We use cookies to provide our clients with the best possible experience. If You continue to use this site, you agree with our cookie policy. Read more »
- Academic Guidance
- Essay Examples
- Essay Topics
- How To Write
- Other Articles
- Research and Sources
- Synonym Explorations
- Writing Tips

Good book report questions

Writing a book report is a common activity students are required to go through today. Reading is one thing but the ability to summarize and analyze information is totally different. One can read a lot of books but still be unable to develop a good book report due to the lack of knowledge of what it should look like. Therefore, students often seek book report help in order to understand how to write one. In this article we are going to provide some good book report questions that will provide guidance as to which direction to go when choosing a format of a book report. Even if you have never faced the challenge of writing one, it is most likely that you will soon receive such assignment. And it is always better to face it prepared knowing what to do. So keep reading to get to know more about how to develop a good one. Even if you have written one or many reports by now, you can still find out more to polish up your writing skills. Questions for a book report provided below will serve a good foundation for every student.

❓ How to Write a Good Book Report
There is a difference between a book report and a book review which everybody should know prior to writing any of these. They are not the same although there are some similarities. A lot of students mix them up turning in reports when reviews are requested and vice versa. Book reports are all about explaining topical details and the storyline of the book. Those writing this type of assignment are to present biographical information about the author of the book (year of birth, marital status, his/her education and worldview, etc.). After the biographical information, there should go a brief summary of the book content – the main characters and the development of the plot.
Now a book review is different as it requires an in-depth analysis in addition to the things mentioned in a book report. The bio of the author along with the summary of the story also belongs in the review but the attention paid to these things should not be so significant. In other words, these things are not central in writing a book review . Instead, they are all considered a background information upon which one may analyze and evaluate the book in general. A book review is then more about analysis and evaluation where students are required to identify the author’s main message and ideas as well as to understand the meaning of symbolic elements present in the text. Now as we have managed to draw the line of separation between a book report and a book review, we can move on to how to write a book report.
Book reports can be of different types and formats. Most common forms of book reports are plot summaries, theme and character analysis. This type of assignment will help you practice expressing your own opinion about different aspects of the text and eventually expressing your thoughts on pretty much any subject in future. But no matter what type of book report you are about to write, there are some common things you have to include into your paper:
- Specify the kind of book report
- Include the title of the book
- Put the name of the author
- Indicate the time when the story takes place
- Mention the location of the events taking place in the book
- List the names of the characters briefly describing each one of them (at least those you will be discussing in the report)
- Add quotations in order to back up your opinions
📄 Plot Summaries
This type of book report assumes one has to explain own opinions about the plot and why he/she believes so. Your purpose should be to describe and characterize the plot and back up your opinions by some examples from the book.
🖋 Character Analysis
Here you can explore the traits of the main characters and how they affect the development of the plot in the book. There are many things you can pay attention to when analyzing the characters, such as clothing, moral flaws, dialogues, actions, etc.
📗 Theme Analysis
This form of book reports allows exploring the themes and big ideas that are interwoven within the entire story. You can simply choose a theme that seems to be the most important or the one you like the most and try to bring some of your thoughts to highlight the topic.
📚 Book Report Questions
What can help you write book reports efficiently is the list of questions to direct your thinking and writing. You can google phrases like “book report questions for high school” or “book report questions for middle school” depending on what your level of writing is. But in order to save some time for you, we have decided to come up with our own list of questions that should help develop a good book report. Therefore, there is no need to type something like “write my book report” in a google search tab in hopes to find someone who will do it all for you. Instead, you may consider the questions to ask for a book report and try to write it on your own. Here is the list:
- What genre does your book belong to? Fiction, non-fiction, etc.
- Do you like the book? Why so? If yes, would you recommend it to your friends?
- Can you come up with another title?
- What is the setting/background information?
- Who are the main characters?
- Are the names of the characters in any way descriptive?
- How does the story start? Why do you think the author chose to start his book this way?
- How does the story develop?
- Did you have any associations coming to your mind when you were reading the story?
- Did you find anything funny in the story?
- What’s your favorite part?
- Is there a problem in the story? What is this problem?
- Do you think that the author could have come up with a better solution (if there is one)?
- Is there the main idea that you can identify?
- Can you identify the purpose of the book?
- What are the lessons the book teaches (if any)?
- Is the topic of the book important? Why?
- Did any of the characters in the book do something you did not quite like?
- Can you identify the main purpose of writing the book?
- Did the book help you generate new ideas?
✅ Final Remarks
Now that you know what book reports are all about, we recommend you to try and write one. But when we say “write one”, we don’t necessarily mean that the very first thing you have to do in order to produce a good book report is to take a pen and start writing something. There are other things one should do before writing. We suggest you jot down the information you would want to take special note of when reading the book. Keep this piece of paper next to you when you read a book. As you read, take notes of the plot, characters and the main idea. Then you can go through the questions listed above – they should help you understand the book better. When you are done with the questions, organize your thoughts into an outline and draft the book report. From there you have to only edit and revise the draft to produce a perfect paper.
- Place an order
- About Writology
- How it Works
- Buy Custom Essays
- Nursing Writing Services
- Do My Assignment
- Buy a Letter of Recommendation
- Buy Research Papers

24 Book Review Questions to Ask Before Writing a Review
By: Author Laura
Posted on Published: 23rd February 2021 - Last updated: 5th September 2024
Categories Book Blogging , Books
Trying to write a book review but don’t know where to start? Don’t worry, these book review questions for a book report will help you on your way!

Writing a book review or book report can feel overwhelming for one of two reasons. Either you have too much to say or nothing to say at all.
In either case, having some structure to your review and a roadmap of questions to answer can be helpful in focussing your thoughts so you can write a useful book review.
These book review questions are designed to get your brain thinking about some of the key issues and interesting points about your book in question.
You certainly don’t have to answer all of them and you don’t need to follow the order I have listed the book report questions below.
RELATED: How to Write a Good Review of a Bad Book
Book Review Questions: General Information
Before you delve into sharing your own opinions, you should share some general information about the book.
This can be to do with its plot, its genre, the setting and whether there is anything readers should be aware of before delving in.
These are good questions to ask about a book as a basic starting point and where you should always begin.
What is the book about?
What genre does this book fit into?
In what time and place is the book set?
Who is the intended audience of the book?
Is the book appropriate for that audience?
Should this book come with any content warnings?
Book Review Questions: Stylistic Points
An author could craft the most fascinating story in the world but if they can’t convey that story with an interesting or logical style then a book may well just fall flat.
Consider whether the author of the book you are reviewing has a particularly interesting style and what is it about their style that shaped the book and your opinion of it.
What style is the book written in?
What point of view is the book written from?
Does the author use any interesting techniques?
Book Review Questions: The Characters
Really compelling characters, whether you love them or hate them, can make a book really stand out. If they don’t feel real then a book can crumble pretty quickly.
Make sure to include some information about the main character (or characters) but there’s no need to mention every single person, there simply isn’t space!
Who are the key characters in the book?
Did the characters feel real?
Are the characters likeable?
Which character did you find most compelling?
Could you relate to the key characters?
Book Review Questions: Your Opinions
Of course, any good book review should contain what you, the reviewer, actually thought about it! These book review questions to ask yourself are some of the most important.
Did you discover a new favourite book or is this one you wish you had never picked up in the first place?
Try to share a balanced view so reader’s of your review can come to their own conclusions about whether this book is worth reading for them. Some points that you might not have liked might be another reader’s favourite trope!
What did you like about the book?
What did you dislike about the book?
What could have been improved?
How did the book make you feel?
How does the book compare to other similar books?
Book Review Questions: Conclusion
Make sure to wrap up your book review with some final reflections about who should read this book, what you learnt from it and what other books it is similar to.
If a reader sees that a book is similar to one they have already read and loved then that’s a great indication that they’ll love this one too.
Would you recommend this book?
What did you learn from reading this?
What sort of reader would like this book?
What other books did this one remind you of?
What star rating would you give this book?
That concludes my list of book questions to ask yourself kick your brain in gear and get you thinking about all the most interesting points of the book you’ve just read.
Do you have any more relevant book review questions to add to the list?
Let me know in the comments below!
Follow me on Instagram and Goodreads for regular book updates!
If you liked this post, check out these: How to Write a Negative Book Review How to Start a Book Blog 36 Easy Book Blog Post Ideas

Founder & Editor of What’s Hot?
Saturday 10th of December 2022
Book report question: What made this book unique from other books you have read?
Thursday 25th of February 2021
This is so so useful.
Tuesday 23rd of February 2021
Very key points here. That first part, where I talk about the synopsis, the intended audience, the genre, that is my biggest struggle.

- Ask LitCharts AI
- Discussion Question Generator
- Essay Prompt Generator
- Quiz Question Generator

- Literature Guides
- Poetry Guides
- Shakespeare Translations
- Literary Terms
How to Write a Book Report
Use the links below to jump directly to any section of this guide:
Book Report Fundamentals
Preparing to write, an overview of the book report format, how to write the main body of a book report, how to write a conclusion to a book report, reading comprehension and book reports, book report resources for teachers .
Book reports remain a key educational assessment tool from elementary school through college. Sitting down to close read and critique texts for their content and form is a lifelong skill, one that benefits all of us well beyond our school years. With the help of this guide, you’ll develop your reading comprehension and note-taking skills. You’ll also find resources to guide you through the process of writing a book report, step-by-step, from choosing a book and reading actively to revising your work. Resources for teachers are also included, from creative assignment ideas to sample rubrics.
Book reports follow general rules for composition, yet are distinct from other types of writing assignments. Central to book reports are plot summaries, analyses of characters and themes, and concluding opinions. This format differs from an argumentative essay or critical research paper, in which impartiality and objectivity is encouraged. Differences also exist between book reports and book reviews, who do not share the same intent and audience. Here, you’ll learn the basics of what a book report is and is not.
What Is a Book Report?
"Book Report" ( ThoughtCo )
This article, written by a professor emeritus of rhetoric and English, describes the defining characteristics of book reports and offers observations on how they are composed.
"Writing a Book Report" (Purdue OWL)
Purdue’s Online Writing Lab outlines the steps in writing a book report, from keeping track of major characters as you read to providing adequate summary material.
"How to Write a Book Report" ( Your Dictionary )
This article provides another helpful guide to writing a book report, offering suggestions on taking notes and writing an outline before drafting.
"How to Write a Successful Book Report" ( ThoughtCo )
Another post from ThoughtCo., this article highlights the ten steps for book report success. It was written by an academic advisor and college enrollment counselor.
What’s the Difference Between a Book Report and an Essay?
"Differences Between a Book Report & Essay Writing" ( Classroom)
In this article from the education resource Classroom, you'll learn the differences and similarities between book reports and essay writing.
"Differences Between a Book Report and Essay Writing" (SeattlePi.com)
In this post from a Seattle newspaper's website, memoirist Christopher Cascio highlights how book report and essay writing differ.
"The Difference Between Essays and Reports" (Solent Online Learning)
This PDF from Southampton Solent University includes a chart demonstrating the differences between essays and reports. Though it is geared toward university students, it will help students of all levels understand the differing purposes of reports and analytical essays.
What’s the Difference Between a Book Report and a Book Review?
"How to Write a Book Review and a Book Report" (Concordia Univ.)
The library at Concordia University offers this helpful guide to writing book report and book reviews. It defines differences between the two, then presents components that both forms share.
"Book Reviews" (Univ. of North Carolina)
The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill’s writing guide shows the step-by-step process of writing book reviews, offering a contrast to the composition of book reports.
Active reading and thoughtful preparation before you begin your book report are necessary components of crafting a successful piece of writing. Here, you’ll find tips and resources to help you learn how to select the right book, decide which format is best for your report, and outline your main points.
Selecting and Finding a Book
"30 Best Books for Elementary Readers" (Education.com)
This article from Education.com lists 30 engaging books for students from kindergarten through fifth grade. It was written by Esme Raji Codell, a teacher, author, and children's literature specialist.
"How to Choose a Good Book for a Report (Middle School)" (WikiHow)
This WikiHow article offers suggestions for middle schoolers on how to choose the right book for a report, from getting started early on the search process to making sure you understand the assignment's requirements.
"Best Book-Report Books for Middle Schoolers" (Common Sense Media)
Common Sense Media has compiled this list of 25 of the best books for middle school book reports. For younger students, the article suggests you check out the site's "50 Books All Kids Should Read Before They're 12."
"50 Books to Read in High School" (Lexington Public Library)
The Lexington, Kentucky Public Library has prepared this list to inspire high school students to choose the right book. It includes both classics and more modern favorites.
The Online Computer Library Center's catalogue helps you locate books in libraries near you, having itemized the collections of 72,000 libraries in 170 countries.
Formats of Book Reports
"Format for Writing a Book Report" ( Your Dictionary )
Here, Your Dictionary supplies guidelines for the basic book report format. It describes what you'll want to include in the heading, and what information to include in the introductory paragraph. Be sure to check these guidelines against your teacher's requirements.
"The Good Old Book Report" (Scholastic)
Nancy Barile’s blog post for Scholastic lists the questions students from middle through high school should address in their book reports.
How to Write an Outline
"Writer’s Web: Creating Outlines" (Univ. of Richmond)
The University of Richmond’s Writing Center shows how you can make use of micro and macro outlines to organize your argument.
"Why and How to Create a Useful Outline" (Purdue OWL)
Purdue’s Online Writing Lab demonstrates how outlines can help you organize your report, then teaches you how to create outlines.
"Creating an Outline" (EasyBib)
EasyBib, a website that generates bibliographies, offers sample outlines and tips for creating your own. The article encourages you to think about transitions and grouping your notes.
"How to Write an Outline: 4 Ways to Organize Your Thoughts" (Grammarly)
This blog post from a professional writer explains the advantages of using an outline, and presents different ways to gather your thoughts before writing.
In this section, you’ll find resources that offer an overview of how to write a book report, including first steps in preparing the introduction. A good book report's introduction hooks the reader with strong opening sentences and provides a preview of where the report is going.
"Step-by-Step Outline for a Book Report" ( Classroom )
This article from Classroom furnishes students with a guide to the stages of writing a book report, from writing the rough draft to revising.
"Your Roadmap to a Better Book Report" ( Time4Writing )
Time4Writing offers tips for outlining your book report, and describes all of the information that the introduction, body, and conclusion should include.
"How to Start a Book Report" ( ThoughtCo)
This ThoughtCo. post, another by academic advisor and college enrollment counselor Grace Fleming, demonstrates how to write a pithy introduction to your book report.
"How to Write an Introduction for a Book Report" ( Classroom )
This brief but helpful post from Classroom details what makes a good book report introduction, down to the level of individual sentences.
The body paragraphs of your book report accomplish several goals: they describe the plot, delve more deeply into the characters and themes that make the book unique, and include quotations and examples from the book. Below are some resources to help you succeed in summarizing and analyzing your chosen text.
Plot Summary and Description
"How Do You Write a Plot Summary?" ( Reference )
This short article presents the goals of writing a plot summary, and suggests a word limit. It emphasizes that you should stick to the main points and avoid including too many specific details, such as what a particular character wears.
"How to Write a Plot for a Book Report" ( The Pen & The Pad )
In this article from a resource website for writers, Patricia Harrelson outlines what information to include in a plot summary for a book report.
"How to Write a Book Summary" (WikiHow)
Using Harry Potter and the Sorcerer’s Stone as an example, this WikiHow article demonstrates how to write a plot summary one step at a time.
Analyzing Characters and Themes
"How to Write a Character Analysis Book Report" ( The Pen & The Pad )
Kristine Tucker shows how to write a book report focusing on character. You can take her suggestions as they are, or consider incorporating them into the more traditional book report format.
"How to Write a Character Analysis" (YouTube)
The SixMinuteScholar Channel utilizes analysis of the film Finding Nemo to show you how to delve deeply into character, prioritizing inference over judgment.
"How to Define Theme" ( The Editor's Blog )
Fiction editor Beth Hill contributes an extended definition of theme. She also provides examples of common themes, such as "life is fragile."
"How to Find the Theme of a Book or Short Story" ( ThoughtCo )
This blog post from ThoughtCo. clarifies the definition of theme in relation to symbolism, plot, and moral. It also offers examples of themes in literature, such as love, death, and good vs. evil.
Selecting and Integrating Quotations
"How to Choose and Use Quotations" (Santa Barbara City College)
This guide from a college writing center will help you choose which quotations to use in your book report, and how to blend quotations with your own words.
"Guidelines for Incorporating Quotes" (Ashford Univ.)
This PDF from Ashford University's Writing Center introduces the ICE method for incorporating quotations: introduce, cite, explain.
"Quote Integration" (YouTube)
This video from The Write Way YouTube channel illustrates how to integrate quotations into writing, and also explains how to cite those quotations.
"Using Literary Quotations" (Univ. of Wisconsin-Madison)
This guide from the University of Wisconsin-Madison’s Writing Center helps you emphasize your analysis of a quotation, and explains how to incorporate quotations into your text.
Conclusions to any type of paper are notoriously tricky to write. Here, you’ll learn some creative ways to tie up loose ends in your report and express your own opinion of the book you read. This open space for sharing opinions that are not grounded in critical research is an element that often distinguishes book reports from other types of writing.
"How to Write a Conclusion for a Book Report" ( Classroom )
This brief article from the education resource Classroom illustrates the essential points you should make in a book report conclusion.
"Conclusions" (Univ. of North Carolina)
The University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill’s Writing Center lays out strategies for writing effective conclusions. Though the article is geared toward analytical essay conclusions, the tips offered here will also help you write a strong book report.
"Ending the Essay: Conclusions" (Harvard College Writing Center)
Pat Bellanca’s article for Harvard University’s Writing Center presents ways to conclude essays, along with tips. Again, these are suggestions for concluding analytical essays that can also be used to tie up a book report's loose ends.
Reading closely and in an engaged manner is the strong foundation upon which all good book reports are built. The resources below will give you a picture of what active reading looks like, and offer strategies to assess and improve your reading comprehension. Further, you’ll learn how to take notes—or “annotate” your text—making it easier to find important information as you write.
How to Be an Active Reader
"Active Reading Strategies: Remember and Analyze What You Read" (Princeton Univ.)
Princeton University’s McGraw Center for Teaching and Learning recommends ten strategies for active reading, and includes sample diagrams.
"Active Reading" (Open Univ.)
The Open University offers these techniques for reading actively alongside video examples. The author emphasizes that you should read for comprehension—not simply to finish the book as quickly as possible.
"7 Active Reading Strategies for Students" ( ThoughtCo )
In this post, Grace Fleming outlines seven methods for active reading. Her suggestions include identifying unfamiliar words and finding the main idea.
"5 Active Reading Strategies for Textbook Assignments" (YouTube)
Thomas Frank’s seven-minute video demonstrates how you can retain the most important information from long and dense reading material.
Assessing Your Reading Comprehension
"Macmillan Readers Level Test" (MacMillan)
Take this online, interactive test from a publishing company to find out your reading level. You'll be asked a number of questions related to grammar and vocabulary.
"Reading Comprehension Practice Test" (ACCUPLACER)
ACCUPLACER is a placement test from The College Board. This 20-question practice test will help you see what information you retain after reading short passages.
"Reading Comprehension" ( English Maven )
The English Maven site has aggregated exercises and tests at various reading levels so you can quiz your reading comprehension skills.
How to Improve Your Reading Comprehension
"5 Tips for Improving Reading Comprehension" ( ThoughtCo )
ThoughtCo. recommends five tips to increase your reading comprehension ability, including reading with tools such as highlighters, and developing new vocabulary.
"How to Improve Reading Comprehension: 8 Expert Tips" (PrepScholar)
This blog post from PrepScholar provides ideas for improving your reading comprehension, from expanding your vocabulary to discussing texts with friends.
CrashCourse video: "Reading Assignments" (YouTube)
This CrashCourse video equips you with tools to read more effectively. It will help you determine how much material you need to read, and what strategies you can use to absorb what you read.
"Improving Reading Comprehension" ( Education Corner )
From a pre-reading survey through post-reading review, Education Corner walks you through steps to improve reading comprehension.
Methods of In-text Annotation
"The Writing Process: Annotating a Text" (Hunter College)
This article from Hunter College’s Rockowitz Writing Center outlines how to take notes on a text and provides samples of annotation.
"How To Annotate Text While Reading" (YouTube)
This video from the SchoolHabits YouTube channel presents eleven annotation techniques you can use for better reading comprehension.
"5 Ways To Annotate Your Books" ( Book Riot )
This article from the Book Riot blog highlights five efficient annotation methods that will save you time and protect your books from becoming cluttered with unnecessary markings.
"How Do You Annotate Your Books?" ( Epic Reads )
This post from Epic Reads highlights how different annotation methods work for different people, and showcases classic methods from sticky notes to keeping a reading notebook.
Students at every grade level can benefit from writing book reports, which sharpen critical reading skills. Here, we've aggregated sources to help you plan book report assignments and develop rubrics for written and oral book reports. You’ll also find alternative book report assessment ideas that move beyond the traditional formats.
Teaching Elementary School Students How to Write Book Reports
"Book Reports" ( Unique Teaching Resources )
These reading templates courtesy of Unique Teaching Resources make great visual aids for elementary school students writing their first book reports.
"Elementary Level Book Report Template" ( Teach Beside Me )
This printable book report template from a teacher-turned-homeschooler is simple, classic, and effective. It asks basic questions, such as "who are the main characters?" and "how did you feel about the main characters?"
"Book Reports" ( ABC Teach )
ABC Teach ’s resource directory includes printables for book reports on various subjects at different grade levels, such as a middle school biography book report form and a "retelling a story" elementary book report template.
"Reading Worksheets" ( Busy Teacher's Cafe )
This page from Busy Teachers’ Cafe contains book report templates alongside reading comprehension and other language arts worksheets.
Teaching Middle School and High School Students How to Write Book Reports
"How to Write a Book Report: Middle and High School Level" ( Fact Monster)
Fact Monster ’s Homework Center discusses each section of a book report, and explains how to evaluate and analyze books based on genre for students in middle and high school.
"Middle School Outline Template for Book Report" (Trinity Catholic School)
This PDF outline template breaks the book report down into manageable sections for seventh and eighth graders by asking for specific information in each paragraph.
"Forms for Writing a Book Report for High School" ( Classroom )
In this article for Classroom, Elizabeth Thomas describes what content high schoolers should focus on when writing their book reports.
"Forms for Writing a Book Report for High School" ( The Pen & The Pad )
Kori Morgan outlines techniques for adapting the book report assignment to the high school level in this post for The Pen & The Pad .
"High School Book Lists and Report Guidelines" (Highland Hall Waldorf School)
These sample report formats, grading paradigms, and tips are collected by Highland Hall Waldorf School. Attached are book lists by high school grade level.
Sample Rubrics
"Book Review Rubric Editable" (Teachers Pay Teachers)
This free resource from Teachers Pay Teachers allows you to edit your book report rubric to the specifications of your assignment and the grade level you teach.
"Book Review Rubric" (Winton Woods)
This PDF rubric from a city school district includes directions to take the assignment long-term, with follow-up exercises through school quarters.
"Multimedia Book Report Rubric" ( Midlink Magazine )
Perfect for oral book reports, this PDF rubric from North Carolina State University's Midlink Magazine will help you evaluate your students’ spoken presentations.
Creative Book Report Assignments
"25 Book Report Alternatives" (Scholastic)
This article from the Scholastic website lists creative alternatives to the standard book report for pre-kindergarteners through high schoolers.
"Fresh Ideas for Creative Book Reports" ( Education World )
Education World offers nearly 50 alternative book report ideas in this article, from a book report sandwich to a character trait diagram.
"A Dozen Ways to Make Amazingly Creative Book Reports" ( We Are Teachers )
This post from We Are Teachers puts the spotlight on integrating visual arts into literary study through multimedia book report ideas.
"More Ideas Than You’ll Ever Use for Book Reports" (Teachnet.com)
This list from Teachnet.com includes over 300 ideas for book report assignments, from "interviewing" a character to preparing a travel brochure to the location in which the book is set.
"Fifty Alternatives to the Book Report" (National Council of Teachers of English)
In this PDF resource from the NCTE's English Journal, Diana Mitchell offers assignment ideas ranging from character astrology signs to a character alphabet.
- PDFs for all 136 Lit Terms we cover
- Downloads of 2009 LitCharts Lit Guides
- Teacher Editions for every Lit Guide
- Explanations and citation info for 42,469 quotes across 2009 books
- Downloadable (PDF) line-by-line translations of every Shakespeare play
Need something? Request a new guide .
How can we improve? Share feedback .
LitCharts is hiring!

- Quizzes, saving guides, requests, plus so much more.
Oral Book Reports: Keys to a Successful Presentation

So, one of your recent assignments was a report on the book read. Hope you have coped with it successfully. And now, your task is to make an oral presentation.
On the one hand, there seems to be nothing complicated about preparing an oral book report. It is just a public performance based on the task you have already completed.
On the other hand, acting in front of the audience is extremely difficult for some students, which means they run the risk of failing their oral book reports.
If you are one of those students, let us present you some secrets of a successful oral book report. First, we will discuss what an oral book report should consist of.
Format of an oral book report
- Start with introducing the book to the audience. Give its title, author’s name, date of publication, genre.
- Pass to the main characters of the book. The following things about the characters should be mentioned: name, gender, age, personality, relations between characters.
- Now, provide details about the setting in your oral book report. Let us remind you that here you should tell when and where the story described in the book takes place.
- Explain the conflict of the book. What are major issues? How do characters change throughout the story?
Tips on how to make a successful oral book report
- You have to be sure in every word of your oral book report. It is impossible if you have not read the book or you do not get it.
- Make note cards with the most important points to be included into your oral book report. However, do not read from these cards, just look up from time to time.
- Try to illustrate your oral book report. Find some pictures related to the book or, at least, the writer’s portrait.
Here, you can also read about an oral book report rubric .

Hopefully Home
craft · teach · live · grow

Book Report Series: Oral Book Reports
This one is the scariest of them all (and sometimes the least popular), so I figured I would tackle it right off in this book report blog series.
The first thing you need to know is this: your students can do oral book reports!
It’s up to you to set the tone for a learning environment in which it’s OK to not be great at everything. Learning is messy.
When I first started trying to do oral book reports, I just knew that I would have a few kids accept a zero rather than try, and/ or there would be tears and/ or vomit. ( Sorry, just keepin’ it real here. )
I had precious students who I knew suffered from social anxiety, and those who I knew were just very, very shy. I was prepared for disaster.
But guess what? There was none!
Was every presentation stellar? Nope. But did everyone try? You betcha. You can do it! They can do it!
Here are some tips to help:
1. Be extremely specific about your expectations.
In the syllabus I hand out to students and parents at the beginning of the year ( get it for free here! ), I include a list of exactly what types of book reports we will be doing and I even include the date they’re due. No surprises.
A couple weeks before the report is due (and after students have begun the independent reading book they selected), I officially introduce the assignment and give them a detailed handout that includes clear requirements and even some step-by-step instructions.
When putting together the handout, I do my best to anticipate any questions or concerns they might have, but I also try to anticipate any ways they might try to cut corners (but still expect a high grade, of course). So I have a requirement for everything. And I spell it all out.
Even though the handout is detailed, I don’t let it speak for itself- we go over it together. After I’m done talking through the entire handout, I take questions. Expect approximately 6,542 questions if you’re doing this with middle schoolers. 🙂 But one of the biggest reasons your kiddos will have so many questions is probably that they’re very nervous about this. They’re just sure they will fail, and worse, they’re just sure everyone will laugh at them.
So tip #2 is where you will save the day.

2. Have a Z.E.R.O.-tolerance policy for laughter.
Now I don’t mean no one can laugh if the presenter says something funny (however, I would caution my class clowns beforehand that their book report doesn’t have to be a comedy show). But I make a huge deal out of the fact that we are NOT going to make fun of someone before, during, or after their presentation.
We are not going to make faces at our friend while he’s talking.
We are not going to sigh or roll our eyes if someone is taking a while to get out what they’re trying to say.
We are not going to comment on the “performance.”
And if someone does? That someone loses points on his own grade. Points off for every offense.
At first that sounds harsh to the offenders, but I found what this strict policy really did was help to alleviate some of the pressure of getting up in front of your classmates and trying to say stuff.
Most teens’ worst fear is being embarrassed. So when you come right out of the shoot with a serious plan in place to help them feel less embarrassed, it seems to alleviate some fears.
Now knowing that everything is funnier when you’re not supposed to laugh, I have a plan in place for that too: I tell them, “if you’re about to lose it, just put your head down until you can get the giggles under control.” Sounds silly, but it helps.
On presentation day, I position myself facing the class, and I look over at the speaker. That way they see how serious I am about monitoring audience behavior.
However you choose to go about it, just be sure that you do everything within your power to let your kiddos know that this presentation is purely academic, meant to be a growing experience for them, and you’re there to make sure that no one uses it as an opportunity for being unkind or making others feel stupid.

3. Ease students’ fear of failing.
While I know that a large part of the fear behind oral book reports is that of looking dumb in front of their peers, another part of the fear is that they will fail the assignment, not for lack of effort or understanding, but for lack of public speaking skills. Reassure them that this will not happen.
That’s why tip #1 is so important. Have really clear expectations for this assignment, and let students know that if they follow directions and do their best, their grade will be just fine. Tell them exactly what you’re going to be grading about the actual speaking part of the project, and model examples of what to do, and what not to do. This will give them a lot more confidence.
4. Require written work beforehand.
This is- whether they know it or not- another confidence-booster for your students. Require them to write an outline of what they plan to say about the book.
Give them an easy-to-follow template of what needs to be in the outline. (Not only does this make it easier for the students to complete, it makes it way easier for you to grade!)
I also like to have students write out short introduction and conclusion paragraphs, to further help them plan, and to reiterate the importance of an engaging beginning and a strong ending.
Again, model examples of these, and give funny examples of what not to do.
Require a rough draft of this outline to be checked a couple days before they’re scheduled to give their presentation.
By requiring written work, you’re giving them a framework for their speech, and you’re guaranteeing that their brain has to at least plan a little what they’re going to say before they find themselves standing in front of the class.
5. Encourage practice.
Once your students have outlined what they plan to say in their report, encourage them to practice. For my teaching style, encourage is a bit of an understatement. I BEG them to practice.
My background is actually speech and drama, so to me, practice is everything, and I try to give them my best practice tips.
I “encourage” them to practice in front of family or friends, but if this feels too awkward, practice in front of your dog, your baby sibling, or in the shower. Whatever works- just practice!
I even offer for them to practice with me ahead of time. (Only one student has ever taken me up on that, and that’s because his mom forced him. Poor thing was so embarrassed, but he ended up getting a good grade!)

6. Let them use a notecard.
Another little thing that I found solicited a sigh of relief from my kiddos was my allowance of speaking from a notecard.
Now with juniors and seniors or gifted students, you may want to skip this step. Do what you feel would give your students the most meaningful learning experience.
I allowed one 3×5 card with large writing front and back, but no full sentences, and no tiny writing all crammed on the card. Why? Because having everything they plan to say all written out will just result in unintelligible mumbling from students whose heads are down, eyes glued to their card, reading the whole thing.
One of the things I grade on in an oral presentation is eye contact, and I know there will be no incentive to make eye contact with their audience if everything is written down.
Also, if they do try to make eye contact with their audience, they will have to come back to their notecard to find their place. If the card is crammed with information, they will most certainly have lost their place.
I “encourage” (I keep using that word because it sounds more friendly and professional than “ stand on one of their desks, waving my arms and screeching at ”) them to just neatly write a few key phrases and ideas they’re likely to forget such as the author’s name and their main points.
7. Offer bonus points.
Yet another way to help students feel like they can be successful with this assignment is to offer a way to earn a few bonus points. This way, students who don’t have the best public speaking skills can make up for it by just doing a little something extra.
My favorite bonus opportunity is to simply require a visual: students can wear a costume piece (like a hat or jacket), use a prop (like a baseball mitt or a stuffed animal), or make a poster.
I always clarify that to earn the bonus points, they must have clearly planned ahead with the item(s) (I’m not going to count holding a pencil they found in the hallway, because the character in their book wrote a letter, as an actual prop), and they must tie it in in their presentation- explain to the class what the significance is.
This just adds an element of fun to the project, and relieves the anxiety of your perfectionists trying maintain that 4.0. I was surprised to see that even my senior high students would don a costume piece or bring a stuffed animal in to get a few bonus points.
8. Take volunteers on presentation day.
I usually start off by allowing anyone who wants to, to volunteer to go first. You’ll usually have a couple takers, and it will be a great way to break the ice, because often those confident enough to go first will probably do a good job, giving yet another good model for the students who still aren’t sure.

9. Wait to tackle this project.
I don’t suggest making this the first (or even second) project of the year. Wait until you’ve gotten to know your students a little better, because the truth is, you will need to grade this a little bit on a case-by-case basis.
English class is not a public speaking class, and while you want to expose them to opportunities to hone those skills, you don’t want to hurt the grade of a student who is otherwise comprehending and moving successfully through the course.
Additionally, your students will feel more comfortable getting up in front of each other after they’ve gotten to know each other a little bit.
10. Grade during the presentations.
Work smarter, not harder, friend!
The great thing about oral presentations is that you don’t have a stack of grading to take home with you! Have students turn in a final draft of that outline they wrote when they come up to speak- give it a quick once-over, and assign it a grade.
Assess their presentation in real time (never try to rely on that memory of yours to conjure up how they did later!), and grade it right then and there. While you may need a moment or two later to glance over their outline a little more, or add up their final score, the bulk of your grading on these will be done, and you should be able to return grades the next day! #teacherwin
In order to do this, you’ll definitely want to use a rubric . If you haven’t already, take a look at this oral book report resource — it has everything you need to teach, introduce, assign, and assess oral book reports or book talks.

11. (Bonus!) Alternatives for students with special needs
While I am a huge proponent of the thought that oral book reports are definitely a doable thing, I do understand that students with certain IEPs or other learning differences may still need some accommodation. And that’s okay!
Here are a couple of options:
- Have the student record his presentation at home, and play it for the class on presentation day.
- Allow the student to write out his book report and read it to the class.
- Shorten the time requirement for their presentation.
- Allow students to present in pairs.
- Allow students to present to small groups, rather than the whole class.
Whew! That was a lot! So, tell me, how do you feel? Are you ready to take on oral book reports in your classroom? Are you an oral presentation veteran, and have some tips to add? Please share in the comments below! 🙂
Also be sure to take a look at the next post in the Book Report Series: Written Reports .
Happy teaching, my friends!

Published by admin
View all posts by admin
I'd love to hear from you! Cancel reply
Find something you liked share the love.
Teachnet.com
Creative perspectives on education and classroom management, more ideas than you’ll ever use for book reports.
October 26, 2010 Teachnet Staff Language Arts , Reading 11
Submitted by Teacher-2-Teacher contributor Kim Robb of Summerland, BC
- Book Report
11 Comments
WOW THATS BIG
Great ideas, but many in the lower half are repeating the first half of the list.
We’ll take a look at editing out some obvious duplicates. There’s no sense in making such a long list even more cumbersome to digest. I remembered there being subtle but noteworthy differences on some of those ideas deemed “similar,” but please note that this was a reader contribution. Feel free to send in or comment with your own suggestions. Thank you for the feedback!
HOW AM I GONNA PICK ONE!
I go to Ockerman as well(; I’m in 7th grade and i had Mrs. Raider last year. I Love you Mrs. Raider and Mrs. Moore(: <3. xD.
hey Mrs.Body thank you for the suggestions and opportunities to show my creative and artistic skills
You can also put jeopardy or make a short movie trailer of the book like it is just about to come in theaters. Also you can do a news broadcast of a seen that is happening in the book
I also think that you can put an idea of having to do a short song or rap of what is happening in your book
woah that is a huge list!!! i might do either 14 or 64!
I really like these ideas!!! They gave me a 120% on my final grade! I know get to graduate!!! Thanks BOB!
This is an amazing list! I don’t know which idea to choose!
Here’s an idea:
Act out the entire book in a two hour movie!
Thanks! BILLY
Comments are closed.
Copyright © 2024 | WordPress Theme by MH Themes
- EXPLORE Random Article
- Happiness Hub
How to Prepare for an Oral Report
Last Updated: April 8, 2021
wikiHow is a “wiki,” similar to Wikipedia, which means that many of our articles are co-written by multiple authors. To create this article, 13 people, some anonymous, worked to edit and improve it over time. This article has been viewed 34,542 times.
Spending long hours working on an oral report can be tedious. You have to research for accuracy, plan the layout, memorize what you are going to say. Knowing that you're going about the preparation in a fruitful way can help make the exercise seem more worthwhile.
What Do You Know About Your Topic?

Putting the Presentation Together

- Make your writing interesting. Be sure to use better words than the standard and obvious "nice" or "big." Rather opt for words such as "gigantic" or "fantastic."

- Make bullet points. These are easier to memorize and read from quickly.

- Don't try to say your oral word for word; this will make you nervous and queasy if you try to remember everything word for word. It can also look a bit over-the-top unless you are engaging in your delivery; avoid simply reciting something learned off-by-heart.
- Tell the story; it doesn't have to be said exactly the way you wrote it––you just need to tell the story. That said, your oral presentation should reflect some of the things you wrote in the report.
Community Q&A
- Ask your crowd if they have any questions, and always be prepared to answer them. If you don't know something, say so and ask the audience if anyone does have the answer or an idea about it. Don't be afraid to draw in the crowd rather than avoid it. Thanks Helpful 9 Not Helpful 0
- Make your visual aid colorful and eye- catching. However, do not let the color take away from the power of your presentation, as it is made to aid your project, not dominate it. Thanks Helpful 6 Not Helpful 3
- Enthusiasm is good; false excitement is cheesy. Look for the right balance. Thanks Helpful 5 Not Helpful 3
- Keep the speech short and to the point. Long drawn out reports are considered boring and risk losing you marks or positive reactions. Thanks Helpful 9 Not Helpful 1
- When you take notes, be absolutely sure that you aren't plagiarizing, copying word for word as written. Reference everything that you have taken from another source, including someone else's line of reasoning. Thanks Helpful 8 Not Helpful 1
You Might Also Like

About this article
Did this article help you.

- About wikiHow
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing a Book Report

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Book reports are informative reports that discuss a book from an objective stance. They are similar to book reviews but focus more on a summary of the work than an evaluation of it. Book reports commonly describe what happens in a work; their focus is primarily on giving an account of the major plot, characters, thesis, and/or main idea of the work. Most often, book reports are a K-12 assignment and range from 250 to 500 words.
Book reviews are most often a college assignment, but they also appear in many professional works: magazines, newspapers, and academic journals. If you are looking to write a book review instead of a book report, please see the OWL resource, Writing a Book Review .
Before You Read
Before you begin to read, consider what types of things you will need to write your book report. First, you will need to get some basic information from the book:
- Publisher location, name of publisher, year published
- Number of Pages
You can either begin your report with some sort of citation, or you can incorporate some of these items into the report itself.
Next, try to answer the following questions to get you started thinking about the book:
- Author: Who is the author? Have you read any other works by this author?
- Genre: What type of book is this: fiction, nonfiction, biography, etc.? What types of people would like to read this kind of book? Do you typically read these kinds of books? Do you like them?
- Title: What does the title do for you? Does it spark your interest? Does it fit well with the text of the book?
- Pictures/Book Jacket/Cover/Printing: What does the book jacket or book cover say? Is it accurate? Were you excited to read this book because of it? Are there pictures? What kinds are there? Are they interesting?
As You Read
While reading a work of fiction, keep track of the major characters. You can also do the same with biographies. When reading nonfiction works, however, look for the main ideas and be ready to talk about them.
- Characters: Who are the main characters? What happens to them? Did you like them? Were there good and bad characters?
- Main Ideas: What is the main idea of the book? What happens? What did you learn that you did not know before?
- Quotes: What parts did you like best? Are there parts that you could quote to make your report more enjoyable?
When You Are Ready to Write
Announce the book and author. Then, summarize what you have learned from the book. Explain what happens in the book, and discuss the elements you liked, did not like, would have changed, or if you would recommend this book to others and why. Consider the following items as well:
- Principles/characters: What elements did you like best? Which characters did you like best and why? How does the author unfold the story or the main idea of the book?
- Organize: Make sure that most of your paper summarizes the work. Then you may analyze the characters or themes of the work.
- Your Evaluation: Choose one or a few points to discuss about the book. What worked well for you? How does this work compare with others by the same author or other books in the same genre? What major themes, motifs, or terms does the book introduce, and how effective are they? Did the book appeal to you on an emotional or logical way?
- Recommend: Would you recommend this book to others? Why? What would you tell them before they read it? What would you talk about after you read it?
Revising/Final Copy
Do a quick double check of your paper:
- Double-check the spelling of the author name(s), character names, special terms, and publisher.
- Check the punctuation and grammar slowly.
- Make sure you provide enough summary so that your reader or instructor can tell you read the book.
- Consider adding some interesting quotes from the reading.
- help_outline help
iRubric: Oral Book Report Presentation Rubric with visual aid
| Rubric Code: By Ready to use Public Rubric Subject: Type: Grade Levels: 6-8, 9-12 |
| Oral Presentation | |||||
| | |||||
| | |||||
| | |||||
| | |||||
| | |||||
| | |||||
| | |||||
| | |||||
- introduction, summary, characters, delivery and visual aid
- Presentation

- Featured Articles
- Report Card Comments
- Needs Improvement Comments
- Teacher's Lounge
- New Teachers
- Our Bloggers
- Article Library
- Featured Lessons
- Every-Day Edits
- Lesson Library
- Emergency Sub Plans
- Character Education
- Lesson of the Day
- 5-Minute Lessons
- Learning Games
- Lesson Planning
- Subjects Center
- Teaching Grammar
- Leadership Resources
- Parent Newsletter Resources
- Advice from School Leaders
- Programs, Strategies and Events
- Principal Toolbox
- Administrator's Desk
- Interview Questions
- Professional Learning Communities
- Teachers Observing Teachers
- Tech Lesson Plans
- Science, Math & Reading Games
- Tech in the Classroom
- Web Site Reviews
- Creating a WebQuest
- Digital Citizenship
- All Online PD Courses
- Child Development Courses
- Reading and Writing Courses
- Math & Science Courses
- Classroom Technology Courses
- A to Z Grant Writing Courses
- Spanish in the Classroom Course
- Classroom Management
- Responsive Classroom
- Dr. Ken Shore: Classroom Problem Solver
- Worksheet Library
- Highlights for Children
- Venn Diagram Templates
- Reading Games
- Word Search Puzzles
- Math Crossword Puzzles
- Geography A to Z
- Holidays & Special Days
- Internet Scavenger Hunts
- Student Certificates
Newsletter Sign Up
Lesson Plans
- General Archive
- Health & Safety
- Interdisciplinary
- Language Arts
- PE & Sports
- Social Science
- Special Ed & Guidance
- Special Themes
- Top LP Features
- Article Archive
- User Submitted LPs
- Box Cars Math Games
- Every Day Edits
- Five Minute Fillers
- Holiday Lessons
- News for Kids
- ShowBiz Science
- Student Engagers
- Work Sheet Library
- More LP Features
- Calculator Lessons
- Coloring Calendars
- Friday Fun Lessons
- Math Machine
- Month of Fun
- Reading Machine
- Tech Lessons
- Writing Bug
- All Work Sheets
- Critical Thinking Work Sheets
- Animals A to Z
- Backpacktivities
- EveryDay Edits
- Hunt the Fact Monster
- It All Adds Up Math Puzzles
- Make Your Own Work Sheets
- Math Cross Puzzles
- Mystery State
- Math Practice 4 You
- Phonics Word Search Puzzles
- Readers Theater Scripts
- Sudoku Puzzles
- Vocabulous!
- Back to School
- Back to School Archive
- Icebreaker Activities
- Preparing for the First Day
- Ideas for All Year
- The Homework Dilemma
- First Year Teachers
- Don't Forget the Substitute
- More Great Ideas for the New School Year
- Early Childhood
- Best Books for Educators
- Assessments
- Award Certificates
- Bulletin Board Resources
- Classroom Organizers
- Graphic Organizers
- Newsletters
- Parent Teacher Communications
- More Templates
Search form
-->fresh ideas for creative book reports.
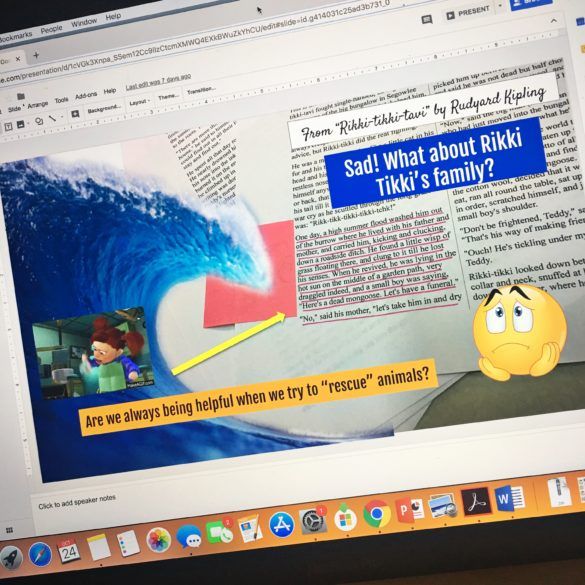
Tired of the same old book report formats? Do your students grumble every time you mention the words book reports? Spice up those old book reports with some new, creative ideas. Education World presents 25 ideas for you to use or adapt. In addition: Ideas for cyber book reports!
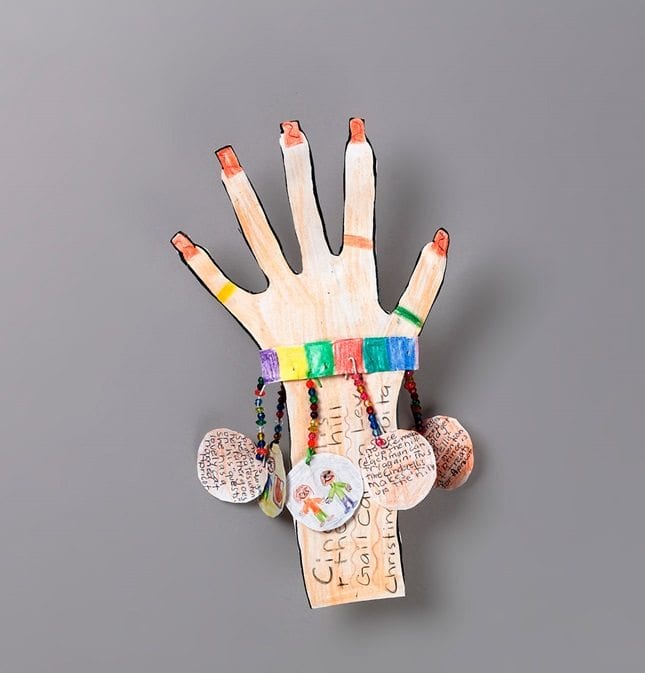





























































IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Include the title of the book. Put the name of the author. Indicate the time when the story takes place. Mention the location of the events taking place in the book. List the names of the characters briefly describing each one of them (at least those you will be discussing in the report) Add quotations in order to back up your opinions.
Book Review Questions: Conclusion. Make sure to wrap up your book review with some final reflections about who should read this book, what you learnt from it and what other books it is similar to. If a reader sees that a book is similar to one they have already read and loved then that's a great indication that they'll love this one too ...
The body paragraphs of your book report accomplish several goals: they describe the plot, delve more deeply into the characters and themes that make the book unique, and include quotations and examples from the book. Below are some resources to help you succeed in summarizing and analyzing your chosen text.
First, we will discuss what an oral book report should consist of. Format of an oral book report. Merely 3 hours, and you will receive your absolutely original paper without plagiarism Check It Out. Start with introducing the book to the audience. Give its title, author's name, date of publication, genre. Pass to the main characters of the book.
3. Ease students' fear of failing. While I know that a large part of the fear behind oral book reports is that of looking dumb in front of their peers, another part of the fear is that they will fail the assignment, not for lack of effort or understanding, but for lack of public speaking skills. Reassure them that this will not happen.
Write and perform an original song that tells the story of the book. After reading a book of poetry, do three of the following: 1) do an oral reading; 2)write an original poem; 3)act out a poem; 4)display a set of pictures which describe the poem; 5)write original music for the poem; 6)add original verses to the poem.
Don't be afraid to jot down details. Make your writing interesting. Be sure to use better words than the standard and obvious "nice" or "big." Rather opt for words such as "gigantic" or "fantastic." 2. Add a little something to your oral report. Perhaps add pictures or make a life size model from the topic.
When writing a book report, it's important to keep a few things in mind. First, avoid repetition by adding a new perspective about the book. Second, be concise and keep your analysis focused on the content your readers are looking for. Third, support your claims and positions with insights from the book and provide evidence for your arguments.
They are similar to book reviews but focus more on a summary of the work than an evaluation of it. Book reports commonly describe what happens in a work; their focus is primarily on giving an account of the major plot, characters, thesis, and/or main idea of the work. Most often, book reports are a K-12 assignment and range from 250 to 500 ...
In the rubric, you need to divide that up into the qualifications for earning those points. Here is an example: 10 points for all accurate and relevant information. 8 points for some confusion or ...
4th Quarter Oral Book Report Presentation Rubric introduction, summary, characters, delivery and visual aid Rubric Code: H92BW2. By lauraflack Ready to use Public Rubric Subject: English Type: Presentation Grade Levels: 6-8, 9-12 ...
Her idea: book report sandwiches! The teacher commissioned a friend to draw slices of ham, tomato, and Swiss cheese; lettuce leaves; a layer of mayonnaise, and a couple of slices of bread. Then she photocopied the drawings onto appropriately colored sheets of paper -- ham on pink, tomato on red, Swiss cheese on yellow, etc.
You've been assigned to give an oral presentation of your book report. This means you already have a general topic—your book. 1. Read through your book report and make a list of the information you feel must be included in your presentation. Most book reports cover information about the book's author, publisher, and a summary of the important
Oral Fluency Tasks in Relation to the Oral Book Reports The term oral fluency used throughout this paper refers to definitions by Hasselgreen (2004) and Schmidt (1992). Hasselgreen (2004) defines L2 oral fluency as the "ability to contribute to what a listener, proficient in the language, would normally perceive as coherent speech, which
And although students don't need to dive deeply into every single book they read, occasionally digging into characters, settings, and themes can help them learn to look beyond the prose. Here are 42 creative book report ideas designed to make reading more meaningful for kids. MiddleWeb. 1. Concrete Found Poem.
Here is everything you need for 5 different types of book reports and post reading projects for middle or high school!Templates, rubrics, handouts, and more, all in both no-prep and editable versions!Click on each product cover above to see detailed previews and more information.What you'll receive: 5. Products. $9.97 $14.85 Save $4.88.
Students can be asked to select which 5 questions to prepare answers for, to ask each other in turn or to be ready to answer any of these in a class discussion. ... It help's me with my book report thanks!!!! Like Like. Reply. Charles DiSilva says: July 24, 2019 at 5:05 am. These questions are really great. Thank you very much. Like Like. Reply.
3-4: basic outline of book, some reading of written text, unable to answer questions in detail, not active in discussions; 0-2: incomplete, no evidence the person actually read the book, short presentation, minimal participation in group discussion; Step 2. Book Report Structure. A book report will have these basic parts. Introduction.
There is more than one way to complete a book report. Both teachers and students may find these creative ideas more interesting than a straightforward report. Write a review of the book. Create the report in the form of a newspaper or blog review. Summarize the book without giving away the plot or the ending.
No more Boring Book Reports. For Teachers 1st - 5th. Students create a paper bag book report. In this book report lesson plan, students choose 5-7 items representing the story. Students fill and decorate their bags and present them to the class. Students describe the significance of the...
Use the outline, questions, and biography book to organize and create your oral presentation. Oral Presentation: Begin your oral book report - try to say something to immediately to get our attention. Speak clearly and loudly enough to be heard easily. You are encouraged to make note cards to guide you through your presentation.
4.9. (12) $1.50. Word Document File. This file includes both a written book report rubric and a book talk rubric. Both rubrics are out of 21 points and focus on the elements of genre, characters, setting, and plot. There are also sections for a critique and on the appearance and/or presentation.
Book Re. ports & Presentations. Long Term Projects: Each month your child will read four (4) chapter books. At the end of the month, students will present one (1) of the books (book report) with a visual. A form of required information for the book report will is posted below. I will model the requirements and give suggestions for the visuals ...