Reported Questions
Reported questions are one form of reported speech .
We usually introduce reported questions with the verb "ask":
- He asked (me) if / whether ... (YES/NO questions)
- He asked (me) why / when / where / what / how ... (question-word questions)
As with reported statements , we may need to change pronouns and tense (backshift) as well as time and place in reported questions.
But we also need to change the word order . After we report a question, it is no longer a question (and in writing there is no question mark). The word order is like that of a normal statement (subject-verb-object).

Reported YES/NO questions
We introduce reported YES/NO questions with ask + if :
Note that in the above example the reported question has no auxiliary "do". But there is pronoun change and backshift.
Note that we sometimes use "whether" instead of "if". The meaning is the same. "Whether" is a little more formal and more usual in writing:
- They asked us if we wanted lunch.
- They asked us whether we wanted lunch.
Reported question-word questions
We introduce reported question-word questions with ask + question word :
Note that in the above example the reported question has no auxiliary "do". But there is pronoun change and backshift.
- YES/NO questions: Do you want tea?
- Question Word questions: Where did you drink tea?
- Choice questions: Do you prefer tea or coffee?
Look at these example sentences:

Reported Speech – Rules, Examples & Worksheet
| Candace Osmond
Candace Osmond
Candace Osmond studied Advanced Writing & Editing Essentials at MHC. She’s been an International and USA TODAY Bestselling Author for over a decade. And she’s worked as an Editor for several mid-sized publications. Candace has a keen eye for content editing and a high degree of expertise in Fiction.
They say gossip is a natural part of human life. That’s why language has evolved to develop grammatical rules about the “he said” and “she said” statements. We call them reported speech.
Every time we use reported speech in English, we are talking about something said by someone else in the past. Thinking about it brings me back to high school, when reported speech was the main form of language!
Learn all about the definition, rules, and examples of reported speech as I go over everything. I also included a worksheet at the end of the article so you can test your knowledge of the topic.
What Does Reported Speech Mean?
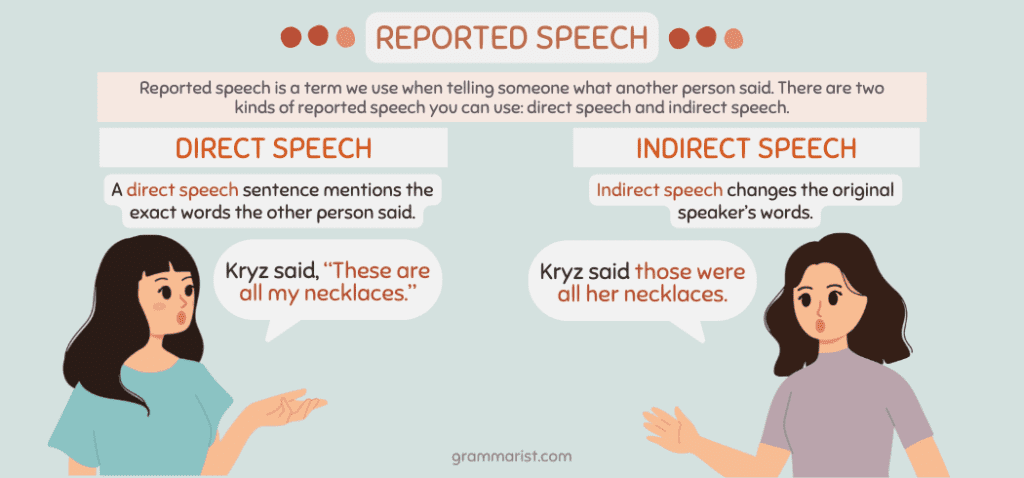
Reported speech is a term we use when telling someone what another person said. You can do this while speaking or writing.
There are two kinds of reported speech you can use: direct speech and indirect speech. I’ll break each down for you.
A direct speech sentence mentions the exact words the other person said. For example:
- Kryz said, “These are all my necklaces.”
Indirect speech changes the original speaker’s words. For example:
- Kryz said those were all her necklaces.
When we tell someone what another individual said, we use reporting verbs like told, asked, convinced, persuaded, and said. We also change the first-person figure in the quotation into the third-person speaker.
Reported Speech Examples
We usually talk about the past every time we use reported speech. That’s because the time of speaking is already done. For example:
- Direct speech: The employer asked me, “Do you have experience with people in the corporate setting?”
Indirect speech: The employer asked me if I had experience with people in the corporate setting.
- Direct speech: “I’m working on my thesis,” I told James.
Indirect speech: I told James that I was working on my thesis.
Reported Speech Structure
A speech report has two parts: the reporting clause and the reported clause. Read the example below:
- Harry said, “You need to help me.”
The reporting clause here is William said. Meanwhile, the reported clause is the 2nd clause, which is I need your help.
What are the 4 Types of Reported Speech?
Aside from direct and indirect, reported speech can also be divided into four. The four types of reported speech are similar to the kinds of sentences: imperative, interrogative, exclamatory, and declarative.
Reported Speech Rules
The rules for reported speech can be complex. But with enough practice, you’ll be able to master them all.
Choose Whether to Use That or If
The most common conjunction in reported speech is that. You can say, “My aunt says she’s outside,” or “My aunt says that she’s outside.”
Use if when you’re reporting a yes-no question. For example:
- Direct speech: “Are you coming with us?”
Indirect speech: She asked if she was coming with them.
Verb Tense Changes
Change the reporting verb into its past form if the statement is irrelevant now. Remember that some of these words are irregular verbs, meaning they don’t follow the typical -d or -ed pattern. For example:
- Direct speech: I dislike fried chicken.
Reported speech: She said she disliked fried chicken.
Note how the main verb in the reported statement is also in the past tense verb form.
Use the simple present tense in your indirect speech if the initial words remain relevant at the time of reporting. This verb tense also works if the report is something someone would repeat. For example:
- Slater says they’re opening a restaurant soon.
- Maya says she likes dogs.
This rule proves that the choice of verb tense is not a black-and-white question. The reporter needs to analyze the context of the action.
Move the tense backward when the reporting verb is in the past tense. That means:
- Present simple becomes past simple.
- Present perfect becomes past perfect.
- Present continuous becomes past continuous.
- Past simple becomes past perfect.
- Past continuous becomes past perfect continuous.
Here are some examples:
- The singer has left the building. (present perfect)
He said that the singers had left the building. (past perfect)
- Her sister gave her new shows. (past simple)
- She said that her sister had given her new shoes. (past perfect)
If the original speaker is discussing the future, change the tense of the reporting verb into the past form. There’ll also be a change in the auxiliary verbs.
- Will or shall becomes would.
- Will be becomes would be.
- Will have been becomes would have been.
- Will have becomes would have.
For example:
- Direct speech: “I will be there in a moment.”
Indirect speech: She said that she would be there in a moment.
Do not change the verb tenses in indirect speech when the sentence has a time clause. This rule applies when the introductory verb is in the future, present, and present perfect. Here are other conditions where you must not change the tense:
- If the sentence is a fact or generally true.
- If the sentence’s verb is in the unreal past (using second or third conditional).
- If the original speaker reports something right away.
- Do not change had better, would, used to, could, might, etc.
Changes in Place and Time Reference
Changing the place and time adverb when using indirect speech is essential. For example, now becomes then and today becomes that day. Here are more transformations in adverbs of time and places.
- This – that.
- These – those.
- Now – then.
- Here – there.
- Tomorrow – the next/following day.
- Two weeks ago – two weeks before.
- Yesterday – the day before.
Here are some examples.
- Direct speech: “I am baking cookies now.”
Indirect speech: He said he was baking cookies then.
- Direct speech: “Myra went here yesterday.”
Indirect speech: She said Myra went there the day before.
- Direct speech: “I will go to the market tomorrow.”
Indirect speech: She said she would go to the market the next day.
Using Modals
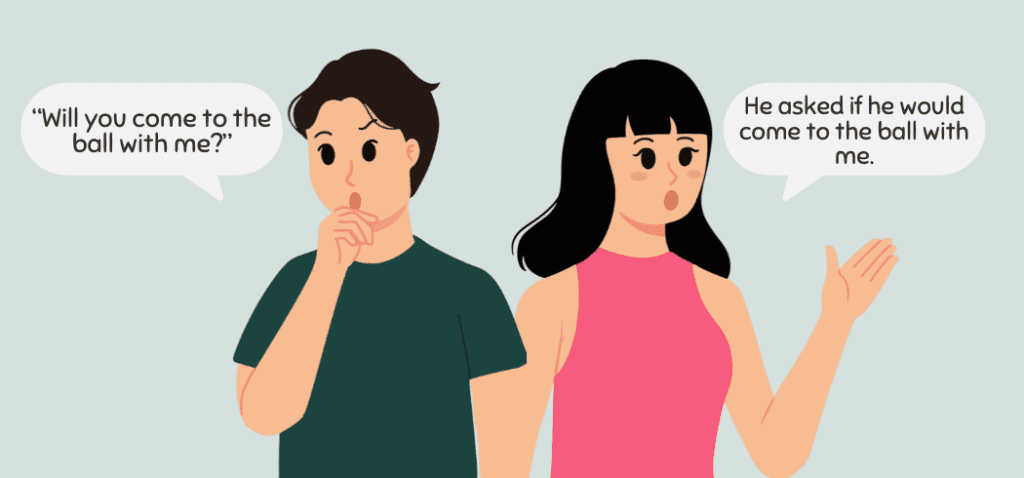

If the direct speech contains a modal verb, make sure to change them accordingly.
- Will becomes would
- Can becomes could
- Shall becomes should or would.
- Direct speech: “Will you come to the ball with me?”
Indirect speech: He asked if he would come to the ball with me.
- Direct speech: “Gina can inspect the room tomorrow because she’s free.”
Indirect speech: He said Gina could inspect the room the next day because she’s free.
However, sometimes, the modal verb should does not change grammatically. For example:
- Direct speech: “He should go to the park.”
Indirect speech: She said that he should go to the park.
Imperative Sentences
To change an imperative sentence into a reported indirect sentence, use to for imperative and not to for negative sentences. Never use the word that in your indirect speech. Another rule is to remove the word please . Instead, say request or say. For example:
- “Please don’t interrupt the event,” said the host.
The host requested them not to interrupt the event.
- Jonah told her, “Be careful.”
- Jonah ordered her to be careful.
Reported Questions
When reporting a direct question, I would use verbs like inquire, wonder, ask, etc. Remember that we don’t use a question mark or exclamation mark for reports of questions. Below is an example I made of how to change question forms.
- Incorrect: He asked me where I live?
Correct: He asked me where I live.
Here’s another example. The first sentence uses direct speech in a present simple question form, while the second is the reported speech.
- Where do you live?
She asked me where I live.
Wrapping Up Reported Speech
My guide has shown you an explanation of reported statements in English. Do you have a better grasp on how to use it now?
Reported speech refers to something that someone else said. It contains a subject, reporting verb, and a reported cause.
Don’t forget my rules for using reported speech. Practice the correct verb tense, modal verbs, time expressions, and place references.
Grammarist is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon.com. When you buy via the links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission at no cost to you.
2024 © Grammarist, a Found First Marketing company. All rights reserved.
What is Reported Speech and how to use it? with Examples
Reported speech and indirect speech are two terms that refer to the same concept, which is the act of expressing what someone else has said. Reported speech is different from direct speech because it does not use the speaker's exact words. Instead, the reporting verb is used to introduce the reported speech, and the tense and pronouns are changed to reflect the shift in perspective. There are two main types of reported speech: statements and questions. 1. Reported Statements: In reported statements, the reporting verb is usually "said." The tense in the reported speech changes from the present simple to the past simple, and any pronouns referring to the speaker or listener are changed to reflect the shift in perspective. For example, "I am going to the store," becomes "He said that he was going to the store." 2. Reported Questions: In reported questions, the reporting verb is usually "asked." The tense in the reported speech changes from the present simple to the past simple, and the word order changes from a question to a statement. For example, "What time is it?" becomes "She asked what time it was." It's important to note that the tense shift in reported speech depends on the context and the time of the reported speech. Here are a few more examples: ● Direct speech: "I will call you later." Reported speech: He said that he would call me later. ● Direct speech: "Did you finish your homework?" Reported speech: She asked if I had finished my homework. ● Direct speech: "I love pizza." Reported speech: They said that they loved pizza.
When do we use reported speech?
Reported speech is used to report what someone else has said, thought, or written. It is often used in situations where you want to relate what someone else has said without quoting them directly. Reported speech can be used in a variety of contexts, such as in news reports, academic writing, and everyday conversation. Some common situations where reported speech is used include: News reports: Journalists often use reported speech to quote what someone said in an interview or press conference. Business and professional communication: In professional settings, reported speech can be used to summarize what was discussed in a meeting or to report feedback from a customer. Conversational English: In everyday conversations, reported speech is used to relate what someone else said. For example, "She told me that she was running late." Narration: In written narratives or storytelling, reported speech can be used to convey what a character said or thought.
How to make reported speech?
1. Change the pronouns and adverbs of time and place: In reported speech, you need to change the pronouns, adverbs of time and place to reflect the new speaker or point of view. Here's an example: Direct speech: "I'm going to the store now," she said. Reported speech: She said she was going to the store then. In this example, the pronoun "I" is changed to "she" and the adverb "now" is changed to "then." 2. Change the tense: In reported speech, you usually need to change the tense of the verb to reflect the change from direct to indirect speech. Here's an example: Direct speech: "I will meet you at the park tomorrow," he said. Reported speech: He said he would meet me at the park the next day. In this example, the present tense "will" is changed to the past tense "would." 3. Change reporting verbs: In reported speech, you can use different reporting verbs such as "say," "tell," "ask," or "inquire" depending on the context of the speech. Here's an example: Direct speech: "Did you finish your homework?" she asked. Reported speech: She asked if I had finished my homework. In this example, the reporting verb "asked" is changed to "said" and "did" is changed to "had." Overall, when making reported speech, it's important to pay attention to the verb tense and the changes in pronouns, adverbs, and reporting verbs to convey the original speaker's message accurately.
How do I change the pronouns and adverbs in reported speech?
1. Changing Pronouns: In reported speech, the pronouns in the original statement must be changed to reflect the perspective of the new speaker. Generally, the first person pronouns (I, me, my, mine, we, us, our, ours) are changed according to the subject of the reporting verb, while the second and third person pronouns (you, your, yours, he, him, his, she, her, hers, it, its, they, them, their, theirs) are changed according to the object of the reporting verb. For example: Direct speech: "I love chocolate." Reported speech: She said she loved chocolate. Direct speech: "You should study harder." Reported speech: He advised me to study harder. Direct speech: "She is reading a book." Reported speech: They noticed that she was reading a book. 2. Changing Adverbs: In reported speech, the adverbs and adverbial phrases that indicate time or place may need to be changed to reflect the perspective of the new speaker. For example: Direct speech: "I'm going to the cinema tonight." Reported speech: She said she was going to the cinema that night. Direct speech: "He is here." Reported speech: She said he was there. Note that the adverb "now" usually changes to "then" or is omitted altogether in reported speech, depending on the context. It's important to keep in mind that the changes made to pronouns and adverbs in reported speech depend on the context and the perspective of the new speaker. With practice, you can become more comfortable with making these changes in reported speech.
How do I change the tense in reported speech?
In reported speech, the tense of the reported verb usually changes to reflect the change from direct to indirect speech. Here are some guidelines on how to change the tense in reported speech: Present simple in direct speech changes to past simple in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: "I like pizza." Reported speech: She said she liked pizza. Present continuous in direct speech changes to past continuous in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: "I am studying for my exam." Reported speech: He said he was studying for his exam. Present perfect in direct speech changes to past perfect in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: "I have finished my work." Reported speech: She said she had finished her work. Past simple in direct speech changes to past perfect in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: "I visited my grandparents last weekend." Reported speech: She said she had visited her grandparents the previous weekend. Will in direct speech changes to would in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: "I will help you with your project." Reported speech: He said he would help me with my project. Can in direct speech changes to could in reported speech. For example: Direct speech: "I can speak French." Reported speech: She said she could speak French. Remember that the tense changes in reported speech depend on the tense of the verb in the direct speech, and the tense you use in reported speech should match the time frame of the new speaker's perspective. With practice, you can become more comfortable with changing the tense in reported speech.
Do I always need to use a reporting verb in reported speech?
No, you do not always need to use a reporting verb in reported speech. However, using a reporting verb can help to clarify who is speaking and add more context to the reported speech. In some cases, the reported speech can be introduced by phrases such as "I heard that" or "It seems that" without using a reporting verb. For example: Direct speech: "I'm going to the cinema tonight." Reported speech with a reporting verb: She said she was going to the cinema tonight. Reported speech without a reporting verb: It seems that she's going to the cinema tonight. However, it's important to note that using a reporting verb can help to make the reported speech more formal and accurate. When using reported speech in academic writing or journalism, it's generally recommended to use a reporting verb to make the reporting more clear and credible. Some common reporting verbs include say, tell, explain, ask, suggest, and advise. For example: Direct speech: "I think we should invest in renewable energy." Reported speech with a reporting verb: She suggested that they invest in renewable energy. Overall, while using a reporting verb is not always required, it can be helpful to make the reported speech more clear and accurate.
How to use reported speech to report questions and commands?
1. Reporting Questions: When reporting questions, you need to use an introductory phrase such as "asked" or "wondered" followed by the question word (if applicable), subject, and verb. You also need to change the word order to make it a statement. Here's an example: Direct speech: "What time is the meeting?" Reported speech: She asked what time the meeting was. Note that the question mark is not used in reported speech. 2. Reporting Commands: When reporting commands, you need to use an introductory phrase such as "ordered" or "told" followed by the person, to + infinitive, and any additional information. Here's an example: Direct speech: "Clean your room!" Reported speech: She ordered me to clean my room. Note that the exclamation mark is not used in reported speech. In both cases, the tense of the reported verb should be changed accordingly. For example, present simple changes to past simple, and future changes to conditional. Here are some examples: Direct speech: "Will you go to the party with me?" Reported speech: She asked if I would go to the party with her. Direct speech: "Please bring me a glass of water." Reported speech: She requested that I bring her a glass of water. Remember that when using reported speech to report questions and commands, the introductory phrases and verb tenses are important to convey the intended meaning accurately.
How to make questions in reported speech?
To make questions in reported speech, you need to use an introductory phrase such as "asked" or "wondered" followed by the question word (if applicable), subject, and verb. You also need to change the word order to make it a statement. Here are the steps to make questions in reported speech: Identify the reporting verb: The first step is to identify the reporting verb in the sentence. Common reporting verbs used to report questions include "asked," "inquired," "wondered," and "wanted to know." Change the tense and pronouns: Next, you need to change the tense and pronouns in the sentence to reflect the shift from direct to reported speech. The tense of the verb is usually shifted back one tense (e.g. from present simple to past simple) in reported speech. The pronouns should also be changed as necessary to reflect the shift in perspective from the original speaker to the reporting speaker. Use an appropriate question word: If the original question contained a question word (e.g. who, what, where, when, why, how), you should use the same question word in the reported question. If the original question did not contain a question word, you can use "if" or "whether" to introduce the reported question. Change the word order: In reported speech, the word order of the question changes from the inverted form to a normal statement form. The subject usually comes before the verb, unless the original question started with a question word. Here are some examples of reported questions: Direct speech: "What time is the meeting?" Reported speech: She asked what time the meeting was. Direct speech: "Did you finish your homework?" Reported speech: He wanted to know if I had finished my homework. Direct speech: "Where are you going?" Reported speech: She wondered where I was going. Remember that when making questions in reported speech, the introductory phrases and verb tenses are important to convey the intended meaning accurately. Here you can find more examples of direct and indirect questions
What is the difference between reported speech an indirect speech?
In reported or indirect speech, you are retelling or reporting what someone said using your own words. The tense of the reported speech is usually shifted back one tense from the tense used in the original statement. For example, if someone said, "I am going to the store," in reported speech you would say, "He/she said that he/she was going to the store." The main difference between reported speech and indirect speech is that reported speech usually refers to spoken language, while indirect speech can refer to both spoken and written language. Additionally, indirect speech is a broader term that includes reported speech as well as other ways of expressing what someone else has said, such as paraphrasing or summarizing.
Examples of direct speech to reported
1. Direct speech: "I am hungry," she said. Reported speech: She said she was hungry. 2. Direct speech: "Can you pass the salt, please?" he asked. Reported speech: He asked her to pass the salt. 3. Direct speech: "I will meet you at the cinema," he said. Reported speech: He said he would meet her at the cinema. 4. Direct speech: "I have been working on this project for hours," she said. Reported speech: She said she had been working on the project for hours. 5. Direct speech: "What time does the train leave?" he asked. Reported speech: He asked what time the train left. 6. Direct speech: "I love playing the piano," she said. Reported speech: She said she loved playing the piano. 7. Direct speech: "I am going to the grocery store," he said. Reported speech: He said he was going to the grocery store. 8. Direct speech: "Did you finish your homework?" the teacher asked. Reported speech: The teacher asked if he had finished his homework. 9. Direct speech: "I want to go to the beach," she said. Reported speech: She said she wanted to go to the beach. 10. Direct speech: "Do you need help with that?" he asked. Reported speech: He asked if she needed help with that. 11. Direct speech: "I can't come to the party," he said. Reported speech: He said he couldn't come to the party. 12. Direct speech: "Please don't leave me," she said. Reported speech: She begged him not to leave her. 13. Direct speech: "I have never been to London before," he said. Reported speech: He said he had never been to London before. 14. Direct speech: "Where did you put my phone?" she asked. Reported speech: She asked where she had put her phone. 15. Direct speech: "I'm sorry for being late," he said. Reported speech: He apologized for being late. 16. Direct speech: "I need some help with this math problem," she said. Reported speech: She said she needed some help with the math problem. 17. Direct speech: "I am going to study abroad next year," he said. Reported speech: He said he was going to study abroad the following year. 18. Direct speech: "Can you give me a ride to the airport?" she asked. Reported speech: She asked him to give her a ride to the airport. 19. Direct speech: "I don't know how to fix this," he said. Reported speech: He said he didn't know how to fix it. 20. Direct speech: "I hate it when it rains," she said. Reported speech: She said she hated it when it rained.
What is Direct and Indirect Speech?
Direct and indirect speech are two different ways of reporting spoken or written language. Let's delve into the details and provide some examples. Click here to read more
Fluent English Grammar
Created by Fluent English Grammar
Privacy Policy
Terms of Service
English EFL
Reported speech
Reported questions
Reported questions.
When we report what people say, we usually change the tense of the verbs to reflect that we are reporting – not giving direct speech. This pattern is followed when we report questions and there are also other important changes between direct questions and reported questions.
Reported questions are one form of reported speech.
We usually introduce reported questions with the verb "ask":
- He asked (me) if / whether ... (YES/NO questions)
- He asked (me) why / when / where / what / how ... (question-word questions)
As with reported statements, we may need to change pronouns and tense (backshift) as well as time and place in reported questions.
But we also need to change the word order . After we report a question, it is no longer a question (and in writing there is no question mark). The word order is like that of a normal statement (subject-verb-object).
Reported YES/NO questions
We introduce reported YES/NO questions with ask + if :
Note that in the above example the reported question has no auxiliary "do". But there is pronoun change and backshift.
Note that we sometimes use "whether" instead of "if". The meaning is the same. "Whether" is a little more formal and more usual in writing:
- They asked us if we wanted lunch.
- They asked us whether we wanted lunch.
Reported question-word questions
We introduce reported question-word questions with ask + question word :
Remember that there are basically three types of question:
- YES/NO questions: Do you want tea?
- Question Word questions: Where did you drink tea?
- Choice questions: Do you prefer tea or coffee?
Reported choice questions have the same structure as Reported YES/NO questions. Questions with the verb BE always have a different structure: Was the tea cold? Where is my tea? You can see all these differences in the examples below.
Look at these example sentences:
Course Curriculum
- Direct and indirect speech 15 mins
- Tense changes in reported speech 20 mins
- Changing time and place in reported speech 20 mins
- Reported questions 20 mins
- Reporting verbs 20 mins
- Reporting orders and requests 15 mins
- Reporting hopes, intentions and promises 20 mins
Welcome to the new Eslbase
While our appearance has changed, you'll still find all the resources that you found before. Thanks for visiting :-)
Search Eslbase
How to use reported questions.
Learn about how to report questions in English grammar. Clear and simple explanation of meaning and use, with examples.

Forming reported questions
These general rules for reported speech also apply.
- Direct speech: “Where are you going?” Reported speech: He asked me where I was going .
- Direct speech: “Why is he shouting?” Reported speech: He asked me why he was shouting .
- Direct speech: “What do you want?” Reported speech: She asked me what I wanted .
- Direct speech: “Who doesn’t like cheese?” Reported speech: She asked me who didn’t like cheese.
- Direct speech: “Do you want me to come?” Reported speech: I asked him if he wanted me to come.
- Direct speech: “Have you fed the dog?” Reported speech: She asked me whether I had fed the dog.
- Direct speech: “Who is the champion?” Reported speech: She asked me who the champion was / She asked me who was the champion.
- Direct speech: “What is your favourite colour?” Reported speech: She asked me what my favourite colour was / She asked me what was my favourite colour.
Related grammar points
Reported Speech Reporting Verbs Say and Tell

Keith Taylor
Keith is the co-founder of Eslbase and School of TEFL . He's been a teacher and teacher trainer for over 20 years, in Indonesia, Australia, Morocco, Spain, Italy, Poland, France and now in the UK.
Grammar for English Teachers
Learn everything you need to feel confident with grammar as a teacher Online course - Save £20 in May
14 comments
Can you change the word order with other verbs that are not “to be”? Example: Where have you been? He asked me where had I been.
Hi – no, you would have to say: “He asked me where I had been.”
Sara Willson
can someone cover this please:
“When do the shops close?” I asked.
I asked when the shops closed.
please can you tell me what is the reported speech of “what was the last book you read? “….please it is very important
AHMED KOHARI
he/she asked me what the last book I read was?
He asked what book I read last
Hi I have a question, my English teacher said we never inverted the subjects in the reported questions. But in your work I saw that you are inverted the subjects in that reported question. Can you tell me why you do this?
Hi , in my book there is exercise that want change sentence from Reported question sentence to direct question My question is ( in past perfect sentence ) how I know that this sentence change to past simple or present perfect. Because both of them in direct speech change to past perfect .
Hi, can you write here the sentence that you need to change?
can you convert this? the student said, “would that my results were different”
It’s very informative… It helped me a lot… Thank you
Hi Yazan She asked me what the last book I read was.
Here’s an example, without the subject and auxiliary inverted first, and then with them inverted:
1. He asked me where was I going. 2. He asked me where I was going.
The second example, with the inversion, is correct for reported speech.
However, you could say the first one like this: 1. He asked me: “Where was I going?”
This is in quite common use in spoken English, and anything which is in common use is acceptable. It’s really a mix of direct and reported speech. With kind of use we would expect just direct speech: 1. He asked me: “Where are you going?”
But as I say, anything which is in common use is acceptable, but may not be “correct” in written English or in tests and exams.
Hope this helps.
Leave your comment (Cancel Reply)
Reported Speech in English Grammar
Direct speech, changing the tense (backshift), no change of tenses, question sentences, demands/requests, expressions with who/what/how + infinitive, typical changes of time and place.
- Lingolia Plus English
Introduction
In English grammar, we use reported speech to say what another person has said. We can use their exact words with quotation marks , this is known as direct speech , or we can use indirect speech . In indirect speech , we change the tense and pronouns to show that some time has passed. Indirect speech is often introduced by a reporting verb or phrase such as ones below.
Learn the rules for writing indirect speech in English with Lingolia’s simple explanation. In the exercises, you can test your grammar skills.
When turning direct speech into indirect speech, we need to pay attention to the following points:
- changing the pronouns Example: He said, “ I saw a famous TV presenter.” He said (that) he had seen a famous TV presenter.
- changing the information about time and place (see the table at the end of this page) Example: He said, “I saw a famous TV presenter here yesterday .” He said (that) he had seen a famous TV presenter there the day before .
- changing the tense (backshift) Example: He said, “She was eating an ice-cream at the table where you are sitting .” He said (that) she had been eating an ice-cream at the table where I was sitting .
If the introductory clause is in the simple past (e.g. He said ), the tense has to be set back by one degree (see the table). The term for this in English is backshift .
The verbs could, should, would, might, must, needn’t, ought to, used to normally do not change.
If the introductory clause is in the simple present , however (e.g. He says ), then the tense remains unchanged, because the introductory clause already indicates that the statement is being immediately repeated (and not at a later point in time).
In some cases, however, we have to change the verb form.
When turning questions into indirect speech, we have to pay attention to the following points:
- As in a declarative sentence, we have to change the pronouns, the time and place information, and set the tense back ( backshift ).
- Instead of that , we use a question word. If there is no question word, we use whether / if instead. Example: She asked him, “ How often do you work?” → She asked him how often he worked. He asked me, “Do you know any famous people?” → He asked me if/whether I knew any famous people.
- We put the subject before the verb in question sentences. (The subject goes after the auxiliary verb in normal questions.) Example: I asked him, “ Have you met any famous people before?” → I asked him if/whether he had met any famous people before.
- We don’t use the auxiliary verb do for questions in indirect speech. Therefore, we sometimes have to conjugate the main verb (for third person singular or in the simple past ). Example: I asked him, “What do you want to tell me?” → I asked him what he wanted to tell me.
- We put the verb directly after who or what in subject questions. Example: I asked him, “ Who is sitting here?” → I asked him who was sitting there.
We don’t just use indirect questions to report what another person has asked. We also use them to ask questions in a very polite manner.
When turning demands and requests into indirect speech, we only need to change the pronouns and the time and place information. We don’t have to pay attention to the tenses – we simply use an infinitive .
If it is a negative demand, then in indirect speech we use not + infinitive .
To express what someone should or can do in reported speech, we leave out the subject and the modal verb and instead we use the construction who/what/where/how + infinitive.
Say or Tell?
The words say and tell are not interchangeable. say = say something tell = say something to someone
How good is your English?
Find out with Lingolia’s free grammar test
Take the test!
Maybe later
Reported Speech (Part 2) – Requests, Orders, and Questions

My colleague asked me to help him update his computer.
Read Reported Speech (Part 1) to learn how to make reported statements.
In Part 2, we will focus on requests, orders, and questions.
1. Requests/orders
- “Asked me to” is used for requests.
- “Told me to” is stronger; it is used for orders/commands.
- The main verb stays in the infinitive: She asked me to make copies. He told me to go to the bank.
2. Yes/no questions
- “Asked if” and “wanted to know if” are equal.
- The main verb changes according to the rules for reported statements : “ Did you turn off the TV?” (past simple) She asked if I had turned off the TV (past perfect)
- We don’t use the auxiliary verbs “do/does/did” in the reported question.
3. Other questions
- “Asked” and “wanted to know” are equal.
- We don’t use the auxiliary verb “do” or “does” in the reported question: “Where does he work?” She wanted to know where he works .
- In questions with the verb “to be,” the word order changes in the reported question: “Where were you born?” (Question word + [to be] + subject) He asked where I was born (Question word + subject + [to be]) He asked where was I born
Reported Speech (Part 2) Quiz
Master the details of english grammar:.

More Espresso English Lessons:
About the author.
Shayna Oliveira
Shayna Oliveira is the founder of Espresso English, where you can improve your English fast - even if you don’t have much time to study. Millions of students are learning English from her clear, friendly, and practical lessons! Shayna is a CELTA-certified teacher with 10+ years of experience helping English learners become more fluent in her English courses.
- Cambridge Dictionary +Plus

Reported speech: indirect speech
Indirect speech focuses more on the content of what someone said rather than their exact words. In indirect speech , the structure of the reported clause depends on whether the speaker is reporting a statement, a question or a command.
Indirect speech: reporting statements
Indirect reports of statements consist of a reporting clause and a that -clause. We often omit that , especially in informal situations:
The pilot commented that the weather had been extremely bad as the plane came in to land. (The pilot’s words were: ‘The weather was extremely bad as the plane came in to land.’ )
I told my wife I didn’t want a party on my 50th birthday. ( that -clause without that ) (or I told my wife that I didn’t want a party on my 50th birthday .)
Indirect speech: reporting questions
Reporting yes-no questions and alternative questions.
Indirect reports of yes-no questions and questions with or consist of a reporting clause and a reported clause introduced by if or whether . If is more common than whether . The reported clause is in statement form (subject + verb), not question form:
She asked if [S] [V] I was Scottish. (original yes-no question: ‘Are you Scottish?’ )
The waiter asked whether [S] we [V] wanted a table near the window. (original yes-no question: ‘Do you want a table near the window? )
He asked me if [S] [V] I had come by train or by bus. (original alternative question: ‘Did you come by train or by bus?’ )
Questions: yes-no questions ( Are you feeling cold? )
Reporting wh -questions
Indirect reports of wh -questions consist of a reporting clause, and a reported clause beginning with a wh -word ( who, what, when, where, why, how ). We don’t use a question mark:
He asked me what I wanted.
Not: He asked me what I wanted?
The reported clause is in statement form (subject + verb), not question form:
She wanted to know who [S] we [V] had invited to the party.
Not: … who had we invited …
Who , whom and what
In indirect questions with who, whom and what , the wh- word may be the subject or the object of the reported clause:
I asked them who came to meet them at the airport. ( who is the subject of came ; original question: ‘Who came to meet you at the airport?’ )
He wondered what the repairs would cost. ( what is the object of cost ; original question: ‘What will the repairs cost?’ )
She asked us what [S] we [V] were doing . (original question: ‘What are you doing?’ )
Not: She asked us what were we doing?
When , where , why and how
We also use statement word order (subject + verb) with when , where, why and how :
I asked her when [S] it [V] had happened (original question: ‘When did it happen?’ ).
Not: I asked her when had it happened?
I asked her where [S] the bus station [V] was . (original question: ‘Where is the bus station?’ )
Not: I asked her where was the bus station?
The teacher asked them how [S] they [V] wanted to do the activity . (original question: ‘How do you want to do the activity?’ )
Not: The teacher asked them how did they want to do the activity?
Questions: wh- questions
Indirect speech: reporting commands
Indirect reports of commands consist of a reporting clause, and a reported clause beginning with a to -infinitive:
The General ordered the troops to advance . (original command: ‘Advance!’ )
The chairperson told him to sit down and to stop interrupting . (original command: ‘Sit down and stop interrupting!’ )
We also use a to -infinitive clause in indirect reports with other verbs that mean wanting or getting people to do something, for example, advise, encourage, warn :
They advised me to wait till the following day. (original statement: ‘You should wait till the following day.’ )
The guard warned us not to enter the area. (original statement: ‘You must not enter the area.’ )
Verbs followed by a to -infinitive
Indirect speech: present simple reporting verb
We can use the reporting verb in the present simple in indirect speech if the original words are still true or relevant at the time of reporting, or if the report is of something someone often says or repeats:
Sheila says they’re closing the motorway tomorrow for repairs.
Henry tells me he’s thinking of getting married next year.
Rupert says dogs shouldn’t be allowed on the beach. (Rupert probably often repeats this statement.)
Newspaper headlines
We often use the present simple in newspaper headlines. It makes the reported speech more dramatic:
JUDGE TELLS REPORTER TO LEAVE COURTROOM
PRIME MINISTER SAYS FAMILIES ARE TOP PRIORITY IN TAX REFORM
Present simple ( I work )
Reported speech
Reported speech: direct speech
Indirect speech: past continuous reporting verb
In indirect speech, we can use the past continuous form of the reporting verb (usually say or tell ). This happens mostly in conversation, when the speaker wants to focus on the content of the report, usually because it is interesting news or important information, or because it is a new topic in the conversation:
Rory was telling me the big cinema in James Street is going to close down. Is that true?
Alex was saying that book sales have gone up a lot this year thanks to the Internet.
‘Backshift’ refers to the changes we make to the original verbs in indirect speech because time has passed between the moment of speaking and the time of the report.
In these examples, the present ( am ) has become the past ( was ), the future ( will ) has become the future-in-the-past ( would ) and the past ( happened ) has become the past perfect ( had happened ). The tenses have ‘shifted’ or ‘moved back’ in time.
The past perfect does not shift back; it stays the same:
Modal verbs
Some, but not all, modal verbs ‘shift back’ in time and change in indirect speech.
We can use a perfect form with have + - ed form after modal verbs, especially where the report looks back to a hypothetical event in the past:
He said the noise might have been the postman delivering letters. (original statement: ‘The noise might be the postman delivering letters.’ )
He said he would have helped us if we’d needed a volunteer. (original statement: ‘I’ll help you if you need a volunteer’ or ‘I’d help you if you needed a volunteer.’ )
Used to and ought to do not change in indirect speech:
She said she used to live in Oxford. (original statement: ‘I used to live in Oxford.’ )
The guard warned us that we ought to leave immediately. (original statement: ‘You ought to leave immediately.’ )
No backshift
We don’t need to change the tense in indirect speech if what a person said is still true or relevant or has not happened yet. This often happens when someone talks about the future, or when someone uses the present simple, present continuous or present perfect in their original words:
He told me his brother works for an Italian company. (It is still true that his brother works for an Italian company.)
She said she ’s getting married next year. (For the speakers, the time at the moment of speaking is ‘this year’.)
He said he ’s finished painting the door. (He probably said it just a short time ago.)
She promised she ’ll help us. (The promise applies to the future.)
Indirect speech: changes to pronouns
Changes to personal pronouns in indirect reports depend on whether the person reporting the speech and the person(s) who said the original words are the same or different.
Indirect speech: changes to adverbs and demonstratives
We often change demonstratives ( this, that ) and adverbs of time and place ( now, here, today , etc.) because indirect speech happens at a later time than the original speech, and perhaps in a different place.
Typical changes to demonstratives, adverbs and adverbial expressions
Indirect speech: typical errors.
The word order in indirect reports of wh- questions is the same as statement word order (subject + verb), not question word order:
She always asks me where [S] [V] I am going .
Not: She always asks me where am I going .
We don’t use a question mark when reporting wh- questions:
I asked him what he was doing.
Not: I asked him what he was doing?

Word of the Day
Your browser doesn't support HTML5 audio
to try to persuade a customer who is already buying something to buy more, or to buy something more expensive

Searching out and tracking down: talking about finding or discovering things

Learn more with +Plus
- Recent and Recommended {{#preferredDictionaries}} {{name}} {{/preferredDictionaries}}
- Definitions Clear explanations of natural written and spoken English English Learner’s Dictionary Essential British English Essential American English
- Grammar and thesaurus Usage explanations of natural written and spoken English Grammar Thesaurus
- Pronunciation British and American pronunciations with audio English Pronunciation
- English–Chinese (Simplified) Chinese (Simplified)–English
- English–Chinese (Traditional) Chinese (Traditional)–English
- English–Dutch Dutch–English
- English–French French–English
- English–German German–English
- English–Indonesian Indonesian–English
- English–Italian Italian–English
- English–Japanese Japanese–English
- English–Norwegian Norwegian–English
- English–Polish Polish–English
- English–Portuguese Portuguese–English
- English–Spanish Spanish–English
- English–Swedish Swedish–English
- Dictionary +Plus Word Lists
To add ${headword} to a word list please sign up or log in.
Add ${headword} to one of your lists below, or create a new one.
{{message}}
Something went wrong.
There was a problem sending your report.
Search form
- B1-B2 grammar
Reported speech
Daisy has just had an interview for a summer job.
Instructions
As you watch the video, look at the examples of reported speech. They are in red in the subtitles. Then read the conversation below to learn more. Finally, do the grammar exercises to check you understand, and can use, reported speech correctly.
Sophie: Mmm, it’s so nice to be chilling out at home after all that running around.
Ollie: Oh, yeah, travelling to glamorous places for a living must be such a drag!
Ollie: Mum, you can be so childish sometimes. Hey, I wonder how Daisy’s getting on in her job interview.
Sophie: Oh, yes, she said she was having it at four o’clock, so it’ll have finished by now. That’ll be her ... yes. Hi, love. How did it go?
Daisy: Well, good I think, but I don’t really know. They said they’d phone later and let me know.
Sophie: What kind of thing did they ask you?
Daisy: They asked if I had any experience with people, so I told them about helping at the school fair and visiting old people at the home, that sort of stuff. But I think they meant work experience.
Sophie: I’m sure what you said was impressive. They can’t expect you to have had much work experience at your age.
Daisy: And then they asked me what acting I had done, so I told them that I’d had a main part in the school play, and I showed them a bit of the video, so that was cool.
Sophie: Great!
Daisy: Oh, and they also asked if I spoke any foreign languages.
Sophie: Languages?
Daisy: Yeah, because I might have to talk to tourists, you know.
Sophie: Oh, right, of course.
Daisy: So that was it really. They showed me the costume I’ll be wearing if I get the job. Sending it over ...
Ollie: Hey, sis, I heard that Brad Pitt started out as a giant chicken too! This could be your big break!
Daisy: Ha, ha, very funny.
Sophie: Take no notice, darling. I’m sure you’ll be a marvellous chicken.
We use reported speech when we want to tell someone what someone said. We usually use a reporting verb (e.g. say, tell, ask, etc.) and then change the tense of what was actually said in direct speech.
So, direct speech is what someone actually says? Like 'I want to know about reported speech'?
Yes, and you report it with a reporting verb.
He said he wanted to know about reported speech.
I said, I want and you changed it to he wanted .
Exactly. Verbs in the present simple change to the past simple; the present continuous changes to the past continuous; the present perfect changes to the past perfect; can changes to could ; will changes to would ; etc.
She said she was having the interview at four o’clock. (Direct speech: ' I’m having the interview at four o’clock.') They said they’d phone later and let me know. (Direct speech: ' We’ll phone later and let you know.')
OK, in that last example, you changed you to me too.
Yes, apart from changing the tense of the verb, you also have to think about changing other things, like pronouns and adverbs of time and place.
'We went yesterday.' > She said they had been the day before. 'I’ll come tomorrow.' > He said he’d come the next day.
I see, but what if you’re reporting something on the same day, like 'We went yesterday'?
Well, then you would leave the time reference as 'yesterday'. You have to use your common sense. For example, if someone is saying something which is true now or always, you wouldn’t change the tense.
'Dogs can’t eat chocolate.' > She said that dogs can’t eat chocolate. 'My hair grows really slowly.' > He told me that his hair grows really slowly.
What about reporting questions?
We often use ask + if/whether , then change the tenses as with statements. In reported questions we don’t use question forms after the reporting verb.
'Do you have any experience working with people?' They asked if I had any experience working with people. 'What acting have you done?' They asked me what acting I had done .
Is there anything else I need to know about reported speech?
One thing that sometimes causes problems is imperative sentences.
You mean like 'Sit down, please' or 'Don’t go!'?
Exactly. Sentences that start with a verb in direct speech need a to + infinitive in reported speech.
She told him to be good. (Direct speech: 'Be good!') He told them not to forget. (Direct speech: 'Please don’t forget.')
OK. Can I also say 'He asked me to sit down'?
Yes. You could say 'He told me to …' or 'He asked me to …' depending on how it was said.
OK, I see. Are there any more reporting verbs?
Yes, there are lots of other reporting verbs like promise , remind , warn , advise , recommend , encourage which you can choose, depending on the situation. But say , tell and ask are the most common.
Great. I understand! My teacher said reported speech was difficult.
And I told you not to worry!
Check your grammar: matching
Check your grammar: error correction, check your grammar: gap fill, worksheets and downloads.
What was the most memorable conversation you had yesterday? Who were you talking to and what did they say to you?

Sign up to our newsletter for LearnEnglish Teens
We will process your data to send you our newsletter and updates based on your consent. You can unsubscribe at any time by clicking the "unsubscribe" link at the bottom of every email. Read our privacy policy for more information.
Reported Speech Exercises
Perfect english grammar.

Here's a list of all the reported speech exercises on this site:
( Click here to read the explanations about reported speech )
Reported Statements:
- Present Simple Reported Statement Exercise (quite easy) (in PDF here)
- Present Continuous Reported Statement Exercise (quite easy) (in PDF here)
- Past Simple Reported Statement Exercise (quite easy) (in PDF here)
- Present Perfect Reported Statement Exercise (quite easy) (in PDF here)
- Future Simple Reported Statement Exercise (quite easy) (in PDF here)
- Mixed Tense Reported Statement Exercise (intermediate) (in PDF here)
- 'Say' and 'Tell' (quite easy) (in PDF here)
Reported Questions:
- Present Simple Reported Yes/No Question Exercise (intermediate) (in PDF here)
- Present Simple Reported Wh Question Exercise (intermediate) (in PDF here)
- Mixed Tense Reported Question Exercise (intermediate) (in PDF here)
Reported Orders and Requests:
- Reported Requests and Orders Exercise (intermediate) (in PDF here)
- Reported Speech Mixed Exercise 1 (difficult) (in PDF here)
- Reported Speech Mixed Exercise 2 (difficult) (in PDF here)

Hello! I'm Seonaid! I'm here to help you understand grammar and speak correct, fluent English.

Read more about our learning method

- Linguapress.com
- English grammar
- Advanced reading
- Intermediate reading
- Language games and puzzles
- Linguapress ›
- English grammar
Reported or indirect questions in English
reported questions and verb tenses in english , preliminary points:.
- a) The main thing to remember is that in reported interrogatives, there is no inversion of subject and verb.
- b) Reported speech can be introduced by a lot of different verbs, but most commonly by expressions such as " He asked...... , I wonder..... " etc.
- When there is no question word (as in model M3 ), indirect questions are introduced by if or whether .
1. Reporting the present: simultaneous reporting.
2. reporting the past: deferred reporting., 2.1. reporting the past from the present ..

2.2. Reporting what was the future in the original question.
- Today that day
- Tomorrow the next day, the following day
- Yesterday the day before, the previous day
- Now then, at that moment ,
- In five minutes' (etc) time five minutes (etc.) later
- Here there

Question forms and reported speech
Question forms and reported speech.
1. Normal word order is used in reported questions, that is, the subject comes before the verb, and it is not necessary to use ‘do’ or ‘did’ :
- “Where does Peter live?” —> She asked him where Peter lived .
2. Yes / no questions : This type of question is reported by using ‘ask’ + ‘if / whether + clause :
- “Do you speak English?” —-> He asked me if I spoke English .
- “Are you British or American?” —-> He asked me whether I was British or American.
- “Is it raining?” —–> She asked if it was raining .
- “Have you got a computer?” ——> He wanted to know whether I had a computer .
- “Can you type?” —–> She asked if I could type .
- “Did you come by train?” ——> He enquired whether I had come by train .
- “Have you been to Bristol before?” ——> She asked if I had been to Bristol before .
3. Question words :
This type of question is reported by using ‘ask’ (or another verb like ‘ask’) + question word + clause. The clause contains the question, in normal word order and with the necessary tense change.
- “What is your name?” he asked me. —–> He asked me what my name was .
- “How old is your mother?”, he asked. ——-> He asked how old her mother was .
- The policeman said to the boy, “Where do you live?” ——-> The policeman asked the boy where he lived .
- “What time does the train arrive?” she asked. ——-> She asked what time the train arrived .
- “When can we have dinner?” she asked. ——> She asked when they could have dinner .
- Peter said to John, “Why are you so late?” ——-> Peter asked the John why he was so late .
Note: See also Summary of Reporting Verbs

SPECIAL OFFER YOUR ENGLISH LANGUAGE LEVEL WITH CERTIFICATE
DOWNLOADABLE and PRINTABLE CErtifiCAte
Sample standard test certificate.

The certificate:
Can be downloaded and printed as a PDF file
Your percentage for the test can be checked against the level at https://english4today.com/tests/

Please register or login for the STANDARD TEST plus CERTIFICATE . Your first and family names are used to complete the certificate information. Your email address is required to validate your registration and to send you the full test results.
Englsh4Today Privacy Policy
In this Privacy Policy, “we”, “us” and “our” refers to: English4Today.com.
This is privacy policy sets out how English4Today uses and protects any information that you provide, whilst using English4Today’s products and services . English4Today may change this policy as and when necessary. In the case of changes to this policy, we will provide a more prominent notice (including email notification of privacy policy changes).
1. What information we collect about you and how we use this information
1.1 Account and Profile Information
You don’t have to create an account to use the non-member sections of this website, such as searching and viewing public information areas, forums, topics and posts. If you do choose to create an account, you must provide us with some personal data so that we can provide our services to you. This includes a display name (for example, “John Doe”), nickname (for example, @john-doe) a username (for example, johnxdoe), a password, and an email address. Your display name and nickname is always public, but you can use either your real name or a pseudonym. After the registration your account display name, nickname and username are the same. We recommend to change display name and nickname to keep the username private and secure. You can change those in your account editing page.Once you have registered and created an account, you have the option of adding to your profile information and adjusting your privacy settings:
- Member Title
- Biography (About Me)
- First name and Family name
- Teacher or Student status
- Your English language level
- Social Network Account addresses
- Location (Country / City or Town)
- And other details you have the option to add to your profile information to be displayed to our community.
Additionally, whilst using English4Today the following information may be collected (not public):
- Internet Protocol (IP) address (not public)
- Geographical location
- Browser type and version (not public)
- Operating system (not public)
- Referral source (not public)
- Length of visit, page views, website navigation and any other related browsing activity
Most activity on English4Today is public, including your profile information mentioned above. You also may choose to publish your location in your profile. Information posted about you by other people who use our forum may also be public. For example, other people may mention you using @nickname in posts.You are responsible for your topics, posts and other information you provide through our services, and you should think carefully about what you make public, especially if it is sensitive information.You may choose to register connecting your account to accounts on another service (e.g. Facebook login), and that other service may send us information about your account on that service. We use the information we receive to provide you features like cross-posting or cross-service authentication, and to operate our community. We create new account in our community for you based on your third party account information you share.
1.2 Contact Information
We use your contact information, such as your email address, to authenticate your account and keep it – and our services – secure, and to help prevent spam, fraud, and abuse. We also use contact information to personalise our services, enable certain account features for example, for login verification, reset password, to send you information about our community and notify on new replies to your subscribed forums and topics. You can also unsubscribe from any email notifications.If you email us, we will keep the content of your message, your email address, and your contact information to respond to your request.
1.3 Private Messages and Non-Public Communications
We provide certain features that let you communicate more privately or control who sees your content. We share the content of your Private Messages with the people you’ve sent them to; we do not use them to serve you ads. When you use features like Private Messages to communicate, remember that recipients have their own copy of your communications on English4Today – even if you delete your copy of those messages from your account – which they may duplicate, store, or re-share.
1.4 Cookies
A cookie is a small piece of data that is stored on your computer or mobile device. Like many websites, we use cookies and similar technologies to collect additional website usage data and to operate our community. Although most web browsers automatically accept cookies, many browsers’ settings can be set to decline cookies or alert you when a website is attempting to place a cookie on your computer. However, many of our community features may not function properly if you disable cookies. We do not support the Do Not Track browser option. You can learn more about how we use cookies and similar technologies here.
We use cookies for the following purposes
1.4.1 Authentication – we use cookies to identify you when you visit our community. When you create a topic or post a reply as guest (not registered user) we store your name and email address in cookies. We use this information to detect current visitor content (topics, posts) and display it to you even if the content is under moderation (not approved by moderators). The name is used to display as topic/post author name. Also we store your name and email in cookies to keep filled these fields when you post a new reply or create a new topic (you don’t heave to fill these information every time you post a content). We recommend don’t use guest posting option on non-personal devices, or at least delete browser cookies when you leave it.
1.4.2 Status – we use cookies to help us to determine if you are logged into our website.
1.4.3 Security – we use cookies as an element of the security measures used to protect user accounts, including preventing fraudulent use of login credentials, and to protect our website and services generally. Cookies used by our service providers
1.4.4 Our service providers use cookies and those cookies may be stored on your computer when you visit our website.
1.4.5 We use Google Analytics to analyse the use of our website. Google Analytics gathers information about website use by means of cookies. The information gathered relating to our website is used to create reports about the use of our website. Google’s privacy policy is available at: https://www.google.com/policies/privacy/ .
1.4.6 We publish Google AdSense interest-based advertisements on our website. These are tailored by Google to reflect your interests. We publish Google AdSense advertisements on our website. To determine your interests, Google will track your behaviour on our website and on other websites across the web using cookies. This behaviour tracking allows Google to tailor the advertisements that you see on other websites to reflect your interests (but we do not publish interest-based advertisements on our website). You can view, delete or add interest categories associated with your browser by visiting: https://adssettings.google.com . You can also opt out of the AdSense partner network cookie using those settings or using the Network Advertising Initiative’s multi-cookie opt-out mechanism at: http://optout.networkadvertising.org . However, these opt-out mechanisms themselves use cookies, and if you clear the cookies from your browser your opt-out will not be maintained. To ensure that an opt-out is maintained in respect of a particular browser, you may wish to consider using the Google browser plug-ins available at: https://support.google.com/ads/answer/7395996 .
1.5 Log Data
We receive information when you view content on or otherwise interact with our community, which we refer to as “Log Data,” even if you have not created an account. For example, when you visit our websites, sign into our community, interact with our email notifications, we may receive information about you. This Log Data includes information such as your IP address, browser type, operating system, the referring web page, pages visited, location, your mobile carrier, device information (including device and application IDs), search terms, and cookie information. We use Log Data to operate our services and ensure their secure, reliable, and robust performance. We use information you provide to us and data we receive, including Log Data and data from third parties, to make inferences like what topics you may be interested in and what languages you speak. This helps us better design our services for you and personalize the content we show you.
2. Information We Share and Disclose
2.1 How we share information we collect
You should be aware that any information you provide on our community – including profile information associated with the account you use to post the information – may be read, collected, and used by any member of the community who access the website. Your posts and certain profile information may remain even after you terminate your account. We urge you to consider the sensitivity of any information you input into these Services. To request removal of your information from publicly accessible websites operated by us, please contact us . In some cases, we may not be able to remove your information, in which case we will let you know if we are unable to and why.
2.2 Sharing with third parties
2.2.1 Service Providers: We share information with third parties that help us operate, provide, improve, integrate, customise, support and market our services. We work with third-party service providers to provide website and application development, hosting, maintenance, backup, storage, virtual infrastructure, payment processing, analysis and other services for us, which may require them to access or use information about you. If a service provider needs to access information about you to perform services on our behalf, they do so under close instruction from us, including policies and procedures designed to protect your information.Our administrators may choose to add new functionality or change the behaviour of the community by installing third party apps within the community. Doing so may give third-party apps access to your account and information about you like your name and email address, and any content you choose to use in connection with those apps. Third-party app policies and procedures are not controlled by us, and this privacy policy does not cover how third-party apps use your information. We encourage you to review the privacy policies of third parties before connecting to or using their applications or services to learn more about their privacy and information handling practices. If you object to information about you being shared with these third parties, please uninstall the contact us and let us know as soon as possible.
Below are the third party services we use on our community:
- Akismet (by Automattic Inc.) – Spam fighting service that protects millions of WordPress sites. Automattic Privacy Policy: https://automattic.com/privacy/
- reCAPTCHA (by Google) – Protects internet users from spam and abuse wherever they go. Google Privacy Policy: https://policies.google.com/privacy
2.2.2 Links to Third Party Sites: Our community may include links that direct you to other websites or services whose privacy practices may differ from ours. If you submit information to any of those third party sites, your information is governed by their privacy policies, not this one. We encourage you to carefully read the privacy policy of any website you visit.
2.2.3 Social Media Widgets: The Services may include links that direct you to other websites or services whose privacy practices may differ from ours. Your use of and any information you submit to any of those third-party sites is governed by their privacy policies, not this one.
2.2.4 Third-Party Widgets: Some of our Services contain widgets and social media features, such as the Facebook “share” or Twitter “tweet” buttons. These widgets and features collect your IP address, which page you are visiting on the Services, and may set a cookie to enable the feature to function properly. Widgets and social media features are either hosted by a third party or hosted directly on our Services. Your interactions with these features are governed by the privacy policy of the company providing it.
2.3 Law, Harm, and the Public Interest
Notwithstanding anything to the contrary in this Privacy Policy or controls we may otherwise offer to you, we may preserve, use, or disclose your personal data if we believe that it is reasonably necessary to comply with a law, regulation, legal process, or governmental request; to protect the safety of any person; to protect the safety or integrity of our platform, including to help prevent spam, abuse, or malicious actors on our services, or to explain why we have removed content or accounts from our services; to address fraud, security, or technical issues; or to protect our rights or property or the rights or property of those who use our services. However, nothing in this Privacy Policy is intended to limit any legal defences or objections that you may have to a third party’s, including a government’s, request to disclose your personal data.
2.4 Non-Personal Information
We share or disclose non-personal data, such as aggregated information like the community statistic (online users, visitors, current viewers of a topic, etc…), the number of people who clicked on a particular link (number of topic views) or voted on a poll in a topic (even if only one did).
3. How to access and control your information
3.1 Accessing or Rectifying Your Personal Data
You have the right to request a copy of your information, to object to our use of your information. If you have registered an account on our community, we provide you with tools and account settings to access, correct, delete, or modify the personal data you provided to us and associated with your account. You can request for downloading your account information, including your created content (posts). You also can request correction, deletion, or modification of your personal data.Your request and choices may be limited in certain cases: for example, if fulfilling your request would reveal information about another person, or if you ask to delete information which we or your administrator are permitted by law or have compelling legitimate interests to keep. Where you have asked us to share data with third parties, for example, by installing third-party apps, you will need to contact those third-party service providers directly to have your information deleted or otherwise restricted.
3.2 Deletion Your Personal Data
You can request for your account deletion. This will include personal data, profile data, created content, logs, etc… Cookies should be deleted from your side. Almost all browsers have an option to delete cookies.Keep in mind that search engines and other third parties may still retain copies of your public information, like your profile information, even after we/you have deleted the information from our community.
3.3 Restrict Processing
3.3.1 Request that we stop using your information : In some cases, you may ask us to stop accessing, storing, using and otherwise processing your information where you believe we don’t have the appropriate rights to do so. For example, if you believe a community account was created for you without your permission or you are no longer an active user, you can request that we delete your account (contact us). Where you gave us consent to use your information for a limited purpose, you can contact us to withdraw that consent, but this will not affect any processing that has already taken place at the time. You can also opt-out of our use of your information for marketing purposes by contacting us. When you make such requests, we may need time to investigate and facilitate your request. If there is delay or dispute as to whether we have the right to continue using your information, we will restrict any further use of your information until the request is honored or the dispute is resolved, provided your administrator does not object (where applicable). If you object to information about you being shared with a third-party app, please disable the app or contact your administrator to do so.
3.3.2 Opt out of communications : You may opt out of receiving email notifications related to your subscribed forums and posts or promotional communications from us by using the unsubscribe link within each email, updating your subscription settings in My Profile > Subscription page, or by contacting us as provided below to have your contact information removed from our promotional email list or registration database.
3.4 Data portability
Data portability is the ability to obtain some of your information in a format you can keep in your devices or share with other communities. Depending on the context, this applies to some of your information, but not to all of your information. Should you request it, we will provide you with an electronic file of your basic account information and the information you create on the spaces you under your sole control, like your topics (only with your posts), your replies in other topics, private messages and conversations (only with your messages), etc…
4. How we store and secure information we collect
We use data hosting service providers to host the information we collect, and we use technical measures to secure your data. While we implement safeguards designed to protect your information, no security system is impenetrable and due to the inherent nature of the Internet, we cannot guarantee that data, during transmission through the Internet or while stored on our systems or otherwise in our care, is absolutely safe from intrusion by others.
5. Children and Our Community
Our community is not directed to children, and you may not use our services if you are under the age of 13. You must also be old enough to consent to the processing of your personal data in your country (in some countries we may allow your parent or guardian to do so on your behalf).
6. Online Privacy Policy Only
This online privacy policy applies only to information collected through our website and not to information collected offline.
7. Your Consent To This Policy
By using our site, you consent to our Privacy Policy.
8. Changes To This Privacy Policy
We may update our Privacy Policy from time to time. We will notify you of any changes by posting the new Privacy Policy on this page.We will let you know via email and/or a prominent notice on our Service, prior to the change becoming effective and update the “effective date” at the top of this Privacy Policy.You are advised to review this Privacy Policy periodically for any changes. Changes to this Privacy Policy are effective when they are posted on this page.
9. Contact Us
If you have any questions about this Privacy Policy, please contact us.
Only fill in if you are not human
By continuing to use this website, you consent to the use of cookies in accordance with our Cookie Policy.
- English Grammar
- Reported Speech
Reported Speech - Definition, Rules and Usage with Examples
Reported speech or indirect speech is the form of speech used to convey what was said by someone at some point of time. This article will help you with all that you need to know about reported speech, its meaning, definition, how and when to use them along with examples. Furthermore, try out the practice questions given to check how far you have understood the topic.

Table of Contents
Definition of reported speech, rules to be followed when using reported speech, table 1 – change of pronouns, table 2 – change of adverbs of place and adverbs of time, table 3 – change of tense, table 4 – change of modal verbs, tips to practise reported speech, examples of reported speech, check your understanding of reported speech, frequently asked questions on reported speech in english, what is reported speech.
Reported speech is the form in which one can convey a message said by oneself or someone else, mostly in the past. It can also be said to be the third person view of what someone has said. In this form of speech, you need not use quotation marks as you are not quoting the exact words spoken by the speaker, but just conveying the message.
Now, take a look at the following dictionary definitions for a clearer idea of what it is.
Reported speech, according to the Oxford Learner’s Dictionary, is defined as “a report of what somebody has said that does not use their exact words.” The Collins Dictionary defines reported speech as “speech which tells you what someone said, but does not use the person’s actual words.” According to the Cambridge Dictionary, reported speech is defined as “the act of reporting something that was said, but not using exactly the same words.” The Macmillan Dictionary defines reported speech as “the words that you use to report what someone else has said.”
Reported speech is a little different from direct speech . As it has been discussed already, reported speech is used to tell what someone said and does not use the exact words of the speaker. Take a look at the following rules so that you can make use of reported speech effectively.
- The first thing you have to keep in mind is that you need not use any quotation marks as you are not using the exact words of the speaker.
- You can use the following formula to construct a sentence in the reported speech.
- You can use verbs like said, asked, requested, ordered, complained, exclaimed, screamed, told, etc. If you are just reporting a declarative sentence , you can use verbs like told, said, etc. followed by ‘that’ and end the sentence with a full stop . When you are reporting interrogative sentences, you can use the verbs – enquired, inquired, asked, etc. and remove the question mark . In case you are reporting imperative sentences , you can use verbs like requested, commanded, pleaded, ordered, etc. If you are reporting exclamatory sentences , you can use the verb exclaimed and remove the exclamation mark . Remember that the structure of the sentences also changes accordingly.
- Furthermore, keep in mind that the sentence structure , tense , pronouns , modal verbs , some specific adverbs of place and adverbs of time change when a sentence is transformed into indirect/reported speech.
Transforming Direct Speech into Reported Speech
As discussed earlier, when transforming a sentence from direct speech into reported speech, you will have to change the pronouns, tense and adverbs of time and place used by the speaker. Let us look at the following tables to see how they work.
Here are some tips you can follow to become a pro in using reported speech.
- Select a play, a drama or a short story with dialogues and try transforming the sentences in direct speech into reported speech.
- Write about an incident or speak about a day in your life using reported speech.
- Develop a story by following prompts or on your own using reported speech.
Given below are a few examples to show you how reported speech can be written. Check them out.
- Santana said that she would be auditioning for the lead role in Funny Girl.
- Blaine requested us to help him with the algebraic equations.
- Karishma asked me if I knew where her car keys were.
- The judges announced that the Warblers were the winners of the annual acapella competition.
- Binsha assured that she would reach Bangalore by 8 p.m.
- Kumar said that he had gone to the doctor the previous day.
- Lakshmi asked Teena if she would accompany her to the railway station.
- Jibin told me that he would help me out after lunch.
- The police ordered everyone to leave from the bus stop immediately.
- Rahul said that he was drawing a caricature.
Transform the following sentences into reported speech by making the necessary changes.
1. Rachel said, “I have an interview tomorrow.”
2. Mahesh said, “What is he doing?”
3. Sherly said, “My daughter is playing the lead role in the skit.”
4. Dinesh said, “It is a wonderful movie!”
5. Suresh said, “My son is getting married next month.”
6. Preetha said, “Can you please help me with the invitations?”
7. Anna said, “I look forward to meeting you.”
8. The teacher said, “Make sure you complete the homework before tomorrow.”
9. Sylvester said, “I am not going to cry anymore.”
10. Jade said, “My sister is moving to Los Angeles.”
Now, find out if you have answered all of them correctly.
1. Rachel said that she had an interview the next day.
2. Mahesh asked what he was doing.
3. Sherly said that her daughter was playing the lead role in the skit.
4. Dinesh exclaimed that it was a wonderful movie.
5. Suresh said that his son was getting married the following month.
6. Preetha asked if I could help her with the invitations.
7. Anna said that she looked forward to meeting me.
8. The teacher told us to make sure we completed the homework before the next day.
9. Sylvester said that he was not going to cry anymore.
10. Jade said that his sister was moving to Los Angeles.
What is reported speech?
What is the definition of reported speech.
Reported speech, according to the Oxford Learner’s Dictionary, is defined as “a report of what somebody has said that does not use their exact words.” The Collins Dictionary defines reported speech as “speech which tells you what someone said, but does not use the person’s actual words.” According to the Cambridge Dictionary, reported speech is defined as “the act of reporting something that was said, but not using exactly the same words.” The Macmillan Dictionary defines reported speech as “the words that you use to report what someone else has said.”
What is the formula of reported speech?
You can use the following formula to construct a sentence in the reported speech. Subject said that (report whatever the speaker said)
Give some examples of reported speech.
Given below are a few examples to show you how reported speech can be written.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

Reported Speech Exercise: Questions
Reported speech exercises | reporting questions.
Do the exercises below about the reported speech (questions) and click on the button to check your answers.
(Before doing the exercise you may want to see the lesson on reported speech )
Transform these questions into reported speech (start the sentence with " she asked him ".)
- What is your name? → She asked him
- Where do you live? → She asked him
- What do you do for a living? → She asked him
- What time do you wake up? → She asked him
- Do you have a shower every morning? → She asked him
- Where did you go last weekend? → She asked him
- Why did you go there? → She asked him
- Did you enjoy going there? → She asked him
- Where are you going next weekend? → She asked him
- Will you be with your friends? → She asked him
- Can you take me with you? → She asked him
- What will the weather be like? → She asked him
- How are we going to get there? → She asked him
- Shall we take anything to eat? → She asked him
- What do you want me to bring? → She asked him
- Where are we going to spend the night? → She asked him
- Shall I take clean blankets? → She asked him
- Can I invite a friend of mine? → She asked him
- Are you sure? → She asked him
- What time shall we get back? → She asked him
Related materials
- Reported speech exercise (mixed)
- Reported speech exercise (questions)
- Reported speech exercise (requests and commands)
- Reported speech lesson

- ELT Concourse home
- A-Z site index
- Teacher training index
- Teacher development
- For teachers
- For trainers
- For managers
- For learners
- About language
- Language questions
- Other areas
- Academic English
- Business English
- Entering ELT
- Courses index
- Basic ELT course
- Language analysis
- Training to train
- Transcription

Indirect or embedded questions

In some analyses, the term embedded question is reserved for the function of being oblique and more polite when asking a question and the term indirect question is used for reported questions. This is not a necessary distinction because the forms are parallel but it is a useful one because the term indirect is often applied to reported speech and separating out the functions is useful when designing a teaching programme.
In the guide to interrogatives on this site, 5 sorts of question are identified. The following, however, only applies to two types of questions:
- Closed Yes / No / Maybe questions such as Have you spent all your money? He did it, didn't he? And alternative questions such as: Are you coming or not?
- Wh- questions such as Where are you going? How is this done? What do you want? Why did you do that? Who called? Who(m) did you ask? Which shop did you go to?
Both these sorts of questions can be formed as embedded questions or as indirect questions in reported speech.
Before we get to considering how indirect questions work syntactically, we need to ask what functions embedded or indirect questions realise. Fundamentally, there are four discrete functions but the forms are parallel.
- Requests: Something like: Could you tell me what his address is? is not a question asking about the hearer's ability; it is a simple request for cooperation.
- Offers: Something like: Let me know if you want my help is also not a question; it's an offer to help.
- Advice: Something like: Couldn't you find out how long it will last? is not a question; it's advice.
- Orders and imperatives Questions can be embedded in imperatives so we get, for example: Find out when the train leaves Tell me what the cost will be and these can, of course, be softened when power relationships are equal so we can also have: Please be good enough to tell me when the train leaves I wonder if you can tell me what the cost will be and so on.
- Reference to a third person When we are unable to pose the question directly to a third person but are asking an intermediary, we often embed the question. For example: Do you know if John drinks red or white wine usually? Does she need to know what time I'm arriving? Let me know whether she wants any help etc.
- Indirect or reported speech In reported speech any question will become embedded in a statement of what someone said so, instead of: *He asked what is my address? which is the form in many languages, English alters the syntax to produce: He asked me what my address is. That is not intuitive and causes learners considerable problems up to and including quite high levels of syntactical mastery. Reported speech, of course, also requires adjustments to pronouns, time adverbials and much else, not least tense forms but they are covered elsewhere in the guide to reported or indirect speech linked in the list of related guides at the end. Such issues will not be considered here.
Only the first of these functions usually requires the use of a question form when the very common forms with can and could are used. Politeness tactics do not always take that form as we shall see.
The syntax of such questions varies depending on the question type and we will take the issues one by one but include examples of all four functions because the forms are identical.
These are open only to three sorts of answer, although the responder may well feel obliged to add further information immediately to clarify the response. For example, the question: Do you want to eat? can be responded to:
- positively with, e.g.: Yes Rather! What a good idea! Do I!? etc.
- or negatively with, e.g.: Not just now No thanks It's too early I'm not hungry
- or by temporising with, e.g.: I'm not sure Maybe If we must Ask me later etc.
The three functions of embedded Yes / No / Maybe questions involve the same syntactical choices.
Overwhelmingly, the choice is to use if or whether to form the embedded syntax, like this:
There are two primary issues:
- There is a difference between, for example Tell me if you need anything which means only tell me when and only when a need arises. It is, in other words conditional on your needing something. I only expect to hear from you if you do. However, Tell me whether you need anything is not contingent because you are to tell me in either case. If you do not need something, you must tell me and if you do need something you must tell me. In other words, the conjunction whether is not conditional. There is no contingency that needs to be satisfied. Using if can sometimes lead to ambiguity so, for example: Let me know me if he wants my help may be considered conditional or not and have two possible meanings: You are to tell me only if he wants my help or I want to know whether or not he wants my help
- The other issue is that when reporting verbalised questions, the use of either if or whether is allowed so we have, for example: "Can I come?" he asked may be reported as He asked whether he could come or as He asked if he could come. On the other hand, when we report internal thoughts such as: "Shall I go?" he asked himself we would normally allow only He wondered whether he would go and not *He wondered if he would go This is more of a tendency than an absolute rule.
- We also see a preference for whether when embedding or reporting alternative questions such as: Are you ready or not? which will usually be embedded or reported as Tell me whether you are ready or not Can you tell me whether you are ready or not? She asked me whether I was ready or not but not as: Tell me if you are ready or not Can you tell me if you are ready or not? She asked me if I was ready or not Again, the forms with if are not unheard of, just rare and slightly unnatural.
There are seven common wh-word s which form normal, unembedded questions: who, what, why, when, which, where, how. Syntactically, these all follow the same rules when they are embedded in any of the four functions we have seen above. Like this:
There are two issues embedded wh-question s. The first is syntactical and important, the second slightly peripheral.
The first issue is the same as the first we encountered with closed questions: syntax.
It bears repeating that this reversion to a declarative statement word order in English is not something that happens in a wide range of other languages, so the forms do not come easily and errors will occur very frequently at all levels.
The second issue is that if the direct question is formed with who, which or what with the verb be as part of the predicate, it is possible to disturb the word order outlined above. For example:
Presenting this small issue to learners who are already struggling to get the usual word ordering of embedded questions right is probably perilous.
The main issue with indirect and embedded questions in English is syntactical rather than semantic. All languages can embed questions for effect but few cultures are so obsessive about using the politeness tactics of which Anglophone nations are so fond. How questions are reported is also very variable across languages with many reserving a special tense for these kinds of grammatical functions and some using subjunctive forms and a bewildering array of other syntactical phenomena.
The first issue is often cultural. While it may be perfectly acceptable and comprehensible to go to an information desk and say: Where is the toilet? it is usually more effective to ask something like: Can you tell me where the toilet is, please?
The second issue is setting the forms in a wider picture of indirect speech. Indirect speech in English often requires quite complex alterations to adverbials of place and time, tense forms and pronoun structures so reporting: "Please would you put these tools back into the garden shed over there before Monday", he said is no mean matter and may result in: He asked us politely to return the tools we had with us to the garden shed on the right of his house before the following Monday. Reported questions, on the other hand, are rarely so complex (although tense shifting is common) and, if learners are already familiar with the politeness tactic of embedding a question, it is a useful way in to a complex grammatical area.
One way to conceptualise how embedded and indirect questions work in English is to explain how they are parallel with the simpler forms. The grammatical structure of ordinary questions is fundamentally either:
What can happen with questions is that the simple noun phrases we have above are replaced by clauses acting as noun phrases (nominalised clauses) so we get, instead:
Once learners can see that the clauses are acting simple as object noun phrases, much becomes clearer (or can do). So for example, if learners can successfully form: Can you tell me the story? Let me know the truth Do you know the right road? etc. They can also form: Can you tell me why he did that ? Let me know when you are coming ? Do you know how to open this ? because the clauses in black are nominalised and acting as simple nouns.
Too often, the teaching of embedded and indirect questions starts and stops with something like: Can tell me ... Could you tell me ... That's short-changing learners somewhat because, as we see above, there are many more ways of structuring an embedded question. Because the structures which follows the introductory signal remain constant, other ways of leading into an embedded question are easy to teach and significantly broaden learners' ability to be precise, deferential or insistent and clear. For example, instead of the modal auxiliary verb, can / could we may have:
Because many of the alternatives are even more polite than the commoner forms (or sometimes less polite when they are imperatives), it is important to set the context and identify the roles of the participants clearly or learners may well be lured into producing stylistic error, of course. Embedded and indirect questions are routinely used between strangers, so common contexts include many service encounters. When embedded questions are used in imperatives, the power relationships need to be borne in mind:
Contact | FAQs | Copyright notice | ELT Concourse charter | Disclaimer and Privacy statement | Search ELT Concourse
Ukraine war latest: Moscow accuses West of being responsible for attacks in Russia; two dead in airstrike on major city
At least two people have been killed and more than a dozen injured in a reported Russian attack on Ukraine's second-largest city of Kharkiv. Russia says it sees the US and UK as responsible for recent attacks on its soil.
Friday 17 May 2024 17:37, UK
Please use Chrome browser for a more accessible video player
- Two dead and 13 injured in Kharkiv attack
- Russia claims UK is 'de facto participant' in conflict | Moscow says it holds US and UK responsible for attacks on Russian soil
- Russian troops advance - but situation 'stabilised', says Zelenskyy
- Putin: Capturing major city 'not part of plan'
- Footage shows oil refinery fire and burning fuel depots after 'massive' overnight attack
- Analysis: Great power politics on display in China visit
- Were Putin and Xi really pictured with their 'nuclear footballs'?
- Live reporting by Brad Young and (earlier) Narbeh Minassian
Ask a question or make a comment
One person has been killed and another eight injured in a Russian missile attack near the Black Sea port of Odesa, a Ukrainian official has said.
Regional governor Oleh Kiper said five people were being treated in hospital. He posted pictures showing emergency workers near the scene of the strike.
Sky News has not independently verified the report.
Odesa has been a frequent target of Russian missile and drone attacks.
President Vladimir Putin used his meeting with Chinese counterpart Xi Jinping to "promote Kremlin narratives feigning interest in peace negotiations", analysts at the Institute for the Study of War say.
The pair signed a joint statement yesterday alluding to Russia's support for the China's proposed peace plan and a possible future Chinese-led negotiation to end the war in Ukraine.
In the statement, they claim both countries support a "sustainable settlement" for the "Ukraine crisis".
The ISW said it has "previously assessed" the Kremlin will "continue to use any calls for peace negotiations to feign interest in negotiations" in the hope of undermining Western support for Ukraine.
Moscow also hopes the West will force Ukraine into negotiations with Russia that make concessions on Ukrainian sovereignty and territorial integrity, the ISW added.
'Decisive' relationship
Meanwhile, the institute says, Mr Putin likely views Moscow's relationship with Beijing as "decisive" in his bid to further mobilise the Russian economy and defence industry to support his war in Ukraine.
"Putin and Xi highlighted bilateral trade and economic cooperation throughout their public speeches," the ISW says, adding the Russian delegation includes officials and businessmen.
"The Russian delegation likely aimed to expand cooperation with their Chinese counterparts that will facilitate increased economic ties between Russia and the PRC [People's Republic of China]."
China has previously signalled concerns its economic relationship with Russia may open it up to sanctions, the ISW says, and Mr Putin "likely intends to head off these concerns as the Russian defence industry grows increasingly reliant on the PRC".
Earlier today, we reported how a purported Ukrainian drone attack caused a fire at an oil refinery in Krasnodar, Russia.
The blaze has forced an emergency shut down at the facility, owned by Rosneft, two sources familiar with the matter have told Reuters.
According to one source, the drones hit the liquefied petroleum gas production unit while the crude distillation unit remained undamaged.
"There was no black smoke during the fire. That means it was just the gas burning", a source said.
Russia's state-run TASS news agency reported the fire was extinguished, citing local authorities.
The Russian defence ministry said air defences downed 44 drones over the Krasnodar region and six over the Belgorod region.
For context: The Tuapse plant's annual capacity is 12 million metric tons, or 240,000 barrels per day.
It produces naphtha, fuel oil, vacuum gasoil and high-sulphur diesel, and supplies fuel mainly Turkey, China, Malaysia and Singapore.
Most Russians would support an end to the war in Ukraine this week - but only if newly-gained territories were not returned.
That's according to the independent Levada Centre , Russia's best known pollster, which ran a survey to canvass public opinion on Vladimir Putin and the war.
While 71% would back an end to the war "this week", this figure drops to just 30% if the condition for peace were to return territories.
Since September last year, Levada reports the level of support for the Russian army has stayed at about 75%, with older respondents more likely to remain in favour.
Mr Putin's approval rating appears to be at about 82%, the pollster reports.
However, those aged between 18 and 24 appear less likely to back M Putin, with 77% not approving of his activities as president.
Former Ukrainian president Petro Poroshenko says no one should trust Vladimir Putin when he says he won't invade Russia's second city, Kharkiv.
The Russian leader does not have an opportunity to capture Kharkiv right now due to Ukraine's defensive forces, he said.
But in Vovchansk, where Mr Poroshenko visited yesterday, the town has been turned into "hell" - with no people or houses left.
"Don't trust Putin. Don't be afraid of Putin," he said.
"I can confirm that our strategy shall be as follows: Ukraine shall win, and Russia, undoubtedly, shall lose."
Moscow says it sees the US and UK as responsible for recent attacks because they are allowing Ukraine to use Western weapons against Russian targets.
The Russian foreign ministry said the UK, US, EU and Kyiv were "playing with fire" over attacks on Russian soil, state news agency Tass reports.
Such actions will not go unanswered, it warned.
"Once again, we should like to unequivocally warn Washington, London, Brussels and other Western capitals, as well as Kyiv, which is under their control, that they are playing with fire. Russia will not leave such encroachments on its territory unanswered."
Earlier today, Russia's ambassador to the UK said the UK was a de facto participant in the war.
This was because it has supplied Kyiv with weapons and shared real-time intelligence, said Andrei Kelin.
The number of victims from a reported Russian airstrike has risen, officials say.
At least two people are now said to have died, with another 13 injured - four of whom are in a "serious condition", regional governor Oleh Syniehubov said.
It is not clear what the attack targeted, but Mr Syniehubov said those injured are civilians.
Reports had initially claimed one person had died and four injured.
Kharkiv, Ukraine's second largest city, and the surrounding region have long been targeted by Russian attacks but the strikes have become more intense in recent months.
Ukraine President Volodymyr Zelenskyy has accused Moscow of seeking to reduce the city to rubble.
A Ukrainian drone hit another oil terminal this morning, this time in the Russian Black Sea port of Novorossiisk, according to sources and footage shared on social media.
The Importpischeprom oil products terminal and Sheskharis oil harbour were struck, with the port shut soon after the attack.
Oil loadings resumed later from Sheskharis, according to industry sources and LSEG data, while activity at Importpischeprom remains suspended.
It came as Russian officials reported another drone attack on an oil refinery, causing a fire in Tuapse, which is roughly 150km southeast of Novorossiisk.
Both are in the Krasnodar region.
Russian oil pipeline monopoly Transneftdid not reply to a request for comment. Its subsidiary, Novorossiisk Commercial Sea Port Group (NCSP), which operates the Sheskharis oil terminal, declined to comment.
Novorossiisk is Russia's largest port on the Black Sea and is a key oil outlet for crude oil and transit in country's south. It also handles grain, coal, mineral fertilisers, timber, containers, food and chemical cargoes.
Four people have been hurt and at least one has died in an airstrike on the city of Kharkiv, according to local officials.
The regional governor says some of those injured are civilians, while it's reported Russia used guided bombs in the attack.
It's not immediately clear what exactly came under attack.
More now on the comments made earlier by the Ukrainian army's commander-in-chief Oleksandr Syrskyi (see our 10.21am post).
He said he expects fighting to intensify as Russia continues to attack Kharkiv - with Sumy the next possible target, roughly 170km northwest.
Russia's attack on Kharkiv has expanded the area of active fighting by almost 70km, he added, which was designed to force Ukraine to divert stretched resources to the region.
In comments on the Telegram messaging app, he said the main focus of Russia's attack is towards the area of Lyptsi and further east in Vovchansk - as our military analyst Michael Clarke reported earlier (1.27pm).
Mr Syrskyi said Russia attacked early after noticing a change in troops, but they "failed to break through".
He added Ukraine "must prevent further advance" by "inflicting maximum losses with air strikes, missile systems, artillery and tank fire".
Be the first to get Breaking News
Install the Sky News app for free

VCU students walk out of commencement during Youngkin address
VCU students who walked out said they were demonstrating support for Palestinians and protesting some of the Republican governor’s crusade against efforts to promote racial equity in education.
RICHMOND — Dozens of Virginia Commonwealth University students walked out of their graduation ceremony Saturday morning as Gov. Glenn Youngkin delivered the commencement address, demonstrating support for Palestinians and protesting some of the Republican’s crusade against efforts to promote racial equity in education.
The selection of Youngkin as speaker drew criticism from some ahead of the ceremony. The university’s chapter of the NAACP this week urged VCU officials to rescind the invitation, and some students in recent days said they would hold a walkout during the ceremony.
College protests over Gaza war

On Saturday, attendees at the commencement were given cards congratulating the graduating class but warning that anyone who disrupted the ceremony was subject to removal.
As Youngkin began his speech, dozens of the graduates in attendance filed out of the Greater Richmond Convention Center, mostly in silence, some holding kaffiyeh scarves and signs aloft. “Teach Black history,” one read. “Book bans [do not equal] respect for learning,” read another.
The protest did not disrupt the program, though an initial burst of applause for the protesters briefly drowned out the governor’s speech. Youngkin pressed on with his address, which included a tribute to his late mother and an extended symphony metaphor.
“The world needs your music,” he said.
Spokesmen for VCU and the governor’s office declined to comment on the walkout.
More than 4,700 VCU students graduated this spring, about 3,000 of them undergraduates. It is a diverse student body, representing 40 countries. More than 900 were first-generation college students, VCU said ahead of the ceremony.
Adding to tensions on Saturday, the ceremony came about two weeks after police used pepper spray to disperse a crowd at a pro-Palestinian demonstration on VCU’s campus. Thirteen people, including six students, were arrested.
The event was among the demonstrations spreading on college campuses around the country, with more than 2,800 arrested as campus officials and protesters facing off in recent weeks. In Virginia, more than 80 people were arrested at Virginia Tech in Blacksburg , a dozen at the University of Mary Washington in Fredericksburg and more than 25 at the University of Virginia .
VCU, in downtown Richmond just a mile west of the state Capitol, has a long tradition of hosting the sitting governor as commencement speaker. Terry McAuliffe (D) gave the address in 2015, as did Robert F. McDonnell (R) in 2011, Tim Kaine (D) in 2008, Mark R. Warner (D) in 2004, Jim Gilmore (R) in 1999 and George Allen (R) in 1997, according to the university.
The VCU chapter of the NAACP sent a letter to university President Michael Rao and the board of visitors Wednesday demanding that the university revoke the governor’s invitation to speak. “Since becoming Governor of Virginia, Youngkin has worked to intimidate and silence educators with anti-racist pedagogies,” the letter stated, citing a short-lived tip line for parents to report the teaching of “divisive concepts” and the reversal of protections for transgender youth.
Asked about the calls to cancel his appearance, Youngkin said Tuesday he hoped the focus would be on the students and their achievements. “I think that anyone who thinks they’re going to disrupt this for their own personal goals, I think it’s misguided,” Youngkin told reporters at an event in Richmond. “Let’s celebrate the students. Let’s honor the students.”
Opposition to Youngkin was due, in part, to the governor’s objections to a proposal to require VCU students to take a course in racial literacy. The school conceived the plan amid the racial reckoning that followed the 2020 murder of George Floyd by Minneapolis police and was still working to implement it when Youngkin raised concerns early this year.
In March, a Youngkin spokesman said the governor was concerned that such a mandate would promote leftist “groupthink.” “Virginia’s public institutions should be teaching our students how to think, not what to think and not advancing ideological conformity,” spokesman Christian Martinez told Virginia Public Media .
On Friday, VCU’s governing board voted against requiring the racial literacy course, but will still make some courses available for interested students.
“Central to the board’s deliberations was a commitment to upholding academic freedom while empowering students with flexibility and autonomy in their educational journey,” VCU said in a written statement after the vote. “The discussion clearly expressed support for the racial literacy classes, and these courses are accessible to students who wish to explore them.”
Outside the convention center, Taya Coates, a mass communications graduate, said she was on the fence about walking out until the students around her started to rise. She decided that she, too, wanted to stand against the governor, who she said didn’t reflect her values.
“It just doesn’t represent our university,” Coates, 23, said of Youngkin’s appearance. Around her, friends embraced and cried. Families cheered for their graduates, posing for photos and remarking about how proud they were of the display.
A smaller group of graduates joined a group of demonstrators outside the convention center. The group marched through the streets chanting “Free Palestine” until they reached Abner Clay Park, about a half mile from the commencement ceremony.
A handful of graduates, still in their caps and gowns, spoke about why they walked out.
Arrington Evans, a political science graduate and member of the NAACP at VCU, said the governor’s actions, particularly his opposition to equity initiatives in education, was in opposition to the kind of work she had been advocating for at VCU.
“This matters more to me, doing right by your classmates and the people in your community, than sitting there doing nothing,” Evans said. “Actions speak louder than words. And that’s what this was.”
In his speech, Youngkin did not acknowledge the protest or make any reference to the politically strife moment. He highlighted some members of the graduating class, including an immigrant from Uganda and another who had overcome cancer. Youngkin advised graduates to “make tomorrow better than today,” choose their “life partner” wisely and be slow to anger.
Before the walkout, Saturday’s graduation began like any other, with robed and smiling graduates waving to relatives and snapping selfies as they marched into the ceremony.
The ceremony wrapped in ordinary fashion two hours later, with black and gold balloons dropping from the ceiling and getting batted around like beach balls.
The walkout was for many a forgettable blip in an otherwise celebratory day. That was a relief to attendees who’d arrived wary of potential disruptions or even violence.
“I’m just hoping that doesn’t happen and we can be here and celebrate these graduates in peace,” LaKeyda Robinson, 45, of Alexandria, said as she watched her “firstborn niece,” Dhasia Allen, walk into the ceremony.
Marcos Chavez, a 54-year-old Bolivian immigrant who works as carpenter in Herndon, was not giving a thought to Gaza or Youngkin. For him, the day was all about his daughter, Natalia. Already the first person in the family to earn a college degree, on Saturday she graduated from VCU’s school of dentistry.
“Right now my focus is on my daughter,” he said. “That’s it.”

- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
Your Health
- Treatments & Tests
- Health Inc.
- Public Health
Why writing by hand beats typing for thinking and learning
Jonathan Lambert

If you're like many digitally savvy Americans, it has likely been a while since you've spent much time writing by hand.
The laborious process of tracing out our thoughts, letter by letter, on the page is becoming a relic of the past in our screen-dominated world, where text messages and thumb-typed grocery lists have replaced handwritten letters and sticky notes. Electronic keyboards offer obvious efficiency benefits that have undoubtedly boosted our productivity — imagine having to write all your emails longhand.
To keep up, many schools are introducing computers as early as preschool, meaning some kids may learn the basics of typing before writing by hand.
But giving up this slower, more tactile way of expressing ourselves may come at a significant cost, according to a growing body of research that's uncovering the surprising cognitive benefits of taking pen to paper, or even stylus to iPad — for both children and adults.
Is this some kind of joke? A school facing shortages starts teaching standup comedy
In kids, studies show that tracing out ABCs, as opposed to typing them, leads to better and longer-lasting recognition and understanding of letters. Writing by hand also improves memory and recall of words, laying down the foundations of literacy and learning. In adults, taking notes by hand during a lecture, instead of typing, can lead to better conceptual understanding of material.
"There's actually some very important things going on during the embodied experience of writing by hand," says Ramesh Balasubramaniam , a neuroscientist at the University of California, Merced. "It has important cognitive benefits."
While those benefits have long been recognized by some (for instance, many authors, including Jennifer Egan and Neil Gaiman , draft their stories by hand to stoke creativity), scientists have only recently started investigating why writing by hand has these effects.
A slew of recent brain imaging research suggests handwriting's power stems from the relative complexity of the process and how it forces different brain systems to work together to reproduce the shapes of letters in our heads onto the page.
Your brain on handwriting
Both handwriting and typing involve moving our hands and fingers to create words on a page. But handwriting, it turns out, requires a lot more fine-tuned coordination between the motor and visual systems. This seems to more deeply engage the brain in ways that support learning.

Shots - Health News
Feeling artsy here's how making art helps your brain.
"Handwriting is probably among the most complex motor skills that the brain is capable of," says Marieke Longcamp , a cognitive neuroscientist at Aix-Marseille Université.
Gripping a pen nimbly enough to write is a complicated task, as it requires your brain to continuously monitor the pressure that each finger exerts on the pen. Then, your motor system has to delicately modify that pressure to re-create each letter of the words in your head on the page.
"Your fingers have to each do something different to produce a recognizable letter," says Sophia Vinci-Booher , an educational neuroscientist at Vanderbilt University. Adding to the complexity, your visual system must continuously process that letter as it's formed. With each stroke, your brain compares the unfolding script with mental models of the letters and words, making adjustments to fingers in real time to create the letters' shapes, says Vinci-Booher.
That's not true for typing.
To type "tap" your fingers don't have to trace out the form of the letters — they just make three relatively simple and uniform movements. In comparison, it takes a lot more brainpower, as well as cross-talk between brain areas, to write than type.
Recent brain imaging studies bolster this idea. A study published in January found that when students write by hand, brain areas involved in motor and visual information processing " sync up " with areas crucial to memory formation, firing at frequencies associated with learning.
"We don't see that [synchronized activity] in typewriting at all," says Audrey van der Meer , a psychologist and study co-author at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology. She suggests that writing by hand is a neurobiologically richer process and that this richness may confer some cognitive benefits.
Other experts agree. "There seems to be something fundamental about engaging your body to produce these shapes," says Robert Wiley , a cognitive psychologist at the University of North Carolina, Greensboro. "It lets you make associations between your body and what you're seeing and hearing," he says, which might give the mind more footholds for accessing a given concept or idea.
Those extra footholds are especially important for learning in kids, but they may give adults a leg up too. Wiley and others worry that ditching handwriting for typing could have serious consequences for how we all learn and think.
What might be lost as handwriting wanes
The clearest consequence of screens and keyboards replacing pen and paper might be on kids' ability to learn the building blocks of literacy — letters.
"Letter recognition in early childhood is actually one of the best predictors of later reading and math attainment," says Vinci-Booher. Her work suggests the process of learning to write letters by hand is crucial for learning to read them.
"When kids write letters, they're just messy," she says. As kids practice writing "A," each iteration is different, and that variability helps solidify their conceptual understanding of the letter.
Research suggests kids learn to recognize letters better when seeing variable handwritten examples, compared with uniform typed examples.
This helps develop areas of the brain used during reading in older children and adults, Vinci-Booher found.
"This could be one of the ways that early experiences actually translate to long-term life outcomes," she says. "These visually demanding, fine motor actions bake in neural communication patterns that are really important for learning later on."
Ditching handwriting instruction could mean that those skills don't get developed as well, which could impair kids' ability to learn down the road.
"If young children are not receiving any handwriting training, which is very good brain stimulation, then their brains simply won't reach their full potential," says van der Meer. "It's scary to think of the potential consequences."
Many states are trying to avoid these risks by mandating cursive instruction. This year, California started requiring elementary school students to learn cursive , and similar bills are moving through state legislatures in several states, including Indiana, Kentucky, South Carolina and Wisconsin. (So far, evidence suggests that it's the writing by hand that matters, not whether it's print or cursive.)
Slowing down and processing information
For adults, one of the main benefits of writing by hand is that it simply forces us to slow down.
During a meeting or lecture, it's possible to type what you're hearing verbatim. But often, "you're not actually processing that information — you're just typing in the blind," says van der Meer. "If you take notes by hand, you can't write everything down," she says.
The relative slowness of the medium forces you to process the information, writing key words or phrases and using drawing or arrows to work through ideas, she says. "You make the information your own," she says, which helps it stick in the brain.
Such connections and integration are still possible when typing, but they need to be made more intentionally. And sometimes, efficiency wins out. "When you're writing a long essay, it's obviously much more practical to use a keyboard," says van der Meer.
Still, given our long history of using our hands to mark meaning in the world, some scientists worry about the more diffuse consequences of offloading our thinking to computers.
"We're foisting a lot of our knowledge, extending our cognition, to other devices, so it's only natural that we've started using these other agents to do our writing for us," says Balasubramaniam.
It's possible that this might free up our minds to do other kinds of hard thinking, he says. Or we might be sacrificing a fundamental process that's crucial for the kinds of immersive cognitive experiences that enable us to learn and think at our full potential.
Balasubramaniam stresses, however, that we don't have to ditch digital tools to harness the power of handwriting. So far, research suggests that scribbling with a stylus on a screen activates the same brain pathways as etching ink on paper. It's the movement that counts, he says, not its final form.
Jonathan Lambert is a Washington, D.C.-based freelance journalist who covers science, health and policy.
- handwriting

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Reported questions are one form of reported speech. direct question. reported question. She said: "Are you cold?" She asked me if I was cold. He said: "Where's my pen?" He asked where his pen was. We usually introduce reported questions with the verb "ask": He asked (me) if / whether ...
Reported Speech Questions: Yes/No Questions. - We use "if" or "whether" to introduce a "yes‑no question". Example: Direct speech: "Did you receive my e-mail?". Reported speech: The teacher asked me if I had received his e-mail. OR The teacher asked me whether I had received his e-mail.
Watch my reported speech video: Here's how it works: We use a 'reporting verb' like 'say' or 'tell'. ( Click here for more about using 'say' and 'tell' .) If this verb is in the present tense, it's easy. We just put 'she says' and then the sentence: Direct speech: I like ice cream. Reported speech: She says (that) she likes ice cream.
You can do this while speaking or writing. There are two kinds of reported speech you can use: direct speech and indirect speech. I'll break each down for you. A direct speech sentence mentions the exact words the other person said. For example: Kryz said, "These are all my necklaces.". Indirect speech changes the original speaker's words.
Reported speech is different from direct speech because it does not use the speaker's exact words. Instead, the reporting verb is used to introduce the reported speech, and the tense and pronouns are changed to reflect the shift in perspective. There are two main types of reported speech: statements and questions. 1.
Reported Questions. When we report what people say, we usually change the tense of the verbs to reflect that we are reporting - not giving direct speech. This pattern is followed when we report questions and there are also other important changes between direct questions and reported questions. Reported questions are one form of reported speech.
When we report questions, the subject comes before the verb. Direct speech: "Where are you going?". Reported speech: He asked me where I was going. Direct speech: "Why is he shouting?". Reported speech: He asked me why he was shouting. Direct speech: "What do you want?". Reported speech: She asked me what I wanted.
Question Sentences. When turning questions into indirect speech, we have to pay attention to the following points:. As in a declarative sentence, we have to change the pronouns, the time and place information, and set the tense back (backshift).; Instead of that, we use a question word.If there is no question word, we use whether/if instead. Example: She asked him, "How often do you work?"
Reported speech: He asked if he would see me later. In the direct speech example you can see the modal verb 'will' being used to ask a question. Notice how in reported speech the modal verb 'will' and the reporting verb 'ask' are both written in the past tense. So, 'will' becomes 'would' and 'ask' becomes 'asked'.
When we use reported speech, we often change the verb tense backwards in time. This can be called "backshift.". Here are some examples in different verb tenses: "I want to go home.". She said she wanted to go home. "I 'm reading a good book.". She said she was reading a good book. "I ate pasta for dinner last night.".
Requests/orders. "Asked me to" is used for requests. "Told me to" is stronger; it is used for orders/commands. She asked me to make copies. He told me to go to the bank. 2. Yes/no questions. "Asked if" and "wanted to know if" are equal. We don't use the auxiliary verbs "do/does/did" in the reported question.
Reported speech: indirect speech - English Grammar Today - a reference to written and spoken English grammar and usage - Cambridge Dictionary
As you watch the video, look at the examples of reported speech. They are in red in the subtitles. Then read the conversation below to learn more. Finally, do the grammar exercises to check you understand, and can use, reported speech correctly. ... In reported questions we don't use question forms after the reporting verb.
Questions and imperatives in indirect speech. Download full-size image from Pinterest. We use the normal order of words in reported questions: subject + verb. We don't use an auxiliary verb like do or did. When we report an order or instruction, we use the form ask or tell someone to do something.
Lots of reported speech exercises - practise using free interactive quizzes. Login Contact Courses Membership Speaking Explanations Exercises Method. ... Reported Questions: Present Simple Reported Yes/No Question Exercise (intermediate) (in PDF here) Present Simple Reported Wh Question Exercise (intermediate)
Reported or indirect questions in English Reported questions and verb tenses in English While expressing reported statements in English is relatively easy to master, putting direct questions into reported speech can often cause problems for the learner. The simplest way to master the rules or structures is to start with a few varied direct questions, and use them as models.
1. Normal word order is used in reported questions, that is, the subject comes before the verb, and it is not necessary to use 'do' or 'did': "Where does Peter live?" —> She asked him where Peter lived. 2. Yes / no questions: This type of question is reported by using 'ask' + 'if / whether + clause: "Do you speak English ...
Andrew, "Will Mandy have lunch with Sue?" Andrew asked me . Justin, "What are you doing?" Justin asked me . Frank, "How much pocket money does Lisa get?" Frank wanted to know . Anne, "Must I do the shopping?" Anne asked . Reported questions in English, Questions, Question, Online Exercise.
Reported speech is the form in which one can convey a message said by oneself or someone else, mostly in the past. It can also be said to be the third person view of what someone has said. In this form of speech, you need not use quotation marks as you are not quoting the exact words spoken by the speaker, but just conveying the message. Q2.
Do the exercises below about the reported speech (questions) and click on the button to check your answers. (Before doing the exercise you may want to see the lesson on reported speech ) Transform these questions into reported speech (start the sentence with " she asked him ".)
for an alternative way to look at reported or embedded questions inter alia: reported or indirect speech: for the in-service guide to the area which includes some consideration of reported questions and reporting verbs: a simpler guide: for the guide to indirect questions in the initial plus section of the site
TikTok and its parent company on Tuesday filed a legal challenge against the United States over a law that President Biden signed last month, which would outlaw the app nationwide unless it found ...
We have reported this morning Russia claimed a Ukrainian drone attack caused a fire at an oil refinery in Krasnodar (see our 6.44am post). Footage shared by The Wall Street Journal's chief foreign ...
President Joe Biden and former President Donald Trump have both accepted an invitation from CNN to debate on June 27, a historically early showdown that will set the tone for the final months of ...
President Biden and Donald Trump have agreed to two debates on June 27 on CNN and Sept. 10 on ABC News, raising the likelihood of the earliest general-election debate in modern history. The early ...
6 min. 0. RICHMOND — Dozens of Virginia Commonwealth University students walked out of their graduation ceremony Saturday morning as Gov. Glenn Youngkin delivered the commencement address ...
By Michael Gold. May 12, 2024. In an extended riff at his rally on Saturday in New Jersey, former President Donald J. Trump returned to a reference that has become a staple of his stump speech ...
The president announced increased taxes on Chinese imports in strategic industries, building on former President Donald J. Trump's tariffs.
Researchers are learning that handwriting engages the brain in ways typing can't match, raising questions about the costs of ditching this age-old practice, especially for kids.
Twelve percent of Democrats hold Mr. Biden responsible, according to New York Times/Siena College polls in Arizona, Georgia, Michigan, Nevada and Wisconsin and a Times/Philadelphia Inquirer/Siena ...