

Chapter 2. Research Design
Getting started.
When I teach undergraduates qualitative research methods, the final product of the course is a “research proposal” that incorporates all they have learned and enlists the knowledge they have learned about qualitative research methods in an original design that addresses a particular research question. I highly recommend you think about designing your own research study as you progress through this textbook. Even if you don’t have a study in mind yet, it can be a helpful exercise as you progress through the course. But how to start? How can one design a research study before they even know what research looks like? This chapter will serve as a brief overview of the research design process to orient you to what will be coming in later chapters. Think of it as a “skeleton” of what you will read in more detail in later chapters. Ideally, you will read this chapter both now (in sequence) and later during your reading of the remainder of the text. Do not worry if you have questions the first time you read this chapter. Many things will become clearer as the text advances and as you gain a deeper understanding of all the components of good qualitative research. This is just a preliminary map to get you on the right road.

Research Design Steps
Before you even get started, you will need to have a broad topic of interest in mind. [1] . In my experience, students can confuse this broad topic with the actual research question, so it is important to clearly distinguish the two. And the place to start is the broad topic. It might be, as was the case with me, working-class college students. But what about working-class college students? What’s it like to be one? Why are there so few compared to others? How do colleges assist (or fail to assist) them? What interested me was something I could barely articulate at first and went something like this: “Why was it so difficult and lonely to be me?” And by extension, “Did others share this experience?”
Once you have a general topic, reflect on why this is important to you. Sometimes we connect with a topic and we don’t really know why. Even if you are not willing to share the real underlying reason you are interested in a topic, it is important that you know the deeper reasons that motivate you. Otherwise, it is quite possible that at some point during the research, you will find yourself turned around facing the wrong direction. I have seen it happen many times. The reason is that the research question is not the same thing as the general topic of interest, and if you don’t know the reasons for your interest, you are likely to design a study answering a research question that is beside the point—to you, at least. And this means you will be much less motivated to carry your research to completion.
Researcher Note
Why do you employ qualitative research methods in your area of study? What are the advantages of qualitative research methods for studying mentorship?
Qualitative research methods are a huge opportunity to increase access, equity, inclusion, and social justice. Qualitative research allows us to engage and examine the uniquenesses/nuances within minoritized and dominant identities and our experiences with these identities. Qualitative research allows us to explore a specific topic, and through that exploration, we can link history to experiences and look for patterns or offer up a unique phenomenon. There’s such beauty in being able to tell a particular story, and qualitative research is a great mode for that! For our work, we examined the relationships we typically use the term mentorship for but didn’t feel that was quite the right word. Qualitative research allowed us to pick apart what we did and how we engaged in our relationships, which then allowed us to more accurately describe what was unique about our mentorship relationships, which we ultimately named liberationships ( McAloney and Long 2021) . Qualitative research gave us the means to explore, process, and name our experiences; what a powerful tool!
How do you come up with ideas for what to study (and how to study it)? Where did you get the idea for studying mentorship?
Coming up with ideas for research, for me, is kind of like Googling a question I have, not finding enough information, and then deciding to dig a little deeper to get the answer. The idea to study mentorship actually came up in conversation with my mentorship triad. We were talking in one of our meetings about our relationship—kind of meta, huh? We discussed how we felt that mentorship was not quite the right term for the relationships we had built. One of us asked what was different about our relationships and mentorship. This all happened when I was taking an ethnography course. During the next session of class, we were discussing auto- and duoethnography, and it hit me—let’s explore our version of mentorship, which we later went on to name liberationships ( McAloney and Long 2021 ). The idea and questions came out of being curious and wanting to find an answer. As I continue to research, I see opportunities in questions I have about my work or during conversations that, in our search for answers, end up exposing gaps in the literature. If I can’t find the answer already out there, I can study it.
—Kim McAloney, PhD, College Student Services Administration Ecampus coordinator and instructor
When you have a better idea of why you are interested in what it is that interests you, you may be surprised to learn that the obvious approaches to the topic are not the only ones. For example, let’s say you think you are interested in preserving coastal wildlife. And as a social scientist, you are interested in policies and practices that affect the long-term viability of coastal wildlife, especially around fishing communities. It would be natural then to consider designing a research study around fishing communities and how they manage their ecosystems. But when you really think about it, you realize that what interests you the most is how people whose livelihoods depend on a particular resource act in ways that deplete that resource. Or, even deeper, you contemplate the puzzle, “How do people justify actions that damage their surroundings?” Now, there are many ways to design a study that gets at that broader question, and not all of them are about fishing communities, although that is certainly one way to go. Maybe you could design an interview-based study that includes and compares loggers, fishers, and desert golfers (those who golf in arid lands that require a great deal of wasteful irrigation). Or design a case study around one particular example where resources were completely used up by a community. Without knowing what it is you are really interested in, what motivates your interest in a surface phenomenon, you are unlikely to come up with the appropriate research design.
These first stages of research design are often the most difficult, but have patience . Taking the time to consider why you are going to go through a lot of trouble to get answers will prevent a lot of wasted energy in the future.
There are distinct reasons for pursuing particular research questions, and it is helpful to distinguish between them. First, you may be personally motivated. This is probably the most important and the most often overlooked. What is it about the social world that sparks your curiosity? What bothers you? What answers do you need in order to keep living? For me, I knew I needed to get a handle on what higher education was for before I kept going at it. I needed to understand why I felt so different from my peers and whether this whole “higher education” thing was “for the likes of me” before I could complete my degree. That is the personal motivation question. Your personal motivation might also be political in nature, in that you want to change the world in a particular way. It’s all right to acknowledge this. In fact, it is better to acknowledge it than to hide it.
There are also academic and professional motivations for a particular study. If you are an absolute beginner, these may be difficult to find. We’ll talk more about this when we discuss reviewing the literature. Simply put, you are probably not the only person in the world to have thought about this question or issue and those related to it. So how does your interest area fit into what others have studied? Perhaps there is a good study out there of fishing communities, but no one has quite asked the “justification” question. You are motivated to address this to “fill the gap” in our collective knowledge. And maybe you are really not at all sure of what interests you, but you do know that [insert your topic] interests a lot of people, so you would like to work in this area too. You want to be involved in the academic conversation. That is a professional motivation and a very important one to articulate.
Practical and strategic motivations are a third kind. Perhaps you want to encourage people to take better care of the natural resources around them. If this is also part of your motivation, you will want to design your research project in a way that might have an impact on how people behave in the future. There are many ways to do this, one of which is using qualitative research methods rather than quantitative research methods, as the findings of qualitative research are often easier to communicate to a broader audience than the results of quantitative research. You might even be able to engage the community you are studying in the collecting and analyzing of data, something taboo in quantitative research but actively embraced and encouraged by qualitative researchers. But there are other practical reasons, such as getting “done” with your research in a certain amount of time or having access (or no access) to certain information. There is nothing wrong with considering constraints and opportunities when designing your study. Or maybe one of the practical or strategic goals is about learning competence in this area so that you can demonstrate the ability to conduct interviews and focus groups with future employers. Keeping that in mind will help shape your study and prevent you from getting sidetracked using a technique that you are less invested in learning about.
STOP HERE for a moment
I recommend you write a paragraph (at least) explaining your aims and goals. Include a sentence about each of the following: personal/political goals, practical or professional/academic goals, and practical/strategic goals. Think through how all of the goals are related and can be achieved by this particular research study . If they can’t, have a rethink. Perhaps this is not the best way to go about it.
You will also want to be clear about the purpose of your study. “Wait, didn’t we just do this?” you might ask. No! Your goals are not the same as the purpose of the study, although they are related. You can think about purpose lying on a continuum from “ theory ” to “action” (figure 2.1). Sometimes you are doing research to discover new knowledge about the world, while other times you are doing a study because you want to measure an impact or make a difference in the world.
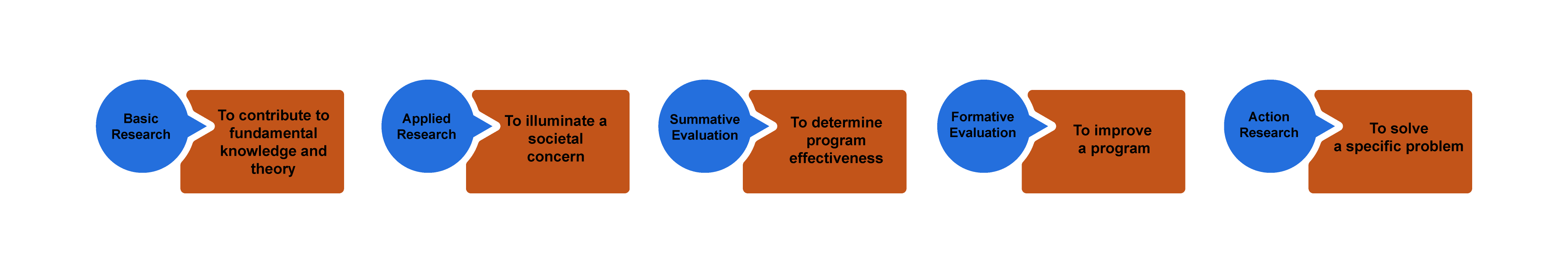
Basic research involves research that is done for the sake of “pure” knowledge—that is, knowledge that, at least at this moment in time, may not have any apparent use or application. Often, and this is very important, knowledge of this kind is later found to be extremely helpful in solving problems. So one way of thinking about basic research is that it is knowledge for which no use is yet known but will probably one day prove to be extremely useful. If you are doing basic research, you do not need to argue its usefulness, as the whole point is that we just don’t know yet what this might be.
Researchers engaged in basic research want to understand how the world operates. They are interested in investigating a phenomenon to get at the nature of reality with regard to that phenomenon. The basic researcher’s purpose is to understand and explain ( Patton 2002:215 ).
Basic research is interested in generating and testing hypotheses about how the world works. Grounded Theory is one approach to qualitative research methods that exemplifies basic research (see chapter 4). Most academic journal articles publish basic research findings. If you are working in academia (e.g., writing your dissertation), the default expectation is that you are conducting basic research.
Applied research in the social sciences is research that addresses human and social problems. Unlike basic research, the researcher has expectations that the research will help contribute to resolving a problem, if only by identifying its contours, history, or context. From my experience, most students have this as their baseline assumption about research. Why do a study if not to make things better? But this is a common mistake. Students and their committee members are often working with default assumptions here—the former thinking about applied research as their purpose, the latter thinking about basic research: “The purpose of applied research is to contribute knowledge that will help people to understand the nature of a problem in order to intervene, thereby allowing human beings to more effectively control their environment. While in basic research the source of questions is the tradition within a scholarly discipline, in applied research the source of questions is in the problems and concerns experienced by people and by policymakers” ( Patton 2002:217 ).
Applied research is less geared toward theory in two ways. First, its questions do not derive from previous literature. For this reason, applied research studies have much more limited literature reviews than those found in basic research (although they make up for this by having much more “background” about the problem). Second, it does not generate theory in the same way as basic research does. The findings of an applied research project may not be generalizable beyond the boundaries of this particular problem or context. The findings are more limited. They are useful now but may be less useful later. This is why basic research remains the default “gold standard” of academic research.
Evaluation research is research that is designed to evaluate or test the effectiveness of specific solutions and programs addressing specific social problems. We already know the problems, and someone has already come up with solutions. There might be a program, say, for first-generation college students on your campus. Does this program work? Are first-generation students who participate in the program more likely to graduate than those who do not? These are the types of questions addressed by evaluation research. There are two types of research within this broader frame; however, one more action-oriented than the next. In summative evaluation , an overall judgment about the effectiveness of a program or policy is made. Should we continue our first-gen program? Is it a good model for other campuses? Because the purpose of such summative evaluation is to measure success and to determine whether this success is scalable (capable of being generalized beyond the specific case), quantitative data is more often used than qualitative data. In our example, we might have “outcomes” data for thousands of students, and we might run various tests to determine if the better outcomes of those in the program are statistically significant so that we can generalize the findings and recommend similar programs elsewhere. Qualitative data in the form of focus groups or interviews can then be used for illustrative purposes, providing more depth to the quantitative analyses. In contrast, formative evaluation attempts to improve a program or policy (to help “form” or shape its effectiveness). Formative evaluations rely more heavily on qualitative data—case studies, interviews, focus groups. The findings are meant not to generalize beyond the particular but to improve this program. If you are a student seeking to improve your qualitative research skills and you do not care about generating basic research, formative evaluation studies might be an attractive option for you to pursue, as there are always local programs that need evaluation and suggestions for improvement. Again, be very clear about your purpose when talking through your research proposal with your committee.
Action research takes a further step beyond evaluation, even formative evaluation, to being part of the solution itself. This is about as far from basic research as one could get and definitely falls beyond the scope of “science,” as conventionally defined. The distinction between action and research is blurry, the research methods are often in constant flux, and the only “findings” are specific to the problem or case at hand and often are findings about the process of intervention itself. Rather than evaluate a program as a whole, action research often seeks to change and improve some particular aspect that may not be working—maybe there is not enough diversity in an organization or maybe women’s voices are muted during meetings and the organization wonders why and would like to change this. In a further step, participatory action research , those women would become part of the research team, attempting to amplify their voices in the organization through participation in the action research. As action research employs methods that involve people in the process, focus groups are quite common.
If you are working on a thesis or dissertation, chances are your committee will expect you to be contributing to fundamental knowledge and theory ( basic research ). If your interests lie more toward the action end of the continuum, however, it is helpful to talk to your committee about this before you get started. Knowing your purpose in advance will help avoid misunderstandings during the later stages of the research process!
The Research Question
Once you have written your paragraph and clarified your purpose and truly know that this study is the best study for you to be doing right now , you are ready to write and refine your actual research question. Know that research questions are often moving targets in qualitative research, that they can be refined up to the very end of data collection and analysis. But you do have to have a working research question at all stages. This is your “anchor” when you get lost in the data. What are you addressing? What are you looking at and why? Your research question guides you through the thicket. It is common to have a whole host of questions about a phenomenon or case, both at the outset and throughout the study, but you should be able to pare it down to no more than two or three sentences when asked. These sentences should both clarify the intent of the research and explain why this is an important question to answer. More on refining your research question can be found in chapter 4.
Chances are, you will have already done some prior reading before coming up with your interest and your questions, but you may not have conducted a systematic literature review. This is the next crucial stage to be completed before venturing further. You don’t want to start collecting data and then realize that someone has already beaten you to the punch. A review of the literature that is already out there will let you know (1) if others have already done the study you are envisioning; (2) if others have done similar studies, which can help you out; and (3) what ideas or concepts are out there that can help you frame your study and make sense of your findings. More on literature reviews can be found in chapter 9.
In addition to reviewing the literature for similar studies to what you are proposing, it can be extremely helpful to find a study that inspires you. This may have absolutely nothing to do with the topic you are interested in but is written so beautifully or organized so interestingly or otherwise speaks to you in such a way that you want to post it somewhere to remind you of what you want to be doing. You might not understand this in the early stages—why would you find a study that has nothing to do with the one you are doing helpful? But trust me, when you are deep into analysis and writing, having an inspirational model in view can help you push through. If you are motivated to do something that might change the world, you probably have read something somewhere that inspired you. Go back to that original inspiration and read it carefully and see how they managed to convey the passion that you so appreciate.
At this stage, you are still just getting started. There are a lot of things to do before setting forth to collect data! You’ll want to consider and choose a research tradition and a set of data-collection techniques that both help you answer your research question and match all your aims and goals. For example, if you really want to help migrant workers speak for themselves, you might draw on feminist theory and participatory action research models. Chapters 3 and 4 will provide you with more information on epistemologies and approaches.
Next, you have to clarify your “units of analysis.” What is the level at which you are focusing your study? Often, the unit in qualitative research methods is individual people, or “human subjects.” But your units of analysis could just as well be organizations (colleges, hospitals) or programs or even whole nations. Think about what it is you want to be saying at the end of your study—are the insights you are hoping to make about people or about organizations or about something else entirely? A unit of analysis can even be a historical period! Every unit of analysis will call for a different kind of data collection and analysis and will produce different kinds of “findings” at the conclusion of your study. [2]
Regardless of what unit of analysis you select, you will probably have to consider the “human subjects” involved in your research. [3] Who are they? What interactions will you have with them—that is, what kind of data will you be collecting? Before answering these questions, define your population of interest and your research setting. Use your research question to help guide you.
Let’s use an example from a real study. In Geographies of Campus Inequality , Benson and Lee ( 2020 ) list three related research questions: “(1) What are the different ways that first-generation students organize their social, extracurricular, and academic activities at selective and highly selective colleges? (2) how do first-generation students sort themselves and get sorted into these different types of campus lives; and (3) how do these different patterns of campus engagement prepare first-generation students for their post-college lives?” (3).
Note that we are jumping into this a bit late, after Benson and Lee have described previous studies (the literature review) and what is known about first-generation college students and what is not known. They want to know about differences within this group, and they are interested in ones attending certain kinds of colleges because those colleges will be sites where academic and extracurricular pressures compete. That is the context for their three related research questions. What is the population of interest here? First-generation college students . What is the research setting? Selective and highly selective colleges . But a host of questions remain. Which students in the real world, which colleges? What about gender, race, and other identity markers? Will the students be asked questions? Are the students still in college, or will they be asked about what college was like for them? Will they be observed? Will they be shadowed? Will they be surveyed? Will they be asked to keep diaries of their time in college? How many students? How many colleges? For how long will they be observed?
Recommendation
Take a moment and write down suggestions for Benson and Lee before continuing on to what they actually did.
Have you written down your own suggestions? Good. Now let’s compare those with what they actually did. Benson and Lee drew on two sources of data: in-depth interviews with sixty-four first-generation students and survey data from a preexisting national survey of students at twenty-eight selective colleges. Let’s ignore the survey for our purposes here and focus on those interviews. The interviews were conducted between 2014 and 2016 at a single selective college, “Hilltop” (a pseudonym ). They employed a “purposive” sampling strategy to ensure an equal number of male-identifying and female-identifying students as well as equal numbers of White, Black, and Latinx students. Each student was interviewed once. Hilltop is a selective liberal arts college in the northeast that enrolls about three thousand students.
How did your suggestions match up to those actually used by the researchers in this study? It is possible your suggestions were too ambitious? Beginning qualitative researchers can often make that mistake. You want a research design that is both effective (it matches your question and goals) and doable. You will never be able to collect data from your entire population of interest (unless your research question is really so narrow to be relevant to very few people!), so you will need to come up with a good sample. Define the criteria for this sample, as Benson and Lee did when deciding to interview an equal number of students by gender and race categories. Define the criteria for your sample setting too. Hilltop is typical for selective colleges. That was a research choice made by Benson and Lee. For more on sampling and sampling choices, see chapter 5.
Benson and Lee chose to employ interviews. If you also would like to include interviews, you have to think about what will be asked in them. Most interview-based research involves an interview guide, a set of questions or question areas that will be asked of each participant. The research question helps you create a relevant interview guide. You want to ask questions whose answers will provide insight into your research question. Again, your research question is the anchor you will continually come back to as you plan for and conduct your study. It may be that once you begin interviewing, you find that people are telling you something totally unexpected, and this makes you rethink your research question. That is fine. Then you have a new anchor. But you always have an anchor. More on interviewing can be found in chapter 11.
Let’s imagine Benson and Lee also observed college students as they went about doing the things college students do, both in the classroom and in the clubs and social activities in which they participate. They would have needed a plan for this. Would they sit in on classes? Which ones and how many? Would they attend club meetings and sports events? Which ones and how many? Would they participate themselves? How would they record their observations? More on observation techniques can be found in both chapters 13 and 14.
At this point, the design is almost complete. You know why you are doing this study, you have a clear research question to guide you, you have identified your population of interest and research setting, and you have a reasonable sample of each. You also have put together a plan for data collection, which might include drafting an interview guide or making plans for observations. And so you know exactly what you will be doing for the next several months (or years!). To put the project into action, there are a few more things necessary before actually going into the field.
First, you will need to make sure you have any necessary supplies, including recording technology. These days, many researchers use their phones to record interviews. Second, you will need to draft a few documents for your participants. These include informed consent forms and recruiting materials, such as posters or email texts, that explain what this study is in clear language. Third, you will draft a research protocol to submit to your institutional review board (IRB) ; this research protocol will include the interview guide (if you are using one), the consent form template, and all examples of recruiting material. Depending on your institution and the details of your study design, it may take weeks or even, in some unfortunate cases, months before you secure IRB approval. Make sure you plan on this time in your project timeline. While you wait, you can continue to review the literature and possibly begin drafting a section on the literature review for your eventual presentation/publication. More on IRB procedures can be found in chapter 8 and more general ethical considerations in chapter 7.
Once you have approval, you can begin!
Research Design Checklist
Before data collection begins, do the following:
- Write a paragraph explaining your aims and goals (personal/political, practical/strategic, professional/academic).
- Define your research question; write two to three sentences that clarify the intent of the research and why this is an important question to answer.
- Review the literature for similar studies that address your research question or similar research questions; think laterally about some literature that might be helpful or illuminating but is not exactly about the same topic.
- Find a written study that inspires you—it may or may not be on the research question you have chosen.
- Consider and choose a research tradition and set of data-collection techniques that (1) help answer your research question and (2) match your aims and goals.
- Define your population of interest and your research setting.
- Define the criteria for your sample (How many? Why these? How will you find them, gain access, and acquire consent?).
- If you are conducting interviews, draft an interview guide.
- If you are making observations, create a plan for observations (sites, times, recording, access).
- Acquire any necessary technology (recording devices/software).
- Draft consent forms that clearly identify the research focus and selection process.
- Create recruiting materials (posters, email, texts).
- Apply for IRB approval (proposal plus consent form plus recruiting materials).
- Block out time for collecting data.
- At the end of the chapter, you will find a " Research Design Checklist " that summarizes the main recommendations made here ↵
- For example, if your focus is society and culture , you might collect data through observation or a case study. If your focus is individual lived experience , you are probably going to be interviewing some people. And if your focus is language and communication , you will probably be analyzing text (written or visual). ( Marshall and Rossman 2016:16 ). ↵
- You may not have any "live" human subjects. There are qualitative research methods that do not require interactions with live human beings - see chapter 16 , "Archival and Historical Sources." But for the most part, you are probably reading this textbook because you are interested in doing research with people. The rest of the chapter will assume this is the case. ↵
One of the primary methodological traditions of inquiry in qualitative research, ethnography is the study of a group or group culture, largely through observational fieldwork supplemented by interviews. It is a form of fieldwork that may include participant-observation data collection. See chapter 14 for a discussion of deep ethnography.
A methodological tradition of inquiry and research design that focuses on an individual case (e.g., setting, institution, or sometimes an individual) in order to explore its complexity, history, and interactive parts. As an approach, it is particularly useful for obtaining a deep appreciation of an issue, event, or phenomenon of interest in its particular context.
The controlling force in research; can be understood as lying on a continuum from basic research (knowledge production) to action research (effecting change).
In its most basic sense, a theory is a story we tell about how the world works that can be tested with empirical evidence. In qualitative research, we use the term in a variety of ways, many of which are different from how they are used by quantitative researchers. Although some qualitative research can be described as “testing theory,” it is more common to “build theory” from the data using inductive reasoning , as done in Grounded Theory . There are so-called “grand theories” that seek to integrate a whole series of findings and stories into an overarching paradigm about how the world works, and much smaller theories or concepts about particular processes and relationships. Theory can even be used to explain particular methodological perspectives or approaches, as in Institutional Ethnography , which is both a way of doing research and a theory about how the world works.
Research that is interested in generating and testing hypotheses about how the world works.
A methodological tradition of inquiry and approach to analyzing qualitative data in which theories emerge from a rigorous and systematic process of induction. This approach was pioneered by the sociologists Glaser and Strauss (1967). The elements of theory generated from comparative analysis of data are, first, conceptual categories and their properties and, second, hypotheses or generalized relations among the categories and their properties – “The constant comparing of many groups draws the [researcher’s] attention to their many similarities and differences. Considering these leads [the researcher] to generate abstract categories and their properties, which, since they emerge from the data, will clearly be important to a theory explaining the kind of behavior under observation.” (36).
An approach to research that is “multimethod in focus, involving an interpretative, naturalistic approach to its subject matter. This means that qualitative researchers study things in their natural settings, attempting to make sense of, or interpret, phenomena in terms of the meanings people bring to them. Qualitative research involves the studied use and collection of a variety of empirical materials – case study, personal experience, introspective, life story, interview, observational, historical, interactional, and visual texts – that describe routine and problematic moments and meanings in individuals’ lives." ( Denzin and Lincoln 2005:2 ). Contrast with quantitative research .
Research that contributes knowledge that will help people to understand the nature of a problem in order to intervene, thereby allowing human beings to more effectively control their environment.
Research that is designed to evaluate or test the effectiveness of specific solutions and programs addressing specific social problems. There are two kinds: summative and formative .
Research in which an overall judgment about the effectiveness of a program or policy is made, often for the purpose of generalizing to other cases or programs. Generally uses qualitative research as a supplement to primary quantitative data analyses. Contrast formative evaluation research .
Research designed to improve a program or policy (to help “form” or shape its effectiveness); relies heavily on qualitative research methods. Contrast summative evaluation research
Research carried out at a particular organizational or community site with the intention of affecting change; often involves research subjects as participants of the study. See also participatory action research .
Research in which both researchers and participants work together to understand a problematic situation and change it for the better.
The level of the focus of analysis (e.g., individual people, organizations, programs, neighborhoods).
The large group of interest to the researcher. Although it will likely be impossible to design a study that incorporates or reaches all members of the population of interest, this should be clearly defined at the outset of a study so that a reasonable sample of the population can be taken. For example, if one is studying working-class college students, the sample may include twenty such students attending a particular college, while the population is “working-class college students.” In quantitative research, clearly defining the general population of interest is a necessary step in generalizing results from a sample. In qualitative research, defining the population is conceptually important for clarity.
A fictional name assigned to give anonymity to a person, group, or place. Pseudonyms are important ways of protecting the identity of research participants while still providing a “human element” in the presentation of qualitative data. There are ethical considerations to be made in selecting pseudonyms; some researchers allow research participants to choose their own.
A requirement for research involving human participants; the documentation of informed consent. In some cases, oral consent or assent may be sufficient, but the default standard is a single-page easy-to-understand form that both the researcher and the participant sign and date. Under federal guidelines, all researchers "shall seek such consent only under circumstances that provide the prospective subject or the representative sufficient opportunity to consider whether or not to participate and that minimize the possibility of coercion or undue influence. The information that is given to the subject or the representative shall be in language understandable to the subject or the representative. No informed consent, whether oral or written, may include any exculpatory language through which the subject or the representative is made to waive or appear to waive any of the subject's rights or releases or appears to release the investigator, the sponsor, the institution, or its agents from liability for negligence" (21 CFR 50.20). Your IRB office will be able to provide a template for use in your study .
An administrative body established to protect the rights and welfare of human research subjects recruited to participate in research activities conducted under the auspices of the institution with which it is affiliated. The IRB is charged with the responsibility of reviewing all research involving human participants. The IRB is concerned with protecting the welfare, rights, and privacy of human subjects. The IRB has the authority to approve, disapprove, monitor, and require modifications in all research activities that fall within its jurisdiction as specified by both the federal regulations and institutional policy.
Introduction to Qualitative Research Methods Copyright © 2023 by Allison Hurst is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Have an account?

Qualitative Research
80 questions

Introducing new Paper mode
No student devices needed. Know more
Triangulation is a validation approach based on the search for the __________ of results obtained by multiple sources and perspectives.
convergence
A researcher who utilizes methods triangulation __________.
mixes research methods with non overlapping strengths and weaknesses
examines multiple theories in order to explain study results
uses multiple methods of data collection to capture a single phenomenon
corroborates the observations of multiple observers
Researchers conducting a qualitative study focus on exploring the world as it occurs __________ in order to capture participants’ perspectives.
artificially
Data collected in qualitative research are analyzed and interpreted and then written using ________.
statistical
passive-voice
third-person
Qualitative research uses the _________ or _________ part of an inclusive scientific method.
Qualitative research focuses on studying particular people, groups, schools, and places.
Qualitative research is just the opinion of the researcher and is based only on idiosyncratic and anecdotal information.
Qualitative research uses an inductive mode of science and often focuses on exploration and discovery.
_______ research usually focuses on the relationships among variables, while ______ attempts to understand concrete human reality in its local context, with all of its complexity.
Answer the first blank only
Quantitative
Qualitative
Which of the following is an example or characteristic of using a “holistic” approach in qualitative research?
Transcribing a distinctive communication pattern of a community member
focusing only on the data available on a single day within a study
Documenting the ethnic background of a study participant
Describing the established cultural norms of a given population
The __________________ of qualitative research contend that knowledge is socially constructed and relativistic.
Epistemology
View of Thought & Behavior
Research Focus
Perspectives on ______________ in qualitative studies are fluid and highly contextualized in qualitative research, providing researchers with many situational perspectives.
The ____________ of qualitative students involves a “wide-angle” lens to capture the entirety, of a phenomenon.
In qualitative research __________ emphasizes individuals’ personal realities and truths rather than objective or universal ones.
Another term for criterion-based selection is __________.
response rate sampling
purposive sampling
typical-case sampling
random sampling
A type of sampling in which the researcher specifies the characteristics of the population of interest and locates individuals with those characteristics is called?
quota sampling
snowball sampling
convenience sampling
__________is a small group of research participants discussing issues in one setting at the same time.
an interview
a focus group
an observation
a questionnaire
In qualitative research, “designs” refers ______?
research methods
research objectives
research studies
Phenomenology-
Describing individuals’ experiences of a particular event, such as the death of a loved one
Addressing research questions through in-depth analysis of a single (small group of people) instance(s) or individuals
Inductively generating a theory explain a process
Describing lives/ stories to add to understanding
Ethnography-
Inductively generating a theory explaining a process
Describing cultural characteristics of a group of people
Narrative Inquiry-
Describing individuals’ experiences of an event, such as the death of a loved one
Describing individuals’ experiences of a event, such as the death of a loved one
Grounded Theory-
A study that intends to describe the shared beliefs and practices of individuals living in a community in the foothills of the Appalachian Mountains would be an example of which type of qualitative research?
phenomenology
ethnography
narrative inquiry
grounded theory
A researcher interviews 20–30 women who are in abusive relationships and from this research she develops a theory to explain the dynamics of abusive relationships. This would likely be an example of which type of qualitative research?
A researcher interviews college students to learn more about their experiences of learning from bad instructors. This would be an example of which type of qualitative research?
absence divergence
The researcher assumes that each case is special and unique. The first level of analysis is being true to, respecting, and capturing the details of the individual cases being studied; cross-case analysis follows from—and depends on—the quality of individual case studies.
unique case orientation
inductive analysis and creative synthesis
holistic perspective
context sensitivity
voice, perspective, and reflexivity
The researcher seeks immersion in the details and specifics of the data to discover important patterns, themes, and interrelationships. Begins by exploring, then confirming; is guided by analytical principles rather than rules. Study ends with a creative synthesis.
The whole phenomenon under study is understood as a complex system that is more than the sum of its parts. The focus is on complex interdependencies and system dynamics that cannot meaningfully be reduced to a few discrete variables and linear, cause-effect relationships.
The researcher places findings in a social, historical, and temporal context and is careful about, even dubious of, the possibility or meaningfulness of generalizations across time and space. Emphasizes instead careful comparative case analyses and extrapolating patterns for possible transferability to and adaptation in new settings.
The qualitative analyst owns and is reflective about her or his own voice and perspective; a credible voice conveys authenticity and trustworthiness. Complete objectivity being impossible and pure subjectivity undermining credibility, the researcher’s focus is on balance—understanding and depicting the world authentically in all its complexity while being self-analytical, politically aware, and reflexive in consciousness.
Qualitative researchers often conduct data collection and analysis ___________ during the study process.
in repeated cycles over time
at a single point in time
Data collection and analysis in qualitative studies are often _________.
triangulated and thematic
statistical and time-limited
Refers to the use of multiple forms of data to capture a single phenomenon. These data provide the opportunity for cross-checking or researcher interpretations.
data triangulation
investigator triangulation
methods triangulation
theory triangulation
Involves the use of multiple observers to record and describe the research participants’ behavior and context. These observers assess the degree to which their observations are corroborated in order to enhance the credibility and defensibility of the results.
investigation triangulation
Refers to the use of a mix of methods for organizing the study and collecting data with an objective of combining different methods that have non overlapping weaknesses and strengths.
Involves the use of a variety of theories and perspectives to explain the phenomena under study (including prior theories and/or other researchers). These contrasting perspectives can provide researchers with insights and help in the development of a more cogent explanation that fits their data.
Use a wide-angle and “deep-angle” lens, examining the breadth and depth of phenomena to learn anything and everything that might be important.
quantitative research
qualitative research
mixed methods research
action research
Which of the following is not a common objective of qualitative research?
Laboratory experimentation
Naturalistic observation
Unobtrusive observation
Holistic descriptions
Which method of research allows qualitative studies' explanations to develop throughout the process?
A specific culture’s language differentiates one concept (e.g., snow) into many varied types not recognized in outside populations. This is known as ______________.
demographic area
mistranslation
epidemiology research
linguistic relativity
Ontology and epistemology are examples of ___________ within the context of research.
philosophical assumptions
theoretical frameworks
analysis techniques
design strategies
In qualitative data collection, which term refers to participants self-reporting instruments?
questionnaires
observations
secondary data
focus groups
After selecting a research topic, what is the next major step in the process of qualitative study?
design the study
collect data
determine research questions
generate findings
Positivism is a belief that all true knowledge must be based on ____.
observation
Postmodernism emphasizes the primacy of individuality, fragmentation, constant change, and _________.
Case study narrative reports include a _______.
discussion of themes issues, and implications
description of invariant structures
discussion of evolving stories and relationships
description of cultural theme contexts
Which theoretical framework utilizes coding to build explanatory models during the data analysis phase?
narrative Inquiry
An established “strength” of qualitative research occurs when data is collected in which kind of setting?
small population pool
naturalistic
unrepeatable
researcher-biased
Qualitative researchers try to understand multiple layers of reality in research settings. Which of the following is NOT an example of one of these layers?
relationships between participants
types of people in a group
results from outside studies
established cultural norms
In qualitative research, the researchers can also be known as the _________ of data collection.
manipulator
The qualitative analysis strategy focusing on complex interdependencies and system dynamics is __________.
inductive analysis
reflexivity
Qualitative studies can often suffer from which limitation?
insight into participants construct interpretation
access to local contexts
cross-case comparisons
lower credibility with some authorities
According to the module, ________ is not considered a key component of qualitative research.
lab results are
special jargons are
quality criteria are
The theoretical framework of “Grounded Theory” originates from....
Which arrow represents the inductive method of qualitative research?
The exploratory arrow
The confirmatory arrow
The arrow from Theory to Hypotheses, Predictions
The arrow from Hypotheses, Predictions to Observations, Data
Qualitative researchers use a ________ approach?
Which major research approach seeks to understand people’s subjective and shared experiences through systematic observation?
Mixed Methods
Describe whether each of the following apply to the ontology, epistemology, view of thought and behavior, or research focus of qualitative research.
subjective, mental, personal, constructed
epistemology
view of though and behavior
research focus
relativism, individual/group justification, varying standards, social construction
view of thought and behavior
personal, social, contextual/situational, fluid, unpredictable
wide-angle and “deep-angle” lens, examining breadth & depth of phenomena, Not interested in generalizing beyond individuals/groups studied
Which three views of human thought and behavior are characteristic of qualitative research?
Choose three answers.
It is fluid
it is predictable
it is personal
it occurs in regular patterns
it is highly situational
Which two characteristics of data collection and analysis are common to the theoretical frameworks of qualitative research?
Choose two answers.
context sensitive
triangulated
time-limited
Which of the following are theoretical frameworks of qualitative research?
experimental
nonexperimental
Which type of qualitative data analysis places a high priority on being true to, respecting, and capturing the details of individual situations?
What is a main strength of qualitative research?
generates results that are relatively independent of the research
leads to a complex understanding about events or phenomenon
produces integrated knowledge that informs theory and practice
empowers practitioners to contribute to knowledge base
Classify each research method as belonging to either the quantitative or qualitative research.
Experimental
qualitative
quantitative
Nonexperimental
Ethnography
Match each type of research report with the corresponding type of qualitative research. Answer options may be used more than once or not at all.
Extensive description of physical and social settings aimed at holistic understanding.
Phenomenology
Narrative Inquiry
Grounded Theory
Account that includes patterns, connections, and insights uncovered.
Rich narrative that lets readers experience phenomenon through eyes of participants.
Holistic narrative that triangulates data and places study into meaningful context.
Methodological descriptions followed by proposed idea built during the study.
Answer the second blank only
Explore all questions with a free account

Continue with email
Continue with phone
- Privacy Policy

Home » Qualitative Research – Methods, Analysis Types and Guide
Qualitative Research – Methods, Analysis Types and Guide
Table of Contents

Qualitative Research
Qualitative research is a type of research methodology that focuses on exploring and understanding people’s beliefs, attitudes, behaviors, and experiences through the collection and analysis of non-numerical data. It seeks to answer research questions through the examination of subjective data, such as interviews, focus groups, observations, and textual analysis.
Qualitative research aims to uncover the meaning and significance of social phenomena, and it typically involves a more flexible and iterative approach to data collection and analysis compared to quantitative research. Qualitative research is often used in fields such as sociology, anthropology, psychology, and education.
Qualitative Research Methods

Qualitative Research Methods are as follows:
One-to-One Interview
This method involves conducting an interview with a single participant to gain a detailed understanding of their experiences, attitudes, and beliefs. One-to-one interviews can be conducted in-person, over the phone, or through video conferencing. The interviewer typically uses open-ended questions to encourage the participant to share their thoughts and feelings. One-to-one interviews are useful for gaining detailed insights into individual experiences.
Focus Groups
This method involves bringing together a group of people to discuss a specific topic in a structured setting. The focus group is led by a moderator who guides the discussion and encourages participants to share their thoughts and opinions. Focus groups are useful for generating ideas and insights, exploring social norms and attitudes, and understanding group dynamics.
Ethnographic Studies
This method involves immersing oneself in a culture or community to gain a deep understanding of its norms, beliefs, and practices. Ethnographic studies typically involve long-term fieldwork and observation, as well as interviews and document analysis. Ethnographic studies are useful for understanding the cultural context of social phenomena and for gaining a holistic understanding of complex social processes.
Text Analysis
This method involves analyzing written or spoken language to identify patterns and themes. Text analysis can be quantitative or qualitative. Qualitative text analysis involves close reading and interpretation of texts to identify recurring themes, concepts, and patterns. Text analysis is useful for understanding media messages, public discourse, and cultural trends.
This method involves an in-depth examination of a single person, group, or event to gain an understanding of complex phenomena. Case studies typically involve a combination of data collection methods, such as interviews, observations, and document analysis, to provide a comprehensive understanding of the case. Case studies are useful for exploring unique or rare cases, and for generating hypotheses for further research.
Process of Observation
This method involves systematically observing and recording behaviors and interactions in natural settings. The observer may take notes, use audio or video recordings, or use other methods to document what they see. Process of observation is useful for understanding social interactions, cultural practices, and the context in which behaviors occur.
Record Keeping
This method involves keeping detailed records of observations, interviews, and other data collected during the research process. Record keeping is essential for ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the data, and for providing a basis for analysis and interpretation.
This method involves collecting data from a large sample of participants through a structured questionnaire. Surveys can be conducted in person, over the phone, through mail, or online. Surveys are useful for collecting data on attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors, and for identifying patterns and trends in a population.
Qualitative data analysis is a process of turning unstructured data into meaningful insights. It involves extracting and organizing information from sources like interviews, focus groups, and surveys. The goal is to understand people’s attitudes, behaviors, and motivations
Qualitative Research Analysis Methods
Qualitative Research analysis methods involve a systematic approach to interpreting and making sense of the data collected in qualitative research. Here are some common qualitative data analysis methods:
Thematic Analysis
This method involves identifying patterns or themes in the data that are relevant to the research question. The researcher reviews the data, identifies keywords or phrases, and groups them into categories or themes. Thematic analysis is useful for identifying patterns across multiple data sources and for generating new insights into the research topic.
Content Analysis
This method involves analyzing the content of written or spoken language to identify key themes or concepts. Content analysis can be quantitative or qualitative. Qualitative content analysis involves close reading and interpretation of texts to identify recurring themes, concepts, and patterns. Content analysis is useful for identifying patterns in media messages, public discourse, and cultural trends.
Discourse Analysis
This method involves analyzing language to understand how it constructs meaning and shapes social interactions. Discourse analysis can involve a variety of methods, such as conversation analysis, critical discourse analysis, and narrative analysis. Discourse analysis is useful for understanding how language shapes social interactions, cultural norms, and power relationships.
Grounded Theory Analysis
This method involves developing a theory or explanation based on the data collected. Grounded theory analysis starts with the data and uses an iterative process of coding and analysis to identify patterns and themes in the data. The theory or explanation that emerges is grounded in the data, rather than preconceived hypotheses. Grounded theory analysis is useful for understanding complex social phenomena and for generating new theoretical insights.
Narrative Analysis
This method involves analyzing the stories or narratives that participants share to gain insights into their experiences, attitudes, and beliefs. Narrative analysis can involve a variety of methods, such as structural analysis, thematic analysis, and discourse analysis. Narrative analysis is useful for understanding how individuals construct their identities, make sense of their experiences, and communicate their values and beliefs.
Phenomenological Analysis
This method involves analyzing how individuals make sense of their experiences and the meanings they attach to them. Phenomenological analysis typically involves in-depth interviews with participants to explore their experiences in detail. Phenomenological analysis is useful for understanding subjective experiences and for developing a rich understanding of human consciousness.
Comparative Analysis
This method involves comparing and contrasting data across different cases or groups to identify similarities and differences. Comparative analysis can be used to identify patterns or themes that are common across multiple cases, as well as to identify unique or distinctive features of individual cases. Comparative analysis is useful for understanding how social phenomena vary across different contexts and groups.
Applications of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research has many applications across different fields and industries. Here are some examples of how qualitative research is used:
- Market Research: Qualitative research is often used in market research to understand consumer attitudes, behaviors, and preferences. Researchers conduct focus groups and one-on-one interviews with consumers to gather insights into their experiences and perceptions of products and services.
- Health Care: Qualitative research is used in health care to explore patient experiences and perspectives on health and illness. Researchers conduct in-depth interviews with patients and their families to gather information on their experiences with different health care providers and treatments.
- Education: Qualitative research is used in education to understand student experiences and to develop effective teaching strategies. Researchers conduct classroom observations and interviews with students and teachers to gather insights into classroom dynamics and instructional practices.
- Social Work : Qualitative research is used in social work to explore social problems and to develop interventions to address them. Researchers conduct in-depth interviews with individuals and families to understand their experiences with poverty, discrimination, and other social problems.
- Anthropology : Qualitative research is used in anthropology to understand different cultures and societies. Researchers conduct ethnographic studies and observe and interview members of different cultural groups to gain insights into their beliefs, practices, and social structures.
- Psychology : Qualitative research is used in psychology to understand human behavior and mental processes. Researchers conduct in-depth interviews with individuals to explore their thoughts, feelings, and experiences.
- Public Policy : Qualitative research is used in public policy to explore public attitudes and to inform policy decisions. Researchers conduct focus groups and one-on-one interviews with members of the public to gather insights into their perspectives on different policy issues.
How to Conduct Qualitative Research
Here are some general steps for conducting qualitative research:
- Identify your research question: Qualitative research starts with a research question or set of questions that you want to explore. This question should be focused and specific, but also broad enough to allow for exploration and discovery.
- Select your research design: There are different types of qualitative research designs, including ethnography, case study, grounded theory, and phenomenology. You should select a design that aligns with your research question and that will allow you to gather the data you need to answer your research question.
- Recruit participants: Once you have your research question and design, you need to recruit participants. The number of participants you need will depend on your research design and the scope of your research. You can recruit participants through advertisements, social media, or through personal networks.
- Collect data: There are different methods for collecting qualitative data, including interviews, focus groups, observation, and document analysis. You should select the method or methods that align with your research design and that will allow you to gather the data you need to answer your research question.
- Analyze data: Once you have collected your data, you need to analyze it. This involves reviewing your data, identifying patterns and themes, and developing codes to organize your data. You can use different software programs to help you analyze your data, or you can do it manually.
- Interpret data: Once you have analyzed your data, you need to interpret it. This involves making sense of the patterns and themes you have identified, and developing insights and conclusions that answer your research question. You should be guided by your research question and use your data to support your conclusions.
- Communicate results: Once you have interpreted your data, you need to communicate your results. This can be done through academic papers, presentations, or reports. You should be clear and concise in your communication, and use examples and quotes from your data to support your findings.
Examples of Qualitative Research
Here are some real-time examples of qualitative research:
- Customer Feedback: A company may conduct qualitative research to understand the feedback and experiences of its customers. This may involve conducting focus groups or one-on-one interviews with customers to gather insights into their attitudes, behaviors, and preferences.
- Healthcare : A healthcare provider may conduct qualitative research to explore patient experiences and perspectives on health and illness. This may involve conducting in-depth interviews with patients and their families to gather information on their experiences with different health care providers and treatments.
- Education : An educational institution may conduct qualitative research to understand student experiences and to develop effective teaching strategies. This may involve conducting classroom observations and interviews with students and teachers to gather insights into classroom dynamics and instructional practices.
- Social Work: A social worker may conduct qualitative research to explore social problems and to develop interventions to address them. This may involve conducting in-depth interviews with individuals and families to understand their experiences with poverty, discrimination, and other social problems.
- Anthropology : An anthropologist may conduct qualitative research to understand different cultures and societies. This may involve conducting ethnographic studies and observing and interviewing members of different cultural groups to gain insights into their beliefs, practices, and social structures.
- Psychology : A psychologist may conduct qualitative research to understand human behavior and mental processes. This may involve conducting in-depth interviews with individuals to explore their thoughts, feelings, and experiences.
- Public Policy: A government agency or non-profit organization may conduct qualitative research to explore public attitudes and to inform policy decisions. This may involve conducting focus groups and one-on-one interviews with members of the public to gather insights into their perspectives on different policy issues.
Purpose of Qualitative Research
The purpose of qualitative research is to explore and understand the subjective experiences, behaviors, and perspectives of individuals or groups in a particular context. Unlike quantitative research, which focuses on numerical data and statistical analysis, qualitative research aims to provide in-depth, descriptive information that can help researchers develop insights and theories about complex social phenomena.
Qualitative research can serve multiple purposes, including:
- Exploring new or emerging phenomena : Qualitative research can be useful for exploring new or emerging phenomena, such as new technologies or social trends. This type of research can help researchers develop a deeper understanding of these phenomena and identify potential areas for further study.
- Understanding complex social phenomena : Qualitative research can be useful for exploring complex social phenomena, such as cultural beliefs, social norms, or political processes. This type of research can help researchers develop a more nuanced understanding of these phenomena and identify factors that may influence them.
- Generating new theories or hypotheses: Qualitative research can be useful for generating new theories or hypotheses about social phenomena. By gathering rich, detailed data about individuals’ experiences and perspectives, researchers can develop insights that may challenge existing theories or lead to new lines of inquiry.
- Providing context for quantitative data: Qualitative research can be useful for providing context for quantitative data. By gathering qualitative data alongside quantitative data, researchers can develop a more complete understanding of complex social phenomena and identify potential explanations for quantitative findings.
When to use Qualitative Research
Here are some situations where qualitative research may be appropriate:
- Exploring a new area: If little is known about a particular topic, qualitative research can help to identify key issues, generate hypotheses, and develop new theories.
- Understanding complex phenomena: Qualitative research can be used to investigate complex social, cultural, or organizational phenomena that are difficult to measure quantitatively.
- Investigating subjective experiences: Qualitative research is particularly useful for investigating the subjective experiences of individuals or groups, such as their attitudes, beliefs, values, or emotions.
- Conducting formative research: Qualitative research can be used in the early stages of a research project to develop research questions, identify potential research participants, and refine research methods.
- Evaluating interventions or programs: Qualitative research can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of interventions or programs by collecting data on participants’ experiences, attitudes, and behaviors.
Characteristics of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research is characterized by several key features, including:
- Focus on subjective experience: Qualitative research is concerned with understanding the subjective experiences, beliefs, and perspectives of individuals or groups in a particular context. Researchers aim to explore the meanings that people attach to their experiences and to understand the social and cultural factors that shape these meanings.
- Use of open-ended questions: Qualitative research relies on open-ended questions that allow participants to provide detailed, in-depth responses. Researchers seek to elicit rich, descriptive data that can provide insights into participants’ experiences and perspectives.
- Sampling-based on purpose and diversity: Qualitative research often involves purposive sampling, in which participants are selected based on specific criteria related to the research question. Researchers may also seek to include participants with diverse experiences and perspectives to capture a range of viewpoints.
- Data collection through multiple methods: Qualitative research typically involves the use of multiple data collection methods, such as in-depth interviews, focus groups, and observation. This allows researchers to gather rich, detailed data from multiple sources, which can provide a more complete picture of participants’ experiences and perspectives.
- Inductive data analysis: Qualitative research relies on inductive data analysis, in which researchers develop theories and insights based on the data rather than testing pre-existing hypotheses. Researchers use coding and thematic analysis to identify patterns and themes in the data and to develop theories and explanations based on these patterns.
- Emphasis on researcher reflexivity: Qualitative research recognizes the importance of the researcher’s role in shaping the research process and outcomes. Researchers are encouraged to reflect on their own biases and assumptions and to be transparent about their role in the research process.
Advantages of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research offers several advantages over other research methods, including:
- Depth and detail: Qualitative research allows researchers to gather rich, detailed data that provides a deeper understanding of complex social phenomena. Through in-depth interviews, focus groups, and observation, researchers can gather detailed information about participants’ experiences and perspectives that may be missed by other research methods.
- Flexibility : Qualitative research is a flexible approach that allows researchers to adapt their methods to the research question and context. Researchers can adjust their research methods in real-time to gather more information or explore unexpected findings.
- Contextual understanding: Qualitative research is well-suited to exploring the social and cultural context in which individuals or groups are situated. Researchers can gather information about cultural norms, social structures, and historical events that may influence participants’ experiences and perspectives.
- Participant perspective : Qualitative research prioritizes the perspective of participants, allowing researchers to explore subjective experiences and understand the meanings that participants attach to their experiences.
- Theory development: Qualitative research can contribute to the development of new theories and insights about complex social phenomena. By gathering rich, detailed data and using inductive data analysis, researchers can develop new theories and explanations that may challenge existing understandings.
- Validity : Qualitative research can offer high validity by using multiple data collection methods, purposive and diverse sampling, and researcher reflexivity. This can help ensure that findings are credible and trustworthy.
Limitations of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research also has some limitations, including:
- Subjectivity : Qualitative research relies on the subjective interpretation of researchers, which can introduce bias into the research process. The researcher’s perspective, beliefs, and experiences can influence the way data is collected, analyzed, and interpreted.
- Limited generalizability: Qualitative research typically involves small, purposive samples that may not be representative of larger populations. This limits the generalizability of findings to other contexts or populations.
- Time-consuming: Qualitative research can be a time-consuming process, requiring significant resources for data collection, analysis, and interpretation.
- Resource-intensive: Qualitative research may require more resources than other research methods, including specialized training for researchers, specialized software for data analysis, and transcription services.
- Limited reliability: Qualitative research may be less reliable than quantitative research, as it relies on the subjective interpretation of researchers. This can make it difficult to replicate findings or compare results across different studies.
- Ethics and confidentiality: Qualitative research involves collecting sensitive information from participants, which raises ethical concerns about confidentiality and informed consent. Researchers must take care to protect the privacy and confidentiality of participants and obtain informed consent.
Also see Research Methods
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Survey Research – Types, Methods, Examples

Descriptive Research Design – Types, Methods and...

Triangulation in Research – Types, Methods and...


One-to-One Interview – Methods and Guide

Exploratory Research – Types, Methods and...

Observational Research – Methods and Guide

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
4.3 Qualitative Research Methodologies
Phenomenology is a research approach that seeks to understand the essence of a particular phenomenon through a detailed exploration of individual experiences. It is especially beneficial for exploring personal experiences such as emotions, perceptions, and awareness. As a budding qualitative researcher, it is imperative that you understand the different qualitative methods to enable you to choose the appropriate methods for your research question. In this chapter, we aim to discuss the most common qualitative methodologies which include descriptive, phenomenology, narrative inquiry, case study, ethnography, action research and grounded theory (Figure 4.2).
Descriptive: A descriptive qualitative study attempts to systematically describe a situation, problem, phenomenon, service or programme. It focuses on discovering the who, what, and where of events or experiences and gaining insights from informants regarding a poorly understood phenomenon. 12 It is also used when more information is required to aid the development and refinement of questionnaires in research projects aiming to gain firsthand knowledge of patients’, relatives’ or professionals’ experiences with a particular topic. 13 This is a good choice for beginner qualitative researchers doing exploratory studies. It uses purposive or convenience sampling, with in-depth interviews as the most common data collection method. 14 Data analysis for this type of qualitative research focuses on a rich descriptive summary of the characteristics (themes) of the phenomena with some interpretation. 14 An example is the study by Cao et al. 2022 that explored the state of education regarding end-of-life care from the perspectives of undergraduate nurses. The findings showed that the undergraduate curriculum related to end-of-life care was disjointed and cultural attitudes toward disease and death impede the undergraduate nurses’ learning and knowledge translation of end-of-life care. 15
Phenomenology is also commonly used in qualitative research, and it is a research approach that seeks to understand the essence of a particular phenomenon through a detailed exploration of individual experiences. It is especially beneficial for exploring personal experiences such as emotions, perceptions, and awareness.that is especially beneficial for exploring personal experiences such as emotions, perceptions, and awareness. 16 It involves in-depth conversations on a specific topic, captures the relationships between people, things, events and situations and describes and explains phenomena from the perspective of those who have experienced it. 17 It explores the dimensions of participants’ experiences. 18 It seeks to understand problems, ideas, and situations in terms of shared understandings and experiences rather than differences. 19 Phenomenological research often employs in-depth, unstructured or semi-structured interviews as a means of data collection. 20 Data analysis typically involves identifying the essential structure or meaning of the experience being studied and then describing it in a way that is understandable to others. The researcher uses a process called the transcendental-phenomenological reduction to bracket off or set aside any preconceived notions of the phenomenon being studied. 21 In this method, researchers use theme analysis to focus on the attributed meaning of participants’ lived experiences rather than influencing findings with their own beliefs. 21 This process allows the researcher to gain a deeper understanding of the phenomenon’s essence as it is lived and experienced by participants. 21 For example, Liao et al. 2021 conducted a study exploring what medical learners experience through narrative medicine and the meanings they ascribe to narrative-based learning. The study identified six themes: feeling hesitation, seeking guidance, shifting roles in narratives, questioning relationships, experiencing transformation, and requesting a safe learning environment. 22
Narrative inquiry: Narrative inquiry is qualitative research that seeks to understand how individuals make meaning of their lives and the world around them through studying their stories and experiences. 23 This qualitative research focuses on marginalised populations, usually individuals or small groups and aims to give voice to their perspective. 24 This approach helps people learn more about the participants’ culture, historical experiences, identity, and lifestyle and is often recorded as a biography, life history, artifacts or traditional story. 25 It captures a wealth of story data, including emotions, beliefs, images, and insights about time. It also considers the relationship between personal experience and the wider social and cultural context. 24 Importantly, it also involves joint investigation and joint meaning-building between participants and researchers. 26 A major benefit of narrative inquiry is that it involves storytelling, and because humans are natural storytellers, the approach makes it easy to elicit stories. 24 Additionally, it facilitates the creation and construction of data through narratives of lived experience and fosters meaning formation, thus providing valuable insight into the complexities of human life, culture, and behavior. 11 This makes it possible to gather in-depth meaning as participants usually reveal themselves in their stories. 27 Narrative inquiry entails collecting data in the form of stories or narratives through interviews, written or visual materials, or other kinds of self-expression. 24 Data analysis in narrative inquiry involves identifying the themes, patterns, and meaning of the stories under consideration and understanding how the stories are formed and related to the individual’s experiences and perspective. 24 An example is the study by Gordon et al. 2015 which explored medical trainees’ experiences of leadership and followership in the interprofessional healthcare workplace. 28 The findings showed that participants most often narrated experiences from the position of follower. 28 Their narratives illustrated many factors that facilitate or inhibit the development of leadership identities. 28 Traditional medical and interprofessional hierarchies persist within the healthcare workplace, and wider healthcare systems can act as barriers to distributed leadership practices. 28
Case Study aids holistic exploration of a phenomenon. It provides powerful stories within social contexts through various data sources. It undertakes the exploration through various lenses to capture continuity and change and reveal multiple facets of the phenomenon. 29 It is an explanatory, descriptive or exploratory analysis of a single case example of a phenomenon. Case study aids researchers in giving a holistic, detailed account of a single case (or more) as it occurs in its real-life context. 30 The purpose of a case study is to understand complex phenomena and to explore new research questions in a real-world setting. 29 There are three main types of qualitative case study design: intrinsic case study, instrumental case study and collective case study. 31 An intrinsic case study is often conducted to learn about a one-of-a-kind phenomenon. 31 This type of case study focuses on a single case or a small number of cases and explores a specific phenomenon or issue in depth. 30,31 The researcher needs to define the phenomenon’s distinctiveness, which separates it from all others. In contrast, the instrumental case study employs a specific instance (some of which may be superior to others) to acquire a more extensive understanding of an issue or phenomenon. 30,31 An instrumental case study uses a single case or a small number of cases to explore a broader research question or problem. 31 The collective case study researches numerous instances concurrently or sequentially to obtain a more comprehensive understanding of a specific subject. 30,31 This type of case study analyses multiple cases to understand a phenomenon or issue from different perspectives. 31 The data collection techniques used in a case study include interviews, observations, or written or visual materials. Data can be collected from various sources, including the case, documents or records, and other relevant individuals. In a case study, data analysis is often inductive, which means that the researcher begins with the data and generates themes, patterns, or insights from it. To examine the data, the researcher may employ a range of approaches, such as coding, memoing, or content analysis. An example of a case study is the study by Lemmen et al. 2021 , which aimed to provide insight into how adopting positive health (PH) in a general practice affects primary care professionals’ (PCP) job satisfaction. 32 The findings of the study identified three themes regarding PCPs’ adoption of PH and job satisfaction, namely adopting and adapting Positive Health, giving substance to Positive Health in practice, and changing financial and organisational structures. 32 Thus, the PCPs adopted PH, which supported PCPs to express, legitimise, and promote their distinctive approach to care work and its value. 32 PH also enabled PCPs to change their financial and organisational structures, freeing time to spend on patients and their own well-being. The changes made by the practice increased the job satisfaction of the PCPs. 32
Ethnography is the study of culture and entails the observation of details of everyday life as they naturally unfold in the real world. It is commonly used in anthropological research focusing on the community 33 . It generally involves researchers directly observing a participant’s natural environment over time. 33 A key feature of ethnography is the fact that natural settings, unadapted for the researchers’ interests, are used. In ethnography, the natural setting or environment is as important as the participants, and such methods have the advantage of explicitly acknowledging that, in the real world, environmental constraints and context influence behaviours and outcomes. 34 Ethnography focuses on the lived culture of a group of people, that is, the knowledge they use to generate and interpret social behaviour. 35 Ethnography often involves a small number of cases or a community, ethnic or social groups. The researcher enters the lived experience of participants in the field and spends considerable time with them to understand their way of life. This research approach increases the strength of the data. 35 An example of ethnographic research is the study by Hinder and Greenhalgh, 2012 . The study sought to produce a richer understanding of how people live with diabetes and why self-management is challenging for some. The study revealed that self-management involved both practical and cognitive tasks (e.g. self-monitoring, menu planning, medication adjustment) and socio-emotional ones (e.g. coping with illness, managing relatives’ input, negotiating access to services or resources). 36 Self-management was hard work and was enabled or constrained by economic, material and socio-cultural conditions within the family, workplace and community. 36 Although this study is old, it provides insight into some of the challenges associated with diabetes. 36 While more devices have helped with diabetes in recent years, some of these challenges may still exist.
Action Research involves a cyclical process of planning, action, observation, and reflection to improve practice or address a problem. It attempts to understand and improve the world via change. 37 The goal of action research is to generate new knowledge and understanding about a specific issue while at the same time taking action to improve the situation. 37 Action research is guided by the desire to take action, so it is not a design. A type of action research is participatory action research. 38 At its core, this is a collaborative, self-reflective enquiry undertaken by researchers and participants to understand and improve upon the practices in which they participate and the situations in which they find themselves. 38 The goal is for the participant to be an equal partner with the researcher. 39 The reflective process is inextricably tied to action, impacted by knowledge of history, culture, and the local context, and is rooted in social connections. 38 It is an inquiry process used to understand and improve complex social systems, such as organisations, communities, or classrooms. 40 Participatory action research draws on qualitative methods such as interviews and observation to inquire about ways to improve the quality of practice. 41 The study by Doherty and O’Brien, 2021 explored midwives’ understandings of burnout, professionally and personally, in the context of contemporary maternity care in Ireland. 42 Multiple factors influenced midwives’ views and understandings of burnout. PAR provided a platform for midwives to examine their ideas and views on burnout with the collaborative support of their midwifery colleagues, via cycles of action and reflection, which is necessary to develop and maintain change. Midwives characterised burnout as continuous stress and tiredness, with an accompanying decline in their coping capacities, motivation, empathy, and/or efficacy. Burnout is unique to the person and is primarily induced and irrevocably tied to excessive workload in midwifery. 42
Grounded theory first described by Glaser and Strauss in 1967, is a framework for qualitative research that suggests that theory must derive from data, unlike other forms of research, which suggest that data should be used to test theory. 43 It is a qualitative research process that entails developing theories based on evidence that has been collected from the participants. 43 Grounded theory may be particularly valuable when little or nothing is known or understood about a problem, situation, or context. 44 The main purpose is to develop a theory that explains patterns and correlations in data and may be utilised to understand and predict the phenomenon under investigation. This method often entails gathering data through interviews, focus groups, questionnaires, surveys, transcripts, letters, government reports, papers, grey literature, music, artefacts, videos, blogs and memos, then analysing it to identify patterns and relationships. 45 Data is analysed via inductive analysis; the researcher starts with observations and data and then builds hypotheses and insights based on the data. In addition, a continual comparison technique is employed, which entails comparing data repeatedly to identify patterns and themes. 46 Furthermore, open, axial and selective coding is used. Open coding divides data into smaller chunks and classifies them based on their qualities and relationships. 47 In axial coding, links between categories and their subcategories are examined with respect to data. 47 Through “selective coding,” all categories are brought together around a “core” category, and categories requiring further explanation include descriptive information. This type of coding is more likely to occur in the final stages of study. 47 An example is the study by Malau-Aduli et al., 2020 ; the study had two main aims – (1) to identify the factors that influence an International Medical Graduate’s (IMG) decision to remain working in regional, rural, and remote areas; (2) to develop a theory, grounded in the data, to explain how these factors are prioritised, evaluated and used to inform a decision to remain working in RRR areas. 48 The findings revealed that the IMG decision-making process involved a complex, dynamic, and iterative process of balancing life goals based on life stage. Many factors were considered when assessing the balance of three primary life goals: satisfaction with work, family, and lifestyle. Another example is the study by Akosah-Twumasi et al. 2020 which explored the perceived role of sub-Saharan African migrant parents living in Australia in the career decision-making processes of their adolescent children. 49 The study showed that the majority of SSA immigrant parents continued to parent in the same manner as they did back home. 49 Interestingly, some parents modified their parenting approaches due to their perceptions of the host nation. 49 However, due to their apparent lack of educational capacity to educate their children, other parents who would otherwise be authoritative turned into trustworthy figures. 49
An Introduction to Research Methods for Undergraduate Health Profession Students Copyright © 2023 by Faith Alele and Bunmi Malau-Aduli is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
9.1 Qualitative research: What is it and when should it be used?
Learning objectives.
- Define qualitative research
- Explain the differences between qualitative and quantitative research
- Identify the benefits and challenges of qualitative research
Qualitative versus quantitative research methods refers to data-oriented considerations about the type of data to collected and how they are analyzed. Qualitative research relies mostly on non-numeric data, such as interviews and observations to understand their meaning, in contrast to quantitative research which employs numeric data such as scores and metrics. Hence, qualitative research is not amenable to statistical procedures, but is coded using techniques like content analysis. Sometimes, coded qualitative data are tabulated quantitatively as frequencies of codes, but this data is not statistically analyzed. Qualitative research has its roots in anthropology, sociology, psychology, linguistics, and semiotics, and has been available since the early 19th century, long before quantitative statistical techniques were employed.
Distinctions from Quantitative Research
In qualitative research, the role of the researcher receives critical attention. In some methods such as ethnography, action research, and participant observation, the researcher is considered part of the social phenomenon, and her specific role and involvement in the research process must be made clear during data analysis. In other methods, such as case research, the researcher must take a “neutral” or unbiased stance during the data collection and analysis processes, and ensure that her personal biases or preconceptions does not taint the nature of subjective inferences derived from qualitative research.
Analysis in qualitative research is holistic and contextual, rather than being reductionist and isolationist. Qualitative interpretations tend to focus on language, signs, and meanings from the perspective of the participants involved in the social phenomenon, in contrast to statistical techniques that are employed heavily in positivist research. Rigor in qualitative research is viewed in terms of systematic and transparent approaches for data collection and analysis rather than statistical benchmarks for construct validity or significance testing.
Lastly, data collection and analysis can proceed simultaneously and iteratively in qualitative research. For instance, the researcher may conduct an interview and code it before proceeding to the next interview. Simultaneous analysis helps the researcher correct potential flaws in the interview protocol or adjust it to capture the phenomenon of interest better. The researcher may even change her original research question if she realizes that her original research questions are unlikely to generate new or useful insights. This is a valuable but often understated benefit of qualitative research, and is not available in quantitative research, where the research project cannot be modified or changed once the data collection has started without redoing the entire project from the start.
Benefits and Challenges of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research has several unique advantages. First, it is well-suited for exploring hidden reasons behind complex, interrelated, or multifaceted social processes, such as inter-firm relationships or inter-office politics, where quantitative evidence may be biased, inaccurate, or otherwise difficult to obtain. Second, it is often helpful for theory construction in areas with no or insufficient pre-existing theory. Third, qualitative research is also appropriate for studying context-specific, unique, or idiosyncratic events or processes. Fourth, it can help uncover interesting and relevant research questions and issues for follow-up research.
At the same time, qualitative research also has its own set of challenges. First, this type of research tends to be more time and resource intensive than quantitative research in data collection and analytic efforts. Too little data can lead to false or premature assumptions, while too much data may not be effectively processed by the researcher. Second, qualitative research requires well-trained researchers who are capable of seeing and interpreting complex social phenomenon from the perspectives of the embedded participants and reconciling the diverse perspectives of these participants, without injecting their personal biases or preconceptions into their inferences. Third, all participants or data sources may not be equally credible, unbiased, or knowledgeable about the phenomenon of interest, or may have undisclosed political agendas, which may lead to misleading or false impressions. Inadequate trust between participants and researcher may hinder full and honest self-representation by participants, and such trust building takes time. It is the job of the qualitative researcher to “see through the smoke” (hidden or biased agendas) and understand the true nature of the problem. Finally, given the heavily contextualized nature of inferences drawn from qualitative research, such inferences do not lend themselves well to replicability or generalizability.
Key Takeaways
- Qualitative research examines words and other non-numeric media
- Analysis in qualitative research is holistic and contextual
- Qualitative research offers unique benefits, while facing challenges to generalizability and replicability
- Qualitative methods – examine words or other media to understand their meaning
Foundations of Social Work Research Copyright © 2020 by Rebecca L. Mauldin is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Neurol Res Pract

How to use and assess qualitative research methods
Loraine busetto.
1 Department of Neurology, Heidelberg University Hospital, Im Neuenheimer Feld 400, 69120 Heidelberg, Germany
Wolfgang Wick
2 Clinical Cooperation Unit Neuro-Oncology, German Cancer Research Center, Heidelberg, Germany
Christoph Gumbinger
Associated data.
Not applicable.
This paper aims to provide an overview of the use and assessment of qualitative research methods in the health sciences. Qualitative research can be defined as the study of the nature of phenomena and is especially appropriate for answering questions of why something is (not) observed, assessing complex multi-component interventions, and focussing on intervention improvement. The most common methods of data collection are document study, (non-) participant observations, semi-structured interviews and focus groups. For data analysis, field-notes and audio-recordings are transcribed into protocols and transcripts, and coded using qualitative data management software. Criteria such as checklists, reflexivity, sampling strategies, piloting, co-coding, member-checking and stakeholder involvement can be used to enhance and assess the quality of the research conducted. Using qualitative in addition to quantitative designs will equip us with better tools to address a greater range of research problems, and to fill in blind spots in current neurological research and practice.
The aim of this paper is to provide an overview of qualitative research methods, including hands-on information on how they can be used, reported and assessed. This article is intended for beginning qualitative researchers in the health sciences as well as experienced quantitative researchers who wish to broaden their understanding of qualitative research.
What is qualitative research?
Qualitative research is defined as “the study of the nature of phenomena”, including “their quality, different manifestations, the context in which they appear or the perspectives from which they can be perceived” , but excluding “their range, frequency and place in an objectively determined chain of cause and effect” [ 1 ]. This formal definition can be complemented with a more pragmatic rule of thumb: qualitative research generally includes data in form of words rather than numbers [ 2 ].
Why conduct qualitative research?
Because some research questions cannot be answered using (only) quantitative methods. For example, one Australian study addressed the issue of why patients from Aboriginal communities often present late or not at all to specialist services offered by tertiary care hospitals. Using qualitative interviews with patients and staff, it found one of the most significant access barriers to be transportation problems, including some towns and communities simply not having a bus service to the hospital [ 3 ]. A quantitative study could have measured the number of patients over time or even looked at possible explanatory factors – but only those previously known or suspected to be of relevance. To discover reasons for observed patterns, especially the invisible or surprising ones, qualitative designs are needed.
While qualitative research is common in other fields, it is still relatively underrepresented in health services research. The latter field is more traditionally rooted in the evidence-based-medicine paradigm, as seen in " research that involves testing the effectiveness of various strategies to achieve changes in clinical practice, preferably applying randomised controlled trial study designs (...) " [ 4 ]. This focus on quantitative research and specifically randomised controlled trials (RCT) is visible in the idea of a hierarchy of research evidence which assumes that some research designs are objectively better than others, and that choosing a "lesser" design is only acceptable when the better ones are not practically or ethically feasible [ 5 , 6 ]. Others, however, argue that an objective hierarchy does not exist, and that, instead, the research design and methods should be chosen to fit the specific research question at hand – "questions before methods" [ 2 , 7 – 9 ]. This means that even when an RCT is possible, some research problems require a different design that is better suited to addressing them. Arguing in JAMA, Berwick uses the example of rapid response teams in hospitals, which he describes as " a complex, multicomponent intervention – essentially a process of social change" susceptible to a range of different context factors including leadership or organisation history. According to him, "[in] such complex terrain, the RCT is an impoverished way to learn. Critics who use it as a truth standard in this context are incorrect" [ 8 ] . Instead of limiting oneself to RCTs, Berwick recommends embracing a wider range of methods , including qualitative ones, which for "these specific applications, (...) are not compromises in learning how to improve; they are superior" [ 8 ].
Research problems that can be approached particularly well using qualitative methods include assessing complex multi-component interventions or systems (of change), addressing questions beyond “what works”, towards “what works for whom when, how and why”, and focussing on intervention improvement rather than accreditation [ 7 , 9 – 12 ]. Using qualitative methods can also help shed light on the “softer” side of medical treatment. For example, while quantitative trials can measure the costs and benefits of neuro-oncological treatment in terms of survival rates or adverse effects, qualitative research can help provide a better understanding of patient or caregiver stress, visibility of illness or out-of-pocket expenses.
How to conduct qualitative research?
Given that qualitative research is characterised by flexibility, openness and responsivity to context, the steps of data collection and analysis are not as separate and consecutive as they tend to be in quantitative research [ 13 , 14 ]. As Fossey puts it : “sampling, data collection, analysis and interpretation are related to each other in a cyclical (iterative) manner, rather than following one after another in a stepwise approach” [ 15 ]. The researcher can make educated decisions with regard to the choice of method, how they are implemented, and to which and how many units they are applied [ 13 ]. As shown in Fig. 1 , this can involve several back-and-forth steps between data collection and analysis where new insights and experiences can lead to adaption and expansion of the original plan. Some insights may also necessitate a revision of the research question and/or the research design as a whole. The process ends when saturation is achieved, i.e. when no relevant new information can be found (see also below: sampling and saturation). For reasons of transparency, it is essential for all decisions as well as the underlying reasoning to be well-documented.

Iterative research process
While it is not always explicitly addressed, qualitative methods reflect a different underlying research paradigm than quantitative research (e.g. constructivism or interpretivism as opposed to positivism). The choice of methods can be based on the respective underlying substantive theory or theoretical framework used by the researcher [ 2 ].
Data collection
The methods of qualitative data collection most commonly used in health research are document study, observations, semi-structured interviews and focus groups [ 1 , 14 , 16 , 17 ].
Document study
Document study (also called document analysis) refers to the review by the researcher of written materials [ 14 ]. These can include personal and non-personal documents such as archives, annual reports, guidelines, policy documents, diaries or letters.
Observations
Observations are particularly useful to gain insights into a certain setting and actual behaviour – as opposed to reported behaviour or opinions [ 13 ]. Qualitative observations can be either participant or non-participant in nature. In participant observations, the observer is part of the observed setting, for example a nurse working in an intensive care unit [ 18 ]. In non-participant observations, the observer is “on the outside looking in”, i.e. present in but not part of the situation, trying not to influence the setting by their presence. Observations can be planned (e.g. for 3 h during the day or night shift) or ad hoc (e.g. as soon as a stroke patient arrives at the emergency room). During the observation, the observer takes notes on everything or certain pre-determined parts of what is happening around them, for example focusing on physician-patient interactions or communication between different professional groups. Written notes can be taken during or after the observations, depending on feasibility (which is usually lower during participant observations) and acceptability (e.g. when the observer is perceived to be judging the observed). Afterwards, these field notes are transcribed into observation protocols. If more than one observer was involved, field notes are taken independently, but notes can be consolidated into one protocol after discussions. Advantages of conducting observations include minimising the distance between the researcher and the researched, the potential discovery of topics that the researcher did not realise were relevant and gaining deeper insights into the real-world dimensions of the research problem at hand [ 18 ].
Semi-structured interviews
Hijmans & Kuyper describe qualitative interviews as “an exchange with an informal character, a conversation with a goal” [ 19 ]. Interviews are used to gain insights into a person’s subjective experiences, opinions and motivations – as opposed to facts or behaviours [ 13 ]. Interviews can be distinguished by the degree to which they are structured (i.e. a questionnaire), open (e.g. free conversation or autobiographical interviews) or semi-structured [ 2 , 13 ]. Semi-structured interviews are characterized by open-ended questions and the use of an interview guide (or topic guide/list) in which the broad areas of interest, sometimes including sub-questions, are defined [ 19 ]. The pre-defined topics in the interview guide can be derived from the literature, previous research or a preliminary method of data collection, e.g. document study or observations. The topic list is usually adapted and improved at the start of the data collection process as the interviewer learns more about the field [ 20 ]. Across interviews the focus on the different (blocks of) questions may differ and some questions may be skipped altogether (e.g. if the interviewee is not able or willing to answer the questions or for concerns about the total length of the interview) [ 20 ]. Qualitative interviews are usually not conducted in written format as it impedes on the interactive component of the method [ 20 ]. In comparison to written surveys, qualitative interviews have the advantage of being interactive and allowing for unexpected topics to emerge and to be taken up by the researcher. This can also help overcome a provider or researcher-centred bias often found in written surveys, which by nature, can only measure what is already known or expected to be of relevance to the researcher. Interviews can be audio- or video-taped; but sometimes it is only feasible or acceptable for the interviewer to take written notes [ 14 , 16 , 20 ].
Focus groups
Focus groups are group interviews to explore participants’ expertise and experiences, including explorations of how and why people behave in certain ways [ 1 ]. Focus groups usually consist of 6–8 people and are led by an experienced moderator following a topic guide or “script” [ 21 ]. They can involve an observer who takes note of the non-verbal aspects of the situation, possibly using an observation guide [ 21 ]. Depending on researchers’ and participants’ preferences, the discussions can be audio- or video-taped and transcribed afterwards [ 21 ]. Focus groups are useful for bringing together homogeneous (to a lesser extent heterogeneous) groups of participants with relevant expertise and experience on a given topic on which they can share detailed information [ 21 ]. Focus groups are a relatively easy, fast and inexpensive method to gain access to information on interactions in a given group, i.e. “the sharing and comparing” among participants [ 21 ]. Disadvantages include less control over the process and a lesser extent to which each individual may participate. Moreover, focus group moderators need experience, as do those tasked with the analysis of the resulting data. Focus groups can be less appropriate for discussing sensitive topics that participants might be reluctant to disclose in a group setting [ 13 ]. Moreover, attention must be paid to the emergence of “groupthink” as well as possible power dynamics within the group, e.g. when patients are awed or intimidated by health professionals.
Choosing the “right” method
As explained above, the school of thought underlying qualitative research assumes no objective hierarchy of evidence and methods. This means that each choice of single or combined methods has to be based on the research question that needs to be answered and a critical assessment with regard to whether or to what extent the chosen method can accomplish this – i.e. the “fit” between question and method [ 14 ]. It is necessary for these decisions to be documented when they are being made, and to be critically discussed when reporting methods and results.
Let us assume that our research aim is to examine the (clinical) processes around acute endovascular treatment (EVT), from the patient’s arrival at the emergency room to recanalization, with the aim to identify possible causes for delay and/or other causes for sub-optimal treatment outcome. As a first step, we could conduct a document study of the relevant standard operating procedures (SOPs) for this phase of care – are they up-to-date and in line with current guidelines? Do they contain any mistakes, irregularities or uncertainties that could cause delays or other problems? Regardless of the answers to these questions, the results have to be interpreted based on what they are: a written outline of what care processes in this hospital should look like. If we want to know what they actually look like in practice, we can conduct observations of the processes described in the SOPs. These results can (and should) be analysed in themselves, but also in comparison to the results of the document analysis, especially as regards relevant discrepancies. Do the SOPs outline specific tests for which no equipment can be observed or tasks to be performed by specialized nurses who are not present during the observation? It might also be possible that the written SOP is outdated, but the actual care provided is in line with current best practice. In order to find out why these discrepancies exist, it can be useful to conduct interviews. Are the physicians simply not aware of the SOPs (because their existence is limited to the hospital’s intranet) or do they actively disagree with them or does the infrastructure make it impossible to provide the care as described? Another rationale for adding interviews is that some situations (or all of their possible variations for different patient groups or the day, night or weekend shift) cannot practically or ethically be observed. In this case, it is possible to ask those involved to report on their actions – being aware that this is not the same as the actual observation. A senior physician’s or hospital manager’s description of certain situations might differ from a nurse’s or junior physician’s one, maybe because they intentionally misrepresent facts or maybe because different aspects of the process are visible or important to them. In some cases, it can also be relevant to consider to whom the interviewee is disclosing this information – someone they trust, someone they are otherwise not connected to, or someone they suspect or are aware of being in a potentially “dangerous” power relationship to them. Lastly, a focus group could be conducted with representatives of the relevant professional groups to explore how and why exactly they provide care around EVT. The discussion might reveal discrepancies (between SOPs and actual care or between different physicians) and motivations to the researchers as well as to the focus group members that they might not have been aware of themselves. For the focus group to deliver relevant information, attention has to be paid to its composition and conduct, for example, to make sure that all participants feel safe to disclose sensitive or potentially problematic information or that the discussion is not dominated by (senior) physicians only. The resulting combination of data collection methods is shown in Fig. 2 .

Possible combination of data collection methods
Attributions for icons: “Book” by Serhii Smirnov, “Interview” by Adrien Coquet, FR, “Magnifying Glass” by anggun, ID, “Business communication” by Vectors Market; all from the Noun Project
The combination of multiple data source as described for this example can be referred to as “triangulation”, in which multiple measurements are carried out from different angles to achieve a more comprehensive understanding of the phenomenon under study [ 22 , 23 ].
Data analysis
To analyse the data collected through observations, interviews and focus groups these need to be transcribed into protocols and transcripts (see Fig. 3 ). Interviews and focus groups can be transcribed verbatim , with or without annotations for behaviour (e.g. laughing, crying, pausing) and with or without phonetic transcription of dialects and filler words, depending on what is expected or known to be relevant for the analysis. In the next step, the protocols and transcripts are coded , that is, marked (or tagged, labelled) with one or more short descriptors of the content of a sentence or paragraph [ 2 , 15 , 23 ]. Jansen describes coding as “connecting the raw data with “theoretical” terms” [ 20 ]. In a more practical sense, coding makes raw data sortable. This makes it possible to extract and examine all segments describing, say, a tele-neurology consultation from multiple data sources (e.g. SOPs, emergency room observations, staff and patient interview). In a process of synthesis and abstraction, the codes are then grouped, summarised and/or categorised [ 15 , 20 ]. The end product of the coding or analysis process is a descriptive theory of the behavioural pattern under investigation [ 20 ]. The coding process is performed using qualitative data management software, the most common ones being InVivo, MaxQDA and Atlas.ti. It should be noted that these are data management tools which support the analysis performed by the researcher(s) [ 14 ].

From data collection to data analysis
Attributions for icons: see Fig. Fig.2, 2 , also “Speech to text” by Trevor Dsouza, “Field Notes” by Mike O’Brien, US, “Voice Record” by ProSymbols, US, “Inspection” by Made, AU, and “Cloud” by Graphic Tigers; all from the Noun Project
How to report qualitative research?
Protocols of qualitative research can be published separately and in advance of the study results. However, the aim is not the same as in RCT protocols, i.e. to pre-define and set in stone the research questions and primary or secondary endpoints. Rather, it is a way to describe the research methods in detail, which might not be possible in the results paper given journals’ word limits. Qualitative research papers are usually longer than their quantitative counterparts to allow for deep understanding and so-called “thick description”. In the methods section, the focus is on transparency of the methods used, including why, how and by whom they were implemented in the specific study setting, so as to enable a discussion of whether and how this may have influenced data collection, analysis and interpretation. The results section usually starts with a paragraph outlining the main findings, followed by more detailed descriptions of, for example, the commonalities, discrepancies or exceptions per category [ 20 ]. Here it is important to support main findings by relevant quotations, which may add information, context, emphasis or real-life examples [ 20 , 23 ]. It is subject to debate in the field whether it is relevant to state the exact number or percentage of respondents supporting a certain statement (e.g. “Five interviewees expressed negative feelings towards XYZ”) [ 21 ].
How to combine qualitative with quantitative research?
Qualitative methods can be combined with other methods in multi- or mixed methods designs, which “[employ] two or more different methods [ …] within the same study or research program rather than confining the research to one single method” [ 24 ]. Reasons for combining methods can be diverse, including triangulation for corroboration of findings, complementarity for illustration and clarification of results, expansion to extend the breadth and range of the study, explanation of (unexpected) results generated with one method with the help of another, or offsetting the weakness of one method with the strength of another [ 1 , 17 , 24 – 26 ]. The resulting designs can be classified according to when, why and how the different quantitative and/or qualitative data strands are combined. The three most common types of mixed method designs are the convergent parallel design , the explanatory sequential design and the exploratory sequential design. The designs with examples are shown in Fig. 4 .

Three common mixed methods designs
In the convergent parallel design, a qualitative study is conducted in parallel to and independently of a quantitative study, and the results of both studies are compared and combined at the stage of interpretation of results. Using the above example of EVT provision, this could entail setting up a quantitative EVT registry to measure process times and patient outcomes in parallel to conducting the qualitative research outlined above, and then comparing results. Amongst other things, this would make it possible to assess whether interview respondents’ subjective impressions of patients receiving good care match modified Rankin Scores at follow-up, or whether observed delays in care provision are exceptions or the rule when compared to door-to-needle times as documented in the registry. In the explanatory sequential design, a quantitative study is carried out first, followed by a qualitative study to help explain the results from the quantitative study. This would be an appropriate design if the registry alone had revealed relevant delays in door-to-needle times and the qualitative study would be used to understand where and why these occurred, and how they could be improved. In the exploratory design, the qualitative study is carried out first and its results help informing and building the quantitative study in the next step [ 26 ]. If the qualitative study around EVT provision had shown a high level of dissatisfaction among the staff members involved, a quantitative questionnaire investigating staff satisfaction could be set up in the next step, informed by the qualitative study on which topics dissatisfaction had been expressed. Amongst other things, the questionnaire design would make it possible to widen the reach of the research to more respondents from different (types of) hospitals, regions, countries or settings, and to conduct sub-group analyses for different professional groups.
How to assess qualitative research?
A variety of assessment criteria and lists have been developed for qualitative research, ranging in their focus and comprehensiveness [ 14 , 17 , 27 ]. However, none of these has been elevated to the “gold standard” in the field. In the following, we therefore focus on a set of commonly used assessment criteria that, from a practical standpoint, a researcher can look for when assessing a qualitative research report or paper.
Assessors should check the authors’ use of and adherence to the relevant reporting checklists (e.g. Standards for Reporting Qualitative Research (SRQR)) to make sure all items that are relevant for this type of research are addressed [ 23 , 28 ]. Discussions of quantitative measures in addition to or instead of these qualitative measures can be a sign of lower quality of the research (paper). Providing and adhering to a checklist for qualitative research contributes to an important quality criterion for qualitative research, namely transparency [ 15 , 17 , 23 ].
Reflexivity
While methodological transparency and complete reporting is relevant for all types of research, some additional criteria must be taken into account for qualitative research. This includes what is called reflexivity, i.e. sensitivity to the relationship between the researcher and the researched, including how contact was established and maintained, or the background and experience of the researcher(s) involved in data collection and analysis. Depending on the research question and population to be researched this can be limited to professional experience, but it may also include gender, age or ethnicity [ 17 , 27 ]. These details are relevant because in qualitative research, as opposed to quantitative research, the researcher as a person cannot be isolated from the research process [ 23 ]. It may influence the conversation when an interviewed patient speaks to an interviewer who is a physician, or when an interviewee is asked to discuss a gynaecological procedure with a male interviewer, and therefore the reader must be made aware of these details [ 19 ].
Sampling and saturation
The aim of qualitative sampling is for all variants of the objects of observation that are deemed relevant for the study to be present in the sample “ to see the issue and its meanings from as many angles as possible” [ 1 , 16 , 19 , 20 , 27 ] , and to ensure “information-richness [ 15 ]. An iterative sampling approach is advised, in which data collection (e.g. five interviews) is followed by data analysis, followed by more data collection to find variants that are lacking in the current sample. This process continues until no new (relevant) information can be found and further sampling becomes redundant – which is called saturation [ 1 , 15 ] . In other words: qualitative data collection finds its end point not a priori , but when the research team determines that saturation has been reached [ 29 , 30 ].
This is also the reason why most qualitative studies use deliberate instead of random sampling strategies. This is generally referred to as “ purposive sampling” , in which researchers pre-define which types of participants or cases they need to include so as to cover all variations that are expected to be of relevance, based on the literature, previous experience or theory (i.e. theoretical sampling) [ 14 , 20 ]. Other types of purposive sampling include (but are not limited to) maximum variation sampling, critical case sampling or extreme or deviant case sampling [ 2 ]. In the above EVT example, a purposive sample could include all relevant professional groups and/or all relevant stakeholders (patients, relatives) and/or all relevant times of observation (day, night and weekend shift).
Assessors of qualitative research should check whether the considerations underlying the sampling strategy were sound and whether or how researchers tried to adapt and improve their strategies in stepwise or cyclical approaches between data collection and analysis to achieve saturation [ 14 ].
Good qualitative research is iterative in nature, i.e. it goes back and forth between data collection and analysis, revising and improving the approach where necessary. One example of this are pilot interviews, where different aspects of the interview (especially the interview guide, but also, for example, the site of the interview or whether the interview can be audio-recorded) are tested with a small number of respondents, evaluated and revised [ 19 ]. In doing so, the interviewer learns which wording or types of questions work best, or which is the best length of an interview with patients who have trouble concentrating for an extended time. Of course, the same reasoning applies to observations or focus groups which can also be piloted.
Ideally, coding should be performed by at least two researchers, especially at the beginning of the coding process when a common approach must be defined, including the establishment of a useful coding list (or tree), and when a common meaning of individual codes must be established [ 23 ]. An initial sub-set or all transcripts can be coded independently by the coders and then compared and consolidated after regular discussions in the research team. This is to make sure that codes are applied consistently to the research data.
Member checking
Member checking, also called respondent validation , refers to the practice of checking back with study respondents to see if the research is in line with their views [ 14 , 27 ]. This can happen after data collection or analysis or when first results are available [ 23 ]. For example, interviewees can be provided with (summaries of) their transcripts and asked whether they believe this to be a complete representation of their views or whether they would like to clarify or elaborate on their responses [ 17 ]. Respondents’ feedback on these issues then becomes part of the data collection and analysis [ 27 ].
Stakeholder involvement
In those niches where qualitative approaches have been able to evolve and grow, a new trend has seen the inclusion of patients and their representatives not only as study participants (i.e. “members”, see above) but as consultants to and active participants in the broader research process [ 31 – 33 ]. The underlying assumption is that patients and other stakeholders hold unique perspectives and experiences that add value beyond their own single story, making the research more relevant and beneficial to researchers, study participants and (future) patients alike [ 34 , 35 ]. Using the example of patients on or nearing dialysis, a recent scoping review found that 80% of clinical research did not address the top 10 research priorities identified by patients and caregivers [ 32 , 36 ]. In this sense, the involvement of the relevant stakeholders, especially patients and relatives, is increasingly being seen as a quality indicator in and of itself.
How not to assess qualitative research
The above overview does not include certain items that are routine in assessments of quantitative research. What follows is a non-exhaustive, non-representative, experience-based list of the quantitative criteria often applied to the assessment of qualitative research, as well as an explanation of the limited usefulness of these endeavours.
Protocol adherence
Given the openness and flexibility of qualitative research, it should not be assessed by how well it adheres to pre-determined and fixed strategies – in other words: its rigidity. Instead, the assessor should look for signs of adaptation and refinement based on lessons learned from earlier steps in the research process.
Sample size
For the reasons explained above, qualitative research does not require specific sample sizes, nor does it require that the sample size be determined a priori [ 1 , 14 , 27 , 37 – 39 ]. Sample size can only be a useful quality indicator when related to the research purpose, the chosen methodology and the composition of the sample, i.e. who was included and why.
Randomisation
While some authors argue that randomisation can be used in qualitative research, this is not commonly the case, as neither its feasibility nor its necessity or usefulness has been convincingly established for qualitative research [ 13 , 27 ]. Relevant disadvantages include the negative impact of a too large sample size as well as the possibility (or probability) of selecting “ quiet, uncooperative or inarticulate individuals ” [ 17 ]. Qualitative studies do not use control groups, either.
Interrater reliability, variability and other “objectivity checks”
The concept of “interrater reliability” is sometimes used in qualitative research to assess to which extent the coding approach overlaps between the two co-coders. However, it is not clear what this measure tells us about the quality of the analysis [ 23 ]. This means that these scores can be included in qualitative research reports, preferably with some additional information on what the score means for the analysis, but it is not a requirement. Relatedly, it is not relevant for the quality or “objectivity” of qualitative research to separate those who recruited the study participants and collected and analysed the data. Experiences even show that it might be better to have the same person or team perform all of these tasks [ 20 ]. First, when researchers introduce themselves during recruitment this can enhance trust when the interview takes place days or weeks later with the same researcher. Second, when the audio-recording is transcribed for analysis, the researcher conducting the interviews will usually remember the interviewee and the specific interview situation during data analysis. This might be helpful in providing additional context information for interpretation of data, e.g. on whether something might have been meant as a joke [ 18 ].
Not being quantitative research
Being qualitative research instead of quantitative research should not be used as an assessment criterion if it is used irrespectively of the research problem at hand. Similarly, qualitative research should not be required to be combined with quantitative research per se – unless mixed methods research is judged as inherently better than single-method research. In this case, the same criterion should be applied for quantitative studies without a qualitative component.
The main take-away points of this paper are summarised in Table Table1. 1 . We aimed to show that, if conducted well, qualitative research can answer specific research questions that cannot to be adequately answered using (only) quantitative designs. Seeing qualitative and quantitative methods as equal will help us become more aware and critical of the “fit” between the research problem and our chosen methods: I can conduct an RCT to determine the reasons for transportation delays of acute stroke patients – but should I? It also provides us with a greater range of tools to tackle a greater range of research problems more appropriately and successfully, filling in the blind spots on one half of the methodological spectrum to better address the whole complexity of neurological research and practice.
Take-away-points
Acknowledgements
Abbreviations, authors’ contributions.
LB drafted the manuscript; WW and CG revised the manuscript; all authors approved the final versions.
no external funding.
Availability of data and materials
Ethics approval and consent to participate, consent for publication, competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Qualitative research involves... -an emergent design: emerges in the field as the researchers make ongoing decisions. -flexible: adjusts to new info. -plan for broad contingencies (time, resources) -pose decision opportunities for study design (when to stop data collection) Characteristics of Qualitative Research Design. -creative and intuitive.
5. Causality and Qualitative Research. Qualitative Design: Control over independent variable. - usually do not conceptualize studies as having independent and dependent variables and rarely manipulate or control any aspect. - all are non-experimental. - goal is to develop an understanding of a phenomena as it exists.
Steps of designing a qualitative study. 1. start with newborn idea/inquiry. 2. discuss with others; study design emerges and evolves; Prospective design that articulates possibilities. 3. formal research proposal written. 4. immerse in data, analyze what's collected and how it's collected.
Characteristics of Qualitative Research: 1) Is conducted in a natural setting (the field), a source of data for close interaction. 2) Relies on the researcher as key instrument in data collection. Researchers do not use or rely on questionnaires or instruments developed by other researchers. 3) Involves multiple methods.
Qualitative research is a systematic, subjective approach used to describe life experiences and give them meaning. It focuses on understanding the whole. It is consistent with holistic philosophy of nursing. Click the card to flip 👆. 1 / 35.
Qualitative research involves collecting and analyzing non-numerical data (e.g., text, video, or audio) to understand concepts, opinions, or experiences. It can be used to gather in-depth insights into a problem or generate new ideas for research. Qualitative research is the opposite of quantitative research, which involves collecting and ...
A method of qualitative analysis in which one reviews data as it is gathered, compares to already interpreted data, and reviews earlier conclusions to see if new data supports or rejects it. Theory is developed and revised as you go. Click the card to flip 👆. 1 / 21.
Qualitative research design typically involves gathering data through methods such as interviews, observations, focus groups, and analysis of documents or artifacts. These methods allow researchers to collect detailed, descriptive information about participants' perspectives, experiences, and contexts. Key characteristics of qualitative ...
Focus Groups. Focus groups resemble qualitative interviews in that a researcher may prepare a guide in advance and interact with participants by asking them questions. But anyone who has conducted both one-on-one interviews and focus groups knows that each is unique. In an interview, usually one member (the research participant) is most active ...
Study with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Which statement is true? a: The quality of qualitative studies depends on the appropriateness of the statistical analysis b: Qualitative design is capable of adjusting to what is being learned during data collection c: Qualitative research does not require approval by an Institutional Review Board or ethical review committee d ...
Figure 2.1. Purpose types from Theory to Action. Adopted from Patton (2002). Basic research involves research that is done for the sake of "pure" knowledge—that is, knowledge that, at least at this moment in time, may not have any apparent use or application. Often, and this is very important, knowledge of this kind is later found to be extremely helpful in solving problems.
Qualitative research involves asking participants about their experiences of things that happen in their lives. It enables researchers to obtain insights into what it feels like to be another person and to understand the world as another experiences it. ... articulating questions, generating hypotheses, and choosing study designs. Can J Hosp ...
Qualitative research involves the studied use and collection of a variety of empirical materials - case study, personal experience, introspective, life story, interview, observational, historical, interactional, and visual texts - that describe routine and problematic moments and meanings in individuals' lives.
While many books and articles guide various qualitative research methods and analyses, there is currently no concise resource that explains and differentiates among the most common qualitative approaches. We believe novice qualitative researchers, students planning the design of a qualitative study or taking an introductory qualitative research course, and faculty teaching such courses can ...
1 pt. A researcher who utilizes methods triangulation __________. mixes research methods with non overlapping strengths and weaknesses. examines multiple theories in order to explain study results. uses multiple methods of data collection to capture a single phenomenon. corroborates the observations of multiple observers.
1. Ethnographic research: In this qualitative method, researchers observe and interact with the study's participants in their real-life environment to understand their culture.For example: A researcher may closely observe a group of members at a gym. In a month, the researcher observes the interactions of the members with trainers, their exercise and equipment preferences, and diets.
Qualitative research is a type of research that explores and provides deeper insights into real-world problems.[1] Instead of collecting numerical data points or intervening or introducing treatments just like in quantitative research, qualitative research helps generate hypothenar to further investigate and understand quantitative data. Qualitative research gathers participants' experiences ...
Qualitative research is defined as an exploratory method that aims to understand complex phenomena, often within their natural settings, by examining subjective experiences, beliefs, attitudes, and behaviors. Unlike quantitative research, which focuses on numerical measurements and statistical analysis, qualitative research employs a range of ...
Chapter 9 Qualitative Methods. Qualitative methods demonstrate a different approach to scholarly inquiry than methods of quantitative research. Although the processes are similar, qualitative methods rely on text and image data, have unique steps in data analysis, and draw on diverse designs. Writing a method section for a proposal or study for ...
Qualitative Research. Qualitative research is a type of research methodology that focuses on exploring and understanding people's beliefs, attitudes, behaviors, and experiences through the collection and analysis of non-numerical data. It seeks to answer research questions through the examination of subjective data, such as interviews, focus ...
Grounded theory first described by Glaser and Strauss in 1967, is a framework for qualitative research that suggests that theory must derive from data, unlike other forms of research, which suggest that data should be used to test theory. 43 It is a qualitative research process that entails developing theories based on evidence that has been ...
Qualitative research has its roots in anthropology, sociology, psychology, linguistics, and semiotics, and has been available since the early 19th century, long before quantitative statistical techniques were employed. Distinctions from Quantitative Research. In qualitative research, the role of the researcher receives critical attention.
Abstract. This paper aims to provide an overview of the use and assessment of qualitative research methods in the health sciences. Qualitative research can be defined as the study of the nature of phenomena and is especially appropriate for answering questions of why something is (not) observed, assessing complex multi-component interventions ...