Is it time to get rid of homework? Mental health experts weigh in.

It's no secret that kids hate homework. And as students grapple with an ongoing pandemic that has had a wide range of mental health impacts, is it time schools start listening to their pleas about workloads?
Some teachers are turning to social media to take a stand against homework.
Tiktok user @misguided.teacher says he doesn't assign it because the "whole premise of homework is flawed."
For starters, he says, he can't grade work on "even playing fields" when students' home environments can be vastly different.
"Even students who go home to a peaceful house, do they really want to spend their time on busy work? Because typically that's what a lot of homework is, it's busy work," he says in the video that has garnered 1.6 million likes. "You only get one year to be 7, you only got one year to be 10, you only get one year to be 16, 18."
Mental health experts agree heavy workloads have the potential do more harm than good for students, especially when taking into account the impacts of the pandemic. But they also say the answer may not be to eliminate homework altogether.
Emmy Kang, mental health counselor at Humantold , says studies have shown heavy workloads can be "detrimental" for students and cause a "big impact on their mental, physical and emotional health."
"More than half of students say that homework is their primary source of stress, and we know what stress can do on our bodies," she says, adding that staying up late to finish assignments also leads to disrupted sleep and exhaustion.
Cynthia Catchings, a licensed clinical social worker and therapist at Talkspace , says heavy workloads can also cause serious mental health problems in the long run, like anxiety and depression.
And for all the distress homework can cause, it's not as useful as many may think, says Dr. Nicholas Kardaras, a psychologist and CEO of Omega Recovery treatment center.
"The research shows that there's really limited benefit of homework for elementary age students, that really the school work should be contained in the classroom," he says.
For older students, Kang says, homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night.
"Most students, especially at these high achieving schools, they're doing a minimum of three hours, and it's taking away time from their friends, from their families, their extracurricular activities. And these are all very important things for a person's mental and emotional health."
Catchings, who also taught third to 12th graders for 12 years, says she's seen the positive effects of a no-homework policy while working with students abroad.
"Not having homework was something that I always admired from the French students (and) the French schools, because that was helping the students to really have the time off and really disconnect from school," she says.
The answer may not be to eliminate homework completely but to be more mindful of the type of work students take home, suggests Kang, who was a high school teacher for 10 years.
"I don't think (we) should scrap homework; I think we should scrap meaningless, purposeless busy work-type homework. That's something that needs to be scrapped entirely," she says, encouraging teachers to be thoughtful and consider the amount of time it would take for students to complete assignments.

The pandemic made the conversation around homework more crucial
Mindfulness surrounding homework is especially important in the context of the past two years. Many students will be struggling with mental health issues that were brought on or worsened by the pandemic , making heavy workloads even harder to balance.
"COVID was just a disaster in terms of the lack of structure. Everything just deteriorated," Kardaras says, pointing to an increase in cognitive issues and decrease in attention spans among students. "School acts as an anchor for a lot of children, as a stabilizing force, and that disappeared."
But even if students transition back to the structure of in-person classes, Kardaras suspects students may still struggle after two school years of shifted schedules and disrupted sleeping habits.
"We've seen adults struggling to go back to in-person work environments from remote work environments. That effect is amplified with children because children have less resources to be able to cope with those transitions than adults do," he explains.
'Get organized' ahead of back-to-school
In order to make the transition back to in-person school easier, Kang encourages students to "get good sleep, exercise regularly (and) eat a healthy diet."
To help manage workloads, she suggests students "get organized."
"There's so much mental clutter up there when you're disorganized. ... Sitting down and planning out their study schedules can really help manage their time," she says.
Breaking up assignments can also make things easier to tackle.
"I know that heavy workloads can be stressful, but if you sit down and you break down that studying into smaller chunks, they're much more manageable."
If workloads are still too much, Kang encourages students to advocate for themselves.
"They should tell their teachers when a homework assignment just took too much time or if it was too difficult for them to do on their own," she says. "It's good to speak up and ask those questions. Respectfully, of course, because these are your teachers. But still, I think sometimes teachers themselves need this feedback from their students."
More: Some teachers let their students sleep in class. Here's what mental health experts say.
More: Some parents are slipping young kids in for the COVID-19 vaccine, but doctors discourage the move as 'risky'
- Future Students
- Current Students
- Faculty/Staff

News and Media
- News & Media Home
- Research Stories
- School's In
- In the Media
You are here
More than two hours of homework may be counterproductive, research suggests.

A Stanford education researcher found that too much homework can negatively affect kids, especially their lives away from school, where family, friends and activities matter. "Our findings on the effects of homework challenge the traditional assumption that homework is inherently good," wrote Denise Pope , a senior lecturer at the Stanford Graduate School of Education and a co-author of a study published in the Journal of Experimental Education . The researchers used survey data to examine perceptions about homework, student well-being and behavioral engagement in a sample of 4,317 students from 10 high-performing high schools in upper-middle-class California communities. Along with the survey data, Pope and her colleagues used open-ended answers to explore the students' views on homework. Median household income exceeded $90,000 in these communities, and 93 percent of the students went on to college, either two-year or four-year. Students in these schools average about 3.1 hours of homework each night. "The findings address how current homework practices in privileged, high-performing schools sustain students' advantage in competitive climates yet hinder learning, full engagement and well-being," Pope wrote. Pope and her colleagues found that too much homework can diminish its effectiveness and even be counterproductive. They cite prior research indicating that homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night, and that 90 minutes to two and a half hours is optimal for high school. Their study found that too much homework is associated with: • Greater stress : 56 percent of the students considered homework a primary source of stress, according to the survey data. Forty-three percent viewed tests as a primary stressor, while 33 percent put the pressure to get good grades in that category. Less than 1 percent of the students said homework was not a stressor. • Reductions in health : In their open-ended answers, many students said their homework load led to sleep deprivation and other health problems. The researchers asked students whether they experienced health issues such as headaches, exhaustion, sleep deprivation, weight loss and stomach problems. • Less time for friends, family and extracurricular pursuits : Both the survey data and student responses indicate that spending too much time on homework meant that students were "not meeting their developmental needs or cultivating other critical life skills," according to the researchers. Students were more likely to drop activities, not see friends or family, and not pursue hobbies they enjoy. A balancing act The results offer empirical evidence that many students struggle to find balance between homework, extracurricular activities and social time, the researchers said. Many students felt forced or obligated to choose homework over developing other talents or skills. Also, there was no relationship between the time spent on homework and how much the student enjoyed it. The research quoted students as saying they often do homework they see as "pointless" or "mindless" in order to keep their grades up. "This kind of busy work, by its very nature, discourages learning and instead promotes doing homework simply to get points," said Pope, who is also a co-founder of Challenge Success , a nonprofit organization affiliated with the GSE that conducts research and works with schools and parents to improve students' educational experiences.. Pope said the research calls into question the value of assigning large amounts of homework in high-performing schools. Homework should not be simply assigned as a routine practice, she said. "Rather, any homework assigned should have a purpose and benefit, and it should be designed to cultivate learning and development," wrote Pope. High-performing paradox In places where students attend high-performing schools, too much homework can reduce their time to foster skills in the area of personal responsibility, the researchers concluded. "Young people are spending more time alone," they wrote, "which means less time for family and fewer opportunities to engage in their communities." Student perspectives The researchers say that while their open-ended or "self-reporting" methodology to gauge student concerns about homework may have limitations – some might regard it as an opportunity for "typical adolescent complaining" – it was important to learn firsthand what the students believe. The paper was co-authored by Mollie Galloway from Lewis and Clark College and Jerusha Conner from Villanova University.
Clifton B. Parker is a writer at the Stanford News Service .
More Stories

⟵ Go to all Research Stories
Get the Educator
Subscribe to our monthly newsletter.
Stanford Graduate School of Education
482 Galvez Mall Stanford, CA 94305-3096 Tel: (650) 723-2109
- Contact Admissions
- GSE Leadership
- Site Feedback
- Web Accessibility
- Career Resources
- Faculty Open Positions
- Explore Courses
- Academic Calendar
- Office of the Registrar
- Cubberley Library
- StanfordWho
- StanfordYou
Improving lives through learning

- Stanford Home
- Maps & Directions
- Search Stanford
- Emergency Info
- Terms of Use
- Non-Discrimination
- Accessibility
© Stanford University , Stanford , California 94305 .
- Second Opinion
- Research & Innovation
- Patients & Families
- Health Professionals
- Recently Visited
- Segunda opinión
- Refer a patient
- MyChart Login
Healthier, Happy Lives Blog
Sort articles by..., sort by category.
- Celebrating Volunteers
- Community Outreach
- Construction Updates
- Family-Centered Care
- Healthy Eating
- Heart Center
- Interesting Things
- Mental Health
- Patient Stories
- Research and Innovation
- Safety Tips
- Sustainability
- World-Class Care
About Our Blog
- Back-to-School
- Pediatric Technology
Latest Posts
- Stanford Heart Team Keeps Extremely Ill Baby Alive With Finesse and Teamwork
- Helping Your Child Cope With Anxiety and Depression
- Kangaroo Care for Premature Babies in the NICU
- Early Diagnosis Is Key for Children With Autism
- Distance Runner Charging Forward After Crawling Across Finish Line

Health Hazards of Homework
March 18, 2014 | Julie Greicius Pediatrics .

A new study by the Stanford Graduate School of Education and colleagues found that students in high-performing schools who did excessive hours of homework “experienced greater behavioral engagement in school but also more academic stress, physical health problems, and lack of balance in their lives.”
Those health problems ranged from stress, headaches, exhaustion, sleep deprivation, weight loss and stomach problems, to psycho-social effects like dropping activities, not seeing friends or family, and not pursuing hobbies they enjoy.
In the Stanford Report story about the research, Denise Pope , a senior lecturer at the Stanford Graduate School of Education and a co-author of the study published in the Journal of Experimental Education , says, “Our findings on the effects of homework challenge the traditional assumption that homework is inherently good.”
The study was based on survey data from a sample of 4,317 students from 10 high-performing high schools in California communities in which median household income exceeded $90,000. Of the students surveyed, homework volume averaged about 3.1 hours each night.
“It is time to re-evaluate how the school environment is preparing our high school student for today’s workplace,” says Neville Golden, MD , chief of adolescent medicine at Stanford Medicine Children’s Health and a professor at the School of Medicine. “This landmark study shows that excessive homework is counterproductive, leading to sleep deprivation, school stress and other health problems. Parents can best support their children in these demanding academic environments by advocating for them through direct communication with teachers and school administrators about homework load.”
Related Posts

Top-ranked group group in Los Gatos, Calif., is now a part of one of the…

The Stanford Medicine Children’s Health network continues to grow with our newest addition, Town and…
- Julie Greicius
- more by this author...
Connect with us:
Download our App:
ABOUT STANFORD MEDICINE CHILDREN'S HEALTH
- Leadership Team
- Vision, Mission & Values
- The Stanford Advantage
- Government and Community Relations
LUCILE PACKARD FOUNDATION FOR CHILDREN'S HEALTH
- Get Involved
- Volunteering Services
- Auxiliaries & Affiliates
- Our Hospital
- Send a Greeting Card
- New Hospital
- Refer a Patient
- Pay Your Bill

Also Find Us on:
- Notice of Nondiscrimination
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Code of Conduct
- Price Transparency
- Stanford School of Medicine
- Stanford Health Care
- Stanford University
Along with Stanford news and stories, show me:
- Student information
- Faculty/Staff information
We want to provide announcements, events, leadership messages and resources that are relevant to you. Your selection is stored in a browser cookie which you can remove at any time using “Clear all personalization” below.

Education scholar Denise Pope has found that too much homework has negative effects on student well-being and behavioral engagement. (Image credit: L.A. Cicero)
A Stanford researcher found that too much homework can negatively affect kids, especially their lives away from school, where family, friends and activities matter.
“Our findings on the effects of homework challenge the traditional assumption that homework is inherently good,” wrote Denise Pope , a senior lecturer at the Stanford Graduate School of Education and a co-author of a study published in the Journal of Experimental Education .
The researchers used survey data to examine perceptions about homework, student well-being and behavioral engagement in a sample of 4,317 students from 10 high-performing high schools in upper-middle-class California communities. Along with the survey data, Pope and her colleagues used open-ended answers to explore the students’ views on homework.
Median household income exceeded $90,000 in these communities, and 93 percent of the students went on to college, either two-year or four-year.
Students in these schools average about 3.1 hours of homework each night.
“The findings address how current homework practices in privileged, high-performing schools sustain students’ advantage in competitive climates yet hinder learning, full engagement and well-being,” Pope wrote.
Pope and her colleagues found that too much homework can diminish its effectiveness and even be counterproductive. They cite prior research indicating that homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night, and that 90 minutes to two and a half hours is optimal for high school.
Their study found that too much homework is associated with:
* Greater stress: 56 percent of the students considered homework a primary source of stress, according to the survey data. Forty-three percent viewed tests as a primary stressor, while 33 percent put the pressure to get good grades in that category. Less than 1 percent of the students said homework was not a stressor.
* Reductions in health: In their open-ended answers, many students said their homework load led to sleep deprivation and other health problems. The researchers asked students whether they experienced health issues such as headaches, exhaustion, sleep deprivation, weight loss and stomach problems.
* Less time for friends, family and extracurricular pursuits: Both the survey data and student responses indicate that spending too much time on homework meant that students were “not meeting their developmental needs or cultivating other critical life skills,” according to the researchers. Students were more likely to drop activities, not see friends or family, and not pursue hobbies they enjoy.
A balancing act
The results offer empirical evidence that many students struggle to find balance between homework, extracurricular activities and social time, the researchers said. Many students felt forced or obligated to choose homework over developing other talents or skills.
Also, there was no relationship between the time spent on homework and how much the student enjoyed it. The research quoted students as saying they often do homework they see as “pointless” or “mindless” in order to keep their grades up.
“This kind of busy work, by its very nature, discourages learning and instead promotes doing homework simply to get points,” Pope said.
She said the research calls into question the value of assigning large amounts of homework in high-performing schools. Homework should not be simply assigned as a routine practice, she said.
“Rather, any homework assigned should have a purpose and benefit, and it should be designed to cultivate learning and development,” wrote Pope.
High-performing paradox
In places where students attend high-performing schools, too much homework can reduce their time to foster skills in the area of personal responsibility, the researchers concluded. “Young people are spending more time alone,” they wrote, “which means less time for family and fewer opportunities to engage in their communities.”
Student perspectives
The researchers say that while their open-ended or “self-reporting” methodology to gauge student concerns about homework may have limitations – some might regard it as an opportunity for “typical adolescent complaining” – it was important to learn firsthand what the students believe.
The paper was co-authored by Mollie Galloway from Lewis and Clark College and Jerusha Conner from Villanova University.
Media Contacts
Denise Pope, Stanford Graduate School of Education: (650) 725-7412, [email protected] Clifton B. Parker, Stanford News Service: (650) 725-0224, [email protected]

Homework Struggles May Not Be a Behavior Problem
Exploring some options to understand and help..
Posted August 2, 2022 | Reviewed by Abigail Fagan
- Mental health challenges and neurodevelopmental differences directly affect children's ability to do homework.
- Understanding what difficulties are getting in the way—beyond the usual explanation of a behavior problem—is key.
- Sleep and mental health needs can take priority over homework completion.
Chelsea was in 10th grade the first time I told her directly to stop doing her homework and get some sleep. I had been working with her since she was in middle school, treating her anxiety disorder. She deeply feared disappointing anyone—especially her teachers—and spent hours trying to finish homework perfectly. The more tired and anxious she got, the harder it got for her to finish the assignments.

One night Chelsea called me in despair, feeling hopeless. She was exhausted and couldn’t think straight. She felt like a failure and that she was a burden to everyone because she couldn’t finish her homework.
She was shocked when I told her that my prescription for her was to go to sleep now—not to figure out how to finish her work. I told her to leave her homework incomplete and go to sleep. We briefly discussed how we would figure it out the next day, with her mom and her teachers. At that moment, it clicked for her that it was futile to keep working—because nothing was getting done.
This was an inflection point for her awareness of when she was emotionally over-cooked and when she needed to stop and take a break or get some sleep. We repeated versions of this phone call several times over the course of her high school and college years, but she got much better at being able to do this for herself most of the time.
When Mental Health Symptoms Interfere with Homework
Kids with mental health or neurodevelopmental challenges often struggle mightily with homework. Challenges can come up in every step of the homework process, including, but not limited to:
- Remembering and tracking assignments and materials
- Getting the mental energy/organization to start homework
- Filtering distractions enough to persist with assignments
- Understanding unspoken or implied parts of the homework
- Remembering to bring finished homework to class
- Being in class long enough to know the material
- Tolerating the fear of not knowing or failing
- Not giving up the assignment because of a panic attack
- Tolerating frustration—such as not understanding—without emotional dysregulation
- Being able to ask for help—from a peer or a teacher and not being afraid to reach out
This list is hardly comprehensive. ADHD , autism spectrum disorder, social anxiety , generalized anxiety, panic disorder, depression , dysregulation, and a range of other neurodevelopmental and mental health challenges cause numerous learning differences and symptoms that can specifically and frequently interfere with getting homework done.

The Usual Diagnosis for Homework Problems is "Not Trying Hard Enough"
Unfortunately, when kids frequently struggle to meet homework demands, teachers and parents typically default to one explanation of the problem: The child is making a choice not to do their homework. That is the default “diagnosis” in classrooms and living rooms. And once this framework is drawn, the student is often seen as not trying hard enough, disrespectful, manipulative, or just plain lazy.
The fundamental disconnect here is that the diagnosis of homework struggles as a behavioral choice is, in fact, only one explanation, while there are so many other diagnoses and differences that impair children's ability to consistently do their homework. If we are trying to create solutions based on only one understanding of the problem, the solutions will not work. More devastatingly, the wrong solutions can worsen the child’s mental health and their long-term engagement with school and learning.
To be clear, we aren’t talking about children who sometimes struggle with or skip homework—kids who can change and adapt their behaviors and patterns in response to the outcomes of that struggle. For this discussion, we are talking about children with mental health and/or neurodevelopmental symptoms and challenges that create chronic difficulties with meeting homework demands.
How Can You Help a Child Who Struggles with Homework?
How can you help your child who is struggling to meet homework demands because of their ADHD, depression, anxiety, OCD , school avoidance, or any other neurodevelopmental or mental health differences? Let’s break this down into two broad areas—things you can do at home, and things you can do in communication with the school.

Helping at Home
The following suggestions for managing school demands at home can feel counterintuitive to parents—because we usually focus on helping our kids to complete their tasks. But mental health needs jump the line ahead of task completion. And starting at home will be key to developing an idea of what needs to change at school.
- Set an end time in the evening after which no more homework will be attempted. Kids need time to decompress and they need sleep—and pushing homework too close to or past bedtime doesn’t serve their educational needs. Even if your child hasn’t been able to approach the homework at all, even if they have avoided and argued the whole evening, it is still important for everyone to have a predictable time to shut down the whole process.
- If there are arguments almost every night about homework, if your child isn’t starting homework or finishing it, reframe it from failure into information. It’s data to put into problem-solving. We need to consider other possible explanations besides “behavioral choice” when trying to understand the problem and create effective solutions. What problems are getting in the way of our child’s meeting homework demands that their peers are meeting most of the time?
- Try not to argue about homework. If you can check your own anxiety and frustration, it can be more productive to ally with your child and be curious with them. Kids usually can’t tell you a clear “why” but maybe they can tell you how they are feeling and what they are thinking. And if your child can’t talk about it or just keeps saying “I don't know,” try not to push. Come back another time. Rushing, forcing, yelling, and threatening will predictably not help kids do homework.

Helping at School
The second area to explore when your neurodiverse child struggles frequently with homework is building communication and connections with school and teachers. Some places to focus on include the following.
- Label your child’s diagnoses and break down specific symptoms for the teachers and school team. Nonjudgmental, but specific language is essential for teachers to understand your child’s struggles. Breaking their challenges down into the problems specific to homework can help with building solutions. As your child gets older, help them identify their difficulties and communicate them to teachers.
- Let teachers and the school team know that your child’s mental health needs—including sleep—take priority over finishing homework. If your child is always struggling to complete homework and get enough sleep, or if completing homework is leading to emotional meltdowns every night, adjusting their homework demands will be more successful than continuing to push them into sleep deprivation or meltdowns.
- Request a child study team evaluation to determine if your child qualifies for services under special education law such as an IEP, or accommodations through section 504—and be sure that homework adjustments are included in any plan. Or if such a plan is already in place, be clear that modification of homework expectations needs to be part of it.
The Long-Term Story
I still work with Chelsea and she recently mentioned how those conversations so many years ago are still part of how she approaches work tasks or other demands that are spiking her anxiety when she finds herself in a vortex of distress. She stops what she is doing and prioritizes reducing her anxiety—whether it’s a break during her day or an ending to the task for the evening. She sees that this is crucial to managing her anxiety in her life and still succeeding at what she is doing.
Task completion at all costs is not a solution for kids with emotional needs. Her story (and the story of many of my patients) make this crystal clear.

Candida Fink, M.D. , is board certified in child/adolescent and general psychiatry. She practices in New York and has co-authored two books— The Ups and Downs of Raising a Bipolar Child and Bipolar Disorder for Dummies.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Therapy Center NEW
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

At any moment, someone’s aggravating behavior or our own bad luck can set us off on an emotional spiral that threatens to derail our entire day. Here’s how we can face our triggers with less reactivity so that we can get on with our lives.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
Our websites may use cookies to personalize and enhance your experience. By continuing without changing your cookie settings, you agree to this collection. For more information, please see our University Websites Privacy Notice .
Neag School of Education
How to use homework to support student success.
- by: Sandra Chafouleas
- January 13, 2022
- Community Engagement

Editor’s Note: Board of Trustees Distinguished Professor Sandra Chafouleas shares insights on supporting students’ homework during the pandemic in the following piece, which originally appeared in Psychology Today , where she publishes a blog.
COVID has brought many changes in education. What does it mean for homework?
School assignments that a student is expected to do outside of the regular school day—that’s homework. The general guideline is 10 minutes of nightly homework per grade level beginning after kindergarten. This amounts to just a few minutes for younger elementary students to up to 2 hours for high school students.
The guidance seems straightforward enough, so why is homework such a controversial topic? School disruptions, including extended periods of remote learning during the COVID-19 pandemic, have magnified the controversies yet also have provided an opportunity to rethink the purpose and value of homework.
Debates about the value of homework center around two primary issues: amount and inequity.
First, the amount of assigned homework may be much more than the recommended guidelines. Families report their children are stressed out over the time spent doing homework. Too much homework can challenge well-being given the restricted time available for sleep, exercise, and social connection. In a 2015 study , for example, parents reported their early elementary children received almost three times the recommended guidelines. In high school, researchers found an average of three hours of homework per night for students living in economically privileged communities.
“ Debates about the value of homework center around two primary issues: amount and inequity.”
Second, homework can perpetuate inequities. Students attending school in less economically privileged communities may receive little to no homework, or have difficulty completing it due to limited access to needed technology. This can translate into fewer opportunities to learn and may contribute to gaps in achievement.
There isn’t a ton of research on the effects of homework, and available studies certainly do not provide a simple answer. For example, a 2006 synthesis of studies suggested a positive influence between homework completion and academic achievement for middle and high school students. Supporters also point out that homework offers additional opportunities to engage in learning and that it can foster independent learning habits such as planning and a sense of responsibility. A more recent study involving 13-year-old students in Spain found higher test scores for those who were regularly assigned homework in math and science, with an optimal time around one hour—which is roughly aligned with recommendations. However, the researchers noted that ability to independently do the work, student effort, and prior achievement were more important contributors than time spent.
Opponents of homework maintain that the academic benefit does not outweigh the toll on well-being. Researchers have observed student stress, physical health problems, and lack of life balance, especially when the time spent goes over the recommended guidelines. In a survey of adolescents , over half reported the amount and type of homework they received to be a primary source of stress in their lives. In addition, vast differences exist in access and availability of supports, such as internet connection, adult assistance, or even a place to call home, as 1.5 million children experience homelessness in the United States
The COVID-19 pandemic has re-energized discussion about homework practices, with the goal to advance recommendations about how, when, and with whom it can be best used. Here’s a summary of key strategies:
Strategies for Educators
Make sure the tasks are meaningful and matched..
First, the motto “ quality over quantity ” can guide decisions about homework. Homework is not busy-work, and instead should get students excited about learning. Emphasize activities that facilitate choice and interest to extend learning, like choose your own reading adventure or math games. Second, each student should be able to complete homework independently with success. Think about Goldilocks: To be effective, assignments should be just right for each learner. One example of how do this efficiently is through online learning platforms that can efficiently adjust to skill level and can be completed in a reasonable amount of time.
Ensure access to resources for task completion.
One step toward equity is to ensure access to necessary resources such as time, space, and materials. Teach students about preparing for homework success, allocating classroom time to model and practice good study habits such as setting up their physical environment, time management, and chunking tasks. Engage in conversations with students and families to problem-solve challenges When needed, connect students with homework supports available through after-school clubs, other community supports, or even within a dedicated block during the school day.
Be open to revisiting homework policies and practices.
The days of penalizing students for not completing homework should be long gone. Homework is a tool for practicing content and learning self-management. With that in mind, provide opportunities for students to communicate needs, and respond by revising assignments or allowing them to turn in on alternative dates. Engage in adult professional learning about high-quality homework , from value (Should I assign this task?) to evaluation (How should this be graded? Did that homework assignment result in expected outcomes?). Monitor how things are going by looking at completion rates and by asking students for their feedback. Be willing to adapt the homework schedule or expectations based on what is learned.
Strategies for Families
Understand how to be a good helper..
When designed appropriately, students should be able to complete homework with independence. Limit homework wars by working to be a good helper. Hovering, micromanaging, or doing homework for them may be easiest in the moment but does not help build their independence. Be a good helper by asking guiding questions, providing hints, or checking for understanding. Focus your assistance on setting up structures for homework success, like space and time.
Use homework as a tool for communication.
Use homework as a vehicle to foster family-school communication. Families can use homework as an opportunity to open conversations about specific assignments or classes, peer relationships, or even sleep quality that may be impacting student success. For younger students, using a daily or weekly home-school notebook or planner can be one way to share information. For older students, help them practice communicating their needs and provide support as needed.
Make sure to balance wellness.
Like adults, children need a healthy work-life balance. Positive social connection and engagement in pleasurable activities are important core principles to foster well-being . Monitor the load of homework and other structured activities to make sure there is time in the daily routine for play. Play can mean different things to different children: getting outside, reading for pleasure, and yes, even gaming. Just try to ensure that activities include a mix of health-focused activities such as physical movement or mindfulness downtime.

The Council for the Accreditation of Educator Preparation (CAEP) accredits the Neag School of Education at the University of Connecticut. Read more about CAEP Accreditation, including the programs covered and the accountability measures .
Some content on this website may require the use of a plug-in, such as Adobe Acrobat Viewer .
- Support the Neag School
Neag School of Education 249 Glenbrook Road, Unit 3064 Charles B. Gentry Building Storrs, CT 06269-3064
860-486-3815 [email protected]
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- HHS Author Manuscripts

Barriers Associated with the Implementation of Homework in Youth Mental Health Treatment and Potential Mobile Health Solutions
Brian e. bunnell.
1 Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Neurosciences, Morsani College of Medicine, University of South Florida, Tampa, FL, USA
2 Biomedical Informatics Center, College of Medicine, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, SC, USA
Lynne S. Nemeth
3 Department of Nursing, College of Nursing, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, SC, USA
Leslie A. Lenert
Nikolaos kazantzis.
4 Cognitive Behavior Therapy Research Unit and School of Psychological Sciences, Monash University, Clayton, VIC, Australia
Esther Deblinger
5 Child Abuse Research Education & Service (CARES) Institute, Rowan University School of Osteopathic Medicine, Stratford, New Jersey, USA
Kristen A. Higgins
Kenneth j. ruggiero.
6 Technology Applications Center for Healthful Lifestyles, College of Nursing, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, SC, USA
Author Contributions
Associated Data
Background:.
Homework, or between-session practice of skills learned during therapy, is integral to effective youth mental health TREATMENTS. However, homework is often under-utilized by providers and patients due to many barriers, which might be mitigated via m Health solutions.
Semi-structured qualitative interviews were conducted with nationally certified trainers in Trauma Focused Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (TF-CBT; n =21) and youth TF-CBT patients ages 8–17 ( n =15) and their caregivers ( n =12) to examine barriers to the successful implementation of homework in youth mental health treatment and potential m Health solutions to those barriers.
The results indicated that many providers struggle to consistently develop, assign, and assess homework exercises with their patients. Patients are often difficult to engage and either avoid or have difficulty remembering to practice exercises, especially given their busy/chaotic home lives. Trainers and families had positive views and useful suggestions for m Health solutions to these barriers in terms of functionality (e.g., reminders, tracking, pre-made homework exercises, rewards) and user interface (e.g., easy navigation, clear instructions, engaging activities).
Conclusions:
This study adds to the literature on homework barriers and potential m Health solutions to those barriers, which is largely based on recommendations from experts in the field. The results aligned well with this literature, providing additional support for existing recommendations, particularly as they relate to treatment with youth and caregivers.
Introduction
Homework, or between-session practice of skills learned during therapy, is one of the most integral, yet underutilized components of high-quality, evidence-based mental health care ( Kazantzis & Deane, 1999 ). Homework activities (e.g., self-monitoring, relaxation, exposure, parent behavior management) are assigned by providers in-session and completed by patients between sessions with the goal of “practicing” therapeutic skills in the environment where they will be most needed ( Kazantzis, Deane, Ronan, & L’Abate, 2005 ). There are numerous benefits to the implementation of homework during mental health treatment ( Kazantzis et al., 2016 ; Kazantzis, Deane, & Ronan, 2004 ). Homework enables the generalization of skills and behaviors learned during therapy, facilitates treatment processes, provides continuity between sessions, allows providers to better grasp patients’ learning, and strengthens that learning, leading to improved maintenance of treatment gains ( Hudson & Kendall, 2002 ; Scheel, Hanson, & Razzhavaikina, 2004 ). Meta-analytic and systematic reviews have shown that homework use by providers and adherence by patients predict increased treatment engagement, decreased treatment dropout, and medium-to-large effects on improvements in clinical outcomes for use (Cohen’s d =.48–.77) and adherence ( d =.45–.54) ( Hudson & Kendall, 2002 ; Kazantzis, Deane, & Ronan, 2000 ; Kazantzis & Lampropoulos, 2002 ; Kazantzis, Whittington, & Dattilio, 2010 ; Mausbach, Moore, Roesch, Cardenas, & Patterson, 2010 ; Scheel et al., 2004 ; Sukhodolsky, Kassinove, & Gorman, 2004 ). Simply put, 68% vs . 32% of patients can be expected to improve when therapy involves homework ( Kazantzis et al., 2010 ).
Despite its many benefits, homework is implemented with variable effectiveness in mental health treatment. Only 68% of general mental health providers and ~55% of family providers report using homework “often” to “almost always” ( Dattilio, Kazantzis, Shinkfield, & Carr, 2011 ; Kazantzis, Lampropoulos, & Deane, 2005 ). Further, providers report using homework in an average of 57% of sessions, although this rate is higher for CBT practitioners (66%) vs . non-CBT practitioners (48%). Moreover, only 25% of providers report using expert recommended systematic procedures for recommending homework (i.e., specifying frequency, duration, and location; writing down homework assignments for patients) ( Kazantzis & Deane, 1999 ). A national survey revealed that 93% or general mental health providers estimate rates of patient adherence to homework to be low to moderate ( Kazantzis, Lampropoulos, et al., 2005 ), and research studies report low to moderate rates of youth/caregiver adherence during treatment (i.e., ~39–63%; ( Berkovits, O’Brien, Carter, & Eyberg, 2010 ; Clarke et al., 1992 ; Danko, Brown, Van Schoick, & Budd, 2016 ; Dattilio et al., 2011 ; Gaynor, Lawrence, & Nelson-Gray, 2006 ; Helbig & Fehm, 2004 ; Lyon & Budd, 2010 ; Simons et al., 2012 ).
Numerous barriers to the successful implementation of homework during mental health treatment have largely been suggested by experts in the field, rather than specifically measured ( Dattilio et al., 2011 ), and have generally been classified as occurring on the provider-, patient-, task-, and environmental-level ( Kazantzis & Shinkfield, 2007 ). Provider-level barriers can relate to the therapeutic relationship and the degree to which a collaborative approach is used, provider beliefs about homework and the patient’s adherence, and providers’ ability to effectively design homework tasks ( Callan et al., 2012 ; Coon, Rabinowitz, Thompson, & Gallagher-Thompson, 2005 ; Friedberg & Mcclure, 2005 ; Garland & Scott, 2002 ; Kazantzis & Shinkfield, 2007 ). Patient-level barriers can include patient avoidance and symptomatology, negative beliefs toward the task, not understanding the rationale or how to do the task, forgetting, and beliefs about their ability to complete homework tasks. ( Bru, Solholm, & Idsoe, 2013 ; Callan et al., 2012 ; Dattilio et al., 2011 ; Friedberg & Mcclure, 2005 ; Garland & Scott, 2002 ; Hudson & Kendall, 2005 ; Kazantzis & Shinkfield, 2007 ; Leahy, 2002 ). Relatedly, core beliefs central to the patients’ psychopathology can be activated during homework–thereby triggering withdrawal and avoidance patterns ( Kazantzis & Shinkfield, 2007 ). Task-level barriers include poor match between tasks and therapy goals, tasks that are perceived as vague or unclear, tasks that are perceived as too difficult or demanding in terms of time or effort, tasks being viewed as boring, and general aversiveness of the idea of completing homework ( Bru et al., 2013 ; Callan et al., 2012 ; Dattilio et al., 2011 ; Friedberg & Mcclure, 2005 ; Garland & Scott, 2002 ; Hudson & Kendall, 2005 ). Environmental factors have been noted to include practical obstacles, lack of family/caregiver support, dysfunctional home environments, lack of time due to busy schedules, and lack of reward or reinforcement ( Callan et al., 2012 ; Dattilio et al., 2011 ; Hudson & Kendall, 2005 ).
The advancement and ubiquitousness of technologies such as m Health resources (e.g., mobile- and web-based apps) provide a tremendous opportunity to overcome barriers to homework use and adherence and resultantly, improve the quality of mental health treatment. m Health solutions to improve access and quality of care, have been widely investigated, are effective in facilitating behavior change, practical, desired by patients and providers, and available at low cost ( Amstadter, Broman-Fulks, Zinzow, Ruggiero, & Cercone, 2009 ; Boschen & Casey, 2008 ; Donker et al., 2013 ; Ehrenreich, Righter, Rocke, Dixon, & Himelhoch, 2011 ; Hanson et al., 2014 ; Heron & Smyth, 2010 ; Krebs & Duncan, 2015 ; Luxton, McCann, Bush, Mishkind, & Reger, 2011 ; Ruggiero, Saunders, Davidson, Cook, & Hanson, 2017 ). Existing m Health resources include features that can support homework implementation (e.g., voice and SMS reminders and feedback, self-monitoring and assessment, and modules and activities that can be used to facilitate between-session practice; Bakker, Kazantzis, Rickwood, & Rickard, 2016 ; Tang & Kreindler, 2017 ), but these resources were not designed with the express intention of addressing barriers to homework implementation, particularly for youth and family patient populations.
The extant literature on barriers to homework implementation is limited in that it is largely based on expert recommendations. Therefore, the first aim of this study was to explore provider, youth, and caregiver patient perspectives on barriers to the successful implementation of homework during youth mental health treatment. Further, m Health solutions to those barriers have not been explored, especially for youth and family patients. Thus, the second and third aims of this study were to obtain suggestions for m Health solutions to homework barriers and explore perceptions on the benefits and challenges associated with those m Health solutions.
Institutional Review Board approval was obtained prior to enrolling any participants in the study. The approach for this study was based on the constructivist grounded theory, which acknowledges the researcher’s prior knowledge and influence in the process and supports and guides conceptual framework development to understand interrelations between constructs ( Charmaz, 2006 ). This qualitative study used a thematic analysis of semi-structured interviews in a sample of nationally certified trainers in Trauma-Focused Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (TFCBT; Cohen, Mannarino, & Deblinger, 2017 ), youth who had engaged in TF-CBT, and their caregivers. The initial goal was to conduct interviews with 15–20 interviewees in each group to achieve theoretical saturation (i.e., no new information was derived), consistent with a prior study by members of the research team which used similar semi-structured interviews with national TF-CBT trainers ( Hanson et al., 2014 ), and recommendations by Morse (2000) given the relatively narrow scope and clear nature of the study. Interviews were conducted until interviewers and the study lead determined that no new pertinent information was being obtained.
Participants
National trainers..
Twenty-one national trainers in TF-CBT were interviewed. National trainers are mental health providers who completed a 15-month TF-CBT Train-the-Trainer program led by the TF-CBT developers. Trainers work extensively with numerous community mental health providers to problem-solve common barriers to clinical practice and thus, provide a unique perspective on the barriers to successful homework implementation and possible m Health solutions to those barriers. An e-mail invitation was sent to a list of approved TF-CBT trainers. Twenty-four trainers responded to this e-mail, 22 of whom agreed to participate in an interview, one of whom was unreachable after initial scheduling. Interviews were completed with a total of 21 trainers, who received a $25 gift card in compensation for their time.
Trainers had been treating children for an average of 23.29 years ( SD =8.80) and had been training providers for an average of 14.95 years ( SD =8.98). In the year prior to the interview, they led an average of 17 provider trainings ( SD =21.67) and trained roughly 345 providers ( SD =339.90). All trainers were licensed, and the majority were Clinical Psychologists (47.6%) and Social Workers (33.3%). The average age of trainers was 47.48 years ( SD =13.63) and the majority were female (71.4%), white (95.2%), and non-Hispanic/Latino (85.7%; see Table 1 ).
Trainer Demographics
Twelve families were interviewed for this study. Families were included if they had one or more youth between the ages of 8 and 17 years-of-age and a caregiver who had engaged in at least four sessions for TF-CBT. These criteria were chosen because TF-CBT is typically recommended for youth between the ages of 8 and 17 years-of-age and it was estimated that four sessions would have likely allowed for adequate time for patients to have received homework assignments, consistent with the authors’ experience and prior TF-CBT literature ( Deblinger, Pollio, & Dorsey, 2016 ; Scheeringa, Weems, Cohen, Amaya-Jackson, & Guthrie, 2011 ). Families were recruited via advertisements online and at local community mental health clinics, and from a participant pool from a prior study ( Davidson et al., 2019 ). Twenty-nine families initially expressed interest in participating in the study. Six families were ineligible because they had not received TF-CBT and contact was lost with six families after their initial contact. Seventeen families were scheduled for an interview, five of which were unreachable after initially being scheduled, and interviews were completed with 12 families. Written informed consent from caregivers and assent from youth above the age of 15 were obtained in-person for four families and via a telemedicine-based teleconsent platform (i.e., https://musc.doxy.me ) for eight families. Families received a $30 gift card in compensation for their time.
A total of 15 youth who had engaged in TF-CBT, and their caregivers ( n =12; three families had two youth who had received treatment) were interviewed. Six youth were still in treatment at the time of their interview and nine had finished treatment an average of 49 weeks ( SD =42.32) prior to the interview. The average age of youth was 13.20 years ( SD =3.19), roughly half were female (53.3%), the majority were white (80%), and all were non-Hispanic/Latino. The average age of caregivers was 44.83 years ( SD =7.90), 66.7% were female, and all were White and non-Hispanic/Latino. Youth and caregivers rated their comfort with technology, in general, on a 10-point Likert scale (i.e., 1–10) with higher scores representing higher levels of comfort. Youth reported being very comfortable with technology (M=9.62, SD =1.12), as did their caregivers (M=7.83, SD =2.63; see Table 2 ).
Family Demographics
Trauma-Focused Cognitive Behavioral Therapy
TF-CBT is a well-established and widely disseminated mental health treatment ( Cohen et al., 2017 ; Deblinger, Mannarino, Cohen, Runyon, & Steer, 2011 ; Silverman et al., 2008 ; Wethington et al., 2008 ). It is a conjoint youth-caregiver mental health treatment typically conducted over ~12, 90-minute sessions that address nine major treatment components (i.e., P sychoeducation; P arenting Skills; R elaxation Skills; A ffective Expression and Modulation Skills; C ognitive Coping and Processing Skills; T rauma Narration and Processing; I n Vivo Exposure; C onjoint Child Parent Activities; and E nhancing Future Safety and Development). TF-CBT also addresses a broad range of symptom domains including trauma- and stress-related disorders, disruptive behavior disorders/behaviors, depression/depressive symptoms, and anxiety disorders ( Cohen et al., 2017 ). TF-CBT was chosen as a model treatment for this study because of its broad symptom focus, inclusion of treatment components used in a variety of youth mental health treatments, and involvement of youth and their caregivers, offering potential to improve the applicability of the study’s results to a range of youth mental health treatment approaches.
Procedures for Data Collection
Interviews were conducted via telephone for trainers, and either in-person or via telephone for families based on their preference. A postdoctoral fellow and masters-level research assistant conducted the interviews, which were audio-recorded and transcribed using a professional transcription service. Interviews included three major components. The first component included demographic questions. The second included a brief orientation to the goal of the study, which was to develop a new technology-based resource to help providers and patients during the implementation of homework during mental health treatment. The third component included questions that aimed to assess perspectives on barriers to homework implementation, elicit suggestions for m Health solutions to those barriers, and examine perceptions on the benefits and challenges associated with m Health solutions to homework barriers. The average duration of interviews was 41 minutes for trainers and 37 minutes for families. See Supplementary Materials for complete interviews.
Data Analysis
Transcribed interviews were coded using NVivo qualitative analysis software. NVivo was used to identify common themes (nodes) as they related to (1) patient-, provider-, task-, and environmental-barriers to homework implementation, (2) suggestions for m Health solutions to homework barriers, and (3) benefits and challenges associated with m Health homework solutions. Initial and secondary coding passes were conducted to identify and refine theme classifications as they emerged and impose a data-derived hierarchy to the nodes identified. Focused coding was used to refine the coding and ensure that data were coded completely with minimal redundancy ( Miles & Huberman, 1994 ). Themes were initially proposed by the first author and reviewed by an expert in qualitative and mixed methods research (the second author) and an internationally recognized expert in the implementation of homework and related barriers during CBT (the fourth author). Divergent perspectives on theme descriptions ( n =2) and classifications ( n =1) were compared until agreement was reached.
Results are organized by the main topics explored in this study, including: 1) barriers to the successful implementation of homework, coded on provider, patient, task, and environmental levels; 2) potential m Health solutions to those homework barriers; and 3) perceived benefits and challenges of those potential m Health solutions. Results within each of these topics are presented first from the perspectives of trainers and second from the perspectives of families.
Barriers to the Successful Implementation of Homework
Trainer perspectives..
As displayed in Table 3 , trainers identified several barriers to homework implementation on the provider-, patient-, task-, and environmental-level.
Trainer Perspectives on Homework Barriers
Provider-Level Barriers.
Many trainers felt that providers tend to have difficulty engaging patients in assigned tasks, leading some providers to become discouraged by low levels of engagement. As stated by one trainer,
“I think they recognize that [homework assignments] do have value, but in terms of what I feel, a lot of clinicians are not having success with families completing homework, so it’s diminishing the sense of value…something they’ve tried to put into place and they are not feeling there’s any success in it.”
Trainers also noted that many providers do not see homework as an integral part of therapy. One trainer commented,
“I think there are a lot of concrete barriers, but to me probably the biggest barrier will be the–I think that still to this day [providers] like to think that therapy happens in that one hour.”
Other interrelated difficulties faced by providers related to their capacity to effectively and consistently develop, assess, and assign meaningful and patient-centered homework exercises.
As stated by one trainer,
“I see a lot of that just shooting from the hip, kind of off the cuff, ‘let’s do this,’ but yet, it’s not backed by anything concrete or tangible…I think probably one of the biggest pieces again is the failure on the clinician’s part to follow that up and too often review it at the end of the session.”
Another said,
“I think clinicians don’t always appreciate how hard it is to actually do homework that requires you to make some behavioral change.”
Barriers also related to providers’ time and resources for implementing homework, as conveyed by one trainer’s comment,
“I mean, these people…every minute of every day is filled up with doing, billing, writing, charting, going to meetings, getting supervision, and seeing patients, and then they go home exhausted.”
Patient-Level Barriers.
Many trainers stated that, similar to some providers, patients often do not see homework as an important part of therapy. Put by one trainer,
“I think that some [patients] just feel that coming to the session is enough and that should resolve everything, and that you know, doing homework is just kind of an extra thing…I don’t really need to do it to benefit from the therapy.”
Perhaps relatedly, trainers also noted that patients generally forget to do homework assignments, and often forget why, how, when, and where assignments should be done.
Task-Level Barriers.
Task-level barriers noted by trainers included assignments not always aligning with patient values or treatment goals and that the term ‘homework’ being aversive to patients of all ages. One trainer commented,
“I think it has to be something that [patients] see the value in. And again, we go back to that engagement and them trusting you as well as you explaining to them why this could be helpful…If it didn’t help, we need to change it.”
Another trainer laughed while stating,
“when we use the word homework, we might as well just throw a stink bomb in the room.”
Environmental-Level Barriers.
Finally, on the environmental-level, many trainers suggested that patients’ home lives are busy and chaotic, leaving little-to-no time for homework.
Explained by one trainer,
“I think that for parents…they have many other things in their life; work, parenting, partnerships that they are working on, just day to day chores or things that they have to do in terms of their family or other responsibilities. So, [homework] often feels like, I think for families, to add another thing…it just feels like a lot.”
Associated barriers included limited caregiver involvement and reinforcement for completing homework assignments. One trainer commented,
“So, let’s not forget that the parents need to be encouraged and checked on to make sure the kid is doing it. They have to work at it – It’s not going to just happen. So, helping the parents to see that they’re going to need to work to make sure the kids do it, because again, the kids would rather eat ice-cream than do the work. I mean change is hard.”
Another stated,
“I would say, lack of reinforcement for homework, so maybe for getting what you assign for homework and not reviewing it or the kiddo or the family learning pretty quickly, you know, why do it, because there’s not a lot of support around it. You know, if [patients] don’t get reinforced, whether tangibly or verbally, they may not continue that.”
Family Perspectives.
Families identified several barriers to homework implementation on the patient-, task-, and environmental-level which were similar to many of those noted by national trainers (see Table 4 ).
Family Perspectives on Homework Barriers
Families believed that patients often avoid homework as a result of their symptoms. In other words, the patient’s unhelpful coping strategies are being triggered.
One caregiver commented,
“Sometimes people don’t even want to dig into their feelings even to do the assignment either, you know. It stirs up things. You know, when you’re dealing with feelings, sometimes you don’t want to experience that feeling…you shut down. You don’t want to feel that at that time.”
“When you already have a child that has ADHD or behavior problems, it’s hard to get them motivated and to get them to do these exercises at home.”
Families also felt that patients simply forget to complete homework or bring it to their next session. One child stated,
“That’s my problem, she’ll give me homework, we met once a week, basically, and I would forget it because I’ve got a lot going on, and when I come in and she’s like, ‘Did you do your homework,’ I’m like, ‘Oh man’.”
Similar to trainers, families felt that patients often forget why, how, when and where assignments should be done. As stated by one caregiver,
“I think sometimes it can also be just, like maybe not fully understanding what is being asked of them to do. I know the therapist will ask them in the office, ‘do you understand?’ and of course the kids always go, ‘yes I do, can I go home now’?”
With respect to task-level barriers, most families viewed homework assignments as boring. General consensus from families was that patients–particularly youth– would more often than not just rather be doing something more interesting.
On the environmental level, all families noted that the home-life of patients is busy and chaotic, leaving little perceived time for homework. Everyday responsibilities such as schoolwork, employment, household chores, and familial responsibilities often take precedence. One caregiver stated,
“Well I think it sounds good in the office and then you get home and you just get quite busy and it gets pushed aside.”
Another commented,
“But I know what he’s saying…sometimes seven-and-a-half hours at school and then sometimes his therapy would be an hour-and-a-half. And thank goodness, his teacher was so flexible that on days he has therapy he did not have homework [for school], but he was just so emotionally and physically drained. When he got home, all he wanted to do was just rest or play. Because that’s the therapy, it can be just exhausting.”
Families also believed that that there is often a lack of reinforcement for completing homework assignments.
m Health Solutions to Homework Barriers
Trainer suggestions..
Trainers provided several suggestions for m Health solutions to homework barriers ( Table 5 ). Most trainers felt that reminders and schedules to help patients remember to complete homework assignments would be a crucial feature. One trainer suggested, “Maybe some kind of reminder feature, something that would kind of record into their daily calendars that they use, or an alarm, or something like a daily reminder…set to the times they are most likely to do the homework.”
Trainer Suggestions for m Health Solutions to Homework Barriers
Trainers also suggested including reports or activity summaries of homework completion along with behavior and symptom tracking tools. One trainer thoughtfully commented, “If the homework app can somehow help to provide some data on the actual implementation of certain skills during the week that would be very valuable because I think the constructive feedback and the positive feedback that’s offered by therapists about performance of those skills between sessions can be really valuable.”
Trainers suggested including a variety of interactive, fun, and rewarding activities that engage children and caregivers. For example, one trainer stated,
“I think the more interactive you can make it between parent and child and the more of a game you can make it…kids are more likely to do that and to kind of use those skills.” All trainers ( n =21) felt that a text message-based system for reminding patients to complete homework assignments would be beneficial.
Family Suggestions.
Families suggested that the main function of the resource should serve to provide reminders (e.g., text messages or push notifications) for patients to complete homework assignments as well as instructions for how and when they should be completed. Another common suggestion was to include a reward system within the resource to reinforce engagement with homework assignments. Some suggestions for this reward system included coins, experience points, levels, and customizable avatar characters. One child thoughtfully related,
“there could be a digital reward system like stars or gems or something. Then it could be redeemed or something in the therapist’s office. Like I remember it was a while ago, I remember my therapist said if I was able to do something that I was having trouble with, we would have like brownies or something the next visit.”
Families also recommended that the resource include interactive and fun activities. The most common suggestion was to “gamify” homework assignments to make them more fun and interesting to patients. For example, a caregiver noted,
“I think that if you are able to play a game or level up after you did your activity…I don’t think you would have a problem with them doing the activity. They would be so excited to be able to play the game.”
Families providers also recommended reports and activity summaries so that progress could be tracked and reported to providers to be reviewed during the next treatment session ( Table 6 ). All families ( n =12) felt that a text message-based system for reminding patients to complete homework assignments would be beneficial.
Family Suggestions for m Health Solutions to Homework Barriers
Benefits and Challenges of m Health Solutions to Homework Barriers
The majority of trainers responded that an m Health solution to homework barriers would increase provider use of ( n =20; 95.2%) and family adherence to ( n =21; 100%) homework during mental health treatment. The majority of trainers also responded that such a resource would positively affect the therapeutic relationship ( n =15; 71.4%), increase treatment efficiency ( n =18; 85.7%), and improve treatment effectiveness ( n =18; 85.7%). Neutral responses were provided by all trainers who did not respond affirmatively to these questions (i.e., no negative responses were provided). Trainers also commented on the potential clinical utility of an m Health homework resource in that it would help providers with tracking and assigning homework and patients with skill development while promoting high levels of engagement in youth patients. Access, comfort with technology, and convenience were also noted benefits (See Table 7 ). One trainer commented,
Trainer Perspectives on Benefits and Challenges relating to m Health Solutions to Homework Barriers No. of Trainers
“I feel like so many people now enjoy so much more doing things on electronics and so definitely in sessions with kids I’m often recommending having a clinician use apps…sometimes technology is the way to really hook families in and engage them.”
“You know everybody has a phone and if we can have some apps where…I mean it’s so exciting to me what you are talking about. I can’t think of a better idea, I really can’t. I mean people always have their phones on them even if you are really, really poor, people tend to have a phone.”
Challenges identified by trainers centered around confidentiality, access and comfort with technology, and potential negative impacts on the therapeutic process. For example, one trainer stated,
“I do not know if people worry about if somebody else saw the app and wondered, ‘oh you are in therapy, oh what happened to you?’ So, some things around privacy issues and confidentiality, but those will be pretty easy to fix.”
The majority of families believed that the an m Health homework resource would make practicing therapy skills at home more fun or interesting ( n =11; 91.7%), would help families practice skills more often ( n =12; 100%), would positively affect the therapeutic relationship ( n =12; 100%), and would improve treatment effectiveness ( n =11; 91.7%). Neutral responses were provided by all families who did not respond affirmatively to these questions (i.e., no negative responses were provided). Families also suggested that an m Health homework resource would have excellent clinical utility, helping to improve communication between providers and families, make treatment and homework more rewarding, encourage more engagement from youth One caregiver commented,
“I think it would encourage the kids to get [homework] done even before the parents. The kids would want to do it on the phone, they love messing with phones.”
“I think by having the reminders, as well as having something there that’s interactive for the kids and the caregivers both. I think it would be a huge help.”
Similar to trainers, challenges noted by families related to confidentiality and some families not having access to the technology or the internet. Additional family perspectives on benefits and challenges are provided in Table 8 .
Family Perspectives on Benefits and Challenges relating to m Health Solutions to Homework Barriers
The aims of this study were to assess barriers to the successful implementation of homework during youth mental health treatment, obtain suggestions for m Health solutions to those barriers, and explore perceptions on the benefits and challenges associated with m Health solutions to homework barriers through semi-structured qualitative interviews with relevant stakeholders. National trainers in TF-CBT provided a unique perspective on the common challenges met by mental health providers and their patients as well as potential solutions to those challenges, particularly given their extensive experience problem-solving common clinical challenges with community mental health providers. Interviews with youth TF-CBT patients and their caregivers provided important perspectives from those most affected by homework barriers in mental health treatment.
Perspectives on Barriers to the Successful Implementation of Homework
Trainer and family perspectives on the various barriers to the successful implementation of homework during mental health treatment aligned well with the heuristic proposed by Kazantzis and Shinkfield (2007) , which classifies barriers as occurring on the provider-, patient-, task-, and environmental-levels. Most of the provider-level barriers noted by trainers were consistent with expert recommendations from the research literature, such as providers’ beliefs relating to homework and patient engagement in homework ( Coon et al., 2005 ; Friedberg & Mcclure, 2005 ; Garland & Scott, 2002 ), difficulty designing homework activities and individualizing them to specific patients ( Kazantzis & Shinkfield, 2007 ), forgetting about homework and running out of time during the session ( Friedberg & Mcclure, 2005 ), difficulty with consistency and not wanting to put too many demands on patients ( Coon et al., 2005 ), and difficulty effectively assessing patient barriers ( Kazantzis & Shinkfield, 2007 ). Experts have proposed a model for practice that directly addresses many of these provider-level barriers by proposing an ideal process for facilitating engagement in homework ( Kazantzis, MacEwan, & Dattilio, 2005 ).
Trainer and family perspectives on the most common patient-level homework barriers were similar and were also consistent with the extant literature. These included patients’ avoidance or symptoms ( Coon et al., 2005 ; Dattilio et al., 2011 ; Friedberg & Mcclure, 2005 ; Garland & Scott, 2002 ; Hudson & Kendall, 2005 ; Leahy, 2002 ), forgetting to complete assignments ( Coon et al., 2005 ; Hudson & Kendall, 2005 ), not understanding when, where, or how to do assignments or the rationale ( Dattilio et al., 2011 ; Friedberg & Mcclure, 2005 ; Garland & Scott, 2002 ), and beliefs about homework tasks and their ability to complete them ( Dattilio et al., 2011 ; Kazantzis & Shinkfield, 2007 ). Interestingly, whereas the most commonly endorsed patient-level barrier by trainers was patients not seeing homework as an integral part of therapy or important, the most commonly endorsed barriers by families included avoidance or symptoms, forgetfulness, and lack of understanding about assignments, reflecting differing views on the more significant barriers faced by patients. This discrepancy in the trainers/providers vs . families’ perspectives regarding between session assignments suggests the importance of therapists’ focusing more time on explaining assignments, discussing potential challenges, emphasizing the benefits of completing assignments in overcoming symptoms/difficulties and ultimately inspiring follow through.
Task-level barriers reported by both trainers and families included assignments not aligning with patient values or treatment goals ( Coon et al., 2005 ; Dattilio et al., 2011 ; Hudson & Kendall, 2005 ). Many trainers reported that the word “homework” is an aversive term to patients, particularly to youth patients. Perhaps relatedly, many families reported that children view homework assignments are boring. Negative associations with homework may be addressed by referring to “homework” as practice assignments, experiments, exercises, or action plans, as recommended by a recent Beck Institute blog post by Drs. Judith Beck and Francine Broder ( Beck & Broder, 2016 ).
Finally, environment-level barriers noted by trainers and families included the home lives of patients being busy and chaotic – leaving little time to complete homework assignments; a lack of caregiver involvement in the case of youth; and a lack of reward or reinforcement for completing homework assignments, all of which have been previously noted ( Bru et al., 2013 ; Coon et al., 2005 ; Dattilio et al., 2011 ; Kazantzis & Shinkfield, 2007 ). In sum, trainer and family perspectives on barriers to the successful implementation of homework were largely consistent with those suggested by experts. Further, there was a general agreement between trainers and families with respect to those barriers. It is important to note the interrelatedness of several barriers within various levels. For example, patients not understanding the importance of homework or seeing it as an integral part of therapy could very much reflect a mismatch in alliance, tasks needed to achieve therapy goals, or a poor therapist rationale and opportunity for client feedback and discussion. Further, a patient’s understanding of the rationale for homework might be dependent on the provider’s skill in its explanation.
Trainers and families provided numerous suggestions for m Health solutions to homework barriers. These functionality and content suggestions included: reminders and schedules to overcome barriers to forgetting; behavior and symptom tracking and reports or activity summaries to assist providers in assessing homework completion; a variety of homework activities to choose from to help providers struggling with developing activities; resources for caregivers to improve caregiver support; and an integrated reward system to make completing homework rewarding and reinforcing for patients. Other suggested features related more to user interface and user experience. For example, interviewees felt that the m Health resource should allow easy navigation to relevant resources; include clear instructions via video, text, and audio to help patients understand and remember how to do assignments; include interactive and fun activities to help make the assignments less boring and less like “homework;” and be patient-centered and developmentally appropriate. Trainers and families also felt that a text message-based system for reminding patients to complete homework assignments would be beneficial, indicating that this approach would provide a good alternative to a purely app-based resource.
As outlined in recent reviews, there are several studies on m Health resources that include the functionality and content features suggested in this study and can also be used to facilitate homework implementation ( Bakker et al., 2016 ; Tang & Kreindler, 2017 ). For example, a number of m Health resources can be used for self-monitoring and symptom tracking, and many have engaging activities that can be used to support between-session learning and skill development in the areas of relaxation, cognitive therapy, imaginal exposure, and parent behavioral management ( Bunnell et al., 2019 ; Jungbluth & Shirk, 2013 ; Kristjánsdóttir et al., 2013 ; Newman, Przeworski, Consoli, & Barr Taylor, 2014 ; Reger et al., 2013 ; Shapiro et al., 2010 ; Whiteside, Ale, Vickers Douglas, Tiede, & Dammann, 2014 ). SMS- and app-based reminders and feedback on progress can also be used to encourage continued engagement in skills practice ( Aguilera & Muñoz, 2011 ; Harrison et al., 2011 ; Reger et al., 2013 ; Wiederhold, Boyd, Sulea, Gaggioli, & Riva, 2014 ). However, as stated previously, most of these resources were not designed with the express intention of addressing barriers to homework implementation, particularly for youth and family patient populations, leaving room for future work in this area.
Trainers and families expressed very positive views on m Health solutions to homework barriers. Trainers felt that m Health would increase provider use and family adherence to homework, positively affect the therapeutic relationship, and increase treatment efficiency and effectiveness. Families felt that it would make practicing therapy skills at home more fun or interesting, help families practice skills more often, positively affect the therapeutic relationship, and improve treatment effectiveness. A potential benefit commonly noted by trainers and families was a high likelihood that youth would engage with the resource given their generally strong interest in technology, and that this would help to reinforce the practice of skills learned during therapy. A particular benefit noted was increased access to helpful resources between-sessions. Trainers and families expressed concerns about issues relating to confidentiality. While they did not view this as a fatal flaw of the resource, they suggested implementing appropriate safeguards to protect patient privacy and clearly explaining data protection to encourage use.
Limitations
There are several limitations to this study. Regarding generalizability of results, the selection of trainers and families interviewed was based on experience with TF-CBT, a specific treatment protocol for childhood trauma. Although interview questions were kept general during interviews, referring to mental health treatment rather than solely to TF-CBT, the views expressed by interviewees may relate more to TF-CBT than other child mental health treatments. However, a strength of this research is that TF-CBT has a broad symptom focus (e.g., PTSD, anxiety, depression, anger, disruptive behavior) and includes treatment components used in numerous youth mental health treatments (e.g., psychoeducation, relaxation, cognitive coping, affective modulation, exposure), which suggests that results would be applicable to a range of child mental health treatments. Additionally, national trainers in TF-CBT have consistent exposure to working closely with community mental health providers and regularly help them to problem-solve common barriers in clinical practice. This added insight into difficulties experienced by numerous mental health providers rather than asking individual providers about their experience. This is a strength of this study but also a potential limitation as not directly measured, thus an assumption. The views of trainers may not be completely representative of the every-day challenges to homework implementation experienced by community mental health providers. Given the small samples size and lack of diversity, the results should be interpreted with caution as they may not reflect the experiences or views of therapists and patients who utilize homework across different treatment approaches, therapy settings, and populations.
With respect to interview questions and results, they tended to focus on barriers and challenges and provided less of an opportunity for trainers and family members to share factors that may have led to successes with homework assignments. Such information could also importantly support the development and presentation of m health solutions by therapists. Relatedly, families were asked about barriers faced by youth and caregivers, and not by providers, which would have provided interesting data on family perspectives on providers’ limitations. Although comfort with technology in general was assessed in youth and caregivers, it was not specified as comfort with m Health, and ratings were not collected from trainers. As such, a potential limitation of this study is that participants’ comfort specifically with mHealth was unknown. Furthermore, this study focused specifically on m Health without a comparison to other low-tech solutions, which might have resulted in inflated levels of interest in m health solutions to homework barriers. A final limitation is that interviews were coded by the first author, and there is potential for variability in coding that was not accounted for (i.e., the same themes might have been classified in different ways). Despite this limitation, themes were reviewed and by an internationally recognized expert in the implementation of homework and related barriers during CBT (the fourth author) and compared until agreement was reached, supporting the derived themes.
Conclusions
This study provides important new information on barriers to the successful implementation of homework during youth mental health treatment, based on perspectives of providers, youth, and caregivers with that treatment experience. This study adds to the literature on these barriers, which has been based largely on recommendations from experts in the field. The results of this study aligned well with this literature, providing additional support for these recommendations. Valuable insights on potential m Health solutions to these homework barriers were also provided. These data are being used to inform the development of an m Health resource that aims to address homework barriers in hopes of improving provider use and patient adherence to homework during youth mental health treatment, with the ultimate goal of improving the quality of care received by patients in community mental health settings.
Supplementary Material
10608_2020_10090_moesm1_esm, acknowledgments.
Compliance with Ethical Standards
Funding. Dr. Bunnell was supported by the National Institute of Mental Health (grant numbers F32 MH108250 and K23 MH118482).
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest
Conflict of Interest. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Research Involving Human Participants and/or Animals
Statement of Human Rights.
Ethics approval. All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Institutional Review Board at the Medical University of South Carolina (Pro00047774) and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Statement on the Welfare of Animals
Ethical approval. This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
- Aguilera A, & Muñoz RF. (2011). Text messaging as an adjunct to CBT in low-income populations: A usability and feasibility pilot study . Professional Psychology: Research and Practice , 42 ( 6 ), 472–478. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Amstadter AB, Broman-Fulks J, Zinzow H, Ruggiero KJ, & Cercone J. (2009). Internet-based interventions for traumatic stress-related mental health problems: A review and suggestion for future research . Clinical Psychology Review , 29 ( 5 ), 410–420. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bakker D, Kazantzis N, Rickwood D, & Rickard N. (2016). Mental health smartphone apps: Review and evidence-based recommendations for future developments . JMIR Mental Health , 3 ( 1 ), e7. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Beck JS, & Broder FR. (2016). The new “Homework” in cognitive behavior therapy . Beck Institute for Cognitive Behavior Therapy . Retrieved November 24, 2019, from https://beckinstitute.org/the-new-homework-in-cognitive-behavior-therapy/ [ Google Scholar ]
- Berkovits MD, O’Brien KA, Carter CG, & Eyberg SM. (2010). Early identification and intervention for behavior problems in primary care: A comparison of two abbreviated versions of parent-child interaction therapy . Behavior Therapy , 41 ( 3 ), 375–387. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Boschen MJ, & Casey LM. (2008). The use of mobile telephones as adjuncts to cognitive behavioral psychotherapy . Professional Psychology: Research and Practice , 39 ( 5 ), 546–552. [ Google Scholar ]
- Bru L, Solholm R, & Idsoe T. (2013). Participants’ experiences of an early cognitive behavioral intervention for adolescents with symptoms of depression . Emotional and Behavioural Difficulties , 18 ( 1 ), 24–43. [ Google Scholar ]
- Bunnell BE, Davidson TM, Winkelmann JR, Maples-Keller JL, Ridings LE, Dahne J, … Ruggiero KJ. (2019). Implementation and utility of an automated text messaging system to facilitate symptom self-monitoring and identify risk for post-traumatic stress disorder and depression in trauma center patients . Telemedicine and E-Health . [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Callan JA, Dunbar-Jacob J, Sereika SM, Stone C, Fasiczka A, Jarrett RB, & Thase ME. (2012). Barriers to cognitive behavioral therapy homework completion scaledepression version: Development and psychometric evaluation . International Journal of Cognitive Therapy , 5 ( 2 ), 219–235. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Charmaz K. (2006). Constructing grounded theory: A practical guide through qualitative analysis . New York, NY: SAGE Publications. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Clarke G, Hops H, Lewinsohn PM, Andrews J, Seeley JR, & Williams J. (1992). Cognitive-behavioral group treatment of adolescent depression: Prediction of outcome . Behavior Therapy , 23 ( 3 ), 341–354. [ Google Scholar ]
- Cohen JA, Mannarino AP, & Deblinger E. (2017). Treating trauma and traumatic grief in children and adolescents , 2nd ed. New York, NY, US: Guilford Press. [ Google Scholar ]
- Coon DW, Rabinowitz YG, Thompson LW, & Gallagher-Thompson D. (2005). Older adults. In Kazantzis N, Deane F, Ronan K, & L’Abate L. (Eds.), Using Homework Assignments in Cognitive Behavior Therapy (pp. 117–152). New York, NY: Routledge. [ Google Scholar ]
- Danko CM, Brown T, Van Schoick L, & Budd KS. (2016). Predictors and correlates of homework completion and treatment outcomes in parent–child interaction therapy . Child and Youth Care Forum , 45 ( 3 ), 467–485. [ Google Scholar ]
- Dattilio FM, Kazantzis N, Shinkfield G, & Carr AG. (2011). A survey of homework use, experience of barriers to homework, and attitudes about the barriers to homework among couples and family therapists . Journal of Marital and Family Therapy , 37 ( 2 ), 121–136. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Davidson TM, Bunnell BE, Saunders BE, Hanson RF, Danielson CK, Cook D, … Ruggiero KJ. (2019). Pilot evaluation of a tablet-based application to improve quality of care in child mental health treatment . Behavior Therapy , 50 ( 2 ), 367–379. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Deblinger E, Mannarino AP, Cohen JA, Runyon MK, & Steer RA. (2011). Trauma-Focused Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for children: Impact of the trauma narrative and treatment length . Depression and Anxiety , 28 ( 1 ), 67–75. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Deblinger E, Pollio E, & Dorsey S. (2016). Applying Trauma-Focused Cognitive–Behavioral Therapy in group format . Child Maltreatment , 21 ( 1 ), 59–73. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Donker T, Petrie K, Proudfoot J, Clarke J, Birch M-R, & Christensen H. (2013). Smartphones for smarter delivery of mental health programs: a systematic review . Journal of Medical Internet Research , 15 ( 11 ), e247. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ehrenreich B, Righter B, Rocke DA, Dixon L, & Himelhoch S. (2011). Are mobile phones and handheld computers being used to enhance delivery of psychiatric treatment ? The Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease , 199 ( 11 ), 886–891. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Friedberg RD, & Mcclure JM. (2005). Adolescents. In Kazantzis N, Deane F, Ronan K, & L’Abate L. (Eds.), Using Homework Assignments in Cognitive Behavior Therapy (pp. 95–116). New York, NY: Routledge. [ Google Scholar ]
- Garland A, & Scott J. (2002). Using homework in therapy for depression . Journal of Clinical Psychology , 58 ( 5 ), 489–498. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gaynor ST, Lawrence PS, & Nelson-Gray RO. (2006). Measuring homework compliance in cognitive-behavioral therapy for adolescent depression: Review, preliminary findings, and implications for theory and practice . Behavior Modification , 30 ( 5 ), 647–672. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hanson RF, Gros KS, Davidson TM, Barr S, Cohen J, Deblinger E, … Ruggiero KJ. (2014). National trainers’ perspectives on challenges to implementation of an empirically-supported mental health treatment . Administration and Policy in Mental Health and Mental Health Services Research , 41 ( 4 ), 522–534. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Harrison V, Proudfoot J, Wee PP, Parker G, Pavlovic DH, & Manicavasagar V. (2011, December). Mobile mental health: Review of the emerging field and proof of concept study . Journal of Mental Health . [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Helbig S, & Fehm L. (2004). Problems with homework in CBT: Rare exception or rather frequent? Behavioural and Cognitive Psychotherapy , 32 ( 3 ), 291–301. [ Google Scholar ]
- Heron KE, & Smyth JM. (2010). Ecological momentary interventions: Incorporating mobile technology into psychosocial and health behaviour treatments . British Journal of Health Psychology , 15 ( 1 ), 1–39. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hudson JL, & Kendall PC. (2002). Showing you can do it: Homework in therapy for children and adolescents with anxiety disorders . Journal of Clinical Psychology , 58 ( 5 ), 525–534. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hudson JL, & Kendall PC. (2005). Children. In Kazantzis N, Deane F, Ronan K, & L’Abate L. (Eds.), Using Homework Assignments in Cognitive Behavior Therapy (pp. 75–94). New York, NY: Routledge. [ Google Scholar ]
- Jungbluth NJ, & Shirk SR. (2013). Promoting homework adherence in cognitive-behavioral therapy for adolescent depression . Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology , 42 ( 4 ), 545–553. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kazantzis N, & Deane FP. (1999). Psychologists’ use of homework assignments in clinical practice . Professional Psychology: Research and Practice , 30 ( 6 ), 581–585. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kazantzis N, Deane FP, & Ronan KR. (2000). Homework assignments in cognitive and behavioral therapy: A meta-analysis . Clinical Psychology: Science and Practice , 7 ( 2 ), 189–202. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kazantzis N, Deane FP, & Ronan KR. (2004). Assessing compliance with homework assingments: Review and recommendations for clinical practice . Journal of Clinical Psychology , 60 ( 6 ), 627–641. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kazantzis N, Deane FP, Ronan KR, & L’Abate L. (2005). Using Homework Assignments in Cognitive Behavior Therapy . New York, NY: Routledge. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kazantzis N, & Lampropoulos GK. (2002). Reflecting on homework in psychotherapy: What can we conclude from research and experience? Journal of Clinical Psychology , 58 ( 5 ), 577–585. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kazantzis N, Lampropoulos GK, & Deane FP. (2005). A national survey of practicing psychologists’ use and attitudes toward homework in psychotherapy . Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology , 73 ( 4 ), 742–748. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kazantzis N, MacEwan J, & Dattilio F. (2005). A guiding model for practice. In Kazantzis N, Deane F, Ronan K, & L’Abate L. (Eds.), Using Homework Assignments in Cognitive Behavior Therapy (pp. 359–407). New York: Routledge. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kazantzis Nikolaos, & Shinkfield G. (2007). Conceptualizing patient barriers to nonadherence with homework assignments . Cognitive and Behavioral Practice , 14 ( 3 ), 317–324. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kazantzis Nikolaos, Whittington C, & Dattilio F. (2010). Meta-analysis of homework effects in cognitive and behavioral therapy: A replication and extension. Clinical Psychology : Science and Practice , 17 ( 2 ), 144–156. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kazantzis Nikolaos, Whittington C, Zelencich L, Kyrios M, Norton PJ, & Hofmann SG. (2016). Quantity and quality of homework compliance: A meta-analysis of relations with outcome in cognitive behavior therapy . Behavior Therapy , 47 ( 5 ), 755–772. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Krebs P, & Duncan DT. (2015). Health app use among US mobile phone owners: A national survey . JMIR MHealth and UHealth , 3 ( 4 ), e101. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kristjánsdóttir ÓB, Fors EA, Eide E, Finset A, Stensrud TL, Van Dulmen S, … Eide H. (2013). A smartphone-based intervention with diaries and therapist-feedback to reduce catastrophizing and increase functioning in women with chronic widespread pain: Randomized controlled trial . Journal of Medical Internet Research , 15 ( 1 ), e5. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Leahy RL. (2002). Improving homework compliance in the treatment of generalized anxiety disorder . Journal of Clinical Psychology , 58 ( 5 ), 499–511. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Luxton DD, McCann RA, Bush NE, Mishkind MC, & Reger GM. (2011). MHealth for mental health: Integrating smartphone technology in behavioral healthcare. Professional Psychology : Research and Practice , 42 ( 6 ), 505–512. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lyon AR, & Budd KS. (2010). A community mental health implementation of Parent–Child Interaction Therapy (PCIT) . Journal of Child and Family Studies , 19 ( 5 ), 654–668. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Mausbach BT, Moore R, Roesch S, Cardenas V, & Patterson TL. (2010). The relationship between homework compliance and therapy outcomes: An updated meta-analysis . Cognitive Therapy and Research , 34 ( 5 ), 429–438. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Miles MB, & Huberman AM. (1994). Qualitative data analysis: An expanded sourcebook . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications. [ Google Scholar ]
- Morse JM. (2000). Determining sample size . Qualitative Health Research , 10 ( 1 ), 3–5. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Newman MG, Przeworski A, Consoli AJ, & Barr Taylor C. (2014). A randomized controlled trial of ecological momentary intervention plus brief group therapy for generalized anxiety disorder . Psychotherapy , 51 ( 2 ), 198–206. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Reger GM, Hoffman J, Riggs D, Rothbaum BO, Ruzek J, Holloway KM, & Kuhn E. (2013). The “PE coach” smartphone application: An innovative approach to improving implementation, fidelity, and homework adherence during prolonged exposure . Psychological Services , 10 ( 3 ), 342–349. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ruggiero KJ, Saunders BE, Davidson TM, Cook DL, & Hanson R. (2017). Leveraging technology to address the quality chasm in children’s evidence-based psychotherapy . Psychiatric Services , 68 , 650–652. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Scheel MJ, Hanson WE, & Razzhavaikina TI. (2004). The process of recommending homework in psychotherapy: A review of therapist delivery methods, client acceptability, and factors that affect compliance . Psychotherapy , 41 ( 1 ), 38–55. [ Google Scholar ]
- Scheeringa MS, Weems CF, Cohen JA, Amaya-Jackson L, & Guthrie D. (2011). Trauma-focused cognitive-behavioral therapy for posttraumatic stress disorder in threethrough six year-old children: a randomized clinical trial . Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry , 52 ( 8 ), 853–860. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Shapiro JR, Bauer S, Andrews E, Pisetsky E, Bulik-Sullivan B, Hamer RM, & Bulik CM. (2010). Mobile therapy: Use of text-messaging in the treatment of bulimia nervosa . International Journal of Eating Disorders , 43 ( 6 ), 513–519. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Silverman WK, Ortiz CD, Viswesvaran C, Burns BJ, Kolko DJ, Putnam FW, & Amaya-Jackson L. (2008). Evidence-based psychosocial treatments for children and adolescents exposed to traumatic events . Journal of Clinical Child & Adolescent Psychology , 37 ( 1 ), 156–183. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Simons AD, Marti CN, Rohde P, Lewis CC, Curry J, & March J. (2012). Does homework “matter” in cognitive behavioral therapy for adolescent depression? Journal of Cognitive Psychotherapy , 26 ( 4 ), 390–404. [ Google Scholar ]
- Sukhodolsky DG, Kassinove H, & Gorman BS. (2004). Cognitive-behavioral therapy for anger in children and adolescents: A meta-analysis . Aggression and Violent Behavior , 9 ( 3 ), 247–269. [ Google Scholar ]
- Tang W, & Kreindler D. (2017). Supporting homework compliance in cognitive behavioural therapy: essential features of mobile apps . JMIR Mental Health , 4 ( 2 ), e20. [ PMC free article ] [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wethington HR, Hahn RA, Fuqua-Whitley DS, Sipe TA, Crosby AE, Johnson RL, … Task Force on Community Preventive Services. (2008). The effectiveness of interventions to reduce psychological harm from traumatic events among children and adolescents . American Journal of Preventive Medicine , 35 ( 3 ), 287–313. 10.1016/j.amepre.2008.06.024 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Whiteside SPH, Ale CM, Vickers Douglas K, Tiede MS, & Dammann JE. (2014). Case examples of enhancing pediatric ocd treatment with a smartphone application . Clinical Case Studies , 13 ( 1 ), 80–94. 10.1177/1534650113504822 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wiederhold BK, Boyd C, Sulea C, Gaggioli A, & Riva G. (2014). Marketing analysis of a positive technology app for the self-management of psychological stress . Studies in Health Technology and Informatics , 199 , 83–87. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
Request More Info
Fill out the form below and a member of our team will reach out right away!
" * " indicates required fields
Is Homework Necessary? Education Inequity and Its Impact on Students

The Problem with Homework: It Highlights Inequalities
How much homework is too much homework, when does homework actually help, negative effects of homework for students, how teachers can help.
Schools are getting rid of homework from Essex, Mass., to Los Angeles, Calif. Although the no-homework trend may sound alarming, especially to parents dreaming of their child’s acceptance to Harvard, Stanford or Yale, there is mounting evidence that eliminating homework in grade school may actually have great benefits , especially with regard to educational equity.
In fact, while the push to eliminate homework may come as a surprise to many adults, the debate is not new . Parents and educators have been talking about this subject for the last century, so that the educational pendulum continues to swing back and forth between the need for homework and the need to eliminate homework.
One of the most pressing talking points around homework is how it disproportionately affects students from less affluent families. The American Psychological Association (APA) explained:
“Kids from wealthier homes are more likely to have resources such as computers, internet connections, dedicated areas to do schoolwork and parents who tend to be more educated and more available to help them with tricky assignments. Kids from disadvantaged homes are more likely to work at afterschool jobs, or to be home without supervision in the evenings while their parents work multiple jobs.”
[RELATED] How to Advance Your Career: A Guide for Educators >>
While students growing up in more affluent areas are likely playing sports, participating in other recreational activities after school, or receiving additional tutoring, children in disadvantaged areas are more likely headed to work after school, taking care of siblings while their parents work or dealing with an unstable home life. Adding homework into the mix is one more thing to deal with — and if the student is struggling, the task of completing homework can be too much to consider at the end of an already long school day.
While all students may groan at the mention of homework, it may be more than just a nuisance for poor and disadvantaged children, instead becoming another burden to carry and contend with.
Beyond the logistical issues, homework can negatively impact physical health and stress — and once again this may be a more significant problem among economically disadvantaged youth who typically already have a higher stress level than peers from more financially stable families .
Yet, today, it is not just the disadvantaged who suffer from the stressors that homework inflicts. A 2014 CNN article, “Is Homework Making Your Child Sick?” , covered the issue of extreme pressure placed on children of the affluent. The article looked at the results of a study surveying more than 4,300 students from 10 high-performing public and private high schools in upper-middle-class California communities.
“Their findings were troubling: Research showed that excessive homework is associated with high stress levels, physical health problems and lack of balance in children’s lives; 56% of the students in the study cited homework as a primary stressor in their lives,” according to the CNN story. “That children growing up in poverty are at-risk for a number of ailments is both intuitive and well-supported by research. More difficult to believe is the growing consensus that children on the other end of the spectrum, children raised in affluence, may also be at risk.”
When it comes to health and stress it is clear that excessive homework, for children at both ends of the spectrum, can be damaging. Which begs the question, how much homework is too much?
The National Education Association and the National Parent Teacher Association recommend that students spend 10 minutes per grade level per night on homework . That means that first graders should spend 10 minutes on homework, second graders 20 minutes and so on. But a study published by The American Journal of Family Therapy found that students are getting much more than that.
While 10 minutes per day doesn’t sound like much, that quickly adds up to an hour per night by sixth grade. The National Center for Education Statistics found that high school students get an average of 6.8 hours of homework per week, a figure that is much too high according to the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD). It is also to be noted that this figure does not take into consideration the needs of underprivileged student populations.
In a study conducted by the OECD it was found that “after around four hours of homework per week, the additional time invested in homework has a negligible impact on performance .” That means that by asking our children to put in an hour or more per day of dedicated homework time, we are not only not helping them, but — according to the aforementioned studies — we are hurting them, both physically and emotionally.
What’s more is that homework is, as the name implies, to be completed at home, after a full day of learning that is typically six to seven hours long with breaks and lunch included. However, a study by the APA on how people develop expertise found that elite musicians, scientists and athletes do their most productive work for about only four hours per day. Similarly, companies like Tower Paddle Boards are experimenting with a five-hour workday, under the assumption that people are not able to be truly productive for much longer than that. CEO Stephan Aarstol told CNBC that he believes most Americans only get about two to three hours of work done in an eight-hour day.
In the scope of world history, homework is a fairly new construct in the U.S. Students of all ages have been receiving work to complete at home for centuries, but it was educational reformer Horace Mann who first brought the concept to America from Prussia.
Since then, homework’s popularity has ebbed and flowed in the court of public opinion. In the 1930s, it was considered child labor (as, ironically, it compromised children’s ability to do chores at home). Then, in the 1950s, implementing mandatory homework was hailed as a way to ensure America’s youth were always one step ahead of Soviet children during the Cold War. Homework was formally mandated as a tool for boosting educational quality in 1986 by the U.S. Department of Education, and has remained in common practice ever since.
School work assigned and completed outside of school hours is not without its benefits. Numerous studies have shown that regular homework has a hand in improving student performance and connecting students to their learning. When reviewing these studies, take them with a grain of salt; there are strong arguments for both sides, and only you will know which solution is best for your students or school.
Homework improves student achievement.
- Source: The High School Journal, “ When is Homework Worth the Time?: Evaluating the Association between Homework and Achievement in High School Science and Math ,” 2012.
- Source: IZA.org, “ Does High School Homework Increase Academic Achievement? ,” 2014. **Note: Study sample comprised only high school boys.
Homework helps reinforce classroom learning.
- Source: “ Debunk This: People Remember 10 Percent of What They Read ,” 2015.
Homework helps students develop good study habits and life skills.
- Sources: The Repository @ St. Cloud State, “ Types of Homework and Their Effect on Student Achievement ,” 2017; Journal of Advanced Academics, “ Developing Self-Regulation Skills: The Important Role of Homework ,” 2011.
- Source: Journal of Advanced Academics, “ Developing Self-Regulation Skills: The Important Role of Homework ,” 2011.
Homework allows parents to be involved with their children’s learning.
- Parents can see what their children are learning and working on in school every day.
- Parents can participate in their children’s learning by guiding them through homework assignments and reinforcing positive study and research habits.
- Homework observation and participation can help parents understand their children’s academic strengths and weaknesses, and even identify possible learning difficulties.
- Source: Phys.org, “ Sociologist Upends Notions about Parental Help with Homework ,” 2018.
While some amount of homework may help students connect to their learning and enhance their in-class performance, too much homework can have damaging effects.
Students with too much homework have elevated stress levels.
- Source: USA Today, “ Is It Time to Get Rid of Homework? Mental Health Experts Weigh In ,” 2021.
- Source: Stanford University, “ Stanford Research Shows Pitfalls of Homework ,” 2014.
Students with too much homework may be tempted to cheat.
- Source: The Chronicle of Higher Education, “ High-Tech Cheating Abounds, and Professors Bear Some Blame ,” 2010.
- Source: The American Journal of Family Therapy, “ Homework and Family Stress: With Consideration of Parents’ Self Confidence, Educational Level, and Cultural Background ,” 2015.
Homework highlights digital inequity.
- Sources: NEAToday.org, “ The Homework Gap: The ‘Cruelest Part of the Digital Divide’ ,” 2016; CNET.com, “ The Digital Divide Has Left Millions of School Kids Behind ,” 2021.
- Source: Investopedia, “ Digital Divide ,” 2022; International Journal of Education and Social Science, “ Getting the Homework Done: Social Class and Parents’ Relationship to Homework ,” 2015.
- Source: World Economic Forum, “ COVID-19 exposed the digital divide. Here’s how we can close it ,” 2021.
Homework does not help younger students.
- Source: Review of Educational Research, “ Does Homework Improve Academic Achievement? A Synthesis of Researcher, 1987-2003 ,” 2006.
To help students find the right balance and succeed, teachers and educators must start the homework conversation, both internally at their school and with parents. But in order to successfully advocate on behalf of students, teachers must be well educated on the subject, fully understanding the research and the outcomes that can be achieved by eliminating or reducing the homework burden. There is a plethora of research and writing on the subject for those interested in self-study.
For teachers looking for a more in-depth approach or for educators with a keen interest in educational equity, formal education may be the best route. If this latter option sounds appealing, there are now many reputable schools offering online master of education degree programs to help educators balance the demands of work and family life while furthering their education in the quest to help others.
YOU’RE INVITED! Watch Free Webinar on USD’s Online MEd Program >>
Be Sure To Share This Article
- Share on Twitter
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Top 11 Reasons to get Your Master of Education Degree
Free 22-page Book

- Master of Education
Related Posts

Homework as a Mental Health Concern It's time for an in depth discussion about homework as a major concern for those pursuing mental health in schools. So many problems between kids and their families, the home and school, and students and teachers arise from conflicts over homework. The topic is a long standing concern for mental health practitioners, especially those who work in schools. Over the years, we have tried to emphasize the idea that schools need to ensure that homework is designed as "motivated practice," and parents need to avoid turning homework into a battleground. These views are embedded in many of the Center documents. At this time, we hope you will join in a discussion of what problems you see arising related to homework and what you recommend as ways to deal with such problems, what positive homework practices you know about, and so forth. Read the material that follows, and then, let us hear from you on this topic. Contact: [email protected] ######################### As one stimulus, here's a piece by Sharon Cromwell from Education World prepared for teachers " The Homework Dilemma: How Much Should Parents Get Involved? " http://www.education-world.com/a_curr/curr053.shtml . What can teachers do to help parents help their children with homework? Just what kind of parental involvement -- and how much involvement -- truly helps children with their homework? The most useful stance parents can take, many experts agree, is to be somewhat but not overly involved in homework. The emphasis needs to be on parents' helping children do their homework themselves -- not on doing it for them. In an Instructor magazine article, How to Make Parents Your Homework Partner s, study-skills consultant Judy Dodge maintains that involving students in homework is largely the teacher's job, yet parents can help by "creating a home environment that's conducive to kids getting their homework done." Children who spend more time on homework, on average, do better academically than children who don't, and the academic benefits of homework increase in the upper grades, according to Helping Your Child With Homework , a handbook by the Office of Education Research and Improvement in the U.S. Department of Education. The handbook offers ideas for helping children finish homework assignments successfully and answers questions that parents and people who care for elementary and junior high school students often ask about homework. One of the Goals 2000 goals involves the parent/school relationship. The goal reads, "Every school will promote partnerships that will increase parental involvement and participation in promoting the social, emotional, and academic growth of children." Teachers can pursue the goal, in part, by communicating to parents their reasons for assigning homework. For example, the handbook states, homework can help children to review and practice what they have learned; prepare for the next day's class; use resources, such as libraries and reference materials; investigate topics more fully than time allows in the classroom. Parents can help children excel at homework by setting a regular time; choosing a place; removing distractions; having supplies and resources on hand; monitoring assignments; and providing guidance. The handbook cautions against actually doing the homework for a child, but talking about the assignment so the child can figure out what needs to be done is OK. And reviewing a completed assignment with a child can also be helpful. The kind of help that works best depends, of course, partly on the child's age. Elementary school students who are doing homework for the first time may need more direct involvement than older students. HOMEWORK "TIPS" Specific methods have been developed for encouraging the optimal parental involvement in homework. TIPS (Teachers Involve Parents in Schoolwork) Interactive Homework process was designed by researchers at Johns Hopkins University and teachers in Maryland, Virginia, and the District of Columbia to meet parents' and teachers' needs, says the Phi Delta Kappa Research Bulletin . The September 1997 bulletin reported the effects of TIPS-Language Arts on middle-grade students' writing skills, language arts report card grades, and attitudes toward TIPS as well as parents' reactions to interactive homework. TIPS interactive homework assignments involve students in demonstrating or discussing homework with a family member. Parents are asked to monitor, interact, and support their children. They are not required to read or direct the students' assignments because that is the students' responsibility. All TIPS homework has a section for home-to-school communication where parents indicate their interaction with the student about the homework. The goals of the TIPS process are for parents to gain knowledge about their children's school work, students to gain mastery in academic subjects by enhancing school lessons at home, and teachers to have an understanding of the parental contribution to student learning. "TIPS" RESULTS Nearly all parents involved in the TIPS program said TIPS provided them with information about what their children were studying in school. About 90 percent of the parents wanted the school to continue TIPS the following year. More than 80 percent of the families liked the TIPS process (44 percent a lot; 36% a little). TIPS activities were better than regular homework, according to 60 percent of the students who participated. About 70 percent wanted the school to use TIPS the next year. According to Phi Delta Kappa Research Bulletin , more family involvement helped students' writing skills increase, even when prior writing skills were taken into account. And completing more TIPS assignments improved students' language arts grades on report cards, even after prior report card grades and attendance were taken into account. Of the eight teachers involved, six liked the TIPS process and intended to go on using it without help or supplies from the researchers. Furthermore, seven of the eight teachers said TIPS "helps families see what their children are learning in class." OTHER TIPS In "How to Make Parents Your Homework Partners," Judy Dodge suggests that teachers begin giving parent workshops to provide practical tips for "winning the homework battle." At the workshop, teachers should focus on three key study skills: Organizational skills -- Help put students in control of work and to feel sure that they can master what they need to learn and do. Parents can, for example, help students find a "steady study spot" with the materials they need at hand. Time-management skills -- Enable students to complete work without feeling too much pressure and to have free time. By working with students to set a definite study time, for example, parents can help with time management. Active study strategies -- Help students to achieve better outcomes from studying. Parents suggest, for instance, that students write questions they think will be on a test and then recite their answers out loud. Related Resources Homework Without Tears by Lee Canter and Lee Hauser (Perennial Library, 1987). A down-to-earth book by well-known experts suggests how to deal with specific homework problems. Megaskills: How Families Can Help Children Succeed in School and Beyond by Dorothy Rich (Houghton Mifflin Company, 1992). Families can help children develop skills that nurture success in and out of school. "Helping Your Student Get the Most Out of Homework" by the National PTA and the National Education Association (1995). This booklet for teachers to use with students is sold in packages of 25 through the National PTA. The Catalog item is #B307. Call 312-549-3253 or write National PTA Orders, 135 South LaSalle Street, Dept. 1860, Chicago, IL 60674-1860. Related Sites A cornucopia of homework help is available for children who use a computer or whose parents are willing to help them get started online. The following LINKS include Internet sites that can be used for reference, research, and overall resources for both homework and schoolwork. Dr. Internet. The Dr. Internet Web site, part of the Internet Public Library, helps students with science and math homework or projects. It includes a science project resource guide Help With Homework. His extensive listing of Internet links is divided into Language Art Links, Science Links, Social Studies Links, Homework Help, Kids Education, and Universities. If students know what they are looking for, the site could be invaluable. Kidz-Net... Links to places where you can get help with homework. An array of homework help links is offered here, from Ask Dr. Math (which provides answers to math questions) to Roget's Thesaurus and the White House. Surfing the Net With Kids: Got Questions? Links to people -- such as teachers, librarians, experts, authors, and other students -- who will help students with questions about homework. Barbara J. Feldman put together the links. Kidsurfer: For Kids and Teens The site, from the National Children's Coalition, includes a Homework/Reference section for many subjects, including science, geography, music, history, and language arts. Homework: Parents' Work, Kid's Work, or School Work? A quick search of this title in the Education Week Archives and you'll find an article presenting a parent's viewpoint on helping children with homework. @#@#@#@@# As another stimulus for the discussion, here is an excerpt from our online continuing education module Enhancing Classroom Approaches for Addressing Barriers to Learning ( https://smhp.psych.ucla.edu ) Turning Homework into Motivated Practice Most of us have had the experience of wanting to be good at something such as playing a musical instrument or participating in a sport. What we found out was that becoming good at it meant a great deal of practice, and the practicing often was not very much fun. In the face of this fact, many of us turned to other pursuits. In some cases, individuals were compelled by their parents to labor on, and many of these sufferers grew to dislike the activity. (A few, of course, commend their parents for pushing them, but be assured these are a small minority. Ask your friends who were compelled to practice the piano.) Becoming good at reading, mathematics, writing, and other academic pursuits requires practice outside the classroom. This, of course, is called homework. Properly designed, homework can benefit students. Inappropriately designed homework, however, can lead to avoidance, parent-child conflicts, teacher reproval, and student dislike of various arenas of learning. Well-designed homework involves assignments that emphasize motivated practice. As with all learning processes that engage students, motivated practice requires designing activities that the student perceives as worthwhile and doable with an appropriate amount of effort. In effect, the intent is to personalize in-class practice and homework. This does not mean every student has a different practice activity. Teachers quickly learn what their students find engaging and can provide three or four practice options that will be effective for most students in a class. The idea of motivated practice is not without its critics. I don't doubt that students would prefer an approach to homework that emphasized motivated practice. But �� that's not preparing them properly for the real world. People need to work even when it isn't fun, and most of the time work isn't fun. Also, if a person wants to be good at something, they need to practice it day in and day out, and that's not fun! In the end, won't all this emphasis on motivation spoil people so that they won't want to work unless it's personally relevant and interesting? We believe that a great deal of learning and practice activities can be enjoyable. But even if they are not, they can be motivating if they are viewed as worthwhile and experienced as satisfying. At the same time, we do recognize that there are many things people have to do in their lives that will not be viewed and experienced in a positive way. How we all learn to put up with such circumstances is an interesting question, but one for which psychologists have yet to find a satisfactory answer. It is doubtful, however, that people have to experience the learning and practice of basic knowledge and skills as drudgery in order to learn to tolerate boring situations. Also in response to critics of motivated practice, there is the reality that many students do not master what they have been learning because they do not pursue the necessary practice activities. Thus, at least for such individuals, it seems essential to facilitate motivated practice. Minimally, facilitating motivated practice requires establishing a variety of task options that are potentially challenging -- neither too easy nor too hard. However, as we have stressed, the processes by which tasks are chosen must lead to perceptions on the part of the learner that practice activities, task outcomes, or both are worthwhile -- especially as potential sources of personal satisfaction. The examples in the following exhibit illustrate ways in which activities can be varied to provide for motivated learning and practice. Because most people have experienced a variety of reading and writing activities, the focus here is on other types of activity. Students can be encouraged to pursue such activity with classsmates and/or family members. Friends with common interests can provide positive models and support that can enhance productivity and even creativity. Research on motivation indicates that one of the most powerful factors keeping a person on a task is the expectation of feeling some sense of satisfaction when the task is completed. For example, task persistence results from the expectation that one will feel smart or competent while performing the task or at least will feel that way after the skill is mastered. Within some limits, the stronger the sense of potential outcome satisfaction, the more likely practice will be pursued even when the practice activities are rather dull. The weaker the sense of potential outcome satisfaction, the more the practice activities themselves need to be positively motivating. Exhibit � Homework and Motivated Practice Learning and practicing by (1) doing using movement and manipulation of objects to explore a topic (e.g., using coins to learn to add and subtract) dramatization of events (e.g., historical, current) role playing and simulations (e.g., learning about democratic vs. autocratic government by trying different models in class; learning about contemporary life and finances by living on a budget) actual interactions (e.g., learning about human psychology through analysis of daily behavior) applied activities (e.g., school newspapers, film and video productions, band, sports) actual work experience (e.g., on-the-job learning) (2) listening reading to students (e.g., to enhance their valuing of literature) audio media (e.g., tapes, records, and radio presentations of music, stories, events) listening games and activities (e.g., Simon Says; imitating rhymes, rhythms, and animal sounds) analyzing actual oral material (e.g., learning to detect details and ideas in advertisements or propaganda presented on radio or television, learning to identify feelings and motives underlying statements of others) (3) looking directly observing experts, role models, and demonstrations visual media visual games and activities (e.g., puzzles, reproducing designs, map activities) analyzing actual visual material (e.g., learning to find and identify ideas observed in daily events) (4) asking information gathering (e.g., investigative reporting, interviewing, and opinion sampling at school and in the community) brainstorming answers to current problems and puzzling questions inquiry learning (e.g., learning social studies and science by identifying puzzling questions, formulating hypotheses, gathering and interpreting information, generalizing answers, and raising new questions) question-and-answer games and activities (e.g., twenty questions, provocative and confrontational questions) questioning everyday events (e.g., learning about a topic by asking people about how it effects their lives) O.K. That's should be enough to get you going. What's your take on all this? What do you think we all should be telling teachers and parents about homework? Let us hear from you ( [email protected] ). Back to Hot Topic Home Page Hot Topic Home Page --> Table of Contents Home Page Search Send Us Email School Mental Health Project-UCLA Center for Mental Health in Schools WebMaster: Perry Nelson ([email protected])

When Is Homework Stressful? Its Effects on Students’ Mental Health

Are you wondering when is homework stressful? Well, homework is a vital constituent in keeping students attentive to the course covered in a class. By applying the lessons, students learned in class, they can gain a mastery of the material by reflecting on it in greater detail and applying what they learned through homework.
However, students get advantages from homework, as it improves soft skills like organisation and time management which are important after high school. However, the additional work usually causes anxiety for both the parents and the child. As their load of homework accumulates, some students may find themselves growing more and more bored.
Students may take assistance online and ask someone to do my online homework . As there are many platforms available for the students such as Chegg, Scholarly Help, and Quizlet offering academic services that can assist students in completing their homework on time.
Negative impact of homework
There are the following reasons why is homework stressful and leads to depression for students and affect their mental health. As they work hard on their assignments for alarmingly long periods, students’ mental health is repeatedly put at risk. Here are some serious arguments against too much homework.
No uniqueness
Homework should be intended to encourage children to express themselves more creatively. Teachers must assign kids intriguing assignments that highlight their uniqueness. similar to writing an essay on a topic they enjoy.
Moreover, the key is encouraging the child instead of criticizing him for writing a poor essay so that he can express himself more creatively.
Lack of sleep
One of the most prevalent adverse effects of schoolwork is lack of sleep. The average student only gets about 5 hours of sleep per night since they stay up late to complete their homework, even though the body needs at least 7 hours of sleep every day. Lack of sleep has an impact on both mental and physical health.
No pleasure
Students learn more effectively while they are having fun. They typically learn things more quickly when their minds are not clouded by fear. However, the fear factor that most teachers introduce into homework causes kids to turn to unethical means of completing their assignments.
Excessive homework
The lack of coordination between teachers in the existing educational system is a concern. As a result, teachers frequently end up assigning children far more work than they can handle. In such circumstances, children turn to cheat on their schoolwork by either copying their friends’ work or using online resources that assist with homework.
Anxiety level
Homework stress can increase anxiety levels and that could hurt the blood pressure norms in young people . Do you know? Around 3.5% of young people in the USA have high blood pressure. So why is homework stressful for children when homework is meant to be enjoyable and something they look forward to doing? It is simple to reject this claim by asserting that schoolwork is never enjoyable, yet with some careful consideration and preparation, homework may become pleasurable.
No time for personal matters
Students that have an excessive amount of homework miss out on personal time. They can’t get enough enjoyment. There is little time left over for hobbies, interpersonal interaction with colleagues, and other activities.
However, many students dislike doing their assignments since they don’t have enough time. As they grow to detest it, they can stop learning. In any case, it has a significant negative impact on their mental health.
Children are no different than everyone else in need of a break. Weekends with no homework should be considered by schools so that kids have time to unwind and prepare for the coming week. Without a break, doing homework all week long might be stressful.
How do parents help kids with homework?
Encouraging children’s well-being and health begins with parents being involved in their children’s lives. By taking part in their homework routine, you can see any issues your child may be having and offer them the necessary support.
Set up a routine
Your student will develop and maintain good study habits if you have a clear and organized homework regimen. If there is still a lot of schoolwork to finish, try putting a time limit. Students must obtain regular, good sleep every single night.
Observe carefully
The student is ultimately responsible for their homework. Because of this, parents should only focus on ensuring that their children are on track with their assignments and leave it to the teacher to determine what skills the students have and have not learned in class.
Listen to your child
One of the nicest things a parent can do for their kids is to ask open-ended questions and listen to their responses. Many kids are reluctant to acknowledge they are struggling with their homework because they fear being labelled as failures or lazy if they do.
However, every parent wants their child to succeed to the best of their ability, but it’s crucial to be prepared to ease the pressure if your child starts to show signs of being overburdened with homework.
Talk to your teachers
Also, make sure to contact the teacher with any problems regarding your homework by phone or email. Additionally, it demonstrates to your student that you and their teacher are working together to further their education.
Homework with friends
If you are still thinking is homework stressful then It’s better to do homework with buddies because it gives them these advantages. Their stress is reduced by collaborating, interacting, and sharing with peers.
Additionally, students are more relaxed when they work on homework with pals. It makes even having too much homework manageable by ensuring they receive the support they require when working on the assignment. Additionally, it improves their communication abilities.
However, doing homework with friends guarantees that one learns how to communicate well and express themselves.
Review homework plan
Create a schedule for finishing schoolwork on time with your child. Every few weeks, review the strategy and make any necessary adjustments. Gratefully, more schools are making an effort to control the quantity of homework assigned to children to lessen the stress this produces.
Bottom line
Finally, be aware that homework-related stress is fairly prevalent and is likely to occasionally affect you or your student. Sometimes all you or your kid needs to calm down and get back on track is a brief moment of comfort. So if you are a student and wondering if is homework stressful then you must go through this blog.
While homework is a crucial component of a student’s education, when kids are overwhelmed by the amount of work they have to perform, the advantages of homework can be lost and grades can suffer. Finding a balance that ensures students understand the material covered in class without becoming overburdened is therefore essential.
Zuella Montemayor did her degree in psychology at the University of Toronto. She is interested in mental health, wellness, and lifestyle.

Psychreg is a digital media company and not a clinical company. Our content does not constitute a medical or psychological consultation. See a certified medical or mental health professional for diagnosis.
- Privacy Policy
© Copyright 2014–2034 Psychreg Ltd
- PSYCHREG JOURNAL
- MEET OUR WRITERS
- MEET THE TEAM

Home » Tips for Teachers » 7 Research-Based Reasons Why Students Should Not Have Homework: Academic Insights, Opposing Perspectives & Alternatives
7 Research-Based Reasons Why Students Should Not Have Homework: Academic Insights, Opposing Perspectives & Alternatives
In recent years, the question of why students should not have homework has become a topic of intense debate among educators, parents, and students themselves. This discussion stems from a growing body of research that challenges the traditional view of homework as an essential component of academic success. The notion that homework is an integral part of learning is being reevaluated in light of new findings about its effectiveness and impact on students’ overall well-being.

The push against homework is not just about the hours spent on completing assignments; it’s about rethinking the role of education in fostering the well-rounded development of young individuals. Critics argue that homework, particularly in excessive amounts, can lead to negative outcomes such as stress, burnout, and a diminished love for learning. Moreover, it often disproportionately affects students from disadvantaged backgrounds, exacerbating educational inequities. The debate also highlights the importance of allowing children to have enough free time for play, exploration, and family interaction, which are crucial for their social and emotional development.
Checking 13yo’s math homework & I have just one question. I can catch mistakes & help her correct. But what do kids do when their parent isn’t an Algebra teacher? Answer: They get frustrated. Quit. Get a bad grade. Think they aren’t good at math. How is homework fair??? — Jay Wamsted (@JayWamsted) March 24, 2022
As we delve into this discussion, we explore various facets of why reducing or even eliminating homework could be beneficial. We consider the research, weigh the pros and cons, and examine alternative approaches to traditional homework that can enhance learning without overburdening students.
Once you’ve finished this article, you’ll know:
- Insights from Teachers and Education Industry Experts →
- 7 Reasons Why Students Should Not Have Homework →
- Opposing Views on Homework Practices →
- Exploring Alternatives to Homework →
Insights from Teachers and Education Industry Experts: Diverse Perspectives on Homework
In the ongoing conversation about the role and impact of homework in education, the perspectives of those directly involved in the teaching process are invaluable. Teachers and education industry experts bring a wealth of experience and insights from the front lines of learning. Their viewpoints, shaped by years of interaction with students and a deep understanding of educational methodologies, offer a critical lens through which we can evaluate the effectiveness and necessity of homework in our current educational paradigm.
Check out this video featuring Courtney White, a high school language arts teacher who gained widespread attention for her explanation of why she chooses not to assign homework.
Here are the insights and opinions from various experts in the educational field on this topic:
“I teach 1st grade. I had parents ask for homework. I explained that I don’t give homework. Home time is family time. Time to play, cook, explore and spend time together. I do send books home, but there is no requirement or checklist for reading them. Read them, enjoy them, and return them when your child is ready for more. I explained that as a parent myself, I know they are busy—and what a waste of energy it is to sit and force their kids to do work at home—when they could use that time to form relationships and build a loving home. Something kids need more than a few math problems a week.” — Colleen S. , 1st grade teacher
“The lasting educational value of homework at that age is not proven. A kid says the times tables [at school] because he studied the times tables last night. But over a long period of time, a kid who is drilled on the times tables at school, rather than as homework, will also memorize their times tables. We are worried about young children and their social emotional learning. And that has to do with physical activity, it has to do with playing with peers, it has to do with family time. All of those are very important and can be removed by too much homework.” — David Bloomfield , education professor at Brooklyn College and the City University of New York graduate center
“Homework in primary school has an effect of around zero. In high school it’s larger. (…) Which is why we need to get it right. Not why we need to get rid of it. It’s one of those lower hanging fruit that we should be looking in our primary schools to say, ‘Is it really making a difference?’” — John Hattie , professor
”Many kids are working as many hours as their overscheduled parents and it is taking a toll – psychologically and in many other ways too. We see kids getting up hours before school starts just to get their homework done from the night before… While homework may give kids one more responsibility, it ignores the fact that kids do not need to grow up and become adults at ages 10 or 12. With schools cutting recess time or eliminating playgrounds, kids absorb every single stress there is, only on an even higher level. Their brains and bodies need time to be curious, have fun, be creative and just be a kid.” — Pat Wayman, teacher and CEO of HowtoLearn.com
7 Reasons Why Students Should Not Have Homework
Let’s delve into the reasons against assigning homework to students. Examining these arguments offers important perspectives on the wider educational and developmental consequences of homework practices.
1. Elevated Stress and Health Consequences

The ongoing debate about homework often focuses on its educational value, but a vital aspect that cannot be overlooked is the significant stress and health consequences it brings to students. In the context of American life, where approximately 70% of people report moderate or extreme stress due to various factors like mass shootings, healthcare affordability, discrimination, racism, sexual harassment, climate change, presidential elections, and the need to stay informed, the additional burden of homework further exacerbates this stress, particularly among students.
Key findings and statistics reveal a worrying trend:
- Overwhelming Student Stress: A staggering 72% of students report being often or always stressed over schoolwork, with a concerning 82% experiencing physical symptoms due to this stress.
- Serious Health Issues: Symptoms linked to homework stress include sleep deprivation, headaches, exhaustion, weight loss, and stomach problems.
- Sleep Deprivation: Despite the National Sleep Foundation recommending 8.5 to 9.25 hours of sleep for healthy adolescent development, students average just 6.80 hours of sleep on school nights. About 68% of students stated that schoolwork often or always prevented them from getting enough sleep, which is critical for their physical and mental health.
- Turning to Unhealthy Coping Mechanisms: Alarmingly, the pressure from excessive homework has led some students to turn to alcohol and drugs as a way to cope with stress.
This data paints a concerning picture. Students, already navigating a world filled with various stressors, find themselves further burdened by homework demands. The direct correlation between excessive homework and health issues indicates a need for reevaluation. The goal should be to ensure that homework if assigned, adds value to students’ learning experiences without compromising their health and well-being.
By addressing the issue of homework-related stress and health consequences, we can take a significant step toward creating a more nurturing and effective educational environment. This environment would not only prioritize academic achievement but also the overall well-being and happiness of students, preparing them for a balanced and healthy life both inside and outside the classroom.
2. Inequitable Impact and Socioeconomic Disparities
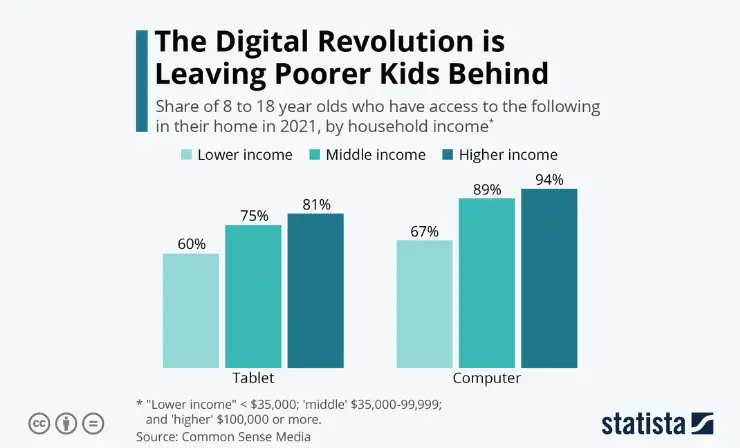
In the discourse surrounding educational equity, homework emerges as a factor exacerbating socioeconomic disparities, particularly affecting students from lower-income families and those with less supportive home environments. While homework is often justified as a means to raise academic standards and promote equity, its real-world impact tells a different story.
The inequitable burden of homework becomes starkly evident when considering the resources required to complete it, especially in the digital age. Homework today often necessitates a computer and internet access – resources not readily available to all students. This digital divide significantly disadvantages students from lower-income backgrounds, deepening the chasm between them and their more affluent peers.
Key points highlighting the disparities:
- Digital Inequity: Many students lack access to necessary technology for homework, with low-income families disproportionately affected.
- Impact of COVID-19: The pandemic exacerbated these disparities as education shifted online, revealing the extent of the digital divide.
- Educational Outcomes Tied to Income: A critical indicator of college success is linked more to family income levels than to rigorous academic preparation. Research indicates that while 77% of students from high-income families graduate from highly competitive colleges, only 9% from low-income families achieve the same . This disparity suggests that the pressure of heavy homework loads, rather than leveling the playing field, may actually hinder the chances of success for less affluent students.
Moreover, the approach to homework varies significantly across different types of schools. While some rigorous private and preparatory schools in both marginalized and affluent communities assign extreme levels of homework, many progressive schools focusing on holistic learning and self-actualization opt for no homework, yet achieve similar levels of college and career success. This contrast raises questions about the efficacy and necessity of heavy homework loads in achieving educational outcomes.
The issue of homework and its inequitable impact is not just an academic concern; it is a reflection of broader societal inequalities. By continuing practices that disproportionately burden students from less privileged backgrounds, the educational system inadvertently perpetuates the very disparities it seeks to overcome.
3. Negative Impact on Family Dynamics

Homework, a staple of the educational system, is often perceived as a necessary tool for academic reinforcement. However, its impact extends beyond the realm of academics, significantly affecting family dynamics. The negative repercussions of homework on the home environment have become increasingly evident, revealing a troubling pattern that can lead to conflict, mental health issues, and domestic friction.
A study conducted in 2015 involving 1,100 parents sheds light on the strain homework places on family relationships. The findings are telling:
- Increased Likelihood of Conflicts: Families where parents did not have a college degree were 200% more likely to experience fights over homework.
- Misinterpretations and Misunderstandings: Parents often misinterpret their children’s difficulties with homework as a lack of attention in school, leading to feelings of frustration and mistrust on both sides.
- Discriminatory Impact: The research concluded that the current approach to homework disproportionately affects children whose parents have lower educational backgrounds, speak English as a second language, or belong to lower-income groups.
The issue is not confined to specific demographics but is a widespread concern. Samantha Hulsman, a teacher featured in Education Week Teacher , shared her personal experience with the toll that homework can take on family time. She observed that a seemingly simple 30-minute assignment could escalate into a three-hour ordeal, causing stress and strife between parents and children. Hulsman’s insights challenge the traditional mindset about homework, highlighting a shift towards the need for skills such as collaboration and problem-solving over rote memorization of facts.
The need of the hour is to reassess the role and amount of homework assigned to students. It’s imperative to find a balance that facilitates learning and growth without compromising the well-being of the family unit. Such a reassessment would not only aid in reducing domestic conflicts but also contribute to a more supportive and nurturing environment for children’s overall development.

4. Consumption of Free Time

In recent years, a growing chorus of voices has raised concerns about the excessive burden of homework on students, emphasizing how it consumes their free time and impedes their overall well-being. The issue is not just the quantity of homework, but its encroachment on time that could be used for personal growth, relaxation, and family bonding.
Authors Sara Bennett and Nancy Kalish , in their book “The Case Against Homework,” offer an insightful window into the lives of families grappling with the demands of excessive homework. They share stories from numerous interviews conducted in the mid-2000s, highlighting the universal struggle faced by families across different demographics. A poignant account from a parent in Menlo Park, California, describes nightly sessions extending until 11 p.m., filled with stress and frustration, leading to a soured attitude towards school in both the child and the parent. This narrative is not isolated, as about one-third of the families interviewed expressed feeling crushed by the overwhelming workload.
Key points of concern:
- Excessive Time Commitment: Students, on average, spend over 6 hours in school each day, and homework adds significantly to this time, leaving little room for other activities.
- Impact on Extracurricular Activities: Homework infringes upon time for sports, music, art, and other enriching experiences, which are as crucial as academic courses.
- Stifling Creativity and Self-Discovery: The constant pressure of homework limits opportunities for students to explore their interests and learn new skills independently.
The National Education Association (NEA) and the National PTA (NPTA) recommend a “10 minutes of homework per grade level” standard, suggesting a more balanced approach. However, the reality often far exceeds this guideline, particularly for older students. The impact of this overreach is profound, affecting not just academic performance but also students’ attitudes toward school, their self-confidence, social skills, and overall quality of life.
Furthermore, the intense homework routine’s effectiveness is doubtful, as it can overwhelm students and detract from the joy of learning. Effective learning builds on prior knowledge in an engaging way, but excessive homework in a home setting may be irrelevant and uninteresting. The key challenge is balancing homework to enhance learning without overburdening students, allowing time for holistic growth and activities beyond academics. It’s crucial to reassess homework policies to support well-rounded development.
5. Challenges for Students with Learning Disabilities
Homework, a standard educational tool, poses unique challenges for students with learning disabilities, often leading to a frustrating and disheartening experience. These challenges go beyond the typical struggles faced by most students and can significantly impede their educational progress and emotional well-being.
Child psychologist Kenneth Barish’s insights in Psychology Today shed light on the complex relationship between homework and students with learning disabilities:
- Homework as a Painful Endeavor: For students with learning disabilities, completing homework can be likened to “running with a sprained ankle.” It’s a task that, while doable, is fraught with difficulty and discomfort.
- Misconceptions about Laziness: Often, children who struggle with homework are perceived as lazy. However, Barish emphasizes that these students are more likely to be frustrated, discouraged, or anxious rather than unmotivated.
- Limited Improvement in School Performance: The battles over homework rarely translate into significant improvement in school for these children, challenging the conventional notion of homework as universally beneficial.
These points highlight the need for a tailored approach to homework for students with learning disabilities. It’s crucial to recognize that the traditional homework model may not be the most effective or appropriate method for facilitating their learning. Instead, alternative strategies that accommodate their unique needs and learning styles should be considered.
In conclusion, the conventional homework paradigm needs reevaluation, particularly concerning students with learning disabilities. By understanding and addressing their unique challenges, educators can create a more inclusive and supportive educational environment. This approach not only aids in their academic growth but also nurtures their confidence and overall development, ensuring that they receive an equitable and empathetic educational experience.
6. Critique of Underlying Assumptions about Learning
The longstanding belief in the educational sphere that more homework automatically translates to more learning is increasingly being challenged. Critics argue that this assumption is not only flawed but also unsupported by solid evidence, questioning the efficacy of homework as an effective learning tool.
Alfie Kohn , a prominent critic of homework, aptly compares students to vending machines in this context, suggesting that the expectation of inserting an assignment and automatically getting out of learning is misguided. Kohn goes further, labeling homework as the “greatest single extinguisher of children’s curiosity.” This critique highlights a fundamental issue: the potential of homework to stifle the natural inquisitiveness and love for learning in children.
The lack of concrete evidence supporting the effectiveness of homework is evident in various studies:
- Marginal Effectiveness of Homework: A study involving 28,051 high school seniors found that the effectiveness of homework was marginal, and in some cases, it was counterproductive, leading to more academic problems than solutions.
- No Correlation with Academic Achievement: Research in “ National Differences, Global Similarities ” showed no correlation between homework and academic achievement in elementary students, and any positive correlation in middle or high school diminished with increasing homework loads.
- Increased Academic Pressure: The Teachers College Record published findings that homework adds to academic pressure and societal stress, exacerbating performance gaps between students from different socioeconomic backgrounds.
These findings bring to light several critical points:
- Quality Over Quantity: According to a recent article in Monitor on Psychology , experts concur that the quality of homework assignments, along with the quality of instruction, student motivation, and inherent ability, is more crucial for academic success than the quantity of homework.
- Counterproductive Nature of Excessive Homework: Excessive homework can lead to more academic challenges, particularly for students already facing pressures from other aspects of their lives.
- Societal Stress and Performance Gaps: Homework can intensify societal stress and widen the academic performance divide.
The emerging consensus from these studies suggests that the traditional approach to homework needs rethinking. Rather than focusing on the quantity of assignments, educators should consider the quality and relevance of homework, ensuring it truly contributes to learning and development. This reassessment is crucial for fostering an educational environment that nurtures curiosity and a love for learning, rather than extinguishing it.
7. Issues with Homework Enforcement, Reliability, and Temptation to Cheat
In the academic realm, the enforcement of homework is a subject of ongoing debate, primarily due to its implications on student integrity and the true value of assignments. The challenges associated with homework enforcement often lead to unintended yet significant issues, such as cheating, copying, and a general undermining of educational values.
Key points highlighting enforcement challenges:
- Difficulty in Enforcing Completion: Ensuring that students complete their homework can be a complex task, and not completing homework does not always correlate with poor grades.
- Reliability of Homework Practice: The reliability of homework as a practice tool is undermined when students, either out of desperation or lack of understanding, choose shortcuts over genuine learning. This approach can lead to the opposite of the intended effect, especially when assignments are not well-aligned with the students’ learning levels or interests.
- Temptation to Cheat: The issue of cheating is particularly troubling. According to a report by The Chronicle of Higher Education , under the pressure of at-home assignments, many students turn to copying others’ work, plagiarizing, or using creative technological “hacks.” This tendency not only questions the integrity of the learning process but also reflects the extreme stress that homework can induce.
- Parental Involvement in Completion: As noted in The American Journal of Family Therapy , this raises concerns about the authenticity of the work submitted. When parents complete assignments for their children, it not only deprives the students of the opportunity to learn but also distorts the purpose of homework as a learning aid.
In conclusion, the challenges of homework enforcement present a complex problem that requires careful consideration. The focus should shift towards creating meaningful, manageable, and quality-driven assignments that encourage genuine learning and integrity, rather than overwhelming students and prompting counterproductive behaviors.
Addressing Opposing Views on Homework Practices
While opinions on homework policies are diverse, understanding different viewpoints is crucial. In the following sections, we will examine common arguments supporting homework assignments, along with counterarguments that offer alternative perspectives on this educational practice.
1. Improvement of Academic Performance

Homework is commonly perceived as a means to enhance academic performance, with the belief that it directly contributes to better grades and test scores. This view posits that through homework, students reinforce what they learn in class, leading to improved understanding and retention, which ultimately translates into higher academic achievement.
However, the question of why students should not have homework becomes pertinent when considering the complex relationship between homework and academic performance. Studies have indicated that excessive homework doesn’t necessarily equate to higher grades or test scores. Instead, too much homework can backfire, leading to stress and fatigue that adversely affect a student’s performance. Reuters highlights an intriguing correlation suggesting that physical activity may be more conducive to academic success than additional homework, underscoring the importance of a holistic approach to education that prioritizes both physical and mental well-being for enhanced academic outcomes.
2. Reinforcement of Learning

Homework is traditionally viewed as a tool to reinforce classroom learning, enabling students to practice and retain material. However, research suggests its effectiveness is ambiguous. In instances where homework is well-aligned with students’ abilities and classroom teachings, it can indeed be beneficial. Particularly for younger students , excessive homework can cause burnout and a loss of interest in learning, counteracting its intended purpose.
Furthermore, when homework surpasses a student’s capability, it may induce frustration and confusion rather than aid in learning. This challenges the notion that more homework invariably leads to better understanding and retention of educational content.
3. Development of Time Management Skills

Homework is often considered a crucial tool in helping students develop important life skills such as time management and organization. The idea is that by regularly completing assignments, students learn to allocate their time efficiently and organize their tasks effectively, skills that are invaluable in both academic and personal life.
However, the impact of homework on developing these skills is not always positive. For younger students, especially, an overwhelming amount of homework can be more of a hindrance than a help. Instead of fostering time management and organizational skills, an excessive workload often leads to stress and anxiety . These negative effects can impede the learning process and make it difficult for students to manage their time and tasks effectively, contradicting the original purpose of homework.
4. Preparation for Future Academic Challenges

Homework is often touted as a preparatory tool for future academic challenges that students will encounter in higher education and their professional lives. The argument is that by tackling homework, students build a foundation of knowledge and skills necessary for success in more advanced studies and in the workforce, fostering a sense of readiness and confidence.
Contrarily, an excessive homework load, especially from a young age, can have the opposite effect . It can instill a negative attitude towards education, dampening students’ enthusiasm and willingness to embrace future academic challenges. Overburdening students with homework risks disengagement and loss of interest, thereby defeating the purpose of preparing them for future challenges. Striking a balance in the amount and complexity of homework is crucial to maintaining student engagement and fostering a positive attitude towards ongoing learning.
5. Parental Involvement in Education

Homework often acts as a vital link connecting parents to their child’s educational journey, offering insights into the school’s curriculum and their child’s learning process. This involvement is key in fostering a supportive home environment and encouraging a collaborative relationship between parents and the school. When parents understand and engage with what their children are learning, it can significantly enhance the educational experience for the child.
However, the line between involvement and over-involvement is thin. When parents excessively intervene by completing their child’s homework, it can have adverse effects . Such actions not only diminish the educational value of homework but also rob children of the opportunity to develop problem-solving skills and independence. This over-involvement, coupled with disparities in parental ability to assist due to variations in time, knowledge, or resources, may lead to unequal educational outcomes, underlining the importance of a balanced approach to parental participation in homework.
Exploring Alternatives to Homework and Finding a Middle Ground

In the ongoing debate about the role of homework in education, it’s essential to consider viable alternatives and strategies to minimize its burden. While completely eliminating homework may not be feasible for all educators, there are several effective methods to reduce its impact and offer more engaging, student-friendly approaches to learning.
Alternatives to Traditional Homework
- Project-Based Learning: This method focuses on hands-on, long-term projects where students explore real-world problems. It encourages creativity, critical thinking, and collaborative skills, offering a more engaging and practical learning experience than traditional homework. For creative ideas on school projects, especially related to the solar system, be sure to explore our dedicated article on solar system projects .
- Flipped Classrooms: Here, students are introduced to new content through videos or reading materials at home and then use class time for interactive activities. This approach allows for more personalized and active learning during school hours.
- Reading for Pleasure: Encouraging students to read books of their choice can foster a love for reading and improve literacy skills without the pressure of traditional homework assignments. This approach is exemplified by Marion County, Florida , where public schools implemented a no-homework policy for elementary students. Instead, they are encouraged to read nightly for 20 minutes . Superintendent Heidi Maier’s decision was influenced by research showing that while homework offers minimal benefit to young students, regular reading significantly boosts their learning. For book recommendations tailored to middle school students, take a look at our specially curated article .
Ideas for Minimizing Homework
- Limiting Homework Quantity: Adhering to guidelines like the “ 10-minute rule ” (10 minutes of homework per grade level per night) can help ensure that homework does not become overwhelming.
- Quality Over Quantity: Focus on assigning meaningful homework that is directly relevant to what is being taught in class, ensuring it adds value to students’ learning.
- Homework Menus: Offering students a choice of assignments can cater to diverse learning styles and interests, making homework more engaging and personalized.
- Integrating Technology: Utilizing educational apps and online platforms can make homework more interactive and enjoyable, while also providing immediate feedback to students. To gain deeper insights into the role of technology in learning environments, explore our articles discussing the benefits of incorporating technology in classrooms and a comprehensive list of educational VR apps . These resources will provide you with valuable information on how technology can enhance the educational experience.
For teachers who are not ready to fully eliminate homework, these strategies offer a compromise, ensuring that homework supports rather than hinders student learning. By focusing on quality, relevance, and student engagement, educators can transform homework from a chore into a meaningful component of education that genuinely contributes to students’ academic growth and personal development. In this way, we can move towards a more balanced and student-centric approach to learning, both in and out of the classroom.
Useful Resources
- Is homework a good idea or not? by BBC
- The Great Homework Debate: What’s Getting Lost in the Hype
- Alternative Homework Ideas
The evidence and arguments presented in the discussion of why students should not have homework call for a significant shift in homework practices. It’s time for educators and policymakers to rethink and reformulate homework strategies, focusing on enhancing the quality, relevance, and balance of assignments. By doing so, we can create a more equitable, effective, and student-friendly educational environment that fosters learning, well-being, and holistic development.
- “Here’s what an education expert says about that viral ‘no-homework’ policy”, Insider
- “John Hattie on BBC Radio 4: Homework in primary school has an effect of zero”, Visible Learning
- HowtoLearn.com
- “Time Spent On Homework Statistics [Fresh Research]”, Gitnux
- “Stress in America”, American Psychological Association (APA)
- “Homework hurts high-achieving students, study says”, The Washington Post
- “National Sleep Foundation’s updated sleep duration recommendations: final report”, National Library of Medicine
- “A multi-method exploratory study of stress, coping, and substance use among high school youth in private schools”, Frontiers
- “The Digital Revolution is Leaving Poorer Kids Behind”, Statista
- “The digital divide has left millions of school kids behind”, CNET
- “The Digital Divide: What It Is, and What’s Being Done to Close It”, Investopedia
- “COVID-19 exposed the digital divide. Here’s how we can close it”, World Economic Forum
- “PBS NewsHour: Biggest Predictor of College Success is Family Income”, America’s Promise Alliance
- “Homework and Family Stress: With Consideration of Parents’ Self Confidence, Educational Level, and Cultural Background”, Taylor & Francis Online
- “What Do You Mean My Kid Doesn’t Have Homework?”, EducationWeek
- “Excerpt From The Case Against Homework”, Penguin Random House Canada
- “How much homework is too much?”, neaToday
- “The Nation’s Report Card: A First Look: 2013 Mathematics and Reading”, National Center for Education Statistics
- “Battles Over Homework: Advice For Parents”, Psychology Today
- “How Homework Is Destroying Teens’ Health”, The Lion’s Roar
- “ Breaking the Homework Habit”, Education World
- “Testing a model of school learning: Direct and indirect effects on academic achievement”, ScienceDirect
- “National Differences, Global Similarities: World Culture and the Future of Schooling”, Stanford University Press
- “When school goes home: Some problems in the organization of homework”, APA PsycNet
- “Is homework a necessary evil?”, APA PsycNet
- “Epidemic of copying homework catalyzed by technology”, Redwood Bark
- “High-Tech Cheating Abounds, and Professors Bear Some Blame”, The Chronicle of Higher Education
- “Homework and Family Stress: With Consideration of Parents’ Self Confidence, Educational Level, and Cultural Background”, ResearchGate
- “Kids who get moving may also get better grades”, Reuters
- “Does Homework Improve Academic Achievement? A Synthesis of Research, 1987–2003”, SageJournals
- “Is it time to get rid of homework?”, USAToday
- “Stanford research shows pitfalls of homework”, Stanford
- “Florida school district bans homework, replaces it with daily reading”, USAToday
- “Encouraging Students to Read: Tips for High School Teachers”, wgu.edu
- Recent Posts

Simona Johnes is the visionary being the creation of our project. Johnes spent much of her career in the classroom working with students. And, after many years in the classroom, Johnes became a principal.
- 28 Exciting Yarn Crafts for Preschool Kids: Igniting Creativity and Fine Motor Skills - April 29, 2024
- 16 Engaging and Educational Cause and Effect Activities for Preschoolers to Boost Cognitive Development - April 24, 2024
- 25 Innovative and Engaging Parts of Speech Activities for Middle School: Fun Grammar Games to Enhance Learning - April 14, 2024
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.


Health Issues

ADHD and Homework

Our eleven-year-old daughter, who has been diagnosed with inattentive-type ADHD, has been doing better since she began treatment with stimulant medication. However, we still have trouble getting her organized around homework. We have tried setting up an office in her room, taking away all the distractions, keeping the area quiet, and not allowing the television to go on until all her homework is done. We don’t seem to be making much progress and, in fact, we are all getting even more frustrated because nothing seems to work. Her teachers still complain that work is not getting turned in, and her grades are still suffering in spite of her teacher always telling us how bright she is.
There is no one-size-fits-all solution to the ideal homework setting. Some children with ADHD work inefficiently in an isolated, quiet setting like their room, and do better in the midst of some action, like at the kitchen table with a radio playing. You might need to try a few different settings until you find the most efficient one.
In addition, you might need to figure out if any other factors are making homework difficult. Think about all the steps involved. Does your child know what all the assignments are? Does she bring the materials home that are necessary for doing the work? Does she have a nightly work plan that fits with her learning style? (She might need to schedule breaks between math and English, or between outlining the report and writing the first 3 paragraphs.) Does she have a system to check on whether all the nightly work is done? Is there a system for checking that her completed work gets turned in on the due date? How does she or you know that work is late? Have you or her teacher set up rewards for progress or consequences for late work? Is there a system for her teacher to communicate with you about late work?
Once you have gone through this type of systematic list of questions, you can begin to solve the problem in an organized way—and you might discover some simple and obvious solutions. If she is taking stimulant medication and she does her homework primarily at a time after it has worn off, you could consider a short-acting extended dose of medication for the early evening.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Are We Talking Too Much About Mental Health?
Recent studies cast doubt on whether large-scale mental health interventions are making young people better. Some even suggest they can have a negative effect.

By Ellen Barry
In recent years, mental health has become a central subject in childhood and adolescence. Teenagers narrate their psychiatric diagnosis and treatment on TikTok and Instagram. School systems, alarmed by rising levels of distress and self-harm, are introducing preventive coursework in emotional self-regulation and mindfulness.
Now, some researchers warn that we are in danger of overdoing it. Mental health awareness campaigns, they argue, help some young people identify disorders that badly need treatment — but they have a negative effect on others, leading them to over-interpret their symptoms and see themselves as more troubled than they are.
The researchers point to unexpected results in trials of school-based mental health interventions in the United Kingdom and Australia: Students who underwent training in the basics of mindfulness , cognitive behavioral therapy and dialectical behavior therapy did not emerge healthier than peers who did not participate, and some were worse off, at least for a while.
And new research from the United States shows that among young people, “self-labeling” as having depression or anxiety is associated with poor coping skills, like avoidance or rumination.
In a paper published last year , two research psychologists at the University of Oxford, Lucy Foulkes and Jack Andrews, coined the term “prevalence inflation” — driven by the reporting of mild or transient symptoms as mental health disorders — and suggested that awareness campaigns were contributing to it.
“It’s creating this message that teenagers are vulnerable, they’re likely to have problems, and the solution is to outsource them to a professional,” said Dr. Foulkes, a Prudence Trust Research Fellow in Oxford’s department of experimental psychology, who has written two books on mental health and adolescence.
Until high-quality research has clarified these unexpected negative effects, they argue, school systems should proceed cautiously with large-scale mental health interventions.
“It’s not that we need to go back to square one, but it’s that we need to press pause and reroute potentially,” Dr. Foulkes said. “It’s possible that something very well-intended has overshot a bit and needs to be brought back in.”
This remains a minority view among specialists in adolescent mental health, who mostly agree that the far more urgent problem is lack of access to treatment.
About 60 percent of young Americans with severe depression receive no treatment, according to Mental Health America, a nonprofit research group. In crisis, desperate families fall back on emergency rooms, where teens often remain for days before a psychiatric bed opens up. There is good reason to embrace a preventive approach, teaching schoolchildren basic skills that might forestall crises later, experts say.
Dr. Foulkes said she understood that her argument runs counter to that consensus, and when she began to present it, she braced for a backlash. To her surprise, she said, many educators reached out to express quiet agreement.
“There’s definitely a fear about being the one to say it,” she said.
A deflating result
In the summer of 2022, the results of a landmark study on mindfulness training in British classrooms landed — like a lead balloon.
The trial, My Resilience in Adolescence, or MYRIAD, was ambitious, meticulous and expansive, following about 28,000 teenagers over eight years. It had been launched in a glow of optimism that the practice would pay off, improving the students’ mental health outcomes in later years.
Half of the teenagers were trained by their teachers to direct their attention to the present moment — breathing, physical sensations or everyday activities — in 10 lessons of 30 to 50 minutes apiece.
The results were disappointing . The authors reported “no support for our hypothesis” that mindfulness training would improve students’ mental health. In fact, students at highest risk for mental health problems did somewhat worse after receiving the training, the authors concluded.
But by the end of the eight-year project, “mindfulness is already embedded in a lot of schools, and there are already organizations making money from selling this program to schools,” said Dr. Foulkes, who had assisted on the study as a postdoctoral research associate. “And it’s very difficult to get the scientific message out there.”
Why, one might ask, would a mental health program do harm?
Researchers in the study speculated that the training programs “bring awareness to upsetting thoughts,” encouraging students to sit with darker feelings, but without providing solutions, especially for societal problems like racism or poverty. They also found that the students didn’t enjoy the sessions and didn’t practice at home.
Another explanation is that mindfulness training could encourage “co-rumination,” the kind of long, unresolved group discussion that churns up problems without finding solutions.
As the MYRIAD results were being analyzed, Dr. Andrews led an evaluation of Climate Schools, an Australian intervention based on the principles of cognitive behavioral therapy, in which students observed cartoon characters navigating mental health concerns and then answered questions about practices to improve mental health.
Here, too, he found negative effects. Students who had taken the course reported higher levels of depression and anxiety symptoms six months and 12 months later.
Co-rumination appears to be higher in girls, who tend to come into the program more distressed, as well as more attuned to their friends, he said. “It might be,” he said, “that they kind of get together and make things a little bit worse for each other.”
Dr. Andrews, a Wellcome Trust research fellow, has since joined an effort to improve Climate Schools by addressing negative effects. And he has concluded that schools should slow down until “we know the evidence base a bit more.” Sometimes, he said, “doing nothing is better than doing something.”
The awareness paradox
One problem with mental health awareness, some research suggests, is that it may not help to put a label to your symptoms.
Isaac Ahuvia, a doctoral candidate at Stony Brook University, recently tested this in a study of 1,423 college students . Twenty-two percent “self-labeled” as having depression, telling researchers “I am depressed” or “I have depression,” but 39 percent met the diagnostic criteria for depression.
He found that the students who self-labeled felt that they had less control over depression and were more likely to catastrophize and less likely to respond to distress by putting their difficulties in perspective, compared with peers who had similar depression symptoms.
Jessica L. Schleider, a co-author of the self-labeling study, said this was no surprise. People who self-label “appear to be viewing depression as a biological inevitability,” she said. “People who don’t view emotions as malleable, view them as set and stuck and uncontrollable, tend to cope less well because they don’t see a point to trying.”
But Dr. Schleider, an associate professor of medical social sciences at Northwestern University and the director of the university’s Lab for Scalable Mental Health, pushed back on the prevalence inflation hypothesis. She disagreed with the claim that students are overdiagnosing themselves, noting that Mr. Ahuvia’s findings suggest otherwise.
Awareness campaigns are bound to have multiple effects, helping some students and not others. And ultimately, she argued, the priority for public health should be reaching young people in the most distress.
“The urgency of the mental health crisis is so clear,” she said. “In the partnerships that I have, the emphasis is on the kids truly struggling right now who have nothing — we need to help them — more so than a possible risk for a subset of kids who aren’t really struggling.”
Maybe, she said, we need to look beyond the “universal, school-assembly-style approach,” to targeted, light-touch interventions, which research has shown can be effective at decreasing anxiety and conduct disorders, especially in younger children.
“There is a risk of throwing the baby out with the bathwater,” Dr. Schleider said. “The response can’t be ‘Forget all of it.’ It should be ‘What about this intervention was unhelpful?’”
Other researchers echoed her concern, pointing to studies that show that on average, students benefit from social and emotional learning courses.
One of the largest, a 2023 meta-analysis of 252 classroom programs in 53 countries, found that students who participated performed better academically, displayed better social skills and had lower levels of emotional distress or behavioral problems. In that context, negative effects in a handful of trials appear modest, the researchers said.
“We clearly have not figured out how to do them yet, but I can’t imagine any population-based intervention that the field got right the first time,” said Dr. Andrew J. Gerber, the president and medical director of Silver Hill Hospital and a practicing child and adolescent psychiatrist.
“Really, if you think about almost everything we do in schools, we don’t have great evidence for it working,” he added. “That doesn’t mean we don’t do it. It just means that we’re constantly thinking about ways to improve it.”
‘We want everyone to have it’
These debates are taking place a long way away from classrooms, where mental health curriculums are increasingly commonplace.
Allyson Kangisser, a counselor at Woodsdale Elementary School in Wheeling, W.Va., said the focus in her school is on basic coping skills. In the early grades, students are asked, “What things can you do to take care of yourself when you’re having big feelings?”
Starting in third grade, they take on more complex material, such as watching cartoon characters to distinguish transient stress from chronic conditions like depression. “We’re not trying to have them diagnose themselves,” Ms. Kangisser said. “We are saying, what do you feel — this one? Or this one?”
At the school’s sixth annual mental health fair last month, Woodsdale students walked through a giant inflatable brain, its lobes neatly labeled. They did yoga stretches and talked about regulating their emotions. Ms. Kangisser said the event is valuable precisely because it is universal, so troubled children are not singled out.
“The mental health fair, everybody does it,” she said. “It’s not ‘You need it, and you don’t.’ We want everyone to have it, because you just never know.”
By the time the students reach college, they will have absorbed enormous amounts of information about mental health — from school, but also from social media and from one another.
Dr. Jessica Gold, chief wellness officer for the University of Tennessee system, said the college students she sees are recognizably different — more comfortable speaking about their emotions and more willing to be vulnerable. They also overuse diagnostic terms and have the self-assurance to question a psychiatrist’s judgment.
“It’s sort of a double-edged sword,” she said. “We want people to talk about this more, but we don’t want that to lead to overdiagnosis or incorrect diagnosis or overtreatment. We want it to lead to normalizing of having feelings.”
Lucy Kim, a Yale senior who has lobbied for better mental health support on campus, described the prevalence inflation hypothesis as “disheartening, dismissive and potentially dangerous,” providing another way to discount the experiences of young people.
“As a college student, I see a generation of young people around me impacted by a depth and breadth of loneliness, exhaustion and disillusionment suggestive of a malaise that goes deeper than the general vicissitudes of life,” said Ms. Kim, 23.
Overdiagnosis does happen, she said, and so does glorification of mental health disorders. But stigma and barriers to treatment remain the bigger problem. “I can confidently say I have never heard anyone respond to disclosures of depression with ‘That’s so cool, I wish I had that, too,’” she said.
Ellen Barry is a reporter covering mental health for The Times. More about Ellen Barry
Managing Anxiety and Stress
Stay balanced in the face of stress and anxiety with our collection of tools and advice..
How are you, really? This self-guided check-in will help you take stock of your emotional well-being — and learn how to make changes .
These simple and proven strategies will help you manage stress , support your mental health and find meaning in the new year.
First, bring calm and clarity into your life with these 10 tips . Next, identify what you are dealing with: Is it worry, anxiety or stress ?
Persistent depressive disorder is underdiagnosed, and many who suffer from it have never heard of it. Here is what to know .
If you notice drastic shifts in your mood during certain times of the year, you could have seasonal affective disorder. Here are answers to your top questions about the condition .
How much anxiety is too much? Here is how to establish whether you should see a professional about it .
China launches campaign to halt school bullying, excessive homework
- Medium Text

Sign up here.
Reporting by Farah Master and the Beijing newsroom; Editing by Bernadette Baum
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. New Tab , opens new tab

World Chevron

Singapore to inaugurate new PM as Lee makes way after 20 years in charge
Singapore will inaugurate Lawrence Wong on Wednesday as its new prime minister and fourth leader since independence six decades ago, completing a carefully calibrated power transfer designed to guarantee continuity in the wealthy city-state.

Send a message to the Office of Communications and Marketing or email us directly at [email protected] .
How do I talk about public health advocacy?
Advocacy is an effective way to support evidence-based health policies, but navigating the process can be tricky! We asked Dr. Ciara Zachary how to get started.
A community member’s guide to getting started. As public health allies, we all have a role to play in teaching, training and advocating for issues of public health importance. Uniting our voices is an effective way to support public officials in making evidence-based decisions on health policy, but navigating the process can be tricky! We asked an expert at the Gillings School for tips on how to get started.
by Ciara Zachary, PhD, MPH, Assistant Professor of Health Policy and Management
Check out a recent Gillings School Inclusive Excellence Community Conversation on “Public Health Advocacy: Gun Violence Prevention as a Public Health Issue,” which includes Dr. Ciara Zachary (starting at 44:10)!
Step 1: Identify your capacity.
Advocacy can take many forms. Think about what skills, knowledge or experiences you can contribute — and what your capacity is to contribute them. Can you write emails or provide transportation? Are you good at organizing? Do you have a compelling story to share? Does your public health knowledge lend itself to a particular issue? Whatever your contribution may be, there is a place for it.

Step 2: Do your homework.
If you are very passionate about an issue, chances are, others are, too. Find a way to get plugged into existing groups so you can best apply your skills instead of trying to do it all or duplicating the efforts of others. Existing groups typically have defined policy goals and understand strategies that are most effective for creating change. Many are also led by those with lived experience who are most impacted by policy or lack thereof.
Step 3: Build relationships.
Relationships are key to mobilizing support. Understand the value you can provide to others, whether that be through education, skills or storytelling. Learn who is being impacted and bring diverse voices into your coalition. Partner with those who have complimentary skills, connections or influence and can establish trusting, friendly relationships with organizations or legislators.
Step 4: Set realistic expectations.
Making progress on policy can happen quickly or very slowly. Expectations that are clearly defined ensure that, when progress moves slower than anticipated, you can maintain energy in a movement, overcome challenges and address concerns of partners who provide resources.
Step 5: Determine your bright line.
A bright-line standard is your way of setting boundaries. Many aspects of policy involve compromise, so it’s important to identify areas where concessions are acceptable — and where they’re not.
Additional considerations:
- Practice self-care. Learn when to step away and take a break before you burn out or become discouraged. Connect with friends who can encourage you, especially when setbacks happen.
- Learn the difference between advocacy and lobbying. While the two actions have overlapping goals, they are not always the same. Advocacy is a broad term that involves raising awareness, educating and supporting programs and policies. Lobbying involves directly urging a lawmaker to take a position on a specific piece of legislation. Many public health organizations encourage advocacy but may not permit lobbying.
- Use the resources you have in public health. If you’re not sure where to begin, check out resources from public health organizations like the American Public Health Association and the National Association of County & City Health Officials.
- Do not undermine community-driven efforts. Advocacy involves collaboration among those who are directly impacted by policy, which means it’s important to ensure that you do not prioritize your own goals over those of the whole community.

Let's stay in touch!
Sign up to our Front Lines newsletter to get the latest news twice a month. ( Sample issue )
More from this issue
- China launches campaign to halt school bullying, excessive homework and boost student's mental health
China launches campaign to halt school bullying, excessive homework and boost student's mental health

Visual Stories

China launches campaign to halt school bullying, excessive homework
HONG KONG (Reuters) – China’s Ministry of Education said on Tuesday it was launching a campaign to address issues including excessive homework and bullying in schools, as part of efforts to boost students’ mental health.
The announcement came a day after the ministry said it was carrying out mental health education for teachers and students, with particular focus on rural migrant children or those “left behind,” whose parents work in large cities for much of the year.
The ministry’s notice, published on its website, detailed 12 negative practices at schools, including encroachment during scheduled breaks, neglect and tolerance of bullying behaviour.
Beijing has, since 2021, tried to reform the education sector and ease academic pressure on students, clamping down on a $120 billion private tutoring industry to cut education costs. Many residents have cited high childcare and education costs as reasons not to have children.
The announcements come after the killing of a 13-year old boy in northern China, whose case triggered a heated media debate over juvenile crime and the plight of children left at home by migrant workers.
Three boys were arrested after they allegedly bullied and killed the student in the small city of Handan on March 10.
(Reporting by Farah Master and the Beijing newsroom; Editing by Bernadette Baum)
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Current Weather »
Coldwater, mi.

- Open access
- Published: 13 May 2024
The impact of the world’s first regulatory, multi-setting intervention on sedentary behaviour among children and adolescents (ENERGISE): a natural experiment evaluation
- Bai Li ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-2706-9799 1 ,
- Selene Valerino-Perea 2 ,
- Weiwen Zhou 3 ,
- Yihong Xie 4 ,
- Keith Syrett 5 ,
- Remco Peters 1 ,
- Zouyan He 4 ,
- Yunfeng Zou 4 ,
- Frank de Vocht 6 , 7 &
- Charlie Foster 1
International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity volume 21 , Article number: 53 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
59 Altmetric
Metrics details
Regulatory actions are increasingly used to tackle issues such as excessive alcohol or sugar intake, but such actions to reduce sedentary behaviour remain scarce. World Health Organization (WHO) guidelines on sedentary behaviour call for system-wide policies. The Chinese government introduced the world’s first nation-wide multi-setting regulation on multiple types of sedentary behaviour in children and adolescents in July 2021. This regulation restricts when (and for how long) online gaming businesses can provide access to pupils; the amount of homework teachers can assign to pupils according to their year groups; and when tutoring businesses can provide lessons to pupils. We evaluated the effect of this regulation on sedentary behaviour safeguarding pupils.
With a natural experiment evaluation design, we used representative surveillance data from 9- to 18-year-old pupils before and after the introduction of the regulation, for longitudinal ( n = 7,054, matched individuals, primary analysis) and repeated cross-sectional ( n = 99,947, exploratory analysis) analyses. We analysed pre-post differences for self-reported sedentary behaviour outcomes (total sedentary behaviour time, screen viewing time, electronic device use time, homework time, and out-of-campus learning time) using multilevel models, and explored differences by sex, education stage, residency, and baseline weight status.
Longitudinal analyses indicated that pupils had reduced their mean total daily sedentary behaviour time by 13.8% (95% confidence interval [CI]: -15.9 to -11.7%, approximately 46 min) and were 1.20 times as likely to meet international daily screen time recommendations (95% CI: 1.01 to 1.32) one month after the introduction of the regulation compared to the reference group (before its introduction). They were on average 2.79 times as likely to meet the regulatory requirement on homework time (95% CI: 2.47 to 3.14) than the reference group and reduced their daily total screen-viewing time by 6.4% (95% CI: -9.6 to -3.3%, approximately 10 min). The positive effects were more pronounced among high-risk groups (secondary school and urban pupils who generally spend more time in sedentary behaviour) than in low-risk groups (primary school and rural pupils who generally spend less time in sedentary behaviour). The exploratory analyses showed comparable findings.
Conclusions
This regulatory intervention has been effective in reducing total and specific types of sedentary behaviour among Chinese children and adolescents, with the potential to reduce health inequalities. International researchers and policy makers may explore the feasibility and acceptability of implementing regulatory interventions on sedentary behaviour elsewhere.
The growing prevalence of sedentary behaviour in school-aged children and adolescents bears significant social, economic and health burdens in China and globally [ 1 ]–[ 3 ]. Sedentary behaviour refers to any waking behaviour characterised by an energy expenditure equal or lower than 1.5 metabolic equivalents (METs) while sitting, reclining, or lying [ 3 ]. Evidence from systematic reviews, meta-analyses and longitudinal studies have shown that excessive sedentary behaviour, in particular recreational screen-based sedentary behaviour, affect multiple dimensions of children and adolescents’ wellbeing, spanning across mental health [ 4 ], cognitive functions/developmental health/academic performance [ 5 ], [ 6 ], quality of life [ 7 ], and physical health [ 8 ]. In China, over 60% of school pupils use part of their sleep time to play mobile phones/digital games and watch TV programmes, and 27% use their sleep time to do homework or other learning activities [ 9 ]. Screen-based, sedentary entertainment has become the leading cause for going to bed late, which is linked to detrimental consequences for children’s physical and mental health [ 10 ]. Notably, academic-related activities such as post-school homework and off campus tutoring also contribute to the increasing amounts of sedentary behaviour. According to the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) report, China is the leading country in time spent on homework by adolescents (14 h/week on average) [ 11 ].
The COVID-19 pandemic exacerbated this global challenge, with children and adolescents reported to have been the most affected group [ 12 ]. Schools are a frequently targeted setting for interventions to reduce sedentary behaviour [ 13 ]. However, school-based interventions have had limited success when delivered under real-world conditions or at scale [ 14 ]. School-based interventions alone have also been unsuccessful in mitigating the trend of increasing sedentary behaviour that is driven by a complex system of interdependent factors across multiple sectors [ 13 ]. Even for parents and carers who intend to restrict screen-based sedentary behaviour and for children who wish to reduce screen-based sedentary behaviour, social factors including peer pressure often form barriers to changing behaviour [ 15 ]. In multiple public health fields such as tobacco control and healthy eating promotion, there has been a notable shift away from downstream (e.g., health education) towards an upstream intervention approach (e.g., sugar taxation). However, regulatory actions for sedentary behaviour are scarce [ 16 ]. World Health Organization (WHO) 2020 guidelines on sedentary behaviour encourage sustainable and scalable approaches for limiting sedentary behaviour and call for more system-wide policies to improve this global challenge [ 8 ]. Up-stream interventions can act on sedentary behaviour more holistically and have the potential to maximise reach and health impact [ 13 ]. In response to this pressing issue, and to widespread demands from many parents/carers, the Chinese government introduced nationwide regulations in 2021 to restrict (i) the amount of homework that teachers can assign, (ii) when (and for how long) online gaming businesses can provide access to young people, and (iii) when tutoring businesses can provide lessons [ 17 ], [ 18 ]. Consultations with WHO officials and reviewers of international health policy interventions confirmed that this is currently the only government-led, multi-setting regulatory intervention on multiple types of sedentary behaviour among school-aged children and adolescents. A detailed description of this programme is available in the Additional File 1 .
We evaluated the impact of this regulatory intervention on sedentary behaviour in Chinese school-aged children and adolescents. We also investigated whether and how intervention effects differed by sex, education stage, geographical area, and baseline weight status.
Study design
The introduction of the nationwide regulation provided a unique opportunity for a natural experiment evaluation where the pre-regulation comparator group data (Wave 1) was compared to the post-regulation group data (Wave 2). Multiple components of the intervention (see Additional File 1 ) were introduced in phases from July 2021 with all components being fully in place by September 2021 [ 17 ], [ 18 ]. This paper follows the STROBE reporting guidance [ 19 ], [ 20 ].
Data source, study population and sampling
We obtained regionally representative data on 99,947 pupils who are resident in the Chinese province of Guangxi as part of Guangxi Centre for Disease Control and Prevention’s (CDC) routine surveillance. The data, available from participants in grade 4 (aged between 9 and 10 years) and higher, were collected using a multi-stage random sampling design (Fig. 1 ) through school visits by trained health professionals following standardised protocols (see Supplementary Fig. 1 , Additional File 1 ). In Wave 1 (data collected from September to November 2020), pupils were randomly selected from schools in 31 urban/rural counties from 14 cities in Guangxi. At least eight schools, including primary, secondary, high schools, and ‘vocational high schools’, were selected from urban counties. Five schools were selected from rural counties. Approximately 80 students were randomly selected from each grade at the schools selected. The same schools were invited to participate in Wave 2 (data collected from September to November 2021), and new schools were invited to replace Wave 1 schools that no longer participated. Children with available data at both Wave 1 and Wave 2 represented approximately 10% of the sample ( n = 7,587). Paper-based questionnaires were administrated to students by trained personnel or teachers. The questionnaires were designed and validated by China National Health Commission, and have been utilised in routine surveillance throughout the country.
Flow diagram of participants included in the ENERGISE study
We used data from the age groups 7–18 years for most analyses. For specific analyses of homework and out-of-campus tutoring, we excluded high school pupils (16–18 years) because the homework and out-of-campus tutoring regulations apply to primary (7–12 years) and middle (13–15 years) school pupils only. Furthermore, participants without socio-demographic data or those who reported medical history of disease, or a physical disability were excluded. This gave us a total sample of 7,054 eligible school-aged children and adolescents with matching data (longitudinal sample).
Outcomes and subgroups
Guangxi CDC used purposively designed questions for surveillance purposes to assess sedentary behaviour outcomes (Table 1 ).
The primary outcomes of interest included: (1) total sedentary behaviour time, (2) homework time, (3) out-of-campus learning (private tutoring) time, and (4) electronic device use time (Table 1 ). We considered electronic device use time, including mobile phones, handheld game consoles, and tablets, the most suitable estimator of online game time (estimand) in the surveillance programme since these are the main devices used for online gaming in China [ 23 ]. Secondary outcomes were: (1) total screen-viewing time, (2) internet-use time, (3) likelihood of meeting international screen-viewing time recommendations, and (4) likelihood of meeting the regulation on homework time (Table 1 ).
We calculated total sedentary behaviour time as the sum of total screen-viewing time (secondary outcome), homework time, and out-of-campus learning time (Table 1 ). Total screen-viewing time represents the sum of electronic device use time per day, TV/video game use time per day, and computer use time per day (Table 1 ). Total screen-viewing time was considered as an alternative estimator of online game time (estimand) since TV/videogame console use time and computer time could also capture the small proportion of children who use these devices for online gaming (Table 1 ). The international screen-viewing time recommendations were based on the American Academy of Paediatrics guidelines [ 21 ]. We did not include internet use time (secondary outcome) in total screen-viewing time, and total sedentary behaviour time, because this measure likely overlaps with other variables.
We defined subgroups by demographic characteristics, including the child’s sex (at birth: girls or boys), date of birth, education stage [primary school or secondary school [including middle school, high school, and ‘occupational schools’]), children’s residency (urban versus rural) and children’s baseline weight status (non-overweight versus overweight/obesity). Each sampling site selected for the survey was classified by the surveillance personnel as urban/rural and as lower-, medium-, or higher-economic level based on the area’s gross domestic product (GDP) per capita. The area’s GDP per capita was measured by the Chinese Centre for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Trained personnel also measured height, and weight using calibrated stadiometers and scales. Children’s weight/height were measured with light clothing and no shoes. Measurements during both waves were undertaken when students lived a normal life (no lockdowns, school were opened normally). We classified weight status (normal weight vs. overweight/obesity) according to the Chinese national reference charts [ 24 ].
Statistical analyses
We treated sedentary behaviour values that exceeded 24-hours per day as missing. We did not exclude extreme values for body mass index from the analyses 25 . Additional information, justifications, and results of implausible and missing values can be found in the Supplementary Table 1 , Additional File 1 .
The assumptions for normality and heteroscedasticity were assessed visually by inspecting residuals. We assessed multicollinearity via variance inflation factors. The outcome variables for linear regression outcomes were transformed using square roots to meet assumptions. We reported descriptive demographic characteristics (age, sex, area of residence, socioeconomic status), weight status, and outcome variables using means (or medians for non-normally distributed data) and proportions [ 26 ]
We ran multilevel models with random effects nested at the school and child levels to compare the outcomes in Wave 1 against Wave 2. We developed separate models for each sedentary behaviour outcome variable. We treated the introduction of the nationwide regulation as the independent binary variable (0 for Wave 1 and 1 for Wave 2). We ran linear models for continuous outcomes, logistic models for binary outcomes, and ordered logistic models for ordinal outcomes in a complete case analysis estimating population average treatment effects [ 27 ]. For the main analysis, in which participants had measurements in both Waves (longitudinal sample), only those with non-missing data at both time points were included.
We estimated marginal effects for each sedentary behaviour outcome. With a self-developed directed acyclic graph (DAG) we identified age (continuous), sex (male/female), area of residence (urban/rural), and socioeconomic status (high/medium/low) as confounders (see Supplementary Figs. 2–4, Additional File 1 ).
We evaluated subgroup effects defined by child’s sex at birth (boys versus girls), child’s stage of education (primary school versus secondary school [including middle school, high school, and ‘occupational schools’]), children’s residency (rural versus urban), and children’s baseline weight status (non-overweight versus overweight/obesity). We also repeated the covariate-adjusted model with interaction terms (between Wave and sex; Wave and child stage of education; Wave and residency; and Wave and weight status). We adjusted for multiple testing using Bonferroni correction ( p 0.05 divided by the number of performed tests for an outcome). The resulting cut-off point of p < 0.005 was used to determine the presence of any interaction effects.
We also conducted exploratory analyses (including subgroup analyses) by evaluating the same models with a representative, cross-sectional sample of 99,947 pupils. This cross-sectional sample included different schools and children at Wave 1 and Wave 2. We therefore used propensity score (PS) weighting to account for sample imbalances in the socio-demographic characteristics. Propensity scores were calculated by conducting a logistic regression, which calculated the likelihood of each individual to be in Wave 2 (dependent variable). Individual’s age, sex, area of residence and the GDP per area were treated as independent variables. Subsequently, inverse probability of treatment weighting was applied to balance the demographic characteristics in the sample in Wave 1 (unexposed to the regulatory intervention) and Wave 2 (exposed to the regulatory intervention). The sample weight for individuals in Wave 1 were calculated using the Eq. 1/ (1-propensity score). The sample weight for individuals in Wave 2 were calculated using the Eq. 1/propensity score [ 28 ].
We only ran linear models for continuous outcomes since it was not possible to run PS-weighted multilevel models with this sample size in Stata. We conducted all statistical analyses in Stata version 16.0.
Participant sample
In our primary, longitudinal analyses, we analysed data from 7,054 children and adolescents. The mean age was 12.3 years (SD, 2.4) and 3,477 (49.3%) were girls (Table 2 ). More detailed information on characteristics of subgroups in the longitudinal sample are presented in the Supplementary Tables 2–5, Additional File 2 .
Primary outcomes
Children and adolescents reported a reduction in their daily mean total sedentary behaviour time by 13.8% (95% CI: -15.9 to -11.7), or 46 min, on average between Waves 1 and 2. Participants were also less likely to report having increased their time spent on homework (adjusted odd ratio/AOR: 0.39; 95% CI: 0.35–0.43) and in out-of-campus learning (AOR: 0.53; 95% CI: 0.47 to 0.59) in Wave 2 in comparison to Wave 1, respectively (Tables 3 and 4 ). We did not find any changes in electronic device use time.
Secondary outcomes
Participants reported reducing their mean daily screen-viewing time by 6.4% (95% CI: -9.6 to -3.3%), or 10 min, on average (Tables 3 and 4 ). Participants were also 20% as likely to meet international screen time recommendations (AOR: 1.20; 95% CI: 1.09 to 1.32) and were 2.79 times as likely to meet the regulatory requirement on homework time (95% CI: 2.47 to 3.14) compared to the reference group (before the introduction of the regulation).
Subgroup analyses
Most screen- and study-related sedentary behaviour outcomes differed by education stage ( p < 0.005) (see Supplementary Tables 6–13, Additional File 2 ), with the reductions being larger in secondary school pupils than in primary school pupils (Tables 3 and 4 , and Table 5 ). Only secondary school pupils reduced their total screen-viewing time (-8.4%; 95% CI: -12.4 to -4.3) and were also 1.41 times as likely to meet screen-viewing recommendations (AOR: 1.41; 95% CI: 1.23 to 1.61) at Wave 2 compared to Wave 1.
Conversely, at Wave 2, primary school pupils reported a lower likelihood of spending more time doing homework (AOR: 0.30; 95%: 0.26 to 0.34) than secondary school pupils (AOR: 0.58; 95% CI: 0.50 to 0.67) compared to their counterparts at Wave 1. At Wave 2, primary school pupils also had a higher likelihood of reporting meeting homework time recommendations (AOR: 3.61; 95% CI: 3.09 to 4.22) than secondary school pupils (middle- and high school) (AOR: 2.11; 95% CI: 1.74 to 2.56) compared to their counterparts at Wave 1 (Table 5 ). There was also a residence interaction effect ( p < 0.001) in total sedentary behaviour time, with participants in urban areas reporting larger reductions (-15.3%; 95% CI: -17.8 to -12.7) than those in rural areas (-11.2%; 95% CI: -15.0 to -7.4). There was no evidence of modifying effects by children’s sex or baseline weight status (Tables 4 and 5 ).
Findings from the exploratory repeated cross-sectional analyses were similar to the findings of the main longitudinal analyses including total sedentary behaviour time, electronic device use time, total screen-viewing time and internet use time (see Supplementary Tables 14–23, Additional File 2 ).
Principal findings
Our study evaluated the impact of the world’s first regulatory, multi-setting intervention on multiple types of sedentary behaviour among school-aged children and adolescents in China. We found that children and adolescents reduced their total sedentary behaviour time, screen-viewing time, homework time and out-of-campus learning time following its implementation. The positive intervention effects on total screen-viewing time (-8.4 vs. -2.3%), and the likelihood of meeting recommendations on screen-viewing time (1.41 vs. 1.02 AOR) were more pronounced in secondary school pupils compared with primary school pupils. Intervention effects on total sedentary behaviour time (-15.3 vs. -11.2%) were more pronounced among pupils living in the urban area (compared to pupils living in the rural area). These subgroup differences imply that the regulatory intervention benefit more the groups known to have a higher rate of sedentary behaviour [ 29 ].
Interestingly, the observed reduction in electronic device use itself did not reach statistical significance following implementation of regulation. This could be viewed as a positive outcome if this is correctly inferred and not the result of reporting bias or measurement error. International data indicated that average sedentary and total screen time have increased among children due to the COVID-19 pandemic [ 12 ]. However, such interesting finding might be explained by the absence of lockdowns in Guangxi during both surveillance waves when most school-aged students outside China were affected by pandemic mitigation measures such as online learning.
Strengths and weaknesses
Our study has several notable strengths. This is the first study to evaluate the impact of multi-setting nationwide regulations on multiple types of sedentary behaviour in a large and regionally representative sample of children and adolescents. Still, to gain a more comprehensive view of the regulatory intervention on sedentary behaviour across China, similar evaluation research should be conducted in other regions of China. Furthermore, access to a rich longitudinal dataset allowed for more robust claims of causality. The available data also allowed us to measure the effect of the intervention on multiple sedentary behaviours including recreational screen-time and academic-related behaviours. Lastly, the large data set allowed us to explore whether the effect of the regulatory intervention varied across important subgroups, suggesting areas for further research and development.
Some limitations need to be taken into consideration when interpreting our findings. First, a common limitation in non-controlled/non-randomised intervention studies is residual confounding. We aimed to limit this by adjusting our analysis for confounders known to impact the variables of interest, but it is impossible to know whether important confounding may still have been present. With maturation bias, it is possible that secular trends are the cause for any observed effects. However, this seems unlikely in our study as older children may spend more time doing homework [ 23 ] and engage more in screen-viewing activities [ 30 ]. In this study, we observed reductions in these outcomes. The use of self-reported outcomes (social desirability bias) was a limitation and might have led to the intervention effects being over-estimated [ 13 ]. However, since our data were collected as part of a routine surveillance programme, pupils were unaware of the evaluation. This might mitigate reporting bias. In addition, the data were collected in Guangxi which might not representative of the whole population in China. Another limitation is using electronic device use time as a proxy measure of online gaming time. It is possible that electronic devices can be used for other purposes. However, mobile phones, handheld game consoles and tablets are the main devices used for online gaming. In this study, electronic device use time provided a practical means of assessing the broad effects of regulatory measures on screen time behaviours, including online gaming, in a large (province level) surveillance programme. In the future, instruments specifically designed to capture online gaming behaviour should be used in surveillance and research work.
Comparisons with other studies
Neither China nor other countries globally have previously implemented and evaluated multi-setting regulatory interventions on multiple types of sedentary behaviour, which makes comparative discussions challenging. In general, results of health behaviour research over the past decades have shown that interventions that address structural and environmental determinants of multiple behaviours to be more effective in comparison with individual-focussed interventions [ 31 ]. Furthermore, the continuous and universal elements of regulatory interventions may be particularly important explanations for the observed reductions in sedentary behaviour. Standalone school and other institution-led interventions may struggle with financial and logistic costs which threaten long-term implementation [ 13 ]. In contrast, the universality element of regulatory intervention can reduce or remove peer pressures and potential stigmatisation among children and teachers that are often associated with more selective/targeted interventions [ 24 ]. Our findings support WHO guidelines for physical activity and sedentary behaviour that encourage sustainable and scalable approaches for limiting sedentary behaviour and call for more system-wide policies to improve this global challenge[ 8 ].
Implications for future policy and research
Our study has important implications for future research and practice both nationally and internationally. Within China, future research should focus on optimising the implementation of the regulatory intervention through implementation research and assess long-term effects of the regulation on both behavioral and health outcomes. Internationally, our findings also provide a promising policy avenue for other countries and communities outside of China to explore the opportunities and barriers to implement such programmes on sedentary behaviour. This exploratory process could start with assessing how key stakeholders (including school-aged children, parents/carers, schoolteachers, health professionals, and policy makers) within different country contexts perceive regulatory actions as an intervention approach for improving health and wellbeing in young people, and how they can be tailored to fit their own contexts. Within public health domains, including healthy eating promotion, tobacco and alcohol control, regulatory intervention approaches (e.g., smoking bans and sugar taxation) have been adopted. However, regulatory actions for sedentary behaviour are scarce [ 19 ]. Within the education sector, some countries recently banned mobile phone use in schools for academic purpose [ 25 ]. While this implies potential feasibility and desirability of such interventions internationally, there is little research on the demand for, and acceptability of, multi-faceted sedentary behaviour regulatory interventions for the purpose of improving health and wellbeing. It will be particularly important to identify and understand any differences in perceptions and feasibility both within (e.g., public versus policy makers) and across countries of differing socio-cultural-political environments.
This natural experiment evaluation indicates that a multi-setting, regulatory intervention on sedentary behaviour has been effective in reducing total sedentary behaviour, and multiple types of sedentary behaviour among Chinese school-aged children and adolescents. Contextually appropriate, regulatory interventions on sedentary behaviour could be explored and considered by researchers and policy makers in other countries.
Data availability
Access to anonymised data used in this study can be requested through the corresponding author BL, subject to approval by the Guangxi CDC. WZ and SVP have full access to all the data in the study and takes responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis.
Abbreviations
Centre for disease control and prevention
Directed acyclic graph
Gross domestic product
Metabolic equivalents
Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development
Bao R, Chen S-T, Wang Y, Xu J, Wang L, Zou L, Cai Y. Sedentary Behavior Research in the Chinese Population: a systematic scoping review. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2020, 17(10).
Nguyen P, Le LK-D, Ananthapavan J, Gao L, Dunstan DW, Moodie M. Economics of sedentary behaviour: a systematic review of cost of illness, cost-effectiveness, and return on investment studies. Prev Med. 2022;156:106964.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
World Health Organization. WHO guidelines on physical activity and sedentary behaviour. In. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2020.
Zhang J, Yang SX, Wang L, Han LH, Wu XY. The influence of sedentary behaviour on mental health among children and adolescents: a systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. J Affect Disord. 2022;306:90–114.
Madigan S, Browne D, Racine N, Mori C, Tough S. Association between Screen Time and children’s performance on a Developmental Screening Test. JAMA Pediatr. 2019;173(3):244–50.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Pagani LS, Fitzpatrick C, Barnett TA, Dubow E. Prospective Associations between Early Childhood Television Exposure and academic, psychosocial, and Physical Well-being by Middle Childhood. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2010;164(5):425–31.
Boberska M, Szczuka Z, Kruk M, Knoll N, Keller J, Hohl DH, Luszczynska A. Sedentary behaviours and health-related quality of life. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Health Psychol Rev. 2018;12(2):195–210.
Fiona CB, Salih SA-A, Stuart B, Katja B, Matthew PB, Greet C, Catherine C, Jean-Philippe C, Sebastien C, Roger C et al. World Health Organization 2020 guidelines on physical activity and sedentary behaviour. British Journal of Sports Medicine 2020, 54(24):1451.
China Sleep Research Association. Sleep White Paper of Chine People’s Health. In. Beijing, China; 2022.
Chaput J-P, Gray CE, Poitras VJ, Carson V, Gruber R, Olds T, Weiss SK, Gorber SC, Kho ME, Sampson M, et al. Systematic review of the relationships between sleep duration and health indicators in school-aged children and youth. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2016;41(6):S266–82. (Suppl. 3)).
OECD. Does Homework Perpetuate inequities in Education? OECD Publishing 2014(46):4.
Trott M, Driscoll R, Iraldo E, Pardhan S. Changes and correlates of screen time in adults and children during the COVID-19 pandemic: a systematic review and meta-analysis. eClinicalMedicine 2022, 48.
van Sluijs EMF, Ekelund U, Crochemore-Silva I, Guthold R, Ha A, Lubans D, Oyeyemi AL, Ding D, Katzmarzyk PT. Physical activity behaviours in adolescence: current evidence and opportunities for intervention. Lancet. 2021;398(10298):429–42.
Cassar S, Salmon J, Timperio A, Naylor P-J, van Nassau F, Contardo Ayala AM, Koorts H. Adoption, implementation and sustainability of school-based physical activity and sedentary behaviour interventions in real-world settings: a systematic review. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Activity. 2019;16(1):120.
Article Google Scholar
Martins J, Costa J, Sarmento H, Marques A, Farias C, Onofre M, Valeiro MG. Adolescents’ perspectives on the barriers and facilitators of physical activity: an updated systematic review of qualitative studies. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2021, 18(9).
Gelius P, Messing S, Tcymbal A, Whiting S, Breda J, Abu-Omar K. Policy Instruments for Health Promotion: a comparison of WHO Policy Guidance for Tobacco, Alcohol, Nutrition and Physical Activity. Int J Health Policy Manage. 2022;11(9):1863–73.
Google Scholar
The General Office of the CPC Central Committee and the General Office of the State. Council issued the opinions on further reducing the Burden of Homework and off-campus training for students in the stage of Compulsory Education. https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/2021-07/24/content_5627132.htm .
Notice of the State Press and Publication Administration on Further Strict. Management to Effectively Prevent Minors from Being Addicted to Online Games. https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/zhengceku/2021-09/01/content_5634661.htm .
Craig P, Cooper C, Gunnell D, Haw S, Lawson K, Macintyre S, Ogilvie D, Petticrew M, Reeves B, Sutton M, et al. Using natural experiments to evaluate population health interventions: new Medical Research Council guidance. J Epidemiol Commun Health. 2012;66(12):1182–6.
Craig P, Campbell M, Bauman A, Deidda M, Dundas R, Fitzgerald N, Green J, Katikireddi SV, Lewsey J, Ogilvie D, et al. Making better use of natural experimental evaluation in population health. BMJ. 2022;379:e070872.
American Academy of Pediatrics. Children, adolescents, and television. Pediatrics. 2001;107(2):423–6.
Bauer CP. Applied Causal Analysis (with R). In. Bookdown; 2020.
Matthay EC, Hagan E, Gottlieb LM, Tan ML, Vlahov D, Adler NE, Glymour MM. Alternative causal inference methods in population health research: evaluating tradeoffs and triangulating evidence. SSM - Popul Health. 2020;10:100526.
Greenberg MT, Abenavoli R. Universal interventions: fully exploring their impacts and potential to produce Population-Level impacts. J Res Educational Eff. 2017;10(1):40–67.
Selwyn N, Aagaard J. Banning mobile phones from classrooms—An opportunity to advance understandings of technology addiction, distraction and cyberbullying. Br J Edu Technol. 2021;52(1):8–19.
Boushey CJ, Harris J, Bruemmer B, Archer SL. Publishing nutrition research: A review of sampling, sample size, statistical analysis, and other key elements of manuscript preparation, Part 2. J Acad Nutr Dietet. 2008;108(4):679–688.
Matthay EC, Hagan E, Gottlieb LM, Tan ML, Vlahov D, Adler NE, Glymour MM. Alternative causal inference methds in population health research:Evaluating tradeoffs nd triangulating evidence. SSM - Population Health. 2020;10:100526.
Chesnaye NC, Stel VS, Tripepi G, Dekker FW, Fu EL, Zoccali C, Jager KJ. An introduction to inverse probability of treatment weighting in observation research. Clin Kid J. 2021;15(1):14–20.
Song C, Gong W, Ding C, Yuan F, Zhang Y, Feng G, Chen Z, Liu A. Physical activity and sedentary behaviour among Chinese children agd 6-17 years: a cross-sectional analysis of 2010-2012 China National Nutrition and Health Survey. BMC Public Health. 2019;19(1):936.
Zhu X, Haegele JA, Tang Y, Wu X. Physical activity and sedentary behaviors of urban chinese children: grade level prevalence and academic burden associations. BioMed Res Int. 2017;2017:7540147.
Rutter H, Bes-Rastrollo M, de Henauw S, Lathi-Koski M, Lehtinen-Jacks S, Mullerova D, Rasmussen F, Rissanen A, Visscher TLS, Lissner L. Balancing upstream and downstream measures to tackle the obesity epidemic: a position statement from the european association for the study of obesity. Obesity Facts. 2017;10(11):61–63.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge Dr Peter Green and Dr Ruth Salway for providing feedback on the initial data analysis plan, and Dr Hugo Pedder and Lauren Scott who provided feedback on the statistical analyses.
This work was funded by the Wellcome Trust through the Global Public Health Research Strand, Elizabeth Blackwell Institute for Health Research. The funder of our study had no role in the design and conduct of the study; collection, management, analysis, and interpretation of the data; preparation, review, or approval of the manuscript; and decision to submit the manuscript for publication.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Centre for Exercise, Nutrition and Health Sciences, School for Policy Studies, University of Bristol, Bristol, UK
Bai Li, Remco Peters & Charlie Foster
Public Health Wales, Cardiff, UK
Selene Valerino-Perea
Department of Nutrition and School Health, Guangxi Center for Disease Control and Prevention, Nanning, Guangxi, China
Weiwen Zhou
School of Public Health, Guangxi Medical University, Nanning, Guangxi, China
Yihong Xie, Zouyan He & Yunfeng Zou
Centre for Health, Law, and Society, School of Law, University of Bristol, Bristol, UK
Keith Syrett
Population Health Sciences, Bristol Medical School, University of Bristol, Bristol, UK
Frank de Vocht
NIHR Applied Research Collaboration West (ARC West), Bristol, UK
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
BL conceived the study idea and obtained the funding with support from WZ, CF, KS, YX, YZ, ZH and RP. BL, CF, FdV and KS designed the study. WZ led data collection and provided access to the data. YX, SVP and ZH cleaned the data. SVP analysed the data with guidance from BL, FdV and CF. BL, SVP and RP drafted the paper which was revised by other authors. All authors read and approved the final manuscript for submission.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Bai Li .
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval and consent to participate.
Ethics approvals were granted by the School for Policy Studies Research Ethics Committee at the University of Bristol (reference number SPSREC/20–21/168) and the Research Ethics Committee at Guangxi Medical University (reference number 0136). Written informed consent was obtained from each participant, and a parent or guardian for participants aged < 20 years.
Consent for publication
The co-authors gave consent for publication.
Competing interests
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential competing interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1
Supplementary material 2, supplementary material 3, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Li, B., Valerino-Perea, S., Zhou, W. et al. The impact of the world’s first regulatory, multi-setting intervention on sedentary behaviour among children and adolescents (ENERGISE): a natural experiment evaluation. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act 21 , 53 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12966-024-01591-w
Download citation
Received : 20 December 2023
Accepted : 04 April 2024
Published : 13 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12966-024-01591-w
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Sedentary behaviour
- Physical activity
- Regulatory intervention
- Health policy
- Screen time
- Natural experiment
- Mental health
- Health promotion
- Child health
International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity
ISSN: 1479-5868
- Submission enquiries: Access here and click Contact Us
- General enquiries: [email protected]
- Skip to main content
- Keyboard shortcuts for audio player
- Your Health
- Treatments & Tests
- Health Inc.
- Public Health
Perspective
When pto stands for 'pretend time off': doctors struggle to take real breaks.
Mara Gordon

A survey shows that doctors have trouble taking full vacations from their high-stress jobs. Even when they do, they often still do work on their time off. Wolfgang Kaehler/LightRocket via Getty Images hide caption
A survey shows that doctors have trouble taking full vacations from their high-stress jobs. Even when they do, they often still do work on their time off.
A few weeks ago, I took a vacation with my family. We went hiking in the national parks of southern Utah, and I was blissfully disconnected from work.
I'm a family physician, so taking a break from my job meant not seeing patients. It also meant not responding to patients' messages or checking my work email. For a full week, I was free.
Taking a real break — with no sneaky computer time to bang out a few prescription refill requests — left me feeling reenergized and ready to take care of my patients when I returned.
But apparently, being a doctor who doesn't work on vacation puts me squarely in the minority of U.S. physicians.
Research published in JAMA Network Open this year set out to quantify exactly how doctors use their vacation time — and what the implications might be for a health care workforce plagued by burnout, dissatisfaction and doctors who are thinking about leaving medicine.
"There is a strong business case for supporting taking real vacation," says Dr. Christine Sinsky , the lead author of the paper. "Burnout is incredibly expensive for organizations."

Shots - Health News
Health workers know what good care is. pandemic burnout is getting in the way.
Researchers surveyed 3,024 doctors, part of an American Medical Association cohort designed to represent the American physician workforce. They found that 59.6% of American physicians took 15 days of vacation or less per year. That's a little more than the average American: Most workers who have been at a job for a year or more get between 10 and 14 days of paid vacation time , according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics.
However, most doctors don't take real vacation. Over 70% of doctors surveyed said they worked on a typical vacation day.
"I have heard physicians refer to PTO as 'pretend time off,'" Sinsky says, referring to the acronym for "paid time off."
Sinsky and co-authors found that physicians who took more than three weeks of vacation a year had lower rates of burnout than those who took less, since vacation time is linked to well-being and job satisfaction .
And all those doctors toiling away on vacation, sitting poolside with their laptops? Sinsky argues it has serious consequences for health care.
Physician burnout is linked to high job turnover and excess health care costs , among other problems.
Still, it can be hard to change the culture of workaholism in medicine. Even the study authors confessed that they, too, worked on vacation.
"I remember when one of our first well-being papers was published," says Dr. Colin West , a co-author of the new study and a health care workforce researcher at the Mayo Clinic. "I responded to the revisions up at the family cabin in northern Minnesota on vacation."
Sinsky agreed. "I do not take all my vacation, which I recognize as a delicious irony of the whole thing," she says.
She's the American Medical Association's vice president of professional satisfaction. If she can't take a real vacation, is there any hope for the rest of us?
I interviewed a half dozen fellow physicians and chatted off the record with many friends and colleagues to get a sense of why it feels so hard to give ourselves a break. Here, I offer a few theories about why doctors are so terrible at taking time off.
We don't want to make more work for our colleagues
The authors of the study in JAMA Network Open didn't explore exactly what type of work doctors did on vacation, but the physicians I spoke to had some ideas.
"If I am not doing anything, I will triage my email a little bit," says Jocelyn Fitzgerald , a urogynecologist at the University of Pittsburgh who was not involved in the study. "I also find that certain high-priority virtual meetings sometimes find their way into my vacations."
Even if doctors aren't scheduled to see patients, there's almost always plenty of work to be done: dealing with emergencies, medication refills, paperwork. For many of us, the electronic medical record (EMR) is an unrelenting taskmaster , delivering a near-constant flow of bureaucratic to-dos.
When I go on vacation, my fellow primary care doctors handle that work for me, and I do the same for them.
But it can sometimes feel like a lot to ask, especially when colleagues are doing that work on top of their normal workload.
"You end up putting people in kind of a sticky situation, asking for favors, and they [feel they] need to pay it back," says Jay-Sheree Allen , a family physician and fellow in preventive medicine at the Mayo Clinic.
She says her practice has a "doctor of the day" who covers all urgent calls and messages, which helps reduce some of the guilt she feels about taking time off.
Still, non-urgent tasks are left for her to complete when she gets back. She says she usually logs in to the EMR when she's on vacation so the tasks don't pile up upon her return. If she doesn't, Allen estimates there will be about eight hours of paperwork awaiting her after a week or so of vacation.
"My strategy, I absolutely do not recommend," Allen says. But "I would prefer that than coming back to the total storm."
We have too little flexibility about when we take vacation
Lawren Wooten , a resident physician in pediatrics at the University of California San Francisco, says she takes 100% of her vacation time. But there are a lot of stipulations about exactly how she uses it.
She has to take it in two-week blocks — "that's a long time at once," she says — and it's hard to change the schedule once her chief residents assign her dates.
"Sometimes I wish I had vacation in the middle of two really emotionally challenging rotations like an ICU rotation and an oncology rotation," she says, referring to the intensive care unit. "We don't really get to control our schedules at this point in our careers."
Once Wooten finishes residency and becomes an attending physician, it's likely she'll have more autonomy over her vacation time — but not necessarily all that much more.
"We generally have to know when our vacations are far in advance because patients schedule with us far in advance," says Fitzgerald, the gynecologist.
Taking vacation means giving up potential pay
Many physicians are paid based on the number of patients they see or procedures they complete. If they take time off work, they make less money.
"Vacation is money off your table," says West, the physician well-being researcher. "People have a hard time stepping off of the treadmill."
A 2022 research brief from the American Medical Association estimated that over 55% of U.S. physicians were paid at least in part based on "productivity," as opposed to earning a flat amount regardless of patient volume. That means the more patients doctors cram into their schedules, the more money they make. Going on vacation could decrease their take-home pay.
But West says it's important to weigh the financial benefits of skipping vacation against the risk of burnout from working too much.
Physician burnout is linked not only to excess health care costs but also to higher rates of medical errors. In one large survey of American surgeons , for example, surgeons experiencing burnout were more likely to report being involved in a major medical error. (It's unclear to what extent the burnout caused the errors or the errors caused the burnout, however.)
Doctors think they're the only one who can do their jobs
When I go on vacation, my colleagues see my patients for me. I work in a small office, so I know the other doctors well and I trust that my patients are in good hands when I'm away.

Doctors have their own diagnosis: 'Moral distress' from an inhumane health system
But ceding that control to colleagues might be difficult for some doctors, especially when it comes to challenging patients or big research projects.
"I think we need to learn to be better at trusting our colleagues," says Adi Shah , an infectious disease doctor at the Mayo Clinic. "You don't have to micromanage every slide on the PowerPoint — it's OK."
West, the well-being researcher, says health care is moving toward a team-based model and away from a culture where an individual doctor is responsible for everything. Still, he adds, it can be hard for some doctors to accept help.
"You can be a neurosurgeon, you're supposed to go on vacation tomorrow and you operate on a patient. And there are complications or risk of complications, and you're the one who has the relationship with that family," West says. "It is really, really hard for us to say ... 'You're in great hands with the rest of my team.'"
What doctors need, says West, is "a little bit less of the God complex."
We don't have any interests other than medicine
Shah, the infectious disease doctor, frequently posts tongue-in-cheek memes on X (formerly known as Twitter) about the culture of medicine. Unplugging during vacation is one of his favorite topics, despite his struggles to follow his own advice.
His recommendation to doctors is to get a hobby, so we can find something better to do than work all the time.
"Stop taking yourself too seriously," he says. Shah argues that medical training is so busy that many physicians neglect to develop any interests other than medicine. When fully trained doctors are finally finished with their education, he says, they're at a loss for what to do with their newfound freedom.
Since completing his training a few years ago, Shah has committed himself to new hobbies, such as salsa dancing. He has plans to go to a kite festival next year.
Shah has also prioritized making the long trip from Minnesota to see his family in India at least twice a year — a journey that requires significant time off work. He has a trip there planned this month.
"This is the first time in 11 years I'm making it to India in summer so that I can have a mango in May," the peak season for the fruit, Shah says.
Wooten, the pediatrician, agrees. She works hard to develop a full life outside her career.
"Throughout our secondary and medical education, I believe we've really been indoctrinated into putting institutions above ourselves," Wooten adds. "It takes work to overcome that."
Mara Gordon is a family physician in Camden, N.J., and a contributor to NPR. She's on X as @MaraGordonMD .
- American Medical Association
- Português Br
- Journalist Pass
Students’ passion projects address big issues in healthcare
Kate Ledger
Share this:

When graduate student Charlotte Hayes began her Ph.D. training in a lab studying brain tumors that affect young children, she was devastated to realize one reality about funding for biomedical research. "Compared to adult cancers, there isn't a lot of money allotted to pediatric cancers, let alone rare brain tumors," she says.
A first-year Ph.D. student at Mayo Clinic Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences , Hayes is also personally knowledgeable about the harsh reality of cancer, having endured surgeries and rounds of chemotherapy for her own cancer, which turned up in her 20s. "During my own ordeal with treatment," she says, "I had a moment where I thought, 'A 5-year-old has to deal with this?' That was absolutely unacceptable to me."
Never one to be told a problem is too big to tackle, she decided to take steps to improve research funding and created a foundation to raise money for pediatric brain tumor research. Hayes is among students from across Mayo Clinic College of Medicine and Science whose energy and vision have led them to devote their spare hours to solving big biomedical problems — and the schools encourage their enthusiasm. Their passion projects are making a mark in medical research and education.
‘I wanted to do something about it’

Hayes' research in the lab of David Daniels, M.D., Ph.D. , studies tumors known as diffuse midline gliomas (DMGs). For children diagnosed with the disease, the prognosis is grim. Spending time in the lab, Hayes realized, "We don't have a lack of ideas, and it's not that we're stuck. The issue is that research is expensive, and we'll never make a dent without funding."
She adds, "I didn't want to sit around and complain about it. I wanted to do something about it."
Hayes, who has been blind since early childhood, had an undergraduate degree in business that prepared her for fundraising. Through online courses she learned web design to create the foundation's website. She read additional medical journal articles about DMG and reached out to families whose children have been affected by it. And she dove into more than 100 pages of government paperwork required to launch a 503(c)(3).
The foundation she established, KIDS MATER TOO, raises money that will go directly to DMG research projects – at Mayo and elsewhere. (The name of the foundation is not a misspelling; it's a play on words about the protective layers that cover the brain, like the dura mater.) The allocation of the funds is determined by a scientific review board, using a double-blind peer-review process to ensure objectivity.
"Charlotte's proactive and altruistic stance demonstrates the positive transformative power one individual can have on society," says Luis Lujan, Ph.D. , associate dean of student affairs. "Her efforts reflect the commitment of our students to affect positive change, which is in line with the values of Mayo Clinic and the Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences."
Hayes also has gotten other graduate students involved in her group's administration. "At this stage," says Hayes, "I'm focused on establishing meaningful relationships with donors, spreading awareness about the disease and continuing my own research. It's been time consuming and tiring, but I would do it all again."
Motivating others to succeed
Back when he was applying to medical school, JR Smith came across a statistic that made an impression on him. "I read that there were more Black men applying and matriculating to medical school in the 1970s than there are today," he says.
One factor contributing to the drop-off, he believed, was an ongoing lack of visual representation of Black men in medicine. He felt he could change that. As he progressed through the medical school application process, he documented his own journey on YouTube.

"I decided to share the strategies that I found helpful to succeed as a premedical and medical student," says Smith, now a fourth-year student at Mayo Clinic Alix School of Medicine . "My hope was that students who resonated with me would be motivated to pursue medicine as a career and have the tools necessary to succeed."
His YouTube channel, Evolving Medic, provides motivation for students pursuing careers in medicine, with strategies and other productivity tips they can use to excel inside and outside their academic responsibilities. (He chooses and describes those that are evidence-based and that he himself has used.) The need hits home: Evolving Medic, with more than 150 videos, has more than 36,000 subscribers. The channel has attracted partnerships with various healthcare-related companies, including a scrubs company and various education-based resources.
"Multiple prospective students to Mayo Clinic Alix School of Medicine have indicated that JR's videos were inspiring to them as they considered pursuing medicine as a career and as they navigated applying to medical school," says Megha Tollefson, M.D. , associate dean of admissions. "He's absolutely had a positive impact on students nationwide."
Smith will continue his training as a resident in orthopedic surgery at Mayo Clinic School of Graduate Medical Education. He intends to continue posting advice for future doctors. "As I progress throughout my career, I'm sure my audience will grow to include physicians as well," he says. "My desire is to share the guidance, resources and knowledge that may be limited for some with the hopes of creating a more equitable environment for all students to succeed."
Mentors make the difference
For Nihal Satyadev, M.D., a first-year neurology resident in Mayo Clinic School of Graduate Medical Education , a passion project focused on Alzheimer's disease made him realize the scope of the problem — and also solidified his career goals to address it.

As a college student and an aspiring clinician, he learned about the ways in which Alzheimer's disease is becoming a public health crisis. Along with classmates, he began an undergraduate club for students interested the topic. "What began as a few friends meeting at my apartment grew into one of the largest student groups on campus and ultimately the leading national youth Alzheimer's nonprofit," he says.
The project led him to reach out to Alzheimer's experts at Mayo Clinic, including Ronald Petersen, M.D., Ph.D. , who became mentors. "Early in the journey," Dr. Satyadev says, "I met with members of Dr. Petersen's team, including [research operations program manager] Angela Lunde at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, who were instrumental in helping me understand the intricacies of population level research and community interventions for dementia."
The initiatives of Youth Movement Against Alzheimer's aim to involve young people in addressing the public health crisis, for instance, by providing companionship to patients and giving time off to family caregivers. Dr. Satyadev was involved for eight years as the group continued to grow, and stepped back as it took on fulltime staff under the management of Hilarity for Charity, the nonprofit started by Lauren and Seth Rogen.
For Dr. Satyadev, the passion project was just a beginning. The connections he has made at Mayo, in particular with neurologist and dementia specialist Gregg Day, M.D. , helped solidify his commitment to becoming a neurologist who specializes in neurodegenerative diseases. Now conducting research projects with Dr. Day during his spare hours, Dr. Satyadev is aiming to develop new strategies to diagnose and treat Alzheimer's disease and related dementias.
"Working on the nonprofit helped me realize addressing this national and global challenge requires a lifetime commitment," he says.
- Timesaving tips for cooking healthy meals Mayo Clinic Minute: Perimenopause and menopause
Related Articles


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
For older students, Kang says, homework benefits plateau at about two hours per night. "Most students, especially at these high achieving schools, they're doing a minimum of three hours, and it's ...
Many students will be struggling with mental health issues that were brought on or worsened by the pandemic, making heavy workloads even harder to balance. ... Is it time to get rid of homework ...
• Reductions in health: In their open-ended answers, many students said their homework load led to sleep deprivation and other health problems. The researchers asked students whether they experienced health issues such as headaches, exhaustion, sleep deprivation, weight loss and stomach problems.
Health Hazards of Homework. Pediatrics. A new study by the Stanford Graduate School of Education and colleagues found that students in high-performing schools who did excessive hours of homework "experienced greater behavioral engagement in school but also more academic stress, physical health problems, and lack of balance in their lives.".
• Reductions in health: In their open-ended answers, many students said their homework load led to sleep deprivation and other health problems. The researchers asked students whether they ...
Key points. Mental health challenges and neurodevelopmental differences directly affect children's ability to do homework. Understanding what difficulties are getting in the way—beyond the usual ...
Mindfulness surrounding homework is especially important in the context of the last two years. Many students will be struggling with mental health issues that were brought on or worsened by the ...
But they were not more invested in the homework itself. They also reported greater academic stress and less time to balance family, friends and extracurricular activities. They experienced more physical health problems as well, such as headaches, stomach troubles and sleep deprivation. "Three hours per night is too much," Galloway says.
Engaging teens in constructive conversations to figure out how they fell behind can be an important lesson unto itself. "Having a 16-year-old who understands, 'When I'm stressed, this is how ...
Research shows that excessive homework leads to increased stress, physical health problems and a lack of balance in students' lives. And studies have shown that more than two hours of daily homework can be counterproductive, yet many teachers assign more.. Homework proponents argue that homework improves academic performance. Indeed, a meta-analysis of research on this issue found a ...
Use a calm voice. When kids feel anxious about homework, they might get angry, yell, or cry. Avoid matching their tone of voice. Take a deep breath and keep your voice steady and calm. Let them know you're there for them. Sometimes kids just don't want to do homework. They complain, procrastinate, or rush through the work so they can do ...
Homework was a leading cause of stress, with 24 percent of parents saying it's an issue. Teenagers say they're suffering, too. A survey by the American Psychological Association found that nearly ...
Use homework as a tool for communication. Use homework as a vehicle to foster family-school communication. Families can use homework as an opportunity to open conversations about specific assignments or classes, peer relationships, or even sleep quality that may be impacting student success. For younger students, using a daily or weekly home ...
Introduction. Homework, or between-session practice of skills learned during therapy, is one of the most integral, yet underutilized components of high-quality, evidence-based mental health care (Kazantzis & Deane, 1999).Homework activities (e.g., self-monitoring, relaxation, exposure, parent behavior management) are assigned by providers in-session and completed by patients between sessions ...
Higher-achieving students — those who may have more homework — are at particular risk for stress-related health issues including sleep deprivation, weight loss, stomach problems and headaches. Source: Stanford University, " Stanford Research Shows Pitfalls of Homework ," 2014.
In fact, a study last year showed that the impact of excessive homework on high schoolers included high stress levels, a lack of balance in children's lives and physical health problems such as ...
Their findings were troubling: Research showed that excessive homework is associated with high stress levels, physical health problems and lack of balance in children's lives; 56% of the ...
Homework as a Mental Health Concern. It's time for an in depth discussion about homework as a major concern for those pursuing mental health in schools. So many problems between kids and their families, the home and school, and students and teachers arise from conflicts over homework. The topic is a long standing concern for mental health ...
Lack of sleep. One of the most prevalent adverse effects of schoolwork is lack of sleep. The average student only gets about 5 hours of sleep per night since they stay up late to complete their homework, even though the body needs at least 7 hours of sleep every day. Lack of sleep has an impact on both mental and physical health.
Examining these arguments offers important perspectives on the wider educational and developmental consequences of homework practices. 1. Elevated Stress and Health Consequences. According to Gitnux, U.S. high school students who have over 20 hours of homework per week are 27% more likely to encounter health issues.
Chinese schoolgirl uses robot to do her homework. Emmy Kang, mental health counselor at Humantold, says studies have shown heavy workloads can be "detrimental" for students and cause a "big ...
There is no one-size-fits-all solution to the ideal homework setting. Some children with ADHD work inefficiently in an isolated, quiet setting like their room, and do better in the midst of some action, like at the kitchen table with a radio playing. You might need to try a few different settings until you find the most efficient one.
May 6, 2024. In recent years, mental health has become a central subject in childhood and adolescence. Teenagers narrate their psychiatric diagnosis and treatment on TikTok and Instagram. School ...
China's Ministry of Education said on Tuesday it was launching a campaign to address issues including excessive homework and bullying in schools, as part of efforts to boost students' mental health.
As public health allies, we all have a role to play in teaching, training and advocating for issues of public health importance. Uniting our voices is an effective way to support public officials in making evidence-based decisions on health policy, but navigating the process can be tricky! ... Step 2: Do your homework. If you are very ...
China's Ministry of Education is addressing issues like excessive homework and bullying in schools through a campaign focusing on mental health education for teachers, students, and rural migrant ...
HONG KONG (Reuters) - China's Ministry of Education said on Tuesday it was launching a campaign to address issues including excessive homework and bullying in schools, as part of efforts to boost ...
Regulatory actions are increasingly used to tackle issues such as excessive alcohol or sugar intake, but such actions to reduce sedentary behaviour remain scarce. World Health Organization (WHO) guidelines on sedentary behaviour call for system-wide policies. The Chinese government introduced the world's first nation-wide multi-setting regulation on multiple types of sedentary behaviour in ...
Physician burnout is linked to high job turnover and excess health care costs, among other problems. Still, it can be hard to change the culture of workaholism in medicine. Even the study authors ...
Students' passion projects address big issues in healthcare. When graduate student Charlotte Hayes began her Ph.D. training in a lab studying brain tumors that affect young children, she was devastated to realize one reality about funding for biomedical research. "Compared to adult cancers, there isn't a lot of money allotted to pediatric ...