- USC Libraries
- Research Guides

Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- 7. The Results
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
The results section is where you report the findings of your study based upon the methodology [or methodologies] you applied to gather information. The results section should state the findings of the research arranged in a logical sequence without bias or interpretation. A section describing results should be particularly detailed if your paper includes data generated from your own research.
Annesley, Thomas M. "Show Your Cards: The Results Section and the Poker Game." Clinical Chemistry 56 (July 2010): 1066-1070.
Importance of a Good Results Section
When formulating the results section, it's important to remember that the results of a study do not prove anything . Findings can only confirm or reject the hypothesis underpinning your study. However, the act of articulating the results helps you to understand the problem from within, to break it into pieces, and to view the research problem from various perspectives.
The page length of this section is set by the amount and types of data to be reported . Be concise. Use non-textual elements appropriately, such as figures and tables, to present findings more effectively. In deciding what data to describe in your results section, you must clearly distinguish information that would normally be included in a research paper from any raw data or other content that could be included as an appendix. In general, raw data that has not been summarized should not be included in the main text of your paper unless requested to do so by your professor.
Avoid providing data that is not critical to answering the research question . The background information you described in the introduction section should provide the reader with any additional context or explanation needed to understand the results. A good strategy is to always re-read the background section of your paper after you have written up your results to ensure that the reader has enough context to understand the results [and, later, how you interpreted the results in the discussion section of your paper that follows].
Bavdekar, Sandeep B. and Sneha Chandak. "Results: Unraveling the Findings." Journal of the Association of Physicians of India 63 (September 2015): 44-46; Brett, Paul. "A Genre Analysis of the Results Section of Sociology Articles." English for Specific Speakers 13 (1994): 47-59; Go to English for Specific Purposes on ScienceDirect;Burton, Neil et al. Doing Your Education Research Project . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2008; Results. The Structure, Format, Content, and Style of a Journal-Style Scientific Paper. Department of Biology. Bates College; Kretchmer, Paul. Twelve Steps to Writing an Effective Results Section. San Francisco Edit; "Reporting Findings." In Making Sense of Social Research Malcolm Williams, editor. (London;: SAGE Publications, 2003) pp. 188-207.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Organization and Approach
For most research papers in the social and behavioral sciences, there are two possible ways of organizing the results . Both approaches are appropriate in how you report your findings, but use only one approach.
- Present a synopsis of the results followed by an explanation of key findings . This approach can be used to highlight important findings. For example, you may have noticed an unusual correlation between two variables during the analysis of your findings. It is appropriate to highlight this finding in the results section. However, speculating as to why this correlation exists and offering a hypothesis about what may be happening belongs in the discussion section of your paper.
- Present a result and then explain it, before presenting the next result then explaining it, and so on, then end with an overall synopsis . This is the preferred approach if you have multiple results of equal significance. It is more common in longer papers because it helps the reader to better understand each finding. In this model, it is helpful to provide a brief conclusion that ties each of the findings together and provides a narrative bridge to the discussion section of the your paper.
NOTE: Just as the literature review should be arranged under conceptual categories rather than systematically describing each source, you should also organize your findings under key themes related to addressing the research problem. This can be done under either format noted above [i.e., a thorough explanation of the key results or a sequential, thematic description and explanation of each finding].
II. Content
In general, the content of your results section should include the following:
- Introductory context for understanding the results by restating the research problem underpinning your study . This is useful in re-orientating the reader's focus back to the research problem after having read a review of the literature and your explanation of the methods used for gathering and analyzing information.
- Inclusion of non-textual elements, such as, figures, charts, photos, maps, tables, etc. to further illustrate key findings, if appropriate . Rather than relying entirely on descriptive text, consider how your findings can be presented visually. This is a helpful way of condensing a lot of data into one place that can then be referred to in the text. Consider referring to appendices if there is a lot of non-textual elements.
- A systematic description of your results, highlighting for the reader observations that are most relevant to the topic under investigation . Not all results that emerge from the methodology used to gather information may be related to answering the " So What? " question. Do not confuse observations with interpretations; observations in this context refers to highlighting important findings you discovered through a process of reviewing prior literature and gathering data.
- The page length of your results section is guided by the amount and types of data to be reported . However, focus on findings that are important and related to addressing the research problem. It is not uncommon to have unanticipated results that are not relevant to answering the research question. This is not to say that you don't acknowledge tangential findings and, in fact, can be referred to as areas for further research in the conclusion of your paper. However, spending time in the results section describing tangential findings clutters your overall results section and distracts the reader.
- A short paragraph that concludes the results section by synthesizing the key findings of the study . Highlight the most important findings you want readers to remember as they transition into the discussion section. This is particularly important if, for example, there are many results to report, the findings are complicated or unanticipated, or they are impactful or actionable in some way [i.e., able to be pursued in a feasible way applied to practice].
NOTE: Always use the past tense when referring to your study's findings. Reference to findings should always be described as having already happened because the method used to gather the information has been completed.
III. Problems to Avoid
When writing the results section, avoid doing the following :
- Discussing or interpreting your results . Save this for the discussion section of your paper, although where appropriate, you should compare or contrast specific results to those found in other studies [e.g., "Similar to the work of Smith [1990], one of the findings of this study is the strong correlation between motivation and academic achievement...."].
- Reporting background information or attempting to explain your findings. This should have been done in your introduction section, but don't panic! Often the results of a study point to the need for additional background information or to explain the topic further, so don't think you did something wrong. Writing up research is rarely a linear process. Always revise your introduction as needed.
- Ignoring negative results . A negative result generally refers to a finding that does not support the underlying assumptions of your study. Do not ignore them. Document these findings and then state in your discussion section why you believe a negative result emerged from your study. Note that negative results, and how you handle them, can give you an opportunity to write a more engaging discussion section, therefore, don't be hesitant to highlight them.
- Including raw data or intermediate calculations . Ask your professor if you need to include any raw data generated by your study, such as transcripts from interviews or data files. If raw data is to be included, place it in an appendix or set of appendices that are referred to in the text.
- Be as factual and concise as possible in reporting your findings . Do not use phrases that are vague or non-specific, such as, "appeared to be greater than other variables..." or "demonstrates promising trends that...." Subjective modifiers should be explained in the discussion section of the paper [i.e., why did one variable appear greater? Or, how does the finding demonstrate a promising trend?].
- Presenting the same data or repeating the same information more than once . If you want to highlight a particular finding, it is appropriate to do so in the results section. However, you should emphasize its significance in relation to addressing the research problem in the discussion section. Do not repeat it in your results section because you can do that in the conclusion of your paper.
- Confusing figures with tables . Be sure to properly label any non-textual elements in your paper. Don't call a chart an illustration or a figure a table. If you are not sure, go here .
Annesley, Thomas M. "Show Your Cards: The Results Section and the Poker Game." Clinical Chemistry 56 (July 2010): 1066-1070; Bavdekar, Sandeep B. and Sneha Chandak. "Results: Unraveling the Findings." Journal of the Association of Physicians of India 63 (September 2015): 44-46; Burton, Neil et al. Doing Your Education Research Project . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2008; Caprette, David R. Writing Research Papers. Experimental Biosciences Resources. Rice University; Hancock, Dawson R. and Bob Algozzine. Doing Case Study Research: A Practical Guide for Beginning Researchers . 2nd ed. New York: Teachers College Press, 2011; Introduction to Nursing Research: Reporting Research Findings. Nursing Research: Open Access Nursing Research and Review Articles. (January 4, 2012); Kretchmer, Paul. Twelve Steps to Writing an Effective Results Section. San Francisco Edit ; Ng, K. H. and W. C. Peh. "Writing the Results." Singapore Medical Journal 49 (2008): 967-968; Reporting Research Findings. Wilder Research, in partnership with the Minnesota Department of Human Services. (February 2009); Results. The Structure, Format, Content, and Style of a Journal-Style Scientific Paper. Department of Biology. Bates College; Schafer, Mickey S. Writing the Results. Thesis Writing in the Sciences. Course Syllabus. University of Florida.
Writing Tip
Why Don't I Just Combine the Results Section with the Discussion Section?
It's not unusual to find articles in scholarly social science journals where the author(s) have combined a description of the findings with a discussion about their significance and implications. You could do this. However, if you are inexperienced writing research papers, consider creating two distinct sections for each section in your paper as a way to better organize your thoughts and, by extension, your paper. Think of the results section as the place where you report what your study found; think of the discussion section as the place where you interpret the information and answer the "So What?" question. As you become more skilled writing research papers, you can consider melding the results of your study with a discussion of its implications.
Driscoll, Dana Lynn and Aleksandra Kasztalska. Writing the Experimental Report: Methods, Results, and Discussion. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University.
- << Previous: Insiderness
- Next: Using Non-Textual Elements >>
- Last Updated: Jun 18, 2024 10:45 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
How to Write the Results/Findings Section in Research
What is the research paper Results section and what does it do?
The Results section of a scientific research paper represents the core findings of a study derived from the methods applied to gather and analyze information. It presents these findings in a logical sequence without bias or interpretation from the author, setting up the reader for later interpretation and evaluation in the Discussion section. A major purpose of the Results section is to break down the data into sentences that show its significance to the research question(s).
The Results section appears third in the section sequence in most scientific papers. It follows the presentation of the Methods and Materials and is presented before the Discussion section —although the Results and Discussion are presented together in many journals. This section answers the basic question “What did you find in your research?”
What is included in the Results section?
The Results section should include the findings of your study and ONLY the findings of your study. The findings include:
- Data presented in tables, charts, graphs, and other figures (may be placed into the text or on separate pages at the end of the manuscript)
- A contextual analysis of this data explaining its meaning in sentence form
- All data that corresponds to the central research question(s)
- All secondary findings (secondary outcomes, subgroup analyses, etc.)
If the scope of the study is broad, or if you studied a variety of variables, or if the methodology used yields a wide range of different results, the author should present only those results that are most relevant to the research question stated in the Introduction section .
As a general rule, any information that does not present the direct findings or outcome of the study should be left out of this section. Unless the journal requests that authors combine the Results and Discussion sections, explanations and interpretations should be omitted from the Results.
How are the results organized?
The best way to organize your Results section is “logically.” One logical and clear method of organizing research results is to provide them alongside the research questions—within each research question, present the type of data that addresses that research question.
Let’s look at an example. Your research question is based on a survey among patients who were treated at a hospital and received postoperative care. Let’s say your first research question is:
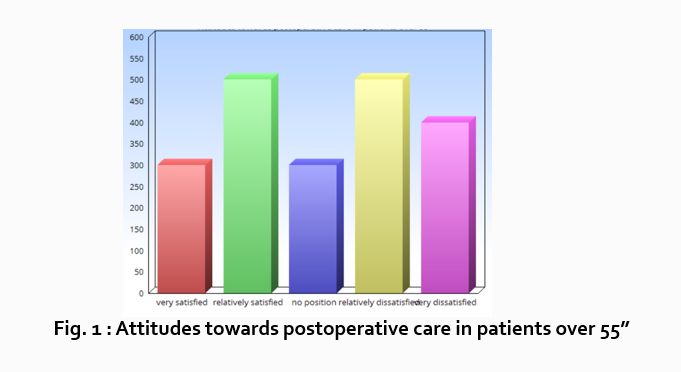
“What do hospital patients over age 55 think about postoperative care?”
This can actually be represented as a heading within your Results section, though it might be presented as a statement rather than a question:
Attitudes towards postoperative care in patients over the age of 55
Now present the results that address this specific research question first. In this case, perhaps a table illustrating data from a survey. Likert items can be included in this example. Tables can also present standard deviations, probabilities, correlation matrices, etc.
Following this, present a content analysis, in words, of one end of the spectrum of the survey or data table. In our example case, start with the POSITIVE survey responses regarding postoperative care, using descriptive phrases. For example:
“Sixty-five percent of patients over 55 responded positively to the question “ Are you satisfied with your hospital’s postoperative care ?” (Fig. 2)
Include other results such as subcategory analyses. The amount of textual description used will depend on how much interpretation of tables and figures is necessary and how many examples the reader needs in order to understand the significance of your research findings.
Next, present a content analysis of another part of the spectrum of the same research question, perhaps the NEGATIVE or NEUTRAL responses to the survey. For instance:
“As Figure 1 shows, 15 out of 60 patients in Group A responded negatively to Question 2.”
After you have assessed the data in one figure and explained it sufficiently, move on to your next research question. For example:
“How does patient satisfaction correspond to in-hospital improvements made to postoperative care?”
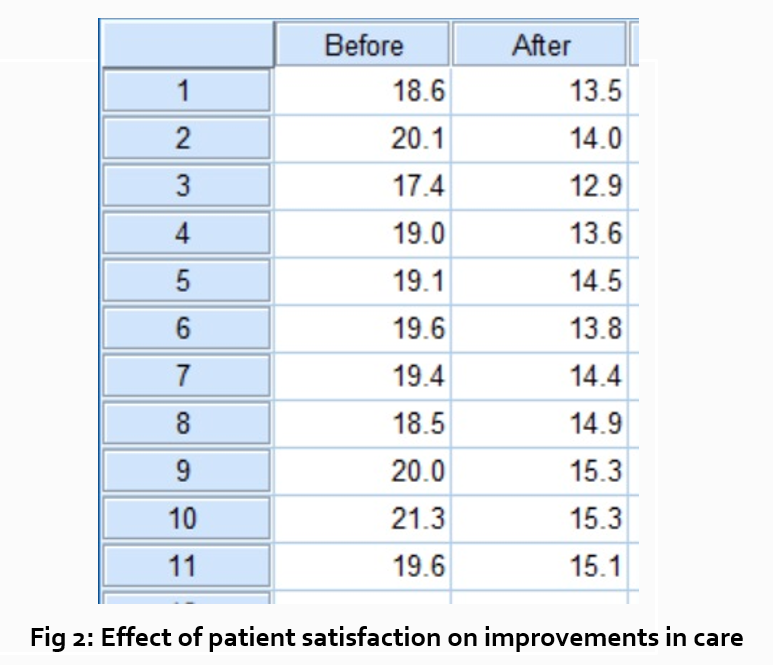
This kind of data may be presented through a figure or set of figures (for instance, a paired T-test table).
Explain the data you present, here in a table, with a concise content analysis:
“The p-value for the comparison between the before and after groups of patients was .03% (Fig. 2), indicating that the greater the dissatisfaction among patients, the more frequent the improvements that were made to postoperative care.”
Let’s examine another example of a Results section from a study on plant tolerance to heavy metal stress . In the Introduction section, the aims of the study are presented as “determining the physiological and morphological responses of Allium cepa L. towards increased cadmium toxicity” and “evaluating its potential to accumulate the metal and its associated environmental consequences.” The Results section presents data showing how these aims are achieved in tables alongside a content analysis, beginning with an overview of the findings:
“Cadmium caused inhibition of root and leave elongation, with increasing effects at higher exposure doses (Fig. 1a-c).”
The figure containing this data is cited in parentheses. Note that this author has combined three graphs into one single figure. Separating the data into separate graphs focusing on specific aspects makes it easier for the reader to assess the findings, and consolidating this information into one figure saves space and makes it easy to locate the most relevant results.
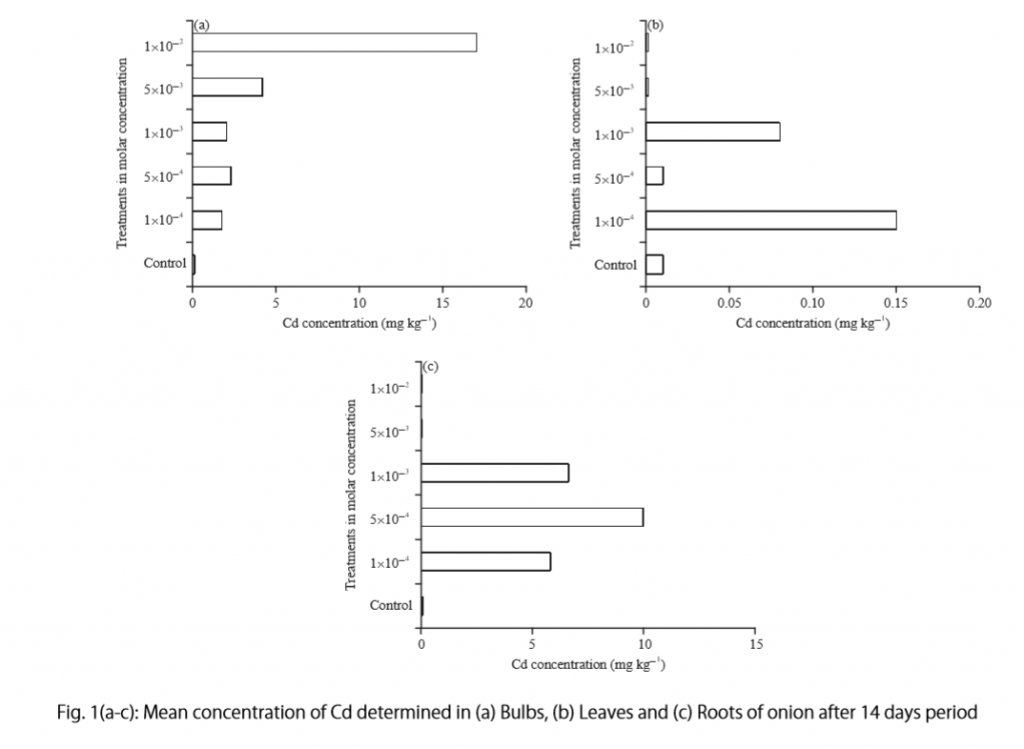
Following this overall summary, the relevant data in the tables is broken down into greater detail in text form in the Results section.
- “Results on the bio-accumulation of cadmium were found to be the highest (17.5 mg kgG1) in the bulb, when the concentration of cadmium in the solution was 1×10G2 M and lowest (0.11 mg kgG1) in the leaves when the concentration was 1×10G3 M.”
Captioning and Referencing Tables and Figures
Tables and figures are central components of your Results section and you need to carefully think about the most effective way to use graphs and tables to present your findings . Therefore, it is crucial to know how to write strong figure captions and to refer to them within the text of the Results section.
The most important advice one can give here as well as throughout the paper is to check the requirements and standards of the journal to which you are submitting your work. Every journal has its own design and layout standards, which you can find in the author instructions on the target journal’s website. Perusing a journal’s published articles will also give you an idea of the proper number, size, and complexity of your figures.
Regardless of which format you use, the figures should be placed in the order they are referenced in the Results section and be as clear and easy to understand as possible. If there are multiple variables being considered (within one or more research questions), it can be a good idea to split these up into separate figures. Subsequently, these can be referenced and analyzed under separate headings and paragraphs in the text.
To create a caption, consider the research question being asked and change it into a phrase. For instance, if one question is “Which color did participants choose?”, the caption might be “Color choice by participant group.” Or in our last research paper example, where the question was “What is the concentration of cadmium in different parts of the onion after 14 days?” the caption reads:
“Fig. 1(a-c): Mean concentration of Cd determined in (a) bulbs, (b) leaves, and (c) roots of onions after a 14-day period.”
Steps for Composing the Results Section
Because each study is unique, there is no one-size-fits-all approach when it comes to designing a strategy for structuring and writing the section of a research paper where findings are presented. The content and layout of this section will be determined by the specific area of research, the design of the study and its particular methodologies, and the guidelines of the target journal and its editors. However, the following steps can be used to compose the results of most scientific research studies and are essential for researchers who are new to preparing a manuscript for publication or who need a reminder of how to construct the Results section.
Step 1 : Consult the guidelines or instructions that the target journal or publisher provides authors and read research papers it has published, especially those with similar topics, methods, or results to your study.
- The guidelines will generally outline specific requirements for the results or findings section, and the published articles will provide sound examples of successful approaches.
- Note length limitations on restrictions on content. For instance, while many journals require the Results and Discussion sections to be separate, others do not—qualitative research papers often include results and interpretations in the same section (“Results and Discussion”).
- Reading the aims and scope in the journal’s “ guide for authors ” section and understanding the interests of its readers will be invaluable in preparing to write the Results section.
Step 2 : Consider your research results in relation to the journal’s requirements and catalogue your results.
- Focus on experimental results and other findings that are especially relevant to your research questions and objectives and include them even if they are unexpected or do not support your ideas and hypotheses.
- Catalogue your findings—use subheadings to streamline and clarify your report. This will help you avoid excessive and peripheral details as you write and also help your reader understand and remember your findings. Create appendices that might interest specialists but prove too long or distracting for other readers.
- Decide how you will structure of your results. You might match the order of the research questions and hypotheses to your results, or you could arrange them according to the order presented in the Methods section. A chronological order or even a hierarchy of importance or meaningful grouping of main themes or categories might prove effective. Consider your audience, evidence, and most importantly, the objectives of your research when choosing a structure for presenting your findings.
Step 3 : Design figures and tables to present and illustrate your data.
- Tables and figures should be numbered according to the order in which they are mentioned in the main text of the paper.
- Information in figures should be relatively self-explanatory (with the aid of captions), and their design should include all definitions and other information necessary for readers to understand the findings without reading all of the text.
- Use tables and figures as a focal point to tell a clear and informative story about your research and avoid repeating information. But remember that while figures clarify and enhance the text, they cannot replace it.
Step 4 : Draft your Results section using the findings and figures you have organized.
- The goal is to communicate this complex information as clearly and precisely as possible; precise and compact phrases and sentences are most effective.
- In the opening paragraph of this section, restate your research questions or aims to focus the reader’s attention to what the results are trying to show. It is also a good idea to summarize key findings at the end of this section to create a logical transition to the interpretation and discussion that follows.
- Try to write in the past tense and the active voice to relay the findings since the research has already been done and the agent is usually clear. This will ensure that your explanations are also clear and logical.
- Make sure that any specialized terminology or abbreviation you have used here has been defined and clarified in the Introduction section .
Step 5 : Review your draft; edit and revise until it reports results exactly as you would like to have them reported to your readers.
- Double-check the accuracy and consistency of all the data, as well as all of the visual elements included.
- Read your draft aloud to catch language errors (grammar, spelling, and mechanics), awkward phrases, and missing transitions.
- Ensure that your results are presented in the best order to focus on objectives and prepare readers for interpretations, valuations, and recommendations in the Discussion section . Look back over the paper’s Introduction and background while anticipating the Discussion and Conclusion sections to ensure that the presentation of your results is consistent and effective.
- Consider seeking additional guidance on your paper. Find additional readers to look over your Results section and see if it can be improved in any way. Peers, professors, or qualified experts can provide valuable insights.
One excellent option is to use a professional English proofreading and editing service such as Wordvice, including our paper editing service . With hundreds of qualified editors from dozens of scientific fields, Wordvice has helped thousands of authors revise their manuscripts and get accepted into their target journals. Read more about the proofreading and editing process before proceeding with getting academic editing services and manuscript editing services for your manuscript.
As the representation of your study’s data output, the Results section presents the core information in your research paper. By writing with clarity and conciseness and by highlighting and explaining the crucial findings of their study, authors increase the impact and effectiveness of their research manuscripts.
For more articles and videos on writing your research manuscript, visit Wordvice’s Resources page.
Wordvice Resources
- How to Write a Research Paper Introduction
- Which Verb Tenses to Use in a Research Paper
- How to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper
- How to Write a Research Paper Title
- Useful Phrases for Academic Writing
- Common Transition Terms in Academic Papers
- Active and Passive Voice in Research Papers
- 100+ Verbs That Will Make Your Research Writing Amazing
- Tips for Paraphrasing in Research Papers
From Data to Discovery: The Findings Section of a Research Paper
Discover the role of the findings section of a research paper here. Explore strategies and techniques to maximize your understanding.
Are you curious about the Findings section of a research paper? Did you know that this is a part where all the juicy results and discoveries are laid out for the world to see? Undoubtedly, the findings section of a research paper plays a critical role in presenting and interpreting the collected data. It serves as a comprehensive account of the study’s results and their implications.
Well, look no further because we’ve got you covered! In this article, we’re diving into the ins and outs of presenting and interpreting data in the findings section. We’ll be sharing tips and tricks on how to effectively present your findings, whether it’s through tables, graphs, or good old descriptive statistics.
Overview of the Findings Section of a Research Paper
The findings section of a research paper presents the results and outcomes of the study or investigation. It is a crucial part of the research paper where researchers interpret and analyze the data collected and draw conclusions based on their findings. This section aims to answer the research questions or hypotheses formulated earlier in the paper and provide evidence to support or refute them.
In the findings section, researchers typically present the data clearly and organized. They may use tables, graphs, charts, or other visual aids to illustrate the patterns, trends, or relationships observed in the data. The findings should be presented objectively, without any bias or personal opinions, and should be accompanied by appropriate statistical analyses or methods to ensure the validity and reliability of the results.
Organizing the Findings Section
The findings section of the research paper organizes and presents the results obtained from the study in a clear and logical manner. Here is a suggested structure for organizing the Findings section:
Introduction to the Findings
Start the section by providing a brief overview of the research objectives and the methodology employed. Recapitulate the research questions or hypotheses addressed in the study.
To learn more about methodology, read this article .
Descriptive Statistics and Data Presentation
Present the collected data using appropriate descriptive statistics. This may involve using tables, graphs, charts, or other visual representations to convey the information effectively. Remember: we can easily help you with that.
Data Analysis and Interpretation
Perform a thorough analysis of the data collected and describe the key findings. Present the results of statistical analyses or any other relevant methods used to analyze the data.
Discussion of Findings
Analyze and interpret the findings in the context of existing literature or theoretical frameworks . Discuss any patterns, trends, or relationships observed in the data. Compare and contrast the results with prior studies, highlighting similarities and differences.
Limitations and Constraints
Acknowledge and discuss any limitations or constraints that may have influenced the findings. This could include issues such as sample size, data collection methods, or potential biases.
Summarize the main findings of the study and emphasize their significance. Revisit the research questions or hypotheses and discuss whether they have been supported or refuted by the findings.
Presenting Data in the Findings Section
There are several ways to present data in the findings section of a research paper. Here are some common methods:
- Tables : Tables are commonly used to present organized and structured data. They are particularly useful when presenting numerical data with multiple variables or categories. Tables allow readers to easily compare and interpret the information presented. Learn how to cite tables in research papers here .
- Graphs and Charts: Graphs and charts are effective visual tools for presenting data, especially when illustrating trends, patterns, or relationships. Common types include bar graphs, line graphs, scatter plots, pie charts, and histograms. Graphs and charts provide a visual representation of the data, making it easier for readers to comprehend and interpret.
- Figures and Images: Figures and images can be used to present data that requires visual representation, such as maps, diagrams, or experimental setups. They can enhance the understanding of complex data or provide visual evidence to support the research findings.
- Descriptive Statistics: Descriptive statistics provide summary measures of central tendency (e.g., mean, median, mode) and dispersion (e.g., standard deviation, range) for numerical data. These statistics can be included in the text or presented in tables or graphs to provide a concise summary of the data distribution.
How to Effectively Interpret Results
Interpreting the results is a crucial aspect of the findings section in a research paper. It involves analyzing the data collected and drawing meaningful conclusions based on the findings. Following are the guidelines on how to effectively interpret the results.
Step 1 – Begin with a Recap
Start by restating the research questions or hypotheses to provide context for the interpretation. Remind readers of the specific objectives of the study to help them understand the relevance of the findings.
Step 2 – Relate Findings to Research Questions
Clearly articulate how the results address the research questions or hypotheses. Discuss each finding in relation to the original objectives and explain how it contributes to answering the research questions or supporting/refuting the hypotheses.
Step 3 – Compare with Existing Literature
Compare and contrast the findings with previous studies or existing literature. Highlight similarities, differences, or discrepancies between your results and those of other researchers. Discuss any consistencies or contradictions and provide possible explanations for the observed variations.
Step 4 – Consider Limitations and Alternative Explanations
Acknowledge the limitations of the study and discuss how they may have influenced the results. Explore alternative explanations or factors that could potentially account for the findings. Evaluate the robustness of the results in light of the limitations and alternative interpretations.
Step 5 – Discuss Implications and Significance
Highlight any potential applications or areas where further research is needed based on the outcomes of the study.
Step 6 – Address Inconsistencies and Contradictions
If there are any inconsistencies or contradictions in the findings, address them directly. Discuss possible reasons for the discrepancies and consider their implications for the overall interpretation. Be transparent about any uncertainties or unresolved issues.
Step 7 – Be Objective and Data-Driven
Present the interpretation objectively, based on the evidence and data collected. Avoid personal biases or subjective opinions. Use logical reasoning and sound arguments to support your interpretations.
Reporting Statistical Significance
When reporting statistical significance in the findings section of a research paper, it is important to accurately convey the results of statistical analyses and their implications. Here are some guidelines on how to report statistical significance effectively:
- Clearly State the Statistical Test: Begin by clearly stating the specific statistical test or analysis used to determine statistical significance. For example, you might mention that a t-test, chi-square test, ANOVA, correlation analysis, or regression analysis was employed.
- Report the Test Statistic: Provide the value of the test statistic obtained from the analysis. This could be the t-value, F-value, chi-square value, correlation coefficient, or any other relevant statistic depending on the test used.
- State the Degrees of Freedom: Indicate the degrees of freedom associated with the statistical test. Degrees of freedom represent the number of independent pieces of information available for estimating a statistic. For example, in a t-test, degrees of freedom would be mentioned as (df = n1 + n2 – 2) for an independent samples test or (df = N – 2) for a paired samples test.
- Report the p-value: The p-value indicates the probability of obtaining results as extreme or more extreme than the observed results, assuming the null hypothesis is true. Report the p-value associated with the statistical test. For example, p < 0.05 denotes statistical significance at the conventional level of α = 0.05.
- Provide the Conclusion: Based on the p-value obtained, state whether the results are statistically significant or not. If the p-value is less than the predetermined threshold (e.g., p < 0.05), state that the results are statistically significant. If the p-value is greater than the threshold, state that the results are not statistically significant.
- Discuss the Interpretation: After reporting statistical significance, discuss the practical or theoretical implications of the finding. Explain what the significant result means in the context of your research questions or hypotheses. Address the effect size and practical significance of the findings, if applicable.
- Consider Effect Size Measures: Along with statistical significance, it is often important to report effect size measures. Effect size quantifies the magnitude of the relationship or difference observed in the data. Common effect size measures include Cohen’s d, eta-squared, or Pearson’s r. Reporting effect size provides additional meaningful information about the strength of the observed effects.
- Be Accurate and Transparent: Ensure that the reported statistical significance and associated values are accurate. Avoid misinterpreting or misrepresenting the results. Be transparent about the statistical tests conducted, any assumptions made, and potential limitations or caveats that may impact the interpretation of the significant results.
Conclusion of the Findings Section
The conclusion of the findings section in a research paper serves as a summary and synthesis of the key findings and their implications. It is an opportunity to tie together the results, discuss their significance, and address the research objectives. Here are some guidelines on how to write the conclusion of the Findings section:
Summarize the Key Findings
Begin by summarizing the main findings of the study. Provide a concise overview of the significant results, patterns, or relationships that emerged from the data analysis. Highlight the most important findings that directly address the research questions or hypotheses.
Revisit the Research Objectives
Remind the reader of the research objectives stated at the beginning of the paper. Discuss how the findings contribute to achieving those objectives and whether they support or challenge the initial research questions or hypotheses.
Suggest Future Directions
Identify areas for further research or future directions based on the findings. Discuss any unanswered questions, unresolved issues, or new avenues of inquiry that emerged during the study. Propose potential research opportunities that can build upon the current findings.
The Best Scientific Figures to Represent Your Findings
Have you heard of any tool that helps you represent your findings through visuals like graphs, pie charts, and infographics? Well, if you haven’t, then here’s the tool you need to explore – Mind the Graph . It’s the tool that has the best scientific figures to represent your findings. Go, try it now, and make your research findings stand out!

Subscribe to our newsletter
Exclusive high quality content about effective visual communication in science.
About Sowjanya Pedada
Sowjanya is a passionate writer and an avid reader. She holds MBA in Agribusiness Management and now is working as a content writer. She loves to play with words and hopes to make a difference in the world through her writings. Apart from writing, she is interested in reading fiction novels and doing craftwork. She also loves to travel and explore different cuisines and spend time with her family and friends.
Content tags
- How it works

How to Write the Dissertation Findings or Results – Steps & Tips
Published by Grace Graffin at August 11th, 2021 , Revised On June 11, 2024
Each part of the dissertation is unique, and some general and specific rules must be followed. The dissertation’s findings section presents the key results of your research without interpreting their meaning .
Theoretically, this is an exciting section of a dissertation because it involves writing what you have observed and found. However, it can be a little tricky if there is too much information to confuse the readers.
The goal is to include only the essential and relevant findings in this section. The results must be presented in an orderly sequence to provide clarity to the readers.
This section of the dissertation should be easy for the readers to follow, so you should avoid going into a lengthy debate over the interpretation of the results.
It is vitally important to focus only on clear and precise observations. The findings chapter of the dissertation is theoretically the easiest to write.
It includes statistical analysis and a brief write-up about whether or not the results emerging from the analysis are significant. This segment should be written in the past sentence as you describe what you have done in the past.
This article will provide detailed information about how to write the findings of a dissertation .
When to Write Dissertation Findings Chapter
As soon as you have gathered and analysed your data, you can start to write up the findings chapter of your dissertation paper. Remember that it is your chance to report the most notable findings of your research work and relate them to the research hypothesis or research questions set out in the introduction chapter of the dissertation .
You will be required to separately report your study’s findings before moving on to the discussion chapter if your dissertation is based on the collection of primary data or experimental work.
However, you may not be required to have an independent findings chapter if your dissertation is purely descriptive and focuses on the analysis of case studies or interpretation of texts.
- Always report the findings of your research in the past tense.
- The dissertation findings chapter varies from one project to another, depending on the data collected and analyzed.
- Avoid reporting results that are not relevant to your research questions or research hypothesis.
Does your Dissertation Have the Following?
- Great Research/Sources
- Perfect Language
- Accurate Sources
If not, we can help. Our panel of experts makes sure to keep the 3 pillars of the Dissertation strong.

1. Reporting Quantitative Findings
The best way to present your quantitative findings is to structure them around the research hypothesis or questions you intend to address as part of your dissertation project.
Report the relevant findings for each research question or hypothesis, focusing on how you analyzed them.
Analysis of your findings will help you determine how they relate to the different research questions and whether they support the hypothesis you formulated.
While you must highlight meaningful relationships, variances, and tendencies, it is important not to guess their interpretations and implications because this is something to save for the discussion and conclusion chapters.
Any findings not directly relevant to your research questions or explanations concerning the data collection process should be added to the dissertation paper’s appendix section.
Use of Figures and Tables in Dissertation Findings
Suppose your dissertation is based on quantitative research. In that case, it is important to include charts, graphs, tables, and other visual elements to help your readers understand the emerging trends and relationships in your findings.
Repeating information will give the impression that you are short on ideas. Refer to all charts, illustrations, and tables in your writing but avoid recurrence.
The text should be used only to elaborate and summarize certain parts of your results. On the other hand, illustrations and tables are used to present multifaceted data.
It is recommended to give descriptive labels and captions to all illustrations used so the readers can figure out what each refers to.
How to Report Quantitative Findings
Here is an example of how to report quantitative results in your dissertation findings chapter;
Two hundred seventeen participants completed both the pretest and post-test and a Pairwise T-test was used for the analysis. The quantitative data analysis reveals a statistically significant difference between the mean scores of the pretest and posttest scales from the Teachers Discovering Computers course. The pretest mean was 29.00 with a standard deviation of 7.65, while the posttest mean was 26.50 with a standard deviation of 9.74 (Table 1). These results yield a significance level of .000, indicating a strong treatment effect (see Table 3). With the correlation between the scores being .448, the little relationship is seen between the pretest and posttest scores (Table 2). This leads the researcher to conclude that the impact of the course on the educators’ perception and integration of technology into the curriculum is dramatic.
Paired Samples
| Mean | N | Std. Deviation | Std. Error Mean | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PRESCORE | 29.00 | 217 | 7.65 | .519 | |
| PSTSCORE | 26.00 | 217 | 9.74 | .661 |
Paired Samples Correlation
| N | Correlation | Sig. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PRESCORE & PSTSCORE | 217 | .448 | .000 |
Paired Samples Test
| Paired Differences | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Std. Deviation | Std. Error Mean | 95% Confidence Interval of the Difference | t | df | Sig. (2-tailed) | |||
| Lower | Upper | ||||||||
| Pair 1 | PRESCORE-PSTSCORE | 2.50 | 9.31 | .632 | 1.26 | 3.75 | 3.967 | 216 | .000 |
Also Read: How to Write the Abstract for the Dissertation.
2. Reporting Qualitative Findings
A notable issue with reporting qualitative findings is that not all results directly relate to your research questions or hypothesis.
The best way to present the results of qualitative research is to frame your findings around the most critical areas or themes you obtained after you examined the data.
In-depth data analysis will help you observe what the data shows for each theme. Any developments, relationships, patterns, and independent responses directly relevant to your research question or hypothesis should be mentioned to the readers.
Additional information not directly relevant to your research can be included in the appendix .
How to Report Qualitative Findings
Here is an example of how to report qualitative results in your dissertation findings chapter;
The last question of the interview focused on the need for improvement in Thai ready-to-eat products and the industry at large, emphasizing the need for enhancement in the current products being offered in the market. When asked if there was any particular need for Thai ready-to-eat meals to be improved and how to improve them in case of ‘yes,’ the males replied mainly by saying that the current products need improvement in terms of the use of healthier raw materials and preservatives or additives. There was an agreement amongst all males concerning the need to improve the industry for ready-to-eat meals and the use of more healthy items to prepare such meals. The females were also of the opinion that the fast-food items needed to be improved in the sense that more healthy raw materials such as vegetable oil and unsaturated fats, including whole-wheat products, to overcome risks associated with trans fat leading to obesity and hypertension should be used for the production of RTE products. The frozen RTE meals and packaged snacks included many preservatives and chemical-based flavouring enhancers that harmed human health and needed to be reduced. The industry is said to be aware of this fact and should try to produce RTE products that benefit the community in terms of healthy consumption.
Looking for dissertation help?
Research prospect to the rescue then.
We have expert writers on our team who are skilled at helping students with dissertations across a variety of disciplines. Guaranteeing 100% satisfaction!

What to Avoid in Dissertation Findings Chapter
- Avoid using interpretive and subjective phrases and terms such as “confirms,” “reveals,” “suggests,” or “validates.” These terms are more suitable for the discussion chapter , where you will be expected to interpret the results in detail.
- Only briefly explain findings in relation to the key themes, hypothesis, and research questions. You don’t want to write a detailed subjective explanation for any research questions at this stage.
The Do’s of Writing the Findings or Results Section
- Ensure you are not presenting results from other research studies in your findings.
- Observe whether or not your hypothesis is tested or research questions answered.
- Illustrations and tables present data and are labelled to help your readers understand what they relate to.
- Use software such as Excel, STATA, and SPSS to analyse results and important trends.
Essential Guidelines on How to Write Dissertation Findings
The dissertation findings chapter should provide the context for understanding the results. The research problem should be repeated, and the research goals should be stated briefly.
This approach helps to gain the reader’s attention toward the research problem. The first step towards writing the findings is identifying which results will be presented in this section.
The results relevant to the questions must be presented, considering whether the results support the hypothesis. You do not need to include every result in the findings section. The next step is ensuring the data can be appropriately organized and accurate.
You will need to have a basic idea about writing the findings of a dissertation because this will provide you with the knowledge to arrange the data chronologically.
Start each paragraph by writing about the most important results and concluding the section with the most negligible actual results.
A short paragraph can conclude the findings section, summarising the findings so readers will remember as they transition to the next chapter. This is essential if findings are unexpected or unfamiliar or impact the study.
Our writers can help you with all parts of your dissertation, including statistical analysis of your results . To obtain free non-binding quotes, please complete our online quote form here .
Be Impartial in your Writing
When crafting your findings, knowing how you will organize the work is important. The findings are the story that needs to be told in response to the research questions that have been answered.
Therefore, the story needs to be organized to make sense to you and the reader. The findings must be compelling and responsive to be linked to the research questions being answered.
Always ensure that the size and direction of any changes, including percentage change, can be mentioned in the section. The details of p values or confidence intervals and limits should be included.
The findings sections only have the relevant parts of the primary evidence mentioned. Still, it is a good practice to include all the primary evidence in an appendix that can be referred to later.
The results should always be written neutrally without speculation or implication. The statement of the results mustn’t have any form of evaluation or interpretation.
Negative results should be added in the findings section because they validate the results and provide high neutrality levels.
The length of the dissertation findings chapter is an important question that must be addressed. It should be noted that the length of the section is directly related to the total word count of your dissertation paper.
The writer should use their discretion in deciding the length of the findings section or refer to the dissertation handbook or structure guidelines.
It should neither belong nor be short nor concise and comprehensive to highlight the reader’s main findings.
Ethically, you should be confident in the findings and provide counter-evidence. Anything that does not have sufficient evidence should be discarded. The findings should respond to the problem presented and provide a solution to those questions.
Structure of the Findings Chapter
The chapter should use appropriate words and phrases to present the results to the readers. Logical sentences should be used, while paragraphs should be linked to produce cohesive work.
You must ensure all the significant results have been added in the section. Recheck after completing the section to ensure no mistakes have been made.
The structure of the findings section is something you may have to be sure of primarily because it will provide the basis for your research work and ensure that the discussions section can be written clearly and proficiently.
One way to arrange the results is to provide a brief synopsis and then explain the essential findings. However, there should be no speculation or explanation of the results, as this will be done in the discussion section.
Another way to arrange the section is to present and explain a result. This can be done for all the results while the section is concluded with an overall synopsis.
This is the preferred method when you are writing more extended dissertations. It can be helpful when multiple results are equally significant. A brief conclusion should be written to link all the results and transition to the discussion section.
Numerous data analysis dissertation examples are available on the Internet, which will help you improve your understanding of writing the dissertation’s findings.
Problems to Avoid When Writing Dissertation Findings
One of the problems to avoid while writing the dissertation findings is reporting background information or explaining the findings. This should be done in the introduction section .
You can always revise the introduction chapter based on the data you have collected if that seems an appropriate thing to do.
Raw data or intermediate calculations should not be added in the findings section. Always ask your professor if raw data needs to be included.
If the data is to be included, then use an appendix or a set of appendices referred to in the text of the findings chapter.
Do not use vague or non-specific phrases in the findings section. It is important to be factual and concise for the reader’s benefit.
The findings section presents the crucial data collected during the research process. It should be presented concisely and clearly to the reader. There should be no interpretation, speculation, or analysis of the data.
The significant results should be categorized systematically with the text used with charts, figures, and tables. Furthermore, avoiding using vague and non-specific words in this section is essential.
It is essential to label the tables and visual material properly. You should also check and proofread the section to avoid mistakes.
The dissertation findings chapter is a critical part of your overall dissertation paper. If you struggle with presenting your results and statistical analysis, our expert dissertation writers can help you get things right. Whether you need help with the entire dissertation paper or individual chapters, our dissertation experts can provide customized dissertation support .
FAQs About Findings of a Dissertation
How do i report quantitative findings.
The best way to present your quantitative findings is to structure them around the research hypothesis or research questions you intended to address as part of your dissertation project. Report the relevant findings for each of the research questions or hypotheses, focusing on how you analyzed them.
How do I report qualitative findings?
The best way to present the qualitative research results is to frame your findings around the most important areas or themes that you obtained after examining the data.
An in-depth analysis of the data will help you observe what the data is showing for each theme. Any developments, relationships, patterns, and independent responses that are directly relevant to your research question or hypothesis should be clearly mentioned for the readers.
Can I use interpretive phrases like ‘it confirms’ in the finding chapter?
No, It is highly advisable to avoid using interpretive and subjective phrases in the finding chapter. These terms are more suitable for the discussion chapter , where you will be expected to provide your interpretation of the results in detail.
Can I report the results from other research papers in my findings chapter?
NO, you must not be presenting results from other research studies in your findings.
You May Also Like
Do dissertations scare you? Struggling with writing a flawless dissertation? Well, congratulations, you have landed in the perfect place. In this blog, we will take you through the detailed process of writing a dissertation. Sounds fun? We thought so!
This article is a step-by-step guide to how to write statement of a problem in research. The research problem will be half-solved by defining it correctly.
Dissertation discussion is where you explore the relevance and significance of results. Here are guidelines to help you write the perfect discussion chapter.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
How To Write The Results/Findings Chapter
For quantitative studies (dissertations & theses).
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewed By: Kerryn Warren (PhD) | July 2021
So, you’ve completed your quantitative data analysis and it’s time to report on your findings. But where do you start? In this post, we’ll walk you through the results chapter (also called the findings or analysis chapter), step by step, so that you can craft this section of your dissertation or thesis with confidence. If you’re looking for information regarding the results chapter for qualitative studies, you can find that here .
Overview: Quantitative Results Chapter
- What exactly the results chapter is
- What you need to include in your chapter
- How to structure the chapter
- Tips and tricks for writing a top-notch chapter
- Free results chapter template
What exactly is the results chapter?
The results chapter (also referred to as the findings or analysis chapter) is one of the most important chapters of your dissertation or thesis because it shows the reader what you’ve found in terms of the quantitative data you’ve collected. It presents the data using a clear text narrative, supported by tables, graphs and charts. In doing so, it also highlights any potential issues (such as outliers or unusual findings) you’ve come across.
But how’s that different from the discussion chapter?
Well, in the results chapter, you only present your statistical findings. Only the numbers, so to speak – no more, no less. Contrasted to this, in the discussion chapter , you interpret your findings and link them to prior research (i.e. your literature review), as well as your research objectives and research questions . In other words, the results chapter presents and describes the data, while the discussion chapter interprets the data.
Let’s look at an example.
In your results chapter, you may have a plot that shows how respondents to a survey responded: the numbers of respondents per category, for instance. You may also state whether this supports a hypothesis by using a p-value from a statistical test. But it is only in the discussion chapter where you will say why this is relevant or how it compares with the literature or the broader picture. So, in your results chapter, make sure that you don’t present anything other than the hard facts – this is not the place for subjectivity.
It’s worth mentioning that some universities prefer you to combine the results and discussion chapters. Even so, it is good practice to separate the results and discussion elements within the chapter, as this ensures your findings are fully described. Typically, though, the results and discussion chapters are split up in quantitative studies. If you’re unsure, chat with your research supervisor or chair to find out what their preference is.

What should you include in the results chapter?
Following your analysis, it’s likely you’ll have far more data than are necessary to include in your chapter. In all likelihood, you’ll have a mountain of SPSS or R output data, and it’s your job to decide what’s most relevant. You’ll need to cut through the noise and focus on the data that matters.
This doesn’t mean that those analyses were a waste of time – on the contrary, those analyses ensure that you have a good understanding of your dataset and how to interpret it. However, that doesn’t mean your reader or examiner needs to see the 165 histograms you created! Relevance is key.
How do I decide what’s relevant?
At this point, it can be difficult to strike a balance between what is and isn’t important. But the most important thing is to ensure your results reflect and align with the purpose of your study . So, you need to revisit your research aims, objectives and research questions and use these as a litmus test for relevance. Make sure that you refer back to these constantly when writing up your chapter so that you stay on track.

As a general guide, your results chapter will typically include the following:
- Some demographic data about your sample
- Reliability tests (if you used measurement scales)
- Descriptive statistics
- Inferential statistics (if your research objectives and questions require these)
- Hypothesis tests (again, if your research objectives and questions require these)
We’ll discuss each of these points in more detail in the next section.
Importantly, your results chapter needs to lay the foundation for your discussion chapter . This means that, in your results chapter, you need to include all the data that you will use as the basis for your interpretation in the discussion chapter.
For example, if you plan to highlight the strong relationship between Variable X and Variable Y in your discussion chapter, you need to present the respective analysis in your results chapter – perhaps a correlation or regression analysis.
Need a helping hand?
How do I write the results chapter?
There are multiple steps involved in writing up the results chapter for your quantitative research. The exact number of steps applicable to you will vary from study to study and will depend on the nature of the research aims, objectives and research questions . However, we’ll outline the generic steps below.
Step 1 – Revisit your research questions
The first step in writing your results chapter is to revisit your research objectives and research questions . These will be (or at least, should be!) the driving force behind your results and discussion chapters, so you need to review them and then ask yourself which statistical analyses and tests (from your mountain of data) would specifically help you address these . For each research objective and research question, list the specific piece (or pieces) of analysis that address it.
At this stage, it’s also useful to think about the key points that you want to raise in your discussion chapter and note these down so that you have a clear reminder of which data points and analyses you want to highlight in the results chapter. Again, list your points and then list the specific piece of analysis that addresses each point.
Next, you should draw up a rough outline of how you plan to structure your chapter . Which analyses and statistical tests will you present and in what order? We’ll discuss the “standard structure” in more detail later, but it’s worth mentioning now that it’s always useful to draw up a rough outline before you start writing (this advice applies to any chapter).
Step 2 – Craft an overview introduction
As with all chapters in your dissertation or thesis, you should start your quantitative results chapter by providing a brief overview of what you’ll do in the chapter and why . For example, you’d explain that you will start by presenting demographic data to understand the representativeness of the sample, before moving onto X, Y and Z.
This section shouldn’t be lengthy – a paragraph or two maximum. Also, it’s a good idea to weave the research questions into this section so that there’s a golden thread that runs through the document.

Step 3 – Present the sample demographic data
The first set of data that you’ll present is an overview of the sample demographics – in other words, the demographics of your respondents.
For example:
- What age range are they?
- How is gender distributed?
- How is ethnicity distributed?
- What areas do the participants live in?
The purpose of this is to assess how representative the sample is of the broader population. This is important for the sake of the generalisability of the results. If your sample is not representative of the population, you will not be able to generalise your findings. This is not necessarily the end of the world, but it is a limitation you’ll need to acknowledge.
Of course, to make this representativeness assessment, you’ll need to have a clear view of the demographics of the population. So, make sure that you design your survey to capture the correct demographic information that you will compare your sample to.
But what if I’m not interested in generalisability?
Well, even if your purpose is not necessarily to extrapolate your findings to the broader population, understanding your sample will allow you to interpret your findings appropriately, considering who responded. In other words, it will help you contextualise your findings . For example, if 80% of your sample was aged over 65, this may be a significant contextual factor to consider when interpreting the data. Therefore, it’s important to understand and present the demographic data.
Step 4 – Review composite measures and the data “shape”.
Before you undertake any statistical analysis, you’ll need to do some checks to ensure that your data are suitable for the analysis methods and techniques you plan to use. If you try to analyse data that doesn’t meet the assumptions of a specific statistical technique, your results will be largely meaningless. Therefore, you may need to show that the methods and techniques you’ll use are “allowed”.
Most commonly, there are two areas you need to pay attention to:
#1: Composite measures
The first is when you have multiple scale-based measures that combine to capture one construct – this is called a composite measure . For example, you may have four Likert scale-based measures that (should) all measure the same thing, but in different ways. In other words, in a survey, these four scales should all receive similar ratings. This is called “ internal consistency ”.
Internal consistency is not guaranteed though (especially if you developed the measures yourself), so you need to assess the reliability of each composite measure using a test. Typically, Cronbach’s Alpha is a common test used to assess internal consistency – i.e., to show that the items you’re combining are more or less saying the same thing. A high alpha score means that your measure is internally consistent. A low alpha score means you may need to consider scrapping one or more of the measures.
#2: Data shape
The second matter that you should address early on in your results chapter is data shape. In other words, you need to assess whether the data in your set are symmetrical (i.e. normally distributed) or not, as this will directly impact what type of analyses you can use. For many common inferential tests such as T-tests or ANOVAs (we’ll discuss these a bit later), your data needs to be normally distributed. If it’s not, you’ll need to adjust your strategy and use alternative tests.
To assess the shape of the data, you’ll usually assess a variety of descriptive statistics (such as the mean, median and skewness), which is what we’ll look at next.

Step 5 – Present the descriptive statistics
Now that you’ve laid the foundation by discussing the representativeness of your sample, as well as the reliability of your measures and the shape of your data, you can get started with the actual statistical analysis. The first step is to present the descriptive statistics for your variables.
For scaled data, this usually includes statistics such as:
- The mean – this is simply the mathematical average of a range of numbers.
- The median – this is the midpoint in a range of numbers when the numbers are arranged in order.
- The mode – this is the most commonly repeated number in the data set.
- Standard deviation – this metric indicates how dispersed a range of numbers is. In other words, how close all the numbers are to the mean (the average).
- Skewness – this indicates how symmetrical a range of numbers is. In other words, do they tend to cluster into a smooth bell curve shape in the middle of the graph (this is called a normal or parametric distribution), or do they lean to the left or right (this is called a non-normal or non-parametric distribution).
- Kurtosis – this metric indicates whether the data are heavily or lightly-tailed, relative to the normal distribution. In other words, how peaked or flat the distribution is.
A large table that indicates all the above for multiple variables can be a very effective way to present your data economically. You can also use colour coding to help make the data more easily digestible.
For categorical data, where you show the percentage of people who chose or fit into a category, for instance, you can either just plain describe the percentages or numbers of people who responded to something or use graphs and charts (such as bar graphs and pie charts) to present your data in this section of the chapter.
When using figures, make sure that you label them simply and clearly , so that your reader can easily understand them. There’s nothing more frustrating than a graph that’s missing axis labels! Keep in mind that although you’ll be presenting charts and graphs, your text content needs to present a clear narrative that can stand on its own. In other words, don’t rely purely on your figures and tables to convey your key points: highlight the crucial trends and values in the text. Figures and tables should complement the writing, not carry it .
Depending on your research aims, objectives and research questions, you may stop your analysis at this point (i.e. descriptive statistics). However, if your study requires inferential statistics, then it’s time to deep dive into those .

Step 6 – Present the inferential statistics
Inferential statistics are used to make generalisations about a population , whereas descriptive statistics focus purely on the sample . Inferential statistical techniques, broadly speaking, can be broken down into two groups .
First, there are those that compare measurements between groups , such as t-tests (which measure differences between two groups) and ANOVAs (which measure differences between multiple groups). Second, there are techniques that assess the relationships between variables , such as correlation analysis and regression analysis. Within each of these, some tests can be used for normally distributed (parametric) data and some tests are designed specifically for use on non-parametric data.
There are a seemingly endless number of tests that you can use to crunch your data, so it’s easy to run down a rabbit hole and end up with piles of test data. Ultimately, the most important thing is to make sure that you adopt the tests and techniques that allow you to achieve your research objectives and answer your research questions .
In this section of the results chapter, you should try to make use of figures and visual components as effectively as possible. For example, if you present a correlation table, use colour coding to highlight the significance of the correlation values, or scatterplots to visually demonstrate what the trend is. The easier you make it for your reader to digest your findings, the more effectively you’ll be able to make your arguments in the next chapter.

Step 7 – Test your hypotheses
If your study requires it, the next stage is hypothesis testing. A hypothesis is a statement , often indicating a difference between groups or relationship between variables, that can be supported or rejected by a statistical test. However, not all studies will involve hypotheses (again, it depends on the research objectives), so don’t feel like you “must” present and test hypotheses just because you’re undertaking quantitative research.
The basic process for hypothesis testing is as follows:
- Specify your null hypothesis (for example, “The chemical psilocybin has no effect on time perception).
- Specify your alternative hypothesis (e.g., “The chemical psilocybin has an effect on time perception)
- Set your significance level (this is usually 0.05)
- Calculate your statistics and find your p-value (e.g., p=0.01)
- Draw your conclusions (e.g., “The chemical psilocybin does have an effect on time perception”)
Finally, if the aim of your study is to develop and test a conceptual framework , this is the time to present it, following the testing of your hypotheses. While you don’t need to develop or discuss these findings further in the results chapter, indicating whether the tests (and their p-values) support or reject the hypotheses is crucial.
Step 8 – Provide a chapter summary
To wrap up your results chapter and transition to the discussion chapter, you should provide a brief summary of the key findings . “Brief” is the keyword here – much like the chapter introduction, this shouldn’t be lengthy – a paragraph or two maximum. Highlight the findings most relevant to your research objectives and research questions, and wrap it up.
Some final thoughts, tips and tricks
Now that you’ve got the essentials down, here are a few tips and tricks to make your quantitative results chapter shine:
- When writing your results chapter, report your findings in the past tense . You’re talking about what you’ve found in your data, not what you are currently looking for or trying to find.
- Structure your results chapter systematically and sequentially . If you had two experiments where findings from the one generated inputs into the other, report on them in order.
- Make your own tables and graphs rather than copying and pasting them from statistical analysis programmes like SPSS. Check out the DataIsBeautiful reddit for some inspiration.
- Once you’re done writing, review your work to make sure that you have provided enough information to answer your research questions , but also that you didn’t include superfluous information.
If you’ve got any questions about writing up the quantitative results chapter, please leave a comment below. If you’d like 1-on-1 assistance with your quantitative analysis and discussion, check out our hands-on coaching service , or book a free consultation with a friendly coach.

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

Thank you. I will try my best to write my results.
Awesome content 👏🏾
this was great explaination
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

Organizing Academic Research Papers: 7. The Results
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Executive Summary
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tertiary Sources
- What Is Scholarly vs. Popular?
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Annotated Bibliography
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- How to Manage Group Projects
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Essays
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Acknowledgements
The results section of the research paper is where you report the findings of your study based upon the information gathered as a result of the methodology [or methodologies] you applied. The results section should simply state the findings, without bias or interpretation, and arranged in a logical sequence. The results section should always be written in the past tense. A section describing results [a.k.a., "findings"] is particularly necessary if your paper includes data generated from your own research.
Importance of a Good Results Section
When formulating the results section, it's important to remember that the results of a study do not prove anything . Research results can only confirm or reject the research problem underpinning your study. However, the act of articulating the results helps you to understand the problem from within, to break it into pieces, and to view the research problem from various perspectives.
The page length of this section is set by the amount and types of data to be reported . Be concise, using non-textual elements, such as figures and tables, if appropriate, to present results more effectively. In deciding what data to describe in your results section, you must clearly distinguish material that would normally be included in a research paper from any raw data or other material that could be included as an appendix. In general, raw data should not be included in the main text of your paper unless requested to do so by your professor.
Avoid providing data that is not critical to answering the research question . The background information you described in the introduction section should provide the reader with any additional context or explanation needed to understand the results. A good rule is to always re-read the background section of your paper after you have written up your results to ensure that the reader has enough context to understand the results [and, later, how you interpreted the results in the discussion section of your paper].
Bates College; Burton, Neil et al. Doing Your Education Research Project . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2008; Results . The Structure, Format, Content, and Style of a Journal-Style Scientific Paper. Department of Biology. Bates College.
Structure and Writing Style
I. Structure and Approach
For most research paper formats, there are two ways of presenting and organizing the results .
- Present the results followed by a short explanation of the findings . For example, you may have noticed an unusual correlation between two variables during the analysis of your findings. It is correct to point this out in the results section. However, speculating as to why this correlation exists, and offering a hypothesis about what may be happening, belongs in the discussion section of your paper.
- Present a section and then discuss it, before presenting the next section then discussing it, and so on . This is more common in longer papers because it helps the reader to better understand each finding. In this model, it can be helpful to provide a brief conclusion in the results section that ties each of the findings together and links to the discussion.
NOTE: The discussion section should generally follow the same format chosen in presenting and organizing the results.
II. Content
In general, the content of your results section should include the following elements:
- An introductory context for understanding the results by restating the research problem that underpins the purpose of your study.
- A summary of your key findings arranged in a logical sequence that generally follows your methodology section.
- Inclusion of non-textual elements, such as, figures, charts, photos, maps, tables, etc. to further illustrate the findings, if appropriate.
- In the text, a systematic description of your results, highlighting for the reader observations that are most relevant to the topic under investigation [remember that not all results that emerge from the methodology that you used to gather the data may be relevant].
- Use of the past tense when refering to your results.
- The page length of your results section is guided by the amount and types of data to be reported. However, focus only on findings that are important and related to addressing the research problem.
Using Non-textual Elements
- Either place figures, tables, charts, etc. within the text of the result, or include them in the back of the report--do one or the other but never do both.
- In the text, refer to each non-textual element in numbered order [e.g., Table 1, Table 2; Chart 1, Chart 2; Map 1, Map 2].
- If you place non-textual elements at the end of the report, make sure they are clearly distinguished from any attached appendix materials, such as raw data.
- Regardless of placement, each non-textual element must be numbered consecutively and complete with caption [caption goes under the figure, table, chart, etc.]
- Each non-textual element must be titled, numbered consecutively, and complete with a heading [title with description goes above the figure, table, chart, etc.].
- In proofreading your results section, be sure that each non-textual element is sufficiently complete so that it could stand on its own, separate from the text.
III. Problems to Avoid
When writing the results section, avoid doing the following :
- Discussing or interpreting your results . Save all this for the next section of your paper, although where appropriate, you should compare or contrast specific results to those found in other studies [e.g., "Similar to Smith [1990], one of the findings of this study is the strong correlation between motivation and academic achievement...."].
- Reporting background information or attempting to explain your findings ; this should have been done in your Introduction section, but don't panic! Often the results of a study point to the need to provide additional background information or to explain the topic further, so don't think you did something wrong. Revise your introduction as needed.
- Ignoring negative results . If some of your results fail to support your hypothesis, do not ignore them. Document them, then state in your discussion section why you believe a negative result emerged from your study. Note that negative results, and how you handle them, often provides you with the opportunity to write a more engaging discussion section, therefore, don't be afraid to highlight them.
- Including raw data or intermediate calculations . Ask your professor if you need to include any raw data generated by your study, such as transcripts from interviews or data files. If raw data is to be included, place it in an appendix or set of appendices that are referred to in the text.
- Be as factual and concise as possible in reporting your findings . Do not use phrases that are vague or non-specific, such as, "appeared to be greater or lesser than..." or "demonstrates promising trends that...."
- Presenting the same data or repeating the same information more than once . If you feel the need to highlight something, you will have a chance to do that in the discussion section.
- Confusing figures with tables . Be sure to properly label any non-textual elements in your paper. If you are not sure, look up the term in a dictionary.
Burton, Neil et al. Doing Your Education Research Project . Los Angeles, CA: SAGE, 2008; Caprette, David R. Writing Research Papers . Experimental Biosciences Resources. Rice University; Hancock, Dawson R. and Bob Algozzine. Doing Case Study Research: A Practical Guide for Beginning Researchers . 2nd ed. New York: Teachers College Press, 2011; Introduction to Nursing Research: Reporting Research Findings. Nursing Research: Open Access Nursing Research and Review Articles. (January 4, 2012); Reporting Research Findings. Wilder Research, in partnership with the Minnesota Department of Human Services. (February 2009); Results . The Structure, Format, Content, and Style of a Journal-Style Scientific Paper. Department of Biology. Bates College; Schafer, Mickey S. Writing the Results . Thesis Writing in the Sciences. Course Syllabus. University of Florida.
Writing Tip
Why Don't I Just Combine the Results Section with the Discussion Section?
It's not unusual to find articles in social science journals where the author(s) have combined a description of the findings from the study with a discussion about their implications. You could do this. However, if you are inexperienced writing research papers, consider creating two sections for each element in your paper as a way to better organize your thoughts and, by extension, your paper. Think of the results section as the place where you report what your study found; think of the discussion section as the place where you interpret your data and answer the "so what?" question. As you become more skilled writing research papers, you may want to meld the results of your study with a discussion of its implications.
- << Previous: Quantitative Methods
- Next: Using Non-Textual Elements >>
- Last Updated: Jul 18, 2023 11:58 AM
- URL: https://library.sacredheart.edu/c.php?g=29803
- QuickSearch
- Library Catalog
- Databases A-Z
- Publication Finder
- Course Reserves
- Citation Linker
- Digital Commons
- Our Website
Research Support
- Ask a Librarian
- Appointments
- Interlibrary Loan (ILL)
- Research Guides
- Databases by Subject
- Citation Help
Using the Library
- Reserve a Group Study Room
- Renew Books
- Honors Study Rooms
- Off-Campus Access
- Library Policies
- Library Technology
User Information
- Grad Students
- Online Students
- COVID-19 Updates
- Staff Directory
- News & Announcements
- Library Newsletter
My Accounts
- Interlibrary Loan
- Staff Site Login
FIND US ON
- Privacy Policy

Home » Evaluating Research – Process, Examples and Methods
Evaluating Research – Process, Examples and Methods
Table of Contents

Evaluating Research
Definition:
Evaluating Research refers to the process of assessing the quality, credibility, and relevance of a research study or project. This involves examining the methods, data, and results of the research in order to determine its validity, reliability, and usefulness. Evaluating research can be done by both experts and non-experts in the field, and involves critical thinking, analysis, and interpretation of the research findings.
Research Evaluating Process
The process of evaluating research typically involves the following steps:
Identify the Research Question
The first step in evaluating research is to identify the research question or problem that the study is addressing. This will help you to determine whether the study is relevant to your needs.
Assess the Study Design
The study design refers to the methodology used to conduct the research. You should assess whether the study design is appropriate for the research question and whether it is likely to produce reliable and valid results.
Evaluate the Sample
The sample refers to the group of participants or subjects who are included in the study. You should evaluate whether the sample size is adequate and whether the participants are representative of the population under study.
Review the Data Collection Methods
You should review the data collection methods used in the study to ensure that they are valid and reliable. This includes assessing the measures used to collect data and the procedures used to collect data.
Examine the Statistical Analysis
Statistical analysis refers to the methods used to analyze the data. You should examine whether the statistical analysis is appropriate for the research question and whether it is likely to produce valid and reliable results.
Assess the Conclusions
You should evaluate whether the data support the conclusions drawn from the study and whether they are relevant to the research question.
Consider the Limitations
Finally, you should consider the limitations of the study, including any potential biases or confounding factors that may have influenced the results.
Evaluating Research Methods
Evaluating Research Methods are as follows:
- Peer review: Peer review is a process where experts in the field review a study before it is published. This helps ensure that the study is accurate, valid, and relevant to the field.
- Critical appraisal : Critical appraisal involves systematically evaluating a study based on specific criteria. This helps assess the quality of the study and the reliability of the findings.
- Replication : Replication involves repeating a study to test the validity and reliability of the findings. This can help identify any errors or biases in the original study.
- Meta-analysis : Meta-analysis is a statistical method that combines the results of multiple studies to provide a more comprehensive understanding of a particular topic. This can help identify patterns or inconsistencies across studies.
- Consultation with experts : Consulting with experts in the field can provide valuable insights into the quality and relevance of a study. Experts can also help identify potential limitations or biases in the study.
- Review of funding sources: Examining the funding sources of a study can help identify any potential conflicts of interest or biases that may have influenced the study design or interpretation of results.
Example of Evaluating Research
Example of Evaluating Research sample for students:
Title of the Study: The Effects of Social Media Use on Mental Health among College Students
Sample Size: 500 college students
Sampling Technique : Convenience sampling
- Sample Size: The sample size of 500 college students is a moderate sample size, which could be considered representative of the college student population. However, it would be more representative if the sample size was larger, or if a random sampling technique was used.
- Sampling Technique : Convenience sampling is a non-probability sampling technique, which means that the sample may not be representative of the population. This technique may introduce bias into the study since the participants are self-selected and may not be representative of the entire college student population. Therefore, the results of this study may not be generalizable to other populations.
- Participant Characteristics: The study does not provide any information about the demographic characteristics of the participants, such as age, gender, race, or socioeconomic status. This information is important because social media use and mental health may vary among different demographic groups.
- Data Collection Method: The study used a self-administered survey to collect data. Self-administered surveys may be subject to response bias and may not accurately reflect participants’ actual behaviors and experiences.
- Data Analysis: The study used descriptive statistics and regression analysis to analyze the data. Descriptive statistics provide a summary of the data, while regression analysis is used to examine the relationship between two or more variables. However, the study did not provide information about the statistical significance of the results or the effect sizes.
Overall, while the study provides some insights into the relationship between social media use and mental health among college students, the use of a convenience sampling technique and the lack of information about participant characteristics limit the generalizability of the findings. In addition, the use of self-administered surveys may introduce bias into the study, and the lack of information about the statistical significance of the results limits the interpretation of the findings.
Note*: Above mentioned example is just a sample for students. Do not copy and paste directly into your assignment. Kindly do your own research for academic purposes.
Applications of Evaluating Research
Here are some of the applications of evaluating research:
- Identifying reliable sources : By evaluating research, researchers, students, and other professionals can identify the most reliable sources of information to use in their work. They can determine the quality of research studies, including the methodology, sample size, data analysis, and conclusions.
- Validating findings: Evaluating research can help to validate findings from previous studies. By examining the methodology and results of a study, researchers can determine if the findings are reliable and if they can be used to inform future research.
- Identifying knowledge gaps: Evaluating research can also help to identify gaps in current knowledge. By examining the existing literature on a topic, researchers can determine areas where more research is needed, and they can design studies to address these gaps.
- Improving research quality : Evaluating research can help to improve the quality of future research. By examining the strengths and weaknesses of previous studies, researchers can design better studies and avoid common pitfalls.
- Informing policy and decision-making : Evaluating research is crucial in informing policy and decision-making in many fields. By examining the evidence base for a particular issue, policymakers can make informed decisions that are supported by the best available evidence.
- Enhancing education : Evaluating research is essential in enhancing education. Educators can use research findings to improve teaching methods, curriculum development, and student outcomes.
Purpose of Evaluating Research
Here are some of the key purposes of evaluating research:
- Determine the reliability and validity of research findings : By evaluating research, researchers can determine the quality of the study design, data collection, and analysis. They can determine whether the findings are reliable, valid, and generalizable to other populations.
- Identify the strengths and weaknesses of research studies: Evaluating research helps to identify the strengths and weaknesses of research studies, including potential biases, confounding factors, and limitations. This information can help researchers to design better studies in the future.
- Inform evidence-based decision-making: Evaluating research is crucial in informing evidence-based decision-making in many fields, including healthcare, education, and public policy. Policymakers, educators, and clinicians rely on research evidence to make informed decisions.
- Identify research gaps : By evaluating research, researchers can identify gaps in the existing literature and design studies to address these gaps. This process can help to advance knowledge and improve the quality of research in a particular field.
- Ensure research ethics and integrity : Evaluating research helps to ensure that research studies are conducted ethically and with integrity. Researchers must adhere to ethical guidelines to protect the welfare and rights of study participants and to maintain the trust of the public.
Characteristics Evaluating Research
Characteristics Evaluating Research are as follows:
- Research question/hypothesis: A good research question or hypothesis should be clear, concise, and well-defined. It should address a significant problem or issue in the field and be grounded in relevant theory or prior research.
- Study design: The research design should be appropriate for answering the research question and be clearly described in the study. The study design should also minimize bias and confounding variables.
- Sampling : The sample should be representative of the population of interest and the sampling method should be appropriate for the research question and study design.
- Data collection : The data collection methods should be reliable and valid, and the data should be accurately recorded and analyzed.
- Results : The results should be presented clearly and accurately, and the statistical analysis should be appropriate for the research question and study design.
- Interpretation of results : The interpretation of the results should be based on the data and not influenced by personal biases or preconceptions.
- Generalizability: The study findings should be generalizable to the population of interest and relevant to other settings or contexts.
- Contribution to the field : The study should make a significant contribution to the field and advance our understanding of the research question or issue.
Advantages of Evaluating Research
Evaluating research has several advantages, including:
- Ensuring accuracy and validity : By evaluating research, we can ensure that the research is accurate, valid, and reliable. This ensures that the findings are trustworthy and can be used to inform decision-making.
- Identifying gaps in knowledge : Evaluating research can help identify gaps in knowledge and areas where further research is needed. This can guide future research and help build a stronger evidence base.
- Promoting critical thinking: Evaluating research requires critical thinking skills, which can be applied in other areas of life. By evaluating research, individuals can develop their critical thinking skills and become more discerning consumers of information.
- Improving the quality of research : Evaluating research can help improve the quality of research by identifying areas where improvements can be made. This can lead to more rigorous research methods and better-quality research.
- Informing decision-making: By evaluating research, we can make informed decisions based on the evidence. This is particularly important in fields such as medicine and public health, where decisions can have significant consequences.
- Advancing the field : Evaluating research can help advance the field by identifying new research questions and areas of inquiry. This can lead to the development of new theories and the refinement of existing ones.
Limitations of Evaluating Research
Limitations of Evaluating Research are as follows:
- Time-consuming: Evaluating research can be time-consuming, particularly if the study is complex or requires specialized knowledge. This can be a barrier for individuals who are not experts in the field or who have limited time.
- Subjectivity : Evaluating research can be subjective, as different individuals may have different interpretations of the same study. This can lead to inconsistencies in the evaluation process and make it difficult to compare studies.
- Limited generalizability: The findings of a study may not be generalizable to other populations or contexts. This limits the usefulness of the study and may make it difficult to apply the findings to other settings.
- Publication bias: Research that does not find significant results may be less likely to be published, which can create a bias in the published literature. This can limit the amount of information available for evaluation.
- Lack of transparency: Some studies may not provide enough detail about their methods or results, making it difficult to evaluate their quality or validity.
- Funding bias : Research funded by particular organizations or industries may be biased towards the interests of the funder. This can influence the study design, methods, and interpretation of results.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

What is a Hypothesis – Types, Examples and...


Scope of the Research – Writing Guide and...

Research Techniques – Methods, Types and Examples

Research Questions – Types, Examples and Writing...

Thesis – Structure, Example and Writing Guide

Background of The Study – Examples and Writing...
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
Research Methods | Definitions, Types, Examples
Research methods are specific procedures for collecting and analyzing data. Developing your research methods is an integral part of your research design . When planning your methods, there are two key decisions you will make.
First, decide how you will collect data . Your methods depend on what type of data you need to answer your research question :
- Qualitative vs. quantitative : Will your data take the form of words or numbers?
- Primary vs. secondary : Will you collect original data yourself, or will you use data that has already been collected by someone else?
- Descriptive vs. experimental : Will you take measurements of something as it is, or will you perform an experiment?
Second, decide how you will analyze the data .
- For quantitative data, you can use statistical analysis methods to test relationships between variables.
- For qualitative data, you can use methods such as thematic analysis to interpret patterns and meanings in the data.
Table of contents
Methods for collecting data, examples of data collection methods, methods for analyzing data, examples of data analysis methods, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about research methods.
Data is the information that you collect for the purposes of answering your research question . The type of data you need depends on the aims of your research.
Qualitative vs. quantitative data
Your choice of qualitative or quantitative data collection depends on the type of knowledge you want to develop.
For questions about ideas, experiences and meanings, or to study something that can’t be described numerically, collect qualitative data .
If you want to develop a more mechanistic understanding of a topic, or your research involves hypothesis testing , collect quantitative data .
| Qualitative | to broader populations. . | |
|---|---|---|
| Quantitative | . |
You can also take a mixed methods approach , where you use both qualitative and quantitative research methods.
Primary vs. secondary research
Primary research is any original data that you collect yourself for the purposes of answering your research question (e.g. through surveys , observations and experiments ). Secondary research is data that has already been collected by other researchers (e.g. in a government census or previous scientific studies).
If you are exploring a novel research question, you’ll probably need to collect primary data . But if you want to synthesize existing knowledge, analyze historical trends, or identify patterns on a large scale, secondary data might be a better choice.
| Primary | . | methods. |
|---|---|---|
| Secondary |
Descriptive vs. experimental data
In descriptive research , you collect data about your study subject without intervening. The validity of your research will depend on your sampling method .
In experimental research , you systematically intervene in a process and measure the outcome. The validity of your research will depend on your experimental design .
To conduct an experiment, you need to be able to vary your independent variable , precisely measure your dependent variable, and control for confounding variables . If it’s practically and ethically possible, this method is the best choice for answering questions about cause and effect.
| Descriptive | . . | |
|---|---|---|
| Experimental |
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
| Research method | Primary or secondary? | Qualitative or quantitative? | When to use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary | Quantitative | To test cause-and-effect relationships. | |
| Primary | Quantitative | To understand general characteristics of a population. | |
| Interview/focus group | Primary | Qualitative | To gain more in-depth understanding of a topic. |
| Observation | Primary | Either | To understand how something occurs in its natural setting. |
| Secondary | Either | To situate your research in an existing body of work, or to evaluate trends within a research topic. | |
| Either | Either | To gain an in-depth understanding of a specific group or context, or when you don’t have the resources for a large study. |
Your data analysis methods will depend on the type of data you collect and how you prepare it for analysis.
Data can often be analyzed both quantitatively and qualitatively. For example, survey responses could be analyzed qualitatively by studying the meanings of responses or quantitatively by studying the frequencies of responses.
Qualitative analysis methods
Qualitative analysis is used to understand words, ideas, and experiences. You can use it to interpret data that was collected:
- From open-ended surveys and interviews , literature reviews , case studies , ethnographies , and other sources that use text rather than numbers.
- Using non-probability sampling methods .
Qualitative analysis tends to be quite flexible and relies on the researcher’s judgement, so you have to reflect carefully on your choices and assumptions and be careful to avoid research bias .
Quantitative analysis methods
Quantitative analysis uses numbers and statistics to understand frequencies, averages and correlations (in descriptive studies) or cause-and-effect relationships (in experiments).
You can use quantitative analysis to interpret data that was collected either:
- During an experiment .
- Using probability sampling methods .
Because the data is collected and analyzed in a statistically valid way, the results of quantitative analysis can be easily standardized and shared among researchers.
| Research method | Qualitative or quantitative? | When to use |
|---|---|---|
| Quantitative | To analyze data collected in a statistically valid manner (e.g. from experiments, surveys, and observations). | |
| Meta-analysis | Quantitative | To statistically analyze the results of a large collection of studies. Can only be applied to studies that collected data in a statistically valid manner. |
| Qualitative | To analyze data collected from interviews, , or textual sources. To understand general themes in the data and how they are communicated. | |
| Either | To analyze large volumes of textual or visual data collected from surveys, literature reviews, or other sources. Can be quantitative (i.e. frequencies of words) or qualitative (i.e. meanings of words). |
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Chi square test of independence
- Statistical power
- Descriptive statistics
- Degrees of freedom
- Pearson correlation
- Null hypothesis
- Double-blind study
- Case-control study
- Research ethics
- Data collection
- Hypothesis testing
- Structured interviews
Research bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Unconscious bias
- Recall bias
- Halo effect
- Self-serving bias
- Information bias
Quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings.
Quantitative methods allow you to systematically measure variables and test hypotheses . Qualitative methods allow you to explore concepts and experiences in more detail.
In mixed methods research , you use both qualitative and quantitative data collection and analysis methods to answer your research question .
A sample is a subset of individuals from a larger population . Sampling means selecting the group that you will actually collect data from in your research. For example, if you are researching the opinions of students in your university, you could survey a sample of 100 students.
In statistics, sampling allows you to test a hypothesis about the characteristics of a population.
The research methods you use depend on the type of data you need to answer your research question .
- If you want to measure something or test a hypothesis , use quantitative methods . If you want to explore ideas, thoughts and meanings, use qualitative methods .
- If you want to analyze a large amount of readily-available data, use secondary data. If you want data specific to your purposes with control over how it is generated, collect primary data.
- If you want to establish cause-and-effect relationships between variables , use experimental methods. If you want to understand the characteristics of a research subject, use descriptive methods.
Methodology refers to the overarching strategy and rationale of your research project . It involves studying the methods used in your field and the theories or principles behind them, in order to develop an approach that matches your objectives.
Methods are the specific tools and procedures you use to collect and analyze data (for example, experiments, surveys , and statistical tests ).
In shorter scientific papers, where the aim is to report the findings of a specific study, you might simply describe what you did in a methods section .
In a longer or more complex research project, such as a thesis or dissertation , you will probably include a methodology section , where you explain your approach to answering the research questions and cite relevant sources to support your choice of methods.
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked, writing strong research questions | criteria & examples.
- What Is a Research Design | Types, Guide & Examples
- Data Collection | Definition, Methods & Examples
More interesting articles
- Between-Subjects Design | Examples, Pros, & Cons
- Cluster Sampling | A Simple Step-by-Step Guide with Examples
- Confounding Variables | Definition, Examples & Controls
- Construct Validity | Definition, Types, & Examples
- Content Analysis | Guide, Methods & Examples
- Control Groups and Treatment Groups | Uses & Examples
- Control Variables | What Are They & Why Do They Matter?
- Correlation vs. Causation | Difference, Designs & Examples
- Correlational Research | When & How to Use
- Critical Discourse Analysis | Definition, Guide & Examples
- Cross-Sectional Study | Definition, Uses & Examples
- Descriptive Research | Definition, Types, Methods & Examples
- Ethical Considerations in Research | Types & Examples
- Explanatory and Response Variables | Definitions & Examples
- Explanatory Research | Definition, Guide, & Examples
- Exploratory Research | Definition, Guide, & Examples
- External Validity | Definition, Types, Threats & Examples
- Extraneous Variables | Examples, Types & Controls
- Guide to Experimental Design | Overview, Steps, & Examples
- How Do You Incorporate an Interview into a Dissertation? | Tips
- How to Do Thematic Analysis | Step-by-Step Guide & Examples
- How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
- How to Write a Strong Hypothesis | Steps & Examples
- Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria | Examples & Definition
- Independent vs. Dependent Variables | Definition & Examples
- Inductive Reasoning | Types, Examples, Explanation
- Inductive vs. Deductive Research Approach | Steps & Examples
- Internal Validity in Research | Definition, Threats, & Examples
- Internal vs. External Validity | Understanding Differences & Threats
- Longitudinal Study | Definition, Approaches & Examples
- Mediator vs. Moderator Variables | Differences & Examples
- Mixed Methods Research | Definition, Guide & Examples
- Multistage Sampling | Introductory Guide & Examples
- Naturalistic Observation | Definition, Guide & Examples
- Operationalization | A Guide with Examples, Pros & Cons
- Population vs. Sample | Definitions, Differences & Examples
- Primary Research | Definition, Types, & Examples
- Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research | Differences, Examples & Methods
- Quasi-Experimental Design | Definition, Types & Examples
- Questionnaire Design | Methods, Question Types & Examples
- Random Assignment in Experiments | Introduction & Examples
- Random vs. Systematic Error | Definition & Examples
- Reliability vs. Validity in Research | Difference, Types and Examples
- Reproducibility vs Replicability | Difference & Examples
- Reproducibility vs. Replicability | Difference & Examples
- Sampling Methods | Types, Techniques & Examples
- Semi-Structured Interview | Definition, Guide & Examples
- Simple Random Sampling | Definition, Steps & Examples
- Single, Double, & Triple Blind Study | Definition & Examples
- Stratified Sampling | Definition, Guide & Examples
- Structured Interview | Definition, Guide & Examples
- Survey Research | Definition, Examples & Methods
- Systematic Review | Definition, Example, & Guide
- Systematic Sampling | A Step-by-Step Guide with Examples
- Textual Analysis | Guide, 3 Approaches & Examples
- The 4 Types of Reliability in Research | Definitions & Examples
- The 4 Types of Validity in Research | Definitions & Examples
- Transcribing an Interview | 5 Steps & Transcription Software
- Triangulation in Research | Guide, Types, Examples
- Types of Interviews in Research | Guide & Examples
- Types of Research Designs Compared | Guide & Examples
- Types of Variables in Research & Statistics | Examples
- Unstructured Interview | Definition, Guide & Examples
- What Is a Case Study? | Definition, Examples & Methods
- What Is a Case-Control Study? | Definition & Examples
- What Is a Cohort Study? | Definition & Examples
- What Is a Conceptual Framework? | Tips & Examples
- What Is a Controlled Experiment? | Definitions & Examples
- What Is a Double-Barreled Question?
- What Is a Focus Group? | Step-by-Step Guide & Examples
- What Is a Likert Scale? | Guide & Examples
- What Is a Prospective Cohort Study? | Definition & Examples
- What Is a Retrospective Cohort Study? | Definition & Examples
- What Is Action Research? | Definition & Examples
- What Is an Observational Study? | Guide & Examples
- What Is Concurrent Validity? | Definition & Examples
- What Is Content Validity? | Definition & Examples
- What Is Convenience Sampling? | Definition & Examples
- What Is Convergent Validity? | Definition & Examples
- What Is Criterion Validity? | Definition & Examples
- What Is Data Cleansing? | Definition, Guide & Examples
- What Is Deductive Reasoning? | Explanation & Examples
- What Is Discriminant Validity? | Definition & Example
- What Is Ecological Validity? | Definition & Examples
- What Is Ethnography? | Definition, Guide & Examples
- What Is Face Validity? | Guide, Definition & Examples
- What Is Non-Probability Sampling? | Types & Examples
- What Is Participant Observation? | Definition & Examples
- What Is Peer Review? | Types & Examples
- What Is Predictive Validity? | Examples & Definition
- What Is Probability Sampling? | Types & Examples
- What Is Purposive Sampling? | Definition & Examples
- What Is Qualitative Observation? | Definition & Examples
- What Is Qualitative Research? | Methods & Examples
- What Is Quantitative Observation? | Definition & Examples
- What Is Quantitative Research? | Definition, Uses & Methods
What is your plagiarism score?
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- v.317(7150); 1998 Jul 4
Looking forward
Making better use of research findings, andrew haines.
a Department of Primary Care and Population Sciences, Royal Free and University College London Schools of Medicine, London NW3 2PF, b Department of Epidemiology and Public Health, University College London Medical School
Anna Donald
There is increasing interest in implementing research findings in practice both because of a growing awareness of the gap between clinical practice and the findings of research and also because of the need to show that public investment in research results in benefits for patients. Improved understanding of the reasons for the uptake of research findings requires insights from a range of disciplines. In order to promote the uptake of research findings it is necessary to identify potential barriers to implementation and to develop strategies to overcome them. Specific interventions that can be used to promote change in practice include using clinical guidelines and computerised decision support systems, developing educational programmes, communicating research findings to patients, and developing strategies for organisational change.
Interest in how best to promote the uptake of research findings has been fuelled by a number of factors including the well documented disparities between clinical practice and research evidence of effective interventions. Examples include interventions in the management of cardiac failure, secondary prevention of heart disease, 1 atrial fibrillation, 2 menorrhagia, 3 and pregnancy and childbirth. 4 In the United Kingdom the advent of the NHS research and development programme has led to greater involvement of NHS personnel in setting priorities 5 and to the establishment of a programme to evaluate different methods of promoting the implementation of research findings. 6 The concept of pay back on research 7 has also been developed, resulting in a framework that can be used to assess the benefits arising from research.
Relying on the passive diffusion of information to keep health professionals’ knowledge up to date is doomed to failure in a global environment in which about 2 million articles on medical issues are published annually. 8 There is also growing awareness that conventional continuing education activities, such as conferences and courses, which focus largely on the passive acquisition of knowledge have little impact on the behaviour of health professionals. 9 The circulation of guidelines without an implementation strategy is also unlikely to result in changes in practice. 10
Summary points
- Reasons for failing to get research findings into practice are many and include the lack of appropriate information at the point of decision making and social, organisational, and institutional barriers to change
- All people within an organisation who will have to implement the change or who can influence change should be involved in developing strategies for change
- Better links between clinical audit, continuing education, and research and development need to be developed
- Evidence of the effectiveness of specific interventions to promote change is still incomplete, but a combination of interventions will probably be needed
- The pressure for more effective and efficient implementation of research findings is likely to grow
Health professionals need to plan for rapid changes in knowledge, something that is likely to persist throughout our professional lifetimes and which encompasses not only diagnostic techniques, drug treatment, behavioural interventions, and surgical procedures but also ways of delivering and organising health services and developing health policy. Many health professionals already feel overburdened, and therefore a radical change in approach is required so that they can manage change rather than feel like its victims. A number of steps are necessary in order to support this process.
Keeping abreast of new knowledge
Health professionals need timely, valid, and relevant information to be available at the point of decision making. Despite extensive investment in information technology by the NHS the rapid delivery of such information is not widely available. Relatively simple prompting and reminder systems can improve clinicians’ performance 11 ; the price of useful databases such as Best Evidence (which comprises Evidence-Based Medicine and the American College of Physicians Journal Club on CD ROM) and The Cochrane Library is little more than the cost of subscribing to a journal. There are an increasing number of journals, such as Evidence-Based Medicine, that review important papers rigorously and present the results in a way that busy clinicians can rapidly absorb. The NHS reviews and dissemination centre in York compiles systematic reviews that are relevant to clinicians and policymakers. Nevertheless, many clinicians still do not receive such information, 12 and more needs to be done to provide a wider range of high quality information that is usable in practice settings.
Librarians’ roles are changing rapidly; in North America, for example, some librarians are involved in clinical practice through programmes such as literature attached to the chart (LATCH). 13 In these programmes, hospital librarians participate in ward rounds and actively support clinical decision making at the bedside. Requests for information are documented in the notes, and articles are subsequently delivered to the ward. Similar programmes could be introduced elsewhere after appropriate evaluation, but information support is also needed in primary care settings. In the United Kingdom many health professionals, such as nurses, may not be permitted to use their hospital library since they are not formally affiliated with the (medical) body that funds them.

Implementing knowledge
Research findings can influence decisions at many levels—in caring for individual patients, in developing practice guidelines, in commissioning health care, in developing prevention and health promotion strategies, in developing policy, in designing educational programmes, and in performing clinical audit—but only if clinicians know how to translate knowledge into action. The acquisition of database searching and critical appraisal skills should give health professionals greater confidence in finding and assessing the quality of publications, but this does not necessarily help in applying new knowledge to day to day problems. 14 Much attention has been paid to the use of best evidence during consultations with individual patients—that is, using evidence based medicine derived largely from epidemiological methods. 15 , 16 However, organisational change is often also necessary to implement clinical change. Even a step as simple as ensuring that all patients with a history of myocardial infarction are offered aspirin requires that a number of smaller steps are taken including identifying patients, contacting them, explaining the rationale, checking for contraindications, and prescribing aspirin or advising patients to buy it over the counter. Furthermore, health professionals have their own experiences, beliefs, and perceptions about appropriate practice; attempts to change practice which ignore these factors are unlikely to succeed. Awareness of these pitfalls has led to greater emphasis on understanding social, behavioural, and organisational factors which may act as barriers to change. 17
A wide spectrum of approaches for promoting implementation has been used. These approaches are underpinned by a number of theoretical perspectives on behavioural change such as cognitive theories which focus on rational information seeking and decision making; management theories which emphasise organisational conditions needed to improve care; learning theories which lead to behavioural approaches involving, for example, audit and feedback and reminder systems; and social influence theories which focus on understanding and using the social environment to promote and reinforce change. 18
Clearly these approaches are not mutually exclusive. For example, the transmission of information from research to single practitioners or small groups of health professionals through educational outreach has a strong educational component but might also include aspects of social influence interventions 19 in pointing out the use of a particular treatment by local colleagues. The marketing strategies used by the pharmaceutical industry depend on segmentation of the target audience into groups that are likely to share characteristics so that a message can be tailored to that group. 20 Similar techniques might be adapted for non-commercial use within the NHS. The evidence for the effectiveness of different approaches and interventions is still incomplete and will be reviewed in a subsequent article in the series. 21 In many cases a combination of approaches will be more effective than a single intervention. 22 No single theoretical perspective has been adequately validated to guide the choice of implementation strategies.
Steps in promoting the uptake of research findings
- Determine that there is an appreciable gap between research findings and practice
- Define the appropriate message (for example, the information to be used)
- Decide which processes need to be altered
- Involve the key players (for example those people who will implement change or who are in a position to influence change)
- Identify the barriers to change and decide how to overcome them
- Decide on specific interventions to promote change (for example the use of guidelines or educational programmes)
- Identify levers for change—that is, existing mechanisms which can be used to promote change (for example, financial incentives to attend educational programmes or placing appropriate questions in professional examinations)
- Determine whether practice has changed in the way desired; use clinical audit to monitor change
The study of the diffusion of innovations—how new ideas are transmitted through social networks—has been influential in illustrating that those who adopt new ideas early tend to differ in a number of ways from those who adopt the ideas later. For example, those who adopt new ideas early tend to have more extensive social and professional networks. 23 Much of the medical literature has a bias towards innovation and the underlying assumption is that innovations are bound to be beneficial. However, in health care the challenge is to promote the uptake of innovations that have been shown to be effective, to delay the spread of those that have not yet been shown to be effective, and to prevent the uptake of ineffective innovations. 24
Although different people can promote the uptake of research findings—including policymakers, commissioning authorities, educators, and provider managers—it is largely clinicians and their patients who will implement findings. A number of steps need to be taken in order to get research findings into practice (box previous page). The characteristics of the message should also be considered; they may influence the degree to which the message is incorporated into practice (box above).
Important characteristics of the message
- Generalisability (settings in which the intervention is relevant)
- Applicability (the patients to whom the intervention is relevant)
- Format and presentation (for example, will there be written or computerised guidelines, will absolute and relative risk reductions be presented)
Other characteristics
- Source of the message (for example, professional organisation, Department of Health)
- Channels of communication (how the message will be disseminated)
- Target audiences (the recipients)
- Timing of the initial launch and frequency of updating
- Mechanism for updating the message
The choice of key players—those people in the organisation who will have to implement change or who can influence change—will depend on the processes to be changed; in primary care, for example, nurses and administrative staff should be involved in many cases, in addition to general practitioners, since their cooperation will be essential for organisational change to be effective. If the innovation involves the acquisition of specific skills, such as training in certain procedures, then those who organise postgraduate and continuing education are also key players.
The identification of barriers to change and the development of strategies to overcome them are likely to be of fundamental importance in promoting the uptake of research findings. Some examples of barriers to the application of research findings to patients are given in the box on the next page. A future article will propose a conceptual framework for analysing and overcoming barriers. 25 Since some of the strongest resistance to change may be related to the experiences and beliefs of health professionals, the early involvement of key players is essential in identifying and, when necessary, overcoming such impediments to change. Barriers need to be reviewed during the process of implementation as their nature may change over time.
Interventions to promote change must be tailored to the problem, audience, and the resources available. Educational outreach, for example, may be particularly appropriate for updating primary care practitioners in the management of specific conditions because they tend to work alone or in small groups. Guidelines based on research evidence may be developed and endorsed by national professional organisations and adapted for local use as part of clinical audit and educational programmes.
Linking research with practice
There need to be closer links between research and practice, so that research is relevant to practitioners’ needs and so that practitioners are willing to participate in research. While there is evidence that some researchers can promote their own work, 26 in general researchers have not been systematically involved in the implementation of their own findings and may not be well equipped to do this. In the United Kingdom, the NHS research and development programme is seeking views about priorities for research through a broad consultation process. 5 Better methods of involving those who are most likely to use the results of research are needed to ensure that research questions are framed appropriately and tested in relevant contexts using interventions that can be replicated in everyday practice. For example, there is little point conducting trials of a new intervention in hospital practice if virtually all of the treatments for a particular disorder are carried out in primary care settings. Contextual relevance is particularly important in studies of the organisation and delivery of services, 27 such as stroke units, hospital at home schemes, and schemes for improving hospital discharge procedures to reduce readmissions among elderly patients. If unaccounted for, differences in skill mix and management structures between innovative services and most providers can make it difficult for providers to have a clear view of how they should best implement findings in their own units.
Interaction between purchasers and providers
—In the NHS, purchasers as well as providers should be involved in applying research findings to practice. Purchasers can help create an environment conducive to change, for example, by ensuring that health professionals have access to information, that libraries are financially supported, and that continuing education and audit programmes are configured to work together to promote effective practice. Purchasers could also ensure that the organisation and delivery of services takes into account the best available research evidence. However, it is clear that the degree of influence exerted by purchasers on the practice of providers is limited, 28 and that priority must be given to helping providers develop the capacity to understand and use research findings.
Making implementation an integral part of training
—For many health professionals, involvement in implementation may be far more relevant to their careers and to the development of the NHS than undertaking laboratory research, yet pressures to undertake research remain strong. Greater encouragement should be given to clinicians to spend time learning to use and implement research findings effectively.
Potential barriers to change
Environmental
In the practice
- Limitations of time
- Limitations of the organisation of the practice (for example, a lack of disease registers or mechanisms to monitor repeat prescribing)
In education
- Inappropriate continuing education and failure to connect with programmes to promote better quality of care
- Lack of incentives to participate in effective educational activities
In health care
- Lack of financial resources
- Lack of defined practice populations
- Health policies which promote ineffective or unproved activities
- Failure to provide practitioners with access to appropriate information
- Influence of the media on patients in creating demands or beliefs
- Impact of disadvantage on patients’ access to care
Factors associated with the practitioner
- Obsolete knowledge
- Influence of opinion leaders (such as health professionals whose views influence their peers)
- Beliefs and attitudes (for example, a previous adverse experience of innovation)
Factors associated with the patient
- Demands for care
- Perceptions or cultural beliefs about appropriate care
Factors which in some circumstances might be perceived as barriers to change can also be levers for change. For example, patients may influence practitioners’ behaviour towards clinically effective practice by requesting interventions that have been proved to be effective. Practitioners might be influenced positively by opinion leaders.
Learning to evaluate and use research findings in daily practice is an important and lifelong part of professional development. This requires not only changes in educational programmes, but also a realignment of institutions so that management structures can support changes in knowledge and the implementation of changes in procedures.
There are major structural difficulties that need to be overcome in the NHS. For example, better coordination at national, regional, and local levels is required between the education and training of health professionals, clinical audit, and research and development. This type of coordination should be a priority for the proposed national institute for clinical excellence in the United Kingdom. 29
It has been suggested that financial considerations, rather than the potential for gaining useful knowledge, affect general practitioners’ choice of continuing education courses. 30 One of the aims of continuing education should be to ensure that practitioners stay up to date with research findings of major importance for patient care and change their practice accordingly. Continuing education activities need to take into account evidence about the ineffectiveness of many traditional approaches. To develop a more integrated approach to promoting the uptake of research findings, health systems need to have coordinated mechanisms that can manage the continuing evolution of medical knowledge.
The advent of research based information that is available to patients 31 and the increasing accessibility of information of variable quality through the internet and other sources suggests that doctors have the potential to act as information brokers and interpreters for patients. Doctors could also work together with user groups representing patients or their carers, a number of which have demonstrated an interest in and commitment to providing quality research based information to their members. 32 The pace of change in knowledge is unlikely to slow. As health systems around the world struggle to reconcile change with limited resources and rising expectations, pressure to implement research findings more effectively and efficiently is bound to grow.
Funding: None.
Conflict of interest: None.
The articles in this series are adapted from Coping with Loss , edited by Colin Murray Parkes and Andrew Markus, which will be published in July.
- Chamberlain University Library
- Chamberlain Library Core
Finding Types of Research
- Evidence-Based Research
On This Guide
About this guide, understand evidence-based practice, identify research study types.
- Quantitative Studies
- Qualitative Studies
- Meta-Analysis
- Systematic Reviews
- Randomized Controlled Trials
- Observational Studies
- Literature Reviews
- Finding Research Tools This link opens in a new window
Throughout your schooling, you may need to find different types of evidence and research to support your course work. This guide provides a high-level overview of evidence-based practice as well as the different types of research and study designs. Each page of this guide offers an overview and search tips for finding articles that fit that study design.
Note! If you need help finding a specific type of study, visit the Get Research Help guide to contact the librarians.
What is Evidence-Based Practice?
One of the requirements for your coursework is to find articles that support evidence-based practice. But what exactly is evidence-based practice? Evidence-based practice is a method that uses relevant and current evidence to plan, implement and evaluate patient care. This definition is included in the video below, which explains all the steps of evidence-based practice in greater detail.
- Video - Evidence-based practice: What it is and what it is not. Medcom (Producer), & Cobb, D. (Director). (2017). Evidence-based practice: What it is and what it is not [Streaming Video]. United States of America: Producer. Retrieved from Alexander Street Press Nursing Education Collection
Quantitative and Qualitative Studies
Research is broken down into two different types: quantitative and qualitative. Quantitative studies are all about measurement. They will report statistics of things that can be physically measured like blood pressure, weight and oxygen saturation. Qualitative studies, on the other hand, are about people's experiences and how they feel about something. This type of information cannot be measured using statistics. Both of these types of studies report original research and are considered single studies. Watch the video below for more information.

Study Designs
Some research study types that you will encounter include:
- Case-Control Studies
- Cohort Studies
- Cross-Sectional Studies
Studies that Synthesize Other Studies
Sometimes, a research study will look at the results of many studies and look for trends and draw conclusions. These types of studies include:
- Meta Analyses
Tip! How do you determine the research article's study type or level of evidence? First, look at the article abstract. Most of the time the abstract will have a methodology section, which should tell you what type of study design the researchers are using. If it is not in the abstract, look for the methodology section of the article. It should tell you all about what type of study the researcher is doing and the steps they used to carry out the study.
Read the book below to learn how to read a clinical paper, including the types of study designs you will encounter.
- Search Website
- Library Tech Support
- Services for Colleagues
Chamberlain College of Nursing is owned and operated by Chamberlain University LLC. In certain states, Chamberlain operates as Chamberlain College of Nursing pending state authorization for Chamberlain University.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- My Bibliography
- Collections
- Citation manager
Save citation to file
Email citation, add to collections.
- Create a new collection
- Add to an existing collection
Add to My Bibliography
Your saved search, create a file for external citation management software, your rss feed.
- Search in PubMed
- Search in NLM Catalog
- Add to Search
Communicating and disseminating research findings to study participants: Formative assessment of participant and researcher expectations and preferences
Affiliations.
- 1 College of Medicine, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, SC, USA.
- 2 College of Health Professions/Healthcare Leadership & Management, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, SC, USA.
- 3 South Carolina Clinical & Translational Research Institute (CTSA), Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, SC, USA.
- 4 SOGI-SES Add Health Study Carolina Population Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, Chapel Hill, NC, USA.
- 5 College of Nursing, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, SC, USA.
- PMID: 32695495
- PMCID: PMC7348011
- DOI: 10.1017/cts.2020.9
Introduction: Translating research findings into practice requires understanding how to meet communication and dissemination needs and preferences of intended audiences including past research participants (PSPs) who want, but seldom receive, information on research findings during or after participating in research studies. Most researchers want to let others, including PSP, know about their findings but lack knowledge about how to effectively communicate findings to a lay audience.
Methods: We designed a two-phase, mixed methods pilot study to understand experiences, expectations, concerns, preferences, and capacities of researchers and PSP in two age groups (adolescents/young adults (AYA) or older adults) and to test communication prototypes for sharing, receiving, and using information on research study findings.
Principal results: PSP and researchers agreed that sharing study findings should happen and that doing so could improve participant recruitment and enrollment, use of research findings to improve health and health-care delivery, and build community support for research. Some differences and similarities in communication preferences and message format were identified between PSP groups, reinforcing the best practice of customizing communication channel and messaging. Researchers wanted specific training and/or time and resources to help them prepare messages in formats to meet PSP needs and preferences but were unaware of resources to help them do so.
Conclusions: Our findings offer insight into how to engage both PSP and researchers in the design and use of strategies to share research findings and highlight the need to develop services and support for researchers as they aim to bridge this translational barrier.
Keywords: Communication; dissemination; research findings; research participant preference; researcher preference.
© The Association for Clinical and Translational Science 2020.
PubMed Disclaimer
Prototype 1: study results email…
Prototype 1: study results email prototype. MUSC, Medical University of South Carolina.
Prototype 2: study results letter…
Prototype 2: study results letter prototype.
Prototype 3: study results MailChimp…
Prototype 3: study results MailChimp prototypes 1 and 2. MUSC, Medical University of…
Similar articles
- Returning study results to research participants: Data access, format, and sharing preferences. Mangal S, Niño de Rivera S, Choi J, Reading Turchioe M, Benda N, Sharko M, Myers A, Goyal P, Dugdale L, Masterson Creber R. Mangal S, et al. Int J Med Inform. 2023 Feb;170:104955. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2022.104955. Epub 2022 Dec 13. Int J Med Inform. 2023. PMID: 36565546 Free PMC article.
- Promoting and supporting self-management for adults living in the community with physical chronic illness: A systematic review of the effectiveness and meaningfulness of the patient-practitioner encounter. Rees S, Williams A. Rees S, et al. JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2009;7(13):492-582. doi: 10.11124/01938924-200907130-00001. JBI Libr Syst Rev. 2009. PMID: 27819974
- Health research participants' preferences for receiving research results. Long CR, Stewart MK, Cunningham TV, Warmack TS, McElfish PA. Long CR, et al. Clin Trials. 2016 Dec;13(6):582-591. doi: 10.1177/1740774516665598. Epub 2016 Aug 24. Clin Trials. 2016. PMID: 27562368 Free PMC article.
- Health professionals' experience of teamwork education in acute hospital settings: a systematic review of qualitative literature. Eddy K, Jordan Z, Stephenson M. Eddy K, et al. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2016 Apr;14(4):96-137. doi: 10.11124/JBISRIR-2016-1843. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2016. PMID: 27532314 Review.
- Communication and dissemination strategies to facilitate the use of health-related evidence. McCormack L, Sheridan S, Lewis M, Boudewyns V, Melvin CL, Kistler C, Lux LJ, Cullen K, Lohr KN. McCormack L, et al. Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep). 2013 Nov;(213):1-520. doi: 10.23970/ahrqepcerta213. Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep). 2013. PMID: 24423078 Free PMC article. Review.
- Dissemination innovation: Using found poetry to return study results to patients and partners facing cancer. Bybee SG, Eaton J, Wong B. Bybee SG, et al. PEC Innov. 2024 May 7;4:100286. doi: 10.1016/j.pecinn.2024.100286. eCollection 2024 Dec. PEC Innov. 2024. PMID: 38770044 Free PMC article.
- Diversity, equity, inclusion, and access are necessary for clinical trial site readiness. Carter-Edwards L, Hidalgo B, Lewis-Hall F, Nguyen T, Rutter J. Carter-Edwards L, et al. J Clin Transl Sci. 2023 Nov 30;7(1):e268. doi: 10.1017/cts.2023.660. eCollection 2023. J Clin Transl Sci. 2023. PMID: 38380391 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
- Diversity, equity, and inclusivity in observational ambulatory assessment: Recommendations from two decades of Electronically Activated Recorder (EAR) research. Kaplan DM, Tidwell CA, Chung JM, Alisic E, Demiray B, Bruni M, Evora S, Gajewski-Nemes JA, Macbeth A, Mangelsdorf SN, Mascaro JS, Minor KS, Noga RN, Nugent NR, Polsinelli AJ, Rentscher KE, Resnikoff AW, Robbins ML, Slatcher RB, Tejeda-Padron AB, Mehl MR. Kaplan DM, et al. Behav Res Methods. 2024 Apr;56(4):3207-3225. doi: 10.3758/s13428-023-02293-0. Epub 2023 Dec 8. Behav Res Methods. 2024. PMID: 38066394
- A series of workshops to present research findings and fill knowledge gap among adolescent girls and young women on sexual and reproductive health in Lebanon: An example of active knowledge dissemination. Korri R, Ivanova O. Korri R, et al. J Glob Health. 2023 Sep 1;13:03044. doi: 10.7189/jogh.13.03044. J Glob Health. 2023. PMID: 37655369 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
- Creating a best practice template for participant communication plans in global health clinical studies. Shelly CE, Logan C, Skorochod B, Wiyeh A, Ndwandwe D, Choko A, Valea I, Titanji BK. Shelly CE, et al. Trials. 2023 Mar 2;24(1):158. doi: 10.1186/s13063-023-07185-4. Trials. 2023. PMID: 36864516 Free PMC article.
- Morrato EH, Concannon TW, Meissner P, Shah ND, Turner BJ. Dissemination and implementation of comparative effectiveness evidence: key informant interviews with clinical and translational science award institutions. Journal of Comparative Effectiveness Research 2013; 2(2): 185–194. - PMC - PubMed
- Zerhouni EA, Alving B. Clinical and translational science awards: a framework for a national research agenda. Translational Research 2006; 148(1): 4–5. - PubMed
- Partridge AH, Winer EP. Informing clinical trial participants about study results. JAMA 2002; 288(3): 363. - PubMed
- Partridge AH, Burstein HJ, Gelman RS, Marcom PK, Winer EP. Do patients participating in clinical trials want to know study results? JNCI Journal of the National Cancer Institute 2003; 95(6): 491–492. - PubMed
- Shalowitz DI, Miller FG. Communicating the results of clinical research to participants: attitudes, practices, and future directions. PLoS Medicine 2008; 5(5): e91, 714–720. - PMC - PubMed
Related information
Grants and funding.
- UL1 TR001450/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full text sources.
- Europe PubMed Central
- PubMed Central
Miscellaneous
- NCI CPTAC Assay Portal
- Citation Manager
NCBI Literature Resources
MeSH PMC Bookshelf Disclaimer
The PubMed wordmark and PubMed logo are registered trademarks of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). Unauthorized use of these marks is strictly prohibited.
Loading metrics
Open Access
Peer-reviewed
Research Article
Functional connectivity changes in the brain of adolescents with internet addiction: A systematic literature review of imaging studies
Roles Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing
Affiliation Child and Adolescent Mental Health, Department of Brain Sciences, Great Ormond Street Institute of Child Health, University College London, London, United Kingdom
Roles Conceptualization, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing
* E-mail: [email protected]
Affiliation Behavioural Brain Sciences Unit, Population Policy Practice Programme, Great Ormond Street Institute of Child Health, University College London, London, United Kingdom
- Max L. Y. Chang,
- Irene O. Lee

- Published: June 4, 2024
- https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmen.0000022
- Peer Review
- Reader Comments
Internet usage has seen a stark global rise over the last few decades, particularly among adolescents and young people, who have also been diagnosed increasingly with internet addiction (IA). IA impacts several neural networks that influence an adolescent’s behaviour and development. This article issued a literature review on the resting-state and task-based functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) studies to inspect the consequences of IA on the functional connectivity (FC) in the adolescent brain and its subsequent effects on their behaviour and development. A systematic search was conducted from two databases, PubMed and PsycINFO, to select eligible articles according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria. Eligibility criteria was especially stringent regarding the adolescent age range (10–19) and formal diagnosis of IA. Bias and quality of individual studies were evaluated. The fMRI results from 12 articles demonstrated that the effects of IA were seen throughout multiple neural networks: a mix of increases/decreases in FC in the default mode network; an overall decrease in FC in the executive control network; and no clear increase or decrease in FC within the salience network and reward pathway. The FC changes led to addictive behaviour and tendencies in adolescents. The subsequent behavioural changes are associated with the mechanisms relating to the areas of cognitive control, reward valuation, motor coordination, and the developing adolescent brain. Our results presented the FC alterations in numerous brain regions of adolescents with IA leading to the behavioural and developmental changes. Research on this topic had a low frequency with adolescent samples and were primarily produced in Asian countries. Future research studies of comparing results from Western adolescent samples provide more insight on therapeutic intervention.
Citation: Chang MLY, Lee IO (2024) Functional connectivity changes in the brain of adolescents with internet addiction: A systematic literature review of imaging studies. PLOS Ment Health 1(1): e0000022. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmen.0000022
Editor: Kizito Omona, Uganda Martyrs University, UGANDA
Received: December 29, 2023; Accepted: March 18, 2024; Published: June 4, 2024
Copyright: © 2024 Chang, Lee. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Data Availability: All relevant data are within the paper and its Supporting information files.
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work.
Competing interests: The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Introduction
The behavioural addiction brought on by excessive internet use has become a rising source of concern [ 1 ] since the last decade. According to clinical studies, individuals with Internet Addiction (IA) or Internet Gaming Disorder (IGD) may have a range of biopsychosocial effects and is classified as an impulse-control disorder owing to its resemblance to pathological gambling and substance addiction [ 2 , 3 ]. IA has been defined by researchers as a person’s inability to resist the urge to use the internet, which has negative effects on their psychological well-being as well as their social, academic, and professional lives [ 4 ]. The symptoms can have serious physical and interpersonal repercussions and are linked to mood modification, salience, tolerance, impulsivity, and conflict [ 5 ]. In severe circumstances, people may experience severe pain in their bodies or health issues like carpal tunnel syndrome, dry eyes, irregular eating and disrupted sleep [ 6 ]. Additionally, IA is significantly linked to comorbidities with other psychiatric disorders [ 7 ].
Stevens et al (2021) reviewed 53 studies including 17 countries and reported the global prevalence of IA was 3.05% [ 8 ]. Asian countries had a higher prevalence (5.1%) than European countries (2.7%) [ 8 ]. Strikingly, adolescents and young adults had a global IGD prevalence rate of 9.9% which matches previous literature that reported historically higher prevalence among adolescent populations compared to adults [ 8 , 9 ]. Over 80% of adolescent population in the UK, the USA, and Asia have direct access to the internet [ 10 ]. Children and adolescents frequently spend more time on media (possibly 7 hours and 22 minutes per day) than at school or sleeping [ 11 ]. Developing nations have also shown a sharp rise in teenage internet usage despite having lower internet penetration rates [ 10 ]. Concerns regarding the possible harms that overt internet use could do to adolescents and their development have arisen because of this surge, especially the significant impacts by the COVID-19 pandemic [ 12 ]. The growing prevalence and neurocognitive consequences of IA among adolescents makes this population a vital area of study [ 13 ].
Adolescence is a crucial developmental stage during which people go through significant changes in their biology, cognition, and personalities [ 14 ]. Adolescents’ emotional-behavioural functioning is hyperactivated, which creates risk of psychopathological vulnerability [ 15 ]. In accordance with clinical study results [ 16 ], this emotional hyperactivity is supported by a high level of neuronal plasticity. This plasticity enables teenagers to adapt to the numerous physical and emotional changes that occur during puberty as well as develop communication techniques and gain independence [ 16 ]. However, the strong neuronal plasticity is also associated with risk-taking and sensation seeking [ 17 ] which may lead to IA.
Despite the fact that the precise neuronal mechanisms underlying IA are still largely unclear, functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) method has been used by scientists as an important framework to examine the neuropathological changes occurring in IA, particularly in the form of functional connectivity (FC) [ 18 ]. fMRI research study has shown that IA alters both the functional and structural makeup of the brain [ 3 ].
We hypothesise that IA has widespread neurological alteration effects rather than being limited to a few specific brain regions. Further hypothesis holds that according to these alterations of FC between the brain regions or certain neural networks, adolescents with IA would experience behavioural changes. An investigation of these domains could be useful for creating better procedures and standards as well as minimising the negative effects of overt internet use. This literature review aims to summarise and analyse the evidence of various imaging studies that have investigated the effects of IA on the FC in adolescents. This will be addressed through two research questions:
- How does internet addiction affect the functional connectivity in the adolescent brain?
- How is adolescent behaviour and development impacted by functional connectivity changes due to internet addiction?
The review protocol was conducted in line with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) guidelines (see S1 Checklist ).
Search strategy and selection process
A systematic search was conducted up until April 2023 from two sources of database, PubMed and PsycINFO, using a range of terms relevant to the title and research questions (see full list of search terms in S1 Appendix ). All the searched articles can be accessed in the S1 Data . The eligible articles were selected according to the inclusion and exclusion criteria. Inclusion criteria used for the present review were: (i) participants in the studies with clinical diagnosis of IA; (ii) participants between the ages of 10 and 19; (iii) imaging research investigations; (iv) works published between January 2013 and April 2023; (v) written in English language; (vi) peer-reviewed papers and (vii) full text. The numbers of articles excluded due to not meeting the inclusion criteria are shown in Fig 1 . Each study’s title and abstract were screened for eligibility.
- PPT PowerPoint slide
- PNG larger image
- TIFF original image
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmen.0000022.g001
Quality appraisal
Full texts of all potentially relevant studies were then retrieved and further appraised for eligibility. Furthermore, articles were critically appraised based on the GRADE (Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development, and Evaluations) framework to evaluate the individual study for both quality and bias. The subsequent quality levels were then appraised to each article and listed as either low, moderate, or high.
Data collection process
Data that satisfied the inclusion requirements was entered into an excel sheet for data extraction and further selection. An article’s author, publication year, country, age range, participant sample size, sex, area of interest, measures, outcome and article quality were all included in the data extraction spreadsheet. Studies looking at FC, for instance, were grouped, while studies looking at FC in specific area were further divided into sub-groups.
Data synthesis and analysis
Articles were classified according to their location in the brain as well as the network or pathway they were a part of to create a coherent narrative between the selected studies. Conclusions concerning various research trends relevant to particular groupings were drawn from these groupings and subgroupings. To maintain the offered information in a prominent manner, these assertions were entered into the data extraction excel spreadsheet.
With the search performed on the selected databases, 238 articles in total were identified (see Fig 1 ). 15 duplicated articles were eliminated, and another 6 items were removed for various other reasons. Title and abstract screening eliminated 184 articles because they were not in English (number of article, n, = 7), did not include imaging components (n = 47), had adult participants (n = 53), did not have a clinical diagnosis of IA (n = 19), did not address FC in the brain (n = 20), and were published outside the desired timeframe (n = 38). A further 21 papers were eliminated for failing to meet inclusion requirements after the remaining 33 articles underwent full-text eligibility screening. A total of 12 papers were deemed eligible for this review analysis.
Characteristics of the included studies, as depicted in the data extraction sheet in Table 1 provide information of the author(s), publication year, sample size, study location, age range, gender, area of interest, outcome, measures used and quality appraisal. Most of the studies in this review utilised resting state functional magnetic resonance imaging techniques (n = 7), with several studies demonstrating task-based fMRI procedures (n = 3), and the remaining studies utilising whole-brain imaging measures (n = 2). The studies were all conducted in Asiatic countries, specifically coming from China (8), Korea (3), and Indonesia (1). Sample sizes ranged from 12 to 31 participants with most of the imaging studies having comparable sample sizes. Majority of the studies included a mix of male and female participants (n = 8) with several studies having a male only participant pool (n = 3). All except one of the mixed gender studies had a majority male participant pool. One study did not disclose their data on the gender demographics of their experiment. Study years ranged from 2013–2022, with 2 studies in 2013, 3 studies in 2014, 3 studies in 2015, 1 study in 2017, 1 study in 2020, 1 study in 2021, and 1 study in 2022.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmen.0000022.t001
(1) How does internet addiction affect the functional connectivity in the adolescent brain?
The included studies were organised according to the brain region or network that they were observing. The specific networks affected by IA were the default mode network, executive control system, salience network and reward pathway. These networks are vital components of adolescent behaviour and development [ 31 ]. The studies in each section were then grouped into subsections according to their specific brain regions within their network.
Default mode network (DMN)/reward network.
Out of the 12 studies, 3 have specifically studied the default mode network (DMN), and 3 observed whole-brain FC that partially included components of the DMN. The effect of IA on the various centres of the DMN was not unilaterally the same. The findings illustrate a complex mix of increases and decreases in FC depending on the specific region in the DMN (see Table 2 and Fig 2 ). The alteration of FC in posterior cingulate cortex (PCC) in the DMN was the most frequently reported area in adolescents with IA, which involved in attentional processes [ 32 ], but Lee et al. (2020) additionally found alterations of FC in other brain regions, such as anterior insula cortex, a node in the DMN that controls the integration of motivational and cognitive processes [ 20 ].
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmen.0000022.g002
The overall changes of functional connectivity in the brain network including default mode network (DMN), executive control network (ECN), salience network (SN) and reward network. IA = Internet Addiction, FC = Functional Connectivity.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmen.0000022.t002
Ding et al. (2013) revealed altered FC in the cerebellum, the middle temporal gyrus, and the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) [ 22 ]. They found that the bilateral inferior parietal lobule, left superior parietal lobule, and right inferior temporal gyrus had decreased FC, while the bilateral posterior lobe of the cerebellum and the medial temporal gyrus had increased FC [ 22 ]. The right middle temporal gyrus was found to have 111 cluster voxels (t = 3.52, p<0.05) and the right inferior parietal lobule was found to have 324 cluster voxels (t = -4.07, p<0.05) with an extent threshold of 54 voxels (figures above this threshold are deemed significant) [ 22 ]. Additionally, there was a negative correlation, with 95 cluster voxels (p<0.05) between the FC of the left superior parietal lobule and the PCC with the Chen Internet Addiction Scores (CIAS) which are used to determine the severity of IA [ 22 ]. On the other hand, in regions of the reward system, connection with the PCC was positively connected with CIAS scores [ 22 ]. The most significant was the right praecuneus with 219 cluster voxels (p<0.05) [ 22 ]. Wang et al. (2017) also discovered that adolescents with IA had 33% less FC in the left inferior parietal lobule and 20% less FC in the dorsal mPFC [ 24 ]. A potential connection between the effects of substance use and overt internet use is revealed by the generally decreased FC in these areas of the DMN of teenagers with drug addiction and IA [ 35 ].
The putamen was one of the main regions of reduced FC in adolescents with IA [ 19 ]. The putamen and the insula-operculum demonstrated significant group differences regarding functional connectivity with a cluster size of 251 and an extent threshold of 250 (Z = 3.40, p<0.05) [ 19 ]. The molecular mechanisms behind addiction disorders have been intimately connected to decreased striatal dopaminergic function [ 19 ], making this function crucial.
Executive Control Network (ECN).
5 studies out of 12 have specifically viewed parts of the executive control network (ECN) and 3 studies observed whole-brain FC. The effects of IA on the ECN’s constituent parts were consistent across all the studies examined for this analysis (see Table 2 and Fig 3 ). The results showed a notable decline in all the ECN’s major centres. Li et al. (2014) used fMRI imaging and a behavioural task to study response inhibition in adolescents with IA [ 25 ] and found decreased activation at the striatum and frontal gyrus, particularly a reduction in FC at inferior frontal gyrus, in the IA group compared to controls [ 25 ]. The inferior frontal gyrus showed a reduction in FC in comparison to the controls with a cluster size of 71 (t = 4.18, p<0.05) [ 25 ]. In addition, the frontal-basal ganglia pathways in the adolescents with IA showed little effective connection between areas and increased degrees of response inhibition [ 25 ].
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmen.0000022.g003
Lin et al. (2015) found that adolescents with IA demonstrated disrupted corticostriatal FC compared to controls [ 33 ]. The corticostriatal circuitry experienced decreased connectivity with the caudate, bilateral anterior cingulate cortex (ACC), as well as the striatum and frontal gyrus [ 33 ]. The inferior ventral striatum showed significantly reduced FC with the subcallosal ACC and caudate head with cluster size of 101 (t = -4.64, p<0.05) [ 33 ]. Decreased FC in the caudate implies dysfunction of the corticostriatal-limbic circuitry involved in cognitive and emotional control [ 36 ]. The decrease in FC in both the striatum and frontal gyrus is related to inhibitory control, a common deficit seen with disruptions with the ECN [ 33 ].
The dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC), ACC, and right supplementary motor area (SMA) of the prefrontal cortex were all found to have significantly decreased grey matter volume [ 29 ]. In addition, the DLPFC, insula, temporal cortices, as well as significant subcortical regions like the striatum and thalamus, showed decreased FC [ 29 ]. According to Tremblay (2009), the striatum plays a significant role in the processing of rewards, decision-making, and motivation [ 37 ]. Chen et al. (2020) reported that the IA group demonstrated increased impulsivity as well as decreased reaction inhibition using a Stroop colour-word task [ 26 ]. Furthermore, Chen et al. (2020) observed that the left DLPFC and dorsal striatum experienced a negative connection efficiency value, specifically demonstrating that the dorsal striatum activity suppressed the left DLPFC [ 27 ].
Salience network (SN).
Out of the 12 chosen studies, 3 studies specifically looked at the salience network (SN) and 3 studies have observed whole-brain FC. Relative to the DMN and ECN, the findings on the SN were slightly sparser. Despite this, adolescents with IA demonstrated a moderate decrease in FC, as well as other measures like fibre connectivity and cognitive control, when compared to healthy control (see Table 2 and Fig 4 ).
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmen.0000022.g004
Xing et al. (2014) used both dorsal anterior cingulate cortex (dACC) and insula to test FC changes in the SN of adolescents with IA and found decreased structural connectivity in the SN as well as decreased fractional anisotropy (FA) that correlated to behaviour performance in the Stroop colour word-task [ 21 ]. They examined the dACC and insula to determine whether the SN’s disrupted connectivity may be linked to the SN’s disruption of regulation, which would explain the impaired cognitive control seen in adolescents with IA. However, researchers did not find significant FC differences in the SN when compared to the controls [ 21 ]. These results provided evidence for the structural changes in the interconnectivity within SN in adolescents with IA.
Wang et al. (2017) investigated network interactions between the DMN, ECN, SN and reward pathway in IA subjects [ 24 ] (see Fig 5 ), and found 40% reduction of FC between the DMN and specific regions of the SN, such as the insula, in comparison to the controls (p = 0.008) [ 24 ]. The anterior insula and dACC are two areas that are impacted by this altered FC [ 24 ]. This finding supports the idea that IA has similar neurobiological abnormalities with other addictive illnesses, which is in line with a study that discovered disruptive changes in the SN and DMN’s interaction in cocaine addiction [ 38 ]. The insula has also been linked to the intensity of symptoms and has been implicated in the development of IA [ 39 ].
“+” indicates an increase in behaivour; “-”indicates a decrease in behaviour; solid arrows indicate a direct network interaction; and the dotted arrows indicates a reduction in network interaction. This diagram depicts network interactions juxtaposed with engaging in internet related behaviours. Through the neural interactions, the diagram illustrates how the networks inhibit or amplify internet usage and vice versa. Furthermore, it demonstrates how the SN mediates both the DMN and ECN.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmen.0000022.g005
(2) How is adolescent behaviour and development impacted by functional connectivity changes due to internet addiction?
The findings that IA individuals demonstrate an overall decrease in FC in the DMN is supported by numerous research [ 24 ]. Drug addict populations also exhibited similar decline in FC in the DMN [ 40 ]. The disruption of attentional orientation and self-referential processing for both substance and behavioural addiction was then hypothesised to be caused by DMN anomalies in FC [ 41 ].
In adolescents with IA, decline of FC in the parietal lobule affects visuospatial task-related behaviour [ 22 ], short-term memory [ 42 ], and the ability of controlling attention or restraining motor responses during response inhibition tests [ 42 ]. Cue-induced gaming cravings are influenced by the DMN [ 43 ]. A visual processing area called the praecuneus links gaming cues to internal information [ 22 ]. A meta-analysis found that the posterior cingulate cortex activity of individuals with IA during cue-reactivity tasks was connected with their gaming time [ 44 ], suggesting that excessive gaming may impair DMN function and that individuals with IA exert more cognitive effort to control it. Findings for the behavioural consequences of FC changes in the DMN illustrate its underlying role in regulating impulsivity, self-monitoring, and cognitive control.
Furthermore, Ding et al. (2013) reported an activation of components of the reward pathway, including areas like the nucleus accumbens, praecuneus, SMA, caudate, and thalamus, in connection to the DMN [ 22 ]. The increased FC of the limbic and reward networks have been confirmed to be a major biomarker for IA [ 45 , 46 ]. The increased reinforcement in these networks increases the strength of reward stimuli and makes it more difficult for other networks, namely the ECN, to down-regulate the increased attention [ 29 ] (See Fig 5 ).
Executive control network (ECN).
The numerous IA-affected components in the ECN have a role in a variety of behaviours that are connected to both response inhibition and emotional regulation [ 47 ]. For instance, brain regions like the striatum, which are linked to impulsivity and the reward system, are heavily involved in the act of playing online games [ 47 ]. Online game play activates the striatum, which suppresses the left DLPFC in ECN [ 48 ]. As a result, people with IA may find it difficult to control their want to play online games [ 48 ]. This system thus causes impulsive and protracted gaming conduct, lack of inhibitory control leading to the continued use of internet in an overt manner despite a variety of negative effects, personal distress, and signs of psychological dependence [ 33 ] (See Fig 5 ).
Wang et al. (2017) report that disruptions in cognitive control networks within the ECN are frequently linked to characteristics of substance addiction [ 24 ]. With samples that were addicted to heroin and cocaine, previous studies discovered abnormal FC in the ECN and the PFC [ 49 ]. Electronic gaming is known to promote striatal dopamine release, similar to drug addiction [ 50 ]. According to Drgonova and Walther (2016), it is hypothesised that dopamine could stimulate the reward system of the striatum in the brain, leading to a loss of impulse control and a failure of prefrontal lobe executive inhibitory control [ 51 ]. In the end, IA’s resemblance to drug use disorders may point to vital biomarkers or underlying mechanisms that explain how cognitive control and impulsive behaviour are related.
A task-related fMRI study found that the decrease in FC between the left DLPFC and dorsal striatum was congruent with an increase in impulsivity in adolescents with IA [ 26 ]. The lack of response inhibition from the ECN results in a loss of control over internet usage and a reduced capacity to display goal-directed behaviour [ 33 ]. Previous studies have linked the alteration of the ECN in IA with higher cue reactivity and impaired ability to self-regulate internet specific stimuli [ 52 ].
Salience network (SN)/ other networks.
Xing et al. (2014) investigated the significance of the SN regarding cognitive control in teenagers with IA [ 21 ]. The SN, which is composed of the ACC and insula, has been demonstrated to control dynamic changes in other networks to modify cognitive performance [ 21 ]. The ACC is engaged in conflict monitoring and cognitive control, according to previous neuroimaging research [ 53 ]. The insula is a region that integrates interoceptive states into conscious feelings [ 54 ]. The results from Xing et al. (2014) showed declines in the SN regarding its structural connectivity and fractional anisotropy, even though they did not observe any appreciable change in FC in the IA participants [ 21 ]. Due to the small sample size, the results may have indicated that FC methods are not sensitive enough to detect the significant functional changes [ 21 ]. However, task performance behaviours associated with impaired cognitive control in adolescents with IA were correlated with these findings [ 21 ]. Our comprehension of the SN’s broader function in IA can be enhanced by this relationship.
Research study supports the idea that different psychological issues are caused by the functional reorganisation of expansive brain networks, such that strong association between SN and DMN may provide neurological underpinnings at the system level for the uncontrollable character of internet-using behaviours [ 24 ]. In the study by Wang et al. (2017), the decreased interconnectivity between the SN and DMN, comprising regions such the DLPFC and the insula, suggests that adolescents with IA may struggle to effectively inhibit DMN activity during internally focused processing, leading to poorly managed desires or preoccupations to use the internet [ 24 ] (See Fig 5 ). Subsequently, this may cause a failure to inhibit DMN activity as well as a restriction of ECN functionality [ 55 ]. As a result, the adolescent experiences an increased salience and sensitivity towards internet addicting cues making it difficult to avoid these triggers [ 56 ].
The primary aim of this review was to present a summary of how internet addiction impacts on the functional connectivity of adolescent brain. Subsequently, the influence of IA on the adolescent brain was compartmentalised into three sections: alterations of FC at various brain regions, specific FC relationships, and behavioural/developmental changes. Overall, the specific effects of IA on the adolescent brain were not completely clear, given the variety of FC changes. However, there were overarching behavioural, network and developmental trends that were supported that provided insight on adolescent development.
The first hypothesis that was held about this question was that IA was widespread and would be regionally similar to substance-use and gambling addiction. After conducting a review of the information in the chosen articles, the hypothesis was predictably supported. The regions of the brain affected by IA are widespread and influence multiple networks, mainly DMN, ECN, SN and reward pathway. In the DMN, there was a complex mix of increases and decreases within the network. However, in the ECN, the alterations of FC were more unilaterally decreased, but the findings of SN and reward pathway were not quite clear. Overall, the FC changes within adolescents with IA are very much network specific and lay a solid foundation from which to understand the subsequent behaviour changes that arise from the disorder.
The second hypothesis placed emphasis on the importance of between network interactions and within network interactions in the continuation of IA and the development of its behavioural symptoms. The results from the findings involving the networks, DMN, SN, ECN and reward system, support this hypothesis (see Fig 5 ). Studies confirm the influence of all these neural networks on reward valuation, impulsivity, salience to stimuli, cue reactivity and other changes that alter behaviour towards the internet use. Many of these changes are connected to the inherent nature of the adolescent brain.
There are multiple explanations that underlie the vulnerability of the adolescent brain towards IA related urges. Several of them have to do with the inherent nature and underlying mechanisms of the adolescent brain. Children’s emotional, social, and cognitive capacities grow exponentially during childhood and adolescence [ 57 ]. Early teenagers go through a process called “social reorientation” that is characterised by heightened sensitivity to social cues and peer connections [ 58 ]. Adolescents’ improvements in their social skills coincide with changes in their brains’ anatomical and functional organisation [ 59 ]. Functional hubs exhibit growing connectivity strength [ 60 ], suggesting increased functional integration during development. During this time, the brain’s functional networks change from an anatomically dominant structure to a scattered architecture [ 60 ].
The adolescent brain is very responsive to synaptic reorganisation and experience cues [ 61 ]. As a result, one of the distinguishing traits of the maturation of adolescent brains is the variation in neural network trajectory [ 62 ]. Important weaknesses of the adolescent brain that may explain the neurobiological change brought on by external stimuli are illustrated by features like the functional gaps between networks and the inadequate segregation of networks [ 62 ].
The implications of these findings towards adolescent behaviour are significant. Although the exact changes and mechanisms are not fully clear, the observed changes in functional connectivity have the capacity of influencing several aspects of adolescent development. For example, functional connectivity has been utilised to investigate attachment styles in adolescents [ 63 ]. It was observed that adolescent attachment styles were negatively associated with caudate-prefrontal connectivity, but positively with the putamen-visual area connectivity [ 63 ]. Both named areas were also influenced by the onset of internet addiction, possibly providing a connection between the two. Another study associated neighbourhood/socioeconomic disadvantage with functional connectivity alterations in the DMN and dorsal attention network [ 64 ]. The study also found multivariate brain behaviour relationships between the altered/disadvantaged functional connectivity and mental health and cognition [ 64 ]. This conclusion supports the notion that the functional connectivity alterations observed in IA are associated with specific adolescent behaviours as well as the fact that functional connectivity can be utilised as a platform onto which to compare various neurologic conditions.
Limitations/strengths
There were several limitations that were related to the conduction of the review as well as the data extracted from the articles. Firstly, the study followed a systematic literature review design when analysing the fMRI studies. The data pulled from these imaging studies were namely qualitative and were subject to bias contrasting the quantitative nature of statistical analysis. Components of the study, such as sample sizes, effect sizes, and demographics were not weighted or controlled. The second limitation brought up by a similar review was the lack of a universal consensus of terminology given IA [ 47 ]. Globally, authors writing about this topic use an array of terminology including online gaming addiction, internet addiction, internet gaming disorder, and problematic internet use. Often, authors use multiple terms interchangeably which makes it difficult to depict the subtle similarities and differences between the terms.
Reviewing the explicit limitations in each of the included studies, two major limitations were brought up in many of the articles. One was relating to the cross-sectional nature of the included studies. Due to the inherent qualities of a cross-sectional study, the studies did not provide clear evidence that IA played a causal role towards the development of the adolescent brain. While several biopsychosocial factors mediate these interactions, task-based measures that combine executive functions with imaging results reinforce the assumed connection between the two that is utilised by the papers studying IA. Another limitation regarded the small sample size of the included studies, which averaged to around 20 participants. The small sample size can influence the generalisation of the results as well as the effectiveness of statistical analyses. Ultimately, both included study specific limitations illustrate the need for future studies to clarify the causal relationship between the alterations of FC and the development of IA.
Another vital limitation was the limited number of studies applying imaging techniques for investigations on IA in adolescents were a uniformly Far East collection of studies. The reason for this was because the studies included in this review were the only fMRI studies that were found that adhered to the strict adolescent age restriction. The adolescent age range given by the WHO (10–19 years old) [ 65 ] was strictly followed. It is important to note that a multitude of studies found in the initial search utilised an older adolescent demographic that was slightly higher than the WHO age range and had a mean age that was outside of the limitations. As a result, the results of this review are biased and based on the 12 studies that met the inclusion and exclusion criteria.
Regarding the global nature of the research, although the journals that the studies were published in were all established western journals, the collection of studies were found to all originate from Asian countries, namely China and Korea. Subsequently, it pulls into question if the results and measures from these studies are generalisable towards a western population. As stated previously, Asian countries have a higher prevalence of IA, which may be the reasoning to why the majority of studies are from there [ 8 ]. However, in an additional search including other age groups, it was found that a high majority of all FC studies on IA were done in Asian countries. Interestingly, western papers studying fMRI FC were primarily focused on gambling and substance-use addiction disorders. The western papers on IA were less focused on fMRI FC but more on other components of IA such as sleep, game-genre, and other non-imaging related factors. This demonstrated an overall lack of western fMRI studies on IA. It is important to note that both western and eastern fMRI studies on IA presented an overall lack on children and adolescents in general.
Despite the several limitations, this review provided a clear reflection on the state of the data. The strengths of the review include the strict inclusion/exclusion criteria that filtered through studies and only included ones that contained a purely adolescent sample. As a result, the information presented in this review was specific to the review’s aims. Given the sparse nature of adolescent specific fMRI studies on the FC changes in IA, this review successfully provided a much-needed niche representation of adolescent specific results. Furthermore, the review provided a thorough functional explanation of the DMN, ECN, SN and reward pathway making it accessible to readers new to the topic.
Future directions and implications
Through the search process of the review, there were more imaging studies focused on older adolescence and adulthood. Furthermore, finding a review that covered a strictly adolescent population, focused on FC changes, and was specifically depicting IA, was proven difficult. Many related reviews, such as Tereshchenko and Kasparov (2019), looked at risk factors related to the biopsychosocial model, but did not tackle specific alterations in specific structural or functional changes in the brain [ 66 ]. Weinstein (2017) found similar structural and functional results as well as the role IA has in altering response inhibition and reward valuation in adolescents with IA [ 47 ]. Overall, the accumulated findings only paint an emerging pattern which aligns with similar substance-use and gambling disorders. Future studies require more specificity in depicting the interactions between neural networks, as well as more literature on adolescent and comorbid populations. One future field of interest is the incorporation of more task-based fMRI data. Advances in resting-state fMRI methods have yet to be reflected or confirmed in task-based fMRI methods [ 62 ]. Due to the fact that network connectivity is shaped by different tasks, it is critical to confirm that the findings of the resting state fMRI studies also apply to the task based ones [ 62 ]. Subsequently, work in this area will confirm if intrinsic connectivity networks function in resting state will function similarly during goal directed behaviour [ 62 ]. An elevated focus on adolescent populations as well as task-based fMRI methodology will help uncover to what extent adolescent network connectivity maturation facilitates behavioural and cognitive development [ 62 ].
A treatment implication is the potential usage of bupropion for the treatment of IA. Bupropion has been previously used to treat patients with gambling disorder and has been effective in decreasing overall gambling behaviour as well as money spent while gambling [ 67 ]. Bae et al. (2018) found a decrease in clinical symptoms of IA in line with a 12-week bupropion treatment [ 31 ]. The study found that bupropion altered the FC of both the DMN and ECN which in turn decreased impulsivity and attentional deficits for the individuals with IA [ 31 ]. Interventions like bupropion illustrate the importance of understanding the fundamental mechanisms that underlie disorders like IA.
The goal for this review was to summarise the current literature on functional connectivity changes in adolescents with internet addiction. The findings answered the primary research questions that were directed at FC alterations within several networks of the adolescent brain and how that influenced their behaviour and development. Overall, the research demonstrated several wide-ranging effects that influenced the DMN, SN, ECN, and reward centres. Additionally, the findings gave ground to important details such as the maturation of the adolescent brain, the high prevalence of Asian originated studies, and the importance of task-based studies in this field. The process of making this review allowed for a thorough understanding IA and adolescent brain interactions.
Given the influx of technology and media in the lives and education of children and adolescents, an increase in prevalence and focus on internet related behavioural changes is imperative towards future children/adolescent mental health. Events such as COVID-19 act to expose the consequences of extended internet usage on the development and lifestyle of specifically young people. While it is important for parents and older generations to be wary of these changes, it is important for them to develop a base understanding of the issue and not dismiss it as an all-bad or all-good scenario. Future research on IA will aim to better understand the causal relationship between IA and psychological symptoms that coincide with it. The current literature regarding functional connectivity changes in adolescents is limited and requires future studies to test with larger sample sizes, comorbid populations, and populations outside Far East Asia.
This review aimed to demonstrate the inner workings of how IA alters the connection between the primary behavioural networks in the adolescent brain. Predictably, the present answers merely paint an unfinished picture that does not necessarily depict internet usage as overwhelmingly positive or negative. Alternatively, the research points towards emerging patterns that can direct individuals on the consequences of certain variables or risk factors. A clearer depiction of the mechanisms of IA would allow physicians to screen and treat the onset of IA more effectively. Clinically, this could be in the form of more streamlined and accurate sessions of CBT or family therapy, targeting key symptoms of IA. Alternatively clinicians could potentially prescribe treatment such as bupropion to target FC in certain regions of the brain. Furthermore, parental education on IA is another possible avenue of prevention from a public health standpoint. Parents who are aware of the early signs and onset of IA will more effectively handle screen time, impulsivity, and minimize the risk factors surrounding IA.
Additionally, an increased attention towards internet related fMRI research is needed in the West, as mentioned previously. Despite cultural differences, Western countries may hold similarities to the eastern countries with a high prevalence of IA, like China and Korea, regarding the implications of the internet and IA. The increasing influence of the internet on the world may contribute to an overall increase in the global prevalence of IA. Nonetheless, the high saturation of eastern studies in this field should be replicated with a Western sample to determine if the same FC alterations occur. A growing interest in internet related research and education within the West will hopefully lead to the knowledge of healthier internet habits and coping strategies among parents with children and adolescents. Furthermore, IA research has the potential to become a crucial proxy for which to study adolescent brain maturation and development.
Supporting information
S1 checklist. prisma checklist..
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmen.0000022.s001
S1 Appendix. Search strategies with all the terms.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmen.0000022.s002
S1 Data. Article screening records with details of categorized content.
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmen.0000022.s003
Acknowledgments
The authors thank https://www.stockio.com/free-clipart/brain-01 (with attribution to Stockio.com); and https://www.rawpixel.com/image/6442258/png-sticker-vintage for the free images used to create Figs 2 – 4 .
- View Article
- PubMed/NCBI
- Google Scholar
- 2. Association AP. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders: DSM-5. 5 ed. Washington, D.C.: American Psychiatric Publishing; 2013.
- 10. Stats IW. World Internet Users Statistics and World Population Stats 2013 [ http://www.internetworldstats.com/stats.htm .
- 11. Rideout VJR M. B. The common sense census: media use by tweens and teens. San Francisco, CA: Common Sense Media; 2019.
- 37. Tremblay L. The Ventral Striatum. Handbook of Reward and Decision Making: Academic Press; 2009.
- 57. Bhana A. Middle childhood and pre-adolescence. Promoting mental health in scarce-resource contexts: emerging evidence and practice. Cape Town: HSRC Press; 2010. p. 124–42.
- 65. Organization WH. Adolescent Health 2023 [ https://www.who.int/health-topics/adolescent-health#tab=tab_1 .
- Open access
- Published: 14 June 2024
Associations between deep venous thrombosis and thyroid diseases: a two-sample bidirectional Mendelian randomization study
- Lifeng Zhang 1 na1 ,
- Kaibei Li 2 na1 ,
- Qifan Yang 1 ,
- Yao Lin 1 ,
- Caijuan Geng 1 ,
- Wei Huang 1 &
- Wei Zeng 1
European Journal of Medical Research volume 29 , Article number: 327 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
199 Accesses
Metrics details
Some previous observational studies have linked deep venous thrombosis (DVT) to thyroid diseases; however, the findings were contradictory. This study aimed to investigate whether some common thyroid diseases can cause DVT using a two-sample Mendelian randomization (MR) approach.
This two-sample MR study used single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) identified by the FinnGen genome-wide association studies (GWAS) to be highly associated with some common thyroid diseases, including autoimmune hyperthyroidism (962 cases and 172,976 controls), subacute thyroiditis (418 cases and 187,684 controls), hypothyroidism (26,342 cases and 59,827 controls), and malignant neoplasm of the thyroid gland (989 cases and 217,803 controls. These SNPs were used as instruments. Outcome datasets for the GWAS on DVT (6,767 cases and 330,392 controls) were selected from the UK Biobank data, which was obtained from the Integrative Epidemiology Unit (IEU) open GWAS project. The inverse variance weighted (IVW), MR-Egger and weighted median methods were used to estimate the causal association between DVT and thyroid diseases. The Cochran’s Q test was used to quantify the heterogeneity of the instrumental variables (IVs). MR Pleiotropy RESidual Sum and Outlier test (MR-PRESSO) was used to detect horizontal pleiotropy. When the causal relationship was significant, bidirectional MR analysis was performed to determine any reverse causal relationships between exposures and outcomes.
This MR study illustrated that autoimmune hyperthyroidism slightly increased the risk of DVT according to the IVW [odds ratio (OR) = 1.0009; p = 0.024] and weighted median methods [OR = 1.001; p = 0.028]. According to Cochran’s Q test, there was no evidence of heterogeneity in IVs. Additionally, MR-PRESSO did not detect horizontal pleiotropy ( p = 0.972). However, no association was observed between other thyroid diseases and DVT using the IVW, weighted median, and MR-Egger regression methods.
Conclusions
This study revealed that autoimmune hyperthyroidism may cause DVT; however, more evidence and larger sample sizes are required to draw more precise conclusions.
Introduction
Deep venous thrombosis (DVT) is a common type of disease that occurs in 1–2 individuals per 1000 each year [ 1 ]. In the post-COVID-19 era, DVT showed a higher incidence rate [ 2 ]. Among hospitalized patients, the incidence rate of this disease was as high as 2.7% [ 3 ], increasing the risk of adverse events during hospitalization. According to the Registro Informatizado Enfermedad Tromboembolica (RIETE) registry, which included data from ~ 100,000 patients from 26 countries, the 30-day mortality rate was 2.6% for distal DVT and 3.3% for proximal DVT [ 4 ]. Other studies have shown that the one-year mortality rate of DVT is 19.6% [ 5 ]. DVT and pulmonary embolism (PE), collectively referred to as venous thromboembolism (VTE), constitute a major global burden of disease [ 6 ].
Thyroid diseases are common in the real world. Previous studies have focused on the relationship between DVT and thyroid diseases, including thyroid dysfunction and thyroid cancer. Some case reports [ 7 , 8 , 9 ] have demonstrated that hyperthyroidism is often associated with DVT and indicates a worse prognosis [ 10 ]. The relationship between thyroid tumors and venous thrombosis has troubled researchers for many years. In 1989, the first case of papillary thyroid carcinoma presenting with axillary vein thrombosis as the initial symptom was reported [ 11 ]. In 1995, researchers began to notice the relationship between thyroid tumors and hypercoagulability [ 12 ], laying the foundation for subsequent extensive research. However, the aforementioned observational studies had limitations, such as small sample sizes, selection bias, reverse causality, and confounding factors, which may have led to unreliable conclusions [ 13 ].
Previous studies have explored the relationship of thyroid disease and DVT and revealed that high levels of thyroid hormones may increase the risk of DVT. Hyperthyroidism promotes a procoagulant and hypofibrinolytic state by affecting the von Willebrand factor, factors VIII, IV, and X, fibrinogen, and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 [ 14 , 15 ]. At the molecular level, researchers believe that thyroid hormones affect coagulation levels through an important nuclear thyroid hormone receptor (TR), TRβ [ 16 ], and participate in pathological coagulation through endothelial dysfunction. Thyroid hormones may have non-genetic effects on the behavior of endothelial cells [ 17 , 18 ]. In a study regarding tumor thrombosis, Lou [ 19 ] found that 303 circular RNAs were differentially expressed in DVT using microarray. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) analysis revealed that the most significantly enriched pathways included thyroid hormone-signaling pathway and endocytosis, and also increased level of proteoglycans in cancer. This indicated that tumor cells and thyroid hormones might interact to promote thrombosis. Based on these studies, we speculated that thyroid diseases, including thyroid dysfunction and thyroid tumors, may cause DVT.
Mendelian randomization (MR) research is a causal inference technique that can be used to assess the causal relationship and reverse causation between specific exposure and outcome factors. If certain assumptions [ 20 ] are fulfilled, genetic variants can be employed as instrumental variables (IVs) to establish causal relationships. Bidirectional MR analysis can clarify the presence of reverse causal relationships [ 21 ], making the conclusions more comprehensive. Accordingly, we aimed to apply a two-sample MR strategy to investigate whether DVT is related to four thyroid diseases, including autoimmune hyperthyroidism, subacute thyroiditis, hypothyroidism, and thyroid cancer.
Study design
MR relies on single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) as IVs. The IVs should fulfill the following three criteria [ 22 ]: (1) IVs should be strongly associated with exposure. (2) Genetic variants must be independent of unmeasured confounding factors that may affect the exposure–outcome association. (3) IVs are presumed to affect the outcome only through their associations with exposure (Fig. 1 ). IVs that met the above requirements were used to estimate the relationship between exposure and outcome. Our study protocol conformed to the STROBE-MR Statement [ 23 ], and all methods were performed in accordance with the relevant guidelines and regulations.
The relationship between instrumental variables, exposure, outcome, and confounding factors
Data sources and instruments
Datasets (Table 1 ) in this study were obtained from a publicly available database (the IEU open genome-wide association studies (GWAS) project [ 24 ] ( https://gwas.mrcieu.ac.uk )). There was no overlap in samples between the data sources of outcome and exposures. Using de-identified summary-level data, privacy information such as overall age and gender were hidden. Ethical approval was obtained for all original work. This study complied with the terms of use of the database.
MR analysis was performed using the R package “TwoSampleMR”. SNPs associated with each thyroid disease at the genome-wide significance threshold of p < 5.0 × 10 –8 were selected as potential IVs. To ensure independence between the genetic variants used as IVs, the linkage disequilibrium (LD) threshold for grouping was set to r 2 < 0.001 with a window size of 10,000 kb. The SNP with the lowest p -value at each locus was retained for analyses.
Statistical analysis
Multiple MR methods were used to infer causal relationships between thyroid diseases and DVT, including the inverse variance weighted (IVW), weighted median, and MR-Egger tests, after harmonizing the SNPs across the GWASs of exposures and outcomes. The main analysis was conducted using the IVW method. Heterogeneity and pleiotropy were also performed in each MR analysis. Meanwhile, the MR-PRESSO Global test [ 25 ] was utilized to detect horizontal pleiotropy. The effect trend of SNP was observed through a scatter plot, and the forest plot was used to observe the overall effects. When a significant causal relationship was confirmed by two-sample MR analysis, bidirectional MR analysis was performed to assess reverse causal relationships by swapping exposure and outcome factors. Parameters were set the same as before. All abovementioned statistical analyses were performed using the package TwoSampleMR (version 0.5.7) in the R program (version 4.2.1).
After harmonizing the SNPs across the GWASs for exposures and outcomes, the IVW (OR = 1.0009, p = 0.024, Table 2 ) and weighted median analyses (OR = 1.001, p = 0.028) revealed significant causal effects between autoimmune hyperthyroidism and DVT risk. Similar results were observed using the weighted median approach Cochran’s Q test, MR-Egger intercept, and MR-PRESSO tests suggested that the results were not influenced by pleiotropy and heterogeneity (Table 2 ). However, the leave-one-out analysis revealed a significant difference after removing some SNPs (rs179247, rs6679677, rs72891915, and rs942495, p < 0.05, Figure S2a), indicating that MR results were dependent on these SNPs (Figure S2, Table S1). No significant effects were observed in other thyroid diseases (Table 2 ). The estimated scatter plot of the association between thyroid diseases and DVT is presented in Fig. 2 , indicating a positive causal relationship between autoimmune hyperthyroidism and DVT (Fig. 2 a). The forest plots of single SNPs affecting the risk of DVT are displayed in Figure S1.
The estimated scatter plot of the association between thyroid diseases and DVT. MR-analyses are derived using IVW, MR-Egger, weighted median and mode. By fitting different models, the scatter plot showed the relationship between SNP and exposure factors, predicting the association between SNP and outcomes
Bidirectional MR analysis was performed to further determine the relationship between autoimmune hyperthyroidism and DVT. The reverse causal relationship was not observed (Table S2), which indicated that autoimmune hyperthyroidism can cause DVT from a mechanism perspective.
This study used MR to assess whether thyroid diseases affect the incidence of DVT. The results showed that autoimmune hyperthyroidism can increase the risk of DVT occurrence, but a reverse causal relationship was not observed between them using bidirectional MR analysis. However, other thyroid diseases, such as subacute thyroiditis, hypothyroidism, and thyroid cancer, did not show a similar effect.
Recently, several studies have suggested that thyroid-related diseases may be associated with the occurrence of DVT in the lower extremities, which provided etiological clues leading to the occurrence of DVT in our subsequent research. In 2006, a review mentioned the association between thyroid dysfunction and coagulation disorders [ 26 ], indicating a hypercoagulable state in patients with hyperthyroidism. In 2011, a review further suggested a clear association between hypothyroidism and bleeding tendency, while hyperthyroidism appeared to increase the risk of thrombotic events, particularly cerebral venous thrombosis [ 27 ]. A retrospective cohort study [ 28 ] supported this conclusion, but this study only observed a higher proportion of concurrent thyroid dysfunction in patients with cerebral venous thrombosis. The relationship between thyroid function and venous thromboembolism remains controversial. Krieg VJ et al. [ 29 ] found that hypothyroidism has a higher incidence rate in patients with chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension and may be associated with more severe disease, which seemed to be different from previous views that hyperthyroidism may be associated with venous thrombosis. Alsaidan [ 30 ] also revealed that the risk of developing venous thrombosis was almost increased onefold for cases with a mild-to-moderate elevation of thyroid stimulating hormone and Free thyroxine 4(FT4). In contrast, it increased twofold for cases with a severe elevation of thyroid stimulating hormone and FT4. Raised thyroid hormones may increase the synthesis or secretion of coagulation factors or may decrease fibrinolysis, which may lead to the occurrence of coagulation abnormality.
Other thyroid diseases are also reported to be associated with DVT. In a large prospective cohort study [ 31 ], the incidence of venous thromboembolism was observed to increase in patients with thyroid cancer over the age of 60. However, other retrospective studies did not find any difference compared with the general population [ 32 ]. In the post-COVID-19 era, subacute thyroiditis has received considerable attention from researchers. New evidence suggests that COVID-19 may be associated with subacute thyroiditis [ 33 , 34 ]. Mondal et al. [ 35 ] found that out of 670 COVID-19 patients, 11 presented with post-COVID-19 subacute thyroiditis. Among them, painless subacute thyroiditis appeared earlier and exhibited symptoms of hyperthyroidism. Another case report also indicated the same result, that is, subacute thyroiditis occurred after COVID-19 infection, accompanied by thyroid function changes [ 36 ]. This led us to hypothesize that subacute thyroiditis may cause DVT through alterations in thyroid function.
This study confirmed a significant causal relationship between autoimmune hyperthyroidism and DVT ( p = 0.02). The data were tested for heterogeneity and gene pleiotropy using MR-Egger, Cochran’s Q, and MR-PRESSO tests. There was no evidence that the results were influenced by pleiotropy or heterogeneity. In the leave-one-out analysis, four of the five selected SNPs showed significant effects of autoimmune hyperthyroidism on DVT, suggesting an impact of these SNPs on DVT outcome. Previous studies have focused on the relationship between hyperthyroidism and its secondary arrhythmias and arterial thromboembolism [ 37 , 38 ]. This study emphasized the risk of DVT in patients with hyperthyroidism, which has certain clinical implications. Prophylactic anticoagulant therapy was observed to help prevent DVT in patients with hyperthyroidism. Unfortunately, the results of this study did not reveal any evidence that suggests a relationship between other thyroid diseases and DVT occurrence. This may be due to the limited database, as this study only included the GWAS data from a subset of European populations. Large-scale multiracial studies are needed in the future.
There are some limitations to this study. First, it was limited to participants of European descent. Consequently, further investigation is required to confirm these findings in other ethnicities. Second, this study did not reveal the relationship between complications of hyperthyroidism and DVT. Additionally, this study selected IVs from the database using statistical methods rather than selecting them from the real population. This may result in weaker effects of the screened IVs and reduce the clinical significance of MR analysis. Moreover, the definitions of some diseases in this study were not clear in the original database, and some of the diseases were self-reported, which may reduce the accuracy of diagnosis. Further research is still needed to clarify the causal relationship between DVT and thyroid diseases based on prospective cohort and randomized controlled trials (RCTs).
This study analyzed large-scale genetic data and provided evidence of a causal relationship between autoimmune hyperthyroidism and the risk of DVT, Compared with the other thyroid diseases investigated. Prospective RCTs or MR studies with larger sample sizes are still needed to draw more precise conclusions.
Availability of data and materials
The IEU open gwas project, https://gwas.mrcieu.ac.uk/
Ortel TL, Neumann I, Ageno W, et al. American society of hematology 2020 guidelines for management of venous thromboembolism: treatment of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. Blood Adv. 2020;4(19):4693–738.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Mehrabi F, Farshbafnadi M, Rezaei N. Post-discharge thromboembolic events in COVID-19 patients: a review on the necessity for prophylaxis. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2023;29:10760296221148476.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Loffredo L, Vidili G, Sciacqua A, et al. Asymptomatic and symptomatic deep venous thrombosis in hospitalized acutely ill medical patients: risk factors and therapeutic implications. Thromb J. 2022;20(1):72.
RIETE Registry. Death within 30 days. RIETE Registry. 2022[2023.8.23]. https://rieteregistry.com/graphics-interactives/dead-30-days/ .
Minges KE, Bikdeli B, Wang Y, Attaran RR, Krumholz HM. National and regional trends in deep vein thrombosis hospitalization rates, discharge disposition, and outcomes for medicare beneficiaries. Am J Med. 2018;131(10):1200–8.
Di Nisio M, van Es N, Büller HR. Deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. Lancet. 2016;388(10063):3060–73.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Aquila I, Boca S, Caputo F, et al. An unusual case of sudden death: is there a relationship between thyroid disorders and fatal pulmonary thromboembolism? A case report and review of literature. Am J Forensic Med Pathol. 2017;38(3):229–32.
Katić J, Katić A, Katić K, Duplančić D, Lozo M. Concurrent deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism associated with hyperthyroidism: a case report. Acta Clin Croat. 2021;60(2):314–6.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Hieber M, von Kageneck C, Weiller C, Lambeck J. Thyroid diseases are an underestimated risk factor for cerebral venous sinus thrombosis. Front Neurol. 2020;11:561656.
Pohl KR, Hobohm L, Krieg VJ, et al. Impact of thyroid dysfunction on short-term outcomes and long-term mortality in patients with pulmonary embolism. Thromb Res. 2022;211:70–8.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Sirota DK. Axillary vein thrombosis as the initial symptom in metastatic papillary carcinoma of the thyroid. Mt Sinai J Med. 1989;56(2):111–3.
CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Raveh E, Cohen M, Shpitzer T, Feinmesser R. Carcinoma of the thyroid: a cause of hypercoagulability? Ear Nose Throat J. 1995;74(2):110–2.
Davey Smith G, Hemani G. Mendelian randomization: genetic anchors for causal inference in epidemiological studies. Hum Mol Genet. 2014;23(R1):R89–98.
Stuijver DJ, van Zaane B, Romualdi E, Brandjes DP, Gerdes VE, Squizzato A. The effect of hyperthyroidism on procoagulant, anticoagulant and fibrinolytic factors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Thromb Haemost. 2012;108(6):1077–88.
PubMed Google Scholar
Son HM. Massive cerebral venous sinus thrombosis secondary to Graves’ disease. Yeungnam Univ J Med. 2019;36(3):273–80.
Elbers LP, Moran C, Gerdes VE, et al. The hypercoagulable state in hyperthyroidism is mediated via the thyroid hormone β receptor pathway. Eur J Endocrinol. 2016;174(6):755–62.
Davis PJ, Sudha T, Lin HY, et al. Thyroid hormone, hormone analogs, and angiogenesis. Compr Physiol. 2015;6(1):353–62.
Mousa SA, Lin HY, Tang HY, et al. Modulation of angiogenesis by thyroid hormone and hormone analogues: implications for cancer management. Angiogenesis. 2014;17(3):463–9.
Lou Z, Li X, Li C, et al. Microarray profile of circular RNAs identifies hsa_circ_000455 as a new circular RNA biomarker for deep vein thrombosis. Vascular. 2022;30(3):577–89.
Hemani G, Bowden J, Davey SG. Evaluating the potential role of pleiotropy in Mendelian randomization studies. Hum Mol Genet. 2018;27(R2):R195–208.
Zhang Z, Li L, Hu Z, et al. Causal effects between atrial fibrillation and heart failure: evidence from a bidirectional Mendelian randomization study. BMC Med Genomics. 2023;16(1):187.
Emdin CA, Khera AV, Kathiresan S. Mendelian randomization. JAMA. 2017;318(19):1925–6.
Skrivankova VW, Richmond RC, Woolf BAR, et al. Strengthening the reporting of observational studies in epidemiology using Mendelian randomization: the STROBE-MR statement. JAMA. 2021;326(16):1614–21.
Hemani G, Zheng J, Elsworth B, et al. The MR-Base platform supports systematic causal inference across the human phenome. Elife. 2018;7: e34408.
Verbanck M, Chen CY, Neale B, Do R. Detection of widespread horizontal pleiotropy in causal relationships inferred from Mendelian randomization between complex traits and diseases. Nat Genet. 2018;50(5):693–8.
Franchini M. Hemostatic changes in thyroid diseases: haemostasis and thrombosis. Hematology. 2006;11(3):203–8.
Franchini M, Lippi G, Targher G. Hyperthyroidism and venous thrombosis: a casual or causal association? A systematic literature review. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2011;17(4):387–92.
Fandler-Höfler S, Pilz S, Ertler M, et al. Thyroid dysfunction in cerebral venous thrombosis: a retrospective cohort study. J Neurol. 2022;269(4):2016–21.
Krieg VJ, Hobohm L, Liebetrau C, et al. Risk factors for chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension—importance of thyroid disease and function. Thromb Res. 2020;185:20–6.
Alsaidan AA, Alruwiali F. Association between hyperthyroidism and thromboembolism: a retrospective observational study. Ann Afr Med. 2023;22(2):183–8.
Walker AJ, Card TR, West J, Crooks C, Grainge MJ. Incidence of venous thromboembolism in patients with cancer—a cohort study using linked United Kingdom databases. Eur J Cancer. 2013;49(6):1404–13.
Ordookhani A, Motazedi A, Burman KD. Thrombosis in thyroid cancer. Int J Endocrinol Metab. 2017;16(1): e57897.
Ziaka M, Exadaktylos A. Insights into SARS-CoV-2-associated subacute thyroiditis: from infection to vaccine. Virol J. 2023;20(1):132.
Henke K, Odermatt J, Ziaka M, Rudovich N. Subacute thyroiditis complicating COVID-19 infection. Clin Med Insights Case Rep. 2023;16:11795476231181560.
Mondal S, DasGupta R, Lodh M, Ganguly A. Subacute thyroiditis following recovery from COVID-19 infection: novel clinical findings from an Eastern Indian cohort. Postgrad Med J. 2023;99(1172):558–65.
Nham E, Song E, Hyun H, et al. Concurrent subacute thyroiditis and graves’ disease after COVID-19: a case report. J Korean Med Sci. 2023;38(18): e134.
Mouna E, Molka BB, Sawssan BT, et al. Cardiothyreosis: epidemiological, clinical and therapeutic approach. Clin Med Insights Cardiol. 2023;17:11795468231152042.
Maung AC, Cheong MA, Chua YY, Gardner DS. When a storm showers the blood clots: a case of thyroid storm with systemic thromboembolism. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab Case Rep. 2021;2021:20–0118.
Download references
Not applicable.
Author information
Lifeng Zhang and Kaibei Li have contributed equally to this work and share the first authorship.
Authors and Affiliations
Department of Vascular Surgery, Hospital of Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, No. 39, Shierqiao Road, Jinniu District, Chengdu, 610072, Sichuan, People’s Republic of China
Lifeng Zhang, Qifan Yang, Yao Lin, Caijuan Geng, Wei Huang & Wei Zeng
Disinfection Supply Center, Hospital of Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, No. 39, Shierqiao Road, Jin Niu District, Chengdu, 610072, Sichuan, People’s Republic of China
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Conception and design: LFZ and WZ. Analysis and interpretation: LFZ, KBL and WZ. Data collection: LFZ, QFY, YL, CJG and WH. Writing the article: LFZ, KBL. Critical revision of the article: LFZ, GFY and WZ. Final approval of the article: LFZ, KBL, YL, CJG, WH, QFY and WZ. Statistical analysis: YL, QFY.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Wei Zeng .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Ethical approval was obtained in all original studies. This study complies with the terms of use of the database.
Competing interests
Additional information, publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1., rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Zhang, L., Li, K., Yang, Q. et al. Associations between deep venous thrombosis and thyroid diseases: a two-sample bidirectional Mendelian randomization study. Eur J Med Res 29 , 327 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40001-024-01933-1
Download citation
Received : 12 September 2023
Accepted : 09 June 2024
Published : 14 June 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s40001-024-01933-1
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Deep venous thrombosis
- Thyroid diseases
- Mendelian randomization analysis
European Journal of Medical Research
ISSN: 2047-783X
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]
What are you looking for?
The inner core began to decrease its speed around 2010, moving slower than the Earth’s surface. (USC Graphic/Edward Sotelo)
USC study confirms the rotation of Earth’s inner core has slowed
A new study provides clear evidence that the inner core began to decrease its speed around 2010.
USC scientists have proven that the Earth’s inner core is backtracking — slowing down — in relation to the planet’s surface, as shown in new research published Wednesday in Nature .
Movement of the inner core has been debated by the scientific community for two decades, with some research indicating that the inner core rotates faster than the planet’s surface. The new USC study provides unambiguous evidence that the inner core began to decrease its speed around 2010, moving slower than the Earth’s surface.
“When I first saw the seismograms that hinted at this change, I was stumped,” said John Vidale , Dean’s Professor of Earth Sciences at the USC Dornsife College of Letters, Arts and Sciences. “But when we found two dozen more observations signaling the same pattern, the result was inescapable. The inner core had slowed down for the first time in many decades. Other scientists have recently argued for similar and different models, but our latest study provides the most convincing resolution.”
The relativity of backtracking and slowing down
The inner core is considered to be reversing and backtracking relative to the planet’s surface due to moving slightly slower instead of faster than the Earth’s mantle for the first time in approximately 40 years. Relative to its speed in previous decades, the inner core is slowing down.
The inner core is a solid iron-nickel sphere surrounded by the liquid iron-nickel outer core. Roughly the size of the moon, the inner core sits more than 3,000 miles under our feet and presents a challenge to researchers: It can’t be visited or viewed. Scientists must use the seismic waves of earthquakes to create renderings of the inner core’s movement.
A new take on a repetitive approach
Vidale and Wei Wang of the Chinese Academy of Sciences utilized waveforms and repeating earthquakes in contrast to other research. Repeating earthquakes are seismic events that occur at the same location to produce identical seismograms.
In this study, the researchers compiled and analyzed seismic data recorded around the South Sandwich Islands from 121 repeating earthquakes that occurred between 1991 and 2023. They have also utilized data from twin Soviet nuclear tests between 1971 and 1974, as well as repeated French and American nuclear tests from other studies of the inner core.
Vidale said the inner core’s slowing speed was caused by the churning of the liquid iron outer core that surrounds it, which generates Earth’s magnetic field, as well as gravitational tugs from the dense regions of the overlying rocky mantle.
The impact on the Earth’s surface
The implications of this change in the inner core’s movement for Earth’s surface can only be speculated. Vidale said the backtracking of the inner core may alter the length of a day by fractions of a second: “It’s very hard to notice, on the order of a thousandth of a second, almost lost in the noise of the churning oceans and atmosphere.”
The USC scientists’ future research aspires to chart the trajectory of the inner core in even greater detail to reveal exactly why it is shifting.
“The dance of the inner core might be even more lively than we know so far,” Vidale said.
About the study: In addition to Vidale, other study authors include Ruoyan Wang of USC Dornsife, Wei Wang of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guanning Pang of Cornell University and Keith Koper of the University of Utah.
This research was supported by the National Science Foundation (EAR-2041892) and the Institute of Geology and Geophysics of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (IGGCAS-201904 and IGGCAS-202204).
Related Articles
Trojan leads clinical trials to improve neurologic rehabilitation, experts converge at usc music, health, and policy workshop, new ai system detects rare epileptic seizures.
- Open access
- Published: 12 June 2024
Global research trends on the relationship between IBD and CRC: a bibliometric analysis from 2000 to 2023
- Hao Zhang 1 na1 ,
- Huiru Xin 2 na1 ,
- Mengqi Zhao 3 na1 ,
- Chenyang Bi 1 ,
- Yafei Xiao 1 ,
- Yifan Li 1 &
- Changjiang Qin 1
Journal of Health, Population and Nutrition volume 43 , Article number: 83 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
149 Accesses
Metrics details
This study aimed to conduct a bibliometric analysis of research articles on the relationship between inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and colorectal cancer (CRC) using CiteSpace to summarize the current research status, hotspots, and trends in this field and present the results visually.
Research articles on the relationship between IBD and CRC published from 2000 to 2023 and in English were selected from the Web of Science Core Collection (Woscc) database. The articles were downloaded as “full record and references”. CiteSpace was used to conduct cooperative, cluster, co-citation, and burst analyses.
The literature search revealed 4244 articles; of which, 5 duplicates were removed, resulting in the inclusion of 4239 articles in this study. The United States of America had the highest number of publications, with Mayo Clinic and Harvard University being the most active institutions, and Bas Oldenburg being the most active author. Collaboration among core authors was inadequate. JA Eaden was the most cited author, and CRC was the most common keyword. Burst analysis indicated that Sun Yat-sen University might be one of the institutions with a large contribution to this research field in the future. Cluster analysis showed that earlier research focused more on microsatellite instability, whereas “gut microbiota” and “oxidative stress” are considered current research hotspots and trends.
At present, the primary focus areas of research are “gut microbiota” and “oxidative stress”. With the improvement of healthcare policies and standards, regular endoscopic monitoring of patients with IBD has become an indispensable diagnostic and therapeutic practice. More drugs will be developed to reduce the risk of progression from IBD to CRC. The findings of this study provide valuable insights into the relationship between IBD and CRC for researchers in the same field.
Introduction
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third most common cancer and the second leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide [ 1 ]. By 2035, the number of new CRC cases is projected to increase to 2.5 million worldwide, surpassing the number of gastric and liver cancer cases. In particular, the most significant increase will be observed in developing countries [ 2 ]. Notably, a more concerning factor is the decreasing age at the diagnosis of CRC [ 3 ]. In recent years, numerous studies have demonstrated the association between the gut environment and genetic factors with CRC, and IBD is considered to play a significant role in the development of CRC [ 4 ].
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), including Crohn’s disease (CD) and ulcerative colitis (UC), is a chronic, relapsing immune-mediated disease with diverse clinical manifestations and varying severity [ 5 ]. Both CD and UC manifest as intestinal inflammation but differ in pathological features, target sites, and clinical presentations. UC primarily affects the colon’s mucosa, with continuous lesions from the rectum upwards, causing diarrhea, abdominal pain, bleeding, and mucus in stools [ 6 ]. CD can occur anywhere in the gastrointestinal tract with discontinuous, full-thickness lesions, leading to ulcers, fistulas, and strictures [ 7 ].
Over the past few decades, numerous studies have demonstrated the relationship between CRC and IBD. Owing to chronic inflammation of the intestinal mucosa, patients with IBD have an increased risk of CRC [ 8 ]. Longer disease duration and extensive UC involvement heighten this risk. Chronic inflammation leads to oxidative stress and DNA damage, activating oncogenes and inactivating tumor suppressor genes, driving the transition from inflammation to cancer, influenced by the host immune response and gut microbiota [ 9 , 10 ].
To date, few studies have summarized research articles on the relationship between IBD and CRC published over the past two decades, facilitating a better analysis of the current research status and future research trends. Bibliometric analysis, which integrates statistical, metrological, and bioinformatic methods, is used to assess the use, output, and dissemination of literature to identify research trends, academic networks, and scholarly contributions and transform complex data into intuitive visual information [ 11 ]. In bibliometric analysis, commonly used metrics include citation count, impact factor, and h-index [ 12 ]. These measures aid in quantifying and evaluating the usage, output, and dissemination of literature. Citation count and impact factor gauge the influence and significance of a publication [ 13 ], while the h-index reflects a researcher’s impact by taking into account both publication quantity and citation frequency [ 14 ]. CiteSpace is a tool used for visualizing and analyzing trends and patterns in scientific literature, facilitating the understanding of research progress in a field of study and the identification and monitoring of research hotspots [ 15 ]. To the best of our knowledge, this bibliometric study is the first to conduct a qualitative analysis of research articles on the relationship between IBD and CRC using CiteSpace.
Data collection and research methodology
The Web of Science (WOS) from Clarivate Analytics is considered one of the leading databases for conducting bibliometric analysis. To minimize potential bias introduced by daily updates, all research articles on the relationship between IBD and CRC were identified and selected exclusively from the Web of Science Core Collection (WoSCC) database [ 16 ] on December 11, 2023. The data sources included the Science Citation Index Expanded, Conference Proceedings Citation Index-Science, Conference Proceedings Citation Index-Social Science & Humanities, Book Citation Index-Science, and Book Citation Index-Social Sciences & Humanities, with the publication type being limited to articles. All relevant articles were selected based on titles (T1) and abstracts (AB). The specific keywords used for the literature search are provided in Supplementary Material . The articles included were published between January 1, 2000, and December 1, 2023, and were published in English. The specific inclusion criteria for research articles are detailed in Figure S1 (Supplementary materials).
CiteSpace (6.1R6) was used as the principal bibliometric analysis tool in this study. Developed by Professor Chaomei Chen at Drexel University in the USA, CiteSpace is a Java-based software that enables visual exploration and knowledge mapping for bibliographic analysis. Through knowledge domain visualization, CiteSpace maps highly cited articles, crucial fields, and emerging topics in literature databases, revealing research trends and patterns [ 17 ]. Studies have shown that the Web of Science database exhibits a superior knowledge-mapping capability when integrated with CiteSpace for visual representation [ 18 ]. Therefore, selecting Web of Science as a data source is both reasonable and effective. For the visual representation of knowledge maps, we followed the fundamental procedures of CiteSpace, including time slicing, threshold setting, modeling, pruning, merging, and mapping. CiteSpace allows the analysis of citation bursts, betweenness centrality, and heterogeneous networks, facilitating the visualization of the current research status and hotspots and emerging research trends [ 15 ]. It integrates three functionalities, namely, bibliometrics, data integration, and visualization [ 19 ]. Basic bibliometric indicators, including countries, authors, institutions, keywords, and citations, can be analyzed using CiteSpace for the systematic visualization of research progress in a field of study and the prediction of future research directions [ 20 ]. In the authors’ analysis, the h-index is an essential metric. Introduced by physicist Jorge E. Hirsch in 2005 [ 14 ], the h-index evaluates both the quantity of a researcher’s publications and the frequency of their citations. This combined measure provides a comprehensive view of a researcher’s academic productivity and impact. In a particular analysis, nodes represent authors, institutions, countries, or keywords. The size of a node indicates the frequency of occurrence or citation, whereas its color represents the year of occurrence or citation. Furthermore, nodes edged in purple signify high centrality, typically indicating hotspots or pivotal points within the field [ 21 ]. The time slice was set from 2000 to 2023, and the included articles were visually analyzed based on countries/regions, authors, institutions, references, and keywords.
Pruning, a key feature of CiteSpace, improves the clarity of network visualization by minimizing link crossings. CiteSpace provides two pruning approaches: Pathfinder and Minimum Spanning Tree. According to Dr. Chaomei Chen, Pathfinder is more efficient in eliminating links. In particular, it can remove non-essential links while preserving critical ones [ 22 ]. Therefore, we selected Pathfinder for pruning.
Quantitative analysis of basic information
Annual growth trend of publications.
The trend of publication growth in a research field reflects the level of interest in the field and the importance of the field. A literature search in the WoSCC database revealed 4244 articles on the relationship between CRC and IBD published between January 1, 2000, and December 1, 2023. We excluded 5 duplicate articles using the duplicate remover feature in CiteSpace, eventually including 4239 articles for visual analysis. As shown in Figure S2 (Supplementary materials), research publications related to the relationship between IBD and CRC showed an overall trend of growth from 2000 to 2023. However, a slight decline was observed in 2001 (-2.78%), 2003 (-6.90%), 2004 (-6.17%), 2008 (-12%), 2011 (-7.95%), 2016 (-3.56%), and 2017 (-0.52%). On the contrary, the annual number of publications was higher in 2002 (24.29%), 2005 (21.05%), 2006 (20.65%), 2010 (33.33%), and 2019 (20.63%).
More than 100 articles were published annually after 2006 (Supplementary Table S1 ), with the fewest articles published in 2001 ( n = 70, 1.65%) and the most articles published in 2022 ( n = 344, 8.12%), averaging 177 articles per year. To predict the number of articles that would be published in 2024, a polynomial regression model was constructed using Microsoft Office Excel 365 (Microsoft, Redmond, WA, USA): y = 0.00574 × 4 − 0.2554 × 3 + 4.0265 × 2 − 14.999x + 87.965. A statistically significant correlation was observed between the year and the number of publications through data fitting (R 2 = 0.9789). It is expected that 421 articles will be published in 2024.
Visualization analysis based on countries/regions
Over the past 24 years, research articles on the relationship between IBD and CRC have been published in more than 100 countries/regions. To analyze the cooperation between countries and compare the number of publications, the time slice was set to 6 years per slice and the top 30 results from each slice were selected. As shown in the distribution map in Fig. 1 A and the bar chart in Fig. 1 C, the top 10 countries/regions (including 5 European countries, 3 Asian countries, and 2 North American countries) published a total of 3876 articles, accounting for 91.44% of the total publication volume. The five countries/regions with the highest number of publications were the United States of America (1293 articles, 30.50%), China (661 articles, 15.59%), Japan (372 articles, 8.78%), England (312 articles, 7.36%), and Germany (293 articles, 6.91%). The five countries with the highest centrality were Belgium (0.44), England (0.41), USA (0.28), Spain (0.22), and Denmark (0.22) (Table 1 ). Centrality values greater than 0.1 indicated a high level of influence in the research field. The USA not only led in publication volume but also had a centrality of 0.28, surpassing most countries/regions in terms of the quantity and quality of research articles on the relationship between IBD and CRC. Belgium had the highest centrality (0.44), demonstrating its prominent influence on the field and the high quality of research articles. Despite a low publication volume (14 articles), Greece had a high centrality of 0.22. Burst analysis (Fig. 1 D) showed that research articles published from 2000 to 2011 were mainly concentrated in European countries/regions and Japan. Germany showed a significantly increased interest in the field from 2006 to 2017. After 2018, developing countries in Asia (such as China, Iran, and Pakistan) and South America (such as Brazil) showed a significantly increased interest in the field. In particular, China had the highest burst strength (41.07), suggesting that the relationship between CRC and IBD will remain a major research hotspot in China in the future. International collaboration was evident among the included countries/regions (Fig. 1 B). Specifically, the USA collaborated with not just neighboring countries (Canada) but also European (UK, Norway, Belgium, and Greece) and Asian (Japan, China, and Korea) countries. On the contrary, China exhibited fewer collaborative efforts, focusing mainly on neighboring countries/regions (such as Japan) and the USA. In particular, it had a close partnership with Japan.

Visualization Analysis of Countries/Regions. ( A ) Distribution of countries in terms of publications. ( B ) Network diagram showing country links; time slice = 6, top 30 per slice; N = 40, E = 90. ( C ) Top 10 most productive countries. ( D ) Top 15 countries in publishing research on the association between IBD and CRC with burst period after 2000
Visualization analysis based on research institutions
The cooperative and co-emerging networks of research institutions demonstrated the level of interdisciplinary research and collaborations between institutions. The time slice was set to 1 year per slice, and the top 10 research institutions from each slice were selected, with similar institutions (such as Harvard University and Harvard Medical School) being merged. The five institutions with the highest publication volume were Mayo Clinic (70), Harvard University (70), University of Washington (40), Cleveland Clinic (37), and University of Toronto (37) (Supplementary Table S2 ). With a centrality of 0.19, Mayo Clinic led in terms of both the number and quality of publications, profoundly influencing the research status of other institutions. Interestingly, Four of these five institutions are located in the United States of America.
Cooperation between institutions was more extensive and closer than that between countries (Fig. 2 A). Mayo Clinic had the most collaborations with domestic and international institutions, such as University of Calif San Francisco, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Uppsala University, Herlev University Hospital, University of Calif San Diego, Radcliffe Infirmary, and Icahn School of Medicine at Mt Sinai. With 32 articles and a centrality of > 0.1, Massachusetts General Hospital had close collaborations with many research institutions both domestically and internationally, indicating that strengthening communication and cooperation is an effective approach to producing excellent results.

Visualization Analysis of Research Institutions, Authors and reference. ( A ) Network diagram showing institution links; Slice length = 1, Top 10 per slice, N = 246, E = 333. ( B ) Network diagram showing literature co-citations link; Slice length = 1; Top 30 per slice, N = 685, E = 3036. ( C ) Network diagram showing author links; Slice length = 1; Top 10 per slice, N = 742, E = 187. ( D ) Network diagram showing co-author links; Slice length = 1; Top 30 per slice, N = 213, E = 609. ( E ) Top 15 institutions in publishing research the association between IBD and CRC with burst period after 2000. ( F ) Top 15 articles related to research the association between IBD and CRC with burst period after 2000
Among Chinese research institutions, Shanghai Jiao Tong University had the highest number of publications and had close collaborations with foreign research institutions, including Karolinska Institutions, University of Calif San Francisco, University of Oxford, Uppsala University, Harvard University, Tongji University, Mayo Clinic, and Icahn School of Medicine at Mt Sinai, with the closest collaboration being with University of Oxford. Other Chinese universities, such as the University of Chinese Academy of Sciences and Nanjing Medical University, had a significant number of articles (more than 10) but rarely collaborated with foreign universities. The University of Chinese Academy of Sciences collaborated exclusively with domestic research institutions, such as Capital Medical University, Zhejiang University, and Chinese Academy of Sciences, with the closest collaboration being with Capital Medical University. Burst analysis (Fig. 2 E) revealed that Mt. Sinai School of Medicine, University of California Los Angeles, and University Medical Center Utrecht were among the first institutions to recognize and comprehensively examine the relationship between IBD and CRC. The burst period for Mt. Sinai School of Medicine was longest, lasting until 2011, whereas that for Mayo Clinic was 2011–2013. The volume and quality of articles published by Mayo Clinic exceeded those of other institutions, highlighting the exceptional research prowess of the institution. In 2018, three of the six institutions experiencing a surge in research activity were from China, highlighting the increasing focus on the field of IBD and CRC within the Chinese scientific community. In particular, Sun Yat-sen University had the highest burst strength at 9.38, indicating its potential for conducting more influential research in the future.
Visualization analysis based on authors and co-cited authors
Author collaboration analysis revealed the status of cooperation among core authors. The time slice was set to 1 year per slice, and the top 10 authors from each slice were selected. The distribution of the number of publications among these 10 authors is shown in Supplementary Table S3 . Bas Oldenburg from the Netherlands UMC had the highest number of publications (17 articles, h-index = 13). His most impactful publication was an article published in Gut in April 2019 [ 23 ]. This article presented a 15-year multi-center, multi-national study that showed that patients with IBD who had two consecutive negative results on colonoscopy during the monitoring period had a lower risk of developing advanced tumors. Furthermore, the results showed four clusters based on authors who published more than five articles each: a cluster led by Hiroki Ikeuchi and Soichiro Ishihara, a cluster led by Bas Oldenburg, a cluster led by David T Rubin, and a cluster led by Mitzi Nagarkatti (Fig. 2 C). Of these four clusters, the cluster led by Bas Oldenburg had the most notable research achievements, with three of the top five authors with high publication volume belonging to this cluster. Research among the four clusters was relatively independent, with rare or almost no collaboration. Timeline analysis showed that research in the cluster led by Hiroki Ikeuchi and Soichiro Ishihara had primarily emerged in recent years and yielded abundant results. An important concern was that all authors had a centrality of < 0.1, indicating limited mutual influence among them.
Author co-citation refers to the citation of at least one article each from two or more authors in one or multiple consecutive articles. Anonymous authors were not included in the co-citation analysis. The time slice was set to 1 year per slice, and the top 30 authors with high citation counts were selected from each time slice. Authors with a total citation count of > 30 were included in network visualization (Fig. 2 D). The top five authors with high citation count and centrality are shown in Supplementary Table S4 . Professor JA Eaden from the United Kingdom had the highest citation count and centrality, highlighting his significant achievements in the research field and the widespread acceptance of his research findings.
Assessment of research hotspots and progress of the relationship between IDB and CRC based on co-cited articles
Analysis of total citations.
Co-citation is defined as the simultaneous citation of two or more articles in a third article. Co-citation analysis is a vital tool in bibliometrics that aids scholars in discovering new research directions, understanding the relationship between different research topics, and assessing mutual influence and collaboration networks within the academic community [ 24 ]. The time slice was set to 1 year per slice, and the 30 most cited articles were selected from each slice to construct a co-citation network map (Fig. 2 B). The top 5 articles with high citation counts are shown in Supplementary Table S5 . The most cited article (82) was published by Professor FA Farraye in 2010 in Gastroenterology . This article provided a comprehensive review of the diagnosis and management of colorectal tumors in patients with IBD. It discussed the history of dysplasia and factors that increase the risk of CRC in patients with IBD, including the duration of the disease, anatomical extent of the disease, concurrent conditions such as primary sclerosing cholangitis, and family history of CRC. The findings specifically suggested that patients with IBD with prolonged disease duration and more extensive disease spread had a higher risk of CRC. Additionally, the article explored monitoring strategies, the role of chemopreventive agents, and the application of new imaging technologies in the management of dysplasia and CRC secondary to IBD [ 25 ]. The second most cited article (60) was published by JA Eaden in Gut in 2001. This article represented a meta-analysis of studies on the risk of CRC in patients with UC. In particular, it analyzed 116 studies involving 54,478 patients. The results showed that the overall prevalence of CRC was 3.7% and 5.4% among patients with UC and pancolitis, respectively. The cumulative risk of CRC increased with the duration of UC or pancolitis: 2% at 10 years, 8% at 20 years, and 18% at 30 years. Pediatric patients with UC had a higher risk of CRC than adult patients. In addition, geographic location affected the risk of CRC, with the risk being higher in the USA and UK than in Scandinavia and other countries [ 26 ]. The third most cited article was published by Professor SC Ng in The Lancet in 2017. Although this article was published in recent years, it had a high citation count, indicating its significant impact on the research field. This article assessed the global incidence and prevalence of IBD (CD and UC) in the 21st century. The results indicated that although the incidence rate of IBD has stabilized in Western countries, it is increasing in recently industrialized countries, such as Brazil. Europe and North America had the highest prevalence rate of IBD at > 0.3%. These findings emphasize the importance of the prevention and effective management of IBD [ 27 ]. Notably, of the top five most cited articles, three articles were published in Gastroenterology , highlighting its significant influence and widespread recognition as a leading academic journal in the field of research on the relationship between IBD and CRC. In the citation network, nodes with a centrality value of > 0.1 were considered key nodes. The article with the highest centrality (0.43) was published by RB Gupta in Gastroenterology in 2007. This article had a significant impact on subsequent research into the relationship between IBD and CRC. It presented a study on a group of patients with UC undergoing regular endoscopic monitoring for dysplasia. The results showed that the severity of inflammation was an independent risk factor for advanced colorectal tumors in patients with UC with a longer disease course [ 28 ].
Analysis of co-citation bursts
Burst analysis allows the identification of research hotspots or trends, facilitating the timely discovery of articles that may significantly influence and guide future research [ 29 ]. Based on the results of burst analysis, Fig. 2 F shows the top 15 articles ranked based on the citation burst strength. The article with the highest citation burst strength was also the most cited article. The article with the second highest citation burst strength was also the second most cited article. The article with the third highest citation burst strength also had a high citation count and was published by Jess T in 2012. This article reported that although the overall risk of CRC in patients with UC was comparable to that in the general population, it was higher in pediatric patients with UC, patients with UC with a longer disease course, or patients with UC with primary sclerosing cholangitis [ 30 ]. Based on the year of citation bursts, an article titled “CRC prevention in ulcerative colitis: a case-control study” was cited extensively in 2000. This article reported that regular treatment with 5-ASA significantly reduced the risk of CRC in patients with UC. Specifically, the use of mesalazine reduced the risk of CRC by 81%, a protective effect that was statistically significant at daily doses of ≥ 1.2 g. The protective effects of sulfasalazine were less pronounced and significant only at higher doses (≥ 2 g/day) [ 31 ]. A recent article titled “CRC in ulcerative colitis: a Scandinavian population-based cohort study” published in The Lancet had a high citation burst. This study compared the risk of CRC between 96,447 patients with UC and 949,207 control individuals from 1969 to 2017. The results showed that the incidence and mortality rates of CRC in patients with UC were higher than those in control individuals. Despite having early-stage tumors, patients with UC had a higher risk of CRC-related mortality. However, this risk decreased over time owing to improvements in treatment methods. These findings emphasize the necessity of improving international monitoring guidelines for CRC [ 32 ].
On analyzing articles with citation bursts, we observed a specific trend. Most articles suggested that patients with IBD, especially those with a longer disease course, had an increased risk of CRC. These articles included studies from various regions and with different populations, further validating the relationship between IBD and the incidence of CRC.
In the context of prolonged inflammatory responses, the mechanisms underlying CRC development are related to abnormalities in cellular signaling pathways, DNA damage, and disruption of DNA repair pathways. This finding holds substantial significance for clinical monitoring and treatment of IBD, indicating that physicians should increase the focus on CRC risk in patients with IBD with a prolonged disease course.
Analysis of the characteristics of co-citation clustering
The clustering function of CiteSpace was used to categorize research themes and exclude outliers. Cluster analysis of articles with citation bursts showed that research themes had undergone significant changes over the past 24 years. In Fig. 3 A, lighter shades of yellow indicate periods closer to the current year. The silhouette coefficient “S” was used to evaluate the appropriateness of clustering. S values of > 0.5 indicated reasonable clustering, whereas S values of > 0.7 indicated convincing clustering. The silhouette coefficients of all clusters shown in Fig. 3 A were > 0.8 (Supplementary Table S6 ). The primary research theme among earlier articles included microsatellite instability (MSI), a molecular marker of defective mismatch repair (MMR) that is present in approximately 15% of CRC cases and is more common in early stages than in advanced stages [ 33 ]. The molecular characteristics of inflammation-related CRC include alterations in p53, MSI, and lack of MUC5AC expression. These mechanisms are different from the typical and serrated mechanisms underlying the pathogenesis of CRC [ 34 ]. A significant increase was observed in the number of studies and review articles in the field of disease surveillance. A study involving a subset of the British population showed that the incidence of synchronous and metachronous tumors in patients with IBD was twice that in patients without IBD, with the difference being statistically significant. IBD-related CRC often occurs in younger patients, with the prognosis being worse than that of sporadic CRC. Consequently, identifying the causes of these differences may facilitate the development of more effective screening, monitoring, and treatment strategies for CRC and its precursors in high-risk populations [ 35 ]. Over the past few years, the focus of research has gradually shifted toward animal disease models, particularly mouse models, facilitating the discovery of new drugs for treating IBD-related CRC. For instance, a study showed that oral administration of GDNPs2 in mouse models of colitis alleviated acute colitis, enhanced intestinal repair, and prevented chronic colitis and colitis-associated cancer. In addition, oral administration of GDNPs2 improved the survival and proliferation of IECs, reduced the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β), and increased the levels of anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-10 and IL-22) in mouse models of colitis. These results indicate that GDNPs2 can mitigate damaging factors while promoting healing [ 36 ]. At present, pathological mechanisms involving the gut microbiome are receiving increasing attention in research on IBD and CRC, with several studies suggesting that IBD is a significant risk factor for CRC.

Analysis of the characteristics of Co-citation clustering and Keywords ( A ) Co-cited References Clustering Diagram. ( B ) Co-cited References Clustering Timeline Diagram. ( C ) Keyword Co-occurrence Network Diagram and Keyword Clustering. ( D ) Top 15 keywords related to research the association between IBD and CRC with burst period after 2000
The co-citation network constructed using temporal nodes generated a timeline graph (Fig. 3 B). The size of circles in this graph indicated the number of citations: the larger the circle, the higher the number of citations. The timeline graph revealed influential research findings in each period. Articles with the highest, second highest, and third highest citation counts were published in 2010, 2001, and 2017, respectively. This finding highlights the continuous emergence of high-quality research articles, validating the importance of the relationship between IBD and CRC. The cluster with the largest title was “#0 undergoing surveillance”, suggesting that regular endoscopic monitoring can effectively prevent the risk of progression to CRC in patients with IBD. A study showed that the incidence rate of CRC among patients with IBD undergoing regular surveillance was lower, with only 17 CRC cases identified in a follow-up assessment of 6823 cases. Most CRC cases (70%) could be attributed to inadequate surveillance conditions before the diagnosis, such as insufficient bowel preparation, inadequate surveillance intervals, or improper dysplasia management. These findings indicate that strict adherence to guidelines on disease surveillance may reduce the incidence of CRC [ 37 ]. The cluster with the largest silhouette coefficient was “#8 regulatory lymphocyte”. Articles in this cluster were similar to each other, showing a strong consistency in research topics or methods. In addition, these articles had good differentiation when compared with articles in other clusters, indicating uniqueness in research themes or directions. Given that regulatory lymphocytes are dysregulated in IBD and CRC, Treg-targeted therapies may be effective in treating or preventing these diseases [ 38 ]. Furthermore, previous studies on the relationship between IBD and CRC were concentrated in four clusters as follows: #5 microsatellite instability, #9 20-year surveillance study, #8 regulatory lymphocyte, and #1 review article. Notably, the clusters #6 gut microbiota and #3 colitis-associated CRC included articles published in recent years, representing the current research directions in the field of IBD and CRC.
Assessment of research hotspot and progress of the relationship between IBD and CRC based on keywords
Analysis of keyword co-occurrence.
Keywords are the essence of a research article. Analyzing keywords helps in summarizing research themes in a particular field, identifying research hotspots, and predicting future research trends. The time slice was set to 1 year per slice, and the top 30 keywords with the highest frequency in each time slice were selected. After similar keywords (e.g., cancer and carcinoma) were merged, a keyword co-occurrence graph was generated using a Pathfinder network (Fig. 3 C). The top 10 keywords with the highest frequency are shown in Table 2 . As disease names, the keywords “CRC”, “IBD”, “ulcerative colitis”, “carcinoma”, “Crohn’s disease”, and “colon cancer” had the highest frequency. Keywords such as “risk”, “expression”, “dysplasia”, and “meta-analysis” highlighted the core focus of research into the relationship between IBD and CRC over the past 24 years. Among the top 10 keywords with centrality values of > 0.1, the keywords other than disease names were “expression” and “dysplasia”. Some studies have indicated that certain genes are aberrantly expressed in inflammation-related CRC. Compared with sporadic CRC (sCRC), IBD-related CRC exhibits strong downregulation of negative regulators of WNT, namely, AXIN2 and RNF43, and a decreased frequency of copy number amplification in HNF4A (a negative regulator of WNT-induced epithelial–mesenchymal transition [EMT]) [ 39 ]. During the progression from UC to CRC, the downregulation of miR-615-5p may induce the upregulation of STC1, promoting tumor development and progression [ 40 ]. IBD-induced carcinogenesis is closely related to the recurrent inflammation and repair of the intestinal mucosa. In particular, intestinal inflammation leads to dysplasia, which eventually leads to CRC. In IBD, large mucosal areas with long-term inflammation are susceptible to tumorigenic transformation, a process referred to as “field cancerization” [ 41 ]. In the keyword co-occurrence network, primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) appeared frequently, with a centrality of 0.1. PSC is a progressive, cholestatic, inflammatory, fibrotic disease closely associated with IBD. Patients with PSC have an increased risk of malignant tumors [ 42 ]. In patients with PSC, abnormal bile acid metabolism leads to oxidative stress and toxic damage to intestinal cells, triggering the activation of intracellular inflammatory pathways and amplification of cell proliferation, consequently increasing the risk of malignant tumors [ 43 ].
Analysis of keyword bursts
Keyword burst analysis not only reflects changes in research hotspots in a field but also predicts future research trends. As shown in Fig. 3 D, changes in keyword bursts over the past 24 years demonstrated the evolution of research hotspots in articles on the relationship between IBD and CRC. “Mutation” was the keyword with the earliest burst, the longest burst duration, and a high burst intensity (18.34). This finding indicates that researchers have been aware of the crucial role of genetic mutations in the progression from IBD to CRC for a long time. Compared with APC mutations, p53 mutations occur earlier in CAC(Colitis Associated Cancer), potentially representing a key initiating event [ 44 ]. Furthermore, APC mutations occur later than is typical in sporadic CRC [ 45 ]. In articles published before 2010, another keyword with a high burst strength (17.22) was microsatellite instability. The two most common somatic genetic abnormalities in CRC are classified as chromosomal instability (CIN) and microsatellite instability (MSI). These abnormalities occur at the same frequency in UC-related CRC and sporadic CRC; however, their timing and frequency are different in the dysplasia-carcinoma sequence associated with UC [ 4 ]. After 2010, the keyword “population-based cohort” began to experience a burst, indicating an increased focus on meta-analyses of population-based cohort studies. Since 2020, the frequency of the keywords “gut microbiota”, “oxidative stress”, and “outcome” has been increasing in research articles on the relationship between IBD and CRC. “Gut microbiota” had the highest burst strength (34.21), indicating that it is a current research hotspot in the field, attracting substantial research interest and resources. Numerous studies have shown that bacteria such as Escherichia coli , ETBF, and Fusobacterium are involved in chronic inflammation and cancer development in patients with IBD. For instance, the enterotoxin produced by ETBF, namely, Bacteroides fragilis toxin, cleaves the cell adhesion molecule E-cadherin, a key component involved in metalloproteinase-mediated cell adhesion [ 46 ]. This toxin can trigger pro-inflammatory and pro-tumorigenic cysteine proteases in colonic epithelial cells, thereby recruiting polymorphonuclear myeloid-derived cells to promote the occurrence of colon cancer [ 47 ]. Additionally, chronic oxidative stress (OS) can lead to the oxidation of biomolecules (nucleic acids, lipids, and proteins) or the activation of inflammatory signaling pathways, resulting in the activation of various transcription factors or the dysregulation of gene and protein expression, which eventually leads to tumor development or cancer cell survival [ 48 ]. We speculate that gut microbiota and oxidative stress will continue to be among the major hotspots in research on IBD and CRC in the future.
Clustering of co-occurring keywords
Figure 3 C demonstrates the main clusters of keywords. The size of the first six clusters was ≥ 10, and their silhouette coefficients were > 0.5, indicating that the clustering was reasonable. The silhouette coefficients of clusters #1-#5 were > 0.7, indicating that the clustering was convincing (Supplementary Table S7 ). Among the four largest cluster categories, “dysplasia” had the highest silhouette coefficient and an earlier average year of study. This finding indicates that dysplasia has been a focus of research on the relationship between IBD and CRC for a long time. With the improvement of healthcare management and the continuous development of endoscopy, screening and monitoring programs involving colonoscopy have been used to detect, identify, or remove dysplastic or CRC tissues. Dysplastic tissues can be removed through endoscopic resection. However, early colectomy should be recommended for patients with IBD with unresectable tumors to reduce the overall incidence and mortality of CRC [ 49 ].
Over the past 24 years, an increasing number of studies have focused on the relationship between IBD and CRC. In this bibliometric study, we systematically searched the WoSCC database for articles on the relationship between IBD and CRC published in English between 2000 and 2023. After excluding duplicate articles and articles that did not meet the selection criteria, we eventually included 4239 research articles from 98 countries. The CiteSpace software was used for the quantitative analysis and visual representation of research progress to identify research hotspots and future research trends.
The number of research articles on the relationship between IBD and CRC increased annually over the past 24 years. The quadratic curve fit of cumulative publications suggested ongoing growth in research on IBD and CRC, reflecting an increasing interest in this research field within the scientific community. The United States of America had the highest publication volume, perhaps due to substantial NIH funding and a significant public health focus on IBD and CRC, driving extensive research and support for understanding, preventing, and treating these diseases. Although China ranked second in terms of publication volume, its centrality score was relatively low, suggesting that the quality and influence of articles published by Chinese researchers need improvement. The Mayo Clinic surpassed other institutions in terms of both publication volume and research quality owing to its robust research prowess and extensive collaboration network. Of the six research institutions that emerged in 2018, three were Chinese, indicating that the relationship between IBD and CRC is becoming a research hotspot in China.
Professor Bas Oldenburg from the Netherlands had the highest number of publications, demonstrating his in-depth research in the field. Professor JA Eaden from the UK had the highest number of co-citations, highlighting his significant influence on research into IBD and CRC. The most cited article (82 citations) was published by Professor FA Farraye in Gastroenterology in 2010. This indicates that the article is of high quality, with its theories, methods, or findings making significant contributions to academic research. It has garnered widespread attention and recognition, significantly impacting subsequent research. Cluster analysis indicated that earlier studies focused more on MSI to investigate the progression of IBD to CRC from a genetic perspective. IBD was consistently validated as a risk factor for CRC in numerous long-term, multicenter, large-sample surveillance studies. In recent years, the research focus has shifted toward the role of the gut microbiome in the progression of IBD to CRC. The largest cluster titled “undergoing surveillance” emphasized the important role of regular endoscopic monitoring in effectively preventing the development of CRC in patients with IBD.
Keyword co-occurrence and burst analysis revealed the main research themes and emerging research trends pertaining to the relationship between IBD and CRC. Earlier studies primarily focused on genetic mutations and MSI to investigate the pivotal roles of specific genes in the progression of IBD to dysplasia and CRC. Chronic inflammation-induced oxidative stress can lead to DNA damage, subsequently triggering the activation of oncogenes and the inactivation of tumor suppressor genes. Defects in the DNA mismatch repair mechanism result in high microsatellite instability (MSI-H), consequently promoting the initiation and development of CRC [ 50 ]. In recent years, gut microbiota and oxidative stress have become major hotspots in research on the relationship between IBD and CRC. The gut microbiome plays a key role in the development of IBD and CRC by regulating intestinal mucosal homeostasis, the intestinal microenvironment, and mucosal immunity. The gut microbiome comprises both probiotics that promote intestinal health and pathogens that cause inflammation and damage the mucosa. It serves as the first line of defense against the invasion of external pathogens; however, it can also stimulate inflammation and produce bacterial toxins that increase the risk of cancer. When the balance between probiotics and pathogens is disrupted, it destroys the normal intestinal homeostasis, leading to mucosal damage, a process referred to as “gut microbiota dysbiosis.” The development of IBD and CRC is closely related to the imbalance of the gut microbiome. In particular, the overgrowth of pathogens leading to inflammation can alter the structure of the gut microbiome and affect intestinal barrier function [ 51 ]. Under physiological conditions, a balance exists between the production of ROS and their elimination by antioxidants. However, under pathological conditions, such as chronic inflammation in IBD, the imbalance between ROS production and antioxidant defenses leads to oxidative stress, thereby exacerbating intestinal mucosal damage and inflammatory responses [ 52 ]. Oxidative stress promotes the progression of IBD and intestinal carcinogenesis by damaging cellular DNA and facilitating molecular events that lead to tumorigenesis.
In keyword clustering analysis, “dysplasia” had the largest silhouette coefficient and an earlier average year of study. Markers of oxidative damage and DNA double-strand breaks are gradually upregulated during the progression of inflammation to dysplasia and, eventually, cancer [ 53 ]. The natural history of dysplasia in colitis progresses from the absence of dysplasia in the intestinal mucosa to indefinite dysplasia, low-grade dysplasia (LGD), high-grade dysplasia (HGD), and invasive cancer. Factors leading to tumorigenesis in IBD can be summarized as follows: (1) genetic alterations (such as chromosomal alterations, MSI, and hypermethylation), (2) mucosal inflammatory mediators, (3) changes in the expression of receptors on epithelial cells, and (4) oxidative stress and gut microbiota [ 54 ]. Endoscopic monitoring of dysplasia is one of the important methods for preventing CRC in patients with IBD. According to the guidelines established by the Surveillance for Colorectal Endoscopic Neoplasia Detection and Management in Inflammatory Bowel Disease Patients (SCENIC), chromoendoscopy for colonoscopy is the optimal endoscopic strategy for identifying dysplasia. Procedures such as endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) and endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) represent various treatment options for colonic dysplastic lesions in patients with IBD [ 55 ].
To the best of our knowledge, this study is the first to conduct a bibliometric analysis of research articles on the relationship between IBD and CRC. We obtained research articles published between 2000 and 2023 from the WoSCC database and conducted an objective and thorough analysis of these articles using CiteSpace. Despite its strengths, this study has some limitations that should be acknowledged. Only original articles published over the past 24 years were selected from the WoSCC database, excluding books, conference abstracts, and other types of articles. Therefore, this literature review may not cover every relevant article published to date. Limiting our review to articles published in English might have introduced potential language bias. Recent publications, particularly those of high quality, might have been underrepresented, emphasizing the requirement for continuous updates in this field. Although our dataset may not encapsulate the entirety of research in this domain, it is comprehensive enough to identify key research trends and focal points.
This bibliometric study shows that the United States of America leads in research pertaining to the relationship between IBD and CRC, whereas China, Japan, and other countries have made significant research progress in this field. At present, gut microbiome and oxidative stress are major focus areas of research on the relationship between IBD and CRC. IBD has been validated as a risk factor for CRC. IBD-related CRC can be prevented through drug therapy (such as 5-ASA), regular endoscopic monitoring, and prompt endoscopic resection of dysplastic mucosal tissue. Future pre-clinical and clinical studies should adopt stricter research methodologies to develop more effective prevention and therapeutic strategies for IBD-related CRC.
Significance and limitations
Significance: 1.This work marks the inaugural bibliometric exploration of the link between IBD and CRC, to the best of our understanding. 2. We sourced our dataset from the WoSCC database, capturing an extensive collection of articles focused on the IBD-CRC correlation. 3. Our methodology ensures an objective and thorough overview of the existing research landscape on this topic.
Limitations: (1) Our analysis spans original articles from the WoSCC database, dated between 2000 and 2023, excluding books, conference abstracts, and other formats from our selection process means our literature review may not cover every relevant work. (2) Limiting our review to English-language articles introduces a potential for language bias. (3) Our study focuses solely on WoSCC, potentially missing relevant research indexed in other databases, which might limit the comprehensiveness of our analysis.
Data availability
No datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
Hossain MS, Karuniawati H, Jairoun AA, Urbi Z, Ooi J, John A, Lim YC, Kibria KMK, Mohiuddin AKM, Ming LC, Goh KW, Hadi MA. Colorectal Cancer: a review of Carcinogenesis, Global Epidemiology, Current challenges, risk factors, preventive and treatment strategies. Cancers (Basel) 14 (2022).
Papamichael D, Audisio RA, Glimelius B, de Gramont A, Glynne-Jones R, Haller D, Kohne CH, Rostoft S, Lemmens V, Mitry E, Rutten H, Sargent D, Sastre J, Seymour M, Starling N, Van Cutsem E, Aapro M. Treatment of colorectal cancer in older patients: International Society of Geriatric Oncology (SIOG) consensus recommendations 2013. Ann Oncol. 2015;26:463–76.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Connell LC, Mota JM, Braghiroli MI, Hoff PM. The rising incidence of younger patients with Colorectal Cancer: questions about Screening, Biology, and treatment. Curr Treat Options Oncol. 2017;18:23.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Dulai PS, Sandborn WJ, Gupta S. Colorectal Cancer and dysplasia in inflammatory bowel disease: a review of Disease Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, and management. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2016;9:887–94.
Bisgaard TH, Allin KH, Keefer L, Ananthakrishnan AN, Jess T. Depression and anxiety in inflammatory bowel disease: epidemiology, mechanisms and treatment. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;19:717–26.
Ordas I, Eckmann L, Talamini M, Baumgart DC, Sandborn WJ. Ulcerative colitis. Lancet. 2012;380:1606–19.
Gajendran M, Loganathan P, Catinella AP, Hashash JG. A comprehensive review and update on Crohn’s disease. Dis Mon. 2018;64:20–57.
Ullman TA, Itzkowitz SH. Intestinal inflammation and cancer. Gastroenterology. 2011;140:1807–16.
Itzkowitz SH, Yio X. Inflammation and cancer IV. Colorectal cancer in inflammatory bowel disease: the role of inflammation. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2004;287:G7–17.
Shah SC, Itzkowitz SH. Colorectal Cancer in inflammatory bowel disease: mechanisms and management. Gastroenterology. 2022;162:715–e7303.
Chang Y, Ou Q, Zhou X, Liu J, Zhang S. Global research trends and focus on the link between colorectal cancer and gut flora: a bibliometric analysis from 2001 to 2021. Front Microbiol. 2023;14:1182006.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Choudhri AF, Siddiqui A, Khan NR, Cohen HL. Understanding bibliometric parameters and analysis. Radiographics. 2015;35:736–46.
Dong P, Loh M, Mondry A. The impact factor revisited. Biomed Digit Libr. 2005;2:7.
Hirsch JE. An index to quantify an individual’s scientific research output. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102:16569–72.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Chen C, CiteSpace II. Detecting and visualizing emerging trends and transient patterns in scientific literature. 57 (2006) 359–77.
Jian C, Jing Z, Yinhang W, Jinlong D, Yuefen P, Quan Q, Shuwen H. Colorectal cancer and gut viruses: a visualized analysis based on CiteSpace knowledge graph. Front Microbiol. 2023;14:1239818.
Synnestvedt MB, Chen C, Holmes JH. CiteSpace II: visualization and knowledge discovery in bibliographic databases. AMIA Annu Symp Proc 2005 (2005) 724-8.
Falagas ME, Pitsouni EI, Malietzis GA, Pappas G. Comparison of PubMed, Scopus, web of Science, and Google Scholar: strengths and weaknesses. FASEB J. 2008;22:338–42.
Xiao Y, Qiu M, Huang W, Hu S, Tan C, Nan F, Jiang X, Wu D, Li M, Li Q, Qin C. Global status of research on radiotherapy for rectal cancer: a bibliometric and visual analysis. Front Public Health. 2022;10:962256.
Liu S, Sun YP, Gao XL, Sui Y. Knowledge domain and emerging trends in Alzheimer’s disease: a scientometric review based on CiteSpace analysis. Neural Regen Res. 2019;14:1643–50.
Zhong D, Li Y, Huang Y, Hong X, Li J, Jin R. Molecular mechanisms of Exercise on Cancer: a Bibliometrics study and visualization analysis via CiteSpace. Front Mol Biosci. 2021;8:797902.
Chen C. Searching for intellectual turning points: progressive knowledge domain visualization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101(Suppl 1):5303–10.
Ten Hove JR, Shah SC, Shaffer SR, Bernstein CN, Castaneda D, Palmela C, Mooiweer E, Elman J, Kumar A, Glass J, Axelrad J, Ullman TA, Colombel JF, Torres J, van Bodegraven AA, Hoentjen F, Jansen JM, de Jong ME, Mahmmod N, van der Meulen-de Jong AE, Ponsioen CY, van der Woude CJ, Itzkowitz SH, Oldenburg B. Consecutive negative findings on colonoscopy during surveillance predict a low risk of advanced neoplasia in patients with inflammatory bowel disease with long-standing colitis: results of a 15-year multicentre, multinational cohort study. Gut. 2019;68:615–22.
Ma D, Yang B, Guan B, Song L, Liu Q, Fan Y, Zhao L, Wang T, Zhang Z, Gao Z, Li S, Xu H. A bibliometric analysis of pyroptosis from 2001 to 2021. Front Immunol. 2021;12:731933.
Farraye F.A., Odze R.D., Eaden J., Itzkowitz S.H. AGA technical review on the diagnosis and management of colorectal neoplasia in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology. 2010;138:746–74. 774 e1-4; quiz e12-3.
Eaden JA, Abrams KR, Mayberry JF. The risk of colorectal cancer in ulcerative colitis: a meta-analysis. Gut. 2001;48:526–35.
Ng SC, Shi HY, Hamidi N, Underwood FE, Tang W, Benchimol EI, Panaccione R, Ghosh S, Wu JCY, Chan FKL, Sung JJY, Kaplan GG. Worldwide incidence and prevalence of inflammatory bowel disease in the 21st century: a systematic review of population-based studies. Lancet. 2017;390:2769–78.
Gupta RB, Harpaz N, Itzkowitz S, Hossain S, Matula S, Kornbluth A, Bodian C, Ullman T. Histologic inflammation is a risk factor for progression to colorectal neoplasia in ulcerative colitis: a cohort study. Gastroenterology. 2007;133:1099–105. quiz 1340-1.
Huang X, Fan X, Ying J, Chen S. Emerging trends and research foci in gastrointestinal microbiome. J Transl Med. 2019;17:67.
Jess T, Simonsen J, Jorgensen KT, Pedersen BV, Nielsen NM, Frisch M. Decreasing risk of colorectal cancer in patients with inflammatory bowel disease over 30 years. Gastroenterology 143 (2012) 375 – 81 e1; quiz e13-4.
Eaden J, Abrams K, Ekbom A, Jackson E, Mayberry J. Colorectal cancer prevention in ulcerative colitis: a case-control study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2000;14:145–53.
Olen O, Erichsen R, Sachs MC, Pedersen L, Halfvarson J, Askling J, Ekbom A, Sorensen HT, Ludvigsson JF. Colorectal cancer in ulcerative colitis: a scandinavian population-based cohort study. Lancet. 2020;395:123–31.
Gelsomino F, Barbolini M, Spallanzani A, Pugliese G, Cascinu S. The evolving role of microsatellite instability in colorectal cancer: a review. Cancer Treat Rev. 2016;51:19–26.
Gene M, Cuatrecasas M, Amat I, Veiga JA, Fernandez Acenero MJ, Fuste Chimisana V, Tarragona J, Jurado I, Fernandez-Victoria R, Martinez Ciarpaglini C, Alenda Gonzalez C, Zac C, Ortega P, de la Obra MT, Fernandez-Figueras M, Esteller, Musulen E. Alterations in p53, microsatellite Stability and Lack of MUC5AC expression as Molecular Features of Colorectal Carcinoma Associated with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Int J Mol Sci 24 (2023).
Birch RJ, Burr N, Subramanian V, Tiernan JP, Hull MA, Finan P, Rose A, Rutter M, Valori R, Downing A, Morris EJA. Inflammatory bowel Disease-Associated Colorectal Cancer Epidemiology and outcomes: an English Population-based study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2022;117:1858–70.
Zhang M, Viennois E, Prasad M, Zhang Y, Wang L, Zhang Z, Han MK, Xiao B, Xu C, Srinivasan S, Merlin D. Edible ginger-derived nanoparticles: a novel therapeutic approach for the prevention and treatment of inflammatory bowel disease and colitis-associated cancer. Biomaterials. 2016;101:321–40.
Mooiweer E, van der Meulen-de AE, Jong CY, Ponsioen CJ, van der Woude AA, van Bodegraven JM, Jansen N, Mahmmod W, Kremer PD, Siersema B, Oldenburg. C.s. Dutch Initiative on, and colitis, incidence of interval Colorectal Cancer among Inflammatory Bowel Disease patients undergoing regular colonoscopic surveillance. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;13:1656–61.
Figliuolo da Paz VR, Jamwal DR, Kiela PR. Intestinal Regulatory T Cells. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1278:141–90.
Rajamaki K, Taira A, Katainen R, Valimaki N, Kuosmanen A, Plaketti RM, Seppala TT, Ahtiainen M, Wirta EV, Vartiainen E, Sulo P, Ravantti J, Lehtipuro S, Granberg KJ, Nykter M, Tanskanen T, Ristimaki A, Koskensalo S, Renkonen-Sinisalo L, Lepisto A, Bohm J, Taipale J, Mecklin JP, Aavikko M, Palin K, Aaltonen LA. Genetic and epigenetic characteristics of inflammatory bowel Disease-Associated Colorectal Cancer. Gastroenterology. 2021;161:592–607.
Sun D, Gong L, Wang X, Chen S, Yi J, Liu X. Pro-inflammatory cytokines promote the occurrence and development of colitis-associated Colorectal Cancer by inhibiting miR-615-5p. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2023;29:1854–64.
Rubin CE, Haggitt RC, Burmer GC, Brentnall TA, Stevens AC, Levine DS, Dean PJ, Kimmey M, Perera DR, Rabinovitch PS. DNA aneuploidy in colonic biopsies predicts future development of dysplasia in ulcerative colitis. Gastroenterology. 1992;103:1611–20.
Kim YS, Hurley EH, Park Y, Ko S. Treatment of primary sclerosing cholangitis combined with inflammatory bowel disease. Intest Res. 2023;21:420–32.
Palmela C, Peerani F, Castaneda D, Torres J, Itzkowitz SH. Inflammatory bowel disease and primary sclerosing cholangitis: a review of the phenotype and Associated Specific features. Gut Liver. 2018;12:17–29.
Leedham SJ, Graham TA, Oukrif D, McDonald SA, Rodriguez-Justo M, Harrison RF, Shepherd NA, Novelli MR, Jankowski JA, Wright NA. Clonality, founder mutations, and field cancerization in human ulcerative colitis-associated neoplasia. Gastroenterology. 2009;136:542–50. e6.
Fogt F, Vortmeyer AO, Goldman H, Giordano TJ, Merino MJ, Zhuang Z. Comparison of genetic alterations in colonic adenoma and ulcerative colitis-associated dysplasia and carcinoma. Hum Pathol. 1998;29:131–6.
Zamani S, Taslimi R, Sarabi A, Jasemi S, Sechi LA, Feizabadi MM. Enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis: a possible Etiological candidate for Bacterially-Induced Colorectal Precancerous and cancerous lesions. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019;9:449.
Yu LC. Microbiota dysbiosis and barrier dysfunction in inflammatory bowel disease and colorectal cancers: exploring a common ground hypothesis. J Biomed Sci. 2018;25:79.
Bardelcikova A, Soltys J, Mojzis J. Oxidative stress, inflammation and colorectal Cancer: an overview. Antioxid (Basel) 12 (2023).
Flynn AD, Valentine JF. Chromoendoscopy for Dysplasia Surveillance in Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2018;24:1440–52.
Fleisher AS, Esteller M, Harpaz N, Leytin A, Rashid A, Xu Y, Liang J, Stine OC, Yin J, Zou TT, Abraham JM, Kong D, Wilson KT, James SP, Herman JG, Meltzer SJ. Microsatellite instability in inflammatory bowel disease-associated neoplastic lesions is associated with hypermethylation and diminished expression of the DNA mismatch repair gene, hMLH1. Cancer Res. 2000;60:4864–8.
CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Pagliari D, Saviano A, Newton EE, Serricchio ML, Dal Lago AA, Gasbarrini A, Cianci R. Gut microbiota-Immune System Crosstalk and Pancreatic disorders. Mediators Inflamm. 2018;2018:7946431.
Pereira C, Gracio D, Teixeira JP, Magro F. Oxidative stress and DNA damage: implications in inflammatory bowel disease. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2015;21:2403–17.
PubMed Google Scholar
Frick A, Khare V, Paul G, Lang M, Ferk F, Knasmuller S, Beer A, Oberhuber G, Gasche C. Overt increase of oxidative stress and DNA damage in Murine and Human Colitis and Colitis-Associated Neoplasia. Mol Cancer Res. 2018;16:634–42.
Azer SA. Overview of molecular pathways in inflammatory bowel disease associated with colorectal cancer development. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;25:271–81.
Khalid S, Abbass A, Khetpal N, Shen B, Navaneethan U. Endoscopic detection and resection of dysplasia in inflammatory bowel disease-techniques with videos. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2019;34:569–80.
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
This study was supported by Natural Science Foundation of Henan Province (232300420049), Postgraduate Cultivating Innovation and Quality Improvement Action Plan of Henan University (SYLYC2022141, SYLYC2023125, SYLYC2023124). Henan Province United Common Project Fund (LHGJ20220663), Henan Provincial Science and Technology Research Project (222102310134) and Ruida Pharmaceutical Clinical Medicine Postgraduate Education Innovation Training Base Project of Henan University (SYLJD2022009). and Program for Innovative Research Team (in Science and Technology) in University of Henan Province (24IRTSTHN041).
Author information
Hao Zhang, Huiru Xin and Mengqi Zhao contributed equally to this work.
Authors and Affiliations
Department of General Surgery, Huaihe Hospital of Henan University, Kaifeng, 475000, China
Hao Zhang, Chenyang Bi, Yafei Xiao, Yifan Li & Changjiang Qin
Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery, Huaihe Hospital of Henan University, Kaifeng, 475000, China
Department of Gastroenterology, Huaihe Hospital of Henan University, Kaifeng, 475000, China
Mengqi Zhao
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
C.Q. and H.Z. contributed to the conception and design of this paper. H.Z., H.X.and M.Z. contributed to all tables and figures and the main manuscript. C.B, Y.X. and Y.L. revised and supplemented the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Changjiang Qin .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate, consent for publication.
We assure that the material is original, and it has not been published elsewhere yet.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1
Rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Zhang, H., Xin, H., Zhao, M. et al. Global research trends on the relationship between IBD and CRC: a bibliometric analysis from 2000 to 2023. J Health Popul Nutr 43 , 83 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s41043-024-00577-5
Download citation
Received : 16 April 2024
Accepted : 04 June 2024
Published : 12 June 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s41043-024-00577-5
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Bibliometric
Journal of Health, Population and Nutrition
ISSN: 2072-1315
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Qualitative Findings. Qualitative research is an exploratory research method used to understand the complexities of human behavior and experiences. Qualitative findings are non-numerical and descriptive data that describe the meaning and interpretation of the data collected. Examples of qualitative findings include quotes from participants ...
Checklist: Research results 0 / 7. I have completed my data collection and analyzed the results. I have included all results that are relevant to my research questions. I have concisely and objectively reported each result, including relevant descriptive statistics and inferential statistics. I have stated whether each hypothesis was supported ...
INTRODUCTION. Scientific research is usually initiated by posing evidenced-based research questions which are then explicitly restated as hypotheses.1,2 The hypotheses provide directions to guide the study, solutions, explanations, and expected results.3,4 Both research questions and hypotheses are essentially formulated based on conventional theories and real-world processes, which allow the ...
Research Results. Research results refer to the findings and conclusions derived from a systematic investigation or study conducted to answer a specific question or hypothesis. These results are typically presented in a written report or paper and can include various forms of data such as numerical data, qualitative data, statistics, charts, graphs, and visual aids.
Doing Case Study Research: A Practical Guide for Beginning Researchers. 2nd ed. New York: Teachers College Press, 2011; Introduction to Nursing Research: Reporting Research Findings. Nursing Research: Open Access Nursing Research and Review Articles. (January 4, 2012); Kretchmer, Paul. Twelve Steps to Writing an Effective Results Section.
Step 1: Consult the guidelines or instructions that the target journal or publisher provides authors and read research papers it has published, especially those with similar topics, methods, or results to your study. The guidelines will generally outline specific requirements for the results or findings section, and the published articles will ...
The findings section of a research paper presents the results and outcomes of the study or investigation. It is a crucial part of the research paper where researchers interpret and analyze the data collected and draw conclusions based on their findings.
1. Reporting Quantitative Findings. The best way to present your quantitative findings is to structure them around the research hypothesis or questions you intend to address as part of your dissertation project. Report the relevant findings for each research question or hypothesis, focusing on how you analyzed them.
the study design. For example, it makes sense to present the results of an ethnographic study as a chronological narrative. Qualitative studies that use thematic coding might break down results by theme or category, whereas quantitative studies might break up findings by research question or statistical test. In most Results sections
The results chapter in a dissertation or thesis (or any formal academic research piece) is where you objectively and neutrally present the findings of your qualitative analysis (or analyses if you used multiple qualitative analysis methods ). This chapter can sometimes be combined with the discussion chapter (where you interpret the data and ...
There are multiple steps involved in writing up the results chapter for your quantitative research. The exact number of steps applicable to you will vary from study to study and will depend on the nature of the research aims, objectives and research questions. However, we'll outline the generic steps below. Step 1 - Revisit your research ...
The results (or findings) section is one of the most important parts of a research paper, in which an author reports the findings of their study in connection to their research question(s). The results section should not attempt to interpret or analyze the findings, only state the facts. In this handout, you will find a description of a results ...
Reporting the findings from a qualitative study in a way that is interesting, meaningful, and trustworthy can be a struggle. ... The example below presents a research question from my study of blended learning at a charter high school (Bingham, 2016), and an excerpt from my findings that answered that research question. I have also included the ...
The researcher interview guide was designed to understand researchers' perspectives on communicating and disseminating research findings to participants; explore past experiences, if any, of researchers with communication and dissemination of research findings to study participants; document any approaches researchers may have used or intend ...
study's findings with those of other studies. In qualitative research, we are open to dif-ferent ways of seeing the world. We make assumptions about how things work. We strive to be open to the reality of others and under-stand different realities. We must listen before we can understand. Analysis of the findings
The results section of the research paper is where you report the findings of your study based upon the information gathered as a result of the methodology [or methodologies] you applied. The results section should simply state the findings, without bias or interpretation, and arranged in a logical sequence. The results section should always be ...
They can determine the quality of research studies, including the methodology, sample size, data analysis, and conclusions. Validating findings: Evaluating research can help to validate findings from previous studies. By examining the methodology and results of a study, researchers can determine if the findings are reliable and if they can be ...
A research design is a strategy for answering your research question using empirical data. Creating a research design means making decisions about: Your overall research objectives and approach. Whether you'll rely on primary research or secondary research. Your sampling methods or criteria for selecting subjects. Your data collection methods.
Research methods are specific procedures for collecting and analyzing data. Developing your research methods is an integral part of your research design. When planning your methods, there are two key decisions you will make. First, decide how you will collect data. Your methods depend on what type of data you need to answer your research question:
Implementing knowledge. Research findings can influence decisions at many levels—in caring for individual patients, in developing practice guidelines, in commissioning health care, in developing prevention and health promotion strategies, in developing policy, in designing educational programmes, and in performing clinical audit—but only if clinicians know how to translate knowledge into ...
The basis of a scientific research study follows a common pattern: Define the question. Gather information and resources. Form hypotheses. Perform an experiment and collect data. Analyze the data ...
If you need help finding a specific type of study, visit the Get Research Help guide to contact the librarians. Understand Evidence-Based Practice. ... Sometimes, a research study will look at the results of many studies and look for trends and draw conclusions. These types of studies include: Meta Analyses;
Access 160+ million publications and connect with 25+ million researchers. Join for free and gain visibility by uploading your research.
Introduction: Translating research findings into practice requires understanding how to meet communication and dissemination needs and preferences of intended audiences including past research participants (PSPs) who want, but seldom receive, information on research findings during or after participating in research studies. Most researchers want to let others, including PSP, know about their ...
The study's methods and findings are years away from being applied to direct patient care, experts said, but there is funding for such efforts. Camille Wesser/Moment RF/Getty Images Related ...
Research study supports the idea that different psychological issues are caused by the functional reorganisation of expansive brain networks, ... The findings answered the primary research questions that were directed at FC alterations within several networks of the adolescent brain and how that influenced their behaviour and development ...
Some previous observational studies have linked deep venous thrombosis (DVT) to thyroid diseases; however, the findings were contradictory. This study aimed to investigate whether some common thyroid diseases can cause DVT using a two-sample Mendelian randomization (MR) approach. This two-sample MR study used single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) identified by the FinnGen genome-wide ...
Movement of the inner core has been debated by the scientific community for two decades, with some research indicating that the inner core rotates faster than the planet's surface. The new USC study provides unambiguous evidence that the inner core began to decrease its speed around 2010, moving slower than the Earth's surface.
Our findings highlight the need for research on HPAI A(H5N1) virus in dairy production. Replication of these findings and extension to other dairy products is needed, including the study of milk ...
This study aimed to conduct a bibliometric analysis of research articles on the relationship between inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and colorectal cancer (CRC) using CiteSpace to summarize the current research status, hotspots, and trends in this field and present the results visually. Research articles on the relationship between IBD and CRC published from 2000 to 2023 and in English were ...