What are the seven sections of a dissertation?

This is the second of three chapters about Dissertations . To complete this reader, read each chapter carefully and then unlock and complete our materials to check your understanding.
– Discuss the overall dissertation structure
– Explore the common elements of a dissertation
– Consider additional elements which may be added
Chapter 1: What is an academic dissertation?
Chapter 2: What are the seven sections of a dissertation?
Chapter 3: What is an effective dissertation topic?
When writing a dissertation , like any type of essay , it’s important that relatively inexperienced writers follow tried and trusted structures and methods so as to convey ideas, arguments and research as clearly and easily as possible. This chapter therefore offers one such prescribed structure that’s particularly used in social-science dissertations, such as for linguistics, psychology or anthropology. Although other subjects may of course use a slightly different number of sections, place these seven sections in a slightly different order, or expect a different weighting for each section, the example structure we’ve included below should cover most dissertation and thesis types that students will be required to produce.
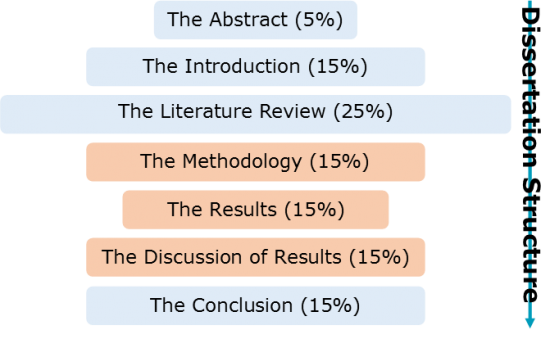
1. The Abstract (5%)
Both the shortest and first-encountered section of a dissertation , the abstract is intended to provide a very brief overview of the entire research project, highlighting to the reader the aims of the dissertation, the background and context of the investigation, the methodology that’s been used, the study’s key findings, and how this particular study has contributed to the field of knowledge.
2. The Introduction (15%)
Following the abstract , the purpose of the introduction is usually to describe the focus of the dissertation by reviewing the topic’s background and context. An introduction may also identify gaps in the research and how the writer intends to fill those gaps, as well as an outline of the scope of the investigation and the general and argumentative structure of the dissertation.
3. The Literature Review (25%)
The largest section of a dissertation is usually the literature review , which aims to provide a detailed discussion of the existing research that’s most relevant to the investigation. This section usually includes a critical review of both non-research and research literature, as well as any theoretical perspectives that require understanding to support and contextualise the study. Additionally, identification and justification of the research gap being filled in this dissertation as well as an explanation of how all of the above features have informed the dissertation are generally included.
4. The Methodology (15%)
The methodology is usually where the primary (and original) research of the dissertation begins. The purpose of this section is to highlight and justify to the reader the approach, design and processes that were followed to collect the findings, such as whether qualitative or quantitative methods were employed and whether questionnaires, interviews or recordings were used to collect the raw data. This section may include the study’s methodological approach, the research design, justification of the methods used, a discussion of the reliability and validity of those methods, and a description of the data collection and analysis procedures.
5. The Results (10%)
The fifth section (which is sometimes combined with the sixth section) of a dissertation is usually focussed on the results . The primary aim of this chapter is to present the results of the study’s primary research in a clear manner that demonstrates how these results address the dissertation’s research questions. Generally, in the results section the writer will present the relevant findings of the study, explain the implications of those findings, present evidence to support those findings, refer back to the methodology and introductory background information, and perhaps also refer forwards to the discussion of results .
6. The Discussion of Results (15%)
While the results section deals with the raw data, the discussion of results is where these findings are contextualised and their significance explained. As well as reminding the reader of the research aims and how the study’s results work to explore these aims, the writer should additionally present a discussion of how these findings have contributed to the dissertation’s hypotheses and therefore to the overall literature. Some time may also be spent interpreting the study’s findings, comparing them to other research, and evaluating their contribution to the literature.
7. The Conclusion (15%)
The final section of a dissertation is called the conclusion , the purpose of which is to remind the reader of the study’s aims, the key methodology, and the findings of the investigation. The writer may also wish to evaluate the significance of the research, commenting on how this research further develops the theory as well as highlighting any limitations that may have become apparent during the investigation. Finally, how this research can be applied practically may also be outlined to the reader, and any research gaps generated by the study explained.
Additional Sections
While these seven sections constitute the bulk of the dissertation , don’t forget to also include a table of contents , a reference list and an appendix if necessary.
Now that we’ve discussed what a dissertation is, when one might be used, and which sections such an extended essay usually contains, the final chapter on this subject is about choosing an effective dissertation topic.
To reference this reader:
Academic Marker (2022) About Dissertations . Available at: https://academicmarker.com/essay-writing/dissertations/about-dissertations/ (Accessed: Date Month Year).
- University of Reading
- University of York

Downloadables
Once you’ve completed all three chapters about dissertations , you might also wish to download our beginner, intermediate and advanced worksheets to test your progress or print for your students. These professional PDF worksheets can be easily accessed for only a few Academic Marks .
Our dissertations academic reader (including all three chapters about this topic) can be accessed here at the click of a button.
Gain unlimited access to our dissertations beginner worksheet, with activities and answer keys designed to check a basic understanding of this reader’s chapters.
To check a confident understanding of this reader’s chapters , click on the button below to download our dissertations intermediate worksheet with activities and answer keys.
Our dissertations advanced worksheet with activities and answer keys has been created to check a sophisticated understanding of this reader’s chapters .
To save yourself 5 Marks , click on the button below to gain unlimited access to all of our dissertations chapters and worksheets. The All-in-1 Pack includes every chapter in this reader, as well as our beginner, intermediate and advanced worksheets in one handy PDF.
Click on the button below to gain unlimited access to our about dissertations teacher’s PowerPoint, which should include everything you’d need to successfully introduce this topic.
Collect Academic Marks
- 100 Marks for joining
- 25 Marks for daily e-learning
- 100-200 for feedback/testimonials
- 100-500 for referring your colleages/friends
- How it works
"Christmas Offer"
Terms & conditions.
As the Christmas season is upon us, we find ourselves reflecting on the past year and those who we have helped to shape their future. It’s been quite a year for us all! The end of the year brings no greater joy than the opportunity to express to you Christmas greetings and good wishes.
At this special time of year, Research Prospect brings joyful discount of 10% on all its services. May your Christmas and New Year be filled with joy.
We are looking back with appreciation for your loyalty and looking forward to moving into the New Year together.
"Claim this offer"
In unfamiliar and hard times, we have stuck by you. This Christmas, Research Prospect brings you all the joy with exciting discount of 10% on all its services.
Offer valid till 5-1-2024
We love being your partner in success. We know you have been working hard lately, take a break this holiday season to spend time with your loved ones while we make sure you succeed in your academics
Discount code: RP0996Y

Writing a Methodology for your Dissertation | Complete Guide & Steps
What is a methodology.
The methodology is perhaps the most challenging and laborious part of the dissertation . Essentially, the methodology helps in understanding the broad, philosophical approach behind the methods of research you chose to employ in your study. The research methodology elaborates on the ‘how’ part of your research.
This means that your methodology chapter should clearly state whether you chose to use quantitative or qualitative data collection techniques or a mix of both.
Your research methodology should explain the following:
- What was the purpose of your research?
- What type of research method was used?
- What were the data-collecting methods?
- How did you analyse the data?
- What kind of resources were used in your research?
- Why did you choose these methods?
You will be required to provide justifications as to why you preferred a certain method over the others. If you are trying to figure out exactly how to write methodology or the structure of a methodology for a dissertation, this article will point you in the right direction.
Students must be sure of why they chose a certain research method over another. “I figured out” or “In my opinion” statements will not be an acceptable justification. So, you will need to come up with concrete academic reasons for your selection of research methods.
What are the Standard Contents of a Research Methodology?
The methodology generally acts as a guideline or plan for exactly how you intend to carry out your research. This is especially true for students who must submit their methodology chapter before carrying out the research.
Your methodology should link back to the literature review and clearly state why you chose certain data collection and analysis methods for your research/dissertation project.
The methodology chapter consists of the following:
- Research Design
- Philosophical Approach
- Data Collection Methods
- Research Limitations
- Ethical Considerations (If Any)
- Data Analysis Methods
For those who are submitting their dissertation as a single paper, their methodology should also touch on any modifications they had to make as their work progressed.
However, it is essential to provide academic justifications for all choices made by the researcher.
How to Choose your Dissertation Methodology and Research Design?
The theme of your research methodology chapter should be related to your literature review and research question (s).
You can visit your college or university library to find textbooks and articles that provide information about the commonly employed research methods .
An intensive reading of such books can help you devise your research philosophy and choose the appropriate methods. Any limitations or weaknesses of your chosen research approach should also be explained, as well as the strategies to overcome them.
To research well, you should read well! Read as many research articles (from reputed journals) as you can. Seeing how other researchers use methods in their studies and why will help you justify, in the long run, your own research method(s).
Regardless of the chosen research approach, you will find researchers who either support it or don’t. Use the arguments for and against articulated in the literature to clarify why you decided to choose the selected research design and why the research limitations are irrelevant to your research.
How to Structure your Dissertation Methodology?
The typical structure of the methodology chapter is as follows:
- Research Design And Strategy
- Methods Of Data Collection And Data Analysis
- Ethical Considerations, Reliability , Limitations And Generalisability
In research jargon, generalisability is termed external validity . It means how generalisable your research findings are to other contexts, places, times, people, etc. External validity is expected to be significantly high, especially in quantitative studies.
According to USC-Research Guides (2017) , a research design’s primary function is to enable the researcher to answer the research questions through evidence effectively. Generally, this section will shed light on how you collected your data.
The researcher will have to justify their choice of data collection methods, such as the one that was reviewed, the use of data tools (interviews, phone surveys, questionnaires, observation, online surveys , etc.) and the like.
Moreover, data sampling choice should also be clearly explained with a focus on how you chose the ethnicity, group, profession and age of the participants.
- What type of questions do you intend to ask the respondents?
- How will they help to answer your research questions ?
- How will they help to test the hypothesis of the dissertation?
It is recommended to prepare these questions at the start of your research. You should develop your research problem and questions. This approach can allow the room to change or modify research questions if your data collection methods do not give the desired results.
It’s a good practice to keep referring to your research questions whilst planning or writing the research design section. This will help your reader recall what the research is about; why you have done what you did. Even though this technique is recommended to be applied at the start of every section within a dissertation, it’s especially beneficial in the methodology section.
In short, you will need to make sure that the data you are going to collect relates to the topic you are exploring. The complexity and length of the research design section will vary depending on your academic subject and the scope of your research, but a well-written research design will have the following characteristics:
- It sheds light on alternative research design options and justifies why your chosen design is the best to address the research problem.
- Clearly specifies the research questions that the research aims to address or the hypothesis to validate.
- Explain how the collected data will help address the research problem and discusses your research methodology to collect the data.
Philosophical Approach Behind Writing a Methodology
This will discuss your chosen philosophy to strengthen your research and the research model. Commonly employed philosophies in academia are
- Interpretivism,
- Positivism/Post-Positivism
- Constructivism
There are several other research philosophies that you could adopt.
The choice of philosophy will depend on many factors, including your academic subject and the type and complexity of the research study. Regardless of which philosophy is used, you will be required to make different assumptions about the world.
Once you have chosen your research philosophy, the next step will describe your research context to answer all the questions, including when, where, why, how and what of your research.
Essentially, as a researcher, you will be required to decide whether you will be using a qualitative method, a quantitative method or a mix of both.
Did you know?
Using both qualitative and quantitative methods leads to the use of a mixed-methods approach. This approach also goes by another seldom-used name: eclectic approach.
The process of data collection is different for each method. Typically, you would want to decide whether you will adopt the positivist approach, defining your hypothesis and testing it against reality.
If this is the case, you will be required to take the quantitative approach, collecting numerical data at a large scale (from 30 or more respondents) and testing your hypotheses with this data.
Collecting data from at least 30 respondents/participants ensures reliable statistical analysis . This is especially true for quantitative studies. If the data contains less than 30 responses, it won’t be enough to carry out reliable statistical analyses on such data.
The other option for you would be to base your research on a qualitative approach, which will point you in a direction where you will be investigating broader areas by identifying people’s emotions and perceptions of a subject.
With a qualitative approach, you will have to collect responses from respondents and look at them in all their richness to develop theories about the field you are exploring.
Finally, you can also use a mix of qualitative and quantitative methods (which is becoming increasingly popular among researchers these days). This method is beneficial if you are interested in putting quantitative data into a real-world context or reflecting different perspectives on a subject.
Research philosophy in the ‘research onion.’
Methods of Data Collection and Data Analysis
This section will require you to clearly specify how you gathered the data and briefly discuss the tools you used to analyse it. For example, you may choose to conduct surveys and/or interviews as part of the data collection process.
Similarly, if you used software such as Excel or SPSS to process the data , you will have to justify your software choice. In this section of your methodology chapter , you will also have to explain how you arrived at your findings and how reliable they are.
It is important to note that your readers or supervisor would want to see a correlation between your findings and the hypothesis/research questions you based your study on at the very beginning.
Your supervisor or dissertation research assistant can play a key role in helping you write the methodology chapter according to established research standards. So, keep your supervisor in the loop to get their contributions and recommendations throughout the process.
In this section, you should briefly describe the methods you’ve used to analyse the data you’ve collected.
Qualitative Methods
The qualitative method includes analysing language, images, audio, videos, or any textual data (textual analysis). The following types of methods are used in textual analysis .
Discourse analysis:
Discourse analysis is an essential aspect of studying a language and its uses in day-to-day life.
Content analysis:
It is a method of studying and retrieving meaningful information from documents Thematic analysis:
It’s a method of identifying patterns of themes in the collected information, such as face-to-face interviews, texts, and transcripts.
Example: After collecting the data, it was checked thoroughly to find the missing information. The interviews were transcribed, and textual analysis was conducted. The repetitions of the text, types of colours displayed, and the tone of the speakers was measured.
Quantitative Methods
Quantitative data analysis is used for analysing numerical data. Include the following points:
- The methods of preparing data before analysing it.
- Which statistical test you have used? (one-ended test, two-ended test)
- The type of software you’ve used.
Ethical Considerations, Reliability and Limitations of a Dissertation Methodology
Other important sections of your methodology are:
Ethical Considerations
Always consider how your research will influence other individuals who are beyond the scope of the study. This is especially true for human subjects. As a researcher, you are always expected to make sure that your research and ideas do not harm anyone in any way.Discussion concerning data protection, data handling and data confidentiality will also be included in this brief segment.
- How did you ensure your participants’/respondents’ anonymity and/or confidentiality?
- Did you remove any identifiable markers after conducting the study (post-test stage) so that readers wouldn’t be able to guess the identity of the participant/respondent?
- Was personal information collected according to the purpose of the research? (For instance, asking respondents their age when it wasn’t even relevant in the study). All such ethical considerations need to be mentioned.
Even though there is no established rule to include ethical considerations and limitations within the methodology section, it’s generally recommended to include it in this section, as it makes more sense than including it, say, after the discussions section or within the conclusion.
This is mainly because limitations almost always occur in the methodology stage of research. And ethical considerations need to be taken while sampling, an important aspect of the research methodology.
Here are some examples of ethical issues that you should be mindful of
- Does your research involve participants recalling episodes of suffering and pain?
- Are you trying to find answers to questions considered culturally sensitive either by participants or the readers?
- Are your research, analysis and findings based on a specific location or a group of people?
All such issues should be categorically addressed and a justification provided for your chosen research methodology by highlighting the study’s benefits.
Reliability
Is your research study and findings reliable for other researchers in your field of work? To establish yourself as a reliable researcher, your study should be both authentic and reliable.
Reliability means the extent to which your research can yield similar results if it was replicated in another setting, at a different time, or under different circumstances. If replication occurs and different findings come to light, your (original) research would be deemed unreliable.
Limitations
Good dissertation writers will always acknowledge the limitations of their research study. Limitations in data sampling can decrease your results’ reliability.
A classic example of research limitation is collecting responses from people of a certain age group when you could have targeted a more representative cross-section of the population.Be humble and admit to your own study’s limitations. Doing so makes your referees, editors, supervisors, readers and anyone else involved in the research enterprise aware that you were also aware of the things that limited your study.
Limitations are NOT the same as implications. Sometimes, the two can be confused. Limitations lead to implications, that is, due to a certain factor being absent in the study (limitation) for instance, future research could be carried out in a setting where that factor is present (implication).
Dissertation Methodology Example
At this point, you might have a basic understanding of how to craft a well-written, organised, accurate methodology section for your dissertation. An example might help bring all the aforementioned points home. Here is a dissertation methodology example in pdf to better understand how to write methodology for a dissertation.
Sample Dissertation Methodology
Does your Research Methodology Have the Following?
- Great Research/Sources
- Perfect Language
- Accurate Sources
If not, we can help. Our panel of experts makes sure to keep the 3 pillars of Research Methodology strong.

Types of Methodologies
A scientific or lab-based study.
A methodology section for a scientific study will need to elaborate on reproducibility and meticulousness more than anything else. If your methods have obvious flaws, the readers are not going to be impressed. Therefore, it is important to ensure that your chosen research methodology is vigorous in nature.
Any information related to the procedure, setup and equipment should be clearly stated so other researchers in your field of study can work with the same method in the future if needed.
Variables that are likely to falsify your data must be taken into the equation to avoid ambiguities. It is recommended to present a comprehensive strategy to deal with these variables when gathering and analysing the data and drawing conclusions.
Statistical models employed as part of your scientific study will have to be justified, and so your methodology should include details of those statistical models.
Another scholar in the future might use any aspect of your methodology as the starting point for their research. For example, they might base their research on your methodology but analyse the data using other statistical models. Hence, this is something you should be mindful of.
Behavioural or Social Sciences-Based Dissertation
Like scientific or lab-based research, a behavioural and social sciences methodology needs to be built along the same lines. The chosen methodology should demonstrate reproducibility and firmness so other scholars can use your whole dissertation methodology or a part of it based on their research needs.
But there are additional issues that the researcher must take into consideration when working with human subjects. As a starting point, you will need to decide whether your analysis will be based on qualitative data, quantitative data or mixed-method of research, where qualitative data is used to provide contextual background to quantitative data or the other way around.
Here are some questions for you to consider:
- Will you observe the participants undertaking some activity, ask them to fill out a questionnaire, or record their responses during the interviews ?
- Will you base your research on existing evidence and datasets and avoid working with human subjects?
- What are the length, width, and reach of your data? Define its scope.
- Is the data highly explicit to the location or cultural setting you carried your study in, or can it be generalised to other situations and frameworks (reliability)? What are your reasons and justifications?
While you will be required to demonstrate that you have taken care of the above questions, it is equally important to make sure that you address your research study’s ethical issues side-by-side.
Of course, the first step in that regard will be to obtain formal approval for your research design from the ethics bodies (such as IRBs – institutional review boards), but still, there will be many more issues that could trigger a sense of grief and discomfort among some of the readers.
Humanities and Arts Dissertation Project
The rigour and dependability of the methods of research employed remain undisputed and unquestionable for humanities and arts-based dissertations as well. However, the way you convince your readers of your dissertation’s thoroughness is slightly different.
Unlike social science dissertation or a scientific study, the methodology of dissertations in arts and humanities subjects needs to be directly linked to the literature review regardless of how innovative your dissertation’s topic might be.
For example, you could demonstrate the relationship between A and B to discover a new theoretical background or use existing theories in a new framework.
The methodology section of humanities and arts-based dissertations is less complex, so there might be no need to justify it in detail. Students can achieve a seamless transition from the literature review to the analysis section.
However, like with every other type of research methodology, it is important to provide a detailed justification of your chosen methodology and relate it to the research problem.
Failing to do so could leave some readers unconvinced of your theoretical foundations’ suitability, which could potentially jeopardise your whole research.
Make sure that you are paying attention to and giving enough information about the social and historical background of the theoretical frameworks your research methodology is based on. This is especially important if there is an essential difference of opinion between your research and the research done on the subject in the past.
A justification of why opposing schools of thought disagree and why you still went ahead to use aspects of these schools of thought in your methodology should be clearly presented for the readers to understand how they would support your readings.
A Dissertation in Creative Arts
Some degree programs in the arts allow students to undertake a portfolio of artworks or creative writing rather than produce an extended dissertation research project.However, in practice, your creative research will be required to be submitted along with a comprehensive evaluative paper, including background information and an explanation that hypothesises your innovative exercise.
While this might seem like an easy thing to do, critical evaluation of someone’s work is highly complex and notorious in nature. This further reinforces the argument of developing a rigorous methodology and adhering to it.
As a scholar, you will be expected to showcase the ability to critically analyse your methodology and show that you are capable of critically evaluating your own creative work.Such an approach will help you justify your method of creating the work, which will give the readers the impression that your research is grounded in theory.
What to Avoid in Methodology?
All chapters of a dissertation paper are interconnected. This means that there will undoubtedly be some information that would overlap between the different chapters of the dissertation .
For example, some of the text material may seem appropriate to both the literature review and methodology sections; you might even end up moving information from pillar to post between different chapters as you edit and improve your dissertation .
However, make sure that you are not making the following a part of your dissertation methodology, even though it may seem appropriate to fit them in there:
A Long Review of Methods Employed by Previous Researchers
It might seem relevant to include details of the models your dissertation methodology is based on. However, a detailed review of models and precedents used by other scholars and theorists will better fit in the literature review chapter, which you can link back to. This will help the readers understand why you decided to go in favour of or against a certain tactic.
Unnecessary Details Readers Might Not be Interested In
There is absolutely no need to provide extensive details of things like lab equipment and experiment procedures. Having such information in the methodology chapter would discourage some readers who might not be interested in your equipment, setup, lab environment, etc.
Your aim as the author of the document will be to retain the readers’ interest and make the methodology chapter as readable as possible.
While it is important to get all the information relating to how others can reproduce your experiment, it is equally important to ensure your methodology section isn’t unnecessarily long. Again, additional information is better to be placed within the appendices chapter.
The methodology is not the section to provide raw data, even if you are only discussing the data collection process. All such information should be moved to the appendices section.
Even if you feel some finding or numerical data is crucial to be presented within the methodology section, you can, at most, make brief comments about such data. Its discussion, however, is only allowed in the discussions section .
What Makes your Methodology Stand Out?
The factors which can determine if your dissertation methodology is ‘great’ depend on many factors, including the level of study you are currently enrolled in.
Undergraduate dissertations are, of course, less complex and less demanding. At most universities in the UK, undergraduate students are required to exhibit the ability to conduct thorough research as they engage for the first time with theoretical and conceptual frameworks in their chosen research area.
As an undergraduate student, you will be expected to showcase the capacity to reproduce what you have learnt from theorists in your academic subject, transform your leanings into a methodology that would help you address the research problem, and test the research hypothesis, as mentioned in the introduction chapter.
A great undergraduate-level dissertation will incorporate different schools of thought and make a valuable contribution to existing knowledge. However, in general, undergraduate-level dissertations’ focus should be to show thorough desk-based and independent research skills.
Postgraduate dissertation papers are much more compound and challenging because they are expected to make a substantial contribution to existing knowledge.
Depending on the academic institute, some postgraduate students are even required to develop a project published by leading academic journals as an approval of their research skills.
It is important to recognise the importance of a postgraduate dissertation towards building your professional career, especially if your work is considered impactful in your area of study and receives citations from multiple scholars, enhancing your reputation in academic communities.
Even if some academics cite your literature review and conclusion in their own work, it is a well-known fact that your methodology framework will result in many more citations regardless of your academic subject.
Other scholars and researchers in your area of study are likely to give much more value to a well-crafted methodology, especially one they can use as the starting point for their own research.
Of course, they can alter, refine and enhance your methodology in one way or another. They can even apply your methodological framework to a new data set or apply it in a completely new situation that is irrelevant to your work.
Finally, postgraduate dissertations are expected to be highly convincing and demonstrate in-depth engagement. They should be reproducible and show rigour, so the findings and conclusions can be regarded as authentic and reliable among scientific and academic communities.
The methodology is the door to success when it comes to dissertation projects. An original methodology that takes into consideration all aspects of research is likely to have an impact on the field of study.
As a postgraduate student, you should ask yourself, Is my dissertation methodology reproducible and transferable? Producing a methodology that others can reproduce in the future is as important as answering research questions .
The methodology chapter can either make or break the grade of your research/dissertation paper. It’s one of the research elements that leave a memorable impression on your readers. So, it would help if you took your time when it comes to choosing the right design and philosophical approach for your research.
Always use authentic academic sources and discuss your plans in detail with your supervisor if you believe your research design or approach has flaws in it.
Did this article help you learn how to write a dissertation methodology and how to structure a dissertation methodology? Let us know in your comments.
Are you struggling to create a thorough and well-rounded dissertation methodology?
Avail of our dissertation writing services ! At ResearchProspect, we have Master’s and PhD qualified dissertation writers for all academic subjects, so you can be confident that the writer we will assign to your dissertation order will be an expert in your field of study. They can help you with your whole dissertation or just a part of it. You decide how much or how little help you need.
You May Also Like
Are you looking for intriguing and trending dissertation topics? Get inspired by our list of free dissertation topics on all subjects.
Looking for an easy guide to follow to write your essay? Here is our detailed essay guide explaining how to write an essay and examples and types of an essay.
Learn about the steps required to successfully complete their research project. Make sure to follow these steps in their respective order.
More Interesting Articles
As featured on.

USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

Splash Sol LLC
- How It Works
- Privacy Policy

Home » Dissertation Methodology – Structure, Example and Writing Guide
Dissertation Methodology – Structure, Example and Writing Guide
- Table of Contents

Dissertation Methodology
In any research, the methodology chapter is one of the key components of your dissertation. It provides a detailed description of the methods you used to conduct your research and helps readers understand how you obtained your data and how you plan to analyze it. This section is crucial for replicating the study and validating its results.
Here are the basic elements that are typically included in a dissertation methodology:
- Introduction : This section should explain the importance and goals of your research .
- Research Design : Outline your research approach and why it’s appropriate for your study. You might be conducting an experimental research, a qualitative research, a quantitative research, or a mixed-methods research.
- Data Collection : This section should detail the methods you used to collect your data. Did you use surveys, interviews, observations, etc.? Why did you choose these methods? You should also include who your participants were, how you recruited them, and any ethical considerations.
- Data Analysis : Explain how you intend to analyze the data you collected. This could include statistical analysis, thematic analysis, content analysis, etc., depending on the nature of your study.
- Reliability and Validity : Discuss how you’ve ensured the reliability and validity of your study. For instance, you could discuss measures taken to reduce bias, how you ensured that your measures accurately capture what they were intended to, or how you will handle any limitations in your study.
- Ethical Considerations : This is where you state how you have considered ethical issues related to your research, how you have protected the participants’ rights, and how you have complied with the relevant ethical guidelines.
- Limitations : Acknowledge any limitations of your methodology, including any biases and constraints that might have affected your study.
- Summary : Recap the key points of your methodology chapter, highlighting the overall approach and rationalization of your research.
Types of Dissertation Methodology
The type of methodology you choose for your dissertation will depend on the nature of your research question and the field you’re working in. Here are some of the most common types of methodologies used in dissertations:
Experimental Research
This involves creating an experiment that will test your hypothesis. You’ll need to design an experiment, manipulate variables, collect data, and analyze that data to draw conclusions. This is commonly used in fields like psychology, biology, and physics.
Survey Research
This type of research involves gathering data from a large number of participants using tools like questionnaires or surveys. It can be used to collect a large amount of data and is often used in fields like sociology, marketing, and public health.
Qualitative Research
This type of research is used to explore complex phenomena that can’t be easily quantified. Methods include interviews, focus groups, and observations. This methodology is common in fields like anthropology, sociology, and education.
Quantitative Research
Quantitative research uses numerical data to answer research questions. This can include statistical, mathematical, or computational techniques. It’s common in fields like economics, psychology, and health sciences.
Case Study Research
This type of research involves in-depth investigation of a particular case, such as an individual, group, or event. This methodology is often used in psychology, social sciences, and business.
Mixed Methods Research
This combines qualitative and quantitative research methods in a single study. It’s used to answer more complex research questions and is becoming more popular in fields like social sciences, health sciences, and education.
Action Research
This type of research involves taking action and then reflecting upon the results. This cycle of action-reflection-action continues throughout the study. It’s often used in fields like education and organizational development.
Longitudinal Research
This type of research involves studying the same group of individuals over an extended period of time. This could involve surveys, observations, or experiments. It’s common in fields like psychology, sociology, and medicine.
Ethnographic Research
This type of research involves the in-depth study of people and cultures. Researchers immerse themselves in the culture they’re studying to collect data. This is often used in fields like anthropology and social sciences.
Structure of Dissertation Methodology
The structure of a dissertation methodology can vary depending on your field of study, the nature of your research, and the guidelines of your institution. However, a standard structure typically includes the following elements:
- Introduction : Briefly introduce your overall approach to the research. Explain what you plan to explore and why it’s important.
- Research Design/Approach : Describe your overall research design. This can be qualitative, quantitative, or mixed methods. Explain the rationale behind your chosen design and why it is suitable for your research questions or hypotheses.
- Data Collection Methods : Detail the methods you used to collect your data. You should include what type of data you collected, how you collected it, and why you chose this method. If relevant, you can also include information about your sample population, such as how many people participated, how they were chosen, and any relevant demographic information.
- Data Analysis Methods : Explain how you plan to analyze your collected data. This will depend on the nature of your data. For example, if you collected quantitative data, you might discuss statistical analysis techniques. If you collected qualitative data, you might discuss coding strategies, thematic analysis, or narrative analysis.
- Reliability and Validity : Discuss how you’ve ensured the reliability and validity of your research. This might include steps you took to reduce bias or increase the accuracy of your measurements.
- Ethical Considerations : If relevant, discuss any ethical issues associated with your research. This might include how you obtained informed consent from participants, how you ensured participants’ privacy and confidentiality, or any potential conflicts of interest.
- Limitations : Acknowledge any limitations in your research methodology. This could include potential sources of bias, difficulties with data collection, or limitations in your analysis methods.
- Summary/Conclusion : Briefly summarize the key points of your methodology, emphasizing how it helps answer your research questions or hypotheses.
How to Write Dissertation Methodology
Writing a dissertation methodology requires you to be clear and precise about the way you’ve carried out your research. It’s an opportunity to convince your readers of the appropriateness and reliability of your approach to your research question. Here is a basic guideline on how to write your methodology section:
1. Introduction
Start your methodology section by restating your research question(s) or objective(s). This ensures your methodology directly ties into the aim of your research.
2. Approach
Identify your overall approach: qualitative, quantitative, or mixed methods. Explain why you have chosen this approach.
- Qualitative methods are typically used for exploratory research and involve collecting non-numerical data. This might involve interviews, observations, or analysis of texts.
- Quantitative methods are used for research that relies on numerical data. This might involve surveys, experiments, or statistical analysis.
- Mixed methods use a combination of both qualitative and quantitative research methods.
3. Research Design
Describe the overall design of your research. This could involve explaining the type of study (e.g., case study, ethnography, experimental research, etc.), how you’ve defined and measured your variables, and any control measures you’ve implemented.
4. Data Collection
Explain in detail how you collected your data.
- If you’ve used qualitative methods, you might detail how you selected participants for interviews or focus groups, how you conducted observations, or how you analyzed existing texts.
- If you’ve used quantitative methods, you might detail how you designed your survey or experiment, how you collected responses, and how you ensured your data is reliable and valid.
5. Data Analysis
Describe how you analyzed your data.
- If you’re doing qualitative research, this might involve thematic analysis, discourse analysis, or grounded theory.
- If you’re doing quantitative research, you might be conducting statistical tests, regression analysis, or factor analysis.
Discuss any ethical issues related to your research. This might involve explaining how you obtained informed consent, how you’re protecting participants’ privacy, or how you’re managing any potential harms to participants.
7. Reliability and Validity
Discuss the steps you’ve taken to ensure the reliability and validity of your data.
- Reliability refers to the consistency of your measurements, and you might discuss how you’ve piloted your instruments or used standardized measures.
- Validity refers to the accuracy of your measurements, and you might discuss how you’ve ensured your measures reflect the concepts they’re supposed to measure.
8. Limitations
Every study has its limitations. Discuss the potential weaknesses of your chosen methods and explain any obstacles you faced in your research.
9. Conclusion
Summarize the key points of your methodology, emphasizing how it helps to address your research question or objective.
Example of Dissertation Methodology
An Example of Dissertation Methodology is as follows:
Chapter 3: Methodology
- Introduction
This chapter details the methodology adopted in this research. The study aimed to explore the relationship between stress and productivity in the workplace. A mixed-methods research design was used to collect and analyze data.
Research Design
This study adopted a mixed-methods approach, combining quantitative surveys with qualitative interviews to provide a comprehensive understanding of the research problem. The rationale for this approach is that while quantitative data can provide a broad overview of the relationships between variables, qualitative data can provide deeper insights into the nuances of these relationships.
Data Collection Methods
Quantitative Data Collection : An online self-report questionnaire was used to collect data from participants. The questionnaire consisted of two standardized scales: the Perceived Stress Scale (PSS) to measure stress levels and the Individual Work Productivity Questionnaire (IWPQ) to measure productivity. The sample consisted of 200 office workers randomly selected from various companies in the city.
Qualitative Data Collection : Semi-structured interviews were conducted with 20 participants chosen from the initial sample. The interview guide included questions about participants’ experiences with stress and how they perceived its impact on their productivity.
Data Analysis Methods
Quantitative Data Analysis : Descriptive and inferential statistics were used to analyze the survey data. Pearson’s correlation was used to examine the relationship between stress and productivity.
Qualitative Data Analysis : Interviews were transcribed and subjected to thematic analysis using NVivo software. This process allowed for identifying and analyzing patterns and themes regarding the impact of stress on productivity.
Reliability and Validity
To ensure reliability and validity, standardized measures with good psychometric properties were used. In qualitative data analysis, triangulation was employed by having two researchers independently analyze the data and then compare findings.
Ethical Considerations
All participants provided informed consent prior to their involvement in the study. They were informed about the purpose of the study, their rights as participants, and the confidentiality of their responses.
Limitations
The main limitation of this study is its reliance on self-report measures, which can be subject to biases such as social desirability bias. Moreover, the sample was drawn from a single city, which may limit the generalizability of the findings.
Where to Write Dissertation Methodology
In a dissertation or thesis, the Methodology section usually follows the Literature Review. This placement allows the Methodology to build upon the theoretical framework and existing research outlined in the Literature Review, and precedes the Results or Findings section. Here’s a basic outline of how most dissertations are structured:
- Acknowledgements
- Literature Review (or it may be interspersed throughout the dissertation)
- Methodology
- Results/Findings
- References/Bibliography
In the Methodology chapter, you will discuss the research design, data collection methods, data analysis methods, and any ethical considerations pertaining to your study. This allows your readers to understand how your research was conducted and how you arrived at your results.
Advantages of Dissertation Methodology
The dissertation methodology section plays an important role in a dissertation for several reasons. Here are some of the advantages of having a well-crafted methodology section in your dissertation:
- Clarifies Your Research Approach : The methodology section explains how you plan to tackle your research question, providing a clear plan for data collection and analysis.
- Enables Replication : A detailed methodology allows other researchers to replicate your study. Replication is an important aspect of scientific research because it provides validation of the study’s results.
- Demonstrates Rigor : A well-written methodology shows that you’ve thought critically about your research methods and have chosen the most appropriate ones for your research question. This adds credibility to your study.
- Enhances Transparency : Detailing your methods allows readers to understand the steps you took in your research. This increases the transparency of your study and allows readers to evaluate potential biases or limitations.
- Helps in Addressing Research Limitations : In your methodology section, you can acknowledge and explain the limitations of your research. This is important as it shows you understand that no research method is perfect and there are always potential weaknesses.
- Facilitates Peer Review : A detailed methodology helps peer reviewers assess the soundness of your research design. This is an important part of the publication process if you aim to publish your dissertation in a peer-reviewed journal.
- Establishes the Validity and Reliability : Your methodology section should also include a discussion of the steps you took to ensure the validity and reliability of your measurements, which is crucial for establishing the overall quality of your research.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Research Objectives – Types, Examples and...


Research Contribution – Thesis Guide

Table of Contents – Types, Formats, Examples

Dissertation – Format, Example and Template

Tables in Research Paper – Types, Creating Guide...

Thesis – Structure, Example and Writing Guide
Academic & Employability Skills
Subscribe to academic & employability skills.
Enter your email address to subscribe to this blog and receive notifications of new posts by email.
Email Address
Writing your dissertation - designing an effective structure
Posted in: dissertations

A well-structured dissertation should be enjoyable to read. It should be logical and coherent, and your argument or line of reasoning should be convincing and easy to follow. Of course, this is easier said than done, so it is vital you spend time planning your structure to ensure success.
A well-built house
It can be difficult to work out where to start designing the structure of your dissertation, with so many elements, sections and ideas to consider. The starting point for sorting out the tangle of wires is your research question(s) . Think of this as the glue that sticks all the various sections and line of reasoning together. Your research question will provide the logic and coherence you need to maintain throughout your dissertation.
Next, break down planning tasks into smaller, achievable parts. So your process could look something like this:
1. Make a list of all the elements and ideas that you need to include. For example:
a. chapter headings
b. notes about analysis
c. ideas for graphical representation
d. ideas for further research
e. alternatively, you could choose to start at stage 2.
2. List the main chapters in the order they will appear.
3. Under each chapter heading, list important sub-headings. For example, your literature review chapter will include several different segments. For each of these you could add a sub-heading based on specific content. Your final sub-heading may be a mini conclusion segment that brings the chapter to a close.
4. Under each sub-heading, list the main content, creating sub-sub-headings if needed. You need to ensure that all the content you want to include has been allocated a place.
5. As you build your structure, you can slot in ideas, references, quotes, clarifications, and conclusions as they occur to you, to make sure they are not lost in the mix.
6. Check that your labelling is consistent and that your structure represents a logical and coherent overview of your research study, and all chapter headings and sub headings link directly to your research question.
7. At this stage, it would be wise to check your structural plan with your supervisor and also take feedback from friends and classmates. It is highly likely they will see something you've missed.
Size matters... but not yet
At this stage, don't worry too much about your word count and the size of each section. It's more important to get started on the process and you can always edit upwards or downwards as you go along.
Write, write, write
It is also really important that you start writing up your dissertation as soon as possible. Don't wait until your research is completed, as the write up may become too intimidating or overwhelming. It may not be pretty at first and it will probably need revisions further down the line, but writing is all about practice and the more you write the better and more expert you will become.
Your supervisor may also wish to see your work in progress, or you may have an interim assessment to complete. She or he may be looking for development and improvement so self-critique is also a critical element in the write up process.
So don't delay... start writing today!
Have you seen, share this:.
- Click to print (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
Click here to cancel reply.
- Email * (we won't publish this)
Write a response
Critical Writing
How you can be a better critical writer: going beyond description Have you ever handed in a piece of writing – an essay or report, for example – and got comments back from your tutor saying that it needs to...

Navigating the dissertation process: my tips for final years
Imagine for a moment... After months of hard work and research on a topic you're passionate about, the time has finally come to click the 'Submit' button on your dissertation. You've just completed your longest project to date as part...

8 ways to beat procrastination
Whether you’re writing an assignment or revising for exams, getting started can be hard. Fortunately, there’s lots you can do to turn procrastination into action.


How To Write The Methodology Chapter
A plain-language explainer – with practical examples.

Overview: The Methodology Chapter
- The purpose of the methodology chapter
- Why you need to craft this chapter (really) well
- How to write and structure the chapter
- Methodology chapter example
- Essential takeaways
What (exactly) is the methodology chapter?
The methodology chapter is where you outline the philosophical foundations of your research and detail the specific methodological choices you’ve made. In other words, the purpose of this chapter is to explain exactly how you designed your study and, just as importantly, why you made those choices.
Your methodology chapter should comprehensively describe and justify all the methodological decisions involved in your study. For instance, the research approach you took (qualitative, quantitative, or mixed methods), your sampling strategy (who you collected data from), how you gathered your data, and how you analysed it. If that sounds a bit daunting, don’t worry – we’ll walk you through all these methodological aspects in this post .

Why is the methodology chapter important?
The methodology chapter plays two important roles in your dissertation or thesis:
Firstly, it demonstrates your understanding of research theory, which is what earns you marks. A flawed research design or methodology would mean flawed results. So, this chapter is vital as it allows you to show the marker that you know what you’re doing and that your results are credible .
Secondly, the methodology chapter is what helps to make your study replicable. In other words, it allows other researchers to undertake your study using the same methodological approach, and compare their findings to yours. This is very important within academic research, as each study builds on previous studies.
The methodology chapter is also important in that it allows you to identify and discuss any methodological issues or problems you encountered (i.e., research limitations ), and to explain how you mitigated the impacts of these.
Now, it’s important to understand that every research project has its limitations , so it’s important to acknowledge these openly and highlight your study’s value despite its limitations . Doing so demonstrates your understanding of research design, which will earn you marks.
Need a helping hand?
How to write up the methodology chapter
First off, it’s worth noting that the exact structure and contents of the methodology chapter will vary depending on the field of research (e.g., humanities, chemistry or engineering) as well as the university . So, be sure to always check the guidelines provided by your institution for clarity and, if possible, review past dissertations from your university. Here we’re going to discuss a generic structure for a methodology chapter typically found in the sciences.
Before you start writing, it’s always a good idea to draw up a rough outline to guide your writing. Don’t just start writing without knowing what you’ll discuss where. If you do, you’ll likely end up with a disjointed, ill-flowing narrative . You’ll then waste a lot of time rewriting in an attempt to try to stitch all the pieces together. Do yourself a favour and start with the end in mind .
Section 1 – Introduction
As with all chapters in your dissertation or thesis, the methodology chapter should have a brief introduction. In this section, you should remind your readers what the focus of your study is, especially the research aims . As we’ve discussed many times on the blog, your methodology needs to align with your research aims, objectives and research questions. Therefore, it’s useful to frontload this component to remind the reader (and yourself!) what you’re trying to achieve.
In this section, you can also briefly mention how you’ll structure the chapter. This will help orient the reader and provide a bit of a roadmap so that they know what to expect. You don’t need a lot of detail here – just a brief outline will do.
Section 2 – The Methodology
The next section of your chapter is where you’ll present the actual methodology. In this section, you need to detail and justify the key methodological choices you’ve made in a logical, intuitive fashion. Importantly, this is the heart of your methodology chapter, so you need to get specific – don’t hold back on the details here. This is not one of those “less is more” situations.
Let’s take a look at the most common components you’ll likely need to cover.
Methodological Choice #1 – Research Philosophy
Research philosophy refers to the underlying beliefs (i.e., the worldview) regarding how data about a phenomenon should be gathered , analysed and used . The research philosophy will serve as the core of your study and underpin all of the other research design choices, so it’s critically important that you understand which philosophy you’ll adopt and why you made that choice. If you’re not clear on this, take the time to get clarity before you make any further methodological choices.
While several research philosophies exist, two commonly adopted ones are positivism and interpretivism . These two sit roughly on opposite sides of the research philosophy spectrum.
Positivism states that the researcher can observe reality objectively and that there is only one reality, which exists independently of the observer. As a consequence, it is quite commonly the underlying research philosophy in quantitative studies and is oftentimes the assumed philosophy in the physical sciences.
Contrasted with this, interpretivism , which is often the underlying research philosophy in qualitative studies, assumes that the researcher performs a role in observing the world around them and that reality is unique to each observer . In other words, reality is observed subjectively .
These are just two philosophies (there are many more), but they demonstrate significantly different approaches to research and have a significant impact on all the methodological choices. Therefore, it’s vital that you clearly outline and justify your research philosophy at the beginning of your methodology chapter, as it sets the scene for everything that follows.

The next thing you would typically discuss in your methodology section is the research type. The starting point for this is to indicate whether the research you conducted is inductive or deductive .
Inductive research takes a bottom-up approach , where the researcher begins with specific observations or data and then draws general conclusions or theories from those observations. Therefore these studies tend to be exploratory in terms of approach.
Conversely , d eductive research takes a top-down approach , where the researcher starts with a theory or hypothesis and then tests it using specific observations or data. Therefore these studies tend to be confirmatory in approach.
Related to this, you’ll need to indicate whether your study adopts a qualitative, quantitative or mixed approach. As we’ve mentioned, there’s a strong link between this choice and your research philosophy, so make sure that your choices are tightly aligned . When you write this section up, remember to clearly justify your choices, as they form the foundation of your study.
Methodological Choice #3 – Research Strategy
Next, you’ll need to discuss your research strategy (also referred to as a research design ). This methodological choice refers to the broader strategy in terms of how you’ll conduct your research, based on the aims of your study.
Several research strategies exist, including experimental , case studies , ethnography , grounded theory, action research , and phenomenology . Let’s take a look at two of these, experimental and ethnographic, to see how they contrast.
Experimental research makes use of the scientific method , where one group is the control group (in which no variables are manipulated ) and another is the experimental group (in which a specific variable is manipulated). This type of research is undertaken under strict conditions in a controlled, artificial environment (e.g., a laboratory). By having firm control over the environment, experimental research typically allows the researcher to establish causation between variables. Therefore, it can be a good choice if you have research aims that involve identifying causal relationships.
Ethnographic research , on the other hand, involves observing and capturing the experiences and perceptions of participants in their natural environment (for example, at home or in the office). In other words, in an uncontrolled environment. Naturally, this means that this research strategy would be far less suitable if your research aims involve identifying causation, but it would be very valuable if you’re looking to explore and examine a group culture, for example.
The next thing you’ll need to detail in your methodology chapter is the time horizon. There are two options here: cross-sectional and longitudinal . In other words, whether the data for your study were all collected at one point in time (cross-sectional) or at multiple points in time (longitudinal).
The choice you make here depends again on your research aims, objectives and research questions. If, for example, you aim to assess how a specific group of people’s perspectives regarding a topic change over time , you’d likely adopt a longitudinal time horizon.
Another important factor to consider is simply whether you have the time necessary to adopt a longitudinal approach (which could involve collecting data over multiple months or even years). Oftentimes, the time pressures of your degree program will force your hand into adopting a cross-sectional time horizon, so keep this in mind.
Methodological Choice #5 – Sampling Strategy
Next, you’ll need to discuss your sampling strategy . There are two main categories of sampling, probability and non-probability sampling.
Probability sampling involves a random (and therefore representative) selection of participants from a population, whereas non-probability sampling entails selecting participants in a non-random (and therefore non-representative) manner. For example, selecting participants based on ease of access (this is called a convenience sample).
The right sampling approach depends largely on what you’re trying to achieve in your study. Specifically, whether you trying to develop findings that are generalisable to a population or not. Practicalities and resource constraints also play a large role here, as it can oftentimes be challenging to gain access to a truly random sample. In the video below, we explore some of the most common sampling strategies. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fSmedyVv-Us Video can't be loaded because JavaScript is disabled: How to use Mendeley Desktop, Web Importer & MS Word Plugin (Full Tutorial) (https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=fSmedyVv-Us) Methodological Choice #6 – Data Collection Method
Next up, you’ll need to explain how you’ll go about collecting the necessary data for your study. Your data collection method (or methods) will depend on the type of data that you plan to collect – in other words, qualitative or quantitative data.
Typically, quantitative research relies on surveys , data generated by lab equipment, analytics software or existing datasets. Qualitative research, on the other hand, often makes use of collection methods such as interviews , focus groups , participant observations, and ethnography.
So, as you can see, there is a tight link between this section and the design choices you outlined in earlier sections. Strong alignment between these sections, as well as your research aims and questions is therefore very important.
Methodological Choice #7 – Data Analysis Methods/Techniques
The final major methodological choice that you need to address is that of analysis techniques . In other words, how you’ll go about analysing your date once you’ve collected it. Here it’s important to be very specific about your analysis methods and/or techniques – don’t leave any room for interpretation. Also, as with all choices in this chapter, you need to justify each choice you make.

With the key methodological choices outlined and justified, the next step is to discuss the limitations of your design. No research methodology is perfect – there will always be trade-offs between the “ideal” methodology and what’s practical and viable, given your constraints. Therefore, this section of your methodology chapter is where you’ll discuss the trade-offs you had to make, and why these were justified given the context.
Methodological limitations can vary greatly from study to study, ranging from common issues such as time and budget constraints to issues of sample or selection bias . For example, you may find that you didn’t manage to draw in enough respondents to achieve the desired sample size (and therefore, statistically significant results), or your sample may be skewed heavily towards a certain demographic, thereby negatively impacting representativeness .
In this section, it’s important to be critical of the shortcomings of your study. There’s no use trying to hide them (your marker will be aware of them regardless). By being critical, you’ll demonstrate to your marker that you have a strong understanding of research theory, so don’t be shy here. At the same time, don’t beat your study to death . State the limitations, why these were justified, how you mitigated their impacts to the best degree possible, and how your study still provides value despite these limitations .
Section 4 – Concluding Summary
Finally, it’s time to wrap up the methodology chapter with a brief concluding summary. In this section, you’ll want to concisely summarise what you’ve presented in the chapter. Here, it can be a good idea to use a figure to summarise the key decisions, especially if your university recommends using a specific model (for example, Saunders’ Research Onion ).

Methodology Chapter Example
In the video below, we walk you through an example of a high-quality research methodology chapter from a dissertation. We also unpack our free methodology chapter template so that you can see how best to structure your chapter.
Wrapping Up
And there you have it – the methodology chapter in a nutshell. As we’ve mentioned, the exact contents and structure of this chapter can vary between universities , so be sure to check in with your institution before you start writing. If possible, try to find dissertations or theses from former students of your specific degree program – this will give you a strong indication of the expectations and norms when it comes to the methodology chapter (and all the other chapters!).
Also, remember the golden rule of the methodology chapter – justify every choice ! Make sure that you clearly explain the “why” for every “what”, and reference credible methodology textbooks or academic sources to back up your justifications.
If you need a helping hand with your research methodology (or any other component of your research), be sure to check out our private coaching service , where we hold your hand through every step of the research journey. Until next time, good luck!

Learn More About Methodology

How To Choose A Tutor For Your Dissertation
Hiring the right tutor for your dissertation or thesis can make the difference between passing and failing. Here’s what you need to consider.

5 Signs You Need A Dissertation Helper
Discover the 5 signs that suggest you need a dissertation helper to get unstuck, finish your degree and get your life back.

Triangulation: The Ultimate Credibility Enhancer
Triangulation is one of the best ways to enhance the credibility of your research. Learn about the different options here.

Research Limitations 101: What You Need To Know
Learn everything you need to know about research limitations (AKA limitations of the study). Includes practical examples from real studies.

In Vivo Coding 101: Full Explainer With Examples
Learn about in vivo coding, a popular qualitative coding technique ideal for studies where the nuances of language are central to the aims.
📄 FREE TEMPLATES
Research Topic Ideation
Proposal Writing
Literature Review
Methodology & Analysis
Academic Writing
Referencing & Citing
Apps, Tools & Tricks
The Grad Coach Podcast
56 Comments
highly appreciated.
This was very helpful!
This was helpful
Thanks ,it is a very useful idea.
Thanks ,it is very useful idea.
Thank you so much, this information is very useful.
Thank you very much. I must say the information presented was succinct, coherent and invaluable. It is well put together and easy to comprehend. I have a great guide to create the research methodology for my dissertation.
Highly clear and useful.
I understand a bit on the explanation above. I want to have some coach but I’m still student and don’t have any budget to hire one. A lot of question I want to ask.
Thank you so much. This concluded my day plan. Thank you so much.
Thanks it was helpful
Great information. It would be great though if you could show us practical examples.
Thanks so much for this information. God bless and be with you
Thank you so so much. Indeed it was helpful
This is EXCELLENT!
I was totally confused by other explanations. Thank you so much!.
justdoing my research now , thanks for the guidance.
Thank uuuu! These contents are really valued for me!
This is powerful …I really like it
Highly useful and clear, thank you so much.
Highly appreciated. Good guide
That was helpful. Thanks
This is very useful.Thank you
Very helpful information. Thank you
This is exactly what I was looking for. The explanation is so detailed and easy to comprehend. Well done and thank you.
Great job. You just summarised everything in the easiest and most comprehensible way possible. Thanks a lot.
Thank you very much for the ideas you have given this will really help me a lot. Thank you and God Bless.
Such great effort …….very grateful thank you
Please accept my sincere gratitude. I have to say that the information that was delivered was congruent, concise, and quite helpful. It is clear and straightforward, making it simple to understand. I am in possession of an excellent manual that will assist me in developing the research methods for my dissertation.
Thank you for your great explanation. It really helped me construct my methodology paper.
thank you for simplifieng the methodoly, It was realy helpful
Very helpful!
Thank you for your great explanation.
The explanation I have been looking for. So clear Thank you
Thank you very much .this was more enlightening.
helped me create the in depth and thorough methodology for my dissertation
Thank you for the great explaination.please construct one methodology for me
I appreciate you for the explanation of methodology. Please construct one methodology on the topic: The effects influencing students dropout among schools for my thesis
This helped me complete my methods section of my dissertation with ease. I have managed to write a thorough and concise methodology!
its so good in deed
wow …what an easy to follow presentation. very invaluable content shared. utmost important.
Peace be upon you, I am Dr. Ahmed Khedr, a former part-time professor at Al-Azhar University in Cairo, Egypt. I am currently teaching research methods, and I have been dealing with your esteemed site for several years, and I found that despite my long experience with research methods sites, it is one of the smoothest sites for evaluating the material for students, For this reason, I relied on it a lot in teaching and translated most of what was written into Arabic and published it on my own page on Facebook. Thank you all… Everything I posted on my page is provided with the names of the writers of Grad coach, the title of the article, and the site. My best regards.
A remarkably simple and useful guide, thank you kindly.
I real appriciate your short and remarkable chapter summary
Bravo! Very helpful guide.
Only true experts could provide such helpful, fantastic, and inspiring knowledge about Methodology. Thank you very much! God be with you and us all!
highly appreciate your effort.
This is a very well thought out post. Very informative and a great read.
THANKS SO MUCH FOR SHARING YOUR NICE IDEA
I love you Emma, you are simply amazing with clear explanations with complete information. GradCoach really helped me to do my assignment here in Auckland. Mostly, Emma make it so simple and enjoyable
Thank you very much for this informative and synthesised version.
thank you, It was a very informative presentation, you made it just to the point in a straightforward way .
Help me write a methodology on the topic “challenges faced by family businesses in Ghana
Well articulated, clear, and concise. I got a lot from this writings. Thanks
Thanks so much; this is very helpful. I appreciate
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Submit Comment
- Print Friendly
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
How to Write a Dissertation Proposal | A Step-by-Step Guide
Published on 14 February 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on 11 November 2022.
A dissertation proposal describes the research you want to do: what it’s about, how you’ll conduct it, and why it’s worthwhile. You will probably have to write a proposal before starting your dissertation as an undergraduate or postgraduate student.
A dissertation proposal should generally include:
- An introduction to your topic and aims
- A literature review of the current state of knowledge
- An outline of your proposed methodology
- A discussion of the possible implications of the research
- A bibliography of relevant sources
Dissertation proposals vary a lot in terms of length and structure, so make sure to follow any guidelines given to you by your institution, and check with your supervisor when you’re unsure.
Make your writing flawless in 1 upload
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Step 1: coming up with an idea, step 2: presenting your idea in the introduction, step 3: exploring related research in the literature review, step 4: describing your methodology, step 5: outlining the potential implications of your research, step 6: creating a reference list or bibliography.
Before writing your proposal, it’s important to come up with a strong idea for your dissertation.
Find an area of your field that interests you and do some preliminary reading in that area. What are the key concerns of other researchers? What do they suggest as areas for further research, and what strikes you personally as an interesting gap in the field?
Once you have an idea, consider how to narrow it down and the best way to frame it. Don’t be too ambitious or too vague – a dissertation topic needs to be specific enough to be feasible. Move from a broad field of interest to a specific niche:
- Russian literature 19th century Russian literature The novels of Tolstoy and Dostoevsky
- Social media Mental health effects of social media Influence of social media on young adults suffering from anxiety
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Like most academic texts, a dissertation proposal begins with an introduction . This is where you introduce the topic of your research, provide some background, and most importantly, present your aim , objectives and research question(s) .
Try to dive straight into your chosen topic: What’s at stake in your research? Why is it interesting? Don’t spend too long on generalisations or grand statements:
- Social media is the most important technological trend of the 21st century. It has changed the world and influences our lives every day.
- Psychologists generally agree that the ubiquity of social media in the lives of young adults today has a profound impact on their mental health. However, the exact nature of this impact needs further investigation.
Once your area of research is clear, you can present more background and context. What does the reader need to know to understand your proposed questions? What’s the current state of research on this topic, and what will your dissertation contribute to the field?
If you’re including a literature review, you don’t need to go into too much detail at this point, but give the reader a general sense of the debates that you’re intervening in.
This leads you into the most important part of the introduction: your aim, objectives and research question(s) . These should be clearly identifiable and stand out from the text – for example, you could present them using bullet points or bold font.
Make sure that your research questions are specific and workable – something you can reasonably answer within the scope of your dissertation. Avoid being too broad or having too many different questions. Remember that your goal in a dissertation proposal is to convince the reader that your research is valuable and feasible:
- Does social media harm mental health?
- What is the impact of daily social media use on 18– to 25–year–olds suffering from general anxiety disorder?
Now that your topic is clear, it’s time to explore existing research covering similar ideas. This is important because it shows you what is missing from other research in the field and ensures that you’re not asking a question someone else has already answered.
You’ve probably already done some preliminary reading, but now that your topic is more clearly defined, you need to thoroughly analyse and evaluate the most relevant sources in your literature review .
Here you should summarise the findings of other researchers and comment on gaps and problems in their studies. There may be a lot of research to cover, so make effective use of paraphrasing to write concisely:
- Smith and Prakash state that ‘our results indicate a 25% decrease in the incidence of mechanical failure after the new formula was applied’.
- Smith and Prakash’s formula reduced mechanical failures by 25%.
The point is to identify findings and theories that will influence your own research, but also to highlight gaps and limitations in previous research which your dissertation can address:
- Subsequent research has failed to replicate this result, however, suggesting a flaw in Smith and Prakash’s methods. It is likely that the failure resulted from…
Next, you’ll describe your proposed methodology : the specific things you hope to do, the structure of your research and the methods that you will use to gather and analyse data.
You should get quite specific in this section – you need to convince your supervisor that you’ve thought through your approach to the research and can realistically carry it out. This section will look quite different, and vary in length, depending on your field of study.
You may be engaged in more empirical research, focusing on data collection and discovering new information, or more theoretical research, attempting to develop a new conceptual model or add nuance to an existing one.
Dissertation research often involves both, but the content of your methodology section will vary according to how important each approach is to your dissertation.
Empirical research
Empirical research involves collecting new data and analysing it in order to answer your research questions. It can be quantitative (focused on numbers), qualitative (focused on words and meanings), or a combination of both.
With empirical research, it’s important to describe in detail how you plan to collect your data:
- Will you use surveys ? A lab experiment ? Interviews?
- What variables will you measure?
- How will you select a representative sample ?
- If other people will participate in your research, what measures will you take to ensure they are treated ethically?
- What tools (conceptual and physical) will you use, and why?
It’s appropriate to cite other research here. When you need to justify your choice of a particular research method or tool, for example, you can cite a text describing the advantages and appropriate usage of that method.
Don’t overdo this, though; you don’t need to reiterate the whole theoretical literature, just what’s relevant to the choices you have made.
Moreover, your research will necessarily involve analysing the data after you have collected it. Though you don’t know yet what the data will look like, it’s important to know what you’re looking for and indicate what methods (e.g. statistical tests , thematic analysis ) you will use.
Theoretical research
You can also do theoretical research that doesn’t involve original data collection. In this case, your methodology section will focus more on the theory you plan to work with in your dissertation: relevant conceptual models and the approach you intend to take.
For example, a literary analysis dissertation rarely involves collecting new data, but it’s still necessary to explain the theoretical approach that will be taken to the text(s) under discussion, as well as which parts of the text(s) you will focus on:
- This dissertation will utilise Foucault’s theory of panopticism to explore the theme of surveillance in Orwell’s 1984 and Kafka’s The Trial…
Here, you may refer to the same theorists you have already discussed in the literature review. In this case, the emphasis is placed on how you plan to use their contributions in your own research.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Upload my document
You’ll usually conclude your dissertation proposal with a section discussing what you expect your research to achieve.
You obviously can’t be too sure: you don’t know yet what your results and conclusions will be. Instead, you should describe the projected implications and contribution to knowledge of your dissertation.
First, consider the potential implications of your research. Will you:
- Develop or test a theory?
- Provide new information to governments or businesses?
- Challenge a commonly held belief?
- Suggest an improvement to a specific process?
Describe the intended result of your research and the theoretical or practical impact it will have:
Finally, it’s sensible to conclude by briefly restating the contribution to knowledge you hope to make: the specific question(s) you hope to answer and the gap the answer(s) will fill in existing knowledge:
Like any academic text, it’s important that your dissertation proposal effectively references all the sources you have used. You need to include a properly formatted reference list or bibliography at the end of your proposal.
Different institutions recommend different styles of referencing – commonly used styles include Harvard , Vancouver , APA , or MHRA . If your department does not have specific requirements, choose a style and apply it consistently.
A reference list includes only the sources that you cited in your proposal. A bibliography is slightly different: it can include every source you consulted in preparing the proposal, even if you didn’t mention it in the text. In the case of a dissertation proposal, a bibliography may also list relevant sources that you haven’t yet read, but that you intend to use during the research itself.
Check with your supervisor what type of bibliography or reference list you should include.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2022, November 11). How to Write a Dissertation Proposal | A Step-by-Step Guide. Scribbr. Retrieved 21 October 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/proposal/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, what is a dissertation | 5 essential questions to get started, what is a literature review | guide, template, & examples, what is a research methodology | steps & tips.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
In this post, we'll be discussing a traditional dissertation/thesis structure and layout, which is generally used for social science research across universities, whether in the US, UK, Europe or Australia. However, some universities may have small variations on this structure (extra chapters, merged chapters, slightly different ordering, etc).
The main heading of "Methods" should be centered, boldfaced, and capitalized. Subheadings within this section are left-aligned, boldfaced, and in title case. You can also add lower level headings within these subsections, as long as they follow APA heading styles. To structure your methods section, you can use the subheadings of ...
For instance, a dissertation research design includes the different resources and data collection techniques and helps establish your ... In the design section of a research paper, describe the research methodology chosen and justify its selection. Outline the data collection methods, participants or samples, instruments used, and procedures ...
The table below illustrates a classic dissertation layout with approximate lengths for each section. Hopkins, D. and Reid, T., 2018. The Academic Skills Handbook: Your Guide to Success in Writing, Thinking and Communicating at University. Sage. Title. Your title should be clear, succinct and tell the reader exactly what your dissertation is about.
Table of Contents. Table of contents is the section of a dissertation that guides each section of the dissertation paper's contents. Depending on the level of detail in a table of contents, the most useful headings are listed to provide the reader the page number on which said information may be found at.
1. The Abstract (5%) Both the shortest and first-encountered section of a dissertation, the abstract is intended to provide a very brief overview of the entire research project, highlighting to the reader the aims of the dissertation, the background and context of the investigation, the methodology that's been used, the study's key findings ...
A Complete Dissertation The Big Picture OVERVIEW Following is a road map that briefly outlines the contents of an entire dissertation. This is a comprehensive overview, and as such is helpful in making sure that at a glance you understand up front the necessary elements that will constitute each section of your dissertation.
acceptable for this section as well as sections 1-E and 1-G to appear in other chapters of the dissertation. CHAPTER 2 REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE Scholarly research is always a leap from the known to the unknown. The literature review and conceptual framework are used to construct a platform of the known from which you jump.
Dissertation & Thesis Outline | Example & Free Templates. Published on June 7, 2022 by Tegan George.Revised on November 21, 2023. A thesis or dissertation outline is one of the most critical early steps in your writing process.It helps you to lay out and organize your ideas and can provide you with a roadmap for deciding the specifics of your dissertation topic and showcasing its relevance to ...
An example of such a design is described in a dissertation by Sangster (1991): An experimental, 2 × 2 factorial, pretest-posttest design was used to test ... this section. The Sampling Design.As is the case with research design in general, the issue of sampling is a complex one. Our purpose, however, and your pur-
The complexity and length of the research design section will vary depending on your academic subject and the scope of your research, but a well-written research design will have the following characteristics: It sheds light on alternative research design options and justifies why your chosen design is the best to address the research problem.
A research design is a strategy for answering your research question using empirical data. Creating a research design means making decisions about: Your overall research objectives and approach. Whether you'll rely on primary research or secondary research. Your sampling methods or criteria for selecting subjects. Your data collection methods.
This section is crucial for replicating the study and validating its results. Here are the basic elements that are typically included in a dissertation methodology: Introduction: This section should explain the importance and goals of your research. Research Design: Outline your research approach and why it's appropriate for your study. You ...
4. Under each sub-heading, list the main content, creating sub-sub-headings if needed. You need to ensure that all the content you want to include has been allocated a place. 5. As you build your structure, you can slot in ideas, references, quotes, clarifications, and conclusions as they occur to you, to make sure they are not lost in the mix. 6.
Acknowledgements. The acknowledgements section is usually optional, and gives space for you to thank everyone who helped you in writing your dissertation. This might include your supervisors, participants in your research, and friends or family who supported you. Abstract. The abstract is a short summary of your dissertation, usually about 150-300 words long.
Phase. Work on the phase in the following courses (enrolled prior to 1/2/2020) Work on the phase in the following courses (enrolled 1/2/2020 and after) Doctoral Phase 1 - Prospectus: Outline of the Planned Dissertation Study. DOC/700 (5 weeks) LDR/711A (8 weeks) RES/709 (8 weeks) RES/724 (8 weeks) Qualitative Methods and Design.
Do yourself a favour and start with the end in mind. Section 1 - Introduction. As with all chapters in your dissertation or thesis, the methodology chapter should have a brief introduction. In this section, you should remind your readers what the focus of your study is, especially the research aims. As we've discussed many times on the blog ...
Table of contents. Step 1: Coming up with an idea. Step 2: Presenting your idea in the introduction. Step 3: Exploring related research in the literature review. Step 4: Describing your methodology. Step 5: Outlining the potential implications of your research. Step 6: Creating a reference list or bibliography.
How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation Introduction. Published on September 7, 2022 by Tegan George and Shona McCombes. Revised on November 21, 2023. The introduction is the first section of your thesis or dissertation, appearing right after the table of contents.Your introduction draws your reader in, setting the stage for your research with a clear focus, purpose, and direction on a relevant ...
Since 2006, Oxbridge Essays has been the UK's leading paid essay-writing and dissertation service. We have helped 10,000s of undergraduate, Masters and PhD students to maximise their grades in essays, dissertations, model-exam answers, applications and other materials. If you would like a free chat about your project with one of our UK staff ...