

Signature Guidelines: Home
Guidance for academic signature blocks.
Before You Graduate
When creating an academic e-mail signature block for Walden University, as well as for most professional correspondence, you should only use the academic credential that you have earned after your name. You should not use amended forms of a degree (e.g., PhD-C or PhD(c)) to indicate partial completion of your program, nor should you use ABD (all-but-dissertation). None of these designations are accepted credentials, and using them may confuse others, including prospective employers. These amended forms are not recognized by Walden University either.
While a doctoral student, you can use any other academic credential you have already earned (including a first doctoral degree, if applicable). For e-mail originating from your Walden account, you should include a designation of your status in the academic program in the signature block on the second line (e.g., doctoral student or doctoral candidate). You should not include any references to other positions you hold outside of the university.
Chris C. Cumberbatch, MSW Student, PhD in Social Work Walden University
When you qualify, you should refer to yourself as a "doctoral candidate" in correspondence, instead of being ABD. Candidacy status says that you are an active, advanced student, pursuing the last part of your doctoral degree. ABD is not an actual degree nor is it a credential; it is often used informally by individuals who did not complete their degree after they have stopped being a student. All amended forms of the doctoral degree credential, indicating partial attainment, should be avoided in your signature, as well. The intention to complete and progress toward a degree are different than actually completing one.
Mary Jane Smith, MBA Doctoral Candidate, Doctor of Business Administration Walden University
Definition of Doctoral Candidacy
The status of “doctoral candidate” is defined as an advanced graduate student who has demonstrated mastery of the knowledge of an academic domain or discipline and a readiness to embark on the capstone project.
A Walden University student is considered a doctoral candidate when the following expectations, as prescribed in the Program of Study, have been completed.
- Academic Coursework
- Core Research Courses
- Academic Residencies (except Residency 4 for PhD students)
- Prospectus, approved by the Academic Program Director or designee following successful rubric examination, and on record with the Office of Student Research Administration
- Other specific requirements stipulated by the academic program
Read more about Doctoral Candidacy in the Student Catalog.
After You Graduate
Upon conferral of your degree, however, you should begin using that new credential on your academic and/or professional correspondence, directly after your name. Also, in most situations, you need only list your highest credential, based on an assumption that you also have the degrees leading up to it. You do not need to spell it out, nor do you need to include your academic specialization. No need to include periods in the abbreviation either.
Joseph J. Johnson, PhD
It is advisable for you to double check the standard in your profession/discipline for the use of “Dr.” as a designation in your e-mail signature. In only a few professional areas is it considered acceptable to use both “Dr.” and your doctoral degree. The preferred convention is to include the degree abbreviation at the end to indicate to everyone that you hold a doctoral degree, and to use Dr. as you would use Mr. or Ms.
An e-mail signature should not be a replacement for your resumé or curriculum vitae, but in some professional contexts, you may choose to include a relevant license or professional credential after your doctoral degree (e.g., LPC, RN). Again, restraint is usually warranted. Even though you have earned them, including an entire alphabet of letters after your name may communicate a level of egocentrism that is not congruent with your intention.
In summary, there are two general rules for academic/professional communications, which includes e-mail signature blocks: (1) only include the degree and credentials that you have earned, and (2) when in doubt about what to include, less is generally more. Specific contexts outside of Walden University may require a different strategy, however, so try to model your signature on professionals at the same level of training in that context.
Get Connected!
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.
Stack Exchange Network
Stack Exchange network consists of 183 Q&A communities including Stack Overflow , the largest, most trusted online community for developers to learn, share their knowledge, and build their careers.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
How should degrees be listed in an e-mail signature?
I have the following degrees:
- PhD in Information Technology (Computer Science concentration)
- MS in Systems Engineering (MSE)
- MS in Engineering Management (MEM)
- BS in Computer Science
What would a proper e-mail signature look like?
- 56 I don't think I have read anyone's email signature even once in my life. IMO, you're overthinking this very much. – user9646 May 31, 2017 at 13:02
- 206 It's also worth mentioning that listing all of your degrees (especially when the list is that long) could come off as obnoxiously pompous to some people. – user51076 May 31, 2017 at 13:46
- 50 And it is generally regarded as incorrect to prefix your title and to repeat it after the name. Even with a single degree, you should either say "Dr. Bob Roberts" or "Bob Roberts, PhD". Saying "Dr. Bob Roberts, PhD" isn't good. So, if you really want to list all of your degrees, you should probably omit the title before your name. Aren't you going to include High School, Junior High, Elementary, and Kindergarden as well? It all seems a bit excessive. I think I would just stick with "Dr. Bob Roberts". Including the rest seems rather unhumble. – MPW May 31, 2017 at 16:14
- Comments are not for extended discussion; this conversation has been moved to chat . – eykanal Jun 4, 2017 at 5:11
12 Answers 12
There is no formal academic convention for email signatures, although your university or institution may have formatting guidelines. You can simply include as much or as little information as you want the recipient to know.
Personally, I think your name and position are sufficient and listing every degree you have is a bit redundant (and, as others have pointed out, pretentious). People will probably infer that you have a BS and MS if you also have a PhD.
- 3 @A.T.Ad: You don't seem to be the person asking the original question, but I would expect your official position to cover your 'area of expertise'. If you feel the need to specify, do so by specifying your position. Don't just rattle off all your degrees. – Falc May 31, 2017 at 15:24
- 27 @A.T.Ad It's not necessarily problematic, it just has the potential to come off as trivially boasting. If it conveys useful information, I wouldn't be too concerned. For example, for a Professor of Ethics with an MS in Biology, listing both might help to inform people of diverse (relevant) experience. However, it's rather pointless for a Professor of Biology to list a PhD, MS and BS all in biology - also mentioning the additional degrees doesn't add anything, except perhaps ego padding. -- Rule of thumb: only list them if they indicate expertise not implied by the most advanced title. – R.M. May 31, 2017 at 15:29
- 11 @A.T.Ad: Do you really think people would go on to read your signature to find out your area of expertise? Just put that on your website. – tomasz May 31, 2017 at 17:51
- 4 @R.M. Just out of curiosity, have you ever actually acted on such information that was included in a signature? Generally when I'm emailing someone I already know who they are and have a reason to email them. If I want to find someone who has expertise in area X I wouldn't send a mail to everyone and then check their signatures to find whom I'm looking for. – Voo May 31, 2017 at 18:55
- 5 @alephzero I don't know where people get their information about German culture. A typical German e-mail signature looks like "Prof. Dr. Christian Schmidt, Institute of Quantum Mechanics, address, phone number, website". Nobody lists qualifications, but some list positions. – user9482 Jun 2, 2017 at 6:48
It's supposed to be an email signature, not a CV. "Dr Bob Roberts" already says that you have a PhD. The rest is redundant, because having a PhD implies that you probably have a master's degree (which nobody cares about, because you have a PhD), and almost certainly have a bachelor's degree (which nobody cares about, because you have a master's). And, hey, you probably got some qualifications in high school, too (which nobody cares about, because you have a bachelor's).
So the only reason for including all that stuff in your signature is tooting your horn. And, in an academic context, it looks crass because you're drawing attention to the obvious. "Oh, look at me, I have a PhD and a master's and a bachelor's!" Well, er, so does everybody else on the academic and research staff. That level of qualifications is implied by the fact that you work here.
If you'll allow me, i'd like to play devil's advocate. Don't list your degrees in your email signature. The signature is there to format email more like a letter. It's not the place to communicate your experience. I'd recommend setting up a personal resume website or a linkedin page to showcase your experience.
Allow your message content to communicate your command of a subject, don't rest on your letters.
- 7 +1 I usually sign my e-mails "Patricia", unless I am being really formal, when I use "Patricia Shanahan", but just for this occasion: Patricia Shanahan, PhD, MSc, BSc, ARCS. – Patricia Shanahan Jun 1, 2017 at 0:21
- 6 @PatriciaShanahan It's good to know that you treat Academia.SE as a really formal environment. :-D – David Richerby Jun 1, 2017 at 14:08
- 4 @PatriciaShanahan Today I learned: the level of formality we attribute to commenting on SE is directly related to the naming conventions of our usernames. :) Apparently you, David, and myself are all quite formal; chuck, not so much. – Bryan Krause ♦ Jun 1, 2017 at 22:12
- 1 I am advocating this - the default should be to keep emails as informal as possible and appropriate. – Sascha Jun 3, 2017 at 12:32
I want to give a different perspective.
Do what is common practise in your institution/region (i. e. what your collegues or other comparable people do).
Here in Austria, it seems to be common practise to list all your titles (maybe except for BSc/BA if you have a MSc/MA because people are not so used to these two titles). I often see multiple doctor titles and honoris causa titles in signatures.
In my view, many people here see a signature (if there is any) as a place where you state your "official" name - and, at least here, this includes your titles. "Bob" in a signature would certainly be viewed as unprofessional and strange. (But then again, I am not sure if the commenters suggesting writing "Bob" are serious or joking.)
While many people on this site view many titles as "bragging", not including them can certainly interpreted as an insult to the others - like you are saying "you guys including so many titles are pretentious".
So in short, do what your environment does.
However, I have never ever seen someone stating the field they received their titles in. (Although there are titles like "BA (FH)" (FH meanging Fachhochschule, "university of applied sciences"), which appear sometimes. Probably they have to be stated in exact this way.)
- 9 The advice to do what other people in the same situation does is excellent. But I think somebody would have to be almost paranoid to interpret somebody not including something in their signature as a judgement on those who do. What next? "OMG, he's wearing a different coloured shirt to me! It must be an insult!" – David Richerby May 31, 2017 at 23:01
- 3 Yeah it's culture dependent. Using just your first name in professional circumstances is quite common in the US, but seems incredibly weird to Germans and Austrians (so no, not a joke to just sign with "Bob"). That said I wouldn't use my titles in emails or conversations, it's more something to put on formal documentation or requests where it really does make a difference (certainly use every title you have when trying to rent an apartment..). There is a bit of a generational divide too it seems to me. – Voo Jun 1, 2017 at 7:16
- 4 Slightly different German perspective. Listing titles is rather uncommon here, but it is common to give rather more details on your institute. For business, full company name, address, phone and tax number and possibly trade registry number etc. are often mandatory. So "blacksaibot, head of IT, company X" would need to give more details on X. – cbeleites unhappy with SX Jun 1, 2017 at 13:11
- 2 Exactly! A year ago I registered at a GP in Czech Republic and now after a year a nurse came to me, "don't you have another title?". Medicine here is all about the titles. It is strange to be called a doctor when you are a patient, but that is how they do that here. They expect all the titles. – Vladimir F Героям слава Jun 1, 2017 at 16:09
- 1 Are we speaking about e-mail signatures in academia or in industry / rest of the world? There is probably a difference between them. (And, by the way, my "use Bob" was serious.) – Federico Poloni Jun 1, 2017 at 22:32
Dr. Bob Roberts
Bob Roberts, Ph.D.
unless one of two things obtain. First, your organization has a set of internal customs or formal rules regarding the signature. Second, if your degrees are in different areas. For example,
Bob Roberts Ph.D. Management Science MS Nursing
For interrelated fields, the Ph.D. supersedes the master's degree and ceases being relevant. It is also relevant to show certifications that are not superseded by the doctorate.
- Nice; Brief and concise! – Alisa Aug 23, 2020 at 3:51
Your signature indicates how you want the person you're writing to address you. If you want be called by your first name, sign "Bob" or "Bob Roberts". If you want to be called "Dr. Roberts", sign "Dr. Bob Roberts".
No one is going to call you "Dr. Bob Roberts PhD IT, MSE, MEM", and what do you really hope to accomplish with that signature?
I never had an email signature. Can't think of something to put there that the person I'm communicating with doesn't know already or can easily find out if interested in having that information.
When something is relevant to the other party I'll mention it in the email, not on the signature. If exchanging more than a few emails, having long signatures becomes annoying (IMO).
As for the question, I'd keep the signature as simple as possible, e.g. John Doe, PhD . This way you're not adding additional lines to your name/signature combo, while still informing everyone that you have a PhD and everything else that comes beforehand.
Another way to do this would be to just include your linkedin profile link. That way anyone interested in learning about your credentials can just click on there. Something else I see common in Academic settings is to link to their personal webpage for the department. That page usually lists their resume, educational credentials, what paper they may have presented in the past, etc. Ofcourse ensure to setup the webpage and add all the relevant information there.
While in grad school I was told by my dissertation advisor that in formal correspondence you should not refer to yourself by Dr. The proper form would be:
Bob Roberts, Ph.D. in and not,
Dr. Bob Roberts.
Medical doctors seem to violate this convention quite frequently though.
- 2 That's because medical doctors are MDs, not PhDs. Also this is very culture specific; in the UK, writing Dr Bob Roberts is far more common than Bob Roberts, PhD. Or, as others have pointed out, just plain old Bob. – astronat supports the strike Jun 2, 2017 at 20:48
- May I guess that you (or rather, your dissertation adviser) are American? Certainly in Commonwealth English, it's normal (and correct) to write "Dr." before someone's name, regardless of what type of doctorate they hold. – Dawood ibn Kareem Jun 3, 2017 at 4:38
- 2 Yes, American. The advice applied to self-references only. Referring to someone else as Dr. would of course be perfectly normal. I guess his point was that you would not introduce yourself as, "Hello, I'm Mr. Bob Roberts", so the same logic should apply to Dr. as a prefix. These are by definition English honorifics intended to address a person with respect. Therefore use in the case of a self-reference would seem inappropriate. I can see why at a medical center people would refer to themselves as Dr. in order to distinguish themselves from the nurses and janitors. – crayguy Jun 4, 2017 at 0:52
You can list your other degrees if they are relevant to your work. For example, if I were an art therapist, a BA in fine art is relevant to my work, so I'd list it. But don't list the BS in Psychology that led to the MS. And you would list any licensure first, if you have it, such as MFT.
I've seen Fred Davidson, M.D. Ph.D
which i personally like because it's all in one line and the fact that the md and the phd are together makes it look more powerful rather than separated.
- 1 This is something of a different case. the MD and PhD degrees both lead to the title "Dr" and, in the context of medical practice or research, it's good to distinguish "I'm an physician" from "I'm an academic" from "I'm both a physician and an academic." – David Richerby Aug 27, 2018 at 15:15
You shouldn't put any of that in your email. There is a general correlation of Ph.D.s who call themselves Dr. or use the ,Ph.D. being the weaker ones. Even if not true in your case, it will still come across that way. And not just to the general public, but other Ph.D. holders. (Same thing applies to retired military ranks unless you are writing a letter to the editor.)
First Last (optional) position and/or org cell phone number email
You include the cell so people can call you. Lots of people use email sigs for finding phone numebrs and get annoyed by others who don't list it. (Of course if it is an email you don't want the cell included, edit it out.) Include the actual email since many email programs or physical printouts list your name in the header but not the email adress
You must log in to answer this question.
Not the answer you're looking for browse other questions tagged email ., hot network questions.
- Is it theoretically possible for the Sun to go dark?
- How can I use a router without gateway?
- Yosemite national park availability
- A short story in French about furniture that leaves a mansion by itself, and comes back some time later
- My players think they found a loophole that gives them infinite poison and XP. How can I add the proper challenges to slow them down?
- Group with a translation invariant ultrafilter
- Customary learning areas for Shavuos?
- Why did Kenny go to Heaven?
- What is the difference between Hof and Bauernhof?
- What's the maximum amount of material that a puzzle with unique solution can have?
- Am I seeing double? What kind of helicopter is this, and how many blades does it actually have?
- How was damno derived from damnum?
- Why is "second" an adverb in "came a close second"?
- How do Authenticators work?
- Windows Server 2022 Support for Intel X520-DA2
- Universal PCB enclosure: what are these cylinders with holes for?
- Should I ask for authorship or ignore?
- Can someone explain the damage distrubution on this aircraft that flew through a hailstorm?
- Is cellulose, blown-in insulation biodegradeable
- Can we combine a laser with a gauss rifle to get a cinematic 'laser rifle'?
- How to make Bash remove quotes after parameter expansion?
- Average value of lattice parameters from cell trajectory
- Structure that holds the twin-engine on an aircraft
- Smallest Harmonic number greater than N

How to Use a Doctorate with Your Name
—- For more on the the use of Port-Nominal Abbreviations , see that page . —- For more on use of an Honorary Doctorate , see that page . How to Use a Doctorate with Your Name
Here are the forms to use when addressing a person addressed as Dr. See the discussion below “How to Use a Doctorate with Your Name 1-2-3-4-5” for more information on who typically does use Dr. as part of their name and who does not.
—- Envelope or address block on letter or email to their office/place of work: ——– (Full Name), (Post-nominal abbreviation for doctorate held). ——– ( Name of office/place of work if appropriate) ——– (Address)
—- Social/Personal envelope: ——– Dr. (Full Name) ——– (Address)
—- Salutation – for both official & social: ——– Dear Dr. (Surname): How to Use a Doctorate with Your Name
Robert Hickey author of “Honor & Respect”
How to Use a Doctorate with Your Name: 1-2-3-4-5
—- #1) Holders of doctorates who work in academia or research institutions are addressed as ‘Dr. (Name)’ professionally and socially in a salutation or conversation. Thus, a Ph.D. professor at a college, a Ph.D. in biology doing scientific research, and a Ph.D. principal at an elementary school all use Dr. (Name) and everybody thinks it is normal.
—- NOTE: At some universities it is traditional to address faculty holding of academic doctorates as ‘Mr. (Name)’ or ‘Professor (Name)’ and not to address as ‘Dr. (Name)’. For those outside the academic community it is acceptable to follow the insider’s rule or to address holders of doctorates as ‘Dr. (Name)’ in writing or oral address.
—- #2) Protestant clergy with doctorates are addressed as ‘Dr. (Name)’ in a salutation or conversation. I specify ‘Protestant’ here because not all clergy is. For example, neither priests – addressed in a salutation or conversation as Father [Name] – nor rabbis – addressed as Rabbi [Name] – holding doctorates are ever addressed as Dr. [Name] . In a salutation or conversation they stick with Father[Name] and Rabbi [Name].
—- #3) Holders of doctorates who work outside academia or research don’t always prefer to be addressed as ‘Dr. (Name)’. in a salutation or conversation. —- —- A) In the USA ‘Dr.’ may be used depending on the work environment and/or when the degree isn’t pertinent to the conversation. E.g., a Ph.D. in finance working at a bank or a Ph.D. in American history working in software development are not likely to insist on being addressed as ‘ Dr. (Name)’ . But always ask for their preference. Use of, or omitting, the honorific can be a sensitive issue to some individuals! —- —- B) And, outside the U.S.A. everyone holding a doctorate will want to be addressed as ‘Dr. (Name)’ in every instance.
—- #4) In hospitals and healthcare environments historically there was a practice that only physicians (medical doctors, osteopaths, dentists, podiatrists, veterinarians, etc. ) are addressed as ‘Dr. (Name)’. This was explained to be out of consideration for the patients who want to know who ‘the doctors’ are and who are nurses and allied healthcare professionals.
—- That made for some unhappy professionals who earned doctorates in hospital administration, pharmacy, physical therapy and nursing, etc. – who felt they too were properly addressed as ‘Dr. (Name)’ . It’s my understanding that today all the holders of doctorates are addressed as Dr. (Name) and hospitals (etc.) have figured out other ways to define which doctor is a physician, which is a physical therapist and which is a nurse anesthetist.
—- #5) All that said, ultimately how one is addressed by others is up to the individual and usually everyone goes along. For example, if you and I meet a woman who identifies herself as ‘Monsignor Alice’ … I think it is unlikely she’s a Roman Catholic Monsignor. And, it’s unusual she has only one name, like Pink, Rhianna, Sting, Cher, or Madonna. But we should directly address her in conversation as ‘Monsignor Alice,’ it’s nice to meet you …’ because that’s what she says her name is. How to Use a Doctorate with Your Name
—- But, when she’s out of range, we will all be talking about her.
—- —- – Robert Hickey
Related Healthcare Links -V — — Chiropractor / Doctor of Chiropractic Medicine -V — — Dentist / Doctor of Dentistry -V — — Medical Doctor / Doctor of Medicine -V — — Military Physician / Armed Services -V — — Optometrist / Doctor of Optometry -V — — Osteopath / Doctor of Osteopathy -V — — Podiatrist / Doctor of Podiatry -V — — Veterinarian / Doctor of Veterinary Medicine
More Related Healthcare Links: -V — — Person holding a doctorate -V — — Pharmacist / Doctor of Pharmacy -V — — Psychologist -V — — Therapist
Related Links: —- —- —- Principal —- —- —- Headmaster —- —- —- President College University —- —- —- President of a School —- —- —- Chancellor —- —- —- Professor
When To Use Dr. (Name) and When To Use (Name), Ph.D.?
My daughter is receiving her Ph.D. and will be teaching. I would like to give her a name plate for her desk. Should it be ‘Dr. (Full Name)’ or ‘(Full Name), Ph.D. ‘? ——————- – AP
Dear AP, How to Use a Doctorate with Your Name
‘(Full Name), Ph.D.’ is the official form of her name. You will use it on the envelope, or in the address block of a letter, when you write to her with regard to her professional pursuits. This is the form the university will use when she is listed among the faculty. It is used by the degree holder, when specifying the exact degree is pertinent – like on business cards or in a list of academics.
‘Dr. (Full Name)’ is the social form of her name. You will use it when you write her name on a personal letter’s envelope, e.g., one sent to her home. This is the form everyone will use on the envelope when they send her a birthday or holiday card. It is rarely used by the degree holder since one does not correctly give oneself an honorific. The degree holder – in their signature or when introducing him or herself – just uses their name … no ‘Dr.’ It’s up to the other person to add the ‘Dr.’ E.g., I just introduce myself as ‘Robert Hickey’ – never ‘Mr. Robert Hickey.’
Sometimes you will observe a physician in a healthcare setting introducing him or herself as ‘Dr. (Name)’ – but there it is for the patient’s benefit to know they are the physician in a field of people wearing seemingly identical white coats!
‘Dr. (Surname)’ is the conversational form of her name. Use it both officially and socially in a letter’s salutation as well as in oral conversation.
So, for an office name plate use the official form of her name – (Full Name), Ph.D.
– Robert Hickey

Doctors present the official form of their name to the public: (Full Name) (Pertinent post-nominals for the service offered). The social form of their name does not include their degree: Dr. (Full Name). In both official and social salutations and conversations patients use Dr. (Name).

If My Doctorate is in Music, am I ‘Dr.’?
I hold a DMA, Doctorate in Music, from a Boston university and am a Church Music Director. Please could you advise me as to whether it is acceptable for the church where I work to list me in the service bulletins as: ‘Dr. (First name) + (Last name) ‘? —————- – CJ
Dear CJ: How to Use a Doctorate with your Name It is correct to list yourself in the bulletin using the professional form of your name … (First name) + (Last name), DMA. It specifies your academic credential in your professional domain.
Among protestant denominations many address their clergy with a doctorate orally and in a salutation as Dr. (Surname). If your church is one of those, and it is your preference is to be Dr. (Surnhttps://formsofaddress.info/wp-admin/post.php?post=13983&action=edit#ame), tell everyone that it is your preference to be addressed Dr. (Surname).
Usually academics and researchers who go by Dr. (Surname) professionally – use Dr. (Surname) socially. But ultimately whether a particular Ph.D. holder is ‘Dr. (Name)’ socially … especially outside of healthcare, academia or research … is at the preference of the bearer. Some insist, some don’t care, others say they answer to anything they are called. Ultimately your name belongs to you and if you want to be Dr. (Surname), then it’s your right to request everyone address you that way.
– Robert Hickey How to Use a Doctorate with your Name
May I Call Myself Dr. (Name) if my Degree Is Not Related to the Service I Offer?
I have a Ph.D. and license in counseling. Recently I sent out an announcement for a yoga class I will be teaching. The state of Colorado says I should not teach yoga as “Dr. (Name)”. How can I convince them I can? ——– – Kevin S., Ph.D., L.P.C., C.M.T., I.K.Y.T.A. , Counseling, Yoga Therapy, Integrative Health & Healing
Dear Dr. Kevin, How to Use a Doctorate with your Name
Your Ph.D. is in a field not related to the service you are offering.
A couple of typical practices I observe in the USA come to mind:
Professionals use with their name the degrees pertinent to their profession service. The degrees and certifications are provided for the benefit of the public so the public can quickly evaluate your credentials.
Here’s what I mean by pertinent . A pastor who would be the Reverend (Full Name) & Pastor (Name) at church on Sundays, would not use the Reverend (Full Name) & Pastor (Name) when teaching English Monday through Friday, at the local high school. That he or she is the Reverend might be mentioned in a complete biography or introduction. It just isn’t part of his/her name at school.
So, I can see if you are using ‘Dr. (Name)’ when offering a class in yoga, and your doctorate is not directly to the service you are offering, say a doctorate physical therapy or kinesthetics …. it would be confusing to me … and the state officials must think it is misleading to the public.
– Robert Hickey How to Use a Doctorate with Your Name

Should I Use Dr. or Ph.D. on an Invitation?
If a person holds a Ph.D., should his or her name be ‘Dr. (name)’ a wedding invitation? Or ‘( Name), Ph.D.’ ? Is this true for the father of the bride? The groom? Is the rule for names on wedding invitations and wedding envelopes different that the guidelines for social correspondence? ————– – Beverly Russell, Winchester, Virginia
Dear Ms. Russell: Wedding invitations and their envelopes are social correspondence. Post-nominal abbreviations ( Ph.D. is a post nominal abbreviation) aren’t used on social correspondence:
—- —- DON’T use Ph.D.
—- —- DO use Dr. (Name)
Another question that typically comes up is whether to use Doctor or Dr. (spelled out or abbreviated) on the invitation or on the mailing envelope?
The rule is to spell out everything and not to use abbreviations unless space is an issue.
But, Mr., Mrs., Dr., and Ms. (for which there is no spelled-out version) are typically used on invitations and when addressing invitations in even the most formal circles. I think ‘Doctor (Name)’ looks oh-so-highly precious, but I know some wedding planners who would wrestle me to the mat on that one.
When Should You Use the Forms on this Page?
You can use these forms of address for any mode of communication: addressing a letter, invitation, card or Email. (If there are differences between the official and social forms of address, I will have mentioned the different forms.) The form noted in the salutation is the same form you say when you say their name in conversation or when you greet them. ___ What I don’t cover on this site are many things I do cover in my book: all the rules of forms of address, about names, international titles, precedence, complimentary closes, details on invitations, place cards, all sorts of introductions , etc. I hope you’ll get a copy of the book if you’d like the further detail.
Not Finding Your Answer?
—- #1) At right on desktops , at the bottom of every page on tablets and phones , is a list of all the offices, officials & topics covered on the site.
—- #2) If you don’t see the official you seek included or your question answered send me an e-mail . I am pretty fast at sending a reply: usually the next day or so (unless I am traveling.) Note: I don’t have mailing or Email addresses for any of the officials and I don’t keep track of offices that exist only in history books.
—- #3) If I think your question is of interest to others, Sometimes I post the question – but always change all the specifics.
— Robert Hickey
Recommended Resources: The Protocol School of Washington (PSOW) and Protocol and Diplomacy International – Protocol Officers Association (PDI-POA) For more information see the Protocol Resources page.
Share This Story, Choose Your Platform!
Doctor of Education Leadership

Additional Information
- Download the Doctoral Viewbook
- Admissions & Aid
America needs transformative leaders in preK–12 education whose passion for education quality and equity is matched by a knowledge of learning and development, the organizational management skills to translate visionary ideas into practical success, and a firm grasp of the role of context and politics in shaping leadership. Graduates of the three-year, multidisciplinary Doctor of Education Leadership (Ed.L.D.) Program at the Harvard Graduate School of Education will be prepared to become those leaders.
The Ed.L.D Program — taught by faculty from the Harvard Graduate School of Education, the Harvard Business School, and the Harvard Kennedy School — will train you for system-level leadership positions in school systems, state and federal departments of education, and national nonprofit organizations. Ed.L.D. is a full-time, three-year program built on a cohort learning model. Cohorts consist of up to 25 students from diverse professional backgrounds (including district/charter management leaders, nonprofit directors, principals, teachers, and policy researchers) who progress through the program together.
All Ed.L.D. students receive a full tuition funding package plus stipends, work opportunities, and a paid third-year residency at a partner organization.
The Ed.L.D. Program prepares graduates to do work for the public good in the American public education sector, whether that be at the system or state level. Specifically, the program is designed to accelerate the progress graduates make toward achieving meaningful impact in influential roles and/or crossing boundaries in the following spaces in the public education sector:
- PreK–12 district or CMO leadership roles : superintendent of schools, chief academic officer, and/or deputy superintendent
- Foundation/philanthropy roles: director, president and CEO, senior fellow
- Education nonprofit roles : president or executive director of backbone or collective impact organizations which support preK–12 schools. Ed.L.D. graduates will lead education nonprofits that explicitly focus on improving outcomes and opportunities for children, families, and communities.
- State or federal education leadership roles : commissioner or deputy commissioner roles. Could also include public education advocacy or education policy advisers to senior government officials.
- Social Entrepreneurship and Innovation roles: Founder, CEO, president
Curriculum Information
The Ed.L.D. curriculum is a balance of multidisciplinary coursework and practice-based learning. Core courses and electives are taught by recognized leaders from across Harvard’s graduate programs in fields like data-based education reform, organizational change and innovation, and effective leadership strategies for urban schools. You will develop and test your leadership skills through team projects and an immersive third-year residency.
All students in the cohort take the same classes in four foundational content areas: learning and teaching, leadership and organizational change, politics and policy, adult development, and leadership inside and out (including one-on-one executive coaching). Courses taken during the first-year focus on practice-based learning and serve as the framework of your first-year experience.
Sample HGSE Courses
- Leading Change
- How People Learn
- Ed.L.D. Proseminar
- Leadership, Entrepreneurship, and Learning
- Race, Equity, and Leadership
- Practicing Leadership Inside and Out
- Sector Change
- The Workplace Lab for System-Level Leaders
View all courses in the Academic Catalog.
Each cohort member works with program advisers to choose an individualized sequence of electives from any of the Harvard graduate schools. You will work closely with the program faculty and staff during your second year to determine the best match with a partner organization for your third-year residency. Matches are driven by mutual interest between the resident and the partner organization, and each student's career and learning goals and geographic preferences.
- Second Year Practicing Leadership Inside and Out
- Driving Change
- Education Sector Nonprofits
- Negotiation Workshop
- Coaching with Equity in Mind
- Ethnic Studies and Education
- Deeper Learning for All: Designing a 21st Century School System
- Institutional Change in School Organizations, Systems, and Sectors
You will take part in a 10-month paid residency at one of our partner organizations. There, you will work on a strategic project which synthesizes your experience and learning into a written Capstone project. You will stay connected to your Ed.L.D. cohort and HGSE through technology and by returning to Harvard periodically for intensive workshops.
Paid Residency
Our partner organizations include school systems and departments of education, as well as some of the nation's most influential and dynamic nonprofit, mission-based for-profit, and philanthropic organizations.
You will be intentionally pushed out of your comfort zones and asked to work systemically and make a significant contribution to the partner organization. In addition, the residency will provide you with the professional mentoring, practical experiences, and network of connections they need to position themselves as future leaders in the education sector.
Strategic Project
You will define (with supervisors from your partner organization) a strategic project on which to focus. You will have the opportunity to lead one or two major efforts on behalf of the organization, such as the creation or implementation of current initiatives. The project allows you to practice and improve leadership skills, add important value to the mission and strategy of the partner organization, work systemically, and hold high-level accountability.
During the residency period, you will produce a written Capstone. The Capstone is a descriptive, analytic, and reflective account of your third-year leadership contributions to a strategic project within an Ed.L.D. partner organization. It is a demonstration of your ability to engage others, develop strategy to successfully address and diagnose challenges, work toward a vision and goals, and learn from the results.
Sample Topics
- Accountability, Coherence, and Improvement: Leadership Reflection and Growth in the Los Angeles Unified School District
- Leadership Development for Entrepreneurial Education Leaders Working to Build Public & Private Sector Support
- Disrupting Teacher Preparation: Lessons in Collaboration and Innovation Across the Learning to Teach Community of Practice
- Pursuing Educational Equality for English Language Learners
Sample Summaries
- Breaking Down Silos in a School District: Findings from an Ed.L.D. Project in Montgomery County
- Expanding Students' Access to Meaningful STEM Learning Opportunities Through Strategic Community Partnerships
- Developing a New Teacher Leadership and Compensation System in Iowa: A Consensus-Based Process
- Finding Great Teachers for Blended-Learning Schools
GSE Theses and Dissertations from Digital Access to Scholarship at Harvard (DASH)
Program Faculty
Ed.L.D. students learn with renowned faculty from the Harvard Graduate School of Education, Harvard Business School, and Harvard Kennedy School. Faculty from the three schools share their individual expertise in the Ed.L.D. Program and work collaboratively to provide a challenging and coherent experience for students. Faculty who teach in the Ed.L.D. core curriculum and advise Ed.L.D. students include:
Faculty Director

Frank D. Barnes
Frank Barnes is faculty director of the Doctor of Education Leadership Program. He has over 30 years experience as an educator, researcher, and organizer. As a chief accountability officer, he led turnaround efforts for large public school districts, including Boston Public Schools and Charlotte-Mecklenburg Schools.
Kathryn Parker Boudett

Ebony N. Bridwell-Mitchell

Jennifer Perry Cheatham

Elizabeth City

Candice Crawford-Zakian

Marshall Ganz

Adria D. Goodson
Deborah helsing.

Monica C. Higgins

Deborah Jewell-Sherman

Lisa Laskow Lahey

Mary Grassa O'Neill

Irvin Leon Scott

Catherine Snow

Michael L. Tushman
Martin west.

Introduce Yourself
Tell us about yourself so that we can tailor our communication to best fit your interests and provide you with relevant information about our programs, events, and other opportunities to connect with us.
Program Highlights
Explore examples of the Doctor of Education Leadership experience and the impact its community is making on the field:
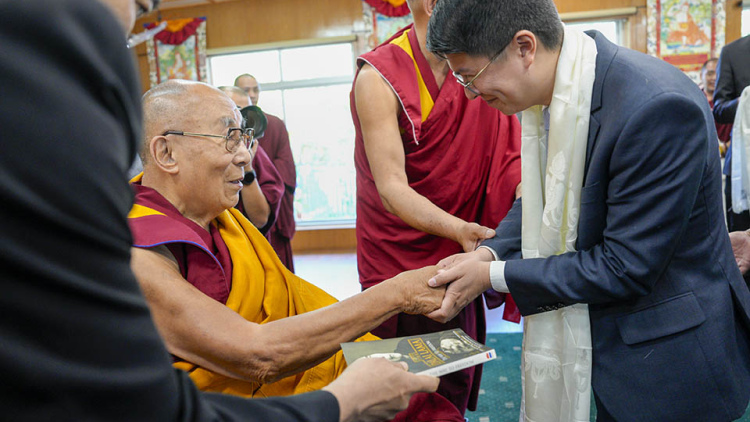

Do We Need Happiness Teachers?
After a trip to meet with the Dalai Lama, an Ed.L.D. student says we do

Combatting Chronic Absenteeism with Family Engagement
As post-COVID absenteeism rates continue unabated, a look at how strong family-school engagement can help
Advertisement
Action Research as Signature Pedagogy in an Education Doctorate Program: The Reality and Hope
- Published: 25 November 2010
- Volume 36 , pages 261–271, ( 2011 )
Cite this article

- Debby Zambo 1
781 Accesses
20 Citations
Explore all metrics
Debates about the education doctorate continue; and, while some individuals focus on the problematic, others work to distinguish this degree from the Ph.D. The author is part of the latter, and in this article I explain how faculty members at one university are using action research as a signature pedagogy to create stewards of practice, that is, school leaders who have the knowledge, skills, and dispositions to pinpoint educational problems, design solutions, and create effective change. A content analysis of action research dissertations was used to prove stewardship. I investigated the challenges that sparked students’ actions; the actions they took in response; and the benefits, if any, they gained from this experience.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others

Embedding Action Research in Philippine Teacher Education

Action Research as an Inquiry-Based Teaching Practice Model for Teacher Education Programs

Teacher Responsive Teaching and Learning Initiatives Through Action Research
Andrews, R., & Grogan, M. (2005). Form should follow function: Removing the Ed.D. dissertation from the Ph.D. straight jacket. UCEA Review, 46 (2), 10–13.
Google Scholar
Bradbury Huang, H. (2007). What is good action research? Action Research, 8 (1), 93–109. doi: 10.1177/1476705310362435
Article Google Scholar
Carnegie Project on the Education Doctorate. (2010). Working principles for the professional practice doctorate in education . College Park, MD: Author.
Erikson, F. (1986). Qualitative methods in research on teaching. In M. C. Wittrock (Ed.), Handbook of research on teaching (3rd ed., pp. 119–161). New York, NY: Macmillan.
Evans, R. (2007). Comments on Shulman, Golde, Bueschel, and Garabedian: Existing practice is not the template. Educational Researcher, 36 (6), 553–559. doi: 10.3102/0013189X07313149
Glaser, B. G., & Strauss, A. L. (1967). The discovery of grounded theory: Strategies for qualitative research . Hawthorne, NY: Aldine De Gruyter.
Golde, C. M. (2006). Signature pedagogies in doctoral education: Are they adaptable for the preparation of educational researchers? Educational Researcher, 36 (6), 344–351. doi: 10.3102/0013189X07308301
Golde, C. M., & Walker, G. E. (2006). Envisioning the future of doctoral education: Preparing stewards of the discipline . San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass.
Greenwood, D. (2007). Teaching/learning action research requires fundamental reforms in public higher education. Action Research, 5 (3), 249–264. doi: 10.1177/1476750307081016
Hendricks, G. (2009). Improving schools through action research: A comprehensive guide for educators . Boston, MA: Pearson/Merrill/Prentice Hall.
Herr, K., & Anderson, G. L. (2005). The action research dissertation: A guide for students and faculty . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Hinchey, P. A. (2008). Action research primer . New York, NY: Peter Lang.
Levine, A. (2005). Educating school leaders. Washington, DC: The Education Schools Project. Retrieved November 12, 2010, from www.edschools.org
Mills, G. E. (2010). Action Research: A Guide for the Teacher Research (43rd Ed.). Boston: Prentice Hall.
Murphy, J., & Vriesenga, M. (2005). Developing professionally anchored dissertations: Lessons from innovative programs. School Leadership Reviews, 1 (1), 33–57.
Perry, J. A., & Imig, D. G. (2008, November/December). A stewardship of practice in education. Change , 42-48.
Pine, G. J. (2009). Teacher action research: Building knowledge democracies . Los Angeles, CA: Sage.
Reason, P., & Bradbury, H. (2001). Inquiry and participation in search of a world worthy of human aspiration. In P. Reason & H. Bradbury (Eds.), Handbook of participatory action research: Participatory inquiry and practice (pp. 1–14). Los Angeles, CA: Sage.
Shulman, L. S. (2005). Signature pedagogies in the professions. Daedalus, 134 (3), 52–59. doi: 10.1162/0011526054622015
Shulman, L. S. (2007). Practical wisdom in the service of professional practice. Educational Researcher, 36 , 560–563. doi: 10.3102/0013189X07313150
Shulman, L. S., Golde, C. M., Bueschel, A. C., & Garabedian, K. J. (2006). Reclaiming education’s doctorates: A critique and a proposal. Educational Researcher, 35 (3), 25–32. doi: 10.3102/0013189X035003025
Strauss, A., & Corbin, J. (1998). Basics of qualitative research: Techniques and procedures for developing grounded theory . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications.
Walker, G. E., Golde, C. M., Jones, L., Bueschel, A. C., & Hutchings, P. (2008). The formation of scholars: Rethinking doctorial education for the twenty-first century . San Francisco, CA: Jossey Bass.
Weber, R. P. (1990). Basic content analysis (2nd ed.). Newbury Park, CA: Sage Publications.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
College of Teacher Education and Leadership, Arizona State University, P.O. Box 37100, Phoenix, AZ, 85069-7100, USA
Debby Zambo
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Debby Zambo .
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Zambo, D. Action Research as Signature Pedagogy in an Education Doctorate Program: The Reality and Hope. Innov High Educ 36 , 261–271 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10755-010-9171-7
Download citation
Published : 25 November 2010
Issue Date : August 2011
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10755-010-9171-7
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Action research dissertation
- Signature pedagogy
- Education doctorate
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

How to use the PhD title and all the little doctorate “rules”
There are many conventions in the academic world that can make it difficult to navigate the PhD title. The PhD title is awarded to those who have completed a doctoral degree but, not many people know how to use it once they have it.
This article will go through everything you need to know about using the PhD title and when you can start using it.
The “rules” are relatively simple and can be broken as they are not officially set in stone – other than when you can officially call yourself a doctor.
There is no one correct answer but it may be misleading if you use the PhD title incorrectly. Here are the recommendations for effective communication.
It very much depends on the setting. Here are some examples of how I would use my PhD titles awarded to me after my PhD degree.
| Situation | Preferred titles |
|---|---|
| Full formal university business | Dr Andrew Stapleton Ph.D, MChem |
| University emails | Dr Andy Stapleton |
| Speaking to a primary school class | Dr Andy |
| Emails to students I am lecturing | Dr Stapleton |
| How I wish to be called while teaching university classes | Andy |
How do you Write PhD correctly after a name? Is it ph d or phd?
It can be confusing to know exactly how to write PhD after your name. Which bits are capitalised? Is there a ‘.’ In the middle?
When writing a name with a PhD after it, the correct way to do so is to use “PhD” or “Ph.D. or Ph.D”
Depending on the preference of the individual, either form can be used.
However, if the individual has a business card that states their degree in full, then the more formal “Doctor of Philosophy” should be used.
It is important to note that using “PhD” without any periods is incorrect; this abbreviation should only be used in informal contexts such as emails or text messages. I tend to use PhD in my YouTube videos and some people have pointed out that this is incorrect…
Following the individual’s preferred format will ensure that their name and credentials are properly represented.
Should you use Dr as well as PhD?
Some people like to use Dr and PhD in their official titles. There are a couple of important points that you need to know about markers and academic titles.
- A person can have more than one marker in their name. For example my full title is Dr Andrew Stapleton, PhD, MChem.
- The doctor title at the front can be used as a variant to the PhD at the end.
It can be a little bit ambiguous if I was to use Dr Andrew Stapleton, PhD as there are two markers. This could mean that I have two PhD’s, it could mean that I have a PhD and a medical doctorate, or it could just be that I want to use both the doctor and the PhD tags for the one degree.
However, in my experience, I still like to use the doctor title at the front and the PhD tag at the end of my name for official purposes.
Academics would rarely use the PhD suffix in everyday communication. They would much rather just use the doctor title.
What is the proper title for a PhD?
The proper title for a PhD is Doctor of Philosophy. However, some teachers and professors like to be referred to without their official title.
If you are not sure about how your professor, lecturer, or friend with a PhD wishes to be officially addressed you can ask them.
Most of the time, I like to refer to my colleagues with their doctor title for official purposes, but I do not include the PhD at the end of their name. That is much better suited to a business card.
Your lecture may wish to be referred to as:
- Dr [last name]
- Dr [first name]
Asking them in the early stages of your relationship is the best way to work out which one they prefer.
If in doubt, always go for the more formal name and nomenclature.
When can you start to use your PhD title after your doctorate?
When you have earned your PhD, you can start using your title immediately. Although, it can be a little bit confusing as to when you have actually passed your PhD. Is it when you have submitted your dissertation? Is it when you have received the comments back?
The University of Adelaide says that you can use it from your conferral date:
Students can be conferred on one of five dates during the year and for PhD students the conferral date will be the first available following the completion of all the academic requirements of your degree, including final thesis lodgement and the disbursement of any outstanding financial obligations to the University.
I started using my PhD title as soon as my confirmation letter arrived at my house. It was the first letter from the University that referred to me as Dr Stapleton. It was incredibly excited.
Generally, it is acceptable to use the title “Dr.” both professionally and socially but socially, people very rarely use it – at least in Australia. But you should never use it if you are a PhD student, PhD candidate or enrolled in a PhD program without a previous PhD qualification.
I do use it in professional settings but it always makes me feel a little bit awkward.
However, there may be some restrictions for certain settings. For example, if have a research degree resulting in a doctor title and you are working in a medical setting – some institutions do not like you to use Dr as it can confuse patients into thinking that you have a medical degree.
Instead, they ask that you use the PhD tag at the end of your name rather than the doctoral title for official and professional communications.
What is the correct way to write PhD?
When writing about someone’s PhD, the correct way is to write the term in full and capitalize each letter.
This should be done for all academic degrees, not just PhDs.
For example, it would be “Doctor of Philosophy” or “PhD” instead of “Ph.D.”, “Dr.”, or “DPhil”.
Additionally, it is common to mention the field of study in which the degree was earned if known, such as “Doctor of Philosophy in Mathematics”. It is also good practice to include the institution that granted the degree if it is a recognized one.
When writing about someone’s PhD, use proper capitalization and include relevant information like field of study and institution if known to ensure accuracy.
How do you put a PhD in a title?
Putting a PhD in a title is not as complicated as it may sound.
Generally speaking, the proper way to list a PhD in an academic or professional setting is by writing “Dr.” before the name, followed by the person’s full name and the appropriate abbreviations for their degree.
For example, if John Smith has earned a doctorate in psychology, his credentials would be listed as “Dr. John Smith, Ph.D.”
In some cases, such as when addressing someone formally in speech or on a business card, it may also be acceptable to list their credentials as “John Smith, Ph.D.”
Depending on context and personal preference, some people may also choose to list their higher degrees after their names by writing out the entire degree instead of just its abbreviation.
For example, John Smith could choose to write his full title as “John Smith, Doctor of Psychology”
However, I have not seen this in real academic life.
Should the font size of Ph.D. be the same as someone’s name?
The question of whether the font size of a Ph.D. should be the same as someone’s name is an interesting one.
On one hand, it could be argued that the Ph.D. deserves to be highlighted and therefore should be given a larger font size than someone’s name to denote its importance.
On the other, it could be argued that this would not be necessary or appropriate, and that treating everyone equally regardless of their title or degree is more important.
It depends on context and usage – if both names appear in the same document then they should likely have the same font size; however, if one appears in a formal setting such as a diploma or certificate, then it may make sense to give it a larger font size than someone’s name to emphasize its importance and significance.
Ph.Ds (or PhDs) are an important academic achievement and should be respected accordingly but without going overboard by giving them overly large fonts sizes which can take away from rather than add to their importance.
Wrapping up – doctoral title rules
this article has been over everything you need to know that using the PhD title properly and effectively.
The doctor title can be used in place of the PhD and for incredibly formal communications, such as a business email or card, you can use both.
However, sometimes using both can cause confusion as to whether or not there is a reason first using both the doctor and PhD tags. Nonetheless, many people still use both.

Dr Andrew Stapleton has a Masters and PhD in Chemistry from the UK and Australia. He has many years of research experience and has worked as a Postdoctoral Fellow and Associate at a number of Universities. Although having secured funding for his own research, he left academia to help others with his YouTube channel all about the inner workings of academia and how to make it work for you.
Thank you for visiting Academia Insider.
We are here to help you navigate Academia as painlessly as possible. We are supported by our readers and by visiting you are helping us earn a small amount through ads and affiliate revenue - Thank you!

2024 © Academia Insider

- Create an email message
- Suggested recipients
- Use @mentions
- Create a signature
- Add attachments
- Check spelling
- Add a reaction
- Out of office replies
- Delay or schedule
- Recall a message
- Automatic forwarding
- Read receipt
- Save a file or draft
- Manual sync
- Create a folder
- Search folders
- Use inbox rules
- Conditional formatting
- Use Favorites
- Use dark mode
- Message font size
- Message list view
- Focused Inbox
- View as conversations
- Filter and sort messages
- Number of messages
- Chat with recipients
- Share an email
- Status in Outlook
- Phishing and suspicious behavior
- Blocked senders
- Protected messages
- Open a protected message
- More to explore

Create and add an email signature in Outlook
In Outlook, you can create one or more personalized signatures for your email messages. Your signature can include text, links, pictures, and images (such as your handwritten signature or a logo).
|
| Or, option below for the version of Outlook you're using. |
Note: If the steps under this New Outlook tab don't work, you may not be using new Outlook for Windows yet. Select Classic Outlook and follow those steps instead.
Create and add an email signature
On the View tab, select View Settings .
Select Accounts > Signatures .
Select New signature , then give it a distinct name.
In the editing box below the new name, type your signature, then format it with the font, color, and styles to get the appearance you want.
Select Save when you're done.
With your new signature selected from the list above the editing box, go to Select default signatures and choose whether to apply the signature to new messages and to replies and forwards.
Select Save again.
Note: If you have a Microsoft account, and you use Outlook and Outlook on the web or Outlook on the web for business, you need to create a signature in both products.
Create your signature and choose when Outlook adds a signature to your messages
If you want to watch how it's done, you can go directly to the video below .
Open a new email message.

Under Select signature to edit , choose New , and in the New Signature dialog box, type a name for the signature.
Under Edit signature , compose your signature. You can change fonts, font colors, and sizes, as well as text alignment. If you want to create a more robust signature with bullets, tables, or borders, use Word to create and format your signature text, then copy and paste it into the Edit signature box. You can also use a pre-designed template to create your signature. Download the templates in Word, customize with your personal information, and then copy and paste into the Edit signature box.
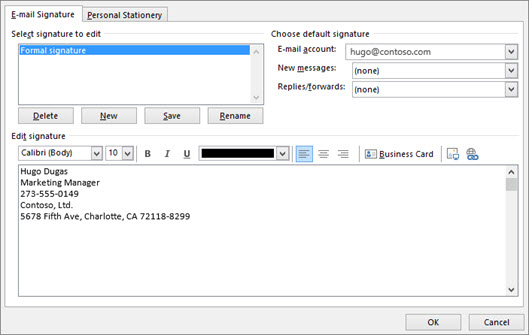
You can add links and images to your email signature, change fonts and colors, and justify the text using the mini formatting bar under Edit signature .
You can also add social media icons and links in your signature or customize one of our pre-designed temlates. For more information, see Create a signature from a template .
To add images to your signature, see Add a logo or image to your signature .
Under Choose default signature , set the following options.
In the E-mail account drop-down box, choose an email account to associate with the signature. You can have different signatures for each email account.
You can have a signature automatically added to all new messages. Go to in the New messages drop-down box and select one of your signatures. If you don't want to automatically add a signature to new messages, choose (none). This option does not add a signature to any messages you reply to or forward.
You can select to have your signature automatically appear in reply and forward messages. In the Replies/forwards drop-down, select one of your signatures. Otherwise, accept the default option of (none).
Choose OK to save your new signature and return to your message. Outlook doesn't add your new signature to the message you opened in Step 1, even if you chose to apply the signature to all new messages. You'll have to add the signature manually to this one message. All future messages will have the signature added automatically. To add the signature manually, select Signature from the Message menu and then pick the signature you just created.
Add a logo or image to your signature
If you have a company logo or an image to add to your signature, use the following steps.
Open a new message and then select Signature > Signatures .
In the Select signature to edit box, choose the signature you want to add a logo or image to.

To resize your image, right-click the image, then choose Picture . Select the Size tab and use the options to resize your image. To keep the image proportions, make sure to keep the Lock aspect ratio checkbox checked.
When you're done, select OK , then select OK again to save the changes to your signature.
Insert a signature manually
If you don't choose to insert a signature for all new messages or replies and forwards, you can still insert a signature manually.
In your email message, on the Message tab, select Signature .
Choose your signature from the fly-out menu that appears. If you have more than one signature, you can select any of the signatures you've created.

See how it's done

Top of page
Note: Outlook on the web is the web version of Outlook for business users with a work or school account.
Automatically add a signature to a message
You can create an email signature that you can add automatically to all outgoing messages or add manually to specific ones.
Select Settings at the top of the page.
Select Mail > Compose and reply .
Under Email signature , type your signature and use the available formatting options to change its appearance.
Select the default signature for new messages and replies.
Manually add your signature to a new message
If you've created a signature but didn't choose to automatically add it to all outgoing messages, you can add it later when you write an email message.
In a new message or reply, type your message.

If you created multiple signatures, choose the signature you want to use for your new message or reply.
When your email message is ready, choose Send .
Note: Outlook.com is the web version of Outlook for users signing in with a personal Microsoft account such as an Outlook.com or Hotmail.com account.
Related articles
Create and add an email signature in Outlook for Mac
Create an email signature from a template

Need more help?
Want more options.
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.

Microsoft 365 subscription benefits

Microsoft 365 training

Microsoft security

Accessibility center
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.

Ask the Microsoft Community

Microsoft Tech Community

Windows Insiders
Microsoft 365 Insiders
Find solutions to common problems or get help from a support agent.

Online support
Was this information helpful?
Thank you for your feedback.
Most Affordable Online Doctorate in Education (EdD) Programs for 2024
Organizations require great leadership to reach their full potential and weather the worst storms. If you are looking to become a more effective and thoughtful manager or team leader, you may be considering a graduate degree program. For people who are further along in their careers and looking for a more flexible option, an online Ed.D. program in organizational leadership may be a good fit. But earning a doctorate degree requires a big investment of both time and money. So Fortune has ranked eight online Doctorate in Education (Ed.D.) programs by affordability. Tuition amounts were compiled using data provided by schools for our ranking of the best online Ed.D. programs in 2022. If schools did not provide the total tuition cost of the program, we multiplied the cost per credit amount by the minimum credit hours required to graduate. Cost per credit amounts were either provided by schools or taken from the program webpage. This ranking was last updated December 2022.
Online Ed.D. from Top-5-Ranked Peabody College

1. Trevecca Nazarene University
- ACCEPTANCE RATE
- CREDITS REQUIRED TO GRADUATE
- RETENTION RATE
2. Abilene Christian University

3. Spalding University

Hawai‘i Pacific University M.Ed. in Educational Leadership

4. Virginia Commonwealth University

5. University of Dayton

6. Drexel University

7. Baylor University

8. Vanderbilt University

Maryville University’s Doctor of Education | Online

- DOI: 10.3102/0013189X07308301
- Corpus ID: 20168720
Signature Pedagogies in Doctoral Education: Are They Adaptable for the Preparation of Education Researchers?
- Chris M. Golde
- Published 1 August 2007
- Educational Researcher
128 Citations
A signature pedagogy in doctoral education: the leader–scholar community.
- Highly Influenced
Action Research as Signature Pedagogy in an Education Doctorate Program: The Reality and Hope
Leadership development of doctoral students in a carnegie project on the education doctorate affiliated ed.d. program, journal clubs as pedagogy for interdisciplinary graduate education, signature pedagogies in support of teachers’ professional learning, program evaluation of an online ed.d. in learning design and technologies: recent graduates’ perspectives, the use of journal clubs in science teacher education, using journal clubs to cultivate a community of practice at the graduate level, the design of doctorate curricula for practising professionals, identity development and mentoring in doctoral education., 28 references, signature pedagogies in the professions.
- Highly Influential
Doctoral Preparation of Scientifically Based Education Researchers
A call for the teaching of writing in graduate education, helping doctoral students write: pedagogies for supervision, the trouble with ed schools, envisioning the future of doctoral education : preparing stewards of the discipline carnegie essays on the doctorate, a new approach to teaching and learning in journal club., literature reviews of, and for, educational research: a commentary on boote and beile’s “scholars before researchers”, a review of journal clubs in postgraduate medical education, scholars before researchers: on the centrality of the dissertation literature review in research preparation, related papers.
Showing 1 through 3 of 0 Related Papers
Email signatures for PhD students (content, tips and examples)

A lot of communication in academia occurs via email. Therefore, the power of a concise and effective email signature should not be underestimated. Find out how to create a professional email signature, and what to include, as a PhD student.
Why PhD students should have professional email signatures
While Zoom, Microsoft Teams and co. become increasingly popular tools of communication, emails remain a key way of communicating in academia.
Some PhD students have to ambition to pursue an academic career, while others already know that they want to leave academia. Regardless of their ambitions, PhD students benefit from establishing all-around academic profiles , to be competitive in the (academic and non-academic) job market.
When getting in touch with people via email, you should make it as easy as possible for them. A proper email signature reminds them who you are, how to find out more about you, and how to contact you.
Don’t take that chance. Instead, help the readers of your emails out by providing them with a proper email signature to establish legitimacy.
Key elements to include in email signatures for PhD students
You may also like: The most useful academic social networking sites for PhD students
Tips for creating a convincing email signature as a PhD student
#1 know your audience when creating an email signature.
It can also make sense to create several email signatures for different purposes.
#2 Keep your email signature short and simple
#3 include hyperlinks in your email signature instead of long web addresses.
One way to reduce the text in an email signature is with hyperlinks.
A popup window will appear where you can include the full hyperlink. Your actual text will look like this:
#4 Should I include a picture in my email signature as a PhD student?
So while it may be encouraged to include a picture in some contexts, in others it may not be appreciated (anymore) if a picture is included.
How to create an email signature as a PhD student
Creating an email signature in outlook.
Under ‘ compose and reply ‘, you can create your email signature:
Creating an email signature in Gmail
After scrolling down for a bit, you will come across ‘ signature ‘. After clicking on ‘ create new ‘, you can give your signature a name and include all relevant information:
Making use of email signature templates
Templates can be a great way to create nicely designed email signatures, also as a PhD student.
4 examples of email signatures for PhD students
In the third example, Joan Doe decided to include her headshot in her email signature. Overall, she went for a bold design. She is a postgraduate student at a school of fine and performance arts and wants this background to be reflected in her email signature. She also provides a link to her ort website and links to her ongoing projects, publications and her ORCID record.
Master Academia
Get new content delivered directly to your inbox, a guide for first year phd students: expectations, responsibilities, advice, how to introduce yourself in a conference presentation (in six simple steps), related articles, the best email signatures for graduate students (with examples), how to organize and structure academic panel discussions, 5 proven ways to find co-authors to collaborate with, how to thrive in academia as an extrovert.
Cookie Consent
To improve the website, the DAAD and third parties set cookies and process usage data . In doing so, the DAAD and third parties transfer usage data to third countries in which there is no level of data protection comparable to that under EU law. By clicking the "Accept all" button, you consent to this processing. You can also find selection options and explanations of these cookies and processing at the end of this page under "Cookies". There you can withdraw consent at any time with effect for the future.
- Privacy Policy
Jump to content
PhD Studies & Research

Science and research in Germany are characterised by a distinguished infrastructure, a wide variety of disciplines, well-equipped research facilities and competent staff. Germany offers various career opportunities for international PhD students and researchers.
Deutscher Akademischer Austauschdienst e.V. Kennedyallee 50 53175 Bonn
All addresses in the DAAD Network
DAAD Newsletters
Receive regular up-to-date information about our work and organisation.
Newsletter - DAAD
Useful Links
- Find Scholarships
- DAAD offices worldwide
Jump to top of page

Scholarships
As you embark on your educational journey, we understand that financial support can make a significant difference. That’s why we’re pleased to offer a variety of scholarships to help you achieve your educational goals.
Doctor of Pharmacy students are encouraged to contact S tudent Financial Aid with questions regarding their scholarship and financial aid eligibility and packages.
- Prospective PharmD Students
- Current PharmD Students
Prospective PharmD students should fill out the optional scholarship essay in the PharmCAS application to be considered for College of Pharmacy scholarships for their P1 year. Scholarships will be awarded on a rolling basis and are limited for incoming P1 students. Typical scholarship amounts range from $5,000-$10,000 for the P1 year and are non-renewable. Additional renewable scholarship opportunities will be available P2-P4 year!
Every eligible student should file the FAFSA at studentaid.gov . The FAFSA is available on October 1 each year. Ohio State’s priority FAFSA submission deadline is February 1. Ohio State’s school code is 003090.
Students are encouraged to contact [email protected] with questions regarding their scholarship and financial aid eligibility and packages.
Continuing PharmD students may apply for College of Pharmacy scholarships through ScholarshipUniverse beginning December 1. Most scholarship applications are due by February 15. ScholarshipUniverse is a scholarship-matching tool that connects Buckeyes to scholarships and university-vetted external scholarships.
Some scholarships require a current FAFSA for consideration. Every eligible student should file the FAFSA at studentaid.gov . The FAFSA is available on October 1 each year. Ohio State’s priority FAFSA submission deadline is February 1. Ohio State’s school code is 003090. Doctor of Pharmacy students are encouraged to contact [email protected] with questions regarding their scholarship and financial aid eligibility and packages.

The George Beecher Kauffman Memorial scholarship has allowed me to wholeheartedly dedicate myself to rotations and research during my last year of pharmacy school. I would not be where I am currently if it wasn’t for scholarships, grants, and lots of loans; I grew up on a dairy farm and my family could not contribute much to my education, but it never stopped me from shooting for the stars.
Beyond providing financial security, flexibility and understanding that ends will meet, the Jason and Jamie George Veteran Scholarship validates that the work I’ve been doing has been worth it - it is recognized and acknowledged.
Receiving the Kathryn R. Kourie Scholarship has been a tremendous blessing on my educational journey. This generous support has alleviated my financial burden and allowed me to fully immerse myself in my studies and extracurricular activities. As I progress in my studies and work towards achieving my career goals, I am determined to pay forward the support I have received by actively contributing to the well-being of others.

ANA Nursing Resources Hub
Search Resources Hub

Nursing Career Pathways
5 min read • April, 25 2023
Nursing is a dynamic, rewarding profession with plenty of room for personal and professional growth. The demand for nurses is high and projected to grow as the baby boomer generation ages, promising excellent job security and earning potential. Are you wondering where to start your nursing career, or have you already started one? We'll show you available nursing career options and how to develop a career plan for the future.
Nursing Careers: Getting Started
Each nursing career path offers unique advantages and may require additional training or degrees. Establishing your goals upfront makes choosing the right nursing pathway easier. Fortunately, the nursing field provides ample opportunity for professional development. Keep in mind that many nurses change specialties or work environments throughout their careers, so whatever you initially decide isn't set in stone.
1. Earn Your Degree
No matter what nursing career you choose, your first step is to earn a post-secondary degree. The main options to consider on your path to becoming a nurse are:
- Licensed practical nurse program: If you want to start working as soon as possible, a certificate program to become a licensed practical nurse (LPN) is your fastest option — you can complete one in about a year. Bridge programs can help you transition from an LPN to a registered nurse (RN) later if you decide to advance your career.
- Nursing diploma: A nursing diploma is a fast and often more affordable path to becoming an RN. This type of program is most often based in a hospital. They aren't as common as degree programs, but if your state has one, you may be able to start working as an RN in less than two years. However, a nursing diploma doesn't provide college credits, so your training won't count toward a degree if you plan to further your career later. You may also earn a lower salary than you would with a college degree. However, with an RN-to-BSN program, you can fast-track your four-year degree later if you want to pursue opportunities that require a Bachelor of Science in Nursing (BSN).
- Associate degree: Earning an Associate Degree in Nursing (ADN) usually takes two to three years. Like a four-year degree, an ADN prepares you to become an RN. Depending on the nursing career pathway you want to pursue, you may need to get a BSN degree later. However, the advantage of an ADN compared to a nursing diploma is that your credits may transfer to your BSN program, making it easier and cheaper to continue your education down the road.
- Bachelor's degree: Compared to other ways to become an entry-level registered nurse, a BSN takes more time and may be more expensive. It usually takes about four years to get a BSN, but having one can make it possible to pursue other nursing career paths that aren't possible with a diploma or ADN alone. For that reason, a BSN is an investment that offers greater earning potential and more opportunities for professional growth throughout your career. Many hospitals and other health care employers now require new hires to have at least a BSN. And most advanced certification and post-graduate programs also require applicants to have one. Getting a BSN is the best option if you're planning a long-term nursing career or pursuing the RN career path with the highest earning potential.
2. Get Your License
Whichever nursing degree or program you decide to pursue, you need to get licensed before you can work as a licensed practical nurse or registered nurse. You must pass a licensure exam called the National Council Licensure Examination (NCLEX for registered nurses or NCLEX-PN for LPNs). This test verifies that you have the knowledge and skills to begin working safely and confidently as an entry-level nurse. Once you pass the exam, you'll receive licensure from your state and can start your nursing career.
3. Secure a Nursing Job
Once you're licensed, you're ready to look for your first nursing job. The median salary for an RN is more than $77,000, but nurses starting out can also expect a decent wage — only about 10% of registered nurses earn less than $60,000 per year. LPNs make, on average, about two thirds as much as an RN — $48,000 per year according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics .
4. Pursue Advanced Certification
Many nurses are content working as RNs or LPNs. But if you're interested in a nursing specialty or becoming a certified nurse practitioner , you have some terrific options. Some specialties require additional training or certifications from bodies like the American Nurses Credentialing Center (ANCC).
Some specialties require post-graduate degrees, such as a Master of Science in Nursing (MSN) or Doctor of Nursing Practice (DNP). Most MSN and DNP programs require a bachelor's degree before applying. If you start out with a diploma or an associate degree, you'll need to finish your BSN before pursuing nursing career pathways that require advanced degrees. Although it takes extra time and expense to get a post-graduate degree, nurses who obtain an advanced specialization have more options for career development and are among the top earners in the nursing profession. Certified Registered Nurse Anesthetists (CRNAs) make the most, earning over $165,000 on average.
More Career Options for Nurses

With all the different nursing paths, titles, advanced certifications, and specialties, a nursing career provides more flexibility than many other professions. You can choose the environment you want to work in, such as a school, hospital, outpatient doctor's office, travel nursing , long-term care, or occupational health setting.
Want even more flexibility? Depending on the nursing career path you choose, the degrees or certifications you earn and the experience you acquire, you can even work in a role that doesn't involve day-to-day patient care, such as medical consulting on legal cases, nursing research , or nursing technology and informatics. And if you have a post-graduate degree, you can pursue an advanced clinical position or a leadership role like a nurse educator, nurse administrator , or director of nursing .
This flexibility is essential for job satisfaction and to avoid one of the most significant issues: nursing burnout . When job stress leads to a lack of motivation, reduced performance, and dissatisfaction, it poses a serious safety risk to nurses and their patients. Having the freedom to pivot your career, change your environment, or move into another nursing specialty can prevent burnout and lead to a fulfilling career.
Learn about the different types of nurses and what nursing school is like as you consider if a career in nursing is right for you.
Images sourced from Getty Images
You May Also Like
Nurse Practitioner Certifications
Presented by ANCC
Family Nurse Practitioner Certification (FNP-BC™)
Price From: $395.00
ANA Member Price: $295.00
Psychiatric-Mental Health Nurse Practitioner (Across the Lifespan) Certification (PMHNP-BC™)
Specialty Certifications
Medical-Surgical Nursing Certification (MEDSURG-BC™)
Nurse Executive Certification (NE-BC®)
Related Resources
Item(s) added to cart
Covering a story? Visit our page for journalists or call (773) 702-8360.
Top Stories
Can you find good health information on tiktok uchicago study advises caution, two uchicago students honored for commitment to environmental work.
- Majority of Americans will pay more for electric vehicles made in U.S., survey finds
UChicago announces 2024 winners of Quantrell and PhD Teaching Awards
The transformative education offered at the University of Chicago begins in the classroom, with the teachers who inspire, engage and inform their students.
UChicago annually recognizes faculty for their incredible teaching and mentoring of undergraduate and graduate students through the Llewellyn John and Harriet Manchester Quantrell Awards , believed to be the nation’s oldest prize for undergraduate teaching; and the Faculty Awards for Excellence in PhD Teaching and Mentoring , which honor faculty for their work with graduate students.
Learn more about this year’s recipients below:
- Quantrell Awards: Fred Chong , Anton Ford , Michele Friedner , Nicholas Hatsopoulos and Chris Kennedy
- PhD Teaching and Mentoring Awards: Marcus Clark , Mikhail Golosov , Sidney Nagel and Miwa Yasui
Llewellyn John and Harriet Manchester Quantrell Awards
Fred chong, the seymour goodman professor in the department of computer science.
Fred Chong’s love of computer science started at an early age, when he immersed himself in the “power of creation” possible with coding.
As an undergraduate student at MIT, where he completed his graduate education, he was captivated by computer architecture, recognizing how the intricate design of the underlying machinery—composed of wires and transistors—enabled the execution of digital logic essential for powering his creations.
In a graduate course on silicon chip design, he gained insight into the construction and spatial arrangement of these components, understanding their impact on performance, cost, and energy consumption.
“It turns out that this spatial view of technology gives the core intuition of why even today's machine designs have a certain speed, cost, and energy consumption – essentially, the smaller the better,” he said.
He now teaches Quantum Computer Systems and Computer Architecture, and has taught Honors Introduction to Computer Science. The University of Chicago marks Chong’s third institution as an instructor, and while he has cherished each experience thus far, he said the learning environment at UChicago is unique.
“The truly exceptional and curious students, coupled with small class sizes, allow me to go deeper into very advanced topics,” Chong said. “Perhaps my favorite part comes from student questions. After 28 years of teaching, I can still get questions that surprise me and make me rethink some of the fundamentals of my field.”
Chong’s courses and research are centrally about understanding the trends in technology and shaping the future of computing. On the last day of class, he typically gives a lecture on some of these trends, and some of the more visionary ideas emerging in the future.
“For the last 10 years or so, this last lecture has focused a bit on quantum computing, which could potentially solve problems that are unsolvable by classical computers,” he said. “If I were to distill this down to a message, it would be to "think outside of the box and be open to what is currently impossible.”
Anton Ford, Associate Professor in the Department of Philosophy
When Anton Ford was in high school, he found a steamer trunk in the basement of his house that contained his parents’ books from college. He spread them on the floor and took the most appealing for himself.
As he recalls, the trunk had a wide variety of books: novels, poetry, history and sociology books, political texts and philosophy books. He said he remembers reading some Platonic dialogues, and developing an interest in Emerson and Nieztsche.
“My tastes have matured,” he said. “But that was my first encounter with philosophy, on the floor of the basement of my childhood home. The trunk itself came to have a sentimental value for me. I brought it with me to college, then to graduate school, and then to my first job, here, at the University of Chicago.”
Ford joined the faculty at UChicago in 2007, and is now an associate professor in philosophy with areas of special interest in Anscombe, Aristotle and Marx. In his classroom, Ford's approach aligns closely with the UChicago ethos of teaching how to think, not what to think.
On the last day of class, he said he hopes his students will leave not so much with a message as with a set of intellectual tools for thinking about the world they will be stepping into.
“The philosophers whose work I tend to teach are systematic thinkers,” he said. “One thing about a system of thought is that it can help one to see the connection between things. Another is that it provides one with intellectual orientation in an infinite variety of new circumstances.”
Through his teaching, Ford aims to empower his students to navigate a transitional phase in their lives with clarity and purpose.
“College is a pivotal moment in life, a point between academic and professional paths,” he said. “Depending on who one happens to meet, what interests one develops, what one encounters in class, what is happening in the world—and much else—one’s future trajectory could change very radically. Not every period of life is like that. Nothing in particular follows from the fact that this is a pivotal moment. But the fact is worth bearing in mind.”
Michele Friedner, Professor in the Department of Comparative Human Development
On her first day of class as an undergraduate in an introduction to Indian religions course, Michele Friedner’s professor insisted that her students look closely at the craters on the moon, and identify the shape of a rabbit — and that they had to keep looking for it until they found it.
The professor used this tactic to encourage her students to try to see things differently from how they appear at surface level, and it resonated with Friedner.
“I loved looking for the rabbit and then finally finding it,” she said. “I never look at the moon the same way anymore. And this is what I want my students to do, too – to learn different ways of seeing and experiencing taken-for-granted objects, processes and practices.”
Now a professor of comparative human development in the College, Friedner said she is not afraid to emulate that same level of “playfulness” when interacting with her students.
“Often, I ask a question that I have not fully formed and that I am still thinking through. I want them to be able to articulate things that are not fully formed while also being aware of the stakes of what we are reading and discussing,” she said.
Friedner teaches courses in disability anthropology and sensory anthropology, as well as classes in the Self, Culture and Society Core sequence. She also teaches a course in the “Big Problems” Curriculum, elective capstone experiences designated for third- and fourth-year students, alongside Jennifer Iverson in the Department of Music, called “Disability and Design” The course involves working with scholars and activists at the forefront of its eponymous fields.
For their final projects, students design a fully accessible policy, playground, restaurant, job interview guide, children’s book and more. Friedner says the course is “wonderful and invigorating” to teach.
“I love teaching disability studies-related courses at UChicago because the students are genuinely excited to consider questions and theories around disability and to grapple with complex embodiments,” she said. “They especially find it useful to reflect upon their own experiences at UChicago and beyond through the lens of disability theory.”
Nicholas Hatsopoulos, Professor in the Department of Organismal Biology and Anatomy
Nicholas Hatsopoulos teaches a course titled "Neuroscience of Consciousness," delving into a subject that has intrigued him since his undergraduate days, when he minored in philosophy.
He has always been fascinated by questions surrounding free will, which propelled him into this field of study. Though consciousness is not his primary area of research as a neuroscience professor, Hatsopoulos said he finds immense joy in engaging with his students and the lively discussions that ensue during his lectures.
“I love the interactions I have with the students and all the questions they ask during my lectures,” he said. “The students here are really smart and inquisitive. They genuinely want to learn and not just get a good grade."
Hatsopoulos fosters an environment of active participation in his classroom. He encourages interruptions and questions, believing that dialogue is essential for deep learning. If he doesn’t know the answer to a question, he is not afraid to say he doesn’t know but says he’ll try to get an answer by the next class.
He assigns students the task of critiquing two papers they read each week, promptly discussing some of the submissions in the following class. Throughout the course, debates on consciousness-related topics stimulate further exploration and critical thinking.
“I want them to interrupt me and ask questions,” he said. "The message I give them at the beginning of the course is telling them that we won't ultimately answer the question as to how consciousness arises from the brain, but hopefully they will learn about some of the experiments and theories and learn some neuroscience in the process.”
Chris Kennedy, Professor in the Department of Linguistics
Chris Kennedy, who has been teaching linguistics at UChicago for nearly 20 years, wasn’t planning to become a linguist.
“I was living in Austin, Texas, playing bass in a punk band,” he remembers. “I had a horrible case of poison ivy one summer and was stuck inside. I asked my now wife/then girlfriend to grab me a book by Noam Chomsky from the Austin Public Library. She brought me a copy of ‘Syntactic Structures,’ and I was hooked.”
In the Department of Linguistics, Kennedy teaches undergraduate and graduate courses in semantics and pragmatics, and the occasional course in syntax. He also helped design and is the faculty director for the new cognitive science major, for which he teaches the two foundational courses alongside instructors in the Psychology Department. He also teaches in the Philosophical Perspectives humanities sequence.
Kennedy says he appreciates UChicago students’ passion for the “acquisition of knowledge,” which he incorporates into his own teaching approach.
“I like to approach my classes with the idea that I am learning the material alongside the students, approaching it from a position of discovery rather than presenting it from a position of authority,” said Kennedy. “Much of the time, this is literally true, because I've found that the best way for me to really understand new ideas, especially from areas outside my own expertise, is by working through them in a classroom full of University of Chicago students. And even when I teach a class on something I’m very familiar with, I like to start from some basic assumptions and then, together with the students, build up the theory from scratch.”
Kennedy threw himself into new material as an undergraduate student and said his curiosity has been a major influence in his career. He recalls coursework in religion and archeology, as well as his primary undergraduate major in Russian language and literature, as formative educational experiences even though they were quite different from the field he works in today.
“Whenever a student asks me what they should study, I say: ‘It doesn’t matter. What matters is that you find the best teachers, and do different things,’” he said.
Faculty Awards for Excellence in PhD Teaching and Mentoring
Marcus clark, professor in the department of medicine.
Marcus Clark is fond of telling people that he loves his work. “My job is really an amalgam of hobbies, the things that I like to do. I just happen to get paid for them.”
As chief of the Section of Rheumatology in the Department of Medicine and director of the Medical Scientist Training Program (MSTP), an NIH-funded training program that pairs medical degrees with PhDs in the biological or physical sciences, he has his hands full. But rather than embracing the role of an administrator, he prefers a hands-on approach to mentoring the next generation of physician-scientists.
“I really get to know each incoming class, what they’re interested in and what their strengths are. I think that the personal touch elevates you from being just an administrator and shows them how to work like a scientist,” he said.
Clark individually mentors, advises and counsels each of the roughly 80 students in the MSTP, making a point to meet them where they are and challenging them to reach their potential how they define it—not according to a predetermined plan. He provides guidance, but not solutions—a “teach a man to fish” philosophy that makes students feel empowered in their career choices. He credits this ability to having been there before, building his own career researching immune system functions and treating patients with psoriatic arthritis and lupus.
“I think I have a good sense of where a student needs to be and how their personal journey can get them there,” he said. “I feel like I’ve done enough in my own career that I can give the students a little bit more space and think about them more. It helps me be like a proud dad in a way. I just want to see them do well.”
Mikhail Golosov, the Homer J. Livingston Professor in Economics and the College
As a graduate student, Mikhail Golosov remembers having tea with his advisor, economist Larry Jones, after a particularly brutal presentation. They talked for hours. As Golosov calmed down, he was able to spot the weaknesses in his research.
“Now, it's probably one of my most famous papers,” Golosov said. “For me, that focus on well-being played a huge role in graduate school.”
Using his own mentors as a model, Golosov’s approach to advising is twofold—guiding students through difficult research questions as well as helping manage the anxieties that might crop up because of them.
“When you start, there is so much uncertainty,” Golosov said. “You don’t know much about research; you don’t know if you’re good at it.”
After taking Golosov’s public finance course, one student was inspired to pursue a related research topic using an unfamiliar methodology.
“Without Mikhail Golosov’s patience, guidance and intelligence, I could not have pursued this project,” the student wrote. “He carefully considers each and every question without prejudice, demystifies the process of research and expresses empathy on its exciting, but frightening uncertainties."
As director of Graduate Studies, Golosov meets with student representatives from each Ph.D. cohort to hear their concerns. If he has the power to make students’ experiences better, Golosov simply will—whether that’s arranging for an accommodation or mediating between faculty and students.
“There are little things we can do that don’t require that much effort that could improve the life of graduate students a lot,” Golosov said. “Whenever I come across them, it gives me a lot of satisfaction.”
“It is rare for a scholar of his stature to demonstrate such a deep commitment to each student's success,” wrote another student. “My growth as an economist and as a member of the academic community is largely attributable to Mike’s influence.”
Sidney Nagel, the Stein-Freiler Distinguished Service Professor of Physics and the College
In Sidney Nagel’s laboratory, graduate students are learning to be physicists—to ask a question about the world no one has yet been able to answer, and then design a way to answer it. It’s not easy, but it is rewarding.
“I want to make sure they understand that doing physics is hard, but that it’s also hard for me, even as long as I’ve been doing it,” Nagel said. “To fight through the ideas to get something crisp and clean at the end is a challenge every time. But we are working on these things together.”
The “joy of common striving,” as Nagel puts it, is the theme that runs through the lab. A former student wrote that Nagel, and other more experienced Ph.D. students in the laboratory, “readily dedicated hours to guide and help me…The sense of support and collaboration permeates the Nagel group completely, out of genuine kindness and alignment of curiosity.”
Among the communal lab activities is something that Nagel believes in deeply: the value of learning to articulate a scientific problem. “That is, can you frame a vision about why this problem is important, why it’s worth doing and where it can lead?” Nagel said.
As members of Nagel’s laboratory transform from students to scientists, each learns how to present this vision through intensive coaching and group feedback.
“When I started grad school, I had no experience in giving scientific presentations, had very limited public speaking skills as a non-native English speaker, and did not enjoy presenting my work to people,” wrote another former student. “He is single-handedly responsible for making me a decent public speaker who loves giving talks.”
Another former student agreed: “He taught me to see the beauty in science, and to share my joy at understanding it with the world.”
Miwa Yasui, Associate Professor in the Crown Family School of Social Work, Policy and Practice
Described by her students and colleagues as an “exceptional,” “creative,” and “devoted lifelong mentor,” Miwa Yasui is a passionate educator whose deep commitment to teaching and student development has made a profound impact at the Crown Family School.
Recognizing that the academic life of a social scientist is never a solitary one, Yasui believes that learning is best cultivated in an environment that fosters collaboration and the sharing of ideas.
“Social sciences is something that you can never do on your own. It requires an entire team of great minds to come together. I’m very grateful for leading the team of students in my research lab from whom I have come to learn about their own interests and journeys, seeing especially how they would continue their intellectual trajectories,” she said.
Her pedagogy is also characterized by an empathetic listening that takes into account the diverse perspectives and lived experiences of her students, often reflected in their classroom discussions.
It is no wonder that she is well-loved among students in her department for being compassionate and attentive to their scholarly and emotional needs.
“Prof. Yasui has provided time and space to empathetically listen to my personal experience, inquire about my family and loved ones and mentor me on the importance of care. I cannot thank her enough for that,” a Crown Family School student said.
Having lived in different countries such as Japan, England, Singapore, and the United States, Yasui is deeply sensitive to the ways in which our human behavior, values, and beliefs are determined by cultural influences. Her research focuses on the intersection between race, culture, and immigration in the context of child development and family processes, and how they contribute to racial disparities in mental health.
Yasui’s conviction for her students is that they will not only become innovative leaders in social work but, more importantly, that their scholarship will also transform the lives of the vulnerable and marginalized.
As a former student gratefully expressed: “Notably, she believed in me.”
—With contributions by Andy Brown, Meredith Davis, Tori Lee, Louise Lerner and Matt Wood.
2024 TEACHING AWARDS
Meet the winners of the Swogger Awards, Booth Prizes and Undergraduate Student Prizes
Get more with UChicago News delivered to your inbox.
Related Topics
Latest news, supply chain software startup freshx takes first place at 2024 nvc.

Class of 2024 learns ‘three little secrets to change the world’

The College

Go 'Inside the Lab' at UChicago
Explore labs through videos and Q and As with UChicago faculty, staff and students

Quantum Computing
Researchers draw inspiration from ancient Alexandria to optimize quantum simulations
National Science Foundation
UChicago to partner on $12 million NSF project to ‘decarbonize’ computing
Around uchicago.

Around Campus
Rockefeller Chapel renovation to add beauty, functionality to historic landmark
Quantrell and PhD Teaching Awards
Campus News
Project to improve accessibility, sustainability of Main Quadrangles
National Academy of Sciences
Five UChicago faculty elected to National Academy of Sciences in 2024

UChicago women’s tennis team wins first NCAA title

UChicago men’s tennis team storms back to win NCAA championship
Biological Sciences Division
“You have to be open minded, planning to reinvent yourself every five to seven years.”

UChicago Class Visits
Atop a Chilean mountain, undergraduate students make cutting-edge astronomical observations

COMMENTS
When creating an academic e-mail signature block for Walden University, as well as for most professional correspondence, you should only use the academic credential that you have earned after your name. You should not use amended forms of a degree (e.g., PhD-C or PhD (c)) to indicate partial completion of your program, nor should you use ABD ...
50. And it is generally regarded as incorrect to prefix your title and to repeat it after the name. Even with a single degree, you should either say "Dr. Bob Roberts" or "Bob Roberts, PhD". Saying "Dr. Bob Roberts, PhD" isn't good. So, if you really want to list all of your degrees, you should probably omit the title before your name.
How to Use a Doctorate with Your Name: 1-2-3-4-5 —-#1) Holders of doctorates who work in academia or research institutions are addressed as 'Dr. (Name)' professionally and socially in a salutation or conversation.Thus, a Ph.D. professor at a college, a Ph.D. in biology doing scientific research, and a Ph.D. principal at an elementary school all use Dr. (Name) and everybody thinks it is ...
The Ed.L.D Program — taught by faculty from the Harvard Graduate School of Education, the Harvard Business School, and the Harvard Kennedy School — will train you for system-level leadership positions in school systems, state and federal departments of education, and national nonprofit organizations. Ed.L.D. is a full-time, three-year ...
The NAFOL's signature pedagogy of doctoral education was outlined. Challenges experienced towards the end of the project were also discussed. Hasgall et al. state in their report about European doctoral education that it is the doctoral community itself that develops the programme, and it is to a lesser extent a top-down dynamic decided by ...
The years since 2005 have seen an explosion of debate about the doctorate in education, much of which appeared in these pages. Shulman, Golde, Bueschel, and Garabedian (2006) proposed that educators reclaim the professional doctorate, partly in response to a critique of doctoral programs in education published by Levine (2005).The public conversation continued with a philosophical critique-and ...
signature pedagogy in our program. Action research is pervasive in our program. It is taught in the core courses (12 hours) and. research courses (9 hours), and it is also supported in Leader ...
Debates about the education doctorate continue; and, while some individuals focus on the problematic, others work to distinguish this degree from the Ph.D. The author is part of the latter, and in this article I explain how faculty members at one university are using action research as a signature pedagogy to create stewards of practice, that is, school leaders who have the knowledge, skills ...
Since 2005 there has been an explosion of interest and debate about alternative futures for the doctorate in education. The authors take the debate from the abstract to the concrete by describing a signature pedagogy in doctoral education that combines theory, applied scholarship, and the wisdom of practice in new ways.
An EdD, also known as a Doctor of Education, is a professional doctorate focused on the practice of education. Both on-campus and online EdD programs provide doctoral students with the tools and skills necessary to implement research-based practices in the classroom. EdD programs are primarily designed to take existing research and apply it to ...
Since 2005 there has been an explosion of interest and debate about alternative futures for the doctorate in education. The authors take the debate from the abstract to the concrete by describing a signature pedagogy in doctoral education that combines theory, applied scholarship, and the wisdom of practice in new ways. They describe "leader-scholar communities," whose goal is to assist and ...
attention to signature pedagogies developed as we saw elements of doctoral programs that occur normally in one discipline but are unusual in others. The research methods for this article are essentially observational. Over the course of the CID we heard faculty and students make passing reference to practices in their doctoral programs that all ...
When writing a name with a PhD after it, the correct way to do so is to use "PhD" or "Ph.D. or Ph.D". Depending on the preference of the individual, either form can be used. However, if the individual has a business card that states their degree in full, then the more formal "Doctor of Philosophy" should be used.
Debates about the education doctorate continue; and, while some individuals focus on the problematic, others work to distinguish this degree from the Ph.D. The author is part of the latter, and in this article I explain how faculty members at one university are using action research as a signature pedagogy to create stewards of practice, that is, school leaders who have the knowledge, skills ...
Since 2005 there has been an explosion of interest and debate about alternative futures for the doctorate in education. The authors take the debate from the abstract to the concrete by describing a signature pedagogy in doctoral education that combines theory, applied scholarship, and the wisdom of practice in new ways. They describe leader-scholar communities, whose goal is to assist and ...
Under Choose default signature, set the following options.. In the E-mail account drop-down box, choose an email account to associate with the signature. You can have different signatures for each email account. You can have a signature automatically added to all new messages. Go to in the New messages drop-down box and select one of your signatures. If you don't want to automatically add a ...
Since 2005 there has been an explosion of interest and debate about alternative futures for the doctorate in education. The authors take the debate from the abstract to the concrete by describing a signature pedagogy in doctoral education that combines theory, applied scholarship, and the wisdom of practice in new ways.
Spalding University ranked No. 6 among Fortune's best online doctorate in education (Ed.D.) programs in 2022. The school doesn't require applicants to submit a GRE score to qualify for ...
Associate vice provost for graduate education at Stanford University; 450 Serra Mall, Building 310, Room 110, Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94305; [email protected].This article was written while she was a senior scholar and research director for The Carnegie Initiative on the Doctorate at the Carnegie Foundation for the Advancement of Teaching.
This article describes two practices that can be considered signature pedagogies of doctoral education, one in neuroscience (the journal club) and one in English studies (the list). The practices are routinely found in these and neighboring disciplines but are not found in other fields. The journal club and the list share the goal of acquainting students with the literature of a field, but ...
Completing a master's degree generally takes 18 months to two years, and a doctoral degree can take another four to eight years. The timeline for completion of a graduate degree will vary depending on the type of degree you pursue, your desired subject area, and the institution you choose to study at, as well as whether you decide to study full-time or part-time.
Key elements to include in email signatures for PhD students. Tips for creating a convincing email signature as a PhD student. #1 Know your audience when creating an email signature. #2 Keep your email signature short and simple. #3 Include hyperlinks in your email signature instead of long web addresses.
signature pedagogy and capstone experience for the Ed.D. Debates, Vision, and Signature Pedagogy ... the Education Doctorate (CPED) and its university affiliates are working to re-envision, re-
2. Social services. Knowledge of human behavior, motivations, interviewing, and data analysis —skills common in psychology degree programs—translate well into the field of social work. Help people cope with the struggles of their everyday lives in a role as a case manager, social services assistant, or child welfare specialist.
PhD Studies & Research. PhD Studies & Research. Science and research in Germany are characterised by a distinguished infrastructure, a wide variety of disciplines, well-equipped research facilities and competent staff. Germany offers various career opportunities for international PhD students and researchers.
Scholarships will be awarded on a rolling basis and are limited for incoming P1 students. Typical scholarship amounts range from $5,000-$10,000 for the P1 year and are non-renewable. Additional renewable scholarship opportunities will be available P2-P4 year! Every eligible student should file the FAFSA at studentaid.gov.
Associate degree: Earning an Associate Degree in Nursing (ADN) usually takes two to three years. Like a four-year degree, an ADN prepares you to become an RN. Depending on the nursing career pathway you want to pursue, you may need to get a BSN degree later. However, the advantage of an ADN compared to a nursing diploma is that your credits may ...
Associate vice provost for graduate education at Stanford University; 450 Serra Mall, Building 310, Room 110, Stanford University, Stanford, CA 94305; [email protected].This article was written while she was a senior scholar and research director for The Carnegie Initiative on the Doctorate at the Carnegie Foundation for the Advancement of Teaching.
Here are some tips to help you order your credentials after your name properly: Use commas. Use commas to separate the abbreviation for each of your credentials. This can make it easier for people to determine where one credential ends and the next credential begins. Double-check abbreviations.
PhD Teaching and Mentoring Awards: Marcus Clark, Mikhail Golosov, Sidney Nagel and Miwa Yasui; Llewellyn John and Harriet Manchester Quantrell Awards ... As an undergraduate student at MIT, where he completed his graduate education, he was captivated by computer architecture, recognizing how the intricate design of the underlying machinery ...