Home Blog Design Understanding Data Presentations (Guide + Examples)

Understanding Data Presentations (Guide + Examples)
In this age of overwhelming information, the skill to effectively convey data has become extremely valuable. Initiating a discussion on data presentation types involves thoughtful consideration of the nature of your data and the message you aim to convey. Different types of visualizations serve distinct purposes. Whether you’re dealing with how to develop a report or simply trying to communicate complex information, how you present data influences how well your audience understands and engages with it. This extensive guide leads you through the different ways of data presentation.
Table of Contents
What is a Data Presentation?
What should a data presentation include, line graphs, treemap chart, scatter plot, how to choose a data presentation type, recommended data presentation templates, common mistakes done in data presentation.
A data presentation is a slide deck that aims to disclose quantitative information to an audience through the use of visual formats and narrative techniques derived from data analysis, making complex data understandable and actionable. This process requires a series of tools, such as charts, graphs, tables, infographics, dashboards, and so on, supported by concise textual explanations to improve understanding and boost retention rate.
Data presentations require us to cull data in a format that allows the presenter to highlight trends, patterns, and insights so that the audience can act upon the shared information. In a few words, the goal of data presentations is to enable viewers to grasp complicated concepts or trends quickly, facilitating informed decision-making or deeper analysis.
Data presentations go beyond the mere usage of graphical elements. Seasoned presenters encompass visuals with the art of data storytelling , so the speech skillfully connects the points through a narrative that resonates with the audience. Depending on the purpose – inspire, persuade, inform, support decision-making processes, etc. – is the data presentation format that is better suited to help us in this journey.
To nail your upcoming data presentation, ensure to count with the following elements:
- Clear Objectives: Understand the intent of your presentation before selecting the graphical layout and metaphors to make content easier to grasp.
- Engaging introduction: Use a powerful hook from the get-go. For instance, you can ask a big question or present a problem that your data will answer. Take a look at our guide on how to start a presentation for tips & insights.
- Structured Narrative: Your data presentation must tell a coherent story. This means a beginning where you present the context, a middle section in which you present the data, and an ending that uses a call-to-action. Check our guide on presentation structure for further information.
- Visual Elements: These are the charts, graphs, and other elements of visual communication we ought to use to present data. This article will cover one by one the different types of data representation methods we can use, and provide further guidance on choosing between them.
- Insights and Analysis: This is not just showcasing a graph and letting people get an idea about it. A proper data presentation includes the interpretation of that data, the reason why it’s included, and why it matters to your research.
- Conclusion & CTA: Ending your presentation with a call to action is necessary. Whether you intend to wow your audience into acquiring your services, inspire them to change the world, or whatever the purpose of your presentation, there must be a stage in which you convey all that you shared and show the path to staying in touch. Plan ahead whether you want to use a thank-you slide, a video presentation, or which method is apt and tailored to the kind of presentation you deliver.
- Q&A Session: After your speech is concluded, allocate 3-5 minutes for the audience to raise any questions about the information you disclosed. This is an extra chance to establish your authority on the topic. Check our guide on questions and answer sessions in presentations here.
Bar charts are a graphical representation of data using rectangular bars to show quantities or frequencies in an established category. They make it easy for readers to spot patterns or trends. Bar charts can be horizontal or vertical, although the vertical format is commonly known as a column chart. They display categorical, discrete, or continuous variables grouped in class intervals [1] . They include an axis and a set of labeled bars horizontally or vertically. These bars represent the frequencies of variable values or the values themselves. Numbers on the y-axis of a vertical bar chart or the x-axis of a horizontal bar chart are called the scale.
Real-Life Application of Bar Charts
Let’s say a sales manager is presenting sales to their audience. Using a bar chart, he follows these steps.
Step 1: Selecting Data
The first step is to identify the specific data you will present to your audience.
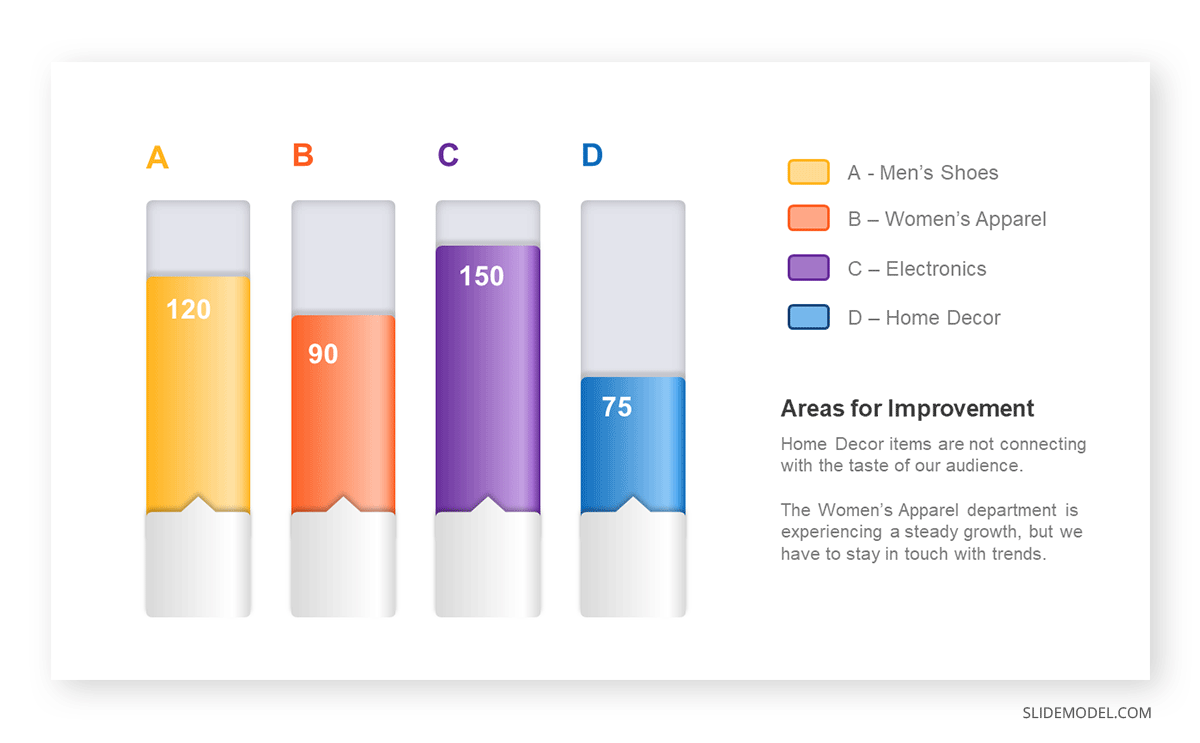
The sales manager has highlighted these products for the presentation.
- Product A: Men’s Shoes
- Product B: Women’s Apparel
- Product C: Electronics
- Product D: Home Decor
Step 2: Choosing Orientation
Opt for a vertical layout for simplicity. Vertical bar charts help compare different categories in case there are not too many categories [1] . They can also help show different trends. A vertical bar chart is used where each bar represents one of the four chosen products. After plotting the data, it is seen that the height of each bar directly represents the sales performance of the respective product.
It is visible that the tallest bar (Electronics – Product C) is showing the highest sales. However, the shorter bars (Women’s Apparel – Product B and Home Decor – Product D) need attention. It indicates areas that require further analysis or strategies for improvement.
Step 3: Colorful Insights
Different colors are used to differentiate each product. It is essential to show a color-coded chart where the audience can distinguish between products.
- Men’s Shoes (Product A): Yellow
- Women’s Apparel (Product B): Orange
- Electronics (Product C): Violet
- Home Decor (Product D): Blue
Bar charts are straightforward and easily understandable for presenting data. They are versatile when comparing products or any categorical data [2] . Bar charts adapt seamlessly to retail scenarios. Despite that, bar charts have a few shortcomings. They cannot illustrate data trends over time. Besides, overloading the chart with numerous products can lead to visual clutter, diminishing its effectiveness.
For more information, check our collection of bar chart templates for PowerPoint .
Line graphs help illustrate data trends, progressions, or fluctuations by connecting a series of data points called ‘markers’ with straight line segments. This provides a straightforward representation of how values change [5] . Their versatility makes them invaluable for scenarios requiring a visual understanding of continuous data. In addition, line graphs are also useful for comparing multiple datasets over the same timeline. Using multiple line graphs allows us to compare more than one data set. They simplify complex information so the audience can quickly grasp the ups and downs of values. From tracking stock prices to analyzing experimental results, you can use line graphs to show how data changes over a continuous timeline. They show trends with simplicity and clarity.
Real-life Application of Line Graphs
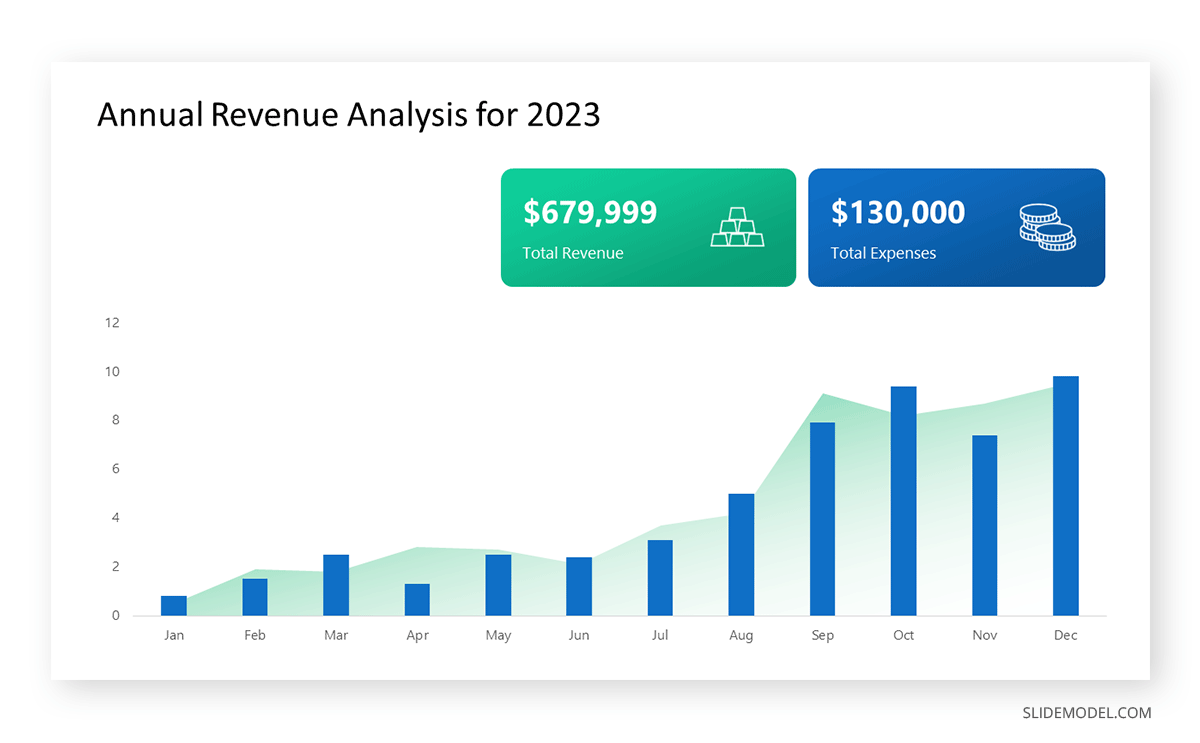
To understand line graphs thoroughly, we will use a real case. Imagine you’re a financial analyst presenting a tech company’s monthly sales for a licensed product over the past year. Investors want insights into sales behavior by month, how market trends may have influenced sales performance and reception to the new pricing strategy. To present data via a line graph, you will complete these steps.
First, you need to gather the data. In this case, your data will be the sales numbers. For example:
- January: $45,000
- February: $55,000
- March: $45,000
- April: $60,000
- May: $ 70,000
- June: $65,000
- July: $62,000
- August: $68,000
- September: $81,000
- October: $76,000
- November: $87,000
- December: $91,000
After choosing the data, the next step is to select the orientation. Like bar charts, you can use vertical or horizontal line graphs. However, we want to keep this simple, so we will keep the timeline (x-axis) horizontal while the sales numbers (y-axis) vertical.
Step 3: Connecting Trends
After adding the data to your preferred software, you will plot a line graph. In the graph, each month’s sales are represented by data points connected by a line.
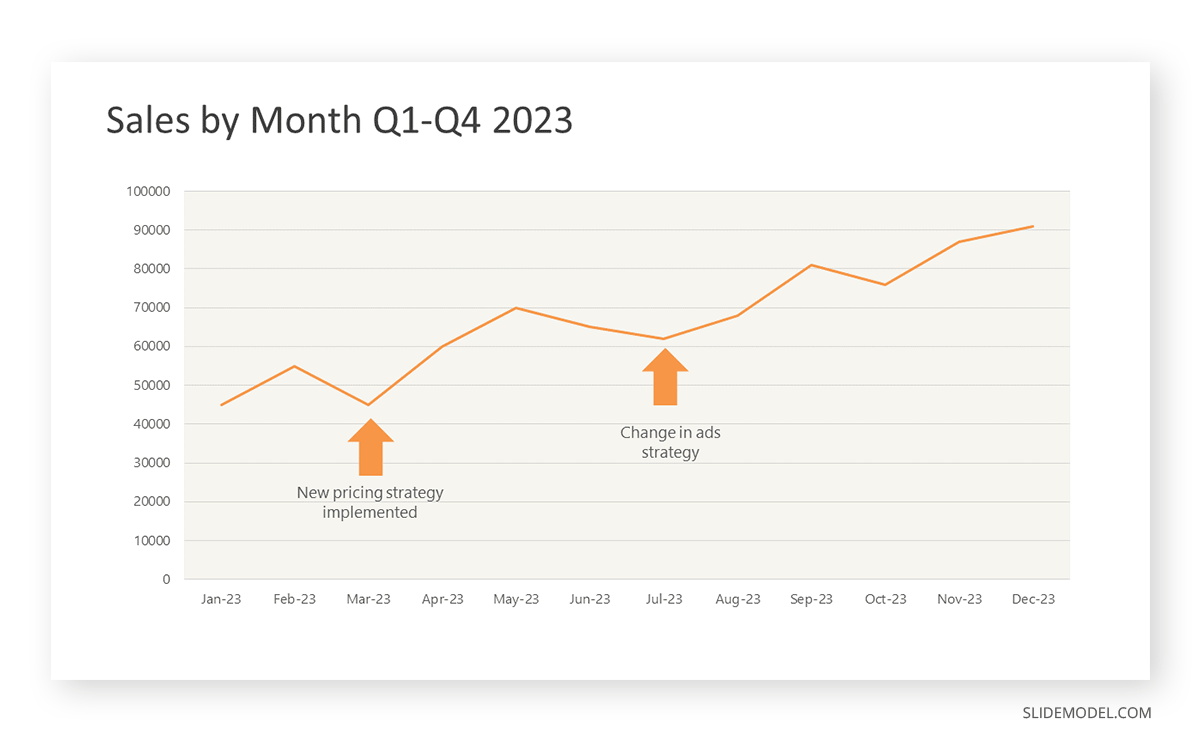
Step 4: Adding Clarity with Color
If there are multiple lines, you can also add colors to highlight each one, making it easier to follow.
Line graphs excel at visually presenting trends over time. These presentation aids identify patterns, like upward or downward trends. However, too many data points can clutter the graph, making it harder to interpret. Line graphs work best with continuous data but are not suitable for categories.
For more information, check our collection of line chart templates for PowerPoint and our article about how to make a presentation graph .
A data dashboard is a visual tool for analyzing information. Different graphs, charts, and tables are consolidated in a layout to showcase the information required to achieve one or more objectives. Dashboards help quickly see Key Performance Indicators (KPIs). You don’t make new visuals in the dashboard; instead, you use it to display visuals you’ve already made in worksheets [3] .
Keeping the number of visuals on a dashboard to three or four is recommended. Adding too many can make it hard to see the main points [4]. Dashboards can be used for business analytics to analyze sales, revenue, and marketing metrics at a time. They are also used in the manufacturing industry, as they allow users to grasp the entire production scenario at the moment while tracking the core KPIs for each line.
Real-Life Application of a Dashboard
Consider a project manager presenting a software development project’s progress to a tech company’s leadership team. He follows the following steps.
Step 1: Defining Key Metrics
To effectively communicate the project’s status, identify key metrics such as completion status, budget, and bug resolution rates. Then, choose measurable metrics aligned with project objectives.
Step 2: Choosing Visualization Widgets
After finalizing the data, presentation aids that align with each metric are selected. For this project, the project manager chooses a progress bar for the completion status and uses bar charts for budget allocation. Likewise, he implements line charts for bug resolution rates.
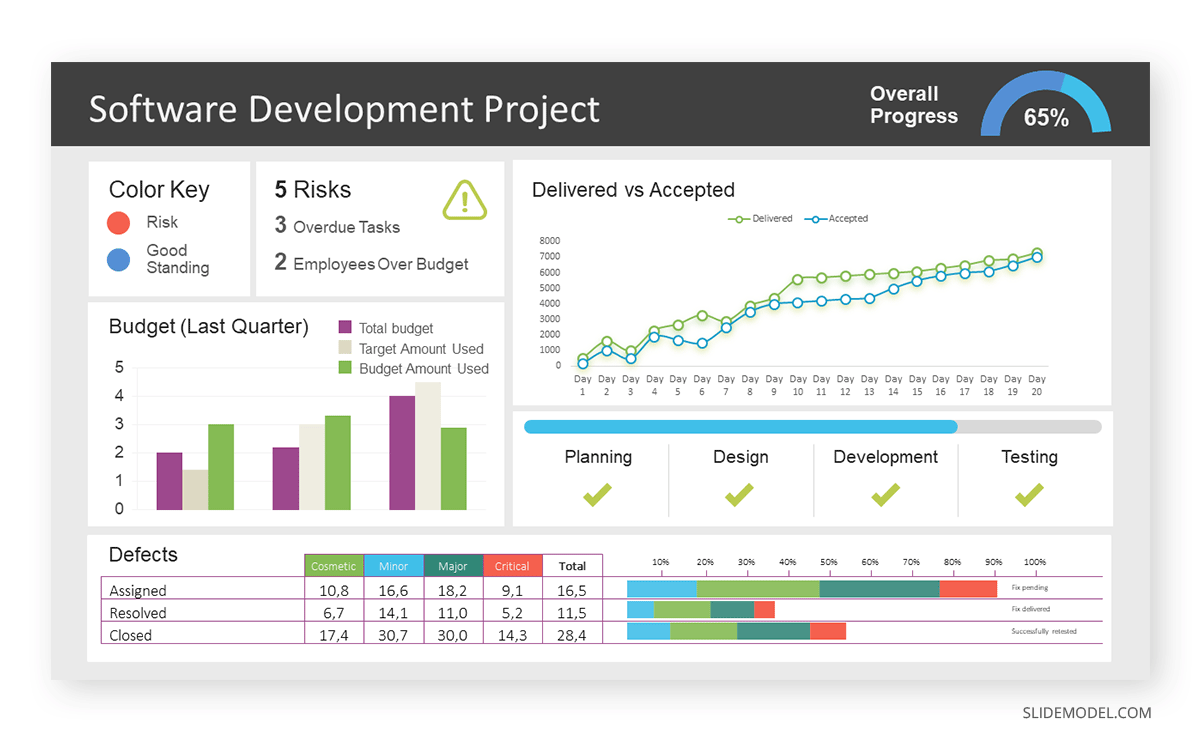
Step 3: Dashboard Layout
Key metrics are prominently placed in the dashboard for easy visibility, and the manager ensures that it appears clean and organized.
Dashboards provide a comprehensive view of key project metrics. Users can interact with data, customize views, and drill down for detailed analysis. However, creating an effective dashboard requires careful planning to avoid clutter. Besides, dashboards rely on the availability and accuracy of underlying data sources.
For more information, check our article on how to design a dashboard presentation , and discover our collection of dashboard PowerPoint templates .
Treemap charts represent hierarchical data structured in a series of nested rectangles [6] . As each branch of the ‘tree’ is given a rectangle, smaller tiles can be seen representing sub-branches, meaning elements on a lower hierarchical level than the parent rectangle. Each one of those rectangular nodes is built by representing an area proportional to the specified data dimension.
Treemaps are useful for visualizing large datasets in compact space. It is easy to identify patterns, such as which categories are dominant. Common applications of the treemap chart are seen in the IT industry, such as resource allocation, disk space management, website analytics, etc. Also, they can be used in multiple industries like healthcare data analysis, market share across different product categories, or even in finance to visualize portfolios.
Real-Life Application of a Treemap Chart
Let’s consider a financial scenario where a financial team wants to represent the budget allocation of a company. There is a hierarchy in the process, so it is helpful to use a treemap chart. In the chart, the top-level rectangle could represent the total budget, and it would be subdivided into smaller rectangles, each denoting a specific department. Further subdivisions within these smaller rectangles might represent individual projects or cost categories.
Step 1: Define Your Data Hierarchy
While presenting data on the budget allocation, start by outlining the hierarchical structure. The sequence will be like the overall budget at the top, followed by departments, projects within each department, and finally, individual cost categories for each project.
- Top-level rectangle: Total Budget
- Second-level rectangles: Departments (Engineering, Marketing, Sales)
- Third-level rectangles: Projects within each department
- Fourth-level rectangles: Cost categories for each project (Personnel, Marketing Expenses, Equipment)
Step 2: Choose a Suitable Tool
It’s time to select a data visualization tool supporting Treemaps. Popular choices include Tableau, Microsoft Power BI, PowerPoint, or even coding with libraries like D3.js. It is vital to ensure that the chosen tool provides customization options for colors, labels, and hierarchical structures.
Here, the team uses PowerPoint for this guide because of its user-friendly interface and robust Treemap capabilities.
Step 3: Make a Treemap Chart with PowerPoint
After opening the PowerPoint presentation, they chose “SmartArt” to form the chart. The SmartArt Graphic window has a “Hierarchy” category on the left. Here, you will see multiple options. You can choose any layout that resembles a Treemap. The “Table Hierarchy” or “Organization Chart” options can be adapted. The team selects the Table Hierarchy as it looks close to a Treemap.
Step 5: Input Your Data
After that, a new window will open with a basic structure. They add the data one by one by clicking on the text boxes. They start with the top-level rectangle, representing the total budget.
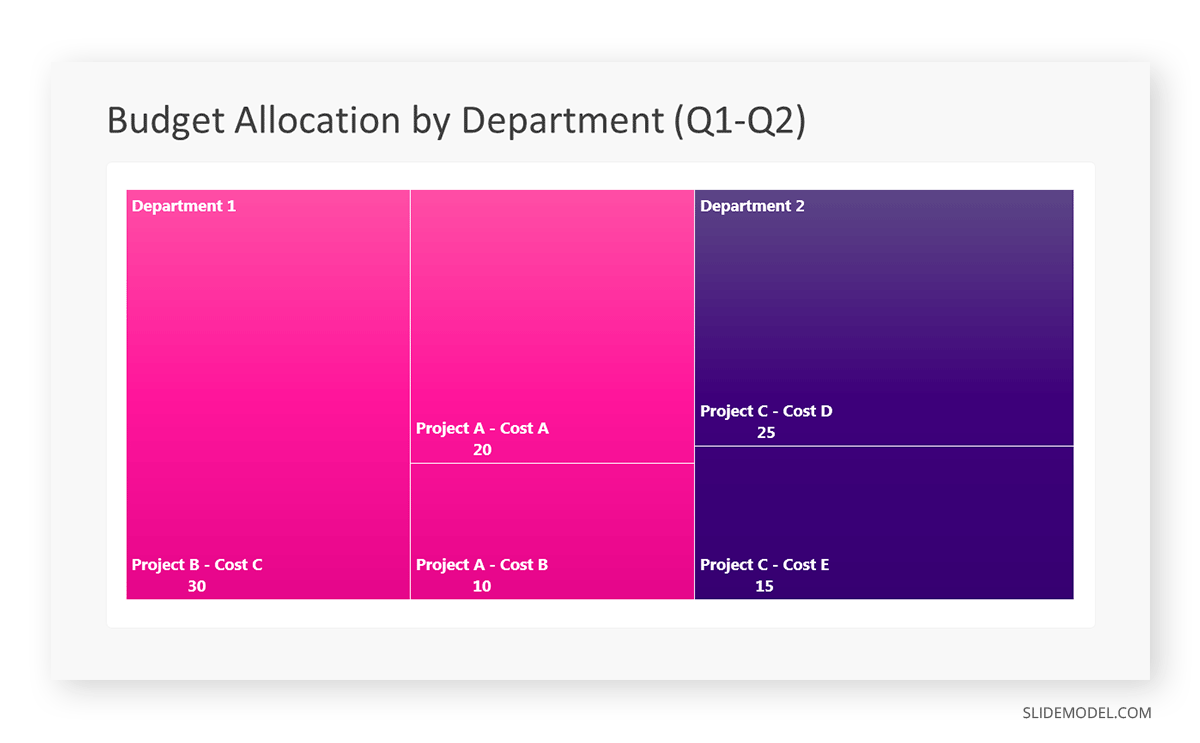
Step 6: Customize the Treemap
By clicking on each shape, they customize its color, size, and label. At the same time, they can adjust the font size, style, and color of labels by using the options in the “Format” tab in PowerPoint. Using different colors for each level enhances the visual difference.
Treemaps excel at illustrating hierarchical structures. These charts make it easy to understand relationships and dependencies. They efficiently use space, compactly displaying a large amount of data, reducing the need for excessive scrolling or navigation. Additionally, using colors enhances the understanding of data by representing different variables or categories.
In some cases, treemaps might become complex, especially with deep hierarchies. It becomes challenging for some users to interpret the chart. At the same time, displaying detailed information within each rectangle might be constrained by space. It potentially limits the amount of data that can be shown clearly. Without proper labeling and color coding, there’s a risk of misinterpretation.
A heatmap is a data visualization tool that uses color coding to represent values across a two-dimensional surface. In these, colors replace numbers to indicate the magnitude of each cell. This color-shaded matrix display is valuable for summarizing and understanding data sets with a glance [7] . The intensity of the color corresponds to the value it represents, making it easy to identify patterns, trends, and variations in the data.
As a tool, heatmaps help businesses analyze website interactions, revealing user behavior patterns and preferences to enhance overall user experience. In addition, companies use heatmaps to assess content engagement, identifying popular sections and areas of improvement for more effective communication. They excel at highlighting patterns and trends in large datasets, making it easy to identify areas of interest.
We can implement heatmaps to express multiple data types, such as numerical values, percentages, or even categorical data. Heatmaps help us easily spot areas with lots of activity, making them helpful in figuring out clusters [8] . When making these maps, it is important to pick colors carefully. The colors need to show the differences between groups or levels of something. And it is good to use colors that people with colorblindness can easily see.
Check our detailed guide on how to create a heatmap here. Also discover our collection of heatmap PowerPoint templates .
Pie charts are circular statistical graphics divided into slices to illustrate numerical proportions. Each slice represents a proportionate part of the whole, making it easy to visualize the contribution of each component to the total.
The size of the pie charts is influenced by the value of data points within each pie. The total of all data points in a pie determines its size. The pie with the highest data points appears as the largest, whereas the others are proportionally smaller. However, you can present all pies of the same size if proportional representation is not required [9] . Sometimes, pie charts are difficult to read, or additional information is required. A variation of this tool can be used instead, known as the donut chart , which has the same structure but a blank center, creating a ring shape. Presenters can add extra information, and the ring shape helps to declutter the graph.
Pie charts are used in business to show percentage distribution, compare relative sizes of categories, or present straightforward data sets where visualizing ratios is essential.
Real-Life Application of Pie Charts
Consider a scenario where you want to represent the distribution of the data. Each slice of the pie chart would represent a different category, and the size of each slice would indicate the percentage of the total portion allocated to that category.
Step 1: Define Your Data Structure
Imagine you are presenting the distribution of a project budget among different expense categories.
- Column A: Expense Categories (Personnel, Equipment, Marketing, Miscellaneous)
- Column B: Budget Amounts ($40,000, $30,000, $20,000, $10,000) Column B represents the values of your categories in Column A.
Step 2: Insert a Pie Chart
Using any of the accessible tools, you can create a pie chart. The most convenient tools for forming a pie chart in a presentation are presentation tools such as PowerPoint or Google Slides. You will notice that the pie chart assigns each expense category a percentage of the total budget by dividing it by the total budget.
For instance:
- Personnel: $40,000 / ($40,000 + $30,000 + $20,000 + $10,000) = 40%
- Equipment: $30,000 / ($40,000 + $30,000 + $20,000 + $10,000) = 30%
- Marketing: $20,000 / ($40,000 + $30,000 + $20,000 + $10,000) = 20%
- Miscellaneous: $10,000 / ($40,000 + $30,000 + $20,000 + $10,000) = 10%
You can make a chart out of this or just pull out the pie chart from the data.
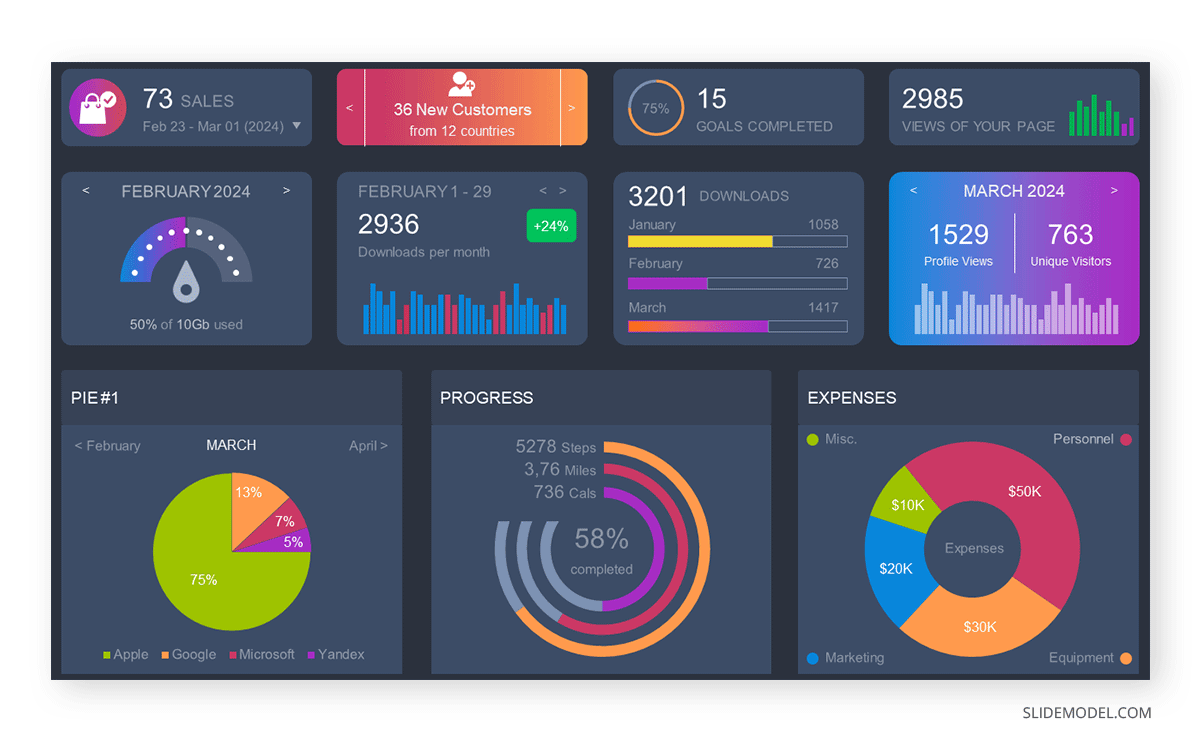
3D pie charts and 3D donut charts are quite popular among the audience. They stand out as visual elements in any presentation slide, so let’s take a look at how our pie chart example would look in 3D pie chart format.
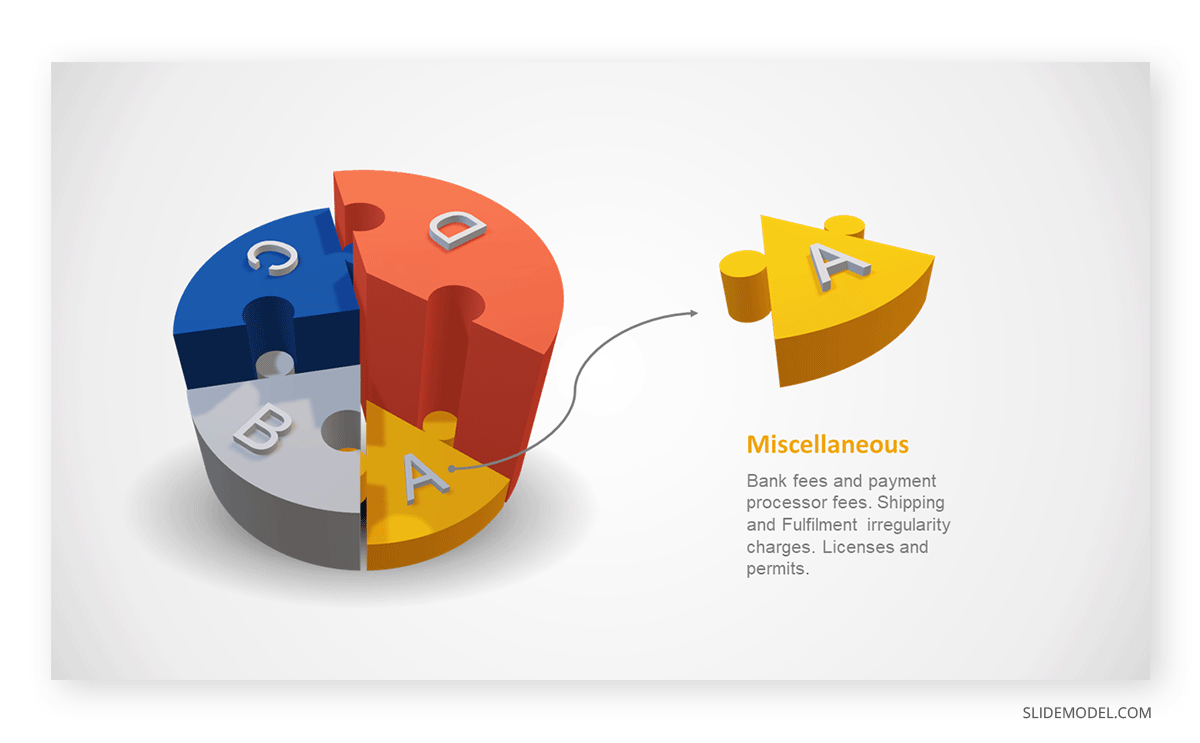
Step 03: Results Interpretation
The pie chart visually illustrates the distribution of the project budget among different expense categories. Personnel constitutes the largest portion at 40%, followed by equipment at 30%, marketing at 20%, and miscellaneous at 10%. This breakdown provides a clear overview of where the project funds are allocated, which helps in informed decision-making and resource management. It is evident that personnel are a significant investment, emphasizing their importance in the overall project budget.
Pie charts provide a straightforward way to represent proportions and percentages. They are easy to understand, even for individuals with limited data analysis experience. These charts work well for small datasets with a limited number of categories.
However, a pie chart can become cluttered and less effective in situations with many categories. Accurate interpretation may be challenging, especially when dealing with slight differences in slice sizes. In addition, these charts are static and do not effectively convey trends over time.
For more information, check our collection of pie chart templates for PowerPoint .
Histograms present the distribution of numerical variables. Unlike a bar chart that records each unique response separately, histograms organize numeric responses into bins and show the frequency of reactions within each bin [10] . The x-axis of a histogram shows the range of values for a numeric variable. At the same time, the y-axis indicates the relative frequencies (percentage of the total counts) for that range of values.
Whenever you want to understand the distribution of your data, check which values are more common, or identify outliers, histograms are your go-to. Think of them as a spotlight on the story your data is telling. A histogram can provide a quick and insightful overview if you’re curious about exam scores, sales figures, or any numerical data distribution.
Real-Life Application of a Histogram
In the histogram data analysis presentation example, imagine an instructor analyzing a class’s grades to identify the most common score range. A histogram could effectively display the distribution. It will show whether most students scored in the average range or if there are significant outliers.
Step 1: Gather Data
He begins by gathering the data. The scores of each student in class are gathered to analyze exam scores.
After arranging the scores in ascending order, bin ranges are set.
Step 2: Define Bins
Bins are like categories that group similar values. Think of them as buckets that organize your data. The presenter decides how wide each bin should be based on the range of the values. For instance, the instructor sets the bin ranges based on score intervals: 60-69, 70-79, 80-89, and 90-100.
Step 3: Count Frequency
Now, he counts how many data points fall into each bin. This step is crucial because it tells you how often specific ranges of values occur. The result is the frequency distribution, showing the occurrences of each group.
Here, the instructor counts the number of students in each category.
- 60-69: 1 student (Kate)
- 70-79: 4 students (David, Emma, Grace, Jack)
- 80-89: 7 students (Alice, Bob, Frank, Isabel, Liam, Mia, Noah)
- 90-100: 3 students (Clara, Henry, Olivia)
Step 4: Create the Histogram
It’s time to turn the data into a visual representation. Draw a bar for each bin on a graph. The width of the bar should correspond to the range of the bin, and the height should correspond to the frequency. To make your histogram understandable, label the X and Y axes.
In this case, the X-axis should represent the bins (e.g., test score ranges), and the Y-axis represents the frequency.
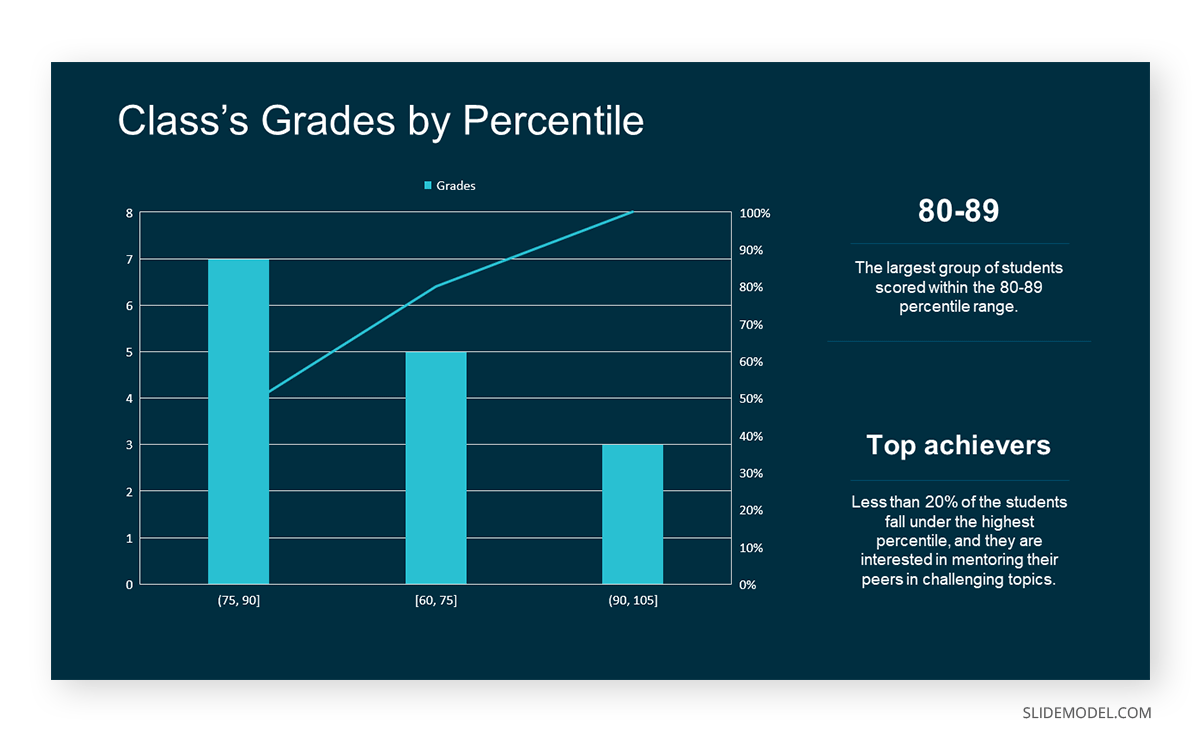
The histogram of the class grades reveals insightful patterns in the distribution. Most students, with seven students, fall within the 80-89 score range. The histogram provides a clear visualization of the class’s performance. It showcases a concentration of grades in the upper-middle range with few outliers at both ends. This analysis helps in understanding the overall academic standing of the class. It also identifies the areas for potential improvement or recognition.
Thus, histograms provide a clear visual representation of data distribution. They are easy to interpret, even for those without a statistical background. They apply to various types of data, including continuous and discrete variables. One weak point is that histograms do not capture detailed patterns in students’ data, with seven compared to other visualization methods.
A scatter plot is a graphical representation of the relationship between two variables. It consists of individual data points on a two-dimensional plane. This plane plots one variable on the x-axis and the other on the y-axis. Each point represents a unique observation. It visualizes patterns, trends, or correlations between the two variables.
Scatter plots are also effective in revealing the strength and direction of relationships. They identify outliers and assess the overall distribution of data points. The points’ dispersion and clustering reflect the relationship’s nature, whether it is positive, negative, or lacks a discernible pattern. In business, scatter plots assess relationships between variables such as marketing cost and sales revenue. They help present data correlations and decision-making.
Real-Life Application of Scatter Plot
A group of scientists is conducting a study on the relationship between daily hours of screen time and sleep quality. After reviewing the data, they managed to create this table to help them build a scatter plot graph:
In the provided example, the x-axis represents Daily Hours of Screen Time, and the y-axis represents the Sleep Quality Rating.
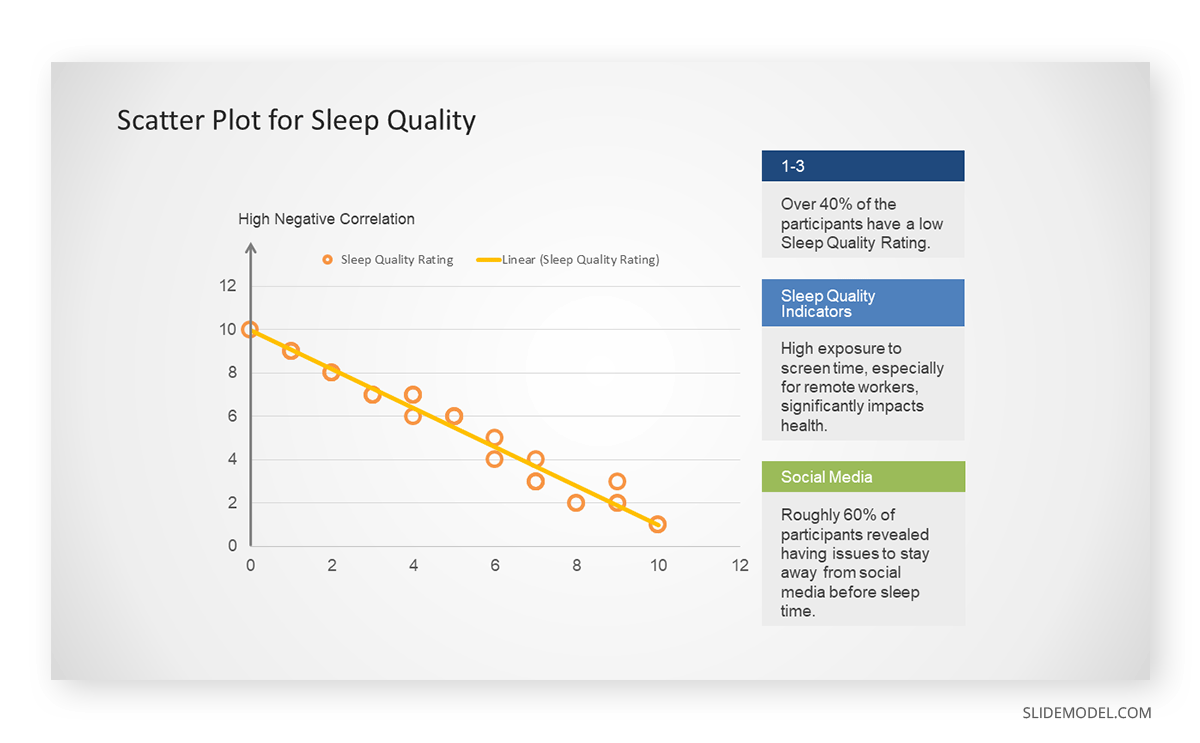
The scientists observe a negative correlation between the amount of screen time and the quality of sleep. This is consistent with their hypothesis that blue light, especially before bedtime, has a significant impact on sleep quality and metabolic processes.
There are a few things to remember when using a scatter plot. Even when a scatter diagram indicates a relationship, it doesn’t mean one variable affects the other. A third factor can influence both variables. The more the plot resembles a straight line, the stronger the relationship is perceived [11] . If it suggests no ties, the observed pattern might be due to random fluctuations in data. When the scatter diagram depicts no correlation, whether the data might be stratified is worth considering.
Choosing the appropriate data presentation type is crucial when making a presentation . Understanding the nature of your data and the message you intend to convey will guide this selection process. For instance, when showcasing quantitative relationships, scatter plots become instrumental in revealing correlations between variables. If the focus is on emphasizing parts of a whole, pie charts offer a concise display of proportions. Histograms, on the other hand, prove valuable for illustrating distributions and frequency patterns.
Bar charts provide a clear visual comparison of different categories. Likewise, line charts excel in showcasing trends over time, while tables are ideal for detailed data examination. Starting a presentation on data presentation types involves evaluating the specific information you want to communicate and selecting the format that aligns with your message. This ensures clarity and resonance with your audience from the beginning of your presentation.
1. Fact Sheet Dashboard for Data Presentation

Convey all the data you need to present in this one-pager format, an ideal solution tailored for users looking for presentation aids. Global maps, donut chats, column graphs, and text neatly arranged in a clean layout presented in light and dark themes.
Use This Template
2. 3D Column Chart Infographic PPT Template
Represent column charts in a highly visual 3D format with this PPT template. A creative way to present data, this template is entirely editable, and we can craft either a one-page infographic or a series of slides explaining what we intend to disclose point by point.
3. Data Circles Infographic PowerPoint Template
An alternative to the pie chart and donut chart diagrams, this template features a series of curved shapes with bubble callouts as ways of presenting data. Expand the information for each arch in the text placeholder areas.
4. Colorful Metrics Dashboard for Data Presentation
This versatile dashboard template helps us in the presentation of the data by offering several graphs and methods to convert numbers into graphics. Implement it for e-commerce projects, financial projections, project development, and more.
5. Animated Data Presentation Tools for PowerPoint & Google Slides
A slide deck filled with most of the tools mentioned in this article, from bar charts, column charts, treemap graphs, pie charts, histogram, etc. Animated effects make each slide look dynamic when sharing data with stakeholders.
6. Statistics Waffle Charts PPT Template for Data Presentations
This PPT template helps us how to present data beyond the typical pie chart representation. It is widely used for demographics, so it’s a great fit for marketing teams, data science professionals, HR personnel, and more.
7. Data Presentation Dashboard Template for Google Slides
A compendium of tools in dashboard format featuring line graphs, bar charts, column charts, and neatly arranged placeholder text areas.
8. Weather Dashboard for Data Presentation
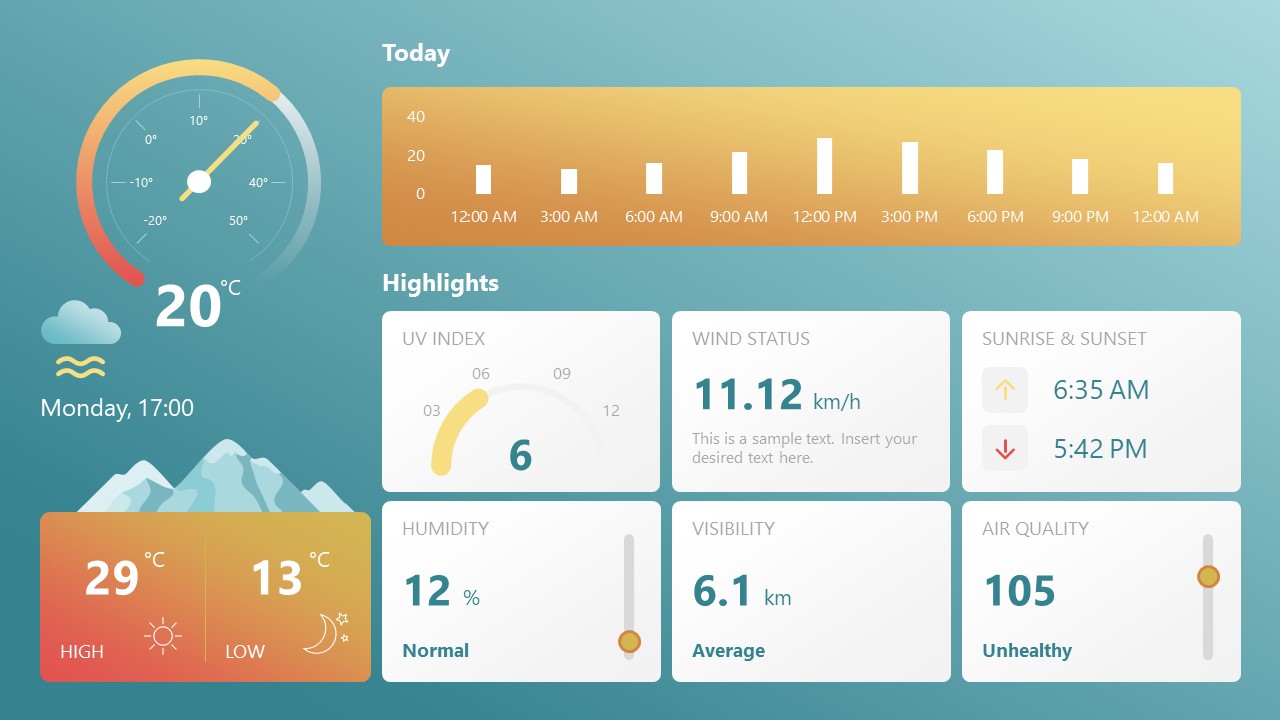
Share weather data for agricultural presentation topics, environmental studies, or any kind of presentation that requires a highly visual layout for weather forecasting on a single day. Two color themes are available.
9. Social Media Marketing Dashboard Data Presentation Template
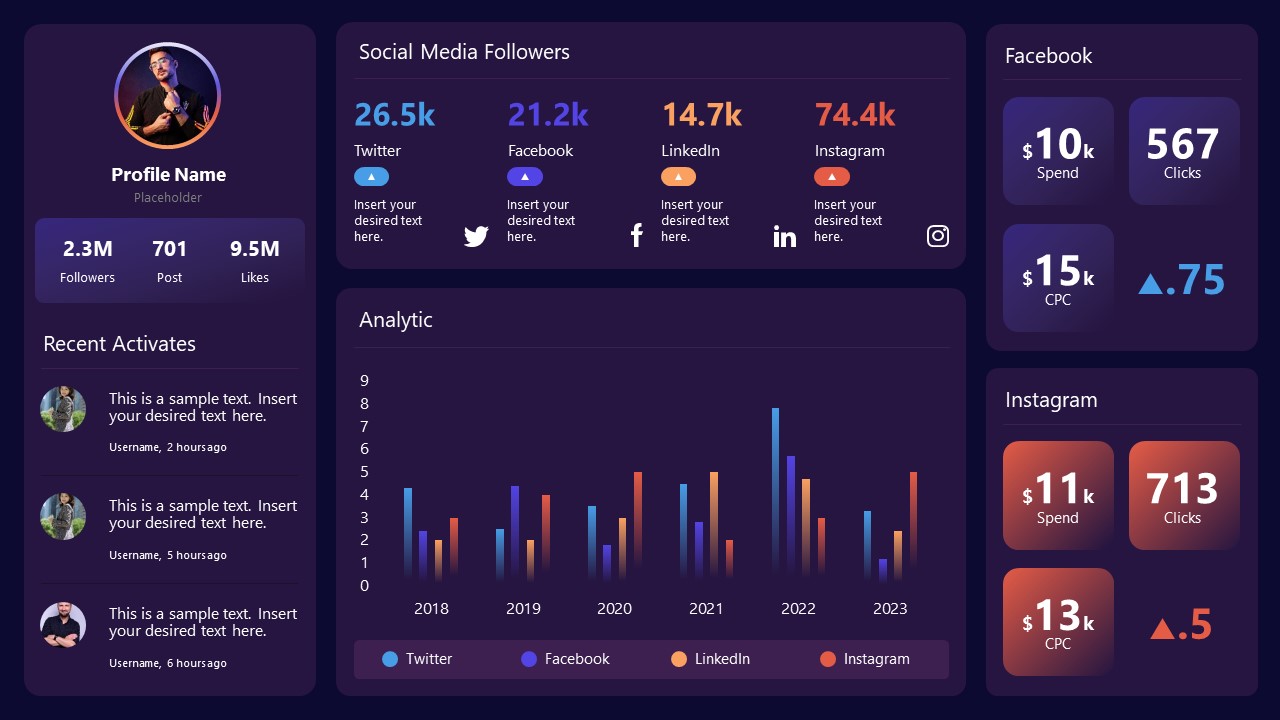
Intended for marketing professionals, this dashboard template for data presentation is a tool for presenting data analytics from social media channels. Two slide layouts featuring line graphs and column charts.
10. Project Management Summary Dashboard Template
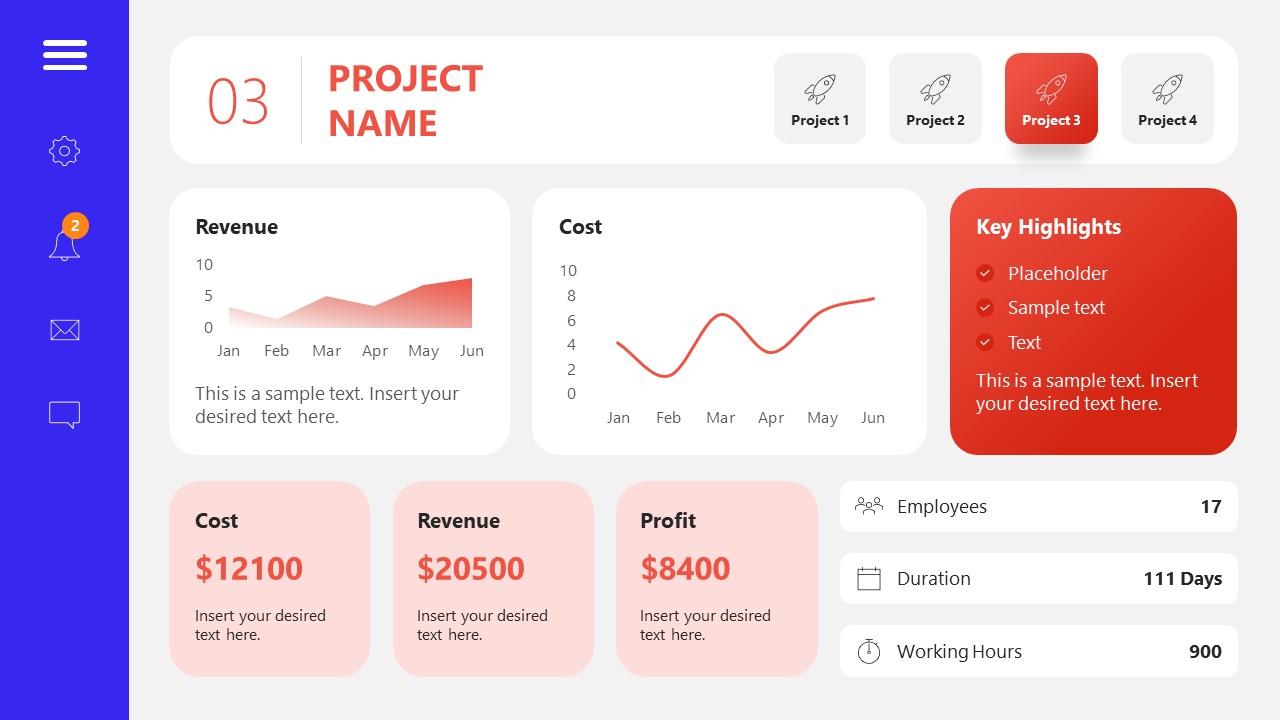
A tool crafted for project managers to deliver highly visual reports on a project’s completion, the profits it delivered for the company, and expenses/time required to execute it. 4 different color layouts are available.
11. Profit & Loss Dashboard for PowerPoint and Google Slides
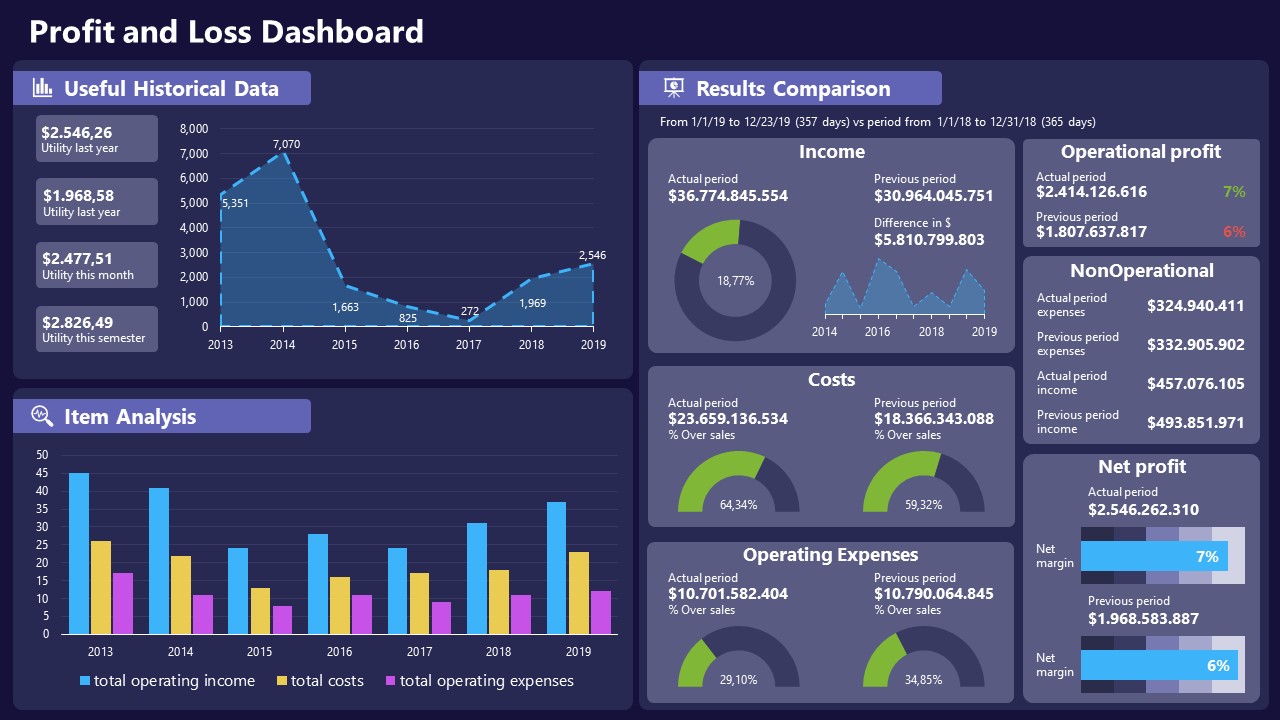
A must-have for finance professionals. This typical profit & loss dashboard includes progress bars, donut charts, column charts, line graphs, and everything that’s required to deliver a comprehensive report about a company’s financial situation.
Overwhelming visuals
One of the mistakes related to using data-presenting methods is including too much data or using overly complex visualizations. They can confuse the audience and dilute the key message.
Inappropriate chart types
Choosing the wrong type of chart for the data at hand can lead to misinterpretation. For example, using a pie chart for data that doesn’t represent parts of a whole is not right.
Lack of context
Failing to provide context or sufficient labeling can make it challenging for the audience to understand the significance of the presented data.
Inconsistency in design
Using inconsistent design elements and color schemes across different visualizations can create confusion and visual disarray.
Failure to provide details
Simply presenting raw data without offering clear insights or takeaways can leave the audience without a meaningful conclusion.
Lack of focus
Not having a clear focus on the key message or main takeaway can result in a presentation that lacks a central theme.
Visual accessibility issues
Overlooking the visual accessibility of charts and graphs can exclude certain audience members who may have difficulty interpreting visual information.
In order to avoid these mistakes in data presentation, presenters can benefit from using presentation templates . These templates provide a structured framework. They ensure consistency, clarity, and an aesthetically pleasing design, enhancing data communication’s overall impact.
Understanding and choosing data presentation types are pivotal in effective communication. Each method serves a unique purpose, so selecting the appropriate one depends on the nature of the data and the message to be conveyed. The diverse array of presentation types offers versatility in visually representing information, from bar charts showing values to pie charts illustrating proportions.
Using the proper method enhances clarity, engages the audience, and ensures that data sets are not just presented but comprehensively understood. By appreciating the strengths and limitations of different presentation types, communicators can tailor their approach to convey information accurately, developing a deeper connection between data and audience understanding.
[1] Government of Canada, S.C. (2021) 5 Data Visualization 5.2 Bar Chart , 5.2 Bar chart . https://www150.statcan.gc.ca/n1/edu/power-pouvoir/ch9/bargraph-diagrammeabarres/5214818-eng.htm
[2] Kosslyn, S.M., 1989. Understanding charts and graphs. Applied cognitive psychology, 3(3), pp.185-225. https://apps.dtic.mil/sti/pdfs/ADA183409.pdf
[3] Creating a Dashboard . https://it.tufts.edu/book/export/html/1870
[4] https://www.goldenwestcollege.edu/research/data-and-more/data-dashboards/index.html
[5] https://www.mit.edu/course/21/21.guide/grf-line.htm
[6] Jadeja, M. and Shah, K., 2015, January. Tree-Map: A Visualization Tool for Large Data. In GSB@ SIGIR (pp. 9-13). https://ceur-ws.org/Vol-1393/gsb15proceedings.pdf#page=15
[7] Heat Maps and Quilt Plots. https://www.publichealth.columbia.edu/research/population-health-methods/heat-maps-and-quilt-plots
[8] EIU QGIS WORKSHOP. https://www.eiu.edu/qgisworkshop/heatmaps.php
[9] About Pie Charts. https://www.mit.edu/~mbarker/formula1/f1help/11-ch-c8.htm
[10] Histograms. https://sites.utexas.edu/sos/guided/descriptive/numericaldd/descriptiven2/histogram/ [11] https://asq.org/quality-resources/scatter-diagram

Like this article? Please share
Data Analysis, Data Science, Data Visualization Filed under Design
Related Articles

Filed under Design • March 27th, 2024
How to Make a Presentation Graph
Detailed step-by-step instructions to master the art of how to make a presentation graph in PowerPoint and Google Slides. Check it out!
Filed under Presentation Ideas • January 6th, 2024
All About Using Harvey Balls
Among the many tools in the arsenal of the modern presenter, Harvey Balls have a special place. In this article we will tell you all about using Harvey Balls.

Filed under Business • December 8th, 2023
How to Design a Dashboard Presentation: A Step-by-Step Guide
Take a step further in your professional presentation skills by learning what a dashboard presentation is and how to properly design one in PowerPoint. A detailed step-by-step guide is here!
Leave a Reply
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Present Your Data Like a Pro
- Joel Schwartzberg

Demystify the numbers. Your audience will thank you.
While a good presentation has data, data alone doesn’t guarantee a good presentation. It’s all about how that data is presented. The quickest way to confuse your audience is by sharing too many details at once. The only data points you should share are those that significantly support your point — and ideally, one point per chart. To avoid the debacle of sheepishly translating hard-to-see numbers and labels, rehearse your presentation with colleagues sitting as far away as the actual audience would. While you’ve been working with the same chart for weeks or months, your audience will be exposed to it for mere seconds. Give them the best chance of comprehending your data by using simple, clear, and complete language to identify X and Y axes, pie pieces, bars, and other diagrammatic elements. Try to avoid abbreviations that aren’t obvious, and don’t assume labeled components on one slide will be remembered on subsequent slides. Every valuable chart or pie graph has an “Aha!” zone — a number or range of data that reveals something crucial to your point. Make sure you visually highlight the “Aha!” zone, reinforcing the moment by explaining it to your audience.
With so many ways to spin and distort information these days, a presentation needs to do more than simply share great ideas — it needs to support those ideas with credible data. That’s true whether you’re an executive pitching new business clients, a vendor selling her services, or a CEO making a case for change.
- JS Joel Schwartzberg oversees executive communications for a major national nonprofit, is a professional presentation coach, and is the author of Get to the Point! Sharpen Your Message and Make Your Words Matter and The Language of Leadership: How to Engage and Inspire Your Team . You can find him on LinkedIn and X. TheJoelTruth
Partner Center

Princeton Correspondents on Undergraduate Research
How to Make a Successful Research Presentation
Turning a research paper into a visual presentation is difficult; there are pitfalls, and navigating the path to a brief, informative presentation takes time and practice. As a TA for GEO/WRI 201: Methods in Data Analysis & Scientific Writing this past fall, I saw how this process works from an instructor’s standpoint. I’ve presented my own research before, but helping others present theirs taught me a bit more about the process. Here are some tips I learned that may help you with your next research presentation:
More is more
In general, your presentation will always benefit from more practice, more feedback, and more revision. By practicing in front of friends, you can get comfortable with presenting your work while receiving feedback. It is hard to know how to revise your presentation if you never practice. If you are presenting to a general audience, getting feedback from someone outside of your discipline is crucial. Terms and ideas that seem intuitive to you may be completely foreign to someone else, and your well-crafted presentation could fall flat.
Less is more
Limit the scope of your presentation, the number of slides, and the text on each slide. In my experience, text works well for organizing slides, orienting the audience to key terms, and annotating important figures–not for explaining complex ideas. Having fewer slides is usually better as well. In general, about one slide per minute of presentation is an appropriate budget. Too many slides is usually a sign that your topic is too broad.

Limit the scope of your presentation
Don’t present your paper. Presentations are usually around 10 min long. You will not have time to explain all of the research you did in a semester (or a year!) in such a short span of time. Instead, focus on the highlight(s). Identify a single compelling research question which your work addressed, and craft a succinct but complete narrative around it.
You will not have time to explain all of the research you did. Instead, focus on the highlights. Identify a single compelling research question which your work addressed, and craft a succinct but complete narrative around it.
Craft a compelling research narrative
After identifying the focused research question, walk your audience through your research as if it were a story. Presentations with strong narrative arcs are clear, captivating, and compelling.
- Introduction (exposition — rising action)
Orient the audience and draw them in by demonstrating the relevance and importance of your research story with strong global motive. Provide them with the necessary vocabulary and background knowledge to understand the plot of your story. Introduce the key studies (characters) relevant in your story and build tension and conflict with scholarly and data motive. By the end of your introduction, your audience should clearly understand your research question and be dying to know how you resolve the tension built through motive.
- Methods (rising action)
The methods section should transition smoothly and logically from the introduction. Beware of presenting your methods in a boring, arc-killing, ‘this is what I did.’ Focus on the details that set your story apart from the stories other people have already told. Keep the audience interested by clearly motivating your decisions based on your original research question or the tension built in your introduction.
- Results (climax)
Less is usually more here. Only present results which are clearly related to the focused research question you are presenting. Make sure you explain the results clearly so that your audience understands what your research found. This is the peak of tension in your narrative arc, so don’t undercut it by quickly clicking through to your discussion.
- Discussion (falling action)
By now your audience should be dying for a satisfying resolution. Here is where you contextualize your results and begin resolving the tension between past research. Be thorough. If you have too many conflicts left unresolved, or you don’t have enough time to present all of the resolutions, you probably need to further narrow the scope of your presentation.
- Conclusion (denouement)
Return back to your initial research question and motive, resolving any final conflicts and tying up loose ends. Leave the audience with a clear resolution of your focus research question, and use unresolved tension to set up potential sequels (i.e. further research).
Use your medium to enhance the narrative
Visual presentations should be dominated by clear, intentional graphics. Subtle animation in key moments (usually during the results or discussion) can add drama to the narrative arc and make conflict resolutions more satisfying. You are narrating a story written in images, videos, cartoons, and graphs. While your paper is mostly text, with graphics to highlight crucial points, your slides should be the opposite. Adapting to the new medium may require you to create or acquire far more graphics than you included in your paper, but it is necessary to create an engaging presentation.
The most important thing you can do for your presentation is to practice and revise. Bother your friends, your roommates, TAs–anybody who will sit down and listen to your work. Beyond that, think about presentations you have found compelling and try to incorporate some of those elements into your own. Remember you want your work to be comprehensible; you aren’t creating experts in 10 minutes. Above all, try to stay passionate about what you did and why. You put the time in, so show your audience that it’s worth it.
For more insight into research presentations, check out these past PCUR posts written by Emma and Ellie .
— Alec Getraer, Natural Sciences Correspondent
Share this:
- Share on Tumblr

Data Collection, Presentation and Analysis
- First Online: 25 May 2023
Cite this chapter

- Uche M. Mbanaso 4 ,
- Lucienne Abrahams 5 &
- Kennedy Chinedu Okafor 6
596 Accesses
This chapter covers the topics of data collection, data presentation and data analysis. It gives attention to data collection for studies based on experiments, on data derived from existing published or unpublished data sets, on observation, on simulation and digital twins, on surveys, on interviews and on focus group discussions. One of the interesting features of this chapter is the section dealing with using measurement scales in quantitative research, including nominal scales, ordinal scales, interval scales and ratio scales. It explains key facets of qualitative research including ethical clearance requirements. The chapter discusses the importance of data visualization as key to effective presentation of data, including tabular forms, graphical forms and visual charts such as those generated by Atlas.ti analytical software.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Bibliography
Abdullah, M. F., & Ahmad, K. (2013). The mapping process of unstructured data to structured data. Proceedings of the 2013 International Conference on Research and Innovation in Information Systems (ICRIIS) , Malaysia , 151–155. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICRIIS.2013.6716700
Adnan, K., & Akbar, R. (2019). An analytical study of information extraction from unstructured and multidimensional big data. Journal of Big Data, 6 , 91. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40537-019-0254-8
Article Google Scholar
Alsheref, F. K., & Fattoh, I. E. (2020). Medical text annotation tool based on IBM Watson Platform. Proceedings of the 2020 6th international conference on advanced computing and communication systems (ICACCS) , India , 1312–1316. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICACCS48705.2020.9074309
Cinque, M., Cotroneo, D., Della Corte, R., & Pecchia, A. (2014). What logs should you look at when an application fails? Insights from an industrial case study. Proceedings of the 2014 44th Annual IEEE/IFIP International Conference on Dependable Systems and Networks , USA , 690–695. https://doi.org/10.1109/DSN.2014.69
Gideon, L. (Ed.). (2012). Handbook of survey methodology for the social sciences . Springer.
Google Scholar
Leedy, P., & Ormrod, J. (2015). Practical research planning and design (12th ed.). Pearson Education.
Madaan, A., Wang, X., Hall, W., & Tiropanis, T. (2018). Observing data in IoT worlds: What and how to observe? In Living in the Internet of Things: Cybersecurity of the IoT – 2018 (pp. 1–7). https://doi.org/10.1049/cp.2018.0032
Chapter Google Scholar
Mahajan, P., & Naik, C. (2019). Development of integrated IoT and machine learning based data collection and analysis system for the effective prediction of agricultural residue/biomass availability to regenerate clean energy. Proceedings of the 2019 9th International Conference on Emerging Trends in Engineering and Technology – Signal and Information Processing (ICETET-SIP-19) , India , 1–5. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICETET-SIP-1946815.2019.9092156 .
Mahmud, M. S., Huang, J. Z., Salloum, S., Emara, T. Z., & Sadatdiynov, K. (2020). A survey of data partitioning and sampling methods to support big data analysis. Big Data Mining and Analytics, 3 (2), 85–101. https://doi.org/10.26599/BDMA.2019.9020015
Miswar, S., & Kurniawan, N. B. (2018). A systematic literature review on survey data collection system. Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Information Technology Systems and Innovation (ICITSI) , Indonesia , 177–181. https://doi.org/10.1109/ICITSI.2018.8696036
Mosina, C. (2020). Understanding the diffusion of the internet: Redesigning the global diffusion of the internet framework (Research report, Master of Arts in ICT Policy and Regulation). LINK Centre, University of the Witwatersrand. https://hdl.handle.net/10539/30723
Nkamisa, S. (2021). Investigating the integration of drone management systems to create an enabling remote piloted aircraft regulatory environment in South Africa (Research report, Master of Arts in ICT Policy and Regulation). LINK Centre, University of the Witwatersrand. https://hdl.handle.net/10539/33883
QuestionPro. (2020). Survey research: Definition, examples and methods . https://www.questionpro.com/article/survey-research.html
Rajanikanth, J. & Kanth, T. V. R. (2017). An explorative data analysis on Bangalore City Weather with hybrid data mining techniques using R. Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Current Trends in Computer, Electrical, Electronics and Communication (CTCEEC) , India , 1121-1125. https://doi/10.1109/CTCEEC.2017.8455008
Rao, R. (2003). From unstructured data to actionable intelligence. IT Professional, 5 , 29–35. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/3426648_From_Unstructured_Data_to_Actionable_Intelligence
Schulze, P. (2009). Design of the research instrument. In P. Schulze (Ed.), Balancing exploitation and exploration: Organizational antecedents and performance effects of innovation strategies (pp. 116–141). Gabler. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-8349-8397-8_6
Usanov, A. (2015). Assessing cybersecurity: A meta-analysis of threats, trends and responses to cyber attacks . The Hague Centre for Strategic Studies. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/319677972_Assessing_Cyber_Security_A_Meta-analysis_of_Threats_Trends_and_Responses_to_Cyber_Attacks
Van de Kaa, G., De Vries, H. J., van Heck, E., & van den Ende, J. (2007). The emergence of standards: A meta-analysis. Proceedings of the 2007 40th Annual Hawaii International Conference on Systems Science (HICSS’07) , USA , 173a–173a. https://doi.org/10.1109/HICSS.2007.529
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Centre for Cybersecurity Studies, Nasarawa State University, Keffi, Nigeria
Uche M. Mbanaso
LINK Centre, University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Africa
Lucienne Abrahams
Department of Mechatronics Engineering, Federal University of Technology, Owerri, Nigeria
Kennedy Chinedu Okafor
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
Mbanaso, U.M., Abrahams, L., Okafor, K.C. (2023). Data Collection, Presentation and Analysis. In: Research Techniques for Computer Science, Information Systems and Cybersecurity. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-30031-8_7
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-30031-8_7
Published : 25 May 2023
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-30030-1
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-30031-8
eBook Packages : Engineering Engineering (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research

The Ultimate Guide to Qualitative Research - Part 3: Presenting Qualitative Data

- Introduction
How do you present qualitative data?
Data visualization.
- Research paper writing
- Transparency and rigor in research
- How to publish a research paper
Table of contents
- Transparency and rigor
Navigate to other guide parts:
Part 1: The Basics or Part 2: Handling Qualitative Data
- Presenting qualitative data
In the end, presenting qualitative research findings is just as important a skill as mastery of qualitative research methods for the data collection and data analysis process . Simply uncovering insights is insufficient to the research process; presenting a qualitative analysis holds the challenge of persuading your audience of the value of your research. As a result, it's worth spending some time considering how best to report your research to facilitate its contribution to scientific knowledge.

When it comes to research, presenting data in a meaningful and accessible way is as important as gathering it. This is particularly true for qualitative research , where the richness and complexity of the data demand careful and thoughtful presentation. Poorly written research is taken less seriously and left undiscussed by the greater scholarly community; quality research reporting that persuades its audience stands a greater chance of being incorporated in discussions of scientific knowledge.
Qualitative data presentation differs fundamentally from that found in quantitative research. While quantitative data tend to be numerical and easily lend themselves to statistical analysis and graphical representation, qualitative data are often textual and unstructured, requiring an interpretive approach to bring out their inherent meanings. Regardless of the methodological approach , the ultimate goal of data presentation is to communicate research findings effectively to an audience so they can incorporate the generated knowledge into their research inquiry.
As the section on research rigor will suggest, an effective presentation of your research depends on a thorough scientific process that organizes raw data into a structure that allows for a thorough analysis for scientific understanding.
Preparing the data
The first step in presenting qualitative data is preparing the data. This preparation process often begins with cleaning and organizing the data. Cleaning involves checking the data for accuracy and completeness, removing any irrelevant information, and making corrections as needed. Organizing the data often entails arranging the data into categories or groups that make sense for your research framework.
Coding the data
Once the data are cleaned and organized, the next step is coding , a crucial part of qualitative data analysis. Coding involves assigning labels to segments of the data to summarize or categorize them. This process helps to identify patterns and themes in the data, laying the groundwork for subsequent data interpretation and presentation. Qualitative research often involves multiple iterations of coding, creating new and meaningful codes while discarding unnecessary ones , to generate a rich structure through which data analysis can occur.
Uncovering insights
As you navigate through these initial steps, keep in mind the broader aim of qualitative research, which is to provide rich, detailed, and nuanced understandings of people's experiences, behaviors, and social realities. These guiding principles will help to ensure that your data presentation is not only accurate and comprehensive but also meaningful and impactful.
While this process might seem intimidating at first, it's an essential part of any qualitative research project. It's also a skill that can be learned and refined over time, so don't be discouraged if you find it challenging at first. Remember, the goal of presenting qualitative data is to make your research findings accessible and understandable to others. This requires careful preparation, a clear understanding of your data, and a commitment to presenting your findings in a way that respects and honors the complexity of the phenomena you're studying.
In the following sections, we'll delve deeper into how to create a comprehensive narrative from your data, the visualization of qualitative data , and the writing and publication processes . Let's briefly excerpt some of the content in the articles in this part of the guide.
ATLAS.ti helps you make sense of your data
Find out how with a free trial of our powerful data analysis interface.
How often do you read a research article and skip straight to the tables and figures? That's because data visualizations representing qualitative and quantitative data have the power to make large and complex research projects with thousands of data points comprehensible when authors present data to research audiences. Researchers create visual representations to help summarize the data generated from their study and make clear the pathways for actionable insights.
In everyday situations, a picture is always worth a thousand words. Illustrations, figures, and charts convey messages that words alone cannot. In research, data visualization can help explain scientific knowledge, evidence for data insights, and key performance indicators in an orderly manner based on data that is otherwise unstructured.
For all of the various data formats available to researchers, a significant portion of qualitative and social science research is still text-based. Essays, reports, and research articles still rely on writing practices aimed at repackaging research in prose form. This can create the impression that simply writing more will persuade research audiences. Instead, framing research in terms that are easy for your target readers to understand makes it easier for your research to become published in peer-reviewed scholarly journals or find engagement at scholarly conferences. Even in market or professional settings, data visualization is an essential concept when you need to convince others about the insights of your research and the recommendations you make based on the data.
Importance of data visualization
Data visualization is important because it makes it easy for your research audience to understand your data sets and your findings. Also, data visualization helps you organize your data more efficiently. As the explanation of ATLAS.ti's tools will illustrate in this section, data visualization might point you to research inquiries that you might not even be aware of, helping you get the most out of your data. Strictly speaking, the primary role of data visualization is to make the analysis of your data , if not the data itself, clear. Especially in social science research, data visualization makes it easy to see how data scientists collect and analyze data.
Prerequisites for generating data visualizations
Data visualization is effective in explaining research to others only if the researcher or data scientist can make sense of the data in front of them. Traditional research with unstructured data usually calls for coding the data with short, descriptive codes that can be analyzed later, whether statistically or thematically. These codes form the basic data points of a meaningful qualitative analysis. They represent the structure of qualitative data sets, without which a scientific visualization with research rigor would be extremely difficult to achieve. In most respects, data visualization of a qualitative research project requires coding the entire data set so that the codes adequately represent the collected data.
A successfully crafted research study culminates in the writing of the research paper . While a pilot study or preliminary research might guide the research design , a full research study leads to discussion that highlights avenues for further research. As such, the importance of the research paper cannot be overestimated in the overall generation of scientific knowledge.
The physical and natural sciences tend to have a clinical structure for a research paper that mirrors the scientific method: outline the background research, explain the materials and methods of the study, outline the research findings generated from data analysis, and discuss the implications. Qualitative research tends to preserve much of this structure, but there are notable and numerous variations from a traditional research paper that it's worth emphasizing the flexibility in the social sciences with respect to the writing process.
Requirements for research writing
While there aren't any hard and fast rules regarding what belongs in a qualitative research paper , readers expect to find a number of pieces of relevant information in a rigorously-written report. The best way to know what belongs in a full research paper is to look at articles in your target journal or articles that share a particular topic similar to yours and examine how successfully published papers are written.
It's important to emphasize the more mundane but equally important concerns of proofreading and formatting guidelines commonly found when you write a research paper. Research publication shouldn't strictly be a test of one's writing skills, but acknowledging the importance of convincing peer reviewers of the credibility of your research means accepting the responsibility of preparing your research manuscript to commonly accepted standards in research.
As a result, seemingly insignificant things such as spelling mistakes, page numbers, and proper grammar can make a difference with a particularly strict reviewer. Even when you expect to develop a paper through reviewer comments and peer feedback, your manuscript should be as close to a polished final draft as you can make it prior to submission.
Qualitative researchers face particular challenges in convincing their target audience of the value and credibility of their subsequent analysis. Numbers and quantifiable concepts in quantitative studies are relatively easier to understand than their counterparts associated with qualitative methods . Think about how easy it is to make conclusions about the value of items at a store based on their prices, then imagine trying to compare those items based on their design, function, and effectiveness.
Qualitative research involves and requires these sorts of discussions. The goal of qualitative data analysis is to allow a qualitative researcher and their audience to make such determinations, but before the audience can accept these determinations, the process of conducting research that produces the qualitative analysis must first be seen as trustworthy. As a result, it is on the researcher to persuade their audience that their data collection process and subsequent analysis is rigorous.
Qualitative rigor refers to the meticulousness, consistency, and transparency of the research. It is the application of systematic, disciplined, and stringent methods to ensure the credibility, dependability, confirmability, and transferability of research findings. In qualitative inquiry, these attributes ensure the research accurately reflects the phenomenon it is intended to represent, that its findings can be understood or used by others, and that its processes and results are open to scrutiny and validation.
Transparency
It is easier to believe the information presented to you if there is a rigorous analysis process behind that information, and if that process is explicitly detailed. The same is true for qualitative research results, making transparency a key element in qualitative research methodologies. Transparency is a fundamental aspect of rigor in qualitative research. It involves the clear, detailed, and explicit documentation of all stages of the research process. This allows other researchers to understand, evaluate, replicate, and build upon the study. Transparency in qualitative research is essential for maintaining rigor, trustworthiness, and ethical integrity. By being transparent, researchers allow their work to be scrutinized, critiqued, and improved upon, contributing to the ongoing development and refinement of knowledge in their field.
Research papers are only as useful as their audience in the scientific community is wide. To reach that audience, a paper needs to pass the peer review process of an academic journal. However, the idea of having research published in peer-reviewed journals may seem daunting to newer researchers, so it's important to provide a guide on how an academic journal looks at your research paper as well as how to determine what is the right journal for your research.
In simple terms, a research article is good if it is accepted as credible and rigorous by the scientific community. A study that isn't seen as a valid contribution to scientific knowledge shouldn't be published; ultimately, it is up to peers within the field in which the study is being considered to determine the study's value. In established academic research, this determination is manifest in the peer review process. Journal editors at a peer-reviewed journal assign papers to reviewers who will determine the credibility of the research. A peer-reviewed article that completed this process and is published in a reputable journal can be seen as credible with novel research that can make a profound contribution to scientific knowledge.
The process of research publication
The process has been codified and standardized within the scholarly community to include three main stages. These stages include the initial submission stage where the editor reviews the relevance of the paper, the review stage where experts in your field offer feedback, and, if reviewers approve your paper, the copyediting stage where you work with the journal to prepare the paper for inclusion in their journal.
Publishing a research paper may seem like an opaque process where those involved with academic journals make arbitrary decisions about the worthiness of research manuscripts. In reality, reputable publications assign a rubric or a set of guidelines that reviewers need to keep in mind when they review a submission. These guidelines will most likely differ depending on the journal, but they fall into a number of typical categories that are applicable regardless of the research area or the type of methods employed in a research study, including the strength of the literature review , rigor in research methodology , and novelty of findings.
Choosing the right journal isn't simply a matter of which journal is the most famous or has the broadest reach. Many universities keep lists of prominent journals where graduate students and faculty members should publish a research paper , but oftentimes this list is determined by a journal's impact factor and their inclusion in major academic databases.

Guide your research to publication with ATLAS.ti
Turn insights into visualizations with our easy-to-use interface. Download a free trial today.
This section is part of an entire guide. Use this table of contents to jump to any page in the guide.
Part 1: The Basics
- What is qualitative data?
- 10 examples of qualitative data
- Qualitative vs. quantitative research
- What is mixed methods research?
- Theoretical perspective
- Theoretical framework
- Literature reviews
- Research questions
- Conceptual framework
- Conceptual vs. theoretical framework
- Focus groups
- Observational research
- Case studies
- Survey research
- What is ethnographic research?
- Confidentiality and privacy in research
- Bias in research
- Power dynamics in research
- Reflexivity
Part 2: Handling Qualitative Data
- Research transcripts
- Field notes in research
- Research memos
- Survey data
- Images, audio, and video in qualitative research
- Coding qualitative data
- Coding frame
- Auto-coding and smart coding
- Organizing codes
- Content analysis
- Thematic analysis
- Thematic analysis vs. content analysis
- Narrative research
- Phenomenological research
- Discourse analysis
- Grounded theory
- Deductive reasoning
- What is inductive reasoning?
- Inductive vs. deductive reasoning
- What is data interpretation?
- Qualitative analysis software
Part 3: Presenting Qualitative Data
- Data visualization - What is it and why is it important?

Skills for Learning : Research Skills
Data analysis is an ongoing process that should occur throughout your research project. Suitable data-analysis methods must be selected when you write your research proposal. The nature of your data (i.e. quantitative or qualitative) will be influenced by your research design and purpose. The data will also influence the analysis methods selected.
We run interactive workshops to help you develop skills related to doing research, such as data analysis, writing literature reviews and preparing for dissertations. Find out more on the Skills for Learning Workshops page.
We have online academic skills modules within MyBeckett for all levels of university study. These modules will help your academic development and support your success at LBU. You can work through the modules at your own pace, revisiting them as required. Find out more from our FAQ What academic skills modules are available?
Quantitative data analysis
Broadly speaking, 'statistics' refers to methods, tools and techniques used to collect, organise and interpret data. The goal of statistics is to gain understanding from data. Therefore, you need to know how to:
- Produce data – for example, by handing out a questionnaire or doing an experiment.
- Organise, summarise, present and analyse data.
- Draw valid conclusions from findings.
There are a number of statistical methods you can use to analyse data. Choosing an appropriate statistical method should follow naturally, however, from your research design. Therefore, you should think about data analysis at the early stages of your study design. You may need to consult a statistician for help with this.
Tips for working with statistical data
- Plan so that the data you get has a good chance of successfully tackling the research problem. This will involve reading literature on your subject, as well as on what makes a good study.
- To reach useful conclusions, you need to reduce uncertainties or 'noise'. Thus, you will need a sufficiently large data sample. A large sample will improve precision. However, this must be balanced against the 'costs' (time and money) of collection.
- Consider the logistics. Will there be problems in obtaining sufficient high-quality data? Think about accuracy, trustworthiness and completeness.
- Statistics are based on random samples. Consider whether your sample will be suited to this sort of analysis. Might there be biases to think about?
- How will you deal with missing values (any data that is not recorded for some reason)? These can result from gaps in a record or whole records being missed out.
- When analysing data, start by looking at each variable separately. Conduct initial/exploratory data analysis using graphical displays. Do this before looking at variables in conjunction or anything more complicated. This process can help locate errors in the data and also gives you a 'feel' for the data.
- Look out for patterns of 'missingness'. They are likely to alert you if there’s a problem. If the 'missingness' is not random, then it will have an impact on the results.
- Be vigilant and think through what you are doing at all times. Think critically. Statistics are not just mathematical tricks that a computer sorts out. Rather, analysing statistical data is a process that the human mind must interpret!
Top tips! Try inventing or generating the sort of data you might get and see if you can analyse it. Make sure that your process works before gathering actual data. Think what the output of an analytic procedure will look like before doing it for real.
(Note: it is actually difficult to generate realistic data. There are fraud-detection methods in place to identify data that has been fabricated. So, remember to get rid of your practice data before analysing the real stuff!)
Statistical software packages
Software packages can be used to analyse and present data. The most widely used ones are SPSS and NVivo.
SPSS is a statistical-analysis and data-management package for quantitative data analysis. Click on ‘ How do I install SPSS? ’ to learn how to download SPSS to your personal device. SPSS can perform a wide variety of statistical procedures. Some examples are:
- Data management (i.e. creating subsets of data or transforming data).
- Summarising, describing or presenting data (i.e. mean, median and frequency).
- Looking at the distribution of data (i.e. standard deviation).
- Comparing groups for significant differences using parametric (i.e. t-test) and non-parametric (i.e. Chi-square) tests.
- Identifying significant relationships between variables (i.e. correlation).
NVivo can be used for qualitative data analysis. It is suitable for use with a wide range of methodologies. Click on ‘ How do I access NVivo ’ to learn how to download NVivo to your personal device. NVivo supports grounded theory, survey data, case studies, focus groups, phenomenology, field research and action research.
- Process data such as interview transcripts, literature or media extracts, and historical documents.
- Code data on screen and explore all coding and documents interactively.
- Rearrange, restructure, extend and edit text, coding and coding relationships.
- Search imported text for words, phrases or patterns, and automatically code the results.
Qualitative data analysis
Miles and Huberman (1994) point out that there are diverse approaches to qualitative research and analysis. They suggest, however, that it is possible to identify 'a fairly classic set of analytic moves arranged in sequence'. This involves:
- Affixing codes to a set of field notes drawn from observation or interviews.
- Noting reflections or other remarks in the margins.
- Sorting/sifting through these materials to identify: a) similar phrases, relationships between variables, patterns and themes and b) distinct differences between subgroups and common sequences.
- Isolating these patterns/processes and commonalties/differences. Then, taking them out to the field in the next wave of data collection.
- Highlighting generalisations and relating them to your original research themes.
- Taking the generalisations and analysing them in relation to theoretical perspectives.
(Miles and Huberman, 1994.)
Patterns and generalisations are usually arrived at through a process of analytic induction (see above points 5 and 6). Qualitative analysis rarely involves statistical analysis of relationships between variables. Qualitative analysis aims to gain in-depth understanding of concepts, opinions or experiences.
Presenting information
There are a number of different ways of presenting and communicating information. The particular format you use is dependent upon the type of data generated from the methods you have employed.
Here are some appropriate ways of presenting information for different types of data:
Bar charts: These may be useful for comparing relative sizes. However, they tend to use a large amount of ink to display a relatively small amount of information. Consider a simple line chart as an alternative.
Pie charts: These have the benefit of indicating that the data must add up to 100%. However, they make it difficult for viewers to distinguish relative sizes, especially if two slices have a difference of less than 10%.
Other examples of presenting data in graphical form include line charts and scatter plots .
Qualitative data is more likely to be presented in text form. For example, using quotations from interviews or field diaries.
- Plan ahead, thinking carefully about how you will analyse and present your data.
- Think through possible restrictions to resources you may encounter and plan accordingly.
- Find out about the different IT packages available for analysing your data and select the most appropriate.
- If necessary, allow time to attend an introductory course on a particular computer package. You can book SPSS and NVivo workshops via MyHub .
- Code your data appropriately, assigning conceptual or numerical codes as suitable.
- Organise your data so it can be analysed and presented easily.
- Choose the most suitable way of presenting your information, according to the type of data collected. This will allow your information to be understood and interpreted better.
Primary, secondary and tertiary sources
Information sources are sometimes categorised as primary, secondary or tertiary sources depending on whether or not they are ‘original’ materials or data. For some research projects, you may need to use primary sources as well as secondary or tertiary sources. However the distinction between primary and secondary sources is not always clear and depends on the context. For example, a newspaper article might usually be categorised as a secondary source. But it could also be regarded as a primary source if it were an article giving a first-hand account of a historical event written close to the time it occurred.
- Primary sources
- Secondary sources
- Tertiary sources
- Grey literature
Primary sources are original sources of information that provide first-hand accounts of what is being experienced or researched. They enable you to get as close to the actual event or research as possible. They are useful for getting the most contemporary information about a topic.
Examples include diary entries, newspaper articles, census data, journal articles with original reports of research, letters, email or other correspondence, original manuscripts and archives, interviews, research data and reports, statistics, autobiographies, exhibitions, films, and artists' writings.
Some information will be available on an Open Access basis, freely accessible online. However, many academic sources are paywalled, and you may need to login as a Leeds Beckett student to access them. Where Leeds Beckett does not have access to a source, you can use our Request It! Service .
Secondary sources interpret, evaluate or analyse primary sources. They're useful for providing background information on a topic, or for looking back at an event from a current perspective. The majority of your literature searching will probably be done to find secondary sources on your topic.
Examples include journal articles which review or interpret original findings, popular magazine articles commenting on more serious research, textbooks and biographies.
The term tertiary sources isn't used a great deal. There's overlap between what might be considered a secondary source and a tertiary source. One definition is that a tertiary source brings together secondary sources.
Examples include almanacs, fact books, bibliographies, dictionaries and encyclopaedias, directories, indexes and abstracts. They can be useful for introductory information or an overview of a topic in the early stages of research.
Depending on your subject of study, grey literature may be another source you need to use. Grey literature includes technical or research reports, theses and dissertations, conference papers, government documents, white papers, and so on.
Artificial intelligence tools
Before using any generative artificial intelligence or paraphrasing tools in your assessments, you should check if this is permitted on your course.
If their use is permitted on your course, you must acknowledge any use of generative artificial intelligence tools such as ChatGPT or paraphrasing tools (e.g., Grammarly, Quillbot, etc.), even if you have only used them to generate ideas for your assessments or for proofreading.
- Academic Integrity Module in MyBeckett
- Assignment Calculator
- Building on Feedback
- Disability Advice
- Essay X-ray tool
- International Students' Academic Introduction
- Manchester Academic Phrasebank
- Quote, Unquote
- Skills and Subject Suppor t
- Turnitin Grammar Checker
{{You can add more boxes below for links specific to this page [this note will not appear on user pages] }}
- Research Methods Checklist
- Sampling Checklist
Skills for Learning FAQs

0113 812 1000
- University Disclaimer
- Accessibility
10 Superb Data Presentation Examples To Learn From
The best way to learn how to present data effectively is to see data presentation examples from the professionals in the field.
We collected superb examples of graphical presentation and visualization of data in statistics, research, sales, marketing, business management, and other areas.
On this page:
How to present data effectively? Clever tips.
- 10 Real-life examples of data presentation with interpretation.
Download the above infographic in PDF
Your audience should be able to walk through the graphs and visualizations easily while enjoy and respond to the story.
[bctt tweet=”Your reports and graphical presentations should not just deliver statistics, numbers, and data. Instead, they must tell a story, illustrate a situation, provide proofs, win arguments, and even change minds.” username=””]
Before going to data presentation examples let’s see some essential tips to help you build powerful data presentations.
1. Keep it simple and clear
The presentation should be focused on your key message and you need to illustrate it very briefly.
Graphs and charts should communicate your core message, not distract from it. A complicated and overloaded chart can distract and confuse. Eliminate anything repetitive or decorative.
2. Pick up the right visuals for the job
A vast number of types of graphs and charts are available at your disposal – pie charts, line and bar graphs, scatter plot , Venn diagram , etc.
Choosing the right type of chart can be a tricky business. Practically, the choice depends on 2 major things: on the kind of analysis you want to present and on the data types you have.
Commonly, when we aim to facilitate a comparison, we use a bar chart or radar chart. When we want to show trends over time, we use a line chart or an area chart and etc.
3. Break the complex concepts into multiple graphics
It’s can be very hard for a public to understand a complicated graphical visualization. Don’t present it as a huge amount of visual data.
Instead, break the graphics into pieces and illustrate how each piece corresponds to the previous one.
4. Carefully choose the colors
Colors provoke different emotions and associations that affect the way your brand or story is perceived. Sometimes color choices can make or break your visuals.
It is no need to be a designer to make the right color selections. Some golden rules are to stick to 3 or 4 colors avoiding full-on rainbow look and to borrow ideas from relevant chart designs.
Another tip is to consider the brand attributes and your audience profile. You will see appropriate color use in the below data presentation examples.
5. Don’t leave a lot of room for words
The key point in graphical data presentation is to tell the story using visuals and images, not words. Give your audience visual facts, not text.
However, that doesn’t mean words have no importance.
A great advice here is to think that every letter is critical, and there’s no room for wasted and empty words. Also, don’t create generic titles and headlines, build them around the core message.
6. Use good templates and software tools
Building data presentation with AI nowadays means using some kind of software programs and templates. There are many available options – from free graphing software solutions to advanced data visualization tools.
Choosing a good software gives you the power to create good and high-quality visualizations. Make sure you are using templates that provides characteristics like colors, fonts, and chart styles.
A small investment of time to research the software options prevents a large loss of productivity and efficiency at the end.
10 Superb data presentation examples
Here we collected some of the best examples of data presentation made by one of the biggest names in the graphical data visualization software and information research.
These brands put a lot of money and efforts to investigate how professional graphs and charts should look.
1. Sales Stage History Funnel Chart
Data is beautiful and this sales stage funnel chart by Zoho Reports prove this. The above funnel chart represents the different stages in a sales process (Qualification, Need Analysis, Initial Offer, etc.) and shows the potential revenue for each stage for the last and this quarter.
The potential revenue for each sales stage is displayed by a different color and sized according to the amount. The chart is very colorful, eye-catching, and intriguing.
2. Facebook Ads Data Presentation Examples
These are other data presentation examples from Zoho Reports. The first one is a stacked bar chart that displays the impressions breakdown by months and types of Facebook campaigns.
Impressions are one of the vital KPI examples in digital marketing intelligence and business. The first graph is designed to help you compare and notice sharp differences at the Facebook campaigns that have the most influence on impression movements.
The second one is an area chart that shows the changes in the costs for the same Facebook campaigns over the months.
The 2 examples illustrate how multiple and complicated data can be presented clearly and simply in a visually appealing way.
3. Sales Opportunity Data Presentation
These two bar charts (stacked and horizontal bar charts) by Microsoft Power Bi are created to track sales opportunities and revenue by region and sales stage.
The stacked bar graph shows the revenue probability in percentage determined by the current sales stage (Lead, Quality, Solution…) over the months. The horizontal bar chart represents the size of the sales opportunity (Small, Medium, Large) according to regions (East, Central, West).
Both graphs are impressive ways for a sales manager to introduce the upcoming opportunity to C-level managers and stakeholders. The color combination is rich but easy to digest.
4. Power 100 Data Visualization
Want to show hierarchical data? Treemaps can be perfect for the job. This is a stunning treemap example by Infogram.com that shows you who are the most influential industries. As you see the Government is on the top.
This treemap is a very compact and space-efficient visualization option for presenting hierarchies, that gives you a quick overview of the structure of the most powerful industries.
So beautiful way to compare the proportions between things via their area size.
When it comes to best research data presentation examples in statistics, Nielsen information company is an undoubted leader. The above professional looking line graph by Nielsen represent the slowing alcoholic grow of 4 alcohol categories (Beer, Wine, Spirits, CPG) for the period of 12 months.
The chart is an ideal example of a data visualization that incorporates all the necessary elements of an effective and engaging graph. It uses color to let you easily differentiate trends and allows you to get a global sense of the data. Additionally, it is incredibly simple to understand.
6. Digital Health Research Data Visualization Example
Digital health is a very hot topic nowadays and this stunning donut chart by IQVIA shows the proportion of different mobile health apps by therapy area (Mental Health, Diabetes, Kidney Disease, and etc.). 100% = 1749 unique apps.
This is a wonderful example of research data presentation that provides evidence of Digital Health’s accelerating innovation and app expansion.
Besides good-looking, this donut chart is very space-efficient because the blank space inside it is used to display information too.
7. Disease Research Data Visualization Examples
Presenting relationships among different variables is hard to understand and confusing -especially when there is a huge number of them. But using the appropriate visuals and colors, the IQVIA did a great job simplifying this data into a clear and digestible format.
The above stacked bar charts by IQVIA represents the distribution of oncology medicine spendings by years and product segments (Protected Brand Price, Protected Brand Volume, New Brands, etc.).
The chart allows you to clearly see the changes in spendings and where they occurred – a great example of telling a deeper story in a simple way.
8. Textual and Qualitative Data Presentation Example
When it comes to easy to understand and good looking textual and qualitative data visualization, pyramid graph has a top place. To know what is qualitative data see our post quantitative vs qualitative data .
9. Product Metrics Graph Example
If you are searching for excel data presentation examples, this stylish template from Smartsheet can give you good ideas for professional looking design.
The above stacked bar chart represents product revenue breakdown by months and product items. It reveals patterns and trends over the first half of the year that can be a good basis for data-driven decision-making .
10. Supply Chain Data Visualization Example
This bar chart created by ClicData is an excellent example of how trends over time can be effectively and professionally communicated through the use of well-presented visualization.
It shows the dynamics of pricing through the months based on units sold, units shipped, and current inventory. This type of graph pack a whole lot of information into a simple visual. In addition, the chart is connected to real data and is fully interactive.
The above data presentation examples aim to help you learn how to present data effectively and professionally.
About The Author
Silvia Valcheva
Silvia Valcheva is a digital marketer with over a decade of experience creating content for the tech industry. She has a strong passion for writing about emerging software and technologies such as big data, AI (Artificial Intelligence), IoT (Internet of Things), process automation, etc.
Leave a Reply Cancel Reply
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Data Visualization 10 Data Presentation Examples For Strategic Communication
10 Data Presentation Examples For Strategic Communication
Written by: Krystle Wong Sep 28, 2023

Knowing how to present data is like having a superpower.
Data presentation today is no longer just about numbers on a screen; it’s storytelling with a purpose. It’s about captivating your audience, making complex stuff look simple and inspiring action.
To help turn your data into stories that stick, influence decisions and make an impact, check out Venngage’s free chart maker or follow me on a tour into the world of data storytelling along with data presentation templates that work across different fields, from business boardrooms to the classroom and beyond. Keep scrolling to learn more!
Click to jump ahead:
10 Essential data presentation examples + methods you should know
What should be included in a data presentation, what are some common mistakes to avoid when presenting data, faqs on data presentation examples, transform your message with impactful data storytelling.
Data presentation is a vital skill in today’s information-driven world. Whether you’re in business, academia, or simply want to convey information effectively, knowing the different ways of presenting data is crucial. For impactful data storytelling, consider these essential data presentation methods:
1. Bar graph
Ideal for comparing data across categories or showing trends over time.
Bar graphs, also known as bar charts are workhorses of data presentation. They’re like the Swiss Army knives of visualization methods because they can be used to compare data in different categories or display data changes over time.
In a bar chart, categories are displayed on the x-axis and the corresponding values are represented by the height of the bars on the y-axis.
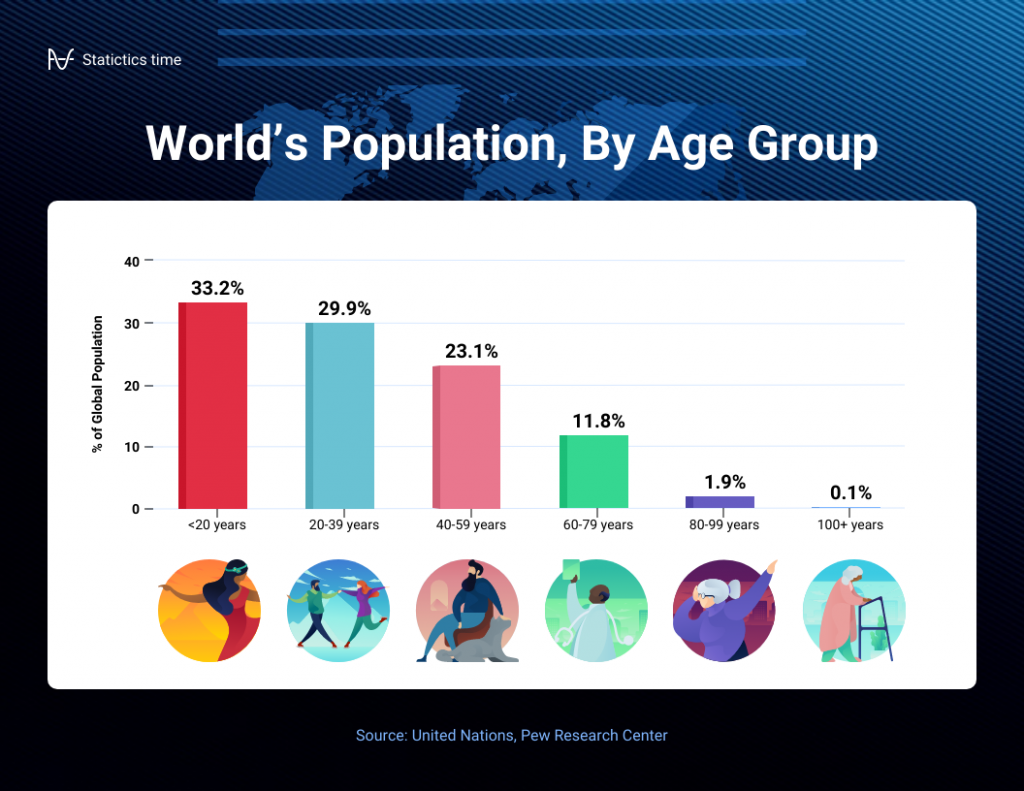
It’s a straightforward and effective way to showcase raw data, making it a staple in business reports, academic presentations and beyond.
Make sure your bar charts are concise with easy-to-read labels. Whether your bars go up or sideways, keep it simple by not overloading with too many categories.
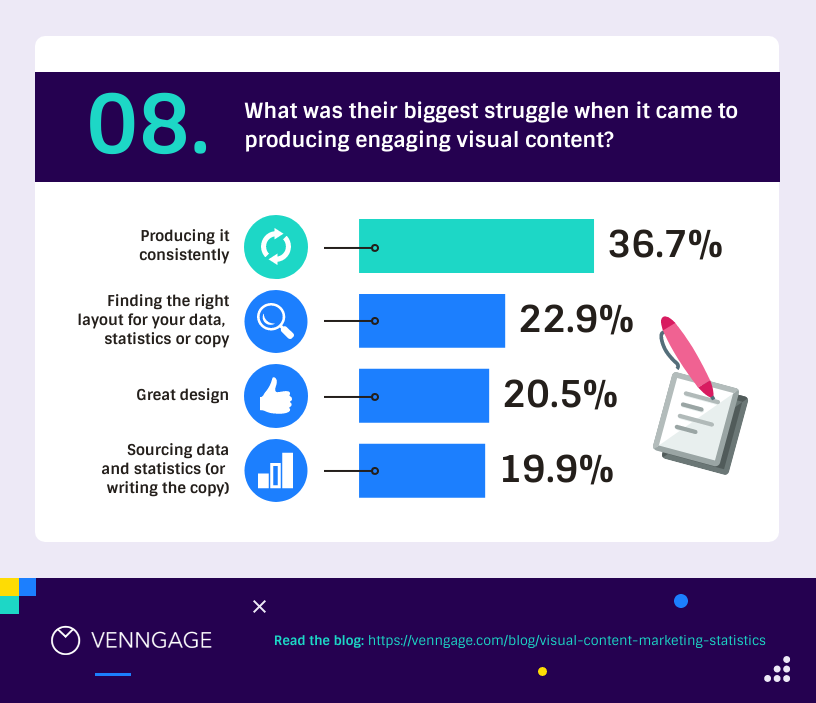
2. Line graph
Great for displaying trends and variations in data points over time or continuous variables.
Line charts or line graphs are your go-to when you want to visualize trends and variations in data sets over time.
One of the best quantitative data presentation examples, they work exceptionally well for showing continuous data, such as sales projections over the last couple of years or supply and demand fluctuations.
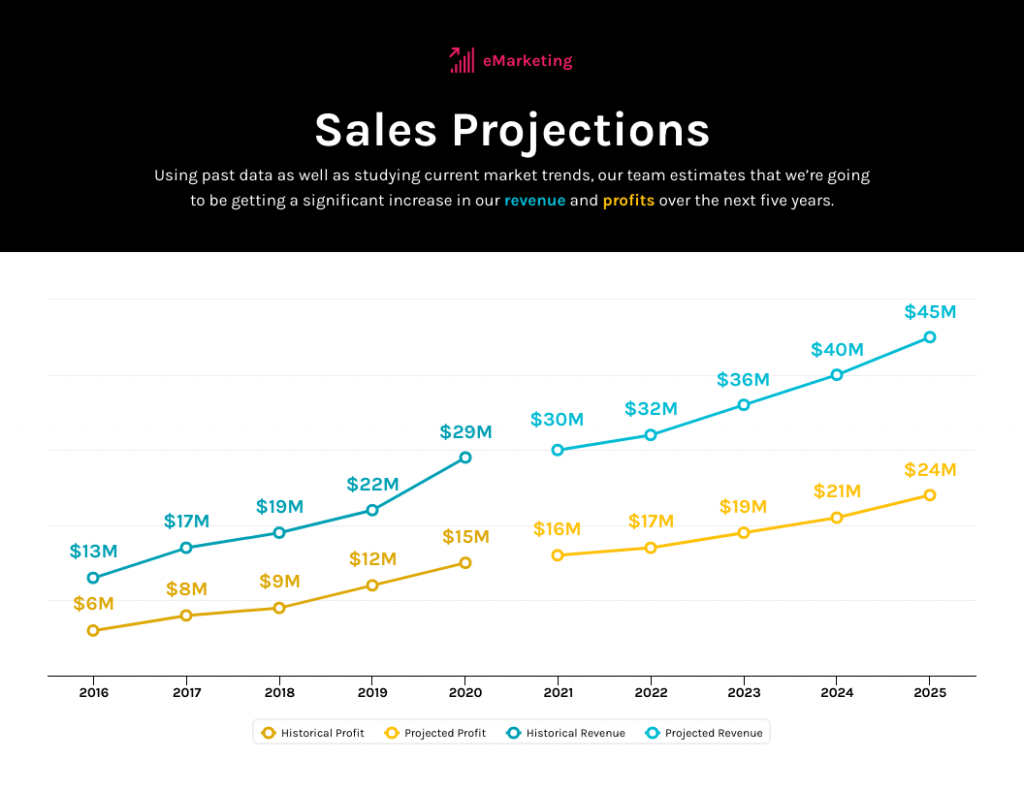
The x-axis represents time or a continuous variable and the y-axis represents the data values. By connecting the data points with lines, you can easily spot trends and fluctuations.
A tip when presenting data with line charts is to minimize the lines and not make it too crowded. Highlight the big changes, put on some labels and give it a catchy title.
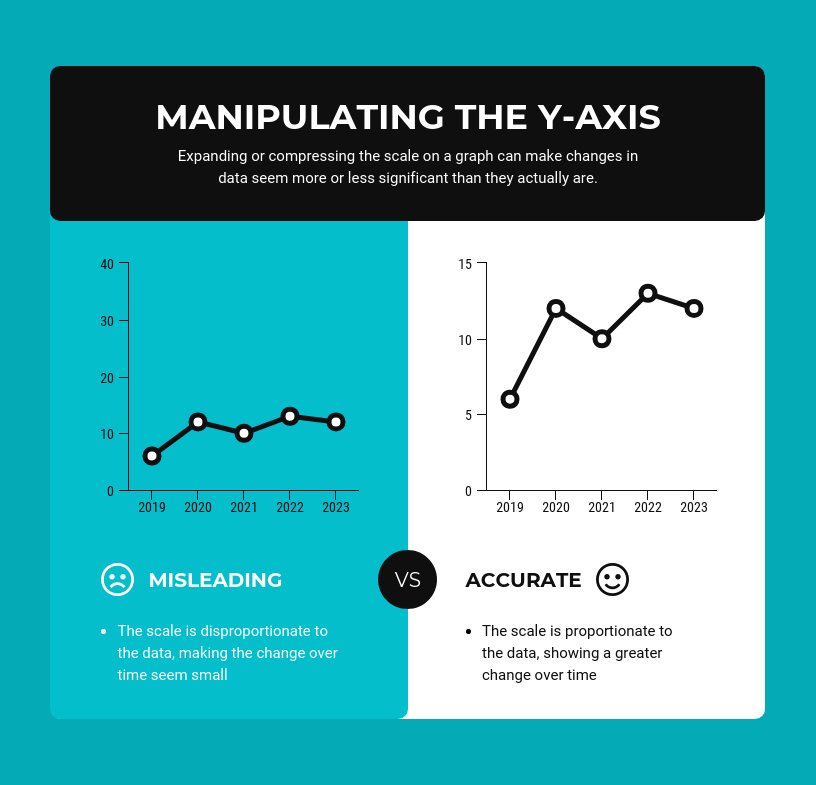
3. Pie chart
Useful for illustrating parts of a whole, such as percentages or proportions.
Pie charts are perfect for showing how a whole is divided into parts. They’re commonly used to represent percentages or proportions and are great for presenting survey results that involve demographic data.
Each “slice” of the pie represents a portion of the whole and the size of each slice corresponds to its share of the total.
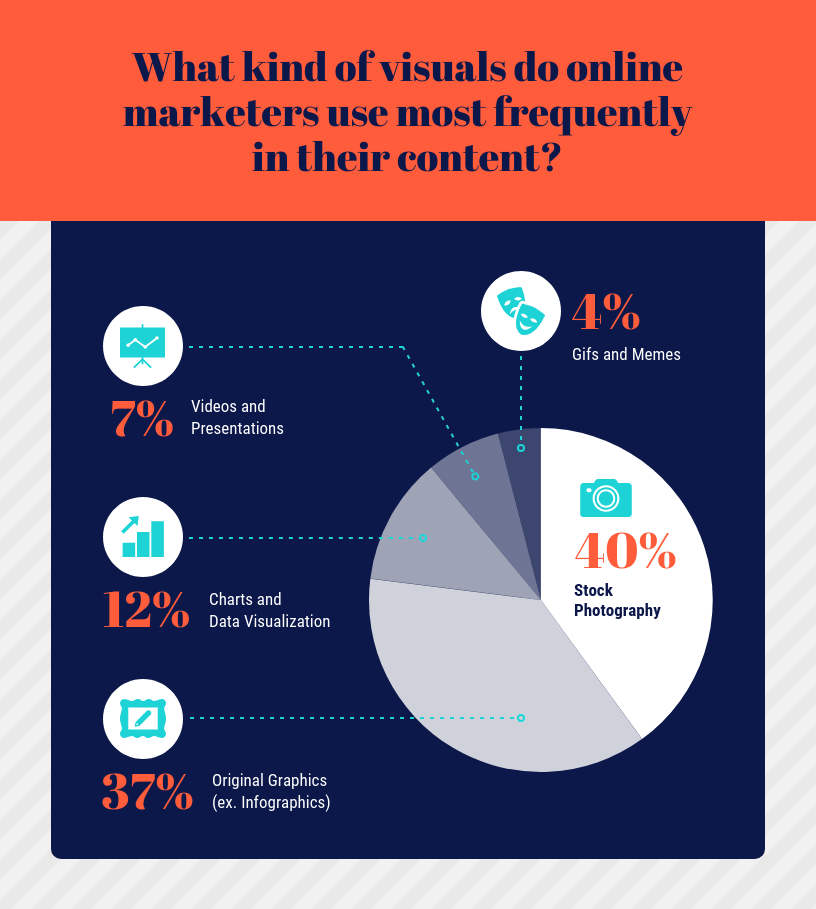
While pie charts are handy for illustrating simple distributions, they can become confusing when dealing with too many categories or when the differences in proportions are subtle.
Don’t get too carried away with slices — label those slices with percentages or values so people know what’s what and consider using a legend for more categories.
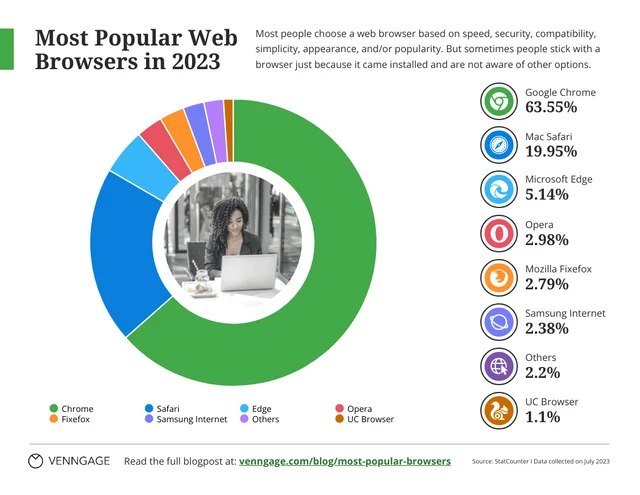

4. Scatter plot
Effective for showing the relationship between two variables and identifying correlations.
Scatter plots are all about exploring relationships between two variables. They’re great for uncovering correlations, trends or patterns in data.
In a scatter plot, every data point appears as a dot on the chart, with one variable marked on the horizontal x-axis and the other on the vertical y-axis.
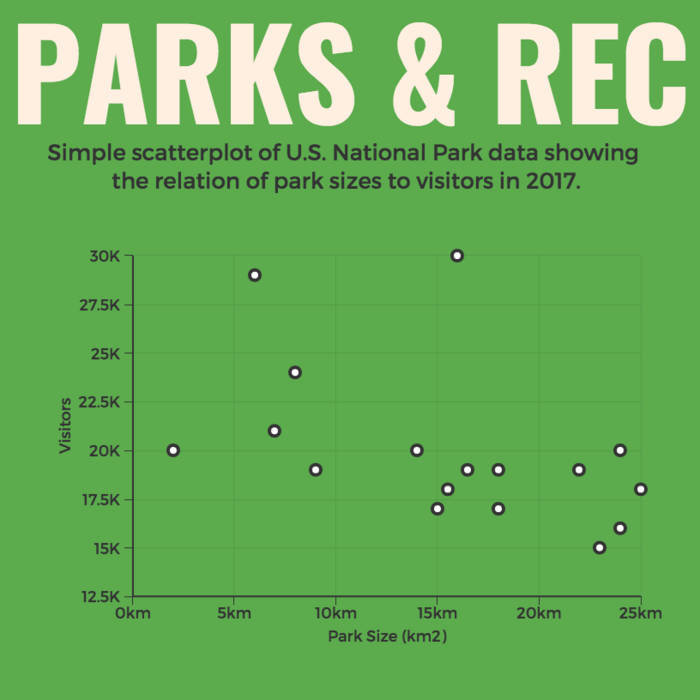
By examining the scatter of points, you can discern the nature of the relationship between the variables, whether it’s positive, negative or no correlation at all.
If you’re using scatter plots to reveal relationships between two variables, be sure to add trendlines or regression analysis when appropriate to clarify patterns. Label data points selectively or provide tooltips for detailed information.
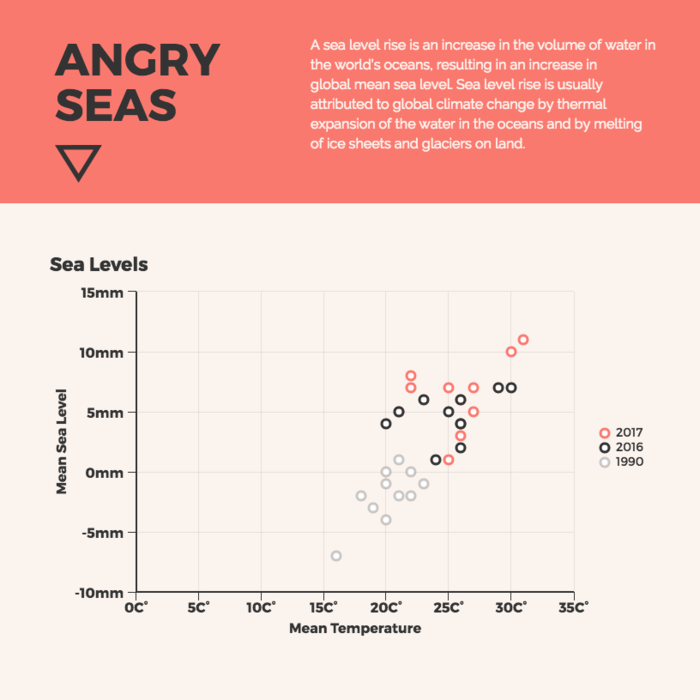
5. Histogram
Best for visualizing the distribution and frequency of a single variable.
Histograms are your choice when you want to understand the distribution and frequency of a single variable.
They divide the data into “bins” or intervals and the height of each bar represents the frequency or count of data points falling into that interval.
Histograms are excellent for helping to identify trends in data distributions, such as peaks, gaps or skewness.
Here’s something to take note of — ensure that your histogram bins are appropriately sized to capture meaningful data patterns. Using clear axis labels and titles can also help explain the distribution of the data effectively.
6. Stacked bar chart
Useful for showing how different components contribute to a whole over multiple categories.
Stacked bar charts are a handy choice when you want to illustrate how different components contribute to a whole across multiple categories.
Each bar represents a category and the bars are divided into segments to show the contribution of various components within each category.
This method is ideal for highlighting both the individual and collective significance of each component, making it a valuable tool for comparative analysis.
Stacked bar charts are like data sandwiches—label each layer so people know what’s what. Keep the order logical and don’t forget the paintbrush for snazzy colors. Here’s a data analysis presentation example on writers’ productivity using stacked bar charts:
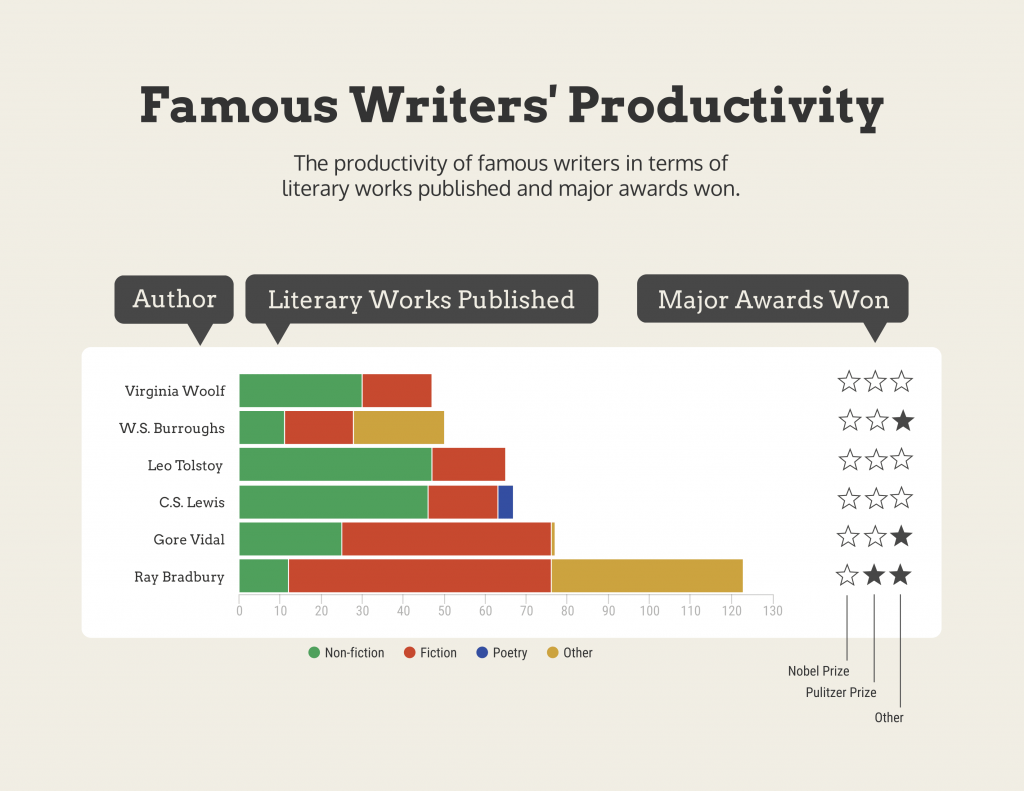
7. Area chart
Similar to line charts but with the area below the lines filled, making them suitable for showing cumulative data.
Area charts are close cousins of line charts but come with a twist.
Imagine plotting the sales of a product over several months. In an area chart, the space between the line and the x-axis is filled, providing a visual representation of the cumulative total.
This makes it easy to see how values stack up over time, making area charts a valuable tool for tracking trends in data.
For area charts, use them to visualize cumulative data and trends, but avoid overcrowding the chart. Add labels, especially at significant points and make sure the area under the lines is filled with a visually appealing color gradient.
8. Tabular presentation
Presenting data in rows and columns, often used for precise data values and comparisons.
Tabular data presentation is all about clarity and precision. Think of it as presenting numerical data in a structured grid, with rows and columns clearly displaying individual data points.
A table is invaluable for showcasing detailed data, facilitating comparisons and presenting numerical information that needs to be exact. They’re commonly used in reports, spreadsheets and academic papers.
When presenting tabular data, organize it neatly with clear headers and appropriate column widths. Highlight important data points or patterns using shading or font formatting for better readability.
9. Textual data
Utilizing written or descriptive content to explain or complement data, such as annotations or explanatory text.
Textual data presentation may not involve charts or graphs, but it’s one of the most used qualitative data presentation examples.
It involves using written content to provide context, explanations or annotations alongside data visuals. Think of it as the narrative that guides your audience through the data.
Well-crafted textual data can make complex information more accessible and help your audience understand the significance of the numbers and visuals.
Textual data is your chance to tell a story. Break down complex information into bullet points or short paragraphs and use headings to guide the reader’s attention.
10. Pictogram
Using simple icons or images to represent data is especially useful for conveying information in a visually intuitive manner.
Pictograms are all about harnessing the power of images to convey data in an easy-to-understand way.
Instead of using numbers or complex graphs, you use simple icons or images to represent data points.
For instance, you could use a thumbs up emoji to illustrate customer satisfaction levels, where each face represents a different level of satisfaction.

Pictograms are great for conveying data visually, so choose symbols that are easy to interpret and relevant to the data. Use consistent scaling and a legend to explain the symbols’ meanings, ensuring clarity in your presentation.
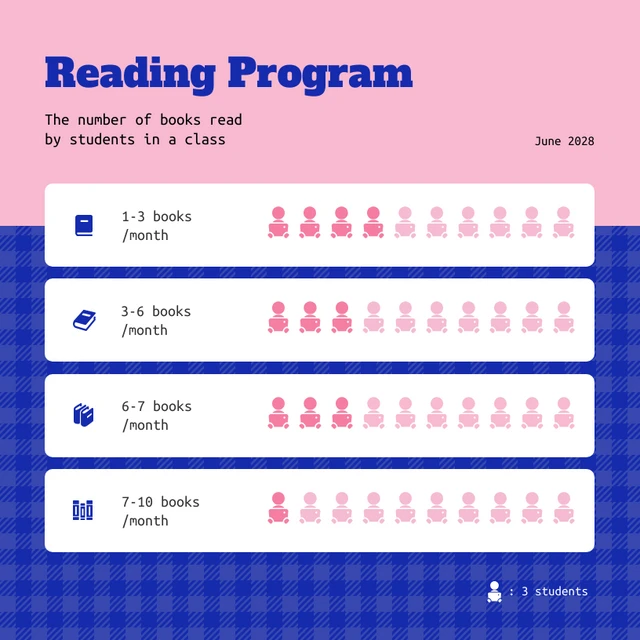
Looking for more data presentation ideas? Use the Venngage graph maker or browse through our gallery of chart templates to pick a template and get started!
A comprehensive data presentation should include several key elements to effectively convey information and insights to your audience. Here’s a list of what should be included in a data presentation:
1. Title and objective
- Begin with a clear and informative title that sets the context for your presentation.
- State the primary objective or purpose of the presentation to provide a clear focus.

2. Key data points
- Present the most essential data points or findings that align with your objective.
- Use charts, graphical presentations or visuals to illustrate these key points for better comprehension.
3. Context and significance
- Provide a brief overview of the context in which the data was collected and why it’s significant.
- Explain how the data relates to the larger picture or the problem you’re addressing.
4. Key takeaways
- Summarize the main insights or conclusions that can be drawn from the data.
- Highlight the key takeaways that the audience should remember.
5. Visuals and charts
- Use clear and appropriate visual aids to complement the data.
- Ensure that visuals are easy to understand and support your narrative.
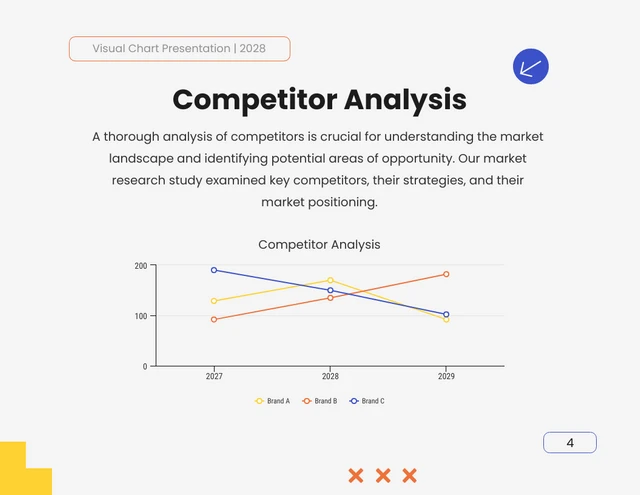
6. Implications or actions
- Discuss the practical implications of the data or any recommended actions.
- If applicable, outline next steps or decisions that should be taken based on the data.
7. Q&A and discussion
- Allocate time for questions and open discussion to engage the audience.
- Address queries and provide additional insights or context as needed.
Presenting data is a crucial skill in various professional fields, from business to academia and beyond. To ensure your data presentations hit the mark, here are some common mistakes that you should steer clear of:
Overloading with data
Presenting too much data at once can overwhelm your audience. Focus on the key points and relevant information to keep the presentation concise and focused. Here are some free data visualization tools you can use to convey data in an engaging and impactful way.
Assuming everyone’s on the same page
It’s easy to assume that your audience understands as much about the topic as you do. But this can lead to either dumbing things down too much or diving into a bunch of jargon that leaves folks scratching their heads. Take a beat to figure out where your audience is coming from and tailor your presentation accordingly.
Misleading visuals
Using misleading visuals, such as distorted scales or inappropriate chart types can distort the data’s meaning. Pick the right data infographics and understandable charts to ensure that your visual representations accurately reflect the data.
Not providing context
Data without context is like a puzzle piece with no picture on it. Without proper context, data may be meaningless or misinterpreted. Explain the background, methodology and significance of the data.
Not citing sources properly
Neglecting to cite sources and provide citations for your data can erode its credibility. Always attribute data to its source and utilize reliable sources for your presentation.
Not telling a story
Avoid simply presenting numbers. If your presentation lacks a clear, engaging story that takes your audience on a journey from the beginning (setting the scene) through the middle (data analysis) to the end (the big insights and recommendations), you’re likely to lose their interest.
Infographics are great for storytelling because they mix cool visuals with short and sweet text to explain complicated stuff in a fun and easy way. Create one with Venngage’s free infographic maker to create a memorable story that your audience will remember.
Ignoring data quality
Presenting data without first checking its quality and accuracy can lead to misinformation. Validate and clean your data before presenting it.
Simplify your visuals
Fancy charts might look cool, but if they confuse people, what’s the point? Go for the simplest visual that gets your message across. Having a dilemma between presenting data with infographics v.s data design? This article on the difference between data design and infographics might help you out.
Missing the emotional connection
Data isn’t just about numbers; it’s about people and real-life situations. Don’t forget to sprinkle in some human touch, whether it’s through relatable stories, examples or showing how the data impacts real lives.
Skipping the actionable insights
At the end of the day, your audience wants to know what they should do with all the data. If you don’t wrap up with clear, actionable insights or recommendations, you’re leaving them hanging. Always finish up with practical takeaways and the next steps.
Can you provide some data presentation examples for business reports?
Business reports often benefit from data presentation through bar charts showing sales trends over time, pie charts displaying market share,or tables presenting financial performance metrics like revenue and profit margins.
What are some creative data presentation examples for academic presentations?
Creative data presentation ideas for academic presentations include using statistical infographics to illustrate research findings and statistical data, incorporating storytelling techniques to engage the audience or utilizing heat maps to visualize data patterns.
What are the key considerations when choosing the right data presentation format?
When choosing a chart format , consider factors like data complexity, audience expertise and the message you want to convey. Options include charts (e.g., bar, line, pie), tables, heat maps, data visualization infographics and interactive dashboards.
Knowing the type of data visualization that best serves your data is just half the battle. Here are some best practices for data visualization to make sure that the final output is optimized.
How can I choose the right data presentation method for my data?
To select the right data presentation method, start by defining your presentation’s purpose and audience. Then, match your data type (e.g., quantitative, qualitative) with suitable visualization techniques (e.g., histograms, word clouds) and choose an appropriate presentation format (e.g., slide deck, report, live demo).
For more presentation ideas , check out this guide on how to make a good presentation or use a presentation software to simplify the process.
How can I make my data presentations more engaging and informative?
To enhance data presentations, use compelling narratives, relatable examples and fun data infographics that simplify complex data. Encourage audience interaction, offer actionable insights and incorporate storytelling elements to engage and inform effectively.
The opening of your presentation holds immense power in setting the stage for your audience. To design a presentation and convey your data in an engaging and informative, try out Venngage’s free presentation maker to pick the right presentation design for your audience and topic.
What is the difference between data visualization and data presentation?
Data presentation typically involves conveying data reports and insights to an audience, often using visuals like charts and graphs. Data visualization , on the other hand, focuses on creating those visual representations of data to facilitate understanding and analysis.
Now that you’ve learned a thing or two about how to use these methods of data presentation to tell a compelling data story , it’s time to take these strategies and make them your own.
But here’s the deal: these aren’t just one-size-fits-all solutions. Remember that each example we’ve uncovered here is not a rigid template but a source of inspiration. It’s all about making your audience go, “Wow, I get it now!”
Think of your data presentations as your canvas – it’s where you paint your story, convey meaningful insights and make real change happen.
So, go forth, present your data with confidence and purpose and watch as your strategic influence grows, one compelling presentation at a time.
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker
10 Methods of Data Presentation with 5 Great Tips to Practice, Best in 2024
Leah Nguyen • 05 April, 2024 • 17 min read
There are different ways of presenting data, so which one is suited you the most? You can end deathly boring and ineffective data presentation right now with our 10 methods of data presentation . Check out the examples from each technique!
Have you ever presented a data report to your boss/coworkers/teachers thinking it was super dope like you’re some cyber hacker living in the Matrix, but all they saw was a pile of static numbers that seemed pointless and didn’t make sense to them?
Understanding digits is rigid . Making people from non-analytical backgrounds understand those digits is even more challenging.
How can you clear up those confusing numbers in the types of presentation that have the flawless clarity of a diamond? So, let’s check out best way to present data. 💎
Table of Contents
- What are Methods of Data Presentations?
- #1 – Tabular
#3 – Pie chart
#4 – bar chart, #5 – histogram, #6 – line graph, #7 – pictogram graph, #8 – radar chart, #9 – heat map, #10 – scatter plot.
- 5 Mistakes to Avoid
- Best Method of Data Presentation
Frequently Asked Questions
More tips with ahaslides.
- Marketing Presentation
- Survey Result Presentation
- Types of Presentation

Start in seconds.
Get any of the above examples as templates. Sign up for free and take what you want from the template library!
What are Methods of Data Presentation?
The term ’data presentation’ relates to the way you present data in a way that makes even the most clueless person in the room understand.
Some say it’s witchcraft (you’re manipulating the numbers in some ways), but we’ll just say it’s the power of turning dry, hard numbers or digits into a visual showcase that is easy for people to digest.
Presenting data correctly can help your audience understand complicated processes, identify trends, and instantly pinpoint whatever is going on without exhausting their brains.
Good data presentation helps…
- Make informed decisions and arrive at positive outcomes . If you see the sales of your product steadily increase throughout the years, it’s best to keep milking it or start turning it into a bunch of spin-offs (shoutout to Star Wars👀).
- Reduce the time spent processing data . Humans can digest information graphically 60,000 times faster than in the form of text. Grant them the power of skimming through a decade of data in minutes with some extra spicy graphs and charts.
- Communicate the results clearly . Data does not lie. They’re based on factual evidence and therefore if anyone keeps whining that you might be wrong, slap them with some hard data to keep their mouths shut.
- Add to or expand the current research . You can see what areas need improvement, as well as what details often go unnoticed while surfing through those little lines, dots or icons that appear on the data board.
Methods of Data Presentation and Examples
Imagine you have a delicious pepperoni, extra-cheese pizza. You can decide to cut it into the classic 8 triangle slices, the party style 12 square slices, or get creative and abstract on those slices.
There are various ways for cutting a pizza and you get the same variety with how you present your data. In this section, we will bring you the 10 ways to slice a pizza – we mean to present your data – that will make your company’s most important asset as clear as day. Let’s dive into 10 ways to present data efficiently.
#1 – Tabular
Among various types of data presentation, tabular is the most fundamental method, with data presented in rows and columns. Excel or Google Sheets would qualify for the job. Nothing fancy.
This is an example of a tabular presentation of data on Google Sheets. Each row and column has an attribute (year, region, revenue, etc.), and you can do a custom format to see the change in revenue throughout the year.
When presenting data as text, all you do is write your findings down in paragraphs and bullet points, and that’s it. A piece of cake to you, a tough nut to crack for whoever has to go through all of the reading to get to the point.
- 65% of email users worldwide access their email via a mobile device.
- Emails that are optimised for mobile generate 15% higher click-through rates.
- 56% of brands using emojis in their email subject lines had a higher open rate.
(Source: CustomerThermometer )
All the above quotes present statistical information in textual form. Since not many people like going through a wall of texts, you’ll have to figure out another route when deciding to use this method, such as breaking the data down into short, clear statements, or even as catchy puns if you’ve got the time to think of them.
A pie chart (or a ‘donut chart’ if you stick a hole in the middle of it) is a circle divided into slices that show the relative sizes of data within a whole. If you’re using it to show percentages, make sure all the slices add up to 100%.
The pie chart is a familiar face at every party and is usually recognised by most people. However, one setback of using this method is our eyes sometimes can’t identify the differences in slices of a circle, and it’s nearly impossible to compare similar slices from two different pie charts, making them the villains in the eyes of data analysts.
Bonus example: A literal ‘pie’ chart! 🥧
The bar chart is a chart that presents a bunch of items from the same category, usually in the form of rectangular bars that are placed at an equal distance from each other. Their heights or lengths depict the values they represent.
They can be as simple as this:
Or more complex and detailed like this example of presentation of data. Contributing to an effective statistic presentation, this one is a grouped bar chart that not only allows you to compare categories but also the groups within them as well.
Similar in appearance to the bar chart but the rectangular bars in histograms don’t often have the gap like their counterparts.
Instead of measuring categories like weather preferences or favourite films as a bar chart does, a histogram only measures things that can be put into numbers.
Teachers can use presentation graphs like a histogram to see which score group most of the students fall into, like in this example above.
Recordings to ways of displaying data, we shouldn’t overlook the effectiveness of line graphs. Line graphs are represented by a group of data points joined together by a straight line. There can be one or more lines to compare how several related things change over time.
On a line chart’s horizontal axis, you usually have text labels, dates or years, while the vertical axis usually represents the quantity (e.g.: budget, temperature or percentage).
A pictogram graph uses pictures or icons relating to the main topic to visualise a small dataset. The fun combination of colours and illustrations makes it a frequent use at schools.
Pictograms are a breath of fresh air if you want to stay away from the monotonous line chart or bar chart for a while. However, they can present a very limited amount of data and sometimes they are only there for displays and do not represent real statistics.
If presenting five or more variables in the form of a bar chart is too stuffy then you should try using a radar chart, which is one of the most creative ways to present data.
Radar charts show data in terms of how they compare to each other starting from the same point. Some also call them ‘spider charts’ because each aspect combined looks like a spider web.
Radar charts can be a great use for parents who’d like to compare their child’s grades with their peers to lower their self-esteem. You can see that each angular represents a subject with a score value ranging from 0 to 100. Each student’s score across 5 subjects is highlighted in a different colour.
If you think that this method of data presentation somehow feels familiar, then you’ve probably encountered one while playing Pokémon .
A heat map represents data density in colours. The bigger the number, the more colour intense that data will be represented.
Most U.S citizens would be familiar with this data presentation method in geography. For elections, many news outlets assign a specific colour code to a state, with blue representing one candidate and red representing the other. The shade of either blue or red in each state shows the strength of the overall vote in that state.
Another great thing you can use a heat map for is to map what visitors to your site click on. The more a particular section is clicked the ‘hotter’ the colour will turn, from blue to bright yellow to red.
If you present your data in dots instead of chunky bars, you’ll have a scatter plot.
A scatter plot is a grid with several inputs showing the relationship between two variables. It’s good at collecting seemingly random data and revealing some telling trends.
For example, in this graph, each dot shows the average daily temperature versus the number of beach visitors across several days. You can see that the dots get higher as the temperature increases, so it’s likely that hotter weather leads to more visitors.
5 Data Presentation Mistakes to Avoid
#1 – assume your audience understands what the numbers represent.
You may know all the behind-the-scenes of your data since you’ve worked with them for weeks, but your audience doesn’t.
Showing without telling only invites more and more questions from your audience, as they have to constantly make sense of your data, wasting the time of both sides as a result.
While showing your data presentations, you should tell them what the data are about before hitting them with waves of numbers first. You can use interactive activities such as polls , word clouds , online quiz and Q&A sections , combined with icebreaker games , to assess their understanding of the data and address any confusion beforehand.
#2 – Use the wrong type of chart
Charts such as pie charts must have a total of 100% so if your numbers accumulate to 193% like this example below, you’re definitely doing it wrong.
Before making a chart, ask yourself: what do I want to accomplish with my data? Do you want to see the relationship between the data sets, show the up and down trends of your data, or see how segments of one thing make up a whole?
Remember, clarity always comes first. Some data visualisations may look cool, but if they don’t fit your data, steer clear of them.
#3 – Make it 3D
3D is a fascinating graphical presentation example. The third dimension is cool, but full of risks.
Can you see what’s behind those red bars? Because we can’t either. You may think that 3D charts add more depth to the design, but they can create false perceptions as our eyes see 3D objects closer and bigger than they appear, not to mention they cannot be seen from multiple angles.
#4 – Use different types of charts to compare contents in the same category
This is like comparing a fish to a monkey. Your audience won’t be able to identify the differences and make an appropriate correlation between the two data sets.
Next time, stick to one type of data presentation only. Avoid the temptation of trying various data visualisation methods in one go and make your data as accessible as possible.
#5 – Bombard the audience with too much information
The goal of data presentation is to make complex topics much easier to understand, and if you’re bringing too much information to the table, you’re missing the point.
The more information you give, the more time it will take for your audience to process it all. If you want to make your data understandable and give your audience a chance to remember it, keep the information within it to an absolute minimum. You should set your session with open-ended questions , to avoid dead-communication!
What are the Best Methods of Data Presentation?
Finally, which is the best way to present data?
The answer is…
There is none 😄 Each type of presentation has its own strengths and weaknesses and the one you choose greatly depends on what you’re trying to do.
For example:
- Go for a scatter plot if you’re exploring the relationship between different data values, like seeing whether the sales of ice cream go up because of the temperature or because people are just getting more hungry and greedy each day?
- Go for a line graph if you want to mark a trend over time.
- Go for a heat map if you like some fancy visualisation of the changes in a geographical location, or to see your visitors’ behaviour on your website.
- Go for a pie chart (especially in 3D) if you want to be shunned by others because it was never a good idea👇
What is chart presentation?
A chart presentation is a way of presenting data or information using visual aids such as charts, graphs, and diagrams. The purpose of a chart presentation is to make complex information more accessible and understandable for the audience.
When can I use charts for presentation?
Charts can be used to compare data, show trends over time, highlight patterns, and simplify complex information.
Why should use charts for presentation?
You should use charts to ensure your contents and visual look clean, as they are the visual representative, provide clarity, simplicity, comparison, contrast and super time-saving!
What are the 4 graphical methods of presenting data?
Histogram, Smoothed frequency graph, Pie diagram or Pie chart, Cumulative or ogive frequency graph, and Frequency Polygon.
Leah Nguyen
Words that convert, stories that stick. I turn complex ideas into engaging narratives - helping audiences learn, remember, and take action.
Tips to Engage with Polls & Trivia
More from AhaSlides

NMDP and CIBMTR to Present New, Promising Stem Cell Transplantation Trial Data at ASCO 2024
Adults with blood cancers receiving peripheral blood stem cell transplant exhibited excellent survival rates and low incidence of life-threatening graft-versus-host-disease
Additional NMDP presentation on population-level access barriers to bone marrow transplant
NMDP and CIBMTR to Present New, Promising Stem Cell Transplantation Trial Data using Mismatched, Unrelated Donors at 2024 ASCO Annual Meeting
MINNEAPOLIS, May 23, 2024 — NMDP℠, a global nonprofit leader in cell therapy, and the CIBMTR® (Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research®), announced that interim results from the ACCESS trial will be presented as an oral abstract on Friday, May 31 at the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) Annual Meeting in Chicago, Ill., demonstrating that adults with hematologic malignancies who received peripheral blood stem cell (PBSC) transplant from HLA-mismatched unrelated donors (MMUD) followed by post-transplant cyclophosphamide (PTCy) graft-versus-host-disease (GvHD) prophylaxis exhibited a 79% overall survival, with a significant 51% GvHD-free, relapse-free survival (GRFS) probability at one-year post transplant. Notably, ASCO also selected this abstract to be presented at its 2024 Best of ASCO program in July.
“We want more patients to survive and thrive — results from ACCESS to-date have shown positive, significant transplant outcomes and good quality of life for patients,” said Monzr M. Al Malki, M.D., Associate Professor, Department of Hematology & Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation, City of Hope; presenting author and ACCESS study co-chair. “These preliminary data provide strong support for inclusion of this novel treatment approach for patients receiving PBSC from partially matched, unrelated donors and advance current evidence demonstrating how more patients can benefit from the potentially curative therapeutic effects of transplant.”
In addition to achieving very good OS and GRFS clinical endpoints, adult participants also exhibited low rates of severe acute and chronic GvHD, both at 9%. The NMDP-sponsored ACCESS trial, conducted through the CIBMTR — a research collaboration between the Medical College of Wisconsin and NMDP — enrolled 70 adult patients with blood cancers and disorders, including acute myeloid leukemia (AML), myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS), and acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), from 13 participating transplant centers, like City of Hope. All patients in this stratum received reduced intensity conditioning, most often fludarabine/melphalan (63%) or fludarabine/busulfan (20%), and PBSCs from donors matched at 5-7 of 8 HLA loci, predominantly at the 7/8 match level (67%). Notably, half of patients enrolled in the trial were people of color.
“Historically, barriers in access to transplant have been inhibited by two factors: the low availability of matched, related sibling donors; and the substantial variance of matched, unrelated donor availability on international registries, particularly for patients with diverse ancestry — many of whom already face significant challenges,” said study co-author Steven M. Devine, M.D., Chief Medical Officer, NMDP; Senior Scientific Director, CIBMTR. “Our research findings advance our ability to offer more options to patients without a fully matched donor, many of whom are ethnically diverse and have been underserved in receiving potentially life-saving cell therapy.”
Addressing Equitable Care: NMDP-led Donor for All Research
Traditionally, finding an available matched, unrelated donor on international registries has been limited for patients with ethnically diverse ancestry – from as low as 29% for Black or African American patients and 48% for Latino and Hispanic patients versus 79% for non-Hispanic Whites. NMDP’s network of transplant centers, many of which participate in CIBMTR trials, are bringing new research to light that is challenging previously established stem cell transplantation science.
ACCESS builds upon findings from the first “Donor for All” trial, a groundbreaking NMDP-sponsored 15-MMUD study , which showed that PTCy was effective in decreasing risk for GvHD in adults with hematologic malignancies receiving bone marrow (BM) transplants from MMUD. Similar to ACCESS, 15-MMUD patients — 48% of whom were ethnically diverse — showed a one-year overall survival (OS) rate of 76% and exhibited a low rate of moderate / severe GvHD. Enrolling now, the OPTIMIZE trial is evaluating whether a reduced dose of PTCy will safely and effectively prevent GvHD while reducing infection risk in patients with hematologic malignancies receiving PBSC HCT from MMUDs. Finally, a recent observational study by the CIBMTR presented at the 2024 Tandem Meetings , reported no discernable differences in OS or GRFS for adult patients with hematologic malignancies using MMUD HCT at an 8/8 or 7/8 HLA match level using PTCy GvHD prophylaxis — increasing the likelihood for patients of all ethnicities of finding a suitable donor to at least 84% and up to 99%.
“Our Donor for All research is the foundational future upon which we are building a new platform protocol using innovative strategies for preventing and treating GvHD, decreasing risk for post-transplant relapse of hematologic malignancies, and in the future, applying MMUD transplant to cure non-malignant conditions, such as sickle cell disease,” said Dr. Devine. “Through CIBMTR, we are showing that science can solve the gap in equitable access to transplant, giving new hope to patients worldwide.”
2024 ASCO Presentation Details
Oral Presentation ( Abstract #6503 ) Friday, May 31; 2:45-5:45 p.m. CDT; Room S100bc
Post-transplant cyclophosphamide-based graft-versus-host disease prophylaxis following mismatched unrelated donor peripheral blood stem cell (PBSC) transplantation
Monzr M. Al Malki, M.D.
Poster Discussion ( Abstract #1528 ) Saturday, June 1; 9 a.m. – noon CDT; Hall A
Identifying states for targeted alloHCT access initiatives using social vulnerability, physician density, and unmet need
Samantha Watters, MPH
About CIBMTR® CIBMTR® (Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research®) is a nonprofit research collaboration between NMDP℠, in Minneapolis, and the Medical College of Wisconsin, in Milwaukee. CIBMTR collaborates with the global scientific community to increase survival and enrich quality of life for patients. CIBMTR facilitates critical observational and interventional research through scientific and statistical expertise, a large network of centers, and a unique database of long-term clinical data for more than 675,000 people who have received hematopoietic cell transplantation and other cellular therapies. Learn more at cibmtr.org .
About NMDP℠ At NMDP℠, we believe each of us holds the key to curing blood cancers and disorders. As a global nonprofit leader in cell therapy, NMDP creates essential connections between researchers and supporters to inspire action and accelerate innovation to find life-saving cures. With the help of blood stem cell donors from the world’s most diverse registry and our extensive network of transplant partners, physicians and caregivers, we’re expanding access to treatment so that every patient can receive their life-saving cell therapy. NMDP. Find cures. Save lives. Learn more at nmdp.org .
- Open access
- Published: 21 May 2024
Effectively teaching cultural competence in a pre-professional healthcare curriculum
- Karen R. Bottenfield 1 ,
- Maura A. Kelley 2 ,
- Shelby Ferebee 3 ,
- Andrew N. Best 1 ,
- David Flynn 2 &
- Theresa A. Davies 1 , 2
BMC Medical Education volume 24 , Article number: 553 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
188 Accesses
Metrics details
There has been research documenting the rising numbers of racial and ethnic minority groups in the United States. With this rise, there is increasing concern over the health disparities that often affect these populations. Attention has turned to how clinicians can improve health outcomes and how the need exists to educate healthcare professionals on the practice of cultural competence. Here we present one successful approach for teaching cultural competence in the healthcare curriculum with the development of an educational session on cultural competence consisting of case-based, role-play exercises, class group discussions, online discussion boards, and a lecture PowerPoint presentation.
Cultural competence sessions were delivered in a pre-dental master’s program to 178 students between 2017 and 2020. From 2017 to 2019, the sessions were implemented as in-person, case-based, role-play exercises. In 2020, due to in-person limitations caused by the COVID-19 pandemic, students were asked to read the role-play cases and provide a reflection response using the online Blackboard Learn discussion board platform. Evaluation of each session was performed using post-session survey data.
Self-reported results from 2017 to 2020 revealed that the role-play exercises improved participant’s understanding of components of cultural competence such as communication in patient encounters (95%), building rapport with patients (94%), improving patient interview skills (95%), and recognition of students own cultural biases when working with patients (93%).
Conclusions
Students were able to expand their cultural awareness and humility after completion of both iterations of the course session from 2017 to 2019 and 2020. This session can be an effective method for training healthcare professionals on cultural competence.
Peer Review reports
It is projected that by the year 2050, racial and ethnic minority groups will make up over 50% of the United States population [ 1 ]. With a more multicultural society, growing concern has emerged over how to address the health disparities that effect these populations and the ways in which healthcare professionals can increase positive health outcomes. Continuing evidence suggests that many patients from racial and ethnic minority groups are not satisfied with the current state of healthcare which has been attributed to implicit bias on the part of physicians and current challenges faced by practitioners who feel underprepared to address these issues due to differences in language, financial status, and healthcare practice [ 2 , 3 , 4 ].
To contend with health disparities and the challenges faced by practitioners working with a more diverse population, healthcare educators have begun to emphasize the importance of educating healthcare workforce on the practice of cultural competence and developing a skilled-based set of behaviors, attitudes and policies that effectively provides care in the wake of cross-cultural situations and differences [ 4 , 5 , 6 ]. There are several curricular mandates from both medical and dental accreditation bodies to address this issue [ 7 , 8 , 9 ], and large amounts of resources, ideas, and frameworks that exist for implementing and training future and current healthcare providers on the inadequacies of the healthcare system and cultural competence [ 10 , 11 , 12 ]. These current institutional guidelines for accreditation and the numerous amounts of resources for training cultural competence, continue to evolve with work documenting the need for blended curriculum that is continuous throughout student education, starting early as we have done here with pre-dental students, including in-person didactic or online sessions, a service learning component, community engagement and a reflective component [ 4 , 5 , 13 , 14 ].
This study investigates teaching cultural competence in a healthcare curriculum. We hypothesized that early educational exposure to cultural competence through role playing case studies, can serve as an effective mechanism for training early pre-doctoral students the practice of cultural competence. Utilizing student self-reported survey data conducted in a predental master’s curriculum, in which two iterations of role-playing case studies were used to teach components of cultural competence, this study aims to evaluate and support research that suggests role-playing case studies as effective means for educating future clinical professionals on the practice of cultural competence.
This study was determined to be exempt by the Institutional Review Board of Boston University Medical Campus, Protocol # H-37,232. Informed consent was received from all subjects.
Data collection
The role-playing, case-based simulated patient encounter exercises were developed and administered at Boston University Chobanian & Avedisian School of Medicine to predental students in the Master of Science in Oral Health Sciences Program (see Table 1 ). From 2017 to 2020, we administered patient encounter cases [see Additional File 1 ] to students ( n = 178) in the program as a portion of a case-based, role-playing exercise to teach the importance of cultural competence and cultural awareness during patient encounters. During years 2017–2019, real actors portrayed the patient and physician. In 2020, the session was conducted online via a discussion board through a Blackboard Course Site. The original case was published as part of a master’s students thesis work in 2021 [ 15 ].
Description of patient encounter cases 1 and 2
Patient Encounter Case 1 [see Additional file 1 ] is composed of two subsections, scenario 1 A and scenario 1B, and is centered around a patient/physician interaction in which a patient who is pregnant presents with pain upon urination. The physician in 1 A is short and terse with the patient, immediately looking at a urine sample, prescribing medication for a urinary tract infection, and telling the patient to return for a follow-up in 2 weeks. In scenario 1B, a similar situation ensues; however, in this scenario the physician takes more time with the patient providing similar care as the physician in 1 A, but asking for more information about the patients personal and medical history. At the conclusion of the scenario, the patient is offered resources for an obstetrician and a dentist based on the information that is provided about the patient’s background. The patient is then sent on their way and asked to follow-up in 2 weeks. The patient does not return.
Patient Encounter Case 2 [see Additional file 1 ] follows a similar format to the Patient Encounter Case 1. In scenario 2 A, the same patient from Case 1 returns with tooth pain after giving birth. The physician in 2 A, like 1 A, is short with the patient and quickly refers the patient to a dentist. In 2B, the physician again takes more time with the patient to receive background information on the patient, make a connection, and provides an antibiotic and dental referral.
Each Patient Encounter Case explored topics such as the importance of building a trusting physician/patient relationship, the importance of asking a patient for patient history, making a connection, and the importance of a physician taking all facets of a patient’s circumstances into consideration [ 15 ].
Session outline
The sessions conducted between 2017 and 2019 were composed of three parts: (1) enactment of an abridged patient encounter facilitated by session administrators, (2) group discussion and reflection during which time students were asked to critically reflect and discuss the theme and key take-aways from the role play exercise, and (3) a PowerPoint presentation emphasizing take-away points from the role-play exercise. At the conclusion of the cultural competence training sessions, students participated in a post-session Qualtrics generated survey administered electronically to assess each student’s feelings about the session [see Additional file 3 ].
Role-play enactment
Facilitators dressed-up in clothing to mimic both the physician and patient for all case scenarios in Patient Encounter Case 1 and Case 2. At the conclusion of the role play portion of each of the cases, the facilitators paused to lead students in a real-time class group discussion. After Case 1, students were asked questions such as: What did you think ? Were the patient’s needs met? Did you expect the patient to return? Following Case 2, similar questions were asked by the facilitators, including: What did you think ? Were the patient’s needs met? Did you expect the patient to accept help?
At the conclusion of this portion of the session, the facilitators led a larger general discussion about both cases and how they related to one another. Finally, the course session concluded with a PowerPoint presentation that reinforced the take-home points from the session [see Additional file 2 ] [ 15 ].
Change in session modality due to COVID-19 pandemic
In Fall 2020, due to the COVID-19 pandemic, the course modality moved to an online platform and consisted of three parts on a Blackboard Discussion Board (Blackboard, Inc.). Students were required to: (1) read each of the Patient Encounter Cases and add a brief reflection comparing the scenarios, (2) then comment on at least two peer’s posts in the discussion forum and (3) attend class to hear a PowerPoint presentation by a course session facilitator on the key take-aways from each scenario [ 15 ].
Student surveys
At the conclusion of the cultural competence training sessions, students participated in a post-session Qualtrics ( https://www.qualtrics.com ) generated survey administered electronically to assess each student’s feelings about the sessions [see Additional file 3 ]. The format of the survey included 5 questions with the following Likert scale response options: strongly agree, agree, disagree, strongly disagree. These post-session surveys were not required but rather optional [ 15 ].
A total of 178 students completed the cultural competence sessions between 2017 and 2020. Of these participants, 112 voluntarily completed a post-session survey on the effectiveness of the course in teaching cultural competence and cultural awareness during patient encounters. Between 2017 and 2019, 99 students completed post-session surveys following sessions with role play exercises. In 2020, 13 students completed post-session surveys following discussion board sessions.
Role-play exercises enhanced cultural competence
In responding to post-session survey questions following cultural competence sessions that included role-play exercises (2017–2019), 71% of students surveyed strongly agreed and 24% agreed that the role-play exercises helped them to identify the importance of communication in patient encounters. In asking participants if the role-play exercises made them more aware of different strategies to improve their patient interview skills, 72% strongly agreed and 23% agreed. Also, 68% of the students strongly agreed and 26% agreed that the exercises helped them to better identify the importance of building rapport and trust during patient encounters. When asked if the exercises helped the students to better understand their own bias and/or cultural awareness when working with patients, the results of the survey showed that 62% of students strongly agreed and 31% agreed with this statement. In addition, most students found the role-play exercises to be enjoyable (72% strongly agreed and 22% agreed). See results shown in Fig. 1 .
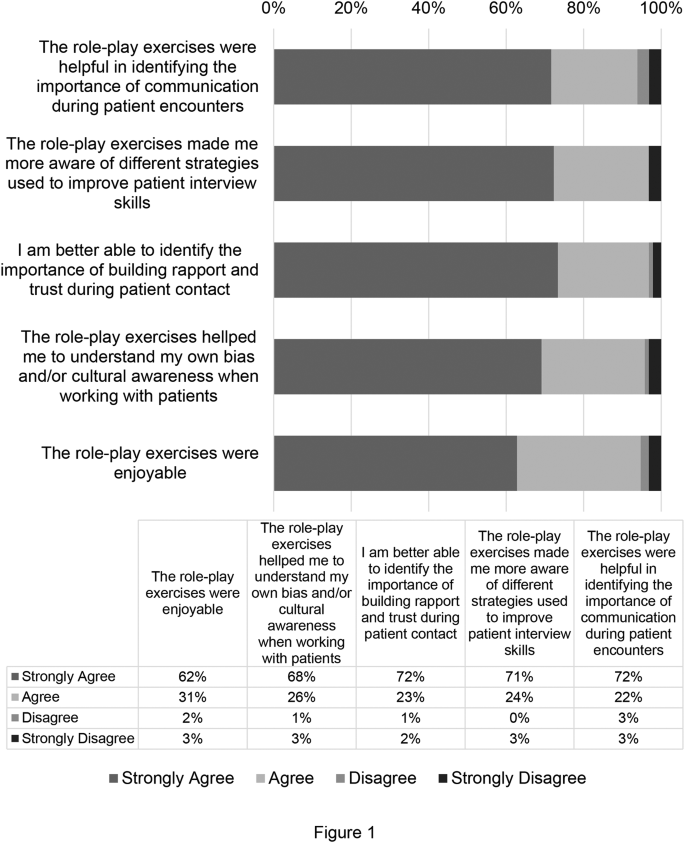
Cultural Competence Session Survey Data from the Year 2017–2019. Survey data from students at Boston University’s Oral Health Sciences Program for the years 2017–2019. Data is presented as percent of respondents ( n = 99)
Discussion boards and reflections enhanced cultural competence
Cultural competence sessions held during 2020 did not include role-play exercises due to the Covid-19 pandemic. Instead, students participated in discussion boards and reflections on Blackboard. In response to the post-session survey question asking if the discussion board exercises were helpful in identifying the importance of communication during patient encounters, 67% of students strongly agreed and 25% agreed with this statement. Also, 75% of students strongly agreed and 17% agreed that the discussion board exercises helped them identify the importance of building rapport and trust during patient contact. When asked if the exercises helped the students to better understand their own bias and/or cultural awareness when working with patients, the results of the survey showed that 67% of students strongly agreed and 25% agreed with this statement. In addition, most students found the discussion board exercises to be enjoyable (67% strongly agreed and 22% agreed). See results shown in Fig. 2 .
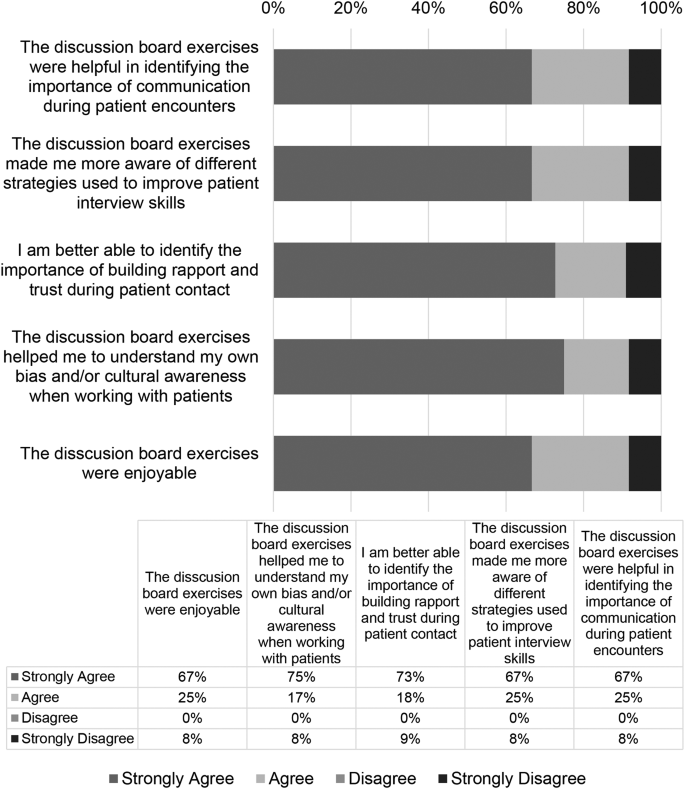
Cultural competence session survey data from the Year 2020. Survey data from students at Boston University’s Oral Health Sciences Program for the year 2020. Data is presented as percent of respondents ( n = 13)
Student responses to the reflection portion of the online cultural competency sessions were recorded and categorized. Five themes were selected and 441 reflection responses were coded using NVivo (Version 12). The results showed that 29% of reflections demonstrated student’s ability to understand a holistic approach to clinical care, 24.3% understood the importance of collecting a patient history, 6.8% recognized the socioeconomic factors during a patient encounter, 27.9% reflected on the importance of the patient clinical relationship, and 12% on the effects on improving health outcomes (Table 1 ). Representative student responses to these themes are shown in Table 1 .
There exists a need to develop novel and effective means for teaching and training the next generation of healthcare professionals the practice of cultural competence. Thus, two iterations of a course session using case-based patient centered encounters were developed to teach these skills to pre-professional dentals students. Overall, the results of this study demonstrated that participation in the course, subsequent group discussion sessions, and take-away PowerPoint sessions significantly improved the participant’s understanding of the importance of communication skills and understanding of socioeconomic, environmental, and cultural disparities that can affect a patient’s health outcome.
According to results from the course session implemented in-person from 2017 to 2019, the role-playing exercise significantly improved participants understanding of important components that can be used to improve health outcomes that may be affected due to health disparities. Students were strongly able to identify the importance of communication in patient encounters, to understand strategies such as communication and compassionate care in patient encounters, identify the importance of building a patient-physician relationship with patients, and were able to recognize their own cultural biases. Similarly, in 2020, even with a change in course modality to on-line learning due to COVID-19, students were able to understand the same key take-aways from the course session as demonstrated by reflections using the discussion board regarding the need for a holistic approach to care, importance of the patient clinician relationship, and importance of taking a patient history. Despite promising implications of both iterations of the session, students completing the session online did not find the same success in “understanding my own bias/and or cultural awareness when working with patients.” This decrease may be attributed to change in course modality and the strengths of the role-play enactment of the patient encounter. It is important to recognize that additional learning components, including video recordings of the role-play enactment, may be necessary if the discussion board is used as the primary learning method in the future.
In contrast to previous studies that attempted to determine the effectiveness of cultural competence training methods, this session had many unique characteristics. The simulated role-playing exercise enabled student participants to see first-hand an interactive patient scenario that could be used as an example for when students begin working with patients or communicating with patients who are culturally diverse. Additionally, the nature of the cases created for the course session which were divided into a part A in which the patient physician was more straightforward when diagnosing and treating the patient and a part B with a more comprehensive and nurturing approach to care, allowed the students to compare the scenarios and make their own assumptions and comments on the effectiveness of each portion of the case. Another strength of this training, was the faculty with cultural competence training were uniquely involved in case creation and facilitation of the course session. According to previous studies with similar aims, it was noted that direct observation and feedback from a faculty member who had cultural competence training and direct contact with patients can provide students with a more memorable and useful experience when educating students [ 12 ]. The facilitators of this session were able to emphasize from their own personal experiences how to work with culturally diverse populations.
An important aspect of the 2020 iteration of the course session in which a discussion board format was used, was that it allowed students who may feel uncomfortable with sharing their thoughts on a case and their own biases, the opportunity to share in a space that may feel safer than in person [ 4 ]. Previous studies have mentioned challenges with online discussion boards [ 4 ] but here we had robust participation, albeit required. Students often contributed more than the required number of comments and they were often lengthy and engaging when responding to peers. Finally, in contrast to previous studies, this course session took place in a pre-professional master’s program, the M.S. in Oral Health Sciences Program at Boston University Chobanian & Avedisian School of Medicine. This program, in which students are given the opportunity to enhance their credentials for professional school, provided students with early exposure to cultural competence training. Students that completed this session in their early pre-professional curriculum should be better prepared than peers who did not receive any cultural competence training until they entered their designated professional school. This session is part of an Evidence Based Dentistry course, which incorporates a larger component of personal reflection that serves to engage students in critical thinking as they begin to develop the skills to be future clinicians. Students that understand different cultures, society and themselves through self-assessments will grow and be best suited in time to treat future patients [ 4 , 16 , 17 ].
One limitation of the present study was the number of survey participants that competed the post-session surveys, as survey completion was not required. Thus, the number of student participants declined over the years, reaching its lowest number of participants in 2020 when the discussion board course session was implemented, and students may have been over surveyed due to the pandemic. Another limitation to this study, was the lack of both a pre and post survey that could be used to determine how student’s understanding of cultural competence had evolved from their entry into the course to the conclusion of the course as well as individual bias and self-reporting measures.
In the future, the course should implement both a role-playing format and subsequent discussion board reflections within the same course session. Studies have shown that alternatives ways of drawing students to reflect whether role play, personal narratives, etc. can be extremely advantageous in developing personal reflection and awareness building competency [ 4 , 16 , 17 , 18 ]. It is noted that role-playing exercises that allow students to provide feedback with student colleagues can provide students with more insight into their own behaviors. It has also been shown in previous studies that student writing and reflection activities can also facilitate student’s reflections on their own beliefs and biases [ 4 , 11 ]. Reflective writing skills are an important and effective means for students to continue to gauge their cultural competence throughout the remainder of their academic training and as future clinicians [ 4 , 17 , 19 ]. Further, students may experience emotional responses through the process of reflective writing as they recognize personal bias or stereotypes, creating a profound and impactful response resulting in enhanced understanding of cultural differences and beliefs [ 4 ]. By combining both learning techniques, students would be able to understand their own bias and their classmates and create a dialogue that could be more beneficial than just one learning method alone. Furthermore, by implementing the discussion board into the role-playing session, as stated previously, students that are more cautious about sharing their point of view or about their own implicit bias in a traditional classroom setting would be able to express their opinions and facilitate a more comprehensive discussion more thoroughly.
Here we show an effective means to utilize role-play of a multi-scenario case-based patient encounter to teach pre-professional healthcare student’s components of cultural competence, emphasizing the importance of provider-patient interactions, holistic patient care, and patient history and socioeconomic factors in provider care. This study contributes to the larger body of work that seeks to address this important aspect of education as it relates to enhancing patient health care outcomes.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Albino JEN, Inglehart MR, Tedesco LA. Dental education and changing oral health care needs: disparities and demands. J Dent Educ. 2012;76(1):75–88.
Article Google Scholar
Constantinou CS, Papageorgiou A, Samoutis G, McCrorie P. Acquire, apply, and activate knowledge: a pyramid model for teaching and integrating cultural competence in medical curricula. Patient Educ Couns. 2018;101(6):1147–51.
DallaPiazza M, Padilla-Register M, Dwarakanath M, Obamedo E, Hill J, Soto-Greene ML. Exploring racism and health: an intensive interactive session for medical students. MedEdPORTAL. 2018;14:10783.
Forsyth CJ, Irving MJ, Tennant M, Short SD, Gilroy JA. Teaching Cultural competence in Dental Education: a systematic review and exploration of implications for indigenous populations in Australia. J Dent Educ. 2017;81(8):956–68.
Betancourt JR. Cultural competence and medical education: many names, many perspectives, one goal. Acad Med. 2006;81(6):499–501.
Jernigan VBB, Hearod JB, Tran K, Norris KC, Buchwald D. An examination of cultural competence training in US medical education guided by the tool for assessing cultural competence training. J Health Disparities Res Pract. 2016;9(3):150–67.
Google Scholar
Behar-Horenstein LS, Warren RC, Dodd VJ, Catalanotto FA. Addressing oral Health disparities Via Educational Foci on Cultural competence. Am J Public Health. 2017;107(S1):S18–23.
Lie D, Boker J, Cleveland E. Using the tool for assessing cultural competence training (TACCT) to measure faculty and medical student perceptions of cultural competence instruction in the first three years of the curriculum. Acad Med. 2006;81(6):557–64.
Holyfield LJ, Miller BH. A tool for assessing cultural competence training in dental education. J Dent Educ. 2013;77(8):990–7.
Vasquez Guzman CE, Sussman AL, Kano M, Getrich CM, Williams RL. A comparative case study analysis of cultural competence training at 15 U.S. medical schools. Acad Med. 2021;96(6):894–9.
Jernigan VB, Hearod JB, Tran K, Norris KC, Buchwald D. An examination of cultural competence training in US medical education guided by the tool for assessing cultural competence training. J Health Dispar Res Pract. 2016;9(3):150–67.
Kripalani S, Bussey-Jones J, Katz MG, Genao I. A prescription for cultural competence in medical education. J Gen Intern Med. 2006;21(10):1116–20.
Mariño R, Satur J, Tuncer E, Tran M, Milford E, Tran VMTH, Tran PQ, Tsai RP. Cultural competence of Australian dental students. BMC Med Educ. 2021;21(1):155.
Beagan BL. Teaching social and cultural awareness to medical students: it’s all very nice to talk about it in theory, but ultimately it makes no difference. Acad Med. 2003;78(6):605–14.
Ferrebee S, Boston University School of Medicine Master’s Thesis. (2021). Effectively Teaching Cultural Competence in Healthcare Education. Available at Boston University Libraries: Open BU: https://open.bu.edu/handle/2144/43838 .
Crosson JC, Deng W, Brazeau C, Boyd L, Soto-Greene M. Evaluating the effect of cultural competency training on medical student attitudes. Fam Med. 2004;36(3):199–203.
Cathryn F, Michelle I, Short S, Tennant M, Gilroy J. Strengthening indigenous cultural competence in dentistry and oral health education: academic perspectives. Eur J Dent Educ. 2019;23(1). https://doi.org/10.1111/eje.12398
DasGupta S, Meyer D, Calero-Breckheimer A, Costley AW, Guillen S. Teaching cultural competency through narrative medicine: intersections of classroom and community. Teach Learn Med. 2006;18(1):14–7.
Woldt JL, Nenad MW. Reflective writing in dental education to improve critical thinking and learning: A systematic review. J Dent Educ. 2021;85(6):778–785. https://doi.org/10.1002/jdd.12561 . Epub 2021 Feb 11. PMID: 33576055.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge Boston University’s Chobanian & Avedisian School of Medicine’s Graduate Medical Science students and study participants.
No funding was used for the completion of this study.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Graduate Medical Sciences, Boston University Chobanian & Avedisian School of Medicine, 72 East Concord Street, L317, R-1017, Boston, MA, 02118, USA
Karen R. Bottenfield, Andrew N. Best & Theresa A. Davies
Department of Medical Sciences & Education, Boston University Chobanian & Avedisian School of Medicine, 72 East Concord Street, Boston, MA, 02118, USA
Maura A. Kelley, David Flynn & Theresa A. Davies
University of Maryland School of Dentistry, 650 W Baltimore Street, Baltimore, MD, 21201, USA
Shelby Ferebee
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
TAD designed the original study concept, taught the classes (roleplay), conducted the surveys, and collected data; MAK designed the original case and PowerPoint, and performed roleplay; DBF and SF evaluated data and drafted original figures; ANB assisted in drafting the manuscript; KRB finalized figures and the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Theresa A. Davies .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
This study was determined to be EXEMPT by the Institutional Review Board of Boston University Medical Campus, Protocol # H-37232.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Informed consent
Informed consent was received from all subjects.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1
Supplementary material 2, supplementary material 3, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Bottenfield, K.R., Kelley, M.A., Ferebee, S. et al. Effectively teaching cultural competence in a pre-professional healthcare curriculum. BMC Med Educ 24 , 553 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05507-x
Download citation
Received : 27 October 2023
Accepted : 02 May 2024
Published : 21 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-024-05507-x
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Communication
BMC Medical Education
ISSN: 1472-6920
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]

- Liberty University
- Jerry Falwell Library
- Special Collections
- < Previous Event
- Next Event >
Home > Conferences and Events > Research Week > 2024 > Oral Presentations > 33

Oral Presentations
Diabetic Management with GLP1-RA Ozempic and Diabetic Education
Presenter Information
Katrina Sivo-Souza , Liberty University Follow
Oral (LUO Remote) - Applied
Description
Diabetes mellitus remains the seventh leading cause of death within the country. This diagnosis can and often does lead to severe complications, creating implications for not only the patient but also families, caregivers, and the community. Most diabetic patients possess a diagnosis of type 2 diabetes mellitus. The healthcare industry continues to implement improvement with diabetic management and complications resulting from diabetes. Research suggests that the standard of care for patients with diabetes begins with lifestyle modification to improve glycemic control. New medications, such as Ozempic (semaglutide), have also been influential in diabetic management. Therefore, this scholarly project intended to study the two methods of medication management with GLP1-RA Ozempic and diabetic education with the hopes of improved glycemic control, improved weight, and improved comprehension of lifestyle management of the diagnosis. Patients with T2DM were tracked for a period of 12 weeks, assessing pre- and post intervention data. The data collected included A1C, weight in pounds, body mass index (BMI), and self care knowledge via a validated questionnaire. Participants were on the medication Ozempic (semaglutide) and received 12 weeks of education. Each participant received education via weekly emails. This scholarly project provided statistically significant evidence that med and the education are useful tools to manage T2DM. The significant results 0.0310 for weight, 0.05 for HbA1C and 0.0001 for Self Care Inventory-Revised. These results support the pairing of GLP1_RA Ozempic with diabetic education is useful for managing T2DM.
Since May 20, 2024
To view the content in your browser, please download Adobe Reader or, alternately, you may Download the file to your hard drive.
NOTE: The latest versions of Adobe Reader do not support viewing PDF files within Firefox on Mac OS and if you are using a modern (Intel) Mac, there is no official plugin for viewing PDF files within the browser window.
- Collections
- Faculty Expert Gallery
- Theses and Dissertations
- Conferences and Events
- Open Educational Resources (OER)
- Explore Disciplines
Advanced Search
- Notify me via email or RSS .
Faculty Authors
- Submit Event
- Expert Gallery Login
Student Authors
- Undergraduate Submissions
- Graduate Submissions
- Honors Submissions
Home | About | FAQ | My Account | Accessibility Statement
Privacy Copyright
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Am J Pharm Educ
- v.74(8); 2010 Oct 11
Presenting and Evaluating Qualitative Research
The purpose of this paper is to help authors to think about ways to present qualitative research papers in the American Journal of Pharmaceutical Education . It also discusses methods for reviewers to assess the rigour, quality, and usefulness of qualitative research. Examples of different ways to present data from interviews, observations, and focus groups are included. The paper concludes with guidance for publishing qualitative research and a checklist for authors and reviewers.
INTRODUCTION
Policy and practice decisions, including those in education, increasingly are informed by findings from qualitative as well as quantitative research. Qualitative research is useful to policymakers because it often describes the settings in which policies will be implemented. Qualitative research is also useful to both pharmacy practitioners and pharmacy academics who are involved in researching educational issues in both universities and practice and in developing teaching and learning.
Qualitative research involves the collection, analysis, and interpretation of data that are not easily reduced to numbers. These data relate to the social world and the concepts and behaviors of people within it. Qualitative research can be found in all social sciences and in the applied fields that derive from them, for example, research in health services, nursing, and pharmacy. 1 It looks at X in terms of how X varies in different circumstances rather than how big is X or how many Xs are there? 2 Textbooks often subdivide research into qualitative and quantitative approaches, furthering the common assumption that there are fundamental differences between the 2 approaches. With pharmacy educators who have been trained in the natural and clinical sciences, there is often a tendency to embrace quantitative research, perhaps due to familiarity. A growing consensus is emerging that sees both qualitative and quantitative approaches as useful to answering research questions and understanding the world. Increasingly mixed methods research is being carried out where the researcher explicitly combines the quantitative and qualitative aspects of the study. 3 , 4
Like healthcare, education involves complex human interactions that can rarely be studied or explained in simple terms. Complex educational situations demand complex understanding; thus, the scope of educational research can be extended by the use of qualitative methods. Qualitative research can sometimes provide a better understanding of the nature of educational problems and thus add to insights into teaching and learning in a number of contexts. For example, at the University of Nottingham, we conducted in-depth interviews with pharmacists to determine their perceptions of continuing professional development and who had influenced their learning. We also have used a case study approach using observation of practice and in-depth interviews to explore physiotherapists' views of influences on their leaning in practice. We have conducted in-depth interviews with a variety of stakeholders in Malawi, Africa, to explore the issues surrounding pharmacy academic capacity building. A colleague has interviewed and conducted focus groups with students to explore cultural issues as part of a joint Nottingham-Malaysia pharmacy degree program. Another colleague has interviewed pharmacists and patients regarding their expectations before and after clinic appointments and then observed pharmacist-patient communication in clinics and assessed it using the Calgary Cambridge model in order to develop recommendations for communication skills training. 5 We have also performed documentary analysis on curriculum data to compare pharmacist and nurse supplementary prescribing courses in the United Kingdom.
It is important to choose the most appropriate methods for what is being investigated. Qualitative research is not appropriate to answer every research question and researchers need to think carefully about their objectives. Do they wish to study a particular phenomenon in depth (eg, students' perceptions of studying in a different culture)? Or are they more interested in making standardized comparisons and accounting for variance (eg, examining differences in examination grades after changing the way the content of a module is taught). Clearly a quantitative approach would be more appropriate in the last example. As with any research project, a clear research objective has to be identified to know which methods should be applied.
Types of qualitative data include:
- Audio recordings and transcripts from in-depth or semi-structured interviews
- Structured interview questionnaires containing substantial open comments including a substantial number of responses to open comment items.
- Audio recordings and transcripts from focus group sessions.
- Field notes (notes taken by the researcher while in the field [setting] being studied)
- Video recordings (eg, lecture delivery, class assignments, laboratory performance)
- Case study notes
- Documents (reports, meeting minutes, e-mails)
- Diaries, video diaries
- Observation notes
- Press clippings
- Photographs
RIGOUR IN QUALITATIVE RESEARCH
Qualitative research is often criticized as biased, small scale, anecdotal, and/or lacking rigor; however, when it is carried out properly it is unbiased, in depth, valid, reliable, credible and rigorous. In qualitative research, there needs to be a way of assessing the “extent to which claims are supported by convincing evidence.” 1 Although the terms reliability and validity traditionally have been associated with quantitative research, increasingly they are being seen as important concepts in qualitative research as well. Examining the data for reliability and validity assesses both the objectivity and credibility of the research. Validity relates to the honesty and genuineness of the research data, while reliability relates to the reproducibility and stability of the data.
The validity of research findings refers to the extent to which the findings are an accurate representation of the phenomena they are intended to represent. The reliability of a study refers to the reproducibility of the findings. Validity can be substantiated by a number of techniques including triangulation use of contradictory evidence, respondent validation, and constant comparison. Triangulation is using 2 or more methods to study the same phenomenon. Contradictory evidence, often known as deviant cases, must be sought out, examined, and accounted for in the analysis to ensure that researcher bias does not interfere with or alter their perception of the data and any insights offered. Respondent validation, which is allowing participants to read through the data and analyses and provide feedback on the researchers' interpretations of their responses, provides researchers with a method of checking for inconsistencies, challenges the researchers' assumptions, and provides them with an opportunity to re-analyze their data. The use of constant comparison means that one piece of data (for example, an interview) is compared with previous data and not considered on its own, enabling researchers to treat the data as a whole rather than fragmenting it. Constant comparison also enables the researcher to identify emerging/unanticipated themes within the research project.
STRENGTHS AND LIMITATIONS OF QUALITATIVE RESEARCH
Qualitative researchers have been criticized for overusing interviews and focus groups at the expense of other methods such as ethnography, observation, documentary analysis, case studies, and conversational analysis. Qualitative research has numerous strengths when properly conducted.
Strengths of Qualitative Research
- Issues can be examined in detail and in depth.
- Interviews are not restricted to specific questions and can be guided/redirected by the researcher in real time.
- The research framework and direction can be quickly revised as new information emerges.
- The data based on human experience that is obtained is powerful and sometimes more compelling than quantitative data.
- Subtleties and complexities about the research subjects and/or topic are discovered that are often missed by more positivistic enquiries.
- Data usually are collected from a few cases or individuals so findings cannot be generalized to a larger population. Findings can however be transferable to another setting.
Limitations of Qualitative Research
- Research quality is heavily dependent on the individual skills of the researcher and more easily influenced by the researcher's personal biases and idiosyncrasies.
- Rigor is more difficult to maintain, assess, and demonstrate.
- The volume of data makes analysis and interpretation time consuming.
- It is sometimes not as well understood and accepted as quantitative research within the scientific community
- The researcher's presence during data gathering, which is often unavoidable in qualitative research, can affect the subjects' responses.
- Issues of anonymity and confidentiality can present problems when presenting findings
- Findings can be more difficult and time consuming to characterize in a visual way.
PRESENTATION OF QUALITATIVE RESEARCH FINDINGS
The following extracts are examples of how qualitative data might be presented:
Data From an Interview.
The following is an example of how to present and discuss a quote from an interview.
The researcher should select quotes that are poignant and/or most representative of the research findings. Including large portions of an interview in a research paper is not necessary and often tedious for the reader. The setting and speakers should be established in the text at the end of the quote.
The student describes how he had used deep learning in a dispensing module. He was able to draw on learning from a previous module, “I found that while using the e learning programme I was able to apply the knowledge and skills that I had gained in last year's diseases and goals of treatment module.” (interviewee 22, male)
This is an excerpt from an article on curriculum reform that used interviews 5 :
The first question was, “Without the accreditation mandate, how much of this curriculum reform would have been attempted?” According to respondents, accreditation played a significant role in prompting the broad-based curricular change, and their comments revealed a nuanced view. Most indicated that the change would likely have occurred even without the mandate from the accreditation process: “It reflects where the profession wants to be … training a professional who wants to take on more responsibility.” However, they also commented that “if it were not mandated, it could have been a very difficult road.” Or it “would have happened, but much later.” The change would more likely have been incremental, “evolutionary,” or far more limited in its scope. “Accreditation tipped the balance” was the way one person phrased it. “Nobody got serious until the accrediting body said it would no longer accredit programs that did not change.”
Data From Observations
The following example is some data taken from observation of pharmacist patient consultations using the Calgary Cambridge guide. 6 , 7 The data are first presented and a discussion follows:
Pharmacist: We will soon be starting a stop smoking clinic. Patient: Is the interview over now? Pharmacist: No this is part of it. (Laughs) You can't tell me to bog off (sic) yet. (pause) We will be starting a stop smoking service here, Patient: Yes. Pharmacist: with one-to-one and we will be able to help you or try to help you. If you want it. In this example, the pharmacist has picked up from the patient's reaction to the stop smoking clinic that she is not receptive to advice about giving up smoking at this time; in fact she would rather end the consultation. The pharmacist draws on his prior relationship with the patient and makes use of a joke to lighten the tone. He feels his message is important enough to persevere but he presents the information in a succinct and non-pressurised way. His final comment of “If you want it” is important as this makes it clear that he is not putting any pressure on the patient to take up this offer. This extract shows that some patient cues were picked up, and appropriately dealt with, but this was not the case in all examples.
Data From Focus Groups
This excerpt from a study involving 11 focus groups illustrates how findings are presented using representative quotes from focus group participants. 8
Those pharmacists who were initially familiar with CPD endorsed the model for their peers, and suggested it had made a meaningful difference in the way they viewed their own practice. In virtually all focus groups sessions, pharmacists familiar with and supportive of the CPD paradigm had worked in collaborative practice environments such as hospital pharmacy practice. For these pharmacists, the major advantage of CPD was the linking of workplace learning with continuous education. One pharmacist stated, “It's amazing how much I have to learn every day, when I work as a pharmacist. With [the learning portfolio] it helps to show how much learning we all do, every day. It's kind of satisfying to look it over and see how much you accomplish.” Within many of the learning portfolio-sharing sessions, debates emerged regarding the true value of traditional continuing education and its outcome in changing an individual's practice. While participants appreciated the opportunity for social and professional networking inherent in some forms of traditional CE, most eventually conceded that the academic value of most CE programming was limited by the lack of a systematic process for following-up and implementing new learning in the workplace. “Well it's nice to go to these [continuing education] events, but really, I don't know how useful they are. You go, you sit, you listen, but then, well I at least forget.”
The following is an extract from a focus group (conducted by the author) with first-year pharmacy students about community placements. It illustrates how focus groups provide a chance for participants to discuss issues on which they might disagree.
Interviewer: So you are saying that you would prefer health related placements? Student 1: Not exactly so long as I could be developing my communication skill. Student 2: Yes but I still think the more health related the placement is the more I'll gain from it. Student 3: I disagree because other people related skills are useful and you may learn those from taking part in a community project like building a garden. Interviewer: So would you prefer a mixture of health and non health related community placements?
GUIDANCE FOR PUBLISHING QUALITATIVE RESEARCH
Qualitative research is becoming increasingly accepted and published in pharmacy and medical journals. Some journals and publishers have guidelines for presenting qualitative research, for example, the British Medical Journal 9 and Biomedcentral . 10 Medical Education published a useful series of articles on qualitative research. 11 Some of the important issues that should be considered by authors, reviewers and editors when publishing qualitative research are discussed below.
Introduction.
A good introduction provides a brief overview of the manuscript, including the research question and a statement justifying the research question and the reasons for using qualitative research methods. This section also should provide background information, including relevant literature from pharmacy, medicine, and other health professions, as well as literature from the field of education that addresses similar issues. Any specific educational or research terminology used in the manuscript should be defined in the introduction.
The methods section should clearly state and justify why the particular method, for example, face to face semistructured interviews, was chosen. The method should be outlined and illustrated with examples such as the interview questions, focusing exercises, observation criteria, etc. The criteria for selecting the study participants should then be explained and justified. The way in which the participants were recruited and by whom also must be stated. A brief explanation/description should be included of those who were invited to participate but chose not to. It is important to consider “fair dealing,” ie, whether the research design explicitly incorporates a wide range of different perspectives so that the viewpoint of 1 group is never presented as if it represents the sole truth about any situation. The process by which ethical and or research/institutional governance approval was obtained should be described and cited.
The study sample and the research setting should be described. Sampling differs between qualitative and quantitative studies. In quantitative survey studies, it is important to select probability samples so that statistics can be used to provide generalizations to the population from which the sample was drawn. Qualitative research necessitates having a small sample because of the detailed and intensive work required for the study. So sample sizes are not calculated using mathematical rules and probability statistics are not applied. Instead qualitative researchers should describe their sample in terms of characteristics and relevance to the wider population. Purposive sampling is common in qualitative research. Particular individuals are chosen with characteristics relevant to the study who are thought will be most informative. Purposive sampling also may be used to produce maximum variation within a sample. Participants being chosen based for example, on year of study, gender, place of work, etc. Representative samples also may be used, for example, 20 students from each of 6 schools of pharmacy. Convenience samples involve the researcher choosing those who are either most accessible or most willing to take part. This may be fine for exploratory studies; however, this form of sampling may be biased and unrepresentative of the population in question. Theoretical sampling uses insights gained from previous research to inform sample selection for a new study. The method for gaining informed consent from the participants should be described, as well as how anonymity and confidentiality of subjects were guaranteed. The method of recording, eg, audio or video recording, should be noted, along with procedures used for transcribing the data.
Data Analysis.
A description of how the data were analyzed also should be included. Was computer-aided qualitative data analysis software such as NVivo (QSR International, Cambridge, MA) used? Arrival at “data saturation” or the end of data collection should then be described and justified. A good rule when considering how much information to include is that readers should have been given enough information to be able to carry out similar research themselves.
One of the strengths of qualitative research is the recognition that data must always be understood in relation to the context of their production. 1 The analytical approach taken should be described in detail and theoretically justified in light of the research question. If the analysis was repeated by more than 1 researcher to ensure reliability or trustworthiness, this should be stated and methods of resolving any disagreements clearly described. Some researchers ask participants to check the data. If this was done, it should be fully discussed in the paper.
An adequate account of how the findings were produced should be included A description of how the themes and concepts were derived from the data also should be included. Was an inductive or deductive process used? The analysis should not be limited to just those issues that the researcher thinks are important, anticipated themes, but also consider issues that participants raised, ie, emergent themes. Qualitative researchers must be open regarding the data analysis and provide evidence of their thinking, for example, were alternative explanations for the data considered and dismissed, and if so, why were they dismissed? It also is important to present outlying or negative/deviant cases that did not fit with the central interpretation.
The interpretation should usually be grounded in interviewees or respondents' contributions and may be semi-quantified, if this is possible or appropriate, for example, “Half of the respondents said …” “The majority said …” “Three said…” Readers should be presented with data that enable them to “see what the researcher is talking about.” 1 Sufficient data should be presented to allow the reader to clearly see the relationship between the data and the interpretation of the data. Qualitative data conventionally are presented by using illustrative quotes. Quotes are “raw data” and should be compiled and analyzed, not just listed. There should be an explanation of how the quotes were chosen and how they are labeled. For example, have pseudonyms been given to each respondent or are the respondents identified using codes, and if so, how? It is important for the reader to be able to see that a range of participants have contributed to the data and that not all the quotes are drawn from 1 or 2 individuals. There is a tendency for authors to overuse quotes and for papers to be dominated by a series of long quotes with little analysis or discussion. This should be avoided.
Participants do not always state the truth and may say what they think the interviewer wishes to hear. A good qualitative researcher should not only examine what people say but also consider how they structured their responses and how they talked about the subject being discussed, for example, the person's emotions, tone, nonverbal communication, etc. If the research was triangulated with other qualitative or quantitative data, this should be discussed.
Discussion.
The findings should be presented in the context of any similar previous research and or theories. A discussion of the existing literature and how this present research contributes to the area should be included. A consideration must also be made about how transferrable the research would be to other settings. Any particular strengths and limitations of the research also should be discussed. It is common practice to include some discussion within the results section of qualitative research and follow with a concluding discussion.
The author also should reflect on their own influence on the data, including a consideration of how the researcher(s) may have introduced bias to the results. The researcher should critically examine their own influence on the design and development of the research, as well as on data collection and interpretation of the data, eg, were they an experienced teacher who researched teaching methods? If so, they should discuss how this might have influenced their interpretation of the results.
Conclusion.
The conclusion should summarize the main findings from the study and emphasize what the study adds to knowledge in the area being studied. Mays and Pope suggest the researcher ask the following 3 questions to determine whether the conclusions of a qualitative study are valid 12 : How well does this analysis explain why people behave in the way they do? How comprehensible would this explanation be to a thoughtful participant in the setting? How well does the explanation cohere with what we already know?
CHECKLIST FOR QUALITATIVE PAPERS
This paper establishes criteria for judging the quality of qualitative research. It provides guidance for authors and reviewers to prepare and review qualitative research papers for the American Journal of Pharmaceutical Education . A checklist is provided in Appendix 1 to assist both authors and reviewers of qualitative data.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Thank you to the 3 reviewers whose ideas helped me to shape this paper.
Appendix 1. Checklist for authors and reviewers of qualitative research.
Introduction
- □ Research question is clearly stated.
- □ Research question is justified and related to the existing knowledge base (empirical research, theory, policy).
- □ Any specific research or educational terminology used later in manuscript is defined.
- □ The process by which ethical and or research/institutional governance approval was obtained is described and cited.
- □ Reason for choosing particular research method is stated.
- □ Criteria for selecting study participants are explained and justified.
- □ Recruitment methods are explicitly stated.
- □ Details of who chose not to participate and why are given.
- □ Study sample and research setting used are described.
- □ Method for gaining informed consent from the participants is described.
- □ Maintenance/Preservation of subject anonymity and confidentiality is described.
- □ Method of recording data (eg, audio or video recording) and procedures for transcribing data are described.
- □ Methods are outlined and examples given (eg, interview guide).
- □ Decision to stop data collection is described and justified.
- □ Data analysis and verification are described, including by whom they were performed.
- □ Methods for identifying/extrapolating themes and concepts from the data are discussed.
- □ Sufficient data are presented to allow a reader to assess whether or not the interpretation is supported by the data.
- □ Outlying or negative/deviant cases that do not fit with the central interpretation are presented.
- □ Transferability of research findings to other settings is discussed.
- □ Findings are presented in the context of any similar previous research and social theories.
- □ Discussion often is incorporated into the results in qualitative papers.
- □ A discussion of the existing literature and how this present research contributes to the area is included.
- □ Any particular strengths and limitations of the research are discussed.
- □ Reflection of the influence of the researcher(s) on the data, including a consideration of how the researcher(s) may have introduced bias to the results is included.
Conclusions
- □ The conclusion states the main finings of the study and emphasizes what the study adds to knowledge in the subject area.

The Health for Life in Singapore (HELIOS) Study: delivering Precision Medicine research for Asian populations
- Find this author on Google Scholar
- Find this author on PubMed
- Search for this author on this site
- ORCID record for Theresia Mina
- ORCID record for Nilanjana Sadhu
- ORCID record for Dorrain Low
- ORCID record for Max Lam
- For correspondence: [email protected]
- Info/History
- Preview PDF
Asian people are under-represented in population-based, clinical, and genomic research. To address this gap, we have initiated the HELIOS longitudinal cohort study, comprising comprehensive behavioural, phenotypic, and genomic measurements from 10,004 Asian men and women of Chinese, Indian or Malay background. Phenotyping has been carried out using validated approaches, that are internationally interoperable. Health record linkage enriches both baseline phenotyping and evaluation of prospective outcomes. The integrated multi-omics data include whole-genome and RNA sequencing, quantification of DNA methylation, and metabolomic profiling. Our data reveal extensive lifestyle, physiological, genomic, and molecular diversity between the distinct Asian ethnic groups, and the biological interconnectivity between functional layers. This includes characterisation of divergent patterns of genome regulation between Asian individuals, that correlate with differences in educational attainment, dietary quality, and adiposity, and which overlap transcription factors and DNA methylation sites linked to the development of diabetes and other chronic diseases. Our unique HELIOS Asian Precision Medicine cohort study represents a state-of-the art platform to enable biomedical researchers to understand the aetiology and pathogenesis of diverse disease outcomes in Asia, and to generate insights that have the potential to improve health outcomes for Asian populations globally.
Competing Interest Statement
B.L.C.C. receives honorarium for obesity-related presentations and/or participates in the advisory board of Novo Nordisk, Abbott Nutrition and DKSH, and all honorariums were paid to Khoo Teck Puat Hospital, Singapore. J.N. receives research funding from Astra Zeneca. J.L. participates in the advisory board of Boehringer Ingelheim and is a council member of National Council Against Drug Abuse, Singapore. G.A.M, K.E.W, and P.A.S are employees of Metabolon. L.P.Y., and Y.Z.X. are employees of Ministry of Health, Singapore. The other authors declare no competing financial interests.
Funding Statement
This study is supported by Singapore Ministry of Health (MOH) National Medical Research Council (NMRC) under its OF-LCG funding scheme (MOH-000271-00), Singapore Translational Research (StaR) funding scheme (NMRC/StaR/0028/2017), the National Research Foundation, Singapore through the Singapore MOH NMRC and the Precision Health Research, Singapore (PRECISE) under the National Precision Medicine programme (NMRC/PRECISE/2020) and intramural funding from Nanyang Technological University, Lee Kong Chian School of Medicine and the National Healthcare Group. RNA sequencing was partially funded by i) Ministry of Education Academic Research Fund Tier 1 Grant (RS09/20), ii) A*STAR-NHMRC Joint Grant Call (A20PRb0138), iii) Start-Up Grant (awarded to M.Loh [PI]) from Lee Kong Chian School of Medicine, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore and iv) Imperial - Nanyang Technological University Collaboration Fund (awarded to M.Loh [PI]). T.M. was funded by Deans Postdoctoral Fellowship from the Lee Kong Chian School of Medicine. This study made use of data generated by Ministry of Health (MOH) and Immigration and Checkpoints Authority (ICA). This study was supported by the Trusted Research and Real-World-Data Utilisation and Sharing Tech platform (TRUST Platform) developed by the Ministry of Health and Smart Nation and Digital Government Office, through the use of its research data analytics facilities. The views expressed are those of the author(s) are not necessarily those of the Government, MOH and ICA investigators or institutional partners. The computational work for this study was partially performed on resources of the National Supercomputing Centre, Singapore (https://www.nscc.sg).
Author Declarations
I confirm all relevant ethical guidelines have been followed, and any necessary IRB and/or ethics committee approvals have been obtained.
The details of the IRB/oversight body that provided approval or exemption for the research described are given below:
Nanyang Technological University Institutional Review Board IRB-2016-11-030
I confirm that all necessary patient/participant consent has been obtained and the appropriate institutional forms have been archived, and that any patient/participant/sample identifiers included were not known to anyone (e.g., hospital staff, patients or participants themselves) outside the research group so cannot be used to identify individuals.
I understand that all clinical trials and any other prospective interventional studies must be registered with an ICMJE-approved registry, such as ClinicalTrials.gov. I confirm that any such study reported in the manuscript has been registered and the trial registration ID is provided (note: if posting a prospective study registered retrospectively, please provide a statement in the trial ID field explaining why the study was not registered in advance).
I have followed all appropriate research reporting guidelines, such as any relevant EQUATOR Network research reporting checklist(s) and other pertinent material, if applicable.
In the previous version, the bibliography was incorrect (only 30 references). In this revised version, we have refreshed the bibligpraphy comprising 62 references.
Data Availability
The HELIOS phenotype and genotype data used in this manuscript are protected and are not publicly available due to data privacy regulations. Data access request can be submitted to the HELIOS Data Access Committee by emailing [email protected] for details. For accessing de-identified National Health and Administrative records linked through TRUST, please contact TRUST platform (https://trustplatform.sg) for details.
View the discussion thread.
Thank you for your interest in spreading the word about medRxiv.
NOTE: Your email address is requested solely to identify you as the sender of this article.

Citation Manager Formats
- EndNote (tagged)
- EndNote 8 (xml)
- RefWorks Tagged
- Ref Manager
- Tweet Widget
- Facebook Like
- Google Plus One
- Addiction Medicine (324)
- Allergy and Immunology (632)
- Anesthesia (168)
- Cardiovascular Medicine (2400)
- Dentistry and Oral Medicine (289)
- Dermatology (207)
- Emergency Medicine (381)
- Endocrinology (including Diabetes Mellitus and Metabolic Disease) (850)
- Epidemiology (11797)
- Forensic Medicine (10)
- Gastroenterology (705)
- Genetic and Genomic Medicine (3769)
- Geriatric Medicine (350)
- Health Economics (637)
- Health Informatics (2408)
- Health Policy (940)
- Health Systems and Quality Improvement (905)
- Hematology (342)
- HIV/AIDS (787)
- Infectious Diseases (except HIV/AIDS) (13347)
- Intensive Care and Critical Care Medicine (769)
- Medical Education (369)
- Medical Ethics (105)
- Nephrology (401)
- Neurology (3524)
- Nursing (199)
- Nutrition (529)
- Obstetrics and Gynecology (681)
- Occupational and Environmental Health (667)
- Oncology (1835)
- Ophthalmology (539)
- Orthopedics (221)
- Otolaryngology (287)
- Pain Medicine (234)
- Palliative Medicine (66)
- Pathology (447)
- Pediatrics (1037)
- Pharmacology and Therapeutics (426)
- Primary Care Research (424)
- Psychiatry and Clinical Psychology (3190)
- Public and Global Health (6184)
- Radiology and Imaging (1291)
- Rehabilitation Medicine and Physical Therapy (751)
- Respiratory Medicine (832)
- Rheumatology (380)
- Sexual and Reproductive Health (373)
- Sports Medicine (324)
- Surgery (405)
- Toxicology (50)
- Transplantation (172)
- Urology (147)

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Understanding Data Presentations (Guide + Examples) Design • March 20th, 2024. In this age of overwhelming information, the skill to effectively convey data has become extremely valuable. Initiating a discussion on data presentation types involves thoughtful consideration of the nature of your data and the message you aim to convey.
TheJoelTruth. While a good presentation has data, data alone doesn't guarantee a good presentation. It's all about how that data is presented. The quickest way to confuse your audience is by ...
Start with response rate and description of research participants (these information give the readers an idea of the representativeness of the research data), then the key findings and relevant statistical analyses. Data should answer the research questions identified earlier. Leave the process of data collection to the methods section.
Turning a research paper into a visual presentation is difficult; there are pitfalls, and navigating the path to a brief, informative presentation takes time and practice. As a TA for GEO/WRI 201: Methods in Data Analysis & Scientific Writing this past fall, I saw how this process works from an instructor's standpoint.
Introduction. Data description is a vital part of any research project and should not be ignored in the rush to start testing hypotheses. There are many reasons for this important process, such as gaining familiarity with the data, looking for unusually high or low values (outliers) and checking the assumptions required for statistical testing.
1. Choose the right format. 2. Follow the design principles. 3. Adapt to your audience. 4. Here's what else to consider. Data presentation is a crucial aspect of any research report, as it ...
Storytelling with data is a highly valued skill in the workforce today and translating data and insights for a non-technical audience is rare to see than it is expected. Here's my five-step routine to make and deliver your data presentation right where it is intended —. 1. Understand Your Data & Make It Seen.
In this article, the techniques of data and information presentation in textual, tabular, and graphical forms are introduced. Text is the principal method for explaining findings, outlining trends, and providing contextual information. A table is best suited for representing individual information and represents both quantitative and ...
The use of graphs in research presentation and the communication of results makes it possible to synthesise large amounts of data and enables users to comprehend the information more easily than if it were presented in mere words or numbers (Cukier 2010).Tufte refers to well-designed graphics as instruments for reasoning about quantitative information and considers them the most powerful way ...
Presentation length. This is my formula to determine how many slides to include in my main presentation assuming I spend about five minutes per slide. (Presentation length in minutes-10 minutes for questions ) / 5 minutes per slide. For an hour presentation that comes out to ( 60-10 ) / 5 = 10 slides.
Abstract. This chapter covers the topics of data collection, data presentation and data analysis. It gives attention to data collection for studies based on experiments, on data derived from existing published or unpublished data sets, on observation, on simulation and digital twins, on surveys, on interviews and on focus group discussions.
Qualitative data presentation differs fundamentally from that found in quantitative research. While quantitative data tend to be numerical and easily lend themselves to statistical analysis and graphical representation, qualitative data are often textual and unstructured, requiring an interpretive approach to bring out their inherent meanings.
Overview. Data analysis is an ongoing process that should occur throughout your research project. Suitable data-analysis methods must be selected when you write your research proposal. The nature of your data (i.e. quantitative or qualitative) will be influenced by your research design and purpose. The data will also influence the analysis ...
Data presentation is a process of comparing two or more data sets with visual aids, such as graphs. Using a graph, you can represent how the information relates to other data. ... Identifying the main ideas of your data and research helps organise your presentation and communicate clearly with your audience about the significance of the ...
Data Analysis and Data Presentation have a practical implementation in every possible field. It can range from academic studies, commercial, industrial and marketing activities to professional practices. In its raw form, data can be extremely complicated to decipher and in order to extract meaningful insights from the data, data analysis is an important step towards breaking down data into ...
DATA PRESENTATION, ANALYSIS AND INTERPRETATION. 4.0 Introduction. This chapter is concerned with data pres entation, of the findings obtained through the study. The. findings are presented in ...
Here we collected some of the best examples of data presentation made by one of the biggest names in the graphical data visualization software and information research. These brands put a lot of money and efforts to investigate how professional graphs and charts should look. 1. Sales Stage History Funnel Chart.
All this gathered information represents the data of the research. For example, ... The forms of data presentation that have been described up to this point illustrated the distribution of a given variable, whether categorical or numerical. In addition, it is possible to present the relationship between two variables of interest, either ...
The data presentation is one of the segments of the methodology in every research depending on the approach. The methodology, therefore, refers to the design and the theory that underpins the ...
8. Tabular presentation. Presenting data in rows and columns, often used for precise data values and comparisons. Tabular data presentation is all about clarity and precision. Think of it as presenting numerical data in a structured grid, with rows and columns clearly displaying individual data points.
Histogram, Smoothed frequency graph, Pie diagram or Pie chart, Cumulative or ogive frequency graph, and Frequency Polygon. Tags: Types of Presentation. How to present the data in a way that even the clueless person in the room can understand? Check out our 10 methods of data presentation for a better idea.
CIBMTR facilitates critical observational and interventional research through scientific and statistical expertise, a large network of centers, and a unique database of long-term clinical data for more than 675,000 people who have received hematopoietic cell transplantation and other cellular therapies. Learn more at cibmtr.org. About NMDP℠
There has been research documenting the rising numbers of racial and ethnic minority groups in the United States. With this rise, there is increasing concern over the health disparities that often affect these populations. Attention has turned to how clinicians can improve health outcomes and how the need exists to educate healthcare professionals on the practice of cultural competence.
Diabetes mellitus remains the seventh leading cause of death within the country. This diagnosis can and often does lead to severe complications, creating implications for not only the patient but also families, caregivers, and the community. Most diabetic patients possess a diagnosis of type 2 diabetes mellitus. The healthcare industry continues to implement improvement with diabetic ...
Oral Presentation #904. IBD Controlled Trials I. May 20, 2024. 4:00-5:30 PM . Economic Impact of Risankizumab Induction Therapy on UC-Related Hospitalizations and Work Productivity: An Analysis of Data from the Phase 3 Induction Study. Poster #Tu1102. Health Economics (Cost of Illness, Cost-Effectiveness, and Health Economic Models) May 21 ...
The purpose of this paper is to help authors to think about ways to present qualitative research papers in the American Journal of Pharmaceutical Education. It also discusses methods for reviewers to assess the rigour, quality, and usefulness of qualitative research. Examples of different ways to present data from interviews, observations, and ...
Asian people are under-represented in population-based, clinical, and genomic research. To address this gap, we have initiated the HELIOS longitudinal cohort study, comprising comprehensive behavioural, phenotypic, and genomic measurements from 10,004 Asian men and women of Chinese, Indian or Malay background. Phenotyping has been carried out using validated approaches, that are ...
In a late-breaking oral presentation, Lilly will report outcome data from the pivotal Phase 3 postMONARCH study evaluating Verzenio in combination with fulvestrant compared to placebo plus fulvestrant for patients with hormone receptor positive (HR+), human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 negative (HER2-) advanced or metastatic breast cancer ...
Custom copilot is pre-populated with information from the file/folder selection. The copilot has a default folder name, branding, description, sources you've selected, and other fields already. You can keep these fields and parameters as-is, or easily update them. Customize the identity with a name change. Customize the grounding knowledge.