CBSE NCERT Solutions
NCERT and CBSE Solutions for free

Class 12 Chemistry Assignments
We have provided below free printable Class 12 Chemistry Assignments for Download in PDF. The Assignments have been designed based on the latest NCERT Book for Class 12 Chemistry . These Assignments for Grade 12 Chemistry cover all important topics which can come in your standard 12 tests and examinations. Free printable Assignments for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry , school and class assignments, and practice test papers have been designed by our highly experienced class 12 faculty. You can free download CBSE NCERT printable Assignments for Chemistry Class 12 with solutions and answers. All Assignments and test sheets have been prepared by expert teachers as per the latest Syllabus in Chemistry Class 12. Students can click on the links below and download all Pdf Assignments for Chemistry class 12 for free. All latest Kendriya Vidyalaya Class 12 Chemistry Assignments with Answers and test papers are given below.
Chemistry Class 12 Assignments Pdf Download
We have provided below the biggest collection of free CBSE NCERT KVS Assignments for Class 12 Chemistry . Students and teachers can download and save all free Chemistry assignments in Pdf for grade 12th. Our expert faculty have covered Class 12 important questions and answers for Chemistry as per the latest syllabus for the current academic year. All test papers and question banks for Class 12 Chemistry and CBSE Assignments for Chemistry Class 12 will be really helpful for standard 12th students to prepare for the class tests and school examinations. Class 12th students can easily free download in Pdf all printable practice worksheets given below.
Topicwise Assignments for Class 12 Chemistry Download in Pdf

Advantages of Class 12 Chemistry Assignments
- As we have the best and largest collection of Chemistry assignments for Grade 12, you will be able to easily get full list of solved important questions which can come in your examinations.
- Students will be able to go through all important and critical topics given in your CBSE Chemistry textbooks for Class 12 .
- All Chemistry assignments for Class 12 have been designed with answers. Students should solve them yourself and then compare with the solutions provided by us.
- Class 12 Students studying in per CBSE, NCERT and KVS schools will be able to free download all Chemistry chapter wise worksheets and assignments for free in Pdf
- Class 12 Chemistry question bank will help to improve subject understanding which will help to get better rank in exams
Frequently Asked Questions by Class 12 Chemistry students
At https://www.cbsencertsolutions.com, we have provided the biggest database of free assignments for Chemistry Class 12 which you can download in Pdf
We provide here Standard 12 Chemistry chapter-wise assignments which can be easily downloaded in Pdf format for free.
You can click on the links above and get assignments for Chemistry in Grade 12, all topic-wise question banks with solutions have been provided here. You can click on the links to download in Pdf.
We have provided here topic-wise Chemistry Grade 12 question banks, revision notes and questions for all difficult topics, and other study material.
We have provided the best collection of question bank and practice tests for Class 12 for all subjects. You can download them all and use them offline without the internet.
Related Posts

Class 12 Mathematics Relations and Functions Assignments

Class 12 Computer Science Assignments

Class 12 Mathematics Determinants Assignments
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- NCERT Solutions for Chemistry Class 12
- NCERT Solutions

Class 12 Chemistry NCERT Solutions - Chapter-wise FREE PDF Download
Access the updated NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry, designed to enhance your understanding and excel in exams. class 12 chemistry NCERT solutions cover the entire syllabus, providing clarity on complex topics and aiding in concept reinforcement. Download the PDF format for the academic year 2024-25 to study at your convenience. Assistance with theoretical concepts or practical applications, these solutions offer step-by-step explanations and practice questions to facilitate learning. One notable advantage of Class 12 chemistry NCERT solutions is its alignment with the curriculum prescribed. You can also check the updated NCERT Syllabus for Class 12 Chemistry created by Vedantu Master Teachers.
NCERT Solutions Class 12 Chemistry | Chapter-wise List
Access Vedantu’s chapter-wise NCERT Chemistry Class 12 Solutions PDFs below. These resources are invaluable for students, offering systematic and precise solutions to every question from the NCERT Textbook . NCERT solution chapter class 12 chemistry Ideal is for comprehensive learning, they assist students in mastering concepts quickly and thoroughly. With Vedantu, students can streamline their study process and achieve academic success in a shorter duration.
The following Chapters have been removed from NCERT Class 12 chemistry for the Academic year 2024-25
The Solid State
Surface Chemistry
General principals and processes of isolation of Elements
The p-Block Elements
Chemistry in Everyday Life
Below is a quick overview of the chapters:
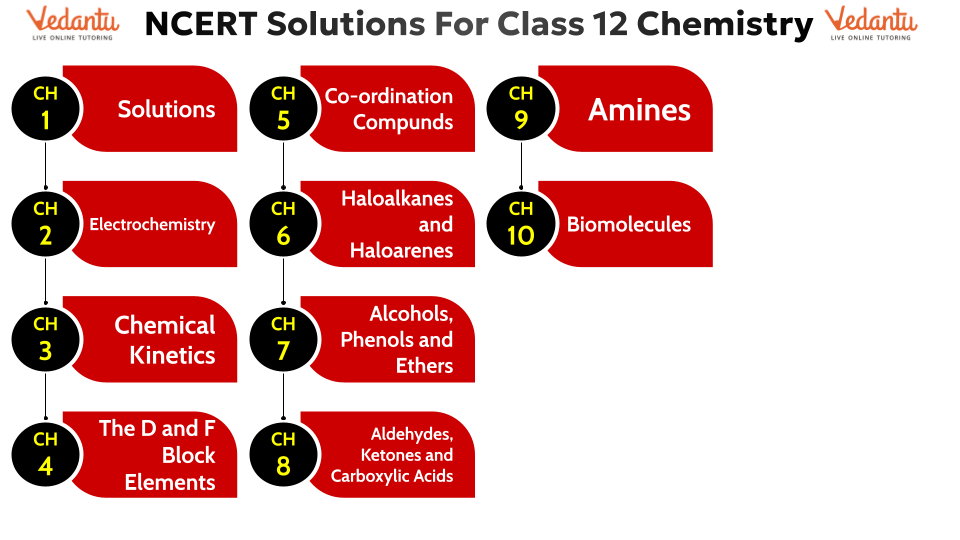
Quick Insights of NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry
NCERT class 12 chemistry solutions - for all the chapters and exercises from Chapters 1 to 10 are provided.
Practicing the textbook questions using these solutions can help students analyse their level of preparation and understanding of concepts.
The chapters are included according to the revised academic year 2024-25 syllabus.
It gives the details about the marks weightage and question paper design for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry.
NCERT class 12 chemistry solutions - provides resources such as class notes, important concepts and formulas exemplar solutions, and other recommended books for further reference.

NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapters Details, and Formulas and Concepts.
Chapter 1- solutions.
Explore the fascinating world of solutions in chemistry, delving into key concepts such as Raoult's Law, Colligative Properties, Determination of Molecular Mass, Types of Solutions, Expression of Concentration, and the Van't Hoff Factor. These topics provide fundamental insights into the behavior of solutes and solvents, offering essential knowledge for understanding solution chemistry and its practical applications.
Class 12 NCERT solutions help the students to go through the formulas easily. Here find the Important formulas of Chapter 1- Solutions to crack your exams.
1. Mole fraction (x)
if the number of moles of A and B are nA and nB respectively, the mole fraction of A and B will be
X A =X/N A +N B , AND X B = ng/П A +П B
2. Molarity (M) = Moles of solute/ Volume of solution in litres
3. Moality (m) = Moles of solute / Mass of solvent in kilograms
4. Parts per million (ppm) = Number of parts of the component 106/Total number of parts of all components of the solution
5. Raoult's law for a solution of volatile solute in volatile solvent :
PA = P A X A
PB = P B * X B
Students can access extra study materials on Solutions , These resources are available for download, offering additional support for your studies.
Chapter 1: Solutions Important Questions
Chapter 1: Solutions Revision Notes
Chapter 1: Solutions NCERT Exemplar Solutions
Chapter 1: Solutions NCERT Books
Chapter 2 - Electrochemistry
In this chapter, we delve into the dynamic world of electrochemistry, covering: Redox reactions, EMF of a cell, Standard electrode potential, Nernst equation, and its applications, the Relationship between Gibbs energy change and EMF Kohlrausch's Law, Electrolysis, the law thereof Dry cell, electrolytic cells, and galvanic cells, Conductance in electrolytic solutions, Lead accumulator, Fuel cells.
Class 12 NCERT solutions help the students to go through the formulas easily. Here, find the Important formulas of Chapter 2- Electrochemistry to crack your exams.
Nernst Equation : This equation relates the equilibrium potential of an electrochemical cell to the concentrations of the reactants and products involved. It's given as:
E = E°-0.0592/n log Q
Gibbs Free Energy Change (Δ G ) : In electrochemistry, this concept is crucial as it determines whether a reaction is spontaneous or not. The relationship between Gibbs free energy change, cell potential, and temperature is given by:Δ𝐺=−𝑛𝐹𝐸.
Students can access extra study materials on Electrochemistry , These resources are available for download, offering additional support for your studies.
Chapter 2: Electrochemistry Important Questions
Chapter 2: Electrochemistry Revision Notes
Chapter 2: Electrochemistry NCERT Exemplar Solutions
Chapter 2: Electrochemistry NCERT Books
Chapter 3 - Chemical Kinetics
The chemical kinetics chapter will give you insight into the Rate of a reaction (Average and instantaneous), factors affecting the rate of reaction: concentration, temperature, catalyst; order and molecularity of a reaction, rate law and specific rate constant, integrated rate equations and half-life (only for zero and first order reactions), the concept of collision theory (elementary idea, no mathematical treatment), activation energy, Arrhenius equation.
Class 12 NCERT solutions help the students to go through the formulas easily. Here find the Important formulas of Chapter 3- Chemical Kinetics to crack your exams.
1. Integrated rate law equation for zero order reaction
k = [R] o [R]/t
Where k is the rate constant and [R] is the initial molar concentration.
2. t 1/2 = [R] o /2k
t 1/2 is the half-life period of zero-order reaction.
3. Integrated rate law equation for first order reaction
k = 2.303/k log [R]/[R]
Where k is the rate constant, [R] is the initial molar concentration, and [R] is the final concentration at a time 't'.
4. Half-life period (t 1/2 ) for the first-order reaction:
t 1/2 = 0.693/k
5. Arhenius epuation
k=Ae-E a /RT
Where 'A' is the frequency factor, Ea is the energy of activation, R is the universal gas constant and T is the absolute temperature.
Students can access extra study materials on Chemical Kinetics , These resources are available for download, offering additional support for your studies.
Chapter 3: Chemical Kinetics Important Questions
Chapter 3: Chemical Kinetics Revision Notes
Chapter 3: Chemical Kinetics NCERT Exemplar Solutions
Chapter 3: Chemical Kinetics NCERT Books
Chapter 4 - d and f Block Elements
The chapter gives insight into the General introduction, electronic configuration, occurrence and characteristics of transition metals, general trends in properties of the first-row transition metals – metallic character, ionization enthalpy, oxidation states, ionic radii, colour, catalytic property, magnetic properties, interstitial compounds, alloy formation, preparation and properties of K 2 Cr 2 O 7 and KMnO 4 . Lanthanoids - Electronic configuration, oxidation states, chemical reactivity, and lanthanoid contraction and its consequences. Actinoids - Electronic configuration, oxidation states, and comparison with lanthanoids.
Class 12 NCERT solutions help the students to go through the formulas easily. Here find the Important formulas of Chapter- 4 d and f block elements to crack your exams.
1.EAN=Number of valence electrons of metal ion−Charge on the metal ion + Number of ligands
2. Magnetic Moment (µ): The magnetic moment of a complex ion is given by the formula:
µ = √n(n+2) BM
3. Crystal Field Stabilization Energy (CFSE): CFSE = -0.4 × ▲ o × n
Students can access extra study materials on d and f block elements , These resources are available for download, offering additional support for your studies.
Chapter 4 : D and F Block Elements Important Questions
Chapter 4 : D and F Block Elements Revision Notes
Chapter 4 : D and F Block Elements NCERT Exemplar Solutions
Chapter 4 : D and F Block Elements NCERT Books
Chapter 5 - Coordination Compounds
Coordination Compounds give the basic Introduction, ligands, coordination number, colour, magnetic properties and shapes, and IUPAC nomenclature of mononuclear coordination compounds. Bonding, Werner's theory, VBT, and CFT; structure and stereoisomerism, importance of coordination compounds (in qualitative analysis, extraction of metals and biological system).
Class 12 NCERT solutions help the students to go through the formulas easily. Here find the Important topics of Chapter 5- Coordination Compounds to crack your exams.
Coordination Number (CN) : The coordination number of a central metal ion in a complex is the total number of ligands attached to it. It is determined experimentally or by the nature of the complex.
Werner's Coordination Theory : Werner proposed the theory of coordination compounds, stating that metal ions exhibit two types of valencies - primary and secondary. Primary valency determines the oxidation state of the metal ion, while secondary valency determines the coordination number and the number of ligands attached to the metal ion.
Stability Constant (Kₛ) : The stability constant (also known as formation constant) is a measure of the stability of a complex ion in solution. It is defined as the equilibrium constant for the formation of the complex ion from its constituent ions.
Isomerism : Coordination compounds exhibit various types of isomerism including structural isomerism (geometric isomerism, linkage isomerism), and stereoisomerism (optical isomerism, geometrical isomerism).
Crystal Field Theory (CFT) : CFT explains the electronic structure and properties of transition metal complexes by considering the interaction between the d orbitals of the metal ion and the ligand's electron pairs.
Students can access extra study materials on Coordination Compounds , These resources are available for download, offering additional support for your studies.
Chapter 5: Coordination Compounds Important Questions
Chapter 5: Coordination Compounds Revision Notes
Chapter 5: Coordination Compounds NCERT Exemplar Solutions
Chapter 5: Coordination Compounds NCERT Books
Chapter 6 - Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
The organic part of Haloalkanes gives the details of depth of Nomenclature, nature of C–X bond, physical and chemical properties, and optical rotation mechanism of substitution reactions.
Haloarenes : Nature of C–X bond, substitution reactions (Directive influence of halogen in monosubstituted compounds only). Uses and environmental effects of - dichloromethane, trichloromethane, tetrachloromethane, iodoform, freons, DDT.
Class 12 NCERT solutions help the students to go through the formulas easily. Here find the Important topics of Chapter 6 - Haloalkanes and Haloarenes to crack your exams.
Nucleophilic Substitution Reaction: Haloalkanes undergo nucleophilic substitution reactions where the halogen atom is replaced by a nucleophile. The general equation for such a reaction is:
R-X+Nu→ R-Nu + X¯
SN1 Reaction Rate Equation: For a first-order nucleophilic substitution reaction (SN1), the rate equation is given by:
Rate = k[R-X]
SN2 Reaction Rate Equation: For a second-order nucleophilic substitution reaction (SN2), the rate equation is given by
Rate = k[Nu¯|[R-X]
Hofmann Elimination (Anti-Elimination): In Hofmann elimination, the leaving group and the hydrogen atom to be removed are anti to each other. This results in the formation of the least substituted alkene. The reaction mechanism involves the E2 mechanism (bimolecular elimination).
Saytzeff Elimination (Syn-Elimination): In Saytzeff elimination, the leaving group and the hydrogen atom to be removed are syn to each other. This results in the formation of the most substituted alkene. The reaction mechanism involves the E1cb mechanism (elimination, unimolecular, conjugate base).
Students can access extra study materials on Haloalkanes and Haloarenes , These resources are available for download, offering additional support for your studies.
Chapter 6: Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Important Questions
Chapter 6: Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Revision Notes
Chapter 6: Haloalkanes and Haloarenes NCERT Exemplar Solutions
Chapter 6: Haloalkanes and Haloarenes NCERT Books
Chapter 7 - Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
In the fascinating world of Organic Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers act as a skeleton to perform several reactions. This chapter will give you the following Learnings :
Alcohols : Nomenclature, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties (of primary alcohols only), identification of primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohols, mechanism of dehydration, and uses with special reference to methanol and ethanol.
Phenols: Nomenclature, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties, acidic nature of phenol, electrophilic substitution reactions, uses of phenols.
Ethers : Nomenclature, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties, uses.
Class 12 NCERT solutions help the students to go through the formulas easily. Here find the Important topics of Chapter 7 - Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers to crack your exams.
Nomenclature: Understanding the IUPAC nomenclature rules for alcohols, phenols, and ethers is crucial. For example:
Alcohols : Named by replacing the -e suffix of the corresponding alkane with -ol.
Phenols : Named by adding the suffix -ol to the name of the parent aromatic hydrocarbon.
Ethers : Named by naming the alkyl groups attached to oxygen in alphabetical order followed by the word ether.
Preparation Methods: There are various methods for the preparation of alcohols, phenols, and ethers. Some important ones include:
Alcohol : From Alkene (Hydration), From Grignard reagent, From Alkyl Halides (Substitution), etc.
Phenols : From Benzene sulfonic acid, From diazonium salts, etc.
Ethers : Williamson synthesis, Dehydration of alcohols, etc.
Reactions of Alcohols: Alcohols undergo various reactions such as:
Oxidation : Alcohols can be oxidized to corresponding aldehydes, ketones, or carboxylic acids depending on the oxidizing agent and conditions.
Esterification : Reaction with carboxylic acids to form esters in the presence of an acid catalyst.
Dehydration : Elimination of water to form alkenes in the presence of a strong acid catalyst.
Reactions of Phenols: Phenols exhibit acidic properties due to the presence of the -OH group attached to the aromatic ring. Important reactions include:
Reaction with metals to form phenoxide ions.
Reaction with alkalis to form salts.
Esterification to form esters.
Williamson Ether Synthesis: This method is used for the preparation of ethers by the reaction of alkyl halides with sodium or potassium alkoxide. The general reaction is: R-X+RO→ R-O-R + X¯
Students can access extra study materials on Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers , These resources are available for download, offering additional support for your studies.
Chapter 7: Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Important Questions
Chapter 7: Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers Revision Notes
Chapter 7: Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers NCERT Exemplar Solutions
Chapter 7: Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers NCERT Books
Chapter 8 - Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acid
Learn more about Aldehydes, Ketones, and Carboxylic Acid and get the following insights from the chapter:
Aldehydes and Ketones : Nomenclature, nature of carbonyl group, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties, mechanism of nucleophilic addition, reactivity of alpha hydrogen in aldehydes, uses. Carboxylic Acids: Nomenclature, acidic nature, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties; uses.
Class 12 NCERT solutions help the students to go through the formulas easily. Here find the Important topics of Chapter 8 - Aldehydes, Ketones, and Carboxylic Acid to crack your exams.
Nomenclature : Understanding the IUPAC nomenclature rules for aldehydes, ketones, and carboxylic acids is crucial.
Preparation Methods :
Aldehydes : From primary alcohols by mild oxidation (PCC, Tollens' reagent, Fehling's solution, etc.)
Ketones : From secondary alcohols by oxidation or from alkyl halides by Friedel-Crafts acylation.
Carboxylic Acids : From primary alcohols by strong oxidation from Grignard reagents, etc.
Reactions of Aldehydes and Ketones :
Nucleophilic Addition : Aldehydes and ketones undergo nucleophilic addition reactions with nucleophiles.
Oxidation : Aldehydes are oxidized to carboxylic acids, whereas ketones are not easily oxidized under mild conditions.
Reactions of Carboxylic Acids :
Esterification : Reaction with alcohols to form esters in the presence of an acid catalyst.
Decarboxylation : Carboxylic acids undergo decarboxylation to produce carbon dioxide and a lower alkane upon heating with soda lime
Acidity of Carboxylic Acids : Carboxylic acids are acidic due to the presence of the carboxyl group.
Students can access extra study materials on Aldehydes, Ketones, and Carboxylic Acid , These resources are available for download, offering additional support for your studies.
Chapter 8: Aldehydes, Ketones, and Carboxylic Acids Important Questions
Chapter 8: Aldehydes, Ketones, and Carboxylic Acids Revision Notes
Chapter 8: Aldehydes, Ketones, and Carboxylic Acids NCERT Exemplar Solutions
Chapter 8: Aldehydes, Ketones, and Carboxylic Acids NCERT Books
Chapter 9 - Amines
The chapter will provide information about Nomenclature, classification, structure, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties, uses, and identification of primary, secondary, and tertiary amines. Diazonium salts: Preparation, chemical reactions and importance in synthetic organic chemistry.
Class 12 NCERT solutions help the students to go through the formulas easily. Here find the Important topics of Chapter 9 - Amines to crack your exams.
Classification of Amines: Amines are classified based on the number of alkyl or aryl groups attached to the nitrogen atom. They can be primary (one alkyl/aryl group), secondary (two alkyl/aryl groups), or tertiary (three alkyl/aryl groups) amines.
Preparation Methods: Amines can be prepared by various methods including:
Reduction of nitro compounds
Reduction of nitriles
Gabriel synthesis
Hoffmann bromamide reaction
Ammonolysis of alkyl halides
Basicity of Amines: Amines are basic due to the presence of a lone pair of electrons on the nitrogen atom. The basicity of amines increases with the availability of lone pairs, which is influenced by the number of alkyl or aryl groups attached to the nitrogen atom.
Hoffmann Bromamide Reaction: This reaction is used for the synthesis of primary amines from a primary amide. The primary amide is treated with bromine and a base to form an isocyanate intermediate, which is then hydrolyzed to yield the primary amine.
Aromatic Amines: Aromatic amines are derivatives of benzene in which one or more hydrogen atoms are replaced by amino groups (-NH 2 ). Aniline is the simplest aromatic amine and is an important precursor in the synthesis of dyes, pharmaceuticals, and other organic compounds.
Students can access extra study materials on Amines , These resources are available for download, offering additional support for your studies.
Chapter 9: Amines Important Questions
Chapter 9: Amines Revision Notes
Chapter 9: Amines NCERT Exemplar Solutions
Chapter 9: Amines NCERT Books
Chapter 10 - Biomolecules
Carbohydrates - Classification (aldoses and ketoses), monosaccharides (glucose and fructose), D-L configuration oligosaccharides (sucrose, lactose, maltose), polysaccharides (starch, cellulose, glycogen); Importance of carbohydrates.
Proteins -Elementary idea of - amino acids, peptide bonds, polypeptides, proteins, structure of proteins - primary, secondary, tertiary structure and quaternary structures (qualitative idea only), denaturation of proteins; enzymes. Hormones - Elementary idea excluding structure.
Vitamins - Classification and functions.
Nucleic Acids: DNA and RNA.
Class 12 NCERT solutions help the students to go through the formulas easily. Here find the Important topics of Chapter 10 - Biomolecules to crack your exams.
Classification of Biomolecules: Biomolecules are classified into four main categories based on their chemical nature and functions:
Carbohydrates : Sugars, starches, cellulose, etc.
Proteins : Polymers of amino acids.
Lipids : Fats, oils, phospholipids, etc.
Nucleic Acids : DNA, RNA, ATP, etc.
Primary Structure of Proteins: The primary structure of a protein refers to the sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide chain. It is determined by the order of amino acids linked by peptide bonds.
Carbohydrate Chemistry: Key concepts in carbohydrate chemistry include:
Monosaccharides : Simple sugars such as glucose, fructose, and galactose.
Disaccharides : Two monosaccharides linked by a glycosidic bond, such as sucrose, lactose, and maltose.
Polysaccharides : Complex carbohydrates formed by the polymerization of monosaccharide units, such as starch, glycogen, and cellulose.
Enzyme Kinetics: Enzymes are biological catalysts that increase the rate of biochemical reactions.
Nucleic Acid Structure: Nucleic acids are polymers of nucleotides and include DNA and RNA. Key concepts include:
DNA Structure : Double helix structure composed of two complementary strands of nucleotides held together by hydrogen bonds.
RNA Structure : Single-stranded molecule involved in protein synthesis and gene expression.
Students can access extra study materials on Biomolecules , These resources are available for download, offering additional support for your studies.
Chapter 10: Amines Important Questions
Chapter 10: Amines Revision Notes
Chapter 10: Amines NCERT Exemplar Solutions
Chapter 10: Amines NCERT Books
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry 2024-25 - Marks Distribution
The CBSE Class 12 Chemistry exam is an important exam for all the students and every student wants to score well in it. Each chapter is allocated with a certain number of marks. Preparing for the Class 12 exam means you have to prepare all the chapters thoroughly. The marks are divided in the following manner:
Benefits of Referring to Vedantu’s NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry
The Vedantu’s Class 12 NCERT Solutions of Chemistry provided here in PDFs offer various benefits, including:
The answers provided here are straightforward.
To facilitate comprehension, solutions are presented in phases.
All of the questions from each chapter are answered.
For effective preparations, comprehend all of the processes outlined in the answers.
Vedantu’s NCERT Solution has planned a detailed study map to help the students understand the topics, important concepts, and formulas to crack their exams.
Along with this, students can also download additional study materials provided by Vedantu, for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry–

FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Chemistry Class 12
1. Is NCERT Book Good for Chemistry Class 12?
NCERT books are the most recommended books of CBSE, which cover 50% of the board questions. The topics in NCERT are explained in detail with relevant images, diagrams and graphs. Moreover, the ease of language and in-depth analysis of chapters makes it preferable for students and teachers.
The topics like organic, inorganic and physical chemistry are also crucial for competitive exams; therefore, understanding the fundamentals via NCERT book will be fruitful as there is a step by step description.
Furthermore, NCERT textbook comes with exam-specific exercises; solving these with the previous year question paper and mock test paper will prove beneficial.
2. What are the Critical Chapters in Class 12 Chemistry?
Almost all chapters are crucial for boards exam, but students can give additional emphasis to specific chapters like:
Kinetic energy
Atomic structure and chemical bonding
Thermodynamic
Electrochemistry
Aldehydes, Ketones, and Carboxylic Acids
These chapters require an in-depth understanding and practise to grasp the context. Students need to highlight the critical sections like in Aldehydes, Ketones, Carboxylic Acids to better understand this chapter. It would help if you also gave weightage to properties of hydrides and anomalous behaviour of second-period elements and products of the given reactions. All these require thorough practise prior to the exam.
3. How to Secure Good Marks in Class 12 Chemistry?
With good preparation of the paper, you can secure a high score. It is advisable to read all the chapters from quality textbooks and revise them regularly. Practising exercises and questions from books will strengthen the fundamentals. Moreover, it would be best if you focus on important topics rather than mastering every bit of the syllabus.
It would be helpful if a student prepares a timetable and allots time for more scoring chapters. Picking the topics with maximum weightage will quicken the revision process. Furthermore, knowing the exam pattern, writing format, appropriate formulas and chemical equation will again help in securing good grades in boards or relevant exams.
4. How many chapters are present in the NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry?
There are a total of 16 chapters in the NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry . If you want to score well in your Class 12 Chemistry exam, you need to finish all of these chapters. The focus of your study should be on the NCERT textbooks , as most of the questions in your board exams will be directly or indirectly from them. You can take the help of Vedantu’s NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry to prepare for the board exams. It contains solutions to all the exercise problems.
5. Is the NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry important for the students?
The NCERT Solutions for Class 12 are very important, the reason for it is that all the questions and examples are as per the CBSE syllabus . You will be able to understand and strengthen your subject by preparing from the class 12 NCERT solutions . All the examples and questions are based on the CBSE syllabus and there are chances that the same questions may come in the exam. The solutions books will help the teachers to explain better and will help you to revise the same topic that is being taught. The main purpose of the Class 12 NCERT solutions is that students can self-analyze their mistakes and improve themselves in that particular area. To score well in Class 12 all students must follow the Solution chapter Class 12 Chemistry.
6. How can I understand Class 12 Chemistry?
To understand Class 12 Chemistry and score well in your exams, the book that you have to focus on is the NCERT. It explains all the concepts in an easy language. Most importantly, the questions in your board exams will be directly or inspired by the NCERT textbooks . What you need is Vedantu’s NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry . You can get the solutions to all the exercise problems and get through the NCERT textbooks quickly.
7. What is the best Solution book for NCERT Class 12 Chemistry?
The best Solution book for NCERT Class 12 Chemistry is the one offered by Vedantu. They provide the solutions to all the exercise problems from NCERT in PDF format so that you can study anytime and anywhere. The top subject-matter experts have created these solutions. This means that they are not only accurate but also written in a way that CBSE accepts. It is the best way of scoring well in Class 12 exams.
8. Where can I get the NCERT Solution for Class 12 Chemistry?
Vedantu offers NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry. Each exercise’s solution is provided in a different PDF for your ease. Here is how you can download them:
Visit the page of NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry on the official website of Vedantu.
Find the chapter for which you want a solution and click on the ‘Download PDF’ link.
The solutions will be downloaded into your system. You’ll also receive a message/ mail with a direct download button of your preferred solution.
With these few simple steps, you will have access to NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry in no time. You can also access study materials from Vedantu’s app. All the resources are free of cost.
9. Are NCERT Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Solutions important for board exams?
Yes, NCERT Solutions Class 12 Chemistry Solutions are crucial for board exams as they offer a clear understanding of the chapter's concepts and help students practice a wide range of questions. By solving these solutions, students can improve their problem-solving skills and score well in exams.
10. What are the important questions for 12th chemistry?
Important questions for 12th Chemistry vary depending on the curriculum and focus areas, but topics like electrochemistry, chemical kinetics, and coordination compounds often carry weight.
11. What are good questions to ask about chemistry?
Good questions to ask about chemistry could revolve around the applications of chemical concepts in everyday life, the latest advancements in the field, or the environmental impact of chemical processes.
12. Who created chemistry?
Chemistry as a formal discipline doesn't have a single creator; it has evolved over centuries through contributions from various scientists such as Antoine Lavoisier, Robert Boyle, and Dmitri Mendeleev.
13. Is 12th chemistry tough?
The difficulty of 12th-grade chemistry can vary from student to student, but it often requires a solid understanding of concepts and regular practice to excel.
14. Which chapter is more important in Chemistry Class 12?
In ncert class 12 chemistry solutions chapters like Electrochemistry, Chemical Kinetics, and Organic Chemistry containing Aldehydes, Ketones, and Carboxylic Acids are often considered more important due to their weightage in exams and their foundational concepts.
15. What is the full form of chemistry?
Chemistry's full form is derived from the word "alchemy" and originates from the Arabic word "al-kīmiyā", meaning "the science of the natural".
16. Which is the easiest chapter in chemistry class 12?
For some students, chapters like "Solutions" may be considered easier in Chemistry Class 12 due to their straightforward concepts and fewer intricate calculations compared to other chapters.
NCERT Solutions for Class 12
Cbse class 12 study materials, important update.
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions in Hindi Medium and English Medium. Get here Exercises Questions and Intext Questions to view online or download in PDF format. These solutions are updated for new academic year 2024-25 for all boards using NCERT Books.
Class 12th Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions Answers
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Exercises
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Intext
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 in Hindi
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 NCERT Book
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Revision Book
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Study Materials
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Assignment 1
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Assignment 2
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Assignment 3
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Assignment 4
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Level 1 Test 1
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Level 2 Test 1
- Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Level 3 Test 1
- Class 12 Chemistry NCERT Solutions
- Class 12 all Subjects NCERT Solutions
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 in PDF format to free download is given below updated for new academic session 2024-25. Download NCERT Books and offline as well as online apps based on latest CBSE Syllabus.
Download App for Class 12

1. Which of the following units is useful in relating concentration of solution with its vapour pressure? (i) mole fraction (ii) parts per million (iii) mass percentage (iv) molality 2. Maximum amount of a solid solute that can be dissolved in a specified amount of a given liquid solvent does not depend upon ____________. (i) Temperature (ii) Nature of solute (iii) Pressure (iv) Nature of solvent 3. An unripe mango placed in a concentrated salt solution to prepare pickle, shrivels because _____________. (i) it gains water due to osmosis. (ii) it loses water due to reverse osmosis. (iii) it gains water due to reverse osmosis. (iv) it loses water due to osmosis. 4. Low concentration of oxygen in the blood and tissues of people living at high altitude is due to ____________. (i) low temperature (ii) low atmospheric pressure (iii) high atmospheric pressure (iv) both low temperature and high atmospheric pressure
5. The value of Henry’s constant KH is _____________. (i) greater for gases with higher solubility. (ii) greater for gases with lower solubility. (iii) constant for all gases. (iv) not related to the solubility of gases. 6. At a given temperature, osmotic pressure of a concentrated solution of a substance _____________. (i) is higher than that at a dilute solution. (ii) is lower than that of a dilute solution. (iii) is same as that of a dilute solution. (iv) cannot be compared with osmotic pressure of dilute solution. 7. Considering the formation, breaking and strength of hydrogen bond, predict which of the following mixtures will show a positive deviation from Raoult’s law? (i) Methanol and acetone. (ii) Chloroform and acetone. (iii) Nitric acid and water. (iv) Phenol and aniline.
8. Which of the following statements is false? (i) Units of atmospheric pressure and osmotic pressure are the same. (ii) In reverse osmosis, solvent molecules move through a semipermeable membrane from a region of lower concentration of solute to a region of higher concentration. (iii) The value of molal depression constant depends on nature of solvent. (iv) Relative lowering of vapour pressure, is a dimensionless quantity. 9. Colligative properties depend on ____________. (i) the nature of the solute particles dissolved in solution. (ii) the number of solute particles in solution. (iii) the physical properties of the solute particles dissolved in solution. (iv) the nature of solvent particles. 10. On dissolving sugar in water at room temperature solution feels cool to touch. Under which of the following cases dissolution of sugar will be most rapid? (i) Sugar crystals in cold water. (ii) Sugar crystals in hot water. (iii) Powdered sugar in cold water. (iv) Powdered sugar in hot water.
1 (i) 2 (iii) 3 (iv) 4 (ii) 5 (ii) 6 (i) 7 (i) 8 (ii) 9 (ii) 10 (iv).
NCERT Books for all classes and subjects, Offline Apps 2024-25 based on new CBSE Syllabus. Ask your doubts related to NIOS or CBSE Board and share your knowledge with your friends and other users through Discussion Forum.

Copyright 2024 by Tiwari Academy | A step towards Free Education

- Class 6 Maths
- Class 6 Science
- Class 6 Social Science
- Class 6 English
- Class 7 Maths
- Class 7 Science
- Class 7 Social Science
- Class 7 English
- Class 8 Maths
- Class 8 Science
- Class 8 Social Science
- Class 8 English
- Class 9 Maths
- Class 9 Science
- Class 9 Social Science
- Class 9 English
- Class 10 Maths
- Class 10 Science
- Class 10 Social Science
- Class 10 English
- Class 11 Maths
- Class 11 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 11 English
- Class 12 Maths
- Class 12 English
- Class 12 Economics
- Class 12 Accountancy
- Class 12 Physics
- Class 12 Chemistry
- Class 12 Biology
- Class 12 Computer Science (Python)
- Class 12 Physical Education
- GST and Accounting Course
- Excel Course
- Tally Course
- Finance and CMA Data Course
- Payroll Course
Interesting
- Learn English
- Learn Excel
- Learn Tally
- Learn GST (Goods and Services Tax)
- Learn Accounting and Finance
- GST Tax Invoice Format
- Accounts Tax Practical
- Tally Ledger List
- GSTR 2A - JSON to Excel
Are you in school ? Do you love Teachoo?
We would love to talk to you! Please fill this form so that we can contact you
You are learning...
Chemistry Class 12
Click on any of the links below to start learning from Teachoo ...
Class 12 is a crucial year for students who want to pursue higher education in chemistry or related fields. It is the year when you have to prepare for competitive exams like JEE, NEET, AIIMS, etc. as well as board exams. It is also the year when you have to learn some of the most advanced and complex topics in chemistry, such as electrochemistry, coordination compounds, organic synthesis, biomolecules, and more.🧪🔬🌡
If you are looking for a way to ace your class 12 chemistry exams and gain a solid foundation for your future studies, you have come to the right place. We have designed an online course that will help you master the concepts and skills of class 12 chemistry in a fun and engaging way.😊
Here are some of the features of our online class 12 chemistry course:
- You will get access to comprehensive and updated video lectures, interactive quizzes, assignments, and notes that cover the entire syllabus of class 12 chemistry.
- You will learn from expert and experienced teachers who have a passion for teaching and a deep knowledge of the subject and the exam pattern.
- You will get personalized feedback and guidance on your progress and performance.
- You will be able to interact with other students and teachers through online forums and live sessions.
Our online class 12 chemistry course will not only help you to score high marks in your exams, but also prepare you for your future endeavors in chemistry or related fields. Whether you want to become a chemist, a doctor, an engineer, or anything else, our online class 12 chemistry course will give you the edge you need.👩⚕️👨🔬👩🎓
Don’t miss this opportunity. Enroll in our online class 12 chemistry course today and start your journey of learning and discovery.🚀
Solutions to CBSE Sample Paper - Chemistry Class 12
What's in it?
Hi, it looks like you're using AdBlock :(
Please login to view more pages. it's free :), solve all your doubts with teachoo black.

NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Solutions
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Solutions contains all the questions with detailed solutions. Students are advised to practice these questions for better understanding of the concepts given in the chapter.
February 23, 2024

Table of Contents
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2: NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Solutions is prepared by our senior and renowned teachers of Physics Wallah primary focus while solving these questions of class 12 in the NCERT textbook, also do read the theory of this Chapter 2 Solutions while going before solving the NCERT questions. Our Physics Wallah team Prepared Other Subjects NCERT Solutions for class 12.
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Overview
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 cover several important topics. It is highly recommended for students to review each topic thoroughly in order to gain a comprehensive understanding of the concepts taught in the chapter and make optimal use of the provided solutions.
These solutions are the result of dedicated efforts by the Physics Wallah teachers aimed at assisting students in grasping the concepts covered in this chapter. By going through and practicing these solutions, the objective is for students to achieve excellent results in their exams effortlessly.
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2
Answer the following Questions of NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2:
Question 1. Calculate the mass percentage of benzene (C 6 H 6 ) and carbon tetrachloride (CCl 4 ) if 22 g of benzene is dissolved in 122 g of carbon tetrachloride.
Alternatively,
Mass percentage of CCl 4 = (100 − 15.28)%
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 3
Question 2. Calculate the mole fraction of benzene in solution containing 30% by mass in carbon tetrachloride.
Solution : Let the total mass of the solution be 100 g and the mass of benzene be 30 g.
∴Mass of carbon tetrachloride = (100 − 30)g
Molar mass of benzene (C 6 H 6 ) = (6 × 12 + 6 × 1) g mol −1
= 78 g mol −1
= 0.3846 mol
Molar mass of carbon tetrachloride (CCl 4 ) = 1 × 12 + 4 × 35.5
= 154 g mol −1
∴Number of moles of CCl 4 = 70 / 154
= 0.4545 mol
Thus, the mole fraction of C 6 H 6 is given as:
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 4
Question 3. Calculate the molarity of each of the following solutions: (a) 30 g of Co(NO 3 ) 2 . 6H 2 O in 4.3 L of solution (b) 30 mL of 0.5 M H 2 SO 4 diluted to 500 mL.
Solution : Molarity is given by:
(a) Molar mass of Co (NO 3 ) 2 .6H 2 O = 59 + 2 (14 + 3 × 16) + 6 × 18
= 291 g mol −1
= 0.103 mol
(b) Number of moles present in 1000 mL of 0.5 M H 2 SO 4 = 0.5 mol
= 0.015 mol
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 5
Question 4. Calculate the mass of urea (NH 2 CONH 2 ) required in making 2.5 kg of 0.25 molal aqueous solution.
Solution : Molar mass of urea (NH 2 CONH 2 ) = 2(1 × 14 + 2 × 1) + 1 × 12 + 1 × 16
= 60 g mol −1
0.25 molar aqueous solution of urea means:
1000 g of water contains 0.25 mol = (0.25 × 60)g of urea
= 15 g of urea
(1000 + 15) g of solution contains 15 g of urea
= 37 g of urea (approximately)
Hence, mass of urea required = 37 g
Question 5. Calculate (a) molality (b) molarity and (c) mole fraction of KI if the density of 20% (mass/mass) aqueous KI is 1.202 g mL -1.
Solution : (a) Molar mass of KI = 39 + 127 = 166 g mol −1
20% (mass/mass) aqueous solution of KI means 20 g of KI is present in 100 g of solution.
20 g of KI is present in (100 − 20) g of water = 80 g of water
= 1.51 m (approximately)
(b) It is given that the density of the solution = 1.202 g mL −1
= 83.19 × 10 −3 L
Question 6. H 2 S, a toxic gas with rotten egg like smell, is used for the qualitative analysis. If the solubility of H 2 S in water at STP is 0.195 m, calculate Henry’s law constant.
Solution : It is given that the solubility of H 2 S in water at STP is 0.195 m, i.e., 0.195 mol of H 2 S is dissolved in 1000 g of water.
= 55.56 mol
At STP, pressure (p) = 0.987 bar
According to Henry’s law:
Question 7. Henry’s law constant for CO 2 in water is 1.67 × 10 8 Pa at 298 K. Calculate the quantity of CO 2 in 500 mL of soda water when packed under 2.5 atm CO 2 pressure at 298 K.
Solution : It is given that:
K H = 1.67 × 10 8 Pa
= 2.533125 × 10 5 Pa
In 500 mL of soda water, the volume of water = 500 mL
[Neglecting the amount of soda present]
We can write:
500 mL of water = 500 g of water
nH 2 0= 27.78 mol of water
Hence, quantity of CO 2 in 500 mL of soda water = (0.042 × 44)g
Question 8. The vapour pressure of pure liquids A and B are 450 and 700 mm Hg respectively, at 350 K. Find out the composition of the liquid mixture if total vapour pressure is 600 mm Hg. Also find the composition of the vapour phase.
p total = 600 mm of Hg
From Raoult’s law, we have:
= 450 × 0.4
= 180 mm of Hg
= 700 × 0.6
= 420 mm of Hg
Now, in the vapour phase:
And, mole fraction of liquid B = 1 − 0.30
Question 9. Vapour pressure of pure water at 298 K is 23.8 mm Hg. 50 g of urea (NH 2 CONH 2 ) is dissolved in 850 g of water. Calculate the vapour pressure of water for this solution and its relative lowering.
Weight of water taken, w 1 = 850 g
Weight of urea taken, w 2 = 50 g
Molecular weight of water, M 1 = 18 g mol −1
Molecular weight of urea, M 2 = 60 g mol −1
Now, we have to calculate vapour pressure of water in the solution. We take vapour pressure as p 1 .
Now, from Raoult’s law, we have:
Hence, the vapour pressure of water in the given solution is 23.4 mm of Hg and its relative lowering is 0.0173.
Question 10. Boiling point of water at 750 mm Hg is 99.63°C. How much sucrose is to be added to 500 g of water such that it boils at 100°C. Molal elevation constant for water is 0.52 K kg mol −1.
Solution : Here, elevation of boiling point ΔT b = (100 + 273) − (99.63 + 273)
Mass of water, w l = 500 g
Molar mass of sucrose (C 12 H 22 O 11 ), M 2 = 11 × 12 + 22 × 1 + 11 × 16
= 342 g mol −1
Molal elevation constant, K b = 0.52 K kg mol −1
We know that:
= 121.67 g (approximately)
Hence, 121.67 g of sucrose is to be added.
Question 11. Calculate the mass of ascorbic acid (Vitamin C, C 6 H 8 O 6 ) to be dissolved in 75 g of acetic acid to lower its melting point by 1.5°C. K f = 3.9 K kg mol −1.
Solution : Mass of acetic acid, w 1 = 75 g
Molar mass of ascorbic acid (C 6 H 8 O 6 ), M 2 = 6 × 12 + 8 × 1 + 6 × 16
= 176 g mol −1
Lowering of melting point, ΔT f = 1.5 K
= 5.08 g (approx)
Hence, 5.08 g of ascorbic acid is needed to be dissolved.
Question 12. Calculate the osmotic pressure in pascals exerted by a solution prepared by dissolving 1.0 g of polymer of molar mass 185,000 in 450 mL of water at 37°C.
Volume of water, V = 450 mL = 0.45 L
Temperature, T = (37 + 273)K = 310 K
= 31 Pa (approximately)
Question 13. Define the term solution. How many types of solutions are formed? Write briefly about each type with an example.
Solution : Homogeneous mixtures of two or more than two components are known as solutions.
There are three types of solutions.
(i) Gaseous solution:
The solution in which the solvent is a gas is called a gaseous solution. In these solutions, the solute may be liquid, solid, or gas. For example, a mixture of oxygen and nitrogen gas is a gaseous solution.
(ii) Liquid solution:
The solution in which the solvent is a liquid is known as a liquid solution. The solute in these solutions may be gas, liquid, or solid.
For example, a solution of ethanol in water is a liquid solution.
(iii) Solid solution:
The solution in which the solvent is a solid is known as a solid solution. The solute may be gas, liquid or solid. For example, a solution of copper in gold is a solid solution.
Question 14. Give an example of solid solution in which the solute is a gas.
Solution : In case a solid solution is formed between two substances (one having very large particles and the other having very small particles), an interstitial solid solution will be formed. For example, a solution of hydrogen in palladium is a solid solution in which the solute is a gas.
Question 15. Define the following terms:
(i) Mole fraction
(ii) Molality
(iii) Molarity
(iv) Mass percentage.
Solution : (i) Mole fraction:
The mole fraction of a component in a mixture is defined as the ratio of the number of moles of the component to the total number of moles of all the components in the mixture.
Mole fraction is denoted by ‘x’.
If in a binary solution, the number of moles of the solute and the solvent are n A and n B respectively, then the mole fraction of the solute in the solution is given by,
Similarly, the mole fraction of the solvent in the solution is given as:
(ii) Molality
Molality (m) is defined as the number of moles of the solute per kilogram of the solvent. It is expressed as:
(iii) Molarity
Molarity (M) is defined as the number of moles of the solute dissolved in one Litre of the solution.
It is expressed as:
(iv) Mass percentage:
The mass percentage of a component of a solution is defined as the mass of the solute in grams present in 100 g of the solution. It is expressed as:
Question 15. Concentrated nitric acid used in laboratory work is 68% nitric acid by mass in aqueous solution. What should be the molarity of such a sample of the acid if the density of the solution is 1.504 g mL −1?
Solution : Concentrated nitric acid used in laboratory work is 68% nitric acid by mass in an aqueous solution. This means that 68 g of nitric acid is dissolved in 100 g of the solution.
Molar mass of nitric acid (HNO 3 ) = 1 × 1 + 1 × 14 + 3 × 16 = 63 g mol −1
= 1.079 mol
Density of solution = 1.504 g mL −1
Question 16. A solution of glucose in water is labelled as 10% w/w, what would be the molality and mole fraction of each component in the solution? If the density of solution is 1.2 g mL −1, then what shall be the molarity of the solution?
Solution : 10% w/w solution of glucose in water means that 10 g of glucose in present in 100 g of the solution i.e., 10 g of glucose is present in (100 − 10) g = 90 g of water.
Molar mass of glucose (C 6 H 12 O 6 ) = 6 × 12 + 12 × 1 + 6 × 16 = 180 g mol −1
= 0.056 mol
= 1 − 0.011
If the density of the solution is 1.2 g mL −1 , then the volume of the 100 g solution can be given as:
Question 17. How many mL of 0.1 M HCl are required to react completely with 1 g mixture of Na 2 CO 3 and NaHCO 3 containing equimolar amounts of both?
Solution : Let the amount of Na 2 CO 3 in the mixture be x g.
Then, the amount of NaHCO 3 in the mixture is (1 − x) g.
Molar mass of Na 2 CO 3 = 2 × 23 + 1 × 12 + 3 × 16
= 106 g mol −1
Molar mass of NaHCO 3 = 1 × 23 + 1 × 1 × 12 + 3 × 16
= 84 g mol −1
According to the question,
⇒ 84x = 106 − 106x
⇒ 190x = 106
⇒ x = 0.5579
= 0.0053 mol
HCl reacts with Na 2 CO 3 and NaHCO 3 according to the following equation.
1 mol of Na 2 CO 3 reacts with 2 mol of HCl.
Therefore, 0.0053 mol of Na 2 CO 3 reacts with 2 × 0.0053 mol = 0.0106 mol.
Similarly, 1 mol of NaHCO 3 reacts with 1 mol of HCl.
Therefore, 0.0053 mol of NaHCO 3 reacts with 0.0053 mol of HCl.
Total moles of HCl required = (0.0106 + 0.0053) mol
= 0.0159 mol
In 0.1 M of HCl,
0.1 mol of HCl is preset in 1000 mL of the solution.
= 159 mL of the solution
Hence, 159 mL of 0.1 M of HCl is required to react completely with 1 g mixture of Na 2 CO 3 and NaHCO 3, containing equimolar amounts of both.
Question 18. A solution is obtained by mixing 300 g of 25% solution and 400 g of 40% solution by mass. Calculate the mass percentage of the resulting solution.
Solution : Total amount of solute present in the mixture is given by,
Total amount of solution = 300 + 400 = 700 g
And, mass percentage (w/w) of the solvent in the resulting solution,
= (100 − 33.57)%
Question 19. An antifreeze solution is prepared from 222.6 g of ethylene glycol (C 2 H 6 O 2 ) and 200 g of water. Calculate the molality of the solution. If the density of the solution is 1.072 g mL −1 , then what shall be the molarity of the solution?
= 62 gmol −1
Total mass of the solution = (222.6 + 200) g
Density of the solution = 1.072 g mL −1
= 394.22 mL
= 0.3942 × 10 −3 L
Question 20. A sample of drinking water was found to be severely contaminated with chloroform (CHCl 3 ) supposed to be a carcinogen. The level of contamination was 15 ppm (by mass):
(i) express this in percent by mass
(ii) determine the molality of chloroform in the water sample.
Solution : (i) 15 ppm (by mass) means 15 parts per million (10 6) of the solution.
= 1.5 × 10 −3 %
(ii) Molar mass of chloroform (CHCl 3 ) = 1 × 12 + 1 × 1 + 3 × 35.5
= 119.5 g mol −1
Now, according to the question,
15 g of chloroform is present in 10 6 g of the solution.
i.e., 15 g of chloroform is present in (10 6 − 15) ≈ 106 g of water.
= 1.26 × 10 −4 m
Question 21. What role does the molecular interaction play in a solution of alcohol and water?
Solution : In pure alcohol and water, the molecules are held tightly by a strong hydrogen bonding. The interaction between the molecules of alcohol and water is weaker than alcohol−alcohol and water−water interactions. As a result, when alcohol and water are mixed, the intermolecular interactions become weaker and the molecules can easily escape. This increases the vapour pressure of the solution, which in turn lowers the boiling point of the resulting solution.
Question 22. Why do gases always tend to be less soluble in liquids as the temperature is raised?
Solution : Solubility of gases in liquids decreases with an increase in temperature. This is because dissolution of gases in liquids is an exothermic process.
Therefore, when the temperature is increased, heat is supplied and the equilibrium shifts backwards, thereby decreasing the solubility of gases.
Question 23. State Henry’s law and mention some important applications?
Solution : Henry’s law states that partial pressure of a gas in the vapour phase is proportional to the mole fraction of the gas in the solution. If p is the partial pressure of the gas in the vapour phase and x is the mole fraction of the gas, then Henry’s law can be expressed as:
K H is Henry’s law constant
Some important applications of Henry’s law are mentioned below.
(i) Bottles are sealed under high pressure to increase the solubility of CO 2 in soft drinks and soda water.
(ii) Henry’s law states that the solubility of gases increases with an increase in pressure. Therefore, when a scuba diver dives deep into the sea, the increased sea pressure causes the nitrogen present in air to dissolve in his blood in great amounts. As a result, when he comes back to the surface, the solubility of nitrogen again decreases and the dissolved gas is released, leading to the formation of nitrogen bubbles in the blood. This results in the blockage of capillaries and leads to a medical condition known as ‘bends’ or ‘decompression sickness’.
Hence, the oxygen tanks used by scuba divers are filled with air and diluted with helium to avoid bends.
(iii) The concentration of oxygen is low in the blood and tissues of people living at high altitudes such as climbers. This is because at high altitudes, partial pressure of oxygen is less than that at ground level. Low-blood oxygen causes climbers to become weak and disables them from thinking clearly. These are symptoms of anoxia.
Question 24. The partial pressure of ethane over a solution containing 6.56 × 10 −3 g of ethane is 1 bar. If the solution contains 5.00 × 10 −2 g of ethane, then what shall be the partial pressure of the gas?
Solution : Molar mass of ethane (C 2 H 6 ) = 2 × 12 + 6 × 1
= 30 g mol −1

= 2.187 × 10 −4 mol
Let the number of moles of the solvent be x.
According to Henry’s law,

= 1.67 × 10 −3 mol
= 7.636 bar
Hence, partial pressure of the gas shall be 7.636 bar.
Question 25. What is meant by positive and negative deviations from Raoult’s law and how is the sign of Δ sol H related to positive and negative deviations from Raoult’s law?
Solution : According to Raoult’s law, the partial vapour pressure of each volatile component in any solution is directly proportional to its mole fraction. The solutions which obey Raoult’s law over the entire range of concentration are known as ideal solutions. The solutions that do not obey Raoult’s law (non-ideal solutions) have vapour pressures either higher or lower than that predicted by Raoult’s law. If the vapour pressure is higher, then the solution is said to exhibit positive deviation, and if it is lower, then the solution is said to exhibit negative deviation from Raoult’s law.

Vapour pressure of a two-component solution showing positive deviation from Raoult’s law

Vapour pressure of a two-component solution showing negative deviation from Raoult’s law
In the case of an ideal solution, the enthalpy of the mixing of the pure components for forming the solution is zero.
Δ sol H = 0
In the case of solutions showing positive deviations, absorption of heat takes place.
∴Δ sol H = Positive
In the case of solutions showing negative deviations, evolution of heat takes place.
∴Δ sol H = Negative
Question 26. An aqueous solution of 2% non-volatile solute exerts a pressure of 1.004 bar at the normal boiling point of the solvent. What is the molar mass of the solute?
Solution : Here,
Vapour pressure of the solution at normal boiling point (p 1 ) = 1.004 bar
Mass of solute, (w 2 ) = 2 g
Mass of solvent (water), (w 1 ) = 98 g
Molar mass of solvent (water), (M 1 ) = 18 g mol −1
According to Raoult’s law,
= 41.35 g mol −1
Hence, the molar mass of the solute is 41.35 g mol −1.
Question 27. Heptane and octane form an ideal solution. At 373 K, the vapour pressures of the two liquid components are 105.2 kPa and 46.8 kPa respectively. What will be the vapour pressure of a mixture of 26.0 g of heptane and 35 g of octane?
We know that,
Molar mass of heptane (C 7 H 16 ) = 7 × 12 + 16 × 1
= 100 g mol −1
Molar mass of octane (C 8 H 18 ) = 8 × 12 + 18 × 1
= 114 g mol −1
∴ Number of moles of octane = 35 /114 mol
And, mole fraction of octane, x 2 = 1 − 0.456
= 0.456 × 105.2
= 47.97 kPa
= 0.544 × 46.8
= 25.46 kPa
Hence, vapour pressure of solution, p total = p 1 + p 2
= 47.97 + 25.46
= 73.43 kPa
Question 28. The vapour pressure of water is 12.3 kPa at 300 K. Calculate vapour pressure of 1 molal solution of a non-volatile solute in it.
Solution : 1 molal solution means 1 mol of the solute is present in 1000 g of the solvent (water).
Molar mass of water = 18 g mol −1
Therefore, mole fraction of the solute in the solution is
It is given that,
⇒ 12.3 − p 1 = 0.2177
⇒ p 1 = 12.0823
= 12.08 kPa (approximately)
Hence, the vapour pressure of the solution is 12.08 kPa.
Question 29. Calculate the mass of a non-volatile solute (molar mass 40 g mol −1 ) which should be dissolved in 114 g octane to reduce its vapour pressure to 80%.
Molar mass of solute, M 2 = 40 g mol −1
Mass of octane, w 1 = 114 g
Molar mass of octane, (C 8 H 18 ), M 1 = 8 × 12 + 18 × 1
Applying the relation,
Hence, the required mass of the solute is 8 g.
Question 30. A solution containing 30 g of non-volatile solute exactly in 90 g of water has a vapour pressure of 2.8 kPa at 298 K. Further, 18 g of water is then added to the solution and the new vapour pressure becomes 2.9 kPa at 298 K. Calculate: molar mass of the solute vapour pressure of water at 298 K.
Solution : (i) Let, the molar mass of the solute be M g mol −1
Applying the relation:
After the addition of 18 g of water:
Again, applying the relation:
Dividing equation (i) by (ii), we have:
Therefore, the molar mass of the solute is 23 g mol −1.
(ii) Putting the value of ‘M’ in equation (i), we have:
Hence, the vapour pressure of water at 298 K is 3.53 kPa.
Page No 60:
Question 31. A 5% solution (by mass) of cane sugar in water has freezing point of 271 K. Calculate the freezing point of 5% glucose in water if freezing point of pure water is 273.15 K.
Solution : Here, ΔT f = (273.15 − 271) K
Molar mass of sugar (C 12 H 22 O 11 ) = 12 × 12 + 22 × 1 + 11 × 16
5% solution (by mass) of cane sugar in water means 5 g of cane sugar is present in (100 − 5)g = 95 g of water.
= 0.0146 mol
= 0.1537 mol kg −1
ΔT f = K f × m
= 13.99 K kg mol −1
Molar of glucose (C 6 H 12 O 6 ) = 6 × 12 + 12 × 1 + 6 × 16
= 180 g mol −1
5% glucose in water means 5 g of glucose is present in (100 − 5) g = 95 g of water.
= 0.0278 mol
= 0.2926 mol kg −1
= 13.99 K kg mol −1 × 0.2926 mol kg−1
= 4.09 K (approximately)
Hence, the freezing point of 5% glucose solution is (273.15 − 4.09) K= 269.06 K.
Question 32. Two elements A and B form compounds having formula AB 2 and AB 4 . When dissolved in 20 g of benzene (C 6 H 6 ), 1 g of AB 2 lowers the freezing point by 2.3 Kwhereas 1.0 g of AB 4 lowers it by 1.3 K. The molar depression constant for benzene is 5.1 Kkg mol −1 . Calculate atomic masses of A and B.
Solution : We know that,
= 110.87 g mol −1
= 196.15 g mol −1
Now, we have the molar masses of AB 2 and AB 4 as 110.87 g mol −1 and 196.15 g mol−1 respectively.
Let the atomic masses of A and B be x and y respectively.
Now, we can write:
Subtracting equation (i) from (ii), we have
⇒ y = 42.64
Putting the value of ‘y’ in equation (1), we have
x + 2 × 42.64 = 110.87
⇒ x = 25.59
Hence, the atomic masses of A and B are 25.59 u and 42.64 u respectively.
Question 33. At 300 K, 36 g of glucose present in a litre of its solution has an osmotic pressure of 4.98 bar. If the osmotic pressure of the solution is 1.52 bars at the same temperature, what would be its concentration?
π = 1.52 bar
R = 0.083 bar L K −1 mol−1
= 0.061 mol
Since the volume of the solution is 1 L, the concentration of the solution would be 0.061 M.
Question 34. Suggest the most important type of intermolecular attractive interaction in the following pairs.
(i) n-hexane and n-octane
(ii) I 2 and CCl 4
(iii) NaClO 4 and water
(iv) methanol and acetone
(v) acetonitrile (CH 3 CN) and acetone (C 3 H 6 O).
Solution : (i) Van der Wall’s forces of attraction.
(ii) Van der Wall’s forces of attraction.
(iii) Ion-diople interaction.
(iv) Dipole-dipole interaction.
(v) Dipole-dipole interaction.
Question 35. Based on solute-solvent interactions, arrange the following in order of increasing solubility in n-octane and explain. Cyclohexane, KCl, CH 3 OH, CH 3 CN.
Solution : n-octane is a non-polar solvent. Therefore, the solubility of a non-polar solute is more than that of a polar solute in the n-octane.
The order of increasing polarity is:
Cyclohexane < CH 3 CN < CH 3 OH < KCl
Therefore, the order of increasing solubility is:
KCl < CH 3 OH < CH 3 CN < Cyclohexane
Question 36. Amongst the following compounds, identify which are insoluble, partially soluble and highly soluble in water?
(i) phenol (ii) toluene (iii) formic acid
(iv) ethylene glycol (v) chloroform (vi) pentanol.
Solution : (i) Phenol (C 6 H 5 OH) has the polar group −OH and non-polar group −C 6 H 5 . Thus, phenol is partially soluble in water.
(ii) Toluene (C 6 H 5 −CH 3 ) has no polar groups. Thus, toluene is insoluble in water.
(iii) Formic acid (HCOOH) has the polar group −OH and can form H-bond with water. Thus, formic acid is highly soluble in water.

(v) Chloroform is insoluble in water.
(vi) Pentanol (C 5 H 11 OH) has polar −OH group, but it also contains a very bulky non-polar −C 5 H 11 group. Thus, pentanol is partially soluble in water.
Question 37. If the density of some lake water is 1.25 g mL −1 and contains 92 g of Na + ions per kg of water, calculate the molality of Na + ions in the lake.
Question 38. If the solubility product of CuS is 6 × 10 −16 , calculate the maximum molarity of CuS in aqueous solution.
Solution : Solubility product of CuS, K sp = 6 × 10 −16
Let s be the solubility of CuS in mol L −1.
= 2.45 × 10 −8 mol L−1
Hence, the maximum molarity of CuS in an aqueous solution is 2.45 × 10 −8 mol L −1.
Question 39. Calculate the mass percentage of aspirin (C 9 H 8 O 4 ) in acetonitrile (CH 3 CN) when 6.5 g of C 9 H 8 O 4 is dissolved in 450 g of CH 3 CN.
Solution : 6.5 g of C 9 H 8 O 4 is dissolved in 450 g of CH 3 CN.
Then, total mass of the solution = (6.5 + 450) g
Question 40. Nalorphene (C 19 H 21 NO 3 ), similar to morphine, is used to combat withdrawal symptoms in narcotic users. Dose of nalorphene generally given is 1.5 mg. Calculate the mass of 1.5 × 10 −3 m aqueous solution required for the above dose.
In 1.5 × 10 −3 m aqueous solution of nalorphene,
This implies that the mass of the solution containing 0.4665 g of nalorphene is 1000.4665 g.
Therefore, mass of the solution containing 1.5 mg of nalorphene is:
Hence, the mass of aqueous solution required is 3.22 g.
Question 41. Calculate the amount of benzoic acid (C 6 H 5 COOH) required for preparing 250 mL of 0.15 M solution in methanol.
Solution : 0.15 M solution of benzoic acid in methanol means,
1000 mL of solution contains 0.15 mol of benzoic acid
= 0.0375 mol of benzoic acid
Molar mass of benzoic acid (C 6 H 5 COOH) = 7 × 12 + 6 × 1 + 2 × 16
= 122 g mol −1
Hence, required benzoic acid = 0.0375 mol × 122 g mol −1
Question 42. The depression in freezing point of water observed for the same amount of acetic acid, trichloroacetic acid and trifluoroacetic acid increases in the order given above. Explain briefly.

Among H, Cl, and F, H is least electronegative while F is most electronegative. Then, F can withdraw electrons towards itself more than Cl and H. Thus, trifluoroacetic acid can easily lose H + ions i.e., trifluoroacetic acid ionizes to the largest extent. Now, the more ions produced, the greater is the depression of the freezing point. Hence, the depression in the freezing point increases in the order:
Acetic acid < trichloroacetic acid < trifluoroacetic acid
Question 43. Calculate the depression in the freezing point of water when 10 g of CH 3 CH 2 CHClCOOH is added to 250 g of water. K a = 1.4 × 10 −3, K f = 1.86 K kg mo l−1.
= 0.0816 mol
Since α is very small with respect to 1, 1 − α ≈ 1
Total moles of equilibrium = 1 − α + α + α
Hence, the depression in the freezing point of water is given as:
Question 44. 19.5 g of CH 2 FCOOH is dissolved in 500 g of water. The depression in the freezing point of water observed is 1.0°C. Calculate the van’t Hoff factor and dissociation constant of fluoroacetic acid.
Now, the value of K a is given as:
Taking the volume of the solution as 500 mL, we have the concentration:
Question 45. Vapour pressure of water at 293 Kis 17.535 mm Hg. Calculate the vapour pressure of water at 293 Kwhen 25 g of glucose is dissolved in 450 g of water.
Mass of glucose, w 2 = 25 g
Mass of water, w 1 = 450 g
Molar mass of glucose (C 6 H 12 O 6 ), M 2 = 6 × 12 + 12 × 1 + 6 × 16
Molar mass of water, M 1 = 18 g mol −1
= 0.139 mol
⇒ 17.535 − p 1 = 0.097
⇒ p 1 = 17.44 mm of Hg
Hence, the vapour pressure of water is 17.44 mm of Hg.
Question 46. Henry’s law constant for the molality of methane in benzene at 298 Kis 4.27 × 10 5 mm Hg. Calculate the solubility of methane in benzene at 298 Kunder 760 mm Hg.
p = 760 mm Hg
k H = 4.27 × 10 5 mm Hg
= 177.99 × 10 −5
= 178 × 10 −5 (approximately)
Hence, the mole fraction of methane in benzene is 178 × 10 −5.
Question 47. 100 g of liquid A (molar mass 140 g mol −1 ) was dissolved in 1000 g of liquid B (molar mass 180 g mol −1 ). The vapour pressure of pure liquid B was found to be 500 torr. Calculate the vapour pressure of pure liquid A and its vapour pressure in the solution if the total vapour pressure of the solution is 475 Torr.
= 0.714 mol
= 5.556 mol
And, mole fraction of B, x B = 1 − 0.114
Therefore, vapour pressure of liquid B in the solution,
= 500 × 0.886
Total vapour pressure of the solution, p total = 475 torr
∵ Vapour pressure of liquid A in the solution,
p A = p total − p B
= 475 − 443
= 280.7 torr
Hence, the vapour pressure of pure liquid A is 280.7 torr.
Question 48. Vapour pressure of pure acetone and chloroform at 328 K are 741.8 mm Hg and 632.8 mm Hg respectively. Assuming that they form ideal solution over the entire range of composition, plot p total ’ p chloroform ’ and p acetone as a function of x acetone . The experimental data observed for different compositions of mixture is.
Solution : From the question, we have the following data

It can be observed from the graph that the plot for the p total of the solution curves downwards. Therefore, the solution shows negative deviation from the ideal behaviour.
Question 49. Benzene and toluene form ideal solution over the entire range of composition. The vapour pressure of pure benzene and toluene at 300 K are 50.71 mm Hg and 32.06 mm Hg respectively. Calculate the mole fraction of benzene in vapour phase if 80 g of benzene is mixed with 100 g of toluene.
And, no. of moles present in 100 g of toluene = 100/92 = 1.087 mol
Hence, mole fraction of benzene in vapour phase is given by:
Question 50. The air is a mixture of a number of gases. The major components are oxygen and nitrogen with approximate proportion of 20% is to 79% by volume at 298 K. The water is in equilibrium with air at a pressure of 10 atm. At 298 Kif the Henry’s law constants for oxygen and nitrogen are 3.30 × 10 7 mm and 6.51 × 10 7 mm respectively, calculate the composition of these gases in water.
Solution : Percentage of oxygen (O 2 ) in air = 20 %
Percentage of nitrogen (N 2 ) in air = 79%
Also, it is given that water is in equilibrium with air at a total pressure of 10 atm, that is, (10 × 760) mm Hg = 7600 mm Hg
= 1520 mm Hg
= 6004 mmHg
Now, according to Henry’s law:
For oxygen:
For nitrogen:
Hence, the mole fractions of oxygen and nitrogen in water are 4.61 ×10 −5and 9.22 × 10−5 respectively.
Question 51. Determine the amount of CaCl 2 (i = 2.47) dissolved in 2.5 litre of water such that its osmotic pressure is 0.75 atm at 27°C.
R = 0.0821 L atm K -1mol-1
M = 1 × 40 + 2 × 35.5
= 111g mol -1
Hence, the required amount of CaCl 2 is 3.42 g.
Question 52. Determine the osmotic pressure of a solution prepared by dissolving 25 mg of K 2 SO 4 in 2 liter of water at 25° C, assuming that it is completely dissociated.
⇒ Total number of ions produced = 3
w = 25 mg = 0.025 g
T = 25 0C = (25 + 273) K = 298 K
Also, we know that:
M = (2 × 39) + (1 × 32) + (4 × 16) = 174 g mol -1
Appling the following relation,
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Solutions FAQs
Organic chemistry is the most important topic for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry exam.
The carbonyl groups in aldehydes and ketones can be oxidized to form the next “oxidation level” compound-carboxylic acid. Adding water to an aldehyde or ketone produces a product called a hydrate or gemdiol (two OH groups on one carbon). The reaction is catalyzed by acids and bases.
“As per my meticulous observation, the difficulty level of the Chemistry paper of Class 12 was high. The questions asked in the paper were tricky, although they were from the NCERT course.
Four elements, hydrogen, carbon, oxygen and nitrogen, are the major components of most organic compounds.
The acidosis is usually attributed to the 'acidic' nature of the ketone bodies (acetoacetate, 3-hydroxybutyrate, and acetone). However, acetoacetate and 3-hydroxybutyrate are produced not as acids but as their conjugate bases, and acetone is neither an acid nor a base.
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 The Solid State
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 English Vistas Chapter 7 Evans Tries an O-Level here

.st1{display:none} Related Articles
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 English Footprints without Feet Chapter 6 The Making of a Scientist
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 English Footprints without Feet Chapter 5 Footprints without Feet
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 English Footprints without Feet Chapter 4 A Question of Trust
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 English Footprints without Feet Chapter 3 The Midnight Visitor
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 English First Flight Chapter 8 Mijbil the Otter
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 English First Flight Chapter 7 Glimpses of India
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 English First Flight Chapter 6 The Hundred Dresses – II
- JAC 9th Result 2024 OUT Anytime Soon Get Download Link Here
- JAC 11th Result 2024 OUT Anytime Soon Get Download Link Here
- JAC 8th Result 2024 Expected to be OUT Soon Check Date and Time

NCERT Books and Solutions for all classes
Assignments Class 12 Chemistry Pdf Download
Students can refer to Assignments for Class 12 Chemistry available for download in Pdf. We have given below links to subject-wise free printable Assignments for Chemistry Class 12 which you can download easily. All assignments have a collection of questions and answers designed for all topics given in your latest NCERT Books for Class 12 Chemistry for the current academic session. All Assignments for Chemistry Grade 12 have been designed by expert faculty members and have been designed based on the type of questions asked in standard 12 class tests and exams. All Free printable Assignments for NCERT CBSE Class 12, practice worksheets, and question banks have been designed to help you understand all concepts properly. Practicing questions given in CBSE NCERT printable assignments for Class 12 with solutions and answers will help you to further improve your understanding. Our faculty have used the latest syllabus for Class 12. You can click on the links below to download all Pdf assignments for class 12 for free. You can get the best collection of Kendriya Vidyalaya Class 12 Chemistry assignments and questions workbooks below.
Class 12 Chemistry Assignments Pdf Download
CBSE NCERT KVS Assignments for Chemistry Class 12 have been provided below covering all chapters given in your CBSE NCERT books. We have provided below a good collection of assignments in Pdf for Chemistry standard 12th covering Class 12 questions and answers for Chemistry. These practice test papers and workbooks with question banks for Class 12 Chemistry Pdf Download and free CBSE Assignments for Class 12 are really beneficial for you and will support in preparing for class tests and exams. Standard 12th students can download in Pdf by clicking on the links below.
Subjectwise Assignments for Class 12 Chemistry

Benefits of Solving Class 12 Chemistry Assignments
- The best collection of Grade 12 assignments for Chemistry have been provided below which will help you in getting better marks in class tests and exams.
- The solved question for Class 12 Chemistry will help you to gain more confidence to attempt all types of problems in exams
- Latest NCERT Books for Class 12 Chemistry have been referred to for designing these assignments
- We have provided step by step solutions for all questions in the Class 12 assignments so that you can understand the solutions in detail.
- We have provided single click download links to all chapterwise worksheets and assignments in Pdf.
- Class 12 practice question banks will support to enhance subject knowledge and therefore help to get better marks in exam
FAQs by Chemistry Students in Class 12
At https://www.ncertbooksolutions.com is the best website that has the biggest collection of free printable assignments for Class 12 Chemistry.
We provide here Standard 12 subject-wise assignments which can be easily downloaded in Pdf format for free. Our teachers have provided these Grade 12 Chemistry test sheets for Chemistry given in your books.
You can click on the links above and get assignments for Chemistry in Grade 12, all chapters and topic-wise question banks with solutions have been provided here. You can click on the links to download in Pdf.
We have provided here subject-wise Grade 12 Chemistry question banks, revision notes and questions for all difficult topics, and other study material. You can download it all without any charge by clicking on the links provided above.
We have provided the best quality question bank for Class 12 for Chemistry available for Pdf Download. You can download them all and use them offline without the internet.
Related Posts:

Related Posts

Assignments Class 12 Mathematics Integrals Pdf Download

Assignments Class 12 Mathematics Differentials Equation Pdf Download

Assignments Class 12 Political Science Pdf Download
- NCERT Exemplar
- Chemistry Exemplar Class 12
NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Chemistry
Ncert exemplar class 12 chemistry – free pdf download (updated for 2023-24).
NCERT Class 12 Chemistry exemplars are provided here to guide students to excel in their CBSE Class 12 examination, as well as graduate entrance examinations. The NCERT Exemplar for Class 12 Chemistry includes solved chapter-wise questions to help students with a quick review of the complete syllabus and perform their best in the exams. Along with questions in the NCERT Exemplar book, this solution has extra questions prepared by the subject experts at BYJU’S, together with questions from previous years’ question papers and sample papers.
By practising questions from this book, students can gain more detailed information regarding the subject, as all the questions are solved by the subject expert team as per the NCERT syllabus (2023-2024).
Class 12 Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Problems Chapter-wise
Students can also access and download NCERT Class 12 Books here.
The Importance of NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Chemistry
- Referring to Class 12 Chemistry NCERT Exemplar will help you become thorough with chemical reactions and numerical problems of organic as well as inorganic parts of Chemistry. Solving the question bank from the exemplar will help you in gaining in-depth knowledge and master the Class 12 Chemistry concepts.
- Many of the questions that appear in the board exam, as well as in the competitive exams such as NEET, JEE, etc., are directly picked up from the Exemplar.
- Solving a variety of conceptual questions and numerical problems enhances skills in solving reasoning-type questions, especially for the inorganic part of Chemistry.
- Information in the NCERT Exemplar is authentic, as it is provided by the NCERT , which follows the CBSE Syllabus.
The Chemistry NCERT Exemplar includes all the important questions that can be asked both in Class 12 board exams and other competitive exams. The NCERT Class 12 Chemistry Exemplar is the best study material for those students preparing for JEE Advanced, NEET, JEE Main , AIIMS, etc., as this book includes a variety of questions in different formats, including short and long answers, multiple-choice questions and other objective type questions.
BYJU’S provides free NCERT Exemplar Solutions, which is available in PDF format. Students can download them easily and use them for their exam preparations. To access many more interesting videos, animations and info-graphics to make learning interesting, download BYJU’S – The Learning App.

Frequently Asked Questions on NCERT Exemplars for Class 12 Chemistry
What are the chapters present in ncert exemplars for class 12 chemistry , will there be questions in the board exam from ncert exemplars for class 12 chemistry, are ncert exemplars for class 12 chemistry pdfs sufficient to score well in the board exam, which are the important chapters in ncert exemplars for class 12 chemistry, leave a comment cancel reply.
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

- Class 12 PCMB Courses
- Class 11 PCMB Courses
- CBSE Class 10 Courses
- CBSE Class 9 Courses
- कक्षा 12 PCMB
- कक्षा 11 PCMB
- कक्षा 10 हिंदी माध्यम
- कक्षा 9 हिंदी माध्यम
- CLASS 12 NOTES
- CLASS 11 NOTES
- CLASS 10 NOTES
- CLASS 9 NOTES
- NCERT Solutions
- Teach with us
- ToppersCBSE App
No products in the cart.
- Revision Notes for CBSE
Cbse class 12 Chemistry Notes Chapter 1
Cbse class 12 chemistry notes chapter 1.
Download PDF of class 12 Chemistry notes Chapter 1 Solution. Notes of chapter 1 Solution contains all the topic as per the syllabus of NCERT. Each topic is explained in very easy language with colored diagrams. Typical topics are divided into parts so that student can understand these topics step by step. Class 12 Chemistry notes Chapter 1 Solution is prepared by our experts as per the latest syllabus and exam pattern Class 12 Chemistry. Derivation of formulas is given in very simple ways after consulting from various books and expert teachers. Also don’t forget to download Class 12 Notes of other Subjects like Physics, Mathematics Formulas sheets, Biology. Along with Notes, we are also providing Online Quizzes for each Chapters of class 12 Chemistry and other subjects. Online Quizzes are given topic wise and contains MCQs with timer to attempt the quizzes. After reading the Class 12 Chemistry Notes of Chapter 1 Solution, students can revise the whole Chapter in Our Online quizzes.
Syllabus Covered
Cbse class 12 chemistry notes chapter 1 solution.
Types of solutions, expression of concentration of solutions of solids in liquids, solubility of gases in liquids, solid solutions, colligative properties – relative lowering of vapour pressure, Raoult’s law, elevation of boiling point, depression of freezing point, osmotic pressure, determination of molecular masses using colligative properties, abnormal molecular mass, Van’t Hoff factor.
Chapter 1. Solution

← Previous Next →
Buy notes of Class 12 Chemistry Notes. We will send printed notes by Speed Post. Online quizzes are also accessible to registered users only.
Buy chemistry notes class 12 big discount , stay connected, revision notes other classes.
- CBSE Class 9 Notes
- CBSE Class 10 Notes
- CBSE Class 11 Notes
- CBSE Class 12 Notes
Quick Buy Notes
- CBSE Class 9 Hindi Medium Notes
- CBSE Class 10 Hindi Medium Notes
- CBSE Class 11 Hindi Medium Notes
- CBSE Class 12 Hindi Medium Notes
AssignmentsBag.com
Assignments Class 12 Chemistry Solutions
Please refer to Assignments Class 12 Chemistry Solutions Chapter 2 with solved questions and answers. We have provided Class 12 Chemistry Assignments for all chapters on our website. These problems and solutions for Chapter 2 Solutions Class 12 Chemistry have been prepared as per the latest syllabus and books issued for the current academic year. Learn these solved important questions to get more marks in your class tests and examinations.
Solutions Assignments Class 12 Chemistry
Question. Which of the following units is useful in relating concentration of solution with its vapour pressure? (A) Mole fraction (B) Parts per million (C) Mass percentage (D) Molality
Question. When 1 mole of benzene is mixed with 1 mole of toluene the vapour will contain: (Given: vapour of benzene = 12.8kPa and vapour pressure of toluene = 3.85 kPa). (A) equal amount of benzene and toluene as it forms an ideal solution (B) unequal amount of benzene and toluene as it forms a non ideal solution (C) higher percentage of benzene (D) higher percentage of toluene
Question. KH value for Ar(g), CO 2 (g), HCHO(g) and CH4(g) are 4.039, 1.67, 1.83 × 10 –5 , and 0.143, respectively.Arrange these gases in the order of their increasing solubility (A) HCHO < CH 4 < CO 2 < Ar (B) HCHO < CO 2 < CH 4 < Ar (C) Ar < CO 2 < CH 4 < HCHO (D) Ar < CH 4 < CO 2 < HCHO
Question. A beaker contains a solution of substance ‘A’.Precipitation of substance ‘A’ takes place when small amount of ‘A’ is added to the solution. The solution is _________. (A) saturated (B) supersaturated (C) unsaturated (D) concentrated
Question. At equilibrium the rate of dissolution of a solid solute in a volatile liquid solvent is __________. (A) less than the rate of crystallisation (B) greater than the rate of crystallisation (C) equal to the rate of crystallisation (D) zero
Question. Which of the following solutions in water has highest boiling point? (A) 1 M NaCl (B) 1 M MgCl 2 (C) 1 M urea (C) 1 M glucose
Question. Which of the following aqueous solutions should have the highest boiling point? (A) 1.0 M NaOH (B) 1.0 M Na 2 SO 4 (C) 1.0 M NH 4 NO 3 (D) 1.0 M KNO 3
Question. A molar solution is one that contains one mole of a solute in (A) 1000 g of the solvent (B) one litre of the solvent (C) one litre of the solution (D) 22.4 litre of the solution
Question. In which mode of expression, the concentration of a solution remains independent of temperature? (A) Molarity (B) Normality (C) Formality (D) Molality
Question. Value of Henry’s constant KH is ________________. (A) Increases with increase in temperature. (B) Decreases with increase in temperature (C) Remains constant (D) First increases then decreases.
Question. For a dilute solution, Raoult’s law states that (A) The lowering of vapour pressure is equal to the mole fraction of solute. (B) The relative lowering of vapour pressure is equal to the mole fraction of solute. (C) The relative lowering of vapour pressure is proportional to the amount of solute in solution. (D) The vapour pressure of the solution is equal to the mole fraction of the solute.
Question. Relative lowering of vapour pressure is a colligative property because _________ . (A) It depends on number of particles of electrolyte solute in solution and does not depend on the nature of the solute particles. (B) It depends on the concentration of a non electrolyte solute in solution as well as on the nature of the solute molecules. (C) Is depends on the concentration of an electrolyte or non-electrolyte solute is solution as well on the nature of solute molecules. (D) None of the above
Question. The unit of ebullioscopic constant is: (A) K kg mol -1 or K (molality) -1 (B) mol kg -1 K -1 or K -1 (molality) (C) kg mol-1 K -1 or K- (molality) -1 (D) K mol kg -1 or K (molality)
Question. The increase in the temperature of the aqueous solution will result in its (A) Molarity to increase (B) Molarity to decrease (C) Mole fraction to increase (D) Mass % to increase
Question. Considering the formation, breaking and strength of hydrogen bond, predict which of the following mixtures will show a positive deviation from Raoult’s law? (A) Methanol and acetone. (B) Chloroform and acetone. (C) Nitric acid and water. (D) Phenol and aniline.
Question. If two liquids A and B form minimum boiling azeotrope at some specific composition, then. (A) A–B interactions are stronger than those between A–A or B–B. (B) vapour pressure of solution increases because more number of molecules of liquids A and B can escape from the solution. (C) vapour pressure of solution decreases because less number of molecules of only one of the liquids escape from the solution. (D) A–B interactions are weaker than those between A–A or B–B.
Question. Consider the figure and mark the correct option.

(A) Water will move from side (A) to side (B) if pressure lower than osmotic pressure is applied on piston (B). (B) Water will move from side (B) to side (A) if pressure greater than osmotic pressure is applied on piston (B). (C) Water will move from side (B) to side (A) if pressure equal to osmotic pressure is applied on piston (B). (D) Water will move from side (A) to side (B) if pressure equal to osmotic pressure is applied on piston (A).
Question. If two liquids A and B form minimum boiling azeotrope at some specific composition then_________. (A) A–B interactions are stronger than those between A–A or B–B. (B) Vapour pressure of solution increases because more number of molecules of liquids A and B can escape from the solution. (C) Vapour pressure of solution decreases because less number of molecules of only one of the liquids escape from the solution. (D) A–B interactions are weaker than those between A–A or B–B.
ASSERTION AND REASON BASED MCQs
Directions: In the following questions, A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by a statement of Reason (R). Mark the correct choice as. (A) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A (B) Both A and R are true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A (C) A is true but R is false (D) A is false and R is True
Question. Assertion (A): Elevation in boiling point is a colligative property. Reason (R): Elevation in boiling point is directly proportional to molarity.
Question. Assertion (A): Molarity of a solution changes with temperature. Reason (R): Molarity is dependent on volume of solution.
Question. Assertion (A): 0.1 M solution of KCl has great osmotic pressure than 0.1 M solution of glucose at same temperature. Reason (R): In solution KCl dissociates to produce more number of particles.
Question. Assertion (A): An ideal solution obeys Henry’s law. Reason (R): In an ideal solution, solute-solute as well as solvent-solvent interactions are similar to solutesolvent interaction.
Question. Assertion (A): Molarity of 0.1 N solution of HCl is 0.1 M. Reason (R): Normality and molarity of a solution are always equal.
Question. Assertion (A): Dimethyl ether is less volatile than ethyl alcohol. Reason (R): Dimethyl ether has greater vapour pressure than ethyl alcohol.
Question. Assertion (A): Molarity of a solution in liquid state changes with temperature. Reason (R): The volume of a solution changes with change in temperature.
Question. Assertion (A): Vapour pressure increase with increase in temperature. Reason (R): With increase in temperature, more molecules of the liquid can go into vapour phase.
Question. Assertion (A): A molar solution is more concentrated than molal solution. Reason (R): A molar solution contains one mole of solute in 1000 mL of solution.
CASE-BASED MCQs
I. Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Scuba apparatus includes a tank of compressed air toted by the diver on his or her back, a hose for carrying air to a mouthpiece, a face mask that covers the eyes and nose, regulators that control air flow, and gauges that indicate depth and how much air remains in the tank. A diver who stays down too long, swims too deep, or comes up too fast can end up with a condition called “the bends.” In this case, bubbles of gas in the blood can cause intense pain, even death. In these following questions a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given.
Choose the correct answer out of the following choices. (A) Assertion and Reason both are correct statements and Reason is correct explanation for Assertion. (B) Assertion and Reason both are correct statements but Reason is not correct explanation for Assertion. (C) Assertion is correct statement but Reason is wrong statement. (D) Assertion is wrong statement but Reason is correct statement.
Question. Assertion: Bends is caused due to formation of nitrogen bubbles in the blood of scuba divers which blocks the capillaries. Reason: Underwater high pressure increases solubility of gases in blood, while as pressure gradually decreases moving towards the surface,gases are released and nitrogen bubbles are formed in blood.
Question. Assertion: Scuba divers may face a medical condition called ‘bends’. Reason: ‘Bends’ can be explained with the help of Henry’s law as it links the partial pressure of gas to that of its mole fraction.
Question. Assertion: Anoxia is a condition experienced by climbers which makes them suddenly agile and unable to think clearly. Reason: At high altitudes the partial pressure of oxygen is less than that at the ground level.
Question. Assertion: Soft drinks and soda water bottles are sealed under high pressure. Reason: High pressure maintains the taste and texture of the soft drinks.
II. Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Raoult’s law states that for a solution of volatile liquids, the partial vapour pressure of each component of the solution is directly proportional to its mole fraction present in solution. Dalton’s law of partial pressure states that the total pressure (ptotal) over the solution phase in the container will be the sum of the partial pressures of the components of the solution and is given as: P total = P 1 +P 2

Question. In comparison to a 0.01 M solution of glucose, the depression in freezing point of a 0.01 M MgCl 2 solution is _____________. (A) the same (B) about twice (C) about three times (D) about six times
Question. What type of deviation from Raoult’s law does the above graph represent ? (A) First positive then negative (B) Negative deviation (C) Positive deviation (D) First negative then positive
Question. Which of the following aqueous solutions should have the highest boiling point ? (A) 1.0 M NaOH (B) 1.0 M Na 2 SO 4 (C) 1.0 M NH 4 NO 3 (D) 1.0 M KNO 3
Question. A solution of two liquids boils at a temperature more than the boiling point of either of them. What type of deviation will be shown by the solution formed in terms of Raoult’s law ? (A) Negative deviation (B) Positive deviation (C) First positive then negative (D) First negative then positive
III. Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
Boiling point or freezing point of liquid solution would be affected by the dissolved solids in the liquid phase. A soluble solid in solution has the effect of raising its boiling point and depressing its freezing point. The addition of non-volatile substances to a solvent decreases the vapor pressure and the added solute particles affect the formation of pure solvent crystals. According to many researches the decrease in freezing point directly correlated to the concentration of solutes dissolved in the solvent. This phenomenon is expressed as freezing point depression and it is useful for several applications such as freeze concentration of liquid food and to find the molar mass of an unknown solute in the solution. Freeze concentration is a high quality liquid food concentration method where water is removed by forming ice crystals. This is done by cooling the liquid food below the freezing point of the solution. The freezing point depression is referred as a colligative property and it is proportional to the molar concentration of the solution (m), along with vapor pressure lowering, boiling point elevation, and osmotic pressure. These are physical characteristics of solutions that depend only on the identity of the solvent and the concentration of the solute. The characters are not depending on the solute’s identity.
Question. When a non volatile solid is added to pure water it will: (a) boil above 100°C and freeze above 0°C (b) boil below 100°C and freeze above 0°C (c) boil above 100°C and freeze below 0°C (d) boil below 100°C and freeze below 0°C
Question. Colligative properties are: (a) dependent only on the concentration of the solute and independent of the solvent’s and solute’s identity. (b) dependent only on the identity of the solute and the concentration of the solute and independent of the solvent’s identity. (c) dependent on the identity of the solvent and solute and thus on the concentration of the solute. (d) dependent only on the identity of the solvent and the concentration of the solute and independent of the solute’s identity.
Question. Assume three samples of juices A, B and C have glucose as the only sugar present in them.The concentration of sample A, B and C are 0.1M,.5M and 0.2 M respectively. Freezing point will be highest for the fruit juice: (a) A (b) B (c) C (d) All have same freezing point
Question. Identify which of the following is a colligative property: (A) freezing point (B) boiling point (C) osmotic pressure (D) all of the above
STATEMENT TYPE QUESTIONS
Question. On the basis of information given below mark the correct option. (i) In bromoethane and chloroethane mixture intermolecular interactions of A-A and B-B type are nearly same as A-B type interactions. (ii) In ethanol and acetone mixture A-A or B-B type intermolecular interactions are stronger than A-B type interactions. (iii) In chloroform and acetone mixture A-A or B-B type intermolecular interactions are weaker than A-B type interactions. (a) Solution (ii) and (iii) will follow Raoult’s law. (b) Solution (i) will follow Raoult’s law. (c) Solution (ii) will show negative deviation from Raoult’s law. (d) Solution (iii) will show positive deviation from Raoult’s law.
Question. Molarity and molality of a solution of NaOH is calculated.If now temperature of the solution is increased then which of the following statement(s) is/are correct ? (i) Molarity of solution decreases (ii) Molality of the solution increases (a) Both statements are correct (b) Statement (i) is correct only (c) Statement (ii) is correct only (d) Both statements are incorrect.
Question. Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct option. (i) Different gases have different KH values at the same temperature. (ii) Higher the value of KH at a given temperature, lower is the solubility of the nature of gas in the liquid. (iii) KH is a function of the nature of the gas. (iv) Solubility of gases increases with increase of temperature. (a) (i), (ii) and (iv) are correct. (b) (ii) and (iv) are correct. (c) (i), (ii) and (iii) are correct. (d) (i) and (iv) are correct
Question. Which observation(s) reflect(s) colligative properties? (i) A 0.5 m NaBr solution has a higher vapour pressure than a 0.5 m BaCl2 solution at the same temperature (ii) Pure water freezes at the higher temperature than pure methanol (iii) a 0.1 m NaOH solution freezes at a lower temperature than pure water Choose the correct answer from the codes given below (a) (i), (ii) and (iii) (b) (i) and (ii) (c) (ii) and (iii) (d) (i) and (iii)
Question. Read the following statements and choose the correct option. (i) Polar solutes dissolve in a polar solvent. (ii) Polar solutes dissolve in a non-polar solvent. (iii) Non-polar solutes dissolve in a non-polar solvent. (iv) Non-polar solutes dissolve in a polar solvent. (a) (i) and (ii) are correct. (b) (i), (ii) and (iii) are correct. (c) (i) and (iii) are correct. (d) (ii) and (iv) are correct.
Question. Study the given statements and choose the correct option. (i) 3.62 mass percentage of sodium hypochlorite in water is used as commercial bleaching solution. (ii) 35% volume percentage of ethylene glycol is used as an antifreeze (as coolent in car engines). (iii) Concentration of dissolved oxygen in a litre of sea water is 5.8 ppm. (a) Statements (i) and (ii) are correct (b) Statements (i) and (iii) are correct (c) Statements (ii) and (iii) are correct (d) Statements (i),(ii) and (iii) are correct
Question. Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct option (i) Osmotic pressure is not a colligative property. (ii) For dilute solutions, osmotic pressure is proportional to the molarity, C of the solution at a given temperature T. (iii) During osmosis ,solvent molecules always flow from higher concentration to lower concentration of solution. (iv) The osmotic pressure has been found to depend on the concentration of the solution (a) (i), (ii) and (iv) are correct (b) (ii) and (iv) are correct (c) (iii), and (iv) are correct (d) (i), (ii) and (iii) are correct
Question. Read the following statements carefully and choose the correct option (i) The vapour pressure of a liquid decreases with increase of temperature. (ii) The liquid boils at the temperature at which its vapour pressure is equal to the atmospheric pressure. (iii) Vapour pressure of the solvent decreases in the presence of non-volatile solute. (iv) Vapour pressure of the pure solvent and solution is a function of temperature. (a) (i), (ii) and (iv) are correct (b) (i), (iii), and (iv) are correct (c) (ii), (iii), and (iv) are correct (d) (i), (ii) and (iii) are correct
Question. “If temperature increases solubility of gas decreases”. For this situation which of the following statement(s) is/are correct ? (i) Reaction is endothermic (ii) Le-chatelier’s principle can be applied (a) Statement (i) and (ii) both are correct (b) Statement (i) is correct only (c) Statement (ii) is correct only (d) Both statement(s) (i) and (ii) are incorrect
MATCHING TYPE QUESTIONS
Question. Match the laws given in the Column-I with expression given in Column-II.

(a) A – (r), B – (t), C – (s), D – (p), E – (q) (b) A – (t), B – (r), C – (q), D – (s), E – (p) (c) A – (p), B – (t), C – (r), D – (q), E – (s) (d) A – (s), B – (p), C – (q), D – (r), E – (t)
Question. Match the columns
Column-I Column-II (A) Na-Hg Amalgam (p) gas – solid (B) H2 in Pd (q) gas – liquid (C) Camphor in nitrogen gas (r) liquid – solid (D) Oxygen dissolved in water (s) solid – gas (a) A – (q), B – (s), C – (r), D – (p) (b) A – (t), B – (p), C – (q), D – (s) (c) A – (r), B – (p), C – (s), D – (q) (d) A – (s), B – (q), C – (p), D – (p)
Question. Match the Column I, II & III and choose the correct option.
Column-I Column-II Column-III (A) Gaseous solutions (p) Solid-liquid (h) Copper dissolved in gold (B) Liquid solutions (q) Solid-solid (i) Chloroform mixed with nitrogen (C) Solid solutions (r) Liquid-gas (j) Common salt dissolved in water (a) (A) – (r) – (h), (B) – (r) – (i), (C) – (p) – (j) (b) (A) – (r) – (i), (B) – (p) – (j), (C) – (q) – (h) (c) (A) – (r) – (j), (B) – (p) – (h), (C) – (q) – (i) (d) (A) – (r) – (j), (B) – (q) – (i), (C) – (p) – (h)
Column -I Column-II (A) Mass percentage (p) Medicine and pharmacy (B) Mass by volume (q) Concentration of pollutants in water (C) ppm (r) Industrial chemical application (D) Volume percentage (s) Liquid solutions (a) A – (q), B – (p), C – (s), D – (r) (b) A – (s), B – (r), C – (p), D – (q) (c) A – (r), B – (q), C – (s), D – (p) (d) A – (r), B – (p), C – (q), D – (s)

(a) A – (s), B – (r), C – (p), D – (q) (b) A – (r), B – (p), C – (s), D – (q) (c) A – (r), B – (s), C – (q), D – (p) (d) A – (q), B – (p), C – (r), D – (s)
ASSERTION-REASON TYPE QUESTIONS
Directions : Each of these questions contain two statements,Assertion and Reason. Each of these questions also has four alternative choices, only one of which is the correct answer. You have to select one of the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) given below. (a) Assertion is correct, reason is correct; reason is a correct explanation for assertion. (b) Assertion is correct, reason is correct; reason is not a correct explanation for assertion (c) Assertion is correct, reason is incorrect (d) Assertion is incorrect, reason is correct.
Question. Assertion : Azeotropic mixtures are formed only by non-ideal solutions and they may have boiling points either greater than both the components or less than both the components. Reason : The composition of the vapour phase is same as that of the liquid phase of an azeotropic mixture.
Question. Assertion : If one component of a solution obeys Raoult’s law over a certain range of composition, the other component will not obey Henry’s law in that range. Reason : Raoult’s law is a special case of Henry’s law.
Question. Assertion : When a solution is separated from the pure solvent by a semi- permeable membrane, the solvent molecules pass through it from pure solvent side to the solution side Reason : Diffusion of solvent occurs from a region of high concentration solution to a region of low concentration solution.
Question. Assertion : Molarity of a solution in liquid state changes with temperature. Reason : The volume of a solution changes with change in temperature.
Question. Assertion : When NaCl is added to water a depression in freezing point is observed. Reason : The lowering of vapour pressure of a solution causes depression in the freezing point.
Question. Assertion : If a liquid solute more volatile than the solvent is added to the solvent, the vapour pressure of the solution may increase i.e., ps > po. Reason : In the presence of a more volatile liquid solute,only the solute will form the vapours and solvent will not.
Question. Assertion : When methyl alcohol is added to water, boiling point of water increases. Reason : When a volatile solute is added to a volatile solvent elevation in boiling point is observed.
CRITICAL THINKING TYPE QUESTIONS
Question. If two liquids A and B form minimum boiling azeotrope at some specific composition then _______. (a) A – B interactions are stronger than those between A – A or B – B (b) vapour pressure of solution increases because more number of molecules of liquids A and B can escape from the solution. (c) vapour pressure of solution decreases because less number of molecules of only one of the liquids escape from the solution (d) A – B interactions are weaker than those between A – A or B – B
Question. Equal masses of methane and oxygen are mixed in an empty container at 25°C. The fraction of the total pressure exerted by oxygen is (a) 1/2 (b) 2/3 (c) 1/3 × 273/298 (d) 1/3
Question. The normality of orthophosphoric acid having purity of 70 % by weight and specific gravity 1.54 is (a) 11 N (b) 22 N (c) 33 N (d) 44 N
Question. KH value for Ar(g), CO 2 (g), HCHO (g) and CH 4 (g) are 40.39,1.67, 1.83 × 10 –5 and 0.413 respectively. Arrange these gases in the order of their increasing solubility. (a) HCHO < CH 4 < CO 2 < Ar (b) HCHO < CO 2 < CH 4 < Ar (c) Ar < CO 2 < CH 4 < HCHO (d) Ar < CH 4 < CO 2 < HCHO
Question. What is the ratio of no. of moles of nitrogen to that of oxygen in a container of 5 litre at atmospheric pressure? (a) 1 : 1.71 (b) 1 : 2 (c) 2 : 1 (d) 1 : 24
Question. Consider a and b are two components of a liquid mixture,their corresponding vapour pressure (mmHg) are respectively 450 and 700 in pure states and total pressure given is 600. Then corresponding composition in liquid phase will be (a) 0.4, 0.6 (b) 0.5, 0.5 (a) 0.6, 0.4 (d) 0.3, 0.7
Question. For a dilute solution containing 2.5 g of a non-volatile nonelectrolyte solute in 100 g of water, the elevation in boiling point at 1 atm pressure is 2°C. Assuming concentration of solute is much lower than the concentration of solvent, the vapour pressure (mm of Hg) of the solution is (take Kb = 0.76 K kg mol –1 ) (a) 724 (b) 740 (c) 736 (d) 718
Question. Which will form maximum boiling point azeotrope (a) HNO 3 + H 2 O solution (b) C 2 H 5 OH + H 2 O solution (c) C 6 H 6 + C 6 H 5 CH 3 solution (d) None of these
Question. Chloroform and acetone are added to each other, Raoult’s law shows negative deviation.what does this suggests ? (a) Exothermic reaction (b) Endothermic reaction (c) Zero change in enthalpy (d) None of these
Question. When a gas is bubbled through water at 298 K, a very dilute solution of the gas is obtained. Henry’s law constant for the gas at 298 K is 100 kbar. If the gas exerts a partial pressure of 1 bar, the number of millimoles of the gas dissolved in one litre of water is (a) 0.555 (b) 5.55 (c) 0.0555 (d) 55.5
Question. Which of the following statements, regarding the mole fraction (x) of a component in solution, is incorrect? (a) 0 ≤ x ≤1 (b) x ≤1 (c) x is always non-negative (d) None of these
Question. Which one of the following gases has the lowest value of Henry’s law constant? (a) N 2 (b) He (c) H 2 (d) CO 2
Question. Someone has added a non electrolyte solid to the pure liquid but forgot that among which of the two beakers he has added that solid. This problem can be solved by checking (a) relative lower in vapour pressure (b) elevation in boiling point (c) depression in Freezing point (d) all above
Question. An 1% solution of KCl (I), NaCl (II), BaCl2 (III) and urea (IV) have their osmotic pressure at the same temperature in the ascending order (molar masses of NaCl, KCl,BaCl 2 and urea are respectively 58.5, 74.5, 208.4 and 60 g mole –1 ). Assume 100% ionization of the electrolytes at this temperature (a) I < III < II < IV (b) III < I < II < IV (c) I < II < III < IV (d) III < IV < I < II
Question. Vapour pressure of benzene at 30°C is 121.8 mm. When 15g of a non-volatile solute is dissolved in 250 g of benzene, its vapour pressure is decreased to 120.2 mm. The molecular weight of the solute is (a) 35.67 g (b) 356.7 g (c) 432.8 g (d) 502.7 g
Question. The difference between the boiling point and freezing point of an aqueous solution containing sucrose (molecular wt = 342 g mole –1 ) in 100 g of water is 105°C. If Kf and Kb of water are 1.86 and 0.51 K kg mol –1 respectively, the weight of sucrose in the solution is about (a) 34.2 g (b) 342 g (c) 7.2 g (d) 72 g
Question. At 300 K the vapour pressure of an ideal solution containing 1 mole of liquid A and 2 moles of liquid B is 500 mm of Hg.The vapour pressure of the solution increases by 25 mm of Hg, if one more mole of B is added to the above ideal solution at 300 K. Then the vapour pressure of A in its pure state is (a) 300 mm of Hg (b) 400 mm of Hg (c) 500 mm of Hg (d) 600 mm of Hg
Question. The boiling point of 0.2 mol kg –1 solution of X in water is greater than equimolal solution of Y in water. Which one of the following statements is true in this case ? (a) Molecular mass of X is greater than the molecular mass of Y. (b) Molecular mass of X is less than the molecular mass of Y. (c) Y is undergoing dissociation in water while X undergoes no change. (d) X is undergoing dissociation in water.
Question. The vapour pressure of a solvent decreases by 10 mm of Hg when a non-volatile solute was added to the solvent. The mole fraction of the solute in the solution is 0.2. What should be the mole fraction of the solvent if the decrease in the vapour pressure is to be 20 mm of Hg ? (a) 0.8 (b) 0.6 (c) 0.4 (d) 0.2
Question. What is the freezing point of a solution containing 8.1 g HBr in 100 g water assuming the acid to be 90% ionised ? (Kf for water = 1.86 K kg mol –1 ) : (a) 0.85°K (b) – 3.53°K (c) 0°K (d) – 0.35°K
Question. 1 g of a non-volatile, non-electrolyte solute of molar mass 250 g/mol was dissolved in 51.2 g of benzene. If the freezing point depression constant Kf of benzene is 5.12 kg K mol –1 . The freezing point of benzene is lowered by (a) 0.3 K (b) 0.5 K (c) 0.2 K (d) 0.4 K
Question. If the elevation in boiling point of a solution of non-volatile, non-electrolytic and non-associating solute in a solvent (Kb = x K kg mol –1 ) is y K, then the depression in freezing point of solution of same concentration would be (Kf of the solvent = z K kg mol –1 ) (a) 2xz/y (b) yz/x (c) xz/y (d) yz/2x
Related Posts

Assignments For Class 12 Mathematics Relations and Functions
Assignments class 12 chemistry polymers.

Assignments Class 12 Biology Molecular Basis of Inheritance
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Unit 1: Solutions
Expressing concentration of solutions.
- Concentration of a solution_Worked Problem (Opens a modal)
- Calculating concentration of a solution Get 5 of 7 questions to level up!
- Henry's Law (Opens a modal)
- Solubility of a substance in a liquid Get 5 of 7 questions to level up!
Vapour pressure of liquid solutions
- Raoult's Law (Opens a modal)
- Raoult's law and vapour pressure of liquids Get 6 of 8 questions to level up!
Ideal and non-ideal solutions
- Ideal and non-ideal solutions (Opens a modal)
- Ideal and non-ideal solutions Get 5 of 7 questions to level up!
Colligative properties
- Colligative properties: Elevation of boiling point (Opens a modal)
- Colligative properties of solutions Get 4 of 5 questions to level up!
Abnormal molar masses
- Abnormal molar masses (Opens a modal)
- Abnormal molar mass and van't Hoff factor Get 4 of 5 questions to level up!

Class 12 Chemistry Answer Key 2024 Out, For Set 1, 2, 3
Students can match their answers with the most accurate CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Answer Key 2024 prepared by the expert facilities of Adda247. Get CBSE Chemistry Class 12 Question Paper Set 1, 2, 3.
Table of Contents
Chemistry Answer key 2024
The Central Board of Secondary Education has successfully conducted the CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Exam 2024 o n 27 February 2024. The chemistry paper was concluded at 01:30 pm, As the completion of the examination we updated the CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Answer Key 2024 on this page. The students appearing in the examination can match their answers with the unofficial Class 12 Chemistry Answer Key 2024 prepared by the expert facilities of Adda247.
Class 12 Chemistry Answer Key 2024
Here we have given the complete CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Answer Key 2024 along with Exam Analysis. In CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Answer Key & Exam Analysis, we will cover the difficulty level of the exam, out-of-syllabus questions, and mistakes in the question paper. CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Answer key 2024 is provided for all sections. Section A consists of 16 multiple-choice questions worth one mark each. Section B consists of five short answer questions worth two marks each. After completion of the CBSE Exam for the Chemistry subject, the students must match their responses with the Chemistry Answer Key provided on this page and must check the CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Exam Analysis.
Start your Preparation with CUET 2024 Arjun 2.0 Science Complete Batch
Answer Key Chemistry Class 12: Overview
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Answer Key 2024 given on this page is error-free and all the answers are framed by the faculties who have years of experience in teaching Class 12 Chemistry. Below we have given the highlights of CBSE Answer Key Chemistry Class 12. The students must check the brief information of CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Answer Key 2024 provided in the table below.

CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Answer Key Set 1 (56/2/1)
SECTION A Questions no. I to 16 are Multiple Choice type Questions, carrying 1 mark each 16×1=16
1. When MnO2 is fused with KOH in air, it gives (A) KMnO4 (B) K2MnO4 (C) MngO7 (D) Mn2O Answer: (B) K2MnO4
2. Ligand EDTA is an example of a: (A) Monodentate ligand (B) Didentate ligand (C) Tridentate ligand (D) Polydentate ligand
Answer:(D) Polydentate ligand
3. Which of the following ligand forms chelate complex? (A) (CO2-) 4 (B) CI (C) NO (D) NH3
Answer:(A) CO 4

Answer: Option C

Answer: Option (d)

Answer: Option A
7. Ethanol on heating with conc, H₂SO₄ at 413 K gives: (A) C2H5OSO3H (B) C₂H-O-CH3 (C) C₂H-O-C2H5 (D) CH2=CH2 Answer:(C) C₂H-O-C2H5
8. An azeotropic solution of two liquids has boiling point lower than either of them when it : (A) is saturated (B) shows positive deviation from Raoult’s law (C) shows negative deviation from Raoult’s law (D) shows no deviation from Raoult’s law Answer:(B) shows positive deviation from Raoult’s law
9. The relative lowering of vapour pressure of an aqueous solution containing non-volatile solute is 0-0225. The mole fraction of the non-volatile solute is: (A) 0.80 (B) 0.725 (C) 0.15 (D) 0.0225 Answer: (D) 0.0225
10. During electrolysis of aqueous solution of NaCl: (A) H₂ (g) is liberated at cathode (B) Na is formed at cathode (C) O2 (g) is liberated at anode (D) Cl2 (g) is liberated at cathode
11. The addition of catalyst during a chemical reaction alters which of the following quantities of the reaction? (A) Enthalpy (B) Activation energy (C) Entropy (D) Internal energy
Answer: (B) Activation energy
12. For the elementary reaction PQ. the rate of disappearance of ‘P’ increases by a factor of 8 upon doubling the concentration of ‘P’. The order of the reaction with respect to ‘P’ is: (A) 3 (B) 4 (C) 2 (D) 1
Answer: (A) 3
For Questions number 13 to 16, two statements are given one labelled as Assertion (A) and the other labelled as Reason (R). Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (A), (B), (C) and (D) as given below. (A) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A). (B) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of the Assertion (A). (C) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false. (D) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
13. Assertion (A): Aliphatic primary amines can be prepared by Gabriel phthalimide synthesis. Reason (R): Alkyl halides undergo nucleophilic substitution with anion formed by phthalimide.
Answer:(A) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A). 14. Assertion (A): Uracil base is present in DNA. Reason (R): DNA undergoes self-replication.
Answer: (D) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true. 15. Assertion (A): Diazonium salts of aromatic amines are more stable than those of aliphatic amines. Reason (R): Diazonium salts of aliphatic amines show resonance.
Answer:(A) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A). 16. Assertion (A): p-nitroaniline is a weaker base than p-toluidine. Reason (R): The electron withdrawing effect of NO2 group in p-nitroaniline makes it a weaker base.
Answer:(A) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).

Chemistry Set 2 Answer Key 2024: Paper Code (56/4/2)
3. Which alkyl halide Dom the given options will undergo a reaction

4. Which of the following stids represents Vitamin C? (A) Banelusric acid (B) Gluconic acid (C) Ascorbic acid (D) Benzoic acid

6. Consider the following reaction

Identify A and B from the given options (A) A-Methanol. B-Potassium formate (B) A-Ethanol. B-Potassium formate (C) A-Methanal, 8-Ethanol (D) A-Methanol, B-Potassium acetate
Answer: (A) A-Methanol. B-Potassium formate
11. Nucleophilic addition of Grignard reagent to ketones followed by hydrolysis with dilute acids forms: (A) Alkene (C) Tertiary alcohol (B) Primary alcohol (D) Secondary alcohol
Answer: (C) Tertiary alcohol
12. Match the reagents required for the given reactions:
(A) 1-(г), П-(p), III-(s), IV(q) (B) 1-(q), II(r), III-(p). IV- (9) (C) 1-(8), II-(q). III-(p). IV(r) (D) 1-(p). II-(s), III-(r). IV- (q)
Answer: (A) 1-(г), П-(p), III-(s), IV(q)

Chemistry Set 3 Answer Key 2024: Paper Code (56/3/3-13)
1. Which of the following ligands is an ambidentate ligand? (A) CO (B) SCN- (C) NH3 (D) H₂O
Answer: (B) SCN-
2. On adding AgNO3 solution to 1 mole of CoCl3. 4NH3, one mole of AgCl is precipitated. The secondary valency of Cois: (A) 6 (C) 3 (B) 4 (D) 7
Answer: (A) 6
3. Which of the following elements of 3d series of transition elements has the lowest Δ a H°? (B) Cr (A) Sc (D) Zn (C) Cu
Answer: (D) Zn

Answer: Option B

6. CH3-O-CH3 when treated with excess HI gives: (A) CH3-OH + CH3-1 (B) 2CH3-OH (C) 2CH3-I (D) CH3-I+CH4
Answer:C) 2CH3-I
Which of the following compounds will not react with benzene sulphonyl chloride? (A) (C2H5)3N (B) C2H5-NH2 (C) (C2H5)2 NΗ (D)C6H5- NH2
Answer:(A) (C2H5)3N
6. Scurvy’ is caused by a deficiency of vitamins: (A) E (B) A (C) C (D) D Answer: (C) C
7. A 1% solution of solute ‘X’ is isotonic with a 6% solution of sucrose (molar mass = 342 g mol¹). The molar mass of solute ‘X’ is: (A) 34-2 g mol-1 (B) 57 g mol-1 (C) 114 g mol-¹ (D) 3-42 g mol 1
10. The half life of a first order reaction with rate constant (k) of 3 min-1 (A) 0.693 min (B) 2.31 min (C) 6.93 min (D) 0.231 min
Answer: (D) 0.231 min
11. Which of the following cells is used in hearing aids? (A) Dry cell (B) Mercury cell (C) Nickel-cadmium cell (D) Fuel cell Answer: (C) Nickel-cadmium cell 12. Aniline on reaction with Bromine water gives: (A) o-bromoaniline (B) 2,4,6-tribromoaniline (C) m-bromoaniline (D) p-bromoaniline
Answer: (B) 2,4,6-tribromoaniline
13. Assertion (A): AmixH and AmixV are zero for an ideal solution. Reason (R): The solution which obeys Raoult’s law over the entire range of concentration is called an ideal solution. Answer: (a)
14. Assertion (A): Rate of reaction decreases with increase in temperature. Reason (R): Number of effective collisions increases with increase in temperature.
Assertion (A): Phenol on reaction with aqueous NaOH gives sodium phenoxide. Reason (R): This reaction supports the acidic nature of phenol.
Asertion (A): Boiling point of butan-1-ol is higher than that of butan-1-amine. Reason (R): Being more polar, butan-1-ol intermolecular hydrogen bonds form stronger compared to as butan-1-amine.
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Answer Key 2024 Set 1
SECTION – A (MCQs)
1. Van’t Hoff factor for K₂SO4 solution, assuming complete ionization is
(A) 1 (B) 3 (C) 13 (D) 2
Answer: (B) 3
5. The rate of a reaction increases sixteen times when the concentration of the reactant increases four times. The order of the reaction is
(A) 2.5 (B) 2.0 (C) 1.5 (D) 0.5
Answer: (B) 2.0
6. Which of the following cell is used in hearing aids?
(A) Mercury cell (B) H2-O2 fuel cell (C) Dry cell (D) Ni-Cd cell
Answer: (A) Mercury cell
7. Isotonic solutions have the same
(A) density (C) osmotic pressure (B) refractive index (D) volume
Answer: (C) osmotic pressure
8. Transition metals are known to make interstitial compounds. Formation of interstitial compounds makes the transition metal
(A) more hard (C) more ductile (B) more soft (D) more metallic
Answer: (A) more hard
9. Auto-oxidation of chloroform in air and light produces a poisonous gas known as
(A) Phosphine (C) Phosgene (B) Mustard gas (D) Tear gas
Answer: (C) Phosgene
10. Out of the following alkenes, the one which will produce tertiary butyl alcohol on acid catalysed hydration is
(A) CH3CH3CH=CH2 (B) CH3CH=CH2 (C) CH3-CH=CH-CH3 (D) (CH3)2C = CH2
Answer: (D) (CH3)2C = CH2
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Answer key 2024 Set 3
Check out the solutions of paper code 56/5/3 section A Mcqs in the table below.
CBSE Class 12th Chemistry Answer key 2024 Set 1
Check out the solutions of paper code 56/1/1 section A Mcqs in the table below.
Class 12 Chemistry Answer Key 2024 & Paper Analysis
Watch the video to get the Class 12 Chemistry Exam Analysis at the earliest.
Answer Key of Chemistry Class 12 CBSE 2024 for Set 1,2,3
Here we will provide the CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Answer key 2024 for Chemistry question sets 1, 2 and 3. A majority of students said that Section A’s Multiple Choice questions are a little bit tricky and they found some difficulties while solving these sections. Candidates can cross-check their answers with the answer key of chemistry class 12 cbse 2024 of Section A.
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Question Paper 2024 PDF
The CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Exam was conducted in multiple sets at different exam centers. Students should assess the difficulty level of the Chemistry Question paper sets that differ from their own. The board question paper has a weightage of 70 points and all questions are mandatory to attempt. Students can access CBSE 12 Chemistry question papers from various sets on this page.
Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper Analysis 2024
After the conclusion of the Exam, we talked to the students as well as the teachers to know the difficulty level of the Paper. Let’s check the test takers’ and subject experts’ reactions on the CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Exam below.
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Paper Analysis by Students
According to general reviews, students regarded the work to be moderate and balanced.
- The paper was NCERT-based and covered all relevant topics.
- The MCQ component of the paper was a little challenging but workable. Section B was easy.
- The long-answer questions were straightforward, if fairly lengthy.
- The short-answer questions were moderately difficult.
- Organic chemistry is frequently the most difficult component of the exam. Students rated organic chemistry this year as moderate. Expected questions regarding conversions and name reactions were posed.
CBSE Class 12th Chemistry Exam Analysis by Teachers
Experts and educators have stated that the chemistry paper was balanced and of moderate difficulty.
- The majority of the questions were direct and based on NCERT. Almost all of the students found the CBSE Class 12 Chemistry paper to be fairly average.
- The paper pattern was consistent with the CBSE sample paper.
- The majority of the paper’s questions ranged from simple to moderate, except for a couple that could have been difficult for pupils.
Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper 2024 Pattern
With calculating the scores with the CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Answer Key 2024 , students must know the Chemistry marking Scheme of Each section. As per the CBSE Class 12 Chemistry sample paper, the CBSE Class 12 Chemistry question paper consists of Five sections. All the sections hold different marks and different types of questions. The board will ask the very short answer type, short answer type, and case-based questions in the CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Examination. Check out the detailed section-wise pattern listed below:
1. Section A consists of 18 Questions carrying 1 mark each [Multiple Choice Questions]
2. Section B consists of 7 questions carrying 2 marks each [Very Short Answer Questions]
3. Section C consists of 5 questions carrying 3 marks each [Short Answer Questions]
4. Section D consists of 2 Questions carrying 4 marks each [Case Based Questons]
5. Section E consists of 2 Questions carrying 5 marks each [Long Answer Questions]
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Answer Key Set 3 Last year
1, A compound CaCl2.6h2O undergoes complete dissociation in water, The Van’t Hoff Factor ‘i’ is:
a) 9, b) 6, c)3, d) . 4
Answer: c) 3
2. For a Zero order reaction of type A →products, the rate equation may be expressed as:

Answer: Option (a)
3. Which of the following Cu 2+ halide is not known?
Answer: Option (b)
Q4. Which of the following structures represents a-D-glucose?

Answer: (a)
- The compounds [Cr(H2O)lCl3, [Cr(H2O) Cl]C12. H2O and [Cr(H2O)4C12]Cl. 2H2O exhibit:
(a) Linkage isomerism (b) Geometrical isomerism (c) . Ionization isomerism (d) Hydrate isomerism
Answer: (d) Hydrate isomerism
- Which of the following alkenes on acid catalysed hydration gives a tertiary alcohol?
(a) 2-Butene
(b) 2-Methylpropene
(c) Propene
(d) 95 1-Butene
Answer: (b) 2-Methylpropene
- When nitrobenzene is heated with tin and concentrated HCl, the product formed is:

- The reaction of 1-phenyl-2-chloropropane with alcoholic KOH gives mainly:
(a) 1-phenylpropene
(b) 3-phenylpropene
(c) 1-phenylpropene 1-phenylpropan-3-ol
(d) 1-phenylypropan-2-ol
Answer: (a) 1-phenylpropene
- Corrosion of iron is:
(a) a decomposition process a photochemical process (b) a photochemical process (c) an electrochemical process (d) a reduction process
Answer: (a) reduction process
- The number of molecules that react with each other in an elementary reaction is a measure of the:
(a) activation energy of the reaction (b) order of the reaction (c) stoichiometry of the reaction (d) molecularity of the reaction
Answer: (d) molecularity of the reaction
11. On hydrolysis, which of the following carbohydrates gives glucose and galactose?
(a) Sucrose (c) Maltose (b) Lactose (d) Cellulose
Answer: (b) Lactose
12. The deficiency of which of the following vitamins causes ‘Rickets’?
(a) Vitamin A (b) Vitamin D (c) Vitamin B (d) Vitamin C
Answer; (b) Vitamin D
13. Which of the following is an ‘Acetal’?

Answer: (d)
For Questions number 15 to 18, two statements are given – one labelled as Assertion (A) and the other labelled as Reason (R). Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given below.
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true and Reason (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A). (b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of the Assertion (A). (c) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false. (d) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
- Assertion (A): When NaCl is added to water, a depression in freezing point is observed.
Reason (R): The vapour pressure of solution is increased which causes depression in freezing point.
Answer:(c) Assertion (A) is true, but Reason (R) is false.
- Assertion (A): Monobromination of aniline can be conveniently done by protecting the amino group by acetylation.
Reason (R): Acetylation decreases the activating effect of the amino group.

Class 12 Chemistry Answer Key last Year
- The magnetic moment of [NiCl4]2-
(a) 1.82 BM (b) 2.82 BM (c) 4.42 BM (d) 5.46 BM (Atomic no : Ni= 28) Answer: (a) 1.82 BM
- Which of the following cell was used in Apollo space programme?
(a) Mercury Cell
(b) Daniel Cell
(c) H2-O2 Fuel cell
(d) Dry Cell
Answer: (c) H2-O2 Fuel cell
- Which one of the following has lowest pKa value?
(a) CH3-COOH
(b) O2N-CH2-COOH
(c) Cl-CH2-COOH
Answer: (b) O2N-CH2-COOH
- Which of the following ions has the electronic configuration 3d6 ?
(a) Ni 3+ (b) Co 3+ (c) Mn 2+ (d) Mn 3+ Answer: (b) CO 3+
- Consider the following standard electrode potential values:
Fe3+ (aq) + e- —> Fe2+ (aq) Eo = + 0.77 V MnO4- (aq) + 8H+ + 5e- —-> Mn2+ (aq) + 4H2O (l) Eo = + 1.51V What is the cell potential for the redox reaction? (a) -2.28 V (b) – 0.74 V (c) + 0.74 V (d) + 2.28 V Answer: (c) +0.74 V
- The following experimental rate data were obtained for a reaction carried out at 25o C:
A(g) + B(g) —-> C(g) + D(g)
- A voltaic cell is made by connecting two half cells represented by half equations below:
Sn2+(aq) + 2e- –>Sn(s)Eo=-0.14 V
Fe3+(aq)+e- –> Fe2+ (aq)Eo=+0.77 V
- Which statement is correct about this voltaic cell?
(a) Fe2+ is oxidised and the voltage of the cell is -0.91 V. (b) Sn is oxidised and the voltage of the cell is 0.91 V. (c) Fe2+ is oxidised and the voltage of the cell is 0.91 V. (d) Sn is oxidised and the voltage of the cell is 0.63 V.
Answer: to be updated
- What are the orders with respect to A(g) and B(g)?
Answer: To be updated
- Which of the following aqueous solution will have highest boiling point?
(a) 1.0 M KCl
(b) 1.0 M K 2 SO4
(c) 2.0 M KCl
(d) 2.0 M K2SO4
- Amides can be converted into amines by the reaction named
(a) Hoffmann degradation
(b) Ammonolysis
(c) Carbylamine
(d) Diazotisation
Answer: (a) Hoffmann degradation
- Which of the following would not be a good choice for reducing nitrobenzene to aniline?
(c) Fe and HCl
(d) Sn and HCl
Answer: (a) LiA l H 4
- Which property of transition metals enables them to behave as catalysts?
(a) High melting point
(b) High ionisation enthalpy
(c) Alloy Formation
(d) Variable oxidation states
Answer: (d) Variable oxidation states
- Which of the following statements is not true about glucose?
(a) It is an aldohexose.
(b) On heating with HI it forms n-hexane.
(c) It is present in pyranose form.
(d) It gives 2,4 DNP test.
Answer: (d) It gives 2,4 DNP test.
- Which of the following alcohols will not undergo oxidation?
(a) Butanol
(b) Butan-2-ol
(c) 2-Methylbutan-2-ol
(d) 3-Methylbutan-2-ol
Answer: ( d) 3-Methylbutan-2-ol
- Four half reactions I to IV are shown below:
- 2Cl- —> Cl2 + 2e-
- 4OH- —-> O2 + 2H2O + 2e-
- Na+ + e- —-> Na
- 2H+ + 2e- —-> H2
Which two of these reactions are most likely to occur when concentrated brine is electrolysed?
(a) I and III
(b) I and IV
(c) II and III
(d) II and IV
For the questions 15 to 18 , two statements are given – one labeled as Assertion (A) and the other labelled as Reason (R ). Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c ), and (d) as given below:
(a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R ) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A). (b) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are true, but Reason (R) is not the correct explanation of the Assertion (A). (c) Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false. (d) Assertion (A) is false, but Reason (R) is true.
- Assertion (A) : Vitamin C cannot be stored in our body.
Reason (R) : Vitamin C is fat soluble and is excreted from the body in urine. Answer: (c) Assertion (A) is true but Reason (R) is false
- Assertion (A) : The half life of a reaction is the time in which the concentration of the reactant is reduced to one half of its initial concentration.
Reason (R) : In first order kinetics when concentration of reactant is doubled, its half life is doubled.
- Assertion (A) : Bromination of benzoic acid gives m-bromobenzoic acid.
Reason (R) : Carboxyl group increases the electron density at the meta position. Answer: (a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R ) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
- Assertion (A): EDTA is a hexadentate ligand.
Reason (R) : EDTA has 2 nitrogen and 4 oxygen donor atoms. Answer: (a) Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R ) are true and (R) is the correct explanation of the Assertion (A).
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Exam Paper Analysis – Last year
We surveyed students to find out what they thought of the CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Paper Review 2024. The overall paper was simple to moderate. The questions were straightforward, and nothing was outside of the syllabus. There were some math problems that tested students’ analytical abilities, but everything else was typical in terms of complexity.
Section A, which consisted of MCQs, was the top-scoring component of the exam, according to our subject experts. For your convenience, the answer key for the Class 12 Chemistry test is provided in the sections below.
Class 12 Chemistry Question Paper PDF of Last year
After Completion of the Exam, here we have provided the CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Papers Pdf of last year. Candidates may download Class 12 Chemistry Question Papers and analyze the Class 12 Chemistry Answer key to calculate their expected scores.
Class 12 Chemistry Answer Key- Previous Year’s Repeated Questions
Q.1: Arrange the following compounds in the increasing order of their property indicated .
i) Acetaldehyde, Benzaldehyde, Acetophenone, Acetone(Reactivity towards HCN)
Answer. Acetaldehyde<Acetone<Benzaldehyde<Acetophenone
iii) CH3CH2OH, CH3CHO, CH3COOH (Boiling point)
Answer. CH3COOH<CH3CH2OH<CH3CHO
Q.2: In a plot of m against the square root of concentration (C12) for strong and weak electrolytes, the value of limiting molar conductivity of a weak electrolyte cannot be obtained graphically. Suggest a way to obtain this value. Also state the related law, if any.
Yes, we can do it by Kohlrausch’s law.
Kohlrausch’s law: a statement in physical chemistry: the migration of an ion at infinite dilution is dependent on the nature of the solvent and on the potential gradient but not on the other ions present.
Q.3: Write reasons for the following statements :
(i) Benzoic acid does not undergo Friedel-Crafts reaction.
No, benzoic acid does not undergo Friedel Craft reaction because the carboxylic group is deactivating and the Lewis acid catalyst and carboxylic group are bonded.
(ii) Oxidation of aldehydes is easier than that of ketones.
oxidation of aldenyde is easier than ketone due to presence of H-atoms linked to carbonyl group carbon which is absent in ketones.
Q.4: Write reasons for the following:
(i) Ethylamine is soluble in water whereas aniline is insoluble.
Ethylamine when added to water forms intermolecular H−bonds with water. Hence it is soluble in water. But aniline Can form H−bonding with water to a very small extent due to the presence of a large hydrophobic −C6H5 group. Hence aniline is insoluble in water.
(ii) Amino group is o- and p-directing in aromatic electrophilic substitution reactions, but aniline on nitration gives a substantial amount of m-nitroaniline.
Nitration is carried out in an acidic medium. In an acidic medium, aniline is protonated to give anilinium ion (which is meta-directing).

For this reason, aniline on nitration gives a substantial amount of m-nitroaniline.
(iii) Amines behave as nucleophiles.
A nucleophile is a substance that is attracted to, and then attacks, a positive or slightly positive part of another molecule or ion. All amines contain an active lone pair of electrons on the very electronegative nitrogen atom. It is these electrons that are attracted to positive parts of other molecules or ions.
b) How will you carry out the following conversions :
i) Nitrobenzene to Aniline
Nitrobenzene is reduced to aniline by Sn and concentrated HCl. Instead of Sn, Zn or Fe also can be used. Aniline salt is given from this reaction. Then aqueous NaOH is added to the aniline salt to get released aniline. This reaction is called nitrobenzene reduction.
- Benzene is a clear, colourless, highly flammable and volatile, liquid compound.
- Aniline is a yellowish to brownish oily liquid with a musty fishy odour organic compound.
ii) Ethanamide to Methanamine

React ethanamine with nitrous acid to form an azo compound, which further reacts with water to form ethanol, which on oxidising gives ethanoic acid. After treating with an excess of ammonia the ethanoic acid becomes ethanamide, which on further reacting with Bomine and a strong base (Hoffmann bromamide degradation reaction) to form methenamine.
iii) Ethanenitrile to Ethanamine
it’s simple reduction of nitriles with lithium aluminium hydride or catalytic hydrogenation produce primary amines. the reaction is
CH3C≡N + H2/Ni OR LiAlH4 → CH3CH2NH2
Q.5(a)(i) Write the electronic configuration of d5 on the basis of crystal field splitting theory if Δ0 < P.
When Δo < P, it is weak field and high spin situation’. As a result one electron entered in eg orbital and 3 electrons in t2g.

(ii) [Fe(CN)6]³- is weakly paramagnetic whereas [Fe(CN)6]4- is diamagnetic. Give reason to support this statement [Atomic no. Fe = 26].
Since CN − is a strong field ligand, it causes the pairing of unpaired electrons. Therefore, there is only one unpaired electron left in the d -orbital.
On the other hand, H 2 O is a weak field ligand. Therefore, it cannot cause the pairing of electrons. This means that the number of unpaired electrons is 5.
(iii) Write the number of ions produced from the complex [Co(NH3)6]C12 in solution.
The given complex can be written as [Co(NH3)6]Cl2. Thus, [Co(NH3)6]+ along with two Cl− ions are produced.
Q.(b)(i) Calculate the spin only magnetic moment of the complex [CoF613-. (Atomic no. of Co = 2 7)
Given ion is M 2+ with the atomic no. 27.
(iii) Which out of the two complexes is more stable and why ?
[Fe(H20)6]3+, [Fe(C204)3]3–
[Fe(C204)3]3– is more stable out of two complexes. The central metal ion is Fe3+ and C2O4 2– is negative bi-dentate ligand which forms more stable complex than neutral or monodentate ligand.

Q.6 (i) Which ion amongst the following is colourless and why?
Ti4+, Cr3+, V3+
(Atomic number of Ti = 22, Cr = 24, V = 23)
Ti is colourless because it is having no unpaired e − e- for excitation to higher energy level and it is colourless.
(ii) Why is Mn²+ much more resistant than Fe²+ towards oxidation?
Mn2+ is much more resistant than Fe2+ towards oxidationAs Mn2+ has stable configuration hence it is resistant towards oxidation. while in Fe2+ electronic configuration is 3d6 so it can lose one electron to give stable configuration 3d5.
(iii) Highest oxidation state of a metal is shown in its oxide or fluoride only. Justify the statement.
The highest oxidation state of a metal is exhibited in its oxide or fluoride only. This is because fluorine (F) and oxygen (O)are the most electronegative elements and the highest oxidation state shown by any transition element is +8.
Q.7 A compound ‘A’ (C2H4O) on oxidation gives ‘B’ (C2H4O2). ‘A’ undergoes an Iodoform reaction to give yellow precipitate and reacts with HCN to form the compound ‘C’. ‘C’ on hydrolysis gives 2-hydroxypropanoic acid. Identify the compounds ‘A’, ‘B’ and ‘C’. Write down equations for the reactions involved.

Q.9(a) Write equations involved in the following reactions :
(i) Ethanamine reacts with acetyl chloride.

(ii) Aniline reacts with bromine water at room temperature.

(iii) Aniline reacts with chloroform and ethanolic potassium hydroxide.
When aniline reacts with chloroform and alcoholic K O H it gives an offensive smelling liquid i.e., phenyl isocyanide as product. It is called as isocyanide test. It is given by aliphatic and aromatic primary amines.

Q.9 (b) (i) Write the IUPAC name for the following organic compound: (CH3CH2)2NCH3
( C H 3 C H 2 ) 2 N C H 3 it is a tertiary amine, and the parent chain is ethanamine. IUPAC name is N – Ethyl – N- methyl ethanamine.
(ii) Write the equations for the following:
(I) Gabriel phthalimide synthesis
Gabriel Phthalimide Synthesis Mechanism has 3 steps. The Synthesis is used to get primary amines from primary alkyl halides and is named after the German scientist Siegmund Gabriel.
The reaction has been generalized for applications in the alkylation of sulfonamides and imides & their deprotection in order to obtain amines. Alkylation of ammonia is quite inefficient, therefore it is substituted with phthalimide anion in the Gabriel synthesis.
(II) Hoffmann bromamide degradation
When an amide is treated with bromine in an aqueous or ethanolic solution of sodium hydroxide, degradation of amide takes place leading to the formation of primary amine. This reaction involving degradation of amide and is popularly known as Hoffmann bromamide degradation reaction. The primary amine thus formed contains one carbon less than the number of carbon atoms in that amide.
RCONH 2 +Br 2 + 4NaOH
R-NH 2 + Na 2 CO 3 + 2NaBr + 2H 2 O
Q.11(a) i) Silver atom has completely filled d-orbitals in its ground state, it is still considered to be a transition element. Justify the statement.
Silver (Ag) belongs to group 11 of d-block and its ground state electronic configuration is 4d10 5s1. It shows an oxidation state of +2 in its compounds like AgO and AgF2 in which its electronic configuration is d9 so it is a transition element.
ii) Why are E° values of Mn and Zn more negative than expected?
Negative E° values of Mn2+ and Zn2+ are because of the stabilities of half-filled (3d5 : Mn2+)and fullyfilled (3d10 : Zn2+) configuration respectively. Ni2+ ion has higher E° value due to highest negative enthalpy of hydration.
iii) Why do transition metals form alloys?
Transition metals have very similar atomic sizes. One metal can easily replace the other metal from its lattice to form solid solution (alloy). Transition metals are miscible with one another in the molten state. The molten state solution of two or more transition metals on cooling forms alloy.
Sharing is caring!
When will CBSE class 12 Chemistry Exam takes place?
The CBSE Chemistry Examination is going to take place on 27 February 2024.
How many Sections are there in the class 12 Chemistry Question paper?
Class 12 Chemistry Question paper has 5 sections with 35 questions for 70 marks.
What is the totals marks of class 12 Chemistry Question paper?
The totals marks of the class 12 Chemistry Question paper is 70 marks
Hi, I am Brajesh (M.Tech, MCA), I Professional Educator having 3 years of experience in school education sector. Aim to provide JEE, NEET, CUET, and Other Entrance exams information in a simple way to help students find clarity and confidence. I provide here easily accessible content on Exam Notifications, Syllabus, Admit Cards, and Results.

Join the Conversation
Keep it up the good work
Great article, the information provided to us. Thank you
Sir we need for physics
nice solutions for class 12 chemistry
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Leave a comment
Trending Articles
- CBSE Class 10 Result 2024
- CBSE Class 12th Result 2024
- CGBSE 10th Result 2024
- NEET Question Paper 2024
- NEET Answer Key 2024 All Sets
- NEET Exam Analysis 2024
- NEET Expected Cut Off 2024

CBSE Board Exam 2024
- CBSE Class 10 Syllabus 2024
- CBSE Class 12 Syllabus 2024
- CBSE Previous Year Papers
- CUET Syllabus
- CUET Previous Year paper
- CUET Participating College & Universities
- JEE Main 2024
- JEE Main Syllabus 2024
- JEE Main Exam Analysis 2023
- NEET 2024
- NEET Syllabus 2024
- NEET State wise Cut off
- NEET Rank Predictor
- NEET OMR Sheet
- NEET College Predictor
Recent Posts
Important exams, ncert solutions.
- NCERT Class 12
- NCERT Class 11
- NCERT Class 10
- NCERT Class 9
NCERT Books
School syllabus.
- CBSE Class 12
- CBSE Class 11
- CBSE Class 10
- CBSE Class 9
- JEE Mains 2024
Our Other Websites
- Teachers Adda
- Bankers Adda
- Current Affairs
- Adda Bengali
- Engineers Adda
- Adda Marathi
- Adda School

Get all your queries solved in one single place. We at Adda247 school strive each day to provide you the best material across the online education industry. We consider your struggle as our motivation to work each day.
Download Adda247 App
Follow us on
- Responsible Disclosure Program
- Cancellation & Refunds
- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy Policy

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
We have provided below the biggest collection of free CBSE NCERT KVS Assignments for Class 12 Chemistry. Students and teachers can download and save all free Chemistry assignments in Pdf for grade 12th. Our expert faculty have covered Class 12 important questions and answers for Chemistry as per the latest syllabus for the current academic year.
Class 12 Chemistry NCERT Solutions (2023-24) The solutions have been especially designed to help the students write concise answers in the board examinations, as well as prepare well for objective questions that the students face in JEE and NEET. Chapter 1 The Solid State. Chapter 2 Solutions. Chapter 3 Electro chemistry.
NCERT Intext Solutions Class 12 Chemistry helps students to understand the questions structured as per the CBSE guidelines. Students will be able to get a clear overview of the concepts covered in each chapter and improve their confidence to score well in the exams. Both chapter-wise and exercise-wise solutions are available on BYJU'S, which ...
on April 1, 2024, 5:12 AM. NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry in Hindi and English Medium updated for session 2024-25. Class 12 Chemistry NCERT Solutions refer to the answers and explanations provided for the questions and exercises found in the Chemistry textbook for the 12th grade published by the National Council of Educational Research ...
The NCERT Chemistry Class 12 Solutions PDF provide a valuable resource for their studies. Understanding the NCERT class 12 Chemistry Chapters becomes essential for building a strong foundation for future studies. The chapter at a glance for Chemistry provides a quick overview, highlighting the key topics covered in each Chemistry Chapter.
on September 2, 2023, 5:13 AM. NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solutions in Hindi Medium and English Medium. Get here Exercises Questions and Intext Questions to view online or download in PDF format. These solutions are updated for new academic year 2024-25 for all boards using NCERT Books.
Chemistry Class 12 questions and solutions in Chapter 2 given here are very simple and easy to understand. Class 12 NCERT Solutions for Chemistry Chapter 2 Solutions. Chapter 2 Solutions of Class 12 Chemistry, is designed as per the CBSE Syllabus for the session 2023-24. This chapter holds approximately 5 marks in the board examination.
The answers to the NCERT books are the best study material for students. Listed below are the chapter-wise NCERT Chemistry Class 12 Solutions CBSE, Karnataka Board PUC. • Chapter 1: The Solid State. • Chapter 2: Solutions. • Chapter 3: Electrochemistry. • Chapter 4: Chemical Kinetics. • Chapter 5: Surface Chemistry.
Here are some of the features of our online class 12 chemistry course: You will get access to comprehensive and updated video lectures, interactive quizzes, assignments, and notes that cover the entire syllabus of class 12 chemistry. You will learn from expert and experienced teachers who have a passion for teaching and a deep knowledge of the ...
NCERT TEXTBOOK QUESTIONS SOLVED. 2.1. Calculate the mass percentage of benzene (C6H6) and carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) if 22 g of benzene is dissolved in 122 g of carbon tetrachloride. Ans: Mass of solution = Mass of C 6 H 6 + Mass of CCl 4. = 22 g+122 g= 144 g. Mass % of benzene = 22/144 x 100 =15.28 %. Mass % of CCl 4 = 122/144 x 100 = 84.72 % ...
Solution: Question 4. Calculate the mass of urea (NH 2 CONH 2) required in making 2.5 kg of 0.25 molal aqueous solution. Solution: Moles of urea = 0.25 mole. Mass of solvent (water) = 1 kg = 1000 g. Molar mass of urea (NH 2 CONH 2) = 14 + 2 + 12 + 16 + 14 + 2 = 60 g mol -1. ∴ Mass of urea in 1000 g of water = 0.25 mol × 60 g mol -1 = 15 g.
Below are the chapter wise details of class 12 NCERT solutions for chemistry. Chapter 1 The Solid State. Chapter 2 Solutions. Chapter 3 Electrochemistry. Chapter 4 Chemical Kinetics. Chapter 5 Surface Chemistry. Chapter 6 General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements. Chapter 7 The p-Block Elements.
This Chemistry Solutions Class 12 chapter consists of topics like the concentration of solutions and various types of solutions. Furthermore, it also consists of solubility of gases and solids in liquid, the vapor pressure in a liquid solution, Raoult's law, abnormal mola masses, non-ideal and ideal solutions, determination of molar masses, etc.
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 3. Question2. Calculate the mole fraction of benzene in solution containing 30% by mass in carbon tetrachloride. Solution : Let the total mass of the solution be 100 g and the mass of benzene be 30 g. ∴Mass of carbon tetrachloride = (100 − 30)g. = 70 g. Molar mass of benzene (C 6 H 6) = (6 × ...
All Assignments for Chemistry Grade 12 have been designed by expert faculty members and have been designed based on the type of questions asked in standard 12 class tests and exams. All Free printable Assignments for NCERT CBSE Class 12, practice worksheets, and question banks have been designed to help you understand all concepts properly.
Solutions Class 12 Notes Chemistry Chapter 2 1. A solution is a homogeneous mixture of two or 9. more chemically non-reacting substances. The components of a solution generally cannot be separated by filtration, settling or centrifuging. 2. A solution may be classified as solid, liquid or a gaseous solution. 3. Solubility is defined as the […]
Class 12 Chemistry NCERT Exemplar Problems Chapter-wise. Download the NCERT Exemplar Class 12 Chemistry PDFs. Chapter 1- Solid State. Chapter 2- Solutions. Chapter 3- Electrochemistry. Chapter 4- Chemical Kinetics. Chapter 5- Surface Chemistry. Chapter 6- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements. Chapter 7- The P-Block Elements.
Download PDF of class 12 Chemistry notes Chapter 1 Solution. Notes of chapter 1 Solution contains all the topic as per the syllabus of NCERT. Each topic is explained in very easy language with colored diagrams. Typical topics are divided into parts so that student can understand these topics step by step. Class 12 Chemistry notes Chapter 1 ...
We have provided Class 12 Chemistry Assignments for all chapters on our website. These problems and solutions for Chapter 2 Solutions Class 12 Chemistry have been prepared as per the latest syllabus and books issued for the current academic year. Learn these solved important questions to get more marks in your class tests and examinations.
Assume that we have 100 g of solution (one can start with any amount of solution because the results obtained will be the same). Solution will contain 20 g of ethylene glycol and 80 g of water. Molar mass of C 2 H 6 O 2 = 12 × 2 + 1 × 6 + 16 × 2 = 62 g mol-1. Moles of C 2H6O2 = −1 20 g 62 g mol = 0.322 mol Moles of water = -1 80 g 18 g ...
UP Class 12 Chemistry. 6 units · 39 skills. Unit 1. Solutions. Unit 2. Haloalkanes and haloarenes. Unit 3. Electrochemistry. Unit 4. Chemical Kinetics. Unit 5. Alcohols, phenols and ethers. ... Colligative properties of solutions Get 4 of 5 questions to level up! Abnormal molar masses. Learn. Abnormal molar masses (Opens a modal)
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Answer Key Set 3 Last year. 1, A compound CaCl2.6h2O undergoes complete dissociation in water, The Van't Hoff Factor 'i' is: a) 9, b) 6, c)3, d) . 4. Answer: c) 3. 2. For a Zero order reaction of type A →products, the rate equation may be expressed as: Answer: Option (a) 3.