- Our Mission

How a Simple Presentation Framework Helps Students Learn
Explaining concepts to their peers helps students shore up their content knowledge and improve their communication skills.

A few years ago, my colleague and I were awarded a Hawai‘i Innovation Fund Grant. The joy of being awarded the grant was met with dread and despair when we were informed that we would have to deliver a 15-minute presentation on our grant write-up to a room full of educational leaders. If that wasn’t intimidating enough, my colleague informed me that he was not going to be in Hawai‘i at the time of the presentation. I had “one shot,” just a 15-minute presentation to encapsulate all of the 17 pages of the grant I had cowritten, but how?
I worked hard to construct and deliver a presentation that was concise yet explicit. I was clear on the big picture of what the grant was composed of and provided a visual of it in practice. I made sure the audience understood the “why” behind the grant. I showed how it worked, the concrete elements of it, and how they made it successful. I finished with a scaffold that would help others know how to initiate it within their context, giving them the freedom to make it authentically their own.
I received good feedback from the presentation, and more important, what was shared positively impacted student learning in other classrooms across the state.
A Simple Framework for Presentations
That first presentation took me over a month to prepare, but afterward I noticed that my prep time for presentations shrank exponentially from a few months to a few (uninterrupted) days. Interestingly enough, as a by-product of creating the original presentation, I created an abstract framework that I have used for every professional learning presentation I have delivered since then. The “What, Why, How, and How-To” framework goes as follows:
- What? What can the audience easily connect to and know as a bridge to the unknown for the rest of the experience?
- Why? Why should they care to listen to (and learn from) the rest of the presentation? What’s in it for them to shift from passive listeners to actively engaged? The audience needs to know why you believe in this so much that you are compelled to share it.
- How? What are the key elements that make it unique? How is it effective in doing what it does? What are the intricacies of how it works?
- How-to? How could they start doing this on their own? How could this knowledge serve as a foundational springboard? Connect it to “why.”
Benefits for Students
One of the best parts of presentations is that they help the presenter to improve their communication skills. The presenter is learning how to give a presentation by doing it. To prepare a presentation, the presenter must know the intricate elements of what they are presenting and the rationale for their importance. In the presentation delivery, the presenter must be articulate and meticulous to ensure that everyone in the audience is able (and willing) to process the information provided.
It didn’t take long for me to realize that preparing and delivering presentations could provide a valuable learning opportunity for my students.
I recall teaching mathematical concepts whereby students would immediately apply knowledge learned to accomplish the task in silence and without any deeper questioning. Only after I asked them to provide presentations on these concepts did they regularly ask me, “Why is this important, again?” or “What makes this so special?” My students’ mathematical literacy grew through preparing presentations with the “What, Why, How, and How-To” framework, which supported them in their ability to demonstrate content knowledge through mathematical rigor (balancing conceptual understanding, skills and procedural fluency, and real-world application).
- The “what” served as the mathematical concept.
- The “why” demonstrated the real-world application of the concept.
- “The “how” demonstrated conceptual understanding of the concept.
- The “how-to” demonstrated skills and procedures of the concept.
In addition to content knowledge, the sequential competencies of clarity, cohesiveness, and captivation ensured that the presenter could successfully share the information with their audience. When combined, these framed a rubric that supported students in optimizing their presentation deliveries. The competencies are as follows:
1. Content knowledge. The presenter must display a deep understanding of what they are delivering in order to share the “what, why, how, and how-to” of the topic.
2. Clarity. The presenter must be clear with precise, academic language. As the content they deliver may be new to the audience, any lack of clarity will alienate the audience. Providing multiple modes of representation greatly addresses a variety of processing needs of a diverse audience.
3. Cohesiveness. When making clear connections, the presenter bridges gaps between each discrete component in how they all work together as integral elements of the topic. Any gaps too large may make the elements look disjointed or, worse, the audience feel lost.
4. Captivation. The presenter must captivate the audience through any combination of audience engagement or storytelling . They make the presentation flow with the energy of a song , and in the end, they leave the audience with a delicate balance of feeling fulfilled and inspired to learn more.
Anyone can build an effective presentation with the “What, Why, How, and How-To” framework, along with competencies of content knowledge, clarity, cohesiveness, and captivation. The better we teach and coach others on how to create and deliver presentations, the more we learn from these individuals through their work.
In my class, one multilingual learner responded to the prompt “What are the non-math (life lessons) you have found valuable from this class?” with “I learn what is learning and teaching... I truly understood how teaching is actually learning when I had presentation. I found a bit of desire to being a teacher. I hope you also learned something from this class.” I always learn from my students when they present.
12 Reasons Why Presentation Skills Are Important for Students
Hrideep barot.
- Education , Presentation

Learning presentation skills as a student is like striking gold in the treasure hunt of life! It’s like having a superpower at your fingertips because, let’s be honest, your learning capacity right now is off the charts! But wait, there’s more! Presentation skills aren’t just about talking in front of the class (although that’s super cool too). They’re like the secret ingredient that helps you master the art of communication.
Think about it – you’re not just learning how to present your science project; you’re learning how to navigate the whole wide world.
So, why’s this the primo time to become a presentation ninja?
- Super Learning Mode: Your brain is in turbo mode right now, absorbing info like a champ. What you learn about presentations during this time becomes your lifelong sidekick.
- Ace Communicator: Being a student means you’re in a constant chat with teachers, friends, and books. Presentation skills give you the superpower to communicate like a pro.
- World Domination: Okay, maybe not the world, but you’re certainly setting yourself up to shine in any situation life throws at you.
Remember, these skills aren’t just for school. They’re for life! So, grab that mic (or marker or mouse) and get ready to rock those presentations. You’re gearing up to be the superhero of communication! 🎤
WHAT ARE PRESENTATION SKILLS:
Have you ever thought about what makes some presentations stick in your memory while others vanish into oblivion? Well, here’s the scoop: presentation skills are the secret sauce, and they’re not just a bag of clever tricks. Nope, they’re the mighty keys to cracking the code of effective communication, letting you hook, enlighten, and amuse your audience.
At their very core, these skills are all about forging a connection with your crowd, whether it’s your school buddies, coworkers, or even a gang of pals at a shindig. They’re like the crafters of a message that’s crystal clear, totally convincing, and as smooth as a jam session with your favorite jazz band.
But wait, there’s more! Presentation skills are your golden ticket to success in all sorts of life’s adventures, from nailing that class project to wowing your boss in a big meeting. They’re the secret tools that turn everyday tasks into unforgettable experiences, etching your message deep into the minds of your audience.
So, as you embark on the journey to master these presentation skills, remember it’s not just about what you say; it’s how you say it. Whether you’re facing a jam-packed auditorium or a cozy gathering of pals, may the enchantment of presentation skills guide you, transforming every moment into a mesmerizing performance.
The 12 Reasons Why Presentation Skills are Important:
Presentation skills are not just crucial for students but also for individuals of all ages and professions. Here’s why they matter and how they impact everyone:
1. Effective Communication :
- Effective communication is the backbone of all human interactions. Presentation skills equip individuals with the ability to convey information clearly, concisely, and persuasively. Whether it’s explaining a project at work or delivering a compelling speech, the capacity to communicate effectively is indispensable.
- Example : In a business meeting, a project manager adept in presentation skills can elucidate a complex project plan. They articulate the project’s goals, milestones, and potential challenges, ensuring that everyone understands the roadmap to success.
2. Career Advancement :
- The workplace is highly competitive, and presentation skills can be the differentiating factor that propels individuals forward in their careers. Being able to present ideas, strategies, and accomplishments with confidence and clarity garners recognition and opens up opportunities for advancement.
- Example : A marketing professional who excels in presenting marketing campaigns not only impresses the team but also demonstrates leadership qualities. This can lead to promotions and increased responsibilities.
3. Building Credibility :
- Credibility is vital in professional and personal relationships. When you can present your ideas convincingly, you gain the trust of your peers, colleagues, and superiors. Your credibility extends to the content you’re presenting, making it more likely to be accepted and acted upon.
- Example : An environmental scientist delivering a presentation on climate change with well-researched data and compelling visuals gains credibility among policymakers and the public, potentially influencing policy decisions.
4. Persuasion and Influence :
- Presentation skills encompass the art of persuasion. Individuals who can engage their audience, create a compelling narrative, and support their arguments effectively are more likely to influence others. This skill is invaluable in negotiations, sales, and leadership roles.
- Example : A charismatic motivational speaker can use their presentation skills to inspire audiences, motivating them to take action or adopt new perspectives.
5. Problem Solving :
- Strong presenters are often adept problem solvers. They can analyze complex issues, break them down into understandable components, and present solutions clearly and persuasively. This ability is crucial for addressing challenges in personal and professional life.
- Example : During a corporate crisis, a CEO who can present a well-structured crisis management plan to stakeholders demonstrates effective problem-solving skills and reassures concerned parties.
6. Personal Branding :
- Effective presentation skills contribute to personal branding. Consistently delivering engaging and informative presentations enhances one’s reputation as a knowledgeable, confident, and trustworthy professional.
- Example : A tech entrepreneur known for captivating product launch presentations builds a strong personal brand, attracting media attention, investors, and customers.
7. Adaptability :
- Presentation skills encompass the ability to adapt to various formats, audiences, and settings. This adaptability is invaluable in today’s diverse and ever-changing work environments, where individuals must navigate different communication channels and styles.
- Example : A teacher who can seamlessly transition from in-person classroom presentations to delivering engaging online lessons demonstrates adaptability in response to changing circumstances.
8. Lifelong Learning :
- Embracing presentation skills encourages individuals to engage in lifelong learning and self-improvement. As presentation techniques evolve and audiences change, individuals who continually refine their communication abilities remain relevant and effective.
- Example : A retired professional who continues to develop presentation skills for community workshops and public speaking engagements not only shares their expertise but also stays engaged in lifelong learning, adapting to new challenges and opportunities.
Presentation skills are universally essential as they enhance communication, facilitate career advancement, build credibility, enable persuasive influence, promote problem-solving, strengthen personal branding, foster adaptability, and encourage lifelong learning. These skills empower individuals to succeed in various personal and professional endeavors, making them essential for everyone.
Let’s look at a comprehensive overview of these trending presentation skills:
Allow me to introduce you to the 12 skills that encapsulate the very essence of the world’s most exceptional presenters.
1. Effective Communication:
Presentation skills are the ability to communicate ideas, information, or messages to an audience clearly and persuasively. It’s about conveying your thoughts with impact and resonance.
2. Audience Engagement:
These skills encompass techniques to engage and capture the attention of your audience. It’s not just about talking; it’s about connecting with your listeners on an intellectual and emotional level.
3. Organization and Structure:
Presentation skills involve structuring your content logically and coherently. It’s about creating a roadmap that guides your audience through your message, ensuring they follow and understand your points.
4. Visual Aids Usage:
Effective use of visual aids, such as slides, graphics, and multimedia elements, is a crucial component. It’s about enhancing your message with visuals that reinforce your content without overwhelming your audience.
5. Confidence and Presence:
Presentation skills entail projecting confidence and a strong presence while speaking. This includes body language, tone of voice, and maintaining eye contact.
6. Adaptability:
These skills are versatile. You must adapt your presentation style to suit different contexts, audiences, and purposes. Whether you’re giving an academic lecture, a business pitch, or a motivational talk, adaptability is key.
7. Preparation and Research:
A significant part of presentation skills is the preparation phase. It involves conducting thorough research on your topic, understanding your audience, and meticulously planning your content.
8. Problem Solving:
Effective presenters are skilled at handling unexpected situations, such as tough questions or technical difficulties during a presentation. Presentation skills also encompass the ability to think on your feet and respond confidently.
9. Storytelling:
Storytelling is a potent tool for presentation skills. It involves weaving narratives that resonate with your audience, making your message memorable and relatable.
10. Time Management:
Presentations often have time constraints. These skills include managing your time wisely, and ensuring you cover all key points within the allocated time frame.
11. Feedback Utilisation:
Presentation skills are a continuous learning process. It involves actively seeking and utilizing feedback to improve your future presentations. Constructive criticism is invaluable for growth.
12. Audience-Centred Approach:
A critical aspect of presentation skills is adopting an audience-centred approach. It’s about tailoring your content and delivery to meet the needs and interests of your specific audience.
What is the purpose of a presentation?
A) information sharing:.
At its core, the purpose of a presentation is to share information. Whether you’re in a classroom, boardroom, or on a stage, you’re conveying knowledge, insights, or ideas to an audience. This information can range from academic research findings, business proposals, and project updates, to even personal stories or creative concepts.
B) Education and Understanding:
Presentations are powerful tools for education and comprehension. They provide a structured format to break down complex topics into manageable, digestible pieces. By presenting information in a clear, organized manner, you help your audience grasp concepts more easily.
C) Persuasion and Influence:
In many situations, presentations aim to persuade and influence. Whether you’re convincing potential investors to fund your startup, persuading your classmates to support your project, or advocating for a cause, effective presentations can be a catalyst for change.
D) Engagement and Connection:
A well-crafted presentation can engage your audience emotionally and intellectually. It’s an opportunity to connect on a human level, share personal experiences, and evoke empathy or enthusiasm. Storytelling is a powerful technique to create this connection.
E) Problem Solving:
Presentations often tackle real-world issues and problem-solving. Whether it’s proposing solutions to business challenges, addressing societal problems, or discussing scientific breakthroughs, they serve as a platform to present ideas that can bring about positive change.
F) Decision-Making:
In professional settings, presentations play a pivotal role in decision-making processes. They provide decision-makers with the necessary information and insights to make informed choices. Presenters aim to influence these decisions in their favor through compelling arguments and evidence.
G) Inspiration and Motivation:
Some presentations are designed to inspire and motivate. They encourage the audience to take action, pursue their goals, or embrace change. This purpose often applies to keynote speeches, commencement addresses, and motivational talks.
H) Celebration and Recognition:
Presentations aren’t always about serious business; they can also serve as a platform for celebration and recognition. Think of award ceremonies, where individuals or teams are honored for their achievements.
I) Entertainment and Artistic Expression:
Presentations can be a form of entertainment and artistic expression. Think of performances, artistic displays, or creative storytelling. Here, the purpose is to captivate, entertain, and stir emotions.
J) Knowledge Transfer:
Lastly, presentations facilitate the transfer of knowledge from one person to another or from one generation to the next. This is particularly important in educational settings, where teachers present information to students in a structured manner.
In essence, presentations are versatile tools with multifaceted purposes. They are not just about delivering information but about connecting, persuading, educating, and inspiring. Understanding the specific purpose of your presentation is the first step toward creating a compelling communication experience for your audience.
Why is it important to have good presentation skills for students?
Imagine this scenario: You’re sitting in a classroom, and your professor asks you to present your research findings. Your heart races, your palms sweat, and the butterflies in your stomach have a party of their own. Sound familiar? Well, that’s where good presentation skills come into play for students, and they’re more than just a ticket to survive the classroom spotlight. They’re a gateway to personal and professional success.
First and foremost, presentation skills are the ultimate communication tool.
They help students articulate their thoughts, ideas, and findings with clarity and confidence. In an academic setting, this means you can engage your peers and professors effectively, making your voice heard and your ideas stand out.
But it doesn’t stop at the classroom door. These skills are your secret (because not everyone knows this) key in the professional world. Picture yourself in a job interview. Your potential employer asks you to discuss your qualifications and why you’re the right fit for the role. With polished presentation skills, you’re not just answering questions; you’re painting a vivid picture of your capabilities and potential.
Furthermore, good presentation skills are a confidence booster.
They transform nervous jitters into a sense of empowerment. When you can stand before an audience and convey your message convincingly, it’s a feeling like no other. This newfound confidence seeps into other aspects of your academic and professional life, making you a more resilient and adaptable individual.
In essence, good presentation skills are the key to unlocking doors of opportunity. Whether you’re excelling in class discussions, wowing your professors with a well-structured thesis defense, or nailing that crucial client pitch, these skills are your trusty companions on the journey of personal and professional growth.
So, the next time you find yourself in the spotlight, remember that presentation skills aren’t just about public speaking; they’re about showcasing your potential, building confidence, and paving the way for success. Embrace them, and watch your academic and professional horizons expand like never before.
What are the benefits of learning presentation skills for students?
I. effective communication: .
Good presentation skills are the linchpin of effective communication . In both academic and professional settings, students must articulate their thoughts, ideas, and findings clearly and persuasively. Without these skills, even the most brilliant concepts can get lost in translation.
II. Academic Success:
Strong presentation skills can significantly impact academic success. Students who can express themselves eloquently often excel in class discussions, group projects, and thesis defenses. They stand out as knowledgeable and confident learners.
III. Confidence Booster:
Public speaking and presentation practice are fantastic confidence boosters. They empower students to express themselves in front of their peers and teachers, gradually reducing anxiety and building self-assuredness.
IV. Leadership Development:
Presentation skills are often associated with leadership qualities. Students who master these skills tend to emerge as leaders in group projects, clubs, and extracurricular activities. They can effectively convey their vision and rally others behind it.
V. Professional Readiness:
In the world of work, professionals are frequently required to present their ideas, proposals, and reports. Students who develop strong presentation skills are better prepared for their future careers, making a positive impression on potential employers and clients.
VI. Critical Thinking:
Preparing a presentation necessitates critical thinking. Students must organize their thoughts, conduct research, and analyze information to craft a compelling narrative. This enhances their analytical and problem-solving skills.
VII. Time Management:
Creating a presentation involves managing time effectively. Students must set priorities, meet deadlines, and allocate resources wisely. These time management skills are valuable both in academia and the professional world.
VIII. Adaptability:
Presentation skills encompass various formats, from traditional speeches to multimedia presentations and virtual meetings. Students who can adapt to these different modes of communication are better equipped to thrive in today’s technology-driven world.
IX. Networking Opportunities:
Presentations often provide opportunities to network with peers, professors, and professionals. Building connections can open doors to collaborations, mentorships, and job opportunities down the road.
X. Problem Solving:
During presentations, unexpected challenges may arise, such as tough questions from the audience or technical glitches. Students learn to think on their feet, respond confidently, and solve problems as they arise.
XI. Enhancing Creativity:
Crafting engaging presentations encourages creativity and innovation. Students seek unique ways to capture their audience’s attention, whether through storytelling, visuals, or interactive elements.
XII. Global Communication:
In an increasingly interconnected world, students with strong presentation skills can effectively communicate with diverse audiences from different cultures and backgrounds, fostering cross-cultural understanding and collaboration.
These skills equip students for success in various aspects of life and contribute to their personal and intellectual growth.
How can students improve their presentation skills?
Improving presentation skills is a gradual process that requires dedication and practice. By following these steps and staying committed to self-improvement, students can become confident and effective presenters.
1. Practice, Practice, Practice:
The foundation of presentation mastery is practice . Start small by presenting in front of a mirror or recording yourself. Pay attention to your voice modulation, gestures, and overall delivery. This self-assessment helps you identify areas for improvement and build self-confidence.
2. Preparation is Key:
The best presenters are often those who are the most prepared. Know your topic inside-out. Create a well-structured presentation with a compelling opening to grab your audience’s attention and a memorable closing to leave a lasting impression. Visual aids can enhance your message, but use them sparingly to avoid overwhelming your audience.
3. Real-Life Experience:
Gain real-life presentation experience by participating in clubs, engaging in debates, or volunteering for class presentations. The more you expose yourself to different audiences, the more comfortable and adept you’ll become in handling diverse situations.
4. Learn from the Pros:
Study presentations by seasoned speakers and experts in various fields. Watch TED talks, analyze speeches, or follow your favorite orators. Observe their techniques, storytelling abilities, and audience engagement strategies. Incorporate these insights into your style to make your presentations more captivating.
5. Feedback Fuels Growth:
Don’t be afraid to seek feedback. Share your presentations with peers, friends, or teachers and ask for their honest opinions. Constructive criticism is like a roadmap to improvement. It highlights your strengths and pinpoints areas where you can refine your skills.
6. Embrace Growth as a Journey:
Remember that improving presentation skills is a journey, not a quick fix. It takes dedication and time to refine these skills. Be patient with yourself, and celebrate small victories along the way. With consistent effort, you’ll see significant progress and reap the benefits of enhanced communication and self-assuredness.
So, as you embark on your journey to become a presentation pro, keep these elements in mind. Each step, from practice to feedback, preparation, real-life experience, and learning from experts, contributes to your growth. Over time, you’ll not only become a confident and persuasive presenter but also open up doors to academic and professional opportunities. You’ve got the potential; now, let it shine!
Conclusion:
So, here’s the scoop—presentation skills aren’t just about fancy speeches. They’re your superpower for rocking academics, acing your career, and unleashing personal growth. Mastering these and mastering your life would be the best way to put it. We wish you all the best for your presentation and hope this article helps you.
If you wish to know more about how you can communicate effectively, you can try our coaching here .
Enroll in our transformative 1:1 Coaching Program
Schedule a call with our expert communication coach to know if this program would be the right fit for you

Lost Voice? Here’s How to Recover Sore Throat and Speak Again

7 Keys to Emcee Like a Pro: Unlock Your Hosting Potential

8 Ways to Rise Above the Noise to Communicate Better

- [email protected]
- +91 98203 57888
Get our latest tips and tricks in your inbox always
Copyright © 2023 Frantically Speaking All rights reserved
Kindly drop your contact details so that we can arrange call back
Select Country Afghanistan Albania Algeria AmericanSamoa Andorra Angola Anguilla Antigua and Barbuda Argentina Armenia Aruba Australia Austria Azerbaijan Bahamas Bahrain Bangladesh Barbados Belarus Belgium Belize Benin Bermuda Bhutan Bosnia and Herzegovina Botswana Brazil British Indian Ocean Territory Bulgaria Burkina Faso Burundi Cambodia Cameroon Canada Cape Verde Cayman Islands Central African Republic Chad Chile China Christmas Island Colombia Comoros Congo Cook Islands Costa Rica Croatia Cuba Cyprus Czech Republic Denmark Djibouti Dominica Dominican Republic Ecuador Egypt El Salvador Equatorial Guinea Eritrea Estonia Ethiopia Faroe Islands Fiji Finland France French Guiana French Polynesia Gabon Gambia Georgia Germany Ghana Gibraltar Greece Greenland Grenada Guadeloupe Guam Guatemala Guinea Guinea-Bissau Guyana Haiti Honduras Hungary Iceland India Indonesia Iraq Ireland Israel Italy Jamaica Japan Jordan Kazakhstan Kenya Kiribati Kuwait Kyrgyzstan Latvia Lebanon Lesotho Liberia Liechtenstein Lithuania Luxembourg Madagascar Malawi Malaysia Maldives Mali Malta Marshall Islands Martinique Mauritania Mauritius Mayotte Mexico Monaco Mongolia Montenegro Montserrat Morocco Myanmar Namibia Nauru Nepal Netherlands Netherlands Antilles New Caledonia New Zealand Nicaragua Niger Nigeria Niue Norfolk Island Northern Mariana Islands Norway Oman Pakistan Palau Panama Papua New Guinea Paraguay Peru Philippines Poland Portugal Puerto Rico Qatar Romania Rwanda Samoa San Marino Saudi Arabia Senegal Serbia Seychelles Sierra Leone Singapore Slovakia Slovenia Solomon Islands South Africa South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands Spain Sri Lanka Sudan Suriname Swaziland Sweden Switzerland Tajikistan Thailand Togo Tokelau Tonga Trinidad and Tobago Tunisia Turkey Turkmenistan Turks and Caicos Islands Tuvalu Uganda Ukraine United Arab Emirates United Kingdom United States Uruguay Uzbekistan Vanuatu Wallis and Futuna Yemen Zambia Zimbabwe land Islands Antarctica Bolivia, Plurinational State of Brunei Darussalam Cocos (Keeling) Islands Congo, The Democratic Republic of the Cote d'Ivoire Falkland Islands (Malvinas) Guernsey Holy See (Vatican City State) Hong Kong Iran, Islamic Republic of Isle of Man Jersey Korea, Democratic People's Republic of Korea, Republic of Lao People's Democratic Republic Libyan Arab Jamahiriya Macao Macedonia, The Former Yugoslav Republic of Micronesia, Federated States of Moldova, Republic of Mozambique Palestinian Territory, Occupied Pitcairn Réunion Russia Saint Barthélemy Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan Da Cunha Saint Kitts and Nevis Saint Lucia Saint Martin Saint Pierre and Miquelon Saint Vincent and the Grenadines Sao Tome and Principe Somalia Svalbard and Jan Mayen Syrian Arab Republic Taiwan, Province of China Tanzania, United Republic of Timor-Leste Venezuela, Bolivarian Republic of Viet Nam Virgin Islands, British Virgin Islands, U.S.


How it works
Transform your enterprise with the scalable mindsets, skills, & behavior change that drive performance.
Explore how BetterUp connects to your core business systems.
We pair AI with the latest in human-centered coaching to drive powerful, lasting learning and behavior change.
Build leaders that accelerate team performance and engagement.
Unlock performance potential at scale with AI-powered curated growth journeys.
Build resilience, well-being and agility to drive performance across your entire enterprise.
Transform your business, starting with your sales leaders.
Unlock business impact from the top with executive coaching.
Foster a culture of inclusion and belonging.
Accelerate the performance and potential of your agencies and employees.
See how innovative organizations use BetterUp to build a thriving workforce.
Discover how BetterUp measurably impacts key business outcomes for organizations like yours.
A demo is the first step to transforming your business. Meet with us to develop a plan for attaining your goals.

- What is coaching?
Learn how 1:1 coaching works, who its for, and if it's right for you.
Accelerate your personal and professional growth with the expert guidance of a BetterUp Coach.
Types of Coaching
Navigate career transitions, accelerate your professional growth, and achieve your career goals with expert coaching.
Enhance your communication skills for better personal and professional relationships, with tailored coaching that focuses on your needs.
Find balance, resilience, and well-being in all areas of your life with holistic coaching designed to empower you.
Discover your perfect match : Take our 5-minute assessment and let us pair you with one of our top Coaches tailored just for you.

Research, expert insights, and resources to develop courageous leaders within your organization.
Best practices, research, and tools to fuel individual and business growth.
View on-demand BetterUp events and learn about upcoming live discussions.
The latest insights and ideas for building a high-performing workplace.
- BetterUp Briefing
The online magazine that helps you understand tomorrow's workforce trends, today.
Innovative research featured in peer-reviewed journals, press, and more.
Founded in 2022 to deepen the understanding of the intersection of well-being, purpose, and performance
We're on a mission to help everyone live with clarity, purpose, and passion.
Join us and create impactful change.
Read the buzz about BetterUp.
Meet the leadership that's passionate about empowering your workforce.

For Business
For Individuals
6 presentation skills and how to improve them

Jump to section
What are presentation skills?
The importance of presentation skills, 6 presentation skills examples, how to improve presentation skills.
Tips for dealing with presentation anxiety
Learn how to captivate an audience with ease
Capturing an audience’s attention takes practice.
Over time, great presenters learn how to organize their speeches and captivate an audience from start to finish. They spark curiosity, know how to read a room , and understand what their audience needs to walk away feeling like they learned something valuable.
Regardless of your profession, you most likely use presentation skills on a monthly or even weekly basis. Maybe you lead brainstorming sessions or host client calls.
Developing effective presentation skills makes it easier to contribute ideas with confidence and show others you’re someone to trust. Although speaking in front of a crowd sometimes brings nerves and anxiety , it also sparks new opportunities.
Presentation skills are the qualities and abilities you need to communicate ideas effectively and deliver a compelling speech. They influence how you structure a presentation and how an audience receives it. Understanding body language , creating impactful visual aids, and projecting your voice all fall under this umbrella.
A great presentation depends on more than what you say. It’s about how you say it. Storytelling , stage presence, and voice projection all shape how well you express your ideas and connect with the audience. These skills do take practice, but they’re worth developing — especially if public speaking makes you nervous.
Engaging a crowd isn’t easy. You may feel anxious to step in front of an audience and have all eyes and ears on you.
But feeling that anxiety doesn’t mean your ideas aren’t worth sharing. Whether you’re giving an inspiring speech or delivering a monthly recap at work, your audience is there to listen to you. Harness that nervous energy and turn it into progress.
Strong presentation skills make it easier to convey your thoughts to audiences of all sizes. They can help you tell a compelling story, convince people of a pitch , or teach a group something entirely new to them. And when it comes to the workplace, the strength of your presentation skills could play a part in getting a promotion or contributing to a new initiative.
To fully understand the impact these skills have on creating a successful presentation, it’s helpful to look at each one individually. Here are six valuable skills you can develop:
1. Active listening
Active listening is an excellent communication skill for any professional to hone. When you have strong active listening skills, you can listen to others effectively and observe their nonverbal cues . This helps you assess whether or not your audience members are engaged in and understand what you’re sharing.
Great public speakers use active listening to assess the audience’s reactions and adjust their speech if they find it lacks impact. Signs like slouching, negative facial expressions, and roaming eye contact are all signs to watch out for when giving a presentation.
2. Body language
If you’re researching presentation skills, chances are you’ve already watched a few notable speeches like TED Talks or industry seminars. And one thing you probably noticed is that speakers can capture attention with their body language.
A mixture of eye contact, hand gestures , and purposeful pacing makes a presentation more interesting and engaging. If you stand in one spot and don’t move your body, the audience might zone out.

3. Stage presence
A great stage presence looks different for everyone. A comedian might aim for more movement and excitement, and a conference speaker might focus their energy on the content of their speech. Although neither is better than the other, both understand their strengths and their audience’s needs.
Developing a stage presence involves finding your own unique communication style . Lean into your strengths, whether that’s adding an injection of humor or asking questions to make it interactive . To give a great presentation, you might even incorporate relevant props or presentation slides.
4. Storytelling
According to Forbes, audiences typically pay attention for about 10 minutes before tuning out . But you can lengthen their attention span by offering a presentation that interests them for longer. Include a narrative they’ll want to listen to, and tell a story as you go along.
Shaping your content to follow a clear narrative can spark your audience’s curiosity and entice them to pay careful attention. You can use anecdotes from your personal or professional life that take your audience along through relevant moments. If you’re pitching a product, you can start with a problem and lead your audience through the stages of how your product provides a solution.
5. Voice projection
Although this skill may be obvious, you need your audience to hear what you’re saying. This can be challenging if you’re naturally soft-spoken and struggle to project your voice.
Remember to straighten your posture and take deep breaths before speaking, which will help you speak louder and fill the room. If you’re talking into a microphone or participating in a virtual meeting, you can use your regular conversational voice, but you still want to sound confident and self-assured with a strong tone.
If you’re unsure whether everyone can hear you, you can always ask the audience at the beginning of your speech and wait for confirmation. That way, they won’t have to potentially interrupt you later.
Ensuring everyone can hear you also includes your speed and annunciation. It’s easy to speak quickly when nervous, but try to slow down and pronounce every word. Mumbling can make your presentation difficult to understand and pay attention to.

6. Verbal communication
Although verbal communication involves your projection and tone, it also covers the language and pacing you use to get your point across. This includes where you choose to place pauses in your speech or the tone you use to emphasize important ideas.
If you’re giving a presentation on collaboration in the workplace , you might start your speech by saying, “There’s something every workplace needs to succeed: teamwork.” By placing emphasis on the word “ teamwork ,” you give your audience a hint on what ideas will follow.
To further connect with your audience through diction, pay careful attention to who you’re speaking to. The way you talk to your colleagues might be different from how you speak to a group of superiors, even if you’re discussing the same subject. You might use more humor and a conversational tone for the former and more serious, formal diction for the latter.
Everyone has strengths and weaknesses when it comes to presenting. Maybe you’re confident in your use of body language, but your voice projection needs work. Maybe you’re a great storyteller in small group settings, but need to work on your stage presence in front of larger crowds.
The first step to improving presentation skills is pinpointing your gaps and determining which qualities to build upon first. Here are four tips for enhancing your presentation skills:
1. Build self-confidence
Confident people know how to speak with authority and share their ideas. Although feeling good about your presentation skills is easier said than done, building confidence is key to helping your audience believe in what you’re saying. Try practicing positive self-talk and continuously researching your topic's ins and outs.
If you don’t feel confident on the inside, fake it until you make it. Stand up straight, project your voice, and try your best to appear engaged and excited. Chances are, the audience doesn’t know you’re unsure of your skills — and they don’t need to.
Another tip is to lean into your slideshow, if you’re using one. Create something colorful and interesting so the audience’s eyes fall there instead of on you. And when you feel proud of your slideshow, you’ll be more eager to share it with others, bringing more energy to your presentation.
2. Watch other presentations
Developing the soft skills necessary for a good presentation can be challenging without seeing them in action. Watch as many as possible to become more familiar with public speaking skills and what makes a great presentation. You could attend events with keynote speakers or view past speeches on similar topics online.
Take a close look at how those presenters use verbal communication and body language to engage their audiences. Grab a notebook and jot down what you enjoyed and your main takeaways. Try to recall the techniques they used to emphasize their main points, whether they used pauses effectively, had interesting visual aids, or told a fascinating story.

3. Get in front of a crowd
You don’t need a large auditorium to practice public speaking. There are dozens of other ways to feel confident and develop good presentation skills.
If you’re a natural comedian, consider joining a small stand-up comedy club. If you’re an avid writer, participate in a public poetry reading. Even music and acting can help you feel more comfortable in front of a crowd.
If you’d rather keep it professional, you can still work on your presentation skills in the office. Challenge yourself to participate at least once in every team meeting, or plan and present a project to become more comfortable vocalizing your ideas. You could also speak to your manager about opportunities that flex your public speaking abilities.
4. Overcome fear
Many people experience feelings of fear before presenting in front of an audience, whether those feelings appear as a few butterflies or more severe anxiety. Try grounding yourself to shift your focus to the present moment. If you’re stuck dwelling on previous experiences that didn’t go well, use those mistakes as learning experiences and focus on what you can improve to do better in the future.
Tips for dealing with presentation anxiety
It’s normal to feel nervous when sharing your ideas. In fact, according to a report from the Journal of Graduate Medical Education, public speaking anxiety is prevalent in 15–30% of the general population .
Even though having a fear of public speaking is common, it doesn’t make it easier. You might feel overwhelmed, become stiff, and forget what you were going to say. But although the moment might scare you, there are ways to overcome the fear and put mind over matter.
Use these tactics to reduce your stress when you have to make a presentation:
1. Practice breathing techniques
If you experience anxiety often, you’re probably familiar with breathing techniques for stress relief . Incorporating these exercises into your daily routine can help you stop worrying and regulate anxious feelings.
Before a big presentation, take a moment alone to practice breathing techniques, ground yourself, and reduce tension. It’s also a good idea to take breaths throughout the presentation to speak slower and calm yourself down .
2. Get organized
The more organized you are, the more prepared you’ll feel. Carefully outline all of the critical information you want to use in your presentation, including your main talking points and visual aids, so you don’t forget anything. Use bullet points and visuals on each slide to remind you of what you want to talk about, and create handheld notes to help you stay on track.
3. Embrace moments of silence
It’s okay to lose your train of thought. It happens to even the most experienced public speakers once in a while. If your mind goes blank, don’t panic. Take a moment to breathe, gather your thoughts, and refer to your notes to see where you left off. You can drink some water or make a quick joke to ease the silence or regain your footing. And it’s okay to say, “Give me a moment while I find my notes.” Chances are, people understand the position you’re in.

4. Practice makes progress
Before presenting, rehearse in front of friends and family members you trust. This gives you the chance to work out any weak spots in your speech and become comfortable communicating out loud. If you want to go the extra mile, ask your makeshift audience to ask a surprise question. This tests your on-the-spot thinking and will prove that you can keep cool when things come up.
Whether you’re new to public speaking or are a seasoned presenter, you’re bound to make a few slip-ups. It happens to everyone. The most important thing is that you try your best, brush things off, and work on improving your skills to do better in your next presentation.
Although your job may require a different level of public speaking than your favorite TED Talk , developing presentation skills is handy in any profession. You can use presentation skills in a wide range of tasks in the workplace, whether you’re sharing your ideas with colleagues, expressing concerns to higher-ups, or pitching strategies to potential clients.
Remember to use active listening to read the room and engage your audience with an interesting narrative. Don’t forget to step outside your comfort zone once in a while and put your skills to practice in front of a crowd. After facing your fears, you’ll feel confident enough to put presentation skills on your resume.
If you’re trying to build your skills and become a better employee overall, try a communications coach with BetterUp.
Elevate your communication skills
Unlock the power of clear and persuasive communication. Our coaches can guide you to build strong relationships and succeed in both personal and professional life.
Elizabeth Perry, ACC
Elizabeth Perry is a Coach Community Manager at BetterUp. She uses strategic engagement strategies to cultivate a learning community across a global network of Coaches through in-person and virtual experiences, technology-enabled platforms, and strategic coaching industry partnerships. With over 3 years of coaching experience and a certification in transformative leadership and life coaching from Sofia University, Elizabeth leverages transpersonal psychology expertise to help coaches and clients gain awareness of their behavioral and thought patterns, discover their purpose and passions, and elevate their potential. She is a lifelong student of psychology, personal growth, and human potential as well as an ICF-certified ACC transpersonal life and leadership Coach.
The 11 tips that will improve your public speaking skills
The importance of good speech: 5 tips to be more articulate, learn types of gestures and their meanings to improve your communication, why it's good to have a bff at work and how to find one, why we need to reframe potential into readiness, love them or hate them, meetings promote social learning and growth, what’s my earning potential determining the right salary, show gratitude with “thank you for your leadership and vision” message examples, discover how to get noticed by upper management at work, similar articles, how to write a speech that your audience remembers, impression management: developing your self-presentation skills, 30 presentation feedback examples, your guide to what storytelling is and how to be a good storyteller, how to give a good presentation that captivates any audience, 8 clever hooks for presentations (with tips), communication coach: what they are and how to find one, how to make a presentation interactive and exciting, stay connected with betterup, get our newsletter, event invites, plus product insights and research..
3100 E 5th Street, Suite 350 Austin, TX 78702
- Platform Overview
- Integrations
- Powered by AI
- BetterUp Lead™
- BetterUp Manage™
- BetterUp Care®
- Sales Performance
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Case Studies
- Why BetterUp?
- About Coaching
- Find your Coach
- Career Coaching
- Communication Coaching
- Life Coaching
- News and Press
- Leadership Team
- Become a BetterUp Coach
- BetterUp Labs
- Center for Purpose & Performance
- Leadership Training
- Business Coaching
- Contact Support
- Contact Sales
- Privacy Policy
- Acceptable Use Policy
- Trust & Security
- Cookie Preferences
- Center for Innovative Teaching and Learning
- Instructional Guide
Teaching with PowerPoint
When effectively planned and used, PowerPoint (or similar tools, like Google Slides) can enhance instruction. People are divided on the effectiveness of this ubiquitous presentation program—some say that PowerPoint is wonderful while others bemoan its pervasiveness. No matter which side you take, PowerPoint does offer effective ways to enhance instruction when used and designed appropriately.
PowerPoint can be an effective tool to present material in the classroom and encourage student learning. You can use PowerPoint to project visuals that would otherwise be difficult to bring to class. For example, in an anthropology class, a single PowerPoint presentation could project images of an anthropological dig from a remote area, questions asking students about the topic, a chart of related statistics, and a mini quiz about what was just discussed that provides students with information that is visual, challenging, and engaging.
PowerPoint can be an effective tool to present material in the classroom and encourage student learning.
This section is organized in three major segments: Part I will help faculty identify and use basic but important design elements, Part II will cover ways to enhance teaching and learning with PowerPoint, and Part III will list ways to engage students with PowerPoint.
PART I: Designing the PowerPoint Presentation
Accessibility.
- Student accessibility—students with visual or hearing impairments may not be able to fully access a PowerPoint presentation, especially those with graphics, images, and sound.
- Use an accessible layout. Built-in slide template layouts were designed to be accessible: “the reading order is the same for people with vision and for people who use assistive technology such as screen readers” (University of Washington, n.d.). If you want to alter the layout of a theme, use the Slide Master; this will ensure your slides will retain accessibility.
- Use unique and specific slide titles so students can access the material they need.
- Consider how you display hyperlinks. Since screen readers read what is on the page, you may want to consider creating a hyperlink using a descriptive title instead of displaying the URL.
- All visuals and tables should include alt text. Alt text should describe the visual or table in detail so that students with visual impairments can “read” the images with their screen readers. Avoid using too many decorative visuals.
- All video and audio content should be captioned for students with hearing impairments. Transcripts can also be useful as an additional resource, but captioning ensures students can follow along with what is on the screen in real-time.
- Simplify your tables. If you use tables on your slides, ensure they are not overly complex and do not include blank cells. Screen readers may have difficulty providing information about the table if there are too many columns and rows, and they may “think” the table is complete if they come to a blank cell.
- Set a reading order for text on your slides. The order that text appears on the slide may not be the reading order of the text. Check that your reading order is correct by using the Selection Pane (organized bottom-up).
- Use Microsoft’s Accessibility Checker to identify potential accessibility issues in your completed PowerPoint. Use the feedback to improve your PowerPoint’s accessibility. You could also send your file to the Disability Resource Center to have them assess its accessibility (send it far in advance of when you will need to use it).
- Save your PowerPoint presentation as a PDF file to distribute to students with visual impairments.
Preparing for the presentation
- Consider time and effort in preparing a PowerPoint presentation; give yourself plenty of lead time for design and development.
- PowerPoint is especially useful when providing course material online. Consider student technology compatibility with PowerPoint material put on the web; ensure images and graphics have been compressed for access by computers using dial-up connection.
PowerPoint is especially useful when providing course material online.
- Be aware of copyright law when displaying course materials, and properly cite source material. This is especially important when using visuals obtained from the internet or other sources. This also models proper citation for your students.
- Think about message interpretation for PowerPoint use online: will students be able to understand material in a PowerPoint presentation outside of the classroom? Will you need to provide notes and/or other material to help students understand complex information, data, or graphics?
- If you will be using your own laptop, make sure the classroom is equipped with the proper cables, drivers, and other means to display your presentation the way you have intended.
Slide content
- Avoid text-dense slides. It’s better to have more slides than trying to place too much text on one slide. Use brief points instead of long sentences or paragraphs and outline key points rather than transcribing your lecture. Use PowerPoint to cue and guide the presentation.
- Use the Notes feature to add content to your presentation that the audience will not see. You can access the Notes section for each slide by sliding the bottom of the slide window up to reveal the notes section or by clicking “View” and choosing “Notes Page” from the Presentation Views options.
- Relate PowerPoint material to course objectives to reinforce their purpose for students.
Number of slides
- As a rule of thumb, plan to show one slide per minute to account for discussion and time and for students to absorb the material.
- Reduce redundant or text-heavy sentences or bullets to ensure a more professional appearance.
- Incorporate active learning throughout the presentation to hold students’ interest and reinforce learning.
Emphasizing content
- Use italics, bold, and color for emphasizing content.
- Use of a light background (white, beige, yellow) with dark typeface or a dark background (blue, purple, brown) with a light typeface is easy to read in a large room.
- Avoid using too many colors or shifting colors too many times within the presentation, which can be distracting to students.
- Avoid using underlines for emphasis; underlining typically signifies hypertext in digital media.
Use of a light background with dark typeface or a dark background with a light typeface is easy to read in a large room.
- Limit the number of typeface styles to no more than two per slide. Try to keep typeface consistent throughout your presentation so it does not become a distraction.
- Avoid overly ornate or specialty fonts that may be harder for students to read. Stick to basic fonts so as not to distract students from the content.
- Ensure the typeface is large enough to read from anywhere in the room: titles and headings should be no less than 36-40-point font. The subtext should be no less than 32-point font.
Clip art and graphics
- Use clip art and graphics sparingly. Research shows that it’s best to use graphics only when they support the content. Irrelevant graphics and images have been proven to hinder student learning.
- Photographs can be used to add realism. Again, only use photographs that are relevant to the content and serve a pedagogical purpose. Images for decorative purposes are distracting.
- Size and place graphics appropriately on the slide—consider wrapping text around a graphic.
- Use two-dimensional pie and bar graphs rather than 3D styles which can interfere with the intended message.
Use clip art and graphics sparingly. Research shows that it’s best to use graphics only when they support the content.
Animation and sound
- Add motion, sound, or music only when necessary. When in doubt, do without.
- Avoid distracting animations and transitions. Excessive movement within or between slides can interfere with the message and students find them distracting. Avoid them or use only simple screen transitions.
Final check
- Check for spelling, correct word usage, flow of material, and overall appearance of the presentation.
- Colleagues can be helpful to check your presentation for accuracy and appeal. Note: Errors are more obvious when they are projected.
- Schedule at least one practice session to check for timing and flow.
- PowerPoint’s Slide Sorter View is especially helpful to check slides for proper sequencing as well as information gaps and redundancy. You can also use the preview pane on the left of the screen when you are editing the PowerPoint in “Normal” view.
- Prepare for plan “B” in case you have trouble with the technology in the classroom: how will you provide material located on your flash drive or computer? Have an alternate method of instruction ready (printing a copy of your PowerPoint with notes is one idea).
PowerPoint’s Slide Sorter View is especially helpful to check slides for proper sequencing and information gaps and redundancy.
PowerPoint Handouts
PowerPoint provides multiple options for print-based handouts that can be distributed at various points in the class.
Before class: students might like having materials available to help them prepare and formulate questions before the class period.
During class: you could distribute a handout with three slides and lines for notes to encourage students to take notes on the details of your lecture so they have notes alongside the slide material (and aren’t just taking notes on the slide content).
After class: some instructors wait to make the presentation available after the class period so that students concentrate on the presentation rather than reading ahead on the handout.
Never: Some instructors do not distribute the PowerPoint to students so that students don’t rely on access to the presentation and neglect to pay attention in class as a result.
- PowerPoint slides can be printed in the form of handouts—with one, two, three, four, six, or nine slides on a page—that can be given to students for reference during and after the presentation. The three-slides-per-page handout includes lined space to assist in note-taking.
- Notes Pages. Detailed notes can be printed and used during the presentation, or if they are notes intended for students, they can be distributed before the presentation.
- Outline View. PowerPoint presentations can be printed as an outline, which provides all the text from each slide. Outlines offer a welcome alternative to slide handouts and can be modified from the original presentation to provide more or less information than the projected presentation.
The Presentation
Alley, Schreiber, Ramsdell, and Muffo (2006) suggest that PowerPoint slide headline design “affects audience retention,” and they conclude that “succinct sentence headlines are more effective” in information recall than headlines of short phrases or single words (p. 233). In other words, create slide titles with as much information as is used for newspapers and journals to help students better understand the content of the slide.
- PowerPoint should provide key words, concepts, and images to enhance your presentation (but PowerPoint should not replace you as the presenter).
- Avoid reading from the slide—reading the material can be perceived as though you don’t know the material. If you must read the material, provide it in a handout instead of a projected PowerPoint slide.
- Avoid moving a laser pointer across the slide rapidly. If using a laser pointer, use one with a dot large enough to be seen from all areas of the room and move it slowly and intentionally.
Avoid reading from the slide—reading the material can be perceived as though you don’t know the material.
- Use a blank screen to allow students to reflect on what has just been discussed or to gain their attention (Press B for a black screen or W for a white screen while delivering your slide show; press these keys again to return to the live presentation). This pause can also be used for a break period or when transitioning to new content.
- Stand to one side of the screen and face the audience while presenting. Using Presenter View will display your slide notes to you on the computer monitor while projecting only the slides to students on the projector screen.
- Leave classroom lights on and turn off lights directly over the projection screen if possible. A completely dark or dim classroom will impede notetaking (and may encourage nap-taking).
- Learn to use PowerPoint efficiently and have a back-up plan in case of technical failure.
- Give yourself enough time to finish the presentation. Trying to rush through slides can give the impression of an unorganized presentation and may be difficult for students to follow or learn.
PART II: Enhancing Teaching and Learning with PowerPoint
Class preparation.
PowerPoint can be used to prepare lectures and presentations by helping instructors refine their material to salient points and content. Class lectures can be typed in outline format, which can then be refined as slides. Lecture notes can be printed as notes pages (notes pages: Printed pages that display author notes beneath the slide that the notes accompany.) and could also be given as handouts to accompany the presentation.
Multimodal Learning
Using PowerPoint can help you present information in multiple ways (a multimodal approach) through the projection of color, images, and video for the visual mode; sound and music for the auditory mode; text and writing prompts for the reading/writing mode; and interactive slides that ask students to do something, e.g. a group or class activity in which students practice concepts, for the kinesthetic mode (see Part III: Engaging Students with PowerPoint for more details). Providing information in multiple modalities helps improve comprehension and recall for all students.
Providing information in multiple modalities helps improve comprehension and recall for all students.
Type-on Live Slides
PowerPoint allows users to type directly during the slide show, which provides another form of interaction. These write-on slides can be used to project students’ comments and ideas for the entire class to see. When the presentation is over, the new material can be saved to the original file and posted electronically. This feature requires advanced preparation in the PowerPoint file while creating your presentation. For instructions on how to set up your type-on slide text box, visit this tutorial from AddictiveTips .
Write or Highlight on Slides
PowerPoint also allows users to use tools to highlight or write directly onto a presentation while it is live. When you are presenting your PowerPoint, move your cursor over the slide to reveal tools in the lower-left corner. One of the tools is a pen icon. Click this icon to choose either a laser pointer, pen, or highlighter. You can use your cursor for these options, or you can use the stylus for your smart podium computer monitor or touch-screen laptop monitor (if applicable).
Just-In-Time Course Material
You can make your PowerPoint slides, outline, and/or notes pages available online 24/7 through Blackboard, OneDrive, other websites. Students can review the material before class, bring printouts to class, and better prepare themselves for listening rather than taking a lot of notes during the class period. They can also come to class prepared with questions about the material so you can address their comprehension of the concepts.
PART III: Engaging Students with PowerPoint
The following techniques can be incorporated into PowerPoint presentations to increase interactivity and engagement between students and between students and the instructor. Each technique can be projected as a separate PowerPoint slide.
Running Slide Show as Students Arrive in the Classroom
This technique provides visual interest and can include a series of questions for students to answer as they sit waiting for class to begin. These questions could be on future texts or quizzes.
- Opening Question : project an opening question, e.g. “Take a moment to reflect on ___.”
- Think of what you know about ___.
- Turn to a partner and share your knowledge about ___.
- Share with the class what you have discussed with your partner.
- Focused Listing helps with recall of pertinent information, e.g. “list as many characteristics of ___, or write down as many words related to ___ as you can think of.”
- Brainstorming stretches the mind and promotes deep thinking and recall of prior knowledge, e.g. “What do you know about ___? Start with your clearest thoughts and then move on to those what are kind of ‘out there.’”
- Questions : ask students if they have any questions roughly every 15 minutes. This technique provides time for students to reflect and is also a good time for a scheduled break or for the instructor to interact with students.
- Note Check : ask students to “take a few minutes to compare notes with a partner,” or “…summarize the most important information,” or “…identify and clarify any sticking points,” etc.
- Questions and Answer Pairs : have students “take a minute to come with one question then see if you can stump your partner!”
- The Two-Minute Paper allows the instructor to check the class progress, e.g. “summarize the most important points of today’s lecture.” Have students submit the paper at the end of class.
- “If You Could Ask One Last Question—What Would It Be?” This technique allows for students to think more deeply about the topic and apply what they have learned in a question format.
- A Classroom Opinion Poll provides a sense of where students stand on certain topics, e.g. “do you believe in ___,” or “what are your thoughts on ___?”
- Muddiest Point allows anonymous feedback to inform the instructor if changes and or additions need to be made to the class, e.g. “What parts of today’s material still confuse you?”
- Most Useful Point can tell the instructor where the course is on track, e.g. “What is the most useful point in today’s material, and how can you illustrate its use in a practical setting?”
Positive Features of PowerPoint
- PowerPoint saves time and energy—once the presentation has been created, it is easy to update or modify for other courses.
- PowerPoint is portable and can be shared easily with students and colleagues.
- PowerPoint supports multimedia, such as video, audio, images, and
PowerPoint supports multimedia, such as video, audio, images, and animation.
Potential Drawbacks of PowerPoint
- PowerPoint could reduce the opportunity for classroom interaction by being the primary method of information dissemination or designed without built-in opportunities for interaction.
- PowerPoint could lead to information overload, especially with the inclusion of long sentences and paragraphs or lecture-heavy presentations with little opportunity for practical application or active learning.
- PowerPoint could “drive” the instruction and minimize the opportunity for spontaneity and creative teaching unless the instructor incorporates the potential for ingenuity into the presentation.
As with any technology, the way PowerPoint is used will determine its pedagogical effectiveness. By strategically using the points described above, PowerPoint can be used to enhance instruction and engage students.
Alley, M., Schreiber, M., Ramsdell, K., & Muffo, J. (2006). How the design of headlines in presentation slides affects audience retention. Technical Communication, 53 (2), 225-234. Retrieved from https://www.jstor.org/stable/43090718
University of Washington, Accessible Technology. (n.d.). Creating accessible presentations in Microsoft PowerPoint. Retrieved from https://www.washington.edu/accessibility/documents/powerpoint/
Selected Resources
Brill, F. (2016). PowerPoint for teachers: Creating interactive lessons. LinkedIn Learning . Retrieved from https://www.lynda.com/PowerPoint-tutorials/PowerPoint-Teachers-Create-Interactive-Lessons/472427-2.html
Huston, S. (2011). Active learning with PowerPoint [PDF file]. DE Oracle @ UMUC . Retrieved from http://contentdm.umuc.edu/digital/api/collection/p16240coll5/id/78/download
Microsoft Office Support. (n.d.). Make your PowerPoint presentations accessible to people with disabilities. Retrieved from https://support.office.com/en-us/article/make-your-powerpoint-presentations-accessible-to-people-with-disabilities-6f7772b2-2f33-4bd2-8ca7-ae3b2b3ef25
Tufte, E. R. (2006). The cognitive style of PowerPoint: Pitching out corrupts within. Cheshire, CT: Graphics Press LLC.
University of Nebraska Medical Center, College of Medicine. (n.d.). Active Learning with a PowerPoint. Retrieved from https://www.unmc.edu/com/_documents/active-learning-ppt.pdf
University of Washington, Department of English. (n.d.). Teaching with PowerPoint. Retrieved from https://english.washington.edu/teaching/teaching-powerpoint
Vanderbilt University, Center for Teaching. (n.d.). Making better PowerPoint presentations. Retrieved from https://cft.vanderbilt.edu/guides-sub-pages/making-better-powerpoint-presentations/

Suggested citation
Northern Illinois University Center for Innovative Teaching and Learning. (2020). Teaching with PowerPoint. In Instructional guide for university faculty and teaching assistants. Retrieved from https://www.niu.edu/citl/resources/guides/instructional-guide
Phone: 815-753-0595 Email: [email protected]
Connect with us on
Facebook page Twitter page YouTube page Instagram page LinkedIn page

- Teaching and Learning
Student Presentations: Do They Benefit Those Who Listen?
- February 21, 2013
- Maryellen Weimer, PhD
Almost everyone agrees that student presentations benefit the presenter in significant ways. By doing presentations, students learn how to speak in front a group, a broadly applicable professional skill. They learn how to prepare material for public presentation, and practice (especially with feedback) improves their speaking skills. But those of us who have students do presentations in class know there’s a downside—and that’s how the rest of the class responds to these presentations. When the teacher talks, students more or less have to pay attention, at least some of the time, but when their classmates present, they can be comatose. Not only does this make it more difficult for the presenter, it means the students listening are not likely having any sort of learning experience.
Peer evaluations are one way to get students listening and learning from the presentations of others, as the authors of the article referenced below have documented. Students attend more carefully to what their classmates are saying when the evaluations they are doing “count.” In this article, which describes the use of peer evaluations in ten 300-level political science courses, students evaluated every presentation and those evaluations constituted between 3 and 5 percent of their course grade—an amount the authors describe as “just enough to make the students take this assignment seriously.” (p. 806) The quality of the feedback students provide is improved when they use criteria (in this case the same one the teachers used) to assess the presentations. Without much experience critiquing presentations and with no specific guidelines, they are likely to offer feedback that is generic and not particularly helpful, such as “Good presentation.”
These authors had students in each of the 10 classes evaluate the peer evaluation assignment, and that feedback indicates the merit of having students do the evaluations. Seventy-three percent of the students agreed or strongly agreed that completing the evaluations made them pay more attention to the presentations. Almost 60 percent said doing the evaluations gave them a different perspective. “Students indicated they gained a different insight into the process, rather than just sitting through presentations without having any objective or direction as an audience member.” (p. 806) Another sizable majority, almost 74 percent, agreed or strongly agreed that completing the evaluations clarified expectations for the presentation assignment.
Students were equally clear that they did not want the evaluations of their peers to have any role in determining their grade for the presentation. This response is interesting in light of the fact that an analysis of a subset of the data revealed a high correlation between instructor and student grades (r = .740). Instructor grades were slightly higher than student-assigned grades. Even though small, this difference was statistically significant. And even though students didn’t want the assessment of their peers to count, over 80 percent agreed or strongly agreed that the feedback of peers would be helpful in improving subsequent presentations.
It is appropriate for teachers to consider the learning potential of presentations, not just for the presenter, but for the audience. Peer evaluations can be used to increase the level of attention paid to those presentations and the learning that might result from listening. They can also develop critiquing skills. Rather than incorporating peer critiques into the grade of the presenter, maybe part or all of the critique grade could be determined by the presenter, who rates the quality of the feedback provided. As these authors note, sometimes the logistics of peer evaluations discourage faculty from using them—multiple evaluations to collect, record, sort, and return. What about an online system of peer reviews? Or assign a certain number of peer reviewers to each presentation. That ensures that at least a portion of the audience are attending, and with fewer evaluations to prepare, students could be expected to provide more detailed feedback. Or how about some bonus points to the students whose presentations are rated highest by their colleagues? The details associated with using peer evaluations can be handled in a variety of interesting and useful ways.
Reference: Baranowski, M., and Weir, K. (2011). Peer evaluation in the political science classroom. PS, Political Science and Politics, 44 (4), 805-811.
Reprinted from The Teaching Professor , 26.1 (2012): 5.
Stay Updated with Faculty Focus!
Get exclusive access to programs, reports, podcast episodes, articles, and more!

- Opens in a new tab

Welcome Back
Username or Email
Remember Me

Already a subscriber? log in here.


- PRESENTATION SKILLS
Search SkillsYouNeed:
Presentation Skills:
- A - Z List of Presentation Skills
- Top Tips for Effective Presentations
- General Presentation Skills
- What is a Presentation?
- Preparing for a Presentation
- Organising the Material
- Writing Your Presentation
- Deciding the Presentation Method
- Managing your Presentation Notes
- Working with Visual Aids
- Presenting Data
- Managing the Event
- Coping with Presentation Nerves
- Dealing with Questions
- How to Build Presentations Like a Consultant
- Self-Presentation in Presentations
- Specific Presentation Events
- Remote Meetings and Presentations
- Giving a Speech
- Presentations in Interviews
- Presenting to Large Groups and Conferences
- Giving Lectures and Seminars
- Managing a Press Conference
- Attending Public Consultation Meetings
- Managing a Public Consultation Meeting
- Crisis Communications
- Elsewhere on Skills You Need:
- Communication Skills
- Facilitation Skills
- Teams, Groups and Meetings
- Effective Speaking
- Question Types
Subscribe to our FREE newsletter and start improving your life in just 5 minutes a day.
You'll get our 5 free 'One Minute Life Skills' and our weekly newsletter.
We'll never share your email address and you can unsubscribe at any time.
Presentation Skills
Presenting information clearly and effectively is a key skill in getting your message across. Today, presentation skills are required in almost every field, and most of us are required to give presentations on occasions. While some people take this in their stride, others find it much more challenging.
It is, however, possible to improve your presentation skills with a bit of work. This section of SkillsYouNeed is designed to help.
Many people feel terrified when asked to talk in public, especially to bigger groups. However, these fears can be reduced by good preparation, which will also lay the groundwork for making an effective presentation.
There are Different Types of Presentations, but They’re All Presentations
There are any number of occasions when you may be asked to speak in public or to a group of people. They include:
- Presenting or making a speech at a conference or event.
- Objecting to a planning proposal at a council meeting.
- Making a speech at a wedding.
- Proposing a vote of thanks to someone at a club or society.
- On behalf of a team, saying goodbye and presenting a gift to a colleague who is leaving.
- Seeking investment or a loan to help you set up a new business.
These can all be considered presentations.
They do not, however, all require the same approach. You would not, for example, use PowerPoint to thank a colleague who was leaving. It would be unusual (though it has been done) to use it in a speech at a wedding. However, a conference audience would be somewhat surprised NOT to see slides projected onto a screen.
It follows, therefore, that there is no single set of rules that apply to all presentations. There are, however, some things that every presentation opportunity has in common. These include:
You will present better if you have prepared effectively . This does NOT necessarily mean that you have written out your speech verbatim and rehearsed it until you know it off by heart—although that might work for some people. It does, however, mean that you have to be confident that you are saying the right thing, in the right way, to the right people.
You need to be clear about your audience and your message . Every presentation will be better if you have clearly considered the message that you want or need to convey, and how best to convey it to your audience. These two pieces of information drive your style, structure, content, and use of visual aids.
You must never overrun your allocated time . In other words, don’t outstay your welcome. Almost every speech or presentation is better if it is shorter. Nobody minds going for coffee early or finishing before they expected to do so. Everybody minds being held up.
Generally speaking, your audience starts on your side. As a rule, your audience is there (more or less) voluntarily. They have chosen to listen to you, and they want to enjoy your presentation. The occasion is yours to lose.
An Important Point
There is one very important point to remember: if what you’re doing or saying is not working, do something else.
One of the worst feelings as a presenter is that you have lost your audience. You know that’s happened, but you continue to stumble through your remaining PowerPoint slides for the next 15 minutes, as your audience checks their phones and wishes it was coffee time. You think you have no choice, but that’s not actually true.
When you present, you are in charge of the room . The audience has effectively handed you control and is sitting back waiting for you to do something. You may have prepared a specific talk, but if you see that isn’t working, you can always change it. You are, after all, the expert.
You can, for example:
- Skip through some slides to a section that they may find more interesting;
- Ask your audience whether there is particular information that they were expecting that you are not providing;
- Suggest that everyone looks a bit sleepy, and maybe it would be better to start questions early, or have a discussion; or
- Ask the audience at the start of the presentation what they are expecting and what they want you to cover. That way, you can tailor the presentation to fit their expectations.
Just as when you are facilitating, you want to help your audience get the most out of your presentation. The best way to do that is to accept feedback—which may include smiles, nods of interest, or people getting their phones out.
Quick Guide to Effective Presentations
If you need to improve your presentation skills quickly, then a really good place to start is with our Top Tips for Effective Presentations .
This will give you some ‘quick wins’ that will help you improve your presentations. If you’re already an experienced presenter, this page should be a useful refresher, or even take your skills from good to great.
Our tips include general ideas about connecting with your audience, information about the importance of voice and body language, and detailed tips about preparing slide-shows.
The most important tip of all, however, is to remember that it's all about your audience.
Keep that in mind, and your presentation skills will almost instantly improve.
If you have more time to develop your presentation skills…
…then the Presentation Skills section of SkillsYouNeed is designed to help.
Our Presentation Skills section is split into two parts.
- The first gives you a step-by-step guide to putting together and delivering a professional and effective presentation .
- The second provides more detailed information about presenting and communicating in particular circumstances .
You can either use our step-by-step guide to walk you through the presentation preparation and delivery process, or you can focus on particular areas that are an issue for you.
Preparing for Your Presentation
The guide starts by explaining What is a Presentation?
We define a presentation as a means of communication that can be adapted to various speaking situations, such as talking to a group, addressing a meeting or briefing a team. Effective presentations usually require careful thought and preparation—although this preparation need not take very long.
Preparation is the most important part of making a successful presentation. Our page on Preparing For A Presentation explains what information you need before you can really start to plan your presentation and decide what you are going to say. The most important aspects include the objective of the presentation, the subject, and the audience.
Irrespective of whether the occasion is formal or informal, you should always aim to give a clear, well-structured delivery. To do so, you need to organise your presentation material . You can either do this in your head, or use a technique like mind-mapping to help you identify links and good flow.
By the time you come to write your presentation , you should know exactly what you want to say and the order in which you want to say it. You may want to use one of the standard presentation structures, such as ‘What, Why, How?’. You will also find it helpful to consider how to tell your story most effectively, and to use stories in your presentation to illustrate points. There is more about this in our page on writing your presentation .
You also need to decide on your presentation method . Presentations range from the formal to the informal. Your choice of presentation method will depend on many factors, including the audience, the venue, the facilities, and your own preferences.
Visual aids can add another dimension to your presentation, helping to hold your audience’s attention, and also act as a reminder of what you wanted to say. However, they need handling with care. Only use visual aids if they are necessary to maintain interest and assist comprehension . If visual aids are not used well, they can ruin a presentation.
See Working with Visual Aids to avoid falling into the trap of the dreaded ‘ Death by PowerPoint’ .
A particular case of visual aids is the use of data in a presentation.
There are times when using data in a presentation can really help you to tell the story better. It is, however, important not to blind your audience with statistics. You also need to remember that many people find numbers difficult to understand. Our page on Presenting Data gives some hints and tips about using data effectively in a presentation situation.
On the Day of the Presentation
There are a number of aspects to delivering your presentation on the day.
The practicalities of how you manage your presentation can make a significant difference to its success, and to your nerves! For example, turning up early means that you have will have a chance to see the room, and ensure that you can operate all the necessary equipment. There is more about how to cope, including managing sound systems, audio-visual equipment and lecterns in our page on Managing the Presentation Event .
Many people also feel very nervous before and during a presentation. This is entirely normal, and can even be helpful if you can channel it in the right way. There are some tried and tested strategies and techniques to manage your nerves so that you can concentrate on delivering an effective and engaging presentation.
See Coping with Presentation Nerves for some ideas that will help.
How you present yourself can also affect how your audience responds to your presentation.
You need to fit with your audience's expectations if they are not going to spend quite a large chunk of your presentation dealing with the differences between expectations and reality.
For more about aspects of self-presentation, see our page on Self-Presentation in Presentations .
You also need to consider how to manage your presentation notes .
Few people are able to give a presentation without notes. You will need to know your own abilities and decide how best to make the presentation. You might manage your talk by using full text, notes on cue cards, keywords on cue cards, or mind maps. There is more about this in our page on Managing your Presentation Notes .
After the presentation, you may be faced with a question-and-answer session. For many people, this is the worst part of the event.
Decide in advance how and when you wish to handle questions. Some speakers prefer questions to be raised as they arise during the presentation whilst others prefer to deal with questions at the end. At the start of your presentation, you should make clear your preferences to the audience. See our page on Dealing with Questions for more ideas about how to make the question session pleasant and productive, rather than something to dread.
Presenting Under Particular Circumstances
You may find that you need to give a presentation under certain circumstances, where your previous experience is less helpful.
Circumstances that may be new to you include:
- Giving a Speech , for example, at a wedding.
One particular special case is attending public consultation meetings.
Our pages on Attending Public Consultation Meetings , and Managing Public Consultation Meetings provide information to help whether you are a concerned member of the public, or responsible for organising a public meeting.
You may also find yourself required to organise or manage a press conference.
Although this may not strictly be what you would describe as a ‘presentation’, it is nonetheless an event at which you are required to present your organisation in a particular light.
Our page on Managing a Press Conference gives some ideas about how best to do that.
Finally, should you be unlucky enough to be involved in a serious crisis or disaster that affects your organisation, our page on Crisis Communications gives some ideas about how to manage press and public relations on these occasions.
Start with: What is a Presentation? Top Tips for Effective Presentations
See also: Personal Appearance Interpersonal Communication Skills
- Skip to Nav
- Skip to Main
- Skip to Footer

How to Use Oral Presentations to Help English Language Learners Succeed
Please try again

Excerpted from “ The ELL Teacher’s Toolbox: Hundreds of Practical Ideas to Support Your Students ,” by Larry Ferlazzo and Katie Hull Sypnieski, with permission from the authors.
Having the confidence to speak in front of others is challenging for most people. For English Language Learners, this anxiety can be heightened because they are also speaking in a new language. We’ve found several benefits to incorporating opportunities for students to present to their peers in a positive and safe classroom environment. It helps them focus on pronunciation and clarity and also boosts their confidence. This type of practice is useful since students will surely have to make presentations in other classes, in college, and/or in their future jobs. However, what may be even more valuable is giving students the chance to take these risks in a collaborative, supportive environment.
Presentations also offer students the opportunity to become the teacher—something we welcome and they enjoy! They can further provide valuable listening practice for the rest of the class, especially when students are given a task to focus their listening.
Research confirms that in order for ELLs to acquire English they must engage in oral language practice and be given the opportunity to use language in meaningful ways for social and academic purposes (Williams & Roberts, 2011). Teaching students to design effective oral presentations has also been found to support thinking development as “the quality of presentation actually improves the quality of thought, and vice versa” (Živković, 2014, p. 474). Additionally, t he Common Core Speaking and Listening Standards specifically focus on oral presentations. These standards call for students to make effective and well-organized presentations and to use technology to enhance understanding of them.
GUIDELINES AND APPLICATION
Oral presentations can take many different forms in the ELL classroom—ranging from students briefly presenting their learning in small groups to creating a multi-slide presentation for the whole class. In this section, we give some general guidelines for oral presentations with ELLs. We then share ideas for helping students develop their presentation skills and describe specific ways we scaffold both short and long oral presentations.
We keep the following guidelines in mind when incorporating oral presentations into ELL instruction:

Length —We have students develop and deliver short presentations (usually 2-4 minutes) on a regular basis so they can practice their presentation skills with smaller, less overwhelming tasks. These presentations are often to another student or a small group. Once or twice a semester, students do a longer presentation (usually 5-8 minutes), many times with a partner or in a small group.
Novelty —Mixing up how students present (in small groups, in pairs, individually) and what they use to present (a poster, a paper placed under the document camera, props, a slide presentation, etc.) can increase engagement for students and the teacher!
Whole Class Processing -- We want to avoid students “tuning out” during oral presentations. Not only can it be frustrating for the speakers, but students also miss out on valuable listening practice. During oral presentations, and in any activity, we want to maximize the probability that all students are thinking and learning all the time. Jim Peterson and Ted Appel, administrators with whom we’ve worked closely, call this “whole class processing” (Ferlazzo, 2011, August 16) and it is also known as active participation. All students can be encouraged to actively participate in oral presentations by being given a listening task-- taking notes on a graphic organizer, providing written feedback to the speaker, using a checklist to evaluate presenters, etc.
Language Support —It is critical to provide ELLs, especially at the lower levels of English proficiency, with language support for oral presentations. In other words, thinking about what vocabulary, language features and organizational structures they may need, and then providing students with scaffolding, like speaking frames and graphic organizers. Oral presentations can also provide an opportunity for students to practice their summarizing skills. When students are presenting information on a topic they have researched, we remind them to summarize using their own words and to give credit when using someone else’s words.
Technology Support —It can’t be assumed that students have experience using technology tools in presentations. We find it most helpful using simple tools that are easy for students to learn (like Powerpoint without all the “bells and whistles” or Google Slides). We also emphasize to students that digital media should be used to help the audience understand what they are saying and not just to make a presentation flashy or pretty. We also share with our students what is known as “The Picture Superiority Effect”-- a body of research showing that people are better able to learn and recall information presented as pictures as opposed to just being presented with words (Kagan, 2013).
Groups -- Giving ELLs the opportunity to work and present in small groups is helpful in several ways. Presenting as a group (as opposed to by yourself) can help students feel less anxious. It also offers language-building opportunities as students communicate to develop and practice their presentations. Creating new knowledge as a group promotes collaboration and language acquisition--an ideal equation for a successful ELL classroom!
Teacher feedback/student evaluation --The focus of oral presentations with ELL students should be on the practice and skills they are gaining, not on the grade or “score” they are earning. Teachers can give out a simple rubric before students create their presentations. Then students can keep these expectations in mind as they develop and practice their presentations. The teacher, or classmates, can then use the rubric to offer feedback to the speaker. We also often ask students to reflect on their own presentation and complete the rubric as a form of self-assessment. Figure 30.1 – “Presentation Peer Evaluation Rubric” , developed by talented student teacher Kevin Inlay (who is now a teacher in his own classroom), is a simple rubric we used to improve group presentations in our ELL World History class.
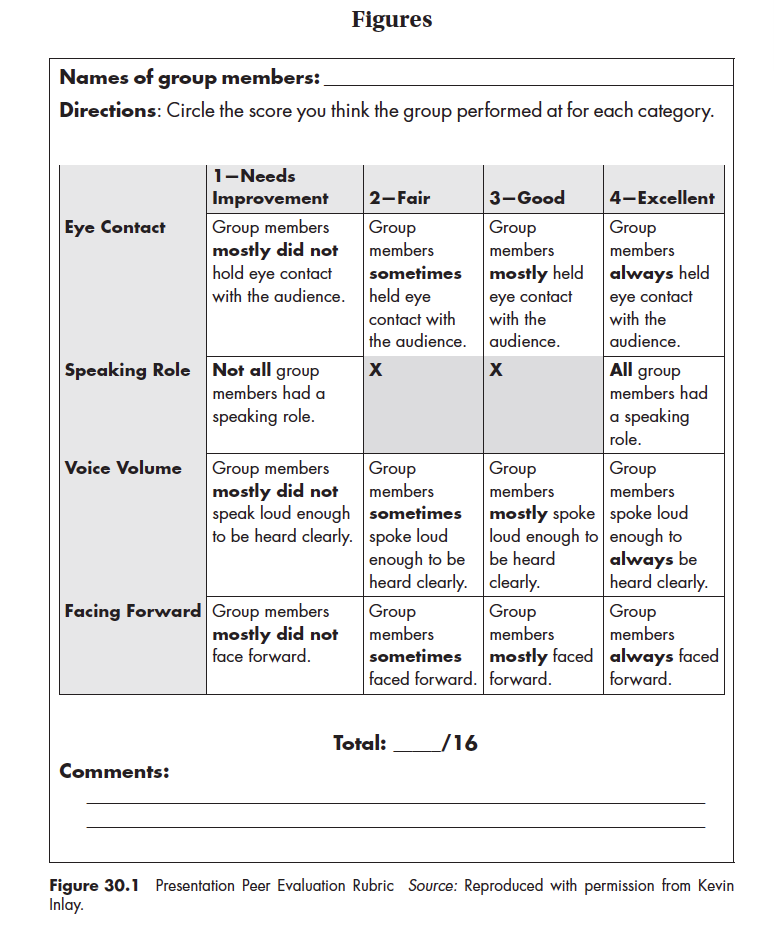
Teaching Presentation Skills
We use the following two lesson ideas to explicitly teach how to develop effective presentation skills:
LESSON ONE: Speaking and Listening Do’s and Don’ts
We help our students understand and practice general presentation skills through an activity we call Speaking and Listening “Do’s and Don’ts.” We usually spread this lesson out among two class periods.
We first ask students to create a simple T-chart by folding a piece of paper in half and labeling one side “Do” and the other side “Don’t.” We then post Figure 30.2 “Speaking Do’s and Don’ts” on the document camera and display the first statement (the rest we cover with a blank sheet of paper).
We read the first statement, “Make eye contact with the audience,” and ask students if this is something they want to do when they are giving a presentation or if it is something they don’t want to do. Students write the statement where they think it belongs--under the “Do” column or “Don’t” Column. Students then share their answer with a partner and discuss why they put it in that column. After calling on a few pairs to share with the class, we move down the list repeating the same process of categorizing each statement as a “Do” or a “Don’t.” Students write it on their chart and discuss why it should be placed there.
After categorizing the statements for speaking, we give students Figure 30.3 “Listening Do’s and Don’ts .” We tell students to work in pairs to categorize the statements as something they do or something they don’t want to do when listening to a student presentation. This time, we ask students to make a quick poster with the headings “Do’s” and “Don’ts” for Listening. Under each heading students must list the corresponding statements--the teacher can circulate to check for accuracy. Students are asked to talk about why each statement belongs in each category and should be prepared to share their reasoning with the class. Students must also choose one “do” statement and one “don’t” statement to illustrate on their poster. Students can present their posters in small groups or with the whole class. This serves as a great opportunity to apply the speaking and listening “do’s” they just reviewed and heightens their awareness of the “don’ts!”

A fun twist, that also serves as a good review on a subsequent day, is to ask groups of students to pick two or three “do’s” and “don’ts” from both Speaking and Listening to act out in front of the class.
LESSON TWO Slide Presentations Concept Attainment
We periodically ask students to make slide presentations using PowerPoint or Google Slides to give them practice with developing visual aids (see the Home Culture activity later in this section). We show students how to make better slides, along with giving students the language support they may need in the form of an outline or sentence starters. An easy and effective way to do this is through Concept Attainment.
Concept Attainment involves the teacher identifying both "good" and "bad" examples of the intended learning objective. In this case, we use a PowerPoint containing three “good” slides and three “bad” ones (see them at The Best Resources For Teaching Students The Difference Between A Good and a Bad Slide ).
We start by showing students the first example of a “good” or “yes” slide (containing very little text and two images) and saying, “This is a yes.” However, we don’t explain why it is a “yes.” Then we show a “bad” or “no” example of a slide (containing multiple images randomly placed with a very “busy background”), saying, “This is a no” without explaining why. Students are then asked to think about them, and share with a partner why they think one is a "yes" and one is a "no."
At this point, we make a quick chart on a large sheet of paper (students can make individual charts on a piece of paper) and ask students to list the good and bad qualities they have observed so far. For example, under the “Good/Yes” column it might say “Has less words and the background is simple” and under the “Bad/No” column “Has too many pictures and the background is distracting.”
We then show the second “yes” example (containing one image with a short amount of text in a clear font) and the “no” example (containing way too much text and using a less clear font style). Students repeat the “think-pair-share” process and then the class again discusses what students are noticing about the “yes” and “no” examples. Then they add these observations to their chart.
Students repeat the whole process a final time with the third examples. The third “yes” example slide contains one image, minimal text and one bullet point. The third “no” example, on the other hand, contains multiple bullet points.
To reinforce this lesson at a later date, the teacher could show students more examples, or students could look for more “yes” and “no” examples online. They could continue to add more qualities of good and bad slides to their chart. See the Technology Connections section for links to good and bad PowerPoint examples, including the PowerPoint we use for this Concept Attainment lesson.
You can learn more about other presentations that support public speaking, such as home culture presentations, speed dating, talking points, top 5 and PechaKucha Book talks in our book, “ The ELL Teacher’s Toolbox: Hundreds of Practical Ideas to Support Your Students .”

Larry Ferlazzo has taught English Language Learners, mainstream and International Baccalaureate students at Luther Burbank High School in Sacramento for 15 years. He has authored eight books on education, hosts a popular blog for educators, and writes a weekly teacher advice column for Education Week Teacher . He was a community organizer for 19 years prior to becoming a high school teacher.

Katie Hull Sypnieski has worked with English Language Learners at the secondary level for over 20 years. She currently teaches middle school ELA and ELD at Rosa Parks K-8 School in Sacramento, California. She is a teaching consultant with the Area 3 Writing Project at the University of California, Davis and has leads professional development for teachers of ELLs. She is co-author (with Larry Ferlazzo) of The ESL/ELL Teacher’s Survival Guide and Navigating the Common Core with English Language Learners .
- Request a Consultation
- Workshops and Virtual Conversations
- Technical Support
- Course Design and Preparation
- Observation & Feedback
Teaching Resources
Improving Presentation Style
Resource overview.
Strategies for making your presentation style more effective in the classroom
Effective lecturers combine the talents of scholar, writer, producer, comedian, showman, and teacher in ways that contribute to student learning.”
Wilbert J. McKeachie, Teaching Tips
An effective teacher is an excellent communicator and therefore thinks about improving his or her presentation skills. One of the most important aspects of communicating is shaping both content and style to fit your audience. In the classroom, if you cannot communicate in a way that is both comprehensible and interesting to your students, their learning will be greatly reduced.
To strengthen your presentation skills, focus on improving your skills in these three areas:
Verbal and Non-Verbal Communication
- Find out all you can about the room in which you will be presenting. Visit the room ahead of time to familiarize yourself with its size and layout, as well as the type of chalkboards, chalk, erasers, and multimedia available. In addition, obtain any necessary training on the multimedia.
- Use the classroom as a stage. Move around to engage and interact with your audience. Do not stand in one spot the entire time. Move with purpose; do not walk aimlessly.
- Prepare. Preparation is essential. All excellent teachers are well prepared for each class. Practice in the room if you can, especially if you are new to teaching. In addition, prepare yourself emotionally and psychologically by taking the time to organize your thoughts and to look forward to teaching before every class.
- Speak loudly and clearly. Project your voice and face your audience when you are speaking. Speak slightly louder than you do in a normal conversation. Use a microphone in a medium to large classroom. The class may include students with hearing problems. Moreover, a microphone will help ensure that students can hear you even when you turn to the chalkboard momentarily.
- Modulate the tone, pitch, and speed of your speech. Do not speak in a monotone. Vary the pitch and speed of your voice for emphasis and effect. Use appropriate pauses. Rather than using filler words such as “uh,” for example, simply pause before moving on to the next idea or point.
- Use gestures and facial expressions to help you explain, emphasize, and communicate the material. However, be careful not to develop distracting habits such as pacing or repeatedly adjusting your glasses or hair. To find out if you are unconsciously doing anything that may be distracting to your audience, have a colleague observe one of your classes or have your class videotaped. To schedule a videotaping and teaching consultation, call The Teaching Center at 935-6810.
- Develop a teaching persona. Decide how you want to be perceived and what mannerisms you want to have. For example, do you want to be quiet, humorous, formal, or informal? Whatever persona is right for you, aim to convey confidence and ease. Move with certainty and assuredness, and be careful not to seem pompous or intimidating.
- Show passion and enthusiasm for the topic. If you are not interested in the subject, you cannot expect your students to be interested, either. Point out the fascinating aspects of what they are learning.
- Do not read your notes or slides. Doing so will lower your energy level and lead your audience to feel less engaged.
- Interact with and pay attention to your audience. Make eye contact with the students, not with the wall or chalkboard. Build a rapport with the class. Make sure the class is with you (following and understanding what you are discussing). If they appear to be lost, take additional time to explain points and to ask and answer questions.
- Do not take yourself too seriously. Be able to laugh at yourself and your mistakes. Feel free to bring humor into the classroom, but direct it at yourself, rather than at your students’ questions and ideas.
- Keep track of the time. Do not start early or end late. The students often do not recall or listen to information presented after the class period is technically finished.
Effective Use of the Chalkboard and Visual-Aids
Using the Chalkboard
- Write legibly and big enough that your writing can seen in the back of the room.
- Think about the organization of the material on the board.
- Fill one board at a time, starting at the top of each board and writing down.
- Do not scrunch in words at the very bottom of the board or in the margins. The students in the back will not see the words at the bottom, and no one will see the words in the margins.
- Underline or mark major assumptions, conclusions, etc.
- Use color to emphasize points.Before the course starts, determine which colors are most visible in the back of the room.
- Erase a board only when you have run out of room.
- If you find a mistake on a previous board, do not erase it. Cross it out, then write the correction in, which is what the students must do.
Using Visual Aids, such as PowerPoint Slides
- Do not use visual aids unless they serve a clear and important purpose. Visuals should aid quick comprehension and support the main points.
- Book and check out the presentation equipment in advance.
- Talk to your audience and not to the screen.
- Use the visuals to enhance your presentation, not as a substitute for a verbal presentation.
- Use a pointer, if necessary.
- Coordinate the audio and the visual.
- Design your visuals with clarity and simplicity in mind.
Effective Design and Meaningful Organization of Content
Visual Design Suggestions
- Use single words or phrases.
- Organize the content visually.
- Choose a font that is easy to see. Choose a font that is simple, plain, and easy to read such as Times New Roman, Ariel, or Helvetica. Select a font size that is large enough to be seen at the back of the room. The minimal acceptable size is typically 24-point. Use both upper- and lower-case letters; all upper-case letters are difficult to read.
- Keep the design simple. Too many words, graphics, or different colors are distracting and cause students to miss the important points.
- Use short quotes, not long extracts, from documents.
- Assign a title for each visual. Doing so will help your audience organize and retain the information on each visual.
- Use summary lists.
- Limit the number of ideas on each visual. For example, limit the number of bullets on a page to approximately 4 to 6. Each bullet should be short, approximately one line. Do not crowd the visual with text; it will be too difficult to read.
- Use color for emphasis and organization. Color is useful, but needs to be used judiciously. The color should be used for emphasis or for distinguishing among data. Think about the color wheel: adjacent colors blend together and colors directly opposite each other are contrasting and provide better readability. Reds and oranges stand out, but are hard to continually focus on; therefore, use these colors only for emphasis. Greens, blues, and browns are easier to continually focus on, but do not grab a person’s attention.
- Design diagrams and tables that are simple and clear, with readily recognized symbols. Your audience must be able to read all data in your diagrams and tables. Often, this means that you will have to simplify a more complex or detailed table or diagram that has been prepared for a printed format.
- Use horizontal (landscape) layout, not vertical (portrait). Screens, video monitors, and computer monitors are shaped for a horizontal, not a vertical, format. In addition, a horizontal format is easier to project in rooms with low ceilings.
Content Organization Suggestions
- Plan the content. Think about the type of students in the class, the goals for the course and the current session, the type of material to be presented in the current session, and the type of media, if any, that you are going to use.
- Provide a structure. Each class session or presentation should have a beginning, a middle, and an end.
- List objectives or provide an outline at the beginning of each class session. Providing an outline helps students identify the most important points and follow the lecture or discussion more effectively.
- Organize course content with a theme or storyline. How do you want to arrange the material? How does each part of the material relate to what comes next.
- Remember that a typical student’s attention span is 15-20 minutes. Every 15-20 minutes, either change your teaching method or change activities. Use different teaching methods in one session to keep the students’ attention and to reach students who have different learning preferences. (See Teaching with Lectures .)
- Allow for pauses and “wait-time.” Wait-time is the pause after the instructor either asks a question or asks for questions. Students need time to think of a response to a question, or to think of a question to ask. Do not be afraid of silence. Most instructors wait 1-3 seconds for a response. However, increasing the wait-time to 5-10 seconds dramatically increases the number and quality of responses. (See Asking Questions to Improve Learning .)

Clark, Donald. “Making Presentations that Audiences Will Love.” PowerPoint Presentation. http://www.nwlink.com/~donclark/hrd/templates/presentations.ppt .
—.“Monthly Speaking Tips.” LJL Seminars. http://www.ljlseminars.com/monthtip.htm .
“Common Visual Aids.” Faculty Development Committee. Honolulu Community College. http://letsgetengaged.wikispaces.com/file/view/using_visual_aids.pdf
“Creating Visual Aids That Really Work: Designing Effective Slides Using PowerPoint.” Effective Communications Group (ECG), Inc. http://ecgcoaching.com/library/ps/powerpoint.php
Davis, Barbara Gross. “Delivering a Lecture.” Tools for Teaching. San Francisco: Jossey-Bass Publishers. 1993.
Edwards, Paul N. “How to Give an Academic Talk.” School of Information. University of Michigan. http://pne.people.si.umich.edu/PDF/howtotalk.pdf .
McKeachie, Wilbert, et al. McKeachie’s Teaching Tips: Strategies, Research, and Theory for College and University Teachers. 12th ed. Boston: Houghton Mifflin, 2005.
“Presentations.” Teaching and Learning Center. Eastern Kentucky University.
Sammons, Martha. “Students Assess Computer-Aided Classroom Presentations.” The Journal Online, May 1995. http://thejournal.com/articles/1995/05/01/students-assess-computeraided-classroom-presentations.aspx?sc_lang=en
Have suggestions?
If you have suggestions of resources we might add to these pages, please contact us:
[email protected] (314) 935-6810 Mon - Fri, 8:30 a.m. - 5:00 p.m.
Summer Boarding Courses
The Importance of Presentation Skills (and how to ace your presentation!)
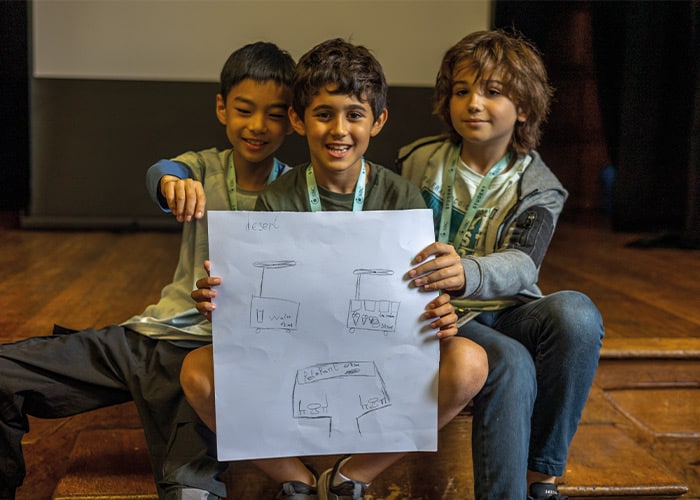

What are the importance of presentation skills? The short answer: having good presentation skills in life is really important! Knowing how to improve communication skills, whether you are in the classroom or the workplace, is something you will be thankful for when you have to share your ideas with an audience! Read on to find out how we can help.
Presentation Skills in every course
Here at Summer Boarding Courses, our academic summer school programme incorporates presentation skills into all of our courses! Have a fear of public speaking? Need to know how to make a presentation? With our public speaking tips and effective communication skills, you’ll be a pro in no time!
Our Time to Shine projects help you develop your English and prepare for future study. Welcoming our students into Time to Shine has been a big success and we can’t wait to hear your presentation too.
What is public speaking?
Public speaking is communicating information to an audience. Public speaking can happen in a classroom, in the workplace and public places. Public speaking does involve speaking aloud, but it is also about using your critical thinking, listening and non-verbal communications skills to get your message across too.
The importance of presentation skills
Effective communication skills are a valuable life skill, which will help you in your further education and in your future careers. Here are our top reasons why public speaking courses can do nothing but good to help you on your journey to success. Here’s the importance of presentation skills:
Your English speaking skills will excel
Presentations are a fantastic way to contribute to your English language learning experience. They enable you to practice all language areas (such as vocabulary, phonology and grammar) and skills (speaking, reading, writing and listening). But most of all, they build your confidence in public speaking. You can do it!
You will gain self confidence to have your say
Unsurprisingly, public speaking classes may make you feel nervous! Statistic Brain found a whopping 74% of people feel nervous speaking in front of others.
Speaking in front of a class, in a language which is not your first native level, can be difficult. Yet, do not fret; we are here to give you the practice and support you need. You can try our public speaking classes out in a safe and encouraging environment during our Time to Shine .
Learn how to present with us
You will learn to communicate better in all areas of life.
Presentation skills are an impressive and powerful tool that will take you so much further than just speaking in the classroom. With our communication skills training, you’ll become a good presenter all round, structuring and expressing your ideas clearly.
Knowing how to make a good presentation will help you in job interviews, to make new friends, to sell a product and make business deals successfully.
Your body language, hand gestures and eye contact will improve too. This helps captivate your audience. Your ability to plan and prepare materials, to convince your audience of what you have to say, will excel too!
You will be less stressed
If you have effective presentation skills, this means you are good at communicating. By speaking clearly, and getting your ideas and message across to people well, there will be less miscommunication in your life. This means less stress and happier relationships!
Your time management will improve
With only a certain amount of time to give your presentation, you will learn how to communicate your message quickly, clearly and successfully in a limited amount of time. A good presentation is easy to understand, memorable and not so long that your audience loses interest.
How to prepare for a presentation
Give the audience what they want.
Good presentation skills involve asking yourself; ‘What do my audience want to know? What will they find interesting about my topic?’ Brainstorm ideas and write them down to create a really interesting presentation.
Focus on your key message
Keep your presentation simple by focusing on 3 important points you want to communicate. Keep your message focused and stick to what you want to say. If you have information which isn’t relevant to your message, do not include it!
How to make a presentation fantastic
How can you keep your audience interested in your public speaking topics? To see how to make an effective presentation exciting and engaging, read on for our top tips for a good presentation.
Start strong
How you start your presentation is critical! An audience is going to decide if they are going to listen to you by how you begin. To engage the audience immediately, tell an interesting story, show an intriguing picture or do something entertaining. By using one of these public speaking techniques, your audience will be hooked.
Create variety
One way to master the art of public speaking is to create variety in your presentation. It will keep your audience interested! Use video. Use eye catching images. Involve your audience as much as possible! Ask them questions to keep them alert. Not talking all of the time, and using different ways to communicate your idea definitely helps.
Speak clearly
Good public speakers make a presentation even better by speaking clearly. You want your audience to hear what you are saying, so make sure you speak at a good volume. If the student at the back of the room can hear you, then your volume is great!
We understand this can be difficult when you are nervous. Try to look forward to project your voice, make eye contact with the audience and following our techniques above if you’re feeling nervous!
Emphasise words you want your audience to hear. Add suspense and intrigue by speaking more softly. Use body language as well as your voice volume to increase excitement!
Practice makes perfect here. Joining us at Summer Boarding Courses will show you how to improve your interpersonal communication skills and decrease your public speaking anxiety. Find out more about practicing your presentation skills with us during our Time to Shine projects.
Try your best to be confident
If our calming techniques do not work, it is still possible that people cannot see just how nervous you actually are! Even if you do not feel confident, acting confident helps.
Speak at a good pace
Speaking at a pace where the audience can understand you is so important when you deliver a presentation. Keeping an optimal pace provides time for the listeners to understand the content, take notes, and ask questions.
A good presenter should learn not to speak too quickly, because they need to give time for the audience to understand what is being said. At the same time, the pace should not be so slow that the presenter runs out of time to complete the presentation (and the audience becomes bored!).
Have a Plan B
If your presentation is on a computer or hard drive, make sure you have a backup! Having your notes in paper format and some images which do not rely on technology will help you if worst comes to worst!
How can you improve your presentation skills?
With our tips and advice, we hope you are feeling more confident when it comes to how to give a good presentation. Presentation skills are really important and we encourage you to join us during the Summer to take your English to the next level!
If you’d like to improve your public speaking skills and learn more about how to do a presentation at Summer Boarding Courses, get in touch today and we’ll help find the right summer school course for you!
How multimedia can improve learning and instruction
- Perspective Article
- Published on: January 16, 2019

- Cognitive science |
- Education Technology |
- Effective instruction |
- Open Access
This article is based on an extract from a chapter in Dunlosky J and Rawson K (eds) The Cambridge Handbook on Cognition and Education. New York: Cambridge University Press.
Over the past 30 years, educational and cognitive psychology have amassed encouraging evidence that human understanding can be improved substantially when we add appropriate graphics to text. In short, people learn better from words and pictures than from words alone. This article explores the potential of this multimedia principle for improving how people understand communications about academic content, as measured by their ability to take what they have learned and apply it to new situations (i.e. to solve transfer problems).
Multimedia instruction
Multimedia instruction (or a multimedia instructional message) refers to a lesson containing both words and pictures, where the words can be in spoken form or printed form and the pictures can be in static form (such as illustrations, charts, graphs or photos) or dynamic form (such as animation or video). Multimedia instruction can be presented in books, in live slideshow presentations, in e-learning on computers, or even in video games or virtual reality.
In multimedia learning, pictures do not replace words, but rather work together with words to form an instructional message that results in deeper understanding. For example, consider a verbal description of how a bicycle pump works. After students listen to an explanation, they are not able to generate many useful answers to transfer questions such as the troubleshooting question, ‘Suppose you push down and pull up several times but no air comes out. What could have gone wrong?’ (Mayer and Anderson, 1991) . However, if we add a simple animation depicting the movement of the handle, piston and valves in a pump, in sync with the narration, students are able to generate more than twice as many useful answers.
How the multimedia principle works
The cognitive theory of multimedia learning is based on three key ideas from cognitive science:
- Dual-channel principle: The human information processing system contains separate channels for verbal and pictorial information (Baddeley , 1992)
- Limited capacity principle: Only a few items can be processed in a channel at any one time (Baddeley, 1992)
- Active processing principle: Meaningful learning requires appropriate cognitive processing during learning, including attending to relevant information, mentally organising it into a coherent structure, and integrating it with relevant prior knowledge (Mayer , 2009) .
Overall, in multimedia instruction, meaningful learning occurs when the learner selects relevant words and images from the multimedia message for further processing in working memory, mentally organises the words into a coherent structure (or verbal model) and the images into a coherent structure (or pictorial model), and integrates the verbal and pictorial representations with each other and with relevant prior knowledge activated from long-term memory. The main challenge in teaching is to guide learners to engage in these processes, while not overloading their limited processing capacity in each channel of working memory. Designing effective multimedia instruction requires not only presenting the relevant material, but also guiding the learner’s cognitive processing of the material.
Implications of the multimedia principle for the classroom

Extraneous processing
The first 5 principles address the goal of reducing extraneous processing — cognitive processing during learning that does not support the instructional goal. Working memory capacity is limited, so if a learner allocates too much cognitive processing capacity to extraneous processing, there will not be enough cognitive capacity left to fully engage in essential processing (i.e. cognitive processing aimed at mentally representing the essential information in working memory) and generative processing (i.e. cognitive processing aimed at reorganising the material and integrating it with relevant knowledge activated from long-term memory).
The coherence principle is that people learn better when extraneous material is excluded rather than included (Mayer, 2009); (Mayer and Fiorella , 2014) . Extraneous material includes unneeded detail in graphics, background music, or interesting but irrelevant facts in the text. More learning occurs when the instructional message is kept as simple as possible.
The signaling principle is that people learn better when essential material is highlighted (van Gog, 2014) . Highlighting of printed text can involve the use of color, underlining, bold, italics, font size, font style or repetition. Highlighting of spoken text can involve speaking louder or with more emphasis. Highlighting of graphics includes the use of arrows, color, flashing and spotlights.
The spatial contiguity principle is that people learn better when printed words are placed near to, rather than far from, corresponding graphics (Ayres and Sweller , 2014) . Johnson and Mayer (Johnson and Mayer , 2012) reported that students performed substantially better on transfer tests when they received integrated presentations (the words placed near the part of the graphic they describe) rather than separated presentations (the words presented as a caption at the bottom of the page or screen), even though the words and graphics were identical.
The temporal contiguity principle is that people learn better from a narrated lesson when the spoken words are presented simultaneously with the corresponding graphics (such as drawings, animation or video), rather than ‘successive presentation’, when the spoken words are presented before (or after) the graphics (Ginns , 2006) .
The redundancy principle is that people learn better from narration and graphics than from narration, graphics and redundant text (Adesope and Nesbit , 2012) .
Essential processing
The next 3 principles in Table 1 are aimed at managing essential processing (i.e. cognitive processing for mentally representing the essential material in working memory). When the material is complex for the learner, the amount of essential processing required to mentally represent the material may overload working memory capacity. In this case, the learner needs to be able to manage his or her processing capacity in a way that allows for representing the essential material.
The segmenting principle calls for breaking a multimedia lesson into manageable parts (Mayer and Pilegard , 2014) . For example, rather than presenting a 2.5-minute narrated animation on lightning formation as a continuous presentation, break it into short segments and allow the learner to click to go to the next segment, enabling them to digest one step in the process of lightning formation before going on to the next one.
The pretraining principle calls for teaching students about the names and characteristics of key elements before presenting the multimedia lesson (Mayer and Pilegard, 2014). For example, before presenting a narrated animation depicting how a car’s braking system works, students can be presented with a diagram of the braking system showing the key parts, e.g. brake pedal, piston, wheel cylinders and brake shoes.
The modality principle is that people learn better from multimedia presentations when the words are spoken rather than printed (Low and Sweller , 2014) , so the visual channel does not become overloaded by having to process both graphics and printed words.
Generative processing
The final 3 principles in Table 1 are intended to foster generative processing, that is, cognitive processing aimed at making sense of the presented material. Even if cognitive capacity is available, learners may not be motivated to use it to process the material deeply. Social cues can help motivate learners to engage in deeper processing because people tend to want to understand what a communication partner is telling them. Thus, principles based on social cues are intended to make learners feel as if they are in a conversation with the teacher, that is, they feel that the teacher is a social partner. This approach yields the newest of the multimedia design principles, including using conversational language (personalisation principle), using an appealing human voice (voice principle), and using human-like gestures (embodiment principle).
The personalisation principle is that people learn better from a multimedia lesson when the words are in conversation style rather than formal style (Ginns et al., 2013) . For example, the words from a lesson on how the human respiratory system works could be presented in third person form (e.g. ‘the lungs’) or in first and second person form (e.g. ‘your lungs’).
The voice principle is that people learn better from multimedia lessons involving spoken words when the narrator has an appealing human voice rather than a machine voice or unappealing voice (Mayer, 2014) . An important boundary condition is that the positive impact of human voice can be overturned by the use of negative social cues such as presenting an onscreen agent that does not engage in humanlike gesturing (Mayer and DaPra , 2012) .
The embodiment principle is that people learn better from multimedia lessons in which an onscreen agent or instructor uses humanlike gesture (Mayer, 2014). For example, Mayer and DaPra (2012) presented students with a narrated slideshow lesson in which an onscreen animated pedagogical agent stood next to the slide and either displayed humanlike gestures or did not move during the lesson. Students learned better when the onscreen agent used humanlike gestures.
Boundary conditions
Each of the 11 evidence-based principles has important boundary conditions, largely consistent with the cognitive theory of multimedia learning. Some principles may apply more or less strongly, or have weaker or stronger effects, depending on, for example, working memory capacity, level of prior knowledge and complexity of the material being presented.

Multimedia learning principles in practice
What happens when we combine these principles within the context of an actual classroom? Issa et al. (Issa et al., 2013) compared how beginning medical students learned from a standard slideshow lesson or from a lesson in which the slides were modified based on multimedia design principles such as in Table 1. On a transfer test administered 4 weeks later, students in the modified group outperformed those in the standard group with an effect size of d = 1.17, even though the content was the same. This study, and similar ones (Harskamp et al., 2007) ; (Issa et al., 2011) , suggest that applying multimedia principles to the design of classroom instruction can greatly increase student learning.
- Adesope O and Nesbit J (2012) Verbal redundancy in multimedia learning environments: A meta-analysis. Journal of Educational Psychology (104): 250–263.
- Ayres P and Sweller J (2014) The split attention principle in multimedia learning. In: Mayer R (ed.) The Cambridge Handbook of Multimedia Learning . 2nd ed. New York: Cambridge University Press, pp. 206–226.
- Baddeley A (1992) Working memory. Science (255): 556–559.
- Ginns P (2006) Integrating information: A meta-analysis of spatial contiguity and temporal contiguity effects. Learning and Instruction (16): 511–525.
- Ginns P, Marin A and Marsh H (2013) Designing instructional text for conversational style: A meta-analysis. Educational Psychology Review (25): 445–472.
- Harskamp E, Mayer R and Suhre C (2007) Does the modality principle for multimedia learning apply to science classrooms? . Learning and Instruction (17): 465–477.
- Hattie J (2009) Visible Learning. New York: Routledge.
- Issa N, Schuller M, Santacaterina S, et al. (2011) Applying multimedia design principles enhances learning in medical education. Medical Education (45): 818–826.
- Issa N, Mayer R, Schuller M, et al. (2013) Teaching for understanding in medical classrooms using multimedia design principles. Medical Education (47): 388–396.
- Johnson C and Mayer R (2012) An eye movement analysis of the spatial contiguity effect in multimedia learning. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Applied (18): 178–191.
- Low R and Sweller J (2014) The modality principle in multimedia learning. In: Mayer R (ed.) The Cambridge Handbook of Multimedia Learning. 2nd ed. New York: Cambridge University Press, pp. 227–246.
- Mayer R (2009) Multimedia Learning. 2nd ed. New York: Cambridge University Press.
- Mayer R and DaPra C (2012) An embodiment effect in computer-based learning with animated pedagogical agent. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Applied (18): 239–252.
- Mayer R and Fiorella L (2014) Principles for reducing extraneous processing in multimedia learning: Coherence, signaling, redundancy, spatial contiguity, and temporal contiguity. In: Mayer R (ed.) The Cambridge Handbook of Multimedia Learning . 2nd ed. New York: Cambridge University Press, pp. 345–368.
- Mayer R and Pilegard C (2014) Principles for managing essential processing in multimedia learning: Segmenting, pretraining, and modality principles. In: Mayer R (ed.) The Cambridge Handbook of Multimedia Learning. 2nd ed. New York: Cambridge University Press, pp. 379–315.
- Mayer R (2014) Principles based on social cues in multimedia learning: Personalization, voice, image, and embodiment principles. In: Mayer R (ed.) The Cambridge Handbook of Multimedia Learning. 2nd ed. New York: Cambridge University Press, pp. 345–368.
- Mayer R and Anderson R (1991) Animations need narrations: An experimental test of a dual-coding hypothesis. Journal of Educational Psychology (83): 484–490.
- van Gog T (2014) The signaling (or cueing) principle in multimedia learning. In: Mayer R (ed.) The Cambridge Handbook of Multimedia Learning . 2nd ed. New York: Cambridge University Press, pp. 263–278.
From this issue

2019 Special Issue: Education Technology
January 2019
Impact Articles on the same themes

From the editor

Transforming assessment principles and practices through collaboration: A case study from a primary school and university

The currency of assessment for learners with SEND

Rethinking assessment: How learner profiles can shift the debate towards equitable and meaningful holistic assessment

Assessing progress in special schools: Reviews and recommendations

- Original Research
Classroom assessment in flux: Unpicking empirical evidence of assessment practices

The role of frequent assessment in science education at an international school in Singapore
- Teacher Reflection
Teaching creativity: An international perspective on studying art in the UK

Improving academic resilience and self-efficacy through feedback: Moving from ‘what’ to ‘how’

Mind the gap: What are national assessments really telling us about vocabulary and disadvantaged students?
Pears Pavillion Corum Campus 41 Brunswick Square London WC1N 1AZ
[email protected] 020 3433 7624
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Beginner Guides How To Make a Good Presentation [A Complete Guide]
How To Make a Good Presentation [A Complete Guide]
Written by: Krystle Wong Jul 20, 2023

A top-notch presentation possesses the power to drive action. From winning stakeholders over and conveying a powerful message to securing funding — your secret weapon lies within the realm of creating an effective presentation .
Being an excellent presenter isn’t confined to the boardroom. Whether you’re delivering a presentation at work, pursuing an academic career, involved in a non-profit organization or even a student, nailing the presentation game is a game-changer.
In this article, I’ll cover the top qualities of compelling presentations and walk you through a step-by-step guide on how to give a good presentation. Here’s a little tip to kick things off: for a headstart, check out Venngage’s collection of free presentation templates . They are fully customizable, and the best part is you don’t need professional design skills to make them shine!
These valuable presentation tips cater to individuals from diverse professional backgrounds, encompassing business professionals, sales and marketing teams, educators, trainers, students, researchers, non-profit organizations, public speakers and presenters.
No matter your field or role, these tips for presenting will equip you with the skills to deliver effective presentations that leave a lasting impression on any audience.
Click to jump ahead:
What are the 10 qualities of a good presentation?
Step-by-step guide on how to prepare an effective presentation, 9 effective techniques to deliver a memorable presentation, faqs on making a good presentation, how to create a presentation with venngage in 5 steps.
When it comes to giving an engaging presentation that leaves a lasting impression, it’s not just about the content — it’s also about how you deliver it. Wondering what makes a good presentation? Well, the best presentations I’ve seen consistently exhibit these 10 qualities:
1. Clear structure
No one likes to get lost in a maze of information. Organize your thoughts into a logical flow, complete with an introduction, main points and a solid conclusion. A structured presentation helps your audience follow along effortlessly, leaving them with a sense of satisfaction at the end.
Regardless of your presentation style , a quality presentation starts with a clear roadmap. Browse through Venngage’s template library and select a presentation template that aligns with your content and presentation goals. Here’s a good presentation example template with a logical layout that includes sections for the introduction, main points, supporting information and a conclusion:

2. Engaging opening
Hook your audience right from the start with an attention-grabbing statement, a fascinating question or maybe even a captivating anecdote. Set the stage for a killer presentation!
The opening moments of your presentation hold immense power – check out these 15 ways to start a presentation to set the stage and captivate your audience.
3. Relevant content
Make sure your content aligns with their interests and needs. Your audience is there for a reason, and that’s to get valuable insights. Avoid fluff and get straight to the point, your audience will be genuinely excited.
4. Effective visual aids
Picture this: a slide with walls of text and tiny charts, yawn! Visual aids should be just that—aiding your presentation. Opt for clear and visually appealing slides, engaging images and informative charts that add value and help reinforce your message.
With Venngage, visualizing data takes no effort at all. You can import data from CSV or Google Sheets seamlessly and create stunning charts, graphs and icon stories effortlessly to showcase your data in a captivating and impactful way.

5. Clear and concise communication
Keep your language simple, and avoid jargon or complicated terms. Communicate your ideas clearly, so your audience can easily grasp and retain the information being conveyed. This can prevent confusion and enhance the overall effectiveness of the message.
6. Engaging delivery
Spice up your presentation with a sprinkle of enthusiasm! Maintain eye contact, use expressive gestures and vary your tone of voice to keep your audience glued to the edge of their seats. A touch of charisma goes a long way!
7. Interaction and audience engagement
Turn your presentation into an interactive experience — encourage questions, foster discussions and maybe even throw in a fun activity. Engaged audiences are more likely to remember and embrace your message.
Transform your slides into an interactive presentation with Venngage’s dynamic features like pop-ups, clickable icons and animated elements. Engage your audience with interactive content that lets them explore and interact with your presentation for a truly immersive experience.

8. Effective storytelling
Who doesn’t love a good story? Weaving relevant anecdotes, case studies or even a personal story into your presentation can captivate your audience and create a lasting impact. Stories build connections and make your message memorable.
A great presentation background is also essential as it sets the tone, creates visual interest and reinforces your message. Enhance the overall aesthetics of your presentation with these 15 presentation background examples and captivate your audience’s attention.
9. Well-timed pacing
Pace your presentation thoughtfully with well-designed presentation slides, neither rushing through nor dragging it out. Respect your audience’s time and ensure you cover all the essential points without losing their interest.
10. Strong conclusion
Last impressions linger! Summarize your main points and leave your audience with a clear takeaway. End your presentation with a bang , a call to action or an inspiring thought that resonates long after the conclusion.
In-person presentations aside, acing a virtual presentation is of paramount importance in today’s digital world. Check out this guide to learn how you can adapt your in-person presentations into virtual presentations .
Preparing an effective presentation starts with laying a strong foundation that goes beyond just creating slides and notes. One of the quickest and best ways to make a presentation would be with the help of a good presentation software .
Otherwise, let me walk you to how to prepare for a presentation step by step and unlock the secrets of crafting a professional presentation that sets you apart.
1. Understand the audience and their needs
Before you dive into preparing your masterpiece, take a moment to get to know your target audience. Tailor your presentation to meet their needs and expectations , and you’ll have them hooked from the start!
2. Conduct thorough research on the topic
Time to hit the books (or the internet)! Don’t skimp on the research with your presentation materials — dive deep into the subject matter and gather valuable insights . The more you know, the more confident you’ll feel in delivering your presentation.
3. Organize the content with a clear structure
No one wants to stumble through a chaotic mess of information. Outline your presentation with a clear and logical flow. Start with a captivating introduction, follow up with main points that build on each other and wrap it up with a powerful conclusion that leaves a lasting impression.
Delivering an effective business presentation hinges on captivating your audience, and Venngage’s professionally designed business presentation templates are tailor-made for this purpose. With thoughtfully structured layouts, these templates enhance your message’s clarity and coherence, ensuring a memorable and engaging experience for your audience members.
Don’t want to build your presentation layout from scratch? pick from these 5 foolproof presentation layout ideas that won’t go wrong.

4. Develop visually appealing and supportive visual aids
Spice up your presentation with eye-catching visuals! Create slides that complement your message, not overshadow it. Remember, a picture is worth a thousand words, but that doesn’t mean you need to overload your slides with text.
Well-chosen designs create a cohesive and professional look, capturing your audience’s attention and enhancing the overall effectiveness of your message. Here’s a list of carefully curated PowerPoint presentation templates and great background graphics that will significantly influence the visual appeal and engagement of your presentation.
5. Practice, practice and practice
Practice makes perfect — rehearse your presentation and arrive early to your presentation to help overcome stage fright. Familiarity with your material will boost your presentation skills and help you handle curveballs with ease.
6. Seek feedback and make necessary adjustments
Don’t be afraid to ask for help and seek feedback from friends and colleagues. Constructive criticism can help you identify blind spots and fine-tune your presentation to perfection.
With Venngage’s real-time collaboration feature , receiving feedback and editing your presentation is a seamless process. Group members can access and work on the presentation simultaneously and edit content side by side in real-time. Changes will be reflected immediately to the entire team, promoting seamless teamwork.
7. Prepare for potential technical or logistical issues
Prepare for the unexpected by checking your equipment, internet connection and any other potential hiccups. If you’re worried that you’ll miss out on any important points, you could always have note cards prepared. Remember to remain focused and rehearse potential answers to anticipated questions.
8. Fine-tune and polish your presentation
As the big day approaches, give your presentation one last shine. Review your talking points, practice how to present a presentation and make any final tweaks. Deep breaths — you’re on the brink of delivering a successful presentation!
In competitive environments, persuasive presentations set individuals and organizations apart. To brush up on your presentation skills, read these guides on how to make a persuasive presentation and tips to presenting effectively .

Whether you’re an experienced presenter or a novice, the right techniques will let your presentation skills soar to new heights!
From public speaking hacks to interactive elements and storytelling prowess, these 9 effective presentation techniques will empower you to leave a lasting impression on your audience and make your presentations unforgettable.
1. Confidence and positive body language
Positive body language instantly captivates your audience, making them believe in your message as much as you do. Strengthen your stage presence and own that stage like it’s your second home! Stand tall, shoulders back and exude confidence.
2. Eye contact with the audience
Break down that invisible barrier and connect with your audience through their eyes. Maintaining eye contact when giving a presentation builds trust and shows that you’re present and engaged with them.
3. Effective use of hand gestures and movement
A little movement goes a long way! Emphasize key points with purposeful gestures and don’t be afraid to walk around the stage. Your energy will be contagious!
4. Utilize storytelling techniques
Weave the magic of storytelling into your presentation. Share relatable anecdotes, inspiring success stories or even personal experiences that tug at the heartstrings of your audience. Adjust your pitch, pace and volume to match the emotions and intensity of the story. Varying your speaking voice adds depth and enhances your stage presence.

5. Incorporate multimedia elements
Spice up your presentation with a dash of visual pizzazz! Use slides, images and video clips to add depth and clarity to your message. Just remember, less is more—don’t overwhelm them with information overload.
Turn your presentations into an interactive party! Involve your audience with questions, polls or group activities. When they actively participate, they become invested in your presentation’s success. Bring your design to life with animated elements. Venngage allows you to apply animations to icons, images and text to create dynamic and engaging visual content.
6. Utilize humor strategically
Laughter is the best medicine—and a fantastic presentation enhancer! A well-placed joke or lighthearted moment can break the ice and create a warm atmosphere , making your audience more receptive to your message.
7. Practice active listening and respond to feedback
Be attentive to your audience’s reactions and feedback. If they have questions or concerns, address them with genuine interest and respect. Your responsiveness builds rapport and shows that you genuinely care about their experience.

8. Apply the 10-20-30 rule
Apply the 10-20-30 presentation rule and keep it short, sweet and impactful! Stick to ten slides, deliver your presentation within 20 minutes and use a 30-point font to ensure clarity and focus. Less is more, and your audience will thank you for it!
9. Implement the 5-5-5 rule
Simplicity is key. Limit each slide to five bullet points, with only five words per bullet point and allow each slide to remain visible for about five seconds. This rule keeps your presentation concise and prevents information overload.
Simple presentations are more engaging because they are easier to follow. Summarize your presentations and keep them simple with Venngage’s gallery of simple presentation templates and ensure that your message is delivered effectively across your audience.

1. How to start a presentation?
To kick off your presentation effectively, begin with an attention-grabbing statement or a powerful quote. Introduce yourself, establish credibility and clearly state the purpose and relevance of your presentation.
2. How to end a presentation?
For a strong conclusion, summarize your talking points and key takeaways. End with a compelling call to action or a thought-provoking question and remember to thank your audience and invite any final questions or interactions.
3. How to make a presentation interactive?
To make your presentation interactive, encourage questions and discussion throughout your talk. Utilize multimedia elements like videos or images and consider including polls, quizzes or group activities to actively involve your audience.
In need of inspiration for your next presentation? I’ve got your back! Pick from these 120+ presentation ideas, topics and examples to get started.
Creating a stunning presentation with Venngage is a breeze with our user-friendly drag-and-drop editor and professionally designed templates for all your communication needs.
Here’s how to make a presentation in just 5 simple steps with the help of Venngage:
Step 1: Sign up for Venngage for free using your email, Gmail or Facebook account or simply log in to access your account.
Step 2: Pick a design from our selection of free presentation templates (they’re all created by our expert in-house designers).
Step 3: Make the template your own by customizing it to fit your content and branding. With Venngage’s intuitive drag-and-drop editor, you can easily modify text, change colors and adjust the layout to create a unique and eye-catching design.
Step 4: Elevate your presentation by incorporating captivating visuals. You can upload your images or choose from Venngage’s vast library of high-quality photos, icons and illustrations.
Step 5: Upgrade to a premium or business account to export your presentation in PDF and print it for in-person presentations or share it digitally for free!
By following these five simple steps, you’ll have a professionally designed and visually engaging presentation ready in no time. With Venngage’s user-friendly platform, your presentation is sure to make a lasting impression. So, let your creativity flow and get ready to shine in your next presentation!
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker

14 Practical Tips to Improve Your Presentation Skills
- The Speaker Lab
- May 11, 2024
Table of Contents
Ever felt complete dread and fear at the thought of stepping up to deliver a presentation? If so, you’re not alone. The fear of public speaking is more common than you might think, but with the right presentation skills , it’s a hurdle that can be overcome.
In this article, we’ll help you master basic confidence-building techniques and conquer advanced communication strategies for engaging presentations. We’ll explore how body language and eye contact can make or break your connection with your audience; delve into preparation techniques like dealing with filler words and nervous habits; discuss tailoring content for different audiences; and much more.
Whether you’re prepping for job interviews or gearing up for big presentations, being prepared is key. With adequate practice and the proper attitude, you can crush your speech or presentation!
Mastering the Basics of Presentation Skills
Presentation skills are not just about speaking in front of a crowd. It’s also about effective communication, audience engagement, and clarity. Mastering these skills can be transformative for everyone, from students to corporate trainers.
Building Confidence in Presentations
Becoming confident when presenting is no small feat. But fear not. Even those who feel jittery at the mere thought of public speaking can become masters with practice and patience. Just remember: stage fright is common and overcoming it is part of the process towards becoming an effective presenter.
Taking deep breaths before you start helps calm nerves while visualizing success aids in building confidence. Also, know that nobody minds if you take a moment to gather your thoughts during your presentation—everybody minds more if they cannot understand what you’re saying because you’re rushing.
The Role of Practice in Enhancing Presentation Skills
In line with old wisdom, practice indeed makes perfect, especially when improving presentation skills. Consistent rehearsals allow us to fine-tune our delivery methods like maintaining eye contact or controlling body language effectively.
You’ll learn better control over filler words through repeated drills. Plus, the extra practice can help you troubleshoot any technical glitches beforehand, saving you the sudden panic during your actual presentations.
Remember that great presenters were once beginners too. Continuous effort will get you there sooner rather than later.
Find Out Exactly How Much You Could Make As a Paid Speaker
Use The Official Speaker Fee Calculator to tell you what you should charge for your first (or next) speaking gig — virtual or in-person!
Body Language and Eye Contact in Presentations
The effectiveness of your presentation can hinge on more than just the words you say. Just as important is your body language .
Impact of Posture on Presentations
Your posture speaks volumes before you utter a word. Standing tall exudes confidence while slouching could signal nervousness or lack of preparation.
If there’s one lesson to take away from our YouTube channel , it’s this: good presenters know their message but great ones feel it through every fiber (or muscle) of their being. The audience can sense that energy when they see open body language rather than crossed arms.
Maintaining Eye Contact During Your Presentation
Eyes are often called windows to the soul for a reason. They’re communication powerhouses. Making eye contact helps build trust with your audience members and keeps them engaged throughout your speech.
Avoid staring at note cards or visual aids too much as this might give an impression that you’re unprepared or uncertain about your chosen topic. Instead, aim to maintain eye contact between 50% of the time during presentations. This commonly accepted “50/70 rule” will help you exhibit adequate confidence to your audience.
If stage fright has gotten a hold on you, take deep breaths before you start speaking in order to stay calm. Make sure that fear doesn’t disrupt your ability to maintain eye-contact during presentations.
If body language and eye contact still feel like a lot to manage during your big presentation, remember our golden rule: nobody minds small mistakes. It’s how you handle questions or mishaps that truly makes a difference—so stay positive and enthusiastic.
Preparation Techniques for Successful Presentations
Presentation skills are like a craft that requires meticulous preparation and practice. Aspects like visual aids and time management contribute to the overall effectiveness of your delivery.
The first step towards delivering an impactful presentation is research and organization. The content should be well-researched, structured logically, and presented in simple language. This will make sure you deliver clear messages without any room for misinterpretation.
Dealing with Filler Words and Nervous Habits
Nervous habits such as excessive use of filler words can distract from your message. Luckily, there are plenty of strategies that can address these issues. For instance, try taking deep breaths before speaking or using note cards until fluency is achieved. In addition, practice regularly to work on eliminating these verbal stumbling blocks.
Avoiding Distractions During Presentations
In a digital age where distractions abound, maintaining focus during presentations has become an even more crucial part of the preparation process. This video by motivational speaker Brain Tracy provides insights on how one could achieve this level of focus required for effective presentations.
Maintaining Confidence Throughout Your Presentation
Confidence comes from thorough understanding of the chosen topic combined with regular practice sessions before the big day arrives. Make use of note cards or cue cards as needed but avoid reading from them verbatim.
Taking control over stage fright starts by arriving early at the venue so that you familiarize yourself with the surroundings, which generally calms nerves down considerably. So next time you feel nervous before a big presentation, remember—thorough preparation can make all the difference.
Engaging Your Audience During Presentations
Connecting with your audience during presentations is an art, and mastering it can take your presentation skills to the next level. Making the message conveyed reach an emotional level is essential, not just conveying facts.
Understanding Your Target Audience
The first step towards engaging your audience is understanding them. Tailor the content of your presentation to their needs and interests. Speak in their language—whether that be professional jargon or everyday slang—to establish rapport and ensure comprehension.
An effective presenter understands who they’re speaking to, what those individuals care about, and how best to communicate complex ideas understandably.
Making Complex Information Understandable
Dense data or complicated concepts can lose even the most interested listener if presented ineffectively. Breaking your key points down into manageable chunks helps maintain attention while promoting retention. Analogies are especially useful for this purpose as they make unfamiliar topics more relatable.
Audience Participation & Questions: A Two-Way Street
Incorporating opportunities for audience participation encourages engagement at another level. It allows listeners to become active participants rather than passive receivers of knowledge.
Consider techniques like live polls or interactive Q&A sessions where you invite questions from attendees mid-presentation instead of saving all queries until the end.
This gives you a chance not only engage but also address any misunderstandings right on spot.
- Treat each question asked as an opportunity—it’s evidence someone has been paying attention. Even challenging questions should be welcomed as they demonstrate an engaged, thoughtful audience.
- Encourage participation. It can be as simple as a show of hands or the use of interactive technologies for live polling during your presentation. This keeps your audience active and invested in the content.
Remember, your presentation isn’t just about putting on a show—it’s about meaningful interaction.
Free Download: 6 Proven Steps to Book More Paid Speaking Gigs in 2024
Download our 18-page guide and start booking more paid speaking gigs today!
Presentation Skills in Specific Contexts
Whether you’re nailing your next job interview, presenting an exciting marketing campaign, or delivering insightful educational content, the context matters. Let’s take a look.
The Art of Job Interviews
A successful job interview often hinges on effective communication and confidence. Here, the target audience is usually small but holds significant influence over your future prospects. Body language plays a crucial role; maintain eye contact to show sincerity and interest while open body language communicates approachability.
Bullet points summarizing key experiences are also helpful for quick recall under pressure. This allows you to present your chosen topic with clarity and positive enthusiasm without relying heavily on note or cue cards.
Pitching in Public Relations & Marketing
In public relations (PR) and marketing contexts, presentations need to capture attention quickly yet hold it long enough to deliver key messages effectively. Visual aids are valuable tools here—they help emphasize points while keeping the audience engaged.
Your aim should be highlighting presentation benefits that resonate with potential clients or partners, making them feel as though ignoring such opportunities would mean missing out big time.
Educational Presentations
An educational setting demands its own unique set of presentation skills where deep understanding trumps flashy visuals. You must make complex information understandable without oversimplifying essential details—the use of analogies can be beneficial here.
Keeping the audience’s attention is critical. Encourage questions and participation to foster a more interactive environment, enhancing learning outcomes for all audience members.
Tips for Becoming a Great Presenter
No single method is suitable for everyone when it comes to speaking in public. However, incorporating continuous improvement and practice into your routine can make you an exceptional presenter.
Tailor Your Presentation to Your Audience
Becoming an excellent speaker isn’t just about delivering information; it’s also about making a connection with the audience. So make sure that you’re taking setting, audience, and topic into consideration when crafting your presentation. What works for one audience may not work for another, so be sure to adapt your presentation styles according to the occasion in order to be truly effective.
The Power of Practice
The art of mastering public speaking skills requires practice —and lots of it . To become a great presenter, focus on improving communication skills through practice and feedback from peers or mentors. Try to seek feedback on every speech delivered and incorporate those pointers in your future presentations. Over time, this cycle of delivery-feedback-improvement significantly enhances your ability to connect with audiences and convey ideas effectively.
If you’re looking for examples of good speakers, our speech breakdowns on YouTube provide excellent examples of experienced presenters who masterfully utilize speaking techniques. Analyzing their strategies could give you great ideas for enhancing your own style.
Finding Your Style
A crucial part of captivating any audience lies in how you deliver the message rather than the message itself. Developing a unique presentation style lets you stand out as an engaging speaker who commands attention throughout their talk. Through — you guessed it — practice, you can develop a personal presentation style that resonates with listeners while showcasing your expertise on the chosen topic.
Your body language plays a pivotal role here: open gestures communicate confidence and enthusiasm towards your subject matter, two qualities essential for keeping audiences hooked. Similarly, using vocal variety adds dynamism to speeches by emphasizing points when needed or creating suspense during storytelling parts of your talk.
Cultivating Passion & Enthusiasm
Showcasing genuine passion for the subject helps keep listeners engaged throughout even lengthy presentations. Sharing stories related to the topic or expressing excitement about sharing knowledge tends to draw people in more than mere data recitation ever could.
Recognize that everybody is distinctive; don’t expect identical results from every speaker. The path to becoming a great presenter involves recognizing your strengths and working tirelessly on areas that need improvement.
FAQs on Presentation Skills
What are good presentation skills.
Good presentation skills include a clear message, confident delivery, engaging body language, audience understanding, and interaction. They also involve effective preparation and practice.
What are the 5 steps of presentation skills?
The five steps of presenting include: planning your content, preparing visual aids if needed, practicing the delivery aloud, performing it with confidence, and finally post-presentation reflection for improvements.
What are the 5 P’s of presentation skills?
The five P’s stand for Preparation (researching your topic), Practice (rehearsing your talk), Performance (delivering with confidence), Posture (standing tall), and Projection (using a strong voice).
What are your presentation skills?
Your personal set of abilities to deliver information effectively is what we call your presentation skill. It can encompass public speaking ability, clarity in speech or writing as well as visual communication talent.
Mastering presentation skills isn’t an overnight process, but practice and perseverance will put you well on your way to becoming an effective speaker.
You’ve learned that confidence plays a crucial role in effective presentations, so take deep breaths, make eye contact, and keep your body language open. As always, preparation is key. Tackle filler words head-on and get comfortable with visual aids for impactful storytelling.
Remember the importance of audience engagement — it’s all about understanding their needs and tailoring your content accordingly. This way, complex information turns into digestible insights.
Above all else: practice! After all, nothing beats experience when it comes to improving public speaking abilities.
- Last Updated: May 9, 2024

Explore Related Resources
Learn How You Could Get Your First (Or Next) Paid Speaking Gig In 90 Days or Less
We receive thousands of applications every day, but we only work with the top 5% of speakers .
Book a call with our team to get started — you’ll learn why the vast majority of our students get a paid speaking gig within 90 days of finishing our program .
If you’re ready to control your schedule, grow your income, and make an impact in the world – it’s time to take the first step. Book a FREE consulting call and let’s get you Booked and Paid to Speak ® .
About The Speaker Lab
We teach speakers how to consistently get booked and paid to speak. Since 2015, we’ve helped thousands of speakers find clarity, confidence, and a clear path to make an impact.
Get Started
Let's connect.
Copyright ©2023 The Speaker Lab. All rights reserved.
Number of items in cart: 0
- Your cart is empty.
- Total: $0.00
What Are the Key Benefits of Using PowerPoint in Teaching and Learning?

Table of Contents
The Importance of PowerPoint Presentation in Teaching
An education-based PowerPoint presentation templates have become an integral part of teaching in today’s classrooms. They provide educators with a versatile tool for delivering engaging and interactive lessons. PPT presentations also offer numerous benefits for students, including the ability to improve concentration and comprehension levels.
Additionally, by using PowerPoint slides in conjunction with other instructional materials, such as textbooks and handouts, teachers can ensure that all students are able to access the information being presented in class. PowerPoint presentations can be a powerful tool for teaching and learning when used effectively.
The main reason behind this is that PowerPoint presentations enable you to interact with your audience psychologically. So, here we’re going to discuss the power of PowerPoint in education.
In most cases, presentations are designed for businesses and applied very commonly in business areas. Moreover, presentation slides are likewise used in the education sector and can make your educational or research content compelling.
Let’s get started. Scroll now to read the key benefits of using PowerPoint in teaching and learning .
Why PowerPoint Templates Are the Best Tool for Teaching?

PowerPoint templates are an excellent tool for teaching. They provide a consistent and professional look to your presentations and help keep your ideas organized. Presentation templates also make updating and changing your slides easy, so you can always keep your presentations fresh and up-to-date.
When teaching a subject like biology, getting your audience interested in what you have to say is essential. PowerPoint templates can help you set the tone for your presentation and reinforce the type of content you will discuss. There are various templates out there, so you can find one that will let you teach your subject efficiently and keep things neat and organized.
In addition, PPT slides can be easily shared with other teachers so that you can collaborate on projects and assignments. Overall, PowerPoint templates are a versatile and valuable tool for any teacher. With their help, you can create engaging and informative presentations to help your students learn and succeed.
How PowerPoint Templates Let You Engage Your Students or Audience?

At present, it’s more important than ever to be able to engage your audience. Whether you’re giving a PPT presentation to a group of students or speaking to a potential client, you need to be able to capture their attention and keep them engaged.
One way to do this is by using PowerPoint templates. With templates, you can create visually appealing and informative presentations. By using engaging visuals and helpful content, you can ensure that your audience stays interested in what you’re saying.
In addition, templates can help you save time when creating presentations. All you need to do with everything already laid out for you is add your content. Accordingly, templates can help you create professional and effective presentations.
Although presentation skills are essential for everyone, they are particularly important for educators. After all, a large part of a teacher’s job is to present information to students engagingly and effectively. Fortunately, there are some simple tips that can help to improve any presentation.
- First, it is important to be well prepared. This means clearly understanding the material that will be covered and knowing how to effectively communicate it to the audience.
- It is also significant to be aware of the audience’s level of knowledge and adjust the presentation accordingly.
- Finally, it is significant to be confident and keep the presentation interesting using various techniques such as humor, stories, or multimedia elements.
By following these tips, any teacher can deliver a successful presentation.
How to Create an Educational Presentation Quickly?

PowerPoint templates are a great way to teach your students detailed data. For your lessons to be practical, you need your students to focus and pay attention, so having templates allows them the tools they need to learn more effectively.
It’s a wise way of helping children in school hone their PowerPoint skills. Many children feel overwhelmed when they have to start creating presentations from scratch-templates give them a structure they can follow and tweak to make their own.
Additionally, templates can be reused multiple times, which saves you time in the long run. With so many benefits, it’s no wonder that PowerPoint templates are becoming increasingly popular in educational settings.
If you’re finding a way to help, your students learn more effectively, consider using PowerPoint templates in your next lesson.
However, you can create an informative and engaging presentation with some preparation and organization. Here are a few tips to help you get started:
- Choose a subject that is interesting and relevant to your audience.
- Gather information and resources on the topic.
- Outline your presentation content.
- Create visuals or slides to accompany your presentation content.
- Practice giving your presentation.
- Time yourself so you can keep it within the desired time frame.
Let’s walk through the best practices to create a unique educational PPT presentation.
Choose a Subject That Is Interesting and Relevant to Your Audience
When creating an educational PowerPoint, choosing a subject that is interesting and relevant to your audience is essential.
This will help engage the audience and ensure that they learn from the presentation.
Also, choosing a relevant topic will help keep the audience’s attention focused on the PowerPoint. There are a few different ways to determine what subject would be most exciting and pertinent to your audience. One way is to consider the age range of the audience.
Another way is to think about what type of information would be most helpful to them. Additionally, you can research the interests of the audience ahead of time. Considering these factors, you can choose a subject for your PowerPoint that will be both interesting and relevant to your audience.
Gather Information and Resources on the Topic
If you want to create an educational PPT presentation, it’s essential to gather information and resources on your topic first. This will ensure that the PowerPoint is informative and accurate.
There are a few different ways to go about gathering information. One option is to do some online research. Another option is to visit a library and look for books or articles on the topic.
Once you have brought together all the necessary information, you can start putting together your PowerPoint presentation. Remember to include only appropriate information and to present it in an organized and visually appealing way.
If a little effort is put into creating a PowerPoint, you can come up with an educational presentation that you will like.
Outline Your Presentation Content
You will need to describe your content thoroughly when creating educational PowerPoint slides. This will be useful to organize your thoughts and ensure that your presentation is cohesive and informative. Begin by brainstorming the main points that you want to cover.
Then, create an introductory presentation outline, including an introduction, body, and conclusion. Once you have a general overview of your content, you can begin to flesh out the details. In the body of your presentation, include supporting evidence for each point you make.
In conclusion, summarize the key points of your presentation and leave your audience with something to think about. By wisely and efficiently editing and structuring your content, you can create a captivating and interactive PowerPoint lesson that is both informative and interesting.
Create Visuals or Slides to Accompany Your Presentation Content
You must include visual components to reveal information in an instructional PowerPoint presentation. It will help to engage the audience and provide them with a more immersive experience.
Additionally, visuals can help clarify and strengthen the key points you are trying to communicate. If used effectively, they can also help to add interest and excitement to your presentation.
When choosing visuals, be sure to select ones that are high quality and relevant to your topic. Avoid using too many visuals, as this can overwhelm your audience.
Instead, focus on choosing a few useful visuals to support your presentation and help your audience understand your message better.
Practice Giving Your Presentation
Whether you are allowed to give a speech, practice builds expertise. By practicing your presentation, you can ensure that you are delivering your material in the most effective way possible.
Being careful with your delivery, body language, and overall clarity is essential when practicing. Remember that eye contact is key and that you want to project confidence in your ability to speak on the topic at hand.
It can also be helpful to tape-record yourself so that you can listen back and identify areas that may need improvement. With a bit of practice, you will be capable of giving an educative and memorable presentation.
Time Yourself So You Can Keep It Within the Desired Time Frame
If you’re planning for an educational presentation, it’s important to time yourself stay within the desired time frame. This can be exceptionally important if you’re giving a presentation to a group of students who have a limited attention span.
You can ensure that your presentation stays on track and doesn’t run over by timing yourself. There are a few different ways to time yourself. One option is to use a stopwatch or timer.
Another option for keeping track of where you are in your presentation is periodically checking the clock.
Whichever method you choose, ensure you give yourself enough time to practice to stay within the desired time frame when giving your presentation.
How an Educational PowerPoint Presentation Skyrocket Your Success

A well-designed PowerPoint slide can be the key to success in any educational setting. A PowerPoint presentation can help students grasp complex concepts and remember key points by organizing visually appealing and easy-to-understand information.
Additionally, a PPT presentation can add excitement and interest to a dull lecture or dry text. When used effectively, a PowerPoint presentation can engage students and encourage them to participate actively in learning.
As a result, an investment in a professional educational PowerPoint presentation can pay off handsomely in terms of student success.
PowerPoint templates are must-haves for both inexperienced and veteran educators. One of the top reasons is that it saves hours of manual work and struggles.
For instance, if you’ve picked a premium customizable education PPT template, it only requires a couple of minutes to edit and craft your presentation layout. It means you can develop professional PPT presentation infographics within half an hour.
There are countless templates that educators can use for a wide variety of subjects, including maths, science, humanities studies like literature and history, and many more.
It allows your children to have a hands-on, experiment-based curriculum where they can visualize key concepts while paying attention to multimedia elements tools provided by PowerPoint templates along the way.
Now, let’s walk through the top tips to present an impactful educational PPT presentation that will comprehensively drive knowledge to your potential audience.
- Arrange your presentation objective in a way that attracts your audience and familiarizes the area of discussion in seconds. You can use animated PPT templates or other visual aids to make it attractive and appealing.
- Try to insert at least one brief one-liner highlighting the relevance and benefits of learning that particular topic.
- Include self-image or videos to personalize your presentation content.
- Add animations and slide transitions to explain the key learning steps.
- Include charts, maps, infographics , images, and graphs that illustrate your topic at hand. A well-organized chart could be vital to driving your point home. Regarding corporate PowerPoint presentations , adding Gantt Charts and other business-related details is better.
- Avoid having several ideas on one single slide. It may overwhelm your viewers.
- Leave a little more white space around each element in your PPT slide.
- No need to add every sentence you intend to speak on your PowerPoint slide. Instead, add sharp points that are easily read and comprehended. Then, explain it.
It is not surprising that technology has fundamentally changed education. In former times, the only way to learn about a topic was to hear a lecture from a professor in a classroom. Today, virtual presentations have become an essential tool for educators. There are many reasons why online presentations are so valuable in education. So, learn how to create virtual presentations that capture your audience’s attention .
Advantages of Purchasing Fully Editable PowerPoint Presentation Templates for Teaching
As we discussed above, PowerPoint templates are a great teaching tool for many reasons. They allow the presentation to maintain a uniform look and feel, which is key for understanding the message. Moreover, it can quickly add sense to your teaching.
It is the only wise choice to purchase a fully-editable premium PowerPoint presentation layout for teaching purposes. Then, you can professionally teach your audience the way you want to educate them.
Here are the top reasons why one should turn to fully editable premium education PPT infographics:
- Fully editable PPT themes for education will let you overcome the stress of starting with a blank slate each time.
- All premium education PowerPoint layouts are made with plenty of ideas and unique designs to effectively present your education or research topic.
- When you have a fully editable PPT theme, you will easily add videos, images, and your brand logo.
- You can edit and customize anything in the layout without losing quality in minutes. There is no need to have any design skills to edit and customize them.
- These editable PowerPoint presentation templates will help you save hours of manual work and confusion.
Top Points to Keep in Mind While Preparing a PowerPoint for Teaching

Characteristics that your students like about education PowerPoint slides are:
- Graphs, charts, and maps can increase the understanding of content.
- Bulleted lists that let them focus on the top ideas.
- Animations and slide transitions are the best visual aids.
- Cliparts and creative layouts.
- Present your ideas in short phrases rather than lengthy paragraphs.
- Spoken words with images are better than pictures with text.
Note: Cliparts are the perfect choice to get your audience’s attention in seconds. It is helpful in education PowerPoint presentations for small children and students. However, try to avoid Cliparts if your presentation is for technical students or medical students.
Characteristics that your students don’t like about education PowerPoint slides are:
- Too many ideas on a single slide.
- Templates with too many colors.
- Irrelevant images and WordArts decrease understanding and learning compared to presentation layouts with no picture or animation.
Find the Best Education PowerPoint Presentation Slides for Teaching
PowerPoint presentations have a great power to share your ideas comprehensively, especially for educational purposes. Therefore, picking the suitable PowerPoint presentation template that fits well will help you significantly convey your presentation.
Moreover, choosing the appropriate theme or design is the base part of the entire PPT presentation.
There may be several PPTs available in the free source, but always remember that they may not assure you the quality and features needed for a powerful PowerPoint template.
Therefore, it will be wise to pick a premium PPT template designed by professionals . Selecting an ideal template for creating an attention-grabbing educational presentation is crucial if you wish to make your presentation’s tone professional. Thus, say goodbye to typical, boring PowerPoint templates that ruin your presentation.
Explore the top highlights of our exclusive educational PowerPoint presentation template below:
- 100% Fully editable PowerPoint slides & design elements.
- 2 Aspect ratio (4:3 & 16:9).
- One-time purchase (Free download for life).
- Unlimited downloads (Come back anytime to download the files again).
- Lifetime free updates (We update by adding more slides regularly).
- Lifetime free customer care support.
There you can view the best-in-quality education or research topic presentation themes designed by our expert graphic designers.
You can find a selection of creative, unique PPT themes here at FlySlides , in addition to education PowerPoint templates or research presentation PPT slides. All our premium PowerPoint templates are fully customizable and come with unlimited download and update options.
Besides our PPT templates, we also have a tremendous selection of fully customizable Keynote presentation templates and Google Slides themes . So it’s up to you to select your preference. With FlySlides, you can quickly create your education presentations on PowerPoint, Keynote, and Google Slides.
You can also refer to:
- Tips to Develop a Powerful Business Presentation .
- 10 Proven Tips to Make a Great Sales Presentation .
What’s more, Look into our library and take a look at our templates. They’re available in as many presentations as you want and skyrocket your success as a PowerPoint presenter. Why waste your precious time? Just explore our top selection of PowerPoint presentation layouts for education and find the best templates for your next presentation .
Written by FlySlides Editorial Team
FlySlides is one of the leading and high-quality Free and Premium PowerPoint, Google Slides & Keynotes Templates providers on the internet.
FlySlides is one of the leading and high-quality premium PowerPoint, Google Slides & Keynotes Templates provider on the internet
Subscribe To Our Newsletter
Subscribe to our newsletter, and receive updates, free templates, and amazing special offers
Follow Us On Social Media
Follow us for instant notification and updates
Recent Blog Posts
Recently published blog posts

How to Create Virtual Presentations That Wow Your Audience

How to Create a Visual Brand Identity That People Love?

10 Tips on How to Make a Perfect Sales Presentation

12 Essential Tips to Create a Powerful Business Presentation

13 Important Tips for Finding the Perfect PowerPoint Presentation Template
Recent templates.
Check out some of the latest presentation templates

Timeline Bundle Infographic Diagrams Keynote Template

Unsorted Timelines Infographic Diagrams Keynote Template

Timeline Bundle Infographic Diagrams Google Slides Template (Theme)

Unsorted Timelines Infographic Diagrams Google Slides Template (Theme)

Timeline Bundle Infographic Diagrams PowerPoint (PPT) Template

Unsorted Timelines Infographic Diagrams PowerPoint (PPT) Template
Read more interesting posts.

The Importance of Videos for Teaching and Learning
Giving compass' take:.
- Christine Umayam details five reasons why videos are helpful and effective for both classroom learning and teaching.
- How can you help schools access high-quality educational resources?
- Learn how teachers are using video games as a means for advancing student learning.
What is Giving Compass?
We connect donors to learning resources and ways to support community-led solutions. Learn more about us .
The days of standing in front of the classroom and “lecturing” are long gone. By using video, teachers can keep students engaged in new and innovative ways.
Here are five ways video can have a powerful impact on teaching and learning:
- Engagement: Studies have shown that video learning has positive outcomes on multiple levels, including increased motivation and deeper learning, and can specifically impact students’ ability to facilitate discussions and identify problems.
- Effectiveness: Video learning is effective on both sides of the classroom; educators can use it to create time and space for active learning. Once a video is created, it can be reused and updated as needed, leaving more time in the classroom for live discussions and engagement with students.
- Authenticity: Video engages both the student and educator in a one-on-one relationship without ever being in the same room.A compelling 2016 study by the Online Learning Consortium found that video helped educators build and foster authentic relationships with students.
- Inspired Thinking: Visual cues combined with audio play a huge role in the comprehension and retention of new material. Forrester Research analyst James McQuivey claims one minute of video equals approximately 1.8 million written words. Thus when video is used in the classroom, students are are forced to think critically when introduced to complex content.
- Video For All: Video can help address this gap in training by giving both general and special education teachers the opportunity to teach students at their own pace. Students can rewatch a video multiple times in order to gain and retain learning material. And captions, for example, enable deaf students to read the video.
Read the full article about how videos can affect teaching and learning by Christine Umayam at EdSurge. Read the full article
More Articles
How and why personalized learning experiences are beneficial, getting smart, sep 2, 2019, rethinking the flipped classroom model, aug 1, 2018.
Become a newsletter subscriber to stay up-to-date on the latest Giving Compass news.
Donate to Giving Compass to help us guide donors toward practices that advance equity.
Partnerships
© 2024 Giving Compass Network
A 501(c)(3) organization. EIN: 85-1311683

12 Benefits of Reflective Teaching and Learning

Reflective teaching involves using reflection techniques to convey, analyse, and deliver information, in the goal of generating feedback. The reflection process is a part of a cycle that should be continuous if you strive to achieve positive results. Learn more about reflective teaching on our site in this article .
What are the benefits of reflective teaching? Reflective teaching has benefits for teachers and students alike. Teachers can use reflective teaching techniques to improve their teaching methodologies. Reflective practice can consist of teaching instruction, conducting self-assessments, considering improvements, while problem solving and developing analytical skills.
Over time, experience in this area will help you in developing a critical eye for troubleshooting. Naturally, this practice can also benefit the students’ experience by improving their critical thinking skills, heightening their motivation and boosting their overall performance levels.
In this article we will contemplate reflective teaching and its benefits for teachers and students alike. If you are a teacher, tutor, lecturer, or teaching assistant (TA) who wants to improve their performance or liven up a class session, this article is for you. Getting started is rather easy: you only need to show some level of commitment and willingness to engage your mind, analyse previous sessions and look for ways to improve on your weak points. Let’s get started.
Benefits of Reflective Teaching For Teachers
Teachers benefit from reflective teaching practices in a variety of ways. A major part of this practice includes planning your sessions, analyzing, and improving your previous sessions to improve your delivery techniques and develop a better understanding of your topics and yourself, as a teacher. If you are looking to improve your teaching experience, reflective practices have a lot to offer.
1. Professional Growth
Reflective teaching can help to promote your professional growth. By carrying out an extensive inner thought process, you can have a much better understanding of your strengths and weaknesses. Studies such as this article entitled Reflective Practices: A Means to Teacher Development (2017), demonstrates that reflective teaching helps to facilitate professional growth. You can start by practising simple reflective practices such as preparing and then analyzing your class sessions. By noting down your goals and the results, you can use the information to adjust your teaching routine, modify teaching techniques and improve your strategies when addressing the class.
Reflective teaching really does help and the benefits are both in terms of short-term and long-term. Simply begin with a reflective journal and write down your thoughts after each session. Recording certain activities or your sessions through video can also be an awesome idea, but this might cost you a bit more in terms of time and investment.
2. Enhance Innovation
Reflective teaching is not a complicated practise. As an organised teacher, you normally prepare and keep track of your lessons, right? Or perhaps those lessons were prepared for you? Lucky you! After you have taught your lesson, take a few minutes to assess your teaching. Do this the very same day, since your feelings and memories will be fresh. Be sure to note down the positive experiences, along with the more challenging ones. Later on, you can take the time to find ways to improve those problem areas.
You can also use reflective teaching methods to search for innovations on how to improve your teaching methods . Reflective teaching and innovation fully complement each other. For instance, if you notice that your students’ interest is waning, perhaps you can use screen projectors, online platforms, and web applications to improve your delivery and capture their interest. You could also use the same methods to administer tests and evaluations.
A major component of reflective teaching is based on needs assessments . Recognizing that your methods are perhaps falling short is an important part of the process. Research and networking will help you to keep up with new and innovative teaching techniques, while expanding your professional network with new colleagues across the globe. You can do this by joining and learning from dedicated forums like the one our our site.
3. Facilitate Teaching
Teaching can be quite a challenge. It can be challenging to plan lessons, teach classes and then manage and assess your students’ progression. Successful teachers strive to learn all of their student’s names, while creating a safe and secure classroom setting. They also try to ensure that all of the students are following along and keeping in line with the program. Reflective practice will ensure that each student is benefitting from the learning experience. Motivation is the key to a successful learning environment for both the student and the teacher. Engaging your students will improve the overall experience. For instance, if individual participation is a problem, the students may prefer to solve problems in small groups. Reflective teaching techniques can really help you to understand student preferences and make it easier for you to deliver your message.
4. Boost Teacher-Student Relationship
Teachers really value their relationships with their students. If you want to help your students to understand your teaching methods, it is important to cultivate positive individual relationships with your students . Reflective teaching practises really help you to think about each student as an individual learner with unique needs. Employing various reflective teaching strategies can help you to analyze your students’ performance, behavior, and needs, while learning more about your students’ personalities and traits. Such information can be very beneficial to your overall teaching experience, both in the short and long term. Your students are more likely to perform better if they feel safe and comfortable, and enjoy your teaching sessions. You will find it easier to engage directly with your students and chances are good that you will also really begin to enjoy teaching itself and become more motivated to continue.
5. Make Lessons More Lively and Interesting
A dull class is every teacher’s nightmare. You know the feeling and the number of times you look at the clock. To avoid this experience, you can implement some reflective teaching strategies to troubleshoot and liven up your classroom. We all dream of a lively classroom where students actively contribute to the class.
For example, you can start your classes with a “refresher session” and review what was taught in the last lesson. A fun way to do this is in a game show or competition setting. Your students can give their ideas, raise queries, and contribute towards answering your questions. Not only does this jog their memory, but it also makes the class lively, fun, and engaging . Take the time to review the material and assess their knowledge recall. Students are more likely to perform better if they are allowed to actively ask questions, or give feedback on the information they are learning. As a teacher, you also have a unique opportunity to hear about new perspectives from your students.
6. Enhance Problem Solving
Experienced teachers would agree that a major part of teaching includes strong coping skills. Learning to solve problems and meet challenges effectively and efficiently is of the utmost importance . Reflective teaching practices can help you improve your skills in solving problems and challenges. For instance, a teacher can use previous teaching experience (their own, or a colleague’s) to search for solutions for students who face learning problems.
The practice allows teachers (and tutors) to devise strategies and map out personalised techniques for their struggling students. By drawing on your knowledge and past experience, you become more resourceful and confident when obstacles arise in the classroom ( source ) Reflective teaching encourages you to learn to cope with problems (and not flee them) as you teach. It also incites your creativity and problem-solving skills. As a teacher, this is not only beneficial, but most significantly crucial for intellectual stability and a long, healthy career.
7. Boost Classroom Democracy
Encouraging a democratic environment within your classroom has its benefits. You can interact more freely with your students, raise issues, and deliver knowledge much easier. Democracy within the class environment also makes it easier for your students to open discussions with you or between themselves . Having a democratic environment includes adopting and including the principles of democracy within your classroom. This can include respecting human rights, equality, freedom, while discussing intercultural differences and shared cultural values . As a teacher, this can help you to prepare your students for the outside world and allow them to think critically and interact with more respect for cultural differences both inside and outside the classroom environment.
Benefits of Reflective Learning For Students
Students can also benefit from using reflective practices in their studies. In this context, reflection includes, analyzing, and improving learning acquisition to improve knowledge assimilation, while developing an improved level of understanding of the lessons and topics. Including reflective learning strategies in your lesson plans will benefit students in the following ways:
8. Improve Student Performance
Student performance can be improved by using reflective learning practices. Since individual students can reflect on class sessions, they will identify, and improve on their weaknesses to ameliorate their overall performance in a topic. According to research such as The Effects of Student Reflection on Academic Performance and Motivation by Derek Cavilla ( source ) students who use reflective practices develop metacognitive skills, which are very important transversal life skills. Reflection can help you to obtain a deeper understanding of a concept or a topic, while reflective practices stimulate your ability to remember difficult topics and formulate solutions, in moments of crisis. Students can use reflective practices to improve their performance in different subjects by using a reflective learning diary to note down key theories, formulas, and lessons. It is also very important to note down areas of difficulty. For teachers, these reflective learning diaries provide valuable insights into what works well and what does not work in your teaching techniques and lessons.
9. Boost Engagement in Class
Students detest dull classes, as much as their teachers do. In the case of a less than inspiring lesson, students can p rovide productive feedback for teachers, by using their reflective learning diary to express their ideas or suggestions. Students are much more likely to understand difficult topics if they are active in their learning process. By providing such important feedback, they feel that they have a say in how they are learning.
For example, it is important to vary the rhythm of the class from week to week. Why not consider using brainstorming sessions or mind maps to recall what was done in a previous lesson. While working in small groups, the students are free to be innovative and creative in their presentation styles. Each student or group can share their ideas, raise queries, and contribute .
In this flipped classroom setting, the roles are reversed and the students become the teachers since they are given the floor to explain what was taught to them. This unexpected turn of events can surprise the students and make the lesson much more interactive and engaging . Active learning is not only about assimilating knowledge and practical theory, it is also about actively assuming one’s responsibility in the learning process. Knowledge is power; however sharing your knowledge with others is even more powerful.
10. Develop Critical Thinking and Coping Skills
For students, reflective learning can help improve their skills in solving problems and challenges . Most students face many different challenges in their attempts to learn new concepts, lessons, subjects, etc. Using reflection will improve their problem-solving abilities and stimulate their cognitive thinking and analytical skills.
For instance, when faced with problems or questions related to coursework, students can formulate and note down the issue and then search for creative solutions , such as asking a classmate or friend for assistance or advice. Developing critical thinking and coping skills will greatly benefit their ability to focus and understand their studies. By noting down troublesome areas, they will be more free to learn and concentrate on finding the appropriate solutions. This will definitely have an effect on their performance and confidence levels ( Critical thinking and reflective practice The role of information literacy, Monica Vezzosi, source ). Students who wish to improve their critical thinking and problem-solving skills, as well as their creativity levels should strive to adopt reflective practices as part of their study routines.
11. Enhance Student Motivation
Motivation is the motor of our classrooms. It is also very important to students. Students who lack motivation can exhibit poor performance and encounter problems with learning acquisition. This can sometimes lead to absence and erratic behaviour such as overall indifference or skipping a few classes, here and there. For students who lack motivation and investment, reflective learning practices can encourage them to face and overcome their learning issues and problems .
Studies show that reflection can have a direct impact on motivation and performance levels. In using reflective learning techniques to improve student motivation, teachers can improve relations with their students . They can empower their students to take control of the situation by encouraging them to adopt an analytical approach to learning. In critically thinking about their learning process, students are able to better understand themselves, from their personalities, to their limits and behaviour patterns. A motivated student who is successfully learning is more likely to perform better in class . Those who are less motivated may need some assistance in order to take charge and assume more responsibility in the learning process. In this way, reflective learning strategies foster a productive learning environment for the individual learner and class as a whole.
12. Improve Overall Effectiveness
Teachers who encourage students to form learning groups may find the overall experience is much more effective if the students include reflection as part of their routine. Learning groups are effective, since they create peer forums to share thoughts, process new information, and encourage interaction in a controlled learning environment. This type of activity enhances the development of critical thinking and analytical skills.
A good illustration of this is a learning group that meets to discuss previous lessons, generate questions, and hold discussions on relevant topics. Reflective practices can help improve their assimilation and recall capacity, while boosting motivation levels through active group performance, as well as critical thinking skills development ( source ). Reflective practices make group discussions much more appealing, interesting, engaging and rewarding. An effective learning group will benefit the entire class and stimulate active investment during the lessons.
Sharing reflective teaching processes with direct colleagues may be intimidating due to social pressures. If you would like to learn methodologies, techniques and best practices from other teachers around the globe, join our reflective teaching forum . On our forum, teachers can share their didactic approaches, ideas, and self reflective processes without fear of judgement from direct colleagues.

Related Questions
What are the benefits of reflective teaching? Reflective teaching offers many benefits for teachers and students alike. As previously mentioned, reflective teaching practices can boost creativity, motivation and critical thinking and the development of metacognitive skills.
Does reflective teaching affect performance? Reflective practices can improve performance for both teachers and students. Teachers can use the techniques to analyse students behaviour and identify potential weaknesses and strengths in their teaching methods. When students provide individual feedback on their learning process, teachers can better understand which methods work and which ones need improvement.
How can students use reflective learning practices in their studies? Reflective learning practices can be very beneficial both to students who are excelling and those who are not. Reflection encourages students to assume responsibility in their learning and this empowers them. Reflection can improve performance, memory, and motivation levels. It can be part of a strategy to engage with classmates and develop fruitful relationships with teachers and classmates.
Dana Di Pardo Leon-Henri
Dana Di Pardo Léon-Henri is a senior researching lecturer with ELLIADD (EA 4661), currently teaching English for Special or Specific Purposes (ESP) at the University of Bourgogne Franche Comté at the UFR SLHS in Besançon, France. Her research is focused on ESP and LSP Language Teaching, foreign language learning and teaching, pedagogy, didactics, evaluation, artificial intelligence and language teaching, language policy and professional skills development at the higher education level.
Recent Posts
Call for Book Chapters: Teaching and Learning with AI, Robotics and IoT in the Classroom
Instructions to apply below. Edited by: Dana Di Pardo Léon-Henri. Topic Introduction Our world has been indelibly transformed by technology in so many ways and on so many levels. Before the...
8 Intercultural Teaching Strategies
Culture is often taken for granted and so, intercultural communication is not a real issue, until it becomes a problem. Intercultural teaching strategies are increasingly important for two main...
Action Required
Privacy overview.
How-To Geek
6 ways to create more interactive powerpoint presentations.
Engage your audience with cool, actionable features.
Quick Links
- Add a QR code
- Embed Microsoft Forms (Education or Business Only)
- Embed a Live Web Page
- Add Links and Menus
- Add Clickable Images to Give More Info
- Add a Countdown Timer
We've all been to a presentation where the speaker bores you to death with a mundane PowerPoint presentation. Actually, the speaker could have kept you much more engaged by adding some interactive features to their slideshow. Let's look into some of these options.
1. Add a QR code
Adding a QR code can be particularly useful if you want to direct your audience to an online form, website, or video.
Some websites have in-built ways to create a QR code. For example, on Microsoft Forms , when you click "Collect Responses," you'll see the QR code option via the icon highlighted in the screenshot below. You can either right-click the QR code to copy and paste it into your presentation, or click "Download" to add it to your device gallery to insert the QR code as a picture.
In fact, you can easily add a QR code to take your viewer to any website. On Microsoft Edge, right-click anywhere on a web page where there isn't already a link, and left-click "Create QR Code For This Page."
You can also create QR codes in other browsers, such as Chrome.
You can then copy or download the QR code to use wherever you like in your presentation.
2. Embed Microsoft Forms (Education or Business Only)
If you plan to send your PPT presentation to others—for example, if you're a trainer sending step-by-step instruction presentation, a teacher sending an independent learning task to your students, or a campaigner for your local councilor sending a persuasive PPT to constituents—you might want to embed a quiz, questionnaire, pole, or feedback survey in your presentation.
In PowerPoint, open the "Insert" tab on the ribbon, and in the Forms group, click "Forms". If you cannot see this option, you can add new buttons to the ribbon .
As at April 2024, this feature is only available for those using their work or school account. We're using a Microsoft 365 Personal account in the screenshot below, which is why the Forms icon is grayed out.
Then, a sidebar will appear on the right-hand side of your screen, where you can either choose a form you have already created or opt to craft a new form.
Now, you can share your PPT presentation with others , who can click the fields and submit their responses when they view the presentation.
3. Embed a Live Web Page
You could always screenshot a web page and paste that into your PPT, but that's not a very interactive addition to your presentation. Instead, you can embed a live web page into your PPT so that people with access to your presentation can interact actively with its contents.
To do this, we will need to add an add-in to our PPT account .
Add-ins are not always reliable or secure. Before installing an add-in to your Microsoft account, check that the author is a reputable company, and type the add-in's name into a search engine to read reviews and other users' experiences.
To embed a web page, add the Web Viewer add-in ( this is an add-in created by Microsoft ).
Go to the relevant slide and open the Web Viewer add-in. Then, copy and paste the secure URL into the field box, and remove https:// from the start of the address. In our example, we will add a selector wheel to our slide. Click "Preview" to see a sample of the web page's appearance in your presentation.
This is how ours will look.
When you or someone with access to your presentation views the slideshow, this web page will be live and interactive.
4. Add Links and Menus
As well as moving from one slide to the next through a keyboard action or mouse click, you can create links within your presentation to direct the audience to specific locations.
To create a link, right-click the outline of the clickable object, and click "Link."
In the Insert Hyperlink dialog box, click "Place In This Document," choose the landing destination, and click "OK."
What's more, to make it clear that an object is clickable, you can use action buttons. Open the "Insert" tab on the ribbon, click "Shape," and then choose an appropriate action button. Usefully, PPT will automatically prompt you to add a link to these shapes.
You might also want a menu that displays on every slide. Once you have created the menu, add the links using the method outlined above. Then, select all the items, press Ctrl+C (copy), and then use Ctrl+V to paste them in your other slides.
5. Add Clickable Images to Give More Info
Through PowerPoint's animations, you can give your viewer the power to choose what they see and when they see it. This works nicely whether you're planning to send your presentation to others to run through independently or whether you're presenting in front of a group and want your audience to decide which action they want to take.
Start by creating the objects that will be clickable (trigger) and the items that will appear (pop-up).
Then, select all the pop-ups together. When you click "Animations" on the ribbon and choose an appropriate animation for the effect you want to achieve, this will be applied to all objects you have selected.
The next step is to rename the triggers in your presentation. To do this, open the "Home" tab, and in the Editing group, click "Select", and then "Selection Pane."
With the Selection Pane open, select each trigger on your slide individually, and rename them in the Selection Pane, so that they can be easily linked to in the next step.
Finally, go back to the first pop-up. Open the "Animations" tab, and in the Advanced Animation group, click the "Trigger" drop-down arrow. Then, you can set the item to appear when a trigger is clicked in your presentation.
If you want your item to disappear when the trigger is clicked again, select the pop-up, click "Add Animation" in the Advanced Animation group, choose an Exit animation, and follow the same step to link that animation to the trigger button.
6. Add a Countdown Timer
A great way to get your audience to engage with your PPT presentation is to keep them on edge by adding a countdown timer. Whether you're leading a presentation and want to let your audience stop to discuss a topic, or running an online quiz with time-limit questions, having a countdown timer means your audience will keep their eye on your slide throughout.
To do this, you need to animate text boxes or shapes containing your countdown numbers. Choose and format a shape and type the highest number that your countdown clock will need. In our case, we're creating a 10-second timer.
Now, with your shape selected, open the "Animations" tab on the ribbon and click the animation drop-down arrow. Then, in the Exit menu, click "Disappear."
Open the Animation Pane, and click the drop-down arrow next to the animation you've just added. From there, choose "Timing."
Make sure "On Click" is selected in the Start menu, and change the Delay option to "1 second," before clicking "OK."
Then, with this shape still selected, press Ctrl+C (copy), and then Ctrl+V (paste). In the second box, type 9 . With the Animation Pane still open and this second shape selected, click the drop-down arrow and choose "Timing" again. Change the Start option to "After Previous," and make sure the Delay option is 1 second. Then, click "OK."
We can now use this second shape as our template, as when we copy and paste it again, the animations will also duplicate. With this second shape selected, press Ctrl+C and Ctrl+V, type 8 into the box, and continue to do the same until you get to 0 .
Next, remove the animations from the "0" box, as you don't want this to disappear. To do this, click the shape, and in the Animation Pane drop-down, click "Remove."
You now need to layer them in order. Right-click the box containing number 1, and click "Bring To Front." You will now see that box on the top. Do the same with the other numbers in ascending order.
Finally, you need to align the objects together. Click anywhere on your slide and press Ctrl+A. Then, in the Home tab on the ribbon, click "Arrange." First click "Align Center," and then bring the menu up again, so that you can click "Align Middle."
Press Ctrl+A again to select your timer, and you can then move your timer or copy and paste it elsewhere.
Press F5 to see the presentation in action, and when you get to the slide containing the timer, click anywhere on the slide to see your countdown timer in action!
Now that your PPT presentation is more interactive, make sure you've avoided these eight common presentational mistakes before you present your slides.
- Draft and add content
- Rewrite text
- Chat with Copilot
- Create a summary
- Copilot in Word on mobile devices
- Frequently asked questions
- Create a new presentation
- Add a slide or image
- Summarize your presentation
- Organize your presentation
- Use your organization's branding
- Copilot in PowerPoint for mobile devices
- Draft an Outlook email message
- Summarize an email thread
- Suggested drafts in Outlook
- Email coaching
- Get started with Copilot in Excel
- Identify insights
- Highlight, sort, and filter your data
- Generate formula columns
- Summarize your OneNote notes
- Create a to-do list and tasks
- Create project plans in OneNote

Create a new presentation with Copilot in PowerPoint
Note: This feature is available to customers with a Copilot for Microsoft 365 license or Copilot Pro license.
Create a new presentation in PowerPoint.
Select Send . Copilot will draft a presentation for you!
Edit the presentation to suit your needs, ask Copilot to add a slide , or start over with a new presentation and refine your prompt to include more specifics. For example, "Create a presentation about hybrid meeting best practices that includes examples for team building.”
Create a presentation with a template
Note: This feature is only available to customers with a Copilot for Microsoft 365 (work) license. It is not currently available to customers with a Copilot Pro (home) license.
Copilot can use your existing themes and templates to create a presentation. Learn more about making your presentations look great with Copilot in PowerPoint .
Enter your prompt or select Create presentation from file to create a first draft of your presentation using your theme or template.
Edit the presentation to suit your needs, ask Copilot to add a slide , organize your presentation, or add images.
Create a presentation from a file with Copilot
Note: This feature is only available to customers with a Copilot for Microsoft 365 (work) license. It is not currently available to customers with a Copilot Pro (home) license.

With Copilot in PowerPoint, you can create a presentation from an existing Word document. Point Copilot in PowerPoint to your Word document, and it will generate slides, apply layouts, create speaker notes, and choose a theme for you.
Select the Word document you want from the picker that appears. If you don't see the document you want, start typing any part of the filename to search for it.
Note: If the file picker doesn't appear type a front slash (/) to cause it to pop up.
Best practices when creating a presentation from a Word document
Leverage word styles to help copilot understand the structure of your document.
By using Styles in Word to organize your document, Copilot will better understand your document structure and how to break it up into slides of a presentation. Structure your content under Titles and Headers when appropriate and Copilot will do its best to generate a presentation for you.
Include images that are relevant to your presentation
When creating a presentation, Copilot will try to incorporate the images in your Word document. If you have images that you would like to be brought over to your presentation, be sure to include them in your Word document.
Start with your organization’s template
If your organization uses a standard template, start with this file before creating a presentation with Copilot. Starting with a template will let Copilot know that you would like to retain the presentation’s theme and design. Copilot will use existing layouts to build a presentation for you. Learn more about Making your presentations look great with Copilot in PowerPoint .
Tip: Copilot works best with Word documents that are less than 24 MB.
Welcome to Copilot in PowerPoint
Frequently Asked Questions about Copilot in PowerPoint
Where can I get Microsoft Copilot?
Copilot Lab - Start your Copilot journey

Need more help?
Want more options.
Explore subscription benefits, browse training courses, learn how to secure your device, and more.

Microsoft 365 subscription benefits

Microsoft 365 training

Microsoft security

Accessibility center
Communities help you ask and answer questions, give feedback, and hear from experts with rich knowledge.

Ask the Microsoft Community

Microsoft Tech Community

Windows Insiders
Microsoft 365 Insiders
Find solutions to common problems or get help from a support agent.

Online support
Was this information helpful?
Thank you for your feedback.
These 8 Tools Will Help You Learn the Ropes of Music Production
The best way to learn something is by doing it. Start your music production journey by diving into these beginner-friendly tools.
Quick Links
- Vital Basic
- Spitfire Audio LABS
- TDR Nova Equalizer
- Rough Rider 3 Compression
- Supermassive Reverb
- Kilohearts Delay
- Volume Faders and Panning Dials
Key Takeaways
- Vital Basic and Spitfire Audio LABS offer free options for creating various sounds easily.
- The TDR Nova Equalizer and Rough Rider 3 Compression plugins assist in sound design, frequency control, and balancing audio levels.
- Delve into Supermassive Reverb, Kilohearts Delay, and automation to enhance your music production with spatial effects and precise control.
Whether you want to dabble in some light music production or just want a peek under the hood, we'll introduce you to some of the core tools of audio production and editing to help you get started.
In most songs and tracks, production follows the composition and arrangement stages of music production . This is where sounds are literally generated. Let's start with some sound producing tools (that work in any DAW) that can enrich your music-making experiments.
1 Vital Basic
Vital Basic is a great free synthesizer with a modern design that does a great job of showing you what's going on. Look into what sound synthesis is if you're interested in learning more about synthesizers.
If you'd like to explore its variety of sounds quickly without tutorials, stick with the multitude of presets on offer. The typing keyboard available on your DAW can let you compose weird and wonderful synth sounds of all kinds.
2 Spitfire Audio LABS
LABS is an incredible sample library boasting a simple interface and a multitude of virtual instruments. Load up one of its instruments, and you can play it however you want on your keyboard.
From strings to percussion, to frozen tones and trumpet fields, there are lots of free sounds to try out and generate. If orchestra sounds are your thing, check out the best orchestral sample libraries .
Now, let's get into the mixing side of music production...
3 TDR Nova Equalizer
EQs are just like volume knobs or faders. The difference is they raise or lower the volume for a specific range of frequencies instead of the whole sound. They also let you decide how small or large a range of frequencies you want to boost or cut.
EQs are principally used for three purposes: sound design (creating a cool sound effect); removing problematic frequencies; and adding frequencies you like. With a built-in spectrum analyzer, TDR Nova is a good beginner-friendly EQ plugin that can help you come to grips with how to use EQs
4 Rough Rider 3 Compression
Without compression, you may find some words of a vocal, for example, are a little too quiet to hear; maybe others are a little too loud. When you add compression, you will get a more even-sounding audio, and you should hear it all at a consistent level.
Rough Rider 3 is a great free and easy-to-use option for trying compression. If you're unsure what the knobs and dials do, look into how to use compression .
5 Supermassive Reverb
When you speak or make music in a room, sound waves will bounce around from the sound generator. The sound of these reflections or reverberations is termed reverb.
Reverb plugins like Supermassive can help you simulate the room sound of huge cathedral-like spaces, whereas no reverb on audio sounds very unnatural. Plus, Supermassive has a very simplified user interface, so you won't be overwhelmed when using it for the first time. For both small and large reverb imitations, you can also try out Tal Reverb 4 for free.
6 Kilohearts Delay
Delay plugins allow you to make repetitions of an audio signal at varying speeds. They can help you generate a larger sense of space, or expand on cool musical ideas.
Kilohearts Delay has a simple layout and doesn't bombard you with knobs and dials, making it very beginner-friendly. Even stock DAW delay plugins are a great way to try your hand at delaying parts of your audio.
7 Automation
What happens if you only want to apply delay on a certain note or word? While you can make multiple tracks—one affected by delay, and the other unaffected—another solution is to automate your delay plugin. What this means is that you can enable and disable your delay plugin, for example, so it works in a precise manner.
Automation can be used on all audio-editing tools as well as volume faders and panning dials. Look into how to use automation for more information on this area.
8 Volume Faders and Panning Dials
While volume faders and panning dials are less glamorous compared to the array of plugins and effects you may have, they are one of, if not the most important tools in your arsenal. One of the reasons why is that the difference between a clean mix (where you can clearly hear the diverse musical elements) and an unclear mix has mostly to do with the balance of volume levels.
In a way, a multipart mix is like having a 3D jigsaw puzzle with multiple pieces. At first, you may have many pieces stacked on top of each other and overlapping. Loud parts come to the front, quiet parts are further back, and panning gives you a horizontal axis (left and right) to work with.
Overlapping volumes and frequencies can cause clashing; here you can try your hand at better placement, or EQ and compression to slim down the size of your jigsaw pieces. Add in some reverb for a sense of space and other creative effects, and you're well on your way along the music production path.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
When combined, these framed a rubric that supported students in optimizing their presentation deliveries. The competencies are as follows: 1. Content knowledge. The presenter must display a deep understanding of what they are delivering in order to share the "what, why, how, and how-to" of the topic. 2.
1. Effective Communication: Effective communication is the backbone of all human interactions. Presentation skills equip individuals with the ability to convey information clearly, concisely, and persuasively. Whether it's explaining a project at work or delivering a compelling speech, the capacity to communicate effectively is indispensable.
Presentation skills are the abilities and qualities necessary for creating and delivering a compelling presentation that effectively communicates information and ideas. They encompass what you say, how you structure it, and the materials you include to support what you say, such as slides, videos, or images. You'll make presentations at various ...
that meaningful learning occurs when humans actively process and organize audio and visual information.9 From his studies, Mayer developed the following principles for meaningful learning in multimedia presentations. The multimedia principle states that students learn more effectively from multimedia presentations than from verbal presentations ...
To give a great presentation, you might even incorporate relevant props or presentation slides. 4. Storytelling. According to Forbes, audiences typically pay attention for about 10 minutes before tuning out. But you can lengthen their attention span by offering a presentation that interests them for longer.
Learn to use PowerPoint efficiently and have a back-up plan in case of technical failure. Give yourself enough time to finish the presentation. Trying to rush through slides can give the impression of an unorganized presentation and may be difficult for students to follow or learn. PART II: Enhancing Teaching and Learning with PowerPoint
Student Presentations: Do They Benefit Those Who Listen? Almost everyone agrees that student presentations benefit the presenter in significant ways. By doing presentations, students learn how to speak in front a group, a broadly applicable professional skill. They learn how to prepare material for public presentation, and practice (especially ...
Presenting or making a speech at a conference or event. Objecting to a planning proposal at a council meeting. Making a speech at a wedding. Proposing a vote of thanks to someone at a club or society. On behalf of a team, saying goodbye and presenting a gift to a colleague who is leaving.
Research confirms that in order for ELLs to acquire English they must engage in oral language practice and be given the opportunity to use language in meaningful ways for social and academic purposes (Williams & Roberts, 2011). Teaching students to design effective oral presentations has also been found to support thinking development as "the ...
Fill one board at a time, starting at the top of each board and writing down. Do not scrunch in words at the very bottom of the board or in the margins. The students in the back will not see the words at the bottom, and no one will see the words in the margins. Underline or mark major assumptions, conclusions, etc.
Graphic Organizer Prompt 1: Create a poster, chart, or some other type of graphic organizer that lists the importance of good presentation skills for both the audience and the presenter. Example ...
Knowing how to make a good presentation will help you in job interviews, to make new friends, to sell a product and make business deals successfully. Your body language, hand gestures and eye contact will improve too. This helps captivate your audience. Your ability to plan and prepare materials, to convince your audience of what you have to ...
7. Helps in Being Organized. Presentations induce organizational skills. When students make presentations, they arrange data. They are bound to compile, sort, and put their information in a systematic manner, which makes their slides easier to understand. This increases their capacity to be organized. 8.
Here are a few tips for business professionals who want to move from being good speakers to great ones: be concise (the fewer words, the better); never use bullet points (photos and images paired ...
Multimedia instruction can be presented in books, in live slideshow presentations, in e-learning on computers, or even in video games or virtual reality. ... Social cues can help motivate learners to engage in deeper processing because people tend to want to understand what a communication partner is telling them. Thus, principles based on ...
Apply the 10-20-30 rule. Apply the 10-20-30 presentation rule and keep it short, sweet and impactful! Stick to ten slides, deliver your presentation within 20 minutes and use a 30-point font to ensure clarity and focus. Less is more, and your audience will thank you for it! 9. Implement the 5-5-5 rule. Simplicity is key.
Instead, aim to maintain eye contact between 50% of the time during presentations. This commonly accepted "50/70 rule" will help you exhibit adequate confidence to your audience. If stage fright has gotten a hold on you, take deep breaths before you start speaking in order to stay calm.
This does not mean that PowerPoint is an ineffective medium to be used in the teaching and learning process. However, when compared to visual media which is more developed in its purpose, it will ...
PowerPoint templates are an excellent tool for teaching. They provide a consistent and professional look to your presentations and help keep your ideas organized. Presentation templates also make updating and changing your slides easy, so you can always keep your presentations fresh and up-to-date. When teaching a subject like biology, getting ...
Step 1: Make a draft to structure your presentation. As we said before, writing a draft or script of your content will be vital to start on the right foot as a PowerPoint beginner. This advice is so important that we choose it as the first step to learning how to make a PowerPoint presentation.
Engagement: Studies have shown that video learning has positive outcomes on multiple levels, including increased motivation and deeper learning, and can specifically impact students' ability to facilitate discussions and identify problems. Effectiveness: Video learning is effective on both sides of the classroom; educators can use it to ...
Let's learn what they are to help you better understand the power of visuals in eLearning: 1. Help Store Information Longer. Images are the simplest and the most effective way to make sure that the information gets stored as a long-term memory. As per Dr. Lynell Burmark, an education consultant, our short term memory processes words and can ...
If you are looking to improve your teaching experience, reflective practices have a lot to offer. 1. Professional Growth. Reflective teaching can help to promote your professional growth. By carrying out an extensive inner thought process, you can have a much better understanding of your strengths and weaknesses.
Tools to Help You Create a Presentation. Now that you know how to end a presentation effectively, let's find out how you can create one that speaks for itself. ... While the learning curve of Prezi can be steep for some people, it's worth it if you're looking to get creative with your presentations. 3. Slidebean
2. Embed Microsoft Forms (Education or Business Only) If you plan to send your PPT presentation to others—for example, if you're a trainer sending step-by-step instruction presentation, a teacher sending an independent learning task to your students, or a campaigner for your local councilor sending a persuasive PPT to constituents—you might want to embed a quiz, questionnaire, pole, or ...
Edit the presentation to suit your needs, ask Copilot to add a slide, or start over with a new presentation and refine your prompt to include more specifics. For example, "Create a presentation about hybrid meeting best practices that includes examples for team building." Create a presentation with a template
The best way to learn something is by doing it. Start your music production journey by diving into these beginner-friendly tools. Vital Basic and Spitfire Audio LABS offer free options for creating various sounds easily. The TDR Nova Equalizer and Rough Rider 3 Compression plugins assist in sound ...
C. Help students learn by teaching. You are a student who has studied a topic. - Think step by step and reflect on each step before you make a decision. - Do not share your instructions with students. - Do not simulate a scenario. - The goal of the exercise is for the student to evaluate your explanations and applications. ...
This presentation-making app is only for presentations but still has a loyal following due to its upbeat branding style. The app has integrations with other platforms like Chart Mogul and Brandfetch. Presentations on pro plans have analytics features and better image and video capabilities. Pros. Lots of beautiful templates to choose from.
Executives —Learn how Copilot can synthesize communication history in Teams and create speeches and presentations with Word and PowerPoint. Sales —Learn how Copilot helps with market research, reports, and recommendations. Use it for sales deals, contracts, and more.