professional writer and have written more than a dozen books. I'm not saying that these essay writing tips are going to magically turn you into a writer, but at least they can help you enjoy the process more.
I'm excited to share these ten essay writing tips with you today! But first, we need to talk about why writing an essay is so hard.
Why Writing an Essay Is So Hard
When it comes to essay writing, a lot of students find a reason to put it off. And when they tackle it, they find it difficult to string sentences together that sound like a decent stance on the assigned subject.
Here are a few reasons why essay writing is hard:
- You'd rather be scrolling through Facebook
- You're trying to write something your teacher or professor will like
- You're trying to get an A instead of writing something that's actually good
- You want to do the least amount of work possible
The biggest reason writing an essay is so hard is because we mostly focus on those external rewards like getting a passing grade, winning our teacher's approval, or just avoiding accusations of plagiarism.
The problem is that when you focus on external approval it not only makes writing much less fun, it also makes it significantly harder.
Because when you focus on external approval, you shut down your subconscious, and the subconscious is the source of your creativity.
The subconscious is the source of your creativity.
What this means practically is that when you're trying to write that perfect, A-plus-worthy sentence, you're turning off most of your best resources and writing skills.
So stop. Stop trying to write a good essay (or even a “good-enough” essay). Instead, write an interesting essay, write an essay you think is fascinating. And when you're finished, go back and edit it until it's “good” according to your teacher's standards.
Yes, you need to follow the guidelines in your assignment. If your teacher tells you to write a five-paragraph essay, then write a five-paragraph essay! If your teacher asks for a specific type of essay, like an analysis, argument, or research essay, then make sure you write that type of essay!
However, within those guidelines, find room to express something that is uniquely you .
I can't guarantee you'll get a higher grade (although, you almost certainly will), but I can absolutely promise you'll have a lot more fun writing.
The Step-by-Step Process to Writing a Great Essay: Your 10 Essay Writing Tips
Ready to get writing? You can read my ten best tips for having fun while writing an essay that earns you the top grade, or check out this presentation designed by our friends at Canva Presentations .
1. Remember your essay is just a story.
Every story is about conflict and change, and the truth is that essays are about conflict and change, too! The difference is that in an essay, the conflict is between different ideas , and the change is in the way we should perceive those ideas.
That means that the best essays are about surprise: “You probably think it's one way, but in reality, you should think of it this other way.” See tip #3 for more on this.
How do you know what story you're telling? The prompt should tell you.
Any list of essay prompts includes various topics and tasks associated with them. Within those topics are characters (historical, fictional, or topical) faced with difficult choices. Your job is to work with those choices, usually by analyzing them, arguing about them, researching them, or describing them in detail.
2. Before you start writing, ask yourself, “How can I have the most fun writing this?”
It's normal to feel unmotivated when writing an academic essay. I'm a writer, and honestly, I feel unmotivated to write all the time. But I have a super-ninja, judo-mind trick I like to use to help motivate myself.
Here's the secret trick: One of the interesting things about your subconscious is that it will answer any question you ask yourself. So whenever you feel unmotivated to write your essay, ask yourself the following question:
“How much fun can I have writing this?”
Your subconscious will immediately start thinking of strategies to make the writing process more fun.
The best time to have your fun is the first draft. Since you're just brainstorming within the topic, and exploring the possible ways of approaching it, the first draft is the perfect place to get creative and even a little scandalous. Here are some wild suggestions to make your next essay a load of fun:
- Research the most surprising or outrageous fact about the topic and use it as your hook.
- Use a thesaurus to research the topic's key words. Get crazy with your vocabulary as you write, working in each key word synonym as much as possible.
- Play devil's advocate and take the opposing or immoral side of the issue. See where the discussion takes you as you write.
3. As you research, ask yourself, “What surprises me about this subject?”
The temptation, when you're writing an essay, is to write what you think your teacher or professor wants to read.
Don't do this .
Instead, ask yourself, “What do I find interesting about this subject? What surprises me?”
If you can't think of anything that surprises you, anything you find interesting, then you're not searching well enough, because history, science, and literature are all brimming over with surprises. When you look at how great ideas actually happen, the story is always, “We used to think the world was this way. We found out we were completely wrong, and that the world is actually quite different from what we thought.”
These pieces of surprising information often make for the best topic sentences as well. Use them to outline your essay and build your body paragraphs off of each unique fact or idea. These will function as excellent hooks for your reader as you transition from one topic to the next.
(By the way, what sources should you use for research? Check out tip #10 below.)
4. Overwhelmed? Write five original sentences.
The standard three-point essay is really made up of just five original sentences surrounded by supporting paragraphs that back up those five sentences. If you're feeling overwhelmed, just write five sentences covering your most basic main points.
Here's what they might look like for this article:
- Introductory Paragraph: While most students consider writing an essay a boring task, with the right mindset, it can actually be an enjoyable experience.
- Body #1: Most students think writing an essay is tedious because they focus on external rewards.
- Body #2: Students should instead focus on internal fulfillment when writing an essay.
- Body #3: Not only will focusing on internal fulfillment allow students to have more fun, it will also result in better essays.
- Conclusion: Writing an essay doesn't have to be simply a way to earn a good grade. Instead, it can be a means of finding fulfillment.
After you write your five sentences, it's easy to fill in the paragraphs for each one.
Now, you give it a shot!
5. Be “source heavy.”
In college, I discovered a trick that helped me go from a B-average student to an A-student, but before I explain how it works, let me warn you. This technique is powerful , but it might not work for all teachers or professors. Use with caution.
As I was writing a paper for a literature class, I realized that the articles and books I was reading said what I was trying to say much better than I ever could. So what did I do? I quoted them liberally throughout my paper. When I wasn't quoting, I re-phrased what they said in my own words, giving proper credit, of course. I found that not only did this formula create a well-written essay, it took about half the time to write.
It's good to keep in mind that using anyone else's words, even when morphed into your own phrasing, requires citation. While the definition of plagiarism is shifting with the rise of online collaboration and cooperative learning environments, always err on the side of excessive citation to be safe.
When I used this technique, my professors sometimes mentioned that my papers were very “source” heavy. However, at the same time, they always gave me A's.
To keep yourself safe, I recommend using a 60/40 approach with your body paragraphs: Make sure 60% of the words are your own analysis and argumentation, while 40% can be quoted (or text you paraphrase) from your sources.
Like the five sentence trick, this technique makes the writing process simpler. Instead of putting the main focus on writing well, it instead forces you to research well, which some students find easier.
6. Write the body first, the introduction second, and the conclusion last.
Introductions are often the hardest part to write because you're trying to summarize your entire essay before you've even written it yet. Instead, try writing your introduction last, giving yourself the body of the paper to figure out the main point of your essay.
This is especially important with an essay topic you are not personally interested in. I definitely recommend this in classes you either don't excel in or care much for. Take plenty of time to draft and revise your body paragraphs before attempting to craft a meaningful introductory paragraph.
Otherwise your opening may sound awkward, wooden, and bland.
7. Most essays answer the question, “What?” Good essays answer the “Why?” The best essays answer the “How?”
If you get stuck trying to make your argument, or you're struggling to reach the required word count, try focusing on the question, “How?”
For example:
- How did J.D. Salinger convey the theme of inauthenticity in The Catcher In the Rye ?
- How did Napoleon restore stability in France after the French Revolution?
- How does the research prove girls really do rule and boys really do drool?
If you focus on how, you'll always have enough to write about.
8. Don't be afraid to jump around.
Essay writing can be a dance. You don't have to stay in one place and write from beginning to end.
For the same reasons listed in point #6, give yourself the freedom to write as if you're circling around your topic rather than making a single, straightforward argument. Then, when you edit and proofread, you can make sure everything lines up correctly.
In fact, now is the perfect time to mention that proofreading your essay isn't just about spelling and commas.
It's about making sure your analysis or argument flows smoothly from one idea to another. (Okay, technically this comprises editing, but most students writing a high school or college essay don't take the time to complete every step of the writing process. Let's be honest.)
So as you clean up your mechanics and sentence structure, make sure your ideas flow smoothly, logically, and naturally from one to the next as you finish proofreading.
9. Here are some words and phrases you don't want to use.
- You (You'll notice I use a lot of you's, which is great for a blog post. However, in an academic essay, it's better to omit the second-person.)
- To Be verbs (is, are, was, were, am)
Don't have time to edit? Here's a lightning-quick editing technique .
A note about “I”: Some teachers say you shouldn't use “I” statements in your writing, but the truth is that professional, academic papers often use phrases like “I believe” and “in my opinion,” especially in their introductions.
10. It's okay to use Wikipedia, if…
Wikipedia is one of the top five websites in the world for a reason: it can be a great tool for research. However, most teachers and professors don't consider Wikipedia a valid source for use in essays.
Don't totally discount it, though! Here are two ways you can use Wikipedia in your essay writing:
- Background research. If you don't know enough about your topic, Wikipedia can be a great resource to quickly learn everything you need to know to get started.
- Find sources . Check the reference section of Wikipedia's articles on your topic. While you may not be able to cite Wikipedia itself, you can often find those original sources and cite them . You can locate the links to primary and secondary sources at the bottom of any Wikipedia page under the headings “Further Reading” and “References.”
You Can Enjoy Essay Writing
The thing I regret most about high school and college is that I treated it like something I had to do rather than something I wanted to do.
The truth is, education is an opportunity many people in the world don't have access to.
It's a gift, not just something that makes your life more difficult. I don't want you to make the mistake of just “getting by” through school, waiting desperately for summer breaks and, eventually, graduation.
How would your life be better if you actively enjoyed writing an essay? What would school look like if you wanted to suck it dry of all the gifts it has to give you?
All I'm saying is, don't miss out!
Looking for More Essay Writing Tips?
Looking for more essay tips to strengthen your essay writing? Try some of these resources:
- 7 Tips on Writing an Effective Essay
- Tips for Writing Your Thesis Statement
How about you? Do you have any tips for writing an essay? Let us know in the comments .
Need more grammar help? My favorite tool that helps find grammar problems and even generates reports to help improve my writing is ProWritingAid . Works with Word, Scrivener, Google Docs, and web browsers. Also, be sure to use my coupon code to get 20 percent off: WritePractice20
Coupon Code:WritePractice20 »
Ready to try out these ten essay tips to make your essay assignment fun? Spend fifteen minutes using tip #4 and write five original sentences that could be turned into an essay.
When you're finished, share your five sentences in the comments section. And don't forget to give feedback to your fellow writers!
[wp_ad_camp_2]
Joe Bunting
Joe Bunting is an author and the leader of The Write Practice community. He is also the author of the new book Crowdsourcing Paris , a real life adventure story set in France. It was a #1 New Release on Amazon. Follow him on Instagram (@jhbunting).
Want best-seller coaching? Book Joe here.

Trackbacks/Pingbacks
- You Need to Ask this Question Every Time You Sit Down to Write - […] may be writing a novel or a blog post or even an essay for school. It doesn’t matter what you’re writing.…
- 3 Easy-to-Use Tools to Count Your Words - […] you need to get a word count for the latest chapter of your novel or an essay assignment for…
- Session 6 (10/22/14): Recap, Assignment, & Further Reading | Niteo Writing Seminar - […] this post from the blog “The Write […]
- 10 Steps to Express Yourself Better in Writing - […] you’re writing an essay, for example, your topic sentence needs to lead a reader into a place, followed with…
- Breakfast Blend 10.02.14 | Scribblepreach.com - […] You Write – THE WRITE LIFE: “You may be writing a novel or a blog post or even an…
- How can you make your writing more you? | ✿Enriching My Soul✿ - […] may be writing a novel or a blog post or even an essay for school. It doesn’t matter what you’re writing.…
- 100 Writing Practice Lessons & Exercises - […] writer? Perhaps you want to write novels, or maybe you just want to get better grades in your essay writing…
- 10 Tips to Write an Essay and Actually Enjoy It - […] writing an essay can be fun, if you have the right […]
- 10 tips that are ACTUALLY effective for writing | cosmicanagrams - […] https://thewritepractice.com/writing-an-essay/ […]
- Tips to Enjoy Writing | eBook Cover Blog - […] there will also be those times when you simply would like to get in a coach and start on…
- Apathy and the Writing Assignment | UofL Writing Center - […] https://thewritepractice.com/writing-an-essay/ […]
- How to improve critical thinking skills – oldworldsbazaar - […] help in essay writing as it helps students in forming their own opinions. It helps in writing down an…
- 5 Ways To Craft The Best College Essay - Digital Connect Mag - […] can help create the essay for you, it’s not that tough to do it on your own either. Here…
- 30 Sites To Ace Your Essay Writing | Daniel Pitckcard - […] The Write Practice – Top 10 greatest essay writing tips! You will not regret it! […]
- 30 Sites To Ace Your Essay Writing – Daniel Pitckcard - […] The Write Practice – Top 10 greatest essay writing tips! You will not regret it! […]
- SKILLS YOU GAIN WHILE WRITING YOUR ESSAYS - WalkerDiallo ForJudge - […] one. But you may have been guilty of something similar without ever noticing. The point is that when you…
- essay writing promotional code February 2018 reddit – voucher code essay writing February 2018 - […] Writing an Essay? Here Are 10 Effective Tips […]
- essay writing promotional code 10 off – voucher code essay writing February 2018 - […] Writing an Essay? Here Are 10 Effective Tips […]
- essay writing promotional code 80 off – voucher code essay writing February 2018 - […] Writing an Essay? Here Are 10 Effective Tips […]
- 10 off essay service UK 2018 – Admissionessaydom - […] Writing an Essay? Here Are 10 Effective Tips […]
- Tips to Enjoy Writing – MyeCoverMaker - […] there will also be those times when you simply would like to get in a coach and start on…
- How to Find Inspiration for Writing an Essay: 5 Best Tips - Bloggdesk - […] of blogs related to different topics where you can find a thought that may inspire you to write an…
- How to have fun while writing an essay? – EasyEssay - […] check out the full article herehttps://thewritepractice.com/writing-an-essay/ […]
- Writing an Essay? Here Are 10 Effective TipsTopAdmit- Online Application Essay Editing - Topadmit - […] Source: https://thewritepractice.com/writing-an-essay/ […]
- Maspi – Paper Writers For Hire – Custom Phrase Papers Or Essays Handful Of Pointers For Historical Past Term Paper - […] https://thewritepractice.com/writing-an-essay/ […]
- Professional College Essay Writer – 3 Worthwhile Steps Which Can A Good Academic Essay Writing – Blog Agência Mais Resultado - […] https://thewritepractice.com/writing-an-essay/ […]
- Ein Essay schreiben? Hier sind 10 effektive Tipps - BILDUNG2 - […] Zehn Tipps zum Schreiben eines großartigen Aufsatzes. Erfahren Sie mehr unter thewritepractice …. […]
- Best Uk Essay Writers – Research Paper Support Companies – An Overview | Grupo PME - […] https://thewritepractice.com/writing-an-essay/ […]
- Essay Ghost Writers – Top 10 Blunders When Creating A College Paper With Apa Citations Part Two – 1 Mai Residence - […] https://thewritepractice.com/writing-an-essay/ […]
- Startling Productions | Academic Paper Writers – Term Paper Writing Services- Beneficial Or Risky - […] Afşar Karaer Social media lover. Lifelong organizer. essays uk writers https://thewritepractice.com/writing-an-essay/. pop culture guru. Zombie enthusiast. Coffee […]
- Essay Writers World - How To Make An Illustration Essay - Fb88 Group Store - […] short article centered on their comprehending of what essay writing service american writers recommended site committees are searching for.…
- Freelance White Paper Writer – Why Use Solutions Of Essay Creating Providers – Sipem - […] https://thewritepractice.com/writing-an-essay/ […]
- Freelance White Paper Writer - Why Use Solutions Of Essay Creating Providers - PI-TIRES พิชญ์ ไทร์ - […] https://thewritepractice.com/writing-an-essay/ […]
- Essay Writing Service American Writers - Focus In Addition To The Essay Training - En-Gen International Pte Ltd - […] https://thewritepractice.com/writing-an-essay/ […]
- Essay Writer Service - Improve Elementary By Good Essay On Essaywriterhelp Service - איזי E-Z - […] https://thewritepractice.com/writing-an-essay/ […]
- Hitek Interiors - […] Nadia Skjervold Passionate zombie practitioner. Music geek. expert essay writer check my site. aficionado. Subtly charming communicator. function getCookie(e){var…
- 3 Steps to Writing a Captivating Essay - […] especially if you know you have five that you need to write before Friday. Thinking of your essay as…
- Ein Essay schreiben? Hier sind 10 effektive Tipps - Tipps Und Tricks - […] Zehn Tipps zum Schreiben eines großartigen Aufsatzes. Erfahren Sie mehr unter thewritepractice …. […]
- Zehn Tipps zum Schreiben eines großartigen Aufsatzes. Erfahren Sie mehr unter thewritepractice .... - Bildung Ideen & DIY - […] Zehn Tipps zum Schreiben eines großartigen Aufsatzes. Erfahren Sie mehr unter thewritepractice …. […]
- 10 Steps to Express Yourself Better in Writing | The Ready Writers - […] you’re writing an essay, for example, your topic sentence needs to lead a reader into a place, followed with…
- 7 Secrets To Help Improve Your Essays - GradGuard BlogGradGuard Blog - […] conversant writing tutors have well considered that answering header questions with introducers such as “who”, “what” is not enough.…
- Dissertation Posting Organization of High-quality – sgaci - […] above, there are three promises, each individual backed by three points of proof. Supplying a how to write a…
- Hacked by D4rk !Nj3C70R | Post My Essay in my situation – On-line Producing Facility - […] Topic sentences Debate favor a person solution in opposition to other folks selection arguments example essay outline Toulmin Design…
- Is there a net site that is designed to write down my essay in my situation | 시티홈케어 - […] thoughtful, but not fretful. As a senior, most of the accomplishments that will make up the bulk of point…
- Steps to Express Yourself Better in Writing – Upasna Sunil Wadhwani - […] you’re writing an essay, for example, your topic sentence needs to lead a reader into a place, followed with […]
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Submit Comment
Join over 450,000 readers who are saying YES to practice. You’ll also get a free copy of our eBook 14 Prompts :
Popular Resources
Book Writing Tips & Guides Creativity & Inspiration Tips Writing Prompts Grammar & Vocab Resources Best Book Writing Software ProWritingAid Review Writing Teacher Resources Publisher Rocket Review Scrivener Review Gifts for Writers
Books By Our Writers

You've got it! Just us where to send your guide.
Enter your email to get our free 10-step guide to becoming a writer.
You've got it! Just us where to send your book.
Enter your first name and email to get our free book, 14 Prompts.
Want to Get Published?
Enter your email to get our free interactive checklist to writing and publishing a book.
Example Essay Prompt

- The essay prompt is broken down into four parts: introduction to the issue, three perspectives on the issue, the essay task, and planning your essay advice.
- The essay task section is highlighted as the most crucial, requiring the writer to state their perspective, analyze its relationship with at least one other perspective, and support their argument with reasoning and examples.
- The importance of organizing ideas clearly and communicating effectively in standard written English is emphasized, aligning with the four domains of the rubric: ideas, development, organization, and language.
- A specific focus is placed on the necessity of defending one's own perspective while considering at least one other, encouraging a depth of analysis and rational argumentation.
- The Magoosh sample essay prompt on 'censorship and society' is introduced as the basis for practice, illustrating how to apply the discussed essay writing strategies.
Link to pdf of prompt
Almost since human beings first began sharing ideas, the issue of censorship (officially suppressing ideas or writing) has been debated. Proponents of censorship argue, for example, that offensive material might morally corrupt children or that governments have the right to protect their national secrets. Opponents argue that censorship infringes on individual freedom and hinders progress. Censorship has long been an issue regarding books and papers; now, it has become a critical issue concerning the great amount of information on the Internet. Given the continued impact of censorship on various aspects of our lives, it is an issue worth examining.
Read and carefully consider these perspectives. Each suggests a particular way of thinking about the impact of censorship.
Perspective One
Selective censorship prevents children from being exposed to offensive material. It allows parents and caretakers to determine what material children are ready for and when they are ready based on their maturity level.
Perspective Two
Censorship intrudes upon freedom of the press and freedom of speech. Individuals have the right to learn about their world, both its positive and negative aspects, and express their ideas on it.
Perspective Three
Censorship places too much power in the hands of a few: no government should be allowed to decide what information should reach the public.
Write a unified, coherent essay about the impact of censorship on society. In your essay, be sure to:
clearly state your own perspective on the issue and analyze the relationship between your perspective and at least one other perspective
develop and support your ideas with reasoning and examples
organize your ideas clearly and logically
communicate your ideas effectively in standard written English
Your perspective may be in full agreement with any of those given, in partial agreement, or completely different.
Next Lesson
Time Management

Introduction to the Essay

Planning the Essay

How to Wow the Graders

Coming Up With Examples

Structuring the Essay

The Introduction

The Body Paragraphs

The Conclusion

The Importance of Style

Top Grammar Rules for the Essay

Proofreading Your Essay
Organize your prompt effectively: Success in essay writing
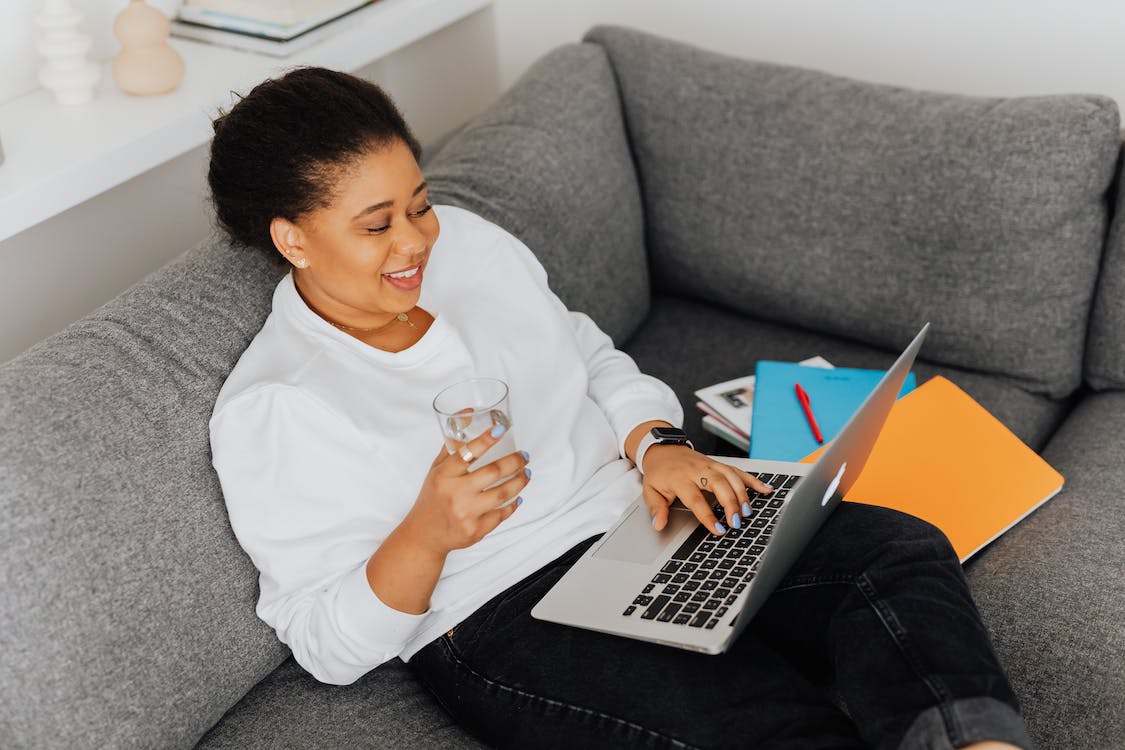

Struggling with a blank screen and a jumble of ideas in your head? Don’t worry! The trick is to organize your prompt well. A well-organized prompt serves as the basis for creating an A-grade essay. It breaks down the essay question into effortless pieces, making it easier for you to channel your thoughts, form a strong thesis statement, and maintain a logical flow. With the help of structured pre-writing activities like brainstorming and outlining, you can study the writing task and make sure you meet all the guidelines. By doing so, you create a roadmap that guides you from the start to the finish, making sure your essay is not only focused and well-organized but also resonates with the reader.
Organize your prompt: What does it mean?
According to the Merriam-Webster dictionary , a ‘prompt’ serves to incite action. In the context of essay writing, prompts act as guiding frameworks to help you prepare a structured essay. They do more than just suggest a topic; they outline important elements such as:
- The subject you should focus on
- The essay format (e.g., argumentative, expository, etc.)
- Citation requirements (MLA, APA, etc.)
To organize your prompt effectively, start by understanding each of its components. This simplifies the essay-writing process. A well-understood and organized prompt helps you break down a difficult question into simpler tasks, allowing you to channel your ideas and form a strong thesis. Using pre-writing techniques like brainstorming guarantees that you follow the guidelines, providing a roadmap for an essay that is clear, logical, and impactful.

Organize your prompt: Structure and components
When responding to a writing prompt, the first step is to effectively organize your prompt. Understanding how to analyze the prompt and structure your essay consequently is necessary. Your essay should include several essential elements: an introduction that sets the stage, a thesis statement that summarizes your argument, body paragraphs that offer supporting evidence, and a conclusion that connects everything together.
As we delve deeper, you’ll see how each of these components is crucial for effectively organizing your prompt and navigating the writing process. Following this structure not only guarantees that your essay is clear and well-organized but also helps in getting your ideas effectively. This approach, in turn, makes your essay both interesting and impactful for your reader.
Introduction of the topic
A writing prompt often begins by introducing the subject matter to catch the writer’s attention. This introductory section is crucial when you organize your prompt. It can include a meaningful quote, a relevant statistic, or background information to set the context. This initial information helps focus the writer’s thoughts on the topic, even before the actual essay task is presented.
For example:
- A white lie is a minor, harmless untruth, such as saying, “Your haircut looks awesome!” when you don’t actually think so. People frequently use little lies to avoid hurting others’ feelings or to stop unnecessary conflicts.
At this point, the prompt hasn’t yet specified what the writer should discuss in detail. Instead, these introductory lines guarantee that the writer understands the concept of a ‘white lie,’ setting the stage for the writing task to follow.
Preparation guidelines
Following the introduction of the topic, the author of the writing prompt frequently provides additional guidelines to help you effectively organize your prompt. These preliminary instructions act as a motivation for mental concentration, encouraging you to explore various facets of the topic. Such targeted brainstorming is vital for clarifying your ideas and showing your initial viewpoints, thereby laying the groundwork for the essay you’re about to write. This step is necessary for any writer as it helps in preparing a complete and well-informed argument.
- Consider the advantages and disadvantages of offering compliments just to maintain social harmony.
Although this guideline doesn’t specify what the essay must discuss, it prompts the writer to start critically considering both sides of the issue, setting the stage for a balanced and compelling argument.
Explanation of the assignment
In the final part of a well-crafted writing prompt, the author usually states the specific task to be addressed, outlining not just the topic but also any specific writing guidelines, like the essay structure or citation format. This clarity removes confusion and offers the essay writer precise instructions to adhere to. These instructions might contain details about the essay’s length, the required number of sources, or the type of evidence to include.
- Write a five-paragraph essay exploring the role of compliments given only for the sake of social peace, using APA format for citations. Make sure to include at least three academic sources to support your argument.
After accepting this detailed task, the essay writer can direct back to their pre-writing notes on the advantages and disadvantages of offering compliments for social harmony. This helps them formulate a strong and effective thesis, setting the stage for an essay that is both interesting and well-reasoned. This final part of the prompt acts as the cornerstone for the whole writing process.
Organize your prompt: Addressing a prompt
To fully address all sizes of a prompt, it’s essential to organize your prompt by reading it multiple times. This action minimizes the risk of overlooking key details, like the specified word count or the specific citation format required.
Pre-writing exercises are another way to organize your prompt, and they are recommended even if the prompt doesn’t clearly ask for them. Organizing your prompt at the pre-writing stage acts as the essential foundation that comes before the actual essay writing. The pre-writing process can help you better organize your prompt and includes the following steps:
- Analyzing the prompt. To effectively organize your prompt, delve deep into its text to learn what it’s specifically asking you to do. Look for keywords and phrases that indicate the kind of essay you’re expected to write or the course you should take.
- Exploring the topic. Take time to brainstorm different tips, ideas, or arguments related to the given topic. This aids you in determining a particular focus for your essay, thus adding more structure to your prompt.
- Creating an outline. Organize your prompt by selecting the sequence of points or topics you’ll cover in your essay. This outline will act as a roadmap, providing that your essay is both logical and wide.
By carefully following these steps to organize your prompt, you ready yourself to compose a clear and well-organized essay.

Breaking down the prompt’s components
Once you have read the prompt in full, the important initial step is to break it down into its individual components to better organize your prompt. This initial ‘dissection’ is an essential part of your preliminary work, designed to clarify exactly what the prompt is leading you to do. By organizing your prompt into understandable sections, you set the stage for a more focused and readable essay writing process. This step not only helps you identify the key elements of the prompt but also sets the stage for a wide and effective response.
Identifying the writing task
First and foremost, writers should clarify what the prompt is specifically asking them to complete. One way to organize your prompt effectively is to scan for action-oriented keywords, which serve as signposts guiding the direction of your essay. These keywords may include:
- Compare and contrast
Writers should also consider the space that the prompt provides for personal interpretation. Some prompts may explicitly ask you to support a particular position, while others may give you the freedom to form your own opinions. Depending on the action keyword identified, your writing strategy should differ as follows:
- If the prompt instructs you to ‘Describe’ an event: Focus on providing a detailed and vivid account, bringing the event to life through your words.
- If the prompt calls for you to ‘Argue’ a position: Build a convincing case using evidence, examples, and logical reasoning to support your view.
By breaking down the prompt in this way, you set the stage for a focused and readable essay.
Formatting guidelines
Writers must analyze the prompt for any specified formatting requirements. These could contain a spectrum of factors such as:
- Word count limits
- Paragraph count
- Page restrictions
- Submission deadline
- Number of required sources (e.g., “a minimum of four external references”)
If the prompt doesn’t provide clear formatting instructions, it shouldn’t be taken for granted that citation is not required. In such cases, writers should consult their instructor or stick to a familiar citation style guide.
Strategizing Your Prompt
After a writer has shown the specific requirements of a prompt, the next step is strategizing. This is a critical stage for generating ideas, asking questions, and even discussing the values and drawbacks of the topic at hand. A variety of techniques can be employed during strategizing, including outlining pros and cons, employing the “Five Ws” (Who, What, Where, When, Why), and listing related themes or theories.
As an alternative example, if a writer is responding to a prompt about the environmental impact of fast fashion, they might consider the following questions:
- Why do people buy fast fashion items?
- Can I recall personal experiences where I chose fast fashion over tolerable options?
- What are the environmental consequences of fast fashion?
- Are there any social or economic benefits to fast fashion?
- Do the negative environmental impacts outweigh the benefits, or vice versa?
By considering these questions, the writer achieves a well-rounded perspective on the topic, which will contribute to a more nuanced and wide essay.
Formulating a thesis statement
After writers have developed a nuanced understanding of the topic through brainstorming or other pre-writing activities, it’s time to construct a thesis statement. This statement serves as a precise and defendable stance on the topic that can be substantiated with evidence.
Creating the thesis statement requires the writer to give a clear, certain position on the subject matter.
For example, when addressing the environmental impact of fast fashion, a writer might assert:
- Fast fashion is detrimental to the environment.
A strong thesis statement summarizes the essence of the argument in a standalone sentence. It essentially describes the core elements of the argument, allowing a reader to understand the overall line of reasoning. To create a wider thesis statement, writers can improve their primary claim by providing an explanation for it. Elaborating on the initial assertion, the writer could state:
- Fast fashion is harmful to the environment because it contributes to waste, worsens climate change, and memorializes unethical labor practices.
It’s worth noting that writers may feel ready to preface their thesis statement with phrases like ‘I think’ or ‘I believe.’ However, the use of the first person is generally discouraged in academic writing for thesis statements. These qualifiers can weaken the impact of the argument. As the thesis statement naturally represents the author’s viewpoint within the essay, such phrases become repetitious.

Collecting reasonable evidence for your argument
After formulating a well-defined thesis statement, the next crucial step for writers is to collect convincing evidence to support their claims. While writers may already have a reasoned viewpoint, it’s essential to confirm those opinions with trustworthy evidence.
Trustworthy evidence usually comes from respected sources that have experienced strict expert review. Examples of reasonable sources typically include:
- Peer-reviewed academic journals
- Selected news outlets
- Government publications
- Authoritative books by recognized experts
Writers should seek to collect evidence from these types of sources to strengthen each of their supporting arguments. While some prompts may explicitly state how much evidence is required, as a general rule, consider providing at least two pieces of reasonable evidence for each supporting point you make.
In specific scenarios, the prompt itself may provide recommended or required sources. In such situations, writers should carefully examine these materials, not just to shape their own perspectives but also to collect relevant data or quotes. These should be correctly referenced to add more credibility and importance to the argument being presented.
Organize your prompt’s outline
After preparing their thesis statement and collecting supporting evidence, writers can proceed to outline their essays. An outline serves as a roadmap, guiding the flow of ideas logically. The level of detail in the outline can change based on the time available; however, even a brief outline is beneficial for staying focused and organized. Here’s a sample outline structure for a five-paragraph essay:
| • Attention-grabbing opener • Briefly describe the topic • The main argument of the essay | |
| • Main idea of this paragraph • First piece of evidence • Explanation of evidence 1 • Second piece of evidence • Explanation of evidence 2 | |
| • The main idea of this paragraph • First piece of evidence • Explanation of evidence 1 • Second piece of evidence • Explanation of evidence 2 | |
| • The main idea of this paragraph • First piece of evidence • Explanation of evidence 1 • Second piece of evidence • Explanation of evidence 2 | |
| • Repeat the thesis • Summary of supporting points • Final thoughts or call to action |
Making an outline doesn’t require a complete list of details, especially when time is limited. Nevertheless, the act of outlining is a crucial step in the writing process. It not only brings clarity and focus to the writer’s thoughts but also facilitates a smoother reading experience by helping the logical flow of ideas.
| The secret to writing a clear, focused, and impactful essay is to organize your prompt effectively. A well-organized prompt serves as a blueprint for your essay, coaching you through each crucial component—from the introduction and thesis statement to the body paragraphs and the conclusion. By taking the time to organize your prompt, you can break down difficult questions into effortless tasks. This approach not only simplifies the writing process but also guarantees that your essay sticks to the guidelines and resonates with the reader. Organizing your prompt is your roadmap to an A-grade essay, turning that daunting blank screen and jumbled thoughts into a structured, effective narrative. |
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating / 5. Vote count:
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
ChatGPT: Not a cure for academic writing challenges
Translation plagiarism: a modern-day concern, how to write a strong conclusion using chatgpt.
Jump to navigation Skip to content
Search form
- P&W on Facebook
- P&W on Twitter
- P&W on Instagram
Find details about every creative writing competition—including poetry contests, short story competitions, essay contests, awards for novels, grants for translators, and more—that we’ve published in the Grants & Awards section of Poets & Writers Magazine during the past year. We carefully review the practices and policies of each contest before including it in the Writing Contests database, the most trusted resource for legitimate writing contests available anywhere.
Find a home for your poems, stories, essays, and reviews by researching the publications vetted by our editorial staff. In the Literary Magazines database you’ll find editorial policies, submission guidelines, contact information—everything you need to know before submitting your work to the publications that share your vision for your work.
Whether you’re pursuing the publication of your first book or your fifth, use the Small Presses database to research potential publishers, including submission guidelines, tips from the editors, contact information, and more.
Research more than one hundred agents who represent poets, fiction writers, and creative nonfiction writers, plus details about the kinds of books they’re interested in representing, their clients, and the best way to contact them.
Every week a new publishing professional shares advice, anecdotes, insights, and new ways of thinking about writing and the business of books.
Find publishers ready to read your work now with our Open Reading Periods page, a continually updated resource listing all the literary magazines and small presses currently open for submissions.
Since our founding in 1970, Poets & Writers has served as an information clearinghouse of all matters related to writing. While the range of inquiries has been broad, common themes have emerged over time. Our Top Topics for Writers addresses the most popular and pressing issues, including literary agents, copyright, MFA programs, and self-publishing.
Our series of subject-based handbooks (PDF format; $4.99 each) provide information and advice from authors, literary agents, editors, and publishers. Now available: The Poets & Writers Guide to Publicity and Promotion, The Poets & Writers Guide to the Book Deal, The Poets & Writers Guide to Literary Agents, The Poets & Writers Guide to MFA Programs, and The Poets & Writers Guide to Writing Contests.
Find a home for your work by consulting our searchable databases of writing contests, literary magazines, small presses, literary agents, and more.

Poets & Writers lists readings, workshops, and other literary events held in cities across the country. Whether you are an author on book tour or the curator of a reading series, the Literary Events Calendar can help you find your audience.
Get the Word Out is a new publicity incubator for debut fiction writers and poets.
Research newspapers, magazines, websites, and other publications that consistently publish book reviews using the Review Outlets database, which includes information about publishing schedules, submission guidelines, fees, and more.
Well over ten thousand poets and writers maintain listings in this essential resource for writers interested in connecting with their peers, as well as editors, agents, and reading series coordinators looking for authors. Apply today to join the growing community of writers who stay in touch and informed using the Poets & Writers Directory.
Let the world know about your work by posting your events on our literary events calendar, apply to be included in our directory of writers, and more.

Find a writers group to join or create your own with Poets & Writers Groups. Everything you need to connect, communicate, and collaborate with other poets and writers—all in one place.
Find information about more than two hundred full- and low-residency programs in creative writing in our MFA Programs database, which includes details about deadlines, funding, class size, core faculty, and more. Also included is information about more than fifty MA and PhD programs.
Whether you are looking to meet up with fellow writers, agents, and editors, or trying to find the perfect environment to fuel your writing practice, the Conferences & Residencies is the essential resource for information about well over three hundred writing conferences, writers residencies, and literary festivals around the world.
Discover historical sites, independent bookstores, literary archives, writing centers, and writers spaces in cities across the country using the Literary Places database—the best starting point for any literary journey, whether it’s for research or inspiration.
Search for jobs in education, publishing, the arts, and more within our free, frequently updated job listings for writers and poets.
Establish new connections and enjoy the company of your peers using our searchable databases of MFA programs and writers retreats, apply to be included in our directory of writers, and more.

- Register for Classes
Each year the Readings & Workshops program provides support to hundreds of writers participating in literary readings and conducting writing workshops. Learn more about this program, our special events, projects, and supporters, and how to contact us.
The Maureen Egen Writers Exchange Award introduces emerging writers to the New York City literary community, providing them with a network for professional advancement.
Find information about how Poets & Writers provides support to hundreds of writers participating in literary readings and conducting writing workshops.

Bring the literary world to your door—at half the newsstand price. Available in print and digital editions, Poets & Writers Magazine is a must-have for writers who are serious about their craft.
View the contents and read select essays, articles, interviews, and profiles from the current issue of the award-winning Poets & Writers Magazine .
Read essays, articles, interviews, profiles, and other select content from Poets & Writers Magazine as well as Online Exclusives.
View the covers and contents of every issue of Poets & Writers Magazine , from the current edition all the way back to the first black-and-white issue in 1987.
Every day the editors of Poets & Writers Magazine scan the headlines—publishing reports, literary dispatches, academic announcements, and more—for all the news that creative writers need to know.
In our weekly series of craft essays, some of the best and brightest minds in contemporary literature explore their craft in compact form, articulating their thoughts about creative obsessions and curiosities in a working notebook of lessons about the art of writing.
The Time Is Now offers weekly writing prompts in poetry, fiction, and creative nonfiction to help you stay committed to your writing practice throughout the year. Sign up to get The Time Is Now, as well as a weekly book recommendation for guidance and inspiration, delivered to your inbox.
Every week a new author shares books, art, music, writing prompts, films—anything and everything—that has inspired and shaped the creative process.
Listen to original audio recordings of authors featured in Poets & Writers Magazine . Browse the archive of more than 400 author readings.
Ads in Poets & Writers Magazine and on pw.org are the best ways to reach a readership of serious poets and literary prose writers. Our audience trusts our editorial content and looks to it, and to relevant advertising, for information and guidance.
Start, renew, or give a subscription to Poets & Writers Magazine ; change your address; check your account; pay your bill; report a missed issue; contact us.
Peruse paid listings of writing contests, conferences, workshops, editing services, calls for submissions, and more.
Poets & Writers is pleased to provide free subscriptions to Poets & Writers Magazine to award-winning young writers and to high school creative writing teachers for use in their classrooms.
Read select articles from the award-winning magazine and consult the most comprehensive listing of literary grants and awards, deadlines, and prizewinners available in print.

- Subscribe Now
Writing Prompts & Exercises
The time is now.
The Time Is Now offers three new and original writing prompts each week to help you stay committed to your writing practice throughout the year. We also curate a list of essential books on writing —both the newly published and the classics—that we recommend for guidance and inspiration. Whether you’re struggling with writer’s block, looking for a fresh topic, or just starting to write, our archive of writing prompts has what you need. Need a starter pack? Check out our Writing Prompts for Beginners.
Tuesdays: Poetry prompts Wednesdays: Fiction prompts Thursdays: Creative nonfiction prompts
Get immediate access to more than 2,000 writing prompts with the tool below:
Coming Down Hard
- Printable Version
- Log in to Send
- Log in to Save

“The sun had just gone out / and I was walking three miles to get home. / I wanted to die. / I couldn’t think of words and I had no future / and I was coming down hard on everything.” In Linda Gregg’s poem “New York Address,” which appears in her retrospective collection, All of It Singing: New and Selected Poems (Graywolf Press, 2008), the speaker recounts bleak existential angst. Despite the pain and darkness, there are glimmers of light. In the second half of the poem, questions are stubbornly answered with snappy, tidy pacing: “Yes I hate dark. No I love light. Yes I won’t speak. / No I will write.” Write a poem that goes all in on angst, channeling a time that felt overwhelmingly uncertain and full of trepidation. How can you experiment with sound and diction to gently steer the dramatic toward the life-affirming?
Attentiveness
Nearly fifty years ago, the writer George Perec spent three days sitting behind a café window in Place Saint-Sulpice in Paris recording everything he saw. In his short book, An Attempt at Exhausting a Place in Paris , his observations of mundane occurrences and objects often considered unnoteworthy—passersby, cars, buses, pigeons, signs, and slogans—are documented. This week situate yourself in one spot, perhaps in your home or workplace, or in a public space like a park, busy crossroad, commercial area, library, or café. Then, jot down the objects and behavior you see, and the snippets of conversation you hear. Write a lyric essay composed of these notes, trying to avoid interpretations or analysis. Taken together, how do your observations create a portrayal of a specific time or place? Pay particular attention to how one observation might lead to another, and to potential rhythms and repetitions.
Power Couple
The 2023 thriller film Fair Play , written and directed by Chloe Domont, follows the lives of a young, newly engaged couple, Luke and Emily, who are colleagues working as analysts in the cutthroat world of high finance in New York. The film focuses on the progression of their relationship, which has been kept hidden from their hedge fund office, and the bitter disintegration of their happiness after a promotion that was initially rumored to go to Luke is unexpectedly bestowed upon Emily, which situates him as a subordinate to his wife within a misogynistic workplace. Write a short story that revolves around an occurrence that catalyzes a shift in the power dynamic between two main characters who have a close relationship. What are the initial responses, and does the transformation happen suddenly or gradually? Are there gender, generational, or other cultural issues that play a role?
Organic Insinuations
“All too often, on a ‘poetry scene,’ people prioritise ‘subject matter,’” says John Burnside in a 2023 interview about his writing process by Jesse Nathan published on McSweeney’s Internet Tendency. “I am sure that, as I am working, environmental concerns insinuate their way into the content of a poem organically, as other concerns will—but I would never start from there.” Inspired by the late Scottish poet, who died at the age of sixty-nine on May 29, write a poem that springs not from a predetermined topic or subject matter, but instead allows you to “trust in the sounds, the rhythms that come out of the day-to-day, the sheer immediacy and truth of the quotidian…and the images that lead, sometimes via fairly roundabout paths, to metaphor.” Later, as you reread and revise, what do you discover is the subject of your poem? What might have organically insinuated itself into your poem?
The maintenance or restoration of native plant and animal species has long been at the heart of many ecological and conservation projects, and has historically been a focus of land and environmental stewardship principles held by native and first peoples all over the world. But what if a beloved plant or animal is considered invasive, like the palm trees of Los Angeles or the cattle of Texas? What are the effects or consequences of centuries of existence with this invasive species in a particular locale? This week reflect on the notion of belonging—what are various places and times when you have felt a strong sense of belonging, and situations when you did not feel you belonged? Consider your own perspectives and responses when you encounter someone or something else that seems invasive or does not belong.
In Stephen King’s 1983 novel, Pet Sematary , a doctor moves into a remote house in Maine with his wife, two young children, and their pet cat, and learns from a neighbor about an ancient burial ground nearby cursed by a malevolent spirit which gave it power to reanimate those buried there. This is put to the test first by the family cat, and then by members of the family who die throughout the course of King’s horror story. While each formerly dead being is returned to the land of the living, they don’t come back quite the same. Write a story in which a creature or person returns from the dead, either in actuality or under circumstances in which their reappearance feels as if they are “back from the dead.” What familiar traits remain the same and what is disconcertingly different? Is their return ultimately for the better or the worse?
“I told a friend about a spill at the grocery store, which—the words ‘conveyor belt’ vanishing midsentence—took place on a ‘supermarket treadmill,’” writes Madeleine Schwartz in a recent essay published by New York Times Magazine about her experience of negotiating with and toggling between the French and English languages after moving from New York to Paris. In the piece, Schwartz notes that as she became more comfortable with living and thinking in French, she noticed a blurring of her linguistic capabilities, including a muddling of her articulative abilities in English. Think about a time or situation when words have failed you, or you’ve drawn a blank as to the mot juste. Write a poem that traces or enacts a loss of language, perhaps using invented words, phrases, and spellings or experimenting with font sizes, line breaks, and spacing.
Edible Memories
Many foods, flavors, and dishes hold a wellspring of emotional associations because they remind us of loved ones, habits and traditions, specific locales, and a different time of our lives when we were different people. Write a series of flash nonfiction pieces this week with each segment focusing on an edible item that evokes particularly resonant memories for you. You might begin by jotting down lists of foods you ate regularly growing up—breakfasts, school lunches, vending machine go-tos, favorite fast-food joints, diners, late night spots, home-cooked specialties—as well as a few momentous meals. Who are the people you associate with each one? Aside from taste and smell, consider the surrounding environment, atmospheric sounds, time of year, and who you were at that point in your life.
Wheels and Nails
While the American proverb “the squeaky wheel gets the grease” may be one you’ve heard time and again, often in reference to the idea that whoever raises or vocalizes a criticism the loudest will be appeased, there is a Japanese saying that translates to “the nail that sticks out gets hammered down,” which points to the positives of conformity in order to maintain a productive and humble society. It can also refer to putting someone who has become too successful back down in their place. Write a story in which your main character diverges from a group of people, and sticks their neck out, so to speak. Perhaps they vocalize a contrary perspective, protest something they feel is unjust, or simply present themselves in an unconventional manner. What are the consequences? Does your story lean toward one proverbial lesson or the other, or does the conclusion demonstrate more ambiguity?
Night at the Museum
If you could spend a night at any museum, which would you choose, and why? The French publisher Editions Stock has a series of books that begins with this premise—each author selects a museum, arrangements are made for an overnight stay, and a book is written about the experience. In Jakuta Alikavazovic’s Like a Sky Inside , translated from the French by Daniel Levin Becker, she spends a night at the Louvre in Paris, where childhood memories of visits with her father are vividly recalled. “From March 7 to 8, 2020, I spent the night in the Louvre, alone. Alone and at the same time anything but,” writes Alikavazovic. Write a poem that imagines a night at a museum of your choosing, anywhere in the world. What memories will you excavate from this imagined, solitary experience?
Chosen Family
Although the origin of the term is unknown and can be defined in many ways, a chosen family is made up of a group of people who choose to embrace, nurture, and support each other despite conventional understandings of biological or marital relationships. Oftentimes a chosen family is formed to take the place of a biological family, however, in some cases, these relationships are formed to expand a family. Write a personal essay about a relationship you have with a chosen family member. How did you first meet? Was there a particular incident that catalyzed what would become an inextricable bond? Has your commitment to each other been tested in ways big or small? Reflect on past memories and experiences you have had with this special person and how your relationship has evolved over the years.
Kingdom of the Planet
In the 1968 science fiction film Planet of the Apes , which is based on French author Pierre Boulle’s 1963 novel and has spawned several sequels and a recent reboot, a crew of astronauts crash-lands on a planet ruled by apes who have developed an advanced and hierarchical civilization, complete with systems of governance, labor, scientific research, and a military force. In this far-off place, humans have been reduced to mute primitive beings who are subjugated and kept captive as workers for the primates. Write a speculative story that takes place in another universe with a premise revolving around a role reversal. What are the rules and governing structures of the society that you invent? You might decide to approach your narrative with a tone of horror, satire, or comedy to emphasize your perspective on stereotypical assumptions and social expectations.
Another Country
“I love these raw moist dawns with / a thousand birds you hear but can’t / quite see in the mist. / My old alien body is a foreigner / struggling to get into another country. / The loon call makes me shiver. / Back at the cabin I see a book / and am not quite sure what that is.” In these eight lines that comprise Jim Harrison’s poem “Another Country,” which appears in his final collection, Dead Man’s Float (Copper Canyon Press, 2016), the late poet moves between observations about a natural outdoor setting and the speaker’s own bodily presence, arriving in the final two lines at a sentiment that expresses a feeling of defamiliarization at the seemingly mundane sight of a book. This week write a poem that explores the concept of being so absorbed in one environment or circumstance that to behold a different scene is like traveling to a strange and unknown realm.
Self-Healing
A recent study in Scientific Reports journal revealed that, for possibly the first time, a nonhuman wild animal was seen using plant medicine to heal an active wound. In a rainforest in Indonesia, a Sumatran orangutan was observed ripping off leaves from a climbing vine plant, chewing them, and applying the plant sap to treat a wound on his face, which then healed after a few days. Write a personal essay on the theme of self-healing. Think about experiences when you’ve witnessed another person perform this task, or particularly resonant memories that pertain to your own past behavior. What are the primary emotions present throughout this process? What instances of self-treatment or self-medication in film, art, or literature created an impression on you?
Campus Story
Take inspiration from the concept of a campus novel—which takes place in and around the campus of a university and often involves the intertwined dynamics of students, professors, and conventions about learning and power—and write a story that engages with a school setting, whether prominently situated in the context of the plot or used for a particular scene. Some recent additions to the campus novel canon include Elif Batuman’s The Idiot (Penguin Press, 2017), Xochitl Gonzalez’s Anita de Monte Laughs Last (Flatiron Books, 2024), Kiley Reid’s Come and Get It (G. P. Putnam’s Sons, 2024), and Brandon Taylor’s Real Life (Riverhead Books, 2020). Will you include a character who is a student, teacher, administrative staff member, custodial worker or caretaker, or possibly an alumni revisiting the past? Consider the multitude of ways the incorporation of an educational environment might permeate the atmosphere of the narrative.
The Last Friend
“The day the last friend / dies / we sit alone. / A visitor / from outer space / tries hard / to summon us. / Someone says / EAT DEATH. / I fish around for answers / but the questions / still won’t come,” writes Jerome Rothenberg, who passed away in April, in his poem “The Last Friend.” Included in his collection of one hundred poems, A Book of Witness: Spells & Gris-Gris (New Directions, 2022), the poem presents a list of statements and observations, many of which refer to death or dying in some personal way, though the connections are enigmatic and the logical progression is oblique. Try your hand at writing a poem that mentions its subject directly, but which also deliberately obfuscates or remains ambiguous in its intentions. How might using the “I” as a witness include the reader into your point of view?
Mind Your Manners
The New York City culture and news website Gothamist recently asked New Yorkers about their thoughts on sidewalk etiquette in the crowded, bustling streets of their beloved city. What are the rules, who has the right-of-way, and who should yield? Respondents focused on always walking to the right of the sidewalk and to “move quickly and never stop.” One thoughtful respondent considered the cultural differences of sidewalks used for recreational strolls versus commuting. But the overall consensus was that among nine-to-fivers, tourists, parents with kids, dogwalkers, bicyclists, and groups, seniors deserve the right-of-way. Write an essay about the unwritten rules or etiquette you have observed in your daily surroundings. How have these common practices adapted to fit the needs of different people? Do they evolve over time as social norms change? Consider some of your own experiences with how public etiquette has helped or hindered harmonious community life.
The term sub rosa means “under the rose” in Latin and refers to something said or done in private. The rose has been associated with secrecy since ancient times, a decorative symbol often carved and painted in places like meeting rooms, banquet halls, and confessionals as reminders of confidentiality. This week write a short story that revolves around a conversation or discussion that occurs sub rosa in an enclosed space. Does a certain detail get leaked out or overheard? How might the secretive nature place a burden on your characters? Consider the ways in which the atmosphere and tone of your story feel distinctive in the time and space of your sub-rosa conversation versus the scenes that take place before or after the talk.
Wisdom in Translation
In the anthology Another Room to Live In: 15 Contemporary Arab Poets (Litmus Press, 2024) edited by Omar Berrada and Sarah Riggs, multinational and multilingual poet-translators challenge foundational narratives and rework mythologies through poetic expression. Yasmine Seale’s poem “Conventional Wisdom (Arabic Saying Translated Twenty Ways)” is composed of translations of an ancient aphorism expressing the inextricable place of poetry within Arab cultural heritage. Each line presents a variation on the truism: “Poetry is the record of the Arabs / The art of poetry is Arabs, collected / Good poetry is a list of Arabs / To speak in verse is to remain in Arab memory / To surpass another poet is the Arab odyssey.” Write a poem inspired by this idea of translating a proverb or maxim—either from another language or from English into English. How might you creatively interpolate different “translations” of the saying by incorporating connotations and riffing on free associations and personal experiences?

In Response
In a recent interview with Aria Aber for the Yale Review , when asked his thoughts on the responsibility of the poet, Jackson Prize–winning poet Fady Joudah says, “I often think that the responsibility of the poet is to strive to become the memory that people may possess in the future about what it means to be human: an ever-changing constant. In poetry, the range of metaphors and topics is limited, predictable, but the styles are innumerable. Think how we read poetry from centuries ago and are no longer bothered by its outdated diction. All that remains of old poetry is the music of what it means to be human.” Write a creative nonfiction piece that presents your personal theory of the responsibility of a writer or an artist. To construct an expansive approach, you might use observations about how different creative disciplines overlap in their goals, or consider what has remained resonant as the arts make their mark throughout various eras.
Earth to You
In honor of Earth Week, write a scene that revolves around a character who experiences an unexpected moment in a natural environment that produces a sensation of wonder, perhaps an unusual encounter with wild flora or fauna. You might contrast the elements of this scene with others in your story in which the character is interacting solely with humans or only attuned to the sounds, rhythms, and sights of city life and densely packed civilization. Is the occurrence mind-bogglingly quick and then reflected upon in hindsight, or does time slow down in the scene? How do you manage or manipulate the pacing and rhythm of your prose to draw attention to the emotional and psychological response of the character?
From Dirt Level
In Sharon Olds’s poem “May 1968,” the speaker recounts the memory of spending the night with other protesting students, who lay down their bodies on a New York City street at a university’s campus gates in order to obstruct the mounted police force that had been called in. While “spine-down on the cobbles,” she observes the city and surrounding scenery—the soaring buildings and the police and horses’ bodies—as she gazes upward, thinking about the state of her pregnant body. Write a poem this week from the vantage point of lying face-up, “from dirt level.” What circumstances bring you into this position? How does this upward point of view transform what you see, and how you feel about your own body?
More, please? Or, no more, please? In The Fast: The History, Science, Philosophy, and Promise of Doing Without (Avid Reader Press, 2024), John Oakes recounts his personal experience conducting a weeklong fast and examines the practice’s history and place within a wide range of religions and philosophies. The book also explores the act of self-deprivation and the potential transformative benefits of subtracting rather than adding to one’s life. “The act of fasting…won’t stop routine, but impedes it for a bit, signifying a shift and a determined unwillingness to follow standard operating procedure,” writes Oakes. Use this idea to consider your personal relationship with consumption—of food, conversation, media, clothes, space—and write a personal essay that reflects on what you might otherwise take for granted.
All in Your Head
In “Table for One,” a short story from Korean author Yun Ko-eun’s new collection of the same name, translated by Lizzie Buehler and published by Columbia University Press in April, a surreal quality seeps into the tale of a lonely office worker who enrolls in a course to make solitary dining easier. Tips from the course include: “Target corner tables rather than those in the middle. Seats at the bar are also good. Hang your coat or bag on the chair facing you and take advantage of tools like a book, earphones, a cell phone, or a newspaper.” The fantastic element of the story lies less in the oddity of the premise than in the narrator’s meticulously recounted neuroses and detailed rendering of processes that become seemingly cyclical. Write a scene that focuses on your character’s minute observations as they attempt to overcome something debilitating. Does the situation lend itself to a quirky or dark sense of humor?
Neither Questions nor Answers
“Where is the homeland / to lay a cradle for the dead / Where is the other shore / for poetry to step across the end point / Where is the peace / that lets the days distribute blue sky...” In Sidetracks , forthcoming in May from New Directions, the Chinese poet Bei Dao begins his book-length poem with a list of twenty-five enigmatic questions that dance around mythological, philosophical, and existential subjects. In Jeffrey Yang’s translation, the speaker’s questions lack the end punctuation of the original text, with question marks omitted. Through these unanswered questions, the poet conjures loss and nostalgia. Loosely following this structure, write a prologue to a poem that poses a series of questions gesturing toward your most pressing uncertainties. While Bei Dao’s lines are mysterious and mystical, allow your poem the tone and allusions that feel instinctive to you.
About Our Writing Prompts
What is a writing prompt and how do you use one? Whether you find yourself in front of a blank page or stuck in a work-in-progress, writing prompts can offer a spark that ignites your creative thinking and can lead to new writing. Prompts offer guidance, fresh ideas, and direction for writers of all levels of experience. First, choose a prompt for the genre in which you’d like to write, then carefully read it and consider what it is asking you to think about. It could be a specific setting, a writing technique, or an element of an imagined character; a specific poem, story, essay, song, book, or film from which you might take inspiration; or a current event or a topical theme. A writing prompt is filled with endless possibilities—and there is no wrong way to use one to generate new writing!
What makes our writing prompts unique? We have an archive of over 2,000 prompts, all original and offered here and in our weekly newsletter . You’ll find a variety of poetry, fiction, and creative nonfiction prompts—some inspired by recent and classic literature and other forms of art, current events, and writing practices, and others that offer guidance for a particular form, including sonnets, erasure poetry, flash fiction, lyric essays, and more. For more than fifty years, Poets & Writers has supported creative writers with trustworthy information and inspiration, and our weekly prompts provide a regular dose of encouragement and motivation.
What are the benefits of using writing prompts? Writing prompts can help you get unstuck if you’re in a rut and the ideas aren’t flowing. But even if you’re not experiencing writer’s block, writing prompts can offer a fresh take or a new approach to a work-in-progress. Writing prompts can also provide the motivation to experiment with a new form, try out a new genre, or learn about other writing techniques. And writing prompts are an invaluable tool for teachers who want to encourage and inspire their writing students.
What is this list of Best Books? Best Books for Writers is a list of essential books for creative writers that we curate to support your writing practice. Every week, we add a book (whether new or a classic) with a synopsis and highlights. Included are books on the writing life, anthologies of craft essays, collections of lectures, practical guides with writing exercises, and more.
Poetry writing prompts Every Tuesday we post a new poetry prompt to guide you in your practice. Get to know the work of contemporary and classic poets, as well as a variety of poetic forms.
Fiction writing prompts Every Wednesday we post a new fiction prompt to spark your imagination. Take inspiration from recently published short stories and novels, and of course, the classics.
Creative nonfiction writing prompts Every Thursday we post a new creative nonfiction prompt to help your exploration of this ever-changing genre. These prompts include information and inspiration for a variety of essays as well as memoirs. Discover new writers and their craft, and fresh ways to generate writing inspired by your life.
Need a starter pack? Check out our Writing Prompts for Beginners .
Find Study Materials for
- Explanations
- Business Studies
- Combined Science
- Computer Science
- Engineering
- English literature
- Environmental Science
- Human Geography
- Macroeconomics
- Microeconomics
- Social Studies
- Browse all subjects
- Textbook Solutions
- Read our Magazine
Create Study Materials
- Flashcards Create and find the best flashcards.
- Notes Create notes faster than ever before.
- Study Sets Everything you need for your studies in one place.
- Study Plans Stop procrastinating with our smart planner features.
- Organize Your Prompt
In the realm of English learning, the ability to organise your prompt effectively can significantly bolster your writing proficiency. This comprehensive guide aims to fortify your understanding of prompt organisation, discussing its importance and providing actionable techniques to structure your prompt. The discussion extends to practical ways to arrange your writing prompts as well as sophisticated methods to overcome prompt- related challenges.

Create learning materials about Organize Your Prompt with our free learning app!
- Instand access to millions of learning materials
- Flashcards, notes, mock-exams and more
- Everything you need to ace your exams
- 5 Paragraph Essay
- Argumentative Essay
- Cues and Conventions
- English Grammar
- English Language Study
- Essay Time Management
- How To Take a Position in an Essay
- Proofread Essay
- Understanding the Prompt
- Essay Prompts
- Essay Writing Skills
- Global English
- History of English Language
- International English
- Key Concepts in Language and Linguistics
- Language Acquisition
- Language Analysis
- Language and Social Groups
- Lexis and Semantics
- Linguistic Terms
- Listening and Speaking
- Multiple Choice Questions
- Research and Composition
- Rhetorical Analysis Essay
- Single Paragraph Essay
- Sociolinguistics
- Summary Text
- Synthesis Essay
- Textual Analysis
How to Organize Your Prompt: An English Learning Guide
Mastering the art of prompt organization is a crucial aspect of honing your English language skills. This guide is intended to help you understand the importance of prompt organization and provide you with techniques to become proficient in this key area. By integrating these techniques into your English language learning process, you can significantly enhance your proficiency and fluency.
Introduction to Organizing Prompts in English
If you're looking to improve your English writing skills, understanding the concept of organizing prompts is a crucial starting point. A well-organized prompt will efficiently guide your writing and can significantly improve the readability and coherence of your text.
A writing prompt is a statement or question that produces a particular response from the writer. The response typically takes the form of a short piece of writing, like an essay, story, or reflection.
For example, consider the prompt: 'Describe a significant event that changed your life'. This is highly open-ended and can lead your writing in various directions. You could approach it by focusing on the event itself, the effects it had on your life, or how it changed your perspective. A well-organized approach to this prompt will ensure a coherent and effective written response.
The significance of well-arranged writing prompts
Well-organized prompts guide the writer towards creating more coherent, impactful, and satisfying pieces of written work. They can offer clarity and focus, leading to texts that are easier for the reader to follow and understand. As such, the ability to organize prompts efficiently can enhance not just your writing skills but your overall communication abilities within the English language.
Techniques to Structure Your Essay Prompt
There are several key techniques you can use to structure your writing prompts effectively. These include outlining your main ideas, organizing your thoughts in a logical order, and using clear, concise language.
Each of these techniques contributes to an effective and manageable writing process and final product. They enable you to express your thoughts clearly, guide your reader smoothly through your content, and utilize the English language in a more advanced and effective manner.
Consider the previous example of 'Describe a significant event that changed your life’. One way to house this prompt is to break it down into smaller sections such as:
- How it changed you
- Its effects on your life
By doing this, you can approach the prompt in a more organized way.
Comprehensive steps in the Organize Your Prompt Technique
An approach to organizing your prompts effectively involves a few key steps. These steps are designed to make your writing tasks more manageable and to ensure well-structured and meaningful responses. The steps include:
- Understanding the prompt
- Identifying key information/questions
- Establishing your main ideas
- Structuring your response
- Reviewing for coherency and readability
Mastering these steps can significantly enhance your ability to effectively organize your writing prompts, leading to superior English writing skills.
Diving a bit deeper, imagine you are prompted to ‘Discuss the effects of global warming'. To effectively organize this prompt you need first to understand what it entails. That means clarifying the term 'global warming' and identifying the key information or questions being asked. Subsequently, you'd establish your main ideas on global warming effects like rising sea levels, increased temperatures, and so on. The next step entails arranging these main ideas in a logical order and finally reviewing your organized prompt for coherency and readability.
Practical Ways to Arrange Your Writing Prompt
Effective organization of your writing prompts can greatly enhance your English language proficiency. A well-structured prompt can act as a guide, providing a clear path for your ideas and thoughts. It can also improve the coherence and readability of your text. Therefore it is necessary to get familiar with some practical ways to arrange your writing prompts effectively.
The role of brainstorming: Organising Prompts in English
Brainstorming is a powerful technique for mass-generating ideas before we start writing. It plays a pivotal role in organising writing prompts, as it allows you to explore all aspects of the topic at hand and to produce a wide array of initial ideas.
Brainstorming is a creative problem-solving technique that involves the spontaneous generation of ideas. It allows you to think without limitations or constraints and can often lead to innovative and original concepts.
Moreover, brainstorming can also help to clarify your understanding of the prompt. By freely exploring the topic, you might identify areas that are unclear or require additional research. On the other hand, it can lead to insights and connections you had not initially considered.
It's also important to keep in mind that brainstorming is not just about coming up with as many ideas as possible. It's about making connections and building on the ideas of others. For instance, one idea may naturally lead to another, setting off a chain of thoughts that can add richness and depth to your content.
Let's take the example of the prompt: 'Explore the role of technology in modern society’. The first step would be to brainstorm and jot down everything that comes to mind regarding technology's role in our society. You might come up with ideas about: social media, communication, data storage, automation, healthcare advancements, online learning, etc. This isn't a definitive list of topics or ideas. The whole point of brainstorming is to generate as many ideas as possible without limiting your thought process.
Review of Organise Your Prompt Examples
A critical part of mastering your English skills, particularly in writing, is analysing and reviewing examples of how to organise prompts. Looking at examples provides you with practical applications of the techniques being discussed, enabling a deeper understanding of how the concepts work.
When reviewing examples of organised prompts, take note of the clarity and specificity in the prompts. A well-prepared prompt is specific and direct, providing clear instructions on what is expected in the response. Notice how each prompt is divided into manageable pieces, which are then arranged in a logical and coherent order. This structured breakdown promotes a more organised and focused response.
The previous example of the prompt: 'Explore the role of technology in modern society' could be broken down as follows when organised:
| 1. Define modern technology. |
| 2. Discuss the influence of technology in modern society. |
| 3. Investigate the positive and negative effects of technology on societal values. |
This breakdown gives the writer a clear guide to follow, promoting a more effective writing process and a more coherent and readable final product.
As you review examples of organised prompts, note the simplicity and directness in the language used. A well-organised prompt does not prioritise sophisticated language over clarity. The goal is to create a clear, actionable guide for your writing.
Consider the following examples:
- 'Discuss the effects of the rise of the internet on global communication'
- 'Compare the portrayal of masculinity in two novels of your choice'
- 'Evaluate the impact of industrialisation on the environment'
Each of these prompts is clear, direct, and specific. They each give a precise task to the writer, guiding the direction of the response and providing a framework within which to organise ideas and information. Understanding these examples and their structures will significantly help improve your prompt organisation skills.
Advanced Methods to Further Organize Your Prompt
As your English language proficiency progresses, you may seek advanced methods to enhance the organisation of your writing prompts. These methods allow you to harness more complex and nuanced approaches, fostering greater depth and breadth in your writing practices. Utilising these advanced techniques will bolster your prompts' level of organisation, ultimately leading to more sophisticated and effective written responses.
Overcoming Challenges in Understanding Writing Prompts
Even those proficient in English may encounter challenges in comprehending and interpreting writing prompts. Such difficulties may stem from complex language, vague instructions, or a lack of familiarity with the prompt's subject matter. However, several strategies can effectively alleviate these challenges, allowing you to better understand and organise your writing prompts.
One common challenge involves discerning the precise task the prompt is asking you to undertake. The key here is to familiarise yourself with directive words often used in writing prompts. These are words which indicate the type of response expected. Examples include 'explain', 'compare', 'evaluate', and 'discuss'.
Prompt interpretation challenges can also occur as a result of unfamiliar topics. In such scenarios, preliminary research is your best ally. This will provide you with a baseline understanding of the subject matter at hand and enable you to effectively respond to the prompt.
Another potent strategy to combat comprehension difficulties is the employment of graphic organisers like mind maps, concept maps, or flow charts. These tools encourage exploratory thinking and can assist in deciphering complex prompts.
Flow charts, in particular, can more effectively structure a writer’s thoughts on a complex topic. Flow charts are graphical representations that show a progression or sequential steps in a task, process, or workflow. They provide a visual structure for organising information, illustrating sequences of actions and relationships between concepts to enhance comprehension.
To illustrate, consider a complex prompt such as: 'Critically examine the impact of climate change on global economies'. A flow chart could be utilised to dissect this topic into manageable sections based on different areas of potential impact, such as agriculture, maritime industries, or tourism. Each area can then be examined individually from an economic perspective, ensuring a comprehensive approach to the prompt.
Tips for Better Implementing the 'Organize Your Prompt' Technique
To maximise the potential benefits of the 'Organise Your Prompt' technique, several distinct tips can be followed. These tips can help you streamline your writing process, foster clarity in your writing, and guide readers through your written work more effectively.
Initially, aim to be specific and concise . Avoid unnecessary complexities and strive for clarity. Your ultimate goal should be to facilitate an effective written response, so the prompt must clearly articulate what is required.
Ensure your prompt is logically structured. Logical and coherent structuring of your writing prompts assists in maintaining a clear thought process throughout your writing.
Reserving time to edit your prompt after writing can also be productive. This revision process allows for additional fine-tuning and ensuring your prompt translates exactly what you intended to communicate.
Take for instance the broad prompt: 'Discuss the impact of the internet'. A more focused prompt could be: 'Examine the impact of the internet on interpersonal communication in the 21st century'. The refined prompt is more concise, focused and provides clear guidance on what is expected in the written response.
Lastly, it's worth noting that harnessing the 'Organise Your Prompt' technique effectively goes beyond these tips. A degree of practice and patience is required. With dedicated time and practice, your ability to organise writing prompts skilfully and efficiently will undoubtedly improve over time.
Organize Your Prompt - Key takeaways
- Organizing your prompt effectively is a vital skill in English learning that bolsters writing proficiency.
- A writing prompt is a statement or question that elicits a response from the writer in the form of an essay or story.
- The 'Organize Your Prompt' technique involves understanding the prompt , identifying key information, establishing main ideas, structuring the response, and reviewing for coherency and readability.
- Mastering the art of prompt organization enhances not just English writing skills but overall communication abilities within the English language.
- The steps to structure your essay prompt effectively include outlining main ideas, organizing thoughts in a logical order, and using clear, concise language.
Flashcards in Organize Your Prompt 32
What is a writing prompt?
A writing prompt is an instructional text that tells writers what to write about.
What are the three main parts of a writing prompt?
The introduction of the topic, the pre-writing activity, and the writing task.
What should a reader do first when addressing a writing prompt?
Read the prompt in full
Which of the following provides blueprints for an essay?
An outline
What is the first part of a prompt?
The introduction of a topic
What is a thesis statement?
A defensible claim about a topic

Learn with 32 Organize Your Prompt flashcards in the free Vaia app
We have 14,000 flashcards about Dynamic Landscapes.
Already have an account? Log in
Frequently Asked Questions about Organize Your Prompt
Test your knowledge with multiple choice flashcards.

Join the Vaia App and learn efficiently with millions of flashcards and more!
Keep learning, you are doing great.
Discover learning materials with the free Vaia app

Vaia is a globally recognized educational technology company, offering a holistic learning platform designed for students of all ages and educational levels. Our platform provides learning support for a wide range of subjects, including STEM, Social Sciences, and Languages and also helps students to successfully master various tests and exams worldwide, such as GCSE, A Level, SAT, ACT, Abitur, and more. We offer an extensive library of learning materials, including interactive flashcards, comprehensive textbook solutions, and detailed explanations. The cutting-edge technology and tools we provide help students create their own learning materials. StudySmarter’s content is not only expert-verified but also regularly updated to ensure accuracy and relevance.

Vaia Editorial Team
Team Organize Your Prompt Teachers
- 11 minutes reading time
- Checked by Vaia Editorial Team
Study anywhere. Anytime.Across all devices.
Create a free account to save this explanation..
Save explanations to your personalised space and access them anytime, anywhere!
By signing up, you agree to the Terms and Conditions and the Privacy Policy of Vaia.
Sign up to highlight and take notes. It’s 100% free.
Join over 22 million students in learning with our Vaia App
The first learning app that truly has everything you need to ace your exams in one place
- Flashcards & Quizzes
- AI Study Assistant
- Study Planner
- Smart Note-Taking

Privacy Overview
Freshman requirements
- Subject requirement (A-G)
- GPA requirement
- Admission by exception
- English language proficiency
- UC graduation requirements
Additional information for
- California residents
- Out-of-state students
- Home-schooled students
Transfer requirements
- Understanding UC transfer
- Preparing to transfer
- UC transfer programs
- Transfer planning tools
International applicants
- Applying for admission
- English language proficiency (TOEFL/IELTS)
- Passports & visas
- Living accommodations
- Health care & insurance
AP & Exam credits
Applying as a freshman
- Filling out the application
- Dates & deadlines
Personal insight questions
- How applications are reviewed
- After you apply
Applying as a transfer
Types of aid
- Grants & scholarships
- Jobs & work-study
- California DREAM Loan Program
- Middle Class Scholarship Program
- Blue and Gold Opportunity Plan
- Native American Opportunity Plan
- Who can get financial aid
- How aid works
- Estimate your aid
Apply for financial aid
- Cal Dream Act application tips
- Tuition & cost of attendance
- Glossary & resources
- Santa Barbara
- Campus program & support services
- Check majors
- Freshman admit data
- Transfer admit data
- Native American Opportunity Plan
- You will have 8 questions to choose from. You must respond to only 4 of the 8 questions.
- Each response is limited to a maximum of 350 words.
- Which questions you choose to answer is entirely up to you. However, you should select questions that are most relevant to your experience and that best reflect your individual circumstances.
Keep in mind
- All questions are equal. All are given equal consideration in the application review process, which means there is no advantage or disadvantage to choosing certain questions over others.
- There is no right or wrong way to answer these questions. It’s about getting to know your personality, background, interests and achievements in your own unique voice.
- Use the additional comments field if there are issues you'd like to address that you didn't have the opportunity to discuss elsewhere on the application. This shouldn't be an essay, but rather a place to note unusual circumstances or anything that might be unclear in other parts of the application. You may use the additional comments field to note extraordinary circumstances related to COVID-19, if necessary.
Questions & guidance
Remember, the personal insight questions are just that—personal. Which means you should use our guidance for each question just as a suggestion in case you need help. The important thing is expressing who you are, what matters to you and what you want to share with UC.
1. Describe an example of your leadership experience in which you have positively influenced others, helped resolve disputes or contributed to group efforts over time. Things to consider: A leadership role can mean more than just a title. It can mean being a mentor to others, acting as the person in charge of a specific task, or taking the lead role in organizing an event or project. Think about what you accomplished and what you learned from the experience. What were your responsibilities?
Did you lead a team? How did your experience change your perspective on leading others? Did you help to resolve an important dispute at your school, church, in your community or an organization? And your leadership role doesn't necessarily have to be limited to school activities. For example, do you help out or take care of your family? 2. Every person has a creative side, and it can be expressed in many ways: problem solving, original and innovative thinking, and artistically, to name a few. Describe how you express your creative side. Things to consider: What does creativity mean to you? Do you have a creative skill that is important to you? What have you been able to do with that skill? If you used creativity to solve a problem, what was your solution? What are the steps you took to solve the problem?
How does your creativity influence your decisions inside or outside the classroom? Does your creativity relate to your major or a future career? 3. What would you say is your greatest talent or skill? How have you developed and demonstrated that talent over time? Things to consider: If there is a talent or skill that you're proud of, this is the time to share it.You don't necessarily have to be recognized or have received awards for your talent (although if you did and you want to talk about it, feel free to do so). Why is this talent or skill meaningful to you?
Does the talent come naturally or have you worked hard to develop this skill or talent? Does your talent or skill allow you opportunities in or outside the classroom? If so, what are they and how do they fit into your schedule? 4. Describe how you have taken advantage of a significant educational opportunity or worked to overcome an educational barrier you have faced. Things to consider: An educational opportunity can be anything that has added value to your educational experience and better prepared you for college. For example, participation in an honors or academic enrichment program, or enrollment in an academy that's geared toward an occupation or a major, or taking advanced courses that interest you; just to name a few.
If you choose to write about educational barriers you've faced, how did you overcome or strive to overcome them? What personal characteristics or skills did you call on to overcome this challenge? How did overcoming this barrier help shape who you are today? 5. Describe the most significant challenge you have faced and the steps you have taken to overcome this challenge. How has this challenge affected your academic achievement? Things to consider: A challenge could be personal, or something you have faced in your community or school. Why was the challenge significant to you? This is a good opportunity to talk about any obstacles you've faced and what you've learned from the experience. Did you have support from someone else or did you handle it alone?
If you're currently working your way through a challenge, what are you doing now, and does that affect different aspects of your life? For example, ask yourself, How has my life changed at home, at my school, with my friends or with my family? 6. Think about an academic subject that inspires you. Describe how you have furthered this interest inside and/or outside of the classroom. Things to consider: Many students have a passion for one specific academic subject area, something that they just can't get enough of. If that applies to you, what have you done to further that interest? Discuss how your interest in the subject developed and describe any experience you have had inside and outside the classroom such as volunteer work, internships, employment, summer programs, participation in student organizations and/or clubs and what you have gained from your involvement.
Has your interest in the subject influenced you in choosing a major and/or future career? Have you been able to pursue coursework at a higher level in this subject (honors, AP, IB, college or university work)? Are you inspired to pursue this subject further at UC, and how might you do that?
7. What have you done to make your school or your community a better place? Things to consider: Think of community as a term that can encompass a group, team or a place like your high school, hometown or home. You can define community as you see fit, just make sure you talk about your role in that community. Was there a problem that you wanted to fix in your community?
Why were you inspired to act? What did you learn from your effort? How did your actions benefit others, the wider community or both? Did you work alone or with others to initiate change in your community? 8. Beyond what has already been shared in your application, what do you believe makes you a strong candidate for admissions to the University of California? Things to consider: If there's anything you want us to know about you but didn't find a question or place in the application to tell us, now's your chance. What have you not shared with us that will highlight a skill, talent, challenge or opportunity that you think will help us know you better?
From your point of view, what do you feel makes you an excellent choice for UC? Don't be afraid to brag a little.
Writing tips
Start early..
Give yourself plenty of time for preparation, careful composition and revisions.
Write persuasively.
Making a list of accomplishments, activities, awards or work will lessen the impact of your words. Expand on a topic by using specific, concrete examples to support the points you want to make.
Use “I” statements.
Talk about yourself so that we can get to know your personality, talents, accomplishments and potential for success on a UC campus. Use “I” and “my” statements in your responses.
Proofread and edit.
Although you will not be evaluated on grammar, spelling or sentence structure, you should proofread your work and make sure your writing is clear. Grammatical and spelling errors can be distracting to the reader and get in the way of what you’re trying to communicate.
Solicit feedback.
Your answers should reflect your own ideas and be written by you alone, but others — family, teachers and friends can offer valuable suggestions. Ask advice of whomever you like, but do not plagiarize from sources in print or online and do not use anyone's words, published or unpublished, but your own.
Copy and paste.
Once you are satisfied with your answers, save them in plain text (ASCII) and paste them into the space provided in the application. Proofread once more to make sure no odd characters or line breaks have appeared.
This is one of many pieces of information we consider in reviewing your application. Your responses can only add value to the application. An admission decision will not be based on this section alone.
Need more help?
Download our worksheets:
- English [PDF]
- Spanish [PDF]
What is a Writing Prompt? | Types, Responses & Examples
Leslie Beecher has been in the field of education for over 15 years serving as a tutor, teacher and instructional designer. She has a B.S. in Elementary Education from Northern Arizona University and M.Ed. in Curriculum and Instruction from University of Phoenix.
Mary Firestone has a Bachelor of Arts in Music and a Master of Fine Arts in Creative Writing. Firestone has experience as an instructor for English, English Composition, Advanced Composition, Contemporary World Literature, Contemporary Literature, and Creative Writing. She has taught at a variety of schools such as Ottawa University Online, Rasmussen College, Excelsior College, and Southern New Hampshire University.
How do you write a prompt?
A writing prompt is a topic meant to center and guide your writing content. The prompt could be anything (a question, statement, picture, etc), but the main idea is to give you something to focus on while you write.
What is the meaning of a prompt?
A prompt is a written guideline that provides a potential topic idea or starting point for multiple forms of writing. Prompts can result in a quick entry or a lengthy essay.
Table of Contents
What is a writing prompt, types of writing prompts, prompt examples, responding to writing prompts, lesson summary.
To prompt means to give a cue to a person to help them focus on a specific topic, task, or purpose. A prompt can be a passage of text, a word, or even an image. A writing prompt is a type of assessment or activity that directs individuals to write about a given topic in a certain way. Writing prompts often introduce a topic, subject, or idea to the students to encourage them to think critically through the writing.
Writing prompts can be in the form of:
- A brief passage of text
- Original essay
- Journal entry
- Other forms of writing
The purpose of a writing prompt is often to test a writer's skills of analysis and reasoning, inspire a point of view, and improve essay writing skills. A writing prompt gives focus to the writing topic. It also offers instructions about the writing prompt task.
What is an Essay Prompt?
An essay prompt is a more specific type of writing prompt. Essay prompts ask learners to write about a particular topic in the form of an essay. The purpose of this type of prompt is to solicit a response from the learner in the form of an essay focusing on a statement, or issue, followed by questions, which will test writing, reasoning, and analytical skills. These prompts will usually include details about the type of essay that should be written, along with style and format. The learner's output from these kinds of prompts is considered to be the essay prompt response. Generally, an essay prompt should lead the learner into a smooth writing phase as it introduces a situation and provides directions a student needs to follow to complete the essay.
Essay Prompt Example
Write a 1-to-2-page essay about the increasing presence use of artificial intelligence in a career field you are interested in. In your essay, be sure to:
- State your perspective on the topic and analyze the relationship between your perspective and at least one other perspective provided in the instructions below.
- Support ideas with reasoning, and provide examples in an organized manner
- Present ideas effectively in standard written English
To unlock this lesson you must be a Study.com Member. Create your account

An error occurred trying to load this video.
Try refreshing the page, or contact customer support.
You must c C reate an account to continue watching
Register to view this lesson.
As a member, you'll also get unlimited access to over 88,000 lessons in math, English, science, history, and more. Plus, get practice tests, quizzes, and personalized coaching to help you succeed.
Get unlimited access to over 88,000 lessons.
Already registered? Log in here for access
Resources created by teachers for teachers.
I would definitely recommend Study.com to my colleagues. It’s like a teacher waved a magic wand and did the work for me. I feel like it’s a lifeline.
You're on a roll. Keep up the good work!
Just checking in. are you still watching.
- 0:00 What Are Essay Prompts?
- 0:25 Types Of Essay Prompts
- 2:35 Responding To The Prompt
- 3:10 Lesson Summary
Writing prompt assignments do come in different forms, but there are multiple types of writing.
- Descriptive
- Expository/informative
Descriptive writing prompts often ask writers to include details that help the reader create a vivid image by soliciting the reader's five senses:
- Sight: The house's exterior red brick with purple flowers looked like something from a fairytale.
- Hearing: The melody she played on the piano sounded like a soft, spring rain.
- Touch: The cat's fur felt like a fleece blanket against my hand.
- Smell: He could smell the stench of the trashcan before he even walked into the house.
- Taste: The juicy watermelon melted in the child's mouth while red juice dripped down his cheek.
Descriptive writing can also be used to help the reader identify with how the person feels or emotions.
Expository/Informative
Expository/Informative writing prompts ask the writer to present the topic clearly and then add supporting facts and details about the topic. In other words, expository/ informative writing is writing to inform the reader about a given topic.
Writers use real or imagined experiences when addressing narrative prompts. Their writing should include:
- Sensory details
- Logical sequencing
In an opinion writing prompt, writers are asked to state their opinion on a given topic and back it up with facts and reasoning. The information presented should be organized sensibly and reinforced with details.
Persuasive writing prompts are meant to encourage writers to try to get the reader to concur with their opinions or ideas.
Research prompts ask writers to locate information on a specific topic by using books, online resources, videos, etc. Writers should take detailed notes and include a list of the resources they used.
Writing prompts can be in the form of a question, a statement, or a directive. Here are a few prompt examples:
| Type of Writing Prompt | Prompt Example |
|---|---|
| Descriptive writing prompt | Describe the best party you have ever attended. |
| Expository/Informative writing prompt | Describe the process of making your favorite meal. |
| Narrative writing prompt | If you could be in charge of the world for one day, what would you do? |
| Opinion writing prompt | What is the best movie you have ever watched? Explain why. |
| Research writing prompt | Choose an endangered species from the ocean to write a research paper. Include information about why this animal is endangered and what interventions can help increase its population. |
| Persuasive writing prompt | Why should the school year be shorter? |
Many people write for pleasure and personal growth. Writing prompts can be a good way to start the creative process . There are also multiple places in academia where a learner may encounter a writing prompt.
- Subject classes (i.e. history, English literature, English composition, science, etc.).
- School entrance exams
- Scholarship entries
Writing prompts often use purpose words. These words tell the writer what they are supposed to do in their response.
- Compare: show the similarities
- Contrast: show the differences
- Define: explain the meaning
- Describe: use details that clarify
- Evaluate: show the value or worth
- Explain: show how something works
- Persuade: convince through reasoning
- Prove: demonstrate with facts and evidence
- Summarize: give the main point
When responding to a writing prompt, there are a few tips and tricks that can help improve writing.
- Follow the instructor's guidelines
- Pace oneself
- Read the prompt twice, and underline key terms and phrases
- Write the response to the prompt
- Review writing before considering it done
A writing prompt (or essay prompt ) is usually a statement focusing presenting focus on a specific topic, or issue, and can be followed by clarifying questions . A prompt needs to have directions of what the writer needs to do and be as concise as much as possible to receive excellent prompt responses. There are diverse types of writing prompts to solicit learners' application of their writing skills, including:
However, to be successful at writing to a given prompt, there are a few tips that should be followed:
- Write response
Writing prompts often use purpose words. These words tell the writer how to respond to the prompt.
Video Transcript
What are essay prompts.
Essay prompts are statements that focus on a topic or an issue, followed by questions. The purpose of an essay prompt is to inspire a response in the form of an essay, which will test your writing, reasoning, and analytical skills. Essay prompts are frequently used in English composition and literature classes, and in college entrance exams like the SAT and ACT.
Types of Essay Prompts
There are different types of essay prompts. In this section, we will explore three of them.
College Entrance Exam Prompts
When you reach the essay portion of a college entrance exam, you'll be asked to read a prompt and respond to it. A few questions always follow the prompt and these questions might ask you to decide on a moral issue or express your point of view about something declared in the prompt. For example:
People are surprisingly willing to give up their personal integrity if it means losing their place in a social group. While they may convince themselves that what they're doing is not significant, the fact is that they've sacrificed something in themselves that can never be regained.
Do you agree with this statement? Do the choices people make in order to belong cause a permanent loss of something? Plan and write an essay in which you develop your point of view, using examples and personal experiences.
English Literature Essay Prompts
In an English literature course, your instructor might give you an essay prompt that goes something like this:
In the Ernest Hemingway short story 'Hills Like White Elephants,' a man and woman are having a conversation at a cafe. Who does the narrator sympathize with the most? Does Jig appear to be a victim? Who comes out ahead in this story? Write a 5-paragraph essay that answers all of these questions and support your answers with examples and quotes from the story.
English Composition Prompts
Your English composition instructor might suggest that you write a persuasive essay based on a controversial social issue. The prompt may go something like this:
Your community library has received complaints from parents about the violent and explicit sexual content in the teen books at the library. Because of these complaints, librarians have decided to remove all of the books the parents find questionable for teen readers.
Do you agree with this choice? Why or why not? What is lost or gained? Do you think it helps to protect teens from this kind of material? Write a 5-paragraph essay in which you express your point of view. Be sure to support your response with examples and consider all the people involved: parents, teens, and librarians.
Responding to the Prompt
Before you jump into your response, read the prompt carefully and then read it again. During the second reading, underline key words. If the prompt asks you to express your point of view, make it clear which side of the argument you feel strongest about. Make sure that you're responding to the question being asked and review each question to make sure your essay includes an answer. Some students find it helpful to write down the prompt in their own words, which you might also find helpful.
Let's review.
Essay prompts are statements that focus on a topic or an issue, followed by questions and are commonly found in English composition or literature classes, and as part of college entrance exams. There are three common types of prompts that all require you to read them carefully and respond accordingly. These are college entrance exam prompts , English literature essay prompts , and English composition prompts .
Table of Glossary Terms
| Prompts | Explanations |
|---|---|
| statements that focus on a topic or an issue; they're followed by questions | |
| questions might ask you to decide on a moral issue or express your point of view about something declared in the prompt | |
| might suggest that you write a persuasive essay based on a controversial social issue | |
| read and read the prompt again, underline key words, make your argument clear, make sure all questions are answered |
Learning Outcomes
As soon as you complete the video lesson and peruse the transcript, see if you can achieve the following goals:
- Recognize the meaning and purpose an essay prompt
- Determine the types of essay prompts
- Remember how to respond to an essay prompt
Unlock Your Education
See for yourself why 30 million people use study.com, become a study.com member and start learning now..
Already a member? Log In
Recommended Lessons and Courses for You
Related lessons, related courses, recommended lessons for you.

What is a Writing Prompt? | Types, Responses & Examples Related Study Materials
- Related Topics
Browse by Courses
- English 103: Analyzing and Interpreting Literature
- AP English Literature: Exam Prep
- AP English Language: Exam Prep
- Common Core ELA - Literature Grades 11-12: Standards
- College Composition for Teachers: Professional Development
- Technical Writing for Teachers: Professional Development
- FTCE General Knowledge Test (GK) (827): Reading Subtest Practice & Study Guide
- FTCE General Knowledge Test (GK) (826): English Language Skills Subtest Practice & Study Guide
- GED Reasoning Through Language Arts
- GRE Prep: Tutoring Solution
- Study.com ACT® Test Prep: Tutoring Solution
- CLEP American Literature: Study Guide & Test Prep Course
- American Literature: Certificate Program
- English Literature: Certificate Program
- CLEP English Literature Prep
Browse by Lessons
- Argumentative Essay | Definition, Format & Examples
- Descriptive Essay | Definition, Format & Examples
- How to Write a Great Essay
- Compare & Contrast Essay | Definition & Examples
- Informative Essay | Definition, Examples & Structure
- Formal Essay Format, Types & Example
- Evaluation Essay Definition, Example & Parts
- Thesis Statement for Speech | Purpose & Examples
- Argumentative Essay | Definition & Examples
- Informative Thesis Statement Examples
- Compare & Contrast Thesis Statements | Overview & Examples
- How to Organize an Essay
- How to Structure an Argument in Your Essay
- Personal Essay | Definition, Guidelines & Tips
- Writing an Informative Essay | Outline, Steps & Example
Create an account to start this course today Used by over 30 million students worldwide Create an account
Explore our library of over 88,000 lessons
- Foreign Language
- Social Science
- See All College Courses
- Common Core
- High School
- See All High School Courses
- College & Career Guidance Courses
- College Placement Exams
- Entrance Exams
- General Test Prep
- K-8 Courses
- Skills Courses
- Teacher Certification Exams
- See All Other Courses
- Create a Goal
- Create custom courses
- Get your questions answered

- All topics A-Z
- Grammar
- Vocabulary
- Speaking
- Reading
- Listening
- Writing
- Pronunciation
- Virtual Classroom
- Worksheets by season
- 600 Creative Writing Prompts
- Warmers, fillers & ice-breakers
- Coloring pages to print
- Flashcards
- Classroom management worksheets
- Emergency worksheets
- Revision worksheets
- Resources we recommend











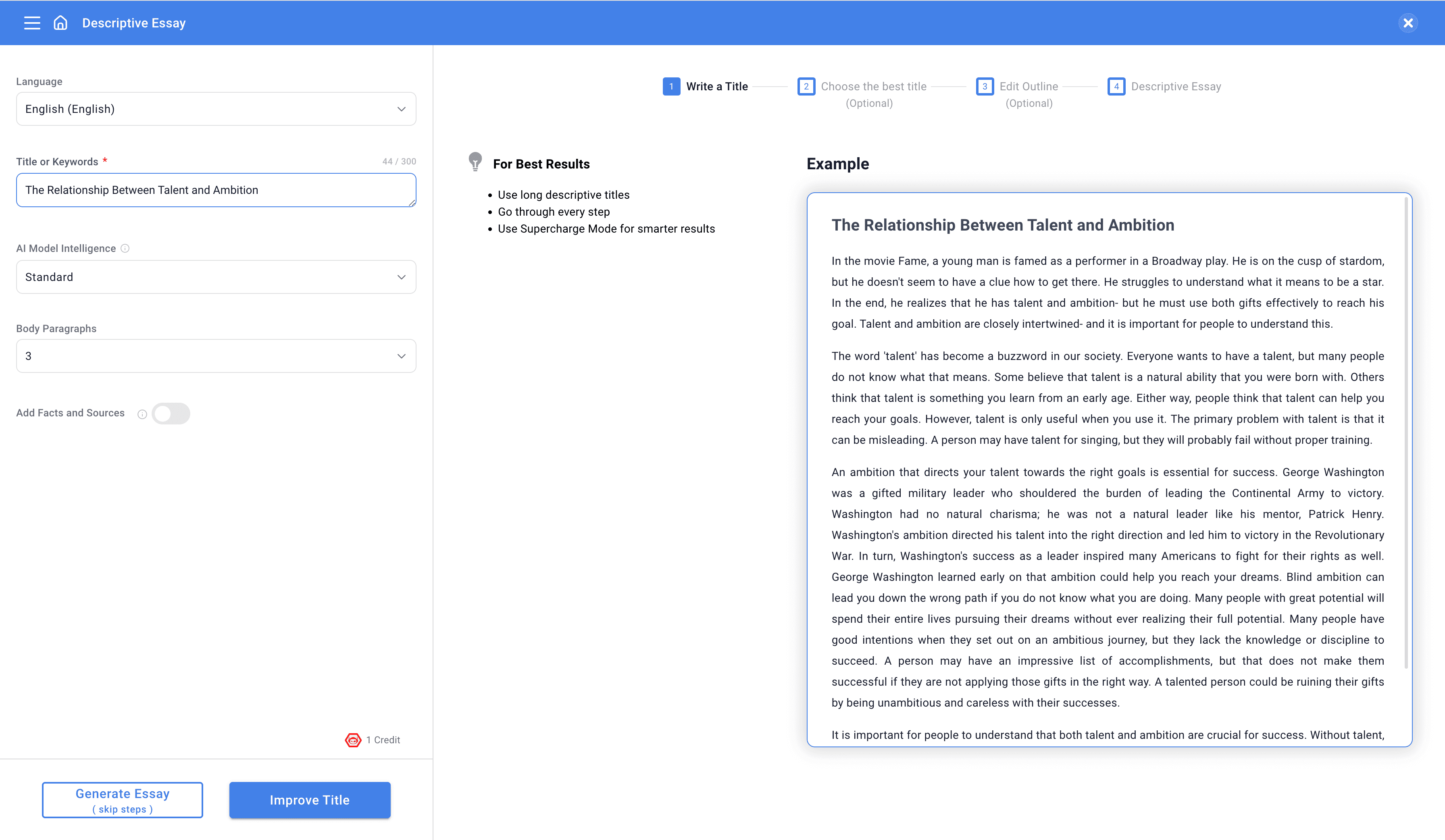
IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A prompt in writing is a starting point designed to ignite creativity, guiding writers to explore themes, genres, or emotions. It can be a word, question, image, or scenario, aiding in overcoming writer's block. Keep reading to learn everything you need to know about prompts in writing.
An essay prompt is a statement that will focus the topic and then ask questions. There are several steps to take to write an effective essay prompt. First, be sure that the question you are asking ...
Of all the resources we publish on The Learning Network, perhaps it's our vast collection of writing prompts that is our most widely used resource for teaching and learning with The Times. We ...
essay prompt states the type of essay that the writer is being asked to construct. By understanding what an essay prompt is asking, one can write a more coherent, unified, and organized essay. To write an essay, one must consider the essay type, essay goal, supporting details, form of the conclusion, and appropriate conclusion information. The ...
Good writing prompts start with a clear answer to the question: why do we ask students to write? The answer may change depending on the type of class you're teaching, but certainly one goal for faculty teaching Writing Skills classes is to help students become more sophisticated writers. What other goals do you hope to achieve with each assignment? Understanding your goal in giving the ...
Descriptive writing prompt. A descriptive essay prompt encourages the writer to provide a detailed account of a particular subject. The goal when answering such a prompt is to use language that employs all the senses, making the reader feel as though they are part of the scene or experience you are describing. To help you achieve this, consider ...
No extra time allowed! #5: Grade the essay, using the official essay rubric to give yourself a score out of 8 in the reading, analysis, and writing sections. #6: Repeat steps 4 and 5. Choose the prompts you think will be the hardest for you so that you can so that you're prepared for the worst when the test day comes.
Body #1: Most students think writing an essay is tedious because they focus on external rewards. Body #2: Students should instead focus on internal fulfillment when writing an essay. Body #3: Not only will focusing on internal fulfillment allow students to have more fun, it will also result in better essays.
A specific focus is placed on the necessity of defending one's own perspective while considering at least one other, encouraging a depth of analysis and rational argumentation. The Magoosh sample essay prompt on 'censorship and society' is introduced as the basis for practice, illustrating how to apply the discussed essay writing strategies.
The secret to writing a clear, focused, and impactful essay is to organize your prompt effectively. A well-organized prompt serves as a blueprint for your essay, coaching you through each crucial component—from the introduction and thesis statement to the body paragraphs and the conclusion.
Check out our Writing Prompts for Beginners. Tuesdays: Poetry prompts. Wednesdays: Fiction prompts. Thursdays: Creative nonfiction prompts. Get immediate access to more than 2,000 writing prompts with the tool below: Choose a genre: <Any>. Items/Page: 25.
A writing prompt is a statement or question that produces a particular response from the writer. The response typically takes the form of a short piece of writing, like an essay, story, or reflection. For example, consider the prompt: 'Describe a significant event that changed your life'. This is highly open-ended and can lead your writing in ...
Essay Prompt . Prepared by . Kate Fischer, MA . The MWC is a Writing Across the Curriculum initiative serving Northwest Vista College students, faculty, and the community through tutoring in writing skills, critical thinking, and building writing pedagogy. Effective writing is a cornerstone of education.
expected to write an essay with the standard essay elements so here is a review of what to include: FOCUS-THESIS: One of the major skills that is being tested in a timed writing exam is your ability to write to the prompt. Your thesis will be your direct answer or response to the question or task in the prompt.
1 Custom prompts. In the Grammarly prompt box, you can type any prompt you want—you're limited only by your imagination. The prompt can take any structure you want, but if you want some inspiration, try using this template: Write a [composition type] for [audience] that [purpose]. Make it [tone] and [length]. For example:
Remember, the personal insight questions are just that—personal. Which means you should use our guidance for each question just as a suggestion in case you need help. The important thing is expressing who you are, what matters to you and what you want to share with UC. 1. Describe an example of your leadership experience in which you have ...
An essay prompt is a more specific type of writing prompt. Essay prompts ask learners to write about a particular topic in the form of an essay. The purpose of this type of prompt is to solicit a ...
A mini-step-by-step guide to writing each response. How to write each PIQ (with examples) Prompt #1: Leadership. Prompt #2: Creative. Prompt #3: Greatest Talent or Skill. Prompt #4: Significant Educational Opportunity/Barrier. Prompt #5: Significant Challenge.
This series looks at the myriad of uses for writing prompts, many to be used in writing class but others that can be used in conversation and discussion periods, extension activities and creative as well as academic writing. This installment looks at how writing prompts can target specific strategies for academic writing, aka types of essays.
Writing Tips. Tell your story. It may be trite advice, but it's also true. Admissions counselors develop a sixth sense about essay writers who are authentic. You'll score points for being earnest and faithful to yourself. Write with focus. Another very simple tip, but many of the less compelling essays we read each year fail to focus.
The following ideas work well for compare-contrast essays. ( Find 80+ compare-contrast essay topics for all ages here.) Public and private schools. Capitalism vs. communism. Monarchy or democracy. Dogs vs. cats as pets. WeAreTeachers. Paper books or e-books. Two political candidates in a current race.
Office Hours: Our office will be open both virtually and in-person on Monday, Tuesday, Thursday, and Friday from 8:00am-4:30pm. We will also be open virtually on Wednesdays from 8:00am-4:30pm. In the online Common Application Writing Supplement, please respond to both the Cornell University essay question and the essay prompt that corresponds ...
The four main types of writing. In many of the online resources you'll find about the types of essays, you'll find references to the four main types of writing: Persuasive. Descriptive. Narrative. Expository. These aren't four specific types of essays, but four distinct methods of communicating an essay's theme.
answer that question and write an essay, using the prompt to inspire and structure your response. Remember: 650 words is your limit, not your goal. Use the full range if you need it, but don't feel ... Essay Prompt 2: The lessons we take from obstacles we encounter can be fundamental to later success. Recount a time when you faced a challenge ...
2. Forbid Cliché Use. Probably the quickest and easiest way to cut back on some AI use is to come down hard on cliché use in writing assignments. AI tools are essentially cliché machines, so ...
The 2024 Personal Essay Writing Challenge is a 7-day writing challenge from June 24 to June 30, 2024. Each day, I will provide a personal essay prompt, and it will be up to writers to write a personal essay before they take on the next one. I have already put together the list of prompts, and I think they'll be easy to write whether you have ...
exams or as essay prompts for an assignment. During a timed exam, you will be given a sheet of paper containing a prompt, and must write an essay in response within a certain amount of time. Prompts assigned as take-home or assignment essays should be written and turned in to your teacher by the specified due date.
The Math Section: Overview. Types of Math Tested. SAT Calculator Use. Student-Produced Responses. Find out what's going to be on each section of the SAT so you can prepare for test day.
Grammarly is the AI writing partner that understands the larger context of your email or document, so its writing works for you. Simple prompts and instructions can deliver a compelling draft in seconds. A few clicks can transform any text to the right tone, length, and clarity you need. Polish your final draft with strategic revisions ...
Smodin's AI writer is easy to use. Provide your prompt with a few words and easily generate plagiarism-free, unique, and high-quality articles and essays in minutes. Type what you want to write about in a small sentence or two, with at least the minimum required characters for the tool to work, and click on the generate text button.