| You might be using an unsupported or outdated browser. To get the best possible experience please use the latest version of Chrome, Firefox, Safari, or Microsoft Edge to view this website. |

How To Write A Business Plan (2024 Guide)

Updated: Apr 17, 2024, 11:59am

Table of Contents
Brainstorm an executive summary, create a company description, brainstorm your business goals, describe your services or products, conduct market research, create financial plans, bottom line, frequently asked questions.
Every business starts with a vision, which is distilled and communicated through a business plan. In addition to your high-level hopes and dreams, a strong business plan outlines short-term and long-term goals, budget and whatever else you might need to get started. In this guide, we’ll walk you through how to write a business plan that you can stick to and help guide your operations as you get started.
Featured Partners
ZenBusiness
$0 + State Fees
Varies By State & Package

On ZenBusiness' Website
Northwest Registered Agent
$39 + State Fees

On Northwest Registered Agent's Website
Tailor Brands
$0 + state fee + up to $50 Amazon gift card
Free expedited filing (within 48 hours)

On Tailor Brands' Website
$0 + State Fee
On Formations' Website
Drafting the Summary
An executive summary is an extremely important first step in your business. You have to be able to put the basic facts of your business in an elevator pitch-style sentence to grab investors’ attention and keep their interest. This should communicate your business’s name, what the products or services you’re selling are and what marketplace you’re entering.
Ask for Help
When drafting the executive summary, you should have a few different options. Enlist a few thought partners to review your executive summary possibilities to determine which one is best.
After you have the executive summary in place, you can work on the company description, which contains more specific information. In the description, you’ll need to include your business’s registered name , your business address and any key employees involved in the business.
The business description should also include the structure of your business, such as sole proprietorship , limited liability company (LLC) , partnership or corporation. This is the time to specify how much of an ownership stake everyone has in the company. Finally, include a section that outlines the history of the company and how it has evolved over time.
Wherever you are on the business journey, you return to your goals and assess where you are in meeting your in-progress targets and setting new goals to work toward.
Numbers-based Goals
Goals can cover a variety of sections of your business. Financial and profit goals are a given for when you’re establishing your business, but there are other goals to take into account as well with regard to brand awareness and growth. For example, you might want to hit a certain number of followers across social channels or raise your engagement rates.
Another goal could be to attract new investors or find grants if you’re a nonprofit business. If you’re looking to grow, you’ll want to set revenue targets to make that happen as well.
Intangible Goals
Goals unrelated to traceable numbers are important as well. These can include seeing your business’s advertisement reach the general public or receiving a terrific client review. These goals are important for the direction you take your business and the direction you want it to go in the future.
The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you’re offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit in the current market or are providing something necessary or entirely new. If you have any patents or trademarks, this is where you can include those too.
If you have any visual aids, they should be included here as well. This would also be a good place to include pricing strategy and explain your materials.
This is the part of the business plan where you can explain your expertise and different approach in greater depth. Show how what you’re offering is vital to the market and fills an important gap.
You can also situate your business in your industry and compare it to other ones and how you have a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
Other than financial goals, you want to have a budget and set your planned weekly, monthly and annual spending. There are several different costs to consider, such as operational costs.
Business Operations Costs
Rent for your business is the first big cost to factor into your budget. If your business is remote, the cost that replaces rent will be the software that maintains your virtual operations.
Marketing and sales costs should be next on your list. Devoting money to making sure people know about your business is as important as making sure it functions.
Other Costs
Although you can’t anticipate disasters, there are likely to be unanticipated costs that come up at some point in your business’s existence. It’s important to factor these possible costs into your financial plans so you’re not caught totally unaware.
Business plans are important for businesses of all sizes so that you can define where your business is and where you want it to go. Growing your business requires a vision, and giving yourself a roadmap in the form of a business plan will set you up for success.
How do I write a simple business plan?
When you’re working on a business plan, make sure you have as much information as possible so that you can simplify it to the most relevant information. A simple business plan still needs all of the parts included in this article, but you can be very clear and direct.
What are some common mistakes in a business plan?
The most common mistakes in a business plan are common writing issues like grammar errors or misspellings. It’s important to be clear in your sentence structure and proofread your business plan before sending it to any investors or partners.
What basic items should be included in a business plan?
When writing out a business plan, you want to make sure that you cover everything related to your concept for the business, an analysis of the industry―including potential customers and an overview of the market for your goods or services―how you plan to execute your vision for the business, how you plan to grow the business if it becomes successful and all financial data around the business, including current cash on hand, potential investors and budget plans for the next few years.
- Best VPN Services
- Best Project Management Software
- Best Web Hosting Services
- Best Antivirus Software
- Best LLC Services
- Best POS Systems
- Best Business VOIP Services
- Best Credit Card Processing Companies
- Best CRM Software for Small Business
- Best Fleet Management Software
- Best Business Credit Cards
- Best Business Loans
- Best Business Software
- Best Business Apps
- Best Free Software For Business
- How to Start a Business
- How To Make A Small Business Website
- How To Trademark A Name
- What Is An LLC?
- How To Set Up An LLC In 7 Steps
- What is Project Management?
- How To Write An Effective Business Proposal

Best Pennsylvania LLC Services In 2024
Best Florida LLC Services In 2024

Best Maryland LLC Services In 2024
Best Texas LLC Services In 2024
Best Arizona LLC Services In 2024
Best California LLC Services In 2024
Julia is a writer in New York and started covering tech and business during the pandemic. She also covers books and the publishing industry.
Find anything you save across the site in your account
How to Write a Killer Business Plan: Your Step-by-Step Guide
All products featured on Architectural Digest are independently selected by our editors. However, when you buy something through our retail links, we may earn an affiliate commission.
If you're wondering how to write a business plan, you’ve likely been considering launching your own design firm for quite a while. You have a ton of ideas—you’ve seen how others have done it, and you’re ready to take a crack at striking out on your own. But where to begin? When getting your new business off the ground, one of your initial steps should be learning how to write a business plan. It’s crucial to structure your ideas formally into a road map for your firm’s success. If you plan to seek funding for your company, you’ll need to draft a traditional business plan; if you’re self-funding, a simple outline will suffice. Scroll on to find AD PRO’s guide, filled with strategies and details on what to include.
Typically, business plans fall into one of three categories:
1. A one-page business plan
This document summarizes your business goals in a simplified format. It’s ideal for introducing your concept to potential investors, who may not have time to peruse a lengthy document. This easy-to-read format, viewable at a glance, is perfect for initial meetings, and it offers a substantial jumping-off point—though you may need a more detailed plan in the future.
2. A lean startup plan
Slightly longer than the one-page plan, this one includes a summary and a bulleted list that contains your firm’s financial information, business strategies, metrics, and forecasts. Since this type of business plan mainly functions as an internal tool, it’s not necessary to include all the sections and information of a formal traditional business plan (see below). This simple-to-navigate five- to 10-page document should contain your strategy, the tasks you need to complete to achieve your goals and their due dates, projected sales, spending, and cash flow. It’s advisable to update this plan regularly (at least twice a year), as it is intended to guide the growth of your company—and help keep all internal members of your team in the loop. As such, it should evolve organically as your business does.
3. An external business plan (a.k.a. a traditional standard plan)
You'll need to create a more formal business plan if you intend to share company information with key players: potential investors to fund your endeavor, banks to support loan applications, or even future employees. Since you’ll be using this document to explain your strategies for your business with those who may finance or join your company, you’ll want to clearly delineate your plan in detailed sections.
Where to begin?
Your business plan is a living document that will evolve with your business. It should plot out how your business will operate, state your goals, and precisely express your vision for your company. Regardless of the type of plan you opt to create, check out these solid tips before you begin drafting the document.
1. Keep it simple
No need to complicate the already stressful process of starting your own business by constructing a convoluted plan. Create a simple bulleted plan that cites goals and your strategies for achieving them, then update it as your company grows. If you choose to draft a traditional business plan, keep it to less than 40 pages. If you’re having trouble distilling the essence of your company down to 30-35 pages, consider hiring an expert to help you write it. Fit Small Business lists Wise Business Plans as its top-choice service, but keep in mind this argument about why it’s often better to do the writing yourself.
Even if you go with a traditional, external business plan, keep it concise. Cut to the chase as quickly and efficiently as possible—you don’t want to lose a potential investor out of boredom! And don’t spend too much time making your business plan pretty. As a designer, your instinct may be to focus on stunning graphics, and while they can indeed enhance the appearance of the document, the actual content is what’s most important. Use graphs, charts, and photos to break up the text and illustrate your message without obscuring it.
2. Know your audience
Tailor your business plan to suit your needs, and craft it so that the intended audience can clearly understand it. Avoid using lingo only an A&D professional would understand—especially if you intend to use the plan as a pitch to investors or for a loan application. Use straightforward rather than insider-y language to avoid alienating your target audience.
3. Know your competition
Never speak disparagingly about your competitors. Get familiar with who they are, know what they are doing well (and poorly), and make it evident in your business plan how you will distinguish your brand from the rest. What makes your company stand out against the competition? Perhaps your firm offers online design services, specializes in custom millwork, or provides clients with assistance from a personal account director. Highlight whatever sets you apart transparently in your business plan.
4. Keep it real
Keep your expectations in check and never inflate your financials. While we encourage you to think positively and believe that your business will succeed financially, do not overestimate your earning potential and revenue forecast. What services will you offer, and how much will you bill for them? What do comparable companies bill for similar services? Make your projections realistic, particularly if you are seeking funding. Explain your business model and how you plan to earn money, as well as the reasoning behind your figures. And be certain to root all financial information in solid facts.
5. Work backward
Figure out what you want to accomplish and by what date, and then backtrack from there. Consider: Where would you like your company to be financially one year from now? What revenue goals would you like to achieve by that time? Then determine what you must do in 12 months, six months, and three months to arrive at your objective in a timely fashion. Work these milestones into your business plan. You'll be pleased as you see results accumulate throughout the year—even more so when you realize your objective by your firm’s one-year anniversary.
6. Just get it started
Don’t let the task of drafting your business plan paralyze you. If you sit down to write and come up empty, start jotting down your ideas—remembering what inspired you to launch your company in the first place—and worry about shaping your formal business plan later.
If it helps you to get started, begin with a simple one-page plan; you can always use that document as an outline and go back and fill in more details later. Remember: No one knows your business better than you do. Let your passion for starting your new company motivate you as you begin writing and don’t be afraid to let that emotion to come through in the final document. It will better convey your vision and help your readers understand what your small business is all about.
The essential components of a business plan
Now that you have an idea of what type of business plan will be right for your company and understand how to approach the task, the question remains: What do you need to include in your business plan? Entrepreneurs have varying ideas on what’s essential and what you can skip. But when starting your first-ever business, consider following the advice of the U.S. Small Business Administration, and make sure that your business plan contains these nine recommended sections.
1. Executive summary
As the single most important part of your business plan, the executive summary should pique the curiosity of your audience. It should be a brief synopsis of your company’s mission, your immediate as well as long-term goals, and your strategies for attaining these goals. Make it evident what exactly your business is: What’s the product or service? Why will your company be successful? What sets it apart from the competition? What do you plan to do differently? Get this information out there immediately. Also, include basic facts about your employees, leadership team, location, and financial statistics.
Sometimes investors will ask to see only your executive summary as they consider whether or not to grant you funding. If they are intrigued by what they read, they will ask for your entire business plan. So be sure to hit the highlights in the executive summary. And while this summary appears first in the document, it’s actually smart to write it last, since it encompasses all components of your plan, whittled down to a brief synopsis. Think of it as the whole document in a nutshell. Don’t let it exceed a page or two.
2. Company overview
Here’s where you go into detail about the concept behind your business, what you do, and what you plan to accomplish. What problem does your firm address? And what are your solutions? What target audience will your small business serve? Name specific businesses, design firms, organizations, and/or clients. Explain what you have to offer and what you’re selling. Be sure to use concrete examples and eliminate superfluous language. Outline what makes your company distinct from the competition. You’ve touched on this point in the executive summary, but go into specific detail in this section. It’s the place where you can toot your own horn—tastefully and succinctly, of course—so take advantage of the opportunity, play up your strengths, and sell your company.
3. Market research
Demonstrate that you understand your industry by doing comprehensive market analysis. Look for emerging trends and themes in the marketplace. Have a crystal-clear picture of who your customer is. Research your potential competitors, see what their strengths and weaknesses are, and determine how you can create more effective solutions. It’s critical that you stay on top of what the competition is offering.
When attempting to discern who your target audience is and who your ideal consumers are, a strong small business plan will identify market segments, the size of each, and additional segments that could be interested in your business. The typical way to distinguish market segments is to use a method called the TAM, SAM, and SOM approach, defined as:
• TAM: Your Total Available or Addressable Market. This group includes everyone you wish to reach with your product/service.
• SAM: Your Segmented Addressable Market or Served Available Market. This is the portion of the total available market you will target.
• SOM: Your Share of the Market. This is a category within your SAM that you will realistically reach in the early days of your business.
Once you establish your market segments, figure out who your ideal customer, or “buyer persona,” is within each segment. In this exercise, you should attribute specific demographics to your buyer persona—for example, a name, gender, income level, and preferences in the marketplace. This fictitious persona of your ideal customer will help you to better understand your consumer base, create stronger marketing and sales tools targeted to your consumer, and be able to attract the right type of client to your business.
4. Organization and management
Delineate your company’s business structure—whether it’s set up as a sole proprietorship, partnership, LLC, C-corp, or S-corp. Explain who is in charge, list your employees by job function, and elaborate on each person’s responsibilities. If you already have staff in place, include employees’ names and experiences, describe what each of your workers is contributing to your small firm, and how each will help it succeed. This is your opportunity to demonstrate how you’ve amassed a stellar team or explain your strategy for attracting and retaining one.
You know the old axiom: A company is only as good as its employees. Kathryn Minshew, CEO and cofounder of career-planning platform The Muse, elaborates on this tenet in a widely circulated piece of advice that was published in Colleen DeBaise's book, Inc.: Start a Successful Business : “The hard part is actually building the team that will embody your company culture and propel you forward.” This is a critical point: You must hire good people who understand your vision and who are dedicated to helping your small business flourish.
5. Description of products or services
Outline the products or services your company offers as specifically as possible. Focus first on what you will initially bring to market, rather than long-term plans. Though it’s exciting to speculate on just how big your company can become—after all, it’s that type of guts, vision, and big thinking that enabled you to launch your own business in the first place—there's no point in focusing too heavily on the distant future in the initial business plan.
You do, however, need to illustrate exactly what your company is offering, so spend a few paragraphs expanding on your concept for products and services. Discuss your service or product’s life cycle, be very specific about how it will impact consumers, and divulge whether you plan to file for copyrights or patents. Also, describe the research and development you plan to do to enhance your offerings in the near future.
6. Marketing and sales
Spelling out your complete sales and marketing strategy will provide you with a point of reference for the future. You’ll likely refer to this section and continue to tweak and update it as your company grows. Here, discuss how you plan to reach your target audience. Be sure that you have your buyer persona explicitly defined before doing this (see number 3 above).
Within the marketing strategy portion of your business plan, delineate how you plan to position your company to consumers and how you will deliver the goods and/or services you will offer. Include a positioning statement that expresses your essential value proposition and distinguishes your competitive edge. According to Bplans , a free online resource for entrepreneurs, your positioning statement needn’t be lengthy; Bplans recommends using this simple formula to construct your statement: “For [target market description] who [target market need], [this product] [how it meets the need]. Unlike [key competition], it [most important distinguishing feature].”
This sales and marketing section is the place to address product and service pricing. Although there is no exact science to setting your pricing, consider the following:
• You must break even. Plan to charge customers enough to cover your costs in creating and delivering goods or services.
• Plan for primary and secondary profit center pricing. You may decide to sell your product or services at cost or less-than-cost to offer an appealing price— but then require support or maintenance that would push the price over the amount that would make it profitable for you.
• Adhere to market rate. Your pricing should be aligned with what your audience expects. You’ll walk a fine line here: You don’t want to alienate potential customers with high pricing, yet you shouldn’t devalue your offerings with pricing that’s too low.
How you will promote and advertise your business should also be addressed in this section. Do you plan to rely on traditional advertising avenues, such as print media? Would an online platform better suit your business and reach your target audience? How about public relations? Outline how you'll get the word out about your new company.
You can also market yourself online through social media channels. It’s a business necessity to have an online presence, and deciding which social media platform will serve you best depends on your target audience. Consider your consumer demographic when deciding on where to focus your time and efforts. You’ll want to make sure to keep your brand message and voice consistent across all marketing, advertising, and promotional materials—in print and online.
7. Funding request
If you’re using your plan to seek funding, this section is where you clearly express how much you need and how you will use it. Will you opt for debt or equity? This is a question you should ponder ahead of time: Are you willing to relinquish equity in your company for the funds to get your business off the ground? What are the terms you’re seeking? What is the length of time in business that your request will cover? Make note of collateral you have to put against loans, if any. Be prepared to explain to potential investors in depth how you will use their funds. Paint them a picture in broad strokes, and highlight the major areas that need funding (for example, purchasing an inventory, funding a marketing budget, etc.).
8. Financial projections
Follow up your funding request with a detailed explanation of future financial plans. Investors want to believe they’re making a sound decision by supporting your business. When do you plan to pay off debt? Do you intend to build up your business and then sell it? Include projections for the next five years.
Don’t fret if you do not have a solid foundation in finance. It’s not as complex to create these financial projections as you might assume. This section is where you might employ some of your design savvy to create visuals such as charts and graphs to spice up otherwise dull financial details.
Your financial forecast should include the following (this information can be projected if your business is not yet established enough to have the actual documents):
• Income statement (a.k.a., profit and loss or P&L): This document essentially shows whether you’re making money. It includes a compilation of all your numbers and data, and shows your expenses deducted from your earnings to reveal whether you’re poised to be profitable.
• Cash flow statement: This statement differs from your P&L in that it’s the record of how much money you have in the bank at any given moment. In this document, you’ll calculate cash you have plus cash you receive minus cash you pay out, which equals your total cash flow. This cash flow statement helps you to understand at what points you may be low on cash (for example, while you’re waiting for a client to pay a bill), indicating that it may not be the optimal time to spend on non-urgent expenses. This document can help you determine how much funding you may need to get your small business up and running.
• Balance sheet: This statement helps determine the net worth of your company. It subtracts your assets and equity from your liabilities to arrive at your company’s net worth. From this balance sheet, investors can see the overall financial picture of your endeavor.
9. Appendix
Here you’ll include any requested documentation, such as résumés, reference letters, credit reports, permits, licenses, contracts, patents, or other legal paperwork. It’s also where you can add any supplemental information that an investor might want or need when considering whether or not to help you with funding.
Keeping these strategies in mind, you should be ready to get started on your business plan. This documentation is essential to plotting the future of your company, so it's important to spend time on it and make sure it represents you and your business in the best way possible.

Finding Investors
How Funding Works
Idea Validation Bootcamp
Pitch Deck Bootcamp
Pitching Investors
Product MVP
Product/MVP
Idea Validation
Customer Acquisition
Emotional Support
How To Write A Business Plan: A Comprehensive Guide
The Startups Team

How To Write A Business Plan: A Comprehensive Guide
A comprehensive, step-by-step guide - complete with real examples - on writing business plans with just the right amount of panache to catch an investor's attention and serve as a guiding star for your business.
Introduction to Business Plans
So you've got a killer startup idea. Now you need to write a business plan that is equally killer.
You fire up your computer, open a Google doc, and stare at the blank page for several minutes before it suddenly dawns on you that, Hm…maybe I have no idea how to write a business plan from scratch after all.
Don't let it get you down. After all, why would you know anything about business planning? For that very reason we have 4 amazing business plan samples to share with you as inspiration.

For most founders, writing a business plan feels like the startup equivalent of homework. It's the thing you know you have to do, but nobody actually wants to do.
Here's the good news: writing a business plan doesn't have to be this daunting, cumbersome chore.
Once you understand the fundamental questions that your business plan should answer for your readers and how to position everything in a way that compels your them to take action, writing a business plan becomes way more approachable.
Before you set fingers to the keyboard to turn your business idea into written documentation of your organizational structure and business goals, we're going to walk you through the most important things to keep in mind (like company description, financials, and market analysis, etc.) and to help you tackle the writing process confidently — with plenty of real life business plan examples along the way to get you writing a business plan to be proud of!
Keep It Short and Simple.
There's this old-school idea that business plans need to be ultra-dense, complex documents the size of a doorstop because that's how you convey how serious you are about your company.
Not so much.
Complexity and length for complexity and length's sake is almost never a good idea, especially when it comes to writing a business plan. There are a couple of reasons for this.
1. Investors Are Short On Time
If your chief goal is using your business plan to secure funding, then it means you intend on getting it in front of an investor. And if there's one thing investors are, it's busy. So keep this in mind throughout writing a business plan.
Investors wade through hundreds of business plans a year. There's no version of you presenting an 80-page business plan to an investor and they enthusiastically dive in and take hours out of their day to pour over the thing front to back.
Instead, they're looking for you to get your point across as quickly and clearly as possible so they can skim your business plan and get to the most salient parts to determine whether or not they think your opportunity is worth pursuing (or at the very least initiating further discussions).
You should be able to refine all of the key value points that investors look for to 15-20 pages (not including appendices where you will detail your financials). If you find yourself writing beyond that, then it's probably a case of either over explaining, repeating information, or including irrelevant details in your business plan (you don't need to devote 10 pages to how you're going to set up your website, for example).
Bottom line: always be on the lookout for opportunities to “trim the fat" while writing a business plan (and pay special attention to the executive summary section below), and you'll be more likely to secure funding.
2. Know Your Audience
If you fill your business plan with buzzwords, industry-specific jargon or acronyms, and long complicated sentences, it might make sense to a handful of people familiar with your niche and those with superhuman attention spans (not many), but it alienates the vast majority of readers who aren't experts in your particular industry. And if no one can understand so much as your company overview, they won't make it through the rest of your business plan.
Your best bet here is to use simple, straightforward language that's easily understood by anyone — from the most savvy of investor to your Great Aunt Bertha who still uses a landline.
How To Format Your Business Plan
You might be a prodigy in quantum mechanics, but if you show up to your interview rocking cargo shorts and lime green Crocs, you can probably guess what the hiring manager is going to notice first.
In the same way, how you present your business plan to your readers equally as important as what you present to them. So don't go over the top with an extensive executive summary, or get lazy with endless bullet points on your marketing strategy.
If your business plan is laden with inconsistent margins, multiple font types and sizes, missing headings and page numbers, and lacks a table of contents, it's going to create a far less digestible reading experience (and totally take away from your amazing idea and hours of work writing a business plan!)
While there's no one right way to format your business plan, the idea here is to ensure that it presents professionally. Here's some easy formatting tips to help you do just that.
If your margins are too narrow, it makes the page look super cluttered and more difficult to read.
A good rule of thumb is sticking to standard one-inch margins all around.
Your business plan is made up of several key sections, like chapters in a book.
Whenever you begin a section (“Traction” for example) you'll want to signify it using a header so that your reader immediately knows what to expect from the content that follows.
This also helps break up your content and keep everything nice and organized in your business plan.
Subheadings
Subheadings are mini versions of headings meant to break up content within each individual section and capture the attention of your readers to keep them moving down the page.
In fact, we're using sub-headers right now in this section for that very purpose!
Limit your business plan to two typefaces (one for headings and one for body copy and subheadings, for example) that you can find in a standard text editor like Microsoft Word or Google Docs.
Only pick fonts that are easy to read and contain both capital and lowercase letters.
Avoid script-style or jarring fonts that distract from the actual content. Modern, sans-serif fonts like Helvetica, Arial, and Proxima Nova are a good way to go.
Keep your body copy between 11 and 12-point font size to ensure readability (some fonts are more squint-inducing than others).
You can offset your headings from your body copy by simply upping the font size and by bolding your subheadings.
Sometimes it's better to show instead of just tell.
Assume that your readers are going to skim your plan rather than read it word-for-word and treat it as an opportunity to grab their attention with color graphics, tables, and charts (especially with financial forecasts), as well as product images, if applicable.
This will also help your reader better visualize what your business model is all about.
Need some help with this?
Our business planning wizard comes pre-loaded with a modular business plan template that you can complete in any order and makes it ridiculously easy to generate everything you need from your value proposition, mission statement, financial projections, competitive advantage, sales strategy, market research, target market, financial statements, marketing strategy, in a way that clearly communicates your business idea.
Refine Your Business Plans. Then Refine Them Some More.
Your business isn't static, so why should your business plan be?
Your business strategy is always evolving, and so are good business plans. This means that the early versions of your business plans probably won't (and shouldn't be) your last. The details of even even the best business plans are only as good as their last update.
As your business progresses and your ideas about it shift, it's important revisit your business plan from time to time to make sure it reflects those changes, keeping everything as accurate and up-to-date as possible. What good is market analysis if the market has shifted and you have an entirely different set of potential customers? And what good would the business model be if you've recently pivoted? A revised business plan is a solid business plan. It doesn't ensure business success, but it certainly helps to support it.
This rule especially holds true when you go about your market research and learn something that goes against your initial assumptions, impacting everything from your sales strategy to your financial projections.
At the same time, before you begin shopping your business plan around to potential investors or bankers, it's imperative to get a second pair of eyes on it after you've put the final period on your first draft.
After you run your spell check, have someone with strong “English teacher skills” run a fine-tooth comb over your plan for any spelling, punctuation, and grammatical errors you may have glossed over. An updated, detailed business plan (without errors!) should be constantly in your business goals.
More than that, your trusty business plan critic can also give you valuable feedback on how it reads from a stylistic perspective. While different investors prefer different styles, the key here is to remain consistent with your audience and business.
Writing Your Business Plan: A Section-By-Section Breakdown
We devoted an entire article carefully breaking down the key components of a business plan which takes a comprehensive look of what each section entails and why.
If you haven't already, you should check that out, as it will act as the perfect companion piece to what we're about to dive into in a moment.
For our purposes here, we're going to look at a few real world business plan examples (as well as one of our own self-penned “dummy” plans) to give you an inside look at how to position key information on a section-by-section basis.
1. Executive Summary
Quick overview.
After your Title Page — which includes your company name, slogan (if applicable), and contact information — and your Table of Contents, the Executive Summary will be the first section of actual content about your business.
The primary goal of your Executive Summary is to provide your readers with a high level overview of your business plan as a whole by summarizing the most important aspects in a few short sentences. Think of your Executive Summary as a kind of “teaser” for your business concept and the information to follow — information which you will explain in greater detail throughout your plan. This isn't the place for your a deep dive on your competitive advantages, or cash flow statement. It is an appropriate place to share your mission statement and value proposition.
Executive Summary Example
Here's an example of an Executive Summary taken from a sample business plan written by the Startups.com team for a fictional company called Culina. Here, we'll see how the Executive Summary offers brief overviews of the Product , Market Opportunity , Traction , and Next Steps .
Culina Tech specializes in home automation and IoT technology products designed to create the ultimate smart kitchen for modern homeowners.
Our flagship product, the Culina Smart Plug, enables users to make any kitchen appliance or cooking device intelligent. Compatible with all existing brands that plug into standard two or three-prong wall outlets, Culina creates an entire network of Wi-Fi-connected kitchen devices that can be controlled and monitored remotely right from your smartphone.
The majority of US households now spend roughly 35% of their energy consumption on appliances, electronics, and lighting. With the ability to set energy usage caps on a daily, weekly or monthly basis, Culina helps homeowners stay within their monthly utility budget through more efficient use of the dishwasher, refrigerator, freezer, stove, and other common kitchen appliances.
Additionally, 50.8% of house fires are caused in the kitchen — more than any other room in the home — translating to over $5 billion in property damage costs per year. Culina provides the preventative intelligence necessary to dramatically reduce kitchen-related disasters and their associated costs and risk of personal harm.
Our team has already completed the product development and design phase, and we are now ready to begin mass manufacturing. We've also gained a major foothold among consumers and investors alike, with 10,000 pre-ordered units sold and $5 million in investment capital secured to date.
We're currently seeking a $15M Series B capital investment that will give us the financial flexibility to ramp up hardware manufacturing, improve software UX and UI, expand our sales and marketing efforts, and fulfill pre-orders in time for the 2018 holiday season.
2. Company Synopsis
Your Company Synopsis section answers two critically important questions for your readers: What painful PROBLEM are you solving for your customers? And what is your elegant SOLUTION to that problem? The combination of these two components form your value proposition.
Company Synopsis Example
Let's look at a real-life company description example from HolliBlu * — a mobile app that connects healthcare facilities with local skilled nurses — to see how they successfully address both of these key aspects. *Note: Full disclosure; Our team worked directly with this company on their business plan via Fundable.

Notice how we get a crystal clear understanding of why the company exists to begin with when they set up the problem — that traditional nurse recruitment methods are costly, inconvenient, and time-consuming, creating significant barriers to providing quality nursing to patients in need.
Once we understand the painful problem that HolliBlu's customers face, we're then directly told how their solution links back directly to that problem — by creating an entire community of qualified nurses and directly connecting them with local employers more cost-effectively and more efficiently than traditional methods.

3. Market Overview
Your Market Overview provides color around the industry that you will be competing in as it relates to your product/service.
This will include statistics about industry size, [growth](https://www.startups.com/library/expert-advice/the-case-for-growing-slowly) rate, trends, and overall outlook. If this part of your business plan can be summed up in one word, it's research .
The idea is to gather as much raw data as you can to make the case for your readers that:
This is a market big enough to get excited about.
You can capture a big enough share of this market to get excited about.
Target Market Overview Example
Here's an example from HolliBlu's business plan:

HolliBlu's Market Overview hits all of the marks — clearly laying out the industry size ($74.8 billion), the Total Addressable Market or TAM (3 million registered nurses), industry growth rate (581,500 new RN jobs through 2018; $355 billion by 2020), and industry trends (movement toward federally-mandated compliance with nurse/patient ratios, companies offering sign-on bonuses to secure qualified nurses, increasing popularity of home-based healthcare).
4. Product (How it Works)
Where your Company Synopsis is meant to shed light on why the company exists by demonstrating the problem you're setting out to solve and then bolstering that with an impactful solution, your Product or How it Works section allows you to get into the nitty gritty of how it actually delivers that value, and any competitive advantage it provides you.
Product (How it Works) Example
In the below example from our team's Culina sample plan, we've divided the section up using subheadings to call attention to product's key features and how it actually works from a user perspective.
This approach is particularly effective if your product or service has several unique features that you want to highlight.

5. Revenue Model
Quite simply, your Revenue Model gives your readers a framework for how you plan on making money. It identifies which revenue channels you're leveraging, how you're pricing your product or service, and why.
Revenue Model Example
Let's take a look at another real world business plan example with brewpub startup Magic Waters Brewpub .*
It can be easy to get hung up on the financial aspect here, especially if you haven't fully developed your product yet. And that's okay. *Note: Full disclosure; Our team worked directly with this company on their business plan via Fundable.
The thing to remember is that investors will want to see that you've at least made some basic assumptions about your monetization strategy.

6. Operating Model
Your Operating Model quite simply refers to how your company actually runs itself. It's the detailed breakdown of the processes, technologies, and physical requirements (assets) that allow you to deliver the value to your customers that your product or service promises.
Operating Model Example
Let's say you were opening up a local coffee shop, for example. Your Operating Model might detail the following:
Information about your facility (location, indoor and outdoor space features, lease amount, utility costs, etc.)
The equipment you need to purchase (coffee and espresso machines, appliances, shelving and storage, etc.) and their respective costs.
The inventory you plan to order regularly (product, supplies, etc.), how you plan to order it (an online supplier) and how often it gets delivered (Mon-Fri).
Your staffing requirements (including how many part or full time employees you'll need, at what wages, their job descriptions, etc.)
In addition, you can also use your Operating Model to lay out the ways you intend to manage the costs and efficiencies associated with your business, including:
The Critical Costs that make or break your business. In the case of our coffee shop example, you might say something like,
“We're estimating the marketing cost to acquire a customer is going to be $25. Our average sale is $45. So long as we can keep our customer acquisition costs below $25 we will have enough margin to grow with.”
Cost Maturation & Milestones that show how your Critical Costs might fluctuate over time.
“If we sell 50 coffees a day, our average unit cost will be $8 on a sale of $10. At that point we're barely breaking even. However as we scale up to 200 coffees a day, our unit costs drop significantly to $4, creating a 100% increase in net income.”
Investment Costs that highlight strategic uses of capital that will have a big Return on Investment (ROI) later.
“We're investing $100,000 into a revolutionary new coffee brewing system that will allow us to brew twice the amount our current output with the same amount of space and staff.”
Operating Efficiencies explaining your capability of delivering your product or service in the most cost effective manner possible while maintaining the highest standards of quality.
“By using energy efficient Ecoboilers, we're able to keep our water hot while minimizing the amount of energy required. Our machines also feature an energy saving mode. Both of these allow us to dramatically cut energy costs.”
7. Competitive Analysis
Like the Market Overview section, you want to show your readers that you've done your homework and have a crazy high level of awareness about your current competitors or any potential competitors that may crop up down the line for your given business model.
When writing your Competitive Analysis, your overview should cover who your closest competitors are, the chief strengths they bring to the table, and their biggest weaknesses .
You'll want to identify at least 3 competitors — either direct, indirect, or a combination of the two. It's an extremely important aspect of the business planning process.
Competition Analysis Example
Here's an example of how HolliBlu lays out their Competitive Analysis section for just one of their competitors, implementing each of the criteria noted above:

8. Customer Definition
Your Customer Definition section allows you to note which customer segment(s) you're going after, what characteristics and habits each customer segment embodies, how each segment uniquely benefits from your product or service, and how all of this ties together to create the ideal portrait of an actual paying customer, and how you'll cultivate and manage customer relationships.
Customer Definition Example

HolliBlu's Customer Definition section is effective for several reasons. Let's deconstruct their first target market segment, hospitals.
What's particularly successful here is that we are explained why hospitals are optimal buyers.
They accomplish this by harkening back to the central problem at the core of the opportunity (when hospitals can't supply enough staff to meet patient demands, they have to resort on costly staffing agencies).
On top of that, we are also told how big of an opportunity going after this customer segment represents (5,534 hospitals in the US).
This template is followed for each of the company's 3 core customer segments. This provides consistency, but more than that, it emphasizes how diligent research reinforces their assumptions about who their customers are and why they'd open their wallets. Keep all of this in mind when you are write your own business plan.
9. Customer Acquisition
Now that you've defined who your customers are for your readers, your Customer Acquisition section will tell them what marketing and sales strategy and tactics you plan to leverage to actually reach the target market (or target markets) and ultimately convert them into paying customers.
marketing Strategy Example

Similar to the exercise you will go through with your Revenue Model, in addition to identifying which channels you're pursuing, you'll also want to detail all of relevant costs associated with your customer acquisition channels.
Let's say you spent $100 on your marketing plan to acquire 100 customers during 2018. To get your CAC, you simply divide the number of customers acquired by your spend, giving you a $1.00 CAC.
10. Traction
This one's huge. Traction tells investors one important thing: that you're business has momentum. It's evidence that you're making forward progress and hitting milestones. That things are happening. It's one of the most critical components of a successful business plan.
Why is this so important? Financial projections are great and all, but if you can prove to investors that your company's got legs before they've even put a dime into it, then it will get them thinking about all the great things you'll be able to accomplish when they do bankroll you.
Traction Example

In our Culina Traction section, we've called attention to several forms of traction, touching on some of the biggest ones that you'll want to consider when writing your own plan.
Have I built or launched my product or service yet?
Have I reached any customers yet?
Have I generated any revenue yet?
Have I forged any strategic industry relationships that will be instrumental in driving growth?
The key takeaway here: the more traction you can show, the more credibility you build with investors. After all, you can't leave it all on market analysis alone.
11. Management Team
Here's what your Management Team section isn't: it's not an exhaustive rundown of each and every position your team members have held over the course of their lives.
Instead, you should tell investors which aspects of your team's experience and expertise directly translates to the success of this company and this industry.
In other words, what applicable, relevant background do they bring to the table?
Management Team Example

Let's be real. The vast majority of startup teams probably aren't stacked with Harvard and Stanford grads. But the thing to home in on is how the prior experience listed speaks directly to how it qualifies that team member's current position.
The word of the day here is relevancy. If it's not relevant, you probably don't need to include it in your typical business plan.
12. Funding
Funding overview.
The ask! This is where you come out and, you guessed it, ask your investors point blank how much money you need to move your business forward, what specific milestones their investment will allow you to reach, how you'll allocate the capital you secure, and what the investor will get in exchange for their investment.
You can also include information about your exit strategy (IPO, acquisition, merger?).
Funding Example
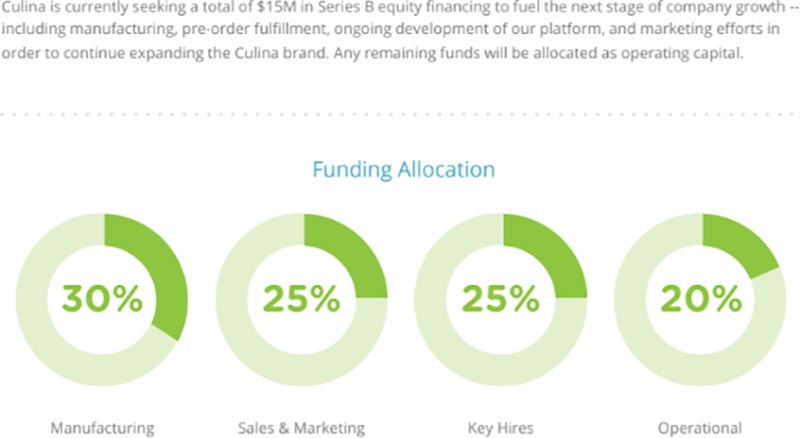
While we've preached against redundancy in your business plan, an exception to the rule is using the Funding section to offer up a very brief recap that essentially says, “here are the biggest reasons you should invest in my company and why it will ultimately benefit you.”
13. Financials
Spreadsheets and numbers and charts, oh my! Yes, it's everybody's “favorite” business plan section: Financials.
Your Financials section will come last and contain all of the forecasted numbers that say to investors that this is a sound investment. This will include things like your sales forecast, expense budget, and break-even analysis. A lot of this will be assumptions, or estimates.
The key here is keeping those estimates as realistic as humanly possible by breaking your figures into components and looking at each one individually.
Financials Example

The balance sheet above illustrates the business' estimated net worth over a three-year period by summarizing its assets (tangible objects owned by the company), liabilities (debt owed to a creditor of the company), and shareholders' equity (source of financing used to fund the assets).
In plain words, the balance sheet is basically a snapshot of your business' financial status by laying out what you own and owe, helping investors determine the level of risk involved and giving them a good understanding of the financial health of the business.
If you're looking to up your game from those outdated Excel-style spreadsheets, our business planning software will help you create clean, sleek, modern financial reports the modern way. Plus, it's as easy to use as it is attractive to look at. You might even find yourself enjoying financial projections, building a cash flow statement, and business planning overall.
You've Got This!
You've committed to writing your business plan and now you've got some tricks of the trade to help you out along the way. Whether you're applying for a business loan or seeking investors, your well-crafted business plan will act as your Holy Grail in helping take your business goals to the next plateau.
This is a ton of work. It's not a few hours and a free business plan template. It's not just a business plan software. We've been there before. Writing your [business plan](https://www.startups.com/library/expert-advice/top-4-business-plan-examples) is just one small step in startup journey. There's a whole long road ahead of you filled with a marketing plan, investor outreach, chasing venture capitalists, actually getting funded, and growing your business into a successful company.
And guess what? We've got helpful information on all of it — and all at your disposal! We hope this guides you confidently on how to write a business plan worth bragging about.
Find this article helpful?
This is just a small sample! Register to unlock our in-depth courses, hundreds of video courses, and a library of playbooks and articles to grow your startup fast. Let us Let us show you!
Ronald Calderon
Great info for feedback my current business plan!
Register to join the discussion.
- Newsletters
- Best Industries
- Business Plans
- Home-Based Business
- The UPS Store
- Customer Service
- Black in Business
- Your Next Move
- Female Founders
- Best Workplaces
- Company Culture
- Public Speaking
- HR/Benefits
- Productivity
- All the Hats
- Digital Transformation
- Artificial Intelligence
- Bringing Innovation to Market
- Cloud Computing
- Social Media
- Data Detectives
- Exit Interview
- Bootstrapping
- Crowdfunding
- Venture Capital
- Business Models
- Personal Finance
- Founder-Friendly Investors
- Upcoming Events
- Inc. 5000 Vision Conference
- Become a Sponsor
- Cox Business
- Verizon Business
- Branded Content
- Apply Inc. 5000 US
Inc. Premium

- How to Write a Great Business Plan: Overview and Objectives
The third in a comprehensive series to help you craft the perfect business plan for your startup.

This article is part of a series on how to write a great business plan .
Providing an overview of your business can be tricky, especially when you're still in the planning stages. If you already own an existing business, summarizing your current operation should be relatively easy; it can be a lot harder to explain what you plan to become .
So start by taking a step back.
Think about what products and services you will provide, how you will provide those items, what you need to have in order to provide those items, exactly who will provide those items... and most importantly, whom you will provide those items to.
Consider our bicycle rental business example. It's serves retail customers. It has an online component, but the core of the business is based on face-to-face transactions for bike rentals and support.
So you'll need a physical location, bikes, racks and tools and supporting equipment, and other brick-and-mortar related items. You'll need employees with a very particular set of skills to serve those customers, and you'll need an operating plan to guide your everyday activities.
Sound like a lot? It boils down to:
- What you will provide
- What you need to run your business
- Who will service your customers, and
- Who your customers are
In our example, defining the above is fairly simple. You know what you will provide to meet your customer's needs. You will of course need a certain quantity of bikes to service demand, but you will not need a number of different types of bikes. You need a retail location, furnished to meet the demands of your business. You need semi-skilled employees capable of sizing, customizing, and repairing bikes.
And you know your customers: Cycling enthusiasts.
In other businesses and industries answering the above questions can be more difficult. If you open a restaurant, what you plan to serve will in some ways determine your labor needs, the location you choose, the equipment you need to purchase... and most importantly will help define your customer. Changing any one element may change other elements; if you cannot afford to purchase expensive kitchen equipment, you may need to adapt your menu accordingly. If you hope to attract an upscale clientele, you may need to invest more in purchasing a prime location and creating an appealing ambience.
So where do you start? Focus on the basics first:
- Identify your industry: Retail, wholesale, service, manufacturing, etc. Clearly define your type of business.
- Identify your customer. You cannot market and sell to customers until you know who they are.
- Explain the problem you solve. Successful businesses create customer value by solving problems. In our rental example, one problem is cycling enthusiasts who don't--or can't--travel with bikes. Another problem is casual cyclists who can't--or choose not to--spend significant sums on their own bikes. The rental shop will solve that problem by offering a lower-cost and convenient alternative.
- Show how you will solve that problem. Our rental shop will offer better prices and enhanced services like remote deliveries, off-hours equipment returns, and online reservations.
If you are still stuck, try answering these questions. Some may pertain to you; others may not.
- Who is my average customer? Who am I targeting? (Unless you plan to open a grocery store, you should be unlikely to answer, "Everyone!")
- What problem do I solve for my customers?
- How will I solve that problem?
- Where will I fail to solve a customer problem... and what can I do to overcome that issue? (In our rental example, one problem is a potential lack of convenience; we will overcome that issue by offering online reservations, on-resort deliveries, and drive-up equipment returns.)
- Where will I locate my business?
- What products, services, and equipment do I need to run my business?
- What skills do my employees need, and how many do I need?
- How will I beat my competition?
- How can I differentiate myself from my competition in the eyes of my customers? (You can have a great plan to beat your competition but you also must win the perception battle among your customers. If customers don't feel you are different... then you aren't truly different. Perception is critical.)
Once you work through this list you will probably end up with a lot more detail than is necessary for your business plan. That is not a problem: Start summarizing the main points. For example, your Business Overview and Objectives section could start something like this:
History and Vision
Blue Mountain Cycle Rentals is a new retail venture that will be located at 321 Mountain Drive, directly adjacent to an extremely popular cycling destination. Our initial goal is to become the premier provider for bicycle rentals. We will then leverage our customer base and position in the market to offer new equipment sales as well as comprehensive maintenance and service, custom equipment fittings, and expert trail advice.
- Achieve the largest market share bicycle rentals in the area
- Generate a net income of $235,000 at the end of the second year of operation
- Minimize rental inventory replacement costs by maintaining a 7% attrition rate on existing equipment (industry average is 12%)
Keys to Success
- Provide high quality equipment, sourcing that equipment as inexpensively as possible through existing relationships with equipment manufacturers and other cycling shops
- Use signage to attract visitors traveling to the national forest, highlighting our cost and service advantage
- Create additional customer convenience factors to overcome a perceived lack of convenience for customers planning to ride roads and trails some distance away from our shop
- Develop customer incentive and loyalty programs to leverage customer relationships and create positive word of mouth
You could certainly include more detail in each section; this is simply a quick guide. And if you plan to develop a product or service, you should thoroughly describe the development process as well as the end result.
The key is to describe what you will do for your customers--if you can't, you won't have any customers.
Next time we'll look at another major component in a business plan: your Products and Services .
More in this series:
- How to Write a Great Business Plan: Key Concepts
- How to Write a Great Business Plan: the Executive Summary
- How to Write a Great Business Plan: Products and Services
- How to Write a Great Business Plan: Market Opportunities
- How to Write a Great Business Plan: Sales and Marketing
- How to Write a Great Business Plan: Competitive Analysis
- How to Write a Great Business Plan: Operations
- How to Write a Great Business Plan: Management Team
- How to Write a Great Business Plan: Financial Analysis
The Daily Digest for Entrepreneurs and Business Leaders
Privacy Policy

- Entrepreneurs / Startups
How to Write a Killer Business Plan
by Francis Nwokike
Writing a business plan is a must for anyone who wants to grow their business, say entrepreneurs themselves . While such a plan doesn’t instantly guarantee you success, it helps evaluate the strong and weak points of your business, understands its position on a market and its competitiveness, and come up with strong, research-based strategies for growth and problem-solving.
We want to say right from the start that there’s no one optimal business plan template . In fact, even the size of a business plan and the level of depth one has to provide vary from one business to another, from one situation to another. However, if you are an owner of a startup currently seeking funding from investors, you might want to consider a more detailed and research-heavy business plan.

That said, will you be able to write such a plan if you are short of time? The answer is yes.
Here’s what you need to do in order to achieve that.
How to write a Killer Business Plan
- Identify a Problem and Offer a Solution.
This is a piece of general advice for everyone who wants to start their own business. Though problems aren’t exactly a thing many of us, entrepreneurs included, like to think about, in business they become opportunities. This is especially true for a competitive market.
What problem does your product or service solve? How is it different from other products or services designed to solve that same problem? You need to answer those questions in as much detail as you can and provide facts and statistics to support those answers.
First, doing so will help you understand the true value of your product or service and maybe even figure out how to market it better. Second, it will demonstrate to potential investors why your business could be a better investment than the ones that belong to your competitors.
- Learn More About Your Customers.
We’ve all heard about the importance of knowing your audience. Yet, some entrepreneurs still don’t know their customers as much as they need to. It’s important to demonstrate that you aren’t one of them, that you know your customers, and know what they want.
You can figure this out with the help of an email survey or even hold interviews with at least 10 of your customers, existing or potential. You can ask your existing customers for some feedback, and so on.
Try to understand how you can use this information to change or improve certain products or services and your business in general. Be sure to include both the information and your conclusions in a business plan.
- Set Clear and Specific Goals.
There probably aren’t many entrepreneurs who start their businesses with no intention of growing big. Most likely, your dreams and ambitions are big or even huge, and that’s great: this will give you the motivation to work hard. However, big dreams and ambitious goals might not be the best solution for a business plan.
Keep in mind : the investors want to see something more realistic, based on facts and solid figures. You have to plan for the next couple of years, not for the future in general, be precise and financially wise.
Indicate a budget that could cover all expenses while leaving some room for growth at the same time. Explain how you’re going to track the progress and measure the results. Do your best to demonstrate how exactly your business will make money.
- Write a Compelling Executive Summary.
An executive summary is a very important section of a business plan. It explains to the investors what your business does or plans on doing in the nearest future (if you are a startup owner).
We cannot overemphasize the importance of this section. If you fail to impress, the investors probably won’t continue reading your plan and make their decision at that point. At the same time, this is your chance to stand out among competitors by explaining how you plan to succeed by doing something they failed to do.
Most likely, you know that already: you’ve probably answered that question to yourself before starting a business. Now you just need to explain it so the others would understand and believe in your business just like you believe in it. Don’t forget to include the financial projections as well to let the investors know how much money do you want to raise.

- Create a Marketing Plan.
Any business needs a strong marketing strategy in order to succeed. And it’s always better to come up with one (and describe one) at that point to both impress the investors and figure this out for yourself.
Think about how you’re going to let people know about your business and how you’ll keep new customers coming. Make sure that your strategy is competitive yet its budget is still reasonable. Adding a marketing strategy to your business plan will make it look stronger and more mature.
- Include an Appendix if Necessary.
You don’t have to write one just for the sake of it. However, if you want to add more data (such as charts, additional calculations, reports, etc.), explain some terms or simply include something that you believe will make your business plan look more thought-out, definitely do so.
- Don’t Forget to Review.
If possible, put aside your business plan for a day (or a couple of hours at least) and review it after. This will help you spot the things you might want to change or elaborate, just as the points that you might have left out. You also have to proofread it to ensure that no typos or grammar errors will ruin the impression.
A strong business plan is vital for both attracting investors and growing your business . It helps you understand where your business is heading, how is it going to survive in the competitive market, and how you will grow it with time.
Therefore, even if you are short of time, make sure that you’ve researched everything you need or turn to any good professional for help. Also, don’t forget to review your business plan from time to time and to update it if necessary. Adjusting it when something changes will help you keep ahead of the competitors even during difficult times.
Furthermore, such a plan will help you understand the real value of your business and its strong sides. We hope that you’ll be able to write a strong and effective business plan with the help of our tips.
Did you use a business plan to grow your business? What tips on business plan writing could you give to our readers? Please share your thoughts and stories in the comments below.
Share this:
Francis Nwokike
Francis Nwokike is the Founder and Chief Editor of The Total Entrepreneurs. A Social Entrepreneur and experienced Disaster Manager. He loves researching and discussing business trends and providing startups with valuable insights into running a profitable business. He created TTE to share ideas and tips to help entrepreneurs run and grow their businesses.
- Next story Pros and Cons of SaaS eCommerce Platforms
- Previous story Fashion Affiliate Programs: The Fashion Bloggers’ Secret Money Machine
Business Ideas
Advice for Landlords Dealing with Cost Increases in Rental Properties and HMOs
12 Businesses that Thrive During a Pandemic
Running a Fleet of Vehicles? 6 Easy Ways to Save on Fleet Costs
Physician Mortgage Loans: Everything You Need to Know
How To Incorporate Sustainability At Your Next Business Event
Importance of Packaging and its Influence on Customer Buying Habits
The Impact of Marketing Strategies on Healthcare Systems
How To Market a Manufacturing Company
How To Spot The Best Digital Marketing Channels For Your Business
Consumer Behavior Examples: How to Tailor Your Marketing Tactics
Tips & How to Setup a Unified Communication System for a Business
How to Use WhatsApp in Desktop Computer
Key Features and Benefits of CPQ Software for Businesses
How Digital Customer Service Is Transforming the Consumer Experience
IT Risks That Any Start-Up Company Is Vulnerable To
Startup Interviews

The Short Jack Ma Story and the Secret behind his Success

Interview with Isaac Mashman, Founder Mashman Ventures

How I Make Money – Efiye Bribena

Interview with Ariel Camus, Founder and CEO of Microverse
Recent Posts
- Smart Ways to Fund Your Business: A Guide for New Entrepreneurs
- User Onboarding: The Key to Boosting Product Engagement
- How Coworking Spaces Are Supporting Startups and Freelancers
- Unlocking Growth: The Strategic Value of Exploring New Investment Opportunities for Growing Businesses
- Understanding COSHH: A Comprehensive Guide to Workplace Hazard Management

COMMENTS
Read our simple guide to learn how to write a business plan quickly and easily. A solid business plan is essential for any new business.
The following steps outline the basics of how to create a business plan, as defined by the U.S. Small Business Administration: Executive Summary – Your company’s value proposition. Company Description – An overview of your company’s history, leadership, locations, and team.
Your business plan is a living document that will evolve with your business. It should plot out how your business will operate, state your goals, and precisely express your vision for your...
A comprehensive, step-by-step guide - complete with real examples - on writing business plans with just the right amount of panache to catch an investor's attention and serve as a guiding star for your business.
Focus on the basics first: Identify your industry: Retail, wholesale, service, manufacturing, etc. Clearly define your type of business. Identify your customer. You cannot market and sell to...
The answer is yes. Here’s what you need to do in order to achieve that. How to write a Killer Business Plan. Identify a Problem and Offer a Solution. This is a piece of general advice for everyone who wants to start their own business.