Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals

Library science articles from across Nature Portfolio
Latest research and reviews.

Emerging landscapes of “alternative-academic” careers in library and information science: Evolutionary patterns and prospects in the Chinese context
- Kuang-Hua Chen
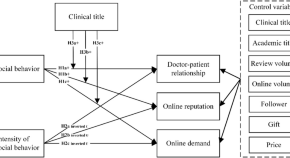
The effect of prosocial behavior and its intensity on doctors’ performance in an online health community
- Yuguang Xie
- Shuping Zhao
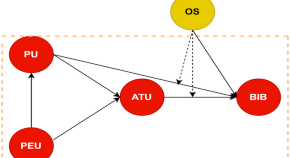
What factors influence the intention to adopt blockchain technology in accounting education?
- Hamood Mohammed Al-Hattami
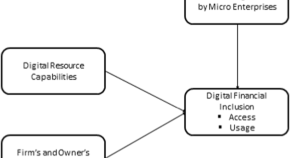
Digital financial inclusion in micro enterprises: understanding the determinants and impact on ease of doing business from World Bank survey
- Mohammad Asif
- Mohammad Wasiq
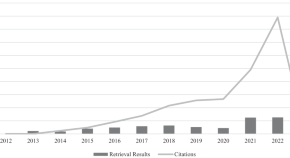
Big data visualisation in regional comprehensive economic partnership: a systematic review
What determines digital accounting systems’ continuance intention? An empirical investigation in SMEs
- Faozi A. Almaqtari
News and Comment
Pandemic publishing poses a new COVID-19 challenge
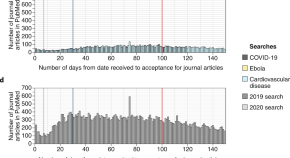
The scientific community’s response to COVID-19 has resulted in a large volume of research moving through the publication pipeline at extraordinary speed, with a median time from receipt to acceptance of 6 days for journal articles. Although the nature of this emergency warrants accelerated publishing, measures are required to safeguard the integrity of scientific evidence.
- Adam Palayew
- Ole Norgaard
- Jeffrey V. Lazarus
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies

Emerging Topics, Challenges, and Strategies for Library and Information Science Education
- Jiangping Chen University of Illinois, Urbana Champaign
- Natalie Taylor University of South Florida
- Abebe Rorissa University of Tennessee, Knoxville
Library and Information Studies (LIS) has become more multidisciplinary and interdisciplinary with the application of advanced information technologies. It evolves from traditional areas that focus on organizing print materials and providing access services to library patrons to applying technologies to collect, organize, retrieve, and analyze digital information in different formats. In recent years, misinformation, DEI (diversity, equity, and inclusiveness), and generative artificial intelligence (AI) based on large language models and other topics have been popular and important topics that attract the attention of educators and scholars in a variety of disciplines. Collaboration is becoming more and more important for LIS scholars in investigating these challenging topics. Significant research has been conducted to explore these topics. Furthermore, academic departments and programs in LIS have started to reassess and provide up-to-date curricula so our graduates can possess the knowledge and skills required to excel in current complicated information environments. There is a need for LIS schools and programs to share their experiences and learn from others on strategies to deal with new topics for educating leading information professionals.
This panel will discuss the emerging topics that are relevant to LIS, the challenges of teaching these new topics, and possible strategies for LIS education. The panelists are program directors or department chairs who have led the curriculum reassessment in their respective schools or programs. We will share our thoughts with the community and provide our experience and lessons for other LIS programs on strategic planning. Specifically, we will try to address the following questions based on recent literature, curriculum, and the practice of respective LIS schools or programs:
- What are the new topics or areas that your program or school has added to your curriculum in recent three years? What are the considerations behind the curriculum decisions?
- What are important topics and/or areas that have not been added? What are the new courses you would recommend LIS programs and schools to offer to master and undergraduate students?
- Based on graduates’ feedback, has your program met the needs of your students? What topics or areas do students need courses or training in?
- What are the top three challenges for educating future information science professionals?
- How does the department or information school gain support from the university administration on new programs?
Following the panelists’ presentation, the panel will invite the audience to share their answers and experiences. We also welcome questions from the audience related to the panelists' presentations. Then, the whole session may move to discuss the specific topic(s) that most of the audience is interested in. Panelists and the audience will interact actively on these topics to achieve the most benefits of the session.
We believe this panel will attract not only program directors, chairs, and deans but also LIS faculty members and students attending ALISE. The LIS leaders, such as program directors, chairs, and deans, could use this opportunity to share and learn from each other on strategic curriculum planning. Faculty and students will benefit from the discussion on new and important research topics and areas, which will help them to develop their research and instruction plans. The panelists and the audience will learn a great deal in this interactive session.
Author Biographies
Dr.Jiangping Chen is the Interim Executive Associate Dean & Visiting Professor at the School of Information Sciences
Dr. Natalie Taylor is an Associate Professor and the Director of the School of Information
Dr. Abebe Rorissa, is Professor and Director of the School of Information Sciences and was the Associate Dean for Faculty Affairs at the College of Communication and Information
Wang, D., Zhou, L., & Chowdhury, G. (2023). Connecting iSchools and society through scientific research: a worldwide exploratory study. Proceedings of the Associations for Information Science and Technology, October 27-31, London, United Kingdom. pp. available at: https://asistdl.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/pra2.844 .

Copyright (c) 2024 Jiangping Chen, Natalie Taylor, Abebe Rorissa

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License .
This proceedings is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
ALA Research & Library Topics
Ala library and information resource center, frequently asked questions about books and reading.
Answers to the questions that we receive most often about books and reading.
Resource Guides
Providing information on the work of the American Library Association, as well as subject-specific resources both for and about libraries.
Professional Resources: A to Z Index of Topics
Professional resources for librarians on a wide range of topics, in alphabetical order.
ALA Publications

Share This Page
College & Research Libraries News ( C&RL News ) is the official newsmagazine and publication of record of the Association of College & Research Libraries, providing articles on the latest trends and practices affecting academic and research libraries.
C&RL News became an online-only publication beginning with the January 2022 issue.
Members of the ACRL Research Planning and Review Committee: Brian D. Quigley (chair) is head of the sciences division at the University of California, Berkeley Library, email: [email protected] . Thomas R. Caswell (vice-chair) is associate dean for academic engagement at the University of Central Florida Libraries, email: [email protected] . Jennie M. Burroughs is senior program advisor and researcher at the University of Minnesota Libraries, email: [email protected] . Laura Costello is director of access and information services at the University of Minnesota Libraries, email: [email protected] . cristalan ‘tal’ ness is linguistics librarian and social sciences resident librarian at the University of Michigan, email: [email protected] . Kristin Van Diest is digital publishing librarian at Texas State University, email: [email protected] . Minglu Wang is research data management librarian at York University, email: [email protected] . Anna Yang is science librarian at Santa Clara University, email: [email protected] .
ALA JobLIST
Advertising Information
- Preparing great speeches: A 10-step approach (254138 views)
- The American Civil War: A collection of free online primary sources (212805 views)
- 2018 top trends in academic libraries: A review of the trends and issues affecting academic libraries in higher education (78537 views)
ACRL Research Planning and Review Committee
2024 Top Trends in Academic Libraries
A Review of the Trends and Issues
T his article explores the topics and issues that have been trending in academic libraries over the past two years. It draws on research and initiatives from librarians across the profession, highlighting the constant change libraries face. The launch of ChatGPT sparked discussions about the potential impact of artificial intelligence, open access and open science initiatives continued to gain momentum, and the lingering effects of COVID-19 on library workspaces and student well-being remained significant. Rich citations to the literature provide opportunities for further exploration.
AI and AI Literacy
Artificial intelligence (AI) has been a trend in academic libraries for several years, but the release of ChatGPT and other generative AI tools has sparked renewed interest in the topic. This could have profound implications for academic libraries in the future. As Andrew M. Cox and Suvodeep Mazumdar note, “There is immense potential for it to increase access to knowledge in fundamental ways, for example through improved search and recommendation, through description of digital materials at scale, through transcription, and through automated translation.” 1 AI also raises a host of ethical and legal issues, ranging from concerns about bias, privacy, non-representative training data, and misinformation to issues around copyright, plagiarism, and exploitation. 2
Due to their ease of use, generative AI tools like ChatGPT have become extremely popular. These tools leverage large language models (LLMs) trained on massive datasets of text or images. LLMs use neural networks and natural language processing to analyze input prompts and generate responses based on the statistical patterns learned from the training data. Beyond ChatGPT, AI is also being incorporated into literature searching, summarization, and programming tools such as Elicit, Semantic Scholar, scite, and Copilot for GitHub. 3 With the growing popularity of these tools among students, faculty are increasingly turning to librarians to help cultivate AI literacy, discussing AI and its impact on literature searching and citations with their classes. 4
Duri Long and Brian Magerko define AI literacy “as a set of competencies that enables individuals to critically evaluate AI technologies; communicate and collaborate effectively with AI; and use AI as a tool online, at home, and in the workplace.” 5 Leo S. Lo outlines a framework to assist librarians and students in developing more effective prompts for generative AI, a process called prompt engineering. As he states, using his framework, “librarians can help students develop critical thinking skills, improve their comprehension of AI-generated content, and optimize AI-based research processes.” 6 It is also important to raise awareness among students of the potential problems associated with AI including accuracy, hallucinations, bias, ethical issues, and environmental impact. Some institutions have begun developing workshop series to discuss and facilitate conversations with students about these issues, 7 and the University of Florida has started an AI Across the Curriculum initiative to introduce all undergraduate students to AI and better prepare them for the future workforce. 8
Academic libraries have also been pursuing possible roles for AI within the library itself. This has included setting up AI research spaces, exploring robotics, investigating ethical issues and implicit bias in machine learning, and experimenting with using AI to classify images, refine metadata, and improve discovery. 9 Many also see a broader role for libraries within the AI landscape. Fiona Bradley calls for libraries to be involved in AI discussions at the national level and notes that “the sector is already participating in consultations and processes to ensure that the future of AI is rights-based, ethical, and transparent.” 10
Open Pedagogy and Instructional Design
Although open educational resource (OER) initiatives are not new, libraries have recently begun expanding their impact by investigating the potential to enrich student learning through open pedagogy. In their timely book, Mary Ann Cullen and Elizabeth Dill explore the foundation, approaches, and implementation of open pedagogy as a strategy for information literacy in higher education. 11 Open pedagogy requires students to be actively involved in the design, creation, and curation of OER learning materials through renewable assignments. These assignments invite students to contribute to the production and dissemination of knowledge, pushing them past more traditional library projects. Wikipedia assignments are among the most popular forms of renewable assignments, encouraging students to find, evaluate, and improve upon the information on its pages. 12 Other examples of renewable assignments include creating research toolkits, online courses, ebooks, and living websites. 13 Each of these renewable assignments allows students to see themselves as active creators of information rather than passive consumers.
According to Eric Werth and Katherine Williams, to increase student motivation, “OER-enabled pedagogy must be structured in a way that allows autonomy, competence, and relatedness.” 14 Aligning OER projects with practical and real-world knowledge can positively impact student engagement. 15 At the heart of this engagement is inclusive practice. By creating a supportive environment where all students have access to the same materials, instructors foster inclusivity in their courses. 16 Instructors can also motivate students to see the value of open pedagogy by helping them find their own interests and passion within these assignments, 17 showing students that they have control over their content, 18 and demonstrating that their work can have a global impact. 19
Concerns have been raised about the high workload and long-term sustainability of open pedagogy. Kate McNally Carter and Ariana Santiago find that “workload was often minimized or entirely overlooked as a factor in many studies in favor of highlighting student success outcomes” and advise working toward sustainability by creating adaptable renewable assignments that can fit into many contexts and subject areas. 20 Bryan McGeary, Christopher Guder, and Ashwini Ganeshan further suggest that broad groups of staff should contribute to this important work for OER-enabled pedagogy to be sustainable. 21
Open Science and Reproducibility
As early advocates for open access and research data management, libraries are now assessing their potential roles in the burgeoning open science movement, which increasingly emphasizes equity, collaboration, reproducibility, security, and privacy in supporting the whole research ecosystem. 22 Much of this recent interest in open science has been spurred by the federal government, with US agencies collaborating on the Year of Open Science campaign, and NASA launching its Transform to Open Science (TOPS) initiative and Open Science 101 virtual training. 23 At the institutional level, many universities and libraries have joined the Higher Education Leadership Initiative for Open Scholarship (HELIOS Open), which aims to collaborate on “a more transparent, inclusive, and trustworthy research ecosystem” through presidential commitment, campus engagement, and communities of practice. 24
As open scholarship gains momentum, libraries face growing calls to expand their roles beyond technical support. Authors from UNESCO emphasize the need for libraries to be “a bridge between local contexts and the global scholarly community,” 25 while LIBER (Association of European Research Libraries) identifies “advancing open science” as a core component of its strategy, aiming for libraries to “stimulate, facilitate, co-develop and manage infrastructures and practices designed to take Open Science to the next level.” 26 Reflecting these calls, a recent book from ACRL positions open science as “an emerging synthesis of the various streams of open.” 27 It recommends changes to incentive structures and urges consolidation of siloed services to create an open infrastructure aligned with open research values and available equally to all researchers. By promoting open practices and facilitating infrastructure development, libraries can solidify their place as leaders in the evolving open scholarship landscape.
As advocates for open science, libraries also contribute to one of its key outcomes: reproducibility. 28 This new area of service requires librarians to become deeply integrated in research communities, understanding researchers’ needs and tools while simultaneously leveraging their unique position as institutional hubs to connect stakeholders and research services partners. 29 Thanks to stricter National Institutes of Health demands for research rigor and reproducibility, health science librarians have emerged as key players in educating researchers on these topics. Their success stories showcase libraries’ potential to deliver valuable instruction in this crucial area, while also underlining the critical need for collaborative partnerships to further enhance research reproducibility services. 30
Open Access and Equitable Publishing
In the wake of recent calls for more open research publication practices, researchers have been exploring the impact of article processing charges, transformative agreements, open access models, and new policy development on equity and access in publishing practices.
Findings show that faculty perceptions of open access publishing have remained virtually the same over the past twenty years, citing commonplace challenges that have yet to be resolved: uncertainty around the prestige of open access journals, confusion around types of open access, and lack of clarity and acceptance of open access in the promotion and tenure process. 31 On the other hand, students increasingly rely on open access articles in their assignments. A study of community college students found that 56.8% of their citations were open access articles, with one key benefit being that they “will still have access to open access search tools after they are no longer in college.” 32
Within that context, many researchers feel that the open access movement has been co-opted by commercial publishers and are advocating for a return to scholar-led publishing communities. Discussing the global limitations of corporate publishing, several authors urge libraries and consortia to support their research communities by avoiding bundled publishing service agreements, contributing to scholar-led initiatives, and redistributing funds to support the Global South. 33 In addition, there is growing understanding that open access does not necessarily mean universal accessibility. Multiple authors have shed light on the inequities within open access publishing, including design practices and publishing cost structures that are exclusionary; researchers recommend libraries focus on integrating accessibility practices into design 34 and support bibliodiversity to emphasize “the critical diversity of authors and scholarly works representing cultures, languages, genres and all kinds of scholarly and scientific endeavours.” 35
A series of new tools and proposals have recently been released to guide libraries and scholars as they work to support a values-driven publishing ecosystem. These guidelines call for systems that enable scholars to choose when their research is made public and decenter the journal article as the sole object of importance in the research lifecycle, 36 encourage libraries to align their publishing infrastructure and practices with key values and ethical frameworks, 37 and propose helping “new and established open access journals in navigating the rapidly changing landscape of open access publishing.” 38
Disrupting and Reconceiving Collection Practices
While there had been actions and initiatives relating to diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) in libraries before 2020, much of that effort consisted of broad advocacy and raising awareness. 39 Libraries are increasingly recognizing that making good on public statements will require firm resource commitments, disruption of existing systems, and sustained action in multiple arenas. 40 This work requires deep reflection and disruption: deconstructing systems for collecting and describing materials, deconstructing myths of librarian authority, and deconstructing student assumptions about information.
In recent years, libraries have begun putting more attention and action into re-evaluating library collections and collection management practices. Auditing collections through a social justice lens or to address colonialist and Euro-centric practices involves re-examining values, defining what “diversity” means in the context of collections, and setting tangible markers for progress. 41 In setting these parameters, it’s important to “embrace imperfection,” 42 which might include defining a more targeted goal or an initial starting point. 43 In each case, these efforts are leading to a re-examination of acquisition practices and systems, including approval plans and demand-driven acquisition programs, which may “amplify biases already present in the higher education and publishing industries.” 44
In addition to reallocating collection funds, libraries acting to make their collections more diverse and inclusive are reconsidering personnel commitments and involving more people in collection activities. Reversing earlier trends, some libraries are increasing staff time on collection development and cataloging, and they are partnering with underrepresented communities to select and describe materials. 45 This involves multiple points of outreach and consultation over the course of a project, and it requires libraries to embrace the complexities that their partners share about working with multiple communities. 46 Regardless of approach, libraries will need to consider how to sustain these improvements in collection building and management practices throughout changes in budgets, leadership, and staffing levels. 47
Politicization of Academic Libraries
The landscape of academic libraries continues to be significantly impacted and shaped by a highly political and polarizing climate. As academic libraries navigate this landscape, it becomes crucial for them to strike a balance between neutrality and civic engagement, acknowledging the inherent political dimensions of their collections, programs, and spaces. They must continue to maintain an active role in the enactment of democracy, despite ongoing and future threats.
Renowned scholar John Buschmann contends in several scholarly publications that libraries historically play an important role in the democratic fabric of society and navigate crises while persisting through terrorist acts, 48 politically charged environments, 49 and pandemics. 50 Even during extreme geopolitical crises like wars and international sanctions, libraries are implicated as active participants in affecting and responding to the complex sociopolitical environment they inhabit. 51 In trying to counter fake news rhetoric, libraries can unintentionally be drawn into political processes by simply providing research services and fighting misinformation and disinformation. 52 In one study, several land-grant university library websites were analyzed and found to indeed be “serving as significant providers of political information during politically turbulent times.” 53
Although censorship of library collections using “book bans” has primarily affected public libraries, academic libraries now find they too are being drawn into this heated dialogue, especially surrounding social justice, DEI, and antiracism initiatives. Zoë Abbie Teel contends that anti-DEI legislation may extend its impact to potentially influence library policies and acquisitions, including “the availability of certain materials’’ that may be seen as promoting DEI. 54 The question of whether libraries can remain “neutral” in the face of social injustice has created debate among library practitioners. 55 Steve Rosato discusses the role of academic librarians and publishers as “vanguards” of critical DEI content, 56 and Annis Lee Adams presents an array of antiracism resources to support library staff, emphasizing the active role libraries play in addressing racial issues. 57 Libraries can also amplify their antiracism resources by partnering with other campus stakeholders. 58 Two articles highlight the need for libraries to actively support inclusivity, with Qing H. Stellwagen and Steven Bingo emphasizing cultural celebrations as a means of creating a sense of community on campus 59 and Silvia Vong discussing the impact of racial capitalism on academic librarians and libraries, specifically focusing on issues of representation and equity within library staff. 60
Anti-DEI Legislation, Academic Freedom, and Unionization
In recent years, academic librarians and library staff have experienced the growing challenge of low morale and burnout. 61 Compounding this for many staff, a recent wave of anti-DEI legislation has been introduced and passed in many states. These laws impose restrictions on DEI offices, staff training, diversity statements, and “identity-based preferences for hiring and admissions,” with one state’s legislation compelling public colleges to designate “agents” to oversee “prohibitions on DEI spending.” 62 Some states have also severed ties with the American Library Association (ALA) 63 amid allegations that the association is constrained by its perspectives on gender ideology and a left-leaning bias. 64
The contentious atmosphere surrounding library associations and the uptick in book challenges, particularly against titles by or about LGBTQIA+ people and people of color or relating to DEI content, 65 have implications for academic libraries and academic freedom in particular. The Association of American University Professors emphasizes the significance of “academic freedom, tenure, and shared governance” in providing a foundation for faculty members. 66 Tenure is seen as a crucial safeguard against the censorship and book banning observed in school libraries, ensuring impartiality and protecting academic libraries. 67
Unions may also play a role in protecting academic freedom. Higher education has witnessed an increase in union activities, strikes, and labor activism recently. 68 The pandemic has played a role in sparking these efforts, with one author suggesting it “exacerbated existing issues and brought up new ones,” 69 and 2023–24 ALA President Emily Drabinski has recognized the role of unions in protecting library workers from extremist groups, censorship, and unsafe conditions. 70 Library unions provide guarantees for fair wages, 71 improved working conditions, 72 the preservation of academic freedom, 73 and protection against unilateral decision-making, such as institutional reorganization and reimagining library workers’ research and roles. 74 The recent increase in union activities reflects a growing recognition of the power of collective bargaining to address the multifaceted challenges facing academic libraries in the current sociopolitical climate.
Post-pandemic Workplace and Hybrid Work Environments
The pandemic triggered widespread soul-searching, leading librarians to re-evaluate their priorities and seek workplaces aligned with their values. Not immune from “The Great Reshuffle,” many library staff have considered leaving their positions due to pandemic stress and lack of intrinsic motivators like work-life balance and growth. In a recent survey of academic librarians, nearly half said they were thinking of leaving their job “about half the time or more.” 75 When they remain, they want to have a role in defining the future. In one study, librarians “repeatedly emphasized the need for working conditions going forward to be governed through collegiality and conversation, rather than defaulting to the pre-pandemic organizational norms.” 76 Andrea Falcone and Lyda Fontes McCartin suggest that libraries must adapt to this shift by prioritizing talent retention through improved compensation, workload management, and flexible work options. 77 At the same time, perceived inequities within libraries and universities can fuel dissatisfaction and burnout. 78 Academic librarians may also risk burnout due to the emotional labor inherent in their work: “Meeting the societal and user expectations of being a librarian requires simultaneously regulating or performing one’s own emotions and interpreting, managing, and responding to the emotions of users.” 79 Effective prevention requires emotional literacy and supportive leadership that acknowledges the emotional toll and promotes decompression strategies, especially for librarians of color who often bear the brunt of this burden. 80
In this new workplace environment, many libraries are embracing flexible work arrangements as one strategy for addressing dissatisfaction and burnout. “Many workers now perceive pre-pandemic work modalities and workplace expectations as unnecessary, unrealistic, and undesirable, and employers have taken notice of the shift in employee attitudes.” 81 In fact, recent surveys have shown that three-quarters of academic libraries now offer hybrid work environments with flexible work arrangements. These same studies note that remote work offers benefits like greater productivity and reduced stress while onsite work fosters better onboarding, engagement, and team building. As a result, even when flexible work arrangements are available, usage by staff varies widely, suggesting a diverse workforce with a range of preferences. 82 To foster trust, knowledge, empathy, and community in such a hybrid environment, institutions must acknowledge its complexities and invest in intentional efforts to rebuild a strong academic workplace culture. 83 This new hybrid environment may also require redesigning staff spaces and setting new priorities for onsite work. The physical office is predicted to transform into a space for building social connections, fostering learning, and sparking innovation, which will necessitate intentional leadership that prioritizes face-to-face interaction and facilitates collaboration within a redesigned office environment. 84

Makerspaces and Tech Spaces
Designed for innovative and creative experimentation, makerspaces are defined as “low- and high-tech communal learning environments where people can create, build, and invent with digital and fabrication tools.” 85 While makerspaces started mostly in engineering departments, libraries quickly adopted the idea to become leaders in innovation through technology. In fact, the library is now the most common place for a makerspace to live on an academic campus. 86 Makerspaces found in academic libraries tend to “focus on digital fabrication, using computerized software-driven equipment,” with 3D printers and laser cutters being “the most commonly described equipment in Makerspaces in the research literature.” 87
As libraries continue to assess their user needs, support for these spaces is increasingly important. However, maintaining a thriving makerspace does not come without challenges, which include proper staffing and financial support for costly technology. 88 Despite these challenges, librarians are collaborating more through their makerspaces to amplify student engagement in the library. While not every endeavor has been successful, initiatives like the 3D Selfie Booth 89 and Game Jam 90 showcase library staff’s creativity and highlight positive interactions with makerspace technology, leading authors to express interest in deeper collaboration.
By analyzing student learning styles against major typologies of learning, the effectiveness of the makerspace on student engagement becomes clear. Students using these spaces learn through creation and interaction—with a community, experts, and a real-world environment. In makerspaces, “students are engaging in both content and culture knowledge and skills along with communication, management, ingenuity, and self-awareness.” 91 Students who visit makerspaces on a regular basis are more inclined to continue their use over time, indicating that ongoing engagement is crucial for students to perceive the usefulness of the space. 92
Makerspaces enable students to build self-efficacy, explore their entrepreneurial spirit, 93 and learn skills that will last them long past their academic career. Evolving alongside patron needs, academic libraries are integrating makerspaces into their future vision, offering access to new technologies, collaborative opportunities, and platforms for exploring personal interests. 94
Supporting Student Well-being Post-pandemic
The changes to learning environments and increased social isolation during the COVID-19 pandemic had a mental health impact on current and incoming college students including increased rates of depression and anxiety. 95 Academic libraries are adopting new strategies to address student mental health and well-being that go beyond scholarship to support for the whole student. 96 The “whole-university” approach is in use in some institutions with libraries serving as a vital part of an interconnected team of university offices working together to support student mental health. 97 These efforts align with trends focused on offering more personalized, socially centered service in libraries, 98 and they also relate to initiatives to support the evolving usage of library space. Students value the library as a social space and visit libraries as a way to overcome social isolation and find community. 99 For example, students in a recent focus group study noted using physical library spaces to socialize and de-stress 100 while librarians at Virginia Commonwealth University created a guide with audio and visual resources to help students re-create the library mood from home during the pandemic. 101 As another way to prioritize student wellness, libraries are adding leisure reading collections to support mindfulness, 102 and they are weaving mindfulness practices into information literacy instruction. 103 Academic librarians have also been looking inward, acknowledging the emotional work involved in supporting students and managing change through the pandemic. 104
The future holds many hurdles for academic librarians, such as the possible impacts of AI on higher education and the uncertainty of recurring operating and materials budgets. We are simultaneously thrilled by the new possibilities for hybrid teamwork and workspaces, the growing demand for diverse viewpoints, and the integration of innovative methods to provide access to our common resources. These challenges will require new policies and practices, but they will also enable us to innovate, adapt, and respond to complex and evolving phenomena in our common pursuit of supporting student achievement and enhancing teaching, learning, and academic research.
- Andrew M. Cox and Suvodeep Mazumdar, “Defining Artificial Intelligence for Librarians,” Journal of Librarianship and Information Science , published ahead of print (December 22, 2022), https://doi.org/10.1177/09610006221142029 , p. 2.
- Fiona Bradley, “Representation of Libraries in Artificial Intelligence Regulations and Implications for Ethics and Practice,” Journal of the Australian Library and Information Association 71, no. 3 (July 3, 2022): 189–200, https://doi.org/10.1080/24750158.2022.2101911 ; Mohammad Hosseini and Kristi Holmes, “The Evolution of Library Workplaces and Workflows via Generative AI,” College & Research Libraries 84, no. 6 (November 1, 2023): 836–42, https://doi.org/10.5860/crl.84.6.836 ; Aileen B. Houston and Edward M. Corrado, “Embracing ChatGPT: Implications of Emergent Language Models for Academia and Libraries,” Technical Services Quarterly 40, no. 2 (April 3, 2023): 76–91, https://doi.org/10.1080/07317131.2023.2187110 .
- Matthew Hutson, “Could AI Help You to Write Your Next Paper?,” Nature 611, no. 7934 (October 31, 2022): 192–93, https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-022-03479-w .
- Lauren Coffey, “AI, the Next Chapter for College Librarians,” Inside Higher Ed , November 3, 2023, https://www.insidehighered.com/news/tech-innovation/libraries/2023/11/03/ai-marks-next-chapter-college-librarians .
- Duri Long and Brian Magerko, “What Is AI Literacy? Competencies and Design Considerations,” in Proceedings of the 2020 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI ‘20: CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Honolulu HI USA: ACM, 2020), 1–16, https://doi.org/10.1145/3313831.3376727 , p. 2.
- Leo S. Lo, “The CLEAR Path: A Framework for Enhancing Information Literacy through Prompt Engineering,” The Journal of Academic Librarianship 49, no. 4 (July 2023): 102720, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acalib.2023.102720 , p. 3.
- Amanda Wheatley and Sandy Hervieux, “Separating Artificial Intelligence from Science Fiction: Creating an Academic Library Workshop Series on AI Literacy,” in The Rise of AI: Implications and Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Academic Libraries , ACRL Publications in Librarianship 78 (Chicago: Association of College & Research Libraries, 2022), 61–70.
- Jane Southworth, Kati Migliaccio, Joe Glover, Ja’Net Glover, David Reed, Christopher McCarty, Joel Brendemuhl, Aaron Thomas, “Developing a Model for AI Across the Curriculum: Transforming the Higher Education Landscape via Innovation in AI Literacy,” Computers and Education: Artificial Intelligence 4 (2023): 100127, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.caeai.2023.100127 .
- Sandy Hervieux and Amanda Wheatley, eds., The Rise of AI: Implications and Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Academic Libraries , ACRL Publications in Librarianship 78 (Chicago: Association of College & Research Libraries, 2022).
- Bradley, “Representation of Libraries in Artificial Intelligence,” 196.
- Mary Ann Cullen and Elizabeth Dill, eds., Intersections of Open Educational Resources and Information Literacy (Chicago: Association of College & Research Libraries, 2022).
- Yolanda Bergstrom-Lynch, Mary Mahoney, and Joelle Thomas, “Empowering Students as OER Creators to Challenge Information Privilege,” in Intersections of Open Educational Resources and Information Literacy , ed. Mary Ann Cullen and Elizabeth Dill (Chicago: Association of College & Research Libraries, 2022), 237–64; Jolie A. L. Gareis, Erin I. Larson, Marcelo Ardón, John A. Berges, Jessica E. Brandt, Kaitlyn M. Busch, Victoria L. S. Chraibi, Elizabeth N. Gallagher, Kelly L. Hondula, Dustin W. Kincaid et al., “Using Wikipedia Assignments to Teach Critical Thinking and Scientific Writing in STEM Courses,” Frontiers in Education 7 (2022), https://doi.org/10.3389/feduc.2022.905777 ; Diana E. Park and Laurie M. Bridges, “Meet Students Where They Are: Centering Wikipedia in the Classroom,” Communications in Information Literacy 16, no. 1 (March 2022): 4–23, https://doi.org/10.15760/comminfolit.2022.16.1.2 ; Paul Anthony Thomas, Matthew Jones, and Spencer Mattingly, “Using Wikipedia to Teach Scholarly Peer Review: A Creative Approach to Open Pedagogy,” Journal of Information Literacy 15, no. 2 (August 6, 2021), https://doi.org/10.11645/15.2.2913 .
- Teresa Schultz and Elena S. Azadbakht, “Exploring Open Pedagogy in a Librarian-Taught Honors Course,” Communications in Information Literacy 17, no. 1 (June 1, 2023): 221–37, https://doi.org/10.15760/comminfolit.2023.17.1.2 ; Torrey Trust, Robert W Maloy, and Sharon Edwards, “College Student Engagement in OER Design Projects: Impacts on Attitudes, Motivation, and Learning,” Active Learning in Higher Education 24, no. 3 (November 1, 2023): 353–71, https://doi.org/10.1177/14697874221081454 ; Peter Daniel Wallis, Jennifer Mae White, and Stephen T. Kerr, “High Structure Renewable Assignments: A Design Study,” Open Praxis 14, no. 1 (January 2022): 39–53, https://doi.org/10.55982/openpraxis.14.1.146 ; Lindsey Gumb, “OER-Enabled Pedagogy Meets Info Lit: Empowering the Next Generation of Open Scholars,” in Intersections of Open Educational Resources and Information Literacy , ed. Mary Ann Cullen and Elizabeth Dill (Chicago: Association of College & Research Libraries, 2022), 49–68.
- Eric Werth and Katherine Williams, “What Motivates Students about Open Pedagogy? Motivational Regulation through the Lens of Self-Determination Theory,” International Review of Research in Open and Distributed Learning 22, no. 3 (August 1, 2021): 34–54, https://doi.org/10.19173/irrodl.v22i3.5373 , p. 48.
- Vanessa Arce and Rena D Grossman, “Students Speak: Animating Stories about the Value of Information,” in Intersections of Open Educational Resources and Information Literacy , ed. Mary Ann Cullen and Elizabeth Dill (Chicago: Association of College & Research Libraries, 2022), 199–211; Trust, Maloy, and Edwards, “College Student Engagement in OER Design Projects.”
- Lauren Hays and Melissa N. Mallon, “Using OER to Promote Inclusion in Higher Education Institutions,” Currents in Teaching & Learning 12, no. 2 (January 2021): 20–33; Wallis, White, and Kerr, “High Structure Renewable Assignments.”
- Eric Werth and Katherine Williams, “Learning to Be Open: Instructor Growth through Open Pedagogy,” Open Learning: The Journal of Open, Distance and e-Learning 38, no. 4 (October 2, 2023): 301–14, https://doi.org/10.1080/02680513.2021.1970520 .
- Erika Bailey and Marisa Petrich, “Grounded in Agency: Privacy Literacy for Student Empowerment,” Alki: The Washington Library Association Journal 38, no. 3 (2022): 31–37.
- Trust, Maloy, and Edwards, “College Student Engagement in OER Design Projects.”
- Kate McNally Carter and Ariana Santiago, “Exploring Sustainability in Library Support for Open Pedagogy Collaborations,” Communications in Information Literacy 17, no. 1 (June 1, 2023): 238–59, https://doi.org/10.15760/comminfolit.2023.17.1.3 , p.241.
- Bryan McGeary, Christopher Guder, and Ashwini Ganeshan, “Opening up Educational Practices through Faculty, Librarian, and Student Collaboration in OER Creation: Moving from Labour-Intensive to Supervisory Involvement,” Partnership: The Canadian Journal of Library & Information Practice & Research 16, no. 1 (January 2021): 1–27, https://doi.org/10.21083/partnership.v16i1.6149 .
- “Open Science Announcements from Federal Agencies,” Science.gov , 2023, https://open.science.gov/ .
- “Take Open Science 101,” NASA Transform to Open Science, 2023, https://nasa.github.io/Transform-to-Open-Science/take-os101/ .
- “Higher Education Leadership Initiative for Open Scholarship,” HELIOS Open, 2024, https://www.heliosopen.org .
- Ana Peršić and Tiffany Straza, “Open Science for All: Implementing the UNESCO Recommendation on Open Science for an Equitable and Just Transition to Open Science,” College & Research Libraries News 84, no. 10 (November 2, 2023), https://doi.org/10.5860/crln.84.10.377 , p. 381.
- “Strategy 2023–2027,” LIBER Europe, 2023, https://libereurope.eu/strategy/ .
- Maria Bonn, Josh Bolick, and Will Cross, eds., Scholarly Communication Librarianship and Open Knowledge (Chicago: Association of College & Research Libraries, 2023), p. 82.
- Joshua Quan, “Toward Reproducibility: Academic Libraries and Open Science,” in Data Science in the Library: Tools and Strategies for Supporting Data-Driven Research and Instruction , ed. Joel Herndon (London: Facet, 2022), 57–68.
- Birgit Schmidt et al., “Emerging Roles and Responsibilities of Libraries in Support of Reproducible Research,” LIBER Quarterly: The Journal of the Association of European Research Libraries 33, no. 1 (2023): 1–21, https://doi.org/10.53377/lq.14947 .
- Fred Willie Zametkin LaPolla et al., “Rigor and Reproducibility Instruction in Academic Medical Libraries,” Journal of the Medical Library Association: JMLA 110, no. 3 (2022): 281–93, https://doi.org/10.5195/jmla.2022.1443 ; Mark MacEachern and Sara Samuel, “Research Reproducibility Activities in Health Sciences Libraries,” Journal of eScience Librarianship 12, no. 2 (August 10, 2023): e650, https://doi.org/10.7191/jeslib.650 .
- Elisabeth Shook and Amy Vecchione, “Faculty Perceptions of Open Access Publishing: Investigating Faculty Publishing Habits to Evaluate Library Collection Alignment,” Journal of Librarianship and Scholarly Communication 10, no. 1 (December 16, 2022), https://doi.org/10.31274/jlsc.13216 .
- Tim Dolan and Duncan Claflin, “Assessing the Value of Subscription Journal Packages and Open Access Journal Articles in a Community College Context,” Journal of Librarianship and Scholarly Communication 11, no. 1 (July 28, 2023), https://doi.org/10.31274/jlsc.15673 .
- Björn Brembs et al., “Replacing Academic Journals,” Royal Society Open Science 10 (July 19, 2023): 230206, https://doi.org/10.1098/rsos.230206 ; Emily Cox, “Research Outputs as Testimony & the APC as Testimonial Injustice in the Global South,” College & Research Libraries 84, no. 4 (2023), https://doi.org/10.5860/crl.84.4.513 ; Katherine Elizabeth Skinner, Catherine Mitchell, and Kristen Ratan, “‘Bundle of Sticks’ and the Value of Interdependence: Building a Tools and Services Collective,” The Journal of Electronic Publishing 25, no. 1 (April 26, 2022), https://doi.org/10.3998/jep.1994 .
- Matthew Weirick Johnson and Salma Abumeeiz, “The Limits of Inclusion in Open Access: Accessible Access, Universal Design, and Open Educational Resources,” Journal of Librarianship and Scholarly Communication 11, no. 1 (August 8, 2023), https://doi.org/10.31274/jlsc.14399 .
- Lai Ma, Jane Buggle, and Marie O’Neill, “Open Access at a Crossroads: Library Publishing and Bibliodiversity,” Insights the UKSG Journal 36 (May 9, 2023): 10, 1–8, https://doi.org/10.1629/uksg.613 , p. 1.
- Bodo Stern, Zoé Ancion, Andreas Björke, Ashley Farley, Marte Qvenild, Katharina Rieck, Joroen Sondervan, Johan Rooryck, Robert Kiley, Maria Karatzia, and Nora Papp., “Towards Responsible Publishing: Seeking Input from the Research Community to a Draft Proposal from cOAlition S,” Zenodo, October 31, 2023, https://doi.org/10.5281/ZENODO.8398480 .
- Sarah Lippincott and Katherine Skinner, “FOREST Framework for Values-Driven Scholarly Communication” (Educopia Institute, 2022), https://www.nextgenlibpub.org/forest-framework ; Library Publishing Coalition, “An Ethical Framework for Library Publishing, Version 2.0,” May 2023, https://librarypublishing.org/resources/ethical-framework/ .
- Alex Mendonça, Andrea Chiarelli, Andy Byers, Andy Nobes, Chris Hartgerink, Clarissa França Dias Carneiro, Elle Malcolmson, Ivonne Lujano, Katie Foxall, Lucia Loffreda et al., “The Open Access Journals Toolkit (English),” Zenodo, June 27, 2023, https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.8017033 .
- Emily P. Jones, Nandita S. Mani, Rebecca B. Carlson, Carolyn G. Welker, Michelle Cawley, and Fei Yu, “Analysis of Anti-Racism, Equity, Inclusion and Social Justice Initiatives in Library and Information Science Literature,” Reference Services Review 50, no. 1 (March 2, 2022): 81–101, https://doi.org/10.1108/RSR-07-2021-0032 .
- Monica Figueroa and Kristan Shawgo, “‘You Can’t Read Your Way out of Racism’: Creating Anti-Racist Action out of Education in an Academic Library,” Reference Services Review 50, no. 1 (2022): 25–39, https://doi.org/10.1108/RSR-06-2021-0025 .
- Kara Bledsoe, Danielle Miriam Cooper, Roger C. Schonfeld, and Oya Y. Rieger, “Leading by Diversifying Collections: A Guide for Academic Library Leadership” (Ithaka S+R, November 9, 2022), https://doi.org/10.18665/sr.317833 .
- Bledsoe et al., “Leading by Diversifying Collections,” 11.
- Renae J. Watson, Khaleedah Thomas, and Kristine Nowak, “Adhocking It: Overcoming the Overwhelm to Start Creating: Equitable and Inclusive Collections Now,” in Practicing Social Justice in Libraries , ed. Alyssa Brissett and Diana Moronta (Routledge, 2023); Jessica M. Abbazio, Avery Boddie, and Ellen Ogihara, “Music Libraries and an Expanding Repertory: Suggested Strategies for Building Diverse Music Library Collections,” Notes (Music Library Association) 78, no. 3 (2022): 353–79, https://doi.org/10.1353/not.2022.0005 ; Veronica Wells, Michele Gibney, and Mickel Paris, “Student Learning and Engagement in a DEI Collection Audit: Applying the ACRL Framework for Information Literacy,” College & Research Libraries News 83, no. 8 (2022), https://doi.org/10.5860/crln.83.8.335 .
- Lori Jahnke, Kyle Tanaka, and Christopher Palazzolo, “Ideology, Policy, and Practice: Structural Barriers to Collections Diversity in Research and College Libraries,” College & Research Libraries 83, no. 2 (2022), https://doi.org/10.5860/crl.83.2.166 , p. 175.
- Bledsoe et al., “Leading by Diversifying Collections.”
- Heather M. Campbell, Christopher S. Dieckman, Nausicaa L. Rose, and Harriet E. Wintermute, “Improving Subject Headings for Iowa Indigenous Peoples,” Library Resources & Technical Services 66, no. 1 (March 11, 2022): 48, https://doi.org/10.5860/lrts.66n1.48 .
- Colleen S. Mullally, Jeremy Whitt, and Kayla Valdivieso, “Starting and Sustaining JEDI Acquisitions and Collections in Academic Libraries: Considerations and Strategies for Success,” in Perspectives on Justice, Equity, Diversity, and Inclusion in Libraries , ed. Nandita S. Mani, Michelle A. Cawley, and Emily P. Jones (IGI Global, 2023), 104–22, https://doi.org/10.4018/978-1-6684-7255-2.ch006 .
- John Buschman, “Libraries, Democracy, and Citizenship: Twenty Years after 9/11,” The Library Quarterly 93, no. 2 (April 1, 2023): 181–201, https://doi.org/10.1086/723850 .
- John Buschman, “Confusion Made Its Masterpiece: The Political Climate of Libraries (and Moving Forward),” The Library Quarterly 91, no. 2 (April 1, 2021): 129–36, https://doi.org/10.1086/713045 .
- John Buschman, “COVID-19 Doesn’t Change Anything: Neoliberalism, Generation-ism, Academic Library Buildings, and Lazy Rivers,” The Journal of Academic Librarianship 48, no. 4 (July 2022): 102558, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acalib.2022.102558 .
- Adebowale Adetayo, Khadijat Ajayi, and Ranmilowo Komolafe, “Wars and Sanctions: Do Libraries Have a Role to Play?,” The Reference Librarian 63, no. 3 (July 3, 2022): 102–17, https://doi.org/10.1080/02763877.2022.2100559 .
- Joe Kohlburn, Jenny Bossaller, Hyerim Cho, Heather Moulaison-Sandy, and Denice Adkins, “Public Libraries and COVID-19: Perceptions and Politics in the United States,” The Library Quarterly 93, no. 1 (January 1, 2023): 7–25, https://doi.org/10.1086/722547 ; Catherine Lockmiller, “Decoding the Misinformation-Legislation Pipeline: An Analysis of Florida Medicaid and the Current State of Transgender Healthcare,” Journal of the Medical Library Association 111, no. 4 (October 2, 2023): 750–61, https://doi.org/10.5195/jmla.2023.1724 .
- Bharat Mehra and Joseph Winberry, “‘Politic Talks’ in Academic Libraries of the South to Address a Global Democracy Recession in the United States: An Exploratory Website Analysis,” in Libraries and the Global Retreat of Democracy: Confronting Polarization, Misinformation, and Suppression , ed. Natalie Greene Taylor et al., Advances in Librarianship 50 (Bingley, UK: Emerald Publishing Limited, 2021), 183–210, https://doi.org/10.1108/S0065-283020210000050008 .
- Zoë Abbie Teel, “Guardians of Freedom: Examining Privacy, Censorship, and Government Legislation in Collection Development,” The Serials Librarian , September 27, 2023, 1–6, https://doi.org/10.1080/0361526X.2023.2245862 .
- Michael Dudley and John Wright, “The Role of Multidimensional Library Neutrality in Advancing Social Justice: Adapting Theoretical Foundations from Political Science and Urban Planning,” Journal of Intellectual Freedom & Privacy 7, no. 3 (2023), https://doi.org/10.5860/jifp.v7i3.7840 .
- Steve Rosato, “Legally Speaking—Banning Bans, aka What’s Happening in Illinois,” Against the Grain (blog), September 30, 2022, https://www.charleston-hub.com/2023/11/legally-speaking-banning-bans-aka-whats-happening-in-illinois/ .
- Annis Lee Adams, “Anti-Racism Resources,” Public Services Quarterly 17, no. 2 (April 3, 2021): 104–11, https://doi.org/10.1080/15228959.2021.1898519 .
- Leta Hendricks and Gene Springs, “Amplifying Antiracism Resources through Intra-University Collaboration,” Collaborative Librarianship 13, no. 1 (April 15, 2022), https://digitalcommons.du.edu/collaborativelibrarianship/vol13/iss1/6 .
- Qing H. Stellwagen and Steven Bingo, “Supporting an Inclusive Campus Community: An Academic Library’s Co-Sponsorship of Asian American and Native Hawaiian/Pacific Islander Heritage Month Celebrations,” Journal of Library Administration 63, no. 3 (April 3, 2023): 358–70, https://doi.org/10.1080/01930826.2023.2177926 .
- Silvia Vong, “Not a Token! A Discussion on Racial Capitalism and Its Impact on Academic Librarians and Libraries,” Reference Services Review 50, no. 1 (March 2, 2022): 127–47, https://doi.org/10.1108/RSR-06-2021-0024 .
- Ann Glusker, Celia Emmelhainz, Natalia Estrada, and Bonita Dyess, “‘Viewed as Equals’: The Impacts of Library Organizational Cultures and Management on Library Staff Morale,” Journal of Library Administration 62, no. 2 (February 17, 2022): 153–89, https://doi.org/10.1080/01930826.2022.2026119 .
- Adrienne Lu, “Here’s What Florida’s Proposed Anti-DEI Regulations Would Ban,” The Chronicle of Higher Education , October 12, 2023, https://www.chronicle.com/article/heres-what-floridas-proposed-anti-dei-regulations-would-ban .
- Andrew Atterbury, “Florida Joins Conservative States Severing Ties with National Library Group,” POLITICO Pro, October 31, 2023, https://subscriber.politicopro.com/article/2023/10/florida-joins-conservative-states-severing-ties-with-national-library-organization-ala-00124516 ; Madalaine Elhabbal, “Montana State Library Commission Breaks Ties with American Library Association Over New President,” CatholicVote (blog), July 11, 2023, https://catholicvote.org/mt-state-library-commission-breaks-ties-with-ala/ .
- Shannon M Oltmann, Toni Samek, and Louise Cooke, “Intellectual Freedom: Waving and Wavering across Three National Contexts,” IFLA Journal 48, no. 3 (October 2022): 439–48, https://doi.org/10.1177/03400352221085294 .
- Raymond Garcia, “American Library Association Reports Record Number of Demands to Censor Library Books and Materials in 2022,” ALAnews, March 2023, https://www.ala.org/news/press-releases/2023/03/record-book-bans-2022 .
- Diana Castillo and Kelly McElroy, “Solidarity Is for Librarians: Lessons from Organizing,” In the Library with the Lead Pipe , August 24, 2022, https://www.inthelibrarywiththeleadpipe.org/2022/solidarity/ .
- David Baca and Lamoya Burks, “Tenure, Critical Race Theory + Academic Libraries,” Texas Library Journal 98, no. 2 (2022): 60–61.
- Ryan Quinn, “Report: Higher Ed Unions and Strikes Surged in 2022, 2023,” Inside Higher Ed , September 1, 2023, https://www.insidehighered.com/news/quick-takes/2023/09/01/higher-ed-unions-strikes-surged-2022-2023 .
- Colleen Flaherty, “When Librarians Unionize,” Inside Higher Ed , January 11, 2022, https://www.insidehighered.com/news/2022/01/12/northwestern-librarians-unionize-following-furloughs-cuts .
- Emily Drabinski, “Facing Threat of Far Right Violence, Library Workers Seek Safety in Unionization,” Truthout, December 16, 2022, https://truthout.org/articles/facing-threat-of-far-right-violence-library-workers-seek-safety-in-unionization/ .
- Liam Knox, “School Starts With a Strike at American University,” Inside Higher Ed , August 22, 2022, https://www.insidehighered.com/news/2022/08/23/american-u-staff-strike-higher-wages .
- Flaherty, “When Librarians Unionize.”
- Castillo and McElroy, “Solidarity Is for Librarians.”
- Josh Moody, “Texas A&M Weighs Sweeping Changes to Library,” Inside Higher Ed , May 15, 2022, https://www.insidehighered.com/news/2022/05/16/texas-am-considers-making-sweeping-changes-library .
- Amy F. Fyn, Amanda Foster Kaufman, and Christina Heady, “Academic Librarian Turnover and Leadership Amidst the Great Reshuffle,” in Forging the Future: ACRL 2023 Proceedings (Chicago: Association of College & Research Libraries, 2023), https://www.ala.org/acrl/conferences/acrl2023/papers , p. 2.
- Amy McLay Paterson, “‘Just The Way We’ve Always Done It’: Who Shapes The New Normal for Academic Libraries?,” Canadian Journal of Academic Librarianship / Revue Canadienne de Bibliothéconomie Universitaire 8 (2022): 1–25, https://doi.org/10.33137/cjal-rcbu.v8.38476 , p.15.
- Andrea Falcone and Lyda Fontes McCartin, “Strategies for Retaining and Sustaining the Academic Librarian Workforce in Times of Crises,” Journal of Library Administration 62, no. 4 (May 19, 2022): 557–63, https://doi.org/10.1080/01930826.2022.2057132 .
- Fyn, Kaufman, and Heady, “Academic Librarian Turnover and Leadership Amidst the Great Reshuffle.”
- Matthew Weirick Johnson and Sylvia Page, “What’s in a Workload? Affect, Burnout, and Complicating Capacity in Academic Librarians,” in Academic Librarian Burnout: Causes and Responses (Chicago: Association of College & Research Libraries, 2022), https://escholarship.org/uc/item/6w86w41v , p. 52.
- Johnson and Page, “What’s in a Workload?”
- Ashlea Green, “Academic Library Employees and Their Work Modality Options and Preferences,” The Journal of Academic Librarianship 49, no. 5 (September 1, 2023): 102764, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acalib.2023.102764 , p. 1.
- Green, “Academic Library Employees and Their Work Modality Options and Preferences”; Daniel Pfeiffer, “New Data Reveal the Future of Remote Work in Libraries,” Choice 360 (blog), February 5, 2024, https://www.choice360.org/libtech-insight/new-data-reveal-the-future-for-remote-work-in-libraries/ .
- Joshua Kim, “Hybrid Work and the University Conversations We Need to Have,” Inside Higher Ed (blog), July 21, 2023, https://www.insidehighered.com/opinion/blogs/learning-innovation/2023/07/21/hybrid-work-and-university-conversations-we-need-have .
- Anne-Laure Fayard, John Weeks, and Mahwesh Khan, “Designing the Hybrid Office,” Harvard Business Review 99, no. 2 (March-April 2021): 114–23.
- Marijel (Maggie) Melo, Kimberly Hirsh, and Laura March, “Makerspaces in Libraries at U.S. Public Colleges and Universities: A Census,” portal: Libraries and the Academy 23, no. 1 (January 2023): 35–43, https://doi.org/10.1353/pla.2023.0007 , p.35.
- Melo, Hirsh, and March, “Makerspaces in Libraries at U.S. Public Colleges and Universities.”
- Emilia C. Bell, Stephanie Piper, and Carmel O’Sullivan, “Users’ Experiences in a Regional Academic Library Makerspace,” Journal of the Australian Library and Information Association 72, no. 2 (April 3, 2023): 135–49, https://doi.org/10.1080/24750158.2023.2202512 .
- Lawren Wilkins and John DeLooper, “If You Build It, Will They Come? Reflections on Creating a Community College Library Makerspace,” Public Services Quarterly 17, no. 4 (October 2, 2021): 276–85, https://doi.org/10.1080/15228959.2021.1887049 .
- Alex Watson, “To Thine Own 3D Selfie Be True: Outreach for an Academic Library Makerspace with a 3D Selfie Booth,” Information Technology and Libraries 42, no. 4 (December 18, 2023), https://doi.org/10.5860/ital.v42i4.15107 .
- Amber Sewell, “Game Jams for Academic Libraries: Lessons Learned from a Collaboration with the Makerspace,” College & Research Libraries News 85, no. 1 (2024), https://doi.org/10.5860/crln.85.1.23 .
- Megan Tomko, Melissa Alemán, Robert Nagel, Wendy Newstetter, Julie Linsey, “A Typology for Learning: Examining How Academic Makerspaces Support Learning for Students,” Journal of Mechanical Design 145, no. 9 (September 1, 2023): 091402, https://doi.org/10.1115/1.4062701 , p. 9.
- Bala Haruna and K. Kiran, “Intrinsic Motivation as a Determinant of Perceived Usefulness of Library Makerspace: The Influence of Learning Dimensions,” Malaysian Journal of Library and Information Science 28, no. 1 (May 11, 2023): 15–34, https://doi.org/10.22452/mjlis.vol28no1.2 .
- Sewell, “Game Jams for Academic Libraries.”
- Sarita S. Rajan, Mohamed Esmail, and Mohamed Musthafa K., “Repositioning Academic Libraries as a Hub of Technology Enhanced Learning Space: Innovations and Challenges,” Library Philosophy and Practice , January 10, 2022, https://digitalcommons.unl.edu/libphilprac/6694 .
- Jad A. Elharake, Faris Akbar, Amyn A. Malik, Walter Gilliam, and Saad B. Omer, “Mental Health Impact of COVID-19 among Children and College Students: A Systematic Review,” Child Psychiatry & Human Development 54, no. 3 (June 1, 2023): 913–25, https://doi.org/10.1007/s10578-021-01297-1 .
- Marta Bladek, “Student Well-Being Matters: Academic Library Support for the Whole Student,” The Journal of Academic Librarianship 47, no. 3 (May 1, 2021): 102349, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acalib.2021.102349 .
- Liz Brewster and Andrew M. Cox, “Taking a ‘Whole-University’ Approach to Student Mental Health: The Contribution of Academic Libraries,” Higher Education Research & Development 42, no. 1 (January 2, 2023): 33–47, https://doi.org/10.1080/07294360.2022.2043249 .
- Sheila Corrall, “The Social Mission of Academic Libraries in Higher Education,” in The Social Future of Academic Libraries: New Perspectives on Communities, Networks, and Engagement , ed. Paul Bracke, Sheila Corrall, and Tim Schlak (London: Facet, 2022), 109–48, https://doi.org/10.29085/9781783304738.007 .
- Yujin Kim and Eunhwa Yang, “Academic Library Spaces and Student Activities during the COVID-19 Pandemic,” The Journal of Academic Librarianship 48, no. 4 (July 1, 2022): 102529, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acalib.2022.102529 .
- Brendan Johnson, “Using the Physical Academic Library to Cope with Academic Stress,” Journal of Library Outreach and Engagement 3 (September 7, 2023): 35–49, https://doi.org/10.21900/j.jloe.v3.956 .
- Megan Hodge, “Library Mood: Re-Creating the Library Experience from Home,” portal: Libraries and the Academy 22, no. 1 (January 6, 2022): 227–40, https://doi.org/10.1353/pla.2022.0002 .
- Pauline Dewan, “Leisure Reading as a Mindfulness Activity: The Implications for Academic Reference Librarians,” The Reference Librarian 64, no. 1 (January 2, 2023): 1–16, https://doi.org/10.1080/02763877.2022.2156968 .
- Selenay Aytac and Diane Mizrachi, “The Mindfulness Framework for Implementing Mindfulness into Information Literacy Instruction,” The Reference Librarian 63, no. 1–2 (April 3, 2022): 43–61, https://doi.org/10.1080/02763877.2022.2030273 .
- Susan Carter, Cecily Andersen, Michaell Turner, and Lorraine Gaunt, “‘What about Us?’ Wellbeing of Higher Education Librarians,” The Journal of Academic Librarianship 49, no. 1 (January 1, 2023): 102619, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acalib.2022.102619 ; Maryellen Nash, Barbara Lewis, Jessica Szempruch, Stephanie Jacobs, and Susan Silver, “Together, Apart: Communication Dynamics among Academic Librarians during the COVID-19 Pandemic,” College & Research Libraries 83, no. 6 (November 2022): 946–65, https://doi.org/10.5860/crl.83.6.946 .
Article Views (Last 12 Months)
Contact ACRL for article usage statistics from 2010-April 2017.
Article Views (By Year/Month)
© 2024 Association of College and Research Libraries , a division of the American Library Association
Print ISSN: 0099-0086 | Online ISSN: 2150-6698
ALA Privacy Policy
ISSN: 2150-6698
Open Access is an initiative that aims to make scientific research freely available to all. To date our community has made over 100 million downloads. It’s based on principles of collaboration, unobstructed discovery, and, most importantly, scientific progression. As PhD students, we found it difficult to access the research we needed, so we decided to create a new Open Access publisher that levels the playing field for scientists across the world. How? By making research easy to access, and puts the academic needs of the researchers before the business interests of publishers.
We are a community of more than 103,000 authors and editors from 3,291 institutions spanning 160 countries, including Nobel Prize winners and some of the world’s most-cited researchers. Publishing on IntechOpen allows authors to earn citations and find new collaborators, meaning more people see your work not only from your own field of study, but from other related fields too.
Brief introduction to this section that descibes Open Access especially from an IntechOpen perspective
Want to get in touch? Contact our London head office or media team here
Our team is growing all the time, so we’re always on the lookout for smart people who want to help us reshape the world of scientific publishing.
Home > Books > Qualitative versus Quantitative Research
Research Methods in Library and Information Science
Submitted: 28 October 2016 Reviewed: 23 March 2017 Published: 28 June 2017
DOI: 10.5772/intechopen.68749
Cite this chapter
There are two ways to cite this chapter:
From the Edited Volume
Qualitative versus Quantitative Research
Edited by Sonyel Oflazoglu
To purchase hard copies of this book, please contact the representative in India: CBS Publishers & Distributors Pvt. Ltd. www.cbspd.com | [email protected]
Chapter metrics overview
6,091 Chapter Downloads
Impact of this chapter
Total Chapter Downloads on intechopen.com
Total Chapter Views on intechopen.com
Overall attention for this chapters
Library and information science (LIS) is a very broad discipline, which uses a wide rangeof constantly evolving research strategies and techniques. The aim of this chapter is to provide an updated view of research issues in library and information science. A stratified random sample of 440 articles published in five prominent journals was analyzed and classified to identify (i) research approach, (ii) research methodology, and (iii) method of data analysis. For each variable, a coding scheme was developed, and the articles were coded accordingly. A total of 78% of the articles reported empirical research. The rest 22% were classified as non‐empirical research papers. The five most popular topics were “information retrieval,” “information behaviour,” “information literacy,” “library services,” and “organization and management.” An overwhelming majority of the empirical research articles employed a quantitative approach. Although the survey emerged as the most frequently used research strategy, there is evidence that the number and variety of research methodologies have been increased. There is also evidence that qualitative approaches are gaining increasing importance and have a role to play in LIS, while mixed methods have not yet gained enough recognition in LIS research.
- library and information science
- research methods
- research strategies
- data analysis techniques
- research articles
Author Information
Aspasia togia *.
- Department of Library Science & Information Systems, Technological Educational Institute (TEI) of Thessaloniki, Greece
Afrodite Malliari
- DataScouting, Thessaloniki, Greece
*Address all correspondence to: [email protected]
1. Introduction
Library and information science (LIS), as its name indicates, is a merging of librarianship and information science that took place in the 1960s [ 1 , 2 ]. LIS is a field of both professional practice and scientific inquiry. As a field of practice, it includes the profession of librarianship as well as a number of other information professions, all of which assume the interplay of the following:
information content,
the people who interact with the content, and
the technology used to facilitate the creation, communication, storage, or transformation of the content [ 3 ].
The disciplinary foundation of LIS, which began in the 1920s, aimed at providing a theoretical foundation for the library profession. LIS has evolved in close relationship with other fields of research, especially computer science, communication studies, and cognitive sciences [ 4 ].
The connection of LIS with professional practice, on one hand, and other research fields on the other has influenced its research orientation and the development of methodological tools and theoretical perspectives [ 5 ]. Research problems are diverse, depending on the research direction, local trends, etc. Most of them relate to the professional practice although there are theoretical research statements as well. LIS research strives to address important information issues, such as these of “ information retrieval, information quality and authenticity, policy for access and preservation, the health and security applications of data mining ”(p. 3) [ 6 ]. The research is multidisciplinary in nature, and it has been heavily influenced by research designs developed in the social, behavioral, and management sciences and to a lesser extent by the theoretical inquiry adopted in the humanities [ 7 ]. Methods used in information retrieval research have been adapted from computer science. The emergence of evidence‐based librarianship in the late 1990s brought a positivist approach to LIS research, since it incorporated many of the research designs and methods used in clinical medicine [ 7 , 8 ]. In addition, LIS has developed its own methodological approaches, a prominent example of which is bibliometrics. Bibliometrics, which can be defined as “ the use of mathematical and statistical methods to study documents and patterns of publication ” (p. 38) [ 9 ], is a native research methodology, which has been extensively used outside the field, especially in science studies [ 10 ].
Library and information science research has been often criticized as being fragmentary, narrowly focused, and oriented to practical problems [ 11 ]. Many authors have noticed limited use of theory in published research and have advocated greater use of theory as a conceptual basis in LIS research [ 4 , 11 – 14 ]. Feehan et al. [ 13 ] claimed that LIS literature has not evolved enough to support a rigid body of its own theoretical basis. Jarvelin and Vakkari [ 15 ] argued that LIS theories are usually vague and conceptually unclear, and that research in LIS has been dominated by a paradigm which “ has made little use of such traditional scientific approaches as foundations and conceptual analysis, or of scientific explanation and theory formulation ” (p. 415). This lack of theoretical contributions may be associated with the fact that LIS emanated from professional practice and is therefore closely linked to practical problems such as the processing and organization of library materials, documentation, and information retrieval [ 15 , 16 ].
In this chapter, after briefly discussing the role of theory in LIS research, we provide an updated view of research issues in the field that will help scholars and students stay informed about topics related to research strategies and methods. To accomplish this, we describe and analyze patterns of LIS research activity as reflected in prominent library journals. The analysis of the articles highlights trends and recurring themes in LIS research regarding the use of multiple methods, the adoption of qualitative approaches, and the employment of advanced techniques for data analysis and interpretation [ 17 ].
2. The role of theory in LIS research
The presence of theory is an indication of research eminence and respectability [ 18 ], as well as a feature of discipline’s maturity [ 19 , 20 ]. Theory has been defined in many ways. “ Any of the following have been used as the meaning of theory: a law, a hypothesis, group of hypotheses, proposition, supposition, explanation, model, assumption, conjecture, construct, edifice, structure, opinion, speculation, belief, principle, rule, point of view, generalization, scheme, or idea ” (p. 309) [ 21 ]. A theory can be described as “ a set of interrelated concepts, definitions, and propositions that explains or predicts events or situations by specifying relations among variables ” [ 22 ]. According to Babbie [ 23 ], research is “ a systematic explanation for the observed facts and laws that related to a particular aspect of life ” (p. 49). It is “ a multiple‐level component of the research process, comprising a range of generalizations that move beyond a descriptive level to a more explanatory level ” [ 24 ] (p. 319). The role of theory in social sciences is, among other things, to explain and predict behavior, be usable in practical applications, and guide research [ 25 ]. According to Smiraglia [ 26 ], theory does not exist in a vacuum but in a system that explains the domains of human actions, the phenomena found in these domains, and the ways in which they are affected. He maintains that theory is developed by systematically observing phenomena, either in the positivist empirical research paradigm or in the qualitative hermeneutic paradigm. Theory is used to formulate hypotheses in quantitative research and confirms observations in qualitative research.
Glazier and Grover [ 24 ] proposed a model for theory‐building in LIS called “circuits of theory.” The model includes taxonomy of theory, developed earlier by the authors [ 11 ], and the critical social and psychological factors that influence research. The purpose of the taxonomy was to demonstrate the relationships among the concepts of research, theory, paradigms, and phenomena. Phenomena are described as “ events experienced in the empirical world ” (p. 230) [ 11 ]. Researchers assign symbols (digital or iconic representations, usually words or pictures) to phenomena, and meaning to symbols, and then they conceptualize the relationships among phenomena and formulate hypotheses and research questions. “ In the taxonomy, empirical research begins with the formation of research questions to be answered about the concepts or hypotheses for testing the concepts within a narrow set of predetermined parameters ” (p. 323) [ 24 ]. Various levels of theories, with implications for research in library and information Science, are described. The first theory level, called substantive theory , is defined as “ a set of propositions which furnish an explanation for an applied area of inquiry ” (p. 233) [ 11 ]. In fact, it may not be viewed as a theory but rather be considered as a research hypothesis that has been tested or even a research finding [ 16 ]. The next level of theory, called formal theory , is defined as “ a set of propositions which furnish an explanation for a formal or conceptual area of inquiry, that is, a discipline ” (p. 234) [ 11 ]. Substantive and formal theories together are usually considered as “middle range” theory in the social sciences. Their difference lies in the ability to structure generalizations and the potential for explanation and prediction. The final level, grand theory , is “ a set of theories or generalizations that transcend the borders of disciplines to explain relationships among phenomena ” (p. 321) [ 24 ]. According to the authors, most research generates substantive level theory, or, alternatively, researchers borrow theory from the appropriate discipline, apply it to the problem under investigation, and reconstruct the theory at the substantive level. Next in the hierarchy of theoretical categories is the paradigm , which is described as “ a framework of basic assumptions with which perceptions are evaluated and relationships are delineated and applied to a discipline or profession ” (p. 234) [ 11 ]. Finally, the most significant theoretical category is the world view , which is defined as “ an individual’s accepted knowledge, including values and assumptions, which provide a ‘filter’ for perception of all phenomena ” (p. 235) [ 11 ]. All the previous categories contribute to shaping the individual’s worldview. In the revised model, which places more emphasis on the impact of social environment on the research process, research and theory building is surrounded by a system of three basic contextual modules: the self, society, and knowledge, both discovered and undiscovered. The interactions and dialectical relationships of these three modules affect the research process and create a dynamic environment that fosters theory creation and development. The authors argue that their model will help researchers build theories that enable generalizations beyond the conclusions drawn from empirical data [ 24 ].
In an effort to propose a framework for a unified theory of librarianship, McGrath [ 27 ] reviewed research articles in the areas of publishing, acquisitions, classification and knowledge organization, storage, preservation and collection management, library collections, and circulations. In his study, he included articles that employed explanatory and predictive statistical methods to explore relationships between variables within and between the above subfields of LIS. For each paper reviewed, he identified the dependent variable, significant independent variables, and the units of analysis. The review displayed explanatory studies “ in nearly every level, with the possible exception of classification, while studies in circulation and use of the library were clearly dominant. A recapitulation showed that a variable at one level may be a unit of analysis at another, a property of explanatory research crucial to the development of theory, which has been either ignored or unrecognized in LIS literature ” (p. 368) [ 27 ]. The author concluded that “explanatory and predictive relationships do exist and that they can be useful in constructing a comprehensive unified theory of librarianship” (p. 368) [ 27 ].
Recent LIS literature provides several analyses of theory development and use in the field. In a longitudinal analysis of information needs and uses of literature, Julien and Duggan [ 28 ] investigated, among other things, to what extent LIS literature was grounded in theory. Articles “ based on a coherent and explicit framework of assumptions, definitions, and propositions that, taken together, have some explanatory power ” (p. 294) were classified as theoretical articles. Results showed that only 18.3% of the research studies identified in the sample of articles examined were theoretically grounded.
Pettigrew and McKechnie [ 29 ] analyzed 1160 journal articles published between 1993 and 1998 to determine the level of theory use in information science research. In the absence of a singular definition of theory that would cover all the different uses of the term in the sample of articles, they operationalized “theory” according to authors’ use of the term. They found that 34.1% of the articles incorporated theory, with the largest percentage of theories drawn from the social sciences. Information science itself was the second most important source of theories. The authors argued that this significant increase in theory use in comparison to earlier studies could be explained by the research‐oriented journals they selected for examination, the sample time, and the broad way in which they defined “theory.” With regard to this last point, that is, their approach of identifying theories only if the author(s) describe them as such in the article, Pettigrew and McKechnie [ 29 ] observed significant differences in how information science researchers perceive theory:
Although it is possible that conceptual differences regarding the nature of theory may be due to the different disciplinary backgrounds of researchers in IS, other themes emerged from our data that suggest a general confusion exists about theory even within subfields. Numerous examples came to light during our analysis in which an author would simultaneously refer to something as a theory and a method, or as a theory and a model, or as a theory and a reported finding. In other words, it seems as though authors, themselves, are sometimes unsure about what constitutes theory. Questions even arose regarding whether the author to whom a theory was credited would him or herself consider his or her work as theory (p. 68).
Kim and Jeong [ 16 ] examined the state and characteristics of theoretical research in LIS journals between 1984 and 2003. They focused on the “theory incident,” which is described as “an event in which the author contributes to the development or the use of theory in his/her paper.” Their study adopted Glazier and Grover’s [ 24 ] model of “circuits of theory.” Substantive level theory was operationalized to a tested hypothesis or an observed relationship, while both formal and grand level theories were identified when they were named as “theory,” “model,” or “law” by authors other than those who had developed them. Results demonstrated that the application of theory was present in 41.4% of the articles examined, signifying a significant increase in the proportion of theoretical articles as compared to previous studies. Moreover, it was evident that both theory development and theory use had increased by the year. Information seeking and use, and information retrieval, were identified as the subfields with the most significant contribution to the development of the theoretical framework.
In a more in‐depth analysis of theory use in Kumasi et al. [ 30 ] qualitatively analyzed the extent to which theory is meaningfully used in scholarly literature. For this purpose, they developed a theory talk coding scheme, which included six analytical categories, describing how theory is discussed in a study. The intensity of theory talk in the articles was described across a continuum from minimal (e.g., theory is discussed in literature review and not mentioned later) through moderate (e.g., multiple theories are introduced but without discussing their relevance to the study) to major (e.g., theory is employed throughout the study). Their findings seem to support the opinion that “ LIS discipline has been focused on the application of specific theoretical frameworks rather than the generation of new theories ” (p. 179) [ 30 ]. Another point the authors made was about the multiple terms used in the articles to describe theory. Words such as “framework,” “model,” or “theory” were used interchangeably by scholars.
It is evident from the above discussion that the treatment of theory in LIS research covers a spectrum of intensity, from marginal mentions to theory revising, expanding, or building. Recent analyses of the published scholarship indicate that the field has not been very successful in contributing to existing theory or producing new theory. In spite of this, one may still assert that LIS research employs theory, and, in fact, there are many theories that have been used or generated by LIS scholars. However, “ calls for additional and novel theory development work in LIS continue, particularly for theories that might help to address the research practice gap ” (p. 12) [ 31 ].
3. Research strategies in LIS
3.1. surveys of research methods.
LIS is a very broad discipline, which uses a wide range of constantly evolving research strategies and techniques [ 32 ]. Various classification schemes have been developed to analyze methods employed in LIS research (e.g., [ 13 , 15 , 17 , 33 – 35 , 38 ]). Back in 1996, in the “research record” column of the Journal of Education for Library and Information Science, Kim [ 36 ] synthesized previous categories and definitions and introduced a list of research strategies, including data collection and analysis methods. The listing included four general research strategies: (i) theoretical/philosophical inquiry (development of conceptual models or frameworks), (ii) bibliographic research (descriptive studies of books and their properties as well as bibliographies of various kinds), (iii) R&D (development of storage and retrieval systems, software, interface, etc.), and (iv) action research, it aims at solving problems and bringing about change in organizations. Strategies are then divided into quantitative and qualitative driven. In the first category are included descriptive studies, predictive/explanatory studies, bibliometric studies, content analysis, and operation research studies. Qualitative‐driven strategies are considered the following: case study, biographical method, historical method, grounded theory, ethnography, phenomenology, symbolic interactionism/semiotics, sociolinguistics/discourse analysis/ethnographic semantics/ethnography of communication, and hermeneutics/interpretive interactionism (p. 378–380) [ 36 ].
Systematic studies of research methods in LIS started in the 1980s and several reviews of the literature have been conducted over the past years to analyze the topics, methodologies, and quality of research. One of the earliest studies was done by Peritz [ 37 ] who carried out a bibliometric analysis of the articles published in 39 core LIS journals between 1950 and 1975. She examined the methodologies used, the type of library or organization investigated, the type of activity investigated, and the institutional affiliation of the authors. The most important findings were a clear orientation toward library and information service activities, a widespread use of the survey methodology, a considerable increase of research articles after 1960, and a significant increase in theoretical studies after 1965.
Nour [ 38 ] followed up on Peritz’s [ 37 ] work and studied research articles published in 41 selected journals during the year 1980. She found that survey and theoretical/analytic methodologies were the most popular, followed by bibliometrics. Comparing these findings to those made by Peritz [ 37 ], Nour [ 38 ] found that the amount of research continued to increase, but the proportion of research articles to all articles had been decreasing since 1975.
Feehan et al. [ 13 ] described how LIS research published during 1984 was distributed over various topics and what methods had been used to study these topics. Their analysis revealed a predominance of survey and historical methods and a notable percentage of articles using more than one research method. Following a different approach, Enger et al. (1989) focused on the statistical methods used by LIS researchers in articles published during 1985 [ 39 ]. They found that only one out of three of the articles reported any use of statistics. Of those, 21% used descriptive statistics and 11% inferential statistics. In addition, the authors found that researchers from disciplines other than LIS made the highest use of statistics and LIS faculty showed the highest use of inferential statistics.
An influential work, against which later studies have been compared, is that of Jarvelin and Vakkari [ 15 ] who studied LIS articles published in 1985 in order to determine how research was distributed over various subjects, what approaches had been taken by the authors, and what research strategies had been used. The authors replicated their study later to include older research published between 1965 and 1985 [ 40 ]. The main finding of these studies was that the trends and characteristics of LIS research remained more or less the same over the aforementioned period of 20 years. The most common topics were information service activities and information storage and retrieval. Empirical research strategies were predominant, and of them, the most frequent was the survey. Kumpulainen [ 41 ], in an effort to provide a continuum with Jarvelin and Vakkeri’s [ 15 ] study, analyzed 632 articles sampled from 30 core LIS journals with respect to various characteristics, including topics, aspect of activity, research method, data selection method, and data analysis techniques. She used the same classification scheme, and she selected the journals based on a slightly modified version of Jarvelin and Vakkari’s [ 15 ] list. Library services and information storage and retrieval emerged again as the most common subjects approached by the authors and survey was the most frequently used method.
More recent studies of this nature include those conducted by Koufogiannakis et al. [ 42 ], Hildreth and Aytac [ 43 ], Hider and Pymm [ 32 ], and Chu [ 17 ]. Koufogiannakis et al. [ 42 ] examined research articles published in 2001 and they found that the majority of them were questionnaire‐based descriptive studies. Comparative, bibliometrics, content analysis, and program evaluation studies were also popular. Information storage and retrieval emerged as the predominant subject area, followed by library collections and management. Hildreth and Aytac [ 43 ] presented a review of the 2003–2005 published library research with special focus on methodology issues and the quality of published articles of both practitioners and academic scholars. They found that most research was descriptive and the most frequent method for data collection was the questionnaire, followed by content analysis and interviews. With regard to data analysis, more researchers used quantitative methods, considerably less used qualitative‐only methods, whereas 61 out of 206 studies included some kind of qualitative analysis, raising the total percentage of qualitative methods to nearly 50%. With regard to the quality of published research, the authors argued that “ the majority of the reports are detailed, comprehensive, and well‐organized ” (p. 254) [ 43 ]. Still, they noticed that the majority of reports did not mention the critical issues of research validity and reliability and neither did they indicate study limitations or future research recommendations. Hider and Pymm [ 32 ] described content analysis of LIS literature “ which aimed to identify the most common strategies and techniques employed by LIS researchers carrying out high‐profile empirical research ” (p. 109). Their results suggested that while researchers employed a wide variety of strategies, they mostly used surveys and experiments. They also observed that although quantitative research accounted for more than 50% of the articles, there was an increase in the use of most sophisticated qualitative methods. Chu [ 17 ] analyzed the research articles published between 2001 and 2010 in three major journals and reported the following most frequent research methods: theoretical approach (e.g., conceptual analysis), content analysis, questionnaire, interview, experiment, and bibliometrics. Her study showed an increase in both the number and variety of research methods but lack of growth in the use of qualitative research or in the adoption of multiple research methods.
In summary, the literature shows a continued interest in the analysis of published LIS research. Approaches include focusing on particular publication years, geographic areas, journal titles, aspects of LIS, and specific characteristics, such as subjects, authorship, and research methods. Despite the abundance of content analyses of LIS literature, the findings are not easily comparable due to differences in the number and titles of journals examined, in the types of the papers selected for analysis, in the periods covered, and in classification schemes developed by the authors to categorize article topics and research strategies. Despite the differences, some findings are consistent among all studies:
Information seeking, information retrieval, and library and information service activities are among the most common subjects studied,
Descriptive research methodologies based on surveys and questionnaires predominate,
Over the years, there has been a considerable increase in the array of research approaches used to explore library issues, and
Data analysis is usually limited to descriptive statistics, including frequencies, means, and standard deviations.
3.2. Data collection and analysis
Articles published between 2011 and 2016 were obtained from the following journals: Library and Information Science Research, College & Research Libraries, Journal of Documentation, Information Processing & Management, and Journal of Academic Librarianship ( Table 1 ). These five titles were selected as data sources because they have the highest 5‐year impact factor of the journals classified in Ulrich’s Serials Directory under the “Library and Information Sciences” subject heading. From the journals selected, only full‐length articles were collected. Editorials, book reviews, letters, interviews, commentaries, and news items were excluded from the analysis. This selection process yielded 1643 articles. A stratified random sample of 440 articles was chosen for in‐depth analysis ( Table 2 ). For the purpose of this study, five strata, corresponding to the five journals, were used. The sample size was determined using a margin of error, 4%, and confidence interval, 95%.
Table 1.
Profile of the journals.
Table 2.
Journal titles.
Each article was classified as either research or theoretical. Articles that employed specific research methodology and presented specific findings of original studies performed by the author(s) were considered research articles. The kind of study may vary (e.g., it could be an experiment, a survey, etc.), but in all cases, raw data had been collected and analyzed, and conclusions were drawn from the results of that analysis. Articles reporting research in system design or evaluation in the information systems field were also regarded as research articles . On the other hand, works that reviewed theories, theoretical concepts, or principles discussed topics of interest to researchers and professionals, or described research methodologies were regarded as theoretical articles [ 44 ] and were classified in the no‐empirical‐research category. In this category, were also included literature reviews and articles describing a project, a situation, a process, etc.
Each article was classified into a topical category according to its main subject. The articles classified as research were then further explored and analyzed to identify (i) research approach, (ii) research methodology, and (iii) method of data analysis. For each variable, a coding scheme was developed, and the articles were coded accordingly. The final list of the analysis codes was extracted inductively from the data itself, using as reference the taxonomies utilized in previous studies [ 15 , 32 , 43 , 45 ]. Research approaches “ are plans and procedures for research ” (p. 3) [ 46 ]. Research approaches can generally be grouped as qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods studies. Quantitative studies aim at the systematic empirical investigation of quantitative properties or phenomena and their relationships. Qualitative research can be broadly defined as “ any kind of research that produces findings not arrived at by means of statistical procedures or other means of quantification ” (p. 17) [ 47 ]. It is a way to gain insights through discovering meanings and explaining phenomena based on the attributes of the data. In mixed model research, quantitative and qualitative approaches are combined within or across the stages of the research process. It was beyond the scope of this study to identify in which stages of a study—data collection, data analysis, and data interpretation—the mixing was applied or to reveal the types of mixing. Therefore, studies using both quantitative and qualitative methods, irrespective of whether they describe if and how the methods were integrated, were coded as mixed methods studies.
Research methodologies , or strategies of inquiry, are types of research models “ that provide specific direction for procedures in a research design ” (p. 11) [ 46 ] and inform the decisions concerning data collection and analysis. A coding schema of research methodologies was developed by the authors based on the analysis of all research articles included in the sample. The methodology classification included 12 categories ( Table 3 ). Each article was classified into one category for the variable research methodology . If more than one research strategy was mentioned (e.g., experiment and survey), the article was classified according to the main strategy.
Table 3.
Coding schema for research methodologies.
Methods of data analysis refer to the techniques used by the researchers to explore the original data and answer their research problems or questions. Data analysis for quantitative researches involves statistical analysis and interpretation of figures and numbers. In qualitative studies, on the other hand, data analysis involves identifying common patterns within the data and making interpretations of the meanings of the data. The array of data analysis methods included the following categories:
Descriptive statistics,
Inferential statistics,
Qualitative data analysis,
Experimental evaluation, and
Other methods,
Descriptive statistics are used to describe the basic features of the data in a study. Inferential statistics investigate questions, models, and hypotheses. Mathematical analysis refers to mathematic functions, etc. used mainly in bibliometric studies to answer research questions associated with citation data. Qualitative data analysis is the range of processes and procedures used for the exploration of qualitative data, from coding and descriptive analysis to identification of patterns and themes and the testing of emergent findings and hypotheses. It was used in this study as an overarching term encompassing various types of analysis, such as thematic analysis, discourse analysis, or grounded theory analysis. The class experimental evaluation was used for system and software analysis and design studies which assesses the newly developed algorithm, tool, method, etc. by performing experiments on selected datasets. In these cases, “experiments” differ from the experimental designs in social sciences. Methods that did not fall into one of these categories (e.g., mathematical analysis, visualization, or benchmarking) were classified as other methods . If both descriptive and inferential statistics were used in an article, only the inferential were recorded. In mixed methods studies, each method was recorded in the order in which it was reported in the article.
Ten percent of the articles were randomly selected and used to establish inter‐rater reliability and provide basic validation of the coding schema. Cohen’s kappa was calculated for each coded variable. The average Cohen’s kappa value was κ = 0.60, p < 0.000 (the highest was 0.63 and lowest was 0.59). This indicates a substantial agreement [ 48 ]. The coding disparities across raters were discussed, and the final codes were determined via consensus.
3.3. Results
3.3.1. topic.
Table 4 presents the distribution of articles over the various topics, for each of which a detailed description is provided. The five most popular topics of the papers in the total sample of 440 articles were “information retrieval,” “information behavior,” “information literacy,” “library services,” and “organization and management.” These areas cover over 60% of all topics studied in the papers. The least‐studied topics (covered in less than eight papers) fall into the categories of “information and knowledge management,” “library information systems,” “LIS theory,” and “infometrics.”
Table 4.
Article topics.
Figure 1 shows how the top five topics are distributed across journals. As expected, the topic “information retrieval” has higher publication frequencies in Information Processing & Management, a journal focusing on system design and issues related to the tools and techniques used in storage and retrieval of information. “Information literacy,” “information behavior,” “library services,” and “organization and management” appear to be distributed almost proportionately in College & Research Libraries. “Information literacy” seems to be a more preferred topic in the Journal of Academic Librarianship, while “information behavior” is more popular in the Journal of Documentation and Library & Information Science Research.

Figure 1.
Distribution of topics across journals.
3.3.2. Research approach and methodology
Of all articles examined, 343 articles, which represent the 78% of the sample, reported empirical research. The rest 22% (N = 97) were classified as non‐empirical research papers. Research articles were coded as quantitative, qualitative, or mixed methods studies. An overwhelming majority (70%) of the empirical research articles employed a quantitative research approach. Qualitative and mixed methods research was reported in 21.6 and 8.5% of the articles, respectively ( Figure 2 ).

Figure 2.
Research approach.
Table 5 presents the distribution of research approaches over the five most famous topics. The quantitative approach clearly prevails in all topics, especially in information retrieval research. However, qualitative designs seem to gain acceptance in all topics (except information retrieval), while in information behavior research, quantitative and qualitative approaches are almost evenly distributed. Mixed methods were quite frequent in information literacy and information behavior studies and less popular in the other topics.
Table 5.
Topics across research approach.
The most frequently used research strategy was survey, accounting for almost 37% of all research articles, followed by system and software analysis and design, a strategy used in this study specifically for research in information systems (Jarvelin & Vakkari, 1990). This result is influenced by the fact that Information Processing & Management addresses issues at the intersection between LIS and computer science, and the majority of its articles present the development of new tools, algorithms, methods and systems, and their experimental evaluation. The third‐ and fourth‐ranking strategies were content analysis and bibliometrics. Case study, experiment, and secondary data analysis were represented by 15 articles each, while the rest of the techniques were underrepresented with considerably fewer articles ( Table 6 ).
Table 6.
Research methodologies.
3.3.3. Methods of data analysis
Table 7 displays the frequencies for each type of data analysis.
Table 7.
Method of data analysis.
Almost half of the empirical research papers examined reported any use of statistics. Descriptive statistics, such as frequencies, means, or standard deviations, were more frequently used compared to inferential statistics, such as ANOVA, regression, or factor analysis. Nearly one‐third of the articles employed some type of qualitative data analysis either as the only method or—in mixed methods studies—in combination with quantitative techniques.
3.4. Discussions and conclusions
The patterns of LIS research activity as reflected in the articles published between 2011 and 2016 in five well‐established, peer‐reviewed journals were described and analyzed. LIS literature addresses many and diverse topics. Information retrieval, information behavior, and library services continue to attract the interest of researchers as they are core areas in library science. Information retrieval has been rated as one of the most famous areas of interest in research articles published between 1965 and 1985 [ 40 ]. According to Dimitroff [ 49 ], information retrieval was the second most popular topic in the articles published in the Bulletin of the Medical Library Association, while Cano [ 50 ] argued that LIS research produced in Spain from 1977 to 1994 was mostly centered on information retrieval and library and information services. In addition, Koufogiannakis et al. [ 42 ] found that information access and retrieval were the domain with the most research, and in Hildreth and Aytac’s [ 43 ] study, most articles were dealing with issues related to users (needs, behavior, information seeking, etc.), services, and collections. The present study provides evidence that the amount of research in information literacy is increasing, presumably due to the growing importance of information literacy instruction in libraries. In recent years, there is an ongoing educational role for librarians, who are more and more actively engaging in the teaching and learning processes, a trend that is reflected in the research output.
With regard to research methodologies, the present study seems to confirm the well‐documented predominance of survey in LIS research. According to Dimitroff [ 49 ], the percentage related to use of survey research methods reported in various studies varied between 20.3 and 41.5%. Powell [ 51 ], in a review of the research methods appearing in LIS literature, pointed out that survey had consistently been the most common type of study in both dissertations and journal articles. Survey reported the most widely used research design by Jarvelin and Vakkari [ 40 ], Crawford [ 52 ], Hildreth and Aytac [ 43 ], and Hider and Pymm [ 32 ]. The majority of articles examined by Koufogiannakis et al. [ 42 ] were descriptive studies using questionnaires/surveys. In addition, survey methods represented the largest proportion of methods used in information behavior articles analyzed by Julien et al. [ 53 ]. There is no doubt that survey has been used more than any other method in LIS research. As Jarvelin and Vakkari [ 15 ] put it, “it appears that the field is so survey‐oriented that almost all problems are seen through a survey viewpoint” (p. 416). Much of survey’s popularity can be ascribed to its being a well‐known, understood, easily conducted, and inexpensive method, which is easy to analyze results [ 41 , 42 ]. However, our findings suggest that while the survey ranks high, a variety of other methods have been also used in the research articles. Content analysis emerged as the third‐most frequent strategy, a finding similar to those of previous studies [ 17 , 32 ]. Although content analysis was not regarded by LIS researchers as a favored research method until recently, its popularity seems to be growing [ 17 ].
Quantitative approaches, which dominate, tend to rely on frequency counts, percentages, and descriptive statistics used to describe the basic features of the data in a study. Fewer studies used advanced statistical analysis techniques, such as t‐tests, correlation, and regressions, while there were some examples of more sophisticated methods, such as factor analysis, ANOVA, MANOVA, and structural equation modeling. Researchers engaging in quantitative research designs should take into consideration the use of inferential statistics, which enables the generalization from the sample being studied to the population of interest and, if used appropriately, are very useful for hypothesis testing. In addition, multivariate statistics are suitable for examining the relationships among variables, revealing patterns and understanding complex phenomena.
The findings also suggest that qualitative approaches are gaining increasing importance and have a role to play in LIS studies. These results are comparable to the findings of Hider and Pymm [ 32 ], who observed significant increases for qualitative research strategies in contemporary LIS literature. Qualitative analysis description varied widely, reflecting the diverse perspectives, analysis methods, and levels of depth of analysis. Commonly used terms in the articles included coding, content analysis, thematic analysis, thematic analytical approach, theme, or pattern identification. One could argue that the efforts made to encourage and promote qualitative methods in LIS research [ 54 , 55 ] have made some impact. However, qualitative research methods do not seem to be adequately utilized by library researchers and practitioners, despite their potential to offer far more illuminating ways to study library‐related issues [ 56 ]. LIS research has much to gain from the interpretive paradigm underpinning qualitative methods. This paradigm assumes that social reality is
the product of processes by which social actors together negotiate the meanings for actions and situations; it is a complex of socially constructed meanings. Human experience involves a process of interpretation rather than sensory, material apprehension of the external physical world and human behavior depends on how individuals interpret the conditions in which they find themselves. Social reality is not some ‘thing’ that may be interpreted in different ways, it is those interpretations (p. 96) [ 57 ].
As stated in the introduction of this chapter, library and information science focuses on the interaction between individuals and information. In every area of LIS research, the connection of factors that lead to and influence this interaction is increasingly complex. Qualitative research searches for “ all aspects of that complexity on the grounds that they are essential to understanding the behavior of which they are a part ” (p. 241) [ 59 ]. Qualitative research designs can offer a more in‐depth analysis of library users, their needs, attitudes, and behaviors.
The use of mixed methods designs was found to be rather rare. While Hildreth and Aytac [ 43 ] found higher percentages of studies using combined methods in data analysis, our results are analogous to those shown by Fidel [ 60 ]. In fact, as in her study, only few of the articles analyzed referred to mixed methods research by name, a finding indicating that “ the concept has not yet gained recognition in LIS research ” (p. 268). Mixed methods research has become an established research approach in the social sciences as it minimizes the weaknesses of quantitative and qualitative research alone and allows researchers to investigate the phenomena more completely [ 58 ].
In conclusion, there is evidence that LIS researchers employ a large number and wide variety of research methodologies. Each research approach, strategy, and method has its advantages and limitations. If the aim of the study is to confirm hypotheses about phenomena or measure and analyze the causal relationships between variables, then quantitative methods might be used. If the research seeks to explore, understand, and explain phenomena then qualitative methods might be used. Researchers can consider the full range of possibilities and make their selection based on the philosophical assumptions they bring to the study, the research problem being addressed, their personal experiences, and the intended audience for the study [ 46 ].
Taking into consideration the increasing use of qualitative methods in LIS studies, an in‐depth analysis of papers using qualitative methods would be interesting. A future study in which the different research strategies and types of analysis used in qualitative methods will be presented and analyzed could help LIS practitioners understand the benefits of qualitative analysis.
Mixed methods used in LIS research papers could be analyzed in future studies in order to identify in which stages of a study, data collection, data analysis, and data interpretation, the mixing was applied and to reveal the types of mixing.
As far as it concerns the quantitative research methods, which predominate in LIS research, it would be interesting to identify systematic relations between more than two variables such as authors’ affiliation, topic, research strategies, etc. and to create homogeneous groups using multivariate data analysis techniques.
- 1. Buckland MK, Liu ZM. History of information science. Annual Review of Information Science and Technology. 1995; 30 :385-416
- 2. Rayward WB. The history and historiography of information science: Some reflections. Information Processing & Management. 1996; 32 (1):3-17
- 3. Wildemuth BM. Applications of Social Research Methods to Questions in Information and Library Science. Westport, CT: Libraries Unlimited; 2009
- 4. Hjørland B. Theory and metatheory of information science: A new interpretation. Journal of Documentation. 1998; 54 (5):606-621. DOI: http://doi.org/10.1108/EUM0000000007183
- 5. Åström F. Heterogeneity and homogeneity in library and information science research. Information Research [Internet]. 2007 [cited 23 April 2017]; 12 (4): poster colisp01 [3 p.]. Available from: http://www.informationr.net/ir/12-4/colis/colisp01.html
- 6. Dillon A. Keynote address: Library and information science as a research domain: Problems and prospects. Information Research [Internet]. 2007 [cited 23 April 2017]; 12 (4): paper colis03 [6 p.]. Available from: http://www.informationr.net/ir/12-4/colis/colis03.html
- 7. Eldredge JD. Evidence‐based librarianship: An overview. Bulletin of the Medical Library Association. 2000; 88 (4):289-302
- 8. Bradley J, Marshall JG. Using scientific evidence to improve information practice. Health Libraries Review. 1995; 12 (3):147-157
- 9. Bibliometrics. In: International Encyclopedia of Information and Library Science. 2nd ed. London, UK: Routledge; 2003. p. 38
- 10. Åström F. Library and Information Science in context: The development of scientific fields, and their relations to professional contexts. In: Rayward WB, editor. Aware and Responsible: Papers of the Nordic‐International Colloquium on Social and Cultural Awareness and Responsibility in Library, Information and Documentation Studies (SCARLID). Oxford, UK: Scarecrow Press; 2004. pp. 1-27
- 11. Grover R, Glazier J. A conceptual framework for theory building in library and information science. Library and Information Science Research. 1986; 8 (3):227-242
- 12. Boyce BR, Kraft DH. Principles and theories in information science. In: W ME, editor. Annual Review of Information Science and Technology. Medford, NJ: Knowledge Industry Publications. 1985; pp. 153-178
- 13. Feehan PE, Gragg WL, Havener WM, Kester DD. Library and information science research: An analysis of the 1984 journal literature. Library and Information Science Research. 1987; 9 (3):173-185
- 14. Spink A. Information science: A third feedback framework. Journal of the American Society for Information Science. 1997; 48 (8):728-740
- 15. Jarvelin K, Vakkari P. Content analysis of research articles in Library and Information Science. Library and Information Science Research. 1990; 12 (4):395-421
- 16. Kim SJ, Jeong DY. An analysis of the development and use of theory in library and information science research articles. Library and Information Science Research. 2006; 28 (4):548-562. DOI: http://doi.org/10.1016/j.lisr.2006.03.018
- 17. Chu H. Research methods in library and information science: A content analysis. Library & Information Science Research. 2015; 37 (1):36-41. DOI: http://doi.org/10.1016/j.lisr.2014.09.003
- 18. Van Maanen J. Different strokes: Qualitative research in the administrative science quarterly from 1956 to 1996. In: Van Maanen J, editor. Qualitative Studies of Organizations. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE; 1998. pp. ix‐xxxii
- 19. Brookes BC. The foundations of information science Part I. Philosophical aspects. Journal of Information Science. 1980; 2 (3/4):125-133
- 20. Hauser L. A conceptual analysis of information science. Library and Information Science Research. 1988; 10 (1):3-35
- 21. McGrath WE. Current theory in Library and Information Science. Introduction. Library Trends. 2002; 50 (3):309-316
- 22. Theory and why it is important - Social and behavioral theories - e-Source Book - OBSSR e-Source [Internet]. Esourceresearch.org. 2017 [cited 23 April 2017]. Available from: http://www.esourceresearch.org/eSourceBook/SocialandBehavioralTheories/3TheoryandWhyItisImportant/tabid/727/Default.aspx
- 23. Babbie E. The practice of social research. 7th ed. Belmont, CA: Wadsworth; 1995
- 24. Glazier JD, Grover R. A multidisciplinary framework for theory building. Library Trends. 2002; 50 (3):317-329
- 25. Glaser B, Strauss AL. The discovery of grounded theory: Strategies for qualitative research. New Brunswick: Aldine Transaction; 1999
- 26. Smiraglia RP. The progress of theory in knowledge organization. Library Trends. 2002; 50 :330-349
- 27. McGrath WE. Explanation and prediction: Building a unified theory of librarianship, concept and review. Library Trends. 2002; 50 (3):350-370
- 28. Julien H, Duggan LJ. A longitudinal analysis of the information needs and uses literature. Library & Information Science Research. 2000; 22 (3):291-309. DOI: http://doi.org/10.1016/S0740‐8188(99)00057‐2
- 29. Pettigrew KE, McKechnie LEF. The use of theory in information science research. Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology. 2001; 52 (1):62-73. DOI: http://doi.org/10.1002/1532‐2890(2000)52:1<62::AID‐ASI1061>3.0.CO;2‐J
- 30. Kumasi KD, Charbonneau DH, Walster D. Theory talk in the library science scholarly literature: An exploratory analysis. Library & Information Science Research. 2013; 35 (3):175-180. DOI: http://doi.org/10.1016/j.lisr.2013.02.004
- 31. Rawson C, Hughes‐Hassell S. Research by Design: The promise of design‐based research for school library research. School Libraries Worldwide. 2015; 21 (2):11-25
- 32. Hider P, Pymm B. Empirical research methods reported in high‐profile LIS journal literature. Library & Information Science Research. 2008; 30 (2):108-114. DOI: http://doi.org/10.1016/j.lisr.2007.11.007
- 33. Bernhard, P. In search of research methods used in information science. Canadian Journal of Information and Library Science. 1993;18(3): 1-35
- 34. Blake VLP. Since Shaughnessy. Collection Management. 1994; 19 (1‐2):1-42. DOI: http://doi.org/10.1300/J105v19n01_01
- 35. Schlachter GA. Abstracts of library science dissertations. Library Science Annual. 1989; 1 :1988-1996
- 36. Kim MT. Research record. Journal of Education for Library and Information Science. 1996; 37 (4):376-383
- 37. Peritz BC. The methods of library science research: Some results from a bibliometric survey. Library Research. 1980; 2 (3):251-268
- 38. Nour MM. A quantitative analysis of the research articles published in core library journals of 1980. Library and Information Science Research. 1985; 7 (3):261-273
- 39. Enger KB, Quirk G, Stewart JA. Statistical methods used by authors of library and infor- mation science journal articles. Library and Information Science Research. 1989; 11 (1): 37-46
- 40. Jarvelin K, Vakkari P. The evolution of library and information science 1965-1985: A content analysis of journal articles. Information Processing and Management. 1993; 29 (1):129-144
- 41. Kumpulainen S. Library and information science research in 1975: Content analysis of the journal articles. Libri. 1991; 41 (1):59-76
- 42. Koufogiannakis D, Slater L, Crumley E. A content analysis of librarianship research. Journal of Information Science. 2004; 30 (3):227-239. DOI: http://doi.org/10.1177/0165551504044668
- 43. Hildreth CR, Aytac S. Recent library practitioner research: A methodological analysis and critique on JSTOR. Journal of Education for Library and Information Science. 2007; 48 (3):236-258
- 44. Gonzales‐Teruel A, Abad‐Garcia MF. Information needs and uses: An analysis of the literature published in Spain, 1990‐2004. Library and Information Science Research. 2007; 29 (1):30-46
- 45. Luo L, Mckinney M. JAL in the past decade: A comprehensive analysis of academic library research. The Journal of Academic Librarianship. 2015; 41 :123-129. DOI: http://doi.org/10.1016/j.acalib.2015.01.003
- 46. Creswell JW. Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Approaches. 3rd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE; 2009
- 47. Strauss A, Corbin J. Basics of Qualitative Research: Grounded Theory Procedures and Techniques. Newbury Park, CA: SAGE Publications; 1990
- 48. Neuendorf KA. The Content Analysis Guidebook. 2nd ed. Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications; 2016
- 49. Dimitroff A. Research for special libraries: A quantitative analysis of the literature. Special Libraries. 1995; 86 (4):256-264
- 50. Cano V. Bibliometric overview of library and information science research in Spain. Journal of the American Society for Information Science. 1999; 50 (8):675-680. DOI: http://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1097‐4571(1999)50:8<675::AID‐ASI5>3.0.CO;2‐B
- 51. Powell RR. Recent trends in research: A methodological essay. Library & Information Science Research. 1999; 21 (1):91-119. DOI: http://doi.org/10.1016/S0740‐8188(99)80007‐3
- 52. Crawford GA. The research literature of academic librarianship: A comparison of college & Research Libraries and Journal of Academic Librarianship. College & Research Libraries. 1999; 60 (3):224-230. DOI: http://doi.org/10.5860/crl.60.3.224
- 53. Julien H, Pecoskie JJL, Reed K. Trends in information behavior research, 1999-2008: A content analysis. Library & Information Science Research. 2011; 33 (1):19-24. DOI: http://doi.org/10.1016/j.lisr.2010.07.014
- 54. Fidel R. Qualitative methods in information retrieval research. Library and Information Science Research. 1993; 15 (3):219-247
- 55. Hernon P, Schwartz C. Reflections (editorial). Library and Information Science Research. 2003; 25 (1):1-2. DOI: http://doi.org/10.1016/S0740‐8188(02)00162‐7
- 56. Priestner A. Going native: Embracing ethnographic research methods in libraries. Revy. 2015; 38 (4):16-17
- 57. Blaikie N. Approaches to social enquiry. Cambridge: Polity; 1993
- 58. Johnson RB, Onwuegbuzie AJ. Mixed methods research: A research paradigm whose time has come. Educational Researcher. 2004; 33 (7):14-26
- 59. Westbrook L. Qualitative research methods: A review of major stages, data analysis techniques, and quality controls. Library & Information Science Research. 1994; 16 (3):241-254
- 60. Fidel R. Are we there yet?: Mixed methods research in library and information science. Library and Information Science Research. 2008; 30 (4):265-272. DOI: http://doi.org/10.1016/j.lisr.2008.04.001
© 2017 The Author(s). Licensee IntechOpen. This chapter is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 License , which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Continue reading from the same book
Edited by Sonyel Oflazoglu Dora
Published: 28 June 2017
By Yusuf Bilgin
3307 downloads
By Kadriye Şahin
1886 downloads
By Seyma Demir and Yasemin Yildirim Usta
1975 downloads
IntechOpen Author/Editor? To get your discount, log in .
Discounts available on purchase of multiple copies. View rates
Local taxes (VAT) are calculated in later steps, if applicable.
Support: [email protected]

IMAGES
VIDEO