

14 Types of Creative Writing
by Melissa Donovan | Apr 6, 2021 | Creative Writing | 20 comments

Which types of creative writing have you tried?
When we talk about creative writing, fiction and poetry often take the spotlight, but there are many other types of creative writing that we can explore.
Most writers develop a preference for one form (and genre) above all others. This can be a good thing, because you can specialize in your form and genre and become quite proficient. However, occasionally working with other types of writing is beneficial. It prevents your work from becoming stale and overladen with form- or genre-specific clichés, and it’s a good way to acquire a variety of techniques that are uncommon in your preferred form and genre but that can be used to enhance it.
Types of Creative Writing
Free writing: Open a notebook or an electronic document and just start writing. Allow strange words and images to find their way to the page. Anything goes! Also called stream-of-consciousness writing, free writing is the pinnacle of creative writing.
Journals: A journal is any written log. You could keep a gratitude journal, a memory journal, a dream journal, or a goals journal. Many writers keep idea journals or all-purpose omni-journals that can be used for everything from daily free writes to brainstorming and project planning.
Diaries: A diary is a type of journal in which you write about your daily life. Some diaries are written in letter format (“Dear Diary…”). If you ever want to write a memoir, then it’s a good idea to start keeping a diary.
Letters: Because the ability to communicate effectively is increasingly valuable, letter writing is a useful skill. There is a long tradition of publishing letters, so take extra care with those emails you’re shooting off to friends, family, and business associates. Hot tip: one way to get published if you don’t have a lot of clips and credits is to write letters to the editor of a news publication.
Memoir: A genre of creative nonfiction , memoirs are books that contain personal accounts (or stories) that focus on specific experiences. For example, one might write a travel memoir.
Essays. Essays are often associated with academic writing, but there are many types of essays, including personal essays, descriptive essays, and persuasive essays, all of which can be quite creative (and not especially academic).
Journalism: Some forms of journalism are more creative than others. Traditionally, journalism was objective reporting on facts, people, and events. Today, journalists often infuse their writing with opinion and storytelling to make their pieces more compelling or convincing.
Poetry: Poetry is a popular but under-appreciated type of writing, and it’s easily the most artistic form of writing. You can write form poetry, free-form poetry, and prose poetry.
Song Lyrics: Song lyrics combine the craft of writing with the artistry of music. Composing lyrics is similar to writing poetry, and this is an ideal type of writing for anyone who can play a musical instrument.
Scripts: Hit the screen or the stage by writing scripts for film, television, theater, or video games. Beware: film is a director’s medium, not a writer’s medium, but movies have the potential to reach a non-reading audience.
Storytelling: Storytelling is the most popular form of creative writing and is found in the realms of both fiction and nonfiction writing. Popular forms of fiction include flash fiction, short stories, novellas, and full-length novels; and there are tons of genres to choose from. True stories, which are usually firsthand or secondhand accounts of real people and events, can be found in essays, diaries, memoirs, speeches, and more. Storytelling is a tremendously valuable skill, as it can be found in all other forms of writing, from poetry to speech writing.
Speeches: Whether persuasive, inspirational, or informative, speech writing can lead to interesting career opportunities in almost any field or industry. Also, speech-writing skills will come in handy if you’re ever asked to write and deliver a speech at an important event, such as a graduation, wedding, or award ceremony.
Vignettes: A vignette is defined as “a brief evocative description, account, or episode.” Vignettes can be poems, stories, descriptions, personal accounts…anything goes really. The key is that a vignette is extremely short — just a quick snippet.
Honorable Mention: Blogs. A blog is not a type of writing; it’s a publishing platform — a piece of technology that displays web-based content on an electronic device. A blog can be used to publish any type of writing. Most blogs feature articles and essays, but you can also find blogs that contain diaries or journals, poetry, fiction, journalism, and more.
Which of these types of creative writing have you tried? Are there any forms of writing on this list that you’d like to experiment with? Can you think of any other types of creative writing to add to this list? Share your thoughts by leaving a comment, and keep writing.

20 Comments
What is “flash” writing or stories.
Flash fiction refers to super short stories, a few hundred words or fewer.
its very helpful especially to those students like me who wasn’t capable or good in doing a creative writing
I’m glad you found this post helpful, Elena.
I also found this to be very helpful, especially because I don’t do very well at writing.
Thanks for letting me know you found this helpful. Like anything else, writing improves with practice.
Thank you Melissa. It’s very helpful!
You’re welcome!
Over all good list. Yes blogs can be publishing platforms but only if something is written first. I read what you wrote on a blog.
Thanks a lot Good job
Are these types of creaitve writing the same or different if I need to teach children’s creative writing? Can you recommend a website to teach these?
Hi Marie. Thanks for your question. I’ve come across many websites for teaching children’s creative writing. I recommend a search on Google, which will lead you to a ton of resources.
these are very helpful when it comes to getting in college or essays or just to improve my writing
Thanks, Donte. I’m glad you found this helpful.
Free writing really helps me get going. For some reason my prose are much better when I am not beholden to an overall plot or narrative with specific defined characters. I like to free writer “excerpts” on theprose.com. It allows me to practice writing and receive feedback at the same time. I am also trying to blog about writing my first novel, both for writing practice and to keep myself accountable. It really helps!
I feel the same way. Free writing is always a fun and creative experience for me.
Was trying to give an inservice on writing skills and the different types of writing.
Your wok here really helped. Thanks.
You’re welcome.
Hi, Melissa can you assist me ? I’m trying to improve my writing skills as quickly as possible. Plz send me some more tips and trick to improve my writing and communication skills.
You are welcome to peruse this website, which is packed with tips for improving your writing. I’d recommend focusing on the categories Better Writing and Writing Tips for writing improvement. You can also subscribe to get new articles send directly to your email. Thanks!
Trackbacks/Pingbacks
- 23 Calming Hobbies to Restore Your Energy | NunziaDreams - […] You can do a lot with creative writing. […]
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .

Subscribe and get The Writer’s Creed graphic e-booklet, plus a weekly digest with the latest articles on writing, as well as special offers and exclusive content.

Recent Posts
- Writing Tips: Be Yourself
- A Must-Read for Storytellers: Save the Cat
- Poetry Prompts for Language Lovers
- Fiction Writing Exercise: The Internal and External Struggles of Your Characters
- 12 Character Writing Tips for Fiction Writers
Write on, shine on!
Pin It on Pinterest

What Is Creative Writing? (Ultimate Guide + 20 Examples)
Creative writing begins with a blank page and the courage to fill it with the stories only you can tell.
I face this intimidating blank page daily–and I have for the better part of 20+ years.
In this guide, you’ll learn all the ins and outs of creative writing with tons of examples.
What Is Creative Writing (Long Description)?
Creative Writing is the art of using words to express ideas and emotions in imaginative ways. It encompasses various forms including novels, poetry, and plays, focusing on narrative craft, character development, and the use of literary tropes.

Table of Contents
Let’s expand on that definition a bit.
Creative writing is an art form that transcends traditional literature boundaries.
It includes professional, journalistic, academic, and technical writing. This type of writing emphasizes narrative craft, character development, and literary tropes. It also explores poetry and poetics traditions.
In essence, creative writing lets you express ideas and emotions uniquely and imaginatively.
It’s about the freedom to invent worlds, characters, and stories. These creations evoke a spectrum of emotions in readers.
Creative writing covers fiction, poetry, and everything in between.
It allows writers to express inner thoughts and feelings. Often, it reflects human experiences through a fabricated lens.
Types of Creative Writing
There are many types of creative writing that we need to explain.
Some of the most common types:
- Short stories
- Screenplays
- Flash fiction
- Creative Nonfiction
Short Stories (The Brief Escape)
Short stories are like narrative treasures.
They are compact but impactful, telling a full story within a limited word count. These tales often focus on a single character or a crucial moment.
Short stories are known for their brevity.
They deliver emotion and insight in a concise yet powerful package. This format is ideal for exploring diverse genres, themes, and characters. It leaves a lasting impression on readers.
Example: Emma discovers an old photo of her smiling grandmother. It’s a rarity. Through flashbacks, Emma learns about her grandmother’s wartime love story. She comes to understand her grandmother’s resilience and the value of joy.
Novels (The Long Journey)
Novels are extensive explorations of character, plot, and setting.
They span thousands of words, giving writers the space to create entire worlds. Novels can weave complex stories across various themes and timelines.
The length of a novel allows for deep narrative and character development.
Readers get an immersive experience.
Example: Across the Divide tells of two siblings separated in childhood. They grow up in different cultures. Their reunion highlights the strength of family bonds, despite distance and differences.
Poetry (The Soul’s Language)
Poetry expresses ideas and emotions through rhythm, sound, and word beauty.
It distills emotions and thoughts into verses. Poetry often uses metaphors, similes, and figurative language to reach the reader’s heart and mind.
Poetry ranges from structured forms, like sonnets, to free verse.
The latter breaks away from traditional formats for more expressive thought.
Example: Whispers of Dawn is a poem collection capturing morning’s quiet moments. “First Light” personifies dawn as a painter. It brings colors of hope and renewal to the world.
Plays (The Dramatic Dialogue)
Plays are meant for performance. They bring characters and conflicts to life through dialogue and action.
This format uniquely explores human relationships and societal issues.
Playwrights face the challenge of conveying setting, emotion, and plot through dialogue and directions.
Example: Echoes of Tomorrow is set in a dystopian future. Memories can be bought and sold. It follows siblings on a quest to retrieve their stolen memories. They learn the cost of living in a world where the past has a price.
Screenplays (Cinema’s Blueprint)
Screenplays outline narratives for films and TV shows.
They require an understanding of visual storytelling, pacing, and dialogue. Screenplays must fit film production constraints.
Example: The Last Light is a screenplay for a sci-fi film. Humanity’s survivors on a dying Earth seek a new planet. The story focuses on spacecraft Argo’s crew as they face mission challenges and internal dynamics.
Memoirs (The Personal Journey)
Memoirs provide insight into an author’s life, focusing on personal experiences and emotional journeys.
They differ from autobiographies by concentrating on specific themes or events.
Memoirs invite readers into the author’s world.
They share lessons learned and hardships overcome.
Example: Under the Mango Tree is a memoir by Maria Gomez. It shares her childhood memories in rural Colombia. The mango tree in their yard symbolizes home, growth, and nostalgia. Maria reflects on her journey to a new life in America.
Flash Fiction (The Quick Twist)
Flash fiction tells stories in under 1,000 words.
It’s about crafting compelling narratives concisely. Each word in flash fiction must count, often leading to a twist.
This format captures life’s vivid moments, delivering quick, impactful insights.
Example: The Last Message features an astronaut’s final Earth message as her spacecraft drifts away. In 500 words, it explores isolation, hope, and the desire to connect against all odds.
Creative Nonfiction (The Factual Tale)
Creative nonfiction combines factual accuracy with creative storytelling.
This genre covers real events, people, and places with a twist. It uses descriptive language and narrative arcs to make true stories engaging.
Creative nonfiction includes biographies, essays, and travelogues.
Example: Echoes of Everest follows the author’s Mount Everest climb. It mixes factual details with personal reflections and the history of past climbers. The narrative captures the climb’s beauty and challenges, offering an immersive experience.
Fantasy (The World Beyond)
Fantasy transports readers to magical and mythical worlds.
It explores themes like good vs. evil and heroism in unreal settings. Fantasy requires careful world-building to create believable yet fantastic realms.
Example: The Crystal of Azmar tells of a young girl destined to save her world from darkness. She learns she’s the last sorceress in a forgotten lineage. Her journey involves mastering powers, forming alliances, and uncovering ancient kingdom myths.
Science Fiction (The Future Imagined)
Science fiction delves into futuristic and scientific themes.
It questions the impact of advancements on society and individuals.
Science fiction ranges from speculative to hard sci-fi, focusing on plausible futures.
Example: When the Stars Whisper is set in a future where humanity communicates with distant galaxies. It centers on a scientist who finds an alien message. This discovery prompts a deep look at humanity’s universe role and interstellar communication.
Watch this great video that explores the question, “What is creative writing?” and “How to get started?”:
What Are the 5 Cs of Creative Writing?
The 5 Cs of creative writing are fundamental pillars.
They guide writers to produce compelling and impactful work. These principles—Clarity, Coherence, Conciseness, Creativity, and Consistency—help craft stories that engage and entertain.
They also resonate deeply with readers. Let’s explore each of these critical components.
Clarity makes your writing understandable and accessible.
It involves choosing the right words and constructing clear sentences. Your narrative should be easy to follow.
In creative writing, clarity means conveying complex ideas in a digestible and enjoyable way.
Coherence ensures your writing flows logically.
It’s crucial for maintaining the reader’s interest. Characters should develop believably, and plots should progress logically. This makes the narrative feel cohesive.
Conciseness
Conciseness is about expressing ideas succinctly.
It’s being economical with words and avoiding redundancy. This principle helps maintain pace and tension, engaging readers throughout the story.
Creativity is the heart of creative writing.
It allows writers to invent new worlds and create memorable characters. Creativity involves originality and imagination. It’s seeing the world in unique ways and sharing that vision.
Consistency
Consistency maintains a uniform tone, style, and voice.
It means being faithful to the world you’ve created. Characters should act true to their development. This builds trust with readers, making your story immersive and believable.
Is Creative Writing Easy?
Creative writing is both rewarding and challenging.
Crafting stories from your imagination involves more than just words on a page. It requires discipline and a deep understanding of language and narrative structure.
Exploring complex characters and themes is also key.
Refining and revising your work is crucial for developing your voice.
The ease of creative writing varies. Some find the freedom of expression liberating.
Others struggle with writer’s block or plot development challenges. However, practice and feedback make creative writing more fulfilling.
What Does a Creative Writer Do?
A creative writer weaves narratives that entertain, enlighten, and inspire.
Writers explore both the world they create and the emotions they wish to evoke. Their tasks are diverse, involving more than just writing.
Creative writers develop ideas, research, and plan their stories.
They create characters and outline plots with attention to detail. Drafting and revising their work is a significant part of their process. They strive for the 5 Cs of compelling writing.
Writers engage with the literary community, seeking feedback and participating in workshops.
They may navigate the publishing world with agents and editors.
Creative writers are storytellers, craftsmen, and artists. They bring narratives to life, enriching our lives and expanding our imaginations.
How to Get Started With Creative Writing?
Embarking on a creative writing journey can feel like standing at the edge of a vast and mysterious forest.
The path is not always clear, but the adventure is calling.
Here’s how to take your first steps into the world of creative writing:
- Find a time of day when your mind is most alert and creative.
- Create a comfortable writing space free from distractions.
- Use prompts to spark your imagination. They can be as simple as a word, a phrase, or an image.
- Try writing for 15-20 minutes on a prompt without editing yourself. Let the ideas flow freely.
- Reading is fuel for your writing. Explore various genres and styles.
- Pay attention to how your favorite authors construct their sentences, develop characters, and build their worlds.
- Don’t pressure yourself to write a novel right away. Begin with short stories or poems.
- Small projects can help you hone your skills and boost your confidence.
- Look for writing groups in your area or online. These communities offer support, feedback, and motivation.
- Participating in workshops or classes can also provide valuable insights into your writing.
- Understand that your first draft is just the beginning. Revising your work is where the real magic happens.
- Be open to feedback and willing to rework your pieces.
- Carry a notebook or digital recorder to jot down ideas, observations, and snippets of conversations.
- These notes can be gold mines for future writing projects.
Final Thoughts: What Is Creative Writing?
Creative writing is an invitation to explore the unknown, to give voice to the silenced, and to celebrate the human spirit in all its forms.
Check out these creative writing tools (that I highly recommend):
Read This Next:
- What Is a Prompt in Writing? (Ultimate Guide + 200 Examples)
- What Is A Personal Account In Writing? (47 Examples)
- How To Write A Fantasy Short Story (Ultimate Guide + Examples)
- How To Write A Fantasy Romance Novel [21 Tips + Examples)

- Onsite training
3,000,000+ delegates
15,000+ clients
1,000+ locations
- KnowledgePass
- Log a ticket
01344203999 Available 24/7
Types of Creative Writing: A Detailed Explanantion
Read the blog and discover different Types of Creative Writing offering insights and examples to help you navigate the world of literary creativity. Explore various forms such as poetry, fiction, non-fiction, and scriptwriting. Discover how each style offers unique ways to express creativity, tell stories, and engage audiences.

Exclusive 40% OFF
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Share this Resource
- Report Writing Course
- Communication and Influencing skill Training
- Effective Communication Skills
- Speed Writing Course
- E-mail Etiquette Training

Creative Writing is a diverse and exciting art that demands Writers to look into their imagination and express their thoughts in unique ways. From short stories to poetry, different Types of Creative Writing which cater to different styles and preferences. In this blog, we will delve into the different Types of Creative Writing, offering insights and examples to help you navigate the world of literary creativity.
Table of Contents
1) What are the various Types of Creative Writing?
a) Fiction writing
b) Poetry
c) Song lyrics
d) Journals and diaries
e) Drama and playwriting
f) Screenwriting
g) Experimental writing
h) Novels
2) Techniques used in Creative Writing
3) Conclusion
What are the various Types of Creative Writing?
Let’s discuss the various Types of Creative Writing:

Fiction writing
Fiction writing is one of the captivating Types of Creative Writing that transports readers into imaginary worlds, introduces them to memorable characters, and explores numerous emotions and themes. Within fiction, there are several distinct forms that Writers can explore to weave intricate tales. These forms include:
Fiction writing is a captivating part of Creative Writing that transports readers into imaginary worlds, introduces them to memorable characters, and explores an array of emotions and themes. Within fiction, there are several distinct forms that Writers can explore to weave intricate tales:
a) Short stories:
Short stories are concise yet potent narratives that distil the essence of a single plot, theme, or character arc. Writers craft short stories to deliver a powerful impact within a limited word count. The brevity of the format challenges Authors to make every word count, focusing on evoking emotions, building tension, and delivering a satisfying resolution in a short span of time.
Novels offer the canvas for Writers to embark on extended journeys of storytelling. With ample space to develop complex characters, intricate plotlines, and detailed settings, novels invite readers to immerse themselves in the fictional world fully. Writers can explore a myriad of themes, emotions, and conflicts, delving deep into the psyche of their characters and creating a lasting impact on the reader.
c) Flash fiction:
Flash fiction is the art of storytelling distilled into its most concise form. Writers embrace the challenge of telling a complete story within just a few hundred words. This form demands precision and creativity, forcing Writers to capture the essence of a narrative in a condensed space.
d) Fan fiction:
Fan fiction is a fascinating genre that allows Writers to extend and reimagine existing fictional universes. Writers create new stories, scenarios, and adventures featuring beloved characters from books, movies, TV shows, or video games. By building upon established foundations, Writers engage in a creative dialogue with the original creators and fellow fans.
d) Historical fiction:

Poetry
Poetry is the language of emotions, a lyrical form of expression that transcends conventional prose. It's one of the most interesting and beautiful Types of Creative Writing that condenses thoughts, feelings, and imagery into evocative verses.
It invites readers to experience the world through a different lens. Within the realm of poetry, various forms and styles allow poets to experiment with rhythm, sound, and language, resulting in a rich tapestry of literary artistry that involves the following:
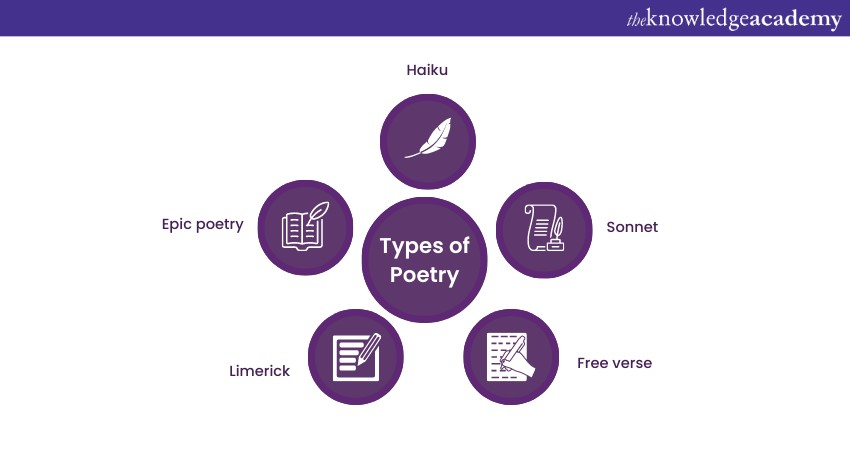
Haiku, originating from Japan, is a minimalist form of poetry that captures the essence of a moment in just three lines. With a syllable structure of 5-7-5, haikus distil nature's beauty and human experiences into concise verses. They often focus on capturing fleeting moments, seasons, and emotions, inviting readers to pause and reflect on the subtleties of life.
The sonnet is a structured and elegant poetic form dating back to the Renaissance. Typically composed of 14 lines, sonnets follow specific rhyme schemes, such as the Shakespearean (ABABCDCDEFEFGG) or the Petrarchan (ABBAABBACDCDCD). Sonnets explore themes of love, beauty, mortality, and the complexities of human emotion.
c) Free verse:
Free verse poetry breaks away from traditional rhyme and meter patterns, allowing poets to experiment with line breaks, rhythm, and imagery. This form gives poets the freedom to let their thoughts flow naturally, creating unique and organic rhythms that reflect the pace of modern life.
d) Limerick:
Limericks are playful and humorous five-line poems with a distinct AABBA rhyme scheme. These witty verses often feature light-hearted language and unexpected twists, making them a favourite for conveying amusing anecdotes and quirky observations.
e) Epic poetry:
Epic poems tell grand narratives of heroes, gods, and legendary quests. With their lengthy verses and intricate storytelling, epic poems like Homer's "The Iliad" and "The Odyssey" have shaped cultures and inspired countless works of literature. These narratives delve into themes of heroism, fate, and the human condition, offering readers an immersive journey through time and imagination.
Unlock your potential in report writing with our Report Writing Training – sign up now for enhanced personal and professional development!
Song lyrics
If you like writing poetry or you think that it can be your forte as a Creative Writer, then you can also try your hand at writing song lyrics. Song lyrics are another one of the most popular Types of Creative Writing.
Practising writing song lyrics is one of the best ways to bring out your creativity, especially if you have a knack for music. Although it sounds interesting and fun, matching the lines in a song lyric can be a challenging task.
You need to think about maintaining not only the intent of the song but also the kind of audience you’ll be approaching. Your song lyrics need to be tangible and understandable, and most importantly, they need to carry out a story and song at the same time.
If you don’t have any proper knowledge of music, then you can try getting help from your friends or peers who have a good knowledge of music and see if your lyrics are going well with the music.
Journals and diaries
Practicing journaling is a good way of regulating someone’s emotions and understand their feelings. If you are unsure what Type of Creative Writing you want to pursue, you can simply start by jotting down the events of your day.
Understanding what you go through every day, not only helps you in your personal development, but also help you to become a good Creative Writer. You can even publish your works as we have seen so many famous people publishing their diary entries. If you want to know where to start, there are several journal entries by famous people, whose works can inspire you to start Writing.
Keeping a journal or diary, is crucial for your mental health, as it helps you to express your feelings in a constructive manner. This also gives you another boost to your writing skills, if you are a budding Writer
Drama and playwriting
Drama and playwriting are artistic forms of Creative Writing that bring narratives to life through the dynamics of performance. These forms of creative expression explore the intricacies of human interaction, emotion, and conflict within the context of staged productions. Let's delve into the world of drama and playwriting, where characters come alive on the stage:
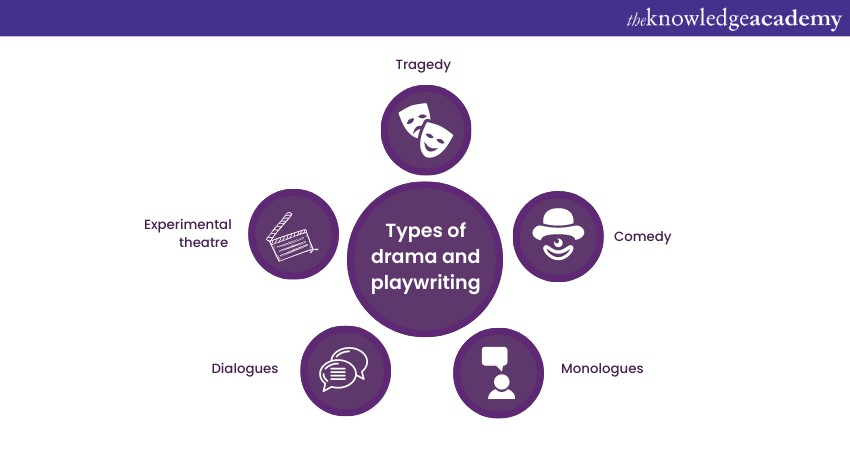
a) Tragedy:
Tragedy is a dramatic genre that delves into the darker aspects of human nature and the inevitability of suffering. Tragic plays often revolve around protagonists who face moral dilemmas, internal struggles, and external forces that ultimately lead to their downfall. Tragedies offer audiences a cathartic experience, allowing them to confront and process complex emotions while reflecting on the human condition.
Comedy is the art of entertainment through humour and light-heartedness. Comedic plays explore the absurdities of human behaviour, social conventions, and misunderstandings. These works aim to amuse and uplift audiences, often featuring witty dialogue, situational comedy, and humorous characters. From slapstick to sattire, comedies provide a diverse range of comedic experiences.
c) Monologues:
Monologues are powerful soliloquies delivered by a single character on stage. They offer insight into the character's thoughts, emotions, and motivations, allowing the audience to connect deeply with their inner world. Monologues provide actors with opportunities to showcase their talent and capture the essence of a character's complexity.
d) Dialogues:
Dialogues are the heart of dramatic interaction. They reveal the relationships between characters, advance the plot, and convey emotions and conflicts. Well-crafted dialogues create tension, build connections, and propel the narrative forward, immersing the audience in the unfolding drama.
e) Experimental theatre:
Experimental theatre pushes the boundaries of traditional forms and conventions. This genre encourages innovative approaches to staging, narrative structure, and performance. Playwrights and directors experiment with non-linear narratives, multimedia elements, immersive environments, and audience interaction to challenge perceptions and evoke thought-provoking responses.
Screenwriting
Screenwriting is the art of crafting stories specifically for the visual medium of film or television. It's a dynamic and collaborative form of writing that serves as the foundation for the creation of compelling on-screen narratives. Here are some key elements of screenwriting:
a) Writing for film:
Film screenwriting involves creating scripts that serve as blueprints for movies. ScreenWriters translate their ideas into a structured format that includes scenes, dialogues, actions, and descriptions. They must balance engaging storytelling with the technical aspects of filmmaking, considering camera angles, pacing, and visual cues.
b) Television scripts:
Television scripts are tailored to episodic formats, such as TV series or miniseries. Writers develop characters, story arcs, and dialogue that span multiple episodes, allowing for character development and plot progression over time. Each episode contributes to the overarching narrative while maintaining its own distinct identity.
c) Adaptation:
Adaptation involves transforming existing source material, such as books, plays, or real-life events, into screenplay format. Writers must distil the essence of the original work while making necessary changes to suit the visual medium and the constraints of time.
d) Dialogue and action:
Effective screenwriting places a strong emphasis on dialogue and action. Dialogue conveys characters' personalities, motivations, and conflicts, while action descriptions provide visual cues for directors, actors, and crew. Both elements work together to create a seamless and engaging on-screen experience.
Unlock your storytelling potential with our Creative Writing Training – embark on a journey of literary discovery today!
Experimental writing
Experimental writing defies traditional conventions, pushing the boundaries of language and structure to create innovative literary works. It challenges readers to engage with unconventional formats, fragmented narratives, and abstract concepts.
Through a stream of consciousness, collage writing, and visual poetry, experimental writing offers a fresh perspective, inviting readers to explore new realms of thought and emotion. It's a playground of creative freedom where Writers experiment with words as artists do with colours, producing compositions that evoke intrigue, reflection, and a deeper understanding of the limitless possibilities of language.
It is often said that good Writers are voracious readers. Well, if we take that into consideration, then there have many times where you might have loved reading novels. All the novels that you have read, or you know of, are one of the premium examples of Creative Writing.
They may vary in length, depending on the subject or genre that you choose to write on. If you are writing a long form novel, then they are divided into number of chapters. If you have a big idea waiting to be broken down into many chapters, then novels are for you.
Techniques used in Creative Writing
If you are wondering how to begin Creative Writing, you can start by following these techniques:
1) Narrative
Determining the narrative of your story is extremely important. If you control the narrative in your story, you can hold your audience’s attention for a long time, whether you are writing novels, novellas, or even short stories. In general, you should remember that whether you are doing Creative Writing or Non-fiction Writing, deciding on a narrative and then maintaining that throughout is crucial.
2) Characterisation
Characterisation is vital in building your story. If you don’t provide the details of your characters and describe their physical features, background, past, etc., you cannot help your reader imagine the situation. It is a crucial step in Creative Writing, enabling you to drive the plot forward and allow your story to build more layers.
Before you build your story, you need to have a solid plot to make your story upon. It is a blueprint to help you establish your story's theme agenda. It can also be referred to as a series of events that will help you build up the narrative. The plot has five parts: exposition or introduction, complications or rising action, climax, slow revelations and then the conclusion. The more solid your plot will be, the more you can create beautiful stories.
From the whimsical realms of children's literature to the thought-provoking depths of creative non-fiction, this blog about the different Types of Creative Writing has unveiled a world of literary possibilities. As pens meet paper and imaginations take flight, we hope this blog will guide you on your journey to weave tales that leave an indelible mark on hearts and minds.
Unlock your potential with our Personal Development Training and embark on a journey of self-discovery and growth.
Frequently Asked Questions
Incorporating Creative Writing skills will help you in your professional growth. Creative Writing helps in effective communication, improved problem-solving abilities, increased empathy, improved mental health, and enhanced creativity.
The factors which influence the organisational structure in various types of Creative Writing are genre, style, narrative, expectations from the audience, length, point of view, cultural and historical context, character development, and more.
The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs , videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA .
The Knowledge Academy offers various Personal Development courses , including Organisational skills training, Emotional Intelligence Training, and Report Writing Course. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Journalism .
Our Business Skills blogs covers a range of topics related to Sports Journalism, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Creative Writing skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Fri 14th Jun 2024
Fri 30th Aug 2024
Fri 11th Oct 2024
Fri 13th Dec 2024
Get A Quote
WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
My employer
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry
- Business Analysis
- Lean Six Sigma Certification
Share this course
Our biggest spring sale.

We cannot process your enquiry without contacting you, please tick to confirm your consent to us for contacting you about your enquiry.
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry.
We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Or select from our popular topics
- ITIL® Certification
- Scrum Certification
- Change Management Certification
- Business Analysis Courses
- Microsoft Azure Certification
- Microsoft Excel Courses
- Microsoft Project
- Explore more courses
Press esc to close
Fill out your contact details below and our training experts will be in touch.
Fill out your contact details below
Thank you for your enquiry!
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go over your training requirements.
Back to Course Information
Fill out your contact details below so we can get in touch with you regarding your training requirements.
* WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
Preferred Contact Method
No preference
Back to course information
Fill out your training details below
Fill out your training details below so we have a better idea of what your training requirements are.
HOW MANY DELEGATES NEED TRAINING?
HOW DO YOU WANT THE COURSE DELIVERED?
Online Instructor-led
Online Self-paced
WHEN WOULD YOU LIKE TO TAKE THIS COURSE?
Next 2 - 4 months
WHAT IS YOUR REASON FOR ENQUIRING?
Looking for some information
Looking for a discount
I want to book but have questions
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go overy your training requirements.
Your privacy & cookies!
Like many websites we use cookies. We care about your data and experience, so to give you the best possible experience using our site, we store a very limited amount of your data. Continuing to use this site or clicking “Accept & close” means that you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about our privacy policy and cookie policy cookie policy .
We use cookies that are essential for our site to work. Please visit our cookie policy for more information. To accept all cookies click 'Accept & close'.

Ebooks, Publishing, and Everything in Between
- Downloads & Pricing
- Advertising
Exploring the Different Types of Creative Writing
- on Sep 26, 2022
- in Writing Tips
- Last update: November 16th, 2023
Writing comes in all forms and sizes. But in order for a work to be considered creative writing, it must come from a place of imagination and emotion.
This is something many people pursuing a creative writing degree online at first struggle to get a handle on. Take for example what Franz Kafa said about creative writing, “Don’t bend; don’t water it down; don’t try to make it logical; don’t edit your own soul according to the fashion. Rather, follow your most intense obsessions mercilessly.”
Many authors who choose to follow Kafka’s advice—to write “mercilessly” and from the soul—find it comforting that their writing doesn’t have to conform to one style. But this variety of types and forms might leave some writers a bit confused.
That’s why, in this article, we are going to walk you through the most popular types of creative writing, with some great examples from authors who absolutely rocked their respective forms.

In this article:
- Creative Writing Definition
- Creative Writing Techniques
- Free Writing
- Journal Diaries
- Personal Essays
- Short Fiction
- Novels/Novellas
What Is Creative Writing?
Think of creative writing as a form of artistic expression. Authors bring this expression to life using their imagination, personal writing style, and personality.
Creative writing is also different from straightforward academic or technical writing. For instance, an economics book like Khalid Ikram’s The Political Economy of Reforms in Egypt is an academic monograph. This means that readers would rightfully expect it to contain analytic rather than creative writing.
So what are some elements that make a written piece more creative than analytic?
Popular Techniques Used in Creative Writing
Despite the fact that creative writing can be “freer” and less traditional than academic writing, it is likely to contain one or more of the following six elements:
1. Literary Devices
Many creative writers use literary devices to convey the meaning and themes of their work. Some common literary devices are allegories , metaphors and similes , foreshadowing , and imagery . These all serve to make the writing more vivid and descriptive .
2. Narrative
Authors often use this technique to engage readers through storytelling. Narrative isn’t limited to novels and short stories; poems, autobiographies, and essays can be considered narratives if they tell a story. This can be fiction (as in novels) or nonfiction (as in memoirs and essays).
3. Point of View
All creative writing must have a point of view; that’s what makes it imaginative and original. The point of view is the perspective from which the author writes a particular piece. Depending on the type of work, the point of view can be first person, third person omniscient, third person limited , mixed (using third- and first-person writing), or—very rarely—second person.
4. Characterization
Characterization is the process by which authors bring their characters to life by assigning them physical descriptions, personality traits, points of view, background and history, and actions. Characterization is key in creative writing because it helps drive the plot forward.
5. Dialogue
An important element used in many creative writing works is dialogue . Assigning
dialogue to characters is a way for authors to show their characters’ different traits without explicitly listing them.
Dialogue also immerses readers in the narrative’s action by highlighting the emotions and tensions between characters. Like characterization, it also helps drive the plot forward.
6. Plot
The plot is the sequence of events that make up a narrative and establish the themes and conflicts of a work . Plots will usually include an exp osi tion (the introduction), rising action (the complications), climax (the peak in action and excitement), falling action (the revelations and slowing down of events), and denouement (the conclusion).

The Main Types of Creative Writing (With Examples)
What’s great about creative writing is that there are so many types to choose from. In this section, we’ll walk you through the most popular types of creative writing, along with some examples.
Type 1: Free writing
Free writing, also known as stream-of-consciousness writing, is a technique that allows words and images to spill onto the page without giving thought to logic, sequence, or grammar. Although authors often use it as an exercise to get rid of the infamous writer’s block , free writing is also useful within a larger work.
For instance, let’s take a look at this excerpt from Toni Morrison’s novel Beloved.
Beloved by Toni Morrison [an excerpt]
the air is heavy I am not dead I am not there is a house there is what she whispered to me I am where she told me I am not dead I sit the sun closes my eyes when I open them I see the face I lost Sethe’s is the face that left me Sethe sees me see her and I see the smile her smiling face is the place for me it is the face I lost she is my face smiling at me
Note how the author uses free writing to convey the character’s disjointed and agitated thoughts. Even punctuation has been set aside here, adding to the rush of the character’s fear and confusion. The imagery is powerful (“the sun closes my eyes”; “her smiling face is the place for me”) and relies on repetitions like “I am not dead” and “I see” to immerse the readers in the character’s disturbed mental state.
Type 2: Journals and Diaries
A journal is a written account of an author’s experiences, activities, and feelings. A diary is an example of a journal, in which an author documents his/her life frequently.
Journals and diaries can be considered creative writing, particularly if they offer more than just a log of events. For instance, if a diary entry discusses how the writer ran into an old friend, it might include details of the writer’s emotions and probably use literary devices to convey these feelings.
It’s almost impossible to read the word “diary” and not think of Anne Frank. Let’s look at this excerpt from her work The Diary of a Young Girl .
Anne Frank: The Diary of a Young Girl [an excerpt]
Saturday, 20 June, 1942: I haven’t written for a few days, because I wanted first of all to think about my diary. It’s an odd idea for someone like me to keep a diary; not only because I have never done so before, but because it seems to me that neither I—nor for that matter anyone else—will be interested in the unbosomings of a thirteen-year-old schoolgirl. Still, what does that matter? I want to write, but more than that, I want to bring out all kinds of things that lie buried deep in my heart.
In the extract above, Anne adopts a reflective tone. She uses the rhetorical question “what does that matter?” to illustrate how she arrived at the conclusion that this diary will help bring out what is “buried deep in her heart.”
In this way, the diary serves as a log of events that happened in Anne’s life, but also as a space for Anne to reflect on them, and to explore her resulting emotions.
Type 3: Memoir
Although they might seem similar at first, memoirs and diaries are two different creative writing types. While diaries offer a log of events recorded at frequent intervals, memoirs allow the writer to select key moments and scenes that help shed light on the writer’s life.
Let’s examine this excerpt from the memoir of Roxanne Gay, author of Bad Feminist .
Hunger: A Memoir of (My) Body by Roxanne Gay:
I ate and ate and ate in the hopes that if I made myself big, my body would be safe. I buried the girl I was because she ran into all kinds of trouble. I tried to erase every memory of her, but she is still there, somewhere . . . I was trapped in my body, one that I barely recognized or understood, but at least I was safe.
Roxanne Gay offers readers a powerful work on anxiety, food, and body image by taking them on a journey through her past . Using evocative imagery in the excerpt above (“I buried the girl I was”; “I was trapped in my body”) the author shares her psychological trauma and resulting tumultuous relationship with food.
As with most memoirs—and diaries—this one is intimate, allowing readers into the dark crevices of the author’s mind. However, unlike a diary, this memoir does not provide an account of the writer’s day-to-day life, but rather focuses on certain events—big and small—that the author feels made her who she is today.
Type 4: Letters
Unlike diary and journal entries—which usually don’t have a specific recipient—letters address one target reader. Many famous authors have had collections of their letters published, revealing a side of them that isn’t visible in other works.
Letter writing uncovers the nature of the relationship between sender and recipient, and can include elements of creative writing such as imagery, opinion, humor, and feeling.
Here is an excerpt from a letter by Truman Capote, author of Breakfast at Tiffany’s and In Cold Blood .
Too Brief a Treat: The Letters of Truman Capote , edited by Gerald Clarke
Dear Bob; Have come, am here, am slowly freezing to death; my fingers are pencils of ice. But really, all told, I think this is quite a place, at least so far. The company is fairly good… I have a bedroom in the mansion (there are bats circulating in some of the rooms, and Leo keeps his light on all night, for the wind blows eerily, doors creak, and the faint cheep cheep of the bats cry in the towers above: no kidding.
In his letter to editor and friend Robert “Bob” Linscott, Truman paints a scene of his new setting . He uses hyperbole (“freezing to death”) and a powerful metaphor (“my fingers are pencils of ice”) to convey the discomforting cold weather. Truman also uses sound imagery (“doors creak”; “wind blows eerily”; “cheep cheep of the bats”) to communicate the creepy, sinister mood to his reader.
Type 5: Personal Essays
Many of us don’t normally think of essays as creative writing, but that’s probably because our minds go to academic research essays. However, there are many types of essays that require creative rather than analytic writing, including discursive essays, descriptive essays, and personal essays.
A personal essay, also known as a narrative essay, is a piece of nonfiction work that offers readers a story drawn from the author’s personal experience. This is different from a memoir, in which the primary focus is on the author and their multiple experiences.
A personal essay, on the other hand, focuses on a message or theme , and the author’s personal experience is there to communicate that theme using memorable characters and setting , as well as engaging events . These, of course, all have to be true, otherwise the personal essay would turn into a fictional short story.
Here is an excerpt from a personal essay by writers Chantha Nguon and Kim Green.
The Gradual Extinction of Softness by Chantha Nguon and Kim Green
In 1975, the Khmer Rouge informed the Cambodian people that we had no history, but we knew it was a lie. Cambodia has a rich past, a mosaic of flavors from near and far: South Indian traders gave us Buddhism and spicy curries; China brought rice noodles and astrology; and French colonizers passed on a love of strong coffee, flan, and a light, crusty baguette. We lifted the best tastes from everywhere and added our own.
The opening of this paragraph establishes the author’s strong and unwavering opinion : “we knew it was a lie.” Instead of providing a history of Cambodia, she demonstrates the country’s rich past by discussing its diverse “flavors”: “spicy curries”; “strong coffee”; “light, crusty baguette”, etc.
Using gustatory imagery , which conveys a sense of taste , the authors reveal their personal version of what makes Cambodia wonderful. The writer communicates the essay’s theme of food and memories through a story of her childhood.
Type 6: Poetry
Robert Frost once wrote: “Poetry is when an emotion has found its thought and the thought has found words.” Good poetry is effective because it uses the power of imagery to convey what it is to be human. Every word in a poem counts, and the best poems are those that evoke the reader’s emotions without unpacking too much.
As one of the most diverse types of creative writing, poetry can come in many forms. Some poets prefer to write in the more traditional forms such as sonnets , villanelles , and haikus , where you have particular structures, rhyme, and rhythm to follow. And others prefer the freedom of free verse and blackout poetry .
Let’s take a look at this excerpt from Maya Angelou’s powerful lyric poem , “Still I Rise.”
“Still I Rise” from And Still I Rise: A Book of Poems by Maya Angelou
Out of the huts of history’s shame I rise Up from a past that’s rooted in pain I rise I’m a black ocean, leaping and wide, Welling and swelling I bear in the tide. Leaving behind nights of terror and fear I rise Into a daybreak that’s wondrously clear I rise Bringing the gifts that my ancestors gave, I am the dream and the hope of the slave. I rise I rise I rise.
Packed with powerful language, this excerpt from Angelou’s poem gives us absolute
chills! The refrain “I rise” is repeated 7 times in these two verses alone,
hammering home the idea that the speaker cannot be defeated.
The imagery, repetition, and rhyme scheme all work together to convey the emotions of pride and resilience. Both verses also rely heavily on metaphors (“I’m a black ocean”; “I am the dream and the hope of the slave”) to convey the speaker’s power. She is not like an ocean or a dream; she is both, and she is unstoppable.
Type 7: Song Lyrics
Song lyrics are in many ways similar to poems, except that lyrics are meant to be sung . They are a form of creative writing that allows writers to surpass the rules of grammar and punctuation in favor of creating rhyme and rhythm . This means that the creativity of a song lyricist is free from the traditional restrictions of language.
Type 8: Scripts
Scriptwriting is a form of creative writing that relies heavily on character dialogue , stage directions , and setting . Scripts are written for films and TV shows (known as screenplays and teleplays), stage plays, commercials, and radio and podcast programs.
Like song lyrics, scripts are written with the intention of reaching a non-reading audience. In other words, scriptwriters must bear in mind how their writing will be 1) interpreted by other storytellers , such as directors, designers, etc., and 2) performed by actors.
Let’s examine the iconic opening scene from the screenplay of the film Forrest Gump .
Forrest Gump , screenplay by Eric Roth [an excerpt]
THE MAN Hello, I’m Forrest. I’m Forrest Gump. She nods, not much interested. He takes an old candy kiss out of his pocket. Offering it to her: FORREST (cont’d) Do you want a chocolate? She shakes “no.” He unwraps it, popping it in his mouth. FORREST (cont’d) I could eat about a million and a half of these. Mama said, “Life was just a box of chocolates. You never know what you gonna get.”
From the dialogue and stage directions in this opening scene, the audience can see that there is something innocent, kind-hearted, and simple about the character Forrest Gump. This is conveyed through the way he introduces himself with a slight repetition (“I’m Forrest. I’m Forrest Gump.”) to a complete stranger, and the way he quotes his mother to her.
Moreover, the action of Forrest “popping” the candy in his mouth is almost childlike , and that the stranger is reluctant to communicate with him foreshadows the fact that the people Forrest meets are initially suspicious of him and his innocence. Thus, the pauses and silences in the scene are just as important to the work as what is explicitly said.
Type 9: Short Fiction
Short fiction is a form of creative fiction writing that typically falls between 5,000 to 10,000 words ; however, there is definitely room to go lower than 5,000 words, depending on the topic.
For instance, flash fiction is a form of short fiction that can be 1,000 words or less. In the case of flash fiction, the author unpacks the “skeleton” of a story in as few words as possible. For instance, legend has it that Ernest Hemingway wrote a 6-word “story”:
For sale: baby shoes, never worn.
In just six words, the reader is led to understand that this is a story of death and loss.
Nevertheless, the average short story is usually structured around the following elements: characterization , setting , plot , and conflict . Many fiction authors start out writing short fiction because it enables them to nail all the essential elements, which they can then expand upon in longer works.
Let’s look at an excerpt from Janet Frame’s short story, “The Bath”
“The Bath” by Janet Frame [an excerpt]
She leaned forward, feeling the pain in her back and shoulder. She grasped the rim of the bath but her fingers slithered from it almost at once. She would not pancic, she told herself; she would try gradually, carefully, to get out. Again she leaned forward; again her grip loosened as if iron hands had deliberately uncurled her stiffened blue fingers from their trembling hold. Her heart began to beat faster, her breath came more quickly, her mouth was dry. She moistened her lips. If I shout for help, she thought, no-one will hear me. No-one in the world will hear me. No-one will know I’m in the bath and can’t get out.
In this paragraph, there is an image of a frail, old woman, physically unable to get out of her bathtub. The diction , or word choice, serves to convey the woman’s sense of fear and helplessness. For instance, words like “grasped,” “slithered,” “uncurled,” and “stiffened,” demonstrate the immense effort it takes for her to try to get out.
The image of her “moistening” her lips illustrates that fear has turned her mouth dry. And the repetition of “no-one” in the last few sentences highlights the woman’s loneliness and entrapment —two of the story’s main themes. Indeed, the bath symbolizes the unavoidable obstacles brought about by old age.
Type 10: Novellas / Novels
Novels are one of the most popular forms of creative writing. Though they vary in length, depending on the subject, they’re generally considered a long form of fiction , typically divided into chapters .
Novellas, on the other hand, are shorter than novels but longer than short stories. Like short stories, novels, and novellas contain characters , plot , dialogue , and setting ; however, their longer forms allow writers a chance to delve much deeper into those elements.
Type 11: Speeches
Speeches are a form of writing similar to essays in that both forms are non-fiction , and both usually entail a discussion of the writer’s personal experiences and include engaging events and a particular theme.
However, speeches differ from essays in that the former are meant to be recited (usually in front of an audience), and tend to be persuasive and inspirational. For instance, think of the purpose of graduation speeches and political speeches: they aim to inspire and move listeners.
One of the most well-known speeches from the 20th century is Martin Luther King’s “I Have a Dream”. Let’s examine the excerpt below:
“I Have a Dream” by Martin Luther King [an excerpt]
Now is the time to make real the promises of democracy. Now is the time to rise from the dark and desolate valley of segregation to the sunlit path of racial justice. Now is the time to lift our nation from the quicksands of racial injustice to the solid rock of brotherhood. Now is the time to make justice a reality for all of God’s children.
What immediately catches the eye (and ear) in this paragraph is the speaker’s usage of anaphora : the repetition of the phrase “now is the time” serves to emphasize the urgency of the matter being discussed (i.e. the prevalence of racial injustice).
The speaker’s repetition of the pronoun “our” is an appeal to his audience’s emotions and their sense of unity. Both he and they are in this together, and thus he is motivating them to take on the challenge as one.
Moreover, the use of figurative language is abundant here and can be found in similar inspirational and motivational styles of creative writing. The imagery created by the metaphor and alliteration in “the d ark and d esolate valley of segregation,” and its juxtaposition with “sunlit path of racial justice,” together aim to convey the speaker’s main message. Segregation has brought nothing but darkness and ruin to American society, but there is hope and light on the path toward racial equality.
Final Thoughts
Creative writing acts as a medium for artistic expression. It can come in a variety of forms, from screenplays and speeches to poetry and flash fiction. But what groups all of these different types of creative writing under the “creative” umbrella, regardless of form, is their display of a writer’s imagination, creativity, and linguistic prowess.
How to Write the Best Book Introduction
Making Use of Humor in Writing
4 Different Types of Writing You Need to Understand
I appreciate you offering such a thought-provoking perspective. It should be useful for academic writing in addition to creative writing, in my opinion. Each method you listed is pertinent and appropriate.
You’re absolutely right! Many of these writing methods can be applied to both creative and academic writing, enhancing the depth and effectiveness of communication.
Robert smith enago
Thank you for sharing this enlightening blog post on the various types of creative writing. Your exploration of different writing methods and styles provides an inspiring perspective on the boundless possibilities within the realm of creativity.
It is remarkable to see how creative writing encompasses an array of forms, each with its unique allure and artistic essence. From poetry, fiction, and drama to screenwriting, creative nonfiction, and even songwriting, each avenue offers writers a chance to express their thoughts, emotions, and imagination in captivating ways.
We truly appreciate your kind words! Creative writing is indeed a vast and fascinating world with endless opportunities for self-expression 🙂
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Currently you have JavaScript disabled. In order to post comments, please make sure JavaScript and Cookies are enabled, and reload the page. Click here for instructions on how to enable JavaScript in your browser.

Kotobee is the complete end-to-end ebook solution for you and your business. Export multiple formats. Deliver securely.
Create, publish, and sell ebooks with ease
Kotobee es la solución completa de ebooks de extremo a extremo para usted y su empresa.
Cree, publique y venda libros electrónicos con facilidad

Recent Posts
- Enhancing Student Engagement: Using Interactive Ebooks for Effective Learning
- How to Make a Book Trailer in 6 Simple Steps
- The Different Types of Characters in a Story Explained
- LMS Integration: Types, Examples, and Best Practices
- How to Edit a Book for Publishing: Tips & Best Practices
- Entries feed
- Comments feed
- WordPress.org
12 Types of Creative Writing to Explore
Kate is an experienced writer who has written hundreds of articles for publication.
Learn about our Editorial Policy .
Creative writing isn't just limited to novels, short stories, and poems; in fact, this type of writing encompasses at least a dozen different types, each suited to specific situations and kinds of personal expression. Try them all to find out which ones you enjoy the most.
You may think of writing a song as a purely musical form of creative expression, but if your song has lyrics, you'll also be doing some creative writing. Lyrics are similar to poetry in that they can have many forms, although some type of rhyme scheme is common. See examples of some of the most popular song lyrics at MetroLyrics .
- 14 Mood Ring Color Meanings Decoded: What They Say About You
- Mercury Retrograde: What It Is, When It Is, & How It Affects You
From haiku to sonnets, there are dozens of different poetic forms to try. In general, the key to writing poetry is to create evocative images and make every word count. You can write about anything, from nature to love to your family . You can even write poems for specific occasions, such as a wedding ceremony or a funeral .
3. Vignettes
Vignettes are a short form of fiction or creative non-fiction that sets up a scene for the reader. There may not be a central conflict to drive the story forward, and there may not even be characters. Length can range from a single paragraph to a few pages. Generally, the entire piece takes place in one location. Ernest Hemingway's In Our Time features several examples of vignettes.
4. Short Fiction
Short fiction offers more of a "story" than a vignette. It includes short stories and even modern fan fiction. Writing a short story is a great way to learn about how fiction is structured, including plot, characters, conflict, and setting. You can even make money writing short fiction. A great example of this genre is A&P by John Updike.
5. Novellas
Longer than a short story but not quite as long as a novel, a novella goes into great detail about all the elements of the story. It may or may not have chapters. Joseph Conrad's Heart of Darkness is a good example of a novella.
Novels are perhaps the best known form of fiction, and you'll see them in many genres, including romance, thrillers, and science fiction. In this long form of fiction, you have time to explore the plot, characters, and other elements more fully. Writing a novel is a huge undertaking and a great way to improve your skills as a writer. If you're considering such a project, look at what works in some of the best novels of all time.
Scripts, for everything from TV commercials to radio programs and even movies, are another form of creative writing. The length can vary significantly, but the key is that the words you write will be recited by actors and recorded. An audience will view or listen to the piece later. Find movie scripts to review as examples of this form of writing.
Like a script in that the dialogue you write will be recited by actors, plays are designed to be performed in front of an audience. They are usually divided into several acts, although short, one-act plays are also popular. Writing a play is a great way to see your story ideas come to life. Arthur Miller's Death of a Salesman is a good example if you're looking for inspiration.
9. Personal Essays
Not all creative writing is made up. In fact, creative non-fiction comes in several important forms. One of these is the personal essay in which the writer explores his or her own life experiences or opinions. Writing an essay on yourself isn't always easy, but it's an important skill to have for everything from college applications to family history.
10. Journals and Diaries
More than just a therapeutic exercise or a way to record the day's events, journals can also be a type of creative writing. This is especially true if you infuse your entries with your emotions and personal experiences. Take some time to read journal writing prompts and try your hand at this creative writing form.
11. Memoirs
A longer form of the personal essay or journal, a memoir is a type of creative nonfiction that explores a person's life or experiences. You can focus on a single period or your entire life. This is different from an autobiography in that it includes feelings and thoughts - not just the facts of what happened. There are even websites with examples of memoirs and tips for writing your own.
12. Letters
Because they contain more than a basic reporting of the facts, letters can also be a type of creative writing. This is especially true if they discuss emotion or opinion. Even love letters can be creative.
Try All the Forms
There are many more forms of writing that can become creative if they expand beyond the basic facts. For instance, some blogs and literary journalism articles are very creative too. There are so many types of creative writing to explore that it makes sense to try them all. You're sure to find one (or several) that you love.
Home › Study Tips › Creative Writing Resources For Secondary School Students
Creative Writing Examples: 9 Types Of Creative Writing
- Published July 28, 2022

Table of Contents
Creative writing takes a lot of brainpower. You want to improve your creative writing skills, but you feel stuck. And nothing’s worse than feeling dry and wrung out of ideas!
But don’t worry. When our creative writing summer school students feel they’re in a rut, they expand their horizons. Because sometimes, all you need is to try something new .
And this article will give you a glimpse into what you need to thrive at creative writing.
Here you’ll find creative writing examples to help give you the creative boost you’re looking for. Are you dreaming of writing a novel but can’t quite get there yet?
No worries! Maybe you’d want to try your hand writing short stories first, or maybe flash fiction. You’ll know more about these in the coming sections.
9 Scintillating Creative Writing Examples
Let’s go through the 9 examples of creative writing and some of their famous pieces penned under each type.
There is hardly a 21st-century teenager who hasn’t laid their hands on a novel or two. A novel is one of the most well-loved examples of creative writing.
It’s a fictional story in prose form found in various genres, including romance, horror, Sci-Fi, Fantasy and contemporary. Novels revolve around characters whose perspectives in life change as they grow through the story. They contain an average of 50,000 to 70,000 words.
Here are some of the most famous novels:
- To Kill a Mockingbird by Harper Lee
- Pride and Prejudice by Jane Austen
- Harry Potter by J.K. Rowling
- The Chronicles of Narnia by C.S. Lewis
- Lord of the Rings by J.R.R. Tolkien
2. Flash Fiction
Flash Fiction is similar to a novel in that it offers plot development and characters. But unlike novels, it’s less than 1000 words. Some even contain fewer than 100 words! Legend has it that the shortest story ever told was Ernest Hemmingway’s six-word story, which goes like this, “For Sale: Baby shoes, never worn.”
Do you know that there are sub-categories of Flash Fiction? There’s the “Sudden Fiction” with a maximum of 750 words. “Microfiction” has 100 words at most. And the “six-word story” contains a single-digit word count.
Remarkable Flash Fiction include:
- The Long and Short of It by Michael A. Arnzen
- Chapter V Ernest Hemingway
- Gasp by Michael A. Arnzen
- Angels and Blueberries by Tara Campbell
- Curriculum by Sejal Shah
3. Short Story
What’s shorter than a novel but longer than flash fiction? Short story. It’s a brief work of fiction that contains anywhere from 1,000 to 10,000 words. Whereas a novel includes a complex plot, often with several characters interacting with each other, a short story focuses on a single significant event or mood. It also has fewer characters.
The best short stories are memorable and evoke strong emotions. They also contain a twist or some type of unexpected resolution.
Check out these famous short stories:
- The Lottery by Shirley Jackson
- The Cask of Amontillado by Edgar Allan Poe
- The Gift of the Magi by O. Henry
- The Sniper by Liam OFlaherty
- A Good Man is Hard to Find by Flannery O’Connor
4. Personal Essay
In a personal essay, you write about your personal experience. What lesson did the experience teach you? And how does it relate to the overarching theme of the essay? Themes can be about anything! From philosophical questions, political realizations, historical discussions, you name it.
Since writing a personal essay involves talking about actual personal events, it’s often called “autobiographical nonfiction.” Its tone is informal and conversational.
Have you observed that applications at universities and companies usually involve submitting personal essays? That’s because having the capability to write clear essays displays your communication and critical thinking skills.
Some of the most famous personal essays include:
- Self-Reliance by Ralph Waldo Emerson
- Once More To The Lake by E.B. White
- What I Think and Feel at 25 by F. Scott Fitzgerald
- Ticket to the Fair by David Foster Wallace
Memoirs and personal essays are autobiographical. But while you use your experiences in a personal essay to share your thoughts about a given theme, a memoir focuses on your life story. What past events do you want to share? And how has your life changed?
In a word, a memoir is all about self-exploration.
Here are among the most famous memoirs:
- I Know Why the Caged Bird Sings by Maya Angelou
- West with the Night by Beryl Markham
- Personal Memoirs of Ulysses S. Grant by Ulysses Grant
- Night By Elie Wiesel
- A Long Way Gone By Ishmael Beah
6. Poetry
Poetry is one of the oldest examples and types of creative writing . Did you know that the oldest poem in the world is the Epic of Gilgamesh, which is known to be 4,000 years old? Poetry is a type of literature that uses aesthetic and rhythmic qualities of language—such as sound, imagery, and metaphor—to evoke meaning.
There are 5 types of rhythmic feet common in poetry: trochee, anapest, dactyl, iamb, and anapest.
The most beloved poems include:
- No Man Is An Island by John Donne
- Still I Rise by Maya Angelou
- Ode to a Nightingale by John Keats
- If You Forget Me by Pablo Neruda
- Fire And Ice by Robert Frost
7. Script (Screenplay)
A script is a type of creative writing (a.k.a. screenwriting) that contains instructions for movies. Instructions indicate the characters’ movements, expressions, and dialogues. In essence, the writer is giving a visual representation of the story.
When a novel says , “Lucy aches for the love she lost,” a script must show . What is the actress of Lucy doing? How can she portray that she is aching for her lost love? All these must be included in screenwriting.
The following are some of the most brilliant scripts:
- Citizen Kane by Herman J. Mankiewicz and Orson Welles
- The Godfather by Mario Puzo and Francis Ford Coppola
- Pulp Fiction by Quentin Tarantino
- The Silence of the Lambs by Ted Tally
- Taxi Driver by Paul Schrader
8. Play (Stageplay)
If screenplay is for movies, stageplay is for live theatre. Here’s another distinction. A screenplay tells a story through pictures and dialogues, whereas a stageplay relies on the actors’ performances to bring the story to life.
That’s why dialogue is THE centre of live performance. A play doesn’t have the benefit of using camera angles and special effects to “show, don’t tell.”
Some of the most renowned plays are:
- Hamlet by William Shakespeare
- The Crucible by Arthur Miller
- A Streetcar Named Desire by Tennessee Williams
- Romeo and Juliet by William Shakespeare
- The Importance of Being Earnest by Oscar Wilde
What was the best speech you heard that moved you to action? Speeches are among the most powerful examples of creative writing. It’s meant to stir the audience and persuade them to think and feel as you do about a particular topic.
When you write a speech, you intend to present it orally. So not only do you have to consider the words you choose and the phrasing. But you also have to think about how you’ll deliver it.
Will the sentences flow smoothly onto each other so as to roll off the tongue? Do the words give you the confidence and conviction you need to express your thoughts and beliefs?
Here are some of the most stirring speeches in history:
- I Have A Dream by Martin Luther King Jr.
- The Gettysburg Address by Abraham Lincoln
- First Inaugural Address by Franklin D. Roosevelt
- I Choose To Live by Sabine Herold
- Address to the Nation on the Challenger by Ronald Reagan
What Are The Elements of Creative Writing?
You’re now familiar with the various examples of creative writing. Notice how creative writing examples fall under different categories. Can you guess what they are? That’s right! Poetry and Prose .
The Prose section can be broken down further into Prose Fiction and Prose Nonfiction.
Where do the Elements of Creative Writing come in? For Prose fiction . If there’s one word that can describe all forms of prose fiction, it’s STORY. So what are the Elements of a Story (Creative Writing?)
The character is a being (person, animal, thing) through which the reader experiences the story. They speak, act, and interact with the environment and other characters.
- Elizabeth Bennet in Pride & Prejudice
- Simba in Lion King
- Woody in Toy Story
The two most essential types of characters are the Protagonist and Antagonist. Who is the Protagonist? They’re the main character, and the story revolves around them. Elizabeth, Simba, and Woody are the protagonists in their stories.
And who is the Antagonist? The one who causes conflict for the protagonist.
The setting answers the question, “when and where does the story set place?” It’s the story’s time and location. Providing context that helps the reader visualise the events in clearer detail.
What is the Plot? It’s the sequence of events in the story. If you break it down, the plot looks like this:
Exposition – you can also call this the introduction. Where you first catch a glimpse of the characters and setting. In the Lion King (Part 1), this is where Simba is introduced to all the animals on top of Pride Rock as the future King.
Rising Action – the story gets complicated. The tension builds, and you see the conflict arise. It’s a time of crisis for the main characters. So what’s the Rising Action for Lion King? It would be when Simba’s uncle Scar murders his father and tells him to “Run away and NEVER return.”
Climax – you’re at the edge of your seat as the story reaches its crescendo. The most defining (and intense) moment arrives when the protagonist faces the conflict (enemy/challenge) head-on. Simba finally goes back to Pride Rock to confront his wicked uncle Scar. And an epic fight begins. Simba even almost falls off a cliff! *gasp
Falling Action – here you catch your breath as the story starts to calm down. The characters unwind and work towards their respective conclusions. Simba didn’t fall off the cliff. Instead, he won the fight. And he roars atop Pride Rock to reclaim his rightful place as King. The lionesses proclaim their joyful acceptance by roaring back.
Resolution – remaining conflict concludes, and the story ends. In Lion King, Pride Land is once again lush and peaceful. And Simba looks on with pride as he introduces his daughter Kiara on top of Pride Rock.
You can think of the theme as the main idea. What meaning is the writer trying to express in the story? The other elements, such as setting, plot, and characters, work together to convey the theme.
Point of View
Through what lens or “eye” does the narrating voice tell the story? There are three points of view common in writing stories:
First Person
In the first person point of view, the narrating voice is the main character. Much of the lines talk of “I” and “me.” Everything you know about the other characters, places, and dialogues in the story comes from the main character’s perspective.
Third Person
From the third person point of view, the narrating voice is separate from the main character. Meaning the narrator uses “he/she/they” when following the main character in the story. There are generally two types of third-person points of view.
Limited. In a third-person limited point of view, the narrator only knows about the main character’s inner world – their thoughts and feelings. But they have no idea about the thoughts and feelings of other characters.
Omniscient. What does “omniscient” mean? All-knowing. So in the Third Person Omniscient point of view, the narrator knows about the feelings and thoughts of all the characters. Not just that of the main character.
In a story that uses a third-person omniscient point of view, the all-knowing narrator sometimes follows the story from multiple characters’ perspectives.
There you have it! By now, you’ve learned about creative writing examples, plus creative elements should you want to write a story. Browse our creative writing tips if you’re looking for a bit of help to engage your audience.
Still feel like you need more heavy-lifting? If it’s a talented Oxford, Cambridge, or Ivy League tutor you need to help you master creative writing, check out these creative writing online courses .
Related Content
Smart career paths: engineering.
17 Types of Creative Writing
- September 14, 2022
- One Comment
What is Creative Writing?
Creative writing is any writing that goes outside the bounds of normal professional, journalistic, academic, or technical forms of literature, typically identified by an emphasis on narrative craft, character development, and the use of literary tropes or with various traditions of poetry and poetics. Due to the looseness of the definition, it is possible for writing such as feature stories to be considered as one of the type of creative writing, even though they fall under journalism because the content of features is specifically focused on narrative and character development. Both fictional and non-fictional works fall into this category of different types of creative writing. This list of different types of creative writing also includes novels, biographies, short stories, and poems. In the academic setting, creative writing is typically separated into fiction and poetry classes, with a focus on writing in an original style, as opposed to imitating pre-existing genres such as crime or horror. Writing for the screen and stage—screenwriting and playwriting—are often taught separately, but fit under the creative writing category as well. Source: Wikipedia
What are the different types of Creative Writing?
Whether you’re a reader or a writer, understanding different types of creative writing can be confusing. The category is so vast and so rich that it is easy to lose your bearings. Worry not- we’ve made a list of the major types of creative writing. Equipped with this, you will be able to tell the difference between all the major types of creative writing!
( P.S – Check out the examples for extra clarification on the types of creative writing. )

Types of Creative Writing
Novels are one of the most popular types of fiction around. Any work of fiction that is of considerable length, and uses characters to tell a story may be considered a novel. The essential components in a novel are generally agreed to be the characters, the plot, the setting, the conflict, and the resolution. The traditional structure for a novel includes the exposition, the climax, and the conclusion. Novels may be standalone or part of a series.
Because novels consist of such a vast category, there are many, many different kinds of novels that form sub-categories. These subcategories may be on the basis of language, genre, style, literary school, time period, or setting.
Example: A Fine Balance by Rohinton Mistry

Learn more about ‘Writing Feature Articles’ from our blog post HERE .

A novella is essentially a short novel. Generally, if a work of fiction is between 20,000-50,000 words, it may be considered a novella and not a novel. Just like novels, novellas can be of many types.
Example: A Flight of Pigeons by Ruskin Bond

Short stories
Short stories are pieces of narrative fiction writing that are considerably shorter than novels and novellas. A short story is prose that deals with imaginary events and characters and are less complex than a novel. They can be of various types, and span most genres.
Example: The Blue Umbrella by Ruskin Bond

Flash Fiction
Flash Fiction is fiction that is shorter than a short story- in other words, a very short story. Structurally, it is similar to a short story but generally less complex. Flash fiction can even be a sentence long, as long as it is an entire story.
Examples: Unseen by Jose Varghese

Brush up on your knowledge of writing styles with our blog post – Different Kinds of Writing Styles with Examples
A vignette is a very short piece of fiction writing. It differs from flash fiction in one crucial aspect. Flash fiction must have a plot. A vignette can be less structured and is generally used to evoke a feeling. It can be a brief account of anything but does not need to follow a strict structure.
Example: Various excellent examples can be found in Ruskin Bond’s ‘It’s A Wonderful Life: Roads to Happiness’.

Narrative Nonfiction
Narrative Nonfiction is writing where real events are narrated in the style of a fictional novel or story. It is also known as literary or creative nonfiction. This is also a vast category under which various types of narratives can be classified. A common and popular example of narrative fiction is travel books and accounts.
Example: Shadow City: A Woman Walks Kabul by Taran Khan

Biography and Autobiography
Biographies and autobiographies are both nonfiction books that narrate the life of a person. Autobiography refers to an account of a person’s life written by said person. A biography is written by someone else. Some biographies are approved by the individual whose story is being told. Other times, especially where historical figures are concerned, many people attempt to write biographies. How a biography is written depends on who is writing it, and why. Where scholarly biographies may be concerned with certain details of someone’s life, a personal biography may focus on completely different details.
Example: And Then One Day: A Memoir by Naseeruddin Shah
Practice is the only way you can improve your writing. So, here’s a list of 8 Free Writing Platforms in India to keep you going.

An essay is a short piece of writing focused on a particular topic. It could be written to analyze, persuade or explain. Essays can be of many different kinds, but broad categories include descriptive, narrative, and argumentative essays. A descriptive essay, as the name implies, focuses on describing an event, an object, or something else. Narrative essays are similar to short narrative nonfiction or fictional short stories. Argumentative essays are opinion pieces that are meant to persuade readers to accept a certain side of an argument, while clearly outlining the debate.
The usual structure of an essay includes an introduction, the main body, and the conclusion. The introduction generally contains a thesis statement, which poses the main question of the essay. The conclusion should include the restatement of the thesis statement. While this does not apply to every essay, for most types it is a useful rule of thumb.
Examples: Walking with the Comrades by Arundhati Roy

Poetry is a form of writing that is difficult to define. According to Merriam-Webster, poetry is ‘writing that uses rhythm, vivid language, and often rhymes to provoke an emotional response.’
Because poetry is so loosely defined, it encompasses vastly different styles from all over the world. Poems may be classified by style, literary school, era, language, region, content, or form. Poems may follow a rigid structure or no structure at all. They are not necessarily narrative in nature. Generally, poems are shorter than prose, though there are works of epic poetry that are novel length and longer.
Example: On Killing A Tree by Gieve Patel

Songwriting
Songwriting may be considered a form of poetry. However, it is specifically poetry that is meant to be sung, with accompanying music. Unlike a poet whose work is meant to be read, the songwriter is concerned much more closely with rhythm, beat, and rhyme.
Songwriting has to take into account that their work will be composed and sung, and be mindful that the lyrics are compatible with the song. Often, songwriters compose the music for their own lyrics, but it is equally common for the composition to be done by someone else.
Example: Empire of Fear by Anoushka Maskey
Rap is a form of songwriting, and by extension, poetry. Associated with hip-hop, rap is a very specific kind of performance poetry. Rap is a type of music that involves fast speech, strong rhyme, and rhythm. It is not sung. It is also strongly associated with street culture and the poetry of resistance and anger.
Examples: On My Own by Brodha V
Screenplays
Screenplays are scripts for movies, TV and web series, and short films. Writing screenplays requires not only an understanding of prose writing but also the movie-making process. For example, it is important to keep in mind that the dialogues written will be spoken on screen by actors. Similarly, a director and cinematographer will decide what the content looks like on screen. Screenplays are divided into scenes and within scenes, shots. The location is clearly established, and dialogues are of utmost importance.
Example: The Disciple by Chaitanya Tamhane
We have gathered information on Screenwriting Agents in India : What do they do? Who are the best ones? for you.

Playwriting
Playwriting is a kind of dramatic writing. It is the writing of scripts that are to be performed on the stage. There are many, many kinds of plays that are different from each other in almost every respect. For example, the absurdist theatre has very little in common with classical theatre, and the respective playwrights use a variety of different tools. However, all plays are supposed to be performed, so there are many practical commonalities between playwrights.
Example: Harlesden High Street by Abhishek Majumdar

A blog is a personalized online platform where a person writes about any topic that is of interest to them. Sometimes, organizations and companies also have a blog with a theme and different writers contribute to it. The style of writing, as well as the content, can vary hugely. Blog writing is a fairly flexible medium that allows for different kinds of expression.
Example: 82 Women Writers on The Himalayan Writing Retreat blog by Vanya Singh

Speeches are generally addressed to the public and have a purpose behind them. Political figures and leaders of all sorts need to make speeches all the time. They may be to inspire, persuade or explain. Speeches are written with a clear aim in mind, and try to evoke strong emotion of some sort.
Example: ‘Tryst with Destiny’ by Jawaharlal Nehru
Merriam Webster defines journalism as the act of collecting and editing news for presentation through the media. Journalists write for different media- print, radio, and television being the most prominent. The presentation of news in all of these follows different formats, as does the job of a journalist. However, the fundamental role of the journalist- the collection of relevant news, and editing remain common.
Example: Newslaundry

Comic Strips/ Graphic Novels
Comic strips and graphic novels are interesting avenues for creative writing. They essentially present a collaboration between writers and artists. The artist draws the comic panels, and the writer writes in them. The way characters and stories are developed through this medium is very different from other types of fiction. The collaborative aspect, as in film and stage, cannot be forgotten.
Example: Corridor by Sarnath Banerjee
Here are 10 Secrets of Ghostwriting in India that I bet you didn’t know.

Letter Writing
Letters are addressed to people and fall into two broad categories. Formal letters, and informal letters. Formal letters are written in an official or professional capacity. For example, letters to the municipality complaining about an issue is a formal letter. Informal letters are more personal in nature and more relaxed in their tone and use of language. For example, a letter written by a sister to her brother is an informal letter.
Example: Letters From A Father to His Daughter by Jawaharlal Nehru

Conclusion
While this list is by no means exhaustive, an effort has been made to include the main types of creative writing. All of the above can be published- but there are also other types of creative writing, like personal diaries and journals that are usually kept private.
We hope this helps you to better navigate the wonderfully chaotic world of reading and writing!
Related posts:
Recent posts.
- Hindi Films About Writers
- 10 Best Books by R.K.Narayan
- 12 Series Based on Books
- 12 Hindi Movies Based on Books
- 12 Best Books by Ruskin Bond
One Response
It is true that creative writing can be very rewarding. It can also be very difficult. your article is very helpful for writers thanks for sharing with us!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
- Workshops/Retreats
- Physical Workshops/Courses
- International Writer's Retreat
- Online Courses
- Custom Workshops
- Support for Writers
- First Draft Club
- Himalayan Book Club
- Destination Book Launch
- French Residency
- Writing Coach
- Stay with Us
- Rooms/Tariffs
- Writing Spaces
- Getting here
- Traveller Safety
- HWR Books & Awards
- In the Media
- Community Impact
( 11am - 5pm )
Email: [email protected]
- Privacy Policy
- Copyright © 2022 The Himalayan Writing Retreat
TRY OUR FREE APP
Write your book in Reedsy Studio. Try the beloved writing app for free today.
Craft your masterpiece in Reedsy Studio
Plan, write, edit, and format your book in our free app made for authors.

Guides • Perfecting your Craft
Last updated on Dec 23, 2022
Creative Writing: 8 Fun Ways to Get Started
Creative writing is a written art form that uses the imagination to tell stories and compose essays, poetry, screenplays, novels, lyrics, and more. It can be defined in opposition to the dry and factual types of writing found in academic, technical, or journalistic texts.
Characterized by its ability to evoke emotion and engage readers, creative writing can tackle themes and ideas that one might struggle to discuss in cold, factual terms.
If you’re interested in the world of creative writing, we have eight fantastic exercises and activities to get you started.

1. Use writing prompts every week

Coming up with ideas for short stories can be challenging, which is why we created a directory of 1700+ creative writing prompts covering a wide range of genres and topics. Writing prompts are flexible in nature, they are meant to inspire you without being too constrictive. Overall, they are a great way to keep your creative muscles limber.

If you’re struggling for motivation, how does a hard deadline and a little prize money sound? Prompts-based writing contests are a fantastic way to dive into creative writing: the combination of due dates, friendly rivalries, prize money, and the potential to have your work published is often just what’s needed to propel you over the finish line.
We run a weekly writing contest over on Reedsy Prompts, where hundreds of writers from all around the world challenge themselves weekly to write a short story between 1,000 and 3,000 words for a chance to win the $250 prize. Furthermore, the community is very active in providing constructive feedback, support, and accountability to each other 一 something that will make your efforts even more worthwhile.
Take a peek at our directory of writing contests which features some of the most prestigious open writing competitions in the world.
2. Start journaling your days

Another easy way to get started with creative writing is to keep a journal. We’re not talking about an hour-by-hour account of your day, but journaling as a way to express yourself without filters and find your ‘voice in writing’. If you’re unsure what to journal about, think of any daily experiences that have had an impact on you, such as…
Special moments . Did you lock yourself out of your house? Or did you catch a beautiful sunset on your way back from groceries? Capture those moments, and how you felt about them.
People . Did you have an unusual exchange with a stranger at the bar? Or did you reconnect with someone you haven’t seen in years? Share your thoughts about it.
World events . Is there something happening in the world right now that is triggering you? That’s understandable. You can reflect on it (and let some steam off) while journaling.
Memories . Did you go down memory lane after a glass of wine? Great, honor those memories by trying to recollect them in detail on paper so that they will always stay vivid in your mind.
Life decisions . Are you having an existential crisis about what to do with your life? Write down your thought process, and the pros and cons of the possible decisions in front of you. You’ll be surprised to discover that, not only is it a great creative writing exercise, but it can also actually help you sort your life out!
If you struggle to write consistently, sign up for our How to Write a Novel course to finish a novel in just 3 months.

NEW REEDSY COURSE
How to Write a Novel
Enroll in our course and become an author in three months.
3. Create an anonymous social media account

Like anonymous blogging, an incognito Twitter account sidesteps the pressure that comes with attaching your name to your work. Anonymously putting tiny stories out into the ether gives you the freedom to create without worrying about the consequences — which is great, so long as you don’t use it as an opportunity to troll people or spread conspiracy theories.
You could use the anonymous account in different ways. For example, you could…
- Tweet from unique points of view (e.g. a dog observing human behavior );
- Create a parody account of real or fictional people (e.g. an English poet from the Middle Ages );
- Challenge yourself to write tiny flash fiction stories that fit into Twitter threads.
Just remember, you’re not doing this to fool anyone into thinking that your account is real: be a good citizen and mark yourself a fiction account in your bio.
But if you’re not really a social media kinda person, you may enjoy our next tip, which is a bit more on the analog side.

GET ACCOUNTABILITY
Meet writing coaches on Reedsy
Industry insiders can help you hone your craft, finish your draft, and get published.

4. Find an old photo and tell its story

Find a random old photo — maybe on the web, maybe from a photo album in a yard sale — and see what catches your attention. Look closely at it and try to imagine the story behind it. What was happening? Who are the people in it and how are they really feeling? Do they share a relationship, and of what kind? What are their goals and dreams?
In other words, bring the photo to life with your imagination. Don't be afraid to take artistic license with your story, as the goal is to be creative and have fun while writing.
How do you know it’s creative writing?

5. Create a character from a random name

Just as our universe started from a few simple elements, you can create a character from a few basic information, like their name, culture, and gender. Reedsy’s handy character name generator can help you with that, offering random names based on archetypes, Medieval roots, fantasy traits and more. A few examples? A Celtic heroine named Fíona O'Keefe, a hero’s sidekick named Aderine, or a Korean track star named Park Kang-Dae.
Once you've chosen their name, begin to develop their personality. Set a timer for 5–10 minutes and write anything that comes to mind about them. It could be a page from their FBI dossier, a childhood diary entry, or simply a scene about them boiling an egg.
Just ‘go with the flow’ and don’t stop writing until your time is up. Repeat the process a few times to further hone the personality. If you like what you end up with, you can always go deeper later with our character profile template .
If a stream-of-consciousness exercise is not your thing, you can try to imagine your character in a specific situation and write down how’d they respond to it. For example, what if they were betrayed by a friend? Or if they were elected in power? To help you imagine situations to put your character in, we made a free template that you can download below.

FREE RESOURCE
Reedsy’s Character Questionnaire
40 questions to help you develop memorable characters.
6. Construct a character by people-watching

People watching is “the action of spending time idly observing people in a public place.” In a non-creepy way, ideally. Sit on a bench on a public square or on a road-side table at your favorite café, and start observing the people around you. Pay attention to any interesting quirks or behaviors, and write it down. Then put on your detective’s hat and try to figure out what that tells you about them.
For example, the man at the table next to you at the restaurant is reading the newspaper. His jacket and hat are neatly arranged next to him. The pages make a whipping sound as he briskly turns them, and he grimaces every time he reads a new article. Try to imagine what he’s reading, and why he’s reacting the way he is. Then, try to build a character with the information you have. It’s a fun creative exercise that will also, hopefully, help you better empathize with strangers.
7. “Map” something you feel strongly about into a new context

Placing your feelings into new contexts can be a powerful creative writing exercise. The idea is to start from something you feel strongly about, and frame it into a completely different context.
For example, suppose your heart is torn apart after you divorce your life-long partner: instead of journaling or crafting an entire novel about it, you could tell a story about a legendary trapeze duo whose partnership has come to an end. If you’re struggling with politicking and petty power dynamics at the office: what if you “mapped” your feelings onto an ant who resents being part of a colony? Directing your frustration at a queen ant can be a fun and cathartic writing experience (that won’t get you in trouble if your co-workers end up reading your story).
8. Capture the moment with a haiku

Haikus are poems from the Japanese tradition that aim to capture, in a few words, daily moments of insight (usually inspired by nature). In a nutshell, it’s about becoming mindful of your surroundings, and notice if you can see something in a new or deeper way 一 then use contrasting imagery to express whatever you noticed.
Here’s an example:
Bright orange bicycle
Speeding through the autumn leaves
A burst of color waves
It may sound a bit complicated, but it shouldn’t be 一 at least not for the purpose of this exercise. Learn the basics of haiku-writing , then challenge yourself to write one per day for a week or month. At the end, you’ll be able to look back at your collection of poems and 一 in the worst case scenario 一 revisit small but significant moments that you would have otherwise forgot about.
Creative writing can be any writing you put your heart and soul into. It could be made for the purpose of expressing your feelings, exploring an idea, or simply entertaining your readers. As you can see there’s many paths to get involved with it, and hundreds of exercises you can use as a starting point. In the next post, we’ll look more in detail at some creative writing examples from some fellow authors.
Join a community of over 1 million authors
Reedsy is more than just a blog. Become a member today to discover how we can help you publish a beautiful book.

Try our novel writing master class — 100% free
Sign up for a free video lesson and learn how to make readers care about your main character.

1 million authors trust the professionals on Reedsy. Come meet them.
Enter your email or get started with a social account:
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to footer
Enchanting Marketing
Writing advice for small business
11 Creative Writing Techniques
Learn how to add pizzazz to any type of writing.
The articles below show you how to use creative writing tools in fiction or non-fiction. Each article features a series of examples so it becomes easier to apply the technique.
List of creative writing techniques
Click the links below to go to a specific section:
Personification
Show don’t tell
Repetition in writing
Contrast in writing
The rule of three in writing
Parallelism
1. Metaphors

Learn how to use metaphors and get inspired by these examples …
Learn how to use metaphors >>
Metaphor examples >>

Get inspired by over 10 simile examples by various authors …
Simile examples >>
3. Analogies

Get inspired by these analogy examples …
Analogy examples >>

Improve your writing style
Learn how to write better and find your voice. Get free writing tips in your inbox.
Get free writing tips >>

Get inspired by these imagery examples …
Imagery examples >>
5. Personification

Learn how to use personification to make your writing sparkle …
Personification examples >>
6. Show don’t tell

Get inspired by these examples of “show, don’t tell” …
Show don’t tell examples >>
7. Repetition in writing

Get inspired by these examples of word repetition …
Examples of repetition in writing >>
8. Contrast in writing

Discover how to use contrast in your writing …
Examples of contrast in writing >>
9. The rule of 3 in writing

Get inspired by these examples of the rule of 3 …
The rule of 3 in writing >>
10. Parallelism in writing

Get inspired by these examples of the parallelism …
Parallelism examples >>
11. Switch the point of view (POV)

Discover how to switch the point of view …
Point of view examples >>
You may also like …

Creative writing examples
Learn how to inject creativity in any writing.

Creative writing exercises
Try these exercises to add a touch of creativity to your writing.
Share this page:

Books and courses
Follow proven templates for specific writing tasks, practice your skills, and get professional feedback so you become a confident business writer. Take on any writing project with gusto. Learn more about books and courses

About Henneke
I never saw myself as a writer, but in my early forties, I learned how to write and discovered the joy of writing. Now, I’d like to empower you to find your voice, share your ideas and inspire your audience. Learn how I can help you
Popular topics
Sales copywriting
Blog writing for business
Your writing voice
Tips for beginning writers
The writing process
Improve your writing skills
Writing examples
Popular blog posts
Recent blog posts
Free Snackable Writing Course
Get 16 concise emails and learn how to write more persuasive content.
Success! Now check your email to confirm your subscription.
There was an error submitting your subscription. Please try again.

Creative Writing 101
You love to write and have been told you have a way with words. So you’ve decided to give writing a try—creative writing.
The problem is, you’re finding it tougher than you thought it would be.
You have a great story idea , but you’re not sure how to turn it into something people will read.
Don’t be discouraged—writing a compelling story can be grueling, even for veterans. Conflicting advice online may confuse you and make you want to quit before you start.
But you know more than you think. Stories saturate our lives.
We tell and hear stories every day in music, on television, in video games, in books, in movies, even in conversation.
- What is Creative Writing?
Creative Writing is prose that tells a story featuring someone who wants something.
That person runs into trouble and begins an adventure, a journey, or a quest, faces obstacles, and is ultimately transformed—for the good or for the bad.
While Creative Writing can also educate and/or entertain, but it does its best work when it emotionally moves the reader.
- Elements of Creative Writing
Writing a story is much like building a house.
You may have all the right tools and design ideas, but if your foundation isn’t solid, even the most beautiful structure won’t stand.
Most storytelling experts agree, these 7 key elements must exist in a story.
Plot (more on that below) is what happens in a story. Theme is why it happens.
Before you begin writing, determine why you want to tell your story.
What message do you wish to convey? What will it teach the reader?
Resist the urge to explicitly state your theme. Just tell the story, and let it make its own point.
Give your readers credit. Subtly weave your theme into the story and trust them to get it.
They may remember a great plot, but you want them thinking about your theme long after they’ve finished reading.
2. Characters
Every story needs believable characters who feel knowable.
In fiction, your main character is the protagonist, also known as the lead or hero/heroine.
The protagonist must have:
- redeemable flaws
- potentially heroic qualities that emerge in the climax
- a character arc (he must be different, better, stronger by the end)
Resist the temptation to create a perfect lead. Perfect is boring. (Even Indiana Jones suffered a snake phobia.)
You also need an antagonist, the villain , who should be every bit as formidable and compelling as your hero.
Don’t make your bad guy bad just because he’s the bad guy. Make him a worthy foe by giving him motives for his actions.
Villains don’t see themselves as bad. They think they’re right! A fully rounded bad guy is much more realistic and memorable.
Depending on the length of your story , you may also need important orbital cast members.
For each character, ask:
- What do they want?
- What or who is keeping them from getting it?
- What will they do about it?
The more challenges your characters face, the more relatable they are.
Much as in real life, the toughest challenges result in the most transformation.
Setting may include a location, time, or era, but it should also include how things look, smell, taste, feel, and sound.
Thoroughly research details about your setting so it informs your writing, but use those details as seasoning, not the main course. The main course is the story.
But, beware.
Agents and acquisitions editors tell me one of the biggest mistakes beginning writers make is feeling they must begin by describing the setting.
That’s important, don’t get me wrong. But a sure way to put readers to sleep is to promise a thrilling story on the cover—only to start with some variation of:
The house sat in a deep wood surrounded by…
Rather than describing your setting, subtly layer it into the story.
Show readers your setting. Don’t tell them. Description as a separate element slows your story to crawl.
By layering in what things look and feel and sound like you subtly register the setting in the theater of readers’ minds.
While they’re concentrating on the action, the dialogue , the tension , the drama, and conflict that keep them turning the pages, they’re also getting a look and feel for your setting.
4. Point of View
POV is more than which perspective you choose to tell your story: First Person ( I, me ), Second Person ( you, your ), or Third Person ( he, she, or it ).
Determine your perspective (POV) character for each scene—the one who serves as your camera and recorder—by deciding who has the most at stake. Who’s story is this?
The cardinal rule is that you’re limited to one perspective character per scene, but I prefer only one per chapter, and ideally one per novel.
Readers experience everything in your story from this character’s perspective.
For a more in-depth explanation of Voice and POV, read A Writer’s Guide to Point of View .
This is the sequence of events that make up a story —in short, what happens. It either compels your reader to keep turning pages or set the book aside.
A successful story answers:
- What happens? (Plot)
- What does it mean? (Theme: see above)
Writing coaches call various story structures by different names, but they’re all largely similar. All such structures include some variation of:
- An inciting incident that changes everything
- A series of crises that build tension
- A resolution (or conclusion)
How effectively you create drama, intrigue, conflict, and tension, determines whether you can grab readers from the start and keep them to the end.
6. Conflict
This is the engine of fiction and crucial to effective nonfiction as well.
Readers crave conflict and what results from it.
If everything in your plot is going well and everyone is agreeing, you’ll quickly bore your reader—the cardinal sin of writing.
If two characters are chatting amicably and the scene feels flat (which it will), inject conflict. Have one say something that makes the other storm out, revealing a deep-seated rift.
Readers will stay with you to find out what it’s all about.
7. Resolution
Whether you’re an Outliner or a Pantser like me (one who writes by the seat of your pants), you must have an idea where your story is going.
How you expect the story to end should inform every scene and chapter. It may change, evolve, and grow as you and your characters do, but never leave it to chance.
Keep your lead character center stage to the very end. Everything he learns through all the complications you plunged him into should, in the end, allow him to rise to the occasion and succeed.
If you get near the end and something’s missing, don’t rush it. Give your ending a few days, even a few weeks if necessary.
Read through everything you’ve written. Take a long walk. Think about it. Sleep on it. Jot notes. Let your subconscious work. Play what-if games. Reach for the heart, and deliver a satisfying ending that resonates .
Give your readers a payoff for their investment by making it unforgettable.
- 14 Types of Creative Writing
Novels are fiction by definition. Lengths typically fall between 75,000 to 100,000 words. The author must create a story that can carry an entire book.
Novellas usually run between 10,000 and 40,000 words and typically follow a single character’s point of view. Otherwise, they tend to feature the structural and narrative elements of a full-length novel. Example: Edith Wharton’s Ethan Frome.
Short Story
Short stories, including super short micro or flash fiction—which can be as short as just a few words, are usually between a thousand and five thousand words and thus must telescope the creative writing techniques and properties of a novel. This creative writing type gained popularity during the 19th century in literary magazines, and many such magazines still carry short stories.
Narrative Nonfiction
Also known as Creative Nonfiction, this form displays techniques and literary styles such as story and tone to convey emotion in nonfiction narratives. A common example is a personal essay.
Biographies capture the stories of individuals whose lives can provide a lesson to readers.
Autobiography
An autobiography is written by the author, about the author, following a chronological account of their life.
As opposed to an autobiography, a memoir emphasizes takeaway value to the reader and is thus theme-oriented. Readers should be able to see themselves in the anecdotes chosen to show life transformation. Creative writing techniques similar to those in a novel will bring the story to life.
Poets use traditional structures such as rhyme, rhythm, and subject matter to tell their stories. They can also experiment with prose-poetry or free verse.
Song lyrics
Song lyrics are another form of poetry, the aim being to tell a story in the fewest, most evocative words possible.
Speeches require creative writing to keep audiences engaged.
A blog is usually based on the writer’s own life and interests. The best ones tell stories readers relate to and interact with.
Journaling, usually intended for the author’s eyes only, can become, in essence, a creatively written diary.
Screenwriting
Screenwriting is a form of scriptwriting specific to television shows, films, and other visual media. Screenwriting relies heavily on dialogue to tell a story, but not exclusively. The writer must include action and response takes.
Playwriting
Playwriting is a form of scriptwriting specific to theater productions, again relying heavily on dialogue and action. Playwriting also requires stage direction suggestions for lighting, sound, and actors.
- 11 Creative Writing Tips
In How to Write a Novel , I cover each step of the writing process:
Come up with a great story idea .
That may sound obvious, but make sure it’s compelling enough to draw you back to the keyboard every day.
Determine whether you’re an Outliner or a Pantser or a Hybrid.
If you’re an Outliner, you prefer to map out everything before you start writing your novel.
If you’re a Pantser, you write by the seat of your pants, putting, as Stephen King advises, interesting characters in difficult situations and writing to find out what happens.
I cover both types and how to structure a novel here .
And though I’m primarily a Pantser, I never start writing a novel without an idea where I’m going — or think I’m going.
Create an unforgettable main character.
Resist the temptation to create a perfect character, even if it’s a superhero. Main characters must exhibit human flaws to make them relatable.
For more on character development, check out my blog posts Your Ultimate Guide to Character Development: 9 Steps to Creating Memorable Heroes , How to Create a Powerful Character Arc , and Character Motivation: How to Craft Realistic Characters .
Expand your idea into a plot.
Regardless of whether you’re a Panster or an Outliner, you need some semblance of a structure.
Dean Koontz calls this the Classic Story Structure (in his How to Write Best-Selling Fiction ):
- Plunge the main character into terrible trouble
- Everything the character does to get out of trouble makes things worse until…
- All appears hopeless
- The qualities the main character develops trying to fix the trouble make him heroic enough to succeed in the end
Conduct your research.
The best fiction must ironically feel believable.
You must research to add flavor and authenticity.
One caveat : Resist the urge to show off your research by loading your story with every esoteric fact you’ve learned. Add specifics the way you would season food. It enhances the experience, but it’s not the main course.
Choose your Voice and Point of View.
Point of View (POV) is more than simply deciding what voice to use:
First Person ( I, me ), Second Person ( you, your ), or Third Person ( he, she, or it ).
It also involves deciding who will be your perspective character, serving as your story’s camera.
The cardinal rule is one POV character per scene .
For a more in-depth explanation, read my post A Writer’s Guide to Point of View .
Start in medias res (in the midst of things).
Grab the reader by the throat on page one.
Avoid what’s called throat clearing—too much scene setting and description. Get to the good stuff—the guts of the story .
The goal of every sentence, in fact of every word , is to compel the reader to read the next.
Intensify your main character’s problems.
Do not give him a break. Remember, conflict is the engine of fiction.
(For more on conflict, read my post Internal and External Conflict: Tips for Creating Unforgettable Characters )
Your main character’s trouble should escalate with his every attempt to fix it.
Make the predicament appear hopeless.
You’ll be tempted to give your protagonist a break, invent an escape, or inject a miracle. Don’t do it!
This darkest, bleakest moment forces your hero to use every new skill and muscle gained through battling those obstacles.
The more hopeless the situation appears, the more powerful your climax will be.
Bring it all to a climax.
This is where your hero faces his toughest test yet. The stakes must be dire, the prospect of failure catastrophic.
The tension that has been building throughout crescendos during an ultimate confrontation, and all the major book-length setups are paid off.
Note: the climax is not the end. The real conclusion ties up loose ends and puts the journey into perspective.
Leave readers wholly satisfied.
A great ending :
- Honors the reader for his investment of time and money.
- Aims for the heart.
- Keeps your hero on stage till the last word.
Don’t rush it.
A fully satisfying ending drops the curtain with a resounding thud.
- More to Think About
1. Carry a writing pad, electronic or otherwise. I like the Moleskine™ notebook .
Ideas can come at any moment. Record ideas for:
- Anything that might expand your story
2. Start small.
Take time to learn the craft and hone your skills on smaller projects before attempting to write a book . A book is not where you start; it’s where you arrive.
Journal. Write a newsletter. Start a blog. Write short stories . Submit articles to magazines, newspapers, or e-zines.
Take a night school or online course in journalism or creative writing. Attend a writers conference.
3. Keep perfectionism in its place.
Reserve it for the editing and revision stage.
While writing, take off that perfectionist cap and just get the story down. At that stage, perfectionism is the enemy of progress.
- Time to Get to Work
Few pleasures in life compare to getting lost in a great story.
Learn how to write creatively, and the characters you birth have the potential to live in readers’ hearts for years.

Are You Making This #1 Amateur Writing Mistake?

Faith-Based Words and Phrases

What You and I Can Learn From Patricia Raybon

Before you go, be sure to grab my FREE guide:
How to Write a Book: Everything You Need to Know in 20 Steps
Just tell me where to send it:

Writing styles may be hard to define, but something separates Hemingway from Steinbeck, Atwood from LeGuin, or Keats from Wordsworth. Though two given writers might dwell on similar themes, every writer expresses a unique writing style, conveyed through elements like word choice, narrative structure, and the author’s own voice.
But what is style in writing? On some level, style is ineffable. It’s also emergent: when you parse the elements of writing styles, you lose something that lives in how you put them together.
This article provides tips for honing style in your own work. We’ll analyze the different types of writing styles, look at examples of different writing styles from famous authors, and suggest different ways to experiment in your own work.
But first, let’s clarify what we mean when we say “writing styles.” What is style in writing?
What is Style in Writing?
Think of writing style as the author’s thumbprint—a unique and indelible mark on the voice and personality of the work. If a writer’s work is a house, style is what adorns that house: the window blinds, the doormat, the freshly painted eaves.
Style is like an author’s thumbprint—a unique and indelible mark on the voice and personality of the work.
Authors doesn’t only hone their style deliberately: writing styles emerge as a result of dedication, the author’s own personality, and a continuous experimentation with language and meaning.
To illustrate what we mean by style, let’s compare two examples of different writing styles from two different works of fiction. Each excerpt talks about the same dilemma—the endurance of memory—but approaches that dilemma in uniquely stylish ways.
“Perhaps you have forgotten. That’s one of the great problems of our modern world, you know. Forgetting. The victim never forgets. Ask an Irishman what the English did to him in 1920 and he’ll tell you the day of the month and the time and the name of every man they killed. Ask an Iranian what the English did to him in 1953 and he’ll tell you. His child will tell you. His grandchild will tell you. And when he has one, his great-grandchild will tell you too. But ask an Englishman—” He flung up his hands in mock ignorance. “If he ever knew, he has forgotten. ‘Move on!’ you tell us. ‘Move on! Forget what we’ve done to you. Tomorrow’s another day!’ But it isn’t, Mr. Brue.” He still had Brue’s hand. “Tomorrow was created yesterday, you see. That is the point I was making to you. And by the day before yesterday, too. To ignore history is to ignore the wolf at the door.”
—John le Carré, A Most Wanted Man
Compare this with the following excerpt:
“The ones who did it can always rationalize their actions and even forget what they did. They can turn away from things they don’t want to see. But the surviving victims can never forget. They can’t turn away. Their memories are passed on from parent to child. That’s what the world is, after all: an endless battle of contrasting memories.”
—Haruki Murakami, 1Q84
Each quote addresses a similar theme : how the perpetrators forget, but the victims always remember, and how that remembering shapes the world. Yet they approach the topic in different ways. John le Carré illustrates his point by examining historical, world-altering events. He uses dialogue and describes the gestures of his characters to punctuate his ideas, and he ends by suggesting that, if we do not remember, then we are infinitely more vulnerable to the metaphorical “wolf at the door.”
Haruki Murakami, by contrast, uses far fewer words to illustrate the same idea. His sentences are less laden with imagery and description; they are merely vehicles to his conclusion that the world is “an endless battle of contrasting memories.”
Each author takes his own route, and each excerpt will connect with the reader in different ways. Such differences in expression are the essence of style. Writing styles showcase how a writer reaches their point, encompassing the totality of the author’s word choice, sentence structures, use of literary devices, etc. It is the gestalt of every decision, both conscious and unconscious, that the writer makes in the text.
What Authors Say About Writing Style
Before we move on, let’s illustrate this point about authors’ writing styles in another way: different quotes from authors on writing styles themselves.
- “Style is the dress of thoughts; and let them be ever so just, if your style is homely, coarse, and vulgar, they will appear to as much disadvantage.” —Philip Dormer Stanhope, Earl of Chesterfield
- “When we see a natural style, we are astonished and delighted; for we expected to see an author, and we find a man.” —Blaise Pascal
- “The essence of a sound style is that it cannot be reduced to rules–that it is a living and breathing thing with something of the devilish in it–that it fits its proprietor tightly yet ever so loosely, as his skin fits him. It is, in fact, quite as seriously an integral part of him as that skin is. . . . In brief, a style is always the outward and visible symbol of a man, and cannot be anything else.” —H.L. Mencken
- “You do not create a style. You work, and develop yourself; your style is an emanation from your own being.” —Katherine Anne Porter
- “Style is that which indicates how the writer takes himself and what he is saying. It is the mind skating circles around itself as it moves forward.” —Robert Frost
- “Style is what unites memory or recollection, ideology, sentiment, nostalgia, presentiment, to the way we express all that. It’s not what we say but how we say it that matters.” —Federico Fellini
- “Proper words in proper places, make the true definition of style.” —Jonathan Swift
- “The web, then, or the pattern, a web at once sensuous and logical, an elegant and pregnant texture: that is style.” —Robert Louis Stevenson
- “Thought and speech are inseparable from each other. Matter and expression are parts of one; style is a thinking out into language.” —Cardinal John Henry Newman
- “Find a subject you care about and which you in your heart feel others should care about. It is this genuine caring, not your games with language, which will be the most compelling and seductive element in your style.” —Stephen King
- “It is only by writing, not dreaming about it, that we develop our own style.” —P.D. James
Elements of Writing Styles
Every author makes key decisions about their writing, and those decisions build over time into a cohesive writing style. What decisions do they have to make? In other words, what are the elements of writing styles?
Creative writing styles are honed through a combination of the following:
- Word choice
- Economy and concision
- Literary devices
- Context and purpose
- The author’s location, time period, and influences
Let’s explore each element in detail.
Elements of Writing Styles: Word Choice
Also called diction, word choice refers to the artistic decisions a writer makes in choosing one word over another, and how those decisions affect the meaning, mood , tone , and ideas conveyed to the reader.
Word choice refers to the artistic decisions a writer makes in choosing one word over another, and how those decisions affect the meaning, mood, tone, and ideas conveyed to the reader.
Take a look at the following two example sentences. Only one word has been changed in each sentence, and those words are synonyms, but the changed word has a huge impact on the way each sentence is read.
- The Union beat The Confederacy during the American Civil War.
- The Union subjugated The Confederacy during the American Civil War.
As you can see, changing “beat” to “subjugated” affects every part of the sentence. The sentence moves from neutral and informative to passionate and descriptive; the idea, once impartial, now comes across as heavily invested in the outcome of the Civil War. A word like “subjugated” transmits to the reader that the Union was extremely powerful, even suggesting that the Confederacy was a victim of the North.
Small details such as word choice can have huge impacts on writing styles. Another important element to consider is syntax.
Elements of Writing Styles: Syntax
Syntax refers to sentence structure—how rearranging the order of words impacts the meaning transmitted to the reader. It is closely related to diction, but where diction is concerned with the choice of words, syntax is concerned with the arrangement of those words, as well as the length and complexity of sentences.
Syntax is concerned with the arrangement of words, as well as the length and complexity of sentences.
Much of syntax is innately learned, especially to native English speakers. For example, an English sentence is typically constructed with the subject first, and then the verb, followed by the object of that verb. See below:
- The quick brown fox (subject) jumped (verb) over the lazy dog (object).
If the daring writer wanted to complicate this syntactical order, they might write “Over the lazy dog, the quick brown fox jumped.” Of course, such experimentations can prove dangerous, as the reader might misinterpret that construction, or read it as shallow or pretentious.
Nonetheless, paying close attention to the structure, length, and word order of sentences can allow writers to develop their writing styles. Here are some other ways one might experiment with syntax:
- Structure (active to passive): The lazy dog was jumped over by the quick brown fox.
- Length : The fox jumped over the dog. OR: The quick, sly, and daring fox jumped right over the lazy and motionless dog.
- Word order : The brown fox jumped quickly over the dog lying lazily.
Notice how each of these syntactical changes affect the rhythm, meaning, and style of the sentences. Some changes certainly worsen the effect of the sentence.
A final element of syntax is punctuation. Commas, colons, semicolons, em-dashes, and periods each have their own specific use in English grammar. How the author decides to use each punctuation mark contributes to the overall style of their sentences.
Elements of Writing Styles: Economy and Concision
All stylish writers know how to use economy and concision. They know how to use fewer words, not more, and they know how to make every word count.
There are certainly rules and guidelines for concise writing. The economic writer knows to:
- Avoid adverbs.
- Use strong, visual verbs.
- Employ prepositions sparingly.
- Only use adjectives when necessary.
- Stay inside the active voice, unless the passive is necessary.
- Provide only the important details.
Later in this article, we dive deeper into concision. Nonetheless, let’s demonstrate this key facet of writing styles.
Here’s a simple, effective sentence:
We careened from California to Maine.
The wordy writer has many reasons to make this sentence more complicated. Perhaps the reader does need more information. But, the writer might also be insecure about their own writing, or else they might think every detail needs to be ornate (a tactic called purple prose ). Here’s the above sentence, written wordier. In parentheses are the rules broken from the list above.
We were driven (5) swiftly (1) and without (3) direction in (3) our little blue Chevy (4, 6), somehow (1) finding (2) our way from California to Maine.
Perhaps the little blue Chevy is important to the story. It does add some personality to the people in the car. Otherwise, this sentence is haphazard, conveying too much to the reader in too many words.
Elements of Writing Styles: Literary Devices
Literary devices are specific writing techniques that forge novel connections and possibilities in language. You are probably familiar with common devices, like metaphors and similes . However, there is a wide range of devices available to creative writers, from the hyperbole to the synecdoche, from the onomatopoeia to the paranomasia .
In any work of creative writing, literary devices are essential to both the author’s meaning and their writing style.
In any work of creative writing, literary devices are essential to both the author’s meaning and their writing style. Sometimes, the device is confined to a single sentence in the text. Other times, various elements of the writing—its plot , characters, and settings—act as metaphors for broader ideas and themes.
Here’s an example of a metaphor that’s daring, stylish, and effective:
“Love is so embarrassing. I bled in your bed. I’m sorry. I have built you a shore with all my best words & still, the waves.”
Out of Bound by Claire Schwartz
This is a striking metaphor, heartbreaking in its imagery. The speaker laments at the imperfectness of love and language: how, no matter how carefully and precisely a lover chooses the words they use to love another, those words are, inevitably, broken down by “the waves.” What do those waves represent? Perhaps the limits of language—the ever-present gap between what is spoken and what is understood. In the same way that love is modified by language, the shore is always modified by the waves.
Many stylistic decisions go into the construction of literary devices, including:
- Which devices are used.
- The images used to convey deeper meanings.
- The word choice and syntax of those devices.
Indeed, the construction of literary devices is closely related to syntax and word choice, but the way that the writer employs those devices and makes connections and comparisons is key to honing an author’s writing style.
To learn more, check out our articles on common literary devices and rhetorical devices .
Elements of Writing Styles: Context and Purpose
While an author’s writing style is the product of their own artistic integrity, some creative writing styles develop in relation to the context and purpose of the writing itself.
Some creative writing styles develop in relation to the context and purpose of the writing itself.
For example, an author might choose to write a murder mystery novel, a middle grade fiction book, and a historical account of the Sino-Japanese War. Each publication would have its own unique writing style, because the writing serves a different purpose in each book, and the author will have to write towards different audiences. We’ll explore this shortly when we look at the different types of writing styles.
In creative writing, the question of audience can matter a great deal. You would not want someone with a hard-boiled writing style to publish a romance novel in the same voice, nor would you expect a law critic to write poetry using the same word choice.
While audience should not define the author’s style and intent, it is a necessary consideration in the editing process before a work is published.
It is also important to note that there are different types of writing styles for different contexts. Let’s review those briefly.
Different Types of Writing Styles
In standard rhetorical analysis, there are four different types of writing styles: narrative, descriptive, persuasive, and expository. We mention a fifth style, the creative style, because certain decisions and elements are available to creative works that are not usually available to other writing styles.
Narrative Writing Styles
At its simplest, narrative is a synonym for storytelling . As such, narrative writing styles employ certain storytelling tactics to communicate a plot with characters, settings , and themes.
Narrative writing styles employ storytelling tactics to communicate a plot with characters, settings, and themes.
Here’s an example of a narrative writing style, which seeks to communicate the essential details for a reader to understand the story:
“There was no possibility of taking a walk that day. We had been wandering, indeed, in the leafless shrubbery an hour in the morning; but since dinner (Mrs. Reed, when there was no company, dined early) the cold winter wind had brought with it clouds so sombre, and a rain so penetrating, that further outdoor exercise was now out of the question.
I was glad of it: I never liked long walks, especially on chilly afternoons: dreadful to me was the coming home in the raw twilight, with nipped fingers and toes, and a heart saddened by the chidings of Bessie, the nurse, and humbled by the consciousness of my physical inferiority to Eliza, John, and Georgiana Reed.” —Opening lines of Jane Eyre by Charlotte Brontë
These two paragraphs give us the essentials. We know that the narrator is a child with an unkind family (character), that they live somewhere bleak and chilly (setting), and that the speaker has been made to feel inferior to her peers (theme).
Narrative writing styles are commonly used in the following:
- Creative nonfiction
- Narrative poetry
- Legal writing
- Marketing and brand development
Descriptive Writing Styles
Descriptive writing seeks to evoke sensory experiences. This type of writing concerns itself with the effective use of imagery , including non-visual forms of imagery like sounds, sights, tastes, smells, and kinesthetic and organic images.
Descriptive writing seeks to evoke sensory experiences.
Here’s an example of a descriptive writing style, which uses imagery and other devices to reconstruct a particular sensory experience through language:
“The flower shop was here and it was my father’s domain, but it was also marvelously other, this place heavy with the drowsy scent of velvet-petaled roses and Provencal freesias in the middle of winter, the damp-earth spring fragrance of just-watered azaleas and cyclamen all mixed up with the headachey smell of bitter chocolate.” —Patricia Hempl, excerpt from The Florist’s Daughter
The writer employs a variety of images, scents, and comparisons to describe the sensual intensity of the flower shop. Details of the shop’s setting, smells, and the narrator’s relationship to the shop itself combine to make this an effective, descriptive passage.
Descriptive writing styles are commonly used in the following:
- Medical writing
Persuasive Writing Styles
Persuasive writing wants to change your mind. By employing logic, argumentation, and various rhetorical strategies, persuasive writers seek to convince you that their argument or interpretation prevails.
Persuasive writing wants to change your mind.
Here’s an example of a persuasive writing style, which uses rhetorical strategies to convince you about a certain worldview:
“Perhaps everybody has a garden of Eden, I don’t know; but they have scarcely seen their garden before they see the flaming sword. Then, perhaps, life only offers the choice of remembering the garden or forgetting it. Either, or: it takes strength to remember, it takes another kind of strength to forget, it takes a hero to do both. People who remember court madness through pain, the pain of the perpetual recurring death of their innocence; people who forget court another kind of madness, the madness of the denial of pain and the hatred of innocence; and the world is mostly divided between madmen who remember and madmen who forget. Heroes are rare.” —James Baldwin, excerpt from Giovanni’s Room
In addition to Baldwin’s lyrical prose style, key elements of this passage try to persuade the reader of the narrator’s worldview. “Garden of Eden” and “flaming sword” are strong visual metaphors, and setting up this worldview as a binary (people who remember or forget) encourages the reader to sort people into one of two categories. While persuasive writing styles usually come off as confident, the narrator’s admission that he doesn’t precisely know the answer to this conundrum helps humanize the conflict he’s debating. Certainly, this is a depressing worldview, and one which the reader is free to disagree with, but the strategies Baldwin takes in constructing this paragraph are certainly compelling.
Persuasive writing styles are commonly used in the following:
Expository Writing Styles
Expository writing wants to tell you about something as neutrally as possible. The goal is to be informative: by conveying something with as little bias and interpretation, expository writing styles stick to the facts. Do note that bias is universal: it is nearly impossible for any text to remove itself from bias completely.
Expository writing wants to tell something as neutrally as possible.
Here’s an example of an expository writing style, which conveys facts in a linear and digestible paragraph:
“On June 13, 1910, Arthur James Balfour lectured the House of Commons on ‘the problems with which we have to deal in Egypt.’ These, he said, ‘belong to a wholly different category’ than those ‘affecting the Isle of Wight or the West Riding of Yorkshire.’ He spoke with the authority of a long-time member of Parliament, former private secretary to Lord Salisbury, former chief secretary for Ireland, former secretary for Scotland, former prime minister, veteran of numerous overseas crises, achievements, and changes.” —Edward W. Said, excerpt from Orientalism
This opening passage of Orientalism sets the scene factually: we learn the time period, some geopolitical issues, and a main actor in all of these events. Yes, the passage does play up the significance of Arthur James Balfour and his many accolades, but this, too, is expository description, letting the reader know exactly who and what we are dealing with.
Expository writing styles are commonly used in the following:
Creative Writing Styles
Creative writing styles combine the previous four types: a creative writer can employ narrative, descriptive, persuasive, and expository strategies in their work. You may have noticed that creative genres, like fiction, nonfiction, and poetry, routinely show up under the categories of writing that employ the above four styles. This is because authors must employ a variety of strategies to tell effective stories.
Creative writers can employ narrative, descriptive, persuasive, and expository strategies in their work.
But, in addition to employing the previous four styles, creative writing also seeks to experiment and find new, artistic possibilities in language. Poetry is an obvious example, as the use of stanzas and line breaks affects how the language is read and interpreted. But there are also countless examples of experimentation in prose, from the use of stream of consciousness to the Oulipian n+7 .
Here’s an example:
“I turned out the light and went into my bedroom, out of the gasoline but I could still smell it. I stood at the window the curtains moved slow out of the darkness touching my face like someone breathing asleep, breathing slow into the darkness again, leaving the touch. After they had gone up stairs Mother lay back in her chair, the camphor handker- chief to her mouth. Father hadn’t moved he still sat beside her holding her hand the bellowing hammering away like no place for it in silence When I was little there was a picture in one of our books, a dark place into which a single weak ray of light came slanting upon two faces lifted out of the shadow. You know what I’d do if I were King? she never was a queen or a fairy she was always a king or a giant or a general I’d break that place open and drag them out and I’d whip them good It was torn out, jagged out. I was glad.” —Excerpt from The Sound and the Fury by William Faulkner
This is, of course, a highly literary and experimental piece of writing, but it demonstrates something distinct to creative writing styles. The italicized portions of text are streams of consciousness—moments where the reader has direct access to the unfiltered thoughts, images, and memories flowing through the character’s mind. Understanding these passages requires close attention to the text, as well as several re-reads. While creative writing styles can be far simpler than this, the point is that a creative writer takes great liberties to experiment with language, in ways distinct to creative writing, which seek to mine the wide varieties of the human experience.
Creative writing styles are commonly used in the following:
- Lyric essays
- Creative journalism
Elements of Writing Styles: The Author’s Location, Time Period, and Influences
Lastly, writers are undeniably influenced by their location, time period, and literary influences. For example, if you’ve ever read a poem or novel from Victorian Era England, you know that the Victorian writers (like the Brontës, Charles Dickens, or Percy Bysshe Shelley) often wrote in elaborate and flowery language. By modern standards, Victorian writing styles might seem overwrought; but, that style was influenced by the era’s appreciation for emotional intensity, as well as the tendency to pay writers per-word.
Writing Styles: Examples and Analyses
Let’s take a look at three writing styles examples. For each writer, we will examine how various stylistic strategies affect the overall mood and interpretation of the text, while also discussing that writer’s influences and likely intent. All examples come from published works of classic literature.
Ernest Hemingway’s Writing Style
Ernest Hemingway once wrote “A writer’s style should be direct and personal, his imagery rich and earthy, and his words simple and vigorous. The greatest writers have the gift of brilliant brevity, are hard workers, diligent scholars and competent stylists.” Hemingway’s writing style certainly lives up to this quote, as his words are often simple, direct, and unadorned.
Here’s an excerpt from his short story “ A Clean, Well-Lighted Place .”
It was very late and everyone had left the cafe except an old man who sat in the shadow the leaves of the tree made against the electric light. In the day time the street was dusty, but at night the dew settled the dust and the old man liked to sit late because he was deaf and now at night it was quiet and he felt the difference. The two waiters inside the cafe knew that the old man was a little drunk, and while he was a good client they knew that if he became too drunk he would leave without paying, so they kept watch on him.”Last week he tried to commit suicide,” one waiter said.
“Why?”
“He was in despair.”
“What about?”
“Nothing.”
“How do you know it was nothing?”
“He has plenty of money.”
Hemingway’s writing style seeks to dispense the precise amount of information necessary for the reader, without any garnishment. Notice the details he provides: the exact time does not matter, only that “it was very late.” Notice, also, a similar pattern with the dialogue. People generally don’t speak in such clipped sentences, but the characters of this story speak to give just enough context for the story’s themes.
Additionally, the visual details, such as the dew settling the dust and the shadows of leaves against the electric light, evoke the sensation of a space that’s quiet and comforting, if also a little bit eerie.
Notice, also, the general lengths of the sentences. The first paragraph is built on longer sentences and clauses, which inevitably juxtaposes sensory details (an old man in the shadow of leaves cast by an electric light.) The effect of these sentences is that time feels slower, as the reader’s focus is on the kaleidoscope of details paused in this one moment in a quiet café.
Finally, pay attention to the lack of pretensity in Hemingway’s word choice. While the story itself deals with complex themes, including the question of nihilism, the language itself is simple, direct, and accessible.
Hemingway got his start in writing as a journalist, then as a short story writer, both of which certainly influenced his economic style. He famously coined the “Iceberg Theory,” which describes writing that focuses on surface-level details without explicitly analyzing underlying themes, rather implying those themes for the reader to interpret. Hemingway was also greatly influenced by World Wars I and II, and his writing style may have been a reaction to these wars, eschewing the flowery language of pre-war literature for a hardened, masculine style.
Toni Morrison’s Writing Style
A master of voice and character, Toni Morrison’s writing style borrows heavily from vernacular, from history, and from her own unique relationship to analogies and metaphors. Morrison frequently plays with sentence lengths and imagery, but her writing never fails to be compelling, lyrical, and delicious to read.
Here’s an excerpt from Recitatif , her only published short story:
My mother danced all night and Roberta’s was sick. That’s why we were taken to St. Bonny’s. People want to put their arms around you when you tell them you were in a shelter, but it really wasn’t bad. No big long room with one hundred beds like Bellevue. There were four to a room, and when Roberta and me came, there was a shortage of state kids, so we were the only ones assigned to 406 and could go from bed to bed if we wanted to. And we wanted to, too. We changed beds every night and for the whole four months we were there we never picked one out as our own permanent bed.It didn’t start out that way. The minute I walked in and the Big Bozo introduced us, I got sick to my stomach. It was one thing to be taken out of your own bed early in the morning—it was something else to be stuck in a strange place with a girl from a whole other race. And Mary, that’s my mother, she was right. Every now and then she would stop dancing long enough to tell me something important and one of the things she said was that they never washed their hair and they smelled funny. Roberta sure did. Smell funny, I mean. So when the Big Bozo (nobody ever called her Mrs. Itkin, just like nobody ever said St. Bonaventure)—when she said, “Twyla, this is Roberta. Roberta, this is Twyla. Make each other welcome.” I said, “My mother won’t like you putting me in here.”
Both lyrical and conversational, Morrison’s style simply makes you want to read more. Pay attention to two things:
One, the lengths of these sentences. Morrison routinely switches from short sentences to longer ones, partially to emphasize important details in short sentences, and partially to keep the pace of the story engaging. The alternation of short and long sentences mirrors a conversational storytelling style.
Two, the childlike voice behind the narration. It is clear that the narrator is a child. Despite being directly stated, this fact is also obvious when certain elements of word choice are analyzed. Phrases like “smell funny” and “Big Bozo” clue the reader towards a speaker whose words and observations are that of a child.
One thing that’s absent from these paragraphs, but very much present in Morrison’s writing style, is the use of surprising comparisons (similes, metaphors, and analogies). This example comes later in “Recitatif”:
“I used to dream a lot and almost always the orchard was there. Two acres, four maybe, of these little apple trees. Hundreds of them. Empty and crooked like beggar women when I first came to St. Bonny’s but fat with flowers when I left.”
The simile “empty and crooked like beggar women” might be shocking to the reader, but it provides great insight into the personality of the narrator. This sentence is also ripe with foreshadowing , since the trees were “fat with flowers” when the narrator leaves St. Bonny’s.
Edgar Allan Poe’s Writing Style
One of America’s most influential writers, Edgar Allan Poe’s poetry and fiction forged new possibilities in the written word. Poe’s writing is often dark, gothic, and tinged with insanity, and his style reflects the problems that haunt his protagonists. Notice how psychosis influences Poe’s writing style in this excerpt from “ The Tell-Tale Heart :”
Poe adapts his style quite well to write a character who is clearly self-aggrandizing and obsessed with his own genius. The storytelling here has lots of repetition , such as “slowly—very, very slowly” and “cautiously-oh, so cautiously—cautiously” which makes the narrator sound in love with his own voice. And, it takes a while for the reader to understand what the narrator is doing, as his erratic behavior, like poking his head into the door for an hour, goes without a clear explanation.
Nonetheless, this writing is typical of Poe’s Gothic style. The use of words like “madman,” “midnight,” “vulture,” and “Evil Eye” give this story the grim moodiness characteristic of Poe’s writing. Additionally, the frequent use of em dashes and lengthy sentences propels the reader slowly, as we come to understand every minute detail that forms the totality of this character’s psychosis. This methodical, psychological writing style helps define Poe as a master of mystery and suspense.
Tips for Honing Your Own Author’s Writing Style
Writing styles develop with time, and there’s no singular thing any writer can do to hone their style. Rather, an attentiveness to language and a willingness to experiment are the best things you can do for yourself as you hone your author’s writing style. Nonetheless, here’s 7 pieces of advice for anyone who wants to write with style, flare, and confidence.
1. Creative Writing Styles: Experiment with Language and Syntax
Take risks in your writing. Be unconventional, and don’t always go for the expected word or phrase. Style doesn’t develop from playing it safe—it develops from making active decisions in the words you use to express your ideas.
What do we mean by taking risks? Here’s an example of a risky sentence, from poet Eduardo C. Corral: “Moss intensifies up the tree, like applause.”
This is a daring comparison: we don’t often think of moss “intensifying,” and so that verb already seems strange and risky. But then the moss itself is compared to applause, so now the visual cue of intensifying moss is being compared to intensifying sound. The product of this simile is that we see moss blooming and expanding across the tree, which makes this an effective and stylish sentence—but there’s a level of risk, faith, and skill involved in making this simile work .
Taking risks allows you to see what works and what doesn’t in your writing. So make bold comparisons! End your paragraphs with em-dashes! Try using four different languages in a single sentence!
Just be sure to review your work after and assess what does and doesn’t work for the reader. And, when you’re not sure what to do, try doing the complete opposite of what seems intuitive. You might find a short sentence works better than a long one, for example.
2. Creative Writing Styles: Experiment with Writing Forms
Creative writing styles often adapt to the form of the writing itself. For example, genre writing styles vary from genre to genre. You wouldn’t expect a writer of hard-boiled noir to have the same terse, simplistic style when writing romance fiction (although I would love to read that).
As you hone your writing style, experiment reading and writing in different forms. Pay attention to how the form demands you to make different stylistic decisions. The words you choose in a love sonnet will be different from the words you choose in a flash essay about your childhood. And, certainly, your sentence lengths will differ when you’re writing literary fiction versus speculative fiction .
Getting into the habit of making these stylistic decisions, and paying attention to those decisions, will help you create a mental framework for the ways you approach writing. Such is the nature of style development.
3. Creative Writing Styles: Consider Character
Character development is an essential part of fiction writing, and it will naturally affect the style you use to write. If you’re writing in first person or third person limited, then your protagonist’s personality will affect everything, because their worldview tinges the way you tell their story. Key observational details and thought processes from main characters naturally bleed into the style of the writing itself.
You can see this in action in the novels of F. Scott Fitzgerald. His second novel, The Beautiful and Damned , is written from the third person limited point of view of Anthony Patch, an unambitious libertine whose personality is defined by wry cynicism and a rigid belief in the purposelessness of life. These personality traits often affect the storytelling, as the reader sees the world through Anthony’s eyes, and thus trudges through a lot of Anthony’s ironic commentary and disdain for others.
Fitzgerald’s next novel, The Great Gatsby , is completely different, both tonally and stylistically. Written from the first person point of view of Nick Carraway, an optimistic bond salesman who wants to immerse himself in the high society of New York’s nouveau riche. Much of the style is poetic and introspective, honing in on the creative chaos of the Jazz Age and the tragedy of the American Dream.
For your own writing, alter your style to reflect the traits of your characters. Style reflects personality, and the person narrating your fiction will certainly want to tell their story in their own way.
4. Creative Writing Styles: Omit Needless Words
While style can take many forms, one thing that all good author’s writing styles have in common is an economy of language. In other words, no word in good writing is excessive or unnecessary. To sharpen your own style, you must omit needless words.
What does that look like? There are two ways to omit needless words: striking out redundancies, and rewriting phrases.
Here’s two examples. First, let’s look at redundancy. A redundancy is when you communicate something multiple times without refining the meaning of your words. Here’s a redundant sentence:
“The girl vaulted over the large gray boulder.”
Nothing is explicitly wrong with this sentence, but several words are giving repeat information. You don’t need the word “over,” because to vault means to jump over something. And, you don’t need the word “large,” because a boulder is, by definition, large. Finally, most rocks are gray, and the word “gray” isn’t offering much useful detail.
A much cleaner sentence would simply be “the girl vaulted the boulder.”
Another example is to rewrite phrases. If you don’t think about your words, it’s easy to communicate something in 10 words when 2 will do. Here’s another example sentence:
“She worked many long hours in order to secure a trade deal with the company.”
God, doesn’t that just read like a corporate memo? It’s passively worded and nondescript. Isolate any phrase in this sentence, and it can be truncated into something much more straightforward. Be sure to avoid phrases like “in order to”—simply “to” will always suffice.
Here’s a cleaner sentence: “She hustled to secure the Nike trade deal.”
Lastly, some categories of words are better than others. Nouns and verbs are necessary for understanding the action of a sentence. Adjectives should be used sparingly, and only when that description is necessary for the reader. Adverbs, which modify verbs, should only be used when there isn’t a sharper verb. For example, “breathing heavily” is much better written as “panting.”
For more advice, check out our article on how to omit needless words .
5. Creative Writing Styles: Read Like a Writer
How do published writers write so well? What did they do to craft such artful sentences, effective plots, or in-depth characters? While you can certainly learn these tricks by taking a writing class , you can also learn them by reading like a writer.
Reading like a writer means paying attention to the construction of a piece of literature and thinking about why that writing works. We did a little bit of this when we examined the above writing styles examples. By examining the elements of writing styles—word choice, sentence structure, character and voice, etc.—we paid attention to what makes each excerpt an effective piece of writing.
Employ those same strategies in the work you read. If there’s an author you like or whose style you admire, pay attention to what makes that style effective. And don’t be afraid to emulate that style in your own work: writers often borrow from each other’s styles and strategies to hone their own voice.
6. Creative Writing Styles: Study Poetry
The writing styles tips in this article primarily pertain to prose writers. But, whether you’re writing poetry, prose, or some secret third thing, reading poetry is essential to honing style.
Poets are masters of language. They know how to build tension, pacing, and rhythm in their sentences. They know how to make that tension correspond with what they’re writing about. They manipulate vowel sounds, constants, tools like rhyme and meter, and a whole other host of poetic devices to move their readers.
Writing poetry is its own separate challenge. Prose writers don’t need to write poetry to master their writing styles. But they absolutely should study poetry. What makes language beautiful? What makes a poem concise? How does the flow of a sentence accentuate its meaning? Asking these questions and listening to the poets will help you experiment in your own pages.
7. Creative Writing Styles: Write Every Day
The key to honing your style is to write every day. A diligent writing practice will train your brain to think about language and make continuous stylistic choices in your work. Even if you can only manage 10 minutes a day on a writing project, or even if you just keep a writing journal, the simple practice of putting thoughts to words and words to pages will naturally sharpen the personality you put into your writing.
Hone Your Own Writing Style at Writers.com
One last piece of advice on writing styles is to read The Elements of Style by Strunk and White. You can find a free copy of it online here . Most of the advice in this book has remained true in the many decades since its publication, and while rules are certainly made to be broken, you should understand the rules first before breaking them.
Want clear, direct feedback on your writing styles and the other elements of your work? Take a look at any of the upcoming creative writing classes at Writers.com! Our instructors are masters of the craft and know how to sharpen your words so that they zing across the page.
Sean Glatch
[…] Writing Styles: What is Style in Writing? […]
very informative and interesting; very useful for all readers.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
A Look Into Creative Writing | Oxford Summer Courses
Exploring the magic of creative writing with oxford summer courses.
Subscribe to our newsletter to receive helpful tips, tutorials, and thought-provoking articles that can inform and inspire your professional development. Sign up here .
Defining Creative Writing
Creative writing , as taught at Oxford Summer Courses, is the process of crafting original and imaginative works of literature, poetry, prose, or scripts. It transcends conventional writing, encouraging individuals to explore language, structure, and narrative. Whether it's a heartfelt poem, a captivating short story, or a thought-provoking novel, creative writing allows us to communicate our unique perspectives and experiences with the world.
The Magic of Imagination
Creative Writing is a catalyst that sparks our creativity and empowers us to breathe life into our ideas on the page. With Oxford Summer Courses, aspiring writers aged 16-24 can embark on an extraordinary journey of creative expression and growth. Immerse yourself in the captivating realms of Oxford and Cambridge as you explore our inspiring creative writing programs. Teleport readers to distant lands, realms of fantasy and creation, introduce them to captivating characters, and craft new worlds through the transformative art of storytelling. Discover more about our creative writing course here . Unleash your imagination and unlock the writer within.
What Are the Different Types of Creative Writing?
Creative Writing comes in many forms, encompassing a range of genres and styles. There are lots of different types of Creative Writing, which can be categorised as fiction or non-fiction. Some of the most popular being:
- Biographies
- Fiction: novels, novellas, short stories, etc.
- Poetry and Spoken word
- Playwriting/Scriptwriting
- Personal essays
At Oxford Summer Courses, students have the opportunity to delve into these various types of Creative Writing during the Summer School.
The Benefits of Creative Writing with Oxford Summer Courses
Engaging in Creative Writing with Oxford Summer Courses offers numerous benefits beyond self-expression. By joining our dedicated Creative Writing summer school programme, you would:
- Foster self-discovery and gain a deeper understanding of your thoughts, emotions, and personal experiences.
- Improve your communication skills, honing your ability to express yourself effectively and engage readers through refined language and storytelling abilities.
- Enhance empathy by exploring diverse perspectives and stepping into the shoes of different characters, broadening your understanding of the world around you.
- Gain new skills for further education or work, expanding your repertoire of writing techniques and abilities to enhance your academic or professional pursuits.
- Nurture your creativity, encouraging you to think outside the box, embrace unconventional ideas, and challenge the status quo, fostering a life-long mindset of innovation and originality.
Embracing the Journey
To embark on a journey of creative writing, embrace curiosity, take risks, and surrender to the flow of imagination. Write regularly, read widely, embrace feedback from tutors and peers at Oxford Summer Courses. Begin to experiment with styles and genres, and stay persistent in your course of action. The path of creative writing requires dedication, practice, and an open mind. Join us as we provide tips to help you start your creative writing journey and unleash your full creative potential under the guidance of industry professionals.
Creative Writing is a remarkable voyage that invites us to unleash our imagination, share our stories, and inspire others. It offers countless personal and professional benefits, nurturing self-expression, empathy, and creativity. So, grab a pen, open your mind, and embark on this enchanting journey of creative writing with Oxford Summer Courses. Let your words paint a vivid tapestry that captivates hearts and minds under the guidance of experienced tutors from Oxford and Cambridge. Join us as we explore the magic of creative writing and discover the transformative power it holds within through the renowned Oxford Summer Courses summer school.
Ready to study Creative Writing? Apply now to Oxford Summer Courses and join a community of motivated learners from around the world. Apply here .
Share this article
Discover the enchantment of creative writing with Oxford Summer Courses. Unleash your imagination, explore different genres, and enhance your communication skills. Nurture self-expression, empathy, and creativity while gaining valuable writing techniques.
Get Our Newsletter
Oxford Summer Courses LTD
18 Beaumont Street, Oxford, OX1 2NA, United Kingdom
+44 01865 818403

Juniors 9-12
Oxford 13-15
Oxford 16-17
Oxford 18-24
Cambridge 13-15
Cambridge 16-17
Advanced Cambridge 18-24
GDPR Notice
Privacy Policy
Terms and Conditions
Sign up to our newsletter
Oxford summer courses is an organisation which contracts with the colleges of the universities of oxford, cambridge and london for the use of facilities, but which has no formal connection with the universities of oxford, cambridge and london., oxford summer courses © 2024, oxford summer courses is a company registered in england and wales with company number 08011543.

What is Creative Writing and Its Types?

Expressing creativity through writing is an art that can be mastered. Are you someone who is looking to hone their creative writing skills? Unlu brings to you online creative writing classes by Ruskin Bond which is a sure-fire way to strengthen your grip on the basics. Now understand the essentials by diving deep into the informative ways of learning and enhancing your writing skills.
Along with this, the learner can expect to get an in-depth understanding of what is creative writing. The many different types of creative writing, like descriptive, expository, or persuasive, can be practiced and improved throughout this course. The classes are curated with a special focus on including the many different ways, types and styles of writing. Once enrolled, the learner can kick start their career in creative writing or even as a freelancer by offering creative content.
So let’s look at the multiple aspects of creative writing and delve deeper into it.
What is Creative Writing?
The term “creative” can be understood in a variety of ways. The following are a few examples of descriptions: “the potential to construct”, “explorative”, “constructive and innovative”, “exemplified by articulation and individuality” are all terms used to describe people who have the ability to create.
Story writing, in which the author creates situations, scenarios, and characters, and often even a setting, is sometimes known as creative writing.
The aim of creative writing is not to educate but to entertain. Its aim is to provoke a reaction by stirring emotions.

Types of Creative Writing
If you remain focused on your goal, whether you are writing essays, business materials, novels, posts, emails, or even just notes in your journal, your writing would be at its finest.
Mentioned below are the 4 different types of creative writing:
1. Expository
Since the term expository includes the word reveal, it is a good descriptor for this style of writing as it reveals, or puts out information.
It is definitely the most typical type of writing you will come across in your daily life. This type of writing can be demonstrated in newspapers, articles, essays, and journals.
A subject would be presented and set out in a clear order in an expository piece, with little regard to the author’s personal opinions. There are five types of expository essays:
- How-to: This is also known as the process essay. This type of essay answers the question, “How-to?” and explains the process to the readers.
- Problem/solution: In this essay, you identify an existing problem or an issue and suggest solutions for the problem.
- Comparison: This type of writing involves comparing two subjects and explaining their similarities and differences.
- Cause and effect: Involves writing about why an issue took place and what are the results of that issue.
2. Descriptive
The aim of descriptive writing is to help the reader imagine a character, an experience, a place, or all of these things together in great detail.
Authors use all five senses to describe the environment. Expository writing limits the writer’s creative expression, while descriptive writing does not. The types of descriptive writing are:
- B iography: A biography is a detailed work about a person. It features facts and information about that person’s life.
- T ravel writing: This writing style enables the author to use a descriptive writing style competently.
- N ature writing: Nature writing describes the beauty of nature. For instance, John Keats’ poems.
3. Persuasive
The aim of persuasive writing, often known as argumentation, is to persuade the reader to adopt the author’s viewpoint. In a typical piece, the writer may share personal views and provide reasons to persuade the reader to agree with them.
While writing a persuasive piece, the following appeals are preferred:
- Ethos – Be credible: Claims are made more believable by appealing to credibility. By writing clearly, the writer builds on their ethos.
- Lagos – Be logical: A writer persuades by appealing to logic. This type of writing requires reputable evidence. Quote by a reliable source, for instance.
- P athos – Appeal to emotions: A writer persuades by appealing to emotions.
Being logical, credible, and appealing to a writer’s emotions becomes imperative while writing persuasively.
4. Narrative
The aim of narrative writing is to showcase a plot, whether it is a true story or an imaginary one. Characters will appear in plot pieces, and the reader will experience what happens to them through the story. Dialogue is often used in narrative prose. The four common types of narrative writing are:
- Linear narrative: A linear narrative depicts the events in the order that they happened.
- Non-linear narrative: A non-linear narrative delivers the events of the story without following the order. It uses flashbacks to change the chronology of a story.
- Quest narrative: A quest narrative is a story where the protagonist works relentlessly to achieve an objective.
- Viewpoint narrative: In viewpoint narrative writing, the subjective perspective of the narrator filters the sensory details.
What are the Elements of Creative Writing?
The process of writing creatively involves many stages and parts that make the writing whole. These elements can make or break the writing and form an essential aspect. Here, we will learn about some of these elements as they make up a huge part of the learning process.
Some of the major elements of writing in a creative manner are as follows-
- Plot : Every piece of writing requires an interesting plot. It acts as the spine of the writing and provides a structure while connecting all the parts of the writing. Having a good plot is essential to the writing’s acceptance and success. The writer should always aim to come up with something unique so as to keep the readers connected and interested.
- Characters : The characters of any piece of writing depend on the plot. It is of utmost importance that the writer expresses the character’s development throughout the writing. This can be achieved by showcasing the changes throughout using vivid details. This is another way of attracting the readers’ attention and keeping them stuck to the piece of writing.
- Theme : For a writing that is creative, an underlying theme or concept is the very basic requirement. The writer should base the plot on a theme that is either unique or discuss a common theme from a different perspective. The intention can be to convey a message to the masses, express one’s own view, or simply enhance the readers’ range of imagination.
- Descriptions : It is important to note that the descriptions can be expressed in a visual manner that would assist in understanding. It is always preferable to describe a major event using visuals as it pulls the audience’s interest and keeps them intrigued.
- Point of view : A writer can express their plot from the first, second, or third person’s viewpoint. This is not fixed and can be chosen by the writer. The use of an appropriate point of view allows the writer to touch on significant points in the storyline and also allows room for the readers’ interpretation to expand.
- Language : Another point of the main focus is the use of language to write creatively. This can involve the usage of metaphors, phrases, and figures of speech. Using such an approach can create a better appeal and makes room for imagination and interpretation.
Creative Writing Tips and Techniques
Keeping in mind some basic techniques can help one in avoiding writer’s block and eases out the entire process of writing while being creative. These techniques can be used by anyone who wishes to stand separate from the crowd and take their writing several notches up. Below are some of these amazing techniques and tips that are sure to enhance the overall writing experience.
- Reading a variety of books
Once a writer gets into the habit of reading on a regular basis, it expands their point of view and fills up their mind with many different approaches, styles, and ways of expressing any situation at hand. This can be achieved by going through different genres, writing styles, etc. Look out for the experts in their genres and understand their work.
- Developing a plot
It is best to draft a plot for the piece of content that is being written. The various developments and stages can be noted down for reference while including twists and turns in the story. This can also assist in establishing a relationship between characters and providing a structure to the work.
- Use literary devices
Such devices can prove to be essential in adding details and hidden meanings ad can be used in the different forms of creative writing. Simile, alliteration, and metaphors turn out to be vital and can be used by the writer in different contexts and ways. This technique can engage the readers and pique their interest.
- Adding dialogues
This is such an important aspect of writing creatively as it adds an emotional touch and holds the power of connecting characters. By including dialogues, the writer can work towards developing the characters in the story in an engrossing way.
How to Start Creative Writing?
In order to write creatively, one needs to start doing the basics and catching up on the must-do things. The process of improvement and expertise requires effort, patience, and time and can be achieved with determination. In this section, all the major aspects have been compiled and can be put into practice to achieve perfection.
- A writer can actively engage in getting in touch with the works of established, renowned writers. This will help in getting insights along with many different ideas and knowledge.
- A writer must jot down all the creative ideas, plots, and approaches that may come to find. Maintaining a journal for the same can turn out to be fruitful in the long run.
- Another useful thing is to write without making any edits. This allows the ideas to flow and makes for a smooth experience of writing. Uninterrupted work will make longer durations of writing easier and will also provide a space to open up with thoughts and let creativity come out.
- A writer can focus on ‘What if?’ situations and unleash their creative side. This activity lets imagination expand and allows the writer to come up with new and distinguished ideas.
Can Creative Writing be Taught?
The art of creative writing does not have to sprout out naturally. It can be taught in classes and hones over time with diligent practice. The process of learning can be aided by enrolling on courses or classes. Anyone who aspires to work on their writing skills can learn it and develop their work’s quality over time. Taking online creative writing classes offers a structured learning path for the writers. It familiarizes them with the in and out of the process and acquaints them with many budding writers working alongside them.
These classes are not limited to handbooks or readings but also include interactive sessions and workshops that allow the writers to engage and grow exponentially. The learnings of these classes can be directly implemented and used in the work and do not require any additional chores. With everything available in one place, the writers can focus and utilize the resources to the best extent.
What are the Forms of Creative Writing?
Now that you know the meaning of creative writing, let us look at the different forms of creative writing. As discussed above, creative writing is explorative and innovative and therefore has several distinct forms.
1. Poetry/Poems
This category of creative writing allows the maximum space for imagination, creative thinking, and exclusive ideas. The poems can be experimented with and are free of any rules or structures. Various styles like Haiku, Ballad, Sonnets and free-verse poems form a part of the category. A few common types of poetry are:
- Haiku: This type of poetry focuses on the beauty and simplicity of nature. The poems are usually three-line stanzas.
- Free verse poems: This is an open form of poetry and hence, does not contain any pattern, rhyme, or structure.
- Ballad: A ballad is a poem that tells a story based on a legend or a folk tale.
- Sonnets: A sonnet is a one-stanza, 14-line poem, written in iambic pentameter.
Novels are certainly the most popular form of creative writing. They allow readers to escape from reality and dip in and out of the new worlds created by the novelists. There are different types of novels. For instance, mysteries, romance, thrillers, science fiction, fantasy, and historical fiction.
3. Short stories
Also known as short fiction, short stories are a form of creative writing that is shorter than a novel and contains just a few characters. They usually fall between 3,000 to 6,000 words and hence, can be read in a single sitting. There are five elements of a short story:
- Character: A person or an animal taking part in an action of short fiction.
- Setting: The time and place when the action is taking place in the story.
- Plot: The foundation of a story with a series of events and character actions that relate to the central conflict.
- Conflict: A struggle between opposing forces is called a conflict in a story.
- Theme: The main idea or belief of a story.
Essay writing requires creative thinking therefore, they are a form of creative writing. Essays are usually associated with academic writing. However, there are different types of essays such as personal essays, descriptive essays, argumentative essays, and narrative essays.
5. Journals
Almost everything you write that does not follow a specific structure is creative writing, including your journals. A journal is a written record of your thoughts and experiences. It preserves your memories and makes you remember things crystal clear.
Understanding your purpose behind creative writing

Expository prose is an appropriate way to present facts. Textbooks, journalism (except opinion and editorial articles), corporate writing, professional writing, essays, and directions all contain facts.
Rich representation in descriptive writing evokes visualisation. You can employ it in fiction, verse, journal publishing and advertisement.
Persuasive writing attempts to persuade the reader to agree with the author’s viewpoint. It finds utility in advertisements as well as opinion and editorial pieces, ratings and job applications
A story is told in narrative prose. Fiction, poems, biographies, and anecdotes all have some degree of narration.
Ways to be More Creative with your Writing
Learn from the best, but there is no need to emulate them. Additionally, it is helpful to read well-known authors as examples of high-quality writing.
Seek out the genre’s highlights, depending on the writing style. If you want to write young adult fiction, look up to classics like J.K. Rowling’s Harry Potter series, R.L. Stine’s Goosebumps world, or Judy Blume’s touching coming-of-age books.
Furthermore, Research the works of Isaac Asimov and Neil Gaiman if you choose to write science fiction. at the same time, do not mistake the voices of these writers for your own. Use your favourite books as a starting point. To be genuinely artistic, you must develop ideas, styles, and a point of view that are distinct from others.
To brainstorm, use the snowflake technique. The snowflake process, developed by author and writing coach Randy Ingermanson, is a method for writing a novel from the ground up by beginning with a simple plot summary and layering in additional components.
It is suitable for a wide range of creative writing projects. To initiate the snowflake process, conceive a big-picture plot concept and write a one-sentence description for it
Moreover, you can Try freewriting for a while. It is the art of writing without a predetermined format, such as outlines, cards, notes, or editorial supervision. In freewriting, the writer follows their own mental instincts, causing ideas and creativity to come to them spontaneously.
Allow the words on the screen to be inspired by the stream of consciousness.
Online Writing Course by Ruskin Bond
Learn writing online with Ruskin Bond, subscribe now!
Related Posts

Relive Diwali Contest Winners Announced: Unwrapping Memories and Spreading Joy

How to Write an ‘Attractive’ Story for Children ?

How to Research for Your Story? Step by Step Guide

How to Write Dialogues for Your Characters?

How to write a Synopsis for a Novel ?

How to Write the Perfect ‘Premise’ for a Story?
Write a comment cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
© 2019 ThemeSphere. Designed by ThemeSphere .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Types of Creative Writing. Free writing: Open a notebook or an electronic document and just start writing. Allow strange words and images to find their way to the page. Anything goes! Also called stream-of-consciousness writing, free writing is the pinnacle of creative writing. Journals: A journal is any written log.
A lot falls under the term 'creative writing': poetry, short fiction, plays, novels, personal essays, and songs, to name just a few. By virtue of the creativity that characterizes it, creative writing is an extremely versatile art. So instead of defining what creative writing is, it may be easier to understand what it does by looking at ...
Types of Creative Writing. Examples of creative writing can be found pretty much everywhere. Some forms that you're probably familiar with and already enjoy include: • Fiction (of every genre, from sci-fi to historical dramas to romances) • Film and television scripts. • Songs. • Poetry.
Creative writing is an art form that transcends traditional literature boundaries. It includes professional, journalistic, academic, and technical writing. This type of writing emphasizes narrative craft, character development, and literary tropes. It also explores poetry and poetics traditions.
Literary techniques you develop with writing plays and screenplays can include satire, motif, dramatic irony, allusion, and diction. 5. Personal essays. Focusing on the author's life and experiences, a personal essay is a form of creative non-fiction that almost acts as an autobiography.
Creative Writing is a diverse and exciting art that demands Writers to look into their imagination and express their thoughts in unique ways. From short stories to poetry, different Types of Creative Writing which cater to different styles and preferences. In this blog, we will delve into the different Types of Creative Writing, offering insights and examples to help you navigate the world of ...
Type 2: Journals and Diaries. A journal is a written account of an author's experiences, activities, and feelings. A diary is an example of a journal, in which an author documents his/her life frequently. Journals and diaries can be considered creative writing, particularly if they offer more than just a log of events.
Some types of creative writing, like poems and songs, have limited space, and therefore tend to be more mysterious and less narrative. Types like novels and plays have room to explore character ...
Creative writing is any writing that goes outside the bounds of normal professional, journalistic, academic, or technical forms of literature, typically identified by an emphasis on narrative craft, character development, and the use of literary tropes or with various traditions of poetry and poetics.Due to the looseness of the definition, it is possible for writing such as feature stories to ...
4. Short Fiction. Short fiction offers more of a "story" than a vignette. It includes short stories and even modern fan fiction. Writing a short story is a great way to learn about how fiction is structured, including plot, characters, conflict, and setting. You can even make money writing short fiction.
Let's go through the 9 examples of creative writing and some of their famous pieces penned under each type. 1. Novels. There is hardly a 21st-century teenager who hasn't laid their hands on a novel or two. A novel is one of the most well-loved examples of creative writing.
Both fictional and non-fictional works fall into this category of different types of creative writing. This list of different types of creative writing also includes novels, biographies, short stories, and poems. In the academic setting, creative writing is typically separated into fiction and poetry classes, with a focus on writing in an ...
Creative writing is a written art form that uses the imagination to tell stories and compose essays, poetry, screenplays, novels, lyrics, and more. It can be defined in opposition to the dry and factual types of writing found in academic, technical, or journalistic texts.
6. Show don't tell. To let readers experience your story, show don't tell. Showing means using sensory details and describing actions to direct a mental movie in your reader's mind. Get inspired by these examples of "show, don't tell" …. Show don't tell examples >>. 7. Repetition in writing.
This creative writing type gained popularity during the 19th century in literary magazines, and many such magazines still carry short stories. Narrative Nonfiction. Also known as Creative Nonfiction, this form displays techniques and literary styles such as story and tone to convey emotion in nonfiction narratives. A common example is a ...
5. Creative writing style. Creative writing's purpose is to entertain, provoke thought, express feelings, and stretch the imagination of the reader. It's a way for writers to express themselves creatively by talking about all sorts of human experiences, like wild adventures, deep thoughts, or trying out new ideas.
Creative Writing Styles. Creative writing styles combine the previous four types: a creative writer can employ narrative, descriptive, persuasive, and expository strategies in their work. You may have noticed that creative genres, like fiction, nonfiction, and poetry, routinely show up under the categories of writing that employ the above four ...
5. Read, read, read. It's a lot harder to get the hang of creative writing if you don't have any references from which to draw. Notable writers throughout history have penned excellent examples of well-written creative work that should be required reading for any budding creative writer.
Discover more about our creative writing course here. Unleash your imagination and unlock the writer within. What Are the Different Types of Creative Writing? Creative Writing comes in many forms, encompassing a range of genres and styles. There are lots of different types of Creative Writing, which can be categorised as fiction or non-fiction.
The many different types of creative writing, like descriptive, expository, or persuasive, can be practiced and improved throughout this course. The classes are curated with a special focus on including the many different ways, types and styles of writing. Once enrolled, the learner can kick start their career in creative writing or even as a ...
15 hours. Best University-level Creative Writing Course (Wesleyan University) 5-6 hours. Best Course to Find Your Voice (Neil Gaiman) 4-5 hours. Best Practical Writing Course With Support (Trace Crawford) 12 hours. Best Course to Overcome Writer's Block: 10-Day Journaling Challenge (Emily Gould) 1-2 hours.