What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.

Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
112 Persuasive Speech Topics That Are Actually Engaging
What’s covered:, how to pick an awesome persuasive speech topic, 112 engaging persuasive speech topics, tips for preparing your persuasive speech.
Writing a stellar persuasive speech requires a carefully crafted argument that will resonate with your audience to sway them to your side. This feat can be challenging to accomplish, but an engaging, thought-provoking speech topic is an excellent place to start.
When it comes time to select a topic for your persuasive speech, you may feel overwhelmed by all the options to choose from—or your brain may be drawing a completely blank slate. If you’re having trouble thinking of the perfect topic, don’t worry. We’re here to help!
In this post, we’re sharing how to choose the perfect persuasive speech topic and tips to prepare for your speech. Plus, you’ll find 112 persuasive speech topics that you can take directly from us or use as creative inspiration for your own ideas!
Choose Something You’re Passionate About
It’s much easier to write, research, and deliver a speech about a cause you care about. Even if it’s challenging to find a topic that completely sparks your interest, try to choose a topic that aligns with your passions.
However, keep in mind that not everyone has the same interests as you. Try to choose a general topic to grab the attention of the majority of your audience, but one that’s specific enough to keep them engaged.
For example, suppose you’re giving a persuasive speech about book censorship. In that case, it’s probably too niche to talk about why “To Kill a Mockingbird” shouldn’t be censored (even if it’s your favorite book), and it’s too broad to talk about media censorship in general.
Steer Clear of Cliches
Have you already heard a persuasive speech topic presented dozens of times? If so, it’s probably not an excellent choice for your speech—even if it’s an issue you’re incredibly passionate about.
Although polarizing topics like abortion and climate control are important to discuss, they aren’t great persuasive speech topics. Most people have already formed an opinion on these topics, which will either cause them to tune out or have a negative impression of your speech.
Instead, choose topics that are fresh, unique, and new. If your audience has never heard your idea presented before, they will be more open to your argument and engaged in your speech.
Have a Clear Side of Opposition
For a persuasive speech to be engaging, there must be a clear side of opposition. To help determine the arguability of your topic, ask yourself: “If I presented my viewpoint on this topic to a group of peers, would someone disagree with me?” If the answer is yes, then you’ve chosen a great topic!
Now that we’ve laid the groundwork for what it takes to choose a great persuasive speech topic, here are over one hundred options for you to choose from.
- Should high school athletes get tested for steroids?
- Should schools be required to have physical education courses?
- Should sports grades in school depend on things like athletic ability?
- What sport should be added to or removed from the Olympics?
- Should college athletes be able to make money off of their merchandise?
- Should sports teams be able to recruit young athletes without a college degree?
- Should we consider video gamers as professional athletes?
- Is cheerleading considered a sport?
- Should parents allow their kids to play contact sports?
- Should professional female athletes be paid the same as professional male athletes?
- Should college be free at the undergraduate level?
- Is the traditional college experience obsolete?
- Should you choose a major based on your interests or your potential salary?
- Should high school students have to meet a required number of service hours before graduating?
- Should teachers earn more or less based on how their students perform on standardized tests?
- Are private high schools more effective than public high schools?
- Should there be a minimum number of attendance days required to graduate?
- Are GPAs harmful or helpful?
- Should schools be required to teach about standardized testing?
- Should Greek Life be banned in the United States?
- Should schools offer science classes explicitly about mental health?
- Should students be able to bring their cell phones to school?
- Should all public restrooms be all-gender?
- Should undocumented immigrants have the same employment and education opportunities as citizens?
- Should everyone be paid a living wage regardless of their employment status?
- Should supremacist groups be able to hold public events?
- Should guns be allowed in public places?
- Should the national drinking age be lowered?
- Should prisoners be allowed to vote?
- Should the government raise or lower the retirement age?
- Should the government be able to control the population?
- Is the death penalty ethical?
Environment
- Should stores charge customers for plastic bags?
- Should breeding animals (dogs, cats, etc.) be illegal?
- Is it okay to have exotic animals as pets?
- Should people be fined for not recycling?
- Should compost bins become mandatory for restaurants?
- Should electric vehicles have their own transportation infrastructure?
- Would heavier fining policies reduce corporations’ emissions?
- Should hunting be encouraged or illegal?
- Should reusable diapers replace disposable diapers?
Science & Technology
- Is paper media more reliable than digital news sources?
- Should automated/self-driving cars be legalized?
- Should schools be required to provide laptops to all students?
- Should software companies be able to have pre-downloaded programs and applications on devices?
- Should drones be allowed in military warfare?
- Should scientists invest more or less money into cancer research?
- Should cloning be illegal?
- Should societies colonize other planets?
- Should there be legal oversight over the development of technology?
Social Media
- Should there be an age limit on social media?
- Should cyberbullying have the same repercussions as in-person bullying?
- Are online relationships as valuable as in-person relationships?
- Does “cancel culture” have a positive or negative impact on societies?
- Are social media platforms reliable information or news sources?
- Should social media be censored?
- Does social media create an unrealistic standard of beauty?
- Is regular social media usage damaging to real-life interactions?
- Is social media distorting democracy?
- How many branches of government should there be?
- Who is the best/worst president of all time?
- How long should judges serve in the U.S. Supreme Court?
- Should a more significant portion of the U.S. budget be contributed towards education?
- Should the government invest in rapid transcontinental transportation infrastructure?
- Should airport screening be more or less stringent?
- Should the electoral college be dismantled?
- Should the U.S. have open borders?
- Should the government spend more or less money on space exploration?
- Should students sing Christmas carols, say the pledge of allegiance, or perform other tangentially religious activities?
- Should nuns and priests become genderless roles?
- Should schools and other public buildings have prayer rooms?
- Should animal sacrifice be legal if it occurs in a religious context?
- Should countries be allowed to impose a national religion on their citizens?
- Should the church be separated from the state?
- Does freedom of religion positively or negatively affect societies?
Parenting & Family
- Is it better to have children at a younger or older age?
- Is it better for children to go to daycare or stay home with their parents?
- Does birth order affect personality?
- Should parents or the school system teach their kids about sex?
- Are family traditions important?
- Should parents smoke or drink around young children?
- Should “spanking” children be illegal?
- Should parents use swear words in front of their children?
- Should parents allow their children to play violent video games?
Entertainment
- Should all actors be paid the same regardless of gender or ethnicity?
- Should all award shows be based on popular vote?
- Who should be responsible for paying taxes on prize money, the game show staff or the contestants?
- Should movies and television shows have ethnicity and gender quotas?
- Should newspapers and magazines move to a completely online format?
- Should streaming services like Netflix and Hulu be free for students?
- Is the movie rating system still effective?
- Should celebrities have more privacy rights?
Arts & Humanities
- Are libraries becoming obsolete?
- Should all schools have mandatory art or music courses in their curriculum?
- Should offensive language be censored from classic literary works?
- Is it ethical for museums to keep indigenous artifacts?
- Should digital designs be considered an art form?
- Should abstract art be considered an art form?
- Is music therapy effective?
- Should tattoos be regarded as “professional dress” for work?
- Should schools place greater emphasis on the arts programs?
- Should euthanasia be allowed in hospitals and other clinical settings?
- Should the government support and implement universal healthcare?
- Would obesity rates lower if the government intervened to make healthy foods more affordable?
- Should teenagers be given access to birth control pills without parental consent?
- Should food allergies be considered a disease?
- Should health insurance cover homeopathic medicine?
- Is using painkillers healthy?
- Should genetically modified foods be banned?
- Should there be a tax on unhealthy foods?
- Should tobacco products be banned from the country?
- Should the birth control pill be free for everyone?
If you need more help brainstorming topics, especially those that are personalized to your interests, you can use CollegeVine’s free AI tutor, Ivy . Ivy can help you come up with original persuasive speech ideas, and she can also help with the rest of your homework, from math to languages.
Do Your Research
A great persuasive speech is supported with plenty of well-researched facts and evidence. So before you begin the writing process, research both sides of the topic you’re presenting in-depth to gain a well-rounded perspective of the topic.
Understand Your Audience
It’s critical to understand your audience to deliver a great persuasive speech. After all, you are trying to convince them that your viewpoint is correct. Before writing your speech, consider the facts and information that your audience may already know, and think about the beliefs and concerns they may have about your topic. Then, address these concerns in your speech, and be mindful to include fresh, new information.
Have Someone Read Your Speech
Once you have finished writing your speech, have someone read it to check for areas of strength and improvement. You can use CollegeVine’s free essay review tool to get feedback on your speech from a peer!
Practice Makes Perfect
After completing your final draft, the key to success is to practice. Present your speech out loud in front of a mirror, your family, friends, and basically, anyone who will listen. Not only will the feedback of others help you to make your speech better, but you’ll become more confident in your presentation skills and may even be able to commit your speech to memory.
Hopefully, these ideas have inspired you to write a powerful, unique persuasive speech. With the perfect topic, plenty of practice, and a boost of self-confidence, we know you’ll impress your audience with a remarkable speech!
Related CollegeVine Blog Posts


Persuasive Speech Example on Love
Why Is Love Not a Gift but a Challenge?
Introduction
When we think about love, we imagine lovely pictures of romantic kisses, exciting adventures, and living happily ever after. Why do we always forget about the other things that stand behind these nice images? Why don’t we remember fights, tears, and broken hearts? The answer is simple – we don’t want to. It is easier to take love as a dream, not reality.
Problem statement
Such unrealistic beliefs are the root of all the conflicts in romantic relationships. We should remember that love is not a blessing or a present of fate. It is a complex and fragile structure built on the foundation of mutual respect, understanding, and trust. And we have to work on our relationships all the time. Otherwise, they won’t last long.
The most important thing that we have to understand is that there is no perfectly compatible partner for every human being. Moreover, most people are totally incompatible. We are too weird for each other. Would you like to meet a person who behaves and thinks exactly like you? If your answer is “yes,” try to recall all the episodes of your life that you regret about or you’re ashamed of. Have you changed your mind? Nobody is perfect, so we have no right to demand perfection from others while we keep making mistakes.
True love is our willingness to be as compatible with our partner as possible. We have to be ready to teach them and to learn from them. That’s one more essential aspect of good relationships. Our partners are the only ones who can honestly tell us about our weaknesses. Parents don’t do that because they love us too much. Our friends don’t do that because they don’t care about our self-development. But when we hear the words of criticism from our loved ones, we take it as an attack.
Remember that our partners don’t want to humiliate us or make fun of us. They simply try to make us into better people.
Another problem that we frequently face in romantic relationships is our partner’s unwillingness to share his or her thoughts and feelings. Let’s imagine a typical situation: your boyfriend or girlfriend is in a bad mood and doesn’t even try to hide this fact. You ask a logical question like, “what’s wrong?” or “is everything okay?” And what do they usually do? Right, they say something meaningless and then start sulking.
The explanation of such irrational behavior is simple: they want to be understood without words. You see, in our imaginary world, true lovers always guess what is on our minds. They don’t need any hints because they love us so much. Nonsense! Of course, they love you. But it doesn’t mean that they can read your thoughts. Your partners are not the parents of a two-year-old child who can’t speak properly. They will do everything to comfort you, but you have to tell them what’s wrong. There is nothing difficult about it.
You see, being loved is easy and delightful. Loving is much more tricky. In truth, loving is a skill that has to be trained. Many people think that loving doesn’t require learning and that we can love someone following our emotions and instincts. That’s so not true.
True love is challenging, hard work. It is teaching and learning. It is your willingness to become a better person for your lover. Love can be a gift, but only a deserved one.
Speech Writing Assistance from EssayShark Essay Writers
We hope that you like this sample, as it’s one of our persuasive speech examples. Our samples help students in situations when they don’t know how to start their own papers. They are written using only reliable and proven sources. Check out persuasive speech topics on our blog to have a clear understanding what aspects to consider in writing. Or use an academic title generator tool to get more ideas for writing.
The worst a student can do without the required writing skills is to struggle with his or her paper. Our site has a team of writers who possess excellent writing skills and know how to deal with different types of papers. You can begin getting our help right after you place an order with your requirements and the deadline. It is important to know that our writer will create a unique paper for you that will meet your expectations. So, the reason for using our paper writing service is significant – you will receive a paper written from scratch. Moreover, each order is completed with an individual approach on our site. It is necessary for us to satisfy all of our customers’ needs, as we want you to come back to us to order more papers.
Stop worrying about your writing problems – we can solve them!
Photo by Stux from Pixabay
- Article review samples
- Bibliography samples
- Biography samples
- Book review samples
- Business paper samples
- Case Study Samples
- Coursework samples
- Critical thinking samples
- Dissertation samples
- Essay samples
- Lab report samples
- Movie review samples
- Poem analysis samples
- Presentation samples
- Research paper samples
- Research proposal samples
- Speech samples
- Summary samples
- Thesis samples
- Uncategorized

Grab our 3 e-books bundle for $27 FREE
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
10 Chapter 10: Persuasive Speaking
Amy Fara Edwards and Marcia Fulkerson, Oxnard College
Victoria Leonard, Lauren Rome, and Tammera Stokes Rice, College of the Canyons
Adapted by Jamie C. Votraw, Professor of Communication Studies, Florida SouthWestern State College
|
|
|
|

Figure 10.1: Abubaccar Tambadou 1
Introduction
The American Society for the Prevention of Cruelty to Animals (ASPCA) was founded on April 10, 1866. You may be familiar with their television commercials. They start with images of neglected and lonely-looking cats and dogs while the screen text says: “Every hour… an animal is beaten or abused. They suffer… alone and terrified…” Cue the sad song and the request for donations on the screen. This commercial causes audiences to run for the television remote because they can’t bear to see those images! Yet it is a very persuasive commercial and has proven to be very successful for this organization. According to the ASPCA website, they have raised $30 million since 2006, and their membership has grown to over 1.2 million people. The audience’s reaction to this commercial showcases how persuasion works! In this chapter, we will define persuasive speaking and examine the strategies used to create powerful persuasive speeches.

Figure 10.2: Caged Dogs 2
Defining Persuasive Speaking
Persuasion is the process of creating, reinforcing, or changing people’s beliefs or actions. It is not manipulation, however! The speaker’s intention should be clear to the audience in an ethical way and accomplished through the ethical use of methods of persuasion. When speaking to persuade, the speaker works as an advocate. In contrast to informative speaking, persuasive speakers argue in support of a position and work to convince the audience to support or do something.
As you learned in chapter five on audience analysis, you must continue to consider the psychological characteristics of the audience. You will discover in this chapter the attitudes, beliefs, and values of the audience become particularly relevant in the persuasive speechmaking process. A key element of persuasion is the speaker’s intent. You must intend to create, reinforce, and/or change people’s beliefs or actions in an ethical way.
Types of Persuasive Speeches
There are three types of persuasive speech propositions. A proposition , or speech claim , is a statement you want your audience to support. To gain the support of our audience, we use evidence and reasoning to support our claims. Persuasive speech propositions fall into one of three categories, including questions of fact, questions of value, and questions of policy. Determining the type of persuasive propositions your speech deals with will help you determine what forms of argument and reasoning are necessary to effectively advocate for your position.
Questions of Fact
A question of fact determines whether something is true or untrue, does or does not exist, or did or did not happen. Questions of fact are based on research, and you may find research that supports competing sides of an argument! You may even find that you change your mind about a subject when researching. Ultimately, you will take a stance and rely on credible evidence to support your position, ethically.
Today there are many hotly contested propositions of fact: humans have walked on the moon, the Earth is flat, Earth’s climate is changing due to human action, we have encountered sentient alien life forms, life exists on Mars, and so on.
Here is an example of a question of fact:
Recreational marijuana does not lead to hard drug use.
Recreational marijuana does lead to hard drug use.
Questions of Value
A question of value determines whether something is good or bad, moral or immoral, just or unjust, fair or unfair. You will have to take a definitive stance on which side you’re arguing. For this proposition, your opinion alone is not enough; you must have evidence and reasoning. An ethical speaker will acknowledge all sides of the argument, and to better argue their point, the speaker will convince the audience why their position is the “best” position.
Here is an example of a question of value:
Recreational marijuana use is immoral .
Recreational marijuana use is moral .
Questions of Policy
A question of policy advances a specific course of action based on facts and values. You are telling the audience what you believe should be done and/or you are asking your audience to act in a particular way to make a change. Whether it is stated or implied, all policy speeches focus on values. To be the most persuasive and get your audience to act, you must determine their beliefs, which will help you organize and argue your proposition.
Persuasive speeches on questions of policy must address three elements: need, plan, and practicality . First, the speaker must demonstrate there is a need for change (i.e., there is a problem). Next, the speaker offers the audience a plan (i.e., the policy solution) to address the problem. Lastly, the speaker shows the audience that the solution is practical . This requires that the speaker demonstrate how their proposed plan will address the identified problem without creating new problems.
Consider the topic of car accidents. A persuasive speech on a question of policy might focus on reducing the number of car accidents on a Florida highway. First, the speaker could use evidence from their research to demonstrate there is a need for change (e.g., statistics showing a higher-than-average rate of accidents). Then, the speaker would offer their plan to address the problem. Imagine their proposed plan was to permanently shut down all Florida highways. Would this plan solve the problem and reduce the number of accidents on Florida highways? Well, yes. But is it practical? No. Will it create new problems? Yes – side roads will be congested, people will miss work, kids will miss school, emergency response teams will be slowed, and tourism will decrease. The speaker could not offer such a plan and demonstrate that it is practical. Alternatively, maybe the speaker advocates for a speed reduction in a particularly problematic stretch of highway or convinces the audience to support increasing the number of highway patrol cars.
Here is an example of a question of policy:
Recreational marijuana use should be legal in all 50 states.
Recreational marijuana use should not be legal in all 50 states.
Persuasive Speech Organizational Patterns
There are several methods of organizing persuasive speeches. Remember, you must use an organizational pattern to outline your speech (think back to chapter eight). Some professors will specify a specific pattern to use for your assignment. Otherwise, the organizational pattern you select should be based on your speech content. What pattern is most logical based on your main points and the goal of your speech? This section will explain five common formats of persuasive outlines: Problem-Solution, Problem-Cause-Solution, Comparative Advantages, Monroe’s Motivated Sequence, and Claim to Proof.
Problem-Solution Pattern
Sometimes it is necessary to share a problem and a solution with an audience. In cases like these, the problem-solution organizational pattern is an appropriate way to arrange the main points of a speech. It’s important to reflect on what is of interest to you, but also what is critical to engage your audience. This pattern is used intentionally because, for most problems in society, the audience is unaware of their severity. Problems can exist at a local, state, national, or global level.
For example, the nation has recently become much more aware of the problem of human sex trafficking. Although the US has been aware of this global issue for some time, many communities are finally learning this problem is occurring in their own backyards. Colleges and universities have become engaged in the fight. Student clubs and organizations are getting involved and bringing awareness to this problem. Everyday citizens are using social media to warn friends and followers of sex-trafficking tricks to look out for.
Let’s look at how you might organize a problem-solution speech centered on this topic. In the body of this speech, there would be two main points; a problem and a solution. This pattern is used for speeches on questions of policy.
Topic: Human Sex Trafficking
General Purpose: To persuade
Specific Purpose: To persuade the audience to support increased legal penalties for sex traffickers.
Thesis (Central Idea): Human sex trafficking is a global challenge with local implications, but it can be addressed through multi-pronged efforts from governments and non-profits.
Preview of Main Points: First, I will define and explain the extent of the problem of sex trafficking within our community while examining the effects this has on the victims. Then, I will offer possible solutions to take the predators off the streets and allow the victims to reclaim their lives and autonomy.
- The problem of human sex trafficking is best understood by looking at the severity of the problem, the methods by which traffickers kidnap or lure their victims, and its impact on the victim.
- The problem of human sex trafficking can be solved by working with local law enforcement, changing the laws currently in place for prosecuting the traffickers and pimps, and raising funds to help agencies rescue and restore victims.
Problem-Cause-Solution Pattern
To review the problem-solution pattern, recall that the main points do not explain the cause of the problem, and in some cases, the cause is not necessary to explain. For example, in discussing the problem of teenage pregnancy, most audiences will not need to be informed about what causes someone to get pregnant. However, there are topics where discussing the cause is imperative to understanding the solution. The Problem-Cause-Solution organizational pattern adds a main point between the problem and solution by discussing the cause of the problem. In the body of the speech, there will be three main points: the problem, the cause, and finally, the solution. This pattern is also used for speeches dealing with questions of policy. One of the reasons you might consider this pattern is when an audience is not familiar with the cause. For example, if gang activity is on the rise in the community you live in, you might need to explain what causes an individual to join a gang in the first place. By explaining the causes of a problem, an audience might be more likely to accept the solution(s) you’ve proposed. Let’s look at an example of a speech on gangs.
Topic: The Rise of Gangs in Miami-Dade County
Specific Purpose: To persuade the audience to urge their school boards to include gang education in the curriculum.
Thesis (Central Idea): The uptick in gang affiliation and gang violence in Miami-Dade County is problematic, but if we explore the causes of the problem, we can make headway toward solutions.
Preview of Main Points: First, I will explain the growing problem of gang affiliation and violence in Miami-Dade County. Then, I will discuss what causes an individual to join a gang. Finally, I will offer possible solutions to curtail this problem and get gangs off the streets of our community.
- The problem of gang affiliation and violence is growing rapidly, leading to tragic consequences for both gang members and their families.
- The causes of the proliferation of gangs can be best explained by feeling disconnected from others, a need to fit in, and a lack of supervision after school hours.
- The problem of the rise in gangs can be solved, or minimized, by offering after-school programs for youth, education about the consequences of joining a gang, and parent education programs offered at all secondary education levels.
Let’s revisit the human sex trafficking topic from above. Instead of using only a problem-solution pattern, the example that follows adds “cause” to their main points.
Preview of Main Points: First, I will define and explain the extent of the problem of sex trafficking within our community while examining the effects this has on the victims. Second, I will discuss the main causes of the problem. Finally, I will offer possible solutions to take the predators off the streets and allow the victims to reclaim their lives.
- The cause of the problem can be recognized by the monetary value of sex slavery.
- The problem of human sex trafficking can be solved by working with local law enforcement, changing the current laws for prosecuting traffickers, and raising funds to help agencies rescue and restore victims.
Comparative Advantages
Sometimes your speech will showcase a problem, but there are multiple potential solutions for the audience to consider. In cases like these, the comparative advantages organizational pattern is an appropriate way to structure the speech. This pattern is commonly used when there is a problem, but the audience (or the public) cannot agree on the best solution. When your goal is to convince the audience that your solution is the best among the options, this organizational pattern should be used.
Consider the hot topic of student loan debt cancellation. There is a rather large divide among the public about whether or not student loans should be canceled or forgiven by the federal government. Once again, audience factors come into play as attitudes and values on the topic vary greatly across various political ideologies, age demographics, socioeconomic statuses, educational levels, and more.
Let’s look at how you might organize a speech on this topic. In the body of this speech, one main point is the problem, and the other main points will depend on the number of possible solutions.
Topic: Federal Student Loan Debt Cancellation
Specific Purpose: To persuade the audience to support the government cancellation of $10,000 in federal student loan debt.
Thesis (Central Idea): Student loans are the largest financial hurdle faced by multiple generations, and debt cancellation could provide needed relief to struggling individuals and families.
Preview of Main Points: First, I will define and explain the extent of the student loan debt problem in the United States. Then, I will offer possible solutions and convince you that the best solution is a debt cancellation of $10,000.
- Student loan debt is the second greatest source of financial debt in the United States and several solutions have been proposed to address the problem created by unusually high levels of educational debt.
- The first proposed solution is no debt cancellation. This policy solution would not address the problem.
- The second proposed solution is $10,000 of debt cancellation. This is a moderate cancellation that would alleviate some of the financial burden faced by low-income and middle-class citizens without creating vast government setbacks.
- The third proposed solution is full debt cancellation. While this would help many individuals, the financial setback for the nation would be too grave.
- As you can see, there are many options for addressing the student loan debt problem. However, the best solution is the cancellation of $10,000.
Monroe’s Motivated Sequence Format
Alan H. Monroe, a Purdue University professor, used the psychology of persuasion to develop an outline for making speeches that will deliver results and wrote about it in his book Monroe’s Principles of Speech (1951). It is now known as Monroe’s Motivated Sequence . This is a well-used and time-proven method to organize persuasive speeches for maximum impact. It is most often used for speeches dealing with questions of policy. You can use it for various situations to create and arrange the components of any persuasive message. The five steps are explained below and should be followed explicitly and in order to have the greatest impact on the audience.
Step One: Attention
In this step, you must get the attention of the audience. The speaker brings attention to the importance of the topic as well as their own credibility and connection to the topic. This step of the sequence should be completed in your introduction like in other speeches you have delivered in class. Review chapter 9 for some commonly used attention-grabber strategies.
Step Two: Need
In this step, you will establish the need; you must define the problem and build a case for its importance. Later in this chapter, you will find that audiences seek logic in their arguments, so the speaker should address the underlying causes and the external effects of a problem. It is important to make the audience see the severity of the problem, and how it affects them, their families, and/or their community. The harm , or problem that needs changing, can be physical, financial, psychological, legal, emotional, educational, social, or a combination thereof. It must be supported by evidence. Ultimately, in this step, you outline and showcase that there is a true problem that needs the audience’s immediate attention. For example, it is not enough to say “pollution is a problem in Florida,” you must demonstrate it with evidence that showcases that pollution is a problem. For example, agricultural runoff is said to cause dangerous algal blooms on Florida’s beaches. You could show this to your audience with research reports, pictures, expert testimony, etc.
Step Three: Satisfaction
In this step, the need must be “satisfied” with a solution. As the speaker, this is when you present the solution and describe it, but you must also defend that it works and will address the causes and symptoms of the problem. Do you recall “need, plan, and practicality”? This step involves the plan and practicality elements. This is not the section where you provide specific steps for the audience to follow. Rather, this is the section where you describe “the business” of the solution. For example, you might want to change the voting age in the United States. You would not explain how to do it here; you would explain the plan – what the new law would be – and its practicality – how that new law satisfies the problem of people not voting. Satisfy the need!
Step Four: Visualization
In this step, your arguments must look to the future either positively or negatively, or both. If positive, the benefits of enacting or choosing your proposed solution are explained. If negative, the disadvantages of not doing anything to solve the problem are explained. The purpose of visualization is to motivate the audience by revealing future benefits or using possible fear appeals by showing future harms if no changes are enacted. Ultimately, the audience must visualize a world where your solution solves the problem. What does this new world look like? If you can help the audience picture their role in this new world, you should be able to get them to act. Describe a future where they fail to act, and the problem persists or is exacerbated. Or, help them visualize a world where their adherence to the steps you outlined in your speech remediates the problem.
Step Five: Action
In the final step of Monroe’s Motivated Sequence, we tell the audience exactly what needs to be done by them . Not a general “we should lower the voting age” statement, but rather, the exact steps for the people sitting in front of you to take. If you really want to move the audience to action, this step should be a full main point within the body of the speech and should outline exactly what you need them to do. It isn’t enough to say “now, go vote!” You need to tell them where to click, who to write, how much to donate, and how to share the information with others in their orbit. In the action step, the goal is to give specific steps for the audience to take, as soon as possible, to move toward solving the problem. So, while the satisfaction step explains the solution overall, the action section gives concrete ways to begin making the solution happen. The more straightforward and concrete you can make the action step, the better. People are more likely to act if they know how accessible the action can be. For example, if you want your audience to be vaccinated against the hepatitis B virus (HBV), you can give them directions to a clinic where vaccinations are offered and the hours of that location. Do not leave anything to chance. Tell them what to do. If you have effectively convinced them of the need/problem, you will get them to act, which is your overall goal.
Claim-to-Proof Pattern
A claim-to-proof pattern provides the audience with reasons to accept your speech proposition (Mudd & Sillars, 1962). State your claim (your thesis) and then prove your point with reasons (main points). The proposition is presented at the beginning of the speech, and in the preview, tells the audience how many reasons will be provided for the claim. Do not reveal too much information until you get to that point in your speech. We all hear stories on the news about someone killed by a handgun, but it is not every day that it affects us directly, or that we know someone who is affected by it. One student told a story of a cousin who was killed in a drive-by shooting, and he was not even a member of a gang.
Here is how the setup for this speech would look:
Thesis and Policy Claim: Handgun ownership in America continues to be a controversial subject, and I believe that private ownership of handguns should have limitations.
Preview: I will provide three reasons why handgun ownership should be limited.
When presenting the reasons for accepting the claim, it is important to consider the use of primacy-recency . If the audience is against your claim, put your most important argument first. For this example, the audience believes in no background checks for gun ownership. As a result, this is how the main points may be written to try and capture the audience who disagrees with your position. We want to get their attention quickly and hold it throughout the speech. You will also need to support these main points. Here is an example:
- The first reason background checks should be mandatory is that when firearms are too easily accessed by criminals, more gun violence occurs.
- A second reason why background checks should be mandatory is that they would lower firearm trafficking.
Moving forward, the speaker would select one or two other reasons to bring into the speech and support them with evidence. The decision on how many main points to have will depend on how much time you have for this speech, and how much research you can find on the topic. If this is a pattern your instructor allows, speak with them about sample outlines. This pattern can be used for fact, value, or policy speeches.
Methods of Persuasion
The three methods of persuasion were first identified by Aristotle, a Greek philosopher in the time of Ancient Greece. In his teachings and book, Rhetoric, he advised that a speaker could persuade their audience using three different methods: Ethos (persuasion through credibility), Pathos (persuasion through emotion), and Logos (persuasion through logic). In fact, he said these are the three methods of persuasion a speaker must rely on.

Figure 10.3: Aristotle 3
By definition, ethos is the influence of a speaker’s credibility, which includes character, competence, and charisma. Remember in earlier chapters when we learned about credibility? Well, it plays a role here, too. The more credible or believable you are, the stronger your ethos. If you can make an audience see you believe in what you say and have knowledge about what you say, they are more likely to believe you and, therefore, be more persuaded by you. If your arguments are made based on credibility and expertise, then you may be able to change someone’s mind or move them to action. Let’s look at some examples.
If you are considering joining the U.S. Air Force, do you think someone in a military uniform would be more persuasive than someone who was not in uniform? Do you think a firefighter in uniform could get you to make your house more fire-safe than someone who was not in uniform? Their uniform contributes to their ethos. Remember, credibility comes from audience perceptions – how they perceive you as the speaker. You may automatically know they understand fire safety without even opening their mouths to speak. If their arguments are as strong as the uniform, you may have already started putting your fire emergency kit together! Ultimately, we tend to believe in people in powerful positions. We often obey authority figures because that’s what we have been taught to do. In this case, it works to help us persuade an audience.
Advertising campaigns also use ethos well. Think about how many celebrities sell you products. Whose faces do you regularly see? Taylor Swift, Kerry Washington, Kylie Jenner, Jennifer Aniston? Do they pick better cosmetics than the average woman, or are they using their celebrity influence to persuade you to buy? If you walk into a store to purchase makeup and remember which ones are Kylie Jenner’s favorite makeup, are you more likely to purchase it? Pop culture has power, which is why you see so many celebrities selling products on social media. Now, Kylie may not want to join you in class for your speech (sorry!), so you will have to be creative with ethos and incorporate experts through your research and evidence. For example, you need to cite sources if you want people to get a flu shot, using a doctor’s opinion or a nurse’s opinion is critical to get people to make an appointment to get the shot. You might notice that even your doctor shares data from research when discussing your healthcare. Similarly, y ou have to be credible. You need to become an authority on your topic, show them the evidence, and persuade them using your character and charisma.
Finally, ethos also relates to ethics. The audience needs to trust you and your speech needs to be truthful. Most importantly, this means ethical persuasion occurs through ethical methods – you should not trick your audience into agreeing with you. It also means your own personal involvement is important and the topic should be something you are either personally connected to or passionate about. For example, if you ask the audience to adopt a puppy from a rescue, will your ethos be strong if you bought your puppy from a pet store or breeder? How about asking your audience to donate to a charity; have you supported them yourself? Will the audience want to donate if you haven’t ever donated? How will you prove your support? Think about your own role in the speech while you are also thinking about the evidence you provide.
The second appeal you should include in your speech is pathos , an emotional appeal . By definition, pathos appeals evoke strong feelings or emotions like anger, joy, desire, and love. The goal of pathos is to get people to feel something and, therefore, be moved to change their minds or to act. You want your arguments to arouse empathy, sympathy, and/or compassion. So, for persuasive speeches, you can use emotional visual aids or thoughtful stories to get the audience’s attention and hook them in. If you want someone to donate to a local women’s shelter organization to help the women further their education at the local community college, you might share a real story of a woman you met who stayed at the local shelter before earning her degree with the help of the organization. We see a lot of advertisement campaigns rely on this. They show injured military veterans to get you to donate to the Wounded Warriors Project , or they show you injured animals to get you to donate to animal shelters. Are you thinking about how your own topic is emotional yet? We hope so!
In addition, we all know that emotions are complex. So, you can’t just tell a sad story or yell out a bad word to shock them and think they will be persuaded. You must ensure the emotions you engage relate directly to the speech and the audience. Be aware that negative emotions can backfire, so make sure you understand the audience, so you will know what will work best. Don’t just yell at people that they need to brush their teeth for two minutes or show a picture of gross teeth; make them see the benefits of brushing for two minutes by showing beautiful teeth too.
Emotional appeals also need to be ethical and incorporated responsibly. Consider a persuasive speech on distracted driving. If your audience is high school or college students, they may be mature enough to see an emotional video or photo depicting the devastating consequences of distracted driving. If you’re teaching an elementary school class about car safety (e.g., keeping your seatbelt on, not throwing toys, etc.), it would be highly inappropriate to scare them into compliance by showing a devastating video of a car accident. As an ethical public speaker, it is your job to use emotional appeals responsibly.
One way to do this is to connect to the theory by Abraham Maslow, Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs, which states that our actions are motivated by basic (physiological and safety), psychological (belongingness, love, and esteem), and self-fulfillment needs (self-actualization). To persuade, we have to connect what we say to the audience’s real lives. Here is a visual of Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs Pyramid:
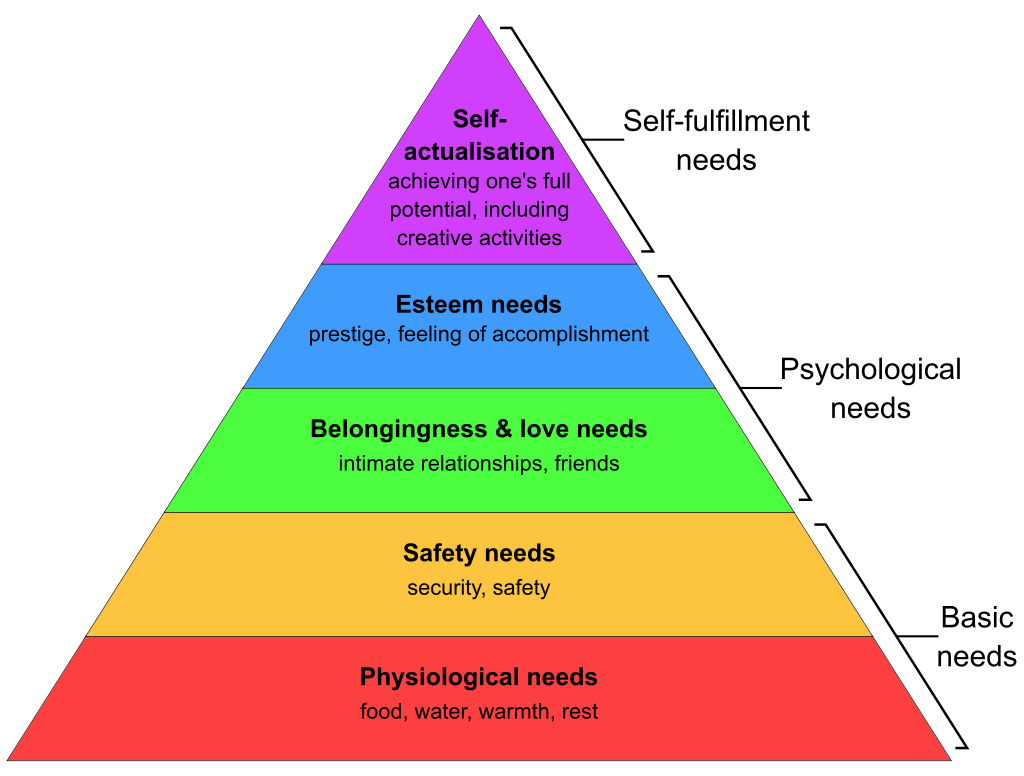
Figure 10.4: Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs 4
Notice the pyramid is largest at the base because our basic needs are the first that must be met. Ever been so hungry you can’t think of anything except when and what you will eat? (Hangry anyone?) Well, you can’t easily persuade people if they are only thinking about food. It doesn’t mean you need to bring snacks to your speech class on the day of your speech (albeit, this might be relevant to a food demonstration speech). Can you think about other ways pathos connects to this pyramid? How about safety and security needs, the second level on the hierarchy? Maybe your speech is about persuading people to purchase more car insurance. You might argue they need more insurance so they can feel safer on the road. Or maybe your family should put in a camera doorbell to make sure the home is safe. Are you seeing how we can use arguments that connect to emotions and needs simultaneously?
The third level in Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs, love and belongingness, is about the need to feel connected to others. This need level is related to the groups of people we spend time with like friends and family. This also relates to the feeling of being “left out” or isolated from others. If we can use arguments that connect us to other humans, emotionally or physically, we will appeal to more of the audience. If your topic is about becoming more involved in the church or temple, you might highlight the social groups one may join if they connect to the church or temple. If your topic is on trying to persuade people to do a walk for charity, you might showcase how doing the event with your friends and family becomes a way of raising money for the charity and carving out time with, or supporting, the people you love. For this need, your pathos will be focused on connection. You want your audience to feel like they belong in order for them to be persuaded. People are more likely to follow through on their commitments if their friends and family do it. We know that if our friends go to the party, we are more likely to go, so we don’t have FOMO (fear of missing out). The same is true for donating money; if your friends have donated to a charity, you might want to be “in” the group, so you would donate also.
Finally, we will end this pathos section with an example that connects Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs to pathos. Maybe your speech is to convince people to remove the Instagram app from their phones, so they are less distracted from their life. You could argue staying away from social media means you won’t be threatened online (safety), you will spend more real-time with your friends (belongingness), and you will devote more time to writing your speech outlines (esteem and achievement). Therefore, you can use Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs as a roadmap for finding key needs that relate to your proposition which helps you incorporate emotional appeals.
The third and final appeal Aristotle described is logos , which, by definition, is the use of logical and organized arguments that stem from credible evidence supporting your proposition. When the arguments in your speech are based on logic, you are utilizing logos. You need experts in your corner to persuade; you need to provide true, raw evidence for someone to be convinced. You can’t just tell them something is good or bad for them, you have to show it through logic. You might like to buy that product, but how much does it cost? When you provide the dollar amount, you provide some logos for someone to decide if they can and want to purchase that product. How much should I donate to that charity? Provide a dollar amount reasonable for the given audience, and you will more likely persuade them. If you asked a room full of students to donate $500.00 to a charity, it isn’t logical. If you asked them to donate $10.00 instead of buying lattes for two days, you might actually persuade them.
So, it is obvious that sources are a part of logos, but so is your own honest involvement with the topics. If you want people to vote, you need to prove voting matters and make logical appeals to vote. We all know many people say, “my vote doesn’t count.” Your speech needs to logically prove that all votes count, and you need to showcase that you always vote in the local and national elections. In this example, we bring together your ethos and your pathos to sell us on the logos. All three appeals together help you make your case. Audiences are not only persuaded by experts, or by emotions, they want it all to make sense! Don’t make up a story to “make it fit”. Instead, find a real story that is truthful, emotional, and one your audience can relate to make your speech logical from beginning to end and, therefore, persuasive.
Reasoning and Fallacies in Your Speech
In this chapter, we have provided you with several important concepts in the persuasive speech process, including patterns of organization and methods of persuasion. Now, we want to make sure your speech content is clear and includes strong and appropriate arguments. You have done extensive research to support the claims you will make in your speech, but we want to help you ensure that your arguments aren’t flawed. Thus, we will now look at different forms of reasoning and fallacies (or errors) to avoid in your logic.
Thus far, you have read how Aristotle’s proofs can and should be used in a persuasive speech. But, you might wonder how that influences the approach you take in writing your speech outline. You already know your research needs to be credible, and one way to do this is through research. Let’s now put this all together by explaining how reasoning is used in a speech, as well as the fallacies, or errors in reasoning, that often occur when speechwriting.
You may have seen graduation requirements include the category of critical thinking, which is the ability to think about what information you are given and make sense of it to draw conclusions. Today, colleges, universities, and employers are seeking individuals who have these critical thinking skills. Critical thinking can include abilities like problem-solving or decision-making. How did you decide on which college to start your higher educational journey? Was it a decision based on finances, being close to home, or work? This decision involved critical thinking. Even if you had an emotional investment in this decision (pathos), you still needed to use logic, or logos, in your thought process. Reasoning is the process of constructing arguments in a logical way. The use of evidence, also known as data , is what we use to prove our claims. We have two basic and important approaches for how we come to believe something is true. These are known as induction and deduction. Let us explain.
Inductive Reasoning
You have probably used inductive reasoning in your life without even knowing it! Inductive reasoning is a type of reasoning in which examples or specific instances are used to provide strong evidence for (though not absolute proof of) the truth of the conclusion (Garcia, 2022). In other words, you are led to a conclusion through your “proof”. With inductive reasoning, we are exposed to several different examples of a situation, and from those examples, we conclude a general truth because there is no theory to test. Think of it this way: you first make an observation, then, observe a pattern, and finally, develop a theory or general conclusion.
For instance, you visit your local grocery store daily to pick up necessary items. You notice that on Sunday, two weeks ago, all the clerks in the store were wearing football jerseys. Again, last Sunday, the clerks wore their football jerseys. Today, also a Sunday, they’re wearing them again. From just these three observations, you may conclude that on Sundays, these supermarket employees wear football jerseys to support their favorite teams. Can you conclude that this pattern holds indefinitely? Perhaps not; the phenomenon may only take place during football season. Hypotheses typically need much testing before confirmation. However, it seems likely that if you return next Sunday wearing a football jersey, you will fit right in.
In another example, imagine you ate an avocado, and soon afterward, the inside of your mouth swelled. Now imagine a few weeks later you ate another avocado and again the inside of your mouth swelled. The following month, you ate yet another avocado, and you had the same reaction as the last two times. You are aware that swelling on the inside of your mouth can be a sign of an allergy to avocados. Using induction, you conclude, more likely than not, you are allergic to avocados.
Data (evidence): After I ate an avocado, the inside of my mouth was swollen (1st time).
Data (evidence): After I ate an avocado, the inside of my mouth was swollen (2nd time).
Data (evidence): I ate an avocado, and the inside of my mouth was swollen (3rd time).
Additional Information: Swollen lips can be a sign of a food allergy.
Conclusion: Likely, I am allergic to avocados.
Inductive reasoning can never lead to absolute certainty. Instead, induction allows you to say, given the examples provided for support, the conclusion is most likely true. Because of the limitations of inductive reasoning, a conclusion will be more credible if multiple lines of reasoning are presented in its support. This is how inductive reasoning works. Now, let’s examine four common methods of inductive reasoning to help you think critically about your persuasive speech.
An analogy allows you to draw conclusions about an object or phenomenon based on similarities to something else (Garcia, 2022). Sometimes the easiest way to understand reasoning is to start with a simple analogy. An avid DIY enthusiast may love to paint -walls, furniture, and objects. To paint well, you need to think about what materials you will need, a knowledge of the specific steps to paint, and the knowledge of how to use an approach to painting so that your paint doesn’t run and your project comes out perfectly! Let’s examine how this example works as an analogy.
Analogies can be figurative or literal. A figurative analogy compares two things that share a common feature, but are still different in many ways. For example, we could say that painting is like baking; they both involve making sure that you have the correct supplies and follow a specific procedure. There are similarities in these features, but there are profound differences. However, a literal analogy is where the two things under comparison have sufficient or significant similarities to be compared fairly (Garcia, 2022). A literal analogy might compare different modalities at the school where your authors teach. If we claim that you should choose Florida SouthWestern State College’s face-to-face courses rather than enrolling in online courses , we could make literal comparisons of the courses offered, available student services, or the classroom atmosphere, for instance.
If we use the more literal analogy of where you choose to go to college, we are using an analogy of two similar “things,” and hopefully, this makes your analogy carry more weight. What this form of reasoning does is lead your audience to a conclusion. When we address fallacies later in this chapter, you will see that comparing two things that are not similar enough could lead you might make an error, or what we call a false analogy fallacy.
Generalization
Another effective form of reasoning is through the use of generalizations. Generalization is a form of inductive reasoning that draws conclusions based on recurring patterns or repeated observations (Garcia, 2022), observing multiple examples and looking for commonalities in those examples to make a broad statement about them. For example, if I tried four different types of keto bread (the new craze), and found that each of them tasted like Styrofoam , I could generalize and say all keto bread is NOT tasty! Or, if in your college experience, you had two professors that you perceived as “bad professors,” you might take a big leap and say that all professors at your campus are “bad.” As you will see later in the discussion on fallacies, this type of reasoning can get us into trouble if we draw a conclusion without sufficient evidence, also known as a hasty generalization. Have you ever drawn a conclusion about a person or group of people after only one or two experiences with them? Have you ever decided you disliked a pizza place because you didn’t like the pizza the first time you tried it? Sometimes, we even do this in our real lives.
Causal Reasoning
Causal reasoning is a form of inductive reasoning that seeks to make cause-effect connections (Garcia, 2022). We don’t typically give this a lot of thought. In the city where one of your authors lives, there are periodic street closures with cones up or signs to redirect drivers. The past several times this has happened, it has been because there was a community 5K run. It is easy to understand why each time I see cones I assume there is a 5K event. However, there could be a completely different cause that I didn’t even think about. The cones could be there due to a major accident or road work.
Reasoning from Sign
Reasoning from sign is a form of inductive reasoning in which conclusions are drawn about phenomena based on events that precede or co-exist with (but do not cause) a subsequent event (Garcia, 2022). In Southern California, a part of the country with some of the worst droughts, one may successfully predict when summer is coming. The lawn begins to die, and the beautiful gardens go limp. All of this occurs before the temperature reaches 113 degrees and before the calendar changes from spring to summer. Based on this observation, there are signs that summer has arrived.
Like many forms of reasoning, it is easy to confuse “reasoning from sign” with “causal reasoning.” Remember, that for this form of reasoning, we looked at an event that preceded another, or co-existed, not an event that occurred later. IF the weather turned to 113 degrees, and then the grass and flowers began to die, then it could be causal.
Deductive Reasoning
The second type of reasoning is known as deductive reasoning , or deduction, which is a conclusion based on the combination of multiple premises that are generally assumed to be true (Garcia, 2022). Whereas with inductive reasoning, we were led to a conclusion, deductive reasoning starts with the overall statement and then identifies examples that support it to reach the conclusion.
Deductive reasoning is built on two statements whose logical relationship should lead to a third statement that is an unquestionably correct conclusion, as in the following example:
Grocery store employees wear football jerseys on Sundays.
Today is Sunday.
Grocery store employees will be wearing football jerseys today.
Suppose the first statement is true (Grocery store employees wear football jerseys on Sundays) and the second statement is true (Today is Sunday). In that case, the conclusion (Grocery store employees will be wearing football jerseys today) is reasonably expected. If a group must have a certain quality, and an individual is a member of that group, then the individual must have that quality.
Unlike inductive reasoning, deductive reasoning allows for certainty as long as certain rules are followed.
Fallacies in Reasoning
As you might recall from our discussion, we alluded to several fallacies. Fallacies are errors in reasoning logic or making a mistake when constructing an inductive or deductive argument. There are dozens of fallacies we could discuss here, but we will highlight those we find to be the most common. Our goal is to help you think through the process of writing your persuasive speech so that it is based on sound reasoning with no fallacies in your arguments.
Table 10.1 describes fifteen fallacies that can be avoided once you understand how to identify them.
Table 10.1: Fallacies
|
|
|
|
|
| Criticizing the person (such as their character or some other attribute) rather than the issue, assumption, or point of view. | “I could never vote for Donald Trump. His hair looks ridiculous.” “I could never vote for Joe Biden. He’s in his 70’s.” |
|
| This occurs when we assert that something is superior because it is new. | “The latest iPhone update is better than any other because it now allows face recognition while wearing a mask.” |
|
| When we try to legitimize a position based on tradition alone; it’s always been done this way. | “Public speaking is only proper when a student is at a lectern in a classroom.” |
|
| Asserting that an argument should be accepted because it is popular and done by others. | “You should buy stock in because the stock prices have soared since the pandemic, and everyone is jumping in!” |
|
| Assuming a conclusion in a premise (saying the same thing twice as both the premise and the conclusion). The argument begins with a claim the speaker is trying to conclude with. | “Of course the use of performance enhancing drugs in sports should be illegal! After all, it’s against the law!” |
|
| Provides only two alternatives when more exist. | “We better eliminate the Social Security system in the United States or our country will go broke.” |
|
| States that since an argument has one thing in common, they will have everything in common. | “As a student, I should be able to look at my notes when I take exams. After all, my doctor looks at his notes about me every time I go into the office. He isn’t expected to memorize my chart!” |
|
| A fallacy that mistakenly assumes that one event causes another, when in fact there are many possible causes. | “I went out of the house for a walk on my street and didn’t wear my mask, so I contracted COVID-19.” (Maybe you contracted COVID-19 from exposure at a birthday party last week). |
|
| Appealing to a rather small sample or unrepresentative number of cases to prove a larger issue. | “So far, I’ve met three British people in England, and they all were nice to me, so all people in the U.K. are nice.” |
|
| Occurs when a conclusion does not follow logically from a premise. | “It’s time to get my nails done. I wonder if my hairstylist is available next week.” “My washing machine is making noise. I better take my car to the shop soon.” |
|
| Introduces irrelevant material into a discussion so that attention is diverted from the real issue; changing the subject or giving an irrelevant response to distract. | Mom: “You got home really late last night.” You: “Did I tell you I’m getting an A in math?” “How can I support the President’s sanctions against Russia if I don’t like his healthcare policy?” |
|
| Assumes consequences for which there is no evidence they will follow an earlier (harmful) act. | “All types of killing, like premeditated murder, or manslaughter, will become legal if we legalize physician-assisted suicide in all states.” “If we decrease the school budget, all the teachers will quit and our kids won’t be able to go to school.” |
|
| Misrepresents a position so that it can more easily be attacked; distorts the opponent’s argument so that no one could agree with it. | “People who are not in favor of eliminating aerosol sprays think it’s okay to destroy the environment.” |
|
| Assuming that a generalization about a class of things/people necessarily applies to everything/person as if there are no exceptions (like stereotyping). | “Oh, you’re a student. You just want to party all the time and don’t want to work hard.” “I heard you were a football player. Football players never try hard in school.” |
|
| Argues that it is okay to do something wrong if someone else did something wrong first. | Julia defends the lie she told her school by saying, “Well, you lied last month when you said you were home with the flu.” |
In this chapter, you can feel confident that you have learned what you need to know to complete an effective persuasive speech. We have defined persuasion, explained speech propositions and patterns, and offered strategies to persuade, including ways to use logic. We also helped you learn more about inductive and deductive reasoning, and all of the various ways these methods help you construct your speeches. Finally, we provided you with the most common fallacies that could trip you up if you aren’t careful. The goal is to be clear, logical, and persuasive! Motivate your audience. Hey, have you been persuaded to start your speech outline yet? We hope so!
Reflection Questions
- What is the difference between propositions of fact, value, and policy?
- How will you determine which pattern of organization to use for your persuasive speech?
- How might you use ethos, pathos, and logos effectively in your speech? How can you write these three proofs into your content?
- What form(s) of reasoning will you use in your speech? How can you ensure you are not using any fallacies?
Appeal to Novelty
Appeal to Tradition
Circular Reasoning
Claim-to-Proof
Critical Thinking
Emotional Appeal
False Analogy
False Cause
Figurative Analogy
Hasty Generalization
Literal Analogy
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs
Monroe’s Motivated Sequence
Non-Sequitur
Primacy-recency
Problem-Cause-Solution
Problem-Solution
Proposition
Question of Fact
Question of Policy
Question of Value
Red Herring
Slippery Slope
Sweeping Generalization
Two Wrongs Make a Right
Garcia, A. R. (2022). Inductive and Deductive Reasoning. Retrieved May 5, 2022, from https://englishcomposition.org/advanced-writing/inductive-and-deductive-reasoning/.
Monroe, A. H. (1949). Principles and types of speech . Glenview, IL: Scott, Foresman and Company.
Mudd, C. S. & Sillars, M.O. (1962), Speech; content and communication. San Francisco, CA: Chandler Publishing Company.
Introduction to Public Speaking Copyright © by Jamie C. Votraw, M.A.; Katharine O'Connor, Ph.D.; and William F. Kelvin, Ph.D. is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
How to Write and Structure a Persuasive Speech
- Homework Tips
- Learning Styles & Skills
- Study Methods
- Time Management
- Private School
- College Admissions
- College Life
- Graduate School
- Business School
- Distance Learning
- M.Ed., Education Administration, University of Georgia
- B.A., History, Armstrong State University
The purpose of a persuasive speech is to convince your audience to agree with an idea or opinion that you present. First, you'll need to choose a side on a controversial topic, then you will write a speech to explain your position, and convince the audience to agree with you.
You can produce an effective persuasive speech if you structure your argument as a solution to a problem. Your first job as a speaker is to convince your audience that a particular problem is important to them, and then you must convince them that you have the solution to make things better.
Note: You don't have to address a real problem. Any need can work as the problem. For example, you could consider the lack of a pet, the need to wash one's hands, or the need to pick a particular sport to play as the "problem."
As an example, let's imagine that you have chosen "Getting Up Early" as your persuasion topic. Your goal will be to persuade classmates to get themselves out of bed an hour earlier every morning. In this instance, the problem could be summed up as "morning chaos."
A standard speech format has an introduction with a great hook statement, three main points, and a summary. Your persuasive speech will be a tailored version of this format.
Before you write the text of your speech, you should sketch an outline that includes your hook statement and three main points.
Writing the Text
The introduction of your speech must be compelling because your audience will make up their minds within a few minutes whether or not they are interested in your topic.
Before you write the full body you should come up with a greeting. Your greeting can be as simple as "Good morning everyone. My name is Frank."
After your greeting, you will offer a hook to capture attention. A hook sentence for the "morning chaos" speech could be a question:
- How many times have you been late for school?
- Does your day begin with shouts and arguments?
- Have you ever missed the bus?
Or your hook could be a statistic or surprising statement:
- More than 50 percent of high school students skip breakfast because they just don't have time to eat.
- Tardy kids drop out of school more often than punctual kids.
Once you have the attention of your audience, follow through to define the topic/problem and introduce your solution. Here's an example of what you might have so far:
Good afternoon, class. Some of you know me, but some of you may not. My name is Frank Godfrey, and I have a question for you. Does your day begin with shouts and arguments? Do you go to school in a bad mood because you've been yelled at, or because you argued with your parent? The chaos you experience in the morning can bring you down and affect your performance at school.
Add the solution:
You can improve your mood and your school performance by adding more time to your morning schedule. You can accomplish this by setting your alarm clock to go off one hour earlier.
Your next task will be to write the body, which will contain the three main points you've come up with to argue your position. Each point will be followed by supporting evidence or anecdotes, and each body paragraph will need to end with a transition statement that leads to the next segment. Here is a sample of three main statements:
- Bad moods caused by morning chaos will affect your workday performance.
- If you skip breakfast to buy time, you're making a harmful health decision.
- (Ending on a cheerful note) You'll enjoy a boost to your self-esteem when you reduce the morning chaos.
After you write three body paragraphs with strong transition statements that make your speech flow, you are ready to work on your summary.
Your summary will re-emphasize your argument and restate your points in slightly different language. This can be a little tricky. You don't want to sound repetitive but will need to repeat what you have said. Find a way to reword the same main points.
Finally, you must make sure to write a clear final sentence or passage to keep yourself from stammering at the end or fading off in an awkward moment. A few examples of graceful exits:
- We all like to sleep. It's hard to get up some mornings, but rest assured that the reward is well worth the effort.
- If you follow these guidelines and make the effort to get up a little bit earlier every day, you'll reap rewards in your home life and on your report card.
Tips for Writing Your Speech
- Don't be confrontational in your argument. You don't need to put down the other side; just convince your audience that your position is correct by using positive assertions.
- Use simple statistics. Don't overwhelm your audience with confusing numbers.
- Don't complicate your speech by going outside the standard "three points" format. While it might seem simplistic, it is a tried and true method for presenting to an audience who is listening as opposed to reading.
- 100 Persuasive Speech Topics for Students
- 5 Tips on How to Write a Speech Essay
- Controversial Speech Topics
- How to Write a Graduation Speech as Valedictorian
- How to Give an Impromptu Speech
- 10 Tips for the SAT Essay
- Basic Tips for Memorizing Speeches, Skits, and Plays
- Mock Election Ideas For Students
- 50 Topics for Impromptu Student Speeches
- How to Write an Interesting Biography
- The Difference Between Liberals and Conservatives
- How to Run for Student Council
- Tips to Write a Great Letter to the Editor
- How to Write a Film Review
- Writing the Parts of a Stage Play Script
- 18 Ways to Practice Spelling Words
Chapter 11: Informative and Persuasive Speaking
11.2 persuasive speaking, learning objectives.
- Explain how claims, evidence, and warrants function to create an argument.
- Identify strategies for choosing a persuasive speech topic.
- Identify strategies for adapting a persuasive speech based on an audience’s orientation to the proposition.
- Distinguish among propositions of fact, value, and policy.
- Choose an organizational pattern that is fitting for a persuasive speech topic.
We produce and receive persuasive messages daily, but we don’t often stop to think about how we make the arguments we do or the quality of the arguments that we receive. In this section, we’ll learn the components of an argument, how to choose a good persuasive speech topic, and how to adapt and organize a persuasive message.
Foundation of Persuasion
Persuasive speaking seeks to influence the beliefs, attitudes, values, or behaviors of audience members. In order to persuade, a speaker has to construct arguments that appeal to audience members. Arguments form around three components: claim, evidence, and warrant. The claim is the statement that will be supported by evidence. Your thesis statement is the overarching claim for your speech, but you will make other claims within the speech to support the larger thesis. Evidence , also called grounds, supports the claim. The main points of your persuasive speech and the supporting material you include serve as evidence. For example, a speaker may make the following claim: “There should be a national law against texting while driving.” The speaker could then support the claim by providing the following evidence: “Research from the US Department of Transportation has found that texting while driving creates a crash risk that is twenty-three times worse than driving while not distracted.” The warrant is the underlying justification that connects the claim and the evidence. One warrant for the claim and evidence cited in this example is that the US Department of Transportation is an institution that funds research conducted by credible experts. An additional and more implicit warrant is that people shouldn’t do things they know are unsafe.
Figure 11.2 Components of an Argument

The quality of your evidence often impacts the strength of your warrant, and some warrants are stronger than others. A speaker could also provide evidence to support their claim advocating for a national ban on texting and driving by saying, “I have personally seen people almost wreck while trying to text.” While this type of evidence can also be persuasive, it provides a different type and strength of warrant since it is based on personal experience. In general, the anecdotal evidence from personal experience would be given a weaker warrant than the evidence from the national research report. The same process works in our legal system when a judge evaluates the connection between a claim and evidence. If someone steals my car, I could say to the police, “I’m pretty sure Mario did it because when I said hi to him on campus the other day, he didn’t say hi back, which proves he’s mad at me.” A judge faced with that evidence is unlikely to issue a warrant for Mario’s arrest. Fingerprint evidence from the steering wheel that has been matched with a suspect is much more likely to warrant arrest.
As you put together a persuasive argument, you act as the judge. You can evaluate arguments that you come across in your research by analyzing the connection (the warrant) between the claim and the evidence. If the warrant is strong, you may want to highlight that argument in your speech. You may also be able to point out a weak warrant in an argument that goes against your position, which you could then include in your speech. Every argument starts by putting together a claim and evidence, but arguments grow to include many interrelated units.

Choosing a Persuasive Speech Topic
As with any speech, topic selection is important and is influenced by many factors. Good persuasive speech topics are current, controversial, and have important implications for society. If your topic is currently being discussed on television, in newspapers, in the lounges in your dorm, or around your family’s dinner table, then it’s a current topic. A persuasive speech aimed at getting audience members to wear seat belts in cars wouldn’t have much current relevance, given that statistics consistently show that most people wear seat belts. Giving the same speech would have been much more timely in the 1970s when there was a huge movement to increase seat-belt use.
Many topics that are current are also controversial, which is what gets them attention by the media and citizens. Current and controversial topics will be more engaging for your audience. A persuasive speech to encourage audience members to donate blood or recycle wouldn’t be very controversial, since the benefits of both practices are widely agreed on. However, arguing that the restrictions on blood donation by men who have had sexual relations with men be lifted would be controversial. I must caution here that controversial is not the same as inflammatory. An inflammatory topic is one that evokes strong reactions from an audience for the sake of provoking a reaction. Being provocative for no good reason or choosing a topic that is extremist will damage your credibility and prevent you from achieving your speech goals.
You should also choose a topic that is important to you and to society as a whole. As we have already discussed in this book, our voices are powerful, as it is through communication that we participate and make change in society. Therefore we should take seriously opportunities to use our voices to speak publicly. Choosing a speech topic that has implications for society is probably a better application of your public speaking skills than choosing to persuade the audience that Lebron James is the best basketball player in the world or that Superman is a better hero than Spiderman. Although those topics may be very important to you, they don’t carry the same social weight as many other topics you could choose to discuss. Remember that speakers have ethical obligations to the audience and should take the opportunity to speak seriously.
You will also want to choose a topic that connects to your own interests and passions. If you are an education major, it might make more sense to do a persuasive speech about funding for public education than the death penalty. If there are hot-button issues for you that make you get fired up and veins bulge out in your neck, then it may be a good idea to avoid those when speaking in an academic or professional context.

Choose a persuasive speech topic that you’re passionate about but still able to approach and deliver in an ethical manner.
Michael Vadon – Nigel Farage – CC BY-SA 2.0.
Choosing such topics may interfere with your ability to deliver a speech in a competent and ethical manner. You want to care about your topic, but you also want to be able to approach it in a way that’s going to make people want to listen to you. Most people tune out speakers they perceive to be too ideologically entrenched and write them off as extremists or zealots.
You also want to ensure that your topic is actually persuasive. Draft your thesis statement as an “I believe” statement so your stance on an issue is clear. Also, think of your main points as reasons to support your thesis. Students end up with speeches that aren’t very persuasive in nature if they don’t think of their main points as reasons. Identifying arguments that counter your thesis is also a good exercise to help ensure your topic is persuasive. If you can clearly and easily identify a competing thesis statement and supporting reasons, then your topic and approach are arguable.
Review of Tips for Choosing a Persuasive Speech Topic
- Not current. People should use seat belts.
- Current. People should not text while driving.
- Not controversial. People should recycle.
- Controversial. Recycling should be mandatory by law.
- Not as impactful. Superman is the best superhero.
- Impactful. Colleges and universities should adopt zero-tolerance bullying policies.
- Unclear thesis. Homeschooling is common in the United States.
- Clear, argumentative thesis with stance. Homeschooling does not provide the same benefits of traditional education and should be strictly monitored and limited.
Adapting Persuasive Messages
Competent speakers should consider their audience throughout the speech-making process. Given that persuasive messages seek to directly influence the audience in some way, audience adaptation becomes even more important. If possible, poll your audience to find out their orientation toward your thesis. I read my students’ thesis statements aloud and have the class indicate whether they agree with, disagree with, or are neutral in regards to the proposition. It is unlikely that you will have a homogenous audience, meaning that there will probably be some who agree, some who disagree, and some who are neutral. So you may employ all of the following strategies, in varying degrees, in your persuasive speech.
When you have audience members who already agree with your proposition, you should focus on intensifying their agreement. You can also assume that they have foundational background knowledge of the topic, which means you can take the time to inform them about lesser-known aspects of a topic or cause to further reinforce their agreement. Rather than move these audience members from disagreement to agreement, you can focus on moving them from agreement to action. Remember, calls to action should be as specific as possible to help you capitalize on audience members’ motivation in the moment so they are more likely to follow through on the action.
There are two main reasons audience members may be neutral in regards to your topic: (1) they are uninformed about the topic or (2) they do not think the topic affects them. In this case, you should focus on instilling a concern for the topic. Uninformed audiences may need background information before they can decide if they agree or disagree with your proposition. If the issue is familiar but audience members are neutral because they don’t see how the topic affects them, focus on getting the audience’s attention and demonstrating relevance. Remember that concrete and proxemic supporting materials will help an audience find relevance in a topic. Students who pick narrow or unfamiliar topics will have to work harder to persuade their audience, but neutral audiences often provide the most chance of achieving your speech goal since even a small change may move them into agreement.
When audience members disagree with your proposition, you should focus on changing their minds. To effectively persuade, you must be seen as a credible speaker. When an audience is hostile to your proposition, establishing credibility is even more important, as audience members may be quick to discount or discredit someone who doesn’t appear prepared or doesn’t present well-researched and supported information. Don’t give an audience a chance to write you off before you even get to share your best evidence. When facing a disagreeable audience, the goal should also be small change. You may not be able to switch someone’s position completely, but influencing him or her is still a success. Aside from establishing your credibility, you should also establish common ground with an audience.

Build common ground with disagreeable audiences and acknowledge areas of disagreement.
Chris-Havard Berge – Shaking Hands – CC BY-NC 2.0.
Acknowledging areas of disagreement and logically refuting counterarguments in your speech is also a way to approach persuading an audience in disagreement, as it shows that you are open-minded enough to engage with other perspectives.
Determining Your Proposition
The proposition of your speech is the overall direction of the content and how that relates to the speech goal. A persuasive speech will fall primarily into one of three categories: propositions of fact, value, or policy. A speech may have elements of any of the three propositions, but you can usually determine the overall proposition of a speech from the specific purpose and thesis statements.
Propositions of fact focus on beliefs and try to establish that something “is or isn’t.” Propositions of value focus on persuading audience members that something is “good or bad,” “right or wrong,” or “desirable or undesirable.” Propositions of policy advocate that something “should or shouldn’t” be done. Since most persuasive speech topics can be approached as propositions of fact, value, or policy, it is a good idea to start thinking about what kind of proposition you want to make, as it will influence how you go about your research and writing. As you can see in the following example using the topic of global warming, the type of proposition changes the types of supporting materials you would need:
- Proposition of fact. Global warming is caused by increased greenhouse gases related to human activity.
- Proposition of value. America’s disproportionately large amount of pollution relative to other countries is wrong .
- Proposition of policy. There should be stricter emission restrictions on individual cars.
To support propositions of fact, you would want to present a logical argument based on objective facts that can then be used to build persuasive arguments. Propositions of value may require you to appeal more to your audience’s emotions and cite expert and lay testimony. Persuasive speeches about policy usually require you to research existing and previous laws or procedures and determine if any relevant legislation or propositions are currently being considered.
“Getting Critical”
Persuasion and Masculinity
The traditional view of rhetoric that started in ancient Greece and still informs much of our views on persuasion today has been critiqued for containing Western and masculine biases. Traditional persuasion has been linked to Western and masculine values of domination, competition, and change, which have been critiqued as coercive and violent (Gearhart, 1979).
Communication scholars proposed an alternative to traditional persuasive rhetoric in the form of invitational rhetoric. Invitational rhetoric differs from a traditional view of persuasive rhetoric that “attempts to win over an opponent, or to advocate the correctness of a single position in a very complex issue” (Bone et al., 2008). Instead, invitational rhetoric proposes a model of reaching consensus through dialogue. The goal is to create a climate in which growth and change can occur but isn’t required for one person to “win” an argument over another. Each person in a communication situation is acknowledged to have a standpoint that is valid but can still be influenced through the offering of alternative perspectives and the invitation to engage with and discuss these standpoints (Ryan & Natalle, 2001). Safety, value, and freedom are three important parts of invitational rhetoric. Safety involves a feeling of security in which audience members and speakers feel like their ideas and contributions will not be denigrated. Value refers to the notion that each person in a communication encounter is worthy of recognition and that people are willing to step outside their own perspectives to better understand others. Last, freedom is present in communication when communicators do not limit the thinking or decisions of others, allowing all participants to speak up (Bone et al., 2008).
Invitational rhetoric doesn’t claim that all persuasive rhetoric is violent. Instead, it acknowledges that some persuasion is violent and that the connection between persuasion and violence is worth exploring. Invitational rhetoric has the potential to contribute to the civility of communication in our society. When we are civil, we are capable of engaging with and appreciating different perspectives while still understanding our own. People aren’t attacked or reviled because their views diverge from ours. Rather than reducing the world to “us against them, black or white, and right or wrong,” invitational rhetoric encourages us to acknowledge human perspectives in all their complexity (Bone et al., 2008).
- What is your reaction to the claim that persuasion includes Western and masculine biases?
- What are some strengths and weaknesses of the proposed alternatives to traditional persuasion?
- In what situations might an invitational approach to persuasion be useful? In what situations might you want to rely on traditional models of persuasion?
Organizing a Persuasive Speech
We have already discussed several patterns for organizing your speech, but some organization strategies are specific to persuasive speaking. Some persuasive speech topics lend themselves to a topical organization pattern, which breaks the larger topic up into logical divisions. Earlier, in Chapter 9 “Preparing a Speech” , we discussed recency and primacy, and in this chapter we discussed adapting a persuasive speech based on the audience’s orientation toward the proposition. These concepts can be connected when organizing a persuasive speech topically. Primacy means putting your strongest information first and is based on the idea that audience members put more weight on what they hear first. This strategy can be especially useful when addressing an audience that disagrees with your proposition, as you can try to win them over early. Recency means putting your strongest information last to leave a powerful impression. This can be useful when you are building to a climax in your speech, specifically if you include a call to action.

Putting your strongest argument last can help motivate an audience to action.
Celestine Chua – The Change – CC BY 2.0.
The problem-solution pattern is an organizational pattern that advocates for a particular approach to solve a problem. You would provide evidence to show that a problem exists and then propose a solution with additional evidence or reasoning to justify the course of action. One main point addressing the problem and one main point addressing the solution may be sufficient, but you are not limited to two. You could add a main point between the problem and solution that outlines other solutions that have failed. You can also combine the problem-solution pattern with the cause-effect pattern or expand the speech to fit with Monroe’s Motivated Sequence.
As was mentioned in Chapter 9 “Preparing a Speech” , the cause-effect pattern can be used for informative speaking when the relationship between the cause and effect is not contested. The pattern is more fitting for persuasive speeches when the relationship between the cause and effect is controversial or unclear. There are several ways to use causes and effects to structure a speech. You could have a two-point speech that argues from cause to effect or from effect to cause. You could also have more than one cause that lead to the same effect or a single cause that leads to multiple effects. The following are some examples of thesis statements that correspond to various organizational patterns. As you can see, the same general topic area, prison overcrowding, is used for each example. This illustrates the importance of considering your organizational options early in the speech-making process, since the pattern you choose will influence your researching and writing.
Persuasive Speech Thesis Statements by Organizational Pattern
- Problem-solution. Prison overcrowding is a serious problem that we can solve by finding alternative rehabilitation for nonviolent offenders.
- Problem–failed solution–proposed solution. Prison overcrowding is a serious problem that shouldn’t be solved by building more prisons; instead, we should support alternative rehabilitation for nonviolent offenders.
- Cause-effect. Prisons are overcrowded with nonviolent offenders, which leads to lesser sentences for violent criminals.
- Cause-cause-effect. State budgets are being slashed and prisons are overcrowded with nonviolent offenders, which leads to lesser sentences for violent criminals.
- Cause-effect-effect. Prisons are overcrowded with nonviolent offenders, which leads to increased behavioral problems among inmates and lesser sentences for violent criminals.
- Cause-effect-solution. Prisons are overcrowded with nonviolent offenders, which leads to lesser sentences for violent criminals; therefore we need to find alternative rehabilitation for nonviolent offenders.
Monroe’s Motivated Sequence is an organizational pattern designed for persuasive speaking that appeals to audience members’ needs and motivates them to action. If your persuasive speaking goals include a call to action, you may want to consider this organizational pattern. We already learned about the five steps of Monroe’s Motivated Sequence in Chapter 9 “Preparing a Speech” , but we will review them here with an example:
- Hook the audience by making the topic relevant to them.
- Imagine living a full life, retiring, and slipping into your golden years. As you get older you become more dependent on others and move into an assisted-living facility. Although you think life will be easier, things get worse as you experience abuse and mistreatment from the staff. You report the abuse to a nurse and wait, but nothing happens and the abuse continues. Elder abuse is a common occurrence, and unlike child abuse, there are no laws in our state that mandate complaints of elder abuse be reported or investigated.
- Cite evidence to support the fact that the issue needs to be addressed.
- According to the American Psychological Association, one to two million elderly US Americans have been abused by their caretakers. In our state, those in the medical, psychiatric, and social work field are required to report suspicion of child abuse but are not mandated to report suspicions of elder abuse.
- Offer a solution and persuade the audience that it is feasible and well thought out.
- There should be a federal law mandating that suspicion of elder abuse be reported and that all claims of elder abuse be investigated.
- Take the audience beyond your solution and help them visualize the positive results of implementing it or the negative consequences of not.
- Elderly people should not have to live in fear during their golden years. A mandatory reporting law for elderly abuse will help ensure that the voices of our elderly loved ones will be heard.
- Call your audience to action by giving them concrete steps to follow to engage in a particular action or to change a thought or behavior.
- I urge you to take action in two ways. First, raise awareness about this issue by talking to your own friends and family. Second, contact your representatives at the state and national level to let them know that elder abuse should be taken seriously and given the same level of importance as other forms of abuse. I brought cards with the contact information for our state and national representatives for this area. Please take one at the end of my speech. A short e-mail or phone call can help end the silence surrounding elder abuse.
Key Takeaways
- Arguments are formed by making claims that are supported by evidence. The underlying justification that connects the claim and evidence is the warrant. Arguments can have strong or weak warrants, which will make them more or less persuasive.
- Good persuasive speech topics are current, controversial (but not inflammatory), and important to the speaker and society.
- When audience members agree with the proposal, focus on intensifying their agreement and moving them to action.
- When audience members are neutral in regards to the proposition, provide background information to better inform them about the issue and present information that demonstrates the relevance of the topic to the audience.
- When audience members disagree with the proposal, focus on establishing your credibility, build common ground with the audience, and incorporate counterarguments and refute them.
- Propositions of fact focus on establishing that something “is or isn’t” or is “true or false.”
- Propositions of value focus on persuading an audience that something is “good or bad,” “right or wrong,” or “desirable or undesirable.”
- Propositions of policy advocate that something “should or shouldn’t” be done.
- Persuasive speeches can be organized using the following patterns: problem-solution, cause-effect, cause-effect-solution, or Monroe’s Motivated Sequence.
- Getting integrated: Give an example of persuasive messages that you might need to create in each of the following contexts: academic, professional, personal, and civic. Then do the same thing for persuasive messages you may receive.
- To help ensure that your persuasive speech topic is persuasive and not informative, identify the claims, evidence, and warrants you may use in your argument. In addition, write a thesis statement that refutes your topic idea and identify evidence and warrants that could support that counterargument.
- Determine if your speech is primarily a proposition of fact, value, or policy. How can you tell? Identify an organizational pattern that you think will work well for your speech topic, draft one sentence for each of your main points, and arrange them according to the pattern you chose.
Bone, J. E., Cindy L. Griffin, and T. M. Linda Scholz, “Beyond Traditional Conceptualizations of Rhetoric: Invitational Rhetoric and a Move toward Civility,” Western Journal of Communication 72 (2008): 436.
Gearhart, S. M., “The Womanization of Rhetoric,” Women’s Studies International Quarterly 2 (1979): 195–201.
Ryan, K. J., and Elizabeth J. Natalle, “Fusing Horizons: Standpoint Hermenutics and Invitational Rhetoric,” Rhetoric Society Quarterly 31 (2001): 69–90.
- Communication in the Real World: An Introduction to Communication Studies. Provided by : University of Minnesota Libraries Publishing edition, 2016. This edition adapted from a work originally produced in 2013 by a publisher who has requested that it not receive attribution.. Located at : https://open.lib.umn.edu/communication/ . License : CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike

Privacy Policy

Improve your practice.
Enhance your soft skills with a range of award-winning courses.
Persuasive Speech Outline, with Examples
March 17, 2021 - Gini Beqiri
A persuasive speech is a speech that is given with the intention of convincing the audience to believe or do something. This could be virtually anything – voting, organ donation, recycling, and so on.
A successful persuasive speech effectively convinces the audience to your point of view, providing you come across as trustworthy and knowledgeable about the topic you’re discussing.
So, how do you start convincing a group of strangers to share your opinion? And how do you connect with them enough to earn their trust?
Topics for your persuasive speech
We’ve made a list of persuasive speech topics you could use next time you’re asked to give one. The topics are thought-provoking and things which many people have an opinion on.
When using any of our persuasive speech ideas, make sure you have a solid knowledge about the topic you’re speaking about – and make sure you discuss counter arguments too.
Here are a few ideas to get you started:
- All school children should wear a uniform
- Facebook is making people more socially anxious
- It should be illegal to drive over the age of 80
- Lying isn’t always wrong
- The case for organ donation
Read our full list of 75 persuasive speech topics and ideas .

Preparation: Consider your audience
As with any speech, preparation is crucial. Before you put pen to paper, think about what you want to achieve with your speech. This will help organise your thoughts as you realistically can only cover 2-4 main points before your audience get bored .
It’s also useful to think about who your audience are at this point. If they are unlikely to know much about your topic then you’ll need to factor in context of your topic when planning the structure and length of your speech. You should also consider their:
- Cultural or religious backgrounds
- Shared concerns, attitudes and problems
- Shared interests, beliefs and hopes
- Baseline attitude – are they hostile, neutral, or open to change?
The factors above will all determine the approach you take to writing your speech. For example, if your topic is about childhood obesity, you could begin with a story about your own children or a shared concern every parent has. This would suit an audience who are more likely to be parents than young professionals who have only just left college.
Remember the 3 main approaches to persuade others
There are three main approaches used to persuade others:
The ethos approach appeals to the audience’s ethics and morals, such as what is the ‘right thing’ to do for humanity, saving the environment, etc.
Pathos persuasion is when you appeal to the audience’s emotions, such as when you tell a story that makes them the main character in a difficult situation.
The logos approach to giving a persuasive speech is when you appeal to the audience’s logic – ie. your speech is essentially more driven by facts and logic. The benefit of this technique is that your point of view becomes virtually indisputable because you make the audience feel that only your view is the logical one.
- Ethos, Pathos, Logos: 3 Pillars of Public Speaking and Persuasion
Ideas for your persuasive speech outline
1. structure of your persuasive speech.
The opening and closing of speech are the most important. Consider these carefully when thinking about your persuasive speech outline. A strong opening ensures you have the audience’s attention from the start and gives them a positive first impression of you.
You’ll want to start with a strong opening such as an attention grabbing statement, statistic of fact. These are usually dramatic or shocking, such as:
Sadly, in the next 18 minutes when I do our chat, four Americans that are alive will be dead from the food that they eat – Jamie Oliver
Another good way of starting a persuasive speech is to include your audience in the picture you’re trying to paint. By making them part of the story, you’re embedding an emotional connection between them and your speech.
You could do this in a more toned-down way by talking about something you know that your audience has in common with you. It’s also helpful at this point to include your credentials in a persuasive speech to gain your audience’s trust.

Obama would spend hours with his team working on the opening and closing statements of his speech.
2. Stating your argument
You should pick between 2 and 4 themes to discuss during your speech so that you have enough time to explain your viewpoint and convince your audience to the same way of thinking.
It’s important that each of your points transitions seamlessly into the next one so that your speech has a logical flow. Work on your connecting sentences between each of your themes so that your speech is easy to listen to.
Your argument should be backed up by objective research and not purely your subjective opinion. Use examples, analogies, and stories so that the audience can relate more easily to your topic, and therefore are more likely to be persuaded to your point of view.
3. Addressing counter-arguments
Any balanced theory or thought addresses and disputes counter-arguments made against it. By addressing these, you’ll strengthen your persuasive speech by refuting your audience’s objections and you’ll show that you are knowledgeable to other thoughts on the topic.
When describing an opposing point of view, don’t explain it in a bias way – explain it in the same way someone who holds that view would describe it. That way, you won’t irritate members of your audience who disagree with you and you’ll show that you’ve reached your point of view through reasoned judgement. Simply identify any counter-argument and pose explanations against them.
- Complete Guide to Debating
4. Closing your speech
Your closing line of your speech is your last chance to convince your audience about what you’re saying. It’s also most likely to be the sentence they remember most about your entire speech so make sure it’s a good one!
The most effective persuasive speeches end with a call to action . For example, if you’ve been speaking about organ donation, your call to action might be asking the audience to register as donors.
Practice answering AI questions on your speech and get feedback on your performance .
If audience members ask you questions, make sure you listen carefully and respectfully to the full question. Don’t interject in the middle of a question or become defensive.
You should show that you have carefully considered their viewpoint and refute it in an objective way (if you have opposing opinions). Ensure you remain patient, friendly and polite at all times.
Example 1: Persuasive speech outline
This example is from the Kentucky Community and Technical College.
Specific purpose
To persuade my audience to start walking in order to improve their health.
Central idea
Regular walking can improve both your mental and physical health.
Introduction
Let’s be honest, we lead an easy life: automatic dishwashers, riding lawnmowers, T.V. remote controls, automatic garage door openers, power screwdrivers, bread machines, electric pencil sharpeners, etc., etc. etc. We live in a time-saving, energy-saving, convenient society. It’s a wonderful life. Or is it?
Continue reading
Example 2: Persuasive speech
Tips for delivering your persuasive speech
- Practice, practice, and practice some more . Record yourself speaking and listen for any nervous habits you have such as a nervous laugh, excessive use of filler words, or speaking too quickly.
- Show confident body language . Stand with your legs hip width apart with your shoulders centrally aligned. Ground your feet to the floor and place your hands beside your body so that hand gestures come freely. Your audience won’t be convinced about your argument if you don’t sound confident in it. Find out more about confident body language here .
- Don’t memorise your speech word-for-word or read off a script. If you memorise your persuasive speech, you’ll sound less authentic and panic if you lose your place. Similarly, if you read off a script you won’t sound genuine and you won’t be able to connect with the audience by making eye contact . In turn, you’ll come across as less trustworthy and knowledgeable. You could simply remember your key points instead, or learn your opening and closing sentences.
- Remember to use facial expressions when storytelling – they make you more relatable. By sharing a personal story you’ll more likely be speaking your truth which will help you build a connection with the audience too. Facial expressions help bring your story to life and transport the audience into your situation.
- Keep your speech as concise as possible . When practicing the delivery, see if you can edit it to have the same meaning but in a more succinct way. This will keep the audience engaged.
The best persuasive speech ideas are those that spark a level of controversy. However, a public speech is not the time to express an opinion that is considered outside the norm. If in doubt, play it safe and stick to topics that divide opinions about 50-50.
Bear in mind who your audience are and plan your persuasive speech outline accordingly, with researched evidence to support your argument. It’s important to consider counter-arguments to show that you are knowledgeable about the topic as a whole and not bias towards your own line of thought.
- Alternatives
7 Best Short Persuasive Speech Examples to Drive Change
Leah Nguyen • 08 April, 2024 • 7 min read
Are you looking for persuasive speches? Persuasion is power, and within a mere three minutes, you can move mountains - or at least change some minds.
But with brevity comes pressure to pack a maximum punch.
So how do you deliver impact concisely and command attention from the get-go? Let us show you some short persuasive speech examples that convince the audience in less than the time to microwave a pizza.
Table of Contents
1-minute short persuasive speech examples, 3-minute short persuasive speech examples, 5-minute short persuasive speech examples, bottom line, frequently asked questions.

Tips for Audience Engagement
- A Persuasive Speech Outline
- How Do You Express Yourself?
- Use live word clouds or live Q&A to survey your audience easier!
- Use brainstorming tool effectively by AhaSlides idea board

Start in seconds.
Get free templates for your next interactive presentation. Sign up for free and take what you want from the template library!
The 1-minute persuasive speeches are similar to a 30-second elevator pitch which constrain what you can do due to their limited time. Here are some examples that stick to a single, compelling call to action for a 1-minute window.

#1. Title: Go Meatless on Mondays
Good afternoon everyone. I'm asking you to join me in adopting a simple change that can positively impact both our health and the planet - going meatless one day a week. On Mondays, commit to leaving meat off your plate and choosing vegetarian options instead. Research shows cutting back on red meat just a bit provides significant benefits. You'll reduce your risk of chronic diseases while lessening your environmental footprint. Meatless Mondays are easy to incorporate into any lifestyle. So starting next week, I hope you'll help raise awareness around sustainable eating by participating. Every small choice matters - will you make this one with me?
#2. Title: Volunteer at the Library
Hello, my name is X and I'm here today to tell you about an exciting opportunity to give back to the community. Our public library is seeking more volunteers to assist patrons and help keep its services running strong. As little as two hours per month of your time would be hugely appreciated. Tasks can include shelving books, reading to children, and assisting seniors with technology. Volunteering is a great way to build skills while feeling fulfilled through serving others. Please consider signing up at the front desk. Our library brings people together - help keep it open for all by offering your time and talents. Thank you for listening!
#3. "Invest in Your Career with Continued Education"
Friends, to stay competitive in today's world we must commit to lifelong learning. A degree alone won't cut it anymore. That's why I'm encouraging you all to consider pursuing additional certifications or classes part-time. It's a great way to boost your skills and open new doors. Just a few hours a week can make a big difference. Companies also love seeing employees who take the initiative to grow. So let's support each other along the way. Who wants to further their career together starting this fall?
These persuasive speech examples clearly state the position and main information within 3 minutes. You can have a tad bit more freedom to express your points compared to the 1-minute speeches.

#1. "Spring Clean Your Social Media"
Hey everyone, social media can be fun but it also eats up a lot of our time if we’re not careful. I know from experience - I was constantly scrolling instead of doing things I enjoy. But I had an epiphany last week - it’s time for a digital detox! So I did some spring cleaning and unfollowed accounts that didn’t spark joy. Now my feed is full of inspiring folks instead of distractions. I feel less pulled to mindlessly browse and more present. Who’s with me in lightening your online load so you can spend more high-quality time in real life? It takes just a few minutes to unsubscribe and you won’t miss the stuff that doesn’t serve you.
#2. "Visit Your Local Farmers Market"
Guys, have you been to the downtown farmers market on Saturdays? It's one of my favourite ways to spend the morning. The fresh veggies and local goods are amazing, and you get to chat with friendly farmers growing their own stuff. I always walk away with breakfast and lunch sorted for days. Even better, shopping directly from farmers means more money goes back into our community. It's a fun outing too - I see lots of neighbours there every weekend. So this Saturday, let's go check it out. Who wants to join me on a trip to support locals? I promise you'll leave full and happy.
#3. "Reduce Food Waste through Composting"
How can we help the planet while saving money? By composting our food scraps, that's how. Did you know food rotting in landfills is a major source of methane gas? But if we compost it naturally, those scraps turn into nutrient-rich soil instead. It's easy to get started with a backyard bin too. Just 30 minutes a week breaks down apple cores, banana peels, coffee grounds - you name it. I promise your garden or community garden will thank you. Who wants to do their part and compost with me from now on?
Covering your information in a few minutes is possible if you have a well-established persuasive speech outline .
Let's look at this 5-minute example on life:

We've all heard the saying "You only live once". But how many of us truly understand this motto and appreciate each day to its maximum? I'm here to persuade you that carpe diem should be our mantra. Life is too precious to take for granted.
Too often we get caught up in daily routines and trivial worries, neglecting to fully experience each moment. We scroll mindlessly through phones instead of engaging with real people and surroundings. Or we work excessive hours without dedicating quality time to relationships and hobbies that feed our souls. What's the point of any of this if not to genuinely live and find joy each day?
The truth is, we really don't know how much time we have. An unforeseen accident or illness could end even the healthiest life in an instant. Yet we trudge through life on autopilot instead of embracing opportunities as they arise. Why not commit to living consciously in the present rather than the hypothetical future? We must make a habit of saying yes to new adventures, meaningful connections, and simple pleasures that spark life within us.
To wrap it up, let this be the era where we stop waiting to truly live. Each sunrise is a gift, so let's open our eyes to experience this wonderful ride called life to its absolute fullest. You never know when it might end, so make each moment count from today forward.
👩💻 How to Make a 5 Minute Presentation with 30 Topic Ideas in 2024
We hope these exemplary short speech examples have inspired and equipped you to craft impactful persuasive openers of your own.
Remember, in just a minute or two, you have the potential to spark real change. So keep messages concise yet vivid, paint compelling pictures through well-chosen words, and above all, leave audiences eager to hear more.
Which is an example of a persuasive speech?
Persuasive speeches present a clear position and utilise arguments, facts and reasoning to convince an audience to accept that particular viewpoint. For example, a speech which is written to convince voters to approve local funding for park upgrades and maintenance.
How do you write a 5-minute persuasive speech?
Choose a specific topic that you are passionate and knowledgeable about. Write an attention-grabbing introduction and develop 2 to 3 main arguments or points to support your thesis/position. Time your practice runs and cut content to fit within 5 minutes, accounting for natural speech pacing
Leah Nguyen
Words that convert, stories that stick. I turn complex ideas into engaging narratives - helping audiences learn, remember, and take action.
Tips to Engage with Polls & Trivia
More from AhaSlides

3 Minute Speech on Friendship
Good Morning to one and all present here. I am going to present a speech about friendship. Friendship is one of the treasures that anyone can possess. God gave us the right to choose friends because they will be with us forever. Our parents and siblings are loving us as they are our own blood. But a friend is someone, who is initially a stranger. Then they take their place in our life above all the other relations. Friendship is nothing but true and pure love without expectations in return.

Role of a Friend
True friends always support each other even during the hardest of times. A true friend is one who feels happy for our success, on the other hand, who feel gloomy for our failures. A true friend may criticize also so that we may come out of our weakness.
He may scold us if we do a mistake and guide the right path. That’s why it is being said that true friend is more precious than any gem in our life. Love from your friend will always be unconditional. They may expect nothing from us but shower their love always.
Friendship – A Divine Relationship
Friendship is a divine relationship, which is beyond the definition of blood relations. It is the only relation that is truly priceless. We may acquire all kinds of pleasures by putting our efforts. But even then life may remain dull, without having someone to share our life with some true friends.
It’s natural that human being always tends to find emotional support and social life. In spite of having everything in life, we may remain in a vacuum. It happens only when we have no such good friend to share our small and small happiness in life. Friends are always there to listen to us unconditionally.
Get the Huge List of 100+ Speech Topics here
There is no Second Chance for True Friendship
Friendship will provide us with thousands of fun moments in life which we may memorize in our old age. But side by side, with times this relation may have moments of crisis. A misunderstanding may crop in and this amazing relation may start weakening.
Always be the first one to save the friendship. God forbid, if due to some unfavorable reason distance ever arises within this relation, we must not let our friend go. Hold his or her hand and apologize for any mistake done. There is nothing more pathetic in anyone’s life than losing a true friend.
Friendship is a relationship that is like a newborn baby. Friendship is always pure and like a bundle of joy which only needs more and more nourishment to grow. Never ignore true friends or take them for granted. We may come across various people at different phases of our life. Many may pretend to be our friends but never go by outward glitter.
At last, I wish to say that a good friendship is very difficult to come across. Therefore, we should appreciate this divine relationship having a base on understanding and feelings. We just need friends to live happily. Lasting friendship is a blessing for everyone.
We don`t need to pretend to be someone else when we spend time with our friends. They give us total freedom to be who we are in reality. We should always be grateful to people who make us happy. A true friend is one of the most precious possessions in anyone’s life.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

Speech for Students
- Speech on India for Students and Children
- Speech on Mother for Students and Children
- Speech on Air Pollution for Students and Children
- Speech about Life for Students and Children
- Speech on Disaster Management for Students and Children
- Speech on Internet for Students and Children
- Speech on Generation Gap for Students and Children
- Speech on Indian Culture for Students and Children
- Speech on Sports for Students and Children
- Speech on Water for Students and Children
16 responses to “Speech on Water for Students and Children”
this was very helpful it saved my life i got this at the correct time very nice and helpful
This Helped Me With My Speech!!!
I can give it 100 stars for the speech it is amazing i love it.
Its amazing!!
Great !!!! It is an advanced definition and detail about Pollution. The word limit is also sufficient. It helped me a lot.
This is very good
Very helpful in my speech
Oh my god, this saved my life. You can just copy and paste it and change a few words. I would give this 4 out of 5 stars, because I had to research a few words. But my teacher didn’t know about this website, so amazing.
Tomorrow is my exam . This is Very helpfull
It’s really very helpful
yah it’s is very cool and helpful for me… a lot of 👍👍👍
Very much helpful and its well crafted and expressed. Thumb’s up!!!
wow so amazing it helped me that one of environment infact i was given a certificate
check it out travel and tourism voucher
thank you very much
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App

- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
The Ezra Klein Show
Nate Silver on Kamala Harris’s Chances and the Mistakes of the ‘Indigo Blob’

By Ezra Klein
Nate Silver on How Kamala Harris Changed the Odds
Nate Silver came to fame in American politics for election forecasting. But before Silver was in politics, he was a poker player. And after getting into politics, he went back to being a poker player. He’s been running through poker championships and out there on tables — partly because he’s been writing a book about risk.
The book is called “ On the Edge: The Art of Risking Everything .” And it applies the frameworks of the gambler to politics, to A.I., to venture capital.
The way Silver thinks about politics I find very useful. So I invited him on my podcast to talk about how that thinking has guided him over the past year and how he’s thinking about the election going forward.
This is an edited transcript of part of our conversation. For the full conversation, watch the video below, or listen to “ The Ezra Klein Show .”
The election forecaster discusses 2024 and what politicians can learn from gamblers.
“Nate Silver came to fame in American politics for election forecasting. He built models that were pretty damn successful at predicting American politics.” “Nate Silver is the founder of fivethirtyeight.com, a polling website that correctly predicted the winner of 49 of the 50 states in the last presidential election.” “Election Oracle, ESPN’s Nate Silver, he predicted every state in the last presidential election.” “And once again, Nate Silver completely nailed it.” “The guy’s amazing.” “But before Silver was in politics, he was a poker player. And after getting into politics, he went back to being a poker player. He’s been running through poker championships and out there on tables —” “Savage, savage bluff by Silver. Oh, my God.” “— partially because he’s been writing a book about risks. The book is called ‘On the Edge: The Art of Risking Everything.’ And it applies the frameworks of, I would say, the gambler, maybe say the poker player, to politics, to AI, to venture capital. Nate, the way he thinks about politics I find very useful. I find that he thinks more clearly about risk and probabilities than a lot of people do and maybe more people should follow. So I wanted to have him on to talk about how that thinking has guided him over the past year and how he’s thinking about it in the election going forward. As always, my email, [email protected].” [THEME MUSIC] “Nate Silver, welcome to the show.” “Thank you, Ezra. Happy to be here.” “Last I looked, your model has Harris winning the election at around 52 percent. It might be mildly different today. But this has been an unusual election. So how much stock do you put in your model right now?” “I think the model is balancing the different factors pretty well. I mean, there are some things you could argue are favorable to Harris, one of which is that for the past few weeks we’ve been in what the model thinks is supposed to be the convention bounce period for republicans, where typically you poll pretty well after your convention. There’s the afterglow of the new nomination and things like that — the afterglow of the VP pick, often, too. And Kamala Harris kind of stomped on Donald Trump’s news cycle. So maybe it’s an overly favorable assumption for Harris. There’s also in polls what’s known as nonpartisan response bias. So when voters get more enthusiastic, you’d rather have that than not as a candidate. But it also means that they sometimes are more likely to respond to polls. At the same time, her momentum has been pretty good, which usually I dismiss. We don’t really kind of know what the baseline is here, right? You know, Hillary Clinton, who was, I think, kind of a terrible candidate, won the popular vote by two points. Is she a little bit better than Hillary Clinton? Probably, right? So can she win by three or four? Well, if you win by three or four, then you win the electoral college in most instances.” “I don’t think many people expected — if you did, I’d like to know it — the turnaround in her numbers we have seen since she’s become the presumptive nominee. She’s gone to net favorables, which I would not have bet a ton of money on at this speed at least. People were looking at a lot of data on Harris and assuming that data was solid. That data was not solid.” “When a candidate’s a hypothetical candidate, you have to treat that polling very carefully. People are — I think it’s a weird thing to ask, you know, what if Gavin Newsom ran against Trump. It’s not the same thing as when you actually have the candidate in front of you, and have the advertisements, and have the news articles, and everything else to actually evaluate. I mean, I think this is, like, on the higher side for a jump in favorables, but, you know, she was amazingly well-organized at getting the entire establishment behind her within literally minutes [LAUGHS]: of Biden announcing that he was going to step down. And so that suggested that maybe she did have more support in the party than she let on. And also, you know, I don’t — I think the Biden people may have been in somewhat bad faith. Maybe not consciously, but I’m not sure they weren’t trying to undermine her. Because the obvious thing to do would be to have this qualified, if not always that politically adept, you know, much, much younger vice president take over for you when you’re about to be 82. But they gave her the border. They gave her voting rights, which is kind of the one major domestic policy area where they got very little done. So I don’t think they gave her a very good hand to play. But meanwhile, she’s getting a lot of reps, and giving speeches, and building connections, and played the game really well. I have a lot of respect for that.” “Well, the key thing, I think, is that Biden had a huge amount of influence over how the party viewed her in both directions. There was a long period, I would say, when the quiet signals out of Biden world were this isn’t going well.” “Yeah.” “And when there was pressure to push Biden off the ticket, those signals got louder — Harris cannot do this. If you get rid of him, you’re going to get her. You’re going to lose. But then the thing you saw happen is a moment Biden actually stepped aside and fully endorsed her. That was a signal so powerful that it functionally won the potential primary for Harris instantly. Nobody was going to go against Joe Biden in that moment. And so, in both directions, Biden had, and the team around him, a lot of influence. When implicitly Biden world told the Democratic Party Harris can’t do it, the Democratic Party believed them. And then when explicitly Biden himself told the Democratic Party and the world Harris could do it, the Democratic Party believed him. And by the way, from what I could tell, it seems he was right. And I don’t blame Biden, I think, for things that happened earlier in the administration. That was a lot of staff talk. And to be fair, it was based on some things. There were problems in her office. There were reasons to be skeptical. But he and they had tremendous power. In a way, this was not, to me, like a mini primary. This was a parliamentary process, right? The party came together and chose a leader through endorsements from elected officials. That’s functionally what happened.” “Yeah, it felt very British. It felt like —” “It felt very British.” “— the Liz Truss kind of thing or something, right, where, yeah. There’s a loss of confidence. Those are fascinating dynamics to study. But yeah, it’s interesting to have the inside view versus the outside view a little bit. And, you know, again, we talk about this in the book a little bit, but I come at a position where I’m more skeptical about the competence of people who work in politics. Right? Even if I like the candidates they endorse — I mean, I plan to plan to vote for Kamala Harris. I would not have voted for Joe Biden, by the way. I think it was deeply irresponsible to nominate him, and I would have voted libertarian or something. But I have a more skeptical view, and I think even the rationales they state out loud are sometimes maybe the rationales they believe or not. But, you know, I think human behavior is pretty strategic when you understand people’s incentives, and kind of information set, and things like that. And I think it was in Biden’s narrow self-interest to make Harris look weaker. And I think that plays a role at all sorts of subconscious margins in terms of how she was treated.” “Well, let’s talk about that skepticism. You and I have known each other a long time. We’re old-school bloggers. And my read of you is that somewhat over the 2016 election, then specifically over the pandemic —” “Yeah.” “— and your experience, I think, with online liberalism in the pandemic, you became much more disillusioned with the people who once felt to you like your group, your coalition, your tribe. There’s been a kind of an alienation for you. Is that a fair read?” “Yeah, I’d say it’s three things, right. Number one, the 2016 aftermath, I thought a lot of the kind of liberal and centrist news media, kind of were in denial about their own role in the ‘But her emails’ stuff and then picked scapegoats for Trump’s victory that were not the real reasons that he won. You know, Russian bot farms have approximately nothing to do with why Donald Trump won the 2016 election. And the Russia stuff, in general, I think was treated with an order of magnitude more importance than it probably objectively had. And blaming Facebook and the tech industry for that, I thought that was irresponsible. And also kind of the obsession over the polls in 2016, where I think there was some revisionist history where the polls actually showed a pretty close race. I mean, we had Trump with a 30 percent chance. And it was kind of the conventional wisdom that assumed that he was dead in the water. So the ability to conveniently lie a little bit or manipulate facts and spin facts, I mean, that was part one. Part two was the pandemic. Absolutely. And, you know, ‘orange man bad,’ I think, was often the reason that people believed a lot of what they believed. Because in some ways, the move to shut down society in some ways kind of went against the values of traditional liberalism, right? There’s a transfer of welfare from younger people [LAUGHS]: and people who are not able to work from home to wealthy suburbanites and older people who you’re protecting their health, but you’re undermining the education of millions and millions and millions of schoolkids around the country, and essential workers are still putting themselves at risk that you deem unacceptable for people who are able to work with laptops to take. So I thought it was very self-serving, and I thought kind of expertise was co-opted and corrupted by political partisans. And then third was the Biden stuff.” “Well, it seemed to me it happened for you before the Biden stuff.” “Yeah. I mean —” “And you were crosswise with a lot of liberals on Twitter. I mean, I came back to Twitter for three weeks during the height of Bidenmania to try to be sort of in touch with that sentiment and mostly stay away from it. But Twitter is a place that groups that exist outside the online hothouse purify inside the online hothouse. So there’s the public health community outside Twitter, and then there’s how it acts inside Twitter — political scientists outside Twitter and then inside Twitter, republicans outside Twitter, then inside Twitter. And my sense was that you ended up in a lot of fights with liberals who had a much lower risk tolerance than you did. And between that and what was, I believe, unfair criticism of the 2016 model, which got the election much more right than most did, that it sort of — you began to see habits of — you call it ‘the village.’ The village is your term for —” “Yeah. And that’s been a term that’s been used by other right. But the village is basically media, politics, government, progressive —” “The establishment.” “The establishment, ‘The New York Times,’ Harvard University.” “The regime.” “The regime. Yeah. The Democratic White House. Maybe not a Republican White House, but that’s a more complicated kind of edge case.” “Or maybe a different Republican White House.” “Yeah.” “Right? George W. Bush was part of the village.” “Absolutely.” “Maybe Donald Trump wasn’t.” “Absolutely.” “I think you’ve also called it the indigo blob in different ways, that you began to see it as a kind of set of aligned cognitive tendencies that you disagreed with. What were they?” “So one of them is the failure to do what I call decoupling. It’s not my term. Decoupling is the act of separating an issue from the context. So the example I give in the book is that if you’re able to say I abhor the Chick-fil-A’s CEO’s position on gay marriage — I don’t know if it’s changed or not, but he was anti-gay marriage, at least for some period of time — but they make a really delicious chicken sandwich. Like, that’s decoupling.” “I abhor their treatment of chickens.” “Yeah.” “I have a strong direct take on Chick-fil-A. I don’t like how they treat chickens.” “O.K. Or you can say or separate out, you know, Michael Jackson, Woody Allen, separate the art from the artist kind of thing. Right? You know, that tendency goes against kind of the tendency on the progressive left to care a lot about the identity of the speaker in terms of the racial or gender identity and in terms of their credentials. And this other world that I call ‘the river,’ the kind of gambling, risk-taking world, all that matters is that you’re right.” “The river is your name for the community of people who think about risk roughly the way you do and are willing to make big bets, willing to accept loss. The river is your — it’s your world of gamblers at all levels of society.” “Capital and lowercase g gambling.” “So hedge funds —” “Expected value.” “— venture capitalists.” “Yeah. And then you get kind of the more —” “Crypto.” “— groundwater stuff where it’s like crypto, and meme stocks, and things like that. It doesn’t matter who you are, it matters that you’re right and you’re able to prove it or bet on it in some way. And that’s very against, I think, the kind of credentialism that you have within the progressive Democratic left, which I also call the indigo blob, because it’s a fusion of purple and blue. There’s not a clear separation between the nonpartisan, centrist media and the left-leaning progressive media that’s kind of rooting for Democrats. Different parts of ‘The New York Times’ have both those functions in place. And as someone who’s kind of more on the nonpartisan side, even though, again, I would prefer to see Kamala Harris than Donald Trump, I think people are exploiting the trust that institutions have earned for political gain. And particularly in the kind of pre-Elon pandemic-era Twitter days, the pile-ons were kind of insane, and 98 percent of people don’t have the tolerance for that. But I didn’t really care because these people are not my friends, and I have a good life outside of Twitter, and because, you know, to some extent, even if you run a newsletter, being a little polarizing is O.K., right? If I have 10 random people yelling at me on Twitter and 10 people sign up to be paid subscribers to ‘Silver Bulletin,’ then I come out like way ahead in that deal. And so I think I couldn’t do my job without running afoul of this group of people.” “Let me ask you about the definition of decoupling there, because I think decoupling is interesting. And I found the examples you pick also interesting but contestable.” “Yeah.” “So in the Chick-fil-A example, I’m between a vegetarian and vegan these days, so I got my own issues with Chick-fil-a, but was not a believer necessarily in boycotting it if you didn’t have my issues. But I understood it as more like a boycott, that theory, right? You don’t want to give money to something that’s going to work against your interests. The question of decoupling art and artist, which I’m more on the side of decoupling, but also has a dimension of — those both strike me as versions of activism, right? What you want to do, what people who hold those positions are trying to do, is affect change in the world by applying consequences to beliefs. And maybe you don’t want that, or you don’t agree that the beliefs they are trying to affect should have those consequences on them. But it’s kind of different than the idea of things are being pressed together that don’t go together. I think an interesting sort of decoupling issue that happened in the pandemic was the same public health voices who were at one point saying you had to be so careful, even outside oftentimes were then pro joining the George Floyd protests, which a lot of people found very upsetting. What people were looking to the public health world for right then was not their views on protests but their views on distancing. And that felt like it coupled things in a way that undermined one to achieve another.” “Well, and they framed it in, like, oh, this is good for public health reasons, right? If they had said, look, I’m a big believer in racial equity; there is a little bit of risk here; but outside, wear a mask, and probably not a huge problem — I mean, that would be honest, right?” “Which ended up being true too.” “Yeah. But instead it was in the name of public health, right? I think people don’t do enough thinking about thinking and don’t read enough of the literature on cognitive biases. Ironically, this is kind of like the expert literature on how powerful the human mind is at confirmation bias, and how powerful a drug political partisanship is, and how smart people are maybe better rationalizes in certain respects. I mean, a lot of irrational traits are like rational on some halfway approximate different version of the universe. You know what I mean?” “My first book was on polarization. And what I understand you as doing in the book in part is making an interesting cut in society between people with different forms of both risk tolerance and thinking about risk. And you write something that caught my eye where you say, quote, ‘COVID made those risk preferences public, worn on our proverbial sleeves and our literal faces.’ And you go on to say, quote, ‘People are becoming more bifurcated in their risk tolerance, and this affects everything from who we hang out with to how we vote.’” “Yeah.” “Tell me about both sides of that — the way that it made risk tolerance visible, but then your view that since then risk tolerance is becoming a deeper cleavage in society.” “I mean, on the one hand, there are lots of signs that risk tolerance is going down, right? Among young people in particular, they’re smoking less, drinking less, doing fewer drugs, having less sex. A different type of risk tolerance, they are less willing to defend free speech norms if it potentially would cause injury to someone. That’s kind of a — free speech is kind of a pro-risk kind of take in some ways because speech can cause effects, of course. On the other hand, you have this boom and bust, and various booms and busts, in crypto. You have Las Vegas bringing in record revenue. You have record revenue in sports betting and things like that. You have the CEO of OpenAI saying, yeah, this might destroy the universe, but it’s worth it. It’s a good gamble to take. You have FTX and all this stuff. And the first trip I made after COVID was to a Casino in Florida, which is every bit the shit show that you think it might be. And the tournament drew record numbers of Poker players. And so it just seems to me like we are in a world now where institutions are less trusted. And some people respond to that by saying, O.K., I make my own rules now, and this is great, and I have lots of agency. And some respond by kind of withdrawing into an online world, or maybe clinging on to beliefs and experts that have lost their credibility, or just by becoming more risk averse. I mean, I think the pandemic also revealed that there’s a lot of differences in introversion versus extroversion. I just can’t deal with being cooped up inside all day. This doesn’t work for me at all. But I think some people kind of secretly like the idea that, O.K., there’s no more FOMO. I can kind of be cozy all day. And that’s fine. There’s differences in desire for human companionship and things like that too.” “Let’s talk about a couple of those people. One of the things that’s kind of fun about the book is you spend time with people whose approach to risk you find sophisticated and interesting.” “Yeah.” “One of them is Peter Thiel. What were your impressions of Peter Thiel? What did he learn spending time with him?” “The first impression is that he’s a weird dude. I interviewed him by phone. And the first question I asked him he took half an hour to answer. So he’s very thoughtful. And the question was what I thought was kind of a softball question. It’s like, if you ran the world 1,000 times or 10,000 times, how often do you think you’d wind up in a situation like the one that you’re in? And it was kind of a nerdy way to ask, do you think you got lucky. Which in Thiel’s case is interesting. There’s an anecdote in the book about this famous or infamous car trip he took with Elon Musk. They were going to pitch Michael Moritz at Sequoia Capital, and Elon had a new McLaren F1 and was going way too fast, and spun out of control in the middle of whichever Sand Hill Road or whatever, and they totaled the car. They could easily have been killed. And instead, they actually hitchhiked to this meeting and saved what was then called Confinity — it was like the future of Paypal, right? And so this twist of fate, twist of good fortune, kind of helped [LAUGHS]: Peter Thiel out. But most people understand, like —” “Wait, how did it help him out? I mean, he didn’t die.” “Well, he didn’t die. So he avoided — yeah, he avoided dying, I guess I’d say. So probably the expectation was not that he’d die. But the point is still that you can easily have a world in which Elon Musk and Peter Thiel are not a part of it if there’s a car going the wrong way and the other side of the road. So most people, when you ask that question — I asked Mark Cuban, for example — they’ll give the politically correct response. Which is, oh, of course I’ve been very lucky, and I’m a talented person, but of course it’s a 1 in a million thing. Right? And Thiel objected to the question. He said, you know, well, if it’s predetermined, then the odds are 100 percent. And if the world’s not predetermined, then the odds are probably approximately zero. But that doesn’t really make sense. Like, how can you perturb the world by exactly this amount? But I think he kind of believes in predestiny a little bit. And —” “As a spiritual thing or as a matter of classical physics?” “There’s a good book by I think Max Chafkin was the journalist — or ‘Chaff-kin’— I don’t how you say his last name — about Peter Thiel called ‘The Contrarian,’ which is convincing that Thiel is actually quite conservative, more than libertarian, and probably quite religious. But I also think that if you ARE one of these people, just the amounts of wealth, and success, and power that Silicon Valley has, I do think some of these people kind of pinch themselves and wonder if they have been one of the chosen ones in some ways or been blessed in some ways, or, maybe the nerdy version of it, think they’re living in a simulation of some kind. Like, what odds would you give yourself that that actually makes sense that you’re the protagonist of the story? It must be kind of weird, right?” “So I used to interview Thiel. Not super regularly but every so often. My impression of him, which has been my impression of a lot of the I would call them ideologist VCs, which is not all VCs, but the ones who are heavily behind or out online and sort of pushing a kind of what I would think of as like VC ideology that leans now right, talking to him always interesting. Because over the course of a conversation, he would offer like 15 or 20 ideas. I would call them more thought experiments than analytical arguments. They were not empirically backed, typically. And you would leave and be like, 13 of those seem genuinely ridiculous to me. Two of them might be very importantly right. I’m not 100 percent sure which are the two and which are the 13. And Peter Thiel, I think, is very — he is a sort of template of the VC mind, and a lot of VCs try to be him. And he’s been very successful. I mean, he’s a guy who has backed a number of very important companies, found a number of very important founders. He is able to do something there. But it is oriented towards being right in important and counterintuitive ways, like, three out of 20 times and doesn’t care about being wrong 17 out of 20 times. Whereas if you think about media, media is oriented towards being right 17 out of 20 times, and the three that it gets wrong are going to be really big because they’re going to be correlated across the entirety of American institutions. But it’s a very different way of thinking about risk. It’s like you want big payouts, not a high betting average.” “And that’s because this is core to the VC mindset. The two things that you hear from every VC, one is the importance of the longer time horizon. So you’re making investments that might not pay off for 10 or 15 years. But number two, even more important, is the asymmetric ability to bet on upside. They are all terrified because they all had an experience early in their career where Mark Zuckerberg walked through their door, or Larry Page or Sergey Brin walked through their door, and they didn’t give them funding. And then they wound up missing on an investment that paid out at 100x or 1000x or 10,000x. And so if you can only lose 1x your money, but you can make 1000x if you have a successful company, then that changes your mindset about everything, and you want to avoid false negatives. You want to avoid missed opportunities. And I think there’s a tendency for a certain type of smart person to provoke, to troll a little bit. I think he’s like that a little bit mean. This is also partly the thing on Twitter, right? I kind of us Twitter sometimes as a sketch pad [LAUGHS]: a little bit for slightly irreverent, half-trollish ideas that might later turn into newsletter posts or something like that, or might be developed further, and probing around and seeing what things land and what don’t. Like a stand mic night at a comedy show or something. And I think that’s how Twitter is meant to be used. But other people use it for enforcing consensus. But we’ve already talked about Twitter. But yeah —” “Well, you can never talk about it enough, particularly with these people. The one thing I will say on that, and I think this is true for virtually everybody I know who has been on that platform for a long period of time, is they will tell you that I have this persona on Twitter.” “Yeah.” “Right? Twitter is not real life. I mean, I use it to provoke. I’m having fun. I’m shitposting. I’m trolling. And people, over time, if they spend a lot of time there, become more like who they are there. That is true for Marc Andreessen, another person who you profile and talk to in the book. It’s true for lots of people in politics I know. Ted Cruz has become his Twitter persona even more than he once was. It happened in Democratic politics I think in 2020. Different campaigns became more like their Twitter incarnations than that person had been in politics before. And I think it has to do with social dynamics. Because over time, the people you get praise from become more persuasive and credible to you. The people who begin to hate you, you sort of repel from. People I think always think they can be playful in their social dynamics, but actually who you end up surrounding yourself, even online, you become them. It’s very, very hard to maintain that kind of separation.” “I mean, clearly, Elon Musk maintained a stance for a while that, oh, I’m just kind of a libertarian moderate. Like, no, he’s kind of like a right-pilled conservative.” “Yeah. And I’m just having fun. I’m posting funny things. He’s his Twitter persona now. You spent some time with Sam Bankman-Fried.” “Yeah.” “Tell me what you learned from him or learned about him.” “I think Sam is kind of insane [CHUCKLES]:, and I’m not very sympathetic to him. I mean, I’m sympathetic in the sense that this is this very dramatic reversal of fortune, where he’s kind of literally emerging and on top of the whole world, and shooting commercials with Tom Brady, and it kind of all collapses, and he becomes very abandoned overnight. So he’s kind of reaching out to a couple of journalists to have conversations because he basically no friends left in the Bahamas anymore. And his parents are there and two of his employees are there, but everyone else has fled the island. Sam is somebody who has to be owned by the river. But, you know, he is unabashedly a part of that world. I mean, he had his tentacles in every part of that world. He was active in Democratic and actually, under the radar, Republican political donations. He was trying to figure out how to get into sports betting legally and things like that. And so he is kind of everywhere. And of course, most of all, with the effect of altruists — in the original plan for the book, there was this awkward transition between the chapter on crypto and the chapter on effective altruism. I’m like, how do I have a natural transition? And then SBF is very important in both worlds, and it’s a very strange connection that somehow crypto profits are funding these people who want to cure malaria or something in Africa. But, you know, I think there are a couple of things. One is that I think people were overly impressed by SBF, partly because he was able to manipulate his self image. I mean, he’s not the most conventionally normal guy, right? But he was very aware that founders — the founder algorithm, the VC algorithm is like we can’t — weirdness is good for VCs. The fact that SBF would play video games in investor pitch meetings or things like that, or dress down, or have a fidget spinner, they’re like, oh, he’s a little bit on the spectrum, and that’s actually probably good for a founder because you want the single-minded devotion. And he’s a little weird, but you want variance, variance, variance.” “Sleeps on a beanbag. Right? There was a real mythos around him.” “Which is kind of carefully constructed. He’s kind of inhabiting a character which is inspired by some inner SBF. And he’s kind of playing that character and then kind of forgets what has ever inner core values, whatever they were, might have been. But he is not a very competent manager of risk. He invested all this money in this Democratic primary for a candidate named Carrick Flynn in Oregon’s — I forget which — six or seventh district, maybe eighth district. And the candidate had been ahead in the polls by 15 points and wound up losing by 15 points. Because to spend $8 million in a congressional primary is kind of insane if you’re not in the New York media market or something. So the candidate would go to people’s houses, and they’d be like, hey, I’m Carrick Flynn. I’m a candidate for the Oregon primary. And they’re like, oh, I have your literature and bring out a stack of 20 flyers that SBF’s super PAC had sent on behalf of Carrick Flynn and made him look like a weird freak backed by this mysterious crypto billionaire. So, yeah, he had a tendency — and this is based on testimony from both the court case and an interview I did with Tara MacAulay I think his her name, his original co-founder at Alameda. He had the kind of often good initial instincts, and being a good estimator is an important skill in my world, but then would kind of double down on that a lot and rationalize things a lot. And there was also a bystander effect problem where so many people vouched for him — Sequoia Capital and all these Oxford philosophers, these effective altruists. And he’s on stage with Bill Clinton or whatever, and he’s invited to the Met Gala, and Tom Brady is shooting commercials with him. So what could possibly be wrong with this guy? I mean, maybe he seems a little bit weird to me, but all these other people are kind of in his corner. But no one was doing the due diligence. And he kind of figured out that despite — there’s a little contradiction in the river, where on the one hand we tend to think of ourselves as being contrarian. On the other hand, we’re pretty big fans of markets, because we know that it’s kind of hard to beat the Las Vegas point spread or it’s hard to beat the S&P 500 Index funds or things like that. So the market judgment is that SBF is a credible actor, and how would I trust my own judgment over the market judgment a little bit. And there was too much deference toward that and too much actually groupthink about SBF, because the problems were evident the whole way. I mean, he told Tyler Cowen that if he could flip a coin to double the amount of utility in the world plus 1 epsilon or something but there’s a 50/50 chance of blowing the world up, that he would take the coin flip and repeatedly.” “So you’re actually getting two earths, but you’re risking a 49 percent chance of it all disappearing.” “And again, I feel compelled to say caveats here of how would you really know that’s what’s happening, blah, blah, blah, whatever. Put that aside. Take the hypothetical — the pure hypothetical. Yeah. Yeah.” “And then you keep on playing the game. So what’s the chance we’re left with anything? Don’t I just Saint Petersburg paradox you into non-existence?” “Well, not necessarily. Maybe Saint Petersburg paradox into an enormously valuable existence. That’s the other option.” “I remember seeing that Tyler Cowen interview and thinking, that’s nuts. But I think it gets at a kind of nuts that there is a bias towards in the world you’re describing. There is an aesthetic around talking in probabilities. There’s an ability to think in probabilities, and there’s an aesthetic around probabilities — people attaching, I would often say, almost random probabilities to things. I see this a lot in Silicon valley, people who I would call it like faux Bayesian reasoning where they’re given some probability, but they have no reason to base the probability — 50 percent of this. And it makes you sound much more precise. It makes you sound like what you’re talking about. SBF was known for always talking in terms of expected value. Which is very appealing to the kinds of people you’re describing, maybe the kind of person even that you are. And people who know how to talk like that get through a lot of filters, because you sort of assume, if they’ve converted everything into probabilities, and they’re great at math, and he worked at Jane Street. I worried about this a lot with effective altruists for a while, which is a group I have a lot more sympathy for than most people now have. But there can be this tendency, I think, to fetishize a certain form of discourse. It’s like the first people into that form of discourse are doing something valuable, and then, after that, I think it can become a kind of costume of sloppy thinking. This worries me about models too. I’m curious how you think about it, because I often find that people talk in terms of probabilities but people hear them in terms of certainties. That somehow talking in terms of probabilities makes people more willing to believe you without actually being skeptical or attaching a failure risk to you.” “Yeah. I mean, there’s two things here. One is just there is a kind of jargon. In some ways I liken being from the river to being from the South of the United States or something, where there’s just a lot of shared cultural norms and unspoken discursive tendencies — it’s just the way we communicate, I think, in the river. But also, it’s really easy to build bad models. Even in narrow problems, like I want to forecast the NFL or something or build an election model, it’s easy to build bad models. And on these open-ended problems, it’s really easy to fall in love with the incomplete model of the world and then forget that — what’s the Kamala Harris coconut tree quote? A model does not fall from a coconut tree. It exists —” “It exists in the context of all that came before it. Sure.” “So a model is supposed to describe something in the real world. And if you lose sight of the real world and it fails to describe the real world, then it’s the model’s fault and your fault for building the model and not the real world’s fault. And that’s a lesson that people, I think, have a lot of trouble learning.” “Bankman-Fried is in prison. Thiel might in some ways be responsible for destroying the Republican ticket this year. I mean, in a close election, JD Vance now seems to have about as much negative value as we’ve seen from a recent Vice President. I’m not saying Peter Thiel’s the only reason Vance got chosen for the ticket, but he is one of the key reasons Vance is in politics. Before now, you would said JD Vance was Peter Thiel’s political bet that paid off best.” “Yeah.” “And now it might be his political bet that pays off worst. You mentioned Bankman-Fried’s political donations, which were kind of disastrous in a direct way sometimes. Also ended up taking a lot of other people down over time. If these guys are so good at making bets or seem to be so good at making bets, what are they missing in politics? As somebody who straddles those worlds, what is not in their models? So both these groups, both the river and the village, are groups of elites. And I think, ironically, both groups’ critiques of one another are kind of true, right? I mean, they kind of can be epistemic trespassers, but they are not very data driven when it comes to politics. And part of it, too, is that if you’re a VC, and you’re evaluating a lot of pitches and a lot of opportunities, you have very quick twitch reflexes for saying, O.K., something about this founder seems smart. Let’s investigate further. Let’s do an initial seed round of investing. But it’s like thin slicing and not necessarily — for this part of the river, the VC part of the river — more profound analytical takes on things. And so you’re surrounded by people that are inclined to agree with you, and you kind of see enemies on the other side. He thought maybe that people had some deeper intuitive sense in 2016 that something was wrong with Hillary Clinton, even though she was ahead in the polls. And to his credit, he did back Trump at a time when that seemed like a big risk to take. It seemed like it was probably going to be the wrong bet, and it seemed like he was losing a lot of credibility. And now, it turns out that he was kind of ahead of the curve. You know, people like Peter Thiel thought that the village had been discredited by 2016 and other things. You can’t really trust the polls, and they said Trump would never do x, y or z. But no, I mean, these guys often are pretty dumb about [LAUGHS]: politics. And it’s the same — the guys in the hedge fund poker game that I play sometimes are the guys that are like, I think Gavin Newsom is going to replace Joe Biden on the ticket. And it’s like, you actually were kind of right about part of this, but why Gavin Newsom? What is the infatuation with Gavin Newsom.” “I heard so many versions of that. I always thought it was so crazy.” “Yeah.” “But, you know, it’s funny. I would say what they’ve often missed, and Thiel’s particular on this, is how human beings react to different human beings. So JD Vance, for instance, wildly underperforms in the Ohio Senate race. And Vance’s problem right now, he’s pushed onto the ticket by, as best we can tell, people like Steve Bannon, Don Trump, Jr., Tucker Carlson, Elon Musk — so the very online, very reactionary pale, the people around Trump. And what is missed about him is he’s kind of offputting. He doesn’t talk to other people in a way they would like to be spoken to. He’s able to make even popular ideas like a child tax credit sound completely bizarre when he talks about them in terms of punishing childless adults — that there is something here, I think, when people look at the world — and I’ve seen this in a lot of different dimensions of these kinds of folks — when they look at the world too much in numbers, the intangibles begin to dissolve for them.” “Although I think some of these tangibles aren’t so intangible. Right? Where you can look at JD Vance’s margins in Ohio, you can look at historically candidates who don’t have experience getting elected to some lower office and then ascending the ranks, underperform. It’s been a factor in our congressional midterm models for years, for example. But, look, in some ways, these VCs are obviously incredibly, deeply flawed people. And so, why do they succeed despite that? I think because the idea of having a longer time horizon, number one, and being willing to make these plus expected value, positive expected value, high risk, but very, very, very high-upside bets, and gathering a portfolio of them repeatedly, and making enough of these bets that you effectively do hedge your risk, those two ideas are so good that it makes up for the fact that these guys often have terrible judgment and are kind of vainglorious assholes — half of them, right? They’re interesting people too. I mean, they’re very interesting I think. And they — I’m happy that the book is able to present, I think, a complete journalistic portrait of some of them. But they have lots and lots of flaws, and it’s made up for by the fact that this is kind of a magic formula for making money.” “Let me get us back to the election. So we mentioned before Harris’s approval ratings have gone from significantly underwater to net favorable very, very fast. She’s now leading in head-to-head polls. More than that, there’s a real deep, whatever Republicans have convinced themselves to the contrary, organic enthusiasm that has unleashed itself around her. She turns out to be very memeable in a way I’m not sure people quite predicted. I know most Democrats didn’t predict this. I don’t think you predicted it. So what was missed here? What wasn’t in the Harris model that should have been?” “Yeah, maybe you really can meme your way to victory. [CHUCKLES]: I don’t know. I wouldn’t necessarily have thought that. I mean, there’s something about how it’s off trend a little bit, and it’s kind of unexpected a little bit. And there’s something about that, that I think people were ready for a vibe shift, right? I think people in politics neglect just how annoying the pedantic, dramatic, no fun tone of politics was and the having to be like serious all the time. And if the worst Republicans can say about Kamala Harris, oh, she laughs a lot, maybe it kind of suits the mood a little bit after so many years of doom and gloom. So maybe it was just spontaneous and lucky. I mean, it’s also the case maybe when Kamala Harris was a candidate for the nomination in 2019, I had these tiers, and the top tier was Joe Biden and Kamala Harris. And the line was always, O.K., I got one of those right and one of those about as wrong as possible. But she was seen as this rising, up-and-coming political talent, and maybe the combination of misaligned strategy in 2019 and then not being marketed well by the White House, and we debated before what the reasons for that are, maybe that was the underperformance. And the rising star that people thought she was kind of the real Kamala Harris after all.” “So Harris ended up choosing Tim Walz, the governor of Minnesota, as her VP pick. You made a case that it should have been Josh Shapiro. Tell me why.” “Pennsylvania, number one. There’s about a 4 percent chance in our model that Harris will lose the election because of Pennsylvania, where she wins the other Midwestern swing states but she’s 19 votes or fewer electoral votes fewer because of Pennsylvania. And if you’re a probabilist, then a 4 percent chance — because campaigns often don’t make a difference, right? If we go into a recession in the third quarter, then Harris will probably lose through no fault of her own. But in the worlds where campaign strategy can make a difference, then the VP being from Pennsylvania is a reasonably big upgrade. And the fact that he has demonstrated his popularity with this very diverse state that’s kind of a microcosm of the US as a whole — in Pennsylvania, you have the Northeast, you have the Midwest, and even you have a little bit of the South creeping in the Appalachian part of the state. You have the suburbs, you have rural areas, and you have one of the biggest cities in the United States. You have a big African-American vote. You have lots of famous colleges and things like that. You have everything there, and he’s 15 points above water approval-wise. And that’s pretty powerful information to work with. I happen to think that Tim Walz is an above-average pick, better than most, better than JD Vance. Not a particularly high bar, but better than a lot of the recent picks. I mean, I think he’s kind of memeable as America’s goofy dad kind of way, and he had a pretty moderate track record in Congress. And again, my premise is that, generally speaking, moderation wins. A lot of people disagree with that, but I think the empirical evidence is strong there. More progressive governance, of course, in Minnesota. But I think it was a somewhat risk-averse decision. Now, if you read —” “Why do you say that? I found this argument you’ve made very weird. So I think there’s a very good chance — I always told people on the VP pick my head says Shapiro and my heart says Walz.” “Yeah.” “I think that because I am a cautious person, if I were running for president, worried about losing Pennsylvania, I would have found it very hard not to pick Shapiro. Because if you don’t pick Shapiro, and you end up in a we lost Pennsylvania scenario, everybody’s going to blame you for blowing the decision that could have won Pennsylvania. In terms of the expected value, both on the front end and the back end, I understood Walz as a choice on vibes, this sort of energy, this momentum she has created. He was sort of able to upend and remake all Democratic messaging in a single morning Joe appearance. There is some intangible charisma to Walz that has made him — developed him overnight, this huge online fan base, that the cautious candidate, the one, listening to the consultants, the one reading Nate Silver polls, that candidate goes with Shapiro. Walz is something else. Why did you say that you understood Walz as risk averse?” “Because I think they were worried about news cycles where the left got mad, and/or the Gaza issue was elevated, and/or you had protests at the convention in Chicago in a couple of weeks. I think they were worried about that, and maybe kind of undermining what is clearly good vibes right now, and maybe overrating — I mean, maybe it’s not. Maybe I just think it’s the lower expected value decision of what gives Kamala Harris a higher chance of winning the electoral college in November.” “I think one of the questions I’ve been reflecting on — because I often think about, where do I disagree with writers I otherwise agree with? And I think I’m typically pretty aligned with you on a bunch of things, or Iglesias, or [INAUDIBLE], or some others. But a lot of you have really gotten into a view that I think takes the median voter theorem almost too seriously. That it’s like as if politics is unidimensional, and how close you are to ideologically the median voter is what decides elections. Which I do think moderation has an effect in. I mean, we see this in the political science research. But that doesn’t have a lot of room in that model for energy, for enthusiasm, for the mediation of politics — the thing that happens in between the candidate and the public for what is happening on social media, for what is happening on cable news. And you can often sort of back out explanations here and there. But I, for instance, think this sort of in retrospect explanation that what led Obama to victory was careful moderation — one of the things he did was moderate on some issues like gay marriage. Another thing he did was unleash astonishing levels of enthusiasm in the electorate for reasons orthogonal in many ways to his policy positions. And so I’m curious how you think about that. Because to me, one of the questions Shapiro and Walz raised, Shapiro and Harris sort of are a lot like each other. I think they sort of come off as the two smartest members of the law review. Right?” “Yeah, that’s interesting —” “Which is like kind of —” “— for sure.” “— not necessary the visual you want — maybe it is but might not be — and that there is something here that is I guess people call it vibes now. I feel like it’s a little dismissive. But how you play out in earned media, in social media, how much people want to talk about you, that feeling of enthusiasm, how do you think about that as somebody who builds models and handicaps politics?” “I mean, look, if you’re literally building a congressional model, there’s a model that forecasts the vote based on fundamentals, which means not the polls if you don’t have polling, for example, based on whatever it is, seven or eight factors. And one of those factors, if you’re incumbent, is how often do you vote with your party. And the more often you buck your party, actually the more often — like Susan Collins or Joe Manchin — then you tend to overperform in your congressional race. Now, that’s also one of eight factors. Right? And even when you have all eight factors, there’s still quite a bit of uncertainty in the race. So to me, it’s like this is something where if you’re used to looking at larger data sets, you can come up with counterexamples of Jon Tester is pretty progressive actually and somehow manages to get reelected in Montana with this kind of maybe Tim Walz-like folksy personality or something —” “Sherrod Brown. Sort of similar to that.” “Also pretty progressive. But if you take all the data from every congressional race since 1990, then it becomes clear in the aggregate, right? And I’d also say, if we could get progressives to the point where — I don’t know who we is in this sentence, because I’m not sure I identify as progressive — liberal but not progressive, I’d say — if we could get them to the point where they said, yes, the median voter theorem is mostly true but sometimes outweighed by other factors. But yeah, to get them to that point, instead of thinking, oh, you win elections by winning the base — I mean, that might have narrowly been true in an earlier —” “Wait, you’re turning this around on progressives. Because I’m asking it of you. I agree that progressives should take the median voter theorem more seriously. But I am asking you whether energy, enthusiasm, media — I just think attention in politics is undertheorized. I think if you look at Donald Trump, and you do a thing that I’ve seen people do, and say, look, he is more like the median voter on certain things like immigration, et cetera, or at least he was perceived as more moderate than Hillary Clinton and that’s why he won, I think that is an undertold story about Donald Trump that is somewhat true. I think that missing the showmanship of Donald Trump, the entertainment value, the energy he unlocks in people. There’s a reason that Trump had Dana White from the UFC and Hulk Hogan on his night of the RNC. So in 2020, Joe Biden’s view is that the election should be about Donald Trump, and Donald Trump’s view is that the election should be about Donald Trump. And that was a theory of attention they both agreed on, and it worked out for Joe Biden. In 2024, Joe Biden’s view is the election should be about Donald Trump. Donald Trump’s view was the election should probably be about Donald Trump. And that was a bad theory of attention. Biden had no way of shifting a narrative that wasn’t any good for him.” “Yeah.” “And so I guess this is what I’m getting at, that one thing that I worry about in some of this thinking among people I like is that attention is important. Candidates have different theories of it, but I don’t know that we know how to think about it as rigorously as I wish we did.” “Look, I agree. I mean, again, with Harris, maybe you do have to revise your views a little bit. I think also maybe in a campaign that’s a sprint and not a marathon, then maybe you never reach the long run. It seems possible. Usually, I’d say don’t worry about momentum over the next two weeks, because inevitably you’re going to have a bad news cycle later on. It’s just how the media works and it’s how elections work. It is possible they can just sprint their way to a memeified victory in this shortened, modified campaign. That they have a good convention, and that she wins whenever the debate is held, and then you’re in October and everyone’s crazy and explicitly partisan, they may be able to sprint to a narrow electoral college victory without having this skeptical news cycle. So that may be an argument for Walz, I think.” “One of the reasons on my mind is not actually Walz. And as I said before, because I do want to say this, I’m not sure who she should have picked as VP. I actually have very conflicted views on this, although I really, really enjoy Tim Walz, and really enjoyed interviewing him, and think he’s a pretty unusual political talent. But I think you could say the same about Josh Shapiro in different ways, and Pennsylvania is a very big state. But I’ve been interested in the shift in — look, you have a campaign staffed by many of the same people, particularly in the first two weeks, and yet the campaign’s tenor has completely changed. The tone of press releases is now they are trying to get you to talk about them and doing that by courting controversy, by being kind of mean in a way. Democrats have not been mean in a long time. That Tim Walz actually made a JD Vance couch joke in his introducing himself as her vice presidential pick speech — let’s put it this way, that is not something that Joe Biden campaign was going to do. They want people to talk about them. They want to court kind of controversy, outrage. They want attention. But I think the reason it’s all on my mind is what I am seeing in them is a radically different relationship to attention than the campaign that the same people were running two weeks ago.” “Yeah. And this why we rely on you for how much these people overlap. Like, that’s not something I really —” “They overlap tremendously.” “Yeah.” “I mean, it’s not the exact same people. Mike Donilon isn’t running things anymore. But there’s enough of the same people here that you’re not dealing with ‘nobody knew how to write these press releases’ a month ago.” “It is interesting that Joe Biden, based on the polling, would probably have been better off in election with low turnout. The one thing that might have saved him is if you get that special election, midterm election, lower turnout where people aren’t very happy about it, but they go to the polls and vote for Biden and the Trump people don’t bother to show up. Because unlike in the past, the marginal voters have been more likely to vote for Trump than for Biden. So maybe by having a really boring campaign, it kind of suited their interests. With Harris, who is bringing back some of the younger voters and some of the voters of color that had defected to Kennedy, or defected to Trump, or defected to sitting out the election, those are also some of the more marginal voters. And so, now, all of a sudden, she probably doesn’t mind as much higher turnout which is going to get young Latino women to vote for her or young Black men to vote for her when they might not have voted for Biden. And so it kind of matches the incentives of where you want to turnout to be on November 5.” “Tim Alberta in the Atlantic had a great piece on the way the Trump campaign was thinking about the race that came out around the time of the debate or right after the debate. And they felt they had Nevada, North Carolina completely locked up — and Georgia — and that this was really a race in three, maybe four states. My understanding is Harris and her team think they have re-expanded the map. They think that Nevada, Arizona, Georgia are for sure back in play. They think that North Carolina might be back in play. Do you think that’s true? Do you think the map has gotten bigger?” “I think that’s right. Because, again, look at the voters that Biden was falling off with. Nevada, people don’t remember, they think of it as kind of libertarian old miners, right? No, Nevada is extremely diverse, and it’s working class voters of color. Big fall-off constituency for Biden. Georgia, you have tons of young professionals, and tons of great colleges and universities, and, of course, tons of Black voters — the same groups that he’s declining from a little bit. North Carolina has been, interestingly, kind of close in the polls. Arizona is the one that didn’t seem to have moved quite as much, though there was one poll yesterday with Harris ahead there. But that’s right. I mean, I think the map has expanded, and it’s obviously plausible again now that she would win Georgia, especially with the Brian Kemp stuff not helping Trump one bit. At the moment — I was playing in a poker tournament, very on-brand, right — when Trump gets shot and has the iconic photo, which I’m not a Trump fan, but you kind of have to admire that, I think a little bit, I think a lot of people assume he’s going to win the election. I mean, with Biden already, he’s not going to lose after this. They try to shoot him, and he has this great photo opportunity, right? And then it seems like he’s at a high water mark. And then he picks JD Vance, and I think got a little arrogant.” [LAUGHS] “Because his initial instinct apparently was not to pick necessarily JD Vance and kind of talked out of it by his sons. And I don’t know what influence Peter Thiel or whatever had. But the VC guys were like, oh, JD Vance is kind of one of us. And he probably is smarter than the average VP or something. But that appeal has been demonstrated not to work. I mean, you saw it with Blake Masters for example, right? It works every now and then. I guess Rick Scott had a background in I don’t know what exactly, but like —” “Medicare fraud.” “O.K., yeah. [LAUGHS]: But for the most part, these —” “The guy the guy ran a health company that was convicted of the single largest Medicare fraud at that point in history.” “What I tell my VC friends is if you have a rich guy, just have him buy a basketball team or something. He’s not going to come across very well to the average voter. And I think they don’t understand that. And then, again, in a poker tournament or a poker home cash game, when you go from having a big stack and you’re kind of like, oh, this is so nice. Man, I’m going to go home and cash out my winnings. Maybe I’ll have a nice little whiskey at the bar or something. And this is going to be — I’ll text my friends about how well my session ran. And then you lose a big pot, and then you lose another big pot, and then you go on tilt. And before long, you have no chips left.” “What is tilt?” “Tilt is playing emotionally, particularly in poker or other forms of gambling. It’s often sparked by a bad beat. Meaning that you got unlucky. Or it can be sparked by getting bluffed and getting mad at your opponent. Or bad luck. Or sometimes you can actually have what’s called winner’s tilt too, where maybe this is what Trump had in picking JD Vance. You have a bunch of things that are going really well. I mean, this election was going about as well as it could for Donald Trump. He’s not a popular guy, yet he had moved ahead in some of the National polls by four or five points. It’s pretty hard to do. I mean, he’s lost the popular vote twice.” “Trump feels very on tilt to me. When you think about him, for Donald Trump, he had been pretty on his message. He was talking a lot about immigration. He was talking a lot about inflation. He was letting it be known that he was thinking about picking Doug Burgum. He seemed to be enjoying this idea that he was — people were longing for a stability They now associated with his presidency rightly or wrongly. They wanted the lower prices back. They don’t like the war in Gaza. They don’t like the war in Ukraine. Maybe Trump is a strong man who can bring it back. And he was kind of playing into that. And since the Harris switch and him beginning to fall in the polls, you feel this old Trump returning. The Trump who goes to Georgia and begins yelling at the governor — the Republican governor — of Georgia. The Trump that goes to the National Association of Black Journalists and begins to talk about how nobody knew Kamala Harris was Black. The Trump who is just trying out attack lines, trying to find something that will work no matter what the kind of cost might be. I mean, your description of him playing emotionally — he’s not listening to anybody right now. He’s flailing.” “And the fact that, according to the reporting, that they weren’t prepared for the eventuality when Joe Biden dropped out was kind of inexcusable. I mean, if you looked at prediction markets, it was immediately a live consideration after the debate. I think they overestimated the degree to which Democrats are a personality cult. I mean, they can be. There was maybe a personality cult around Obama, or Bill Clinton, or things like that. But there wasn’t one around Joe Biden. He was kind of always the candidate of the party. And it was not in the party’s interest any longer to have him as their nominee. And so the Democratic Party is capable and powerful in a way the GOP is not. And they extrapolated from their views to how Democrats would behave and underestimated the smart decision that the party was capable of making.” “I talked to Republicans about this, about why they weren’t more prepared, and one thing I heard from them is they just didn’t think Biden was going to step aside. I mean, if you’re a party that has completely bent the knee to Donald Trump and is now years and years into not being able to convince Donald Trump of functionally anything, it might shift your sense of how people in power, particularly the apex of power, act. It’s one reason — this is a place where you and I’ve been a little bit different — I’ve been more on the side of Joe Biden did something difficult that deserves praise. Because — and I think you see this in how Republicans were thinking — leaders just often don’t do this. The kind of personality that gets you to that point is not the kind of personality that leaves power gracefully. It’s why, when people are talking about dictators, there’s endlessly this talk of how to create golden parachutes for dictators. You’re dealing with a kind of human being that has told a story about their own essentialness. Going back to your point about Elon Musk and feeling like you’re the main character of global life — particularly you’ve become the American president — you sort of were the main character of global life for a while — that does something to you. Those people don’t give it up easily.” “No. And if you look at the history of — before there was whichever Amendment it was, 20-something Amendment —” “22.” “— that prevents you from running for more than two terms, it was pretty routine for candidates to tease — Woodrow Wilson had a stroke and wanted a third term. Harry Truman had like a 32 percent approval rating and wanted a third term, second full term. Old men are often pretty stubborn. And I think the most interesting thing is that if Harris wins — or maybe comes close, but mostly if she wins — what that will say about the primary system, right? Maybe we should go back to giving a larger role to superdelegates for example.” “I want to end on a part of your book I found really interesting, which is about the physical experience of risk — in gambling, but in other things. You talk about pain tolerance. You talk about how the body feels when you’re behind on a hand and you’re losing your chips. You’ve talked about being on tilt. But I see it in politics too. I mean, there is a physical question that comes into the decisions you make. I see it on this podcast. There are times when a question is physically uncomfortable for me to ask another person. Tell me a bit about how you think about this relationship between the body and the ability to act under pressure to make intuitive decisions in moments of very high stress.” “So human beings have tens of thousands of years of evolutionary pressure which is inclined to respond in a heightened way to moments that are high stakes, that are high-stress moments. If you’ve ever been in a situation where you saw someone’s life in danger or your own life was in danger — you know, I was in LA in January, and there was an armed robbery outside the place where I was trying to get just a cup of coffee. And time kind of slows down a little bit in situations like that. And you don’t realize how stressed out you are until I texted my partner and be like, LOL, almost got shot, ha, ha. And I was kind of like, oh yeah, I was too cool for school. And then an hour later, I’m getting some tacos or something and I almost break down. It’s like, oh my god, it could have gone really, really badly. Public speaking also triggers this for people because objectively it’s a pretty high-stakes thing. If you’re playing a $1 or $2 poker game, and it’s nothing for you, your body will when you’re playing a $100-200 game where it really matters — you will just know. You’ll experience that stress. Even if you suppress it consciously, it will still affect the way that you’re literally kind of ingesting your five senses. So if your heart rate goes up, that has discernible effects. But actually, your body is providing you with more information. You’re taking in more in these kind of short bursts of time. People who can master that zone — and I use the term zone intentionally, because it’s very related to being ‘in the zone’ like Michael Jordan used to talk about, or golfers, or hockey goalies, or whatever else — learning to master that and relish that is a very powerful skill. Because you are experiencing physical stress whether you want to or not.” “How much is that, in your view, in your experience, learnable, and how much of it is a kind of natural physical intelligence some people have and some people don’t?” “I think it’s actually quite learnable. It’s a little bit like if you’ve been on mushrooms before [LAUGHS]: then you kind of learn, oh, this is the part of the brain that is — this is the things that look a little funny when you’re on mushrooms, right? You can kind of maybe tone it up or tone it down a little bit. So it’s very much like that. I mean, it’s terrifying the first time it happens. But when you start to recognize it, and you kind of make a conscious effort to slow down a little bit, and take your time, and try to execute the basics, it’s not as much about trying to be a hero. It’s about trying to execute the basics. Because when everyone’s losing their shit, if you can do your basic ABC blocking and tackling, then you’re ahead of 95 percent of people. And keeping bandwidth free for dealing with emergency situations, that will take you very far.” “It’s funny, because that feels to me like a very important question that is hard to test in politics.” “Yeah.” “People have to make profound decisions under incredibly high stress. And we have simulacrums of it. The debate, in a way, is a simulacrum of that. Very, very high stress. Speeches on teleprompters are not very good analogies for that. But this question of how good is a person at that moment —” “I mean —” “— how do you evaluate that?” “I mean, Trump, after getting shot, kind of performed very well. And I think, again, the Harris moment of leaping right into action to secure the nomination also has to be seen as very good performance under stress. And Biden’s failure under stress — I mean, he went to some kind of spiral of some kind or another, physical, or mental, or whatever else. So those kind of three pivotal moments — the assassination, the debate, and then Harris seizing the nomination in record time — speak to the difference in performance. And that’s why the two of them, Harris and Trump, are still candidates for the presidency, and Biden is not.” “I was just reading Nancy Pelosi’s new book before I was reading yours, because I just had her on the show, and she talks about how, above all, she says, that what a Speaker of the House needs is intuition. They need to be able to act. And she says that the key thing is you have to act fast. Because every moment you don’t act, your options are diminishing. And I ended up thinking, then, when reading your book, of it. Because what she was describing is quite, I think, for her, physical. Like something in her knows how to act and is unafraid to act in those moments. The thing that was crucial about her, I think, in this process, inside the Democratic Party of getting Biden out, is she was willing to act in public to take the pressure of that in ways very few people were. And somebody had to be doing that in public to create space for others to be considering it in private. But you look at her career, and she has this sort of intuitive capability to know when to move. And there’s something in it that I don’t think she can explain how she does it, but it makes her a fascinating leader. People believe that she will act. And she will act because something in her knows when to act, and she’s unafraid.” “Yeah. So is gut instinct overrated or underrated? Well, it depends on how much experience you have, right? Poker players have — because now poker is actually kind of a solved game. There are computer solvers they’re called that spit out this very complicated solution to poker. Hard to execute in practice, but it’s technically speaking a solved game. However, the best poker players can have uncannily good instincts based on reading physical tells, just the kind of vibe someone gives off. And if — you know, I played a lot of Poker and writing this book, more live poker than I have in the past, and you develop a sixth sense. Not all the time. It helps if you’re well rested. But you develop a sixth sense for whether someone has a strong hand or something. Like they’re glowing green or something almost sometimes. And you can test it, because you can say, I know that I’m supposed to fold this hand here. It’s a little bit too weak to call against a bluff. But I just have a sense that he’s bluffing. And lo and behold, you’re right more often than you’d think — more often than you need to be to make that call correct based on the odds that you’re getting from the pot. So if Nancy Pelosi has decades and decades of experience in politics and reading the moves of how the coalition is moving, I mean, that’s something where intuition probably plays a pretty good role. And also the fact that being willing to work with incomplete information — I mean, I don’t know how much longer Biden could have — maybe they could have run out the clock [LAUGHS]: potentially.” “Oh, they 100 percent could of. That day when he sent that letter to congressional Democrats and said, I’m not leaving — this conversation is over, stop trying to overturn the will of the primary voters — I was getting congressional Democrats telling me, this is done. It’s a fait accompli. He’s quelled the rebellion. It looked to me like he had. I was talking to other people. They said, 10 percent shot he’s out. Nancy Pelosi goes on ‘Morning Joe’ two days later and says, we’re really looking forward to him making a decision. And I asked her about it. And I said, what was happening? I mean, he had just sent that letter. And she said, yeah, but that was just a letter.” “Yeah.” “I didn’t accept the letter as anything but a letter. I mean, there are some people who were unhappy with the letter. Let me say it a different — some said that some people were unhappy with the letter. I’ll put it in somebody else’s mouth. Because it was a — I don’t think — it didn’t sound like Joe Biden to me.” “I’m like, oh, you read a bluff.” “So I think Nancy Pelosi might be pretty good at poker.” “Good place to end. Always our final question — what are three books you’d recommend to the audience.” “So one book is pertinent to the discussion that we had a moment ago, which is called ‘The Hour Between Dog and Wolf.’ It’s written by John Coates, who is an academic economist who then became a derivatives trader, I think, for Deutsche Bank in New York and found out that the traders that he studied were really weird. Like these traders would have strange physical and mental stress responses to the market rising or falling. And he was so fascinated by it that he went back and became a neuroscientist and basically did studies of traders. So you test the testosterone of like an options trader or a guy who works at a hedge fund and see how it varies from day to day and correlates with performance. So yeah, so he studies the physical responses of risk-takers, and the book is called ‘The Hour Between Dog and Wolf.’ So that’s one recommendation. Number two, in a totally different direction, ‘The Making of the Atomic Bomb’ by Richard Rhodes. We didn’t talk as much about some of the AI stuff today, but at the end of the book there’s a pretty long, elaborate comparison between the Manhattan Project and the building of these large language models that some people think could be potentially very dangerous. And nuclear weapons are, I think, a pivot point in human history, and this book is kind of the best history of that. The third is called ‘Addiction by Design,’ by Natasha Schüll. And Natasha is an NYU anthropologist who studied Las Vegas as her thesis basically. She did a lot of reporting just about the properties of slot machines, and how addictive they are, and about the kind of casino gambling industry in general. And of course, she draws metaphors between that and the rest of society.” “Nate Silver, thank you very much.” “Thank you, Ezra.” [THEME MUSIC]

The last I looked, your model has Kamala Harris winning the election at around 52 percent — it might be a little different today. But this has been an unusual election. How much stock do you put in your model right now?
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Love is Something we should but don't fear or prepare for. A version of hell or heaven. Love is the one thing that is shown off as amazing or something that everyone will find. Or it is abundantly pushed off as a fairytale ending. love is an obnoxious emotion. Due to the fact love is the one thing that will make you or break you. WRITING A PERSUASIVE ESSAY about love - 19203791
Writing a stellar persuasive speech requires a carefully crafted argument that will resonate with your audience to sway them to your side. This feat can be challenging to accomplish, but an engaging, thought-provoking speech topic is an excellent place to start.
Persuasive Speech Example on Love Why Is Love Not a Gift but a Challenge? Introduction When we think about love, we imagine lovely pictures of romantic kisses, exciting adventures, and living happily ever after. Why do we always forget about the other things that stand behind these nice images? Why don't we remember fights, tears, and broken ...
The audience's reaction to this commercial showcases how persuasion works! In this chapter, we will define persuasive speaking and examine the strategies used to create powerful persuasive speeches. Figure 10.2: Caged Dogs 2 Defining Persuasive Speaking Persuasion is the process of creating, reinforcing, or changing people's beliefs or actions.
Explanation: A persuasive speech example would aim to convince the audience to adopt a new belief or take action on an issue. The speech would be structured with a strong organization, starting with an introduction that clearly states the issue, followed by body paragraphs that provide substantial evidence—such as quotations, examples, expert ...
We've compiled a list of 110 persuasive speech topics—broken down by category—for you to choose from or use as inspiration. Use the set of three questions we shared above to determine which of these interesting persuasive speech topics is right for you. Art, Media, and Culture.
The purpose of a persuasive speech is to convince your audience to agree with an idea or opinion that you present. First, you'll need to choose a side on a controversial topic, then you will write a speech to explain your position, and convince the audience to agree with you. You can produce an effective persuasive speech if you structure your ...
We produce and receive persuasive messages daily, but we don't often stop to think about how we make the arguments we do or the quality of the arguments that we receive. In this section, we'll learn the components of an argument, how to choose a good persuasive speech topic, and how to adapt and organize a persuasive message.
Persuasive Speech Outline, with Examples. A persuasive speech is a speech that is given with the intention of convincing the audience to believe or do something. This could be virtually anything - voting, organ donation, recycling, and so on. A successful persuasive speech effectively convinces the audience to your point of view, providing ...
Learn how to write a persuasive speech that keeps your audience engaged and convinced. Follow these steps to choose a topic, research your arguments, organize your speech, and more.
Short persuasive speech examples. #1. Title: Go Meatless on Mondays. Good afternoon everyone. I'm asking you to join me in adopting a simple change that can positively impact both our health and the planet - going meatless one day a week. On Mondays, commit to leaving meat off your plate and choosing vegetarian options instead.
3 Minute Speech on Friendship. Good Morning to one and all present here. I am going to present a speech about friendship. Friendship is one of the treasures that anyone can possess. God gave us the right to choose friends because they will be with us forever. Our parents and siblings are loving us as they are our own blood.
Hey guys it's me your friend today I wanna tell you about what is ️ love. Love is our life it is great thing in our life if we love someone then it is good and we should love all our Indians to increase our personality and respect towards others. We know that love is great thing among all others.
Biden's communications strategy was designed to make Trump bigger. Harris's strategy is to make him smaller. "These guys are just weird," Tim Walz said on "Morning Joe," and it stuck.
So this could be a controversial topic that I am using for my persuasive speech but I want to use that opportunity or I may never have that opportunity again (my teacher seems cool and not the kind of person that would think lefty unlike my Filipino teacher last s.y) I want to talk about the 'woke' culture (delusional people, ppl who force the undoctrine perspective & lgbtq members who wants ...
Free speech is kind of a pro-risk take in some ways because speech can cause effects, of course. On the other hand, you have various booms and busts in crypto. You have Las Vegas bringing in ...
If you are in need of a persuasive speech for school, college or work, here is an example of a persuasive speech. It is a very informative speech, but why not have a look at the statistics on NASA's website?
Answer 10 people found it helpful profile gardneradrian30 report flag outlined Answer: persuasive speech about why people should connect more with nature with 100 words Advertisement
If you were giving a persuasive speech about a topic, you are passionate about, describe how you would use AT LEAST THREE different nonverbal cues such as pacing, inflection, volume, body movements, and why you would incorporate these.
Type of paper: Speeches Subject: Environment Words: 239 Pollution is one of the biggest challenges faced by the world today. All the countries are adopting more and more laws on pollution reduction. Still, governmental actions cannot guarantee the complete elimination of this problem.
I LOVE THE IMAGE KSKFUDJSKFBEWJKAS I LOVE BOKUTO I LOVE HAIIYUU U ARE CULTURED MWAH MWAH MWAH HAVE A GREAT WEEKEND AND GOOD LUCK WITH UR PROJECT
In a persuasive speech about the importance of environmental conservation, the speak cites the research findings of a renowned climate scientist. Which rhetorical appeal is