- Reviews / Why join our community?
- For companies
- Frequently asked questions

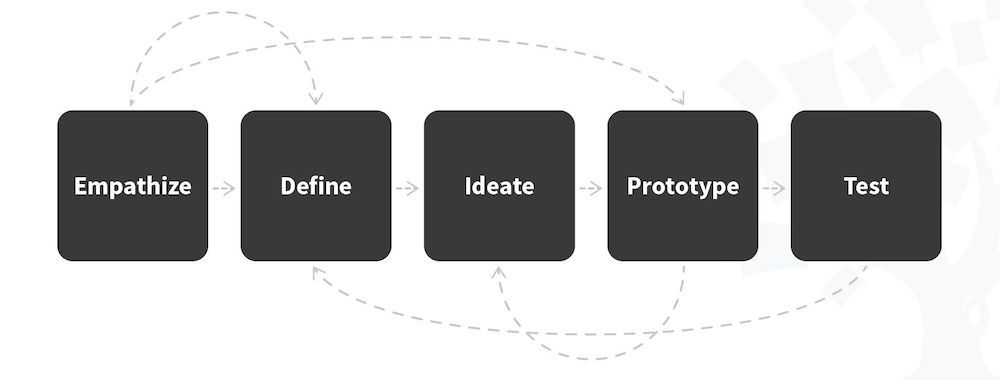
The 5 Stages in the Design Thinking Process
Design thinking is a methodology which provides a solution-based approach to solving problems. It’s extremely useful when used to tackle complex problems that are ill-defined or unknown—because it serves to understand the human needs involved, reframe the problem in human-centric ways, create numerous ideas in brainstorming sessions and adopt a hands-on approach to prototyping and testing. When you know how to apply the five stages of design thinking you will be impowered because you can apply the methodology to solve complex problems that occur in our companies, our countries, and across the world.
Design thinking is a non-linear, iterative process that can have anywhere from three to seven phases, depending on whom you talk to. We focus on the five-stage design thinking model proposed by the Hasso Plattner Institute of Design at Stanford (the d.school) because they are world-renowned for the way they teach and apply design thinking.
What are the 5 Stages of the Design Thinking Process
The five stages of design thinking, according to the d.school, are:
Empathize : research your users' needs .
Define : state your users' needs and problems.
Ideate : challenge assumptions and create ideas.
Prototype : start to create solutions.
Test : try your solutions out.
Let’s dive into each stage of the design thinking process.
- Transcript loading…
Hasso-Platner Institute Panorama
Ludwig Wilhelm Wall, CC BY-SA 3.0 <https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0>, via Wikimedia Commons
Stage 1: Empathize—Research Your Users' Needs

Empathize: the first phase of design thinking, where you gain real insight into users and their needs.
© Teo Yu Siang and the Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-NC-SA 3.0.
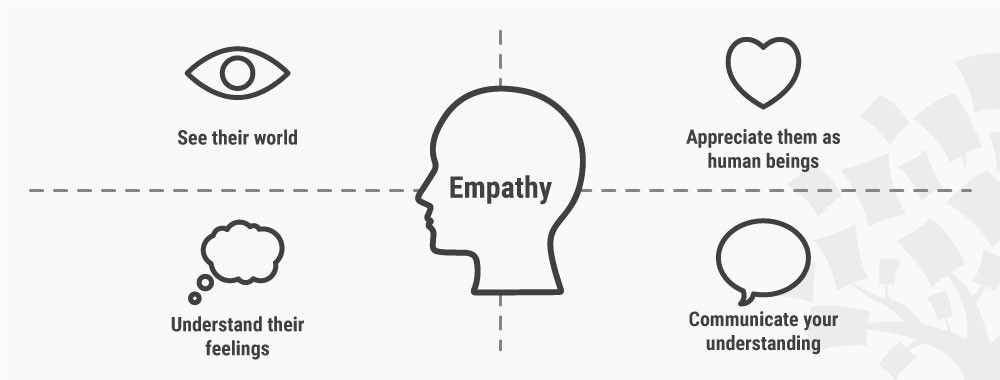
The first stage of the design thinking process focuses on user-centric research . You want to gain an empathic understanding of the problem you are trying to solve. Consult experts to find out more about the area of concern and conduct observations to engage and empathize with your users. You may also want to immerse yourself in your users’ physical environment to gain a deeper, personal understanding of the issues involved—as well as their experiences and motivations . Empathy is crucial to problem solving and a human-centered design process as it allows design thinkers to set aside their own assumptions about the world and gain real insight into users and their needs.
Depending on time constraints, you will gather a substantial amount of information to use during the next stage. The main aim of the Empathize stage is to develop the best possible understanding of your users, their needs and the problems that underlie the development of the product or service you want to create.
Stage 2: Define—State Your Users' Needs and Problems

Define: the second phase of design thinking, where you define the problem statement in a human-centered manner.
In the Define stage, you will organize the information you have gathered during the Empathize stage. You’ll analyze your observations to define the core problems you and your team have identified up to this point. Defining the problem and problem statement must be done in a human-centered manner .
For example, you should not define the problem as your own wish or need of the company: “We need to increase our food-product market share among young teenage girls by 5%.”
You should pitch the problem statement from your perception of the users’ needs: “Teenage girls need to eat nutritious food in order to thrive, be healthy and grow.”
The Define stage will help the design team collect great ideas to establish features, functions and other elements to solve the problem at hand—or, at the very least, allow real users to resolve issues themselves with minimal difficulty. In this stage, you will start to progress to the third stage, the ideation phase, where you ask questions to help you look for solutions: “How might we encourage teenage girls to perform an action that benefits them and also involves your company’s food-related product or service?” for instance.
Stage 3: Ideate—Challenge Assumptions and Create Ideas

Ideate: the third phase of design thinking, where you identify innovative solutions to the problem statement you’ve created.
During the third stage of the design thinking process, designers are ready to generate ideas. You’ve grown to understand your users and their needs in the Empathize stage, and you’ve analyzed your observations in the Define stage to create a user centric problem statement. With this solid background, you and your team members can start to look at the problem from different perspectives and ideate innovative solutions to your problem statement .
There are hundreds of ideation techniques you can use—such as Brainstorm, Brainwrite , Worst Possible Idea and SCAMPER . Brainstorm and Worst Possible Idea techniques are typically used at the start of the ideation stage to stimulate free thinking and expand the problem space. This allows you to generate as many ideas as possible at the start of ideation. You should pick other ideation techniques towards the end of this stage to help you investigate and test your ideas, and choose the best ones to move forward with—either because they seem to solve the problem or provide the elements required to circumvent it.
Stage 4: Prototype—Start to Create Solutions

Prototype: the fourth phase of design thinking, where you identify the best possible solution.
The design team will now produce a number of inexpensive, scaled down versions of the product (or specific features found within the product) to investigate the key solutions generated in the ideation phase. These prototypes can be shared and tested within the team itself, in other departments or on a small group of people outside the design team.
This is an experimental phase, and the aim is to identify the best possible solution for each of the problems identified during the first three stages . The solutions are implemented within the prototypes and, one by one, they are investigated and then accepted, improved or rejected based on the users’ experiences.
By the end of the Prototype stage, the design team will have a better idea of the product’s limitations and the problems it faces. They’ll also have a clearer view of how real users would behave, think and feel when they interact with the end product.
Stage 5: Test—Try Your Solutions Out

Test: the fifth and final phase of the design thinking process, where you test solutions to derive a deep understanding of the product and its users.
Designers or evaluators rigorously test the complete product using the best solutions identified in the Prototype stage. This is the final stage of the five-stage model; however, in an iterative process such as design thinking, the results generated are often used to redefine one or more further problems. This increased level of understanding may help you investigate the conditions of use and how people think, behave and feel towards the product, and even lead you to loop back to a previous stage in the design thinking process. You can then proceed with further iterations and make alterations and refinements to rule out alternative solutions. The ultimate goal is to get as deep an understanding of the product and its users as possible.
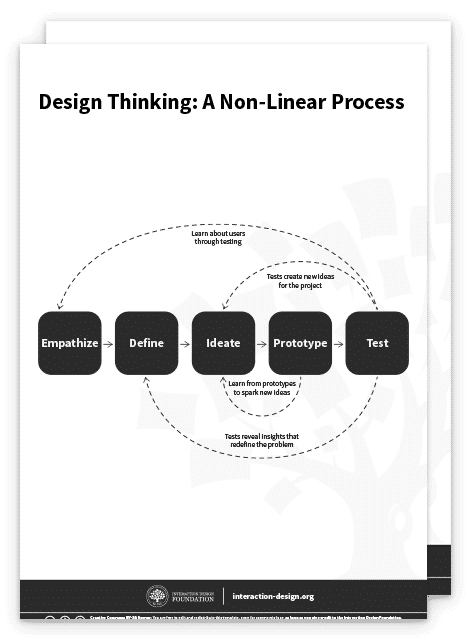
Did You Know Design Thinking is a Non-Linear Process?
We’ve outlined a direct and linear design thinking process here, in which one stage seemingly leads to the next with a logical conclusion at user testing . However, in practice, the process is carried out in a more flexible and non-linear fashion . For example, different groups within the design team may conduct more than one stage concurrently, or designers may collect information and prototype throughout each stage of the project to bring their ideas to life and visualize the problem solutions as they go. What’s more, results from the Test stage may reveal new insights about users which lead to another brainstorming session (Ideate) or the development of new prototypes (Prototype).
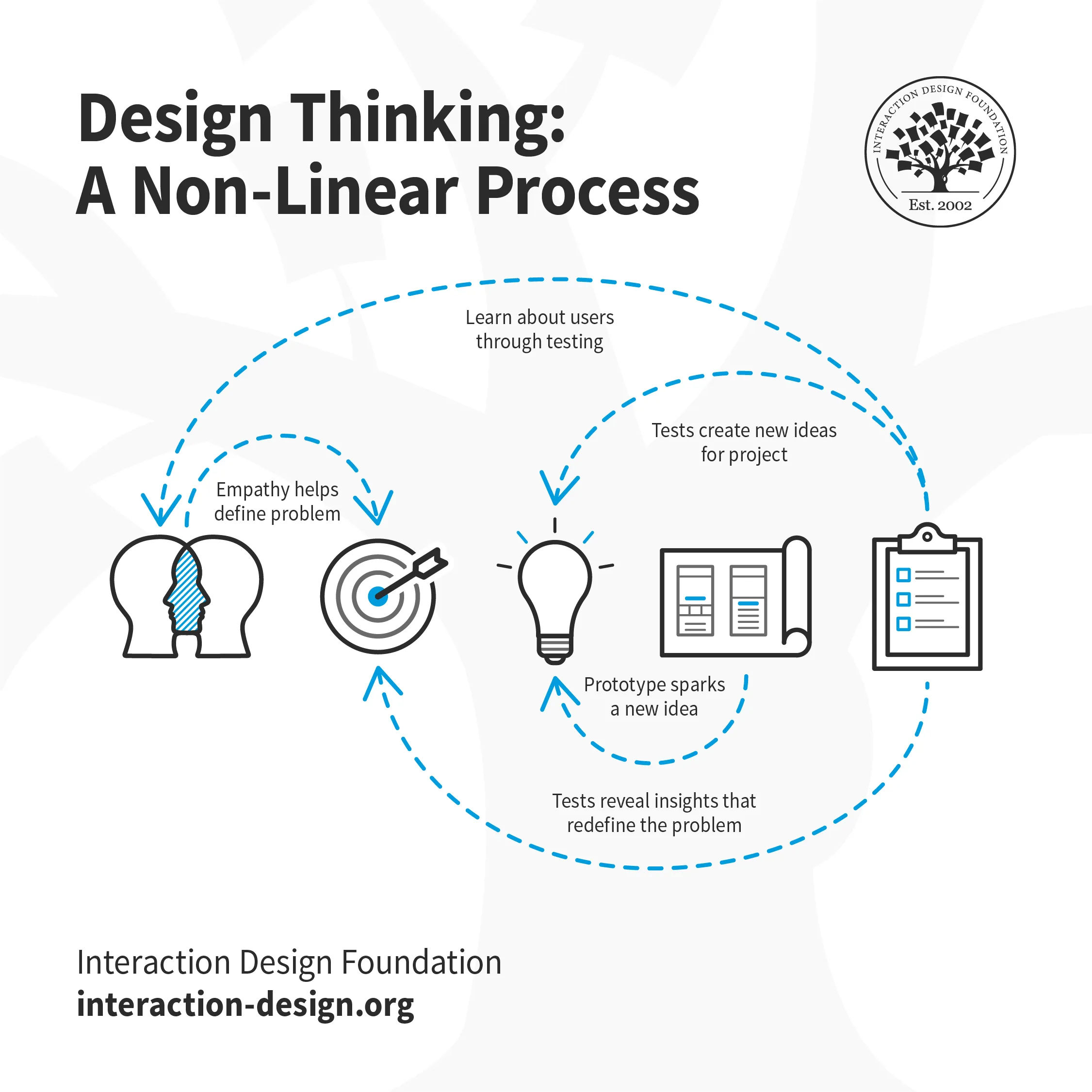
It is important to note the five stages of design thinking are not always sequential. They do not have to follow a specific order, and they can often occur in parallel or be repeated iteratively. The stages should be understood as different modes which contribute to the entire design project, rather than sequential steps.
The design thinking process should not be seen as a concrete and inflexible approach to design; the component stages identified should serve as a guide to the activities you carry out. The stages might be switched, conducted concurrently or repeated several times to gain the most informative insights about your users, expand the solution space and hone in on innovative solutions.
This is one of the main benefits of the five-stage model. Knowledge acquired in the latter stages of the process can inform repeats of earlier stages . Information is continually used to inform the understanding of the problem and solution spaces, and to redefine the problem itself. This creates a perpetual loop, in which the designers continue to gain new insights, develop new ways to view the product (or service) and its possible uses and develop a far more profound understanding of their real users and the problems they face.
The Take Away
Design thinking is an iterative, non-linear process which focuses on a collaboration between designers and users. It brings innovative solutions to life based on how real users think, feel and behave.
This human-centered design process consists of five core stages Empathize, Define, Ideate, Prototype and Test.
It’s important to note that these stages are a guide. The iterative, non-linear nature of design thinking means you and your design team can carry these stages out simultaneously, repeat them and even circle back to previous stages at any point in the design thinking process.
References & Where to Learn More
Take our Design Thinking course which is the ultimate guide when you want to learn how to you can apply design thinking methods throughout a design thinking process. Herbert Simon, The Sciences of the Artificial (3rd Edition), 1996.
d.school, An Introduction to Design Thinking PROCESS GUIDE , 2010.
Gerd Waloszek, Introduction to Design Thinking , 2012.
Hero Image: © the Interaction Design Foundation, CC BY-NC-SA 3.0.
Design Thinking: The Ultimate Guide

Get Weekly Design Insights
Topics in this article, what you should read next, what is design thinking and why is it so popular.
- 1.6k shares
Personas – A Simple Introduction

- 1.5k shares
Stage 2 in the Design Thinking Process: Define the Problem and Interpret the Results

- 1.3k shares
What is Ideation – and How to Prepare for Ideation Sessions
- 1.2k shares
Affinity Diagrams: How to Cluster Your Ideas and Reveal Insights

- 2 years ago
Stage 1 in the Design Thinking Process: Empathise with Your Users
- 3 years ago
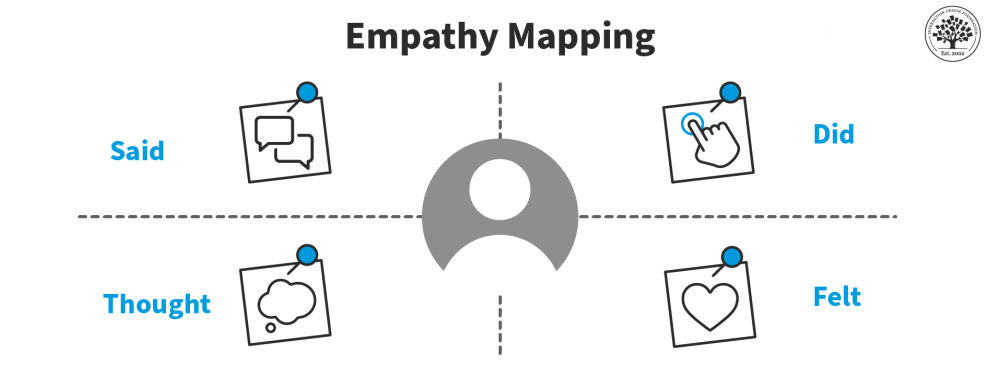
Empathy Map – Why and How to Use It
What Is Empathy and Why Is It So Important in Design Thinking?
10 Insightful Design Thinking Frameworks: A Quick Overview
Define and Frame Your Design Challenge by Creating Your Point Of View and Ask “How Might We”

- 1.1k shares
Open Access—Link to us!
We believe in Open Access and the democratization of knowledge . Unfortunately, world-class educational materials such as this page are normally hidden behind paywalls or in expensive textbooks.
If you want this to change , cite this article , link to us, or join us to help us democratize design knowledge !
Privacy Settings
Our digital services use necessary tracking technologies, including third-party cookies, for security, functionality, and to uphold user rights. Optional cookies offer enhanced features, and analytics.
Experience the full potential of our site that remembers your preferences and supports secure sign-in.
Governs the storage of data necessary for maintaining website security, user authentication, and fraud prevention mechanisms.
Enhanced Functionality
Saves your settings and preferences, like your location, for a more personalized experience.
Referral Program
We use cookies to enable our referral program, giving you and your friends discounts.
Error Reporting
We share user ID with Bugsnag and NewRelic to help us track errors and fix issues.
Optimize your experience by allowing us to monitor site usage. You’ll enjoy a smoother, more personalized journey without compromising your privacy.
Analytics Storage
Collects anonymous data on how you navigate and interact, helping us make informed improvements.
Differentiates real visitors from automated bots, ensuring accurate usage data and improving your website experience.
Lets us tailor your digital ads to match your interests, making them more relevant and useful to you.
Advertising Storage
Stores information for better-targeted advertising, enhancing your online ad experience.
Personalization Storage
Permits storing data to personalize content and ads across Google services based on user behavior, enhancing overall user experience.
Advertising Personalization
Allows for content and ad personalization across Google services based on user behavior. This consent enhances user experiences.
Enables personalizing ads based on user data and interactions, allowing for more relevant advertising experiences across Google services.
Receive more relevant advertisements by sharing your interests and behavior with our trusted advertising partners.
Enables better ad targeting and measurement on Meta platforms, making ads you see more relevant.
Allows for improved ad effectiveness and measurement through Meta’s Conversions API, ensuring privacy-compliant data sharing.
LinkedIn Insights
Tracks conversions, retargeting, and web analytics for LinkedIn ad campaigns, enhancing ad relevance and performance.
LinkedIn CAPI
Enhances LinkedIn advertising through server-side event tracking, offering more accurate measurement and personalization.
Google Ads Tag
Tracks ad performance and user engagement, helping deliver ads that are most useful to you.
Share Knowledge, Get Respect!
or copy link
Cite according to academic standards
Simply copy and paste the text below into your bibliographic reference list, onto your blog, or anywhere else. You can also just hyperlink to this article.
New to UX Design? We’re giving you a free ebook!

Download our free ebook The Basics of User Experience Design to learn about core concepts of UX design.
In 9 chapters, we’ll cover: conducting user interviews, design thinking, interaction design, mobile UX design, usability, UX research, and many more!
New to UX Design? We’re Giving You a Free ebook!
Eberly Center
Teaching excellence & educational innovation, creating assignments.
Here are some general suggestions and questions to consider when creating assignments. There are also many other resources in print and on the web that provide examples of interesting, discipline-specific assignment ideas.
Consider your learning objectives.
What do you want students to learn in your course? What could they do that would show you that they have learned it? To determine assignments that truly serve your course objectives, it is useful to write out your objectives in this form: I want my students to be able to ____. Use active, measurable verbs as you complete that sentence (e.g., compare theories, discuss ramifications, recommend strategies), and your learning objectives will point you towards suitable assignments.
Design assignments that are interesting and challenging.
This is the fun side of assignment design. Consider how to focus students’ thinking in ways that are creative, challenging, and motivating. Think beyond the conventional assignment type! For example, one American historian requires students to write diary entries for a hypothetical Nebraska farmwoman in the 1890s. By specifying that students’ diary entries must demonstrate the breadth of their historical knowledge (e.g., gender, economics, technology, diet, family structure), the instructor gets students to exercise their imaginations while also accomplishing the learning objectives of the course (Walvoord & Anderson, 1989, p. 25).
Double-check alignment.
After creating your assignments, go back to your learning objectives and make sure there is still a good match between what you want students to learn and what you are asking them to do. If you find a mismatch, you will need to adjust either the assignments or the learning objectives. For instance, if your goal is for students to be able to analyze and evaluate texts, but your assignments only ask them to summarize texts, you would need to add an analytical and evaluative dimension to some assignments or rethink your learning objectives.
Name assignments accurately.
Students can be misled by assignments that are named inappropriately. For example, if you want students to analyze a product’s strengths and weaknesses but you call the assignment a “product description,” students may focus all their energies on the descriptive, not the critical, elements of the task. Thus, it is important to ensure that the titles of your assignments communicate their intention accurately to students.
Consider sequencing.
Think about how to order your assignments so that they build skills in a logical sequence. Ideally, assignments that require the most synthesis of skills and knowledge should come later in the semester, preceded by smaller assignments that build these skills incrementally. For example, if an instructor’s final assignment is a research project that requires students to evaluate a technological solution to an environmental problem, earlier assignments should reinforce component skills, including the ability to identify and discuss key environmental issues, apply evaluative criteria, and find appropriate research sources.
Think about scheduling.
Consider your intended assignments in relation to the academic calendar and decide how they can be reasonably spaced throughout the semester, taking into account holidays and key campus events. Consider how long it will take students to complete all parts of the assignment (e.g., planning, library research, reading, coordinating groups, writing, integrating the contributions of team members, developing a presentation), and be sure to allow sufficient time between assignments.
Check feasibility.
Is the workload you have in mind reasonable for your students? Is the grading burden manageable for you? Sometimes there are ways to reduce workload (whether for you or for students) without compromising learning objectives. For example, if a primary objective in assigning a project is for students to identify an interesting engineering problem and do some preliminary research on it, it might be reasonable to require students to submit a project proposal and annotated bibliography rather than a fully developed report. If your learning objectives are clear, you will see where corners can be cut without sacrificing educational quality.
Articulate the task description clearly.
If an assignment is vague, students may interpret it any number of ways – and not necessarily how you intended. Thus, it is critical to clearly and unambiguously identify the task students are to do (e.g., design a website to help high school students locate environmental resources, create an annotated bibliography of readings on apartheid). It can be helpful to differentiate the central task (what students are supposed to produce) from other advice and information you provide in your assignment description.
Establish clear performance criteria.
Different instructors apply different criteria when grading student work, so it’s important that you clearly articulate to students what your criteria are. To do so, think about the best student work you have seen on similar tasks and try to identify the specific characteristics that made it excellent, such as clarity of thought, originality, logical organization, or use of a wide range of sources. Then identify the characteristics of the worst student work you have seen, such as shaky evidence, weak organizational structure, or lack of focus. Identifying these characteristics can help you consciously articulate the criteria you already apply. It is important to communicate these criteria to students, whether in your assignment description or as a separate rubric or scoring guide . Clearly articulated performance criteria can prevent unnecessary confusion about your expectations while also setting a high standard for students to meet.
Specify the intended audience.
Students make assumptions about the audience they are addressing in papers and presentations, which influences how they pitch their message. For example, students may assume that, since the instructor is their primary audience, they do not need to define discipline-specific terms or concepts. These assumptions may not match the instructor’s expectations. Thus, it is important on assignments to specify the intended audience http://wac.colostate.edu/intro/pop10e.cfm (e.g., undergraduates with no biology background, a potential funder who does not know engineering).
Specify the purpose of the assignment.
If students are unclear about the goals or purpose of the assignment, they may make unnecessary mistakes. For example, if students believe an assignment is focused on summarizing research as opposed to evaluating it, they may seriously miscalculate the task and put their energies in the wrong place. The same is true they think the goal of an economics problem set is to find the correct answer, rather than demonstrate a clear chain of economic reasoning. Consequently, it is important to make your objectives for the assignment clear to students.
Specify the parameters.
If you have specific parameters in mind for the assignment (e.g., length, size, formatting, citation conventions) you should be sure to specify them in your assignment description. Otherwise, students may misapply conventions and formats they learned in other courses that are not appropriate for yours.
A Checklist for Designing Assignments
Here is a set of questions you can ask yourself when creating an assignment.
- Provided a written description of the assignment (in the syllabus or in a separate document)?
- Specified the purpose of the assignment?
- Indicated the intended audience?
- Articulated the instructions in precise and unambiguous language?
- Provided information about the appropriate format and presentation (e.g., page length, typed, cover sheet, bibliography)?
- Indicated special instructions, such as a particular citation style or headings?
- Specified the due date and the consequences for missing it?
- Articulated performance criteria clearly?
- Indicated the assignment’s point value or percentage of the course grade?
- Provided students (where appropriate) with models or samples?
Adapted from the WAC Clearinghouse at http://wac.colostate.edu/intro/pop10e.cfm .
CONTACT US to talk with an Eberly colleague in person!
- Faculty Support
- Graduate Student Support
- Canvas @ Carnegie Mellon
- Quick Links
Creative Ways to Design Assignments for Student Success
There are many creative ways in which teachers can design assignments to support student success. We can do this while simultaneously not getting bogged down with the various obstructions that keep students from both completing and learning from the assignments. For me, assignments fall into two categories: those that are graded automatically, such as SmartBook® readings and quizzes in Connect®; and those that I need to grade by hand, such as writing assignments.
For those of us teaching large, introductory classes, most of our assignments are graded automatically, which is great for our time management. But our students will ultimately deliver a plethora of colorful excuses as to why they were not completed and why extensions are warranted. How do we give them a little leeway to make the semester run more smoothly, so there are fewer worries about a reading that was missed or a quiz that went by too quickly? Here are a few tactics I use.
Automatically graded assignments:
Multiple assignment attempts
- This eases the mental pressure of a timed assignment and covers computer mishaps or human error on the first attempt.
- You can deduct points for every attempt taken if you are worried about students taking advantage.
Automatically dropped assignments
- Within a subset or set of assignments, automatically drop a few from grading. This can take care of all excuses for missing an assignment.
- Additionally, you can give a little grade boost to those who complete all their assignments (over a certain grade).
Due dates
- Consider staggering due dates during the week instead of making them all due on Sunday night.
- Set the due date for readings the night before you cover the material, so students are prepared.
Requirements
- If we want our students to read, then make a reading assignment a requirement of a quiz.
The tactics above might be applied to written assignments, too. An easy way to bolster a student’s interest and investment in these longer assignments is to give them a choice. This could be in the topic, location of study, or presentation style. For example, if you want them to analyze the susceptibility of a beach to hurricane threat, why not let them choose the location? In this way, you will also be gaining a lot of new information for your own use.
With a small amount of effort, we can design our classes, so students concentrate on learning the subject matter rather than the logistics of completing the assignments.
Attending a conference?
Checkout if mcgraw hill will be in attendance:.
- Columbia University in the City of New York
- Office of Teaching, Learning, and Innovation
- University Policies
- Columbia Online
- Academic Calendar
- Resources and Technology
- Resources and Guides
Getting Started with Creative Assignments
Creative teaching and learning can be cultivated in any course context to increase student engagement and motivation, and promote thinking skills that are critical to problem-solving and innovation. This resource features examples of Columbia faculty who teach creatively and have reimagined their course assessments to allow students to demonstrate their learning in creative ways. Drawing on these examples, this resource provides suggestions for creating a classroom environment that supports student engagement in creative activities and assignments.
On this page:
- The What and Why of Creative Assignments
Examples of Creative Teaching and Learning at Columbia
- How To Get Started
Cite this resource: Columbia Center for Teaching and Learning (2022). Getting Started with Creative Assignments. Columbia University. Retrieved [today’s date] from https://ctl.columbia.edu/resources-and-technology/resources/creative-assignments/
The What and Why of Creative Assignments
Creative assignments encourage students to think in innovative ways as they demonstrate their learning. Thinking creatively involves combining or synthesizing information or course materials in new ways and is characterized by “a high degree of innovation, divergent thinking, and risk-taking” (AAC&U). It is associated with imagination and originality, and additional characteristics include: being open to new ideas and perspectives, believing alternatives exist, withholding judgment, generating multiple approaches to problems, and trying new ways to generate ideas (DiYanni, 2015: 41). Creative thinking is considered an important skill alongside critical thinking in tackling contemporary problems. Critical thinking allows students to evaluate the information presented to them while creative thinking is a process that allows students to generate new ideas and innovate.
Creative assignments can be integrated into any course regardless of discipline. Examples include the use of infographic assignments in Nursing (Chicca and Chunta, 2020) and Chemistry (Kothari, Castañeda, and McNeil, 2019); podcasting assignments in Social Work (Hitchcock, Sage & Sage, 2021); digital storytelling assignments in Psychology (Sheafer, 2017) and Sociology (Vaughn and Leon, 2021); and incorporating creative writing in the economics classroom (Davis, 2019) or reflective writing into Calculus assignment ( Gerstle, 2017) just to name a few. In a 2014 study, organic chemistry students who elected to begin their lab reports with a creative narrative were more excited to learn and earned better grades (Henry, Owens, and Tawney, 2015). In a public policy course, students who engaged in additional creative problem-solving exercises that included imaginative scenarios and alternative solution-finding showed greater interest in government reform and attentiveness to civic issues (Wukich and Siciliano, 2014).
The benefits of creative assignments include increased student engagement, motivation, and satisfaction (Snyder et al., 2013: 165); and furthered student learning of course content (Reynolds, Stevens, and West, 2013). These types of assignments promote innovation, academic integrity, student self-awareness/ metacognition (e.g., when students engage in reflection through journal assignments), and can be made authentic as students develop and apply skills to real-world situations.
When instructors give students open-ended assignments, they provide opportunities for students to think creatively as they work on a deliverable. They “unlock potential” (Ranjan & Gabora and Beghetto in Gregerson et al., 2013) for students to synthesize their knowledge and propose novel solutions. This promotes higher-level thinking as outlined in the revised Bloom’s Taxonomy’s “create” cognitive process category: “putting elements together to form a novel coherent whole or make an original product,” this involves generating ideas, planning, and producing something new.
The examples that follow highlight creative assignments in the Columbia University classroom. The featured Columbia faculty taught creatively – they tried new strategies, purposefully varied classroom activities and assessment modalities, and encouraged their students to take control of what and how they were learning (James & Brookfield, 2014: 66).

Dr. Cruz changed her course assessment by “moving away from high stakes assessments like a final paper or a final exam, to more open-ended and creative models of assessments.” Students were given the opportunity to synthesize their course learning, with options on topic and format of how to demonstrate their learning and to do so individually or in groups. They explored topics that were meaningful to them and related to the course material. Dr. Cruz noted that “This emphasis on playfulness and creativity led to fantastic final projects including a graphic novel interpretation, a video essay that applied critical theory to multiple texts, and an interactive virtual museum.” Students “took the opportunity to use their creative skills, or the skills they were interested in exploring because some of them had to develop new skills to produce these projects.” (Dr. Cruz; Dead Ideas in Teaching and Learning , Season 3, Episode 6). Along with their projects, students submitted an artist’s statement, where they had to explain and justify their choices.
Dr. Cruz noted that grading creative assignments require advanced planning. In her case, she worked closely with her TAs to develop a rubric that was shared with students in advance for full transparency and emphasized the importance of students connecting ideas to analytical arguments discussed in the class.
Watch Dr. Cruz’s 2021 Symposium presentation. Listen to Dr. Cruz talk about The Power of Blended Classrooms in Season 3, Episode 6 of the Dead Ideas in Teaching and Learning podcast. Get a glimpse into Dr. Cruz’s online classroom and her creative teaching and the design of learning experiences that enhanced critical thinking, creativity, curiosity, and community by viewing her Voices of Hybrid and Online Teaching and Learning submission.

As part of his standard practice, Dr. Yesilevskiy scaffolds assignments – from less complex to more complex – to ensure students integrate the concepts they learn in the class into their projects or new experiments. For example, in Laboratory 1, Dr. Yesilevskiy slowly increases the amount of independence in each experiment over the semester: students are given a full procedure in the first experiment and by course end, students are submitting new experiment proposals to Dr. Yesilevskiy for approval. This is creative thinking in action. Students not only learned how to “replicate existing experiments, but also to formulate and conduct new ones.”
Watch Dr. Yesilevskiy’s 2021 Symposium presentation.
How Do I Get Started?: Strategies to Support Creative Assignments
The previous section showcases examples of creative assignments in action at Columbia. To help you support such creative assignments in your classroom, this section details three strategies to support creative assignments and creative thinking. Firstly, re-consider the design of your assignments to optimize students’ creative output. Secondly, scaffold creative assignments using low-stakes classroom activities that build creative capacity. Finally, cultivate a classroom environment that supports creative thinking.
Design Considerations for Creative Assignments
Thoughtfully designed open-ended assignments and evaluation plans encourage students to demonstrate their learning in authentic ways. When designing creative assignments, consider the following suggestions for structuring and communicating to your students about the assignment.
Set clear expectations . Students may feel lost in the ambiguity and complexity of an open-ended assignment that requires them to create something new. Communicate the creative outcomes and learning objectives for the assignments (Ranjan & Gabora, 2013), and how students will be expected to draw on their learning in the course. Articulare how much flexibility and choice students have in determining what they work on and how they work on it. Share the criteria or a rubric that will be used to evaluate student deliverables. See the CTL’s resource Incorporating Rubrics Into Your Feedback and Grading Practices . If planning to evaluate creative thinking, consider adapting the American Association of Colleges and Universities’ creative thinking VALUE rubric .
Structure the project to sustain engagement and promote integrity. Consider how the project might be broken into smaller assignments that build upon each other and culminate in a synthesis project. The example presented above from Dr. Yesilevskiy’s teaching highlights how he scaffolded lab complexity, progressing from structured to student-driven. See the section below “Activities to Prepare Students for Creative Assignments” for sample activities to scaffold this work.
Create opportunities for ongoing feedback . Provide feedback at all phases of the assignment from idea inception through milestones to completion. Leverage office hours for individual or group conversations and feedback on project proposals, progress, and issues. See the CTL’s resource on Feedback for Learning . Consider creating opportunities for structured peer review for students to give each other feedback on their work. Students benefit from learning about their peers’ projects, and seeing different perspectives and approaches to accomplishing the open-ended assignment. See the CTL’s resource Peer Review: Intentional Design for Any Course Context .
Share resources to support students in their work. Ensure all students have access to the resources they will need to be successful on the assigned project. Connect students with campus resources that can help them accomplish the project’s objectives. For instance, if students are working on a research project – connect them to the Library instruction modules “ From Books to Bytes: Navigating the Research Ecosystem ,” encourage them to schedule a consultation with a specialist for research support through Columbia Libraries , or seek out writing support. If students will need equipment to complete their project, remind them of campus resources such as makerspaces (e.g., The Makerspace @ Columbia in Room 254 Engineering Terrace/Mudd; Design Center at Barnard College); borrowing equipment (e.g., Instructional Media and Technology Services (IMATS) at Barnard; Gabe M. Wiener Music & Arts Library ).
Ask students to submit a self-reflection with their project. Encourage students to reflect on their process and the decisions they made in order to complete the project. Provide guiding questions that have students reflect on their learning, make meaning, and engage their metacognitive thinking skills (see the CTL’s resource of Metacognition ). Students can be asked to apply the rubric to their work or to submit a creative statement along with their work that describes their intent and ownership of the project.
Collect feedback from students and iterate. Invite students to give feedback on the assigned creative project, as well as the classroom environment and creative activities used. Tell students how you will use their suggestions to make improvements to activities and assignments, and make adjustments to the classroom environment. See the CTL’s resource on Early and Mid-Semester Student Feedback .
Low-Stakes Activities to Prepare Students for Creative Assignments
The activities described below are meant to be scaffolded opportunities leading to a larger creative project. They are low-stakes, non-graded activities that make time in the classroom for students to think, brainstorm, and create (Desrochers and Zell, 2012) and prepare them to do the creative thinking needed to complete course assignments. The activities can be adapted for any course context, with or without the use of technology, and can be done individually or collaboratively (see the CTL’s resource on Collaborative Learning to explore digital tools that are available for group work).
Brainstorming
Brainstorming is a process that students can engage in to generate as many ideas as possible related to a topic of study or an assignment topic (Sweet et al., 2013: 87). As they engage in this messy and jugement-free work, students explore a range of possibilities. Brainstorming reveals students’ prior knowledge (Ambrose et al., 2010: 29). Brainstorm activities are useful early on to help create a classroom culture rooted in creativity while also serving as a potential icebreaker activity that helps instructors learn more about what prior knowledge and experiences students are bringing to the course or unit of study. This activity can be done individually or in groups, and in class or asynchronously. Components may include:
- Prompt students to list off (individually or collaboratively) their ideas on a whiteboard, free write in a Google Doc or some other digital space.
- Provide formative feedback to assist students to further develop their ideas.
- Invite students to reflect on the brainstorm process, look over their ideas and determine which idea to explore further.
Mind mapping
A mind map, also known as a cognitive or concept map, allows students to visually display their thinking and knowledge organization, through lines connecting concepts, arrows showing relationships, and other visual cues (Sweet et al., 2013: 89; Ambrose et al. 2010: 63). This challenges students to synthesize and be creative as they display words, ideas, tasks or principles (Barkley, 2010: 219-225). A mind mapping activity can be done individually or in groups, and in class or asynchronously. This activity can be an extension of a brainstorming session, whereby students take an idea from their brainstormed list and further develop it.
Components of a mind mapping activity may include:
- Prompt students to create a map of their thinking on a topic, concept, or question. This can be done on paper, on a whiteboard, or with digital mind mapping or whiteboard tools such as Google Drawing.
- Provide formative feedback on the mind maps.
- Invite students to reflect on their mind map, and determine where to go next.
Digital storytelling
Digital storytelling involves integrating multimedia (images, text, video, audio, etc.) and narrative to produce immersive stories that connect with course content. Student-produced stories can promote engagement and learning in a way that is both personal and universal (McLellan, 2007). Digital storytelling contributes to learning through student voice and creativity in constructing meaning (Rossiter and Garcia, 2010).
Tools such as the CTL-developed Mediathread as well as EdDiscussion support collaborative annotation of media objects. These annotations can be used in writing and discussions, which can involve creating a story. For freeform formats, digital whiteboards allow students to drop in different text and media and make connections between these elements. Such storytelling can be done collaboratively or simply shared during class. Finally, EdBlogs can be used for a blog format, or Google Slides if a presentation format is better suited for the learning objective.
Asking questions to explore new possibilities
Tap into student imagination, stimulate curiosity, and create memorable learning experiences by asking students to pose “What if?” “why” and “how” questions – how might things be done differently; what will a situation look like if it is viewed from a new perspective?; or what could a new approach to solving a problem look like? (James & Brookfield, 2014: 163). Powerful questions are open-ended ones where the answer is not immediately apparent; such questions encourage students to think about a topic in new ways, and they promote learning as students work to answer them (James & Brookfield, 2014: 163). Setting aside time for students to ask lots of questions in the classroom and bringing in questions posed on CourseWorks Discussions or EdDiscussion sends the message to students that their questions matter and play a role in learning.
Cultivate Creative Thinking in the Classroom Environment
Create a classroom environment that encourages experimentation and thinking from new and diverse perspectives. This type of environment encourages students to share their ideas without inhibition and personalize the meaning-making process. “Creative environments facilitate intentional acts of divergent (idea generation, collaboration, and design thinking) and convergent (analysis of ideas, products, and content created) thinking processes.” (Sweet et al., 2013: 20)
Encourage risk-taking and learning from mistakes . Taking risks in the classroom can be anxiety inducing so students will benefit from reassurance that their creativity and all ideas are welcome. When students bring up unexpected ideas, rather than redirecting or dismissing, seize it as an opportunity for a conversation in which students can share, challenge, and affirm ideas (Beghetto, 2013). Let students know that they can make mistakes, “think outside of the box” without penalty (Desrochers and Zell, 2012), and embrace failure seeing it as a learning opportunity.
Model creative thinking . Model curiosity and how to ask powerful questions, and encourage students to be curious about everything (Synder et al., 2013, DiYanni, 2015). Give students a glimpse into your own creative thinking process – how you would approach an open-ended question, problem, or assignment? Turn your own mistakes into teachable moments. By modeling creative thinking, you are giving students permission to engage in this type of thinking.
Build a community that supports the creative classroom environment. Have students get to know and interact with each other so that they become comfortable asking questions and taking risks in front of and with their peers. See the CTL’s resource on Community Building in the Classroom . This is especially important if you are planning to have students collaborate on creative activities and assignments and/or engage in peer review of each other’s work.
Plan for play. Play is integral to learning (Cavanagh, 2021; Eyler, 2018; Tatter, 2019). Play cultivates a low stress, high trust, inclusive environment, as students build relationships with each. This allows students to feel more comfortable in the classroom and motivates them to tackle more difficult content (Forbes, 2021). Set aside time for play (Ranjan & Gabora, 2013; Sinfield, Burns, & Abegglen, 2018). Design for play with purpose grounded in learning goals. Create a structured play session during which students experiment with a new topic, idea, or tool and connect it to curricular content or their learning experience. Play can be facilitated through educational games such as puzzles, video games, trivia competitions, scavenger hunts or role-playing activities in which students actively apply knowledge and skills as they act out their role (Eyler, 2018; Barkley, 2010). For an example of role-playing games explore Reacting to the Past , an active learning pedagogy of role-playing games developed by Mark Carnes at Barnard College.
The CTL is here to help!
CTL consultants are happy to support instructors as they design activities and assignments that promote creative thinking. Email [email protected] to schedule a consultation.
Ambrose et al. (2010). How Learning Works: 7 Research-Based Principles for Smart Teaching. Jossey-Bass.
Barkley, E. F., Major, C. H., and Cross, K. P. (2014). Collaborative Learning Techniques: A Handbook for College Faculty .
Barkley, E. F. (2010) Student Engagement Techniques: A Handbook for College Faculty.
Beghetto, R. (2013). Expect the Unexpected: Teaching for Creativity in the Micromoments. In M.B. Gregerson, H.T. Snyder, and J.C. Kaufman (Eds.). Teaching Creatively and Teaching Creativity . Springer.
Cavanagh, S. R. (2021). How to Play in the College Classroom in a Pandemic, and Why You Should . The Chronicle of Higher Education. February 9, 2021.
Chicca, J. and Chunta, K, (2020). Engaging Students with Visual Stories: Using Infographics in Nursing Education . Teaching and Learning in Nursing. 15(1), 32-36.
Davis, M. E. (2019). Poetry and economics: Creativity, engagement and learning in the economics classroom. International Review of Economics Education. Volume 30.
Desrochers, C. G. and Zell, D. (2012). Gave projects, tests, or assignments that required original or creative thinking! POD-IDEA Center Notes on Instruction.
DiYanni, R. (2015). Critical and creative thinking : A brief guide for teachers . John Wiley & Sons, Incorporated.
Eyler, J. R. (2018). How Humans Learn. The Science and Stories Behind Effective College Teaching. West Virginia University Press.
Forbes, L. K. (2021). The Process of Play in Learning in Higher Education: A Phenomenological Study. Journal of Teaching and Learning. Vol. 15, No. 1, pp. 57-73.
Gerstle, K. (2017). Incorporating Meaningful Reflection into Calculus Assignments. PRIMUS. Problems, Resources, and Issues in Mathematics Undergraduate Studies. 29(1), 71-81.
Gregerson, M. B., Snyder, H. T., and Kaufman, J. C. (2013). Teaching Creatively and Teaching Creativity . Springer.
Henry, M., Owens, E. A., and Tawney, J. G. (2015). Creative Report Writing in Undergraduate Organic Chemistry Laboratory Inspires Non Majors. Journal of Chemical Education , 92, 90-95.
Hitchcock, L. I., Sage, T., Lynch, M. and Sage, M. (2021). Podcasting as a Pedagogical Tool for Experiential Learning in Social Work Education. Journal of Teaching in Social Work . 41(2). 172-191.
James, A., & Brookfield, S. D. (2014). Engaging imagination : Helping students become creative and reflective thinkers . John Wiley & Sons, Incorporated.
Jackson, N. (2008). Tackling the Wicked Problem of Creativity in Higher Education.
Jackson, N. (2006). Creativity in higher education. SCEPTrE Scholarly Paper , 3 , 1-25.
Kleiman, P. (2008). Towards transformation: conceptions of creativity in higher education.
Kothari, D., Hall, A. O., Castañeda, C. A., and McNeil, A. J. (2019). Connecting Organic Chemistry Concepts with Real-World Context by Creating Infographics. Journal of Chemistry Education. 96(11), 2524-2527.
McLellan, H. (2007). Digital Storytelling in Higher Education. Journal of Computing in Higher Education. 19, 65-79.
Ranjan, A., & Gabora, L. (2013). Creative Ideas for Actualizing Student Potential. In M.B. Gregerson, H.T. Snyder, and J.C. Kaufman (Eds.). Teaching Creatively and Teaching Creativity . Springer.
Rossiter, M. and Garcia, P. A. (2010). Digital Storytelling: A New Player on the Narrative Field. New Directions for Adult and Continuing Education. No. 126, Summer 2010.
Sheafer, V. (2017). Using digital storytelling to teach psychology: A preliminary investigation. Psychology Learning & Teaching. 16(1), 133-143.
Sinfield, S., Burns, B., & Abegglen, S. (2018). Exploration: Becoming Playful – The Power of a Ludic Module. In A. James and C. Nerantzi (Eds.). The Power of Play in Higher Education . Palgrave Macmillan.
Reynolds, C., Stevens, D. D., and West, E. (2013). “I’m in a Professional School! Why Are You Making Me Do This?” A Cross-Disciplinary Study of the Use of Creative Classroom Projects on Student Learning. College Teaching. 61: 51-59.
Sweet, C., Carpenter, R., Blythe, H., and Apostel, S. (2013). Teaching Applied Creative Thinking: A New Pedagogy for the 21st Century. Stillwater, OK: New Forums Press Inc.
Tatter, G. (2019). Playing to Learn: How a pedagogy of play can enliven the classroom, for students of all ages . Harvard Graduate School of Education.
Vaughn, M. P. and Leon, D. (2021). The Personal Is Political Art: Using Digital Storytelling to Teaching Sociology of Sexualities. Teaching Sociology. 49(3), 245-255.
Wukich, C. and Siciliano, M. D. (2014). Problem Solving and Creativity in Public Policy Courses: Promoting Interest and Civic Engagement. Journal of Political Science Education . 10, 352-368.
CTL resources and technology for you.
- Overview of all CTL Resources and Technology
This website uses cookies to identify users, improve the user experience and requires cookies to work. By continuing to use this website, you consent to Columbia University's use of cookies and similar technologies, in accordance with the Columbia University Website Cookie Notice .

Strategies for Effective Assignment Design
As students progress through their degree programs, it becomes increasingly important for them to learn the major genres, research strategies, and writing conventions of their field. Because writing expectations vary across disciplinary and professional contexts, students benefit from transparent explanation of what those expectations are, how to achieve them, and why they’re important. This can be accomplished through carefully designed formal assignments.
Experts in Writing across the Curriculum argue that students learn most successfully when formal assignments engage them with “authentic research projects that promote disciplinary ways of inquiry and argument and are written in real disciplinary genres. [1] from the National Survey of Student Engagement shows that deep learning depends less on the amount of writing assigned in a course than on the design of the writing assignments themselves. According to this and other research, effective assignments have the following three features: [2] a meaning-constructing task, clear explanations of expectations, and interactive components.
Engage students in meaning-making
A meaning-constructing task asks students to bring their own critical thinking to bear on problems that matter to both the writer and the intended audience. A meaning-constructing task typically presents students with a disciplinary problem, asks them to formulate their own problems, or otherwise engages them in active critical thinking in a specific rhetorical context.

Provide clear expectations
Effective assignments clearly present the instructor’s expectations for a successful performance. Ideally, the assignment prompt also explains the purpose of the assignment in terms of the course’s learning goals and presents the instructor’s evaluation criteria.
Include interactive components
Interactive activities situate writing as a process of inquiry and discovery, promote productive talk about the writer’s emerging ideas, and encourage multiple drafts and global revision.
Create a Rhetorical Context
Creating a rhetorical context for your assignments means considering the role students will play in their writing, the audience they are meant to address, the format (or genre) of the writing task, and the task they are meant to accomplish. The mnemonic RAFT is helpful to recall these four components. [3]
Having a role helps students understand the kind of change they hope to bring about in their audience’s view of the subject matter. Without a specific role to play other than “student,” writers in your class might assume that their purpose is simply to regurgitate information to the instructor.
Specifying an audience goes hand-in-hand with establishing the student’s role. By identifying an audience, the instructor can help students see how their writing might influence a reader’s stance.
Format/Genre
By specifying a genre (e.g., experimental report, op-ed piece, proposal), the assignment helps students transfer earlier genre knowledge to the current task and make decisions about document design, organization, and style. It also helps instructors clarify expectations about length, citation style, etc. More important still, the rhetorical awareness enabled by writing in a specific genre also creates an awareness of a discourse community at work. To students, college writing assignments often appear to be an isolated transaction between student and teacher. Students assume that strange features of the assignment reflect the idiosyncrasies of the instructor rather than the conventions of a larger community. When instructors assign authentic genres there is an opportunity to make discourse community values and expectations explicit.
Task (Problem-Focused)
The task itself sets forth the subject matter of the assignment. Unlike topic-focused tasks (e.g., research/write about X), which can lead to unfocused papers that merely report information, a truly engaging task is typically embedded in disciplinary “problems” and disciplinary ways of thinking and argumentation. A problem-focused task should give students agency to bring their own critical thinking to bear on the subject matter—that is, to engage them in making their own meaning.
Use Transparent Assignment Design
Often an assignment that seems clear to you can be confusing to your students. While designing your assignments, ask yourself what might be unclear to your students—what assumptions might you be making about their procedural or background knowledge? Scholar Mary Ann Winkelmas
Align writing activities and assignments clearly with learning objectives
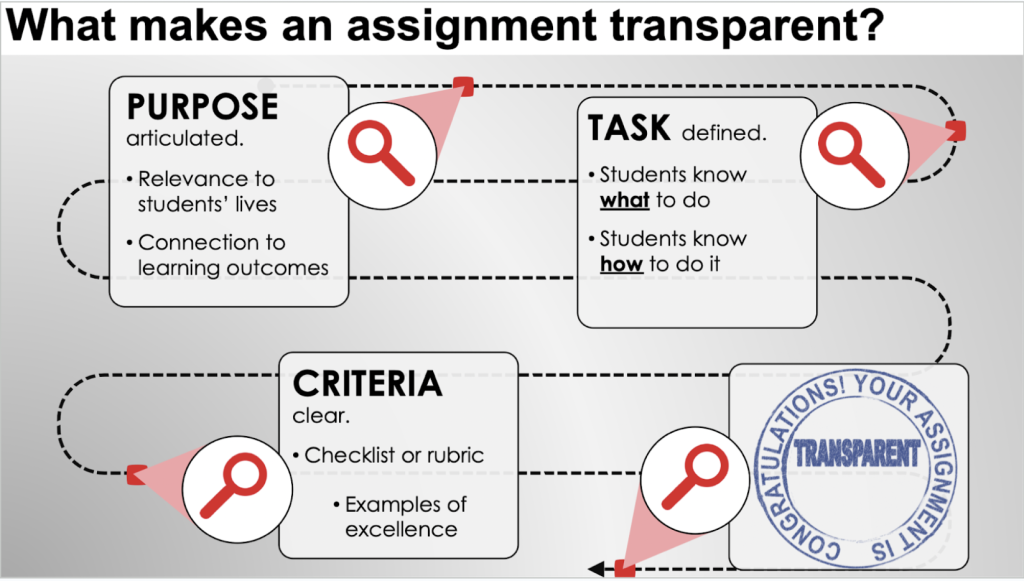
The goal of transparent assignment design is to “to make learning processes explicit and equally accessible for all students” (winkelmes et al., 2019, p. 1)., make clear the purpose, task, and criteria for success., for more information visit tilt (transparency in teaching and learning).
Example: Less Transparent
Assignment from an Introductory Communications Course
1. Select a professional in your prospective academic discipline and/or career filed that is considered an expert in an area in which you are interested 2. Secure an interview with the professional for a date and time that is convenient for both of you. 3. Prepare 8-10 questions to ask the professional about their knowledge of a particular academic discipline/career field. 4. Conduct a 20-30 minute, face-to-face interview to gather knowledge that will help you make an informed decision about the major/career you are considering. You will want to audio/video record the interview with the interviewee’s permission 5. Prepare a typed transcript of the questions and answers using the audio/ video recording 6. Write a 400-500 word reflection paper in which you address the following items: a. Who you selected and why? b. What you learned from them that is most interesting? c. What this assignment helped you learn about your major/career decision? 7. What questions you still have? 8. Submit the typed transcript and reflection paper to your instructor

Revised EXAMPLE: More Transparent
Communications 100E, Interview Assignment Used by permission of Katharine Johnson, University of Nevada, Las Vegas
Due dates: - Sept 30 - Draft interview questions - October 15 - Transcript of interviews - November 17 - Report
Purpose : The purpose of this assignment is to help you make an informed decision about the major/career you are considering.
Skills : This assignment will help you practice the following skills that are essential to your success in school and professional life: - Accessing and collecting information from appropriate primary and secondary sources - Synthesizing information to develop informed views - Composing a well-organized, clear, concise report to expand your knowledge on a subject in your major.
Knowledge : This assignment will also help you to become familiar with the following important content knowledge in this discipline: - Issues facing professionals in a field - Scholarly research formats for documenting sources and creating reference pages (i.e., bibliographies).
Task : To complete this assignment you should: 1. Secure an interview with two professionals in hour prospective academic discipline and/or career field who are considered experts. 2. Schedule the interviews with the professionals at a date and time that is convenient for both of you. 3. Prepare 8-10 questions to ask the professionals about their expertise in a particular academic or career field. The questions must be based on a review of the filed using 5 credible sources as defined by the librarian in our research module. Sources should be cited using APA formatting. 4. Conduct a 2 -3 -minute, face-to-face interview with each professional to gather knowledge that will help you make an informed decision about the major/career you are considering. You will want to audio/video record the interview with the interviewee’s permission. 5. Prepare a typed transcript of the interviews 6. Compare and contrast the information provided by both professionals in an 8-page (1.5 spaced, 12point Times New Roman font, 1 inch margins) report that documents the advantages and disadvantages of a career in the selected field.
Criteria for success : Please see the attached rubric.Type your textbox content here.
Information Literacy Skills Needed for Research Writing
Asking students to engage authentic, discipline-specific problems requires a kind of dismantling of the commonly encountered “research paper” culture in which students think of research as going to the library to find sources that can be summarized, paraphrased, and quoted. To move from “research paper” culture to a culture in which research projects are written in disciplinary genres, instructors need to help students develop the following skills related to information literacy: [4]
Click "next" in the bottom right corner to continue reading this chapter.
Consider the Novice-Expert Framework
Consider backward design.
- Bean and Melzer, p. 64-65 ↵
- All of this section excerpted and paraphrased from Bean and Melzer, pp. 66-68 ↵
- All of this section excerpted and paraphrased from Bean and Melzer, pp. 200-202 ↵
- Bizup, Joseph. “BEAM: A Rhetorical Vocabulary for Teaching Research-Based Writing.” Rhetoric Review, 2008, Vol.27 (1), p.72-86. DOI: 10.1080/07350190701738858 ↵
Locally Sourced: Writing Across the Curriculum Sourcebook Copyright © by [email protected] is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Assignment Design and Assessment
Assignments are a major part of pedagogy. Designing assignments can therefore be one of the most influential elements of classroom teaching. Thoughtful assignment design can support student learning by helping students practice meaningful tasks that carry on into their careers or across the curriculum.
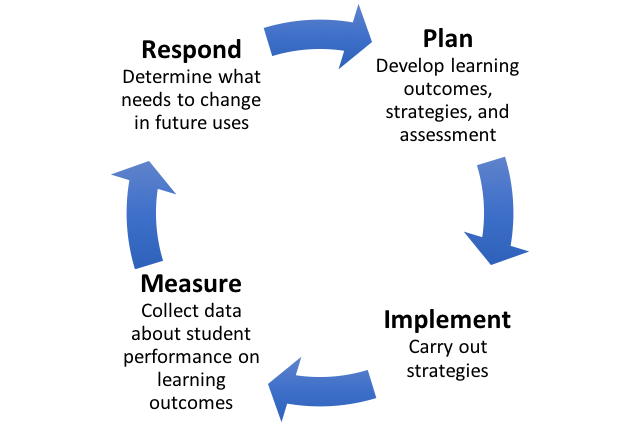
The graphic below illustrates how assessment can provide a continuous process of planning, measuring, analyzing results, and using the results to make informed decisions that lead to improvements. Because learning is a process that is driven by the products it produces at each stage, it is important to think about how assignments are designed and assessed so that they can support student learning.
Below are several videos describing a range of assessment techniques:
Transparency in Assignments
Transparent assignments promote students’ conscious understanding of how they learn. Research from the Transparency in Teaching and Learning Project has shown that when students understand the task, its purpose, and the criteria for evaluating their work, they are more motivated. That doesn’t mean we don’t give students challenging work, rather, that we help them understand the struggles we design for them.
Our adaptation of Palmer’s transparent assignment template is a great tool for helping faculty think through how to make the learning process clear to students.
Click on the links below for exemplary assignments from a range of disciplines at UCF.
- Humanities Assignment
- Business Assignment
- Public Administration Assignment
- Public Speaking Assignment and Evaluation Sheet
- Biomedical Science Assignment and Peer Review Sheet
- General Group Project Assignment
More Information About Assessment
For information about UCF’s Academic Learning Compacts (ALCs), see Operational Excellence and Assessment Support .
Read more about providing students with effective feedback here: https://lsa.umich.edu/sweetland/instructors/teaching-resources/giving-feedback-on-student-writing.html

- Join Our Listserv
- Request a Consult
- Search Penn's Online Offerings

- Assignment Design: Is AI In or Out?
Generative AI
- Rachel Hoke
This page provides examples for designing AI out of or into your assignments. These ideas are intended to provide a starting point as you consider how assignment design can limit or encourage certain uses of AI to help students learn. CETLI is available to consult with you about ways you might design AI out of or into your assignments.
Considerations for Crafting Assignments
- Connect to your goals. Assignments support the learning goals of your course, and decisions about how students may or may not use AI should be based on these goals.
- Designing ‘in’ doesn’t mean ‘all in’. Incorporating certain uses of AI into an assignment doesn’t mean you have to allow all uses, especially those that would interfere with learning.
- Communicate to students . Think about how you will explain the assignment’s purpose and benefits to your students, including the rationale for your guidelines on AI use.
Design Out: Limit AI Use
Very few assignments are truly AI-proof, but some designs are more resistant to student AI use than others. Along with designing assignments in ways that deter the use of AI, inform students about your course AI policies regarding what is and is not acceptable as well as the potential consequences for violating these terms.
Assignments that ask students to refer to something highly specific to your course or not easily searchable online will make it difficult for AI to generate a response. Examples include asking students to:
- Summarize, discuss, question, or otherwise respond to content from an in-class activity, a specific part of your lecture, or a classmate’s discussion comments.
- Relate course content to issues that have local context or personal relevance. The more recent and specific the topic, the more poorly AI will perform.
- Respond to visual or multimedia material as part of their assignment. AI has difficulty processing non-text information.
Find opportunities for students to present, discuss their work, and respond to questions from others. To field questions live requires students to demonstrate their understanding of the topic, and the skill of talking succinctly about one’s work and research is valuable for students in many disciplines. You might ask students to:
- Create an “elevator pitch” for a research idea and submit it as a short video, then watch and respond to peers’ ideas.
- Give an in-class presentation with Q&A that supplements submitted written work.
- Meet with you or your TA to discuss their ideas and receive constructive feedback before or after completing the assignment.
This strategy allows students to show how they have thought about the work that they’ve done and places value on their awareness of their learning. For instance, students might:
- Briefly write about a source or approach they considered but decided not to use and why.
- Discuss a personal connection they made to the learning material.
- Submit a reflection on how the knowledge or skills gained from the assignment apply to their professional practice.
Consider asking students to show the stages of their work or submit assignments in phases, so you can review the development of their ideas or work over time. Explaining the value of the thinking students will do in taking on the work themselves can help deter students’ dependence on AI. Additionally, this strategy helps keep students on track so they do not fall behind and feel pressure to use AI inappropriately. For materials handed in with the final product, it can give you a way to refer back to their process. You may ask students to:
- Submit an outline, list of sources, discussion of a single piece of data, explanation of their approach, or first draft before the final product.
- Meet briefly with an instructor to discuss their approach or work in progress.
- Submit the notes they have taken on sources to prepare their paper, presentation, or project.
Prior to beginning an exam or submitting an assignment, you may ask students to confirm that they have followed the policies regarding academic integrity and AI. This can be particularly helpful for an assignment with different AI guidelines than others in your course. You might:
- Ask students to affirm a statement that all submitted work is their own.
- Ask students to confirm their understanding of your generative AI policy at the start of the assignment.
If you decide to limit student’s use of AI in their work:
- Communicate the policy early, often and in a variety of ways.
- Be Transparent. Clearly explain the reasoning behind your decision to limit or exclude the use of AI in the assignment, focusing on how the assignment relates to the course’s learning objectives and how the use of AI limits the intended learning outcomes.
Design In: Encourage AI Use
You may find that assignments that draw upon generative AI can help your students develop the thinking and skills that are valuable in your field. Careful planning is important to ensure that the designed use of AI furthers your objectives and benefits students. Become familiar with the tasks that AI does and does not do well, and explore how careful prompting can influence its output. These examples represent only a small fraction of potential uses and aim to provide a starting point for considering assignments you might adapt for your courses.
Consider using AI tools to generate original content for students to analyze. You might ask students to:
- Compare multiple versions of an AI-generated approach to problem-solving based on the same task.
- Analyze case studies generated by AI.
- Determine and implement strategies for fact-checking AI-generated assertions to examine the value of information sources.
Generative AI may support students as they take on more advanced thinking by offering help and feedback in real time. For instance, students can:
- Input a provided prompt that guides AI to act as a tutor on an assignment. Prompts can lead the AI tutor to review material, answer questions, and help students use problem-solving strategies to find a solution.
- Ask AI to support the writing process by having it review an essay and provide feedback with explicit instructions to help identify weaknesses in an argument. Consider asking students to turn in the transcript of their discussion with the AI as part of the assignment.
- Use AI for coaching (guidance) through complex tasks like helping students without coding skills create code to analyze materials when the learning goal is data analysis rather than coding.
To support students in learning how to test their ideas, to understand what is arguable, or to practice voicing ideas with feedback, generative AI can be prompted to participate in a conversation. You might ask students to:
- Instruct AI to respond as someone unfamiliar with the course material and engage in a dialogue explaining a concept to the AI.
- Find common ground in a discussion of a controversial issue by asking AI to take a counterposition in the debate. The student could question the AI’s contradictions or identify oversimplifications while focusing on defining their own position.
- Engage with AI as it role-plays a persona like a stakeholder in a case study or a patient in a clinical conversation.
Students can engage with AI as a thought partner at the start or end stages of a project, without allowing AI to do everything. The parts of the task AI does and the parts students should do will depend on the type of learning you want them to accomplish. You might ask students to:
- Use AI to draft an initial hypothesis. Then, the student gathers, synthesizes, and cites evidence that supports or refutes the argument. Finally, the student submits the original AI output along with their finished product.
- Brainstorm with AI, using the tool to generate many possible positions or projects. Students decide which one to pursue and why.
- Develop an initial draft of code on their own, ask AI for assistance to revise or debug, and evaluate the effectiveness of AI in improving the final product.
The specific prompts a user gives to an AI tool strongly determine the quality of its output. Learning to write effective prompts can help students use AI to its fullest potential. Students might:
- Prompt AI to generate responses on a topic the student knows a lot about and evaluate how different prompt characteristics impact the quality and accuracy of AI responses.
- Research applications of prompt engineering that are emerging in their field or discipline.
- Create custom instructions for AI to help with a specific, challenging task. Share their results with peers and evaluate the effectiveness of each others’ results.
If you allow students to utilize AI in their work:
- Make it clear that students are responsible for any inaccuracies in content or citations generated by AI, and that they should own whatever positions they take in submissions.
- Set and communicate clear expectations for when and how AI contributions must be acknowledged or cited.
- Consider barriers that prevent equitable access to high-quality AI tools . S tudents may also have varying levels of AI knowledge and experience us ing the tools. CETLI can assist you in developing an inclusive plan to ensure students can complete the assignment.
If students may use AI with proper attribution, APA , MLA , and Chicago styles each offer recommendations for how to cite AI-generated contributions.
Harvard’s metaLAB AI Pedagogy Project provides additional sample assignments designed to incorporate AI, which are free to use, share, or adapt with appropriate attribution.
CETLI Can Help
CETLI staff are available to discuss ideas or concerns related to generative AI and your teaching, and we can work with your program or department to facilitate conversations about this technology. Contact CETLI to learn more .
- Course Policies & Communication
More Resources
- Supporting Your Students
- Inclusive & Equitable Teaching
- Teaching with Technology
- Generative AI & Your Teaching
- Structured Active In-class Learning (SAIL)
- Syllabus Language & Policies
- Academic Integrity
- Course Evaluations
- Teaching Online
- Course Roster, Classroom & Calendar Info
- Policies Concerning Student-Faculty Interactions
- For New Faculty
- Teaching Grants for Faculty
Academic Resources
- Academic Calendar
- Academic Catalog
- Academic Success
- BlueM@il (Email)
- Campus Connect
- DePaul Central
- Desire2Learn (D2L)
Campus Resources
- Campus Security
- Campus Maps
University Resources
- Technology Help Desk
Information For
- Alumni & Friends
- Current Students
- Faculty & Staff
- Teaching Guides
- How Students Learn
- Course Design
- Instructional Methods
Aligning with Learning Goals
Critical thinking, deterring plagiarism, integrative learning.
- Feedback & Grading
- Learning Activities
- Flex Teaching
- Online Teaching
- Scholarship of Teaching and Learning
- Reflective Practice
- Inclusive Teaching
- Teaching at DePaul
- Support Services
- Technology Tools
Teaching Commons > Teaching Guides > Assignment Design
Assignment Design

Here's a short list of some general assignment design strategies that apply to a wide variety of disciplines.

A number of strategies for deterring plagiarism are discussed, including asking your students to write about current topics relevant to your course and staging essay assignments throughout the quarter.
Integrative learning occurs when students make connections among ideas and experiences in order to transfer learning to new contexts.
- Assignment Design
- Office of the Provost
- Teaching and Learning
- Faculty Collaborative for Teaching Innovation
- Digital Resources for Teaching (DRT)
Sections: General Principles of Assignment Design Additional Resources
General Principles of Assignment Design
Assignments: Make Them Effective, Engaging, and Equitable. At their best, assignments are one of the most important learning experiences for students in a course. Students grapple with course content, deepen their understanding, form new ideas, connections, and questions, and show how they are achieving the course or program learning outcomes. Assignments can also affirm students' social identities, interests, and abilities in ways that foster belonging and academic success.
Characteristics of Effective, Engaging, and Equitable Assignments
- Address the central learning outcomes/objectives of your courses. This ensures the relevancy of the assignment (students won’t wonder why they’re doing it) and provides you with an assessment of student learning that tells you about the progress your students are making.
- Interesting and challenging . What assignments are most memorable to you? Chances are they asked you to apply knowledge to an interesting problem or to do it in a creative way. Assignments can be seen as more relevant when they connect to a real world problem or situation, or when students imagine they are presenting the information to a real world audience (e.g., policy makers), or when they can bring in some aspect of their own experience. Assignments can also be contextualized to reflect the values or priorities of the institution.
- Purpose: Why are you asking students to do the assignment? How does it connect with course learning objectives and support broader skill development that students can draw upon well after your class is over? Often the purpose is very clear to us but we don’t always spell it out for our students.
- Tasks: What steps will students need to take to complete the assignment successfully? Laying this out helps students organize what they need to do and when.
- Criteria for Success: What does excellence look like? This can be described through text or a rubric that aligns expectations with the key elements of the assignment.
- Utility value: How can you make adjustments that allow students to perceive the assignment has more value, either professionally, academically, or personally?
- Inclusive content: Is the assignment equally accessible to all students? If examples are drawn from the dominant culture, they are less accessible to students from other cultures. Structuring assignments so that content is equally familiar to all students reduces educational equity gaps by limiting the effects of prior knowledge and privilege.
- Flexibility and variety: Consider how much flexibility and variety you’re offering in your assignments. This allows students to show what they have learned regardless of their academic strengths or familiarity with particular assignment types. Can students choose among different formats for how they’ll present their assignment (paper, podcast or infographic); is there variety in formats across all the course assignments? Multi-modal assignments allow students to represent what they know in various ways and are therefore more equitable by design.
- Support assignments with instructional activities. Planning learning activities that support students’ best work on their assignments is another critical component. This can include having students read model articles in the style in which you are asking them to prepare their own assignment, discuss or apply the rubric to a sample paper, or break the assignment into smaller pieces so that students can get feedback from you or peers on how they are progressing. Another way to support students is to make clear the role of tools like ChatGPT: if it’s used, how can students use it effectively and responsibly? More generally, all major assignments provide opportunities for important discussions about academic integrity and its relevance to work in one’s discipline, higher education, and personal development.
- Provide opportunities for feedback and revision (especially if high-stakes) . Students may receive feedback on their progress or drafts in a variety of ways: peer, faculty, or a library partner. The Columbia Center for Teaching and Learning identifies four characteristics of effective feedback: Targeted and Concise; Focused; Action-Oriented; and Timely.
For assignments that ask students to write in the style of a particular discipline and draw upon research, SCU’s Success in Writing, Information, and Research Literacy (SWIRL) project has developed guidance for faculty in assignment design and instruction to improve student writing and critical use of information.
You can download the WRITE assignment design tool and learn more at the SWIRL website. Members of the SWIRL team welcome individual consultations with faculty on assignment design. You are welcome to contact them for feedback on any assignment you’re designing.
Additional Resources:
Columbia Center for Teaching and Learning (2021). Feedback for Learning. Columbia University. Retrieved [February 26, 2024] from https://ctl.columbia.edu/resources-and-technology/resources/feedback-for-learning/
Hobbs H. T., Singer-Freeman K. E., Robinson C. (2021). Considering the effects of assignment choices on equity gaps. Research and Practice in Assessment, 16 (1), 49–62.
SWIRL : For assignments that ask students to write in the style of a particular discipline and draw upon research, SCU’s Success in Writing, Information, and Research Literacy (SWIRL) project has developed guidance for faculty in assignment design and instruction to improve student writing and critical use of information. You can download the WRITE assignment design tool and learn more at the SWIRL website.
Transparency in Higher Education Project: Examples and Resources. Copyright © 2009-2023 M.A. Winkelmes. Retrieved [February 26, 2024] from https://tilthighered.com/tiltexamplesandresources
Winkelmes, M., Boye, A., & Tapp, S. (Eds.). (2019). Transparent design in higher education teaching and leadership. Stylus Publishing.
Page authors: Chris Bachen
Last updated: March 5, 2024
Teaching, Learning, & Professional Development Center
- Teaching Resources
- TLPDC Teaching Resources
How Do I Create Meaningful and Effective Assignments?
Prepared by allison boye, ph.d. teaching, learning, and professional development center.
Assessment is a necessary part of the teaching and learning process, helping us measure whether our students have really learned what we want them to learn. While exams and quizzes are certainly favorite and useful methods of assessment, out of class assignments (written or otherwise) can offer similar insights into our students' learning. And just as creating a reliable test takes thoughtfulness and skill, so does creating meaningful and effective assignments. Undoubtedly, many instructors have been on the receiving end of disappointing student work, left wondering what went wrong… and often, those problems can be remedied in the future by some simple fine-tuning of the original assignment. This paper will take a look at some important elements to consider when developing assignments, and offer some easy approaches to creating a valuable assessment experience for all involved.
First Things First…
Before assigning any major tasks to students, it is imperative that you first define a few things for yourself as the instructor:
- Your goals for the assignment . Why are you assigning this project, and what do you hope your students will gain from completing it? What knowledge, skills, and abilities do you aim to measure with this assignment? Creating assignments is a major part of overall course design, and every project you assign should clearly align with your goals for the course in general. For instance, if you want your students to demonstrate critical thinking, perhaps asking them to simply summarize an article is not the best match for that goal; a more appropriate option might be to ask for an analysis of a controversial issue in the discipline. Ultimately, the connection between the assignment and its purpose should be clear to both you and your students to ensure that it is fulfilling the desired goals and doesn't seem like “busy work.” For some ideas about what kinds of assignments match certain learning goals, take a look at this page from DePaul University's Teaching Commons.
- Have they experienced “socialization” in the culture of your discipline (Flaxman, 2005)? Are they familiar with any conventions you might want them to know? In other words, do they know the “language” of your discipline, generally accepted style guidelines, or research protocols?
- Do they know how to conduct research? Do they know the proper style format, documentation style, acceptable resources, etc.? Do they know how to use the library (Fitzpatrick, 1989) or evaluate resources?
- What kinds of writing or work have they previously engaged in? For instance, have they completed long, formal writing assignments or research projects before? Have they ever engaged in analysis, reflection, or argumentation? Have they completed group assignments before? Do they know how to write a literature review or scientific report?
In his book Engaging Ideas (1996), John Bean provides a great list of questions to help instructors focus on their main teaching goals when creating an assignment (p.78):
1. What are the main units/modules in my course?
2. What are my main learning objectives for each module and for the course?
3. What thinking skills am I trying to develop within each unit and throughout the course?
4. What are the most difficult aspects of my course for students?
5. If I could change my students' study habits, what would I most like to change?
6. What difference do I want my course to make in my students' lives?
What your students need to know
Once you have determined your own goals for the assignment and the levels of your students, you can begin creating your assignment. However, when introducing your assignment to your students, there are several things you will need to clearly outline for them in order to ensure the most successful assignments possible.
- First, you will need to articulate the purpose of the assignment . Even though you know why the assignment is important and what it is meant to accomplish, you cannot assume that your students will intuit that purpose. Your students will appreciate an understanding of how the assignment fits into the larger goals of the course and what they will learn from the process (Hass & Osborn, 2007). Being transparent with your students and explaining why you are asking them to complete a given assignment can ultimately help motivate them to complete the assignment more thoughtfully.
- If you are asking your students to complete a writing assignment, you should define for them the “rhetorical or cognitive mode/s” you want them to employ in their writing (Flaxman, 2005). In other words, use precise verbs that communicate whether you are asking them to analyze, argue, describe, inform, etc. (Verbs like “explore” or “comment on” can be too vague and cause confusion.) Provide them with a specific task to complete, such as a problem to solve, a question to answer, or an argument to support. For those who want assignments to lead to top-down, thesis-driven writing, John Bean (1996) suggests presenting a proposition that students must defend or refute, or a problem that demands a thesis answer.
- It is also a good idea to define the audience you want your students to address with their assignment, if possible – especially with writing assignments. Otherwise, students will address only the instructor, often assuming little requires explanation or development (Hedengren, 2004; MIT, 1999). Further, asking students to address the instructor, who typically knows more about the topic than the student, places the student in an unnatural rhetorical position. Instead, you might consider asking your students to prepare their assignments for alternative audiences such as other students who missed last week's classes, a group that opposes their position, or people reading a popular magazine or newspaper. In fact, a study by Bean (1996) indicated the students often appreciate and enjoy assignments that vary elements such as audience or rhetorical context, so don't be afraid to get creative!
- Obviously, you will also need to articulate clearly the logistics or “business aspects” of the assignment . In other words, be explicit with your students about required elements such as the format, length, documentation style, writing style (formal or informal?), and deadlines. One caveat, however: do not allow the logistics of the paper take precedence over the content in your assignment description; if you spend all of your time describing these things, students might suspect that is all you care about in their execution of the assignment.
- Finally, you should clarify your evaluation criteria for the assignment. What elements of content are most important? Will you grade holistically or weight features separately? How much weight will be given to individual elements, etc? Another precaution to take when defining requirements for your students is to take care that your instructions and rubric also do not overshadow the content; prescribing too rigidly each element of an assignment can limit students' freedom to explore and discover. According to Beth Finch Hedengren, “A good assignment provides the purpose and guidelines… without dictating exactly what to say” (2004, p. 27). If you decide to utilize a grading rubric, be sure to provide that to the students along with the assignment description, prior to their completion of the assignment.
A great way to get students engaged with an assignment and build buy-in is to encourage their collaboration on its design and/or on the grading criteria (Hudd, 2003). In his article “Conducting Writing Assignments,” Richard Leahy (2002) offers a few ideas for building in said collaboration:
• Ask the students to develop the grading scale themselves from scratch, starting with choosing the categories.
• Set the grading categories yourself, but ask the students to help write the descriptions.
• Draft the complete grading scale yourself, then give it to your students for review and suggestions.
A Few Do's and Don'ts…
Determining your goals for the assignment and its essential logistics is a good start to creating an effective assignment. However, there are a few more simple factors to consider in your final design. First, here are a few things you should do :
- Do provide detail in your assignment description . Research has shown that students frequently prefer some guiding constraints when completing assignments (Bean, 1996), and that more detail (within reason) can lead to more successful student responses. One idea is to provide students with physical assignment handouts , in addition to or instead of a simple description in a syllabus. This can meet the needs of concrete learners and give them something tangible to refer to. Likewise, it is often beneficial to make explicit for students the process or steps necessary to complete an assignment, given that students – especially younger ones – might need guidance in planning and time management (MIT, 1999).
- Do use open-ended questions. The most effective and challenging assignments focus on questions that lead students to thinking and explaining, rather than simple yes or no answers, whether explicitly part of the assignment description or in the brainstorming heuristics (Gardner, 2005).
- Do direct students to appropriate available resources . Giving students pointers about other venues for assistance can help them get started on the right track independently. These kinds of suggestions might include information about campus resources such as the University Writing Center or discipline-specific librarians, suggesting specific journals or books, or even sections of their textbook, or providing them with lists of research ideas or links to acceptable websites.
- Do consider providing models – both successful and unsuccessful models (Miller, 2007). These models could be provided by past students, or models you have created yourself. You could even ask students to evaluate the models themselves using the determined evaluation criteria, helping them to visualize the final product, think critically about how to complete the assignment, and ideally, recognize success in their own work.
- Do consider including a way for students to make the assignment their own. In their study, Hass and Osborn (2007) confirmed the importance of personal engagement for students when completing an assignment. Indeed, students will be more engaged in an assignment if it is personally meaningful, practical, or purposeful beyond the classroom. You might think of ways to encourage students to tap into their own experiences or curiosities, to solve or explore a real problem, or connect to the larger community. Offering variety in assignment selection can also help students feel more individualized, creative, and in control.
- If your assignment is substantial or long, do consider sequencing it. Far too often, assignments are given as one-shot final products that receive grades at the end of the semester, eternally abandoned by the student. By sequencing a large assignment, or essentially breaking it down into a systematic approach consisting of interconnected smaller elements (such as a project proposal, an annotated bibliography, or a rough draft, or a series of mini-assignments related to the longer assignment), you can encourage thoughtfulness, complexity, and thoroughness in your students, as well as emphasize process over final product.
Next are a few elements to avoid in your assignments:
- Do not ask too many questions in your assignment. In an effort to challenge students, instructors often err in the other direction, asking more questions than students can reasonably address in a single assignment without losing focus. Offering an overly specific “checklist” prompt often leads to externally organized papers, in which inexperienced students “slavishly follow the checklist instead of integrating their ideas into more organically-discovered structure” (Flaxman, 2005).
- Do not expect or suggest that there is an “ideal” response to the assignment. A common error for instructors is to dictate content of an assignment too rigidly, or to imply that there is a single correct response or a specific conclusion to reach, either explicitly or implicitly (Flaxman, 2005). Undoubtedly, students do not appreciate feeling as if they must read an instructor's mind to complete an assignment successfully, or that their own ideas have nowhere to go, and can lose motivation as a result. Similarly, avoid assignments that simply ask for regurgitation (Miller, 2007). Again, the best assignments invite students to engage in critical thinking, not just reproduce lectures or readings.
- Do not provide vague or confusing commands . Do students know what you mean when they are asked to “examine” or “discuss” a topic? Return to what you determined about your students' experiences and levels to help you decide what directions will make the most sense to them and what will require more explanation or guidance, and avoid verbiage that might confound them.
- Do not impose impossible time restraints or require the use of insufficient resources for completion of the assignment. For instance, if you are asking all of your students to use the same resource, ensure that there are enough copies available for all students to access – or at least put one copy on reserve in the library. Likewise, make sure that you are providing your students with ample time to locate resources and effectively complete the assignment (Fitzpatrick, 1989).
The assignments we give to students don't simply have to be research papers or reports. There are many options for effective yet creative ways to assess your students' learning! Here are just a few:
Journals, Posters, Portfolios, Letters, Brochures, Management plans, Editorials, Instruction Manuals, Imitations of a text, Case studies, Debates, News release, Dialogues, Videos, Collages, Plays, Power Point presentations
Ultimately, the success of student responses to an assignment often rests on the instructor's deliberate design of the assignment. By being purposeful and thoughtful from the beginning, you can ensure that your assignments will not only serve as effective assessment methods, but also engage and delight your students. If you would like further help in constructing or revising an assignment, the Teaching, Learning, and Professional Development Center is glad to offer individual consultations. In addition, look into some of the resources provided below.
Online Resources
“Creating Effective Assignments” http://www.unh.edu/teaching-excellence/resources/Assignments.htm This site, from the University of New Hampshire's Center for Excellence in Teaching and Learning, provides a brief overview of effective assignment design, with a focus on determining and communicating goals and expectations.
Gardner, T. (2005, June 12). Ten Tips for Designing Writing Assignments. Traci's Lists of Ten. http://www.tengrrl.com/tens/034.shtml This is a brief yet useful list of tips for assignment design, prepared by a writing teacher and curriculum developer for the National Council of Teachers of English . The website will also link you to several other lists of “ten tips” related to literacy pedagogy.
“How to Create Effective Assignments for College Students.” http:// tilt.colostate.edu/retreat/2011/zimmerman.pdf This PDF is a simplified bulleted list, prepared by Dr. Toni Zimmerman from Colorado State University, offering some helpful ideas for coming up with creative assignments.
“Learner-Centered Assessment” http://cte.uwaterloo.ca/teaching_resources/tips/learner_centered_assessment.html From the Centre for Teaching Excellence at the University of Waterloo, this is a short list of suggestions for the process of designing an assessment with your students' interests in mind. “Matching Learning Goals to Assignment Types.” http://teachingcommons.depaul.edu/How_to/design_assignments/assignments_learning_goals.html This is a great page from DePaul University's Teaching Commons, providing a chart that helps instructors match assignments with learning goals.
Additional References Bean, J.C. (1996). Engaging ideas: The professor's guide to integrating writing, critical thinking, and active learning in the classroom . San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
Fitzpatrick, R. (1989). Research and writing assignments that reduce fear lead to better papers and more confident students. Writing Across the Curriculum , 3.2, pp. 15 – 24.
Flaxman, R. (2005). Creating meaningful writing assignments. The Teaching Exchange . Retrieved Jan. 9, 2008 from http://www.brown.edu/Administration/Sheridan_Center/pubs/teachingExchange/jan2005/01_flaxman.pdf
Hass, M. & Osborn, J. (2007, August 13). An emic view of student writing and the writing process. Across the Disciplines, 4.
Hedengren, B.F. (2004). A TA's guide to teaching writing in all disciplines . Boston: Bedford/St. Martin's.
Hudd, S. S. (2003, April). Syllabus under construction: Involving students in the creation of class assignments. Teaching Sociology , 31, pp. 195 – 202.
Leahy, R. (2002). Conducting writing assignments. College Teaching , 50.2, pp. 50 – 54.
Miller, H. (2007). Designing effective writing assignments. Teaching with writing . University of Minnesota Center for Writing. Retrieved Jan. 9, 2008, from http://writing.umn.edu/tww/assignments/designing.html
MIT Online Writing and Communication Center (1999). Creating Writing Assignments. Retrieved January 9, 2008 from http://web.mit.edu/writing/Faculty/createeffective.html .
Contact TTU
Center for Teaching Innovation
Ai in assignment design.
Using generative artificial intelligence (AI) can be both productive and limiting—it can help students to create and revise content, yet it also has the potential to undermine the process by which students create. When incorporated effectively into assignments, generative AI can be leveraged to stimulate students' ability to apply essential knowledge and develop critical thinking skills.
As you explore the possible uses of generative AI in your course, note that establishing a general familiarity with generative AI and being mindful of accessibility and ethical concerns will be helpful.
The following process may help you determine how to best incorporate generative AI into your course assignments.
Affirm What You Actually Want to Assess
As you decide how you might incorporate AI into your course, it’s important to revisit your current course assessment plan, most importantly your course learning outcomes —that is, the skills and knowledge you want students to learn and demonstrate by the end of your course. Once you have a clear idea of the specific skills/knowledge you want to assess, the following questions can help determine whether or not your current assignments are effective and assessing what you want them to assess:
- Does my assignment call for the same type of thinking skills that are articulated in my class outcomes? For example, if my course learning outcome calls for students to analyze major themes in a work, is there risk of my final assignment prompting students to do more (e.g., synthesize multiple themes across multiple works) or to do less (e.g., merely identify a theme) than this outcome? If so, there may be a misalignment that can easily be addressed.
- Does my assignment call for the same type of thinking skills that students have actually practiced in class? For example, if I am asking students to generate a research prospectus, have I given them adequate opportunity to develop—and receive feedback on—this skill in class?
- Depending on your discipline, is there a need for an additional course outcome that honors what students now need to know about the use of generative AI in your course/field?
Explore When & How Generative AI Can Facilitate Student Learning
Once you have affirmed your learning outcomes and ensured that your assignments are properly aligned with those outcomes, think about if, when, and how it might make sense to incorporate generative AI. Is there a way to leverage generative AI to engage students in deeper learning, provide meaningful practice, or help scaffold your assignments?
Consider the usefulness of generative AI to serve as:
- Have students analyze AI-generated texts to articulate what constitutes “good” (and not so good) responses to prompts.
- Have students analyze AI-generated texts and engage in error analysis to develop more nuanced and discipline-specific writing skills.
- Leverage the use of generative AI platforms to help students become more discerning. This can help students develop the critical thinking and information literacy skills required to effectively and responsibly use such platforms.
- Have students revise AI-generated texts to develop critical thinking skills.
- Have students engage with a generative AI platform as a tutor.
- Facilitate students’ responsible, self-guided use of generative AI to develop select discipline specific skills (e.g., coding in computer science courses)
- Have students use generative AI to off-load repetitive tasks.
- Have students use generative AI to conduct preliminary analysis of data sets to confirm broad takeaways and affirm that their more nuanced analysis is heading in the right direction.
Identify When Generative AI Cannot Facilitate Student Learning
It is often the case that students cannot—or should not—leverage generative AI to promote or demonstrate their own learning. To help ensure that your assignment design highlights students’ unique perspectives and underscores the importance of a (non-generative AI informed) discipline-specific process, consider how to emphasize metacognition, authentic application, thematic connection, or personal reflection.
Even if another part of an assignment calls for the use of generative AI, the following strategies may supplement the uses of AI highlighted above and foster deep and meaningful learning:
- Have students identify the successes and challenges they experienced throughout the completion of a project.
- Have students set incremental goals throughout a project, highlighting next steps of a discipline-specific process, resources they used, and the steps about which they are enthusiastic/nervous.
- Have students self-assess their work, identifying strengths and weaknesses of their product/effort.
- Have students engage in problem-based learning projects, ideally in authentic settings (e.g., problems that focus on our local community, real-world challenges, real-world industries, etc.).
- Have students present projects (and engage with) authentic audiences (e.g., real stakeholders, discipline-specific research partners, native-speaking language partners, etc.)
- Have students connect select reading(s) to course experiences (e.g., labs, field experiences, class discussions).
- Leverage Canvas-based tools that promote student-to-student interactions (e.g., Hypothesis for social annotation or FeedbackFruits for peer review and feedback).
- Have students provide a reflective rationale for choices made throughout the completion of a class project (e.g., an artist statement, response to a reflection prompt about personal relevance of source selections)
- Have students connect course experiences/motivations to their own lived experiences.
Create Transparent Assignment Materials
Once you have thought about whether or not generative AI can be effectively incorporated into your assignments, it is important to create assignment materials that are transparent (Winkelmes, et al., 2019). Specifically, this means creating ways to communicate to students the task you are are requiring, along with its purpose and evaluative criteria:
- Task. Students will benefit from having a clear and accessible set of directions for the project or assignment you are asking them to complete.
- Purpose. Students are often more motivated when they understand why a particular task is worth doing and what specific knowledge or skills they will develop by completing the assigned task.
- Evaluative Criteria. Students benefit from having a clear sense of how their work will be evaluated and a full understanding of what good work looks like.
Communicate Your Expectations for Generative AI Use
Regardless of the extent to which you incorporate the use of generative AI into your assignment design, it is essential to communicate your expectations to students. Sharing clear directions for assignments, communicating how students can be successful in your class, and promoting academic integrity serves both you and your students well.
Example Assignment Policy Language for Generative AI Use
The following language on the use of generative AI may be helpful as you create directions for specific assignments. Please note that the following sample language does not reflect general, course-level perspectives on the use of generative AI tools. For sample course-level statements, see AI & Academic Integrity .
Prohibiting AI Use for a Specific Assignment
Allowing the use of generative ai for a specific assignment with attribution.
For full details on how to properly cite AI-generated work, please see the APA Style article, How to Cite ChatGPT . "
Encouraging the Use of Generative AI for a Specific Assignment with Attribution
For full details on how to properly cite AI- generated work, please see the APA Style article, How to Cite ChatGPT ."
Confer with Colleagues
There is almost always a benefit to discussing an assessment plan with colleagues, either within or beyond your department. Remember, too, that CTI offers consultations on any topic related to teaching and learning, and we are delighted to collaboratively review your course assessment plan. Visit our Consultations page to learn more, or contact us to set up a consultation.
2023 EducaUse Horizon Report | Teaching and Learning Edition. (2023, May 8). EDUCAUSE Library. https://library.educause.edu/resources/2023/5/2023-educause-horizon-report-teaching-and-learning-edition
Antoniak, M. (2023, June 22). Using large language models with care - AI2 blog. Medium. https://blog.allenai.org/using-large-language-models-with-care-eeb17b0aed27
Dinnar, S. M., Dede, C., Johnson, E., Straub, C. and Korjus, K. (2021), Artificial Intelligence and Technology in Teaching Negotiation. Negotiation Journal, 37: 65-82. https://doi.org/10.1111/nejo.12351
Jensen, T., Dede, C., Tsiwah, F., & Thompson, K. (2023, July 27). Who Does the Thinking: The Role of Generative AI in Higher Education. YouTube. International Association of Universities. Retrieved July 27, 2023.
OpenAI. (2023, February 16.). How should AI systems behave, and who should decide? https://openai.com/blog/how-should-ai-systems-behave
Winkelmes, M. A., Boye, A., & Tapp, S. (2019). Transparent design in higher education
teaching and leadership: A guide to implementing the transparency framework institution-wide to improve learning and retention. Sterling, VA: Stylus Publishing .
The Cowbell
News and Resources from UWGB's Center for the Advancement of Teaching and Learning
Assignment Design
There’s a fine line between assignment design and assessment strategies . In short, designing good assignments is one means of assessing your students’ learning on a larger scale.
Assignments help measure student learning in your course. Effective assignment design in your course involves aligning your assignments with learning outcomes. When assignments and outcomes are aligned, good grades and good learning go hand in hand ( https://www.cmu.edu/teaching/designteach/design/assessments.html ).
Assessments fall into one of two categories, formative or summative .
Formative assessments are typically low-stakes and help students identify their strengths and weaknesses so that they can improve their learning. Routine formative assessments also help instructors identify the areas where students are struggling and adapt their teaching accordingly.
Summative assessments evaluate student learning (such as at the end of a unit of instruction). Summative assessments are generally higher stakes (like midterm exams and final projects).
Assignments are what students actually ‘do’ as part of those assessments.
Incorporating a mix of assignment activities in your course can help students practice and demonstrate their mastery of outcomes in multiple ways. Consider ways you can design your assignments so that they better mirror the application of knowledge in real-world scenarios. Assignments designed in this way are often referred to as Authentic Assessments ( Authentic-assessment.pdf (uwex.edu)). One type of highly authentic assessment is the long-term project which challenges students to solve a problem or complete a challenge requiring the application of course concepts ( Project_Based_Learning.pdf (uwex.edu) ).
More details and examples can be found in the tabbed content box below. Please also consider signing up for a CATL consultation with one of our instructional designers for some personalized assistance in developing your ideas for assignments and ensuring that they align with your course outcomes .
(Adapted from Carnegie Mellon's: Design and Teach a Course )
Assessments should provide instructors and students with evidence of how well students have mastered the course outcomes.
There are two major reasons for aligning assessments with learning outcomes.
- Alignment increases the probability that we will provide students with the opportunities to learn and practice knowledge and skills that instructors will require students know in the objectives and in the assessments. (Teaching to the assessment is a good thing.)
- When instructors align assessments with outcomes, students are more likely to translate "good grades" into "good learning." Conversely, when instructors misalign assessments with objectives, students will focus on getting good grades on the assessments, rather than focusing on mastering the material that the instructor finds important.
Instructors may use different types of assessments to measure student proficiency in a learning objective. Moreover, instructors may use the same activity to measure different objectives. To ensure a more accurate assessment of student proficiency, many instructional designers recommend that you use different kinds of activities so that students have multiple ways to practice and demonstrate their knowledge and skills.
Formative assessment
The goal of formative assessment is to monitor student learning to provide ongoing feedback that can be used by instructors to improve their teaching and by students to improve their learning. More specifically, formative assessments:
- help students identify their strengths and weaknesses and target areas that need work
- help faculty recognize where students are struggling and address problems immediately
Formative assessments are generally low stakes , which means that they have low or no point value. Examples of formative assessments include asking students to:
- draw a concept map in class to represent their understanding of a topic
- submit one or two sentences identifying the main point of a lecture
- turn in a research proposal for early feedback
Summative assessment
The goal of summative assessment is to evaluate student learning at the end of an instructional unit by comparing it against some standard or benchmark.
Summative assessments are often high stakes , which means that they have a high point value. Examples of summative assessments include:
- a midterm exam
- a final project
- a senior recital
Information from summative assessments can be used formatively when students or faculty use it to guide their efforts and activities in subsequent courses.
Formative Assessments:
- Reading quizzes
- Concept map
- Muddiest point
- Pro/con grid
- Focused paraphrasing
- Reflective journal
- Virtual lab/game
- Webconference
- Debate (synchronous or asynchronous)
- Participant research
- Peer review
Summative Assessments:
- Presentation
- Portfolio project
Carnegie Mellon University on Aligning Assessments with Objectives with examples.
Items to consider when weighing your assessment options:
If you are thinking about using discussions, be sure to think about the following:.
- What kind of questions/situations do you want the students to discuss? Is it complex enough to allow students to build knowledge beyond the textbook? Will the discussion help students meet your objectives (and develop an answer for your essential questions)?
- What are your expectations for discussions? Should students participate (post) a certain number of times, with a certain number of words, and reply to a certain number of people?
- What is your role in the discussion (traffic cop, the person who clarifies issues, will you respond to every post)?
If you are thinking about using quizzes, be sure to think about the following:
- What type of questions will help your students meet the objectives of the course? Are you going to grade essay questions or just let the computer grade multiple choice questions?
- What is the place for academic integrity? Are you going to randomize questions, randomize answers, restrict time, restrict the answers that students can see after completing the exam?
- How are you going to populate your quiz? Are you going to write the questions or use questions that come from a textbook publisher?
If you are thinking of using essays, be sure to think about the following:
- Will these essays/papers help students to meet the course objectives, which ones? Is the length of the essay appropriate?
- What do you think about plagiarism checkers such as TurnItIn?
- To what extent will you allow students to submit drafts, and will you provide feedback on drafts, or will you use a peer review system?
Other items to consider:
- Are you thinking about using an alternative assignment? If so, you may want to talk with an instructional technologist or designer.
- Consider the type of feedback you will provide for each assignment. What should students expect from you; how will you communicate those expectations; and how soon will you provide feedback (realistically)?
Further resources
Small teaching online.
This book (requires UWGB login) contains many tips that are easy to integrate into your distance education class. The chapter on “ surfacing backward design” contains many tips for assessment for online classes, many of which are adaptable to all distance modalities.
CATL Resources
- Collaborative Learning Assignments (Toolbox article)
- Administering Tests and Quizzes (including alternatives) (Toolbox article)
- Writing Good Multiple Choice Questions ( TeAch Tuesday , YouTube)
Tip sheets from UW-System
UW-System put together some tip sheets for common sticking points in assessment for distance education.
- Writing effective multiple choice questions
- Authentic assessments
- Unproctored online assessments
- Project-based learning
Department Info
- Center for the Advancement of Teaching and Learning , CL 405 UW-Green Bay, 2420 Nicolet Drive Green Bay , WI 54311-7001
- (920) 465-2541 [email protected]
- Events & Programs
UW-Green Bay
- University of Wisconsin-Green Bay 2420 Nicolet Drive Green Bay , WI 54311 , USA
- UW-Green Bay Mission
- College Portrait
- Connect with UWGB: facebook twitter flickr youtube
- General Contact: (920) 465-2000 or [email protected]
- Report a website issue
- Privacy Policy
- Emergency Information: emergency.uwgb.edu
- Online Learning
- Arts & Performances
- Cofrin Library
- Departments & People
- Faculty & Staff
- A to Z index
- Departments
- CTLI Newsletter
- Designing a Course
- Inclusive & Anti-Oppressive Pedagogy
- Building Community
- Active Learning Strategies
- Grading for Growth
- Guides & Templates
- Classroom Technology
- Educational Apps
- Generative AI
- Using Technology Purposefully
- Upcoming Events
- Archive & Recordings
- Book Groups
- Faculty Learning Community
- Thank an Educator Program
- University Resources
- CTLI Consultations
- New VTSU Faculty – Getting Started
- Center for Teaching & Learning Innovation Staff
- Advisory Committee
- Newsletter Archive
- CTLI News Blog
Transparent Assignment Design
The goal of Transparent Assignment Design is to “to make learning processes explicit and equally accessible for all students” (Winkelmes et al., 2019, p. 1). The development of a transparent assignment involves providing students with clarity on the purpose of the assignment, the tasks required, and criteria for success as shown in the figure below. The inclusion of these elements as well as the provision of examples can be beneficial in enabling your students to do their best work!

Example A: Sociology
Example B: Science 101
Example C: Psychology
Example D: Communications
Authors of Examples A-D describe the outcomes of their assignment revisions
Example E: Biology
Discussion Questions (about Examples A-E)
Example F: Library research Assignment
Example G: Criminal Justice In-Class activity
Example H: Criminal Justice Assignment
Example I: Political Science Assignment
Example J: Criteria for Math Writing
Example K – Environmental History
Example L – Calculus
Example M – Algebra
Example N – Finance
Transparent Assignments Promote Equitable Opportunities for Students’ Success Video Recording
Transparent Assignment Design Faculty Workshop Video Recording
- Transparent Assignment Template for instructors (Word Document download)
- Checklist for Designing Transparent Assignments
- Assignment Cues to use when designing an assignment (adapted from Bloom’s Taxonomy) for faculty
- Transparent Equitable Learning Readiness Assessment for Teachers
- Transparent Assignment Template for students (to help students learn to parse assignments also to frame a conversation to gather feedback from your students about how to make assignments more transparent and relevant for them)
- Measuring Transparency: A Learning-focused Assignment Rubric (Palmer, M., Gravett, E., LaFleur, J.)
- Transparent Equitable Learning Framework for Students (to frame a conversation with students about how to make the purposes, tasks and criteria for class activities transparent and relevant for them)
- Howard, Tiffiany, Mary-Ann Winkelmes, and Marya Shegog. “ Transparency Teaching in the Virtual Classroom: Assessing the Opportunities and Challenges of Integrating Transparency Teaching Methods with Online Learning.” Journal of Political Science Education, June 2019.
- Ou, J. (2018, June), Board 75 : Work in Progress: A Study of Transparent Assignments and Their Impact on Students in an Introductory Circuit Course Paper presented at 2018 ASEE Annual Conference & Exposition , Salt Lake City, Utah.
- Palmer, M. S., Gravett, E. O., & LaFleur, J. (2018). Measuring transparency: A learning‐focused assignment rubric. To Improve the Academy, 37(2), 173-187. doi:10.1002/tia2.20083
- Winkelmes, M., Allison Boye and Suzanne Tapp, ed.s. (2019). Transparent Design in Higher Education Teaching and Leadership. Stylus Publishing.
- Humphreys, K., Winkelmes, M.A., Gianoutsos, D., Mendenhall, A., Fields, L.A., Farrar, E., Bowles-Terry, M., Juneau-Butler, G., Sully, G., Gittens, S. Cheek, D. (forthcoming 2018). Campus-wide Collaboration on Transparency in Faculty Development at a Minority-Serving Research University. In Winkelmes, Boye, Tapp, (Eds.), Transparent Design in Higher Education Teaching and Leadership.
- Copeland, D.E., Winkelmes, M., & Gunawan, K. (2018). Helping students by using transparent writing assignments. In T.L. Kuther (Ed.), Integrating Writing into the College Classroom: Strategies for Promoting Student Skills, 26-37. Retrieved from the Society for the Teaching of Psychology website.
- Winkelmes, Mary-Ann, Matthew Bernacki, Jeffrey Butler, Michelle Zochowski, Jennifer Golanics, and Kathryn Harriss Weavil. “A Teaching Intervention that Increases Underserved College Students’ Success.”Peer Review (Winter/Spring 2016).
- Transparency and Problem-Centered Learning. (Winter/Spring 2016) Peer Review vol.18, no. 1/2.b
- Winkelmes, Mary-Ann. Small Teaching Changes, Big Learning Benefits.” ACUE Community ‘Q’ Blog, December, 2016.
- Winkelmes, Mary-Ann. “Helping Faculty Use Assessment Data to Provide More Equitable Learning Experiences.” NILOA Guest Viewpoints. Urbana, IL: University of Illinois and Indiana University, National Institute for Learning Outcomes Assessment, March 17, 2016.
- Gianoutsos, Daniel, and Mary-Ann Winkelmes.“Navigating with Transparency: Enhancing Underserved Student Success through Transparent Learning and Teaching in the Classroom and Beyond.” Proceedings of the Pennsylvania Association of Developmental Educators (Spring 2016).
- Sodoma, Brian.“The End of Busy Work.” UNLV Magazine 24,1 (Spring 2016): 16-19.
- Cook, Lisa and Daniel Fusch. One Easy Way Faculty Can Improve Student Success.” Academic Impressions (March 10, 2016).
- Head, Alison and Kirsten Hosteller. “Mary-Ann Winkelmes: Transparency in Teaching and Learning,” Project Information Literacy, Smart Talk Interview, no. 25. Creative Commons License 3.0 : 2 September 2015.
- Winkelmes, Mary-Ann, et al. David E. Copeland, Ed Jorgensen, Alison Sloat, Anna Smedley, Peter Pizor, Katharine Johnson, and Sharon Jalene. “Benefits (some unexpected) of Transparent Assignment Design.” National Teaching and Learning Forum, 24, 4 (May 2015), 4-6.
- Winkelmes, Mary-Ann. “Equity of Access and Equity of Experience in Higher Education.” National Teaching and Learning Forum, 24, 2 (February 2015), 1-4.
- Cohen, Dov, Emily Kim, Jacinth Tan, Mary-Ann Winkelmes, “A Note-Restructuring Intervention Increases Students’ Exam Scores.” College Teaching vol. 61, no. 3 (2013): 95-99.
- Winkelmes, Mary-Ann.”Transparency in Teaching: Faculty Share Data and Improve Students’ Learning.” Liberal Education Association of American Colleges and Universities (Spring 2013).
- Winkelmes, Mary-Ann. “Transparency in Learning and Teaching: Faculty and students benefit directly from a shared focus on learning and teaching processes.” NEA Higher Education Advocate (January 2013): 6 – 9.
- Bhavsar, Victoria Mundy. (2020). A Transparent Assignment to Encourage Reading for a Flipped Course, College Teaching, 68:1, 33-44, DOI: 10.1080/87567555.2019.1696740
- Bowles-Terry, Melissa, John C. Watts, Pat Hawthorne, and Patricia Iannuzzi. “ Collaborating with Teaching Faculty on Transparent Assignment Design .” In Creative Instructional Design: Practical Applications for Librarians, edited by Brandon K. West, Kimberly D. Hoffman, and Michelle Costello, 291–311. Atlanta: American Library Association, 2017.
- Leuzinger, Ryne and Grallo, Jacqui, “ Reaching First- Generation and Underrepresented Students through Transparent Assignment Design .” (2019). Library Faculty Publications and Presentations. 11. https://digitalcommons.csumb.edu/lib_fac/11
- Fuchs, Beth, “ Pointing a Telescope Toward the Night Sky: Transparency and Intentionality as Teaching Techniques ” (2018). Library Presentations. 188. https://uknowledge.uky.edu/libraries_present/188
- Ferarri, Franca; Salis, Andreas; Stroumbakis, Kostas; Traver, Amy; and Zhelecheva, Tanya, “ Transparent Problem-Based Learning Across the Disciplines in the Community College Context: Issues and Impacts ” (2015).NERA Conference Proceedings 2015. 9. https://opencommons.uconn.edu/nera-2015/9
- Milman, Natalie B. Tips for Success: The Online Instructor’s (Short) Guide to Making Assignment Descriptions More Transparent . Distance Learning. Greenwich Vol. 15, Iss. 4, (2018): 65-67. 3
- Winkelmes, M. (2023). Introduction to Transparency in Learning and Teaching. Perspectives In Learning, 20 (1). Retrieved from https://csuepress.columbusstate.edu/pil/vol20/iss1/2
- Brown, J., et al. (2023). Perspectives in Learning: TILT Special Issue, 20 (1). Retrieved from https://csuepress.columbusstate.edu/pil/vol20/iss1/
- Winkelmes, M. (2022). “Assessment in Class Meetings: Transparency Reduces Systemic Inequities.” In Henning, G. W., Jankowski, N. A., Montenegro, E., Baker, G. R., & Lundquist, A. E. (Eds.). (2022). Reframing Assessment to Center Equity: Theories, Models, and Practices. Stylus Publishing, LLC.
Citation : TILT Higher Ed © 2009-2023 by Mary-Ann Winkelmes . Retrieved from https://tilthighered.com/
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License .
- Staff Directory
- Workshops and Events
- For Students
- Implement Universal Design for Learning with Assignments
by Mohammad Ahmed | May 14, 2024 | Accessibility , How-tos , Instructional design , Services , Universal Design for Learning

This post is the second installment in a series on Universal Design for Learning. For more information, please see previous installments in this series .
When you are designing assignments to help your class practice new concepts, you can set up your students for success by implementing the principles of Universal Design for Learning (UDL). This involves creating tasks that provide multiple means of representation, expression, and engagement to accommodate the diverse needs and preferences of all learners. Providing multiple options for assignments involves offering students various ways to engage with the material, demonstrate their understanding, and express their learning.
When implementing UDL in your course, be sure to explain the rationale behind different assignment formats. This will make it clear to students that through engaging with various formats they get a variety of ways to practice their knowledge and can develop far stronger skills in order to achieve greater mastery. Also highlight the link between the different formats, for example, that all of these formats contribute to the main learning objectives of the course and that one format is not “easier” or “harder”. Lastly, provide them with necessary feedback to improve their learning irrespective of the format they choose. Below are some strategies you can use to designing assignments with UDL:
- Provide Clear Instructions: Clearly articulate the assignment objectives, expectations, and grading criteria. Consider providing written, spoken, and visual instructions to accommodate different learning preferences. A format-agnostic rubric will help to organize this, and we have resources available for you .
- Offer Multiple Options : Provide students with choices on how they can demonstrate their understanding of the material. This could include options such as written essays, oral presentations, multimedia projects, artistic creations, or hands-on demonstrations.
- Use Varied Formats : Present assignment materials in multiple formats to accommodate different learning styles. Offer readings in text, audio, and video formats, and provide visual aids such as diagrams, charts, and infographics to support comprehension. Allow students to choose the format in which they present their work. Options could include written reports, oral presentations, multimedia presentations (i.e. videos, audios), posters or infographics, or digital portfolios. Some tools that can support this such as Immersive Reader , Panopto Videos , and the OneButton Studio .
- Support Accessibility : Ensure that assignment materials are accessible to all students, including those with disabilities. Use accessible document formats , provide alternative text for images, and consider the needs of students who may require accommodations such as screen readers or captioning.
- Offer Feedback Options : Provide students with options for receiving feedback on their assignments, such as written comments, audio recordings, or face-to-face meetings. Speedgrader is a great resource for written and audio comments. Tailor feedback to individual student needs and preferences. Offer students options for receiving feedback on their assignments. Allow them to choose their preferred method of feedback, such as written comments, audio recordings, video feedback, or face-to-face meetings.
- Promote Reflection : Incorporate opportunities for students to reflect on their learning process and evaluate their own progress. Encourage metacognitive strategies such as goal setting, self-assessment, and reflection journals.
Each one of these strategies can become overwhelming, so start small. Don’t implement all of them at once; instead choose one strategy and implement it into 1 assignment or assessment. This is what Thomas Tobin calls the +1 method 1 : one activity that you already do plus one new, easy strategy. To read more about his strategy you can download his free pdf book UDL for FET Practitioners: Guidance for Implementing Universal Design for Learning .
Let’s take feedback options, for example. After using SpeedGrader to grade the students’ exams, many faculty and instructors typically offer some text feedback; however, you can easily implement a UDL strategy by also offering verbal feedback through the recorded audio button near the bottom of the feedback panel in SpeedGrader. You can make this a 1+1 goal for the next quarter, and as you become more proficient with this strategy you can slowly increase it to monthly and then weekly implementations.
By providing multiple options for UDL assignments, you can accommodate diverse learning styles, preferences, and abilities, and empower students to take ownership of their learning experiences.
Further Resources:
- Review Academic Technology Solutions’ full list of Teaching Tools .
- Learn About Universal Design for Learnin g from CAST.
- Explore the University of Chicago’s Center for Digital Accessibility .
- Request an instructional design consultation with LDT instructional designers.
- Request digital media consultation and development services in support of teaching materials and the presentation of research.
- Request custom workshops for departments or programs who want to tailor the content to their instructors or subject area.
- Join us in office hours , virtual or hybrid, during which you can ask any questions you may have.
- Join our online workshops on various topics related to teaching with technology.
1 Tobin, T. J. (2021). UDL for FET Practitioners. SOLAS. April 15, 2024, https://www.ahead.ie/udlforfet-guidance .
Search Blog
Subscribe by email.
Please, insert a valid email.
Thank you, your email will be added to the mailing list once you click on the link in the confirmation email.
Spam protection has stopped this request. Please contact site owner for help.
This form is protected by reCAPTCHA and the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
Recent Posts
- Build Proficiency for Language Learners by Assessing AI Outputs: Insights from a UChicago Instructor’s Experimentation
- Making the Most of Ed Discussion
- Create Accessible Instructional Videos
- Digitize Paper-Based Assignments with Gradescope
- A/V Equipment
- Accessibility
- Canvas Features/Functions
- Digital Accessibility
- Faculty Success Stories
- Instructional design
- Multimedia Development
- Surveys and Feedback
- Symposium for Teaching with Technology
- Uncategorized
- Universal Design for Learning
- Visualization
All You Need To Know About The Assignment Of Design Rights
Contributor
Industrial design
Industrial designs are part of the aesthetic sector, but they're also meant to be used as a blueprint for the production of industrial or handcrafted goods. The ornamental or aesthetic part of a practical object that must appeal to the sense of sight and may consist of the shape, pattern, and/or colour of the article is known as industrial design. To be protected, an industrial design must be new and original. For a period of five, ten, or fifteen years, industrial designs are protected against unlawful duplication or replication.
According to Section 2(d) of the Designs Act, 2000, design refers to "only the features of shape, configuration, pattern or ornament or composition of lines or color or a combination thereof applied to any article, whether two dimensional or three dimensional or in both forms, by any industrial process or means, whether manual, mechanical or chemical, separate or combined, which in the finished article appeal to and are judged solely by the eye," but it excludes "any mode or principle or construction", as defined in clause (v) of sub-section of Section 2 of the Trade and Merchandise Marks Act, 1958, property mark or artistic works as defined under Section 2(c) of the Copyright Act, 1957.
Assignment of Design rights
Assignment is a legal phrase that refers to the transfer of rights, property, or other benefits from one person to another (the "assignor"). Both contract and property law make use of this term. The term can relate to either the act of transferring or the transferred rights/property/benefits.
Section 30 of the Design Act of 2000( Hereinafter referred to as "Act"), as amended by Rules 32, 33, 34, and 35 of the Design Rules of 2001, recognizes design assignment contracts and establishes a method for their recording. Section 30(1) of the Design Act provides that if a person acquires the copyright in a registered design through assignments, transmission, or other legal means, he may apply to the Controller in the specified form to register his title. According to Section 30(3) of the Design Act of 2000, an assignment must be in writing, and the agreement between the parties must be reduced to the form of an instrument embodying all of the terms and conditions governing their rights and obligations, and the application for registration of title under such instrument must be filed in the prescribed manner with the Controller within the stipulated time-that is, within six months of the execution date. The person registered as the proprietor of the design has the absolute right to assign the design rights, according to Section 30(4) of the Design Act of 2000.
Only if the design's Copyright is statutorily recognised under the requirements of the Designs Act, 2000, is it protected. Similarly, third-party rights obtained through assignments or licences are only effective if they are properly registered in accordance with the Act's requirements and the Rules enacted thereunder. Under design law, there is no concept of a common law licence.
Assignment of the Semiconductor Integrated Circuits Layout Design
An electronic circuit made on the surface of semiconductor material is known as a semiconductor integrated circuit. Integrated circuits have transformed the field of electronics by being employed in practically all electronic devices currently in use. The sheer quantity of electronic appliances we use on a daily basis demonstrates the significance of semiconductor integrated circuits or chips in today's environment.
The layout or arrangement of the chip determines its ability to perform a specific function. As a result, a second enactment was required to protect the chip designer's investment. In India, the Semiconductor Integrated Circuits Layouts Design Act of 2000 would provide this protection.This was done in accordance with India's commitments under the TRIPS Agreement.
'An assignment in writing by act of the parties concerned,' according to Section 2(b) of the Semiconductor Integrated Circuits Layout-Design Act, 2000. According to Section 19 of the Act, the registration of the design, as well as all subsequent assignments, will serve as prima facie evidence of its validity.
Assignments and Transmissions are covered in Chapter V of the Semiconductor Integrated Circuits Layouts Design Act, 2000. Section 20 of the Semiconductor Integrated Circuits Layouts Design Act of 2000 gives the owner of a layout design the authority to assign the layout design and to issue effective receipts for any money received in exchange for the assignment.This is subject to the provisions of the aforementioned Act, as well as any rights that appear to be vested in another person based on the register. A registered layout-design is assignable and transmissible with or without the goodwill of the business involved under Section 21 of the Semiconductor Integrated Circuits Layouts Design Act, 2000.According to Section 22 of the Semiconductor Integrated Circuits Layouts Design Act, 2000, when an integrated circuit layout is assigned without goodwill, the assignment will not take effect unless the assignee applies to the Registrar for directions with respect to the assignment not later than six months from the date on which the assignment is made or within such extended period, if any, not exceeding three months in the aggregate, as the Registrar may allow. The assignee must register the title with the registrar, according to Section 23 of the Semiconductor Integrated Circuits Layouts Design Act, 2000.If the matter is still before the registrar or an appeal from an order therefrom is pending, Section 24 of the Semiconductor Integrated Circuits Layouts Design Act, 2000 prohibits the assignee from utilizing the registration as proof of title.
These rights can be assigned with the help of Assignment Agreements
Assignment agreements deal with the transfer of intellectual property rights from one person or organisation to another. An Intellectual Property Agreement (IP Agreement) or an Intellectual Property Assignment Agreement is a documented and enforceable contract that completes and formalizes a purchase and sale of intellectual property rights between two organisations. Copyrights, trademarks, and/or patents are examples of intellectual property that can be purchased. Assignment agreements differ from licence agreements in that an assignment agreement transfers ownership of intellectual property from the assignor to the assignee, whereas a licence agreement merely allows the licensee to use the intellectual property for a certain time.
An assignment agreement cannot be compared to a negotiating document since in a negotiation, the transferee may obtain a superior title than the transferor, which cannot occur in an assignment/transfer.
An assignment agreement may include a complete and exclusive sale of the rights, granting the assignee complete ownership of the intellectual property rights to exploit them in any way, shape, or form it sees fit, subject to any constraints set forth in the agreement. These contracts are governed in India under the Indian Contract Act of 1872 and the Indian Stamp Act of 1899.
Process of Assignment under Designs Act, 2000
- After a design is registered, an application for ownership under Rule 33 of the Design Rules, 2001 must be made to the Controller for the registration of title in the new owner's name.
- The agreement of assignment must be written, and all of the parties' concerns should be provided in the form of the instrument comprising all of the terms and conditions, according to Rule 37 of the Design Rules.
- After all requirements have been completed and the assignment of rights has been registered with the register of designs, the assignment of rights will be enforceable from that date.
- Within six months of the instrument's implementation date, a title registration application must be submitted. This period can be extended for an additional six months.
The Design Act of 2000 and the Copyright Act of 1957 protect the rights of the original designer and deal with the transfer of rights to succeeding owners. The Assignment Agreement assists two parties in transferring intellectual property rights to one another for product development and commercial purposes. Section 30 of the Design Act and Rules 32-35 of the Design Rules, 2001 deal with design assignment agreements. If they are not carefully written as required by law, these assignment agreements give birth to legal and equitable rights in law and raise a slew of concerns.As a result, it's a good idea to include Assignment Agreement terms that handle concerns like governing law, jurisdiction, and Alternative Dispute Resolution to ensure that disagreements are resolved quickly. It is a legally binding agreement that must adhere to all applicable laws. The enforceability of assignment agreements encourages these individuals to develop innovative technologies that benefit society in the long run. In addition to adhering to these Rules, it is critical to ensure that the agreement properly identifies who owns what. The task must be specific, as well as the duration for which the individual will be the owner of the intellectual property.This would serve as a safeguard in the event of a potential dispute over the Design's ownership.
The content of this article is intended to provide a general guide to the subject matter. Specialist advice should be sought about your specific circumstances.

Intellectual Property
Mondaq uses cookies on this website. By using our website you agree to our use of cookies as set out in our Privacy Policy.
Should you give job applicants an assignment during the interview process? Be thoughtful about the ask

Hiring is a time-consuming and expensive endeavor. Companies need candidates who offer the right skills and experience for a given role, and who align with their organization’s vision and mission.
To find the best fit, many companies still lean on a strategy that continues to generate debate : the assignment. Some candidates believe their experience and interviews should give prospective employers enough information to determine whether they will fit the role. Employers have to ask themselves whether they are willing to turn off a strong candidate by asking them to do additional work.
Is the assignment valuable enough to the evaluation process that they cannot move someone forward without it? Sometimes it is—sometimes they help an employer decide between two strong candidates. And if they are necessary, how can employers make assignments fair and equitable for the candidate or candidates?
When done right, assignments help assess practical skills and problem-solving abilities, giving a clearer picture of a candidate beyond what their resume or interview reveals. But employers should be thoughtful about the ask. While it may make sense for roles that require specific technical expertise or creative thinking, it isn’t appropriate for all roles—so assignments should always be given with a clear reason for why they are needed.
Plus, they don’t just benefit the employer. For job seekers, an assignment during the interview process might also help them stand out from the competition. It can also offer a window into what their day-to-day in the new role might entail. Remember that the candidate should be interviewing the company, too. Having a test run of the work they’d be asked to do is a great way to see whether they believe the role is a fit.
However, there is a rift in how people perceive the assignment as part of the interview process. Workers today span many generations, each with unique values and expectations. Whereas older workers often prioritize stability and loyalty, younger millennials and Gen Zers are more focused on flexibility and work well-being, Indeed data shows .
This mindset impacts the amount of time and energy a candidate is willing to devote to each application. After multiple rounds of interviews and prep, taking on an in-depth assignment may feel like a bridge too far—especially if the expectations for the assignment are not clearly communicated ahead of time.
Some candidates are wary of providing free labor to a company that may use their work and not hire them. Hiring managers should be clear about how the work will be used. They may also consider offering compensation if the assignment requires more than a couple hours of someone’s time, or if they plan to use the work without hiring the candidate.
The key for early career candidates in particular is to ensure their time and efforts are respected. This is a win-win for employers: By providing clarity and transparency, they not only elicit the additional information they want from candidates, but they demonstrate that the organization is transparent and fair.
Equity is also imperative: Which candidates are being asked to complete assignments? Is the hiring team consistent in giving out assignments across ages, experience levels, and roles? There should always be a process and clear evaluation criteria in place to ensure fairness.
As we adapt to the rapidly evolving world of work, we must continue to think critically about each step in the hiring process. Candidate assignments can be a valuable tool, but only with appropriate respect for job seekers’ time and contributions.
With the right strategy, we can bridge the gap between generations in the workplace and build a hiring culture that values efficiency, talent, and integrity.
Eoin Driver is the global vice president of talent at Indeed.
More must-read commentary:
- Fannie Mae CEO: Beyoncé is right. Climate change has already hit the housing market—and homeowners aren’t prepared
- Congress could soon spell the end of employment arbitration—but it’s not all good news for American workers
- Outdated laws prevent gig economy workers from getting benefits. This pilot program shows the path forward
- No, combustion engines won’t be supplanted by electric vehicles—and they’re critical for sustainable transport
The opinions expressed in Fortune.com commentary pieces are solely the views of their authors and do not necessarily reflect the opinions and beliefs of Fortune .
Latest in Commentary

Corporate America is mobilizing to support democracy in 2024 and beyond. Here’s how

Big Tech is pouring billions into British AI investments—but the U.K. risks becoming a sidekick to U.S. tech giants

American families are struggling with debt. When it gets forgiven, the tax code treats it like extra income

The myth that money supply controls inflation is being revived. Here’s how it failed its most ardent believer—Margaret Thatcher

I grew up in Kenya’s biggest slum and know from experience: International aid must shift toward community-based organizations

Gen AI looks easy. That’s what makes it so hard
Most popular.

Amazon raised warehouse wages to $15 an hour 5 years ago. Today, half of workers surveyed told researchers they struggle to afford food or rent

Florida HBCU launches investigation after record $238 million ‘gift’ from 30-year-old hemp mogul is deemed likely worthless: ‘I wanted it to be real’

Thousands of North Koreans stole Americans’ identities and took remote-work tech jobs at Fortune 500 companies, DOJ says

France admits it’s lost control of parts of New Caledonia, the world’s third-largest producer of critical EV metal nickel

Young adults are getting cold feet about their highly anticipated $84 trillion wealth transfer

Billionaire investor Ray Dalio warns U.S. is ‘on the brink’ and estimates a more than 1 in 3 chance of civil war

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Designing Assignments for Learning. The rapid shift to remote teaching and learning meant that many instructors reimagined their assessment practices. Whether adapting existing assignments or creatively designing new opportunities for their students to learn, instructors focused on helping students make meaning and demonstrate their learning ...
Design thinking is a methodology which provides a solution-based approach to solving problems. It's extremely useful when used to tackle complex problems that are ill-defined or unknown—because it serves to understand the human needs involved, reframe the problem in human-centric ways, create numerous ideas in brainstorming sessions and adopt a hands-on approach to prototyping and testing.
04. Create graphs and charts people want to look at. Graphs and charts tend to draw someone's eye. If you see a page full of text, or a presentation full of bullet points, these picture representations of your work tend to be where people look first. Sometimes, they even set the tone for what someone is about to read.
Design assignments that are interesting and challenging. This is the fun side of assignment design. Consider how to focus students' thinking in ways that are creative, challenging, and motivating. Think beyond the conventional assignment type! For example, one American historian requires students to write diary entries for a hypothetical ...
With a small amount of effort, we can design our classes, so students concentrate on learning the subject matter rather than the logistics of completing the assignments. About the Author Gina Seegers Szablewski has taught large introductory geology classes at the University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee for over 20 years with a total of nearly 20,000 ...
Assignment design principles and strategies: Backwards design, alignment, scaffolding, feedback, and transparency. Applying a principle or strategy to improve an assignment. Developing and using rubrics. Helping students with assignments. Joining an assignment design community: Assignments Across Disciplines.
To help you support such creative assignments in your classroom, this section details three strategies to support creative assignments and creative thinking. Firstly, re-consider the design of your assignments to optimize students' creative output. Secondly, scaffold creative assignments using low-stakes classroom activities that build ...
Designing Effective Writing Assignments. One of the best ways for students to determine what they know, think, and believe about a given subject is to write about it. To support students in their writing, it is important to provide them with a meaningful writing task, one that has an authentic purpose, clear guidelines, and engages students in ...
Exercise 1: Improve an assignment. Brainstorm in your breakout group choose one or more way to improve the assignment: Identify the hidden skills or knowledge explicit by creating learning outcomes or objectives. Devise an activity that gives students practice with required skills. Clarify the instructions.
Align writing activities and assignments clearly with learning objectives; The goal of Transparent Assignment Design is to "to make learning processes explicit and equally accessible for all students" (Winkelmes et al., 2019, p. 1). Make clear the purpose, task, and criteria for success. For more information visit TILT (Transparency in ...
Assignments are a major part of pedagogy. Designing assignments can therefore be one of the most influential elements of classroom teaching. Thoughtful assignment design can support student learning by helping students practice meaningful tasks that carry on into their careers or across the curriculum.. The graphic below illustrates how assessment can provide a continuous process of planning ...
Connect to your goals. Assignments support the learning goals of your course, and decisions about how students may or may not use AI should be based on these goals. Designing 'in' doesn't mean 'all in'. Incorporating certain uses of AI into an assignment doesn't mean you have to allow all uses, especially those that would interfere ...
Assignment Design Strategies. Here's a short list of some general assignment design strategies that apply to a wide variety of disciplines. Aligning with Learning Goals When we're clear about our goals for student learning, we can then choose assignments that ask students to do work that will likely result in their achievement of those goals. ...
Assignments can also be contextualized to reflect the values or priorities of the institution. Follow the principles of Transparent Assignment Design. This approach reflects an explicit attempt to create more equity across students with different levels of academic experience by making assignment goals and expectations very clear, enabling all ...
Table of contents. Step 1: Define your variables. Step 2: Write your hypothesis. Step 3: Design your experimental treatments. Step 4: Assign your subjects to treatment groups. Step 5: Measure your dependent variable. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about experiments.
This site, from the University of New Hampshire's Center for Excellence in Teaching and Learning, provides a brief overview of effective assignment design, with a focus on determining and communicating goals and expectations. Gardner, T. (2005, June 12).
Assignment Design 2.0 comes with its own challenges. As Hutchings, Jankowski, and Schultz noted, the assignment design process has thus far been largely a "private" activity for faculty. Building a classroom assignment that can be used for institutional assessment requires that the assignment design process become public and more ...
Random Assignment in Experiments | Introduction & Examples. Published on March 8, 2021 by Pritha Bhandari.Revised on June 22, 2023. In experimental research, random assignment is a way of placing participants from your sample into different treatment groups using randomization. With simple random assignment, every member of the sample has a known or equal chance of being placed in a control ...
AI in Assignment Design. Using generative artificial intelligence (AI) can be both productive and limiting—it can help students to create and revise content, yet it also has the potential to undermine the process by which students create. When incorporated effectively into assignments, generative AI can be leveraged to stimulate students ...
Assignment Design. There's a fine line between assignment design and assessment strategies. In short, designing good assignments is one means of assessing your students' learning on a larger scale. Assignments help measure student learning in your course. Effective assignment design in your course involves aligning your assignments with ...
Transparent Assignment Design. The goal of Transparent Assignment Design is to "to make learning processes explicit and equally accessible for all students" (Winkelmes et al., 2019, p. 1). The development of a transparent assignment involves providing students with clarity on the purpose of the assignment, the tasks required, and criteria ...
Below are some strategies you can use to designing assignments with UDL: Provide Clear Instructions: Clearly articulate the assignment objectives, expectations, and grading criteria. Consider providing written, spoken, and visual instructions to accommodate different learning preferences. A format-agnostic rubric will help to organize this, and ...
Catalyzing assignment design activity on your campus: Lessons from NILOA's assignment library initiative, makes the case for the value of a focus on assignment design, and highlights features of powerful assignments. It describes the NILOA "charrette" model as well as adaptations and examples from campuses. In addition,
Assignment activity is comprised of five primary components: assignment design, as-signment completion, assignment marking, comment on assignment results, and as-signment review. Among them, assignment design takes the lead, as well-designed as-signments can alleviate excessive schoolwork and boost students' overall growth. A detailed ...
Assignment is a legal phrase that refers to the transfer of rights, property, or other benefits from one person to another (the "assignor"). Both contract and property law make use of this term. The term can relate to either the act of transferring or the transferred rights/property/benefits. Section 30 of the Design Act of 2000 ( Hereinafter ...
However, there is a rift in how people perceive the assignment as part of the interview process. Workers today span many generations, each with unique values and expectations. Whereas older ...
BTEC Assignment Brief Qualification Pearson BTEC Level 3 National Foundation Diploma in Information Technology Unit number and title Unit 4: Programming Learning aim(s) (For NQF only) B: Design a software solution to meet client requirements C Develop a software solution to meet client requirements Assignment title Programming Development Assessor Dr Liguang Chen Issue date 16/04/2024 Hand in ...