The HTML Presentation Framework
Created by Hakim El Hattab and contributors


Hello There
reveal.js enables you to create beautiful interactive slide decks using HTML. This presentation will show you examples of what it can do.
Vertical Slides
Slides can be nested inside of each other.
Use the Space key to navigate through all slides.
Basement Level 1
Nested slides are useful for adding additional detail underneath a high level horizontal slide.
Basement Level 2
That's it, time to go back up.

Not a coder? Not a problem. There's a fully-featured visual editor for authoring these, try it out at https://slides.com .
Pretty Code
Code syntax highlighting courtesy of highlight.js .
Even Prettier Animations
Point of view.
Press ESC to enter the slide overview.
Hold down the alt key ( ctrl in Linux) and click on any element to zoom towards it using zoom.js . Click again to zoom back out.
(NOTE: Use ctrl + click in Linux.)
Auto-Animate
Automatically animate matching elements across slides with Auto-Animate .
Touch Optimized
Presentations look great on touch devices, like mobile phones and tablets. Simply swipe through your slides.
Add the r-fit-text class to auto-size text
Hit the next arrow...
... to step through ...
... a fragmented slide.
Fragment Styles
There's different types of fragments, like:
fade-right, up, down, left
fade-in-then-out
fade-in-then-semi-out
Highlight red blue green
Transition Styles
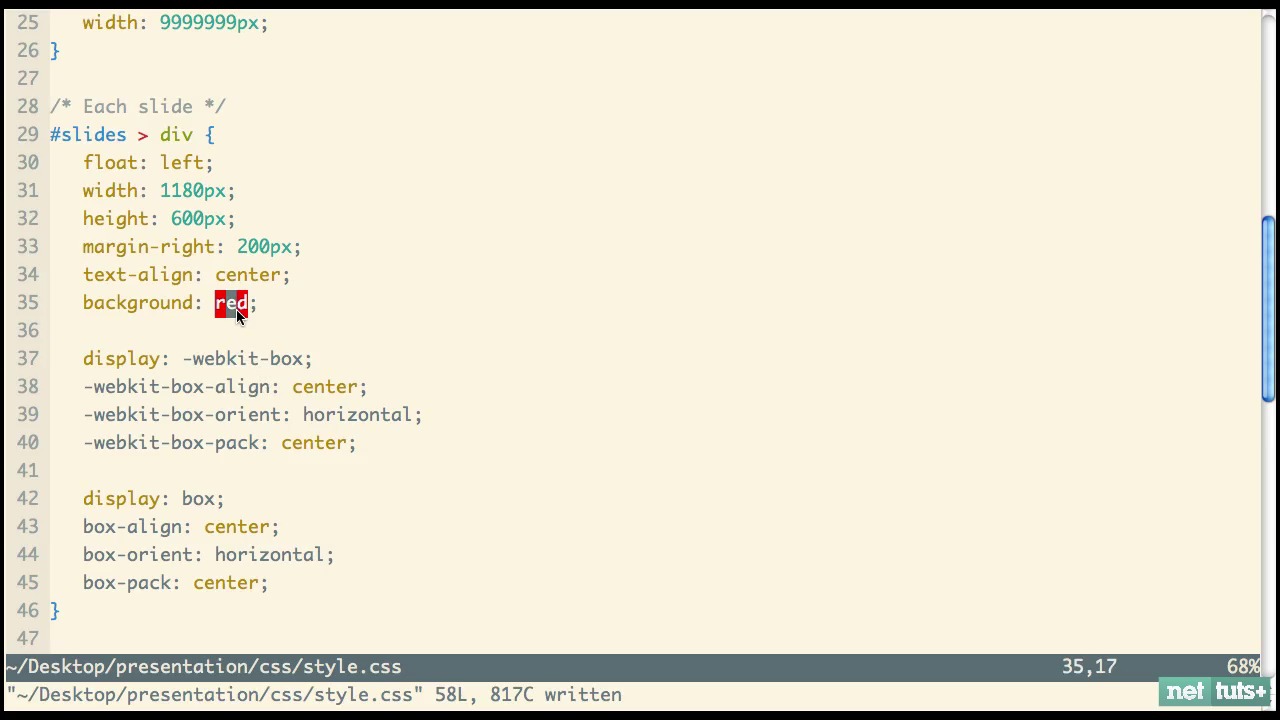
You can select from different transitions, like: None - Fade - Slide - Convex - Concave - Zoom
Slide Backgrounds
Set data-background="#dddddd" on a slide to change the background color. All CSS color formats are supported.
Image Backgrounds
Tiled backgrounds, video backgrounds, ... and gifs, background transitions.
Different background transitions are available via the backgroundTransition option. This one's called "zoom".
You can override background transitions per-slide.
Iframe Backgrounds
Since reveal.js runs on the web, you can easily embed other web content. Try interacting with the page in the background.
Marvelous List
- No order here
Fantastic Ordered List
- One is smaller than...
- Two is smaller than...
Tabular Tables
| Item | Value | Quantity |
|---|---|---|
| Apples | $1 | 7 |
| Lemonade | $2 | 18 |
| Bread | $3 | 2 |
Clever Quotes
These guys come in two forms, inline: The nice thing about standards is that there are so many to choose from and block:
“For years there has been a theory that millions of monkeys typing at random on millions of typewriters would reproduce the entire works of Shakespeare. The Internet has proven this theory to be untrue.”
Intergalactic Interconnections
You can link between slides internally, like this .
Speaker View
There's a speaker view . It includes a timer, preview of the upcoming slide as well as your speaker notes.
Press the S key to try it out.
Export to PDF
Presentations can be exported to PDF , here's an example:
Global State
Set data-state="something" on a slide and "something" will be added as a class to the document element when the slide is open. This lets you apply broader style changes, like switching the page background.
State Events
Additionally custom events can be triggered on a per slide basis by binding to the data-state name.
Take a Moment
Press B or . on your keyboard to pause the presentation. This is helpful when you're on stage and want to take distracting slides off the screen.
- Right-to-left support
- Extensive JavaScript API
- Auto-progression
- Parallax backgrounds
- Custom keyboard bindings
- Try the online editor - Source code & documentation
Create Stunning Presentations on the Web
reveal.js is an open source HTML presentation framework. It's a tool that enables anyone with a web browser to create fully-featured and beautiful presentations for free.
Presentations made with reveal.js are built on open web technologies. That means anything you can do on the web, you can do in your presentation. Change styles with CSS, include an external web page using an <iframe> or add your own custom behavior using our JavaScript API .
The framework comes with a broad range of features including nested slides , Markdown support , Auto-Animate , PDF export , speaker notes , LaTeX support and syntax highlighted code .
Ready to Get Started?
It only takes a minute to get set up. Learn how to create your first presentation in the installation instructions !
Online Editor
If you want the benefits of reveal.js without having to write HTML or Markdown try https://slides.com . It's a fully-featured visual editor and platform for reveal.js, by the same creator.
Supporting reveal.js
This project was started and is maintained by @hakimel with the help of many contributions from the community . The best way to support the project is to become a paying member of Slides.com —the reveal.js presentation platform that Hakim is building.

Slides.com — the reveal.js presentation editor.
Become a reveal.js pro in the official video course.

Practical SQL course for Product Managers, Marketers, Designers, Software Engineers, CEOs and more. Learn with hundreds of bite-sized exercises which could be applied in real job right away.
How to Make Slideshow in HTML: Your Quick and Easy Guide
If you’ve ever wondered how to make a slideshow in HTML , today’s your lucky day. I’m here to break it down for you, step-by-step, making the process as clear and easy as possible. While it might sound complicated at first glance, with a bit of understanding and practice, you’ll be creating stunning slideshows in no time.
HTML (HyperText Markup Language) is the backbone of every website we visit on the internet. With its partner in crime CSS (Cascading Style Sheets), they allow us to create visually engaging web pages with ease. A slideshow is just one of many interactive elements that can enhance your web project, enriching the user experience.
In this guide, I’ll walk you through each phase of creating an HTML slideshow – from crafting the structure using HTML tags, styling it with CSS rules, and adding functionality with JavaScript or jQuery if needed. By the end of this article, not only will you have acquired a new skill set but also gained confidence in your ability to manipulate these powerful tools effectively.
Understanding HTML for Slideshow Creation
Diving into the world of HTML, it’s crucial to grasp the foundational elements first. HTML, or Hyper Text Markup Language, is the building block of most web pages. It’s a way to structure content on the web and create visual presentations like slideshows.
When we talk about creating a slideshow using HTML, we’re often referring to leveraging a combination of div tags and CSS properties. Just imagine each slide as an individual div . You need to define that div in your HTML file like this:
In this snippet, we’ve created a simple division or ‘container’ with a single paragraph inside it. This represents one slide in our slideshow.
But here’s where things get interesting! While you can use multiple div tags for different slides, you could also leverage other HTML elements for variety. For instance, an image tag <img> can be used within your slide container along with some text within paragraph <p> or heading <h1> , <h2> , etc., tags.
It might look something like this:
Apart from static content like text and images, you can even incorporate interactive elements into your slides using form input tags such as buttons ( <button> ), dropdowns ( <select> ), etc.
HTML is truly versatile when it comes to crafting engaging slideshows! But remember – while knowing how to manipulate these tags is important, understanding their interaction with CSS and JavaScript will truly unlock their potential for dynamic webpage design.
Essential Tools Required for HTML Slideshow
Creating an HTML slideshow might seem like a daunting task, especially if you’re new to coding. However, I’m here to assure you that it’s not as complex as it may first appear. With the right tools in hand, anyone can create an interactive and engaging slideshow for their website.
Firstly, let’s talk about the most fundamental tool – a text editor. While there are numerous options available such as Sublime Text, Atom or even Notepad++, my personal recommendation is Visual Studio Code (VS Code). It’s free, versatile and has an array of plugins which can simplify your coding experience significantly.
Next up is your web browser. This will be used to preview your slideshow as you build it. Chrome and Firefox offer great developer tools allowing you to inspect elements on your webpage and debug any errors that might pop up.
Now onto the real meat of our toolset: HTML, CSS, and JavaScript. Thinking of them as building blocks:
- HTML (HyperText Markup Language) forms the foundation or structure of your webpage.
- CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) comes next adding style; color schemes, fonts etc., breathing life into your HTML skeleton.
- Lastly comes JavaScript , making everything interactive. In terms of slideshows this could mean transitioning between images when a button is clicked.
Here’s a simple example of these three working together:
In this code, HTML is creating a space for our slideshow, CSS is specifying the size of that space and JavaScript is cycling through an array of image URLs, updating the src attribute of our <img> element every three seconds.
If you’re looking to expand on your slideshow functionality or make it more visually appealing, there are several libraries available such as jQuery and Bootstrap. They offer pre-built components which can be customized to fit into your webpage seamlessly.
Remember, practice makes perfect. So don’t shy away from coding your own HTML slideshows. It’s a fantastic way to learn and understand how websites work!
Step-by-Step Guide: Building Your First HTML Slideshow
Let’s dive into the fun part! We’re going to create a simple yet sophisticated HTML slideshow. Don’t worry if you’re new to coding – it’s really not as intimidating as it might seem.
Firstly, we’ll need to set up our HTML document. This is the backbone of your webpage and where all the magic happens. Start with a basic structure that includes the !DOCTYPE declaration, html, head, and body tags. It should look something like this:
Next comes adding our images for the slideshow within the body section of our code. We’ll use div tags here, which are essentially containers for content on your page. For each image in your slideshow, create a new div tag and nest an img tag inside it with the source (src) attribute pointing to your image file. Here’s what it would look like:
We’ve added a CSS class “slide” to each div so we can style them later.
Now to bring life into our static images – we want them changing automatically creating a dynamic feel! To achieve this effect, you’ll likely find JavaScript most helpful due its ability for controlling time-based events.
Consider using setInterval() function which allows us to run certain code every x milliseconds. In this case, that’d be switching between images in our slideshow:
In the snippet above, we’re hiding all images by default and then displaying one image at a time. When the last image is shown, it goes back to the first.
Finally, let’s not forget about styling our slideshow. With CSS you can customize your slideshow’s appearance to match your website’s aesthetic. Here’s an example of how that might look:
And voila! You’ve just created your first HTML slideshow! Practice makes perfect, so don’t hesitate to experiment with different styles and functionalities. Happy coding!
Common Mistakes and Troubleshooting in Making HTML Slideshows
I’ve seen many people stumble while creating HTML slideshows. It’s not uncommon to come across a few hiccups along the way. So, let’s shed some light on these common mistakes and how you can troubleshoot them.
One of the most frequent mistakes is forgetting to include the Doctype declaration at the beginning of your HTML file. Without it, your slideshow might not display correctly across different browsers. Here’s an example:
Another common error is neglecting to close tags properly, which can lead to elements appearing out of place or not displaying at all. Always double-check that each opening tag has its corresponding closing tag like this:
Sometimes, it’s easy to overlook file paths when linking images or scripts essential for your slideshow. Providing incorrect file paths will prevent those resources from loading correctly – make sure you’re referring to the right location!
Lastly, not optimizing images for web use can slow down your slideshow significantly. Large image files take longer time to load and may cause delays between transitions in your slideshow.
As for troubleshooting issues with HTML slideshows, using browser developer tools should be your go-to strategy! These tools allow you to inspect elements directly in the browser and identify any coding errors causing problems in real-time.
Here are some quick tips:
- Check console logs for any error messages.
- Use ‘Inspect Element’ feature to view associated CSS rules.
- Use Network tab to verify if resources are being loaded successfully.
Remember, everyone makes mistakes when they’re learning something new – it’s all part of the process. Keep practicing, and you’ll surely master the art of creating HTML slideshows!
Conclusion: Mastering the Art of Creating a Slideshow in HTML
I’ve taken you through the steps and shared my knowledge on creating a slideshow using HTML. And I’m confident that you’re now better equipped to handle this task. It’s not just about getting it done, it’s about mastering the art.
Let’s recap what we’ve covered:
- Understanding how to use the <div> tag to create containers for our slides.
- Learning how to style these divs using CSS properties like background-image , height , and width to give shape and substance to our slideshow.
- Discovering the power of JavaScript in manipulating our HTML elements, making them interactive and dynamic.
For example, here’s a simple slide structure:
And remember, there are many ways you can customize your slideshow. You could add navigation buttons with more tags like <button> or introduce transitions with CSS animations.
This whole process isn’t just about learning a new skill; it’s also about enhancing your creativity. Can’t wait to see what amazing slideshows you’ll design!
HTML is such an indispensable tool in web development. From creating basic structures like paragraphs and headings with tags like <p> and <h> , respectively, to crafting intricate layouts with divs – there are endless possibilities.
The beauty lies not only in understanding each HTML tag but also knowing when and where to use them effectively – that’s where true mastery begins!
In essence, building a slideshow in HTML might seem complex at first glance but once broken down into parts – defining structure with HTML, styling with CSS, adding interactivity with JavaScript – it becomes less daunting!
So keep practicing those codes. Each time you do, you’re one step closer towards becoming an expert web developer. Happy coding!
Cristian G. Guasch
Related articles.
- How to Make a Vertical Line in HTML: A Simple Guide for Beginners
- How to Disable a Button in HTML: Your Quick and Easy Guide
- How to Make Checkboxes in HTML: My Simple Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Make a Popup in HTML: A Simple, Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners
- How to Float an Image in HTML: Simplifying Web Design for Beginners
- How to Use iFrame in HTML: A Comprehensive Beginner’s Guide
- How to Add Audio in HTML: A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners
- How to Print in HTML: Your Essential Guide for Webpage Printing
- How to Draw Lines in HTML: A Swift and Simple Guide for Beginners
- How to Add Canonical Tag in HTML: Your Easy Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Use Span in HTML: Unleashing Your Web Design Potential
- How to Embed Google Map in HTML: A Quick and Easy Guide for Beginners
- How to Add SEO Keywords in HTML: My Simplified Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Add a GIF in HTML: A Simple Guide for Beginners
- How to Change Fonts in HTML: Your Ultimate Guide to Web Typography
- How to Make an Ordered List in HTML: A Straightforward Guide for Beginners
- How to Add Bullet Points in HTML: Your Quick and Easy Guide
- How to Move Text in HTML: My Expert Guide for Web Developers
- How to Unbold Text in HTML: A Straightforward Guide for Beginners
- How to Create Pages in HTML: A Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners
- How to Use PHP in HTML: An Expert’s Guide for Seamless Integration
- How to Make Multiple Pages in HTML: A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners
- How to Embed a Website in HTML: Your Simple Guide to Seamless Integration
- How to Create a Box in HTML: A Simple Guide for Beginners
- How to Make a Search Bar in HTML: Simplified Steps for Beginners
- How to Add Padding in HTML: A Simple Guide for Web Design Beginners
- How to Send HTML Email in Outlook: Your Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Make a Form in HTML: Your Easy Guide for Better Web Design
- How to Put Text Next to an Image in HTML: A Simple Guide for Beginners
- How to Use Div in HTML: Your Ultimate Guide on Mastering Division Tags
- How to Wrap Text in HTML: Mastering the Art of Web Design
- How to Redirect to Another Page in HTML: A Simple, Effective Guide for Beginners
- How to Center a Div in HTML: My Expert Guide for Perfect Alignment
- How to Add a Target Attribute in HTML: A Simple Guide for Beginners
- How to Link Email in HTML: My Simple Guide for Beginners
- How to Use JavaScript in HTML: A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners
- How to Make List in HTML: A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners
- How to Make a Button in HTML: A Simple Guide for Beginners
- How to Add a Line Break in HTML: Your Quick and Easy Guide
- How to Embed a Video in HTML: A Simplified Guide for Beginners
- How to Add a Favicon in HTML: Your Easy Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Change Font Size in HTML: A Simple Guide for Beginners
- How to Center a Table in HTML: Streamlining Your Web Design Skills
- How to Add Space in HTML: Your Guide for a Cleaner Code Layout
- How to Change Image Size in HTML: Your Quick and Easy Guide
- How to Indent in HTML: A Simple Guide for Beginners
- How to Add a Link in HTML: Your Easy Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Make a Table in HTML: Your Ultimate Guide to Mastery
- How to Add an Image in HTML: A Step-by-Step Tutorial for Beginners
- How to Italicize in HTML: A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners

DEV Community
Posted on Jan 11, 2019
How To Build A Captivating Presentation Using HTML, CSS, & JavaScript
Building beautiful presentations is hard. Often you're stuck with Keynote or PowerPoint, and the templates are extremely limited and generic. Well not anymore.
Today, we're going to learn how to create a stunning and animated presentation using HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
If you're a beginner to web development, don't fret! This tutorial will be easy enough to keep up with. So let's slide right into it!

We're going to be using an awesome framework called Reveal.js . It provides robust functionality for creating interesting and customizable presentations.
- Head over to the Reveal.js repository and clone the project (you can also fork this to your GitHub namespace).

- Change directories into your newly cloned folder and run npm install to download the package dependencies. Then run npm start to run the project.

The index.html file holds all of the markup for the slides. This is one of the downsides of using Reveal.js; all of the content will be placed inside this HTML file.

Built-In Themes
Reveal includes 11 built-in themes for you to choose from:

Changing The Theme
- Open index.html
- Change the CSS import to reflect the theme you want to use

The theme files are:
- solarized.css
Custom Themes
It's quite easy to create a custom theme. Today, I'll be using my custom theme from a presentation I gave called "How To Build Kick-Ass Website: An Introduction To Front-end Development."
Here is what my custom slides look like:

Creating A Custom Theme
- Open css/theme/src inside your IDE. This holds all of the Sass files ( .scss ) for each theme. These files will be transpiled to CSS using Grunt (a JavaScript task runner). If you prefer to write CSS, go ahead and just create the CSS file inside css/theme.
- Create a new .scss file. I will call mine custom.scss . You may have to stop your localhost and run npm run build to transpile your Sass code to CSS.
- Inside the index.html file, change the CSS theme import in the <head> tag to use the name of the newly created stylesheet. The extension will be .css , not .scss .
- Next, I created variables for all of the different styles I wanted to use. You can find custom fonts on Google Fonts. Once the font is downloaded, be sure to add the font URL's into the index.html file.
Here are the variables I chose to use:
- Title Font: Viga
- Content Font: Open Sans
- Code Font: Courier New
- Cursive Font: Great Vibes
- Yellow Color: #F9DC24
- Add a .reveal class to the custom Sass file. This will wrap all of the styles to ensure our custom theme overrides any defaults. Then, add your custom styling!
Unfortunately, due to time constraints, I'll admit that I used quite a bit of !important overrides in my CSS. This is horrible practice and I don't recommend it. The reveal.css file has extremely specific CSS styles, so I should have, if I had more time, gone back and ensured my class names were more specific so I could remove the !importants .
Mixins & Settings
Reveal.js also comes with mixins and settings you can leverage in your custom theme.
To use the mixins and settings, just import the files into your custom theme:
Mixins You can use the vertical-gradient, horizontal-gradient, or radial-gradient mixins to create a neat visual effect.
All you have to do is pass in the required parameters (color value) and voila, you've got a gradient!
Settings In the settings file, you'll find useful variables like heading sizes, default fonts and colors, and more!

The structure for adding new content is:
.reveal > .slides > section
The <section> element represents one slide. Add as many sections as you need for your content.
Vertical Slides
To create vertical slides, simply nest sections.
Transitions
There are several different slide transitions for you to choose from:
To use them, add a data-transition="{name}" to the <section> which contains your slide data.
Fragments are great for highlighting specific pieces of information on your slide. Here is an example.
To use fragments, add a class="fragment {type-of-fragment}" to your element.
The types of fragments can be:
- fade-in-then-out
- fade-in-then-semi-out
- highlight-current-blue
- highlight-red
- highlight-green
- highlight-blue
You can additionally add indices to your elements to indicate in which order they should be highlighted or displayed. You can denote this using the data-fragment-index={index} attribute.
There are way more features to reveal.js which you can leverage to build a beautiful presentation, but these are the main things which got me started.
To learn more about how to format your slides, check out the reveal.js tutorial . All of the code for my presentation can be viewed on GitHub. Feel free to steal my theme!
Top comments (18)
Templates let you quickly answer FAQs or store snippets for re-use.
- Joined Oct 2, 2018
I really love reveal.js. I haven't spoken in a while so I haven't used it. I've always used their themes and never thought about making my own. This is probably super useful for company presentations, too. I'm SO over google slides. Trying to format code in those is a nightmare LOL
- Location Stockholm
- Education Siena College
- Work Software Engineer at Spotify
- Joined Dec 21, 2018
Yeah it is time consuming, but the result is much better
- Location Antibes, France
- Work Senior Software Engineer at Spotify
- Joined Oct 16, 2017
The best thing in this - and now I'm not being ironic - is that while you work on a not so much technical task - creating a presentation - you still have to code. And the result is nice.
On the other hand, I know what my presentation skills teachers would say. Well, because they said it... :) If you really want to deliver a captivating presentation, don't use slides at all. Use the time to prepare what you want to say.
I'm not that good - yet, but taking their advice, if must I use few slides, with little information on them and with minimal graphical distractions. My goal is to impress them by what I say, not is what behind my head.
I'm going to a new training soon, where the first day we have to deliver a presentation supported by slides at a big auditorium and the next day we have to go back and forget about the slides and just get on stage and speak. I can't wait for it.
- Location Lake Villa, IL
- Education Bachelor in Electronics Engineering
- Work Computer & Technology Enthusiast
- Joined Oct 8, 2017
How about github.com/team-fluxion/slide-gazer ?
It's my fourth attempt at creating a simple presentation tool to help one present ideas quickly without having to spend time within a presentation editor like Microsoft PowerPoint. It directly converts markdown documents into elegant presentations with a few features and is still under development.
- Location Singapore
- Work Web Developer at FirstCom Solutions
- Joined Jan 15, 2019
Yup, RevealJS is awesome !
Previously I either used PPT or Google Slides. One is a paid license and the other requires an internet connection.
The cool thing about it is that since it's just HTML files behind the scenes, the only software you need to view it with is a web browser. Has amazing syntax-highlighting support via PrismJS. And as a web developer, it makes it simple to integrate other npm packages if need be...
I actually just used it to present a talk this week!
- Email [email protected]
- Location Indianapolis, IN
- Education Purdue University
- Pronouns he/him
- Work Senior Frontend Engineer at Whatnot
- Joined Aug 3, 2017
Great article, Emma! I love Reveal and this is a great write up for using it!
- Location New Delhi, India 🇮🇳
- Joined Dec 5, 2018
I think its a coincidence 😅 I was just starting to think to use reveal.js and suddenly you see this post 🤩
- Location Saratoga Springs,NY
- Education BA, University of Michigan
- Work Documentarian
- Joined Sep 7, 2018
Check out slides.com If you want to skip the heavy lifting and/or use a presentation platform based on reveal.js.
Everything is still easy to customize. The platform provides a UI to work from and an easy way to share your stuff.
BTW - I have no affiliation with slides.com, or even a current account. I used the service a few years back when I regularly presented and wanted to get over PowerPoint, Google Slides, Prezi, etc.
- Location Toronto, ON
- Education MFA in Art Video Syracuse University 2013 😂
- Work Rivalry
- Joined May 31, 2017
Well I guess you get to look ultra pro by skipping the moment where you have to adjust for display detection and make sure your notes don’t show because you plugged your display connector in 😩 But If the conference has no wifi then we’re screwed I guess
- Location Palm Bay, FL
- Education FullSail University
- Work Developer Relations Manager at MetaMask
- Joined Sep 16, 2018
I like Reveal, but I still have not moved past using Google docs slides because every presentation I do has to be done yesterday. Hoping that I can use Reveal more often this year as I get more time to work on each presentation.
- Email [email protected]
- Location Abuja Nigeria
- Work Project Manager Techibytes Media
- Joined Feb 19, 2019
Well this is nice and I haven't tried it maybe because I haven't spoken much in meet ups but I think PowerPoint is still much better than going all these steps and what if I have network connection issues that day then I'm scrolled right?
- Email [email protected]
- Joined Apr 16, 2018
Using Node and Soket.io remote control (meant to be used on phones) for my school's computer science club, it also features some more goodies which are helpful when having multiple presentations. It can be modded to use these styling techniques effortlessly. Feel free to fork!
SBCompSciClub / prez-software
A synchronized role based presentation software using node, prez-software.
TODO: Make system to easily manage multiple presentations Add Hash endocing and decoding for "sudo" key values TODO: Document Code
Run on Dev Server
npm i nodemon app.js Nodemon? - A life saving NPM module that is ran on a system level which automatically runs "node (file.js)" when files are modified. Download nodemon by running npm i -g nodemon
Making a Presentation
- Copy an existing presentation folder
- Change the folder name (which should be located at public/slides) with the name day[num of day] ex(day2)
Making a Slide
Making a slide is pretty simple. Just add a HTML section. <section> <!--slide content--> </section> inside the span with the class of "prez-root". Also keep in mind that you will need to copy and pate the markup inside the prez root to the other pages (viewer & controller).
Adding Text
You may add text however you desire, but for titles use the…
Awesome post! I’m glad I’m not the only one who likes libraries. 😎
- Location Los Angeles
- Education Engineering, Physics, and Math
- Joined Sep 6, 2018
Fantastic post. I just loved it.
- Location France
- Work Co-Founder of Depot
- Joined Sep 2, 2017
Awesome introduction! I feel like I need to give this a try the next time I create a presentation.
Some comments may only be visible to logged-in visitors. Sign in to view all comments.
Are you sure you want to hide this comment? It will become hidden in your post, but will still be visible via the comment's permalink .
Hide child comments as well
For further actions, you may consider blocking this person and/or reporting abuse

React Mindset: How New React Developers Should Think
Amir H. Moayeri - Sep 16

How to start a Shadcn project from scratch
OpenSource - Sep 23

Day 6:Understanding Stack and Heap in JavaScript
Aman Kumar - Sep 4

Mastering React.js: How to Build Fast, Scalable, and Performant Web Apps
Sabyasachi Mondal - Sep 13

We're a place where coders share, stay up-to-date and grow their careers.
Create beautiful stories
WebSlides makes HTML presentations easy. Just the essentials and using lovely CSS.
WebSlides 1.5.0 Github
Why WebSlides?
Good karma & Productivity.
An opportunity to engage.
WebSlides is about good karma. This is about telling the story, and sharing it in a beautiful way. HTML and CSS as narrative elements.
Work better, faster.
Designers, marketers, and journalists can now focus on the content. Simply choose a demo and customize it in minutes.
WebSlides is really easy
Each parent <section> in the #webslides element is an individual slide.
Code is clean and scalable. It uses intuitive markup with popular naming conventions. There's no need to overuse classes or nesting. Making an HTML presentation has never been so fast .
→ Simple Navigation
Slide counter, 40 + beautiful components, vertical rhythm, 500 + svg icons, webslides demos.
Contribute on Github . View all ›

If you need help, here's just some tutorials. Just a basic knowledge of HTML is required:
- Components · Classes .
- WebSlides on Codepen .
- WebSlides Media: images, videos...
Built to expand
The best way to inspire with your content is to connect on a personal level:
- Background images: Unsplash .
- CSS animations: Animate.css .
- Longforms: Animate on scroll .
Ready to Start?
Create your own stories instantly. 120+ premium slides ready to use.
Free Download Pay what you want.
People share content that makes them feel inspired. WebSlides is a very effective way to engage young audiences, customers, and teams.
@jlantunez , @ant_laguna , and @luissacristan .
Unsupported browser
This site was designed for modern browsers and tested with Internet Explorer version 10 and later.
It may not look or work correctly on your browser.
Create Presentation Slides with HTML and CSS
- Bahasa Indonesia
As I sifted through the various pieces of software that are designed for creating presentation slides, it occurred to me: why learn yet another program, when I can instead use the tools that I'm already familiar with? With a bit of fiddling, we can easily create beautiful presentations with HTML and CSS. I'll show you how today!
Screencasts:
- Creating The Markup (preview video)
- Building Sample Slides
- Load The Slides
- Styling and JavaScript
- Event Listeners
- Completing the JavaScript
- Custom Slide-Styling
Screencast 1: Create the Markup

Screencast 2: Building Sample Slides
Screencast 3: Load the Slides

Screencast 4: Styling and Continued JavaScript
Screencast 5: Event Listeners
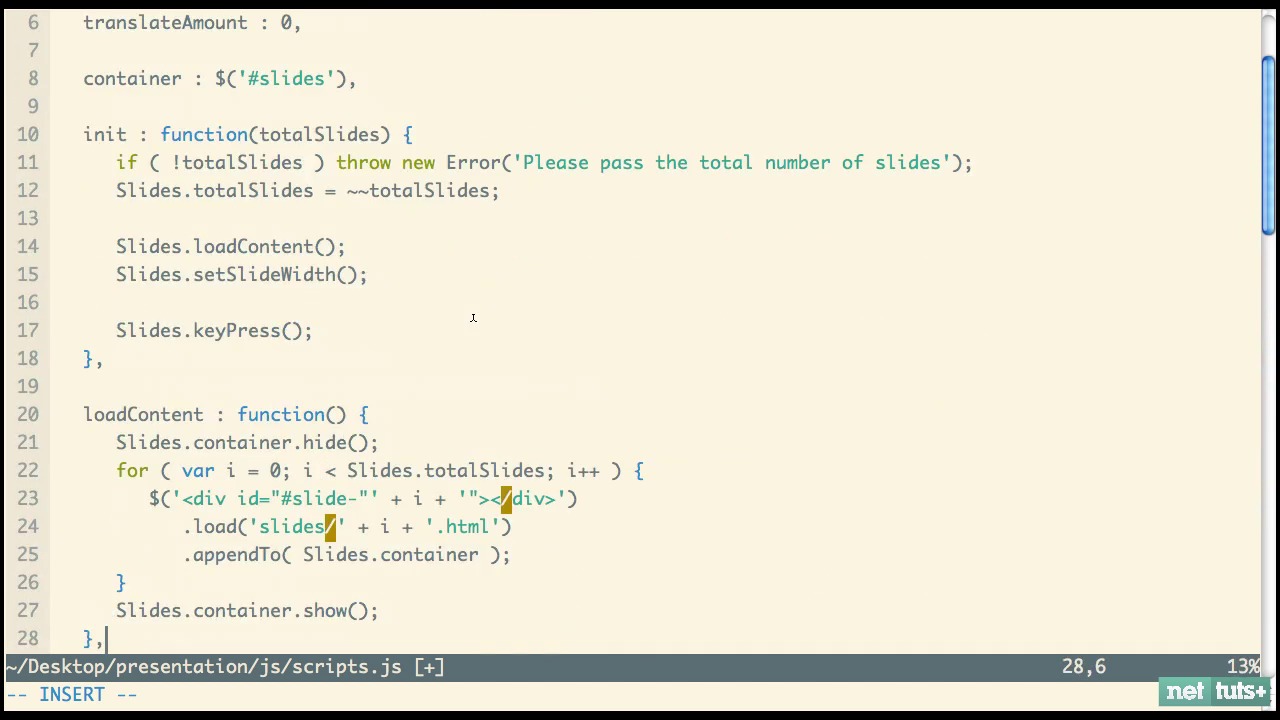
Screencast 6: Completing the JavaScript
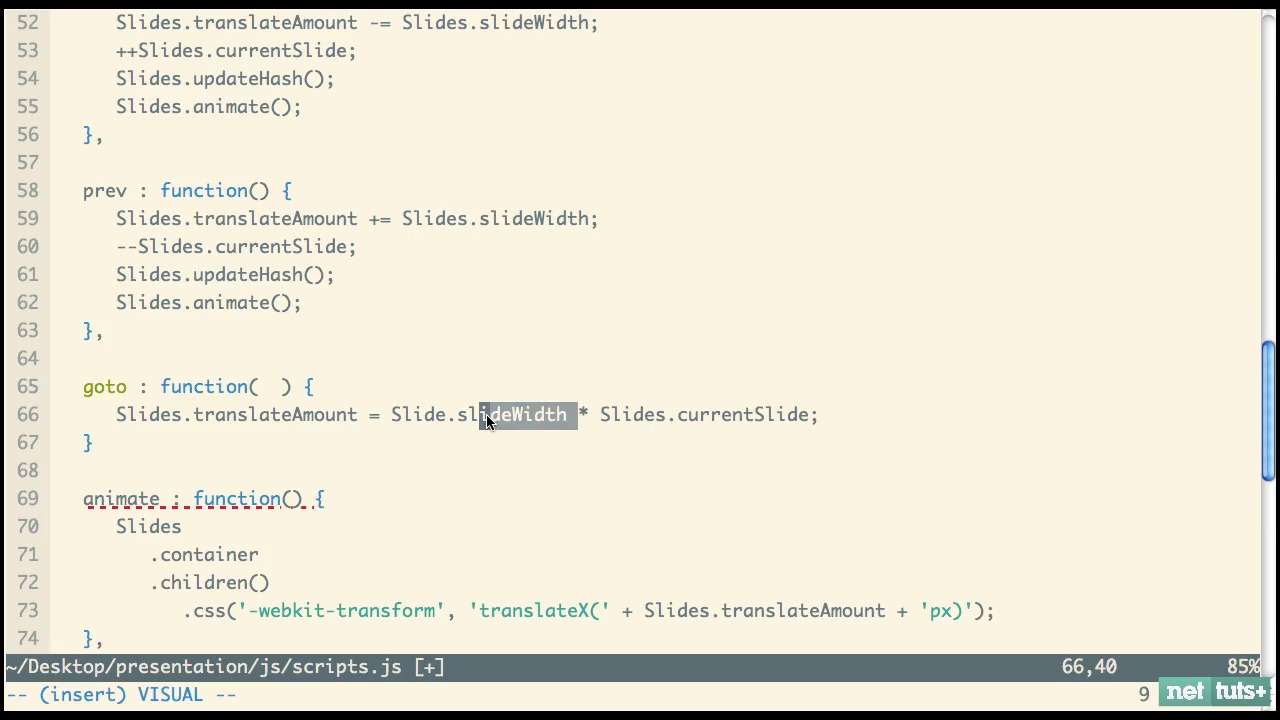
Screencast 7: Custom Slide Styling
- [email protected]
Bootstraphunter
Free and Premium Bootstrap Templates and Themes
How to Create Presentation Slides with HTML and CSS
- March 15, 2022
As I sifted through the various pieces of software that are designed for creating presentation slides, it occurred to me: why learn yet another program, when I can instead use the tools that I’m already familiar with?
We can easily create beautiful and interactive presentations with HTML, CSS and JavaScript, the three basic web technologies. In this tutorial, we’ll use modern HTML5 markup to structure our slides, we’ll use CSS to style the slides and add some effects, and we’ll use JavaScript to trigger these effects and reorganize the slides based on click events.
This tutorial is perfect for those of you new to HTML5, CSS and JavaScript, who are looking to learn something new by building.
Here’s the final preview of the presentation slide we’re going to build:
You can also find the complete source code in the GitHub repo .
Let’s begin.
Table of Contents
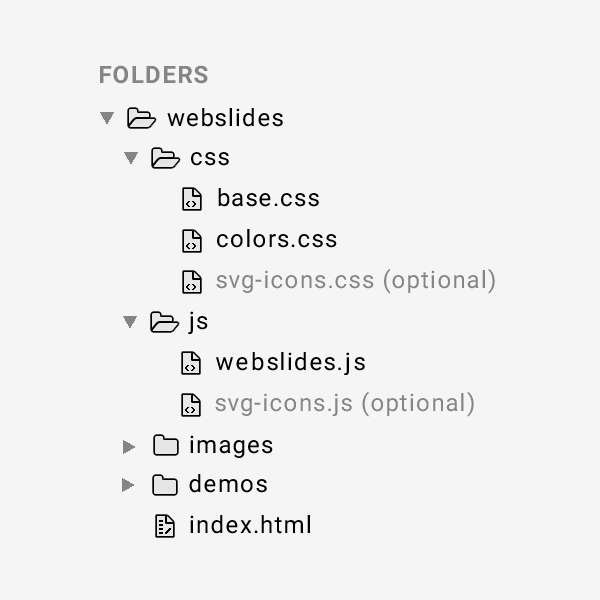
1. Create the Directory Structure
Before we get started, let’s go ahead and create our folder structure; it should be fairly simple. We’ll need:
index.html css/style.css js/scripts.js
This is a simple base template. Your files remain blank for the time being. We’ll fill that shortly.
2. Create the Starter Markup
Let’s begin by creating the base markup for our presentation page. Paste the following snippet into your index.html file.
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang=”en”> <head> <meta charset=”UTF-8″> <meta name=”viewport” content=”width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0″> <meta http-equiv=”X-UA-Compatible” content=”ie=edge”> <title>Document</title> <link rel=”stylesheet” href=”css/style.css”>
<!– Font Awesome Icon CDN –> <link rel=”stylesheet” href=”https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/font-awesome/6.0.0/css/all.min.css” integrity=”sha512-9usAa10IRO0HhonpyAIVpjrylPvoDwiPUiKdWk5t3PyolY1cOd4DSE0Ga+ri4AuTroPR5aQvXU9xC6qOPnzFeg==” crossorigin=”anonymous” referrerpolicy=”no-referrer” /> </head> <body> <div class=”container” <div id=”presentation-area”> <!– slides go here –> </div> </div> <script src=”js/index.js” type=”text/javascript”></script> </body> </html>
From the base markup, you can tell that we are importing Font Awesome Icons, our stylesheet ( style.css ) and our JavaScript ( index.js ).
Now we’ll add the HTML markup for the actual slides inside the <div> wrapper:
<section class=”presentation”>
<!– Slide 1 –> <div class=”slide show”> <div class=”heading”> Presentation on C# </div> <div class=”content grid center”> <h3 class=”title”> What is C# ? <br /> All You Need To Know </h3> </div> </div>
<!– Slide 1 –> <div class=”slide”> <div class=”heading”> Overview </div> <div class=”content grid center”> <h3 class=”title”> Introduction to C+ </h3> <p class=”sub-title”> Basic and Advanced Concepts </p> <p>Lecture No. 1</p> <p>My Email Address</p> <p><a href=””> [email protected] </a></p> </div> </div>
<!– Add 5 more slides here –> </section>
We have seven slides in total, and each slide is comprised of the heading section and the content section.
Only one slide will be shown at a time. This functionality is handled by the .show class which will be implemented later on in our stylesheet.
Using JavaScript, later on, we’ll dynamically add the .show class to the active slide on the page.
Below the slides, we’ll add the markup for our slide’s counter and tracker:
<div id=”presentation-area”> <!– <section class=”slides”><-></section> –> <section class=”counter”> 1 of 6 </section> </div>
Later on, we’ll use JavaScript to update the text content as the user navigates through the slides.
Finally, we’ll add the slide navigator just below the counter:
<div id=”presentation-area”> <!– <section class=”slides”><-></section> –> <!– <section class=”counter”><-></section> –> <section class=”navigation”> <button id=”full-screen” class=”btn-screen show”> <i class=”fas fa-expand”></i> </button>
<button id=”small-screen” class=”btn-screen”> <i class=”fas fa-compress”></i> </button>
<button id=”left-btn” class=”btn”> <i class=”fas fa-solid fa-caret-left”></i> </button>
<button id=”right-btn” class=”btn”> <i class=”fa-solid fa-caret-right”></i> </button> </section> </div>
This section consists of four buttons responsible for navigating left and right and switching between full-screen mode and small-screen mode. Again, we’ll use the class .show to regulate which button appears at a time.
That’ll be all for the HTML part, let’s move over to styling.
3. Make It Pretty
Our next step takes place within our stylesheet. We’ll be focusing on both aesthetics as well as functionality here. To make each slide translate from left to right, we’ll need to target the class .show with a stylesheet to show the element.
Here’s the complete stylesheet for our project:
* { margin: 0; padding: 0; box-sizing: border-box; font-family: sans-serif; transition: all 0.5s ease; }
body { width: 100vw; height: 100vh; display: flex; align-items: center; justify-content: center; }
ul { margin-left: 2rem; }
ul li, a { font-size: 1.2em; }
.container { background: #212121; width: 100%; height: 100%; position: relative; display: flex; align-items: center; justify-content: center; }
#presentation-area { width: 1000px; height: 500px; position: relative; background: purple; }
/* Styling all three sections */ #presentation-area .presentation { width: 100%; height: 100%; overflow: hidden; background: #ffffff; position: relative; }
#presentation-area .counter { position: absolute; bottom: -30px; left: 0; color: #b6b6b6; }
#presentation-area .navigation { position: absolute; bottom: -45px; right: 0; }
/* On full screen mode */ #presentation-area.full-screen { width: 100%; height: 100%; overflow: hidden; }
#presentation-area.full-screen .counter { bottom: 15px; left: 15px; }
#presentation-area.full-screen .navigation { bottom: 15px; right: 15px; }
#presentation-area.full-screen .navigation .btn:hover { background: #201e1e; color: #ffffff; }
#presentation-area.full-screen .navigation .btn-screen:hover { background: #201e1e; } /* End full screen mode */
/* Buttons */ .navigation button { width: 30px; height: 30px; border: none; outline: none; margin-left: 0.5rem; font-size: 1.5rem; line-height: 30px; text-align: center; cursor: pointer; }
.navigation .btn { background: #464646; color: #ffffff; border-radius: 0.25rem; opacity: 0; transform: scale(0); }
.navigation .btn.show { opacity: 1; transform: scale(1); visibility: visible; }
.navigation .btn-screen { background: transparent; color: #b6b6b6; visibility: hidden; }
.btn-screen.show { opacity: 1; transform: scale(1); visibility: visible; }
.btn-screen.hover { color: #ffffff; box-shadow: 0px 10px 30px rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1); } /* End Buttons */
/* content */ .presentation .content { padding: 2em; width: 100%; height: calc(100% – 100px); z-index: 11; }
.presentation .content.grid { display: grid; }
.presentation .content.grid.center { justify-content: center; align-items: center; text-align: center; }
.content .title { font-size: 3em; color: purple; }
.content .sub-title { font-size: 2.5em; color: purple; }
.content p { font-size: 1.25em; margin-bottom: 1rem; } /* End Content Stylesheet */
/* Slide */ .presentation .slide { position: absolute; top: 0; left: 0; width: 100%; height: 100%; background: #ffffff; opacity: 0; transform: scale(0); visibility: none; }
.slide.show { opacity: 1; transform: scale(1); visibility: visible; }
.slide .heading { padding: 2rem; background: purple; font-size: 2em; font-weight: bold; color: #ffffff; }
4. Enable Slide Navigation
Whenever we click on the left or right icon, we want the next slide or previous slide to appear. We also want to be able to toggle between full-screen mode and small-screen mode.
Furthermore, we want the slide’s counter to display the accurate slide number on every slide. All these features will be enabled with JavaScript.
Inside js/index.js , we’ll begin by storing references to the presentation wrapper, the slides, and the active slide:
let slidesParentDiv = document.querySelector(‘.slides’); let slides = document.querySelectorAll(‘.slide’); let currentSlide = document.querySelector(‘.slide.show’);
Next, we’ll store references to the slide counter and both of the slide navigators (left and right icons):
var slideCounter = document.querySelector(‘.counter’); var leftBtn = document.querySelector(‘#left-btn’); var rightBtn = document.querySelector(‘#right-btn’);
Then store references to the whole presentation container and both button icons for going into full screen and small screen mode:
let presentationArea = document.querySelector(‘#presentation-area’); var fullScreenBtn = document.querySelector(‘#full-screen’); var smallScreenBtn = document.querySelector(‘#small-screen’);
Now that we’re done with the references, we’ll initialize some variables with default values:
var screenStatus = 0; var currentSlideNo = 1 var totalSides = 0;
screenStatus represents the screen orientation. 0 represents a full screen mode and 1 represents a small screen mode.
currentSlideNo represents the current slide number, which as expected is the first slide. totalSlides is initialized with 0, but this will be replaced by the actual number of our slides.
Moving the Presentation to the Next and Previous Slides
Next, we’ll add click event listeners to the left button, right button, full screen button and small screen button:
leftBtn.addEventListener(‘click’, moveToLeftSlide); rightBtn.addEventListener(‘click’, moveToRightSlide);
fullScreenBtn.addEventListener(‘click’, fullScreenMode); smallScreenBtn.addEventListener(‘click’, smallScreenMode);
We bind corresponding functions that will run when the click event is triggered on the corresponding element.
Here are the two functions responsible for changing the slide:
function moveToLeftSlide() { var tempSlide = currentSlide; currentSlide = currentSlide.previousElementSibling; tempSlide.classList.remove(‘show’); currentSlide.classList.add(‘show’); }
function moveToRightSlide() { var tempSlide = currentSlide; currentSlide = currentSlide.nextElementSibling; tempSlide.classList.remove(‘show’); currentSlide.classList.add(‘show’); }
In the function moveToLeftSlide, we basically access the previous sibling element (ie. the previous slide), remove the .show class on the current slide and add it to that sibling. This will move the presentation to the previous slide.
We do the exact opposite of this in the function moveToRightSlide. Because nextElementSibling is the opposite of previousElementSibling, we’ll be getting the next sibling instead.
Code for Showing the Presentation in Full Screen and Small Screen
Recall that we also added click event listeners to the full screen and small screen icons.
Here’s the function responsible for toggling full-screen mode:
function fullScreenMode() { presentationArea.classList.add(‘full-screen’); fullScreenBtn.classList.remove(‘show’); smallScreenBtn.classList.add(‘show’);
screenStatus = 1; }
function smallScreenMode() { presentationController.classList.remove(‘full-screen’); fullScreenBtn.classList.add(‘show’); smallScreenBtn.classList.remove(‘show’);
screenStatus = 0; }
Recall that presentationArea refers to the element that wraps the whole presentation. By adding the class full-screen to this element, we trigger the CSS that will expand it to take up the whole screen.
Since we’re now in full-screen mode, we need to show the icon for reverting back to the small screen by adding the class .show to it. Finally, we update the variable screenStatus to 1.
For the smallScreenMode function, the opposite is done – we remove the class full-screen, show the expand button icon, and reupdate screenStatus.
Hidding Left and Right Icons in First and Last Slides
Now, we need to invent a way to hide both the left and right buttons when we’re on the first slide and last slide respectively.
We’ll use the following two functions to achieve this:
function hideLeftButton() { if(currentSlideNo == 1) { toLeftBtn.classList.remove(‘show’); } else { toLeftBtn.classList.add(‘show’); } }
function hideRightButton() { if(currentSlideNo === totalSides) { toRightBtn.classList.remove(‘show’); } else { toRightBtn.classList.add(‘show’); } }
Both these functions perform a very simple task: they check for the current slide number and hide the left and right buttons when the presentation is pointing to the first and last slide respectively.
Updating and Displaying Slide Number
Because we’re making use of the variable currentSlideNo to hide or show the left and right button icons, we need a way to update it as the user navigates through the slides.
We also need to display to the user what slide he or she is currently viewing.
We’ll create a function getCurrentSlideNo to update the current slide number:
function getCurrentSlideNo() { let counter = 0;
slides.forEach((slide, i) => { counter++
if(slide.classList.contains(‘show’)){ currentSlideNo = counter; } });
We start the counter at 0, and for each slide on the page, we increment the counter. We assign the active counter (ie. with the class .show) to the currentSlideNo variable.
With that in place, we create another function that inserts some text into the slide counter:
function setSlideNo() { slideNumber.innerText = `${currentSlideNo} of ${totalSides}` }
So if we were on the second slide for example, the slide’s counter will read as: 2 of 6
Putting Everything Together
To ensure that all of these functions run in harmony, we’ll run them in a newly created init function that we’ll execute at start of the script, just below the references:
function init() {
getCurrentSlideNo(); totalSides = slides.length setSlideNo(); hideLeftButton(); hideRightButton(); }
We must also run init() at the bottom of both the moveToLeftSlide and moveToRightSlide functions:
function moveToLeftSlide() { // other code
function moveToRightSlide() { // other code
This will ensure that the function init runs every time the user navigates left or right in the presentation.
Wrapping Up
I hope this tutorial helped you understand basic web development better. Here we built a presentation slideshow from scratch using HTML, CSS and JavaScript.
With this project, you should have learned some basic HTML, CSS and JavaScript syntax to help you with web development.
Recent Posts
- How Flatlogic Started Their Business
- Gulp is back – did it ever leave?
- Solving Memory Leaks in Node.js has Never Been Easier, Introducing the Latest Version of N|Solid
- Svelte 5 is almost here
- JSR isn’t another tool, it’s a fundamental shift
Navigation Menu
Search code, repositories, users, issues, pull requests..., provide feedback.
We read every piece of feedback, and take your input very seriously.
Saved searches
Use saved searches to filter your results more quickly.
To see all available qualifiers, see our documentation .
- Notifications You must be signed in to change notification settings
Create HTML presentations in seconds —
webslides/WebSlides
Folders and files.
| Name | Name | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 560 Commits | ||||
Repository files navigation
Webslides = create stories with karma.
Finally, everything you need to make HTML presentations, landings, and longforms in a beautiful way. Just a basic knowledge of HTML and CSS is required. Designers, marketers, and journalists can now focus on the content. — https://webslides.tv/demos .
Simply choose a demo and customize it in seconds. Latest version: webslides.tv/webslides-latest.zip .
What's in the download?
The download includes demos and images (devices and logos). All content is for demo purposes only. Images are property of their respective owners.
- Navigation (horizontal and vertical sliding): remote presenters, touchpad, keyboard shortcuts, and swipe.
- Slide counter.
- Permalinks: go to a specific slide.
- Click to nav.
- Simple CSS alignments. Put content wherever you want (vertical centering...)
- 40+ components: background images/videos, quotes, cards, covers...
- Flexible blocks with auto-fill and equal height.
- Fonts: Roboto, Maitree (Serif), and San Francisco.
- Vertical rhythm (use multiples of 8).
- Code is clean and scalable. It uses intuitive markup with popular naming conventions. There's no need to overuse classes or nesting.
- Each parent <section> in the #webslides element is an individual slide.
Vertical Sliding
Css syntax (classes).
- Typography: .text-landing , .text-data , .text-intro ...
- Background Colors: .bg-primary , .bg-apple , .bg-blue ...
- Background Images: .background , .background-center-bottom ...
- Cards: .card-50 , .card-40 ...
- Flexible Blocks: .flexblock.clients , .flexblock.metrics ...
You can add:
- Unsplash photos
- animate.css
- particles.js
- Animate on scroll (Useful for longform articles)
- Do not miss our demos .
- Plugin Docs
- Plugin Development
- WebSlides was created by @jlantunez using Cactus .
- Javascript: @Belelros and @LuisSacristan .
- Based on SimpleSlides , by @JennSchiffer .
Releases 12
Used by 192.
Contributors 14
- JavaScript 49.3%
jQuery Script - Free jQuery Plugins and Tutorials
10 best html presentation frameworks in javascript (2024 update), what is html presentation framework.
An HTML Presentation Framework helps you create a fullscreen web presentation to showcase your web content just like Apple Keynote and Microsoft PowerPoint.
It separates your HTML content into several fullscreen pages (slides) so that the visitors are able to navigate between these slides with certain operations (mouse wheel, arrow keys, touch events, etc).
The Best HTML Presentation Framework
You have been tasked with building an HTML5 presentation application, but where should you start? As there are many frameworks to choose from, it can be challenging to know where to begin.
In this post, we're going to introduce you the 10 best JavaScript HTML presentation frameworks to help developers generate professional, nice-looking presentations using JavaScript, HTML, and CSS. Have fun.
Originally Published Feb 2020, up date d Feb 27 2024
Table of contents:
- jQuery HTML Presentation Frameworks
- Vanilla JS HTML Presentation Frameworks
Best jQuery HTML Presentation Frameworks
Full page presentations with jquery and css animations.
A vertical full-page presentation app (also called fullscreen page slider) implemented in JavaScript (jQuery) and CSS animations.
[ Demo ] [ Download ]
jQuery Amazing Scrolling Presentation Plugin - scrolldeck
scrolldeck is a cool jQuery plugin that make it easier to create amazing scrolling presentation like Slide Animation s, Image Slides and parallax effects for your project.
Easy Dynamic Presentation Plugin In jQuery - Presentation.js
A jQuery-powered presentation plugin that allows users to create better professional-looking presentations, with awesome jQuery and/or CSS 3 animations.

jQuery Plugin To Create Amazing Presentations - mb.disclose
An awesome jQuery plugin that provides an amazing way to present Html contents in carousel like presentations. You can customize the CSS3 powered animations for each Html element using Html5 data-* attributes.

Responsive Web Presentation Plugin For jQuery - sectionizr
A really simple jQuery web presentation plugin which presents any html contents in a responsive, fullscreen, carousel-style page UI. Supports both horizontal and vertical scrolling.

Best Vanilla JS HTML Presentation Frameworks
Beautiful html presentation library - reveal.js.
reveal.js is an open source HTML presentation framework. It's a tool that enables anyone with a web browser to create fully-featured and beautiful presentations for free.
Presentations made with reveal.js are built on open web technologies. That means anything you can do on the web, you can do in your presentation. Change styles with CSS, include an external web page using an iframe or add your own custom behavior using our JavaScript API.

Fullscreen Scrolling Presentation In JavaScript – Pageable
A lightweight JavaScript library to generate a fullscreen scrolling presentation where the users are allowed to scroll through sectioned pages with drag, swipe, and mouse wheel events.

Amazing Presentation Framework With CSS3 - impress.js
An amazing Presentation framework for modern bowsers. Based on CSS3 transforms and transitions. It doesn't depend on any external stylesheets. It adds all of the styles it needs for the presentation to work.

Slidev aims to provide the flexibility and interactivity for developers to make their presentations even more interesting, expressive, and attractive by using the tools and technologies they are already familiar with.
When working with WYSIWYG editors, it is easy to get distracted by the styling options. Slidev remedies that by separating the content and visuals. This allows you to focus on one thing at a time, while also being able to reuse the themes from the community. Slidev does not seek to replace other slide deck builders entirely. Rather, it focuses on catering to the developer community.

Shower HTML presentation engine
Shower HTML presentation engine built on HTML, CSS and vanilla JavaScript. Works in all modern browsers. Themes are separated from engine. Fully keyboard accessible. Printable to PDF.

Conclusion:
There is no one right answer. The right presentation framework for you depends on your own project requirements, as well as your personal preferences. However, with the ten HTML presentation frameworks listed above to choose from, you are bound to find one that suits your specific needs.
Looking for more jQuery plugins or JavaScript libraries to create awesome HTML Presentations on the web & mobile? Check out the jQuery Presentation and JavaScript Presentation sections.
- 10 Best Mobile-friendly One Page Scroll Plugins
- Prev: Weekly Web Design & Development News: Collective #330
- Next: Weekly Web Design & Development News: Collective #331

You Might Also Like
7 Best JavaScript Timeago Plugins For Human-readable Datetime Format

Top 100 Best Free jQuery Plugins From 2013

7 Best Youtube Lazy Loaders To Improve Page Speed (2024 Update)

10 Best JavaScript Dark Mode Solutions (2024 Update)

Top 100 Best Free jQuery Plugins From 2014
10 Best Free GDPR Cookie Consent Banner Plugins In JavaScript
Add Your Review
How to Create a Slideshow with HTML, CSS, and JavaScript

A web slideshow is a sequence of images or text that consists of showing one element of the sequence in a certain time interval.
For this tutorial you can create a slideshow by following these simple steps:
Write some markup
Write styles to hide slides and show only one slide..
To hide the slides you have to give them a default style. It'll dictate that you only show one slide if it is active or if you want to show it.
Change the slides in a time interval.
The first step to changing which slides show is to select the slide wrapper(s) and then its slides.
When you select the slides you have to go over each slide and add or remove an active class depending on the slide that you want to show. Then just repeat the process for a certain time interval.
Keep it in mind that when you remove an active class from a slide, you are hiding it because of the styles defined in the previous step. But when you add an active class to the slide, you are overwritring the style display:none to display:block , so the slide will show to the users.
Codepen example following this tutorial
If you read this far, thank the author to show them you care. Say Thanks
Learn to code for free. freeCodeCamp's open source curriculum has helped more than 40,000 people get jobs as developers. Get started

HTML BASICS Slides Presentation
Click to access all Slides..
This slide presentation shows basics of HTML.
HTML and XHTML are the foundation of all web development. HTML is used as the graphical user interface in client-side programs written in JavaScript. Server-side languages like PHP and Java also receive data from web pages and use HTML as the output mechanism. The emerging Ajax technologies likewise use HTML and XHTML as their visual engine. HTML was once a very loosely-defined language with very little standardization, but as it has become more important, the need for standards has become more apparent. Regardless of whether you choose to write HTML or XHTML, understanding the current standards will help you provide a solid foundation that will simplify all your other web coding. Fortunately HTML and XHTML are actually simpler than they used to be, because much of the functionality has moved to CSS.
Common Elements
Every page (HTML or XHTML shares certain elements in common.) All are essentially plain text files, with the .html extension. HTML files should not be created with a word processor, but in some type of editor that creates plain text. Every page has a large container (HTML or XHTML) and two major subcontainers, the head and the body. The head area contains information useful behind the scenes, such as CSS formatting instructions and JavaScript code. The body contains the part of the page that is visible to the user.
Tags and Attributes
An HTML document is based on the notion of tags. A tag is a piece of text inside angle brackets (<>). Tags typically have a beginning and an end, and usually contain some sort of text inside them. For example, a paragraph is normally denoted like this:
The <p> indicates the beginning of a paragraph. Text is then placed inside the tag, and the end of the paragraph is denoted by an end tag, which is similar to the start tag but with a slash (</p>.) It is common to indent content in a multi-line tag, but it is also legal to place tags on the same line:
Tags are sometimes enhanced by attributes, which are name value pairs that modify the tag. For example, the tag (used to embed an image into a page) usually includes the following attributes:
The src attribute describes where the image file can be found, and the alt attribute describes alternate text that is displayed if the image is unavailable.
Nested tags
Tags can be (and frequently are) nested inside each other. Tags cannot overlap, so <a><b></a></b> is not legal, but <a><b></b></a> is fine.
HTML VS XHTML
HTML has been around for some time. While it has done its job admirably, that job has expanded far more than anybody expected. Early HTML had very limited layout support. Browser manufacturers added many competing standards and web developers came up with clever workarounds, but the result is a lack of standards and frustration for web developers. The latest web standards (XHTML and the emerging HTML 5.0 standard) go back to the original purpose of HTML: to describe the structure of the data only, and leave all formatting to CSS (Please see the DZone CSS Refcard Series). XHTML is nothing more than HTML code conforming to the stricter standards of XML. The same style guidelines are appropriate whether you write in HTML or XHTML (but they tend to be enforced in XHTML):
Most of the requirements of XHTML turn out to be good practice whether you write HTML or XHTML. I recommend using XHTML strict so you can validate your code and know it follows the strictest standards.
XHTML has a number of flavors. The strict type is recommended, as it is the most up-to-date standard which will produce the most predictable results. You can also use a transitional type (which allows deprecated HTML tags) and a frameset type, which allows you to add frames. For most applications, the strict type is preferred.
HTML Template
The following code can be copied and pasted to form the foundation of a basic web page:
The structure of your web pages is critical to the success of programs based on those pages, so use a validating tool to ensure you haven't missed anything
| Validating Tool | Description |
| WC3 | The most commonly used validator is online at http://validator.w3.org this free tool checks your page against the doctype you specify and ensures you are following the standards. This acts as a 'spell-checker' for your code and warns you if you made an error like forgetting to close a tag. |
| HTML Tidy | There's an outstanding free tool called HTML tidy which not only checks your pages for validity, but also fixes most errors automatically. Download this tool at http://tidy.sourceforge.net/ or (better) use the HTML validator extension to build tidy into your browser. |
| HTML Validator extension | The extension mechanism of Firefox makes it a critical tool for web developers. The HTML Validator extension is an invaluable tool. It automatically checks any page you view in your browser against both the w3 validation engine and tidy. It can instantly find errors, and repair them on the spot with tidy. With this free extension available at http://users.skynet. be/mgueury/mozilla/ , there's no good reason not to validate your code. |
USEFUL OPEN SOURCE TOOLS
Some of the best tools for web development are available through the open source community at no cost at all. Consider these application as part of your HTML toolkit:
| Open Source Tool | Description |
| Aptana | http://www.aptana.com/ This free programmer's editor (based on Eclipse) is a full-blown IDE customized for HTML / XHTML, CSS, JavaScript, and Ajax. It offers code completion, syntax highlighting, and FTP support within the editor. |
| Web Developer Toolbar | https://www.addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/addon/60 This Firefox extension adds numerous debugging and web development tools to your browser. |
| Firebug | https://addons.mozilla.org/en-US/firefox/addon/1843 is an add-on that adds full debugging capabilities to the browser. The firebug lite version even works with IE. |
PAGE STRUCTURE ELEMENTS
The following elements are part of every web page.
| Element | Description |
| <html></html> | Surrounds the entire page |
| <head></head> | Contains header information (metadata, CSS styles, JavaScript code) |
| <title></title> | Holds the page title normally displayed in the title bar and used in search results |
| <body></body> | Contains the main body text. All parts of the page normally visible are in the body |
KEY STRUCTURAL ELEMENTS
Most pages contain the following key structural elements:
| Element | Name | Description |
| <h1> </h1> | Heading 1 | Reserved fo strongest emphasis |
| <h2> </h2> | Heading 2 | Secondary level heading. Headings go down to level 6, but <h1> through <h3> are most common |
| <p> </p> | Paragraph | Most of the body of a page should be enclosed in paragraphs |
| <div> </div> | Division | Similar to a paragraph, but normally marks a section of a page. Divs usually contain paragraphs |
LISTS AND DATA
Web pages frequently incorporate structured data so HTML includes several useful list and table tag
| Element | Name | Description |
| <ul></ul> | Unordered list | Normally these lists feature bullets (but that can be changed with CSS) |
| <ol></ol> | Ordered list | These usually are numbered, but this can be changed with CSS |
| <li></li> | List item | Used to describe a list item in an unordered list or an ordered list |
| <dl></dl> | Definition list | Used for lists with name-value pairs |
| <dt></dt> | Definition term | The name in a name-value pair. Used in definition lists |
| <dd></dd> | Definition description | The value (or definition) of a name, value pair |
| <table></table> | Table | Defines beginning and end of a table |
| <tr></tr> | Table row | Defines a table row. A table normally consists of several <tr> pairs (one per row) |
| <td></td> | Table data | Indicates data in a table cell. <td> tags occur within <tr> (which occur within <table>) |
| <th></th> | Table heading | Indicates a table cell to be treated as a heading with special formatting |
Standard List Types
HTML supports three primary list types. Ordered lists and unordered lists are the primary list types. By default, ordered lists use numeric identifiers, and unordered lists use bullets.
However, you can use the list-style-type CSS attribute to change the list marker to one of several types.
Lists can be nested inside each other
Definition lists
The special definition list is used for name / value pairs. The definition term (dt) is a word or phrase that is used as the list marker, and the definition data is normally a paragraph:
Use of tables
Tables were used in the past to overcome the page-layout shortcomings of HTML. That use is now deprecated in favor of CSS-based layout. Use tables only as they were intended, to display tabular data.
A table mainly consists of a series of table rows (tr.) Each table row consists of a number of table data (td) elements. The table heading (th) element can be used to indicate a table cell should be marked as a heading.
The rowspan and colspan attributes can be used to make a cell span more than one row or column.
Each row of a table should have the same number of columns, and each column should have the same number of rows. Use of the span attribute may require adjustment to other rows or columns.
LINKS AND IMAGES
Links and images are both used to incorporate external resources into a page. Both are reliant on URIs (Universal Resource Indicators), commonly referred to as URLs or addresses.
<a> (anchor) The anchor tag is used to provide the basic web link:
In this example, http://www.example.com is the site to be visited. The text "link to example.com" will be highlighted as a link.
absolute and relative references
<link>
The link tag is used primarily to pull in external CSS files:
<img>
The img tag is used in to attach an image. Valid formats are .jpg, .png, and .gif. An image should always be accompanied by an alt attribute describing the contents of the image.
Image formatting attributes (height, width, and align) are deprecated in favour of CSS.
SPECIALTY MARKUP
HTML / XHTML includes several specialty tags. These are used to describe special purpose text. They have default styling, but of course the styles can be modified with CSS.
<quote>
The quote tag is intended to display a single line quote:
Quote is an inline tag. If you need a block level quote, use <blockquote>.
<pre>
The <pre> tag is used for pre-formatted text. It is sometimes used for code listings or ASCII art because it preserves carriage returns. Pre-formatted text is usually displayed in a fixed-width font.
<code>
The code format is used to manage pre-formatted text, especially code listings. It is very similar to pre.
<blockquote>
This tag is used to mark multi-line quotes. Frequently it is set off with special fonts and indentation through CSS. It is a block-level tag.
<span>
The span tag is a vanilla inline tag. It has no particular formatting of its own. It is intended to be used with a class or ID when you want to apply style to an inline chunk of code.
The em tag is used for standard emphasis. By default, <em> italicizes text, but you can use CSS to make any other type of emphasis you wish.
<strong>
This tag represents strong emphasis. By default, it is bold, but you can modify the formatting with CSS.
Forms are the standard user input mechanism in HTML / XHTML. You will need another language like JavaScript or PHP to read the contents of the form elements and act upon them.
Form Structure
A number of tags are used to describe the structure of the form. Begin by looking over a basic form:
The <form></form> pair describes the form. In XHTML strict, you must indicate the form's action property. This is typically the server-side program that will read the form. If there is no such program, you can set the action to null ("") The method attribute is used to determine whether the data is sent through the get or post mechanism.
Most form elements are inline tags, and must be encased in a block element. The fieldset is designed exactly for this purpose. Its default appearance draws a box around the form. You can have multiple fieldsets inside a single form.
You can add a legend inside a fieldset. This describes the purpose of the fieldset.
A label is a special inline element that describes a particular field. A label can be paired with an input element by putting that element's ID in the label's for attribute.
The input element is a general purpose inline element. It is meant to be used inside a form, and it is the basis for several types of more specific input. The subtype is indicated by the type attribute. Input elements usually include an id attribute (used for CSS and JavaScript identification) and / or a name attribute (used in server-side programming.) The same element can have both a name and an id.
This element allows a single line of text input:
Passwords display just like textboxes, except rather than showing the text as it is typed, an asterisk appears for each letter. Note that the data is not encoded in any meaningful way. Typing text into a password field is still entirely unsecure.
Radio Button
Radio buttons are used in a group. Only one element of a radio group can be selected at a time. Give all members of a radio group the same name value to indicate they are part of a group.
Attaching a label to a radio button means the user can activate the button by clicking on the corresponding label. For best results, use the selected attribute to force one radio button to be the default.
Checkboxes are much like radio buttons, but they are independent. Like radio buttons, they can be associated with a label.
Hidden fields hold data that is not visible to the user (although it is still visible in the code) It is primarily used to preserve state in server-side programs.
Note that the data is still not protected in any meaningful way.
Buttons are used to signal user input. Buttons can be created through the input tag:
This will create a button with the caption "launch the missiles." When the button is clicked, the page will attempt to run a JavaScript function called "launchMissiles()" Standard buttons are usually used with JavaScript code on the client. The same button can also be created with this alternate format:
This second form is preferred because buttons often require different CSS styles than other input elements. This second form also allows an <img> tag to be placed inside the button, making the image act as the button.
The reset button automatically resets all elements in its form to their default values. It doesn't require any other attributes.
Select / option
Drop-down lists can be created through the select / option mechanism. The select tag creates the overall structure, which is populated by option elements.
The select has an id (for client-side code) or name (for serverside code) identifier. It contains a number of options. Each option has a value which will be returned to the program. The text between <option> and </option> is the value displayed to the user. In some cases (as in this example) the value displayed to the user is not the same as the value used by programs.
Multiple Selections
You can also create a multi-line selection with the select and option tags:
DEPRECATED FORMATTING TAGS
Certain tags common in older forms of HTML are no longer recommended as CSS provides much better alternatives.
The font tag was used to set font color, family (typeface) and size. Numerous CSS attributes replace this capability with much more flexible alternatives. See the CSS refcard for details.
I (italics)
HTML code should indicate the level of emphasis rather than the particular stylistic implications. Italicizing should be done through CSS. The <em> tag represents emphasized text. It produces italic output unless the style is changed to something else. The <i> tag is no longer necessary and is not recommended. Add font-style: italic to the style of any element that should be italicized.
Like italics, boldfacing is considered a style consideration. Use the <strong> tag to denote any text that should be strongly emphasized. By default, this will result in boldfacing the enclosed text. You can add bold emphasis to any style with the font-weight: bold attribute in CSS.
DEPRECATED TECHNIQUES
In addition to the deprecated tags, there are also techniques which were once common in HTML that are no longer recommended.
Frames have been used as a layout mechanism and as a technique for keeping one part of the page static while dynamically loading other parts of the page in separate frames. Use of frames has proven to cause major usability problems. Layout is better handled through CSS techniques, and dynamic page generation is frequently performed through server-side manipulation or AJAX.
Table-based design
Before CSS became widespread, HTML did not have adequate page formatting support. Clever designers used tables to provide an adequate form of page layout. CSS provides a much more flexible and powerful form of layout than tables, and keeps the HTML code largely separated from the styling markup.
HTML ENTITIES
Sometimes you need to display a special character in a web page. HTML has a set of special characters for exactly this purpose. Each of these entities begins with the ampersand(&) followed by a code and a semicolon.
| Character | Name | Code | Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| Non-breaking space | Adds white space | ||
| < | Used to display HTML code or mathematics | ||
| > | Greater than | > | Used to display HTML code or mathematics |
| & | Ampersand | & | If you're not displaying an entity but really want the & symbol |
| © | Copyright | © | Copyright symbol |
| ® | Registered trademark | ® | Registered trademark |
HTML 5 / CSS3 PREVIEW
New technologies are on the horizon. Firefox 3.5 now has support for significant new HTML 5 features, and CSS 3 is not far behind. While the following should still be considered experimental, they are likely to become very important tools in the next few years. Firefox 3.5, Safari 4 (and a few other recent browsers) support the following new features:
Audio and video tags
Finally the browsers have direct support for audio and video without plugin technology. These tags work much like the img tag.
The HTML 5 standard currently supports Ogg Theora video, Ogg Vorbis audio, and wav audio. The Ogg formats are opensource alternatives to proprietary formats, and plenty of free tools convert from more standard video formats to Ogg. The autoplay option causes the element to play automatically. The controls element places controls directly into the page.
The code between the beginning and ending tag will execute if the browser cannot process the audio or video tag. You can place alternate code here for embedding alternate versions (Flash, for example)
The canvas tag offers a region of the page that can be drawn upon (usually with Javascript.) This creates the possibility of real interactive graphics without requiring plugins like Flash.
This is actually a CSS improvement, but it's much needed. It allows you to define a font-face in CSS and include a ttf font file from the server. You can then use this font face in your ordinary CSS and use the downloaded font. If this becomes a standard, we will finally have access to reliable downloadable fonts on the web, which will usher in web typography at long last.
Follow us on Facebook and Twitter for latest update.
It will be nice if you may share this link in any developer community or anywhere else, from where other developers may find this content. Thanks.
https://www.w3resource.com/slides/basics-of-html-5.php
- Weekly Trends and Language Statistics
- Stack Overflow for Teams Where developers & technologists share private knowledge with coworkers
- Advertising & Talent Reach devs & technologists worldwide about your product, service or employer brand
- OverflowAI GenAI features for Teams
- OverflowAPI Train & fine-tune LLMs
- Labs The future of collective knowledge sharing
- About the company Visit the blog
Collectives™ on Stack Overflow
Find centralized, trusted content and collaborate around the technologies you use most.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
Get early access and see previews of new features.
Embed a Powerpoint in a Web Page
Is there any way to embed a PowerPoint slide show in an HTML page using just the standard tags etc? I tried using a iframe, but that just results in the PowerPoint being downloaded.
I am looking for a way to show the slide show using only standard stuff. I realize I could use google docs or flash or something, but I'd rather have a simple implementation.
Does the web just not know how to process a PowerPoint presentation?
- possible duplicate of Embed Powerpoint into HTML – Marko Commented Aug 18, 2011 at 0:29
- 2 I said I do not want to use google docs. – Snowy Coder Girl Commented Aug 18, 2011 at 0:30
- 1 It lists other possible solutions, look at the answers below the accepted one. – Marko Commented Aug 18, 2011 at 0:31
- I saw ones about Flash and other applications, but I'll look deeper some more. – Snowy Coder Girl Commented Aug 18, 2011 at 0:37
- Google docs is the simple implementation. – djlumley Commented Aug 18, 2011 at 2:11
11 Answers 11
Plain and simple...this is the best method to embed any Microsoft or Adobe file into a HTML website.
- 2 I wonder why the hell your answer doesn't get more upvotes. It's the closest one to the original intention of the asker. – EugZol Commented Oct 18, 2017 at 16:34
- 6 This answer won't work for presentations on an internal website. – NetMage Commented Aug 2, 2019 at 19:53
- 3 <iframe width="100%" height="630" src=" docs.google.com/viewer?url=your_file&embedded=true " ></iframe> – Alexis Cabrera Mondeja Commented Apr 6, 2020 at 1:53
- 1 JS var url = encodeURIComponent(originalURl); HTML: <iframe src=' view.officeapps.live.com/op/embed.aspx?src=$ {url}' width='100%' height='600px' frameborder='0'> – Anil Commented May 7, 2020 at 15:12
- 3 As of 2022, I can't get the above answer to work. I've updated the url to a real deck in the github sharepoint that I uploaded. I assume the view.officeapps.live.com/op/embed... isn't there any more. – Lance Kind Commented Feb 24, 2022 at 16:50
Just to update this question - as there is a new way to embed Powerpoints in a web page. If you have an account on OneDrive , do the following using Powerpoint Online (accessing Powerpoint via the browser) to embed a Powerpoint:

- 2 this was unexpectedly easy! – Gregg Bursey Commented May 11, 2017 at 21:37
- Hey, please give me solution for without putting ppt on the drive and take from the server then how do they do it? – user7918630 Commented Sep 7, 2017 at 10:22
- 1 requires viewers to have a microsoft account. not a good solution for a public website. – sspence65 Commented Dec 22, 2020 at 10:44
Web browsers don't understand power point, but there are solutions besides Flash.
You could export it to HTML or a PDF. Or you could also upload to site like slideshare and make use of their players which are built for this problem.
- 1 +1, thanks for the help. I have decided to use YouTube (see answer). Thanks again. ^_^ – Snowy Coder Girl Commented Aug 18, 2011 at 2:07
- Hey, please give me solution for without putting ppt on the drive and take from the server then how do they do it? – user7918630 Commented Sep 7, 2017 at 10:23
I have decided to take a hack route and upload the powerpoint onto YouTube and then just include the youtube video in the iframe.
I know, it's cheap, but it's also easy.
I eventually checked my page as XHTML Strict, which does not support the <iframe> tag. So I used the object tag instead.
I tried answer posted by Shane, which looks exactly right and how MS used to have PPT viewing online earlier but it didn't worked for me. After doing some research I found out that the link has changed a bit.
So use: https://view.officeapps.live.com/op/ view.aspx instead of https://view.officeapps.live.com/op/ embed.aspx
Note: Link to PPT need to be publicly accessible.
- 2 I like more google docs viewer works with docs, pptx, pdf, etc. <iframe width="100%" height="630" src=" docs.google.com/viewer?url=your_file&embedded=true " ></iframe> – Alexis Cabrera Mondeja Commented Apr 6, 2020 at 2:05
- Animations and effects present in a PPT won't work with google docs viewers. – SumitK Commented Apr 7, 2020 at 6:29
- But you can use "Open With" and use Google presentations App. – Alexis Cabrera Mondeja Commented Apr 8, 2020 at 14:07
- I'm not sure if that can be done directly via a link like we can with MS. Also I believe to use Google Slides user need to be signed in with an Google account. – SumitK Commented Apr 9, 2020 at 15:21
Use Microsoft skydrive, upload your power point to this site and use this code
http://skydrive.live.com/redir.aspx?cid=20f065afc1acdb2e&page=view&resid=20F065AFC1ACDB2E!723&parid=20F065AFC1ACDB2E!719 is the URL of the powerpoint file.
You have to replace SD20F065AFC1ACDB2E!723 for your own string of the corresponding URL
- <iframe src=" r.office.microsoft.com/r/… " width="402" height="327" frameborder="0" scrolling="no"></iframe> – Carlos Soto Johnson Commented Jul 8, 2012 at 4:13
- Look the code of this site, crc.tc/powerpointDemo.html and replace SD20F065AFC1ACDB2E!723 with your own power point skidrive URL identifier – Carlos Soto Johnson Commented Jul 8, 2012 at 4:21
Upload a PowerPoint document on your Google Drive and then 'Share' it with everyone (make it public): Sharing your pptx doc
Then, go to File > Publish to the web > hit the publish button.
Go to Embed and copy the embed code and paste it to your web page
Copy embed code
Works Best for me.
Goto MS View Office Documents Online Page
Enter link to PPT file Note: This link should be publicly Accessible
Click on Create URL.
Link to view office documents online will be generated.
Paste this link to any webpage or as iframe src attribute.
You are all set!! :)
I was able to do this by saving the PPT as an mp4 (Save As > MPEG-4 Video (*.mp4)) and then using the video tag.
If you are using Google slides you could easily publish it on the web and also embed the slide in an iframe.
Go to google slides -> file-> sharing -> embed and copy the code

and then in your HTML file use the below code to show slides in fullscreen mode.
why not use prezi, I just use it in my work, very easy and useful.

Not the answer you're looking for? Browse other questions tagged html powerpoint or ask your own question .
- The Overflow Blog
- Masked self-attention: How LLMs learn relationships between tokens
- Deedy Das: from coding at Meta, to search at Google, to investing with Anthropic
- Featured on Meta
- User activation: Learnings and opportunities
- Preventing unauthorized automated access to the network
- Feedback Requested: How do you use the tagged questions page?
Hot Network Questions
- If Voyager is still an active NASA spacecraft, does it have a flight director? Is that a part time job?
- Is it ethical to edit grammar, spelling, and wording errors in survey questions after the survey has been administered, prior to publication?
- In John 3:16, what is the significance of Jesus' distinction between the terms 'world' and 'everyone who believes' within the context?
- How to do automated content publishing from CLI in XMCloud
- How do we define a non-standard model of natural numbers in ZFC, including predecessor operations?
- Bevel edges by Geometry nodes by using attribute on a vertex after solidify modifier
- Does this work for page turns in a busy violin part?
- Where is this NPC's voice coming from?
- How do I avoid getting depressed after receiving edits?
- On a glassed landmass, how long would it take for plants to grow?
- Why would an ocean world prevent the creation of ocean bases but allow ships?
- What causes, and how to avoid, finger numbness?
- Infinite sequence of uniform random variables
- Did Classical Latin authors ever incorrectly utilize an Ablative of Location for nouns that utilize the Locative Case?
- How do you tell someone to offer something to everyone in a room by taking it physically to everyone in the room so everyone can have it?
- If two subgroups intersect in only the identity, do their cosets intersect in at most one element?
- Player sprite becomes smaller during attack animation (Java)
- The most common one (L)
- Java class subset of C++ std::list with efficient std::list::sort()
- How to sub-align expressions and preserve equation numbering?
- Easily unload gravel from pickup truck
- What is the criterion for oscillatory motion?
- Does a passenger jet detect excessive weight in the tail after it's just landed?
- Purpose of sleeve on sledge hammer handle
5 of the Best Free HTML5 Presentation Systems
Share this article
Google Slides Template
Frequently asked questions (faqs) about html5 presentation systems.
- it’s quicker to add a few HTML tags than use a WYSIWYG interface
- you can update a presentation using a basic text editor on any device
- files can be hosted on the web; you need never lose a PPT again
- you can easily distribute a presentation without viewing software
- it’s not PowerPoint and your audience will be amazed by your technical prowess.
- you require web coding skills
- positioning, effects and transitions are more limited
- few systems offer slide notes (it’s a little awkward to show them separately)
- it’s more difficult to print handouts
- S5 — A Simple Standards-Based Slide Show System ( download )
- CSSS — CSS-based SlideShow System ( download )
- Slides ( download )
- HTML5Rocks (no direct downloads, but you can copy the source)
What are the key features to look for in an HTML5 presentation system?
When choosing an HTML5 presentation system, consider features such as ease of use, customization options, and compatibility with various devices. The system should have an intuitive interface that allows you to create presentations without any coding knowledge. Customization options are important for personalizing your presentation to match your brand or style. Additionally, the system should be compatible with different devices, including desktops, laptops, tablets, and smartphones, to ensure your audience can view your presentation without any issues.
How does HTML5 improve the presentation experience compared to traditional methods?
HTML5 enhances the presentation experience by offering interactive and dynamic content. Unlike traditional methods, HTML5 allows for the integration of multimedia elements like videos, audio, and animations directly into the presentation. This makes the presentation more engaging and interactive for the audience. Additionally, HTML5 presentations are web-based, meaning they can be accessed from any device with an internet connection, providing convenience and flexibility for both the presenter and the audience.
Are HTML5 presentations compatible with all browsers?
HTML5 presentations are generally compatible with all modern web browsers, including Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Safari, and Microsoft Edge. However, there may be slight variations in how different browsers render HTML5 content. Therefore, it’s always a good idea to test your presentation on multiple browsers to ensure it displays correctly.
Can I use HTML5 presentation systems for professional purposes?
Yes, HTML5 presentation systems are suitable for a variety of professional purposes. They can be used for business presentations, educational lectures, product demonstrations, and more. The ability to incorporate multimedia elements and interactive features makes HTML5 presentations a powerful tool for conveying complex information in an engaging and understandable way.
How can I make my HTML5 presentation accessible to all users?
To make your HTML5 presentation accessible, ensure that all content is readable and navigable for users with different abilities. This includes providing alternative text for images, captions for videos, and using clear and simple language. Additionally, make sure your presentation is responsive, meaning it adjusts to fit different screen sizes and orientations.
Can I convert my existing PowerPoint presentations to HTML5?
Yes, many HTML5 presentation systems offer the ability to import and convert PowerPoint presentations. This allows you to leverage your existing content while benefiting from the enhanced features and capabilities of HTML5.
Do I need to know how to code to use HTML5 presentation systems?
While having some knowledge of HTML5 can be beneficial, many HTML5 presentation systems are designed to be user-friendly and do not require any coding skills. These systems often feature drag-and-drop interfaces and pre-designed templates to help you create professional-looking presentations with ease.
Can I share my HTML5 presentations online?
Yes, one of the major advantages of HTML5 presentations is that they can be easily shared online. You can publish your presentation on your website, share it via email, or even embed it in a blog post or social media update.
Are HTML5 presentations secure?
HTML5 presentations are as secure as any other web content. However, it’s important to follow best practices for web security, such as using secure hosting platforms and regularly updating your software to protect against potential vulnerabilities.
Can I track the performance of my HTML5 presentations?
Yes, many HTML5 presentation systems include analytics features that allow you to track viewer engagement and behavior. This can provide valuable insights into how your audience interacts with your presentation, helping you to improve and refine your content over time.
Craig is a freelance UK web consultant who built his first page for IE2.0 in 1995. Since that time he's been advocating standards, accessibility, and best-practice HTML5 techniques. He's created enterprise specifications, websites and online applications for companies and organisations including the UK Parliament, the European Parliament, the Department of Energy & Climate Change, Microsoft, and more. He's written more than 1,000 articles for SitePoint and you can find him @craigbuckler .

- Full Stack Course
- React Native
- CSS Frameworks
- JS Frameworks
- Web Development
How to create a slideshow with HTML and CSS ?
A slideshow can be used to display text or images that continuously scroll from one slide to the other to display its content. This article shows an approach to building a slideshow with the use of only HTML and CSS . It consumes less browser memory and takes less computation power as there is no JavaScript involved.
JavaScript-based sliders make the web page slower and also do not work if the user has disabled JavaScript in the browser.
It uses the approach of using animation keyframes to scroll through each of the slides by modifying each of the slide’s margin-left properties during the animation. The animation type can be specified so that the slides can be animated as per the required duration and effect. In this article, we will learn how to build a slideshow using HTML & CSS.
- Use separate div sections for each slide to contain the text content. This allows for individual content definitions on each slide.
- Employ the slide-wrapper class to encapsulate all slides, enabling consistent animation effects and easy application of CSS properties to each slide.
- Utilize the overflow property to clip excess content, ensuring that the content within each slide remains visible, and any overflow is hidden.
- Apply the float property to align contents to the left, providing a structured layout for the slide elements.
- A pply the: nth-child() selector to style elements based on their position in a group of siblings. This allows for individualized styling, such as background color, based on the order of each slide.
Example: In this example, we will see the design of slideshow with HTML and CSS .
Similar Reads
- Web Technologies
- Web Templates
Please Login to comment...
- Top Language Learning Apps in 2024
- Top 20 Free VPN for iPhone in 2024: October Top Picks
- How to Underline in Discord
- How to Block Someone on Discord
- GeeksforGeeks Practice - Leading Online Coding Platform
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
W3.CSS Colors
Web building, w3.css slideshow.

Manual Slideshow
Displaying a manual slideshow with W3.CSS is very easy.
Just create many elements with the same class name:
JavaScript Explained
First, set the slideIndex to 1. (First picture)
Then call showDivs() to display the first image.
When the user clicks one of the buttons call plusDivs() .
The plusDivs() function subtracts one or adds one to the slideIndex.
The showDiv() function hides ( display="none" ) all elements with the class name "mySlides", and displays ( display="block" ) the element with the given slideIndex.
If the slideIndex is higher than the number of elements (x.length), the slideIndex is set to zero.
If the slideIndex is less than 1 it is set to number of elements (x.length).
Advertisement
Automatic Slideshow

To display an automatic slideshow is even simpler.
You only need a little different JavaScript:
HTML Slides
The slides do not have to be images.
They can be any HTML content:
Lorem ipsum
Slideshow caption.

Add a caption text for each image slide with the w3-display-* classes (topleft, topmiddle, topright, bottomleft, bottommiddle, bottomright, left, right or middle):
Slideshow Indicators
An example of using buttons to indicate how many slides there are in the slideshow, and which slide the user is currently viewing.

Another example:
Images as Indicators
An example of using images as indicators:
Multiple Slideshows on the Same Page
To operate multiple slideshows on one page, you must class the members of each slideshow group with different classes:
Animated Slides
Slide or fade in an element from the top, bottom, left or right of the screen with the w3-animate-* classes.

Faded Animation
The w3-animate-fading class fades an element in and out (takes about 10 seconds).

COLOR PICKER

Contact Sales
If you want to use W3Schools services as an educational institution, team or enterprise, send us an e-mail: [email protected]
Report Error
If you want to report an error, or if you want to make a suggestion, send us an e-mail: [email protected]
Top Tutorials
Top references, top examples, get certified.

HTML Slidy: Slide Shows in HTML and XHTML
Dave Raggett , < [email protected] > Hit the space bar or swipe left for next slide
Slide Shows in HTML and XHTML
- You can now create accessible slide shows with ease
- Advance to next slide with mouse click, space bar or swipe left
- Move forward/backward between slides with Cursor Left, Cursor Right, Pg Up and Pg Dn keys, or swipe left or right
- Home key for first slide, End key for last slide
- The " C " key for an automatically generated table of contents, or click on "contents" on the toolbar or swipe up or down
- Function F11 to go full screen and back
- The " F " key toggles the display of the footer
- Try it now to see how to include notes for handouts (this is explained in the notes following this slide)
- use S and B keys for manual control (or < and >, or the - and + keys on the number pad
- Use CSS to set a relative font size on a given slide to make the content bigger or smaller than on other slides
- Switching off JavaScript reveals all slides
- Now move to next slide to see how it works
Copyright © 2005-2010 W3C ® ( MIT , ERCIM , Keio ), All Rights Reserved.
For handouts, its often useful to include extra notes using a div element with class="handout" following each slide, as in:
What you need to do
- Each presentation is a single XHTML file
- The div element will be created automatically for h1 elements that are direct children of the body element.
- Use regular markup within each slide
- The slide show style sheet: http://www.w3.org/Talks/Tools/Slidy2/styles/slidy.css
- The slide show script: http://www.w3.org/Talks/Tools/Slidy2/scripts/slidy.js
- Or you can link to the compressed version of the script which is about one seventh the size, see http://www.w3.org/Talks/Tools/Slidy2/scripts/slidy.js.gz
- If you are using XHTML, remember to use </script> and </style> as per Appendix C.3
To get the W3C Blue Style
The head element should include the following link to the style sheet:
The body element's content should start with the following markup:
This adds the logos on the top left and right corners of the slide.
You are of course welcome to create your own slide designs. You can provide different styles and backgrounds for different slides (more details later).
Use the meta element with name="copyright" for use in the slide show footer:
Upgrading from previous versions of Slidy
- This uses a new version of the HTML Slidy script
- Only adds one global name "w3c_slidy"
- Doesn't interfere with other scripts that set event handers such as onload on body element
- Works for slides delivered as text/html and application/xhtml+xml
- New presentation timer feature
- Initial prompt on first slide to help newcomers to Slidy
- Better support for styling slides and printing them
- See slidy.css , and w3c-blue.css
- But old presentations will work unchanged as they refer to the old script!
To use it off-line
- You can download slidy.zip and unzip it to create a Slidy directory on your machine
- If you have cvs access to the W3C site you can check out the Slidy directory
- Remember to periodically check for updates
- Use relative URIs depending on your local setup to access the appropriate files. Use the same directory structure as on the W3C server, ie, ".../2005/Talks/...".
- Run a Web server on your machine so that the directory above can be accessed via http://localhost/Talks/Tools/Slidy2 and use the URIs of the form "/Talks/Tools/Slidy2/styles/slidy.css", "/Talks/Tools/Slidy2/scripts/slidy.js".
- In both cases you can then publish your files on the W3C server unchanged.
- NOTE Internet Explorer on Windows XP now disables scripting for web pages loaded directly from the local file system, a work around is to use another browser, e.g. Firefox or Opera
- Please feel free to create your own designs, and help us to build a gallery of Slidy styles.
- My Google TechTalk (1st Feb 2006) uses a notebook themed style
Timing Your Presentation
- Sometimes it is handy to know just how much time you have to left to finish your presentation
- To get this feature, add the following markup to the content of the head element, replacing 5 by the duration of your presentation in minutes <meta name="duration" content="5" />
- The time left in minutes and seconds is shown in the footer next to the slide number
- The clock starts to run when you move away from the first slide
- Moving back to the first slide pauses the clock
Generate a Title Page
If you want a separate title page with the W3C blue style, the first slide should be as follows:
The w3c-blue.css style sheet looks for the classes "slide" and "cover" on div and img elements using the CSS selector div.slide.cover
This technique can be used to assign your slides to different classes with a different appearence for each such class.
Slidy also allows you to use different background markup for different slides, based upon shared class names, as in "foo" below. Backgrounds without additional class names are always shown except when the slide isn't transparent. You may need to tweak your custom style sheet.
Incremental display of slide contents
For incremental display, use class="incremental", for instance:
- First bullet point
- Second bullet point
- Third bullet point
which is marked up as follows:
An element is incrementally revealed if its parent element has class="incremental" or if itself has that attribute. Text nodes are not elements and are revealed when their parent element is revealed. You can use class="incremental" on any element except for <br />. Use class="non-incremental" to override the effect of setting the parent element's class to incremental.
Note: you will see a red asterisk on the left of the toolbar when there is still something more to reveal.
Create outline lists with hidden content
You can make your bullet points or numbered list items into outlines that you can expand or collapse
- The Slidy script will then treat the list as an outline list.
- Clicking on outline list items will expand/collapse block-level elements within that list item.
- Click on the above to make this list item collapse again.
- Users will then see expand/collapse icons as appropriate and may click anywhere on the list item to change its state. This particular list item can't be expanded or collapsed.
- By default Slidy hides all the block level elements within the outline list items unless you have specified class="expand".
- Such pre-expanded items can be collapsed by clicking on them.
- Microsoft says it will be supported by IE7 along with many fixes for other CSS woes in IE6.
Make your images scale with the browser window size
For adaptive layout, use percentage widths on images, together with CSS positioning:
- CSS positioning is simpler and more reliable than using tables
To work around a CSS rendering bug in IE relating to margins, you can set display:inline on floated elements.
Incremental display of layered images
These can be marked up using CSS relative positioning, e.g.
You should also use transparent GIF images to avoid the IE/Win bug for alpha channel in PNG. A fix is expected in IE 7. A work around is available on skyzyx.com. My thanks to ACID2 for the graphics.
How to center content vertically and horizontally
Within the div element for your slide:
and style it with the following:
The above styling is included in w3c-blue.css , which is designed to be used with slidy.css , but you are encouraged to develop your own style sheet with your own look and feel.
Include SVG Content
Inclusion of SVG content can be done using the object element, for example:

has been achieved by:
This ensures that the enclosed png is displayed when the browser has no plugin installed or can't display SVG directly. Providing such a fall back is very important! Don't forget the alt text for people who can't see the image.
However, there are caveats, see the next slide!
Caveats with SVG+object
Adobe has recently withdrawn support for its SVG Viewer, so you are recommended to consider alternatives . If you still using the Adobe SVG viewer you should be aware of bugs when using the it with IE, Namely:
- Most modern browsers generally support SVG SVG Tiny 1.1 or better natively without the need for a plugin
- If you need to use Internet Explorer you are advised to upgrade to IE9 which includes native support for SVG.
- Patches to Internet Explorer mean that the Adobe SVG Viewer version 3.03 no longer works with IE6. You are therefore recommended to uninstall version 3.03 and instead install Adobe SVG Viewer 6.0 preview if this is available to to you.
- IE6 makes a copy of the SVG file on the local disc when displaying it; but doesn't pass the original URI to the plugin
- As a result relative references from within the SVG to external resources (scripts, CSS, images, other SVG) will break.
- The work around is to use absolute references within your SVG.
- On Windows, the Adobe SVG plugin doesn't respect the CSS z-index property, and if used on backgrounds will always show through other content
Additional Remarks
- Slides are auto-numbered on the slide show footer
- It works out which slide you want and hides the rest
- You can even link between slides in the same slide show
- Previous versions of Slidy used square brackets, which will also work.
- Note that the browser's back/forward buttons may not work as you might expect due to browser problems.
- Adding "title" to the list of classes for div elements that serve as title pages will render the corresponding entry in the table of contents in bold italic text (press "C" now for an example)
- the following requests fonts to be one step smaller than the Slidy default for the current window width, and positive integers will make the fonts correspondingly larger
- Slidy uses JavaScript to dynamically set the font size on the body element, but it is okay to specify relative font changes on other elements within your own style sheet, e.g.
- You are encouraged to ensure your markup is valid. HTML Tidy can be used to find and correct common markup problems
- The slide show script and style sheet can be used freely under W3C's software licensing and document use policies
- At XTech2006 I gave this presentation on Slidy ( Paper ).
Localization and automatic translation
Slidy now includes support for localization
- The tool bar is localized according to the language of the presentation
- This is taken from the xml:lang or lang attributes on the html element
- The help file is selected based upon your browser's language preferences
- As of 29th July 2010, the languages supported are: English, Spanish, Catalonian, Czech, Dutch, German, Polish, French, Hungarian, Italian, Greek, Japanese, Chinese, Russian and Swedish
- If you would like to contribute localizations for other languages, please get in touch with Dave Raggett <[email protected]>
- The following illustrates what was used for Spanish
Note: Slidy now works with current slides translated into French . Use right mouse button to open frame without Google header. To disable automatic translation of the content of particular elements add class="notranslate" , see breaking the language barrier .
Future Plans
Recent additions have included a table of contents, and a way to hide and reveal content in the spirit of outline lists. The script has been rewritten to make it easier to combine with other scripts, e.g. for UI controls, and support swipes for navigation on touch screen devices. Further work is anticipated on the following:
- Opportunities for graphics designers!
- Bob Ferris has worked on a number of UI extensions which could be incorporated into the W3C slidy script.
- Using scripts to dynamically convert SVG Tiny to VML
- Note that IE9 introduces native SVG support, so it may no longer be worth working on SVG to VML for rendering of SVG
- Using contentEditable when available, otherwise falling back to textarea and plain text conventions
- Using XMLHttpRequest to dynamically reflect changes to server
- Using XMLHttpRequest to listen for navigation commands
- Using VoIP for accompanying audio and teleconferencing
- Synchronizing recorded spoken presentation with currently viewed slide
- and export to PDF via PrinceXML
If you have comments, suggestions for improvements, or would like to volunteer your help with further work on Slidy, please contact Dave Raggett < [email protected] >
Acknowledgements
- My thanks to everyone who sent in bug reports and feature requests
- Opera Software for implementing CSS @media projection and promoting the idea of using the Web for presentations with Opera Show
- Tantek Çelik for his pioneering work on applying JavaScript for slide presentations on other browsers
- Eric Meyer for taking this further with the excellent S5
- W3C's slidemaker tool , which uses a perl script to split an html file up into one file per slide with navigation buttons
- Early versions of HTML Tidy which supported a means to create presentations via splitting html files on h2 elements
- Many sites with advice on JavaScript work arounds for browser variations
- Microsoft for pioneering contentEditable and XMLHTTP which both provide tremendous opportunities for Web applications
- Microsoft Office which provided the impetus for creating Slidy as a Web-based alternative to the ubiquitous use of PowerPoint
Note that while Slidy and S5 were developed independently, both support the use of the class values "slide" and "handout" for div elements. Slidy doesn't support the "layout" class featured in S5 and Opera Show, but instead provides a more flexible alternative with the "background" class, which enables different backgrounds on different slides.
The following people have contributed localizations:
- Emmanuelle Gutiérrez y Restrepo, Spanish
- Joan V. Baz, Catalan
- Jakub Vrána, Czech
- Ruud Steltenpool, Dutch
- Beat Vontobel, German
- Krzysztof Kotowicz, Polish
- Tamas Horvath, Hungarian
- Creso Moraes, Brazilian Portuguese
- Giuseppe Scollo, Italian
- Konstantinos Koukopoulos, Greek
- Yoshikazu Sawa (澤 義和), Japanese
- Shelley Shyan, Chinese
- Andrew Pantyukhin, Russian
- Saasha Metsärantala, Swedish
The following people have contributed bug reports:
- Gerald Senarclens de Grancy
- Steve Robertson
- Ivan Herman
- Steve Bratt
- Peter Patel-Schneider
- Matthew Coller
- Rune Heggtveit
- Gopal Venkatesan
- Cay Horstmann
- Schuyler Duveen
- Matteo Nannini
- Ralph Swick
- Jakub Vrána
- Philip Bolt
- Jonathan Chetwynd
- Nicolas Frisby
Douglas Crockford for jsmin which was used to minify the script before compressing it with gzip.
- For Business
How to embed PowerPoint presentation in HTML?
Have you ever needed to add a slideshow to your website or blog without inserting it just as an image? In this article, we’ll show several ways on how to embed PowerPoint in HTML. Read on and select a suitable option.

Why embed a PowerPoint in HTML?
Embedding a PowerPoint presentation into HTML pages offers a convenient way to showcase, distribute and share your slides on the web.
By integrating a presentation into your site or application, you provide a more interactive and engaging experience for users since they are able to access the slideshow online and don’t need to have PowerPoint software installed on their computers or mobile devices.
Additionally, if you embed PowerPoint in HTML iframe, you can customize the appearance and functionality of the presentation, such as adding navigation controls or interactive elements.
1. Embed PPTX in HTML via ONLYOFFICE Workspace
In ONLYOFFICE Workspace , a productivity platform for managing your files, emails, projects, etc., there is an option to generate an embedding code for any file, including presentations.
- Go to the Documents module and click Share next to the required PPTX file.
- Click Add link -> Save.
- In the drop-down menu, select Embedding settings .
- If needed, adjust the settings such as width and height.
- Copy the embedding code and insert it to your HTML page.
Alternatively, you are able to do the same actions right from the opened presentation editor via the Collaboration tab.
GET ONLYOFFICE WORKSPACE
2. How to embed PowerPoint into HTML on your WordPress or Drupal site
The ONLYOFFICE Docs suite is seamlessly integrated with popular and widely-used CMS platforms like WordPress and Drupal . This way, you can easily insert presentations into your WordPress or Drupal website.
For example, when creating a new WordPress post, you can add the ONLYOFFICE block and then upload a new file or select one from the Media Library.
The added PPTX will be displayed as the ONLYOFFICE logo with the file name in the currently edited post. After the post is published, your WordPress site visitors will have access to this file for viewing in the Embedded mode.
GET ONLYOFFICE DOCS
Check our tutorials to learn more about ONLYOFFICE integration with WordPress and Drupal .
3. Embedding options for developers
For developers and integrators, a further option to embed a PowerPoint in HTML is provided via ONLYOFFICE DocSpace .
It is a room-based collaborative environment which empowers you with an extensive array of customization options, enabling you to enhance the functionality of your web applications and tailor them precisely to your requirements.
CREATE FREE ACCOUNT
So, you can seamlessly integrate specific DocSpace rooms with the needed slides into your web application.
Check the detailed guide
If you are an experienced user, you can also embed PowerPoint in HTML iframe using the basic concepts of the open API as well as a tutorial for inline editors .
ONLYOFFICE DOCS FOR DEVELOPERS
Useful links
ONLYOFFICE Presentation Editor
ONLYOFFICE Workspace
ONLYOFFICE DocSpace
ONLYOFFICE for developers
Integrations with popular services & platforms
Create your free ONLYOFFICE account
Recent posts.

How to add consistent table stylings with an ONLYOFFICE macro

ONLYOFFICE hits 100,000 views on TikTok

How to create a personal education plan

How To Embed PowerPoint In HTML/Website?
Ever wonder how to post a PowerPoint presentation to your website or blog without just posting an image of it? Embedding PowerPoint presentations in an HTML website can do this. You can share your beautifully designed PowerPoint presentations on your webpage, attracting many people and increasing traffic.
You can present dynamic material and attract users by integrating interactive slideshows right into web pages. Embedding PowerPoint in the website enables users to access the content without the requirement of additional software and makes them extensively utilized for business, education, and various other uses.
Let us check out how to embed PowerPoint in HTML or a website.
How to Embed PowerPoint in HTML/Website?
Using the following two methods, you can embed PowerPoint on a website or HTML. Both of these methods are compatible with Windows, Mac, and Web. Let’s check them out:
- Using PowerPoint Web
- Using OneDrive
Method 1: Using PowerPoint Web
To embed PowerPoint presentation in HTML using PowerPoint Web:
- Open “PowerPoint Web” from your browser and go to “File.” You will see the “Open option.” Select the presentation you want to embed on your website.
- Again, go to “File” and select “Share.”
- Click on” Embed” from the “drop-down menu.” Wait a few seconds for a “new menu” to show up, and hit “Generate.” Now, your presentation will be previewed in front of you.
- You can change the dimensions of your presentation according to your audience.
- Next, from the “Embed Code textbox,” copy the code.
- Paste the code into the body of your website.
- Save your site. And now you have successfully embedded a PowerPoint presentation into a website.
Method 2: Using OneDrive
To embed PowerPoint presentations in HTML using OneDrive:
- Open your Presentation. Remove any notes or personal details if you have any.
- Next, upload your “PPT” to your personal OneDrive account.
- On your OneDrive, go to recent documents and select your presentation.
- Click on the “Embed button” appearing at the top of the page.
- Copy the “HTML code” that appears in front of your screen.
- Paste the copied code on your website and save it. Your PowerPoint presentation will now be embedded in your website.
READ MORE: How To Covert Keynote To PowerPoint
However, the imbibing option is not entirely functional because you won’t be able to update or change the fonts. There are no extra features because it is only available for viewing on the web. But you can resize it, search the document for particular phrases, print the paper, download it, and use several other tools that Microsoft offers.
Embedding PPT in HTML is an effective way to increase engagement on your website. You can share the required information through an amazing slideshow. By following the steps above, you can easily embed PowerPoint in your website. You can either use PowerPoint Web or your OneDrive account at your convenience.
Stay updated on our website to keep reading such useful blogs.
Can I Change The Font Of My PowerPoint Presentation After Embedding It On A Website?
No, changing the font after embedding PowerPoint in HTML or a website is impossible as it is converted into a PDF or PPTX form. If you wish to change the font, you must do it in your original presentation and reupload the file.
Can I Embed Multiple PowerPoint Files On The Same Website?
Yes, you certainly can. You can embed as many PowerPoint presentations as you want, repeating the same procedure.
Is There Any Limitation On The Size Of The PowerPoint File To Be Uploaded To A Website?
No, there is no limitation on the size of the PowerPoint presentation. The upload time may be affected depending on the size of your PPT file.
Can I Include Videos In My PowerPoint Presentation While Embedding Them On A Website?
Yes, you can include videos within the presentation. However, it may sometimes not function properly and contain some lags. So it is always advisable to include the videos separately if you are embedding PowerPoint in website.
Can I Use The Embed Function Directly From The PowerPoint Application On My Device?
No, you cannot directly use the embed function from the PowerPoint application. You have to either use PowerPoint Web or upload it to your OneDrive account and then embed it.
Table Of Content
Related presentations.

Customer Testimonial Template

Contact Us Template

About Me Template
Related posts from the same category.

8 Apr, 2020 | SlideUpLift
How To Embed A YouTube Video In PowerPoint
There may be many occasions where you'd like your audiences to watch a video to better understand your argument or notion. Adding a video to your presentation can help retain

15 May, 2023 | SlideUpLift
How To Embed Fonts In PowerPoint
Have you ever opened a PowerPoint presentation only to comprehend that the fonts used in it are completely different from the ones you have on your computer? This can be

3 Feb, 2023 | SlideUpLift
How To Make A Graph In PowerPoint?
Do you need help communicating data effectively in your presentations? Data visualization is an essential tool in today's world as it helps represent complex data sets in a simple and

25 Jan, 2018 | SlideUpLift
How To Add Annotations In PowerPoint | How To Add Comments In PowerPoint
This PowerPoint tutorial explains how to add annotations in PowerPoint in simple steps. Often presentations are used in business discussions and interactive sessions. During the discussion, you might need to

8 Dec, 2022 | SlideUpLift
How To Use Transparency In PowerPoint?
PowerPoint's user-friendly design has made it a top choice among many, one of the key contributing factors to its immense popularity. Microsoft PowerPoint is one of the most used software

30 Apr, 2021 | SlideUpLift
Learn How To Communicate In Several Languages In PowerPoint
In this tutorial, we will learn how to change language in PowerPoint. Presentations are an essential part of the business world. Businesses and professionals use presentations to inform, educate, motivate

28 Feb, 2023 | SlideUpLift
How To Track Changes in PowerPoint: Methods and Best Practices
PowerPoint is a widely used presentation tool frequently used in group settings where several people can make additions to the same presentation. When multiple persons edit the same file, tracking

11 Sep, 2024 | SlideUpLift
How To Create Puzzle Pieces In PowerPoint [+Templates]
The jigsaw puzzle is the perfect design element that you can use for your strategy presentations; it helps with the storytelling aspect of your presentation by showing how the pieces

18 Oct, 2022 | SlideUpLift
How to make a Curved Arrows in PowerPoint | PowerPoint Tutorial
Curved Arrows Cyclic diagrams show the process and series of events that interact repetitively through the cycle. Such diagrams depict the flow of one step following another repeatedly, which means

PowerPoint Hack: How To Create Sections In PowerPoint And How To Zoom In PowerPoint
This PowerPoint tutorial is about How To Create Sections In PowerPoint. Imagine that you are about to begin your business presentation to a room full of clients, and you remember
Related Tags And Categories
Forgot Password?
Privacy Overview
Necessary cookies are absolutely essential for the website to function properly. This category only includes cookies that ensures basic functionalities and security features of the website. These cookies do not store any personal information
Any cookies that may not be particularly necessary for the website to function and is used specifically to collect user personal data via ads, other embedded contents are termed as non-necessary cookies. It is mandatory to procure user consent prior to running these cookies on your website.
- Accessibility Options:
- Skip to Content
- Skip to Search
- Skip to footer
- Office of Disability Services
- Request Assistance
- 305-284-2374
- High Contrast
- School of Architecture
- College of Arts and Sciences
- Miami Herbert Business School
- School of Communication
- School of Education and Human Development
- College of Engineering
- School of Law
- Rosenstiel School of Marine, Atmospheric, and Earth Science
- Miller School of Medicine
- Frost School of Music
- School of Nursing and Health Studies
- The Graduate School
- Division of Continuing and International Education
- People Search
- Class Search
- IT Help and Support
- Privacy Statement
- Student Life
- University of Miami
- Division of University Communications
- Office of Media Relations
- Miller School of Medicine Communications
- Hurricane Sports
- UM Media Experts
- Emergency Preparedness
- Connection and Transition
- Diversity and Inclusion
- Student Engagement
- Well-Being and Resiliency
- Departments and Areas
- 'Canes Care for 'Canes
- Latest Headlines
- Student Affairs
- Subscribe to News@TheU Newsletter
- UM NEWS HOME
Kevin Kruger Reflects on the Evolution of Higher Education
By Jen Rau 09-26-2024
On Monday, September 23, the University of Miami’s Division of Student Affairs and Alumni Engagement had the honor of hosting Kevin Kruger, former President of the National Association of Student Personnel Administrators (NASPA), in the Shalala Student Center Ballroom. With over 40 years of experience in higher education, Kruger delivered a profound reflection on the evolving challenges and opportunities within student affairs and higher education leadership.
Attendees included staff from Student Affairs, Alumni Engagement, Center for Student Navigation and Success, Human Resources, Strategy and Transformation, and Auxiliary Services.
Kruger’s presentation provided a comprehensive look back at his extensive career, focusing on the significant evolutions he has witnessed within the field. He underscored the need for continued support of low-income and first-generation students, emphasizing the importance of meeting their needs at every stage of their educational journey. He also identified mental health and well-being of students as institutional priorities.
Pat Whitely, senior vice president for student affairs and alumni engagement, who has served the University of Miami for over 40 years, invited Kruger to speak. Whitely, a national leader in student affairs, recently co-chaired the search for the next NASPA president and has been recognized for her extensive contributions to higher education. Reflecting on the event, she remarked, “Kruger’s presentation was thought-provoking and filled with invaluable insights and data, providing our teams with strategies to elevate their work and further support for student success.”
Kruger also addressed pressing campus issues, including the need for innovation to address belonging and well-being across diverse student populations and navigating financial constraints. His analysis offered a roadmap for collaboration between student affairs professionals and academic staff to tackle these critical challenges effectively.
Addressing the pressing issues on university campuses, Kruger called for continued innovation to tackle challenges such as belonging and mental health, finding commonalities across diverse student populations, and navigating fiscal constraints. His insights offered a valuable perspective on how student affairs professionals and academic staff can collaborate to address these critical issues and support student success.
This event reinforced the importance of professional development for university staff as the institution continues to prioritize student success. Kruger’s insights will inspire ongoing efforts to enhance the support provided to students, ensuring their continued growth and achievement within the University of Miami community.

Division of Student Affairs
- 1252 Memorial Drive Coral Gables , FL 33146
- 305-284-4922 305-284-4922
- [email protected]
- UM News and Events
- Alumni & Friends
- 'Cane Watch
Tools and Resources
- Academic Calendar
- Department Search
- Parking & Transportation
- social-facebook
- social-twitter
- social-youtube
- social-instagram
Copyright: 2024 University of Miami. All Rights Reserved. Emergency Information Privacy Statement & Legal Notices Title IX & Gender Equity Website Feedback
Individuals with disabilities who experience any technology-based barriers accessing the University’s websites or services can visit the Office of Workplace Equity and Inclusion .
- Today's news
- Reviews and deals
- Climate change
- 2024 election
- Newsletters
- Fall allergies
- Health news
- Mental health
- Sexual health
- Family health
- So mini ways
- Unapologetically
- Buying guides
Entertainment
- How to Watch
- My Portfolio
- Latest News
- Stock Market
- The Morning Brief
- Biden Economy
- Stocks: Most Actives
- Stocks: Gainers
- Stocks: Losers
- Trending Tickers
- World Indices
- US Treasury Bonds Rates
- Top Mutual Funds
- Options: Highest Open Interest
- Options: Highest Implied Volatility
- Basic Materials
- Communication Services
- Consumer Cyclical
- Consumer Defensive
- Financial Services
- Industrials
- Real Estate
- Stock Comparison
- Advanced Chart
- Currency Converter
- Credit Cards
- Balance Transfer Cards
- Cash-back Cards
- Rewards Cards
- Travel Cards
- Credit Card Offers
- Best Free Checking
- Student Loans
- Personal Loans
- Car insurance
- Mortgage Refinancing
- Mortgage Calculator
- Editor's Picks
- Investing Insights
- Trending Stocks
- Morning Brief
- Opening Bid
- Fantasy football
- Pro Pick 'Em
- College Pick 'Em
- Fantasy baseball
- Fantasy hockey
- Fantasy basketball
- Download the app
- Daily fantasy
- Scores and schedules
- GameChannel
- World Baseball Classic
- Premier League
- CONCACAF League
- Champions League
- Motorsports
- Horse racing
New on Yahoo
- Privacy Dashboard
Yahoo Finance
Pacira Announces the Presentation of 104-Week Safety and Efficacy Data Following Local Administration of PCRX-201 for Moderate to Severe Osteoarthritis of the Knee
In this article:.
-- Poster to be presented at ACR Convergence annual meeting --
TAMPA, Fla., Sept. 26, 2024 (GLOBE NEWSWIRE) -- Pacira BioSciences, Inc. (NASDAQ: PCRX), the industry leader in the delivery of innovative, non-opioid pain therapies, today announced the upcoming presentation of new data in support of its gene therapy candidate, PCRX-201 (enekinragene inzadenovec). The data will be presented at the American College of Rheumatology’s annual ACR Convergence meeting, being held in Washington, D.C. November 14–19.
Presentation Title: Sustained Clinical Effects After a Single Intra-articular Injection of PCRX-201 for Moderate-to-Severe Osteoarthritis of the Knee
Presented By: Stanley Cohen, MD, a board-certified rheumatologist and Co-Medical Director of the Metroplex Clinical Research Center in Dallas, TX
Date & Time: Sunday, November 17 from 10:30 am – 12:30 pm EST
PCRX-201 is a locally administered gene therapy, designed to produce interleukin-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra), a naturally occurring, anti-inflammatory protein with a proven mechanism of action that reduces interleukin-1 (IL-1) signaling, a known factor in the development and progression of osteoarthritis of the knee. Unlike systemically administered gene therapies, PCRX-201 delivers the medicine where it matters and uses an inducible promoter to mimic the body’s natural response to inflammation by “turning on” the expression of IL-1Ra when inflammation is present in the joint to reduce pain and disability and potentially slow structural progression.
In March 2024, PCRX-201 became the first-ever gene therapy product candidate in osteoarthritis to receive Regenerative Medicine Advanced Therapy (RMAT) designation from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
RMAT designation provides the benefits of intensive FDA guidance on efficient drug development, including the ability for early interactions with the FDA to discuss surrogate or intermediate endpoints, potential ways to support accelerated approval and satisfy post-approval requirements, potential priority review of the Biologics License Application (BLA), and other opportunities to expedite development and review. PCRX-201 was also granted Advanced Therapy Medicinal Products (ATMP) designation by the European Medicines Agency in May 2023.
About Pacira BioSciences Pacira BioSciences delivers innovative, non-opioid pain therapies to transform the lives of patients. Pacira has three commercial-stage non-opioid treatments: EXPAREL ® (bupivacaine liposome injectable suspension), a long-acting local analgesic currently approved for infiltration, fascial plane block, and as an interscalene brachial plexus nerve block for postsurgical pain management; ZILRETTA ® (triamcinolone acetonide extended-release injectable suspension), an extended-release, intra-articular injection indicated for the management of osteoarthritis knee pain; and ioveraº ® , a novel, handheld device for delivering immediate, long-acting, drug-free pain control using precise, controlled doses of cold temperature to a targeted nerve. The company is also advancing the development of PCRX-201, a novel locally administered gene therapy with the potential to treat large prevalent diseases like osteoarthritis. To learn more about Pacira, visit www.pacira.com .
CONTACT: Investor Contact: Susan Mesco, (973) 451-4030 [email protected] Media Contact: Sara Marino, (973) 248-7005 [email protected]
Recommended Stories

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Inside the newly created presentation folder, create a new file and call it index.html. Now, enter the following code, which contains the needed references to the WebSlides' files (make sure the ...
Create Stunning Presentations on the Web. reveal.js is an open source HTML presentation framework. It's a tool that enables anyone with a web browser to create fully-featured and beautiful presentations for free. Presentations made with reveal.js are built on open web technologies. That means anything you can do on the web, you can do in your ...
In the function moveToLeftSlide, we basically access the previous sibling element (i.e. the previous slide), remove the .show class on the current slide, and add it to that sibling. This will move the presentation to the previous slide. We do the exact opposite of this in the function moveToRightSlide.Because nextElementSibling is the opposite of previousElementSibling, we'll be getting the ...
HTML, or Hyper Text Markup Language, is the building block of most web pages. It's a way to structure content on the web and create visual presentations like slideshows. When we talk about creating a slideshow using HTML, we're often referring to leveraging a combination of div tags and CSS properties.
Making a Presentation. Copy an existing presentation folder; Change the folder name (which should be located at public/slides) with the name day[num of day] ex(day2) Making a Slide. Making a slide is pretty simple. Just add a HTML section. <section> <!--slide content--> </section> inside the span with the class of "prez-root". Also keep in mind ...
A framework for easily creating beautiful presentations using HTML. Reveal.js HTML Presentations Made Easy. Created by Hakim El Hattab / @hakimel. Heads Up. ... Presentations can be exported to PDF, below is an example that's been uploaded to SlideShare. Take a Moment.
WebSlides is the easiest way to make HTML presentations. Just choose a demo and customize it in minutes. 120+ slides ready to use. Good karma. WebSlides is a beautiful solution for telling stories. ... HTML and CSS as narrative elements. Work better, faster. Designers, marketers, and journalists can now focus on the content. Simply choose a ...
HTML/CSS. As I sifted through the various pieces of software that are designed for creating presentation slides, it occurred to me: why learn yet another program, when I can instead use the tools that I'm already familiar with? With a bit of fiddling, we can easily create beautiful presentations with HTML and CSS. I'll show you how today!
Create the Starter Markup. 3. Make It Pretty. 4. Enable Slide Navigation. Moving the Presentation to the Next and Previous Slides. Code for Showing the Presentation in Full Screen and Small Screen. Hidding Left and Right Icons in First and Last Slides. Updating and Displaying Slide Number.
Learn the basics of HTML in a fun and engaging video tutorial. Templates. We have created a bunch of responsive website templates you can use - for free! Web Hosting. Host your own website, and share it to the world with W3Schools Spaces. Create a Server. Create your own server using Python, PHP, React.js, Node.js, Java, C#, etc. ...
WebSlides = Create stories with Karma. Finally, everything you need to make HTML presentations, landings, and longforms in a beautiful way. Just a basic knowledge of HTML and CSS is required. Designers, marketers, and journalists can now focus on the content. — https://webslides.tv/demos.
Best Vanilla JS HTML Presentation Frameworks Beautiful HTML Presentation Library - reveal.js. reveal.js is an open source HTML presentation framework. It's a tool that enables anyone with a web browser to create fully-featured and beautiful presentations for free. Presentations made with reveal.js are built on open web technologies.
The first step to changing which slides show is to select the slide wrapper (s) and then its slides. When you select the slides you have to go over each slide and add or remove an active class depending on the slide that you want to show. Then just repeat the process for a certain time interval. Keep it in mind that when you remove an active ...
HTML is used as the graphical user interface in client-side programs written in JavaScript. Server-side languages like PHP and Java also receive data from web pages and use HTML as the output mechanism. The emerging Ajax technologies likewise use HTML and XHTML as their visual engine.
If you have an account on OneDrive, do the following using Powerpoint Online (accessing Powerpoint via the browser) to embed a Powerpoint: Click 'File', then 'Share', then 'Embed'. Click the 'Generate' button to generate HTML code to be embedded. Copy the 'Embed Code' and paste it in the HTML of a website. answered Aug 1, 2014 at 7:41.
This series of short videos explores Reveal.js, an HTML Presentation Framework for making beautiful web presentations. In this fourth video, we'll look at ad...
Google Slides Template. As you'd expect, Google has their own HTML5 presentation template (as well as the one offered in Google Docs). It's fairly basic when compared to Reveal.js or Impress ...
In this article, you will learn how to create a full-screen search Bar. Here You will be required to create two divs. One for the overlay container and the other for the overlay content container. HTML Code: The first step is to create an HTML file. Here we will create the basic structure for the search bar. Here we will also use an icon for the se
The showDiv () function hides (display="none") all elements with the class name "mySlides", and displays (display="block") the element with the given slideIndex. If the slideIndex is higher than the number of elements (x.length), the slideIndex is set to zero. If the slideIndex is less than 1 it is set to number of elements (x.length).
Home key for first slide, End key for last slide. The " C " key for an automatically generated table of contents, or click on "contents" on the toolbar or swipe up or down. Function F11 to go full screen and back. The " F " key toggles the display of the footer. The " A " key toggles display of current vs all slides.
Click Add link -> Save. In the drop-down menu, select Embedding settings. If needed, adjust the settings such as width and height. Copy the embedding code and insert it to your HTML page. Alternatively, you are able to do the same actions right from the opened presentation editor via the Collaboration tab. GET ONLYOFFICE WORKSPACE.
Method 1: Using PowerPoint Web. To embed PowerPoint presentation in HTML using PowerPoint Web: Open "PowerPoint Web" from your browser and go to "File.". You will see the "Open option.". Select the presentation you want to embed on your website. Again, go to "File" and select "Share.". Click on" Embed" from the "drop ...
Kruger's presentation provided a comprehensive look back at his extensive career, focusing on the significant evolutions he has witnessed within the field. He underscored the need for continued support of low-income and first-generation students, emphasizing the importance of meeting their needs at every stage of their educational journey.
KalVista Pharmaceuticals Announces Nine Abstracts Accepted for Presentation at the HAEi Global Angioedema Forum (GAF) September 26, 2024 06:30 AM Eastern Daylight Time.
Presentation Title: Sustained Clinical Effects After a Single Intra-articular Injection of PCRX-201 for Moderate-to-Severe Osteoarthritis of the Knee Presented By: Stanley Cohen, MD, a board ...