Curriculum / Math / 4th Grade / Unit 2: Multi-Digit Multiplication / Lesson 9

Multi-Digit Multiplication
Lesson 9 of 18
Criteria for Success
Tips for teachers, anchor tasks.
Problem Set
Target Task
Additional practice.
Lesson Notes
There was an error generating your document. Please refresh the page and try again.
Generating your document. This may take a few seconds.
Are You Sure?
Are you sure you want to delete this note? This action cannot be undone.
Multiply four-digit numbers by one-digit numbers.
Common Core Standards
Core standards.
The core standards covered in this lesson
Number and Operations in Base Ten
4.NBT.B.5 — Multiply a whole number of up to four digits by a one-digit whole number, and multiply two two-digit numbers, using strategies based on place value and the properties of operations. Illustrate and explain the calculation by using equations, rectangular arrays, and/or area models.
Foundational Standards
The foundational standards covered in this lesson
3.NBT.A.3 — Multiply one-digit whole numbers by multiples of 10 in the range 10—90 (e.g., 9 × 80, 5 × 60) using strategies based on place value and properties of operations.
4.NBT.A.1 — Recognize that in a multi-digit whole number, a digit in one place represents ten times what it represents in the place to its right. For example, recognize that 700 ÷ 70 = 10 by applying concepts of place value and division.
4.NBT.B.4 — Fluently add and subtract multi-digit whole numbers using the standard algorithm.
Operations and Algebraic Thinking
3.OA.B.5 — Apply properties of operations as strategies to multiply and divide. Students need not use formal terms for these properties. Example: Knowing that 8 × 5 = 40 and 8 × 2 = 16, one can find 8 × 7 as 8 × (5 + 2) = (8 × 5) + (8 × 2) = 40 + 16 = 56. (Distributive property.) Example: If 6 × 4 = 24 is known, then 4 × 6 = 24 is also known (Commutative property of multiplication.) 3 × 5 × 2 can be found by 3 × 5 = 15, then 15 × 2 = 30, or by 5 × 2 = 10, then 3 × 10 = 30. (Associative property of multiplication.)
3.OA.C.7 — Fluently multiply and divide within 100, using strategies such as the relationship between multiplication and division (e.g., knowing that 8 × 5 = 40, one knows 40 ÷ 5 = 8) or properties of operations. By the end of Grade 3, know from memory all products of two one-digit numbers.
The essential concepts students need to demonstrate or understand to achieve the lesson objective
- Multiply a four-digit whole number by a one-digit whole number using area models and the partial products algorithm.
- Understand that partial products can be written in increasing or decreasing order when recording them vertically.
- Estimate products by rounding factors to the largest place value.
- Solve one-step word problems involving multiplication of four-digit by one-digit numbers (on the Problem Set and Extra Practice Problems) (MP.4).
Suggestions for teachers to help them teach this lesson
Note that the last Criteria for Success is not addressed in the Anchor Tasks below, since each problem type involving multiplication has been explored in previous lessons. However, if it seems students need additional practice with any type (particularly multiplicative compare with larger unknown), then you can use the values in Anchor Task 2 in the context of a word problem.
Unlock features to optimize your prep time, plan engaging lessons, and monitor student progress.
Tasks designed to teach criteria for success of the lesson, and guidance to help draw out student understanding
25-30 minutes
A student solved 4 × 2,387 below:

a. How is this different from the way we recorded partial products previously?
b. Did this way of recording the partial products give the correct product? Use an area model and/or the way we recorded partial products yesterday to check.
Guiding Questions
Student response.
Upgrade to Fishtank Plus to view Sample Response.
Estimate the product. Then use any method to solve.
a. $$8 \times 5,289$$
b. $$3,067 \times 6$$
15-20 minutes
- Problem Set Answer Key
Discussion of Problem Set
- Can you represent #3 with an area model to solve even though it’s a problem involving arrays? Why or why not?
- Whenever there is a 0 in a factor, what does that mean about how many sections of an area model there will be? What about how many partial products there will be in the partial products algorithm?
- In #4, can you use the expression (6 x 5,000) + (6 x 400) + (6 x 70) + (6 x 9) to solve 6 x 5,479? How is this related to the partial products algorithm?
- I think the product in #2c is 1,490. What mistake do you think I made? What if I thought the answer was 149?
- Did you use any strategies from Lesson 6 to solve any problems on today’s Problem Set? For example, #2c or #5c?
A task that represents the peak thinking of the lesson - mastery will indicate whether or not objective was achieved
5-10 minutes
Which strategy for multiplying 5,712 and 4 should result in the correct product?
a. Explain why the expression (4,000 + 20 + 5) × 6 can or cannot be used to find the value of 4,025 × 6.
b. Compute 4,025 × 6.
A pencil is 7 inches long. The Empire State Building is 2,492 times as tall as a pencil. How tall, in inches, is the Empire State Building?
The Extra Practice Problems can be used as additional practice for homework, during an intervention block, etc. Daily Word Problems and Fluency Activities are aligned to the content of the unit but not necessarily to the lesson objective, therefore feel free to use them anytime during your school day.
Extra Practice Problems
- Extra Practice Problems Answer Key
Word Problems and Fluency Activities
Help students strengthen their application and fluency skills with daily word problem practice and content-aligned fluency activities.
Multiply two-, three-, and four-digit numbers by one-digit numbers and assess the reasonableness of the product.
Topic A: Multiplicative Comparison
Solve multiplicative comparison problems with a larger unknown. Distinguish multiplicative comparison from additive comparison.
4.OA.A.1 4.OA.A.2
Solve multiplicative comparison problems with a smaller unknown.
Solve multiplicative comparison problems with an unknown multiplier. Interpret a multiplication equation as a comparison.
Create a free account to access thousands of lesson plans.
Already have an account? Sign In
Topic B: Multiplication of up to Four-Digit Whole Numbers by One-Digit Whole Numbers
Multiply 10, 100, and 1,000 by one- and two-digit numbers.
Multiply multiples of 10, 100, and 1,000 by one-digit numbers. Estimate multi-digit products by rounding numbers to their largest place value.
Multiply two-, three-, and four-digit numbers by one-digit numbers using a variety of mental strategies.
Multiply two-digit numbers by one-digit numbers.
Multiply three-digit numbers by one-digit numbers.
Topic C: Multiplication of Two-Digit Whole Numbers by Two-Digit Whole Numbers
Multiply two-digit multiples of 10 by two-digit multiples of 10. Estimate multi-digit products by rounding numbers to their largest place value.
Multiply two-digit multiples of 10 by two-digit numbers.
Multiply two-digit numbers by two-digit numbers using a variety of mental strategies.
Multiply two-digit by two-digit numbers using four partial products.
Multiply two-digit by two-digit numbers using two partial products and assess the reasonableness of the product.
Topic D: Multi-Step Word Problems
Abstract the formulas for the area and perimeter of a rectangle and apply those formulas in real-world and mathematical problems involving multiplication, addition, and subtraction.
4.MD.A.3 4.OA.A.3
Solve two-step word problems involving multiplication, addition, and subtraction.
4.OA.A.2 4.OA.A.3
Solve multi-step word problems involving multiplication, addition, and subtraction.
Request a Demo
See all of the features of Fishtank in action and begin the conversation about adoption.
Learn more about Fishtank Learning School Adoption.
Contact Information
School information, what courses are you interested in, are you interested in onboarding professional learning for your teachers and instructional leaders, any other information you would like to provide about your school.

We Handle Materials So You Can Focus on Students
We've got you covered with rigorous, relevant, and adaptable math lesson plans for free

Strategies for Teaching Multi-Digit Multiplication
- Freebies , Math , Planning , Strategies

Common Core requires that we teach students strategies before we introduce them to the traditional algorithms. When it comes to teaching multi-digit multiplication, it’s common for teachers to focus solely on the partial products method and forget about the rest. Instead, I like to scaffold my students’ learning first so that they are ready for both partial products and the traditional algorithm with more concrete methods.

It’s important that we are teaching students in the way that they learn best. One method of scaffolding is to start all concepts in a concrete manner and then work toward a more abstract manner. I talk about this in my post, Teaching Math so Students Get It . In this case of teaching my students how to multiply multi-digit numbers, I first start with the area model, then work up to the box model, introduce the distributive property, and then move into the partial products method. Depending on your grade level and standards, then you may teach the traditional algorithm after. This allows for scaffolding, instead of rescuing students later on.
The Area Model as a Multi-Digit Multiplication Strategy
When I introduce my students to the area model, I first remind them of what this model looks like with basic multiplication numbers, such as 7 x 8. I provide students with base-ten blocks and have them create an array. Then I ask them to “just try” creating one with a larger number such as 27 x 4. Then, depending on how that goes, we will create the model. I will either model it or guide them. I remind students of place value and together we first create the sides of our array. For instance, in the problem 27 x 4, we create the two tens and the seven ones using our base ten blocks on one side and create the four ones on the other.
Next, we have to fill in the space to create an array. I express that we could do this with actual one base ten blocks, but it would take us a long time. Instead, it would be best to use the larger ones that would fit. This is an important step because later they will need this when they get to double digits and with understanding division. Once everything is filled in, we now count our total blocks for that section and add them up to get our final answer. You can see this in the anchor charts below, found in my fourth grade multi-digit multiplication math workshop unit (or found on TpT here ).
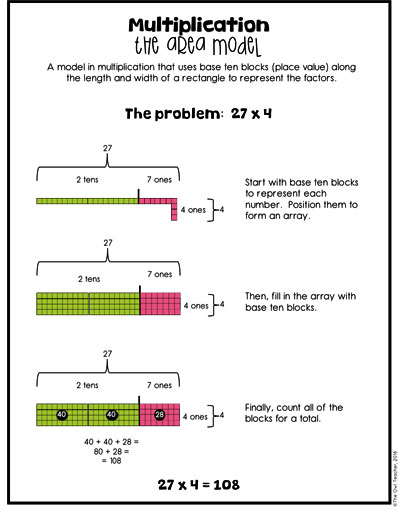
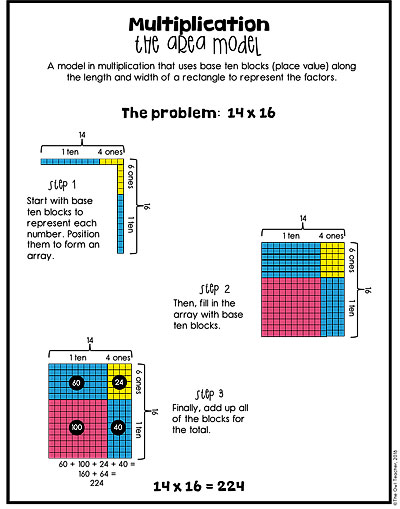
Using the area model with 2-digit numbers by 2-digit numbers is essentially the same, except the area model is just a bit larger. (I don’t recommend moving into the 2-digit by 2-digit model until after you have had plenty of practice with all of the multi-digit numbers by 1 digit. This post is to assist all multi-digit multiplication needs.) This area model typically involves more tens and hundreds.
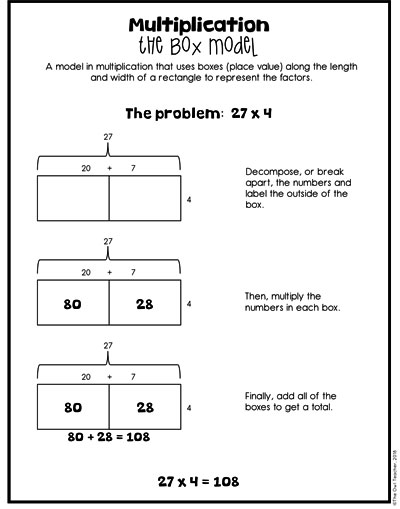
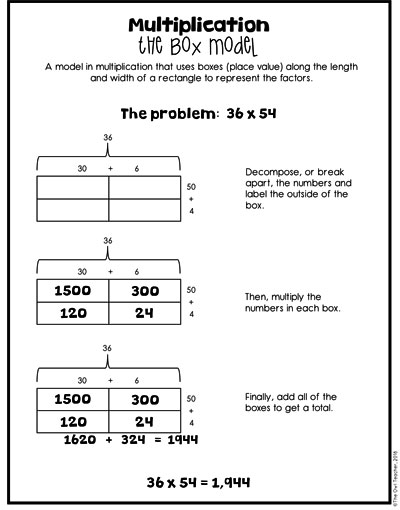
The Box Model as a Multi-Digit Multiplication Strategy
The box model follows the area model perfectly!
As seen in the image below, I typically create an area model first and then draw boxes around it to show my students the relationship between the two. Instead of actually usually manipulatives (concrete), we are now moving into drawing our models. In fact, in my math workshop and in my class, I often have my students draw symbols of the base-ten blocks after they have created the area model, so the transition is even nicer.
Now students are in the semi-concrete or representational stage. They are drawing the boxes and placing the numbers outside the box so that they can determine the answers for each box through multiplication.
The box model is really no different except that now they are not physically manipulating any base-ten blocks. This is a great time to mention decomposing, because that will be something you’ll be mentioning a lot during both the distributive property and later in other concepts, such as area.
When I talk about decomposing, I like to remind my students that this is really no different than what they did when they broke numbers up into the expanded form.
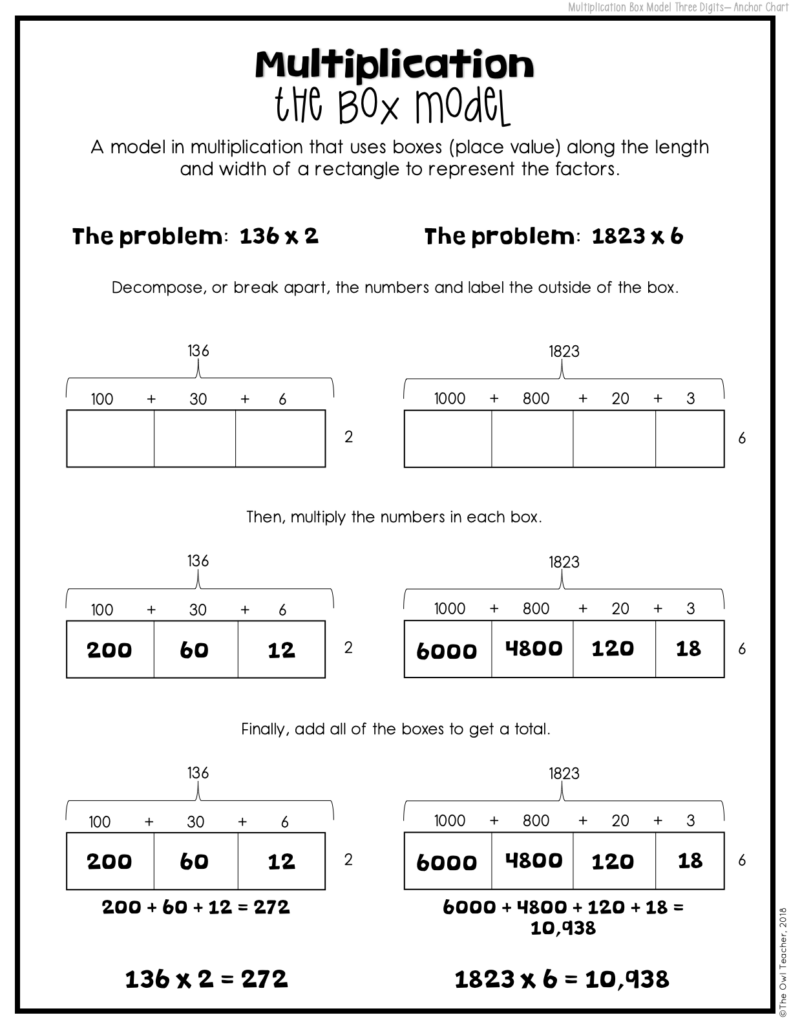
When students work on the 2-digit numbers by 2-digit numbers, they are now working with a 4-square box. Just as before, they are only multiplying the boxes in a grid-like way and then adding them up. See the charts below for a more detailed explanation.
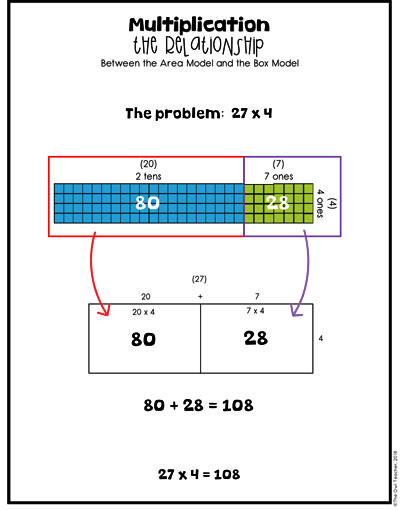
The Distributive Model as a Multi-Digit Multiplication Strategy
For some reason, teachers don’t like to tackle the distributive property and/or the students fear it. But, if you have worked your way up using the previous methods, this strategy isn’t as scary as it appears.
Since we just talked about decomposing numbers in the last strategy, students should now know they can take the larger number and break it up into smaller numbers. I give them the freedom to choose how they break it up. Then I provide them with boxes to break it up and multiply away!
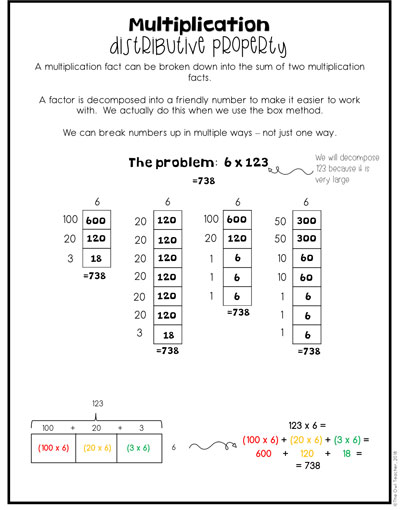
Down at the bottom of this distributive property chart (above), you can see that I have turned the box sideways and have used colored pens. I did this intentionally before I moved into partial products. I wanted to make sure students are seeing what each box is made up of. For instance, the first box (in red) is 100 x 6, the second box (in yellow-orange) is 20 x 6, and the third box is 3 x 6. Then I showed them how it’s written out and added up. I did this for two reasons. First, because they will see this again when we get to partial products (next), and second because they will see it when they learn to use the distributive property in algebra (FOIL) later.
Partial Products as a Multi-Digit Multiplication Strategy
Most teachers are likely aware of the Partial Products method. In case you are not, it’s really just taking the larger number and breaking it out into expanded form and then having the other factor multiply each of the expanded form factors. Then they are added up to get the final product. (See chart below.)
You’ll notice that my colors are back. Whenever possible, I use colors to help differentiate each step. I remind students that we are using the distributive property (which is not scary now!) and decompose our larger number into the expanded form. Then we multiply each new factor one at a time. I always write each new product with the multiplication problem next to it so students can see where I got it from. Then, after we have found all the products to each of those, we add them up to find our final product. This strategy also helps later when introducing the “placeholder” in the traditional algorithm.
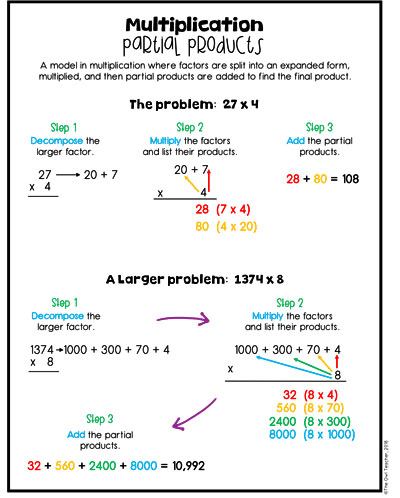
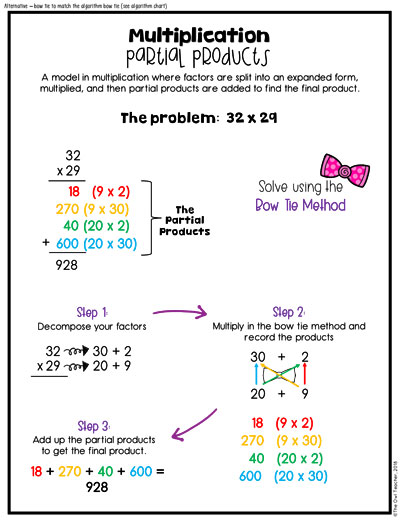
When we get to double digits, it is the same thing, but I like to introduce a method called the “bow tie method.” Just as before, students would decompose both factors into an expanded form. Then they multiply in a bow tie method. If you look at the illustration below, you can see this method through the use of the colors. I actually have my students draw it on their papers to help them so they don’t miss a factor as they are multiplying. As they work through the bow tie method, they record the products for each one. Once finished, they add the products together to get the final product.
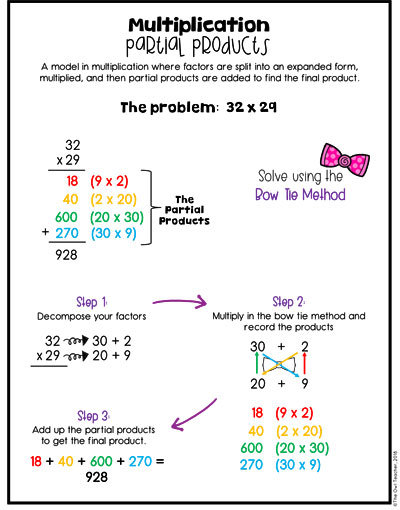
Understandably, if you prefer to have your students begin preparing for the traditional algorithm, you could have them do the “bow tie” method in the traditional algorithm motions, like in the chart below. Overall, the point of the “bow tie” method is to make sure no factors are missed or hit twice.
For students to truly be ready for multi-digit multiplication with the traditional algorithm, they must first go through the strategies that Common Core requires. This requires us to also teach in the way that students learn best. If you want your students to do well with multi-digit multiplication, you will need to scaffold the concepts by first starting with the concrete method of using an area model, working to a semi-concrete, representational model of the box method, and then into both the distributive property and the partial products method.
Using just one method will not cut it. Students need this gradual release with multi-digit multiplication before they’ll be ready or they just won’t fully understand the concept and be successful.
Grab the FREEBIE!
To help your students practice these strategies, I have a freebie to get you started! Click here to download the freebie!
Then check out my multi-digit multiplication lesson plans, games, and activities that go along with these anchor charts so that you can save time lesson planning today. Purchase the 4th grade Large Numbers Multiplication Math Workshop Unit here on my website or found on TpT by clicking here .
Check out these related 4th Grade Math Workshop Units!
- freebie , Multi-Digit , Multiplication , Strategies
FIND IT NOW!
Check me out on tpt.

CHECK THESE OUT
MW5 Unit 3 Multiplying and Dividing Whole Numbers

5th Grade Math Workshop Growing Bundle- 9 Units
Want to save time?
COPYRIGHT © 2016-2024. The Owl Teacher | Privacy page | Disclosure Page | Shipping | Returns/Refunds
BOGO on EVERYTHING!

Reading & Math for K-5
- Kindergarten
- Learning numbers
- Comparing numbers
- Place Value
- Roman numerals
- Subtraction
- Multiplication
- Order of operations
- Drills & practice
- Measurement
- Factoring & prime factors
- Proportions
- Shape & geometry
- Data & graphing
- Word problems
- Children's stories
- Leveled stories
- Sight words
- Sentences & passages
- Context clues
- Cause & effect
- Compare & contrast
- Fact vs. fiction
- Fact vs. opinion
- Main idea & details
- Story elements
- Conclusions & inferences
- Sounds & phonics
- Words & vocabulary
- Reading comprehension
- Early writing
- Numbers & counting
- Simple math
- Social skills
- Other activities
- Dolch sight words
- Fry sight words
- Multiple meaning words
- Prefixes & suffixes
- Vocabulary cards
- Other parts of speech
- Punctuation
- Capitalization
- Narrative writing
- Opinion writing
- Informative writing
- Cursive alphabet
- Cursive letters
- Cursive letter joins
- Cursive words
- Cursive sentences
- Cursive passages
- Grammar & Writing
Breadcrumbs
- Math drills
- Multi-digit multiplication

Download & Print Only $5.60
Multi-digit multiplication worksheets
Multiplication and regrouping.
These worksheets proceed stepwise from simple multiplying small numbers mentally to multiplication of large numbers in columns with regrouping . Emphasis is on the regrouping algorithm.
We also have multiplication facts worksheets and thousands of math worksheets by grade level .

Sample multiplication worksheet
What is K5?
K5 Learning offers free worksheets , flashcards and inexpensive workbooks for kids in kindergarten to grade 5. Become a member to access additional content and skip ads.

Our members helped us give away millions of worksheets last year.
We provide free educational materials to parents and teachers in over 100 countries. If you can, please consider purchasing a membership ($24/year) to support our efforts.
Members skip ads and access exclusive features.
Learn about member benefits
This content is available to members only.
Join K5 to save time, skip ads and access more content. Learn More
- → Curriculum
- → 5th Grade
- → Unit 2: Whole Number & Decimal Operations
Multiply Multi-Digit Whole Numbers Lesson Plan
Get the lesson materials.

Multi Digit Multiplication Whole Numbers Guided Notes with Doodles Sketch Notes

Ever wondered how to teach multi-digit multiplication of whole numbers in an engaging way to your 5th-grade students?
In this lesson plan, students will learn about multiplying multi-digit whole numbers using the standard algorithm and their real-life applications. Through artistic, interactive guided notes, check for understanding, practice activities like a doodle & color by number activity, and a maze worksheet, students will gain a comprehensive understanding of multi-digit multiplication.
The lesson ends with a real-life example that explores how multi-digit multiplication of whole numbers is used in practical, everyday situations such as order purchases, merchandise organization. Then, they reflect on their learning and mastery of this topic through self assessments and short prompts.
- Standard : CCSS 5.NBT.B.5
- Topic : Factors, Multiples & Divisibility
- Grade : 5th Grade
- Type : Lesson Plans
Learning Objectives
After this lesson, students will be able to use the standard algorithm to:
Multiply two-digit numbers by one-digit numbers
Multiply two-digit numbers by two-digit numbers
Multiply three-digit numbers by one-digit numbers
Multiply three-digit numbers by two-digit numbers
Prerequisites
Before this lesson, students should be familiar with:
Basic understanding of regrouping or carrying over in addition and subtraction
Colored pencils or markers
Multi Digit Multiplication Whole Numbers Guided Notes with Doodles
Key Vocabulary
Multi-Digit
Whole Numbers
Introduction

As a hook, ask students why knowing how to multiply multi-digit whole numbers is important in everyday life. Refer to the last page of the guided notes as well as the FAQs below for ideas.
Use the first page of the guided notes to introduce multiplying 2-digit numbers by 1-digit numbers. Walk through the steps involved in this multiplication process while students fill in the blanks on their guided notes (pg. 1), emphasizingƒsetting up the problem by stacking the numbers to the right. Model the first two or three examples on the page so they see how to use the steps. Students will then see how to multiple 3-digit numbers by 2-digit numbers. Model the multiplication process using examples and emphasize the significance of placing zeroes when moving to the next place value.
Use the second page of the guided notes to allow students to practice how to use the standard algorithm to multiple whole numbers. There are 3 levels of practice that increases in difficulty. Level 1 contains multiplication of 2-digit by 1-digit numbers. Level 2 contains multiplication of 2-digit by 2-digit numbers. Level 3 contains multiplication multiplication of 3-digit by 2-digit numbers.
Based on student responses, reteach concepts that students need extra help with. If your class has a wide range of proficiency levels, you can pull out students for reteaching, and have more advanced students begin work on the practice exercises.

Continue with the third page of the guided notes for a fun maze activity ! Students will solve multi-digit multiplication problems to escape the maze. Walk around to answer student questions.
Then, use the fourth page of the guided notes for a fun color by number activity . Students solve math problems to unlock colors to fill in an image. Fast finishers can also be assigned this activity for extra practice. Alternatively, you can assign it as homework for the remainder of the class.
Real-Life Application

Use the last page of the guided notes, called real life applications, to bring the class back together, and introduce the concept of using multidigit multiplication in real-world scenarios. Students read about how it can be used in calculating the total cost of purchasing multiple items at a store, determining the area of a rectangular garden, or organizing merchandise in a factory. Then, they reflect on their learning and confidence about this math topic.

Additional Self-Checking Digital Practice
If you’re looking for digital practice for multiplying whole numbers, try my Pixel Art activities in Google Sheets. Every answer is automatically checked, and correct answers unlock parts of a mystery picture. It’s incredibly fun, and a powerful tool for differentiation.
Here’s 1 activity to explore:
Multiplying Multi-Digit Whole Numbers Pixel Art | Products | Google Sheets
Additional Print Practice
A fun, no-prep way to practice multiplying whole numbers is Doodle Math — they’re a fresh take on color by number or color by code. It includes multiple levels of practice, perfect for a review day or sub plan.
Here are 1 activity to try:
Multidigit Multiplication Doodle Math Twist on Color by Number | Product
What are multi-digit whole numbers? Open
Multi-digit whole numbers are numbers that consist of two or more digits, without any decimal or fraction parts.
How can I multiply multi-digit whole numbers? Open
To multiply multi-digit whole numbers, follow these steps:
Place the numbers so that one number is above the other, and stacked to the right.
Multiply each digit of the bottom number by each digit of the top number, starting from the rightmost place value.
Carry over, if needed.
Repeat with the next digit on the bottom. Place zeroes in the appropriate spot, if needed.
Add the partial products together to get the final product.
Why is it important to learn how to multiply multi-digit whole numbers? Open
Learning to multiply multi-digit whole numbers is important because:
It helps in solving real-world problems involving large quantities.
It builds a strong foundation for more advanced math concepts.
It improves mental math skills and overall math proficiency.
Can you provide examples of practice problems for multiplying multi-digit whole numbers that are similar to the ones in the guided notes? Open
Sure! Here are a few examples:
What strategies can I use to solve multi-digit multiplication problems? Open
Some helpful strategies for solving multi-digit multiplication problems include:
Partial products method
Lattice method
Standard algorithm method
*In this guided notes, only the standard algorithm is used.
How can I check my answers when multiplying multi-digit whole numbers? Open
You can check your answers by:
Estimating the product and comparing it to the actual answer.
Using a calculator to verify the multiplication.
Reversing the operation (division) to see if you get back the original numbers.
Are there any real-life applications of multiplying multi-digit whole numbers? Open
Yes, multiplying multi-digit whole numbers is used in various real-life situations such as:
Calculating total costs when buying multiple items
Determining area and perimeter of objects
Solving problems related to time, distance, and speed
Want more ideas and freebies?
Get my free resource library with digital & print activities—plus tips over email.
Number & Operations in Base Ten – 4th Grade
Use place value understanding and properties of operations to perform multi-digit arithmetic..
CCSS.Math.Content.4.NBT.B.5 Multiply a whole number of up to four digits by a one-digit whole number, and multiply two two-digit numbers, using strategies based on place value and the properties of operations. Illustrate and explain the calculation by using equations, rectangular arrays, and/or area models.
Teacher Notes The teacher needs to understand how place value helps students find the product in multi-digit multiplication problem. It is important to use multi-digit multiplication problems to reenforce place value. Example: "Four tens times three tens is twelve tens. Regroup and put one in the hundreds and two in the tens." Students who develop flexibility in breaking numbers apart have a better understanding of the importance of place value and the distributive property in multi-digit multiplication.
Student Knowledge Goals
Vocabulary area model Commutative Property of Multiplication Distributive Property of Multiplication over Addition equal groups equation factor Identity Property of Multiplication partial product place value product rectangular array strategy
Lessons Engage NY Module 3 B-4 – Interpret and represent patterns when multiplying by 10, 100, and 1,000 in arrays and numerically. Engage NY Module 3 B-5 – Multiply multiples of 10, 100, and 1,000 by single digits, recognizing patterns. Engage NY Module 3 B-6 – Multiply two-digit multiples of 10 by two-digit multiples of 10 with the area model. Engage NY Module 3 C-7 – Multiplication of up to Four Digits by Single-Digit: Use place value disks to represent two-digit by one-digit multiplication. Engage NY Module 3 C-8 – Extend the use of place value disks to represent three- and four-digit by one-digit multiplication. Engage NY Module 3 C-9 – Multiply three- and four-digit numbers by one-digit numbers applying the standard algorithm. Engage NY Module 3 C-10 – Multiply three- and four-digit numbers by one-digit numbers applying the standard algorithm. Engage NY Module 3 C-11 – Multiply three- and four-digit numbers by one-digit numbers applying the standard algorithm.
Student Video Lessons Learn Zillion - Multiply Multi-Digit Whole Numbers Learn Zillion - Solve multiplication problems Study Jams – Distributive Property Virtual Nerd – Multiplication
Online Problems, Games, and Assessments Khan Academy – Questions and Video Lessons Multiply 1-digit numbers by 2-digit numbers Multiply 1-digit numbers by 3-digit or 4-digit numbers Multiplication patterns over increasing place values Properties of multiplication Distributive property: find the missing factor Multiply using the distributive property Multiply a 2-digit number by a 2-digit number: complete the missing steps Multiply a 2-digit number by a 2-digit number Multiply numbers ending in zeroes
Printables Multiplication – Single & Multi-Digit 4.NBT.B.5 - 60 pages of PDF worksheets
- Notifications 0

- Add Friend ($5)

As a registered member you can:
- View all solutions for free
- Request more in-depth explanations for free
- Ask our tutors any math-related question for free
- Email your homework to your parent or tutor for free
- Grade 5 Eureka - Answer Keys Module 2

Explanation:
During the 2011 season, a quarterback passed for 302 yards per game. He played in all 16 regular season games that year.
a . For how many total yards did the quarterback pass?
b . If he matches this passing total for the next 13 seasons, how many yards will he pass for in his career?
Yes, email page to my online tutor. ( if you didn't add a tutor yet, you can add one here )
Thank you for doing your homework!
Submit Your Question

Addition (Basic)
Addition (Multi-Digit)
Algebra & Pre-Algebra
Comparing Numbers
Daily Math Review (Math Buzz)
Division (Basic)
Division (Long Division)
Hundreds Charts
Measurement
Multiplication (Basic)
Multiplication (Multi-Digit)
Order of Operations
Place Value
Probability
Skip Counting
Subtraction
Telling Time
Word Problems (Daily)
More Math Worksheets
Reading Comprehension
Reading Comprehension Gr. 1
Reading Comprehension Gr. 2
Reading Comprehension Gr. 3
Reading Comprehension Gr. 4
Reading Comprehension Gr. 5
Reading Comprehension Gr. 6
Reading & Writing
Reading Worksheets
Cause & Effect
Daily ELA Review (ELA Buzz)
Fact & Opinion
Fix the Sentences
Graphic Organizers
Synonyms & Antonyms
Writing Prompts
Writing Story Pictures
Writing Worksheets
More ELA Worksheets
Consonant Sounds
Vowel Sounds
Consonant Blends
Consonant Digraphs
Word Families
More Phonics Worksheets
Early Literacy
Build Sentences
Sight Word Units
Sight Words (Individual)
More Early Literacy
Punctuation
Subjects and Predicates
More Grammar Worksheets
Spelling Lists
Spelling Grade 1
Spelling Grade 2
Spelling Grade 3
Spelling Grade 4
Spelling Grade 5
Spelling Grade 6
More Spelling Worksheets
Chapter Books
Charlotte's Web
Magic Tree House #1
Boxcar Children
More Literacy Units
Animal (Vertebrate) Groups
Butterfly Life Cycle
Electricity
Matter (Solid, Liquid, Gas)
Simple Machines
Space - Solar System
More Science Worksheets
Social Studies
Maps (Geography)
Maps (Map Skills)
More Social Studies
Columbus Day
Veterans Day
More Holiday Worksheets
Puzzles & Brain Teasers
Brain Teasers
Logic: Addition Squares
Mystery Graph Pictures
Number Detective
Lost in the USA
More Thinking Puzzles
Teacher Helpers
Teaching Tools
Award Certificates
More Teacher Helpers
Pre-K and Kindergarten
Alphabet (ABCs)
Numbers and Counting
Shapes (Basic)
More Kindergarten
Worksheet Generator
Word Search Generator
Multiple Choice Generator
Fill-in-the-Blanks Generator
More Generator Tools
Full Website Index
5th Grade Common Core: 5.NBT.7

Logged in members can use the Super Teacher Worksheets filing cabinet to save their favorite worksheets.
Quickly access your most used files AND your custom generated worksheets!
Please login to your account or become a member and join our community today to utilize this helpful feature.

PDF with answer key:
PDF no answer key:
5.4 Wrapping Up Multiplication and Division with Multi-Digit Numbers
- Students use the standard algorithm to multiply multi-digit whole numbers. They divide whole numbers up to four-digits by two-digits divisors using strategies based on place value and properties of operations.
Section A Goals
- Multiply multi-digit whole numbers using the standard algorithm.
Section B Goals
- Divide multi-digit whole numbers using strategies based on place value, properties of operations, and the relationship between multiplication and division.
Section C Goals
- Multiply and divide to solve real-world and mathematical problems involving area and volume.
Section A: Multi-digit Multiplication Using the Standard Algorithm
Estimate and find products, partial products in diagrams, partial products in algorithms, standard algorithm: one-digit and multi-digit numbers with composing, standard algorithm: multi-digit numbers without composing, standard algorithm: multi-digit numbers with composing.
PLC Activity
Build Multiplication Fluency
Multiplication fluency, section b: multi-digit division using partial quotients, world’s record folk dance, different partial quotients, an algorithm using partial quotients, divide using partial quotients, practice an algorithm using partial quotients, find missing side lengths, world’s record noodle soup, fractions as partial quotients (optional), section c: let’s put it to work, lots of milk, shipping trash, food waste journal (optional).
- Texas Go Math
- Big Ideas Math
- Engageny Math
- McGraw Hill My Math
- enVision Math
- 180 Days of Math
- Math in Focus Answer Key
- Math Expressions Answer Key
- Privacy Policy
McGraw Hill My Math Grade 5 Chapter 2 Lesson 10 Answer Key Multiply by Two-Digit Numbers
All the solutions provided in McGraw Hill Math Grade 5 Answer Key PDF Chapter 2 Lesson 10 Multiply by Two-Digit Numbers will give you a clear idea of the concepts.
McGraw-Hill My Math Grade 5 Answer Key Chapter 2 Lesson 10 Multiply by Two-Digit Numbers
Find 44 × 12. Estimate 44 × 10 = ____
Helpful Hint By estimating first, you can determine if your answer is reasonable.
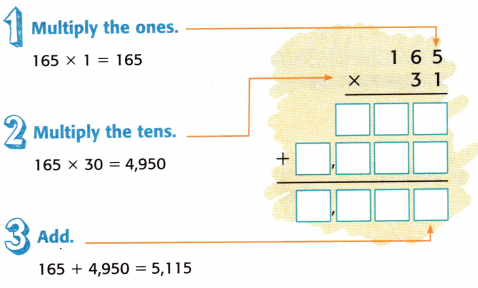
Guided Practice
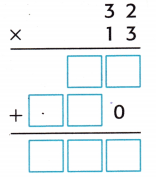
Independent Practice
Estimate. Then multiply. Use your estimate to check your answer.
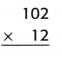
Question 8. 21 × 42 = ____ Answer: 882
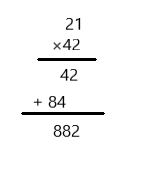
Question 9. 69 × 14 = ____ Answer: 996
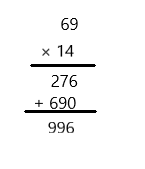
Question 10. 83 × 367 = ____ Answer: 30461
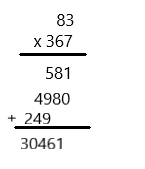
Problem Solving
Question 14. Marshall’s mother buys 2 boxes of granola bars each week. Each box contains 8 granola bars. If she continues buying 2 boxes each week, how many granola bars will she buy in a year (1 year = 52 weeks)? Answer: 832 granola bars.
Explanation: If Marshall’s mother continues to buy two boxes each week Marshall’s mother will have 832.
Question 15. Mathematical PRACTICE 5 Use Math Tools A delivery truck travels 278 miles each day. How far does it travel in 25 days? Answer: 6950
Explanation: Given, Speed = 278 miles Time = 25 days Distance = Speed × time = 278 × 25 = 6950
Question 16. A cow can eat 25 pounds of hay a day. At that rate, how many pounds of hay can a cow eat in 31 days? Answer: 775 pounds
Explanation: The cow eats 25 pounds of hay a day. Can a cow eat in 31 days? 25 × 31 = 775 So the cow eats 775 pounds of hay in 31 days.
Hot Problems
Question 17. Mathematical PRACTICE 2 Use Number Sense Find 235 × 124. Use the same strategy that you used for multiplying by a two-digit number except include multiplying by the hundreds place. Answer: 29140
Explanation: 235 × 124 = 29140
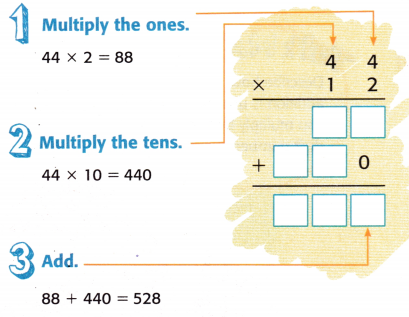
Question 18. ? Building on the Essential Question How do you multiply by two-digit numbers? Answer: Step 1: Estimate the product using the nearest ‘tens‘ to verify the answer. Step 2: Multiply any one of the numbers by the ‘ones’ digit of the second number. Step 3: Multiply the number by the tens digit of the number. Step 4: Finally, add the two partial products to get the final product and verify it with the estimated product.
McGraw Hill My Math Grade 5 Chapter 2 Lesson 10 My Homework Answer Key
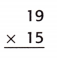
Question 3. 470 × 56 = ____ Answer: 26320
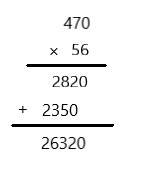
Question 4. Ms. Jenkins was arranging chairs for a school awards assembly. Each row contained 15 chairs. If there were 21 rows, how many chairs had to be arranged? Answer: 315 chairs had to be arranged.
Explanation: Jenkins was arranging chairs for a school awards assembly No of chairs in each row = 15 Then multiply the number of chairs in 21 rows 15 × 21 = 315
Question 5. Leon earns $14 an hour. How much does he earn in 4 weeks if he works 12 hours each week? Answer: $672
Explanation: He worked a total of 12 × 4 = 48 Then multiply that by 14 × 28 =672 $672
Question 6. Mathematical PRACTICE 5 Use Math Tools Without actually calculating, how much greater is the product of 98 × 50 than the product of 97 × 50? Answer: (98 – 97) × 50 = 1 × 50 = 50 98 × 50 is greater than 97 × 50 by 50.
Explanation: (5 × 12 + 8 × 14) × 12 (60 + 112) × 12 172 × 12 $2064 The buckets indicate the money earned each week.
Test Practice
Question 8. Each day there are 12 tours at the glass factory. Twenty-eight people can go on a tour. How many people can tour the glass factory each day? A. 236 people B. 280 people C. 336 people D. 436 people Answer: 336 people
Explanation: Each day there are 12 tours at the glass factory, and on each tour 28 people can assist, in order to know how many people can tour the glass factory 12 × 28 = X 336 = X
Fluency Practice Mathematical practice 6
Fluency Practice
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
We use the same model for the multi digit numbers and two digit numbers. For both numbers we multiply from the right side of a number. Example for two digit number 2 x 12 = 24. for multi digit numbers 2 x 123 = 246. McGraw Hill My Math Grade 4 Chapter 4 Lesson 9 My Homework Answer Key. Multiply. Check for reasonableness. Question 1. Answer:
Lesson 9 Multiply by a Multi-Digit Number; Lesson 10 Problem-Solving Investigation: Estimate or Exact Answer ... McGraw-Hill My Math 4th Grade Volume 1 Answer Key Chapter 5 Multiply with Two-Digit Numbers. Chapter 5 Multiply with Two-Digit Numbers; ... McGraw Hill Math Grade 4 Answers cover the concepts in Homework Practice, Cumulative ...
4.NBT.A.1. Number and Operations in Base Ten. 4.NBT.A.1 — Recognize that in a multi-digit whole number, a digit in one place represents ten times what it represents in the place to its right. For example, recognize that 700 ÷ 70 = 10 by applying concepts of place value and division. Search. 4.NBT.B.4. Number and Operations in Base Ten.
Lesson 8 Estimate Products; Lesson 9 Multiply by One-Digit Numbers; Lesson 10 Multiply by Two-Digit Numbers; McGraw Hill My Math Grade 5 Chapter 2 Check My Progress; McGraw Hill My Math Grade 5 Chapter 2 Review Answer Key; McGraw-Hill My Math Grade 5 Volume 1 Answers Key Chapter 3 Divide by a One-Digit Divisor. Chapter 3 Divide by a One-Digit ...
Chapter 4: Multiply with One-Digit Numbers. Lesson 1: Multiples of 10, 100, and 1,000; Lesson 2: Round to Estimate Products; Lesson 3: Hands On: Use Place Value to Multiply; Lesson 4: Hands On: Use Models to Multiply; Lesson 5: Multiply by a Two-Digit Number; Lesson 6: Hands On: Model Regrouping; Lesson 7: The Distributive Property; Lesson 8 ...
5. Writing numbers up to 1,000 in words: convert digits to words. 6. Writing numbers up to 100,000 in words: convert digits to words. 7. Writing numbers up to one million in words: convert digits to words. 8. Spell word names for numbers up to one million. Lesson 2: Read and Write Multi-Digit Numbers.
Use the table below to find videos, mobile apps, worksheets and lessons that supplement My Math 4 Volume 1 Common Core. My Math 4 Volume 1 Common Core grade 4 workbook & answers help online. Grade: 4, Title: My Math 4 Volume 1 Common Core, Publisher: McGraw-Hill, ISBN: 21150230.
Using the area model with 2-digit numbers by 2-digit numbers is essentially the same, except the area model is just a bit larger. (I don't recommend moving into the 2-digit by 2-digit model until after you have had plenty of practice with all of the multi-digit numbers by 1 digit. This post is to assist all multi-digit multiplication needs.)
Multiply whole tens by whole hundreds and thousands. 60 x 8,000 =. Multiply whole hundreds. 400x700 =. Multiply whole thousands. 5,000 x 9,000 =. Multiplying by whole tens and hundreds- missing factor. ___ x 200 = 3,400. Sample multiplication worksheet.
Common core worksheets and activities for 4.NBT.5 / Number And Operations In Base Ten / Use Place Value Understanding And Properties Of Operations To Perform Multi-Digit Arithmetic. / Multiply a whole number of up to four digits by a one-digit whole number, and multiply two two-digit numbers, using strategies based on place value and the properties of operations.
This printable includes 5 pages of multi-digit multiplication practice along with answer key for your students. This resource includes the following:-4 digit x 1 digit-2 digit x 2 digit-3 digit x 2 digit-4 digit x 2 digit-Mixed Practice of all of the aboveIt is aligned to the following 4th and 5th grade CCSS math standards:CCSS.MATH.CONTENT.4.NBT.B.5Multiply a whole number of up to four digits ...
Unit 1 Place value. Unit 2 Addition, subtraction, and estimation. Unit 3 Multiply by 1-digit numbers. Unit 4 Multiply by 2-digit numbers. Unit 5 Division. Unit 6 Factors, multiples and patterns. Unit 7 Equivalent fractions and comparing fractions. Unit 8 Add and subtract fractions. Unit 9 Multiply fractions.
To multiply multi-digit whole numbers, follow these steps: Place the numbers so that one number is above the other, and stacked to the right. Multiply each digit of the bottom number by each digit of the top number, starting from the rightmost place value. Repeat with the next digit on the bottom. Place zeroes in the appropriate spot, if needed.
McGraw-Hill My Math Grade 4 Answer Key Chapter 9 Lesson 9 Multiply Fractions by Whole Numbers. You can use models and equations to multiply a fraction by a whole number. Math in My World Example 1 Each card on a trivia game has 6 questions. Each question represents \(\frac{1}{6}\) of the questions on the card. Caleb correctly answered 4 of the ...
Number & Operations in Base Ten - 4th Grade Use place value understanding and properties of operations to perform multi-digit arithmetic. CCSS.Math.Content.4.NBT.B.5 Multiply a whole number of up to four digits by a one-digit whole number, and multiply two two-digit numbers, using strategies based on place value and the properties of operations. Illustrate and explain…
Practice multiplying multi-digit numbers in this multiplication worksheet that's filled with equations, from easy to challenging. Assess kids' ability to multiply and divide multi-digit numbers. Offering over 40 regrouping problems, this worksheet is a great way to practice your multiplication skills.
Topic A: Multiplicative Comparison Word Problems. Topic B: Multiplication by 10, 100, and 1,000. Topic C: Multiplication of up to Four Digits by Single-Digit Numbers. Topic D: Multiplication Word Problems. Topic E: Division of Tens and Ones with Successive Remainders. Topic F: Reasoning with Divisibility.
Lesson 9: Multiply by One-Digit Numbers 1. Multiply by 1-digit numbers. 2. Multiply by 1-digit numbers: word problems ... Lesson 10: Multiply by Two-Digit Numbers 1. Multiply by 2-digit numbers: complete the missing steps. 2. Multiply 2-digit numbers by 2-digit numbers. 3. Multiply by 2-digit numbers: word problems ...
Email your homework to your parent or tutor for free; ... Lesson 9: Fluently multiply multi-digit whole number. Please share this page with your friends on FaceBook. Question 1 (request help) Jeffery bought 203 sheets of stickers. Each sheet has a dozen stickers. ... Yes, email page to my online tutor.
Common core worksheets and activities for 5.NBT.7 / Number And Operations In Base Ten / Perform Operations With Multi-Digit Whole Numbers And With Decimals To Hundredths. / Add, subtract, multiply, and divide decimals to hundredths, using concrete models or drawings and strategies based on place value, properties of operations, and/or the relationship between addition and subtraction; relate ...
Step 1: Line the numbers up by place value. Step 2: Multiply the bottom number by each digit of the top number. Step 3: Start with the ones. Step 4: Next, multiply the tens. McGraw Hill My Math Grade 5 Chapter 2 Lesson 9 My Homework Answer Key. Practice. Estimate. Then multiply. Use your estimate to check your answer. Question 1. Answer: 144 ...
Multiply multi-digit whole numbers using the standard algorithm. Section B Goals. Divide multi-digit whole numbers using strategies based on place value, properties of operations, and the relationship between multiplication and division. Section C Goals. Multiply and divide to solve real-world and mathematical problems involving area and volume.
Step 2: Multiply any one of the numbers by the 'ones' digit of the second number. Step 3: Multiply the number by the tens digit of the number. Step 4: Finally, add the two partial products to get the final product and verify it with the estimated product. McGraw Hill My Math Grade 5 Chapter 2 Lesson 10 My Homework Answer Key. Practice ...