An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Indian J Anaesth
- v.60(9); 2016 Sep

How to write a research proposal?
Department of Anaesthesiology, Bangalore Medical College and Research Institute, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India
Devika Rani Duggappa
Writing the proposal of a research work in the present era is a challenging task due to the constantly evolving trends in the qualitative research design and the need to incorporate medical advances into the methodology. The proposal is a detailed plan or ‘blueprint’ for the intended study, and once it is completed, the research project should flow smoothly. Even today, many of the proposals at post-graduate evaluation committees and application proposals for funding are substandard. A search was conducted with keywords such as research proposal, writing proposal and qualitative using search engines, namely, PubMed and Google Scholar, and an attempt has been made to provide broad guidelines for writing a scientifically appropriate research proposal.
INTRODUCTION
A clean, well-thought-out proposal forms the backbone for the research itself and hence becomes the most important step in the process of conduct of research.[ 1 ] The objective of preparing a research proposal would be to obtain approvals from various committees including ethics committee [details under ‘Research methodology II’ section [ Table 1 ] in this issue of IJA) and to request for grants. However, there are very few universally accepted guidelines for preparation of a good quality research proposal. A search was performed with keywords such as research proposal, funding, qualitative and writing proposals using search engines, namely, PubMed, Google Scholar and Scopus.
Five ‘C’s while writing a literature review

BASIC REQUIREMENTS OF A RESEARCH PROPOSAL
A proposal needs to show how your work fits into what is already known about the topic and what new paradigm will it add to the literature, while specifying the question that the research will answer, establishing its significance, and the implications of the answer.[ 2 ] The proposal must be capable of convincing the evaluation committee about the credibility, achievability, practicality and reproducibility (repeatability) of the research design.[ 3 ] Four categories of audience with different expectations may be present in the evaluation committees, namely academic colleagues, policy-makers, practitioners and lay audiences who evaluate the research proposal. Tips for preparation of a good research proposal include; ‘be practical, be persuasive, make broader links, aim for crystal clarity and plan before you write’. A researcher must be balanced, with a realistic understanding of what can be achieved. Being persuasive implies that researcher must be able to convince other researchers, research funding agencies, educational institutions and supervisors that the research is worth getting approval. The aim of the researcher should be clearly stated in simple language that describes the research in a way that non-specialists can comprehend, without use of jargons. The proposal must not only demonstrate that it is based on an intelligent understanding of the existing literature but also show that the writer has thought about the time needed to conduct each stage of the research.[ 4 , 5 ]
CONTENTS OF A RESEARCH PROPOSAL
The contents or formats of a research proposal vary depending on the requirements of evaluation committee and are generally provided by the evaluation committee or the institution.
In general, a cover page should contain the (i) title of the proposal, (ii) name and affiliation of the researcher (principal investigator) and co-investigators, (iii) institutional affiliation (degree of the investigator and the name of institution where the study will be performed), details of contact such as phone numbers, E-mail id's and lines for signatures of investigators.
The main contents of the proposal may be presented under the following headings: (i) introduction, (ii) review of literature, (iii) aims and objectives, (iv) research design and methods, (v) ethical considerations, (vi) budget, (vii) appendices and (viii) citations.[ 4 ]
Introduction
It is also sometimes termed as ‘need for study’ or ‘abstract’. Introduction is an initial pitch of an idea; it sets the scene and puts the research in context.[ 6 ] The introduction should be designed to create interest in the reader about the topic and proposal. It should convey to the reader, what you want to do, what necessitates the study and your passion for the topic.[ 7 ] Some questions that can be used to assess the significance of the study are: (i) Who has an interest in the domain of inquiry? (ii) What do we already know about the topic? (iii) What has not been answered adequately in previous research and practice? (iv) How will this research add to knowledge, practice and policy in this area? Some of the evaluation committees, expect the last two questions, elaborated under a separate heading of ‘background and significance’.[ 8 ] Introduction should also contain the hypothesis behind the research design. If hypothesis cannot be constructed, the line of inquiry to be used in the research must be indicated.
Review of literature
It refers to all sources of scientific evidence pertaining to the topic in interest. In the present era of digitalisation and easy accessibility, there is an enormous amount of relevant data available, making it a challenge for the researcher to include all of it in his/her review.[ 9 ] It is crucial to structure this section intelligently so that the reader can grasp the argument related to your study in relation to that of other researchers, while still demonstrating to your readers that your work is original and innovative. It is preferable to summarise each article in a paragraph, highlighting the details pertinent to the topic of interest. The progression of review can move from the more general to the more focused studies, or a historical progression can be used to develop the story, without making it exhaustive.[ 1 ] Literature should include supporting data, disagreements and controversies. Five ‘C's may be kept in mind while writing a literature review[ 10 ] [ Table 1 ].
Aims and objectives
The research purpose (or goal or aim) gives a broad indication of what the researcher wishes to achieve in the research. The hypothesis to be tested can be the aim of the study. The objectives related to parameters or tools used to achieve the aim are generally categorised as primary and secondary objectives.
Research design and method
The objective here is to convince the reader that the overall research design and methods of analysis will correctly address the research problem and to impress upon the reader that the methodology/sources chosen are appropriate for the specific topic. It should be unmistakably tied to the specific aims of your study.
In this section, the methods and sources used to conduct the research must be discussed, including specific references to sites, databases, key texts or authors that will be indispensable to the project. There should be specific mention about the methodological approaches to be undertaken to gather information, about the techniques to be used to analyse it and about the tests of external validity to which researcher is committed.[ 10 , 11 ]
The components of this section include the following:[ 4 ]
Population and sample
Population refers to all the elements (individuals, objects or substances) that meet certain criteria for inclusion in a given universe,[ 12 ] and sample refers to subset of population which meets the inclusion criteria for enrolment into the study. The inclusion and exclusion criteria should be clearly defined. The details pertaining to sample size are discussed in the article “Sample size calculation: Basic priniciples” published in this issue of IJA.
Data collection
The researcher is expected to give a detailed account of the methodology adopted for collection of data, which include the time frame required for the research. The methodology should be tested for its validity and ensure that, in pursuit of achieving the results, the participant's life is not jeopardised. The author should anticipate and acknowledge any potential barrier and pitfall in carrying out the research design and explain plans to address them, thereby avoiding lacunae due to incomplete data collection. If the researcher is planning to acquire data through interviews or questionnaires, copy of the questions used for the same should be attached as an annexure with the proposal.
Rigor (soundness of the research)
This addresses the strength of the research with respect to its neutrality, consistency and applicability. Rigor must be reflected throughout the proposal.
It refers to the robustness of a research method against bias. The author should convey the measures taken to avoid bias, viz. blinding and randomisation, in an elaborate way, thus ensuring that the result obtained from the adopted method is purely as chance and not influenced by other confounding variables.
Consistency
Consistency considers whether the findings will be consistent if the inquiry was replicated with the same participants and in a similar context. This can be achieved by adopting standard and universally accepted methods and scales.
Applicability
Applicability refers to the degree to which the findings can be applied to different contexts and groups.[ 13 ]
Data analysis
This section deals with the reduction and reconstruction of data and its analysis including sample size calculation. The researcher is expected to explain the steps adopted for coding and sorting the data obtained. Various tests to be used to analyse the data for its robustness, significance should be clearly stated. Author should also mention the names of statistician and suitable software which will be used in due course of data analysis and their contribution to data analysis and sample calculation.[ 9 ]
Ethical considerations
Medical research introduces special moral and ethical problems that are not usually encountered by other researchers during data collection, and hence, the researcher should take special care in ensuring that ethical standards are met. Ethical considerations refer to the protection of the participants' rights (right to self-determination, right to privacy, right to autonomy and confidentiality, right to fair treatment and right to protection from discomfort and harm), obtaining informed consent and the institutional review process (ethical approval). The researcher needs to provide adequate information on each of these aspects.
Informed consent needs to be obtained from the participants (details discussed in further chapters), as well as the research site and the relevant authorities.
When the researcher prepares a research budget, he/she should predict and cost all aspects of the research and then add an additional allowance for unpredictable disasters, delays and rising costs. All items in the budget should be justified.
Appendices are documents that support the proposal and application. The appendices will be specific for each proposal but documents that are usually required include informed consent form, supporting documents, questionnaires, measurement tools and patient information of the study in layman's language.
As with any scholarly research paper, you must cite the sources you used in composing your proposal. Although the words ‘references and bibliography’ are different, they are used interchangeably. It refers to all references cited in the research proposal.
Successful, qualitative research proposals should communicate the researcher's knowledge of the field and method and convey the emergent nature of the qualitative design. The proposal should follow a discernible logic from the introduction to presentation of the appendices.
Financial support and sponsorship
Conflicts of interest.
There are no conflicts of interest.
Advertisement

- Previous Issue
- Previous Article
- Next Article
Preparation of the Investigator for a Proposal
The research proposal, insights into the reviewer's perspective, conclusions, writing successful research proposals for medical science .
(Schwinn) Professor of Anesthesiology and Surgery; Associate Professor of Pharmacology/Cancer Biology, Duke University Medical Center; Senior Fellow, Duke Pepper Aging Center.
(DeLong) Associate Professor, Division of Biometry and Medical Informatics, Duke University Medical Center.
(Shafer) Staff Anesthesiologist, Palo Alto VA Health Care System; Associate Professor of Anesthesia, Stanford University.
- Split-Screen
- Article contents
- Figures & tables
- Supplementary Data
- Peer Review
- Open the PDF for in another window
- Cite Icon Cite
- Get Permissions
- Search Site
Debra A. Schwinn , Elizabeth R. DeLong , Steven L. Shafer; Writing Successful Research Proposals for Medical Science . Anesthesiology 1998; 88:1660–1666 doi: https://doi.org/10.1097/00000542-199806000-00031
Download citation file:
- Ris (Zotero)
- Reference Manager
HIGH-QUALITY research proposals are required to obtain funds for the basic and clinical sciences. In this era of diminishing revenues, the ability to compete successfully for peer-reviewed research money is essential to create and maintain scientific programs. Ideally, the essentials of “grantsmanship” are learned through observation and participation in grant preparation, but the training environment experienced by most physicians typically focuses on clinical skills. Most physicians are never exposed to a research environment and therefore do not learn how to write grants. The result is that many clinical studies, even when designed by skilled clinicians and those that address important clinical questions, often do not compete successfully with proposals written by basic scientists. This creates a perception that clinical studies are not favorably viewed by research review committees. The opposite is probably closer to the truth; research review committees are very keen to fund excellent clinical research. Although greater numbers of researchers with Ph.D. degrees have applied for National Institutes of Health (NIH) grants compared with researchers with M.D. degrees over the last 10 yr, funding rates (percent applications funded) have remained approximately the same for these investigators ( Figure 1 ; 1995 success rates: all degrees, 6,759 [26.8%]; M.D. - Ph.D., 370 [23.1%]; M.D., 1,518 [28.1%]; Ph.D., 4,746 [26.8%]; other degree, 125 [23.1%]).[section]
![medical research proposal examples Figure 1. Overall success rates for NIH funding of scientific applications, 1986 - 1995. No difference in funding rate is observed between applicants holding M.D. versus Ph.D. degrees. As the success rate for first-time applications was 11.3% in 1993, it is apparent that resubmission of a revised application significantly increases the overall chance of having research proposal ultimately funded.[section]](https://asa2.silverchair-cdn.com/asa2/content_public/journal/anesthesiology/88/6/10.1097_00000542-199806000-00031/4/m_31ff1.png?Expires=1718730435&Signature=t8YukTWktVTwoTVfgcnkddXgA7GvpyrxHXJDcavRxewV4poA7PAtjGqBpBS4UdKXdKjw4a6rt0hczCJi18B3ggQJFZY9MVeUBKihRm2l~gsH4LrnWKoXUqPU0~kJEsIWvVv6tmDWGFNPuz0d-upwxoBYvgms40zmF06EYWFcJeLjKhms4SG5onYiJFju1I-w1eIJ3J3emzSQHRFE~DcnWGI4fx5GXy3G1x06jEY87j5MX8HxDRKV0pLrYmXnHhg0ThxSMJcuQlGoR2FuJE13~-CIAqMeD156DnMiuIC0ltNuCacO28MKuG-7TvgYE6l14Oyx7WX0bfmgF5C8YzXJ2w__&Key-Pair-Id=APKAIE5G5CRDK6RD3PGA)
Figure 1. Overall success rates for NIH funding of scientific applications, 1986 - 1995. No difference in funding rate is observed between applicants holding M.D. versus Ph.D. degrees. As the success rate for first-time applications was 11.3% in 1993, it is apparent that resubmission of a revised application significantly increases the overall chance of having research proposal ultimately funded.[section]
Capable medical researchers ultimately write research proposals for funding by the NIH. Standards of excellence for NIH grants are high (only the top [almost equal to] 20% of grants are funded). Research questions posed must be hypothesis driven; the investigator must be qualified to perform the study; and preliminary evidence should be presented demonstrating that the research is feasible and will answer the questions posed. The goal of this article is to review important elements of successful research proposals, with emphasis on funding sources available to the anesthesiology community. Two important anesthesia-specific organizations exist to support anesthesia research - The Foundation for Anesthesia Education and Research (FAER, an organization under the auspices of the American Society of Anesthesiologists) and the International Anesthesiology Research Society (IARS).
Successful applications for research support from FAER and IARS have many of the characteristics of grants funded by the NIH and other peer-reviewed funding sources. These characteristics include (1) a highly qualified investigator(s);(2) for junior investigators, a mentor with a successful track record in scientific investigation, peer-reviewed funding, and mentorship of fellows and faculty;(3) a supportive academic environment; and (4) a scientifically sound proposal. Each of these characteristics is discussed in the subsequent sections.
Training of the Investigator
One of the most important components of a successful research proposal is a well-trained investigator. Training in clinical anesthesia is not training in research methodology or scientific thinking; it does not prepare an individual for a career in investigation. Although obvious for basic science research, clinical research also requires commitment of a minimum of 1 yr of dedicated training with a good mentor, and more typically 2 - 3 yr in the field of the proposed research. The applicant also needs to demonstrate commitment to a career in investigation. Several years of scientific training is the first demonstration of such commitment. Research proposals must document institutional support for nonclinical time, and the investigator must provide evidence that this time has been used wisely and will continue to be dedicated to the proposed research.
The research proposal must document a track record of productivity by the investigator. This expectation increases as the training and career of the investigator progresses. Fellowship awards do not have an expectation of prior research training, so publications from prior research are not expected. At the fellowship level, outstanding letters of recommendation, undergraduate and medical school performance, and related accomplishments are most important. Because previous training is not required of the fellowship applicant, prior success of the mentor (publications and track record with previous trainees) weighs heavily in the fellowship review. For junior faculty, peer-reviewed publications are expected from the fellowship period. Young Investigator Annoucements (from FAER) and several new IARS awards require several years as a successful junior faculty member, so expectations of demonstrated research success are further increased. The investigator must demonstrate (1) rigorous training, (2) commitment to research, (3) an appropriate career path, and (4) a track record of productive work. None of these are trivial issues, and none can be easily accomplished without making a commitment to research early in the academic career.
The quality of the mentor is another important aspect of awards granted to fellows and junior faculty. Identification of a mentor is explicitly required for FAER and certain junior level NIH grant applications. First and foremost, the mentor must be a successful investigator. Criteria for this include a track record of publication in the area of the proposed research, continued peer-reviewed funding, and a history of successfully training young investigators. Although mentorship is not considered heavily in more senior grant applications, input from a more experienced investigator often remains beneficial throughout one's career (as we can personally attest to). In addition to the mentor, high-quality coinvestigators, collaborators, and consultants also play important roles in strengthening a research proposal.
Environment
Good research is best accomplished in a supportive, cooperative environment. Because of the changing climate of clinical medicine, researchers (both clinical and basic science) face increasing pressure to minimize research time. It is not possible to become a successful investigator in one's spare time. Documentation of adequate nonclinical time for research (not for committee meetings or other unrelated tasks) is essential. Receiving funding at a junior level often enables the department to match funds or to guarantee nonclinical time to the budding investigator. In general, the more non-clinical time available to an investigator, the more competitive the application.
Other important elements of the environment include people, space, and institutional resources. People include mentors, consultants who can help with specific methodologies, statistical support, helpful colleagues, experienced technicians, a clinical research team, and a dedicated chairperson. There must be adequate space for performing the proposed studies, office space for research personnel, and storage space for equipment and supplies. Institutional resources include related departmental and interdepartmental seminar series, a critical mass of investigators in a related area, instrument development and repair shops, and necessary laboratory space and common facilities.
Criteria for a sound research proposal are the same whether the proposal is submitted to NIH, FAER, IARS, or other funding sources. In crafting a proposal, it is essential to consider the perspective of the reviewer; therefore, items of interest to the reviewer are listed after general definition of the grant proposal.
Review committees receive dozens of grants. NIH study sections may review as many as 150 proposals during one session. Typically, only two or three reviewers are assigned to read each grant in detail, but everyone is expected to read each abstract. Hence, the abstract is often one of the most important parts of the research proposal. The abstract should address the significance of the question and the overall topic, state the hypothesis, and point out key preliminary data. Additionally, the abstract should provide a synopsis of methodologies planned. In the end, the reviewer must be convinced that the applicant is uniquely (or ideally) suited to undertake this important study by the end of this concise paragraph.
Body of the Grant
Specific Aims. The specific aims section is critically important in a scientific proposal. It is here that the investigator crystallizes the overall goal of the research and states specific hypotheses.
Beginning with the specific aims, the proposal must be well written and logically organized. A poorly organized grant application is difficult to review, even if the science is otherwise excellent. Typically, the specific aims begin with a short introduction (one paragraph), followed by a formally stated hypothesis. The hypothesis must be answerable by the research methods proposed. Generally, two or three specific aims are outlined with subheadings where appropriate. Organization of the specific aims is often temporal, starting with a proposed mechanism or the first set of studies in a clinical project. In general, the specific aims section should be no longer than one page.
Background and Significance. The background section provides an opportunity to bring reviewers up to date on current research in the area of the proposal. This section should summarize succinctly studies from the literature and related work published by the investigator. The most crucial aspect of the background is to build a case for significance of the proposed research regarding the ultimate clinical application or mechanistic understanding. Ideally, the background section should demonstrate that the current proposal is a logical extension of previous studies in the field and will provide new information and novel insights. In general, the background section should be about one fourth of the length of the grant proposal.
Preliminary Data. Preliminary data provide the opportunity for the investigator to demonstrate his or her ability to perform the proposed research. The goal in presenting preliminary data is to convince the reviewer that the investigator is capable of performing the proposed studies and that the mechanisms proposed are plausible. Good preliminary data support novel (or even unlikely) hypotheses. Each experimental method proposed should be accompanied by preliminary data demonstrating facility and expertise with related preparations. For example, if the investigator proposes using a specific electrophysiologic technique to study an ion channel, evidence demonstrating that this technique has been used by the investigator with other ion channels and a Figure showingresults from pilot experiments on the channel of interest would suffice. In clinical studies, demonstration of a working investigative team and the ability to enroll a given number of patients per week is helpful. Figures or tables help to convey the message in a succinct manner. They also conserve space in the proposal and create a more impressive effect. Although it is best if the applicant has generated his or her own preliminary data, for training awards, preliminary data from the mentor's laboratory is entirely appropriate. An effective way to organize preliminary data is to present it in the same order as the specific aims (e.g., C.1 preliminary data corresponds to A.1 specific aims, C.2 preliminary data corresponds to A.2 specific aims, etc.). Presentation of preliminary data usually takes about one fourth to one third of the length of the grant application.
Methods. The methods are the guts of the research proposal. Unfortunately, many investigators run out of steam by the time they reach the methods, leaving reviewers unconvinced by the proposed methodology. Ideally, the model being investigated should be broken down into simple, logical components, each accompanied by a description of specific experiments/interventions to be performed. The investigator should assume that at least one reviewer is an expert in each method presented. Therefore, enough detail should be provided to convince an expert that the experiment or technique is being performed properly. Methods presented as a list of recipes, requiring the reviewer to guess which method applies to each study, are recipes for disaster. Individual experimental techniques should be state of the art. In addition, approaching a problem from several angles is often helpful. “Lingo” of the field should be avoided; it is very annoying to reviewers to have to look up unexplained abbreviations or to have models alluded to rather than described. For training grants, methods should involve techniques currently being performed in the laboratory of the mentor. An effective way to organize the methods section is to follow the same order as the preliminary data and specific aims sections (e.g., D.1 methods corresponds to C.1 preliminary data and A.1 specific aims, etc.).
The methods sections should include a description of the design, conduct, and analysis of each study being proposed. Common errors in design include lack of specification of primary outcome, lack of randomization or blinding in clinical trials, inadequate justification of sample size, failure to adjust the total study number for expected dropouts/failed experiments or patient refusal, and use of single drug doses or concentrations rather than development of dose - response or concentration - response relations. Common errors in conducting research include lack of confirmation of drug concentrations, inadequate reproducibility of final results, lack of standardization of procedures, inadequate follow-up, incomplete data recording, and overall lack of organization.
Inadequate or inappropriate statistical methods can be a major weakness of a grant proposal. Many investigators feel confident with all aspects of their methods except the statistical section. Because statistical issues underlie the design and analysis strategy for every study, the input of a biostatistician is essential in planning the research and writing the grant application. Statistical considerations include specification of the primary end points that drive power calculations. Common statistical errors in research proposals include lack of sample size/power calculations, treating continuous variables as dichotomous, repeated t tests when a more comprehensive modeling approach should be taken, application of statistical tests that assume normality without verifying assumptions, failure to consider covariate effects, and failure to distinguish between interindividual and intraindividual variability. The investigator should be familiar with the concept of statistical power and be prepared to estimate some of the quantities needed to formulate an alternative hypothesis appropriately. The statistical analysis should be clearly outlined with specific methodology directed toward the hypotheses of the study. A statistical reviewer is unlikely to be convinced by a statement that “appropriate statistical methodology will be used” or by a barrage of nonspecific statistical jargon. At least one full paragraph (and sometimes an entire page) of the research proposal should be devoted to statistical analysis. Often several smaller statistics sections are appropriately included after each method is presented.
Even the best methods have potential problems and weaknesses. It is critical that the methods section discuss potential problems that may be encountered during the study and state how the investigator proposes to deal with these problems creatively. Reviewers tend to be impressed when the investigator presents potential problems that never occurred to them, because it suggests that the investigator is an expert in this area of research. A time line and organizational plan (who will be responsible for what) should also be included in the methods section so the reviewers can determine whether the investigator is being realistic in his or her approach. The methods section is typically one third to one half of the length of the entire grant proposal.
Introduction to Revised Application. Because so few grant applications are funded on their first submission (11.5% in 1993), the new investigator should not be unduly alarmed if his or her application is not funded. When a grant application has been unsuccessful, an investigator should revise the application and reapply, even if the original score was “noncompetitive”(meaning the grant was in the lower 50% of applications). Often the reviewers suggest key changes that will improve the application significantly. When submitting a revised application, an introduction (placed before the specific aims section) is used to discuss how criticisms of the original grant have been addressed in the revised proposal. Because the reviewer's comments are intended to be helpful, it is important to address each concern carefully in the revised proposal (changed text should be highlighted in the revised application by italic, bold, or identifying lines in the margin), with changes outlined in the introduction section. Angry responses to reviewers do not facilitate funding of the revised application. Remember that reviewers usually have a copy of the prior review, and they expect corrections or, when appropriate, an explanation of why you have chosen not to incorporate some suggestions from a prior review. Time taken to revise an application is well spent; as Figure 1 demonstrates, investigators who persist in revising and resubmitting their applications have an increased chance ([almost equal to] 20% with no previous NIH support, [almost equal to] 35% if previously funded) of ultimately being funded.[section]
In writing a research grant, it is helpful to consider the reviewer's perspective. Key features considered by reviewers include significance, approach, and feasibility. It is wise for the investigator to reread his or her application before submission with these features in mind. The NIH recently has published two documents on-line that discuss review criteria; examination of these documents before submission of a research proposal may prove helpful. These include the Report of the Committee on Rating Grant Applications[double vertical bar] and Review Criteria for Rating Unsolicited Research Grants.#
Significance
First and foremost, is the investigator asking an important question? There are two general ways research studies can be significant. The first is to demonstrate clinical significance. The litmus test for clinical significance is whether the proposed research will improve patient care. The second is elucidation of fundamental mechanisms underlying disease or biologic processes. The ideal research question succeeds in being significant in both areas.
The reviewer assesses whether the research plan can support or refute the stated hypothesis. In addition, the reviewer assesses whether the methodologies used provide adequate or, better yet, elegant approaches to the problem. Recently, the NIH has mandated an increasing emphasis on innovation in research. [1] **
Review committees generally are composed of individuals with expertise in many scientific areas. Additionally, study sections often retain outside reviewers with expertise in the proposed research area. The investigator should assume that his or her methods will be critiqued by at least one expert. Therefore, the investigator should not propose a method that would strike the world's expert in the field as being simplistic, inappropriate, or nonsensical, because the world's expert just might be one of the reviewers. Conversely, some reviewers do not have expertise in the proposed area of research. To ensure that the nonexpert is convinced of the validity and importance of proposed methodologies, the overall proposal should be written with a logical flow of ideas that build from basic to sophisticated concepts. Beginning each portion of the methods section with a short introduction for the nonexpert, followed by a more detailed description of the proposed methods, is an effective strategy to address the needs of both expert and nonexpert reviewers.
Feasibility
The investigator must convince reviewers that the chosen approach is feasible. Preliminary data provide the best demonstration of feasibility. Feasibility is often demonstrated by a track record of publications or peer-reviewed grant support for the applicant or mentor using the proposed experimental approach. Feasibility also can be demonstrated by appropriate statistical analysis of the proposal. For example, a power analysis and corresponding data on the number of patients with the required characteristics at the investigator's institution helps convince reviewers that a clinical study is feasible.
Anesthesiology Funding Sources
Funding for research performed by anesthesiologists is available from many sources. Because the discipline of anesthesiology overlaps many other fields, anesthesiologists have the opportunity to apply for research funds from agencies as diverse as the American Academy of Pediatrics, American Cancer Society, American Heart Association (national and local), American Thoracic Society, American Society for Regional Anesthesiology, critical care societies, Department of Veterans Affairs, National Science Foundation, Shriners, Society for Cardiovascular Anesthesiology, Society for Obstetrics and Perinatology, National Aeronautics and Space Aviation, NIH, and many other private foundations. Grants from FAER and IARS are available specifically to the anesthesiology community.
It is important that anesthesiologists continue to apply for NIH grants. For fiscal year 1996, the NIH awarded 149 research grants (including career development grants, R29, R01, and program project grants) to departments of anesthesiology, totaling $21 million in direct costs ([almost equal to]$31 million in total costs). Because of the diversity of research projects in anesthesiology, these grants were awarded by 14 different institutes, centers, and divisions within the NIH. In analyzing data for three recent review sessions (June 1996, October 1996, and February 1997) from the surgery, anesthesiology, and trauma study section, 26% of anesthesiology applications scored in the top 20th percentile, and 31% scored in the top 25th percentile; clearly no bias exists against anesthesiology in this predominantly surgical study section, at least in this limited sample (Alison Cole, anesthesiology representative for the National Institute of General Medicine Science at the NIH, personal communication, December, 1997). Table 1
Table 1. Number of Recipients of NIH Research Project Annoucements

A brief list of funding opportunities available to anesthesiologists early in their career is shown in Table 2 . Several sites are available on the World Wide Web ( Table 3 ) to facilitate access to grant/training resources for anesthesiologists. We have created an additional website ( http://pkpd.icon.palo-alto.med.va.gov/grants/grants.htm ), which provides access to more comprehensive lists of funding agencies and direct links to funding sources. This website also contains example grants designed to illustrate the grant writing principles discussed in this article.
Table 2. Potential Funding Sources

Table 3. Grant/Training Resources on the WWW

Successful grant applications require a well-trained investigator who carefully outlines a hypothesis-driven research proposal. Unique to FAER and IARS research committees is that the reviewers are mostly investigators and practicing anesthesiologists. These reviewers fully appreciate the importance of clinical research and enthusiastically support high-quality clinical studies. Although descriptive clinical studies are interesting to practicing clinicians, from a scientific perspective, clinical research must be driven by testable hypotheses. Without a testable hypothesis, clinical research cannot pass the test of adequate significance required for funding.
It is our hope that by demystifying the grant writing and review process that more anesthesiologists will be encouraged to submit proposals for research funding. As part of this effort, we strongly encourage residents and fellows interested in research careers to obtain adequate research training and to apply for appropriate fellowship/junior faculty awards early in their careers.
[section] NIH Extramural Data and Trends, Fiscal Years 1986 - 1995. Bethesda, Office of Reports and Analysis (component of the Office of Extramural Research), National Institutes of Health. (Published on-line and periodically updated. http://www.nih.gov/grants/award/award.htm ).
[double vertical bar] Report of the Committee on Rating Grant Applications. Revised 5/17/96. Bethesda, National Institutes of Health. (Published on-line. http://www.nih.gov/grants/peer/rga.pdf ).
# Review Criteria for Rating Unsolicited Research Grants. NIH Guide, Vol. 26, No. 22, 6/27/97. Bethesda, National Institutes of Health. (Published on-line. http://www.nih.gov/grants/guide/1997/97.06.27/notice-review-criter9.html ).
** Brown KS: A winning strategy for grant application: Focus on impact. The Scientist 1997; April 8:13–4
Citing articles via
Most viewed, email alerts, related articles, social media, affiliations.
- ASA Practice Parameters
- Online First
- Author Resource Center
- About the Journal
- Editorial Board
- Rights & Permissions
- Online ISSN 1528-1175
- Print ISSN 0003-3022
- Anesthesiology
- ASA Monitor

- Terms & Conditions Privacy Policy
- Manage Cookie Preferences
- © Copyright 2024 American Society of Anesthesiologists
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account

ISP Proposal Samples
You must have Adobe Acrobat Reader to view or print these PDF files. Click the button below to download a free copy:
Section 'Sub' Navigation:
- Introduction
- Role of Committee
- Expectations
- Past ISP Titles and Chairs
- Sample Proposals
- Helpful Hints
- Proposal Review Process
- Time Frames
- Completing the ISP
- Elective Credit
- Contact ISP Coordinator
- AudioVisual Support
- Body Donation Program
- Central Administration
- Educational Technology
- Professional Development Center
- Simulation Training Center
- MedEd Site Index
Page 'Breadcrumb' Navigation:
Site 'Main' Navigation:
- ASA Divisional Offices/Centers
- Admissions Office
- Financial Aid Office
- Student Affairs Office
- Diversity & Community Partnerships
- Global Health & Academic Concentration
- Medical Scientist Training Program
- Problem Based Learning Recruitment
- Schedules and Calendars
- Visiting Senior Students
- SOM Block Schedule
- UGME Divisional Offices/Centers
- ACA Preceptor
- Educational Support Services
- ISP Handbook
- Medical Education Technology and Evaluation
- Medical Teaching Laboratory
- Credentials Verification
- House Officer
- Benefits & Liability Insurance
- Medical License, DEA Registration & EPCS Enrollment
- Visiting Residents
- Program Coordinators & Directors
- Policies & Notices
- Anonymous Feedback
- GME Orientation
- Continuing Medical Education
- Alumni Affairs
- Business Office
- Equipment Replacement
- MedEd Support Services
- Medical Education Technology
- Medical Education
- School of Medicine
- UC San Diego Health System
- UC San Diego Health Sciences
Official Web Site of the University of California, San Diego. Copyright © 2024 Regents of the University of California. All rights reserved. Webmaster
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research process
- How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
Published on 30 October 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George. Revised on 13 June 2023.
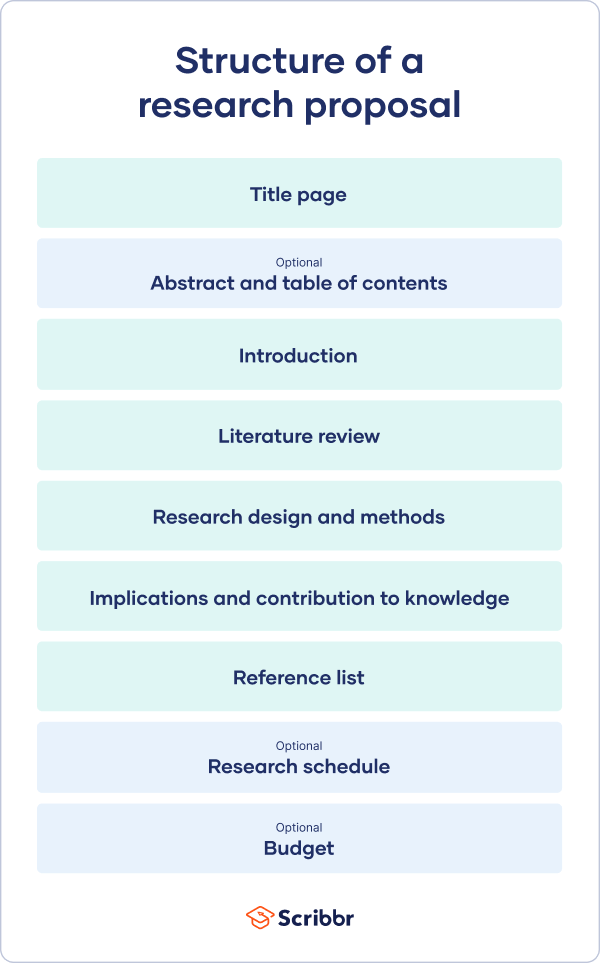
A research proposal describes what you will investigate, why it’s important, and how you will conduct your research.
The format of a research proposal varies between fields, but most proposals will contain at least these elements:
Introduction
Literature review.
- Research design
Reference list
While the sections may vary, the overall objective is always the same. A research proposal serves as a blueprint and guide for your research plan, helping you get organised and feel confident in the path forward you choose to take.
Table of contents
Research proposal purpose, research proposal examples, research design and methods, contribution to knowledge, research schedule, frequently asked questions.
Academics often have to write research proposals to get funding for their projects. As a student, you might have to write a research proposal as part of a grad school application , or prior to starting your thesis or dissertation .
In addition to helping you figure out what your research can look like, a proposal can also serve to demonstrate why your project is worth pursuing to a funder, educational institution, or supervisor.
Research proposal length
The length of a research proposal can vary quite a bit. A bachelor’s or master’s thesis proposal can be just a few pages, while proposals for PhD dissertations or research funding are usually much longer and more detailed. Your supervisor can help you determine the best length for your work.
One trick to get started is to think of your proposal’s structure as a shorter version of your thesis or dissertation , only without the results , conclusion and discussion sections.
Download our research proposal template
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We’ve included a few for you below.
- Example research proposal #1: ‘A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management’
- Example research proposal #2: ‘ Medical Students as Mediators of Change in Tobacco Use’
Like your dissertation or thesis, the proposal will usually have a title page that includes:
- The proposed title of your project
- Your supervisor’s name
- Your institution and department
The first part of your proposal is the initial pitch for your project. Make sure it succinctly explains what you want to do and why.
Your introduction should:
- Introduce your topic
- Give necessary background and context
- Outline your problem statement and research questions
To guide your introduction , include information about:
- Who could have an interest in the topic (e.g., scientists, policymakers)
- How much is already known about the topic
- What is missing from this current knowledge
- What new insights your research will contribute
- Why you believe this research is worth doing
As you get started, it’s important to demonstrate that you’re familiar with the most important research on your topic. A strong literature review shows your reader that your project has a solid foundation in existing knowledge or theory. It also shows that you’re not simply repeating what other people have already done or said, but rather using existing research as a jumping-off point for your own.
In this section, share exactly how your project will contribute to ongoing conversations in the field by:
- Comparing and contrasting the main theories, methods, and debates
- Examining the strengths and weaknesses of different approaches
- Explaining how will you build on, challenge, or synthesise prior scholarship
Following the literature review, restate your main objectives . This brings the focus back to your own project. Next, your research design or methodology section will describe your overall approach, and the practical steps you will take to answer your research questions.
To finish your proposal on a strong note, explore the potential implications of your research for your field. Emphasise again what you aim to contribute and why it matters.
For example, your results might have implications for:
- Improving best practices
- Informing policymaking decisions
- Strengthening a theory or model
- Challenging popular or scientific beliefs
- Creating a basis for future research
Last but not least, your research proposal must include correct citations for every source you have used, compiled in a reference list . To create citations quickly and easily, you can use our free APA citation generator .
Some institutions or funders require a detailed timeline of the project, asking you to forecast what you will do at each stage and how long it may take. While not always required, be sure to check the requirements of your project.
Here’s an example schedule to help you get started. You can also download a template at the button below.
Download our research schedule template
If you are applying for research funding, chances are you will have to include a detailed budget. This shows your estimates of how much each part of your project will cost.
Make sure to check what type of costs the funding body will agree to cover. For each item, include:
- Cost : exactly how much money do you need?
- Justification : why is this cost necessary to complete the research?
- Source : how did you calculate the amount?
To determine your budget, think about:
- Travel costs : do you need to go somewhere to collect your data? How will you get there, and how much time will you need? What will you do there (e.g., interviews, archival research)?
- Materials : do you need access to any tools or technologies?
- Help : do you need to hire any research assistants for the project? What will they do, and how much will you pay them?
Once you’ve decided on your research objectives , you need to explain them in your paper, at the end of your problem statement.
Keep your research objectives clear and concise, and use appropriate verbs to accurately convey the work that you will carry out for each one.
I will compare …
A research aim is a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear in your introduction at the end of your problem statement , before your research objectives.
Research objectives are more specific than your research aim. They indicate the specific ways you’ll address the overarching aim.
A PhD, which is short for philosophiae doctor (doctor of philosophy in Latin), is the highest university degree that can be obtained. In a PhD, students spend 3–5 years writing a dissertation , which aims to make a significant, original contribution to current knowledge.
A PhD is intended to prepare students for a career as a researcher, whether that be in academia, the public sector, or the private sector.
A master’s is a 1- or 2-year graduate degree that can prepare you for a variety of careers.
All master’s involve graduate-level coursework. Some are research-intensive and intend to prepare students for further study in a PhD; these usually require their students to write a master’s thesis . Others focus on professional training for a specific career.
Critical thinking refers to the ability to evaluate information and to be aware of biases or assumptions, including your own.
Like information literacy , it involves evaluating arguments, identifying and solving problems in an objective and systematic way, and clearly communicating your ideas.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. & George, T. (2023, June 13). How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved 21 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/the-research-process/research-proposal-explained/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, what is a literature review | guide, template, & examples, how to write a results section | tips & examples.
How to prepare a research proposal in the health sciences?
Affiliations.
- 1 Servicio de Aparato Digestivo, Hospital Universitario de La Princesa, Instituto de Investigación Sanitaria Princesa (IIS-IP), Universidad Autónoma de Madrid, Centro de Investigación Biomédica en Red de Enfermedades Hepáticas y Digestivas (CIBEREHD), Madrid, España. Electronic address: [email protected].
- 2 Servicio de Aparato Digestivo, Hospital Universitario de La Princesa, Instituto de Investigación Sanitaria Princesa (IIS-IP), Universidad Autónoma de Madrid, Centro de Investigación Biomédica en Red de Enfermedades Hepáticas y Digestivas (CIBEREHD), Madrid, España.
- PMID: 33277051
- DOI: 10.1016/j.gastrohep.2020.07.028
Knowing how to properly prepare a research proposal is a real challenge - and being able to prepare an excellent research proposal is increasingly a requirement to compete for funding with assurances of success. With this in mind, we aim to share with the reader our experience (in many cases, unsuccessful) as applicants on the most important aspects of preparing a research proposal and securing its approval and funding. This article aims not only to list theoretical recommendations but also to share some personal and eminently practical suggestions on the following elements of a research proposal: the title, the abstract, the introduction, the objectives, the methodology, the work plan or schedule, the proposal's consistency and coherence, its viability, its applicability, the importance of the principal investigator and the research team, the proposal's limitations and alternatives, its budget, its references, and, finally, the research proposal's form or wording. In summary, a research proposal is a carefully written plan that includes all the scientific, ethical and logistical aspects of the study to be conducted. Writing a good research proposal requires considerable effort and a great deal of time, but it's worth it.
Keywords: Ciencias de la salud; Health sciences; Protocol; Protocolo; Proyecto de investigación; Research proposal.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier España, S.L.U. All rights reserved.
- Guidelines as Topic*
- Research Design / standards*
- Research Support as Topic
- Writing / standards*
Writing a research proposal
The format of a research proposal varies depending on what or who it is required by. They can vary in length, ie. be very concise or quite long and detailed. Also the headings for the different sections can vary. Therefore, this guide deals with the research proposal in its most generic form, which should be easily modifiable to fit the criteria for any research body.
The ultimate aim of any research proposal is to convince people that your research is important, has not been done before, is worthwhile and is feasible. Hence you have to make a strong argument for your research. The language used should be clear and easy to understand, as often non-experts will assess it. Some funders may, and the Research Ethics Committee application form will, want a ‘lay’ summary in addition to your basic proposal document. It is usually only in the background and methodology sections that writers tend to assume that the intended audience has a particular knowledge of their research area.
Additionally, it is crucial that different sections of your research proposal should link or follow on from each other, eg. the research question should link with the methodology. This may sound obvious, but revisions of one section can lead to mis-matches. Check this before submitting your proposal!
Typical stages in a research proposal
1. The purpose of a research proposal is:
- To help to focus on a relevant and current topic.
- To identify a gap or inadequacy in the research literature.
- To make sure that these are your ideas, and to help you to focus and crystallise your ideas.
- To help you to focus on what the actual stages involved in the research process will be, eg. the exact methodology and data analysis that will be adopted.
- To justify a proposed research project to a particular audience, eg. supervisor, departmental or faculty committee, external funding body etc.
2. Some strategies before you start:
- Search through literature for topic related articles and books, ie. search through databases/catalogues/journals etc.
- Look at what is already being done in the area i.e. existing data and research.
- Read critically, ie. look for interesting and suitable gaps – areas for research.
- Talk to your employer for approval – there is no point in starting research that you will not be allowed to complete.
- Talk to your local research and development teams. They will be able to tell you the specific criteria for any research proposal and may highlight some issues that you have overlooked.
- Talk to experts or supervisors in the field – in person, phone, letters, e-mail.
- If it is helpful, use concept maps to link ideas, and or formulate questions that the literature review should address.
3. Identifying your research question:
Any research proposal needs to have a clear research question for it to succeed. Without a clear question research will become confused and lack direction. Subsequent analysis will be difficult because the research question is key to forming your hypothesis or aims, and later analysis.
Do start by writing a question, not a statement. This will help clarify exactly what the issue is that you are trying to find a solution to. Hypotheses, aims etc can then follow from this.
Your research question should:
- Be as clear and concise as you can make it. Don’t use multi-barrelled questions if you can avoid them.
- Be informative – state your population of interest, locality etc.
- Avoid technical jargon – this is the golden rule in most areas of research proposals. Remember that your research question is what will capture the interest of the reader / assessor.
- Relate to the proposal title – often the research question is quoted as the title of the proposal.
- Relate to the aim of the research – again, the research question is often quoted as the research aim.
It should be obvious from your question alone what the project will aim to do, and on who.
4. Project title:
The title should be brief but informative. It is important that it is clear and easy to understand, and describes what your proposed research is. As previously stated, this is often the research question.
5. Abstract or summary:
This is a very important section which bears a disproportionate share of responsibility for success or failure of a proposal, as it may act as the initial ‘hook’.
It needs to be written for a wider audience, so technical vocabulary has to be limited. The abstract also needs to come quickly to the proposed research. Abstracts for grant proposals usually begin with the objective or purpose of the study, move on to methodology (procedures and design), and close with a modest but precise statement of the projects’ significance.
The significance should:
- Be about one paragraph – if it needs any longer it is advisable to rethink your research or break it down into more manageable chunks.
- Explain to the reader why the study is “significant”, in the sense of advancing general knowledge.
- Explain what the benefits to the patient / health community are.
- Encourage funding.
Although you present this first in the document, write it last so that its content accurately reflects the whole proposal.
6. Introduction:
The introduction is also written so that a more general audience can easily obtain a general idea of what the project is about, and the major concepts involved. It will also typically begin with the purpose of the proposed research. The introduction will typically be quite short, leaving the detail to the background and methodology sections.
7. Background:
It is only in the background and methodology sections that writers tend to assume that their intended audience is a specialist in their research area, and so use more technical language.
This section will include the literature review.
The purpose of a literature review is as follows:
- To become familiar with the research area and keep up to date with the current research in your area of interest.
- Identify an appropriate research question.
- Establish a theoretical framework for the research.
- Justify the need for the research.
Through the actual process of writing the literature review you, the researcher, can explore the relevant literature, formulate a problem, defend the value of the research, and compare the findings and ideas with your own. The literature review establishes a context and orientates the reader to your research topic.
The common structure of the literature review is likened to a “funnel effect”, which goes from general to more specific studies etc directly relating your intended project, ending with your research question, problem or objective.
In summary the stages of a literature review are as follows:
- General statement(s) about the field of research – the setting.
- More specific statements about the previous research.
- Statements that indicate the need for more investigation.
- Very specific statement(s) of the research question, problem or objective.
Your Trust librarians will be able to help with appropriate literature searching techniques if required.
8. Methodology:
The method or methodology section describes the steps you will follow in conducting your research. It is a very important section as assessors will scrutinise it to evaluate the feasibility and likelihood of successful completion of your proposed research.
Examine methodology sections of research articles in your research area. Arrange to discuss your research with a statistical and/or methodological specialist (Trust and other local research clinics / groups). Discuss with other researchers in your discipline the methodologies they have adopted. Consult methodology texts and statistical packages.
Overview of research:
Population/sample to be studied, including:
- How you have arrived at the sample size.
- How they will be recruited.
- Location of the research.
- Restrictions/limiting conditions.
- Sampling technique.
- Procedures.
- Analysis tools and methods.
9. Timescale:
10. Budget:
11. Ethical considerations:
- Benefits vs risks of the involvement in the project.
- Receipt of informed consent.
- Protection of participants (including data protection and storage issues).
- Privacy, minimising discomfort etc.
- Community values.
12. Dissemination strategy:
- The targets of your research eg. staff, patients, service users or carers,
- services locally and/or nationally,
- policies that drive the above services.
13. Bibliography and references:
Good luck with your project!
Useful reading: Bowling A (2002), Research Methods in Health: Investigating Health and Health Services 2Rev Ed edition, Open University Press Polgar S and Thomas SA. (4 th Edition 2004) Introduction to Research in the Health Sciences. Churchill Livingstone. MRC Good Research Practice Guidance

- Research Process
Writing a Scientific Research Project Proposal
- 5 minute read
- 103.1K views
Table of Contents
The importance of a well-written research proposal cannot be underestimated. Your research really is only as good as your proposal. A poorly written, or poorly conceived research proposal will doom even an otherwise worthy project. On the other hand, a well-written, high-quality proposal will increase your chances for success.
In this article, we’ll outline the basics of writing an effective scientific research proposal, including the differences between research proposals, grants and cover letters. We’ll also touch on common mistakes made when submitting research proposals, as well as a simple example or template that you can follow.
What is a scientific research proposal?
The main purpose of a scientific research proposal is to convince your audience that your project is worthwhile, and that you have the expertise and wherewithal to complete it. The elements of an effective research proposal mirror those of the research process itself, which we’ll outline below. Essentially, the research proposal should include enough information for the reader to determine if your proposed study is worth pursuing.
It is not an uncommon misunderstanding to think that a research proposal and a cover letter are the same things. However, they are different. The main difference between a research proposal vs cover letter content is distinct. Whereas the research proposal summarizes the proposal for future research, the cover letter connects you to the research, and how you are the right person to complete the proposed research.
There is also sometimes confusion around a research proposal vs grant application. Whereas a research proposal is a statement of intent, related to answering a research question, a grant application is a specific request for funding to complete the research proposed. Of course, there are elements of overlap between the two documents; it’s the purpose of the document that defines one or the other.
Scientific Research Proposal Format
Although there is no one way to write a scientific research proposal, there are specific guidelines. A lot depends on which journal you’re submitting your research proposal to, so you may need to follow their scientific research proposal template.
In general, however, there are fairly universal sections to every scientific research proposal. These include:
- Title: Make sure the title of your proposal is descriptive and concise. Make it catch and informative at the same time, avoiding dry phrases like, “An investigation…” Your title should pique the interest of the reader.
- Abstract: This is a brief (300-500 words) summary that includes the research question, your rationale for the study, and any applicable hypothesis. You should also include a brief description of your methodology, including procedures, samples, instruments, etc.
- Introduction: The opening paragraph of your research proposal is, perhaps, the most important. Here you want to introduce the research problem in a creative way, and demonstrate your understanding of the need for the research. You want the reader to think that your proposed research is current, important and relevant.
- Background: Include a brief history of the topic and link it to a contemporary context to show its relevance for today. Identify key researchers and institutions also looking at the problem
- Literature Review: This is the section that may take the longest amount of time to assemble. Here you want to synthesize prior research, and place your proposed research into the larger picture of what’s been studied in the past. You want to show your reader that your work is original, and adds to the current knowledge.
- Research Design and Methodology: This section should be very clearly and logically written and organized. You are letting your reader know that you know what you are going to do, and how. The reader should feel confident that you have the skills and knowledge needed to get the project done.
- Preliminary Implications: Here you’ll be outlining how you anticipate your research will extend current knowledge in your field. You might also want to discuss how your findings will impact future research needs.
- Conclusion: This section reinforces the significance and importance of your proposed research, and summarizes the entire proposal.
- References/Citations: Of course, you need to include a full and accurate list of any and all sources you used to write your research proposal.
Common Mistakes in Writing a Scientific Research Project Proposal
Remember, the best research proposal can be rejected if it’s not well written or is ill-conceived. The most common mistakes made include:
- Not providing the proper context for your research question or the problem
- Failing to reference landmark/key studies
- Losing focus of the research question or problem
- Not accurately presenting contributions by other researchers and institutions
- Incompletely developing a persuasive argument for the research that is being proposed
- Misplaced attention on minor points and/or not enough detail on major issues
- Sloppy, low-quality writing without effective logic and flow
- Incorrect or lapses in references and citations, and/or references not in proper format
- The proposal is too long – or too short
Scientific Research Proposal Example
There are countless examples that you can find for successful research proposals. In addition, you can also find examples of unsuccessful research proposals. Search for successful research proposals in your field, and even for your target journal, to get a good idea on what specifically your audience may be looking for.
While there’s no one example that will show you everything you need to know, looking at a few will give you a good idea of what you need to include in your own research proposal. Talk, also, to colleagues in your field, especially if you are a student or a new researcher. We can often learn from the mistakes of others. The more prepared and knowledgeable you are prior to writing your research proposal, the more likely you are to succeed.
Language Editing Services
One of the top reasons scientific research proposals are rejected is due to poor logic and flow. Check out our Language Editing Services to ensure a great proposal , that’s clear and concise, and properly referenced. Check our video for more information, and get started today.

- Manuscript Review
Research Fraud: Falsification and Fabrication in Research Data

Research Team Structure
You may also like.

Descriptive Research Design and Its Myriad Uses

Five Common Mistakes to Avoid When Writing a Biomedical Research Paper

Making Technical Writing in Environmental Engineering Accessible

To Err is Not Human: The Dangers of AI-assisted Academic Writing

When Data Speak, Listen: Importance of Data Collection and Analysis Methods

Choosing the Right Research Methodology: A Guide for Researchers

Why is data validation important in research?

Writing a good review article
Input your search keywords and press Enter.
- AI Content Shield
- AI KW Research
- AI Assistant
- SEO Optimizer
- AI KW Clustering
- Customer reviews
- The NLO Revolution
- Press Center
- Help Center
- Content Resources
- Facebook Group
Medical Research Proposal Sample & Guide
Table of Contents
A medical research proposal sample is a great way to understand what your proposal should look like. It can give you the structure and guidance needed to create a successful proposal. Well-written medical research proposals help researchers stand out from other applicants and boost their chances of being selected or funded. Read on to find out what a medical research proposal entails and how to write yours with our easy sample.
What Is a Medical Research Proposal?
A medical research proposal is a document that outlines the purpose and methodology of a proposed research project . It includes information about what the researcher intends to study, how they plan to conduct their research and measurement for success or failure. The proposal also explains why the research is essential, what ethical considerations need to be considered, and the potential risks associated with it.
Why Is a Medical Research Proposal Necessary?
A medical research proposal is essential because it outlines the critical information and details necessary to complete a project successfully. This document ensures that everyone understands their position and how they will contribute resources, time, and effort to make the project successful. It also helps researchers to secure funding from sponsors and provide transparency for potential participants in the study.
What to Include in a Medical Research Proposal?
A medical research proposal should include the following:
- A brief description of the project, outlining the purpose and goals.
- An explanation of how you plan to collect data; through surveys or interviews with participants?
- List any ethical considerations involved, including who will have access to the collected information and how it will be stored securely.
- Budget required for the research and any timeline associated with the completion of the study.
- Samples from past researchers, so you can learn more about what makes a successful medical research proposal.
Steps on How to Write a Medical Research Proposal
It is important to remember that all proposals, no matter the topic, should follow specific steps to make them effective and organized. Here are a few steps to guide you:

Brainstorm and Outline the Problem
The first step is to brainstorm the project you are proposing, making sure that it has relevance in medicine. Determine what issue you are trying to address through your research and explain it clearly as a problem statement.
Describe Your Project
Provide detailed information on your project, the aims, the expected outcomes, and any methods used to achieve them.
Break It Into Small Sections
Once you have a clear vision of what you want to accomplish, break it down into small sections to effectively convey your thoughts.
Set Your Objectives
Set specific objectives for your project and explain how you plan to achieve them.
Outline Your Methodology
Describe the processes used to collect data, analyze results, and draw conclusions from the research.
Discuss Ethical Considerations
Explain any ethical considerations relevant to your proposed project, such as privacy and consent.
Write a Budget
Outline the cost of the project, including any equipment or materials needed.
Proofread the Proposal
Make sure to read through your proposal carefully before submitting it and ask someone else to do so, if possible.
Medical Research Proposal Sample
To help you get started with your medical research proposal, here is an example: Project Aims: This project aims to study air pollution’s effects on public health in a particular city. Objectives: To investigate how air pollution impacts public health in the target city and how to mitigate it. Methodology: Data will be collected through surveys, interviews with residents, and environmental air quality sampling. Ethical Considerations: All participants in the project must be informed of the risks involved and consent to its use for research purposes. Personal information will be kept confidential and only used for research purposes. Budget: The budget allocated for this project is $5000.
Developing a medical research proposal requires careful consideration and organization. Consequently, a medical research proposal sample might serve as an excellent starting point when writing your own project .

Abir Ghenaiet
Abir is a data analyst and researcher. Among her interests are artificial intelligence, machine learning, and natural language processing. As a humanitarian and educator, she actively supports women in tech and promotes diversity.
Explore All Proposal Generator Articles
Creative terms and conditions agreement in business proposal.
In business, proposals are essential for securing contracts and agreements with clients. However, a proposal is only complete with terms…
- Proposal Generator

Free guide to a statement of proposal sample
A statement of proposal is a document that outlines a proposed project or initiative in detail. It is typically used…
Free Proposal Letter for Training and Development for a Head Start
Training and development are essential to improve employees’ skills, knowledge, and productivity. A well-crafted training proposal can help an organization…
Detailed Guide to Free HR Consulting Proposal
HR consulting is an essential service for businesses of all sizes. HR consultants provide expert guidance to organizations on various…
Key Guide to Better Remote Work Proposal
The rise of remote work has been a significant trend in the business world over the last few years. With…
Guide to Free E-Commerce Proposal Template
E-commerce has become one of the most popular ways of doing business recently. With the increasing number of people using…
- Search Menu
- Browse content in Arts and Humanities
- Browse content in Archaeology
- Anglo-Saxon and Medieval Archaeology
- Archaeological Methodology and Techniques
- Archaeology by Region
- Archaeology of Religion
- Archaeology of Trade and Exchange
- Biblical Archaeology
- Contemporary and Public Archaeology
- Environmental Archaeology
- Historical Archaeology
- History and Theory of Archaeology
- Industrial Archaeology
- Landscape Archaeology
- Mortuary Archaeology
- Prehistoric Archaeology
- Underwater Archaeology
- Urban Archaeology
- Zooarchaeology
- Browse content in Architecture
- Architectural Structure and Design
- History of Architecture
- Residential and Domestic Buildings
- Theory of Architecture
- Browse content in Art
- Art Subjects and Themes
- History of Art
- Industrial and Commercial Art
- Theory of Art
- Biographical Studies
- Byzantine Studies
- Browse content in Classical Studies
- Classical History
- Classical Philosophy
- Classical Mythology
- Classical Literature
- Classical Reception
- Classical Art and Architecture
- Classical Oratory and Rhetoric
- Greek and Roman Papyrology
- Greek and Roman Epigraphy
- Greek and Roman Law
- Greek and Roman Archaeology
- Late Antiquity
- Religion in the Ancient World
- Digital Humanities
- Browse content in History
- Colonialism and Imperialism
- Diplomatic History
- Environmental History
- Genealogy, Heraldry, Names, and Honours
- Genocide and Ethnic Cleansing
- Historical Geography
- History by Period
- History of Emotions
- History of Agriculture
- History of Education
- History of Gender and Sexuality
- Industrial History
- Intellectual History
- International History
- Labour History
- Legal and Constitutional History
- Local and Family History
- Maritime History
- Military History
- National Liberation and Post-Colonialism
- Oral History
- Political History
- Public History
- Regional and National History
- Revolutions and Rebellions
- Slavery and Abolition of Slavery
- Social and Cultural History
- Theory, Methods, and Historiography
- Urban History
- World History
- Browse content in Language Teaching and Learning
- Language Learning (Specific Skills)
- Language Teaching Theory and Methods
- Browse content in Linguistics
- Applied Linguistics
- Cognitive Linguistics
- Computational Linguistics
- Forensic Linguistics
- Grammar, Syntax and Morphology
- Historical and Diachronic Linguistics
- History of English
- Language Evolution
- Language Reference
- Language Acquisition
- Language Variation
- Language Families
- Lexicography
- Linguistic Anthropology
- Linguistic Theories
- Linguistic Typology
- Phonetics and Phonology
- Psycholinguistics
- Sociolinguistics
- Translation and Interpretation
- Writing Systems
- Browse content in Literature
- Bibliography
- Children's Literature Studies
- Literary Studies (Romanticism)
- Literary Studies (American)
- Literary Studies (Asian)
- Literary Studies (European)
- Literary Studies (Eco-criticism)
- Literary Studies (Modernism)
- Literary Studies - World
- Literary Studies (1500 to 1800)
- Literary Studies (19th Century)
- Literary Studies (20th Century onwards)
- Literary Studies (African American Literature)
- Literary Studies (British and Irish)
- Literary Studies (Early and Medieval)
- Literary Studies (Fiction, Novelists, and Prose Writers)
- Literary Studies (Gender Studies)
- Literary Studies (Graphic Novels)
- Literary Studies (History of the Book)
- Literary Studies (Plays and Playwrights)
- Literary Studies (Poetry and Poets)
- Literary Studies (Postcolonial Literature)
- Literary Studies (Queer Studies)
- Literary Studies (Science Fiction)
- Literary Studies (Travel Literature)
- Literary Studies (War Literature)
- Literary Studies (Women's Writing)
- Literary Theory and Cultural Studies
- Mythology and Folklore
- Shakespeare Studies and Criticism
- Browse content in Media Studies
- Browse content in Music
- Applied Music
- Dance and Music
- Ethics in Music
- Ethnomusicology
- Gender and Sexuality in Music
- Medicine and Music
- Music Cultures
- Music and Media
- Music and Religion
- Music and Culture
- Music Education and Pedagogy
- Music Theory and Analysis
- Musical Scores, Lyrics, and Libretti
- Musical Structures, Styles, and Techniques
- Musicology and Music History
- Performance Practice and Studies
- Race and Ethnicity in Music
- Sound Studies
- Browse content in Performing Arts
- Browse content in Philosophy
- Aesthetics and Philosophy of Art
- Epistemology
- Feminist Philosophy
- History of Western Philosophy
- Metaphysics
- Moral Philosophy
- Non-Western Philosophy
- Philosophy of Language
- Philosophy of Mind
- Philosophy of Perception
- Philosophy of Science
- Philosophy of Action
- Philosophy of Law
- Philosophy of Religion
- Philosophy of Mathematics and Logic
- Practical Ethics
- Social and Political Philosophy
- Browse content in Religion
- Biblical Studies
- Christianity
- East Asian Religions
- History of Religion
- Judaism and Jewish Studies
- Qumran Studies
- Religion and Education
- Religion and Health
- Religion and Politics
- Religion and Science
- Religion and Law
- Religion and Art, Literature, and Music
- Religious Studies
- Browse content in Society and Culture
- Cookery, Food, and Drink
- Cultural Studies
- Customs and Traditions
- Ethical Issues and Debates
- Hobbies, Games, Arts and Crafts
- Lifestyle, Home, and Garden
- Natural world, Country Life, and Pets
- Popular Beliefs and Controversial Knowledge
- Sports and Outdoor Recreation
- Technology and Society
- Travel and Holiday
- Visual Culture
- Browse content in Law
- Arbitration
- Browse content in Company and Commercial Law
- Commercial Law
- Company Law
- Browse content in Comparative Law
- Systems of Law
- Competition Law
- Browse content in Constitutional and Administrative Law
- Government Powers
- Judicial Review
- Local Government Law
- Military and Defence Law
- Parliamentary and Legislative Practice
- Construction Law
- Contract Law
- Browse content in Criminal Law
- Criminal Procedure
- Criminal Evidence Law
- Sentencing and Punishment
- Employment and Labour Law
- Environment and Energy Law
- Browse content in Financial Law
- Banking Law
- Insolvency Law
- History of Law
- Human Rights and Immigration
- Intellectual Property Law
- Browse content in International Law
- Private International Law and Conflict of Laws
- Public International Law
- IT and Communications Law
- Jurisprudence and Philosophy of Law
- Law and Politics
- Law and Society
- Browse content in Legal System and Practice
- Courts and Procedure
- Legal Skills and Practice
- Primary Sources of Law
- Regulation of Legal Profession
- Medical and Healthcare Law
- Browse content in Policing
- Criminal Investigation and Detection
- Police and Security Services
- Police Procedure and Law
- Police Regional Planning
- Browse content in Property Law
- Personal Property Law
- Study and Revision
- Terrorism and National Security Law
- Browse content in Trusts Law
- Wills and Probate or Succession
- Browse content in Medicine and Health
- Browse content in Allied Health Professions
- Arts Therapies
- Clinical Science
- Dietetics and Nutrition
- Occupational Therapy
- Operating Department Practice
- Physiotherapy
- Radiography
- Speech and Language Therapy
- Browse content in Anaesthetics
- General Anaesthesia
- Neuroanaesthesia
- Clinical Neuroscience
- Browse content in Clinical Medicine
- Acute Medicine
- Cardiovascular Medicine
- Clinical Genetics
- Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology and Diabetes
- Gastroenterology
- Genito-urinary Medicine
- Geriatric Medicine
- Infectious Diseases
- Medical Toxicology
- Medical Oncology
- Pain Medicine
- Palliative Medicine
- Rehabilitation Medicine
- Respiratory Medicine and Pulmonology
- Rheumatology
- Sleep Medicine
- Sports and Exercise Medicine
- Community Medical Services
- Critical Care
- Emergency Medicine
- Forensic Medicine
- Haematology
- History of Medicine
- Browse content in Medical Skills
- Clinical Skills
- Communication Skills
- Nursing Skills
- Surgical Skills
- Browse content in Medical Dentistry
- Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery
- Paediatric Dentistry
- Restorative Dentistry and Orthodontics
- Surgical Dentistry
- Medical Ethics
- Medical Statistics and Methodology
- Browse content in Neurology
- Clinical Neurophysiology
- Neuropathology
- Nursing Studies
- Browse content in Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Gynaecology
- Occupational Medicine
- Ophthalmology
- Otolaryngology (ENT)
- Browse content in Paediatrics
- Neonatology
- Browse content in Pathology
- Chemical Pathology
- Clinical Cytogenetics and Molecular Genetics
- Histopathology
- Medical Microbiology and Virology
- Patient Education and Information
- Browse content in Pharmacology
- Psychopharmacology
- Browse content in Popular Health
- Caring for Others
- Complementary and Alternative Medicine
- Self-help and Personal Development
- Browse content in Preclinical Medicine
- Cell Biology
- Molecular Biology and Genetics
- Reproduction, Growth and Development
- Primary Care
- Professional Development in Medicine
- Browse content in Psychiatry
- Addiction Medicine
- Child and Adolescent Psychiatry
- Forensic Psychiatry
- Learning Disabilities
- Old Age Psychiatry
- Psychotherapy
- Browse content in Public Health and Epidemiology
- Epidemiology
- Public Health
- Browse content in Radiology
- Clinical Radiology
- Interventional Radiology
- Nuclear Medicine
- Radiation Oncology
- Reproductive Medicine
- Browse content in Surgery
- Cardiothoracic Surgery
- Gastro-intestinal and Colorectal Surgery
- General Surgery
- Neurosurgery
- Paediatric Surgery
- Peri-operative Care
- Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
- Surgical Oncology
- Transplant Surgery
- Trauma and Orthopaedic Surgery
- Vascular Surgery
- Browse content in Science and Mathematics
- Browse content in Biological Sciences
- Aquatic Biology
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics and Computational Biology
- Developmental Biology
- Ecology and Conservation
- Evolutionary Biology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Microbiology
- Molecular and Cell Biology
- Natural History
- Plant Sciences and Forestry
- Research Methods in Life Sciences
- Structural Biology
- Systems Biology
- Zoology and Animal Sciences
- Browse content in Chemistry
- Analytical Chemistry
- Computational Chemistry
- Crystallography
- Environmental Chemistry
- Industrial Chemistry
- Inorganic Chemistry
- Materials Chemistry
- Medicinal Chemistry
- Mineralogy and Gems
- Organic Chemistry
- Physical Chemistry
- Polymer Chemistry
- Study and Communication Skills in Chemistry
- Theoretical Chemistry
- Browse content in Computer Science
- Artificial Intelligence
- Computer Architecture and Logic Design
- Game Studies
- Human-Computer Interaction
- Mathematical Theory of Computation
- Programming Languages
- Software Engineering
- Systems Analysis and Design
- Virtual Reality
- Browse content in Computing
- Business Applications
- Computer Security
- Computer Games
- Computer Networking and Communications
- Digital Lifestyle
- Graphical and Digital Media Applications
- Operating Systems
- Browse content in Earth Sciences and Geography
- Atmospheric Sciences
- Environmental Geography
- Geology and the Lithosphere
- Maps and Map-making
- Meteorology and Climatology
- Oceanography and Hydrology
- Palaeontology
- Physical Geography and Topography
- Regional Geography
- Soil Science
- Urban Geography
- Browse content in Engineering and Technology
- Agriculture and Farming
- Biological Engineering
- Civil Engineering, Surveying, and Building
- Electronics and Communications Engineering
- Energy Technology
- Engineering (General)
- Environmental Science, Engineering, and Technology
- History of Engineering and Technology
- Mechanical Engineering and Materials
- Technology of Industrial Chemistry
- Transport Technology and Trades
- Browse content in Environmental Science
- Applied Ecology (Environmental Science)
- Conservation of the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Environmental Sustainability
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Environmental Science)
- Management of Land and Natural Resources (Environmental Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environmental Science)
- Nuclear Issues (Environmental Science)
- Pollution and Threats to the Environment (Environmental Science)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Environmental Science)
- History of Science and Technology
- Browse content in Materials Science
- Ceramics and Glasses
- Composite Materials
- Metals, Alloying, and Corrosion
- Nanotechnology
- Browse content in Mathematics
- Applied Mathematics
- Biomathematics and Statistics
- History of Mathematics
- Mathematical Education
- Mathematical Finance
- Mathematical Analysis
- Numerical and Computational Mathematics
- Probability and Statistics
- Pure Mathematics
- Browse content in Neuroscience
- Cognition and Behavioural Neuroscience
- Development of the Nervous System
- Disorders of the Nervous System
- History of Neuroscience
- Invertebrate Neurobiology
- Molecular and Cellular Systems
- Neuroendocrinology and Autonomic Nervous System
- Neuroscientific Techniques
- Sensory and Motor Systems
- Browse content in Physics
- Astronomy and Astrophysics
- Atomic, Molecular, and Optical Physics
- Biological and Medical Physics
- Classical Mechanics
- Computational Physics
- Condensed Matter Physics
- Electromagnetism, Optics, and Acoustics
- History of Physics
- Mathematical and Statistical Physics
- Measurement Science
- Nuclear Physics
- Particles and Fields
- Plasma Physics
- Quantum Physics
- Relativity and Gravitation
- Semiconductor and Mesoscopic Physics
- Browse content in Psychology
- Affective Sciences
- Clinical Psychology
- Cognitive Psychology
- Cognitive Neuroscience
- Criminal and Forensic Psychology
- Developmental Psychology
- Educational Psychology
- Evolutionary Psychology
- Health Psychology
- History and Systems in Psychology
- Music Psychology
- Neuropsychology
- Organizational Psychology
- Psychological Assessment and Testing
- Psychology of Human-Technology Interaction
- Psychology Professional Development and Training
- Research Methods in Psychology
- Social Psychology
- Browse content in Social Sciences
- Browse content in Anthropology
- Anthropology of Religion
- Human Evolution
- Medical Anthropology
- Physical Anthropology
- Regional Anthropology
- Social and Cultural Anthropology
- Theory and Practice of Anthropology
- Browse content in Business and Management
- Business Ethics
- Business Strategy
- Business History
- Business and Technology
- Business and Government
- Business and the Environment
- Comparative Management
- Corporate Governance
- Corporate Social Responsibility
- Entrepreneurship
- Health Management
- Human Resource Management
- Industrial and Employment Relations
- Industry Studies
- Information and Communication Technologies
- International Business
- Knowledge Management
- Management and Management Techniques
- Operations Management
- Organizational Theory and Behaviour
- Pensions and Pension Management
- Public and Nonprofit Management
- Strategic Management
- Supply Chain Management
- Browse content in Criminology and Criminal Justice
- Criminal Justice
- Criminology
- Forms of Crime
- International and Comparative Criminology
- Youth Violence and Juvenile Justice
- Development Studies
- Browse content in Economics
- Agricultural, Environmental, and Natural Resource Economics
- Asian Economics
- Behavioural Finance
- Behavioural Economics and Neuroeconomics
- Econometrics and Mathematical Economics
- Economic History
- Economic Systems
- Economic Methodology
- Economic Development and Growth
- Financial Markets
- Financial Institutions and Services
- General Economics and Teaching
- Health, Education, and Welfare
- History of Economic Thought
- International Economics
- Labour and Demographic Economics
- Law and Economics
- Macroeconomics and Monetary Economics
- Microeconomics
- Public Economics
- Urban, Rural, and Regional Economics
- Welfare Economics
- Browse content in Education
- Adult Education and Continuous Learning
- Care and Counselling of Students
- Early Childhood and Elementary Education
- Educational Equipment and Technology
- Educational Strategies and Policy
- Higher and Further Education
- Organization and Management of Education
- Philosophy and Theory of Education
- Schools Studies
- Secondary Education
- Teaching of a Specific Subject
- Teaching of Specific Groups and Special Educational Needs
- Teaching Skills and Techniques
- Browse content in Environment
- Applied Ecology (Social Science)
- Climate Change
- Conservation of the Environment (Social Science)
- Environmentalist Thought and Ideology (Social Science)
- Natural Disasters (Environment)
- Social Impact of Environmental Issues (Social Science)
- Browse content in Human Geography
- Cultural Geography
- Economic Geography
- Political Geography
- Browse content in Interdisciplinary Studies
- Communication Studies
- Museums, Libraries, and Information Sciences
- Browse content in Politics
- African Politics
- Asian Politics
- Chinese Politics
- Comparative Politics
- Conflict Politics
- Elections and Electoral Studies
- Environmental Politics
- European Union
- Foreign Policy
- Gender and Politics
- Human Rights and Politics
- Indian Politics
- International Relations
- International Organization (Politics)
- International Political Economy
- Irish Politics
- Latin American Politics
- Middle Eastern Politics
- Political Behaviour
- Political Economy
- Political Institutions
- Political Methodology
- Political Communication
- Political Philosophy
- Political Sociology
- Political Theory
- Politics and Law
- Politics of Development
- Public Policy
- Public Administration
- Quantitative Political Methodology
- Regional Political Studies
- Russian Politics
- Security Studies
- State and Local Government
- UK Politics
- US Politics
- Browse content in Regional and Area Studies
- African Studies
- Asian Studies
- East Asian Studies
- Japanese Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Middle Eastern Studies
- Native American Studies
- Scottish Studies
- Browse content in Research and Information
- Research Methods
- Browse content in Social Work
- Addictions and Substance Misuse
- Adoption and Fostering
- Care of the Elderly
- Child and Adolescent Social Work
- Couple and Family Social Work
- Developmental and Physical Disabilities Social Work
- Direct Practice and Clinical Social Work
- Emergency Services
- Human Behaviour and the Social Environment
- International and Global Issues in Social Work
- Mental and Behavioural Health
- Social Justice and Human Rights
- Social Policy and Advocacy
- Social Work and Crime and Justice
- Social Work Macro Practice
- Social Work Practice Settings
- Social Work Research and Evidence-based Practice
- Welfare and Benefit Systems
- Browse content in Sociology
- Childhood Studies
- Community Development
- Comparative and Historical Sociology
- Economic Sociology
- Gender and Sexuality
- Gerontology and Ageing
- Health, Illness, and Medicine
- Marriage and the Family
- Migration Studies
- Occupations, Professions, and Work
- Organizations
- Population and Demography
- Race and Ethnicity
- Social Theory
- Social Movements and Social Change
- Social Research and Statistics
- Social Stratification, Inequality, and Mobility
- Sociology of Religion
- Sociology of Education
- Sport and Leisure
- Urban and Rural Studies
- Browse content in Warfare and Defence
- Defence Strategy, Planning, and Research
- Land Forces and Warfare
- Military Administration
- Military Life and Institutions
- Naval Forces and Warfare
- Other Warfare and Defence Issues
- Peace Studies and Conflict Resolution
- Weapons and Equipment

- < Previous chapter
- Next chapter >

87Chapter 4 Writing your research proposal
- Published: November 2011
- Cite Icon Cite
- Permissions Icon Permissions
In many ways it’s a reflection of yourself as a researcher and an insight into your proposed work. A poorly written proposal has the ability to wreck a project and embarrass the researcher before it has even begun. Similarly, a well-constructed proposal bodes well for the success of the project and displays the researcher in a good light amongst their peers and supervisors. The research proposal identifies: • What the topic is, both in terms of background and the individual area of interest. • What you plan to accomplish and why it needs doing. • What in particular you are trying to find out, i.e. the research question. • How you will get the answer to your question, i.e. your methodology. • What others will learn from it and why it is worth learning. • How long it will take. • How much money it will cost. Through your research proposal you are attempting to convince potential supporters that your project is worth doing, you are scientifically competent to run it, and are in possession of the necessary management skills to ensure its completion. The proposal concisely describes the key elements of the study process, although in sufficient depth to permit evaluation. It is a stand-alone document that must contain evidence of an answerable question, demonstrate your grasp of the literature, and also clearly show that your methodology is sound. A research time-table is required to demonstrate a realistic appreciation of how the study will progress through time. The research proposal serves many purposes to many different parties. Amongst these purposes, some of the key ones are: • Acting as a route map and timetable for all involved in your project. • Giving a clear overview of your planned work to ensure favourable decision at ethical review. • Gaining funding to carry out your proposed study. • Securing a place to undertake a higher scientific degree. • Being an opportunity to ‘blow your own trumpet’ on paper. Although there are several bodies who will be obliged to see your proposal, there is a reasonable chance it will end up being wider read than this, so a coherent piece of work will reflect well on you.
Signed in as
Institutional accounts.
- GoogleCrawler [DO NOT DELETE]
- Google Scholar Indexing
Personal account
- Sign in with email/username & password
- Get email alerts
- Save searches
- Purchase content
- Activate your purchase/trial code
- Add your ORCID iD
Institutional access
Sign in with a library card.
- Sign in with username/password
- Recommend to your librarian
- Institutional account management
- Get help with access
Access to content on Oxford Academic is often provided through institutional subscriptions and purchases. If you are a member of an institution with an active account, you may be able to access content in one of the following ways:
IP based access
Typically, access is provided across an institutional network to a range of IP addresses. This authentication occurs automatically, and it is not possible to sign out of an IP authenticated account.
Sign in through your institution
Choose this option to get remote access when outside your institution. Shibboleth/Open Athens technology is used to provide single sign-on between your institution’s website and Oxford Academic.
- Click Sign in through your institution.
- Select your institution from the list provided, which will take you to your institution's website to sign in.
- When on the institution site, please use the credentials provided by your institution. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
- Following successful sign in, you will be returned to Oxford Academic.
If your institution is not listed or you cannot sign in to your institution’s website, please contact your librarian or administrator.
Enter your library card number to sign in. If you cannot sign in, please contact your librarian.
Society Members
Society member access to a journal is achieved in one of the following ways:
Sign in through society site
Many societies offer single sign-on between the society website and Oxford Academic. If you see ‘Sign in through society site’ in the sign in pane within a journal:
- Click Sign in through society site.
- When on the society site, please use the credentials provided by that society. Do not use an Oxford Academic personal account.
If you do not have a society account or have forgotten your username or password, please contact your society.
Sign in using a personal account
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members. See below.
A personal account can be used to get email alerts, save searches, purchase content, and activate subscriptions.
Some societies use Oxford Academic personal accounts to provide access to their members.
Viewing your signed in accounts
Click the account icon in the top right to:
- View your signed in personal account and access account management features.
- View the institutional accounts that are providing access.
Signed in but can't access content
Oxford Academic is home to a wide variety of products. The institutional subscription may not cover the content that you are trying to access. If you believe you should have access to that content, please contact your librarian.
For librarians and administrators, your personal account also provides access to institutional account management. Here you will find options to view and activate subscriptions, manage institutional settings and access options, access usage statistics, and more.
Our books are available by subscription or purchase to libraries and institutions.
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Rights and permissions
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
- Postgraduate
Research degrees
- Examples of Research proposals
- Apply for 2024
- Find a course
- Accessibility
Examples of research proposals
How to write your research proposal, with examples of good proposals.
Research proposals
Your research proposal is a key part of your application. It tells us about the question you want to answer through your research. It is a chance for you to show your knowledge of the subject area and tell us about the methods you want to use.
We use your research proposal to match you with a supervisor or team of supervisors.
In your proposal, please tell us if you have an interest in the work of a specific academic at York St John. You can get in touch with this academic to discuss your proposal. You can also speak to one of our Research Leads. There is a list of our Research Leads on the Apply page.
When you write your proposal you need to:
- Highlight how it is original or significant
- Explain how it will develop or challenge current knowledge of your subject
- Identify the importance of your research
- Show why you are the right person to do this research
- Research Proposal Example 1 (DOC, 49kB)
- Research Proposal Example 2 (DOC, 0.9MB)
- Research Proposal Example 3 (DOC, 55.5kB)
- Research Proposal Example 4 (DOC, 49.5kB)
Subject specific guidance
- Writing a Humanities PhD Proposal (PDF, 0.1MB)
- Writing a Creative Writing PhD Proposal (PDF, 0.1MB)
- About the University
- Our culture and values
- Academic schools
- Academic dates
- Press office
Our wider work
- Business support
- Work in the community
- Donate or support
Connect with us
York St John University
Lord Mayor’s Walk
01904 624 624
York St John London Campus
6th Floor Export Building
1 Clove Crescent
01904 876 944
- Policies and documents
- Module documents
- Programme specifications
- Quality gateway
- Admissions documents
- Access and Participation Plan
- Freedom of information
- Accessibility statement
- Modern slavery and human trafficking statement
© York St John University 2024
Colour Picker
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua. Dui id ornare arcu odio.
Felis bibendum ut tristique et egestas quis ipsum. Et netus et malesuada fames ac turpis egestas. Faucibus pulvinar elementum integer enim neque volutpat ac. Hac habitasse platea dictumst vestibulum rhoncus.
Nec ullamcorper sit amet risus nullam eget felis eget. Eget felis eget nunc lobortis mattis aliquam faucibus purus.
- Privacy Policy

Home » How To Write A Research Proposal – Step-by-Step [Template]
How To Write A Research Proposal – Step-by-Step [Template]
Table of Contents

How To Write a Research Proposal
Writing a Research proposal involves several steps to ensure a well-structured and comprehensive document. Here is an explanation of each step:
1. Title and Abstract
- Choose a concise and descriptive title that reflects the essence of your research.
- Write an abstract summarizing your research question, objectives, methodology, and expected outcomes. It should provide a brief overview of your proposal.
2. Introduction:
- Provide an introduction to your research topic, highlighting its significance and relevance.
- Clearly state the research problem or question you aim to address.
- Discuss the background and context of the study, including previous research in the field.
3. Research Objectives
- Outline the specific objectives or aims of your research. These objectives should be clear, achievable, and aligned with the research problem.
4. Literature Review:
- Conduct a comprehensive review of relevant literature and studies related to your research topic.
- Summarize key findings, identify gaps, and highlight how your research will contribute to the existing knowledge.
5. Methodology:
- Describe the research design and methodology you plan to employ to address your research objectives.
- Explain the data collection methods, instruments, and analysis techniques you will use.
- Justify why the chosen methods are appropriate and suitable for your research.
6. Timeline:
- Create a timeline or schedule that outlines the major milestones and activities of your research project.
- Break down the research process into smaller tasks and estimate the time required for each task.
7. Resources:
- Identify the resources needed for your research, such as access to specific databases, equipment, or funding.
- Explain how you will acquire or utilize these resources to carry out your research effectively.
8. Ethical Considerations:
- Discuss any ethical issues that may arise during your research and explain how you plan to address them.
- If your research involves human subjects, explain how you will ensure their informed consent and privacy.
9. Expected Outcomes and Significance:
- Clearly state the expected outcomes or results of your research.
- Highlight the potential impact and significance of your research in advancing knowledge or addressing practical issues.
10. References:
- Provide a list of all the references cited in your proposal, following a consistent citation style (e.g., APA, MLA).
11. Appendices:
- Include any additional supporting materials, such as survey questionnaires, interview guides, or data analysis plans.
Research Proposal Format
The format of a research proposal may vary depending on the specific requirements of the institution or funding agency. However, the following is a commonly used format for a research proposal:
1. Title Page:
- Include the title of your research proposal, your name, your affiliation or institution, and the date.
2. Abstract:
- Provide a brief summary of your research proposal, highlighting the research problem, objectives, methodology, and expected outcomes.
3. Introduction:
- Introduce the research topic and provide background information.
- State the research problem or question you aim to address.
- Explain the significance and relevance of the research.
- Review relevant literature and studies related to your research topic.
- Summarize key findings and identify gaps in the existing knowledge.
- Explain how your research will contribute to filling those gaps.
5. Research Objectives:
- Clearly state the specific objectives or aims of your research.
- Ensure that the objectives are clear, focused, and aligned with the research problem.
6. Methodology:
- Describe the research design and methodology you plan to use.
- Explain the data collection methods, instruments, and analysis techniques.
- Justify why the chosen methods are appropriate for your research.
7. Timeline:
8. Resources:
- Explain how you will acquire or utilize these resources effectively.
9. Ethical Considerations:
- If applicable, explain how you will ensure informed consent and protect the privacy of research participants.
10. Expected Outcomes and Significance:
11. References:
12. Appendices:
Research Proposal Template
Here’s a template for a research proposal:
1. Introduction:
2. Literature Review:
3. Research Objectives:
4. Methodology:
5. Timeline:
6. Resources:
7. Ethical Considerations:
8. Expected Outcomes and Significance:
9. References:
10. Appendices:
Research Proposal Sample
Title: The Impact of Online Education on Student Learning Outcomes: A Comparative Study
1. Introduction
Online education has gained significant prominence in recent years, especially due to the COVID-19 pandemic. This research proposal aims to investigate the impact of online education on student learning outcomes by comparing them with traditional face-to-face instruction. The study will explore various aspects of online education, such as instructional methods, student engagement, and academic performance, to provide insights into the effectiveness of online learning.
2. Objectives
The main objectives of this research are as follows:
- To compare student learning outcomes between online and traditional face-to-face education.
- To examine the factors influencing student engagement in online learning environments.
- To assess the effectiveness of different instructional methods employed in online education.
- To identify challenges and opportunities associated with online education and suggest recommendations for improvement.
3. Methodology
3.1 Study Design
This research will utilize a mixed-methods approach to gather both quantitative and qualitative data. The study will include the following components:
3.2 Participants
The research will involve undergraduate students from two universities, one offering online education and the other providing face-to-face instruction. A total of 500 students (250 from each university) will be selected randomly to participate in the study.
3.3 Data Collection
The research will employ the following data collection methods:
- Quantitative: Pre- and post-assessments will be conducted to measure students’ learning outcomes. Data on student demographics and academic performance will also be collected from university records.
- Qualitative: Focus group discussions and individual interviews will be conducted with students to gather their perceptions and experiences regarding online education.
3.4 Data Analysis
Quantitative data will be analyzed using statistical software, employing descriptive statistics, t-tests, and regression analysis. Qualitative data will be transcribed, coded, and analyzed thematically to identify recurring patterns and themes.
4. Ethical Considerations
The study will adhere to ethical guidelines, ensuring the privacy and confidentiality of participants. Informed consent will be obtained, and participants will have the right to withdraw from the study at any time.
5. Significance and Expected Outcomes
This research will contribute to the existing literature by providing empirical evidence on the impact of online education on student learning outcomes. The findings will help educational institutions and policymakers make informed decisions about incorporating online learning methods and improving the quality of online education. Moreover, the study will identify potential challenges and opportunities related to online education and offer recommendations for enhancing student engagement and overall learning outcomes.
6. Timeline
The proposed research will be conducted over a period of 12 months, including data collection, analysis, and report writing.
The estimated budget for this research includes expenses related to data collection, software licenses, participant compensation, and research assistance. A detailed budget breakdown will be provided in the final research plan.
8. Conclusion
This research proposal aims to investigate the impact of online education on student learning outcomes through a comparative study with traditional face-to-face instruction. By exploring various dimensions of online education, this research will provide valuable insights into the effectiveness and challenges associated with online learning. The findings will contribute to the ongoing discourse on educational practices and help shape future strategies for maximizing student learning outcomes in online education settings.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How To Write A Proposal – Step By Step Guide...

Grant Proposal – Example, Template and Guide

How To Write A Business Proposal – Step-by-Step...

Business Proposal – Templates, Examples and Guide

Proposal – Types, Examples, and Writing Guide

How to choose an Appropriate Method for Research?
6+ SAMPLE Medical Research Proposal in PDF | MS Word
Medical research proposal | ms word, 6+ sample medical research proposal, what is a medical research proposal, things to think about to prepare for a medical research proposal, what should the medical research proposal contain, how to structure your medical research proposal, medical researches of various types, why is funding important for medical research, what distinguishes a good research proposal from a bad one, why are you required to submit a research proposal, what is the purpose of your research proposal, and why is it crucial, how long should my research proposal be.

Medical Student Research Proposal

Medical Research Request For Proposal

Medical Health Research Project Proposal

Sample Medical Research Proposal

Bio-Medical Research Proposal

Medical Research Council Proposal
Medical Research Proposal in DOC
Share this post on your network, file formats, word templates, google docs templates, excel templates, powerpoint templates, google sheets templates, google slides templates, pdf templates, publisher templates, psd templates, indesign templates, illustrator templates, pages templates, keynote templates, numbers templates, outlook templates, you may also like these articles, 25+ sample construction company proposal in ms word.
Navigating the intricate world of construction demands a seasoned company with a proven track record. Our comprehensive guide on the Construction Company Proposal is your blueprint to understanding the…
8+ SAMPLE Drama Proposal in PDF

Julia Child said: “Drama is very important in life: You have to come on with a bang. You never want to go out with a whimper. Everything can have…
browse by categories
- Questionnaire
- Description
- Reconciliation
- Certificate
- Spreadsheet
Information
- privacy policy
- Terms & Conditions
All Formats
Table of Contents
Proposal template bundle, 5 steps to make a medical research proposal, step 1: collect source material, step 2: devise a plan, step 3: identify problems, step 4: set goals, step 5: evaluate and assess, 17+ medical research proposal templates, 1. simple medical research proposal template, 2. undergraduate medical student research proposal, 3. medical research proposal template, 4. sample medical research proposal, 5. medical clinical research proposal example, 6. medical study research proposal in pdf, 7. basic medical research proposal in pdf, 8. medical ph.d. project research proposal, 9. bio-medical pharmacology research proposal template, 10. medical public health issues research proposal in pdf, 11. medical research request for proposal, 12. medical research proposal format, 13. medical student research proposal in pdf, 14. medical research proposal submission form, 15. medical research proposal format in doc, 16. medical research proposal in doc, 17. simple medical thesis research proposal template, 18. medical research proposal letter template, proposal templates, 17+ medical research proposal templates in pdf | doc.
To create a medical research proposal, you need to find valuable information and create a complicated document. The proposal is mainly devised for investors, academic heads, or other people who would value the legitimacy of your project proposal and assess the merit. For successful research proposals, you need to follow certain guidelines for efficiency. We have all sorts of medical research proposal templates for users with specific needs. Whether it’s for a clinical Ph.D. research on public health issues or an undergraduate letter over pharmacology, we got them all right here. Or if you are wondering, you can use proposal templates that bring ready-made documents for your benefit!

- Google Docs
- Apple Pages

More in Proposal Templates
Hospital medical certificate template, medical certificate for casual leave template, hospital death certificate template, online medical report template, medical summary report template, medical incident report template, medical report template, patient report template, clinical evaluation report template, medical status report template.
- Proposal Templates – 170+ Free Word, PDF, Format Download!
- 57+ Training Proposal Templates in PDF | Google Docs | MS Word | Pages
- 7+ Logistics Proposal Templates in PDF
- 13+ Recruitment Proposal Templates in Google Docs | MS Word | Pages | PDF | MS Excel
- 12+ Logistics Business Proposal Templates in PDF
- 67+ Project Proposal in PDF , Docs
- 39+ Sponsorship Proposal Templates – Free Word, Excel, PDF Format Download!
- 23+ Funding Proposal Templates – DOC, PDF, Excel, Apple Pages, Google Docs
- 22+ Bid Proposal Templates – Word, PDF, Google Docs, Apple Pages
- 16+ School Project Proposal Templates – Word, PDF
- 11+ Product Business Proposal Templates – Sample, Example
- 10+ Travel Insurance Document Templates in Google Docs | Google Sheets | Excel | Word | Numbers | Pages | PDF
- 10+ Longevity Insurance Document Templates in Google Docs | Word | Pages | PDF
- 10+ Auto Insurance Templates in Google Docs | Word | Pages | PDF
- 10+ Homeowners Insurance Templates in Google Docs | Word | Pages | PDF
File Formats
Word templates, google docs templates, excel templates, powerpoint templates, google sheets templates, google slides templates, pdf templates, publisher templates, psd templates, indesign templates, illustrator templates, pages templates, keynote templates, numbers templates, outlook templates.

Medical Proposal

If you are looking for medical proposal templates , this article is for you. We’ve put together a list of 10 options that you’ll find useful. Each template is available for free download. So, instead of creating yours from scratch, you can download any of these and it as a guide and inspiration to write a good medical proposal. Check them out below.
Best Medical Proposal Examples & Templates
1. sample medical proposal template.

- Google Docs
Size: A4, US
Your medical idea may be the next big thing. In fact, the idea may just be one of the best services you can offer your community. But, you need to remember that your ideas can’t come to fruition unless you are sure it’s something people would be willing to buy. This calls for a comprehensive proposal . If your medical service proposal clicks, you can be sure that different people will buy your idea and support you in whatever way you need. The best way to start writing a proposal fast is to use a custom medical proposal template. And here is a unique example that you’ll definitely love.
2. Simple Medical Business Proposal Template

Why would anyone choose to work with your medical business and not your competitor? This is an important question. In essence, it helps you to determine if the medical business would be useful to the target audience. But how exactly do you write a proposal that will get the hook you need? You can do so by doing research. Then, you can use the data that you collected to justify the content of your document. Now that you have collected the data you need, it’s time to put it into a professional format using a high-quality medical proposal template. Download this example.
3. Printable Medical Proposal Template
Size: 64 KB
People write medical proposals for two reasons. First, they want to communicate and implement ideas they believe will help the community. Second, they need to secure support from different bodies to realize the goal of the medical project. However, many of these proposals fail because they don’t address a problem in-depth. If you want your medical project proposal to gain the attention it deserves, you need to prove that it can solve a problem in the best way possible. The best way to go about this is to do your research and come up with concrete information. Check this sample for inspiration.
4. Medical Research Template Example

Size: 294 KB
So you have a medical research topic that you would like to work on. And you are certain that the subject can help many people in the community. However, you don’t have a reasonable budget plan to fund the project. What do you do? Well, the best thing would be to write a comprehensive medical proposal. Then, share it with entities you would like to help you. Remember, a good medical research proposal is the one that highlights the problem of concern as well as the objective of the research. Check out this sample template for more ideas. The file is free to download.
5. Business Proposal for Medical Coding Solutions

Size: 463 KB
Medical coding is a business in demand. At least you have an opportunity to give it a shot because there is a thriving market out there. But first, you need to start with the basics. You need to do your research, understand your target, and then write them a proposal. The proposal here is more like your marketing pitch . So, you need to make sure the proposal is clear, comprehensive, and communicate the right message to the right audience. Here is a well-written example that you should have a look at. This template is free to download, just click the link above.
6. Printable Medical Billing Proposal Template

Size: 108 KB
Did you know that there is a high demand for medical billing services today? So, if you are skilled and have experience in this area, there is a market out there waiting for you. Your success rate depends on how you market your services . You first need to have a unique proposal that your potential buyer won’t help but look read. And if you can capture their attention with your proposal, you bet that’s marketing half done. So, how do you write a good medical billing proposal? You can do that by getting ideas from this sample proposal template. You can download the template for free by clicking the download link above.
7. Simple Research Proposal Template

Writing a medical research proposal isn’t difficult. But there are rules to follow. At the very least, you need to spend time brainstorming ideas. Remember, the goal of your proposal is to win your target over. And if you nail it in the brainstorming stage, you can attract attention to the actual proposal. A good proposal is clear and direct to the point. Grab the attention of your target with the title of the proposal. If you do, you have their attention. The document should also show a list of your aims (objectives). Download this sample template and check the format of the research proposal.
8. Medical Grant Proposal Checklist

Size: 65 KB
Maybe you have never written a medical grant proposal and you are looking for a good example to use as a guide. Or, maybe it has been a while since you wrote one and you are just looking for some inspiration. Whatever the case, you will find this example template quite useful. Click the link above to download this document for free.
9. Mobile Medical Care Project Proposal

Size: 137 KB
If you would like to pitch your mobile medical project ideas to a specific audience, you will need to write a mobile medical proposal. Check out this sample proposal template for some ideas. The template is available for free download.
10. Medical Service Proposal Template

Size: 157 KB
Would you like to request for a proposal for a medical service fast? There is an easier way to do that. You only need a well-written template and you are good to get started. Here’s a sample template that you can download and use.
Proposal Maker
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Generate a proposal for a new school recycling program
Compose a proposal for a school field trip to a science museum.

COMMENTS
steps. It begins with selecting a study topic, reviewing. the literature, setting goals, choosing a study design and. appropriate statistical tools, and formulating a research proposal. to obtain ...
It puts the proposal in context. 3. The introduction typically begins with a statement of the research problem in precise and clear terms. 1. The importance of the statement of the research problem 5: The statement of the problem is the essential basis for the construction of a research proposal (research objectives, hypotheses, methodology ...
1 Sample Research Proposal Resident: John Smith, PGY2 Research Mentor: Jane Doe, MD, Section of General Internal Medicine Date of Proposal: February 5, 2009 I. Title of Proposed Research Project Medical Students as Mediators of Change in Tobacco Use II. Specific Aims In conducting this study, we will accomplish the following specific aims:
Research proposal examples. Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: "A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management" Example research proposal #2: "Medical Students as Mediators of ...
Writing the proposal of a research work in the present era is a challenging task due to the constantly evolving trends in the qualitative research design and the need to incorporate medical advances into the methodology. ... The details pertaining to sample size are discussed in the article "Sample size calculation: Basic priniciples ...
Common statistical errors in research proposals include lack of sample size/power calculations, treating continuous variables as dichotomous, repeated t tests when a more comprehensive modeling approach should be taken, application of statistical tests that assume normality without verifying assumptions, failure to consider covariate effects ...
ISP Proposal Samples. Analysis of a. Scientific or. Medical Problem. Community Service & Leadership. Medical Education. Scientific Research. Focused Clinical Multidisciplinary. SMP1 - [71 kb]
Research proposal examples. Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: 'A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management' Example research proposal #2: 'Medical Students as Mediators of ...
Science*. Writing / standards*. Knowing how to properly prepare a research proposal is a real challenge - and being able to prepare an excellent research proposal is increasingly a requirement to compete for funding with assurances of success. With this in mind, we aim to share with the reader our experience (in many cases, unsucc ….
Typical stages in a research proposal. 1. The purpose of a research proposal is: To help to focus on a relevant and current topic. To identify a gap or inadequacy in the research literature. To make sure that these are your ideas, and to help you to focus and crystallise your ideas.
Abstract: This is a brief (300-500 words) summary that includes the research question, your rationale for the study, and any applicable hypothesis. You should also include a brief description of your methodology, including procedures, samples, instruments, etc. Introduction: The opening paragraph of your research proposal is, perhaps, the most ...
Introduction. Research is an activity aimed at obtaining new knowledge and applying it to solve problems or questions. Scientific research, in particular, uses the steps of scientific method to study a certain aspect of reality, either theoretically or experimentally. 1 The basis of the research process is the research proposal or protocol, a document that outlines in detail the organisation ...
research grant proposal. − Receiving relevant and up-to-date information about new research methods. − Establishing collaborative associations with peers. − Constructive feedback on research proposals and throughout the research process. − Assistance in the development of a long-term research and writing plan.
Research Proposal Template Biomedical Research: General Page 2 Methods . Human Subjects This section describes your proposed study population and, if the study is prospective, how you will identify and enroll participants and obtain their informed consent. The bulleted list gives examples of elements you may need to describe (the first three items
If you plan to apply for a medical education research grant, writing a strong proposal can help you rise above the competition. These expert recommendations will be useful as you pursue future funding opportunities.. Writing a compelling grant proposal requires strategic thinking and research, especially if you want to increase your chances of attracting a particular funder, according to a ...
A medical research proposal sample is a great way to understand what your proposal should look like. It can give you the structure and guidance needed to create a successful proposal. Well-written medical research proposals help researchers stand out from other applicants and boost their chances of being selected or funded.
The research proposal serves many purposes to many different parties. Amongst these purposes, some of the key ones are: Acting as a route map and timetable for all involved in your project. Giving a clear overview of your planned work to ensure favourable decision at ethical review.
Research proposals. Your research proposal is a key part of your application. It tells us about the question you want to answer through your research. It is a chance for you to show your knowledge of the subject area and tell us about the methods you want to use. We use your research proposal to match you with a supervisor or team of supervisors.
Here is an explanation of each step: 1. Title and Abstract. Choose a concise and descriptive title that reflects the essence of your research. Write an abstract summarizing your research question, objectives, methodology, and expected outcomes. It should provide a brief overview of your proposal. 2.
Step 5: Tie Loose Ends. Finish your proposal with a few lines that summarize the problem, solution, and benefits. Restate essential concepts or data you want your audience to remember in your proposal to make it stand out. Examine your proposal for consistency of thought and to see if the components work together.
Medical Clinical Research Proposal Example. bumc.bu.edu. Details. File Format. PDF; Size: 102 KB Download Now. Having this Medical Research Proposal Example with you will simplify a lot of problems for your proposed research. This is an example of a well-written research proposal so that you don't have to look for more elsewhere. With goals ...
Sample Applications & More. Several NIAID investigators have graciously agreed to share their exceptional applications and summary statements as samples to help the research community. Below the list of applications, you'll also find example forms, sharing plans, letters, emails, and more. Find more guidance at NIAID's Apply for a Grant.
Size: 137 KB. Download. If you would like to pitch your mobile medical project ideas to a specific audience, you will need to write a mobile medical proposal. Check out this sample proposal template for some ideas. The template is available for free download. 10. Medical Service Proposal Template. ftp.ci.missoula.mt.us. Details.
Step 4: Define the Project Deliverables. Defining your project deliverables is a crucial step during the project proposal process. Stakeholders want to know just what it is you're going to be delivering to them at the end of the project. This could be a product, a program, an upgrade in technology or something similar.