How to Write About Coronavirus in a College Essay
Students can share how they navigated life during the coronavirus pandemic in a full-length essay or an optional supplement.
Writing About COVID-19 in College Essays

Getty Images
Experts say students should be honest and not limit themselves to merely their experiences with the pandemic.
The global impact of COVID-19, the disease caused by the novel coronavirus, means colleges and prospective students alike are in for an admissions cycle like no other. Both face unprecedented challenges and questions as they grapple with their respective futures amid the ongoing fallout of the pandemic.
Colleges must examine applicants without the aid of standardized test scores for many – a factor that prompted many schools to go test-optional for now . Even grades, a significant component of a college application, may be hard to interpret with some high schools adopting pass-fail classes last spring due to the pandemic. Major college admissions factors are suddenly skewed.
"I can't help but think other (admissions) factors are going to matter more," says Ethan Sawyer, founder of the College Essay Guy, a website that offers free and paid essay-writing resources.
College essays and letters of recommendation , Sawyer says, are likely to carry more weight than ever in this admissions cycle. And many essays will likely focus on how the pandemic shaped students' lives throughout an often tumultuous 2020.
But before writing a college essay focused on the coronavirus, students should explore whether it's the best topic for them.

Writing About COVID-19 for a College Application
Much of daily life has been colored by the coronavirus. Virtual learning is the norm at many colleges and high schools, many extracurriculars have vanished and social lives have stalled for students complying with measures to stop the spread of COVID-19.
"For some young people, the pandemic took away what they envisioned as their senior year," says Robert Alexander, dean of admissions, financial aid and enrollment management at the University of Rochester in New York. "Maybe that's a spot on a varsity athletic team or the lead role in the fall play. And it's OK for them to mourn what should have been and what they feel like they lost, but more important is how are they making the most of the opportunities they do have?"
That question, Alexander says, is what colleges want answered if students choose to address COVID-19 in their college essay.
But the question of whether a student should write about the coronavirus is tricky. The answer depends largely on the student.
"In general, I don't think students should write about COVID-19 in their main personal statement for their application," Robin Miller, master college admissions counselor at IvyWise, a college counseling company, wrote in an email.
"Certainly, there may be exceptions to this based on a student's individual experience, but since the personal essay is the main place in the application where the student can really allow their voice to be heard and share insight into who they are as an individual, there are likely many other topics they can choose to write about that are more distinctive and unique than COVID-19," Miller says.
Opinions among admissions experts vary on whether to write about the likely popular topic of the pandemic.
"If your essay communicates something positive, unique, and compelling about you in an interesting and eloquent way, go for it," Carolyn Pippen, principal college admissions counselor at IvyWise, wrote in an email. She adds that students shouldn't be dissuaded from writing about a topic merely because it's common, noting that "topics are bound to repeat, no matter how hard we try to avoid it."
Above all, she urges honesty.
"If your experience within the context of the pandemic has been truly unique, then write about that experience, and the standing out will take care of itself," Pippen says. "If your experience has been generally the same as most other students in your context, then trying to find a unique angle can easily cross the line into exploiting a tragedy, or at least appearing as though you have."
But focusing entirely on the pandemic can limit a student to a single story and narrow who they are in an application, Sawyer says. "There are so many wonderful possibilities for what you can say about yourself outside of your experience within the pandemic."
He notes that passions, strengths, career interests and personal identity are among the multitude of essay topic options available to applicants and encourages them to probe their values to help determine the topic that matters most to them – and write about it.
That doesn't mean the pandemic experience has to be ignored if applicants feel the need to write about it.
Writing About Coronavirus in Main and Supplemental Essays
Students can choose to write a full-length college essay on the coronavirus or summarize their experience in a shorter form.
To help students explain how the pandemic affected them, The Common App has added an optional section to address this topic. Applicants have 250 words to describe their pandemic experience and the personal and academic impact of COVID-19.
"That's not a trick question, and there's no right or wrong answer," Alexander says. Colleges want to know, he adds, how students navigated the pandemic, how they prioritized their time, what responsibilities they took on and what they learned along the way.
If students can distill all of the above information into 250 words, there's likely no need to write about it in a full-length college essay, experts say. And applicants whose lives were not heavily altered by the pandemic may even choose to skip the optional COVID-19 question.
"This space is best used to discuss hardship and/or significant challenges that the student and/or the student's family experienced as a result of COVID-19 and how they have responded to those difficulties," Miller notes. Using the section to acknowledge a lack of impact, she adds, "could be perceived as trite and lacking insight, despite the good intentions of the applicant."
To guard against this lack of awareness, Sawyer encourages students to tap someone they trust to review their writing , whether it's the 250-word Common App response or the full-length essay.
Experts tend to agree that the short-form approach to this as an essay topic works better, but there are exceptions. And if a student does have a coronavirus story that he or she feels must be told, Alexander encourages the writer to be authentic in the essay.
"My advice for an essay about COVID-19 is the same as my advice about an essay for any topic – and that is, don't write what you think we want to read or hear," Alexander says. "Write what really changed you and that story that now is yours and yours alone to tell."
Sawyer urges students to ask themselves, "What's the sentence that only I can write?" He also encourages students to remember that the pandemic is only a chapter of their lives and not the whole book.
Miller, who cautions against writing a full-length essay on the coronavirus, says that if students choose to do so they should have a conversation with their high school counselor about whether that's the right move. And if students choose to proceed with COVID-19 as a topic, she says they need to be clear, detailed and insightful about what they learned and how they adapted along the way.
"Approaching the essay in this manner will provide important balance while demonstrating personal growth and vulnerability," Miller says.
Pippen encourages students to remember that they are in an unprecedented time for college admissions.
"It is important to keep in mind with all of these (admission) factors that no colleges have ever had to consider them this way in the selection process, if at all," Pippen says. "They have had very little time to calibrate their evaluations of different application components within their offices, let alone across institutions. This means that colleges will all be handling the admissions process a little bit differently, and their approaches may even evolve over the course of the admissions cycle."
Searching for a college? Get our complete rankings of Best Colleges.
10 Ways to Discover College Essay Ideas

Tags: students , colleges , college admissions , college applications , college search , Coronavirus
2025 Best Colleges

Search for your perfect fit with the U.S. News rankings of colleges and universities.
College Admissions: Get a Step Ahead!
Sign up to receive the latest updates from U.S. News & World Report and our trusted partners and sponsors. By clicking submit, you are agreeing to our Terms and Conditions & Privacy Policy .
Ask an Alum: Making the Most Out of College
You May Also Like
Avoid money problems in med school.
Sammy Allen Nov. 15, 2024

Seek Mentors at U.S. Colleges
Anayat Durrani Nov. 13, 2024

10 HBCUs With Low Acceptance Rates
Cole Claybourn Nov. 13, 2024

Applying to College as Undecided Major
Anthony Todd Carlisle Nov. 11, 2024

How to Make a College List
Cole Claybourn Nov. 6, 2024

Weighing LSAT Test Prep Options
Gabriel Kuris Nov. 4, 2024

Data Privacy Tips for College Students
Cole Claybourn Nov. 4, 2024

Preparing for Your First Job Post-Grad
Sarah Wood Oct. 31, 2024

5 Ways to Decrease Medical School Costs
Anayat Durrani Oct. 31, 2024

Graduate School with Student Loan Debt
A.R. Cabral Oct. 31, 2024

An official website of the United States government
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock icon ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Advanced Search
- Journal List

The impact of COVID-19 on student experiences and expectations: Evidence from a survey ☆
Esteban m aucejo, jacob french, maria paola ugalde araya, basit zafar.
- Author information
- Article notes
- Copyright and License information
Corresponding author.
Received 2020 Jun 10; Revised 2020 Aug 17; Accepted 2020 Aug 19; Issue date 2020 Nov.
Since January 2020 Elsevier has created a COVID-19 resource centre with free information in English and Mandarin on the novel coronavirus COVID-19. The COVID-19 resource centre is hosted on Elsevier Connect, the company's public news and information website. Elsevier hereby grants permission to make all its COVID-19-related research that is available on the COVID-19 resource centre - including this research content - immediately available in PubMed Central and other publicly funded repositories, such as the WHO COVID database with rights for unrestricted research re-use and analyses in any form or by any means with acknowledgement of the original source. These permissions are granted for free by Elsevier for as long as the COVID-19 resource centre remains active.
In order to understand the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on higher education, we surveyed approximately 1500 students at one of the largest public institutions in the United States using an instrument designed to recover the causal impact of the pandemic on students' current and expected outcomes. Results show large negative effects across many dimensions. Due to COVID-19: 13% of students have delayed graduation, 40% have lost a job, internship, or job offer, and 29% expect to earn less at age 35. Moreover, these effects have been highly heterogeneous. One quarter of students increased their study time by more than 4 hours per week due to COVID-19, while another quarter decreased their study time by more than 5 hours per week. This heterogeneity often followed existing socioeconomic divides. Lower-income students are 55% more likely than their higher-income peers to have delayed graduation due to COVID-19. Finally, we show that the economic and health related shocks induced by COVID-19 vary systematically by socioeconomic factors and constitute key mediators in explaining the large (and heterogeneous) effects of the pandemic.
Keywords: COVID-19, Higher education, Expectations, Survey
Due to COVID: 13% of students delayed graduation, 40% lost a job, internship, or offer, and 29% expect to earn less at 35.
The effects of the pandemic have been highly heterogeneous.
Lower-income students are 55% more likely than their higher-income peers to have delayed graduation due to COVID-19.
COVID-19's economic and health shocks vary by socioeconomic status and act as key mediators explaining pandemic's effects.
1. Introduction
The disruptive effects of the COVID-19 outbreak have impacted almost all sectors of our society. Higher education is no exception. Anecdotal evidence paints a bleak picture for both students and universities. According to the American Council on Education, enrollment is likely to drop by 15% in the fall of 2020, while at the same time many institutions may have to confront demands for large tuition cuts if classes remain virtual. 1 In a similar vein, students face an increasingly uncertain environment, where financial and health shocks (for example, lack of resources to complete their studies or fear of becoming seriously sick), along with the transition to online learning may have affected their academic performance, educational plans, current labor market participation, and expectations about future employment.
This paper attempts to shed light on the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on college students. First, we describe and quantify the causal effects of the COVID-19 outbreak on a wide set of students' outcomes/expectations. In particular, we analyze enrollment and graduation decisions, academic performance, major choice, study and social habits, remote learning experiences, current labor market participation, and expectations about future employment. Second, we study how these effects differ along existing socioeconomic divides and whether the pandemic has exacerbated existing inequalities. Finally, we present suggestive evidence on the mechanisms behind the heterogeneous COVID-19 effects by quantifying the relationship between individual-level (financial and health) shocks and students' academic decisions and labor market expectations.
For this purpose, we surveyed about 1500 undergraduate students at Arizona State University (ASU), one of the largest public universities in the United States, in late April 2020. The survey was explicitly designed to not only collect student outcomes and expectations after the onset of the pandemic, but also to recover counterfactual outcomes in the absence of the outbreak. Specifically, the survey asked students about their current experiences/expectations and what those experiences/expectations would have been had it not been for the pandemic. Because we collect information conditional on both states of the world (with the COVID-19 pandemic, and without) from each student , we can directly analyze how each student believes COVID-19 has impacted their current and future outcomes. 2 For example, by asking students about their current GPA in a post-COVID-19 world and their expected GPA in the absence of COVID-19, we can back out the subjective treatment effect of COVID-19 on academic performance. The credibility of our approach depends on: (1) students having well-formed beliefs about outcomes in the counterfactual scenario. This is a plausible assumption in our context since the counterfactual state is a realistic and relevant one - it was the status quo less than two months before the survey, and (2) there being no systematic bias in the reporting of the data - an assumption that is implicitly made when using any survey data. 3
Our findings on academic outcomes indicate that COVID-19 has led to a large number of students delaying graduation (13%), withdrawing from classes (11%), and intending to change majors (12%). Moreover, approximately 50% of our sample separately reported a decrease in study hours and in their academic performance. Predicting the longer-term impact of the pandemic on student achievement is more difficult, but students reported that they expect to take a break from college in the fall 2020 semester at more than twice the rate in previous years. Historically, 28% of students who fail to re-enroll do not return to ASU or another university after 5 years (authors' calculations from ASU first-time freshmen transcript data for the 2012–2014 spring semesters), suggesting that the pandemic may have a lasting impact on the educational achievement of current students. We also find that students report a decreased preference for online instruction as a result of their recent experiences.
As expected, the COVID-19 outbreak also had large negative effects on students' current labor market participation and expectations about post-college labor outcomes. Working students suffered a 31% decrease in their wages and a 37% drop in weekly hours worked, on average. Moreover, around 40% of students lost a job, internship, or a job offer, and 61% reported to have a family member that experienced a reduction in income. The pandemic also had a substantial impact on students' expectations about their labor market prospects post-college. For example, their perceived probability of finding a job before graduation decreased by almost 20%, and their expected earnings when 35 years old (around 15 years from the outbreak) declined by approximately 2.5%. This last finding suggests that students expect the pandemic to have a long-lasting impact on their labor market prospects, which is qualitatively consistent with the literature on graduating during a recession. For instance, Oreopoulos et al. (2012) and Schwandt and von Wachter (2019) find significant reductions in earnings 5 and 10 years after graduation, respectively, and Kahn (2010) finds an even longer-lasting effect on wages. On the other hand, although we are measuring the probability of finding a job before graduating, not unemployment directly, our estimated quantitative effect on students' expectations of finding a job seems to be larger relative to the literature ( Kahn, 2010 ; Altonji et al., 2016 ; and Rothstein, 2020 ).
The data also show that while all subgroups of the population have experienced negative effects due to the outbreak, the size of the effects are heterogeneous. For example, compared to their more affluent peers, lower-income students are 55% more likely to delay graduation due to COVID-19 and are 41% more likely to report that COVID-19 impacted their major choice. Further, COVID-19 nearly doubled the gap between higher- and lower-income students' expected GPA. 4 There also is substantial variation in the pandemic's effect on preference for online learning, with Honors students and males revising their preferences down more than 2.5 times as much as their peers. However, despite appearing to be more disrupted by the switch to online learning, the impact of COVID-19 on Honors students' academic outcomes is consistently smaller than the impact on non-Honors students.
Finally, we evaluate the extent to which mitigating factors associated with more direct economic and health shocks from the pandemic (for example, a family member losing income due to COVID-19, or the expected probability of hospitalization if contracting COVID-19) can explain the heterogeneity in pandemic effects. We find that both types of shock (economic and health) are systematically correlated with students' COVID-19 experiences. For example, the expected probability of delaying graduation due to COVID-19 increases by approximately 25% if either a student's subjective probability of being late on a debt payment in the following 90 days (a measure of financial fragility) or subjective probability of requiring hospitalization conditional on contracting COVID-19 increases by one standard deviation. As expected, the magnitude of health and economic shocks are not homogeneous across the student population. The average of the principal component for the economic and health shocks is about 0.3–0.4 standard deviations higher for students from lower-income families. Importantly, we find that the disparate economic and health impacts of COVID-19 can explain 40% of the delayed graduation gap (as well as a substantial part of the gap for other outcomes) between lower- and higher-income students. This analysis should be viewed as descriptive in nature and not necessarily causal, since omitted factors that are correlated both with the shocks and the outcomes may be driving these relationships.
To our knowledge, this is the first paper to shed light on the effects of COVID-19 on college students' experiences. The treatment effects that we find are large in economic terms. Whether students are overreacting in their response to the COVID-19 shock is not clear. We do find that previous cumulative GPA is a strong predictor of expected semester GPA without COVID-19, suggesting that students' reported expectations are meaningful. However, we know that individuals generally tend to overweight recent experiences ( Malmendier and Nagel, 2016 ; Kuchler and Zafar, 2019 ). Whether students' subjective treatment effects are “correct” in some ex-post sense is beside the point. As long as students are reporting their subjective beliefs without any systematic bias, it is the perceived treatment effects, not actual ones, – regardless of whether they are correct or not – which are fundamental to understanding choices. For example, if students (rightly or wrongly) perceive a negative treatment effect of COVID-19 on the returns to a college degree, this belief will have an impact on their future human capital decisions (such as continuing with their education, choice of major, etc.).
Our results underscore the fact that the COVID-19 shock is likely to exacerbate socioeconomic disparities in higher education. This is consistent with findings regarding the impacts of COVID-19 on K-12 students. Kuhfeld et al. (2020) project that school closures are likely to lead to significant learning losses in math and reading. However, they estimate heterogeneous effects, and conclude that high-performing students are likely to make gains. Likewise, Chetty et al. (2020) find that, post-COVID, student progress on an online math program decreased significantly more in poorer ZIP codes. Our analysis reveals that the heterogeneous economic and health burden imposed by COVID-19 can partially explain these varying impacts. This suggests that by addressing the economic and health impacts imposed by COVID-19, policy makers may be able to prevent COVID-19 from widening existing gaps in higher education.
2.1. Survey
Our data come from an original survey of undergraduate students at Arizona State University (ASU), one of the largest public universities in the United States. Like other higher educational institutions in the US, the Spring 2020 semester started in person. However, in early March during spring break, the school announced that instruction would be transitioned online and that students were advised not to return to campus.
The study was advertised on the My ASU website, accessible only through the student's ASU ID and password. Undergraduate students were invited to participate in an online survey about their experiences and expectations in light of the COVID-19 pandemic, for which they would be paid $10. The study was posted during the second to last week of instruction for the spring semester (April 23rd). Our sample size was constrained by the research funds to 1500 students, and the survey was closed once the desired sample size was reached, which happened within 3 days of posting the survey.
The survey was programmed in Qualtrics. It collected data on students' demographics and family background, their current experiences (both for academic outcomes and non-academic outcomes), and their future expectations. Importantly for the purposes of this study, the survey collected data on what these outcomes/expectations would have been in the counterfactual state, without COVID-19. The survey instrument (with only the relevant sections) can be found here .
2.2. Sample
A total of 1564 respondents completed the survey. 5 90 respondents were ineligible for the study (such as students enrolled in graduate degree programs or diploma programs) and were dropped from the sample. Finally, responses in the 1st and 99th percentile of survey duration were further excluded, leading to a final sample size of 1446. The survey took 38 min to complete, on average (median completion time was 26 min).
The first five columns of Table 1 show how our sample compares with the broader ASU undergraduate population and the average undergraduate student at other large flagship universities (specifically, the largest public universities in each state). Relative to the ASU undergraduate population, our sample has a significantly higher proportion of first-generation students (that is, students with no parent with a college degree), and a smaller proportion of international students. The demographic composition of our sample compares reasonably well with that of students in flagship universities. Our sample is also positively selected in terms of SAT/ACT scores relative to these two populations. The sample may also differ from the student body at other large public schools in that 30% report living on campus, which is not always the norm at other large institutions and may play an important role in how disruptive the pandemic has been. 6
Summary statistics.
Notes: Data in columns (2), (3) and (8) is from IPEDS 2018. The flagship universities are the 4-year public universities with the highest number of undergraduate students in each state. Means for these columns are weighted by total number of undergraduates in each institution. ACT and SAT data are weighted averages of 2018–2015 years from IPEDS. P -value columns show the p -value of a difference in means test between the two columns indicated by the numbers in the heading.
Data in the ASU column from a different source. This data includes everyone taking at least one class for credit during the Spring semester of 2018 and attended ASU as their first full-time university. Income and first generation variables for the ASU data are constructed with the data of the first available year, which it is not the first year of college for most of the sample.
Students with no parent with a college degree.
Family income in thousands of dollars.
The largest public universities in each state.
Top 10 universities according to the US News Ranking 2020.
The better performance on admission tests could be explained by the high proportion of Honors students in our sample (22% compared to 18% in the ASU population). The last four columns of Table 1 show how Honors students compare with ASU students and the average college student at a top-10 university. We see that they perform better than the average ASU student (which is expected) and just slightly worse than the average college student at a top-10 university. The share of white Honors students in our sample (60%) is higher than the proportion in the ASU population and much higher than the proportion of white students in the top-10 universities.
Overall, we believe our sample of ASU students is a reasonable representation of students at other large public schools, while the Honors students may provide insight into the experiences of students at more elite Institutions. Though, it is important to acknowledge that elite institutions may have additional resources to address a global pandemic.

3. Analytic framework
We next outline a simple analytic framework that guides the empirical analysis. Let O i ( COVID – 19) be the potential outcome of individual i associated with COVID-19 treatment. We are interested in the causal impact of COVID-19 on student outcomes:
where the first term on the right-hand side is student i 's outcome in the state of the world with COVID-19, and the second term being student i 's outcome in the state of the world without COVID-19. Recovering the treatment effect at the individual level entails comparison of the individual's outcomes in two alternate states of the world. With standard data on realizations, a given individual is observed in only one state of the world (in our case, COVID – 19 = 1). The alternate outcomes are counterfactual and unobserved. A large econometric and statistics literature studies how to identify these counterfactual outcomes and moments of the counterfactual outcomes (such as average treatment effects) from realized choice data (e.g., Heckman and Vytlacil, 2005 ; Angrist and Pischke, 2009 ; Imbens and Rubin, 2015 ). Instead, the approach we use in this paper is to directly ask individuals for their expected outcomes in both states of the world. From the collected data, we can then directly calculate the individual-level subjective treatment effect. As an example, consider beliefs about end-of-semester GPA. The survey asked students “ What semester-level GPA do you expect to get at the end of this semester ?” This is the first-term on the right-hand side of Eq. (1) . The counterfactual is elicited as follows “ Were it not for the COVID-19 pandemic , what semester-level GPA would you have expected to get at the end of the semester ?”. The difference in the responses to these two questions gives us the subjective expected treatment effect of COVID-19 on the student's GPA. For certain binary outcomes in the survey, we directly ask students for the Δ i . For example, regarding graduation plans, we simply ask a student if the Δ i is positive, negative, or zero: “ How has the COVID-19 pandemic affected your graduation plan ? [ graduate later ; graduation plan unaffected ; graduate earlier ].”
The approach we use in this paper follows a small and growing literature that uses subjective expectations to understand decision-making under uncertainty. Specifically, Arcidiacono et al. (2020) and Wiswall and Zafar (2020) ask college students about their beliefs for several outcomes associated with counterfactual choices of college majors, and estimate the ex-ante treatment effects of college majors on career and family outcomes. Shapiro and Giustinelli (2019) use a similar approach to estimate the subjective ex-ante treatment effects of health on labor supply. There is one minor distinction from these papers: while these papers elicit ex-ante treatment effects, in our case, we look at outcomes that have been observed (for example, withdrawing from a course during the semester) as well as those that will be observed in the future (such as age 35 earnings). Thus, some of our subjective treatment effects are ex-post in nature while others are ex-ante.
The soundness of our approach depends on a key assumption that students have well-formed expectations for outcomes in both the realized state and the counterfactual state. Since the outcomes we ask about are absolutely relevant and germane to students, they should have well-formed expectations for the realized state. In addition, given that the counterfactual state is the one that had been the status quo in prior semesters (and so students have had prior experiences in that state of the world), their ability to have expectations for outcomes in the counterfactual state should not be a controversial assumption. 7 As evidence that students' expectations exhibit meaningful variation, Appendix Fig. A1 shows that previous cumulative GPA is a strong predictor of expected semester GPA with COVID-19.
4. Empirical analysis
4.1. treatment effects.
We start with the analysis of the aggregate-level treatment effects, which are presented in Table 2 . The outcomes are organized in two groups, academic and labor market (see Appendix Table A1 for a complete list of outcomes). The first two columns of the table show the average beliefs for those outcomes where the survey elicited beliefs in both states of the world. The average treatment effects shown in column (3) are of particular interest. Since we can compute the individual-level treatment effects, columns (4)–(7) of the table show the cross-sectional heterogeneity in the treatment effects.
Subjective treatment effects.
Notes: Δ : change. Prop. Δ >0: proportion of students for whom the individual level Δ is positive. Prop. Δ =0: proportion of students for whom the individual level Δ is zero. 25th and 75th percentiles of the cross-sectional distribution of Δ . Standard deviation in parentheses. ( ∗ : p <0.1, ∗∗ : p <0.05, ∗∗∗ : p <0.01).
Unconditional, based on the whole sample.
Conditional on having a job.
With and without COVID-19 levels are in dollars and Δ = percentage points difference.
With and without COVID-19 levels are in thousands of dollars and Δ = percentage points difference.
We see that the average treatment effects are statistically and economically significant for all outcomes. The average impacts on academic outcomes, shown in Panel A, are mostly negative. For example, the average subjective treatment effect of COVID-19 on semester-level GPA is a decline of 0.17 points. More than 50% of the students in our sample expect a decrease in their GPA due to the treatment (versus only 7% expecting an increase). Additionally, 13% of the participants delayed their graduation, 11% withdrew from a class during the spring semester, and 12% stated that their major choice was impacted by COVID-19. 8
While almost no students report planning to drop out due to COVID-19, on average they expect to take a break from ASU in the fall 2020 semester at nearly twice the historical rate. Admittedly, the decision to take a break during a pandemic may be different than in more normal times. However, a substantial increase in the share of students failing to continue their studies is concerning, as historically 28% of students who fail to re-enroll for a fall semester do not return to ASU or another university within 5 years.
Regarding the impact of the pandemic on major choice, students who report that COVID-19 impacted their major choice were more likely to be in lower-paying majors before the pandemic; mean pre-COVID major-specific annual earnings were $43,053 ($46,943) for students whose major choice was (not) impacted by COVID-19. 9 Impacted students were also 9.3 percentage points less likely to be in a science, technology, engineering, or math (STEM) major before COVID-19. 10 We are only able to observe pre- and post-COVID major choices for the subset of students who had switched their major by the date of the survey. 11 Within this selected subsample of switchers, students chose to move into higher paying majors, with an average change in first-year earnings of $3,340. These patterns are generally consistent with the finding that students tend to gravitate towards higher-paying majors when exposed to adverse economic conditions when in college ( Blom et al., 2019 ).
An interesting and perhaps unanticipated result reported in Table 2 is that, on average, students are 4 percentage points less likely to opt for online instruction if given the choice between online and in-person instruction due to their experience with online instruction during the pandemic. 12 13 However, there is a substantial amount of variation in terms of the direction of the effect: 31% (47%) of the participants are now more (less) likely to enroll in online classes. We explore this heterogeneity in more detail in the next section, but it seems that prior experience with online classes somewhat ameliorates the negative experience; the average treatment effect for students with prior experience in online classes is a 2.4 percentage points decrease in their likelihood of enrolling in online classes, versus a 9.5 percentage points decline for their counterparts (difference statistically significant at the 0.1% level).
This large variation in the treatment effects of COVID-19 is apparent in several of the other outcomes, such as study hours, where the average treatment effect of COVID-19 on weekly study hours is −0.9 (that is, students spend 0.9 less hours studying per week due to COVID-19). The interquartile range of the across-subject treatment effect demonstrates substantial variation, with the pandemic decreasing study time by 5 hours at the 25th percentile and increasing study time by 4 hours at the 75th.
Overall, these results suggest that COVID-19 represents a substantial disruption to students' academic experiences, and is likely to have lasting impacts through changes in major/career and delayed graduation timelines. Students' negative experiences with online teaching, perhaps due to the abruptness of the transition, also has implications for the willingness of students to take online classes in the future.
Turning to Panel B in Table 2 , we see that students' current and expected labor market outcomes were substantially disrupted by COVID-19. As for the extensive margin of current employment, on average, 29% of the students lost the jobs they were working at prior to the pandemic (67% of the students were working prior to the pandemic), 13% of students had their internships or job offers rescinded, and 61% of the students reported that a close family member had lost their job or experienced an income reduction. The last statistic is in line with findings from other surveys of widespread economic disruption across the US. 14 Respondents experienced an average decrease of 11.5 hours of work per week and a 21% decrease in weekly earnings, although there was no change in weekly earnings for 52% of the sample, which again reflects substantial variation in the effects of COVID-19 across students.
In terms of labor market expectations, on average, students foresee a 13 percentage points decrease in the probability of finding a job by graduation, a reduction of 2% in their reservation wages, and a 2.3% decrease in their expected earnings at age 35.
The significant changes in reservation wages and expected earnings at age 35 demonstrate that students expect the treatment effects of COVID-19 to be long-lasting. Qualitatively, this is broadly consistent with the literature on graduating during recession. Oreopoulos et al. (2012) finds that graduating during a recession in which the unemployment rate increases 5% implies an initial loss in earnings of 9%, that decreases to 4.5% within 5 years and disappears after 10 years for a sample of male college graduates in Canada. Similarly, Schwandt and von Wachter (2019) find a 2.6% reduction in earnings 10 years after graduation for a 3-percentage point increase in unemployment at graduation, and Kahn (2010) finds an even longer-lasting effect on wages.
A large literature has investigated the impact of graduating during recessions on unemployment rates. Kahn (2010) finds that during the 1980's recession, the probability of being employed right after graduation for white males was largely unaffected by economic conditions. Altonji et al. (2016) only find what they term modest impacts. On the other hand, Rothstein (2020) finds that, for 22 to 23-year-olds graduating from college during the Great Recession, the probability of being employed decreases by 0.7 percentage point for every 1 percentage point increase in the unemployment rate. Using the estimates in Rothstein (2020) and the approximate 10 percentage point increase in the unemployment rate during April 2020, a back-of-the-envelope calculation indicates a 7 percentage point reduction in the probability of being employed for the graduating cohort in our sample. We find that students who are graduating in spring or summer 2020 expect a 35 percentage point decline in the likelihood of finding a job before graduation. While it is difficult to precisely map pre-graduation job finding rates to unemployment over the subsequent year, a 7 percentage point increase in unemployment appears low compared to the impact on students' expectations. It could be the case that the literature estimates are not appropriate for a situation as unexpected and different as a global pandemic, where the economic recession goes hand in hand with health concerns. Having said that, it could also be that students are overreacting to the COVID-19 shock. Data that tracks students' expectations and outcomes over time may be able to shed light on this.
4.2. Heterogeneous effects
We next explore demographic heterogeneity in the treatment effects of COVID-19. Fig. 1 plots the average treatment effects across several relevant demographic divisions including gender, race, parental education, and parental income. Honors college status and cohort are also included as interesting dimensions of heterogeneity in the COVID-19 context. The figure shows the impacts for six of the more economically meaningful outcomes from Table 2 (additional outcomes can be found in Appendix Fig. A2 ).
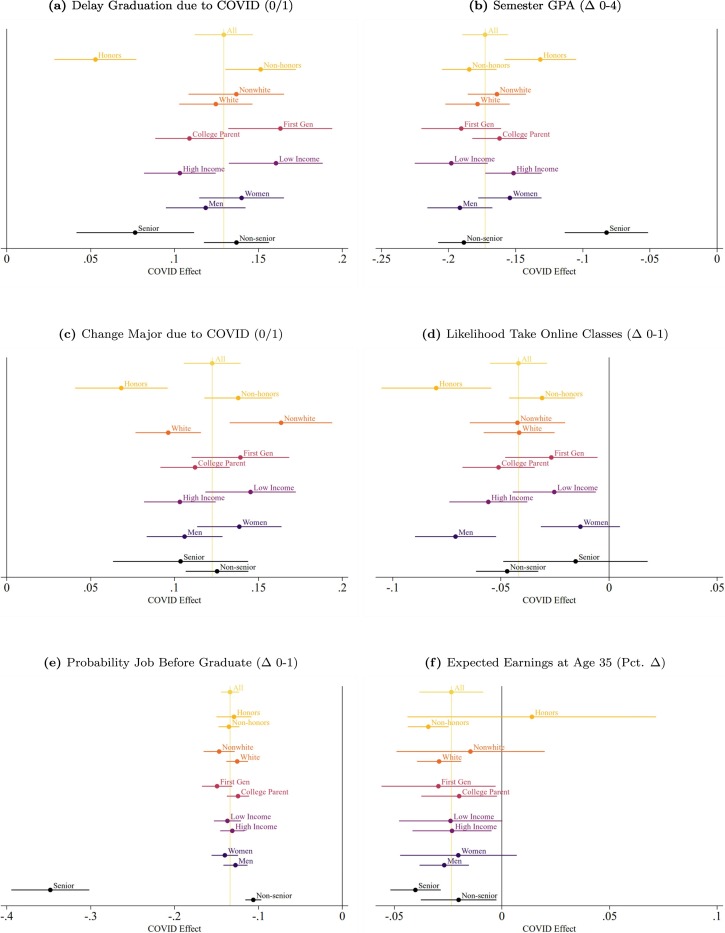
Treatment effects by demographic group.
(a) Delay Graduation due to COVID (0/1)
(b) Semester GPA ( Δ 0–4)
(c) Change major due to COVID (0/1)
(d) Likelihood take online classes ( Δ 0–1)
(e) Probability job before graduate ( Δ 0–1)
(f) Expected earnings at age 35 (Pct. Δ )
Notes: bars denote 90% confidence interval.
At least four patterns of note emerge from Fig. 1 . First, compared to their classmates, students from disadvantaged backgrounds (lower-income students defined as those with below-median parental income, racial minorities, and first-generation students) experienced larger negative impacts for the academic outcomes, as shown in the first three panels of the figure. 15 The trends are most striking for lower-income students, who are 55% more likely to delay graduation due to COVID-19 than their more affluent classmates (0.16 increase in the proportion of those expecting to delay graduation versus 0.10), expect 30% larger negative effects on their semester GPA due to COVID-19, and are 41% more likely to report that COVID-19 impacted their major choice (these differences are statistically significant at the 5% level). For some academic outcomes, COVID-19 had similarly disproportionate effects on nonwhite and first-generation students, with nonwhite students being 70% more likely to report changing their major preference compared to their white peers and first-generation students being 50% more likely to delay their graduation than students with college-educated parents. Thus, while on average COVID-19 negatively impacted several measures of academic achievement for all subgroups, the effects are significantly more pronounced for socioeconomic groups which were predisposed towards worse academic outcomes pre-COVID. 16 The pandemic's widening of existing achievement gaps can be seen directly in students' expected Semester GPA. Without COVID-19, lower-income students expected a 0.052 lower semester GPA than their higher-income peers. With COVID-19, this gap nearly doubles to 0.098. 17
Second, Panel (d) of Fig. 1 shows that the switch to online learning was substantially harder for some demographic groups; for example, men are 7 percentage points less likely to opt for an online version of a course as a result of COVID-19, while women do not have a statistically significant change in their online preferences. We also see that Honors students revise their preferences by more than 2.5 times the amount of non-Honors students. As we show later (in Table 4 ), these gaps persist after controlling for household income, major, and cohort, suggesting that the switch to online learning mid-semester may have been substantially more disruptive for males and Honors students. While the effect of COVID-19 on preferences for online learning looks similar for males and Honors students, our survey evidence indicates that different mechanisms underpin these shifts. Based on qualitative evidence, it appears that Honors students had a negative reaction to the transition to online learning because they felt less challenged, while males were more likely to struggle with the learning methods available through the online platform. 18 One speculative explanation for the gender difference is that consumption value of college amenities is higher for men (however, Jacob et al. (2018) , find little gender difference in willingness to pay for the amenities they consider).
Composition of COVID effects.
Notes: Standard errors in parentheses bootstrapped with 1000 replications. Each column reports results from a separate OLS regression of the dependent variable onto the covariates (row variables). Dependent variables measured in percentage points. ( ∗ : p <0.1, ∗∗ : p <0.05, ∗∗∗ : p <0.01).
The third trend worth highlighting from Fig. 1 is that Honors students were better able to mitigate the negative effect of COVID-19 on their academic outcomes (panels a, b, and c), despite appearing to be more disrupted by the move to online learning (panel d). Honors students report being less than half as likely as non-Honors students to delay graduation and change their major due to COVID-19. Extrapolating from these patterns provides suggestive evidence that academic impacts for students attending elite schools– the group more comparable to these Honors students– are likely to have been small relative to the impacts for the average student at large public schools.
Finally, the last two panels of Fig. 1 present the COVID effect on two labor market expectations and show much less meaningful heterogeneity across demographic groups compared to the academic outcomes in previous panels. This suggests that, while students believe COVID-19 will impact both their academic outcomes and future labor market outcomes, they do not believe there is a strong connection between these domains. Supporting this observation, the individual-specific treatment effect on semester GPA is only weakly correlated with the individual-specific treatment effects on finding a job before graduation (corr = 0.0497, p = 0.065) and expected earnings at 35 (corr = 0.0467, p = 0.077).
The one notable exception to the lack of heterogeneity in panels (e) and (f) of Fig. 1 are seniors, who on average revised their subjective probability of finding a job before graduation three times as much as other cohorts. Appendix Fig. A3 further breaks down the estimated COVID-19 effects by expected year of graduation. Perhaps unsurprisingly, the 2020 cohort expects much larger effects on immediate job market outcomes such as reservation wages and probability of finding a job before graduation. While average expected changes to job market outcomes are noisier for academically younger students, perhaps reflecting additional uncertainty about the longer-term impacts of COVID-19, they appear to anticipate meaningful changes to their future labor market prospects. Conversely, younger students also expected larger disruptions to academic outcomes such as semester GPA and study time.
5. Understanding the heterogeneous effects
This section presents mediation analysis on the drivers of the underlying heterogeneity in the treatment effects. The COVID-19 pandemic serves as both an economic and a health shock. However, these shocks may have been quite heterogeneous across the various groups, and that could partly explain the heterogeneous treatment effects we documented in the previous section.
5.1. Economic and health mediating factors
We proxy for the financial and health shocks due to COVID-19 by relying on a small but relevant set of covariates which capture more fundamental or first-order disruptions from the pandemic. Financial shocks are characterized based on whether a student lost a job due to COVID-19, whether a student's family members lost income due to COVID-19, the change in a student's monthly earnings due to COVID-19, and the likelihood a student will fail to fully meet debt payments in the next 90 days. To measure health shocks, we consider a student's belief about the likelihood that they will be hospitalized if they contract COVID-19, a student's belief about the likelihood that they will have contracted COVID-19 by summer, and a student's subjective health assessment. Finally, in order to summarize the combined effect of each set of proxies, we construct principal component scores as one-dimensional measures of the financial and health shock to students. 19
Table 3 reports summary statistics of the different economic and health proxies by demographic group. Given the results in Fig. 1 , the remainder of the analysis will focus on three socioeconomic divisions: parental income, gender, and Honors college status. Our data indicate that lower-income students faced larger health and economic shocks as compared to their more affluent peers. In particular, they are almost 10 percentage points more likely to expect to default on their debt payments compared to their higher-income counterparts. Additionally, lower-income students are 16 percentage points more likely to have had a close family member experience an income reduction due to COVID-19. Regarding the health proxies, lower-income students rate their health as worse than higher-income students and perceive a higher probability of being hospitalized if they catch the virus. Finally, the differences in economic and health shocks between lower and higher-income students, as summarized by the principle components of the selected proxy variables, are statistically significant.
Summary statistics for economic and health proxies.
Notes: P-value columns report the p-value of a difference in means test between the two columns indicated by the numbers in the heading.
The mean of the first factor of a PCA that uses the measures in the corresponding panel.
1 through 5 scale where higher numbers mean better health.
Columns (5)–(7) of Table 3 show that both economic and health shocks are larger for non-Honors students. In fact, the average differences in the principal component scores for both the economic and health factors is larger for these two groups than for the income groups. Likewise, the last three columns of the table show that women experienced larger COVID-19 shocks due to economic and health factors. These differences are partly driven by the fact that, in our sample, females are more likely to report that they belong to a lower-income household than males (50% vs. 42%).
In short, Table 3 makes clear that the impacts of COVID-19 on the economic well-being and health of students have been quite heterogeneous, with lower-income and lower-ability students being more adversely affected.
5.2. The role of economic and health shocks on explaining the COVID-19 effects
To investigate the role of economic and health shocks in explaining the heterogeneous treatment effects (in Section 4.2 ), we estimate the following specification:
where Δ i is the COVID-19 treatment effect for outcome O on student i . Demog i is a vector including indicators for gender, lower-income, Honors status, and dummies for cohort year and major. FinShock i and HealthShock i are vectors containing the shock proxies or their principal component. Finally, ε i denotes an idiosyncratic shock.
The parameters of interest are α 2 and α 3 . A causal interpretation of these parameters requires FinShock i and HealthShock i to be independent of ε i . This seems unlikely in our context as unobservables correlated with FinShock i and HealthShock i may also modulate COVID-19's impact on academic outcomes. Therefore, we prefer to interpret α 2 and α 3 as simple correlations. Nevertheless, we believe this descriptive evidence can be informative from a policy perspective.
Table 4 shows estimates of Eq. (2) for four different outcomes ( Appendix Table A2 shows the estimates for additional outcomes). For each outcome, five specifications are reported ranging from controlling for only demographic variables in the first specification to controlling for both economic and health factors in the fourth specification. Finally, the last column includes only the principal component of each shock to provide insight about overall effects, given that certain shock proxies show high levels of correlation (see Appendix Table A4 for the correlations within each set of proxies).
Several important messages emerge from Table 4 . First, both shocks are (economically and statistically) significant correlates of the COVID-19 effects on students' outcomes. In particular, F-tests show that the financial and health shock proxies are jointly significant across almost all specifications. 20 This is also reflected in the statistical significance of the principal components. Moreover, the fact that the effect of key proxy variables remains robust when we simultaneously control for both shocks demonstrates the robustness of our results. For example, we find that a 50 percentage point increase in the probability of being late on debt payments is associated with an increase in the probability of delaying graduation and switching majors due to COVID-19 of 6.9 and 6.4 percentage points respectively. These effects are large given that they represent more than half of the overall COVID-19 treatment effect for these variables. Similarly, we find that an analogous increase in the probability of hospitalization if contracting COVID-19 is associated with a 6 and 5 percentage points increase in the probability of delaying graduation and switching majors due to COVID-19.
Second, in terms of labor market expectations, we find that the change in the expected probability of finding a job before graduation strongly depends on having a family member that lost income (which is also correlated with the student himself losing a job). In particular, the size of this effect represents 32% of the overall COVID-19 treatment effect. Therefore, this finding suggests that students' labor market expectations are driven in large part by personal/family experiences.
Third, although the proxies play an important role in explaining the pandemic's impact on students, there is still a substantial amount of variation in COVID-19 treatment effects left unexplained. Across the four outcomes in Table 4 , the full set of proxies explain less than a quarter of the variation in outcomes across individuals. Appendix Fig. A4 visualizes this variation by plotting the distribution of several continuous outcomes with and without controls. While the interquartile range noticeably shrinks after conditioning on the proxy variables, these plots highlight the large amount of variation in treatment effects remaining after conditioning on the proxies.
Finally, our results show that the financial and health shocks play an important role in explaining the heterogeneous effects of the COVID-19 outbreak. In particular, columns (4) and (9) demonstrate that economic and health factors together can explain approximately 40% and 70% of the income gap in COVID-19's effect on delayed graduation and changing major respectively. The gap between Honors and non-Honors students is likewise reduced by 27% and 39% for the same outcomes. Taken together, these results imply that differences in the magnitude of COVID-19's economic and health impact can explain a significant proportion of the demographic gaps in COVID-19's effect on the decision to delay graduation, the decision to change major, and preferences for online learning. These results are important and suggest that focusing on the needs of students who experienced larger financial or health shocks from COVID-19 may be an effective way to minimize the disparate disruptive effects and prevent COVID-19 from exacerbating existing achievement gaps in higher education.
6. Conclusions
This paper provides the first systematic analysis of the effects of COVID-19 on higher education. To study these effects, we surveyed 1500 students at Arizona State University, and present quantitative evidence showing the negative effects of the pandemic on students' outcomes and expectations. For example, we find that 13% of students have delayed graduation due to COVID-19. Expanding upon these results, we show that the effects of the pandemic are highly heterogeneous, with lower-income students 55% more likely to delay graduation compared to their higher-income counterparts. We further show that the negative economic and health impacts of COVID-19 have been significantly more pronounced for less advantaged groups, and that these differences can partially explain the underlying heterogeneity that we document. Our results suggest that by focusing on addressing the economic and health burden imposed by COVID-19, as measured by a relatively narrow set of mitigating factors, policy makers may be able to prevent COVID-19 from widening existing achievement gaps in higher education.
Declaration of competing interest
The authors declare that they have no relevant or material financial interests that relate to the research described in this paper. There are no declarations of interest.
Noah Deitrick and Adam Streff provided excellent research assistance. All errors that remain are ours.
See, the New York Times article “ After Coronavirus , Colleges Worry : Will Students Come Back ?” (April 15, 2020) for a discussion surrounding students' demands for tuition cuts.
In some cases, instead of asking students for the outcomes in both states of the world, we directly ask for the difference. For example, the survey asked how the pandemic had affected the student's graduation date.
This approach has been used successfully in several other settings, such as to construct career and family returns to college majors ( Arcidiacono et al., 2020 ; Wiswall and Zafar, 2020 ), and the causal impact of health on retirement ( Shapiro and Giustinelli, 2019 ).
The income gap in GPA increased from 0.052 to 0.098 on a 4 point scale. It is significant at the 1% level in both scenarios.
The 64 people taking the survey at the moment the target sample size (1500) was reached were allowed to finish.
59% of Honors students in our sample report living on campus.
This is different from asking students in normal times about their expected outcomes in a state with online teaching and no campus activities (COVID-19) since most students would not have had any experience with this counterfactual prior to March this year.
Altonji et al. (2016) finds a small but positive effect on the probability of attending graduate school when graduating into a recession. This is suggestive evidence that students try to avoid entering the labor market when economic conditions are adverse. Our results on delayed graduation are consistent with students avoiding entering the labor market at inopportune times.
For this calculation, we take earnings data from the US Department of Education College Scorecard dataset. Major-specific earnings are calculated using median first-year earnings for ASU graduates in 2015 and 2016 by two-digit CIP code. Observable earnings averaged within major category.
STEM major designation made using two-digit CIP code and The STEM Designated Degree Program from the US Department of Homeland Security.
This includes 77 respondents, or 43% of those who say COVID-19 impacted their major choice.
The relevant survey question read: “ Suppose you are given the choice to take a course online/remote or in-person . [ Had you NOT had experience with online/remote classes this semester ], what is the percent chance that you would opt for the online/remote option ?”
This result is in line with a survey about eLearning experiences across different universities in Washington and New York that concludes that 75% of the students are unhappy with the quality of their classes after moving to online learning due to COVID-19.
According to the US Census Bureau Household Pulse Survey Week 3, 48% of the surveyed households have experienced a loss in employment income since March 13 2020.
The cutoff for median parental income in our sample is $80,000.
Based on analysis of ASU administrative data including transcripts, we find that, relative to their counterparts, first-generation, lower-income, and non-white students drop out at higher rates, take longer to graduate, have lower GPAs at graduation, and are more likely to switch majors when in college (see Appendix Table A3 ).
The difference is significant at 1% in both cases.
Honors students were as likely as non-Honors students to say that classes got easier after they went online but, conditional on saying classes got easier, were 47% more likely to say “homework/test questions got easier.” Conversely, males were marginally more likely to say classes got harder after they went online (10% more likely, p = 0.055) and, conditional on this, were 14% more likely to say that “online material is not clear”.
Eigenvalues indicate the presence of only one principal component for each of the shocks.
The only exception is the financial shock when explaining changes in the probability of taking classes online.
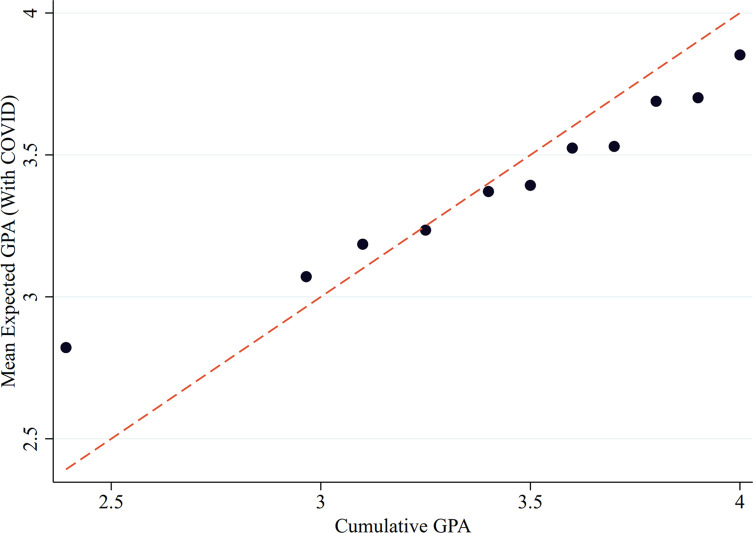
Expected and previous academic performance.
Notes: Figure plots mean expected GPA with COVID-19 against students' cumulative GPA up to the spring 2020 semester. The 45 degree line is also plotted for reference.
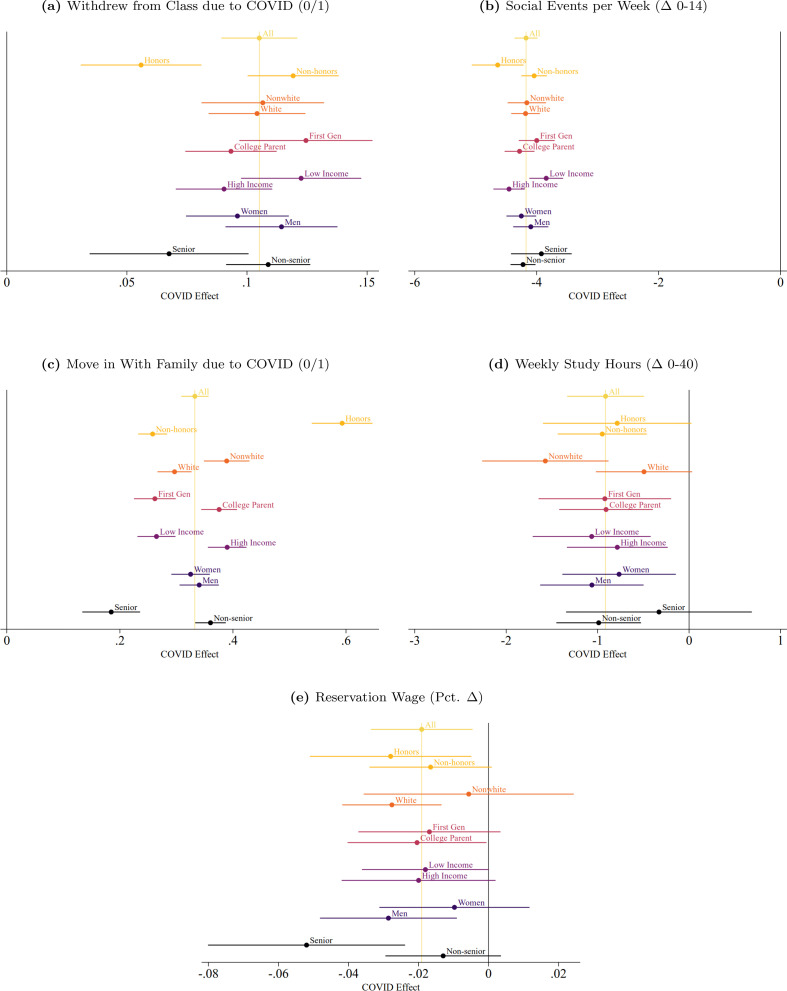
More treatment effects by demographic group.
(a) Withdrew from Class due to COVID (0/1); (b) Social Events per Week ( Δ 0–14); (c) Move in With Family due to COVID (0/1); (d) Weekly Study Hours ( Δ 0–40); (e) Reservation Wage (Pct. Δ )
Notes: Bars denote 90% confidence interval.
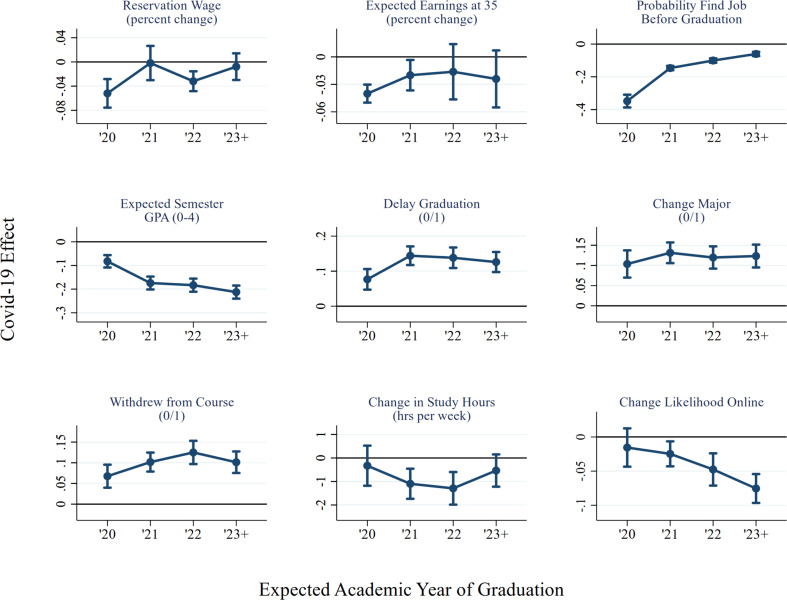
Cohort trends.
Notes: Figure plots average COVID-19 effects for a series of outcomes. The x-axis variable in each panel is expected academic year of graduation (after COVID), with summer graduation dates included in the previous academic year. Bars denote 90% confidence interval.
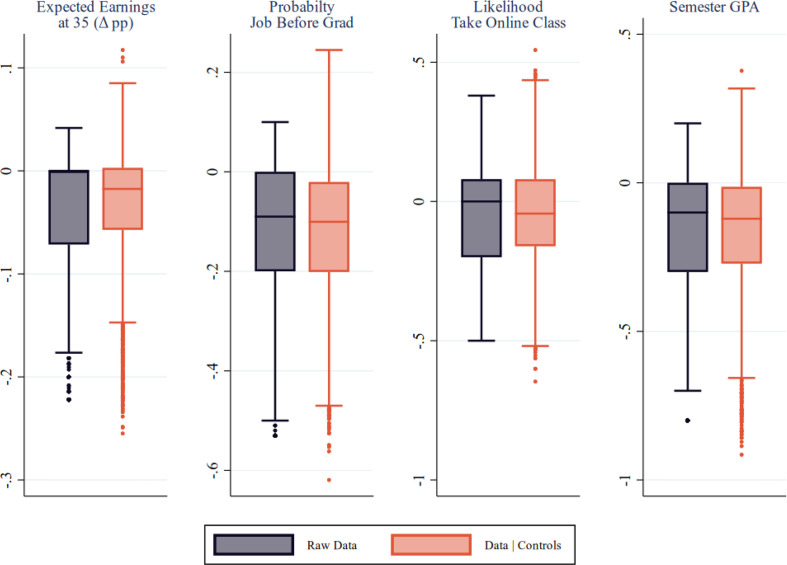
Distribution of individual effects.
Notes: Data winsorized below 5% and above 95%. Controls include cohort fixed effects, major fixed effects, and the economic/health proxies in Table 3 . Conditional distribution adjusted to preserve unconditional mean. Within each plot: middle line represents median, edges of box represent interquatile range (IQR), edge of whisker represents the adjacent values or the 25th(75th) percentile plus(minus) 1.5 times the IQR. Outlier observations past adjacent values plotted as individual points.
How the importance of this reason for choosing a major change due to COVID-19. −1: decreased, 0: stayed the same, 1:increased.
How the time allocated to each activity changed due to COVID-19. −1: decreased, 0: stayed the same, 1:increased.
Composition of COVID effects: more outcomes.
Notes: Standard errors in parentheses bootstrapped with 1000 replications. Each column reports results from a separate OLS regression of the dependent variable onto the covariates (row variables). Dependent variables measured in percentage points (except GPA). ( ∗ : p <0.1, ∗∗ : p <0.05, ∗∗∗ : p <0.01).
Existing achievement gaps.
Notes: Sample includes all first time freshman at ASU's main campus who started within the last 10 years. N = 58,426. ( ∗ : p <0.1, ∗∗ : p <0.05, ∗∗∗ : p <0.01).
Correlation of shock proxies.
Notes: Table reports correlation matrix for indicated variables.
- Altonji J., Arcidiacono P., Maurel A. Handbook of the Economics of Education. vol. 5. Elsevier; Cambridge, MA: 2016. The analysis of field choice in college and graduate school: determinants and wage effects; pp. 305–396. [ Google Scholar ]
- Angrist J.D., Pischke J.-S. Princeton University Press; Princeton: 2009. Mostly Harmless Econometrics: An Empiricist’s Companion. OCLC: ocn231586808. [ Google Scholar ]
- Arcidiacono P., Hotz V.J., Maurel A., Romano T. Ex ante returns and occupational choice. J. Polit. Econ. 2020 (forthcoming) [ Google Scholar ]
- Blom E., Cadena B.C., Keys B.J. 2019. Investment Over the Business Cycle: Insights from College Major Choice. (Working Paper) [ Google Scholar ]
- Chetty R., Friedman J.N., Hendren N., Stepner M. 2020, May. Real-Time Economics: A New Platform to Track the Impacts of COVID-19 on People, Businesses, and Communities Using Private Sector Data. [ Google Scholar ]
- Heckman J.J., Vytlacil E. Structural equations, treatment effects, and econometric policy evaluation. Econometrica. 2005, May;73(3):669–738. [ Google Scholar ]
- Imbens G., Rubin D.B. Causal inference: for statistics, social and biomedical sciences: an introduction. OCLC. 2015;985493948 [ Google Scholar ]
- Jacob B., McCall B., Stange K. College as country club: do colleges cater to students’ preferences for consumption? J. Labor Econ. 2018;36(2):40. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kahn L.B. The long-term labor market consequences of graduating from college in a bad economy. Labour Econ. 2010, April;17(2):303–316. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kuchler T., Zafar B. Personal experiences and expectations about aggregate outcomes. J. Financ. 2019, October;74(5):2491–2542. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kuhfeld M., Soland J., Tarasawa B., Johnson A., Ruzek E., Liu J. 2020, May. Projecting the Potential Impacts of COVID-19 School Closures on Academic Achievement. Publisher: EdWorkingPapers.com. [ Google Scholar ]
- Malmendier U., Nagel S. Learning from inflation experiences *. Q. J. Econ. 2016, February;131(1):53–87. [ Google Scholar ]
- Oreopoulos P., von Wachter T., Heisz A. The short- and long-term career effects of graduating in a recession. Am. Econ. J. Appl. Econ. 2012, January;4(1):1–29. [ Google Scholar ]
- Rothstein J. 2020, May. The Lost Generation? Labor Market Outcomes for Post Great Recession Entrants. [ Google Scholar ]
- Schwandt H., von Wachter T. Unlucky cohorts: estimating the long-term effects of entering the labor market in a recession in large cross-sectional data sets. J. Labor Econ. 2019;37(S1):S161–S198. [ Google Scholar ]
- Shapiro M., Giustinelli P. 2019, July. SeaTE: Subjective ex Ante Treatment Effect of Health on Retirement. [ Google Scholar ]
- Wiswall M., Zafar B. Human capital investments and expectations about career and family. J. Polit. Econ. 2020 (forthcoming) [ Google Scholar ]
- View on publisher site
- PDF (1.8 MB)
- Collections
Similar articles
Cited by other articles, links to ncbi databases.
- Download .nbib .nbib
- Format: AMA APA MLA NLM
Add to Collections

Covid-19’s Impact on Students’ Academic and Mental Well-Being
The pandemic has revealed—and exacerbated—inequities that hold many students back. Here’s how teachers can help.
Your content has been saved!
The pandemic has shone a spotlight on inequality in America: School closures and social isolation have affected all students, but particularly those living in poverty. Adding to the damage to their learning, a mental health crisis is emerging as many students have lost access to services that were offered by schools.
No matter what form school takes when the new year begins—whether students and teachers are back in the school building together or still at home—teachers will face a pressing issue: How can they help students recover and stay on track throughout the year even as their lives are likely to continue to be disrupted by the pandemic?
New research provides insights about the scope of the problem—as well as potential solutions.
The Achievement Gap Is Likely to Widen
A new study suggests that the coronavirus will undo months of academic gains, leaving many students behind. The study authors project that students will start the new school year with an average of 66 percent of the learning gains in reading and 44 percent of the learning gains in math, relative to the gains for a typical school year. But the situation is worse on the reading front, as the researchers also predict that the top third of students will make gains, possibly because they’re likely to continue reading with their families while schools are closed, thus widening the achievement gap.
To make matters worse, “few school systems provide plans to support students who need accommodations or other special populations,” the researchers point out in the study, potentially impacting students with special needs and English language learners.
Of course, the idea that over the summer students forget some of what they learned in school isn’t new. But there’s a big difference between summer learning loss and pandemic-related learning loss: During the summer, formal schooling stops, and learning loss happens at roughly the same rate for all students, the researchers point out. But instruction has been uneven during the pandemic, as some students have been able to participate fully in online learning while others have faced obstacles—such as lack of internet access—that have hindered their progress.
In the study, researchers analyzed a national sample of 5 million students in grades 3–8 who took the MAP Growth test, a tool schools use to assess students’ reading and math growth throughout the school year. The researchers compared typical growth in a standard-length school year to projections based on students being out of school from mid-March on. To make those projections, they looked at research on the summer slide, weather- and disaster-related closures (such as New Orleans after Hurricane Katrina), and absenteeism.
The researchers predict that, on average, students will experience substantial drops in reading and math, losing roughly three months’ worth of gains in reading and five months’ worth of gains in math. For Megan Kuhfeld, the lead author of the study, the biggest takeaway isn’t that learning loss will happen—that’s a given by this point—but that students will come back to school having declined at vastly different rates.
“We might be facing unprecedented levels of variability come fall,” Kuhfeld told me. “Especially in school districts that serve families with lots of different needs and resources. Instead of having students reading at a grade level above or below in their classroom, teachers might have kids who slipped back a lot versus kids who have moved forward.”
Disproportionate Impact on Students Living in Poverty and Students of Color
Horace Mann once referred to schools as the “great equalizers,” yet the pandemic threatens to expose the underlying inequities of remote learning. According to a 2015 Pew Research Center analysis , 17 percent of teenagers have difficulty completing homework assignments because they do not have reliable access to a computer or internet connection. For Black students, the number spikes to 25 percent.
“There are many reasons to believe the Covid-19 impacts might be larger for children in poverty and children of color,” Kuhfeld wrote in the study. Their families suffer higher rates of infection, and the economic burden disproportionately falls on Black and Hispanic parents, who are less likely to be able to work from home during the pandemic.
Although children are less likely to become infected with Covid-19, the adult mortality rates, coupled with the devastating economic consequences of the pandemic, will likely have an indelible impact on their well-being.
Impacts on Students’ Mental Health
That impact on well-being may be magnified by another effect of school closures: Schools are “the de facto mental health system for many children and adolescents,” providing mental health services to 57 percent of adolescents who need care, according to the authors of a recent study published in JAMA Pediatrics . School closures may be especially disruptive for children from lower-income families, who are disproportionately likely to receive mental health services exclusively from schools.
“The Covid-19 pandemic may worsen existing mental health problems and lead to more cases among children and adolescents because of the unique combination of the public health crisis, social isolation, and economic recession,” write the authors of that study.
A major concern the researchers point to: Since most mental health disorders begin in childhood, it is essential that any mental health issues be identified early and treated. Left untreated, they can lead to serious health and emotional problems. In the short term, video conferencing may be an effective way to deliver mental health services to children.
Mental health and academic achievement are linked, research shows. Chronic stress changes the chemical and physical structure of the brain, impairing cognitive skills like attention, concentration, memory, and creativity. “You see deficits in your ability to regulate emotions in adaptive ways as a result of stress,” said Cara Wellman, a professor of neuroscience and psychology at Indiana University in a 2014 interview . In her research, Wellman discovered that chronic stress causes the connections between brain cells to shrink in mice, leading to cognitive deficiencies in the prefrontal cortex.
While trauma-informed practices were widely used before the pandemic, they’re likely to be even more integral as students experience economic hardships and grieve the loss of family and friends. Teachers can look to schools like Fall-Hamilton Elementary in Nashville, Tennessee, as a model for trauma-informed practices .
3 Ways Teachers Can Prepare
When schools reopen, many students may be behind, compared to a typical school year, so teachers will need to be very methodical about checking in on their students—not just academically but also emotionally. Some may feel prepared to tackle the new school year head-on, but others will still be recovering from the pandemic and may still be reeling from trauma, grief, and anxiety.
Here are a few strategies teachers can prioritize when the new school year begins:
- Focus on relationships first. Fear and anxiety about the pandemic—coupled with uncertainty about the future—can be disruptive to a student’s ability to come to school ready to learn. Teachers can act as a powerful buffer against the adverse effects of trauma by helping to establish a safe and supportive environment for learning. From morning meetings to regular check-ins with students, strategies that center around relationship-building will be needed in the fall.
- Strengthen diagnostic testing. Educators should prepare for a greater range of variability in student learning than they would expect in a typical school year. Low-stakes assessments such as exit tickets and quizzes can help teachers gauge how much extra support students will need, how much time should be spent reviewing last year’s material, and what new topics can be covered.
- Differentiate instruction—particularly for vulnerable students. For the vast majority of schools, the abrupt transition to online learning left little time to plan a strategy that could adequately meet every student’s needs—in a recent survey by the Education Trust, only 24 percent of parents said that their child’s school was providing materials and other resources to support students with disabilities, and a quarter of non-English-speaking students were unable to obtain materials in their own language. Teachers can work to ensure that the students on the margins get the support they need by taking stock of students’ knowledge and skills, and differentiating instruction by giving them choices, connecting the curriculum to their interests, and providing them multiple opportunities to demonstrate their learning.
The pandemic has had devastating impacts on learning. What will it take to help students catch up?
Subscribe to the brown center on education policy newsletter, megan kuhfeld , megan kuhfeld director of growth modeling and data analytics - nwea jim soland , jim soland assistant professor, school of education and human development - university of virginia, affiliated research fellow - nwea karyn lewis , and karyn lewis vice president of research and policy partnerships - nwea emily morton emily morton research scientist - nwea.
March 3, 2022
As we reach the two-year mark of the initial wave of pandemic-induced school shutdowns, academic normalcy remains out of reach for many students, educators, and parents. In addition to surging COVID-19 cases at the end of 2021, schools have faced severe staff shortages , high rates of absenteeism and quarantines , and rolling school closures . Furthermore, students and educators continue to struggle with mental health challenges , higher rates of violence and misbehavior , and concerns about lost instructional time .
As we outline in our new research study released in January, the cumulative impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on students’ academic achievement has been large. We tracked changes in math and reading test scores across the first two years of the pandemic using data from 5.4 million U.S. students in grades 3-8. We focused on test scores from immediately before the pandemic (fall 2019), following the initial onset (fall 2020), and more than one year into pandemic disruptions (fall 2021).
Average fall 2021 math test scores in grades 3-8 were 0.20-0.27 standard deviations (SDs) lower relative to same-grade peers in fall 2019, while reading test scores were 0.09-0.18 SDs lower. This is a sizable drop. For context, the math drops are significantly larger than estimated impacts from other large-scale school disruptions, such as after Hurricane Katrina—math scores dropped 0.17 SDs in one year for New Orleans evacuees .
Even more concerning, test-score gaps between students in low-poverty and high-poverty elementary schools grew by approximately 20% in math (corresponding to 0.20 SDs) and 15% in reading (0.13 SDs), primarily during the 2020-21 school year. Further, achievement tended to drop more between fall 2020 and 2021 than between fall 2019 and 2020 (both overall and differentially by school poverty), indicating that disruptions to learning have continued to negatively impact students well past the initial hits following the spring 2020 school closures.
These numbers are alarming and potentially demoralizing, especially given the heroic efforts of students to learn and educators to teach in incredibly trying times. From our perspective, these test-score drops in no way indicate that these students represent a “ lost generation ” or that we should give up hope. Most of us have never lived through a pandemic, and there is so much we don’t know about students’ capacity for resiliency in these circumstances and what a timeline for recovery will look like. Nor are we suggesting that teachers are somehow at fault given the achievement drops that occurred between 2020 and 2021; rather, educators had difficult jobs before the pandemic, and now are contending with huge new challenges, many outside their control.
Clearly, however, there’s work to do. School districts and states are currently making important decisions about which interventions and strategies to implement to mitigate the learning declines during the last two years. Elementary and Secondary School Emergency Relief (ESSER) investments from the American Rescue Plan provided nearly $200 billion to public schools to spend on COVID-19-related needs. Of that sum, $22 billion is dedicated specifically to addressing learning loss using “evidence-based interventions” focused on the “ disproportionate impact of COVID-19 on underrepresented student subgroups. ” Reviews of district and state spending plans (see Future Ed , EduRecoveryHub , and RAND’s American School District Panel for more details) indicate that districts are spending their ESSER dollars designated for academic recovery on a wide variety of strategies, with summer learning, tutoring, after-school programs, and extended school-day and school-year initiatives rising to the top.
Comparing the negative impacts from learning disruptions to the positive impacts from interventions
To help contextualize the magnitude of the impacts of COVID-19, we situate test-score drops during the pandemic relative to the test-score gains associated with common interventions being employed by districts as part of pandemic recovery efforts. If we assume that such interventions will continue to be as successful in a COVID-19 school environment, can we expect that these strategies will be effective enough to help students catch up? To answer this question, we draw from recent reviews of research on high-dosage tutoring , summer learning programs , reductions in class size , and extending the school day (specifically for literacy instruction) . We report effect sizes for each intervention specific to a grade span and subject wherever possible (e.g., tutoring has been found to have larger effects in elementary math than in reading).
Figure 1 shows the standardized drops in math test scores between students testing in fall 2019 and fall 2021 (separately by elementary and middle school grades) relative to the average effect size of various educational interventions. The average effect size for math tutoring matches or exceeds the average COVID-19 score drop in math. Research on tutoring indicates that it often works best in younger grades, and when provided by a teacher rather than, say, a parent. Further, some of the tutoring programs that produce the biggest effects can be quite intensive (and likely expensive), including having full-time tutors supporting all students (not just those needing remediation) in one-on-one settings during the school day. Meanwhile, the average effect of reducing class size is negative but not significant, with high variability in the impact across different studies. Summer programs in math have been found to be effective (average effect size of .10 SDs), though these programs in isolation likely would not eliminate the COVID-19 test-score drops.
Figure 1: Math COVID-19 test-score drops compared to the effect sizes of various educational interventions

Source: COVID-19 score drops are pulled from Kuhfeld et al. (2022) Table 5; reduction-in-class-size results are from pg. 10 of Figles et al. (2018) Table 2; summer program results are pulled from Lynch et al (2021) Table 2; and tutoring estimates are pulled from Nictow et al (2020) Table 3B. Ninety-five percent confidence intervals are shown with vertical lines on each bar.
Notes: Kuhfeld et al. and Nictow et al. reported effect sizes separately by grade span; Figles et al. and Lynch et al. report an overall effect size across elementary and middle grades. We were unable to find a rigorous study that reported effect sizes for extending the school day/year on math performance. Nictow et al. and Kraft & Falken (2021) also note large variations in tutoring effects depending on the type of tutor, with larger effects for teacher and paraprofessional tutoring programs than for nonprofessional and parent tutoring. Class-size reductions included in the Figles meta-analysis ranged from a minimum of one to minimum of eight students per class.
Figure 2 displays a similar comparison using effect sizes from reading interventions. The average effect of tutoring programs on reading achievement is larger than the effects found for the other interventions, though summer reading programs and class size reduction both produced average effect sizes in the ballpark of the COVID-19 reading score drops.
Figure 2: Reading COVID-19 test-score drops compared to the effect sizes of various educational interventions

Source: COVID-19 score drops are pulled from Kuhfeld et al. (2022) Table 5; extended-school-day results are from Figlio et al. (2018) Table 2; reduction-in-class-size results are from pg. 10 of Figles et al. (2018) ; summer program results are pulled from Kim & Quinn (2013) Table 3; and tutoring estimates are pulled from Nictow et al (2020) Table 3B. Ninety-five percent confidence intervals are shown with vertical lines on each bar.
Notes: While Kuhfeld et al. and Nictow et al. reported effect sizes separately by grade span, Figlio et al. and Kim & Quinn report an overall effect size across elementary and middle grades. Class-size reductions included in the Figles meta-analysis ranged from a minimum of one to minimum of eight students per class.
There are some limitations of drawing on research conducted prior to the pandemic to understand our ability to address the COVID-19 test-score drops. First, these studies were conducted under conditions that are very different from what schools currently face, and it is an open question whether the effectiveness of these interventions during the pandemic will be as consistent as they were before the pandemic. Second, we have little evidence and guidance about the efficacy of these interventions at the unprecedented scale that they are now being considered. For example, many school districts are expanding summer learning programs, but school districts have struggled to find staff interested in teaching summer school to meet the increased demand. Finally, given the widening test-score gaps between low- and high-poverty schools, it’s uncertain whether these interventions can actually combat the range of new challenges educators are facing in order to narrow these gaps. That is, students could catch up overall, yet the pandemic might still have lasting, negative effects on educational equality in this country.
Given that the current initiatives are unlikely to be implemented consistently across (and sometimes within) districts, timely feedback on the effects of initiatives and any needed adjustments will be crucial to districts’ success. The Road to COVID Recovery project and the National Student Support Accelerator are two such large-scale evaluation studies that aim to produce this type of evidence while providing resources for districts to track and evaluate their own programming. Additionally, a growing number of resources have been produced with recommendations on how to best implement recovery programs, including scaling up tutoring , summer learning programs , and expanded learning time .
Ultimately, there is much work to be done, and the challenges for students, educators, and parents are considerable. But this may be a moment when decades of educational reform, intervention, and research pay off. Relying on what we have learned could show the way forward.
Related Content
Megan Kuhfeld, Jim Soland, Beth Tarasawa, Angela Johnson, Erik Ruzek, Karyn Lewis
December 3, 2020
Lindsay Dworkin, Karyn Lewis
October 13, 2021
Early Childhood Education Education Access & Equity Education Policy K-12 Education
Governance Studies
U.S. States and Territories
Brown Center on Education Policy
Melissa Arnold Lyon
November 18, 2024
Mary Helen Immordino-Yang, Douglas R. Knecht
Christine Apiot Okudi, Ellen Chigwanda, Thinley Choden, Sumbal Naveed, Mary Otieno, Jamila Razzaq, Nasrin Siddiqa, Jennifer L. O’Donoghue
November 14, 2024

IMAGES