- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Critique Report
- Writing Reports
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Events FAQ
- Grammar Guide

How to Write a Summary (Examples Included)

By Ashley Shaw

Have you ever recommended a book to someone and given them a quick overview? Then you’ve created a summary before!
Summarizing is a common part of everyday communication. It feels easy when you’re recounting what happened on your favorite show, but what do you do when the information gets a little more complex?
Written summaries come with their own set of challenges. You might ask yourself:
- What details are unnecessary?
- How do you put this in your own words without changing the meaning?
- How close can you get to the original without plagiarizing it?
- How long should it be?
The answers to these questions depend on the type of summary you are doing and why you are doing it.
A summary in an academic setting is different to a professional summary—and both of those are very different to summarizing a funny story you want to tell your friends.
One thing they all have in common is that you need to relay information in the clearest way possible to help your reader understand. We’ll look at some different forms of summary, and give you some tips on each.
Let’s get started!
What Is a Summary?
How do you write a summary, how do you write an academic summary, what are the four types of academic summaries, how do i write a professional summary, writing or telling a summary in personal situations, summarizing summaries.
A summary is a shorter version of a larger work. Summaries are used at some level in almost every writing task, from formal documents to personal messages.
When you write a summary, you have an audience that doesn’t know every single thing you know.
When you want them to understand your argument, topic, or stance, you may need to explain some things to catch them up.
Instead of having them read the article or hear every single detail of the story or event, you instead give them a brief overview of what they need to know.
Academic, professional, and personal summaries each require you to consider different things, but there are some key rules they all have in common.
Let’s go over a few general guides to writing a summary first.

1. A summary should always be shorter than the original work, usually considerably.
Even if your summary is the length of a full paper, you are likely summarizing a book or other significantly longer work.
2. A summary should tell the reader the highlights of what they need to know without giving them unnecessary details.
3. It should also include enough details to give a clear and honest picture.
For example, if you summarize an article that says “ The Office is the greatest television show of all time,” but don’t mention that they are specifically referring to sitcoms, then you changed the meaning of the article. That’s a problem! Similarly, if you write a summary of your job history and say you volunteered at a hospital for the last three years, but you don’t add that you only went twice in that time, it becomes a little dishonest.
4. Summaries shouldn’t contain personal opinion.
While in the longer work you are creating you might use opinion, within the summary itself, you should avoid all personal opinion. A summary is different than a review. In this moment, you aren’t saying what you think of the work you are summarizing, you are just giving your audience enough information to know what the work says or did.

Now that we have a good idea of what summaries are in general, let’s talk about some specific types of summary you will likely have to do at some point in your writing life.
An academic summary is one you will create for a class or in other academic writing. The exact elements you will need to include depend on the assignment itself.
However, when you’re asked for an academic summary, this usually this means one of five things, all of which are pretty similar:
- You need to do a presentation in which you talk about an article, book, or report.
- You write a summary paper in which the entire paper is a summary of a specific work.
- You summarize a class discussion, lesson, or reading in the form of personal notes or a discussion board post.
- You do something like an annotated bibliography where you write short summaries of multiple works in preparation of a longer assignment.
- You write quick summaries within the body of another assignment . For example, in an argumentative essay, you will likely need to have short summaries of the sources you use to explain their argument before getting into how the source helps you prove your point.

Regardless of what type of summary you are doing, though, there are a few steps you should always follow:
- Skim the work you are summarizing before you read it. Notice what stands out to you.
- Next, read it in depth . Do the same things stand out?
- Put the full text away and write in a few sentences what the main idea or point was.
- Go back and compare to make sure you didn’t forget anything.
- Expand on this to write and then edit your summary.
Each type of academic summary requires slightly different things. Let’s get down to details.
How Do I Write a Summary Paper?
Sometimes teachers assign something called a summary paper . In this, the entire thing is a summary of one article, book, story, or report.
To understand how to write this paper, let’s talk a little bit about the purpose of such an assignment.
A summary paper is usually given to help a teacher see how well a student understands a reading assignment, but also to help the student digest the reading. Sometimes, it can be difficult to understand things we read right away.
However, a good way to process the information is to put it in our own words. That is the point of a summary paper.

A summary paper is:
- A way to explain in our own words what happened in a paper, book, etc.
- A time to think about what was important in the paper, etc.
- A time to think about the meaning and purpose behind the paper, etc.
Here are some things that a summary paper is not:
- A review. Your thoughts and opinions on the thing you are summarizing don’t need to be here unless otherwise specified.
- A comparison. A comparison paper has a lot of summary in it, but it is different than a summary paper. In this, you are just saying what happened, but you aren’t saying places it could have been done differently.
- A paraphrase (though you might have a little paraphrasing in there). In the section on using summary in longer papers, I talk more about the difference between summaries, paraphrases, and quotes.

Because a summary paper is usually longer than other forms of summary, you will be able to chose more detail. However, it still needs to focus on the important events. Summary papers are usually shorter papers.
Let’s say you are writing a 3–4 page summary. You are likely summarizing a full book or an article or short story, which will be much longer than 3–4 pages.
Imagine that you are the author of the work, and your editor comes to you and says they love what you wrote, but they need it to be 3–4 pages instead.
How would you tell that story (argument, idea, etc.) in that length without losing the heart or intent behind it? That is what belongs in a summary paper.
How Do I Write Useful Academic Notes?
Sometimes, you need to write a summary for yourself in the form of notes or for your classmates in the form of a discussion post.
You might not think you need a specific approach for this. After all, only you are going to see it.
However, summarizing for yourself can sometimes be the most difficult type of summary. If you try to write down everything your teacher says, your hand will cramp and you’ll likely miss a lot.
Yet, transcribing doesn’t work because studies show that writing things down (not typing them) actually helps you remember them better.
So how do you find the balance between summarizing the lessons without leaving out important points?
There are some tips for this:
- If your professor writes it on the board, it is probably important.
- What points do your textbooks include when summarizing information? Use these as a guide.
- Write the highlight of every X amount of time, with X being the time you can go without missing anything or getting tired. This could be one point per minute, or three per five minutes, etc.
How Do I Create an Annotated Biography?
An annotated bibliography requires a very specific style of writing. Often, you will write these before a longer research paper . They will ask you to find a certain amount of articles and write a short annotation for each of them.
While an annotation is more than just a summary, it usually starts with a summary of the work. This will be about 2–3 sentences long. Because you don’t have a lot of room, you really have to think about what the most important thing the work says is.
This will basically ask you to explain the point of the article in these couple of sentences, so you should focus on the main point when expressing it.
Here is an example of a summary section within an annotation about this post:
“In this post, the author explains how to write a summary in different types of settings. She walks through academic, professional, and personal summaries. Ultimately, she claims that summaries should be short explanations that get the audience caught up on the topic without leaving out details that would change the meaning.”

Can I Write a Summary Within an Essay?
Perhaps the most common type of summary you will ever do is a short summary within a longer paper.
For example, if you have to write an argumentative essay, you will likely need to use sources to help support your argument.
However, there is a good chance that your readers won’t have read those same sources.
So, you need to give them enough detail to understand your topic without spending too much time explaining and not enough making your argument.
While this depends on exactly how you are using summary in your paper, often, a good amount of summary is the same amount you would put in an annotation.
Just a few sentences will allow the reader to get an idea of the work before moving on to specific parts of it that might help your argument.
What’s the Difference Between Summarizing, Paraphrasing, and Using Quotes?
One important thing to recognize when using summaries in academic settings is that summaries are different than paraphrases or quotes.
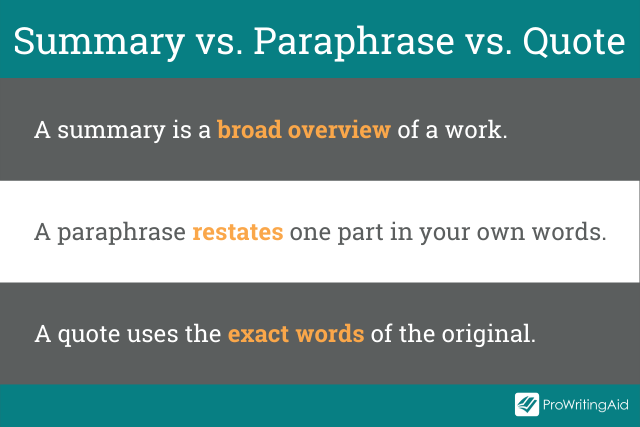
A summary is broader and more general. A paraphrase, on the other hand, puts specific parts into your own words. A quote uses the exact words of the original. All of them, however, need to be cited.
Let’s look at an example:
Take these words by Thomas J. Watson:
”Would you like me to give you a formula for success? It’s quite simple, really. Double your rate of failure. You are thinking of failure as the enemy of success. But it isn’t as all. You can be discouraged by failure—or you can learn from it. So go ahead and make mistakes. Make all you can. Because, remember, that’s where you will find success.”
Let’s say I was told to write a summary, a paraphrase, and a quote about this statement. This is what it might look like:
Summary: Thomas J. Watson said that the key to success is actually to fail more often. (This is broad and doesn’t go into details about what he says, but it still gives him credit.)
Paraphrase: Thomas J. Watson, on asking if people would like his formula for success, said that the secret was to fail twice as much. He claimed that when you decide to learn from your mistakes instead of being disappointed by them, and when you start making a lot of them, you will actually find more success. (This includes most of the details, but it is in my own words, while still crediting the source.)
Quote: Thomas J. Watson said, ”Would you like me to give you a formula for success? It’s quite simple, really. Double your rate of failure. You are thinking of failure as the enemy of success. But it isn’t at all. You can be discouraged by failure—or you can learn from it. So go ahead and make mistakes. Make all you can. Because, remember, that’s where you will find success.” (This is the exact words of the original with quotation marks and credit given.)
Avoiding Plagiarism
One of the hardest parts about summarizing someone else’s writing is avoiding plagiarism .

That’s why I have a few rules/tips for you when summarizing anything:
1. Always cite.
If you are talking about someone else’s work in any means, cite your source. If you are summarizing the entire work, all you probably need to do (depending on style guidelines) is say the author’s name. However, if you are summarizing a specific chapter or section, you should state that specifically. Finally, you should make sure to include it in your Work Cited or Reference page.
2. Change the wording.
Sometimes when people are summarizing or paraphrasing a work, they get too close to the original, and actually use the exact words. Unless you use quotation marks, this is plagiarism. However, a good way to avoid this is to hide the article while you are summarizing it. If you don’t have it in front of you, you are less likely to accidentally use the exact words. (However, after you are done, double check that you didn’t miss anything important or give wrong details.)
3. Use a plagiarism checker.
Of course, when you are writing any summary, especially academic summaries, it can be easy to cross the line into plagiarism. If this is a place where you struggle, then ProWritingAid can help.
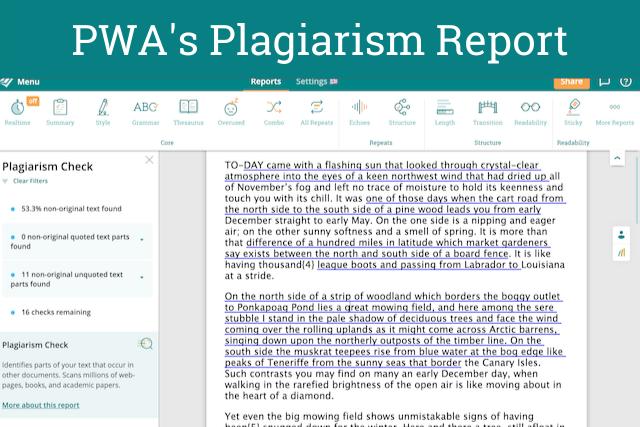
Just use our Plagiarism Report . It’ll highlight any unoriginal text in your document so you can make sure you are citing everything correctly and summarizing in your own words.
Find out more about ProWritingAid plagiarism bundles.
Along with academic summaries, you might sometimes need to write professional summaries. Often, this means writing a summary about yourself that shows why you are qualified for a position or organization.
In this section, let’s talk about two types of professional summaries: a LinkedIn summary and a summary section within a resume.
How Do I Write My LinkedIn Bio?
LinkedIn is all about professional networking. It offers you a chance to share a brief glimpse of your professional qualifications in a paragraph or two.
This can then be sent to professional connections, or even found by them without you having to reach out. This can help you get a job or build your network.
Your summary is one of the first things a future employer might see about you, and how you write yours can make you stand out from the competition.

Here are some tips on writing a LinkedIn summary :
- Before you write it, think about what you want it to do . If you are looking for a job, what kind of job? What have you done in your past that would stand out to someone hiring for that position? That is what you will want to focus on in your summary.
- Be professional . Unlike many social media platforms, LinkedIn has a reputation for being more formal. Your summary should reflect that to some extent.
- Use keywords . Your summary is searchable, so using keywords that a recruiter might be searching for can help them find you.
- Focus on the start . LinkedIn shows the first 300 characters automatically, and then offers the viewer a chance to read more. Make that start so good that everyone wants to keep reading.
- Focus on accomplishments . Think of your life like a series of albums, and this is your speciality “Greatest Hits” album. What “songs” are you putting on it?

How Do I Summarize My Experience on a Resume?
Writing a professional summary for a resume is different than any other type of summary that you may have to do.
Recruiters go through a lot of resumes every day. They don’t have time to spend ages reading yours, which means you have to wow them quickly.
To do that, you might include a section at the top of your resume that acts almost as an elevator pitch: That one thing you might say to a recruiter to get them to want to talk to you if you only had a 30-second elevator ride.

If you don’t have a lot of experience, though, you might want to skip this section entirely and focus on playing up the experience you do have.
Outside of academic and personal summaries, you use summary a lot in your day-to-day life.
Whether it is telling a good piece of trivia you just learned or a funny story that happened to you, or even setting the stage in creative writing, you summarize all the time.
How you use summary can be an important consideration in whether people want to read your work (or listen to you talk).
Here are some things to think about when telling a story:
- Pick interesting details . Too many and your point will be lost. Not enough, and you didn’t paint the scene or give them a complete idea about what happened.
- Play into the emotions . When telling a story, you want more information than the bare minimum. You want your reader to get the emotion of the story. That requires a little bit more work to accomplish.
- Focus. A summary of one story can lead to another can lead to another. Think about storytellers that you know that go off on a tangent. They never seem to finish one story without telling 100 others!

To wrap up (and to demonstrate everything I just talked about), let’s summarize this post into its most essential parts:
A summary is a great way to quickly give your audience the information they need to understand the topic you are discussing without having to know every detail.
How you write a summary is different depending on what type of summary you are doing:
- An academic summary usually gets to the heart of an article, book, or journal, and it should highlight the main points in your own words. How long it should be depends on the type of assignment it is.
- A professional summary highlights you and your professional, academic, and volunteer history. It shows people in your professional network who you are and why they should hire you, work with you, use your talents, etc.
Being able to tell a good story is another form of summary. You want to tell engaging anecdotes and facts without boring your listeners. This is a skill that is developed over time.
Take your writing to the next level:

20 Editing Tips from Professional Writers
Whether you are writing a novel, essay, article, or email, good writing is an essential part of communicating your ideas., this guide contains the 20 most important writing tips and techniques from a wide range of professional writers..
Be confident about grammar
Check every email, essay, or story for grammar mistakes. Fix them before you press send.
Ashley Shaw
Ashley Shaw is a former editor and marketer/current PhD student and teacher. When she isn't studying con artists for her dissertation, she's thinking of new ways to help college students better understand and love the writing process. You can follow her on Twitter, or, if you prefer animal accounts, follow her rabbits, Audrey Hopbun and Fredra StaHare, on Instagram.
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via:

Summarizing
by jleemcga | Aug 18, 2023 | Resources for Students , Writing Resources
What is summarizing?
A summary of a text is a short overview of the main ideas written in your own words. While paraphrasing involves expressing specific ideas or details from a larger text in your own words, we generally summarize whole texts (whether it is an essay, article, chapter, book, et cetera). So, in order to ensure our summaries are not too wordy or confusing, we only cover the main ideas or argument presented within a whole text.

It’s best to summarize when you’re contextualizing a topic by letting your readers know about the current, ongoing conversation. By summarizing relevant sources, you’re providing your audience with an overview of what has already been said about this topic to help them understand how you’ll be adding to it. Summarizing material within your paper allows you to:
- Condense key ideas or arguments relevant to your paper
- Simplify the connection between a source and your own writing
How do I summarize?
To approach summarizing a source, try the following steps:
- First make sure you carefully read the original source material to understand it. Like paraphrasing, summarizing effectively requires an accurate understanding of the source material
- Identify all the main ideas from the text. It helps to look for the thesis or overall claim the author is presenting, as well as any important reasons they give to back their claim. Basically, you’re looking for why their argument is what it is
- When you begin your summary, you might use a TAG line. This stands for Title, Author, Genre and allows you to formally introduce the text before you summarize its ideas. An example of a TAG line is: In the article “Stuck on the Streets of San Francisco in a Driverless Car”, Cade Metz reports … TAG lines add a helpful framework for the summary
- Be sure not to include any specific examples, details, or evidence from the text. In summaries, we don’t describe the author’s examples (this would be like rewriting the entire text). Instead, we offer a map of the main idea and major points
- Once you finish writing your summary, check to make sure your summary concisely and accurately captures the author’s main ideas
- Remember to cite!
Examples of summarizing
Here is an example of a writer summarizing a main idea from the source Social Death: Racialized Rightlessness and the Criminalization of the Unprotected by Lisa Marie Cacho in their essay about a Salvadoran poet and her poetry’s relationship to reclaiming identity:
The ambiguity that is scored onto the bodies of Salvadoran migrants creates an impoverished sense of time and freedom by keeping these individuals indefinitely “temporary,” an ephemera that imposes a constant threat against safety and belonging for Salvadorans in the US. This weaponization of time also contributes to the condition of social death that Cacho describes as being prevalent for people of color, and particularly immigrants, in the US. According to Cacho, part of the criminalization of people of color within the US— not based on one’s behavior, but by their appearance— is heightened further by the notion of documentation. The rhetoric surrounding immigration in the US ultimately aims to invalidate those without documentation by using slurs like “illegal” (Cacho).
Note: The writer quotes some key terms, like “temporary” or “illegal” that the author emphasizes in the original source but describes the main ideas of the source in their own words. Note, too, that the summary focuses on the big-picture ideas of the source without mentioning examples that are too specific.
Things to keep in mind when summarizing
Some important things to remain mindful of while summarizing in your assignments are:
- There is no specified length for writing summaries; they may be a few sentences or a few paragraphs depending on your writing project. For most academic essays, a summary of a few sentences to a short paragraph is appropriate. Concision is key
- Do not include your opinions on the topic or the author’s ideas in your summary; your ideas are important, but summary is a genre of writing that requires objectivity
- Do not include specific details or examples from the text—just focus on the big picture ideas

Our Newest Resources!
- Best Practices for Emailing Instructors and Professors
- Incorporating Headings & Subheadings
- Revision vs. Proofreading
- Engaging With Sources Effectively
- The Dos and Don’ts of Using Tables and Figures in Your Writing
Additional Resources
- Black Lives Matter Writing Contest
- Graduate Writing Consultants
- Instructor Resources
- Student Resources
- Quick Guides and Handouts
- Self-Guided and Directed Learning Activities
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Happiness Hub Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Write a Summary
Last Updated: July 26, 2024 Approved
Sample Summaries
Reviewing the piece, writing the summary in your own words, revising your draft into a coherent summary, expert q&a.
This article was co-authored by Richard Perkins . Richard Perkins is a Writing Coach, Academic English Coordinator, and the Founder of PLC Learning Center. With over 24 years of education experience, he gives teachers tools to teach writing to students and works with elementary to university level students to become proficient, confident writers. Richard is a fellow at the National Writing Project. As a teacher leader and consultant at California State University Long Beach's Global Education Project, Mr. Perkins creates and presents teacher workshops that integrate the U.N.'s 17 Sustainable Development Goals in the K-12 curriculum. He holds a BA in Communications and TV from The University of Southern California and an MEd from California State University Dominguez Hills. wikiHow marks an article as reader-approved once it receives enough positive feedback. This article received 26 testimonials and 89% of readers who voted found it helpful, earning it our reader-approved status. This article has been viewed 1,833,871 times.
Writing a summary is a great way to process the information you read, whether it’s an article or a book. If you’re assigned a summary in school, the best way to approach it is by reviewing the piece you’re summarizing. Read it thoroughly and take notes on the major points you want to include in your summary. When you get to writing your summary, rely on your memory first to make sure the summary is in your own words. Then, revise it to ensure that your writing is clear and the grammar, punctuation, and spelling are all perfect.
How do you write a good summary?
Start by reviewing the piece and identifying what the major points of it are. Highlight the author and the name of their work first, and then try to recall all of the major plot points from memory. Tighten up your draft by ensuring that your content is in chronological order, and by checking for errors or repetition.

- The author might also state their thesis more plainly by saying something like "my argument is...." or I believe...
- In a fiction piece, the author will more likely emphasize themes. So if you notice that love - discussions or descriptions of it, for example - come up a lot, one of the main points of the piece is probably love.

- To put something in your own words, write it down as if you were explaining or describing it to a friend. In that case, you wouldn't just read what the author wrote. Do the same when you're writing down the major points in your own words.

- For fiction pieces, this means avoiding rewriting every single thing that happens in the piece. Focus instead on the major plot points and the main motivator for those points. Don't include everything that happens to the character along the way.

- For example, you can start with something like “George Shaw’s '‘Pygmalion’' is a play that addresses issues of class and culture in early twentieth-century England.”

- If you absolutely must use the original author’s words, put them in quotation marks. This tells your reader those words aren’t yours. Not doing this is academic plagiarism, and it can get you in a lot of trouble.
- Make sure you format the quote correctly!

- For example, you might think that Hamlet spends a lot of time thinking and not a lot of time acting. You can say something like, "Hamlet is a man of thought, rather than action," instead of saying, "Why doesn't Hamlet do something once in a while?"

- In fiction pieces, you can say something like "Shakespeare's Hamlet then spends a lot of time brooding on the castle ramparts." This tells your reader you're talking about Shakespeare's play, not inventing your own story.

- For example, in a summary of an article about the cause of the American Revolution, you might have a paragraph that summarizes the author's arguments about taxes, and another about religious freedom. You can say something like, "Although some colonists believed that taxes should entitle them to representation in Parliament, the author also argues that other colonists supported the Revolution because they believed they were entitled to representation in heaven on their own terms."

- Don't use spell-checker for spelling errors. It will catch if you spell something wrong, but not if you use the wrong spelling of a word. For example, it won't catch that you used "there" when you meant "their."

- Generally, a summary should be around one quarter the length of the original piece. So if the original piece is 4 pages long, your summary should be no more than 1 page. [13] X Research source

- Not only should they be comparing your work for accuracy, ask them to read it for flow and summation. They should be able understand what happened in the article or story by reading your summary alone. Don't hesitate to ask for criticism; then weigh those criticisms and make valid changes.

- If you notice an author has made the same point multiple times, though, it’s a good indicator that this is an important point, and it should definitely be in your summary. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
Tips from our Readers
- Start your summary out with where the story takes place, or something that is on the first page or in the first chapter.
- Look at the chapter title of the book.This might help summarize the chapter as you start working on your summary.

You Might Also Like

- ↑ http://teacher.scholastic.com/reading/bestpractices/comprehension/authorsmainidea.pdf
- ↑ Richard Perkins. Writing Coach & Academic English Coordinator. Expert Interview. 1 September 2021.
- ↑ http://utminers.utep.edu/omwilliamson/engl0310/summaryhints.htm
- ↑ https://public.wsu.edu/~mejia/Summary.htm
- ↑ http://www.hunter.cuny.edu/rwc/handouts/the-writing-process-1/invention/Guidelines-for-Writing-a-Summary
About This Article

Before you write a summary, read the piece you’re summarizing, then make notes on what you think the main point and major supporting arguments are. When you’re ready to draft your summary, start with the author and title, then use your own words to write what you think the author’s main point is in each section. Be sure to focus on what the author thinks and feels rather than what you do! Finally, reread your summary and check it for good spelling, punctuation, and grammar. For more suggestions from our reviewer about polishing your summary and improving transitions, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Dec 9, 2016
Did this article help you?
Kylee Harris
Jan 21, 2021
Munazza Batool
May 21, 2017
Nalini Sengupta
Feb 27, 2017
Feb 5, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter
- How it works

Writing a Summary – Explanation & Examples
Published by Alvin Nicolas at October 17th, 2023 , Revised On October 17, 2023
In a world bombarded with vast amounts of information, condensing and presenting data in a digestible format becomes invaluable. Enter summaries.
A summary is a brief and concise account of the main points of a larger body of work. It distils complex ideas, narratives, or data into a version that is quicker to read and easier to understand yet still retains the essence of the original content.
Importance of Summaries
The importance of summarising extends far beyond just making reading more manageable. In academic settings, summaries aid students in understanding and retaining complex materials, from textbook chapters to research articles. They also serve as tools to showcase one’s grasp of the subject in essays and reports.
In professional arenas, summaries are pivotal in business reports, executive briefings, and even emails where key points need to be conveyed quickly to decision-makers. Meanwhile, summarising skills come into play in our personal lives when we relay news stories to friends, recap a movie plot, or even scroll through condensed news or app notifications on our smartphones.
Why Do We Write Summaries?
In our modern information age, the sheer volume of content available can be overwhelming. From detailed research papers to comprehensive news articles, the quest for knowledge is often met with lengthy and complex resources. This is where the power of a well-crafted summary comes into play. But what drives us to create or seek out summaries? Let’s discuss.
Makes Important Things Easy to Remember
At the heart of summarisation is the goal to understand. A well-written summary aids in digesting complex material. By distilling larger works into their core points, we reinforce the primary messages, making them easier to remember. This is especially crucial for students who need to retain knowledge for exams or professionals prepping for a meeting based on a lengthy report.
Simplification of Complex Topics
Not everyone is an expert in every field. Often, topics come laden with jargon, intricate details, and nuanced arguments. Summaries act as a bridge, translating this complexity into accessible and straightforward content. This is especially beneficial for individuals new to a topic or those who need just the highlights without the intricacies.
Aid in Researching and Understanding Diverse Sources
Researchers, writers, and academics often wade through many sources when working on a project. This involves finding sources of different types, such as primary or secondary sources , and then understanding their content. Sifting through each source in its entirety can be time-consuming. Summaries offer a streamlined way to understand each source’s main arguments or findings, making synthesising information from diverse materials more efficient.
Condensing Information for Presentation or Sharing
In professional settings, there is often a need to present findings, updates, or recommendations to stakeholders. An executive might not have the time to go through a 50-page report, but they would certainly appreciate a concise summary highlighting the key points. Similarly, in our personal lives, we often summarise movie plots, book stories, or news events when sharing with friends or family.
Characteristics of a Good Summary
Crafting an effective summary is an art. It’s more than just shortening a piece of content; it is about capturing the essence of the original work in a manner that is both accessible and true to its intent. Let’s explore the primary characteristics that distinguish a good summary from a mediocre one:
Conciseness
At the core of a summary is the concept of brevity. But being concise doesn’t mean leaving out vital information. A good summary will:
- Eliminate superfluous details or repetitive points.
- Focus on the primary arguments, events, or findings.
- Use succinct language without compromising the message.
Objectivity
Summarising is not about infusing personal opinions or interpretations. A quality summary will:
- Stick to the facts as presented in the original content.
- Avoid introducing personal biases or perspectives.
- Represent the original author’s intent faithfully.
A summary is meant to simplify and make content accessible. This is only possible if the summary itself is easy to understand. Ensuring clarity involves:
- Avoiding jargon or technical terms unless they are essential to the content. If they are used, they should be clearly defined.
- Structuring sentences in a straightforward manner.
- Making sure ideas are presented in a way that even someone unfamiliar with the topic can grasp the primary points.
A jumble of ideas, no matter how concise, will not make for a good summary. Coherence ensures that there’s a logical flow to the summarised content. A coherent summary will:
- Maintain a logical sequence, often following the structure of the original content.
- Use transition words or phrases to connect ideas and ensure smooth progression.
- Group related ideas together to provide structure and avoid confusion.
Steps of Writing a Summary
The process of creating a compelling summary is not merely about cutting down content. It involves understanding, discerning, and crafting. Here is a step-by-step guide to writing a summary that encapsulates the essence of the original work:
Reading Actively
Engage deeply with the content to ensure a thorough understanding.
- Read the entire document or work first to grasp its overall intent and structure.
- On the second read, underline or highlight the standout points or pivotal moments.
- Make brief notes in the margins or on a separate sheet, capturing the core ideas in your own words.
Identifying the Main Idea
Determine the backbone of the content, around which all other details revolve.
- Ask yourself: “What is the primary message or theme the author wants to convey?”
- This can often be found in the title, introduction, or conclusion of a piece.
- Frame the main idea in a clear and concise statement to guide your summary.
List Key Supporting Points
Understand the pillars that uphold the main idea, providing evidence or depth to the primary message.
- Refer back to the points you underlined or highlighted during your active reading.
- Note major arguments, evidence, or examples that the author uses to back up the main idea.
- Prioritise these points based on their significance to the main idea.
Draft the Summary
Convert your understanding into a condensed, coherent version of the original.
- Start with a statement of the main idea.
- Follow with the key supporting points, maintaining logical order.
- Avoid including trivial details or examples unless they’re crucial to the primary message.
- Use your own words, ensuring you are not plagiarising the original content.
Fine-tune your draft to ensure clarity, accuracy, and brevity.
- Read your draft aloud to check for flow and coherence.
- Ensure that your summary remains objective, avoiding any personal interpretations or biases.
- Check the length. See if any non-essential details can be removed without sacrificing understanding if it is too lengthy.
- Ensure clarity by ensuring the language is straightforward, and the main ideas are easily grasped.
The research done by our experts have:
- Precision and Clarity
- Zero Plagiarism
- Authentic Sources

Dos and Don’ts of Summarising Key Points
Summarising, while seemingly straightforward, comes with its nuances. Properly condensing content demands a balance between brevity and fidelity to the original work. To aid in crafting exemplary summaries, here is a guide on the essential dos and don’ts:
Use your Own Words
This ensures that you have truly understood the content and are not merely parroting it. It also prevents issues of plagiarism.
Tip: After reading the original content, take a moment to reflect on it. Then, without looking at the source, write down the main points in your own words.
Attribute Sources Properly
Giving credit is both ethical and provides context to readers, helping them trace back to the original work if needed. How to cite sources correctly is a skill every writer should master.
Tip: Use signal phrases like “According to [Author/Source]…” or “As [Author/Source] points out…” to seamlessly incorporate attributions.
Ensure Accuracy of the Summarised Content
A summary should be a reliable reflection of the original content. Distorting or misrepresenting the original ideas compromises the integrity of the summary.
Tip: After drafting your summary, cross-check with the original content to ensure all key points are represented accurately and ensure you are referencing credible sources .
Avoid Copy-Pasting Chunks of Original Content
This not only raises plagiarism concerns but also shows a lack of genuine engagement with the material.
Tip: If a particular phrase or sentence from the original is pivotal and cannot be reworded without losing its essence, use block quotes , quotation marks, and attribute the source.
Do not Inject your Personal Opinion
A summary should be an objective reflection of the source material. Introducing personal biases or interpretations can mislead readers.
Tip: Stick to the facts and arguments presented in the original content. If you find yourself writing “I think” or “In my opinion,” reevaluate the sentence.
Do not Omit Crucial Information
While a summary is meant to be concise, it shouldn’t be at the expense of vital details that are essential to understanding the original content’s core message.
Tip: Prioritise information. Always include the main idea and its primary supports. If you are unsure whether a detail is crucial, consider its impact on the overall message.
Examples of Summaries
Here are a few examples that will help you get a clearer view of how to write a summary.
Example 1: Summary of a News Article
Original Article: The article reports on the recent discovery of a rare species of frog in the Amazon rainforest. The frog, named the “Emerald Whisperer” due to its unique green hue and the soft chirping sounds it makes, was found by a team of researchers from the University of Texas. The discovery is significant as it offers insights into the biodiversity of the region, and the Emerald Whisperer might also play a pivotal role in understanding the ecosystem balance.
Summary: Researchers from the University of Texas have discovered a unique frog, termed the “Emerald Whisperer,” in the Amazon rainforest. This finding sheds light on the region’s biodiversity and underscores the importance of the frog in ecological studies.
Example 2: Summary of a Research Paper
Original Paper: In a study titled “The Impact of Urbanisation on Bee Populations,” researchers conducted a year-long observation on bee colonies in three urban areas and three rural areas. Using specific metrics like colony health, bee productivity, and population size, the study found that urban environments saw a 30% decline in bee populations compared to rural settings. The research attributes this decline to factors like pollution, reduced green spaces, and increased temperatures in urban areas.
Summary: A study analysing the effects of urbanisation on bee colonies found a significant 30% decrease in bee populations in urban settings compared to rural areas. The decline is linked to urban factors such as pollution, diminished greenery, and elevated temperatures.
Example 3: Summary of a Novel
Original Story: In the novel “Winds of Fate,” protagonist Clara is trapped in a timeless city where memories dictate reality. Throughout her journey, she encounters characters from her past, present, and imagined future. Battling her own perceptions and a menacing shadow figure, Clara seeks an elusive gateway to return to her real world. In the climax, she confronts the shadow, which turns out to be her own fear, and upon overcoming it, she finds her way back, realising that reality is subjective.
Summary: “Winds of Fate” follows Clara’s adventures in a surreal city shaped by memories. Confronting figures from various phases of her life and battling a symbolic shadow of her own fear, Clara eventually discovers that reality’s perception is malleable and subjective.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long is a summary.
A summary condenses a larger piece of content, capturing its main points and essence. It is usually one-fourth of the original content.
What is a summary?
A summary is a concise representation of a larger text or content, highlighting its main ideas and points. It distils complex information into a shorter form, allowing readers to quickly grasp the essence of the original material without delving into extensive details. Summaries prioritise clarity, brevity, and accuracy.
When should I write a summary?
Write a summary when you need to condense lengthy content for easier comprehension and recall. It’s useful in academic settings, professional reports, presentations, and research to highlight key points. Summaries aid in comparing multiple sources, preparing for discussions, and sharing essential details of extensive materials efficiently with others.
How can I summarise a source without plagiarising?
To summarise without plagiarising: Read the source thoroughly, understand its main ideas, and then write the summary in your own words. Avoid copying phrases verbatim. Attribute the source properly. Use paraphrasing techniques and cross-check your summary against the original to ensure distinctiveness while retaining accuracy. Always prioritise understanding over direct replication.
What is the difference between a summary and an abstract?
A summary condenses a text, capturing its main points from various content types like books, articles, or movies. An abstract, typically found in research papers and scientific articles, provides a brief overview of the study’s purpose, methodology, results, and conclusions. Both offer concise versions, but abstracts are more structured and specific.
You May Also Like
When researching or exploring a new topic, the distinction between primary and secondary sources is paramount. The validity, reliability, and relevance of the information you gather will heavily depend on the type of source you consult.
A tertiary source is an information source that compiles, analyses, and synthesises both primary and secondary sources.
Primary sources refer to original, unmediated documents or records that have not been altered or transformed by interpretation or commentary. They provide first-hand accounts, evidence, or direct testimony concerning a subject or event under investigation.
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works
Home / Guides / Writing Guides / Parts of a Paper / How to Write a Summary
How to Write a Summary
Introduction.
In this lesson, you will learn how to summarize a text accurately.
Guide Overview
Summarizing.
- Tips for summarizing: introducing the main idea
- Tips for summarizing: transitions
- The final summary
A summary is a much shorter version of a text, with only the most essential information.
Below, you can read the main points from each section of the Scholastic News article Running Into History :
- Roberta “Bobbi” Gibb was the first woman to run in the Boston Marathon.
- Gibb had to disguise herself as a man to participate in the race because people didn’t think women could run that far at the time.
- Gibb helped open the race to other women.
To turn this information into a summary, you will need to add a few things!
Tips for Summarizing: Introducing the Main Idea
When you write your summary, it’s important to follow a few steps.
First, start your summary by identifying the title, author and type of text.
You should include the information above and a brief explanation of the author’s major point in the first sentence of your summary.
Example : The Scholastic News article, “Running Into History,” explains how Roberta “Bobbi” Gibb changed the Boston Marathon.
Tips for Summarizing: Transitions
Have you ever read a text that was robotic and choppy? When that happens, the information is hard to follow and not very interesting! To avoid this, use transitions between the main points of your summary.
Look at the list of Transitional Words and Phrases from the University of Wisconsin. These can help your writing flow! Every few sentences, use summarizing language that reminds the reader that they are reading a summary. Summarizing transitions include “ The author claims… ” or “ The article explains… ”
The Final Summary
After adding in an introductory sentence and transitions to the main points of the text, the next step is to complete the summary .
Read the summary of the Scholastic News article below. Notice how 8 paragraphs of text have been shortened into a one-paragraph summary!
The Scholastic News article, “Running Into History,” explains how Roberta “Bobbi” Gibb changed the Boston Marathon.Gibb was the first woman to run in the Boston Marathon. She had to disguise herself as a man to participate in the race because people didn’t think women could run that far at the time. According to the article, Gibb’s success in the marathon helped to open the race up to other women.
In this lesson, you learned how to:
- summarize informational texts using main ideas and transitional words and phrases
EasyBib Writing Resources
Writing a paper.
- Academic Essay
- Argumentative Essay
- College Admissions Essay
- Expository Essay
- Persuasive Essay
- Research Paper
- Thesis Statement
- Writing a Conclusion
- Writing an Introduction
- Writing an Outline
- Writing a Summary
EasyBib Plus Features
- Citation Generator
- Essay Checker
- Expert Check Proofreader
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tools
Plagiarism Checker
- Spell Checker
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
Grammar and Plagiarism Checkers
Grammar Basics
Plagiarism Basics
Writing Basics
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started
Have a thesis expert improve your writing
Check your thesis for plagiarism in 10 minutes, generate your apa citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Working with sources
- How to Write a Summary | Guide & Examples
How to Write a Summary | Guide & Examples
Published on 25 September 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 12 May 2023.
Summarising , or writing a summary, means giving a concise overview of a text’s main points in your own words. A summary is always much shorter than the original text.
There are five key steps that can help you to write a summary:
- Read the text
- Break it down into sections
- Identify the key points in each section
- Write the summary
- Check the summary against the article
Writing a summary does not involve critiquing or analysing the source. You should simply provide an accurate account of the most important information and ideas (without copying any text from the original).
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
When to write a summary, step 1: read the text, step 2: break the text down into sections, step 3: identify the key points in each section, step 4: write the summary, step 5: check the summary against the article, frequently asked questions.
There are many situations in which you might have to summarise an article or other source:
- As a stand-alone assignment to show you’ve understood the material
- To keep notes that will help you remember what you’ve read
- To give an overview of other researchers’ work in a literature review
When you’re writing an academic text like an essay , research paper , or dissertation , you’ll integrate sources in a variety of ways. You might use a brief quote to support your point, or paraphrase a few sentences or paragraphs.
But it’s often appropriate to summarize a whole article or chapter if it is especially relevant to your own research, or to provide an overview of a source before you analyse or critique it.
In any case, the goal of summarising is to give your reader a clear understanding of the original source. Follow the five steps outlined below to write a good summary.

The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
You should read the article more than once to make sure you’ve thoroughly understood it. It’s often effective to read in three stages:
- Scan the article quickly to get a sense of its topic and overall shape.
- Read the article carefully, highlighting important points and taking notes as you read.
- Skim the article again to confirm you’ve understood the key points, and reread any particularly important or difficult passages.
There are some tricks you can use to identify the key points as you read:
- Start by reading the abstract . This already contains the author’s own summary of their work, and it tells you what to expect from the article.
- Pay attention to headings and subheadings . These should give you a good sense of what each part is about.
- Read the introduction and the conclusion together and compare them: What did the author set out to do, and what was the outcome?
To make the text more manageable and understand its sub-points, break it down into smaller sections.
If the text is a scientific paper that follows a standard empirical structure, it is probably already organised into clearly marked sections, usually including an introduction, methods, results, and discussion.
Other types of articles may not be explicitly divided into sections. But most articles and essays will be structured around a series of sub-points or themes.
Now it’s time go through each section and pick out its most important points. What does your reader need to know to understand the overall argument or conclusion of the article?
Keep in mind that a summary does not involve paraphrasing every single paragraph of the article. Your goal is to extract the essential points, leaving out anything that can be considered background information or supplementary detail.
In a scientific article, there are some easy questions you can ask to identify the key points in each part.
| Introduction | or problem was addressed? formulated? |
|---|---|
| Methods | |
| Results | |
| Discussion/conclusion |
If the article takes a different form, you might have to think more carefully about what points are most important for the reader to understand its argument.
In that case, pay particular attention to the thesis statement —the central claim that the author wants us to accept, which usually appears in the introduction—and the topic sentences that signal the main idea of each paragraph.
Now that you know the key points that the article aims to communicate, you need to put them in your own words.
To avoid plagiarism and show you’ve understood the article, it’s essential to properly paraphrase the author’s ideas. Do not copy and paste parts of the article, not even just a sentence or two.
The best way to do this is to put the article aside and write out your own understanding of the author’s key points.
Examples of article summaries
Let’s take a look at an example. Below, we summarise this article , which scientifically investigates the old saying ‘an apple a day keeps the doctor away’.
An article summary like the above would be appropriate for a stand-alone summary assignment. However, you’ll often want to give an even more concise summary of an article.
For example, in a literature review or research paper, you may want to briefly summarize this study as part of a wider discussion of various sources. In this case, we can boil our summary down even further to include only the most relevant information.
Citing the source you’re summarizing
When including a summary as part of a larger text, it’s essential to properly cite the source you’re summarizing. The exact format depends on your citation style , but it usually includes an in-text citation and a full reference at the end of your paper.
You can easily create your citations and references in APA or MLA using our free citation generators.
APA Citation Generator MLA Citation Generator
Finally, read through the article once more to ensure that:
- You’ve accurately represented the author’s work
- You haven’t missed any essential information
- The phrasing is not too similar to any sentences in the original.
If you’re summarising many articles as part of your own work, it may be a good idea to use a plagiarism checker to double-check that your text is completely original and properly cited. Just be sure to use one that’s safe and reliable.
A summary is a short overview of the main points of an article or other source, written entirely in your own words.
Save yourself some time with the free summariser.
A summary is always much shorter than the original text. The length of a summary can range from just a few sentences to several paragraphs; it depends on the length of the article you’re summarising, and on the purpose of the summary.
With the summariser tool you can easily adjust the length of your summary.
You might have to write a summary of a source:
- As a stand-alone assignment to prove you understand the material
- For your own use, to keep notes on your reading
- To provide an overview of other researchers’ work in a literature review
- In a paper , to summarise or introduce a relevant study
To avoid plagiarism when summarising an article or other source, follow these two rules:
- Write the summary entirely in your own words by paraphrasing the author’s ideas.
- Reference the source with an in-text citation and a full reference so your reader can easily find the original text.
An abstract concisely explains all the key points of an academic text such as a thesis , dissertation or journal article. It should summarise the whole text, not just introduce it.
An abstract is a type of summary , but summaries are also written elsewhere in academic writing . For example, you might summarise a source in a paper , in a literature review , or as a standalone assignment.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, May 12). How to Write a Summary | Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 9 September 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/working-sources/how-to-write-a-summary/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to paraphrase | step-by-step guide & examples, how to quote | citing quotes in harvard & apa, apa referencing (7th ed.) quick guide | in-text citations & references.
)
How to write a summary
Published March 31, 2021. Updated June 2, 2022.
Summary definition
A summary provides an overview of something produced by a writer.
Overview of summary writing
One should read the material multiple times before starting to write a summary. A quick initial read will help to identify the general argument and structure, positioning you to contextualize each part. Annotation can help you process and understand the whole. Making an outline of the text can help identify the argument and its construction. You should never substitute a summary for analysis. When you fully understand both the argument and its construction, you can start writing the summary. Start with the main idea or argument. Follow it with the major points that you have outlined either in the margins or on a separate piece of paper.
Worried about your writing? Submit your paper for a Chegg Writing essay check , or for an Expert Check proofreading . Both can help you find and fix potential writing issues.
What is a summary?
A summary provides an overview of something produced by another writer or by someone working in a different medium. It should address the work as a whole and have the appropriate citation or attribution. In addition, you need to paraphrase the text in your own words without ever borrowing (plagiarizing) the original author’s own. Finally, you must keep strictly to the original material, leaving the summary free of commentary or bias.
Most likely you will want to read the material multiple times.
- A quick initial read to help you to identify the general argument and structure, positioning you to contextualize each part
- An attentive read and annotation to help you process and understand the whole
- A final once-over in which you reverse outline the piece, writing the main point or function of each section in the margins
When you fully understand both the argument and its construction, you’re ready to write the summary. Start with the main idea or argument. Follow it with the major points that you’ve outlined either in the margins or on a separate piece of paper.
- Read the text multiple times and take careful notes.
- Outline the piece’s structure, the way the writer puts together their argument or report.
- Cover the whole thing.
- Paraphrase.
- Include proper attribution or citation.
- Go into the details.
- Reproduce general context or definitions you can assume your audience to know already.
- Copy whole phrases or sentences.
- Add your opinion of the piece.
When to write a summary
There are several reasons you might need to summarize someone else’s work. Summary can be useful—or even necessary—in all of the following contexts.
- You need to keep track of multiple arguments and texts in your own notes.
- Your teacher assigned the summary as an assignment. The purpose may be for you to demonstrate comprehension of an important idea or to engage with another paper’s construction in order to improve your own writing.
- You need to use the piece, as a whole, as evidence or context in a paper.
- You need to produce a literature review as part of a dissertation or similar project.
Be careful with these last two. They both require summary, but be sure that you summarize only what is necessary.
When to avoid summary
Summary becomes problematic when writers confuse it with or substitute it for analysis. Keep these two things distinct. In high school and college, most academic essay assignments call for argument and analysis.
How to identify summary
While it seems like this should be simple, sometimes summary masquerades as analysis. Particularly, when you are working on difficult material, the effort you put into basic comprehension can make paraphrase seem analytical when it’s not.
Here are some warning signs that your paper may have too much summary:
- You outline another essay’s argument rather than positioning yourself with regards to it.
- In literature papers, you describe setting, plot, or characters that would be familiar to someone who has read the book.
- Your paper is organized chronologically. You go through the plot or argument in the order that the writer presents it.
- You use the word “about.” (This story is about… This argument is about…)
- You describe established themes or symbols or identify literary devices instead of digging into any of these. Applying common labels doesn’t count as analysis.
How to shift into analysis
In analysis, you dig into material, looking for the how and why rather than the what. In an essay, you make an argument that pulls all of this analysis together. Here are a couple prompts that can help you shift towards analysis.
Interrogate the text
Assume a skeptical position in relationship to the text. Ask yourself:
- What is reliable information? What isn’t?
- What biases does it reveal or assumptions does it assume?
- If it makes an argument, where is that argument strong? Where is it weak?
- Are opinion and fact kept clearly separate?
While these questions clearly apply to other essays, you can also use them when it comes to the narrators or narrative voice of literary material.
Focus on points of tension
What thematic contrasts drive the work? For example, the text may be preoccupied with the relationship between appearance and reality. While identifying this tension isn’t enough, turning your attention to how and why these things come into conflict can often get you thinking in a more analytical direction.
You can also take this prompt in a more structural direction. If there are different forms, sections, or media, how do these interact? How do they interpret one another in unexpected ways?
Before you turn in that paper, don’t forget to cite your sources in APA format , MLA format , or a style of your choice.
Key takeaways
- A summary needs to provide a complete overview in your own words without adding any commentary or bias.
- You may want to read the piece multiple times.
- Making an outline of the text can help you identify the argument and its construction.
- You should never substitute summary for analysis. These are distinct modes that do different things.

What’s included with a Chegg Writing subscription
- Unlimited number of paper scans
- Plagiarism detection: Check against billions of sources
- Expert proofreading for papers on any subject
- Grammar scans for 200+ types of common errors
- Automatically create & save citations in 7,000+ styles
- Cancel subscription anytime, no obligation
- How to Write a Summary
Proficient students understand that summarizing , identifying what is most important and restating the text (or other media) in your own words, is an important tool for college success.
After all, if you really know a subject, you will be able to summarize it. If you cannot summarize a subject, even if you have memorized all the facts about it, you can be absolutely sure that you have not learned it. And, if you truly learn the subject, you will still be able to summarize it months or years from now.
Proficient students may monitor their understanding of a text by summarizing as they read. They understand that if they can write a one- or two-sentence summary of each paragraph after reading it, then that is a good sign that they have correctly understood it. If they can not summarize the main idea of the paragraph, they know that comprehension has broken down and they need to use fix-up strategies to repair understanding.
Summary Writing Format
- When writing a summary, remember that it should be in the form of a paragraph.
- A summary begins with an introductory sentence that states the text’s title, author and main point of the text as you see it.
- A summary is written in your own words.
- A summary contains only the ideas of the original text. Do not insert any of your own opinions, interpretations, deductions or comments into a summary.
- Identify in order the significant sub-claims the author uses to defend the main point.
- Copy word-for-word three separate passages from the essay that you think support and/or defend the main point of the essay as you see it.
- Cite each passage by first signaling the work and the author, put “quotation marks” around the passage you chose, and put the number of the paragraph where the passages can be found immediately after the passage.
- Using source material from the essay is important. Why? Because defending claims with source material is what you will be asked to do when writing papers for your college professors.
- Write a last sentence that “wraps” up your summary; often a simple rephrasing of the main point.
Example Summary Writing Format
In the essay Santa Ana , author Joan Didion’s main point is ( state main point ). According to Didion “… passage 1 …” (para.3). Didion also writes “… passage 2 …” (para.8). Finally, she states “… passage 3 …” (para. 12) Write a last sentence that “wraps” up your summary; often a simple rephrasing of the main point.
- Provided by : Lumen Learning. Located at : http://lumenlearning.com/ . License : CC BY: Attribution
- Authored by : Paul Powell. Provided by : Central Community College. Project : Kaleidoscope Open Course Initiative. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Authored by : Elisabeth Ellington and Ronda Dorsey Neugebauer. Provided by : Chadron State College. Project : Kaleidoscope Open Course Initiative. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Table of Contents
Instructor Resources (Access Requires Login)
- Overview of Instructor Resources
An Overview of the Writing Process
- Introduction to the Writing Process
- Introduction to Writing
- Your Role as a Learner
- What is an Essay?
- Reading to Write
- Defining the Writing Process
- Videos: Prewriting Techniques
- Thesis Statements
- Organizing an Essay
- Creating Paragraphs
- Conclusions
- Editing and Proofreading
- Matters of Grammar, Mechanics, and Style
- Peer Review Checklist
- Comparative Chart of Writing Strategies
Using Sources
- Quoting, Paraphrasing, and Avoiding Plagiarism
- Formatting the Works Cited Page (MLA)
- Citing Paraphrases and Summaries (APA)
- APA Citation Style, 6th edition: General Style Guidelines
Definition Essay
- Definitional Argument Essay
- How to Write a Definition Essay
- Critical Thinking
- Video: Thesis Explained
- Effective Thesis Statements
- Student Sample: Definition Essay
Narrative Essay
- Introduction to Narrative Essay
- Student Sample: Narrative Essay
- "Shooting an Elephant" by George Orwell
- "Sixty-nine Cents" by Gary Shteyngart
- Video: The Danger of a Single Story
- How to Write an Annotation
- Writing for Success: Narration
Illustration/Example Essay
- Introduction to Illustration/Example Essay
- "She's Your Basic L.O.L. in N.A.D" by Perri Klass
- "April & Paris" by David Sedaris
- Writing for Success: Illustration/Example
- Student Sample: Illustration/Example Essay
Compare/Contrast Essay
- Introduction to Compare/Contrast Essay
- "Disability" by Nancy Mairs
- "Friending, Ancient or Otherwise" by Alex Wright
- "A South African Storm" by Allison Howard
- Writing for Success: Compare/Contrast
- Student Sample: Compare/Contrast Essay
Cause-and-Effect Essay
- Introduction to Cause-and-Effect Essay
- "Cultural Baggage" by Barbara Ehrenreich
- "Women in Science" by K.C. Cole
- Writing for Success: Cause and Effect
- Student Sample: Cause-and-Effect Essay
Argument Essay
- Introduction to Argument Essay
- Rogerian Argument
- "The Case Against Torture," by Alisa Soloman
- "The Case for Torture" by Michael Levin
- How to Write a Summary by Paraphrasing Source Material
- Writing for Success: Argument
- Student Sample: Argument Essay
- Grammar/Mechanics Mini-lessons
- Mini-lesson: Subjects and Verbs, Irregular Verbs, Subject Verb Agreement
- Mini-lesson: Sentence Types
- Mini-lesson: Fragments I
- Mini-lesson: Run-ons and Comma Splices I
- Mini-lesson: Comma Usage
- Mini-lesson: Parallelism
- Mini-lesson: The Apostrophe
- Mini-lesson: Capital Letters
- Grammar Practice - Interactive Quizzes
- De Copia - Demonstration of the Variety of Language
- Style Exercise: Voice
Helpful Test
How to write a summary in 7 steps (with examples).
Summarizing may seem like a simple task, but it entails a lot more than just rephrasing sentences.
Crafting a well-crafted summary involves extracting the essential information from a text while maintaining its fundamental message.
Summarizing is a handy skill that can save you time, improve your attention to detail, and help you better understand complex topics.
These are some of the simple steps that can help you write a summary with confidence:
1. Read the text carefully
Before you even think about summarizing, it is important to read the text you want to summarize carefully.
Whether it’s an article, a book chapter, or any other piece of writing, take notes on the key ideas and important details.
Reading through the text multiple times is recommended, ensuring that you don’t miss anything essential.
2. Identify the main points
Now that you’ve thoroughly read the text, it’s time to determine the main ideas, arguments, or positions presented.
These are the key points that need to be included in your summary. Look for topic sentences, headings, or repeated information as clues.
Identifying the main points may be the most critical step, so be sure to take your time and reflect on what you’ve read.
3. Condense the information
Once you’ve identified the main points, it’s time to condense that information into a concise summary.
Focus on capturing the key ideas without including unnecessary details. Use your own words to explain the content, maintaining the original meaning.
You can condense the information further by grouping similar points together, using subheadings, or removing redundant information.
4. Organize the summary
Your summary should be structured in a logical manner. You can choose to organize it chronologically, by importance, or by following the structure of the original text.
Each paragraph should focus on a specific main point.
Be sure to create a clear introduction and conclusion that provide context and a summary of the overall message.
5. Use transitional phrases
To coherence and flow in your summary, make use of transitional phrases.
These phrases serve as connectors between different ideas and help provide a smooth transition between paragraphs.
For example, phrases such as “In addition,” “Furthermore,” or “On the other hand” can be used to introduce new points, provide additional information, or present contrasting ideas.
Using these transitional phrases will help you enhance the overall structure of your summary.
They act as signposts for your readers, guiding them through the logical progression of the ideas in your summary.
6. Check for accuracy
After completing your summary, thoroughly review it to ensure an accurate representation of the original text.
Take the time to carefully examine each sentence and paragraph, checking for any misinterpretation or omission of crucial details.
Additionally, if needed, conduct fact-checking to verify the accuracy of the information presented. Taking these steps will help ensure the integrity and reliability of your summary.
7. Revise and edit
Take a moment to review and revise your summary carefully. Ensure it is crystal clear, concise, and grammatically correct.
Craft it with finesse, eliminating any unnecessary words or sentences to maintain its brevity.
While doing so, consider adding a touch more detail to enrich its content and provide a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
Examples of Summaries
1. “the snowy day” by ezra jack keats.
“The Snowy Day” is a timeless children’s book written and illustrated by Ezra Jack Keats. The story follows a young boy named Peter who wakes up to a winter wonderland after a fresh snowfall. Excitedly, Peter ventures out into the snowy cityscape, exploring his neighborhood and engaging in various activities. From making footprints in the snow to creating snow angels and even trying to save a snowball for later, Peter’s adventures capture the joy and excitement of a snowy day. With its vivid illustrations and simple yet profound storytelling, “The Snowy Day” celebrates the beauty of winter and the wonder of childhood.
2. “Goodnight Moon” by Margaret Wise Brown
“Goodnight Moon” is a beloved children’s book written by Margaret Wise Brown. The story follows a young bunny as it prepares to go to sleep. Throughout the book, the bunny says goodnight to various objects in its room, such as the moon, stars, toys, and even the quiet old lady whispering “hush.” The rhyming text and gentle illustrations create a soothing atmosphere, making it a perfect bedtime story for little readers. “Goodnight Moon” has become a classic bedtime tale cherished by generations of children and their parents.
3. “Green Eggs and Ham” by Dr. Seuss
“Green Eggs and Ham” is a delightful children’s book by Dr. Seuss that tells the story of a persistent character named Sam-I-Am and his attempt to convince another character to try green eggs and ham. The main character, who initially refuses to try the strange dish, encounters Sam-I-Am in various locations, persistently offering him the unconventional meal. As the story progresses, Sam-I-Am presents multiple scenarios and locations where the green eggs and ham can be enjoyed. Eventually, the reluctant character agrees to try the dish and discovers that he actually enjoys it. The book teaches children about open-mindedness, trying new things, and not judging something without experiencing it firsthand.
How do you start a summary?
Here are a few examples of effective starting lines for a summary:
- “In [title], [author] explores…”
- “This [genre] [title] delves into…”
- “With [topic] as its focus, [title]…”
- “From the mind of [author], [title] takes readers on a journey…”
- “Set in [setting], [title] follows the story of…”
Crafting the perfect opening line for a summary can differ based on the content and target audience. However you do it, try to encapsulate the essential elements and captivate the reader right from the start.
How short should a summary be?
A summary should be concise and succinct, capturing the main ideas without unnecessary details. It should aim to provide a clear and objective overview of the content.
Keep in mind that the length of a summary may vary depending on the specific requirements or context. Generally, a summary should be no more than one-third to one-fourth the length of the original text.
This ensures brevity while effectively conveying the essential information through numbered lists, bullet points, and contrast.
Summarizing is more than just rephrasing a piece of writing. It is a critical skill that requires attention to detail, an understanding of the material, and concise writing.
Following these simple steps will help you write a summary that is both informative and engaging.
Summarizing effectively takes practice, so don’t be discouraged if your first attempt isn’t perfect.
Keep reading and summarizing, and soon you’ll find that it becomes a natural and useful tool in your skillset.
Welcome to the site. Our aim is to help students improve in their studies/exams. We believe each students learn in a different and unique ways our website provides information on variety of learning techniques and subjects to boost a person skills area. We provide a wide range of questions and answers on the following subjects: Mathematics, English Language, Human and Social Biology, Social Studies, Principle of Accounts, Information Technology, Physics, Science, Biology, and Chemistry. Sample SBA, Exam tips, and much more. We aim to enable persons to practice a subject they might find challenging. All quizzes consist of mostly past paper questions, which will help persons to get better exam passes. We advise that participants continue to practice these quizzes to gain further knowledge. Motto: Helping you advance in learning one blog at a time!!!!
10 Best Tips For Writing A Good Summary
5 best freelance developers for programming jobs on fiverr, you may also like, what are the rules of descriptive essay, 3 effective note-taking strategies for test-taking, the importance of staying hydrated during test-taking, the power of positive self-talk and visualization in..., 5 best tips for understanding and managing test-taking..., how to use spaced repetition for long-term retention, is getting enough sleep before an exam essential..., the impact of sleep on test performance and..., how to use mnemonic devices for test preparation.
- Terms of Conditions
- Privacy Policy
Helpful Test Copyright @ 2022
- All eBooks & Audiobooks
- Academic eBook Collection
- Home Grown eBook Collection
- Off-Campus Access
- Literature Resource Center
- Opposing Viewpoints
- ProQuest Central
- Course Guides
- Citing Sources
- Library Research
- Websites by Topic
- Book-a-Librarian
- Research Tutorials
- Use the Catalog
- Use Databases
- Use Films on Demand
- Use Home Grown eBooks
- Use NC LIVE
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary vs. Secondary
- Scholarly vs. Popular
- Make an Appointment
- Writing Tools
- Annotated Bibliographies
- Summaries, Reviews & Critiques
- Writing Center
Service Alert

Article Summaries, Reviews & Critiques
Writing an article summary.
- Writing an article REVIEW
- Writing an article CRITIQUE
- Citing Sources This link opens in a new window
- About RCC Library
Text: 336-308-8801
Email: [email protected]
Call: 336-633-0204
Schedule: Book-a-Librarian
Like us on Facebook
Links on this guide may go to external web sites not connected with Randolph Community College. Their inclusion is not an endorsement by Randolph Community College and the College is not responsible for the accuracy of their content or the security of their site.
When writing a summary, the goal is to compose a concise and objective overview of the original article. The summary should focus only on the article's main ideas and important details that support those ideas.
Guidelines for summarizing an article:
- State the main ideas.
- Identify the most important details that support the main ideas.
- Summarize in your own words.
- Do not copy phrases or sentences unless they are being used as direct quotations.
- Express the underlying meaning of the article, but do not critique or analyze.
- The summary should be about one third the length of the original article.
Your summary should include:
- Give an overview of the article, including the title and the name of the author.
- Provide a thesis statement that states the main idea of the article.
- Use the body paragraphs to explain the supporting ideas of your thesis statement.
- One-paragraph summary - one sentence per supporting detail, providing 1-2 examples for each.
- Multi-paragraph summary - one paragraph per supporting detail, providing 2-3 examples for each.
- Start each paragraph with a topic sentence.
- Use transitional words and phrases to connect ideas.
- Summarize your thesis statement and the underlying meaning of the article.
Adapted from "Guidelines for Using In-Text Citations in a Summary (or Research Paper)" by Christine Bauer-Ramazani, 2020
Additional Resources
All links open in a new window.
How to Write a Summary - Guide & Examples (from Scribbr.com)
Writing a Summary (from The University of Arizona Global Campus Writing Center)
- Next: Writing an article REVIEW >>
- Last Updated: Mar 15, 2024 9:32 AM
- URL: https://libguides.randolph.edu/summaries
Free Text Summarizer
Try our other writing services

Want to be 100% sure your summary is plagiarism-free?
Make your life easier with the free summarizer tool.
Academic research
Speed up your academic research by extracting key points.
Every day use
Reduce your reading time by summarizing long blocks of text within seconds.
Easily condense transcripts of long meetings into concise bullet points.
Difficult text
Simplify hard-to-read paragraphs, sentences or complete articles with 1 click.

Why use this summarizer?
- 100% free: Generate unlimited summaries without paying a penny
- Accurate: Get a reliable and trustworthy summary of your original text without any errors
- No signup: Use it without giving up any personal data
- Secure: No summary data is stored, guaranteeing your privacy
- Speed: Get an accurate summary within seconds, thanks to AI
- Flexible: Adjust summary length to get more (or less) detailed summaries
How to use this summarizer
1. insert, paste or download your text, 2. pick the way you want to summarize, 3. adjust your summary length, 4. get your summary in seconds.
2 ways of summarizing your text
1. key sentences.
Extracts the key points of your text and turns them into digestible bullet points
2. Concise paragraphs
Summarizes your text in a concise paragraph
Summarize your text today
| 💸 Free | Unlimited text summarization |
|---|---|
| 🤖 AI-powered | Extract key points in seconds |
| 🎯 Accurate | Ideal for academic research |
| 🗎 Summarize any text | Articles, paragraphs & essays |
Want to make sure your summary doesn’t contain any plagiarism?
Scribbr & academic integrity.
Scribbr is committed to protecting academic integrity. Our plagiarism checker , AI Detector , Citation Generator , proofreading services , paraphrasing tool , grammar checker , summarizer, and free Knowledge Base content are designed to help students produce quality academic papers.
We make every effort to prevent our software from being used for fraudulent or manipulative purposes.
Ask our team
Want to contact us directly? No problem. We are always here for you.
- Email [email protected]
- Start live chat
- Call +1 (510) 822-8066
- WhatsApp +31 20 261 6040

Frequently asked questions
Yes, it can. The AI has been trained on a big dataset, so technical or complex data won’t be a problem for the text summarizer .
The text summarizer is accessible on both desktop and mobile.
This text summarizer can condense long text within seconds.
At the moment, a maximum of 600 words can be summarized at once, within a few seconds. Want to summarize more? Just paste another block of text. There’s no limit on how much text you can summarize with our text summarizer .
The text summarizer can give you a longer or shorter summary, depending on your wishes. Want a more detailed summary? Just adjust the summary length at the top.

What Is a Summary In Writing? (Explained + 40 Examples)
In my 20+ years of writing essays, research articles, short stories, blog posts, and books, I’ve summarized thousands of times.
Here is my summary answer about “What is a summary in writing?”
A summary in writing is the craft of distilling vast oceans of text into droplets of essence, a skill as crucial as it is challenging . At the core, summary writing is the distillation of essential points from a larger text, preserving the original message and intent. It balances brevity and clarity.
As contradictory as it might sound, there is a lot more to say about summary in writing.
The Essence of Summarization

Table of Contents
Over the years, I’ve learned that a successful summary does two things well—it provides clarity to the reader and respects the original work’s integrity.
Brevity and clarity are the twin pillars of a good summary.
My mantra, “As short as possible and as long as necessary,” and a favorite quote I align with—attributed to Einstein—”Things should be as simple as possible, but no simpler,” encapsulate my approach to summaries.
Achieving this balance is more an art than a science, a dance between being concise and being clear.
My guideline—keeping things as short as necessary but as long as needed—is a testament to this balancing act.
It’s about not just shrinking text size but ensuring every word counts, every sentence conveys meaning, and the essence of the text is untouched.
Types of Summaries
Below are some common types of summaries you need to know:
- Descriptive Summaries: These provide an overview of the main points of a text, without offering analysis or interpretation. Descriptive summaries focus on summarizing the content in a clear and concise manner, making them useful for providing an overview or introduction to a topic.
- Analytical Summaries: Analytical summaries go beyond simply recounting the main points of a text; they also analyze and evaluate the content. These summaries often delve into the author’s arguments, evidence, and conclusions, offering insights into the text’s significance and implications.
- Informative Summaries: Informative summaries aim to convey the most important information from a text, often condensing complex ideas into simpler language. These summaries are commonly used in academic writing, where the goal is to provide readers with a clear understanding of the text’s main points.
- Critical Summaries: Critical summaries involve not only summarizing the content of a text but also critiquing it. Writers may highlight strengths and weaknesses, identify biases or gaps in the argument, and offer their own perspective on the text’s merits or limitations.
- Abstracts: Abstracts are concise summaries of longer documents, such as research papers or articles. They typically include a brief overview of the purpose, methodology, results, and conclusions of the study, allowing readers to quickly grasp the key findings and significance of the research.
Crafting the Perfect Summary
Summarizing is not a random act but a structured process.
It starts with a thorough reading, understanding the text’s main arguments, themes, and nuances.
Then, identifying the core elements that are indispensable to the message.
The challenge is to weave these elements into a cohesive, shorter narrative that stands on its own while reflecting the original text’s spirit.
Personal Insights and Techniques
Through trial and error, I’ve honed specific techniques that aid in summarization:
- Highlighting Key Points: As I read, I highlight or note down crucial information and standout ideas.
- Structuring the Summary: I create a rough outline, deciding the order of points based on their relevance and the original work’s flow.
- Rewriting with Precision: This step involves rewriting the highlighted points in my own words, ensuring clarity and conciseness without diluting the message.
Template for Writing a Summary
Crafting a summary can be simplified by following a structured template.
While each summary may vary in complexity and content, this general template provides a framework to guide your summarization process:
- Introduction: Begin by introducing the text and its author, providing necessary context for the summary. Identify the main topic or thesis of the text and briefly outline its purpose and significance.
- Main Points: Summarize the main points or arguments presented in the text, focusing on the most essential information. Use concise language and avoid unnecessary details or tangents.
- Supporting Details: Provide supporting evidence or examples to reinforce the main points of the text. Select key quotations, statistics, or anecdotes that best illustrate the author’s ideas.
- Analysis: Analyze the text’s content, identifying any underlying themes, patterns, or implications. Consider the author’s purpose, audience, and rhetorical strategies, and evaluate the effectiveness of their argument or message.
- Conclusion: Conclude the summary by summarizing the overall message or takeaway of the text. Reflect on the significance of the text’s content and its relevance to the broader context or field of study.
Here is a great video on how to summarize in writing:
The Role of Experience in Writing Summaries
Experience plays a critical role in mastering summarization.
In my life, I’ve learned that every word in a summary must earn its place. This discernment comes from practice and familiarity with a wide range of texts.
It comes down to what words and ideas to leave in and what to leave out.
Experience has taught me when to cut deeper and when to allow a bit more space for explanation or narrative, always guided by the principle of making things as simple as possible but no simpler.
Original Research and Testing
My curiosity led me to conduct a series of experiments comparing different summarization techniques across various text types.
I assessed the outcomes based on reader comprehension, retention, and feedback.
The Impact of Testing Different Techniques
My research involved comparing various summarization strategies to identify the most effective approaches for different text types.
This hands-on testing revealed that the audience’s needs significantly influence the summary’s structure and content.
For instance, summaries intended for academic audiences prioritized accuracy and conciseness, while those for a general audience often leaned towards engaging narratives and essential takeaways.
Findings and Insights
One key insight from this research was the importance of adaptability.
A one-size-fits-all approach to summarization doesn’t work.
Tailoring the summary to the text type and intended audience increases effectiveness and satisfaction. Additionally, iterative testing highlighted the value of feedback in refining summaries.
Incorporating reader feedback into the summarization process can significantly enhance clarity and relevance.
40 Examples of Summaries
In the spirit of showing rather than telling, let’s dissect examples of summaries from various genres.
For brevity’s sake, I’ll categorize these examples and provide insights into what makes each effective.
Research Articles/Essays
- The Impact of Climate Change on Coastal Ecosystems: Summarizes key findings on the degradation of coastal ecosystems due to rising temperatures, including potential long-term effects and mitigation strategies.
- Technological Advancements in Renewable Energy: Details the latest advancements in solar and wind energy technologies, highlighting efficiency improvements and the path toward sustainable energy solutions.
- Behavioral Economics and Consumer Decision Making: Explores how psychological factors influence economic decisions, offering insights into improving marketing strategies and consumer education.
- The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare: Discusses the integration of AI in diagnostics and patient care, emphasizing potential benefits and ethical considerations.
- Educational Reforms and Student Outcomes: Analyzes the impact of recent educational reforms on student performance and equity, suggesting further research directions and policy implications.
- Microplastics in Marine Environments: Examines the sources, distribution, and ecological impacts of microplastics, proposing methods for reduction and cleanup.
- Mental Health in the Workplace: Investigates the correlation between workplace environment and employee mental health, recommending strategies for creating supportive work cultures.
- Sustainable Agriculture Practices: Reviews sustainable farming techniques and their effectiveness in promoting biodiversity, soil health, and food security.
- The Influence of Social Media on Political Discourse: Evaluates how social media platforms have transformed political communication, voter behavior, and public opinion formation.
- Advances in Alzheimer’s Research: Presents recent breakthroughs in understanding the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease, with a focus on potential therapeutic targets and preventive measures.
Work Reports
- Annual Marketing Strategy Review: Summarizes the performance of last year’s marketing campaigns, key metrics achieved, lessons learned, and strategies for the upcoming year.
- Quarterly Sales Report: Details sales performance by region and product line, comparing results against targets, analyzing trends, and suggesting actionable insights for improvement.
- Customer Satisfaction Survey Analysis: Compiles findings from recent customer surveys, highlighting areas of strength and opportunities for service enhancement.
- IT Infrastructure Upgrade Project Summary: Outlines the objectives, progress, challenges, and next steps in the company’s IT infrastructure overhaul, including budget and timeline updates.
- Employee Training Program Evaluation: Reviews the outcomes of the latest employee training initiatives, assessing effectiveness in skill development and impact on performance.
- Competitor Analysis Report: Provides an overview of key competitors’ strategies, market positioning, product offerings, and potential threats or opportunities.
- Supply Chain Optimization Study: Summarizes findings from a study on supply chain efficiencies, identifying bottlenecks and recommending solutions for cost reduction and speed.
- Risk Management Assessment: Evaluates the company’s exposure to various risks, including financial, operational, and reputational risks, proposing mitigation strategies.
- Sustainability Initiatives Progress Report: Tracks the progress of corporate sustainability efforts, including environmental impact reductions, community engagement, and sustainability goals.
- New Product Development Update: Offers a snapshot of the development stages, challenges encountered, market research findings, and estimated launch timeline for a new product.
- The Echo of the Ocean : A novel about a marine biologist uncovering a groundbreaking discovery about sea life communication, while navigating personal challenges and ethical dilemmas.
- Futures Past : A science fiction saga exploring the consequences of time travel on human history, ethics, and personal identity through intertwined narratives.
- Mind Over Matter : A non-fiction exploration of the power of the human mind to overcome physical limitations, featuring real-life stories of resilience and scientific insights.
- The Last Emperor’s Secret – Historical fiction set in ancient China, revolving around a palace conspiracy, hidden treasures, and the quest for truth.
- Green Horizons : An environmental science book discussing innovative solutions to climate change, from renewable energy to conservation strategies, aimed at a general audience.
- Heartstrings : A collection of short stories delving into the complexities of human relationships, love, loss, and redemption, across diverse cultures and situations.
- Digital Frontiers : Examines the digital revolution’s impact on society, economy, and individual lives, offering insights into future trends and ethical considerations.
- Culinary Journeys : A travelogue that takes readers on a gastronomical tour around the world, exploring the history and stories behind iconic dishes and ingredients.
- The Art of Innovation : A guide to fostering creativity and innovation in the workplace, with case studies from leading companies and practical tips for teams.
- Voices of the Forest : A fantasy novel featuring a young hero’s adventure in a mystical forest, battling dark forces to save their homeland with the help of enchanted creatures.
Short Stories
- The Last Light : A poignant tale about a lighthouse keeper’s final night before the automation of his lighthouse, reflecting on the changes and constants in life.
- Crossroads : Explores the moment a young man stands at a crossroad, literal and metaphorical, contemplating the diverging paths of his future.
- Echoes of War : Follows a veteran’s struggle with returning to civilian life, haunted by memories of the battlefield, and his journey towards healing.
- A Stitch in Time : A whimsical story about a seamstress who discovers her sewing machine can repair more than just clothes, mending broken hearts and dreams.
- The Glass Forest : Details an explorer’s discovery of a mysterious forest where trees are made of glass, symbolizing beauty and fragility.
- Shadows on the Moon : A science fiction piece about a colony on the moon dealing with the psychological effects of living in perpetual darkness and light.
- Invisible Ties : Explores the unseen connections between strangers on a crowded subway, each carrying their own stories and struggles.
- The Color of Autumn : Captures a painter’s attempt to paint the perfect autumn scene, reflecting on the impermanence of life and the enduring beauty of nature.
- Whispers in the Wind : Tells the story of a small village where the wind carries voices from the past, and a young girl learns the history of her ancestors.
- Ripples : A narrative about the impact of a single act of kindness, following its ripple effects through the lives of various people in a community.
The 5 Biggest Mistakes Writers Make When Summarizing
Summarizing is an art, but like any craft, it’s prone to pitfalls.
Here are the five most common mistakes writers make when summarizing, along with tips on how to avoid them.
Summarizing may seem straightforward, but it’s deceptively complex.
One of the biggest mistakes writers make is oversimplifying or overcomplicating the summary, leading to confusion or loss of crucial information.
Another common error is failing to capture the essence of the original text, resulting in a summary that misses the mark.
Additionally, inadequate understanding of the audience can lead to summaries that are either too technical or too simplistic for the intended readership. Lastly, neglecting to cite sources or provide proper attribution in summaries can result in accusations of plagiarism or intellectual dishonesty.
The 5 Biggest Mistakes
- Oversimplifying or Overcomplicating: Striking the right balance between brevity and clarity is key.
- Missing the Essence: Ensure the summary captures the core message and key points of the original text.
- Audience Misalignment: Tailor the summary to the audience’s knowledge level and interests.
- Lack of Attribution: Always cite sources and provide proper credit for ideas and information.
- Ignoring Structure and Flow: A well-structured summary enhances readability and comprehension.
Final Thoughts: What Is a Summary In Writing?
Summarization is more than a writing skill—it’s a critical thinking exercise that challenges you to understand deeply, analyze critically, and communicate effectively.
In my two decades of writing, I’ve seen firsthand how a well-crafted summary can open doors to understanding, make knowledge more accessible, and bridge the gap between complex ideas and a broader audience.
Read This Next:
- What Is TNR In Writing? (Explained w/ Examples)
- What Is Generative Writing? [Ultimate Guide + 100 Examples]
- What Is A Cold Open In Writing? (Tips, Examples, Guide)
- What Is A Universal Statement In Writing? (Explained)
MigrationConfirmed set by Tish
Courtesy the Odegaard Writing & Research Center
http://depts.washington.edu/owrc
Writing a summary response essay
Finally, combine the steps writing a summary response essay write the summary-response. To understand better what are the main stages of your future essay, we offer you an example of a summary response essay outline with short and simple guidelines on what should be in each part of your paper. Analyzing the reasons why some people have confused running with religion, wriing writing a summary response essay rezponse on his own personal experience, pointing out that running does make the writing a summary response essay «feel better, look better, have respose energy, and think more clearly. Armed latest essay writing topics for ielts these questions to ask as I write, maybe I can really put substance into my random thoughts. Afterward, use "authors" or the last name of the first author and "et al. Computer Science. But it doesn't mean that your essay will be divided into two separate parts. In order to present information in a more logical order and lead your audience to the main ideas gradually, there are some essay structure rules following which will help you with making your writing really perfect. Your email address. Her overall thrust is a major point for that part of the article. In order to write well, you need to practice good reading skills. The author develops her ideas and connects them to her thesis by using strong sources. Introduction Very often students are required to perform different academic assignments during their educational process, such as writing an analysis, thesis, research papers, various articles, and essays, etc. Sentence 3: Write a sentence that brings this information together and states how your opinion or thought relates to the author's main idea. Then, for the response paragraph, create a separate thesis statement A brief statement that identifies a writer's thoughts, opinions, or conclusions about a topic. In the summary paragraph, it is important to maintain the order of these supporting details.
Video Writing a summary response essay

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
How to Write a Summary | Guide & Examples
How to Summarize an Essay: Proven Strategies and Tips
How to Write a Summary (Examples Included)
How to Summarize an Article: Techniques & Tips
How to Write a Great Summary
A summary of a text is a short overview of the main ideas written in your own words. While paraphrasing involves expressing specific ideas or details from a larger text in your own words, we generally summarize whole texts (whether it is an essay, article, chapter, book, et cetera). So, in order to ensure our summaries are not too wordy or ...
Writing a Summary
How to Write a Summary: 15 Steps (with Pictures)
How to Write a Summary
Here are a few examples that will help you get a clearer view of how to write a summary. Example 1: Summary of a News Article. Original Article: The article reports on the recent discovery of a rare species of frog in the Amazon rainforest. The frog, named the "Emerald Whisperer" due to its unique green hue and the soft chirping sounds it ...
How to Write a Summary, Analysis, and Response Essay ...
How to Write a Summary: 4 Tips for Writing a Good Summary
When you write your summary, it's important to follow a few steps. First, start your summary by identifying the title, author and type of text. You should include the information above and a brief explanation of the. author's major point in the first sentence of your summary. Example: The Scholastic News article, "Running Into.
How to Write a Summary | Guide & Examples - Scribbr
A final once-over in which you reverse outline the piece, writing the main point or function of each section in the margins. * See terms and conditions. When you fully understand both the argument and its construction, you're ready to write the summary. Start with the main idea or argument. Follow it with the major points that you've ...
How to Write a Summary | English Composition 1
Write objectively. Summaries should not report your opinion on the matter, but should accurately reflect the author's ideas and style. Nevertheless, make note of your evaluative comments and opinions outside of the summary because they may prove useful when writing your paper. 5. Document the publishing information for later reference.
Taking these steps will help ensure the integrity and reliability of your summary. 7. Revise and edit. Take a moment to review and revise your summary carefully. Ensure it is crystal clear, concise, and grammatically correct. Craft it with finesse, eliminating any unnecessary words or sentences to maintain its brevity.
Article Summaries, Reviews & Critiques - RCC Library
Free AI Text Summarizer
A summary in writing is the craft of distilling vast oceans of text into droplets of essence, a skill as crucial as it is challenging. At the core, summary writing is the distillation of essential points from a larger text, preserving the original message and intent. It balances brevity and clarity. As contradictory as it might sound, there is ...
Preparing to Write: To write a good summary it is important to thoroughly understand the material you are working with. Here are some preliminary steps in writing a summary. Skim the text, noting in your mind the subheadings. If there are no subheadings, try to divide the text into sections. Consider why you have been assigned the text. Try to.
AI Text Summarizer
Writing a summary response essay. Finally, combine the steps writing a summary response essay write the summary-response. To understand better what are the main stages of your future essay, we offer you an example of a summary response essay outline with short and simple guidelines on what should be in each part of your paper.