- Impact of Globalization on Australia Words: 1192
- Globalization Concept and Its Impact on the State Words: 1907
- Contemporary Globalization and Its Impact Words: 1108
- The Impact of Racism on Globalization Words: 4995
- Impacts of Globalization on the Developing Countries Words: 2315
- Globalization: Impact and Consequences Words: 599
- Globalization Impacts on Trade and Employment Words: 1723
- Globalization and its Impact on the World Words: 583
- Globalization, Its Defenders and Critics Words: 903
- Issues in the International Politics: Globalization Words: 1444
- Globalization: More Positive Effects Than Negative Ones Words: 1643
- The Pitfalls of Globalization Words: 568

Globalization and Its Impact on Society
Introduction, changes brought about by globalization.
Globalization is the process of the ongoing assimilation of the world’s largest nations. It is well currently underway in all regions of the universe. It is complicated connectivity between conservatism and liberalism that comprises both advantages and disadvantages, including emboldening and demeaning people and organizations. Ambassadors, legislators, and lawmakers must meet and deal with countries’ needs and desires as more countries, individuals, and civilizations acclimate to the ever-changing international organizations. Statesmanship can take multiple shapes, including peace negotiations, authored constitutional provisions, experiential learning, and much more. Culture is a well-known term that has remained essentially unchanged in the description. On the other hand, globalization in international relations has had a continual direct and indirect impact on society. Thus, as discussed in this essay, while globalization supports technology, worldwide collaboration, and the use of prominent brands, its danger results in the loss of high-wage employment, rising wealth disparity, and the erosion of cultural awareness.
Moreover, the above occurrence boosts advanced worldwide technologies, the legibility of quick, verbal teamwork, and the utilization of successful brands. This phenomenon connects civilizations and international affairs on many different levels, including economic principles, politics, and societal problems. Furthermore, the above manifestation has been used by international relations to reach its objectives of cultural knowledge. Foreign politics are concerned with how nations, individuals, and institutions interact, and globalization significantly impacts these global events. Therefore, acknowledging the above incidence in international affairs is critical not only for the coming years of government entities, individuals, and companies but also for the existence of humanity.
In today’s consistent, symbiotic, and volatile world, many of the top stories are global relations. Whether that’s the ongoing aspect of globalization, it is a complicated connectedness among democratic capitalism that includes advantages and disadvantages that embolden and disenfranchise people and organizations (Li & Huang, 2021). Globalization, on either hand, is a common phrase used by government entities, businesses, academics, and a variety of non-governmental institutions. It also represents a new conceptual framework in the worldwide economy and political interactions.
While member states dominated the global economic and political scenario for decades, regional and global institutions now play significant roles in society. These institutions include the World Bank, Bank for International Settlements, and North American Free Trade Agreement (Schmitz & Weinen, 2020). National authorities have lost several of their significance, and maybe their abilities in this “Global Village” favor these United Nations agencies. As a collective phenomenon between many people, businesses, and government agencies from various countries, globalization is facilitated by information systems and influenced by international economic integration. This procedure affects the earth, heritage, government systems, financial progress and prosperity, and individual body health in communities today.
Learning has improved over time, leveling the playing ground for all commercial entities to conduct business operations. Companies worldwide can now compete on a single international platform, while consumers today can purchase from anywhere in the world. Globalization led to the introduction of worldwide service charge commercial transactions. Thus, corporate establishments have more rights to operate beyond their boundaries because mainstream media allows people to connect worldwide. With increased information exchange, vital data can be exchanged between people and enterprises worldwide (Schmitz & Weinen, 2020).
Moreover, environmental protection initiatives have increased their efforts in promoting the conservation of natural habitats worldwide. In addition, the international community effect has continued to grow as language differences are continually being fragmented, resulting in more diverse cultural philosophies. Globalization has resulted in an increase in data transmission between spatially distant locations. Furthermore, places on the single global market have a free exchange of products and investments.
Households and companies have easy access to a wide variety of goods. The emergence of the worldwide production marketplace has been brought about by globalization. The free movement of people from different countries positively impacts society. Discussions are used to resolve climate change issues such as cross-border pollution, overexploitation in the oceans, and global warming. Finally, there has been an increase in cross-border data flow via satellite systems, the web, and wireless cell phones.
Notwithstanding all of the individual and other significant barriers, the efficiency of globalization and the partnership working of people and countries will help address the downsides. It will strengthen the prevention of migration innate in third-world and backward country countries and reduce existing inequalities, which will help minimize the effects of the above occurrence (Imene et al., 2021). All of the facts mentioned above are the night before going to bed and labor-intensive processes. Still, they will significantly strengthen their institutional enterprises are unaffected, whereas international organizations and restrictions limit their choice. Globalization has undermined state sovereignty, according to another prevalent notion. On the one hand, international trade restricts nation-states’ capability to regulate their internal business operations.
On the other hand, international institutions and the laws that govern them limit such countries’ decision-making powers. Regardless of the assumption that globalization brought better living and economic stability, its negative implications have been widely condemned. The manifestation mentioned above has significant environmental, political, and social consequences on the financial system.
In conclusion, globalization seems to have a bright destiny ahead of it. The global economic system will become more linked and connected as study and creativity, development, and generalizability improve the inherent high movement of present and future civilizations aids in this. Exogenous elements related to globalization’s consequences will considerably impact country policies and decisions, although national authorities remain relevant. Developing civilizations will be the most impacted due to their improvement needs and the ensuing demand for research and innovation competencies to address their development and growth concerns.
Imene, C., Ali, D., & El Hadi, L. (2021). Globalization of economy: Strengthening of inequalities between countries and the possibility of reducing them. International Journal of Econometrics and Financial Management , 9 (1), 1-5. Web.
Li, L., & Huang, G. (2021). “Advantages and disadvantages” of individual proactive behavior in organizations. Advances in Psychological Science , 29 (8), 1484. Web.
Schmitz, G., & Weinen, J. (2020). Increased traffic safety through V2X information exchange. Atzelectronics Worldwide , 15 (6), 46-49. Web.
Cite this paper
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2022, November 21). Globalization and Its Impact on Society. https://studycorgi.com/globalization-and-its-impact-on-society/
"Globalization and Its Impact on Society." StudyCorgi , 21 Nov. 2022, studycorgi.com/globalization-and-its-impact-on-society/.
StudyCorgi . (2022) 'Globalization and Its Impact on Society'. 21 November.
1. StudyCorgi . "Globalization and Its Impact on Society." November 21, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/globalization-and-its-impact-on-society/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "Globalization and Its Impact on Society." November 21, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/globalization-and-its-impact-on-society/.
StudyCorgi . 2022. "Globalization and Its Impact on Society." November 21, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/globalization-and-its-impact-on-society/.
This paper, “Globalization and Its Impact on Society”, was written and voluntary submitted to our free essay database by a straight-A student. Please ensure you properly reference the paper if you're using it to write your assignment.
Before publication, the StudyCorgi editorial team proofread and checked the paper to make sure it meets the highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, fact accuracy, copyright issues, and inclusive language. Last updated: September 17, 2024 .
If you are the author of this paper and no longer wish to have it published on StudyCorgi, request the removal . Please use the “ Donate your paper ” form to submit an essay.
Home — Essay Samples — Sociology — Globalization — The Economic and Social Impact of Globalization
The Economic and Social Impact of Globalization
- Categories: Globalization
About this sample

Words: 760 |
Published: Aug 1, 2024
Words: 760 | Pages: 2 | 4 min read
Table of contents
The economic impact of globalization, the social impact of globalization, the environmental impact of globalization.

Cite this Essay
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing style below:
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Dr. Karlyna PhD
Verified writer
- Expert in: Sociology

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
1 pages / 619 words
1 pages / 713 words
4 pages / 1960 words
2 pages / 451 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Globalization
Hurrell, A., & Woods, N. (1995). Globalization and Inequality. The Millennium Debate: International Studies, 23(4), 443-464.Financial Times Magazine. (2019). Defining Globalization: A Comprehensive Look. Retrieved from Wolf, M. [...]
Homogenization refers to the process of making something uniform or similar throughout. In the context of society, homogenization can be seen as the process of making cultures, traditions, and practices more uniform or similar [...]
Globalization is the key word of having this huge world coming very small. It has changed the way many people think, behave, react, talk, dress and take actions in different fields. It made the international aspects from all [...]
Globalization is a multifaceted phenomenon that has reshaped the world in numerous ways. It refers to the increasing interconnectedness and interdependence of the world's markets and businesses. This process has accelerated in [...]
I’d like to begin with explaining the term Globalization with help of the definitions as follows: Globalization refers to all those processes by which the peoples of the world are incorporated into a single world society, [...]
Globalization is erasing country borders. It’s expanding something to a worldwide scale, and generally making the world a little bit smaller. When you think of globalization in terms of sports, the best example is soccer. Soccer [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
- Skip to main content
- Skip to secondary menu
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
A Plus Topper
Improve your Grades
Impact of Globalization Essay | Essay on Impact of Globalization for Students and Children in English
February 13, 2024 by Prasanna
Impact of Globalization Essay: Since the decline of communalism, Globalization has become one of the most controversial and debating issues among people around the World. Globalization has a different definition to different people, and whether it has a positive impact today or was better for yesterday is still questionable. Although a part of the population questions its existence, it has significantly impacted both developed and developing countries’ economies. Globalization cannot simply be related to being political as it has had significant effects on cultural, ideological, and social aspects of people around the World.
To understand the impact of Globalization, it is important to know what it is. One of the popular political scientist, James Rosenau, described the term as a currently popular label and accounted for people’s norms, goods, ideas, services, activities, and currencies that are localized and practiced in a confined area. As per World Health Organization, Globalization is defined as the interdependence and interconnection of people in a local place with the people around the World. The two main elements that need to work here is the ease of flow of goods, services, and activities of people from one place to another and the incorporation and change in policies that allow the easy flow of exchange around the areas.
You can also find more Essay Writing articles on events, persons, sports, technology and many more.
Worldwide Interdependence
Globalization is a complex procedure that includes the trends and tendencies of the economic, cultural, and social spheres of the people and places around the World. The process is huge and not easily predictable but organized as well. The liberation of investment and trade, Social networks worldwide, technological innovation, and entrepreneurship are the four major factors of Globalization.
Many political scientists believe that the two major forces that make Globalization effective are technological innovation and entrepreneurship. However, it is impossible to prove that the process works without the intervention of other factors. With the adoption and evolution of market-related laws and policies in local and international fields, the governments have played a significant role by allowing economic integration of special activities and giving major independence to welcome the outside World. Globalization’s financial aspect is the major force that acts as a driving agent for both the political and social parts. Due to the colonization by Europe in various countries, some of the practices and cultural lifestyle is adopted by the people deep inside the African villages.
Globalization Plays a Role in the Worldwide Development
Globalization has made way for the countries to develop rapidly. However, the development is not even because some countries are growing quickly in comparison to others. The interconnection between the countries helped decrease poverty, but it does not equally support global community members. The developing countries lie in a depriving position while the developed countries enjoy all the interconnection benefits. However, when we take a close look at the impact of Globalization worldwide, we can conclude that it has both positive and negative effects on both developed and developing countries.
Globalization has proven to make a positive impact on the quality of life of people in developing countries. Funding from foreign countries and industrialized nations are helping many developing countries to decrease poverty. These funds are spent on improving the social, health, transport structure, and education of developing countries, helping them with a standard of living.
Today, the developing countries can openly communicate and trade through transport, labor, technology, management, and other benefits from other industrialized countries.
The impact of Globalization around the World
Globalization has its backdrops that dually affect both the developed and developing countries. However, considering the positive side to be heavier, people still believe it to be beneficial and aim for a better standard of living for all the poor people around the Globe.
World Trade and Globalizationz
According to political scientists, the impact of Globalization and trade on developing countries and industrialized countries is obvious that has a positive impact on the economic development of the nations. However, economic progress is not possible if the member countries and governments do not allow free trade flow without any limitations. The liberalization of trade will help the free flow of goods and services with an increasing profit to the producer country and the export countries. In the past decade, Uganda has proven to improve its economic situation by allowing free trade flow and restricting laws.
Trade is emerging as a trend in various underdeveloped and developing countries. With the reducing restrictions of trade, labor requirement and demand of manufacturers has risen. Many such industrialists migrate their business and production to developing countries, increasing employment and wealth among poor people. The hosting countries get several benefits from such a situation. Firstly, increase in employment opportunities as a lot of labor and workforce is required in industries. Import of new technology automatically activates with the welcome of new foreign sectors. Therefore, training local employees gives another opportunity for employment for the hosting countries. Often these foreign industries distribute their work and machine factories in various other countries and states. In such cases, the widespread chance of employment paves the way for Globalization.
Globalization Increases Competition Among Countries
With the increase in creativity and innovation, local and Global competition is an automatic result of Globalization. The competition among the producers ensures the quality of the product and the efficiency of producing goods. One of the major positive effects of Globalization is access to foreign interests, culture, and entertainment via music, movies, apparel, and television broadcasts. The cooperation among the government officials and the focus on similar goals has helped distribute knowledge among different underprivileged countries. With Globalization, the news and another kind of interactions can be done faster than expected.
However, with numerous positive effects of Globalization, there are several negative impacts as well, which the critics put together to criticize the concept in developing countries. According to reports of 2004, Globalization’s negative impact has no greater examples than countries like China and India.
Negative Impact of Globalization on Developing Countries
According to political scientists, the major negative impact of Globalization is poverty. Although it is said to have decreased poverty in developing countries, the Secretary-General of the United Nations, Kofi Annan, says that only a few countries are enjoying Globalization’s benefits. In contrast, most developing countries are left behind in the dark. It is not possible to evaluate the effect of Globalization on poverty. However, according to a survey, Sub Saharan Africa shows increased poverty by eighty-two million, central Asia and Europe by fourteen million, and the Caribbean and Latin America by eight million. However, Globalization alone is not responsible for poverty in developing countries, weak reforms, governance, lack of economic policies and ideas. Like Zygmunt Bauman, popular political figures claimed that Globalization makes the industrialized countries rich and the poor developing countries poorer.
Globalization helped several African colonies; however, today, most of them are dependent on large wealthy countries over the years. The African colonies are known for their largely consuming economy. The weak agricultural practice and growth make the overall economy worse in Africa. With the decline of trade and import facilities in the late 90s, the region’s per capita income has slowly reduced. The survey of social and economic conditions of Africa has an external debt of a million dollars.
Impact of Globalization on Health and Diseases
Globalization has made a serious impact on the hygiene of infectious and deadly diseases. It has given the developing countries the opportunity to restraint, prevent and eradicate the infection quickly. The reason why deadly diseases are increasing worldwide is because of the technological challenges that led to the increase of harmful emissions, resulting in global warming. The increase in mosquito breeding in open waters, bathing in pools, and other ways to be contaminated with the Schistosoma’s larvae might result in harmful diseases. With the use of western diets in developing countries, food-related diseases started increasing in the long run.
The western style that took place through Globalization has led the adults and the youth to lose their core values leading to several diseases like AIDS or HIV that have a long-term effect on the country’s society and economy. Before the liberalization came into practice, the coffee farmers of Uganda had a Coffee Marketing Board organized by the Government that worked as a middle man between the farmers and the foreign buyers. Even though the farmer’s infrastructure cost was to be paid, they were assured of a standard price. However, with the introduction of Globalization, Coffee making board was abolished, and the farmers had to shelter in the unpredictability of the world market.
Impact of Globalization on Employment
With the introduction of Globalization, the structure of employment opportunities in developing nations has taken a turn. Before the inception of Globalization, the main source of occupation and economy in developing countries was based on agriculture among both men and women. With the introduction of foreign industrial corporations, the section of people has shifted their occupation from agriculture and joined industries as laborers required for mass production. This led to a small scale of people working in the fields. Evidence shows the decrease of male workers in agricultural areas by sixty-two percent and the female workers by fourteen percent. The increasing unstable income and unemployment with no guarantee of their future result from the employment structure in the developing countries.
Globalization has led to mass unemployment as multinational companies outsource their services. The three main changes that Globalization leads people to are the changes in their income as laborers, changes in prices, and household production-consumption. Before Globalization, there was a difference between skilled and unskilled laborers. However, with serialization, the demand for educated workers gradually increased in the developing countries. Among several debates, the only conclusion found to be similar is that there has been the development of inequalities with Globalization in developing nations.
Impact of Globalization on Cultural Boundaries
Before Globalization came into existence, the native countries had their own culture and practices. It leads to the extinction of various native languages in developing countries. Today, people are keen to learn the common language around the Globe, English, and thus, the cessation of languages is taking place rapidly. The blend of western and local culture has led to the declination of cultural barriers, which has led people’s individuality and culture to fade away. The imbibing of extremist ideas and adaptation of multiple cultures has led to multiculturalism, causing terrorist attacks and suicide terrorism in countries like Sudan, Egypt, Tunisia, Somalia, and many more.
The free trade areas in the developing countries that welcome the foreign investors have turned to adapt more negative points than positives. The female workers of factories are physically and verbally abused to keep up with the foreign industrialists’ production demands, as mentioned in 2003, “The Hidden Face of Globalization”. To maximize production and profit, many multinational companies avoid maintaining a secure and safe environment for their workers. The Philco Ford assembly plant in Taiwan was recorded to kill twelve female workers due to toxic fumes. All these are also leading to a toxic environment harming the eco-friendly areas of the developing countries. Other than these, human trafficking, cheap labor, and other illegal practices are also a result of Globalization.
Impact of Globalization Essay Conclusion
Globalization is a complex procedure that is currently the topic of debate around the World. Since it has both positive and negative impacts on the developed and developing countries, many countries face economic wrath and a serious lack of growth and development. It is the leaders of developed countries’ responsibility to take measures and try to remove poverty from the developing countries and improve their style of living. Imposing various rational laws and reforms for a better guide of liberalization will help the developing countries. All the developing countries must get equal opportunities rather than focusing on a few countries to develop into a better country both in economy and health.
- Picture Dictionary
- English Speech
- English Slogans
- English Letter Writing
- English Essay Writing
- English Textbook Answers
- Types of Certificates
- ICSE Solutions
- Selina ICSE Solutions
- ML Aggarwal Solutions
- HSSLive Plus One
- HSSLive Plus Two
- Kerala SSLC
- Distance Education

- History & Society
- Science & Tech
- Biographies
- Animals & Nature
- Geography & Travel
- Arts & Culture
- Games & Quizzes
- On This Day
- One Good Fact
- New Articles
- Lifestyles & Social Issues
- Philosophy & Religion
- Politics, Law & Government
- World History
- Health & Medicine
- Browse Biographies
- Birds, Reptiles & Other Vertebrates
- Bugs, Mollusks & Other Invertebrates
- Environment
- Fossils & Geologic Time
- Entertainment & Pop Culture
- Sports & Recreation
- Visual Arts
- Demystified
- Image Galleries
- Infographics
- Top Questions
- Britannica Kids
- Saving Earth
- Space Next 50
- Student Center
- Introduction
- “Davos” culture
The international “faculty club”
Nongovernmental organizations, transnational workers.
- The persistence of local culture
- The compression of time and space
- Entertainment
- Religion and globalization
- Demographic influences
- Challenges to national sovereignty and identity
- Anti-globalism movements and the Internet
- Localized responses
- Borrowing and “translating” popular culture
- Subjectivity of meaning—the case of Titanic
- The ties that still bind

- Who controls the Internet?
- Is the Internet “making us stupid”?
- Is cancel culture (or “callout culture”) good for society?

cultural globalization
Our editors will review what you’ve submitted and determine whether to revise the article.
- CORE - Hybridity in Cultural Globalization
- National Center for Biotechnology Information - PubMed Central - Cultural syndromes in the era of globalization
- Seoul National University - S-Space - Cultural Globalization: Challenges and Responses
- BBC Future - Does globalization mean we will become one culture?
- Colorado Community College System’s Open Textbook - PPSC HIS 1120: The World: 1500-Present - Globalization
- Table Of Contents
cultural globalization , phenomenon by which the experience of everyday life, as influenced by the diffusion of commodities and ideas, reflects a standardization of cultural expressions around the world. Propelled by the efficiency or appeal of wireless communications , electronic commerce , popular culture , and international travel, globalization has been seen as a trend toward homogeneity that will eventually make human experience everywhere essentially the same. This appears, however, to be an overstatement of the phenomenon. Although homogenizing influences do indeed exist, they are far from creating anything akin to a single world culture .
Emergence of global subcultures
Some observers argue that a rudimentary version of world culture is taking shape among certain individuals who share similar values, aspirations , or lifestyles. The result is a collection of elite groups whose unifying ideals transcend geographical limitations.
“ Davos ” culture
One such cadre, according to political scientist Samuel Huntington in The Clash of Civilizations (1998), comprises an elite group of highly educated people who operate in the rarefied domains of international finance, media, and diplomacy. Named after the Swiss town that began hosting annual meetings of the World Economic Forum in 1971, these “ Davos ” insiders share common beliefs about individualism , democracy , and market economics. They are said to follow a recognizable lifestyle, are instantly identifiable anywhere in the world, and feel more comfortable in each other’s presence than they do among their less-sophisticated compatriots.
The globalization of cultural subgroups is not limited to the upper classes. Expanding on the concept of Davos culture, sociologist Peter L. Berger observed that the globalization of Euro-American academic agendas and lifestyles has created a worldwide “faculty club”—an international network of people who share similar values, attitudes, and research goals. While not as wealthy or privileged as their Davos counterparts, members of this international faculty club wield tremendous influence through their association with educational institutions worldwide and have been instrumental in promoting feminism, environmentalism, and human rights as global issues. Berger cited the antismoking movement as a case in point: the movement began as a singular North American preoccupation in the 1970s and subsequently spread to other parts of the world, traveling along the contours of academe’s global network.
Another global subgroup comprises “ cosmopolitans” who nurture an intellectual appreciation for local cultures . As pointed out by Swedish anthropologist Ulf Hannerz, this group advocates a view of global culture based not on the “replication of uniformity” but on the “organization of diversity.” Often promoting this view are nongovernmental organizations (NGOs) that lead efforts to preserve cultural traditions in the developing world. By the beginning of the 21st century, institutions such as Cultural Survival were operating on a world scale, drawing attention to indigenous groups who are encouraged to perceive themselves as “first peoples”—a new global designation emphasizing common experiences of exploitation among indigenous inhabitants of all lands. By sharpening such identities, these NGOs have globalized the movement to preserve indigenous world cultures.
Another group stems from the rise of a transnational workforce. Indian-born anthropologist Arjun Appadurai has studied English-speaking professionals who trace their origins to South Asia but who live and work elsewhere. They circulate in a social world that has multiple home bases, and they have gained access to a unique network of individuals and opportunities. For example, many software engineers and Internet entrepreneurs who live and work in Silicon Valley , California, maintain homes in—and strong social ties to—Indian states such as Maharashtra and Punjab .
- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- AI Essentials for Business
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Creating Brand Value
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading Change and Organizational Renewal
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
4 Effects of Globalization on the Environment

- 15 Apr 2021
Globalization —defined in the online course Global Business as the increased flow of goods, services, capital, people, and ideas across international boundaries—has brought many changes in its wake.
While globalization can positively and negatively impact society, its effect on the environment is primarily negative. Here’s a breakdown of how globalization impacts society and the environment and what business leaders can do to reduce these negative consequences.
How Does Globalization Affect Society?
The world has become more connected than ever before through the increase in technological advancements and economic integrations. Advanced economies are formed as domestic businesses transform into international ones and further contribute to the spread of technology around the world.
There are several benefits of globalization , such as increased international trade and cooperation and less international aggression. Social globalization —the sharing of ideas and information between countries—has led to innovation in the medical, technological, and environmental preservation industries.
Additionally, globalization has improved the quality of life in several developing nations. This includes implementing efficient transportation systems and ensuring accessibility to services such as education and healthcare.
However, globalization can also have negative effects on society, such as increased income inequality and substandard working conditions in developing countries that produce goods for wealthier nations. Income inequality is directly related to globalization as it further increases the gap between more advanced and developing areas of a nation. As a result, it can also increase the risk of societal violence.
Along with its societal effects, globalization has a lasting impact on the environment—and typically not a positive one.
Access your free e-book today.
What Are the Effects of Globalization on the Environment?

1. Increased Transport of Goods
One of the primary results of globalization is that it opens businesses up to new markets in which they can sell goods and source labor, raw materials, and components.
Both of these realities mean finished products travel farther now than ever before—potentially halfway around the globe. In the past, products were more likely to be produced, sold, and consumed locally. This increased transport of goods can impact the environment in several ways, including:
- Increased emissions: The farther a product travels, the more fuel is consumed, and a greater level of greenhouse gas emissions is produced. According to a report by the International Transport Forum , CO2 emissions from transport will increase 16 percent by 2050. These emissions contribute to pollution, climate change , and ocean acidification around the world and have been shown to significantly impact biodiversity.
- Habitat destruction: Transportation—especially when land-based—requires infrastructure like roads and bridges. The development of such infrastructure can lead to issues including habitat loss and pollution. The more ships that travel by sea, the greater the chances for major oil spills or leaks that damage the delicate marine environment.
- Invasive species: Every shipping container and vessel presents an opportunity for a living organism—from plants to animals to fungus—to hitch a ride to a new location where it can become invasive and grow without checks and balances that might be present in its natural environment.
2. Economic Specialization
One often-overlooked side effect of globalization is that it allows nations and geographical regions to focus on their economic strengths while relying on trading partners for goods they don’t produce themselves. This economic specialization often boosts productivity and efficiency.
Unfortunately, overspecialization can threaten forest health and lead to serious environmental issues, often in the form of habitat loss, deforestation, or natural resource overuse. A few examples include:
- Illegal deforestation in Brazil due to an increase in the country’s cattle ranching operations, which requires significant land for grazing
- Overfishing in coastal areas that include Southeast Asia, which has significantly contributed to reduced fish populations and oceanic pollution
- Overdependence on cash crops, such as coffee, cacao, and various fruits, which has contributed to habitat loss, especially in tropical climates
It’s worth considering that globalization has allowed some nations to specialize in producing various energy commodities, such as oil, natural gas, and timber. Nations that depend on energy sales to fund a large portion of their national budgets, along with those that note “energy security” as a priority, are more likely to take intervening actions in the market in the form of subsidies or laws that make transitioning to renewable energy more difficult.
The main byproduct of these energy sources comes in the form of greenhouse gas emissions, which significantly contribute to global warming and climate change.
3. Decreased Biodiversity
Increased greenhouse gas emissions, ocean acidification, deforestation (and other forms of habitat loss or destruction), climate change, and the introduction of invasive species all work to reduce biodiversity around the globe.
According to the World Wildlife Fund’s recent Living Planet Report , the population sizes of all organisms—including mammals, birds, fish, amphibians, and reptiles—have decreased 68 percent since 1970. Latin America and Africa—two rapidly developing regions important to global trade—have seen disproportionate levels of biodiversity loss, especially among environmentally sensitive fish, reptiles, and amphibians.
While this decrease in biodiversity has many causes, it’s widely believed that the issues listed above have contributed in part.
4. Increased Awareness
While many of globalization’s environmental effects have been negative, its increase has heightened environmental awareness worldwide.
Greater connectivity and higher rates of international travel have made it easier than ever for individuals to see the effects of deforestation, habitat loss, and climate change on the environment. This, in turn, has contributed to new laws, regulations, and processes that limit negative effects.

Globalization as a Threat and an Opportunity
Globalization has allowed society to enjoy many benefits, including increased global cooperation, reduced risk of global conflict, and lower prices for goods and commodities. Unfortunately, it’s also led to serious negative effects on the environment.
Since it isn’t feasible for globalization to end or reverse, it’s likely the situation will worsen until nations, governing bodies, and other organizations are compelled to implement laws and regulations that limit negative effects.
Businesses and industries that operate globally have an incentive to take whatever voluntary actions they can to reduce the potential for negative consequences. Doing so can not only provide an organization greater control over its initiatives, but also a powerful marketing and communication tool .
Some ways businesses address climate change include:
- Transitioning to renewable energy sources
- Choosing greener infrastructures or equipment
- Reducing energy consumption
- Creating credible climate transition plans
- Raising awareness among employees
In addition, investing in renewable energy and packaging, embracing responsible land-use management, and shifting goods production to move closer to the end customer are all viable options that businesses can and should consider. The challenge lies in balancing a desire to embrace corporate social responsibility with the need to turn a profit and run a successful business.
Are you interested in breaking into a global market? Sharpen your knowledge of the international business world with our four-week Global Business course. In addition, explore our Business and Climate Change course to help your organization adapt to and embrace business risks and opportunities created by climate change, as well as our other online courses related to business in society .
This post was updated on February 28, 2024. It was originally published on April 15, 2021.

About the Author

Is globalization an engine of economic development?
All people living in today's world have experienced some of the benefits of globalization: the expansion of foreign trade has meant that vaccines and antibiotics produced in a handful of countries have been widely used all over the world to eradicate diseases and treat deadly infections. Since 1900, life expectancy has increased in every country in the world , and global average life expectancy has more than doubled .
Globalization has also been a key driver of unprecedented economic growth and as a result, we now live in a world with much less poverty .
Yet these achievements are the product of multiple forces, and globalization is only one of them. The increasing potential of governments to collect revenues and redistribute resources through social transfers has been another important factor contributing to improved standards of living around the world. Neither free market capitalism nor social democracy alone has been responsible for economic development. On the contrary, they often work together.
In this blog post, we discuss in more detail the evidence behind these claims.
The rise of globalization
International trade has been part of the world economy for thousands of years . Despite this long history, the importance of foreign trade was modest until the beginning of the 19th century—the sum of worldwide exports and imports never exceeded 10% of global output before 1800 .
Then around 1820 things started to change quickly. Around that time, technological advances and political liberalism triggered what we know today as the 'first wave of globalization'.
This first wave of globalization came to an end with the beginning of the First World War, when the decline of liberalism and the rise of nationalism led to a collapse in international trade. But this was temporary and after the Second World War, trade started growing again. This second wave of globalization, which continues today, has seen international trade grow faster than ever before. Today, around 60% of all goods and services produced in the world are shipped across country borders. (In our entry on International Trade you find more details regarding the particular features that characterize the first and second waves of globalization.)
The chart here shows the remarkable growth of foreign trade since 1800. The series shows the value of world exports in constant prices—world exports have been indexed, so that values are relative to the value of exports in the year 1913.
The broad trend in this chart is striking: Trade followed an exponential path. Other metrics of trade, such as the share of imports and exports in global output , tell the same story.
In just a few generations, globalization completely changed the world economy.
The correlation between globalization, economic growth and poverty reductions
In the period in which international trade expanded, the average world income increased substantially and the share of the population living in extreme poverty went down continuously.
GDP per capita is a common metric used for measuring national average incomes. By this measure, average incomes followed a similar growth pattern to international trade. For thousands of years, global GDP per capita had a negligible growth rate: technological progress in the preindustrial world produced people rather than prosperity . Over the course of the 19th century, however, alongside the first wave of globalization, this changed substantially. In this period, economic growth started accelerating and global GDP per capita has been growing constantly over the last two centuries—with the exception of lower growth rates during the years between the two world wars. (You can read more about these trends in our entry on Economic Growth .)
Regarding extreme poverty, the available evidence shows that up until 1800, the vast majority of people around the world lived in extreme deprivation , with only a tiny elite enjoying higher standards of living. In the 19th century we began making progress and the share of people living in extreme poverty started to slowly decline. This trend is shown in the chart here. As we can see, today, two hundred years later, the share of people living in extreme poverty is less than 10%. This is an achievement that would have been unthinkable to our ancestors. 1
The stark trend in the incidence of poverty is particularly remarkable if we consider that the world population increased 7-fold over the same period. In a world without economic growth, such an increase in the population would have resulted in less and less consumption for everyone. And yet, as the chart shows if you switch to the 'absolute' view, the exact opposite happened: in a time of unprecedented population growth, we managed to lift more and more people out of poverty.
Living with less than 1.90 dollars per day is difficult by any standard—the term 'extreme poverty' is appropriate. However, recent estimates show that no matter what global poverty line you choose, the share of people below that poverty line has declined . (In our entry on Global Extreme Poverty you can find more evidence supporting this important historical achievement.)
The link between globalization and absolute poverty
The fact that trade and average incomes followed similar upward trajectories in a period of unprecedented poverty reduction is of course not proof of a causal relationship. However, both evidence and theory suggest that what we observe is more than an accidental correlation.
Trade facilitates efficiency gains that are materialized in aggregate economic growth. From a conceptual point of view, international trade contributes to economic growth by allowing nations to specialize, in order to produce goods that they are relatively efficient at producing, while importing other goods. There is substantial empirical evidence backing this causal mechanism .
If trade leads to growth in average incomes, what does this mean for poverty? In a much-cited 2002 academic article, David Dollar and Aart Kraay empirically showed that on average, the income of the poorest grew one-for-one with average national incomes over the last four decades of the 20th century. 2 This means that trade has helped raise the incomes of the poor as much as it has helped raise average incomes. More recent articles have confirmed the original findings from Dollar and Kraay. 3
When taken together, the evidence thus tells us that globalization has contributed to reducing poverty around the world.
The link between globalization and inequality
That globalization is good for the poor is a statement that is true on average . In some countries and in some periods the poor did better than average, and sometimes they did worse.
Looking at the long-run average effect is very helpful to form an opinion regarding broad trends. However, these broad trends are not necessarily informative about how trade has affected the distribution of incomes generally; nor about how trade has affected specific groups of people in specific periods.
The same economic principles that suggest we should lend serious consideration to the efficiency gains from trade, suggest that we should do likewise for the distributional consequences from trade. If globalization generates growth by allowing countries to specialize in the production of goods that intensively use locally abundant resources, it is natural to expect that differences in the way resources are endowed will translate into differences in the way benefits are reaped.
If we take a look at the data, we observe that the process of globalization and growth that led to historical achievements in poverty reductions went along with a substantial increase in global income inequality .
The chart shows this by comparing the global income distribution at three points in time: 1800, 1975, and 2015. We can see that the world today is both much richer and more unequal than it was in 1800.
There are two forces that can drive global income inequality : within-country differences in incomes, and between-country differences in incomes. Which of the two is driving the trend we observe in this chart? The evidence suggests that it is the latter—global inequality increased in the period 1800-1975 because the countries that industrialized earlier grew faster.
In 1800, only a few countries had achieved economic growth while the majority of the world still lived in poverty. In the following century, more and more countries achieved sustained economic growth, and the global income distribution became much more unequal: there was a clear divergence between early-industrialized countries (where extreme forms of poverty were virtually eradicated) and the rest of the world. In the following decades and up until today, early-industrialized countries have continued growing, but the biggest changes have taken place at the bottom of the distribution. Today, global income inequality is lower than it was in 1975. But still, despite the ‘catch-up growth’ in recent decades, our world today is both much richer and more unequal than it was in 1800.
So, what does the data tell us about globalization? Over the last century, the gains from international trade were substantial and generally equally distributed within countries, but global inequality increased because for a long period early-industrialized countries had larger gains to distribute among their citizens.
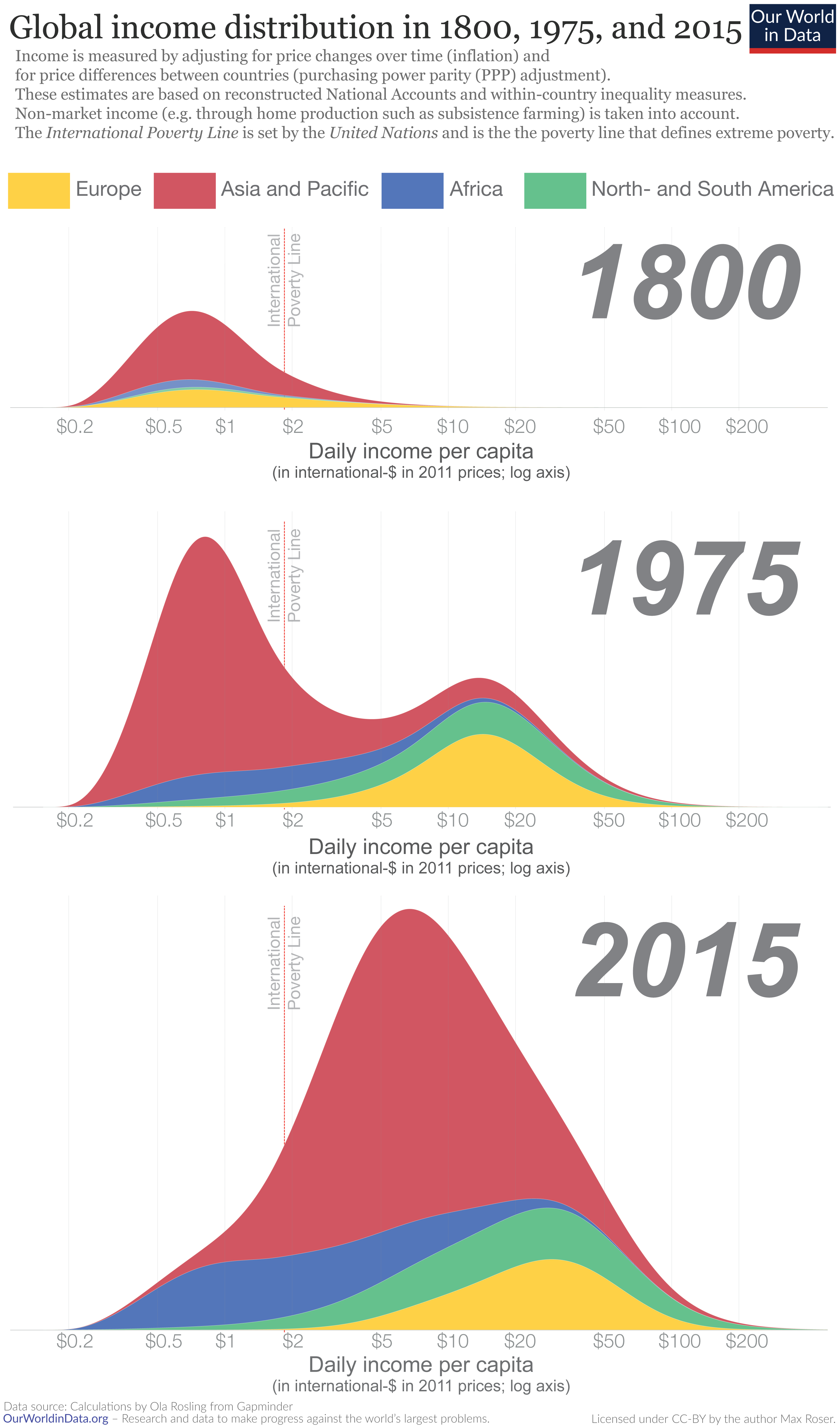
The distribution of the gains from trade
The above conclusion that globalization has not had substantial effects on global inequality may seem paradoxical to some people—there is substantial evidence of growing inequality in many countries, including countries that have vehemently pursued trade liberalization. A notable case in point is the US, where income inequality has been on the rise in the last four decades, with incomes for the bottom 10% growing much more slowly than incomes for the top 10% . (You can read more about these within-country trends in our entry on Income Inequality .)
How can we reconcile these two empirical facts? In a recent article, Elhanan Helpman provides an answer informed by a meta-analysis of the available evidence: factors such as automation, technological changes, and market frictions, have contributed to the rise of inequality more than growth in international trade has. 4
If this is the case, then why has the view that globalization is bad for the working class captured the political debate in rich countries? Part of the answer has to do with the fact that people are misinformed about the evidence. But another important reason is that, while globalization may not have been the prime cause of growing inequality within many rich countries, it remains true that there are specific groups of people who have not reaped many of the benefits from globalization in recent years.
Daniel Trefler published a paper in 2004 showing that the 1989 free trade agreement between the US and Canada temporarily increased (for about three years) the level of unemployment in Canada. 5 And David Autor and colleagues published another much cited article in 2013 showing that imports from China had diverging effects on employment across various geographical zones in the US, with employment declining more in zones where industries were more exposed to import competition from China. 6
These effects on specific groups are real and need to be taken into account, even if they do not imply that ‘globalization is bad for the poor’. Public policies should protect and compensate workers whose earnings are adversely affected by globalization. And as a matter of fact, public policies in rich countries have done this to some degree in the past. As painful as job losses are for the affected workers, it is thanks to unemployment benefits and other safety-net policies that we do not observe unemployment leading to widespread extreme poverty in rich countries.
Which way forward?
Has globalization been an engine of economic development? The answer is yes. Globalization has had a positive effect on economic growth, contributing to rising living standards and the reduction of extreme poverty across the world.
Can we conclude from this that we should strive for a ‘hyper-globalized’ world economy in which there is completely free trade with no room for public policy and regulation? The answer is no.
The point is that the worldwide historical achievements that we can attribute to globalization are not independent of other factors, including the potential of governments to redistribute resources. Indeed, as the last chart here shows, the process of globalization that we have experienced in the last couple of centuries took place at the same time as governments increased their potential for taxing and redirecting resources through public policies, particularly social transfers.
How much integration in global markets would be optimal? I would be skeptical of anyone who offers a definitive answer. But it seems unlikely that the optimal degree of integration is either of the two extremes—neither ‘hyper-protectionism’ nor ‘hyper-globalization’ is likely to be the answer.
Policies aimed at liberalizing trade, and policies aimed at providing social safety nets, are often advocated by different groups, and it is common for these groups to argue that they are in conflict. But both economic theory and the empirical evidence from the successful fight against extreme poverty suggests this is a mistake: globalization and social policy should be treated as complements rather than substitutes.
The data in the chart here measures ‘extreme poverty’ as defined by the World Bank; people are considered to live in extreme poverty if they have to get by with less than 1.90 ‘international dollars’ per day. International dollars are a hypothetical currency that corrects incomes for differences in price levels in different countries as well as for inflation (explained by us here ).
Dollar, David, and Aart Kraay. "Growth is Good for the Poor." Journal of economic growth 7.3 (2002): 195-225.
See, for example, Dollar and Kraay (2004), "Trade, growth, and poverty." The Economic Journal 114.493 (2004) ; and Dollar, Kleineberg and Kraay (2014), "Growth, inequality, and social welfare : cross-country evidence." Policy Research Working Paper.
Helpman, Elhanan. Globalization and Wage Inequality. No. w22944. National Bureau of Economic Research, 2016.
Trefler, Daniel. "The long and short of the Canada-US free trade agreement." The American Economic Review 94.4 (2004): 870-895.
David, H., David Dorn, and Gordon H. Hanson. "The China syndrome: Local labor market effects of import competition in the United States." The American Economic Review 103.6 (2013): 2121-2168.
Cite this work
Our articles and data visualizations rely on work from many different people and organizations. When citing this article, please also cite the underlying data sources. This article can be cited as:
BibTeX citation
Reuse this work freely
All visualizations, data, and code produced by Our World in Data are completely open access under the Creative Commons BY license . You have the permission to use, distribute, and reproduce these in any medium, provided the source and authors are credited.
The data produced by third parties and made available by Our World in Data is subject to the license terms from the original third-party authors. We will always indicate the original source of the data in our documentation, so you should always check the license of any such third-party data before use and redistribution.
All of our charts can be embedded in any site.
Our World in Data is free and accessible for everyone.
Help us do this work by making a donation.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Globalization Essay
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
When discussing the drawbacks and benefits of globalization, essays tend to be on the longer side. The example below is a brief exploration of this complex subject. Learn more in this concise globalization pros and cons essay.
Introduction
- Benefits and Disadvantages of Globalization
Reducing Negative Effects
In today’s world, globalization is a process that affects all aspects of people’s lives. It also has a crucial impact on businesses and governments as it provides opportunities for development while causing significant challenges. This paper discusses the advantages and disadvantages of globalization using evidence from academic sources. The report also suggests how governments and companies may implement to reduce the negative impact of the process.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Globalization
Globalization is a complex concept that can be defined by the process of interaction between organizations, businesses, and people on an international scale, which is driven by international trade. Some people may associate it with uniformity, while others can perceive it as the cause of diversification. The reason for such a difference in public opinion is that globalization has both advantages and disadvantages that should be analyzed.
The most significant positive aspects of globalization include global economic growth, the elimination of barriers between nations, and the establishment of competition between countries, which can potentially lead to a decrease in prices. Globalization supports free trade, creates jobs, and helps societies to become more tolerant towards each other. In addition, this process may increase the speed of financial and commercial operations, as well as reduce the isolation of poor populations (Burlacu, Gutu, & Matei, 2018; Amavilah, Asongu, & Andrés, 2017).
The disadvantages of globalization are that it causes the transfer of jobs from developed to lower-cost countries, a decrease in the national intellectual potential, the exploitation of labor, and a security deficit. Moreover, globalization leads to ecological deficiency (Ramsfield, Bentz, Faccoli, Jactel, & Brockerhoff, 2016). In addition, this process may result in multinational corporations influencing political decisions and offering unfair working conditions to their employees.
Firms and governments can work on eliminating the negative effects of globalization in the following ways. For example, countries should work on microeconomic policies, such as enhancing opportunities for education and career training and establishing less rigid labor markets. In addition, governments can build the necessary institutional infrastructure to initiate economic growth. To solve the problem of poor working conditions, it is vital to establish strict policies regarding minimum wages and the working environment for employees. A decrease in the national intellectual potential may be addressed by offering a broad range of career opportunities with competitive salaries, as well as educating future professionals on how their skills can solve problems on the local level.
Companies, in their turn, may invest in technologies that may lead to more flexible energy infrastructure, lower production costs, and decrease carbon emissions. They can also establish strong corporate cultures to support their workers and provide them with an opportunity to share their ideas and concerns. Such an approach may eliminate employees’ migration to foreign organizations and increase their loyalty to local organizations. It is vital for companies to develop policies aimed at reducing a negative impact on the environment as well by using less destructive manufacturing alternatives and educating their employees on ecology-related issues.
Globalization has a significant impact on companies, governments, and the population. It can be considered beneficial because it helps to eliminate barriers between nations, causes competition between countries, and initiates economic growth. At the same time, globalization may result in a decrease in the national intellectual potential, the exploitation of labor, and ecology deficiency. To address these problems, organizations and governments can develop policies to enhance the population’s education, improve working conditions, and reduce carbon emissions.
Amavilah, V., Asongu, S. A., & Andrés, A. R. (2017). Effects of globalization on peace and stability: Implications for governance and the knowledge economy of African countries. Technological Forecasting and Social Change , 122 (C), 91-103.
Burlacu, S., Gutu, C., & Matei, F. O. (2018). Globalization – Pros and cons. Calitatea , 19 (S1), 122-125.
Ramsfield, T. D., Bentz, B. J., Faccoli, M., Jactel, H., & Brockerhoff, E. G. (2016). Forest health in a changing world: Effects of globalization and climate change on forest insect and pathogen impacts. Forestry , 89 (3), 245-252.
- Globalization of Bollywood and Its Effects on the UAE
- Globalization and Its Impact on the 21st Century Global Marketplace
- Disease Ecology Definition
- How Does Iron Deficiency Affect Pregnancy?
- Ecology: Definition & Ecological Fallacy
- Multinational Corporations Economic Implications
- Globalisation and Labour Market
- Impact of Globalisation on Labour
- The Origins of the Modern World
- Containerized Shipping Influence on World Economies
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2021, June 9). Advantages and Disadvantages of Globalization Essay. https://ivypanda.com/essays/advantages-and-disadvantages-of-globalization/
"Advantages and Disadvantages of Globalization Essay." IvyPanda , 9 June 2021, ivypanda.com/essays/advantages-and-disadvantages-of-globalization/.
IvyPanda . (2021) 'Advantages and Disadvantages of Globalization Essay'. 9 June.
IvyPanda . 2021. "Advantages and Disadvantages of Globalization Essay." June 9, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/advantages-and-disadvantages-of-globalization/.
1. IvyPanda . "Advantages and Disadvantages of Globalization Essay." June 9, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/advantages-and-disadvantages-of-globalization/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "Advantages and Disadvantages of Globalization Essay." June 9, 2021. https://ivypanda.com/essays/advantages-and-disadvantages-of-globalization/.
IvyPanda uses cookies and similar technologies to enhance your experience, enabling functionalities such as:
- Basic site functions
- Ensuring secure, safe transactions
- Secure account login
- Remembering account, browser, and regional preferences
- Remembering privacy and security settings
- Analyzing site traffic and usage
- Personalized search, content, and recommendations
- Displaying relevant, targeted ads on and off IvyPanda
Please refer to IvyPanda's Cookies Policy and Privacy Policy for detailed information.
Certain technologies we use are essential for critical functions such as security and site integrity, account authentication, security and privacy preferences, internal site usage and maintenance data, and ensuring the site operates correctly for browsing and transactions.
Cookies and similar technologies are used to enhance your experience by:
- Remembering general and regional preferences
- Personalizing content, search, recommendations, and offers
Some functions, such as personalized recommendations, account preferences, or localization, may not work correctly without these technologies. For more details, please refer to IvyPanda's Cookies Policy .
To enable personalized advertising (such as interest-based ads), we may share your data with our marketing and advertising partners using cookies and other technologies. These partners may have their own information collected about you. Turning off the personalized advertising setting won't stop you from seeing IvyPanda ads, but it may make the ads you see less relevant or more repetitive.
Personalized advertising may be considered a "sale" or "sharing" of the information under California and other state privacy laws, and you may have the right to opt out. Turning off personalized advertising allows you to exercise your right to opt out. Learn more in IvyPanda's Cookies Policy and Privacy Policy .

Teasing out the disruptive effects of globalization
Professor Gordon Hanson pursues a lifelong fascination with the movements of people, the evolution of labor markets, and why place matters.

Q: How do your research and teaching connect to the solution of pressing problems in the world today?

“Place matters in terms of your material well-being. Where you live has an outsized impact on the quality of jobs available to you and your capacity to enjoy the benefits of globalization and technological progress.”
Q: What surprising things have you come across in your work?
One thing that's been surprising to me is that in many regions hard hit by global competition—which often see dramatic reductions in employment—workers don’t leave. We’ve long had this notion that the United States labor market is dynamic and flexible, such that if we lose jobs in one part of the economy, we’ll simply create jobs in another part of economy. Workers will relocate from one place to another in response. Yet, as we’ve come to appreciate the adverse impacts of globalization, we’ve seen that job loss tends to persist over extended periods of time. Relatively few workers migrate out and relatively few new firms open up shop to hire displaced labor. Job loss ends up creating concentrated and long-lived pockets of disruption in large part because people don’t move out of declining regions. If we want to find solutions to the persistent regional economic divides that exist in the United States, we need to start with the idea that we must generate new employment in distressed places, rather than thinking that we can convince people in distressed places to move somewhere else.
Q: You’re teaching “ Urban Economic Policy ” (SUP-680). What is the most important thing you want students to take away from your class?
Place matters in terms of your material well-being. Where you live has an outsized impact on the quality of jobs available to you and your capacity to enjoy the benefits of globalization and technological progress. If we want to create a vibrant economy and with widespread economic opportunity, it is essential that economic growth and development be as regionally inclusive as possible.
Q: How have your life experiences influenced your academic direction?
When I was a child, my parents were mission doctors working in northern Thailand. I grew up learning about how modern medicine can help address health challenges in parts of the world that—at least at that time—had poorly developed health systems. How do we deal with the challenges of infectious disease? How do we bring new technology to communities where people may not be comfortable with modern methods? We moved back to California in 1970 to live in Fresno County, which would see one of the largest influxes of immigrant workers anywhere in the country. On a personal level, immigration changed who I went to school with; at a community level, immigration allowed Fresno to grow and prosper. While immigration added cultural richness and diversity, it also created social tension within the community—between rival schools and between rival groups within schools. Without necessarily articulating it or thinking about it analytically at the time, I grew up surrounded by the impacts of globalization. Later, when I encountered economics in college, I realized, “Wow, you know, I can use this to understand the stuff that I’ve lived through.”
Immigrant agricultural workers critical to U.S. food security amid COVID-19 outbreak harvest romaine lettuce on a machine with heavy plastic dividers that separate workers from each other in Greenfield, California.
Photo by Brent Stirton; faculty portrait by Martha Stewart

More from HKS
First research findings measure covid-19 prevalence in u.s. prisons, jails, “a very, very serious headache on economic activity”: q&a with ricardo hausmann..
Get smart & reliable public policy insights right in your inbox.
Advertisement
The impact of economic, social, and political globalization and democracy on life expectancy in low-income countries: are sustainable development goals contradictory?
- Published: 18 January 2021
- Volume 23 , pages 13508–13525, ( 2021 )
Cite this article

- Arif Eser Guzel ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-5072-9527 1 ,
- Unal Arslan 1 &
- Ali Acaravci 1
114k Accesses
49 Citations
10 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
The 17 Sustainable Development Goals announced by the United Nations are important guides for the development processes of developing countries. However, achieving all of these goals is only possible if the goals are consistent with each other. It has been observed in the literature that possible contradictions between these goals are ignored. Therefore, the main purpose of this study is to investigate whether two sustainable development goals (SDGs) of the UN are contradictory or supporting each other in low-income countries. These SDGs are “Good Health and Well-Being” (SDG3) and “Partnerships for the Goals” (SDG17). For this purpose, the role of globalization and democracy in life expectancy is empirically investigated in 16 low-income countries over the period 1970–2017. While globalization has been used as an indicator of the partnership between countries, democracy has been used as an indicator of accountability and cooperation between governments and societies. According to estimations of the continuous-updated fully modified (CUP-FM) and bias-adjusted ordinary least squares (BA-OLS), globalization and its subcomponents such as economic, social, and political globalization affect life expectancy positively. Democracy also increases life expectancy in those countries. The GDP per capita is also used as a control variable. Our results show that a higher level of per capita income is positively associated with higher levels of life expectancy. In conclusion, no contradiction was found between SDG3 and SDG17 in those countries. Achieving a healthier society requires economic, social, and political integration between governments and societies.
Similar content being viewed by others

The Human Development Index as the Key Indicator for Measuring the Quality of Life of the Population in Altai Krai

Comparing Life Expectancy Determinants Between Indonesia and Oman from 1980 to 2020

Human Development Index
Explore related subjects.
- Medical Ethics
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
The main problem of economics is to increase economic development and social welfare. Increasing the social welfare level is a complex process that depends on economic and non-economic factors. Achieving economic development or increasing the level of welfare depends on achieving and sustaining the main objectives in political, economic, and social areas. Today, development is no longer a process that can be realized through policies implemented by governments alone. It requires cooperation between governments and societies. While cooperation between different countries requires globalization in the economic, social, and political fields, democracy is the way to ensure cooperation between governments and societies.
Health is one of the most important indicators of social welfare. Besides being one of the indicators of development, it is one of the determinants of human capital formation which is necessary for economic development. Individuals living in developed countries live a healthier life compared to those living in less developed countries. While the differences between the levels of development of countries determine the health conditions, at the same time, improvement of public health paves the way for economic development. Healthy people have higher opportunities to earn a higher income than unhealthy people. Individuals with higher incomes can benefit from better nutrition and access to health services. Therefore, economic development and improvement of health conditions represent a two-way process. In this context, the determination of the variables that will enable the achievement of the goal of a healthier society is especially important in explaining the economic differences between developing countries and developed countries. Because of its importance, health-related goals have an important place both among the Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) announced by the United Nations.
The world leaders with the support of international funding organizations announced the Millennium Declaration in September 2000 at the United Nations Headquarters in New York. They committed their nations to a new international partnership to achieve some development targets having with the final deadline of 2015. The Millennium Development Goals (MDGs) consist of 8 goals, 21 targets, and 60 related indicators covering a wide spectrum of development areas such as “End Poverty and Hunger (MDG 1),” “Universal Education (MDG 2),” “Gender Equality (MDG 3),” “Child Health (MDG 4),” “Maternal Health (MDG 5),” “Combat HIV/AIDS (MDG 6),” “Environmental Sustainability (MDG 7),” and “Global Partnership (MDG 8).” As we see, three of the goals are directly associated with the health status of the people. In the deadline of 2015, according to “Health in 2015: From MDGs to SDGs” report of the World Health Organization (WHO), there are improvements in health-related targets such as child health, maternal health, and combat with HIV/AIDS. Globally, HIV, tuberculosis, and malaria targets have been met. Also, the child mortality rate was reduced by 53% and maternal mortality by 43% (WHO 2016 ). On a global view, although health-related problems are largely resolved, the situation is not as good for low-income countries. As shown in Fig. 1 , significant differences exist between developing countries and developed countries in achieving health-related goals.
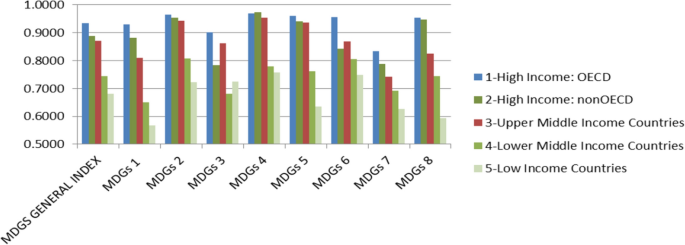
Source Halisçelik and Soytas (2015)
World Bank Income Groups’ MDGs Index Values in 2015.
According to MDGs, indexes in the context of health status show that the goals desired in terms of health are not attained in low-income countries compared to other income groups. After the deadline of MDGs, the United Nations has announced 17 SDGs, and “Good Health and Well-Being” takes its place as the third goal. Since achieving these goals requires the cooperation of countries and societies, “Partnership for the Goals” is determined as the seventeenth SDG. According to the United Nations ( 2019 ), the main indicators of global partnerships are trade, foreign direct investments, remittances, financial integration technology transfers, data monitoring and accountability, internet usage, and political integration among countries. In our study, while globalization is used as a proxy indicator of global cooperation, democracy is an indicator of cooperation between societies and governments. Democracy also refers to accountability levels of governments.
Globalization can simply be defined as the process of international integration which has economic, social, and political dimensions (Dreher 2006 ). Many countries have adapted to this process and have enjoyed the welfare effects of globalization by implementing necessary economic and institutional transformation. However, some countries still suffer from poor adaption to global markets. According to the KOF Globalization Index published by the Swiss Economic Institute ( 2020 ), low-income countries have the lowest globalization level compared to other income groups. They also suffer from bad health conditions such as low life expectancy, communicable diseases, and high mortality rates according to MDG indexes given above. At this point, the literature is divided into two parts. The first one blames globalization and argues that poverty and as a result of this, low life expectancy derives from the inequality created by globalization itself (Buss 2002 ). The second group mostly focuses on the benefits of free trade, capital mobility, and technology transfers (Rao and Vadlamannati 2011 ). The low-income countries also suffer from low institutional quality in the context of democracy and political rights. According to Freedom House’s list of electoral democracies, the countries without electoral democracy are mostly the low-income countries in the Middle East, North Africa, Sub-Saharan Africa, and Southeast Asia (Freedom House 2019 ).
The main question of our study is to determine whether the problem of low life expectancy in low-income countries is due to the low levels of globalization and weak political institutions in these countries. To answer this question, the role of economic, social, and political globalization and democracy in life expectancy in those countries is empirically investigated. This study provides several contributions to previous literature. First, we provide a new perspective in the context of sustainable development goals. Previous studies mostly focused on how to achieve SDGs, while possible conflicts between the goals were mostly ignored especially in the context of health. Such conflicts between sustainable development goals in the literature have mostly focused on the impact of economic growth and globalization on the sustainable environment (Ulucak and Bilgili 2018 ; Zafar et al. 2019a ). Those studies are mostly addressed the relationship between SDG7, SDG8, SDG13, and SDG17 (Zafar et al. 2019b ). To the best of our knowledge, it is the first study that investigates the relationship between SDG3 and SDG17. It is also important to examine this relationship in low-income countries since they still suffer from low levels of life expectancy, less adaptation to globalization, and poor democratic institutions compared to other income groups. Previous works mostly provide global evidence, while only a few studies focus on less developed countries. Achieving these 17 goals put forward by the United Nations at the same time is possible only if these goals do not conflict with each other. Second, empirical works in previous literature consist of traditional estimation methods called first-generation tests. In the analysis of panel data, the estimators considering cross-sectional dependence are called the second-generation estimators. Cross-sectional dependency simply refers to the situation when the shock that occurs in one country affects other countries as well. The source of this problem encountered in panel data analysis is the economic, financial, and political integration among countries (Menyah et al. 2014 ). The ignorance of cross-sectional dependence results in biased and inconsistent estimates and wrong inferences (De Hoyos and Sarafidis 2006 ; Chudik and Pesaran 2013 ). Low-income countries are mostly African countries where there is a rising trend in terms of integration to global markets and institutions (Beck et al. 2011 ). Using estimation techniques that consider cross-sectional dependence in those countries prevents misleading results. As the literature is divided into two parts about the effects of globalization on human well-being, fresh evidence via robust estimation methods is required in order to provide proper policy implications. To fill this gap, our work provides second-generation estimations.
2 Literature review
To improve the health conditions of a country, the welfare of the poor should be improved as well. Poverty is detrimental to access to health services. Therefore, the positive impact of globalization on health first emerged with its positive effects on economic growth (Labonté et al. 2009 : 10). The effects of globalization on growth were mostly driven by free trade, international specialization, technology transfers, knowledge spillovers, and competitive markets. It also offers broader opportunities for entrepreneurs and paves the way for innovation (Grossman and Helpman 2015 : 101). As expected, poverty rates significantly reduced in the last two decades because of the integration of developing economies to global markets (Harrison 2006 ). When trade liberalization and income increases are considered together, people's access to treatments and medications can be easier and life expectancy may be prolonged. However, we should consider other possibilities in the context of spreading communicable diseases. As Deaton ( 2004 ) mentioned before, access to cheap and easy travel can increase the rate of spread of communicable diseases. Migration is also another fact to take into account. Particularly rising sexual tourism and migrant sex workers increase the spread of sexually transmitted diseases such as HIV/AIDS. But today there are improved treatment methods to solve these problems. Even HIV-infected people can survive with antiretroviral therapy, and it also reduces sexual transmission of the infection (Dollar 2001 ; Cohen et al. 2011 ). Due to the high cost of advanced drugs as in the case of antiretroviral therapy, it should be accepted that people in low-income countries will have trouble accessing the drugs (Buss 2002 ). There are approaches known as the unequal exchange that globalization increases inequality among countries and that developed countries are more profitable from the globalization process (Love, 1980 ). It may also increase domestic income inequality. There are a few studies that came with the conclusion that globalization rises inequality (Dreher and Gaston 2008 ; Ha 2012 ), but Bergh and Nilsson ( 2010 ) suggested a different perspective. Due to extensive R&D investments and scientific activities, developed countries can find new treatment methods and supply advanced drugs. The only way to access that knowledge and these drugs are trade and integration between developed and underdeveloped countries. Globalization can play an important role in improving the health conditions of low-income countries to the extent that it can provide these linkages. One should also notice that wider markets and higher returns are important factors that motivate entrepreneurs. Buss ( 2002 ) claimed that the intellectual property rights of advanced drugs belong to private firms in developed countries, and because of the strong protection of property rights, less developed countries have trouble accessing them. However, rising global human rights became an important step to advance public health issues against economic concerns in the trade of pharmaceutical products.
The human rights approach focuses on how globalization affected disadvantaged people worldwide (Chapman 2009 ). It is an important instrument in the suppression of the inequality created by economic globalization. Because of the pressure on the government about human rights, disadvantaged people are becoming able to meet their basic human needs. The role of political globalization on this point is forcing governments to adopt global institutions. It increases the number of international organizations in which a country is a member. This makes governments more accountable in the global area and forcing them to pay attention to protect human rights. Gelleny and McCoy ( 2001 ) also claimed that integration among countries leads to political stability. Therefore, governments' tendency to violate human rights in order to maintain their power becomes lesser. Moreover, as social dimensions of globalization expand and communication opportunities among people in different countries increase, the possibility of human rights violations being discovered by other people increases (Dreher et al. 2012 ). Governments that know the international sanctions required by these violations have to be more cautious against human rights violations. Social globalization also provides cultural integration among the world’s people, and it changes lifestyles and consumption patterns worldwide. The consequences of this change can have positive and negative effects. First, increased urban population and sedentary lifestyles may enhance prepared food consumption and reduce daily movements which result in rising obesity and diabetes (Hu 2011 ). Second, although rapidly increasing consumption options and diversity are known as welfare indicators, they also can cause stress which is known as an important determinant of many diseases both psychological and physical (Cutler et al. 2006 ). Third, due to knowledge spillovers and communication technology, people can learn about healthy nutrition and protection from communicable diseases. Thus, unhealthy but traditional consumption patterns and lifestyles may change. These days we experience the coronavirus epidemic and we see once again the importance of globalization. Countries are aware of infectious diseases in different parts of the world in a very short time and can take measures to stop the spread of the virus. The changes created by social and political globalization play a major role in this emergence. Social globalization enables people in very remote areas of the world to communicate with each other, while political globalization forces governments to be transparent about infectious diseases.
With economic globalization, increased economic activity may lead to urbanization. One may think about unhealthy conditions of an urban area such as environmental degradation, air and water pollution, higher crime rates, and stress which reduce life expectancy. However, according to Kabir ( 2008 ), people living in an urban area can benefit from improved medical care, easy access to pharmacy, and to the hospitals that use higher technology. They can also get a better education and can enjoy better socioeconomic conditions.
Democracy can be considered as another determinant of life expectancy. In order to solve the health problems of the poor, people should draw the attention of the government. Sen ( 1999 ) claimed that the instrumental role of democracy in solving problems is enabling people to express and support their claims. Thus, the attention of politicians can be attracted to the problems of the poor. Politicians who have never tasted poverty do not have the urge to take action against the problems of the poor at the right time. Another linkage can be established through accountability (Besley and Kudamatsu 2006 ). In democracies, governments have an obligation to account to citizens for what purposes the resources were used. Thus, resources can be allocated to solve important public issues such as quality of life, communicable diseases, and mortality.
Compared to theoretical discussions, previous literature provides a lack of empirical evidence. Barlow and Vissandjee ( 1999 ) examined the determinants of life expectancy with cross-sectional data available in 1990 for 77 developed and developing countries. According to regression results, per capita income, literacy rate, and lower fertility are important determinants of life expectancy while living in a tropical area decreasing it. Another finding in this study shows that health expenditures in those countries failed to increase life expectancy. Following this study, Or ( 2000 ) analyzed the determinants of health outcomes in 21 industrialized OECD countries covering the period 1970–1992. This study presents gender-specific estimates separately for men and women. Fixed effects estimation results reveal a significant negative relationship between public health expenditure and women's premature death. The relationship also occurs for men, while GDP per capita dropped from the regression model due to high collinearity. Furthermore, GDP per capita and the proportion of white-collar workers reduce premature death for both men and women, while alcohol consumption increases it.
Franco et al. ( 2004 ) analyzed the impact of democracy on health utilizing political rights data of 170 countries. Empirical results show that people living in democracies enjoy better health conditions such as longer life expectancy, better maternal health, and lower child mortality. Following this, Besley and Kudamatsu ( 2006 ) investigated the nexus between democracy and health outcomes utilizing panel data from the 1960s to the 2000s. In their study, they used life expectancy at birth and child mortality variables for 146 countries as indicators of health outcomes. According to results, democracy has a positive and significant effect on life expectancy at birth and it also reduces child mortality. Safaei ( 2006 ) also investigated the impact of democracy on life expectancy and adult and child mortality rates with the data of 32 autocratic, 13 incoherent, and 72 democratic countries. According to the OLS estimation results, improving democratic institutions increases life expectancy and reduces child and adult mortality rates. Another finding of the study is that socioeconomic factors such as income, education, and access to health care services are important determinants of health status.
Owen and Wu ( 2007 ) found a positive relationship between trade openness and health outcomes using a panel of 219 countries. Health outcome measures of this study are infant mortality and life expectancy. Trade openness is one of the most important dimensions of globalization.
Kabir ( 2008 ) analyzed the determinants of life expectancy in 91 developing countries. Empirical results obtained are the opposite of the expected. According to results, per capita income, literacy rate, per capita health expenditure, and urbanization have no significant impact on life expectancy. On the other hand, the number of physicians has a positive and significant impact on life expectancy, while malnutrition reduces it. As a dummy variable, living in Sub-Saharan Africa is another factor that reduces life expectancy due to communicable diseases like HIV, malaria, etc.
Bergh and Nilsson ( 2010 ) used a panel of 92 countries in the period 1970–2005 to investigate the relationship between globalization and life expectancy. They used social, political, and economic globalization data separately, and the results show a significant positive effect of economic globalization on life expectancy at birth. But no significant relationship was found between social globalization, political globalization, and life expectancy. They also used average years of education, urban population, the number of physicians, and nutrition as control variables and the effect of economic globalization was still positive and significant.
Welander et al. ( 2015 ) examined the effects of globalization and democracy on child health in their panel data analysis for 70 developing countries covering the period 1970–2009. According to the results, globalization significantly reduces child mortality. In addition, democracy improves child health and it also increases the beneficial effects of globalization on child health. Following this study, Tausch ( 2015 ) analyzed the role of globalization in life expectancy in 99 countries. The results of OLS estimates show that globalization leads to inequality, and therefore, it reduces health performance in terms of life expectancy and infant mortality. These results are contradictory to positive views on the role of globalization in public health. However, in 19 of 99 countries, globalization increases public health performance. Ali and Audi ( 2016 ) also analyzed the role of globalization in life expectancy in Pakistan. According to ARDL estimation results, life expectancy is positively associated with higher levels of globalization. Another study on the Pakistan case proposed by Alam et al. ( 2016 ) concluded that foreign direct investment and trade openness which are important indicators of economic globalization affects life expectancy positively.
Patterson and Veenstra ( 2016 ) concluded that electoral democracies provide better health conditions compared to other countries. Their analysis includes annual data from 168 countries covering the period 1960–2010. Empirical results show democracy has a significant positive impact on life expectancy and it reduces infant mortality.
In their recent study, Shahbaz et al. ( 2019 ) investigated the impact of globalization, financial development, and economic growth on life expectancy. The authors used nonlinear time series analysis methods utilizing the data of 16 Sub-Saharan African countries over the period 1970–2012. Their results show that globalization, financial development, and economic growth affect life expectancy positively in 14 of 16 Sub-Saharan African countries.
The previous literature provides a lack of evidence in the context of globalization, democracy, and life expectancy relationship. There are also methodological weaknesses in previous empirical studies. First, it can be observed that previous studies are mostly based on traditional estimation methods. Second, the panel data analyses are based on the first-generation estimators that assume cross-sectional independence. This assumption is hard to satisfy due to integration among countries. In addition, ignoring the cross-sectional dependence results in inconsistent estimations. Particularly in empirical work in the context of globalization which refers to economic, political, and cultural integration among countries, considering the cross-sectional dependence becomes more important. Therefore, in order to make a methodological contribution to previous literature, we used second-generation panel time series methods considering cross-sectional dependence.
3 Methodology and data
According to the United Nations, achieving sustainable development goals requires global cooperation and partnership. Therefore, “partnerships for goals” has taken its place as the 17th sustainable development target. However, it was emphasized that some sub-goals should be realized in order to reach this goal. These include improving international resource mobility, helping developing countries to attain debt sustainability, promoting the transfer of information and technology between developed and developing countries, an open and rule-based free trade system, encouraging public–private and civil society partnerships, increasing transparency and accountability, and high quality and reliable data (United Nations 2019 ). In our empirical work, economic, social, and political globalization and democracy variables were used as proxies of the subcomponents of SDG17. In addition, the life expectancy at birth variable that mostly used in related literature as a proxy of health status and well-being, it is used in our study as a proxy of SDG3. In this study, we investigated the role of globalization and democracy in life expectancy in 16 low-income countries. Footnote 1 Following Barlow and Vissandjee ( 1999 ) and ( 2000 ), GDP per capita is used as a control variable in order to mitigate omitted variable bias. Our dataset is covering the period 1970–2017. Following the related literature, we present our model as follows:
where lex is life expectancy at birth which refers to the average number of years a newborn is expected to live. Life expectancy at birth data is provided by World Bank ( 2019 ) World Development Indicators. Life expectancy at birth indicates the number of years a newborn infant would live if prevailing patterns of mortality at the time of its birth were to stay the same throughout its life. The dataset is consisting of a weighted average of collected data from several co-founders. In Eq. 1 , X refers to the KOF Globalization Index developed by Dreher ( 2006 ). This index has been used in previous literature as a proxy of SDG17 (Saint Akadiri et al. 2020 ). The current version of the data published by the Swiss Economic Institute is revised by Gygli et al. ( 2019 ). The globalization variables are between 0–100, and 100 refers to the highest globalization level. In our analysis, we used subcomponents of globalization index such as economic (EC), social (SOS), and political (POL) globalization in addition to overall globalization (GLB). Due to high collinearity, the effects of different types of globalization are analyzed separately. Models 1, 2, 3, and 4 represent the estimations with overall, economic, social, and political globalization indexes, respectively. The democracy variable ( dem ) is provided from the Polity IV project dataset (Marshall and Jaggers 2002 ). While the increases in this indicator represent a more democratic regime, the decreases represent a more autocratic regime. Finally, gdp is real GDP per capita (constant 2010 $) and it is provided from World Bank World Development Indicators. All variables transformed to the logarithmic form except democracy due to negative values. In the estimation of the model, the panel data analysis methods are used.
3.1 Cross-sectional dependence
Traditional panel data methods are based on the assumption that no cross-sectional dependence exists among cross section units. However, this assumption is hard to satisfy due to rising economic, social, and political integration between countries. The estimations do not take this process into account may cause inconsistent results. Such results may also lead to incorrect inferences (Chudik and Pesaran, 2013 ). The existence of cross-sectional dependence in variables and the error term is obtained from the model analyzed with Pesaran ( 2004 ) \({\text{CD}}_{{{\text{LM}}}}\) and Pesaran et al. ( 2008 ) bias-adjusted LM test. These techniques are robust whether N > T and T > N. Therefore, \({CD}_{LM}\) and bias-adjusted LM ( \({LM}_{adj})\) tests are found to be appropriate and their test statistics can be calculated as follows:
Equation 2 shows the calculation of Pesaran ( 2004 ) \({CD}_{LM},\) and Eq. 3 is Pesaran et al. ( 2008 ) bias-adjusted LM test statistic. \({V}_{Tij}\) , \({\mu }_{Tij}\) , and \({\widehat{\rho }}_{ij},\) respectively, represent variance, mean, and the correlation between cross section units. The null and alternative hypothesis for both test statistics; \({H}_{0}\) : No cross-sectional dependence exist; \({H}_{1}\) : Cross-sectional dependence exist.
In the selection of stationarity tests and long-run estimators, the existence of cross-sectional dependence will be decisive. If the null of no cross-sectional dependence is rejected, second-generation methods that assume cross-sectional dependence should be used in order to provide unbiased and consistent estimation results.
3.2 Slope homogeneity
Pesaran and Yamagata ( 2008 ) proposed a method to examine slope heterogeneity in panel data analysis based on the Swamy ( 1970 )’s random coefficient model.
The calculation of the test statistic of Swamy’s model is given in Eq. 4 .
In Eq. 4 , \({\stackrel{\sim }{\beta }}_{i}\) and \({\overbrace{\beta }}_{WFE},\) respectively, indicate the parameters obtained from pooled OLS and weighted fixed effects estimation, while \({M}_{T}\) is the identity matrix. The test statistic obtained from Swamy’s model is improved by Pesaran et al. ( 2008 ) as follows:
where \(\stackrel{\sim }{S}\) is the Swamy test statistic and k is a number of explanatory variables. \({\stackrel{\sim }{\Delta }}_{adj}\) is a bias-adjusted version of \(\stackrel{\sim }{\Delta }\) . \({\stackrel{\sim }{Z}}_{it}\) =k and \(Var\left({\stackrel{\sim }{Z}}_{it}\right)=2k(T-k-1)/T+1\) . The null and alternative hypothesis for both test statistics is given below.
The rejection of the null hypothesis shows that slope coefficients of Eq. 1 are heterogeneous. In the selection of panel data estimation methods, the results of those preliminary analysis are taken into account.
3.3 Unit root test
Pesaran ( 2006 ) suggested a factor modeling approach to solve the cross-sectional dependency problem. This approach is simply based on adding cross-sectional averages to the models as proxies of unobserved common factors. The Cross-sectionally Augmented Dickey–Fuller (CADF) unit root test developed by Pesaran ( 2007 ) is based on that factor modelling approach. This method is an augmented form of Augmented Dickey–Fuller (ADF) regression with lagged cross-sectional average and its first difference to deal with cross-sectional dependence (Baltagi, 2008 : 249). This method considers the cross-sectional dependence and can be used, while N > T and T > N. The CADF regression is:
\({\stackrel{-}{y}}_{t}\) is the average of all N observations. To prevent serial correlation, the regression must be augmented with lagged first differences of both \({y}_{it}\) and \({\stackrel{-}{y}}_{t}\) as follows:
After the calculation of CADF statistics for each cross section ( \({CADF}_{i}\) ), Pesaran ( 2007 ) calculates the CIPS statistic as average of CADF statistics.
If the calculated CIPS statistic exceeds the critical value, it means that the unit root hypothesis is rejected. After the preliminary analysis of unit root, the existence of a long-run relationship between the variables in our model will be investigated via Westerlund and Edgerton ( 2007 ) cointegration test. After this, the long-run coefficients will be estimated using the continuous-updated fully modified (CUP-FM) estimator developed by Bai and Kao ( 2006 ) and Bias-adjusted OLS estimator developed by Westerlund ( 2007 ).
3.4 Cointegration test and long-run relationship
In this study, the cointegration relationship was investigated by Westerlund and Edgerton ( 2007 ) LM bootstrap test. This method considers cross-sectional dependence and provides robust results in small samples (Westerlund and Edgerton, 2007 ). This method is based on the following equation
where \({n}_{ij}\) is an independent and identically distributed process with zero mean and var( \({n}_{ij})\) = \({{\sigma }_{i}}^{2}\) . Westerlund and Edgerton ( 2007 ) suggested following LM test in order to test the null of cointegration
where \({S}_{it}\) is partial sum process of the fully modified estimate of \({z}_{it}\) and \({\widehat{w}}_{i}^{-2}\) is the estimated long-run variance of \({u}_{it}\) conditional on \(\Delta {x}_{it}^{^{\prime}}\) . If the calculated LM statistic is below the critical value, the null of cointegration will be accepted. The critical values will be provided using the bootstrap method in order to prevent cross-sectional dependence.
In the estimation of long-run coefficients, the CUP-FM estimator was used and this method is based on the following regression
where \({\widehat{\lambda }}_{i}^{^{\prime}}\) refers to the estimated factor loadings and \(\hat{y}_{{i,t}}^{ + } = y_{{i,t}} - \left( {\lambda _{i} ^{\prime } \hat{\Omega }_{{F \in i}} + \hat{\Omega }_{{\mu \in i}} } \right)\hat{\Omega }_{{ \in i}}^{{ - 1}} {{\Delta }}x_{{i,t}}\) indicates the transformation of the dependent variable for endogeneity correction. According to Bai and Kao ( 2006 ), CUP-FM estimator is robust under cross-sectional dependence. However, the assumption that the number of common factors (k) is known cannot be satisfied in practice (Westerlund, 2007 ). Therefore, Westerlund ( 2007 ) suggested a bias-adjusted estimator (BA-OLS) following the methodology of Bai and Kao ( 2006 ) except in the context of determining the number of common factors. The author suggested the estimation of k using an information criterion as
where \(IC\left(k\right)\) is the information criterion. In this study, we determined the number of common factors via the Bayesian information criterion (BIC) as follows.
In the equation above, V(k) is the estimated variance of \({\widehat{u}}_{it}\) based on k factors. By minimizing the BIC, we obtain \(\widehat{k}\) . Westerlund ( 2007 ) showed that the estimation of k provides better results compared to CUP-FM estimator assuming k is known. Both of the estimators require cointegrated variables in the long run.
3.5 Empirical results and discussion
The results of Pesaran ( 2004 ) \({CD}_{LM}\) and Pesaran et al. ( 2008 ) bias-adjusted LM tests are given in Table 1 .
The results given in Table 1 show that the null of no cross-sectional dependence is rejected at 1% according to both \({CD}_{LM}\) and \({LM}_{adj}\) test statistics in all variables. In addition, in the error terms obtained from models 1, 2, 3, and 4 the null of no cross-sectional dependence is rejected at 1%. These results show that the methods to be used in the analysis of the stationarity of the variables and the determination of the long-run relationship should consider the cross-sectional dependence.
The results of homogeneity tests developed by Pesaran and Yamagata ( 2008 ) are given in Table 2 . According to the results, the null of homogeneity is accepted at %1 in all models. Therefore, estimators assume parameter homogeneity are used in our analysis.
After the preliminary analysis of cross-sectional dependence, the CADF unit root test developed by Pesaran ( 2007 ) is found to be appropriate for our model because of its robustness under cross-sectional dependence. The results of the CADF unit root test are given in Table 3 .
In the analysis of unit root, constant and trend terms are both considered at level, while only constant term is added at first difference. Maximum lag level is determined as 3, while optimum lag level is determined by F joint test from general to particular. According to results, the null of unit root is accepted for all variables, while calculated CIPS statistics of first-differenced variables exceed 1% critical value. All variables have a unit root, and their first differences are stationary ( \({I}_{1})\) . Therefore, in order to determine the existence of a long-run relationship, we applied Westerlund and Edgerton ( 2007 ) panel cointegration test. This method considers cross-sectional dependence and can be used, while the series are integrated in the same order. The results are shown in Table 4 .
Constant and trend are both considered in the analysis of cointegration, and critical values are obtained from 5000 bootstrap replications. The results show that the null of cointegration is accepted for all models. There is a long-run relationship between life expectancy, globalization, democracy, and GDP per capita. After determining the cointegration relationship, we estimated long-run coefficients utilizing CUP-FM and BA-OLS estimators proposed by Bai and Kao ( 2006 ) and Westerlund ( 2007 ), respectively.
The long-run estimation results given in Table 5 show that overall, economic, social, and political globalization are positively associated with life expectancy at 1% significance level according to both CUP-FM and BA-OLS estimators. The results show that a 1% increase in globalization index increases life expectancy %0.014 and %0.015 according to CUP-FM and BA-OLS estimators, respectively. The impact of economic, social and political globalization indexes is 0.013%, 0.011%, and 0.015% according to CUP-FM estimation results while 0.014%, 0.012%, and 0.017% according to both estimators, respectively.
Our results confirms the findings of Owen and Wu ( 2007 ), Ali and Audi ( 2016 ), and Shahbaz et al. ( 2019 ) who found a positive relationship between globalization and life expectancy. Our empirical work also supports the evidence of Bergh and Nilsson ( 2010 ) in terms of positive effect of economic globalization on life expectancy. While the authors found no significant impact of social and political globalization on life expectancy, our results show that life expectancy is positively associated with both social and political globalization. The results we found contradict Tausch ( 2015 )’s evidences in 80 of 99 countries. However, according to his results, in 19 of 99 countries, globalization affects health positively. When these countries are examined, it is seen that 14 of them are countries in the low and lower-middle income groups. In this sense, it can be said that the evidence we found for low-income countries is in line with the author's evidence. As Dreher ( 2006 ) mentioned, despite its possible inequality effects, the net effect of globalization on development is mostly positive and our empirical work supports that idea. The effect of democracy on life expectancy is also positive and significant at 1% which confirms the findings of Franco et al. ( 2004 ) and Besley and Kudamatsu ( 2006 ). In electoral democracies, people living in poverty and suffering from health problems can easily attract the attention of policymakers compared to autocracies. This leads to the reallocation of resources to solve the primary problems of the society. In the context of sustainable development goals, our results show that there is no conflict between SDG3 (good health and well-being) and SDG17 (partnerships for the goals). The improvement of the health conditions of the poor countries depends on global partnership and economic, social, and political integration among countries. In addition, democracy is an important tool in achieving the goal of a healthy society, as it fosters accountability, transparency, and partnership between governments and the societies they rule. As stated in the introduction section, low-income countries show low performance in terms of health-related sustainable development goals, and their connections with global markets are weak compared to other countries. At the same time, democratic institutions are not developed. Our work supports the idea that in order to achieve SDG3, global partnership and democracy are required.
The GDP per capita that used as a control variable has a positive impact on life expectancy at a 1% level. These results support the evidence of Barlow and Vissandjee ( 1999 ), Or ( 2000 ), and Shahbaz et al. ( 2019 ). Individuals living in countries with high per capita income are expected to have higher welfare and have a longer life expectancy (Judge, 1995 ). In low-income countries where people still suffer from having difficulty in meeting basic human needs, increasing per capita income may lead to better nutritional status, easier access to advanced treatment methods and technology.
4 Conclusion
In this study, the effects of globalization and democracy on life expectancy are empirically investigated in low-income countries. While globalization and democracy indexes are used as proxy indicators of “Partnerships for the Goals (SDG 17),” life expectancy used a proxy of “Good Health and Well-Being (SDG 3).” With this, it is aimed to examine the existence of contradiction between those SDGs. In the estimation of the long-run relationship between the variables, second-generation panel data analysis methods that consider cross-sectional dependency are used. According to the results, the globalization index and its subcomponents such as economic, social, and political globalization are important instruments to achieve a healthier society. In addition, higher levels of democracy lead to higher levels of life expectancy. Finally, GDP per capita growth improves health status of countries.
The findings obtained from our study show that economic, social, and political integration of countries and democracy accelerate the process of achieving a healthier society. Therefore, it is seen that SDG3 and SDG17 targets are compatible with each other. In order to achieve SDG3, economic, social, and political integration between countries should be encouraged and democratic institutions should be improved. Policy makers should remove the barriers on globalization, and they should promote participation on international organizations and public–private and civil society partnerships.
Those countries are Benin, Burkina Faso, Burundi, Central African Republic, Chad, Democratic Republic of Congo, The Gambia, Haiti, Madagascar, Malawi, Mali, Nepal, Niger, Rwanda, Sierra Leone, and Togo.
Alam, M. S., Raza, S. A., Shahbaz, M., & Abbas, Q. (2016). Accounting for contribution of trade openness and foreign direct investment in life expectancy: The long-run and short-run analysis in Pakistan. Social Indicators Research, 129 (3), 1155–1170.
Article Google Scholar
Ali A, & Audi M (2016). The impact of income inequality, environmental degradation and globalization on life expectancy in Pakistan: An empirical analysis. MPRA Working Paper, No. 71112.
Bai, J., & Kao, C. (2006). On the estimation and inference of a panel cointegration model with cross-sectional dependence In panel data econometrics theoretical contributions and empirical applications . Bingley: Emerald Group Publishing Limited.
Google Scholar
Baltagi, B. (2008). Econometric analysis of panel data . New York: Wiley.
Barlow, R., & Vissandjee, B. (1999). Determinants of national life expectancy. Canadian Journal of Development Studies/Revue canadienne d’études du développement, 20 (1), 9–29.
Beck, T., Maimbo, S. M., Faye, I., & Triki, T. (2011). Financing Through the crisis and beyond . Africa: The World Bank.
Book Google Scholar
Bergh, A., & Nilsson, T. (2010). Good for living? On the relationship between globalization and life expectancy. World Development, 38 (9), 1191–1203.
Besley, T., & Kudamatsu, M. (2006). Health and democracy. American Economic Review, 96 (2), 313–318.
Buss, P. M. (2002). Globalization and disease: In an unequal world, unequal health! Cadernos de Saúde Pública, 18, 1783–1788.
Chapman, A. R. (2009). Globalization, human rights, and the social determinants of health. Bioethics, 23 (2), 97–111.
Chudik A, & Pesaran, MH (2013) Large panel data models with cross-sectional dependence: a survey. CAFE Research Paper , (13.15).
Cohen, M. S., Chen, Y. Q., McCauley, M., Gamble, T., Hosseinipour, M. C., Kumarasamy, N., & Godbole, S. V. (2011). Prevention of HIV-1 infection with early antiretroviral therapy. New England journal of medicine, 365 (6), 493–505.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Cutler, D., Deaton, A., & Lleras-Muney, A. (2006). The determinants of mortality. Journal of economic perspectives, 20 (3), 97–120.
De Hoyos, R. E., & Sarafidis, V. (2006). Testing for cross-sectional dependence in panel-data models. The stata journal, 6 (4), 482–496.
Deaton, A. (2004). Health in an age of globalization (No. w10669) . Cambridge: National Bureau of Economic Research.
Dollar, D. (2001). Is globalization good for your health? Bulletin of the world Health Organization, 79, 827–833.
CAS Google Scholar
Dreher, A. (2006). Does globalization affect growth? Evidence from a new index of globalization. Applied economics, 38 (10), 1091–1110.
Dreher, A., & Gaston, N. (2008). Has globalization increased inequality? Review of International Economics , 16 (3), 516–536.
Dreher, A., Gassebner, M., & Siemers, L. H. (2012). Globalization, economic freedom, and human rights. Journal of Conflict Resolution, 56 (3), 516–546.
Franco, Á., Álvarez-Dardet, C., & Ruiz, M. T. (2004). Effect of democracy on health: Ecological study. BMJ, 329 (7480), 1421–1423.
Freedom House (2019). List of Electoral Democracies in 2019. https://freedomhouse.org/report-types/freedom-world (Access Date: 11.13.2019).
Gelleny, R. D., & McCoy, M. (2001). Globalization and government policy independence: The issue of taxation. Political Research Quarterly, 54 (3), 509–529.
Grossman, G. M., & Helpman, E. (2015). Globalization and growth. American Economic Review, 105 (5), 100–104.
Gygli, S., Haelg, F., Potrafke, N., & Sturm, J. E. (2019). The KOF globalisation index–revisited. The Review of International Organizations , 14 , 543–574.
Ha, E. (2012). Globalization, government ideology, and income inequality in developing countries. The journal of Politics, 74 (2), 541–557.
Halisçelik, E., & Soytas, M. A. (2019). Sustainable development from millennium 2015 to Sustainable Development Goals 2030. Sustainable Development, 27 (4), 545–572.
Harrison, A. (2006). Globalization and poverty (No. w12347) . Cambridge: National Bureau of Economic Research.
Hu, F. B. (2011). Globalization of diabetes: the role of diet, lifestyle, and genes. Diabetes Care, 34 (6), 1249–1257.
Judge, K. (1995). Income distribution and life expectancy: A critical appraisal. BMJ, 311 (7015), 1282–1285.
Kabir, M. (2008). Determinants of life expectancy in developing countries. The journal of Developing areas, 41, 185–204.
Labonté, R., Schrecker, T., Packer, C., & Runnels, V. (Eds.). (2009). Globalization and health: Pathways, evidence and policy . Abingdon: Routledge.
Love, J. L. (1980). Raul Prebisch and the origins of the doctrine of unequal exchange. Latin American Research Review, 15 (3), 45–72.
Marshall, M. G., & Jaggers, K. (2002). Polity IV Project: Political regime characteristics and transitions, 1800–2002: Dataset users’ manual . Maryland: University of Maryland.
Menyah, K., Nazlioglu, S., & Wolde-Rufael, Y. (2014). Financial development, trade openness and economic growth in African countries: New insights from a panel causality approach. Economic Modelling, 37, 386–394.
Or, Z. (2000). Determinants of health outcomes in industrialized countries: A pooled, cross-country, time-series analysis. OECD Economic Studies, 1, 53–78.
Owen, A. L., & Wu, S. (2007). Is trade good for your health? Review of International Economics, 15 (4), 660–682.
Patterson, A. C., & Veenstra, G. (2016). Politics and population health: Testing the impact of electoral democracy. Health & place, 40, 66–75.
Pesaran MH (2004) General diagnostic tests for cross section dependence in panels. CESifo Working Paper (No. 1229).
Pesaran, M. H. (2006). Estimation and inference in large heterogeneous panels with a multifactor error structure. Econometrica , 74 (4), 967–1012.
Pesaran, M. H. (2007). A simple panel unit root test in the presence of cross-section dependence. Journal of applied econometrics, 22 (2), 265–312.
Pesaran, M. H., & Yamagata, T. (2008). Testing slope homogeneity in large panels. Journal of Econometrics, 142 (1), 50–93.
Pesaran, M. H., Ullah, A., & Yamagata, T. (2008). A bias-adjusted LM test of error cross-section independence. The Econometrics Journal, 11 (1), 105–127.
Rao, B. B., & Vadlamannati, K. C. (2011). Globalization and growth in the low income African countries with the extreme bounds analysis. Economic Modelling, 28 (3), 795–805.
Safaei, J. (2006). Is democracy good for health? International Journal of Health Services, 36 (4), 767–786.
Saint Akadiri, S., Alola, A. A., Olasehinde-Williams, G., & Etokakpan, M. U. (2020). The role of electricity consumption, globalization and economic growth in carbon dioxide emissions and its implications for environmental sustainability targets. Science of The Total Environment, 708, 134653.
Sen, A. (1999). Development as freedom . New York: Knopf.
Shahbaz, M., Shafiullah, M., & Mahalik, M. K. (2019). The dynamics of financial development, globalisation, economic growth and life expectancy in sub-Saharan Africa. Australian Economic Papers, 58 (4), 444–479.
Swamy, P. A. (1970). Efficient inference in a random coefficient regression model. Econometrica: Journal of the Econometric Society, 38, 311–323.
Swiss Economic Institute. (2020). KOF Globalization Index. https://kof.ethz.ch/en/forecasts-and-indicators/indicators/kof-globalisation-index.html (Access Date: December, 2019).
Tausch, A. (2015). Is globalization really good for public health? The International journal of health planning and management, 31 (4), 511–536.
The United Nations (2019). Sustainable Development Goal Indicators. https://unstats.un.org/sdgs/indicators/Global%20Indicator%20Framework%20after%202019%20refinement_Eng.pdf (Access Date: 25.12.2019).
Ulucak, R., & Bilgili, F. (2018). A reinvestigation of EKC model by ecological footprint measurement for high, middle and low income countries. Journal of cleaner production, 188, 144–157.
Welander, A., Lyttkens, C. H., & Nilsson, T. (2015). Globalization, democracy, and child health in developing countries. Social Science and Medicine, 136, 52–63.
Westerlund, J. (2007). Estimating cointegrated panels with common factors and the forward rate unbiasedness hypothesis. Journal of Financial Econometrics, 5 (3), 491–522.
Westerlund, J., & Edgerton, D. L. (2007). A panel bootstrap cointegration test. Economics Letters, 97 (3), 185–190.
World Bank (2019). World Development Indicators. https://databank.worldbank.org/source/world-development-indicators (Access Date: December, 2019).
World Health Organization. (2016). Health in 2015: from MDGs to SDGs 2015 . Geneva: World Health Organization.
Zafar, M. W., Saud, S., & Hou, F. (2019a). The impact of globalization and financial development on environmental quality: Evidence from selected countries in the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). Environmental science and pollution research, 26 (13), 13246–13262.
Zafar, M. W., Shahbaz, M., Hou, F., & Sinha, A. (2019b). From nonrenewable to renewable energy and its impact on economic growth: The role of research & development expenditures in Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation countries. Journal of cleaner production, 212, 1166–1178.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Economics, Faculty of Economics and Administrative Sciences, Hatay Mustafa Kemal University, Hatay, Turkey
Arif Eser Guzel, Unal Arslan & Ali Acaravci
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Arif Eser Guzel .
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Guzel, A.E., Arslan, U. & Acaravci, A. The impact of economic, social, and political globalization and democracy on life expectancy in low-income countries: are sustainable development goals contradictory?. Environ Dev Sustain 23 , 13508–13525 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-01225-2
Download citation
Received : 30 April 2020
Accepted : 04 January 2021
Published : 18 January 2021
Issue Date : September 2021
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-021-01225-2
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Life expectancy
- Globalization
- Low-income countries
- Sustainable development
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
How our interconnected world is changing
Globalization isn’t going away, but it is changing, according to recent research from the McKinsey Global Institute (MGI). In this episode of The McKinsey Podcast , MGI director Olivia White speaks with global editorial director Lucia Rahilly about the flows of goods, knowledge, and labor that drive global integration—and about what reshaping these flows might mean for our interconnected future.
After, global brewer AB InBev has flourished in the throes of what its CFO Fernando Tennenbaum describes as the recent “twists and turns.” Find out how in this excerpt from “ How to thrive in a downturn: A CFO perspective ,” recorded in December 2022 as part of our McKinsey Live series. 1 Please note that market conditions may have changed since this interview was conducted in December 2022.
The McKinsey Podcast is cohosted by Roberta Fusaro and Lucia Rahilly.
This transcript has been edited for clarity and length.
Globalization is here to stay
Lucia Rahilly: Pundits and other public figures have wrongly predicted the demise of globalization for what seems like years. Now, given the war in Ukraine and other disruptions, many are once again sounding its death knell. What does this new MGI research tell us about the fate of globalization? Is it really in retreat?
Olivia White: The flows of goods, the real tangible stuff, have leveled off after nearly 20-plus years of growing at twice the rate of GDP. But the flows of goods kept pace with GDP and even rose a little bit, surprisingly, in the past couple of years. Since GDP has been growing, that means actual ties have gotten stronger.
One of the most striking findings from this research was that flows representing knowledge and know-how, such as IP and data, and flows of services and international students have accelerated and are now growing faster than the flow of goods. Flows of data grew by more than 40 percent per annum over the past ten years.
Lucia Rahilly: Goods are a smaller share of total flows, a smaller share of economic output, than in the past. That doesn’t necessarily sound like a bad thing. Could it be a sign of progress?
Olivia White: The fact that certain goods are growing less quickly than other types of flows shows this shift in our economy and what’s most important to the way the economy functions. It comes on the back of a long history of different factors that influence growth and shifts in the way patterns work. What’s happening, in part, is that a variety of countries are producing more domestically—first and foremost China. That has been driving a lot of the flow down, if you take the longitudinal view, over the past ten years versus before.
The world remains interdependent
Lucia Rahilly: How interdependent would you say we are at this stage? Could you give us some examples of the ways we’re interconnected?
Olivia White: The top line is, every region in the world depends on another significant region for at least 25 percent of a flow it values most.
In general, regions that are manufacturing regions—Europe, Asia–Pacific, and China, if we look at it on its own because it’s such a large economy—depend very strongly on the rest of the world for resources: food to some degree, but really energy and minerals of different sorts. I’ll give you a few examples.
In general, regions that are manufacturing regions depend very strongly on the rest of the world for resources: food to some degree, but really energy and minerals. Olivia White
China imports over 25 percent of its minerals, from places as far-flung as Brazil, Chile, and South Africa. China imports energy, particularly in the form of oil from the Middle East and Russia. Europe is emblematic of these forms of dependency on energy. It was dependent on Russia for over 50 percent of its energy, but now that has drastically changed.
In some other regions in the world—places that are resource rich, like the Middle East, sub-Saharan Africa, and Latin America—those places are highly dependent on the rest of the world for their manufactured goods. Well over half the world’s population lives in those places. They import well over 50 percent of their electronics and similar amounts of their pharmaceuticals. They are highly dependent on other parts of the world for things that are really quite critical to development and for modern life.
North America is somewhat of a different story. We don’t have any single spot of quite as great a dependency, at least at the broad category level. We import close to 25 percent of what we use in net value terms across the spectrum, both of resources and of manufactured goods.
This doesn’t yet speak of data and IP, where, for example, the US and Europe are fairly significant producers/exporters. A country like China is a very large consumer of IP.
Lucia Rahilly: How interdependent are we in terms of the global workforce?
Olivia White: This is quite striking. We asked how many workers in regions outside North America serve North American demand. And we asked the same question for Europe. It turns out that 60 million people in regions outside North America serve North American demand, and in Europe the corresponding number is 50 million.
These numbers are very substantial versus the working populations in those countries. So when you consider how much of what North Americans or Europeans are consuming could be produced onshore, by onshore labor, the answer is not even remotely close to those sorts of numbers—at least given the means of production or the way services are delivered today and the role people play in that.
Lucia Rahilly: Let’s turn to some of the categories of flows that have increased in recent years. What’s driving growth in global flows now that the trade in goods has stabilized?
Olivia White: Flows linked to knowledge and know-how. Knowledge services that have historically grown more slowly than manufactured goods and resources, with increased global connection over time, have flipped over the past ten years.
Professional services, such as engineering services, are among those more traditional trade flows that have been growing fastest, at about 6 percent a year, versus resources, which have slowed to just around two percent. Anything that involves real know-how—engineering, but also providing, say, call center support—is in that category.
The flows of IP are growing even faster. Now, IP is tricky because accounting for it is a very tricky thing to do. But it roughly looks at flows of the fun stuff. In the report we talk about Squid Game , but IP also includes movies, streaming platforms, music, and any sort of cultural elements that we consume.
It’s also important to consider flows of patents and ideas and the way countries or companies will use ideas or know-how developed in one country to help what they do broadly across the world. Those flows have been growing at roughly 6 percent per year as well.
There are data flows—the flows of packets of data. For example, if we were in different countries while conducting this interview there would be the flows between us. There are also flows linked to our ever-expanding use of cloud and data localization. Data transfer is happening more and more quickly.
The flows of international students have also been rising. That was mightily interrupted by the pandemic, for reasons I don’t need to belabor, but these flows seem to be rebounding. It’s important to consider the degree to which those will jump back on their accelerated growth trajectory.
Want to subscribe to The McKinsey Podcast ?
How covid-19 has affected global flows.
Lucia Rahilly: You mentioned flows of international students dropping off during COVID, for the obvious reasons. Did other flows generally drop off during the pandemic? Or were there examples of flows that were particularly resilient throughout that period?
Olivia White: There’s some variation, but many flows were remarkably resilient—resilient in a way that’s a bit counter to the general narrative about what happened during the pandemic.
The flows of resources and manufactured goods jumped reasonably significantly in 2020 and 2021, both to levels of about 6 percent per year on an annualized basis. To some degree, what was happening is that cross-border flows stepped in to replace interrupted domestic production. Flows from Asia came in, for example, to the US or to Europe. We’ve seen some flows go in reverse directions. There was a bunch of interruption in domestic production, which was quite surprising.
Flows of capital also jumped quite a lot as people needed to shift the way they were financing themselves. Multinationals needed to shift the way they were financing themselves. Some were moving liquidity to different parts of the world under times of financial stress. But those jumped to levels of growth in the tens of digits from what had actually been reversed growth for the past ten years. All those things jumped. IP jumped a little bit; data remained high. So these flows have been remarkably resilient.
The good and bad news about resource concentration
Lucia Rahilly: You invoked concentration a bit when you talked about Europe being dependent on Russia for 50 percent of its energy. Can you say a bit more about what concentration means in this context and how it affects the dynamics of the way we’re connected globally?
Olivia White: From the global perspective, there are some products that truly originate in only a few places in the world, and all of us across the globe are dependent on those few places for our supply. Iron ore is quite concentrated, and cobalt is concentrated in the DRC [Democratic Republic of the Congo].
The second type of concentration is viewed from the standpoint of an individual country. Lucia, you talked about Europe and gas dependency.
For example, Germany was getting gas from only a very concentrated set of sources. These are places where, for a variety of reasons, countries have built up dependencies on just a small number of other countries.
Why has this happened? Why are we in this position? Cost is one reason. People have made decisions based on economic factors. Another reason is regional preference. Not all goods are created equal, even if they fall in the same category.
The third reason is preferential trade agreements between different countries or other forms of tariffs or taxes that shape the way flows occur. We’re in a world in which suddenly people are realizing they have to contemplate the consequences associated with concentration—not of suppliers, but of the country of origin from which they’re buying things.
Lucia Rahilly: It sounds like concentration also increases efficiency in some cases where those disruptions don’t occur. Is concentration always a bad thing? If we rethink concentration, can we expect to see some loss of efficiency in the interim?
Olivia White: No, it’s not always a bad thing. But there are a lot of considerations to make that involve costs, involve geopolitical relationships, involve the role that various countries want to play themselves, how they’re thinking about development, how they’re thinking about their workforces. All those things have to be part of the mix.
Imagine three or four different countries, each with three trading partners, and they’re largely different trading partners. Swapping off who’s supplied by whom is a huge problem of coordination.
How global chains will evolve
Lucia Rahilly: Geopolitical risks have obviously trained a policy spotlight on reimagining these global value chains, whether for security reasons or to strengthen resilience more generally. Accepting that the world remains interdependent, how do we see trade flows continuing to evolve in coming years?
Olivia White: Broadly speaking, there are four categories of potential evolution. Semiconductors are most prominent in public discussion. Electronics, more broadly, is one of the fastest-moving value chains since 1995, with 21 percentage points of share movement per decade. Pharmaceuticals and the mining of critical minerals are other examples. And they will be part of what shifts the way that flows crisscross the globe.
Second category: textiles and apparel. This category is not as sensitive in a geopolitical sense as some of the things I was talking about before. This category is one where you actually do have new hub creation right now. Consumer electronics, other forms of electric equipment that aren’t particularly sensitive, possibly fall in that category too.
Third category: IT services and financial intermediation or professional services. That will reconfigure the ways in which services flow.
Fourth and finally, there’s the stuff that’s just going to be steady—food and beverages, paper and printing. There’s no particular reason to expect that there are strong forcing mechanisms that will change the way those things are flowing across the world right now. They’re things that have remained relatively steady for the past ten or more years.
Global flows are necessary for a net-zero transition
Lucia Rahilly: Do we have a view on whether the evolving state of global flows is helping or hindering the net-zero transition ?
Olivia White: The way I’d put it is, there is no way we move quickly toward a net-zero transition without global flows. There are certainly things about global flows that are tricky from a net-zero perspective. It costs carbon to ship things and move things a long way. But in order for net zero to be attainable, we need to make sure that energy-generating technologies and fuels are able to flow across the world.
Energy-generating technologies include both the minerals that underpin construction of those technologies and the actual manufacturing. So, in the first category, think nickel and lithium. In the second category, think about the actual manufacturing of solar panels. The minerals themselves are processed in only a few countries around the world. So people are going to have to move them from one place to another. Maybe the world could have broader diversification of such things, but on average, the timeline from discovering a mineral to being able to produce it at scale is well in excess of 16 years. If we want to move fast, we have the luxury to move things across the world. Meeting cost curves for manufacturing at scale and in locations where you have at least some established presence is going to be important.
The final element that’s crucial with respect to net zero is cross-border capital flows. It’s really important that developing countries are able to finance shifts in the way that energy is produced and consumed in their countries, which means they may have to both spend more, at least as a ratio of GDP, and have less ability to spend, given other forms of development imperative.
Multinationals and global resilience
Lucia Rahilly: What’s the role of major multinational companies as we look ahead toward reimagining the future of our global connectedness?
Olivia White: The first thing that needs to be recognized is that major multinational corporations play an outsize role in global flows today. Multinationals are responsible for about 30 percent of trade. They’re responsible for 60 percent of exports and 82 percent of exports of knowledge-intensive goods. So they disproportionately drive flows, especially the ones associated with knowledge. And therefore, they’re going to be the center of managing for their own resilience, but also in a collective sense, for the resilience of the world.
The future of global flows
Lucia Rahilly: The media tends to focus on what some see as globalization’s imminent demise. Accepting that global ties continue to bind and connect us across the world, it’s also natural for folks to have pretty strong reactions to these intense and ongoing global disruptions that we’ve experienced in recent years. How would you sum up the way we think about the future of globalization at a high level?
Olivia White: The world we live in right now is highly dependent on flows. Will those flows reconfigure and shift? Yes, absolutely. They have in the past, and they will in the future.
Lucia Rahilly: Do we see anything in the research to indicate that the world is actually moving toward decoupling, which is also very much part of the media narrative?
Olivia White: If you look along regional lines, individual regions can’t be independent. If you just start to play with what sorts of decoupling of regions would be possible, you see very quickly that it’s not something you can do.
Now, is it possible that you would get groups of countries that become more strongly interconnected among themselves and less strongly connected with others? Absolutely. It’s possible to move in that direction. The question becomes, is there an actual decoupling, or do you just have a shift in degree? As with most things in the world, the answer tends toward the shift in degree rather than an abrupt or sharp true change or decoupling.
Lucia Rahilly: Does greater regionalization improve resilience?
Olivia White: To some degree you can say, “Look, if I’m self-sufficient, I’m more resilient.” On the other hand, all of a sudden you depend on yourself for everything, and that’s a point of vulnerability in the same way that getting it only from one other person would be a problem.
There are a whole host of reasons some degree of regionalization might help. You’ve got things closer to you. But dependency just on a few sets of people, whether or not they’re in your region, means you’ve got dependency on just a few points of potential weaknesses rather than a broad web, which in general is a more resilient and robust structure.
Lucia Rahilly: Thanks so much, Olivia. That was such an interesting discussion.
Olivia White: A real pleasure, Lucia. Thank you.
Roberta Fusaro: One example of resilience is AB InBev. Here to talk about how it’s prospering in the face of worldwide disruption is its CFO, Fernando Tennenbaum. This excerpt, “ How to thrive in a downturn: A CFO perspective ,” from our McKinsey Live series, was recorded in December 2022.
Lucia Rahilly: Fernando, we’re confronting an unusual constellation of disruptions: inflation, high interest rates driving up the cost of capital, geopolitical turbulence unexpectedly upending supply chains and sending energy prices spiking—it’s genuinely a volatile moment. Tell us, how is AB InBev faring in the current context?
Fernando Tennenbaum: We’re fortunate to be in a resilient category. Despite these twists and turns in different parts of the world, beer sales have been quite strong. That said, inflation has turned out to be much higher than expected. 2 Market conditions may have changed since this interview was conducted. We need to ensure our operations are in sync with the market, to meet this unique moment. We need to understand the state of the consumer and adjust our operations accordingly.
In emerging markets like Latin America and Africa, inflation is not new news. There are different levels of inflation, but inflation has been a part of these economies for a very long time. Consumers are more used to it, companies are more used to it—and it’s probably a more straightforward discussion.
Lucia Rahilly: You’ve spent much of your career in Latin America where, as you said, inflation has historically been much higher and more volatile than in the US or in Western Europe. Walk us through some of the lessons that we in the US, for example, could learn from.
Fernando Tennenbaum: Make sure that you’re always looking at your customers, and that you’re always keeping up with inflation. You should avoid lagging too much, and you should avoid overpricing compared with inflation. If you do too little or too much, you start disturbing the health of the consumer. If you get it right, it’s probably a good thing for the business. You have to make sure you navigate the rising cost environment while ensuring that the consumer is in a good place, your product is in a good place, and the category is a healthy one. It’s a balancing act.
You should avoid lagging too much, and you should avoid overpricing compared with inflation. If you do too little or too much, you start disturbing the health of the consumer. Fernando Tennenbaum
Lucia Rahilly: AB InBev has a diverse portfolio of brands. Volumes are good. Are customers trading up or down, during this period, between your premium and mass-market brands?
Fernando Tennenbaum: Premiumization continues to be a trend, and consumers continue to trade up to premium brands. Over the course of this year, people often asked whether consumers were trading down—and we see no evidence of trading down. That is true for the US, that is true for Africa, and that is true for Latin America—which is quite unique.
I don’t know if the future will be different; the world is changing so fast. But if you were to ask me ten years from now, I’d expect premium to be even bigger than it is today.
Lucia Rahilly: Let’s talk about uncertainty. The economy could play out in many different ways. How do you manage for that?
Fernando Tennenbaum: Let’s take our debt portfolio. Now is the moment that interest rates are going up. Inflation and borrowing are going up. Overall, this tends to be bad news—but for us, it’s quite the opposite because we don’t have any debt maturing in the next three years. We prepared for this when we saw the world going to a very different place at the beginning of 2020.
We ended up raising some long-term debt and repaying all our short-term debt. Now we’re left with a debt portfolio that has an average maturity of 16 years and no meaningful amount of debt maturing in the next three years—all at a fixed rate. Since we don’t need to refinance, we’re actually buying back our debt. Rising interest rates can be good when you can buy back debt cheaper than it cost to issue.
Lucia Rahilly: You became CFO at AB InBev in 2020, when pandemic uncertainty was at its peak. Talk to us about how you navigated that period.
Fernando Tennenbaum: The first thing we did in 2020 was pump up our cash position. Not that we needed it, but I felt it would give operations peace of mind. To be prepared, we started borrowing a lot of money. And we started taking care of our people. We needed to make sure our people were safe—that was priority number one.
Once we made sure our employees were safe, our operations were safe, then we looked at opportunities and started to fast-forward. I remember we looked at May, for example, and started to see a lot of markets doing well in terms of volume. We had a lot of cash. We started buying back some debt, especially near-term debt, to create even more optionality for the future.
We also accelerated our digital transformation. The moment was uniquely suited for it. Digital was a much better way to reach customers at a time when everybody was afraid to meet in person. In hindsight, the company ended up in a much better place today than it was three years ago—in terms of our portfolio, our digital transformation, and even financially—because we acted very quickly and created a lot of optionality during the first few months of the pandemic.
Lucia Rahilly: Any mistakes to avoid?
Fernando Tennenbaum: Looking back, I wouldn’t have done anything massively different. If I had known the outcome, I might have done things differently. But without knowing the outcome, I felt that the way we managed and the optionality we created set us up well.
Lucia Rahilly: Brewing is such an agriculturally dependent business, and agriculture has been significantly disrupted, both because of the war in Ukraine and because of climate-related risk. As CFO, how do you think about sustainability in terms of longer-term value creation?
Fernando Tennenbaum: Sustainability cuts across the whole of our business. We have a lot of local suppliers—20,000 local farmers. Our brewing processes are natural. The more efficient we are there, the more sustainable we are and, actually, the more profitable we are. We have local operations, and we sell to the local community. And most of our customers are very small entrepreneurs. The more we help them, the better they can run their business. And we say beer is inclusive because we have two billion consumers.
Lucia Rahilly: Is packaging also part of the sustainability approach?
Fernando Tennenbaum: Definitely. For example, we have returnable glass bottles. That’s very efficient, very sustainable, and from an economic standpoint, that’s probably the most profitable packaging we have. It’s also the most affordable for consumers. So it’s good for us, good for the environment, and good for the consumers.
Lucia Rahilly: You said beer is inclusive in part because so many of us drink it. How else do you approach inclusion at AB InBev?
Fernando Tennenbaum: Our two billion consumers are very different from one another. We need to make sure that, as a company, we reflect our consumers. Whenever we look at our colleagues, we need to make sure they reflect the societies where we operate—and we operate in very different societies.
A diverse and inclusive team is going to be a better team. That also applies to our suppliers. For example, if you think about suppliers in Africa, some are very poor. They manage to get access to technology, which means we can track whether they’re receiving the funds we pay them. We can track where agricultural commodities are being sourced. So how we financially empower them is also a very important part of our sustainability strategy.
Lucia Rahilly: Looking ahead, how are you thinking about innovation and investment in technology, in order to enable growth?
Fernando Tennenbaum: Innovation is a key component of beer, and there are two sides to that. One is innovation in products. The other is packaging. In Mexico, for example, we have different pack sizes for different consumption occasions and consumer needs.
Beyond that, there’s also technological innovation. Take our B2B platform, which we started piloting in 2019. Now, three or four years later, we have around $30 billion of GMV [gross merchandise value] in our e-commerce platform, which is accessible in more than 19 countries. That’s the optimal portfolio to improve customer engagement at their point of sale. Before we launched our B2B platform, we used to spend seven minutes per week interacting with our customers. Today, with our B2B platform, we interact with them 30 minutes per week. We increased the number of points of sales. For example, in Brazil, we used to have 700,000 customers, and now we have more than a million customers. Previously, they were buying our products from a distributor. Now we can reach them directly with the B2B system in place.
This connection with our customers means we can do a lot of other things, like our online marketplace, where third-party products generated an annualized GMV of $850 million, up from zero four years ago. That marketplace now continues to grow and to deliver a lot of value for our customers and for ourselves.
Lucia Rahilly: One more question: If you could give one piece of advice to a brand-new CFO of a large, multinational corporation, what would it be in this market?
Fernando Tennenbaum: Make sure you plan for different scenarios. The world is moving very fast, and you can’t expect it to unfold in a certain way. But if you have options, are agile in making decisions, and have a very engaged team, then regardless of the twists and turns, you are able to meet the moment. And you are definitely able to deliver on your objectives.
Lucia Rahilly: I lied. I’m going to ask you one more. How do you see, for these new CFOs, the relationship between sustainability and inclusivity and growth? Do you see those in tension?
Fernando Tennenbaum: There is this myth that you are either sustainable or profitable. At least at AB InBev, we’re sure they go hand in hand. The more sustainable you are, the more profitable you are, and the more value you create for your different stakeholders.
Fernando Tennenbaum is the CFO of Anheuser-Busch InBev. Olivia White is a director of the McKinsey Global Institute and a senior partner in McKinsey’s Bay Area office. Roberta Fusaro is an editorial director in the Waltham, Massachusetts, office, and Lucia Rahilly is global editorial director and deputy publisher of McKinsey Global Publishing and is based in the New York office.
Comments and opinions expressed by interviewees are their own and do not represent or reflect the opinions, policies, or positions of McKinsey & Company or have its endorsement.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

Global flows: The ties that bind in an interconnected world

On the cusp of a new era?

Globalization’s next chapter
ENCYCLOPEDIC ENTRY
Globalization.
Globalization is a term used to describe the increasing connectedness and interdependence of world cultures and economies.
Anthropology, Sociology, Social Studies, Civics, Economics
Freight Trains
Freight trains waiting to be loaded with cargo to transport around the United Kingdom. This cargo comes from around the world and contains all kinds of goods and products.
Photograph by Bloomberg

Globalization is a term used to describe how trade and technology have made the world into a more connected and interdependent place. Globalization also captures in its scope the economic and social changes that have come about as a result. It may be pictured as the threads of an immense spider web formed over millennia, with the number and reach of these threads increasing over time. People, money, material goods, ideas, and even disease and devastation have traveled these silken strands, and have done so in greater numbers and with greater speed than ever in the present age. When did globalization begin? The Silk Road, an ancient network of trade routes across China, Central Asia, and the Mediterranean used between 50 B.C.E. and 250 C.E., is perhaps the most well-known early example of exchanging ideas, products, and customs. As with future globalizing booms, new technologies played a key role in the Silk Road trade. Advances in metallurgy led to the creation of coins; advances in transportation led to the building of roads connecting the major empires of the day; and increased agricultural production meant more food could be trafficked between locales. Along with Chinese silk, Roman glass, and Arabian spices, ideas such as Buddhist beliefs and the secrets of paper-making also spread via these tendrils of trade. Unquestionably, these types of exchanges were accelerated in the Age of Exploration, when European explorers seeking new sea routes to the spices and silks of Asia bumped into the Americas instead. Again, technology played an important role in the maritime trade routes that flourished between old and newly discovered continents. New ship designs and the creation of the magnetic compass were key to the explorers’ successes. Trade and idea exchange now extended to a previously unconnected part of the world, where ships carrying plants, animals, and Spanish silver between the Old World and the New also carried Christian missionaries. The web of globalization continued to spin out through the Age of Revolution, when ideas about liberty , equality , and fraternity spread like fire from America to France to Latin America and beyond. It rode the waves of industrialization , colonization , and war through the eighteenth, nineteenth, and twentieth centuries, powered by the invention of factories, railways, steamboats, cars, and planes. With the Information Age, globalization went into overdrive. Advances in computer and communications technology launched a new global era and redefined what it meant to be “connected.” Modern communications satellites meant the 1964 Summer Olympics in Tokyo could be watched in the United States for the first time. The World Wide Web and the Internet allowed someone in Germany to read about a breaking news story in Bolivia in real time. Someone wishing to travel from Boston, Massachusetts, to London, England, could do so in hours rather than the week or more it would have taken a hundred years ago. This digital revolution massively impacted economies across the world as well: they became more information-based and more interdependent. In the modern era, economic success or failure at one focal point of the global web can be felt in every major world economy. The benefits and disadvantages of globalization are the subject of ongoing debate. The downside to globalization can be seen in the increased risk for the transmission of diseases like ebola or severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), or in the kind of environmental harm that scientist Paul R. Furumo has studied in microcosm in palm oil plantations in the tropics. Globalization has of course led to great good, too. Richer nations now can—and do—come to the aid of poorer nations in crisis. Increasing diversity in many countries has meant more opportunity to learn about and celebrate other cultures. The sense that there is a global village, a worldwide “us,” has emerged.
Media Credits
The audio, illustrations, photos, and videos are credited beneath the media asset, except for promotional images, which generally link to another page that contains the media credit. The Rights Holder for media is the person or group credited.
Production Managers
Program specialists, specialist, content production, last updated.
March 6, 2024
User Permissions
For information on user permissions, please read our Terms of Service. If you have questions about how to cite anything on our website in your project or classroom presentation, please contact your teacher. They will best know the preferred format. When you reach out to them, you will need the page title, URL, and the date you accessed the resource.
If a media asset is downloadable, a download button appears in the corner of the media viewer. If no button appears, you cannot download or save the media.
Text on this page is printable and can be used according to our Terms of Service .
Interactives
Any interactives on this page can only be played while you are visiting our website. You cannot download interactives.
Related Resources
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
The State of Globalization in 2022
- Steven A. Altman
- Caroline R. Bastian

Its collapse has been vastly overstated, according to an analysis of international flows of trade, capital, information, and people.
As companies contemplate adjustments to their global strategies, it is important to recognize how much continuity there still is even in a period of wrenching change. The idea of a world where economic efficiency alone drives patterns of international flows was always a myth. Globalization has always been an uneven process, with cross-country differences and international conflicts significantly dampening international flows. That’s a big part of why — even before the present crisis in Ukraine — only about 20% of global economic output ended up in a different country from where it was produced. As the landscape shifts, global strategies must be updated, but managers should avoid the costly overreactions that tend to follow major shocks to globalization.
Russia’s invasion of Ukraine has led to a new round of predictions that the end of globalization is nigh , much like we saw at the beginning of the Covid-19 pandemic . However, global cross-border flows have rebounded strongly since the early part of the pandemic. In our view, the war will likely reduce many types of international business activity and cause some shifts in their geography, but it will not lead to a collapse of international flows.
- Steven A. Altman is a senior research scholar, adjunct assistant professor, and director of the DHL Initiative on Globalization at the NYU Stern Center for the Future of Management .
- CB Caroline R. Bastian is a research scholar at the DHL Initiative on Globalization.
Partner Center
- Tools and Resources
- Customer Services
- Original Language Spotlight
- Alternative and Non-formal Education
- Cognition, Emotion, and Learning
- Curriculum and Pedagogy
- Education and Society
- Education, Change, and Development
- Education, Cultures, and Ethnicities
- Education, Gender, and Sexualities
- Education, Health, and Social Services
- Educational Administration and Leadership
- Educational History
- Educational Politics and Policy
- Educational Purposes and Ideals
- Educational Systems
- Educational Theories and Philosophies
- Globalization, Economics, and Education
- Languages and Literacies
- Professional Learning and Development
- Research and Assessment Methods
- Technology and Education
- Share Facebook LinkedIn Twitter
Article contents
Globalization and education.
- Liz Jackson Liz Jackson University of Hong Kong
- https://doi.org/10.1093/acrefore/9780190264093.013.52
- Published online: 26 October 2016
Few would deny that processes of globalization have impacted education around the world in many important ways. Yet the term “globalization” is relatively new, and its meaning or nature, conceptualization, and impact remain essentially contested within the educational research community. There is no global consensus on the exact time period of its occurrence or its most significant shaping processes, from those who focus on its social and cultural framings to those that hold global political-economic systems or transnational social actors as most influential. Intersecting questions also arise regarding whether its influence on human communities and the world should be conceived of as mostly good or mostly bad, which have significant implications for debates regarding the relationship between globalization and education. Competing understandings of globalization also undergird diverse methodologies and perspectives in expanding fields of research into the relationship between education and globalization.
There are many ways to frame the relationship of globalization and education. Scholars often pursue the topic by examining globalization’s perceived impact on education, as in many cases global convergence around educational policies, practices, and values has been observed in the early 21st century. Yet educational borrowing and transferal remains unstraightforward in practice, as educational and cultural differences across social contexts remain, while ultimate ends of education (such as math competencies versus moral cultivation) are essentially contested. Clearly, specificity is important to understand globalization in relation to education. As with globalization generally, globalization in education cannot be merely described as harmful or beneficial, but depends on one’s position, perspective, values, and priorities.
Education and educators’ impacts on globalization also remain a worthwhile focus of exploration in research and theorization. Educators do not merely react to globalization and related processes, but purposefully interact with them, as they prepare their students to respond to challenges and opportunities posed by processes associated with globalization. As cultural and political-economic considerations remain crucial in understanding globalization and education, positionality and research ethics and reflexivity remain important research concerns, to understand globalization not just as homogeneity or oppressive top-down features, but as complex and dynamic local and global intersections of people, ideas, and goods, with unclear impacts in the future.
- globalization
- economic integration
- education borrowing
- global studies in education
- comparative education
- education development
Few would deny that processes of globalization have impacted education around the world in many important ways. Yet the term “globalization” is relatively new, and its meaning or nature, conceptualization, and impact remain essentially contested within the educational research community. Competing understandings of globalization undergird diverse methodologies and perspectives in the expanding web of fields researching the relationship between education and globalization examined below. The area of educational research which exploded at the turn of the 21st century requires a holistic view. Rather than take sides within this contentious field, it is useful to examine major debates and trends, and indicate where readers can learn more about particular specialist areas within the field and other relevant strands of research.
The first part below considers the development of the theorization and conceptualization of globalization and debates about its impact that are relevant to education. The next section examines the relationship between education and globalization as explored by the educational research community. There are many ways to frame the relationship between globalization and education. First explored here is the way that globalization can be seen to impact education, as global processes and practices have been observed to influence many educational systems’ policies and structures; values and ideals; pedagogy; curriculum and assessment; as well as broader conceptualizations of teacher and learner, and the good life. However, there is also a push in the other direction—through global citizenship education, education for sustainable development, and related trends—to understand education and educators as shapers of globalization, so these views are also explored here. The last section highlights relevant research directions.
The Emergence of Globalization(s)
At the broadest level, globalization can be defined as a process or condition of the cultural, political, economic, and technological meeting and mixing of people, ideas, and resources, across local, national, and regional borders, which has been largely perceived to have increased in intensity and scale during the late 20th and early 21st centuries. However, there is no global consensus on the exact time period of its occurrence, or its most significant shaping processes, from social and cultural framings to those that hold global political-economic systems or transnational social actors as most influential. Intersecting questions also arise regarding whether its influence on human communities and the world should be conceived as mostly good or mostly bad, which have clear and significant implications for understanding debates regarding the relationship between globalization and education.
Conceptualizing Globalization
Globalization is a relatively recent concept in scholarly research, becoming popular in public, academic, and educational discourse only in the 1980s. However, many leading scholars of globalization have argued that the major causes or shapers of globalization, particularly the movement and mixing of elements beyond a local or national level, is at least many centuries old; others frame globalization as representing processes inherent to the human experience, within a 5,000–10,000-year time frame. 1 Conceptualizations of globalization have typically highlighted cultural, political-economic, and/or technological aspects of these processes, with different researchers emphasizing and framing the relationships among these different aspects in diverse ways in their theories.
Cultural framings: Emphasizing the cultural rather than economic or political aspects of globalization, Roland Robertson pinpointed the occurrence of globalization as part of the process of modernity in Europe (though clearly similar processes were occurring in many parts of the world), particularly a growing mutual recognition among nationality-based communities. 2 As people began identifying with larger groups, beyond their family, clan, or tribe, “relativization” took place, as people saw others in respective outside communities similarly developing national or national-like identities. 3 Through identifying their own societies as akin to those of outsiders, people began measuring their cultural and political orders according to a broader, international schema, and opening their eyes to transnational inspirations for internal social change.
Upon mutual recognition of nations, kingdoms, and the like as larger communities that do not include all of humanity, “emulation” stemming from comparison of the local to the external was often a next step. 4 While most people and communities resisted, dismissed, or denied the possibility of a global human collectivity, they nonetheless compared their own cultures and lives with those beyond their borders. Many world leaders across Eurasia looked at other “civilizations” with curiosity, and began increasing intercultural and international interactions to benefit from cultural mixing, through trade, translation of knowledge, and more. With emulation and relativization also came a sense of a global standard of values, for goods and resources, and for the behavior and organization of individuals and groups in societies, though ethnocentrism and xenophobia was also often a part of such “global” comparison. 5
Political-economic framings: In political theory and popular understanding, nationalism has been a universalizing discourse in the modern era, wherein individuals around the world have been understood to belong to and identify primarily with largely mutually exclusive national or nation-state “imagined communities.” 6 In this context, appreciation for and extensive investigation of extranational and international politics and globalization were precluded for a long time in part due to the power of nationalistic approaches. However, along with the rise historically of nationalist and patriotic political discourse, theories of cosmopolitanism also emerged. Modern cosmopolitanism as a concept unfolded particularly in the liberalism of Immanuel Kant, who argued for a spirit of “world citizenship” toward “perpetual peace,” wherein people recognize themselves as citizens of the world. 7 Martha Nussbaum locates cosmopolitanism’s roots in the more distant past, however, observing Diogenes the Cynic (ca. 404–323 bce ) in Ancient Greece famously identifying as “a citizen of the world.” 8 This suggests that realization of commonality, common humanity, and the risks of patriotism and nationalism as responses to relativization and emulation have enabled at least a “thin” kind of global consciousness for a very long time, as a precursor to today’s popular awareness of globalization, even if such a global consciousness was in ancient history framed within regional rather than planetary discourse.
In the same way as culturally oriented globalization scholars, those theorizing from an economic and/or political perspective conceive the processes of globalization emerging most substantively in the 15th and 16th centuries, through the development of the capitalist world economic system and the growth of British- and European-based empires holding vast regions of land in Africa, Asia, and the Americas as colonies to enhance trade and consumption within empire capitals. According to Immanuel Wallerstein’s world system theory, which emerged before globalization theory, in the 1970s, the capitalist world economic system is one of the most essential framing elements of the human experience around the world in the modern (or postmodern) era. 9 Interaction across societies primarily for economic purposes, “ not bounded by a unitary political structure,” characterizes the world economy, as well as a capitalist order, which conceives the main purpose of international economic exchange as being the endless generation and accumulation of capital. 10 A kind of global logic was therein introduced, which has expanded around the globe as we now see ourselves as located within an international financial system.
Though some identify world system theory as an alternative or precursor to globalization theories (given Wallerstein’s own writing, which distinguished his view from globalization views 11 ), its focus on a kind of planetary global logic interrelates with globalization theories emerging in the 1980s and 1990s. 12 Additionally, its own force and popularity in public and academic discussions enabled the kind of global consciousness and sense of global interrelation of people which we can regard as major assumptions underpinning the major political-economic theories of globalization and the social imaginary of globalization 13 that came after.
Globalization emerged within common discourse as the process of international economic and political integration and interdependency was seen to deepen and intensify during and after the Cold War era of international relations. At that time, global ideologies were perceived which spanned diverse cultures and nation-states, while global economic and military interdependency became undeniable facts of the human condition. Thus, taking world systems theory as a starting point, global capitalism models have theorized the contemporary economic system, recognizing aspects of world society not well suited to the previously popular nationalistic ways of thinking about international affairs. Leslie Sklair 14 and William Robinson 15 highlighted the transnational layer of capitalistic economic activity, including practices, actors and social classes, and ideologies of international production and trade, elaborated by Robinson as “an emergent transnational state apparatus,” a postnational or extranational ideological, political, and practical system for societies, individuals, and groups to interact in the global space beyond political borders. 16 Globalization is thus basically understood as a process or condition of contemporary human life, at the broadest level, rather than a single event or activity.
Technological framings: In the 1980s and 1990s, the impact of technology on many people’s lives, beliefs, and activities rose tremendously, altering the global political economy by adding an intensity of transnational communication and (financial and information) trading capabilities. Manuel Castells argued that technological advancements forever altered the economy by creating networks of synchronous or near-synchronous communication and trade of information. 17 Anthony Giddens likewise observed globalization’s essence as “time-space distanciation”: “the intensification of worldwide social relations which link distant localities in such a way that local happenings are shaped by events occurring many miles away and vice versa.” 18 As information became present at hand with the widespread use of the Internet, a postindustrial society has also been recognized as a feature of globalization, wherein skills and knowledge to manipulate data and networks become more valuable than producing goods or trading material resources.
Today, globalization is increasingly understood as having interrelating cultural, political-economic, and technological dimensions, and theorists have thus developed conceptualizations and articulations of globalization that work to emphasize the ways that these aspects intersect in human experience. Arjun Appadurai’s conception of global flows frames globalization as taking place as interactive movements or waves of interlinked practices, people, resources, and ideologies: ethnoscapes, mediascapes, technoscapes, finanscapes, and ideoscapes. 19 Ethnoscapes are waves of people moving across cultures and borders, while mediascapes are moving local, national, and international constructions of information and images. Technoscapes enable (and limit) interactions of peoples, cultures, and resources through technology, while finanscapes reflect intersection values and valuations; human, capital, and national resources; and more. Ideoscapes reflect competing, interacting, reconstructing ideologies, cultures, belief systems, and understandings of the world and humanity. Through these interactive processes, people, things, and ideas move and move each other, around the world. 20
Evaluating Globalization
While the explanatory function of Appadurai’s vision of globalization’s intersecting dimensions is highlighted above, many theories of globalization emphasize normative positions in relation to the perceived impact of global and transnational processes and practices on humanity and the planet. Normative views of globalization may be framed as skeptical , globalist , or transformationalist . As Fazal Rizvi and Bob Lingard note, these are ideal types, rather than clearly demarcated practical parties or camps of theorists, though they have become familiar and themselves a part of the social imaginary of globalization (that is, the way globalization is perceived in normative and empirical ways by ordinary people rather than researchers). 21 The positions are also reflected in the many educational discourses relating to globalization, despite their ideological rather than simply empirical content.
Skeptical views: Approaches to globalization in research that are described as skeptical may question or problematize globalization discourse in one of two different ways. The first type of skepticism questions the significance of globalization. The second kind of skepticism tends to embrace the idea of globalization, but regards its impact on people, communities, and/or the planet as negative or risky, overall.
As discussed here, global or international processes are hardly new, while globalization became a buzzword only in the last decades of the 20th century. Thus a first type of skeptic may charge that proponents of globalization or globalization theory are emphasizing the newness of global processes for ulterior motives, as a manner of gaining attention for their work, celebrating that which should instead be seen as problematic capitalist economic relations, for example. Alternatively, some argue that the focus on globalization in research, theorization, and popular discourse fails to recognize the agency of people and communities as actors in the world today, and for this reason should be avoided and replaced by a focus on the “transnational.” As Michael Peter Smith articulates, ordinary individual people, nation-states, and their practices remain important within the so-called global system; a theory of faceless, ahistorical globalization naturalizes global processes and precludes substantive elaboration of how human (and national) actors have played and continue to play primary roles in the world through processes of knowledge and value construction, and through interpersonal and transnational activities. 22
The second strand of globalization skepticism might be referred to as antiglobalist or antiglobalization positions. Thinkers in this vein regard globalization as a mark of our times, but highlight the perceived negative impacts of globalization on people and communities. Culturally, this can include homogenization and loss of indigenous knowledge, and ways of life, or cultural clashes that are seen to arise out of the processes of relativization and emulation in some cases. George Ritzer coined the term “McDonaldization” to refer to the problematic elements of the rise of a so-called global culture. 23 More than simply the proliferation of McDonalds fast-food restaurants around the world, McDonaldization, according to Ritzer, includes a valuation of efficiency over humanity in production and consumption practices, a focus on quantity over quality, and control and technology over creativity and culture. Global culture is seen as a negative by others who conceive it as mainly the product of a naïve cultural elite of international scholars and business people, in contrast with “low-end globalization,” which is the harsher realities faced by the vast majority of people not involved in international finance, diplomacy, or academic research. 24
Alternatively, Benjamin Barber 25 and Samuel Huntington 26 have focused on “Jihad versus McWorld” and the “clash of civilizations,” respectively, as cultures can be seen to mix in negative and unfriendly ways in the context of globalization. Although Francis Fukuyama and other hopeful globalists perceived a globalization of Western liberal democracy at the turn of the 21st century, 27 unforeseen global challenges such as terrorism have fueled popular claims by Barber and Huntington that cultural differences across major “civilizations” (international ideological groupings), particularly of liberal Western civilization and fundamentalist Islam, preclude their peaceful relativization, homogenization, and/or hybridization, and instead function to increase violent interactions of terrorism and war.
Similarly, but moving away from cultural aspects of globalization, Ulrich Beck highlighted risk as essential to understanding globalization, as societies face new problems that may be related to economy or even public health, and as their interdependencies with others deepen and increase. 28 Beck gave the example of Mad Cow disease (bovine spongiform encephalopathy) as one instance where much greater and more broadly distributed risks have been created through global economic and political processes. Skeptical economic theories of globalization likewise highlight how new forms of inequality emerge as global classes and labor markets are created. For instance, Michael Hardt and Antonio Negri argue that a faceless power impersonally oppresses grassroots people despite the so-called productivity of globalization (that is, the growth of capital it enables) from a capitalist economic orientation. 29 It is this faceless but perceived inhumane power that has fueled globalization protests, particularly of the meetings of the World Trade Organization in the 1990s and 2000s, in the United States and Europe.
In light of such concerns, Walden Bello argued for “deglobalization,” a reaction and response by people that aims to fight against globalization and reorient communities to local places and local lifestyles. Bello endorsed a radical shift to a decentralized, pluralistic system of governance from a political-economic perspective. 30 Similarly, Colin Hines argues for localization, reclaiming control over local economies that should become as diverse as possible to rebuild stability within communities. 31 Such ideas have found a broad audience, as movements to “buy local” and “support local workers” have spread around the world rapidly in the 2000s.
Globalist views: Globalists include researchers and advocates who highlight the benefits of globalization to different communities and in various areas of life, often regarding it as necessary or natural. Capitalist theories of globalization regard it as ideal for production and consumption, as greater specialism around the world increases efficiency. 32 The productive power of globalization is also highlighted by Giddens, who sees the potential for global inclusivity and enhanced creative dialogue arising (at least in part) from global processes. 33 In contrast with neoliberal (pro-capitalism) policies, Giddens propagated the mixture of the market and state interventions (socialism and Keynesian economy), and believed that economic policies with socially inclusive ideas would influence social and educational policies and thus promote enhanced social development.
The rise of global culture enhances the means for people to connect with one another to improve life and give it greater meaning, and can increase mutual understanding. As democracy becomes popular around the world as a result of global communication processes, Scott Burchill has argued that universal human rights can be achieved to enhance global freedom in the near future. 34 Joseph Stiglitz likewise envisioned a democratizing globalization that can include developing countries on an equal basis and transform “economic beings” to “human beings” with values of community and social justice. 35 Relatedly, some globalists contend against skeptics that cultural and economic-political or ideological hybridity and “glocalization,” as well as homogenization or cultural clashes, often can and do take place. Under glocalization , understood as local-level globalization processes (rather than top-down intervention), local actors interact dynamically with, and are not merely oppressed by, ideas, products, things, and practices from outside and beyond. Thus, while we can find instances of “Jihad” and “McWorld,” so too can we find Muslims enjoying fast food, Westerners enjoying insights and activities from Muslim and Eastern communities, and a variety of related intercultural dialogues and a dynamic reorganization of cultural and social life harmoniously taking place.
Transformationalist views: Globalization is increasingly seen by educators (among others) around the globe to have both positive and negative impacts on communities and individuals. Thus, most scholars today hold nuanced, middle positions between skepticism and globalism, such as David Held and Anthony McGrew’s transformationalist stance. 36 As Rizvi and Lingard note, globalization processes have material consequences in the world that few would flatly deny, while people increasingly do see themselves as interconnected around the globe, by technology, trade, and more. 37 On the other hand, glocalization is often a mixed blessing, from a comparative standpoint. Global processes do not happen outside of political and economic contexts, and while some people clearly benefit from them, others may not appear to benefit from or desire processes and conditions related to globalization.
Thus, Rizvi and Lingard identify globalization “as an empirical fact that describes the profound shifts that are taking place in the world; as an ideology that masks various expression of power and a range of political interests; and as a social imaginary that expresses the sense people have of their own identity and how it relates to the rest of the world, and … their aspirations and expectations.” 38 Such an understanding of globalization enables its continuous evaluation in terms of dynamic interrelated practices, processes, and ideas, as experienced and engaged with by people and groups within complex transnational webs of organization. Understandings of globalization thus link to education in normative and empirical ways within research. It is to the relationship of globalization to education that we now turn.
Historical Background
Globalization and education are highly interrelated from a historical view. At the most basic level, historical processes that many identify as essential precursors to political-economic globalization during the late modern colonial and imperialist eras influenced the development and rise of mass education. Thus, what we commonly see around the world today as education, mass schooling of children, could be regarded as a first instance of globalization’s impact on education, as in many non-Western contexts traditional education had been conceived as small-scale, local community-based, and as vocational or apprenticeship education, and/or religious training. 39 In much of Africa, Asia, the Middle East, and the indigenous Americas and Australasia, institutionalized formal schools emerged for the first time within colonial or (often intersecting) missionary projects, for local elite youth and children of expatriate officials.
The first educational scholarship with a global character from a historical point of view would thus be research related to colonial educational projects, such as in India, Africa, and East Asia, which served to create elite local communities to serve colonial officials, train local people to work in economic industries benefiting the colony, and for preservation of the status quo. Most today would describe this education as not part of an overall development project belonging to local communities, but as a foreign intervention for global empire maintenance or social control. As postcolonial educational theorists such as Paulo Freire have seen it, this education sought to remove and dismiss local culture as inferior, and deny local community needs for the sake of power consolidation of elites, and it ultimately served as a system of oppression on psychological, cultural, and material levels. 40 It has been associated by diverse cultural theorists within and outside the educational field with the loss of indigenous language and knowledge production, with moral and political inculcation, and with the spread of English as an elite language of communication across the globe. 41
Massification of education in the service of local communities in most developing regions roughly intersected with the period after the Second World War and in the context of national independence movements, wherein nationally based communities reorganized as politically autonomous nation-states (possibly in collaboration with former colonial parties). In 1945 , the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) emerged, as the United Nations recognized education as critical for future global peace and prosperity, preservation of cultural diversity, and global progress toward stability, economic flourishing, and human rights. UNESCO has advocated for enhancement of quality and access to education around the world through facilitating the transnational distribution of educational resources, establishing (the discourse of) a global human right to education, promoting international transferability of educational and teaching credentials, developing mechanisms for measuring educational achievement across countries and regions, and supporting national and regional scientific and cultural developments. 42 The World Bank, Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), and United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF) have engaged in similar work.
Thus, the first modern global educational research was that conducted by bodies affiliated with or housed under UNESCO, such as the International Bureau of Education, the UNESCO Institute for Statistics, and the International Institute of Educational Planning, which are regarded as foundational bodies sponsoring international and comparative research. In research universities, educational borrowing across international borders became one significant topic of research for an emerging field of scholars identified as comparative educational researchers. Comparative education became a major field of educational inquiry in the first half of the 20th century, and expanded in the 1950s and 1960s. 43 Comparative educational research then focused on aiding developing countries’ education and improving domestic education through cross-national examinations of educational models and achievement. Today, comparative education remains one major field among others that focuses on globalization and education, including international education and global studies in education.
Globalization as a contemporary condition or process clearly shapes education around the globe, in terms of policies and values; curriculum and assessment; pedagogy; educational organization and leadership; conceptions of the learner, the teacher, and the good life; and more. Though, following the legacy of the primacy of a nation-state and systems-theory levels of analysis, it is traditionally conceived that educational ideas and changes move from the top, such as from UNESCO and related bodies and leading societies, to the developing world, we find that often glocalization and hybridity, rather than simple borrowing, are taking place. On the other hand, education is also held by scholars and political leaders to be a key to enhancing the modern (or postmodern) human condition, as a symbol of progress of the global human community, realized as global citizenship education, education for sustainable development, and related initiatives. 44 The next subsections consider how globalization processes have been explored in educational research as shapers of education, and how education and educators can also be seen to influence globalization.
Research on Globalization’s Impact on Education
Global and transnational processes and practices have been observed to influence and impact various aspects of contemporary education within many geographical contexts, and thus the fields of research related to education and globalization are vast: they are not contained simply within one field or subfield, but can be seen to cross subdisciplinary borders, in policy studies, curriculum, pedagogy, higher education studies, assessment, and more. As mentioned previously, modern education can itself be seen as one most basic instance of globalization, connected to increased interdependency of communities around the world in economic and political affairs first associated with imperialism and colonialism, and more recently with the capitalist world economy. And as the modern educational system cannot be seen as removed or sealed off from cultural and political-economic processes involved in most conceptualizations of globalization, the impacts of globalization processes upon education are often considered wide-ranging, though many are also controversial.
Major trends: From a functionalist perspective, the globalization of educational systems has been influenced by new demands and desires for educational transferability, of students and educators. In place of dichotomous systems in terms of academic levels and credentialing, curriculum, and assessment, increasing convergence can be observed today, as it is recognized that standardization makes movement of people in education across societies more readily feasible, and that such movement of people can enhance education in a number of ways (to achieve diversity, to increase specialization and the promotion of dedicated research centers, to enhance global employability, and so on). 45 Thus, the mobility and paths of movement of students and academics, for education and better life opportunities, have been a rapidly expanding area of research. A related phenomenon is that of offshore university and school campuses—the mobility of educational institutions to attract and recruit new students (and collect fees), such as New York University in Abu Dhabi and Shanghai. By implication, education is often perceived as becoming more standardized around the globe, though hybridity can also be observed at the micro level.
How economic integration under globalization impacts local educational systems has been traced by Rizvi and Lingard. 46 As they note, from a broad view, the promotion of neoliberal values in the context of financial adjustment and restructuring of poorer countries under trade and debt agreements led by intergovernmental organizations, most notably the OECD, encouraged, first, fiscal discipline in educational funding (particularly impacting the payment of educators in many regions) and, second, the redistribution of funds to areas of education seen as more economically productive, namely primary education, and to efforts at privatization and deregulation of education. While the educational values of countries can and do vary, from democracy and peace, to social justice and equity, and so on, Rizvi and Lingard also observed that social and economic efficiency views have become dominant within governments and their educational policy units. 47 Though human capital theory has always supported the view that individuals gain proportionately according to the investment in their education and training, this view has become globalized in recent decades to emphasize how whole societies can flourish under economic interdependency via enhanced education.
These policy-level perspectives have had serious implications for how knowledge and thus curriculum are increasingly perceived. As mentioned previously, skills for gaining knowledge have taken precedent over knowledge accumulation, with the rise of technology and postindustrial economies. In relation, “lifelong learning,” learning to be adaptive to challenges outside the classroom and not merely to gain academic disciplinary knowledge, has become a focal point for education systems around the globe in the era of globalization. 48 Along with privatization of education, as markets are seen as more efficient than government systems of provision, models of educational choice and educational consumption have become normalized as alternatives to the historical status quo of traditional academic or intellectual, teacher-centered models. Meanwhile, the globalization of educational testing—that is, the use of the same tests across societies around the world—has had a tremendous impact on local pedagogies, assessment, and curricula the world over. Though in each country decision-making structures are not exactly the same, many societies face pressure to focus on math, science, and languages over other subjects, as a result of the primacy of standardized testing to measure and evaluate educational achievement and the effectiveness of educational systems. 49
However, there remains controversy over what education is the best in the context of relativization and emulation of educational practices and students, and therefore the 2010s have seen extraordinary transfers of educational approaches, not just from core societies to peripheral or developing areas, but significant horizontal movements of educational philosophies and practices from West to East and East to West. With the rise of global standardized tests such as the OECD’s Programme for International Student Assessment (PISA), educational discourse in Western societies has increasingly emphasized the need to reorient education to East Asian models (such as Singapore or Shanghai), seen as victors of the tests. 50 On the other hand, many see Finland’s educational system as ideal in relation to its economic integration in society and focus on equity in structure and orientation, and thus educators in the Middle East, East Asia, and the United States have also been seen to consider emulating Finnish education in the 2010s. 51
Evaluations: From a normative point of view, some regard changes to local education in many contexts brought about by globalization as harmful and risky. Freire’s postcolonial view remains salient to those who remain concerned that local languages and indigenous cultural preservation are being sacrificed for elite national and international interests. 52 There can be no doubt that language diversity has been decreasing over time, while indigenous knowledge is being reframed within globalist culture as irrelevant to individual youths’ material needs. 53 Many are additionally skeptical of the sometimes uncritical adoption of educational practices, policies, and discourse from one region of the globe to another. In many countries in Africa and the Middle East, ideas and curricula are borrowed from the United Kingdom, the United States, or Finland in an apparently hasty manner, only to be discarded for the next reform, when it is not found to fit neatly and efficiently within the local educational context (for instance, given local educational values, structures and organizations, and educator and student views). 54 Others argue, in parallel to globalization skeptics, that globalization’s major impact on education has actually been the promotion of a thin layer of aspirational, cosmopolitan values among global cultural elites, who largely overlook the realities, problems, and challenges many face. 55
On the other hand, the case for globalization as a general enhancer of education worldwide has compelling evidence as well. Due to the work of UNESCO, the OECD, and related organizations, educational attainment has become more equitable globally, by nation, race, gender, class, and other markers of social inequality; and educational access has been recognized as positively aligned with personal and national economic improvement, according to quantitative educational researchers. 56 (David Hill, Nigel Greaves, and Alpesh Maisuria argue from a Marxist viewpoint that education in conjunction with global capitalism reinforces rather than decreases inequality and inequity; yet they also note that capitalism can be and often has been successfully regulated to diminish rather than increase inequality generally across countries. 57 ) As education has been effectively conceived as a human right in the era of globalization, societies with historically uneven access to education are on track to systematically enhance educational quality and access.
Changes to the way knowledge and the learner have been conceived, particularly with the rise of ubiquitous technology, are also often regarded as positive overall. People around the world have more access to information than ever before with the mass use of the Internet, and students of all ages can access massive open online courses (MOOCs); dynamic, data-rich online encyclopedias; and communities of like-minded scholars through social networks and forums. 58 In brick-and-mortar classrooms, educators and students are more diverse than ever due to enhanced educational mobility, and both are exposed to a greater variety of ideas and perspectives that can enhance learning for all participants. Credentials can be earned from reputable universities online, with supervision systems organized by leading scholars in global studies in education in many cases. Students have more choices when it comes to learning independently or alongside peers, mentors, or experts, in a range of disciplines, vocations, and fields.
The truth regarding how globalization processes and practices are impacting contemporary education no doubt lies in focusing somewhere in between the promises and the risks, depending on the context in question: the society, the educational level, the particular community, and so on. Particularly with regard to the proposed benefits of interconnectivity and networked ubiquitous knowledge spurred by technology, critics contend that the promise of globalization for enhancing education has been severely overrated. Elites remain most able to utilize online courses and use technologies due to remaining inequalities in material and human resources. 59 At local levels, globalization in education (more typically discussed as internationalization) remains contentious in many societies, as local values, local students and educators, and local educational trends can at times be positioned as at odds with the priorities of globalization, of internationalizing curricula, faculty, and student bodies. As part of the social imaginary of globalization, international diversity can become a buzzword, while cultural differences across communities can result in international students and faculty members becoming ghettoized on campus. 60 International exchanges of youth and educators for global citizenship education can reflect political and economic differences between communities, not merely harmonious interconnection and mutual appreciation. 61 In this context of growing ambivalence, education and educators are seen increasingly as part of the solution to the problems and challenges of the contemporary world that are associated with globalization, as educators can respond to such issues in a proactive rather than a passive way, to ensure globalization’s challenges do not exceed its benefits to individuals and communities.
Education’s Potential Impact on Globalization
As globalization is increasingly regarded with ambivalence in relation to the perceived impact of global and transnational actors and processes on local educational systems, educators are increasingly asked not to respond passively to globalization, through enacting internationalization and global economic agendas or echoing simplistic conceptualizations or evaluations of globalization via their curriculum. Instead, education has been reframed in the global era as something youth needs, not just to accept globalization but to interact with it in a critical and autonomous fashion. Two major trends have occurred in curriculum and pedagogy research, wherein education is identified as an important potential shaper of globalization. These are global citizenship education (also intersecting with what are called 21st-century learning and competencies) and education for sustainable development.
Global citizenship education: Global citizenship education has been conceived by political theorists and educational philosophers as a way to speak back to globalization processes seen as harmful to individuals and communities. As Martha Nussbaum has argued, educators should work to develop in students feelings of compassion, altruism, and empathy that extend beyond national borders. 62 Kathy Hytten has likewise written that students need to learn today as part of global citizenship education not just feelings of sympathy for people around the world, but critical skills to identify root causes of problems that intersect the distinction of local and global, as local problems can be recognized as interconnected with globalization processes. 63 In relation to this, UNESCO and nongovernmental organizations and foundations such as Oxfam and the Asia Society have focused on exploring current practices and elaborating best practices from a global comparative standpoint for the dissemination of noncognitive, affective, “transversal” 21st-century competencies, to extend civic education in the future in the service of social justice and peace, locally and globally. 64
Questions remain in this area in connection with implementation within curriculum and pedagogy. A first question is whether concepts of altruism, empathy, and even harmony, peace, and justice, are translatable, with equivalent meanings across cultural contexts. There is evidence that global citizenship education aimed at educating for values to face the potential harms of globalization is converging around the world on such aims as instilling empathy and compassion, respect and appreciation of diversity, and personal habits or virtues of open-mindedness, curiosity, and creativity. However, what these values, virtues, and dispositions look like, how they are demonstrated, and their appropriate expressions remain divergent as regards Western versus Eastern and African societies (for example). 65 By implication, pedagogical or curriculum borrowing or transferral in this area may be problematic, even if some basic concepts are shared and even when best practices can be established within a cultural context.
Additionally, how these skills, competencies, and dispositions intersect with the cognitive skills and political views of education across societies with different cultures of teaching and learning also remains contentious. In line with the controversies over normative views of globalization, whether the curriculum should echo globalist or skeptical positions remains contested by educators and researchers in the field. Some argue that a focus on feelings can be overrated or even harmful in such education, given the immediacy and evidence of global social justice issues that can be approached rationally and constructively. 66 Thus, token expressions of cultural appreciation can be seen to preclude a deeper engagement with social justice issues if the former becomes a goal in itself. On the other hand, the appropriate focus on the local versus the global, and on the goods versus the harms of globalization, weighs differently across and within societies, from one individual educator to the next. Thus, a lack of evidence of best practices in relation to the contestation over ultimate goals creates ambivalence at the local level among many educators about what and how to teach global citizenship or 21st-century skills, apart from standardized knowledge in math, science, and language.
Education for sustainable development: Education for sustainable development is a second strand of curriculum and pedagogy that speaks back to globalization and that is broadly promoted by UNESCO and related intergovernmental and nongovernmental organizations. Education for sustainable development is, like global citizenship education, rooted in globalization’s impact upon individuals in terms of global consciousness. Like global citizenship, education for sustainable development also emphasizes global interconnection in relation to development and sustainability challenges. It is also a broad umbrella term that reflects an increasingly wide array of practices, policies, and programs, formal and informal, for instilling virtues and knowledge and skills seen to enable effective responses to challenges brought about by globalization. 67 In particular, education for sustainable development has seen global progress, like globalization, as enmeshed in intersecting cultural, social, and economic and political values and priorities. Education for All is an interrelated complementary thread of UNESCO work, which sees access to education as a key to social justice and development, and the improvement of human quality of life broadly. In developed societies, environmental sustainability has come to be seen as a pressing global issue worth curricular focus, as behaviors with regard to consumption of natural resources impact others around the world, as well as future generations. 68
A diversity of practices and views also marks this area of education, resulting in general ambiguity about overall aims and best means. Controversies over which attitudes of sustainability are most important to inculcate, and whether it is important to inculcate them, intertwine with debates over what crises are most pertinent and what skills and competencies students should develop. Measures are in place for standardizing sustainability knowledge in higher education worldwide, as well as for comparing the development of prosustainability attitudes. 69 However, some scholars argue that both emphases miss the point, and that education for sustainable development should first be about changing cultures to become more democratic, creative, and critical, developing interpersonal and prosocial capabilities first, as the challenges of environmental sustainability and global development are highly complex and dynamic. 70 Thus, as globalization remains contested in its impacts, challenges, and promise at local levels, so too does the best education that connects positively with globalization to enhance local and global life. In this rich and diverse field, as processes of convergence and hybridity of glocalization continue to occur, the promise of globalization and the significance of education in relation to it will no doubt remain lively areas of debate in the future, as globalization continues to impact communities in diverse ways.
Research Considerations
There is no shortage of normative and explanatory theories about globalization, each of which points to particular instances and evidence about domains and contexts of globalization. However, when it comes to understanding the interconnections of globalization and education, some consensus regarding best practices for research has emerged. In fields of comparative and international education and global studies in education, scholars are increasingly calling today for theories and empirical investigations that are oriented toward specificity, particularity, and locality, in contrast with the grand theories of globalization elaborated by political scholars. However, a challenge is that such scholarship should not be reduced artificially to one local level in such a way as to exclude understanding of international interactions, in what has been called in the research community “methodological nationalism.” 71 Such reductive localism or nationalism can arise particularly in comparative education research, as nation-states have been traditional units for comparative analysis, but are today recognized as being too diverse from one to the next to be presumed similar (while global processes impact them in disparate ways). 72 Thus, Rizvi has articulated global ethnography as a focused approach to the analysis of international educational projects that traces interconnections and interactions of local and global actors. 73 In comparative educational research, units of analysis must be critically pondered and selected, and it is also possible to make comparisons across levels within one context (for instance, from local educational interactions to higher-level policy-making processes in one society). 74
Qualitative and quantitative analyses can be undertaken to measure global educational achievements, values, policy statements, and more; yet researcher reflexivity and positionality, what is traditionally conceived of as research ethics, is increasingly seen as vital for researchers in this politically and ethically contentious field. Although quantitative research remains important for highlighting convergences in data in global educational studies, such research cannot tell us what we should do, as it does not systematically express peoples’ values and beliefs about the aims of education, or their experiences of globalization, and so on, particularly effectively. On the other hand, normative questions about how people’s values intersect with globalization and related educational processes can give an in-depth view of one location or case, but should be complemented by consideration of generalizable trends. 75
In either case, cultural assumptions can interfere or interact in problematic or unintentional ways with methodologies of data gathering and analysis, for instance, when questions or codes (related to race, ethnicity, or class, for example) are applied across diverse sites by researchers, who may not be very familiar and experienced across divergent cultural contexts. 76 Thus, beyond positionality, the use of collaborative research teams has become popular in global and comparative educational research, to ensure inevitable cultural and related differences across research domains are sufficiently addressed in the research process. 77 In this context, researchers must also contend with the challenges of collaborating across educational settings, as new methods of engaging, saving, and sharing data at distance through technology continue to unfold in response to ongoing challenges with data storage, data security, and privacy.
Among recent strands of educational research fueled by appreciation for globalization is the exploration of the global economy of knowledge. Such research may consider the practices and patterns of movement, collaboration, research production and publication, and authorship of researchers, and examine data from cultural, political, and economic perspectives, asking whose knowledge is regarded as valid and most prized, and what voices dominate in conversations and discourse around globalization and education, such as in classrooms studying global studies in education, or in leading research journals. 78 Related research emerging includes questions such as who produces knowledge, who is the subject of knowledge, and where are data gathered, as recurring historical patterns may appear to be reproduced in contemporary scholarship, wherein those from the global North are more active in investigating and elaborating knowledge in the field, while those from the global South appear most often as subjects of research. As globalization of education entails the globalization of knowledge itself, such inquiries can be directed to various sites and disciplines outside of education, in considering how communication, values, and knowledge are being dynamically revised today on a global scale through processes of globalization.
Research that focuses on globalization and education uses a wide array of approaches and methods, topics, and orientations, as well as diverse theoretical perspectives and normative assumptions. The foregoing sections have explored this general field, major debates, and topics; the relationships have been traced between globalization and education; and there have been brief comments on considerations for research. One key point of the analysis has been that the way globalization is conceived has implications for how its relationship with education is understood. This is important, for as is illustrated here, the ways of conceptualizing globalization are diverse, in terms of how the era of globalization is framed chronologically (as essential to the human condition, to modernity, or as a late 20th-century phenomena), what its chief characteristics are from cultural, political-economic, and technological views, and whether its impact on human life and history is seen as good or bad. A broad consideration of viewpoints has highlighted the emergence of a middle position within research literature: there is most certainly an intertwined meeting and movement of peoples, things, and ideas around the globe; and clearly, processes associated with globalization have good and bad aspects. However, these processes are uneven, and they can be seen to impact different communities in various ways, which are clearly not, on the whole, simply all good or all bad.
That the processes associated with globalization are interrelated with the history and future of education is undeniable. In many ways global convergence around educational policies, practices, and values can be observed in the early 21st century. Yet educational borrowing and transferral remain unstraightforward in practice, as educational and cultural differences across social contexts remain, while the ultimate ends of education (such as math competencies versus moral cultivation) are essentially contested. Thus, specificity is important to understand globalization in relation to education. As with globalization generally, globalization in education cannot be merely described as harmful or beneficial, but depends on one’s position in power relations, and on one’s values and priorities for local and global well-being.
Education and educators’ impact on globalization also remains an important area of research and theorization. Educators are no longer expected merely to react to globalization, they must purposefully interact with it, preparing students around the world to respond to globalization’s challenges. As cultural and political-economic considerations remain crucial in understanding major aspects of both globalization and education, positionality and research ethics and reflexivity remain important research concerns, to understand globalization not just as homogeneity or oppressive top-down features, but as complex and dynamic local, global, and transnational intersections of people, ideas, and goods, with unclear impacts in the future.
- Besley, T. , & Peters, M. A. (Eds.). (2012). Interculturalism: Education and dialogue . New York: Peter Lang.
- Bray, M. , Adamson, R. , & Mason, M. (2015). Comparative education research: Approaches and methods . Hong Kong: Comparative Education Research Centre, University of Hong Kong.
- Held, D. , & McGrew, A. (Eds.). (2000). The global transformation reader: An introduction to the globalization debate . Cambridge, U.K.: Polity.
- Ritzer, G. (Ed.). (2007). The Blackwell companion to globalization . Malden, MA: Blackwell.
- Rizvi, F. , & Lingard, R. (2010). Globalizing educational policy . London: Routledge.
- Robinson, W. I. (2003). Transnational conflicts: Central America, social change, and globalization . London: Verso.
- Sklair, L. (2002). Globalization: Capitalism and its alternatives . New York: Oxford University Press.
- Stiglitz, J. (2006). Making globalization work . New York: W. W. Norton.
- Walby, S. (2009). Globalization and inequalities . London: SAGE.
- Wallerstein, I. (1974). The modern world system . New York: Academic.
1. W. I. Robinson (2007), Theories of globalization, in G. Ritzer (Ed.), The Blackwell Companion to Globalization (pp. 125–143) (Malden, MA: Blackwell).
2. R. Robertson (1992), Globalization: Social theory and global culture (Thousand Oaks: SAGE, 1992).
3. Robertson, Globalization .
4. Robertson, Globalization.
5. For an historical example of how negative cultural comparison has interconnected with international political relations, see H. Kotef (2015), Little Chinese feet encased in iron shoes: Freedom, movement, gender, and empire in Western political thought, Political Theory, 43 , 334–355.
6. B. Anderson (1983), Imagined communities (London: Verso).
7. Anderson, Imagined communities.
8. M. Nussbaum (1996), For love of country? (Boston: Boston Press).
9. I. Wallerstein (1974), The modern world system (New York: Academic Press).
10. I. Wallerstein (2000), Globalization or the age of transition? International Sociology, 15 , 249–265.
11. Wallerstein, Globalization.
12. Robinson, Theories.
13. F. Rizvi and B. Lingard (2010), Globalizing educational policy (London: Routledge).
14. L. Sklair (2002), Globalization: Capitalism and its alternatives (New York: Oxford University Press).
15. W. I. Robinson (2003), Transnational conflicts: Central America, social change, and globalization (London: Verso)
16. Robinson, Theories.
17. M. Castells (1996), The rise of the network society (Oxford: Blackwell).
18. A. Giddens (1990), The consequences of modernity (Cambridge, U.K.: Polity), 64 ; see also D. Harvey (1990), The condition of post-modernity (London: Blackwell).
19. A. Appadurai (1997), Modernity at large: Cultural dimensions of globalization (Minneapolis: University of Minnesota Press).
20. See also D. Held , A. G. McGrew , D. Goldblatt , and J. Perraton (1999), Global transformations: Politics, economics, and culture (Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press) ; M. Waters (1995), Globalization (London: Routledge).
21. Rizvi and Lingard, Globalizing.
22. M. P. Smith (2001), Transnational urbanism: Locating globalization (Oxford: Blackwell).
23. G. Ritzer (1993), The McDonaldization of society (Boston: Pine Forge).
24. G. Mathews (2011), Ghetto at the center of the world (Hong Kong: Hong Kong University Press).
25. B. Barber (1995), Jihad versus McWorld (New York: Random House).
26. S. Huntington (1993), The clash of civilizations? Foreign Affairs, 72 (3), 22–49.
27. F. Fukuyama (1992), The end of history and the last man (London: Free Press).
28. U. Beck (1992), The risk society: Toward a new modernity (Cambridge, U.K.: Polity).
29. M. Hardt and A. Negri (2000), Empire (Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press) ; Hardt and Negri (2004), Multitude: War and democracy in the age of empire (New York: Penguin).
30. W. Bello (2004), Deglobalization: Ideas for a new world economy (London: New York University Press) ; Bello (2013), Capitalism’s last stand? Deglobalization in the age of austerity (London: Zed Books).
31. C. Hines (2000), Localization: A global manifesto (New York: Routledge).
32. See D. Harvey (1989), The condition of post-modernity: An enquiry into the conditions of cultural change (Oxford: Blackwell).
33. A. Giddens (1990), The consequences of modernity (Cambridge, U.K.: Polity).
34. S. Burchill (2009), Liberalism, in S. Burchill , A. Linklater , R. Devetak , J. Donnelly , T. Nardin , M. Paterson , C. Reus-Smit , and J. True (Eds.) (pp. 57–85), Theories of international relations (New York: Palgrave Macmillan).
35. See, for instance, J. Stiglitz (2006), Making globalization work (New York: W. W. Norton).
36. D. Held and A. McGrew (Eds.) (2000), The global transformation reader: An introduction to the globalization debate (Cambridge, U.K.: Polity).
37. Rizvi and Lingard, Globalizing.
38. Rizvi and Lingard, Globalizing , 24.
39. T. Reagan (2000), Non-Western educational traditions: Alternative approaches to educational thought (Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum). Of course, scholars such as Michael P. Smith would reject describing these processes as belonging to globalization, as people, nations, and communities played significant roles.
40. P. Freire (1972), Pedagogy of the oppressed (Victoria: Penguin).
41. B. Ashcroft , G. Griffiths , and H. Tiffin (Eds.) (1995), The post-colonial studies reader (London: Routledge).
42. R. E. Wanner (2015), UNESCO’s origins, achievements, problems and promise: An inside/outside perspective from the US (Hong Kong: Comparative Education Research Centre/University of Hong Kong).
43. M. Manzon (2011), Comparative education: The construction of a field (Hong Kong: Comparative Education Research Centre/University of Hong Kong).
44. S. Walby (2009), Globalization and inequalities (London: SAGE).
45. See for instance J. Stier (2004), Taking a critical stance toward internationalization ideologies in higher education: idealism, instrumentalism and educationalism, Globalisation, Societies and Education, 2 , 1–28.
46. Rizvi and Lingard, Globalizing .
47. Rizvi and Lingard, Globalizing .
48. Rizvi and Lingard, Globalizing .
49. Rizvi and Lingard, Globalizing .
50. See for instance M. S. Tucker and L. Darling-Hammond (2011), Surpassing Shanghai: An agenda for American education built on the world’s leading systems (Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press).
51. See for instance P. Sahlberg (2014), Finnish lessons 2.0: What can the world learn from educational change in Finland? (New York: Teachers College Press).
52. A. Darder (2015), Paulo Freire and the continuing struggle to decolonize education, in M. A Peters and T. Besley (Eds.), Paulo Freire: The global legacy (pp. 55–78) (New York: Peter Lang).
53. S. J. Shin (2009), Bilingualism in schools and society (London: Routledge) ; H. Norberg-Hodge (2009), Ancient futures: Lessons from Ladakh for a globalizing world (San Francisco: Sierra Club).
54. L. Jackson (2015), Challenges to the global concept of student-centered learning with special reference to the United Arab Emirates: “Never Fail a Nahayan,” Educational Philosophy and Theory, 47 , 760–773.
55. T. Besley (2012), Narratives of intercultural and international education: Aspirational values and economic imperatives, in T. Besley and M. A. Peters (Eds.), Interculturalism: Education and dialogue (pp. 87–112) (New York: Peter Lang).
56. W. J. Jacob and D. B. Holsinger (2008), Inequality in education: A critical analysis, in D. B. Holsinger and W. J. Jacob (Eds.), Inequality in education: Comparative and international perspectives (pp. 1–33) (Hong Kong: Comparative Education Research Centre/University of Hong Kong).
57. D. Hill , N. M. Greaves , and A. Maisuria (2008), Does capitalism inevitably increase inequality? in D. B. Holsinger and W. J. Jacob (Eds.), Inequality in education: Comparative and international perspectives (pp. 59–85) (Hong Kong: Comparative Education Research Centre/University of Hong Kong).
58. D. M. West (2013), Digital schools : How technology can transform education (Washington, DC: Brookings Institute Press) ; N. Burbules and T. Callister (2000), Watch IT: The risks and promises of technologies for education (Boulder, CO: Westview).
59. Burbules and Callister, Watch IT.
60. Stier, Critical Stance.
61. See for example, S. K. Gallwey and G. Wilgus (2014), Equitable partnerships for mutual learning or perpetuator of North-South power imbalances? Ireland–South Africa school links, Compare: A Journal of Comparative and International Education, 44 , 522–544.
62. M. C. Nussbaum (2001), Upheavals of thought: The intelligence of emotions (Cambridge, U.K.: Cambridge University Press).
63. K. Hytten (2009), Education for critical democracy and compassionate globalization, in R. Glass (Ed.), Philosophy of Education 2008 (pp. 330–332) (Urbana, IL: Philosophy of Education Society).
64. See for example, Report to the UNESCO of the International Commission on Education for the Twenty-First Century (1996), Learning: The treasure within (Paris: UNESCO) ; Asia Society (2015), A Rosetta Stone for noncognitive skills: Understanding, assessing, and enhancing noncognitive skills in primary and secondary education (New York: Asia Society).
65. See S. Y. Kang (2006), Identity-centered multicultural care theory: White, Black, and Korean caring, Educational Foundations, 20 (3–4), 35–49 ; L. Jackson (2016), Altruism, non-relational caring, and global citizenship education, in M. Moses (Ed.), Philosophy of Education 2014 (Urbana, IL: Philosophy of Education).
66. Jackson, Altruism.
67. L. Jackson (2016), Education for sustainable development: From environmental education to broader view, in E. Railean , G. Walker , A. Elçi , and L. Jackson (Eds.), Handbook of research on applied learning theory and design in modern education (pp. 41–64) (Hershey, PA: IGI Press).
68. Jackson, Education for Sustainable Development.
69. Jackson, Education for Sustainable Development.
70. P. Vare and W. Scott (2007), Learning for change: Exploring the relationship between education and sustainable development, Journal of Education for Sustainable Development, 1 , 191–198.
71. P. Kennedy (2011), Local lives and global transformations: Towards a world society (London: Palgrave).
72. M. Manzon (2015), Comparing places, in M. Bray , B. Adamson , and M. Mason (Eds.), Comparative education research: Approaches and methods (pp. 85–121) (Hong Kong: Comparative Education Research Centre/University of Hong Kong).
73. F. Rizvi (2009), Global mobility and the challenges of educational policy and research, in T. S. Popkewitz and F. Rizvi (Eds.), Globalization and the study of education (pp. 268–289) (Oxford: Blackwell).
74. Manzon, Comparing places.
75. G. P. Fairbrother , Qualitative and quantitative approaches to comparative education, in Bray , Adamson , and Mason (Eds.), Comparative education research (pp. 39–62).
76. L. Jackson (2015), Comparing race, class, and gender, in Bray , Adamson , and Mason (Eds.), Comparative education research (pp. 195–220).
77. M. Bray , B. Adamson , and M. Mason (2015), Different models, different emphases, different insights, in Bray , Adamson , and Mason (Eds.), Comparative education research , 421.
78. See, for instance, H. Tange and S. Miller (2015), Opening the mind? Geographies of knowledge and curricular practices, Higher Education , 1–15.
Related Articles
- Biographical Approaches in Education
- Decolonial Philosophy and Education
- Postcolonialism and Education
- The World Bank and Educational Assistance
- Teacher Unions
- European Studies and Research in Adult Learning and Education
- Critical Perspectives on the Political Economy of Higher Education in India and Globally
- Education for Sustainable Development (ESD) in Asia
- Commercialization in Education
- Globalization of Educational Knowledge and Research
- Indigenous School Education in Brazil
- Educational Policy and Development
- Critical English for Academic Purposes
- Cosmopolitanism and Education
- Homeschooling in the United States
- Constructions of Justice, Marginalization, and Belonging in Education
- Neoliberalism and Education
- Educational Attainment and Integration of Foreign Students in Spain
Printed from Oxford Research Encyclopedias, Education. Under the terms of the licence agreement, an individual user may print out a single article for personal use (for details see Privacy Policy and Legal Notice).
date: 29 September 2024
- Cookie Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Legal Notice
- Accessibility
- [185.148.24.167]
- 185.148.24.167
Character limit 500 /500

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Introduction. Globalization is the process of the ongoing assimilation of the world's largest nations. It is well currently underway in all regions of the universe. It is complicated connectivity between conservatism and liberalism that comprises both advantages and disadvantages, including emboldening and demeaning people and organizations.
Globalization is a complex phenomenon that has a big influence on various fields of human life, including economics, society, and culture. Even though trade between countries has existed since time immemorial, in the 21st-century, globalization has become an integral part of the world's development. While businesses try to expand on a global ...
Its first positive effect is that it makes it possible for different countries to exchange their products. The second positive effect of globalization is that it promotes international trade and growth of wealth as a result of economic integration and free trade among countries. However, globalization is also associated with negative effects.
Nations can easily trade, socialize, share ideas, and assist each other in different spheres of life. Get a custom essay on The Effect of Globalization on a World Culture. Improved international relations have enabled the movement of factors of production among nations with minimal barriers to trade. The cooperation has led to social, political ...
This essay will explore the various aspects of globalization, discussing its implications and effects on different aspects of society. Through an analysis of credible sources and evidence, it will be argued that while globalization has undoubtedly brought numerous benefits, it also poses significant challenges that must be addressed.
Impact of Globalization Essay Conclusion Globalization is a complex procedure that is currently the topic of debate around the World. Since it has both positive and negative impacts on the developed and developing countries, many countries face economic wrath and a serious lack of growth and development.
In economics, globalization can be defined as the process in which businesses, organizations, and countries begin operating on an international scale. Globalization is most often used in an economic context, but it also affects and is affected by politics and culture. In general, globalization has been shown to increase the standard of living ...
Overall, what are the advantages of globalization? The advantages of globalization are actually much like the advantages of technological improvement. They have very similar effects: they raise output in countries, raise productivity, create more jobs, raise wages, and lower prices of products in the world economy.
glocalization. cultural globalization, phenomenon by which the experience of everyday life, as influenced by the diffusion of commodities and ideas, reflects a standardization of cultural expressions around the world. Propelled by the efficiency or appeal of wireless communications, electronic commerce, popular culture, and international travel ...
While this decrease in biodiversity has many causes, it's widely believed that the issues listed above have contributed in part. 4. Increased Awareness. While many of globalization's environmental effects have been negative, its increase has heightened environmental awareness worldwide. Greater connectivity and higher rates of international ...
Essay On Impact Of Globalisation On Society. 1905 Words8 Pages. With the re-emergence of globalization in the 1970s, globalization has not only transformed the world into what it has become today, but it has also impacted and influenced almost every aspect of our modern lives. Globalization is defined as a process of interaction and ...
Since 1900, life expectancy has increased in every country in the world, and global average life expectancy has more than doubled. Globalization has also been a key driver of unprecedented economic growth and as a result, we now live in a world with much less poverty. Yet these achievements are the product of multiple forces, and globalization ...
Collective and Individual Ministerial Responsibility in India's Parliamentary System. THE INDIAN DIASPORA: Global Contributions, Challenges, & Government Initiatives. India's Constitutional Amendments: Flexibility & Rigidity for a Dynamic Democracy. Indian Parliamentary Forums: Initiatives and their Impact since 2005.
Paradoxically, it underlies both the dynamics of global crises (e.g., rising inequality, climate change) and the possibilities for ameliorating them. In this review, we introduce globalization as a multifaceted process and elaborate its psychological effects with respect to identity, culture, and collective action.
Globalization supports free trade, creates jobs, and helps societies to become more tolerant towards each other. In addition, this process may increase the speed of financial and commercial operations, as well as reduce the isolation of poor populations (Burlacu, Gutu, & Matei, 2018; Amavilah, Asongu, & Andrés, 2017).
Globalization. Teasing out the disruptive effects of globalization. May 07, 2020. Gordon Hanson joined Harvard Kennedy School this year as the Peter Wertheim Professor in Urban Policy. His work addresses problems at the knotty intersection of economics, international trade, and immigration—problems that feel especially relevant and complex ...
Therefore, the positive impact of globalization on health first emerged with its positive effects on economic growth (Labonté et al. 2009: 10). The effects of globalization on growth were mostly driven by free trade, international specialization, technology transfers, knowledge spillovers, and competitive markets.
Globalization isn't going away, but it is changing, according to recent research from the McKinsey Global Institute (MGI). In this episode of The McKinsey Podcast, MGI director Olivia White speaks with global editorial director Lucia Rahilly about the flows of goods, knowledge, and labor that drive global integration—and about what reshaping these flows might mean for our interconnected ...
adjective. having to do with the ocean. metallurgy. noun. field of science and technology concerned with metals and their production and purification. microcosm. noun. complete miniature world. Globalization is a term used to describe the increasing connectedness and interdependence of world cultures and economies.
The State of Globalization in 2021. Trade, capital, and information flows have stabilized, recovered, and even grown in the past year. Summary. As the coronavirus swept the world, closing borders ...
The State of Globalization in 2022. by Steven A. Altman and Caroline R. Bastian. April 12, 2022. David Malan/Getty Images. Summary. As companies contemplate adjustments to their global strategies ...
Scholars often pursue the topic by examining globalization's perceived impact on education, as in many cases global convergence around educational policies, practices, and values has been observed in the early 21st century. ... recognizing aspects of world society not well suited to the previously popular nationalistic ways of thinking about ...