Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
Collection 29 March 2022

2021 Top 25 Health Sciences Articles
We are pleased to share with you the 25 most downloaded Nature Communications articles* in health sciences published in 2021. (Please note we have a separate collection on the Top 25 COVID-19 papers .) Featuring authors from around the world, these papers highlight valuable research from an international community.
Browse all Top 25 subject area collections here .
*Data obtained from SN Insights (based on Digital Science's Dimensions) and normalised to account for articles published later in the year.
Research highlights

Association of sleep duration in middle and old age with incidence of dementia
Sleep dysregulation has been linked to dementia, but it is unknown whether sleep duration earlier in life is associated with dementia risk. Here, the authors show higher dementia risk associated with short sleep duration (six hours or less) in a longitudinal study of middle and older age adults.
- Séverine Sabia
- Aurore Fayosse
- Archana Singh-Manoux
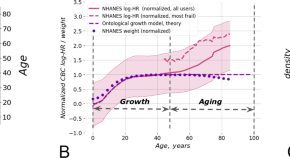
Longitudinal analysis of blood markers reveals progressive loss of resilience and predicts human lifespan limit
Aging is associated with an increased risk of chronic diseases and functional decline. Here, the authors investigate the fluctuations of physiological indices along aging trajectories and observed a characteristic decrease in the organism state recovery rate.
- Timothy V. Pyrkov
- Konstantin Avchaciov
- Peter O. Fedichev
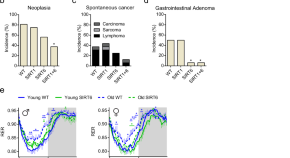
Restoration of energy homeostasis by SIRT6 extends healthy lifespan
Aging is associated with increased frailty and disrupted energy homeostasis. Here, the authors show that SIRT6 overexpression extends the lifespan of male and female mice and demonstrate that SIRT6 optimizes energy homeostasis in old age, which delays frailty and preserves healthy aging.
- A. Roichman
- S. Elhanati
- H. Y. Cohen
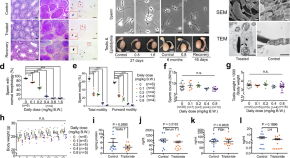
Triptonide is a reversible non-hormonal male contraceptive agent in mice and non-human primates
No male contraceptive pills are currently available. Here, the authors use triptonide, a compound derived from a Chinese plant, to deform sperm so that they cannot move properly, thereby causing reversible infertility in male mice and monkeys.
- Zongliang Chang
- Weibing Qin
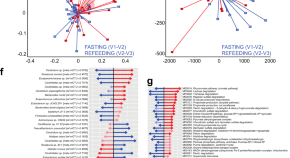
Fasting alters the gut microbiome reducing blood pressure and body weight in metabolic syndrome patients
Nutritional modification including fasting has been shown to reduce cardiometabolic risk linked to western diet. Here the authors show implementation of fasting resulted in alterations to the intestinal microbiota, and circulating immune cells, improving blood pressure and body weight in patients with metabolic syndrome.
- András Maifeld
- Hendrik Bartolomaeus
- Sofia K. Forslund
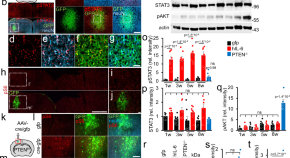
Transneuronal delivery of hyper-interleukin-6 enables functional recovery after severe spinal cord injury in mice
The CNS has limited ability to regenerate following injury, Here, the authors show that a single injection of AAV-hyper-interleukin-6 in the sensory motor cortex results in corticospinal and raphe spinal tracts regeneration in the injured spinal cord as well as functional recovery in mice.
- Marco Leibinger
- Charlotte Zeitler
- Dietmar Fischer
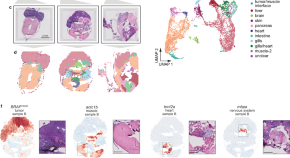
Spatially resolved transcriptomics reveals the architecture of the tumor-microenvironment interface
During tumor progression, cancer cells contact different neighboring cell types, but it is unclear how these interactions affect cancer cell behavior. Here, the authors use spatially resolved transcriptomics and single-cell RNA-seq to study the role of cilia at the tumormicroenvironment interface.
- Miranda V. Hunter
- Reuben Moncada
- Richard M. White
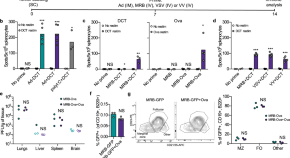
Adjuvant oncolytic virotherapy for personalized anti-cancer vaccination
Viruses expressing tumour antigens can prime and boost anti-tumour immunity but the efficiency of this approach depends on the capacity of the virus to infect the host. Here, the authors show that vaccination with oncolytic viruses co-administered with tumour antigenic peptides is as efficient as antigen-engineered oncolytic viruses.
- K. Geoffroy
- M.-C. Bourgeois-Daigneault
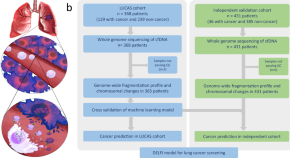
Detection and characterization of lung cancer using cell-free DNA fragmentomes
DNA from tumour cells can be detected in the blood of cancer patients. Here, the authors show that cell free DNA fragmentation patterns can identify lung cancer patients and when this information is further interrogated it can be used to predict lung cancer histological subtype.
- Dimitrios Mathios
- Jakob Sidenius Johansen
- Victor E. Velculescu
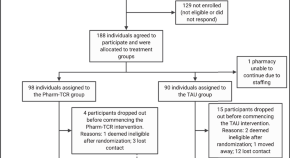
A randomized controlled trial of pharmacist-led therapeutic carbohydrate and energy restriction in type 2 diabetes
Community pharmacists are accessible healthcare providers with expertise in medication management. Here the authors show that a low-carbohydrate, low-energy diet implemented by community pharmacists reduced diabetes medication use and improved glucose control in people with type 2 diabetes.
- Cody Durrer
- Sean McKelvey
- Jonathan P. Little

A metabolome atlas of the aging mouse brain
Metabolites play an important role in physiology, yet the complexity of the metabolome and its interaction with disease and aging is poorly understood. Here the authors present a comprehensive atlas of the mouse brain metabolome and how it changes during aging.
- Oliver Fiehn
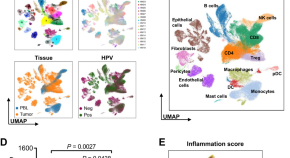
Investigating immune and non-immune cell interactions in head and neck tumors by single-cell RNA sequencing
The tumor microenvironment (TME) has an important role in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC) progression. Here, using single-cell RNA sequencing and multiplexed imaging, the authors report the cellular complexity of the TME in patients with HNSCC, exploring inflammatory status, stromal heterogeneity and immune checkpoint receptor-ligand interactions.
- Cornelius H. L. Kürten
- Aditi Kulkarni
- Robert L. Ferris
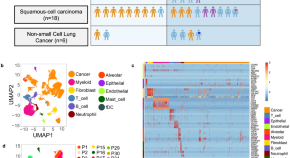

Single-cell profiling of tumor heterogeneity and the microenvironment in advanced non-small cell lung cancer
Comprehensive profiles of tumour and microenvironment are critical to understand heterogeneity in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Here, the authors profile 42 late-stage NSCLC patients with single-cell RNA-seq, revealing immune landscapes that are associated with cancer subtype or heterogeneity.
- Fengying Wu
- Caicun Zhou
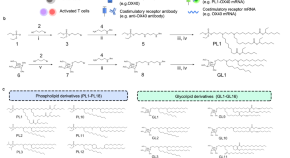
Biomimetic nanoparticles deliver mRNAs encoding costimulatory receptors and enhance T cell mediated cancer immunotherapy
Antibodies targeting OX40 or CD137, two T cell costimulatory receptors, have been shown to improve antitumor immunity. Here the authors design a phospholipid-derived nanoparticle to deliver OX40 or CD137 mRNA to T cells in vivo, improving efficacy of anti-OX40 and anti-CD137 antibody therapy in preclinical tumor models.
- Xinfu Zhang
- Yizhou Dong
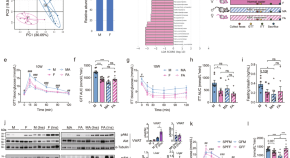
Sexual dimorphism in glucose metabolism is shaped by androgen-driven gut microbiome
Male sex is a risk factor for impaired glucose metabolism and type 2 diabetes. Here the authors identify that androgen modulates the gut microbiome, which drives insulin resistance and contributes to sexual dimorphism in glucose metabolism in mice.
- Weiqing Wang
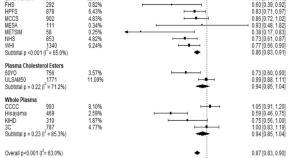
Blood n-3 fatty acid levels and total and cause-specific mortality from 17 prospective studies
Associations between of omega-3 fatty acids and mortality are not clear. Here the authors report that, based on a pooled analysis of 17 prospective cohort studies, higher blood omega-3 fatty acid levels correlate with lower risk of all-cause mortality.
- William S. Harris
- Nathan L. Tintle
- The Fatty Acids and Outcomes Research Consortium (FORCE)
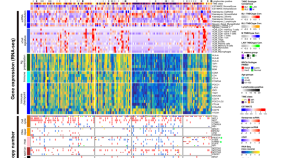
Multi-omics analysis identifies therapeutic vulnerabilities in triple-negative breast cancer subtypes
Triple negative breast cancer can be divided into additional subtypes. Here, using omics analyses, the authors show that in the mesenchymal subtype expression of MHC-1 is repressed and that this can be restored by using drugs that target subunits of the epigenetic modifier PRC2.
- Brian D. Lehmann
- Antonio Colaprico
- X. Steven Chen
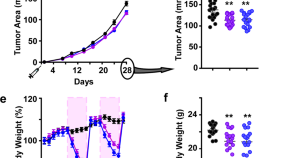
Daily caloric restriction limits tumor growth more effectively than caloric cycling regardless of dietary composition
Caloric restriction (CR) has been shown as an effective intervention to reduce tumorigenesis, but alternative less stringent dietary interventions have also been considered. Here, the authors show that in a murine model of breast cancer CR has a larger effect on preventing tumorigenesis and metastasis compared to periodic caloric cycling.
- Laura C. D. Pomatto-Watson
- Monica Bodogai
- Rafael de Cabo
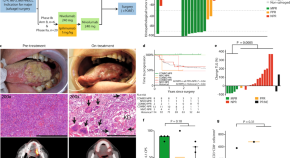
Neoadjuvant immunotherapy with nivolumab and ipilimumab induces major pathological responses in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Immune checkpoint blockade has become standard care for patients with recurrent metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). Here the authors present the results of a non-randomized phase Ib/IIa trial, reporting safety and efficacy of neoadjuvant nivolumab monotherapy and nivolumab plus ipilimumab prior to standard-of-care surgery in patients with HNSCC. .
- Joris L. Vos
- Joris B. W. Elbers
- Charlotte L. Zuur
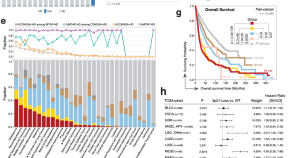
9p21 loss confers a cold tumor immune microenvironment and primary resistance to immune checkpoint therapy
The molecular mechanisms of resistance to immune checkpoint therapy remain elusive. Here, the authors perform immunogenomic analysis of TCGA data and data from clinical trials for antiPD-1/PD-L1 therapy and highlight the association of 9p21 loss with a cold tumor microenvironment and resistance to therapy.
- Guangchun Han
- Guoliang Yang
- Linghua Wang
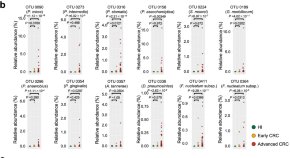
Gut bacteria identified in colorectal cancer patients promote tumourigenesis via butyrate secretion
Several bacteria in the gut microbiota have been associated with colorectal cancer (CRC) but it is not completely clear whether they have a role in tumourigenesis. Here, the authors show enrichment of 12 bacterial taxa in two cohorts of CRC patients and that two Porphyromonas species accelerate CRC onset through butyrate secretion.
- Shintaro Okumura
- Yusuke Konishi
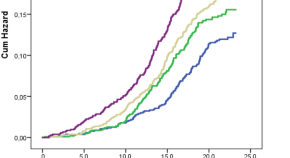
Elevated circulating follistatin associates with an increased risk of type 2 diabetes
Follistatin promotes in type 2 diabetes (T2D) pathogenesis in model animals and is elevated in patients with T2D. Here the authors report that plasma follistatin associates with increased risk of incident T2D in two longitudinal cohorts, and show that follistatin regulates insulin-induced suppression lipolysis in cultured human adipocytes.
- Chuanyan Wu
- Yang De Marinis
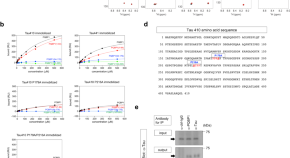
Tau activates microglia via the PQBP1-cGAS-STING pathway to promote brain inflammation
Brain inflammation generally accelerates neurodegeneration but the mechanisms of this are not fully characterised. Here the authors show that PQBP1 in microglia is important for sensing extrinsic Tau 3 R/4 R proteins and triggers an innate immune response through cGAS and STING resulting in cognitive impairment.
- Hiroki Shiwaku
- Hitoshi Okazawa
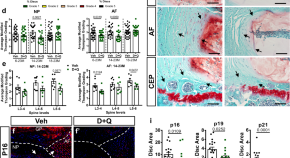
Long-term treatment with senolytic drugs Dasatinib and Quercetin ameliorates age-dependent intervertebral disc degeneration in mice
Intervertebral disc degeneration is a leading cause of chronic back pain and disability. Here the authors show that long term treatment with senolytic compounds Dasatinib and Quercetin reduces disc senescence burden and ameliorates age-dependent degeneration in mice.
- Emanuel J. Novais
- Victoria A. Tran
- Makarand V. Risbud
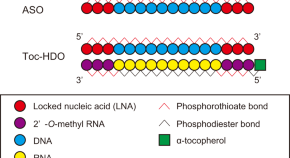
DNA/RNA heteroduplex oligonucleotide technology for regulating lymphocytes in vivo
Using gene silencing to regulate lymphocyte function is a promising therapeutic approach for autommunity, inflammation and cancer. Here the authors use a heteroduplex oligonucleotide for improved potency, efficacy and longer retention times.
- Masaki Ohyagi
- Tetsuya Nagata
- Takanori Yokota
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies

IMAGES
VIDEO