Topics index

| eISSN: | 2585-2906 |

- How it works


Useful Links
How much will your dissertation cost?
Have an expert academic write your dissertation paper!
Dissertation Services

Get unlimited topic ideas and a dissertation plan for just £45.00
Order topics and plan

Get 1 free topic in your area of study with aim and justification
Yes I want the free topic

Midwifery Dissertation Topics
Published by Owen Ingram at January 3rd, 2023 , Revised On August 16, 2023
There have been midwives around for decades now. The role of midwives has not changed much with the advent of modern medicine, but their core function remains the same – to provide care and comfort to pregnant women during childbirth.
It is possible to be a midwife in the healthcare industry, but it is not always a rewarding or challenging career. Here are five things you didn’t know about midwifery nursing to help you decide if it could be the right career choice for you.
The profession of midwifery involves caring for women and newborns during pregnancy, childbirth, and the first few days following birth. Registered nurses are trained with four additional years of education along with major research on methods involve in midwifery and writing on midwifery dissertation topics, while midwives provide natural health care for mothers and children.
As a midwife, your role is to promote healthy pregnancies and births while respecting women’s rights and dignity. Midwives provide care to patients at every stage of life, from preconception to postpartum, family planning to home delivery to breastfeeding support.
Important Links: Child Health Nursing Dissertation Topics , Adult Nursing Topics , Critical Care Nursing Dissertation Topics . These links will help you to get a broad experience or knowledge about the latest trends and practices in academics.
Midwifery Is A Good Fit for the Following:
● Those who want to work with women, especially those at risk of giving birth in a hospital setting. ● Those who enjoy helping people and solving problems. ● Those who like to be creative and solve complex problems. ● Those who want to help others and make a difference in their lives.
Midwifery is a career with many benefits for both the midwife and the baby. They are well-trained and experienced in caring for pregnant women and newborns and often have access to the exceptional care that other nurses may not have.
Related Links:
- Evidence-based Practice Nursing Dissertation Topics
- Child Health Nursing Dissertation Topics
- Adult Nursing Dissertation Topics
- Critical Care Nursing Dissertation Topics
- Dementia Nursing Dissertation Topics
- Palliative Care Nursing Dissertation Topics
- Mental Health Nursing Dissertation Topics
- Nursing Dissertation Topics
- Coronavirus (COVID-19) Nursing Dissertation Topics
Midwifery Dissertation Topics With Research Aim
Topic:1 adolescence care.
Research Aim: Focus on comprehensive medical, psychological, physical, and mental health assessments to provide a better quality of care to patients.
Topic:2 Alcohol Abuse
Reseasrch Aim: Closely studying different addictions and their treatments to break the habit of drug consumption among individuals.
Topic:3 Birth Planning
Research Aim: Comprehensive birth planning between parents discussing the possible consequences of before, between, and after labour.
Topic:4 Community midwifery
Research Aim: Studying different characters in community midwifery and the midwife’s role in providing care for the infant during the early days of the child’s birth.
Topic:5 Contraception
Research Aim: Understand the simplicity of contraception to prevent pregnancy by stopping egg production that results in the fertilization of egg and sperm in the later stages.
Topic:6 Electronic fetal monitoring
Research Aim: In-depth study of electronic fetal monitoring to track the health of your baby during the womb, record construction per minute, and make a count of your baby’s heart rate.
Topic:7 Family planning
Research Aim: Importance to follow the basic rhythm methods for the couple to prevent pregnancy and use protection during the vaginal sex to plan a family without fertility treatments.
Topic:8 Foetal and newborn care
Research Aim: Expansion of the maternal-fetal and newborn care services to improve the nutritional quality of infants after delivery during their postnatal care time.
Topic:9 Foetal well being
Carefully tracking indications for the rise in heart rate of the fetal by weekly checkups to assess the overall well-being of the fetal.
Topic:10 Gender-based violence
Research Aim: Studying the consequences of male desire for a child that results in gender-based violence, harming the child’s physical and mental health.
Topic:11 Health promotion
Research Aim: Working on practices that help in controlling the amount of pollution of people, taking care of their overall health, and improving quality of life through adapting best health practices.
Topic:12 High-risk pregnancy
Research Aim: Calculating the ordinary risks of a high-risk pregnancy and how it affects a pregnant body resulting in a baby with poor health or any by-birth diseases, increasing the chance for complications.
Topic:13 HIV infection
Research Aim: Common causes of HIV infection and their long-term consequences on the body’s immune system. An in-depth study into the acquired immunodeficiency and the results leading to this.
Topic:14 Human Rights
Creating reports on human rights and their link with the freedom of thought, conscience, religion, belief, and other factors.
Topic:15 Infection prevention and control
Research Aim: Practices for infection prevention and control using efficient approaches for patients and health workers to avoid harmful substances in the environment.
Topic:16 Infertility and pregnancy
Research Aim: Evaluating the percentage of infertility and pregnancy, especially those facing no prior births, and who have high chances of infertility and pregnancy complications.
Hire an Expert Writer
Orders completed by our expert writers are
- Formally drafted in an academic style
- Free Amendments and 100% Plagiarism Free – or your money back!
- 100% Confidential and Timely Delivery!
- Free anti-plagiarism report
- Appreciated by thousands of clients. Check client reviews

I/O Example
Midwives are nurses who provide continuous support to the mother before, during, and after labour. Midwives also help with newborn care and educate parents on how to care for their children.
How Much Do Midwives Make?
The salary of a midwife varies depending on the type of work, location, and experience of the midwife. Midwives generally earn $132,950 per year. The average annual salary for entry-level midwives is $102,390.
The minimum requirement for becoming a midwifery nurse is a bachelor’s degree in nursing, with the option of pursuing a master’s degree.
An accredited educational exam can also lead to certification as a nurse-midwife (CNM). The American College of Nurse-Midwives (ACNM) enables you to practice independently as a midwife.
There are many pros and cons to working as a midwife. As a midwife, you have the following pros and cons:
- Midwives have the opportunity to help women during one of the most memorable moments in their lives.
- Midwives can positively impact the health of mothers and their children.
- Midwives can work in many hospitals, clinics, and homes.
- In midwifery, there are many opportunities for continuing education and professional development.
- You will often have to work nights and weekends, which can be mentally draining.
- You will have to travel a lot since most births occur in hospitals or centres in different areas.
- You will have to deal with stressors such as complex patients and uncooperative families.
- You will be dealing with a lot of pain, so you need to be able to handle it without medication or other treatment methods.
A career in midwifery is a great fit for those with a passion for health and wellness, an interest in helping people, and a desire to work in a supportive environment.
It is important to become involved in your local midwifery community if you are contemplating a career in midwifery – the best source of learning is your major research work, along with writing a lengthy thesis document on midwifery dissertation topics that will submit to your university to progress your midwifery career.
Free Dissertation Topic
Phone Number
Academic Level Select Academic Level Undergraduate Graduate PHD
Academic Subject
Area of Research
Frequently Asked Questions
How to find midwifery dissertation topics.
To find midwifery dissertation topics:
- Explore childbirth challenges or trends.
- Investigate maternal and infant health.
- Consider cultural or ethical aspects.
- Review recent research in midwifery.
- Focus on gaps in knowledge.
- Choose a topic that resonates with your passion and career goals.
You May Also Like
Here is a list of Geography Dissertation Topics to help you choose the one studies anyone as per your requirements.
A nurse who specializes in adult nursing assists the elderly with eating, bathing, dressing, and other daily tasks. It requires compassion, patience, excellent communication skills, and physical strength to succeed in this career.
Family law dissertation topics are included in a section of UK law. This topic is more of a minor category in terms of your broader research. Family law dissertations are challenging.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
This website is intended for healthcare professionals

- { $refs.search.focus(); })" aria-controls="searchpanel" :aria-expanded="open" class="hidden lg:inline-flex justify-end text-gray-800 hover:text-primary py-2 px-4 lg:px-0 items-center text-base font-medium"> Search
Search menu
Join our community of midwives.
Access our full range of content and never miss an issue
Latest content from British Journal of Midwifery

Mental wellbeing during summer
As the height of summer approaches (and with the weather in England seeming to have caught up to the season!), many of our readers at higher education institutions will no doubt be enjoying a more...

Transforming midwifery care
‘My dreams have changed – I am no longer just “doing my job”. I see the...
Epidural analgesia in labour and the risk of emergency caesarean: a retrospective observational study
This was a retrospective review of birth outcomes for 200 consecutive labours of women for whom the author provided any intrapartum care between 21 July 2020 and 24 June 2022. Intrapartum care was...
Local cultural perspectives of birth preparedness: a qualitative study in a rural subdistrict of Indonesia
This descriptive study used a qualitative approach to obtain rich, meaningful and detailed information about local cultural perspectives of birth preparedness in a rural subdistrict of East Java...
Midwifery students' experiences of learning to be ‘with woman’: a scoping review
This scoping review was conducted according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Scoping Reviews, as outlined by the Joanna Briggs Institute (Aromataris and Munn, 2020). A priori protocol was...
Latest CPD from CPD Launchpad
Call for a national stoma strategy, exercise and activity after stoma surgery, maternal mental health and breastfeeding duration: the role of optimism and coping strategies.

Breastfeeding knowledge assessment tools among nursing and midwifery students: a systematic review
This systematic review was conducted to identify tools that have been developed to evaluate breastfeeding knowledge and practice among nursing and midwifery students. The review followed the Preferred...

R v Noor: a landmark case in female genital mutilation prosecution
The WHO (2024) classifies female genital mutilation into four types. Type 1 is the partial or total removal of the clitoral glans (the external and visible part of the clitoris, which is a sensitive...

Biomechanics of childbirth
The title of the article says ‘using biomechanics’, although the author did not use biomechanics. In the introduction, the author states, ‘with advances in three-dimensional models of the human body...
Furthering our understanding
Your free revalidation toolkit.
A free revalidation portfolio and CPD resource for nurses and midwives.
Sponsored content

Neonatal outcomes following one previous caesarean section
A retrospective cohort design was used to compare data from women/pregnant people who elected for a vaginal birth after previous caesarean section to those opting for elective repeat caesarean...
Editor's pick
‘My dreams have changed – I am no longer just “doing my job”. I see the importance of giving the mother information so that she can understand the care we are offering and truly consent. This is...
More from The British Journal of Midwifery

Breast self-examination among community midwife and lady health visitor students in Pakistan
This descriptive cross-sectional study was conducted at the Horizon School of Nursing and Health Sciences in Karachi from December 2022–April 2023.

Impact of the midwife-led care model on mode of birth: a systematic review and meta-analysis

The diversity debate: is midwifery higher education addressing the challenges of systemic racism?
The RCM has been sending freedom of information requests to UK universities since 2010. However, their request in 2023 (which formed the basis of the subsequent report on which this series is based)...

Cultivating patient safety culture in midwifery practices through incident reporting
Incident reporting is more than a historical account of an incident; it is a proactive step toward identifying solutions and fostering an environment of learning (Hamed and Konstantinidis, 2022)....

Moving talks at the Primary Care Show
A few weeks ago, I attended this year's Primary Care Show at the National Exhibition Centre in Birmingham. I was very pleased to be able to speak with some of you about the journal and have the time...

Supporting families with baby loss
My name is Kirsty Knight, and I founded 4Louis with my parents, Bob and Tracey McGurrell, after losing my first child, Louis, to stillbirth in 2009. Louis' death turned our world upside down, and it...
Participants were recruited using an existing database of 1505 individuals who had previously taken part in studies on breastfeeding carried out by the second author and colleagues (Keevash et al,...
Digital mentoring on expressing breast milk for working mothers
This quasi-experimental study was a randomised control group, using a pre-test, post-test design. The participants were women recruited while pregnant for the previous study, who had since given...
Measure to improve: a pilot study of Birthrate Plus in the Netherlands
Birthrate Plus has been validated as a patient acuity measurement tool in the UK (Royal College of Midwives, 2018). To assess its value in a different setting, and to measure staffing levels, a pilot...
Want the latest BJM content?
Sign up for our newsletter to stay up to date.

Anaemia prevalence and risk factors in pregnant women in Oman: a retrospective case-control study
The study used a retrospective design to identify pregnant women with anaemia by examining medical records from the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology at the Sultan Qaboos University Hospital in...

Delivering care to women with congenital heart disease: the role of clinical nurse specialist
The joint cardiac and obstetric service at the Royal Brompton and Chelsea and Westminster Hospital, was established by Professor Phillip Steer and Dr Jane Sommerville in 1988. This was then expanded...

Threat to low-risk birth environments
While all areas of maternity services are currently struggling, the past 3 years in the UK have placed the provision of low-risk labour care at a serious disadvantage (National Institute for Health...

Prisons and midwifery
‘…if a pregnant woman receives a prison sentence, she may come directly from a violent domestic background, which “increases the risk of miscarriage, infection, premature birth, and injury or death...
Why choose British Journal of Midwifery?
BJM supports midwives by sharing expertise and advice to help you build confidence, grow professionally and improve care.
What's included
Evidence-based best practice
Peer-reviewed research
Practical guidance
CPD support
Subscriptions start:
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List

Midwifery-led researches for evidence-based practice: Clinical midwives engagement in research in Ethiopia, 2021
Keflie yohannes gebresilassie.
1 Midwifery Directorate, University of Gondar, Gondar, Ethiopia
Adhanom Gebreegziabher Baraki
2 Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, University of Gondar, Gondar, Ethiopia
Belayneh Ayanaw Kassie
3 Midwifery Directorate, School of Midwifery, University of Gondar, Gondar, Ethiopia
Sintayehu Daba Wami
4 Department of Environmental and Occupational Health and Safety, University of Gondar, Gondar, Ethiopia
Associated Data
All relevant data are within the paper and its Supporting information files.
Introduction
Health workers involvement in research had an impact on studies and whole system. They influence the clinical practice and help to implement evidences. Although International Confederation of Midwives (ICM) put research as one of the midwifery competencies and professional development activity, clinical midwives are poorly involved in research. Therefore, this study is aimed to assess clinical midwives engagement in research and bridge the gap through applicable strategies.
Institution-based cross-sectional study was conducted among clinical midwives working at public health facilities of Central and North Gondar Zone, Ethiopia from September to October, 2020 G.C. A structured and pre-tested self-administered questionnaire was used to collect data and entered into Epi-info version 7. Descriptive statistics was used to describe study population. Bi-variable and multi-variable logistic regression analysis was performed using STATA Version 14 and significance level declared at 95% confidence interval, p-value ≤ 0.05 and respective odds ratios.
Out of 335 clinical midwives, 314 were participated making the response rate 93.7%. Among the midwives, one hundred seventy two (54.8%) (95% CI: 49.08%, 60.37) have good skill on conducting a research. Clinical midwives with mothers with formal education [AOR: 1.90, 95% CI: (1.03, 3.51), currently work on referral hospitals [AOR: 2.33, 95% CI: (1.19, 4.53)] and having good level of knowledge on research [AOR: 2.19, 95% CI: (1.25, 3.82)] have significant association with having good research skill. Forty eight (15.2%) (95% CI: 11.5%, 19.7%) ever participated in research during their clinical practice. Clinical midwives who have good knowledge on research [AOR: 0.31, 95% CI: (0.14, 0.70)] are about 0.3 times less likely to participate on research than who have poor knowledge [AOR: 0.31, 95% CI: (0.14, 0.70)].
Conclusion and recommendation
Although more than half have good research skill, only a small proportion of midwives were involved in research. Capacity building activities are crucial to strengthen midwives skill on research and ensure their involvement.
Health workers involvement in research had an impact on studies and whole system. They influence the clinical practice and help to implement evidences [ 1 ]. The new approach named clinical academics had health care and academic roles, thus they combine practice with research [ 2 ]. Despite these recommendations [ 3 ], most college and universities didn’t have clinical academic [ 4 ] and they are not appropriately utilizing their potentials.
Health workers involved in research activities have various reasons that includes individual interest, as part of the curriculum, to improve service quality through shred of evidences, prior experience and/or exposure, professional development and financial benefits [ 1 ]. Nevertheless, International Confederation of Midwives (ICM) has put continuous professional development including research activities as one of midwifery competencies [ 5 ].
Clinical midwives perceived research as other professions role, especially the academic [ 6 ]. They had to aware of and involve in research to improve the clinical care [ 7 ] and overall quality of midwifery services as they can identify health problems for research from their experience.
Although research capacity building for clinical midwives is recommended [ 8 ], most involve as data collector and not more than that. Individuals were capacitated with training, support, workshops and using technologies. In low and middle-income countries projects, partnership and network had built health research capacity. However the lack of empirical research has become a challenge to see their effectiveness [ 9 ].
Once ability to influence practice with research, difficulties to work with the academics [ 1 ], and communication skills could affect their motivation [ 10 ] and confidence [ 11 ] to conduct research were individual barriers for conducting a research. Organizational leadership and management and research recognitions [ 1 ] also had an effect on research capacity. Resources for research such as dedicated time [ 12 , 13 ], research expertise [ 14 ], access to research findings [ 15 ] and opportunities [ 1 ]; availability of funding [ 12 , 14 , 16 ] and investment on research activity [ 15 , 17 ] could limit once research capacity and ability to conduct research. Other studies added that building research partnerships [ 10 ], having research culture [ 16 ], professional development opportunities and inadequate salaries [ 14 , 15 ] as cause to poorly involve in research. At Supra-organizational level, health research policies and governance [ 10 ] had an influence on participation and involvement in research.
Despite the observed gaps and limiting factors, scientific studies are lacking to study clinical midwives engagement in research and contributing factors. Thus, this study was done to bridge the gaps, which will help to set appropriate strategies and interventions to conduct midwifery-led researches. The study will be a baseline for conducting further studies and results will have an input for School of Midwifery at University of Gondar to improve the curriculum and built midwifery student’s research capacity at undergraduate level.
Methodology
Study design, setting, study population and sampling.
Institution-based cross-sectional study was conducted among clinical midwives working at public health facilities of Central and North Gondar Zone, Ethiopia, from September to October 2020 G.C. The study area covers two of the four zones of Amhara region (Central, west, north and south Gondar Zones), in which around 6,335,757 estimated populations are living. There are a total of 23 public hospitals and 222 health center. In North and Central Gondar Zone, around 350 trained registered clinical midwives are working in these institutions. All Midwives working in clinical setting of Central and North Gondar Zone were considered as the source and study population. All registered midwives working in the study area were included, whereas those who are working in administrative and academic area, midwives who are sick and unable to respond were excluded from the study.
Data collection and quality control
Before actual data collection, discussion was done on prevention measures of the current pandemic, Corona-Virus (Covid-19) and basic protective materials (Sanitizer, face mask and glove) were given for data collectors and supervisors. A structured pre-tested self-administered questionnaire was used to collect the data. The tool was developed by referring different literatures [ 18 ], first prepared in English and translated back into Amharic, the local language. The tool was checked for consistency statistically using Cronbach’s alpha. Training was given for five data collectors and supervisor on the objective of the study and confidentiality for two days. Pretest was done on 5% of sample size among midwives working other than the study area and necessary correction done. The collected data was assessed for completeness and accuracy on daily basis. The tool has socio-demographic and academic characteristics; questions for assessing research skill and participation. Clinical Midwives are a registered midwives working in the clinical setting/area. A participant who answers more than 50% of the skill assessment questions will be considered as having good skill on research. Similarly, a participant will be considered as practicing (conducting) research if s/he has ever involved in part of a research other than one conducted as a partial fulfillment of his or her midwifery study.
Data management and analysis procedure
Data was entered into Epi-info version 7 and exported to STATA version 14 for further analysis. Descriptive analysis like frequencies, percentages, means and standard deviations computed for all variables. Model fitness was tested with Hosmer and Lemeshow goodness of fit and both bi-variable and multivariate logistic regression models were carried out to estimate the association. Variables with a p -value of less than 0.2 in the bi-variable analysis were entered into the multivariable logistic regression analysis. Both Crude Odds Ratio (COR) and Adjusted Odds Ratio (AOR) with their corresponding 95% confidence intervals were estimated. Finally, variables with a P-value of less than 0.05 in multivariable logistic regression model were considered as significantly associated with knowledge and attitude towards research.
1. Socio demographic and academic characteristics
Out of 335 clinical midwives 314 were participated making the response rate 93.7%. Age of the midwives range from 18 to 50 years, with median age of 27 years old. More three fifth (66.9%) of the midwives age was between 25 to 29 years. Among all midwives, more than half (52.9%) were male, while two hundred seventy four (87.3%) were Urban dwellers. More than three fifth (63.1%) of the midwives’ were Bachelor degree holders, while majority (73.6%) were graduated from governmental colleges. Nearly there fifth of the midwives (58.6%) study with regular educational program ( Table 1 ).
| Variable | Number (#) | Percentage (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Less than or equal to 24 | 35 | 11.2 |
| 25–29 | 210 | 66.9 |
| 30 and above | 69 | 21.9 |
| Male | 166 | 52.9 |
| Female | 148 | 47.1 |
| Orthodox Christian | 293 | 93.3 |
| Muslim | 19 | 6.1 |
| Protestant | 2 | 0.6 |
| Urban | 274 | 87.3 |
| Rural | 40 | 12.7 |
| No formal Education | 237 | 75.5 |
| Have Formal education | 77 | 24.5 |
| No formal Education | 220 | 70.1 |
| Have Formal education | 94 | 29.9 |
| Diploma (level IV) | 98 | 31.2 |
| Degree | 198 | 63.1 |
| Masters and above | 18 | 5.7 |
| Governmental | 231 | 73.6 |
| Private | 83 | 26.4 |
| Regular | 184 | 58.6 |
| Extension | 130 | 41.4 |
| Yes | 216 | 68.8 |
| No | 98 | 31.2 |
| Specialized/Referral Hospital | 93 | 29.6 |
| General/Primary Hospital | 71 | 22.2 |
| Health Center | 150 | 47.8 |
| Labor and delivery Room | 220 | 70.1 |
| Family planning Room | 100 | 31.8 |
| Comprehensive Abortion Care Room | 53 | 16.9 |
| Antenatal Care Room | 138 | 43.9 |
| Others Specify** | 20 | 6.4 |
| <2 year | 43 | 13.7 |
| 2–4 | 114 | 36.3 |
| >4 | 157 | 50 |
| <4000 | 41 | 13.1 |
| 4000 and above | 184 | 58.6 |
| Not willing to mention | 89 | 28.3 |
Others*—dead
Others**—Gyn ward, Postnatal care, Youth Friendly Service, Immunization
2. Clinical midwives research skill and practice
2.1 skill of clinical midwives to conduct a research.
Among the midwives, one hundred seventy two have good skill on conducting a research making the magnitude 54.8% (95% CI: 49.08%, 60.37).
Among the midwives, nearly half (48.4%) reported as having high skill on identifying research problems, while 132 (42%) have high skill on conducting literature review. More than two fifth (42.7%) and one hundred twenty three (39.2%) of the midwives reported as having poor skill on data management and data analysis using software respectively. Clinical midwives reported as they have high skill on applying for research funding (35%) and to give advice for less experienced researchers (28.7%). ( Table 2 ).
| Variable | Poor skill | Moderate Skill | High Skill |
|---|---|---|---|
| Identify research Problems | 93 (29.6%) | 69 (22%) | 152 (48.4%) |
| Conduct literature Review | 90 (28.7%) | 92 (29.3%) | 132 (42%) |
| Tool development and data collection | 93 (29.6%) | 65 (20.7%) | 156 (49.7%) |
| Data management using software | 134 (42.7%) | 60 (19.1%) | 120 (38.2%) |
| Conduct Data analysis | 123 (39.2%) | 78 (24.8%) | 113 (36%) |
| Interpret analyzed data | 110 (35%) | 83 (26.4%) | 121 (38.5%) |
| Write discussion and conclusion | 109 (34.7%) | 77 (24.5%) | 128 (40.8%) |
| Put references using software | 95 (30.3%) | 83 (26.4%) | 136 (43.3%) |
| Write manuscript for publication | 133 (42.4%) | 92 (29.3%) | 89 (28.3%) |
| Present research findings in conferences | 108 (34.4%) | 81 (25.8%) | 125 (39.8%) |
| Give advice for less experienced researchers | 125 (39.8%) | 99 (31.5%) | 90 (28.7%) |
| Applying for research funding | 102 (32.5%) | 102 (32.5%) | 110 (35%) |
2 . 1 . 1 . Factors associated with clinical midwives skill on research . To identify factors, bi-variable and multi-variable logistic regression analysis was carried out for seven explanatory variables. In multi-variable analysis; Mother educational status of having formal education; currently working on referral health facilities; having good level of knowledge on research and taking prior research course have a positive significant association with skill on research ( Table 3 ).
| Variable | Level of research skill | Crude Odds Ratio [95% CI] | Adjusted Odds Ratio [95% CI] | P-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Good | Poor | ||||
| Less than equal to 24 | 17 (5.4%) | 18 (5.7%) | 1 | 1 | |
| 25 to 29 | 106(33.8%) | 104(33.1%) | 1.08 [0.53, 2.21] | 0.95 [0.43, 2.08] 1.52 | |
| 30 and above | 49 (15.6%) | 20 (6.4%) | 2.59 [1.12, 6.02] | [0.60, 3.85] | |
| No formal education | 116 (36.9%) | 121 (38.5%) | 1 | 1 | |
| Have formal Education | 56 (17.8%) | 21 (6.7%) | 2.78 [1.58, 4.88] | ||
| Governmental | 146 (46.5%) | 85 (27.1%) | 3.77 [2.21, 6.43] | 1.56 [0.82, 2.97] | |
| Private | 26 (8.3%) | 57 (18.2%) | 1 | 1 | |
| Referral Hospitals | 70 (22.3%) | 23 (7.3%) | 4.44 [2.50, 7.87] | ||
| General/Primary Hospital | 41 (13.1%) | 30 (9.6%) | 1.99 [1.13, 3.54] | 1.77 [0.93, 3.38] | |
| Health Center | 61 (19.4%) | 89 (28.3%) | 1 | 1 | |
| Yes | 144 (45.9%) | 72 (22.9%) | 5.00 [2.97, 8.42] | 1.95 [0.99, 3.82] | 0.05 |
| No | 28 (8.9%) | 70 (22.3%) | 1 | 1 | |
| Good | 109 (34.7%) | 45 (14.3%) | 3.73 [2.33, 5.97] | ||
| Poor | 63 (20.1%) | 97 (30.9%) | 1 | 1 | |
| Yes | 35 (11.1%) | 13 (4.1%) | 2.54 [1.28, 5.01] | 1.26 [0.59, 2.71] | |
| No | 137 (43.6%) | 129 (41.1%) | 1 | 1 | |
Clinical midwives who take prior research course were about 1.9 times more likely to have good research skill than their counterparts. [AOR: 1.95, 95% CI: (1.00, 3.82)].
Clinical midwives who have mothers with formal education are about 1.9 times more likely to have good research skill. [AOR: 1.90, 95% CI: (1.03, 3.51)].
Clinical midwives who currently work on specialized/referral hospitals were about 2.3 times more likely to have good research skill than their counterparts. [AOR: 2.33, 95% CI: (1.19, 4.53)].
Clinical midwives who have good level of knowledge on research are about 2.2 times more likely to have good research skill than their counterparts. [AOR: 2.19, 95% CI: (1.25, 3.82)].
2.2. Clinical midwives involvement in conducting research
Among all the midwives, forty eight (15.2%) (95% CI: 11.5%, 19.7%) ever participated in research during their clinical practice. ( Fig 1 ).

More than half (52.1%) have involved in one research activities, while thirty (9.6%) have a responsibility of data collection in the research they involved. Nearly three fifth (72.9%) believe that the research they involved in contributed to the policy and/or the clinical practice in any way. Among the midwives, twenty three (7.3%) ever present at conferences and 13 (4.1%) ever publish research findings. ( Table 4 ).
| Variable | Number | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Yes | 48 | 15.2 |
| No | 266 | 84.8 |
| (n = 48) | ||
| One | 25 | 52.1 |
| Two and above | 23 | 47.9 |
| Coordination of a research project | 18 | 5.7 |
| Selection of research problems | 27 | 8.6 |
| Review of the literature | 18 | 5.7 |
| Recruitment of participants | 17 | 5.4 |
| Data collection | 31 | 9.9 |
| Data management and analysis | 11 | 3.5 |
| Writing research report / manuscript preparation | 16 | 5.1 |
| Midwife | 34 | 70.8 |
| Physicians/Doctors | 17 | 35.4 |
| Nurse and Other public health professionals | 27 | 32.6 |
| Yes | 35 | 72.9 |
| No | 13 | 27.1 |
| Yes | 23 | 7.3 |
| No | 291 | 92.7 |
| Yes | 13 | 4.1 |
| No | 301 | 95.8 |
| One | 8 | 61.5 |
| Two and above | 5 | 38.5 |
2 . 2 . 1 . Factors associated with clinical midwives practice on a research . To identify factors, bi-variable and multi-variable logistic regression analysis was carried out for five explanatory variables that have association with outcome variable. In multi-variable analysis; knowledge level on research course have a negative significant association with participation on research. ( Table 5 ).
| Variable | Participate on Research | Crude Odds Ratio [95% CI] | Adjusted Odds Ratio [95% CI] | P-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yes | No | ||||
| Male | 33 (10.5%) | 133 (42.4%) | 0.46 [0.24, 0.88] | 0.55 [0.27, 1.10] | |
| Female | 15 (4.8%) | 133 (42.4%) | 1 | 1 | |
| Governmental | 44 (14%) | 187(59.6%) | 0.22 [0.08, 0.62] | 0.57 [0.18, 1.80] | |
| Private | 4 (1.3%) | 79 (25.2%) | 1 | 1 | |
| Yes | 45 (14.3%) | 171 (54.5%) | 0.12 [0.34, 0.40] | 0.30 [0.80, 1.11] | |
| No | 3 (1.0%) | 95 (30.3%) | 1 | 1 | |
| Good | 39 (12.4%) | 115 (36.6%) | 0.18 [0.08, 0.38] | ||
| Poor | 9 (2.9%) | 151 (48.1%) | 1 | 1 | |
| Good | 35 (11.1%) | 137 (43.6%) | 0.39 [0.20, 0.78] | 0.72 [0.34, 1.50] | |
| Poor | 13 (4.1%) | 129 (41.1%) | 1 | 1 | |
Clinical midwives who have good knowledge on research are about 0.3 times less likely to participate on research than who have poor knowledge. [AOR: 0.31, 95% CI: (0.14, 0.70)].
The ICM strongly recommends involvement of midwives in research to provide high quality midwifery services [ 19 ]. This study was conducted to assess clinical midwife’s engagement on research and associated factors in Northwest Ethiopia. A total of three hundred fourteen midwives working at public health facilities were participated and majority (63.1%) were registered midwives with Bachelor degree holders.
Only nearly above half (50.6%) of the midwives say that their facility has continuous professional development program for staffs including midwives and this indicate that there is a limited opportunity to upgrade oneself. Unless there is no adequate and continual support to midwives, quality of midwifery services provided for the women could be affected [ 20 ]. A study in Tanzania was also evident that lack of evidence-based practices supported with research could result to poor service provision for patients (30% to 40%) and to have poor health outcomes [ 21 ]. A recent studies review highlighted that midwifery and nurses research publication are increased and suggested to have capacity building activities for strengthening the observed result [ 22 ]. Although it is not found significant, level of income is associated with quality of midwives performance on provision of care as evidenced by a study conducted in Gaza [ 23 ]. Professional benefits such as good salary might have an effect on midwives motivation and retention.
A significant proportion (52.9%) of midwives also responded that their health facilities doesn’t conduct research activities relevant to clinical practice. This might be due to that majority (64.5%) of midwives work on Primary Health Care units (Health Centers and Primary Hospitals). In Ethiopian health care system, facilities are not expected to conduct research activities unless they have teaching role, in addition to patient care service [ 24 ]. Midwives also reported that in addition to poor support from their facility (63.1%) and other professionals (60.2%), there are no opportunities to participate in research conferences (52.9%). As a result midwives poorly utilized research findings in their clinical service [ 25 ]. Moreover lack of dedicated time and poor implementation of research findings further deteriorate the application of research in the clinical practice [ 26 ].
In our study higher odds of good research skill was noted among midwives with formal maternal education (1.9 times) and it has an effect on academic performance [ 27 ].
Midwives who work on specialized/referral hospitals were found to have higher good research skill (2.3 times) than who work in primary health care facilities (health centers). This finding is supported with recent study conducted in North Gondar [ 25 ] and might be reasoned with that in referral health facilities there might be different opportunities to learn about research and related activities as they are teaching hospitals. Moreover these facilities are more likely to utilize research findings in their day too day clinical practice [ 25 ].
Having good research knowledge was associated with having good skill on research (2.2 times). Both research knowledge and skill are crucial to conduct a research as they are interrelated competencies.
Our study found that a small proportion of midwives (15.2%) ever participated in research during their clinical practice, in which 9.6% as data collector. This indicate that there is limited opportunities for midwives to be involved in research activities. Although a higher proportion (36.4%) of Australian nurses were reported as they involved in research, there is still a deficiency in health professional’s engagement in research activities [ 28 ]. In Latin America and the Caribbean, a review of studies also found that there is gap on midwifery-led researches, where most (95.8%) studies were nurses-led [ 29 ]. In our study, although more than three fifth (70.8%) of the midwives reported as they participated in a midwives-led researches, their capacity could be improved if they have the opportunity to work collaboratively with other disciplines such as public health experts, epidemiologists and physicians. Nearly three fifth (72.9%) believe that the research they involved in contributed to the policy and/or the clinical practice in any way. This is indicate that midwives have a positive understanding on the research activities they involved in. As they know the practical setting, they can identify and suggest on the real problem that will benefit the woman and her child [ 7 ].
Although midwives have good knowledge on research, they were less likely (0.3 times) to ever participate on research than who have poor knowledge. This indicate that there is limited opportunities for midwives with adequate research knowledge. This might be due to that a significant proportion of midwives (47.8%) work on health centers and opportunities are scarce.
The study find that research capacity of clinical midwives is not adequate. Only small proportion (15.2%) of midwives participated in research and having good knowledge on research was associated with it. Similarly research skill was associated with mothers with formal education, currently working in specialized /referral health facilities, and having good knowledge on research.
Recommendation
Ethiopian Ministry of Health better to capacitate health facilities to conduct local researches, particularly primary and general hospitals. It is also better to give priority and support health professionals working in the clinical setting to conduct research and related activities. With the existing continuous professional development programs, Regional Health Bureau better to expand opportunities for clinical midwives working in the region.
Ethiopian Midwifery Association (EMwA), University of Gondar and School of Midwifery better to contribute a lot to support clinical midwives with capacity building activities on research such as training, create opportunities and arrange conferences so that they can be involved and conduct researches in their clinical practice. Strengthening the integration of the school and hospital midwifery coordinator is also crucial to work collaboratively and share experience on research and related activities. Moreover it is good to provide dedicated time for clinical service providers including midwives to participate in research and related activities.
Supporting information
Acknowledgments.
We are indebted to the University of Gondar for the approval of the ethical clearance. The authors also forward their gratitude to study participants, data collectors and supervisors who participated in the study.
Funding Statement
The authors received no specific funding for this work.
Data Availability
Strengthening Midwifery Research
- First Online: 06 January 2021
Cite this chapter

- Joy Kemp 4 ,
- Gaynor D. Maclean 5 &
- Nester Moyo 6
902 Accesses
1 Citations
Considering research as an integral part of midwifery education and an indispensable tool in evidence-based practice provides the starting point in this chapter. Network theory is considered prior to exploring midwifery research networks and other initiatives in this context. Examples of initiatives to promote research through universities and professional associations are provided. Priority areas for midwifery research are explored, and the importance of high-quality research is considered in the context of providing evidence upon which safe practice can be based. The chapter concludes by considering the place of midwifery research in the wider context of health care and its significance in the development of the profession of midwifery.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Additional Resources for Reflection and Further Study
Visit the website of the Lugina Africa Midwives Research Network (LAMRN) at: http://lamrn.org/ Examine the ambitions and achievements of this network and consider how such a network may be replicated in other regions.
Explore the website of the Journal of Asian Midwifery (JAM) at: https://ecommons.aku.edu/jam/ Reflect on the aims and scope of the journal and consider its role in promoting midwifery research and enhancing evidence-based practice.
Readers may wish to compare and contrast the activities of the two structures described above and consider what strengths could be gleaned from both in order to establish a wider network for undertaking and disseminating midwifery research.
Google Scholar
World Health Organization (2019) Setting the research agenda: read about the current and ongoing research priorities in maternal, newborn and adolescent health at: https://www.who.int/maternal_child_adolescent/research/en/ . Recent research publications are regularly updated here too.
Soltani H, Low LK, Duxbury A et al (2016) Global midwifery research priorities: an international survey. Int J Childbirth 6(1):5–18 Consider these in the context of your own practice and experience
Article Google Scholar
In the context of global research priorities, explore what the National Institute of Health Research (NIHR) Global Health Research Group are doing to address stillbirth and perinatal mortality in Sub-Saharan Africa: https://sites.manchester.ac.uk/stillbirth-prevention-africa/ . Accessed 23 Oct 2019.
Abuya T et al (2015) Exploring the prevalence of disrespect and abuse during childbirth in Kenya. PLoS One 10(4):e0123606. Accessed 3 Oct 2019. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0123606
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
African Journal of Midwifery (2017) African J Midwifery & Women’s Health. MA Healthcare. http://www.magonlinelibrary.com/toc/ajmw/current . Accessed 12 Mar 2020
American College of Nurse-Midwives (2019) Midwifery Research Interest Groups. American College of Nurse Midwives. http://www.midwife.org/Midwifery-Research-Interest-Groups . Accessed 15 Oct 2019
Australian College of Midwives (2019) Research and innovation: Australian College of Midwives: https://www.midwives.org.au/interest-group/research-and-innovation . Accessed 15 Oct 2019
Azmoud E, Aradmehr M, Dehghani F (2018) Midwives’ attitude and barriers of evidence based practice in maternity care. Malay J Med Sci 25(3):120–128. https://doi.org/10.21315/mjms2018.25.3.12
Barnes S (2019) Empowered midwives could save lives. New Security Beat, Wilson Center, Environmental Change and Security. https://www.newsecuritybeat.org/2019/08/empowered-midwives-save-lives/ . Accessed 16 Oct 2019
Begeley C, Mccarron M, Huntley-Moore S et al (2014) Successful research capacity building in academic nursing and midwifery in Ireland: an exemplar. Nurse Educ Today 34(5):754–760
Bogdan-Lovis E, Sousa A (2006) The contextual influence of professional culture: certified nurse-midwives’ knowledge of and reliance on evidence-based practice. Soc Sci Med 62(11):2681–2693
Bogren M, Doraiswamy S, Erlandsson K (2017) Building a new generation of midwifery faculty members in Bangladesh. J Asian Midwives 4(2):52–58
Bonilla H, Ortiz-Llorens BM et al (2018) Implementation of a programme to develop research projects in a school of midwifery in Santiago. Chile Midwifery 64:60–62
Bowser D, Hill K (2010) Exploring evidence for disrespect and abuse in facility-based childbirth: report of a landscape analysis. USAID-TRAction Project, University Research Corporation, LLC, and Harvard School of Public Health, Bethesda, MD. http://www.tractionproject.org/sites/default/files/Respectful_Care_at_Birth_9-20-101_Final.pdf
Brucker M, Schwarz B (2002) Fact or fiction? International Confederation of Midwives Triennial Conference Proceedings. Austria, Vienna
Burrowes S, Holcombe SJ, Jara D et al (2017) Midwives’ and patients’ perspectives on disrespect and abuse during labor and delivery care in Ethiopia: a qualitative study. BMC Preg Childbirth Open Access 17:263. https://bmcpregnancychildbirth.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12884-017-1442-1 . Accessed 8 Oct 2019
Directorate General of Nursing and Midwifery (2017) National Guidelines for Midwives, Directorate General of Nursing and Midwifery, Bangladesh. http://dgnm.gov.bd/cmsfiles/files/SOP%20for%20Midwives.pdf . Accessed 23 Oct 2019
Doctoral Midwifery Research Society (2020) DMRS background and membership. https://www.doctoralmidwiferysociety.org/ . Accessed 3 Jun 2020
Einstein A, Shaw GB (2009) Einstein on cosmic religion: and other opinions and other aphorisms. Dover, New York
European Midwives Associations (2019) EU Research. European Midwives Association. http://www.europeanmidwives.com/eu/eu-research . Accessed 15 Oct 2019
Forss K, Maclean G (2007) Evaluation of the Africa midwives research network. A study commissioned by the Swedish International Development Cooperation Agency. Sida, Stockholm
Forss K, Birungi H, Saasa O (2000) Sector wide approaches: from principles to practice. A study commissioned by the Department of Foreign Affairs, Dublin, Ireland. Final report 13/11/2000 Andante – tools for thinking AB. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/252177958_Sector_wide_approaches_from_principles_to_practice . Accessed 26 Oct 2019
Glacken M, Chaney D (2004) Perceived barriers and facilitators to implementing research findings in the Irish practice setting. J Clin Nurs 13(6):731–740. Accessed 3 Jun 2020. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2702.2004.00941.x
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Goyet S, Sauvegrain P, Schantz C et al (2018) State of midwifery research in France. Midwifery 64(101–109):2018
Granovetter M (1973) The strength of weak ties. Am J Sociol 78:1360–1380
Guyatt GH, Sackett DL, Sinclair JC et al (1995) Users’ Guides to the Medical Literature: IX. A Method for Grading Health Care Recommendations. JAMA 274(22):18001804. Accessed 16 Oct 2019. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.1995.03530220066035
Hommelstad J, Ruland CM (2004) Norwegian nurses’ perceived barriers and facilitators to research use. Assoc Perioper Reg Nurs J 79(3):621–634. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0001-2092(06)60914-9
Hunter B (2013) Implementing research evidence into practice some reflections on the challenges. Evid Based Midwifery 11(3):76–80
International Confederation of Midwives (2014) Basic and ongoing education for midwives: position statement. strengthening midwifery globally: PS2008_001 V2014. International Confederation of Midwives, The Hague. https://www.internationalmidwives.org/assets/files/statement-files/2019/06/basic-and-ongoing-education-for-midwives-eng-letterhead.pdf . Accessed 15 Oct 2019
International Confederation of Midwives (2018) Research Standing Committee: https://www.internationalmidwives.org/our-work/research/research-standing-committee.html [last accessed 09.11.2020]
International Confederation of Midwives (2019) Research: Midwifery led research. International Confederation of Midwives, The Hague. https://www.internationalmidwives.org/our-work/research/ . Accessed 23 Oct 2019
Iribarren S, Larsen B, Santos F et al (2018) Clinical nursing and midwifery research in Latin American and Caribbean countries: a scoping review. Int J Nurs Pract 24(2):e12623. Accessed 18 Oct 2019. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijn.12623
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Kajermo KN, Boström A-M, Thompson DS et al (2010) The BARRIERS scale—the barriers to research utilization scale: a systematic review. Implement Sci 32(5):1–22. https://doi.org/10.1186/1748-5908-5-32
Kennedy HP, Cheyney M, Dahlen H et al (2018) Asking different questions: research priorities to improve the quality of care for every woman, every child. Lancet Glob Health. Revised May 2018. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/birt.12361 . Accessed 28 May 2020
Khammarnia M, Haj Mohammadi M, Amani Z et al (2015) Barriers to implementation of evidence-based practice in Zahedan teaching hospitals, Iran, 2014. Nurs Res Pract:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/357140
Kolfenbach M, Birdsall K (2015) (2015) international cooperation: strengthening midwifery in Central Asia. J Asian Midwives 2(2):57–61
Koninklijke Nederlandse Organisatie van Verloskundigen (KNOV) (2013) Midwifery Research Network, Dutch Midwives Association. https://www.knov.nl/vakkennis-en-wetenschap/tekstpagina/117-2/midwifery-research-network/hoofdstuk/45/midwifery-research-network/ . Accessed 15 Oct 2019
Laisser R, Chimwaza A, Omoni G et al (2019) Crisis: an educational game to reduce mortality and morbidity. Afr J Midwifery Women Health 13:1–6. https://doi.org/10.12968/AJMW.2018.0025
Lavender T, Omoni G, Laisser et al (2019) Evaluation of an educational board game to improve use of the partograph in sub-Saharan Africa: a quasi-experimental study. Sex Reprod Healthc (20) 54–59
Lugina African Midwives Research Network (2019) The Lugina Africa Midwives Research Network. http://lamrn.org/ . Accessed 4 Jun 2020
Luyben A, Winjen H, Oblasser C et al (2013) The current state of development of midwifery and midwifery research in four European countries. Midwifery 29(5):417–424. Accessed 1 Jun 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.midw.2012.10.008
Maclean GD, Forss K (2010) An evaluation of the Africa midwives research network. Midwifery 26:e1–e8
Maclean G, Laisser R (2020) The use of educational games in midwifery. Afr J Midwifery Women Health 14(91):1–10
Mills J, Yates K, Harrison H et al (2016) Using a community of inquiry framework to teach a nursing and midwifery research subject: an evaluative study. Nurse Educ Today 43:34–39
Munro J, Spiby H (2001) Evidence into practice for midwifery-led care: part 2. Br J Midwifery 9:771–774
Munro J, Spiby H (2010) The nature and use of evidence in midwifery care: evidence-based midwifery. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/242188203_1_The_Nature_and_Use_of_Evidence_in_Midwifery_Care . Accessed 28 May 2020
Muoni T (2014) Decision-making, intuition and the midwife: understanding heuristics. BJM 20(1). Published Online: 16 Aug 2013. Accessed 26 Oct 2019. https://doi.org/10.12968/bjom.2012.20.1.52
Nanda G, Switlick K, Lule E (2005) Accelerating progress towards achieving the MDG to improve maternal health: a collection of promising approaches. Health, Nutrition & Population Discussion Paper. The International Bank for Reconstruction and Development/The World Bank, Washington, DC, p 20433
National Institute of Health Research (2020) Stillbirth prevention in sub-Saharan Africa. The National Institute of Health Research and University of Manchester. https://sites.manchester.ac.uk/stillbirth-prevention-africa/ . Accessed 4 Jun 2020
Ndwiga C, Maingi G, Serwanga J et al (2017) Exploring provider perspectives on respectful maternity care in Kenya: “Work with what you have”. Reprod Health 14:99. Accessed 8 Oct 2019. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12978-017-0364-8
New Zealand College of Midwives (2019) Research: New Zealand College of Midwives. https://www.midwife.org.nz/midwives/research/ . Accessed 15 Oct 2019
Nohria N, Eccles RG (eds) (1992) Networks and organisations: structure, form and action. Harvard Business School Press, Boston
Olsson A, Adolfsson A (2011) Midwife’s experiences of using intuition as a motivating element in conveying assurance and care. Health 3:453–461. Accessed 26 Oct 2019. https://doi.org/10.4236/health.2011.37075
Perrow C (1986) Complex organisations: a critical essay. Random House, New York
Piore MJ (1990) Fragments of a cognitive theory of technological change and organizational behaviour. In: Nohria N, Eccles RG (eds) Networks and organisations: structure, form and action. Harvard Business School Press, Boston
Porter ME (1990) The competitive advantages of nations. Free Press, New York
Book Google Scholar
Renfrew MJ (1997) The development of evidence-based practice. Br J Midwifery 5(2):100–104
Royal College of Midwives (2019) Evidence-based midwifery. Royal College of Midwives publications. https://www.rcm.org.uk/publications . Accessed 26 Oct 2019
Sackett DL, Rosenberg WM, Gray JA et al (1996) Evidence-based medicine: what it is and what it isn't. Editorial: BMJ. Accessed 16 Oct 2019. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.312.7023.71
Siwha J, Roth C (2004) Evidence-based practice. Ch 4. In: Henderson C, Macdonald S (eds) Mayes Midwifery. Bailliėre Tindall, Edinburgh
Soltani H, Low LK, Schuiling KD et al (2016) Global midwifery research priorities: an international survey. Int J Childbirth 6(1):5–1
Sun C, Larson E (2015) Clinical nursing and midwifery research in African countries: a scoping review. Int J Nurs Stud 52(5):1011–1016
Sun C, Dohrn J, Klopper H et al (2015) Clinical nursing and midwifery research priorities in eastern and southern African countries: results from a Delphi survey. Nurs Res 64(6):466–475
Sweileh WM, Al-Jabi SW, Zyoud SH et al (2019) Nursing and midwifery research activity in Arab countries from 1950 to 2017. [Review]. BMC Health Serv Res 19(1):340. Accessed 18 Oct 2019. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-019-4178-y
The Partnership for Maternal Newborn & Child Health (2011) A Global Review of the Key Interventions Related to Reproductive, Maternal, Newborn and Child Health (RMNCH). Geneva, Switzerland: PMNCH.
United Nations Population Fund (2014) State of the world’s midwifery: a universal pathway to women’s health. A United Nations publication, New York
van Wagner V (2017) Midwives using research: evidence-based practice and evidence-informed midwifery. Chapter 12. In: Comprehensive midwifery: the role of the midwife in health care practice, education and research. Press Books, Open Library. https://ecampusontario.pressbooks.pub/cmroleofmidwifery/chapter/midwives-using-research-evidence-based-practice-evidence-informed-midwifery/ . Accessed 28 May 2020
Wickham S (2000) Evidence-informed midwifery 3: evaluating midwifery evidence. Midwifery Today Autumn:45–46
World Health Organization (2016a) WHO and partners call for better working conditions for midwives. World Health Organization, Geneva. https://www.who.int/news-room/detail/13-10-2016-who-and-partners-call-for-better-working-conditions-for-midwives . Accessed 16 Oct 2019
World Health Organization (2016b) Midwives’ voices, midwives’ realities. Findings from a global consultation on providing quality midwifery care. Originally published under ISBN 978 92 4 151054 7. World Health Organization, Geneva. https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/250376/9789241510547-eng.pdf;jsessionid=6F7EFCDDC808DE4828446A6FF8B7844B?sequence=1 . Accessed 4 Jun 2020
World Health Organization (2018a) Midwives are essential to the provision of quality of care in all settings, globally. World Health Organization, Geneva. International Day of the Midwife 2018: https://www.who.int/news-room/commentaries/detail/midwives-are-essential-to-the-provision-of-quality-of-care-in-all-settings-globally . Accessed 16 Oct 2019
World Health Organization (2018b) World Health Organization Collaborating Centres: fact sheet. https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/documents/about-us/factsheetwhocc2018.pdf?sfvrsn=8c7166ee_2 . Accessed 3 Jun 2020
World Health Organization (2019a) Maternal mental health. Sexual and reproductive health. World Health Organization, Geneva. https://www.who.int/mental_health/maternal-child/maternal_mental_health/en/ . Accessed 12 Apr 2019
World Health Organization (2019b) Comprehensive mental health action plan 2013–2020. World Health Organization, Geneva. https://www.who.int/mental_health/action_plan_2013/en/ . Accessed 12 Apr 2019
World Health Organization (2020) World Health Organization news-room fact sheet: nursing and midwifery. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/nursing-and-midwifery . Accessed 3 Jun 2020
Yahui HC, Swaminathan N (2017) Knowledge, attitudes, and barriers towards evidence-based practice among physiotherapists in Malaysia. Hong Kong Physiother J 37:10–18
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Global Professional Advisor, The Royal College of Midwives, London, UK
Maternal and Newborn Health, Department of Interprofessional Health, Swansea University, Swansea, UK
Gaynor D. Maclean
Global Midwifery Advisor, The Hague, Zuid-Holland, The Netherlands
Nester Moyo
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Joy Kemp .
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Kemp, J., Maclean, G.D., Moyo, N. (2021). Strengthening Midwifery Research. In: Global Midwifery: Principles, Policy and Practice. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-46765-4_12
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-46765-4_12
Published : 06 January 2021
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-030-46764-7
Online ISBN : 978-3-030-46765-4
eBook Packages : Medicine Medicine (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- Open access
- Published: 27 November 2021
The State of the World’s Midwifery 2021 report: findings to drive global policy and practice
- Andrea Nove ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-5272-3014 1 ,
- Petra ten Hoope-Bender 2 ,
- Martin Boyce 1 ,
- Sarah Bar-Zeev 3 ,
- Luc de Bernis 1 ,
- Geeta Lal 3 ,
- Zoë Matthews 4 ,
- Million Mekuria 2 &
- Caroline S. E. Homer 5
Human Resources for Health volume 19 , Article number: 146 ( 2021 ) Cite this article
10k Accesses
34 Citations
32 Altmetric
Metrics details
The third global State of the World’s Midwifery report (SoWMy 2021) provides an updated evidence base on the sexual, reproductive, maternal, newborn and adolescent health (SRMNAH) workforce. For the first time, SoWMy includes high-income countries (HICs) as well as low- and middle-income countries. This paper describes the similarities and differences between regions and income groups, and discusses the policy implications of these variations. SoWMy 2021 estimates a global shortage of 900,000 midwives, which is particularly acute in low-income countries (LICs) and in Africa. The shortage is projected to improve only slightly by 2030 unless additional investments are made. The evidence suggests that these investments would yield important returns, including: more positive birth experiences, improved health outcomes, and inclusive and equitable economic growth. Most HICs have sufficient SRMNAH workers to meet the need for essential interventions, and their education and regulatory environments tend to be strong. Upper-middle-income countries also tend to have strong policy environments. LICs and lower-middle-income countries tend to have a broader scope of practice for midwives, and many also have midwives in leadership positions within national government. Key regional variations include: major midwife shortages in Africa and South-East Asia but more promising signs of growth in South-East Asia than in Africa; a strong focus in Africa on professional midwives (rather than associate professionals: the norm in many South-East Asian countries); heavy reliance on medical doctors rather than midwives in the Americas and Eastern Mediterranean regions and parts of the Western Pacific; and a strong educational and regulatory environment in Europe but a lack of midwife leaders at national level. SoWMy 2021 provides stakeholders with the latest data and information to inform their efforts to build back better and fairer after COVID-19. This paper provides a number of policy responses to SoWMy 2021 that are tailored to different contexts, and suggests a variety of issues to consider in these contexts. These suggestions are supported by the inclusion of all countries in the report, because it is clear which countries have strong SRMNAH workforces and enabling environments and can be viewed as exemplars within regions and income groups.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
Despite the significant progress over the past two decades in improving outcomes for sexual, reproductive, maternal, newborn and adolescent health (SRMNAH), progress has been uneven. Maternal mortality, neonatal mortality and stillbirth rates remain high in many countries, a large number of women give birth without assistance from a skilled health provider, there is a considerable amount of unmet need for modern contraception, and quality of care is often suboptimal [ 1 ].
Resilient health systems grounded in primary health care are vital to the health and well-being of every woman, newborn and adolescent. The COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the importance of resilient health systems, especially health workforces. The Global Strategy on Human Resources for Health stresses that without an effective health workforce no health system is viable and universal health coverage cannot be achieved [ 2 ]. High-quality SRMNAH care requires a competent, educated, motivated and well supported workforce. Improving SRMNAH requires increased commitment to, and investment in, the health workforce.
The third global State of the World’s Midwifery (SoWMy) report was published in May 2021 by the United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA), the International Confederation of Midwives (ICM) and the World Health Organization (WHO), to provide an updated evidence base and detailed analysis of the progress and challenges to delivering effective coverage of high-quality midwifery services [ 1 ]. The first two SoWMy reports in 2011 and 2014 [ 3 , 4 ] led to some substantial advances, political commitments and achievements in a number of countries [ 5 ]. However, more needs to be done as a matter of urgency: Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) 3 and 5 will not be met by 2030 without increased commitment to and investment in the education, recruitment, deployment, retention and management of midwives and other SRMNAH workers.
Just prior to the publication of the main SoWMy report, the SoWMy team published a study which concluded that universal coverage of a set of essential “midwife-delivered interventions” (i.e., which are known to be linked to lower mortality rates and which can be delivered in their entirety by a midwife educated to global standards who is working within an enabling environment) could avert approximately two-thirds of the world’s maternal and neonatal deaths and stillbirths, saving over four million lives per year by 2035 [ 6 ].
SoWMy 2011 and SoWMy 2014 focused exclusively on the low- and middle-income countries with the highest rates of maternal and neonatal mortality, whereas all 194 WHO Member States were eligible for inclusion in the 2021 report. The objective of this paper is to describe the observed similarities and differences between different regions and income groups, and to discuss the policy and strategy implications of these variations.
SoWMy 2021 approach and key findings
The two main data reporting mechanisms for SoWMy 2021 were: the WHO National Health Workforce Accounts (NHWA) platform [ 7 ] and the ICM Global Midwives Associations Map Survey [ 8 ]. The NHWA platform, established in October 2017 as the WHO official reporting system for health workforce statistics, is updated on an ongoing basis with government-validated data that have been checked for consistency. The ICM survey was completed in 2019–2020 by professional midwife associations or UNFPA country offices, and validated by the competent national authorities. Full details of the methods used have been published elsewhere [ 9 ].
The analysis uses three key concepts to measure workforce availability and accessibility: (i) “need”, defined as the amount of health worker time that would be required to achieve universal coverage of a set of essential SRMNAH interventions, (ii) “supply”, defined as the amount of SRMNAH worker Footnote 1 time available to spend on SRMNAH interventions, and (iii) “demand”, defined as the economic capacity of a country to employ health workers.
In relation to “need”, SoWMy 2021 estimates that in 2019, approximately 6.5 billion health worker hours were required to meet all of the world's need for essential SRMNAH interventions. Just over half of these hours (55%) are for maternal and newborn interventions, 8% for adolescent sexual and reproductive health (SRH) interventions, and the remaining 37% for other SRH interventions such as contraception and sexually transmitted infections. The workforce must, therefore, have the competencies to meet a wide variety of SRMNAH needs across the life course in addition to pregnancy and childbirth interventions.
SoWMy 2021 estimates a global shortage of 900,000 midwives. If current trends of increased supply continue, this is projected to decrease only slightly (to 750,000) by 2030. It also estimates that the current SRMNAH workforce cannot meet more than 75% of the world’s need for essential SRMNAH interventions. In reality, it is likely that the workforce meets far less than 75% of the need, due to issues, such as: geographical maldistribution, poor working environments, the costs of accessing care, weak commodity supply chains, and gaps in quality of care due to, inter alia , poor quality education and regulation, and gender discrimination in the workforce.
SoWMy 2021 projects estimates of “demand” forward to 2030 and predicts that most countries will have a mismatch between the supply of SRMNAH workers and the number the country can afford to employ. About half of countries will have a demand-based shortage, i.e., they will produce fewer SRMNAH workers than their economy can support, and about half will have a demand-based oversupply, i.e., they will produce more than their economy can support (assuming spending priorities remain unchanged).
Investing in midwives can clearly yield important returns, including: more positive birth experiences, improved health outcomes, inclusive and equitable economic growth. Although the causal mechanism for these improved outcomes is not clear, SoWMy 2021 suggests that it is related to the unique philosophy of midwifery which takes a life-course approach and focuses on woman-centred, preventive, supportive care within a functioning referral system should medical intervention be required.
The impact of COVID-19 on the midwifery workforce is still being evaluated, but it is clear that many midwives and other SRMNAH workers were not sufficiently protected from infection and lost their lives due to the virus (SoWMy 2021 is dedicated to them), and many more are suffering from burnout, exhaustion and trauma. Health systems worldwide need to plan for replacing the losses and supporting the remaining health workforce to stay in post and provide high-quality care. This provides an opportunity to make improvements to SRMNAH care via strategic investments in the workforce. The dependence of the SRMNAH workforce on women (SoWMy 2021 reported that 93% of midwives, 89% of nurses and 50% of SRMNAH doctors Footnote 2 are women) means that a gender-transformative approach is needed, to address the gender-related challenges encountered by women in the health workforce.
To help bring about this transformation and develop an SRMNAH workforce that is sufficiently large, qualified and supported to meet all of the need for high-quality care, SoWMy 2021 calls for investment in four areas (Fig. 1 ).

Summary of investments needed for midwifery
Income group patterns
The SoWMy 2021 analysis is based on country income group classifications as they were in November 2020 (Additional file 1 : Table S2 provides a list of countries in each income group). It provides clear evidence of a major mismatch between the need for midwives, nurses and doctors and the overall supply. High-income countries (HICs) account for 11% of the need and 41% of the supply, whereas low-income countries (LICs) account for 14% of the need and 2% of the supply.
For nurses and doctors, the pattern is the same: on average, HICs have the highest density, Footnote 3 followed by upper-middle-income countries (UMICs), then lower-middle-income countries (LMICs), then LICs. For midwives, however, the density is higher in middle-income countries than in HICs. The figures are skewed by Indonesia: a large middle-income country with many midwives, but even if Indonesia is excluded, midwife density is similar in HICs and middle-income countries. In other words, the greater supply of SRMNAH workers in HICs is largely due to their having more doctors and nurses.
LICs tend to have the lowest density of all three types of SRMNAH worker, but on average, a quarter of the available SRMNAH worker time is from midwives, compared with less than 10% in HICs. In LMICs, the percentage is even higher: about a third of the available SRMNAH worker time is from midwives. However, a large majority of the midwives in LMICs are classed as associate professionals rather than professionals (see notes under Additional file 1 : Table S1 for details), implying that their range of skills and competencies is relatively limited.
Mapping of supply against need in the SoWMy 2021 report shows that HICs have sufficient SRMNAH workers to meet all of the need, and that UMICs have enough to meet most of the need. Needs-based shortages are most severe in LICs but also evident in LMICs: three-quarters of the global shortage of 900,000 midwives comes from LICs and LMICs.
Based on current trends, most of the projected growth in supply to 2030 is expected to occur in LMICs, rather than in LICs, where the shortage is most profound. This pattern is emphasized by the SoWMy 2021 analysis of the extent to which supply in 2030 will match economic demand. About half of all countries are projected to produce fewer SRMNAH workers than they can afford to employ (i.e., they will have a demand-based shortage), but nearly all of the countries projected to have a severe demand-based shortage are LICs and LMICs.
The education and regulatory environment for midwives tends to be stronger in HICs and UMICs than in LMICs and LICs. For example, HICs and UMICs are more likely to: offer midwife education programmes which meet ICM recommendations for duration of course, have midwives educating midwives, offer postgraduate study in midwifery, and have legislation and regulatory systems which recognise midwifery and nursing as distinct professions. Most HICs have laws/policies for the prevention of physical or verbal attacks on health workers, compared to only about half of UMICs, LMICs and LICs.
However, other indicators of the strength of the midwifery profession reveal relative strengths in LICs and LMICs. For example, the percentage of LICs with a professional association specifically for midwives is similar to the percentage in HICs and UMICs. Most UMICs and LICs reported at least one midwife in a leadership position within the national ministry of health (MoH), Footnote 4 compared with just one in five HICs. Midwives in LICs and LMICs tend to have a broader scope of practice, with far fewer restrictions to the number of basic emergency obstetric and newborn care (BEmONC) signal functions and contraceptive methods which they can provide.
Regional patterns
Inequity between the need for and availability of SRMNAH workers is also evident between WHO regions (see Additional file 1 : Table S3 for a list of countries in each region). SoWMy 2021 shows that Africa and South-East Asia account for half of the world’s need for SRMNAH worker time, but just 20% of the world’s midwives, nurses and doctors. By contrast, Europe and the Americas account for 20% of the need but 50% of the supply.
Although Africa has the lowest density of SRMNAH workers overall, relative to the overall size of the workforce this region has the highest proportion of professional midwives, and nearly 40% of the available SRMNAH worker time is from midwives. Africa stands out as having the most severe SRMNAH worker shortage in the world: it accounts for over half of the global shortage, the workforce can meet no more than half of the need, and in reality it almost certainly meets much less than half. These challenges, coupled with rapid population growth in many African countries, mean that the situation is predicted to improve only slightly by 2030 unless there is significant additional investment.
Midwives in Africa tend to have a broader scope of practice than those in other regions: they are generally authorized to perform all seven BEmONC signal functions and provide all modern methods of contraception. Africa also has a high proportion of countries with midwife leaders in the national MoH: it is second only to the Americas on this indicator. About half of responding countries in this region offer postgraduate study in midwifery. On the other hand, many African countries rely on midwife educators who are not themselves midwives to teach pre-service education programmes, indicating a shortage of suitably qualified midwives to teach the next generation. Fewer than half of African countries report that their midwives must provide evidence of continuing professional development (CPD), which calls into question whether the skills of the midwifery workforce are routinely kept up-to-date.
The Americas is the region with the lowest midwife density and the highest nurse density: indicating that this region relies very heavily on nurses as providers of SRMNAH interventions. Fewer than half of responding countries in this region offer a postgraduate qualification in midwifery. Despite this, most responding countries report that midwifery is recognised as a separate profession, that it has a separately regulatory system, that there is a professional association specifically for midwives and that there are midwife leaders in the national MoH.
The Eastern Mediterranean region has the second lowest SRMNAH worker density after Africa and accounts for almost 20% of the global midwife shortage. Its SRMNAH workforce can meet no more than 70% of the need (and like Africa, probably meets much less than this). In contrast to Africa, however, current trends suggest that the situation will be much improved by 2030. Most of the midwives in the Eastern Mediterranean region are professionals, but most of its nurses are associate professionals. Relative to the number of midwives and nurses, the region has a lot of doctors in its SRMNAH workforce, indicating a medicalized SRMNAH care system in many countries in the region.
The Eastern Mediterranean region is one of only two regions, where the vast majority of midwife educators are themselves midwives (the other being Europe). However, fewer than half of countries in this region offer a postgraduate qualification in midwifery, fewer than half have a separate regulation system for midwives and only half require midwives to provide evidence of CPD to continue practising. Some countries in the region restrict the midwife’s scope of practice, e.g., fewer than half of countries authorize midwives to conduct manual placenta removal and manual vacuum aspiration.
The overall density of SRMNAH workers in Europe is similar to the Americas, but midwife density is 2.5 times higher in Europe than in the Americas, and nearly all of Europe’s midwives are professionals rather than associate professionals. As noted above, most European countries use midwives to educate midwives, and it is the only region in which the majority of countries offer a postgraduate qualification in midwifery. Similarly, nearly all countries have a separate regulatory system for midwives and an association specifically for midwives. On the other hand, very few countries in this region have a midwife leader in the national MoH and the scope of practise of midwives is often restricted, e.g., very few countries permit midwives to perform vacuum extraction and manual vacuum aspiration, and midwives do not tend to be authorized to provide modern contraceptives.
A large proportion of the SRMNAH workers in South-East Asia are midwives, but nearly all of this region’s midwives are associate professionals rather than professionals and, therefore, can provide a smaller number of essential SRMNAH interventions. About half of responding countries in this region offer a postgraduate qualification in midwifery. The scope of practise of midwives is broader than in all other regions except Africa. However, only about half of the reporting countries in this region have legislation recognizing midwifery as distinct from nursing, only about two-thirds have a separate regulatory system for midwives, and fewer than one in three have a midwife leader in the national MoH.
The Western Pacific region has a relatively high midwife density, second only to South-East Asia, and nearly all of its midwives are professionals. However, in this region, less than 10% of the available SRMNAH worker time comes from midwives, because there is an even higher density of nurses and doctors. Nearly all responding countries in this region have a separate regulatory system for midwives and a professional association specifically for midwives, and the scope of practice of a midwife tends to be broad (the main exception being that fewer than half of countries in this region authorize midwives to perform manual vacuum aspiration). However, fewer than half of countries offer a postgraduate qualification in midwifery, fewer than half have midwife leaders in the national MoH, and fewer than half require periodic evidence of CPD.
Limitations
Although all 194 WHO Member States submitted at least one data item to the SoWMy 2021 report, no country provided validated data for all of the SoWMy 2021 indicators. For several indicators the number of responding countries was well below 100. Therefore, it is possible that some of the regional and income group results presented in SoWMy 2021 and described in this paper do not accurately represent the situation in that region or income group. This particularly affects the indicators relating to midwife education, regulation and scope of practice, three critical issues for midwifery development and maternal and perinatal health. There is an urgent need for better data availability and quality in many countries. The SoWMy 2021 webappendices [ 9 ] provide details of which countries provided data for each indicator.
The regional and income group estimates for health worker numbers and density are weighted by population size, so larger countries have a stronger impact on the average than smaller countries. While not a limitation as such, it is important to bear this in mind when interpreting the figures. Furthermore, regional and income group averages can mask important variations between and within countries. Within each region and income group, there will be countries which are typical of the group of countries within it, and others which are not.
The policy implications of SoWMy 2021
For the first time in the history of SoWMy, the 2021 report is truly global and, therefore, includes a wider range of analyses, including a new method of estimating demand-based workforce shortages (or oversupplies) as well as estimating needs-based shortages. This makes the report relevant to all countries, and in this paper we have attempted to highlight this broad applicability. It also allows us to draw conclusions about how the policy implications of the data in the report may be different in different contexts.
The main stories from the data on SRMNAH workforce supply are the major global shortage of SRMNAH workers and the inequity between higher and lower income countries—in particular the urgent need to address the severe shortages in LICs and in the African region to achieve the health-related SDGs. Many LICs are projected still to have severe needs-based SRMNAH worker shortages in 2030. It should be noted that the needs-based shortage estimates in SoWMy 2021 are separate from the demand-based shortage estimates: it is possible for a country to have neither type of shortage, just one type, or both types. A needs-based shortage brings with it an imperative to increase production of SRMNAH workers. However, if this is coupled with a demand-based oversupply, then increased production is likely to lead to ‘brain drain’ if the country does not have the fiscal space to employ all of the SRMNAH workers it produces. Many LICs are in this situation, which means efforts are required both to increase the supply of SRMNAH workers and to boost market-based demand to ensure that the increased supply of qualified individuals can get jobs in the health sector.
Even among HICs and UMICs, very few countries are predicted to achieve a good match between supply and economic demand, which implies the need for better workforce planning systems across the board.
Some of the SoWMy 2021 indicators relating to quality of care indicate widespread systemic issues. For example, the only region in which most countries offer a postgraduate qualification in midwifery is Europe, which perhaps partly explains why so many LMICs and LICs in other regions rely on other types of health professional to teach midwives. Stronger midwifery departments in universities would encourage further study and research on midwifery, and encourage midwives to take the lead in the education and research which is greatly needed. Similarly, in most regions fewer than half of countries have a requirement for periodic proof of CPD as part of midwifery regulation. Coupled with the well-documented weaknesses in midwife pre-service education in many countries [ 10 ], this means that many of the world’s midwives may lack the competencies to provide high-quality care.
The dependence in HICs and UMICs—especially in the Americas region—on doctors and nurses to provide SRMNAH interventions raises questions about whether the lower mortality rates for women and newborns observed (on average) in these settings come at the expense of access to the unique philosophy and model of care provided by midwives, which has been shown to facilitate positive birth experiences and improve other types of health outcomes. This concern is underlined by the finding that the scope of practice of midwives tends to be more restricted in HICs and UMICs (especially in Europe and the Eastern Mediterranean) than in LMICs and LICs. SoWMy 2021 points out that midwives who are educated and regulated according to global standards can meet around 90% of the need for essential SRMNAH interventions, but this is achievable only if they are authorized to operate to their full scope of practice within an enabling work environment [ 11 ].
Similarly, the heavy reliance in some LMICs on associate professional midwives calls into question their ability to provide midwifery services across the full continuum of care, so the high density of midwives in LMICs—especially those in South-East Asia—may not translate to widespread access to high quality midwifery care. By contrast, nearly all of Africa’s midwives are classed as professionals, perhaps indicating a greater appreciation of the potential of midwives to meet most of the need for essential SRMNAH interventions, even if currently this region does not have anywhere near enough of them and quality of care can still be poor.
Addressing the issues highlighted in SoWMy 2021 requires strong leadership for the midwifery profession, focusing on the four areas of investment shown in Fig. 1 . Yet only half of countries have midwife leaders in the national MoH, and the proportion is much lower than this in HICs, especially in Europe and South-East Asia. The creation of leadership roles for midwives, and the inclusion of midwives in candidate lists for existing leadership roles, will be important to ensure that appropriate investments in midwifery are made.
Since the first SoWMy report in 2011, there has been much progress in midwifery, including greater recognition of the importance of quality of care, widespread accreditation systems for health worker education institutions, and greater recognition of midwifery as a distinct profession. On the other hand, many of the issues highlighted in the two previous SoWMy reports remain of concern, such as workforce shortages, an inadequate working environment, low-quality education and training, and limitations in health workforce data.
Governments and relevant stakeholders are urged to use SoWMy 2021 to inform their efforts to build back better and fairer from the COVID-19 pandemic, forging stronger primary health-care systems as a pathway to UHC and fostering a more equitable world. It is hoped that the pandemic will be a catalyst for change given the heightened profile of health workers. SoWMy 2021 can help make this happen.
Availability of data and materials
The data sets analysed for the SoWMy 2021 report are available from the National Health Workforce Accounts platform ( https://apps.who.int/nhwaportal/ ) and the ICM Midwives Hub platform ( https://www.globalmidwiveshub.org/ ).
SoWMy 2021 used International Standard Classification of Occupations codes to define the SRMNAH workforce—see Additional file 1 : Table S1 for details.
SoWMy 2021 uses the term “SRMNAH doctors” to refer to general practitioners, obstetricians/gynaecologists and paediatricians: the three types of doctor most likely to provide SRMNAH interventions.
Health worker density is the number of health workers per head of population.
The phrase “leadership position” was defined as referring to a number of management, supervisory and executive titles, including: Chief Midwife, Midwife Advisor, national Midwife Director, maternal advisory position.
Abbreviations
Basic emergency obstetric and newborn care
Continuing professional development
High-income country
International Confederation of Midwives
Low-income country
Lower-middle-income country
Ministry of Health
National Health Workforce Accounts
Sustainable development goals
State of the World’s Midwifery
Sexual and reproductive health
- Sexual, reproductive, maternal, newborn and adolescent health
Upper-middle-income country
United Nations Population Fund
World Health Organization
United Nations Population Fund, International Confederation of Midwives, World Health Organization. State of the world's midwifery 2021. New York: United Nations Population Fund; 2021.
World Health Organization. Global strategy on human resources for health: workforce 2030. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2016.
Google Scholar
United Nations Population Fund. World Health Organization, International Confederation of Midwives. State of the world’s midwifery: delivering health, saving lives. New York: United Nations Population Fund; 2011.
United Nations Population Fund, World Health Organization, International Confederation of Midwives: State of the world's midwifery: a universal pathway. A woman's right to health. New York: United Nations Population Fund; 2014.
Oliver K, Parolin Z. Assessing the policy and practice impact of an international policy initiative: the State of the World’s Midwifery 2014. BMC Health Serv Res. 2018;18:499.
Article Google Scholar
Nove A, Friberg IK, de Bernis L, McConville F, Moran AC, Najjemba M, Ten Hoope-Bender P, Tracy S, Homer CSE. Potential impact of midwives in preventing and reducing maternal and neonatal mortality and stillbirths: a Lives Saved Tool modelling study. Lancet Glob Health. 2021;9:e24–32.
World Health Organization. National health workforce accounts (NHWA). 2021. https://www.who.int/hrh/statistics/nhwa/en/ . Accessed 7 February 2021.
International Confederation of Midwives, Direct Relief. Global midwives hub. 2021. https://www.globalmidwiveshub.org/ . Accessed 15 Feb 2021.
United Nations Population Fund. The state of the world's midwifery 2021: webappendices. 2021. https://www.unfpa.org/sowmy-webappendices . Accessed 22 Oct 2021.
World Health Organization. United Nations Population Fund, United Nations Children’s Fund, International Confederation of Midwives. Strengthening quality midwifery education for universal health coverage 2030: framework for action. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2019.
International Confederation of Midwives. Building the enabling environment for midwives: a call to action for policy makers. 2021. https://internationalmidwives.org/our-work/other-resources/icm-enabling-environment-policy-brief-(2021).html . Accessed 2 Oct 2021.
Download references
Acknowledgements
SoWMy 2021, on which this paper is based, was developed with the support of a large number of people and organizations who are named in the ’contributors and acknowledgements’ section of the report.
Funding for the SoWMy report and this paper was provided by the New Venture Fund. The funder had no role in the study design, data collection, data analysis/interpretation or writing.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Novametrics Ltd, Duffield, DE56 4HQ, UK
Andrea Nove, Martin Boyce & Luc de Bernis
UNFPA, 7 rue de Varembé, 1202, Geneva, Switzerland
Petra ten Hoope-Bender & Million Mekuria
UNFPA, 605 Third Avenue, New York, NY, 10158, USA
Sarah Bar-Zeev & Geeta Lal
University of Southampton, Southampton, SO17 1BJ, UK
Zoë Matthews
Burnet Institute, 85 Commercial Road, Melbourne, VIC, 3004, Australia
Caroline S. E. Homer
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
CH, LdB, PHB, SBZ and ZM conceptualized the paper. AN wrote the initial draft. All authors provided substantive comments on the initial draft and approved the final version.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Andrea Nove .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: table s1..
Health occupations classed as part of the SRMNAH workforce. Table S2. List of WHO Member States by World Bank income group, 2020. Table S3. List of WHO Member States by WHO region, 2020.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Nove, A., ten Hoope-Bender, P., Boyce, M. et al. The State of the World’s Midwifery 2021 report: findings to drive global policy and practice. Hum Resour Health 19 , 146 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12960-021-00694-w
Download citation
Received : 11 October 2021
Accepted : 16 November 2021
Published : 27 November 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12960-021-00694-w
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Human resources for health
- Health workforce
Human Resources for Health
ISSN: 1478-4491
- Submission enquiries: Access here and click Contact Us
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Click through the PLOS taxonomy to find articles in your field.
For more information about PLOS Subject Areas, click here .
Loading metrics
Open Access
Peer-reviewed
Research Article
Midwifery-led researches for evidence-based practice: Clinical midwives engagement in research in Ethiopia, 2021
Roles Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal analysis, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing
* E-mail: [email protected]
Affiliation Midwifery Directorate, University of Gondar, Gondar, Ethiopia
Roles Conceptualization, Methodology, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – review & editing
Affiliation Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics, University of Gondar, Gondar, Ethiopia
Roles Data curation, Methodology, Supervision, Validation, Writing – review & editing
Affiliation Midwifery Directorate, School of Midwifery, University of Gondar, Gondar, Ethiopia
Roles Methodology, Validation, Writing – review & editing
Affiliation Department of Environmental and Occupational Health and Safety, University of Gondar, Gondar, Ethiopia
- Keflie Yohannes Gebresilassie,
- Adhanom Gebreegziabher Baraki,
- Belayneh Ayanaw Kassie,
- Sintayehu Daba Wami

- Published: June 3, 2022
- https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0268697
- Reader Comments
Introduction
Health workers involvement in research had an impact on studies and whole system. They influence the clinical practice and help to implement evidences. Although International Confederation of Midwives (ICM) put research as one of the midwifery competencies and professional development activity, clinical midwives are poorly involved in research. Therefore, this study is aimed to assess clinical midwives engagement in research and bridge the gap through applicable strategies.
Institution-based cross-sectional study was conducted among clinical midwives working at public health facilities of Central and North Gondar Zone, Ethiopia from September to October, 2020 G.C. A structured and pre-tested self-administered questionnaire was used to collect data and entered into Epi-info version 7. Descriptive statistics was used to describe study population. Bi-variable and multi-variable logistic regression analysis was performed using STATA Version 14 and significance level declared at 95% confidence interval, p-value ≤ 0.05 and respective odds ratios.
Out of 335 clinical midwives, 314 were participated making the response rate 93.7%. Among the midwives, one hundred seventy two (54.8%) (95% CI: 49.08%, 60.37) have good skill on conducting a research. Clinical midwives with mothers with formal education [AOR: 1.90, 95% CI: (1.03, 3.51), currently work on referral hospitals [AOR: 2.33, 95% CI: (1.19, 4.53)] and having good level of knowledge on research [AOR: 2.19, 95% CI: (1.25, 3.82)] have significant association with having good research skill. Forty eight (15.2%) (95% CI: 11.5%, 19.7%) ever participated in research during their clinical practice. Clinical midwives who have good knowledge on research [AOR: 0.31, 95% CI: (0.14, 0.70)] are about 0.3 times less likely to participate on research than who have poor knowledge [AOR: 0.31, 95% CI: (0.14, 0.70)].
Conclusion and recommendation
Although more than half have good research skill, only a small proportion of midwives were involved in research. Capacity building activities are crucial to strengthen midwives skill on research and ensure their involvement.
Citation: Gebresilassie KY, Baraki AG, Kassie BA, Wami SD (2022) Midwifery-led researches for evidence-based practice: Clinical midwives engagement in research in Ethiopia, 2021. PLoS ONE 17(6): e0268697. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0268697
Editor: Felix Bongomin, Gulu University, UGANDA
Received: November 20, 2021; Accepted: May 4, 2022; Published: June 3, 2022
Copyright: © 2022 Gebresilassie et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Data Availability: All relevant data are within the paper and its Supporting information files.
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work.
Competing interests: The authors declare that no competing interest exist.
Health workers involvement in research had an impact on studies and whole system. They influence the clinical practice and help to implement evidences [ 1 ]. The new approach named clinical academics had health care and academic roles, thus they combine practice with research [ 2 ]. Despite these recommendations [ 3 ], most college and universities didn’t have clinical academic [ 4 ] and they are not appropriately utilizing their potentials.
Health workers involved in research activities have various reasons that includes individual interest, as part of the curriculum, to improve service quality through shred of evidences, prior experience and/or exposure, professional development and financial benefits [ 1 ]. Nevertheless, International Confederation of Midwives (ICM) has put continuous professional development including research activities as one of midwifery competencies [ 5 ].
Clinical midwives perceived research as other professions role, especially the academic [ 6 ]. They had to aware of and involve in research to improve the clinical care [ 7 ] and overall quality of midwifery services as they can identify health problems for research from their experience.
Although research capacity building for clinical midwives is recommended [ 8 ], most involve as data collector and not more than that. Individuals were capacitated with training, support, workshops and using technologies. In low and middle-income countries projects, partnership and network had built health research capacity. However the lack of empirical research has become a challenge to see their effectiveness [ 9 ].
Once ability to influence practice with research, difficulties to work with the academics [ 1 ], and communication skills could affect their motivation [ 10 ] and confidence [ 11 ] to conduct research were individual barriers for conducting a research. Organizational leadership and management and research recognitions [ 1 ] also had an effect on research capacity. Resources for research such as dedicated time [ 12 , 13 ], research expertise [ 14 ], access to research findings [ 15 ] and opportunities [ 1 ]; availability of funding [ 12 , 14 , 16 ] and investment on research activity [ 15 , 17 ] could limit once research capacity and ability to conduct research. Other studies added that building research partnerships [ 10 ], having research culture [ 16 ], professional development opportunities and inadequate salaries [ 14 , 15 ] as cause to poorly involve in research. At Supra-organizational level, health research policies and governance [ 10 ] had an influence on participation and involvement in research.
Despite the observed gaps and limiting factors, scientific studies are lacking to study clinical midwives engagement in research and contributing factors. Thus, this study was done to bridge the gaps, which will help to set appropriate strategies and interventions to conduct midwifery-led researches. The study will be a baseline for conducting further studies and results will have an input for School of Midwifery at University of Gondar to improve the curriculum and built midwifery student’s research capacity at undergraduate level.
Methodology
Study design, setting, study population and sampling.
Institution-based cross-sectional study was conducted among clinical midwives working at public health facilities of Central and North Gondar Zone, Ethiopia, from September to October 2020 G.C. The study area covers two of the four zones of Amhara region (Central, west, north and south Gondar Zones), in which around 6,335,757 estimated populations are living. There are a total of 23 public hospitals and 222 health center. In North and Central Gondar Zone, around 350 trained registered clinical midwives are working in these institutions. All Midwives working in clinical setting of Central and North Gondar Zone were considered as the source and study population. All registered midwives working in the study area were included, whereas those who are working in administrative and academic area, midwives who are sick and unable to respond were excluded from the study.
Data collection and quality control
Before actual data collection, discussion was done on prevention measures of the current pandemic, Corona-Virus (Covid-19) and basic protective materials (Sanitizer, face mask and glove) were given for data collectors and supervisors. A structured pre-tested self-administered questionnaire was used to collect the data. The tool was developed by referring different literatures [ 18 ], first prepared in English and translated back into Amharic, the local language. The tool was checked for consistency statistically using Cronbach’s alpha. Training was given for five data collectors and supervisor on the objective of the study and confidentiality for two days. Pretest was done on 5% of sample size among midwives working other than the study area and necessary correction done. The collected data was assessed for completeness and accuracy on daily basis. The tool has socio-demographic and academic characteristics; questions for assessing research skill and participation. Clinical Midwives are a registered midwives working in the clinical setting/area. A participant who answers more than 50% of the skill assessment questions will be considered as having good skill on research. Similarly, a participant will be considered as practicing (conducting) research if s/he has ever involved in part of a research other than one conducted as a partial fulfillment of his or her midwifery study.
Data management and analysis procedure
Data was entered into Epi-info version 7 and exported to STATA version 14 for further analysis. Descriptive analysis like frequencies, percentages, means and standard deviations computed for all variables. Model fitness was tested with Hosmer and Lemeshow goodness of fit and both bi-variable and multivariate logistic regression models were carried out to estimate the association. Variables with a p -value of less than 0.2 in the bi-variable analysis were entered into the multivariable logistic regression analysis. Both Crude Odds Ratio (COR) and Adjusted Odds Ratio (AOR) with their corresponding 95% confidence intervals were estimated. Finally, variables with a P-value of less than 0.05 in multivariable logistic regression model were considered as significantly associated with knowledge and attitude towards research.
1. Socio demographic and academic characteristics
Out of 335 clinical midwives 314 were participated making the response rate 93.7%. Age of the midwives range from 18 to 50 years, with median age of 27 years old. More three fifth (66.9%) of the midwives age was between 25 to 29 years. Among all midwives, more than half (52.9%) were male, while two hundred seventy four (87.3%) were Urban dwellers. More than three fifth (63.1%) of the midwives’ were Bachelor degree holders, while majority (73.6%) were graduated from governmental colleges. Nearly there fifth of the midwives (58.6%) study with regular educational program ( Table 1 ).
- PPT PowerPoint slide
- PNG larger image
- TIFF original image
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0268697.t001
2. Clinical midwives research skill and practice
2.1 skill of clinical midwives to conduct a research..
Among the midwives, one hundred seventy two have good skill on conducting a research making the magnitude 54.8% (95% CI: 49.08%, 60.37).
Among the midwives, nearly half (48.4%) reported as having high skill on identifying research problems, while 132 (42%) have high skill on conducting literature review. More than two fifth (42.7%) and one hundred twenty three (39.2%) of the midwives reported as having poor skill on data management and data analysis using software respectively. Clinical midwives reported as they have high skill on applying for research funding (35%) and to give advice for less experienced researchers (28.7%). ( Table 2 ).
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0268697.t002
2 . 1 . 1 . Factors associated with clinical midwives skill on research . To identify factors, bi-variable and multi-variable logistic regression analysis was carried out for seven explanatory variables. In multi-variable analysis; Mother educational status of having formal education; currently working on referral health facilities; having good level of knowledge on research and taking prior research course have a positive significant association with skill on research ( Table 3 ).
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0268697.t003
Clinical midwives who take prior research course were about 1.9 times more likely to have good research skill than their counterparts. [AOR: 1.95, 95% CI: (1.00, 3.82)].
Clinical midwives who have mothers with formal education are about 1.9 times more likely to have good research skill. [AOR: 1.90, 95% CI: (1.03, 3.51)].
Clinical midwives who currently work on specialized/referral hospitals were about 2.3 times more likely to have good research skill than their counterparts. [AOR: 2.33, 95% CI: (1.19, 4.53)].
Clinical midwives who have good level of knowledge on research are about 2.2 times more likely to have good research skill than their counterparts. [AOR: 2.19, 95% CI: (1.25, 3.82)].
2.2. Clinical midwives involvement in conducting research.
Among all the midwives, forty eight (15.2%) (95% CI: 11.5%, 19.7%) ever participated in research during their clinical practice. ( Fig 1 ).
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0268697.g001
More than half (52.1%) have involved in one research activities, while thirty (9.6%) have a responsibility of data collection in the research they involved. Nearly three fifth (72.9%) believe that the research they involved in contributed to the policy and/or the clinical practice in any way. Among the midwives, twenty three (7.3%) ever present at conferences and 13 (4.1%) ever publish research findings. ( Table 4 ).
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0268697.t004
2 . 2 . 1 . Factors associated with clinical midwives practice on a research . To identify factors, bi-variable and multi-variable logistic regression analysis was carried out for five explanatory variables that have association with outcome variable. In multi-variable analysis; knowledge level on research course have a negative significant association with participation on research. ( Table 5 ).
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0268697.t005
Clinical midwives who have good knowledge on research are about 0.3 times less likely to participate on research than who have poor knowledge. [AOR: 0.31, 95% CI: (0.14, 0.70)].
The ICM strongly recommends involvement of midwives in research to provide high quality midwifery services [ 19 ]. This study was conducted to assess clinical midwife’s engagement on research and associated factors in Northwest Ethiopia. A total of three hundred fourteen midwives working at public health facilities were participated and majority (63.1%) were registered midwives with Bachelor degree holders.
Only nearly above half (50.6%) of the midwives say that their facility has continuous professional development program for staffs including midwives and this indicate that there is a limited opportunity to upgrade oneself. Unless there is no adequate and continual support to midwives, quality of midwifery services provided for the women could be affected [ 20 ]. A study in Tanzania was also evident that lack of evidence-based practices supported with research could result to poor service provision for patients (30% to 40%) and to have poor health outcomes [ 21 ]. A recent studies review highlighted that midwifery and nurses research publication are increased and suggested to have capacity building activities for strengthening the observed result [ 22 ]. Although it is not found significant, level of income is associated with quality of midwives performance on provision of care as evidenced by a study conducted in Gaza [ 23 ]. Professional benefits such as good salary might have an effect on midwives motivation and retention.
A significant proportion (52.9%) of midwives also responded that their health facilities doesn’t conduct research activities relevant to clinical practice. This might be due to that majority (64.5%) of midwives work on Primary Health Care units (Health Centers and Primary Hospitals). In Ethiopian health care system, facilities are not expected to conduct research activities unless they have teaching role, in addition to patient care service [ 24 ]. Midwives also reported that in addition to poor support from their facility (63.1%) and other professionals (60.2%), there are no opportunities to participate in research conferences (52.9%). As a result midwives poorly utilized research findings in their clinical service [ 25 ]. Moreover lack of dedicated time and poor implementation of research findings further deteriorate the application of research in the clinical practice [ 26 ].
In our study higher odds of good research skill was noted among midwives with formal maternal education (1.9 times) and it has an effect on academic performance [ 27 ].
Midwives who work on specialized/referral hospitals were found to have higher good research skill (2.3 times) than who work in primary health care facilities (health centers). This finding is supported with recent study conducted in North Gondar [ 25 ] and might be reasoned with that in referral health facilities there might be different opportunities to learn about research and related activities as they are teaching hospitals. Moreover these facilities are more likely to utilize research findings in their day too day clinical practice [ 25 ].
Having good research knowledge was associated with having good skill on research (2.2 times). Both research knowledge and skill are crucial to conduct a research as they are interrelated competencies.
Our study found that a small proportion of midwives (15.2%) ever participated in research during their clinical practice, in which 9.6% as data collector. This indicate that there is limited opportunities for midwives to be involved in research activities. Although a higher proportion (36.4%) of Australian nurses were reported as they involved in research, there is still a deficiency in health professional’s engagement in research activities [ 28 ]. In Latin America and the Caribbean, a review of studies also found that there is gap on midwifery-led researches, where most (95.8%) studies were nurses-led [ 29 ]. In our study, although more than three fifth (70.8%) of the midwives reported as they participated in a midwives-led researches, their capacity could be improved if they have the opportunity to work collaboratively with other disciplines such as public health experts, epidemiologists and physicians. Nearly three fifth (72.9%) believe that the research they involved in contributed to the policy and/or the clinical practice in any way. This is indicate that midwives have a positive understanding on the research activities they involved in. As they know the practical setting, they can identify and suggest on the real problem that will benefit the woman and her child [ 7 ].
Although midwives have good knowledge on research, they were less likely (0.3 times) to ever participate on research than who have poor knowledge. This indicate that there is limited opportunities for midwives with adequate research knowledge. This might be due to that a significant proportion of midwives (47.8%) work on health centers and opportunities are scarce.
The study find that research capacity of clinical midwives is not adequate. Only small proportion (15.2%) of midwives participated in research and having good knowledge on research was associated with it. Similarly research skill was associated with mothers with formal education, currently working in specialized /referral health facilities, and having good knowledge on research.
Recommendation
Ethiopian Ministry of Health better to capacitate health facilities to conduct local researches, particularly primary and general hospitals. It is also better to give priority and support health professionals working in the clinical setting to conduct research and related activities. With the existing continuous professional development programs, Regional Health Bureau better to expand opportunities for clinical midwives working in the region.
Ethiopian Midwifery Association (EMwA), University of Gondar and School of Midwifery better to contribute a lot to support clinical midwives with capacity building activities on research such as training, create opportunities and arrange conferences so that they can be involved and conduct researches in their clinical practice. Strengthening the integration of the school and hospital midwifery coordinator is also crucial to work collaboratively and share experience on research and related activities. Moreover it is good to provide dedicated time for clinical service providers including midwives to participate in research and related activities.
Supporting information
S1 dataset..
https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0268697.s001
Acknowledgments
We are indebted to the University of Gondar for the approval of the ethical clearance. The authors also forward their gratitude to study participants, data collectors and supervisors who participated in the study.
- View Article
- Google Scholar
- 2. Carrick-Sen D, Richardson A, Moore A, Dolan S. Transforming healthcare through clinical academic roles in nursing, midwifery and allied health professions: A practical resource for healthcare provider organisations. Report, The Association of UK University Hospitals, London, November. 2016.
- PubMed/NCBI
- 6. Harvey M, Land L. Research methods for nurses and midwives: theory and practice: Sage; 2016.
- 15. ESSENCE. Seven principles for strengthening research capacity in low-and middle-income countries: simple ideas in a complex world. 2014.
- 19. Role of the Midwife in Research. International Confederation of Mdwives 2014.
- 24. Primary health care systems (PRIMASYS): case study from Ethiopia, abridged version. World Health Organization. 2017.
Journals in Midwifery
Journal of obstetric, gynecologic & neonatal nursing.
- ISSN: 0884-2175
- 5 Year impact factor: 1.9
- Impact factor: 1.8

Nursing for Women's Health
- ISSN: 1751-4851

Open Access is an initiative that aims to make scientific research freely available to all. To date our community has made over 100 million downloads. It’s based on principles of collaboration, unobstructed discovery, and, most importantly, scientific progression. As PhD students, we found it difficult to access the research we needed, so we decided to create a new Open Access publisher that levels the playing field for scientists across the world. How? By making research easy to access, and puts the academic needs of the researchers before the business interests of publishers.
We are a community of more than 103,000 authors and editors from 3,291 institutions spanning 160 countries, including Nobel Prize winners and some of the world’s most-cited researchers. Publishing on IntechOpen allows authors to earn citations and find new collaborators, meaning more people see your work not only from your own field of study, but from other related fields too.
Brief introduction to this section that descibes Open Access especially from an IntechOpen perspective
Want to get in touch? Contact our London head office or media team here
Our team is growing all the time, so we’re always on the lookout for smart people who want to help us reshape the world of scientific publishing.
Home > Books > Maternal-Fetal Medicine
Selected Topics in Midwifery Care

Book metrics overview
13,991 Chapter Downloads
Impact of this book and its chapters
Total Chapter Downloads on intechopen.com
Total Chapter Views on intechopen.com
Overall attention for this book and its chapters
Total Chapter Citations
Book Citations

Academic Editor
University of Ljubljana , Slovenia
Published 08 February 2019
Doi 10.5772/intechopen.74444
ISBN 978-1-78985-534-0
Print ISBN 978-1-78985-533-3
eBook (PDF) ISBN 978-1-83962-033-1
Copyright year 2019
Number of pages 136
Midwifery across the globe faces different issues. In some countries the autonomy of the profession is a tradition, while in some societies midwives struggle to practice autonomously the basic competencies. In one part of the world the medicalisation of childbirth is the main issue, preventing the natural processes of pregnancy and childbirth to flow at their own pace, while in other parts of the ...
Midwifery across the globe faces different issues. In some countries the autonomy of the profession is a tradition, while in some societies midwives struggle to practice autonomously the basic competencies. In one part of the world the medicalisation of childbirth is the main issue, preventing the natural processes of pregnancy and childbirth to flow at their own pace, while in other parts of the world midwives struggle with lack of resources to provide safe midwifery care. The authors of this book practice midwifery in different cultures and within different social contexts. They have to deal with different obstacles and seek solutions to diverse problems. With their contributions, they offer an insight into their thinking, their dilemmas, and the problems of midwifery practices in their countries. However, despite different backgrounds, they all have in common a uniform goal - a wish to offer women optimal midwifery care and to improve midwifery services.
By submitting the form you agree to IntechOpen using your personal information in order to fulfil your library recommendation. In line with our privacy policy we won’t share your details with any third parties and will discard any personal information provided immediately after the recommended institution details are received. For further information on how we protect and process your personal information, please refer to our privacy policy .
Cite this book
There are two ways to cite this book:
Edited Volume and chapters are indexed in
Table of contents.
By Thembelihle Sylvia Patience Ngxongo
By Johanna Mmabojalwa Mathibe-Neke and Seipati Suzan Masitenyane
By Ruth Mielke
By John Kuumuori Ganle and Ebenezer Krampah
By Julius Dohbit, Vetty Agala, Pamela Chinwa-Banda, Betty Anane- Fenin, Omosivie Maduka, Ufuoma Edewor, Ibimonye Porbeni, Fru Angwafo and Rosemary Ogu
By Sevde Aksu
IMPACT OF THIS BOOK AND ITS CHAPTERS
13,991 Total Chapter Downloads
3,944 Total Chapter Views
14 Crossref Citations
4 Web of Science Citations
39 Dimensions Citations
13 Altmetric Score
Order a print copy of this book
Hardcover | Printed Full Colour
Available on

Delivered by

£119 (ex. VAT)*
FREE SHIPPING WORLDWIDE
* Residents of European Union countries need to add a Book Value-Added Tax Rate based on their country of residence. Institutions and companies, registered as VAT taxable entities in their own EU member state, will not pay VAT by providing IntechOpen with their VAT registration number. This is made possible by the EU reverse charge method.
As an IntechOpen Author/Editor, you can buy this book for an Exclusive Author price with discounts from 30% to 50% on retail price.
Log in to your Author Panel to purchase a book at the discounted price.
For any assistance during ordering process, contact us at [email protected]
Related books
Sexology in midwifery.
Edited by Ana Polona Mivšek
Preterm Birth
Edited by John Morrison
Cesarean Delivery
Edited by Raed Salim
Ectopic Pregnancy
Edited by Michael Kamrava
Pregnancy and Birth Outcomes
Edited by Wei Wu
Multiple Pregnancy
Edited by Julio Elito Jr.
Edited by Hassan Abduljabbar
Maternal and Child Health
Edited by Miljana Z. Jovandaric
Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
Edited by Miroslav Radenkovic
Preeclampsia
Call for authors, submit your work to intechopen.

IntechOpen Author/Editor? To get your discount, log in .
Discounts available on purchase of multiple copies. View rates
Local taxes (VAT) are calculated in later steps, if applicable.
Support: [email protected]
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- My Bibliography
- Collections
- Citation manager
Save citation to file
Email citation, add to collections.
- Create a new collection
- Add to an existing collection
Add to My Bibliography
Your saved search, create a file for external citation management software, your rss feed.
- Search in PubMed
- Search in NLM Catalog
- Add to Search
Midwifery care research: what questions are being asked? What lessons have been learned?
Affiliation.
- 1 Midwifery Program, University of Michigan School of Nursing, Ann Arbor 48109-0482, USA. [email protected]
- PMID: 10772732
- DOI: 10.1016/s1526-9523(99)00017-3
Purpose: To create and critically evaluate a research database about midwifery care that identifies topics studied, research methods, results, funding, publication data, and implications for a future midwifery research agenda.
Methods: Systematic literature review. Studies included were 1) data-based research; 2) about midwifery care or practice; 3) in the United States; and 4) published between 1984-1998. The CINAHL and MEDLINE electronic databases were searched using a defined strategy, and relevant journals and bibliographies were searched by hand.
Results: This 15-year review identified 140 studies of midwifery care published in 161 papers. A midwife was the lead author on 60%. Sixty percent were published in the Journal of Nurse-Midwifery. Six to 15 studies were published each year, and both the number of publications and funding increased over the time period. The six major areas of focus were: 1) midwifery management, 2) structure of care, 3) midwifery practice, 4) midwife-physician comparisons, 5) place of birth, and 6) care of vulnerable populations.
Discussion: Although retrospective descriptive studies still predominate, more prospective studies, randomized controlled trials, multi-site studies, and quasi-experimental designs are being conducted. Qualitative methods are helping to measure nontraditional outcomes. A research agenda should be established based on discussion and debate within the profession. Midwife investigators need to build research teams and collaborate with other disciplines. Key areas for future research include alternative therapies, breastfeeding, cost-effectiveness, cultural studies, gynecology, health policy, menopause, postpartum care, substance abuse interventions, and the woman's experience of birth and midwifery care.
PubMed Disclaimer
Similar articles
- Telemedicine for the Medicare population: pediatric, obstetric, and clinician-indirect home interventions. Hersh WR, Wallace JA, Patterson PK, Shapiro SE, Kraemer DF, Eilers GM, Chan BK, Greenlick MR, Helfand M. Hersh WR, et al. Evid Rep Technol Assess (Summ). 2001 Aug;(24 Suppl):1-32. Evid Rep Technol Assess (Summ). 2001. PMID: 11569328 Free PMC article.
- Health professionals' experience of teamwork education in acute hospital settings: a systematic review of qualitative literature. Eddy K, Jordan Z, Stephenson M. Eddy K, et al. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2016 Apr;14(4):96-137. doi: 10.11124/JBISRIR-2016-1843. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2016. PMID: 27532314 Review.
- The experiences of midwives and nurses collaborating to provide birthing care: a systematic review. Macdonald D, Snelgrove-Clarke E, Campbell-Yeo M, Aston M, Helwig M, Baker KA. Macdonald D, et al. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015 Nov;13(11):74-127. doi: 10.11124/jbisrir-2015-2444. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015. PMID: 26657466 Review.
- How has the impact of 'care pathway technologies' on service integration in stroke care been measured and what is the strength of the evidence to support their effectiveness in this respect? Allen D, Rixson L. Allen D, et al. Int J Evid Based Healthc. 2008 Mar;6(1):78-110. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-1609.2007.00098.x. Int J Evid Based Healthc. 2008. PMID: 21631815
- Midwifery care of poor and vulnerable women, 1925-2003. Raisler J, Kennedy H. Raisler J, et al. J Midwifery Womens Health. 2005 Mar-Apr;50(2):113-21. doi: 10.1016/j.jmwh.2004.12.010. J Midwifery Womens Health. 2005. PMID: 15749297 Review.
- Parenting confidence and needs for parents of newborns in taiwan. Kuo CP, Chuang HL, Lee SH, Liao WC, Chang LY, Lee MC. Kuo CP, et al. Iran J Pediatr. 2012 Jun;22(2):177-84. Iran J Pediatr. 2012. PMID: 23056883 Free PMC article.
- The experience of perinatal care at a birthing center: a qualitative pilot study. Pewitt AT. Pewitt AT. J Perinat Educ. 2008 Summer;17(3):42-50. doi: 10.1624/105812408X329593. J Perinat Educ. 2008. PMID: 19436419 Free PMC article.
- Critical views on postpartum care expressed by new mothers. Rudman A, Waldenström U. Rudman A, et al. BMC Health Serv Res. 2007 Nov 5;7:178. doi: 10.1186/1472-6963-7-178. BMC Health Serv Res. 2007. PMID: 17983479 Free PMC article.
Publication types
- Search in MeSH
LinkOut - more resources
Full text sources.
- Elsevier Science

- Citation Manager
NCBI Literature Resources
MeSH PMC Bookshelf Disclaimer
The PubMed wordmark and PubMed logo are registered trademarks of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). Unauthorized use of these marks is strictly prohibited.

Click here to place an order for topic brief service to get instant approval from your professor.
Best Midwifery Dissertation Topics Ideas & Examples
Table of Contents
List of Midwifery dissertations Topics and Some Tips for Selecting Better Dissertation Topics in Midwifery
Many students feel difficulty in pursuing their studies in midwifery, let alone making a selection of topics for the dissertation. If you are searching for examples of midwifery literature review topics, midwifery research topics, midwifery dissertation titles , midwifery dissertation topics, or midwifery research questions this post is for you.
Do you belong to the above group of students who are not only shy but are also confused about how to make a selection of dissertation topics in midwifery for the midwifery dissertation?
Let’s first define what midwifery means and what its importance is in our social and medical structure.
What is Midwifery?
Midwifery is a healthcare profession that provides care to childbearing women during pregnancy, labor, and birth and during the postpartum period. They take care of the newborn and the mother. They also provide primary care to women which includes primary care to women, gynecological examination of women, family planning, and menopausal care.
In the nursing profession, students may be asked to write a dissertation on any topic of midwifery.
Tips for Selecting Midwifery Dissertation Topics
Like any dissertation in which it is difficult to choose a topic and write it, midwifery dissertations also students face the same problem. So, it is not an exception. However, one must know the important areas for the selection of the topic for the dissertation. Therefore, prior to the final selection of the topic, there are some important tips that would help students in selecting midwifery dissertation topics. These tips are as follows.
- The students must be sure that they are going to discuss one of the most important topics in the subject.
- The dissertation on midwifery must touch on some of the serious problems which are faced by mothers and newborns.
- The students must take care that their topic is specific, and it is not broad in its nature.
- If someone has chosen a narrow topic, he/she must expand it through research and writing.
- Clear attention should be given to traditional midwifery dissertation topics in order to know their content and scope.
- The topic chosen must be aimed at explaining the profession in greater detail. The students choose the research topic which can help to improve the healthcare of mothers and their children.
- The students must enhance their basic knowledge for a better understanding of the subject.
Prenatal Care:
- The role of midwives in promoting healthy prenatal behaviors
- Assessing the effectiveness of prenatal education programs
- Addressing cultural barriers in accessing prenatal care
Postpartum Care:
- Strategies for improving postpartum support for new mothers.
- The impact of postpartum depression on maternal health outcomes
- Exploring alternative postpartum care models, such as home visits
Labor and Delivery:
- Examining the use of pain management techniques during labor
- Investigating the influence of birth environment on labor outcomes
- Evaluating the role of midwives in reducing cesarean section rates
Maternal Health:
- Addressing disparities in maternal healthcare access
- Exploring the impact of maternal nutrition on birth outcomes
- Investigating interventions to reduce maternal mortality rates globally.
Neonatal Care:
- Assessing the effectiveness of breastfeeding support in neonatal care units
- Exploring the role of midwives in neonatal resuscitation
- Investigating best practices for kangaroo care in low-resource settings
Women’s Health:
- Examining midwifery-led models of women’s health care
- Investigating the role of midwives in promoting sexual and reproductive health
- Addressing cultural taboos surrounding women’s health issues
Family Planning:
- Evaluating the impact of contraceptive counseling provided by midwives
- Exploring the role of midwives in providing abortion care
- Assessing barriers to accessing family planning services in rural areas
Midwifery Education and Training:
- Assessing the effectiveness of simulation training in midwifery education
- Exploring innovative teaching methods in midwifery programs
- Investigating strategies for mentorship and professional development in midwifery
Midwifery Ethics and Legal Issues:
- Examining ethical dilemmas faced by midwives in clinical practice.
- Exploring legal frameworks for midwifery practice across different countries
- Assessing the impact of litigation on midwifery practice
Mental Health in Pregnancy and Childbirth:
- Investigating the prevalence of anxiety disorders in pregnant women
- Exploring interventions for addressing trauma in childbirth
- Assessing the role of midwives in identifying and supporting women with perinatal mental health issues
Integrative Medicine in Midwifery Practice:
- Exploring the integration of complementary therapies in midwifery care
- Assessing the safety and efficacy of herbal remedies during pregnancy and childbirth
- Investigating cultural practices and rituals surrounding pregnancy and birth
Technology in Midwifery:
- Examining the use of telemedicine in midwifery practice
- Exploring the impact of mobile health applications on maternal and neonatal health outcomes
- Assessing the role of artificial intelligence in improving prenatal diagnosis and monitoring
LGBTQ+ Inclusive Care:
- Investigating the experiences of LGBTQ+ individuals in maternity care settings
- Assessing cultural competency training in midwifery education programs
- Exploring strategies for creating inclusive and affirming birth environments
Global Health and Midwifery:
- Examining the role of midwives in addressing maternal and neonatal health disparities in low-income countries
- Investigating the impact of international partnerships on improving midwifery services
- Assessing the cultural appropriateness of western midwifery models in diverse global contexts
Midwifery and Public Health:
- Exploring the role of midwives in promoting breastfeeding initiation and duration
- Assessing the impact of midwifery-led prenatal care on birth outcomes
- Investigating strategies for reducing maternal and neonatal morbidity and mortality through public health interventions
More Midwifery Dissertation Topics
In light of the above guidance, students can choose any topic from the following given midwifery dissertation topics.
- The impact of maternal obesity on birth outcomes
- The use of midwife-led continuity of care models in maternity care
- The role of midwives in promoting breastfeeding
- The use of technology in midwifery practice
- The impact of cultural diversity on midwifery care
- The use of midwifery-led care in low-risk pregnancies
- The role of midwives in reducing maternal mortality rates
- The use of telehealth in midwifery practice
- The impact of poverty on maternal and newborn health
- The use of water birth in midwifery practice
- The role of midwives in promoting maternal mental health
- The use of midwifery-led care in premature births
- The impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on midwifery practice
- The use of aromatherapy in midwifery practice
- The role of midwives in promoting gender equity in maternal health
- The use of midwifery-led care in home births
- The impact of policy changes on midwifery practice
- The use of midwifery-led care in rural and remote areas
- The role of midwives in promoting maternal and newborn nutrition
- The use of hypnobirthing in midwifery practice
- The impact of midwifery-led care on maternal satisfaction
- The use of midwifery-led care in women with complications in pregnancy
- The role of midwives in promoting maternal and child health
- The use of midwifery-led care in family planning
- The impact of the integration of midwifery practice and primary care
- The use of midwifery-led care in women with a history of trauma
- The role of midwives in promoting gender-sensitive care
- The use of midwifery-led care in low-income communities
- The impact of midwifery education on quality of care
- The use of midwifery-led care in women with chronic conditions.
- Role of a midwife: The role of the midwife in the present healthcare environments.
- Midwifery profession: Nursing and Midwifery-two identical yet different professions. Are they likely to go together? Or one will replace the other? What are the Prospects of males working in the midwifery profession?
- Improvements are needed in the midwifery profession in light of scientific developments in the health and childcare fields.
- The state of midwifery in developed and underdeveloped countries.
- Midwifery field: Discuss the latest practices in nursing and midwifery fields.
- The evolution of midwifery from ancient times to modern times.
- The relation between nursing and midwifery.
- The role of prenatal counseling in the growth of a child.
- Critical analysis of midwifery as the profession dominated by women.
- Midwifery service: How to improve midwifery services to less privileged women?
- What is the future growth of the midwifery profession?
- Pregnant women: Do the midwives influence decision-making and facilitate informed choices among pregnant women?
- Midwives’ descriptions and perceptions of pregnant women with problems of substance abuse .
- Comparison of midwife-led and consultant-led care of healthy women at low risk of childbirth complications in the Republic of Ireland: a randomized trial (the MidU study)
Midwifery is a noble profession with a lot of growth potential. There could be more thought-provoking nursing dissertation topics for research in this field. Interested in further details, call us for more Midwifery Dissertation topics.
Related posts:
- 87 Dementia dissertation topics in nursing
- 54 Adult Nursing Dissertation Topics ideas with examples
- 56 Best Critical Care Nursing Research Topics ideas with examples
- Dissertation topics in Nursing (101 Ideas) for dissertation writing
Custom Midwifery Dissertation Topics Brief Service
Paid topic mini proposal (500 words).
You will get the topics first and then the mini proposal which includes:
- An explanation why we choose this topic.
- 2-3 research questions.
- Key literature resources identification.
- Suitable methodology including raw sample size and data collection method
- View a Sample of Service
Note: After submitting your order please must check your email [inbox/spam] folders for order confirmation and login details. If the email goes in spam please mark not as spam to avoid any communication gap between us.
Get An Expert Dissertation Writing Help To Achieve Good Grades
By placing an order with us, you can get;
- Writer consultation before payment to ensure your work is in safe hands.
- Free topic if you don't have one
- Draft submissions to check the quality of the work as per supervisor's feedback
- Free revisions
- Complete privacy
- Plagiarism Free work
- Guaranteed 2:1 (With help of your supervisor's feedback)
- 2 Instalments plan
- Special discounts
Other Posts
- 250+ Best Nursing Dissertation Topics for Healthcare Students in 2024 March 13, 2020 -->
- 56 Best Critical Care Nursing Research Topics ideas with examples November 18, 2021 -->
- 87 Dementia dissertation topics in nursing November 18, 2021 -->
- Adult Nursing Dissertation Topics ideas with examples November 18, 2021 -->
- Nursing Literature Review Topics and Examples February 6, 2020 -->
- Nursing Research Proposal Topics and Examples February 7, 2020 -->
WhatsApp and Get 35% off promo code now!
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Open access
- Published: 31 August 2024
Knowledge mapping and evolution of research on older adults’ technology acceptance: a bibliometric study from 2013 to 2023
- Xianru Shang ORCID: orcid.org/0009-0000-8906-3216 1 ,
- Zijian Liu 1 ,
- Chen Gong 1 ,
- Zhigang Hu 1 ,
- Yuexuan Wu 1 &
- Chengliang Wang ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-2208-3508 2
Humanities and Social Sciences Communications volume 11 , Article number: 1115 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
- Science, technology and society
The rapid expansion of information technology and the intensification of population aging are two prominent features of contemporary societal development. Investigating older adults’ acceptance and use of technology is key to facilitating their integration into an information-driven society. Given this context, the technology acceptance of older adults has emerged as a prioritized research topic, attracting widespread attention in the academic community. However, existing research remains fragmented and lacks a systematic framework. To address this gap, we employed bibliometric methods, utilizing the Web of Science Core Collection to conduct a comprehensive review of literature on older adults’ technology acceptance from 2013 to 2023. Utilizing VOSviewer and CiteSpace for data assessment and visualization, we created knowledge mappings of research on older adults’ technology acceptance. Our study employed multidimensional methods such as co-occurrence analysis, clustering, and burst analysis to: (1) reveal research dynamics, key journals, and domains in this field; (2) identify leading countries, their collaborative networks, and core research institutions and authors; (3) recognize the foundational knowledge system centered on theoretical model deepening, emerging technology applications, and research methods and evaluation, uncovering seminal literature and observing a shift from early theoretical and influential factor analyses to empirical studies focusing on individual factors and emerging technologies; (4) moreover, current research hotspots are primarily in the areas of factors influencing technology adoption, human-robot interaction experiences, mobile health management, and aging-in-place technology, highlighting the evolutionary context and quality distribution of research themes. Finally, we recommend that future research should deeply explore improvements in theoretical models, long-term usage, and user experience evaluation. Overall, this study presents a clear framework of existing research in the field of older adults’ technology acceptance, providing an important reference for future theoretical exploration and innovative applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
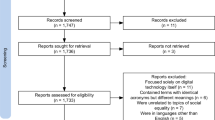
Research progress and intellectual structure of design for digital equity (DDE): A bibliometric analysis based on citespace
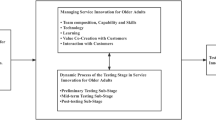
Exploring the role of interaction in older-adult service innovation: insights from the testing stage

Smart device interest, perceived usefulness, and preferences in rural Alabama seniors
Introduction.
In contemporary society, the rapid development of information technology has been intricately intertwined with the intensifying trend of population aging. According to the latest United Nations forecast, by 2050, the global population aged 65 and above is expected to reach 1.6 billion, representing about 16% of the total global population (UN 2023 ). Given the significant challenges of global aging, there is increasing evidence that emerging technologies have significant potential to maintain health and independence for older adults in their home and healthcare environments (Barnard et al. 2013 ; Soar 2010 ; Vancea and Solé-Casals 2016 ). This includes, but is not limited to, enhancing residential safety with smart home technologies (Touqeer et al. 2021 ; Wang et al. 2022 ), improving living independence through wearable technologies (Perez et al. 2023 ), and increasing medical accessibility via telehealth services (Kruse et al. 2020 ). Technological innovations are redefining the lifestyles of older adults, encouraging a shift from passive to active participation (González et al. 2012 ; Mostaghel 2016 ). Nevertheless, the effective application and dissemination of technology still depends on user acceptance and usage intentions (Naseri et al. 2023 ; Wang et al. 2023a ; Xia et al. 2024 ; Yu et al. 2023 ). Particularly, older adults face numerous challenges in accepting and using new technologies. These challenges include not only physical and cognitive limitations but also a lack of technological experience, along with the influences of social and economic factors (Valk et al. 2018 ; Wilson et al. 2021 ).
User acceptance of technology is a significant focus within information systems (IS) research (Dai et al. 2024 ), with several models developed to explain and predict user behavior towards technology usage, including the Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) (Davis 1989 ), TAM2, TAM3, and the Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology (UTAUT) (Venkatesh et al. 2003 ). Older adults, as a group with unique needs, exhibit different behavioral patterns during technology acceptance than other user groups, and these uniquenesses include changes in cognitive abilities, as well as motivations, attitudes, and perceptions of the use of new technologies (Chen and Chan 2011 ). The continual expansion of technology introduces considerable challenges for older adults, rendering the understanding of their technology acceptance a research priority. Thus, conducting in-depth research into older adults’ acceptance of technology is critically important for enhancing their integration into the information society and improving their quality of life through technological advancements.
Reviewing relevant literature to identify research gaps helps further solidify the theoretical foundation of the research topic. However, many existing literature reviews primarily focus on the factors influencing older adults’ acceptance or intentions to use technology. For instance, Ma et al. ( 2021 ) conducted a comprehensive analysis of the determinants of older adults’ behavioral intentions to use technology; Liu et al. ( 2022 ) categorized key variables in studies of older adults’ technology acceptance, noting a shift in focus towards social and emotional factors; Yap et al. ( 2022 ) identified seven categories of antecedents affecting older adults’ use of technology from an analysis of 26 articles, including technological, psychological, social, personal, cost, behavioral, and environmental factors; Schroeder et al. ( 2023 ) extracted 119 influencing factors from 59 articles and further categorized these into six themes covering demographics, health status, and emotional awareness. Additionally, some studies focus on the application of specific technologies, such as Ferguson et al. ( 2021 ), who explored barriers and facilitators to older adults using wearable devices for heart monitoring, and He et al. ( 2022 ) and Baer et al. ( 2022 ), who each conducted in-depth investigations into the acceptance of social assistive robots and mobile nutrition and fitness apps, respectively. In summary, current literature reviews on older adults’ technology acceptance exhibit certain limitations. Due to the interdisciplinary nature and complex knowledge structure of this field, traditional literature reviews often rely on qualitative analysis, based on literature analysis and periodic summaries, which lack sufficient objectivity and comprehensiveness. Additionally, systematic research is relatively limited, lacking a macroscopic description of the research trajectory from a holistic perspective. Over the past decade, research on older adults’ technology acceptance has experienced rapid growth, with a significant increase in literature, necessitating the adoption of new methods to review and examine the developmental trends in this field (Chen 2006 ; Van Eck and Waltman 2010 ). Bibliometric analysis, as an effective quantitative research method, analyzes published literature through visualization, offering a viable approach to extracting patterns and insights from a large volume of papers, and has been widely applied in numerous scientific research fields (Achuthan et al. 2023 ; Liu and Duffy 2023 ). Therefore, this study will employ bibliometric methods to systematically analyze research articles related to older adults’ technology acceptance published in the Web of Science Core Collection from 2013 to 2023, aiming to understand the core issues and evolutionary trends in the field, and to provide valuable references for future related research. Specifically, this study aims to explore and answer the following questions:
RQ1: What are the research dynamics in the field of older adults’ technology acceptance over the past decade? What are the main academic journals and fields that publish studies related to older adults’ technology acceptance?
RQ2: How is the productivity in older adults’ technology acceptance research distributed among countries, institutions, and authors?
RQ3: What are the knowledge base and seminal literature in older adults’ technology acceptance research? How has the research theme progressed?
RQ4: What are the current hot topics and their evolutionary trajectories in older adults’ technology acceptance research? How is the quality of research distributed?
Methodology and materials
Research method.
In recent years, bibliometrics has become one of the crucial methods for analyzing literature reviews and is widely used in disciplinary and industrial intelligence analysis (Jing et al. 2023 ; Lin and Yu 2024a ; Wang et al. 2024a ; Xu et al. 2021 ). Bibliometric software facilitates the visualization analysis of extensive literature data, intuitively displaying the network relationships and evolutionary processes between knowledge units, and revealing the underlying knowledge structure and potential information (Chen et al. 2024 ; López-Robles et al. 2018 ; Wang et al. 2024c ). This method provides new insights into the current status and trends of specific research areas, along with quantitative evidence, thereby enhancing the objectivity and scientific validity of the research conclusions (Chen et al. 2023 ; Geng et al. 2024 ). VOSviewer and CiteSpace are two widely used bibliometric software tools in academia (Pan et al. 2018 ), recognized for their robust functionalities based on the JAVA platform. Although each has its unique features, combining these two software tools effectively constructs mapping relationships between literature knowledge units and clearly displays the macrostructure of the knowledge domains. Particularly, VOSviewer, with its excellent graphical representation capabilities, serves as an ideal tool for handling large datasets and precisely identifying the focal points and hotspots of research topics. Therefore, this study utilizes VOSviewer (version 1.6.19) and CiteSpace (version 6.1.R6), combined with in-depth literature analysis, to comprehensively examine and interpret the research theme of older adults’ technology acceptance through an integrated application of quantitative and qualitative methods.
Data source
Web of Science is a comprehensively recognized database in academia, featuring literature that has undergone rigorous peer review and editorial scrutiny (Lin and Yu 2024b ; Mongeon and Paul-Hus 2016 ; Pranckutė 2021 ). This study utilizes the Web of Science Core Collection as its data source, specifically including three major citation indices: Science Citation Index Expanded (SCIE), Social Sciences Citation Index (SSCI), and Arts & Humanities Citation Index (A&HCI). These indices encompass high-quality research literature in the fields of science, social sciences, and arts and humanities, ensuring the comprehensiveness and reliability of the data. We combined “older adults” with “technology acceptance” through thematic search, with the specific search strategy being: TS = (elder OR elderly OR aging OR ageing OR senile OR senior OR old people OR “older adult*”) AND TS = (“technology acceptance” OR “user acceptance” OR “consumer acceptance”). The time span of literature search is from 2013 to 2023, with the types limited to “Article” and “Review” and the language to “English”. Additionally, the search was completed by October 27, 2023, to avoid data discrepancies caused by database updates. The initial search yielded 764 journal articles. Given that searches often retrieve articles that are superficially relevant but actually non-compliant, manual screening post-search was essential to ensure the relevance of the literature (Chen et al. 2024 ). Through manual screening, articles significantly deviating from the research theme were eliminated and rigorously reviewed. Ultimately, this study obtained 500 valid sample articles from the Web of Science Core Collection. The complete PRISMA screening process is illustrated in Fig. 1 .
Presentation of the data culling process in detail.
Data standardization
Raw data exported from databases often contain multiple expressions of the same terminology (Nguyen and Hallinger 2020 ). To ensure the accuracy and consistency of data, it is necessary to standardize the raw data (Strotmann and Zhao 2012 ). This study follows the data standardization process proposed by Taskin and Al ( 2019 ), mainly executing the following operations:
(1) Standardization of author and institution names is conducted to address different name expressions for the same author. For instance, “Chan, Alan Hoi Shou” and “Chan, Alan H. S.” are considered the same author, and distinct authors with the same name are differentiated by adding identifiers. Diverse forms of institutional names are unified to address variations caused by name changes or abbreviations, such as standardizing “FRANKFURT UNIV APPL SCI” and “Frankfurt University of Applied Sciences,” as well as “Chinese University of Hong Kong” and “University of Hong Kong” to consistent names.
(2) Different expressions of journal names are unified. For example, “International Journal of Human-Computer Interaction” and “Int J Hum Comput Interact” are standardized to a single name. This ensures consistency in journal names and prevents misclassification of literature due to differing journal names. Additionally, it involves checking if the journals have undergone name changes in the past decade to prevent any impact on the analysis due to such changes.
(3) Keywords data are cleansed by removing words that do not directly pertain to specific research content (e.g., people, review), merging synonyms (e.g., “UX” and “User Experience,” “aging-in-place” and “aging in place”), and standardizing plural forms of keywords (e.g., “assistive technologies” and “assistive technology,” “social robots” and “social robot”). This reduces redundant information in knowledge mapping.
Bibliometric results and analysis
Distribution power (rq1), literature descriptive statistical analysis.
Table 1 presents a detailed descriptive statistical overview of the literature in the field of older adults’ technology acceptance. After deduplication using the CiteSpace software, this study confirmed a valid sample size of 500 articles. Authored by 1839 researchers, the documents encompass 792 research institutions across 54 countries and are published in 217 different academic journals. As of the search cutoff date, these articles have accumulated 13,829 citations, with an annual average of 1156 citations, and an average of 27.66 citations per article. The h-index, a composite metric of quantity and quality of scientific output (Kamrani et al. 2021 ), reached 60 in this study.
Trends in publications and disciplinary distribution
The number of publications and citations are significant indicators of the research field’s development, reflecting its continuity, attention, and impact (Ale Ebrahim et al. 2014 ). The ranking of annual publications and citations in the field of older adults’ technology acceptance studies is presented chronologically in Fig. 2A . The figure shows a clear upward trend in the amount of literature in this field. Between 2013 and 2017, the number of publications increased slowly and decreased in 2018. However, in 2019, the number of publications increased rapidly to 52 and reached a peak of 108 in 2022, which is 6.75 times higher than in 2013. In 2022, the frequency of document citations reached its highest point with 3466 citations, reflecting the widespread recognition and citation of research in this field. Moreover, the curve of the annual number of publications fits a quadratic function, with a goodness-of-fit R 2 of 0.9661, indicating that the number of future publications is expected to increase even more rapidly.
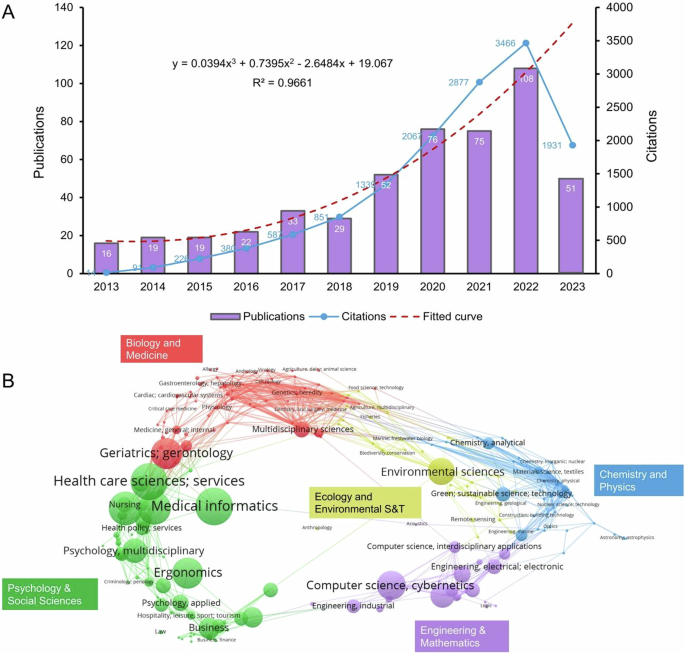
A Trends in trends in annual publications and citations (2013–2023). B Overlay analysis of the distribution of discipline fields.
Figure 2B shows that research on older adults’ technology acceptance involves the integration of multidisciplinary knowledge. According to Web of Science Categories, these 500 articles are distributed across 85 different disciplines. We have tabulated the top ten disciplines by publication volume (Table 2 ), which include Medical Informatics (75 articles, 15.00%), Health Care Sciences & Services (71 articles, 14.20%), Gerontology (61 articles, 12.20%), Public Environmental & Occupational Health (57 articles, 11.40%), and Geriatrics & Gerontology (52 articles, 10.40%), among others. The high output in these disciplines reflects the concentrated global academic interest in this comprehensive research topic. Additionally, interdisciplinary research approaches provide diverse perspectives and a solid theoretical foundation for studies on older adults’ technology acceptance, also paving the way for new research directions.
Knowledge flow analysis
A dual-map overlay is a CiteSpace map superimposed on top of a base map, which shows the interrelationships between journals in different domains, representing the publication and citation activities in each domain (Chen and Leydesdorff 2014 ). The overlay map reveals the link between the citing domain (on the left side) and the cited domain (on the right side), reflecting the knowledge flow of the discipline at the journal level (Leydesdorff and Rafols 2012 ). We utilize the in-built Z-score algorithm of the software to cluster the graph, as shown in Fig. 3 .
The left side shows the citing journal, and the right side shows the cited journal.
Figure 3 shows the distribution of citing journals clusters for older adults’ technology acceptance on the left side, while the right side refers to the main cited journals clusters. Two knowledge flow citation trajectories were obtained; they are presented by the color of the cited regions, and the thickness of these trajectories is proportional to the Z-score scaled frequency of citations (Chen et al. 2014 ). Within the cited regions, the most popular fields with the most records covered are “HEALTH, NURSING, MEDICINE” and “PSYCHOLOGY, EDUCATION, SOCIAL”, and the elliptical aspect ratio of these two fields stands out. Fields have prominent elliptical aspect ratios, highlighting their significant influence on older adults’ technology acceptance research. Additionally, the major citation trajectories originate in these two areas and progress to the frontier research area of “PSYCHOLOGY, EDUCATION, HEALTH”. It is worth noting that the citation trajectory from “PSYCHOLOGY, EDUCATION, SOCIAL” has a significant Z-value (z = 6.81), emphasizing the significance and impact of this development path. In the future, “MATHEMATICS, SYSTEMS, MATHEMATICAL”, “MOLECULAR, BIOLOGY, IMMUNOLOGY”, and “NEUROLOGY, SPORTS, OPHTHALMOLOGY” may become emerging fields. The fields of “MEDICINE, MEDICAL, CLINICAL” may be emerging areas of cutting-edge research.
Main research journals analysis
Table 3 provides statistics for the top ten journals by publication volume in the field of older adults’ technology acceptance. Together, these journals have published 137 articles, accounting for 27.40% of the total publications, indicating that there is no highly concentrated core group of journals in this field, with publications being relatively dispersed. Notably, Computers in Human Behavior , Journal of Medical Internet Research , and International Journal of Human-Computer Interaction each lead with 15 publications. In terms of citation metrics, International Journal of Medical Informatics and Computers in Human Behavior stand out significantly, with the former accumulating a total of 1,904 citations, averaging 211.56 citations per article, and the latter totaling 1,449 citations, with an average of 96.60 citations per article. These figures emphasize the academic authority and widespread impact of these journals within the research field.
Research power (RQ2)
Countries and collaborations analysis.
The analysis revealed the global research pattern for country distribution and collaboration (Chen et al. 2019 ). Figure 4A shows the network of national collaborations on older adults’ technology acceptance research. The size of the bubbles represents the amount of publications in each country, while the thickness of the connecting lines expresses the closeness of the collaboration among countries. Generally, this research subject has received extensive international attention, with China and the USA publishing far more than any other countries. China has established notable research collaborations with the USA, UK and Malaysia in this field, while other countries have collaborations, but the closeness is relatively low and scattered. Figure 4B shows the annual publication volume dynamics of the top ten countries in terms of total publications. Since 2017, China has consistently increased its annual publications, while the USA has remained relatively stable. In 2019, the volume of publications in each country increased significantly, this was largely due to the global outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic, which has led to increased reliance on information technology among the elderly for medical consultations, online socialization, and health management (Sinha et al. 2021 ). This phenomenon has led to research advances in technology acceptance among older adults in various countries. Table 4 shows that the top ten countries account for 93.20% of the total cumulative number of publications, with each country having published more than 20 papers. Among these ten countries, all of them except China are developed countries, indicating that the research field of older adults’ technology acceptance has received general attention from developed countries. Currently, China and the USA were the leading countries in terms of publications with 111 and 104 respectively, accounting for 22.20% and 20.80%. The UK, Germany, Italy, and the Netherlands also made significant contributions. The USA and China ranked first and second in terms of the number of citations, while the Netherlands had the highest average citations, indicating the high impact and quality of its research. The UK has shown outstanding performance in international cooperation, while the USA highlights its significant academic influence in this field with the highest h-index value.
A National collaboration network. B Annual volume of publications in the top 10 countries.
Institutions and authors analysis
Analyzing the number of publications and citations can reveal an institution’s or author’s research strength and influence in a particular research area (Kwiek 2021 ). Tables 5 and 6 show the statistics of the institutions and authors whose publication counts are in the top ten, respectively. As shown in Table 5 , higher education institutions hold the main position in this research field. Among the top ten institutions, City University of Hong Kong and The University of Hong Kong from China lead with 14 and 9 publications, respectively. City University of Hong Kong has the highest h-index, highlighting its significant influence in the field. It is worth noting that Tilburg University in the Netherlands is not among the top five in terms of publications, but the high average citation count (130.14) of its literature demonstrates the high quality of its research.
After analyzing the authors’ output using Price’s Law (Redner 1998 ), the highest number of publications among the authors counted ( n = 10) defines a publication threshold of 3 for core authors in this research area. As a result of quantitative screening, a total of 63 core authors were identified. Table 6 shows that Chen from Zhejiang University, China, Ziefle from RWTH Aachen University, Germany, and Rogers from Macquarie University, Australia, were the top three authors in terms of the number of publications, with 10, 9, and 8 articles, respectively. In terms of average citation rate, Peek and Wouters, both scholars from the Netherlands, have significantly higher rates than other scholars, with 183.2 and 152.67 respectively. This suggests that their research is of high quality and widely recognized. Additionally, Chen and Rogers have high h-indices in this field.
Knowledge base and theme progress (RQ3)
Research knowledge base.
Co-citation relationships occur when two documents are cited together (Zhang and Zhu 2022 ). Co-citation mapping uses references as nodes to represent the knowledge base of a subject area (Min et al. 2021). Figure 5A illustrates co-occurrence mapping in older adults’ technology acceptance research, where larger nodes signify higher co-citation frequencies. Co-citation cluster analysis can be used to explore knowledge structure and research boundaries (Hota et al. 2020 ; Shiau et al. 2023 ). The co-citation clustering mapping of older adults’ technology acceptance research literature (Fig. 5B ) shows that the Q value of the clustering result is 0.8129 (>0.3), and the average value of the weight S is 0.9391 (>0.7), indicating that the clusters are uniformly distributed with a significant and credible structure. This further proves that the boundaries of the research field are clear and there is significant differentiation in the field. The figure features 18 cluster labels, each associated with thematic color blocks corresponding to different time slices. Highlighted emerging research themes include #2 Smart Home Technology, #7 Social Live, and #10 Customer Service. Furthermore, the clustering labels extracted are primarily classified into three categories: theoretical model deepening, emerging technology applications, research methods and evaluation, as detailed in Table 7 .
A Co-citation analysis of references. B Clustering network analysis of references.
Seminal literature analysis
The top ten nodes in terms of co-citation frequency were selected for further analysis. Table 8 displays the corresponding node information. Studies were categorized into four main groups based on content analysis. (1) Research focusing on specific technology usage by older adults includes studies by Peek et al. ( 2014 ), Ma et al. ( 2016 ), Hoque and Sorwar ( 2017 ), and Li et al. ( 2019 ), who investigated the factors influencing the use of e-technology, smartphones, mHealth, and smart wearables, respectively. (2) Concerning the development of theoretical models of technology acceptance, Chen and Chan ( 2014 ) introduced the Senior Technology Acceptance Model (STAM), and Macedo ( 2017 ) analyzed the predictive power of UTAUT2 in explaining older adults’ intentional behaviors and information technology usage. (3) In exploring older adults’ information technology adoption and behavior, Lee and Coughlin ( 2015 ) emphasized that the adoption of technology by older adults is a multifactorial process that includes performance, price, value, usability, affordability, accessibility, technical support, social support, emotion, independence, experience, and confidence. Yusif et al. ( 2016 ) conducted a literature review examining the key barriers affecting older adults’ adoption of assistive technology, including factors such as privacy, trust, functionality/added value, cost, and stigma. (4) From the perspective of research into older adults’ technology acceptance, Mitzner et al. ( 2019 ) assessed the long-term usage of computer systems designed for the elderly, whereas Guner and Acarturk ( 2020 ) compared information technology usage and acceptance between older and younger adults. The breadth and prevalence of this literature make it a vital reference for researchers in the field, also providing new perspectives and inspiration for future research directions.
Research thematic progress
Burst citation is a node of literature that guides the sudden change in dosage, which usually represents a prominent development or major change in a particular field, with innovative and forward-looking qualities. By analyzing the emergent literature, it is often easy to understand the dynamics of the subject area, mapping the emerging thematic change (Chen et al. 2022 ). Figure 6 shows the burst citation mapping in the field of older adults’ technology acceptance research, with burst citations represented by red nodes (Fig. 6A ). For the ten papers with the highest burst intensity (Fig. 6B ), this study will conduct further analysis in conjunction with literature review.
A Burst detection of co-citation. B The top 10 references with the strongest citation bursts.
As shown in Fig. 6 , Mitzner et al. ( 2010 ) broke the stereotype that older adults are fearful of technology, found that they actually have positive attitudes toward technology, and emphasized the centrality of ease of use and usefulness in the process of technology acceptance. This finding provides an important foundation for subsequent research. During the same period, Wagner et al. ( 2010 ) conducted theory-deepening and applied research on technology acceptance among older adults. The research focused on older adults’ interactions with computers from the perspective of Social Cognitive Theory (SCT). This expanded the understanding of technology acceptance, particularly regarding the relationship between behavior, environment, and other SCT elements. In addition, Pan and Jordan-Marsh ( 2010 ) extended the TAM to examine the interactions among predictors of perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, subjective norm, and convenience conditions when older adults use the Internet, taking into account the moderating roles of gender and age. Heerink et al. ( 2010 ) adapted and extended the UTAUT, constructed a technology acceptance model specifically designed for older users’ acceptance of assistive social agents, and validated it using controlled experiments and longitudinal data, explaining intention to use by combining functional assessment and social interaction variables.
Then the research theme shifted to an in-depth analysis of the factors influencing technology acceptance among older adults. Two papers with high burst strengths emerged during this period: Peek et al. ( 2014 ) (Strength = 12.04), Chen and Chan ( 2014 ) (Strength = 9.81). Through a systematic literature review and empirical study, Peek STM and Chen K, among others, identified multidimensional factors that influence older adults’ technology acceptance. Peek et al. ( 2014 ) analyzed literature on the acceptance of in-home care technology among older adults and identified six factors that influence their acceptance: concerns about technology, expected benefits, technology needs, technology alternatives, social influences, and older adult characteristics, with a focus on differences between pre- and post-implementation factors. Chen and Chan ( 2014 ) constructed the STAM by administering a questionnaire to 1012 older adults and adding eight important factors, including technology anxiety, self-efficacy, cognitive ability, and physical function, based on the TAM. This enriches the theoretical foundation of the field. In addition, Braun ( 2013 ) highlighted the role of perceived usefulness, trust in social networks, and frequency of Internet use in older adults’ use of social networks, while ease of use and social pressure were not significant influences. These findings contribute to the study of older adults’ technology acceptance within specific technology application domains.
Recent research has focused on empirical studies of personal factors and emerging technologies. Ma et al. ( 2016 ) identified key personal factors affecting smartphone acceptance among older adults through structured questionnaires and face-to-face interviews with 120 participants. The study found that cost, self-satisfaction, and convenience were important factors influencing perceived usefulness and ease of use. This study offers empirical evidence to comprehend the main factors that drive smartphone acceptance among Chinese older adults. Additionally, Yusif et al. ( 2016 ) presented an overview of the obstacles that hinder older adults’ acceptance of assistive technologies, focusing on privacy, trust, and functionality.
In summary, research on older adults’ technology acceptance has shifted from early theoretical deepening and analysis of influencing factors to empirical studies in the areas of personal factors and emerging technologies, which have greatly enriched the theoretical basis of older adults’ technology acceptance and provided practical guidance for the design of emerging technology products.
Research hotspots, evolutionary trends, and quality distribution (RQ4)
Core keywords analysis.
Keywords concise the main idea and core of the literature, and are a refined summary of the research content (Huang et al. 2021 ). In CiteSpace, nodes with a centrality value greater than 0.1 are considered to be critical nodes. Analyzing keywords with high frequency and centrality helps to visualize the hot topics in the research field (Park et al. 2018 ). The merged keywords were imported into CiteSpace, and the top 10 keywords were counted and sorted by frequency and centrality respectively, as shown in Table 9 . The results show that the keyword “TAM” has the highest frequency (92), followed by “UTAUT” (24), which reflects that the in-depth study of the existing technology acceptance model and its theoretical expansion occupy a central position in research related to older adults’ technology acceptance. Furthermore, the terms ‘assistive technology’ and ‘virtual reality’ are both high-frequency and high-centrality terms (frequency = 17, centrality = 0.10), indicating that the research on assistive technology and virtual reality for older adults is the focus of current academic attention.
Research hotspots analysis
Using VOSviewer for keyword co-occurrence analysis organizes keywords into groups or clusters based on their intrinsic connections and frequencies, clearly highlighting the research field’s hot topics. The connectivity among keywords reveals correlations between different topics. To ensure accuracy, the analysis only considered the authors’ keywords. Subsequently, the keywords were filtered by setting the keyword frequency to 5 to obtain the keyword clustering map of the research on older adults’ technology acceptance research keyword clustering mapping (Fig. 7 ), combined with the keyword co-occurrence clustering network (Fig. 7A ) and the corresponding density situation (Fig. 7B ) to make a detailed analysis of the following four groups of clustered themes.
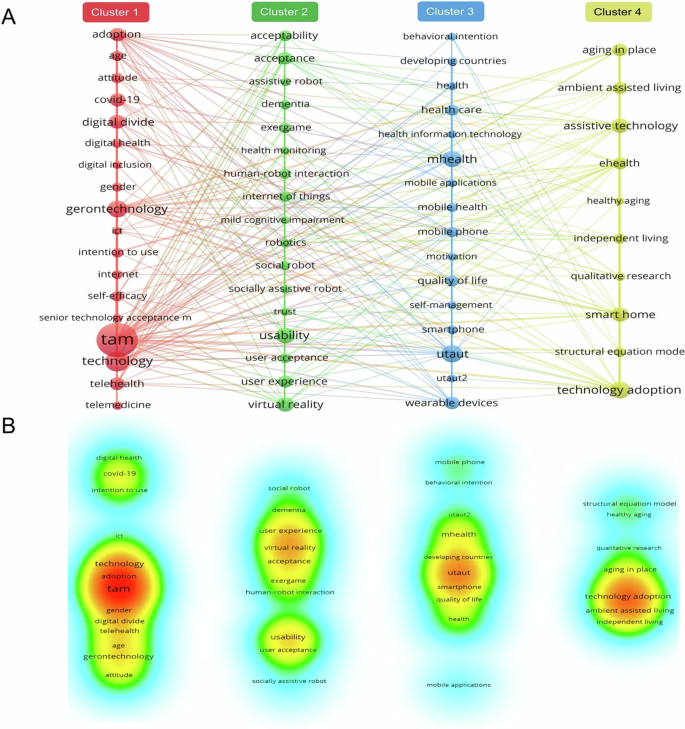
A Co-occurrence clustering network. B Keyword density.
Cluster #1—Research on the factors influencing technology adoption among older adults is a prominent topic, covering age, gender, self-efficacy, attitude, and and intention to use (Berkowsky et al. 2017 ; Wang et al. 2017 ). It also examined older adults’ attitudes towards and acceptance of digital health technologies (Ahmad and Mozelius, 2022 ). Moreover, the COVID-19 pandemic, significantly impacting older adults’ technology attitudes and usage, has underscored the study’s importance and urgency. Therefore, it is crucial to conduct in-depth studies on how older adults accept, adopt, and effectively use new technologies, to address their needs and help them overcome the digital divide within digital inclusion. This will improve their quality of life and healthcare experiences.
Cluster #2—Research focuses on how older adults interact with assistive technologies, especially assistive robots and health monitoring devices, emphasizing trust, usability, and user experience as crucial factors (Halim et al. 2022 ). Moreover, health monitoring technologies effectively track and manage health issues common in older adults, like dementia and mild cognitive impairment (Lussier et al. 2018 ; Piau et al. 2019 ). Interactive exercise games and virtual reality have been deployed to encourage more physical and cognitive engagement among older adults (Campo-Prieto et al. 2021 ). Personalized and innovative technology significantly enhances older adults’ participation, improving their health and well-being.
Cluster #3—Optimizing health management for older adults using mobile technology. With the development of mobile health (mHealth) and health information technology, mobile applications, smartphones, and smart wearable devices have become effective tools to help older users better manage chronic conditions, conduct real-time health monitoring, and even receive telehealth services (Dupuis and Tsotsos 2018 ; Olmedo-Aguirre et al. 2022 ; Kim et al. 2014 ). Additionally, these technologies can mitigate the problem of healthcare resource inequality, especially in developing countries. Older adults’ acceptance and use of these technologies are significantly influenced by their behavioral intentions, motivational factors, and self-management skills. These internal motivational factors, along with external factors, jointly affect older adults’ performance in health management and quality of life.
Cluster #4—Research on technology-assisted home care for older adults is gaining popularity. Environmentally assisted living enhances older adults’ independence and comfort at home, offering essential support and security. This has a crucial impact on promoting healthy aging (Friesen et al. 2016 ; Wahlroos et al. 2023 ). The smart home is a core application in this field, providing a range of solutions that facilitate independent living for the elderly in a highly integrated and user-friendly manner. This fulfills different dimensions of living and health needs (Majumder et al. 2017 ). Moreover, eHealth offers accurate and personalized health management and healthcare services for older adults (Delmastro et al. 2018 ), ensuring their needs are met at home. Research in this field often employs qualitative methods and structural equation modeling to fully understand older adults’ needs and experiences at home and analyze factors influencing technology adoption.
Evolutionary trends analysis
To gain a deeper understanding of the evolutionary trends in research hotspots within the field of older adults’ technology acceptance, we conducted a statistical analysis of the average appearance times of keywords, using CiteSpace to generate the time-zone evolution mapping (Fig. 8 ) and burst keywords. The time-zone mapping visually displays the evolution of keywords over time, intuitively reflecting the frequency and initial appearance of keywords in research, commonly used to identify trends in research topics (Jing et al. 2024a ; Kumar et al. 2021 ). Table 10 lists the top 15 keywords by burst strength, with the red sections indicating high-frequency citations and their burst strength in specific years. These burst keywords reveal the focus and trends of research themes over different periods (Kleinberg 2002 ). Combining insights from the time-zone mapping and burst keywords provides more objective and accurate research insights (Wang et al. 2023b ).
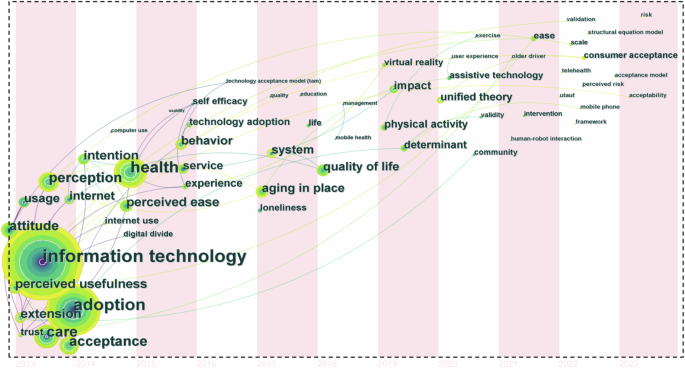
Reflecting the frequency and time of first appearance of keywords in the study.
An integrated analysis of Fig. 8 and Table 10 shows that early research on older adults’ technology acceptance primarily focused on factors such as perceived usefulness, ease of use, and attitudes towards information technology, including their use of computers and the internet (Pan and Jordan-Marsh 2010 ), as well as differences in technology use between older adults and other age groups (Guner and Acarturk 2020 ). Subsequently, the research focus expanded to improving the quality of life for older adults, exploring how technology can optimize health management and enhance the possibility of independent living, emphasizing the significant role of technology in improving the quality of life for the elderly. With ongoing technological advancements, recent research has shifted towards areas such as “virtual reality,” “telehealth,” and “human-robot interaction,” with a focus on the user experience of older adults (Halim et al. 2022 ). The appearance of keywords such as “physical activity” and “exercise” highlights the value of technology in promoting physical activity and health among older adults. This phase of research tends to make cutting-edge technology genuinely serve the practical needs of older adults, achieving its widespread application in daily life. Additionally, research has focused on expanding and quantifying theoretical models of older adults’ technology acceptance, involving keywords such as “perceived risk”, “validation” and “UTAUT”.
In summary, from 2013 to 2023, the field of older adults’ technology acceptance has evolved from initial explorations of influencing factors, to comprehensive enhancements in quality of life and health management, and further to the application and deepening of theoretical models and cutting-edge technologies. This research not only reflects the diversity and complexity of the field but also demonstrates a comprehensive and in-depth understanding of older adults’ interactions with technology across various life scenarios and needs.
Research quality distribution
To reveal the distribution of research quality in the field of older adults’ technology acceptance, a strategic diagram analysis is employed to calculate and illustrate the internal development and interrelationships among various research themes (Xie et al. 2020 ). The strategic diagram uses Centrality as the X-axis and Density as the Y-axis to divide into four quadrants, where the X-axis represents the strength of the connection between thematic clusters and other themes, with higher values indicating a central position in the research field; the Y-axis indicates the level of development within the thematic clusters, with higher values denoting a more mature and widely recognized field (Li and Zhou 2020 ).
Through cluster analysis and manual verification, this study categorized 61 core keywords (Frequency ≥5) into 11 thematic clusters. Subsequently, based on the keywords covered by each thematic cluster, the research themes and their directions for each cluster were summarized (Table 11 ), and the centrality and density coordinates for each cluster were precisely calculated (Table 12 ). Finally, a strategic diagram of the older adults’ technology acceptance research field was constructed (Fig. 9 ). Based on the distribution of thematic clusters across the quadrants in the strategic diagram, the structure and developmental trends of the field were interpreted.
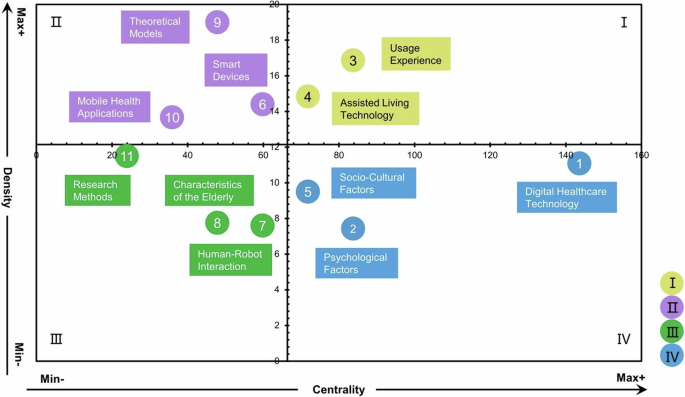
Classification and visualization of theme clusters based on density and centrality.
As illustrated in Fig. 9 , (1) the theme clusters of #3 Usage Experience and #4 Assisted Living Technology are in the first quadrant, characterized by high centrality and density. Their internal cohesion and close links with other themes indicate their mature development, systematic research content or directions have been formed, and they have a significant influence on other themes. These themes play a central role in the field of older adults’ technology acceptance and have promising prospects. (2) The theme clusters of #6 Smart Devices, #9 Theoretical Models, and #10 Mobile Health Applications are in the second quadrant, with higher density but lower centrality. These themes have strong internal connections but weaker external links, indicating that these three themes have received widespread attention from researchers and have been the subject of related research, but more as self-contained systems and exhibit independence. Therefore, future research should further explore in-depth cooperation and cross-application with other themes. (3) The theme clusters of #7 Human-Robot Interaction, #8 Characteristics of the Elderly, and #11 Research Methods are in the third quadrant, with lower centrality and density. These themes are loosely connected internally and have weak links with others, indicating their developmental immaturity. Compared to other topics, they belong to the lower attention edge and niche themes, and there is a need for further investigation. (4) The theme clusters of #1 Digital Healthcare Technology, #2 Psychological Factors, and #5 Socio-Cultural Factors are located in the fourth quadrant, with high centrality but low density. Although closely associated with other research themes, the internal cohesion within these clusters is relatively weak. This suggests that while these themes are closely linked to other research areas, their own development remains underdeveloped, indicating a core immaturity. Nevertheless, these themes are crucial within the research domain of elderly technology acceptance and possess significant potential for future exploration.
Discussion on distribution power (RQ1)
Over the past decade, academic interest and influence in the area of older adults’ technology acceptance have significantly increased. This trend is evidenced by a quantitative analysis of publication and citation volumes, particularly noticeable in 2019 and 2022, where there was a substantial rise in both metrics. The rise is closely linked to the widespread adoption of emerging technologies such as smart homes, wearable devices, and telemedicine among older adults. While these technologies have enhanced their quality of life, they also pose numerous challenges, sparking extensive research into their acceptance, usage behaviors, and influencing factors among the older adults (Pirzada et al. 2022 ; Garcia Reyes et al. 2023 ). Furthermore, the COVID-19 pandemic led to a surge in technology demand among older adults, especially in areas like medical consultation, online socialization, and health management, further highlighting the importance and challenges of technology. Health risks and social isolation have compelled older adults to rely on technology for daily activities, accelerating its adoption and application within this demographic. This phenomenon has made technology acceptance a critical issue, driving societal and academic focus on the study of technology acceptance among older adults.
The flow of knowledge at the level of high-output disciplines and journals, along with the primary publishing outlets, indicates the highly interdisciplinary nature of research into older adults’ technology acceptance. This reflects the complexity and breadth of issues related to older adults’ technology acceptance, necessitating the integration of multidisciplinary knowledge and approaches. Currently, research is primarily focused on medical health and human-computer interaction, demonstrating academic interest in improving health and quality of life for older adults and addressing the urgent needs related to their interactions with technology. In the field of medical health, research aims to provide advanced and innovative healthcare technologies and services to meet the challenges of an aging population while improving the quality of life for older adults (Abdi et al. 2020 ; Wilson et al. 2021 ). In the field of human-computer interaction, research is focused on developing smarter and more user-friendly interaction models to meet the needs of older adults in the digital age, enabling them to actively participate in social activities and enjoy a higher quality of life (Sayago, 2019 ). These studies are crucial for addressing the challenges faced by aging societies, providing increased support and opportunities for the health, welfare, and social participation of older adults.
Discussion on research power (RQ2)
This study analyzes leading countries and collaboration networks, core institutions and authors, revealing the global research landscape and distribution of research strength in the field of older adults’ technology acceptance, and presents quantitative data on global research trends. From the analysis of country distribution and collaborations, China and the USA hold dominant positions in this field, with developed countries like the UK, Germany, Italy, and the Netherlands also excelling in international cooperation and research influence. The significant investment in technological research and the focus on the technological needs of older adults by many developed countries reflect their rapidly aging societies, policy support, and resource allocation.
China is the only developing country that has become a major contributor in this field, indicating its growing research capabilities and high priority given to aging societies and technological innovation. Additionally, China has close collaborations with countries such as USA, the UK, and Malaysia, driven not only by technological research needs but also by shared challenges and complementarities in aging issues among these nations. For instance, the UK has extensive experience in social welfare and aging research, providing valuable theoretical guidance and practical experience. International collaborations, aimed at addressing the challenges of aging, integrate the strengths of various countries, advancing in-depth and widespread development in the research of technology acceptance among older adults.
At the institutional and author level, City University of Hong Kong leads in publication volume, with research teams led by Chan and Chen demonstrating significant academic activity and contributions. Their research primarily focuses on older adults’ acceptance and usage behaviors of various technologies, including smartphones, smart wearables, and social robots (Chen et al. 2015 ; Li et al. 2019 ; Ma et al. 2016 ). These studies, targeting specific needs and product characteristics of older adults, have developed new models of technology acceptance based on existing frameworks, enhancing the integration of these technologies into their daily lives and laying a foundation for further advancements in the field. Although Tilburg University has a smaller publication output, it holds significant influence in the field of older adults’ technology acceptance. Particularly, the high citation rate of Peek’s studies highlights their excellence in research. Peek extensively explored older adults’ acceptance and usage of home care technologies, revealing the complexity and dynamics of their technology use behaviors. His research spans from identifying systemic influencing factors (Peek et al. 2014 ; Peek et al. 2016 ), emphasizing familial impacts (Luijkx et al. 2015 ), to constructing comprehensive models (Peek et al. 2017 ), and examining the dynamics of long-term usage (Peek et al. 2019 ), fully reflecting the evolving technology landscape and the changing needs of older adults. Additionally, the ongoing contributions of researchers like Ziefle, Rogers, and Wouters in the field of older adults’ technology acceptance demonstrate their research influence and leadership. These researchers have significantly enriched the knowledge base in this area with their diverse perspectives. For instance, Ziefle has uncovered the complex attitudes of older adults towards technology usage, especially the trade-offs between privacy and security, and how different types of activities affect their privacy needs (Maidhof et al. 2023 ; Mujirishvili et al. 2023 ; Schomakers and Ziefle 2023 ; Wilkowska et al. 2022 ), reflecting a deep exploration and ongoing innovation in the field of older adults’ technology acceptance.
Discussion on knowledge base and thematic progress (RQ3)
Through co-citation analysis and systematic review of seminal literature, this study reveals the knowledge foundation and thematic progress in the field of older adults’ technology acceptance. Co-citation networks and cluster analyses illustrate the structural themes of the research, delineating the differentiation and boundaries within this field. Additionally, burst detection analysis offers a valuable perspective for understanding the thematic evolution in the field of technology acceptance among older adults. The development and innovation of theoretical models are foundational to this research. Researchers enhance the explanatory power of constructed models by deepening and expanding existing technology acceptance theories to address theoretical limitations. For instance, Heerink et al. ( 2010 ) modified and expanded the UTAUT model by integrating functional assessment and social interaction variables to create the almere model. This model significantly enhances the ability to explain the intentions of older users in utilizing assistive social agents and improves the explanation of actual usage behaviors. Additionally, Chen and Chan ( 2014 ) extended the TAM to include age-related health and capability features of older adults, creating the STAM, which substantially improves predictions of older adults’ technology usage behaviors. Personal attributes, health and capability features, and facilitating conditions have a direct impact on technology acceptance. These factors more effectively predict older adults’ technology usage behaviors than traditional attitudinal factors.
With the advancement of technology and the application of emerging technologies, new research topics have emerged, increasingly focusing on older adults’ acceptance and use of these technologies. Prior to this, the study by Mitzner et al. ( 2010 ) challenged the stereotype of older adults’ conservative attitudes towards technology, highlighting the central roles of usability and usefulness in the technology acceptance process. This discovery laid an important foundation for subsequent research. Research fields such as “smart home technology,” “social life,” and “customer service” are emerging, indicating a shift in focus towards the practical and social applications of technology in older adults’ lives. Research not only focuses on the technology itself but also on how these technologies integrate into older adults’ daily lives and how they can improve the quality of life through technology. For instance, studies such as those by Ma et al. ( 2016 ), Hoque and Sorwar ( 2017 ), and Li et al. ( 2019 ) have explored factors influencing older adults’ use of smartphones, mHealth, and smart wearable devices.
Furthermore, the diversification of research methodologies and innovation in evaluation techniques, such as the use of mixed methods, structural equation modeling (SEM), and neural network (NN) approaches, have enhanced the rigor and reliability of the findings, enabling more precise identification of the factors and mechanisms influencing technology acceptance. Talukder et al. ( 2020 ) employed an effective multimethodological strategy by integrating SEM and NN to leverage the complementary strengths of both approaches, thus overcoming their individual limitations and more accurately analyzing and predicting older adults’ acceptance of wearable health technologies (WHT). SEM is utilized to assess the determinants’ impact on the adoption of WHT, while neural network models validate SEM outcomes and predict the significance of key determinants. This combined approach not only boosts the models’ reliability and explanatory power but also provides a nuanced understanding of the motivations and barriers behind older adults’ acceptance of WHT, offering deep research insights.
Overall, co-citation analysis of the literature in the field of older adults’ technology acceptance has uncovered deeper theoretical modeling and empirical studies on emerging technologies, while emphasizing the importance of research methodological and evaluation innovations in understanding complex social science issues. These findings are crucial for guiding the design and marketing strategies of future technology products, especially in the rapidly growing market of older adults.
Discussion on research hotspots and evolutionary trends (RQ4)
By analyzing core keywords, we can gain deep insights into the hot topics, evolutionary trends, and quality distribution of research in the field of older adults’ technology acceptance. The frequent occurrence of the keywords “TAM” and “UTAUT” indicates that the applicability and theoretical extension of existing technology acceptance models among older adults remain a focal point in academia. This phenomenon underscores the enduring influence of the studies by Davis ( 1989 ) and Venkatesh et al. ( 2003 ), whose models provide a robust theoretical framework for explaining and predicting older adults’ acceptance and usage of emerging technologies. With the widespread application of artificial intelligence (AI) and big data technologies, these theoretical models have incorporated new variables such as perceived risk, trust, and privacy issues (Amin et al. 2024 ; Chen et al. 2024 ; Jing et al. 2024b ; Seibert et al. 2021 ; Wang et al. 2024b ), advancing the theoretical depth and empirical research in this field.
Keyword co-occurrence cluster analysis has revealed multiple research hotspots in the field, including factors influencing technology adoption, interactive experiences between older adults and assistive technologies, the application of mobile health technology in health management, and technology-assisted home care. These studies primarily focus on enhancing the quality of life and health management of older adults through emerging technologies, particularly in the areas of ambient assisted living, smart health monitoring, and intelligent medical care. In these domains, the role of AI technology is increasingly significant (Qian et al. 2021 ; Ho 2020 ). With the evolution of next-generation information technologies, AI is increasingly integrated into elder care systems, offering intelligent, efficient, and personalized service solutions by analyzing the lifestyles and health conditions of older adults. This integration aims to enhance older adults’ quality of life in aspects such as health monitoring and alerts, rehabilitation assistance, daily health management, and emotional support (Lee et al. 2023 ). A survey indicates that 83% of older adults prefer AI-driven solutions when selecting smart products, demonstrating the increasing acceptance of AI in elder care (Zhao and Li 2024 ). Integrating AI into elder care presents both opportunities and challenges, particularly in terms of user acceptance, trust, and long-term usage effects, which warrant further exploration (Mhlanga 2023 ). These studies will help better understand the profound impact of AI technology on the lifestyles of older adults and provide critical references for optimizing AI-driven elder care services.
The Time-zone evolution mapping and burst keyword analysis further reveal the evolutionary trends of research hotspots. Early studies focused on basic technology acceptance models and user perceptions, later expanding to include quality of life and health management. In recent years, research has increasingly focused on cutting-edge technologies such as virtual reality, telehealth, and human-robot interaction, with a concurrent emphasis on the user experience of older adults. This evolutionary process demonstrates a deepening shift from theoretical models to practical applications, underscoring the significant role of technology in enhancing the quality of life for older adults. Furthermore, the strategic coordinate mapping analysis clearly demonstrates the development and mutual influence of different research themes. High centrality and density in the themes of Usage Experience and Assisted Living Technology indicate their mature research status and significant impact on other themes. The themes of Smart Devices, Theoretical Models, and Mobile Health Applications demonstrate self-contained research trends. The themes of Human-Robot Interaction, Characteristics of the Elderly, and Research Methods are not yet mature, but they hold potential for development. Themes of Digital Healthcare Technology, Psychological Factors, and Socio-Cultural Factors are closely related to other themes, displaying core immaturity but significant potential.
In summary, the research hotspots in the field of older adults’ technology acceptance are diverse and dynamic, demonstrating the academic community’s profound understanding of how older adults interact with technology across various life contexts and needs. Under the influence of AI and big data, research should continue to focus on the application of emerging technologies among older adults, exploring in depth how they adapt to and effectively use these technologies. This not only enhances the quality of life and healthcare experiences for older adults but also drives ongoing innovation and development in this field.
Research agenda
Based on the above research findings, to further understand and promote technology acceptance and usage among older adults, we recommend future studies focus on refining theoretical models, exploring long-term usage, and assessing user experience in the following detailed aspects:
Refinement and validation of specific technology acceptance models for older adults: Future research should focus on developing and validating technology acceptance models based on individual characteristics, particularly considering variations in technology acceptance among older adults across different educational levels and cultural backgrounds. This includes factors such as age, gender, educational background, and cultural differences. Additionally, research should examine how well specific technologies, such as wearable devices and mobile health applications, meet the needs of older adults. Building on existing theoretical models, this research should integrate insights from multiple disciplines such as psychology, sociology, design, and engineering through interdisciplinary collaboration to create more accurate and comprehensive models, which should then be validated in relevant contexts.
Deepening the exploration of the relationship between long-term technology use and quality of life among older adults: The acceptance and use of technology by users is a complex and dynamic process (Seuwou et al. 2016 ). Existing research predominantly focuses on older adults’ initial acceptance or short-term use of new technologies; however, the impact of long-term use on their quality of life and health is more significant. Future research should focus on the evolution of older adults’ experiences and needs during long-term technology usage, and the enduring effects of technology on their social interactions, mental health, and life satisfaction. Through longitudinal studies and qualitative analysis, this research reveals the specific needs and challenges of older adults in long-term technology use, providing a basis for developing technologies and strategies that better meet their requirements. This understanding aids in comprehensively assessing the impact of technology on older adults’ quality of life and guiding the optimization and improvement of technological products.
Evaluating the Importance of User Experience in Research on Older Adults’ Technology Acceptance: Understanding the mechanisms of information technology acceptance and use is central to human-computer interaction research. Although technology acceptance models and user experience models differ in objectives, they share many potential intersections. Technology acceptance research focuses on structured prediction and assessment, while user experience research concentrates on interpreting design impacts and new frameworks. Integrating user experience to assess older adults’ acceptance of technology products and systems is crucial (Codfrey et al. 2022 ; Wang et al. 2019 ), particularly for older users, where specific product designs should emphasize practicality and usability (Fisk et al. 2020 ). Researchers need to explore innovative age-appropriate design methods to enhance older adults’ usage experience. This includes studying older users’ actual usage preferences and behaviors, optimizing user interfaces, and interaction designs. Integrating feedback from older adults to tailor products to their needs can further promote their acceptance and continued use of technology products.
Conclusions
This study conducted a systematic review of the literature on older adults’ technology acceptance over the past decade through bibliometric analysis, focusing on the distribution power, research power, knowledge base and theme progress, research hotspots, evolutionary trends, and quality distribution. Using a combination of quantitative and qualitative methods, this study has reached the following conclusions:
Technology acceptance among older adults has become a hot topic in the international academic community, involving the integration of knowledge across multiple disciplines, including Medical Informatics, Health Care Sciences Services, and Ergonomics. In terms of journals, “PSYCHOLOGY, EDUCATION, HEALTH” represents a leading field, with key publications including Computers in Human Behavior , Journal of Medical Internet Research , and International Journal of Human-Computer Interaction . These journals possess significant academic authority and extensive influence in the field.
Research on technology acceptance among older adults is particularly active in developed countries, with China and USA publishing significantly more than other nations. The Netherlands leads in high average citation rates, indicating the depth and impact of its research. Meanwhile, the UK stands out in terms of international collaboration. At the institutional level, City University of Hong Kong and The University of Hong Kong in China are in leading positions. Tilburg University in the Netherlands demonstrates exceptional research quality through its high average citation count. At the author level, Chen from China has the highest number of publications, while Peek from the Netherlands has the highest average citation count.
Co-citation analysis of references indicates that the knowledge base in this field is divided into three main categories: theoretical model deepening, emerging technology applications, and research methods and evaluation. Seminal literature focuses on four areas: specific technology use by older adults, expansion of theoretical models of technology acceptance, information technology adoption behavior, and research perspectives. Research themes have evolved from initial theoretical deepening and analysis of influencing factors to empirical studies on individual factors and emerging technologies.
Keyword analysis indicates that TAM and UTAUT are the most frequently occurring terms, while “assistive technology” and “virtual reality” are focal points with high frequency and centrality. Keyword clustering analysis reveals that research hotspots are concentrated on the influencing factors of technology adoption, human-robot interaction experiences, mobile health management, and technology for aging in place. Time-zone evolution mapping and burst keyword analysis have revealed the research evolution from preliminary exploration of influencing factors, to enhancements in quality of life and health management, and onto advanced technology applications and deepening of theoretical models. Furthermore, analysis of research quality distribution indicates that Usage Experience and Assisted Living Technology have become core topics, while Smart Devices, Theoretical Models, and Mobile Health Applications point towards future research directions.
Through this study, we have systematically reviewed the dynamics, core issues, and evolutionary trends in the field of older adults’ technology acceptance, constructing a comprehensive Knowledge Mapping of the domain and presenting a clear framework of existing research. This not only lays the foundation for subsequent theoretical discussions and innovative applications in the field but also provides an important reference for relevant scholars.
Limitations
To our knowledge, this is the first bibliometric analysis concerning technology acceptance among older adults, and we adhered strictly to bibliometric standards throughout our research. However, this study relies on the Web of Science Core Collection, and while its authority and breadth are widely recognized, this choice may have missed relevant literature published in other significant databases such as PubMed, Scopus, and Google Scholar, potentially overlooking some critical academic contributions. Moreover, given that our analysis was confined to literature in English, it may not reflect studies published in other languages, somewhat limiting the global representativeness of our data sample.
It is noteworthy that with the rapid development of AI technology, its increasingly widespread application in elderly care services is significantly transforming traditional care models. AI is profoundly altering the lifestyles of the elderly, from health monitoring and smart diagnostics to intelligent home systems and personalized care, significantly enhancing their quality of life and health care standards. The potential for AI technology within the elderly population is immense, and research in this area is rapidly expanding. However, due to the restrictive nature of the search terms used in this study, it did not fully cover research in this critical area, particularly in addressing key issues such as trust, privacy, and ethics.
Consequently, future research should not only expand data sources, incorporating multilingual and multidatabase literature, but also particularly focus on exploring older adults’ acceptance of AI technology and its applications, in order to construct a more comprehensive academic landscape of older adults’ technology acceptance, thereby enriching and extending the knowledge system and academic trends in this field.
Data availability
The datasets analyzed during the current study are available in the Dataverse repository: https://doi.org/10.7910/DVN/6K0GJH .
Abdi S, de Witte L, Hawley M (2020) Emerging technologies with potential care and support applications for older people: review of gray literature. JMIR Aging 3(2):e17286. https://doi.org/10.2196/17286
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Achuthan K, Nair VK, Kowalski R, Ramanathan S, Raman R (2023) Cyberbullying research—Alignment to sustainable development and impact of COVID-19: Bibliometrics and science mapping analysis. Comput Human Behav 140:107566. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2022.107566
Article Google Scholar
Ahmad A, Mozelius P (2022) Human-Computer Interaction for Older Adults: a Literature Review on Technology Acceptance of eHealth Systems. J Eng Res Sci 1(4):119–126. https://doi.org/10.55708/js0104014
Ale Ebrahim N, Salehi H, Embi MA, Habibi F, Gholizadeh H, Motahar SM (2014) Visibility and citation impact. Int Educ Stud 7(4):120–125. https://doi.org/10.5539/ies.v7n4p120
Amin MS, Johnson VL, Prybutok V, Koh CE (2024) An investigation into factors affecting the willingness to disclose personal health information when using AI-enabled caregiver robots. Ind Manag Data Syst 124(4):1677–1699. https://doi.org/10.1108/IMDS-09-2023-0608
Baer NR, Vietzke J, Schenk L (2022) Middle-aged and older adults’ acceptance of mobile nutrition and fitness apps: a systematic mixed studies review. PLoS One 17(12):e0278879. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0278879
Barnard Y, Bradley MD, Hodgson F, Lloyd AD (2013) Learning to use new technologies by older adults: Perceived difficulties, experimentation behaviour and usability. Comput Human Behav 29(4):1715–1724. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2013.02.006
Berkowsky RW, Sharit J, Czaja SJ (2017) Factors predicting decisions about technology adoption among older adults. Innov Aging 3(1):igy002. https://doi.org/10.1093/geroni/igy002
Braun MT (2013) Obstacles to social networking website use among older adults. Comput Human Behav 29(3):673–680. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2012.12.004
Article MathSciNet Google Scholar
Campo-Prieto P, Rodríguez-Fuentes G, Cancela-Carral JM (2021) Immersive virtual reality exergame promotes the practice of physical activity in older people: An opportunity during COVID-19. Multimodal Technol Interact 5(9):52. https://doi.org/10.3390/mti5090052
Chen C (2006) CiteSpace II: Detecting and visualizing emerging trends and transient patterns in scientific literature. J Am Soc Inf Sci Technol 57(3):359–377. https://doi.org/10.1002/asi.20317
Chen C, Dubin R, Kim MC (2014) Emerging trends and new developments in regenerative medicine: a scientometric update (2000–2014). Expert Opin Biol Ther 14(9):1295–1317. https://doi.org/10.1517/14712598.2014.920813
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Chen C, Leydesdorff L (2014) Patterns of connections and movements in dual‐map overlays: A new method of publication portfolio analysis. J Assoc Inf Sci Technol 65(2):334–351. https://doi.org/10.1002/asi.22968
Chen J, Wang C, Tang Y (2022) Knowledge mapping of volunteer motivation: A bibliometric analysis and cross-cultural comparative study. Front Psychol 13:883150. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.883150
Chen JY, Liu YD, Dai J, Wang CL (2023) Development and status of moral education research: Visual analysis based on knowledge graph. Front Psychol 13:1079955. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.1079955
Chen K, Chan AH (2011) A review of technology acceptance by older adults. Gerontechnology 10(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.4017/gt.2011.10.01.006.00
Chen K, Chan AH (2014) Gerontechnology acceptance by elderly Hong Kong Chinese: a senior technology acceptance model (STAM). Ergonomics 57(5):635–652. https://doi.org/10.1080/00140139.2014.895855
Chen K, Zhang Y, Fu X (2019) International research collaboration: An emerging domain of innovation studies? Res Policy 48(1):149–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.respol.2018.08.005
Chen X, Hu Z, Wang C (2024) Empowering education development through AIGC: A systematic literature review. Educ Inf Technol 1–53. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-024-12549-7
Chen Y, Chen CM, Liu ZY, Hu ZG, Wang XW (2015) The methodology function of CiteSpace mapping knowledge domains. Stud Sci Sci 33(2):242–253. https://doi.org/10.16192/j.cnki.1003-2053.2015.02.009
Codfrey GS, Baharum A, Zain NHM, Omar M, Deris FD (2022) User Experience in Product Design and Development: Perspectives and Strategies. Math Stat Eng Appl 71(2):257–262. https://doi.org/10.17762/msea.v71i2.83
Dai J, Zhang X, Wang CL (2024) A meta-analysis of learners’ continuance intention toward online education platforms. Educ Inf Technol 1–36. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-024-12654-7
Davis FD (1989) Perceived usefulness, perceived ease of use, and user acceptance of information technology. MIS Q 13(3):319–340. https://doi.org/10.2307/249008
Delmastro F, Dolciotti C, Palumbo F, Magrini M, Di Martino F, La Rosa D, Barcaro U (2018) Long-term care: how to improve the quality of life with mobile and e-health services. In 2018 14th International Conference on Wireless and Mobile Computing, Networking and Communications (WiMob), pp. 12–19. IEEE. https://doi.org/10.1109/WiMOB.2018.8589157
Dupuis K, Tsotsos LE (2018) Technology for remote health monitoring in an older population: a role for mobile devices. Multimodal Technol Interact 2(3):43. https://doi.org/10.3390/mti2030043
Ferguson C, Hickman LD, Turkmani S, Breen P, Gargiulo G, Inglis SC (2021) Wearables only work on patients that wear them”: Barriers and facilitators to the adoption of wearable cardiac monitoring technologies. Cardiovasc Digit Health J 2(2):137–147. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cvdhj.2021.02.001
Fisk AD, Czaja SJ, Rogers WA, Charness N, Sharit J (2020) Designing for older adults: Principles and creative human factors approaches. CRC Press. https://doi.org/10.1201/9781420080681
Friesen S, Brémault-Phillips S, Rudrum L, Rogers LG (2016) Environmental design that supports healthy aging: Evaluating a new supportive living facility. J Hous Elderly 30(1):18–34. https://doi.org/10.1080/02763893.2015.1129380
Garcia Reyes EP, Kelly R, Buchanan G, Waycott J (2023) Understanding Older Adults’ Experiences With Technologies for Health Self-management: Interview Study. JMIR Aging 6:e43197. https://doi.org/10.2196/43197
Geng Z, Wang J, Liu J, Miao J (2024) Bibliometric analysis of the development, current status, and trends in adult degenerative scoliosis research: A systematic review from 1998 to 2023. J Pain Res 17:153–169. https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S437575
González A, Ramírez MP, Viadel V (2012) Attitudes of the elderly toward information and communications technologies. Educ Gerontol 38(9):585–594. https://doi.org/10.1080/03601277.2011.595314
Guner H, Acarturk C (2020) The use and acceptance of ICT by senior citizens: a comparison of technology acceptance model (TAM) for elderly and young adults. Univ Access Inf Soc 19(2):311–330. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10209-018-0642-4
Halim I, Saptari A, Perumal PA, Abdullah Z, Abdullah S, Muhammad MN (2022) A Review on Usability and User Experience of Assistive Social Robots for Older Persons. Int J Integr Eng 14(6):102–124. https://penerbit.uthm.edu.my/ojs/index.php/ijie/article/view/8566
He Y, He Q, Liu Q (2022) Technology acceptance in socially assistive robots: Scoping review of models, measurement, and influencing factors. J Healthc Eng 2022(1):6334732. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/6334732
Heerink M, Kröse B, Evers V, Wielinga B (2010) Assessing acceptance of assistive social agent technology by older adults: the almere model. Int J Soc Robot 2:361–375. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12369-010-0068-5
Ho A (2020) Are we ready for artificial intelligence health monitoring in elder care? BMC Geriatr 20(1):358. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-020-01764-9
Hoque R, Sorwar G (2017) Understanding factors influencing the adoption of mHealth by the elderly: An extension of the UTAUT model. Int J Med Inform 101:75–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2017.02.002
Hota PK, Subramanian B, Narayanamurthy G (2020) Mapping the intellectual structure of social entrepreneurship research: A citation/co-citation analysis. J Bus Ethics 166(1):89–114. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-019-04129-4
Huang R, Yan P, Yang X (2021) Knowledge map visualization of technology hotspots and development trends in China’s textile manufacturing industry. IET Collab Intell Manuf 3(3):243–251. https://doi.org/10.1049/cim2.12024
Article ADS Google Scholar
Jing Y, Wang C, Chen Y, Wang H, Yu T, Shadiev R (2023) Bibliometric mapping techniques in educational technology research: A systematic literature review. Educ Inf Technol 1–29. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-023-12178-6
Jing YH, Wang CL, Chen ZY, Shen SS, Shadiev R (2024a) A Bibliometric Analysis of Studies on Technology-Supported Learning Environments: Hotopics and Frontier Evolution. J Comput Assist Learn 1–16. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcal.12934
Jing YH, Wang HM, Chen XJ, Wang CL (2024b) What factors will affect the effectiveness of using ChatGPT to solve programming problems? A quasi-experimental study. Humanit Soc Sci Commun 11:319. https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-024-02751-w
Kamrani P, Dorsch I, Stock WG (2021) Do researchers know what the h-index is? And how do they estimate its importance? Scientometrics 126(7):5489–5508. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-021-03968-1
Kim HS, Lee KH, Kim H, Kim JH (2014) Using mobile phones in healthcare management for the elderly. Maturitas 79(4):381–388. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.maturitas.2014.08.013
Article MathSciNet PubMed Google Scholar
Kleinberg J (2002) Bursty and hierarchical structure in streams. In Proceedings of the eighth ACM SIGKDD international conference on Knowledge discovery and data mining, pp. 91–101. https://doi.org/10.1145/775047.775061
Kruse C, Fohn J, Wilson N, Patlan EN, Zipp S, Mileski M (2020) Utilization barriers and medical outcomes commensurate with the use of telehealth among older adults: systematic review. JMIR Med Inform 8(8):e20359. https://doi.org/10.2196/20359
Kumar S, Lim WM, Pandey N, Christopher Westland J (2021) 20 years of electronic commerce research. Electron Commer Res 21:1–40. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10660-021-09464-1
Kwiek M (2021) What large-scale publication and citation data tell us about international research collaboration in Europe: Changing national patterns in global contexts. Stud High Educ 46(12):2629–2649. https://doi.org/10.1080/03075079.2020.1749254
Lee C, Coughlin JF (2015) PERSPECTIVE: Older adults’ adoption of technology: an integrated approach to identifying determinants and barriers. J Prod Innov Manag 32(5):747–759. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpim.12176
Lee CH, Wang C, Fan X, Li F, Chen CH (2023) Artificial intelligence-enabled digital transformation in elderly healthcare field: scoping review. Adv Eng Inform 55:101874. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aei.2023.101874
Leydesdorff L, Rafols I (2012) Interactive overlays: A new method for generating global journal maps from Web-of-Science data. J Informetr 6(2):318–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joi.2011.11.003
Li J, Ma Q, Chan AH, Man S (2019) Health monitoring through wearable technologies for older adults: Smart wearables acceptance model. Appl Ergon 75:162–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apergo.2018.10.006
Article ADS PubMed Google Scholar
Li X, Zhou D (2020) Product design requirement information visualization approach for intelligent manufacturing services. China Mech Eng 31(07):871, http://www.cmemo.org.cn/EN/Y2020/V31/I07/871
Google Scholar
Lin Y, Yu Z (2024a) An integrated bibliometric analysis and systematic review modelling students’ technostress in higher education. Behav Inf Technol 1–25. https://doi.org/10.1080/0144929X.2024.2332458
Lin Y, Yu Z (2024b) A bibliometric analysis of artificial intelligence chatbots in educational contexts. Interact Technol Smart Educ 21(2):189–213. https://doi.org/10.1108/ITSE-12-2022-0165
Liu L, Duffy VG (2023) Exploring the future development of Artificial Intelligence (AI) applications in chatbots: a bibliometric analysis. Int J Soc Robot 15(5):703–716. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12369-022-00956-0
Liu R, Li X, Chu J (2022) Evolution of applied variables in the research on technology acceptance of the elderly. In: International Conference on Human-Computer Interaction, Cham: Springer International Publishing, pp 500–520. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-05581-23_5
Luijkx K, Peek S, Wouters E (2015) “Grandma, you should do it—It’s cool” Older Adults and the Role of Family Members in Their Acceptance of Technology. Int J Environ Res Public Health 12(12):15470–15485. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph121214999
Lussier M, Lavoie M, Giroux S, Consel C, Guay M, Macoir J, Bier N (2018) Early detection of mild cognitive impairment with in-home monitoring sensor technologies using functional measures: a systematic review. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform 23(2):838–847. https://doi.org/10.1109/JBHI.2018.2834317
López-Robles JR, Otegi-Olaso JR, Porto Gomez I, Gamboa-Rosales NK, Gamboa-Rosales H, Robles-Berumen H (2018) Bibliometric network analysis to identify the intellectual structure and evolution of the big data research field. In: International Conference on Intelligent Data Engineering and Automated Learning, Cham: Springer International Publishing, pp 113–120. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-03496-2_13
Ma Q, Chan AH, Chen K (2016) Personal and other factors affecting acceptance of smartphone technology by older Chinese adults. Appl Ergon 54:62–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apergo.2015.11.015
Ma Q, Chan AHS, Teh PL (2021) Insights into Older Adults’ Technology Acceptance through Meta-Analysis. Int J Hum-Comput Interact 37(11):1049–1062. https://doi.org/10.1080/10447318.2020.1865005
Macedo IM (2017) Predicting the acceptance and use of information and communication technology by older adults: An empirical examination of the revised UTAUT2. Comput Human Behav 75:935–948. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2017.06.013
Maidhof C, Offermann J, Ziefle M (2023) Eyes on privacy: acceptance of video-based AAL impacted by activities being filmed. Front Public Health 11:1186944. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2023.1186944
Majumder S, Aghayi E, Noferesti M, Memarzadeh-Tehran H, Mondal T, Pang Z, Deen MJ (2017) Smart homes for elderly healthcare—Recent advances and research challenges. Sensors 17(11):2496. https://doi.org/10.3390/s17112496
Article ADS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Mhlanga D (2023) Artificial Intelligence in elderly care: Navigating ethical and responsible AI adoption for seniors. Available at SSRN 4675564. 4675564 min) Identifying citation patterns of scientific breakthroughs: A perspective of dynamic citation process. Inf Process Manag 58(1):102428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ipm.2020.102428
Mitzner TL, Boron JB, Fausset CB, Adams AE, Charness N, Czaja SJ, Sharit J (2010) Older adults talk technology: Technology usage and attitudes. Comput Human Behav 26(6):1710–1721. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2010.06.020
Mitzner TL, Savla J, Boot WR, Sharit J, Charness N, Czaja SJ, Rogers WA (2019) Technology adoption by older adults: Findings from the PRISM trial. Gerontologist 59(1):34–44. https://doi.org/10.1093/geront/gny113
Mongeon P, Paul-Hus A (2016) The journal coverage of Web of Science and Scopus: a comparative analysis. Scientometrics 106:213–228. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-015-1765-5
Mostaghel R (2016) Innovation and technology for the elderly: Systematic literature review. J Bus Res 69(11):4896–4900. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbusres.2016.04.049
Mujirishvili T, Maidhof C, Florez-Revuelta F, Ziefle M, Richart-Martinez M, Cabrero-García J (2023) Acceptance and privacy perceptions toward video-based active and assisted living technologies: Scoping review. J Med Internet Res 25:e45297. https://doi.org/10.2196/45297
Naseri RNN, Azis SN, Abas N (2023) A Review of Technology Acceptance and Adoption Models in Consumer Study. FIRM J Manage Stud 8(2):188–199. https://doi.org/10.33021/firm.v8i2.4536
Nguyen UP, Hallinger P (2020) Assessing the distinctive contributions of Simulation & Gaming to the literature, 1970–2019: A bibliometric review. Simul Gaming 51(6):744–769. https://doi.org/10.1177/1046878120941569
Olmedo-Aguirre JO, Reyes-Campos J, Alor-Hernández G, Machorro-Cano I, Rodríguez-Mazahua L, Sánchez-Cervantes JL (2022) Remote healthcare for elderly people using wearables: A review. Biosensors 12(2):73. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios12020073
Pan S, Jordan-Marsh M (2010) Internet use intention and adoption among Chinese older adults: From the expanded technology acceptance model perspective. Comput Human Behav 26(5):1111–1119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2010.03.015
Pan X, Yan E, Cui M, Hua W (2018) Examining the usage, citation, and diffusion patterns of bibliometric map software: A comparative study of three tools. J Informetr 12(2):481–493. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joi.2018.03.005
Park JS, Kim NR, Han EJ (2018) Analysis of trends in science and technology using keyword network analysis. J Korea Ind Inf Syst Res 23(2):63–73. https://doi.org/10.9723/jksiis.2018.23.2.063
Peek ST, Luijkx KG, Rijnaard MD, Nieboer ME, Van Der Voort CS, Aarts S, Wouters EJ (2016) Older adults’ reasons for using technology while aging in place. Gerontology 62(2):226–237. https://doi.org/10.1159/000430949
Peek ST, Luijkx KG, Vrijhoef HJ, Nieboer ME, Aarts S, van der Voort CS, Wouters EJ (2017) Origins and consequences of technology acquirement by independent-living seniors: Towards an integrative model. BMC Geriatr 17:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-017-0582-5
Peek ST, Wouters EJ, Van Hoof J, Luijkx KG, Boeije HR, Vrijhoef HJ (2014) Factors influencing acceptance of technology for aging in place: a systematic review. Int J Med Inform 83(4):235–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2014.01.004
Peek STM, Luijkx KG, Vrijhoef HJM, Nieboer ME, Aarts S, Van Der Voort CS, Wouters EJM (2019) Understanding changes and stability in the long-term use of technologies by seniors who are aging in place: a dynamical framework. BMC Geriatr 19:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12877-019-1241-9
Perez AJ, Siddiqui F, Zeadally S, Lane D (2023) A review of IoT systems to enable independence for the elderly and disabled individuals. Internet Things 21:100653. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iot.2022.100653
Piau A, Wild K, Mattek N, Kaye J (2019) Current state of digital biomarker technologies for real-life, home-based monitoring of cognitive function for mild cognitive impairment to mild Alzheimer disease and implications for clinical care: systematic review. J Med Internet Res 21(8):e12785. https://doi.org/10.2196/12785
Pirzada P, Wilde A, Doherty GH, Harris-Birtill D (2022) Ethics and acceptance of smart homes for older adults. Inform Health Soc Care 47(1):10–37. https://doi.org/10.1080/17538157.2021.1923500
Pranckutė R (2021) Web of Science (WoS) and Scopus: The titans of bibliographic information in today’s academic world. Publications 9(1):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/publications9010012
Qian K, Zhang Z, Yamamoto Y, Schuller BW (2021) Artificial intelligence internet of things for the elderly: From assisted living to health-care monitoring. IEEE Signal Process Mag 38(4):78–88. https://doi.org/10.1109/MSP.2021.3057298
Redner S (1998) How popular is your paper? An empirical study of the citation distribution. Eur Phys J B-Condens Matter Complex Syst 4(2):131–134. https://doi.org/10.1007/s100510050359
Sayago S (ed.) (2019) Perspectives on human-computer interaction research with older people. Switzerland: Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-06076-3
Schomakers EM, Ziefle M (2023) Privacy vs. security: trade-offs in the acceptance of smart technologies for aging-in-place. Int J Hum Comput Interact 39(5):1043–1058. https://doi.org/10.1080/10447318.2022.2078463
Schroeder T, Dodds L, Georgiou A, Gewald H, Siette J (2023) Older adults and new technology: Mapping review of the factors associated with older adults’ intention to adopt digital technologies. JMIR Aging 6(1):e44564. https://doi.org/10.2196/44564
Seibert K, Domhoff D, Bruch D, Schulte-Althoff M, Fürstenau D, Biessmann F, Wolf-Ostermann K (2021) Application scenarios for artificial intelligence in nursing care: rapid review. J Med Internet Res 23(11):e26522. https://doi.org/10.2196/26522
Seuwou P, Banissi E, Ubakanma G (2016) User acceptance of information technology: A critical review of technology acceptance models and the decision to invest in Information Security. In: Global Security, Safety and Sustainability-The Security Challenges of the Connected World: 11th International Conference, ICGS3 2017, London, UK, January 18-20, 2017, Proceedings 11:230-251. Springer International Publishing. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-51064-4_19
Shiau WL, Wang X, Zheng F (2023) What are the trend and core knowledge of information security? A citation and co-citation analysis. Inf Manag 60(3):103774. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.im.2023.103774
Sinha S, Verma A, Tiwari P (2021) Technology: Saving and enriching life during COVID-19. Front Psychol 12:647681. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.647681
Soar J (2010) The potential of information and communication technologies to support ageing and independent living. Ann Telecommun 65:479–483. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12243-010-0167-1
Strotmann A, Zhao D (2012) Author name disambiguation: What difference does it make in author‐based citation analysis? J Am Soc Inf Sci Technol 63(9):1820–1833. https://doi.org/10.1002/asi.22695
Talukder MS, Sorwar G, Bao Y, Ahmed JU, Palash MAS (2020) Predicting antecedents of wearable healthcare technology acceptance by elderly: A combined SEM-Neural Network approach. Technol Forecast Soc Change 150:119793. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2019.119793
Taskin Z, Al U (2019) Natural language processing applications in library and information science. Online Inf Rev 43(4):676–690. https://doi.org/10.1108/oir-07-2018-0217
Touqeer H, Zaman S, Amin R, Hussain M, Al-Turjman F, Bilal M (2021) Smart home security: challenges, issues and solutions at different IoT layers. J Supercomput 77(12):14053–14089. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11227-021-03825-1
United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (2023) World population ageing 2023: Highlights. https://www.un.org/zh/193220
Valk CAL, Lu Y, Randriambelonoro M, Jessen J (2018) Designing for technology acceptance of wearable and mobile technologies for senior citizen users. In: 21st DMI: Academic Design Management Conference (ADMC 2018), Design Management Institute, pp 1361–1373. https://www.dmi.org/page/ADMC2018
Van Eck N, Waltman L (2010) Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics 84(2):523–538. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11192-009-0146-3
Vancea M, Solé-Casals J (2016) Population aging in the European Information Societies: towards a comprehensive research agenda in eHealth innovations for elderly. Aging Dis 7(4):526. https://doi.org/10.14336/AD.2015.1214
Venkatesh V, Morris MG, Davis GB, Davis FD (2003) User acceptance of information technology: Toward a unified view. MIS Q 27(3):425–478. https://doi.org/10.2307/30036540
Wagner N, Hassanein K, Head M (2010) Computer use by older adults: A multi-disciplinary review. Comput Human Behav 26(5):870–882. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2010.03.029
Wahlroos N, Narsakka N, Stolt M, Suhonen R (2023) Physical environment maintaining independence and self-management of older people in long-term care settings—An integrative literature review. J Aging Environ 37(3):295–313. https://doi.org/10.1080/26892618.2022.2092927
Wang CL, Chen XJ, Yu T, Liu YD, Jing YH (2024a) Education reform and change driven by digital technology: a bibliometric study from a global perspective. Humanit Soc Sci Commun 11(1):1–17. https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-024-02717-y
Wang CL, Dai J, Zhu KK, Yu T, Gu XQ (2023a) Understanding the Continuance Intention of College Students Toward New E-learning Spaces Based on an Integrated Model of the TAM and TTF. Int J Hum-comput Int 1–14. https://doi.org/10.1080/10447318.2023.2291609
Wang CL, Wang HM, Li YY, Dai J, Gu XQ, Yu T (2024b) Factors Influencing University Students’ Behavioral Intention to Use Generative Artificial Intelligence: Integrating the Theory of Planned Behavior and AI Literacy. Int J Hum-comput Int 1–23. https://doi.org/10.1080/10447318.2024.2383033
Wang J, Zhao W, Zhang Z, Liu X, Xie T, Wang L, Zhang Y (2024c) A journey of challenges and victories: a bibliometric worldview of nanomedicine since the 21st century. Adv Mater 36(15):2308915. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202308915
Wang J, Chen Y, Huo S, Mai L, Jia F (2023b) Research hotspots and trends of social robot interaction design: A bibliometric analysis. Sensors 23(23):9369. https://doi.org/10.3390/s23239369
Wang KH, Chen G, Chen HG (2017) A model of technology adoption by older adults. Soc Behav Personal 45(4):563–572. https://doi.org/10.2224/sbp.5778
Wang S, Bolling K, Mao W, Reichstadt J, Jeste D, Kim HC, Nebeker C (2019) Technology to Support Aging in Place: Older Adults’ Perspectives. Healthcare 7(2):60. https://doi.org/10.3390/healthcare7020060
Wang Z, Liu D, Sun Y, Pang X, Sun P, Lin F, Ren K (2022) A survey on IoT-enabled home automation systems: Attacks and defenses. IEEE Commun Surv Tutor 24(4):2292–2328. https://doi.org/10.1109/COMST.2022.3201557
Wilkowska W, Offermann J, Spinsante S, Poli A, Ziefle M (2022) Analyzing technology acceptance and perception of privacy in ambient assisted living for using sensor-based technologies. PloS One 17(7):e0269642. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0269642
Wilson J, Heinsch M, Betts D, Booth D, Kay-Lambkin F (2021) Barriers and facilitators to the use of e-health by older adults: a scoping review. BMC Public Health 21:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-021-11623-w
Xia YQ, Deng YL, Tao XY, Zhang SN, Wang CL (2024) Digital art exhibitions and psychological well-being in Chinese Generation Z: An analysis based on the S-O-R framework. Humanit Soc Sci Commun 11:266. https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-024-02718-x
Xie H, Zhang Y, Duan K (2020) Evolutionary overview of urban expansion based on bibliometric analysis in Web of Science from 1990 to 2019. Habitat Int 95:102100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.habitatint.2019.10210
Xu Z, Ge Z, Wang X, Skare M (2021) Bibliometric analysis of technology adoption literature published from 1997 to 2020. Technol Forecast Soc Change 170:120896. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2021.120896
Yap YY, Tan SH, Choon SW (2022) Elderly’s intention to use technologies: a systematic literature review. Heliyon 8(1). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e08765
Yu T, Dai J, Wang CL (2023) Adoption of blended learning: Chinese university students’ perspectives. Humanit Soc Sci Commun 10:390. https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-023-01904-7
Yusif S, Soar J, Hafeez-Baig A (2016) Older people, assistive technologies, and the barriers to adoption: A systematic review. Int J Med Inform 94:112–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2016.07.004
Zhang J, Zhu L (2022) Citation recommendation using semantic representation of cited papers’ relations and content. Expert Syst Appl 187:115826. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eswa.2021.115826
Zhao Y, Li J (2024) Opportunities and challenges of integrating artificial intelligence in China’s elderly care services. Sci Rep 14(1):9254. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-60067-w
Article ADS MathSciNet PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Download references
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Social Science Foundation of Shaanxi Province in China (Grant No. 2023J014).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Art and Design, Shaanxi University of Science and Technology, Xi’an, China
Xianru Shang, Zijian Liu, Chen Gong, Zhigang Hu & Yuexuan Wu
Department of Education Information Technology, Faculty of Education, East China Normal University, Shanghai, China
Chengliang Wang
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Conceptualization, XS, YW, CW; methodology, XS, ZL, CG, CW; software, XS, CG, YW; writing-original draft preparation, XS, CW; writing-review and editing, XS, CG, ZH, CW; supervision, ZL, ZH, CW; project administration, ZL, ZH, CW; funding acquisition, XS, CG. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. All authors have read and approved the re-submission of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Chengliang Wang .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
Ethical approval was not required as the study did not involve human participants.
Informed consent
Informed consent was not required as the study did not involve human participants.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Shang, X., Liu, Z., Gong, C. et al. Knowledge mapping and evolution of research on older adults’ technology acceptance: a bibliometric study from 2013 to 2023. Humanit Soc Sci Commun 11 , 1115 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-024-03658-2
Download citation
Received : 20 June 2024
Accepted : 21 August 2024
Published : 31 August 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-024-03658-2
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies

Home » Blog » Dissertation » Topics » Nursing » Midwifery » Midwifery Dissertation Topics List (30 Examples) For Your Research

Midwifery Dissertation Topics List (30 Examples) For Your Research
Mark Dec 14, 2019 Jun 5, 2020 Midwifery , Nursing No Comments
As a student, if you are finding Midwifery dissertation topics, you have visited the right site. We offer a wide range of midwifery dissertation topics and project topics on midwifery. As the field has evolved, the research topics on midwifery are based on new and emerging concepts and ideas. You can choose any of the […]

As a student, if you are finding midwifery dissertation topics, you have visited the right site. We offer a wide range of midwifery dissertation topics and project topics on midwifery. As the field has evolved, the research topics on midwifery are based on the new and emerging concepts and ideas.
You can choose any of the give topic for your research in midvfery and our team can offer quality dissertations according to your requirements.
A list Of midwifery dissertaton topics
Emerging trends in midwifery and obstetrical nursing.
Modern trends of the N education in midwives and modern methods in practical training.
The impact of delayed umbilical cord clamping after birth.
How the cell-free DNA screening is helpful in identifying genetic problems in the baby?
Limiting interventions during low-risk labor.
The concept of cost containment in healthcare deliver.
The importance of family centred care and natural childbirth environment.
An interpretive research on the disparity between women’s expectations and experience during childbirth.
Systematic literature review on the extrauterine life management focusing on lung functions in new born.
To analyse the role of perinatal care to pregnant women.
Studying the treatment alternatives for urogenital infections in rural women.
Conducting a systematic review on how midwifery students plan their career.
Strategies adopted by midwives to advise pregnant women about nutritional values and healthy food consumption.
Studying the impact of Hepatitis B in pregnant women.
Analysing how frequent miscarriages are linked with higher anticardiolip antibodies.
Studying the relationship between perinatal mortality rates and physical activity levels.
How can nurses recommend preventive strategies to avoid sexual transmission of Zika virus to new born?
Evaluating the attitude of women related to the implementation of basic immunisation programs in village.
Analysing the modern trends of the education in midwives and new methods in practical training.
To study the advance trends in gynaecology and obstetrics.
The role of midwives in saving the lives of unborn foetus.
Exploring the global trends in nursing and midwifery education.
Analysing the role of optimal midwifery decision-making during second-stage labour.
To study the integration of clinical reasoning into midwifery practice.
A literature review on labouring in water.
Exploring the experiences of mothers in caring for children with complex needs.
An ethnography of independent midwifery in Asian countries.
To explore the perceptions of control in midwifery assisted childbirth.
Analysing the decision-making between nurse-midwives and clients regarding the formulation of a birth plan.
The role of Vitamin D supplementation during pregnancy .
Topic With Mini-Proposal (Paid Service)
Along with a topic, you will also get;
- An explanation why we choose this topic.
- 2-3 research questions.
- Key literature resources identification.
- Suitable methodology with identification of raw sample size, and data collection method
- View a sample of topic consultation service
Get expert dissertation writing help to achieve good grades
- Writer consultation before payment to ensure your work is in safe hands.
- Free topic if you don't have one
- Draft submissions to check the quality of the work as per supervisor's feedback
- Free revisions
- Complete privacy
- Plagiarism Free work
- Guaranteed 2:1 (With help of your supervisor's feedback)
- 2 Instalments plan
- Special discounts
Other Posts
- Dementia Nursing Dissertation Topics (26 Examples) For Your Research June 13, 2020 -->
- Critical Care Nursing Dissertation Topics (25 Examples) For Research June 12, 2020 -->
- Adult nursing Dissertation Topics (28 Examples) For Your Research December 17, 2019 -->
- Dissertation Topics In Nursing (30 Examples) For Research Writing June 14, 2017 -->
Message Us On WhatsApp
- Open access
- Published: 28 August 2024
Perspectives of midwives on the use of Kaligutim (local oxytocin) for induction of labour among pregnant women in the government hospitals in Tamale
- Ahmad Sukerazu Alhassan 1 ,
- Shivera Dakurah 2 &
- Joseph Lasong 1
BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth volume 24 , Article number: 561 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
The use of herbal medicine and/or its products is common throughout the world. In Tamale Metropolis, pregnant women frequently use local oxytocin to induce labour, as shown by the fact that 90% of midwives reported managing patients who used kaligutim (local oxytocin) to speed up labour. Early career midwives are also aware of this and have personally observed it being used by their clients. The purpose of the study was to assess midwives’ opinions on pregnant women’s use of the well-known kaligutim (local oxytocin) for labour induction in the Tamale Metropolis.
A facility-based, quantitative, cross-sectional research design was used for the study. A total of 214 working midwives from Tamale’s three main public hospitals participated. Data for the study were gathered through a standardized questionnaire. For the analysis and presentation of the data, descriptive and analytical statistics, such as basic frequencies, percentages, Fisher’s exact test, chi square test and multivariate analysis, were employed.
According to the findings of this study, the safety, dosages, and contraindications of kaligutim during pregnancy and labour are unknown. The cessation of contractions was reported by 44 (22.4%) of the respondents whose clients used local oxytocin. The study also revealed that women in Tamale metropolis use “walgu”, a spiritual form of oxytocin, to induce and augment labour. Respondents who responded, “yes” to baby admission to the new-born care unit were 25% more likely to use kaligutim (local oxytocin) than were those who responded, “no” to baby admission to the new-born care unit (AOR = 0.25 95% CI (0.01, 0.53), P = 0.021).
Conclusions
It can be concluded that using kaligutim to start labour has negative effects on both the mother and the foetus. Additional research is required to evaluate the efficacy, effectiveness, biochemical makeup, and safety of these herbal medicines, particularly during pregnancy and delivery, as well as the spiritual significance of kaligutim (Walgu) and its forms.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
Herbal medicines, traditional treatments, and traditional practitioners are the main source of health care for many millions of people, and sometimes the only source of care [ 1 ]. Herbal medicines include herbs, herbal materials, herbal preparations and finished herbal products, that contain as active ingredients parts of plants, or other plant materials, or combinations [ 1 , 2 ]. Women in both developed and developing countries use herbal medicine before pregnancy and during pregnancy and delivery, which has several consequences [ 3 ]. The use of herbal medicine has a long history, tracing its roots back to ancient and biblical days when there was no Orthodox medicine. Currently, both developed and developing countries use herbal medicine due to the presence of many traditional medicine practitioners [ 4 ].
Many cultures worldwide use herbal medicine to induce or accelerate labour, and the incidence of labour induction to shorten the duration of labour is on the rise. Most herbal medicine users are pregnant women who have no formal education, who have a low level of income and who mostly stay far from health facilities [ 5 ]. The majority of pregnant women use herbal medicine through the oral route and have confidence in its efficacy, safety and effectiveness [ 6 ]. Herbal medicine is used by women for maternal health-related issues, such as to induce abortion and labour, to correct infertility, for the treatment of pregnancy-related issues, for breast milk secretion and for general wellbeing during pregnancy [ 5 ].
Women who use herbal medicine during pregnancy and/or labour usually have a high risk of postpartum complications [ 7 ]. The use of herbal uterotonics can lead to hyperstimulation of the uterus, foetal asphyxia and several other adverse effects of labour [ 8 ]. Moreover, traditional medicine used by pregnant women is associated with several complications, including a ruptured uterus, a fresh still birth, a macerated still birth, a caesarean section and even death [ 9 ]. These herbal medicines have both uterotonic and nonuterotonic effects on labour and delivery and are mostly used to induce or augment labour in prolonged labour or postdate or to relax or widen the pelvis for delivery [ 8 ].
Maternal and neonatal deaths are still major challenges for most developing countries, with obstetric complications, especially postpartum haemorrhage (P.P.H.) being the major cause of maternal mortality [ 10 ]. The delivery of healthcare services is still poor quality in developing nations [ 11 ]. Maternal and foetal mortality and morbidity have remained high due to inadequate health services and inadequate emergency obstetric treatment. Childbirth is accompanied by numerous customs that are subject to ethnological research and are often rooted in traditional medicine or religion. Cultural influences and sociodemographic characteristics play an important role in a woman’s decision to seek maternal and child health services.
The induction of labour is the process of artificially starting labour by stimulating the uterus with oxytocin or manually through the rupture of amniotic membranes. This process is usually not risk free, and most women find it to be uncomfortable [ 12 ]. The induction of labour is an obstetric procedure recommended when the benefits to the baby and mother outweigh the benefits of continuing the pregnancy. The procedure usually involves complications and failures and must be performed under close monitoring, proper selection of clients and good preparation [ 13 ].
Labour induction also changes the normal physiological processes that accompany childbirth and increases the risk of adverse pregnancy outcomes such as postpartum haemorrhage, neonatal mortality, foetal distress, uterine rapture and premature birth [ 14 ]. Oxytocin is a natural hormone produced by the hypothalamus and is responsible for the activation of sensory nerves during labour and breastfeeding [ 15 ]. Clinically, commercially manufactured synthetic oxytocin is administered to commence or increase uterine activity to reduce the duration of labour [ 16 ].
The induction of labour is not free from risk and must be performed with caution because the procedure involves hyperstimulation of the uterus and foetal distress. Herbal medicine used by pregnant women has long-term effects on both mothers and babies [ 17 ]. Many pregnant women in the Tamale Metropolis use prepackaged herbal medicine before and during pregnancy [ 18 ]. Health-related factors such as cost, distance, access and unavailability of medications influence the utilization of herbal medicine by pregnant women [ 17 ].
All women should be given a prophylactic dose of oxytocin as soon as they give birth. If they start to haemorrhage, they should also be given a treatment dose of oxytocin, which is greater than the prophylactic dose [ 19 ]. There is also a traditional manufactured form of oxytocin (kaligutim) that pregnant women use to start labour. Kaligutim is the local name for the mixture of some special plant parts or a combination of plants prepared and given to pregnant women to start or accelerate the process of labour in the northern part of Ghana [ 17 ].
Ideally, women should take medical drugs during pregnancy (folic acid and fersolate) to help prevent birth defects and congenital malformations such as neural tube defects of the foetus and spinal bifida during pregnancy [ 20 ]. However, in recent decades, women worldwide have used herbal medications during pregnancy and labour, with some taking both herbal medicine and orthodox medicine at the same time [ 21 ]. However, little is known about the use and safety of these medicines, especially during pregnancy, and their dosages, indications and contraindications are not known [ 22 ].
There are studies on herbal medicine use by women during pregnancy and labour, but there is currently no literature on the use of Kaligutim (local oxytocin) for labour induction among pregnant women in Ghana, but similar studies have been conducted in Uganda, Malawi, Tanzania, and Nigeria. Despite the efforts of the government and other nongovernmental organizations to ensure maximum coverage of skilled delivery to help reduce maternal and neonatal mortalities, women still use locally prepared oxytocin to induce labour. Although herbal medicine is commonly used by pregnant women, healthcare providers, especially midwives, are often unprepared to communicate effectively with patients or make proper decisions concerning complementary and alternative medicine use, especially during pregnancy and labour [ 23 ].
It is well known that herbs have played a vital role since the precolonial era during pregnancy, delivery and postpartum care in many parts of the country, but there are still few data on the use of herbs among pregnant women in Ghana [ 24 ]. Towards the end of pregnancy, many women are tired and eager to welcome their babies into the world. Moreover, as the expected date of delivery approaches, these women are given local oxytocin by their mothers’ in-laws, grandmothers, mothers, or TBAs or even by the women themselves to start labour at home before going to the health facility [ 25 ].
Medicinal plants that are used to hasten or speed up labour are mostly taken towards the end of pregnancy or the beginning of labour [ 26 ]. Even after delivery, these herbs may be found in small amounts in the mother’s breast, and some may cross the placental barrier and have harmful effects on the baby. The use of herbal medication by pregnant women is inevitable given that up to 80% of people who live in developing nations rely on traditional medicine for their healthcare needs [ 18 ].
The situation in Ghana, especially Northern Ghana, is not different, as pregnant women continue to use herbs despite the availability of health facilities [ 24 ]. The use of herbal medicine (kaligutim) among the Ghanaian population is alarming. Pregnant women in Tamale use herbal products at a rate of 42.5% prior to pregnancy and 52.7% during pregnancy [ 27 ]. Residents of Tamales who seek healthcare services in hospitals or herbal clinics are therefore at a greater risk of experiencing adverse consequences from drug-herb interactions [ 28 ].
Herbal product manufacturers should clearly state that pregnancy is a contraindication, and vendors should use caution when selling these items to pregnant women [ 27 ]. The use of Kaligutim (local oxytocin) by pregnant women is a maternal and child health problem. Herbal medicine used by pregnant women has long-term effects on both mothers and babies [ 17 ]. Unfortunately, maternal, and neonatal deaths may occur, and hence, there is a need to examine midwives’ perspectives on local oxytocin use during labour, its effects on the progress and outcome of labour, and the relationship between kaligutim use and birth outcomes among pregnant women in the three major government hospitals in Tamale Metropolis.
Theoretical foundation
This study adopted and adapted Andersen’s (1968) behavioural model of healthcare service utilization (use and nonuse of health services [ 29 ]. Andersen’s healthcare utilization model is a conceptual model aimed at demonstrating the factors that lead to the use/nonuse of health services [ 29 ]. This study was guided by Andersen’s behavioural model of health service use as a theoretical framework to identify the effects of Kaligutim on the progress and outcome of labour and to establish the relationship between the use of Kaligutim and nonuse of kaligutim and birth outcomes. The behavioural model is a multilevel model that incorporates both individual and contextual determinants of health service use.
Conceptual framework
Many people rely on products made from medicinal plants to maintain their health or treat illness, and current general development trends in developing and developed countries suggest that the consumption of medicinal plants is unlikely to decline in the short to medium term because of the benefits to consumers, producers, and society as a whole [ 29 ]. Therefore, there is a need to increase our understanding of what motivates the consumption of medicinal plants, despite the barriers to the establishment of solid evidence on the safety and efficacy of herbal medicines and related products [ 29 ].
This unified conceptual framework offers a step towards establishing a comprehensive approach to understanding the experiences midwives encounter when their clients use herbal medicine to induce their labour. The exposure variable in this study refers to kaligutim (local oxytocin) used by pregnant women in the three major government hospitals to induce labour through several routes, including oral, rectal, and vaginal routes, among others. When oxytocin is used by pregnant women, it can produce several results that can be immediate or late.
The results elicited on labour are termed the outcome variables, which can be immediate outcomes (the progress of labour) or outcomes after delivery (the outcome of labour). The progression of labour includes three stages: progressive dilatation of the cervix from 1 cm to 10 cm, delivery of the baby and expulsion of the placenta. Several factors can be used to determine the progress of labour (obstructed labour, prolonged labour, nature of uterine contractions, precipitated labour, foetal distress, and poor progress of labour).
The outcome of labour on the hand refers to what happens during the delivery of the baby, how the baby was delivered, foetal conditions and maternal conditions. The following factors were used for the purpose of this study to determine the outcome of labour (mode of delivery, postpartum haemorrhage, ruptured uterus, cervical tear, birth asphyxia, uterine atony, maternal mortality, and neonatal mortality). This study focused on the immediate effects of Kaligutim (on labour progress) and the effects of Kaligutim after delivery (on labour outcomes) and the relationship between the use of Kaligutim and birth outcomes.
The study was carried out in Tamale, which is the capital city of the northern region of Ghana. According to the 2021 World Urbanization Review, Tamales has an estimated population of 671,812 people. Tamale still has a blend of typical rural and urban communities, although it has attained the status of a metropolitan area. There are three major government hospitals in Tamale: Tamale Central Hospital, Tamale West Hospital and Tamale Teaching Hospital. The Tamale Teaching Hospital is the only tertiary facility in the northern region and serves as the main reference centre for the five regions of the north.
Study population
The main study population was midwives working in Tamale Metropolis. The sampling frame was all midwives practicing in the three major hospitals in Tamale Metropolis who were willing to participate in the study.
Study design
A facility-based cross-sectional research design was used for this study. A cross-sectional study is a type of observational study design carried out at one point in time or over a short period of time to estimate the prevalence of the outcome of interest for a given population for the purpose of public health planning [ 30 ]. This study adopted a quantitative research approach to obtain information.
Sampling technique
A purposive sampling technique was used for this study. Purposive sampling is a nonprobability sampling method in which participants are selected for inclusion in the sample based on their characteristics, knowledge, or experiences. This is because of the midwives’ knowledge, experiences, and objective of the study.
Sample size calculation
Total number of midwives = 458
Yamane formula (1967) was used with a confidence interval of 95% and a margin of error of 5%.
N = population size (458).
n = the sample size (?)
e = margin of error (5%).
n \(\:=\frac{N}{1\:+N\left(e\right)2}\)
n= \(\:\frac{458}{1\:+458\left(0.05\right)2}\)
n = 214.01 = 214.
Sample size = 214 midwives.
Inclusion criteria
All midwives practicing in the three major government hospitals in Tamale Metropolis who were willing to participate in the study were included.
All midwives in the three-government hospital with experience with kaligutim use during labour were also included in the study.
Exclusion criteria
All midwives who were not practising at the three major government hospitals in Tamale Metropolis were excluded from the study.
Midwives who were practicing at the three major government hospitals in Tamale and who were not willing to participate in the study were also excluded from the study.
All midwives who did not have experience with kaligutim use for the induction of labour were excluded from the study.
Data collection instrument
The data collection tool that was used for the study was a standardized questionnaire. The questionnaire was constructed by reviewing various documents, including existing questionnaires that have been used in previous research. Close-ended questions with few open-ended questions were used as the question format. It was designed in line with the objectives of the study to help obtain the necessary information needed for the study. The questionnaire was pretested with midwives before the actual data collection took place.
Data management and analysis
Data collected from the field were coded, cleaned, and entered into the Statistical Package for Social Services (SPSS) version 21.0. Descriptive and analytical statistics, including simple frequencies and percentages, were used for the analysis and presentation of the data. The relationships between predictor and outcome variables were assessed by means of bivariate (chi-square test) analysis to determine potential predictors of kaligutim (local oxytocin) at p values less than 0.05. Adjusted odds ratios were reported, and p values less than 0.05 were deemed to indicate statistical significance at the 95% confidence level after multivariate analysis.
Ethical consideration
The following ethical principles guided this study: respect for persons, beneficence, and justice for all. These principles are based on the human rights that must be protected during any research project, including the right to self-determination, privacy, anonymity, confidentiality, fair treatment and protection from discomfort and harm. First, an introductory letter was obtained from the University for Development Studies authorities. This letter was then presented to the authorities of the three major government hospitals in Tamale, namely, Tamale West Hospital (T.W.H.), Tamale Central Hospital (T.C.H.) and Tamale Teaching Hospital (TTH.), to seek permission to undertake the study. Ethical clearance was also obtained from the Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology (KNUST) (CHRPE/AP/332/22).
Permission was once sought through a consent form to which participants were asked to consent if they were willing to participate in the study. The participants were assured of the confidentiality of all the information they were going to provide. They were also encouraged to participate in the study as much as they could but were also made aware that the study was voluntary and that they could withdraw at any point in time during the process if needed. There was no compensation for the study participants.
The study revealed that 45% of the respondents were between the ages of 20 and 30. Most of the respondents were in their twenties or thirties. Those who were in the first half of their work life constituted 73% of the respondents, while 17% were in the second half of their working life. The majority of the respondents were diploma midwives, representing 48% of the respondents; post basic midwives, constituting 32%; and degree and master’s holders, representing 19% and 1%, respectively. Staff midwives composed the largest group of respondents, while Principal Midwifery officers composed the group with the lowest participation in the study. The lowest rank in midwifery practice in the study was staff midwives, and the highest was principal midwifery officers. This is presented in Table 1 .
The experience of using local oxytocin to induce labour
Approximately 90% of the respondents have prior knowledge or heard that some of their clients take local oxytocin at home to start labour, and only 10% of respondents have no prior knowledge of that. Approximately 63.4% of the respondents encountered local oxytocin cases more than three times every week. This is presented in Fig. 1 .
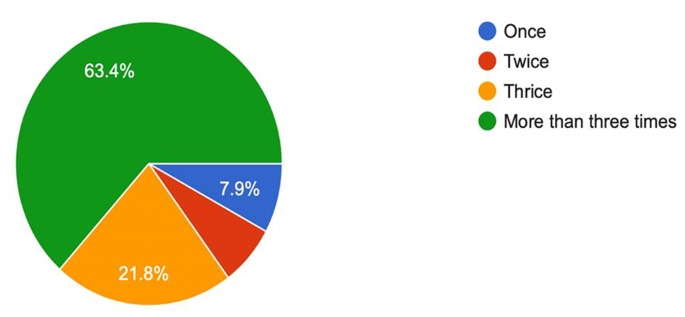
Average number of local oxytocin cases per week
Approximately 72.9% of the respondents said that their clients had ever induced labour during the previous C/S, and 59.6% of the respondents said that they met clients who also induced their labour during twin pregnancy. Another 64.5% of the respondents said that they also met clients with large babies who also induced labour using local oxytocin, while 86.2% of the respondents said that they also met clients who induced labour with local oxytocin even when they had grand multiparity. Another 11.3% of the respondents said that they met clients who used local oxytocin to induce labour during transverse lies, and 15.3% of the respondents said that they had experienced when clients with mal presentations used local oxytocin to induce labour. This is presented in Fig. 2 .
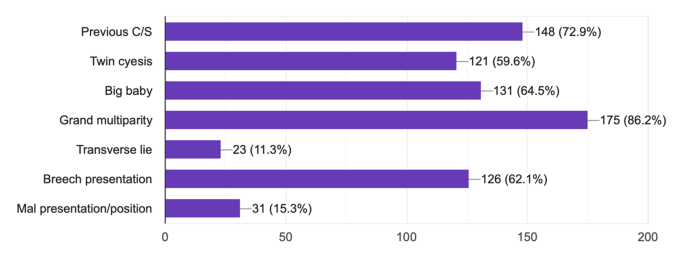
Induction of labour by clients through local oxytocin under certain conditions
The study additionally asked midwives to report on how pregnant women who had taken local oxytocin to induce labour coped during their care. Midwives were expected to respond whether the women they cared for experienced good, difficult, bad, painful, life-threatening, terrible, or normal labour. As shown in Fig. 3 , generally, the experience that pregnant women experience when they use local oxytocin to induce labour is not good. A total of 93.5% of the respondents said that the women who used local oxytocin had very bad experiences.
Experience of using local oxytocin to induce labour
The study further revealed that 15.2% of the respondents had experienced situations where some pregnant women died because of the use of local oxytocin.
Effects of local oxytocin on the progress of labour
The effects of local oxytocin (Kaligutim) on the progress of labour were diverse. The study revealed that the effects of Kaligutim on the progress of labour are negative, as it causes prolonged labour for some, obstructed labour for others, precipitated labour, and poor progress of labour for others. With obstructed labour being the leading effect of kaligutim on the progress of labour, most of the respondents chose caesarean section as the preferred delivery for most clients who used kaligutim at birth. The use of local oxytocin also has some effect on the amniotic fluid of pregnant women, as 99% of the midwives who responded to the study said that there were some levels of stain of the amniotic fluid, and only 1% said it was clear. It is evident from the study that for most pregnant women who use local oxytocin, there is hyperstimulation of the uterus, as most of the midwives confirmed this for the study. Most pregnant women who use kaligutim suffer excessive contractions, which could have an effect on both mothers and babies. Again, more than half (53.75) of the respondents also said that their foetal heart rate was above 160 bpm. The majority (77.65) of the respondents said that there was no cessation of the contractions for those who took the local oxytocin. The results are presented in Table 2 .
Impact of local oxytocin on the outcome of labour
To understand how local oxytocin impacts labour, the study went further to ask participants what the mode of delivery was for those who used Kaligutim. According to the data, caesarean section is the mode of delivery for most women (56.5%) who use local oxytocin, and most are unable to achieve spontaneous delivery. This has contributed to the increasing number of caesarean sections recorded daily. Most of the babies had an Apgar score of 4/10 to 6/10. Many babies born to mothers who used herbal oxytocin were born with moderate birth asphyxia (69.6%) and severe birth asphyxia (24%). The study also reported that 20.8% of midwives reported that hysterectomy was carried out on their clients who had used herbal preparations to induce or hasten labour. This is alarming because many women have their uterus removed as a result of herbal oxytocin (kaligutm) usage. Most clients who used Kaligutim experienced postpartum haemorrhage after delivery. It was also evident that some pregnant women (34.5%) had uterine atony, although it cannot be said that Kaligutim was the cause of uterine atony. Several pregnant women (65.3 years old) who used Kaligutim also developed a ruptured uterus. See Table 3 .
Relationship between kaligutim (local oxytocin) use and birth outcome
Table 4 shows the associations between kaligutim (local oxytocin) use and birth outcomes among the respondents. Fisher’s exact test and the chi-square test showed that several birth outcome variables were significantly associated with kaligutim (local oxytocin). Do women who go through the normal process of labour and those who use kaligutim to induce their labour have the same birth outcome? (P value = 0.021), what was the foetal wellbeing? (P value = 0.041), When do most neonates whose mothers have taken Kaligutim die? (P value = 0.038), was baby admitted at the Newborn Care Unit? (P value = 0.001), were significantly associated with kaligutim. Additionally, having recorded a maternal death because of the use of Kaligutim (p value = 0.002) was also significantly associated with kaligutim, as presented in Table 4 .
Multivariate analysis of birth outcome predictors of Kaligutim (local oxytocin) among pregnant women in three major government hospitals in Tamale metropolis
In Table 5 , three birth outcome variables strongly depicted kaligutim use among the respondents: foetal wellbeing, admission to the new-born care unit, and death of most neonates because of the use of Kaligutim by their mothers. Respondents who responded, “yes” to baby admission to the Newborn Care Unit were 25% more likely to use kaligutim (local oxytocin) than were those who responded “no” to baby admission to the Newborn Care Unit [(AOR = 0.25 95% CI (0.01, 0.53), P = 0.021)].
Discussions
Although the respondents cut across with regard to the number of years of experience, most of the respondents were early career midwives. The fact that these early career midwives are familiar with and have experienced the use of local oxytocin by their clients shows that it is widely used by pregnant women in the Tamale metropolis. Approximately 90% of respondents were aware of the usage of kaligutim (local oxytocin) for inducing labour at home before going to the hospital for delivery. However, a study conducted in the Ashanti region of Ghana revealed that midwives and other healthcare professionals lack proper knowledge about herbal medicine usage among pregnant women, even though this information is urgently needed so that appropriate action may be taken to address the issue [ 31 ]. The study findings also demonstrated that pregnant women frequently utilize local oxytocin and that many of them are unaware of the potential negative effects that these herbs may have on them in certain circumstances. Figure 2 shows that the use of local oxytocin was not limited to only one condition. These findings further show that the use of local oxytocin by pregnant women is widespread and that pregnant women do not know the effect that local oxytocin can have on them when they have certain conditions. Additionally, pregnant women are ignorant of the fact that local oxytocin can be contraindicated under certain conditions and must be avoided. Hence, it may put the life of the pregnant mother and her baby in danger.
Although herbal medicines are natural, not all herbs are safe to use while pregnant. Thus, expectant mothers should consult their midwives for guidance before taking herbal remedies. The experience that pregnant women have when they use local oxytocin to induce labour is not a positive one. A total of 188 respondents, or 93.5% of the respondents, stated that the women who used local oxytocin had a very unpleasant experience. This is supported by additional research results showing that between 50 and 80% of pregnant women use traditional plant remedies, which could have adverse perinatal effects [ 32 ]. The statistics indicate that local oxytocin is frequently used by pregnant women in the Tamale Metropolis. Most of the midwives reported seeing these cases virtually daily. This finding supports a study conducted in Ghana’s Ashanti region (Kumasi), which revealed that knowledge of herbal medicine is widely shared and that there is evidence of an increase in the usage of herbs [ 33 ].
The study revealed that local oxytocin (Kaligutim) has a diverse range of effects on the progress of labour, including precipitating labour, prolonging labour, obstructing labour, and slowing labour. The partograph is a great tool for keeping track of labour progress and serving as a warning system for abnormalities in normal labour, which helps to prevent obstructed labour and improves maternal and foetal outcomes [ 34 ]. This is supported by the study’s findings, which indicate that using a partograph to monitor labour progress and identify any deviations is essential [ 34 ].
According to this study, most midwives, who make up 65.2% of the respondents, also claimed that pregnant women who use local oxytocin (Kaligutim) have excessive contractions, while only 71 of them, or 34.8% of the respondents, claimed that they do not notice excessive contractions in their clients. This is supported by research performed in Zambia, which revealed that these herbal medicines also elicit greater than normal uterine contractions [ 26 ].
Most pregnant women who use kaligutim experience excessive contractions, which may have an impact on both the mother and the unborn child. Similarly, other authors have also claimed that using herbal remedies during labour causes stronger and more frequent uterine contractions, which do not necessarily result in cervical dilatation [ 35 ]. This was confirmed in the study’s findings, which also noted that herbal oxytocin not only produces excessive uterine contractions but also may cause contractions to cease, as 44 (22.4%) of the respondents reported that those who took local oxytocin had a halt in contractions. Intravenous fluids such as normal saline and Ringer’s lactate are used to flush out the local oxytocin in the system and CS in the case of an emergency. Nifedipine is also given in certain circumstances to prevent contractions.
According to the study, 121 midwives, or 59.6% of the respondents, stated that caesarean sections were the preferred method of delivery for women who used kaligutim to induce labour. Both [ 36 ] in South Africa and [ 34 ] in Western Uganda reported these findings. Moderate birth asphyxia (69.6%) and severe birth asphyxia (23%) are common in newborns whose mothers utilize herbal oxytocin. According to the survey, 20.8% of midwives said they had performed hysterectomy procedures on clients who had utilized herbal induction or hastening methods to induce labour.
One of the main causes of maternal deaths worldwide, including in Ghana, is postpartum haemorrhage [ 10 ]. 91% of midwives said that when their patients use herbal oxytocin during labour, more of them suffer from postpartum haemorrhage. This is corroborated by research by Frank (2018), who found a connection between postpartum haemorrhage and the use of herbal medications during labour [ 37 ]. In contrast, other studies [ 38 ] have shown that using herbal medication during childbirth is linked to a lower risk of postpartum haemorrhage. Individuals who experienced postpartum haemorrhage were managed with uterine massage, intravenous fluids, Cytotec, repairs to tears, expulsion of retained products, blood transfusions, cervical repairs, and catheter use.
This report supports the findings of a study conducted in the Ugandan village of Kiganda, where the researcher [ 37 ] reported that the use of herbal medicines has been linked to labour induction, which can cause significant birth canal tearing, postpartum haemorrhage, uterine atony, a raptured uterus, and, if untreated, maternal mortality. Medical experts who are aware of the dangers of herbal remedies and who are obliged to advise patients against using them do so themselves. The majority of women who use herbal preparations during pregnancy have a high school education or higher, according to evidence showing that more than 57.5% of pregnant women who use herbs have a high school diploma or higher, which is consistent with findings from Saudi Arabia by [ 39 ] that show that formal education cannot even prevent women from taking herbs during pregnancy and labour.
Kaligutim also causes excessive uterine contractions, foetal discomfort, excessive uterine stimulation, uterine atony, PPH, birth hypoxia, and premature bearing down, claims this study. This is supported by the results of a study carried out in Europe, where researchers [ 40 ] found that the majority of herbal drugs taken by pregnant women have undesirable side effects. An Iranian study, however, revealed that utilizing herbal treatments during labour can lessen discomfort, speed up the process, and enhance both the quality of a woman’s delivery experience and her odds of having a healthy baby [ 41 ].
According to the study’s findings, three birth outcome variables strongly affected kaligutim (local oxytocin) use among the respondents: foetal wellbeing, admission to the newborn care unit, and death of most neonates as a result of the use of Kaligutim by their mothers. Respondents who responded, “yes to baby” and were admitted to the new-born care unit were 25% more likely to use kaligutim (local oxytocin) than were those who responded, “no to baby” and were admitted to the new-born care unit (AOR = 0.25 95% CI (0.01, 0.53), P = 0.021). This is probably one of the effects of taking local oxytocin. These infants were hospitalized for a variety of reasons, including asphyxia, respiratory distress, and low Apgar scores.
Additionally, the study results indicated that respondents who responded that a still birth outcome affected foetal wellbeing were 1.9 times more likely to use kaligutim (local oxytocin) than those who responded no to having live births were (AOR = 1.9 95% CI (0.01, 1.21), P = 0.047)]. This finding is consistent with findings from a sub-Saharan African study that showed that herbal medications used to speed up and induce labour have uterotonic effects and increase the risk of neonatal asphyxia attributable to uterine hyperstimulation [ 42 ]. This could be ascribed to the fact that the respondents wanted fast and easy delivery, which subsequently caused this effect.
Another interesting finding was that respondents who responded that having a birth asphyxia outcome to foetal wellbeing were 0.16 times more likely to use kaligutim (local oxytocin) than were those who responded no to having live births (AOR = 0.16, 95% CI (0.08, 3.08), P = 0.047). This result is similar to that of [ 42 ], who conducted their study in sub-Saharan Africa. This could be a result of the effects of kaligutim on foetal well-being, which results in birth asphyxia.
Furthermore, newborns whose mothers used kaligutim during labour and who died within the first hour of birth were 3.4 times more likely to use kaligutim (local oxytocin) than those whose mothers used kaligutim during labour [AOR = 3.4 95% CI (0.74, 1.5), P = 0.045]. In support of the findings from this study, a study on the consumption of herbal drugs among pregnant women in rural Malawi revealed that consumption was linked to pregnancy-related issues and that users had a greater risk of neonatal mortality/morbidity within the first hour of life than nonusers [ 14 ]. This could be attributed to the dangers this herb poses to the foetus during delivery.
Newborns whose mothers used kaligutim during labor and who died within the first week of life were 2.23 times more likely to use kaligutim (local oxytocin) than those whose mothers used intrauterine kaligutim [(AOR = 2.23 95% CI (0.00, 0.02), P = 0.045)]. This is supported by findings from a Malawian study that revealed that the use of labour-inducing plants during pregnancy has negative effects on obstetric and labour outcomes, such as uterine rapture, which can cause neonatal mortality and morbidity [ 35 ]. This could be attributed to the fact that PPH, uterine rapture, cervical tear, DIC, and hypoxia were the main causes of death.
Every life matter, which is why mothers’ lives and that of their newborn babies must be safeguarded at all costs. A sufficient level of knowledge is always vital since it exacerbates doubt. Therefore, it is crucial that people are informed of their rights, their health, and the services they can utilize to maintain and improve health to have a healthy increasing population. Although herbal medicine could be effective in treating certain ailments associated with pregnancy and delivery and is easily accessible to pregnant women, especially in rural communities, the possibility of overdose, drug-herb interactions, contraindications, and the unhygienic conditions under which they are prepared may influence both maternal and neonatal conditions.
The results showed that the use of kaligutim by pregnant women in Tamale Metropolis is on the rise. This means that much needs to be done to do away with the use of kaligutim, and this must start with midwives. Pregnancies and births can be improved with a healthy and qualified midwifery care model in improving and protecting women’s and newborn health in Tamale.
It can be concluded that the use of this herbal medicine (Kaligutim) poses a greater long-term health challenge for mothers and their babies. Midwives and other healthcare workers in the Tamale Metropolis must therefore intensify their public health campaigns against the use of Kaligutim for labour induction.
Recommendations
The findings of the study have important implications for maternal and child health. The nonuse of kaligutim (local oxytocin) for the induction of labour is the best option for pregnant women. Pregnant women should visit the hospital for all their health needs during the entire pregnancy. This will help prevent adverse pregnancy and labour outcomes as well as maternal and neonatal mortalities and morbidities.
Future researchers should perform further studies on the spiritual aspects of kaligutim (Walgu) and its types. Like synthetic oxytocin, an Islamic form of oxytocin is prepared by Mallams and causes uterine contractions and dilates the cervix.
However, studies should also be conducted on the efficiency, effectiveness and biochemical composition of these herbal preparations and their safety, especially during pregnancy and delivery. Samples of these herbal preparations should be taken for laboratory investigations.
Data availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this article and its supplementary information files are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
World Health Organization. WHO traditional medicine strategy: 2014–2023. World Health Organization;2013. Accessed 20 Nov 2023.
Fokunang CN, Ndikum V, Tabi OY, Jiofack RB, Ngameni B, Guedje NM et al. Traditional medicine: past, present and future research and development prospects and integration in the National Health System of Cameroon. Afr J Trad Complement Alt Med. 2011;8(3).
John LJ, Shantakumari N. Herbal medicines use during pregnancy: a review from the Middle East. Oman Med J. 2015;30(4):229.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Mekuria AB, Erku DA, Gebresillassie BM, Birru EM, Tizazu B, Ahmedin A. Prevalence and associated factors of herbal medicine use among pregnant women on antenatal care follow-up at University of Gondar referral and teaching hospital, Ethiopia: a cross-sectional study. BMC Complement Alt Med. 2017;17:1–7.
Google Scholar
Shewamene Z, Dune T, Smith CA. The use of traditional medicine in maternity care among African women in Africa and the diaspora: a systematic review. BMC Complement Alt Med. 2017;17:1–6.
Nyeko R, Tumwesigye NM, Halage AA. Prevalence and factors associated with use of herbal medicines during pregnancy among women attending postnatal clinics in Gulu district, Northern Uganda. BMC Preg Childbirth. 2016;1–12.
Fukunaga R, Morof D, Blanton C, Ruiz A, Maro G, Serbanescu F. Factors associated with local herb use during pregnancy and labor among women in Kigoma region, Tanzania, 2014–2016. BMC Preg Childbirth. 2020;20:1–1.
Article Google Scholar
Tripathi V, Stanton C, Anderson FW. Traditional preparations used as uterotonics in Sub-saharan Africa and their pharmacologic effects. Int J Gynecol Obstet. 2013;120(1):16–22.
Maliwichi-Nyirenda CP, Maliwichi LL. Medicinal plants used to induce labour and traditional techniques used in determination of onset of labour in pregnant women in Malawi: a case study of Mulanje district. J Med Plants Res. 2010;4(24):2609.
Amanuel T, Dache A, Dona A. Postpartum Hemorrhage and its Associated factors among women who gave birth at Yirgalem General Hospital, Sidama Regional State, Ethiopia. Health Res Serv Manag Epidemiol. 2021;8:1–7.
James PB, Wardle J, Steel A, Adams J. Traditional, complementary and alternative medicine use in Sub-saharan Africa: a systematic review. BMJ Glob Health. 2018;3(5).
Coates D, Homer C, Wilson A, Deady L, Mason E, Foureur M, et al. Induction of labour indications and timing: a systematic analysis of clinical guidelines. Women Birth. 2020;33(3):219–30.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Lawani OL, Onyebuchi AK, Iyoke CA, Okafo CN, Ajah LO. Obstetric outcome and significance of labour induction in a health resource poor setting. Obstet Gynecol Int. 2014;2014(1):419621.
PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Zamawe C, King C, Jennings HM, Fottrell E. Associations between the use of herbal medicines and adverse pregnancy outcomes in rural Malawi: a secondary analysis of randomised controlled trial data. BMC Complement Alt Med. 2018;18:1–8.
Roopasree B, Joseph J, Mukkadan JK. Oxytocin-functions: an overview. MOJ Anat Physiol. 2019;6:128–33.
Espada-Trespalacios X, Ojeda F, Perez-Botella M, Milà Villarroel R, Bach Martinez M, Figuls Soler H, et al. Oxytocin administration in low-risk women, a retrospective analysis of birth and neonatal outcomes. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021;18(8):4375.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Ayelyini B, Yidana A, Ziblim SD. The Use of Indigenous Medicine among women during pregnancy and labour in rural Ghana. Cent Afr J Public Health. 2019;5(3):120–8. https://doi.org/10.11648/j.cajph.20190503.14 .
Kwame Ameade EP, Zakaria AP, Abubakar L, Sandow R. Herbal medicine usage before and during pregnancy – a study in Northern Ghana. Int J Complement Alt Med. 2018;11(4).
Jhpiego. Business Case: Investing in production of high-quality oxytocin for low-resource settings–Final report December 2014. 2014. http://www.conceptfoundation.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/06/BusinessCase_Oxytocin_web.pdf . Accesed 25 Jan 2024.
Barišić T, Pecirep A, Milićević R, Vasilj A, Tirić D. What do pregnant women know about harmful effects of medication and herbal remedies use during pregnancy? Psychiatr Danub. 2017;29(1):804–11.
PubMed Google Scholar
Ameade EPK, Ibrahim M, Ibrahim HS, Habib RH, Gbedema SY. Concurrent Use of Herbal and Orthodox Medicines among Residents of Tamale, Northern Ghana, Who Patronize Hospitals and Herbal Clinics. Evidence-based Complement Alt Med. 2018;2018(2002).
Illamola SM, Amaeze OU, Krepkova LV, Birnbaum AK, Karanam A, Job KM, et al. Use of herbal medicine by pregnant women: what physicians need to know. Front Pharmacol. 2020;10:1483.
Bahall M, Legall G. Knowledge, attitudes, and practices among health care providers regarding complementary and alternative medicine in Trinidad and Tobago. BMC Complement Alt Med. 2017;17:1–9.
Peprah P, Agyemang-duah W, Arthur-holmes F, Budu HI, Abalo EM, Okwei R et al. ‘ we are nothing without herbs ’ : a story of herbal remedies use during pregnancy in rural Ghana. BMC Complement Altern Med.2019;1–12.
Kamatenesi-Mugisha M, Oryem-Origa H. Medicinal plants used to induce labour during childbirth in western Uganda. J Ethnopharmacol. 2007;109(1):1–9.
Ngoma CM. Use of Herbal Medicines to induce labour by pregnant women: a systematic review of literature. JOJ Nurs Heal Care. 2017;2(3):7–12.
Ameade EK, Zakaria AP, Abubakar L, Sandow R. Herbal medicine usage before and during pregnancy—a study in Northern Ghana. Int J Complement Alt Med. 2018;11(4):235–42.
Ameade EP, Ibrahim M, Ibrahim HS, Habib RH, Gbedema SY. Concurrent use of herbal and orthodox medicines among residents of Tamale, Northern Ghana, who patronize hospitals and herbal clinics. Evidence-Based Complement Alt Med. 2018;2018(1):1289125.
Andersen RM. Revisiting the behavioral Model and Access to Medical Care: does it Matter? J Health Soc Behav. 1995;1–10. https://doi.org/10.2307/2137284 .
Smith-Hall C, Larsen HO, Pouliot M. People, plants and health: a conceptual framework for assessing changes in medicinal plant consumption. J Ethnobiolo Ethnomed. 2012;8:1–1.
Levin KA. Study design III: cross-sectional studies. Evid-Based Dent. 2006;7(1):24–5.
Beste J, Asanti D, Nsabimana D, Anastos K, Mutimura E, Merkatz I, et al. Use of Traditional Botanical Medicines during pregnancy in Rural Rwanda. J Glob Health Perspect. 2015;2015:1–10.
Adusi-Poku Y, Vanotoo L, Detoh E, Oduro J, Nsiah R, Natogmah A. Type of herbal medicines utilized by pregnant women attending ante-natal clinic in Offinso North district: are orthodox prescribers aware? Ghana Med J. 2016;49(4):227.
Agyei-Baffour P, Kudolo A, Quansah DY, Boateng D. Integrating herbal medicine into mainstream healthcare in Ghana: clients’ acceptability, perceptions and disclosure of use. BMC Complement Alt Med. 2017;17(1):1–9.
Mukasa PK, Kabakyenga J, Senkungu JK, Ngonzi J, Kyalimpa M, Roosmalen VJ. Uterine rupture in a teaching hospital in Mbarara, western Uganda, unmatched case-control study. Reprod Health. 2013;10(1):1–6.
Lampiao F, Maliwichi-Nyirenda C, Mponda J, Tembo L, Clements C. A preliminary investigation of the effects of labour inducing plant, cissampelos mucronata, on the outcomesof pregnancy using rat models. Malawi Med J. 2018;30(3):159–61.
Kekana LS, Sebitloane MH. Ingestion of herbal medication during pregnancy and adverse perinatal outcomes. S Afr J Obstet Gynaecol. 2020;26(2):1–5.
Buyondo BF. Use of Herbal Medicines in Preparation for Labour and its determinants among pregnant women at Kiganda Health Centre Iv-Mubende District. Angew Chemie Int Edu. 2018;6(11):951–2.
Koh LM, Percival B, Pauley T, Pathak S. Complementary therapy and alternative medicine: effects on induction of labour and pregnancy outcome in low risk post-dates women. Heliyon. 2019;5(11). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02787 .
Al-Ghamdi S, Aldossari K, Al-Zahrani J, Al-Shaalan F, Al-Sharif S, Al-Khurayji H, et al. Prevalence, knowledge and attitudes toward herbal medication use by Saudi women in the central region during pregnancy, during labor and after delivery. BMC Complement Alt Med. 2017;17(1):1–9.
Gruber CW, O’Brien M. Uterotonic plants and their bioactive constituents. Planta Med. 2011;77(03):207–20.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Zahra A. Lavender aromatherapy massages in reducing labor pain and duration of labor: a randomized controlled trial. Afr J Pharm Pharmacol. 2013;7(8):456–430.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We thank the Management and Healthcare Staff of the Tamale West Hospital (T.W.H), Tamale Central Hospital (T.C.H) and Tamale Teaching Hospital (TTH) for their support throughout the data collection process. We acknowledge the contributions of all the midwives who shared their knowledge and experiences with us, your efforts are well appreciated.
No funding was available for the study.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Population and Reproductive Health, School of Public Health, University for Development Studies, P. O. Box 1883, Tamale, Northern Region, Ghana
Ahmad Sukerazu Alhassan & Joseph Lasong
Nandom Nursing and Midwifery Training College, Upper West Region, Nandom, Ghana
Shivera Dakurah
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
ASA and SD conceptualised and drafted the research proposal. ASA, SD, and JL performed the statistical analysis, assisted with interpretation of the results, and co-drafted the manuscript. All authors contributed to the discussion of the paper, read, and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Ahmad Sukerazu Alhassan .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
An introductory letter from the University for Development Studies was presented to the three government hospitals, Tamale West Hospital (T.W.H), Tamale Central Hospital (T.C.H) and Tamale Teaching Hospital (TTH) to seek for permission to undertake the study. Ethical clearance was also obtained from the Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology (KNUST) with reference number (CHRPE/AP/332/22). Permission was also sought through a consent form of which participants were asked to consent to if they were willing to participate in the study. They were assured of confidentiality of every information they were going to provide. All other methods were performed in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations on subject selection and participation.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Alhassan, A.S., Dakurah, S. & Lasong, J. Perspectives of midwives on the use of Kaligutim (local oxytocin) for induction of labour among pregnant women in the government hospitals in Tamale. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 24 , 561 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-024-06745-z
Download citation
Received : 15 April 2024
Accepted : 08 August 2024
Published : 28 August 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-024-06745-z
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Local oxytocin
- Herbal medicine
- Traditional medicine
BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth
ISSN: 1471-2393
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Explore the latest full-text research PDFs, articles, conference papers, preprints and more on MIDWIFERY RESEARCH. Find methods information, sources, references or conduct a literature review on ...
The Journal of Midwifery & Women's Health (JMWH) is the official journal of the American College of Nurse-Midwives. Within a culture of inclusion and antiracism, JMWH advocates for health equity, access to quality care for all persons, and excellence in midwifery. Articles published in JMWH include new research and current knowledge across a broad range of clinical and interprofessional topics ...
Relaxation techniques. Reproduction. Reproductive psychology. S. Screening for gynaecological cancer. Screening tests in midwifery. Sexual and reproductive health. Smoking cessation. Social sciences.
The profession of midwifery involves caring for women and newborns during pregnancy, childbirth, and the first few days following birth. Registered nurses are trained with four additional years of education along with major research on methods involve in midwifery and writing on midwifery dissertation topics, while midwives provide natural health care for mothers and children.
Background Strengthening the capacity of midwives to deliver high-quality maternal and newborn health services has been highlighted as a priority by global health organisations. To support low-income and middle-income countries (LMICs) in their decisions about investments in health, we aimed to estimate the potential impact of midwives on reducing maternal and neonatal deaths and stillbirths ...
British Journal of Midwifery (BJM) is the leading clinical journal for midwives, promoting excellence in midwifery and women's health.
Midwifery is officially recognised by the European Midwives Association. Midwifery publishes the latest peer reviewed research to inform the safety, quality, outcomes and experiences of care during pregnancy, labour, birth, postnatal and beyond for childbearing women, their infants and families. …. View full aims & scope.
Midwives' roles in sexual and reproductive health and rights (SRHR) continue to evolve and an understanding of the profession's role in health systems is essential in creating evidence-informed policies. Countries across all income levels face challenges with providing high-quality SRHR and achieving effective coverage [1].
To synthesise international research that relates to midwives' use of best available evidence in practice settings and identify key issues relating to the translation of latest evidence into everyday maternity care.Midwifery is a research‐informed ...
Health workers involvement in research had an impact on studies and whole system. They influence the clinical practice and help to implement evidences. Although International Confederation of Midwives (ICM) put research as one of the midwifery competencies ...
Considering research as an integral part of midwifery education and an indispensable tool in evidence-based practice provides the starting point in this chapter. Network theory is considered prior to exploring midwifery research networks and other initiatives in this...
The third global State of the World's Midwifery report (SoWMy 2021) provides an updated evidence base on the sexual, reproductive, maternal, newborn and adolescent health (SRMNAH) workforce. For the first time, SoWMy includes high-income countries (HICs) as well as low- and middle-income countries. This paper describes the similarities and differences between regions and income groups, and ...
Research is an integral part of a midwife's role, enabling the critique of current evidence-. based practice and facilitating involvement or support in research endeavors. The work of a. research ...
Introduction Health workers involvement in research had an impact on studies and whole system. They influence the clinical practice and help to implement evidences. Although International Confederation of Midwives (ICM) put research as one of the midwifery competencies and professional development activity, clinical midwives are poorly involved in research. Therefore, this study is aimed to ...
The journal is highly visual, with full-color images, figures, tables, boxes, and additional resources to enhance readers' understanding and implementation of information into practice areas.Topics broadly include emerging and future clinical challenges; development, implementation, and evaluation of interdisciplinary projects; diseases and ...
We argue that the current favor toward quantitative research and expertise in midwifery academia risks the future of midwifery research by the lack of equal development of qualitative experts, diluting qualitative research rigor within the profession, and limiting the kinds of questions asked.
The role of a research midwife can be very varied and include designing studies, recruiting and gaining consent, collecting and analysing data, and disseminating results. The research midwife role ...
Aims and objectives To synthesise international research that relates to midwives' use of best available evidence in practice settings and identify key issues relating to the translation of latest evidence into everyday maternity care.
Midwifery across the globe faces different issues. In some countries the autonomy of the profession is a tradition, while in some societies midwives struggle to practice autonomously the basic competencies. In one part of the world the medicalisation of childbirth is the main issue, preventing the natural processes of pregnancy and childbirth to flow at their own pace, while in other parts of ...
Abstract Purpose: To create and critically evaluate a research database about midwifery care that identifies topics studied, research methods, results, funding, publication data, and implications for a future midwifery research agenda.
Research Questions The phenomena under study are the skills and knowledge acquired by midwives post-qualification to care for women within a birth centre setting. The main research questions are: 1.
List of Midwifery dissertations Topics and Some Tips for Selecting Better Dissertation Topics in Midwifery Many students feel difficulty in pursuing their studies in midwifery, let alone making a selection of topics for the dissertation. If you are searching for examples of midwifery literature review topics, midwifery research topics, midwifery dissertation titles, midwifery dissertation ...
PDF | https://www.intechopen.com/books/selected-topics-in-midwifery-care | Find, read and cite all the research you need on ResearchGate
Research method. In recent years, bibliometrics has become one of the crucial methods for analyzing literature reviews and is widely used in disciplinary and industrial intelligence analysis (Jing ...
A list of midwifery dissertation topics for student in the field of healthcare, nursing. Get dissertation help on midwifery dissertation research topics.
The use of herbal medicine and/or its products is common throughout the world. In Tamale Metropolis, pregnant women frequently use local oxytocin to induce labour, as shown by the fact that 90% of midwives reported managing patients who used kaligutim (local oxytocin) to speed up labour. Early career midwives are also aware of this and have personally observed it being used by their clients.
In this video we've discussed UGC NET 2024 I Paper-1 Research Aptitude Sure Topic by Shefali Mishra for UGC NET, SET exams and all other teaching exams. #ug...