| |  Sign up for our free weekly newsletter and receive top education news, lesson ideas, teaching tips and more! No thanks, I don't need to stay current on what works in education! COPYRIGHT 1996-2016 BY EDUCATION WORLD, INC. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. COPYRIGHT 1996 - 2024 BY EDUCATION WORLD, INC. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. - SchoolNotes.com
- The Educator's Network
  ChatGPT for TeachersTrauma-informed practices in schools, teacher well-being, cultivating diversity, equity, & inclusion, integrating technology in the classroom, social-emotional development, covid-19 resources, invest in resilience: summer toolkit, civics & resilience, all toolkits, degree programs, trauma-informed professional development, teacher licensure & certification, how to become - career information, classroom management, instructional design, lifestyle & self-care, online higher ed teaching, current events, advice on creating homework policies.  Getting students to work on their homework assignments is not always a simple task. Teachers need to take the initiative to create homework policies that encourage students to work hard to improve their achievement in the classroom setting. Educational leadership starts with making a policy that helps students learn and achieve while competing with extracurricular activities and the interests of students. Set high standardsHomework policies need to have high standards to encourage students to work hard on achieving the best possible results. Student achievement in school improves when teachers set high standards and tell students that they are expected to meet the standards set in the classroom. By setting high standards for the homework policy, teachers are ensuring that the students will be more willing to work on getting assignments done. The policies for homework that teachers and parents create can help improve student understanding of materials and result in better grades and scores on standardized tests. Focus on study skillsTeaching students in their early education is a complicated task. Teachers need to balance the age of the students with the expected school, state and federal educational standards. Although the temptation to create a homework policy that focuses on repetition and traditional assignments can make the policy easy to create, it also removes the focus from establishing strong study skills and habits to engage students in education. Creating a homework policy for younger students in the elementary grades should avoid traditional assignments and focus on building study skills and encouraging learning. Older students after elementary school are ready to take on written assignments rather than using technology and other tools. Putting more focus on study skills will set a stronger foundation for homework in the future. As students get into higher grades, the type of assignments will focus on writing with a pen or pencil. The age of the student must be considered and the goal is to create a strong foundation for the future. Involve the parentsGetting parents involved in the homework policy will encourage students to study and complete the assigned tasks. Asking parents to get involved to facilitate assignments will ensure students are learning without the parents completing the assignment for their child. The goal of involving the parents in the homework policy is getting the family to take an interest in ensuring the assignments are completed. The best assignments will allow the student to manage the work without seeking answers from a parent. That allows parents to supervise and encourage their child without giving the answers. Give consequences for incomplete assignmentsHomework is an important part of providing educational leadership in the classroom. Although parental involvement and high standards can help encourage students to study, it is also important to clearly state the consequences if assignments are incomplete or not turned in on time. A clear homework policy will lay out the possible consequences of avoiding assignments or turning in incomplete work. Consequences can vary based on the student grade level and age, but can include lowering the grades on a report card or taking away classroom privileges. Although it is important to provide details about the consequences of avoiding the assignments, teachers can also use a reward system to motivate students to complete their work. Rewards can focus on the entire class or on individual rewards, depending on the situation. For example, teachers can give a small candy when students complete five assignments in a row. Consequences and rewards can serve as a motivating factor when it comes to the homework policy. By clearly stating the potential downsides and the benefits to the student, it is easier for students to focus on the work. Creating homework policies is part of educational leadership in the classroom. Although homework must focus on helping students achieve, it also needs to clearly state the expectations and give details about the benefits and consequences of different actions. By giving a clear policy from the first day of school, the students will know what to expect and can gain motivation to work on achieving the best results. You may also like to read- The Homework Debate: How Homework Benefits Students
- Creating Better Online Students: A Guide for Teachers
- Ending the Homework Debate: Expert Advice on What Works
- Elementary Students and Homework: How Much Is Too Much?
- The Homework Debate: The Case Against Homework
- FERPA Advice for New Teachers
 Categorized as: Tips for Teachers and Classroom Resources Tagged as: Leadership and Administration - Online & Campus Doctorate (EdD) in Administra...
- Early Childhood Education: Resources, Theorie...
- Online & Campus Bachelor's in Early Childhood...
 Frog Education - Schools & Education
- Professional Development
- Special Projects
- Global Initiatives
 The power of a good homework policyPublished 18th March 2019 by Frog Education With the homework debate continuing to rage and be fuelled by all parties involved, could publishing a robust homework policy help take some of the headache out of home learning?What is a homework policy. The idea of a homework policy is for the school to officially document and communicate their process for homework. The policy should outline what is expected of teachers when setting homework and from students in completing home learning tasks. It is a constructive document through which the school can communicate to parents, teachers, governors and students the learning objectives for homework. Do schools have to have a homework policy? It is a common misconception that schools are required by the government to set homework. Historically the government provided guidelines on the amount of time students should spend on home learning. This was withdrawn in 2012 and autonomy was handed to headteachers and school leaders to determine what and how much homework is set. Therefore, schools are not required by Ofsted or the DfE to have a homework policy in place. The removal of official guidelines, however, does not give pupils the freedom to decide if they complete homework or not. Damian Hinds , Education Secretary, clarified that although schools are not obliged to set homework, when they do, children need to complete it in line with their school’s homework policy; “we trust individual school head teachers to decide what their policy on homework will be, and what happens if pupils don’t do what’s set.” The majority of primary and secondary schools do set homework. Regardless of the different views on the topic, the schools that do incorporate homework into their learning processes, must see value in it. Clearly communicating that value will demonstrate clarity and create alliance for everyone involved – both in and outside of school. This is where the publication of a good homework policy can help. 5 Benefits of publishing a good homework policy #1 Manages students' workload Studies have shown a correlation between student anxiety and demanding amounts of homework. One study found that in more affluent areas, school children are spending three hours per evening on homework. This is excessive. Secondary school students’ study between eight and ten subjects, which means they will have day-to-day contact with a number of teachers. If there is no clear homework policy to provide a guide, it would be feasible for an excessive amount of homework to be set. A homework policy that sets out the expected amount of time students should spend on homework will help prevent an overload. This makes it more realistic for children to complete homework tasks and minimise the detrimental effect it could have on family time, out-of-school activities or students’ overall health and well-being. #2 Creates opportunity for feedback and review The simple act of having an official document in place will instigate opportunities for regular reviews. We often consider the impact of homework on students but teachers are also working out-of-hours and often work overtime . One reason is the need to set quality homework tasks, mark them and provide valuable feedback. No-one, therefore, wants home learning to become about setting homework for homework’s sake. A regular review of the policy will invite feedback which the school can use to make appropriate changes and ensure the policy is working for both teachers and students, and serves the school’s homework learning objectives. #3 Connects parents with education Parents’ engagement in children’s education has a beneficial impact on a child’s success in school. Homework provides a great way for parents to become involved and have visibility of learning topics, offer support where needed and understand their child’s progress. A good homework policy creates transparency for parents. It helps them to understand the value the school places on homework and what the learning objectives are. If parents understand this, it will help set a foundation for them to be engaged in their child’s education. #4 Gives students a routine and creates good habits Whether children are going into the workplace or furthering their education at university, many aspects of a student’s future life will require, at times, work to be completed outside of traditional 9-5 hours as well as independently. This is expected at university (students do not research and write essays in the lecture theatre or their seminars) and will perhaps become more important in the future workplace with the growth of the gig economy (freelancing) and the rise of remote working . A homework policy encourages a consistency for out-of-school learning and helps students develop productive working practices and habits for continued learning and independent working. #5 Helps students retain information they have learned A carefully considered and well-constructed home learning policy will help teachers set homework that is most effective for reinforcing what has been taught. A good homework policy will indicate how to set productive homework tasks and should limit the risk of less effective homework being set, such as just finishing-off work from a lesson and repetition or memorisation tasks. What makes a good homework policy? A good homework policy will determine how much homework is appropriate and what type is most effective for achieving a school’s learning objectives. Publishing the homework policy – although it might not unify everyone’s views on the matter – fosters good communication across the school, sets out expectations for teachers and pupils, and makes that significant connection between parents and their children’s education. But most importantly, if the policy is regularly reviewed and evaluated, it can ensure home learning remains beneficial to pupils’ progress, is of value to teachers and, ultimately, is worth the time and effort that everyone puts into it. Frog 's Homework Solu tion If you'd like to see better results from homework and independent learning, you should see HomeLearning in action! - Set and mark online and offline homework in seconds - Access 300,000 curriculum-mapped quizzes using FrogPlay - Track homework setting and completions in MarkBook - Provide full visibility for parents, leaders, staff and pupils - Encourage independent learning Get a demo of HomeLearning : Speak to FrogBack to Blog Listing - Home Learning
- homework policy
Related Posts We believe that every child can be given a unique and personal education, and that this can be delivered by today’s teachers without increasing workload through the clever use of technology. +44 (0)1422 250800 [email protected] Dean Clough Mills, Halifax HX3 5AX Find on Google Maps   How to Write the Perfect Homework PolicyAuthor: Naimish Gohil Posted: 10 May 2017 Estimated time to read: 4 mins Homework is an integral part to the learning process and as such, each school should have a clear homework policy readily available to teachers, students and parents that sets out your expectations when it comes to home-learning .  A clear and effective homework policy will mean that quality and quantity of homework can be easily tracked and all stakeholders are on the same page. We've created our own Homework Policy that you can adapt for use in your school or use as an outline when creating your own policy: 1. IntroductionThis is the school’s policy for the provision of homework to pupils and has been drawn up in accordance with guidance from the DFE and Sutton Education Trust. It must be recognised that parents play a vital role in the education of their child, therefore it is important and valuable to have a good home-school partnership, of which a homework policy must address. 2. Homework - A definitionHomework is defined as any work or activity that students are asked to undertake outside of lesson time, either on their own or with the aid of parents and carers. Homework doesn’t necessarily have to be completed at home but can be completed in free periods and after-school homework clubs. We see work completed outside of lesson time as a valuable part of a student’s learning. 3. The purpose of homework The school regards the purpose of homework as being to: - Provide learners with the opportunity to work on an activity that is relevant to learning outcomes, or that contributes to gaining qualifications/accreditations.
- Develop an effective partnership between the school, parents and carers in pursuing the academic aims of the school and the development of their child.
- Consolidate and reinforce skills and understanding prior to the following lesson, particularly in English and Mathematics.
- Extend learning across the curriculum, for example through additional reading.
- Encourage pupils as they get older to develop the confidence, self-discipline and independence to develop organisational skills.
As a school, we encourage children to pursue out-of-school activities. Homework should be used to effectively reinforce and/or extend what is learned in school. We hope that children will feel a sense of personal satisfaction in a task completed well and that their efforts will be recognised and praised both at home and at school. Homework tasks should be undertaken to the best of their ability. We hope that parents and carers will be willing and able to give their active support to ensure that work completed at home is done so conscientiously and in the best possible conditions. 4. Current practice At the beginning of the academic year, each year group will be informed about what is expected of them with regards to homework. 5. Time to be spent completing homeworkBased on current good practice, we ask pupils to spend the following amount of time on homework: Years 7 to 9: 1 - 2 hours per day Years 10 & 11: 1 - 3 hours per day Pupils may be expected to undertake a variety of homework activities. These activities will differ depending on the teacher and subject. Examples include: Reading tasks, numeracy tests, spelling tests, quizzes, project work, classwork extensions, coursework, essays and research activities. As a general rule, teachers will not usually set substantial homework tasks to be completed for the next day, pupils will have at least two days to complete any work set. 6. Pupil feedbackThe school recognises the importance of providing prompt and actionable feedback to pupils, parents and carers. Feedback will include how well homework tasks have been tackled, and the knowledge, skills and understanding developed. A variety of methods will be used to provide feedback, such as an appropriate comment of praise, appreciation or area for improvement. Any given feedback will vary according to the age of the pupil. 7. Where to access the school homework policyThe school will use newsletters to inform parents and carers about the school’s homework policy and secure their involvement. The homework policy, as well as useful information for parents in supporting their child’s learning, is displayed on the school website. Parents’ Evenings and New Intake Evenings will be used to promote this partnership and obtain feedback (e.g. English and Mathematics workshops). Homework questionnaires will be used where appropriate to ascertain parent views. Parents will be consulted about any significant changes to the policy that are being considered by the governing body. 8. Reviewing the policyThe homework policy will be reviewed every year. Where significant changes to the policy are felt to be required, proposals will be presented to the governing body and parents consulted.  Get a roundup of our articles once per month. Subscribe to Email UpdatesRecent posts, can ai be used for curric..., let's talk about homework..., should we be worried abou..., using character education..., popular posts, what is behaviourism, how has technology changed education for schools, the impact of effective classroom management, the difference between formative and summative assessments. - Homework (22)
- Teacher Wellbeing (21)
- Student Wellbeing (20)
- Distance Learning (15)
- Classroom Management (14)
- Mental Health (13)
- Ofsted (12)
- Wellbeing (12)
- Skills (11)
- Teacher Workload (11)
- Parental Engagement (10)
- Satchel One MIS (10)
- Staff Wellbeing (10)
- Teachers (10)
- School Culture (9)
- Behaviour Management (8)
- School Improvement (8)
- School Management (8)
- Teacher Resources (8)
- Back to School (7)
- Parental Involvement (7)
- Parents (7)
- Pedagogy (7)
- Student & Parent Resources (7)
- Students (7)
- Assessment (6)
- Cloud-based MIS (6)
- Covid-19 (6)
- Guest Blog (6)
- Leadership (6)
- Online Safety (6)
- Technology (6)
- Bullying (5)
- Digital Literacy (5)
- Marking (5)
- Ofsted framework (5)
- School Closures (5)
- Lesson Plans (4)
- Network Managers (4)
- Revision (4)
- Teacher (4)
- Teaching (4)
- Attendance (3)
- Autonomy (3)
- Data Management (3)
- Education Reform (3)
- Education Technology (3)
- Feedback (3)
- Gender Equality (3)
- Network Manager Resources (3)
- SLT Resources (3)
- School Technology (3)
- Student Engagement (3)
- Students & Parents (3)
- Summer Holidays (3)
- Articles (2)
- Attainment 8 and Progress 8 (2)
- Autonomous Learning (2)
- Children (2)
- Classroom (2)
- Classroom Techniques (2)
- Communication (2)
- Differentiated Homework (2)
- Education (2)
- Education Technolgy (2)
- Embracing Technology (2)
- Exam Results (2)
- Grading (2)
- Home-school Communication (2)
- Homework Debate (2)
- Homework Policy (2)
- Raising Standards (2)
- Reading (2)
- Reducing Workload (2)
- Saving Time (2)
- School Marketing (2)
- School Reopenings (2)
- Security (2)
- Sidekick (2)
- Software Training (2)
- Strategy (2)
- Teaching Crisis (2)
- Teaching and Learning (2)
- Time Management (2)
- Time-saving (2)
- Tips & Tricks (2)
- Workload (2)
- Abuse in the Classroom (1)
- Anti-bullying (1)
- Appreciation (1)
- Attainment 8 (1)
- Benefits of Homework (1)
- Body Image (1)
- British Values (1)
- Career Advice (1)
- Character Education (1)
- Collaboration (1)
- Collaborative Learning (1)
- Continuing Professional Development (1)
- Conversation (1)
- Cost of living (1)
- Cyber-bullying (1)
- Cyberbullying (1)
- Damian Hinds (1)
- Digital Classroom (1)
- Dyslexia Awareness (1)
- E Learning (1)
- Eating Disorders (1)
- Education Secretary (1)
- Empathy (1)
- Exam-ready (1)
- Flipped Classroom (1)
- Formative Assessment (1)
- Girls in STEM (1)
- Global Education (1)
- Global Learning (1)
- Government (1)
- Healthy Eating (1)
- Homework Excuses (1)
- Inspire (1)
- International Learning (1)
- Internet Access (1)
- Interventions (1)
- Job Satisfaction (1)
- Language (1)
- Lead by Example (1)
- Learning Environment (1)
- Manager (1)
- National Curriculum (1)
- Outstanding (1)
- Parent Tips for Homework (1)
- Parent-teacher Relationships (1)
- Parents Evening (1)
- Phased Reopenings (1)
- Physical Health (1)
- Planning (1)
- Preparation (1)
- Productivity (1)
- Progress 8 (1)
- Quality Assurance (1)
- Recognition (1)
- Safeguarding (1)
- School Improvements (1)
- Schools (1)
- Secondary School (1)
- Senior Leaders (1)
- Sharing (1)
- Sharing Best Practice (1)
- Show My Homework (1)
- Slow Processing (1)
- Social Media (1)
- Soft Skills (1)
- Software (1)
- Student (1)
- Student Independence (1)
- Summative Assessment (1)
- Super Union (1)
- Support (1)
- Teaching Schools (1)
- Technology in the classroom (1)
- Tracking & Monitoring (1)
- Training (1)
- Truancy (1)
- Year 6 SATs (1)
- example (1)
- first day of school (1)
- gained time (1)
- homework benefits (1)
- influence (1)
- ofsted inspections (1)
- practice (1)
- quiz creation (1)
- raising awareness (1)
- satchel (1)
- school involvement (1)
- well-balanced education (1)
FREE quiz toolBrowse through over 500k questions created by teachers on Neeto , create a quiz and share back to Satchel One. It's free!  - Satchel One learning platform
- About Satchel
- Get in touch
- Back to all blog posts
Center for American Progress Homework and Higher StandardsHow Homework Stacks Up to the Common CoreCAP analysis found that homework is generally aligned to Common Core State Standards, but additional policy changes would make it more valuable.  Education, Education, K-12, Modernizing and Elevating the Teaching Profession Media ContactMishka espey. Senior Manager, Media Relations [email protected] Government AffairsMadeline shepherd. Director, Federal Affairs In this article Introduction and summaryFor as long as homework has been a part of school life in the United States, so too has the debate over its value. In 1900, a prominent magazine published an article on the evils of homework titled, “A National Crime at the Feet of Parents.” 1 The author, Edward Bok, believed that homework or too much school learning outside the classroom deprived children of critical time to play or participate in other activities at home. The very next year, California, influenced by those concerns, enacted a statewide prohibition on homework for students under the age of 15. 2 In 1917, the state lifted the ban, which has often been the case as districts have continually swung back and forth on the issue. 3 InProgress Stay informed on the most pressing issues of our time.This site is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply. More than 100 years later, homework remains a contentious issue, and the debate over its value rages on, with scholars coming down on both sides of the argument. Homework skeptic Alfie Kohn has questioned the benefit of homework, arguing that its positive effects are mythical, and in fact, it can disrupt the family dynamic. 4 He questions why teachers continue to assign homework given its mixed research base. Taking the opposite view, researchers Robert Marzano and Debra Pickering have voiced their support for purposeful homework that reinforces learning outside of school hours but still leaves time for other activities. 5 In 1989, prominent homework scholar Harris Cooper published a meta-analysis of more than 100 studies on homework in a survey that found a correlation between homework and performance on standardized tests, but only for certain grade levels. According to Cooper’s research, for students in late-elementary grades through high-school, there was a link between homework and improved standardized test performance. However, there was no evidence of the same correlation for younger students. 6 Even without a connection to academic achievement, Cooper still recommended assigning homework to younger students because it helps “develop good study habits, foster positive attitudes toward school, and communicate to students the idea that learning takes work at home as well as school.” 7 Far from academia, parents—not surprisingly—are some of homework’s most ardent supporters and, also, its most vocal critics. For better or worse, many parents help or are involved in their child’s homework in some way. As a result, homework can shape family dynamics and weeknight schedules. If a child receives too much homework, or only busywork, it can cause stress within families and resentment among parents. 8 Some parents report spending hours each night helping their children. For instance, a 2013 article in The Atlantic detailed a writer’s attempt to complete his 13-year-old daughter’s homework for a week. The headline simply read: “My Daughter’s Homework Is Killing Me.” 9 The father reported falling asleep trying to thoughtfully complete homework, which took around three hours per night. 10 On the other hand, some parents appreciate the glimpse into their child’s daily instruction and value homework’s ability to build positive learning habits. It is no surprise that the debate over homework often spills onto the pages of newspapers and magazines, with calls to abolish homework regularly appearing in the headlines. In 2017, the superintendent of Marion County Public Schools in Florida joined districts in Massachusetts and Vermont in announcing a homework ban. To justify his decision, he used research from the University of Tennessee that showed that homework does not improve student achievement. 11 Most recently, in December 2018, The Wall Street Journal published a piece that argued that districts were “Down With Homework”—banning it, placing time caps or limiting it to certain days, or no longer grading it—in order to give students more time to sleep, read, and spend time with family. 12 Given the controversy long surrounding the issue of homework, in late spring 2018, the Center for American Progress conducted an online survey investigating the quality of students’ homework. The survey sought to better understand the nature of homework as well as whether the homework assigned was aligned to rigorous academic standards. Based on the best knowledge of the authors, the CAP survey and this report represent the first-ever national study of homework rigor and alignment to the Common Core State Standards—rigorous academic standards developed in a state-led process in 2010, which are currently in place in 41 states and Washington, D.C. The CAP study adds to existing research on homework by focusing on the quality of assignments rather than the overall value of homework of any type. There are previous studies that considered parental involvement and the potential stress on parents related to homework, but the authors believe that this report represents the first national study of parent attitudes toward homework. 13 For the CAP study, the authors used the Amazon Mechanical Turk (MTurk) online survey tool to collect from parents their child’s actual homework assignments. Specifically, as part of the survey, the authors asked parents to submit a sample of their child’s most recent math or language arts homework assignment and have the child complete questions to gauge if the assignment was challenging, as well as how long it took to complete the assignment. In all, 372 parents responded to the survey, with CAP analyzing 187 homework assignments. Admittedly, the methodological approach has limitations. For one, it’s a convenience sample, which means people were not selected randomly; and broadly speaking, the population on the MTurk site is younger and whiter than the U.S. population as a whole. However, research has shown that MTurk yields high-quality, nationally representative results, with data that are at least as reliable as those obtained via traditional methods. 14 In addition, the homework sample is not from a single classroom or school over the course of a year; rather, it is a snapshot of homework across many classrooms during the span of a few weeks in May 2018. The assumption is that looking at assignments from many classrooms over a short period of time helps to construct a composite picture of mathematics and language arts homework. Moreover, the design of the CAP study has clear advantages. Many of the previous existing studies evaluated homework in a single district, whereas the CAP study draws from a national sample, and despite its limitations, the authors believe that the findings are robust and contribute significantly to the existing research on homework. Three key findings from the CAP survey:- Homework is largely aligned to the Common Core standards. The authors found that the homework submitted is mostly aligned to Common Core standards content. The alignment index that the authors used evaluated both topic and skill. As previously noted, the analysis is a snapshot of homework and, therefore, does not allow the authors to determine if homework over the course of a year covered all the topics represented in the standards.
- Homework is often focused on low-level skills in the Common Core standards, particularly in the earlier grades. While the authors’ analysis shows that there was significant alignment between Common Core and the topics represented in the homework studied, most of the assignments were fairly rote and often did not require students to demonstrate the full depth of knowledge required of the content standards. There was clear emphasis on procedural knowledge, and an even stronger emphasis on memorization and recall in language arts. Common Core content standards, on the other hand, require students to demonstrate deeper knowledge skills, such as the ability to analyze, conceptualize, or generate. 15
- Homework frequently fails to challenge students. Nearly half of the parents who responded to the CAP survey reported that homework is too easy for their child. In particular, parents of primary-grade children were most likely to agree or strongly agree that the homework assignment they submitted was too easy for their child.
Based on these key findings, CAP recommends that states, districts, and schools improve the quality of homework and increase opportunities for students to practice rigorous grade-level content at home. Specifically, the authors—drawing from this survey and other existing research on homework—recommend the following actions to improve the role of homework in education: - Schools and districts should develop homework policies that emphasize strategic, rigorous homework. In many cases, the homework debate is limited and short-sighted. Currently, many arguments focus on whether or not students should have homework at all, and there are entire school districts that have simply banned homework. Instead of debating the merits of banning homework, reformers and practitioners should focus on improving the rigor and effectiveness of all instructional materials, including
Districts, schools, and teachers should ensure that the total amount of homework students receive does not exceed the 10-minute rule—that is to say, no more than 10 minutes of homework multiplied by the student’s grade level. 16 According to research, any more than that can be counterproductive. 17 Also, too much homework may be an unnecessary burden on families and parents. Homework should be engaging and aligned to Common Core standards, which allow students to develop deeper-level learning skills—such as analysis or conceptualization—that help them increase retention of content. - Districts and schools should periodically audit homework to make sure it is challenging and aligned to standards. Rather than implementing homework bans, district policymakers and school principals should regularly review examples of homework assignments to ensure that it is aligned to grade-level standards and requires students to demonstrate conceptual learning. In instances where the district or school finds that homework assignments are not aligned or take too much or too little time to complete, they should help teachers improve homework assignments by recommending instructional materials that may make it easier for them to identify appropriate, grade-level homework assignments.
- Schools and districts should provide access to technology and other supports that can make it easier for students to complete rigorous schoolwork at home. Technology can also provide additional support or scaffolding at home, allowing more students to complete homework without help from adults or older siblings. For instance, programs such as the Khan Academy can give students rigorous homework that’s aligned to Common Core standards. 18 Unfortunately, many households across the nation still do not have adequate access to devices or internet at home. Schools and districts should consider options to ensure that all students can benefit from technology and broadband. Greater access to technology can help more students benefit from continual innovation and new tools. While most of these technologies are not yet research-based, and the use of devices may not be appropriate for younger children, incorporating new tools into homework may be a low-cost method to improve the quality of student learning.
- Curriculum reform and instructional redesign should focus on homework. There are many states and districts that are reforming curriculum or adopting different approaches to instruction, including personalized learning. Curriculum reform and personalized learning are tied to greater academic outcomes and an increase in motivation. Homework should also be a focus of these and other efforts; states and districts should consider how textbooks or other instructional materials can provide resources or examples to help teachers assign meaningful homework that will complement regular instruction.
The findings and recommendations of this study are discussed in detail below. Homework must be rigorous and aligned to content standardsAll homework is not created equal. The CAP study sought to evaluate homework quality—specifically, if homework is aligned to rigorous content standards. The authors believe that access to grade-level content at home will increase the positive impact of adopting more rigorous content standards, and they sought to examine if homework is aligned to the topics and skill level in the content standards. The 10-minute ruleAccording to Harris Cooper, homework is a valuable tool, but there is such a thing as too much. In 2006, Cooper and his colleagues argued that spending a lot of time on homework can be counterproductive. He believes that research supports the 10-minute rule—that students should be able to complete their homework in no more than 10 minutes multiplied by their grade. For example, this would amount to 20 minutes for a second-grade student, 50 minutes for a fifth-grade student, and so on. 19 The Common Core, developed by the National Governors Association and the Council of Chief State School Officers, established a set of benchmarks for “what students should know and be able to do” in math and language arts by the end of the academic year in kindergarten through high school. 20 The math standards focus on fewer concepts but in more depth and ask students to develop different approaches to solve similar problems. In language arts, the standards moved students away from narrative-based assignments, instead concentrating on using evidence to build arguments and reading more nonfiction. The Common Core is not silent in the cognitive demand needed to demonstrate mastery for each standard. 21 For example, a second grade math standard is “[s]olve word problems involving dollar bills, quarters, dimes, nickels, and pennies, using $ and ¢ symbols appropriately.” For this standard, a second-grader has not mastered the standard if they are only able to identifying the name and value of every. Remember, apply, integrate: Levels of cognitive demand or depth of knowledgeThere are numerous frameworks to describe levels of cognitive skills. One of the most prominent of these models, Bloom’s taxonomy, identifies six categories of cognition. The original levels and terms were knowledge, comprehension, application, analysis, synthesis, and evaluation; however, these terms have changed slightly over time. 22 Learning does not necessarily follow a linear process, and certainly, all levels of cognitive demand are important. Yet these categories require individuals to demonstrate a different level of working knowledge of a topic. With the advent of standards-based reform, the role of cognitive skill—particularly in the area of assessment—has become a much more explicit component of curriculum materials. Over the past two decades, cognitive science has shown that individuals of any age retain information longer when they demonstrate deeper learning and make their own meaning with the content—using skills such as the abilities to conjecture, generalize, prove, and more—as opposed to only committing ideas to memory or performing rote procedures, using skills such as the ability to memorize or recall. In essence, Common Core created rigorous expectations to guide the instruction of students in all states that chose to adopt its standards. These standards aimed to increase college preparedness and make students more competitive in the workforce. Policymakers, advocates, and practitioners hoped that Common Core would create greater consistency in academic rigor across states. In addition, with the classroom and homework aligned to these standards, many anticipated that students would graduate from high school prepared for college or career. As of 2017, 41 states and the District of Columbia have adopted and are working to implement the standards, although many of these states have modified them slightly. 23 In this study, the authors evaluated homework to determine if it was aligned to Common Core standards in two ways: First, does it reflect grade-level content standards; second, does it require students to use skills similar to those required to demonstrate proficiency in a content area. This multitiered approach is critical to evaluating alignment between standards and instruction—in this case homework. Instruction must teach content and help students develop necessary levels of cognitive skill. Curricula for each grade should include instructional materials that are sequenced and rigorous, thus enabling students to develop an understanding of all content standards. In spring 2018, the Center for American Progress used Amazon Mechanical Turk (MTurk) to administer a survey. MTurk is a crowdsourcing marketplace managed by Amazon; it allows organizations to virtually administer surveys for a diverse sample. 24 The CAP survey asked parents to submit a sample of their child’s most recent math or language arts homework assignment and complete a few questions to gauge if the assignment was challenging, as well as how long it took for the student to complete the assignment. A total of 372 parents responded to the survey, and CAP analyzed 187 homework assignments. Of the 372 parents who participated in the survey, 202, or about 54 percent of respondents, submitted samples of their child’s homework assignment. The researchers dropped a total of 15 homework submissions from analysis either because the subject matter was not math or language arts—but rather, science, music, or social studies—or because the authors could not examine the specific content, for example, in cases where parents only provided a copy of the cover of a textbook. Of the remaining homework samples submitted, 72 percent (134 samples) focused on mathematics content, while the remaining 28 percent (53 samples) represented language arts content. 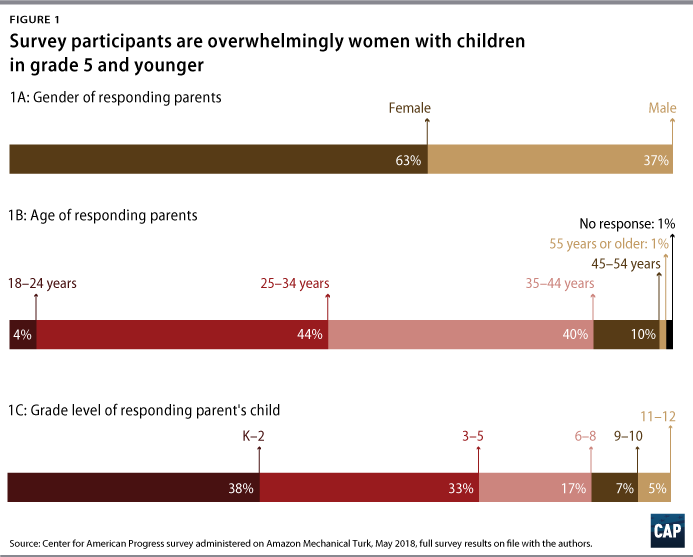 Of the 372 responding parents, 234—or 63 percent—were female, and 126—or 37 percent—were male. Forty-eight percent of parents responding to the survey were under the age of 34, while almost 90 percent of respondents were under the age of 45. There was an unequal distribution of parents representing elementary and secondary grade levels. Seventy-one percent of the total sample were parents with students in primary (K-2) and elementary (3-5) grades. (See Methodology section below) Based on the analysis, the authors’ drew the following conclusions: Homework is largely aligned to Common Core standards, especially the topics in the standardsThe authors found that the submitted homework, for the most part, was aligned to Common Core standards content or within the so-called “good” range based on content expert evaluations. As described in the Methodology, the authors used an alignment index that does not require a homework assignment to exactly mirror the content standards—both topic and skill level—for evaluators to note that it is within a good range. For context, the study’s alignment index has a range of 0.00 to 1.00, where 0.00 indicates no content in common whatsoever between the two descriptions—perfect misalignment—and 1.00 indicates complete agreement between the two descriptions—perfect alignment. Generally speaking, what one might call “good” alignment for instruction tends to range on the alignment index between 0.4 and 0.6, with a measure of 0.5 serving as a median indicator of good alignment. The analysis is a snapshot of homework and, therefore, does not allow the authors to determine if homework over the course of a year covered all required standards. In other words, it is difficult to say how many of the standards for a given grade are covered across a full school year, simply because of the limited sample of assignments. The alignment index evaluates both topic and skill, but there was particular alignment in topic areas. For instance, there was a strong emphasis in the topic areas of number sense and operations for primary math homework. When combined with the third-most emphasized topic, measurement, these three areas accounted for more than 90 percent of primary mathematics homework content. The actual math content standards for the primary grades also placed heavy emphasis on the topic areas of number sense, operations, and measurement—though they accounted for only about 80 percent of primary math content. 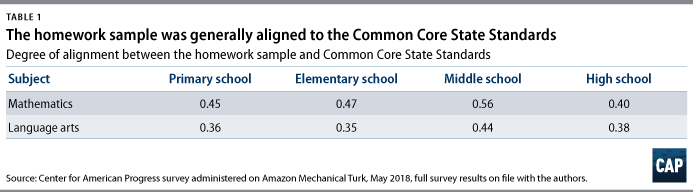 In general, across all age groups, math homework was more closely aligned to content standards—both topic and skill level—than language arts. The alignment results for middle school math were particularly strong, at 0.56, based on 27 homework samples. The stronger alignment among math homework samples may be in part due to the fact that there were more math assignments in the sample than language arts assignments. Larger samples offer more opportunities to show alignment. As a result, smaller samples may underestimate alignment. The table below presents the alignment indices, which were calculated using the homework samples collected for each grade band. Homework is often focused on low-level skills in the standards, particularly in younger gradesWhile the authors’ analysis shows that there was significant alignment in the topic of standards and homework assignments, most of the homework did not require students to demonstrate the full depth of knowledge required of content standards. The analysis uncovered an emphasis on procedural knowledge, with an even stronger emphasis on memorization and recall in language arts. Content standards, on the other hand, require students to demonstrate deeper-knowledge skills, such as the ability to analyze, conceptualize, or generate. 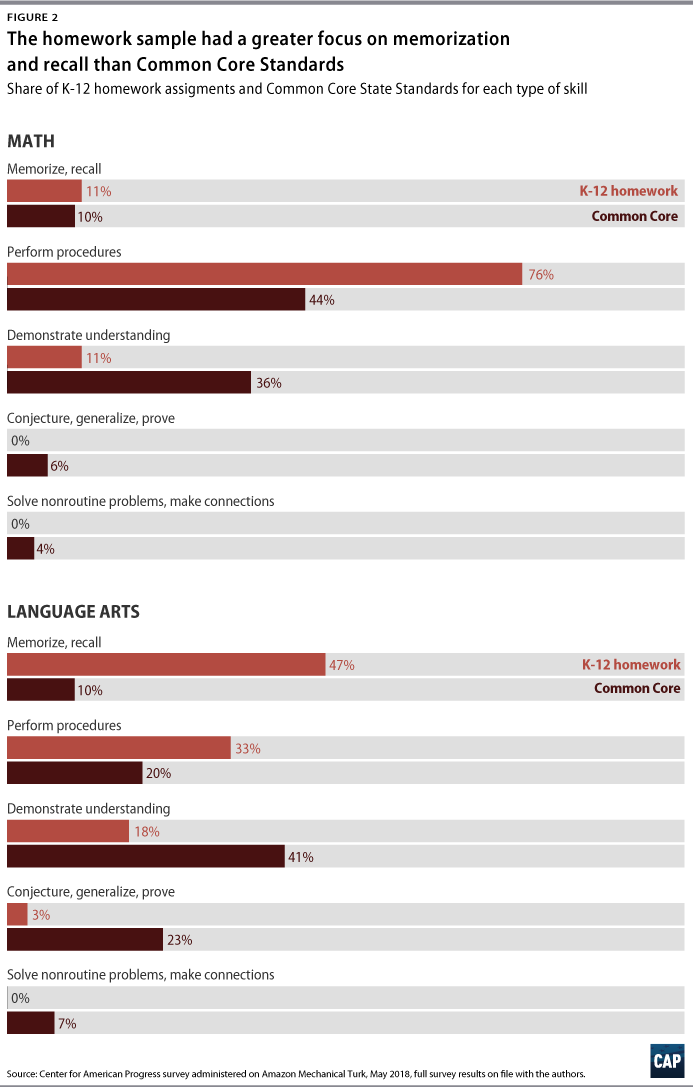 Of five performance expectation categories across math and language arts that the authors used to measure alignment between standards and homework, there was a disproportionate emphasis on skills that require a lower level of knowledge or understanding. In grades K-2, for instance, the content standards emphasize the performance expectations of “procedures,” or computation, and “demonstrate,” or understanding, but the homework samples submitted primarily emphasized the procedures level of performance expectation. Similarly, homework for grades three through five focused almost entirely on the performance expectation of procedures, rather than standards that emphasized both procedures and demonstrate. 25 As seen with the middle school grades, high school math standards—despite a continued emphasis on procedures—show increased emphasis on the more challenging performance expectations of “demonstrate understanding” and “conjecture, generalize, prove.” Interestingly, this shift toward more challenging performance expectations is most visible for the topic areas of geometric concepts and functions, in both the standards and the homework samples submitted by parents of high school students. Parents report that homework frequently does not challenge studentsNearly half of parents that participated in the survey reported that homework does not challenge their child. In particular, parents of primary-grade children were most likely to agree or strongly agree that the homework assignment they submitted was too easy for their child—58 percent for language arts and 55 percent for math. 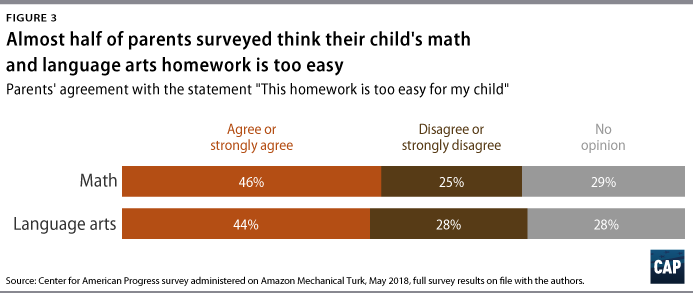 Parents’ opinions about homework difficulty varied between mathematics and language arts assignments. Forty-eight percent of parents who submitted a mathematics assignment and 44 percent of parents who submitted a language arts assignment reported that it was too easy for their child. There was some variance across grade spans as well. As noted above, parents of primary-grade children were most likely to find the homework assignments too easy for their child. Meanwhile, parents that submitted high school math homework were also more likely to agree or strongly agree that the assignments were too easy, with 50 percent agreeing or strongly agreeing and only 33 percent disagreeing or strongly disagreeing with the statement. While there were clear trends in parent opinions, it is important to acknowledge that the sample size for each subset was small. The comments of surveyed parents echoed this finding. One parent noted that “most homework that they are assigned seems like nothing more than busy work.” Another parent said: “The homework is not strong enough to build conceptual knowledge. It assumes that the child already has that knowledge.” Meanwhile, another parent commented: “Homework is way oversimplified and they don’t seem to spend much time on it. It’s a bit sad that English and math don’t seem to require what they used to. I remember much longer and harder worksheets to complete when I was a child.” 26 Weak homework samplesWithin the sample of homework assignments, there were some that fell short of rigorous. For instance, one assignment listed 24 pairs of numbers—three and nine, 24 and 21, and so on—and asked the student to circle the smaller number in order to build numbers sense. While homework can be critical when establishing foundational knowledge, repetitive activities such as this often fail to engage students and, instead, overemphasize rote learning. Asking a student to list or name a number of a lesser value, for instance, would make this assignment more interactive. A second example from kindergarten asked a student to create an uppercase and lowercase letter “f” by filling in dots with paint. The parent who submitted it highlighted the limited utility of the assignment, emphasizing that it does not hold students to high expectations. What’s more, the homework only gave the student two opportunities to practice writing the letter, both in a nonauthentic way. Indeed, the assignment focused more on filling in circles than it did constructing letters. While this task might help build a kindergartener’s hand-eye coordination, it does little to support language arts. Exemplary homework samplesWhile many of the assignments submitted focused on procedures and, for math, computation, it is worth acknowledging some of the more exemplary types of homework included in the samples. These offer examples of how homework can challenge students, engage rigorous cognitive processes, and demonstrate that content standards at all levels—not just middle and high school—can support challenging homework that pushes students to think critically. For example, one math homework assignment asked a student to identify which individuals possessed each of four groups of shapes based on the following description: Ally, Bob, Carl, and Dana each have a set of shapes. - Bob has no triangles.
- The number of rectangles that Dana has is the same as the number of triangles that Carl has.
This example is interesting on two counts. First, the assignment goes beyond procedure, requiring the student to analyze the various sets of shapes in order to determine which set belongs to which individual. It is also interesting insofar as it demonstrates a common real-world situation: There is usually more than one way to solve a problem, and sometimes, there is more than one correct answer. Similarly, another example asked a student to determine actions that would help students beautify the school. The header of the assignment read, “Make a Decision: Keep Our School Beautiful!” The assignment had various boxes, each with a question above, such as, “Should we recycle?” or “Should we make art?” The assignment asked the student to “(1) think about each choice, (2) consider how each choice would affect them and others in the school community, (3) write their ideas in boxes below.” In doing so, it required primary students to analyze and generate ideas—both of which are skills that promote deeper learning. RecommendationsHomework offers a valuable window into the curricula, assessment practices, and instructional preferences of teachers. It provides insight into classroom learning as well as the types of knowledge and skills the teacher believes will reinforce that instruction at home. This analysis shows that the content and value of homework varies. While most homework within the sample was aligned to content standards, there is still a significant need to increase the rigor of homework and create opportunities for students to use higher-order skills. Overall, schools and districts should pay more attention to homework as a reform lever. A growing body of research shows that homework is connected to learning outcomes, and as a result, schools and districts should ensure that policies help teachers provide meaningful assignments. 27 Based on this survey and the existing research on homework quality, the authors identified recommendations that can help increase the quality of homework: Schools and districts should develop homework policies that emphasize strategic, rigorous homeworkIn many cases, the current debate over homework is short-sighted. Many arguments focus on whether or not students should have homework. There are entire school districts that have simply banned homework altogether. However, the debate should move beyond the merit of homework. Research shows that homework is linked to better performance on standardized assessments, especially in higher grades. 28 Many homework scholars also believe that a reasonable homework load can help develop important work habits. 29 Therefore, instead of eliminating homework outright, schools, districts, and advocates should focus on improving its rigor and effectiveness. As discussed throughout, homework should be an extension of instruction during the school day. Accordingly, policymakers and schools must make changes to homework that are in concert with curriculum reform. Like all instruction, homework should be aligned to states’ rigorous content standards and should engage students in order to promote deeper learning and retention. To do this, homework should ask students to use higher-order skills, such as the ability to analyze or evaluate. However, schools and districts, rather than simply assigning longer, more complicated assignments to make homework seem more challenging, should make strategic shifts. Homework assignments should be thought-provoking. But there is a such thing as too much homework. Districts and schools should ensure that teachers follow the research-supported 10-minute rule. 30 Also, teachers, schools, and districts should consider resources to set all students up for success when faced with more rigorous home assignments; homework should never be a burden or source of stress for families and parents. Districts and schools should audit homework to make sure it is challenging and aligned to standardsRather than implementing homework bans, district policymakers and schools should regularly review homework samples to ensure that they are aligned to grade-level standards, are engaging, require students to demonstrate higher-order skills, and adhere to the 10-minute rule. The audit should review multiple homework assignments from each classroom and consider how much time children are receiving from all subject areas, when appropriate. The district or school should ask for ongoing feedback from students, parents, and guardians in order to collect a comprehensive representation of the learning experience at home. In instances where the district or school principal finds that homework assignments are not aligned to grade-level standards or take too much or too little time to complete, they should help the school or teachers improve them by recommending instructional materials that may make it easier for teachers to identify appropriate, grade-level homework assignments. In addition, if parents or students identify challenges to complete assignments at home, the district or school should identify solutions to ensure that all students have access to the resources and support they need to complete homework. Schools and districts should provide access to technology and other supports that make it easier for students to complete homeworkTechnology can go a long way to improve homework and provide additional support or scaffolding at home. For instance, programs such as the Khan Academy—which provides short lessons through YouTube videos and practice exercises—can give students rigorous homework that is aligned to the Common Core standards. Unfortunately, many households across the nation still do not have adequate access to devices or internet at home. A 2017 ACT survey found that 14 percent of students only have access to one technology device at home. 31 Moreover, federal data from 2013 found that about 40 percent of households with school-age children do not have access to broadband. 32 It is likely that the percentage has decreased with time, but internet access remains a significant problem. Schools and districts should adopt programs to ensure that all students can benefit from technology and broadband. For instance, Salton City, California, installed a Wi-Fi router in a school bus. Every night, the bus parks near a neighborhood with low internet connectivity, serving as a hot spot for students. 33 Moreover, greater access to technology can help more students benefit from new innovative resources. While most of these technologies are not yet research-based, and the use of devices may not be appropriate for younger children, incorporating new tools into homework may be a low-cost option to improve the quality of student learning. For instance, ASSISTments is a free web-based tool that provides immediate feedback as students complete homework or classwork. It has been proven to raise student outcomes. 34 Other online resources can complement classroom learning as well. There are various organizations that offer students free lessons in the form of YouTube videos, while also providing supplementary practice exercises and materials for educators. LearnZillion, for example, provides its users with high-quality lessons that are aligned to the Common Core standards. 35 Curriculum reform and instruction design should focus on homeworkThere are many states and districts that are engaging in curriculum reform. Many of these recent reform efforts show promise. In an analysis of the curricula and instructional materials used by the nation’s 30 largest school districts, the Center for American Progress found that approximately one-third of materials adopted or recommended by these districts were highly rated and met expectations for alignment. 36 Homework should be a focus of curriculum reform, and states and districts should consider how textbooks or other instructional materials can provide resources or examples to help teachers assign meaningful homework that will complement regular classroom instruction. Personalized learning—which tailors instruction and learning environments to meet each student’s individual interests and needs—is also gaining traction as a way to increase declining engagement in schools and increase student motivation. 37 These ideas are also relevant to homework quality. A 2010 study found that when students were offered a choice of homework assignment, they were more motivated to do the work, reported greater competence in the assignments, and performed better on unit tests, compared with peers that did not have choice in homework. 38 The study also suggested that offering students a choice improved the rate of completion of assignments. 39 Districts and schools should help implement more student-centered approaches to all instruction—in the classroom and at home. When it comes to change management, experts often advise to look for low-hanging fruit—the simplest and easiest fixes. 40 In education, homework reform is low-hanging fruit. Research shows that quality homework and increasing student achievement are positively correlated; and yet, the authors’ analysis shows that some schools may not be taking advantage of a valuable opportunity to support student achievement. Instead of mirroring the cognitive demand in rigorous content standards, homework assigned to students is often weak or rote. But it does not have to be this way. More rigorous, insightful homework is out there. Policymakers and schools need to move beyond the debate of whether or not to assign work outside of school hours and do their own due diligence—or, put another way, their own homework—before assigning homework to students in this nation’s schools. MethodologyAs mentioned above, the authors used the Amazon Mechanical Turk (MTurk) online survey tool to collect from parents their child’s actual homework assignments. Specifically, as part of the survey, the authors asked parents to submit a sample of their child’s most recent math or language arts homework assignment and have the child complete questions to gauge if the assignment was challenging, as well as how long it took to complete the assignment. In all, 372 parents responded to the survey, with CAP analyzing 187 homework assignments. The submissions of samples were analyzed by a group of analysts under the supervision of John L. Smithson, researcher emeritus at the University of Wisconsin-Madison. Measuring alignmentThe homework samples were reviewed by two teams of content analysts—one for mathematics and one for language arts—who were asked to describe the academic content represented by the submitted homework, as well as the performance expectation. Each team consisted of three analysts who possessed the relevant content expertise and experience in methodology used to gather the descriptive data. The teams used a taxonomy-based methodology that was developed by education researchers Andrew Porter and John Smithson during Porter’s tenure as director of the Wisconsin Center for Education Research at the University of Wisconsin-Madison. 41 Researchers both nationally and internationally have subsequently used this approach to content description for decades in order to examine issues of alignment as well as to support program evaluation and inform school improvement efforts. The U.S. Department of Education also recognizes the validity of this approach. Specifically, the Education Department completes a peer review of states’ annual assessment program’s alignment to state academic content standards. 42 The Porter/Smithson approach is one of a handful of alignment methodologies that has been determined to meet these federal requirements. 43 The Porter/Smithson approach is unique because it defines instructional content as a two-dimensional construct consisting of topic and cognitive demand, or skill. This approach to describing cognitive skill is similar to Bloom’s, which the authors have described above. It has five categories: recall, process, analyze, integrate, and conceptual understanding. The Porter/Smithson approach is the most stringent of alignment indicators, as it looks at both topic and cognitive demand; it is also possibly the most challenging to interpret because the final alignment score considers two dimensions. 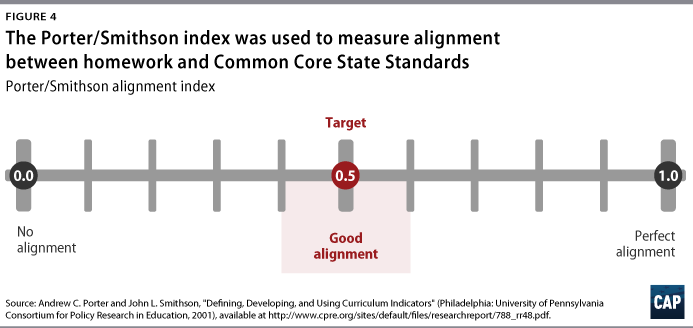 The alignment index has a range of 0.00 to 1.00, where 0.00 indicates no content in common whatsoever between the two descriptions—perfect misalignment—and 1.00 indicates complete agreement between the two descriptions—perfect alignment. A measure of 1.00 is exceedingly unlikely, requiring perfect agreement across every cell that makes up the content description. In practice, this is only seen when comparing a document to itself. For instance, very high alignment measures—more than 0.70—have been noted when comparing different test forms used for a particular grade-level state assessment; but those are instances where high alignment is desired. In terms of instructional alignment—in other words, how well instruction is aligned to the standards—a measure of 1.00 is not the goal. For this reason, the authors did not expect any analysis of homework alignment, no matter how well designed, to have a measure of or close to 1.00. Generally speaking, what one might call “good” alignment for instruction tends to range between 0.4 and 0.6 on the alignment index, with a measure of 0.5 serving as a median indicator of good alignment. The description of the content standards represents the goal of instructional practice—the destination, not the journey. As such, it does not indicate the best path for achieving those goals. The 0.5 indicator measure represents a middle road where teachers are balancing the expectations of the content standards with the immediate learning needs of their students. LimitationsThe authors acknowledge that the analysis has shortcomings. The sample was relatively small and does not directly mirror the national population of parents of elementary and secondary school students. As such, the sample does not necessarily reflect the views or homework experiences of the larger U.S. population. Limited sample sizeThe current study analyzes a snapshot of homework across many classrooms, rather than homework from a single classroom or school. The assumption is that looking at individual homework assignments across many classrooms will help to construct a composite picture of mathematics and language arts homework that will be somewhat reflective of the picture one would get from following many classrooms for many days. If the sample is large enough with a wide enough geographical spread, that assumption serves researchers well enough. For the current study, however, the number of homework samples available for each grade band were, in some cases, quite small—as low as five assignments each for middle and high school language arts. The largest sample sizes were for primary and elementary math, with 47 and 41 homework assignments collected, respectively. However, even 47 is a fairly small sample size for drawing inferences about a full year of homework. Selection biasThe respondents that participated in this study were a reasonably diverse group in terms of age, gender, and ethnicity, but there are notable differences between the makeup of the parents represented in the study and the makeup of parents of school-age children more generally. Respondents were predominantly female, with women making up almost two-thirds—63 percent—of the sample. They also tended to be parents of younger school-age children, with 71 percent of the respondents reporting on children from the bottom half of the K-12 system—grades K-5. Finally, in terms of race and ethnicity, the sample overrepresented Asian American families and underrepresented African American families. These groups comprised 14 percent and 8 percent of respondents, respectively, compared with national averages of 6 percent and 12 percent. Because the sample does not well reflect the population of parents of elementary and secondary students, the authors considered possible selection biases that may help to explain the differences in sample and overall population and that may have affected certain members of the population more than others. For instance, the authors administered the survey using MTurk, which may have skewed the sample. In general, the population on the site is younger and whiter than the U.S. population as a whole. However, research has shown that MTurk yields high-quality, nationally representative results, with data that are at least as reliable as those obtained via traditional methods. 44 The researchers also targeted California and Texas in order to increase the diversity of the sample. In addition, accessibility could have led to selection bias. Despite broad internet access in 2018, there remain families in low-income locales where internet access is not readily available for parents. It is also possible that older parents are less likely to be as active on the internet as younger parents, further contributing to selection bias. About the authorsUlrich Boser is a senior fellow at the Center for American Progress. He is also the founder and CEO of The Learning Agency. Meg Benner is a senior consultant at the Center. John Smithson is the researcher emeritus at the University of Wisconsin-Madison. AcknowledgementsThe authors would like to thank Sarah Shapiro, a former research assistant at the Center for American Progress, for her support developing the survey. They also appreciate the valuable feedback of Catherine Brown, senior fellow for Education Policy at the Center for American Progress; Tom Loveless, senior fellow at the Brookings Institution; Lisette Partelow, director of K-12 Special Initiatives at the Center; and Scott Sargrad, vice president of K-12 Education Policy at the Center. Conflicts of interestThe author, Ulrich Boser, has a financial relationship with the creators of the online homework tool ASSISTments. - Tom Loveless, “How Well Are American Students Learning?” (Washington: Brown Center on Education Policy , 2014), available at https://www.brookings.edu/wp-content/uploads/2016/06/2014-Brown-Center-Report_FINAL-4.pdf .
- Seema Mehta, “Some schools are cutting back on hoomework,” Los Angeles Times , March 22, 2009, available at http://articles.latimes.com/2009/mar/22/local/me-homework22 .
- Alfie Kohn, “Rethinking Homework,” Principal , January/February 2007, available at https://www.alfiekohn.org/article/rethinking-homework/ .
- Robert J. Marzano and Debra J. Pickering, “The Case For and Against Homework,” Educational Leadership 64 (6) (2007): 74–79, available at http://www.ascd.org/publications/educational-leadership/mar07/vol64/num06/The-Case-For-and-Against-Homework.aspx .
- Michael Winerip, “Homework Bound,” The New York Times , January 3, 1999, available at https://www.nytimes.com/1999/01/03/education/homework-bound.html .
- Marzano and Pickering, “The Case For and Against Homework.”
- Brian P. Gill and Seven L. Schlossman, “Villain or Savior? The American Discourse on Homework, 1850-2003,” Theory Into Practice 43 (3) (2004): 174–181, available at http://www.history.cmu.edu/docs/schlossman/Villiain-or-Savior.pdf .
- Karl Taro Greenfeld, “My Daughter’s Homework Is Killing Me,” The Atlantic , October 2013, available at https://www.theatlantic.com/magazine/archive/2013/10/my-daughters-homework-is-killing-me/309514/ .
- Fox News, “Florida students in Marion County will no longer be assigned homework, superintendent says,” July 13, 2017, available at https://www.foxnews.com/us/florida-students-in-marion-county-will-no-longer-be-assigned-homework-superintendent-says ; Kate Edwards, “East Tennessee schools consider ‘no homework policy’,” WJHL, September 13, 2016, available at https://www.wjhl.com/news/east-tennessee-schools-consider-no-homework-policy/871720275 .
- Tawnell D. Hobbs, “Down With Homework, Say U.S. School Districts,” The Wall Street Journal, December 12, 2018, available at https://www.wsj.com/articles/no-homework-its-the-new-thing-in-u-s-schools-11544610600 .
- Marzano and Pickering, “The Case For and Against Homework”; Gill and Schlossman, “Villain or savior?”.
- Matthew J. C. Crump, John V. McDonnell, and Todd M. Gureckis, “Evaluating Amazon’s Mechanical Turk as a Tool for Experimental Behavioral Research,” PLOS ONE 8 (3) (2013): 1–18, available at https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article/file?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0057410&type=printable .
- Common Core requires students to demonstrate conceptual understanding of topics and use the information to analyze and make their own meaning. The abilities to analyze, conceptualize, and generate denote higher-order cognitive skills. The authors describe hierarchies of cognitive skills later in the report. Many of the standards use these verbs to describe what is expected. Common Core State Standards Initiative, “About the Standards,” available at http://www.corestandards.org/about-the-standards/ (last accessed January 2019).
- Robert J. Marzano and Debra J. Pickering, “The Case For and Against Homework.”
- Khan Academy, “Common Core,” available at https://www.khanacademy.org/commoncore (last accessed February 2019).
- Common Core State Standards Initiative, “What are educational standards?”, available at http://www.corestandards.org/faq/what-are-educational-standards/ (last accessed January 2019).
- William G. Huitt, “Bloom et al.’s Taxonomy of the Cognitive Domain” (Valdosta, GA: Valdosta State University, 2011), available at http://www.edpsycinteractive.org/topics/cognition/bloom.pdf .
- Solomon Friedberg and others, “The State of State Standards Post-Common Core” (Washington: Thomas B. Fordham Institute, 2018), available at http://edex.s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/publication/pdfs/(08.22)%20The%20State%20of%20State%20Standards%20Post-Common%20Core.pdf .
- Amazon Mechanical Turk, “Home,” available at https://www.mturk.com/ (last accessed January 2019).
- Common Core State Standards Initiative, “Read the Standards,” available at http://www.corestandards.org/read-the-standards/ (last accessed February 2019).
- Center for American Progress survey administered on Amazon Mechanical Turk, May 2018, full survey results on file with the authors.
- Lauraine Genota, “‘Homework Gap’ Hits Minority, Impoverished Students Hardest, Survey Finds,” Education Week , September 19, 2018, available at https://blogs.edweek.org/edweek/DigitalEducation/2018/09/homework_gap_education_equity_ACT_survey.html .
- John B. Horrigan, “The numbers behind the broadband ‘homework gap’,” Pew Research Center, April 20, 2015, available at http://www.pewresearch.org/fact-tank/2015/04/20/the-numbers-behind-the-broadband-homework-gap/ .
- Nichole Dobo, “What to do for kids with no internet at home? How about parking a wifi-enabled school bus near their trailer park?”, The Hechinger Report , December 23, 2014, available at https://hechingerreport.org/kids-no-internet-home-parking-wifi-enabled-school-bus-near-trailer-park/ .
- Alison Duffy, “Study Shows WPI-developed Math Homework Tool Closes the Learning Gap,” Worcester Polytechnic Institute, October 24, 2016, available at https://www.wpi.edu/news/study-shows-wpi-developed-math-homework-tool-closes-learning-gap .
- Sean Cavanagh, “LearnZillion Going After District Curriculum Business, Aims to Compete With Big Publishers,” EdWeek Market Brief, June 6, 2018, available at https://marketbrief.edweek.org/marketplace-k-12/learnzillion-going-district-curriculum-business-aims-compete-big-publishers/ .
- Lisette Partelow and Sarah Shapiro, “Curriculum Reform in the Nation’s Largest School Districts” (Washington: Center for American Progress, 2018), available at https://americanprogress.org/wp-content/uploads/sites/2/2018/08/DistrictCurricula-report3.pdf .
- TNTP, “The Opportunity Myth” (New York: 2018), available at https://tntp.org/assets/documents/TNTP_The-Opportunity-Myth_Web.pdf ; Gallup, “Gallup Student Poll: Measure What Matters Most for Student Success,” available at https://www.gallup.com/education/233537/gallup-student-poll.aspx?utm_source=link_newsv9&utm_campaign=item_211028&utm_medium=copy&_ga=2.248421390.86741706.1543204564-175832835.1543204564 (last accessed January 2019).
- Erika A. Patall, Harris Cooper, and Susan R. Wynn, “The Effectiveness and Relative Importance of Choice in the Classroom,” Journal of Educational Psychology , 102 (4) (2010): 896–915, available at https://www.immagic.com/eLibrary/ARCHIVES/GENERAL/JOURNALS/E101100P.pdf .
- Jeremy Eden and Terri Long, “Forget the strategic transformation, going after the low-hanging fruit reaps more rewards,” The Globe and Mail, June 24, 2014, available at https://www.theglobeandmail.com/report-on-business/careers/management/bagging-simple-cheap-ideas/article19311957/ .
- U.S. Department of Education, “A State’s Guide to the U.S. Department of Education’s Assessment Peer Review Process” (Washington: 2018), available at https://www2.ed.gov/admins/lead/account/saa/assessmentpeerreview.pdf .
- Ellen Forte, “Evaluating Alignment in Large-Scale Standards-Based Assessment Systems” (Washington: Council of Chief State School Officers, 2017) available at https://ccsso.org/sites/default/files/2018-07/TILSA%20Evaluating%20Alignment%20in%20Large-Scale%20Standards-Based%20Assessment%20Systems.pdf .
- Kevin J. Mullinix and others, “The Generalizability of Survey Experiments,” Journal of Experimental Political Science 2 (2) (2015): 109–138, available at https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/journal-of-experimental-political-science/article/generalizability-of-survey-experiments/72D4E3DB90569AD7F2D469E9DF3A94CB .
The positions of American Progress, and our policy experts, are independent, and the findings and conclusions presented are those of American Progress alone. A full list of supporters is available here . American Progress would like to acknowledge the many generous supporters who make our work possible. Ulrich BoserFormer Senior Fellow Senior Consultant John SmithsonEvaluating the Role of HomeworkWinter 2022 By Alison Baran  Doing Our HomeworkA sign of the times, through the pandemic lens. - Homework was never intended to make up for “learning loss”; it is a tool for reinforcement and enrichment.
- Caregivers are more overwhelmed than ever before. Many are not in the position to support children with their homework.
- Students have the right to socialize with their peers and engage in extracurricular activities that bring them happiness. During the height of the pandemic, children and teens had limited, if any, opportunities to socialize.
- More than a third (37%) of teens surveyed say their mental health has worsened throughout the pandemic, according to a study done by the Morgan Stanley Alliance for Children’s Mental Health (2021). It is important that all constituents—faculty, administrators, caregivers—have a clear understanding and shared language about the expectations around giving and receiving homework. More than ever, we need to be working together in our schools with the express purpose of putting the mental health needs of our students first.
- Children have the right to playtime, extracurricular activities, downtime, and adequate sleep.
- Teachers should assign homework with a clear sense of why it is being given.
- The purpose of the homework assignment should be articulated to the students, including the fact that a certain task might be a challenge. Research shows that when children know why they are doing the homework, they are more engaged and inspired.
- Tasks should be personally relevant to students and should allow for choices. Children are motivated when they have ownership in their learning.
- Over the course of time, the kinds of homework should vary depending on what is happening in class.
- Homework assignments better serve students when they feel competent and confident with the material being assigned.
- Children deserve feedback about the homework that they have completed.
- Teachers should differentiate for individual needs across all grade levels. This might mean adjusting number of math facts, amount of reading, etc.
- Parents have the right to control their child’s time outside of school without being judged.
- If you have doubts about whether the assignment will further learning, consider that the default might be to have no homework, or think about conducting an experiment of not doing homework for a set period of time.
Readings and Resources- The Battle Over Homework: Common Ground for Administrators, Teachers, and Parents by Harris Cooper
- The Homework Myth: Why Our Kids Get Too Much of a Bad Thing by Alfie Kohn
- Rethinking Homework: Best Practices that Support Diverse Needs by Cathy Vatterott
- “ The Case for (Quality) Homework ,” by Janine Bempechat, Education Next , Winter 2019
- “ The Lost Cause of Homework Reform ,” by Brian Gill and Steven Schlossman, American Journal of Education , November 2000
- “ New York School District Weighs Banning Homework ,” by Alexa Lardieri, U.S. News & World Report , May 31, 2018
- “ Why this superintendent is banning homework—and asking kids to read instead ,” by Valerie Strauss, The Washington Post , July 17, 2017
Alison Baran is a fourth grade teacher at The Park School of Baltimore in Maryland. She’s also the lower school new faculty coordinator.  The Benefit of Leadership Coaching for School HeadsA head-turned-leadership coach explains how coaching can help heads become more effective leaders.. Read the Post Advertisement  Homework and Children in Grades 3–6: Purpose, Policy and Non-Academic Impact- Original Paper
- Open access
- Published: 12 January 2021
- Volume 50 , pages 631–651, ( 2021 )
Cite this articleYou have full access to this open access article  - Melissa Holland ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-8349-7168 1 ,
- McKenzie Courtney 2 ,
- James Vergara 3 ,
- Danielle McIntyre 4 ,
- Samantha Nix 5 ,
- Allison Marion 6 &
- Gagan Shergill 1
20k Accesses 17 Citations 127 Altmetric 16 Mentions Explore all metrics Increasing academic demands, including larger amounts of assigned homework, is correlated with various challenges for children. While homework stress in middle and high school has been studied, research evidence is scant concerning the effects of homework on elementary-aged children. The objective of this study was to understand rater perception of the purpose of homework, the existence of homework policy, and the relationship, if any, between homework and the emotional health, sleep habits, and parent–child relationships for children in grades 3–6. Survey research was conducted in the schools examining student ( n = 397), parent ( n = 442), and teacher ( n = 28) perception of homework, including purpose, existing policy, and the childrens’ social and emotional well-being. Preliminary findings from teacher, parent, and student surveys suggest the presence of modest impact of homework in the area of emotional health (namely, student report of boredom and frustration ), parent–child relationships (with over 25% of the parent and child samples reporting homework always or often interferes with family time and creates a power struggle ), and sleep (36.8% of the children surveyed reported they sometimes get less sleep) in grades 3–6. Additionally, findings suggest misperceptions surrounding the existence of homework policies among parents and teachers, the reasons teachers cite assigning homework, and a disconnect between child-reported and teacher reported emotional impact of homework. ConclusionsPreliminary findings suggest homework modestly impacts child well-being in various domains in grades 3–6, including sleep, emotional health, and parent/child relationships. School districts, educators, and parents must continue to advocate for evidence-based homework policies that support children’s overall well-being. Similar content being viewed by others Understanding the Quality of Effective HomeworkRelationships between perceived parental involvement in homework, student homework behaviors, and academic achievement: differences among elementary, junior high, and high school students.  Collaboration between School and Home to Improve Subjective Well-being: A New Chinese Children’s Subjective Well-being ScaleAvoid common mistakes on your manuscript. IntroductionChildren’s social-emotional health is moving to the forefront of attention in schools, as depression, anxiety, and suicide rates are on the rise (Bitsko et al. 2018 ; Child Mind Institute 2016 ; Horowitz and Graf 2019 ; Perou et al. 2013 ). This comes at a time when there are also intense academic demands, including an increased focus on academic achievement via grades, standardized test scores, and larger amounts of assigned homework (Pope 2010 ). This interplay between the rise in anxiety and depression and scholastic demands has been postulated upon frequently in the literature, and though some research has looked at homework stress as it relates to middle and high school students (Cech 2008 ; Galloway et al. 2013 ; Horowitz and Graf 2019 ; Kackar et al. 2011 ; Katz et al. 2012 ), research evidence is scant as to the effects of academic stress on the social and emotional health of elementary children. Literature ReviewThe following review of the literature highlights areas that are most pertinent to the child, including homework as it relates to achievement, the achievement gap, mental health, sleep, and parent–child relationships. Areas of educational policy, teacher training, homework policy, and parent-teacher communication around homework are also explored. Homework and AchievementWith the authorization of No Child Left Behind and the Common Core State Standards, teachers have felt added pressures to keep up with the tougher standards movement (Tokarski 2011 ). Additionally, teachers report homework is necessary in order to complete state-mandated material (Holte 2015 ). Misconceptions on the effectiveness of homework and student achievement have led many teachers to increase the amount of homework assigned. However, there has been little evidence to support this trend. In fact, there is a significant body of research demonstrating the lack of correlation between homework and student success, particularly at the elementary level. In a meta-analysis examining homework, grades, and standardized test scores, Cooper et al. ( 2006 ) found little correlation between the amount of homework assigned and achievement in elementary school, and only a moderate correlation in middle school. In third grade and below, there was a negative correlation found between the variables ( r = − 0.04). Other studies, too, have evidenced no relationship, and even a negative relationship in some grades, between the amount of time spent on homework and academic achievement (Horsley and Walker 2013 ; Trautwein and Köller 2003 ). High levels of homework in competitive high schools were found to hinder learning, full academic engagement, and well-being (Galloway et al. 2013 ). Ironically, research suggests that reducing academic pressures can actually increase children’s academic success and cognitive abilities (American Psychological Association [APA] 2014 ). International comparison studies of achievement show that national achievement is higher in countries that assign less homework (Baines and Slutsky 2009 ; Güven and Akçay 2019 ). In fact, in a recent international study conducted by Güven and Akçay ( 2019 ), there was no relationship found between math homework frequency and student achievement for fourth grade students in the majority of the countries studied, including the United States. Similarly, additional homework in science, English, and history was found to have little to no impact on respective test scores in later grades (Eren and Henderson 2011 ). In the 2015 “Programme of International Student Assessment” results, Korea and Finland are ranked among the top countries in reading, mathematics, and writing, yet these countries are among those that assign the least amount of homework (Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development [OECD] 2016 ). Homework and Mental WellnessAcademic stress has been found to play a role in the mental well-being of children. In a study conducted by Conner et al. ( 2009 ), students reported feeling overwhelmed and burdened by their exceeding homework loads, even when they viewed homework as meaningful. Academic stress, specifically the amount of homework assigned, has been identified as a common risk factor for children’s increased anxiety levels (APA 2009 ; Galloway et al. 2013 ; Leung et al. 2010 ), in addition to somatic complaints and sleep disturbance (Galloway et al. 2013 ). Stress also negatively impacts cognition, including memory, executive functioning, motor skills, and immune response (Westheimer et al. 2011 ). Consequently, excessive stress impacts one’s ability to think critically, recall information, and make decisions (Carrion and Wong 2012 ). Homework and SleepSleep, including quantity and quality, is one life domain commonly impacted by homework and stress. Zhou et al. ( 2015 ) analyzed the prevalence of unhealthy sleep behaviors in school-aged children, with findings suggesting that staying up late to study was one of the leading risk factors most associated with severe tiredness and depression. According to the National Sleep Foundation ( 2017 ), the recommended amount of sleep for elementary school-aged children is 9 – 11 h per night; however, approximately 70% of youth do not get these recommended hours. According to the MetLife American Teacher Survey ( 2008 ), elementary-aged children also acknowledge lack of sleep. Perfect et al. ( 2014 ) found that sleep problems predict lower grades and negative student attitudes toward teachers and school. Eide and Showalter ( 2012 ) conducted a national study that examined the relationship between optimum amounts of sleep and student performance on standardized tests, with results indicating significant correlations ( r = 0.285–0.593) between sleep and student performance. Therefore, sleep is not only impacted by academic stress and homework, but lack of sleep can also impact academic functioning. Homework and the Achievement GapHomework creates increasing achievement variability among privileged learners and those who are not. For example, learners with more resources, increased parental education, and family support are likely to have higher achievement on homework (Hofferth and Sandberg 2001 ; Moore et al. 2018 ; Ndebele 2015 ; OECD 2016 ). Learners coming from a lower socioeconomic status may not have access to quiet, well-lit environments, computers, and books necessary to complete their homework (Cooper 2001 ; Kralovec and Buell 2000 ). Additionally, many homework assignments require materials that may be limited for some families, including supplies for projects, technology, and transportation. Based on the research to date, the phrase “the homework gap” has been coined to describe those learners who lack the resources necessary to complete assigned homework (Moore et al. 2018 ). Parent–Teacher Communication Around HomeworkCommunication between caregivers and teachers is essential. Unfortunately, research suggests parents and teachers often have limited communication regarding homework assignments. Markow et al. ( 2007 ) found most parents (73%) report communicating with their child’s teacher regarding homework assignments less than once a month. Pressman et al. ( 2015 ) indicated children in primary grades spend substantially more time on homework than predicted by educators. For example, they found first grade students had three times more homework than the National Education Association’s recommendation of up to 20 min of homework per night for first graders. While the same homework assignment may take some learners 30 min to complete, it may take others up to 2 or 3 h. However, until parents and teachers have better communication around homework, including time completion and learning styles for individual learners, these misperceptions and disparities will likely persist. Parent–Child Relationships and HomeworkTrautwein et al. ( 2009 ) defined homework as a “double-edged sword” when it comes to the parent–child relationship. While some parental support can be construed as beneficial, parental support can also be experienced as intrusive or detrimental. When examining parental homework styles, a controlling approach was negatively associated with student effort and emotions toward homework (Trautwein et al. 2009 ). Research suggests that homework is a primary source of stress, power struggle, and disagreement among families (Cameron and Bartel 2009 ), with many families struggling with nightly homework battles, including serious arguments between parents and their children over homework (Bennett and Kalish 2006 ). Often, parents are not only held accountable for monitoring homework completion, they may also be accountable for teaching, re-teaching, and providing materials. This is particularly challenging due to the economic and educational diversity of families. Pressman et al. ( 2015 ) found that as parents’ personal perceptions of their abilities to assist their children with homework declined, family-related stressors increased. Teacher TrainingAs homework plays a significant role in today’s public education system, an assumption would be made that teachers are trained to design homework tasks to promote learning. However, only 12% of teacher training programs prepare teachers for using homework as an assessment tool (Greenberg and Walsh 2012 ), and only one out of 300 teachers reported ever taking a course regarding homework during their training (Bennett and Kalish 2006 ). The lack of training with regard to homework is evidenced by the differences in teachers’ perspectives. According to the MetLife American Teacher Survey ( 2008 ), less experienced teachers (i.e., those with 5 years or less years of experience) are less likely to to believe homework is important and that homework supports student learning compared to more experienced teachers (i.e., those with 21 plus years of experience). There is no universal system or rule regarding homework; consequently, homework practices reflect individual teacher beliefs and school philosophies. Educational and Homework PolicyPolicy implementation occurs on a daily basis in public schools and classrooms. While some policies are made at the federal level, states, counties, school districts, and even individual school sites often manage education policy (Mullis et al. 2012 ). Thus, educators are left with the responsibility to implement multi-level policies, such as curriculum selection, curriculum standards, and disability policy (Rigby et al. 2016 ). Despite educational reforms occurring on an almost daily basis, little has been initiated with regard to homework policies and practices. To date, few schools provide specific guidelines regarding homework practices. District policies that do exist are not typically driven by research, using vague terminology regarding the quantity and quality of assignments. Greater variations among homework practices exist when comparing schools in the private sector. For example, Montessori education practices the philosophy of no examinations and no homework for students aged 3–18 (O’Donnell 2013 ). Abeles and Rubenstein ( 2015 ) note that many public school districts advocate for the premise of 10 min of homework per night per grade level. However, there is no research supporting this premise and the guideline fails to recognize that time spent on homework varies based on the individual student. Sartain et al. ( 2015 ) analyzed and evaluated homework policies of multiple school districts, finding the policies examined were outdated, vague, and not student-focused. The reasons cited for homework assignment, as identified by teachers, are varied, such as enhancing academic achievement through practice or teaching self-discipline. However, not all types of practice are equally effective, particularly if the student is practicing the skill incorrectly (Dean et al. 2012 ; Trautwein et al. 2009 ). The practice of reading is one of the only assignments consistently supported by research to be associated with increased academic achievement (Hofferth and Sandberg 2001 ). Current literature supports 15–20 min of daily allocated time for reading practice (Reutzel and Juth 2017 ). Additionally, research supports project-based learning to deepen learners’ practice and understanding of academic material (Williams 2018 ). Research also shows that homework only teaches responsibility and self-discipline when parents have that goal in mind and systematically structure and supervise homework (Kralovec and Buell 2000 ). Non-academic activities, such as participating in chores (University of Minnesota 2002 ) and sports (Hofferth and Sandberg 2001 ) were found to be greater predictors of later success and effective problem-solving. Consistent with the pre-existing research literature, the following hypotheses are offered: Homework will have some negative correlation with children’s social-emotional well-being. The purposes cited for the assignment of homework will be varied between parents and teachers. Schools will lack well-formulated and understood homework policies. Homework will have some negative correlation with children’s sleep and parent–child relationships. This quantitative study explored, via perception-based survey research, the social and emotional health of elementary children in grades 3 – 6 and the scholastic pressures they face, namely homework. The researchers implemented newly developed questionnaires addressing student, teacher, and parent perspectives on homework and on children’s social-emotional well-being. Researchers also examined perspectives on the purpose of homework, the existence of school homework policies, and the perceived impact of homework on children’s sleep and family relationships. Given the dearth of prior research in this area, a major goal of this study was to explore associations between academic demands and child well-being with sufficient breadth to allow for identification of potential associations that may be examined more thoroughly by future research. These preliminary associations and item-response tendencies can serve as foundation for future studies with causal, experimental, or more psychometrically focused designs. A conceptual framework for this study is offered in Fig. 1 .  Conceptual framework Research QuestionsWhat is the perceived impact of homework on children’s social-emotional well-being across teachers, parents, and the children themselves? What are the primary purposes of homework according to parents and teachers? How many schools have homework policies, and of those, how many parents and teachers know what the policy is? What is the perceived impact of homework on children’s sleep and parent–child relationships? The present quantitative descriptive study is based on researcher developed instruments designed to explore the perceptions of children, teachers and parents on homework and its impact on social-emotional well-being. The use of previously untested instruments and a convenience sample preclude any causal interpretations being drawn from our results. This study is primarily an initial foray into the sparsely researched area of the relationship of homework and social-emotional health, examining an elementary school sample and incorporating multiple perspectives of the parents, teachers, and the children themselves.  ParticipantsThe participants in this study were children in six Northern California schools in grades third through sixth ( n = 397), their parents ( n = 442), and their teachers ( n = 28). The mean grade among children was 4.56 (minimum third grade/maximum sixth grade) with a mean age of 9.97 (minimum 8 years old/maximum 12 years old). Approximately 54% of the children were male and 45% were female, with White being the most common ethnicity (61%), followed by Hispanic (30%), and Pacific Islander (12%). Subjects were able to mark more than one ethnicity. Detailed participant demographics are available upon request. InstrumentsThe instruments used in this research include newly developed student, parent, and teacher surveys. The research team formulated a number of survey items that, based on existing research and their own professional experience in the schools, have high face validity in measuring workload, policies, and attitudes surrounding homework. Further psychometric development of these surveys and ascertation of construct and content validity is warranted, with the first step being their use in this initial perception-based study. Each of the surveys, developed specifically for this study, are discussed below. Student SurveyThe Student Survey is a 15-item questionnaire wherein the child was asked closed- and open-ended questions regarding their perspectives on homework, including how homework makes them feel. Parent SurveyThe Parent Survey is a 23-item questionnaire wherein the children’s parents were asked to respond to items regarding their perspectives on their child’s homework, as well as their child’s social-emotional health. Additionally, parents were asked whether their child’s school has a homework policy and, if so, if they know what that policy specifies. Teacher SurveyThe Teacher Survey is a 22-item questionnaire wherein the children’s teacher was asked to respond to items regarding their perspectives of the primary purposes of homework, as well as the impact of homework on children’s social-emotional health. Additionally, teachers were asked whether their school has a homework policy and, if so, what that policy specifies. Data was collected by the researchers after following Institutional Review Board procedures from the sponsoring university. School district approval was obtained by the lead researcher. Upon district approval, individual school approval was requested by the researchers by contacting site principals, after which, teachers of grades 3 – 6 at those schools were asked to voluntarily participate. Each participating teacher was provided a packet including the following: a manila envelope, Teacher Instructions, Administration Guide, Teacher Survey, Parent Packet, and Student Survey. Surveys and classrooms were de-identified via number assignment. Teachers then distributed the Parent Packet to each child’s guardian, which included the Parent Consent and Parent Survey, corresponding with the child’s assigned number. A coded envelope was also enclosed for parents/guardians to return their completed consent form and survey, if they agreed to participate. The Parent Consent form detailed the purpose of the research, the benefits and risks of participating in the research, confidentiality, and the voluntary nature of completing the survey. Parents who completed the consent form and survey sent the completed materials in the enclosed envelope, sealed, to their child’s teacher. After obtaining returned envelopes, with parent consent, teachers were instructed to administer the corresponding numbered survey to the children during a class period. Teachers were also asked to complete their Teacher Survey. All completed materials were to be placed in envelopes provided to each teacher and returned to the researchers once data was collected. Analysis of DataThis descriptive and quantitative research design utilized the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) to analyze data. The researchers developed coding keys for the parent, teacher, and student surveys to facilitate data entry into SPSS. Items were also coded based on the type of data, such as nominal or ordinal, and qualitative responses were coded and translated where applicable and transcribed onto a response sheet. Some variables were transformed for more accurate comparison across raters. Parent, teacher, and student ratings were analyzed, and frequency counts and percentages were generated for each item. Items were then compared across and within rater groups to explore the research questions. The data analysis of this study is primarily descriptive and exploratory, not seeking to imply causal relationships between variables. Survey item response results associated with each research questionnaire are summarized in their respective sections below. The first research question investigated in this study was: “What is the perceived impact of homework on children’s social-emotional well-being across teachers, parents, and children?” For this question the examiners looked at children’s responses to how homework makes them feel from a list of feelings. As demonstrated in Table 1 , approximately 44% of children feel “Bored” and about 25% feel “Annoyed” and “Frustrated” toward homework. Frequencies and percentages are reported in Table 1 . Similar to the student survey, parents also responded to a question regarding their child’s emotional experience surrounding homework. Based on parent reports, approximately 40% of parents perceive their child as “Frustrated” and about 37% acknowledge their child feeling “Stress/Anxiety.” Conversely, about 37% also report their child feels “Competence.” These results are reported in Table 1 . Additionally, parents and teachers both responded to the question, “How does homework affect your student’s social and emotional health?” One notable finding from parent and teacher reports is that nearly half of both parents and teachers reported homework has “No Effect” on children’s social and emotional health. Frequencies and percentages are reported in Table 2 . The second research question investigated in this study was: “What are parent and teacher perspectives on the primary purposes of homework?” For this question the examiners looked at three specific questions across parent and teacher surveys. Parents responded to the questions, “Does homework relate to your child’s learning?” and “How often is homework busy work?” While the majority of parents reported homework “Always” (45%) or “Often” (39%) relates to their child’s learning, parents also feel homework is “Often” (29%) busy work. The corresponding frequencies and percentages are summarized in Table 3 . Additionally, teachers were asked, “What are the primary reasons you assign homework?” The primary purposes of homework according to the teachers in this sample are “Skill Practice” (82%), “Develop Work Ethic” (61%), and “Teach Independence and Responsibility” (50%). The frequencies and percentages of teacher responses are displayed in Table 4 . Notably, on this survey item, teachers were instructed to choose one response (item), but the majority of teachers chose multiple items. This suggests teachers perceive themselves as assigning homework for a variety of reasons. The third research question investigated was, “How many schools have homework policies, and of those, how many parents and teachers know what the policy is?” For this question the examiners analyzed parent and teacher responses to the question, “Does your school have a homework policy?” Frequencies and percentages are displayed in Table 5 . Notably, only two out of the six schools included in this study had homework policies. Results indicate that both parents and teachers are uncertain regarding whether or not their school had a homework policy. The fourth research question investigated was, “What is the perceived impact of homework on children’s sleep and parent–child relationships?” Children were asked if they get less sleep because of homework and parents were asked if their child gets less sleep because of homework. Finally, teachers were asked about the impact of sleep on academic performance. Frequencies and percentages of student, parent, and teacher data is reported in Table 6 . Results indicate disagreement among parents and children on the impact of homework on sleep. While the majority of parents do not feel their child gets less sleep because of homework (77%), approximately 37% of children report sometimes getting less sleep because of homework. On the other hand, teachers acknowledge the importance of sleep in relation to academic performance, as nearly 93% of teachers report sleep always or often impacts academic performance. To investigate the perceived impact of homework on the parent–child relationship, parents were asked “How does homework impact your child’s relationships?” Almost 30% of parents report homework “Brings us Together”; however, 24% report homework “Creates a Power Struggle” and nearly 18% report homework “Interferes with Family Time.” Additionally, parents and children were both asked to report if homework gets in the way of family time. Frequencies and percentages are reported in Table 7 . Data was further analyzed to explore potentially significant differences between parents and children on this perception as described below. In order to prepare for analysis of significant differences between parent and child perceptions regarding homework and family time, a Levene’s test for equality of variances was conducted. Results of the Levene’s test showed that equal variances could not be assumed, and results should be interpreted with caution. Despite this, a difference in mean responses on a Likert-type scale (where higher scores equal greater perceived interference with family time) indicate a disparity in parent ( M = 2.95, SD = 0.88) and child ( M = 2.77, SD = 0.99) perceptions, t (785) = 2.65, p = 0.008. Results suggest that children were more likely to feel that homework interferes with family time than their parents. However, follow up testing where equal variances can be assumed is warranted upon further data collection. The purpose of this research was to explore perceptions of homework by parents, children, and teachers of grades 3–6, including how homework relates to child well-being, awareness of school homework policies and the perceived purpose of homework. A discussion of the results as it relates to each research question is explored. Perceived Impact of Homework on Children’s Social-Emotional Well-Being Across Teachers, Parents, and StudentsAccording to self-report survey data, children in grades 3–6 reported that completing homework at home generates various feelings. The majority of responses indicated that children felt uncomfortable emotions such as bored, annoyed, and frustrated; however, a subset of children also reported feeling smart when completing homework. While parent and teacher responses suggest parents and teachers do not feel homework affects children’s social-emotional health, children reported that homework does affect how they feel. Specifically, many children in this study reported experiencing feelings of boredom and frustration when thinking about completing homework at home. If the purpose of homework is to enhance children’s engagement in their learning outside of school, educators must re-evaluate homework assignments to align with best practices, as indicated by the researchers Dean et al. ( 2012 ), Vatterott ( 2018 ), and Sartain et al. ( 2015 ). Specifically, educators should consider effects of the amount and type of homework assigned, balancing the goal of increased practice and learning with potential effects on children’s social-emotional health. Future research could incorporate a control group and/or test scores or other measures of academic achievement to isolate and better understand the relationships between homework, health, and scholastic achievement. According to parent survey data, the perceived effects of homework on their child’s social and emotional well-being appear strikingly different compared to student perceptions. Nearly half of the parents who participated in the survey reported that homework does not impact their child’s social-emotional health. Additionally, more parents indicated that homework had a positive effect on child well-being compared to a negative one. However, parents also acknowledge that homework generates negative emotions such as frustration, stress and anxiety in their children. Teacher data indicates that, overall, teachers do not appear to see a negative impact on their students’ social-emotional health from homework. Similar to parent responses, nearly half of teachers report that homework has no impact on children’s social-emotional health, and almost one third of teachers reported a positive effect. These results are consistent with related research which indicates that teachers often believe that homework has positive impacts on student development, such as developing good study habits and a sense of responsibility (Bembenutty 2011 ). It should also be noted, not a single teacher reported the belief that homework negatively impacts children’s’ social and emotional well-being, which indicates clear discrepancies between teachers’ perceptions and children’s feelings. Further research is warranted to explore and clarify these discrepancies. Primary Purposes of Homework According to Teachers and ParentsResults from this study suggest that the majority of parents believe that homework relates and contributes to their child’s learning. This finding supports prior research which indicates that parents often believe that homework has long-term positive effects and builds academic competencies in students (Cooper et al. 2006 ). Notably, however, nearly one third of parents also indicate that homework is often given as busy work by teachers. Teachers reported that they assigned homework to develop students’ academic skills, work ethic, and teach students responsibility and promote independence. While teachers appear to have good intentions regarding the purpose of homework, research suggests that homework is not an effective nor recommended practice to achieve these goals. Household chores, cooking, volunteer experiences, and sports may create more conducive learning opportunities wherein children acquire work ethic, responsibility, independence, and problem-solving skills (Hofferth and Sandberg 2001 ; University of Minnesota 2002 ). Educators should leverage the use of homework in tandem with other student life experiences to best foster both academic achievement and positive youth development more broadly. Homework PoliciesAs evident from parent responses, the majority of parents are unaware if their child’s school has a homework policy and many teachers are also uncertain as to whether their school provides restrictions or guidelines for homework (e.g., amount, type, and purpose). Upon contacting school principals, it was determined that only two of the six schools have a school-wide homework policy. Current data indicates the professionals responsible for assigning homework appear to be unclear about whether their school has policies for homework. Additionally, there appears to be a disconnect between parents and teachers regarding whether homework policies do exist among the sampled schools. The research in the current study is consistent with previous research indicating that policies, if they do exist, are often vague and not communicated clearly to parents (Sartain et al. 2015 ). This study suggests that homework policies in these districts require improved communication between administrators, teachers, and parents. Perceived Impact of Homework on Children’s Sleep and Parent–Child RelationshipsRegarding the importance of sleep on academic performance, nearly all of the teachers included in this study acknowledged the impact that sleep has on academic performance. There was disagreement among children and parents on the actual impact that homework has on children’s sleep. Over one third of children report that homework occasionally detracts from their sleep; however, many parents may be unaware of this impact as more than three quarters of parents surveyed reported that homework does not impact their child’s sleep. Thus, while sleep is recognized as highly important for academic achievement, homework may be adversely interfering with students’ full academic potential by compromising their sleep. In regard to homework’s impact on the parent child-relationship, parents in this survey largely indicated that homework does not interfere in their parent–child relationship. However, among the parents who do notice an impact, the majority report that homework can create a power struggle and diminish their overall family time. These results are consistent with Cameron and Bartell’s ( 2009 ) research which found that parents often believe that excessive amounts of homework often cause unnecessary family stress. Likewise, nearly one third of children in this study reported that homework has an impact on their family time. This study provides the foundation for additional research regarding the impact of academic demands, specifically homework, on children’s social-emotional well-being, including sleep, according to children, parents, and teachers. Additionally, the research provides some information on reasons teachers assign homework and a documentation of the lack of school homework policies, as well as the misguided knowledge among parents and teachers about such policies. The preexisting literature and meta-analyses indicate homework has little to no positive effect on elementary-aged learners’ academic achievement (Cooper et al. 2006 ; Trautwein and Köller 2003 ; Wolchover 2012 ). This led to the question, if homework is not conducive to academic achievement at this level, how might it impact other areas of children’s lives? This study provides preliminary information regarding the possible impact of homework on the social-emotional health of elementary children. The preliminary conclusions from this perception research may guide districts, educators, and parents to advocate for evidence-based homework policies that support childrens’ academic and social-emotional health. If homework is to be assigned at the elementary level, Table 8 contains recommended best practices for such assignment, along with a sample of specific guidelines for districts, educators, and parents (Holland et al. 2015 ). Limitations and Recommendations for Future ResearchDue to the preliminary nature of this research, some limitations must be addressed. First, research was conducted using newly developed parent, teacher, and student questionnaires, which were not pilot tested or formally validated. Upon analyzing the data, the researchers discovered limitations within the surveys. For example, due to the nature of the survey items, the variables produced were not always consistently scaled. This created challenges when making direct comparisons. Additionally, this limited the sophistication of the statistical procedures that could be used, and reliability could not be calculated in typical psychometric fashion (e.g., Cronbach’s Alpha). Secondly, the small sample size may limit the generalizability of the results, especially in regard to the limited number of teachers (n = 28) we were able to survey. Although numerous districts and schools were contacted within the region, only three districts granted permission. These schools may systematically differ from other schools in the region and therefore do not necessarily represent the general population. Third, this research is based on perception, and determining the actual impacts of homework on child wellness would necessitate a larger scale, better controlled study, examining variables beyond simple perception and eliminating potentially confounding factors. It is possible that individuals within and across rater groups interpreted survey items in different ways, leading to inconsistencies in the underlying constructs apparently being measured. Some phrases such as “social-emotional health” can be understood to mean different things by different raters, which could have affected the way raters responded and thus the results of this study. Relatedly, causal links between homework and student social-emotional well-being cannot be established through the present research design and future research should employ the use of matched control groups who do not receive homework to better delineate the direct impact of homework on well-being. Finally, interpretations of the results are limited by the nested nature of the data (parent and student by teacher). The teachers, parents, and students are not truly independent groups, as student and parent perceptions on the impact of homework likely differ as a function of the classroom (teacher) that they are in, as well as the characteristics of the school they attend, their family environment, and more. The previously mentioned challenge of making direct comparisons across raters due to the design of the surveys, as well as small sample size of teachers, limited the researchers’ ability to address this issue. Future research may address this limitation by collecting data and formulating related lines of inquiry that are more conducive to the analysis of nested data. At this time, this survey research is preliminary. An increased sample size and replication of results is necessary before further conclusions can be made. Researchers should also consider obtaining data from a geographically diverse population that mirrors the population in the United States, and using revised surveys that have undergone a rigorous validation process. Abeles, V., & Rubenstein, G. (2015). Beyond measure: Rescuing an overscheduled, overtested, underestimated generation . New York: Simon & Schuster. Google Scholar American Psychological Association (APA). (2009). Stress in America 2009 . https://bit.ly/39FiTk3 . American Psychological Association (APA). (2014). Stress in America: Are teens adopting adults’ stress habits? https://bit.ly/2SIiurC . Baines, L. A., & Slutsky, R. (2009). Developing the sixth sense: Play. Educational HORIZONS , 87 (2), 97–101. https://bit.ly/39LLGU4 . Bembenutty, H. (2011). The last word: An interview with harris cooper—Research, policies, tips, and current perspectives on homework. Journal of Advanced Academics, 22 (2), 340–349. https://doi.org/10.1177/1932202X1102200207 . Article Google Scholar Bennett, S., & Kalish, N. (2006). The case against homework: How homework is hurting our children and what we can do about it . New York: Crown Publishers. Bitsko, R. H., Holbrook, J. R., Ghandour, R. M., Blumberg, S. J., Visser, S. N., Perou, R., & Walkup, J. T. (2018). Epidemiology and impact of health care provider:Diagnosed anxiety and depression among US children. Journal of Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics, 39 (5), 395. https://doi.org/10.1097/DBP.0000000000000571 . Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar Cameron, L., & Bartell, L. (2009). The researchers ate the homework! Toronto: Canadian Education Association. Carrion, V. G., & Wong, S. S. (2012). Can traumatic stress alter the brain? Understanding the implications of early trauma on brain development and learning. Journal of Adolescent Health, 51 (2), S23–S28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jadohealth.2012.04.010 . Cech, S. J. (2008). Poll of US teens finds heavier homework load, more stress over grades. Education Week, 27 (45), 9. Child Mind Institute. Children’s mental health report . (2015). https://bit.ly/2SSzE4v . Child Mind Institute. (2016). 2016 children’s mental health report . https://bit.ly/2SQ9kbj . Conner, J., Pope, D., & Galloway, M. (2009). Success with less stress. Educational Leadership, 67, 54–58. Cooper, H. (2001). Homework for all–in moderation. Educational leadership, 58 (7), 34–38. Cooper, H., Robinson, J. C., & Patall, E. A. (2006). Does homework improve academic achievement? A synthesis of research, 1987–2003. Review of Educational Research, 76 (1), 1–62. https://doi.org/10.3102/00346543076001001 . Dean, C. B., Hubbell, E. R., Pitler, H., & Stone, B. J. (2012). Classroom instruction that works: Research-based strategies for increasing student achievement . Alexandria: ASCD. Eide, E. R., & Showalter, M. H. (2012). Sleep and student achievement. Eastern Economic Journal, 38 (4), 512–524. https://doi.org/10.1057/eej.2011.33 . Eren, O., & Henderson, D. J. (2011). Are we wasting our children’s time by giving them more homework? Economics of Education Review, 30 (5), 950–961. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.econedurev.2011.03.011 . Galloway, M., Conner, J., & Pope, D. (2013). Nonacademic effects of homework in privileged, high-performing high schools. The Journal of Experimental Education, 81 (4), 490–510. https://doi.org/10.1080/00220973.2012.745469 . Greenberg, J., & Walsh, K. (2012). What teacher preparation programs teach about k-12 assessment: A review . Washington: National Council on Teacher Quality. Güven, U., & Akçay, A. O. (2019). Trends of homework in mathematics: Comparative research based on TIMSS study. International Journal of Instruction., 12 (1), 1367–1382. Hofferth, S. L., & Sandberg, J. F. (2001). How American children spend their time. Journal of Marriage and Family, 63 (2), 295–308. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1741-3737.2001.00295.x . Holland, M. L., Sisson, H., & Abeles, V. (2015, January). Academic demands, homework, and social–emotional health. NASP Communique, 45 (5), 10. Holte, K. (2015). Homework in primary school: Could it be made more child-friendly? Studia Paedagogica, 21 (4), 13–33. https://doi.org/10.5817/SP2016-4-1 . Horowitz, J. M., & Graf, N. (2019). Most U.S. teens see anxiety and depression as a major problem among their peers. Pew Research Center. https://pewrsr.ch/32kUmhU . Horsley, M., & Walker, R. (2013). Reforming homework: Practices, learning and policies . South Yarra: Palgrave Macmillan. Kackar, H. Z., Shumow, L., Schmidt, J. A., & Grzetich, J. (2011). Age and gender differences in adolescents’ homework experiences. Journal of Applied Developmental Psychology, 32 (2), 70–77. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.appdev.2010.12.005 . Katz, I., Buzukashvili, T., & Feingold, L. (2012). Homework stress: Construct validation of a measure. The Journal of Experimental Education, 80 (4), 405–421. https://doi.org/10.1080/00220973.2011.610389 . Kralovec, E., & Buell, J. (2000). The end of homework: How homework disrupts families, overburdens children, and limits learning . Boston: Beacon Press. Leung, G. S., Yeung, K. C., & Wong, D. F. (2010). Academic stressors and anxiety in children: The role of paternal support. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 19 (1), 90–100. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-009-9288-4 . Markow, D., Kim, A., & Liebman, M. (2007). The Metlife survey of the American teacher . New York: Metlife, Inc. https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED530021.pdf . MetLife. (2008). MetLife American teacher survey grades the state of homework . (ED500012). https://www.metlife.com/aboutus/newsroom/2008/february/metlife-american-teacher-survey-grades-the-state-of-homework/ . Moore, R., Vitale, D., & Stawinoga, N. (2018). The digital divide and educational equity: A look at students with very limited access to electronic devices at home (Insights in Education and Work) . Iowa City: ACT Inc. Mullis, I. V. S., Martin, M. O., Minnich, C. A., Stanco, G. M., Arora, A., & Centurino, V. A. S. (2012). TIMSS 2011 encyclopedia: Education policy and curriculum in mathematics and science (Vols. 1, 2). Chestnut Hill, MA: TIMSS & PIRLS International Study Center, Boston College. https://timssandpirls.bc.edu/timss2011/encyclopedia-timss.html . National Sleep Foundation. (2017). How much sleep do babies and kids need? https://bit.ly/37E157D . Ndebele, M. (2015). Socio-economic factors affecting parents’ involvement in homework: Practices and perceptions from eight Johannesburg public primary schools. Perspectives in Education, 33 (3), 72–91. O’Donnell, M. (2013). Maria Montessori: A critical introduction to key themes and debates . Bloomsbury Academic: Bloomsbury Academic. Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). (2016). PISA 2015 results in focus. https://bit.ly/2T1NUb0 . Perfect, M. M., Levine-Donnerstein, D., Archbold, K., Goodwin, J. L., & Quan, S. F. (2014). The contribution of sleep problems to academic and psychosocial functioning. Psychology in the Schools, 51 (3), 273–295. https://doi.org/10.1002/pits.21746 . Perou, R., Bitsko, R. H., Blumberg, S. J., Pastor, R., Ghandour, R. M., Gfroerer, J. C., et al. (2013). Mental health surveillance among children: United States, 2005–2011. MMWR, 62 (2), 1–35. Pope, D. (2010). Beyond ‘doing school’: From ‘stressed-out’ to ‘engaged in learning.’ Education Canada, 50 (1), 4–8. Pressman, R. M., Sugarman, D. B., Nemon, M. L., Desjarlais, J., Owens, J. A., & Schettini-Evans, A. (2015). Homework and family stress: With consideration of parents’ self-confidence, educational level, and cultural background. The American Journal of Family Therapy, 43 (4), 297–313. https://doi.org/10.1080/01926187.2015.1061407 . Reutzel, D. R., & Juth, S. (2017). Supporting the development of silent reading fluency: An evidence-based framework for the intermediate grades (3–6). International Electronic Journal of Elementary Education, 7 (1), 27–46. Rigby, J. G., Woulfin, S. L., & März, V. (2016). Understanding how structure and agency influence education policy implementation and organizational change. American Journal of Education, 122 (3), 295–302. https://doi.org/10.1086/685849 . Sartain, C., Glenn, L., Jones, J., Merritt, D., (2015). A policy analysis of district homework policies [Doctoral dissertation, Saint Louis University]. ProQuest Dissertations and Theses. https://bit.ly/2vSDxOT . Sisson, H. F. (2015). Academic demands on the social-emotional health of primary and secondary grade students [Master’s thesis, California State University, Sacramento]. Sacramento State Scholarworks. https://bit.ly/2vNyMGq . Tokarski, J. E. (2011). Thoughtful homework or busywork: Impact on student success [Master’s thesis, Dominican University of California]. Dominican Scholar. https://bit.ly/38UrQWw . Trautwein, U., & Köller, O. (2003). The relationship between homework and achievement: Still much of a mystery. Educational Psychology Review, 15 (2), 115–145. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1023460414243 . Trautwein, U., Niggli, A., Schnyder, I., & Lüdtke, O. (2009). Between-teacher differences in homework assignments and the development of students’ homework effort, homework emotions, and achievement. Journal of Educational Psychology, 101 (1), 176–189. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.101.1.176 . University of Minnesota (2002). Involving children in household tasks: Is it worth the effort . https://bit.ly/2TkcUe7 Vatterott, C. (2018). Rethinking homework: Best practices that support diverse needs (2nd ed.). Alexandria: ASCD. Westheimer, K., Abeles, V., & Truebridge, S. (2011). End the race: A facilitation guide and companion resource to the film race to nowhere . Reel Link Films. https://bit.ly/2T1FG2D . Williams, D. L. (2018). The impact of project-based learning on fourth-grade students’ understanding in reading. [Doctoral dissertation, Capella University] ProQuest Dissertations and Theses. https://bit.ly/2SIjvzD . Wolchover, N. (2012, March 30). Too much homework can lower test scores, researchers say. Huffington Post . https://bit.ly/38EdJoi . Zhou, Y., Siu, A. F., & Wai, S. T. (2015). Influences of unhealthy sleep behaviors on the excessive daytime sleepiness and depressive symptoms in children. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 24 (7), 2120–2126. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-014-0013-6 . Download references Author informationAuthors and affiliations. College of Education, California State University, 6000 J Street, Sacramento, CA, 95819, USA Melissa Holland & Gagan Shergill Buckeye Union School District, 5049 Robert J. Mathews Parkway, El Dorado Hills, CA, 95762, USA McKenzie Courtney Institute for Social Research, CSUS, 304 S Street, Suite 333, Sacramento, CA, 95811, USA James Vergara Dry Creek Joint Elementary School District, 8849 Cook Riolo Road, Roseville, CA, 95747, USA Danielle McIntyre Natomas Unified School District, 1901 Arena Blvd, Sacramento, CA, 95834, USA Samantha Nix Panama-Buena Vista Union School District, 4200 Ashe Rd, Bakersfield, CA, 93313, USA Allison Marion You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar ContributionsAll authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by all authors. All authors contributed on this first draft and on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. Corresponding authorCorrespondence to Melissa Holland . Ethics declarationsConflict of interest. All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. Ethics ApprovalEthics approval was granted by the Institutional Review Board at the sponsoring university. This research was approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) at the sponsoring university. Data was collected by the researchers after following the IRB procedures. This study was performed in accordance with the ethical standards as laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments. Consent to ParticipateConsent forms used in this research available upon request addressed to the corresponding author. Access to Data and MaterialAvailable upon request addressed to the corresponding author. Additional informationPublisher's note. Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. Rights and permissionsOpen Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . Reprints and permissions About this articleHolland, M., Courtney, M., Vergara, J. et al. Homework and Children in Grades 3–6: Purpose, Policy and Non-Academic Impact. Child Youth Care Forum 50 , 631–651 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10566-021-09602-8 Download citation Accepted : 05 January 2021 Published : 12 January 2021 Issue Date : August 2021 DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10566-021-09602-8 Share this articleAnyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content: Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article. Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative - Social emotional health
- Elementary students
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
- About the Hub
- Announcements
- Faculty Experts Guide
- Subscribe to the newsletter
Explore by Topic- Arts+Culture
- Politics+Society
- Science+Technology
- Student Life
- University News
- Voices+Opinion
- About Hub at Work
- Gazette Archive
- Benefits+Perks
- Health+Well-Being
- Current Issue
- About the Magazine
- Past Issues
- Support Johns Hopkins Magazine
- Subscribe to the Magazine
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.  Credit: August de Richelieu Does homework still have value? A Johns Hopkins education expert weighs inJoyce epstein, co-director of the center on school, family, and community partnerships, discusses why homework is essential, how to maximize its benefit to learners, and what the 'no-homework' approach gets wrong. By Vicky Hallett The necessity of homework has been a subject of debate since at least as far back as the 1890s, according to Joyce L. Epstein , co-director of the Center on School, Family, and Community Partnerships at Johns Hopkins University. "It's always been the case that parents, kids—and sometimes teachers, too—wonder if this is just busy work," Epstein says. But after decades of researching how to improve schools, the professor in the Johns Hopkins School of Education remains certain that homework is essential—as long as the teachers have done their homework, too. The National Network of Partnership Schools , which she founded in 1995 to advise schools and districts on ways to improve comprehensive programs of family engagement, has developed hundreds of improved homework ideas through its Teachers Involve Parents in Schoolwork program. For an English class, a student might interview a parent on popular hairstyles from their youth and write about the differences between then and now. Or for science class, a family could identify forms of matter over the dinner table, labeling foods as liquids or solids. These innovative and interactive assignments not only reinforce concepts from the classroom but also foster creativity, spark discussions, and boost student motivation. "We're not trying to eliminate homework procedures, but expand and enrich them," says Epstein, who is packing this research into a forthcoming book on the purposes and designs of homework. In the meantime, the Hub couldn't wait to ask her some questions: What kind of homework training do teachers typically get?Future teachers and administrators really have little formal training on how to design homework before they assign it. This means that most just repeat what their teachers did, or they follow textbook suggestions at the end of units. For example, future teachers are well prepared to teach reading and literacy skills at each grade level, and they continue to learn to improve their teaching of reading in ongoing in-service education. By contrast, most receive little or no training on the purposes and designs of homework in reading or other subjects. It is really important for future teachers to receive systematic training to understand that they have the power, opportunity, and obligation to design homework with a purpose. Why do students need more interactive homework?If homework assignments are always the same—10 math problems, six sentences with spelling words—homework can get boring and some kids just stop doing their assignments, especially in the middle and high school years. When we've asked teachers what's the best homework you've ever had or designed, invariably we hear examples of talking with a parent or grandparent or peer to share ideas. To be clear, parents should never be asked to "teach" seventh grade science or any other subject. Rather, teachers set up the homework assignments so that the student is in charge. It's always the student's homework. But a good activity can engage parents in a fun, collaborative way. Our data show that with "good" assignments, more kids finish their work, more kids interact with a family partner, and more parents say, "I learned what's happening in the curriculum." It all works around what the youngsters are learning. Is family engagement really that important?At Hopkins, I am part of the Center for Social Organization of Schools , a research center that studies how to improve many aspects of education to help all students do their best in school. One thing my colleagues and I realized was that we needed to look deeply into family and community engagement. There were so few references to this topic when we started that we had to build the field of study. When children go to school, their families "attend" with them whether a teacher can "see" the parents or not. So, family engagement is ever-present in the life of a school. My daughter's elementary school doesn't assign homework until third grade. What's your take on "no homework" policies?There are some parents, writers, and commentators who have argued against homework, especially for very young children. They suggest that children should have time to play after school. This, of course is true, but many kindergarten kids are excited to have homework like their older siblings. If they give homework, most teachers of young children make assignments very short—often following an informal rule of 10 minutes per grade level. "No homework" does not guarantee that all students will spend their free time in productive and imaginative play. Some researchers and critics have consistently misinterpreted research findings. They have argued that homework should be assigned only at the high school level where data point to a strong connection of doing assignments with higher student achievement . However, as we discussed, some students stop doing homework. This leads, statistically, to results showing that doing homework or spending more minutes on homework is linked to higher student achievement. If slow or struggling students are not doing their assignments, they contribute to—or cause—this "result." Teachers need to design homework that even struggling students want to do because it is interesting. Just about all students at any age level react positively to good assignments and will tell you so. Did COVID change how schools and parents view homework?Within 24 hours of the day school doors closed in March 2020, just about every school and district in the country figured out that teachers had to talk to and work with students' parents. This was not the same as homeschooling—teachers were still working hard to provide daily lessons. But if a child was learning at home in the living room, parents were more aware of what they were doing in school. One of the silver linings of COVID was that teachers reported that they gained a better understanding of their students' families. We collected wonderfully creative examples of activities from members of the National Network of Partnership Schools. I'm thinking of one art activity where every child talked with a parent about something that made their family unique. Then they drew their finding on a snowflake and returned it to share in class. In math, students talked with a parent about something the family liked so much that they could represent it 100 times. Conversations about schoolwork at home was the point. How did you create so many homework activities via the Teachers Involve Parents in Schoolwork program?We had several projects with educators to help them design interactive assignments, not just "do the next three examples on page 38." Teachers worked in teams to create TIPS activities, and then we turned their work into a standard TIPS format in math, reading/language arts, and science for grades K-8. Any teacher can use or adapt our prototypes to match their curricula. Overall, we know that if future teachers and practicing educators were prepared to design homework assignments to meet specific purposes—including but not limited to interactive activities—more students would benefit from the important experience of doing their homework. And more parents would, indeed, be partners in education. Posted in Voices+Opinion You might also likeNews network. - Johns Hopkins Magazine
- Get Email Updates
- Submit an Announcement
- Submit an Event
- Privacy Statement
- Accessibility
Discover JHU- About the University
- Schools & Divisions
- Academic Programs
- Plan a Visit
- my.JohnsHopkins.edu
- © 2024 Johns Hopkins University . All rights reserved.
- University Communications
- 3910 Keswick Rd., Suite N2600, Baltimore, MD
- X Facebook LinkedIn YouTube Instagram
Is Homework Good for Kids? Here’s What the Research SaysA s kids return to school, debate is heating up once again over how they should spend their time after they leave the classroom for the day. The no-homework policy of a second-grade teacher in Texas went viral last week , earning praise from parents across the country who lament the heavy workload often assigned to young students. Brandy Young told parents she would not formally assign any homework this year, asking students instead to eat dinner with their families, play outside and go to bed early. But the question of how much work children should be doing outside of school remains controversial, and plenty of parents take issue with no-homework policies, worried their kids are losing a potential academic advantage. Here’s what you need to know: For decades, the homework standard has been a “10-minute rule,” which recommends a daily maximum of 10 minutes of homework per grade level. Second graders, for example, should do about 20 minutes of homework each night. High school seniors should complete about two hours of homework each night. The National PTA and the National Education Association both support that guideline. But some schools have begun to give their youngest students a break. A Massachusetts elementary school has announced a no-homework pilot program for the coming school year, lengthening the school day by two hours to provide more in-class instruction. “We really want kids to go home at 4 o’clock, tired. We want their brain to be tired,” Kelly Elementary School Principal Jackie Glasheen said in an interview with a local TV station . “We want them to enjoy their families. We want them to go to soccer practice or football practice, and we want them to go to bed. And that’s it.” A New York City public elementary school implemented a similar policy last year, eliminating traditional homework assignments in favor of family time. The change was quickly met with outrage from some parents, though it earned support from other education leaders. New solutions and approaches to homework differ by community, and these local debates are complicated by the fact that even education experts disagree about what’s best for kids. The research The most comprehensive research on homework to date comes from a 2006 meta-analysis by Duke University psychology professor Harris Cooper, who found evidence of a positive correlation between homework and student achievement, meaning students who did homework performed better in school. The correlation was stronger for older students—in seventh through 12th grade—than for those in younger grades, for whom there was a weak relationship between homework and performance. Cooper’s analysis focused on how homework impacts academic achievement—test scores, for example. His report noted that homework is also thought to improve study habits, attitudes toward school, self-discipline, inquisitiveness and independent problem solving skills. On the other hand, some studies he examined showed that homework can cause physical and emotional fatigue, fuel negative attitudes about learning and limit leisure time for children. At the end of his analysis, Cooper recommended further study of such potential effects of homework. Despite the weak correlation between homework and performance for young children, Cooper argues that a small amount of homework is useful for all students. Second-graders should not be doing two hours of homework each night, he said, but they also shouldn’t be doing no homework. Not all education experts agree entirely with Cooper’s assessment. Cathy Vatterott, an education professor at the University of Missouri-St. Louis, supports the “10-minute rule” as a maximum, but she thinks there is not sufficient proof that homework is helpful for students in elementary school. “Correlation is not causation,” she said. “Does homework cause achievement, or do high achievers do more homework?” Vatterott, the author of Rethinking Homework: Best Practices That Support Diverse Needs , thinks there should be more emphasis on improving the quality of homework tasks, and she supports efforts to eliminate homework for younger kids. “I have no concerns about students not starting homework until fourth grade or fifth grade,” she said, noting that while the debate over homework will undoubtedly continue, she has noticed a trend toward limiting, if not eliminating, homework in elementary school. The issue has been debated for decades. A TIME cover in 1999 read: “Too much homework! How it’s hurting our kids, and what parents should do about it.” The accompanying story noted that the launch of Sputnik in 1957 led to a push for better math and science education in the U.S. The ensuing pressure to be competitive on a global scale, plus the increasingly demanding college admissions process, fueled the practice of assigning homework. “The complaints are cyclical, and we’re in the part of the cycle now where the concern is for too much,” Cooper said. “You can go back to the 1970s, when you’ll find there were concerns that there was too little, when we were concerned about our global competitiveness.” Cooper acknowledged that some students really are bringing home too much homework, and their parents are right to be concerned. “A good way to think about homework is the way you think about medications or dietary supplements,” he said. “If you take too little, they’ll have no effect. If you take too much, they can kill you. If you take the right amount, you’ll get better.” More Must-Reads from TIME- Breaking Down the 2024 Election Calendar
- Heman Bekele Is TIME’s 2024 Kid of the Year
- The Reintroduction of Kamala Harris
- What a $129 Frying Pan Says About America’s Eating Habits
- A Battle Over Fertility Law in China
- The 1 Heart-Health Habit You Should Start When You’re Young
- Cuddling Might Help You Get Better Sleep
- The 50 Best Romance Novels to Read Right Now
Write to Katie Reilly at [email protected]  What’s the Right Amount of Homework?Decades of research show that homework has some benefits, especially for students in middle and high school—but there are risks to assigning too much. Many teachers and parents believe that homework helps students build study skills and review concepts learned in class. Others see homework as disruptive and unnecessary, leading to burnout and turning kids off to school. Decades of research show that the issue is more nuanced and complex than most people think: Homework is beneficial, but only to a degree. Students in high school gain the most, while younger kids benefit much less. The National PTA and the National Education Association support the “ 10-minute homework guideline ”—a nightly 10 minutes of homework per grade level. But many teachers and parents are quick to point out that what matters is the quality of the homework assigned and how well it meets students’ needs, not the amount of time spent on it. The guideline doesn’t account for students who may need to spend more—or less—time on assignments. In class, teachers can make adjustments to support struggling students, but at home, an assignment that takes one student 30 minutes to complete may take another twice as much time—often for reasons beyond their control. And homework can widen the achievement gap, putting students from low-income households and students with learning disabilities at a disadvantage. However, the 10-minute guideline is useful in setting a limit: When kids spend too much time on homework, there are real consequences to consider. Small Benefits for Elementary StudentsAs young children begin school, the focus should be on cultivating a love of learning, and assigning too much homework can undermine that goal. And young students often don’t have the study skills to benefit fully from homework, so it may be a poor use of time (Cooper, 1989 ; Cooper et al., 2006 ; Marzano & Pickering, 2007 ). A more effective activity may be nightly reading, especially if parents are involved. The benefits of reading are clear: If students aren’t proficient readers by the end of third grade, they’re less likely to succeed academically and graduate from high school (Fiester, 2013 ). For second-grade teacher Jacqueline Fiorentino, the minor benefits of homework did not outweigh the potential drawback of turning young children against school at an early age, so she experimented with dropping mandatory homework. “Something surprising happened: They started doing more work at home,” Fiorentino writes . “This inspiring group of 8-year-olds used their newfound free time to explore subjects and topics of interest to them.” She encouraged her students to read at home and offered optional homework to extend classroom lessons and help them review material. Moderate Benefits for Middle School StudentsAs students mature and develop the study skills necessary to delve deeply into a topic—and to retain what they learn—they also benefit more from homework. Nightly assignments can help prepare them for scholarly work, and research shows that homework can have moderate benefits for middle school students (Cooper et al., 2006 ). Recent research also shows that online math homework, which can be designed to adapt to students’ levels of understanding, can significantly boost test scores (Roschelle et al., 2016 ). There are risks to assigning too much, however: A 2015 study found that when middle school students were assigned more than 90 to 100 minutes of daily homework, their math and science test scores began to decline (Fernández-Alonso, Suárez-Álvarez, & Muñiz, 2015 ). Crossing that upper limit can drain student motivation and focus. The researchers recommend that “homework should present a certain level of challenge or difficulty, without being so challenging that it discourages effort.” Teachers should avoid low-effort, repetitive assignments, and assign homework “with the aim of instilling work habits and promoting autonomous, self-directed learning.” In other words, it’s the quality of homework that matters, not the quantity. Brian Sztabnik, a veteran middle and high school English teacher, suggests that teachers take a step back and ask themselves these five questions : - How long will it take to complete?
- Have all learners been considered?
- Will an assignment encourage future success?
- Will an assignment place material in a context the classroom cannot?
- Does an assignment offer support when a teacher is not there?
More Benefits for High School Students, but Risks as WellBy the time they reach high school, students should be well on their way to becoming independent learners, so homework does provide a boost to learning at this age, as long as it isn’t overwhelming (Cooper et al., 2006 ; Marzano & Pickering, 2007 ). When students spend too much time on homework—more than two hours each night—it takes up valuable time to rest and spend time with family and friends. A 2013 study found that high school students can experience serious mental and physical health problems, from higher stress levels to sleep deprivation, when assigned too much homework (Galloway, Conner, & Pope, 2013 ). Homework in high school should always relate to the lesson and be doable without any assistance, and feedback should be clear and explicit. Teachers should also keep in mind that not all students have equal opportunities to finish their homework at home, so incomplete homework may not be a true reflection of their learning—it may be more a result of issues they face outside of school. They may be hindered by issues such as lack of a quiet space at home, resources such as a computer or broadband connectivity, or parental support (OECD, 2014 ). In such cases, giving low homework scores may be unfair. Since the quantities of time discussed here are totals, teachers in middle and high school should be aware of how much homework other teachers are assigning. It may seem reasonable to assign 30 minutes of daily homework, but across six subjects, that’s three hours—far above a reasonable amount even for a high school senior. Psychologist Maurice Elias sees this as a common mistake: Individual teachers create homework policies that in aggregate can overwhelm students. He suggests that teachers work together to develop a school-wide homework policy and make it a key topic of back-to-school night and the first parent-teacher conferences of the school year. Parents Play a Key RoleHomework can be a powerful tool to help parents become more involved in their child’s learning (Walker et al., 2004 ). It can provide insights into a child’s strengths and interests, and can also encourage conversations about a child’s life at school. If a parent has positive attitudes toward homework, their children are more likely to share those same values, promoting academic success. But it’s also possible for parents to be overbearing, putting too much emphasis on test scores or grades, which can be disruptive for children (Madjar, Shklar, & Moshe, 2015 ). Parents should avoid being overly intrusive or controlling—students report feeling less motivated to learn when they don’t have enough space and autonomy to do their homework (Orkin, May, & Wolf, 2017 ; Patall, Cooper, & Robinson, 2008 ; Silinskas & Kikas, 2017 ). So while homework can encourage parents to be more involved with their kids, it’s important to not make it a source of conflict. Connect with us to understand how we can help you.State* Andhra Pradesh Chhattisgarh Delhi Gujarat Haryana Himachal Pradesh Karnataka Madhya Pradesh Maharashtra Odisha Punjab Rajasthan Tamil Nadu Telangana Uttar Pradesh Uttarakhand Others - Solution Products* School Loans Smart Learning Maths and Science labs Digital Smart Classroom School ERP and Fee Management Integrated Curriculum Solution School Bus Insurance School Uniform
- I authorize Varthana to connect with me over call and WhatsApp overriding my registration with NDNC
 - Board of Directors
- Our Investors
- School Solution
- VCARE – Varthana care for you
 How To Create An Effective Homework Policy In School? - by Team Varthana
- Posted on January 12, 2024
- in Education
Homework, for us, brings to mind endless writing without a clear reason, often leading to missing out on evening games. We didn’t enjoy it in school and never really questioned why. Since homework is an integral part of the educational experience, providing students with opportunities to reinforce learning, develop essential skills, and cultivate a sense of responsibility is the criteria. However, creating an effective homework policy requires careful consideration, especially in the diverse and dynamic educational landscape of India. A homework policy is a set of guidelines, rules, and principles established by educational institutions to govern the assigning, completion, and evaluation of homework assignments. This policy outlines the expectations and responsibilities of students, teachers, and parents regarding homework. It serves as a framework to ensure that homework is purposeful, relevant, and contributes to the overall learning objectives of the educational institution. What are the Key Components of a Homework Policy in School?1. purpose of homework and the educational philosophy:. This includes reinforcing classroom learning, developing independent study skills, and fostering a sense of responsibility. 2. Guidelines for Homework Assignment:Such as complexity, relevance to the curriculum, and differentiation to accommodate varying student abilities. 3. Time Allocation:Specifies the recommended time students should spend on homework each day, including extracurricular activities and rest. 4. Parental Involvement:Supporting their children with homework, communication channels between teachers and parents, and a conducive environment for learning at home. 5. Feedback and Evaluation:Providing timely and constructive feedback on homework assignments, emphasizing feedback as a tool for improvement. 6. Technology Integration:Guidelines for the use of digital tools and ensuring accessibility for all students. 7. Flexibility and Accommodations:Considering the diverse needs and circumstances, include allowing for alternative assignments or extended deadlines when necessary. 8. Collaborative Learning:Through group projects, peer reviews, or other cooperative activities that foster teamwork and communication skills . Also Read: 7 techniques to boost communication skills for teachers and administrators 9. Alignment with Curriculum:Ensures that homework assignments align with the broader curriculum goals and contribute to the mastery of key concepts and skills. 10. Cultural Sensitivity:Acknowledges cultural diversity and ensures that homework assignments are culturally sensitive and inclusive.  Also Read: Leveraging Tech: 5-Step Guide for Teachers & Parents to Support Students with Special Needs Homework Policies for Each Phase of School EducationHomework policy for kindergarten:, 1. purposeful play and exploration:. Homework in kindergarten should emphasize purposeful play and exploration. Activities may involve simple art projects, interactive games, or reading together with parents to foster a love for learning. 2. Limited Duration:Keep homework sessions short, typically not exceeding 10-15 minutes. Kindergarten students have short attention spans, and the emphasis should be on enjoyable and age-appropriate learning experiences. 3. Parental Engagement:Encourage parents to engage with their child during homework time, making it a positive and bonding experience. Homework may involve activities that promote fine motor skills, creativity, and basic literacy. Homework Policy for Elementary School:1. balanced subjects:. Assign homework that covers a range of subjects, supporting a well-rounded education. This can include math problems, reading assignments, science experiments, and simple research projects. 2. Development of Basic Skills:Homework should focus on developing foundational skills, such as reading comprehension, basic math operations, and written expression. It provides opportunities for independent practice and reinforces what is taught in class. 3. Parental Support:Encourage parents to provide support as needed, fostering a positive home-learning environment. Homework can serve as a communication tool between teachers and parents, keeping them informed about what is happening in the classroom. Homework Policy for Primary School:1. subject-specific assignments:. As students move into primary school, homework may become more subject-specific. Assignments can include math exercises, reading comprehension tasks, science projects, and social studies research. 2. Preparation for Higher Grades:Homework serves as preparation for higher grades by introducing students to more structured assignments. It encourages time management and responsibility while reinforcing the importance of daily practice. 3. Feedback and Assessment:Use homework for formative assessment , providing constructive feedback to guide students’ progress. This feedback loop helps identify areas of strength and areas needing improvement. Also Read: 5 formative assessment techniques for real time feedback Homework Policy for Secondary School:1. diverse subjects and specializations:. Homework in secondary school becomes more diverse as students take on different subjects and potentially specialize in certain areas. Assignments may include essays, research projects, and problem-solving tasks. 2. Preparation for Exams:Homework plays a crucial role in preparing students for exams. It reinforces learning, allows for deeper exploration of topics, and helps students develop study strategies for upcoming assessments. 3. Independent Learning:Encourage independent learning skills. Secondary school students should be capable of managing their workload, researching independently, and applying critical thinking skills to their assignments. Homework Policy for High School:1. advanced academic rigor:. High school homework involves advanced academic rigor, often requiring critical analysis, research, and synthesis of information. Assignments may be more extensive and may contribute to overall course grades. 2. College and Career Preparation:Homework in high school prepares students for college or vocational pursuits. It emphasizes skills such as research, time management, and effective communication, essential for success in higher education and future careers. 3. Balance and Well-Being:Acknowledge the increased academic demands and extracurricular commitments in high school. Strive for a balance that promotes student well-being, considering the importance of mental health and a holistic educational experience. Homework Policy for Pre-University College (PUC):1. academic specialization:. Homework in PUC is often more specialized, focusing on subjects relevant to the chosen course of study. Assignments may be research-intensive, requiring students to delve deeply into their chosen field. 2. Critical Thinking and Research:Emphasize critical thinking and research skills. PUC homework should challenge students to think analytically, apply theoretical knowledge to practical scenarios, and engage in independent scholarly inquiry. 3. Transition to Higher Education:Homework in PUC serves as a bridge to higher education. It helps students adapt to the expectations of college-level coursework, where independent research and self-directed learning become increasingly important. 4. Preparation for Examinations:PUC homework is closely tied to exam preparation, helping students develop effective study habits, time management skills, and a comprehensive understanding of the subjects they are studying. Tips for Creating an Effective Homework Policy for Students1. understanding cultural dynamics:. A homework policy should be sensitive to the diversities, acknowledging that students may come from varied socio-economic backgrounds and have different levels of support at home. Tailoring homework assignments to be inclusive and culturally relevant ensures that all students can engage meaningfully with the material. 2. Balancing Academic Rigor and Well-being:While academic excellence is a priority, it’s essential to strike a balance between challenging students and safeguarding their mental health. The pressure-cooker environment of education can be overwhelming, so a well-crafted homework policy should consider the recommended guidelines for the amount of homework assigned, ensuring it aligns with developmental needs and does not contribute to excessive stress. 3. Clear Communication with Parents:Transparent communication with parents is crucial for the success of any homework policy. Schools should clearly articulate the purpose of homework, its role in the learning process, and the expected level of parental involvement . Regular updates and parent-teacher meetings can facilitate a collaborative approach, fostering a supportive learning environment at home. Also Read: 5 formative assessment techniques for real-time feedback 4. Differentiated Homework Assignments: Recognizing the diverse learning styles and abilities of students, teachers should design homework that allows for differentiation. Tailoring assignments to cater to varying levels of proficiency ensures that each student is appropriately challenged and has the opportunity to succeed . Also Read: Tips for Parents to help their children succeed in school 5. Aligning Homework with Curriculum Goals:The homework policy should be closely aligned with the broader curriculum goals of the school. Assignments should reinforce classroom learning, providing students with opportunities to apply theoretical knowledge in practical contexts. This alignment ensures that homework serves as a meaningful extension of the educational experience rather than a disconnected task. 6. Promoting Self-directed Learning:A well-designed homework policy encourages self-directed learning and critical thinking. Assignments that prompt students to explore topics independently, ask questions, and connect learning across subjects foster a sense of curiosity and intellectual engagement. 7. Incorporating Technology Thoughtfully:In the digital age, incorporating technology into homework assignments can enhance the learning experience. However, it’s essential to do so thoughtfully, considering accessibility issues and ensuring that technology complements the learning objectives rather than becoming a distraction. 8. Providing Timely and Constructive Feedback:Feedback is a crucial component of the learning process. Teachers should establish a system for providing timely and constructive feedback on homework assignments. This not only helps students understand their strengths and areas for improvement but also fosters a culture of continuous learning. 9. Encouraging Collaborative Learning:Homework assignments that encourage collaboration can be beneficial in schools. Group projects, peer reviews, and cooperative learning activities promote teamwork, communication skills, and a sense of shared responsibility. 10. Flexibility and Adaptability:Recognizing that students may face unforeseen challenges at home or in their personal lives, a flexible and adaptable homework policy allows for accommodations when needed. Teachers should be understanding and responsive to individual student needs, ensuring that the policy is a tool for support rather than a source of additional stress. Also Read: How can school leaders help parents get to know the school staff better? A well-designed homework policy is a valuable tool for creating a positive and effective learning environment. In all phases of school education, it’s essential to consider the developmental needs of students, provide clear communication between teachers and parents, and maintain a balance that promotes both academic success and overall well-being. Homework should be purposeful, aligned with educational goals, and conducive to the development of lifelong learning skills. Additionally, an effective homework policy contributes to the overall well-being of students by striking a balance between academic rigor and the importance of a holistic educational experience. Latest BlogsRajasthan graduate revives father’s legacy by building a school that uplifts society, august 23, 2024, how is project-based learning helpful for students, july 11, 2024, building a brighter future: how parent involvement boosts student achievement, july 12, 2024, most viewed blogs, this software engineer from up now leads a school, bringing quality education to every village child, level up learning: how to improve memory for studying, july 15, 2024, bloom’s taxonomy: your guide to designing powerful learning activities, july 17, 2024. - Activities (9)
- AI in Education (1)
- Announcement (1)
- Career Guidance (11)
- Classroom Management (35)
- Courses (2)
- Customer stories (130)
- Customer Story (3)
- Diversity in Education (12)
- Education (370)
- Education Awareness (6)
- Examination (3)
- Festive Learning (1)
- Financial Literacy (1)
- Mental health (15)
- Parent's Guide (13)
- Parents engagement (1)
- School finance (35)
- School Guide (20)
- School Infrastructure (11)
- School Leadership (19)
- School Loan (33)
- School Management (4)
- STEM Learning (11)
- Student Apps (1)
- Student loan (1)
- Student Productivity (11)
- teacher training (1)
- Teacher's Guide (25)
- Teachers training (2)
- Technology in Education (17)
- Uncategorized (7)
Dear Varthana Customer, We have an information update regarding your loan/s with us. Your details are submitted successfully. You can see how this popup was set up in our step-by-step guide: https://wppopupmaker.com/guides/auto-opening-announcement-popups/ - Please select:
- Return to page
- Aims, Vision & Values
- Equality Information and Objectives
- Headteacher's Welcome
- OFSTED Report
- School Development Priorities
- School Performance
- School Staff
- Symphony Learning Trust
- Teacher Training
- Financial Information
- GDPR & Privacy Notices
- Inclusion & SEND
- Mental Health & Wellbeing
- More-Able Learners
- Open Days Autumn 2023
- Orchard Primary School Food Bank
- Pupil Premium
- Remote Education
- Test Application
- The School Day
- Latest News
- Letters Home
- School Closure
- School Newsletters
- Yearly Overview
- Assessment Information
- Code of Conduct
- Extra-Curricular Opportunities
- Parents' Association
- Prevent Strategy
- Questionnaires & Parent Review
- Safeguarding
- School Meals
- Working With Parents
- Wrap-Around Childcare
- British Values Statement
- Curriculum Provision
- Character Education Statement
- Phonics & Reading
- Sports Premium & Sporting Provision
- ABA - Anti-Bullying Ambassadors
- Pupil Leadership Council
- School Council
- Concerns and Complaints
 Select from: « Back to latest news Homework Policy (2023) Click here to download this policyAims of the policy Through implementation of this policy, we aim to: - Give pupils the opportunity to extend their learning in areas of personal interest
- Ensure a consistent approach throughout the school
- To encourage children to develop the confidence, independence, self-discipline and motivation needed to study on their own and prepare them for the next phase of education
- To make set homework relevant and meaningful for the child linked to work done at school
- Make expectations about homework clear to children, parents and other carers
- Provide opportunities for parents and children to work together, thereby, fostering an effective partnership between home and school
« Back to all policies Sorry. You need to upgrade your browserYou are using internet explorer 8. This is considered an out of date browser. This website has been developed with modern browsers in mind to allow it to display at its best in a wide variety of viewing situations - including mobile viewing. But we haven't supported older browsers like IE8. Please upgrade to the latest version of Internet Explorer - or try Mozilla Firefox or Google Chrome. Both are excellent browsers.  © 2009 - 2024 Orchard Community Primary School. All rights reserved. Home Site map Privacy Policy & Cookies Admin Primary School website design by Peter Bourne Communications  |


































COMMENTS
Learn how to assign homework that is relevant, challenging, and meaningful for students. Find out how homework can help teachers differentiate learning, increase student participation, and build lifelong skills.
August 2017. Following an established REL Northeast & Islands research protocol, we conducted a search for recent research on homework policies and practices. We focused on identifying resources that specifically addressed research on policies and practices for homework for various grade levels based on its impact on student achievement.
Adams Homework Policy Ensuring that homework is beneficial requires a balanced approach and clear communication between the student, the teacher and the family. Homework that is assigned should be purposeful, appropriate to the age level of the student, and tailored to the needs of the child and their family. Reasons for assigning homework include practicing […]
Build Flexibility Into Your Homework Policy EducationWorld is pleased to present this professional development resource shared by Dr. Jane Bluestein, an expert in relationship-building, positive school climate and effective instruction.. Any teacher who has ever given out homework has certainly encountered a student the next day saying, "I don't have my assignment."
Creating homework policies is part of educational leadership in the classroom. Although homework must focus on helping students achieve, it also needs to clearly state the expectations and give details about the benefits and consequences of different actions. By giving a clear policy from the first day of school, the students will know what to ...
The school administrator will: • Review the established homework policy with the teaching staff. • Ensure that the teaching staff monitors and follows guidelines above. • Develop specific guidelines within the framework of the general policy where needed. • Provide professional development workshops and/or informational materials regarding
A good homework policy creates transparency for parents. It helps them to understand the value the school places on homework and what the learning objectives are. If parents understand this, it will help set a foundation for them to be engaged in their child's education. #4 Gives students a routine and creates good habits.
Learn how to create a clear and effective homework policy for your school, with examples and tips. Find out the purpose, definition, time, feedback and review of homework.
Schools and districts should develop homework policies that emphasize strategic, rigorous homework In many cases, the current debate over homework is short-sighted. Many arguments focus on whether ...
How does homework affect student well-being and achievement? This article explores the history, research, and challenges of homework policies in schools, and offers some suggestions for rethinking homework practices.
With the beginning of the school year right around the corner, this is the perfect time to start thinking about changing up your homework policy. Leave a comment down below about your about your ...
Background Increasing academic demands, including larger amounts of assigned homework, is correlated with various challenges for children. While homework stress in middle and high school has been studied, research evidence is scant concerning the effects of homework on elementary-aged children. Objective The objective of this study was to understand rater perception of the purpose of homework ...
The necessity of homework has been a subject of debate since at least as far back as the 1890s, according to Joyce L. Epstein, co-director of the Center on School, Family, and Community Partnerships at Johns Hopkins University. "It's always been the case that parents, kids—and sometimes teachers, too—wonder if this is just busy work ...
A s kids return to school, debate is heating up once again over how they should spend their time after they leave the classroom for the day.. The no-homework policy of a second-grade teacher in ...
Genesee Hill Elementary Homework Policy Because we know… That homework can be a valuable way to extend, reinforce and refine learning; That reading is the best way to become a better reader; That writing supports reading and helps develop critical thinking skills; That knowing math facts at a level of automaticity (meaning, instant recall) provides […]
The school's Homework Policy should be made available to the school community, particularly at the time of enrolment. Parents/caregivers of students experiencing difficulties completing homework need to be confident that these concerns can be discussed with the teacher, and that guidance and assistance will be provided. ...
Too much, however, is harmful. And homework has a greater positive effect on students in secondary school (grades 7-12) than those in elementary. "Every child should be doing homework, but the ...
He suggests that teachers work together to develop a school-wide homework policy and make it a key topic of back-to-school night and the first parent-teacher conferences of the school year. Parents Play a Key Role. Homework can be a powerful tool to help parents become more involved in their child's learning (Walker et al., 2004). It can ...
the teacher's homework policies and practices but also as ways to communicate to their children that they ... (2003). Interactive homework in middle schools: Effects on family involvement and science achievement. Journal of Educational Research, 96, 323-338. Xu, J. (2004). Family help and homework management in urban and rural secondary ...
Homework Policies for Each Phase of School Education Homework Policy for Kindergarten: 1. Purposeful Play and Exploration: Homework in kindergarten should emphasize purposeful play and exploration. Activities may involve simple art projects, interactive games, or reading together with parents to foster a love for learning. 2. Limited Duration:
Homework Policies for School Districts, Schools, and Classrooms. Show details Hide details. Harris Cooper. The Battle Over Homework: Common Ground for Administrators, Teachers, and Parents. 2007. SAGE Knowledge. Book chapter . The Homework Assignment. Show details Hide details. Harris Cooper.
Homework Policy (2023) Click here to download this policy. Aims of the policy. Through implementation of this policy, we aim to: Give pupils the opportunity to extend their learning in areas of personal interest. Ensure a consistent approach throughout the school. To encourage children to develop the confidence, independence, self-discipline ...
Primary school. Shadwell Primary School in Leeds has a homework policy that covers: When pupils take books home for reading. How long they should spend reading at home. English and maths homework. Spelling and times tables expectations. Additional half-termly homework tasks, such as a learning log and key instant recall facts.