
Expert business plan and financial models


How to Present Your Business’ Location & Facility
- September 4, 2024

When drafting a business plan, detailing your business’s location and facility is not merely about stating an address or describing a building. Instead it’s about showcasing how your choice of location and the specifics of your facility are important to your business’s success.
This section of your business plan goes beyond mere logistics. Indeed it communicates to potential investors, partners, and lenders the thought process behind selecting a location that enhances market visibility, customer access, and operations efficiency.
In this guide, we’ll guide you through the importance of these elements and how to incorporate them in your business plan. Let’s dive in!
Why Do We Include it in a Business Plan?
In a business plan, the section on a business’s location and facility is crucial for providing readers with essential context about where and how the company operates.
This information typically resides in the business overview section. It should includes details on location and facilities helps stakeholders understand the strategic choices behind site selection. Especially it should be clear as how these decisions support the business’s operations, market presence (visibility), and growth potential.
It conveys to investors, lenders, and partners the thoughtfulness behind location selection (highlighting access to markets, resources, and talent – see more on that below) while the description of the facility underscores the business’s capacity for production, service delivery, and scalability.
Why Location is Important
The choice of location and facility is more than just a logistical decision; it is a strategic one that can significantly influence the overall success and growth trajectory of a business.
Indeed, a prime location enhances visibility, ensuring your business is easily accessible and noticeable to your target market . This visibility is crucial for attracting foot traffic in retail, but it’s equally important for businesses in the service sector to be within reach of their client base.
Furthermore, being situated in a vibrant, thriving area can boost brand recognition and help in crafting a strong, positive public perception.
Simplify operations
Operational efficiency is yet another factor directly impacted by the choice of location. The right location minimizes logistical hurdles and can significantly reduce costs and time associated with transportation and distribution.
For businesses that rely heavily on shipping or receiving goods, being near major highways, ports, or logistics hubs can streamline operations and improve supply chain efficiency.
Access to talent
Access to talent is another critical consideration that depends heavily on location. Operating in or near urban centers or regions known for specific industries can make it easier to attract and retain skilled employees.
For example, proximity to universities, technical schools, and other educational institutions can also be beneficial, providing a steady pipeline of qualified graduates eager to join the workforce. This access to a diverse talent pool can drive innovation, enhance service delivery, and ultimately contribute to the competitive edge of a business.
Why Facility is Important
It’s very important to give details on the business’ facility especially if it is a customer-facing or a manufacturing / supply-side operations business.
For customer-facing businesses (clinics, hotels, restaurants gyms, retail stores, real estate agencies, etc.), the facility’s design, ambiance, and accessibility play a significant role in attracting and retaining customers.
For manufacturing or supply-side operations (brewery, equipment rental, courier, storage, etc.), a facility with the right technical specifications and equipment ensures quality and efficiency in production and supply chain.
Important factors to include here:
- Size and Scalability: Guide readers on choosing a facility size that not only meets current needs but also allows for future growth.
- Layout Efficiency: Discuss how the layout affects operational efficiency, employee productivity, and customer satisfaction.
- Technology and Infrastructure: Highlight the necessity of technological infrastructure and other facilities for business operations.
- Safety and Compliance: Remind readers of the importance of safety standards and compliance with regulations in facility selection.
How to Present Location and Facility in Your Business Plan
Here are 5 simple steps to present location and facility in your business plan:
- Describe the Location: Provide detailed information about the business location, including the address, the geographical area, and why this location is strategic.
- Outline the Facilities: Describe the physical premises of the business. Include details about the size, layout, capacity, and any unique features of the facility.
- Justify the Choices: Explain why the chosen location and facility are optimal for the business objectives. Include data or research that supports these choices.
- Visual Elements: Encourage the use of photographs, maps, and floor plans to give readers a visual understanding of the location and facility.
- Future Plans: Discuss any future plans for expansion or relocation, if applicable, and how this fits into the business’s growth strategy.
Related Posts

How Much It Costs to Open a Chiropractic Clinic: Examples
- September 18, 2024
- Startup Costs

How Much It Costs to Start a Medical Practice: Examples & Budget
- September 14, 2024

How Much It Costs to Start a Pilates Studio: Examples & Budget
Privacy overview.
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| BIGipServerwww_ou_edu_cms_servers | session | This cookie is associated with a computer network load balancer by the website host to ensure requests are routed to the correct endpoint and required sessions are managed. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-advertisement | 1 year | Set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin, this cookie is used to record the user consent for the cookies in the "Advertisement" category . |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| CookieLawInfoConsent | 1 year | Records the default button state of the corresponding category & the status of CCPA. It works only in coordination with the primary cookie. |
| elementor | never | This cookie is used by the website's WordPress theme. It allows the website owner to implement or change the website's content in real-time. |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| __cf_bm | 30 minutes | This cookie, set by Cloudflare, is used to support Cloudflare Bot Management. |
| language | session | This cookie is used to store the language preference of the user. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| _ga | 2 years | The _ga cookie, installed by Google Analytics, calculates visitor, session and campaign data and also keeps track of site usage for the site's analytics report. The cookie stores information anonymously and assigns a randomly generated number to recognize unique visitors. |
| _ga_QP2X5FY328 | 2 years | This cookie is installed by Google Analytics. |
| _gat_UA-189374473-1 | 1 minute | A variation of the _gat cookie set by Google Analytics and Google Tag Manager to allow website owners to track visitor behaviour and measure site performance. The pattern element in the name contains the unique identity number of the account or website it relates to. |
| _gid | 1 day | Installed by Google Analytics, _gid cookie stores information on how visitors use a website, while also creating an analytics report of the website's performance. Some of the data that are collected include the number of visitors, their source, and the pages they visit anonymously. |
| browser_id | 5 years | This cookie is used for identifying the visitor browser on re-visit to the website. |
| WMF-Last-Access | 1 month 18 hours 11 minutes | This cookie is used to calculate unique devices accessing the website. |
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Building Your Business
- Becoming an Owner
- Business Plans
How to Write the Operations Plan Section of a Business Plan
Susan Ward wrote about small businesses for The Balance for 18 years. She has run an IT consulting firm and designed and presented courses on how to promote small businesses.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/SusanWardLaptop2crop1-57aa62eb5f9b58974a12bac9.jpg)
How to Write the Operations Plan Section of the Business Plan
Stage of development section, production process section, the bottom line, frequently asked questions (faqs).
The operations plan is the section of your business plan that gives an overview of your workflow, supply chains, and similar aspects of your business. Any key details of how your business physically produces goods or services will be included in this section.
You need an operations plan to help others understand how you'll deliver on your promise to turn a profit. Keep reading to learn what to include in your operations plan.
Key Takeaways
- The operations plan section should include general operational details that help investors understand the physical details of your vision.
- Details in the operations plan include information about any physical plants, equipment, assets, and more.
- The operations plan can also serve as a checklist for startups; it includes a list of everything that must be done to start turning a profit.
In your business plan , the operations plan section describes the physical necessities of your business's operation, such as your physical location, facilities, and equipment. Depending on what kind of business you'll be operating, it may also include information about inventory requirements, suppliers, and a description of the manufacturing process.
Staying focused on the bottom line will help you organize this part of the business plan.
Think of the operating plan as an outline of the capital and expense requirements your business will need to operate from day to day.
You need to do two things for the reader of your business plan in the operations section: show what you've done so far to get your business off the ground and demonstrate that you understand the manufacturing or delivery process of producing your product or service.
When you're writing this section of the operations plan, start by explaining what you've done to date to get the business operational, then follow up with an explanation of what still needs to be done. The following should be included:
Production Workflow
A high-level, step-by-step description of how your product or service will be made, identifying the problems that may occur in the production process. Follow this with a subsection titled "Risks," which outlines the potential problems that may interfere with the production process and what you're going to do to negate these risks. If any part of the production process can expose employees to hazards, describe how employees will be trained in dealing with safety issues. If hazardous materials will be used, describe how these will be safely stored, handled, and discarded.
Industry Association Memberships
Show your awareness of your industry's local, regional, or national standards and regulations by telling which industry organizations you are already a member of and which ones you plan to join. This is also an opportunity to outline what steps you've taken to comply with the laws and regulations that apply to your industry.
Supply Chains
An explanation of who your suppliers are and their prices, terms, and conditions. Describe what alternative arrangements you have made or will make if these suppliers let you down.
Quality Control
An explanation of the quality control measures that you've set up or are going to establish. For example, if you intend to pursue some form of quality control certification such as ISO 9000, describe how you will accomplish this.
While you can think of the stage of the development part of the operations plan as an overview, the production process section lays out the details of your business's day-to-day operations. Remember, your goal for writing this business plan section is to demonstrate your understanding of your product or service's manufacturing or delivery process.
When writing this section, you can use the headings below as subheadings and then provide the details in paragraph format. Leave out any topic that does not apply to your particular business.
Do an outline of your business's day-to-day operations, including your hours of operation and the days the business will be open. If the business is seasonal, be sure to say so.
The Physical Plant
Describe the type, size, and location of premises for your business. If applicable, include drawings of the building, copies of lease agreements, and recent real estate appraisals. You need to show how much the land or buildings required for your business operations are worth and tell why they're important to your proposed business.
The same goes for equipment. Besides describing the equipment necessary and how much of it you need, you also need to include its worth and cost and explain any financing arrangements.
Make a list of your assets , such as land, buildings, inventory, furniture, equipment, and vehicles. Include legal descriptions and the worth of each asset.
Special Requirements
If your business has any special requirements, such as water or power needs, ventilation, drainage, etc., provide the details in your operating plan, as well as what you've done to secure the necessary permissions.
State where you're going to get the materials you need to produce your product or service and explain what terms you've negotiated with suppliers.
Explain how long it takes to produce a unit and when you'll be able to start producing your product or service. Include factors that may affect the time frame of production and describe how you'll deal with potential challenges such as rush orders.
Explain how you'll keep track of inventory .
Feasibility
Describe any product testing, price testing, or prototype testing that you've done on your product or service.
Give details of product cost estimates.
Once you've worked through this business plan section, you'll not only have a detailed operations plan to show your readers, but you'll also have a convenient list of what needs to be done next to make your business a reality. Writing this document gives you a chance to crystallize your business ideas into a clear checklist that you can reference. As you check items off the list, use it to explain your vision to investors, partners, and others within your organization.
What is an operations plan?
An operations plan is one section of a company's business plan. This section conveys the physical requirements for your business's operations, including supply chains, workflow , and quality control processes.
What is the main difference between the operations plan and the financial plan?
The operations plan and financial plan tackle similar issues, in that they seek to explain how the business will turn a profit. The operations plan approaches this issue from a physical perspective, such as property, routes, and locations. The financial plan explains how revenue and expenses will ultimately lead to the business's success.
Module 12: Managing Processes
Facility location and layout, learning outcomes.
- Explain facility location
- Explain facility layout
Facility Location
Of all the pieces of the planning puzzle, facility location is the most strategic and critical. Once you build a new manufacturing facility, you have made a substantial investment of time, resources, and capital that can’t be changed for a long time. Selecting the wrong location can be disastrous. Some of the key factors that influence facility location are the following:
- Proximity to customers, suppliers, and skilled labor
- Environmental regulations
- Financial incentives offered by state and local development authorities
- Quality-of-life considerations
- Potential for future expansion
The next step, after planning the production process, is deciding on plant layout—how equipment, machinery, and people will be arranged to make the production process as efficient as possible.
Practice Question
Facility layout.
After the site location decision has been made, the next focus in production planning is the facility’s layout. The goal is to determine the most efficient and effective design for the particular production process. A manufacturer might opt for a U-shaped production line, for example, rather than a long, straight one, to allow products and workers to move more quickly from one area to another.
Service organizations must also consider layout, but they are more concerned with how it affects customer behavior. It may be more convenient for a hospital to place its freight elevators in the center of the building, for example, but doing so may block the flow of patients, visitors, and medical personnel between floors and departments.
There are four main types of facility layouts: process, product, fixed-position, and cellular.
The process layout arranges workflow around the production process. All workers performing similar tasks are grouped together. Products pass from one workstation to another (but not necessarily to every workstation). For example, all grinding would be done in one area, all assembling in another, and all inspection in yet another. The process layout is best for firms that produce small numbers of a wide variety of products, typically using general-purpose machines that can be changed rapidly to new operations for different product designs. For example, a manufacturer of custom machinery would use a process layout.

Figure 1. An Example of a Process Facility Layout. Source: Adapted from Operations Management, 9th edition, by Gaither/Frazier.
Products that require a continuous or repetitive production process use the product (or assembly-line ) layout . When large quantities of a product must be processed on an ongoing basis, the workstations or departments are arranged in a line with products moving along the line. Automobile and appliance manufacturers, as well as food-processing plants, usually use a product layout. Service companies may also use a product layout for routine processing operations.

Figure 2. An Example of a Product Facility Layout. Source: Adapted from Operations Management, 9th edition, by Gaither/Frazier.
In the following video, Jansen, a Swiss steel maker, describes how the company’s offices were designed to maximize the productivity and creativity of its engineers:
You can view the transcript for “Office Space – Jansen” (opens in new window) or text alternative for “Office Space – Jansen” (opens in new window ).
Some products cannot be put on an assembly line or moved about in a plant. A fixed-position layout lets the product stay in one place while workers and machinery move to it as needed. Products that are impossible to move—ships, airplanes, and construction projects—are typically produced using a fixed-position layout. Limited space at the project site often means that parts of the product must be assembled at other sites, transported to the fixed site, and then assembled. The fixed-position layout is also common for on-site services such as housecleaning services, pest control, and landscaping.

Figure 3. An Example of a Fixed-Position Facility Layout. Source: Adapted from Operations Management, 9th edition, by Gaither/Frazier.
To see an excellent example of fixed-position layout, watch the following video that shows how Boeing builds an airplane. (Note that this video has no narration; only instrumental music. Access audio description by using the widget below the video.)
Access the text alternative for “Making of a Boeing Airplane” (opens in new window).
Cellular layouts combine some aspects of both product and fixed-position layouts. Work cells are small, self-contained production units that include several machines and workers arranged in a compact, sequential order. Each work cell performs all or most of the tasks necessary to complete a manufacturing order. There are usually five to 10 workers in a cell, and they are trained to be able to do any of the steps in the production process. The goal is to create a team environment wherein team members are involved in production from beginning to end.
- Facility Location. Authored by : Linda Williams and Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Facility Location and Layout. Authored by : Linda Williams and Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Practice Questions. Authored by : Robert Danielson. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- rover 200 framing line. Authored by : spencer cooper. Located at : https://www.flickr.com/photos/spenceyc/7481166880/ . License : CC BY-ND: Attribution-NoDerivatives
- Office Space: Jansen. Provided by : BBC. Located at : https://youtu.be/aT-eZXDLQl0 . License : CC BY-NC-ND: Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives
- Facility Layout. Provided by : OpenStax CNX. Located at : http://cnx.org/contents/[email protected] . License : CC BY: Attribution . License Terms : Download for free at http://cnx.org/contents/[email protected]
- Modification of Image: Process Facility Layout. Authored by : OpenStax CNX; Modification by Lumen Learning. Located at : http://cnx.org/contents/[email protected] . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Making of a Boeing air plane. Authored by : Dial647. Located at : https://youtu.be/-ovNi1cB7a4 . License : All Rights Reserved . License Terms : Standard YouTube License


Business Location Analysis: The Key to Strategic Decision Making
.png)
- Remove the current class from the content27_link item as Webflows native current state will automatically be applied.
- To add interactions which automatically expand and collapse sections in the table of contents, select the content27_h-trigger element, add an element trigger, and select Mouse click (tap).
- For the 1st click, select the custom animation Content 27 table of contents [Expand], and for the 2nd click, select the custom animation Content 27 table of contents [Collapse].
- In the Trigger Settings, deselect all checkboxes other than Desktop and above. This disables the interaction on tablet and below to prevent bugs when scrolling.
Table Of Content
Location, location, location! It's a mantra we've all heard before, but how many of us truly understand its significance in the business world? This isn't just about picking any spot on the map. It's about making strategic choices that propel your business towards remarkable growth and success. Let's delve into the crucial factors to consider during business location analysis.
What is business location analysis?
Business location analysis is the process of studying and evaluating potential physical locations for business operations. It's the cornerstone of strategic planning, with a powerful influence on a company's performance, profitability, and overall success. The significance of choosing the right location cannot be overstated—it provides easy access to customers, employees, and suppliers, and can greatly enhance your brand's visibility.
Choosing the right business location is a crucial step in your company's journey. It's more than just a place—it's the setting for your story and the stage for your success.
Why do businesses use location analysis?

Location analysis pops up as a champion in the realm of business operations, offering a strategic edge to businesses across the globe. It's more than just pinning a spot on the map – it's about designing a roadmap to successful business outcomes. It's the silent hero behind boosting your business' competitive edge, accessibility, and brand visibility.
1. Competitive Edge: Become the Market Leader
Location analysis aids in identifying the best locales to set foot in, where competition is minimal and opportunities are abundant. This is where the magic of strategic positioning comes into play.
By understanding the competition landscape, businesses can strategically place themselves in a position that sets them apart, helping them get ahead in the race.
2. Customer Accessibility: Be Where Your Customers Are
Location analysis also plays a vital role in making businesses more accessible to customers. It’s not about being in the most popular spot, but being in the right spot where customers can easily find and reach you.
- Convenience: A location that's easy for customers to reach can significantly boost your business.
- Visibility: Being in a spot where you’re easily seen can naturally attract more customers.
3. Brand Visibility: Shine Above the Rest
Brand visibility is about more than just being seen – it’s about being remembered. Location analysis helps position your business in an area that not only garners high foot traffic, but also aligns with your brand identity.
Whether it's a bustling city center or a serene suburb, the right location can amplify your brand’s presence, ensuring you're not just seen, but also remembered.
4. Optimizing Operational Efficiency
Location analysis optimizes business efficiency. A strategic location enhances logistics, influencing factors such as supply chain efficiency , distribution convenience, delivery speed, and employee commute. The right location streamlines operations, saving time and resources.
Beyond operations, an ideal location grants access to crucial business services like banking, legal, and marketing consultancy. It facilitates not just survival, but also growth.
Because when we think location, we think efficiency. And in business, efficiency isn't just a buzzword - it's a lifeline. So, are you ready to optimize?
Components of Effective Business Location Analysis:

Data Collection:
Any savvy entrepreneur knows that location is key. But how do you determine the right location for your business? It starts with data collection. You'll need to gather and analyze a variety of data types to make an informed decision. Let's break it down:
- Demographic Data: This is the first type of information you need. Who are your customers? What are their ages, income levels, and occupations? You'll want a location surrounded by your target demographic.
- Traffic Data: How many people walk or drive by the potential location each day? More foot traffic could lead to more customers. But remember, that traffic needs to align with your target demographic.
- Competition Data: What other businesses are in the area? Other businesses could be complementary, boosting your sales. Or they could be competitors, potentially taking away customers.
Remember, data should guide your decision, but it shouldn't make it. Use the data to inform your choices and align them with your business goals.
It's a tricky balance, but armed with the right data, you can make a choice that sets your business up for success.
2. Spatial Analysis & Visualization:
Gas Station Density in Saudi Arabia's Key Regions
When it comes to running a successful business, location is key. That's where Spatial Analysis and Visualization come into play, taking us on a deep dive into the world of Geographic Information Systems (GIS).
GIS serves as a powerful tool in the analysis and interpretation of geographic relationships, patterns, and trends. It integrates hardware, software, and data to capture, store, analyze, and interpret all forms of geographically referenced information. Essentially, it allows us to view and understand data in ways that reveal relationships, patterns, and trends in the form of maps, globes, reports, and charts.
"A Geographic Information System (GIS) helps businesses to visualize, question, analyze, and interpret data to understand relationships, patterns, and trends."
- Mapping: GIS converts complex data into a visual format, simplifying the process of decision making. It can display demographic data, consumer behavior, and competitor locations in an easy-to-understand map.
- Analysis: GIS analyzes the data to identify patterns and trends. It provides insights into the best locations for business expansion or the areas that are most profitable.
Incorporating GIS into your business location analysis allows you to make informed decisions based on concrete data. It's like turning on a light in a dark room, illuminating opportunities and potential challenges that were previously hidden.
Benefits of Using GISExamplesEnhanced Decision MakingChoosing the best location for a new store or officeImproved CommunicationVisualizing potential business growth areas for stakeholdersIncreased EfficiencyRouting deliveries to reduce fuel consumption and save time
As we dive deeper into the realm of location analysis, it's crucial to recognize the role of Geographic Information System (GIS). In today's tech-savvy world, GIS tools are transforming the way businesses analyze their location choices. These powerful tools offer a range of benefits, all contributing to a more informed and smart decision making.
3. Predictive Analytics:

Imagine having a crystal ball that foretells how your business would fare in different locations before you even set foot there. That's precisely what predictive analytics offers! This remarkable blend of technology and statistical methods can help you anticipate potential performance in various locations based on historical data, customer behavior, market trends, and more.
How does it work?
- Predictive models gather data: First, these tools collect a wealth of valuable data from various sources, such as customer databases, demographic information, and market research.
- They analyze the data: Next, they use advanced algorithms to analyze this data, identifying patterns and trends that could impact business performance.
- They forecast future outcomes: Based on these patterns, the models can then make predictions about how a business might perform in different locations.
Businesses can use these forecasts to guide their location-based decisions, helping them choose spots with the highest potential for success. But remember, while predictive analytics can be an incredibly valuable tool, it's not infallible. It's always important to consider other factors, such as your business goals, target audience , and competition, to make the most informed decision possible.
Ultimately, predictive analytics is like a compass guiding your business through the complex landscape of location-based decision-making. It helps you avoid the pitfalls of choosing a location based on gut feelings alone and increases your chances of setting up shop in the most favorable locations.
Real-world Applications and Success Stories:
Let's look at some real-world applications and success stories that exemplify the power of strategic business location analysis.
Case Study 1: Starbucks
Starbucks, a global coffee juggernaut, is renowned for its strategic location choices. The company uses a sophisticated location analysis system, incorporating data like traffic flow, area demographics, and nearby businesses. This strategy has been key in their worldwide growth and success. source
Case Study 2: Walmart
Walmart, a multinational retail corporation, stands as a testament to the effectiveness of location analysis. The company focuses on establishing its stores in small towns, where competition is minimal. This strategy, combined with its vast product range and competitive pricing, has led to Walmart's dominance in the retail market. source
Case Study 3: McDonald's
McDonald's, a global fast-food chain, attributes much of its success to location analysis. The company strategically places its restaurants near highway exits, busy city centers, and suburbs. This approach, paired with their quick service and popular menu, has solidified McDonald's status as a fast-food leader. source
In conclusion, these case studies highlight the immense power of location analysis in business strategy. It demonstrates how, with careful consideration and smart decision-making, businesses can leverage location to maximize brand visibility, profitability, and growth.
Challenges in Business Location Analysis:
Choosing a business location is akin to playing a high-stakes game of chess. One wrong move can spell disaster for your venture. Yet, while choosing the right location can be daunting, understanding common pitfalls can ease the process.
- Common Pitfalls and Misconceptions: Many entrepreneurs fall prey to the misconception that a cheap location means higher profits. It's crucial to understand that a location's value is not solely determined by its cost, but also by its accessibility, demographic alignment, and potential for growth. Weigh these factors before making a decision.
- Overcoming Data Inaccuracies: Quality data is the bedrock of informed decision-making. Ensure the data you base your choice on is accurate, up-to-date, and relevant. Misinterpreted or outdated data can lead to costly mistakes.
- The Evolving Nature of Neighborhoods and Local Markets: Neighborhoods and markets are fluid, continually changing and evolving. A location that seems perfect today might not be the same in a few years. Always consider long-term projections and future growth trends in your analysis.
Remember: You're not just choosing a location, you're choosing a future. Make sure it's one where your business can thrive.
How xMap Can Empower Your Location Analysis?
Unlock the potential of your business with xMap , a cutting-edge platform that transforms location analysis. With a plethora of features at your disposal, xMap empowers you to make strategic, data-backed decisions about your business location. Here's how:
- Data Visualization:
xMap's intuitive interface presents data in a visually appealing and easy-to-understand format. This enables businesses to analyze complex data sets effectively and make informed location decisions.
- Comprehensive Database:
database of all the restaurants in dubai with their key information
With xMap, gain access to a vast database of demographic, geographic, and economic data that can be crucial in selecting the perfect location for your business.
- Advanced Analytics:
Use the power of xMap's advanced analytics to uncover hidden patterns, trends, and insights that can significantly impact your location strategy.
With xMap, the power to choose the right location for your business is literally at your fingertips. The platform's unique combination of data richness and user-friendly design makes it an invaluable tool for businesses of all sizes.
Now, let's talk benefits. The advantages of incorporating xMap into your business strategy are manifold:
- Increased Profitability: By providing you with actionable insights based on data, xMap aids in selecting locations that promise maximum profitability.
- Improved Decision Making: xMap's data visualization and advanced analytics facilitate better, quicker decision-making, saving valuable time and resources.
- Competitive Edge: With access to comprehensive data and analytics, you can stay ahead of the competition and identify untapped market opportunities.
Ready to take your business to new heights? Don't wait any longer to harness the power of location analytics with xMap. Whether you're a small startup or a well-established corporation, xMap has got you covered. Explore xMap today or get in touch for a personalized demo.

Subscribe for advanced Data analysis Tips and Reports

Get in Touch
Whatever your goal or project size, we will handle it. We will ensure you 100% satisfication.
"We focus on delivering quality data tailored to businesses needs from all around the world. Whether you are a restaurant, a hotel, or even a gym, you can empower your operations' decisions with geo-data.”


What is Plant Location? Factors, Analysis, Significance, Selection Criteria
- Post last modified: 3 September 2023
- Reading time: 16 mins read
- Post category: Production Management

What is Plant Location?
Plant location refers to the process of selecting a suitable site or place for establishing a manufacturing facility or industrial plant. It is a critical decision for businesses, as the location of a plant can significantly impact the company’s overall success and competitiveness. Plant location considerations are important across various industries, including manufacturing, agriculture, energy generation, and more.
Table of Content
- 1 What is Plant Location?
- 2.1 Availability of Raw Materials
- 2.2 Proximity to Market
- 2.3 Transportation
- 2.4 Availability of Labour
- 2.5 Availability of Power, Fuel or Gas
- 2.6 Supply of Water
- 2.7 Climatic Conditions
- 3 Location Analysis
- 4 Significance of Plant Location
- 5.1 Materials
- 5.2 Machinery
- 5.4 Safety and Security
- 5.5 Future Operations
Entrepreneurs face a major problem with plant location in deciding the best location for their factory or plant. The utmost care must be exercised in selecting the plant location and many different factors must be taken into account. Primarily, the plant must be located where the minimum cost of production and distribution can be obtained but, other factors such as room for expansion and safe living conditions for plant operation as well as the surrounding community are also important. The location of the plant can also have a crucial effect on the profitability of a project.
For example, Consumer industries like televisions, washing machines and other luxury goods are set up near the marketing centers, while producer industries like steel mills are located near the vicinity of raw materials. Plant location is the choice of region and the site selection to set up a business or a factory.
The choice is primarily made after considering all the benefits and costs of various alternative areas. Moreover, it is a strategic plan which cannot be changed after deciding. The location chosen should be selected according to the specific circumstances and requirements. Each entrepreneur has an individual plant and makes an optimum attempt.
Factors Influencing Plant Location
There are several factors that influence plant location. Moreover, moving forward by resolving all other problems and considering these factors leads to success in business. The major factors affecting the plant location are listed as follows:
Availability of Raw Materials
Proximity to market, transportation, availability of labour, availability of power, fuel or gas, supply of water, climatic conditions.
The source of raw materials is one of the most important factors influencing the selection of a plant location. Attention should be given to the purchased price of raw materials, distance from the source of supply, freight and transportation expenses, availability and reliability of supply, purity of raw materials and storage requirements.
The location of markets or intermediate distribution centers affect the cost of product distribution and time required for shipping. Proximity to major markets is important consideration in the selection of the plant location because the buyer usually finds advantageous to purchase from near-by sources.
The transportation of materials and products to and from plant will be an overriding consideration in the selection of plant location. If practicable, a site that it is close to at least two major forms of transport: road, rail, waterway or a seaport, should be selected. Road transport is being increasingly used, and is suitable for local distribution from a central warehouse.
Rail transport will be cheaper for long-distance transport. If possible, the plant location should have access to all three types of transportation. There is usually a need for convenient rail and air transportation facilities between the plant and the main company headquarters, and the effective transportation facilities for the plant personnel are necessary.
Labour will be needed for the construction of plant and its operation. Skilled construction workers will usually be brought in from outside the site, but there should be an adequate pool of unskilled labours available locally; and labour suitable for training to operate the plant. Skilled tradesmen will be needed for plant maintenance. Local trade union customs and restrictive practices will have to be considered when assessing the availability and suitability of labour for recruitment and training.
It is important for an organisation to ensure the continuous supply of power, fuel and gas before selecting a plant location. For example, the location of thermal power plants and steel plants near coal fields is crucial for reducing cost of the fuel transportation.
Water is important for survival. It is required for processing in industries like chemical, sugar and paper industries. Also, water is used for drinking and sanitary purposes. It is important for an organisation to investigate a quality and probable source of supply. In addition, the chemical properties like hardness, alkalinity and acidity level of water should be checked. Apart from that, a thorough study should be conducted related to the disposal of water like effluents, solids, chemicals and other waste products.
The climate of a region where the plant is to be located has great impact on both capital and operational costs. Various aspects related to climatic conditions to be considered by an organisation include the level of snow fall or rain fall in the region, humidity, velocity of wind, frequency of natural calamities and so on.
In most plant locations, the target is to reduce cost. Some items of cost, like freight, could also be higher for one city and lower for the other city, but power costs, for instance, may have the reverse pattern. A little labour supply may cause labour rates to be bid up beyond rates measured during a location survey.
The sort of labour available may indicate future training expenditures. Thus, although a comparative analysis of varied locations may point toward one community, an appraisal of intangible factors could also be the idea of the choice to pick another. The example of a managerial decision with multiple criteria, where trade-offs must be made between the varied values and criteria.
Location Analysis
Every organisation attempts to find an ideal or optimum location. An optimum location is a place where the product cost is less with a huge market share and less risk. To find such location, an organisation needs to perform vast analysis. Business location analysis is a reliable process where an organisation weighs down the pros and cons of each alternative site.
Location analysis is based on the following aspects:
- Demographic analysis
- Competitive analysis
- Site economics
- Trade area analysis
- Traffic analysis
The following are the objectives of location analysis:
- To make sure the smooth running of the business
- To hold minimum investment and operational cost
- To co-ordinate with government policies
- To promote employee welfare
Significance of Plant Location
Strategic significance of plant location is connected with capacity decisions. Plant location involves commitment towards resources to a long-range plan. The criterion for the selection of location should be profit maximisation and cost minimisation. If the costs of products are uniform altogether, then the criterion becomes one among minimising relevant costs. Plant location is generally a stable decision that cannot be changed frequently and requires a lot of cost and efforts.
Any wrong decision can bring huge losses for the organisation. Therefore, it is important for an organisation to consider all the factors that impact the plant location before making the selection. If all processes and costs are independent of location, choices are going to be guided by proximity to potential customers or clients or similar and competing organisations and centres of economic activity generally.
Plant Location Selection Criteria
Most new investments in land, machines, buildings and expertise are made for the long run. This is furthermore important in terms of manufacturing plants. Being the global business environment, the company requires a location that every single day it holds a major role in the new production plant. Organisations can have several reasons to start the location selection process for their new manufacturing plant, cost reduction, the capacity expansion for business growth, new market entries, the pools of labour coping with geopolitical developments.
The factors that play a crucial role in plant location selection are as follows:
Safety and Security
Future operations.
- The layout of the productive equipment will depend on the characteristics of the product to be managed at the facility, as well as different parts and materials to work on.
- Main factors to be considered: size, shape, volume, weight and the physical-chemical characteristics, since they influence the manufacturing methods and storage and material handling processes.
- The sequence and order of operations will affect plant layout as well, taking into account the variety and quantity to produce.
- Having information about the processes, machinery, tools and necessary equipment, as well as their use and requirements is essential to design a correct layout.
- The methods and time studies to improve the processes are closely linked to the plant layout.
- Regarding machinery, we have to consider the type, total availability for each type, as well as quantity of tools and equipment.
- Labour has to be organised in the production process (direct labour, supervision etc.)
- Environment considerations: employees’ safety, light conditions, ventilation, temperature, noise, etc.
- Process considerations: personnel qualifications, flexibility, number of workers required at a given time as well as the type of work to be performed by them.
- Safety always be a consideration in the design or layout of the facility.
- A company can design the most efficient production layout but if it places employees at risk or places the product at risk from the layout, it cannot be implemented.
- Providing a quality product with the least amount of movement and material handling is important, but the most important asset that any company has is its employees. If the safety of those employees is jeopardised, the layout should not imperil employee’s safety.
- Every plan should include a consideration for the future of operations. Whether it is a manufacturing facility that needs to consider future products or variations of the same product or a distribution centre that needs to consider future storage requirements and product configurations, as well as the ability to expand capacity in the future.
- It is important to forecast future changes to avoid having an inefficient plant layout in a short term.
- Flexibility can be reached keeping the original layout as free as possible regarding fixed characteristics, allowing the adjustment to emergencies and variations of the normal process activities.
- Possible future extensions of the facility must be taken into account, as well as the feasibility of production during re-layout.
You Might Also Like
Quality certifications and award, what is quality measurement, cost of quality, learning from quality gurus, what is material handling objectives, principles, control, what is dmaic process, what is quality improvement basics, models and tools, what is inventory categories, importance, cost of holding inventory, what is purchasing management meaning, importance, aspects, objectives,, process of purchasing management, garvin eight dimensions quality framework, what is quality circle objectives, advantages, factors,, types of production system, what is economic order quantity advantage, limitations, leave a reply cancel reply.
You must be logged in to post a comment.
World's Best Online Courses at One Place
We’ve spent the time in finding, so you can spend your time in learning
Digital Marketing
Personal Growth

Development
- Start Business
- Grow Business
How to Select a Factory Location for Manufacturing Business in 14 Steps
- by Next What Business Research Team
- December 5, 2023
Choosing and selecting a factory location rightfully is a difficult task for entrepreneurs, especially for beginners. The right plant location is a ‘make or break’ decision from an owner’s point of view.
The location of the business is the most important factor influencing its success or failure. It is a long-term decision that should take into consideration not only the present requirements of the organization but also its future expansion plans. Choosing an inappropriate factory location may be very difficult and expensive to rectify.
Also, the location of a plant has a bearing on the layout of machinery and equipment as well as on the process of production. There is no ideal location for all or even one firm at all times. The choice of location depends on several important factors. It is influenced by the products being manufactured and the production and distribution costs.
A sound business plan should be the foundation of your site-selection process, detailing the goods the plant will produce, the number of goods the plant will produce, five years of production planning, and future growth expectations.
The objective of a locational plan is to find out the optimum or best location for the particular plant. Such a location not only results in the lowest cost per unit but also facilitates the orderly growth of the firm. In this article, we intend to explore 14 things to consider in selecting a factory location.
Related: Things To Consider Before Starting a Manufacturing Busines s
Table of Contents
14 Steps to Follow Before Selecting a Factory Location
#1. availability of raw materials.
Raw materials are the basic components of finished products. This is one of the most important considerations when selecting a factory location.
If your required raw materials are perishable items, then you must tend to locate the plant nearer to the raw material source. Moreover, it also reduces transportation costs which affects hugely the cost of production.
#2. Proximity to Market
Every finished product needs to go to the market for consumer consumption. Here also transportation overhead increases the cost of the finished product.
In case you are initiating a fully export-oriented plant, the availability of processing facilities gains importance in deciding the location of one’s industry. Export Promotion Zones (EPZ) are such examples.
#3. Infrastructural Facilities
This is important because all supporting services are required for the successful operation of the plant. The availability of communication facilities is also an important part of the infrastructure.
Existing vibrant infrastructure in the vicinity is much preferred to the need-based infrastructure getting developed after the plant commissioning.
Related: Things To Consider In Purchasing Machine & Equipment
#4. Government Policy
The Government offers several incentives, concessions, tax holidays for a few years, cheaper power supply, factory sheds, etc., to attract entrepreneurs to set up industries in less developed and backward areas. In this scenario, you must prioritize this factor in selecting a factory location.
#5. Get N.O.C
Neighbours play sometimes a vital role in getting license permissions from different Govt. authorities. If you are establishing the plant near a domestic area, then authorities may ask you to get a ‘No Objection’ from your neighbours.
#6. Availability of Manpower
Local availability of skilled and semi-skilled manpower will add to the efficient running of the plant. Besides, you must study labour relations through turnover rates, absenteeism, and the liveliness of trade unionism in a particular area.
#7. Availability Of Utilities
Utilities like electricity, water resources, etc. play an important role in almost every factory’s operation. Stable and uninterrupted power is a required magnitude, without fluctuations in voltage and frequency is important for the successful operation of the plant.
#8. Local Laws, Regulations, and Taxation
You must check the laws related to the pollution control board. In food products, you must check the FPO regulations. In the case of the wood industry, you must maintain the distance from forestry. Taxation is also an important factor as well as a State Subject.
In some highly competitive consumer products, its high quantum may turn out to be the negative factor while its relief may become the final deciding factor for some other industries.
Related: How to Register a Company/ Startup
#9. Ecology & Pollution
Nowadays, there is a great deal of awareness towards the maintenance of natural ecological balance. Regarding the effect of pollution from the specific type of plants, social obligations are to be met.
The nature of the site selected should preferably have some advantages to meet these requirements. You must be careful about effluent disposal, in the cases, it is needed.
#10. Distance from Your Residence
Yes, it’s important. In a small-scale factory operation, an entrepreneur plays a vital role. You should not select a place that has adequate distance from your residence.
#11. Competition
If you are dealing with an innovative product and your plant is in an industrial zone, then you might face competition in manufacturing automation from other companies.
#12. Incentives, Land costs. Subsidies for Backward Areas
In some cases, the Government offers several incentives, concessions, tax holidays, cheaper lands, assured and cheaper power supply, price concessions for departmental (state) purchases, etc. to make the backward areas also conducive for setting up industries. You must take into consideration these issues in selecting a factory location.
Read: Best Small Manufacturing Business Ideas
#13. Climatic Conditions
Climatic conditions affect both people and manufacturing activity. Additionally, certain industries require a specific type of climatic conditions to produce their goods. For example, jute and textile manufacturing industries require high humidity.
#14. Political conditions
The stability of the political environment is essential for industrial growth. It builds confidence and political instability causes a lack of confidence among the prospective and present entrepreneurs to venture into the industry which is filled with risks.
Hence, the most advantageous location is that at which the cost of gathering material and fabricating it plus the cost of distributing the finished product to the customers will be at a minimum. The choice of an optimum location requires a judicious balancing of all these factors.
This list of 14 things to consider in selecting a factory location helps you to get almost the right plant location for your manufacturing operation.
Discover more from NextWhatBusiness
Subscribe to get the latest posts sent to your email.
Type your email…
Search from the site
Industry | December 28, 2021
How to plan & design a manufacturing plant layout? (video examples included)
Our experts at Visual Components discuss how to plan and design a manufacturing plant layout with a simulation case. We review the benefits, process, and necessity for a high-quality plant layout in your business organization.
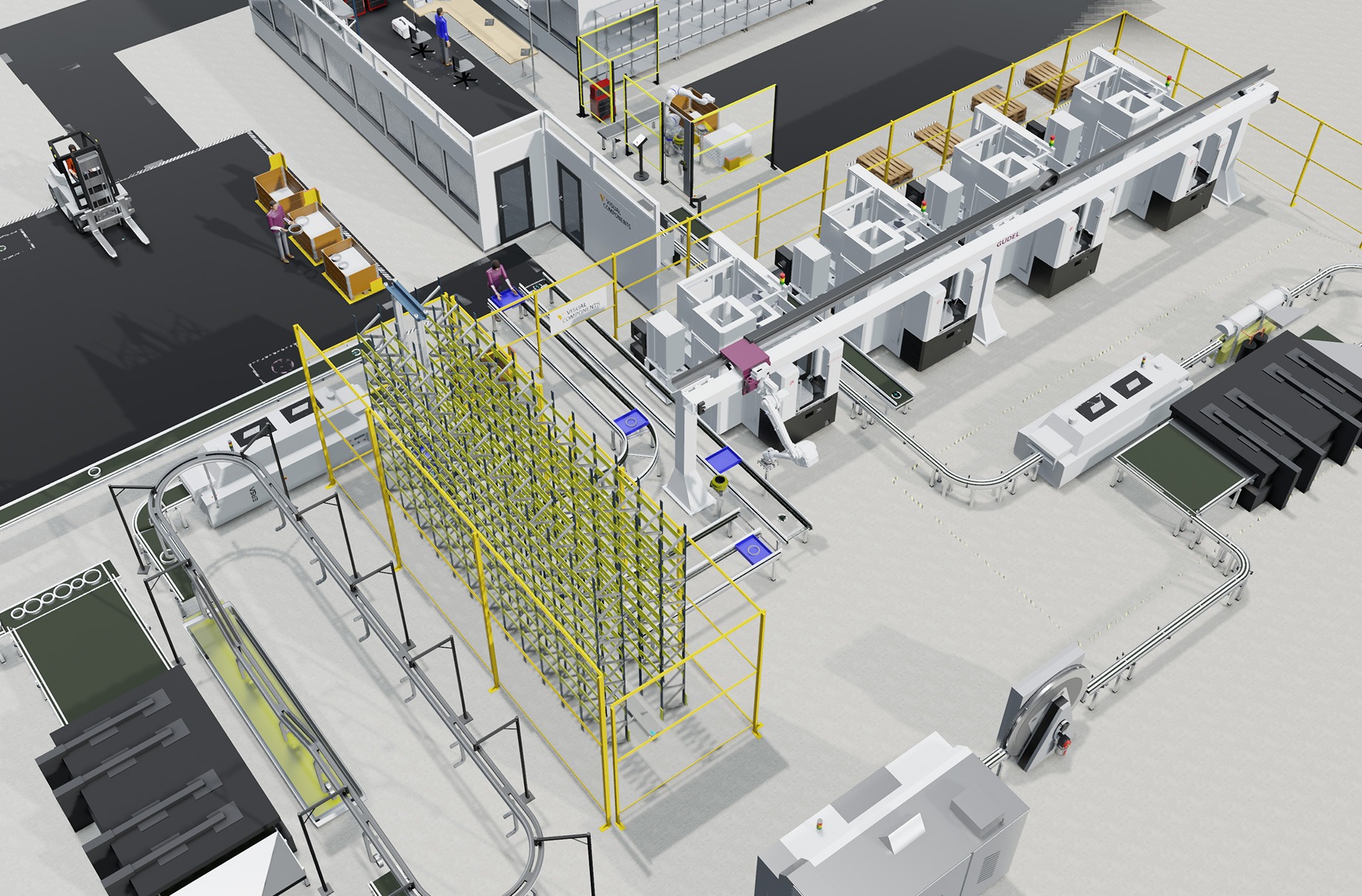

When it comes to running a manufacturing facility, there are a lot of things to consider. As an owner or manager, you’re probably looking for ways to speed up your process, improve your yield, and increase your profit. Did you know that a simple plant layout can achieve all three of these goals?
Layouts are often overlooked, despite their huge money-saving potential.
In this piece, we’ll discuss what is meant by a plant layout, some benefits of a layout, an example, and our step-by-step process for laying out a plant.
These are the topics we’ll cover. You can also jump to the part that interests you the most
- What is meant by a plant layout?
- What is a lean plant layout?
- What are the characteristics of a good plant layout?
- Plant layout design benefits
Plant layout example
- Step-by-step plant layout design process
- Case: tire assembly and warehousing layout
Let’s go!
What is meant by a plant layout?
The plant layout definition is simple: it’s a way to draw your facility’s building, equipment, and major components on paper. It’s typically done through 2D CAD (2-dimensional Computer-Aided Drafting and Design) software.
The designer will use real-world dimensions of your equipment and facility and layout a scaled model of your plant. Without using real dimensions, the final layout won’t be as helpful for your plant.
In a lot of cases, the designer will submit a final layout that allows the viewer to fly through the building, seeing the equipment in motion and observing how the process looks. Since everything is a scale model, the viewer can find out how much distance there is between equipment, for walkways, and so on.
Since it’s all done on paper, this can be done before getting equipment or before having a warehouse. It also allows the designer to change the layout as much as they’d like.
The layout includes a lot of different features:
- How product moves through your building
- Equipment
- Building floorplan
- Dimensional distances between everything
- Visualization of your process
What is a lean plant layout?
If you take the concept one step further, you can start optimizing everything. In a lean plant layout, the designer will start incorporating lean principles into the floorplan.
A big principle in lean layouts is adding sections for different operations. If your process has multiple steps, like cutting, organizing, and packing your product, then it will be broken into different physical areas.
Cutting will be done in one zone, organizing in another, and packing in a third. This also groups together the required machinery and personnel to expedite the process.
Why does this work? Material and people travel shorter distances, the layout is more compact, and everything is streamlined.
There are a lot of other concepts that go into lean principles (a lean layout). For the sake of brevity, we’ll leave it there.
What are the characteristics of a good plant layout?
Knowing whether a plant layout is good or not really depends on your operations and needs. In general, there are a few characteristics to look for:
- Effectively uses the space . One of the limiting factors in your operation is how much space you have. You can’t just invent new space, so you have to get creative with the space you have. A good plant layout effectively uses every square inch of operation space.
- Accessible design . At the end of the day, there should be enough space between items for the full floorplan to be accessible. This means that material handlers need enough space for themselves as well as the product they’re carrying around the building.
- Flexibility for future growth . Make sure that the floorplan isn’t going to constrict your operation. A lot of manufacturing plants benefit by adding a potential for 20-40% growth. This doesn’t mean that you have to predict exactly how much you’ll grow in a decade, just design with future growth in mind.
- Has your operation in mind . You need a layout that works for your individual operation. There are very few cookie-cutter solutions that fit the needs of your business — your layout is the same way. A good plant layout is specialized to what your business needs.
If you want to oversimplify this idea, a good plant layout is one that achieves the goals of your operation while optimizing every possible parameter.
Plant layout design benefits
Why do people spend so much time putting together a plant layout? There are a number of benefits. Let’s quickly review some of the top reasons why people opt for a plant layout in their business organization.
Reduce cycle time
Cycle time is a term that quantifies how long it takes a business to make a product. It’s the combination of every process step that’s required to make your end product.
With a good plant layout, everything is set up with the operation in mind. As a result, businesses will see a reduced cycle time.
Increase operational speed
On top of an overall speed increase, you’ll find speed increases in every step of the process. This goes back to the idea of splitting your operation into different zones.
Rather than an operator walking across your warehouse to perform a task, everything will be centralized. Think of it as storing the knives next to the cutting board in your kitchen.
Maximize your square footage
Depending on where you’re located, the price of your land could be your biggest expense. Due to that fact, most people want to maximize their square footage.
With a manufacturing plant layout, you have the ability to move equipment around on paper in order to maximize your square footage.
The designer can do things like relocating, rotating, and reorienting equipment to see which option makes the most sense for your facility. Clearly, this is a lot faster and less expensive than physically changing around equipment and testing the new layout.
Visualize and tweak your operational process
Once things are laid out, it might help you to see a potential shortcut in your operation. Maybe you can save time and money by moving one step of your process to another part of the cycle.
This is highly dependent on your operation, but we’ve seen it happen in the past: a company thinks their operation is optimized until they do a plant layout and notice some shortcomings.
Maximize profits
When you combine all of these factors, you’re left with one big benefit: maximized profits. This is the major reason why a lot of businesses opt for putting together a plant layout.
You save time, space, and create more products each year. That should sound like millions of dollar signs annually.
To help illustrate this idea, let’s look at an example. Our team at Visual Components lead the design for a company called Midea.
Here’s a case study of one of our previous clients, Midea . They’re the world’s largest producer of major appliances. Before adding a new, high-end production line, they decided to get a plant layout.
Our simulation looked at the real-world size and operational speed of their different machines. We worked closely with their team to understand how the process works, what the limiting factors were, and what kind of flow their operation had.
After we produced some rounds of layouts, we arrived at, what both parties deemed to be, the best possible arrangement. We saved their operation a lot:
- Floor space used was reduced by 10%
- Production capacity increased 10%
- Reduced product defects by 10x
- Construction schedule expedited 20%
- Total project cost savings: $879,000, roughly 15%
- Long-term labor cost reduction, operational efficiency increase, and projected profit increase
This project for Midea shows the importance of lean plant layouts. We foresee an increase in their profits year over year — this isn’t just a short-term, upfront cost saving. The future of their operation will benefit thanks to an initial plant layout.
Step-by-step plant layout design process with a case example
Curious about what the plant layout design process looks like? Here’s a step-by-step process that we typically follow for our clients. Here’s our workflow for planning and building a plant layout:
1. Understanding clients’ needs
It all starts with understanding our clients’ needs. Before a plant layout can be generated, some information about the operation needs to be explored.
This entails a few conversations going over some basics like floor space, equipment, flow, and more.
For example, our customer Firac received a clear request from their client — to automate a manual screw tightening process. Read the whole story.
2. Planning manufacturing system design
Now it’s time to start drafting. Different companies will opt for different manufacturing programs in this step.
Some companies will only provide a 2D layout with no motion included. Others will use a 3D layout that shows how the equipment will move and how the product goes through the cycle.
At Visual Components, we typically use a 2D layout for the building and add a static 3D layout on top. This overlay ensures dimensional accuracy which is paramount in making a plant layout.
3. Equipment selection
Now it’s time to select and add equipment. This will go right into our static 3D layout, so it can be changed later.
Things like the overall size, motion constraints, and equipment parameters will be inputted during this step. This is done to ensure the model is precise and accurate.
As you probably noticed from our Midea case study, the equipment physically moves and operates in our model. During this step, we’re making sure our clients get the best visual of their potential layout.
To help our clients save time on equipment selection, we offer ready-made components. Visual Components eCatalog has a library of virtual models of robots, machines, and equipment from dozens of leading brands in industrial automation. We have over 1,500 pre-defined and ready-to-use components, to be exact.
4. Layout design
Once the equipment is selected, the designer can start moving around components. This is part of the optimization process where items are moved around until they’re in the perfect place.
Since the equipment and building are already drawn on the computer, this step is more of a “drag and drop” process. On the computer, the designer will move around equipment, change its orientation, and find the best place for the physical pieces.
Jump to 2:34-5:50 in the video below to see how it works in practice.
5. Define the flow
In step 5, we’ll start optimizing the flow. There are three major parts of this step:
- Defining the products
- Defining the processes
- Defining the process flow
There’s some overlap between this and the first step on the list. However, this step focuses on optimizing everything from a layout perspective.
This might mean changing the location of equipment, storage, and walkways to improve the overall process.
The flow is how the material cycle looks in your operation. In other words, when you trace the product from raw material to shipment, that’s the flow.
Jump to 6:43-9:22 in the same video below to see how it works in practice.
6. Simulation
With all of these parameters in mind, our team is ready to put together a simulation. The simulation will show the material and how it physically moves down the line.
A simulation is a 3D video that shows a flyby through your facility. It shows how the equipment and product move throughout. The Midea video discussed earlier is a great example of a simulation that our team makes.
However, this isn’t the final stage. Part of the simulation entails finding bottlenecks. This is where your operation is slowing down and hurting the production speed.
After finding a bottleneck, our team will work to alleviate them. Removing even one bottleneck in your operation can result in a huge performance improvement.
Some of our design software comes with plant layout analysis that aides us in targeting and alleviating these bottlenecks. This is another benefit of using computer-based plant layouts.
Read more: Manufacturing simulation: how it works and why you should do it?
7. Modify And Validate the Changes
The final stage is all about making changes to improve the design. We typically target metrics when it comes to the use of space, operation cycle time, and the ability for product defects.
These changes result in faster speeds and more room for profit within your business on an annual scale.
If this layout is done before construction, you’ll also find some construction cost savings built into this step.
The validation stage involves our clients and getting valuable feedback from you.
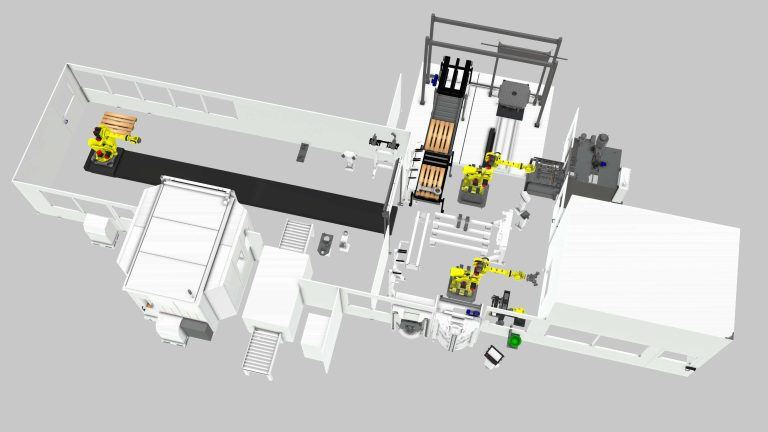
Case: Tire assembly and warehousing layout
Let’s discuss a case where the task was to design, simulate, analyze and optimize a manufacturing and warehousing system based on predefined production and layout goals.
This case is about a tire assembly and warehousing facility that is capable of handling a certain number of tires before they are supplied to a downstream assembly line. We can assume that the downstream is a car manufacturing plant.
Products and product variants
The product that we had to work with in this case was tires however there were many product variants.
First, we had three tires types meaning tires in three different materials.
Next, we had five tire sizes in the three tire types. These sizes are represented in different colors of tire rims.
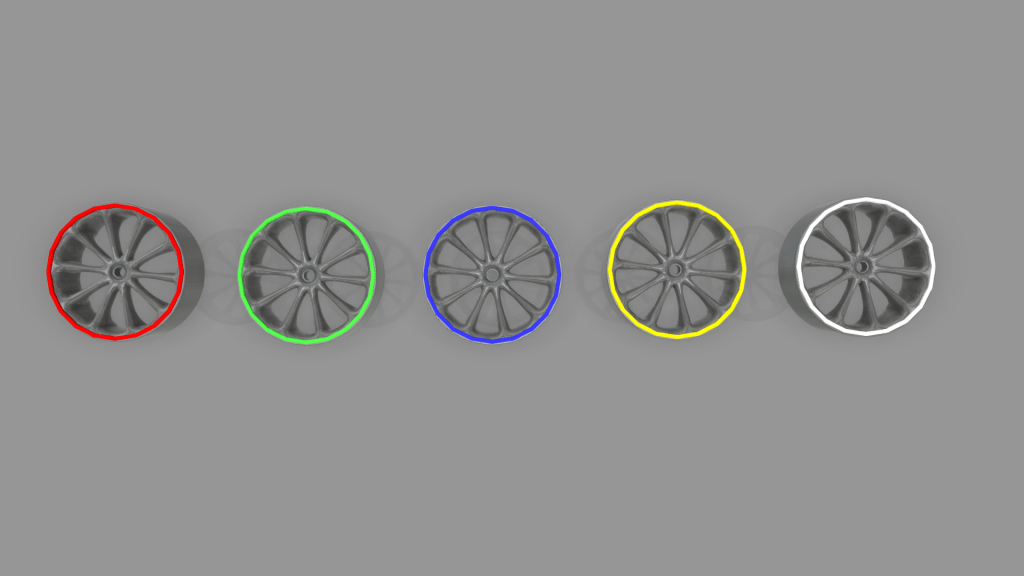

So including all the product variants, we had to design a system that could handle 15 different tires.
Production goals
Once the products and product variants were clear, the next step was to evaluate the pre-defined goals. Here’s the list of the production goals that we had to meet,
- The customer needed a setup that was capable of handling all these tires in batches of 4.
- The downstream assembly required that this tire plant could supply 720 tires per hour regardless of how many it can store. The main objective was to have a functional system that provides uninterrupted supply to the downstream assembly regardless of how many tires it could store.
- Since we were working with batches of 4, 720 tires per hour meant that the goal was to supply 3 sets of tires per minute.
Layout goals
Based on the production goals, there were also some layout goals,
- There must be enough buffer to recover from possible machine downtime.
- There must be enough warehouse to store tires for 5 hours of production meaning 900 sets in 5 hours and they must be available at all times to ensure any downtime does not interrupt the downstream supply.
- Also, in addition to storage, we needed to ensure that we had enough conveyor capacity to handle this amount and variety of products.
Layout overview and functionality
Their layout was then designed based on the given production and layout goals. Here is a video for a closer look at the layout design and functionality of different sections,
1. The tire types are fed to the robot cell as a batch of 4.
2. Next, Tire rims which represent different sizes of the tires are incoming through conveyors behind the robot cell.
3. The robot cell is designed with 4 assembly lines. Each of these has a Yaskawa HP20RD robot on top of a smart pedestal with a tire tool. This tire tool helps to pick the tire type, lubricate it and assemble it with the rim.
4. Once Assembled, these tires go through a different set of machines where they are fixed and balanced before they are ready to be stored in the warehouse.
5. The tires are then sent towards the warehousing side with five storage sections, one for each tire size and four cartesian robots.
6. Each of these robots has certain tasks assigned to them shortly explained here,
- The first red cartesian robot sorts the tires by sizes onto their specific conveyors
- The second dark grey cartesian robot picks one stack of tires at a time and places them in their relevant tire size storage section.
- The third dark grey cartesian robot with beige pillars stores the tires by their sizes in the storage section and also supplies the sets forward when needed.
- The fourth steel-blue robot that is closer to the entrance of the warehousing collects the supplied stacks of tires released by the previous robot and places them in the rack. These racks are then picked and stored by the forklift in the next storage area.
7. From the last storage, the tires are then supplied to the downstream assembly as they’re needed.
Performance evaluation of the designed systems
Initially, two scenarios were designed and their simulation performance was evaluated.
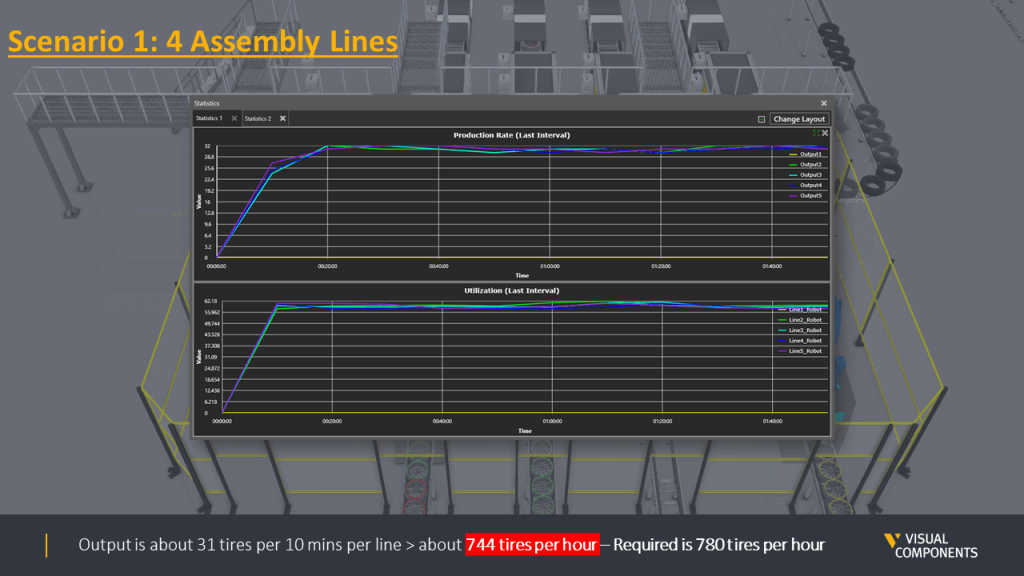
The first scenario consisted of 4 robot assembly lines.
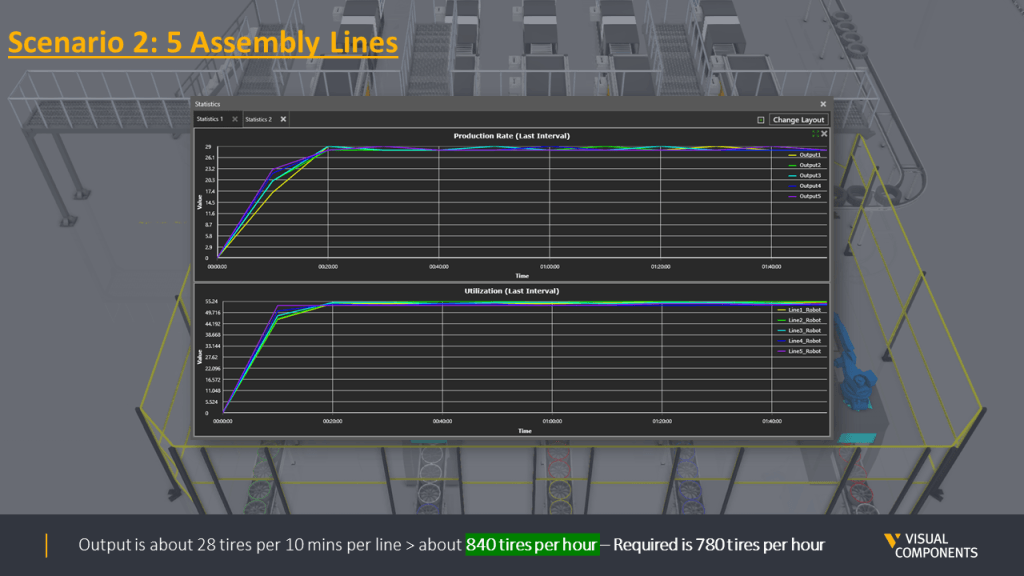
The second one had 5 robots assembly lines.
Later, we realized that machine breakdowns are not taken into account in the first two scenarios. Machine breakdowns could be due to many reasons but the most common reason for a production stoppage is usually Maintenance. So, the Maintenance times or Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) averaging 150 seconds were added to the machines in the robot cell. Also, the maintenance cycle was defined which meant the machine maintenance had to be carried out after every 30 tires were produced.
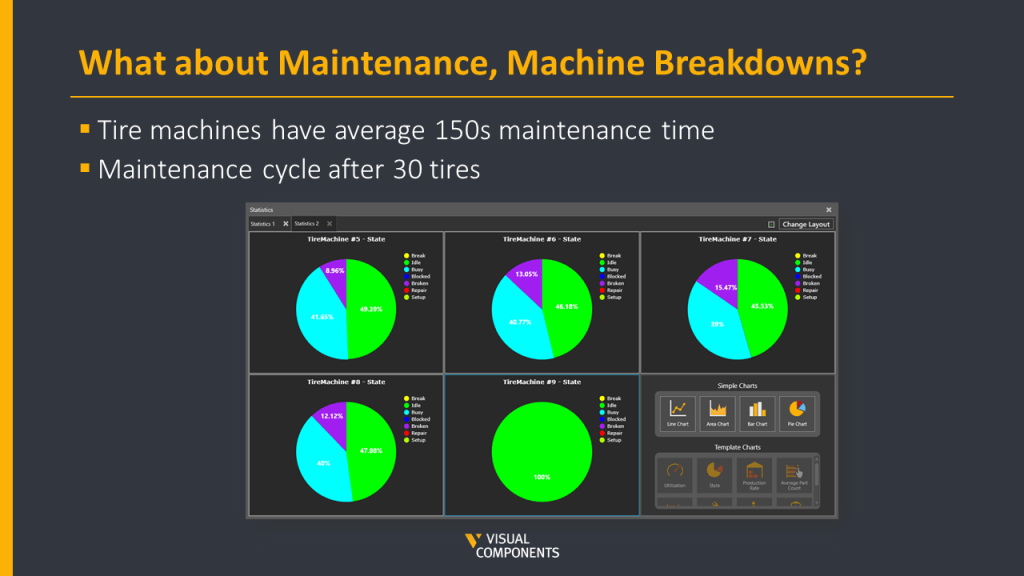
After these metrics were clear and defined, two more scenarios were built, basically, the same and 1st and 2nd scenarios but now with MTBF values included.
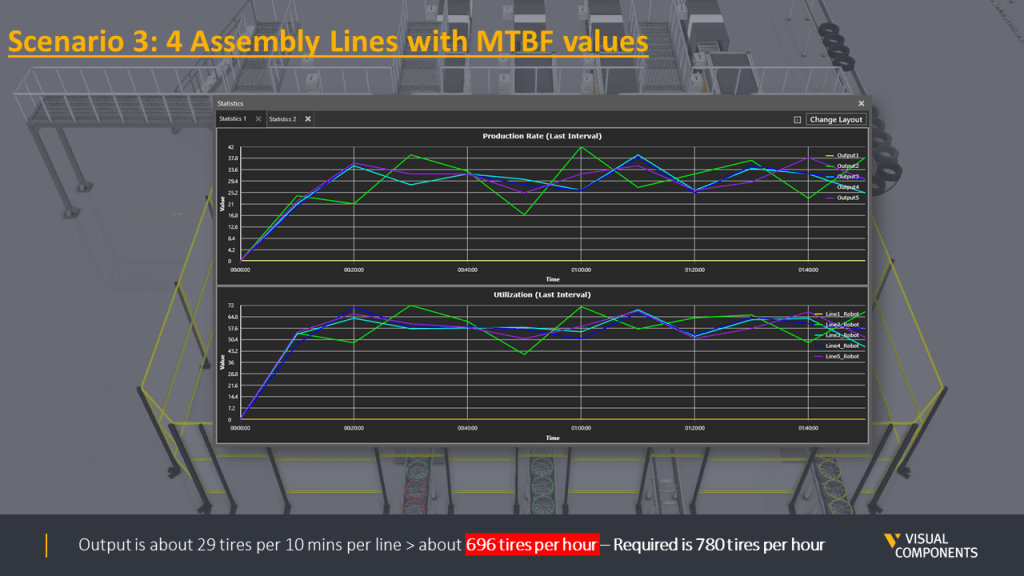
Overall, four scenarios were designed and simulated. Here is the summary of all scenarios with their production output.
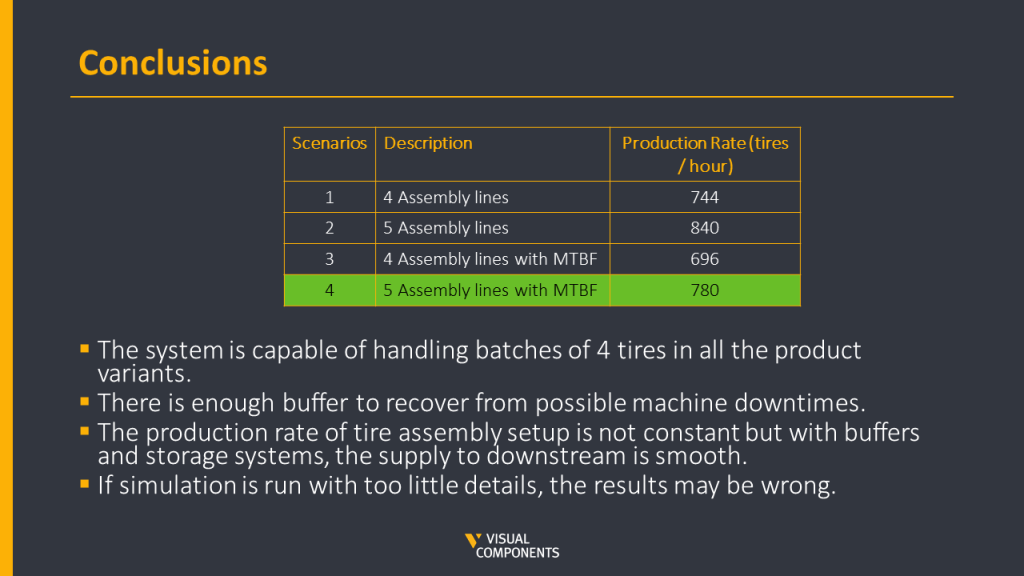
The difference in the production output is quite clear between scenarios where MTBF values were not considered and once they were. Based on the scenarios, it was safe to say that Scenario four with five assembly lines was able to generate the required goal of 780 tires per hour. This scenario was then locked as the final design for this case.
Summary of case results
Some important conclusions of this case were,
- The designed system was capable of handling batches of four tires in all the product variants.
- There was enough buffer to recover from possible machine downtimes.
- The production rate of tire assembly was not constant after the maintenance times were added but with enough buffers and storage systems, the supply to downstream was smooth.
- The last but one of the most important lessons to learn from this case was if the simulation is run with too few details, the results may be wrong like the clear difference between the production outputs in the first two scenarios compared to the last two.
Conclusion
We just reviewed how to plan and design a manufacturing plant layout. Now, you should know the benefits and process that goes into making a layout for your plant. With Visual Components , designing a plant layout is more logical, visual, and easier to do. Contact us today to get started. We’ll show you how your operation can save time and money thanks to our services.
Curious to learn more on the topic? Be sure to download our eBook about planning and optimizing your manufacturing plant layout.
Further reading
Boosting production line efficiency: a guide on improving production output
Production efficiency is the cornerstone of success in manufacturing. It measures the effectiveness of resource utilization in the manufacturing process, aiming to maximize output while minimizing costs and waste. The...
An introduction to virtual commissioning
Virtual commissioning is reshaping the manufacturing landscape by employing computer simulations for testing and optimizing production systems before they're physically built. This approach not only simplifies the setup process and...
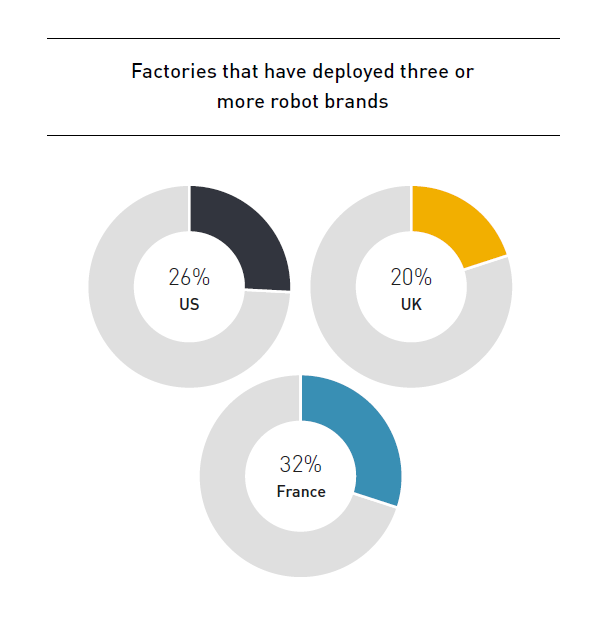
Are manufacturers really ready for the digital era? (survey results)
Legacy equipment and outdated practices can seem like relics from another age, especially as the world zooms ahead with digital innovations. Yet, they're more prevalent in the manufacturing sector than...
Account Management
Log in to manage your policy, generate a certificate of insurance (COI), make a payment, and more.
Log in to your account to update your information or manage your policy.
Download a Certificate of Insurance (COI) to provide to your employer.
Make a Payment
Make a one-time payment, set up autopay, or update your payment information.
Submit a notice of an incident or claim in just minutes.
Topics on this page:
What Is a Business Location Strategy?
Why is a business location strategy important, how to choose a business location, examples of business location strategies that worked and why, final thoughts, business location strategy: a complete guide to finding your optimal location.
Jul 24, 2024

You have a great idea for a business. The plan is ready to go, and you have your financing lined up. Now, you just need to choose your location to get started—but the right decision is not always obvious and calls for careful analysis.
In this guide, we’ll explain the concept behind business location strategy and some key considerations to keep in mind when choosing the best spot for your business. Plus, we’ll provide some examples of real business owners’ location strategies and how they worked out.
A business location strategy is your plan to find the optimal location for an organization. This requires an analysis of company goals and objectives and finding a location that meets them. Your company’s location strategy should align with any overriding corporate structure or strategy.
Some businesses require foot traffic, such as retail and restaurants. Medical practices and other healthcare facilities might prioritize patient access or proximity to growing neighborhoods. Yet others serve B2B customers, so location objectives may focus more on expense reduction.
Having a strategy in place for choosing your business’ location is important because it allows you to make better decisions about choosing a location that balances all the things you need.
Business location, regardless of your industry, affects your operating costs and your stakeholders.
Think About Your Customers
Think about the type of customer you hope to attract. If your business location is off the beaten path, is difficult to find, or does not offer parking, that can be an issue. If you’re not in a safe neighborhood or one that’s well-lit and you have hours after dark, that can also be a problem.
An urgent care clinic, for example, may be fine in a strip mall with enough parking. However, a surgery center may need a more discreet location.
If your business caters to locals, you may be fine in a city center or congested area. If people travel from out of town, you’ll probably want to be near a major roadway.
If you run a B2B business, most of your business dealings might be handled face-to-face, online, or on the phone. In that case, where your business is located might not matter to your customers.
Think About Your Employees
Your business’ location can make a big difference in attracting and retaining employees.
For example, easy access to free parking or public transportation to and from can play a role. If an employee has to pay for parking every day, it cuts into their paycheck. You may prefer to open your business in a location with restaurants or coffee shops nearby to make it easy for employees to grab a meal or take a break.
Think About Your Suppliers
If your business needs to store substantial inventory, think about your supply chain. Faster delivery cuts down on your costs and gets products back in stock more quickly. Locations without street parking or in a difficult-to-access area may increase costs for deliveries.
“Site selection is a process of elimination,” said Christine Wong Rambo , CEcD, MBA, certified economic developer, and president and founder at the economic development marketing firm Upsize Marketing Strategies .
Data should be your guide when choosing real estate for your business.
Data-Driven Site Selection
“The site selection process is driven by data,” said Rambo. “Collecting this type of data may be challenging if a company is not using a site selection consultant. Companies can partner with state, regional, or local economic development organizations to gather this information based on the company’s criteria.”
For example, in the healthcare sector, it’s common to do cohort analysis to find patterns in patients and care. The Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality provides detailed information on medical expenditures for cohort analysis.
Site selection criteria include a range of attributes, including:
- Real estate costs
- Site work needed
- Cost of doing business, including taxes
- Market potential
- Competition
- Potential for future expansion
- Neighborhood reputation
- Available infrastructure
Consider Key Metrics
The elements or metrics most important to your business will determine your ideal business location. However, nearly every organization will have some common themes.
According to Rambo, most optimal locations will:
- Meet consumer or production demands
- Improve operational efficiency and costs due to proximity to other resources
- Lower overall business costs
- Offer sustainability and potential for growth
- Meet workforce requirements
- Provide a more favorable business climate
Consumer businesses that carry large inventories will want to consider the cost of warehouse space and distance from shipping hubs.
Access to a Skilled Workforce
“For the professional services sector, the ability to recruit a skilled workforce and proximity or access to a major client would be important considerations,” said Rambo.
Healthcare facilities, clinics, and medical practices may want to be located near hospitals or universities that train medical professionals for easier access to potential employees. Field service businesses may want to be near a community college, vocational tech school, or career training center. Businesses with a less-skilled labor force that pays lower wages may need to be near public transportation.
Access to Customers
“Your business can optimize its operations and market reach if it’s located in the right location,” said Michael Hammelburger, CEO at business consulting firm The Bottom Line Group . “This is especially true for retailers and food-related establishments that take advantage of heavy foot traffic in areas during rush hour. When situated in the right location, they can reach more people and thus have the potential to sell more.”
For consumer-facing businesses, accessibility and safety for customers are key considerations. The same applies to healthcare facilities. Patients have to be able to access your facility easily and feel safe when doing so.
Consider the Long-Term Implications
Your business location strategy should be far-ranging to accommodate your future plans. If you are open to the possibility of expanding your footprint in the future, you want to make sure there’s enough real estate nearby to make that a reality—even if it may be years down the road.
“When you start a business, you may have assumptions on what business you are in, where you are located, and where your customers are,” said Joseph Meyer, financial consultant and business strategist at The Dollar Soldier . “These assumptions are locked in for your business. If you try to change those assumptions after you start, the risk of business failure grows.”
The assumptions you make today about your business location strategy can help or hinder your efforts down the road.
For businesses that rely on foot traffic or get regular visits from customers or patients, location is crucial. For example, 62% of patients said they selected a physician based on the convenience of the location . Fifty-eight percent of patients that had a choice of hospitals to use said they prioritized locations as a key factor in their choice.
The only factor that was more important than location was whether a practice or facility accepted a patient’s health insurance. After that key consideration, location ranked second.
For businesses that don’t rely on foot traffic or customer visits, the location selection strategy is quite different. Mold Busters , a field service company that handles mold removal, wanted a central location that was close to their customers.
“Our teams out in the field may gather supplies and equipment in the morning then travel to customers,” said Charles Leduc, Mold Buster’s COO. “A location that provides minimal miles in between locations or jobs helps keep expenses down.”
Ralph Severson , president at Flooring Masters , agreed.
“Our crews must be able to get the equipment and supplies that they need each morning with minimal travel time,” Severson said.
At the same time, Severson said they wanted a location that balanced the convenience with lower costs.
“We chose our location because it is only 10 minutes from Louisville, Kentucky, the most densely populated city in the area, but we are north of the Ohio River in Indiana, where overhead costs are lower,” he said.
The right location for your business plays an important role in your success. Businesses need to assess their overall goals and think carefully about how they are serving their customers and employees to optimize their strategy.
Ready to take the next step in protecting your career and business? Take a few minutes to learn more about our suite of insurance products and find out how Berxi can help you.
Image courtesy of iStock.com/ Orbon Alija
Last updated on Jul 24, 2024. Originally published on Aug 25, 2021.
- Small Business
- Mental Health
- Fitness & Wellness
- Real Estate
- Optometrist
The views expressed in this article are those of the author and do not necessarily reflect those of Berxi™ or Berkshire Hathaway Specialty Insurance Company. This article (subject to change without notice) is for informational purposes only, and does not constitute professional advice. Click here to read our full disclaimer
The product descriptions provided here are only brief summaries and may be changed without notice. The full coverage terms and details, including limitations and exclusions, are contained in the insurance policy. If you have questions about coverage available under our plans, please review the policy or contact us at 833-242-3794 or [email protected] . “20% savings” is based on industry pricing averages.
Berxi™ is a part of Berkshire Hathaway Specialty Insurance ( BHSI ). Insurance products are distributed through Berkshire Hathaway Global Insurance Services, California License # 0K09397. BHSI is part of Berkshire Hathaway’s National Indemnity group of insurance companies, consisting of National Indemnity and its affiliates, which hold financial strength ratings of A++ from AM Best and AA+ from Standard & Poor’s. The rating scales can be found at www.ambest.com and www.standardandpoors.com , respectively.
No warranty, guarantee, or representation, either expressed or implied, is made as to the correctness, accuracy, completeness, adequacy, or sufficiency of any representation or information. Any opinions expressed herein are subject to change without notice.
The information on this web site is not intended or implied to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis or treatment, and does not purport to establish a standard of care under any circumstances. All content, including text, graphics, images and information, contained on or available through this web site is for general information purposes only based upon the information available at the time of presentation, and does not constitute medical, legal, regulatory, compliance, financial, professional, or any other advice.
BHSI makes no representation and assumes no responsibility or liability for the accuracy of information contained on or available through this web site, and such information is subject to change without notice. You are encouraged to consider and confirm any information obtained from or through this web site with other sources, and review all information regarding any medical condition or treatment with your physician or medical care provider. NEVER DISREGARD PROFESSIONAL MEDICAL ADVICE OR DELAY SEEKING MEDICAL TREATMENT BECAUSE OF SOMETHING THAT YOU HAVE READ ON OR ACCESSED THROUGH THIS WEB SITE.
BHSI is not a medical organization, and does not recommend, endorse or make any representation about the efficacy, appropriateness or suitability of any specific tests, products, procedures, treatments, services, opinions, health care providers or other information contained on or available through this web site. BHSI IS NOT RESPONSIBLE FOR, AND EXPRESSLY DISCLAIMS ALL LIABILITY FOR, ANY ADVICE, COURSE OF TREATMENT, DIAGNOSIS OR ANY OTHER SERVICES OR PRODUCTS THAT YOU OBTAIN AFTER REVIEWING THIS WEB SITE.
Want Berxi articles delivered straight to your inbox? Sign up for our monthly newsletter below!
" * " indicates required fields
How we use your email address Berxi will not sell or rent your email address to third parties unless otherwise notified. Other than where necessary to administer your insurance policy or where required by law, Berxi will not disclose your email address to third parties. Your email address is required to identify you for access to the Berxi website. You may also receive newsletters, product updates, and communications about quotes and policies.
Paul Dughi is a contributing writer for Berxi, as well as a journalist and freelance writer. He has held executive management positions in the media industry for the past 25 years.
Related Articles

The Difference Between a Career Mentor & an Accountability Partner
Stephanie Lica Jul 24, 2024

How to Pay Yourself as a Small Business Owner
Lauren Garcia Jul 24, 2024

The Big List of Tax Deductions for Real Estate Agents & Business Owners
Kathryn Flynn Jul 24, 2024

How To Choose a Location for Your New Manufacturing Plant

Site selection is critical to business success. Whether your company is planning to commission its first facility or you’re expanding to add additional sites, learning how to choose a location for your new manufacturing plant is essential to a successful opening or move.
A key factor to keep in mind is that site selection is a long-range decision. Once you’ve chosen where to situate a manufacturing plant, it’s unlikely you’ll pick up stakes and move anytime soon, barring some catastrophic event. So while present considerations will influence the decision, always keep an eye on the future as well.
When you’re thinking about how to choose a location for your new manufacturing plant, start with these considerations:
Raw Materials
If a location makes it difficult or impossible to easily source the materials your products are made from, get those raw materials to the plant and resupply them when needed; that location is unlikely to make your short list. Distance from suppliers is one of the first things you should consider.
Infrastructure
Every manufacturing plant will have different infrastructure needs, depending on its size and the product it makes. It’s likely, however, that every business will need:
- Power: Calculate and project the amount and cost of electric, solar, wind, or fuel-generated power the plant will require, both initially and several years into the future. Research the local power producing infrastructure for locations you’re considering. Are the local power grid and fuel lines already at their capacity? Costs for power fluctuate broadly, so this will be an imprecise calculation, but it’s necessary to get an idea of the costs.
- Water: Some forms of manufacturing consume a lot of water. Can the prospective location supply sufficient water for the plant, and does it have the necessary infrastructure to manage wastewater properly?
- Communications: Communication considerations extend far beyond cell service, although that’s an important part of the equation. Communications also include broadband availability, speed, and capacity. While you can store data in the cloud at facilities thousands of miles away, companies are increasingly considering co-locating their data centers with production facilities to speed communications and retain control over information security.
- Roads, Trains, Airports: Will people and goods move easily to and from a facility located in the site you’re assessing? Examine the locale’s plans for transportation improvements and whether they’ll be in place by the time your plant opens.
Available Labor Force
It’s no secret that skilled labor is in short supply. Between retiring “boomers” and a new generation woefully unprepared in STEM fields, employers struggle to find the workforce they need to be productive. Professional and experienced site selection consultants will always include an analysis of the available local labor force in their reports. However, you should also examine local educational and training resources for preparing the future workforce, and whether those resources could realistically supply the number of trained workers your plant will need for years to come.
Cost is a consideration for any decision a business makes. It’s important to itemize the costs you expect to incur in commissioning a new plant:
- Construction, Lease, or Purchase: Build, rent, or buy? Map out several scenarios. It may always seem cheaper to rent or buy an existing facility than to build one, but costs to retrofit or reconfigure an existing site can climb to the point that building a new site seems reasonable.
- Labor: The so-called “Great Resignation” that occurred during the pandemic, and continues, changed the labor cost dynamic. Workers are less willing to accept low paying jobs with unpredictable schedules.
- Taxes: Tax rates can be another unpredictable variable, but experts who understand the local economic and regulatory atmosphere may be able to project tax rates and costs for your business in the location you’re considering.
Governmental Policies and Incentives
As you narrow your list of potential locations, incentives take on a more prominent role in decision making. State and local governments may have enacted laws that incentivize all prospective employers, or they may, within the bounds of the law, be able to create a customized package of incentives to lure your business to their city or state. These may include discounts on building and land costs, infrastructure improvements, discounts on utility rates, job training programs, tax cuts, and more.
Negotiating an incentives package is best left to an experienced site selection company, with professionals who understand what’s possible and what’s pie in the sky, and who can get the best deal for your business.

Logistics: Transportation and Distribution
Distance from your suppliers for raw materials is part of the logistics issue but so is distance from distributors and customers. If you’ll be exporting nearly all your products, you’ll need proximity to seaports and airports.
If you distribute locally and nationally, then trucks, roads, and rails become critical. Analyze the journey of your product from manufacture to end user, and identify the logistical challenges that may slow or disrupt your supply and distribution chains.
Competition
What kind of facilities are already operating in the areas you’re considering? If they employ a workforce that requires similar skills, what can you offer to prospective employees that’s better?
During site selection, you’ll also be competing against other businesses hoping to win incentives and concessions as part of their decision to locate in the area. Define what would make your manufacturing plant more attractive to the decision makers who have the authority to offer incentives.
Sustainability and Climate
Manufacturing operations have environmental impacts that must be taken seriously in order to obtain buy-in from local communities. Moreover, climate change is a reality that affects plant design. Develop a communications plan that will address NIMBY concerns early in the process.
The state of Texas learned the cost of delaying adaptations to climate change the hard way during the winter of 2021, when freeze-offs at well heads and frozen equipment at gas processing plants, combined with a surge in demand, crippled the natural gas supply system, leaving thousands without gas-generated electric power.
It’s reasonable to examine the potential for climate related disasters at any site on your list, from hurricanes to blizzards.
Community Resources and Quality of Life
Whatever site you end up choosing, many of your employees will take up residence in the selected community. Does the city or town have the resources to attract additional skilled labor? Examine schools, day cares, recreational opportunities and facilities, arts and culture, restaurants and shopping, and institutions of higher education.
These are only some of the many considerations that make up a complex matrix of factors that go into how to choose a location for your new manufacturing plant. For help navigating this process, partner with WDG Consultants. We provide fully integrated consulting advisory services for all aspects of the manufacturing plant site selection process.

- 3DConfigure
- Wet Lab Gallery
- Tech Lab Gallery
- Industrial Furniture Gallery
- Products Gallery
- Verticals Gallery
- Design Workbenches
- Submit Custom Request
How to Select the Location of Your New Manufacturing Plant
11/29/2017 | 152 Likes | Manufacturing , Assembly , Heavy Duty , Industrial Facilities , Material Handling ,
Determining where to locate your next manufacturing plant can be a difficult decision, and it’s one that requires significant due diligence. We take a comprehensive look at the key factors — from the availability of skilled workers to effective corporate tax rates and quality of life issues — that can make your manufacturing relocation plan a success.
First, a quick disclaimer: as well all know, no two manufacturing operations are alike. For example, the needs of a specialized, R&D-driven medical devices company will be different from a price-sensitive, mass-market consumer goods operation. Likewise, an OEM electronics component supplier whose output delivery needs to be timed to the minute to satisfy a major automotive manufacturing plant will have different location requirements than a manufacturer processing raw materials sourced from a mining operation in Wyoming.
In other words, even though we’re presenting a comprehensive framework of manufacturing relocation factors, we hope it’s obvious that the importance of any one factor will be determined by the specific needs of your organization! Having said that, let’s take a look at hard costs first, followed by indirect, soft costs. Then we’ll look at some future trends to consider when weighing a manufacturing relocation decision, followed by a short list of some of the leading low-cost domestic and foreign locations. Finally, we’ll take stock of the pros and cons that could influence your own decision.

Manufacturing Relocation: Direct Hard Cost Factors to Consider
In this section, we’ll look at five relocation factors that can have a direct, measurable impact on the bottom line.
1. Supply Chain Infrastructure / Logistics and Access to Customer Markets
Does the candidate location bring you closer to your customer markets? Moving your manufacturing plant closer to your customers can help you increase profits or build up market share by speeding up delivery times, reducing inventory, and cutting costs.
Can you build an efficient, end-to-end supply chain in the candidate city, or will delivery of some components or raw materials be compromised by long distances or unreliable connections? Will weather conditions create unacceptable delays during part of the year?
We recommend performing a complete review of the region’s infrastructure, e.g. deepwater ports, freight rail access, trucking and highway connections, international airports, expediting and transshipment services, as well as Internet, communication, power and water utilities to determine if they are reliable and efficient enough to meet your specific needs.
2. Effective Corporate Tax Rates and Incentives
For each candidate location, it’s crucial to calculate the total impact of local, state, and national taxes, including property-based taxes. Quite a few jurisdictions offer tax breaks and rebates to companies in exchange for activities that benefit their community, such as renovating existing facilities or remediating brown-field sites, investing in targeted industries that create new jobs or conducting research and development activities.
(If your customer includes the Federal Government, don’t overlook preferential contract treatment set-asides — through the HUBZone program, for example — for companies headquartered in historically low-income census tracts.)
It’s also becoming more common for major companies, such as Boeing or Amazon, to conduct highly-publicized campaigns when choosing the location of a new facility. Many cities, regions, and states are willing to negotiate multi-year tax incentives or abatements in exchange for creating new jobs or locating facilities in their jurisdictions. Incentives may be available at the country level as well; for example, France has become notably more aggressive in courting tech-oriented companies .
3. Tax Domiciles, Exchange Rates and Economic Conditions
While smaller manufacturing companies are likely to keep things simple by limiting themselves to domestic operations, large corporations, such as Apple and Nike, have recently been thrust into the news as details of their highly complex tax domicile and ownership structures have been leaked to the press.
That’s quite a bit beyond our remit to provide that level of corporate advice*, as we’d rather stick to much more transparent considerations, such as exchange rates and general economic conditions. With respect to exchange rates, quite a few multi-national companies find it advantageous to hedge against dramatic shifts in exchange rates by having multiple manufacturing bases around the world. When one currency goes up, production can shift to a location with a more favorable exchange rate. And countries with long-term economic growth (and rising consumer incomes) obviously make better candidates for locating consumer goods manufacturing plants — unless your goal is to export 100% of the goods from countries with very low, depressed wages.
*We do note that proposed changes to the US Corporate tax code now before Congress (as of late November 2017) are worth careful monitoring as potential changes to the tax code may encourage US companies to repatriate their foreign-earned profits back to the USA.
4. Business Regulatory Regimes and Customs/Trade Agreements
Substantial trade agreements (such as NAFTA in North America), customs unions (such as the European Union), and special economic zones (such as China’s Shenzhen, the city immediately north of Hong Kong) have helped create regional manufacturing zones, where goods in process (as well as completed goods) can travel across country borders with minimal delays or customs duties. Harmonizing regulations across borders has also reduced non-tariff-based trade barriers. This combination has led to the development of highly-sophisticated manufactured goods supply chains; for example, oftentimes the individual components of automobiles produced North America make multiple trips across the Mexican, US, and Canadian borders before final assembly.
There are also new agreements are on the horizon that may impact manufacturing relocation decisions as well, such as the revived negotiations for a pan-Pacific trade agreement (once known as the Trans-Pacific Partnership) that will stretch from Canada to Chile, to New Zealand and Australia, to Japan and, potentially, Korea. (The US has opted out, and China has yet to be invited.)
On the one hand, so important are the ramifications of major trade agreements and customs unions, such as NAFTA and the EU, that they can be considered in some cases to be the sole determining factor when deciding where to locate a new manufacturing plant. On the other hand, these agreements can be politically controversial: witness the UK’s vote to leave the EU over issues such as free movement of people — despite repeated warnings from companies, such as Honda and Airbus, that a ‘hard’ Brexit would put their UK manufacturing operations at risk. Similarly, many American workers have come to resent NAFTA, for whom the agreement represents nothing more than jobs shifting to Mexico. However, changes to the NAFTA agreement recently proposed by the US trade representatives may prove just as disruptive to workers in the Detroit automobile industry as it will to mid-west farmers who depend upon grain sales to Mexico.
North American automotive manufacturing experts discuss ways that changes proposed by the US Administration to NAFTA’s rules-of-origin content regulation will affect North American manufacturing competitiveness.
The bottom line: when choosing a manufacturing location, have your eyes wide open to potential treaty and regulatory regime changes that may be on the horizon. Carefully investigate business regulations, permitting times (maddeningly long in Brazil and Greece), environmental regulations, and labor rules that would apply in your proposed new location. For example, European Union rules governing environmental pollution (such as the elimination of lead in manufacturing processes) and greenhouse gas reduction can be surprisingly strict, as can requirements for compensation and notice due to workers facing potential layoffs.
5. Business Operating Costs
Performing due diligence on direct business operating costs is next. You’ll want to collect data on these areas:
Facility / Real Estate Costs
What is the market for purchasing or leasing real estate? Will it be more advantageous to build or rent a new facility or renovate an existing one? Can you get an option for potential expansion? What are the tax implications (mentioned above) for owned property, including tools and inventory?
Utility Costs
Is the country self-sufficient in energy or could its supplies be disrupted by an energy boycott or cutoff? Are the utility costs favorable and services reliable? Will you need to budget for more than just emergency backup generators? Industries with high energy demands, such as data centers or aluminum alloy manufacturers, tend to gravitate to locations with low-cost energy resources, such as hydroelectric power.
Labor Unions and Wage Costs
What is the availability of skilled workers required for your manufacturing plant? What are the current local wage rates and minimum wage standards? Are there local training centers that graduate workers with the skills you need, or will you need to invest in training programs or pay to relocate staff? Are most manufacturing plants unionized in this location? Does the location have open or closed shop union regulations? How would you characterize the labor union’s relationship with local industry?
Employee Benefits such as Healthcare, Pensions, Unemployment, Insurance
What are the customary employee benefits in this location?
For example, will defined-benefit retirement plans (e.g. traditional pensions) or defined-contribution retirement plans (e.g. 401K) planned-benefit pensions be required as part of the compensation package?
What about employer-provided healthcare plans? Keep in mind that outside the USA most healthcare plans do not require employer contributions, these are provided either by direct insurance plans paid directly by individuals or funded by the government directly.
Is the employer responsible for paying unemployment, occupational accident or life insurance policy premiums in the proposed location? While these are benefits typically offered by American companies, this can vary worldwide.
Manufacturing Relocation: Indirect and Soft Cost Factors to Consider
Now let’s take stock of some of the indirect factors that you should consider when undertaking a manufacturing plant location analysis.
1. Network Effect / Industry Clusters / Talent and Knowledge Base
Historically, many industries tend to cluster in certain geographic areas. Examples of this include the auto and truck industry in Detroit, computers and software in Silicon Valley, pharmaceuticals in New Jersey, entertainment and media in Los Angeles, and finance in New York City or London. If there is such a cluster of industry in your sector, you should weigh potential pros and cons of the “network effect” that comes from being located near your competitors. When a region is known for a particular industry segment, it can attract talent and support institutional “know-how” that takes many beneficial forms, from informal industry contacts to educational programs in area schools and universities. It could also lead to job poaching or worse, such as compromising industrial secrets, which may lead you to decide to avoid being located anywhere near a competitor!
2. Business Transparency and Criminal Activity
As Americans, we tend to think of successful business transactions in terms of offering the best deal, the best product, the best service. As such, the idea that you have to pay a bribe to a potential customer or an official to secure a deal, or obtain a license or agreement doesn’t happen that often (not the least of which because it’s illegal this country). However, this level of business transaction transparency is not universal around the world. Paying money to customers, government officials, and organized crime figures can be commonplace in some parts of the world, which in turn, can pose problems for Americans who want to avoid these practices and also avoid violating American law. The stakes can be even higher. Criminal activities can be life-threatening in countries such as Mexico, Honduras, or El Salvador, where kidnapping company officials (or their spouses or children) for exorbitant ransoms are not unheard of. In these regions, hiring bodyguard protection and the use of secure, armored vehicles are considered a good investment.
3. Cost of Living for Employees
Can your employees afford to live well in the proposed location or will high or rising costs drive up wage costs? Take a look at housing affordability, the effective income tax rates (for national, state, and city taxes, if applicable) as well a property taxes.
Is there a way for employees to get to work efficiently, such as via a cost-effective public transportation system? Will they spend hours commuting to work — either because the road/transit system is poor and overcrowded or the commute distance between the manufacturing plant and affordable housing is too far?
4. Quality of Life Consideration
Health and safety.
What’s the homicide rate? How many deaths occur on the highway due to accidents? Are there drug and crime epidemics in the region? Do the area’s hospitals and doctors provide sufficient preventative and emergency care?
Educational Institutions
Are the public schools high quality, or will it be necessary for employees to educate their children privately, for example, at expensive, English-language international schools?
Are there institutions of higher learning that can attract candidates and provide a source of skilled, creative employees?
Cultural Institutions, Language, Religious Worship
Does the city offer museums, symphonies, theater and other enriching cultural institutions? Will company executives and family members need to learn a foreign language? Does the city or state allow for freedom of assembly and religious worship?
Diversity and Inclusion
Are the city and its workforce culturally and racially diverse? If located abroad, are there equal opportunities for women, or will female managers or expat family members find themselves excluded from many aspects of daily work and home life? Will LGBT employees and expat family members be accepted or discriminated against?
Recreation and Leisure
Are there amateur or professional sports teams in the city or region?
Are there plenty of outdoor and leisure activities to promote good health and mental well-being?
Can you Future Proof Your Manufacturing Plant Decisions?
It’s hard to predict the future, but it’s a useful exercise to think about potentially disruptive changes that could have an effect on your choice of a manufacturing location. It’s easy to get blindsided by unexpected developments… after all, even Michael Bloomberg, founder of the eponymous Bloomberg financial intelligence and media company, was caught out by the unexpected plans for the UK to exit the European Union just as he opened up Bloomberg’s spanking new European headquarters — in London!
Some of the items on this future possible developments checklist to consider include:
- Continued impact of smart, manufacturing automation and robots .
- Jobs that will be replaced by automation .
- The increasing importance of sustainability and the impact of renewable energy on manufacturing.
Top Lowest Cost USA Manufacturing Plant Locations
So, what do you think are the best locations in the US for siting your next manufacturing plant? For many, it’s not the west coast — detractors point to overcrowding and high costs, especially in real estate and salaries. (In fact, some investors are taking a second look at the mid-west as a place to invest in new tech startups .) Yet, Elon Musk has made a successful go at it, building Tesla cars in the expensive Bay Area and rocket ships along the coast east of Los Angeles.
As we said at the beginning of this article, the answer to which is the right manufacturing location for you is dependent on your industry sector and your particular mix of requirements. So we’ve turned to KPMG, who has handily enough undertaken a sector-by-sector analysis of different cities , here in the USA and abroad, and ranked them.
On a cost basis only, KPMG found these were the lowest-cost cities for operating manufacturing facilities in the US in 2016:
- Shreveport, LA
- Montgomery, AL
- Savannah, GA
- Baton Rouge, LA
- Nashville, TN
- New Orleans, LA
- Lexington, KY
- Gulfport-Biloxi, MS
Indeed, some famous names in manufacturing have moved to these cities, including Airbus (Mobile, AL), Gulfstream (Savannah, GA), Hyundai (Montgomery, AL), Lockheed Martin Corp/NASA (New Orleans, LA), Nissan (Nashville, TN), and Northrup-Grumman ( New Orleans, LA).
States with Lower Tax Rates
These states have no personal income tax:
- South Dakota
However, income tax rates are not the complete picture: sales tax, property tax, and other local taxes can affect the effective tax rate. Kiplingers publishes a comprehensive ranking of each state , which is worth evaluating to see how your candidate location ranks among the other states.
What about taxes on manufacturing facilities? According to the Tax Foundation, these states have the lowest tax rates for labor-intensive manufacturing facilities :
- Wyoming (4.3%)
- Virginia (4.3%)
- Georgia (4.6%)
- Maryland (4.9%)
- Nebraska (5.5%)
- Missouri (5.8%)
- Arizona (6%)
- South Dakota (6.0%)
- Louisiana (6.9%)
- Michigan (6.3%)
States with Low Cost of Living
In addition to taxes, there are many other factors which keep the cost of living lower in certain states. For example, states with moderate weather have reduced the need for winter heating or summer cooling. Housing, local utility rates, the cost of food, healthcare, insurance, and transportation can drive up the cost of living in a particular location.
CNBC recently published a report that ranked each state according to its cost of living . The ten cheapest states were:
- Mississippi
Open Shop States
For some, the site location selection will be influenced by laws governing labor unions. These states have “open shop” laws (also known as “Right-to-Work” laws) which make joining a labor union optional for individual employees. In 2017, over half of the states have open shop laws:
- North Carolina
- North Dakota
- South Carolina
- West Virginia
Top Low-Cost Global Manufacturing Plant Locations
What about international locations?
During 2016, KPMG found that, among ten major western economies, the strong US dollar made America the most expensive among these ten countries. Mexico came out on top, as the most cost-effective in KPMG’s ranking. Here is the list, from least to most expensive.
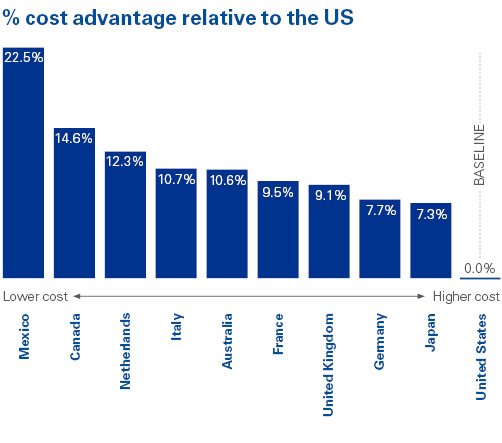
- Netherlands
However, the KPMG study didn’t investigate cities and countries that are increasingly making themselves known for inexpensive manufacturing, such as Poland, Romania, and Bulgaria in eastern Europe and Malaysia, India, Thailand, Indonesia, and Vietnam in Asia.
The consulting firm Deloitte performed a worldwide analysis that ranked countries according to their manufacturing competitiveness . While KPMG ranked the USA as the highest cost manufacturing location, Deoitte’s ranks the US as the most competitive overall. By the year 2020, Deloitte anticipates that the top 20 most competitive manufacturing companies will be ranked like this, with the US still the most competitive:
- United States
- South Korea
- United Kingdom
- Switzerland
- Czech Republic
Deloitte’s 2020 forecasts indicate that India and Vietnam will each move up six slots (compared to 2016), and Malaysia and Indonesia will each move up four slots. Along with Thailand, these countries, dubbed the “MITI V” group by Deloitte , are poised to be more competitive than China in the manufacture of labor-intensive products, such as commodity textiles, toys, and basic consumer goods.
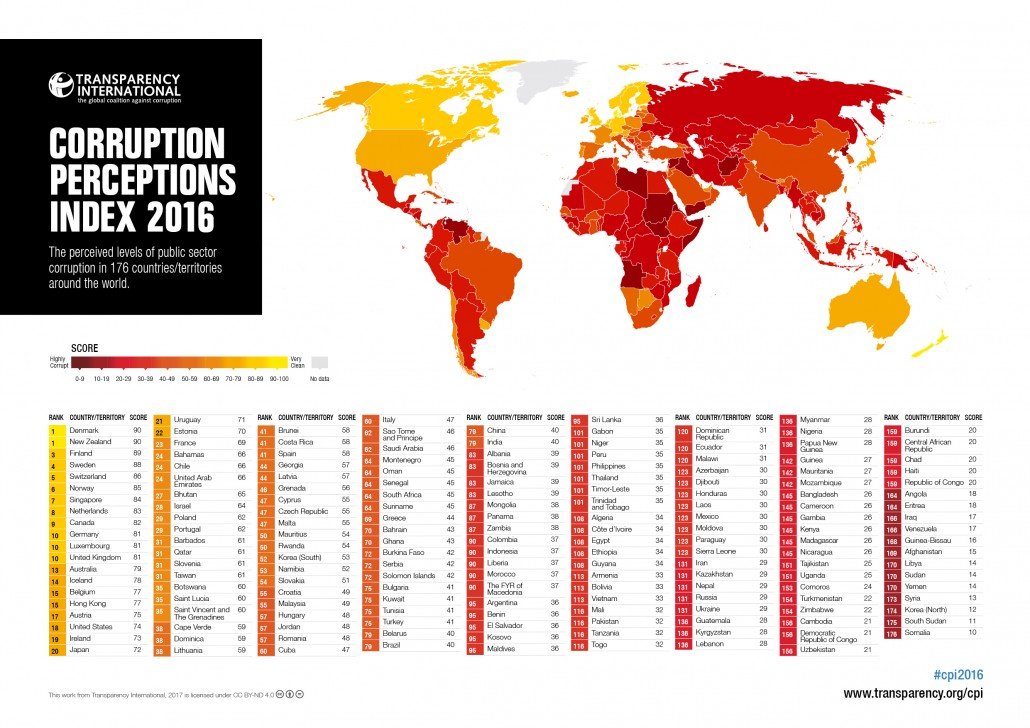
The cost of corruption, especially bribery and extortion, is another important consideration for your manufacturing facility site selection criteria. This map from Transparency International shows the relative rankings of countries in 2016 . Denmark and New Zealand are tied for the least corrupt countries. The United States has slipped to #18.
Weighing the Pros and Cons: Why Formaspace is in Austin, Texas
Decisions get made for a variety of reasons.
As for Formaspace, we looked at the pros and cons and found that for us, locating our factory headquarters in Austin, Texas was the right location:
- We are fortunate that our region in Texas has steel manufacturers so that we can get high-quality steel locally.
- Being located in the center of the country speeds up shipping times and reduces costs for our customers.
- Austin is well-known for the University of Texas, as well as many cultural activities and festivals, including the Austin City Limits music festival and SXSW Conference for the film, interactive, and music industries.
- We enjoy good weather (despite complaining about the heat in July and August), and there are plenty of outdoor recreational activities, including cycling, hiking, and water sports.
- On the other hand, the city has grown very fast (too many of you have come!), and now it’s difficult to get around during many times of the day; new roads and public transportation projects have been slow to close the gap.
- Austin is no longer inexpensive either; housing prices have increased dramatically in recent years, making it harder to live close to the city.
Nonetheless, we’re proud to be here and wouldn’t have it any other way!
Formaspace Can Help Make Your Manufacturing Relocation a Success
When you are ready to build, renovate, or expand your manufacturing operations, you should involve Formaspace early in the process.
Our Formaspace Design Consults can work with your architect and space planners to lend our extensive advice on how to make your manufacturing facility as efficient and productive as possible — from the executive office to the production floor to the warehouse. The process starts with a Formaspace Rapid Plant Assessment : our manufacturing experts review your plans and make recommendations on ways to improve efficiency, from implementing lean manufacturing methods to proposing technical furniture solutions, such as custom manufacturing workbenches , to make your manufacturing plant more productive than ever.

Find out why Fortune 500 companies like Dell, General Electric, and Lockheed Martin turn to Formaspace to help them create productive spaces that can have a major positive impact on their bottom line.
Learn more. Contact your friendly Formaspace Design Consultant today. Just fill out your information in the quick contact form below, and get the conversation started.

- Hospitality
- Business Location Intelligence
- Competitor Analysis
- What Makes a Franchise Unsuccessful and Unprofitable? (2021)
- How to choose the right location for your franchise in California?
- What is Franchise Territory and How to Determine It? (2021)
- 7 Steps to your next retail location
- 5 Tips for selecting a perfect retail location
How much does location matter in a retail business?
- Restaurant Labor Costs: Everything You Need to Know (2021)
- Restaurant Competitive Advantage: 6 Tips to Gain an Edge
- Get Started
10 Factors to Consider During Business Location Analysis (2021)
Selecting the best location for your new business is a decision that you should not take hastily.
Your first consideration in terms of comfort and cost concerns is to go on a quest to find the perfect location for your business.
In this article, we are going to shed more light on the concept of business location selection and then go deeper to discuss the terms of business location analysis and business location strategy and talk about their importance on business location selection.
Business Location Analysis: Definition and Objectives
Location refers to the choice of the region and the selection of a particular location for establishing a business or a factory.
But the choice is made only after the cost and benefits of the various alternative sites are considered.
It is a strategic decision, which can not be changed once it has been undertaken.
If the location is only changed at a considerable loss, it should be selected according to its requirements and circumstances. Every plant is a case in its own right.
A businessman will attempt to find the most suitable or ideal location.
An ideal location is one where the cost of the product is kept to a minimum, with a large market share, the least risk, and the highest social gain.
It is the location of the highest net benefit or which offers minimum unit cost of production and distribution.
Business Location Analysis Definition
Location analysis is a dynamic procedure in which entrepreneurs evaluate and compare the suitability or otherwise of alternative sites for choosing the best site for a given client. It is composed of the following:
1. Demographic Analysis
This includes the analysis of population in the region in terms of total population (in numbers), age distribution, per capita income, level of education, occupational structure, etc.
2. Trade Area Analysis
This is the analysis of the geographic area that offers the company continued clientele.
This analysis would also consider the possibility of entering the trade area from alternate locations.
3. Competitive Analysis
This analysis helps in assessing the nature, location, size, and quality of competition in a given area of trade.
4. Traffic Analysis
To get a rough understanding of the number of potential customers passing through the proposed site during the working hours of the location, the traffic analysis is aimed at determining possible locations in terms of foot and car traffic passing through a site.
5. Site Economics
Under this section, alternative sites are analyzed in terms of establishment costs and operational costs.
Establishment costs are the costs incurred for permanent physical facilities but operational costs are incurred for running a business on a day-to-day basis, these are often called running costs.
Business Location Analysis Objectives
The location of a business needs to be determined while keeping the following targets in mind:
1. Holding Minimum Investment And Operating Costs
The primary goal of choosing a suitable location is to ensure minimal investment and lower operating costs.
This could be achieved by locating the business in a place where raw materials, labor, transportation, and power are readily, regularly, and sufficiently available.
2. To Make Sure The Business Operation Is Smooth
Another goal of the optimal location is to ensure the business operations are running smoothly.
This could be achieved if the business is located in a place where banking, communication, transportation, repair, and maintenance services are easily and regularly available.
3. To Improve Welfare Of The Employees
If the business is located where educational recreational, media and religious needs of the employees are met, they will definitely feel attached to the business and develop loyalty and commitment to it.
4. To Coordinate With The Government Policies And Regulations
Whilst selecting a location, the entrepreneur must ensure that their decision does not conflict with the policy of balanced regional development issued by the government.
Business Location Strategy Factors
Being in the right location is a crucial ingredient in the success of a business.
If a business chooses the wrong location, it may not have sufficient access to customers, workers, transportation, materials, etc.
Consequently, location often plays a significant role in the profit and overall success of a business.
A location strategy is a plan to achieve the optimal location for a company by identifying the needs and goals of the company and searching for locations with offerings that are compatible with those needs and goals.
In general, that means the company will try to maximize opportunities while minimizing costs and risks.
The location strategy of a business should adhere to its overall corporate strategy, and be part of that plan.
Therefore, if a company dreams and plans to become, for example, a global leader in fashion production, it must consider establishing plants and warehouses in regions that are consistent with its strategy and optimally positioned to serve its global clients.
Executives and managers of a company usually develop a business location strategy but companies however, may select consultants (or economic development groups) to undertake the task of developing a location strategy, or at least assist in the process, especially if they have little experience in location selection.
The standard formulation of a business location strategy includes the following factors:
- Facilities: Planning facilities requires deciding what sort of room a organization would be required, considering its short-term and long-term objectives.
- Feasibility: Analysis of feasibility is an assessment of the various running costs and other considerations related to the different locations.
- Logistics: Logistics assessment is the examination of the transport choices and costs for the manufacturing and warehousing facilities in question.
- Labor: Analysis of labor determines whether or not prospective locations can meet the labor needs of a company, given its short-term and long-term objectives.
- Community and Site: Evaluation of the Community and site includes understanding whether or not a business and a prospective community and site would be compatible in the long term.
- Trade Zones: Companies will want to consider the advantages that free-trade zones provide, which are closed facilities supervised by customs services where goods can be brought in without the normal customs requirement. There are some 170 free-trade zones in the United States and other countries have them too.
- Political Risk: Companies considering expanding and spreading to other countries must take political risk into consideration when establishing a business location strategy. Because a number of countries do not have stable political environments, if companies plan long-term operations in such countries, they must be prepared for upheaval and turmoil.
- Governmental Regulation: Companies can also face government barriers and severe constraints and regulation if they plan to expand to other countries. Therefore, when developing location plans, businesses need to investigate regulatory – as well as cultural – challenges in other countries.
- Environmental regulation: The various environmental regulations that could affect their operations at different locations should be considered by companies. Environmental regulation can also impact the relationship of a company with the environment surrounding a prospective venue.
- Incentives: Incentive negotiation is the process of negotiating land between a business and a group, including any incentives that the business may obtain, such as tax cuts. Incentives can play an important part in the selection of a site by a business.
Companies may also have to look at other aspects of prospective locations and communities, depending on the type of business. Based on these considerations, businesses are able to choose a site that best serves their needs and helps them develop a business location strategy and therefore achieve their objectives.
Requirements Of The Company
The initial part of developing a business location strategy is to determine what a firm will need from its locations.
These needs then serve as some of the primary criteria that a business uses to evaluate various options. Some of the basic criteria that an organization has to remember are:
- Size: A business has to determine the size of the property or the facility it requires for its actions.
- Traffic: If you are in the service business, your company must obtain statistics on traffic volumes or the number of pedestrians passing by a prospective location every day.
- Population: If you are running a service or a manufacturing activity, your company needs to analyze the population of prospective locations to ensure a sufficient number of potential clients (if a service business is in discussion) or a sufficient number of qualified or trainable employees. Additionally, manufacturers also benefit from being close to their customers, because customer proximity reduces shipping time and cost and increases customer responsiveness for the company.
- Total costs: Companies should determine the maximum total cost of a new location that they are willing to pay. Total costs include costs related to production, property, labor, taxation, services, and construction. More baffling costs, such as materials for shipping and costs of supplies transportation and the loss of customer responsiveness should also be considered if it moves further away from the customer base.
- Infrastructure: Businesses need to consider what their infrastructure requirements are going to be, including what modes of transport they will need and what types of telecommunications services and equipment they will require for their operations.
- Suppliers: All businesses need to consider the types of suppliers they will need close to their locations. Additionally, having nearby suppliers can help companies lower their cost of production.
In addition to these specific criteria, businesses have to take their particular specifications of prospective locations into consideration. These requirements may be consistent with their overall corporate strategy and corporate goals, and with their specific industries.
Business Location Strategy Trends
Over the last thirty years, globalization and technology have been the greatest drivers of change in the business location selection process.
In recent decades, location activity has been very high due to technological changes, economic growth, international expansion and globalization, and corporate consolidation, mergers, and acquisitions.
Price, infrastructure, labor characteristics, policy and political problems, and the environment are the top five location considerations for global companies.
The availability and quality of labor force, the quality and reliability of utilities, the quality and reliability of transportation modes, telecommunications systems, wage rates, worker motivation, government stability records and industrial relations laws are crucial sub-factors.
Other sub-factors such as patent protection, availability of management resources and specific skills, and cost of system and integration are becoming increasingly important.
Whereas wages and the environment of industrial relations are important factors in making decisions about multinational locations, the main determinant is by far the market size of the host country.
Moreover, global economic considerations have become dominant in the business location strategy, as businesses consider the advantages offered by various locations in terms of positioning themselves on international markets and against other competitors.
In general, when companies seek new locations, they strive to keep operating and start-up costs low, and so they often choose locations to achieve these goals in collaboration with economic development groups.
Companies also now expect to move faster than in the past to new facilities so they tend to focus more on leasing facilities than buying land and building new facilities.
Plus, by leasing equipment and facilities, businesses can migrate every few years if they are required by the market.
Mapchise Technology
Technology, in particular communications technology, has not only been a catalyst of change, but also facilitated the location selection process.
Managers can get initial information via the Internet and promotional software on alternative locations.
Site selection agencies are increasingly using Geographic Information System (GIS) technology, and email has become the most powerful and popular mode of communication in the quest and through negotiation of business locations.
Location databases have allowed businesses to do their own initial screening, thereby reducing their need to rely on economic developers to provide only very basic information and position details — such as commuting habits and workforce characteristics.
This is where Mapchise comes to play. Mapchise is a platform for analytics and location management, designed to expand and manage current and prospecting locations.
The primary purpose is intended for multi-chain prospecting and management.
Analytics Map is built on demographic analysis for prospect locations. This concept is the primary product and principal selling point of Mapchise.
It consists of three different sources of data: Demographics and Socio-demographic (still in production), Commercial Real Estate, and Residential Property. Socio-demographic is a categorization of different age groups, race, and income.
The main features of this product include:
- Commercial Real Estate Data (Data is for all of US)
- Competitor analysis
- Customized target demographic reports to clients needs
- Socio-demographic data
- Real estate data
- Traffic and regional market analysis
- Territory zoning to prevent canabolization
- Different layers customized to clients target demographic
Why Choose Mapchise?
- It provides all the data you need to open a location easily. The data is also proprietary so it won’t be found online for free.
- Task management system is designed and built for multi-chain stores and ease of use by corporate and store management.
- Fully Customizable analytics system designed for the users target market and target demographic, the map and data are built around users provided target market. After answering a few simple demographic questions, the map is fully customized to users’ input.
- Competition Analysis on the map
- Task management system is incorporated into the map for easier management of all locations tasks
How To Find The Best Location For Your Business?
Every business owner has to figure out how the location will (or will not) contribute to the success of a business — and select a spot according to it.
Although when you are looking for a space to house your business, there are many issues to consider, make sure you ask yourself these four important questions:
- Is location significant to the success of your business?
What kind of location would be best for your business?
How much rent you can afford to pay.
- Is the location you have in my mind appropriate for what you want to do there?
Is Location Significant To The Success Of Your Business?
The classic “location, location, location” advice for some businesses is right on the mark— location can bring the difference between feast or famine into reality.
But location may be far less important for other businesses than finding affordable rental space.
In fact, for some businesses, the location is almost irrelevant: service businesses that do all their work at the locations of their customers (such as roofers and plumbers) and businesses that have little public contact (such as mail order companies, Internet-based businesses, and wholesalers).
Picking a low-cost spot in an out-of-the-way location might be a benefit because these types of businesses can pass on rent savings to their clients and their profit margin.
The key to choosing a profitable location is to evaluate the factors that will increase the amount of customers for your company. Ask yourself questions such as:
- Will customers be walking to your location?
- Will customers drive and, if yes, where will they park around your area?
- If you locate near other similar businesses, will you receive more customers?
- Will the reputation of the neighborhood or even of a specific building help you attract more customers?
Bear in mind that different types of businesses draw clients in different ways.
Foot traffic versus car traffic is one of the main distinctions.
For example, if you are opening an urban coffee shop, you can expect your customer volume to be the highest if there is plenty of pedestrian traffic nearby during the hours you plan to keep your business open.
On the other hand, the most suitable locale for an auto repair shop is a well-traveled street where many drivers will see the shop, and are able to easily pull into the lot.
Note also that it would be of benefit to your business to be around similar businesses that already attract the same type of customers you are planning attract.
For example, a women’s clothing store will certainly profit from being close to other clothing shops because many people who shop for clothes prefer to spend at least a few hours in a given location.
In the end, the perfect location for any business is a very individual matter. Spend some time finding out the consumer preferences you would like to draw to your business, and then pick the most suitable location that meets all your needs.
Chances are that you will eventually rent out instead of buying a space for your business.
Most small businesses do not posses the funds to purchase real estate, and in any case it is not necessarily a smart idea to saddle the company with high interest payments.
When looking for a commercial space to lease, one obvious and important concern is finding a location that you can afford.
When preparing your financials (as part of your business plan), you would have calculated how much rent your company will be able to pay on a monthly basis, considering its expected sales and other expenses.
How to assess the average rent in any area?
Agents and brokers are excellent sources of rental cost knowledge in different neighbourhoods.
They will generally give you an average figure for the cost of commercial space per square foot per year in a given area. If you have this number, you can compare it to other spaces you are considering to rent.
If you have not already done so, check out the average rental costs in your area to make sure that the amount you have budgeted for rent makes sense, considering the cost of commercial space in your area, and how important your location is to your business.
For instance, if you decide that location is very important to the success of your business, make sure your budget would allow you to rent a good space given the average cost of space in your area.
If not, then your business plan may need to be reworked.
Is The Location You Have In My Mind Appropriate For What You Want To Do There?
The biggest consideration when choosing a business location is sometimes not where it is but what it is.
The building facilities must be suitable for (or adaptable to) your business. For instance, if you intend to open a coffeehouse, you need a place with limited kitchen facilities, at least.
Unless you are able to convince the landlord to put in the necessary equipment — plumbing, electrical work, and the rest — it is highly unlikely that it will be worth it to lay out the cash to do it yourself.
In short, if a building lacks something substantial that is essential for your business, you should probably look for something else.
Communications Wiring
Another consideration that is important for many businesses these days is having access to modern phone and other data lines that are required by the business.
When considering a particular space, ask the agent or the landlord for communications wiring details, such as whether the space is connected to a fiber optic network or wired for DSL or T1 line (high-volume Internet connections).
Even try to find out who the landlord sold the rights to the risers (wire conduits) in the building. A commercial landlord can not be involved in exclusive contracts with a single provider of telecommunications, such as MCI or AT&T.
It could however be expensive to bring in another provider of your choice.
Electricity and Air Conditioning
Besides high-tech communications wiring, when choosing a business space, do not overlook plain-old electrical power as an important consideration.
Make sure that every room you are looking at has enough power for your needs, both in terms of space outlets and the capacity of the circuits.
If you are going to be operating machinery or other electricity-hungry equipment, find out how much energy the circuits can tolerate from the landlord, and if a generator is available during power outages.
Moreover, if you are going to keep sensitive computer equipment in your office, ask the landlord how many hours of air conditioning will be included in the terms of your lease, and if necessary negotiate longer hours.
Another growing requirement for many businesses is sufficient car parking.
If a significant percentage of your customers come to your establishment by car and there is not enough parking at your chosen spot, looking elsewhere is probably the best alternative.
In addition, the city planning or zoning board can not allow you to function in a space with inadequate parking.
Zoning Rules
At last, the location that you choose for your business needs to be legally acceptable for whatever you plan to execute there.
A certain spot may be good for business, but you are asking for trouble if it is not zoned for what you are planning to do.
You must never sign a lease without being sure that you will be allowed to operate what you are planning in that space.
Your city planning or zoning board will determine what activities are allowed at a given location.
If your zoning board is having a problem with any of your business activities and you are not willing to work out a way to accommodate your company, you may need to find another space for your business.
Never Miss an Article
Sign up for our email list to get relevant content about your industry
More Resources
Other relevant articles, related reads, location intelligence and hospitality industry.
- Sam Nikaein
How to Identify Retail Target Market? (8 Simple Tips)
Copyright © 2020 mapchise all rights reserved., terms of use.
Automated page speed optimizations for fast site performance

Business Location Analysis Example – Site Selection in Business Plan
Proper site selection for your business influences whether you succeed or fail in making money. Your business location analysis should take into account demographics, psychographics, census and other data. Whether you’re trying to decide where to open a new store or where to locate a second office, follow this business plan location analysis example to maximize your chances of success in site selection.
Table of Contents
Location Analysis Definition
Location analysis definition : using data to figure out where to locate your business.
Determining where to put your store, office or even online presence requires careful thought. If you get this wrong, you could be trapped with a commercial lease that costs you a lot of money but doesn’t result in getting new customers.
Business Plan Location Analysis
There is a saying that the three most important considerations in business are location, location, location. If you’re starting a new business that operates primarily offline, location is critical. You want to be near your customers.
But is it critical for online businesses, too? Yes, in a different way. Online location is akin to having the right domain name, online advertising, and search engine optimization so that prospects can find your business.
In two slightly different ways, location is still an important part of doing business. A business plan has two purposes and will serve one or both: 1) raise additional capital and 2) outline in detail how you can succeed in your business (like a user’s manual).
Essentially, you want to answer two questions:
- How can I succeed here?
You will need to answer both of these questions for your site selection analysis.
Site Selection
Answering “why here,” for a brick and mortar location, will address the physical address (or addresses) where your business will take place.
For an online business, “why here” will address your website’s domain, web hosting service, and presence in search results.
Some of this material may overlap with your marketing plan (download a free sample marketing plan ).
Provide data for each of these elements in your business location analysis:
- The elements that attracted you to this location.
- The process you went through to identify this location as the location of choice; in other words, how you narrowed it down from the entire city to the specific location, or from the vast range of URLs to the specific URL you will use.
- Demographic analysis of the people in the area. Be sure to focus in on the make-up of your target market. If you market to women ages 18- 35, talk about what the overall demographic makeup is in your area and (in greater detail) the demographics of the areas women ages 18 – 35.
- Traffic patterns (for example: Time of day – are there rush hours when you’ll be busier?)
- Refer to your marketing plan section where you might talk about how your signage will receive greater exposure at certain times or how your advertising appropriately targets your market.
- Access to future employees: are there enough people qualified to work for your business in the area?
- Competition in the area.
Location Analysis Example
Food chain Whole Foods , now owned by Amazon, picks their locations based on many factors, not just population density in a neighborhood. They found that one of the key drivers that determines whether patrons will shop at their grocery stores is their level of education. As a result, their site selection process looks at locations with a higher per capita level of college degrees.
Costco takes into account population trends to ensure that the neighborhoods in which they locate their stores can sustain sales of their bulk-packaged products.
Walmart uses advertisements to see how far people will go to buy products at their stores. They track usage of mobile advertisements and create a geofence boundary to identify who goes where to buy what. This analysis helps them with their site selection for new stores.
Business Location Analysis
Next, analyze the data you gathered above. This is an important step because it shows the considerations and thought process you put into your business location analysis. Many location analysis examples overlook this part.
Including only the data reduces your chances of success. Add these elements to put perspective on your reasoning:
- Challenges you will overcome. For example, is it difficult to make a left turn across traffic to get to your store? Do people have to “feed the meter”? Those could substantially reduce your target market.
- What your competitors are doing and what you will do differently. You probably already did quite a bit of this in the marketing plan section of your business plan, but this has a slightly different focus and you may want to reference some of those ideas.
- Outline best case scenario and contingency plans, referencing your marketing plan against your demographics.
- Highlight the strategies you can use to access the area’s workforce as your business grows. A good indicator is the presence of companies like yours, which provides an opportunity for you to recruit qualified employees.
- Find competitors in the same area, or in an area of similar demographics, and identify what they’re doing to be successful.
Avoid picking a new location just because it has cheap rent. Signing such a business lease could spell disaster for your business because you may not have access to the clientele and workforce you need to succeed. Paying a little more for for the right address can boost your profits in a big way.
Do the research and think through the implications of your data to dramatically improve your chances of success at your new location.
Like this? Share it with your network:
I need help with:, popular topics:.
- Learning SEO
- Generating Sales
- Writing a Marketing Plan
- Writing a Business Plan
- Leading My Team
- Free Marketing Webinars
- Starting My First Business
Got a Question?
Get personalized expert answers to your business questions – free.
Affiliate Disclosure : This post may contain affiliate links, meaning we get a commission if you decide to purchase something using one of our links at no extra cost to you.
You Might Also Like...

Should I Give a Discount on My Consulting Fees?

SEO Title Tag Makeover: 4 Powerful Examples

5 Steps to Design an Effective Employee Engagement Action Plan

4 Actionable Steps to Find a Mentor for Your Business

5 Effective Scheduling Tips To Boost Your Productivity

Business Coaching vs Executive Coaching: 10 Examples

7 Employee Satisfaction Secrets: Nurturing a Happy Small Business Team

Secure Your First 10 Investors: Step-by-Step Startup Guide

SEO Coaching and Marketing Courses
Get More Business
Marketing tools.
- SEO Keyword Tool
- MSP Website Content Kit
- Done-for-You Content
- Graphic Design Tool
- Webinar Automation
- Getting Referrals
- Hubspot Marketing Automation
Popular Downloads
- Marketing Plan Example
- MSP Marketing Plan
- Life Coach Business Plan
- Consulting Business Plan
- How to Write a Business Plan
- Clothing Line Business Plan
- Restaurant Business Plan
- Personal Trainer Business Plan
- Trucking Business Plan
- Pizza Restaurant Business Plan
Free Guides
- B2B SaaS SEO Best Practices
- MSP SEO Marketing Playbook
- Buyer Persona Examples
- How to Increase Google Rankings
- New Client Welcome Package
- How to Create a Happy Customer
- Brand Development Guide
- SaaS Metrics Dashboard
- Marketing and SEO Videos
- Salary Calculator
- Executive Coaching Newsletter
- Contributing Content
- Affiliate Disclosure
Don't bother with copy and paste.
Get this complete sample business plan as a free text document.
Pie Restaurant Business Plan
Start your own pie restaurant business plan
UPer Crust Pies
Executive summary executive summary is a brief introduction to your business plan. it describes your business, the problem that it solves, your target market, and financial highlights.">.
UPer Crust Pies will specialize in meat, vegetable and fruit pies made using old-country traditional family recipes from the UP – Michigan’s Upper Peninsula. Our pies will be baked fresh everyday and sold hot directly to customers through our retail stores. We will also sell frozen pies in lunch and family sizes that can be cooked at home in an oven or microwave. Our products are low fat and free of genetically modified ingredients and will be complemented by an assortment of fresh premium salads and desserts.
By importing our products directly from a private label bakery in the UP we avoid high labor costs, expensive investment in manufacturing and production equipment, and additional warehousing and production facility costs. Our major costs will be limited to product purchasing, shipping and cold storage.
We have plans to expand the company through further retail outlets and are focused on developing a business model that is favorable to franchise possibilities. With an exclusive import license that could be used to sell frozen product through supermarkets and bulk wholesale food chains, UPer Crust Pies could quickly and clearly establish itself as the market leader.
We have identified four main keys to our success. The first is to secure stores in highly visible locations. The second will be our unique value-for-money product line. The third will be a focus on superior customer service and education, and the fourth key will be employee retention through training and internal promotion.
The proposed business location for the first UPer Crust Pies store will be in downtown Yubetchatown. At this stage five possible sites are being considered in three areas. UPer Crust Pies will target three market segments within the core metro district. Our largest target market is young adults and business people (42%). Our next largest market, and the one with the greatest growth potential, is families with children (36%), and our final target market will be 15-24 year olds which includes students (22%).
Our marketing strategy will be to attract new customers, educate those customers and then create a loyal customer base. UPer Crust Pies will attract consumers through highly visible signage, print media advertising, flyers, entertainment book coupons, word-of-mouth advertising and strategic alliances.
Our sales strategy includes hiring employees who genuinely enjoy their jobs. We will continually assess all aspects of the business and interact with our customers personally, evaluating food choices for popularity and keeping favorites on the menu as we rotate weekly and seasonal specials.
UPer Crust Pies is a Limited Liability Company. All membership shares are currently owned by Lina and Olie Mackinac-Gogebic, with the intent of using a portion of shares to raise capital. UPer Crust Pies is currently seeking a bank loan with an additional private investment contribution from outside investors. The majority of these funds will be used for corporate design, remodeling and lease payments three months prior to opening.
Start-up costs include initial inventory for the first store including shipping and cold storage fees associated with the product. Equipment assets such as a commercial oven, pie warmers, ambient display cases, refrigerators, freezers and miscellaneous one-time furnishings must be purchased. In addition, UPer Crust Pies anticipates the need for liquid cash for operating expenses, unforseen expenses and to help cover wages for the first three months of business.
UPer Crust Pies has forecasted a modest growth rate for the first year of business. In the second year, the company will add two more stores and in the third year, an additional two stores. The addition of these stores will increase the gross revenue in the second and third years. Compared to industry standards we have forecasted a very conservative growth rate for the first three years of operations.
1.1 Objectives
- Achieve first year sales above $120,000.
- Maintain a healthy average gross margin.
- Develop a business model that is favorable to expansion.
- Establish five store locations by the end of the third year.
1.2 Mission
Customer satisfaction and education are our paramount missions. We will endeavor to meet the highest standards of excellence through superb customer service and consistent product delivery in a friendly and comforting environment.
We seek fair and responsible profit, enough to keep the company financially healthy and ensure continued growth and development. Responsible profit will fairly compensate owners and investors for their risk and reward employees for their hard work, loyalty and commitment.
Employee welfare, participation, and training are equally important to our success. Every employee will be treated fairly, with dignity and the utmost respect. It is our responsibility to provide employees with a friendly, comfortable and challenging work environment with opportunities for growth and development.
1.3 Keys to Success
- Locations: visibility, high traffic patterns, convenient access.
- Store design: visually attractive, relaxed atmosphere, fast and efficient operations.
- Unique products: differentiation, competitive pricing, no direct competition.
- Quality controls: genetically modified free policy, consistency, clean presentation.
- Service: cheerful, professional, articulate and informative.
- Marketing: positive image, educational, word-of-mouth advertising.
- Employee retention: training, ongoing education, recognition programs.
Company Summary company overview ) is an overview of the most important points about your company—your history, management team, location, mission statement and legal structure.">
UPer Crust Pies is a specialty meat and fruit pie retailer importing its products from Michigan’s Upper Peninsula. At present there are only two small competitors servicing the entire U.S.A. UPer Crust Pies will offer hot ready-to-go meat and fruit pies and frozen take-home options as well as an assortment of fresh salads and cold beverages.
We are considering five possible locations for its first store in downtown Yubetchatown. The company has plans to expand with an additional four stores in the local megalopolis over the next three years. Implementing a sound business model into our first store will aid expansion plans and open up the possibility of franchising.
UPer Crust Pies is currently seeking a bank loan and an additional private investment contribution from outside investors and family members.
Major costs include initial inventory purchases, equipment purchases, shop rental, personnel wages, site remodeling, marketing and various other operating expenses. Projected gross sales for the first year of business are expected to be over $120,000.
2.1 Company Ownership
UPer Crust Pies is a Limited Liability Company. All membership shares are currently owned by Lina and Olie Mackinac-Gogebic, with the intent of using a portion of these shares to raise private investment through outside investors and family members.
If all funds are raised, based on the investment requirements established in the financial section of this plan, Lina and Olie Mackinac-Gogebic will maintain ownership of no less than 51% of the company.

2.2 Start-up Summary
Start-up expenses and assets are shown below, and the majority of these funds will be used for corporate design, re-modeling and to pay rent for three months prior to opening.
No legal costs will be incurred as the owners have agreed to trade a stock option with the company’s legal counsel in return for on-going legal services.
Start-up assets include initial inventory for the first store including purchasing, packaging, shipping and cold storage fees associated with buying the product inventory. Purchases of equipment assets such as a commercial oven, pie warmers, ambient display cases, refrigerators and freezers and miscellaneous one-time furnishings are necessary. The company anticipates the need for liquid cash for operating expenses, unforseen company expenses and to help cover wages for the first three months of business.
| Start-up | |
| Requirements | |
| Start-up Expenses | |
| Legal | $0 |
| Stationery | $600 |
| Liability insurance | $2,000 |
| Rent (3 months prior to opening) | $8,000 |
| Computer | $1,200 |
| Licenses | $700 |
| Corporate design | $9,000 |
| Web design & implementation | $3,500 |
| Lease-hold improvements | $20,000 |
| Total Start-up Expenses | $45,000 |
| Start-up Assets | |
| Cash Required | $118,000 |
| Start-up Inventory | $12,000 |
| Other Current Assets | $0 |
| Long-term Assets | $65,000 |
| Total Assets | $195,000 |
| Total Requirements | $240,000 |
UPer Crust Pies will specialize in quality pies and pastries, imported frozen from the Upper Peninsula of Michigan and baked fresh every day. The premium taste, presentation and quality of our pies will not only be unique in Yubetchatown and the greater megalopolis area, but in the entire United States.
UPer Crust Pies are low in fat, free of genetically modified ingredients and made with premium ingredients. After oven baking, pies are put into warmers and held at a steady temperature to ensure rapid service and high customer satisfaction.
The company will also sell frozen pies that can be taken home and cooked in an oven or microwave. New technology in manufacturing has enabled New Zealand producers to develop a pie that can be heated by microwave in less than three minutes with the pastry remaining flaky as if it had been cooked in a convection oven for thirty minutes.
Our pies experience will be complemented by an assortment of premium salads and desserts as well as cold beverages. Savory samples will also be offered to first-time visitors.
What is a Pie?
The meat pie is a traditional old-country food consisting of savory fillings in a pastry shell. Traditional fillings include beef and cheese, steak, bacon and egg, and chicken and vegetable to name a few.
Usually eaten hot from a paper bag, with flaky golden pastry and savory fillings, the pie is unpretentious comfort food. UPer Crust Pies will bring the Upper Peninsula pie experience to the U.S. and endeavor to establish the humble meat pie as gourmet fare for Americans while bringing a taste of home to “UPers” living throughout America.
The Menu
The Classic Pie Selection (6.25 oz)
- Beef : Lean savory ground beef in a smooth sauce with fresh herbs and spices in a low-fat pastry.
- Steak : Prime lean steak in rich hearty gravy wrapped in a low-fat flaky pastry.
- Chicken & Vegetable : Chicken breast with garden vegetables in creamy white sauce and wrapped in a low-fat flaky pastry.
- Bacon & Egg : One egg cracked on top of a lean slice of shoulder bacon wrapped in a low-fat flaky pastry.
- Potato Top : A traditional Shepherds pie with lean ground minced beef and a creamy mashed potato topping.
- Steak & Mushroom : Chunky steak prepared in a smooth dark sauce with fresh sliced mushrooms in a low-fat flaky pastry.
- Steak & Cheese : Chunky steak in a dark gravy mixed with pizza blended cheese and wrapped in a low-fat flaky pastry.
- Beef & Cheese : Ground beef in rich gravy mixed with pizza blended cheese and wrapped in a low-fat flaky pastry.
The Gourmet Pie Selection (9.5 oz)
- Thai Chicken : Succulent chicken breast in a creamy oriental sauce wrapped in a light low-fat flaky pastry.
- Bacon & Egg : Two whole eggs cracked on top of lean shoulder bacon, wrapped in a low-fat flaky pastry.
- Beef, Cheese & Tomato : Ground beef in dark gravy with low fat cheese, garden tomatoes and wrapped in a low-fat flaky pastry.
- Chicken & Vegetable : Succulent chicken breast and garden vegetables in a creamy white sauce wrapped in low-fat flaky pastry.
- Butter Chicken : Chicken breast in a smooth, creamy Indian delight prepared in a low-fat flaky pastry.
- Cracked Pepper : Prime strips of beef in rich creamy sauce complimented with spicy cracked pepper corns.
- Beef, Bacon & Double Cheese : Lean beef in a rich gravy, creamy cheese sauce and slices of bacon wrapped in a low-fat flaky pastry.
- Steak & Cheese : Chunky steak in a rich hearty gravy with fresh herbs and spices, wrapped in a low-fat flaky pastry.
- Vegetarian : Garden vegetables prepared in a smooth creamy sauce and wrapped in a true light vegetable pastry.
Rolls & Savories: Sausage rolls, beef rolls, garlic and cheese rolls and small savories all wrapped in a low-fat flaky pastry.
Desserts & Fruit Pies: Low-fat lattice-top dessert pies in cherry, apple, apricot, custard, apple and a selection of cheese cakes.
Salads: Caesar Salad, Greek Salad, French Salad, Potato Salad, Fruit Salad.
Cold Beverages: Coke, Sprite, 7-Up, Carrot, Apple and Orange Juice, spring water, energy drinks.
Market Analysis Summary how to do a market analysis for your business plan.">
The market we will engage in first is the downtown Yubetchatown district. Yubetchatown is centrally located in the Bigriver Valley, home to approximately 3.5 million people. It is an integral part of greater Megalopolis.
Yubetchatown is the seventh largest city in the state with a population of 84,560 and a geographic area of 29 square miles. With a growth rate of 8.5% Yubetchatown’s population is projected to grow well over 100,000 by 2008. It is anticipated that Yubetchatown will become the largest city in south Bigriver Valley.
Yubetchatown’s trade area consists of approximately 160,000 residents and is home to a diverse economic base including corporate offices, retail, industrial and manufacturing companies and one of the largest warehouse and distribution centers in North America.
The median household income in the Yubetchatown area is around $91,000 and the median age is 34 years old. Of the south Bigriver Valley population 13% are under 14, 14.5% are 15-24, 21.5 % are 25-34, 36% are 35-59 and 15% are over 60 years of age.
Demographically the UPer Crust Pie customer will come from all age and income levels of the market. Within this population we will focus on three separate groups with different needs: 15-24 year olds (including students), young adults and business people (25-34) and families with children under 14.
4.1 Market Segmentation
UPer Crust Pies intends to market to a wide customer base. However, we have defined the following groups as targeted segments that contribute to our growth projections:
- Families with Children
The largest target market is young adults and businesspeople. Our next largest market and the one with the greatest growth potential is families with children followed by the 15-24 year-old segment.

| Market Analysis | |||||||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | Year 4 | Year 5 | |||
| Potential Customers | Growth | CAGR | |||||
| 15-24 Year Olds | 2% | 80,662 | 82,275 | 83,921 | 85,599 | 87,311 | 2.00% |
| Young Adults and Businesspeople | 3% | 122,282 | 125,950 | 129,729 | 133,621 | 137,630 | 3.00% |
| Families with Children | 3% | 115,498 | 118,963 | 122,532 | 126,208 | 129,994 | 3.00% |
| Total | 2.75% | 318,442 | 327,188 | 336,182 | 345,428 | 354,935 | 2.75% |
4.2 Target Market Segment Strategy
Young adults and businesspeople have the potential of providing large volume sales to the company during the peak hours of 11 a.m. to 2 p.m. The lunch business is driven by individuals. Many go out to lunch to get out of the office setting or have business meetings at lunch either in or out of the office. We will endeavor to accommodate surrounding businesses placing phone-in orders for business meetings. Satisfaction of this group will provide a vital long-term revenue stream.
Families with children are a growing population, both numerically and in their choice for convenient foods. Two-income families have less time to prepare meals so they are an easy group to market to because their lifestyle is very specific. We will aggressively target single and working mothers who tend to turn to fast and convenient food choices to accommodate family demands. By targeting this group, we not only generate a large volume of immediate business, but also create long-term customers in their children.
Our downtown location and increasing customer base will probably draw in customers outside of our targeted groups to include visitors and downtown shoppers. We believe these customers will be glad to pay a reasonable price for our products in exchange for high quality, great taste and the uniqueness they receive.
4.3 Service Business Analysis
The United States Fast Food Industry
The U.S. has 277,208 fast-food outlets from coast to coast, that’s one for every 1,000 people. According to the U.S. department of Agriculture, consumption of food away from home accounted for 47% of total food expenditures in 2001, up from 45% in 1990 and 26% in 1960. The National Restaurant Association estimates that by 2010, total sales in the fast food industry will exceed $577 billion. At that time, consumers will spend 53% of every food dollar on meals, snacks and beverages away from home.
The strong demand for takeout food, prepared and packaged for busy customers to eat at home, should continue to grow solidly over the next few years, especially with a significant decline in the cost difference between dining out and cooking at home. The NPD Group, Inc.’s 2003 Consumer Spending Survey indicated the recent drop in the economy has encouraged more people to eat ‘on-the-go’ fast foods. Food on the run has now become the food of choice from executives to blue collar workers. According to Technomic Inc., a Chicago based research firm, take out sales accounted for 67% of total sales at the top 25 limited service chains.
The NPD 2003 Consumer Spending Survey also found that 18 to 34 year olds are turning towards new dining venues that are more likely to serve specialty foods like, sandwiches, Mexican wraps and home meal replacements instead of fried foods. NPD found that consumers frequenting these types of outlets are interested in higher quality food preparation and taste, better physical eating conditions and superior customer service, and are willing to pay a higher price.
Increases in income, especially when coupled with exposure to new and different foods, will stimulate Americans’ continuing quest for increased variety in their diets. Technomic Inc. suggests the most successful food companies in 2020 are likely to be those that tap most effectively into Americans’ appreciation for diversity in their lives, especially the insatiable desire for new and different food choices.
The United States Pie Industry
The U.S. Retailer’s Bakery Association stated in 2001 that bakeries will become the new springboard for successful retail meal programs. The Association believes there are unlimited opportunities for fresh pizza, quiche, pot pies, vegetable pies, soup, pasta and sandwiches.
According to the Bakery Production & Marketing Red Book, total U.S. fresh pie sales for 2003 were $204,567,600 compared to fresh pie sales in 2000 which totaled $182,602,096. Total U.S. frozen pie sales were $339,121,696 in 2003, a substantial increase when compared to 2000 sales of $141,488,000.
An estimated 70% of total pie sales in the U.S., including both frozen and fresh pies, are sweet pies. Although statistics complied by the American Institute of Baking stated that frozen pot pies contributed $68,705,000 to the total figure of $141,488,000 frozen pie sales in 2000.
An increase in consumer demand for the convenience of pot pies corresponds with U.S. consumer’s passion for meat and poultry. In 2002 total meat consumption (red meat, poultry and fish) reached 195 pounds per person, 57 pounds more than the average annual consumption in the 1950s. Each American consumed an average of 7 pounds more red meat than in the 1950s, 46 pounds more poultry and 4 pounds more fish and shellfish.
The Upper Peninsula Pie Industry
The pie is considered the national food of Michigan’s Upper Peninsula and the pie making business is a serious endeavor. Pie sales contributed substantially to the UP’s economy according to a statistics report in 2002.
UP brand Chequamegon is the present market leader in fresh pies with a 54.7% market share, well ahead of their closest competitor on 15% share. Chequamegon offers fresh single and multi-pack pies in as well as a range of sausage rolls and savories. Chequamegon also produces frozen family pies, single pies, frozen single sausage rolls and unbaked sausage rolls.
According to Rosemary Ontonagon, marketing manager for Chequamegon, frozen family pies and multi-pack pies are being used as convenient value-for-money family meal solutions. Single pies are purchased with snacking in mind, being a handy product for households to have on hand for hungry family members. Sausage rolls and savories are being used for more social occasions.
4.3.1 Competition and Buying Patterns
Within the restaurant and fast food industry there are several different segments:
- Fast food: McDonald’s, Burger King
- Pizza: delivery and dine in
- Buffets: all you can eat
- Lounges: combining food and alcohol
- Fine dining: typically restaurants at the highest price point
- Fast-casual: combination of fast service and sit down dining
Local Competitors
The Tintagel Pasty Company
The Tintagel Pasty Company has been operating since 1998. The company recently opened its second store, a small retail outlet on Bass Street in the heart of downtown which is supplied by their original store. The company is owned and operated by Anne Thracite, a Cornish woman with no previous baking or relevant industry experience.
Limited planning and organization have affected the company and there are no procedures or sufficient systems in place to deal with rapid expansion or substantial increases in production. The company is presently struggling to fulfill the demands of having a second retail outlet, regularly running out of product or unable to fulfill customer requests during peak times of the year. The quality of the company’s products can vary from week to week. Product is sometimes overcooked or very dry and equipment is not reliable. Product is sometimes baked twice and then sold frozen to customers in order to fulfill demands.
The company’s products include six varieties of beef pie, three varieties of Chicken pie and one vegetable pie. Pies come in Lunch size (5 inch, $3.25 to $3.75), Family size (9 inch, $10.75) and Party size (2 inch, $10.00 per dozen). There are also spinach and sausage rolls ($2.50 each) and rotational weekly specials that include, Thai Curry Chicken, Indian Butter Chicken, plain Chicken, Ham and Brie, and Beef Stroganoff. Of the customers that have entered both stores, one in five has asked for sweet pies and desserts.
All product ingredients are presently bought by the owner and purchased at locally. Beverages are out-sourced and delivered weekly by Fizzy Beverage also locally based. Cornish dry foods sold through the store are imported by the owner through her brother in Falmouth, Cornwall, U.K.
The estimated gross profit for the company after the cost of goods in 2000 was $70,185, in 2001 $69,531, 2002 $82,029, in 2003 $100,729 and in 2004 around $132,353. Shipping of frozen product accounts for around 30% of the gross profit for each year. These figures show a healthy growth rate of over 20% in the last 3 years of business. Based on income and expenses over the last five years, wages have averaged between 25-30%, cost of goods around 20% and rent around 20%.
These figures do not take into account the gross profit of the new Bass Street store which started operations in late October 2004. Gross profit after three months of business at this store was $22,730. Based on the present growth rate and an influx of tourists during the summer months the annual gross profit of the Pike Street store alone is estimated to be between $90,000 and $100,000 gross.
The Quern Flour Bakery (Tidalborestad)
The Quern Flour Bakery is based in Tidalborestad, on the East Coast and has been operating since December 2003. Maltese owner and operator Siggiewi Gozo is a former corporate recruiter with an Masters Degree in Psychology who originally came to Tidalborestad for a job with a national sportswear company. He has no previous baking or relevant industry experience.
A one man shoe-string operation, Siggiewi works 15 hour days to make between 700 and 900 pies per week. In early 2004 Gozo was making and selling about 400 pies per month. In January of 2005 he sold 4,000 in bars and Irish pubs alone. Business is now good enough for him to take on extra staff and to scout a bigger location for the bakery. Currently he operates out of a rented nightclub kitchen after hours.
Quern Flour produces seven varieties for the Tidalborestad market, including steak and mushroom, beef and cheese and a shepherd’s pie. He also makes a breakfast egg and bacon pie and a sausage roll. He sells his pies to several midtown pubs, caters events around town and delivers by the dozen directly to customers’ homes by bicycle or subway. Quern Flour Bakery now offers overnight shipping via FedEx anywhere in the country.
The majority of his clientele hail from British Mediterranean areas. There are around 2,300 Maltese and Gibraltarian customers in Tidalborestad that make up the company’s customer base. Quern Flour supplies around six restaurants and pubs with frozen and hot pies within the Tidalborestad area. Gozo also caters for holiday parties and his pies were served at some consulates during morning tea in 2004.
All the ingredients considered carefully. The flagship ‘chunky steak’ pie is made from sirloin steak and all cuts of meat are inspected to make sure there is no gristle. To develop the perfect pie crust, Quern Flour Bakery sources special margarine directly from Malta.
Quern Flour Bakery pies retail for up to $5.00, and last year the company turned over $90,000 gross. Based on the current market Siggiewi Gozo expects the company to quadruple turnovers by 2005.
Buying Patterns
The most difficult function in predicting customer buying patterns is following the fine line of baking too much product or not having enough product left to serve customers late in the day. Despite implementing sophisticated POS systems that track hourly sales figures, there is no predictable pattern of daily activity. One Tuesday could be a sellout and the next Tuesday there could be pie warmers left full of product.
Despite customer unpredictability, buying patterns typically revolve around several different factors:
- Quality . The menu items must meet minimum levels of quality for people to be willing to spend money on the food, particularly when there are so many different options available.
- Location . Proximity to home or work is very important; so is convenient parking for the end-of-workday traffic stopping to pick up hot food to go or frozen meal solutions.
- Price . Low price or lowest price is not essential. Many customers associate low price with lower quality.
- Convenience . People tend to eat out because it’s quicker than preparing a meal themselves.
- Uniqueness . As consumers seek variety and new experiences, the challenge is to stand out from competitors, not only as an alternative fast food option, but as one that offers consistently high-quality food and a distinctive atmosphere.
The proposed business location for the first UPer Crust store will be in downtown Yubetchatown. Five possible sites are being considered in three areas: the new Yubetchatown Station presently under construction, central downtown Yubetchatown, and the area of Chambers Street and 18th Avenue.
Each will need approximately 500-700 square feet. This area will include freezer space for on-site storage of frozen product. The operating space will consist of an oven, counter and serving area, pie warmers and ambient display cases, cold beverage display, an eating area and a restroom.
The stores will be located on high traffic commuter routes and close to shopping facilities in order to catch customers going to or from work, while they are out for lunch, or on a shopping expedition. The business will operate from Monday through Sunday. Hours of operation will depend entirely on the area and final location of each store.
5.1 Facilities and Equipment
Pie warmers are custom designed and manufactured display cases. Chilled and ambient display cases that house salads, desserts and cold beverages, uniform in design, will also be purchased. Commercial ovens, cash registers and point of sale (POS) accounting systems will be necessary capital asset acquisitions.
5.2 Suppliers and Alliances
UPer Crust Pies is in negotiations with two Michigan Upper Peninsula pie manufacturers to supply frozen pies, rolls and a small selection of dessert pies. It will establish a relationship with a reputable shipping company and a freight agent to aid in the smooth transition of product from the UP to our distribution center.
The company is also currently seeking reputable organizations to supply its stores with fresh salads and desserts on a daily basis, and will also establish contracts with a beverage company to provide popular product brands. Credit and delivery policies will be established; to avoid fluctuating costs the company will endeavor to build a fixed product rate into the contracts.
UPer Crust Pies wishes to establish long-term loyal relationships with its suppliers. Factors such as history, reliability, reputation, delivery system, service, product guarantees and liability issues will be crucial in the final decision. Due to the company’s expansion plans in years two and three, it is important that our suppliers have regional and possibly national coverage.
5.3 Inventory
Our imported products will be stored locally with a company that specializes in cold storage. Lead time for ordering, production, shipping and receiving is expected to be two months, although this will depend on sales volumes and product demand during the first year of business. This lead time will be reviewed constantly and altered in accordance with company expansion and seasonal demands.
Frozen and chilled pastries will be distributed to stores on a weekly basis, dependant on turnover, and will be kept frozen on site. Perishables such as salads and some desserts will be delivered fresh directly to our stores on a daily or two- to three-day schedule. Cold beverages will also be delivered directly to stores according to demand. A small back-up supply of products will also be kept on site.
5.4 Legal Environment
A submission of application for a food license to the State Department of Health will include prepared plans and specifications for review and approval before the construction or remodeling of the initial establishment. The application fee is $300.00.
The State Department of Health will conduct one or more pre-operational inspections to verify that the establishment is constructed and equipped in accordance with the approved plans and in compliance with the Food Code.
The State Department of Health also requires that each employee possess a Food Handlers Permit. This permit is $10.00 and is obtained after a simple exam.
The company will adhere to the State Department of Health and U.S. Food and Drug Administration Food Code standards. An appropriate insurance policy will also be taken out in accordance with State Department of Health regulations.
5.5 Policies and Procedures
Establishing company policies and procedures will be important the company’s growth and employee development. The following policies and procedures will be adopted:
- Development of an employee policy handbook
- Development of a company procedures and systems handbook
- Clearly defined employee job descriptions, training, reviews and monthly meetings
- An open-door policy for employee suggestions and concerns
The company’s credit policy will be to accept only cash, Visa or MasterCard credit cards.
Strategy and Implementation Summary
UPer Crust Pies will penetrate the commuter and captive consumer markets by setting up stores in highly visible and accessible locations. With the proliferation of coffee and fast-food chains across America, customers expect product consistency. Although our unique products will initially captivate a curious market and compete on a consistency level, it will be our fast and cheerful customer service that will differentiate us from competitors and keep our customers returning.
UPer Crust Pies has identified its market as busy, mobile people whose time is already at a premium. This market desires exciting, new-tasting products with familiar ingredients for lunch time or while commuting to or from work or school.
Strategic Assumptions:
- Every resident in the greater Yubetchatown area is a potential customer.
- Each location gives us an opportunity to increase customer awareness.
- Marketing to our target segments will expose us to additional new customers.
6.1 Competitive Edge
UPer Crust Pies’ unique products and focus on the customers experience will give it a significant market edge and differentiate the company from its competitors.
The company has several distinct advantages over its two leading competitors; its authentic products, modern baking and presentation equipment, and the latest operating systems and technology.
A fast and unique food alternative: We offer our customers a completely new experience through our pies, pastries, salads and desserts. The look, feel and taste of our products when compared to the competition will initially establish a sense of curiosity, followed by a value for money reputation and eventually a loyal following of pie lovers and connoisseurs.
Products are made from the finest quality ingredients and are low in fat and free of genetically modified foods. Many products, such as the authentic Upper Peninsula pies, will not be available anywhere else.
Our products will be served fast and ready to consume and will be an alternative to the usual fast-food options available in today’s market.
The importance of the experience: With so many fast food restaurants and prepared foods being offered at grocery markets, the customer experience becomes extremely important as an effective way of distinguishing offerings. It is this experience that remains in the customer’s mind well after they have consumed their food. This memory is what is communicated to their friends and colleagues.
We realize that our business is a lot more than just pies. It’s our pies, our people and the experience the customers have in our stores. The store environment will play a major role in a positive customer experience. The cleanliness, smoke-free environment, color scheme and nostalgic Upper Peninsula/Great Lakes images will create a completely new experience.
6.2 Marketing Strategy
The focus of our marketing strategy will be to attract new customers, educate those customers and create a loyal base. Our goal is to be known as a unique food experience with superior customer service.
The following marketing strategies will be employed in the first year of business:
Signage: Highly visible, eye catching and recognizable signs and logos at each store.
Print media advertising: Weekly and monthly food and dining out guides will be used for print advertising.
Flyers: Distributed to local businesses to create customer awareness, accompanied with buy-one get one-free coupons during our Grand Opening.
Entertainment book coupons: Create initial customer awareness and economic incentive to try our products. The effectiveness of these books diminishes after approximately eight months and UPer Crust Pies will turn to more cost effective marketing.
Word of mouth: Unsurpassed customer service and our unique products will help develop strong word-of-mouth advertising and in turn help extend the company brand.
Alliances: Although the company is primarily in the fast-food industry, it’s unique products and cultural origins could be used as a tourism vehicle to promote the Upper Peninsula through a strategic alliance with Michigan Tourism.
6.3 Sales Strategy
We intend to succeed by giving our customers a combination of delicious food in an appealing environment with outstanding customer service. Once a customer enters our store, it is our job to make sure their experience with us is enjoyable. To establish a loyal customer base, it is vitally important we develop repeat business.
Our pies will be cooked throughout the day, ensuring they can be served with confidence while guaranteeing our customers supreme freshness and taste. We will also offer fresh baked samples free of charge to those who enter our store for the first time.
We need to offer fast service at peak times. To speed up customer service, at least two employees will be servicing customers. One employee will be preparing the customer’s order, the other one will be taking care of the sales transaction. All sales data logged on our computerized POS system will be analyzed for marketing purposes.
We will offer punch cards, meal deals and weekly menu specials and keep accurate track of what types of pies and associated foods sell well through a customer feedback program. With this information we will be able to streamline our food line to match local tastes and encourage more people to eat at the pie shop.
We need to sell the company as well as the product. All employees will go through a comprehensive training process on how to offer customers the finest experience. Employees will be empowered to resolve issues and are encouraged to seek assistance from managers for any conflicts they are unable to resolve.
Part of our mission is to educate our customers about pies. However, this must be done in a respectful fashion. Our knowledge is a resource, and must never be used to make a customer feel uncomfortable or ignorant.
In the first year of business we will implement a Point-of-Sale (POS) computerized cash register system that will make tracking and managing receipts and charitable contributions more robust. We will seek a professional who has experience in how to tie in POS systems to the Internet and inventory controls. This individual’s knowledge will also help establish technology guidelines for the company.
Our sales strategy requires consistently high quality food and fast service in a relaxed atmosphere. We can accomplish this by:
- Hiring employees who appreciate our unique products.
- Continually assessing the quality of all aspects of the business and immediately addressing any issues.
- Interacting with our customers personally, so they know that their feedback goes directly to the owners.
- Evaluating food choices and keeping favorites on the menu as we rotate weekly and seasonal specials.
6.3.1 Sales Forecast
Our sales forecast shows modest estimates for the first year of operations beginning in July 2005. Cost control is a critical focus for UPer Crust Pies. Because we are importing our product from Michigan, we will negotiate a flat purchase price for the first three years of business to compensate for fluctuating economic conditions. We have projected a 60% gross mark up over the first three years of business. Keeping costs low while increasing sales will be vital to the company’s profitability in subsequent years.
UPer Crust Pies envisions the first three months of sales to be fairly slow due to limited product awareness, the competitive nature of the market and existing customer loyalty. We have therefore forecasted a 5% growth rate over the first year. In the second year, UPer Crust Pies will add two more stores and in the third year, an additional two stores. The addition of these stores will nearly triple the gross revenue in the second year and increase half again as much in the third year. Compared to industry standards we have taken a very conservative 10% growth rate over the first three years of operations.
Not projected in this sales forecast is the possibility of additional revenue generated from shipping via an e-commerce facility to be added to our website in year two. Based on current market research, shipping could be a significant profit center. We would sell frozen products that could be shipped overnight via DHL or FedEx to customers throughout the U.S. Shipping would also become an integral part of the company’s marketing plan to help develop brand recognition and build product awareness.
We understand product sales will also vary according to the season. Dessert and salad sales in the summer months are expected to be slightly higher since more people will be having barbecues and picnics requiring ad-on products. Pie and pastry sales should be higher in winter because of food oriented holidays and pies tend to be viewed as a comfort food. It is anticipated that sales of sodas during the summer months should be substantially higher.
Please note that the sales forecast for the first year reflects store number one at a 5% growth rate. In the second year, the forecast reflects the combined sales of three stores at a 10% growth rate, and in the third year, the combined sales of five stores at a 10% growth rate.
| Sales Forecast | |||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Sales | |||
| Pies & Pastry | $56,149 | $185,298 | $308,820 |
| Pies & Pastry (Frozen) | $36,531 | $120,552 | $200,921 |
| Desserts | $18,726 | $61,796 | $102,993 |
| Desserts (Frozen) | $5,444 | $17,965 | $29,942 |
| Salads | $3,586 | $11,834 | $19,723 |
| Cold Beverages | $3,154 | $10,408 | $17,347 |
| Total Sales | $123,589 | $407,853 | $679,746 |
| Direct Cost of Sales | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 |
| Pies & Pastry | $19,652 | $61,904 | $103,173 |
| Pies & Pastry (Frozen) | $12,786 | $40,276 | $67,127 |
| Desserts | $6,554 | $20,645 | $34,409 |
| Desserts (Frozen) | $1,905 | $6,001 | $10,001 |
| Salads | $1,255 | $3,953 | $6,589 |
| Cold Beverages | $1,104 | $3,478 | $5,796 |
| Subtotal Direct Cost of Sales | $43,256 | $136,257 | $227,095 |
Web Plan Summary
In the first year of operation UPer Crust Pies will establish a basic Internet presence. The website will be a virtual business card and portfolio for the company with a simple yet contemporary design to keep up with the latest trends in user interface. The site will have general information about the company, its products, prices, store locations, hours of operation and contact information.
In year two, the company will launch an e-commerce facility for customer ordering and shipping of frozen products throughout the U.S.
7.1 Website Marketing Strategy
Marketing efforts will start with our existing brick-and-mortar store customer base, informing them of our Internet presence and encouraging their word-of-mouth recommendations. Further awareness will be heightened by utilizing search engine submissions, URL links and e-mail marketing.
The company website and email address will be referenced on all printed material and correspondence including menus, business cards and advertising media.
The launching of our e-commerce facility for shipping in year two will also be marketed in our stores through word of mouth and on all printed media. Expansion into outside sales will help us to create greater community awareness.
7.2 Development Requirements
Development Costs
- Site design: $1000 – $2,000.
- Website name registration for www.UPerCrustPies.com is $149.00 for 10 years.
- Site implementation: UPer Crust Pies will utilize the programming services of a friend with 12 years of experience in software development, including custom programming, data management and Web development.
Ongoing Costs
- Site hosting: $19.95 per month. Includes 250 MB Disk Space, 10 GB Data transfer and 20 POP e-mailboxes. (Year 1)
- Fully integrated e-commerce site hosting: $99.95 per month. Includes 5,000 MB Disk Space, 200 GB Data transfer and 200 POP e-mailboxes, storefront and shopping cart, secure online credit card processing and payment options. (Year 2)
- Search engine submission: $44.95 per month. Guaranteed placement in Google and Yahoo! (Year 2)
- Site design changes: Free of charge; however, material for changes such as photography, new logos or designs may incur a fee but will be considered part of the marketing budget.
Management Summary management summary will include information about who's on your team and why they're the right people for the job, as well as your future hiring plans.">
The strength of our management team positions us for success. We have assembled a team that embraces different disciplines with expertise in all areas of the business. Overhead for management will be kept to a minimum and initially all managers will be hands-on workers. There is no intention of having a top-heavy organization that drains profits and complicates decisions.
UPer Crust Pies’ management style will encourage all employees to learn as much as possible about all aspects of the business and be involved in decision making where appropriate. The company respects its community of co-workers, and will treat all workers well. It is important to us that they enjoy their jobs, feel part of the company and are well rewarded for their work.
In addition to the day-to-day operations, the management team, as principals within the company, will oversee product development, purchasing, positioning, pricing, inventory control and approval of all financial obligations of the company. They will plan, develop, and establish customer service policies and objectives, write employee job descriptions and draft an employee manual for all employee-related policies. They will:
- Manage working capital, including receivables, inventory and cash.
- Perform financial forecasting, budgeting, cash flow analysis and external financing requirements.
- Prepare financial analyses for guiding management, including income and expense reports.
- Prepare budgets and financial forecasts and arrange for audits of the company’s accounts.
8.1 Management Team
Lina Mackinac-Gogebic, CEO – Accounting, Marketing, Legal, Human Resources
Confidential and proprietary information removed from this sample plan.
Olie Mackinac-Gogebic, COO – Operations, Marketing, Financial, Business Development
Misty Glade – Vendor Relationships, Sales, Recruitment, Training
Full Time Employee – Operations, Inventory, Store Development
Advisory Board
8.2 Personnel Plan
UPer Crust Pies will be slow to hire people in the first year of operation, but very loyal to those who are hired. Initially all employees will be part time as the majority of work will be done by the owner. As the company grows, we intend to hire employees with relevant skills and reward them accordingly. From that point, we intend to increase the responsibilities of each employee as opposed to hiring more people.
Retail and restaurant businesses live or die on customer service, yet their employees have among the lowest pay and worst benefits of any industry. We know we have great products, but it’s the way those products are delivered that will determine our success. We realize that our employees are our biggest asset and that the image of our company is built by the people who work for us.
Compensation for employees will include direct monetary payments and as the business progresses, performance bonuses will be paid to full-time employees. Because this is a small business, employees will be paid a comfortable wage that is fair to both the employees and the business.
Our opening employment goal is one full-time and one part-time employee with an additional two full-time and three part-time employees by the end of the second year. All employees with be trained in food handling and store procedures and will be required to hold a food handlers permit.
Our employee policies will include:
- Weekly management meetings
- Monthly employee meetings
- On-going training
- Performance reviews every six months
- Performance incentives
- Encouragement of creativity
| Personnel Plan | |||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Olie Mackinac-Gogebic | $27,040 | $27,040 | $29,120 |
| Misty Glade | $0 | $27,040 | $29,140 |
| Full-time Employee 1 | $0 | $27,040 | $27,040 |
| Lina Mackinac-Gogebic | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Full-time Employee 2 | $0 | $0 | $24,960 |
| Full-time Employee 3 | $0 | $0 | $24,960 |
| Part-time Employee 1 | $7,000 | $7,000 | $9,000 |
| Part-time Employee 2 | $0 | $7,000 | $9,000 |
| Part-time Employee 3 | $0 | $7,000 | $9,000 |
| Name or Title or Group | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total People | 2 | 6 | 8 |
| Total Payroll | $34,040 | $102,120 | $162,220 |
Financial Plan investor-ready personnel plan .">
A bank relationship will be established as soon as possible. Sales could very well increase at a much sharper rate than assumed in these conservative projections. Sharper sales will result in a greater need for funds in support of inventory and store growth and a line of credit will need to be established.
We will set a budget for marketing and advertising and will continue to reinvest residual profits into company expansion and personnel.
Sales growth will be aggressive during the first 18 months as we sharpen our product line and inventory to better meet our customer’s requirements. Although we anticipate substantial growth in years two and three we are forecasting a very conservative 10% growth rate.
- Salaries and rent are two major expenses. Depreciation will also increase as the company develops.
- The owners will not take any profits out of the business and will be paid as an employees.
- Payoff of private investment is expected within four to five years.
9.1 Start-up Funding
Total startup funding amounts are shown in the table below. This includes initial start-up expenses, liquid cash for operating expenses, unforseen expenses, to help cover wages, and also includes start-up inventory. This inventory will include the purchase and storage costs of frozen products, purchasing of cold beverages and daily delivery of fresh salads and various other desserts.
The purchase of long-term assets that will include an oven, two pie warmers, an ambient display case, freezers and refrigerators, a dishwasher and microwave, a three-compartment sink, decor and furnishings, utensils, a cash register and Point-Of-Sale software and accessories.
A long-term loan has been secured for the purchase of the long-term assets.
A first round of private investment from outside investors and family members will begin in April 2005. A second round will commence at the end of April 2006 for the purchase of further inventory and long-term assets to service the next two stores.
Profits will be reinvested and the owners will be employees collecting a very modest wage. This will ensure that any operating debts incurred are paid for within the shortest possible time period.
| Start-up Funding | |
| Start-up Expenses to Fund | $45,000 |
| Start-up Assets to Fund | $195,000 |
| Total Funding Required | $240,000 |
| Assets | |
| Non-cash Assets from Start-up | $77,000 |
| Cash Requirements from Start-up | $118,000 |
| Additional Cash Raised | $0 |
| Cash Balance on Starting Date | $118,000 |
| Total Assets | $195,000 |
| Liabilities and Capital | |
| Liabilities | |
| Current Borrowing | $0 |
| Long-term Liabilities | $170,000 |
| Accounts Payable (Outstanding Bills) | $0 |
| Other Current Liabilities (interest-free) | $0 |
| Total Liabilities | $170,000 |
| Capital | |
| Planned Investment | |
| Investor 1 | $8,000 |
| Investor 2 | $8,000 |
| Investor 3 | $8,000 |
| Investor 4 | $8,000 |
| Investor 5 | $8,000 |
| Investor 6 | $10,000 |
| Investor 7 | $10,000 |
| Investor 8 | $10,000 |
| Additional Investment Requirement | $0 |
| Total Planned Investment | $70,000 |
| Loss at Start-up (Start-up Expenses) | ($45,000) |
| Total Capital | $25,000 |
| Total Capital and Liabilities | $195,000 |
| Total Funding | $240,000 |
9.2 Important Assumptions
Payroll burden is calculated at an estimated 12.65% made up of 7.65% for social security and medicare, 2% for unemployment, and 3% for worker’s compensation.
The tax rate has been left at 0% in the first year plan due to accumulated losses carried forward and that as an LLC the the owners will be taxed personally.
Our long-term interest rate is 6%.
Our State Sales tax is 4%. This does not affect our total profitability, but monthly payments to the State does impact our cash flow and cash balance.
Our financial plan depends on important assumptions. Our key underlying assumptions are:
- A slow-growth economy without major recession.
- Access to sufficient capital to sustain the company’s projected growth plan.
9.3 Break-even Analysis
Our break-even analysis is summarized by the following chart and table.

| Break-even Analysis | |
| Monthly Revenue Break-even | $10,862 |
| Assumptions: | |
| Average Percent Variable Cost | 35% |
| Estimated Monthly Fixed Cost | $7,060 |
9.4 Projected Profit and Loss
The following table and charts indicate projected profit and loss.

| Pro Forma Profit and Loss | |||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Sales | $123,589 | $407,853 | $679,746 |
| Direct Cost of Sales | $43,256 | $136,257 | $227,095 |
| Other Costs of Sales | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Cost of Sales | $43,256 | $136,257 | $227,095 |
| Gross Margin | $80,333 | $271,596 | $452,651 |
| Gross Margin % | 65.00% | 66.59% | 66.59% |
| Expenses | |||
| Payroll | $34,040 | $102,120 | $162,220 |
| Marketing/Promotion | $3,000 | $9,000 | $15,000 |
| Depreciation | $9,285 | $9,285 | $9,285 |
| Rent | $24,000 | $72,000 | $120,000 |
| Utilities | $2,700 | $8,100 | $13,500 |
| Liability insurance | $2,400 | $7,200 | $12,000 |
| Payroll Taxes | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Legal fees | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Accounting | $1,200 | $3,600 | $6,000 |
| Bank Service Charges | $1,500 | $5,000 | $7,000 |
| Telephone/Cell Phone | $900 | $1,500 | $2,100 |
| License and Permits | $500 | $1,500 | $2,500 |
| Cold Storage | $2,500 | $6,000 | $12,000 |
| Office Supplies | $500 | $1,000 | $2,000 |
| Repairs and Maintenance | $1,000 | $2,500 | $6,000 |
| Gas/Auto Expenses | $1,000 | $2,000 | $5,000 |
| Postage | $200 | $400 | $1,200 |
| Total Operating Expenses | $84,725 | $231,205 | $375,805 |
| Profit Before Interest and Taxes | ($4,392) | $40,391 | $76,846 |
| EBITDA | $4,893 | $49,676 | $86,131 |
| Interest Expense | $9,810 | $9,060 | $8,160 |
| Taxes Incurred | $0 | $9,399 | $0 |
| Net Profit | ($14,202) | $21,932 | $68,686 |
| Net Profit/Sales | -11.49% | 5.38% | 10.10% |
9.5 Projected Cash Flow
Our projected cash flow is outlined in the following chart and table.

| Pro Forma Cash Flow | |||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Cash Received | |||
| Cash from Operations | |||
| Cash Sales | $123,589 | $407,853 | $679,746 |
| Subtotal Cash from Operations | $123,589 | $407,853 | $679,746 |
| Additional Cash Received | |||
| Sales Tax, VAT, HST/GST Received | $4,944 | $16,314 | $27,190 |
| New Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Other Liabilities (interest-free) | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Long-term Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Sales of Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Sales of Long-term Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Investment Received | $0 | $60,000 | $60,000 |
| Subtotal Cash Received | $128,533 | $484,167 | $766,936 |
| Expenditures | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 |
| Expenditures from Operations | |||
| Cash Spending | $34,040 | $102,120 | $162,220 |
| Bill Payments | $89,311 | $294,893 | $461,222 |
| Subtotal Spent on Operations | $123,351 | $397,013 | $623,442 |
| Additional Cash Spent | |||
| Sales Tax, VAT, HST/GST Paid Out | $4,466 | $16,314 | $27,190 |
| Principal Repayment of Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Other Liabilities Principal Repayment | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Long-term Liabilities Principal Repayment | $12,000 | $14,000 | $16,000 |
| Purchase Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Purchase Long-term Assets | $65,000 | $30,000 | $30,000 |
| Dividends | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Subtotal Cash Spent | $204,817 | $457,327 | $696,631 |
| Net Cash Flow | ($76,284) | $26,840 | $70,304 |
| Cash Balance | $41,716 | $68,556 | $138,861 |
9.6 Projected Balance Sheet
The following table explains the projected balance sheet.
| Pro Forma Balance Sheet | |||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Assets | |||
| Current Assets | |||
| Cash | $41,716 | $68,556 | $138,861 |
| Inventory | $16,744 | $52,744 | $87,906 |
| Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Current Assets | $58,460 | $121,300 | $226,767 |
| Long-term Assets | |||
| Long-term Assets | $130,000 | $160,000 | $190,000 |
| Accumulated Depreciation | $9,285 | $18,570 | $27,855 |
| Total Long-term Assets | $120,715 | $141,430 | $162,145 |
| Total Assets | $179,175 | $262,730 | $388,912 |
| Liabilities and Capital | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 |
| Current Liabilities | |||
| Accounts Payable | $9,899 | $25,522 | $39,018 |
| Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Other Current Liabilities | $478 | $478 | $478 |
| Subtotal Current Liabilities | $10,376 | $26,000 | $39,496 |
| Long-term Liabilities | $158,000 | $144,000 | $128,000 |
| Total Liabilities | $168,376 | $170,000 | $167,496 |
| Paid-in Capital | $70,000 | $130,000 | $190,000 |
| Retained Earnings | ($45,000) | ($59,202) | ($37,270) |
| Earnings | ($14,202) | $21,932 | $68,686 |
| Total Capital | $10,798 | $92,730 | $221,416 |
| Total Liabilities and Capital | $179,175 | $262,730 | $388,912 |
| Net Worth | $10,798 | $92,730 | $221,416 |
9.7 Business Ratios
Projected business ratios are provided in the table below. The final column, Industry Profile, shows ratios for the Fast-Food Restaurant, Independent industry, as determined by the Standard Industry Classification (SIC) Index code 7999.
| Ratio Analysis | ||||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | Industry Profile | |
| Sales Growth | 0.00% | 230.01% | 66.66% | 8.67% |
| Percent of Total Assets | ||||
| Inventory | 9.35% | 20.08% | 22.60% | 3.24% |
| Other Current Assets | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 37.31% |
| Total Current Assets | 32.63% | 46.17% | 58.31% | 45.97% |
| Long-term Assets | 67.37% | 53.83% | 41.69% | 54.03% |
| Total Assets | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% |
| Current Liabilities | 5.79% | 9.90% | 10.16% | 17.94% |
| Long-term Liabilities | 88.18% | 54.81% | 32.91% | 22.26% |
| Total Liabilities | 93.97% | 64.71% | 43.07% | 40.20% |
| Net Worth | 6.03% | 35.29% | 56.93% | 59.80% |
| Percent of Sales | ||||
| Sales | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% |
| Gross Margin | 65.00% | 66.59% | 66.59% | 59.05% |
| Selling, General & Administrative Expenses | 76.49% | 61.21% | 56.49% | 39.24% |
| Advertising Expenses | 7.51% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 1.96% |
| Profit Before Interest and Taxes | -3.55% | 9.90% | 11.31% | 1.92% |
| Main Ratios | ||||
| Current | 5.63 | 4.67 | 5.74 | 1.04 |
| Quick | 4.02 | 2.64 | 3.52 | 0.66 |
| Total Debt to Total Assets | 93.97% | 64.71% | 43.07% | 50.22% |
| Pre-tax Return on Net Worth | -131.51% | 33.79% | 31.02% | 6.90% |
| Pre-tax Return on Assets | -7.93% | 11.93% | 17.66% | 13.87% |
| Additional Ratios | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Net Profit Margin | -11.49% | 5.38% | 10.10% | n.a |
| Return on Equity | -131.51% | 23.65% | 31.02% | n.a |
| Activity Ratios | ||||
| Inventory Turnover | 2.78 | 3.92 | 3.23 | n.a |
| Accounts Payable Turnover | 10.02 | 12.17 | 12.17 | n.a |
| Payment Days | 27 | 21 | 25 | n.a |
| Total Asset Turnover | 0.69 | 1.55 | 1.75 | n.a |
| Debt Ratios | ||||
| Debt to Net Worth | 15.59 | 1.83 | 0.76 | n.a |
| Current Liab. to Liab. | 0.06 | 0.15 | 0.24 | n.a |
| Liquidity Ratios | ||||
| Net Working Capital | $48,083 | $95,300 | $187,271 | n.a |
| Interest Coverage | -0.45 | 4.46 | 9.42 | n.a |
| Additional Ratios | ||||
| Assets to Sales | 1.45 | 0.64 | 0.57 | n.a |
| Current Debt/Total Assets | 6% | 10% | 10% | n.a |
| Acid Test | 4.02 | 2.64 | 3.52 | n.a |
| Sales/Net Worth | 11.45 | 4.40 | 3.07 | n.a |
| Dividend Payout | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | n.a |
Risk Management
New restaurants and fast-food outlets often make one of two mistakes: they are either unprepared or under prepared for opening. Initial poor service or product quality discourages customers from returning. Many first businesses spend all of their efforts at opening and are unable to maintain the quality customers expect on return visits, decreasing word-of-mouth advertising and leading to poor revenues.
UPer Crust Pies will be as prepared as it can possibly be with back–up equipment, alternative suppliers and at least three month’s inventory of frozen product.
Initial costs will be planned accordingly and kept to a minimum. The company recognizes the importance of its image, first-time impressions and customer service and it will not sacrifice this in order to satisfy the bottom line.
It is anticipated that marketing costs will be significantly higher in the first three months of business. Marketing activities will be closely monitored and constantly analyzed to decide what marketing activities are successful and what are not. A marketing budget will be set for the first store and for each subsequent store.
UPer Crust Pies will establish a loyal and long-term relationship with our suppliers and always pay on time. We wish to establish fixed-product rates with our suppliers as a buffer to avoid fluctuating economic conditions that may affect our purchasing capabilities.
Changes in importation policies and health regulations will always affect UPer Crust Pies. We need to establish a strong working relationship with the relevant authorities to ensure all procedures are followed correctly and ensure that we have a steady supply of product.
Because our products are unknown to the general consumer, marketing activities are vitally important. We plan on implementing several marketing strategies as outlined in the marketing section of this business plan. To establish product and brand awareness, we will give-away small samples to encourage first timers to try our products. Although we have quality products, building a loyal customer base will take time. We realize that training and empowerment of our employees will be reflected in their customer service and that word-of-mouth advertising will be paramount to our success.
| Sales Forecast | |||||||||||||
| Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | ||
| Sales | |||||||||||||
| Pies & Pastry | 5% | $3,644 | $4,559 | $3,772 | $3,208 | $5,426 | $6,020 | $3,934 | $5,360 | $4,234 | $5,426 | $5,435 | $5,131 |
| Pies & Pastry (Frozen) | 5% | $2,208 | $2,100 | $2,976 | $2,685 | $3,024 | $3,930 | $3,114 | $3,168 | $3,546 | $3,103 | $3,258 | $3,421 |
| Desserts | 5% | $1,536 | $1,707 | $1,213 | $1,442 | $1,392 | $1,299 | $1,730 | $1,548 | $1,625 | $1,451 | $1,792 | $1,992 |
| Desserts (Frozen) | 5% | $504 | $396 | $331 | $347 | $397 | $551 | $514 | $422 | $443 | $465 | $489 | $585 |
| Salads | 5% | $413 | $360 | $370 | $292 | $235 | $206 | $188 | $232 | $230 | $322 | $321 | $418 |
| Cold Beverages | 5% | $263 | $212 | $198 | $208 | $254 | $196 | $246 | $253 | $279 | $279 | $365 | $399 |
| Total Sales | $8,568 | $9,334 | $8,859 | $8,183 | $10,729 | $12,201 | $9,726 | $10,983 | $10,356 | $11,046 | $11,659 | $11,946 | |
| Direct Cost of Sales | Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | |
| Pies & Pastry | $1,638 | $1,638 | $1,638 | $1,638 | $1,638 | $1,638 | $1,638 | $1,638 | $1,638 | $1,638 | $1,638 | $1,638 | |
| Pies & Pastry (Frozen) | $1,066 | $1,066 | $1,066 | $1,066 | $1,066 | $1,066 | $1,066 | $1,066 | $1,066 | $1,066 | $1,066 | $1,066 | |
| Desserts | $546 | $546 | $546 | $546 | $546 | $546 | $546 | $546 | $546 | $546 | $546 | $546 | |
| Desserts (Frozen) | $159 | $159 | $159 | $159 | $159 | $159 | $159 | $159 | $159 | $159 | $159 | $159 | |
| Salads | $105 | $105 | $105 | $105 | $105 | $105 | $105 | $105 | $105 | $105 | $105 | $105 | |
| Cold Beverages | $92 | $92 | $92 | $92 | $92 | $92 | $92 | $92 | $92 | $92 | $92 | $92 | |
| Subtotal Direct Cost of Sales | $3,605 | $3,605 | $3,605 | $3,605 | $3,605 | $3,605 | $3,605 | $3,605 | $3,605 | $3,605 | $3,605 | $3,605 | |
| Personnel Plan | |||||||||||||
| Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | ||
| Olie Mackinac-Gogebic | 0% | $2,253 | $2,253 | $2,253 | $2,253 | $2,253 | $2,253 | $2,253 | $2,253 | $2,253 | $2,253 | $2,253 | $2,253 |
| Misty Glade | 0% | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Full-time Employee 1 | 0% | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Lina Mackinac-Gogebic | 0% | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Full-time Employee 2 | 0% | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Full-time Employee 3 | 0% | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Part-time Employee 1 | 0% | $583 | $583 | $583 | $583 | $583 | $583 | $583 | $583 | $583 | $583 | $583 | $583 |
| Part-time Employee 2 | 0% | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Part-time Employee 3 | 0% | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Name or Title or Group | 0% | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total People | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | |
| Total Payroll | $2,837 | $2,837 | $2,837 | $2,837 | $2,837 | $2,837 | $2,837 | $2,837 | $2,837 | $2,837 | $2,837 | $2,837 | |
| Pro Forma Profit and Loss | |||||||||||||
| Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | ||
| Sales | $8,568 | $9,334 | $8,859 | $8,183 | $10,729 | $12,201 | $9,726 | $10,983 | $10,356 | $11,046 | $11,659 | $11,946 | |
| Direct Cost of Sales | $3,605 | $3,605 | $3,605 | $3,605 | $3,605 | $3,605 | $3,605 | $3,605 | $3,605 | $3,605 | $3,605 | $3,605 | |
| Other Costs of Sales | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Total Cost of Sales | $3,605 | $3,605 | $3,605 | $3,605 | $3,605 | $3,605 | $3,605 | $3,605 | $3,605 | $3,605 | $3,605 | $3,605 | |
| Gross Margin | $4,963 | $5,729 | $5,254 | $4,578 | $7,124 | $8,597 | $6,121 | $7,378 | $6,751 | $7,441 | $8,054 | $8,341 | |
| Gross Margin % | 57.93% | 61.38% | 59.31% | 55.95% | 66.40% | 70.46% | 62.94% | 67.18% | 65.19% | 67.37% | 69.08% | 69.82% | |
| Expenses | |||||||||||||
| Payroll | $2,837 | $2,837 | $2,837 | $2,837 | $2,837 | $2,837 | $2,837 | $2,837 | $2,837 | $2,837 | $2,837 | $2,837 | |
| Marketing/Promotion | $250 | $250 | $250 | $250 | $250 | $250 | $250 | $250 | $250 | $250 | $250 | $250 | |
| Depreciation | $774 | $774 | $774 | $774 | $774 | $774 | $774 | $774 | $774 | $774 | $774 | $774 | |
| Rent | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | |
| Utilities | $225 | $225 | $225 | $225 | $225 | $225 | $225 | $225 | $225 | $225 | $225 | $225 | |
| Liability insurance | $200 | $200 | $200 | $200 | $200 | $200 | $200 | $200 | $200 | $200 | $200 | $200 | |
| Payroll Taxes | 13% | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Legal fees | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Accounting | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | $100 | |
| Bank Service Charges | $125 | $125 | $125 | $125 | $125 | $125 | $125 | $125 | $125 | $125 | $125 | $125 | |
| Telephone/Cell Phone | $75 | $75 | $75 | $75 | $75 | $75 | $75 | $75 | $75 | $75 | $75 | $75 | |
| License and Permits | $42 | $42 | $42 | $42 | $42 | $42 | $42 | $42 | $42 | $42 | $42 | $42 | |
| Cold Storage | $208 | $208 | $208 | $208 | $208 | $208 | $208 | $208 | $208 | $208 | $208 | $208 | |
| Office Supplies | $42 | $42 | $42 | $42 | $42 | $42 | $42 | $42 | $42 | $42 | $42 | $42 | |
| Repairs and Maintenance | $83 | $83 | $83 | $83 | $83 | $83 | $83 | $83 | $83 | $83 | $83 | $83 | |
| Gas/Auto Expenses | 15% | $83 | $83 | $83 | $83 | $83 | $83 | $83 | $83 | $83 | $83 | $83 | $83 |
| Postage | $17 | $17 | $17 | $17 | $17 | $17 | $17 | $17 | $17 | $17 | $17 | $17 | |
| Total Operating Expenses | $7,060 | $7,060 | $7,060 | $7,060 | $7,060 | $7,060 | $7,060 | $7,060 | $7,060 | $7,060 | $7,060 | $7,060 | |
| Profit Before Interest and Taxes | ($2,097) | ($1,331) | ($1,806) | ($2,482) | $64 | $1,536 | ($939) | $318 | ($309) | $381 | $994 | $1,281 | |
| EBITDA | ($1,323) | ($558) | ($1,032) | ($1,708) | $837 | $2,310 | ($165) | $1,092 | $465 | $1,155 | $1,768 | $2,054 | |
| Interest Expense | $845 | $840 | $835 | $830 | $825 | $820 | $815 | $810 | $805 | $800 | $795 | $790 | |
| Taxes Incurred | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Net Profit | ($2,942) | ($2,171) | ($2,641) | ($3,312) | ($761) | $716 | ($1,754) | ($492) | ($1,114) | ($419) | $199 | $491 | |
| Net Profit/Sales | -34.34% | -23.26% | -29.81% | -40.48% | -7.10% | 5.87% | -18.04% | -4.48% | -10.76% | -3.79% | 1.71% | 4.11% | |
| Pro Forma Cash Flow | |||||||||||||
| Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | ||
| Cash Received | |||||||||||||
| Cash from Operations | |||||||||||||
| Cash Sales | $8,568 | $9,334 | $8,859 | $8,183 | $10,729 | $12,201 | $9,726 | $10,983 | $10,356 | $11,046 | $11,659 | $11,946 | |
| Subtotal Cash from Operations | $8,568 | $9,334 | $8,859 | $8,183 | $10,729 | $12,201 | $9,726 | $10,983 | $10,356 | $11,046 | $11,659 | $11,946 | |
| Additional Cash Received | |||||||||||||
| Sales Tax, VAT, HST/GST Received | 4.00% | $343 | $373 | $354 | $327 | $429 | $488 | $389 | $439 | $414 | $442 | $466 | $478 |
| New Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| New Other Liabilities (interest-free) | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| New Long-term Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Sales of Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Sales of Long-term Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| New Investment Received | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Subtotal Cash Received | $8,911 | $9,707 | $9,214 | $8,510 | $11,158 | $12,689 | $10,115 | $11,422 | $10,770 | $11,488 | $12,125 | $12,424 | |
| Expenditures | Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | |
| Expenditures from Operations | |||||||||||||
| Cash Spending | $2,837 | $2,837 | $2,837 | $2,837 | $2,837 | $2,837 | $2,837 | $2,837 | $2,837 | $2,837 | $2,837 | $2,837 | |
| Bill Payments | $343 | $10,295 | $10,090 | $4,485 | $10,280 | $10,075 | $4,470 | $10,065 | $4,460 | $10,255 | $10,050 | $4,445 | |
| Subtotal Spent on Operations | $3,180 | $13,131 | $12,926 | $7,321 | $13,116 | $12,911 | $7,306 | $12,901 | $7,296 | $13,091 | $12,886 | $7,281 | |
| Additional Cash Spent | |||||||||||||
| Sales Tax, VAT, HST/GST Paid Out | $0 | $343 | $373 | $354 | $327 | $429 | $488 | $389 | $439 | $414 | $442 | $466 | |
| Principal Repayment of Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Other Liabilities Principal Repayment | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Long-term Liabilities Principal Repayment | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | $1,000 | |
| Purchase Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Purchase Long-term Assets | $5,417 | $5,417 | $5,417 | $5,417 | $5,417 | $5,417 | $5,417 | $5,417 | $5,417 | $5,417 | $5,417 | $5,417 | |
| Dividends | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Subtotal Cash Spent | $9,597 | $19,891 | $19,717 | $14,093 | $19,860 | $19,757 | $14,211 | $19,707 | $14,152 | $19,922 | $19,745 | $14,165 | |
| Net Cash Flow | ($686) | ($10,184) | ($10,503) | ($5,582) | ($8,703) | ($7,068) | ($4,096) | ($8,285) | ($3,382) | ($8,434) | ($7,620) | ($1,741) | |
| Cash Balance | $117,314 | $107,130 | $96,627 | $91,045 | $82,342 | $75,274 | $71,178 | $62,893 | $59,511 | $51,076 | $43,457 | $41,716 | |
| Pro Forma Balance Sheet | |||||||||||||
| Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | ||
| Assets | Starting Balances | ||||||||||||
| Current Assets | |||||||||||||
| Cash | $118,000 | $117,314 | $107,130 | $96,627 | $91,045 | $82,342 | $75,274 | $71,178 | $62,893 | $59,511 | $51,076 | $43,457 | $41,716 |
| Inventory | $12,000 | $14,395 | $16,791 | $13,186 | $15,581 | $17,977 | $14,372 | $16,767 | $13,163 | $15,558 | $17,953 | $14,349 | $16,744 |
| Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Current Assets | $130,000 | $131,710 | $123,921 | $109,813 | $106,626 | $100,319 | $89,646 | $87,945 | $76,056 | $75,069 | $69,030 | $57,806 | $58,460 |
| Long-term Assets | |||||||||||||
| Long-term Assets | $65,000 | $70,417 | $75,833 | $81,250 | $86,667 | $92,083 | $97,500 | $102,917 | $108,333 | $113,750 | $119,167 | $124,583 | $130,000 |
| Accumulated Depreciation | $0 | $774 | $1,548 | $2,321 | $3,095 | $3,869 | $4,643 | $5,416 | $6,190 | $6,964 | $7,738 | $8,511 | $9,285 |
| Total Long-term Assets | $65,000 | $69,643 | $74,286 | $78,929 | $83,572 | $88,215 | $92,858 | $97,500 | $102,143 | $106,786 | $111,429 | $116,072 | $120,715 |
| Total Assets | $195,000 | $201,352 | $198,207 | $188,742 | $190,198 | $188,534 | $182,504 | $185,446 | $178,199 | $181,855 | $180,459 | $173,878 | $179,175 |
| Liabilities and Capital | Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | |
| Current Liabilities | |||||||||||||
| Accounts Payable | $0 | $9,952 | $9,947 | $4,142 | $9,937 | $9,932 | $4,128 | $9,923 | $4,118 | $9,913 | $9,908 | $4,103 | $9,899 |
| Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Other Current Liabilities | $0 | $343 | $373 | $354 | $327 | $429 | $488 | $389 | $439 | $414 | $442 | $466 | $478 |
| Subtotal Current Liabilities | $0 | $10,295 | $10,320 | $4,497 | $10,265 | $10,362 | $4,616 | $10,312 | $4,557 | $10,327 | $10,350 | $4,570 | $10,376 |
| Long-term Liabilities | $170,000 | $169,000 | $168,000 | $167,000 | $166,000 | $165,000 | $164,000 | $163,000 | $162,000 | $161,000 | $160,000 | $159,000 | $158,000 |
| Total Liabilities | $170,000 | $179,295 | $178,320 | $171,497 | $176,265 | $175,362 | $168,616 | $173,312 | $166,557 | $171,327 | $170,350 | $163,570 | $168,376 |
| Paid-in Capital | $70,000 | $70,000 | $70,000 | $70,000 | $70,000 | $70,000 | $70,000 | $70,000 | $70,000 | $70,000 | $70,000 | $70,000 | $70,000 |
| Retained Earnings | ($45,000) | ($45,000) | ($45,000) | ($45,000) | ($45,000) | ($45,000) | ($45,000) | ($45,000) | ($45,000) | ($45,000) | ($45,000) | ($45,000) | ($45,000) |
| Earnings | $0 | ($2,942) | ($5,113) | ($7,754) | ($11,067) | ($11,828) | ($11,112) | ($12,866) | ($13,358) | ($14,472) | ($14,891) | ($14,692) | ($14,202) |
| Total Capital | $25,000 | $22,058 | $19,887 | $17,246 | $13,933 | $13,172 | $13,888 | $12,134 | $11,642 | $10,528 | $10,109 | $10,308 | $10,798 |
| Total Liabilities and Capital | $195,000 | $201,352 | $198,207 | $188,742 | $190,198 | $188,534 | $182,504 | $185,446 | $178,199 | $181,855 | $180,459 | $173,878 | $179,175 |
| Net Worth | $25,000 | $22,058 | $19,887 | $17,246 | $13,933 | $13,172 | $13,888 | $12,134 | $11,642 | $10,528 | $10,109 | $10,308 | $10,798 |

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Look Beyond the Obvious in Plant Location
- Roger W. Schmenner
When on-site expansion has become impractical, companies must decide whether to relocate or to open branches. Although the location decision may appear straightforward, if it chiefly involves financial assessments, the company faces unexpected pitfalls, according to this author. He discusses the relative advantages of relocation and new branches in light of a company’s unique problems […]
For many managers, plant location decision making merely refers to the selection of a site for a new plant, and for some the choice is straightforward: select the least costly site. Often a consultant is brought in or a management team assembled with the sole purpose of scouring the South or the Far East, Mexico or Puerto Rico, for low-wage, low-cost, low-tax sites so that plant location can contribute to “the bottom line.” This mode of thinking invites disaster, as numerous companies have found out.
- RS Mr. Schmenner is a research associate of the Harvard-MIT Joint Center for Urban Studies and is now, under a grant from the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development, engaged in research on the plant location decision making of the Fortune “500” companies during the 1970s. His most recent HBR article is “Before You Build a Big Factory”(July–August 1976).
Partner Center

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Business location. In this section, you need to state the full location and the exact address of the business. If possible, ensure that your business is listed on Google Maps so that readers can view the location easily. Mention all of the locations if you have more than one branch.
7.1 OBJECTIVES. After studying this lesson, you should be able to: Describe the concepts of plant location and plant layout. Identify the various factors to be considered for selection of plant location-from state/area to the specific site. Distinguish among the alternative patterns of plant layout.
Here are 5 simple steps to present location and facility in your business plan: Describe the Location: Provide detailed information about the business location, including the address, the geographical area, and why this location is strategic. Outline the Facilities: Describe the physical premises of the business.
Here's how to write the operations plan section of the business plan, including details on writing the development and production process sections. ... The Physical Plant . Describe the type, size, and location of premises for your business. If applicable, ... SMART Goals: Examples for Business. Should My LLC Be Taxed as an S Corp or C Corp?
Facility Layout. After the site location decision has been made, the next focus in production planning is the facility's layout. The goal is to determine the most efficient and effective design for the particular production process. A manufacturer might opt for a U-shaped production line, for example, rather than a long, straight one, to ...
4. Optimizing Operational Efficiency. Location analysis optimizes business efficiency. A strategic location enhances logistics, influencing factors such as supply chain efficiency, distribution convenience, delivery speed, and employee commute. The right location streamlines operations, saving time and resources.
4 Significance of Plant Location. 5 Plant Location Selection Criteria. 5.1 Materials. 5.2 Machinery. 5.3 Labour. 5.4 Safety and Security. 5.5 Future Operations. Entrepreneurs face a major problem with plant location in deciding the best location for their factory or plant. The utmost care must be exercised in selecting the plant location and ...
Here also transportation overhead increases the cost of the finished product. In case you are initiating a fully export-oriented plant, the availability of processing facilities gains importance in deciding the location of one's industry. Export Promotion Zones (EPZ) are such examples. #3. Infrastructural Facilities.
Here is a video for a closer look at the layout design and functionality of different sections, 1. The tire types are fed to the robot cell as a batch of 4. 2. Next, Tire rims which represent different sizes of the tires are incoming through conveyors behind the robot cell. 3.
A business location strategy is your plan to find the optimal location for an organization. This requires an analysis of company goals and objectives and finding a location that meets them. ... Examples of Business Location Strategies That Worked and Why. For businesses that rely on foot traffic or get regular visits from customers or patients ...
These are only some of the many considerations that make up a complex matrix of factors that go into how to choose a location for your new manufacturing plant. For help navigating this process, partner with WDG Consultants. We provide fully integrated consulting advisory services for all aspects of the manufacturing plant site selection process.
Manufacturing Relocation: Indirect and Soft Cost Factors to Consider. Now let's take stock of some of the indirect factors that you should consider when undertaking a manufacturing plant location analysis. 1. Network Effect / Industry Clusters / Talent and Knowledge Base.
The location strategy of a business should adhere to its overall corporate strategy, and be part of that plan. Therefore, if a company dreams and plans to become, for example, a global leader in fashion production, it must consider establishing plants and warehouses in regions that are consistent with its strategy and optimally positioned to ...
Location Analysis Example. Food chain Whole Foods, now owned by Amazon, picks their locations based on many factors, not just population density in a neighborhood. They found that one of the key drivers that determines whether patrons will shop at their grocery stores is their level of education. As a result, their site selection process looks ...
Operations. The operations section in our business plan examples covers the day-to-day workflows for your business to deliver your product or service. What's included here fully depends on the type of business. Typically you can expect to add details on your business location, sourcing and fulfillment, use of technology, and any partnerships or ...
A good business plan guides you through each stage of starting and managing your business. You'll use your business plan as a roadmap for how to structure, run, and grow your new business. It's a way to think through the key elements of your business. Business plans can help you get funding or bring on new business partners.
Pies come in Lunch size (5 inch, $3.25 to $3.75), Family size (9 inch, $10.75) and Party size (2 inch, $10.00 per dozen). There are also spinach and sausage rolls ($2.50 each) and rotational weekly specials that include, Thai Curry Chicken, Indian Butter Chicken, plain Chicken, Ham and Brie, and Beef Stroganoff.
Mr. Schmenner is a research associate of the Harvard-MIT Joint Center for Urban Studies and is now, under a grant from the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development, engaged in research on ...