
Literature Review Basics
- What is a Literature Review?
- Synthesizing Research
- Using Research & Synthesis Tables
- Additional Resources

About the Research and Synthesis Tables
Research Tables and Synthesis Tables are useful tools for organizing and analyzing your research as you assemble your literature review. They represent two different parts of the review process: assembling relevant information and synthesizing it. Use a Research table to compile the main info you need about the items you find in your research -- it's a great thing to have on hand as you take notes on what you read! Then, once you've assembled your research, use the Synthesis table to start charting the similarities/differences and major themes among your collected items.
We've included an Excel file with templates for you to use below; the examples pictured on this page are snapshots from that file.
- Research and Synthesis Table Templates This Excel workbook includes simple templates for creating research tables and synthesis tables. Feel free to download and use!
Using the Research Table

This is an example of a research table, in which you provide a basic description of the most important features of the studies, articles, and other items you discover in your research. The table identifies each item according to its author/date of publication, its purpose or thesis, what type of work it is (systematic review, clinical trial, etc.), the level of evidence it represents (which tells you a lot about its impact on the field of study), and its major findings. Your job, when you assemble this information, is to develop a snapshot of what the research shows about the topic of your research question and assess its value (both for the purpose of your work and for general knowledge in the field).
Think of your work on the research table as the foundational step for your analysis of the literature, in which you assemble the information you'll be analyzing and lay the groundwork for thinking about what it means and how it can be used.
Using the Synthesis Table

This is an example of a synthesis table or synthesis matrix , in which you organize and analyze your research by listing each source and indicating whether a given finding or result occurred in a particular study or article ( each row lists an individual source, and each finding has its own column, in which X = yes, blank = no). You can also add or alter the columns to look for shared study populations, sort by level of evidence or source type, etc. The key here is to use the table to provide a simple representation of what the research has found (or not found, as the case may be). Think of a synthesis table as a tool for making comparisons, identifying trends, and locating gaps in the literature.
How do I know which findings to use, or how many to include? Your research question tells you which findings are of interest in your research, so work from your research question to decide what needs to go in each Finding header, and how many findings are necessary. The number is up to you; again, you can alter this table by adding or deleting columns to match what you're actually looking for in your analysis. You should also, of course, be guided by what's actually present in the material your research turns up!
- << Previous: Synthesizing Research
- Next: Additional Resources >>
- Last Updated: Sep 26, 2023 12:06 PM
- URL: https://usi.libguides.com/literature-review-basics
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Critical Reviews
How to Write an Article Review (With Examples)
Last Updated: April 24, 2024 Fact Checked
Preparing to Write Your Review
Writing the article review, sample article reviews, expert q&a.
This article was co-authored by Jake Adams . Jake Adams is an academic tutor and the owner of Simplifi EDU, a Santa Monica, California based online tutoring business offering learning resources and online tutors for academic subjects K-College, SAT & ACT prep, and college admissions applications. With over 14 years of professional tutoring experience, Jake is dedicated to providing his clients the very best online tutoring experience and access to a network of excellent undergraduate and graduate-level tutors from top colleges all over the nation. Jake holds a BS in International Business and Marketing from Pepperdine University. There are 13 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 3,094,247 times.
An article review is both a summary and an evaluation of another writer's article. Teachers often assign article reviews to introduce students to the work of experts in the field. Experts also are often asked to review the work of other professionals. Understanding the main points and arguments of the article is essential for an accurate summation. Logical evaluation of the article's main theme, supporting arguments, and implications for further research is an important element of a review . Here are a few guidelines for writing an article review.
Education specialist Alexander Peterman recommends: "In the case of a review, your objective should be to reflect on the effectiveness of what has already been written, rather than writing to inform your audience about a subject."
Article Review 101
- Read the article very closely, and then take time to reflect on your evaluation. Consider whether the article effectively achieves what it set out to.
- Write out a full article review by completing your intro, summary, evaluation, and conclusion. Don't forget to add a title, too!
- Proofread your review for mistakes (like grammar and usage), while also cutting down on needless information.

- Article reviews present more than just an opinion. You will engage with the text to create a response to the scholarly writer's ideas. You will respond to and use ideas, theories, and research from your studies. Your critique of the article will be based on proof and your own thoughtful reasoning.
- An article review only responds to the author's research. It typically does not provide any new research. However, if you are correcting misleading or otherwise incorrect points, some new data may be presented.
- An article review both summarizes and evaluates the article.

- Summarize the article. Focus on the important points, claims, and information.
- Discuss the positive aspects of the article. Think about what the author does well, good points she makes, and insightful observations.
- Identify contradictions, gaps, and inconsistencies in the text. Determine if there is enough data or research included to support the author's claims. Find any unanswered questions left in the article.

- Make note of words or issues you don't understand and questions you have.
- Look up terms or concepts you are unfamiliar with, so you can fully understand the article. Read about concepts in-depth to make sure you understand their full context.

- Pay careful attention to the meaning of the article. Make sure you fully understand the article. The only way to write a good article review is to understand the article.

- With either method, make an outline of the main points made in the article and the supporting research or arguments. It is strictly a restatement of the main points of the article and does not include your opinions.
- After putting the article in your own words, decide which parts of the article you want to discuss in your review. You can focus on the theoretical approach, the content, the presentation or interpretation of evidence, or the style. You will always discuss the main issues of the article, but you can sometimes also focus on certain aspects. This comes in handy if you want to focus the review towards the content of a course.
- Review the summary outline to eliminate unnecessary items. Erase or cross out the less important arguments or supplemental information. Your revised summary can serve as the basis for the summary you provide at the beginning of your review.

- What does the article set out to do?
- What is the theoretical framework or assumptions?
- Are the central concepts clearly defined?
- How adequate is the evidence?
- How does the article fit into the literature and field?
- Does it advance the knowledge of the subject?
- How clear is the author's writing? Don't: include superficial opinions or your personal reaction. Do: pay attention to your biases, so you can overcome them.

- For example, in MLA , a citation may look like: Duvall, John N. "The (Super)Marketplace of Images: Television as Unmediated Mediation in DeLillo's White Noise ." Arizona Quarterly 50.3 (1994): 127-53. Print. [9] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source

- For example: The article, "Condom use will increase the spread of AIDS," was written by Anthony Zimmerman, a Catholic priest.

- Your introduction should only be 10-25% of your review.
- End the introduction with your thesis. Your thesis should address the above issues. For example: Although the author has some good points, his article is biased and contains some misinterpretation of data from others’ analysis of the effectiveness of the condom.

- Use direct quotes from the author sparingly.
- Review the summary you have written. Read over your summary many times to ensure that your words are an accurate description of the author's article.

- Support your critique with evidence from the article or other texts.
- The summary portion is very important for your critique. You must make the author's argument clear in the summary section for your evaluation to make sense.
- Remember, this is not where you say if you liked the article or not. You are assessing the significance and relevance of the article.
- Use a topic sentence and supportive arguments for each opinion. For example, you might address a particular strength in the first sentence of the opinion section, followed by several sentences elaborating on the significance of the point.

- This should only be about 10% of your overall essay.
- For example: This critical review has evaluated the article "Condom use will increase the spread of AIDS" by Anthony Zimmerman. The arguments in the article show the presence of bias, prejudice, argumentative writing without supporting details, and misinformation. These points weaken the author’s arguments and reduce his credibility.

- Make sure you have identified and discussed the 3-4 key issues in the article.

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://libguides.cmich.edu/writinghelp/articlereview
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4548566/
- ↑ Jake Adams. Academic Tutor & Test Prep Specialist. Expert Interview. 24 July 2020.
- ↑ https://guides.library.queensu.ca/introduction-research/writing/critical
- ↑ https://www.iup.edu/writingcenter/writing-resources/organization-and-structure/creating-an-outline.html
- ↑ https://writing.umn.edu/sws/assets/pdf/quicktips/titles.pdf
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/research_and_citation/mla_style/mla_formatting_and_style_guide/mla_works_cited_periodicals.html
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4548565/
- ↑ https://writingcenter.uconn.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/593/2014/06/How_to_Summarize_a_Research_Article1.pdf
- ↑ https://www.uis.edu/learning-hub/writing-resources/handouts/learning-hub/how-to-review-a-journal-article
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/editing-and-proofreading/
About This Article

If you have to write an article review, read through the original article closely, taking notes and highlighting important sections as you read. Next, rewrite the article in your own words, either in a long paragraph or as an outline. Open your article review by citing the article, then write an introduction which states the article’s thesis. Next, summarize the article, followed by your opinion about whether the article was clear, thorough, and useful. Finish with a paragraph that summarizes the main points of the article and your opinions. To learn more about what to include in your personal critique of the article, keep reading the article! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Prince Asiedu-Gyan
Apr 22, 2022
Did this article help you?
Sammy James
Sep 12, 2017
Juabin Matey
Aug 30, 2017
Oct 25, 2023
Vanita Meghrajani
Jul 21, 2016

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Develop the tech skills you need for work and life
The Tech Edvocate
- Advertisement
- Home Page Five (No Sidebar)
- Home Page Four
- Home Page Three
- Home Page Two
- Icons [No Sidebar]
- Left Sidbear Page
- Lynch Educational Consulting
- My Speaking Page
- Newsletter Sign Up Confirmation
- Newsletter Unsubscription
- Page Example
- Privacy Policy
- Protected Content
- Request a Product Review
- Shortcodes Examples
- Terms and Conditions
- The Edvocate
- The Tech Edvocate Product Guide
- Write For Us
- Dr. Lynch’s Personal Website
- The Edvocate Podcast
- Assistive Technology
- Child Development Tech
- Early Childhood & K-12 EdTech
- EdTech Futures
- EdTech News
- EdTech Policy & Reform
- EdTech Startups & Businesses
- Higher Education EdTech
- Online Learning & eLearning
- Parent & Family Tech
- Personalized Learning
- Product Reviews
- Tech Edvocate Awards
- School Ratings
Teaching Reading To Struggling Students: Everything You Need to Know
Rhyming capacity: everything you need to know, phonological awareness: everything you need to know, product review of kate spade’s bloom: the perfect mother’s day gift, learning to read: everything you need to know, product review of the arzopa z1c portable monitor, how to teach phonics: everything you need to know, reading groups: everything you need to know, product review of the ultenic p30 grooming kit, reading anxiety in children: everything you need to know, how to write an article review (with sample reviews) .

An article review is a critical evaluation of a scholarly or scientific piece, which aims to summarize its main ideas, assess its contributions, and provide constructive feedback. A well-written review not only benefits the author of the article under scrutiny but also serves as a valuable resource for fellow researchers and scholars. Follow these steps to create an effective and informative article review:
1. Understand the purpose: Before diving into the article, it is important to understand the intent of writing a review. This helps in focusing your thoughts, directing your analysis, and ensuring your review adds value to the academic community.
2. Read the article thoroughly: Carefully read the article multiple times to get a complete understanding of its content, arguments, and conclusions. As you read, take notes on key points, supporting evidence, and any areas that require further exploration or clarification.
3. Summarize the main ideas: In your review’s introduction, briefly outline the primary themes and arguments presented by the author(s). Keep it concise but sufficiently informative so that readers can quickly grasp the essence of the article.
4. Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses: In subsequent paragraphs, assess the strengths and limitations of the article based on factors such as methodology, quality of evidence presented, coherence of arguments, and alignment with existing literature in the field. Be fair and objective while providing your critique.
5. Discuss any implications: Deliberate on how this particular piece contributes to or challenges existing knowledge in its discipline. You may also discuss potential improvements for future research or explore real-world applications stemming from this study.
6. Provide recommendations: Finally, offer suggestions for both the author(s) and readers regarding how they can further build on this work or apply its findings in practice.
7. Proofread and revise: Once your initial draft is complete, go through it carefully for clarity, accuracy, and coherence. Revise as necessary, ensuring your review is both informative and engaging for readers.
Sample Review:
A Critical Review of “The Effects of Social Media on Mental Health”
Introduction:
“The Effects of Social Media on Mental Health” is a timely article which investigates the relationship between social media usage and psychological well-being. The authors present compelling evidence to support their argument that excessive use of social media can result in decreased self-esteem, increased anxiety, and a negative impact on interpersonal relationships.
Strengths and weaknesses:
One of the strengths of this article lies in its well-structured methodology utilizing a variety of sources, including quantitative surveys and qualitative interviews. This approach provides a comprehensive view of the topic, allowing for a more nuanced understanding of the effects of social media on mental health. However, it would have been beneficial if the authors included a larger sample size to increase the reliability of their conclusions. Additionally, exploring how different platforms may influence mental health differently could have added depth to the analysis.
Implications:
The findings in this article contribute significantly to ongoing debates surrounding the psychological implications of social media use. It highlights the potential dangers that excessive engagement with online platforms may pose to one’s mental well-being and encourages further research into interventions that could mitigate these risks. The study also offers an opportunity for educators and policy-makers to take note and develop strategies to foster healthier online behavior.
Recommendations:
Future researchers should consider investigating how specific social media platforms impact mental health outcomes, as this could lead to more targeted interventions. For practitioners, implementing educational programs aimed at promoting healthy online habits may be beneficial in mitigating the potential negative consequences associated with excessive social media use.
Conclusion:
Overall, “The Effects of Social Media on Mental Health” is an important and informative piece that raises awareness about a pressing issue in today’s digital age. Given its minor limitations, it provides valuable
3 Ways to Make a Mini Greenhouse ...
3 ways to teach yourself to play ....
Matthew Lynch
Related articles more from author.
How to Order a Phone Book: 8 Steps

3 Ways to Mix Quikrete
How to Throw a Spiral: 13 Steps

4 Ways to Make Colored Fire

How to Repair a Cracked Mirror: 13 Steps
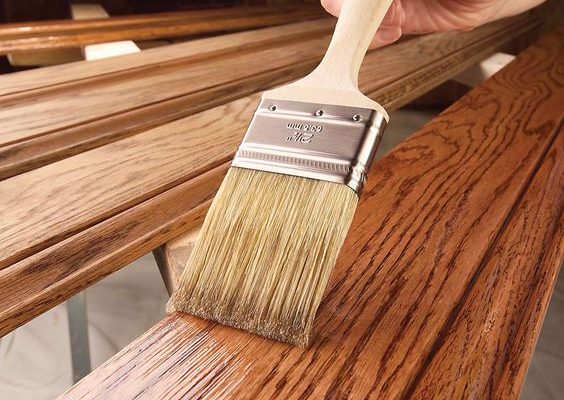

How to Varnish Wood
- Research Guides
- Vanderbilt University Libraries
- Peabody Library
Literature Reviews
Literature review table.
- Steps to Success: The Literature Review Process
- Literature Reviews Webinar Recording
- Writing Like an Academic
- Publishing in Academic Journals
- Managing Citations This link opens in a new window
- Literature Review Table Template Peabody Librarians have created a sample literature review table to use to organize your research. Feel free to download this file and use or adapt as needed.
- << Previous: Literature Reviews Webinar Recording
- Next: Writing Like an Academic >>
- Last Updated: Feb 29, 2024 4:20 PM
- URL: https://researchguides.library.vanderbilt.edu/peabody/litreviews

Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing a Literature Review

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays). When we say “literature review” or refer to “the literature,” we are talking about the research ( scholarship ) in a given field. You will often see the terms “the research,” “the scholarship,” and “the literature” used mostly interchangeably.
Where, when, and why would I write a lit review?
There are a number of different situations where you might write a literature review, each with slightly different expectations; different disciplines, too, have field-specific expectations for what a literature review is and does. For instance, in the humanities, authors might include more overt argumentation and interpretation of source material in their literature reviews, whereas in the sciences, authors are more likely to report study designs and results in their literature reviews; these differences reflect these disciplines’ purposes and conventions in scholarship. You should always look at examples from your own discipline and talk to professors or mentors in your field to be sure you understand your discipline’s conventions, for literature reviews as well as for any other genre.
A literature review can be a part of a research paper or scholarly article, usually falling after the introduction and before the research methods sections. In these cases, the lit review just needs to cover scholarship that is important to the issue you are writing about; sometimes it will also cover key sources that informed your research methodology.
Lit reviews can also be standalone pieces, either as assignments in a class or as publications. In a class, a lit review may be assigned to help students familiarize themselves with a topic and with scholarship in their field, get an idea of the other researchers working on the topic they’re interested in, find gaps in existing research in order to propose new projects, and/or develop a theoretical framework and methodology for later research. As a publication, a lit review usually is meant to help make other scholars’ lives easier by collecting and summarizing, synthesizing, and analyzing existing research on a topic. This can be especially helpful for students or scholars getting into a new research area, or for directing an entire community of scholars toward questions that have not yet been answered.
What are the parts of a lit review?
Most lit reviews use a basic introduction-body-conclusion structure; if your lit review is part of a larger paper, the introduction and conclusion pieces may be just a few sentences while you focus most of your attention on the body. If your lit review is a standalone piece, the introduction and conclusion take up more space and give you a place to discuss your goals, research methods, and conclusions separately from where you discuss the literature itself.
Introduction:
- An introductory paragraph that explains what your working topic and thesis is
- A forecast of key topics or texts that will appear in the review
- Potentially, a description of how you found sources and how you analyzed them for inclusion and discussion in the review (more often found in published, standalone literature reviews than in lit review sections in an article or research paper)
- Summarize and synthesize: Give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: Don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically Evaluate: Mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: Use transition words and topic sentence to draw connections, comparisons, and contrasts.
Conclusion:
- Summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance
- Connect it back to your primary research question
How should I organize my lit review?
Lit reviews can take many different organizational patterns depending on what you are trying to accomplish with the review. Here are some examples:
- Chronological : The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time, which helps familiarize the audience with the topic (for instance if you are introducing something that is not commonly known in your field). If you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order. Try to analyze the patterns, turning points, and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred (as mentioned previously, this may not be appropriate in your discipline — check with a teacher or mentor if you’re unsure).
- Thematic : If you have found some recurring central themes that you will continue working with throughout your piece, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic. For example, if you are reviewing literature about women and religion, key themes can include the role of women in churches and the religious attitude towards women.
- Qualitative versus quantitative research
- Empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the research by sociological, historical, or cultural sources
- Theoretical : In many humanities articles, the literature review is the foundation for the theoretical framework. You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts. You can argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach or combine various theorical concepts to create a framework for your research.
What are some strategies or tips I can use while writing my lit review?
Any lit review is only as good as the research it discusses; make sure your sources are well-chosen and your research is thorough. Don’t be afraid to do more research if you discover a new thread as you’re writing. More info on the research process is available in our "Conducting Research" resources .
As you’re doing your research, create an annotated bibliography ( see our page on the this type of document ). Much of the information used in an annotated bibliography can be used also in a literature review, so you’ll be not only partially drafting your lit review as you research, but also developing your sense of the larger conversation going on among scholars, professionals, and any other stakeholders in your topic.
Usually you will need to synthesize research rather than just summarizing it. This means drawing connections between sources to create a picture of the scholarly conversation on a topic over time. Many student writers struggle to synthesize because they feel they don’t have anything to add to the scholars they are citing; here are some strategies to help you:
- It often helps to remember that the point of these kinds of syntheses is to show your readers how you understand your research, to help them read the rest of your paper.
- Writing teachers often say synthesis is like hosting a dinner party: imagine all your sources are together in a room, discussing your topic. What are they saying to each other?
- Look at the in-text citations in each paragraph. Are you citing just one source for each paragraph? This usually indicates summary only. When you have multiple sources cited in a paragraph, you are more likely to be synthesizing them (not always, but often
- Read more about synthesis here.
The most interesting literature reviews are often written as arguments (again, as mentioned at the beginning of the page, this is discipline-specific and doesn’t work for all situations). Often, the literature review is where you can establish your research as filling a particular gap or as relevant in a particular way. You have some chance to do this in your introduction in an article, but the literature review section gives a more extended opportunity to establish the conversation in the way you would like your readers to see it. You can choose the intellectual lineage you would like to be part of and whose definitions matter most to your thinking (mostly humanities-specific, but this goes for sciences as well). In addressing these points, you argue for your place in the conversation, which tends to make the lit review more compelling than a simple reporting of other sources.

- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
Common Assignments: Literature Review Matrix
Literature review matrix.
As you read and evaluate your literature there are several different ways to organize your research. Courtesy of Dr. Gary Burkholder in the School of Psychology, these sample matrices are one option to help organize your articles. These documents allow you to compile details about your sources, such as the foundational theories, methodologies, and conclusions; begin to note similarities among the authors; and retrieve citation information for easy insertion within a document.
You can review the sample matrixes to see a completed form or download the blank matrix for your own use.
- Literature Review Matrix 1 This PDF file provides a sample literature review matrix.
- Literature Review Matrix 2 This PDF file provides a sample literature review matrix.
- Literature Review Matrix Template (Word)
- Literature Review Matrix Template (Excel)
Related Resources
Didn't find what you need? Email us at [email protected] .
- Previous Page: Commentary Versus Opinion
- Next Page: Professional Development Plans (PDPs)
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.

Get Started
Take the first step and invest in your future.

Online Programs
Offering flexibility & convenience in 51 online degrees & programs.

Prairie Stars
Featuring 15 intercollegiate NCAA Div II athletic teams.

Find your Fit
UIS has over 85 student and 10 greek life organizations, and many volunteer opportunities.

Arts & Culture
Celebrating the arts to create rich cultural experiences on campus.

Give Like a Star
Your generosity helps fuel fundraising for scholarships, programs and new initiatives.

Bragging Rights
UIS was listed No. 1 in Illinois and No. 3 in the Midwest in 2023 rankings.
- Quick links Applicants & Students Important Apps & Links Alumni Faculty and Staff Community Admissions How to Apply Cost & Aid Tuition Calculator Registrar Orientation Visit Campus Academics Register for Class Programs of Study Online Degrees & Programs Graduate Education International Student Services Study Away Student Support Bookstore UIS Life Dining Diversity & Inclusion Get Involved Health & Wellness COVID-19 United in Safety Residence Life Student Life Programs UIS Connection Important Apps UIS Mobile App Advise U Canvas myUIS i-card Balance Pay My Bill - UIS Bursar Self-Service Email Resources Bookstore Box Information Technology Services Library Orbit Policies Webtools Get Connected Area Information Calendar Campus Recreation Departments & Programs (A-Z) Parking UIS Newsroom Connect & Get Involved Update your Info Alumni Events Alumni Networks & Groups Volunteer Opportunities Alumni Board News & Publications Featured Alumni Alumni News UIS Alumni Magazine Resources Order your Transcripts Give Back Alumni Programs Career Development Services & Support Accessibility Services Campus Services Campus Police Facilities & Services Registrar Faculty & Staff Resources Website Project Request Web Services Training & Tools Academic Impressions Career Connect CSA Reporting Cybersecurity Training Faculty Research FERPA Training Website Login Campus Resources Newsroom Campus Calendar Campus Maps i-Card Human Resources Public Relations Webtools Arts & Events UIS Performing Arts Center Visual Arts Gallery Event Calendar Sangamon Experience Center for Lincoln Studies ECCE Speaker Series Community Engagement Center for State Policy and Leadership Illinois Innocence Project Innovate Springfield Central IL Nonprofit Resource Center NPR Illinois Community Resources Child Protection Training Academy Office of Electronic Media University Archives/IRAD Institute for Illinois Public Finance
Request Info

How to Review a Journal Article

- Request Info Request info for.... Undergraduate/Graduate Online Study Away Continuing & Professional Education International Student Services General Inquiries
For many kinds of assignments, like a literature review , you may be asked to offer a critique or review of a journal article. This is an opportunity for you as a scholar to offer your qualified opinion and evaluation of how another scholar has composed their article, argument, and research. That means you will be expected to go beyond a simple summary of the article and evaluate it on a deeper level. As a college student, this might sound intimidating. However, as you engage with the research process, you are becoming immersed in a particular topic, and your insights about the way that topic is presented are valuable and can contribute to the overall conversation surrounding your topic.
IMPORTANT NOTE!!
Some disciplines, like Criminal Justice, may only want you to summarize the article without including your opinion or evaluation. If your assignment is to summarize the article only, please see our literature review handout.
Before getting started on the critique, it is important to review the article thoroughly and critically. To do this, we recommend take notes, annotating , and reading the article several times before critiquing. As you read, be sure to note important items like the thesis, purpose, research questions, hypotheses, methods, evidence, key findings, major conclusions, tone, and publication information. Depending on your writing context, some of these items may not be applicable.
Questions to Consider
To evaluate a source, consider some of the following questions. They are broken down into different categories, but answering these questions will help you consider what areas to examine. With each category, we recommend identifying the strengths and weaknesses in each since that is a critical part of evaluation.
Evaluating Purpose and Argument
- How well is the purpose made clear in the introduction through background/context and thesis?
- How well does the abstract represent and summarize the article’s major points and argument?
- How well does the objective of the experiment or of the observation fill a need for the field?
- How well is the argument/purpose articulated and discussed throughout the body of the text?
- How well does the discussion maintain cohesion?
Evaluating the Presentation/Organization of Information
- How appropriate and clear is the title of the article?
- Where could the author have benefited from expanding, condensing, or omitting ideas?
- How clear are the author’s statements? Challenge ambiguous statements.
- What underlying assumptions does the author have, and how does this affect the credibility or clarity of their article?
- How objective is the author in his or her discussion of the topic?
- How well does the organization fit the article’s purpose and articulate key goals?
Evaluating Methods
- How appropriate are the study design and methods for the purposes of the study?
- How detailed are the methods being described? Is the author leaving out important steps or considerations?
- Have the procedures been presented in enough detail to enable the reader to duplicate them?
Evaluating Data
- Scan and spot-check calculations. Are the statistical methods appropriate?
- Do you find any content repeated or duplicated?
- How many errors of fact and interpretation does the author include? (You can check on this by looking up the references the author cites).
- What pertinent literature has the author cited, and have they used this literature appropriately?
Following, we have an example of a summary and an evaluation of a research article. Note that in most literature review contexts, the summary and evaluation would be much shorter. This extended example shows the different ways a student can critique and write about an article.
Chik, A. (2012). Digital gameplay for autonomous foreign language learning: Gamers’ and language teachers’ perspectives. In H. Reinders (ed.), Digital games in language learning and teaching (pp. 95-114). Eastbourne, UK: Palgrave Macmillan.
Be sure to include the full citation either in a reference page or near your evaluation if writing an annotated bibliography .
In Chik’s article “Digital Gameplay for Autonomous Foreign Language Learning: Gamers’ and Teachers’ Perspectives”, she explores the ways in which “digital gamers manage gaming and gaming-related activities to assume autonomy in their foreign language learning,” (96) which is presented in contrast to how teachers view the “pedagogical potential” of gaming. The research was described as an “umbrella project” consisting of two parts. The first part examined 34 language teachers’ perspectives who had limited experience with gaming (only five stated they played games regularly) (99). Their data was recorded through a survey, class discussion, and a seven-day gaming trial done by six teachers who recorded their reflections through personal blog posts. The second part explored undergraduate gaming habits of ten Hong Kong students who were regular gamers. Their habits were recorded through language learning histories, videotaped gaming sessions, blog entries of gaming practices, group discussion sessions, stimulated recall sessions on gaming videos, interviews with other gamers, and posts from online discussion forums. The research shows that while students recognize the educational potential of games and have seen benefits of it in their lives, the instructors overall do not see the positive impacts of gaming on foreign language learning.
The summary includes the article’s purpose, methods, results, discussion, and citations when necessary.
This article did a good job representing the undergraduate gamers’ voices through extended quotes and stories. Particularly for the data collection of the undergraduate gamers, there were many opportunities for an in-depth examination of their gaming practices and histories. However, the representation of the teachers in this study was very uneven when compared to the students. Not only were teachers labeled as numbers while the students picked out their own pseudonyms, but also when viewing the data collection, the undergraduate students were more closely examined in comparison to the teachers in the study. While the students have fifteen extended quotes describing their experiences in their research section, the teachers only have two of these instances in their section, which shows just how imbalanced the study is when presenting instructor voices.
Some research methods, like the recorded gaming sessions, were only used with students whereas teachers were only asked to blog about their gaming experiences. This creates a richer narrative for the students while also failing to give instructors the chance to have more nuanced perspectives. This lack of nuance also stems from the emphasis of the non-gamer teachers over the gamer teachers. The non-gamer teachers’ perspectives provide a stark contrast to the undergraduate gamer experiences and fits neatly with the narrative of teachers not valuing gaming as an educational tool. However, the study mentioned five teachers that were regular gamers whose perspectives are left to a short section at the end of the presentation of the teachers’ results. This was an opportunity to give the teacher group a more complex story, and the opportunity was entirely missed.
Additionally, the context of this study was not entirely clear. The instructors were recruited through a master’s level course, but the content of the course and the institution’s background is not discussed. Understanding this context helps us understand the course’s purpose(s) and how those purposes may have influenced the ways in which these teachers interpreted and saw games. It was also unclear how Chik was connected to this masters’ class and to the students. Why these particular teachers and students were recruited was not explicitly defined and also has the potential to skew results in a particular direction.
Overall, I was inclined to agree with the idea that students can benefit from language acquisition through gaming while instructors may not see the instructional value, but I believe the way the research was conducted and portrayed in this article made it very difficult to support Chik’s specific findings.
Some professors like you to begin an evaluation with something positive but isn’t always necessary.
The evaluation is clearly organized and uses transitional phrases when moving to a new topic.
This evaluation includes a summative statement that gives the overall impression of the article at the end, but this can also be placed at the beginning of the evaluation.
This evaluation mainly discusses the representation of data and methods. However, other areas, like organization, are open to critique.

How to Write an Article Review: Tips and Examples

Did you know that article reviews are not just academic exercises but also a valuable skill in today's information age? In a world inundated with content, being able to dissect and evaluate articles critically can help you separate the wheat from the chaff. Whether you're a student aiming to excel in your coursework or a professional looking to stay well-informed, mastering the art of writing article reviews is an invaluable skill.
Short Description
In this article, our research paper writing service experts will start by unraveling the concept of article reviews and discussing the various types. You'll also gain insights into the art of formatting your review effectively. To ensure you're well-prepared, we'll take you through the pre-writing process, offering tips on setting the stage for your review. But it doesn't stop there. You'll find a practical example of an article review to help you grasp the concepts in action. To complete your journey, we'll guide you through the post-writing process, equipping you with essential proofreading techniques to ensure your work shines with clarity and precision!
What Is an Article Review: Grasping the Concept
A review article is a type of professional paper writing that demands a high level of in-depth analysis and a well-structured presentation of arguments. It is a critical, constructive evaluation of literature in a particular field through summary, classification, analysis, and comparison.
If you write a scientific review, you have to use database searches to portray the research. Your primary goal is to summarize everything and present a clear understanding of the topic you've been working on.
Writing Involves:
- Summarization, classification, analysis, critiques, and comparison.
- The analysis, evaluation, and comparison require the use of theories, ideas, and research relevant to the subject area of the article.
- It is also worth nothing if a review does not introduce new information, but instead presents a response to another writer's work.
- Check out other samples to gain a better understanding of how to review the article.
Types of Review
When it comes to article reviews, there's more than one way to approach the task. Understanding the various types of reviews is like having a versatile toolkit at your disposal. In this section, we'll walk you through the different dimensions of review types, each offering a unique perspective and purpose. Whether you're dissecting a scholarly article, critiquing a piece of literature, or evaluating a product, you'll discover the diverse landscape of article reviews and how to navigate it effectively.
.webp)
Journal Article Review
Just like other types of reviews, a journal article review assesses the merits and shortcomings of a published work. To illustrate, consider a review of an academic paper on climate change, where the writer meticulously analyzes and interprets the article's significance within the context of environmental science.
Research Article Review
Distinguished by its focus on research methodologies, a research article review scrutinizes the techniques used in a study and evaluates them in light of the subsequent analysis and critique. For instance, when reviewing a research article on the effects of a new drug, the reviewer would delve into the methods employed to gather data and assess their reliability.
Science Article Review
In the realm of scientific literature, a science article review encompasses a wide array of subjects. Scientific publications often provide extensive background information, which can be instrumental in conducting a comprehensive analysis. For example, when reviewing an article about the latest breakthroughs in genetics, the reviewer may draw upon the background knowledge provided to facilitate a more in-depth evaluation of the publication.
Need a Hand From Professionals?
Address to Our Writers and Get Assistance in Any Questions!
Formatting an Article Review
The format of the article should always adhere to the citation style required by your professor. If you're not sure, seek clarification on the preferred format and ask him to clarify several other pointers to complete the formatting of an article review adequately.
How Many Publications Should You Review?
- In what format should you cite your articles (MLA, APA, ASA, Chicago, etc.)?
- What length should your review be?
- Should you include a summary, critique, or personal opinion in your assignment?
- Do you need to call attention to a theme or central idea within the articles?
- Does your instructor require background information?
When you know the answers to these questions, you may start writing your assignment. Below are examples of MLA and APA formats, as those are the two most common citation styles.
Using the APA Format
Articles appear most commonly in academic journals, newspapers, and websites. If you write an article review in the APA format, you will need to write bibliographical entries for the sources you use:
- Web : Author [last name], A.A [first and middle initial]. (Year, Month, Date of Publication). Title. Retrieved from {link}
- Journal : Author [last name], A.A [first and middle initial]. (Publication Year). Publication Title. Periodical Title, Volume(Issue), pp.-pp.
- Newspaper : Author [last name], A.A [first and middle initial]. (Year, Month, Date of Publication). Publication Title. Magazine Title, pp. xx-xx.
Using MLA Format
- Web : Last, First Middle Initial. “Publication Title.” Website Title. Website Publisher, Date Month Year Published. Web. Date Month Year Accessed.
- Newspaper : Last, First M. “Publication Title.” Newspaper Title [City] Date, Month, Year Published: Page(s). Print.
- Journal : Last, First M. “Publication Title.” Journal Title Series Volume. Issue (Year Published): Page(s). Database Name. Web. Date Month Year Accessed.
Enhance your writing effortlessly with EssayPro.com , where you can order an article review or any other writing task. Our team of expert writers specializes in various fields, ensuring your work is not just summarized, but deeply analyzed and professionally presented. Ideal for students and professionals alike, EssayPro offers top-notch writing assistance tailored to your needs. Elevate your writing today with our skilled team at your article review writing service !
.jpg)
The Pre-Writing Process
Facing this task for the first time can really get confusing and can leave you unsure of where to begin. To create a top-notch article review, start with a few preparatory steps. Here are the two main stages from our dissertation services to get you started:
Step 1: Define the right organization for your review. Knowing the future setup of your paper will help you define how you should read the article. Here are the steps to follow:
- Summarize the article — seek out the main points, ideas, claims, and general information presented in the article.
- Define the positive points — identify the strong aspects, ideas, and insightful observations the author has made.
- Find the gaps —- determine whether or not the author has any contradictions, gaps, or inconsistencies in the article and evaluate whether or not he or she used a sufficient amount of arguments and information to support his or her ideas.
- Identify unanswered questions — finally, identify if there are any questions left unanswered after reading the piece.
Step 2: Move on and review the article. Here is a small and simple guide to help you do it right:
- Start off by looking at and assessing the title of the piece, its abstract, introductory part, headings and subheadings, opening sentences in its paragraphs, and its conclusion.
- First, read only the beginning and the ending of the piece (introduction and conclusion). These are the parts where authors include all of their key arguments and points. Therefore, if you start with reading these parts, it will give you a good sense of the author's main points.
- Finally, read the article fully.
These three steps make up most of the prewriting process. After you are done with them, you can move on to writing your own review—and we are going to guide you through the writing process as well.
Outline and Template
As you progress with reading your article, organize your thoughts into coherent sections in an outline. As you read, jot down important facts, contributions, or contradictions. Identify the shortcomings and strengths of your publication. Begin to map your outline accordingly.
If your professor does not want a summary section or a personal critique section, then you must alleviate those parts from your writing. Much like other assignments, an article review must contain an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. Thus, you might consider dividing your outline according to these sections as well as subheadings within the body. If you find yourself troubled with the pre-writing and the brainstorming process for this assignment, seek out a sample outline.
Your custom essay must contain these constituent parts:
- Pre-Title Page - Before diving into your review, start with essential details: article type, publication title, and author names with affiliations (position, department, institution, location, and email). Include corresponding author info if needed.
- Running Head - In APA format, use a concise title (under 40 characters) to ensure consistent formatting.
- Summary Page - Optional but useful. Summarize the article in 800 words, covering background, purpose, results, and methodology, avoiding verbatim text or references.
- Title Page - Include the full title, a 250-word abstract, and 4-6 keywords for discoverability.
- Introduction - Set the stage with an engaging overview of the article.
- Body - Organize your analysis with headings and subheadings.
- Works Cited/References - Properly cite all sources used in your review.
- Optional Suggested Reading Page - If permitted, suggest further readings for in-depth exploration.
- Tables and Figure Legends (if instructed by the professor) - Include visuals when requested by your professor for clarity.
Example of an Article Review
You might wonder why we've dedicated a section of this article to discuss an article review sample. Not everyone may realize it, but examining multiple well-constructed examples of review articles is a crucial step in the writing process. In the following section, our essay writing service experts will explain why.
Looking through relevant article review examples can be beneficial for you in the following ways:
- To get you introduced to the key works of experts in your field.
- To help you identify the key people engaged in a particular field of science.
- To help you define what significant discoveries and advances were made in your field.
- To help you unveil the major gaps within the existing knowledge of your field—which contributes to finding fresh solutions.
- To help you find solid references and arguments for your own review.
- To help you generate some ideas about any further field of research.
- To help you gain a better understanding of the area and become an expert in this specific field.
- To get a clear idea of how to write a good review.
View Our Writer’s Sample Before Crafting Your Own!
Why Have There Been No Great Female Artists?
Steps for Writing an Article Review
Here is a guide with critique paper format on how to write a review paper:
.webp)
Step 1: Write the Title
First of all, you need to write a title that reflects the main focus of your work. Respectively, the title can be either interrogative, descriptive, or declarative.
Step 2: Cite the Article
Next, create a proper citation for the reviewed article and input it following the title. At this step, the most important thing to keep in mind is the style of citation specified by your instructor in the requirements for the paper. For example, an article citation in the MLA style should look as follows:
Author's last and first name. "The title of the article." Journal's title and issue(publication date): page(s). Print
Abraham John. "The World of Dreams." Virginia Quarterly 60.2(1991): 125-67. Print.
Step 3: Article Identification
After your citation, you need to include the identification of your reviewed article:
- Title of the article
- Title of the journal
- Year of publication
All of this information should be included in the first paragraph of your paper.
The report "Poverty increases school drop-outs" was written by Brian Faith – a Health officer – in 2000.
Step 4: Introduction
Your organization in an assignment like this is of the utmost importance. Before embarking on your writing process, you should outline your assignment or use an article review template to organize your thoughts coherently.
- If you are wondering how to start an article review, begin with an introduction that mentions the article and your thesis for the review.
- Follow up with a summary of the main points of the article.
- Highlight the positive aspects and facts presented in the publication.
- Critique the publication by identifying gaps, contradictions, disparities in the text, and unanswered questions.
Step 5: Summarize the Article
Make a summary of the article by revisiting what the author has written about. Note any relevant facts and findings from the article. Include the author's conclusions in this section.
Step 6: Critique It
Present the strengths and weaknesses you have found in the publication. Highlight the knowledge that the author has contributed to the field. Also, write about any gaps and/or contradictions you have found in the article. Take a standpoint of either supporting or not supporting the author's assertions, but back up your arguments with facts and relevant theories that are pertinent to that area of knowledge. Rubrics and templates can also be used to evaluate and grade the person who wrote the article.
Step 7: Craft a Conclusion
In this section, revisit the critical points of your piece, your findings in the article, and your critique. Also, write about the accuracy, validity, and relevance of the results of the article review. Present a way forward for future research in the field of study. Before submitting your article, keep these pointers in mind:
- As you read the article, highlight the key points. This will help you pinpoint the article's main argument and the evidence that they used to support that argument.
- While you write your review, use evidence from your sources to make a point. This is best done using direct quotations.
- Select quotes and supporting evidence adequately and use direct quotations sparingly. Take time to analyze the article adequately.
- Every time you reference a publication or use a direct quotation, use a parenthetical citation to avoid accidentally plagiarizing your article.
- Re-read your piece a day after you finish writing it. This will help you to spot grammar mistakes and to notice any flaws in your organization.
- Use a spell-checker and get a second opinion on your paper.
The Post-Writing Process: Proofread Your Work
Finally, when all of the parts of your article review are set and ready, you have one last thing to take care of — proofreading. Although students often neglect this step, proofreading is a vital part of the writing process and will help you polish your paper to ensure that there are no mistakes or inconsistencies.
To proofread your paper properly, start by reading it fully and checking the following points:
- Punctuation
- Other mistakes
Afterward, take a moment to check for any unnecessary information in your paper and, if found, consider removing it to streamline your content. Finally, double-check that you've covered at least 3-4 key points in your discussion.
And remember, if you ever need help with proofreading, rewriting your essay, or even want to buy essay , our friendly team is always here to assist you.
Need an Article REVIEW WRITTEN?
Just send us the requirements to your paper and watch one of our writers crafting an original paper for you.
What Is A Review Article?
How to write an article review, how to write an article review in apa format, related articles.
.webp)
What’s Included: Literature Review Template
This template is structure is based on the tried and trusted best-practice format for formal academic research projects such as dissertations and theses. The literature review template includes the following sections:
- Before you start – essential groundwork to ensure you’re ready
- The introduction section
- The core/body section
- The conclusion /summary
- Extra free resources
Each section is explained in plain, straightforward language , followed by an overview of the key elements that you need to cover. We’ve also included practical examples and links to more free videos and guides to help you understand exactly what’s required in each section.
The cleanly-formatted Google Doc can be downloaded as a fully editable MS Word Document (DOCX format), so you can use it as-is or convert it to LaTeX.
PS – if you’d like a high-level template for the entire thesis, you can we’ve got that too .
FAQs: Literature Review Template
What format is the template (doc, pdf, ppt, etc.).
The literature review chapter template is provided as a Google Doc. You can download it in MS Word format or make a copy to your Google Drive. You’re also welcome to convert it to whatever format works best for you, such as LaTeX or PDF.
What types of literature reviews can this template be used for?
The template follows the standard format for academic literature reviews, which means it will be suitable for the vast majority of academic research projects (especially those within the sciences), whether they are qualitative or quantitative in terms of design.
Keep in mind that the exact requirements for the literature review chapter will vary between universities and degree programs. These are typically minor, but it’s always a good idea to double-check your university’s requirements before you finalize your structure.
Is this template for an undergrad, Master or PhD-level thesis?
This template can be used for a literature review at any level of study. Doctoral-level projects typically require the literature review to be more extensive/comprehensive, but the structure will typically remain the same.
Can I modify the template to suit my topic/area?
Absolutely. While the template provides a general structure, you should adapt it to fit the specific requirements and focus of your literature review.
What structural style does this literature review template use?
The template assumes a thematic structure (as opposed to a chronological or methodological structure), as this is the most common approach. However, this is only one dimension of the template, so it will still be useful if you are adopting a different structure.
Does this template include the Excel literature catalog?
No, that is a separate template, which you can download for free here . This template is for the write-up of the actual literature review chapter, whereas the catalog is for use during the literature sourcing and sorting phase.
How long should the literature review chapter be?
This depends on your university’s specific requirements, so it’s best to check with them. As a general ballpark, literature reviews for Masters-level projects are usually 2,000 – 3,000 words in length, while Doctoral-level projects can reach multiples of this.
Can I include literature that contradicts my hypothesis?
Yes, it’s important to acknowledge and discuss literature that presents different viewpoints or contradicts your hypothesis. So, don’t shy away from existing research that takes an opposing view to yours.
How do I avoid plagiarism in my literature review?
Always cite your sources correctly and paraphrase ideas in your own words while maintaining the original meaning. You can always check our plagiarism score before submitting your work to help ease your mind.
Do you have an example of a populated template?
We provide a walkthrough of the template and review an example of a high-quality literature research chapter here .
Can I share this literature review template with my friends/colleagues?
Yes, you’re welcome to share this template in its original format (no editing allowed). If you want to post about it on your blog or social media, all we ask is that you reference this page as your source.
Do you have templates for the other dissertation/thesis chapters?
Yes, we do. You can find our full collection of templates here .
Can Grad Coach help me with my literature review?
Yes, you’re welcome to get in touch with us to discuss our private coaching services , where we can help you work through the literature review chapter (and any other chapters).

How to Write an Article Review: Template & Examples
An article review is an academic assignment that invites you to study a piece of academic research closely. Then, you should present its summary and critically evaluate it using the knowledge you’ve gained in class and during your independent study. If you get such a task at college or university, you shouldn’t confuse it with a response paper, which is a distinct assignment with other purposes (we’ll talk about it in detail below).
Our specialists will write a custom essay specially for you!
In this article, prepared by Custom-Writing experts, you’ll find:
- the intricacies of article review writing;
- the difference between an article review and similar assignments;
- a step-by-step algorithm for review composition;
- a couple of samples to guide you throughout the writing process.
So, if you wish to study our article review example and discover helpful writing tips, keep reading.
❓ What Is an Article Review?
- ✍️ Writing Steps
📑 Article Review Format
🔗 references.
An article review is an academic paper that summarizes and critically evaluates the information presented in your selected article.

The first thing you should note when approaching the task of an article review is that not every article is suitable for this assignment. Let’s have a look at the variety of articles to understand what you can choose from.
Popular Vs. Scholarly Articles
In most cases, you’ll be required to review a scholarly, peer-reviewed article – one composed in compliance with rigorous academic standards. Yet, the Web is also full of popular articles that don’t present original scientific value and shouldn’t be selected for a review.
Just in 1 hour! We will write you a plagiarism-free paper in hardly more than 1 hour
Not sure how to distinguish these two types? Here is a comparative table to help you out.
Article Review vs. Response Paper
Now, let’s consider the difference between an article review and a response paper:
- If you’re assigned to critique a scholarly article , you will need to compose an article review .
- If your subject of analysis is a popular article , you can respond to it with a well-crafted response paper .
The reason for such distinctions is the quality and structure of these two article types. Peer-reviewed, scholarly articles have clear-cut quality criteria, allowing you to conduct and present a structured assessment of the assigned material. Popular magazines have loose or non-existent quality criteria and don’t offer an opportunity for structured evaluation. So, they are only fit for a subjective response, in which you can summarize your reactions and emotions related to the reading material.
All in all, you can structure your response assignments as outlined in the tips below.
✍️ How to Write an Article Review: Step by Step
Here is a tried and tested algorithm for article review writing from our experts. We’ll consider only the critical review variety of this academic assignment. So, let’s get down to the stages you need to cover to get a stellar review.
Receive a plagiarism-free paper tailored to your instructions. Cut 20% off your first order!
Read the Article
As with any reviews, reports, and critiques, you must first familiarize yourself with the assigned material. It’s impossible to review something you haven’t read, so set some time for close, careful reading of the article to identify:
- Its topic.
- Its type.
- The author’s main points and message.
- The arguments they use to prove their points.
- The methodology they use to approach the subject.
In terms of research type , your article will usually belong to one of three types explained below.
Summarize the Article
Now that you’ve read the text and have a general impression of the content, it’s time to summarize it for your readers. Look into the article’s text closely to determine:
- The thesis statement , or general message of the author.
- Research question, purpose, and context of research.
- Supporting points for the author’s assumptions and claims.
- Major findings and supporting evidence.
As you study the article thoroughly, make notes on the margins or write these elements out on a sheet of paper. You can also apply a different technique: read the text section by section and formulate its gist in one phrase or sentence. Once you’re done, you’ll have a summary skeleton in front of you.
Evaluate the Article
The next step of review is content evaluation. Keep in mind that various research types will require a different set of review questions. Here is a complete list of evaluation points you can include.
Get an originally-written paper according to your instructions!
Write the Text
After completing the critical review stage, it’s time to compose your article review.
The format of this assignment is standard – you will have an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. The introduction should present your article and summarize its content. The body will contain a structured review according to all four dimensions covered in the previous section. The concluding part will typically recap all the main points you’ve identified during your assessment.
It is essential to note that an article review is, first of all, an academic assignment. Therefore, it should follow all rules and conventions of academic composition, such as:
- No contractions . Don’t use short forms, such as “don’t,” “can’t,” “I’ll,” etc. in academic writing. You need to spell out all those words.
- Formal language and style . Avoid conversational phrasing and words that you would naturally use in blog posts or informal communication. For example, don’t use words like “pretty,” “kind of,” and “like.”
- Third-person narrative . Academic reviews should be written from the third-person point of view, avoiding statements like “I think,” “in my opinion,” and so on.
- No conversational forms . You shouldn’t turn to your readers directly in the text by addressing them with the pronoun “you.” It’s vital to keep the narrative neutral and impersonal.
- Proper abbreviation use . Consult the list of correct abbreviations , like “e.g.” or “i.e.,” for use in your academic writing. If you use informal abbreviations like “FYA” or “f.i.,” your professor will reduce the grade.
- Complete sentences . Make sure your sentences contain the subject and the predicate; avoid shortened or sketch-form phrases suitable for a draft only.
- No conjunctions at the beginning of a sentence . Remember the FANBOYS rule – don’t start a sentence with words like “and” or “but.” They often seem the right way to build a coherent narrative, but academic writing rules disfavor such usage.
- No abbreviations or figures at the beginning of a sentence . Never start a sentence with a number — spell it out if you need to use it anyway. Besides, sentences should never begin with abbreviations like “e.g.”
Finally, a vital rule for an article review is properly formatting the citations. We’ll discuss the correct use of citation styles in the following section.
When composing an article review, keep these points in mind:
- Start with a full reference to the reviewed article so the reader can locate it quickly.
- Ensure correct formatting of in-text references.
- Provide a complete list of used external sources on the last page of the review – your bibliographical entries .
You’ll need to understand the rules of your chosen citation style to meet all these requirements. Below, we’ll discuss the two most common referencing styles – APA and MLA.
Article Review in APA
When you need to compose an article review in the APA format , here is the general bibliographical entry format you should use for journal articles on your reference page:
- Author’s last name, First initial. Middle initial. (Year of Publication). Name of the article. Name of the Journal, volume (number), pp. #-#. https://doi.org/xx.xxx/yyyy
Horigian, V. E., Schmidt, R. D., & Feaster, D. J. (2021). Loneliness, mental health, and substance use among US young adults during COVID-19. Journal of Psychoactive Drugs, 53 (1), pp. 1-9. https://doi.org/10.1080/02791072.2020.1836435
Your in-text citations should follow the author-date format like this:
- If you paraphrase the source and mention the author in the text: According to Horigian et al. (2021), young adults experienced increased levels of loneliness, depression, and anxiety during the pandemic.
- If you paraphrase the source and don’t mention the author in the text: Young adults experienced increased levels of loneliness, depression, and anxiety during the pandemic (Horigian et al., 2021).
- If you quote the source: As Horigian et al. (2021) point out, there were “elevated levels of loneliness, depression, anxiety, alcohol use, and drug use among young adults during COVID-19” (p. 6).
Note that your in-text citations should include “et al.,” as in the examples above, if your article has 3 or more authors. If you have one or two authors, your in-text citations would look like this:
- One author: “According to Smith (2020), depression is…” or “Depression is … (Smith, 2020).”
- Two authors: “According to Smith and Brown (2020), anxiety means…” or “Anxiety means (Smith & Brown, 2020).”
Finally, in case you have to review a book or a website article, here are the general formats for citing these source types on your APA reference list.
Article Review in MLA
If your assignment requires MLA-format referencing, here’s the general format you should use for citing journal articles on your Works Cited page:
- Author’s last name, First name. “Title of an Article.” Title of the Journal , vol. #, no. #, year, pp. #-#.
Horigian, Viviana E., et al. “Loneliness, Mental Health, and Substance Use Among US Young Adults During COVID-19.” Journal of Psychoactive Drugs , vol. 53, no. 1, 2021, pp. 1-9.
In-text citations in the MLA format follow the author-page citation format and look like this:
- According to Horigian et al., young adults experienced increased levels of loneliness, depression, and anxiety during the pandemic (6).
- Young adults experienced increased levels of loneliness, depression, and anxiety during the pandemic (Horigian et al. 6).
Like in APA, the abbreviation “et al.” is only needed in MLA if your article has 3 or more authors.
If you need to cite a book or a website page, here are the general MLA formats for these types of sources.
✅ Article Review Template
Here is a handy, universal article review template to help you move on with any review assignment. We’ve tried to make it as generic as possible to guide you in the academic process.
📝 Article Review Examples
The theory is good, but practice is even better. Thus, we’ve created three brief examples to show you how to write an article review. You can study the full-text samples by following the links.
📃 Men, Women, & Money
This article review examines a famous piece, “Men, Women & Money – How the Sexes Differ with Their Finances,” published by Amy Livingston in 2020. The author of this article claims that men generally spend more money than women. She makes this conclusion from a close analysis of gender-specific expenditures across five main categories: food, clothing, cars, entertainment, and general spending patterns. Livingston also looks at men’s approach to saving to argue that counter to the common perception of women’s light-hearted attitude to money, men are those who spend more on average.
📃 When and Why Nationalism Beats Globalism
This is a review of Jonathan Heidt’s 2016 article titled “When and Why Nationalism Beats Globalism,” written as an advocacy of right-wing populism rising in many Western states. The author illustrates the case with the election of Donald Trump as the US President and the rise of right-wing rhetoric in many Western countries. These examples show how nationalist sentiment represents a reaction to global immigration and a failure of globalization.
📃 Sleep Deprivation
This is a review of the American Heart Association’s article titled “The Dangers of Sleep Deprivation.” It discusses how the national organization concerned with the American population’s cardiovascular health links the lack of high-quality sleep to far-reaching health consequences. The organization’s experts reveal how a consistent lack of sleep leads to Alzheimer’s disease development, obesity, type 2 diabetes, etc.
✏️ Article Review FAQ
A high-quality article review should summarize the assigned article’s content and offer data-backed reactions and evaluations of its quality in terms of the article’s purpose, methodology, and data used to argue the main points. It should be detailed, comprehensive, objective, and evidence-based.
The purpose of writing a review is to allow students to reflect on research quality and showcase their critical thinking and evaluation skills. Students should exhibit their mastery of close reading of research publications and their unbiased assessment.
The content of your article review will be the same in any format, with the only difference in the assignment’s formatting before submission. Ensure you have a separate title page made according to APA standards and cite sources using the parenthetical author-date referencing format.
You need to take a closer look at various dimensions of an assigned article to compose a valuable review. Study the author’s object of analysis, the purpose of their research, the chosen method, data, and findings. Evaluate all these dimensions critically to see whether the author has achieved the initial goals. Finally, offer improvement recommendations to add a critique aspect to your paper.
- Scientific Article Review: Duke University
- Book and Article Reviews: William & Mary, Writing Resources Center
- Sample Format for Reviewing a Journal Article: Boonshoft School of Medicine
- Research Paper Review – Structure and Format Guidelines: New Jersey Institute of Technology
- Article Review: University of Waterloo
- Article Review: University of South Australia
- How to Write a Journal Article Review: University of Newcastle Library Guides
- Writing Help: The Article Review: Central Michigan University Libraries
- Write a Critical Review of a Scientific Journal Article: McLaughlin Library
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email

Short essays answer a specific question on the subject. They usually are anywhere between 250 words and 750 words long. A paper with less than 250 words isn’t considered a finished text, so it doesn’t fall under the category of a short essay. Essays of such format are required for...

High school and college students often face challenges when crafting a compare-and-contrast essay. A well-written paper of this kind needs to be structured appropriately to earn you good grades. Knowing how to organize your ideas allows you to present your ideas in a coherent and logical manner This article by...

If you’re a student, you’ve heard about a formal essay: a factual, research-based paper written in 3rd person. Most students have to produce dozens of them during their educational career. Writing a formal essay may not be the easiest task. But fear not: our custom-writing team is here to guide...

Narrative essays are unlike anything you wrote throughout your academic career. Instead of writing a formal paper, you need to tell a story. Familiar elements such as evidence and arguments are replaced with exposition and character development. The importance of writing an outline for an essay like this is hard...

A précis is a brief synopsis of a written piece. It is used to summarize and analyze a text’s main points. If you need to write a précis for a research paper or the AP Lang exam, you’ve come to the right place. In this comprehensive guide by Custom-Writing.org, you’ll...

A synthesis essay requires you to work with multiple sources. You combine the information gathered from them to present a well-rounded argument on a topic. Are you looking for the ultimate guide on synthesis essay writing? You’ve come to the right place! In this guide by our custom writing team,...

Do you know how to make your essay stand out? One of the easiest ways is to start your introduction with a catchy hook. A hook is a phrase or a sentence that helps to grab the reader’s attention. After reading this article by Custom-Writing.org, you will be able to...

Critical thinking is the process of evaluating and analyzing information. People who use it in everyday life are open to different opinions. They rely on reason and logic when making conclusions about certain issues. A critical thinking essay shows how your thoughts change as you research your topic. This type...

Process analysis is an explanation of how something works or happens. Want to know more? Read the following article prepared by our custom writing specialists and learn about: process analysis and its typesa process analysis outline tipsfree examples and other tips that might be helpful for your college assignment So,...

A visual analysis essay is an academic paper type that history and art students often deal with. It consists of a detailed description of an image or object. It can also include an interpretation or an argument that is supported by visual evidence. In this article, our custom writing experts...

Want to know how to write a reflection paper for college or school? To do that, you need to connect your personal experiences with theoretical knowledge. Usually, students are asked to reflect on a documentary, a text, or their experience. Sometimes one needs to write a paper about a lesson...

A character analysis is an examination of the personalities and actions of protagonists and antagonists that make up a story. It discusses their role in the story, evaluates their traits, and looks at their conflicts and experiences. You might need to write this assignment in school or college. Like any...
Jump to navigation

Cochrane Training
Chapter 14: completing ‘summary of findings’ tables and grading the certainty of the evidence.
Holger J Schünemann, Julian PT Higgins, Gunn E Vist, Paul Glasziou, Elie A Akl, Nicole Skoetz, Gordon H Guyatt; on behalf of the Cochrane GRADEing Methods Group (formerly Applicability and Recommendations Methods Group) and the Cochrane Statistical Methods Group
Key Points:
- A ‘Summary of findings’ table for a given comparison of interventions provides key information concerning the magnitudes of relative and absolute effects of the interventions examined, the amount of available evidence and the certainty (or quality) of available evidence.
- ‘Summary of findings’ tables include a row for each important outcome (up to a maximum of seven). Accepted formats of ‘Summary of findings’ tables and interactive ‘Summary of findings’ tables can be produced using GRADE’s software GRADEpro GDT.
- Cochrane has adopted the GRADE approach (Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation) for assessing certainty (or quality) of a body of evidence.
- The GRADE approach specifies four levels of the certainty for a body of evidence for a given outcome: high, moderate, low and very low.
- GRADE assessments of certainty are determined through consideration of five domains: risk of bias, inconsistency, indirectness, imprecision and publication bias. For evidence from non-randomized studies and rarely randomized studies, assessments can then be upgraded through consideration of three further domains.
Cite this chapter as: Schünemann HJ, Higgins JPT, Vist GE, Glasziou P, Akl EA, Skoetz N, Guyatt GH. Chapter 14: Completing ‘Summary of findings’ tables and grading the certainty of the evidence. In: Higgins JPT, Thomas J, Chandler J, Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, Welch VA (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions version 6.4 (updated August 2023). Cochrane, 2023. Available from www.training.cochrane.org/handbook .
14.1 ‘Summary of findings’ tables
14.1.1 introduction to ‘summary of findings’ tables.
‘Summary of findings’ tables present the main findings of a review in a transparent, structured and simple tabular format. In particular, they provide key information concerning the certainty or quality of evidence (i.e. the confidence or certainty in the range of an effect estimate or an association), the magnitude of effect of the interventions examined, and the sum of available data on the main outcomes. Cochrane Reviews should incorporate ‘Summary of findings’ tables during planning and publication, and should have at least one key ‘Summary of findings’ table representing the most important comparisons. Some reviews may include more than one ‘Summary of findings’ table, for example if the review addresses more than one major comparison, or includes substantially different populations that require separate tables (e.g. because the effects differ or it is important to show results separately). In the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (CDSR), all ‘Summary of findings’ tables for a review appear at the beginning, before the Background section.
14.1.2 Selecting outcomes for ‘Summary of findings’ tables
Planning for the ‘Summary of findings’ table starts early in the systematic review, with the selection of the outcomes to be included in: (i) the review; and (ii) the ‘Summary of findings’ table. This is a crucial step, and one that review authors need to address carefully.
To ensure production of optimally useful information, Cochrane Reviews begin by developing a review question and by listing all main outcomes that are important to patients and other decision makers (see Chapter 2 and Chapter 3 ). The GRADE approach to assessing the certainty of the evidence (see Section 14.2 ) defines and operationalizes a rating process that helps separate outcomes into those that are critical, important or not important for decision making. Consultation and feedback on the review protocol, including from consumers and other decision makers, can enhance this process.
Critical outcomes are likely to include clearly important endpoints; typical examples include mortality and major morbidity (such as strokes and myocardial infarction). However, they may also represent frequent minor and rare major side effects, symptoms, quality of life, burdens associated with treatment, and resource issues (costs). Burdens represent the impact of healthcare workload on patient function and well-being, and include the demands of adhering to an intervention that patients or caregivers (e.g. family) may dislike, such as having to undergo more frequent tests, or the restrictions on lifestyle that certain interventions require (Spencer-Bonilla et al 2017).
Frequently, when formulating questions that include all patient-important outcomes for decision making, review authors will confront reports of studies that have not included all these outcomes. This is particularly true for adverse outcomes. For instance, randomized trials might contribute evidence on intended effects, and on frequent, relatively minor side effects, but not report on rare adverse outcomes such as suicide attempts. Chapter 19 discusses strategies for addressing adverse effects. To obtain data for all important outcomes it may be necessary to examine the results of non-randomized studies (see Chapter 24 ). Cochrane, in collaboration with others, has developed guidance for review authors to support their decision about when to look for and include non-randomized studies (Schünemann et al 2013).
If a review includes only randomized trials, these trials may not address all important outcomes and it may therefore not be possible to address these outcomes within the constraints of the review. Review authors should acknowledge these limitations and make them transparent to readers. Review authors are encouraged to include non-randomized studies to examine rare or long-term adverse effects that may not adequately be studied in randomized trials. This raises the possibility that harm outcomes may come from studies in which participants differ from those in studies used in the analysis of benefit. Review authors will then need to consider how much such differences are likely to impact on the findings, and this will influence the certainty of evidence because of concerns about indirectness related to the population (see Section 14.2.2 ).
Non-randomized studies can provide important information not only when randomized trials do not report on an outcome or randomized trials suffer from indirectness, but also when the evidence from randomized trials is rated as very low and non-randomized studies provide evidence of higher certainty. Further discussion of these issues appears also in Chapter 24 .
14.1.3 General template for ‘Summary of findings’ tables
Several alternative standard versions of ‘Summary of findings’ tables have been developed to ensure consistency and ease of use across reviews, inclusion of the most important information needed by decision makers, and optimal presentation (see examples at Figures 14.1.a and 14.1.b ). These formats are supported by research that focused on improved understanding of the information they intend to convey (Carrasco-Labra et al 2016, Langendam et al 2016, Santesso et al 2016). They are available through GRADE’s official software package developed to support the GRADE approach: GRADEpro GDT (www.gradepro.org).
Standard Cochrane ‘Summary of findings’ tables include the following elements using one of the accepted formats. Further guidance on each of these is provided in Section 14.1.6 .
- A brief description of the population and setting addressed by the available evidence (which may be slightly different to or narrower than those defined by the review question).
- A brief description of the comparison addressed in the ‘Summary of findings’ table, including both the experimental and comparison interventions.
- A list of the most critical and/or important health outcomes, both desirable and undesirable, limited to seven or fewer outcomes.
- A measure of the typical burden of each outcomes (e.g. illustrative risk, or illustrative mean, on comparator intervention).
- The absolute and relative magnitude of effect measured for each (if both are appropriate).
- The numbers of participants and studies contributing to the analysis of each outcomes.
- A GRADE assessment of the overall certainty of the body of evidence for each outcome (which may vary by outcome).
- Space for comments.
- Explanations (formerly known as footnotes).
Ideally, ‘Summary of findings’ tables are supported by more detailed tables (known as ‘evidence profiles’) to which the review may be linked, which provide more detailed explanations. Evidence profiles include the same important health outcomes, and provide greater detail than ‘Summary of findings’ tables of both of the individual considerations feeding into the grading of certainty and of the results of the studies (Guyatt et al 2011a). They ensure that a structured approach is used to rating the certainty of evidence. Although they are rarely published in Cochrane Reviews, evidence profiles are often used, for example, by guideline developers in considering the certainty of the evidence to support guideline recommendations. Review authors will find it easier to develop the ‘Summary of findings’ table by completing the rating of the certainty of evidence in the evidence profile first in GRADEpro GDT. They can then automatically convert this to one of the ‘Summary of findings’ formats in GRADEpro GDT, including an interactive ‘Summary of findings’ for publication.
As a measure of the magnitude of effect for dichotomous outcomes, the ‘Summary of findings’ table should provide a relative measure of effect (e.g. risk ratio, odds ratio, hazard) and measures of absolute risk. For other types of data, an absolute measure alone (such as a difference in means for continuous data) might be sufficient. It is important that the magnitude of effect is presented in a meaningful way, which may require some transformation of the result of a meta-analysis (see also Chapter 15, Section 15.4 and Section 15.5 ). Reviews with more than one main comparison should include a separate ‘Summary of findings’ table for each comparison.
Figure 14.1.a provides an example of a ‘Summary of findings’ table. Figure 15.1.b provides an alternative format that may further facilitate users’ understanding and interpretation of the review’s findings. Evidence evaluating different formats suggests that the ‘Summary of findings’ table should include a risk difference as a measure of the absolute effect and authors should preferably use a format that includes a risk difference .
A detailed description of the contents of a ‘Summary of findings’ table appears in Section 14.1.6 .
Figure 14.1.a Example of a ‘Summary of findings’ table
Summary of findings (for interactive version click here )
a All the stockings in the nine studies included in this review were below-knee compression stockings. In four studies the compression strength was 20 mmHg to 30 mmHg at the ankle. It was 10 mmHg to 20 mmHg in the other four studies. Stockings come in different sizes. If a stocking is too tight around the knee it can prevent essential venous return causing the blood to pool around the knee. Compression stockings should be fitted properly. A stocking that is too tight could cut into the skin on a long flight and potentially cause ulceration and increased risk of DVT. Some stockings can be slightly thicker than normal leg covering and can be potentially restrictive with tight foot wear. It is a good idea to wear stockings around the house prior to travel to ensure a good, comfortable fit. Participants put their stockings on two to three hours before the flight in most of the studies. The availability and cost of stockings can vary.
b Two studies recruited high risk participants defined as those with previous episodes of DVT, coagulation disorders, severe obesity, limited mobility due to bone or joint problems, neoplastic disease within the previous two years, large varicose veins or, in one of the studies, participants taller than 190 cm and heavier than 90 kg. The incidence for the seven studies that excluded high risk participants was 1.45% and the incidence for the two studies that recruited high-risk participants (with at least one risk factor) was 2.43%. We have used 10 and 30 per 1000 to express different risk strata, respectively.
c The confidence interval crosses no difference and does not rule out a small increase.
d The measurement of oedema was not validated (indirectness of the outcome) or blinded to the intervention (risk of bias).
e If there are very few or no events and the number of participants is large, judgement about the certainty of evidence (particularly judgements about imprecision) may be based on the absolute effect. Here the certainty rating may be considered ‘high’ if the outcome was appropriately assessed and the event, in fact, did not occur in 2821 studied participants.
f None of the other studies reported adverse effects, apart from four cases of superficial vein thrombosis in varicose veins in the knee region that were compressed by the upper edge of the stocking in one study.
Figure 14.1.b Example of alternative ‘Summary of findings’ table
14.1.4 Producing ‘Summary of findings’ tables
The GRADE Working Group’s software, GRADEpro GDT ( www.gradepro.org ), including GRADE’s interactive handbook, is available to assist review authors in the preparation of ‘Summary of findings’ tables. GRADEpro can use data on the comparator group risk and the effect estimate (entered by the review authors or imported from files generated in RevMan) to produce the relative effects and absolute risks associated with experimental interventions. In addition, it leads the user through the process of a GRADE assessment, and produces a table that can be used as a standalone table in a review (including by direct import into software such as RevMan or integration with RevMan Web), or an interactive ‘Summary of findings’ table (see help resources in GRADEpro).
14.1.5 Statistical considerations in ‘Summary of findings’ tables
14.1.5.1 dichotomous outcomes.
‘Summary of findings’ tables should include both absolute and relative measures of effect for dichotomous outcomes. Risk ratios, odds ratios and risk differences are different ways of comparing two groups with dichotomous outcome data (see Chapter 6, Section 6.4.1 ). Furthermore, there are two distinct risk ratios, depending on which event (e.g. ‘yes’ or ‘no’) is the focus of the analysis (see Chapter 6, Section 6.4.1.5 ). In the presence of a non-zero intervention effect, any variation across studies in the comparator group risks (i.e. variation in the risk of the event occurring without the intervention of interest, for example in different populations) makes it impossible for more than one of these measures to be truly the same in every study.
It has long been assumed in epidemiology that relative measures of effect are more consistent than absolute measures of effect from one scenario to another. There is empirical evidence to support this assumption (Engels et al 2000, Deeks and Altman 2001, Furukawa et al 2002). For this reason, meta-analyses should generally use either a risk ratio or an odds ratio as a measure of effect (see Chapter 10, Section 10.4.3 ). Correspondingly, a single estimate of relative effect is likely to be a more appropriate summary than a single estimate of absolute effect. If a relative effect is indeed consistent across studies, then different comparator group risks will have different implications for absolute benefit. For instance, if the risk ratio is consistently 0.75, then the experimental intervention would reduce a comparator group risk of 80% to 60% in the intervention group (an absolute risk reduction of 20 percentage points), but would also reduce a comparator group risk of 20% to 15% in the intervention group (an absolute risk reduction of 5 percentage points).
‘Summary of findings’ tables are built around the assumption of a consistent relative effect. It is therefore important to consider the implications of this effect for different comparator group risks (these can be derived or estimated from a number of sources, see Section 14.1.6.3 ), which may require an assessment of the certainty of evidence for prognostic evidence (Spencer et al 2012, Iorio et al 2015). For any comparator group risk, it is possible to estimate a corresponding intervention group risk (i.e. the absolute risk with the intervention) from the meta-analytic risk ratio or odds ratio. Note that the numbers provided in the ‘Corresponding risk’ column are specific to the ‘risks’ in the adjacent column.
For the meta-analytic risk ratio (RR) and assumed comparator risk (ACR) the corresponding intervention risk is obtained as:
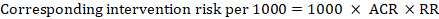
As an example, in Figure 14.1.a , the meta-analytic risk ratio for symptomless deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is RR = 0.10 (95% CI 0.04 to 0.26). Assuming a comparator risk of ACR = 10 per 1000 = 0.01, we obtain:
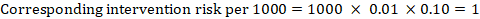
For the meta-analytic odds ratio (OR) and assumed comparator risk, ACR, the corresponding intervention risk is obtained as:
Upper and lower confidence limits for the corresponding intervention risk are obtained by replacing RR or OR by their upper and lower confidence limits, respectively (e.g. replacing 0.10 with 0.04, then with 0.26, in the example). Such confidence intervals do not incorporate uncertainty in the assumed comparator risks.
When dealing with risk ratios, it is critical that the same definition of ‘event’ is used as was used for the meta-analysis. For example, if the meta-analysis focused on ‘death’ (as opposed to survival) as the event, then corresponding risks in the ‘Summary of findings’ table must also refer to ‘death’.
In (rare) circumstances in which there is clear rationale to assume a consistent risk difference in the meta-analysis, in principle it is possible to present this for relevant ‘assumed risks’ and their corresponding risks, and to present the corresponding (different) relative effects for each assumed risk.
The risk difference expresses the difference between the ACR and the corresponding intervention risk (or the difference between the experimental and the comparator intervention).
For the meta-analytic risk ratio (RR) and assumed comparator risk (ACR) the corresponding risk difference is obtained as (note that risks can also be expressed using percentage or percentage points):
As an example, in Figure 14.1.b the meta-analytic risk ratio is 0.41 (95% CI 0.29 to 0.55) for diarrhoea in children less than 5 years of age. Assuming a comparator group risk of 22.3% we obtain:
For the meta-analytic odds ratio (OR) and assumed comparator risk (ACR) the absolute risk difference is obtained as (percentage points):
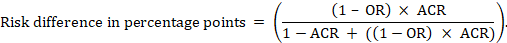
Upper and lower confidence limits for the absolute risk difference are obtained by re-running the calculation above while replacing RR or OR by their upper and lower confidence limits, respectively (e.g. replacing 0.41 with 0.28, then with 0.55, in the example). Such confidence intervals do not incorporate uncertainty in the assumed comparator risks.
14.1.5.2 Time-to-event outcomes
Time-to-event outcomes measure whether and when a particular event (e.g. death) occurs (van Dalen et al 2007). The impact of the experimental intervention relative to the comparison group on time-to-event outcomes is usually measured using a hazard ratio (HR) (see Chapter 6, Section 6.8.1 ).
A hazard ratio expresses a relative effect estimate. It may be used in various ways to obtain absolute risks and other interpretable quantities for a specific population. Here we describe how to re-express hazard ratios in terms of: (i) absolute risk of event-free survival within a particular period of time; (ii) absolute risk of an event within a particular period of time; and (iii) median time to the event. All methods are built on an assumption of consistent relative effects (i.e. that the hazard ratio does not vary over time).
(i) Absolute risk of event-free survival within a particular period of time Event-free survival (e.g. overall survival) is commonly reported by individual studies. To obtain absolute effects for time-to-event outcomes measured as event-free survival, the summary HR can be used in conjunction with an assumed proportion of patients who are event-free in the comparator group (Tierney et al 2007). This proportion of patients will be specific to a period of time of observation. However, it is not strictly necessary to specify this period of time. For instance, a proportion of 50% of event-free patients might apply to patients with a high event rate observed over 1 year, or to patients with a low event rate observed over 2 years.
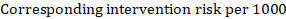
As an example, suppose the meta-analytic hazard ratio is 0.42 (95% CI 0.25 to 0.72). Assuming a comparator group risk of event-free survival (e.g. for overall survival people being alive) at 2 years of ACR = 900 per 1000 = 0.9 we obtain:
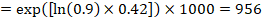
so that that 956 per 1000 people will be alive with the experimental intervention at 2 years. The derivation of the risk should be explained in a comment or footnote.
(ii) Absolute risk of an event within a particular period of time To obtain this absolute effect, again the summary HR can be used (Tierney et al 2007):
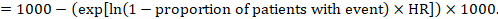
In the example, suppose we assume a comparator group risk of events (e.g. for mortality, people being dead) at 2 years of ACR = 100 per 1000 = 0.1. We obtain:
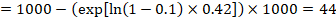
so that that 44 per 1000 people will be dead with the experimental intervention at 2 years.
(iii) Median time to the event Instead of absolute numbers, the time to the event in the intervention and comparison groups can be expressed as median survival time in months or years. To obtain median survival time the pooled HR can be applied to an assumed median survival time in the comparator group (Tierney et al 2007):
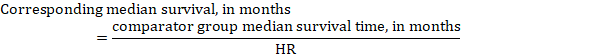
In the example, assuming a comparator group median survival time of 80 months, we obtain:
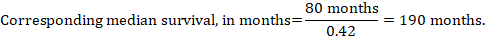
For all three of these options for re-expressing results of time-to-event analyses, upper and lower confidence limits for the corresponding intervention risk are obtained by replacing HR by its upper and lower confidence limits, respectively (e.g. replacing 0.42 with 0.25, then with 0.72, in the example). Again, as for dichotomous outcomes, such confidence intervals do not incorporate uncertainty in the assumed comparator group risks. This is of special concern for long-term survival with a low or moderate mortality rate and a corresponding high number of censored patients (i.e. a low number of patients under risk and a high censoring rate).
14.1.6 Detailed contents of a ‘Summary of findings’ table
14.1.6.1 table title and header.
The title of each ‘Summary of findings’ table should specify the healthcare question, framed in terms of the population and making it clear exactly what comparison of interventions are made. In Figure 14.1.a , the population is people taking long aeroplane flights, the intervention is compression stockings, and the control is no compression stockings.
The first rows of each ‘Summary of findings’ table should provide the following ‘header’ information:
Patients or population This further clarifies the population (and possibly the subpopulations) of interest and ideally the magnitude of risk of the most crucial adverse outcome at which an intervention is directed. For instance, people on a long-haul flight may be at different risks for DVT; those using selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) might be at different risk for side effects; while those with atrial fibrillation may be at low (< 1%), moderate (1% to 4%) or high (> 4%) yearly risk of stroke.
Setting This should state any specific characteristics of the settings of the healthcare question that might limit the applicability of the summary of findings to other settings (e.g. primary care in Europe and North America).
Intervention The experimental intervention.
Comparison The comparator intervention (including no specific intervention).
14.1.6.2 Outcomes
The rows of a ‘Summary of findings’ table should include all desirable and undesirable health outcomes (listed in order of importance) that are essential for decision making, up to a maximum of seven outcomes. If there are more outcomes in the review, review authors will need to omit the less important outcomes from the table, and the decision selecting which outcomes are critical or important to the review should be made during protocol development (see Chapter 3 ). Review authors should provide time frames for the measurement of the outcomes (e.g. 90 days or 12 months) and the type of instrument scores (e.g. ranging from 0 to 100).
Note that review authors should include the pre-specified critical and important outcomes in the table whether data are available or not. However, they should be alert to the possibility that the importance of an outcome (e.g. a serious adverse effect) may only become known after the protocol was written or the analysis was carried out, and should take appropriate actions to include these in the ‘Summary of findings’ table.
The ‘Summary of findings’ table can include effects in subgroups of the population for different comparator risks and effect sizes separately. For instance, in Figure 14.1.b effects are presented for children younger and older than 5 years separately. Review authors may also opt to produce separate ‘Summary of findings’ tables for different populations.
Review authors should include serious adverse events, but it might be possible to combine minor adverse events as a single outcome, and describe this in an explanatory footnote (note that it is not appropriate to add events together unless they are independent, that is, a participant who has experienced one adverse event has an unaffected chance of experiencing the other adverse event).
Outcomes measured at multiple time points represent a particular problem. In general, to keep the table simple, review authors should present multiple time points only for outcomes critical to decision making, where either the result or the decision made are likely to vary over time. The remainder should be presented at a common time point where possible.
Review authors can present continuous outcome measures in the ‘Summary of findings’ table and should endeavour to make these interpretable to the target audience. This requires that the units are clear and readily interpretable, for example, days of pain, or frequency of headache, and the name and scale of any measurement tools used should be stated (e.g. a Visual Analogue Scale, ranging from 0 to 100). However, many measurement instruments are not readily interpretable by non-specialist clinicians or patients, for example, points on a Beck Depression Inventory or quality of life score. For these, a more interpretable presentation might involve converting a continuous to a dichotomous outcome, such as >50% improvement (see Chapter 15, Section 15.5 ).
14.1.6.3 Best estimate of risk with comparator intervention
Review authors should provide up to three typical risks for participants receiving the comparator intervention. For dichotomous outcomes, we recommend that these be presented in the form of the number of people experiencing the event per 100 or 1000 people (natural frequency) depending on the frequency of the outcome. For continuous outcomes, this would be stated as a mean or median value of the outcome measured.
Estimated or assumed comparator intervention risks could be based on assessments of typical risks in different patient groups derived from the review itself, individual representative studies in the review, or risks derived from a systematic review of prognosis studies or other sources of evidence which may in turn require an assessment of the certainty for the prognostic evidence (Spencer et al 2012, Iorio et al 2015). Ideally, risks would reflect groups that clinicians can easily identify on the basis of their presenting features.
An explanatory footnote should specify the source or rationale for each comparator group risk, including the time period to which it corresponds where appropriate. In Figure 14.1.a , clinicians can easily differentiate individuals with risk factors for deep venous thrombosis from those without. If there is known to be little variation in baseline risk then review authors may use the median comparator group risk across studies. If typical risks are not known, an option is to choose the risk from the included studies, providing the second highest for a high and the second lowest for a low risk population.
14.1.6.4 Risk with intervention
For dichotomous outcomes, review authors should provide a corresponding absolute risk for each comparator group risk, along with a confidence interval. This absolute risk with the (experimental) intervention will usually be derived from the meta-analysis result presented in the relative effect column (see Section 14.1.6.6 ). Formulae are provided in Section 14.1.5 . Review authors should present the absolute effect in the same format as the risks with comparator intervention (see Section 14.1.6.3 ), for example as the number of people experiencing the event per 1000 people.
For continuous outcomes, a difference in means or standardized difference in means should be presented with its confidence interval. These will typically be obtained directly from a meta-analysis. Explanatory text should be used to clarify the meaning, as in Figures 14.1.a and 14.1.b .
14.1.6.5 Risk difference
For dichotomous outcomes, the risk difference can be provided using one of the ‘Summary of findings’ table formats as an additional option (see Figure 14.1.b ). This risk difference expresses the difference between the experimental and comparator intervention and will usually be derived from the meta-analysis result presented in the relative effect column (see Section 14.1.6.6 ). Formulae are provided in Section 14.1.5 . Review authors should present the risk difference in the same format as assumed and corresponding risks with comparator intervention (see Section 14.1.6.3 ); for example, as the number of people experiencing the event per 1000 people or as percentage points if the assumed and corresponding risks are expressed in percentage.
For continuous outcomes, if the ‘Summary of findings’ table includes this option, the mean difference can be presented here and the ‘corresponding risk’ column left blank (see Figure 14.1.b ).
14.1.6.6 Relative effect (95% CI)
The relative effect will typically be a risk ratio or odds ratio (or occasionally a hazard ratio) with its accompanying 95% confidence interval, obtained from a meta-analysis performed on the basis of the same effect measure. Risk ratios and odds ratios are similar when the comparator intervention risks are low and effects are small, but may differ considerably when comparator group risks increase. The meta-analysis may involve an assumption of either fixed or random effects, depending on what the review authors consider appropriate, and implying that the relative effect is either an estimate of the effect of the intervention, or an estimate of the average effect of the intervention across studies, respectively.
14.1.6.7 Number of participants (studies)
This column should include the number of participants assessed in the included studies for each outcome and the corresponding number of studies that contributed these participants.
14.1.6.8 Certainty of the evidence (GRADE)
Review authors should comment on the certainty of the evidence (also known as quality of the body of evidence or confidence in the effect estimates). Review authors should use the specific evidence grading system developed by the GRADE Working Group (Atkins et al 2004, Guyatt et al 2008, Guyatt et al 2011a), which is described in detail in Section 14.2 . The GRADE approach categorizes the certainty in a body of evidence as ‘high’, ‘moderate’, ‘low’ or ‘very low’ by outcome. This is a result of judgement, but the judgement process operates within a transparent structure. As an example, the certainty would be ‘high’ if the summary were of several randomized trials with low risk of bias, but the rating of certainty becomes lower if there are concerns about risk of bias, inconsistency, indirectness, imprecision or publication bias. Judgements other than of ‘high’ certainty should be made transparent using explanatory footnotes or the ‘Comments’ column in the ‘Summary of findings’ table (see Section 14.1.6.10 ).
14.1.6.9 Comments
The aim of the ‘Comments’ field is to help interpret the information or data identified in the row. For example, this may be on the validity of the outcome measure or the presence of variables that are associated with the magnitude of effect. Important caveats about the results should be flagged here. Not all rows will need comments, and it is best to leave a blank if there is nothing warranting a comment.
14.1.6.10 Explanations
Detailed explanations should be included as footnotes to support the judgements in the ‘Summary of findings’ table, such as the overall GRADE assessment. The explanations should describe the rationale for important aspects of the content. Table 14.1.a lists guidance for useful explanations. Explanations should be concise, informative, relevant, easy to understand and accurate. If explanations cannot be sufficiently described in footnotes, review authors should provide further details of the issues in the Results and Discussion sections of the review.
Table 14.1.a Guidance for providing useful explanations in ‘Summary of findings’ (SoF) tables. Adapted from Santesso et al (2016)
14.2 Assessing the certainty or quality of a body of evidence
14.2.1 the grade approach.
The Grades of Recommendation, Assessment, Development and Evaluation Working Group (GRADE Working Group) has developed a system for grading the certainty of evidence (Schünemann et al 2003, Atkins et al 2004, Schünemann et al 2006, Guyatt et al 2008, Guyatt et al 2011a). Over 100 organizations including the World Health Organization (WHO), the American College of Physicians, the American Society of Hematology (ASH), the Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technology in Health (CADTH) and the National Institutes of Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) in the UK have adopted the GRADE system ( www.gradeworkinggroup.org ).
Cochrane has also formally adopted this approach, and all Cochrane Reviews should use GRADE to evaluate the certainty of evidence for important outcomes (see MECIR Box 14.2.a ).
MECIR Box 14.2.a Relevant expectations for conduct of intervention reviews
For systematic reviews, the GRADE approach defines the certainty of a body of evidence as the extent to which one can be confident that an estimate of effect or association is close to the quantity of specific interest. Assessing the certainty of a body of evidence involves consideration of within- and across-study risk of bias (limitations in study design and execution or methodological quality), inconsistency (or heterogeneity), indirectness of evidence, imprecision of the effect estimates and risk of publication bias (see Section 14.2.2 ), as well as domains that may increase our confidence in the effect estimate (as described in Section 14.2.3 ). The GRADE system entails an assessment of the certainty of a body of evidence for each individual outcome. Judgements about the domains that determine the certainty of evidence should be described in the results or discussion section and as part of the ‘Summary of findings’ table.
The GRADE approach specifies four levels of certainty ( Figure 14.2.a ). For interventions, including diagnostic and other tests that are evaluated as interventions (Schünemann et al 2008b, Schünemann et al 2008a, Balshem et al 2011, Schünemann et al 2012), the starting point for rating the certainty of evidence is categorized into two types:
- randomized trials; and
- non-randomized studies of interventions (NRSI), including observational studies (including but not limited to cohort studies, and case-control studies, cross-sectional studies, case series and case reports, although not all of these designs are usually included in Cochrane Reviews).
There are many instances in which review authors rely on information from NRSI, in particular to evaluate potential harms (see Chapter 24 ). In addition, review authors can obtain relevant data from both randomized trials and NRSI, with each type of evidence complementing the other (Schünemann et al 2013).
In GRADE, a body of evidence from randomized trials begins with a high-certainty rating while a body of evidence from NRSI begins with a low-certainty rating. The lower rating with NRSI is the result of the potential bias induced by the lack of randomization (i.e. confounding and selection bias).
However, when using the new Risk Of Bias In Non-randomized Studies of Interventions (ROBINS-I) tool (Sterne et al 2016), an assessment tool that covers the risk of bias due to lack of randomization, all studies may start as high certainty of the evidence (Schünemann et al 2018). The approach of starting all study designs (including NRSI) as high certainty does not conflict with the initial GRADE approach of starting the rating of NRSI as low certainty evidence. This is because a body of evidence from NRSI should generally be downgraded by two levels due to the inherent risk of bias associated with the lack of randomization, namely confounding and selection bias. Not downgrading NRSI from high to low certainty needs transparent and detailed justification for what mitigates concerns about confounding and selection bias (Schünemann et al 2018). Very few examples of where not rating down by two levels is appropriate currently exist.
The highest certainty rating is a body of evidence when there are no concerns in any of the GRADE factors listed in Figure 14.2.a . Review authors often downgrade evidence to moderate, low or even very low certainty evidence, depending on the presence of the five factors in Figure 14.2.a . Usually, certainty rating will fall by one level for each factor, up to a maximum of three levels for all factors. If there are very severe problems for any one domain (e.g. when assessing risk of bias, all studies were unconcealed, unblinded and lost over 50% of their patients to follow-up), evidence may fall by two levels due to that factor alone. It is not possible to rate lower than ‘very low certainty’ evidence.
Review authors will generally grade evidence from sound non-randomized studies as low certainty, even if ROBINS-I is used. If, however, such studies yield large effects and there is no obvious bias explaining those effects, review authors may rate the evidence as moderate or – if the effect is large enough – even as high certainty ( Figure 14.2.a ). The very low certainty level is appropriate for, but is not limited to, studies with critical problems and unsystematic clinical observations (e.g. case series or case reports).
Figure 14.2.a Levels of the certainty of a body of evidence in the GRADE approach. *Upgrading criteria are usually applicable to non-randomized studies only (but exceptions exist).
14.2.2 Domains that can lead to decreasing the certainty level of a body of evidence
We now describe in more detail the five reasons (or domains) for downgrading the certainty of a body of evidence for a specific outcome. In each case, if no reason is found for downgrading the evidence, it should be classified as 'no limitation or not serious' (not important enough to warrant downgrading). If a reason is found for downgrading the evidence, it should be classified as 'serious' (downgrading the certainty rating by one level) or 'very serious' (downgrading the certainty grade by two levels). For non-randomized studies assessed with ROBINS-I, rating down by three levels should be classified as 'extremely' serious.
(1) Risk of bias or limitations in the detailed design and implementation
Our confidence in an estimate of effect decreases if studies suffer from major limitations that are likely to result in a biased assessment of the intervention effect. For randomized trials, these methodological limitations include failure to generate a random sequence, lack of allocation sequence concealment, lack of blinding (particularly with subjective outcomes that are highly susceptible to biased assessment), a large loss to follow-up or selective reporting of outcomes. Chapter 8 provides a discussion of study-level assessments of risk of bias in the context of a Cochrane Review, and proposes an approach to assessing the risk of bias for an outcome across studies as ‘Low’ risk of bias, ‘Some concerns’ and ‘High’ risk of bias for randomized trials. Levels of ‘Low’. ‘Moderate’, ‘Serious’ and ‘Critical’ risk of bias arise for non-randomized studies assessed with ROBINS-I ( Chapter 25 ). These assessments should feed directly into this GRADE domain. In particular, ‘Low’ risk of bias would indicate ‘no limitation’; ‘Some concerns’ would indicate either ‘no limitation’ or ‘serious limitation’; and ‘High’ risk of bias would indicate either ‘serious limitation’ or ‘very serious limitation’. ‘Critical’ risk of bias on ROBINS-I would indicate extremely serious limitations in GRADE. Review authors should use their judgement to decide between alternative categories, depending on the likely magnitude of the potential biases.
Every study addressing a particular outcome will differ, to some degree, in the risk of bias. Review authors should make an overall judgement on whether the certainty of evidence for an outcome warrants downgrading on the basis of study limitations. The assessment of study limitations should apply to the studies contributing to the results in the ‘Summary of findings’ table, rather than to all studies that could potentially be included in the analysis. We have argued in Chapter 7, Section 7.6.2 , that the primary analysis should be restricted to studies at low (or low and unclear) risk of bias where possible.
Table 14.2.a presents the judgements that must be made in going from assessments of the risk of bias to judgements about study limitations for each outcome included in a ‘Summary of findings’ table. A rating of high certainty evidence can be achieved only when most evidence comes from studies that met the criteria for low risk of bias. For example, of the 22 studies addressing the impact of beta-blockers on mortality in patients with heart failure, most probably or certainly used concealed allocation of the sequence, all blinded at least some key groups and follow-up of randomized patients was almost complete (Brophy et al 2001). The certainty of evidence might be downgraded by one level when most of the evidence comes from individual studies either with a crucial limitation for one item, or with some limitations for multiple items. An example of very serious limitations, warranting downgrading by two levels, is provided by evidence on surgery versus conservative treatment in the management of patients with lumbar disc prolapse (Gibson and Waddell 2007). We are uncertain of the benefit of surgery in reducing symptoms after one year or longer, because the one study included in the analysis had inadequate concealment of the allocation sequence and the outcome was assessed using a crude rating by the surgeon without blinding.
(2) Unexplained heterogeneity or inconsistency of results
When studies yield widely differing estimates of effect (heterogeneity or variability in results), investigators should look for robust explanations for that heterogeneity. For instance, drugs may have larger relative effects in sicker populations or when given in larger doses. A detailed discussion of heterogeneity and its investigation is provided in Chapter 10, Section 10.10 and Section 10.11 . If an important modifier exists, with good evidence that important outcomes are different in different subgroups (which would ideally be pre-specified), then a separate ‘Summary of findings’ table may be considered for a separate population. For instance, a separate ‘Summary of findings’ table would be used for carotid endarterectomy in symptomatic patients with high grade stenosis (70% to 99%) in which the intervention is, in the hands of the right surgeons, beneficial, and another (if review authors considered it relevant) for asymptomatic patients with low grade stenosis (less than 30%) in which surgery appears harmful (Orrapin and Rerkasem 2017). When heterogeneity exists and affects the interpretation of results, but review authors are unable to identify a plausible explanation with the data available, the certainty of the evidence decreases.
(3) Indirectness of evidence
Two types of indirectness are relevant. First, a review comparing the effectiveness of alternative interventions (say A and B) may find that randomized trials are available, but they have compared A with placebo and B with placebo. Thus, the evidence is restricted to indirect comparisons between A and B. Where indirect comparisons are undertaken within a network meta-analysis context, GRADE for network meta-analysis should be used (see Chapter 11, Section 11.5 ).
Second, a review may find randomized trials that meet eligibility criteria but address a restricted version of the main review question in terms of population, intervention, comparator or outcomes. For example, suppose that in a review addressing an intervention for secondary prevention of coronary heart disease, most identified studies happened to be in people who also had diabetes. Then the evidence may be regarded as indirect in relation to the broader question of interest because the population is primarily related to people with diabetes. The opposite scenario can equally apply: a review addressing the effect of a preventive strategy for coronary heart disease in people with diabetes may consider studies in people without diabetes to provide relevant, albeit indirect, evidence. This would be particularly likely if investigators had conducted few if any randomized trials in the target population (e.g. people with diabetes). Other sources of indirectness may arise from interventions studied (e.g. if in all included studies a technical intervention was implemented by expert, highly trained specialists in specialist centres, then evidence on the effects of the intervention outside these centres may be indirect), comparators used (e.g. if the comparator groups received an intervention that is less effective than standard treatment in most settings) and outcomes assessed (e.g. indirectness due to surrogate outcomes when data on patient-important outcomes are not available, or when investigators seek data on quality of life but only symptoms are reported). Review authors should make judgements transparent when they believe downgrading is justified, based on differences in anticipated effects in the group of primary interest. Review authors may be aided and increase transparency of their judgements about indirectness if they use Table 14.2.b available in the GRADEpro GDT software (Schünemann et al 2013).
(4) Imprecision of results
When studies include few participants or few events, and thus have wide confidence intervals, review authors can lower their rating of the certainty of the evidence. The confidence intervals included in the ‘Summary of findings’ table will provide readers with information that allows them to make, to some extent, their own rating of precision. Review authors can use a calculation of the optimal information size (OIS) or review information size (RIS), similar to sample size calculations, to make judgements about imprecision (Guyatt et al 2011b, Schünemann 2016). The OIS or RIS is calculated on the basis of the number of participants required for an adequately powered individual study. If the 95% confidence interval excludes a risk ratio (RR) of 1.0, and the total number of events or patients exceeds the OIS criterion, precision is adequate. If the 95% CI includes appreciable benefit or harm (an RR of under 0.75 or over 1.25 is often suggested as a very rough guide) downgrading for imprecision may be appropriate even if OIS criteria are met (Guyatt et al 2011b, Schünemann 2016).
(5) High probability of publication bias
The certainty of evidence level may be downgraded if investigators fail to report studies on the basis of results (typically those that show no effect: publication bias) or outcomes (typically those that may be harmful or for which no effect was observed: selective outcome non-reporting bias). Selective reporting of outcomes from among multiple outcomes measured is assessed at the study level as part of the assessment of risk of bias (see Chapter 8, Section 8.7 ), so for the studies contributing to the outcome in the ‘Summary of findings’ table this is addressed by domain 1 above (limitations in the design and implementation). If a large number of studies included in the review do not contribute to an outcome, or if there is evidence of publication bias, the certainty of the evidence may be downgraded. Chapter 13 provides a detailed discussion of reporting biases, including publication bias, and how it may be tackled in a Cochrane Review. A prototypical situation that may elicit suspicion of publication bias is when published evidence includes a number of small studies, all of which are industry-funded (Bhandari et al 2004). For example, 14 studies of flavanoids in patients with haemorrhoids have shown apparent large benefits, but enrolled a total of only 1432 patients (i.e. each study enrolled relatively few patients) (Alonso-Coello et al 2006). The heavy involvement of sponsors in most of these studies raises questions of whether unpublished studies that suggest no benefit exist (publication bias).
A particular body of evidence can suffer from problems associated with more than one of the five factors listed here, and the greater the problems, the lower the certainty of evidence rating that should result. One could imagine a situation in which randomized trials were available, but all or virtually all of these limitations would be present, and in serious form. A very low certainty of evidence rating would result.
Table 14.2.a Further guidelines for domain 1 (of 5) in a GRADE assessment: going from assessments of risk of bias in studies to judgements about study limitations for main outcomes across studies
Table 14.2.b Judgements about indirectness by outcome (available in GRADEpro GDT)
Intervention:
Comparator:
Direct comparison:
Final judgement about indirectness across domains:
14.2.3 Domains that may lead to increasing the certainty level of a body of evidence
Although NRSI and downgraded randomized trials will generally yield a low rating for certainty of evidence, there will be unusual circumstances in which review authors could ‘upgrade’ such evidence to moderate or even high certainty ( Table 14.3.a ).
- Large effects On rare occasions when methodologically well-done observational studies yield large, consistent and precise estimates of the magnitude of an intervention effect, one may be particularly confident in the results. A large estimated effect (e.g. RR >2 or RR <0.5) in the absence of plausible confounders, or a very large effect (e.g. RR >5 or RR <0.2) in studies with no major threats to validity, might qualify for this. In these situations, while the NRSI may possibly have provided an over-estimate of the true effect, the weak study design may not explain all of the apparent observed benefit. Thus, despite reservations based on the observational study design, review authors are confident that the effect exists. The magnitude of the effect in these studies may move the assigned certainty of evidence from low to moderate (if the effect is large in the absence of other methodological limitations). For example, a meta-analysis of observational studies showed that bicycle helmets reduce the risk of head injuries in cyclists by a large margin (odds ratio (OR) 0.31, 95% CI 0.26 to 0.37) (Thompson et al 2000). This large effect, in the absence of obvious bias that could create the association, suggests a rating of moderate-certainty evidence. Note : GRADE guidance suggests the possibility of rating up one level for a large effect if the relative effect is greater than 2.0. However, if the point estimate of the relative effect is greater than 2.0, but the confidence interval is appreciably below 2.0, then some hesitation would be appropriate in the decision to rate up for a large effect. Another situation allows inference of a strong association without a formal comparative study. Consider the question of the impact of routine colonoscopy versus no screening for colon cancer on the rate of perforation associated with colonoscopy. Here, a large series of representative patients undergoing colonoscopy may provide high certainty evidence about the risk of perforation associated with colonoscopy. When the risk of the event among patients receiving the relevant comparator is known to be near 0 (i.e. we are certain that the incidence of spontaneous colon perforation in patients not undergoing colonoscopy is extremely low), case series or cohort studies of representative patients can provide high certainty evidence of adverse effects associated with an intervention, thereby allowing us to infer a strong association from even a limited number of events.
- Dose-response The presence of a dose-response gradient may increase our confidence in the findings of observational studies and thereby enhance the assigned certainty of evidence. For example, our confidence in the result of observational studies that show an increased risk of bleeding in patients who have supratherapeutic anticoagulation levels is increased by the observation that there is a dose-response gradient between the length of time needed for blood to clot (as measured by the international normalized ratio (INR)) and an increased risk of bleeding (Levine et al 2004). A systematic review of NRSI investigating the effect of cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors on cardiovascular events found that the summary estimate (RR) with rofecoxib was 1.33 (95% CI 1.00 to 1.79) with doses less than 25mg/d, and 2.19 (95% CI 1.64 to 2.91) with doses more than 25mg/d. Although residual confounding is likely to exist in the NRSI that address this issue, the existence of a dose-response gradient and the large apparent effect of higher doses of rofecoxib markedly increase our strength of inference that the association cannot be explained by residual confounding, and is therefore likely to be both causal and, at high levels of exposure, substantial. Note : GRADE guidance suggests the possibility of rating up one level for a large effect if the relative effect is greater than 2.0. Here, the fact that the point estimate of the relative effect is greater than 2.0, but the confidence interval is appreciably below 2.0 might make some hesitate in the decision to rate up for a large effect
- Plausible confounding On occasion, all plausible biases from randomized or non-randomized studies may be working to under-estimate an apparent intervention effect. For example, if only sicker patients receive an experimental intervention or exposure, yet they still fare better, it is likely that the actual intervention or exposure effect is larger than the data suggest. For instance, a rigorous systematic review of observational studies including a total of 38 million patients demonstrated higher death rates in private for-profit versus private not-for-profit hospitals (Devereaux et al 2002). One possible bias relates to different disease severity in patients in the two hospital types. It is likely, however, that patients in the not-for-profit hospitals were sicker than those in the for-profit hospitals. Thus, to the extent that residual confounding existed, it would bias results against the not-for-profit hospitals. The second likely bias was the possibility that higher numbers of patients with excellent private insurance coverage could lead to a hospital having more resources and a spill-over effect that would benefit those without such coverage. Since for-profit hospitals are likely to admit a larger proportion of such well-insured patients than not-for-profit hospitals, the bias is once again against the not-for-profit hospitals. Since the plausible biases would all diminish the demonstrated intervention effect, one might consider the evidence from these observational studies as moderate rather than low certainty. A parallel situation exists when observational studies have failed to demonstrate an association, but all plausible biases would have increased an intervention effect. This situation will usually arise in the exploration of apparent harmful effects. For example, because the hypoglycaemic drug phenformin causes lactic acidosis, the related agent metformin was under suspicion for the same toxicity. Nevertheless, very large observational studies have failed to demonstrate an association (Salpeter et al 2007). Given the likelihood that clinicians would be more alert to lactic acidosis in the presence of the agent and over-report its occurrence, one might consider this moderate, or even high certainty, evidence refuting a causal relationship between typical therapeutic doses of metformin and lactic acidosis.

14.3 Describing the assessment of the certainty of a body of evidence using the GRADE framework
Review authors should report the grading of the certainty of evidence in the Results section for each outcome for which this has been performed, providing the rationale for downgrading or upgrading the evidence, and referring to the ‘Summary of findings’ table where applicable.
Table 14.3.a provides a framework and examples for how review authors can justify their judgements about the certainty of evidence in each domain. These justifications should also be included in explanatory notes to the ‘Summary of Findings’ table (see Section 14.1.6.10 ).
Chapter 15, Section 15.6 , describes in more detail how the overall GRADE assessment across all domains can be used to draw conclusions about the effects of the intervention, as well as providing implications for future research.
Table 14.3.a Framework for describing the certainty of evidence and justifying downgrading or upgrading
14.4 Chapter information
Authors: Holger J Schünemann, Julian PT Higgins, Gunn E Vist, Paul Glasziou, Elie A Akl, Nicole Skoetz, Gordon H Guyatt; on behalf of the Cochrane GRADEing Methods Group (formerly Applicability and Recommendations Methods Group) and the Cochrane Statistical Methods Group
Acknowledgements: Andrew D Oxman contributed to earlier versions. Professor Penny Hawe contributed to the text on adverse effects in earlier versions. Jon Deeks provided helpful contributions on an earlier version of this chapter. For details of previous authors and editors of the Handbook , please refer to the Preface.
Funding: This work was in part supported by funding from the Michael G DeGroote Cochrane Canada Centre and the Ontario Ministry of Health.
14.5 References
Alonso-Coello P, Zhou Q, Martinez-Zapata MJ, Mills E, Heels-Ansdell D, Johanson JF, Guyatt G. Meta-analysis of flavonoids for the treatment of haemorrhoids. British Journal of Surgery 2006; 93 : 909-920.
Atkins D, Best D, Briss PA, Eccles M, Falck-Ytter Y, Flottorp S, Guyatt GH, Harbour RT, Haugh MC, Henry D, Hill S, Jaeschke R, Leng G, Liberati A, Magrini N, Mason J, Middleton P, Mrukowicz J, O'Connell D, Oxman AD, Phillips B, Schünemann HJ, Edejer TT, Varonen H, Vist GE, Williams JW, Jr., Zaza S. Grading quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. BMJ 2004; 328 : 1490.
Balshem H, Helfand M, Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Kunz R, Brozek J, Vist GE, Falck-Ytter Y, Meerpohl J, Norris S, Guyatt GH. GRADE guidelines: 3. Rating the quality of evidence. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011; 64 : 401-406.
Bhandari M, Busse JW, Jackowski D, Montori VM, Schünemann H, Sprague S, Mears D, Schemitsch EH, Heels-Ansdell D, Devereaux PJ. Association between industry funding and statistically significant pro-industry findings in medical and surgical randomized trials. Canadian Medical Association Journal 2004; 170 : 477-480.
Brophy JM, Joseph L, Rouleau JL. Beta-blockers in congestive heart failure. A Bayesian meta-analysis. Annals of Internal Medicine 2001; 134 : 550-560.
Carrasco-Labra A, Brignardello-Petersen R, Santesso N, Neumann I, Mustafa RA, Mbuagbaw L, Etxeandia Ikobaltzeta I, De Stio C, McCullagh LJ, Alonso-Coello P, Meerpohl JJ, Vandvik PO, Brozek JL, Akl EA, Bossuyt P, Churchill R, Glenton C, Rosenbaum S, Tugwell P, Welch V, Garner P, Guyatt G, Schünemann HJ. Improving GRADE evidence tables part 1: a randomized trial shows improved understanding of content in summary of findings tables with a new format. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2016; 74 : 7-18.
Deeks JJ, Altman DG. Effect measures for meta-analysis of trials with binary outcomes. In: Egger M, Davey Smith G, Altman DG, editors. Systematic Reviews in Health Care: Meta-analysis in Context . 2nd ed. London (UK): BMJ Publication Group; 2001. p. 313-335.
Devereaux PJ, Choi PT, Lacchetti C, Weaver B, Schünemann HJ, Haines T, Lavis JN, Grant BJ, Haslam DR, Bhandari M, Sullivan T, Cook DJ, Walter SD, Meade M, Khan H, Bhatnagar N, Guyatt GH. A systematic review and meta-analysis of studies comparing mortality rates of private for-profit and private not-for-profit hospitals. Canadian Medical Association Journal 2002; 166 : 1399-1406.
Engels EA, Schmid CH, Terrin N, Olkin I, Lau J. Heterogeneity and statistical significance in meta-analysis: an empirical study of 125 meta-analyses. Statistics in Medicine 2000; 19 : 1707-1728.
Furukawa TA, Guyatt GH, Griffith LE. Can we individualize the 'number needed to treat'? An empirical study of summary effect measures in meta-analyses. International Journal of Epidemiology 2002; 31 : 72-76.
Gibson JN, Waddell G. Surgical interventions for lumbar disc prolapse: updated Cochrane Review. Spine 2007; 32 : 1735-1747.
Guyatt G, Oxman A, Vist G, Kunz R, Falck-Ytter Y, Alonso-Coello P, Schünemann H. GRADE: an emerging consensus on rating quality of evidence and strength of recommendations. BMJ 2008; 336 : 3.
Guyatt G, Oxman AD, Akl EA, Kunz R, Vist G, Brozek J, Norris S, Falck-Ytter Y, Glasziou P, DeBeer H, Jaeschke R, Rind D, Meerpohl J, Dahm P, Schünemann HJ. GRADE guidelines: 1. Introduction-GRADE evidence profiles and summary of findings tables. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011a; 64 : 383-394.
Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Kunz R, Brozek J, Alonso-Coello P, Rind D, Devereaux PJ, Montori VM, Freyschuss B, Vist G, Jaeschke R, Williams JW, Jr., Murad MH, Sinclair D, Falck-Ytter Y, Meerpohl J, Whittington C, Thorlund K, Andrews J, Schünemann HJ. GRADE guidelines 6. Rating the quality of evidence--imprecision. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011b; 64 : 1283-1293.
Iorio A, Spencer FA, Falavigna M, Alba C, Lang E, Burnand B, McGinn T, Hayden J, Williams K, Shea B, Wolff R, Kujpers T, Perel P, Vandvik PO, Glasziou P, Schünemann H, Guyatt G. Use of GRADE for assessment of evidence about prognosis: rating confidence in estimates of event rates in broad categories of patients. BMJ 2015; 350 : h870.
Langendam M, Carrasco-Labra A, Santesso N, Mustafa RA, Brignardello-Petersen R, Ventresca M, Heus P, Lasserson T, Moustgaard R, Brozek J, Schünemann HJ. Improving GRADE evidence tables part 2: a systematic survey of explanatory notes shows more guidance is needed. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2016; 74 : 19-27.
Levine MN, Raskob G, Landefeld S, Kearon C, Schulman S. Hemorrhagic complications of anticoagulant treatment: the Seventh ACCP Conference on Antithrombotic and Thrombolytic Therapy. Chest 2004; 126 : 287S-310S.
Orrapin S, Rerkasem K. Carotid endarterectomy for symptomatic carotid stenosis. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2017; 6 : CD001081.
Salpeter S, Greyber E, Pasternak G, Salpeter E. Risk of fatal and nonfatal lactic acidosis with metformin use in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2007; 4 : CD002967.
Santesso N, Carrasco-Labra A, Langendam M, Brignardello-Petersen R, Mustafa RA, Heus P, Lasserson T, Opiyo N, Kunnamo I, Sinclair D, Garner P, Treweek S, Tovey D, Akl EA, Tugwell P, Brozek JL, Guyatt G, Schünemann HJ. Improving GRADE evidence tables part 3: detailed guidance for explanatory footnotes supports creating and understanding GRADE certainty in the evidence judgments. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2016; 74 : 28-39.
Schünemann HJ, Best D, Vist G, Oxman AD, Group GW. Letters, numbers, symbols and words: how to communicate grades of evidence and recommendations. Canadian Medical Association Journal 2003; 169 : 677-680.
Schünemann HJ, Jaeschke R, Cook DJ, Bria WF, El-Solh AA, Ernst A, Fahy BF, Gould MK, Horan KL, Krishnan JA, Manthous CA, Maurer JR, McNicholas WT, Oxman AD, Rubenfeld G, Turino GM, Guyatt G. An official ATS statement: grading the quality of evidence and strength of recommendations in ATS guidelines and recommendations. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2006; 174 : 605-614.
Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Brozek J, Glasziou P, Jaeschke R, Vist GE, Williams JW, Jr., Kunz R, Craig J, Montori VM, Bossuyt P, Guyatt GH. Grading quality of evidence and strength of recommendations for diagnostic tests and strategies. BMJ 2008a; 336 : 1106-1110.
Schünemann HJ, Oxman AD, Brozek J, Glasziou P, Bossuyt P, Chang S, Muti P, Jaeschke R, Guyatt GH. GRADE: assessing the quality of evidence for diagnostic recommendations. ACP Journal Club 2008b; 149 : 2.
Schünemann HJ, Mustafa R, Brozek J. [Diagnostic accuracy and linked evidence--testing the chain]. Zeitschrift für Evidenz, Fortbildung und Qualität im Gesundheitswesen 2012; 106 : 153-160.
Schünemann HJ, Tugwell P, Reeves BC, Akl EA, Santesso N, Spencer FA, Shea B, Wells G, Helfand M. Non-randomized studies as a source of complementary, sequential or replacement evidence for randomized controlled trials in systematic reviews on the effects of interventions. Research Synthesis Methods 2013; 4 : 49-62.
Schünemann HJ. Interpreting GRADE's levels of certainty or quality of the evidence: GRADE for statisticians, considering review information size or less emphasis on imprecision? Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2016; 75 : 6-15.
Schünemann HJ, Cuello C, Akl EA, Mustafa RA, Meerpohl JJ, Thayer K, Morgan RL, Gartlehner G, Kunz R, Katikireddi SV, Sterne J, Higgins JPT, Guyatt G, Group GW. GRADE guidelines: 18. How ROBINS-I and other tools to assess risk of bias in nonrandomized studies should be used to rate the certainty of a body of evidence. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2018.
Spencer-Bonilla G, Quinones AR, Montori VM, International Minimally Disruptive Medicine W. Assessing the Burden of Treatment. Journal of General Internal Medicine 2017; 32 : 1141-1145.
Spencer FA, Iorio A, You J, Murad MH, Schünemann HJ, Vandvik PO, Crowther MA, Pottie K, Lang ES, Meerpohl JJ, Falck-Ytter Y, Alonso-Coello P, Guyatt GH. Uncertainties in baseline risk estimates and confidence in treatment effects. BMJ 2012; 345 : e7401.
Sterne JAC, Hernán MA, Reeves BC, Savović J, Berkman ND, Viswanathan M, Henry D, Altman DG, Ansari MT, Boutron I, Carpenter JR, Chan AW, Churchill R, Deeks JJ, Hróbjartsson A, Kirkham J, Jüni P, Loke YK, Pigott TD, Ramsay CR, Regidor D, Rothstein HR, Sandhu L, Santaguida PL, Schünemann HJ, Shea B, Shrier I, Tugwell P, Turner L, Valentine JC, Waddington H, Waters E, Wells GA, Whiting PF, Higgins JPT. ROBINS-I: a tool for assessing risk of bias in non-randomised studies of interventions. BMJ 2016; 355 : i4919.
Thompson DC, Rivara FP, Thompson R. Helmets for preventing head and facial injuries in bicyclists. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2000; 2 : CD001855.
Tierney JF, Stewart LA, Ghersi D, Burdett S, Sydes MR. Practical methods for incorporating summary time-to-event data into meta-analysis. Trials 2007; 8 .
van Dalen EC, Tierney JF, Kremer LCM. Tips and tricks for understanding and using SR results. No. 7: time‐to‐event data. Evidence-Based Child Health 2007; 2 : 1089-1090.
For permission to re-use material from the Handbook (either academic or commercial), please see here for full details.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Turk J Urol
- v.39(Suppl 1); 2013 Sep
How to clearly articulate results and construct tables and figures in a scientific paper?
The writing of the results section of a scientific paper is very important for the readers for clearly understanding of the study. This review summarizes the rules for writing the results section of a scientific paper and describes the use of tables and figures.
Introduction
Medical articles consist of review articles, case reports, and letters to the editor which are prepared with the intention of publishing in journals related to the medical discipline of the author. For an academician to be able to progress in carreer, and make his/her activities known in the academic environment, require preparation of the protocol of his/her academic research article, and acquiring sufficient information, and experience related to the composition of this article. In this review article, the information related to the writing of the ‘Results’ section, and use of tables, and figures will be presented to the attention of the readers.
Writing the ‘Results’ section
The ‘Results’ section is perhaps the most important part of a research article. In fact the authors will share the results of their research/study with their readers. Renown British biologist Thomas Henry Huxley (1825–1895) indicated his feelings as “The great tragedy of science: the slaying of a beautiful hypothesis by an ugly fact.” which emphasizes the importance of accurately, and impressively written results.
In essence results provide a response for the question” What is found in the research performed?”. Therefore, it is the most vital part of the article. As a priority, while drafting the ‘Results’ section of a manuscript one should not firstly write down methods in the ‘Material and Method’ section. The first sentence should give information about the number of patients who met the inclusion criteria, and thus enrolled in the study. [ 1 ] Besides information about the number of patients excluded from the study, and the reasons for exclusion is very important in that they will enlighten the readers, and reviewers who critically evaluate the manuscript, and also reflect the seriousness of the study. On the other hand, the results obtained should be recorded in chronological order, and without any comments. [ 2 ] In this section use of simple present tense is more appropriate. The findings should be expressed in brief, lucid, and explicable words. The writing style should not be boring for the reader. During writing process of a research article, a generally ill-conceived point is that positive, and significant findings are more important, attractive, and valuable, while negative, and insignificant findings are worthless, and less attractive. A scientific research is not performed to confirm a hypothesis, rather to test it. Not only positive, and significant results are worth writing, on the other hand negative or statistically insignificant result which support fallacy of a widely accepted opinion might be valuable. Therefore, all findings obtained during research should be inclıuded in the ‘Results’ section. [ 1 ]
While writing the ‘Results’ section, the sequence of results, tabulated data, and information which will be illustrated as figures should be definitively indicated. In indicating insignificant changes, do not use expressions as “decreased” or “increased”, these words should be reserved for significant changes. If results related to more than one parameter would be reported, it is appropriate to write the results under the subheading of its related parameter so as to facilitate reading, and comprehension of information. [ 2 ] Only data, and information concerning the study in question should be included in the ‘Results’ section. Results not mentioned in this section should not be included in the ‘Discussion’ and ‘Summary’ sections. Since the results obtained by the authors are cited in the ‘Results’ section, any reference should not be indicated in this section. [ 3 ]
In the ‘Results’ section, numerical expressions should be written in technically appropriate terms. The number of digits (1, 2 or 3 digits) to be written after a comma (in Turkish) or a point (in especially American English) should be determined The number of digits written after the punctuation marks should not be changed all throughout the text. Data should be expressed as mean/median ± standard deviation. Data as age, and scale scores should be indicated together with ranges of values. Absolute numerical value corresponding to a percentage must be also indicated. P values calculated in statistical analysis should be expressed in their absolute values. While writing p values of statistically significant data, instead of p<0.05 the actual level of significance should be recorded. If p value is smaller than 0.001, then it can be written as p <0.01. [ 2 ] While writing the ‘Results’ section, significant data which should be recalled by the readers must be indicated in the main text. It will be appropriate to indicate other demographic numerical details in tables or figures.
As an example elucidating the abovementioned topics a research paper written by the authors of this review article, and published in the Turkish Journal of Urology in the year 2007 (Türk Üroloji Dergisi 2007;33:18–23) is presented below:
“A total of 9 (56.2%) female, and 7 (43.8%) male patients with were included in this study. Mean age of all the patients was 44.3±13.8 (17–65) years, and mean dimensions of the adrenal mass was 4.5±3.4 (1–14) cm. Mean ages of the male, and female patients were 44.1 (30–65), and 42.4 (17–64) years, while mean diameters of adrenal masses were 3.2 (1–5), and 4.5 (1–14) cm (p age =0.963, p mass size =0.206). Surgical procedures were realized using transperitoneal approach through Chevron incision in 1 (6.2%), and retroperitoneal approach using flank incision with removal of the 11. rib in 15 (93.7%) patients. Right (n=6; 37.5%), and left (n=2; 12.5%) adrenalectomies were performed. Two (12.5%) patients underwent bilateral adrenalectomy in the same session because of clinical Cushing’s syndrome persisted despite transsphenoidal hipophysectomy. Mean operative time, and length of the hospital stay were 135 (65–190) min, and 3 (2–6) days, respectively. While resecting 11. rib during retroperitoneal adrenalectomy performed in 1 patient, pleura was perforated for nearly 1.5 cm. The perforated region was drained, and closed intraoperatively with 4/0 polyglyctan sutures. The patient did not develop postoperative pneumothorax. In none of the patients postoperative complications as pneumothorax, bleeding, prolonged drainage were seen. Results of histopathological analysis of the specimens retrieved at the end of the operation were summarized in Table 1 .” Table 1. Histopathological examination results of the patients Histopathological diagnosis Men n (%) Women n (%) Total n (%) Adrenal cortical adenoma 5 (31.3) 6 (37.6) 11 (68.8) Pheochromocytoma 1 (6.2) 1 (6.2) 2 (12.6) Ganglioneuroma 1 (6.2) - 1 (6.2) Myelolipoma - 1 (6.2) 1 (6.2) Adrenal carcinoma - 1 (6.2) 1 (6.2) Total 7 (43.7) 9 (56.2) 16 (100) Open in a separate window
Use of tables, and figures
To prevent the audience from getting bored while reading a scientific article, some of the data should be expressed in a visual format in graphics, and figures rather than crowded numerical values in the text. Peer-reviewers frequently look at tables, and figures. High quality tables, and figures increase the chance of acceptance of the manuscript for publication.
Number of tables in the manuscript should not exceed the number recommended by the editorial board of the journal. Data in the main text, and tables should not be repeated many times. Tables should be comprehensible, and a reader should be able to express an opinion about the results just at looking at the tables without reading the main text. Data included in tables should comply with those mentioned in the main text, and percentages in rows, and columns should be summed up accurately. Unit of each variable should be absolutely defined. Sampling size of each group should be absolutely indicated. Values should be expressed as values±standard error, range or 95% confidence interval. Tables should include precise p values, and level of significance as assessed with statistical analysis should be indicated in footnotes. [ 2 ] Use of abbreviations in tables should be avoided, if abbreviations are required they should be defined explicitly in the footnotes or legends of the tables. As a general rule, rows should be arranged as double-spaced Besides do not use pattern coloring for cells of rows, and columns. Values included in tables should be correctly approximated. [ 1 , 2 ]
As an example elucidating the abovementioned topics a research paper written by the authors of this review article, and published in the Turkish Journal of Urology in the year 2007 (Türk Üroloji Dergisi 2007;33:18–23).is shown in Table 1 .
Most of the readers priorly prefer to look at figures, and graphs rather than reading lots of pages. Selection of appropriate types of graphs for demonstration of data is a critical decision which requires artist’s meticulousness. As is the case with tables, graphs, and figures should also disploay information not provided in the text. Bar, line, and pie graphs, scatter plots, and histograms are some examples of graphs. In graphs, independent variables should be represented on the horizontal, and dependent variables on the vertical axis. Number of subjects in every subgroup should be indicated The labels on each axis should be easily understandable. [ 2 ] The label of the Y axis should be written vertically from bottom to top. The fundamental point in writing explanatory notes for graphs, and figures is to help the readers understand the contents of them without referring to the main text. Meanings of abbreviations, and acronyms used in the graphs, and figures should be provided in explanatory notes. In the explanatory notes striking data should be emphasized. Statistical tests used, levels of significance, sampling size, stains used for analyses, and magnification rate should be written in order to facilitate comprehension of the study procedures. [ 1 , 2 ]
Flow diagram can be utilized in the ‘Results’ section. This diagram facilitates comprehension of the results obtained at certain steps of monitorization during the research process. Flow diagram can be used either in the ‘Results’ or ‘Material and Method’ section. [ 2 , 3 ]
Histopathological analyses, surgical technique or radiological images which are considered to be more useful for the comprehension of the text by the readers can be visually displayed. Important findings should be marked on photos, and their definitions should be provided clearly in the explanatory legends. [ 1 ]
As an example elucidating the abovementioned issues, graphics, and flow diagram in the ‘Results’ section of a research paper written by the authors of this review article, and published in the World Journal of Urology in the year 2010 (World J Urol 2010;28:17–22.) are shown in Figures 1 , and and2 2 .

a The mean SHIM scores of the groups before and after treatment. SHIM sexual health inventory for male. b The mean IPSS scores of the groups before and after treatment. IPSS international prostate symptom score

Flowchart showing patients’ progress during the study. SHIM sexual health inventory for male, IIEF international index of erectile function, IPSS international prostate symptom score, QoL quality of life, Q max maximum urinary flow rate. PRV post voiding residual urine volume
In conclusion, in line with the motto of the famous German physicist Albert Einstein (1879–1955). ‘If you are out to describe the truth, leave elegance to the tailor .’ results obtained in a scientific research article should be expressed accurately, and with a masterstroke of a tailor in compliance with certain rules which will ensure acceptability of the scientific manuscript by the editorial board of the journal, and also facilitate its intelligibility by the readers.
We’re independently supported by our readers and we may earn a commission when you buy through our links.
What are you looking for?
Search ideas for you, article furniture review.
Sheridan Grant
Content Specialist
Sheridan is a writer from Hamilton, Ontario. She has a passion for writing about what she loves and learning new things along the way. Her topics of expertise include skincare and beauty, home decor, and DIYing.
Table of Contents
About Article Furniture

Say your favorite home decor and furniture store in 3…2..1. Article Furniture ! If that wasn’t your answer, we’ve got news for you. With a wide selection of mid-century styles for all spaces, it’s easy to deck your entire home in this brand’s pieces.
Chances are that if you’ve searched for some new pieces, you’ve come across Article. It’s clear the brand is a popular choice with its impressive following of 924k on Instagram and 371k on Facebook.
On top of that, Article has featured in popular media outlets such as Forbes, Vogue, and Retail Insider, for its admirable traction in the industry and varying selection of stunning home furnishings.
So, does this brand truly live up to the hype? This Article Furniture review is here to help you find out! We’ll tour you through all there is to know about the brand, including in-depth product reviews, customer ratings, and important FAQs, to help you decide if these pieces are the thing you need to complete your space.
Overview of Article Furniture

Article Furniture is the brainchild of a group of friends who are engineers: Aamir Baig, Fraser Hall, Sam Prochazka, and Andy Prochazka. The quartet recognized all the deficiencies in the furniture world and decided to create a space that offered direct-to-consumer products at a lower cost without compromising on quality.
So, in 2013, Article was born. Well, technically, Bryght was born, but they changed the name to Article in 2016. And we’re glad they did because it’s a true reflection of the products it sells. While the ideas are drafted in Vancouver, the furniture is made in different locations around the world that are committed to providing the best of the best .
Being one of the first places to purchase furniture solely online, Article’s business has skyrocketed, and reviews speak clearly of the brand’s roaring success.
We’ll dive deeper into that later, but it’s worth mentioning that the products have made a home for themselves in millions of houses across North America.
Now that you know a little more about where the brand originated, this Article Furniture review will take a quick peek at what makes it special today with some highlights.
- Wide selection of high quality, durable, and functional furniture that adds depth and style to any space
- Shop bundles by room
- Financing option available
- Free delivery on orders over $999
- 30-day satisfaction guarantee
- Free exchanges
- One year warranty
- Direct-to-consumer

When it comes to decorating, we know it can be hard to find all the right pieces and create a space that looks like your vision. Luckily, Article does too.
The wide variety of options allows you to curate a collection of items that you truly love , yet all the pieces fit together easily, producing an elegant design of beautiful pieces, whether they are standing alone or decorating the same space.
So, whether you’re after a sofa fit for both you and your pup, an extra seat at your dining table, or a mirror to reflect the beauty of all your other Article pieces, this is the brand for you.
Next, this Article Furniture review will look at the top-selling choices to help you start designing your space!
Furniture can be a broad term, encompassing anything from bar stools to bed frames.
To help you better understand the wide range of furniture pieces that Article carries and the overall aesthetic, this Article Furniture review will take you through some of the brand’s best-selling works.
Article Furniture Seno Dining Table Review

When it’s time to sit down for a delicious homemade meal, it only makes sense to place it on a table that enhances the moment’s charm. Make the main event of your dining space the Seno Dining Table .
With a simple design and long rectangular shape, this table will let all the food do the talking. But, on the off chance that you’re not hosting a dinner party on a daily basis, it will still be a stunning sight to behold when the sun shines through your window and dances on the deep walnut wood.
It’s also available in a soft, neutral oak if that’s more your speed. The lengthy mid-century tapered legs flatter the table’s rectangular shape and stretch the height of the room by creating negative space.
The Article Furniture Seno Dining Table retails for a range of prices depending on the number of seats:
- Table for 2-3: $469
- Table for 3-4: $749
- Table for 4-6: $949
- Table for 6-8: $1099
- Table for 8+: $1299
Looking for a set of dining chairs to pair with this earthy table? Keep reading this Article Furniture review, because we might have found a match made in heaven!
Article Furniture Quarry Gray Dining Chair Review

To complement your Seno Dining Table , opt for the Quarry Dining Chairs . The frame of these seats is crafted from hearty walnut wood and conforms to a classic and minimal shape.
The seat and backrest are comfortably padded, so you won’t need to worry about a backache while snacking or working from home. These chairs aren’t made for the dining room only, though, as they’ll fit easily alongside the sofa in your living room or the breakfast nook next to your kitchen.
The Article Furniture Quarry Gray Dining Chair is available in five different seat colors, including salmon pink and deep navy blue, though they’re all matched with a deep walnut frame for $139 each.
Article Furniture Seno 63 Media Unit Review

When you’re chilling and catching up on your favorite shows, the TV isn’t the only thing you stare at. The unit it sits on shouldn’t be an eyesore, whether your eyes are glued to the screen, or you’re spending time in the living room.
Why not rest it on something beautiful, like the Article Furniture Seno 63 Media Unit ? This TV stand is crafted from solid wood, low to the ground for perfect eye-level viewing.
Plus, there are two cabinet doors and shelves to store all the items you need on hand in the living room, whether extra books or board games.
With simple mcm legs, the Seno 63 Media Unit is 63” wide and is available in a deep warm-toned walnut or a light-toned oak for $899 .
Article Couch Review
If you’ve gone through couch after couch and are starting to feel like a sofa as stylish as it is comfortable will never make its way into your life, it might be time to gander at an Article couch.
These bestsellers will knock your shoes off (literally, because you’ll be tossing them off to cuddle up on one of these bad boys in no time).
Article Timber Charme Sofa Review

Are you ready to be charmed by the Article Timber Charme Sofa ? This three-seater couch is pillowy soft, upholstered with natural and supple leather, resting upon a sturdy light wood frame.
The armrests are also cushioned so you can lay back comfortably, and the seats are super deep, perfect for decorating with all your cozy throw pillows and blankets. As a bonus, the leather is an excellent option if you have pets since it’s as durable as it is buttery soft!
The Article Furniture Timber Charme Sofa is available in three classic options: a deep black, a chocolate brown, or a caramel tan, for $1999 .
Article Ceni Lagoon Sofa Review

If you’re going for a super 70s feel, the Article Ceni Lagoon Sofa is right up your alley. While it’s low to the ground, it will definitely be high on your list of things to buy for your new living room!
This sofa is upholstered in a durable and soft fabric, resting on a solid wood frame. The foam cushions are easy to sink into and loose on the couch, so they’re easy to arrange when trying to get comfy (though that won’t be hard).
There are 6 colors to choose from, including a swoon-worthy angelic white and a deep turquoise that screams “take me home.” The Ceni Lagoon Sofa is available in a roomy loveseat option for $949 or a three-seater for $1149 .
Article Abisko Quartz Sofa Review

With a modular, contemporary shape, the Article Abisko Quartz Sofa will bring plenty of eye-catching detail into your space.
The low armrests are perfect for resting your head on, and the long shape is perfect for laying down to catch some afternoon zzz’s. The seat is soft and comfortable, without being too firm or sinking in too deeply. The upholstery is silky and durable, easy to spot clean with a dry cloth.
It even arrives in two separate pieces, easy for hauling into apartment buildings or moving in all by yourself. Plus, it comes with two super soft throw pillows stuffed with down filling, all of which are resting upon sleek black metal legs.
The Abisko Sofa comes in three colors: a moody navy blue, a soft cloudy white, or a light airy gray for $1399 .
Who Is Article Furniture For?

This one’s for you, home decor fanatics and interior decorators. When it comes to making your house into a home, a reflection of who you truly are, it’s essential to shop for items made at the same standards you hold yourself.
With a wide selection of high-quality furniture, Article makes it easy to find pieces that suit your space and align with your interests. Plus, all the styles are so beautiful and intricate that they pair easily together, creating a cohesive look.
This way, you’ll never have to sacrifice an item you love out of fear it won’t match your other items.
Article Furniture Reviews: What Do Customers Think?

At this point in our Article Furniture review, it only makes sense to look at what customers are saying. We sourced comments from Better Business Bureau, the brand’s website, Reseller Ratings, and TrustPilot to help determine if the brand is truly worth the buy! Before we dive in, let’s take a look at how some of the top sellers are rated:
- Timber Charme Sofa: 4.7/5 stars out of 1279 reviews
- Seno 63 Media Unit: 4.8/5 stars out of 470 reviews
- Seno Dining Table: 4.7/5 stars out of 505 reviews
- Quarry Gray Dining Chair: 4.7/5 stars out of 204 reviews
If we’re talking report cards, let’s just say Article Furniture is getting straight A’s. Literally, Better Business Bureau grades the brand with a solid A for its awe-inspiring approach to customer service and quality designs . What complaints there are have all been answered by their fantastic customer service.
On Reseller Ratings, Article receives 4.14/5 stars out of 5580 reviews. One shopper rates the brand 5/5 stars for the exceptional customer service: “I could not have asked for a better experience with Article. I ordered this chair on Monday and by Wednesday it was set up in my home. It was quick, easy and I really appreciated the reminders from them.”
Another buyer states that Article has truly won them over: “ We purchased the Timber Charme sofa from Article and we were (and are!) floored by the quality and comfort. It’s a big ol’ leather hug that sits deep and smells incredible. The leather is a gorgeous tan and is so smooth to the touch. We are Article people for life!”
421 shoppers on Trustpilot rate the brand 4.7/5 stars . One customer explains a high quality experience with both the product and the service , writing, “I ordered some outdoor furniture and covers and couldnt be happier! The product quality is excellent and a lot less expensive than most of what I looked at!”
She went on to say, “I initially ordered the wrong size covers for the chairs ans the exchange was simple. I would recommend this company and its products to anyone!”
Article definitely seems to be having a love affair with plenty of buyers, stealing their hearts and often becoming central to their home design. Plus, the brand’s customer service is only a phone call (or the click of a button) away.
Is Article Furniture Worth It?

Now that we’ve seen all there is to know about the brand, you might be wondering if we deem it worth the buy. With a plethora of glowing customer reviews, a wide selection of quality pieces, and tons of great promos and deals (more on that later), it’s easy for this Article Furniture review to say the brand is worth a try !
Yes, Article Furniture can be pricey. But when you think about the number of times you’ll have to buy that same MDF shelf versus owning a piece for years to come that might even eventually be passed down through the generations, the total costs tend to even out, and it starts to make sense that quality furniture comes at a price for a reason!
Article Furniture Promotions & Discounts

Looking for some deals on your new home decor pieces? Here’s what this Article Furniture review found:
- Sign up for the newsletter to receive special discounts and offers
- Visit the sale section for up to 35% off
- Discounts on bundles
Where to Buy Article Furniture

article.com is your one-stop-shop for all your modern furniture and decor needs! This direct-to-consumer method cuts out the middleman—cutting costs in the process!

Who owns Article Furniture?
Article is currently owned by the same group of engineers who founded it: Aamir Baig, Fraser Hall, Sam Prochazka, and Andy Prochazka.
Where is Article Furniture made?
Article Furniture is made by manufacturers all over the world, including locations in Vietnam, China, Indonesia, and India. The brand is big on sourcing craftspeople dedicated to producing the most high-quality pieces, so they come from a wide range of locations.
Plus, Article clarifies that they ensure all locations follow specific ethical and sustainable guidelines to ensure workers are treated fairly, production goes smoothly, and is environmentally friendly!
What is Article Furniture’s Shipping Policy?
This Article Furniture review found that the brand currently only ships within the USA and Canada due to ongoing rules and regulations.
When it comes to getting the products to you, Article offers contactless delivery straight to your front door. Of course, some pieces are pretty heavy, and you can always opt for in-room delivery.
In both cases, the team will wear the proper PPE and physically distance, contactless delivery costing a flat rate of $49 ( free for orders over $999 ) and in-room delivery and assembly costing $99 .
More rural locations can be more expensive to ship to, such as areas outside the contiguous US and less populated regions of Canada like PEI. You can simply enter your zip or postal code to determine shipping costs.
Once you have placed your order, the company will reach out with directions for delivery, including tracking information, choosing a date, and notification of arrival.
What is Article Furniture’s Return Policy?
If you’re not in love with your Article Furniture order, you can exchange it for free or opt to return it. The brand offers clear guidelines for its return and exchange policy:
- Start the return within 30 days of delivery
- The product must be in original condition
- Items must be with their original packaging (or there will be a $50 repackaging fee)
To start a return:
- Contact the brand
- Enter the products you’d like to return with an explanation why
- Confirm all information is correct
- Download and print your return label. While exchanges are free, there is a return shipping fee of $49 for most pieces and $19 for smaller items.
- Arrange collection on a day of your choosing
After the brand has received and inspected the return, they will issue a refund, excluding the return fee or any repackaging charges.
On top of this, there is also a one-year warranty, so if you experience any issues following the 30 day return period, you can simply get in touch with the brand to troubleshoot the problem!
How to Contact Article Furniture
We hope you enjoyed our Article Furniture review! If you have any further questions for the brand, please contact them using the following methods:
- The live chat function on the website
- Call 1 (888) 746-3455
- Fill out the email form on the website
- Visit them in person or send mail to the office address:
1010 Raymur Avenue
Vancouver, BC
Canada V6A 3T2
Article Furniture’s customer service operates weekdays between 9:00 AM-8:00 PM and weekends between 10:00 AM-8:00 PM EDT.
Check out similar brands you might like:
Swoon Furniture Review
Bassett Furniture Review
Novogratz Furniture Review
Feather Furniture Review
Our team is dedicated to finding and telling you more about the web’s best products. If you purchase through our links, we may receive a commission. Our editorial team is independent.
Ask the community or leave a comment
Customer reviews, leave a review, ask the community or leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This field is required
This field is required Please use a valid email
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
You may also be interested in

Thesis Nootropics Review

Alo Yoga Review

Jill Health Review

The Million Roses Review

Paint Your Life Review
- Open access
- Published: 19 April 2024
Person-centered care assessment tool with a focus on quality healthcare: a systematic review of psychometric properties
- Lluna Maria Bru-Luna 1 ,
- Manuel Martí-Vilar 2 ,
- César Merino-Soto 3 ,
- José Livia-Segovia 4 ,
- Juan Garduño-Espinosa 5 &
- Filiberto Toledano-Toledano 5 , 6 , 7
BMC Psychology volume 12 , Article number: 217 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
305 Accesses
Metrics details
The person-centered care (PCC) approach plays a fundamental role in ensuring quality healthcare. The Person-Centered Care Assessment Tool (P-CAT) is one of the shortest and simplest tools currently available for measuring PCC. The objective of this study was to conduct a systematic review of the evidence in validation studies of the P-CAT, taking the “Standards” as a frame of reference.
First, a systematic literature review was conducted following the PRISMA method. Second, a systematic descriptive literature review of validity tests was conducted following the “Standards” framework. The search strategy and information sources were obtained from the Cochrane, Web of Science (WoS), Scopus and PubMed databases. With regard to the eligibility criteria and selection process, a protocol was registered in PROSPERO (CRD42022335866), and articles had to meet criteria for inclusion in the systematic review.
A total of seven articles were included. Empirical evidence indicates that these validations offer a high number of sources related to test content, internal structure for dimensionality and internal consistency. A moderate number of sources pertain to internal structure in terms of test-retest reliability and the relationship with other variables. There is little evidence of response processes, internal structure in measurement invariance terms, and test consequences.
The various validations of the P-CAT are not framed in a structured, valid, theory-based procedural framework like the “Standards” are. This can affect clinical practice because people’s health may depend on it. The findings of this study show that validation studies continue to focus on the types of validity traditionally studied and overlook interpretation of the scores in terms of their intended use.
Peer Review reports
Person-centered care (PCC)
Quality care for people with chronic diseases, functional limitations, or both has become one of the main objectives of medical and care services. The person-centered care (PCC) approach is an essential element not only in achieving this goal but also in providing high-quality health maintenance and medical care [ 1 , 2 , 3 ]. In addition to guaranteeing human rights, PCC provides numerous benefits to both the recipient and the provider [ 4 , 5 ]. Additionally, PCC includes a set of necessary competencies for healthcare professionals to address ongoing challenges in this area [ 6 ]. PCC includes the following elements [ 7 ]: an individualized, goal-oriented care plan based on individuals’ preferences; an ongoing review of the plan and the individual’s goals; support from an interprofessional team; active coordination among all medical and care providers and support services; ongoing information exchange, education and training for providers; and quality improvement through feedback from the individual and caregivers.
There is currently a growing body of literature on the application of PCC. A good example of this is McCormack’s widely known mid-range theory [ 8 ], an internationally recognized theoretical framework for PCC and how it is operationalized in practice. This framework forms a guide for care practitioners and researchers in hospital settings. This framework is elaborated in PCC and conceived of as “an approach to practice that is established through the formation and fostering of therapeutic relationships between all care providers, service users, and others significant to them, underpinned by values of respect for persons, [the] individual right to self-determination, mutual respect, and understanding” [ 9 ].
Thus, as established by PCC, it is important to emphasize that reference to the person who is the focus of care refers not only to the recipient but also to everyone involved in a care interaction [ 10 , 11 ]. PCC ensures that professionals are trained in relevant skills and methodology since, as discussed above, carers are among the agents who have the greatest impact on the quality of life of the person in need of care [ 12 , 13 , 14 ]. Furthermore, due to the high burden of caregiving, it is essential to account for caregivers’ well-being. In this regard, studies on professional caregivers are beginning to suggest that the provision of PCC can produce multiple benefits for both the care recipient and the caregiver [ 15 ].
Despite a considerable body of literature and the frequent inclusion of the term in health policy and research [ 16 ], PCC involves several complications. There is no standard consensus on the definition of this concept [ 17 ], which includes problematic areas such as efficacy assessment [ 18 , 19 ]. In addition, the difficulty of measuring the subjectivity involved in identifying the dimensions of the CPC and the infrequent use of standardized measures are acute issues [ 20 ]. These limitations and purposes motivated the creation of the Person-Centered Care Assessment Tool (P-CAT; [ 21 ]), which emerged from the need for a brief, economical, easily applied, versatile and comprehensive assessment instrument to provide valid and reliable measures of PCC for research purposes [ 21 ].
Person-centered care assessment tool (P-CAT)
There are several instruments that can measure PCC from different perspectives (i.e., the caregiver or the care recipient) and in different contexts (e.g., hospitals and nursing homes). However, from a practical point of view, the P-CAT is one of the shortest and simplest tools and contains all the essential elements of PCC described in the literature. It was developed in Australia to measure the approach of long-term residential settings to older people with dementia, although it is increasingly used in other healthcare settings, such as oncology units [ 22 ] and psychiatric hospitals [ 23 ].
Due to the brevity and simplicity of its application, the versatility of its use in different medical and care contexts, and its potential emic characteristics (i.e., constructs that can be cross-culturally applicable with reasonable and similar structure and interpretation; [ 24 ]), the P-CAT is one of the most widely used tests by professionals to measure PCC [ 25 , 26 ]. It has expanded to several countries with cultural and linguistic differences. Since its creation, it has been adapted in countries separated by wide cultural and linguistic differences, such as Norway [ 27 ], Sweden [ 28 ], China [ 29 ], South Korea [ 30 ], Spain [ 25 ], and Italy [ 31 ].
The P-CAT comprises 13 items rated on a 5-point ordinal scale (from “strongly disagree” to “strongly agree”), with high scores indicating a high degree of person-centeredness. The scale consists of three dimensions: person-centered care (7 items), organizational support (4 items) and environmental accessibility (2 items). In the original study ( n = 220; [ 21 ]), the internal consistency of the instrument yielded satisfactory values for the total scale ( α = 0.84) and good test-retest reliability ( r =.66) at one-week intervals. A reliability generalization study conducted in 2021 [ 32 ] that estimated the internal consistency of the P-CAT and analyzed possible factors that could affect the it revealed that the mean α value for the 25 meta-analysis samples (some of which were part of the validations included in this study) was 0.81, and the only variable that had a statistically significant relationship with the reliability coefficient was the mean age of the sample. With respect to internal structure validity, three factors (56% of the total variance) were obtained, and content validity was assessed by experts, literature reviews and stakeholders [ 33 ].
Although not explicitly stated, the apparent commonality between validation studies of different versions of the P-CAT may be influenced by an influential decades-old validity framework that differentiates three categories: content validity, construct validity, and criterion validity [ 34 , 35 ]. However, a reformulation of the validity of the P-CAT within a modern framework, which would provide a different definition of validity, has not been performed.
Scale validity
Traditionally, validation is a process focused on the psychometric properties of a measurement instrument [ 36 ]. In the early 20th century, with the frequent use of standardized measurement tests in education and psychology, two definitions emerged: the first defined validity as the degree to which a test measures what it intends to measure, while the second described the validity of an instrument in terms of the correlation it presents with a variable [ 35 ].
However, in the past century, validity theory has evolved, leading to the understanding that validity should be based on specific interpretations for an intended purpose. It should not be limited to empirically obtained psychometric properties but should also be supported by the theory underlying the construct measured. Thus, to speak of classical or modern validity theory suggests an evolution in the classical or modern understanding of the concept of validity. Therefore, a classical approach (called classical test theory, CTT) is specifically differentiated from a modern approach. In general, recent concepts associated with a modern view of validity are based on (a) a unitary conception of validity and (b) validity judgments based on inferences and interpretations of the scores of a measure [ 37 , 38 ]. This conceptual advance in the concept of validity led to the creation of a guiding framework to for obtaining evidence to support the use and interpretation of the scores obtained by a measure [ 39 ].
This purpose is addressed by the Standards for Educational and Psychological Testing (“Standards”), a guide created by the American Educational Research Association (AERA), the American Psychological Association (APA) and the National Council on Measurement in Education (NCME) in 2014 with the aim of providing guidelines to assess the validity of the interpretations of scores of an instrument based on their intended use. Two conceptual aspects stand out in this modern view of validity: first, validity is a unitary concept centered on the construct; second, validity is defined as “the degree to which evidence and theory support the interpretations of test scores for proposed uses of tests” [ 37 ]. Thus, the “Standards” propose several sources that serve as a reference for assessing different aspects of validity. The five sources of valid evidence are as follows [ 37 ]: test content, response processes, internal structure, relations to other variables and consequences of testing. According to AERA et al. [ 37 ], test content validity refers to the relationship of the administration process, subject matter, wording and format of test items to the construct they are intended to measure. It is measured predominantly with qualitative methods but without excluding quantitative approaches. The validity of the responses is based on analysis of the cognitive processes and interpretation of the items by respondents and is measured with qualitative methods. Internal structure validity is based on the interrelationship between the items and the construct and is measured by quantitative methods. Validity in terms of the relationship with other variables is based on comparison between the variable that the instrument intends to measure and other theoretically relevant external variables and is measured by quantitative methods. Finally, validity based on the results of the test analyses consequences, both intended and unintended, that may be due to a source of invalidity. It is measured mainly by qualitative methods.
Thus, although validity plays a fundamental role in providing a strong scientific basis for interpretations of test scores, validation studies in the health field have traditionally focused on content validity, criterion validity and construct validity and have overlooked the interpretation and use of scores [ 34 ].
“Standards” are considered a suitable validity theory-based procedural framework for reviewing the validity of questionnaires due to its ability to analyze sources of validity from both qualitative and quantitative approaches and its evidence-based method [ 35 ]. Nevertheless, due to a lack of knowledge or the lack of a systematic description protocol, very few instruments to date have been reviewed within the framework of the “Standards” [ 39 ].
Current study
Although the P-CAT is one of the most widely used instruments by professionals and has seven validations [ 25 , 27 , 28 , 29 , 30 , 31 , 40 ], no analysis has been conducted of its validity within the framework of the “Standards”. That is, empirical evidence of the validity of the P-CAT has not been obtained in a way that helps to develop a judgment based on a synthesis of the available information.
A review of this type is critical given that some methodological issues seem to have not been resolved in the P-CAT. For example, although the multidimensionality of the P-CAT was identified in the study that introduced it, Bru-Luna et al. [ 32 ] recently stated that in adaptations of the P-CAT [ 25 , 27 , 28 , 29 , 30 , 40 ], the total score is used for interpretation and multidimensionality is disregarded. Thus, the multidimensionality of the original study was apparently not replicated. Bru-Luna et al. [ 32 ] also indicated that the internal structure validity of the P-CAT is usually underreported due to a lack of sufficiently rigorous approaches to establish with certainty how its scores are calculated.
The validity of the P-CAT, specifically its internal structure, appears to be unresolved. Nevertheless, substantive research and professional practice point to this measure as relevant to assessing PCC. This perception is contestable and judgment-based and may not be sufficient to assess the validity of the P-CAT from a cumulative and synthetic angle based on preceding validation studies. An adequate assessment of validity requires a model to conceptualize validity followed by a review of previous studies of the validity of the P-CAT using this model.
Therefore, the main purpose of this study was to conduct a systematic review of the evidence provided by P-CAT validation studies while taking the “Standards” as a framework.
The present study comprises two distinct but interconnected procedures. First, a systematic literature review was conducted following the PRISMA method ( [ 41 ]; Additional file 1; Additional file 2) with the aim of collecting all validations of the P-CAT that have been developed. Second, a systematic description of the validity evidence for each of the P-CAT validations found in the systematic review was developed following the “Standards” framework [ 37 ]. The work of Hawkins et al. [ 39 ], the first study to review validity sources according to the guidelines proposed by the “Standards”, was also used as a reference. Both provided conceptual and pragmatic guidance for organizing and classifying validity evidence for the P-CAT.
The procedure conducted in the systematic review is described below, followed by the procedure for examining the validity studies.
Systematic review
Search strategy and information sources.
Initially, the Cochrane database was searched with the aim of identifying systematic reviews of the P-CAT. When no such reviews were found, subsequent preliminary searches were performed in the Web of Science (WoS), Scopus and PubMed databases. These databases play a fundamental role in recent scientific literature since they are the main sources of published articles that undergo high-quality content and editorial review processes [ 42 ]. The search formula was as follows. The original P-CAT article [ 21 ] was located, after which all articles that cited it through 2021 were identified and analyzed. This approach ensured the inclusion of all validations. No articles were excluded on the basis of language to avoid language bias [ 43 ]. Moreover, to reduce the effects of publication bias, a complementary search in Google Scholar was also performed to allow the inclusion of “gray” literature [ 44 ]. Finally, a manual search was performed through a review of the references of the included articles to identify other articles that met the search criteria but were not present in any of the aforementioned databases.
This process was conducted by one of the authors and corroborated by another using the Covidence tool [ 45 ]. A third author was consulted in case of doubt.
Eligibility criteria and selection process
The protocol was registered in PROSPERO, and the search was conducted according to these criteria. The identification code is CRD42022335866.
The articles had to meet the following criteria for inclusion in the systematic review: (a) a methodological approach to P-CAT validations, (b) an experimental or quasiexperimental studies, (c) studies with any type of sample, and (d) studies in any language. We discarded studies that met at least one of the following exclusion criteria: (a) systematic reviews or bibliometric reviews of the instrument or meta-analyses or (b) studies published after 2021.
Data collection process
After the articles were selected, the most relevant information was extracted from each article. Fundamental data were recorded in an Excel spreadsheet for each of the sections: introduction, methodology, results and discussion. Information was also recorded about the limitations mentioned in each article as well as the practical implications and suggestions for future research.
Given the aim of the study, information was collected about the sources of validity of each study, including test content (judges’ evaluation, literature review and translation), response processes, internal structure (factor analysis, design, estimator, factor extraction method, factors and items, interfactor R, internal replication, effect of the method, and factor loadings), and relationships with other variables (convergent, divergent, concurrent and predictive validity) and consequences of measurement.
Description of the validity study
To assess the validity of the studies, an Excel table was used. Information was recorded for the seven articles included in the systematic review. The data were extracted directly from the texts of the articles and included information about the authors, the year of publication, the country where each P-CAT validation was produced and each of the five standards proposed in the “Standards” [ 37 ].
The validity source related to internal structure was divided into three sections to record information about dimensionality (e.g., factor analysis, design, estimator, factor extraction method, factors and items, interfactor R, internal replication, effect of the method, and factor loadings), reliability expression (i.e., internal consistency and test-retest) and the study of factorial invariance according to the groups into which it was divided (e.g., sex, age, profession) and the level of study (i.e., metric, intercepts). This approach allowed much more information to be obtained than relying solely on source validity based on internal structure. This division was performed by the same researcher who performed the previous processes.
Study selection and study characteristics
The systematic review process was developed according to the PRISMA methodology [ 41 ].
The WoS, Scopus, PubMed and Google Scholar databases were searched on February 12, 2022 and yielded a total of 485 articles. Of these, 111 were found in WoS, 114 in Scopus, 43 in PubMed and 217 in Google Scholar. In the first phase, the title and abstracts of all the articles were read. In this first screening, 457 articles were eliminated because they did not include studies with a methodological approach to P-CAT validation and one article was excluded because it was the original P-CAT article. This resulted in a total of 27 articles, 19 of which were duplicated in different databases and, in the case of Google Scholar, within the same database. This process yielded a total of eight articles that were evaluated for eligibility by a complete reading of the text. In this step, one of the articles was excluded due to a lack of access to the full text of the study [ 31 ] (although the original manuscript was found, it was impossible to access the complete content; in addition, the authors of the manuscript were contacted, but no reply was received). Finally, a manual search was performed by reviewing the references of the seven studies, but none were considered suitable for inclusion. Thus, the review was conducted with a total of seven articles.
Of the seven studies, six were original validations in other languages. These included Norwegian [ 27 ], Swedish [ 28 ], Chinese (which has two validations [ 29 , 40 ]), Spanish [ 25 ], and Korean [ 30 ]. The study by Selan et al. [ 46 ] included a modification of the Swedish version of the P-CAT and explored the psychometric properties of both versions (i.e., the original Swedish version and the modified version).
The item selection and screening process are illustrated in detail in Fig. 1 .
PRISMA 2020 flow diagram for new systematic reviews including database searches
Validity analysis
To provide a clear overview of the validity analyses, Table 1 descriptively shows the percentages of items that provide information about the five standards proposed by the “Standards” guide [ 37 ].
The table shows a high number of validity sources related to test content and internal structure in relation to dimensionality and internal consistency, followed by a moderate number of sources for test-retest and relationship with other variables. A rate of 0% is observed for validity sources related to response processes, invariance and test consequences. Below, different sections related to each of the standards are shown, and the information is presented in more detail.
Evidence based on test content
The first standard, which focused on test content, was met for all items (100%). Translation, which refers to the equivalence of content between the original language and the target language, was met in the six articles that conducted validation in another language and/or culture. These studies reported that the validations were translated by bilingual experts and/or experts in the area of care. In addition, three studies [ 25 , 29 , 40 ] reported that the translation process followed International Test Commission guidelines, such as those of Beaton et al. [ 47 ], Guillemin [ 48 ], Hambleton et al. [ 49 ], and Muñiz et al. [ 50 ]. Evaluation by judges, who referred to the relevance, clarity and importance of the content, was divided into two categories: expert evaluation (a panel of expert judges for each of the areas to consider in the evaluation instrument) and experiential evaluation (potential participants testing the test). The first type of evaluation occurred in three of the articles [ 28 , 29 , 46 ], while the other occurred in two [ 25 , 40 ]. Only one of the items [ 29 ] reported that the scale contained items that reflected the dimension described in the literature. The validity evidence related to the test content presented in each article can be found in Table 2 .
Evidence based on response processes
The second standard, related to the validity of the response process, was obtained according to the “Standards” from the analysis of individual responses: “questioning test takers about their performance strategies or response to particular items (…), maintaining records that monitor the development of a response to a writing task (…), documentation of other aspects of performance, like eye movement or response times…” [ 37 ] (p. 15). According to the analysis of the validity of the response processes, none of the articles complied with this evidence.
Evidence based on internal structure
The third standard, validity related to internal structure, was divided into three sections. First, the dimensionality of each study was examined in terms of factor analysis, design, estimator, factor extraction method, factors and items, interfactor R, internal replication, effect of the method, and factor loadings. Le et al. [ 40 ] conducted an exploratory-confirmatory design while Sjögren et al. [ 28 ] conducted a confirmatory-exploratory design to assess construct validity using confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) and investigated it further using exploratory factor analysis (EFA). The remaining articles employed only a single form of factor analysis: three employed EFA, and two employed CFA. Regarding the next point, only three of the articles reported the factor extraction method used, including Kaiser’s eigenvalue, criterion, scree plot test, parallel analysis and Velicer’s MAP test. Instrument validations yielded a total of two factors in five of the seven articles, while one yielded a single dimension [ 25 ] and the other yielded three dimensions [ 29 ], as in the original instrument. The interfactor R was reported only in the study by Zhong and Lou [ 29 ], whereas in the study by Martínez et al. [ 25 ], it could be easily obtained since it consisted of only one dimension. Internal replication was also calculated in the Spanish validation by randomly splitting the sample into two to test the correlations between factors. The effectiveness of the method was not reported in any of the articles. This information is presented in Table 3 in addition to a summary of the factor loadings.
The second section examined reliability. All the studies presented measures of internal consistency conducted in their entirety with Cronbach’s α coefficient for both the total scale and the subscales. The ω coefficient of McDonald was not used in any case. Four of the seven articles performed a test-retest test. Martínez et al. [ 25 ] conducted a test-retest after a period of seven days, while Le et al. [ 40 ] and Rokstad et al. [ 27 ] performed it between one and two weeks later and Sjögren et al. [ 28 ] allowed approximately two weeks to pass after the initial test.
The third section analyzes the calculation of invariance, which was not reported in any of the studies.
Evidence based on relationships with other variables
In the fourth standard, based on validity according to the relationship with other variables, the articles that reported it used only convergent validity (i.e., it was hypothesized that the variables related to the construct measured by the test—in this case, person-centeredness—were positively or negatively related to another construct). Discriminant validity hypothesizes that the variables related to the PCC construct are not correlated in any way with any other variable studied. No article (0%) measured discriminant evidence, while four (57%) measured convergent evidence [ 25 , 29 , 30 , 46 ]. Convergent validity was obtained through comparisons with instruments such as the Person-Centered Climate Questionnaire–Staff Version (PCQ-S), the Staff-Based Measures of Individualized Care for Institutionalized Persons with Dementia (IC), the Caregiver Psychological Elder Abuse Behavior Scale (CPEAB), the Organizational Climate (CLIOR) and the Maslach Burnout Inventory (MBI). In the case of Selan et al. [ 46 ], convergent validity was assessed on two items considered by the authors as “crude measures of person-centered care (i.e., external constructs) giving an indication of the instruments’ ability to measure PCC” (p. 4). Concurrent validity, which measures the degree to which the results of one test are or are not similar to those of another test conducted at more or less the same time with the same participants, and predictive validity, which allows predictions to be established regarding behavior based on comparison between the values of the instrument and the criterion, were not reported in any of the studies.
Evidence based on the consequences of testing
The fifth and final standard was related to the consequences of the test. It analyzed the consequences, both intended and unintended, of applying the test to a given sample. None of the articles presented explicit or implicit evidence of this.
The last two sources of validity can be seen in Table 4 .
Table 5 shows the results of the set of validity tests for each study according to the described standards.
The main purpose of this article is to analyze the evidence of validity in different validation studies of the P-CAT. To gather all existing validations, a systematic review of all literature citing this instrument was conducted.
The publication of validation studies of the P-CAT has been constant over the years. Since the publication of the original instrument in 2010, seven validations have been published in other languages (taking into account the Italian version by Brugnolli et al. [ 31 ], which could not be included in this study) as well as a modification of one of these versions. The very unequal distribution of validations between languages and countries is striking. A recent systematic review [ 51 ] revealed that in Europe, the countries where the PCC approach is most widely used are the United Kingdom, Sweden, the Netherlands, Northern Ireland, and Norway. It has also been shown that the neighboring countries seem to exert an influence on each other due to proximity [ 52 ] such that they tend to organize healthcare in a similar way, as is the case for Scandinavian countries. This favors the expansion of PCC and explains the numerous validations we found in this geographical area.
Although this approach is conceived as an essential element of healthcare for most governments [ 53 ], PCC varies according to the different definitions and interpretations attributed to it, which can cause confusion in its application (e.g., between Norway and the United Kingdom [ 54 ]). Moreover, facilitators of or barriers to implementation depend on the context and level of development of each country, and financial support remains one of the main factors in this regard [ 53 ]. This fact explains why PCC is not globally widespread among all territories. In countries where access to healthcare for all remains out of reach for economic reasons, the application of this approach takes a back seat, as does the validation of its assessment tools. In contrast, in a large part of Europe or in countries such as China or South Korea that have experienced decades of rapid economic development, patients are willing to be involved in their medical treatment and enjoy more satisfying and efficient medical experiences and environments [ 55 ], which facilitates the expansion of validations of instruments such as the P-CAT.
Regarding validity testing, the guidelines proposed by the “Standards” [ 37 ] were followed. According to the analysis of the different validations of the P-CAT instrument, none of the studies used a structured validity theory-based procedural framework for conducting validation. The most frequently reported validity tests were on the content of the test and two of the sections into which the internal structure was divided (i.e., dimensionality and internal consistency).
In the present article, the most cited source of validity in the studies was the content of the test because most of the articles were validations of the P-CAT in other languages, and the authors reported that the translation procedure was conducted by experts in all cases. In addition, several of the studies employed International Test Commission guidelines, such as those by Beaton et al. [ 47 ], Guillemin [ 48 ], Hambleton et al. [ 49 ], and Muñiz et al. [ 50 ]. Several studies also assessed the relevance, clarity and importance of the content.
The third source of validity, internal structure, was the next most often reported, although it appeared unevenly among the three sections into which this evidence was divided. Dimensionality and internal consistency were reported in all studies, followed by test-retest consistency. In relation to the first section, factor analysis, a total of five EFAs and four CFAs were presented in the validations. Traditionally, EFA has been used in research to assess dimensionality and identify key psychological constructs, although this approach involves a number of inconveniences, such as difficulty testing measurement invariance and incorporating latent factors into subsequent analyses [ 56 ] or the major problem of factor loading matrix rotation [ 57 ]. Studies eventually began to employ CFA, a technique that overcame some of these obstacles [ 56 ] but had other drawbacks; for example, the strict requirement of zero cross-loadings often does not fit the data well, and misspecification of zero loadings tends to produce distorted factors [ 57 ]. Recently, exploratory structural equation modeling (ESEM) has been proposed. This technique is widely recommended both conceptually and empirically to assess the internal structure of psychological tools [ 58 ] since it overcomes the limitations of EFA and CFA in estimating their parameters [ 56 , 57 ].
The next section, reliability, reports the total number of items according to Cronbach’s α reliability coefficient. Reliability is defined as a combination of systematic and random influences that determine the observed scores on a psychological test. Reporting the reliability measure ensures that item-based scores are consistent, that the tool’s responses are replicable and that they are not modified solely by random noise [ 59 , 60 ]. Currently, the most commonly employed reliability coefficient in studies with a multi-item measurement scale (MIMS) is Cronbach’s α [ 60 , 61 ].
Cronbach’s α [ 62 ] is based on numerous strict assumptions (e.g., the test must be unidimensional, factor loadings must be equal for all items and item errors should not covary) to estimate internal consistency. These assumptions are difficult to meet, and their violation may produce small reliability estimates [ 60 ]. One of the alternative measures to α that is increasingly recommended by the scientific literature is McDonald’s ω [ 63 ], a composite reliability measure. This coefficient is recommended for congeneric scales in which tau equivalence is not assumed. It has several advantages. For example, estimates of ω are usually robust when the estimated model contains more factors than the true model, even with small samples, or when skewness in univariate item distributions produces lower biases than those found when using α [ 59 ].
The test-retest method was the next most commonly reported internal structure section in these studies. This type of reliability considers the consistency of the scores of a test between two measurements separated by a period [ 64 ]. It is striking that test-retest consistency does not have a prevalence similar to that of internal consistency since, unlike internal consistency, test-retest consistency can be assessed for practically all types of patient-reported outcomes. It is even considered by some measurement experts to report reliability with greater relevance than internal consistency since it plays a fundamental role in the calculation of parameters for health measures [ 64 ]. However, the literature provides little guidance regarding the assessment of this type of reliability.
The internal structure section that was least frequently reported in the studies in this review was invariance. A lack of invariance refers to a difference between scores on a test that is not explained by group differences in the structure it is intended to measure [ 65 ]. The invariance of the measure should be emphasized as a prerequisite in comparisons between groups since “if scale invariance is not examined, item bias may not be fully recognized and this may lead to a distorted interpretation of the bias in a particular psychological measure” [ 65 ].
Evidence related to other variables was the next most reported source of validity in the studies included in this review. Specifically, the four studies that reported this evidence did so according to convergent validity and cited several instruments. None of the studies included evidence of discriminant validity, although this may be because there are currently several obstacles related to the measurement of this type of validity [ 66 ]. On the one hand, different definitions are used in the applied literature, which makes its evaluation difficult; on the other hand, the literature on discriminant validity focuses on techniques that require the use of multiple measurement methods, which often seem to have been introduced without sufficient evidence or are applied randomly.
Validity related to response processes was not reported by any of the studies. There are several methods to analyze this validity. These methods can be divided into two groups: “those that directly access the psychological processes or cognitive operations (think aloud, focus group, and interviews), compared to those which provide indirect indicators which in turn require additional inference (eye tracking and response times)” [ 38 ]. However, this validity evidence has traditionally been reported less frequently than others in most studies, perhaps because there are fewer clear and accepted practices on how to design or report these studies [ 67 ].
Finally, the consequences of testing were not reported in any of the studies. There is debate regarding this source of validity, with two main opposing streams of thought. On the one hand [ 68 , 69 ]) suggests that consequences that appear after the application of a test should not derive from any source of test invalidity and that “adverse consequences only undermine the validity of an assessment if they can be attributed to a problem of fit between the test and the construct” (p. 6). In contrast, Cronbach [ 69 , 70 ] notes that adverse social consequences that may result from the application of a test may call into question the validity of the test. However, the potential risks that may arise from the application of a test should be minimized in any case, especially in regard to health assessments. To this end, it is essential that this aspect be assessed by instrument developers and that the experiences of respondents be protected through the development of comprehensive and informed practices [ 39 ].
This work is not without limitations. First, not all published validation studies of the P-CAT, such as the Italian version by Brugnolli et al. [ 31 ], were available. These studies could have provided relevant information. Second, many sources of validity could not be analyzed because the studies provided scant or no data, such as response processes [ 25 , 27 , 28 , 29 , 30 , 40 , 46 ], relationships with other variables [ 27 , 28 , 40 ], consequences of testing [ 25 , 27 , 28 , 29 , 30 , 40 , 46 ], or invariance [ 25 , 27 , 28 , 29 , 30 , 40 , 46 ] in the case of internal structure and interfactor R [ 27 , 28 , 30 , 40 , 46 ], internal replication [ 27 , 28 , 29 , 30 , 40 , 46 ] or the effect of the method [ 25 , 27 , 28 , 29 , 30 , 40 , 46 ] in the case of dimensionality. In the future, it is hoped that authors will become aware of the importance of validity, as shown in this article and many others, and provide data on unreported sources so that comprehensive validity studies can be performed.
The present work also has several strengths. The search was extensive, and many studies were obtained using three different databases, including WoS, one of the most widely used and authoritative databases in the world. This database includes a large number and variety of articles and is not fully automated due to its human team [ 71 , 72 , 73 ]. In addition, to prevent publication bias, gray literature search engines such as Google Scholar were used to avoid the exclusion of unpublished research [ 44 ]. Finally, linguistic bias was prevented by not limiting the search to articles published in only one or two languages, thus avoiding the overrepresentation of studies in one language and underrepresentation in others [ 43 ].
Conclusions
Validity is understood as the degree to which tests and theory support the interpretations of instrument scores for their intended use [ 37 ]. From this perspective, the various validations of the P-CAT are not presented in a structured, valid, theory-based procedural framework like the “Standards” are. After integration and analysis of the results, it was observed that these validation reports offer a high number of sources of validity related to test content, internal structure in dimensionality and internal consistency, a moderate number of sources for internal structure in terms of test-retest reliability and the relationship with other variables, and a very low number of sources for response processes, internal structure in terms of invariance, and test consequences.
Validity plays a fundamental role in ensuring a sound scientific basis for test interpretations because it provides evidence of the extent to which the data provided by the test are valid for the intended purpose. This can affect clinical practice as people’s health may depend on it. In this sense, the “Standards” are considered a suitable and valid theory-based procedural framework for studying this modern conception of questionnaire validity, which should be taken into account in future research in this area.
Although the P-CAT is one of the most widely used instruments for assessing PCC, as shown in this study, PCC has rarely been studied. The developers of measurement tests applied to the health care setting, on which the health and quality of life of many people may depend, should use this validity framework to reflect the clear purpose of the measurement. This approach is important because the equity of decision making by healthcare professionals in daily clinical practice may depend on the source of validity. Through a more extensive study of validity that includes the interpretation of scores in terms of their intended use, the applicability of the P-CAT, an instrument that was initially developed for long-term care homes for elderly people, could be expanded to other care settings. However, the findings of this study show that validation studies continue to focus on traditionally studied types of validity and overlook the interpretation of scores in terms of their intended use.
Data availability
All data relevant to the study were included in the article or uploaded as additional files. Additional template data extraction forms are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
American Educational Research Association
American Psychological Association
Confirmatory factor analysis
Organizational Climate
Caregiver Psychological Elder Abuse Behavior Scale
Exploratory factor analysis
Exploratory structural equation modeling
Staff-based Measures of Individualized Care for Institutionalized Persons with Dementia
Maslach Burnout Inventory
Multi-item measurement scale
Maximum likelihood
National Council on Measurement in Education
Person-Centered Care Assessment Tool
- Person-centered care
Person-Centered Climate Questionnaire–Staff Version
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
International Register of Systematic Review Protocols
Standards for Educational and Psychological Testing
weighted least square mean and variance adjusted
Web of Science
Institute of Medicine. Crossing the quality chasm: a new health system for the 21st century. Washington, DC: National Academy; 2001.
Google Scholar
International Alliance of Patients’ Organizations. What is patient-centred healthcare? A review of definitions and principles. 2nd ed. London, UK: International Alliance of Patients’ Organizations; 2007.
World Health Organization. WHO global strategy on people-centred and integrated health services: interim report. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2015.
Britten N, Ekman I, Naldemirci Ö, Javinger M, Hedman H, Wolf A. Learning from Gothenburg model of person centred healthcare. BMJ. 2020;370:m2738.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Van Diepen C, Fors A, Ekman I, Hensing G. Association between person-centred care and healthcare providers’ job satisfaction and work-related health: a scoping review. BMJ Open. 2020;10:e042658.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Ekman N, Taft C, Moons P, Mäkitalo Å, Boström E, Fors A. A state-of-the-art review of direct observation tools for assessing competency in person-centred care. Int J Nurs Stud. 2020;109:103634.
American Geriatrics Society Expert Panel on Person-Centered Care. Person-centered care: a definition and essential elements. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2016;64:15–8.
Article Google Scholar
McCormack B, McCance TV. Development of a framework for person-centred nursing. J Adv Nurs. 2006;56:472–9.
McCormack B, McCance T. Person-centred practice in nursing and health care: theory and practice. Chichester, England: Wiley; 2016.
Nolan MR, Davies S, Brown J, Keady J, Nolan J. Beyond person-centred care: a new vision for gerontological nursing. J Clin Nurs. 2004;13:45–53.
McCormack B, McCance T. Person-centred nursing: theory, models and methods. Oxford, UK: Wiley-Blackwell; 2010.
Book Google Scholar
Abraha I, Rimland JM, Trotta FM, Dell’Aquila G, Cruz-Jentoft A, Petrovic M, et al. Systematic review of systematic reviews of non-pharmacological interventions to treat behavioural disturbances in older patients with dementia. The SENATOR-OnTop series. BMJ Open. 2017;7:e012759.
Anderson K, Blair A. Why we need to care about the care: a longitudinal study linking the quality of residential dementia care to residents’ quality of life. Arch Gerontol Geriatr. 2020;91:104226.
Bauer M, Fetherstonhaugh D, Haesler E, Beattie E, Hill KD, Poulos CJ. The impact of nurse and care staff education on the functional ability and quality of life of people living with dementia in aged care: a systematic review. Nurse Educ Today. 2018;67:27–45.
Smythe A, Jenkins C, Galant-Miecznikowska M, Dyer J, Downs M, Bentham P, et al. A qualitative study exploring nursing home nurses’ experiences of training in person centred dementia care on burnout. Nurse Educ Pract. 2020;44:102745.
McCormack B, Borg M, Cardiff S, Dewing J, Jacobs G, Janes N, et al. Person-centredness– the ‘state’ of the art. Int Pract Dev J. 2015;5:1–15.
Wilberforce M, Challis D, Davies L, Kelly MP, Roberts C, Loynes N. Person-centredness in the care of older adults: a systematic review of questionnaire-based scales and their measurement properties. BMC Geriatr. 2016;16:63.
Rathert C, Wyrwich MD, Boren SA. Patient-centered care and outcomes: a systematic review of the literature. Med Care Res Rev. 2013;70:351–79.
Sharma T, Bamford M, Dodman D. Person-centred care: an overview of reviews. Contemp Nurse. 2016;51:107–20.
Ahmed S, Djurkovic A, Manalili K, Sahota B, Santana MJ. A qualitative study on measuring patient-centered care: perspectives from clinician-scientists and quality improvement experts. Health Sci Rep. 2019;2:e140.
Edvardsson D, Fetherstonhaugh D, Nay R, Gibson S. Development and initial testing of the person-centered Care Assessment Tool (P-CAT). Int Psychogeriatr. 2010;22:101–8.
Tamagawa R, Groff S, Anderson J, Champ S, Deiure A, Looyis J, et al. Effects of a provincial-wide implementation of screening for distress on healthcare professionals’ confidence and understanding of person-centered care in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2016;14:1259–66.
Degl’ Innocenti A, Wijk H, Kullgren A, Alexiou E. The influence of evidence-based design on staff perceptions of a supportive environment for person-centered care in forensic psychiatry. J Forensic Nurs. 2020;16:E23–30.
Hulin CL. A psychometric theory of evaluations of item and scale translations: fidelity across languages. J Cross Cult Psychol. 1987;18:115–42.
Martínez T, Suárez-Álvarez J, Yanguas J, Muñiz J. Spanish validation of the person-centered Care Assessment Tool (P-CAT). Aging Ment Health. 2016;20:550–8.
Martínez T, Martínez-Loredo V, Cuesta M, Muñiz J. Assessment of person-centered care in gerontology services: a new tool for healthcare professionals. Int J Clin Health Psychol. 2020;20:62–70.
Rokstad AM, Engedal K, Edvardsson D, Selbaek G. Psychometric evaluation of the Norwegian version of the person-centred Care Assessment Tool. Int J Nurs Pract. 2012;18:99–105.
Sjögren K, Lindkvist M, Sandman PO, Zingmark K, Edvardsson D. Psychometric evaluation of the Swedish version of the person-centered Care Assessment Tool (P-CAT). Int Psychogeriatr. 2012;24:406–15.
Zhong XB, Lou VW. Person-centered care in Chinese residential care facilities: a preliminary measure. Aging Ment Health. 2013;17:952–8.
Tak YR, Woo HY, You SY, Kim JH. Validity and reliability of the person-centered Care Assessment Tool in long-term care facilities in Korea. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2015;45:412–9.
Brugnolli A, Debiasi M, Zenere A, Zanolin ME, Baggia M. The person-centered Care Assessment Tool in nursing homes: psychometric evaluation of the Italian version. J Nurs Meas. 2020;28:555–63.
Bru-Luna LM, Martí-Vilar M, Merino-Soto C, Livia J. Reliability generalization study of the person-centered Care Assessment Tool. Front Psychol. 2021;12:712582.
Edvardsson D, Innes A. Measuring person-centered care: a critical comparative review of published tools. Gerontologist. 2010;50:834–46.
Hawkins M, Elsworth GR, Nolte S, Osborne RH. Validity arguments for patient-reported outcomes: justifying the intended interpretation and use of data. J Patient Rep Outcomes. 2021;5:64.
Sireci SG. On the validity of useless tests. Assess Educ Princ Policy Pract. 2016;23:226–35.
Hawkins M, Elsworth GR, Osborne RH. Questionnaire validation practice: a protocol for a systematic descriptive literature review of health literacy assessments. BMJ Open. 2019;9:e030753.
American Educational Research Association, American Psychological Association. National Council on Measurement in Education. Standards for educational and psychological testing. Washington, DC: American Educational Research Association; 2014.
Padilla JL, Benítez I. Validity evidence based on response processes. Psicothema. 2014;26:136–44.
PubMed Google Scholar
Hawkins M, Elsworth GR, Hoban E, Osborne RH. Questionnaire validation practice within a theoretical framework: a systematic descriptive literature review of health literacy assessments. BMJ Open. 2020;10:e035974.
Le C, Ma K, Tang P, Edvardsson D, Behm L, Zhang J, et al. Psychometric evaluation of the Chinese version of the person-centred Care Assessment Tool. BMJ Open. 2020;10:e031580.
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Int J Surg. 2021;88:105906.
Falagas ME, Pitsouni EI, Malietzis GA, Pappas G. Comparison of PubMed, Scopus, web of Science, and Google Scholar: strengths and weaknesses. FASEB J. 2008;22:338–42.
Grégoire G, Derderian F, Le Lorier J. Selecting the language of the publications included in a meta-analysis: is there a tower of Babel bias? J Clin Epidemiol. 1995;48:159–63.
Arias MM. Aspectos metodológicos Del metaanálisis (1). Pediatr Aten Primaria. 2018;20:297–302.
Covidence. Covidence systematic review software. Veritas Health Innovation, Australia. 2014. https://www.covidence.org/ . Accessed 28 Feb 2022.
Selan D, Jakobsson U, Condelius A. The Swedish P-CAT: modification and exploration of psychometric properties of two different versions. Scand J Caring Sci. 2017;31:527–35.
Beaton DE, Bombardier C, Guillemin F, Ferraz MB. Guidelines for the process of cross-cultural adaptation of self-report measures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2000;25:3186–91.
Guillemin F. Cross-cultural adaptation and validation of health status measures. Scand J Rheumatol. 1995;24:61–3.
Hambleton R, Merenda P, Spielberger C. Adapting educational and psychological tests for cross-cultural assessment. Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates; 2005.
Muñiz J, Elosua P, Hambleton RK. International test commission guidelines for test translation and adaptation: second edition. Psicothema. 2013;25:151–7.
Rosengren K, Brannefors P, Carlstrom E. Adoption of the concept of person-centred care into discourse in Europe: a systematic literature review. J Health Organ Manag. 2021;35:265–80.
Alharbi T, Olsson LE, Ekman I, Carlström E. The impact of organizational culture on the outcome of hospital care: after the implementation of person-centred care. Scand J Public Health. 2014;42:104–10.
Bensbih S, Souadka A, Diez AG, Bouksour O. Patient centered care: focus on low and middle income countries and proposition of new conceptual model. J Med Surg Res. 2020;7:755–63.
Stranz A, Sörensdotter R. Interpretations of person-centered dementia care: same rhetoric, different practices? A comparative study of nursing homes in England and Sweden. J Aging Stud. 2016;38:70–80.
Zhou LM, Xu RH, Xu YH, Chang JH, Wang D. Inpatients’ perception of patient-centered care in Guangdong province, China: a cross-sectional study. Inquiry. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1177/00469580211059482 .
Marsh HW, Morin AJ, Parker PD, Kaur G. Exploratory structural equation modeling: an integration of the best features of exploratory and confirmatory factor analysis. Annu Rev Clin Psychol. 2014;10:85–110.
Asparouhov T, Muthén B. Exploratory structural equation modeling. Struct Equ Model Multidiscip J. 2009;16:397–438.
Cabedo-Peris J, Martí-Vilar M, Merino-Soto C, Ortiz-Morán M. Basic empathy scale: a systematic review and reliability generalization meta-analysis. Healthc (Basel). 2022;10:29–62.
Flora DB. Your coefficient alpha is probably wrong, but which coefficient omega is right? A tutorial on using R to obtain better reliability estimates. Adv Methods Pract Psychol Sci. 2020;3:484–501.
McNeish D. Thanks coefficient alpha, we’ll take it from here. Psychol Methods. 2018;23:412–33.
Hayes AF, Coutts JJ. Use omega rather than Cronbach’s alpha for estimating reliability. But… Commun Methods Meas. 2020;14:1–24.
Cronbach LJ. Coefficient alpha and the internal structure of tests. Psychometrika. 1951;16:297–334.
McDonald R. Test theory: a unified approach. Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum; 1999.
Polit DF. Getting serious about test-retest reliability: a critique of retest research and some recommendations. Qual Life Res. 2014;23:1713–20.
Ceylan D, Çizel B, Karakaş H. Testing destination image scale invariance for intergroup comparison. Tour Anal. 2020;25:239–51.
Rönkkö M, Cho E. An updated guideline for assessing discriminant validity. Organ Res Methods. 2022;25:6–14.
Hubley A, Zumbo B. Response processes in the context of validity: setting the stage. In: Zumbo B, Hubley A, editors. Understanding and investigating response processes in validation research. Cham, Switzerland: Springer; 2017. pp. 1–12.
Messick S. Validity of performance assessments. In: Philips G, editor. Technical issues in large-scale performance assessment. Washington, DC: Department of Education, National Center for Education Statistics; 1996. pp. 1–18.
Moss PA. The role of consequences in validity theory. Educ Meas Issues Pract. 1998;17:6–12.
Cronbach L. Five perspectives on validity argument. In: Wainer H, editor. Test validity. Hillsdale, MI: Erlbaum; 1988. pp. 3–17.
Birkle C, Pendlebury DA, Schnell J, Adams J. Web of Science as a data source for research on scientific and scholarly activity. Quant Sci Stud. 2020;1:363–76.
Bramer WM, Rethlefsen ML, Kleijnen J, Franco OH. Optimal database combinations for literature searches in systematic reviews: a prospective exploratory study. Syst Rev. 2017;6:245.
Web of Science Group. Editorial selection process. Clarivate. 2024. https://clarivate.com/webofsciencegroup/solutions/%20editorial-selection-process/ . Accessed 12 Sept 2022.
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the casual helpers for their aid in information processing and searching.
This work is one of the results of research project HIM/2015/017/SSA.1207, “Effects of mindfulness training on psychological distress and quality of life of the family caregiver”. Main researcher: Filiberto Toledano-Toledano Ph.D. The present research was funded by federal funds for health research and was approved by the Commissions of Research, Ethics and Biosafety (Comisiones de Investigación, Ética y Bioseguridad), Hospital Infantil de México Federico Gómez, National Institute of Health. The source of federal funds did not control the study design, data collection, analysis, or interpretation, or decisions regarding publication.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Departamento de Educación, Facultad de Ciencias Sociales, Universidad Europea de Valencia, 46010, Valencia, Spain
Lluna Maria Bru-Luna
Departamento de Psicología Básica, Universitat de València, Blasco Ibáñez Avenue, 21, 46010, Valencia, Spain
Manuel Martí-Vilar
Departamento de Psicología, Instituto de Investigación de Psicología, Universidad de San Martín de Porres, Tomás Marsano Avenue 242, Lima 34, Perú
César Merino-Soto
Instituto Central de Gestión de la Investigación, Universidad Nacional Federico Villarreal, Carlos Gonzalez Avenue 285, 15088, San Miguel, Perú
José Livia-Segovia
Unidad de Investigación en Medicina Basada en Evidencias, Hospital Infantil de México Federico Gómez Instituto Nacional de Salud, Dr. Márquez 162, 06720, Doctores, Cuauhtémoc, Mexico
Juan Garduño-Espinosa & Filiberto Toledano-Toledano
Unidad de Investigación Multidisciplinaria en Salud, Instituto Nacional de Rehabilitación Luis Guillermo Ibarra Ibarra, México-Xochimilco 289, Arenal de Guadalupe, 14389, Tlalpan, Mexico City, Mexico
Filiberto Toledano-Toledano
Dirección de Investigación y Diseminación del Conocimiento, Instituto Nacional de Ciencias e Innovación para la Formación de Comunidad Científica, INDEHUS, Periférico Sur 4860, Arenal de Guadalupe, 14389, Tlalpan, Mexico City, Mexico
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
L.M.B.L. conceptualized the study, collected the data, performed the formal anal- ysis, wrote the original draft, and reviewed and edited the subsequent drafts. M.M.V. collected the data and reviewed and edited the subsequent drafts. C.M.S. collected the data, performed the formal analysis, wrote the original draft, and reviewed and edited the subsequent drafts. J.L.S. collected the data, wrote the original draft, and reviewed and edited the subsequent drafts. J.G.E. collected the data and reviewed and edited the subsequent drafts. F.T.T. conceptualized the study and reviewed and edited the subsequent drafts. L.M.B.L. conceptualized the study and reviewed and edited the subsequent drafts. M.M.V. conceptualized the study and reviewed and edited the subsequent drafts. C.M.S. reviewed and edited the subsequent drafts. J.G.E. reviewed and edited the subsequent drafts. F.T.T. conceptualized the study; provided resources, software, and supervision; wrote the original draft; and reviewed and edited the subsequent drafts.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Filiberto Toledano-Toledano .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Commissions of Research, Ethics and Biosafety (Comisiones de Investigación, Ética y Bioseguridad), Hospital Infantil de México Federico Gómez, National Institute of Health. HIM/2015/017/SSA.1207, “Effects of mindfulness training on psychological distress and quality of life of the family caregiver”.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1
Rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Bru-Luna, L.M., Martí-Vilar, M., Merino-Soto, C. et al. Person-centered care assessment tool with a focus on quality healthcare: a systematic review of psychometric properties. BMC Psychol 12 , 217 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-024-01716-7
Download citation
Received : 17 May 2023
Accepted : 07 April 2024
Published : 19 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-024-01716-7
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Person-centered care assessment tool
BMC Psychology
ISSN: 2050-7283
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Table set for Honda's massive bet on Canada's electric vehicle sector
What to watch for as honda announces its new presence in canada's ev industry.

Social Sharing
When word of Honda's soon-to-be-announced electric vehicle investment leaked to Bloomberg News on Sunday, Ontario Premier Doug Ford saw an opening to boast about his government's success in getting into the automotive battery business.
"We've overtaken China and knocked them off the pedestal for the first time ever," he told the First Nations Major Project Coalition conference on Monday morning, referring to Canada's top spot in a recent global supply chain ranking . "That's absolutely huge."
Expect more superlatives when Honda Canada makes its official announcement in Alliston, Ont., on Thursday, as government and industry leaders celebrate the fact that the company behind some of Canada's most popular models is settling in for the long haul in Canada's EV sector.
"This may be Honda's biggest bet anywhere on the planet," Flavio Volpe, the president of the Automotive Manufacturers Association of Canada, told CBC News. He called it a "double down" on Canada and "an announcement that I think will be heard around the world."
Honda doesn't make speculative bets, he said. "They've been in Canada for almost 40 years. They've never retreated, they've never gone back. This is, for Canadian suppliers, an extremely bankable customer to get."
- Honda expected to announce multi-billion dollar deal to assemble EVs in Ontario: sources
Enjoying the hype this announcement is generating means ignoring, for the time being, the fact that most of Northern Ontario's critical minerals are years (if not decades) away from powering all the new EVs Canadians will be federally mandated to purchase after 2035 to meet federal carbon emissions targets.
It means overlooking the fact that Ford's government remains well short of the Indigenous partnerships and permissions it will need to fulfil its Ring of Fire mining aspirations. It means dismissing the failure to date of early consumer incentives and spiking spring gas prices to set off a rush of EV sales, and the fact that many of the new EVs on Ontario's roads were imported from a Tesla gigafactory in Shanghai.
"Here in Ontario, we've become a world leader in the electric vehicle revolution," Ford bragged.
How big is 'big'?
Ford said the deal coming this week will be "double the size of Volkswagen."
The $7 billion VW battery plant now under construction in St. Thomas, Ont., covers roughly 150 hectares — over 200 football fields. It's "like a city in itself," Ford said.
It was not clear from Ford's comments if he meant Honda's new operation will cover twice the acreage of the Volkswagen plant, or if its investment is double the size of the Volkswagen deal. Either way, it's historic.

In January, the Japanese news outlet Nikkei was the first to report Honda was considering an investment of 2 trillion yen (about $18 billion Cdn) to start up an EV supply chain in Canada.
Ford's economic development minister, Vic Fedeli, appeared to confirm Thursday's figures could be on that scale when speaking to reporters at Queen's Park on Monday.
Ontario's EV investments "went from zero to $28 billion in three years," he said, before hedging slightly.
"If the premier, if his comments are correct," he added, "then next week we'll be announcing $43 billion in EV, or a number in and around there."
So is Honda about to invest $15 billion in Ontario?
Not so fast. In a subsequent report published Tuesday, Nikkei said Honda was preparing a one-trillion yen announcement (approximately $8.8 billion.)
As the premier told his Monday audience, "stay tuned."
How much will taxpayers contribute?
The timing of Honda's announcement was a business decision — but it's a happy coincidence for Prime Minister Justin Trudeau that it fell in the midst of his ministers' post-budget marketing tour.
Only a few months after Trudeau signalled that the federal government was running out of money for automotive subsidies — prompting fears that Toyota Canada would hit the brakes on further Ontario expansion — a change in government tactics apparently paid off.
Canada's share of North American manufacturing could have been in jeopardy if the federal and provincial governments hadn't stepped up with both investment tax credits and production subsidies to compete with the Inflation Reduction Act introduced by U.S. President Joe Biden.
Those billions were enough to land Ontario its first two battery plants: the VW plant in St. Thomas and the Stellantis facility in Windsor. But the Trudeau government warned at the time that their production subsidies aren't sustainable.
The sweeteners offered to land this Honda deal are more predictable because they're based on the value of Honda's investment, not future production levels.
In the 2023 federal budget, the Liberals introduced a clean manufacturing investment tax credit that rebates 30 per cent of the cost of new machinery and equipment. Its implementation legislation, C-59, has yet to pass; the Liberals hope it receives royal assent by June.
Last week, the 2024 federal budget introduced a ten per cent electric vehicle supply chain investment tax credit to offset the cost of buildings. Companies receiving the tax credit must invest in three parts of the EV supply chain: EV assembly, battery production and production of cathode active material for those batteries.
Finance Minister Chrystia Freeland's department took the lead in federal talks with Honda; her budget forecasts a $80 million expenditure on this tax credit over the next five years. The federal government has hinted it anticipates about $800 million in investment on eligible buildings between now and 2029.
Honda appears set to be the first — and possibly the only — carmaker to make the vertical investments required to access this credit, with an expansion of its facilities in Alliston as well as other yet-to-be announced expansions in Ontario.

Honda expected to announce plans to build EVs in Canada
CBC News has not confirmed that a site earmarked for EV battery production in St. Clair township near Sarnia, Ont. , is part of Honda's negotiations. Fedeli said Monday that land in Wilmot township near Waterloo, Ont ., was not part of Honda's plans.
Quebec's economy minister, Pierre Fitzgibbon, told reporters at the National Assembly Tuesday that he was in talks to land a piece of Honda's business at the industrial park in Bécancour, Que., where other automotive giants are setting up cathode materials manufacturing.
Fitzgibbon admitted he was outbid by Ontario .
To help attract EV investment, Ontario's 2023 provincial budget included a 10 per cent refundable corporate income tax credit for eligible investments in buildings, machinery and equipment, worth up to $2 million a year for individual corporations.
The Toronto Star has reported that when the Stellantis deal was in jeopardy, the federal government convinced the Ford government to pile on more provincial subsidies in return for federal cooperation on the environmental assessments required to build Highway 413.
It's not known whether a similar last-minute squeeze happened in the Honda talks. Ontario Finance Minister Peter Bethlenfalvy's statement in reaction to the April 16 federal budget nodded to this Highway 413 quid pro quo and revived Ontario's demand for the federal government to "eliminate duplicative reviews and processes that are slowing down" Ring of Fire projects.
Are more Japanese investments coming?
Volpe said the new rules hammered out during the NAFTA renegotiation talks anticipated the transition to electrified powertrain products and batteries by making sure carmakers couldn't source components offshore (China, mainly) without risking tariffs.
During a 2023 visit to Canada, Japanese Prime Minister Fumio Kishida called China a "central challenge."
Geopolitically, Japan is far more comfortable working with Canada to source the critical minerals its automotive engineers need.
Last September, Japan's economy, trade and investment minister Yasutoshi Nishimura visited Ottawa with a delegation of Japanese businesspeople from its battery supply chain association ( BASC ) and corporations like Panasonic Energy, Asahi-Kasei, Mitsubishi, Mitsui and Sumitomo. They signed memoranda of cooperation with Canadian companies about sharing technology and business intelligence.
- Climate warrior Jane Goodall isn't sold on carbon taxes and electric vehicles
- Analysis What Tesla's troubles tell us about the EV industry
- U.S. eases vehicle emissions rules, but overall reduction targets remain unchanged
This week's Honda announcement will be Canada's biggest EV investment deal so far. But it wasn't the first and it's not expected to be the last.
Now that Honda's seen enough to place its bet and become Ontario's third EV battery maker, attention will turn to whether Toyota might reconsider becoming the fourth — and whether Canada's clean power grids can accommodate more ambition.
"Every single car company is spending all of their future R&D dollars on electrified product or fuel cell project product, anything that's zero emission," Volpe said, dismissing the naysayers who've lost faith due to slow consumer sales.
"We all know where we're going."
ABOUT THE AUTHOR

Senior reporter
Janyce McGregor joined the CBC's parliamentary bureau in 2001, after starting her career with TVOntario's Studio 2. Her public broadcaster "hat trick" includes casual stints as a news and current affairs producer with the BBC's World Service in London. After two decades of producing roles, she's now a senior reporter filing for CBC Online, Radio and Television. News tips: [email protected]
- Follow Janyce on Twitter
Related Stories
I made Ina Garten's spring spaghetti carbonara and had dinner ready in 30 minutes
- I made Ina Garten's spring green spaghetti carbonara to celebrate the new season.
- The pasta features pancetta, peas, asparagus, and Parmesan cheese.
- I loved how light and creamy the pasta was — it's the perfect easy spring dinner.

April showers bring May flowers — and plenty of new dishes to cook. And if you're looking for a quick and easy pasta that's as bright as the new season, look no further than Ina Garten's spring green spaghetti carbonara.
"Spaghetti carbonara is true Italian comfort food, but it's incredibly rich," Garten writes in her "Modern Comfort Food" cookbook. "I updated it with lots of fresh green vegetables like English peas, snow peas, and asparagus."
Garten's spring green spaghetti carbonara is ready in 30 minutes — a perfect quick weeknight dinner that will still impress your family and friends.
Here's how to make it.
Ina Garten's spring carbonara pasta comes packed with plenty of veggies.
To make Garten's spring green spaghetti carbonara for six, you'll need:
- 12 ounces of spaghetti (she recommends De Cecco)
- 8 ounces of small-diced pancetta
- 1 cup of shelled fresh peas or frozen peas
- ½ pound of snow peas
- 12-14 thin asparagus (bottom third discarded)
- 5 scallions
- ¼ cup of fresh chives
- 1 lemon (zest and juice)
- ½ cup of heavy cream
- 2 extra-large eggs
- 2 extra-large egg yolks
- ¾ cup freshly grated Italian Parmesan cheese
It should be noted that I made Garten's pasta for three people, so I split her measurements in half.
I always do all my prep before I start cooking — a lesson I learned the hard way the first time I tried to make a carbonara.
Once you really get cooking with a carbonara, things need to be mixed together very quickly to achieve maximum creaminess (and to ensure you won't be eating any raw egg).
This time around, I wanted to make sure I had every single step prepped so that I wouldn't be stressed once it was time to put the pasta together.
To start, I cut my asparagus into two-inch pieces and diagonally sliced my scallions, as Garten had instructed.
I also prepped the snow peas and chives.
I julienned the snow peas, following Garten's recipe, and minced my chives.
I also got my lemon ready to go.
I zested the lemon first, then juiced it. Since different parts of the lemon are required for different steps, I made sure to put the zest and juice in separate bowls.
My last step of prep was filling a large bowl with hot tap water.
Garten recommends using "the hottest tap water" to help heat the bowl, which is where you'll later mix the pasta with the carbonara sauce.
Per her instructions, I set the full bowl aside while I cooked the pasta and pancetta. Garten says you should only pour the hot water out of the bowl "just before you drain the pasta."
It was time to get cooking! First, I got my pancetta going.
I drizzled some olive oil into a sauté pan over medium heat and then added the pancetta, which I cooked for around eight minutes.
Garten recommends stirring your pancetta occasionally and cooking until it's browned. Once your pancetta is ready, transfer it to a plate lined with paper towels and set aside.
As my pancetta cooked, I started on my pasta.
I brought a large pot of salted water to a boil, then added my spaghetti. I cooked the pasta for eight minutes, stirring the noodles occasionally.
Once the eight minutes were up, I saved a cup of the pasta water and then added some of the veggies.
I put the pasta water aside — which is important for the carbonara sauce — then threw my snow peas, frozen peas, and asparagus into the spaghetti, letting them cook together for two more minutes.
Just before I drained my pasta, I prepped the carbonara sauce.
I dumped the hot tap water out of the bowl, then added the cream, egg, egg yolk, and some of the pasta water — Garten recommends using ¼ cup if you're making this dish for six — and used a whisk to mix everything together.
After two minutes were up, I drained my spaghetti and veggies.
It was time to turn this pasta into a spaghetti carbonara!
I added my noodles and veggies to the bowl with the carbonara sauce.
I tossed everything together with tongs for a minute, making sure the spaghetti absorbed the sauce. I also added just a bit more pasta water to help keep the sauce creamy.
Then, I threw in the rest of the ingredients.
I added the Parmesan cheese to the pasta, as well as the pancetta, scallions, chives, lemon zest, and lemon juice, along with some salt and pepper.
After giving everything a good toss, I admired the bright and pretty pasta dish.
It's easy to see why Garten wants to make this pasta for her friends in the spring. The green of the veggies and the red of the pancetta pop really nicely against the spaghetti, making this pasta very Instagram-friendly.
You can also make a huge serving of this dish in no time at all. Even though I split Garten's measurements in half, we still had more than enough food for three people. And the entire dish took less than 30 minutes to make, with most of the cooking time just spent on prep.
I added some extra chives and Parmesan before serving the carbonara — which everyone loved.
I won't lie, I was a little apprehensive of this dish when I first read the recipe. I'm a huge fan of Garten's comforting red-sauce pastas , and her spring carbonara seemed, well, a little too green .
But I was pleasantly surprised. The carbonara sauce is creamy without being too heavy, and it's balanced perfectly with the fresh flavors from all the veggies. The pancetta also adds a nice crunch and umami to the pasta — I only wish there had been a bit more of it!
I served the dish to my parents, who both loved it as well. My dad called it "light and lemony," while my mom thought it'd be ideal for a barbecue .
"I'd never think to put all of these things together, but they tasted very good," she added. "It's light and refreshing."
Overall, this was definitely one of my favorites among Garten's lighter pasta dishes, and I think it's perfect for a spring dinner party . The carbonara sauce — and all those pretty veggies — makes it feel a little more special.
- Main content
- Open access
- Published: 23 April 2024
Relationship between workplace spirituality with organization-based self-esteem and workplace deviant behaviors among Iranian nurses
- Behzad Sirousi Moez 1 ,
- Amir Sadeghi ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-9300-1066 2 ,
- Leili Tapak ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-4378-3143 3 &
- Zahra Purfarzad ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-1719-2152 4
BMC Nursing volume 23 , Article number: 262 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
22 Accesses
Metrics details
Despite the numerous studies conducted on workplace spirituality, there is still lack of studies that have explored the relationship between workplace spirituality with organization-based self-esteem and workplace deviant behaviors. This study aims to examine the relationship between workplace spirituality with organization-based self-esteem and workplace deviant behaviors among Iranian nurses.
236 nurses from 5 hospitals participated in this descriptive, analytical, and cross-sectional study from August to December 2022. Data was gathered by four questionnaires: demographic information, workplace spirituality, organization-based self-steam, and workplace deviant behaviors. The data were analyzed by SPSS 26 based on descriptive and inferential statistics (Independent Two-sample t Test, Pearson correlation coefficient and multiple regression).
Based on the findings, nurses had a moderate level of perception of workplace spirituality and organization-based self-esteem while having a low level of perception regarding the occurrence of workplace deviate behaviors. Results of Pearson correlation coefficient test showed a positive and statistically significant relationship between workplace spirituality and organization-based self-esteem. Additionally, there was an inverse and significant relationship between workplace spirituality and organization-based self-esteem with workplace deviant behaviors. Results of multiple regression analyses indicate that by controlling the demographic characteristics of nurses, the meaningful work and sense of community have a significant relationship with organization-based self-esteem. Furthermore, by controlling the demographic characteristics of nurses, permanent employment status, sense of community, alignment with the organization’s values, and organization-based self-esteem have a significant relationship with workplace deviant behavior.
Conclusions
The study suggests that organizations must prioritize promoting workplace spirituality and organization-based self-esteem to ensure a healthy work environment and prevent workplace deviant behaviors.
Peer Review reports
Introduction
Workplace deviant behavior is a common problem among employees in work organizations. Workplace deviant behavior refers to “voluntary behavior that violates significant organizational norms and in so doing threatens the wellbeing of an organization, its members, or both” [ 1 ]. Examples of such behavior include absenteeism, tardiness, bribery, theft, wasting the organization’s resources, sexual harassment, rumor-spreading [ 2 , 3 ]. Unfortunately, workplace deviant behaviors are a common and costly challenge in healthcare centers and organizations, just like in other organizations [ 4 ]. Nurses, under stressful working conditions, are susceptible to workplace deviant behaviors due to reasons such as staff shortages, heavy workload, unclear duties, and inadequate equipment. However, limited studies have been conducted in this area among nurses [ 5 ].
One of the factors that determine workplace deviant behavior is workplace spirituality. Deviant behavior in the workplace reduces when a person has a good spiritual experience at work [ 6 ]. The employees who have a sense of spirituality in the workplace tend to be more satisfied with their jobs and less likely to engage in unethical behavior. Additionally, individuals who have a spiritual inclination tend to exhibit ethical behavior in their workplace. This is because they tend to work better in teams, show greater kindness and fairness, are more aware of others’ needs, and demonstrate traits such as honesty and trust [ 7 ]. The social control theory suggests that people are less likely to participate in deviant behavior at work if they have strong connections with social institutions like co-workers and religion. These bonds can be broken down into four elements: attachment, commitment, involvement, and belief in wider social values [ 8 ]. When employees do not experience spirituality in the workplace, they may feel angry, resentful, or dissatisfied and target their organization or colleagues with negative work behaviors [ 9 ]. According to the social exchange theory, workplace deviant behaviors can be seen as the result of an unfavorable social exchange between employees and their organization [ 10 ].
In order to establish workplace spirituality, it is imperative that employees not only comprehend the meaning and purpose of their work, but also experience a sense of solidarity and connection with their colleagues. Additionally, the values shared by employees must align with the organization’s values [ 11 ]. If the organization fails to meet their expectations, employees may react negatively, which is why it is crucial for organizations to consider workplace spirituality [ 12 ]. By implementing workplace spirituality, organizations can enhance employee organization-based self-esteem [ 13 ]. Organization based self-esteem is defined as, “the degree to which an individual believes him/herself to be capable, significant and worthy as an organizational member” [ 14 ]. Organizations that make their employees feel important, effective and valuable will witness a significant boost in their employees’ self-esteem levels [ 15 ]. Effective interactions are crucial for conveying an employee’s value to the organization. It is essential for employees to receive positive feedback from their colleagues to enhance their perception of their own value [ 16 ]. In this regard, the findings of study of Siriattakul et al. (2020) showed that spiritual leadership is effective on employees’ organizational self-esteem [ 17 ]. On the other hand, when employees’ organization-based self-esteem is damaged, they view themselves as less competent and valuable, which can lead to workplace deviant behavior [ 18 , 19 ].
Workplace spirituality is an undoubtedly novel concept that has recently emerged in the management and business literature [ 20 ]. The positive impact of workplace spirituality cannot be underestimated as an increasing number of employees seek value, support, and meaning in their work [ 21 ]. It is, therefore, not surprising that workplace spirituality is becoming increasingly prevalent in organizations, and research is shifting towards examining and explaining the dimensions and indicators of workplace spirituality, as well as the factors that affect it or are affected by it [ 22 ]. On the other hand, obtaining sufficient knowledge about the levels of workplace deviant behaviors can enable hospital and nursing managers, as well as nurses themselves, to develop and implement intervention strategies to potentially reduce deviant behaviors in hospitals [ 23 ]. Although some studies have shown a correlation between workplace spirituality and deviant behaviors [ 24 ], the findings of the study showed that there was no significant direct correlation between spirituality and deviant behaviors [ 25 ]. Therefore, this study aimed to determine the relationship between workplace spirituality with organization-based self-esteem and workplace deviant behaviors among Iranian nurses.
Study design, sample and setting
A descriptive correlational and cross-sectional study was conducted in five hospitals affiliated with Hamadan University of Medical Sciences. The study population included all nurses working in these hospitals during the sampling period (from August to December 2022). The following formula was used to calculate the sample size for correlation studies:
Based on previous studies [ 10 ], a correlation coefficient of 0.18, a power of 80%, an estimation error of 0.05%, and a 10% potential dropout rate, we have estimated a sample size of 250 nurses. We utilized a proportional stratified random sampling method to select the nurses based on the number of nurses employed in each hospital. This ensured that each center had an appropriate share of nurses in the sample. Subsequently, 250 nurses were randomly selected from each hospital’s list of nurses using a simple random sampling method and a table of random numbers. To be included in the study, nurses were required to have at least a bachelor’s degree in nursing, a minimum of one year of clinical experience, satisfaction, and willingness to participate. The exclusion criteria were a lack of willingness to cooperate or continue participation in any stage of the research and incomplete questionnaires.
Data collection tools
Demographic information questionnaire.
The first questionnaire collected demographic data, including age, gender, service history, type of employment, marital status, level of education, and type of work shift.
The scale of workplace spirituality
The second questionnaire measured workplace spirituality. The questionnaire was based on a standard tool introduced by Milliman et al. (2003) which was designed by Ashmos and Dachon (2000) [ 26 ]. The Persian version of this questionnaire was approved by Alizadeh in 2015. It comprised 20 items grouped into three components: meaningful work (6 items), sense of community (7 items), and alignment with the organization’s values (7 items) [ 27 ]. Participants rated their agreement with each statement on a 5-point Likert scale (1 for completely disagree to 5 for completely agree). In the present study, the average score of the questionnaire and its components was calculated by dividing the total score by the number of items and reported from 1 to 5. A higher average score indicates more workplace spirituality. This questionnaire’s validity and reliability have been confirmed in various studies [ 26 , 27 , 28 ]. The reliability of the instrument for each dimension ranges from 0.88 to 0.94 according to Milliman et al.‘s study, using Cronbach’s α [ 26 ]. Additionally, a study conducted in Iran reported the Cronbach’s alpha of the questionnaire to be 0.882 [ 27 ].. In the study conducted by Farmahini Farahani et al. on Iranian nurses, Cronbach’s alpha of the questionnaire was calculated for each subscale. The results were as follows: meaningful work (α = 0.824), sense of community (α = 0.784), and alignment with organizational values (α = 0.862) [ 28 ]. In the present study, the reliability of the questionnaire was calculated for each subscale: meaningful work (α = 0.894), sense of community (α = 0.861), and alignment with organizational values (α = 0.90).
Organizational-based self-esteem scale
The third questionnaire measured organization-based self-esteem using the organization-based self-esteem scale created by Pierce et al. (1989). It included 10 statements that evaluated employees’ beliefs and their value in the organization’s environment. Participants rated their agreement with each statement on a 5-point Likert scale (1 for completely disagree to 5 for completely agree). In the present study, the average total score of the questionnaire was obtained by dividing the total score by the number of items and was reported from 1 to 5. A higher average score indicates higher organization-based self-esteem [ 14 ]. The validity and reliability of this questionnaire have been confirmed in various studies [ 29 , 30 ]. Pierce et al., reported the Cronbach’s alpha of the questionnaire to be 0.91 [ 14 ]. In studies conducted in Iran, Tahmasabi (2020) [ 29 ], and Nami et al. (2020) [ 30 ] reported Cronbach’s alpha values of 0.94 and 0.91, respectively, for this scale. The results of Cronbach’s alpha coefficients in the present study was reported as 0.883.
The workplace deviance behaviors scale
The fourth questionnaire was used to measure workplace deviant behaviors. The questionnaire was designed by Robinson and Bennett (1995) and included 19 items that measured two components of deviant behaviors: interpersonal deviant behaviors (7 items) and organizational deviant behaviors (12 items) [ 1 ]. Participants indicated how often they observed behaviors that were harmful to the organization or other employees at their workplace. The answers were on a 7-point scale from 1 (never) to 7 (every day). The average score of this questionnaire ranges from 1 to 7. A higher mean score indicates a higher deviant behavior in the workplace. Based on the obtained score, the behaviors were classified into three levels: 1–3 for low, 3–5 for moderate, and 5–7 for high [ 5 ]. The validity and reliability of this questionnaire have been confirmed in various studies [ 4 , 5 , 23 ]. Hashish (2020) calculated Cronbach’s alpha coefficients to check the internal reliability of the tool. For interpersonal deviant behaviors, the alpha coefficient was 0.973, and for organizational deviant behaviors, it was 0.980 [ 5 ]. Babamiri et al. (2022) reported the value of Cronbach’s alpha for the two components of interpersonal and organizational deviant behaviors, equal to 0.91 and 0.93, respectively [ 4 ]. Kake Mam et al. (2021) reported Cronbach’s alpha coefficients in their study for the components of interpersonal and organizational deviant behaviors, respectively, 0.93 and 0.91 [ 23 ]. In the present study, the reliability of the questionnaire was calculated for each subscale: interpersonal deviant behaviors (α = 0.906), and organizational deviant behaviors (α = 0.923).
Data collection
The code of ethics IR.UMSHA.REC.1401.159 was obtained from the ethics committee of the research and technology department of Hamadan University of Medical Sciences in Iran. A written permit for field operations was obtained from the research and technology department of the university, and the educational and medical centers were visited with the introduction letter of this department. The questionnaires were provided by the researcher to the nurses in the service area in person and inside a packet. Upon explaining the study objectives and the questionnaire completion process along with assuring their information confidentiality, the person was requested to provide written informed consent only if they met the entry criteria and agreed to participate. The questionnaires were anonymous and identified for record-keeping purposes. The nurses were instructed to complete the questionnaire during their rest period in the nurses’ rest room. The questionnaires were to be submitted inside the provided packet. Nurses were given a 6-hour sample time to complete and submit the questionnaire. If they were unable to complete it, more time was given to them. A total of 250 questionnaires were distributed across five hospitals. 236 questionnaires were analyzed, while 13 were excluded due to outliers and unanswered questions. The response rate to the questionnaires was 94.4%.
Data analysis
The data was analyzed using statistical software SPSS version 26. Descriptive statistics were used to calculate and report central and dispersion indicators, frequency, and percentage. Inferential statistics were also performed using Independent Two-sample t Test, Pearson’s correlation coefficient, and multiple regression. The significance level of statistical analysis was considered as p < 0.05.
Ethical considerations
The study adhered to ethical guidelines by obtaining approval from the hospital management beforehand, ensuring that all participants provided informed consent, maintaining anonymity and confidentiality of the questionnaires, allowing participants to withdraw at any point, and relying only on reliable sources for data collection. The present study was confirmed by the Ethics Committee at Hamadan University of Medical Sciences (IR.UMSHA.REC.1401.159).
Characteristics of participants
The study showed that the majority of participating nurses were female (68.2%) and married (74.6%). Most of the nurses had a bachelor’s degree (86.4%), and were officially employed (59.3%). The majority of them worked rotating shifts (80.9%). The study also revealed a clear difference in the perception of workplace deviant behaviors between nurses with a master’s degree or higher and those with a bachelor’s degree ( p = 0.035). However, there was no significant difference in the scores for workplace spirituality, organization-based self-esteem, and workplace deviant behaviors based on demographic variables such as gender, marital status, level of education, employment status, and shift worked ( p > 0.05) (Table 1 ).
The research showed that the average age of nurses who participated was 33.49 years, with a standard deviation of 5.83 years. Their work experience was an average of 9.55 years, with a standard deviation of 5.38 years. The study found that there was a significant and direct linear relationship between the variables of age and work experience and the variables of spirituality in the work environment and organization-based self-esteem ( p < 0.01). However, Pearson’s correlation coefficients showed that there was no significant relationship between the variables of age and work experience of nurses with workplace deviant behaviors ( p > 0.05) (Table 1 ).
Descriptive statistics
According to the nurses’ perception, the average score of the total workplace spirituality was 3.11, with a standard deviation of 0.74. Among the components of this variable, the sense of community had the highest mean (3.28, with a standard deviation of 0.75), while alignment with the organization’s values had the lowest mean value (2.81, with a standard deviation of 0.87). Additionally, the average score of nurses’ organizational self-esteem was 3.69, with a standard deviation of 0.62. The mean and standard deviation of deviant behaviors in the workplace were 1.96 and 0.82, respectively. The interpersonal deviant behavior component had a higher average than the organizational deviant behavior component (Table 2 ).
Correlations of workplace spirituality, organization-based self-esteem, and workplace deviant behaviors
Results of Pearson correlation coefficient test showed a positive and statistically significant relationship between workplace spirituality and organization-based self-esteem ( r = 0.517, p < 0.001). Additionally, there was an inverse and significant relationship between workplace spirituality ( r =-0.390, p < 0.001) and organization-based self-esteem ( r =-0.424, p < 0.001) with workplace deviant behaviors (Table 2 ).
Associations of general characteristics and components of workplace spirituality with organization-based self-esteem
Results of multiple regression analyses indicate that by controlling the demographic characteristics of nurses, the meaningful work (β = 0.207, p = 0.023) and sense of community (β = 0.241, p = 0.019) components of workplace spirituality have a significant relationship with organization-based self-esteem. The components of workplace spirituality predict 28.8% of the variance in the organization-based self-esteem while controlling demographic characteristics (Table 3 ).
Associations of general characteristics, components of workplace spirituality, and organization-based self-esteem with workplace deviant behaviors
Results of multiple regression analyses indicate that by controlling the demographic characteristics of nurses, permanent employment status (β = 0.209, p = 0.003), sense of community (β=-0.244, p = 0.020), alignment with the organization’s values (β=-0.191, p = 0.020), and organization-based self-esteem (β=-0.311, p < 0.001) have a significant relationship with workplace deviant behaviors. The components of workplace spirituality and organization-based self-esteem predict 27.8% of the variance of workplace deviant behaviors while controlling demographic characteristics (Table 3 ).
This study showed that nurses had an average level of workplace spirituality. This finding was consistent with some previous studies [ 28 ]. However, there were also studies that reported a higher level of workplace spirituality [ 2 , 31 ]. The perception of workplace spirituality among nurses can vary depending on their religious, cultural, and personal beliefs. This may be the reason for the difference in the studies. In some cultures, spirituality in the work environment is linked to personal satisfaction and a sense of purpose. Nurses may see spirituality as a way to find meaning in their work, communicate with their patients more deeply, and cope with the stress and emotional demands of their jobs. In Eastern cultures, workplace spirituality can be related to the concept of harmony and balance. Nurses may see spirituality as a way to create a harmonious work environment and promote positive relationships with colleagues and patients. In religious and native cultures, spirituality in the work environment may be rooted in the relationship between man and God or nature. Nurses may see spirituality as a way to respect the natural world and promote healing through traditional practices and rituals, or they may perceive it as a way to be close to and obey God. Therefore, the understanding of spirituality in the work environment among nurses can be a phenomenon dependent on people’s lived experience and can be understood in different ways by nurses with different cultural backgrounds and personal beliefs. The findings of the study showed that the component of sense of community had the highest mean among the components of workplace spirituality, while alignment with the organization’s values had the lowest. This means that nurses gave more importance to the group aspect of workplace spirituality.
The present study found that nurses generally have a medium to high level of their organization-based self-esteem. This finding was consistent with some previous studies [ 32 , 33 ]. However, some studies have reported lower levels of organization-based self-esteem compared to the present study [ 34 ]. The study also found that nurses reported low levels of workplace deviant behavior. This finding was consistent with some previous studies [ 2 , 5 , 23 ]. However, the use of self-report questionnaires may lead to an underestimation of the actual levels of deviant behavior. A study conducted in Pakistan evaluated deviant work behaviors of nurses by surveying their colleagues instead of the nurses themselves. The results showed that the level of deviant behavior was evaluated as average [ 35 ]. Interestingly, the study found that nurses reported a higher level of interpersonal deviant behavior compared to organizational deviant behavior. This may be due to nurses perceiving their organization as a source of support and strength. However, if nurses feel that their organization is not supportive or does not recognize their role, they may be more likely to engage in organizational deviant behavior.
The results of present study showed that there is a positive relationship between workplace spirituality and organization-based self-esteem The results are consistent with previous studies [ 17 , 30 ]. There are several reasons that can explain this relationship. Firstly, workplace spirituality can provide nurses with a sense of purpose and meaning in their work. When nurses feel that their work aligns with their personal values and beliefs, it can increase their sense of worth and organization-based self-esteem. Secondly, workplace spirituality can act as a coping mechanism for stress and emotional challenges that nurses often face in their roles. When nurses feel more capable and flexible in their work environment, they are likely to experience a boost in their self-esteem. Thirdly, workplace spirituality can strengthen the sense of sociality and support among nurses, which can positively impact their self-esteem. Lastly, when nurses feel that their work is guided by moral principles, it can increase their self-esteem, as they perceive themselves as more capable and charitable individuals. In conclusion, further research and qualitative insights from nurses themselves can provide a more comprehensive understanding of the underlying mechanisms of this relationship.
The results of this study indicate that increased perception of workplace spirituality among nurses is associated with a decrease workplace deviant behaviors. The results are consistent with previous studies [ 2 , 36 ], while some studies have reported no significant relationship [ 10 , 25 , 37 ]. Furthermore, the study also reveals that an increase in nurses’ perception of organizational self-esteem is associated with a decrease in deviant behaviors, which is in line with other studies [ 18 , 19 ]. Workplace spirituality underscores moral and human-centered values, promoting a greater sense of personal responsibility among nurses. When nurses feel connected to a higher purpose or values in their work environment, deviant behaviors that conflict with their moral principles become less likely. Additionally, spirituality in the workplace contributes to nurses’ psychological well-being by creating a sense of meaning, purpose and satisfaction, which reduces the likelihood of deviant behaviors. The study suggests that cultivating a work environment that promotes spirituality can help create a positive and supportive organizational culture, leading to greater sociality, trust, and respect among nurses, and reducing the occurrence of deviant behaviors. Spirituality in the workplace also serves as a coping mechanism for nurses, enabling them to deal with stress, conflicts, and challenges in a constructive manner, rather than resorting to deviant behaviors. Qualitative studies that encourage open dialogue and reflection on how spirituality in the workplace can positively affect behavior and the overall workplace environment are crucial for further understanding this relationship among nurses.
Limitations
The study has several limitations that could affect the validity of the results. Firstly, the sample size of nurses was limited to only five hospitals. This could significantly reduce the representativeness of the sample and limit the generalization of the findings. Additionally, the cross-sectional design of the study can limit our understanding of causality and changes over time. The use of self-reported data may also lead to response bias and affect the accuracy of the results. It’s worth noting that the negative load of deviant work behaviors may lead to bias in response, which could further affect the validity of the results. Moreover, the demographic structure of nurses was not homogenous, which could also affect the accuracy of the findings. Lastly, due to time constraints, other possible effective variables were not included, which could have a significant impact on the results.
The study found that promoting workplace spirituality can control deviant work behaviors and increase organization-based self-esteem among nurses. It recommends that nursing management should take action to foster spirituality to promote positive work behaviors among nurses. While further research is needed to explore the mechanisms involved, this study provides constructive recommendations for nursing management and education to create a more positive and ethical work environment for nurses.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge all nurses who participated in this research. This study was extracted from a master's thesis in Hamadan University of Medical Sciences (NO.140104212864), Iran. The authors appreciate Hamadan University of Medical Sciences for financially supporting this research.
This study is part of the Msc thesis of the first author at Hamadan University of Medical Sciences (NO.140104212864) in Iran.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Student Research Committee, School of Nursing and Midwifery, Hamadan University of Medical Sciences, Hamadan, Iran
Behzad Sirousi Moez
Department of Nursing, School of Nursing and Midwifery, Hamadan University of Medical Sciences, Hamadan, Iran
Amir Sadeghi
Department of Biostatistics, School of Public Health and Modeling of Noncommunicable Diseases Research Center, Hamadan University of Medical Sciences, Hamadan, Iran
Leili Tapak
Department of Nursing, Malayer School of Nursing, Chronic Diseases (Home Care) Research Center, Hamadan University of Medical Sciences, Hamadan, Iran
Zahra Purfarzad
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Study conception and design: B.S., A.S, L.T, and Z.P; Data collection: B.S; Data analysis and interpretation: L.T, Z.P; Drafting of the article: B.S and Z.P. Critical review of the manuscript: A.S and L.T. All the authors have carefully reviewed the article and approved the final draft.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Zahra Purfarzad .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
The study was approved by ethics committee at Hamadan University of Medical Sciences (IR.UMSHA.REC.1401.159). Participation was voluntary. Consent was obtained and confidentiality kept.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Moez, B.S., Sadeghi, A., Tapak, L. et al. Relationship between workplace spirituality with organization-based self-esteem and workplace deviant behaviors among Iranian nurses. BMC Nurs 23 , 262 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12912-024-01908-x
Download citation
Received : 11 February 2024
Accepted : 01 April 2024
Published : 23 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12912-024-01908-x
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Workplace spirituality
- Organization-based self-esteem
- Workplace deviant behaviors
BMC Nursing
ISSN: 1472-6955
- General enquiries: [email protected]
Specialty medical injectable drug program, requirements and drug policy updates for April
New specialty medical injectable updates and requirements announced April 2024.
Review the following tables to determine changes to our specialty medical injectable drug programs.
SPECIALTY MEDICAL INJECTABLE DRUGS ADDED TO REVIEW AT LAUNCH
For UnitedHealthcare Commercial business
Note: Drugs added to Review at Launch may not yet be available in the marketplace.
Review the UnitedHealthcare Commercial Plan Review at Launch Medication List .
For questions, please contact your broker or UnitedHealthcare representative.
SPECIALTY MEDICAL INJECTABLE DRUGS ADDED TO MEDICATION SOURCING FOR OUTPATIENT HOSPITAL PROVIDERS ONLY
For UnitedHealthcare commercial business
Review the UnitedHealthcare Commercial Plan Medication Sourcing List .
UPDATES TO DRUG PROGRAM REQUIREMENTS AND DRUG POLICIES
For UnitedHealthcare commercial business effective July 1, 2024
UnitedHealthcare will honor all approved prior authorizations on file until the end date on the authorization or the date the member’s eligibility changes. Providers don’t need to submit a new notification/prior authorization request for members who already have an authorization for these medications on the effective date noted above. Upon prior authorization renewal, the updated policy will apply.
More articles
Broker - page template - more news experience fragment, current broker or employer group client.
Access uhceservices to check commissions, manage eligibility, request ID cards and more.
- Open supplemental data
- Reference Manager
- Simple TEXT file
People also looked at
Case report article, malignant peritoneal mesothelioma presenting with bilateral hydronephrosis and renal insufficiency: a case report and literature review.

- 1 Department of Urology, Guiqian International General Hospital, Guiyang, China
- 2 Department of Pathology, Guiqian International General Hospital, Guiyang, China
Introduction: Malignant peritoneal mesothelioma (MPM) is an extremely rare tumor with nonspecific clinical manifestations, making diagnosis challenging.
Case presentation: Herein, we report a case of MPM with occult onset presenting with bilateral hydronephrosis and renal insufficiency. A 30-year-old man was admitted to the Urology Department because of recurrent bilateral lower back pain. The etiology was unclear after a series of laboratory tests, imaging examinations, bone marrow aspiration, renal puncture biopsy, ascites examination, ureteroscopy, and so on. Finally, MPM was diagnosed by laparoscopic exploration and biopsy. Moreover, during the course of the disease, the patient's bilateral ureters were compressed, and the obstruction could not be relieved after the placement of ordinary ureteral stents. Percutaneous nephrostomy or metal ureteral stenosis was appropriate in managing malignant ureteral obstruction as it could improve renal function.
Conclusions: The onset of this case was insidious, and the diagnosis was difficult, with a poor prognosis. To date, only a handful of cases have been reported. We hope this case can provide some enlightenment for our clinical work.
Introduction
Malignant peritoneal mesothelioma (MPM) is an aggressive neoplasm that can rapidly spread within the abdominal area. Patients with peritoneal mesothelioma usually present with an abdominal mass, ascites, and abdominal pain. Herein, we report a case with bilateral hydronephrosis and renal insufficiency as the first symptoms. The case was extremely challenging to diagnose, which was finally confirmed based on laparoscopic exploration and biopsy. This study aimed to provide clinical evidence for the diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis of rare MPM.
Case presentation
A 30-year-old man was admitted to the Urology Department because of repeated bilateral lower back pain for 3 months. At the onset of the illness, computed tomography (CT) scans revealed bilateral hydronephrosis, and the serum creatinine (SCr) level was 123 μmol/L. Symptoms improved after the placement of bilateral ureteral stents. However, the back pain recurred 1 month later, accompanied by abdominal distension, nausea, and vomiting. Enhanced CT scans revealed bilateral hydronephrosis, splenomegaly, and ascites. Hydronephrosis had aggravated, with SCr levels increasing to 305 µmol/L. A transurethral cystoscopy revealed no lower urinary tract obstruction. Ureteroscopy indicated narrowing of the lower part of the bilateral ureter, approximately 6 cm from the ureteral opening. During hospitalization, the patient's condition continued to deteriorate, with a progressive decrease in urine volume. The highest SCr level was 470 μmol/L. A plain CT scan revealed bilateral hydronephrosis, splenomegaly, abdominal effusion, peritoneal thickening with exudative changes, and intestinal wall thickening, with no significant mass observed. We performed a bilateral percutaneous nephrostomy (PCN) and abdominal catheterization. Ascites analysis revealed no definite malignant cells. Serum IgG4 level testing yielded negative results. A renal needle biopsy indicated moderate to severe chronic tubulointerstitial injury. Finally, laparoscopic exploration was performed, and intraoperative findings revealed numerous small, shiny, whitish nodules carpeting all visualized peritoneal surfaces and some parts of the intestinal tubes. The tumor infiltrated the entire omentum, forming a large, firm mass ( Figure 1 ). A biopsy of the omentum itself confirmed the diagnosis of peritoneal mesothelioma. Histological findings revealed fibrous tissue hyperplasia with inflammatory cell infiltration and papillary hyperplasia of the overlying mesothelium. The immunohistochemical (IHC) markers were as follows: calretinin (+), CK (+), desmin (-), HMB45 (-), Ki-67 (10%+), CD34 (-), MC (HBME-1) (+), melan-A (-), and B-catenin (+) ( Figure 2 ).
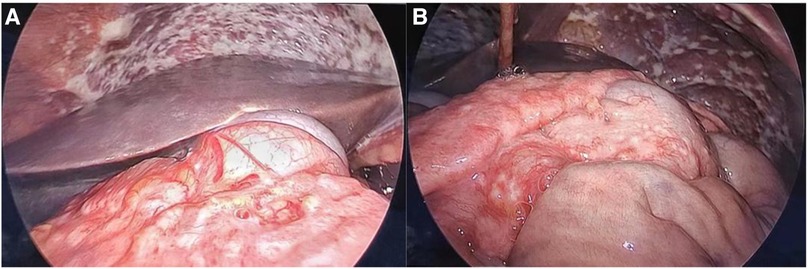
Figure 1 . ( A ) Numerous small nodules carpeting all visualized peritoneal and some parts of intestinal tube surfaces. ( B ) Tumor infiltrating the entire omentum and forming a large, firm mass.
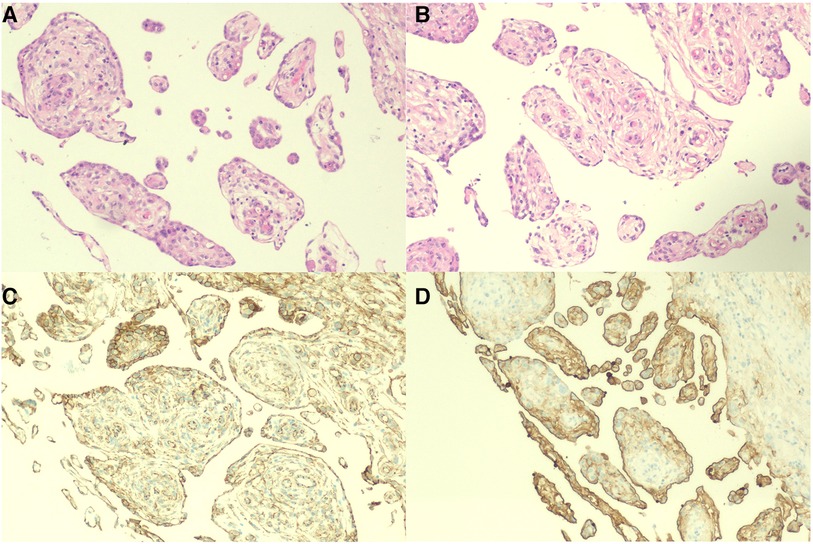
Figure 2 . Histology and immunohistochemistry of the omentum. ( A , B ) Mass of cells lined with a papillary structure of monolayer flat/cuboidal mesothelial cells with a milder nucleus and acidophilic cytoplasm (H&E, ×100). ( C , D ) Immunohistochemistry results for calretinin and MC (HBME-1) (×100).
Unfortunately, the patient refused to undergo therapy and chose to be discharged for recuperation. During the follow-up, he died at home 1 month after discharge.
Discussion and conclusions
Malignant peritoneal mesothelioma is an aggressive neoplasm of the serosal membranes, first reported by Miller and Wynn in 1908 ( 1 ). It accounts for approximately 25% of malignant mesotheliomas. Asbestos exposure is a well-recognized high-risk pathogenic factor for MPM ( 2 ). The patient was a deaf–mute construction worker with no clear history of asbestos exposure. Patients with peritoneal mesothelioma usually present with abdominal pain, distention, ascites, and an abdominal mass. Hydronephrosis rarely occurs as the first symptom. We searched PubMed for articles addressing peritoneal mesothelioma and hydronephrosis and found five relevant articles, screened by title and abstract. Two articles were finally included in the review. Detailed case data of four patients were obtained ( Table 1 ).
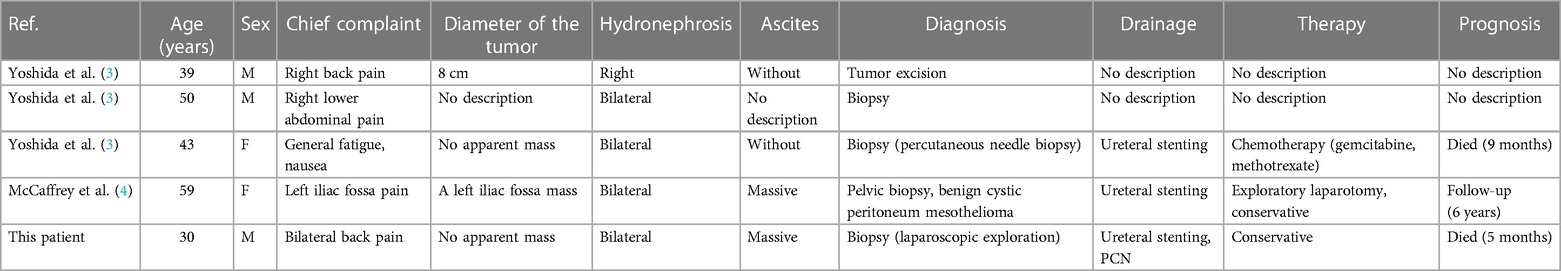
Table 1 . Characteristics of four cases of peritoneal mesothelioma presenting with hydronephrosis, as screened from PubMed and our patient.
Among these cases, the majority had a survival period of only a few months after the first diagnosis. Four out of five presented with combined bilateral hydronephrosis. Ureteral stenting was initially used in the majority of patients to drain hydronephrosis. Renal function improvement was observed in two patients. Therefore, the drainage mode should be considered when dealing with ureteral obstruction. There is no consensus on the optimal method for malignant ureteral obstruction (MUO). Some studies ( 5 ) showed that the postoperative stent failure rate of extrinsic malignant ureteral obstruction was 42%–45%. However, there was no difference in median survival compared with PCN. Metallic stents and some new material stents provide more options. The type and level of obstruction, renal insufficiency, degree of hydroneurosis, and length of obstruction >3 cm have been identified as predictors of stent failure in MUO patients. Accordingly, all these aspects should be taken into consideration. Clinician preference and patient comfort are also important factors.
Diagnosing MPM is extremely challenging, as it is characterized by irregular or nodular peritoneal or mesenteric thickening, omental mass, and ascites in imaging evaluations. The accuracy of ascitic cytology is only 50% ( 6 ). Laparoscopy is superior to CT in the evaluation of localized peritoneal metastases. The gold standard for MPM diagnosis is pathological examination. Morphologically, there are mainly three subtypes of MPM: epithelioid, sarcomatoid, and biphasic. Epithelioid MPM is the most common and least aggressive subtype, accounting for approximately 60% of cases. Our patient belongs to the epithelioid type, as evidenced by the histological findings showing papillary hyperplasia of the overlying mesothelium. However, the diffused growth pattern of the tumor and the limited tissue obtained by laparoscopic biopsy present challenges for pathological examination. In combination with the prognosis of the patient, it can be mixed with a few sarcomatoid types. IHC staining is the most valuable and feasible method for the differential diagnosis of MPM ( 7 ). The recognized positive markers are calretinin, CK 5/6, WT-1, HBME-1, thrombomodulin, podoplanin, mesothelin, and D2-40, while the negative markers are TTF1, carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), Ber Ep4, B72.3, MOC31, and CD15. It is recommended to use at least two positive and two negative markers for differential diagnosis ( 8 ).
In 2011, Yan et al. ( 9 ) proposed a TNM staging system based on the extent of peritoneal disease burden (T), intra-abdominal nodal metastasis (N), and extra-abdominal metastasis (M) to standardize and guide the clinical treatment and prognostic evaluation of MPM. The T stage is determined by calculating the peritoneal carcinomatosis index (PCI). This assessment combines lesion size (0–3) with tumor distribution (abdominopelvic and mesenteric regions 0–13) to quantify the extent of disease as a numerical score (PCI-0 to 39). The 5-year survival rates of stage I, II, and III patients were reported to be 87%, 53%, and 29%, respectively. The patient’s PCI was >30, categorizing MPM as stage III (T4). This staging was an independent prognostic factor for malignant peritoneal mesothelioma.
Cytoreductive surgery (CRS) combined with hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) is the initial preferred treatment for MPM. An analysis by the US HIPEC Collaborative, including 130 patients with MPM (all histologic subtypes included) who underwent CRS-HIPEC, reported a 5-year OS of 67.8% and a conditional OS of 89.7%. The strongest predictor of long-term survival is complete cytoreduction ( 10 ). Our patient presented with diffuse MPM, with extensive peritoneal, small bowel serosal, or mesentery involvement, which is not amenable to complete cytoreduction. The proposed treatment plan is intravenous chemotherapy and HIPEC, and immunosuppressive therapy can be added if physical conditions allow. The current preferred intraperitoneal chemotherapy is cisplatin alone or in combination with cisplatin/doxorubicin, the most commonly used combination therapy. Systemic therapy is an alternative treatment for inoperable patients. The International Expanded Access Program assessed pemetrexed regimens for 109 patients with MPM. Patients received pemetrexed, pemetrexed plus cisplatin, or pemetrexed plus carboplatin as either first-line or second-line therapy. For patients who received pemetrexed plus cisplatin, the 1-year survival rate was 57.4%. For patients who received pemetrexed alone, the median survival rate was 10.3 months, and the 1-year survival rate was 41.5%. Survival rates are not available for pemetrexed plus carboplatin ( 11 ). In recent years, molecular therapy and immunotherapy have attracted increasing attention. BAP1, TP53, NF2, and ALK, which are commonly mutated genes in MPM ( 12 ), are expected to become potential therapeutic targets. A phase II study evaluated the activity of pembrolizumab in 64 mesothelioma patients who had been treated with one or two chemotherapy regimens. Among these patients, only eight (12.5%) had MPM, and they exhibited lower overall response rates than patients with pleural mesothelioma in the study. Whether PDL1 expression is predictive of benefit remains unknown. In another cohort study evaluating the clinical efficacy of immunotherapy in patients with advanced MPM, the overall response rate was 19%, with a reported median progression-free survival (PFS) of 5.5 months ( 13 ) . Immunotherapy is an exciting future direction for MPM, and we look forward to the results of more clinical trials.
Peritoneal mesothelioma with bilateral hydronephrosis as the first symptom is rare and the diagnosis can be confirmed by laparoscopic exploration biopsy when necessary. Because of severe ureteral compression, PCN, or metal stents with high tension, offer more advantages than ordinary stents in improving renal function.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
This study involving humans was approved by the ethics committee of the Guiqian International General Hospital. The studies were conducted in accordance with local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. Written informed consent was obtained from the participant/patient(s) for the publication of this case report.
Author contributions
JL: Conceptualization, Data curation, Validation, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing. JP: Resources, Writing – review & editing. CZ: Investigation, Software, Validation, Writing – review & editing. LW: Formal analysis, Validation, Writing – review & editing. HZ: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Methodology, Project administration, Writing – review & editing.
The authors declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fsurg.2024.1342657/full#supplementary-material
1. Miller J, Wynn WH. A malignant tumour arising from the endothelium of the peritoneum, and producing a mucoid ascitic fluid. J Pathol Bacteriol . (1908) 12:267–78. doi: 10.1002/path.1700120212
Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
2. Broeckx G, Pauwels P. Malignant peritoneal mesothelioma: a review. Transl Lung Cancer Res . (2018) 7(5):537–42. doi: 10.21037/tlcr.2018.10.04
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
3. Yoshida T, Nishimura K, Uemurai M, Harada Y, Kanno N, Miyoshi S, et al. Peritoneal mesothelioma presented with bilateral hydronephrosis: a case report. Hinyokika Kiyo. Acta Urol Jpn . (2006) 52(5):363–6. PMID: 16758726.
PubMed Abstract | Google Scholar
4. McCaffrey JC, Foo FJ, Dalal N, Siddiqui KH. Benign multicystic peritoneal mesothelioma associated with hydronephrosis and colovesical fistula formation: report of a case. Tumori . (2009) 95(6):808–10. doi: 10.1177/030089160909500626
5. Chung SY, Stein RJ, Landsittel D, Davies BJ, Cuellar DC, Hrebinko RL, et al. 15-year experience with the management of extrinsic ureteral obstruction with indwelling ureteral stents. J Urol . (2004) 172(2):592–5. doi: 10.1097/01.ju.0000130510.28768.f5
6. Manzini VP, Recchia L, Cafferata M, Porta C, Siena S, Giannetta L, et al. Malignant peritoneal mesothelioma: a multicenter study on 81 cases. Ann Oncol . (2010) 21(2):348–53. doi: 10.1093/annonc/mdp307
7. Marchevsky AM. Application of immunohistochemistry to the diagnosis of malignant mesothelioma. Arch Pathol Lab Med . (2008) 132(3):397–401. doi: 10.5858/2008-132-397-AOITTD
8. Suster S, Moran CA. Applications and limitations of immunohistochemistry in the diagnosis of malignant mesothelioma. Adv Anat Pathol . (2006) 13(6):316–29. doi: 10.1097/01.pap.0000213064.05005.64
9. Yan TD, Deraco M, Elias D, Glehen O, Levine EA, Moran BJ, et al. A novel tumor-node-metastasis (TNM) staging system of diffuse malignant peritoneal mesothelioma using outcome analysis of a multi-institutional database. Cancer . (2011) 117(9):1855–63. doi: 10.1002/cncr.25640
10. Steadman JA, Grotz TE. Principles of surgical management of peritoneal mesothelioma. J Natl Compr Canc Netw . (2023) 21(9):981–6. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2023.7055
11. Ettinger DS, Wood DE, Stevenson J, Aisner DL, Akerley L, Bauman JR, et al. Mesothelioma: peritoneal, version 2.2023, NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw . (2023) 21(9):961–79. doi: 10.6004/jnccn.2023.0045
12. Kim JE, Kim D, Hong YS, Kim KP, Yoon YK, Lee DH, et al. Mutational profiling of malignant mesothelioma revealed potential therapeutic targets in EGFR and NRAS. Transl Oncol . (2018) 11(2):268–74. doi: 10.1016/j.tranon.2018.01.005
13. Menezes MB, Lima R, Dunões I, Inácio M, Dinis R. A complete response to pembrolizumab in malignant peritoneal mesothelioma: a case report. Cureus . (2024) 16(1):e52716. doi: 10.7759/cureus.52716
Keywords: peritoneal mesothelioma, hydronephrosis, percutaneous nephrostomy, ureteral stent, case report
Citation: Luo J, Pan J, Zhong C, Wang L and Zhang H (2024) Malignant peritoneal mesothelioma presenting with bilateral hydronephrosis and renal insufficiency: a case report and literature review. Front. Surg. 11:1342657. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2024.1342657
Received: 22 November 2023; Accepted: 3 April 2024; Published: 24 April 2024.
Reviewed by:
© 2024 Luo, Pan, Zhong, Wang and Zhang. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Heng Zhang [email protected]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Tip 1: provide detailed information about frameworks and methods. Literature summary tables are not only meant to provide an overview of basic information (authors, country, purpose and findings) about included articles, but they should also provide detailed information about the theoretical and conceptual frameworks and the methods used in the included article.
This is an example of a research table, in which you provide a basic description of the most important features of the studies, articles, and other items you discover in your research.The table identifies each item according to its author/date of publication, its purpose or thesis, what type of work it is (systematic review, clinical trial, etc.), the level of evidence it represents (which ...
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
Identify the article. Start your review by referring to the title and author of the article, the title of the journal, and the year of publication in the first paragraph. For example: The article, "Condom use will increase the spread of AIDS," was written by Anthony Zimmerman, a Catholic priest. 4.
2. Read the article thoroughly: Carefully read the article multiple times to get a complete understanding of its content, arguments, and conclusions. As you read, take notes on key points, supporting evidence, and any areas that require further exploration or clarification. 3. Summarize the main ideas: In your review's introduction, briefly ...
Tip 2: include strengths and limitations for eac h article. Critical appraisal of individual articles included in a. review is crucial for increasing the rigour of the review. Despite using ...
Peabody Librarians have created a sample literature review table to use to organize your research. Feel free to download this file and use or adapt as needed. << Previous: Literature Reviews Webinar Recording; Next: Writing Like an Academic >> Last Updated: Feb 29, 2024 4:20 PM;
Tip 4: compose potential themes from each article during summary writing. While developing literature summary tables, many authors use themes or subthemes reported in the given articles as the key results of their own review.
This section lists all references cited in the review article text or its figures and tables. The references should be formatted according to journal style guidelines. ... Most review articles are between 4000 and 6000 words in length and as a rule of thumb, 80-90% of the text should be within the main section/devoted to the core topic—make ...
The best proposals are timely and clearly explain why readers should pay attention to the proposed topic. It is not enough for a review to be a summary of the latest growth in the literature: the ...
Writing a Literature Review. A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels ...
Literature Review Matrix. As you read and evaluate your literature there are several different ways to organize your research. Courtesy of Dr. Gary Burkholder in the School of Psychology, these sample matrices are one option to help organize your articles. These documents allow you to compile details about your sources, such as the foundational ...
Writing a literature review requires a range of skills to gather, sort, evaluate and summarise peer-reviewed published data into a relevant and informative unbiased narrative. Digital access to research papers, academic texts, review articles, reference databases and public data sets are all sources of information that are available to enrich ...
For many kinds of assignments, like a literature review, you may be asked to offer a critique or review of a journal article.This is an opportunity for you as a scholar to offer your qualified opinion and evaluation of how another scholar has composed their article, argument, and research.That means you will be expected to go beyond a simple summary of the article and evaluate it on a deeper ...
Preparation of the review article. Steps, and targets of constructing a good review article are listed in Table 3. To write a good review article the items in Table 3 should be implemented step by step. [11-13]
A review article is a type of professional paper writing that demands a high level of in-depth analysis and a well-structured presentation of arguments. It is a critical, constructive evaluation of literature in a particular field through summary, classification, analysis, and comparison. ... Tables and Figure Legends (if instructed by the ...
The literature review template includes the following sections: Before you start - essential groundwork to ensure you're ready. The introduction section. The core/body section. The conclusion /summary. Extra free resources. Each section is explained in plain, straightforward language, followed by an overview of the key elements that you ...
Review articles on some journals, but not allowed on others (see below). Glossary List of 1 sentence definitions; optional on some journals. ... Tables should be provided as part of the article ...
Article Review vs. Response Paper . Now, let's consider the difference between an article review and a response paper: If you're assigned to critique a scholarly article, you will need to compose an article review.; If your subject of analysis is a popular article, you can respond to it with a well-crafted response paper.; The reason for such distinctions is the quality and structure of ...
If explanations cannot be sufficiently described in footnotes, review authors should provide further details of the issues in the Results and Discussion sections of the review. Table 14.1.a Guidance for providing useful explanations in 'Summary of findings' (SoF) tables. Adapted from Santesso et al (2016)
This review summarizes the rules for writing the results section of a scientific paper and describes the use of tables and figures. Keywords: Figure, paper, results, table, writing. Introduction. Medical articles consist of review articles, case reports, and letters to the editor which are prepared with the intention of publishing in journals ...
A review ar cle is a cri cal analysis of the literatur e in a. speci c area of knowledge through outline, classi ca on, comparison, etc. A good review ar cle requires brie ng, analysing, and syn ...
Timber Charme Sofa: 4.7/5 stars out of 1279 reviews. Seno 63 Media Unit: 4.8/5 stars out of 470 reviews. Seno Dining Table: 4.7/5 stars out of 505 reviews. Quarry Gray Dining Chair: 4.7/5 stars out of 204 reviews. If we're talking report cards, let's just say Article Furniture is getting straight A's.
Review Article. Share on. Recent Advances in Functional Hydrogel for Repair of Abdominal Wall Defects: A Review ... The article usage is presented with a three- to four-day delay and will update daily once available. Due to this delay, usage data will not appear immediately following publication. ... Tables. Share Share. Share article link ...
The person-centered care (PCC) approach plays a fundamental role in ensuring quality healthcare. The Person-Centered Care Assessment Tool (P-CAT) is one of the shortest and simplest tools currently available for measuring PCC. The objective of this study was to conduct a systematic review of the evidence in validation studies of the P-CAT, taking the "Standards" as a frame of reference.
Never mind the fact that consumer sales have yet to live up to the superlatives: Honda is about to cast a massive vote of confidence in Canada's electric vehicle sector. Here's what we know so far ...
Ina Garten's easy spring green spaghetti carbonara pasta features pancetta, peas, and asparagus. It only takes 30 minutes to make.
Workplace deviant behavior is a common problem among employees in work organizations. Workplace deviant behavior refers to "voluntary behavior that violates significant organizational norms and in so doing threatens the wellbeing of an organization, its members, or both" [].Examples of such behavior include absenteeism, tardiness, bribery, theft, wasting the organization's resources ...
New specialty medical injectable updates and requirements announced April 2024.
Two articles were finally included in the review. Detailed case data of four patients were obtained . Table 1. Table 1. Characteristics of four cases of peritoneal mesothelioma presenting with hydronephrosis, as screened from PubMed and our patient. Among these cases, the majority had a survival period of only a few months after the first ...