- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case AskWhy Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research

Research Hypothesis: What It Is, Types + How to Develop?

A research study starts with a question. Researchers worldwide ask questions and create research hypotheses. The effectiveness of research relies on developing a good research hypothesis. Examples of research hypotheses can guide researchers in writing effective ones.
In this blog, we’ll learn what a research hypothesis is, why it’s important in research, and the different types used in science. We’ll also guide you through creating your research hypothesis and discussing ways to test and evaluate it.
What is a Research Hypothesis?
A hypothesis is like a guess or idea that you suggest to check if it’s true. A research hypothesis is a statement that brings up a question and predicts what might happen.
It’s really important in the scientific method and is used in experiments to figure things out. Essentially, it’s an educated guess about how things are connected in the research.
A research hypothesis usually includes pointing out the independent variable (the thing they’re changing or studying) and the dependent variable (the result they’re measuring or watching). It helps plan how to gather and analyze data to see if there’s evidence to support or deny the expected connection between these variables.
Importance of Hypothesis in Research
Hypotheses are really important in research. They help design studies, allow for practical testing, and add to our scientific knowledge. Their main role is to organize research projects, making them purposeful, focused, and valuable to the scientific community. Let’s look at some key reasons why they matter:
- A research hypothesis helps test theories.
A hypothesis plays a pivotal role in the scientific method by providing a basis for testing existing theories. For example, a hypothesis might test the predictive power of a psychological theory on human behavior.
- It serves as a great platform for investigation activities.
It serves as a launching pad for investigation activities, which offers researchers a clear starting point. A research hypothesis can explore the relationship between exercise and stress reduction.
- Hypothesis guides the research work or study.
A well-formulated hypothesis guides the entire research process. It ensures that the study remains focused and purposeful. For instance, a hypothesis about the impact of social media on interpersonal relationships provides clear guidance for a study.
- Hypothesis sometimes suggests theories.
In some cases, a hypothesis can suggest new theories or modifications to existing ones. For example, a hypothesis testing the effectiveness of a new drug might prompt a reconsideration of current medical theories.
- It helps in knowing the data needs.
A hypothesis clarifies the data requirements for a study, ensuring that researchers collect the necessary information—a hypothesis guiding the collection of demographic data to analyze the influence of age on a particular phenomenon.
- The hypothesis explains social phenomena.
Hypotheses are instrumental in explaining complex social phenomena. For instance, a hypothesis might explore the relationship between economic factors and crime rates in a given community.
- Hypothesis provides a relationship between phenomena for empirical Testing.
Hypotheses establish clear relationships between phenomena, paving the way for empirical testing. An example could be a hypothesis exploring the correlation between sleep patterns and academic performance.
- It helps in knowing the most suitable analysis technique.
A hypothesis guides researchers in selecting the most appropriate analysis techniques for their data. For example, a hypothesis focusing on the effectiveness of a teaching method may lead to the choice of statistical analyses best suited for educational research.
Characteristics of a Good Research Hypothesis
A hypothesis is a specific idea that you can test in a study. It often comes from looking at past research and theories. A good hypothesis usually starts with a research question that you can explore through background research. For it to be effective, consider these key characteristics:
- Clear and Focused Language: A good hypothesis uses clear and focused language to avoid confusion and ensure everyone understands it.
- Related to the Research Topic: The hypothesis should directly relate to the research topic, acting as a bridge between the specific question and the broader study.
- Testable: An effective hypothesis can be tested, meaning its prediction can be checked with real data to support or challenge the proposed relationship.
- Potential for Exploration: A good hypothesis often comes from a research question that invites further exploration. Doing background research helps find gaps and potential areas to investigate.
- Includes Variables: The hypothesis should clearly state both the independent and dependent variables, specifying the factors being studied and the expected outcomes.
- Ethical Considerations: Check if variables can be manipulated without breaking ethical standards. It’s crucial to maintain ethical research practices.
- Predicts Outcomes: The hypothesis should predict the expected relationship and outcome, acting as a roadmap for the study and guiding data collection and analysis.
- Simple and Concise: A good hypothesis avoids unnecessary complexity and is simple and concise, expressing the essence of the proposed relationship clearly.
- Clear and Assumption-Free: The hypothesis should be clear and free from assumptions about the reader’s prior knowledge, ensuring universal understanding.
- Observable and Testable Results: A strong hypothesis implies research that produces observable and testable results, making sure the study’s outcomes can be effectively measured and analyzed.
When you use these characteristics as a checklist, it can help you create a good research hypothesis. It’ll guide improving and strengthening the hypothesis, identifying any weaknesses, and making necessary changes. Crafting a hypothesis with these features helps you conduct a thorough and insightful research study.
Types of Research Hypotheses
The research hypothesis comes in various types, each serving a specific purpose in guiding the scientific investigation. Knowing the differences will make it easier for you to create your own hypothesis. Here’s an overview of the common types:
01. Null Hypothesis
The null hypothesis states that there is no connection between two considered variables or that two groups are unrelated. As discussed earlier, a hypothesis is an unproven assumption lacking sufficient supporting data. It serves as the statement researchers aim to disprove. It is testable, verifiable, and can be rejected.
For example, if you’re studying the relationship between Project A and Project B, assuming both projects are of equal standard is your null hypothesis. It needs to be specific for your study.
02. Alternative Hypothesis
The alternative hypothesis is basically another option to the null hypothesis. It involves looking for a significant change or alternative that could lead you to reject the null hypothesis. It’s a different idea compared to the null hypothesis.
When you create a null hypothesis, you’re making an educated guess about whether something is true or if there’s a connection between that thing and another variable. If the null view suggests something is correct, the alternative hypothesis says it’s incorrect.
For instance, if your null hypothesis is “I’m going to be $1000 richer,” the alternative hypothesis would be “I’m not going to get $1000 or be richer.”
03. Directional Hypothesis
The directional hypothesis predicts the direction of the relationship between independent and dependent variables. They specify whether the effect will be positive or negative.
If you increase your study hours, you will experience a positive association with your exam scores. This hypothesis suggests that as you increase the independent variable (study hours), there will also be an increase in the dependent variable (exam scores).
04. Non-directional Hypothesis
The non-directional hypothesis predicts the existence of a relationship between variables but does not specify the direction of the effect. It suggests that there will be a significant difference or relationship, but it does not predict the nature of that difference.
For example, you will find no notable difference in test scores between students who receive the educational intervention and those who do not. However, once you compare the test scores of the two groups, you will notice an important difference.
05. Simple Hypothesis
A simple hypothesis predicts a relationship between one dependent variable and one independent variable without specifying the nature of that relationship. It’s simple and usually used when we don’t know much about how the two things are connected.
For example, if you adopt effective study habits, you will achieve higher exam scores than those with poor study habits.
06. Complex Hypothesis
A complex hypothesis is an idea that specifies a relationship between multiple independent and dependent variables. It is a more detailed idea than a simple hypothesis.
While a simple view suggests a straightforward cause-and-effect relationship between two things, a complex hypothesis involves many factors and how they’re connected to each other.
For example, when you increase your study time, you tend to achieve higher exam scores. The connection between your study time and exam performance is affected by various factors, including the quality of your sleep, your motivation levels, and the effectiveness of your study techniques.
If you sleep well, stay highly motivated, and use effective study strategies, you may observe a more robust positive correlation between the time you spend studying and your exam scores, unlike those who may lack these factors.
07. Associative Hypothesis
An associative hypothesis proposes a connection between two things without saying that one causes the other. Basically, it suggests that when one thing changes, the other changes too, but it doesn’t claim that one thing is causing the change in the other.
For example, you will likely notice higher exam scores when you increase your study time. You can recognize an association between your study time and exam scores in this scenario.
Your hypothesis acknowledges a relationship between the two variables—your study time and exam scores—without asserting that increased study time directly causes higher exam scores. You need to consider that other factors, like motivation or learning style, could affect the observed association.
08. Causal Hypothesis
A causal hypothesis proposes a cause-and-effect relationship between two variables. It suggests that changes in one variable directly cause changes in another variable.
For example, when you increase your study time, you experience higher exam scores. This hypothesis suggests a direct cause-and-effect relationship, indicating that the more time you spend studying, the higher your exam scores. It assumes that changes in your study time directly influence changes in your exam performance.
09. Empirical Hypothesis
An empirical hypothesis is a statement based on things we can see and measure. It comes from direct observation or experiments and can be tested with real-world evidence. If an experiment proves a theory, it supports the idea and shows it’s not just a guess. This makes the statement more reliable than a wild guess.
For example, if you increase the dosage of a certain medication, you might observe a quicker recovery time for patients. Imagine you’re in charge of a clinical trial. In this trial, patients are given varying dosages of the medication, and you measure and compare their recovery times. This allows you to directly see the effects of different dosages on how fast patients recover.
This way, you can create a research hypothesis: “Increasing the dosage of a certain medication will lead to a faster recovery time for patients.”
10. Statistical Hypothesis
A statistical hypothesis is a statement or assumption about a population parameter that is the subject of an investigation. It serves as the basis for statistical analysis and testing. It is often tested using statistical methods to draw inferences about the larger population.
In a hypothesis test, statistical evidence is collected to either reject the null hypothesis in favor of the alternative hypothesis or fail to reject the null hypothesis due to insufficient evidence.
For example, let’s say you’re testing a new medicine. Your hypothesis could be that the medicine doesn’t really help patients get better. So, you collect data and use statistics to see if your guess is right or if the medicine actually makes a difference.
If the data strongly shows that the medicine does help, you say your guess was wrong, and the medicine does make a difference. But if the proof isn’t strong enough, you can stick with your original guess because you didn’t get enough evidence to change your mind.
How to Develop a Research Hypotheses?
Step 1: identify your research problem or topic..
Define the area of interest or the problem you want to investigate. Make sure it’s clear and well-defined.
Start by asking a question about your chosen topic. Consider the limitations of your research and create a straightforward problem related to your topic. Once you’ve done that, you can develop and test a hypothesis with evidence.
Step 2: Conduct a literature review
Review existing literature related to your research problem. This will help you understand the current state of knowledge in the field, identify gaps, and build a foundation for your hypothesis. Consider the following questions:
- What existing research has been conducted on your chosen topic?
- Are there any gaps or unanswered questions in the current literature?
- How will the existing literature contribute to the foundation of your research?
Step 3: Formulate your research question
Based on your literature review, create a specific and concise research question that addresses your identified problem. Your research question should be clear, focused, and relevant to your field of study.
Step 4: Identify variables
Determine the key variables involved in your research question. Variables are the factors or phenomena that you will study and manipulate to test your hypothesis.
- Independent Variable: The variable you manipulate or control.
- Dependent Variable: The variable you measure to observe the effect of the independent variable.
Step 5: State the Null hypothesis
The null hypothesis is a statement that there is no significant difference or effect. It serves as a baseline for comparison with the alternative hypothesis.
Step 6: Select appropriate methods for testing the hypothesis
Choose research methods that align with your study objectives, such as experiments, surveys, or observational studies. The selected methods enable you to test your research hypothesis effectively.
Creating a research hypothesis usually takes more than one try. Expect to make changes as you collect data. It’s normal to test and say no to a few hypotheses before you find the right answer to your research question.
Testing and Evaluating Hypotheses
Testing hypotheses is a really important part of research. It’s like the practical side of things. Here, real-world evidence will help you determine how different things are connected. Let’s explore the main steps in hypothesis testing:
- State your research hypothesis.
Before testing, clearly articulate your research hypothesis. This involves framing both a null hypothesis, suggesting no significant effect or relationship, and an alternative hypothesis, proposing the expected outcome.
- Collect data strategically.
Plan how you will gather information in a way that fits your study. Make sure your data collection method matches the things you’re studying.
Whether through surveys, observations, or experiments, this step demands precision and adherence to the established methodology. The quality of data collected directly influences the credibility of study outcomes.
- Perform an appropriate statistical test.
Choose a statistical test that aligns with the nature of your data and the hypotheses being tested. Whether it’s a t-test, chi-square test, ANOVA, or regression analysis, selecting the right statistical tool is paramount for accurate and reliable results.
- Decide if your idea was right or wrong.
Following the statistical analysis, evaluate the results in the context of your null hypothesis. You need to decide if you should reject your null hypothesis or not.
- Share what you found.
When discussing what you found in your research, be clear and organized. Say whether your idea was supported or not, and talk about what your results mean. Also, mention any limits to your study and suggest ideas for future research.
The Role of QuestionPro to Develop a Good Research Hypothesis
QuestionPro is a survey and research platform that provides tools for creating, distributing, and analyzing surveys. It plays a crucial role in the research process, especially when you’re in the initial stages of hypothesis development. Here’s how QuestionPro can help you to develop a good research hypothesis:
- Survey design and data collection: You can use the platform to create targeted questions that help you gather relevant data.
- Exploratory research: Through surveys and feedback mechanisms on QuestionPro, you can conduct exploratory research to understand the landscape of a particular subject.
- Literature review and background research: QuestionPro surveys can collect sample population opinions, experiences, and preferences. This data and a thorough literature evaluation can help you generate a well-grounded hypothesis by improving your research knowledge.
- Identifying variables: Using targeted survey questions, you can identify relevant variables related to their research topic.
- Testing assumptions: You can use surveys to informally test certain assumptions or hypotheses before formalizing a research hypothesis.
- Data analysis tools: QuestionPro provides tools for analyzing survey data. You can use these tools to identify the collected data’s patterns, correlations, or trends.
- Refining your hypotheses: As you collect data through QuestionPro, you can adjust your hypotheses based on the real-world responses you receive.
A research hypothesis is like a guide for researchers in science. It’s a well-thought-out idea that has been thoroughly tested. This idea is crucial as researchers can explore different fields, such as medicine, social sciences, and natural sciences. The research hypothesis links theories to real-world evidence and gives researchers a clear path to explore and make discoveries.
QuestionPro Research Suite is a helpful tool for researchers. It makes creating surveys, collecting data, and analyzing information easily. It supports all kinds of research, from exploring new ideas to forming hypotheses. With a focus on using data, it helps researchers do their best work.
Are you interested in learning more about QuestionPro Research Suite? Take advantage of QuestionPro’s free trial to get an initial look at its capabilities and realize the full potential of your research efforts.
LEARN MORE FREE TRIAL
MORE LIKE THIS

Total Experience in Trinidad & Tobago — Tuesday CX Thoughts
Oct 29, 2024

You Can’t Please Everyone — Tuesday CX Thoughts
Oct 22, 2024
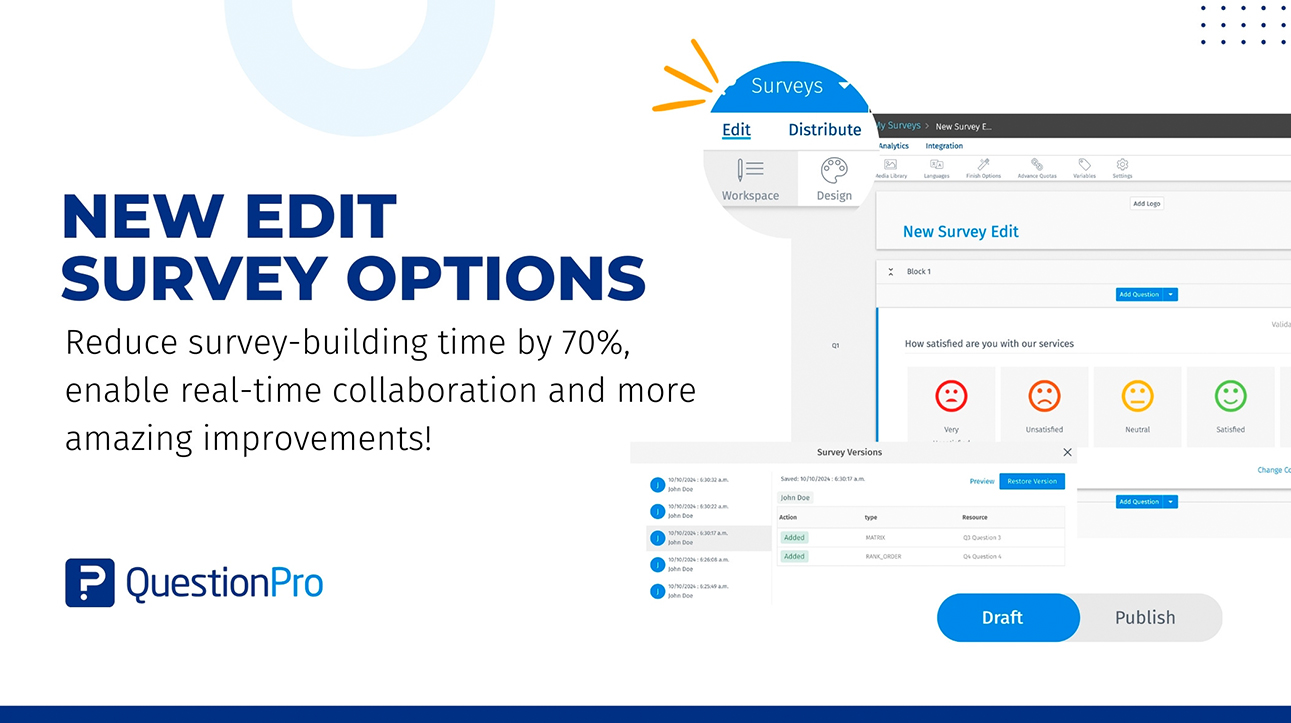
Edit survey: A new way of survey building and collaboration
Oct 10, 2024

Pulse Surveys vs Annual Employee Surveys: Which to Use
Oct 4, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Tuesday CX Thoughts (TCXT)
- Uncategorized
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
Educational resources and simple solutions for your research journey

What is a Research Hypothesis: How to Write it, Types, and Examples

Any research begins with a research question and a research hypothesis . A research question alone may not suffice to design the experiment(s) needed to answer it. A hypothesis is central to the scientific method. But what is a hypothesis ? A hypothesis is a testable statement that proposes a possible explanation to a phenomenon, and it may include a prediction. Next, you may ask what is a research hypothesis ? Simply put, a research hypothesis is a prediction or educated guess about the relationship between the variables that you want to investigate.
It is important to be thorough when developing your research hypothesis. Shortcomings in the framing of a hypothesis can affect the study design and the results. A better understanding of the research hypothesis definition and characteristics of a good hypothesis will make it easier for you to develop your own hypothesis for your research. Let’s dive in to know more about the types of research hypothesis , how to write a research hypothesis , and some research hypothesis examples .
Table of Contents
What is a hypothesis ?
A hypothesis is based on the existing body of knowledge in a study area. Framed before the data are collected, a hypothesis states the tentative relationship between independent and dependent variables, along with a prediction of the outcome.
What is a research hypothesis ?
Young researchers starting out their journey are usually brimming with questions like “ What is a hypothesis ?” “ What is a research hypothesis ?” “How can I write a good research hypothesis ?”
A research hypothesis is a statement that proposes a possible explanation for an observable phenomenon or pattern. It guides the direction of a study and predicts the outcome of the investigation. A research hypothesis is testable, i.e., it can be supported or disproven through experimentation or observation.

Characteristics of a good hypothesis
Here are the characteristics of a good hypothesis :
- Clearly formulated and free of language errors and ambiguity
- Concise and not unnecessarily verbose
- Has clearly defined variables
- Testable and stated in a way that allows for it to be disproven
- Can be tested using a research design that is feasible, ethical, and practical
- Specific and relevant to the research problem
- Rooted in a thorough literature search
- Can generate new knowledge or understanding.
How to create an effective research hypothesis
A study begins with the formulation of a research question. A researcher then performs background research. This background information forms the basis for building a good research hypothesis . The researcher then performs experiments, collects, and analyzes the data, interprets the findings, and ultimately, determines if the findings support or negate the original hypothesis.
Let’s look at each step for creating an effective, testable, and good research hypothesis :
- Identify a research problem or question: Start by identifying a specific research problem.
- Review the literature: Conduct an in-depth review of the existing literature related to the research problem to grasp the current knowledge and gaps in the field.
- Formulate a clear and testable hypothesis : Based on the research question, use existing knowledge to form a clear and testable hypothesis . The hypothesis should state a predicted relationship between two or more variables that can be measured and manipulated. Improve the original draft till it is clear and meaningful.
- State the null hypothesis: The null hypothesis is a statement that there is no relationship between the variables you are studying.
- Define the population and sample: Clearly define the population you are studying and the sample you will be using for your research.
- Select appropriate methods for testing the hypothesis: Select appropriate research methods, such as experiments, surveys, or observational studies, which will allow you to test your research hypothesis .
Remember that creating a research hypothesis is an iterative process, i.e., you might have to revise it based on the data you collect. You may need to test and reject several hypotheses before answering the research problem.
How to write a research hypothesis
When you start writing a research hypothesis , you use an “if–then” statement format, which states the predicted relationship between two or more variables. Clearly identify the independent variables (the variables being changed) and the dependent variables (the variables being measured), as well as the population you are studying. Review and revise your hypothesis as needed.
An example of a research hypothesis in this format is as follows:
“ If [athletes] follow [cold water showers daily], then their [endurance] increases.”
Population: athletes
Independent variable: daily cold water showers
Dependent variable: endurance
You may have understood the characteristics of a good hypothesis . But note that a research hypothesis is not always confirmed; a researcher should be prepared to accept or reject the hypothesis based on the study findings.

Research hypothesis checklist
Following from above, here is a 10-point checklist for a good research hypothesis :
- Testable: A research hypothesis should be able to be tested via experimentation or observation.
- Specific: A research hypothesis should clearly state the relationship between the variables being studied.
- Based on prior research: A research hypothesis should be based on existing knowledge and previous research in the field.
- Falsifiable: A research hypothesis should be able to be disproven through testing.
- Clear and concise: A research hypothesis should be stated in a clear and concise manner.
- Logical: A research hypothesis should be logical and consistent with current understanding of the subject.
- Relevant: A research hypothesis should be relevant to the research question and objectives.
- Feasible: A research hypothesis should be feasible to test within the scope of the study.
- Reflects the population: A research hypothesis should consider the population or sample being studied.
- Uncomplicated: A good research hypothesis is written in a way that is easy for the target audience to understand.
By following this research hypothesis checklist , you will be able to create a research hypothesis that is strong, well-constructed, and more likely to yield meaningful results.

Types of research hypothesis
Different types of research hypothesis are used in scientific research:
1. Null hypothesis:
A null hypothesis states that there is no change in the dependent variable due to changes to the independent variable. This means that the results are due to chance and are not significant. A null hypothesis is denoted as H0 and is stated as the opposite of what the alternative hypothesis states.
Example: “ The newly identified virus is not zoonotic .”
2. Alternative hypothesis:
This states that there is a significant difference or relationship between the variables being studied. It is denoted as H1 or Ha and is usually accepted or rejected in favor of the null hypothesis.
Example: “ The newly identified virus is zoonotic .”
3. Directional hypothesis :
This specifies the direction of the relationship or difference between variables; therefore, it tends to use terms like increase, decrease, positive, negative, more, or less.
Example: “ The inclusion of intervention X decreases infant mortality compared to the original treatment .”
4. Non-directional hypothesis:
While it does not predict the exact direction or nature of the relationship between the two variables, a non-directional hypothesis states the existence of a relationship or difference between variables but not the direction, nature, or magnitude of the relationship. A non-directional hypothesis may be used when there is no underlying theory or when findings contradict previous research.
Example, “ Cats and dogs differ in the amount of affection they express .”
5. Simple hypothesis :
A simple hypothesis only predicts the relationship between one independent and another independent variable.
Example: “ Applying sunscreen every day slows skin aging .”
6 . Complex hypothesis :
A complex hypothesis states the relationship or difference between two or more independent and dependent variables.
Example: “ Applying sunscreen every day slows skin aging, reduces sun burn, and reduces the chances of skin cancer .” (Here, the three dependent variables are slowing skin aging, reducing sun burn, and reducing the chances of skin cancer.)
7. Associative hypothesis:
An associative hypothesis states that a change in one variable results in the change of the other variable. The associative hypothesis defines interdependency between variables.
Example: “ There is a positive association between physical activity levels and overall health .”
8 . Causal hypothesis:
A causal hypothesis proposes a cause-and-effect interaction between variables.
Example: “ Long-term alcohol use causes liver damage .”
Note that some of the types of research hypothesis mentioned above might overlap. The types of hypothesis chosen will depend on the research question and the objective of the study.


Research hypothesis examples
Here are some good research hypothesis examples :
“The use of a specific type of therapy will lead to a reduction in symptoms of depression in individuals with a history of major depressive disorder.”
“Providing educational interventions on healthy eating habits will result in weight loss in overweight individuals.”
“Plants that are exposed to certain types of music will grow taller than those that are not exposed to music.”
“The use of the plant growth regulator X will lead to an increase in the number of flowers produced by plants.”
Characteristics that make a research hypothesis weak are unclear variables, unoriginality, being too general or too vague, and being untestable. A weak hypothesis leads to weak research and improper methods.
Some bad research hypothesis examples (and the reasons why they are “bad”) are as follows:
“This study will show that treatment X is better than any other treatment . ” (This statement is not testable, too broad, and does not consider other treatments that may be effective.)
“This study will prove that this type of therapy is effective for all mental disorders . ” (This statement is too broad and not testable as mental disorders are complex and different disorders may respond differently to different types of therapy.)
“Plants can communicate with each other through telepathy . ” (This statement is not testable and lacks a scientific basis.)
Importance of testable hypothesis
If a research hypothesis is not testable, the results will not prove or disprove anything meaningful. The conclusions will be vague at best. A testable hypothesis helps a researcher focus on the study outcome and understand the implication of the question and the different variables involved. A testable hypothesis helps a researcher make precise predictions based on prior research.
To be considered testable, there must be a way to prove that the hypothesis is true or false; further, the results of the hypothesis must be reproducible.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on research hypothesis
1. What is the difference between research question and research hypothesis ?
A research question defines the problem and helps outline the study objective(s). It is an open-ended statement that is exploratory or probing in nature. Therefore, it does not make predictions or assumptions. It helps a researcher identify what information to collect. A research hypothesis , however, is a specific, testable prediction about the relationship between variables. Accordingly, it guides the study design and data analysis approach.
2. When to reject null hypothesis ?
A null hypothesis should be rejected when the evidence from a statistical test shows that it is unlikely to be true. This happens when the test statistic (e.g., p -value) is less than the defined significance level (e.g., 0.05). Rejecting the null hypothesis does not necessarily mean that the alternative hypothesis is true; it simply means that the evidence found is not compatible with the null hypothesis.
3. How can I be sure my hypothesis is testable?
A testable hypothesis should be specific and measurable, and it should state a clear relationship between variables that can be tested with data. To ensure that your hypothesis is testable, consider the following:
- Clearly define the key variables in your hypothesis. You should be able to measure and manipulate these variables in a way that allows you to test the hypothesis.
- The hypothesis should predict a specific outcome or relationship between variables that can be measured or quantified.
- You should be able to collect the necessary data within the constraints of your study.
- It should be possible for other researchers to replicate your study, using the same methods and variables.
- Your hypothesis should be testable by using appropriate statistical analysis techniques, so you can draw conclusions, and make inferences about the population from the sample data.
- The hypothesis should be able to be disproven or rejected through the collection of data.
4. How do I revise my research hypothesis if my data does not support it?
If your data does not support your research hypothesis , you will need to revise it or develop a new one. You should examine your data carefully and identify any patterns or anomalies, re-examine your research question, and/or revisit your theory to look for any alternative explanations for your results. Based on your review of the data, literature, and theories, modify your research hypothesis to better align it with the results you obtained. Use your revised hypothesis to guide your research design and data collection. It is important to remain objective throughout the process.
5. I am performing exploratory research. Do I need to formulate a research hypothesis?
As opposed to “confirmatory” research, where a researcher has some idea about the relationship between the variables under investigation, exploratory research (or hypothesis-generating research) looks into a completely new topic about which limited information is available. Therefore, the researcher will not have any prior hypotheses. In such cases, a researcher will need to develop a post-hoc hypothesis. A post-hoc research hypothesis is generated after these results are known.
6. How is a research hypothesis different from a research question?
A research question is an inquiry about a specific topic or phenomenon, typically expressed as a question. It seeks to explore and understand a particular aspect of the research subject. In contrast, a research hypothesis is a specific statement or prediction that suggests an expected relationship between variables. It is formulated based on existing knowledge or theories and guides the research design and data analysis.
7. Can a research hypothesis change during the research process?
Yes, research hypotheses can change during the research process. As researchers collect and analyze data, new insights and information may emerge that require modification or refinement of the initial hypotheses. This can be due to unexpected findings, limitations in the original hypotheses, or the need to explore additional dimensions of the research topic. Flexibility is crucial in research, allowing for adaptation and adjustment of hypotheses to align with the evolving understanding of the subject matter.
8. How many hypotheses should be included in a research study?
The number of research hypotheses in a research study varies depending on the nature and scope of the research. It is not necessary to have multiple hypotheses in every study. Some studies may have only one primary hypothesis, while others may have several related hypotheses. The number of hypotheses should be determined based on the research objectives, research questions, and the complexity of the research topic. It is important to ensure that the hypotheses are focused, testable, and directly related to the research aims.
9. Can research hypotheses be used in qualitative research?
Yes, research hypotheses can be used in qualitative research, although they are more commonly associated with quantitative research. In qualitative research, hypotheses may be formulated as tentative or exploratory statements that guide the investigation. Instead of testing hypotheses through statistical analysis, qualitative researchers may use the hypotheses to guide data collection and analysis, seeking to uncover patterns, themes, or relationships within the qualitative data. The emphasis in qualitative research is often on generating insights and understanding rather than confirming or rejecting specific research hypotheses through statistical testing.
Editage All Access is a subscription-based platform that unifies the best AI tools and services designed to speed up, simplify, and streamline every step of a researcher’s journey. The Editage All Access Pack is a one-of-a-kind subscription that unlocks full access to an AI writing assistant, literature recommender, journal finder, scientific illustration tool, and exclusive discounts on professional publication services from Editage.
Based on 22+ years of experience in academia, Editage All Access empowers researchers to put their best research forward and move closer to success. Explore our top AI Tools pack, AI Tools + Publication Services pack, or Build Your Own Plan. Find everything a researcher needs to succeed, all in one place – Get All Access now starting at just $14 a month !
Related Posts

What is Correlational Research: Definition, Types, and Examples

What is Research Protocol? How to Write It (with Examples)
- Interesting
- Scholarships
- UGC-CARE Journals
What is Hypothesis in Research? Types, Examples, & Importance
Research Hypothesis - Learn its types, importance, and how to test one for groundbreaking discoveries.
A research hypothesis is an “educated guess” about relationships/differences in the possible result of scientific research. It should be a precise and testable statement. A good hypothesis converts the research question into a specific statement about the relationship between two or more research variables to predict an expected outcome. It is important to know about the research hypothesis and its type for every researcher .
What is Hypothesis in Research?
In the world of research, a hypothesis is like a smart guess that scientists make. It’s a statement they propose to test out through experiments and analysis. This guess is based on what they already know, the theories they’ve learned, and what they’ve observed.
Example: Imagine you have a plant that seems droopy. You (the scientist) want to figure out why.
Smart Guess (Hypothesis): You think maybe the plant needs more water. This is your educated guess based on what you know about plants (they need water to survive).
Testing the Guess (Experiment): You decide to give the plant more water and see if it perks up.
Types of Hypotheses in Research
There are two kinds of hypotheses:
1. Null Hypothesis (H0)
The null hypothesis states that the two variables under investigation have no relationship which means one variable does not affect the other variable. It claims that the findings are purely coincidental and have no presence in the validity of the hypothesis being investigated.
This one says there’s no real difference or connection between the things being studied. It’s like saying “nothing special is happening.”
Example 1: Null Hypothesis
Nothing Happens (Null Hypothesis): This guess (H0) says that giving the plant more water won’t make a difference. Maybe it needs more sunlight instead.
2. Alternative Hypothesis (H1 or Ha)
The alternative hypothesis states the effect of a relationship between one variable to another variable . In this, the result of the study is not due to the chance of occurrence in the study.
Also, we accept the alternative hypothesis if the null hypothesis is denied. We do not accept the alternative hypothesis if the null hypothesis is not rejected.
This one suggests there is a real difference or connection between the things. It’s the opposite of the null hypothesis
Example 1: Alternative Hypothesis
Plant Gets Happy (Alternative Hypothesis): This guess (H1) says that more water is what the plant needs.
Finding the Answer: If your plant revives after a while, it supports your guess that it needs more water (H1). But if it stays droopy, then your guess was wrong (H0 might be true, and it needs something else).
This is how scientists use experiments to test their smart guesses (hypotheses) and learn more about the world!
Example 2: Null Hypothesis and Alternative Hypothesis
For instance, let’s imagine researchers are studying how a new medicine affects blood pressure. Their hypotheses might look something like this:
- Null Hypothesis (H0): There’s no significant difference in blood pressure between the people who take the medicine and those who don’t.
- Alternative Hypothesis (H1): There is a significant difference in blood pressure between the people who take the medicine and those who don’t.
After forming this hypothesis, scientists do experiments to gather data that either supports or disproves what they’ve guessed. This helps them learn more about the world and how things work.
3. Simple Hypothesis:
A simple hypothesis proposes a relationship between two variables. It predicts a direct cause-and-effect relationship without considering other factors.
Example: If students study for longer hours, their test scores will improve.
4. Complex Hypothesis:
A complex hypothesis accounts for multiple variables and their interactions. It predicts how these variables might influence each other.
Example: The interaction between students’ study habits, teacher effectiveness, and classroom environment will determine their test scores.
5. Associative Hypothesis:
An associative hypothesis suggests that two variables are related or associated with each other. However, it does not imply a cause-and-effect relationship.
Example: There is a positive association between exercise frequency and overall health.
6. Causal Hypothesis:
A causal hypothesis proposes that one variable directly causes a change in another variable. It implies a cause-and-effect relationship.
Example: Increased consumption of sugary beverages causes weight gain in adolescents.
Examples of Hypothesis from Question to Statements
Question: Are health and mental stress-related?
Statement: I predict that health and mental stress are related
Question: How do the teaching practices in Area X and Area Y differ?
Statement: It is hypothesized that the teaching practices in X is different from that of Y
Directional and Non-Directional Hypothesis
Defining the research hypotheses is one of the crucial steps in framing a scientific quantitative research study . Further, it can be classified into Directional, and Non-Directional Hypothesis.
7. Non-Directional Hypothesis
The non-directional hypothesis is a two-tailed hypothesis where the direction of prediction is not specified, In this, the independent variable will affect the dependent variable.
8. Directional Hypothesis
The directional hypothesis is a one-tailed hypothesis that uses the characteristics of the independent variable’s effect on the dependent variable to predict the exact direction of the effect.
Examples of Directional, Non-Directional Hypothesis
Non – Non-Directional Hypothesis: I predict that health and mental stress are related
Directional Hypothesis : I predict that health and mental stress are inversely related
Non-Directional Hypothesis : It is hypothesized that test performance and anxiety will be significantly related
Directional Hypothesis : It is hypothesized that as anxiety increases, test performance will decrease
Question: Do animals care about the color of their food?
Null Hypothesi s: Animals never express food preference based on color.
Negation to Form Null and Alternative Hypothesis:
Null hypothesis: “ x is equal to y .” Alternative hypothesis “ x is not equal to y .” Alternative hypothesis “ x is less than y , ”Null hypothesis: “ x is at least y .” Null hypothesis: “ x is at most y .” Alternative hypothesis “ x is greater than y .” Taylor, Courtney. ThoughtCo.

Significance of Hypothesis in Research
The hypothesis is like the starting point of a treasure hunt in research. They give researchers a map to follow, guiding them toward what they want to find out. The following six points are the importance and significance of the hypothesis in research.
1. Giving Direction
Think of a hypothesis as a compass. They show researchers where to go and what to look for in their studies. Without them, research can feel like wandering in the dark.
2. Testing Ideas
Just like in a science experiment, hypotheses help researchers test their theories. It’s like saying, “I think this might be true. Let’s find out!”
3. Organizing the Hunt
Hypotheses help researchers plan their journey. They decide what data to collect and how to collect it, keeping everything organized and focused.
4. Making Sense of Clues
Once researchers gather data, hypotheses act as a guidebook. They help make sense of the information collected, showing whether it supports their ideas or points in a different direction.
5. Adding to the Map
Every study, whether it proves or disproves a hypothesis, adds to our understanding of the world. It’s like discovering new places on the map of knowledge.
6. Helping in Real Life
Research based on hypotheses isn’t just for academics. It can lead to practical discoveries and decisions that affect our lives, like new medicines or better teaching methods.
So, think of hypotheses as the spark that ignites the research journey, guiding scientists toward discoveries and deeper understanding.
Testing a Hypothesis in Research
Testing a hypothesis in research is like conducting a science experiment to see if your idea holds water. Here’s how it works:
1. Setting Up the Experiment
First, you design a study or experiment to gather data related to your hypothesis. This could involve anything from surveys and interviews to lab experiments or observations in the field.
2. Collecting Data
Next, you collect information or data according to your research design. This could be measurements, observations, or responses to questions, depending on your specific hypothesis and methods.
3. Analyzing the Data
Once you’ve gathered your data, it’s time to roll up your sleeves and crunch the numbers. You use statistical methods and other analytical tools to make sense of the information you’ve collected.
4. Comparing with Expectations
Here’s where the rubber meets the road. You compare your findings with what you expected based on your hypothesis. Did the data support your idea, or did it throw a curveball?
5. Drawing Conclusions
Based on your analysis, you conclude whether your hypothesis is supported by the evidence. If the data aligns with your predictions, you might have a winner. If not, it’s back to the drawing board.
6. Communicating Results
Finally, you share your findings with the world. This could be through a research paper, conference presentation, or scientific journal publication. It’s your chance to contribute to the collective knowledge of your field.

Key Takeaways About Hypothesis in Research
- What it is: A hypothesis in research is an educated guess about the relationship between variables. It’s a tentative statement that guides your investigation and predicts the outcome of your study. [hypothesis in research meaning]
- Research hypothesis (alternative hypothesis): This predicts a specific relationship between the variables you’re studying (e.g., students who use flashcards will score higher on exams). [types of hypothesis in research]
- Null hypothesis: This proposes no relationship between the variables (e.g., there is no difference in exam scores between students who use flashcards and those who don’t). [null hypothesis in research]
- A hypothesis helps you design a research methodology – it dictates what data you collect and how you analyze it. [hypothesis in research methodology]
- Testing the hypothesis is the core of the scientific method – it allows you to see if your prediction is supported by evidence. [testing the hypothesis in research]
- Example: Let’s say you’re researching the effectiveness of exercise on memory. Your hypothesis could be: “Students who engage in regular aerobic exercise will have better recall on memory tests compared to students who do not exercise regularly.”
Hand-Picked Related Articles
Types of Research Variable in Research with Example
How to Write a Research Article? Good Manuscript Structure
Differences Between Quantitative and Qualitative Research
- Alternative Hypothesis
- Directional Hypothesis
- hypothesis in research
- hypothesis in research methodology
- Hypthesis Types
- importance of hypothesis in research
- meaning of hypothesis in research
- Non-Directional Hypothesis
- Null Hypothesis
- null hypothesis in research
- Research Hypothesis
- research hypothesis example
- Research Methodology
- significance of hypothesis in research
- testing a hypothesis in research
- types of research hypothesis
- what is a hypothesis in research
- What is Research Hypothesis
What is a Scopus Indexed Journal?
Ethnographic research examples: exploring cultures through immersive study, advantages and disadvantages of qualitative research methodologies.
[…] What is Research Hypothesis? […]
A research Hypothesis is a proposed explaination for a phenomeon. For the Hypothesis to a scientific method requires that one can test it.
Research is a scientific approach of answering a research question, solving a research problem, or generating new knowledge through a systematic and orderly collection, organization, and analysis of data with the ultimate goal of making the findings of research useful in decision-making.
t is based on the work of others. It can be replicated and doable . It is generalisable to other settings. It is based on some logical rationale and tied to theory. … It generates new questions or is cyclical in nature. It is incremental. It addresses directly or indirectly some real problem in the world.
LEAVE A REPLY Cancel reply
Log in to leave a comment
Most Popular
Scopus indexed journals list 2024, top 7 artificial intelligence (ai) tools in scientific research 2024, ugc phd excellence citation to recognize outstanding research, strategies to end the science nobel drought in india, why mahatma gandhi never won the nobel prize for peace, nomination and selection of nobel prize laureates, the roadmap to nobel prize-worthy research, annas archive – download research papers for free, best for you, 24 best online plagiarism checker free – 2024, what is a phd a comprehensive guide for indian scientists and aspiring researchers, popular posts, unethical journal publications, popular category.
- POSTDOC 317
- Interesting 259
- Journals 236
- Fellowship 134
- Research Methodology 103
- All Scopus Indexed Journals 94
Mail Subscription

iLovePhD is a research education website to know updated research-related information. It helps researchers to find top journals for publishing research articles and get an easy manual for research tools. The main aim of this website is to help Ph.D. scholars who are working in various domains to get more valuable ideas to carry out their research. Learn the current groundbreaking research activities around the world, love the process of getting a Ph.D.
Contact us: [email protected]
Google News
Copyright © 2024 iLovePhD. All rights reserved
- Artificial intelligence

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The statement of the hypothesis is based on a certain concept i.e. it could be either related to the theory or the pre-assumption of the researcher about certain variables i.e. educated guess. This leads to linkin…
A research hypothesis is an assumption or a tentative explanation for a specific process observed during research. Unlike a guess, research hypothesis is a calculated, educated guess proven or disproven through …
In this blog, we’ll learn what a research hypothesis is, why it’s important in research, and the different types used in science. We’ll also guide you through creating your research hypothesis and discussing ways to test and evaluate it.
A research hypothesis is a statement that proposes a possible explanation for an observable phenomenon or pattern. It guides the direction of a study and predicts the outcome of the investigation. A research hypothesis is …
A hypothesis states your predictions about what your research will find. It is a tentative answer to your research question that has not yet been tested. For some research …
A good hypothesis converts the research question into a specific statement about the relationship between two or more research variables to predict an expected outcome. It is important to know about the research …
A hypothesis is an essential part of the scientific method and helps to guide the research process by providing a clear focus for investigation. It enables scientists to …