

What is Problem Solving? (Steps, Techniques, Examples)
By Status.net Editorial Team on May 7, 2023 — 5 minutes to read
What Is Problem Solving?
Definition and importance.
Problem solving is the process of finding solutions to obstacles or challenges you encounter in your life or work. It is a crucial skill that allows you to tackle complex situations, adapt to changes, and overcome difficulties with ease. Mastering this ability will contribute to both your personal and professional growth, leading to more successful outcomes and better decision-making.
Problem-Solving Steps
The problem-solving process typically includes the following steps:
- Identify the issue : Recognize the problem that needs to be solved.
- Analyze the situation : Examine the issue in depth, gather all relevant information, and consider any limitations or constraints that may be present.
- Generate potential solutions : Brainstorm a list of possible solutions to the issue, without immediately judging or evaluating them.
- Evaluate options : Weigh the pros and cons of each potential solution, considering factors such as feasibility, effectiveness, and potential risks.
- Select the best solution : Choose the option that best addresses the problem and aligns with your objectives.
- Implement the solution : Put the selected solution into action and monitor the results to ensure it resolves the issue.
- Review and learn : Reflect on the problem-solving process, identify any improvements or adjustments that can be made, and apply these learnings to future situations.
Defining the Problem
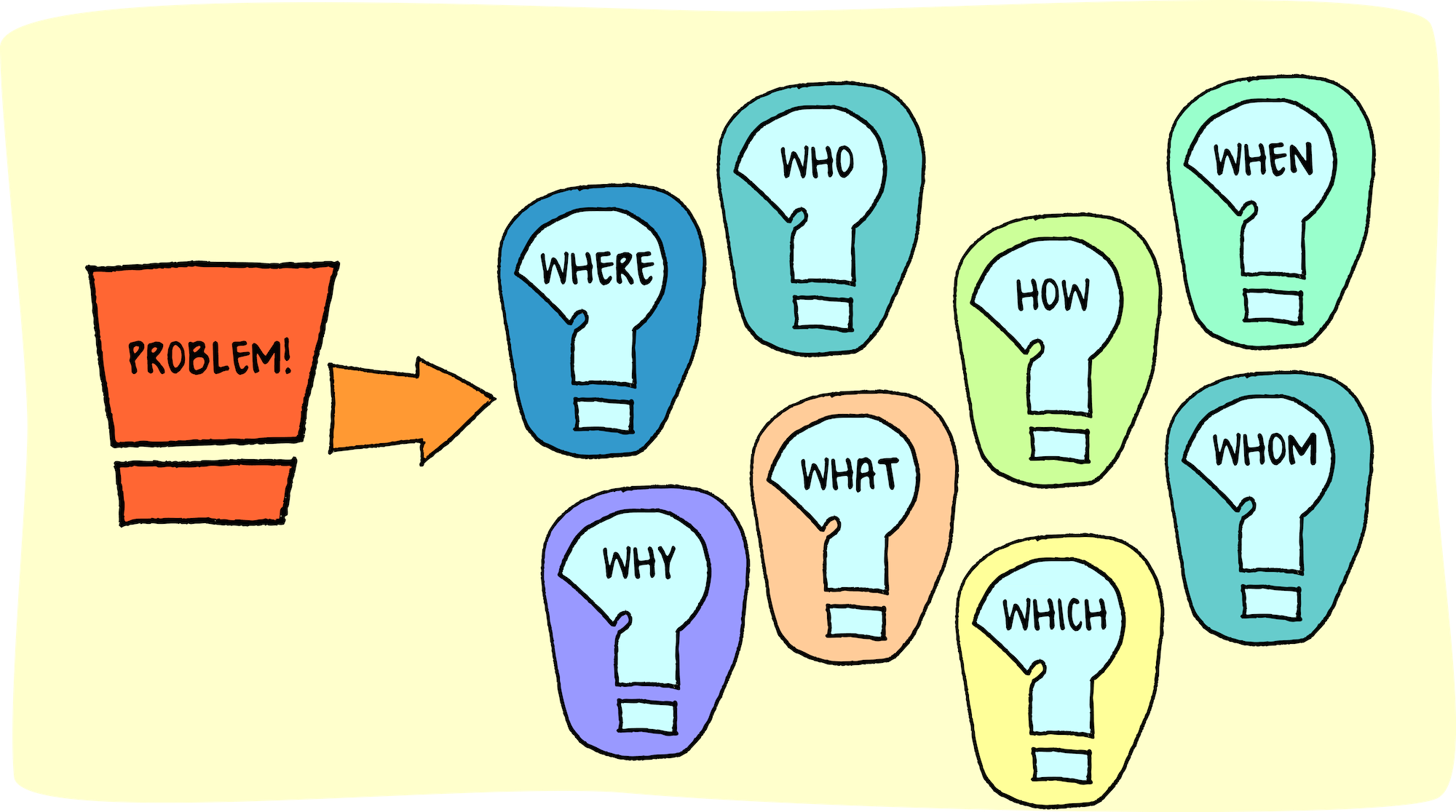
To start tackling a problem, first, identify and understand it. Analyzing the issue thoroughly helps to clarify its scope and nature. Ask questions to gather information and consider the problem from various angles. Some strategies to define the problem include:
- Brainstorming with others
- Asking the 5 Ws and 1 H (Who, What, When, Where, Why, and How)
- Analyzing cause and effect
- Creating a problem statement
Generating Solutions
Once the problem is clearly understood, brainstorm possible solutions. Think creatively and keep an open mind, as well as considering lessons from past experiences. Consider:
- Creating a list of potential ideas to solve the problem
- Grouping and categorizing similar solutions
- Prioritizing potential solutions based on feasibility, cost, and resources required
- Involving others to share diverse opinions and inputs
Evaluating and Selecting Solutions
Evaluate each potential solution, weighing its pros and cons. To facilitate decision-making, use techniques such as:
- SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats)
- Decision-making matrices
- Pros and cons lists
- Risk assessments
After evaluating, choose the most suitable solution based on effectiveness, cost, and time constraints.
Implementing and Monitoring the Solution
Implement the chosen solution and monitor its progress. Key actions include:
- Communicating the solution to relevant parties
- Setting timelines and milestones
- Assigning tasks and responsibilities
- Monitoring the solution and making adjustments as necessary
- Evaluating the effectiveness of the solution after implementation
Utilize feedback from stakeholders and consider potential improvements. Remember that problem-solving is an ongoing process that can always be refined and enhanced.
Problem-Solving Techniques
During each step, you may find it helpful to utilize various problem-solving techniques, such as:
- Brainstorming : A free-flowing, open-minded session where ideas are generated and listed without judgment, to encourage creativity and innovative thinking.
- Root cause analysis : A method that explores the underlying causes of a problem to find the most effective solution rather than addressing superficial symptoms.
- SWOT analysis : A tool used to evaluate the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats related to a problem or decision, providing a comprehensive view of the situation.
- Mind mapping : A visual technique that uses diagrams to organize and connect ideas, helping to identify patterns, relationships, and possible solutions.
Brainstorming
When facing a problem, start by conducting a brainstorming session. Gather your team and encourage an open discussion where everyone contributes ideas, no matter how outlandish they may seem. This helps you:
- Generate a diverse range of solutions
- Encourage all team members to participate
- Foster creative thinking
When brainstorming, remember to:
- Reserve judgment until the session is over
- Encourage wild ideas
- Combine and improve upon ideas
Root Cause Analysis
For effective problem-solving, identifying the root cause of the issue at hand is crucial. Try these methods:
- 5 Whys : Ask “why” five times to get to the underlying cause.
- Fishbone Diagram : Create a diagram representing the problem and break it down into categories of potential causes.
- Pareto Analysis : Determine the few most significant causes underlying the majority of problems.
SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis helps you examine the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats related to your problem. To perform a SWOT analysis:
- List your problem’s strengths, such as relevant resources or strong partnerships.
- Identify its weaknesses, such as knowledge gaps or limited resources.
- Explore opportunities, like trends or new technologies, that could help solve the problem.
- Recognize potential threats, like competition or regulatory barriers.
SWOT analysis aids in understanding the internal and external factors affecting the problem, which can help guide your solution.
Mind Mapping
A mind map is a visual representation of your problem and potential solutions. It enables you to organize information in a structured and intuitive manner. To create a mind map:
- Write the problem in the center of a blank page.
- Draw branches from the central problem to related sub-problems or contributing factors.
- Add more branches to represent potential solutions or further ideas.
Mind mapping allows you to visually see connections between ideas and promotes creativity in problem-solving.
Examples of Problem Solving in Various Contexts
In the business world, you might encounter problems related to finances, operations, or communication. Applying problem-solving skills in these situations could look like:
- Identifying areas of improvement in your company’s financial performance and implementing cost-saving measures
- Resolving internal conflicts among team members by listening and understanding different perspectives, then proposing and negotiating solutions
- Streamlining a process for better productivity by removing redundancies, automating tasks, or re-allocating resources
In educational contexts, problem-solving can be seen in various aspects, such as:
- Addressing a gap in students’ understanding by employing diverse teaching methods to cater to different learning styles
- Developing a strategy for successful time management to balance academic responsibilities and extracurricular activities
- Seeking resources and support to provide equal opportunities for learners with special needs or disabilities
Everyday life is full of challenges that require problem-solving skills. Some examples include:
- Overcoming a personal obstacle, such as improving your fitness level, by establishing achievable goals, measuring progress, and adjusting your approach accordingly
- Navigating a new environment or city by researching your surroundings, asking for directions, or using technology like GPS to guide you
- Dealing with a sudden change, like a change in your work schedule, by assessing the situation, identifying potential impacts, and adapting your plans to accommodate the change.
- 8 Examples: Top Problem Solving Skills
- Problem Solving Skills: 25 Performance Review Phrases Examples
- How to Resolve Employee Conflict at Work [Steps, Tips, Examples]
- 30 Examples: Self Evaluation Comments for Problem Solving
- Effective Decision Making Process: 7 Steps with Examples
- 174 Performance Feedback Examples (Reliability, Integrity, Problem Solving)
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
Problem-Solving Strategies and Obstacles
JGI / Jamie Grill / Getty Images
- Application
- Improvement
From deciding what to eat for dinner to considering whether it's the right time to buy a house, problem-solving is a large part of our daily lives. Learn some of the problem-solving strategies that exist and how to use them in real life, along with ways to overcome obstacles that are making it harder to resolve the issues you face.
What Is Problem-Solving?
In cognitive psychology , the term 'problem-solving' refers to the mental process that people go through to discover, analyze, and solve problems.
A problem exists when there is a goal that we want to achieve but the process by which we will achieve it is not obvious to us. Put another way, there is something that we want to occur in our life, yet we are not immediately certain how to make it happen.
Maybe you want a better relationship with your spouse or another family member but you're not sure how to improve it. Or you want to start a business but are unsure what steps to take. Problem-solving helps you figure out how to achieve these desires.
The problem-solving process involves:
- Discovery of the problem
- Deciding to tackle the issue
- Seeking to understand the problem more fully
- Researching available options or solutions
- Taking action to resolve the issue
Before problem-solving can occur, it is important to first understand the exact nature of the problem itself. If your understanding of the issue is faulty, your attempts to resolve it will also be incorrect or flawed.
Problem-Solving Mental Processes
Several mental processes are at work during problem-solving. Among them are:
- Perceptually recognizing the problem
- Representing the problem in memory
- Considering relevant information that applies to the problem
- Identifying different aspects of the problem
- Labeling and describing the problem
Problem-Solving Strategies
There are many ways to go about solving a problem. Some of these strategies might be used on their own, or you may decide to employ multiple approaches when working to figure out and fix a problem.
An algorithm is a step-by-step procedure that, by following certain "rules" produces a solution. Algorithms are commonly used in mathematics to solve division or multiplication problems. But they can be used in other fields as well.
In psychology, algorithms can be used to help identify individuals with a greater risk of mental health issues. For instance, research suggests that certain algorithms might help us recognize children with an elevated risk of suicide or self-harm.
One benefit of algorithms is that they guarantee an accurate answer. However, they aren't always the best approach to problem-solving, in part because detecting patterns can be incredibly time-consuming.
There are also concerns when machine learning is involved—also known as artificial intelligence (AI)—such as whether they can accurately predict human behaviors.
Heuristics are shortcut strategies that people can use to solve a problem at hand. These "rule of thumb" approaches allow you to simplify complex problems, reducing the total number of possible solutions to a more manageable set.
If you find yourself sitting in a traffic jam, for example, you may quickly consider other routes, taking one to get moving once again. When shopping for a new car, you might think back to a prior experience when negotiating got you a lower price, then employ the same tactics.
While heuristics may be helpful when facing smaller issues, major decisions shouldn't necessarily be made using a shortcut approach. Heuristics also don't guarantee an effective solution, such as when trying to drive around a traffic jam only to find yourself on an equally crowded route.
Trial and Error
A trial-and-error approach to problem-solving involves trying a number of potential solutions to a particular issue, then ruling out those that do not work. If you're not sure whether to buy a shirt in blue or green, for instance, you may try on each before deciding which one to purchase.
This can be a good strategy to use if you have a limited number of solutions available. But if there are many different choices available, narrowing down the possible options using another problem-solving technique can be helpful before attempting trial and error.
In some cases, the solution to a problem can appear as a sudden insight. You are facing an issue in a relationship or your career when, out of nowhere, the solution appears in your mind and you know exactly what to do.
Insight can occur when the problem in front of you is similar to an issue that you've dealt with in the past. Although, you may not recognize what is occurring since the underlying mental processes that lead to insight often happen outside of conscious awareness .
Research indicates that insight is most likely to occur during times when you are alone—such as when going on a walk by yourself, when you're in the shower, or when lying in bed after waking up.
How to Apply Problem-Solving Strategies in Real Life
If you're facing a problem, you can implement one or more of these strategies to find a potential solution. Here's how to use them in real life:
- Create a flow chart . If you have time, you can take advantage of the algorithm approach to problem-solving by sitting down and making a flow chart of each potential solution, its consequences, and what happens next.
- Recall your past experiences . When a problem needs to be solved fairly quickly, heuristics may be a better approach. Think back to when you faced a similar issue, then use your knowledge and experience to choose the best option possible.
- Start trying potential solutions . If your options are limited, start trying them one by one to see which solution is best for achieving your desired goal. If a particular solution doesn't work, move on to the next.
- Take some time alone . Since insight is often achieved when you're alone, carve out time to be by yourself for a while. The answer to your problem may come to you, seemingly out of the blue, if you spend some time away from others.
Obstacles to Problem-Solving
Problem-solving is not a flawless process as there are a number of obstacles that can interfere with our ability to solve a problem quickly and efficiently. These obstacles include:
- Assumptions: When dealing with a problem, people can make assumptions about the constraints and obstacles that prevent certain solutions. Thus, they may not even try some potential options.
- Functional fixedness : This term refers to the tendency to view problems only in their customary manner. Functional fixedness prevents people from fully seeing all of the different options that might be available to find a solution.
- Irrelevant or misleading information: When trying to solve a problem, it's important to distinguish between information that is relevant to the issue and irrelevant data that can lead to faulty solutions. The more complex the problem, the easier it is to focus on misleading or irrelevant information.
- Mental set: A mental set is a tendency to only use solutions that have worked in the past rather than looking for alternative ideas. A mental set can work as a heuristic, making it a useful problem-solving tool. However, mental sets can also lead to inflexibility, making it more difficult to find effective solutions.
How to Improve Your Problem-Solving Skills
In the end, if your goal is to become a better problem-solver, it's helpful to remember that this is a process. Thus, if you want to improve your problem-solving skills, following these steps can help lead you to your solution:
- Recognize that a problem exists . If you are facing a problem, there are generally signs. For instance, if you have a mental illness , you may experience excessive fear or sadness, mood changes, and changes in sleeping or eating habits. Recognizing these signs can help you realize that an issue exists.
- Decide to solve the problem . Make a conscious decision to solve the issue at hand. Commit to yourself that you will go through the steps necessary to find a solution.
- Seek to fully understand the issue . Analyze the problem you face, looking at it from all sides. If your problem is relationship-related, for instance, ask yourself how the other person may be interpreting the issue. You might also consider how your actions might be contributing to the situation.
- Research potential options . Using the problem-solving strategies mentioned, research potential solutions. Make a list of options, then consider each one individually. What are some pros and cons of taking the available routes? What would you need to do to make them happen?
- Take action . Select the best solution possible and take action. Action is one of the steps required for change . So, go through the motions needed to resolve the issue.
- Try another option, if needed . If the solution you chose didn't work, don't give up. Either go through the problem-solving process again or simply try another option.
You can find a way to solve your problems as long as you keep working toward this goal—even if the best solution is simply to let go because no other good solution exists.
Sarathy V. Real world problem-solving . Front Hum Neurosci . 2018;12:261. doi:10.3389/fnhum.2018.00261
Dunbar K. Problem solving . A Companion to Cognitive Science . 2017. doi:10.1002/9781405164535.ch20
Stewart SL, Celebre A, Hirdes JP, Poss JW. Risk of suicide and self-harm in kids: The development of an algorithm to identify high-risk individuals within the children's mental health system . Child Psychiat Human Develop . 2020;51:913-924. doi:10.1007/s10578-020-00968-9
Rosenbusch H, Soldner F, Evans AM, Zeelenberg M. Supervised machine learning methods in psychology: A practical introduction with annotated R code . Soc Personal Psychol Compass . 2021;15(2):e12579. doi:10.1111/spc3.12579
Mishra S. Decision-making under risk: Integrating perspectives from biology, economics, and psychology . Personal Soc Psychol Rev . 2014;18(3):280-307. doi:10.1177/1088868314530517
Csikszentmihalyi M, Sawyer K. Creative insight: The social dimension of a solitary moment . In: The Systems Model of Creativity . 2015:73-98. doi:10.1007/978-94-017-9085-7_7
Chrysikou EG, Motyka K, Nigro C, Yang SI, Thompson-Schill SL. Functional fixedness in creative thinking tasks depends on stimulus modality . Psychol Aesthet Creat Arts . 2016;10(4):425‐435. doi:10.1037/aca0000050
Huang F, Tang S, Hu Z. Unconditional perseveration of the short-term mental set in chunk decomposition . Front Psychol . 2018;9:2568. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2018.02568
National Alliance on Mental Illness. Warning signs and symptoms .
Mayer RE. Thinking, problem solving, cognition, 2nd ed .
Schooler JW, Ohlsson S, Brooks K. Thoughts beyond words: When language overshadows insight. J Experiment Psychol: General . 1993;122:166-183. doi:10.1037/0096-3445.2.166
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Happiness Hub Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Personal Development
- Problem Solving
How to Improve Problem Solving Skills
Last Updated: July 24, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Erin Conlon, PCC, JD . Erin Conlon is an Executive Life Coach, the Founder of Erin Conlon Coaching, and the host of the podcast "This is Not Advice." She specializes in aiding leaders and executives to thrive in their career and personal lives. In addition to her private coaching practice, she teaches and trains coaches and develops and revises training materials to be more diverse, equitable, and inclusive. She holds a BA in Communications and History and a JD from The University of Michigan. Erin is a Professional Certified Coach with The International Coaching Federation. There are 11 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 241,687 times.
The ability to solve problems applies to more than just mathematics homework. Analytical thinking and problem-solving skills are a part of many jobs, ranging from accounting and computer programming to detective work and even creative occupations like art, acting, and writing. While individual problems vary, there are certain general approaches to problem-solving like the one first proposed by mathematician George Polya in 1945. By following his principles of understanding the problem, devising a plan, carrying out the plan, and looking back, you can improve your problem-solving and tackle any issue systematically.
Define the problem clearly.

- Try to formulate questions. Say that as a student you have very little money and want to find an effective solution. What is at issue? Is it one of income – are you not making enough money? Is it one of over-spending? Or perhaps you have run into unexpected expenses or your financial situation has changed?
State your objective.

- Say that your problem is still money. What is your goal? Perhaps you never have enough to go out on the weekend and have fun at the movies or a club. You decide that your goal is to have more spending cash. Good! With a clear goal, you have better defined the problem.
Gather information systematically.

- To solve your money shortage, for example, you would want to get as detailed a picture of your financial situation as possible. Collect data through your latest bank statements and to talk to a bank teller. Track your earnings and spending habits in a notebook, and then create a spreadsheet or chart to show your income alongside your expenditures.
Analyze information.

- Say you have now collected all your bank statements. Look at them. When, how, and from where is your money coming? Where, when, and how are you spending it? What is the overall pattern of your finances? Do you have a net surplus or deficit? Are there any unexplained items?
Generate possible solutions.

- Your problem is a lack of money. Your goal is to have more spending cash. What are your options? Without evaluating them, come up with possible options. Perhaps you can acquire more money by getting a part-time job or by taking out a student loan. On the other hand, you might try to save by cutting your spending or by lowering other costs.
- Divide and conquer. Break the problem into smaller problems and brainstorm solutions for them separately, one by one.
- Use analogies and similarities. Try to find a resemblance with a previously solved or common problem. If you can find commonalities between your situation and one you've dealt with before, you may be able to adapt some of the solutions for use now.
Evaluate the solutions and choose.

- How can you raise money? Look at expenditures – you aren’t spending much outside of basic needs like tuition, food, and housing. Can you cut costs in other ways like finding a roommate to split rent? Can you afford to take a student loan just to have fun on the weekend? Can you spare time from your studies to work part-time?
- Each solution will produce its own set of circumstances that need evaluation. Run projections. Your money problem will require you to draw up budgets. But it will also take personal consideration. For example, can you cut back on basic things like food or housing? Are you willing to prioritize money over school or to take on debt?
Implement a solution.

- You decide to cut costs, because you were unwilling to take on debt, to divert time away from school, or to live with a roommate. You draw up a detailed budget, cutting a few dollars here and there, and commit to a month-long trial.
Review and evaluate the outcome.

- The results of your trial are mixed. On one hand, you have saved enough during the month for fun weekend activities. But there are new problems. You find that you must choose between spending cash and buying basics like food. You also need a new pair of shoes but can’t afford it, according to your budget. You may need to a different solution.
Adjust if necessary.

- After a month, you decide to abandon your first budget and to look for part-time work. You find a work-study job on campus. Making a new budget, you now have extra money without taking too much time away from your studies. You may have an effective solution.
Do regular mental exercises.

- Word games work great. In a game like “Split Words,” for example, you have to match word fragments to form words under a given theme like “philosophy.” In the game, “Tower of Babel,” you will need to memorize and then match words in a foreign language to the proper picture.
- Mathematical games will also put your problem solving to the test. Whether it be number or word problems, you will have to activate the parts of your brain that analyze information. For instance: “James is half as old now as he will be when he is 60 years older than he was six years before he was half as old as he is now. How old will James be when his age is twice what it was 10 years after he was half his current age?”
Play video games.

- Play something that will force you to think strategically or analytically. Try a puzzle game like Tetris. Or, perhaps you would rather prefer a role-playing or strategy game. In that case, something like “Civilization” or “Sim-City” might suit you better.
Take up a hobby.

- Web design, software programming, jigsaw puzzles, Sudoku, and chess are also hobbies that will force you to think strategically and systematically. Any of these will help you improve your overall problem solving.
Expert Q&A
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://www.healthywa.wa.gov.au/Articles/N_R/Problem-solving
- ↑ https://asq.org/quality-resources/problem-solving
- ↑ https://ctb.ku.edu/en/table-of-contents/evaluate/evaluate-community-interventions/collect-analyze-data/main
- ↑ https://www.mindtools.com/pages/article/newCT_96.htm
- ↑ https://www.skillsyouneed.com/ips/problem-solving.html
- ↑ Erin Conlon, PCC, JD. Executive Life Coach. Expert Interview. 31 August 2021.
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5930973/
- ↑ https://www.theguardian.com/lifeandstyle/2018/oct/13/mental-exercises-to-keep-your-brain-sharp
- ↑ https://www.apa.org/monitor/2014/02/video-game
- ↑ https://www.nature.com/articles/d41586-018-05449-7
About This Article

To improve your problem-solving skills, start by clearly defining the problem and your objective or goal. Next, gather as much information as you can about the problem and organize the data by rewording, condensing, or summarizing it. Then, analyze the information you've gathered, looking for important links, patterns, and relationships in the data. Finally, brainstorm possible solutions, evaluate the solutions, and choose one to implement. For tips on implementing solutions successfully, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Georgia Williams
Mar 10, 2023
Did this article help you?
Mar 8, 2017
Alexis Stevens
Sep 23, 2016

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
Introduction to Problem Solving Skills
What is problem solving and why is it important.
The ability to solve problems is a basic life skill and is essential to our day-to-day lives, at home, at school, and at work. We solve problems every day without really thinking about how we solve them. For example: it’s raining and you need to go to the store. What do you do? There are lots of possible solutions. Take your umbrella and walk. If you don't want to get wet, you can drive, or take the bus. You might decide to call a friend for a ride, or you might decide to go to the store another day. There is no right way to solve this problem and different people will solve it differently.
Problem solving is the process of identifying a problem, developing possible solution paths, and taking the appropriate course of action.
Why is problem solving important? Good problem solving skills empower you not only in your personal life but are critical in your professional life. In the current fast-changing global economy, employers often identify everyday problem solving as crucial to the success of their organizations. For employees, problem solving can be used to develop practical and creative solutions, and to show independence and initiative to employers.
Throughout this case study you will be asked to jot down your thoughts in idea logs. These idea logs are used for reflection on concepts and for answering short questions. When you click on the "Next" button, your responses will be saved for that page. If you happen to close the webpage, you will lose your work on the page you were on, but previous pages will be saved. At the end of the case study, click on the "Finish and Export to PDF" button to acknowledge completion of the case study and receive a PDF document of your idea logs.
What Does Problem Solving Look Like?
The ability to solve problems is a skill, and just like any other skill, the more you practice, the better you get. So how exactly do you practice problem solving? Learning about different problem solving strategies and when to use them will give you a good start. Problem solving is a process. Most strategies provide steps that help you identify the problem and choose the best solution. There are two basic types of strategies: algorithmic and heuristic.
Algorithmic strategies are traditional step-by-step guides to solving problems. They are great for solving math problems (in algebra: multiply and divide, then add or subtract) or for helping us remember the correct order of things (a mnemonic such as “Spring Forward, Fall Back” to remember which way the clock changes for daylight saving time, or “Righty Tighty, Lefty Loosey” to remember what direction to turn bolts and screws). Algorithms are best when there is a single path to the correct solution.
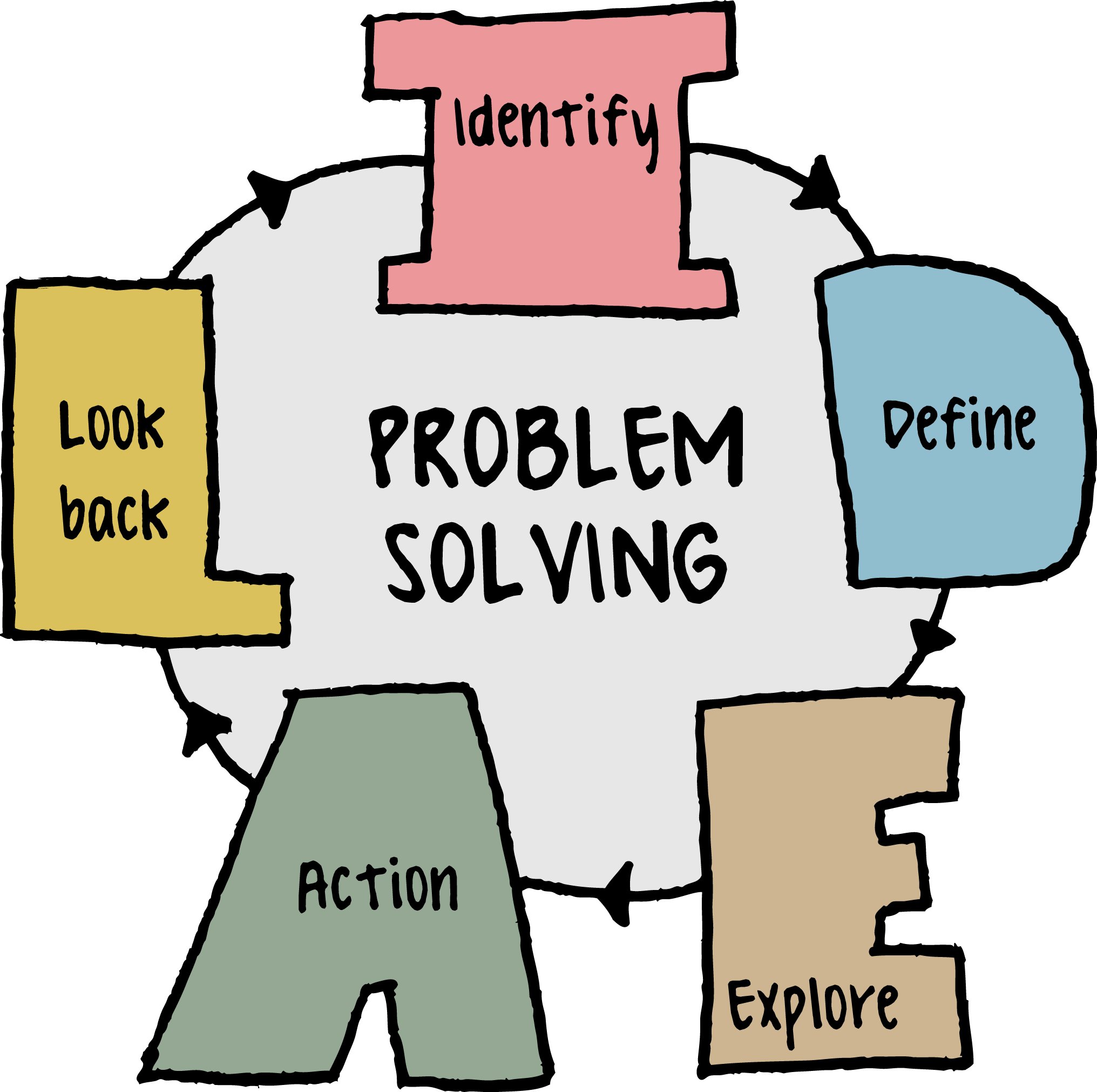
But what do you do when there is no single solution for your problem? Heuristic methods are general guides used to identify possible solutions. A popular one that is easy to remember is IDEAL [ Bransford & Stein, 1993 ] :
- I dentify the problem
- D efine the context of the problem
- E xplore possible strategies
- A ct on best solution
IDEAL is just one problem solving strategy. Building a toolbox of problem solving strategies will improve your problem solving skills. With practice, you will be able to recognize and use multiple strategies to solve complex problems.
Watch the video
What is the best way to get a peanut out of a tube that cannot be moved? Watch a chimpanzee solve this problem in the video below [ Geert Stienissen, 2010 ].
[PDF transcript]
Describe the series of steps you think the chimpanzee used to solve this problem.
- [Page 2: What does Problem Solving Look Like?] Describe the series of steps you think the chimpanzee used to solve this problem.
Think of an everyday problem you've encountered recently and describe your steps for solving it.
- [Page 2: What does Problem Solving Look Like?] Think of an everyday problem you've encountered recently and describe your steps for solving it.
Developing Problem Solving Processes
Problem solving is a process that uses steps to solve problems. But what does that really mean? Let's break it down and start building our toolbox of problem solving strategies.
What is the first step of solving any problem? The first step is to recognize that there is a problem and identify the right cause of the problem. This may sound obvious, but similar problems can arise from different events, and the real issue may not always be apparent. To really solve the problem, it's important to find out what started it all. This is called identifying the root cause .
Example: You and your classmates have been working long hours on a project in the school's workshop. The next afternoon, you try to use your student ID card to access the workshop, but discover that your magnetic strip has been demagnetized. Since the card was a couple of years old, you chalk it up to wear and tear and get a new ID card. Later that same week you learn that several of your classmates had the same problem! After a little investigation, you discover that a strong magnet was stored underneath a workbench in the workshop. The magnet was the root cause of the demagnetized student ID cards.
The best way to identify the root cause of the problem is to ask questions and gather information. If you have a vague problem, investigating facts is more productive than guessing a solution. Ask yourself questions about the problem. What do you know about the problem? What do you not know? When was the last time it worked correctly? What has changed since then? Can you diagram the process into separate steps? Where in the process is the problem occurring? Be curious, ask questions, gather facts, and make logical deductions rather than assumptions.
Watch Adam Savage from Mythbusters, describe his problem solving process [ ForaTv, 2010 ]. As you watch this section of the video, try to identify the questions he asks and the different strategies he uses.
Adam Savage shared many of his problem solving processes. List the ones you think are the five most important. Your list may be different from other people in your class—that's ok!
- [Page 3: Developing Problem Solving Processes] Adam Savage shared many of his problem solving processes. List the ones you think are the five most important.
“The ability to ask the right question is more than half the battle of finding the answer.” — Thomas J. Watson , founder of IBM
Voices From the Field: Solving Problems
In manufacturing facilities and machine shops, everyone on the floor is expected to know how to identify problems and find solutions. Today's employers look for the following skills in new employees: to analyze a problem logically, formulate a solution, and effectively communicate with others.
In this video, industry professionals share their own problem solving processes, the problem solving expectations of their employees, and an example of how a problem was solved.
Meet the Partners:
- Taconic High School in Pittsfield, Massachusetts, is a comprehensive, fully accredited high school with special programs in Health Technology, Manufacturing Technology, and Work-Based Learning.
- Berkshire Community College in Pittsfield, Massachusetts, prepares its students with applied manufacturing technical skills, providing hands-on experience at industrial laboratories and manufacturing facilities, and instructing them in current technologies.
- H.C. Starck in Newton, Massachusetts, specializes in processing and manufacturing technology metals, such as tungsten, niobium, and tantalum. In almost 100 years of experience, they hold over 900 patents, and continue to innovate and develop new products.
- Nypro Healthcare in Devens, Massachusetts, specializes in precision injection-molded healthcare products. They are committed to good manufacturing processes including lean manufacturing and process validation.
Making Decisions
Now that you have a couple problem solving strategies in your toolbox, let's practice. In this exercise, you are given a scenario and you will be asked to decide what steps you would take to identify and solve the problem.
Scenario: You are a new employee and have just finished your training. As your first project, you have been assigned the milling of several additional components for a regular customer. Together, you and your trainer, Bill, set up for the first run. Checking your paperwork, you gather the tools and materials on the list. As you are mounting the materials on the table, you notice that you didn't grab everything and hurriedly grab a few more items from one of the bins. Once the material is secured on the CNC table, you load tools into the tool carousel in the order listed on the tool list and set the fixture offsets.
Bill tells you that since this is a rerun of a job several weeks ago, the CAD/CAM model has already been converted to CNC G-code. Bill helps you download the code to the CNC machine. He gives you the go-ahead and leaves to check on another employee. You decide to start your first run.
What problems did you observe in the video?
- [Page 5: Making Decisions] What problems did you observe in the video?
- What do you do next?
- Try to fix it yourself.
- Ask your trainer for help.
As you are cleaning up, you think about what happened and wonder why it happened. You try to create a mental picture of what happened. You are not exactly sure what the end mill hit, but it looked like it might have hit the dowel pin. You wonder if you grabbed the correct dowel pins from the bins earlier.
You can think of two possible next steps. You can recheck the dowel pin length to make sure it is the correct length, or do a dry run using the CNC single step or single block function with the spindle empty to determine what actually happened.

- Check the dowel pins.
- Use the single step/single block function to determine what happened.
You notice that your trainer, Bill, is still on the floor and decide to ask him for help. You describe the problem to him. Bill asks if you know what the end mill ran into. You explain that you are not sure but you think it was the dowel pin. Bill reminds you that it is important to understand what happened so you can fix the correct problem. He suggests that you start all over again and begin with a dry run using the single step/single block function, with the spindle empty, to determine what it hit. Or, since it happened at the end, he mentions that you can also check the G-code to make sure the Z-axis is raised before returning to the home position.
- Run the single step/single block function.
- Edit the G-code to raise the Z-axis.
You finish cleaning up and check the CNC for any damage. Luckily, everything looks good. You check your paperwork and gather the components and materials again. You look at the dowel pins you used earlier, and discover that they are not the right length. As you go to grab the correct dowel pins, you have to search though several bins. For the first time, you are aware of the mess - it looks like the dowel pins and other items have not been put into the correctly labeled bins. You spend 30 minutes straightening up the bins and looking for the correct dowel pins.
Finally finding them, you finish setting up. You load tools into the tool carousel in the order listed on the tool list and set the fixture offsets. Just to make sure, you use the CNC single step/single block function, to do a dry run of the part. Everything looks good! You are ready to create your first part. The first component is done, and, as you admire your success, you notice that the part feels hotter than it should.
You wonder why? You go over the steps of the process to mentally figure out what could be causing the residual heat. You wonder if there is a problem with the CNC's coolant system or if the problem is in the G-code.
- Look at the G-code.
After thinking about the problem, you decide that maybe there's something wrong with the setup. First, you clean up the damaged materials and remove the broken tool. You check the CNC machine carefully for any damage. Luckily, everything looks good. It is time to start over again from the beginning.
You again check your paperwork and gather the tools and materials on the setup sheet. After securing the new materials, you use the CNC single step/single block function with the spindle empty, to do a dry run of the part. You watch carefully to see if you can figure out what happened. It looks to you like the spindle barely misses hitting the dowel pin. You determine that the end mill was broken when it hit the dowel pin while returning to the start position.
After conducting a dry run using the single step/single block function, you determine that the end mill was damaged when it hit the dowel pin on its return to the home position. You discuss your options with Bill. Together, you decide the best thing to do would be to edit the G-code and raise the Z-axis before returning to home. You open the CNC control program and edit the G-code. Just to make sure, you use the CNC single step/single block function, to do another dry run of the part. You are ready to create your first part. It works. You first part is completed. Only four more to go.
As you are cleaning up, you notice that the components are hotter than you expect and the end mill looks more worn than it should be. It dawns on you that while you were milling the component, the coolant didn't turn on. You wonder if it is a software problem in the G-code or hardware problem with the CNC machine.
It's the end of the day and you decide to finish the rest of the components in the morning.
- You decide to look at the G-code in the morning.
- You leave a note on the machine, just in case.
You decide that the best thing to do would be to edit the G-code and raise the Z-axis of the spindle before it returns to home. You open the CNC control program and edit the G-code.
While editing the G-code to raise the Z-axis, you notice that the coolant is turned off at the beginning of the code and at the end of the code. The coolant command error caught your attention because your coworker, Mark, mentioned having a similar issue during lunch. You change the coolant command to turn the mist on.
- You decide to talk with your supervisor.
- You discuss what happened with a coworker over lunch.
As you reflect on the residual heat problem, you think about the machining process and the factors that could have caused the issue. You try to think of anything and everything that could be causing the issue. Are you using the correct tool for the specified material? Are you using the specified material? Is it running at the correct speed? Is there enough coolant? Are there chips getting in the way?
Wait, was the coolant turned on? As you replay what happened in your mind, you wonder why the coolant wasn't turned on. You decide to look at the G-code to find out what is going on.
From the milling machine computer, you open the CNC G-code. You notice that there are no coolant commands. You add them in and on the next run, the coolant mist turns on and the residual heat issues is gone. Now, its on to creating the rest of the parts.
Have you ever used brainstorming to solve a problem? Chances are, you've probably have, even if you didn't realize it.
You notice that your trainer, Bill, is on the floor and decide to ask him for help. You describe the problem with the end mill breaking, and how you discovered that items are not being returned to the correctly labeled bins. You think this caused you to grab the incorrect length dowel pins on your first run. You have sorted the bins and hope that the mess problem is fixed. You then go on to tell Bill about the residual heat issue with the completed part.
Together, you go to the milling machine. Bill shows you how to check the oil and coolant levels. Everything looks good at the machine level. Next, on the CNC computer, you open the CNC G-code. While looking at the code, Bill points out that there are no coolant commands. Bill adds them in and when you rerun the program, it works.
Bill is glad you mentioned the problem to him. You are the third worker to mention G-code issues over the last week. You noticed the coolant problems in your G-code, John noticed a Z-axis issue in his G-code, and Sam had issues with both the Z-axis and the coolant. Chances are, there is a bigger problem and Bill will need to investigate the root cause .
Talking with Bill, you discuss the best way to fix the problem. Bill suggests editing the G-code to raise the Z-axis of the spindle before it returns to its home position. You open the CNC control program and edit the G-code. Following the setup sheet, you re-setup the job and use the CNC single step/single block function, to do another dry run of the part. Everything looks good, so you run the job again and create the first part. It works. Since you need four of each component, you move on to creating the rest of them before cleaning up and leaving for the day.
It's a new day and you have new components to create. As you are setting up, you go in search of some short dowel pins. You discover that the bins are a mess and components have not been put away in the correctly labeled bins. You wonder if this was the cause of yesterday's problem. As you reorganize the bins and straighten up the mess, you decide to mention the mess issue to Bill in your afternoon meeting.
You describe the bin mess and using the incorrect length dowels to Bill. He is glad you mentioned the problem to him. You are not the first person to mention similar issues with tools and parts not being put away correctly. Chances are there is a bigger safety issue here that needs to be addressed in the next staff meeting.
In any workplace, following proper safety and cleanup procedures is always important. This is especially crucial in manufacturing where people are constantly working with heavy, costly and sometimes dangerous equipment. When issues and problems arise, it is important that they are addressed in an efficient and timely manner. Effective communication is an important tool because it can prevent problems from recurring, avoid injury to personnel, reduce rework and scrap, and ultimately, reduce cost, and save money.
You now know that the end mill was damaged when it hit the dowel pin. It seems to you that the easiest thing to do would be to edit the G-code and raise the Z-axis position of the spindle before it returns to the home position. You open the CNC control program and edit the G-code, raising the Z-axis. Starting over, you follow the setup sheet and re-setup the job. This time, you use the CNC single step/single block function, to do another dry run of the part. Everything looks good, so you run the job again and create the first part.
At the end of the day, you are reviewing your progress with your trainer, Bill. After you describe the day's events, he reminds you to always think about safety and the importance of following work procedures. He decides to bring the issue up in the next morning meeting as a reminder to everyone.
In any workplace, following proper procedures (especially those that involve safety) is always important. This is especially crucial in manufacturing where people are constantly working with heavy, costly, and sometimes dangerous equipment. When issues and problems arise, it is important that they are addressed in an efficient and timely manner. Effective communication is an important tool because it can prevent problems from recurring, avoid injury to personnel, reduce rework and scrap, and ultimately, reduce cost, and save money. One tool to improve communication is the morning meeting or huddle.
The next morning, you check the G-code to determine what is wrong with the coolant. You notice that the coolant is turned off at the beginning of the code and also at the end of the code. This is strange. You change the G-code to turn the coolant on at the beginning of the run and off at the end. This works and you create the rest of the parts.
Throughout the day, you keep wondering what caused the G-code error. At lunch, you mention the G-code error to your coworker, John. John is not surprised. He said that he encountered a similar problem earlier this week. You decide to talk with your supervisor the next time you see him.
You are in luck. You see your supervisor by the door getting ready to leave. You hurry over to talk with him. You start off by telling him about how you asked Bill for help. Then you tell him there was a problem and the end mill was damaged. You describe the coolant problem in the G-code. Oh, and by the way, John has seen a similar problem before.
Your supervisor doesn't seem overly concerned, errors happen. He tells you "Good job, I am glad you were able to fix the issue." You are not sure whether your supervisor understood your explanation of what happened or that it had happened before.
The challenge of communicating in the workplace is learning how to share your ideas and concerns. If you need to tell your supervisor that something is not going well, it is important to remember that timing, preparation, and attitude are extremely important.
It is the end of your shift, but you want to let the next shift know that the coolant didn't turn on. You do not see your trainer or supervisor around. You decide to leave a note for the next shift so they are aware of the possible coolant problem. You write a sticky note and leave it on the monitor of the CNC control system.
How effective do you think this solution was? Did it address the problem?
In this scenario, you discovered several problems with the G-code that need to be addressed. When issues and problems arise, it is important that they are addressed in an efficient and timely manner. Effective communication is an important tool because it can prevent problems from recurring and avoid injury to personnel. The challenge of communicating in the workplace is learning how and when to share your ideas and concerns. If you need to tell your co-workers or supervisor that there is a problem, it is important to remember that timing and the method of communication are extremely important.
You are able to fix the coolant problem in the G-code. While you are glad that the problem is fixed, you are worried about why it happened in the first place. It is important to remember that if a problem keeps reappearing, you may not be fixing the right problem. You may only be addressing the symptoms.
You decide to talk to your trainer. Bill is glad you mentioned the problem to him. You are the third worker to mention G-code issues over the last week. You noticed the coolant problems in your G-code, John noticed a Z-axis issue in his G-code, and Sam had issues with both the Z-axis and the coolant. Chances are, there is a bigger problem and Bill will need to investigate the root cause .
Over lunch, you ask your coworkers about the G-code problem and what may be causing the error. Several people mention having similar problems but do not know the cause.
You have now talked to three coworkers who have all experienced similar coolant G-code problems. You make a list of who had the problem, when they had the problem, and what each person told you.
| Person | When | Problem Description |
|---|---|---|
| Sam | last week | No coolant commands in G-code |
| John | Yesterday | Coolant was turned off and there were Z-axis problems |
| Me | today | Coolant was turned off at both beginning and end of program |
When you see your supervisor later that afternoon, you are ready to talk with him. You describe the problem you had with your component and the damaged bit. You then go on to tell him about talking with Bill and discovering the G-code issue. You show him your notes on your coworkers' coolant issues, and explain that you think there might be a bigger problem.
You supervisor thanks you for your initiative in identifying this problem. It sounds like there is a bigger problem and he will need to investigate the root cause. He decides to call a team huddle to discuss the issue, gather more information, and talk with the team about the importance of communication.
Root Cause Analysis

Root cause analysis ( RCA ) is a method of problem solving that identifies the underlying causes of an issue. Root cause analysis helps people answer the question of why the problem occurred in the first place. RCA uses clear cut steps in its associated tools, like the "5 Whys Analysis" and the "Cause and Effect Diagram," to identify the origin of the problem, so that you can:
- Determine what happened.
- Determine why it happened.
- Fix the problem so it won’t happen again.
RCA works under the idea that systems and events are connected. An action in one area triggers an action in another, and another, and so on. By tracing back these actions, you can discover where the problem started and how it developed into the problem you're now facing. Root cause analysis can prevent problems from recurring, reduce injury to personnel, reduce rework and scrap, and ultimately, reduce cost and save money. There are many different RCA techniques available to determine the root cause of a problem. These are just a few:
- Root Cause Analysis Tools
- 5 Whys Analysis
- Fishbone or Cause and Effect Diagram
- Pareto Analysis

How Huddles Work

Communication is a vital part of any setting where people work together. Effective communication helps employees and managers form efficient teams. It builds trusts between employees and management, and reduces unnecessary competition because each employee knows how their part fits in the larger goal.
One tool that management can use to promote communication in the workplace is the huddle . Just like football players on the field, a huddle is a short meeting where everyone is standing in a circle. A daily team huddle ensures that team members are aware of changes to the schedule, reiterated problems and safety issues, and how their work impacts one another. When done right, huddles create collaboration, communication, and accountability to results. Impromptu huddles can be used to gather information on a specific issue and get each team member's input.
The most important thing to remember about huddles is that they are short, lasting no more than 10 minutes, and their purpose is to communicate and identify. In essence, a huddle’s purpose is to identify priorities, communicate essential information, and discover roadblocks to productivity.
Who uses huddles? Many industries and companies use daily huddles. At first thought, most people probably think of hospitals and their daily patient update meetings, but lots of managers use daily meetings to engage their employees. Here are a few examples:
- Brian Scudamore, CEO of 1-800-Got-Junk? , uses the daily huddle as an operational tool to take the pulse of his employees and as a motivational tool. Watch a morning huddle meeting .
- Fusion OEM, an outsourced manufacturing and production company. What do employees take away from the daily huddle meeting .
- Biz-Group, a performance consulting group. Tips for a successful huddle .
Brainstorming
One tool that can be useful in problem solving is brainstorming . Brainstorming is a creativity technique designed to generate a large number of ideas for the solution to a problem. The method was first popularized in 1953 by Alex Faickney Osborn in the book Applied Imagination . The goal is to come up with as many ideas as you can in a fixed amount of time. Although brainstorming is best done in a group, it can be done individually. Like most problem solving techniques, brainstorming is a process.
- Define a clear objective.
- Have an agreed a time limit.
- During the brainstorming session, write down everything that comes to mind, even if the idea sounds crazy.
- If one idea leads to another, write down that idea too.
- Combine and refine ideas into categories of solutions.
- Assess and analyze each idea as a potential solution.
When used during problem solving, brainstorming can offer companies new ways of encouraging staff to think creatively and improve production. Brainstorming relies on team members' diverse experiences, adding to the richness of ideas explored. This means that you often find better solutions to the problems. Team members often welcome the opportunity to contribute ideas and can provide buy-in for the solution chosen—after all, they are more likely to be committed to an approach if they were involved in its development. What's more, because brainstorming is fun, it helps team members bond.
- Watch Peggy Morgan Collins, a marketing executive at Power Curve Communications discuss How to Stimulate Effective Brainstorming .
- Watch Kim Obbink, CEO of Filter Digital, a digital content company, and her team share their top five rules for How to Effectively Generate Ideas .
Importance of Good Communication and Problem Description

Communication is one of the most frequent activities we engage in on a day-to-day basis. At some point, we have all felt that we did not effectively communicate an idea as we would have liked. The key to effective communication is preparation. Rather than attempting to haphazardly improvise something, take a few minutes and think about what you want say and how you will say it. If necessary, write yourself a note with the key points or ideas in the order you want to discuss them. The notes can act as a reminder or guide when you talk to your supervisor.
Tips for clear communication of an issue:
- Provide a clear summary of your problem. Start at the beginning, give relevant facts, timelines, and examples.
- Avoid including your opinion or personal attacks in your explanation.
- Avoid using words like "always" or "never," which can give the impression that you are exaggerating the problem.
- If this is an ongoing problem and you have collected documentation, give it to your supervisor once you have finished describing the problem.
- Remember to listen to what's said in return; communication is a two-way process.
Not all communication is spoken. Body language is nonverbal communication that includes your posture, your hands and whether you make eye contact. These gestures can be subtle or overt, but most importantly they communicate meaning beyond what is said. When having a conversation, pay attention to how you stand. A stiff position with arms crossed over your chest may imply that you are being defensive even if your words state otherwise. Shoving your hands in your pockets when speaking could imply that you have something to hide. Be wary of using too many hand gestures because this could distract listeners from your message.
The challenge of communicating in the workplace is learning how and when to share your ideas or concerns. If you need to tell your supervisor or co-worker about something that is not going well, keep in mind that good timing and good attitude will go a long way toward helping your case.
Like all skills, effective communication needs to be practiced. Toastmasters International is perhaps the best known public speaking organization in the world. Toastmasters is open to anyone who wish to improve their speaking skills and is willing to put in the time and effort to do so. To learn more, visit Toastmasters International .
Methods of Communication
Communication of problems and issues in any workplace is important, particularly when safety is involved. It is therefore crucial in manufacturing where people are constantly working with heavy, costly, and sometimes dangerous equipment. As issues and problems arise, they need to be addressed in an efficient and timely manner. Effective communication is an important skill because it can prevent problems from recurring, avoid injury to personnel, reduce rework and scrap, and ultimately, reduce cost and save money.
There are many different ways to communicate: in person, by phone, via email, or written. There is no single method that fits all communication needs, each one has its time and place.
In person: In the workplace, face-to-face meetings should be utilized whenever possible. Being able to see the person you need to speak to face-to-face gives you instant feedback and helps you gauge their response through their body language. Be careful of getting sidetracked in conversation when you need to communicate a problem.
Email: Email has become the communication standard for most businesses. It can be accessed from almost anywhere and is great for things that don’t require an immediate response. Email is a great way to communicate non-urgent items to large amounts of people or just your team members. One thing to remember is that most people's inboxes are flooded with emails every day and unless they are hyper vigilant about checking everything, important items could be missed. For issues that are urgent, especially those around safety, email is not always be the best solution.
Phone: Phone calls are more personal and direct than email. They allow us to communicate in real time with another person, no matter where they are. Not only can talking prevent miscommunication, it promotes a two-way dialogue. You don’t have to worry about your words being altered or the message arriving on time. However, mobile phone use and the workplace don't always mix. In particular, using mobile phones in a manufacturing setting can lead to a variety of problems, cause distractions, and lead to serious injury.
Written: Written communication is appropriate when detailed instructions are required, when something needs to be documented, or when the person is too far away to easily speak with over the phone or in person.
There is no "right" way to communicate, but you should be aware of how and when to use the appropriate form of communication for your situation. When deciding the best way to communicate with a co-worker or manager, put yourself in their shoes, and think about how you would want to learn about the issue. Also, consider what information you would need to know to better understand the issue. Use your good judgment of the situation and be considerate of your listener's viewpoint.
Did you notice any other potential problems in the previous exercise?
- [Page 6:] Did you notice any other potential problems in the previous exercise?
Summary of Strategies
In this exercise, you were given a scenario in which there was a problem with a component you were creating on a CNC machine. You were then asked how you wanted to proceed. Depending on your path through this exercise, you might have found an easy solution and fixed it yourself, asked for help and worked with your trainer, or discovered an ongoing G-code problem that was bigger than you initially thought.
When issues and problems arise, it is important that they are addressed in an efficient and timely manner. Communication is an important tool because it can prevent problems from recurring, avoid injury to personnel, reduce rework and scrap, and ultimately, reduce cost, and save money. Although, each path in this exercise ended with a description of a problem solving tool for your toolbox, the first step is always to identify the problem and define the context in which it happened.
There are several strategies that can be used to identify the root cause of a problem. Root cause analysis (RCA) is a method of problem solving that helps people answer the question of why the problem occurred. RCA uses a specific set of steps, with associated tools like the “5 Why Analysis" or the “Cause and Effect Diagram,” to identify the origin of the problem, so that you can:
Once the underlying cause is identified and the scope of the issue defined, the next step is to explore possible strategies to fix the problem.
If you are not sure how to fix the problem, it is okay to ask for help. Problem solving is a process and a skill that is learned with practice. It is important to remember that everyone makes mistakes and that no one knows everything. Life is about learning. It is okay to ask for help when you don’t have the answer. When you collaborate to solve problems you improve workplace communication and accelerates finding solutions as similar problems arise.
One tool that can be useful for generating possible solutions is brainstorming . Brainstorming is a technique designed to generate a large number of ideas for the solution to a problem. The method was first popularized in 1953 by Alex Faickney Osborn in the book Applied Imagination. The goal is to come up with as many ideas as you can, in a fixed amount of time. Although brainstorming is best done in a group, it can be done individually.
Depending on your path through the exercise, you may have discovered that a couple of your coworkers had experienced similar problems. This should have been an indicator that there was a larger problem that needed to be addressed.
In any workplace, communication of problems and issues (especially those that involve safety) is always important. This is especially crucial in manufacturing where people are constantly working with heavy, costly, and sometimes dangerous equipment. When issues and problems arise, it is important that they be addressed in an efficient and timely manner. Effective communication is an important tool because it can prevent problems from recurring, avoid injury to personnel, reduce rework and scrap, and ultimately, reduce cost and save money.
One strategy for improving communication is the huddle . Just like football players on the field, a huddle is a short meeting with everyone standing in a circle. A daily team huddle is a great way to ensure that team members are aware of changes to the schedule, any problems or safety issues are identified and that team members are aware of how their work impacts one another. When done right, huddles create collaboration, communication, and accountability to results. Impromptu huddles can be used to gather information on a specific issue and get each team member's input.
To learn more about different problem solving strategies, choose an option below. These strategies accompany the outcomes of different decision paths in the problem solving exercise.
- View Problem Solving Strategies Select a strategy below... Root Cause Analysis How Huddles Work Brainstorming Importance of Good Problem Description Methods of Communication
Communication is one of the most frequent activities we engage in on a day-to-day basis. At some point, we have all felt that we did not effectively communicate an idea as we would have liked. The key to effective communication is preparation. Rather than attempting to haphazardly improvise something, take a few minutes and think about what you want say and how you will say it. If necessary, write yourself a note with the key points or ideas in the order you want to discuss them. The notes can act as a reminder or guide during your meeting.
- Provide a clear summary of the problem. Start at the beginning, give relevant facts, timelines, and examples.
In person: In the workplace, face-to-face meetings should be utilized whenever possible. Being able to see the person you need to speak to face-to-face gives you instant feedback and helps you gauge their response in their body language. Be careful of getting sidetracked in conversation when you need to communicate a problem.
There is no "right" way to communicate, but you should be aware of how and when to use the appropriate form of communication for the situation. When deciding the best way to communicate with a co-worker or manager, put yourself in their shoes, and think about how you would want to learn about the issue. Also, consider what information you would need to know to better understand the issue. Use your good judgment of the situation and be considerate of your listener's viewpoint.
"Never try to solve all the problems at once — make them line up for you one-by-one.” — Richard Sloma
Problem Solving: An Important Job Skill
Problem solving improves efficiency and communication on the shop floor. It increases a company's efficiency and profitability, so it's one of the top skills employers look for when hiring new employees. Recent industry surveys show that employers consider soft skills, such as problem solving, as critical to their business’s success.
The 2011 survey, "Boiling Point? The skills gap in U.S. manufacturing ," polled over a thousand manufacturing executives who reported that the number one skill deficiency among their current employees is problem solving, which makes it difficult for their companies to adapt to the changing needs of the industry.
In this video, industry professionals discuss their expectations and present tips for new employees joining the manufacturing workforce.
Quick Summary
- [Quick Summary: Question1] What are two things you learned in this case study?
- What question(s) do you still have about the case study?
- [Quick Summary: Question2] What question(s) do you still have about the case study?
- Is there anything you would like to learn more about with respect to this case study?
- [Quick Summary: Question3] Is there anything you would like to learn more about with respect to this case study?
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.

Health & Nursing
Courses and certificates.
- Bachelor's Degrees
- View all Business Bachelor's Degrees
- Business Management – B.S. Business Administration
- Healthcare Administration – B.S.
- Human Resource Management – B.S. Business Administration
- Information Technology Management – B.S. Business Administration
- Marketing – B.S. Business Administration
- Accounting – B.S. Business Administration
- Finance – B.S.
- Supply Chain and Operations Management – B.S.
- Communications – B.S.
- User Experience Design – B.S.
- Accelerated Information Technology Bachelor's and Master's Degree (from the School of Technology)
- Health Information Management – B.S. (from the Leavitt School of Health)
- View all Business Degrees
Master's Degrees
- View all Business Master's Degrees
- Master of Business Administration (MBA)
- MBA Information Technology Management
- MBA Healthcare Management
- Management and Leadership – M.S.
- Accounting – M.S.
- Marketing – M.S.
- Human Resource Management – M.S.
- Master of Healthcare Administration (from the Leavitt School of Health)
- Data Analytics – M.S. (from the School of Technology)
- Information Technology Management – M.S. (from the School of Technology)
- Education Technology and Instructional Design – M.Ed. (from the School of Education)
Certificates
- Supply Chain
- Accounting Fundamentals
- Digital Marketing and E-Commerce
Bachelor's Preparing For Licensure
- View all Education Bachelor's Degrees
- Elementary Education – B.A.
- Special Education and Elementary Education (Dual Licensure) – B.A.
- Special Education (Mild-to-Moderate) – B.A.
- Mathematics Education (Middle Grades) – B.S.
- Mathematics Education (Secondary)– B.S.
- Science Education (Middle Grades) – B.S.
- Science Education (Secondary Chemistry) – B.S.
- Science Education (Secondary Physics) – B.S.
- Science Education (Secondary Biological Sciences) – B.S.
- Science Education (Secondary Earth Science)– B.S.
- View all Education Degrees
Bachelor of Arts in Education Degrees
- Educational Studies – B.A.
Master of Science in Education Degrees
- View all Education Master's Degrees
- Curriculum and Instruction – M.S.
- Educational Leadership – M.S.
- Education Technology and Instructional Design – M.Ed.
Master's Preparing for Licensure
- Teaching, Elementary Education – M.A.
- Teaching, English Education (Secondary) – M.A.
- Teaching, Mathematics Education (Middle Grades) – M.A.
- Teaching, Mathematics Education (Secondary) – M.A.
- Teaching, Science Education (Secondary) – M.A.
- Teaching, Special Education (K-12) – M.A.
Licensure Information
- State Teaching Licensure Information
Master's Degrees for Teachers
- Mathematics Education (K-6) – M.A.
- Mathematics Education (Middle Grade) – M.A.
- Mathematics Education (Secondary) – M.A.
- English Language Learning (PreK-12) – M.A.
- Endorsement Preparation Program, English Language Learning (PreK-12)
- Science Education (Middle Grades) – M.A.
- Science Education (Secondary Chemistry) – M.A.
- Science Education (Secondary Physics) – M.A.
- Science Education (Secondary Biological Sciences) – M.A.
- Science Education (Secondary Earth Science)– M.A.
- View all Technology Bachelor's Degrees
- Cloud Computing – B.S.
- Computer Science – B.S.
- Cybersecurity and Information Assurance – B.S.
- Data Analytics – B.S.
- Information Technology – B.S.
- Network Engineering and Security – B.S.
- Software Engineering – B.S.
- Accelerated Information Technology Bachelor's and Master's Degree
- Information Technology Management – B.S. Business Administration (from the School of Business)
- User Experience Design – B.S. (from the School of Business)
- View all Technology Master's Degrees
- Cybersecurity and Information Assurance – M.S.
- Data Analytics – M.S.
- Information Technology Management – M.S.
- MBA Information Technology Management (from the School of Business)
- Full Stack Engineering
- Web Application Deployment and Support
- Front End Web Development
- Back End Web Development
3rd Party Certifications
- IT Certifications Included in WGU Degrees
- View all Technology Degrees
- View all Health & Nursing Bachelor's Degrees
- Nursing (RN-to-BSN online) – B.S.
- Nursing (Prelicensure) – B.S. (Available in select states)
- Health Information Management – B.S.
- Health and Human Services – B.S.
- Psychology – B.S.
- Health Science – B.S.
- Public Health – B.S.
- Healthcare Administration – B.S. (from the School of Business)
- View all Nursing Post-Master's Certificates
- Nursing Education—Post-Master's Certificate
- Nursing Leadership and Management—Post-Master's Certificate
- Family Nurse Practitioner—Post-Master's Certificate
- Psychiatric Mental Health Nurse Practitioner —Post-Master's Certificate
- View all Health & Nursing Degrees
- View all Nursing & Health Master's Degrees
- Nursing – Education (BSN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Nursing – Leadership and Management (BSN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Nursing – Nursing Informatics (BSN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Nursing – Family Nurse Practitioner (BSN-to-MSN Program) – M.S. (Available in select states)
- Nursing – Psychiatric Mental Health Nurse Practitioner (BSN-to-MSN Program) – M.S. (Available in select states)
- Nursing – Education (RN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Nursing – Leadership and Management (RN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Nursing – Nursing Informatics (RN-to-MSN Program) – M.S.
- Master of Healthcare Administration
- Master of Public Health
- MBA Healthcare Management (from the School of Business)
- Business Leadership (with the School of Business)
- Supply Chain (with the School of Business)
- Accounting Fundamentals (with the School of Business)
- Digital Marketing and E-Commerce (with the School of Business)
- Back End Web Development (with the School of Technology)
- Front End Web Development (with the School of Technology)
- Web Application Deployment and Support (with the School of Technology)
- Full Stack Engineering (with the School of Technology)
- Single Courses
- Course Bundles
Apply for Admission
Admission requirements.
- New Students
- WGU Returning Graduates
- WGU Readmission
- Enrollment Checklist
- Accessibility
- Accommodation Request
- School of Education Admission Requirements
- School of Business Admission Requirements
- School of Technology Admission Requirements
- Leavitt School of Health Admission Requirements
Additional Requirements
- Computer Requirements
- No Standardized Testing
- Clinical and Student Teaching Information
Transferring
- FAQs about Transferring
- Transfer to WGU
- Transferrable Certifications
- Request WGU Transcripts
- International Transfer Credit
- Tuition and Fees
- Financial Aid
- Scholarships
Other Ways to Pay for School
- Tuition—School of Business
- Tuition—School of Education
- Tuition—School of Technology
- Tuition—Leavitt School of Health
- Your Financial Obligations
- Tuition Comparison
- Applying for Financial Aid
- State Grants
- Consumer Information Guide
- Responsible Borrowing Initiative
- Higher Education Relief Fund
FAFSA Support
- Net Price Calculator
- FAFSA Simplification
- See All Scholarships
- Military Scholarships
- State Scholarships
- Scholarship FAQs
Payment Options
- Payment Plans
- Corporate Reimbursement
- Current Student Hardship Assistance
- Military Tuition Assistance
WGU Experience
- How You'll Learn
- Scheduling/Assessments
- Accreditation
- Student Support/Faculty
- Military Students
- Part-Time Options
- Virtual Military Education Resource Center
- Student Outcomes
- Return on Investment
- Students and Gradutes
- Career Growth
- Student Resources
- Communities
- Testimonials
- Career Guides
- Skills Guides
- Online Degrees
- All Degrees
- Explore Your Options
Admissions & Transfers
- Admissions Overview
Tuition & Financial Aid
Student Success
- Prospective Students
- Current Students
- Military and Veterans
- Commencement
- Careers at WGU
- Advancement & Giving
- Partnering with WGU
WESTERN GOVERNORS UNIVERSITY
Developing your problem-solving skills.

Problem-Solving Skills
Problem-solving skills enhance your ability to identify a difficult or unforeseen situation and determine an appropriate solution.
Using the right problem-solving approach will empower you to offer practical solutions in your professional and personal life anytime you’re faced with a problem.
This page covers different types of problem-solving skills, why they matter, and how to acquire them.
Why Are Problem-Solving Skills Important?
Problem-solving skills are crucial in empowering individuals to handle large or small obstacles throughout various aspects of life. Here are just a few ways that these skills can help you:
- Overcoming challenges: Life will always present you with problems that may hinder your personal or professional progress. Problem-solving skills empower you to identify solutions, giving you control over your future.
- Enhancing decision-making: Problem-solving skills help you assess problems as they come, gauge all the possible solutions, and make the best decision.
- Promoting innovation: Practical problem-solving skills encourage creative thinking, enabling you to develop innovative ideas. You can then evaluate these ideas to identify effective solutions to tackle obstacles.
- Increasing efficiency: Problem-solving skills help individuals and organizations improve efficiency and save time and resources. You are assured of increased productivity if you can identify the root cause of a problem, get the appropriate solution, and implement it promptly.
- Building resilience: Since problems are part of everyone’s day-to-day life, being equipped with problem-solving skills will enable you to respond quickly and rationally to unforeseen situations and not succumb to setbacks.
What Are the Benefits of Having Problem-Solving Skills?
When you frequently apply your problem-solving skills, you become more proficient at analyzing, resolving, and adapting to challenges.
In the workplace, people with strong problem-solving skills apply a combination of creative thinking and analytical skills to help them become more confident when making decisions in the face of challenges.
They’re better equipped to handle the challenges their job brings Problem solvers can observe, judge, and act quickly when faced with adversity.
Problem-solving skills enable you to prioritize, plan, and execute your strategies. You also learn how to think outside the box and identify opportunities in problems.

Examples of Problem-Solving Skills
Problem-solving skills are effective in helping you identify the source of a problem and how to solve it with a structured approach.
Here are some skills associated with problem-solving:
- Analyzing data: When addressing a number of problems, it’s important to gather relevant for a thorough understanding of the issue and its underlying causes.
- Brainstorming creative solutions: Brainstorming allows you to find the right information from the different causes of the problem and develop innovative solutions.
- Researching to gather relevant information: Having clarity on your research goals and digging into reliable resources to get relevant information.
- Use critical thinking to evaluate options: This involves objective questioning, analyzing, and systematically assessing available options. You should be able to differentiate facts from opinions.
- Implementing logical and systematic approaches: Exploring the key components of each option to understand their practicality and relevance to the problem. Use predefined criteria to evaluate the options and then conduct a SWOT (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, threats) analysis to determine their viability.
- Collaborating with others to find solutions: Team members gather to offer their input, giving potential solutions and collectively analyzing them to solve the problem.
- Creative thinking: This may include generating new ideas to solve problems. It involves brainstorming, mind mapping, lateral thinking, and analogical reasoning.
- Decision-making: This is the capability to evaluate options, weigh pros and cons, and make informed decisions based on available information.
- Problem identification: The ability to recognize and define problems accurately and clearly.
- Problem structuring: The skill involves taking complicated or vague problems and dissecting them into smaller subproblems that are easier to understand and solve.
How Can I Use Problem-Solving Skills?
Problem-solving skills will have a lasting impact on your life. In your personal and professional life, you will encounter many challenges requiring you to use problem-solving skills.
Here are some instances where you’ll use problem-solving skills:
Career Success
Problem-solving skills will help you tackle challenges at any workplace, make informed decisions, and help the organizations you work with to succeed., personal growth, these skills equip you to overcome everyday life obstacles, like managing personal finances, resolving conflicts in relationships, and more..
Innovation and Entrepreneurship
By solving problems, you can generate creative ideas, develop innovative solutions, and even solve societal problems.
Decision-Making
Making big and small decisions by gathering alternatives, evaluating outcomes, and deciding on the best course of action.
How Can I Learn Problem-Solving Skills?
At wgu, we offer several programs and courses that focus on teaching and enhancing problem-solving skills. , here are ways you can learn problem-solving skills at wgu., school of business.
You’ll learn how to apply problem-solving skills in the world of entrepreneurship and business. For example, our Bachelor of Science in Business Administration–Human Resource Management, offers problem-solving skills as a key component.
With business degree programs, you will learn to:
- Generate a solution to a problem.
- Conduct research to find solutions to a problem.
- Articulate findings and resolutions to a problem.
- Apply contextual reasoning to understand problems.
- Analyze data for the nature and extent of a problem.
School of Technology
You’ll learn how to apply problem-solving skills within the ever-evolving world of IT. We have different bachelor of science degrees in Cloud Computing, such as Muilticloud Track, Amazon Web Services Track, and BS in Cloud Computing - Azure Track.
With IT-related degree programs, you will learn to:
- Select appropriate problem-solving techniques.
- Resolve a challenge using a problem-solving process.
- Recommend multiple solutions for a variety of problems.
- Implement approaches to address complex problems.
- Identify problems using various common frameworks.
School of Education
You’ll learn how problem-solving skills are crucial in the education sector. For example, our Master of Science in Educational Leadership covers problem-solving in the School of Education courses.
With education degree programs, you will learn to:
- Implement problem-solving skills for issue resolution.
- Solve complex problems.
- Identify the cause of a problem.
- Solve problems in the manner most appropriate for each problem.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the steps involved in the problem-solving process?
The problem-solving process involves the following steps:
- Problem identification: Clearly state the problem, what makes you view it as a problem, and how you discovered it.
- Problem analysis: Gather data to help you fully understand the problem and its root causes.
- Generating potential solutions: Look for all the possible ideas from different angles to solve the problem.
- Evaluating alternatives: Scrutinize the available options to identify the best idea.
- Implementing the chosen solution: Follow through on the necessary steps to resolve the problem.
- Reviewing the results: Gather feedback to test the results against your expectations.
How can I improve my critical thinking skills to enhance my problem-solving?
You can improve your critical thinking skills through the following:
- Logical reasoning: Embrace creative hobbies, learn new skills, and socialize with others.
- Evaluating evidence: Determine the relevance and quality of the evidence available to challenge or support claims.
- Considering multiple perspectives: Being open to learning from your peers and adjusting your views accordingly.
What are some effective techniques for generating creative solutions to problems?
Creative problem solving (CPS) is about innovatively solving problems. The techniques below will aid you in the CPS process:
- Brainstorming: Gather relevant parties and spontaneously contribute ideas to offer the solution.
- Mind mapping: Capture and organize any form of information and ideas in a structured way to enhance your logical and creative thinking.
- Analogical reasoning: Use analogies to simplify complex scenarios to makes them easy to comprehend.
How can problem-solving skills be applied in everyday life?
Picture this: your car breaks down while running errands. It’s important to identify the problem with your car and analyze the symptoms and potential root causes of the breakdown, such as mechanical issues or battery failure. You decide that a faulty batter is the issue so you start to identify potential solutions.
The solutions may include calling for roadside assistance, finding a mechanic nearby, or seeking help from friends or family. You then evaluate the potential solutions by weighing in factors such as cost, time, and convenience. The best solution you find may be to call a nearby friend to help you jump-start the car and get back on the road to complete your errands.
This is an everyday occurrence in which problem-solving skills are applicable. Other situations may vary with the degree of difficulty, urgency, and solutions required.
Are specific problem-solving skills valuable in a team or collaborative setting?
Yes. With effective communication, effective conflict resolution strategies, active listening, and consensus building, team members can build healthy working relationships and succeed in their daily decision-making processes.
Find Your Degree
Discovering the right degree program that aligns with your goals is a crucial step. You can begin the journey toward achieving personal growth and advancement. Take our degree quiz to help you identify the degree program that best suits your interests and embark on a path of knowledge and future success.
The University
For students.
- Student Portal
- Alumni Services
Most Visited Links
- Business Programs
- Student Experience
- Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion
- Student Communities
Daring Leadership Institute: a groundbreaking partnership that amplifies Brené Brown's empirically based, courage-building curriculum with BetterUp’s human transformation platform.

What is Coaching?
Types of Coaching
Discover your perfect match : Take our 5-minute assessment and let us pair you with one of our top Coaches tailored just for you.
Find your coach
-1.png)
We're on a mission to help everyone live with clarity, purpose, and passion.
Join us and create impactful change.
Read the buzz about BetterUp.
Meet the leadership that's passionate about empowering your workforce.

For Business
For Individuals
10 Problem-solving strategies to turn challenges on their head

Jump to section
What is an example of problem-solving?
What are the 5 steps to problem-solving, 10 effective problem-solving strategies, what skills do efficient problem solvers have, how to improve your problem-solving skills.
Problems come in all shapes and sizes — from workplace conflict to budget cuts.
Creative problem-solving is one of the most in-demand skills in all roles and industries. It can boost an organization’s human capital and give it a competitive edge.
Problem-solving strategies are ways of approaching problems that can help you look beyond the obvious answers and find the best solution to your problem .
Let’s take a look at a five-step problem-solving process and how to combine it with proven problem-solving strategies. This will give you the tools and skills to solve even your most complex problems.
Good problem-solving is an essential part of the decision-making process . To see what a problem-solving process might look like in real life, let’s take a common problem for SaaS brands — decreasing customer churn rates.
To solve this problem, the company must first identify it. In this case, the problem is that the churn rate is too high.
Next, they need to identify the root causes of the problem. This could be anything from their customer service experience to their email marketing campaigns. If there are several problems, they will need a separate problem-solving process for each one.
Let’s say the problem is with email marketing — they’re not nurturing existing customers. Now that they’ve identified the problem, they can start using problem-solving strategies to look for solutions.
This might look like coming up with special offers, discounts, or bonuses for existing customers. They need to find ways to remind them to use their products and services while providing added value. This will encourage customers to keep paying their monthly subscriptions.
They might also want to add incentives, such as access to a premium service at no extra cost after 12 months of membership. They could publish blog posts that help their customers solve common problems and share them as an email newsletter.
The company should set targets and a time frame in which to achieve them. This will allow leaders to measure progress and identify which actions yield the best results.

Perhaps you’ve got a problem you need to tackle. Or maybe you want to be prepared the next time one arises. Either way, it’s a good idea to get familiar with the five steps of problem-solving.
Use this step-by-step problem-solving method with the strategies in the following section to find possible solutions to your problem.
1. Identify the problem
The first step is to know which problem you need to solve. Then, you need to find the root cause of the problem.
The best course of action is to gather as much data as possible, speak to the people involved, and separate facts from opinions.
Once this is done, formulate a statement that describes the problem. Use rational persuasion to make sure your team agrees .
2. Break the problem down
Identifying the problem allows you to see which steps need to be taken to solve it.
First, break the problem down into achievable blocks. Then, use strategic planning to set a time frame in which to solve the problem and establish a timeline for the completion of each stage.
3. Generate potential solutions
At this stage, the aim isn’t to evaluate possible solutions but to generate as many ideas as possible.
Encourage your team to use creative thinking and be patient — the best solution may not be the first or most obvious one.
Use one or more of the different strategies in the following section to help come up with solutions — the more creative, the better.
4. Evaluate the possible solutions
Once you’ve generated potential solutions, narrow them down to a shortlist. Then, evaluate the options on your shortlist.
There are usually many factors to consider. So when evaluating a solution, ask yourself the following questions:
- Will my team be on board with the proposition?
- Does the solution align with organizational goals ?
- Is the solution likely to achieve the desired outcomes?
- Is the solution realistic and possible with current resources and constraints?
- Will the solution solve the problem without causing additional unintended problems?

5. Implement and monitor the solutions
Once you’ve identified your solution and got buy-in from your team, it’s time to implement it.
But the work doesn’t stop there. You need to monitor your solution to see whether it actually solves your problem.
Request regular feedback from the team members involved and have a monitoring and evaluation plan in place to measure progress.
If the solution doesn’t achieve your desired results, start this step-by-step process again.
There are many different ways to approach problem-solving. Each is suitable for different types of problems.
The most appropriate problem-solving techniques will depend on your specific problem. You may need to experiment with several strategies before you find a workable solution.
Here are 10 effective problem-solving strategies for you to try:
- Use a solution that worked before
- Brainstorming
- Work backward
- Use the Kipling method
- Draw the problem
- Use trial and error
- Sleep on it
- Get advice from your peers
- Use the Pareto principle
- Add successful solutions to your toolkit
Let’s break each of these down.
1. Use a solution that worked before
It might seem obvious, but if you’ve faced similar problems in the past, look back to what worked then. See if any of the solutions could apply to your current situation and, if so, replicate them.
2. Brainstorming
The more people you enlist to help solve the problem, the more potential solutions you can come up with.
Use different brainstorming techniques to workshop potential solutions with your team. They’ll likely bring something you haven’t thought of to the table.
3. Work backward
Working backward is a way to reverse engineer your problem. Imagine your problem has been solved, and make that the starting point.
Then, retrace your steps back to where you are now. This can help you see which course of action may be most effective.
4. Use the Kipling method
This is a method that poses six questions based on Rudyard Kipling’s poem, “ I Keep Six Honest Serving Men .”
- What is the problem?
- Why is the problem important?
- When did the problem arise, and when does it need to be solved?
- How did the problem happen?
- Where is the problem occurring?
- Who does the problem affect?
Answering these questions can help you identify possible solutions.
5. Draw the problem
Sometimes it can be difficult to visualize all the components and moving parts of a problem and its solution. Drawing a diagram can help.
This technique is particularly helpful for solving process-related problems. For example, a product development team might want to decrease the time they take to fix bugs and create new iterations. Drawing the processes involved can help you see where improvements can be made.

6. Use trial-and-error
A trial-and-error approach can be useful when you have several possible solutions and want to test them to see which one works best.
7. Sleep on it
Finding the best solution to a problem is a process. Remember to take breaks and get enough rest . Sometimes, a walk around the block can bring inspiration, but you should sleep on it if possible.
A good night’s sleep helps us find creative solutions to problems. This is because when you sleep, your brain sorts through the day’s events and stores them as memories. This enables you to process your ideas at a subconscious level.
If possible, give yourself a few days to develop and analyze possible solutions. You may find you have greater clarity after sleeping on it. Your mind will also be fresh, so you’ll be able to make better decisions.
8. Get advice from your peers
Getting input from a group of people can help you find solutions you may not have thought of on your own.
For solo entrepreneurs or freelancers, this might look like hiring a coach or mentor or joining a mastermind group.
For leaders , it might be consulting other members of the leadership team or working with a business coach .
It’s important to recognize you might not have all the skills, experience, or knowledge necessary to find a solution alone.
9. Use the Pareto principle
The Pareto principle — also known as the 80/20 rule — can help you identify possible root causes and potential solutions for your problems.
Although it’s not a mathematical law, it’s a principle found throughout many aspects of business and life. For example, 20% of the sales reps in a company might close 80% of the sales.
You may be able to narrow down the causes of your problem by applying the Pareto principle. This can also help you identify the most appropriate solutions.
10. Add successful solutions to your toolkit
Every situation is different, and the same solutions might not always work. But by keeping a record of successful problem-solving strategies, you can build up a solutions toolkit.
These solutions may be applicable to future problems. Even if not, they may save you some of the time and work needed to come up with a new solution.

Improving problem-solving skills is essential for professional development — both yours and your team’s. Here are some of the key skills of effective problem solvers:
- Critical thinking and analytical skills
- Communication skills , including active listening
- Decision-making
- Planning and prioritization
- Emotional intelligence , including empathy and emotional regulation
- Time management
- Data analysis
- Research skills
- Project management
And they see problems as opportunities. Everyone is born with problem-solving skills. But accessing these abilities depends on how we view problems. Effective problem-solvers see problems as opportunities to learn and improve.
Ready to work on your problem-solving abilities? Get started with these seven tips.
1. Build your problem-solving skills
One of the best ways to improve your problem-solving skills is to learn from experts. Consider enrolling in organizational training , shadowing a mentor , or working with a coach .
2. Practice
Practice using your new problem-solving skills by applying them to smaller problems you might encounter in your daily life.
Alternatively, imagine problematic scenarios that might arise at work and use problem-solving strategies to find hypothetical solutions.

3. Don’t try to find a solution right away
Often, the first solution you think of to solve a problem isn’t the most appropriate or effective.
Instead of thinking on the spot, give yourself time and use one or more of the problem-solving strategies above to activate your creative thinking.

4. Ask for feedback
Receiving feedback is always important for learning and growth. Your perception of your problem-solving skills may be different from that of your colleagues. They can provide insights that help you improve.
5. Learn new approaches and methodologies
There are entire books written about problem-solving methodologies if you want to take a deep dive into the subject.
We recommend starting with “ Fixed — How to Perfect the Fine Art of Problem Solving ” by Amy E. Herman.
6. Experiment
Tried-and-tested problem-solving techniques can be useful. However, they don’t teach you how to innovate and develop your own problem-solving approaches.
Sometimes, an unconventional approach can lead to the development of a brilliant new idea or strategy. So don’t be afraid to suggest your most “out there” ideas.
7. Analyze the success of your competitors
Do you have competitors who have already solved the problem you’re facing? Look at what they did, and work backward to solve your own problem.
For example, Netflix started in the 1990s as a DVD mail-rental company. Its main competitor at the time was Blockbuster.
But when streaming became the norm in the early 2000s, both companies faced a crisis. Netflix innovated, unveiling its streaming service in 2007.
If Blockbuster had followed Netflix’s example, it might have survived. Instead, it declared bankruptcy in 2010.
Use problem-solving strategies to uplevel your business
When facing a problem, it’s worth taking the time to find the right solution.
Otherwise, we risk either running away from our problems or headlong into solutions. When we do this, we might miss out on other, better options.
Use the problem-solving strategies outlined above to find innovative solutions to your business’ most perplexing problems.
If you’re ready to take problem-solving to the next level, request a demo with BetterUp . Our expert coaches specialize in helping teams develop and implement strategies that work.
Understand Yourself Better:
Big 5 Personality Test
Elizabeth Perry, ACC
Elizabeth Perry is a Coach Community Manager at BetterUp. She uses strategic engagement strategies to cultivate a learning community across a global network of Coaches through in-person and virtual experiences, technology-enabled platforms, and strategic coaching industry partnerships. With over 3 years of coaching experience and a certification in transformative leadership and life coaching from Sofia University, Elizabeth leverages transpersonal psychology expertise to help coaches and clients gain awareness of their behavioral and thought patterns, discover their purpose and passions, and elevate their potential. She is a lifelong student of psychology, personal growth, and human potential as well as an ICF-certified ACC transpersonal life and leadership Coach.
8 creative solutions to your most challenging problems
5 problem-solving questions to prepare you for your next interview, 31 examples of problem solving performance review phrases, what are metacognitive skills examples in everyday life, what is lateral thinking 7 techniques to encourage creative ideas, leadership activities that encourage employee engagement, learn what process mapping is and how to create one (+ examples), how much do distractions cost 8 effects of lack of focus, 10 organizational skills that will put you a step ahead, the pareto principle: how the 80/20 rule can help you do more with less, thinking outside the box: 8 ways to become a creative problem solver, 3 problem statement examples and steps to write your own, 10 examples of principles that can guide your approach to work, contingency planning: 4 steps to prepare for the unexpected, stay connected with betterup, get our newsletter, event invites, plus product insights and research..
3100 E 5th Street, Suite 350 Austin, TX 78702
- Platform overview
- Integrations
- Powered by AI
- BetterUp Lead™
- BetterUp Manage™
- BetterUp Care®
- Sales Performance
- Diversity & Inclusion
- Case studies
- ROI of BetterUp
- What is coaching?
- About Coaching
- Find your Coach
- Career Coaching
- Communication Coaching
- Personal Coaching
- News and Press
- Leadership Team
- Become a BetterUp Coach
- BetterUp Briefing
- Center for Purpose & Performance
- Leadership Training
- Business Coaching
- Contact Support
- Contact Sales
- Privacy Policy
- Acceptable Use Policy
- Trust & Security
- Cookie Preferences
Very Big Brain
everything cognitive enhancing

- Body-Brain Connection
How to Strengthen Problem-Solving Skills in Everyday Life

Problem-solving is an essential skill that we rely on in both personal and professional settings. From minor inconveniences to complex challenges, we are constantly presented with situations that require us to find effective solutions. Strengthening your problem-solving abilities can improve decision-making, reduce stress, and lead to more successful outcomes.
Whether you’re facing a difficult task at work, managing personal relationships, or navigating everyday life, honing your problem-solving skills is key. By cultivating a strategic mindset, staying mentally sharp, and using the right techniques, you can become more effective at identifying solutions to problems. Some individuals also use brain supplements like nootropics to support mental clarity, focus, and cognitive performance, making problem-solving easier and more efficient.
Ask the Right Questions
The benefits of a step-by-step approach, techniques to foster creativity, stress management techniques for problem-solving, embrace a growth mindset, daily practices to sharpen problem-solving skills, define the problem clearly.
The first step to solving any problem is understanding exactly what the problem is. Many people jump into problem-solving mode without fully analyzing the situation, which can lead to incomplete solutions or overlooked details. Taking the time to clearly define the problem will help you identify the best approach and ensure that you are solving the right issue.
To clearly define a problem, start by asking questions that help you get to the root of the issue. For example, what is the real challenge here? What are the contributing factors? Who is affected by this problem, and why? By breaking the problem down and examining all of its aspects, you can gain a deeper understanding of what needs to be addressed.
In both personal and professional settings, it’s important to differentiate between symptoms and root causes. While it’s tempting to address surface-level symptoms, solving the root cause will prevent the problem from reoccurring. Taking time to ask the right questions and fully define the problem sets the stage for more effective solutions.
Break the Problem into Manageable Steps
Large, complex problems can feel overwhelming, leading to procrastination or poor decision-making. Breaking a problem into smaller, manageable steps makes it easier to approach systematically and keeps you focused on the next actionable task. This step-by-step approach not only simplifies the problem but also helps reduce stress and mental fatigue.
Breaking a problem down into smaller parts allows you to tackle each aspect one at a time. This reduces overwhelm and helps you stay organized throughout the process. For example, if you’re working on a challenging project at work, break it down into research, planning, execution, and review stages. Focus on completing one stage before moving to the next, allowing for greater clarity and concentration.
- Identify Sub-Problems: Break the larger problem into smaller sub-problems that can be addressed independently. This makes the overall challenge more manageable and gives you a clear starting point.
- Create Actionable Steps: Turn each sub-problem into a specific action step that you can take to move forward. Having a clear plan of action keeps you focused and reduces the chances of becoming overwhelmed.
For individuals seeking enhanced cognitive performance during problem-solving, some find that using nootropics supports mental clarity and sustained focus, making it easier to work through each step without losing momentum.

Use Creative Problem-Solving Techniques
Creative problem-solving involves looking beyond traditional solutions and thinking outside the box to find new, innovative approaches. This technique is particularly useful when facing complex challenges or when conventional methods aren’t working. Cultivating creativity in problem-solving can lead to unexpected breakthroughs and more effective solutions.
One popular creative problem-solving method is brainstorming. During a brainstorming session, you generate as many ideas as possible without immediately judging or discarding them. This helps you explore a wide range of possibilities before narrowing down your options. Another effective technique is mind mapping, which involves visually organizing ideas and solutions in a diagram, helping you see connections that might not be immediately obvious.
- Brainstorming: Write down every idea, no matter how unconventional, and explore each one before deciding on the best solution. You might be surprised by the creative insights that emerge.
- Mind Mapping: Draw a visual representation of the problem, with the central issue in the middle and branches representing possible solutions. This helps you see relationships and generate new ideas.
Creative problem-solving requires mental flexibility and the ability to see beyond traditional approaches. Many individuals use brain supplements like nootropics to enhance cognitive flexibility, supporting innovative thinking and creativity during the problem-solving process.
Stay Calm and Manage Stress
Problem-solving is much more difficult when you’re feeling stressed or overwhelmed. High stress levels can cloud judgment, reduce cognitive function, and make it harder to think clearly. Learning how to manage stress effectively is essential for maintaining mental sharpness and approaching problems with a clear, focused mindset.
One of the best ways to reduce stress while problem-solving is to practice mindfulness. Mindfulness helps you stay present and focused on the task at hand, rather than becoming distracted by anxiety or worry about the outcome. Taking regular breaks to breathe deeply, meditate, or step away from the problem for a few minutes can also help you reset and return to the issue with fresh energy.
Physical activity, such as going for a walk or engaging in light exercise, can reduce stress and boost mental clarity, helping you approach problems with a clearer perspective. Staying calm under pressure allows you to think more rationally, helping you find more effective solutions to the challenges you face.
For those looking for additional support in managing stress and maintaining focus, some turn to brain supplements like nootropics to enhance cognitive resilience. These supplements may help reduce mental fatigue, promote calmness, and support better decision-making during stressful situations.
Learn from Mistakes and Adapt
Not every solution will work perfectly the first time. Learning from mistakes and remaining adaptable is a key part of strengthening your problem-solving skills. When a solution doesn’t lead to the desired outcome, it’s important to analyze what went wrong and adjust your approach accordingly.
A growth mindset—the belief that skills and abilities can be developed through effort and learning—helps you view challenges as opportunities for growth. Rather than becoming discouraged by setbacks, see them as valuable learning experiences. Each mistake brings you closer to understanding the problem more deeply and finding the right solution.
Take time to reflect on what went wrong, whether it was a flaw in the solution itself or in the approach you used. This reflection helps you adapt your problem-solving techniques and develop more effective strategies for the future. By staying flexible and open to learning, you strengthen your overall problem-solving abilities.
Adaptability and a willingness to learn from mistakes are essential for long-term success. Many individuals find that using nootropics helps improve cognitive flexibility, making it easier to adjust their strategies and think critically about what changes need to be made.
Practice Problem-Solving Regularly
Like any skill, problem-solving improves with practice. The more you challenge your brain to find solutions, the sharper and more effective your problem-solving skills become. Incorporating problem-solving exercises into your daily routine helps keep your mind sharp and better prepared to tackle challenges as they arise.
One way to practice problem-solving regularly is to engage in puzzles, logic games, or brainteasers. These exercises challenge your brain to think critically and explore different approaches to finding solutions. Additionally, applying problem-solving techniques to everyday challenges, such as organizing your schedule or resolving a conflict, provides valuable real-world practice.
Another effective practice is to reflect on recent challenges you’ve faced and analyze how you approached them. Consider what worked, what didn’t, and how you could improve your approach in the future. By making problem-solving a regular part of your daily routine, you strengthen your mental agility and become more confident in handling any issues that arise.
Some individuals use brain supplements like nootropics to support cognitive performance and problem-solving skills, helping them stay sharp and focused even during complex challenges. Nootropics can provide an additional mental boost, enhancing clarity, focus, and creativity while solving problems.
How to improve your problem solving skills and build effective problem solving strategies

Design your next session with SessionLab
Join the 150,000+ facilitators using SessionLab.
Recommended Articles
A step-by-step guide to planning a workshop, 54 great online tools for workshops and meetings, how to create an unforgettable training session in 8 simple steps.
- 18 Free Facilitation Resources We Think You’ll Love
Effective problem solving is all about using the right process and following a plan tailored to the issue at hand. Recognizing your team or organization has an issue isn’t enough to come up with effective problem solving strategies.
To truly understand a problem and develop appropriate solutions, you will want to follow a solid process, follow the necessary problem solving steps, and bring all of your problem solving skills to the table. We’ll forst look at what problem solving strategies you can employ with your team when looking for a way to approach the process. We’ll then discuss the problem solving skills you need to be more effective at solving problems, complete with an activity from the SessionLab library you can use to develop that skill in your team.
Let’s get to it!
Problem solving strategies
What skills do i need to be an effective problem solver, how can i improve my problem solving skills.
Problem solving strategies are methods of approaching and facilitating the process of problem-solving with a set of techniques , actions, and processes. Different strategies are more effective if you are trying to solve broad problems such as achieving higher growth versus more focused problems like, how do we improve our customer onboarding process?
Broadly, the problem solving steps outlined above should be included in any problem solving strategy though choosing where to focus your time and what approaches should be taken is where they begin to differ. You might find that some strategies ask for the problem identification to be done prior to the session or that everything happens in the course of a one day workshop.
The key similarity is that all good problem solving strategies are structured and designed. Four hours of open discussion is never going to be as productive as a four-hour workshop designed to lead a group through a problem solving process.
Good problem solving strategies are tailored to the team, organization and problem you will be attempting to solve. Here are some example problem solving strategies you can learn from or use to get started.
Use a workshop to lead a team through a group process
Often, the first step to solving problems or organizational challenges is bringing a group together effectively. Most teams have the tools, knowledge, and expertise necessary to solve their challenges – they just need some guidance in how to use leverage those skills and a structure and format that allows people to focus their energies.
Facilitated workshops are one of the most effective ways of solving problems of any scale. By designing and planning your workshop carefully, you can tailor the approach and scope to best fit the needs of your team and organization.
Problem solving workshop
- Creating a bespoke, tailored process
- Tackling problems of any size
- Building in-house workshop ability and encouraging their use
Workshops are an effective strategy for solving problems. By using tried and test facilitation techniques and methods, you can design and deliver a workshop that is perfectly suited to the unique variables of your organization. You may only have the capacity for a half-day workshop and so need a problem solving process to match.
By using our session planner tool and importing methods from our library of 700+ facilitation techniques, you can create the right problem solving workshop for your team. It might be that you want to encourage creative thinking or look at things from a new angle to unblock your groups approach to problem solving. By tailoring your workshop design to the purpose, you can help ensure great results.
One of the main benefits of a workshop is the structured approach to problem solving. Not only does this mean that the workshop itself will be successful, but many of the methods and techniques will help your team improve their working processes outside of the workshop.
We believe that workshops are one of the best tools you can use to improve the way your team works together. Start with a problem solving workshop and then see what team building, culture or design workshops can do for your organization!
Run a design sprint
Great for:
- aligning large, multi-discipline teams
- quickly designing and testing solutions
- tackling large, complex organizational challenges and breaking them down into smaller tasks
By using design thinking principles and methods, a design sprint is a great way of identifying, prioritizing and prototyping solutions to long term challenges that can help solve major organizational problems with quick action and measurable results.
Some familiarity with design thinking is useful, though not integral, and this strategy can really help a team align if there is some discussion around which problems should be approached first.
The stage-based structure of the design sprint is also very useful for teams new to design thinking. The inspiration phase, where you look to competitors that have solved your problem, and the rapid prototyping and testing phases are great for introducing new concepts that will benefit a team in all their future work.
It can be common for teams to look inward for solutions and so looking to the market for solutions you can iterate on can be very productive. Instilling an agile prototyping and testing mindset can also be great when helping teams move forwards – generating and testing solutions quickly can help save time in the long run and is also pretty exciting!
Break problems down into smaller issues
Organizational challenges and problems are often complicated and large scale in nature. Sometimes, trying to resolve such an issue in one swoop is simply unachievable or overwhelming. Try breaking down such problems into smaller issues that you can work on step by step. You may not be able to solve the problem of churning customers off the bat, but you can work with your team to identify smaller effort but high impact elements and work on those first.
This problem solving strategy can help a team generate momentum, prioritize and get some easy wins. It’s also a great strategy to employ with teams who are just beginning to learn how to approach the problem solving process. If you want some insight into a way to employ this strategy, we recommend looking at our design sprint template below!
Use guiding frameworks or try new methodologies
Some problems are best solved by introducing a major shift in perspective or by using new methodologies that encourage your team to think differently.
Props and tools such as Methodkit , which uses a card-based toolkit for facilitation, or Lego Serious Play can be great ways to engage your team and find an inclusive, democratic problem solving strategy. Remember that play and creativity are great tools for achieving change and whatever the challenge, engaging your participants can be very effective where other strategies may have failed.
LEGO Serious Play
- Improving core problem solving skills
- Thinking outside of the box
- Encouraging creative solutions
LEGO Serious Play is a problem solving methodology designed to get participants thinking differently by using 3D models and kinesthetic learning styles. By physically building LEGO models based on questions and exercises, participants are encouraged to think outside of the box and create their own responses.
Collaborate LEGO Serious Play exercises are also used to encourage communication and build problem solving skills in a group. By using this problem solving process, you can often help different kinds of learners and personality types contribute and unblock organizational problems with creative thinking.
Problem solving strategies like LEGO Serious Play are super effective at helping a team solve more skills-based problems such as communication between teams or a lack of creative thinking. Some problems are not suited to LEGO Serious Play and require a different problem solving strategy.
Card Decks and Method Kits
- New facilitators or non-facilitators
- Approaching difficult subjects with a simple, creative framework
- Engaging those with varied learning styles
Card decks and method kids are great tools for those new to facilitation or for whom facilitation is not the primary role. Card decks such as the emotional culture deck can be used for complete workshops and in many cases, can be used right out of the box. Methodkit has a variety of kits designed for scenarios ranging from personal development through to personas and global challenges so you can find the right deck for your particular needs.
Having an easy to use framework that encourages creativity or a new approach can take some of the friction or planning difficulties out of the workshop process and energize a team in any setting. Simplicity is the key with these methods. By ensuring everyone on your team can get involved and engage with the process as quickly as possible can really contribute to the success of your problem solving strategy.
Source external advice
Looking to peers, experts and external facilitators can be a great way of approaching the problem solving process. Your team may not have the necessary expertise, insights of experience to tackle some issues, or you might simply benefit from a fresh perspective. Some problems may require bringing together an entire team, and coaching managers or team members individually might be the right approach. Remember that not all problems are best resolved in the same manner.
If you’re a solo entrepreneur, peer groups, coaches and mentors can also be invaluable at not only solving specific business problems, but in providing a support network for resolving future challenges. One great approach is to join a Mastermind Group and link up with like-minded individuals and all grow together. Remember that however you approach the sourcing of external advice, do so thoughtfully, respectfully and honestly. Reciprocate where you can and prepare to be surprised by just how kind and helpful your peers can be!
Mastermind Group
- Solo entrepreneurs or small teams with low capacity
- Peer learning and gaining outside expertise
- Getting multiple external points of view quickly
Problem solving in large organizations with lots of skilled team members is one thing, but how about if you work for yourself or in a very small team without the capacity to get the most from a design sprint or LEGO Serious Play session?
A mastermind group – sometimes known as a peer advisory board – is where a group of people come together to support one another in their own goals, challenges, and businesses. Each participant comes to the group with their own purpose and the other members of the group will help them create solutions, brainstorm ideas, and support one another.
Mastermind groups are very effective in creating an energized, supportive atmosphere that can deliver meaningful results. Learning from peers from outside of your organization or industry can really help unlock new ways of thinking and drive growth. Access to the experience and skills of your peers can be invaluable in helping fill the gaps in your own ability, particularly in young companies.
A mastermind group is a great solution for solo entrepreneurs, small teams, or for organizations that feel that external expertise or fresh perspectives will be beneficial for them. It is worth noting that Mastermind groups are often only as good as the participants and what they can bring to the group. Participants need to be committed, engaged and understand how to work in this context.
Coaching and mentoring
- Focused learning and development
- Filling skills gaps
- Working on a range of challenges over time
Receiving advice from a business coach or building a mentor/mentee relationship can be an effective way of resolving certain challenges. The one-to-one format of most coaching and mentor relationships can really help solve the challenges those individuals are having and benefit the organization as a result.
A great mentor can be invaluable when it comes to spotting potential problems before they arise and coming to understand a mentee very well has a host of other business benefits. You might run an internal mentorship program to help develop your team’s problem solving skills and strategies or as part of a large learning and development program. External coaches can also be an important part of your problem solving strategy, filling skills gaps for your management team or helping with specific business issues.
Now we’ve explored the problem solving process and the steps you will want to go through in order to have an effective session, let’s look at the skills you and your team need to be more effective problem solvers.
Problem solving skills are highly sought after, whatever industry or team you work in. Organizations are keen to employ people who are able to approach problems thoughtfully and find strong, realistic solutions. Whether you are a facilitator , a team leader or a developer, being an effective problem solver is a skill you’ll want to develop.
Problem solving skills form a whole suite of techniques and approaches that an individual uses to not only identify problems but to discuss them productively before then developing appropriate solutions.
Here are some of the most important problem solving skills everyone from executives to junior staff members should learn. We’ve also included an activity or exercise from the SessionLab library that can help you and your team develop that skill.
If you’re running a workshop or training session to try and improve problem solving skills in your team, try using these methods to supercharge your process!
Active listening
Active listening is one of the most important skills anyone who works with people can possess. In short, active listening is a technique used to not only better understand what is being said by an individual, but also to be more aware of the underlying message the speaker is trying to convey. When it comes to problem solving, active listening is integral for understanding the position of every participant and to clarify the challenges, ideas and solutions they bring to the table.
Some active listening skills include:
- Paying complete attention to the speaker.
- Removing distractions.
- Avoid interruption.
- Taking the time to fully understand before preparing a rebuttal.
- Responding respectfully and appropriately.
- Demonstrate attentiveness and positivity with an open posture, making eye contact with the speaker, smiling and nodding if appropriate. Show that you are listening and encourage them to continue.
- Be aware of and respectful of feelings. Judge the situation and respond appropriately. You can disagree without being disrespectful.
- Observe body language.
- Paraphrase what was said in your own words, either mentally or verbally.
- Remain neutral.
- Reflect and take a moment before responding.
- Ask deeper questions based on what is said and clarify points where necessary.
Active Listening #hyperisland #skills #active listening #remote-friendly This activity supports participants to reflect on a question and generate their own solutions using simple principles of active listening and peer coaching. It’s an excellent introduction to active listening but can also be used with groups that are already familiar with it. Participants work in groups of three and take turns being: “the subject”, the listener, and the observer.
Analytical skills
All problem solving models require strong analytical skills, particularly during the beginning of the process and when it comes to analyzing how solutions have performed.
Analytical skills are primarily focused on performing an effective analysis by collecting, studying and parsing data related to a problem or opportunity.
It often involves spotting patterns, being able to see things from different perspectives and using observable facts and data to make suggestions or produce insight.
Analytical skills are also important at every stage of the problem solving process and by having these skills, you can ensure that any ideas or solutions you create or backed up analytically and have been sufficiently thought out.
Nine Whys #innovation #issue analysis #liberating structures With breathtaking simplicity, you can rapidly clarify for individuals and a group what is essentially important in their work. You can quickly reveal when a compelling purpose is missing in a gathering and avoid moving forward without clarity. When a group discovers an unambiguous shared purpose, more freedom and more responsibility are unleashed. You have laid the foundation for spreading and scaling innovations with fidelity.
Collaboration
Trying to solve problems on your own is difficult. Being able to collaborate effectively, with a free exchange of ideas, to delegate and be a productive member of a team is hugely important to all problem solving strategies.
Remember that whatever your role, collaboration is integral, and in a problem solving process, you are all working together to find the best solution for everyone.
Marshmallow challenge with debriefing #teamwork #team #leadership #collaboration In eighteen minutes, teams must build the tallest free-standing structure out of 20 sticks of spaghetti, one yard of tape, one yard of string, and one marshmallow. The marshmallow needs to be on top. The Marshmallow Challenge was developed by Tom Wujec, who has done the activity with hundreds of groups around the world. Visit the Marshmallow Challenge website for more information. This version has an extra debriefing question added with sample questions focusing on roles within the team.
Communication
Being an effective communicator means being empathetic, clear and succinct, asking the right questions, and demonstrating active listening skills throughout any discussion or meeting.
In a problem solving setting, you need to communicate well in order to progress through each stage of the process effectively. As a team leader, it may also fall to you to facilitate communication between parties who may not see eye to eye. Effective communication also means helping others to express themselves and be heard in a group.
Bus Trip #feedback #communication #appreciation #closing #thiagi #team This is one of my favourite feedback games. I use Bus Trip at the end of a training session or a meeting, and I use it all the time. The game creates a massive amount of energy with lots of smiles, laughs, and sometimes even a teardrop or two.
Creative problem solving skills can be some of the best tools in your arsenal. Thinking creatively, being able to generate lots of ideas and come up with out of the box solutions is useful at every step of the process.
The kinds of problems you will likely discuss in a problem solving workshop are often difficult to solve, and by approaching things in a fresh, creative manner, you can often create more innovative solutions.
Having practical creative skills is also a boon when it comes to problem solving. If you can help create quality design sketches and prototypes in record time, it can help bring a team to alignment more quickly or provide a base for further iteration.
The paper clip method #sharing #creativity #warm up #idea generation #brainstorming The power of brainstorming. A training for project leaders, creativity training, and to catalyse getting new solutions.
Critical thinking
Critical thinking is one of the fundamental problem solving skills you’ll want to develop when working on developing solutions. Critical thinking is the ability to analyze, rationalize and evaluate while being aware of personal bias, outlying factors and remaining open-minded.
Defining and analyzing problems without deploying critical thinking skills can mean you and your team go down the wrong path. Developing solutions to complex issues requires critical thinking too – ensuring your team considers all possibilities and rationally evaluating them.
Agreement-Certainty Matrix #issue analysis #liberating structures #problem solving You can help individuals or groups avoid the frequent mistake of trying to solve a problem with methods that are not adapted to the nature of their challenge. The combination of two questions makes it possible to easily sort challenges into four categories: simple, complicated, complex , and chaotic . A problem is simple when it can be solved reliably with practices that are easy to duplicate. It is complicated when experts are required to devise a sophisticated solution that will yield the desired results predictably. A problem is complex when there are several valid ways to proceed but outcomes are not predictable in detail. Chaotic is when the context is too turbulent to identify a path forward. A loose analogy may be used to describe these differences: simple is like following a recipe, complicated like sending a rocket to the moon, complex like raising a child, and chaotic is like the game “Pin the Tail on the Donkey.” The Liberating Structures Matching Matrix in Chapter 5 can be used as the first step to clarify the nature of a challenge and avoid the mismatches between problems and solutions that are frequently at the root of chronic, recurring problems.
Data analysis
Though it shares lots of space with general analytical skills, data analysis skills are something you want to cultivate in their own right in order to be an effective problem solver.
Being good at data analysis doesn’t just mean being able to find insights from data, but also selecting the appropriate data for a given issue, interpreting it effectively and knowing how to model and present that data. Depending on the problem at hand, it might also include a working knowledge of specific data analysis tools and procedures.
Having a solid grasp of data analysis techniques is useful if you’re leading a problem solving workshop but if you’re not an expert, don’t worry. Bring people into the group who has this skill set and help your team be more effective as a result.
Decision making
All problems need a solution and all solutions require that someone make the decision to implement them. Without strong decision making skills, teams can become bogged down in discussion and less effective as a result.
Making decisions is a key part of the problem solving process. It’s important to remember that decision making is not restricted to the leadership team. Every staff member makes decisions every day and developing these skills ensures that your team is able to solve problems at any scale. Remember that making decisions does not mean leaping to the first solution but weighing up the options and coming to an informed, well thought out solution to any given problem that works for the whole team.
Lightning Decision Jam (LDJ) #action #decision making #problem solving #issue analysis #innovation #design #remote-friendly The problem with anything that requires creative thinking is that it’s easy to get lost—lose focus and fall into the trap of having useless, open-ended, unstructured discussions. Here’s the most effective solution I’ve found: Replace all open, unstructured discussion with a clear process. What to use this exercise for: Anything which requires a group of people to make decisions, solve problems or discuss challenges. It’s always good to frame an LDJ session with a broad topic, here are some examples: The conversion flow of our checkout Our internal design process How we organise events Keeping up with our competition Improving sales flow
Dependability
Most complex organizational problems require multiple people to be involved in delivering the solution. Ensuring that the team and organization can depend on you to take the necessary actions and communicate where necessary is key to ensuring problems are solved effectively.
Being dependable also means working to deadlines and to brief. It is often a matter of creating trust in a team so that everyone can depend on one another to complete the agreed actions in the agreed time frame so that the team can move forward together. Being undependable can create problems of friction and can limit the effectiveness of your solutions so be sure to bear this in mind throughout a project.
Team Purpose & Culture #team #hyperisland #culture #remote-friendly This is an essential process designed to help teams define their purpose (why they exist) and their culture (how they work together to achieve that purpose). Defining these two things will help any team to be more focused and aligned. With support of tangible examples from other companies, the team members work as individuals and a group to codify the way they work together. The goal is a visual manifestation of both the purpose and culture that can be put up in the team’s work space.
Emotional intelligence
Emotional intelligence is an important skill for any successful team member, whether communicating internally or with clients or users. In the problem solving process, emotional intelligence means being attuned to how people are feeling and thinking, communicating effectively and being self-aware of what you bring to a room.
There are often differences of opinion when working through problem solving processes, and it can be easy to let things become impassioned or combative. Developing your emotional intelligence means being empathetic to your colleagues and managing your own emotions throughout the problem and solution process. Be kind, be thoughtful and put your points across care and attention.
Being emotionally intelligent is a skill for life and by deploying it at work, you can not only work efficiently but empathetically. Check out the emotional culture workshop template for more!
Facilitation
As we’ve clarified in our facilitation skills post, facilitation is the art of leading people through processes towards agreed-upon objectives in a manner that encourages participation, ownership, and creativity by all those involved. While facilitation is a set of interrelated skills in itself, the broad definition of facilitation can be invaluable when it comes to problem solving. Leading a team through a problem solving process is made more effective if you improve and utilize facilitation skills – whether you’re a manager, team leader or external stakeholder.
The Six Thinking Hats #creative thinking #meeting facilitation #problem solving #issue resolution #idea generation #conflict resolution The Six Thinking Hats are used by individuals and groups to separate out conflicting styles of thinking. They enable and encourage a group of people to think constructively together in exploring and implementing change, rather than using argument to fight over who is right and who is wrong.
Flexibility
Being flexible is a vital skill when it comes to problem solving. This does not mean immediately bowing to pressure or changing your opinion quickly: instead, being flexible is all about seeing things from new perspectives, receiving new information and factoring it into your thought process.
Flexibility is also important when it comes to rolling out solutions. It might be that other organizational projects have greater priority or require the same resources as your chosen solution. Being flexible means understanding needs and challenges across the team and being open to shifting or arranging your own schedule as necessary. Again, this does not mean immediately making way for other projects. It’s about articulating your own needs, understanding the needs of others and being able to come to a meaningful compromise.
The Creativity Dice #creativity #problem solving #thiagi #issue analysis Too much linear thinking is hazardous to creative problem solving. To be creative, you should approach the problem (or the opportunity) from different points of view. You should leave a thought hanging in mid-air and move to another. This skipping around prevents premature closure and lets your brain incubate one line of thought while you consciously pursue another.
Working in any group can lead to unconscious elements of groupthink or situations in which you may not wish to be entirely honest. Disagreeing with the opinions of the executive team or wishing to save the feelings of a coworker can be tricky to navigate, but being honest is absolutely vital when to comes to developing effective solutions and ensuring your voice is heard.
Remember that being honest does not mean being brutally candid. You can deliver your honest feedback and opinions thoughtfully and without creating friction by using other skills such as emotional intelligence.
Explore your Values #hyperisland #skills #values #remote-friendly Your Values is an exercise for participants to explore what their most important values are. It’s done in an intuitive and rapid way to encourage participants to follow their intuitive feeling rather than over-thinking and finding the “correct” values. It is a good exercise to use to initiate reflection and dialogue around personal values.
Initiative
The problem solving process is multi-faceted and requires different approaches at certain points of the process. Taking initiative to bring problems to the attention of the team, collect data or lead the solution creating process is always valuable. You might even roadtest your own small scale solutions or brainstorm before a session. Taking initiative is particularly effective if you have good deal of knowledge in that area or have ownership of a particular project and want to get things kickstarted.
That said, be sure to remember to honor the process and work in service of the team. If you are asked to own one part of the problem solving process and you don’t complete that task because your initiative leads you to work on something else, that’s not an effective method of solving business challenges.
15% Solutions #action #liberating structures #remote-friendly You can reveal the actions, however small, that everyone can do immediately. At a minimum, these will create momentum, and that may make a BIG difference. 15% Solutions show that there is no reason to wait around, feel powerless, or fearful. They help people pick it up a level. They get individuals and the group to focus on what is within their discretion instead of what they cannot change. With a very simple question, you can flip the conversation to what can be done and find solutions to big problems that are often distributed widely in places not known in advance. Shifting a few grains of sand may trigger a landslide and change the whole landscape.
Impartiality
A particularly useful problem solving skill for product owners or managers is the ability to remain impartial throughout much of the process. In practice, this means treating all points of view and ideas brought forward in a meeting equally and ensuring that your own areas of interest or ownership are not favored over others.
There may be a stage in the process where a decision maker has to weigh the cost and ROI of possible solutions against the company roadmap though even then, ensuring that the decision made is based on merit and not personal opinion.
Empathy map #frame insights #create #design #issue analysis An empathy map is a tool to help a design team to empathize with the people they are designing for. You can make an empathy map for a group of people or for a persona. To be used after doing personas when more insights are needed.
Being a good leader means getting a team aligned, energized and focused around a common goal. In the problem solving process, strong leadership helps ensure that the process is efficient, that any conflicts are resolved and that a team is managed in the direction of success.
It’s common for managers or executives to assume this role in a problem solving workshop, though it’s important that the leader maintains impartiality and does not bulldoze the group in a particular direction. Remember that good leadership means working in service of the purpose and team and ensuring the workshop is a safe space for employees of any level to contribute. Take a look at our leadership games and activities post for more exercises and methods to help improve leadership in your organization.
Leadership Pizza #leadership #team #remote-friendly This leadership development activity offers a self-assessment framework for people to first identify what skills, attributes and attitudes they find important for effective leadership, and then assess their own development and initiate goal setting.
In the context of problem solving, mediation is important in keeping a team engaged, happy and free of conflict. When leading or facilitating a problem solving workshop, you are likely to run into differences of opinion. Depending on the nature of the problem, certain issues may be brought up that are emotive in nature.
Being an effective mediator means helping those people on either side of such a divide are heard, listen to one another and encouraged to find common ground and a resolution. Mediating skills are useful for leaders and managers in many situations and the problem solving process is no different.
Conflict Responses #hyperisland #team #issue resolution A workshop for a team to reflect on past conflicts, and use them to generate guidelines for effective conflict handling. The workshop uses the Thomas-Killman model of conflict responses to frame a reflective discussion. Use it to open up a discussion around conflict with a team.
Planning
Solving organizational problems is much more effective when following a process or problem solving model. Planning skills are vital in order to structure, deliver and follow-through on a problem solving workshop and ensure your solutions are intelligently deployed.
Planning skills include the ability to organize tasks and a team, plan and design the process and take into account any potential challenges. Taking the time to plan carefully can save time and frustration later in the process and is valuable for ensuring a team is positioned for success.
3 Action Steps #hyperisland #action #remote-friendly This is a small-scale strategic planning session that helps groups and individuals to take action toward a desired change. It is often used at the end of a workshop or programme. The group discusses and agrees on a vision, then creates some action steps that will lead them towards that vision. The scope of the challenge is also defined, through discussion of the helpful and harmful factors influencing the group.
Prioritization
As organisations grow, the scale and variation of problems they face multiplies. Your team or is likely to face numerous challenges in different areas and so having the skills to analyze and prioritize becomes very important, particularly for those in leadership roles.
A thorough problem solving process is likely to deliver multiple solutions and you may have several different problems you wish to solve simultaneously. Prioritization is the ability to measure the importance, value, and effectiveness of those possible solutions and choose which to enact and in what order. The process of prioritization is integral in ensuring the biggest challenges are addressed with the most impactful solutions.
Impact and Effort Matrix #gamestorming #decision making #action #remote-friendly In this decision-making exercise, possible actions are mapped based on two factors: effort required to implement and potential impact. Categorizing ideas along these lines is a useful technique in decision making, as it obliges contributors to balance and evaluate suggested actions before committing to them.
Project management
Some problem solving skills are utilized in a workshop or ideation phases, while others come in useful when it comes to decision making. Overseeing an entire problem solving process and ensuring its success requires strong project management skills.
While project management incorporates many of the other skills listed here, it is important to note the distinction of considering all of the factors of a project and managing them successfully. Being able to negotiate with stakeholders, manage tasks, time and people, consider costs and ROI, and tie everything together is massively helpful when going through the problem solving process.
Record keeping
Working out meaningful solutions to organizational challenges is only one part of the process. Thoughtfully documenting and keeping records of each problem solving step for future consultation is important in ensuring efficiency and meaningful change.
For example, some problems may be lower priority than others but can be revisited in the future. If the team has ideated on solutions and found some are not up to the task, record those so you can rule them out and avoiding repeating work. Keeping records of the process also helps you improve and refine your problem solving model next time around!
Personal Kanban #gamestorming #action #agile #project planning Personal Kanban is a tool for organizing your work to be more efficient and productive. It is based on agile methods and principles.
Research skills
Conducting research to support both the identification of problems and the development of appropriate solutions is important for an effective process. Knowing where to go to collect research, how to conduct research efficiently, and identifying pieces of research are relevant are all things a good researcher can do well.
In larger groups, not everyone has to demonstrate this ability in order for a problem solving workshop to be effective. That said, having people with research skills involved in the process, particularly if they have existing area knowledge, can help ensure the solutions that are developed with data that supports their intention. Remember that being able to deliver the results of research efficiently and in a way the team can easily understand is also important. The best data in the world is only as effective as how it is delivered and interpreted.
Customer experience map #ideation #concepts #research #design #issue analysis #remote-friendly Customer experience mapping is a method of documenting and visualizing the experience a customer has as they use the product or service. It also maps out their responses to their experiences. To be used when there is a solution (even in a conceptual stage) that can be analyzed.
Risk management
Managing risk is an often overlooked part of the problem solving process. Solutions are often developed with the intention of reducing exposure to risk or solving issues that create risk but sometimes, great solutions are more experimental in nature and as such, deploying them needs to be carefully considered.
Managing risk means acknowledging that there may be risks associated with more out of the box solutions or trying new things, but that this must be measured against the possible benefits and other organizational factors.
Be informed, get the right data and stakeholders in the room and you can appropriately factor risk into your decision making process.
Decisions, Decisions… #communication #decision making #thiagi #action #issue analysis When it comes to decision-making, why are some of us more prone to take risks while others are risk-averse? One explanation might be the way the decision and options were presented. This exercise, based on Kahneman and Tversky’s classic study , illustrates how the framing effect influences our judgement and our ability to make decisions . The participants are divided into two groups. Both groups are presented with the same problem and two alternative programs for solving them. The two programs both have the same consequences but are presented differently. The debriefing discussion examines how the framing of the program impacted the participant’s decision.
Team-building
No single person is as good at problem solving as a team. Building an effective team and helping them come together around a common purpose is one of the most important problem solving skills, doubly so for leaders. By bringing a team together and helping them work efficiently, you pave the way for team ownership of a problem and the development of effective solutions.
In a problem solving workshop, it can be tempting to jump right into the deep end, though taking the time to break the ice, energize the team and align them with a game or exercise will pay off over the course of the day.
Remember that you will likely go through the problem solving process multiple times over an organization’s lifespan and building a strong team culture will make future problem solving more effective. It’s also great to work with people you know, trust and have fun with. Working on team building in and out of the problem solving process is a hallmark of successful teams that can work together to solve business problems.
9 Dimensions Team Building Activity #ice breaker #teambuilding #team #remote-friendly 9 Dimensions is a powerful activity designed to build relationships and trust among team members. There are 2 variations of this icebreaker. The first version is for teams who want to get to know each other better. The second version is for teams who want to explore how they are working together as a team.
Time management
The problem solving process is designed to lead a team from identifying a problem through to delivering a solution and evaluating its effectiveness. Without effective time management skills or timeboxing of tasks, it can be easy for a team to get bogged down or be inefficient.
By using a problem solving model and carefully designing your workshop, you can allocate time efficiently and trust that the process will deliver the results you need in a good timeframe.
Time management also comes into play when it comes to rolling out solutions, particularly those that are experimental in nature. Having a clear timeframe for implementing and evaluating solutions is vital for ensuring their success and being able to pivot if necessary.
Improving your skills at problem solving is often a career-long pursuit though there are methods you can use to make the learning process more efficient and to supercharge your problem solving skillset.
Remember that the skills you need to be a great problem solver have a large overlap with those skills you need to be effective in any role. Investing time and effort to develop your active listening or critical thinking skills is valuable in any context. Here are 7 ways to improve your problem solving skills.
Share best practices
Remember that your team is an excellent source of skills, wisdom, and techniques and that you should all take advantage of one another where possible. Best practices that one team has for solving problems, conducting research or making decisions should be shared across the organization. If you have in-house staff that have done active listening training or are data analysis pros, have them lead a training session.
Your team is one of your best resources. Create space and internal processes for the sharing of skills so that you can all grow together.
Ask for help and attend training
Once you’ve figured out you have a skills gap, the next step is to take action to fill that skills gap. That might be by asking your superior for training or coaching, or liaising with team members with that skill set. You might even attend specialized training for certain skills – active listening or critical thinking, for example, are business-critical skills that are regularly offered as part of a training scheme.
Whatever method you choose, remember that taking action of some description is necessary for growth. Whether that means practicing, getting help, attending training or doing some background reading, taking active steps to improve your skills is the way to go.
Learn a process
Problem solving can be complicated, particularly when attempting to solve large problems for the first time. Using a problem solving process helps give structure to your problem solving efforts and focus on creating outcomes, rather than worrying about the format.
Tools such as the seven-step problem solving process above are effective because not only do they feature steps that will help a team solve problems, they also develop skills along the way. Each step asks for people to engage with the process using different skills and in doing so, helps the team learn and grow together. Group processes of varying complexity and purpose can also be found in the SessionLab library of facilitation techniques . Using a tried and tested process and really help ease the learning curve for both those leading such a process, as well as those undergoing the purpose.
Effective teams make decisions about where they should and shouldn’t expend additional effort. By using a problem solving process, you can focus on the things that matter, rather than stumbling towards a solution haphazardly.
Create a feedback loop
Some skills gaps are more obvious than others. It’s possible that your perception of your active listening skills differs from those of your colleagues.
It’s valuable to create a system where team members can provide feedback in an ordered and friendly manner so they can all learn from one another. Only by identifying areas of improvement can you then work to improve them.
Remember that feedback systems require oversight and consideration so that they don’t turn into a place to complain about colleagues. Design the system intelligently so that you encourage the creation of learning opportunities, rather than encouraging people to list their pet peeves.
While practice might not make perfect, it does make the problem solving process easier. If you are having trouble with critical thinking, don’t shy away from doing it. Get involved where you can and stretch those muscles as regularly as possible.
Problem solving skills come more naturally to some than to others and that’s okay. Take opportunities to get involved and see where you can practice your skills in situations outside of a workshop context. Try collaborating in other circumstances at work or conduct data analysis on your own projects. You can often develop those skills you need for problem solving simply by doing them. Get involved!
Use expert exercises and methods
Learn from the best. Our library of 700+ facilitation techniques is full of activities and methods that help develop the skills you need to be an effective problem solver. Check out our templates to see how to approach problem solving and other organizational challenges in a structured and intelligent manner.
There is no single approach to improving problem solving skills, but by using the techniques employed by others you can learn from their example and develop processes that have seen proven results.
Try new ways of thinking and change your mindset
Using tried and tested exercises that you know well can help deliver results, but you do run the risk of missing out on the learning opportunities offered by new approaches. As with the problem solving process, changing your mindset can remove blockages and be used to develop your problem solving skills.
Most teams have members with mixed skill sets and specialties. Mix people from different teams and share skills and different points of view. Teach your customer support team how to use design thinking methods or help your developers with conflict resolution techniques. Try switching perspectives with facilitation techniques like Flip It! or by using new problem solving methodologies or models. Give design thinking, liberating structures or lego serious play a try if you want to try a new approach. You will find that framing problems in new ways and using existing skills in new contexts can be hugely useful for personal development and improving your skillset. It’s also a lot of fun to try new things. Give it a go!
Encountering business challenges and needing to find appropriate solutions is not unique to your organization. Lots of very smart people have developed methods, theories and approaches to help develop problem solving skills and create effective solutions. Learn from them!
Books like The Art of Thinking Clearly , Think Smarter, or Thinking Fast, Thinking Slow are great places to start, though it’s also worth looking at blogs related to organizations facing similar problems to yours, or browsing for success stories. Seeing how Dropbox massively increased growth and working backward can help you see the skills or approach you might be lacking to solve that same problem. Learning from others by reading their stories or approaches can be time-consuming but ultimately rewarding.
A tired, distracted mind is not in the best position to learn new skills. It can be tempted to burn the candle at both ends and develop problem solving skills outside of work. Absolutely use your time effectively and take opportunities for self-improvement, though remember that rest is hugely important and that without letting your brain rest, you cannot be at your most effective.
Creating distance between yourself and the problem you might be facing can also be useful. By letting an idea sit, you can find that a better one presents itself or you can develop it further. Take regular breaks when working and create a space for downtime. Remember that working smarter is preferable to working harder and that self-care is important for any effective learning or improvement process.
Want to design better group processes?
Over to you
Now we’ve explored some of the key problem solving skills and the problem solving steps necessary for an effective process, you’re ready to begin developing more effective solutions and leading problem solving workshops.
Need more inspiration? Check out our post on problem solving activities you can use when guiding a group towards a great solution in your next workshop or meeting. Have questions? Did you have a great problem solving technique you use with your team? Get in touch in the comments below. We’d love to chat!
James Smart is Head of Content at SessionLab. He’s also a creative facilitator who has run workshops and designed courses for establishments like the National Centre for Writing, UK. He especially enjoys working with young people and empowering others in their creative practice.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Going from a mere idea to a workshop that delivers results for your clients can feel like a daunting task. In this piece, we will shine a light on all the work behind the scenes and help you learn how to plan a workshop from start to finish. On a good day, facilitation can feel like effortless magic, but that is mostly the result of backstage work, foresight, and a lot of careful planning. Read on to learn a step-by-step approach to breaking the process of planning a workshop into small, manageable chunks. The flow starts with the first meeting with a client to define the purposes of a workshop.…

Effective online tools are a necessity for smooth and engaging virtual workshops and meetings. But how do you choose the right ones? Do you sometimes feel that the good old pen and paper or MS Office toolkit and email leaves you struggling to stay on top of managing and delivering your workshop? Fortunately, there are plenty of great workshop tools to make your life easier when you need to facilitate a meeting and lead workshops. In this post, we’ll share our favorite online tools you can use to make your life easier and run better workshops and meetings. In fact, there are plenty of free online workshop tools and meeting…

How does learning work? A clever 9-year-old once told me: “I know I am learning something new when I am surprised.” The science of adult learning tells us that, in order to learn new skills (which, unsurprisingly, is harder for adults to do than kids) grown-ups need to first get into a specific headspace. In a business, this approach is often employed in a training session where employees learn new skills or work on professional development. But how do you ensure your training is effective? In this guide, we'll explore how to create an effective training session plan and run engaging training sessions. As team leader, project manager, or consultant,…
Design your next workshop with SessionLab
Join the 150,000 facilitators using SessionLab
Sign up for free
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Career Planning
- Skills Development
What Are Problem-Solving Skills?
Definition & Examples of Problem-Solving Skills
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/ADHeadshot-Cropped-b80e40469d5b4852a68f94ad69d6e8bd.jpg)
- Problem-solving skills help you determine why an issue is happening and how to resolve that issue.
Problem-solving is considered a soft skill (a personal strength) rather than a hard skill that's learned through education or training. You can improve your problem-solving skills by familiarizing yourself with common issues in your industry and learning from more experienced employees. Learn more about problem-solving skills and how they work.
Problem-solving skills help you solve issues quickly and effectively. It's one of the key skills that employers seek in job applicants, as employees with these skills tend to be self-reliant. Problem-solving skills require quickly identifying the underlying issue and implementing a solution.
How Problem-Solving Skills Work
Problem-solving starts with identifying the issue. For example, a teacher might need to figure out how to improve student performance on a writing proficiency test. To do that, the teacher will review the writing tests looking for areas of improvement. They might see that students can construct simple sentences, but they're struggling with writing paragraphs and organizing those paragraphs into an essay.
To solve the problem, the teacher would work with students on how and when to write compound sentences, how to write paragraphs, and ways to organize an essay.
Theresa Chiechi / The Balance
Problem-Solving Steps
There are five steps typically used in problem-solving.
1. Analyze Contributing Factors
To solve a problem, you must find out what caused it. This requires you to gather and evaluate data, isolate possible contributing circumstances, and pinpoint what needs to be addressed for a resolution.
To do this, you'll use skills like :
- Data gathering
- Data analysis
- Fact-finding
- Historical analysis
2. Generate Interventions
Once you’ve determined the cause, brainstorm possible solutions. Sometimes this involves teamwork since two (or more) minds are often better than one. A single strategy is rarely the obvious route to solving a complex problem; devising a set of alternatives helps you cover your bases and reduces your risk of exposure should the first strategy you implement fail.
This involves skills like :
- Brainstorming
- Creative thinking
- Forecasting
- Project design
- Project planning
3. Evaluate Solutions
Depending on the nature of the problem and your chain of command, evaluating the best solutions may be performed by assigned teams or team leads, or forwarded to corporate decision-makers. Whoever makes the decision must evaluate potential costs, required resources, and possible barriers to successful solution implementation.
This requires several skills, including:
- Corroboration
- Test development
- Prioritizing
4. Implement a Plan
Once a course of action has been decided, it must be implemented along with benchmarks that can quickly and accurately determine whether it’s working. Plan implementation also involves letting personnel know about changes in standard operating procedures.
This requires skills like:
- Project management
- Project implementation
- Collaboration
- Time management
- Benchmark development
5. Assess the Solution's Effectiveness
Once a solution is implemented, the best problem-solvers have systems in place to evaluate if and how quickly it's working. This way, they know as soon as possible whether the issue has been resolved or whether they’ll have to change their response to the problem mid-stream.
This requires:
- Communication
- Customer feedback
- Follow-through
- Troubleshooting
Examples of Problem-Solving Skills
Here's an example of showing your problem-solving skills in a cover letter.
When I was first hired as a paralegal, I inherited a backlog of 25 sets of medical records that needed to be summarized, each of which was hundreds of pages long. At the same time, I had to help prepare for three major cases, and there weren’t enough hours in the day. After I explained the problem to my supervisor, she agreed to pay me to come in on Saturday mornings to focus on the backlog. I was able to eliminate the backlog in a month.
Here's another example of how to show your problem-solving skills in a cover letter:
When I joined the team at Great Graphics as Artistic Director, the designers had become uninspired because of a former director who attempted to micro-manage every step in the design process. I used weekly round-table discussions to solicit creative input and ensured that each designer was given full autonomy to do their best work. I also introduced monthly team-based competitions that helped build morale, spark new ideas, and improve collaboration.
Highlighting Problem-Solving Skills
- Since this is a skill that's important to most employers, put them front and center on your resume, cover letter, and in interviews.
If you're not sure what to include, look to previous roles—whether in academic, work, or volunteer settings—for examples of challenges you met and problems you solved. Highlight relevant examples in your cover letter and use bullet points in your resume to show how you solved a problem.
During interviews, be ready to describe situations you've encountered in previous roles, the processes you followed to address problems, the skills you applied, and the results of your actions. Potential employers are eager to hear a coherent narrative of the ways you've used problem-solving skills .
Interviewers may pose hypothetical problems for you to solve. Base your answers on the five steps and refer to similar problems you've resolved, if possible. Here are tips for answering problem-solving interview questions , with examples of the best answers.
Key Takeaways
- It's one of the key skills that employers seek in job applicants.
- Problem-solving starts with identifying the issue, coming up with solutions, implementing those solutions, and evaluating their effectiveness.
- Coaching Skills Training
- Coaching TIPS²™
- Continuous Improvement Coaching
- Courageous Conversations Workshop
- Executive Coaching Program
- Feedback 360
- Safety Coaching
- Sales Coaching Training Program
- Free Consultation
- Applied Strategic Thinking®
- Strategic Leadership Course
- Strategic Teaming
- Strategy Development Processes and Services
- Communication Training for Managers
- Conflict and Collaboration
- Confronting Racism Workshop
- Delegation & Accountability
- Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion Workshop
- Flexible Leadership
- Leading Change
- Leading Groups to Solutions
- Leading Innovation
- Mid-Level Management Training
- Qualities of Leadership
- Bottom Line Leadership
- Customized Leadership Development Programs
- Leadership Development Program Design
- Mini-MBA & Operational Finance
- Problem Solving and Decision Making in the Workplace
- Transition to Leadership
- Virtual Leadership
- High-Performance Teamwork
- Leadership Team Alignment Workshop
- Orienteering
- Corporate Outdoor Training and Team Building
- Retreats for Teams
- Innovation Skills Training
- Personal Impact Workshop
- Supervisor Training Programs
- Customization of CMOE’s Learning Library
- Full Curriculum Development and Design
- Learning & Development Advisory Services
- Bottom Line Leadership Training
- Consulting Services
- Leadership Retreats
- Learning and Development Consulting Services
- Needs Analysis and Organization Assessments
- Transformation & Change Solutions
- Facilitator Training Workshop
- Empathic Leadership
- Supervisor Development Series
- All Courses
- Digital Learning
- Books and Publications
- Assessments and Surveys
- Clients Served
- History and Experience
- Meet the CMOE Team
- Testimonials
- Articles & Tools
- Scenario Templates
- Certified Partners
- Event Resources
- Industry Insights
- Resource Library
- Video Library
- News and Events
- Professional Accreditation and Continuing Education Units
- Surveys & Assessments
How to Improve Problem Solving Skills [10 Ways]
While it might seem like some people are just born with stronger problem-solving skills, there are strategies that anyone can use to improve them.
That’s right, it’s possible to significantly enhance your abilities in this area — and the best part is, most of these activities are also pretty fun!
What Are Problem Solving Skills?
Before we get to the engaging activities, let’s refine our understanding of problem-solving skills, which are any techniques that help you consistently:
- Understand the causes of problems
- Overcome short-term crises
- Create strategies to solve longer-term problems
- Turn problems into opportunities
What Problem Solving Skills Should I Have?
You’ll be able to solve problems in your role better as you grow in your industry-specific knowledge. But there are also a few universal problem solving skills we all need:
- Defining the Problem: Deeply understanding a problem through research , leading to better solutions. Research can include interviewing, reading books and emails, analyzing financial data, searching your organization’s intranet, and organizing your findings.
- Brainstorming: Creating a myriad of new solutions quickly. In group brainstorms, allow everyone to state ideas. Appreciate all input, and avoid criticism. Then, organize solutions into groups around common themes.
- Analyzing: Using disciplined thought processes to evaluate each possible solution. Besides listing their costs and benefits, you might apply deductive reasoning, game theory, and the rules of logic (including fallacies) to them.
- Managing Risk: Anticipating and trying to avoid the downsides of key solutions. Your team can list potential risks, rate how likely each is, predict a date by which each might either happen or no longer be an issue, and devise ways to reduce those risks.
- Deciding: The ability to decide on a solution and move forward with it. After an appropriate amount of time, an analysis of possible solutions, and feedback from team members, a designated decider must choose and implement a solution.
- Managing Emotions: Applying emotional intelligence in order to improve your and your team members’ ability to think clearly. This requires you to recognize emotions in yourself and others, manage feelings, and channel emotions into useful work.
10 Exciting Ways to Improve Problem Solving Skills
Use these ten creative ways to improve problem solving skills, develop more strategic ways of thinking , and train your brain to do more.
1. Dance Your Heart Out
Did you know that dancing has a positive impact on neural processing, possibly developing new neural pathways to go around dopamine-depleted blockages in the brain?
This means that if you engage in ballet or another form of structured dance, doing so may facilitate convergent thinking . In other words, it may help you find a single, appropriate answer to a problem. If you need help with divergent thinking (finding multiple answers to a problem), engaging in more improvised types of dance such as hip-hop or tap might just do the trick.
2. Work out Your Brain with Logic Puzzles or Games
The winning strategy when playing chess, Sudoku, a Rubik’s Cube, or other brain-boosting games is actually to work the problem backward, not forward. The same strategy can apply to realistic strategic-thinking situations.
To build up your brain muscle and develop new problem-solving techniques, practice some logic puzzles and other games .
3. Get a Good Night’s Sleep
More than any other sleeping or awake state, Rapid Eye Movement (REM) sleep directly enhances creative processing in the brain. REM sleep helps “stimulate associative networks, allowing the brain to make new and useful associations between unrelated ideas” and are “not due to selective memory enhancements” such as memory consolidation, which occurs when awake.
4. Work out to Some Tunes
A study of cardiac rehabilitation patients tested verbal fluency after exercising with and without music. Results showed that when they listened to music while working out, participants more than doubled their scores on verbal fluency tests in contrast to when they worked out in silence. According to the study’s lead author, “The combination of music and exercise may stimulate and increase cognitive arousal while helping to organize the cognitive output.”
Get Your Free Toolkit to Identify Your Strengths and Minimize Your Weaknesses. Click Here to Download Your Toolkit Today.
5. keep an “idea journal” with you, 6. participate in yoga.
The powerful combination of body awareness, breathing, and meditation that is required during yoga practice has been shown to significantly raise cognitive test scores. Other results from a University of Illinois study include shorter reaction times, more accuracy, and increased attention.
7. Eat Some Cheerios (And Then Think About It)
The Cheerios Effect is the name physicists have given to the event that happens when the last few cheerios in a bowl always cling to each other. The cause of this occurrence is surface tension.
The takeaway is that when it comes to experiencing tension while trying to solve a problem, cling to those around you. Rely on others’ experiences and ideas, even those from different career fields. Draw connections. Brainstorm. Work together to get the job done.
8. Use Mind Maps to Help Visualize the Problem
Mind Maps , a visual snapshot of a problem and its possible solutions, can help focus the mind, stimulate the brain, increase the capacity for creative thinking, and generate more ideas for solutions.
Make a Mind Map by drawing your problem as the central idea. Add “main branches” consisting of all the reasons for the problem. Use “sub-branches” to explore further details.
Next, make a separate Mind Map of all possible solutions to the central problem. Add “main branches” showing all the ways that your problem can be solved, such as colleagues that can help, techniques you can apply, and other resources you can use. Add “sub-branches” to further explore the details. Make a final branch with the most suitable solution for the main problem. Use “sub-branches” for details.
Through this exercise, you should be able to see which “branch” or option is the most practical, time-saving, and cost-effective problem solving method .
9. Create “Psychological Distance”
What is psychological distance? According to the construal level theory (CLT), it’s “anything that we do not experience as occurring now, here, and to ourselves.” Some examples include taking another person’s perspective or thinking of the problem as unlikely.
Scientists have shown that by increasing the mental distance between us and our problem, we’ll have an increase in creative solutions. This happens because thinking more abstractly helps us form unexpected connections between seemingly unrelated concepts, thus allowing our minds to increase its problem solving capacity.
10. Play Some Soccer
A link has been found between our brain’s “executive functions” and sports success . When in action, our brains are quickly multitasking between moving, anticipating, strategizing, reacting, and performing. Doing all these things at once requires an enormous amount of brain activity.
This can be related to our working world when we plan, reason, monitor our actions and problem solve all at once. Therefore, it may be concluded that when you play soccer or any other fast-moving sport, you’re rewiring your brain to be quicker at thinking, processing, and reacting to problems.
To learn more about how to develop your problem-solving and decision making capabilities or to receive training on applied strategic thinking skills , contact CMOE today!
Recommended For You:
Leadership development workshops, get exclusive content delivered straight to your inbox.
When you subscribe to our blog and become a CMOE Insider.
And the best part?
It's 100% free.
As Featured In:
The Better Business Bureau has determined that CMOE meets accreditation standards. These standards verify that CMOE’s product quality and competence enhance customer trust and confidence.
©2024 Center for Management & Organization Effectiveness. All rights reserved.

MSU Extension
Problem-solving skills are an important factor in academic success.
Elizabeth Gutierrez, Michigan State University Extension - May 11, 2012
Updated from an original article written by [email protected]..
Parents and caregivers can ensure their children's success by teaching and modeling effective problem-solving at home.

Helping your child learn how to problem solve is a critical skill for school readiness. Parents and caregivers are a child’s first and most important teacher; therefore, modeling good problem solving skills is very important. Children learn by watching parents and caregivers handle different situations and solve problems. If a parent handles problems by yelling, throwing things, hitting, grabbing or using other unacceptable strategies, a child will learn to do the same thing.
Often, adults will prevent their children from seeing all conflicts or disagreements. Remember, it is important for children to see adults negotiate differences, compromise and resolve conflicts. Learning to negotiate differences in a constructive way and allowing children to see how this is done is very effective and important. If parent and caregivers handle these situations privately, there is no example for the child/children to learn from.
Children can learn how to be assertive verbally as a result of seeing and listening to how adults resolve conflict. Another simple way a child can learn how to be assertive verbally is by role-playing with puppets and through pretend play with an adult. When using these techniques, it is important to help your child think of constructive ways to respond to different situations. By using puppets and role-play, your child can also learn about how others may feel in specific situations. When using these techniques, it is important not to criticize or label the child for past misbehavior.
There are some basic steps to problem solving from Incredible Years :
- Identify the problem.
- List the possible solutions or courses of action.
- Weigh the possible solutions.
- Choose a solution to try.
- Put the solution into practice.
- Evaluate the solution.
Using effective problem solving techniques will help children avoid conflict with others in a school setting and in their everyday lives. It will also strengthen children’s beginning empathy skills and help them learn more positive attributions about another person’s intentions. Effective problem solving skills is essential for academic and social success.
For more articles on child development, academic success, parenting and life skill development, please visit the Michigan State University Extension website.
This article was published by Michigan State University Extension . For more information, visit https://extension.msu.edu . To have a digest of information delivered straight to your email inbox, visit https://extension.msu.edu/newsletters . To contact an expert in your area, visit https://extension.msu.edu/experts , or call 888-MSUE4MI (888-678-3464).
Did you find this article useful?

Ready to grow with 4-H? Sign up today!
new - method size: 3 - Random key: 0, method: tagSpecific - key: 0
You Might Also Be Interested In

MI Community Minutes: Strengthening Irontown with Negaunee City Manager Nate Heffron
Published on March 1, 2022

MSU Soil Testing Update
Published on May 15, 2023

ac3-podcast-episode-6
Published on February 28, 2022
The Scoop on the Poop Power Up
Published on March 1, 2020
The Progression of Bt Resistance
Published on December 13, 2019
MIFruitcast: Michigan Fruit Economics with Chris Bardenhagen
Published on January 18, 2024
- child & family development
- early childhood development
- msu extension
- social and emotional development
- child & family development,
- early childhood development,
- msu extension,
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
How to Learn from Your Mistakes and Make Better Decisions
- Cheryl Strauss Einhorn

Six questions to help you figure out what you need to do differently this time around.
We all have scores of decisions to make every day, and we often want to move quickly, telling ourselves that speed equals efficiency. But true efficiency sometimes requires slowing down, being mindful, and especially looking back at the decisions we’ve made that didn’t go as we’d hoped. Too often we don’t want to spend time and mental energy revisiting the past, especially if it contains uncomfortable missteps. But stopping and looking carefully at those mistakes is exactly what can help us make better decisions moving forward. Think of your past decisions as a dataset that you can mine for insights. They can help you identify biases and assumptions that may be holding you back, develop strategies to shift your behavior going forward, and ultimately feel more confident that your process will lead to positive outcomes. A series of six questions can help you apply lessons from your past decisions to your current situation.
Stacey, the chief executive of a nonprofit focused on energy efficiency, wanted to bolster her leadership team by creating a chief operating officer position. Her first two hires to fill the role were unsuccessful: Neither lasted a full year on the job. These were time-consuming and resource-intensive mistakes.
- Cheryl Strauss Einhorn is the founder and CEO of Decisive, a decision sciences company using her AREA Method decision-making system for individuals, companies, and nonprofits looking to solve complex problems. Decisive offers digital tools and in-person training, workshops, coaching and consulting. Cheryl is a long-time educator teaching at Columbia Business School and Cornell and has won several journalism awards for her investigative news stories. She’s authored two books on complex problem solving, Problem Solved for personal and professional decisions, and Investing In Financial Research about business, financial, and investment decisions. Her new book, Problem Solver, is about the psychology of personal decision-making and Problem Solver Profiles. For more information please watch Cheryl’s TED talk and visit areamethod.com .
Partner Center
Effective Problem Solving Techniques: Critical Thinking, Six Thinking Hats, and Solution Development
Integrating critical thinking and creative approaches to problem solving, how to use the “six thinking hats” model for problem solving, how to effectively solve your problems, how to define personal success, step 3: creating a list of questions to solve the problem, how to find solutions to all your questions, how to develop a successful solution, 1. in-depth problem research, 2. idea generation, 3. action plan development, 1. gather all ideas and responses to form a fully developed solution, 2. explore multiple solutions and evaluate them, 3. think of ways to improve the best solution, 4. consider revising your solution, 5. brainstorm additional steps to enhance your solution, 6. the developed solution must meet all established criteria, problem solving: how to use resources and time efficiently.
In today’s fast-paced world, where challenges become increasingly complex, the ability to solve problems efficiently is a key skill. While a creative approach has long been recognized as a powerful tool for discovering new pathways, adding critical thinking into the mix can deliver even more outstanding results. The fusion of these two types of thinking unlocks innovative solutions that might not be evident when each is used separately.
The Harson Thinking Model is one of the most powerful methods for synergistically utilizing both hemispheres of the brain—the creative and the analytical parts. According to the theory, the right hemisphere is responsible for creativity and intuition, while the left manages logical reasoning and analysis. When these capabilities are combined, the result is highly productive thinking.
For example, imagine an architect designing a new city park. A creative approach might lead to original ideas and unconventional solutions, such as green rooftops or interactive landscapes. However, critical thinking is essential to evaluate the feasibility of these ideas: cost analysis, infrastructure capabilities, and material longevity assessments. Without leveraging both mindsets, the project may either remain a mere creative concept or become overly practical, losing its unique flair.
Another example is the development of a new marketing strategy. A creative director might come up with unique advertising campaign concepts, utilizing unconventional approaches and innovative consumer engagement methods. On the other hand, an analyst measures the success of these ideas by conducting market research and analyzing data to confirm their effectiveness. Only through the synergy of these two approaches can a company achieve optimal results.
Moreover, alternating between critical thinking and creative approaches fosters an iterative process: critical reflection helps refine initial creative ideas, making them more concrete and viable. This is particularly essential for complex projects or unconventional challenges, where both originality and meticulous execution are required.
Utilizing Harson’s thinking model not only aids in finding better solutions for professional and business tasks but can also transform everyday life. For example, when planning a family vacation, combining a creative approach in choosing unique locations and activities with a critical analysis of logistics and budget can create unforgettable moments without stretching beyond your means.
Thus, Harson’s productive thinking model enables a broad perspective on problems, uncovering optimal and innovative solutions. Incorporating this model into daily practice can significantly boost effectiveness in both professional endeavors and personal life.
The “Six Thinking Hats” model, developed by renowned psychologist and author Edward de Bono, is a powerful tool for solving creative problems using critical thinking. This methodology helps organize your thought process and view the problem from multiple perspectives, significantly increasing the chances of finding an effective solution.
Each “hat” represents a specific approach to thinking, and using them in sequence allows you to structure your thought process:
- White Hat: Involves collecting and analyzing facts, data, and information. It’s crucial to evaluate the situation objectively at this stage to understand what is truly happening. For instance, if your company’s Sales have declined, identify the specific factors affecting this — it could be the economic climate, marketing strategies, product quality, and so on.
- Red Hat: Leverages emotions and intuition. This step helps you recognize internal feelings and reactions, both your own and those of your colleagues. Additionally, it’s essential to note if someone on the team feels unjustified anxiety or enthusiasm, as these emotions can impact decisions.
- Black Hat: Assesses potential risks and obstacles. What is the primary issue or problem you’re facing? For example, what threats and challenges might arise in implementing a particular solution? This phase allows you to identify potential pitfalls in advance and prepare for them accordingly.
- Yellow Hat: Focuses on positive aspects and opportunities. Here, you analyze what will be considered a success. What benefits and advantages will the new solution bring? For instance, introducing new technology might enhance processes and increase efficiency.
- Green Hat: Encourages the generation of creative ideas and possible solutions. In this stage, you brainstorm as many options and approaches as possible to address the problem. For example, conduct a brainstorming session with your team where everyone can propose their innovative ideas.
- Blue Hat: Organizes and manages the thinking process. This involves resource allocation and action planning for the selected solution. It’s crucial to create a plan, distribute responsibilities, and determine key milestones. For example, if your plan requires additional resources, compile a list of necessary tools and specialists to help bring the idea to life.
This approach helps you view the problem from multiple perspectives, leading to a more comprehensive analysis. By applying the “Six Thinking Hats” model, you can enhance team communication, uncover hidden opportunities, and find optimal solutions to complex challenges. Remember, critical thinking is a skill that improves with practice. Don’t hesitate to experiment and discover new strategies for problem-solving!
Everyone encounters problems, and regardless of their scale, having the ability to solve them is a crucial life skill. Before jumping into action, it’s essential to clearly understand the issue at hand. Asking yourself a few key questions can help you get to the heart of the matter:
- What exactly is the problem?
- Which aspects of the situation are out of balance?
- What can be improved and how?
- What specific complaints are clients making (if it pertains to business)?
These questions will help you define the problem’s boundaries and approach its resolution with greater confidence. For instance, if you’re managing a project and clients are complaining about delivery delays, it’s crucial to identify where the bottleneck is occurring. In a business context, this might mean reviewing logistics processes or finding new suppliers.
Once the problem is defined, it’s beneficial to examine it from all angles by asking additional questions such as: What factors contribute to its development? Who stands to benefit from its resolution? What benefits will you personally gain? For example, by improving customer service quality, you not only address complaints but also enhance your reputation and boost client loyalty.
To solve the problem effectively, gather all available information and verify its accuracy. Sometimes, a problem may seem insurmountable at first glance, but with deeper analysis, solutions often come to light. The right approach can dispel fears surrounding the problem’s magnitude and allow you to take concrete steps. For instance, if the issue is low team productivity, you might consider surveying your employees to determine what is hindering their efficiency.
Anticipate the potential consequences of both addressing and not addressing the issue in advance. This approach enables a clear assessment of the risks and benefits associated with each possible outcome. For instance, when implementing a new Project management system, you may initially encounter adaptation challenges. However, in the long run, this decision could lead to significant improvements in processes and overall performance.
At some point in life, everyone reflects on what success truly means. What defines success? How can we achieve it? The answers to these questions vary from person to person because success is a deeply personal concept that inspires, instills pride, and brings joy from reaching our goals. Crucially, success is determined solely by our individual standards and expectations. To delve deeper into this, let’s consider four key questions that can help you identify your personal vision of success.
First Question: What is the outcome of a successful decision? This question prompts us to clearly outline what we want to achieve. For example, if career growth signifies success to you, what’s your ultimate goal? Perhaps it’s becoming a director or starting your own business. If it pertains to your personal life, maybe you envision a harmonious family with children. It’s vital to have a precise understanding of what you define as success.
Second Question: What outcome do you absolutely want to avoid? Identifying undesirable outcomes is equally important in understanding success. For instance, in terms of financial success, a negative result might be “not losing investments.” In sports, it could be “avoiding injuries on the way to high performance.” Having a clear idea of the unwanted scenario helps steer your energy correctly and avoid critical mistakes.
Third Question: What resources do you have, and how willing are you to utilize them? This isn’t limited to material resources such as money or equipment but also includes intangible assets like knowledge, skills, and time. For example, if you aim to master a new profession but lack the relevant education, it might be beneficial to invest some time in courses or self-study. Or, if your goal is to build perfect relationships, consider which personal traits you need to develop.
Question Four: How will you measure success? Success can be tangible (like a certain amount of money in the bank) or intangible (such as a sense of satisfaction in life). It’s crucial to choose specific indicators. For example, if your goal is to become more sociable, success metrics might include the number of new acquaintances you make each week or the level of trust others have in you.
For a visual example, imagine someone aspiring to physical health. Their success might be measured by their stamina levels, the number of pounds lost, or how effortlessly they can climb stairs without feeling winded.
The journey to success is a personal endeavor, and it will not always be smooth or easy. However, by using this four-question method, you can clearly understand where you want to go and how to track your progress. Remember, success is not a destination but a process, and the key to it lies within each of us.
In this stage, we dive into Creative thinking , compiling a list of questions that will guide us towards an effective solution. This process is grounded on the information we meticulously gathered and analyzed during the earlier phases of our research.
Brainstorming is our key tool here. The more “How can I…?” and “How can we…?” questions we generate, the more diverse our approaches to solving the problem will become. For instance, if you’re developing a new product, your questions might include: “How can we enhance its functionality?” or “How can we make it more appealing to our target audience?” Numerous such questions will provide various perspectives, unveiling new opportunities and possibilities.
Once you have a sufficiently long list of questions, it’s crucial not to get overwhelmed by the abundance of ideas. Select the three most important, focused questions by consciously filtering out the less significant ones. For example, if you’re addressing a team issue, critical questions might be: “How can we improve team communication?”, “How can we boost employee motivation?”, “What resources are needed to achieve our goal?” This will help you stay focused on key aspects and maintain direction towards solving the problem.
Pay special attention to the most crucial question—the one that holds the key to overcoming the problem. This question should be highlighted and given priority in the solution-seeking process. For instance, in many business situations, this question could be: “How can we increase profits without sacrificing quality?”
The journey of personal growth and self-improvement starts with seeking answers to the wide range of questions that accompany every stage of life. These questions can span from technical issues to complex ethical dilemmas, requiring deep thought. It’s no secret that each day brings new challenges, and to grow and advance, it’s crucial to learn how to effectively find answers to them. But how can we do so most efficiently?
The first and perhaps most important step is to make time for this task. Imagine a quiet morning where you can sit peacefully with a cup of coffee and spend a few minutes listing the questions currently on your mind. This process not only helps you think through pressing issues but also allows you to see them from a new perspective. For instance, if you’re dealing with a pressing work situation, taking this quiet time can help you evaluate it more objectively.
Once you’ve gathered your list of questions, the next step is to search for answers. Start by identifying the most critical and complex questions, as these often require the most attention. For example, improving your professional skills will demand more resources and time than deciding on a vacation destination.
For each question, try to come up with at least 10 possible solutions. Utilize a variety of resources: books, articles, the internet, and consultations with friends or colleagues. The key is to be both creative and thorough in your approach. For instance, if you need to enhance your language skills, consider options such as joining language clubs, taking online courses, watching movies in the original language, and practicing with native speakers.
At the initial stage, don’t limit yourself—explore even the most unusual solutions. Among the answers you propose, there might be some rather eccentric ideas, and that’s perfectly fine. Here, it’s not about the quantity but the variety and the ability to think outside the box. For instance, if you want to increase your physical activity, beyond the standard gym workouts and jogging, you could look into dancing, martial arts, or even taking walks while listening to audiobooks.
Make sure to jot down all the answers you come up with, as they will become your primary tool in the process of self-improvement. Keeping records helps you organize your thoughts and develop a clear action plan. For example, maintaining a journal or notes can significantly enhance the effectiveness of your approach to tasks of any complexity.
So, the process of seeking answers is not just about solving specific questions, but also an important step in personal development, enabling you to grow and become more mindful with each passing day.
Creating a successful solution is a complex and multifaceted process. It requires not just a deep understanding of the task at hand, but also a creative approach, strategic planning, and consideration of numerous external and internal factors. Imagine you’re building a skyscraper: to ensure it’s sturdy and long-lasting, you need to thoroughly analyze the soil, choose quality materials, develop a reliable blueprint, and only then can you start construction. The same goes for developing solutions—every step is crucial. Let’s explore the actions that can lead you to success.
The first step towards creating a successful solution is comprehensive research of the problem. Think of it like writing a book: before you start the actual writing process, you need to gather as much information as possible about the characters, time period, setting, conflict, and other details. Similarly, examine the problem from all angles: its causes, potential consequences, and future prospects. For instance, if the goal is to improve customer service in a restaurant, it’s important to understand what specifically affects this aspect, such as service speed, staff courtesy, and food quality.
After thorough analysis, it’s time to get creative. Brainstorming is an excellent tool for generating a variety of ideas. Organize a group session where everyone can contribute their thoughts without fear of criticism. Remember the famous inventor Thomas Edison? He succeeded by not being afraid to experiment. Edison once said, “I have not failed. I’ve just found 10,000 ways that won’t work.” It’s important not to stop at the first idea that comes to mind, but to explore numerous options and combinations.
Once the best ideas have been selected, it’s time for the planning stage. A clear and detailed action plan serves as a roadmap to the final goal. This plan should cover every detail: what will be done, when it will happen, how it will be executed, the necessary resources, and who will be responsible for each task. Think of it like a movie script or the blueprint for a major project: without a clear structure and step-by-step planning, success is unlikely. For instance, when creating a marketing campaign for a new product, you should outline the timeline, define the target audience, devise promotional strategies, choose distribution channels, and establish methods for analyzing results.
It’s also crucial to monitor the plan’s progress and make adjustments as needed to adapt to changing conditions and requirements. A successful solution isn’t a static product but a dynamic process that demands continuous attention and improvement. By following these essential steps, you can develop truly effective and lasting solutions for any challenge.
This step is crucial for creating a successful project or solving any problem. It’s vital to leverage all available resources, including expert opinions, insights from colleagues, and even external sources. For example, if you’re working on improving a product, make sure to consider user feedback, explore market trends, and study competitors. Once you have all the necessary data, the next stage is to synthesize the information. Carefully and meticulously combine all the ideas, eliminate contradictions, and fill in gaps to form a fully developed and logical solution.
Let’s explore a few examples for better understanding. Imagine you’re developing a new marketing strategy for your brand. You start by surveying your team, seeking opinions from marketing experts, and analyzing market data. Consequently, you gather a plethora of varied ideas: some suggest focusing on social media, others recommend enhancing your presence on YouTube, and another group proposes organizing offline events to increase brand recognition. Your task is to seamlessly merge these ideas into a cohesive strategy that considers all aspects and viewpoints.
Another example: you’re developing new software. Utilize the experience of your developers, feedback from beta testers, and the needs of end-users. By correctly synthesizing this information, you can create a product that offers high usability, functionality, and performance, meeting the demands of all stakeholders.
Before committing to a final decision, it’s crucial to explore several potential solutions. This approach allows you to examine the problem from various perspectives and select the best solution that meets all your requirements and success criteria.
Finding alternative solutions involves both creative and analytical thinking. For instance, if you’re developing a new product, consider different materials or technologies that might be used. One material could be cheaper but less durable, whereas another might meet all your specifications but be significantly more expensive. Evaluating these factors will help you choose the optimal solution.
Let’s take another example from project management . Suppose you need to implement a new task management system. You might consider several software options: one could offer more features but be complex to learn, while another might be easier to use but with limited functionality. By comparing these options based on cost, training time, and user-friendliness, you can select the most well-rounded choice.
Thus, analyzing multiple options and evaluating them based on key parameters such as cost, time, resources, and long-term benefits is essential for making the best decision. Avoid jumping to the first solution you find; a thorough analysis will ensure the best results.
Have you found the most suitable solution? Don’t stop there! There’s always room for improvement, optimization, and increased efficiency. Even the best solution often has hidden potential for enhancements and tweaks.
Take a software product as an example. Imagine you’ve developed an application that processes data at a certain speed. Upon analyzing its performance, you might discover that optimizing the algorithms or using more modern libraries can significantly boost its efficiency. Additionally, switching to asynchronous data processing could reduce user wait times.
Another example is logistics. Suppose you’ve identified the optimal route for delivering goods. But then you decide to implement a tracking system that not only allows real-time monitoring of the shipment but also enables quick route adjustments in case of unforeseen issues like traffic jams or roadworks. This would cut delivery times and improve customer satisfaction.
Enhancing the best solution is an ongoing process of analysis and exploring alternatives. Conduct testing, gather feedback, and use these insights to make small but meaningful adjustments. For instance, if you’re providing a service to clients, ask for their opinions. You might find that minor changes in the application’s interface or the service process structure could greatly improve user convenience, ultimately leading to customer loyalty and an increase in clients.
Never underestimate the power of small improvements. Even minor changes can lead to significant results, whereas a mentality of “it’s good enough” rarely drives progress. Your dedication to perfection and attention to detail will always pay off.
If you believe your current solution could be optimized and improved, it’s worthwhile to seriously consider revising it. This gives you the chance to re-evaluate your approaches, processes, and even the technologies you’re using. It’s important to return to the modeling stage and reassess all aspects of project implementation to ensure your updated solution meets your requirements and success criteria.
Start by analyzing your data; you might discover bottlenecks that were previously overlooked. For instance, you could find that your computational algorithms contain redundant steps that slow down the process. Often, small changes such as optimizing loops or using more efficient data structures can significantly enhance system performance.
Explore the use of new technologies and tools. Modern approaches, such as machine learning or distributed computing, might offer more efficient ways to solve your challenges. For example, if you are dealing with large data sets, leveraging platforms like Apache Hadoop or Spark could dramatically speed up data processing and analysis.
Your team also plays a crucial role in revising the solution. Collective brainstorming sessions and code reviews can generate ideas and approaches that one individual might miss. Agile methodologies, for instance, are a fantastic example of how flexible response to change and continuous improvement based on feedback can enhance product development.
Finally, thoroughly test the new solution. Automated testing and the use of CI/CD (continuous integration and delivery) can drastically reduce the time between changes and deployments, allowing for quicker identification and correction of issues. This also ensures the stability and reliability of your product.
To not just improve but significantly enhance your solution, consider additional steps that will help you achieve the best possible outcome. Depending on your specific context, focusing on your unique requirements and success criteria will be crucial. Here are a few suggestions that might be helpful:
1. Conduct In-Depth Research: Before implementing new steps, it’s vital to thoroughly understand the current problem and its root causes. For instance, if you are developing a new product, gather feedback from your target audience and conduct surveys and interviews.
2. Implement Testing and Optimization Phases: Evaluate interim results at each stage of your solution’s implementation. For example, if you’re enhancing a corporate system, regularly collect data on its effectiveness and perform A/B testing of different strategies.
3. Leverage Modern Technologies: Technological advancements offer a plethora of tools and solutions that can significantly boost the efficiency of your project. For instance, if you’re improving a marketing strategy, use analytics and artificial intelligence to predict customer behavior.
4. Consult Experts: An external perspective can unveil new aspects and approaches to solving your problem. Enlisting specialists in a specific field can help you avoid many pitfalls and speed up the process of achieving your goals.
5. Invest in Continuous Learning and Development: Constantly upgrading your skills and learning new methodologies will keep you at the forefront of your industry. Attending conferences, seminars, and participating in professional communities can provide fresh ideas and inspiration.
By following these steps, you will not only enhance your solution but also gain a deep understanding of the process and success criteria, ultimately leading to the maximization of your goals.
When developing an innovative solution, it’s crucial that it fully meets all established criteria for successful task completion. This ensures maximum efficiency and satisfies the expectations of all stakeholders involved. For instance, in developing a new mobile app, the criteria might include user-friendliness, high performance, data security, and an attractive design. An app that launches quickly, protects user data, and features an intuitive interface is likely to be deemed successful.
In a different scenario, such as creating a new teaching method, key criteria could include measurable improvements in student knowledge, active interaction between students and teachers, and adaptability to various learning styles. A method that leads to tangible academic improvements, actively engages all participants, and easily adjusts to different needs can be considered to meet all the success criteria.
Therefore, developing a solution that fully adheres to all established criteria requires careful analysis, meticulous planning, and continuous testing throughout all development stages. This approach significantly increases the likelihood of achieving optimal results and long-term effectiveness.
Everyone faces various challenges in life, whether they’re professional tasks or personal hurdles. For many, some of these problems can become genuine tests, demanding significant time and resources. To seize opportunities and tackle issues promptly, it’s crucial to identify who and what to involve in resolving the problem most effectively and efficiently.
Imagine a complex work scenario: a project deadline is looming, and the team encounters technical difficulties. Panic and confusion will only make things worse. The key to a successful resolution lies in wisely allocating resources and time. The goal is to solve the problem with minimal expenditure of resources and time. This calls for a model that guides you through systematic and step-by-step problem solving.
The proposed model is a simple yet effective method for solving problems, requiring only paper and a pen. It consists of five steps and helps you quickly ascertain the resources and time needed to address the problem.
- Problem Identification: Determine the core issue. For instance, is your computer failing to boot up due to a technical malfunction or a system error?
- Information Gathering: Collect all necessary data and facts. Review device specifications, browse forums or guides, and seek advice from colleagues or experts.
- Resource Analysis: Evaluate your available resources. Can you resolve the issue on your own, or do you need external specialists? Consider the time frame and financial costs.
- Plan Development: Create a clear and realistic action plan. Outline multiple strategies and opt for the one that demands the least resources and time.
- Implementation and Evaluation: Put your chosen plan into action and check if you’ve achieved the desired result. If something goes awry, analyze the mistakes and make necessary adjustments.
The key is to accurately identify what you need to solve the problem at hand. Use the proposed model to ensure that resources are allocated correctly.
This approach can also be tested and visualized on paper. Such a method will allow you to assess your capabilities and choose the most effective solution. For example, before a major presentation, run through all the details in advance using this model to avoid any unwelcome surprises at the crucial moment.
In the end, by utilizing this simple yet effective model, you significantly boost your chances of successfully addressing various problems, saving valuable time and resources.

- Leadership Skills
- Strategic Thinking Skills
5 Problem-Solving Skills That Drive Business Growth
Search SkillsYouNeed:
Rhubarb The blog at SkillsYouNeed
- Rhubarb Front Page -guidelines for contributors-
- 3 Must-Have Leadership Skills to Effectively Manage and Seamlessly Deliver Staff Augmentation Services
- Essential Tips for Resource Management Success
- Skills You Need to Succeed with Project Management and 10 Essential Dashboards to Boost Efficiency
- The Role of Staffing Agencies in Boosting Remote Work Productivity
- There’s Both EQ and IQ Incorporated in Leadership: Is It Developed Skill or Inborn Talent?
- Soft Skills Development: How to Initiate Soft Skill Training in the Workplace
- Leadership Development: Elevating Your Team to New Heights
- Developing a Recruitment Strategy for Higher Education Institutions
- Automating HR Work with Web-Scraping
- Business Planning and Performance Management: The Human Element in Maximizing Software Solutions
- How to Develop a Culture that Empowers Employee Growth
- Teamwork in T-Shirt Printing: Collaborative Skills for Creative Success
- How Effective Communication Enhances Idea Management in Teams
- Strategic Planning for Long-Term Business Success
- Key Administrative Skills for Business Management
- The Hidden Costs of Workplace Injuries and How to Avoid Them
- Forming and Maintaining a Healthy Team
- Effective Resource Management for Modern Employers
- Developing Effective Workplace Communication Strategies
- Exploring the Critical Connection Between Confidence & Leadership
- Essential Coaching Skills for Strong Leadership
- Exploring the Importance of Emotional Intelligence in Workplace Leadership
- Skills and Strategies Organizations Can Teach to Prevent Child Abuse
- Disney's Path Forward: How Leadership Can Maximize Investor Returns?
Subscribe to our FREE newsletter and start improving your life in just 5 minutes a day.
You'll get our 5 free 'One Minute Life Skills' and our weekly newsletter.
We'll never share your email address and you can unsubscribe at any time.
Problems are a regular part of our lives. They are natural in any business. And your success will largely depend on how you solve these problems and how much effort you put into addressing them.
In the early stages of business development, you will face many challenges. Whether it's handling operational inefficiencies or managing customer expectations, problem-solving skills are essential for driving growth.
In this article, we will reveal five key problem-solving skills that every entrepreneur and leader who wants to lead a team should possess. These qualities help you tackle immediate challenges and prepare your business for sustainable long-term growth.
Analytical Thinking: Breaking Down Complex Problems
Any problem can seem overwhelmingly complicated until you break it down into many small components, each of which requires one specific action. This is known as analytical thinking — the ability to recognize the main challenge, identify the key goals to overcome it, and compile a list of tasks to achieve them. For example, if you are faced with negative customer feedback, analytical thinking will help you to highlight the key points in it, find the roots of the problem in employee performance and product issues, and change the company's management policy to address these.
Analytical thinking is also related to the ability to read data and see certain trends. Studying metrics allows you to find out what works well in your business and what doesn't work at all. By making data-driven decisions, businesses can develop more effective strategies tailored to specific challenges. You don't have to rely on your brain alone to do this. Online financial management platforms like Wallester have user-friendly dashboards for quick diagnostics and detailed analytics to break down specific small parts of the problem.
Key takeaway : Cultivating analytical thinking allows businesses to understand problems in depth, ensuring the solutions implemented are relevant and effective.
Creativity: Finding Innovative Solutions
If a problem seems insurmountable, the solution may simply lie elsewhere. To find it, you should think outside the box and come up with innovative solutions that others might overlook. To do this, you should evaluate the problem not only from the traditional perspective of a businessperson but also from other angles — as a customer, an employee, or an independent observer.
For example, if a startup has a problem finding qualified personnel, it can temporarily replace certain positions with artificial intelligence and present it as a test of innovative technologies. With the right marketing, this can turn a negative reaction into a positive one.
Key takeaway : Encourage creativity within your team to explore fresh ideas that can address challenges in ways traditional methods cannot.
Adaptability: Adjusting to Changing Circumstances
Business is a dynamic entity whose development is more like a sinusoidal curve than a straight line. Companies experience ups and downs caused by changes in markets and target audiences. They have to plan for growth but also be prepared for downturns. Being adaptive means developing strategies that include “B,” “C,” and sometimes even “D” plans.
Adaptive leaders can recognize that certain solutions no longer work. They have the strength to abandon old methods in favor of new ones. They use flexible tools that can also adapt to current circumstances. For example, the Wallester platform allows you to instantly close corporate cards that have become unnecessary after the completion of a particular project. This helps reduce company costs and simplify control over the targeted use of funds.
Key takeaway : Cultivate adaptability within your leadership and teams to respond quickly and efficiently to new challenges, ensuring your business remains competitive.
Collaboration: Leveraging Team Expertise
No one can run a large-scale successful business alone. For a company to grow, develop, and improve its performance, you need to delegate authority. Only in this way will it be flexible and dynamic enough to remain competitive.
Teamwork allows you to create a synergistic effect — together, the team has much more knowledge, skills, and experience than each employee individually. And that's not to mention the potential for finding creative, non-standard solutions during brainstorming sessions. The secret to success in collaboration is to be able to trust but maintain invisible threads of control that will help identify the problem in time and take measures to overcome the crisis.
Key takeaway : Foster collaboration within your team to generate innovative, well-rounded solutions that everyone is invested in.
Decision-Making: Acting on Solutions with Confidence
Determining how to grow your company and overcome challenges is only half the battle. You should also make carefully considered but timely and confident decisions about which solutions to implement and how to execute them. Strong decision-making skills are essential for turning insights into actions that drive business growth.
But it's important to understand that decision-making is not about being ready to jump into action when you see the first best way to solve a problem. It's the ability to quickly assess pros and cons, identify risks, and choose methods of hedging them before taking action. This requires critical thinking and the confidence to commit to a course of action, even when faced with uncertainty.
Key takeaway: Develop decision-making skills within your leadership team to implement solutions swiftly, ensuring your business can address problems before they escalate.
Problem-solving is a multifaceted set of skills and abilities that stimulates business development and makes it sustainable. First of all, a manager must be able to analyze problems and break them down into small parts to set specific tasks. They need creativity, adaptability, and the ability to delegate authority. But no less important will be the timely adoption of informed decisions that will make the company competitive by taking into account current circumstances.
Continue to: Innovation Skills Brainstorming Techniques
See also: Harnessing Creativity in Problem-Solving: Innovations for Overcoming Challenges How to Create A Small Business Growth Strategy Strategic Planning for Long-Term Business Success
Math Fluency Is All About Problem-Solving. Do We Teach It That Way?

- Share article
To learn math, students must build a mental toolbox of facts and procedures needed for different problems.
But students who can recall these foundational facts in isolation often struggle to use them flexibly to solve complex, real-world problems , known as procedural fluency.
“Mathematics is not just normalizing procedures and implementing them when somebody tells you to use that procedure. Mathematics is solving problems,” said Bethany Rittle-Johnson, a professor of psychology and human development at Peabody College in Vanderbilt University, who studies math instruction. “To solve problems, we have to figure out what strategy to use when—and that tends to get too little attention.”
In a series of ongoing experiments, Rittle-Johnson and her colleagues find students develop better procedural fluency when they get opportunities to compare and contrast problem-solving approaches and justify the approaches they use in different situations. While some students may develop this skill on their own, most need explicit instruction, she found.
Rittle-Johnson spoke with Education Week about how teachers can use such comparisons to help students develop a deeper understanding of math. This interview has been edited for space and clarity.
For more on the best research-based strategies on improving math instruction, see Education Week’s new math mini-course .
How often do teachers talk to students about multiple strategies, and how to select them, in math problem-solving?
Students in the [United States] are very rarely doing rich contextual problems. Even more rarely, they’re being asked to compare strategies to solve them. I don’t hear teachers talk about [using different strategies] a lot, and textbooks tend to do a pretty bad job of explaining it.

For example, in Algebra 1, solving systems of equations, there are many standard solutions strategies that are taught in separate chapters and textbooks, ... but I see shockingly little time spent having students think and compare and choose which strategy to use. In one study where teachers were trained [to compare math strategies], only about 20 percent did in the classroom—and only about 5 percent of teachers who [did not receive training.]
Sometimes I hear teachers say, “Well, multiple strategies, that’s great for my high-end learners, but I don’t want to show that to my struggling learners. … So maybe multiple strategies is the ideal, but I’m not going to get to it because I’m tight on time and my kids are behind.” But we hear from struggling learners that they really appreciate the multiple strategies and we see that it helps them, too, across the grade bands and across contexts.
How can teachers decide when to bring in and compare different strategies while introducing a new math concept?
We find comparisons can be useful in all different phases of instruction.
It can be helpful for kids to have had some time to think about one strategy before they think about multiple strategies, maybe at most a lesson. But the risk is in general, if you wait too long, kids just get attached to one strategy. You run the risk of kids becoming really attached to one strategy, and then they become more resistant to wanting to think about and use multiple strategies.
What does this sort of comparison look like in the classroom?
One best practice is to have the steps of the different strategies written out. It can be kids’ strategies that they wrote on the board. It can be projecting strategies from textbooks or your solutions, but one thing we know is: Make sure both strategies are visible so that kids don’t have to remember. Then we ask kids to think about similarities and differences and think about, when is each a good strategy?
Sometimes we have students compare correct and incorrect strategies and explain the concepts that make the correct strategy correct. Just because you teach kids correct ways of doing things, that doesn’t mean the incorrect strategies disappear. Students really need help thinking and reasoning through why those are wrong.
What are the more common struggles for teachers to teach multiple strategies?
The No. 1 barrier we face is time. Teachers just feel they’re under so much pressure to cover so much content that they feel like they can’t take the time to do this, and that they see the value and the payoff in it. It does pay off for what is assessed [in standardized math tests], but it’s not directly assessed, and so that makes teachers nervous.
Also, sometimes teachers really don’t like to say this way is better than this other way. Even though mathematicians would say, “yeah, this way is clearly better in this context, and this other way is clearly better in that context,” ... sometimes teachers feel uncomfortable that they’re making a value judgment.
But the evidence is really clear that it’s helpful to show correct and incorrect examples and talk through them.
New Mini-Course: Teaching Math
Sign up for edweek update, edweek top school jobs.

Sign Up & Sign In


COMMENTS
In insight problem-solving, the cognitive processes that help you solve a problem happen outside your conscious awareness. 4. Working backward. Working backward is a problem-solving approach often ...
The problem-solving process typically includes the following steps: Identify the issue: Recognize the problem that needs to be solved. Analyze the situation: Examine the issue in depth, gather all relevant information, and consider any limitations or constraints that may be present. Generate potential solutions: Brainstorm a list of possible ...
Learning problem-solving techniques is a must for working professionals in any field. No matter your title or job description, the ability to find the root cause of a difficult problem and formulate viable solutions is a skill that employers value. Learning the soft skills and critical thinking techniques that good problem solvers use can help ...
Problem-solving is a mental process that involves discovering, analyzing, and solving problems. The ultimate goal of problem-solving is to overcome obstacles and find a solution that best resolves the issue. The best strategy for solving a problem depends largely on the unique situation. In some cases, people are better off learning everything ...
Recognizing these signs can help you realize that an issue exists. Decide to solve the problem. Make a conscious decision to solve the issue at hand. Commit to yourself that you will go through the steps necessary to find a solution. Seek to fully understand the issue. Analyze the problem you face, looking at it from all sides.
There are several ways you can work to improve your ability to solve problems, including: Practice. Spending time practicing various problems can help you get more comfortable with the problem-solving process. Consider working with someone else in your field to solve hypothetical problems that are realistic within your industry.
On the other hand, you might try to save by cutting your spending or by lowering other costs. Use some strategies to help you come up with solutions: Divide and conquer. Break the problem into smaller problems and brainstorm solutions for them separately, one by one. Use analogies and similarities.
Good problem solving skills empower you not only in your personal life but are critical in your professional life. In the current fast-changing global economy, employers often identify everyday problem solving as crucial to the success of their organizations. For employees, problem solving can be used to develop practical and creative solutions ...
Critical thinking, research, creativity, analytical skills, communication skills, decision-making skills, and adaptability are the 7 most important problem-solving skills you need to succeed personally and professionally. You'll likely hear the term 'problem-solving skills' tossed around when it comes to acing your college applications or ...
Problem-solving requires observational skills, lateral thinking, and critical analysis abilities. Using a combination of these skills can help you identify the issue and determine the underlying cause that's creating the problem. "You can never solve a problem on the level on which it was created." — Albert Einstein.
Problem-solving skills will help you tackle challenges at any workplace, make informed decisions, and help the organizations you work with to succeed. Personal Growth. These skills equip you to overcome everyday life obstacles, like managing personal finances, resolving conflicts in relationships, and more. Innovation and Entrepreneurship.
Brainstorm options to solve the problem. Select an option. Create an implementation plan. Execute the plan and monitor the results. Evaluate the solution. Read more: Effective Problem Solving Steps in the Workplace. 2. Collaborative. This approach involves including multiple people in the problem-solving process.
2. Break the problem down. Identifying the problem allows you to see which steps need to be taken to solve it. First, break the problem down into achievable blocks. Then, use strategic planning to set a time frame in which to solve the problem and establish a timeline for the completion of each stage. 3.
14 types of problem-solving strategies. Here are some examples of problem-solving strategies you can practice using to see which works best for you in different situations: 1. Define the problem. Taking the time to define a potential challenge can help you identify certain elements to create a plan to resolve them.
Becoming a better problem solver involves using an efficient problem-solving process. When faced with a problem, follow these steps to assist you in finding a solution: 1. Identify what the issue really is. Oftentimes, it takes research and careful thought to identify what the underlying issue behind a problem is.
Many people jump into problem-solving mode without fully analyzing the situation, which can lead to incomplete solutions or overlooked details. Taking the time to clearly define the problem will help you identify the best approach and ensure that you are solving the right issue. Ask the Right Questions
By using this problem solving process, you can often help different kinds of learners and personality types contribute and unblock organizational problems with creative thinking. Problem solving strategies like LEGO Serious Play are super effective at helping a team solve more skills-based problems such as communication between teams or a lack ...
Problem-solving skills help you determine why an issue is happening and how to resolve that issue. It's one of the key skills that employers seek in job applicants. Problem-solving starts with identifying the issue, coming up with solutions, implementing those solutions, and evaluating their effectiveness. Since this is a skill that's important ...
Draw connections. Brainstorm. Work together to get the job done. 8. Use Mind Maps to Help Visualize the Problem. Mind Maps, a visual snapshot of a problem and its possible solutions, can help focus the mind, stimulate the brain, increase the capacity for creative thinking, and generate more ideas for solutions.
Finding a suitable solution for issues can be accomplished by following the basic four-step problem-solving process and methodology outlined below. Step. Characteristics. 1. Define the problem. Differentiate fact from opinion. Specify underlying causes. Consult each faction involved for information. State the problem specifically.
Evaluate the solution. Using effective problem solving techniques will help children avoid conflict with others in a school setting and in their everyday lives. It will also strengthen children's beginning empathy skills and help them learn more positive attributions about another person's intentions. Effective problem solving skills is ...
They can help you identify biases and assumptions that may be holding you back, develop strategies to shift your behavior going forward, and ultimately feel more confident that your process will ...
Mathematics provides a systematic and logical framework for problem-solving and critical thinking. The study of math helps to develop analytical skills, logical reasoning, and problem-solving abilities that can be applied to many areas of life. By using critical thinking skills to solve math problems, we can develop a deeper understanding of ...
By applying the "Six Thinking Hats" model, you can enhance team communication, uncover hidden opportunities, and find optimal solutions to complex challenges. Remember, critical thinking is a skill that improves with practice. Don't hesitate to experiment and discover new strategies for problem-solving! How to Effectively Solve Your Problems
These qualities help you tackle immediate challenges and prepare your business for sustainable long-term growth. Analytical Thinking: Breaking Down Complex Problems. Any problem can seem overwhelmingly complicated until you break it down into many small components, each of which requires one specific action.
In this article, we'll explore proven steps that can help you transform workplace challenges into opportunities for growth and innovation. Whether you're a team leader or an individual contributor, mastering these problem-solving techniques will equip you to tackle even the most daunting issues with confidence and creativity.
For example, in Algebra 1, solving systems of equations, there are many standard solutions strategies that are taught in separate chapters and textbooks, ... but I see shockingly little time spent ...