.png)

Case Studies for Product Management: A Deep Dive
We can all agree that applying real-world product management strategies is crucial for success.
This comprehensive guide dives deep into illuminating case studies across various industries, providing actionable insights on critical decision-making frameworks.
Introduction to Product Management Case Studies
Product management involves overseeing a product from conception to production to ensure it meets customer needs. Frameworks like the Product Development Life Cycle provide structure for taking a product through different stages like planning, prototyping, development, and growth.
Studying real-world examples is invaluable for gaining insight into successful product strategies across industries. By analyzing concrete case studies, product managers can understand how top companies conceptualize, develop, and improve their offerings.
Defining Product Management and its Frameworks
The role of a product manager is to understand customer needs and guide development of solutions. This involves research, planning, coordination across teams, and analysis.
Some key frameworks provide processes for product managers:
- Product Development Life Cycle - Conceptualization, Development, Growth, Maturity Decline
- Jobs To Be Done - Focusing on the job the customer aims to get done
- Design Thinking - Empathizing, Defining, Ideating, Prototyping, Testing
These frameworks help structure product decisions and strategy.
Importance of Best Case Studies for Product Management
Analyzing detailed examples of product management in action provides:
- Real-world demonstrations of frameworks
- Examples of product development decisions
- Insights into product successes and failures
- Strategies across industries and product types
By studying case studies, product managers can learn best practices to apply in their own work.
Overview of Industries and Product Case Study Examples
Upcoming sections will explore product management case studies from:
- Technology - Software, hardware, apps
- Retail & ecommerce - Online and brick-and-mortar stores
- Financial services - Banks, investment platforms
- Healthcare - Electronic medical records, patient apps
Specific companies like Apple, Nike, Intuit, Kaiser Permanente will be used to demonstrate product decisions.
What are case studies for Product management?
Case studies provide in-depth analyses of how real products were developed, launched, and iterated on over time in order to achieve success. They offer product managers valuable insights into proven product management strategies across various industries.
By examining case studies, product managers can learn how top companies approached critical activities like:
- Conducting market research
- Defining product requirements based on user needs
- Prioritizing features and functionality
- Developing prototypes and minimum viable products (MVPs)
- Designing effective user experiences
- Iterating based on user feedback
- Tracking key metrics and optimizing
- Developing go-to-market strategies
- Scaling successfully
Additionally, case studies allow readers to understand the reasoning behind key decisions, including both successes and failures. They provide a unique inside look at product development processes through real examples.
Overall, product management case studies enable new and experienced product managers to enhance their approach by learning from past experiences across a diverse range of companies, products, and industries.
How to make structure in case studies for Product management?
Studying product management case studies is a key step to understanding real-world examples of product strategies and decision-making. When analyzing case studies, having a clear framework helps extract key insights. Here are four steps to structure your analysis:
Evaluate the Need
- What customer problem does the product solve?
- How was the need validated through research?
- What metrics indicate the market size and demand?
Validate the Solution
- How does the product solution address the key pain points?
- Were experiments and prototypes done to validate assumptions?
- What early traction or usage metrics demonstrate solution fit?
Set Goals and KPIs
- What key goals and objectives guide the product roadmap?
- How do key performance indicators track progress towards goals?
- What metrics align to the customer and business goals?
Evaluate Decisions and Outcomes
- What key decisions shaped the product strategy and features?
- How did experiments and iterations impact the product direction?
- What final business and customer results were achieved?
Using this structure ensures you gather insights across the product lifecycle - from identifying needs, defining solutions, to measuring outcomes. Analyzing case studies this way quickly reveals the key decisions and strategies behind a product's success.
What are the 4 types of case study?
Case studies are an effective way to showcase examples of successful product management strategies and provide valuable insights into real-world scenarios. There are four main types of case studies:
Illustrative Case Studies
These provide a descriptive overview of a product, business, or industry. They tell the story of a product's development, struggles and successes. Illustrative case studies help set the scene and provide context.
Exploratory Case Studies
Also known as pilot case studies, these are condensed case studies performed before implementing a large scale investigation. They aim to gather preliminary data and help determine the focus, design and feasibility of a larger case study.
Cumulative Case Studies
These aggregate quantitative information from several sites or sources. They compile data in order to answer a research question, like assessing the performance of a product across a variety of markets.
Critical Instance Case Studies
These examine a single instance of intense interest. They provide valuable insights from a business success or failure. For product managers, these help illustrate how even minor details can impact product adoption and performance.
How to prepare for case study interview for product manager?
Preparing for a case study interview as a product manager candidate requires focused preparation across four key areas:
Understanding the Case Study
- Research the company, product, industry, and business context thoroughly to identify potential issues and scenarios the case study may present.
- Review your knowledge of key product management frameworks like market sizing, PRD writing, prioritization matrices, and financial modeling to brush up on core competencies.
Knowing the Interviewers
- Understand the background and seniority level of the interviewers. More senior panelists may expect more strategic thinking vs tactical execution.
- Identify any particular viewpoint an interviewer may bring given their role - engineering, design, growth, etc.
Setting Assumptions
- Clarify any assumptions you can make about the case details upfront instead of getting derailed later.
- Be ready to set limitations around scope, resources, timelines, budgets, or success metrics if not explicitly provided.
Applying Strategy
- Use an open-ended, discovery-based approach for broad business challenges without an obvious solution path.
- Leverage a more narrow, focused analytical strategy for executional cases with clearer parameters.
Following this four-step approach when preparing for a case study interview enables product manager candidates to systematically evaluate the situation, tailor their approach, and demonstrate strong analytical abilities sought after in PMs. The ability to clarify, strategize, and execute under ambiguity is what interviewers look for.
Product Development Case Studies
This section features examples of innovative and user-focused product development processes that led to successful outcomes.
Apple iPod's Intuitive Design Principles
Apple's development of the iPod is a great case study for simple, intuitive product design centered around understanding user needs. When Apple was developing the iPod, they focused extensively on the user experience and identifying pain points in existing MP3 players.
Some key insights that guided the iPod's design:
- Users wanted to easily carry their whole music library with them
- Managing and scrolling through huge song libraries was tedious
- Existing players had complex, confusing controls
To address these issues, Apple designed the click wheel interface to make scrolling through songs incredibly simple and fast. The intuitive menu system also made adding songs easy. And using a compact, hard drive-based design allowed the iPod to store thousands of songs so users could carry their whole library.
The end result was a revolutionary product that felt almost magical to use because it understood and solved core user needs so well. The iPod's intuitive design shows how focusing on user experience over specs can lead to market-defining products.
Iterative Improvement in Google Maps
Google Maps exemplifies a data-driven, iterative approach to product improvement. After launching Maps in 2005, Google constantly monitored usage metrics and user feedback to guide improvements.
Some key iterative changes:
- Added more business information and integrated reviews after seeing people search for places
- Improved driving directions with features like traffic data and alternative routes based on user complaints
- Added Street View and walking directions to address user needs beyond just driving
This methodical improvement process, driven by real user data, allowed Google Maps to completely dominate digital mapping and navigation despite strong competition from established players like MapQuest early on.
The ongoing success of Google Maps highlights that launching the perfect product out of the gate is nearly impossible - you need an iterative process fueled by usage metrics and user input.
Amazon Kindle: Filling the Market Gap
The Amazon Kindle provides an excellent case study in identifying and addressing gaps in existing markets. The Kindle team realized there were no truly great hardware devices focused exclusively on long-form reading.
They saw an opportunity to create a better reading experience by analyzing pain points with physical books:
- Books can be heavy and bulky during travel
- Finding new books means physically going to stores
- Paying for individual books adds up in cost
To solve these user problems, Amazon designed the Kindle ereader hardware to be extremely portable while giving on-demand access to Amazon's massive ebook library.
Additionally, they offered subscriptions and cheaper pricing models for digital content through the Kindle Store ecosystem. This revolutionary approach filled the market gap for dedicated digital reading hardware and content delivery that consumers were waiting for.
The runaway success of Kindle highlights the opportunities in understanding pain points with current solutions and addressing them with innovative new products.
Product Management Case Study Framework
Case studies provide invaluable insights into real-world applications of product management best practices. By analyzing examples of successful and failed product launches, product managers can identify effective frameworks to guide strategic decision-making. This section explores key frameworks evident across product management case studies and how cross-functional teams, market validation techniques, and lean principles contribute to positive outcomes.
Utilizing Cross-Functional Teams
Collaborative teams comprising diverse expertise increase the likelihood of creating products that effectively solve customer needs. Case studies demonstrate that supporting collaboration between product managers, engineers, designers, and business stakeholders leads to:
- Enhanced understanding of customer problems
- Validation of product solutions against real user needs
- Improved transparency and buy-in across organizations
For example, the case study XYZ shows that increased coordination between product and engineering during development boosted software quality by 34%. Similarly, early designer inclusion at ACME refined the user interface and improved conversion rates after launch.
Market Research and Validation
Case studies consistently highlight the importance of upfront market analysis and continuous customer validation to create successful products. Common factors include:
- Comprehensive competitor analysis to identify market white space
- Dedicated qualitative and quantitative market research around problem/solution fit
- Multiple rounds of prototype tests with target users at each product stage gate
The case study for 123Workforce illustrates this. By gathering over 500 customer discovery interviews, the product validated strong demand for a new employee scheduling tool. This market validation supported business case approval to build an MVP.
Lean Product Development Techniques
Case studies demonstrate that lean principles enable effective product iteration based on real user feedback versus internal assumptions. Specifically:
- Minimum viable product (MVP) releases help fail fast and cheaply
- Continuous build-measure-learn loops rapidly incorporate user inputs
- Evidence-based prioritization focuses on the highest customer value features
For example, PlanHub’s early MVP launch gathered inputs from initial users to refine core features rather than overinvesting upfront. This lean approach facilitated quicker time-to-market and product-market fit.
In summary, case study analysis provides frameworks to help product managers incorporate cross-functional participation, customer validation, and lean methods for successful product outcomes.
Product Launch and Marketing Case Studies
This section highlights creative, strategic product launches and marketing initiatives that generated significant consumer interest.
Dropbox's Innovative Referral Program
Dropbox pioneered referral marketing in the SaaS industry with its onboarding flow that rewarded users for sharing the product. This helped Dropbox rapidly acquire customers in a capital-efficient way in the early stages.
Some key aspects of Dropbox's referral scheme that made it effective:
- Frictionless sharing: Users could easily access a unique referral link to share Dropbox with friends and family. The seamless referral integration incentivized sharing.
- Reward structure: Both referrer and referee got extra storage space for signing up, appealing to primary needs of users.
- Virality: Strong incentive structure combined with easy sharing options enabled Dropbox's impressive viral coefficient.
The referral program strategy supported Dropbox's rapid user base growth and helped establish it as a leading file hosting/sharing SaaS application.
Leveraging Slack's Freemium Model
Slack employed a tactical shift from a paid-only model to a freemium pricing strategy. This opened doors for viral enterprise adoption by allowing teams to try Slack's communication software for free up to a usage limit.
Key aspects that made Slack's freemium work:
- Generous free tier: The free version provided enough value for small teams to collaborate. This established stickiness.
- Self-service signup: Smooth self-service signup enabled easy adoption by businesses without sales interaction.
- Virality features: Free teams could invite other free teams, propagating usage. Upgrades were natural with business growth.
Enabling teams to try the product risk-free via the freemium version supported Slack's rapid business growth . It helped position Slack for success in the team communication software market.
Peloton's Premium Positioning
Peloton pioneered the high-tech fitness bike concept with integrated digital content. Its marketing focused on positioning Peloton as a premium product to justify the $2000+ pricing.
Strategic aspects of Peloton's positioning:
- Targeted high-income consumers who valued premium brands as status symbols. This supported the elevated pricing.
- Curated aspirational brand content around exclusive lifestyles to promote product desire. Raked in sales despite pricing.
- Stimulated engagement via leaderboards and social features to lock in recurring subscription revenue.
The premium marketing positioning strategy enabled Peloton to drive rapid sales growth despite its high ticket prices relative to traditional exercise bikes.
Product Management Case Study Interview Insights
Case study interviews are a crucial part of the product management interview process. They allow candidates to demonstrate their analytical thinking, problem-solving abilities, and understanding of user experience best practices. Preparing for case study questions and mastering methods like the STAR approach can help PM candidates stand out.
Mastering the STAR Method
The STAR method is an effective framework for structuring responses to case study interview questions. STAR stands for:
- Situation - Set the context by concisely outlining the background of the case study.
- Task - Describe the problem you need to solve or goals you need to achieve.
- Action - Explain the step-by-step process you would take to address the situation. Show your analytical approach.
- Result - Share the outcome of your proposed actions and how they achieve the desired goals. Quantify the impact if possible.
Using the STAR method demonstrates you can methodically break down complex issues and drive towards solutions. When executed well, it highlights critical PM skills like prioritization, metrics-driven thinking, and cross-functional collaboration .
Analytical Thinking and Problem-Solving
Case study interviews evaluate your comfort with ambiguity and your capacity to structure unclear problems. Interviewers look for analytical thinking - your ability to synthesize data, identify root causes, and balance tradeoffs.
Shine a light on your analytical abilities by:
- Asking clarifying questions before diving into solutions
- Mapping out all stakeholders and components of the system
- Determining which metrics are most important and relevant to track
- Proposing hypotheses before making decisions
- Quantifying the impact of your recommendations with estimates
This showcases your aptitude for breaking down and solving complex product challenges.
Highlighting User Experience Outcomes
While analytics are crucial, PMs must balance quantitative rigor with qualitative empathy. Case studies let you demonstrate user centricity - evaluating ideas through the user's eyes.
To highlight UX sensibilities, discuss how your solutions:
- Simplify or improve key user flows
- Reduce friction during onboarding
- Increase retention by solving pain points
- Improve satisfaction via new delighters
This underscores the customer value created and your ability to advocate for users. Quantify improvements to showcase your user focus.
Ongoing Product Management Case Studies
This section focuses on outstanding examples of continually evolving products by listening to users and proactively addressing their needs.
Duolingo: Mastering App Gamification
Duolingo has refined their app over time to balance user enjoyment and motivation to drive engagement. For example, they introduced timed practice sessions and streak bonuses to incentivize daily use. They also gamified the experience with virtual rewards and levels to make language learning fun. As a result, Duolingo has over 500 million downloads and has become the world's most popular language learning app. Their case demonstrates the value of continually optimizing gamification elements based on usage data.
Amazon: A Culture of Customer Obsession
Amazon's customer-centric culture focuses on constant refinement of the user experience. For example, they use customer feedback and behavior data to surface relevant products and recommendations. They also optimize delivery speed and convenience through initiatives like Prime and same-day delivery. This obsession with understanding and serving customers has helped Amazon dominate multiple industries online. Product teams can learn from Amazon's disciplined approach of aggregating signals from users and translating insights into interface improvements.
Uber: Strategic Market Expansion
Rather than rapidly expanding globally, Uber tailored its rollout strategy city-by-city. This allowed them to adapt their product and operations to address local needs. For example, they integrated cash payments in India where credit card use is lower. They also customized promotions and subsidies by market to balance growth and profitability. Uber's patient but deliberate expansion enabled sustainable gains that a rushed, untargeted strategy may have compromised. Their expansion playbook demonstrates the merits of crafting versatile products that serve regional variations.
Key Takeaways and Best Practices
The product management case studies explored demonstrate several essential insights and best practices:
The Centrality of User-Centricity
Deep understanding of user needs and putting the customer first were critical success factors across many examples. Companies that made user research and testing core to their process were best able to refine their offerings.
The Power of Continuous Iteration
Few companies got their product right from day one. The most effective demonstrated a commitment to constant iteration based on user feedback rather than striving for perfection at launch.
Innovative Strategies in Action
We saw clever approaches to pricing, promotion and user acquisition. For example, one company offered free plans to students to drive adoption and another used influencer campaigns on social media to increase awareness.
Latest Posts
.jpg)
This article will explore how product management side projects can catalyze professional development by allowing you to experiment with new methodologies and enhance your skillset.
.jpg)
This comprehensive guide promises to equip you with a structured approach to tackling product case studies. You'll gain frameworks to methodically analyze prompts and craft insightful solutions.
.jpg)
Through real-world application, valuable feedback, and community engagement with groups like The Product Folks, PMs can significantly accelerate their skill development and expertise in the dynamic field of product management.
Come For the Content Stay For the Community


6 Product Management Case Studies You Can't Miss

Associate Product Marketer at Zeda.io.
Mahima Arora
Created on:
June 26, 2024
Updated on:
8 mins read
.webp)
Transform Insights into Impact
Build Products That Drive Revenue and Delight Customers!
Product management case studies are detailed analyses of how a product was conceptualized, developed, and marketed. A typical product management case study contains the following:
- The pain points and expectations of the user
- Competing products in the market
- Development , delivery, and iteration methods
- Marketing strategies implemented to relay the product’s value proposition
- How the product was received
- Lessons for the product team
So, why should you learn about the development of a product in so much detail? The answer lies in the sixth bullet.
Let’s look at how reading case studies related to product management can help you.
How product management case studies help you
Here’s why reading product management case studies is a worthwhile investment of your time. A well-written case study:
- Gives you an in-depth understanding of real product problems : Meeting or exceeding the expectations of the customers is always challenging. Whether it is technical complexities, budget limitations, or organizational miscommunication, a case study helps you recognize the source of the problem which led to the development of a less-desirable product.
- Contains practical insights outside of the theory : Even a layman can learn the steps of SaaS product management . However, seasoned product managers know that developing a successful product takes more than learning the development steps. These case studies contain tons of real-life scenarios and the lessons that come with them.
- Educates you and makes you a better product manager: Product management case study examples take you through the journey of developing a product, which helps you improve your existing approach toward product development. You will also learn better ways to manage your team and resources.
In simple terms, a product management case study helps teams learn lessons that they can emulate to develop a more profitable product.
In this article, let’s look at six product management case studies that are a must-read for every product manager.
1. Slack: Initial product launch strategy

Stewart Butterfield started a gaming company called Tiny Speck to change the world of massively multiplayer online role-playing games (MMORPG). Him and his team created Glitch which was quite different from other games in that genre such as World of Warcraft.
Glitch was a 2D game that did not have the violent aspects that typical MMORPG games had at the time. It allowed extensive character personalization and Butterfield described it as “Monty Python crossed with Dr. Seuss on acid”.
While building Glitch, Butterfield and his team used the Internet Relay Chat (IRC), an online chat tool popular in the 80s and 90s. However, it fell short as the team found it difficult to keep track of past conversations, which motivated them to build their own communication tool.
As they developed Glitch, their internal chat tool gained more features based on their needs.
Despite lots of support from investors, Glitch was unable to attract enough players to keep running profitably and Butterfield eventually shut it down in 2012 .
After six months, in early 2013, Butterfield renamed their internal communication tool Slack - acronym for Searchable Log of All Conversation and Knowledge and requested his friends and colleagues to try it out and give feedback — they all loved it.
By May 2013, Slack was ready for the big reveal which posed a new challenge — executing the perfect launch strategy to drive demand.
Slack’s Challenge: Nailing the initial product launch
While launching an app that can have such an impact on how organizations work, it is crucial to get it right. At the time, there weren’t many team messaging apps and most teams had conversations via email.
Slack needed a significant number of early adopters to validate their hypotheses about team collaboration and collect data that will help them improve its services further. Consequently, this increased the stakes for the first launch.
How did Slack do it
CEO Stewart Butterfield revealed that on the first day of the launch, Slack welcomed 8000 new users which rose to 15000 at the end of the second week. The credit for this initial success, he explains, went primarily to social media.
Social media helped Slack deliver its PR pieces through its genuine users. This led to a snowballing effect because people interacted with people.
Slack recorded over 18 million active users in 2020.
Although the impact of social media-based word-of-mouth marketing will have different levels of success as it depends on factors such as the type of product and its use cases, you should have a social media marketing strategy to spread the word.
Suggested Read: Leveraging VoC-driven AI Insights to Build Revenue-generating Products
2. Superhuman: Finding product-market fit

Superhuman is a premium email service for busy teams and professionals who need more of everything; speed, usability, and personalization. Apart from superb design, Superhuman processes and executes any request within 100ms.
Rahul Vohra built Rapportive in 2010 — a plugin that adds social profiles to Gmail which was later acquired by LinkedIn . This gave Vohra an intimate view of email and quickly realized that things will progressively get worse.
In his words, “I could see Gmail getting worse every single year, becoming more cluttered, using more memory, consuming more CPU, slowing down your machine, and still not working properly offline.”
He also brought attention to the number of plugins people used, “And on top of that, people were installing plugins like ours, Rapportive, but also Boomerang, Mixmax, Clearbit, you name it, they had it. And each plugin took those problems of clutter, memory, CPU, performance offline, and made all of them dramatically worse.”
Vohra had one question in his mind — how different would the email experience be if it was designed today instead of 12 years ago?
Superhuman was born to give professionals the email experience that they have been long waiting for. Smooth, easy on the eyes, and most importantly, blazingly fast.
But, there was one elephant in the room.
The idea of building a better email service than the existing players sounded great. However, going against some of the biggest brands of Silicon Valley required more than a bad personal experience with Gmail.
The Superhuman team needed evidence that such a product is actually desirable.
Superhuman’s Challenge: Establishing product-market fit
The team at Superhuman was competing against the email services of Apple, Google, and Microsoft which made the product-market fit quite crucial.
But how do you know whether you have achieved product-market fit?
How did Superhuman do it
Vohra and his team came up with an innovative idea to measure product-market fit by testing crucial hypotheses and focusing on the right target audience.
Superhuman had two hypotheses :
- People are dissatisfied with Gmail and how slow it is.
- People are also dissatisfied with third-party email clients and how buggy they were.
In a product management case study , Vohra explained how to find the right audience — the users who would be ‘very disappointed’ if they could no longer use your product. After identifying them, all you have to do is build the product as they want it.
3. Medium: “Highlights” feature

Evan Williams co-founded Blogger and Twitter which has helped millions of people share their thoughts with the world. Although both platforms became quite popular, they still couldn’t deliver the best reading experience to their users. Blogger allowed readers to browse topics by authors only and Twitter made it difficult for authors to aptly describe themselves.
He quickly recognized the need for a publishing platform that delivers a diverse experience for the readers and allows the authors to speak their hearts.
That’s how Medium was born. It enabled readers to browse articles by topics and authors, helping them to gain different perspectives on any particular subject. It also allowed everyone from professional programmers to amateur chefs to share their insights with the world as they wanted it.
The developers slowly added more features to Medium such as tags, linked images, social cards, and sharing drafts as it evolved through the years.
One of the many notable features of the platform is the “Highlight” feature — where you can select any particular post section and treat it as a mini-post. You can comment on the Highlight or tweet it, which is handy for both personal revision and sharing interesting snippets with others.
Suggested Read: Want to become a Product Coach?
Medium’s Challenge: Determining whether “Highlights” added value
Medium faced a challenge while determining a metric that can give them an accurate assessment of the desirability of this feature. In other words, they needed a metric that would tell them whether the “Highlights” feature made user interactions better and more rewarding.
How did Medium do it
The team at Medium solved the challenge by shifting their focus to one crucial metric rather than multiple vanity metrics such as organic visits and retention time which signifies how much value your users are getting out of your product based on retention rate.
For Medium, it was Total Time Reading (TTR) . It is calculated by estimating the average read time which is the number of words divided by the average reading speed (about 265 WPM) and adding the time spent by the reader lingering over good paragraphs by tracking scrolling speed.
4. Ipsy: Managing distribution

Michelle Phan started her journey as a YouTuber who recognized the importance of makeup in someone’s self-expression. She has been sharing beauty tips and makeup tutorials with her audience since 2007.
While on a trip to Thailand, she observed how little girls scrambled to pay for makeup samples in front of vending machines. Five years later, she launched a subscription-based Glam Bag program — where the customers will receive 4-5 deluxe-sized samples of makeup products.
MyGlam, as it was known back then, quickly gained over half-a-million monthly subscribers which created one of the biggest online beauty communities.
Phan quickly realized what she wanted to do — to build a brand for women who wanted to share their perspectives on beauty and meet like-minded people with similar interests and styles.
Ipsy , which comes from the Latin root “ipse” meaning “self”, was created by Phan, Marcelo Camberos, Jennifer Goldfarb, and Richard Frias to expand the user experience.
Although Phan knew how to convert viewers into paying customers, executing a marketing strategy by scaling it up was challenging.
Ipsy’s Challenge: Managing a content distribution strategy
The first makeup tutorial by Michelle Phan has now over 12 million views. Videos like that helped Phan get her first subscribers on her MyGlam program.
This shows the importance and impact of influencer-led content on revenue for businesses in the beauty industry.
However, running an influencer content distribution strategy involves collaborating with multiple passionate influencers. It was challenging to find like-minded influencers who will promote only one brand. Moreover, when working with influencers, it's important to implement effective content moderation to make sure the posted content aligns with your goals.
Phan and her team had a simple solution for this.
How did Ipsy do it
Phan and Spencer McClung, EVP of Media and Partnerships at Ipsy, partnered with beauty influencers like Bethany Mota, Promise Phan, Jessica Harlow, and Andrea Brooks who were already subscribed to MyGlam to create content exclusively for Ipsy.
In a case study analysis, McClung revealed that it put Ipsy on a content-based growth loop where the content was created by both the influencers and customers for the beauty community.
Sponsored content for products by influencers helped them increase their reach and helped Ipsy get more loyal customers. This growth loop gained Ipsy over 3 million monthly subscribers .
Suggested Read: Pivoting equals failure?🤯
5. Stitch Fix: Mastering personalization

Katrina Lake, the founder of Stitch Fix , realized back in 2011 that apparel shopping needed an upgrade. eCommerce failed to meet the expectations of the shoppers and retail shops were falling short in terms of options.
In an interview with The Cut , she revealed "Searching online for jeans is a ridiculously bad experience. And I realized that if I imagined a different future, I could create it."
After realizing that no one has merged data and fashion shopping, she set out to make a difference. She started a personal styling service out of her apartment in 2011 when she was pursuing her MBA from Harvard.
Lake relied on SurveyMonkey to keep track of her customer’s preferences and charged $20 as a styling fee. In late 2012 Eric Colson, then the VP of data science and engineering at Netflix, joined Lake on her journey of crafting the future of retail.
Lake and Colson wanted to give their customers much more than just personalized recommendations.
Stitch Fix’s Challenge: Building a personalized store
Stitch Fix wanted to give their customers more than just personalized recommendations — they wanted to build a personalized store for them where everything they look at, from clothes to accessories, matches their flavor.
But everyone’s body dimensions, preferences, budgets, and past choices are unique which can make building a personalized store difficult.
The team at Stitch Fix found a simple yet effective solution for this challenge.
How did Stitch Fix do it
Katrina Lake, CEO of Stitch Fix, revealed in a case study that personalization is crucial for the onboarding, retention, and monetization of customers.
When signing up, Stitch Fix asks you a few questions about your fashion choices and picks clothes that look the best on you. Furthermore, the collections in your personal store will keep improving as it continuously learns more about your personal preferences.
Also, there is no subscription fee which makes Stitch Fix a great option for occasional shoppers. Suggested Read: Canva’s Success Tale in the World of Design
6. Pinterest: User retention

Ben Silbermann started his tech career at Google’s customer support department. Although he loved the company and believed in its vision, he quickly became frustrated as he wasn’t allowed to build products.
With support from his girlfriend (now wife) Divya and a college friend Paul Sciarra (co-founder), Ben created an app called “Tote” in 2009 which was described as a “catalog for the phone”. Tote allowed users to catalog their favorite items and will be alerted whenever they were on sale so they can make a purchase.
However, the users used it to share their collections with each other instead. Ben recalled how he collected insects as a kid and loved sharing his collection with others. He recognized how people, in general, love to do that.
And, just like that, Pinterest was born where users can “pin” whatever they are interested in and add it to their personal collections.
Pinterest quickly became a hit and entered the global market.
Despite huge success within the US, Pinterest struggled to retain users globally. The team realized that the primary reason users churned is that something stopped them from getting the product’s core value — building personal collections.
Pinterest’s Challenge: Helping customers quickly realize the core value
There are many things that can prevent a user from accessing a product’s core value and one of them is internal friction within the product.
Pinterest’s product folks zeroed in on the one feature that was the gateway to the product’s core value — the “Pin It” feature.
Users outside the US simply couldn’t relate to the term, even though all it did was save the item they like to their personal collection.
How did Pinterest do it
The “Pin It” feature of Pinterest is linked directly to its brand identity. Casey Winters, former growth product lead at Pinterest, suggested changing it to “Save”, particularly in areas outside of the US.
As of the third quarter of 2022, it has over 445 million monthly users all over the world exploring various “ideas” to build collections for sharing with their friends.
Casey concludes in the product management case study that checking whether the users are getting your product’s core value is pivotal in solving most of your growth challenges.
Key Takeaways
Case studies for product management contain in-depth insights that help product teams improve their approach toward their product’s ideation, analysis , development, and commercialization.
The six product management case study examples we reviewed above give these crucial insights:
- Slack : Don’t forget to use social media for marketing your product before its launch.
- Superhuman : Focus on the users that will be “very disappointed” if they can’t use your product anymore to achieve product-market fit.
- Medium : Track the one metric that tells you whether your users are getting value from your product rather than vanity metrics such as organic traffic.
- Ipsy : Partner with influencers to educate your target audience on how to get the most out of your product.
- Stitch Fix : Learn about what your users want and recommend them just that.
- Pinterest : Continuously experiment by changing multiple variables to uncover new growth opportunities.
To put these lessons into practice, you need to provide your team with the right tools that help them interact with your users, learn about their preferences, monitor their usage data, plan the next steps, and manage product development effectively.
Zeda.io is a product management super-app that allows you to do just that. You can run your entire product management process , from ideation to delivery, in one place. Zeda.io comes with over 5000 integrations with Zapier, enabling you to hit the ground running in no time.
Start your free trial today . Also, looking for the latest trends in AI, UX, product management, and startups? Join our biweekly newsletter now! We distill complex topics into actionable insights just for you. Hit the 'Subscribe' button and never miss out on these valuable updates. Act now – because in the fast-paced world of tech, staying ahead matters! Subscribe here.
- What is a product management case study?
Answer: A product management case study is a detailed analysis of how a product was developed and iterated over time for maximum success. These studies help product managers learn from others and improve their own approach toward product management.
- How do you prepare a product management case?
Answer: You can prepare a product management case study in four steps — understand customer needs, monitor the stages of development, identify the factors that affected the course of product development, and extract takeaways.
- What are the 3 major areas of product management?
Answer: Discovery — recognizing the need for a product, planning — creating a roadmap to plan the product’s development, and development — the various sprints through which a product is developed are three major areas of product management.
- What are the 7 steps of product planning?
Answer: Concept development, competitive analysis, market research, MVP development, introduction, product lifecycle, and sunset are the seven steps of product planning.
- What are the 5 dimensions of product management?
Answer: Reliability, usability, functionality, maintainability, and efficiency are the five dimensions of product management.
- What are the 4 P's of product management?
Answer: Product, price, place, and promotion are the 4Ps of product management which represent four crucial aspects product teams should simultaneously focus on while developing a product.
- What are the 5 phases of the product management process?
Answer: Idea generation, screening, concept development, product development, and commercialization are the five phases of the product management process .

Join Product Café Newsletter!
Sip on the freshest insights in Product Management, UX, and AI — straight to your inbox.
By subscribing, I agree to receive communications by Zeda.
IN THIS ARTICLE:
Latest articles
%2520(1).webp)
Product Feedback Management - The Ultimate Guide
Product feedback management is no longer about getting customer responses. It is about listening to the customer's requirements and creating a solution for them.

Product-Led Growth: The End-user is the king
Product Led Growth should keep the users at the center and ensure that the users find the product meaningful and get value out of it.

Product-Market Fit: What it is and Why is it important?
The success of a startup is highly dependent on Product-Market fit. What is Product-Market fit and how do you achieve PMF?
AI-powered product discovery for customer-focused teams
A Systems View Across Time and Space
- Open access
- Published: 17 July 2023
New product development process and case studies for deep-tech academic research to commercialization
- Pravee Kruachottikul 1 , 2 ,
- Poomsiri Dumrongvute ORCID: orcid.org/0009-0009-7461-5888 3 ,
- Pinnaree Tea-makorn 4 ,
- Santhaya Kittikowit 5 &
- Arisara Amrapala 6
Journal of Innovation and Entrepreneurship volume 12 , Article number: 48 ( 2023 ) Cite this article
14k Accesses
8 Citations
1 Altmetric
Metrics details
This research proposes a new product development (NPD) framework for innovation-driven deep-tech research to commercialization and tested it with three case studies of different exploitation methods. The proposed framework, called Augmented Stage-Gate, integrates the next-generation Agile Stage-Gate development process with lean startup and design thinking approaches. The framework consists of six stages and five gates and focuses on critical thinking to help entrepreneurs avoid psychological traps and make the right decisions. Early activities focus on scouting for potential socioeconomically impactful deep-tech research, developing a business case, market analysis, and strategy for problem–solution fit, and then, moving to a build–measure–learn activity with a validated learning feedback loop. Next, suitable exploitation methods are decided using weight factor analysis, developing intellectual property (IP) strategy, completing the university technology transfer process, and participating in fundraising. To pass each gate, the committee board members, consisting of tech, business, IP and regulatory, and domain experts, will evaluate the passing criteria to decide Go/No-Go. Applying the framework to the case studies results in successful university research commercialization. The model, case study, and lessons learned in this paper can be useful for other deep-tech incubator programs to successfully launch deep-tech research for commercialization. The case studies’ positive outcomes validate the Augmented Stage-Gate framework, yet their success is not entirely guaranteed due to external factors like regulatory constraints, entrepreneur characteristics, timing, and the necessary ecosystem or infrastructure, particularly in emerging markets. These factors should be taken into account for future research purposes.
Introduction
Deep-tech innovation is a new wave of impactful innovation that drives the economy and society. Unlike digital innovations such as mobile apps and digital platforms that disrupted many old-fashioned businesses in past decades, deep-tech is unique, high-value, hard-to-reproduce technological or scientific advances that will improve the technological frontier or disrupt existing solutions and result in socio-economic impacts (De la Tour et al., 2017 ). Deep-tech innovation is usually led by megatrends and unmet needs (Linden & Fenn, 2003 ).
Thailand, a developing country, relies heavily on traditional businesses such as sales, marketing, and services. Thailand’s gross expenditure on R&D (GERD) is lower than that of other middle-to-high income countries. In 2018, Thailand spent 1.11% of gross domestic product (GDP) (182 billion baht) compared with an average of 1.41% for the upper-middle-income group and 2.43% for high income countries. GERD was expected to reach 2% of GPD in 2027 but this was revised to 1.46% due to the COVID-19 pandemic, assuming no new measures to boost R&D investment. Nevertheless, various government policies require stimulus to R&D spending, especially for SMEs and innovation-driven enterprises through the Thai Bay-Dole Act (Office of National Higher Education Science Research and Innovation Policy Council, 2021 ). Therefore, deep-tech innovation applied to Thai businesses could be a potent new driver for its economy. Since most deep-tech originates from academia, researchers, patents, or publications, it is unlikely to be successful and sustainable without real demand from users or direction from the business side. This is because traditional academia focuses heavily on research, publication, and prototype development (Fellnhofer, 2016 ), rather than building a product that is ready for commercial use (Hicks et al., 2009 ). Promoting entrepreneurship, which is a combination of art and process to pursue opportunities and turn into a business regardless of resources, among academia can be helpful to create environments that support innovation development (Barringer & Ireland, 2012 ).
Moreover, many deep-tech innovations require a large amount of funding at the initial stage to build a prototype, perform user validation, and develop a business strategy. Additionally, deep-tech innovation is new, and the industry may not be clear about market needs or potential buyers. Therefore, the technology acceptance model (TAM) is used to understand predictors of human behavior toward potential acceptance or rejection of the technology, particularly technologies related to information and communication technology (ICT) (Lee et al., 2003 ). It can also provide a useful tool to assess the success of new technology introductions and help understand the drivers of acceptance to proactively design interventions targeted at users that may be less inclined to adopt new systems (Venkatesh et al., 2003 ). After validating the market and technology, it is time to decide on commercialization options (Yaldiz & Bailey, 2019 ).
For deep-tech innovation to become successful exploitation from the research ideation stage until commercialization, it requires a product development model suitable for university research initiation and developing market environment. Meanwhile, many pieces of prior research on the NPD model and case studies were primarily conducted based on developed countries where the product development was done within the established company ecosystem (Cocchi et al., 2021 ; Cooper, 2016 ; Cooper & Sommer, 2016 , 2018 ; Salvato & Laplume, 2020 ; Walrave et al., 2022 ; Wuest et al., 2014 ). However, this study highlighted the importance of a specific NPD model in the academic initiative context with low resources and a lack of infrastructure setting, which generally happens within developing countries (Ravi & Janodia, 2022a ). This study is essential to promote deep-tech in Thailand and to help other developing countries that require a new growth potential to drive the economy. Consequently, to accelerate deep-tech innovation in Thailand, the Chulalongkorn University Technology Center (UTC) was established in 2019 as a platform to spring-board academic research to commercialization and facilitate among stakeholders within the ecosystem based on triple helix model, which promotes the way of working that the government, private sector, and academia must collaborate to form a solid, deep-tech innovation ecosystem (Leydesdorff & Etzkowitz, 1998 ) to support manpower, finance, know-how, production facilities, regulation, and sandbox testing in order to expedite the speed of innovation development.
This study uses qualitative research and observation based on the actual case studies of the UTC portfolio research teams. The goal is to understand the pain points, needs, obstacles, and processes required for the successful exploitation of their project and then extract the vital insightful factors for applying to the NPD model, which will be later discussed in the Methods section.
To develop the proposed NPD model, several related NPD studies have been reviewed. Then the next-generation stage-gate development system integrated with agile development, lean startup, and design thinking methods is selected and then applied together with the insights obtained from qualitative research as the NPD model to develop successful business-driven deep-tech innovation. The effectiveness of the model is later tested and confirmed using both experts and observation, which will be later described further in the Results section. This framework, which we call the Augmented Stage-Gate framework, is important for successful innovation and is based on critical thinking. Because human decisions are influenced by the subconscious, it is essential to make decisions based on the results of logical reasoning and avoid psychological traps (Linden & Fenn, 2003 ).
In addition, three case studies are explained and discussed. Applying the Augmented Stage-Gate framework results in successful commercialization process in all three cases where the teams transferred the technology via a spin-off startup with a patent, non-profit use with trade secret, and licensing. The benefits of this study can be used as a framework and case study for successful deep-tech innovation development and commercialization, especially in the context of developing markets and academic research initiation. Several options are proposed and discussed. Finally, the study makes several recommendations for future research, including its application to other vertical deep-tech innovation areas.
Literature review
In this section, the literature on the NPD model, TAM model, and product readiness assessment is discussed. Generally, the NPD model, is a nonlinear and iterative process based on a problem-solving approach that is used for the conception, development, and launch of new products or services. It can help management understand user insights, challenge assumptions, redefine problems, and create innovative solutions to prototype and test with target users to successfully launch in the market. In addition, the NPD process is based on critical thinking, which is the ability to look at events, conditions, or thoughts with a careful eye and make decisions about the reliability and validity of the knowledge according to standards of logic (Seferoglu & Akbiyik, 2006 ). It involves identifying and analyzing informational sources for credibility, indicating previous knowledge, making connections, and deducing conclusions (Thurman, 2009 ). Higher-order thinking ability provides the opportunity to analyze the existing knowledge or situation to correct mistakes and complete deficits to reach correct conclusions (Howard et al., 2015 ). In this study, the authors select Stage-Gate, which is a macro idea-to-launch product development planning process that involves the Go/No-Go decision-making (Cooper & Kleinschmidt, 2001 ), as the baseline NPD framework because the model is easy to understand among stakeholders in a simple linear system format that consists of detailed guidelines for every stage and explains the criteria for management to make a decision whether to allow the development to pass each gate. These unique characteristics of Stage-Gate model strongly fit within the context of our study. While its principles can be applied, the Stage-Gate model, including the number of stages, activities, and gate criteria, has to be adjusted according to our objectives using the insights obtained from this study.
After the core concept of Stage-Gate model was chosen, several modern State-Gate models were reviewed. The next-generation Stage-Gate process that comes with the Triple A system and spiral concept that promotes the development process to be adaptive, flexible, iterative, and accelerated using a feedback loop from user validation (Cooper, 2016 ) can be applied to the model. Furthermore, there was a study of applying Agile project management methods, which highlights a process that is a dynamic planning process that is adaptive and flexible to changes in product development, into a traditional Stage-Gate system, called Agile-Stage-Gate Hybrids. The results looked promising for faster product releases, quicker and better responses to changing customer requirements, and improved team communication and morale (Cooper, 2016 ). Moreover, case studies in manufacturers conducted by R. Cooper in 2018 also supported the earlier finding; yet it also added some challenges in terms of management buy-in, resources needed and allocation, and fluid product definitions and development plans (Cooper & Sommer, 2018 ). These insights are also similar to the study by Zasa et al. ( 2020 ) who highlighted that agile project management will increase interaction among project stakeholders and help break big tasks into small and achievable action items (called sprints ) within a short period of time. They also suggested that successful implementation required the integration between traditional project planning modes and the agile method, cultural change, and perceptions of all stakeholders in the organization (Zasa et al., 2020 ).
Therefore, by applying modern concepts of Stage-Gate like triple A system with spiral concept and agile development, the earlier Stage-Gate baseline model can be improved in many ways. That is, the model becomes more adaptive and flexible to changing customer requirements and situations, increasingly improved team communication and morale, and further highlights on an iterative process to promote interfacing between the development team and the target user. Moreover, the importance of interfacing with users iteratively for business assumption validation is also similar to the principle of lean startup and design thinking. The lean startup encourages startups to challenge business growth hypotheses and use them to build the minimal viable product (MVP), then test and validate with the real user to learn whether it is required to pivot or preserve. This can be repeated many times during the NPD process; an approach called build–measure–learn (Ries, 2011 ). On the other hand, design thinking uses a designer’s sensibility and methods to match people’s needs to what is technologically feasible and a viable business strategy that can be converted into customer value and market opportunity (Brown, 2008 ).
In addition, the TAM can be useful to consider during the NPD process, in particular with ICT-related technologies. It can provide information regarding the probability of success during the introduction of a new technology and the key drivers of user acceptance to enable proactively designed interventions and strategies targeted at populations of users who may not be inclined to adopt new systems (Venkatesh et al., 2003 ).
Lastly, the authors review the study of product readiness assessment. This is important for our context because there is a misalignment issue from different stakeholders when evaluating the readiness of the new product development. This is a typical problem found when the product is not ready for commercial. Yet the team has to communicate readiness level with stakeholders for different purposes such as fundraising, selling, field testing, etc. The first assessment is the technology readiness level (TRL) which was introduced by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) in the 1970s. It is a well-recognized and useful tool to determine the maturity of new technologies. It is also a discipline-independent program that enables more effective assessment and communication. Its nine assessment levels are beneficial to determine the readiness of new technology and/or capability during the technology life cycle, which includes the completion of systems analysis and conceptual design studies, determination from several design options, and decision to start full-scale development (Mankins, 2009 ). Another assessment is the investment readiness level (IRL) proposed by Steve Blank in 2013, which is also divided into nine levels. IRL is used to evaluate how investment-ready a technology is by validating its business model to help investors assess the risk of investment (Blank, 2014 ). Investment readiness can be defined as a set of business development processes that increase business venture readiness as candidates for equity investors (Aernoudt et al., 2007 ). Alternatively, it is the capacity of the business venture to look for external funding, especially from an equity investor, to understand the specific needs required by an investor and be able to give an investor an attractive business proposal with high confidence (European Commission, 2006 ). Entrepreneurs need information and advice on the advantages of raising equity financing, what it means, and how to become investment-ready (Mason & Kwok, 2010 ). In addition, Australia National Investment Council. & Marsden Jacob Associates ( 1995 ) proposed that businesses that are not investment-ready are primarily the result of a lack of information. This means that they do not know about the role of equity finance and are unaware of what is involved in raising money, what is required to attract investors, and how to convincingly express their investment proposals (Australia National Investment Council. & Marsden Jacob Associates., 1995 ).
In this research, the authors use the next-generation stage-gate process as the baseline for the NPD process and then propose the modified NPD framework for new deep technologies that are more suitable for academic research initiation to commercialization in developing markets, called the Augmented Stage-Gate framework. The framework was designed using the insights obtained from in-depth interviews of 19 research teams who had been working on deep tech research and entered the three-month entrepreneurship development program in 2019. The interview was conducted at the end of the program and focused on understanding the pain points in the research-to-commercialization process in terms of entrepreneurship, business development, networking, financial, technology transfer process, progress assessment, and goal. After careful analysis, several recommendations were proposed and integrated into the Augmented Stage-Gate framework as shown in Table 1 .
The Augmented Stage-Gate framework highlights more on the Agile development process, flexible entrepreneurial development program, progress assessment using TRL and IRL, process management specialist to guide along the academic research to commercialization journey and bring in a network of business partners and legal experts to support. Its structure is divided into six stages (innovation ideation, build business case, development, test and validation, launch, and scale-up) with five gates (screening, go to development, go to test, go to commercial, and post-launch review). Here, stage means the process for work to be completed, and gate is for the Go or No-Go decision-making. TRL and IRL assessments, as shown in Table 2 , can be used to evaluate progress in terms of technology and business readiness at each stage.
The Augmented Stage-Gate framework applies the principle of the next-generation Stage-Gate’s triple A system and spiral development, which aims to overcome the typical challenges when handling undefined requirements during initial development, and Agile development, which aims to increase interaction among project stakeholders and help break big tasks into small and achievable action items (Sprints). This is because most customers are uncertain about their needs and so the product definition prior to development is unclear. The triple A model promotes each stage to be adaptive and flexible, agile, and accelerated while the spiral development concept promotes experimentation. This is also similar to what Isaacson ( 2011 ) described Steve Jobs’ philosophy during his development career at Apple that encouraged project teams to fail often, fail quickly, and fail cheaply. With the benefits obtained from the Augmented Stage-Gate core concept, the product design and definition can adapt to new information, customer feedback, and changing conditions along with multiple iterations of validation activities with users or customers throughout the NPD cycle. In addition, it is important to understand that the details of the process and its functions may differ from project to project, especially with deep tech, academic research initiative, and emerging market environment. Therefore, a flexible gating process must be leaner, faster, adaptive, and risk based. Experienced project teams, mentors, and stage-gate committees are also important to guide startup work throughout the NPD process. Additionally, even though the NPD model is represented in a simple linear format, in reality, it is common that each step can be repeated many times and also go back and forth between stages, depending on the readiness, criteria, and requirement to pass each stage.
Then the effectiveness of the Augmented Stage-Gate framework was tested with three cases, to be discussed in Sect. 4. The cases were research teams that joined UTC in 2019 after the new framework had been designed and completed the final stage of the framework by September 2022. The teams were willing to participate in the study. We gathered the information for the cases via observations and interviews.
The authors directly observed the teams as they moved through each stage of the framework. Tangible results such as actual sales, contract execution, regulatory approval, and certifications, were recorded. The authors also had access to relevant documents related to the development process since the teams were required to submit a progress checklist and presentation slides. Information reported (as appropriate to each stage) includes team, research and development progress, regulatory process, business plan, project planning and concept, product design, milestones, risk assessment, technology verification and validation (MVP), market validation, legal activities, IP status, implementation and operations, sales and marketing, and financial activities. These documents were collected and analyzed for the case studies.
In addition to observation, the authors interviewed the stage-gate committees and two or three people from each team (the principal investigator and 1–2 team members). The interviewees were asked to describe the team’s journey, how they applied the Augmented-Stage-Gate framework, and the results they achieved. The interviews also explored any significant challenges encountered during implementation, along with the solutions that the teams developed.
The interviews were recorded and transcribed, with the transcriptions used to create a final summary of the case. The summary was then reviewed and approved by the interviewees. In some cases, we went back to the interviewees multiple times to get additional information or to conduct follow-up interviews when the implementation and results had become clearer.
The Augmented Stage-Gate process of new product development
The proposed Augmented Stage-Gate process, as shown in Fig. 1 , is divided into six stages. In addition, the below detail explains the objective, activity, and criteria to pass the gate of each stage (as also summarized in Table 3 ).
Stage 0: innovation ideation stage. As a technology incubation office, one of the important roles at UTC is to search for impactful deep-tech research in focused areas that potentially impact our way of life and attitudes in all aspects. To achieve this, UTC has been working with various business partners and consultants to gain market insights while studying market research information for mega trends. Using this information, UTC scouts, classifies, and prioritizes potential research projects. After finding candidates, UTC works closely with them through various programs such as boot camp, workshop, and mentoring to develop the entrepreneurial knowledge and skill in order to help conduct an initial business feasibility study. Another advantage is to give entrepreneurs an understanding of the business journey, challenges, and exit plan so that they can prepare themselves with both skills and morale to be ready before launching. Moreover, the entrepreneurial development program is provided in a flexible format both online and offline to suit with the availability of researchers who might have other full-time jobs at the beginning. Usually, the business model canvas (Osterwalder et al., 2005 ), with its nine building blocks template, is used to communicate a firm’s or product’s value proposition, infrastructure, customers, and finances to stakeholders. After completion, the team is ready for the official screening, where the committee board consisting of business, technology, and legal experts will evaluate each research project.
The first step is to identify the target customer and study the user journey to understand the pain points and user insights. Additionally, lead users—advanced users who deal with an individual problem very intensively (von Hippel, 1986 )—are a subset of target users and can be helpful for the research team to test, validate, and gain valuable feedback on the early development product. Like design thinking, the concept starts with understanding the way customers do things and why, their physical and emotional needs, how they think about the world, and what is meaningful to them. This can be done by carefully observing, engaging, watching, and listening to the users and stakeholders, and then crafting a meaningful and actionable problem statement that focuses on the insights and needs (Brown, 2008 ).
The second step is to analyze internal and external market data. This process aims to understand the business environment and will allow us to better plan so that the threats and opportunities associated with the target area of the business are understood. An internal analysis examines factors within the research project and its co-founding team. The preferred analysis is a SWOT (Strength, Weakness, Opportunity, Threat). Meanwhile, an external analysis examines the wider business environment outside the research project. A popular tool for this is the PESTEL five-force analysis. The key to this process is to ensure that there is market demand to continue the tech-market fit development process.
The third step is to complete an initial financial management strategy, including profit and loss analysis, cash flow planning, and fundraising, that can help the entrepreneur understand the business from a financial perspective in different scenarios and help the business thrive. Because deep-tech product development usually requires a large amount of money and lengthy development time, careful planning in this step is much cheaper regarding business risk. It can avoid cash flow issues that may cause the company to go bankrupt or project delays. Moreover, financial planning can be used to estimate how much investment is needed in each venture development stage so that the entrepreneur can develop a successful fundraising strategy for investors or government grant agencies.
The next step is a preliminary study of the IP landscape. This gives the research project a high-level perspective on the constraints and opportunities regarding the potential exploitation and freedom to operate of IP rights. The researchers can conduct this by themselves or consult with the university IP office since normally the university provides IP support through its Technology Transfer Office (TTO) and IP Practicum Clinic, or by outsourcing services to specialized law firms.
After that, it is time for regulatory planning to help the research team understand and anticipate what regulations are required for each target market. For instance, Med Tech requires FDA (Food and Drug Administration) for commercialization, IRB (Institutional Review Board) for conducting a clinical trial in humans, and GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice) for manufacturing medical devices. Meanwhile, the PDPA (Personal Data Protection Act) is required to use personal data. Generally, the university technology office can be a helpful resource for regulatory advice.
Finally, since deep-tech initiates from academic research by nature, the original research team usually consists mainly of tech-savvy people. Therefore, to become a successful venture, it is crucial to find co-founders with business skills to join the team. Business case competitions or networking events within the university ecosystem can help form an organic partnership.
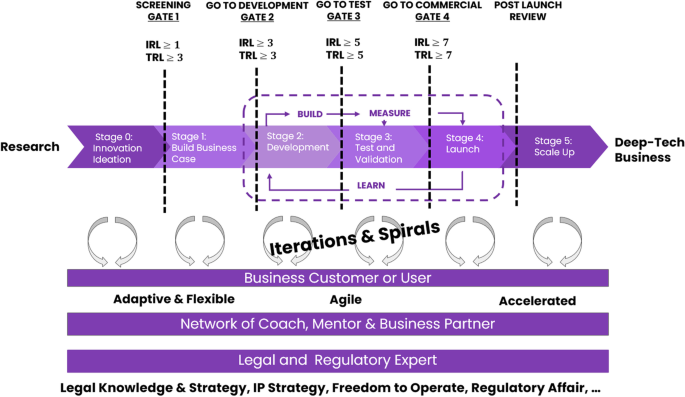
Augmented Stage-Gate framework
Stage 1: build business case stage. The main activity focuses on developing and validating the business model with target users by demonstrating the prototype and then measuring customer satisfaction, interest, or purchase intent. Usually, the prototype in this stage can be nonfunctional and developed based on the concepts of rapid, rough, and right. For example, AI and computer science technology can use UX/UI (user experience and user interface) and wireframe, which is a schematic or blueprint that is useful for thinking and communicating about the software structure among team members, as a prototype to validate the end-to-end solution idea with the user. Moreover, a network of mentors, domain experts, or key opinion leaders, which are mostly university alumni, can be useful resource because they are knowledgeable and experienced, in which they can give truthful advice and validate the solution idea. Another important thing is to interact with real users or customers as early as possible because today users’ roles have become more significant as a new source of innovation than in the past, when innovation was created solely from producers and supplied to consumers via goods and services, as described in Schumpeter’s theory of innovation in 1934 (Schumpeter, 1934 ). By working together, the research team can provide product knowledge, engineering, and manufacturing for innovative users to think and be creative (von Hippel, 1976 ), which means innovators receive an incentive to engage with users to develop innovative designs (Baldwin & von Hippel, 2011 ).
Stage 2: development stage. The main objective in this stage is to develop a workable and functional MVP, validate with the target user, and refine the business model. That is, it aims to improve technology progress and business strategy so that business risk can be reduced. However, it is noted that due to the Agile concept, the startup should target to break the development plan into small and achievable action items so that their hypothesis can be tested and learned often. In addition, validating the MVP in the closest real environment or sandbox, which refers to the environment that allows some players under specific conditions, to enter the market with fewer administrative constraints (e.g., licenses) or legislative requirements (Tsai et al., 2020 ), is recommended to move the MVP and business closer to the commercial version.
Stage 3: test and validation stage. The goal in this stage is to obtain a commercial version of the MVP and business model. To do that, the lean startup’s validated learning concept is applied to this stage because it can show whether the innovation development and business are moving in the correct direction according to the business model. If not, the innovation can be pivoted; a structural course correction to test a new fundamental hypothesis about the product, strategy, and engine of growth. To make the validated learning successful, cause-and-effect questions with actionable and quantitative metrics are essential. After the new features of the MVP are developed, it will be measured with the user to determine if it demonstrates business growth according to the underlying hypothesis, a process can be repeated many times. The benefit of embracing validated learning is to substantially shorten the developmental cycle.
Stage 4: launch stage. The main goal for this stage is to introduce the market of commercial products. The technology development team participates in a build–measure–learn activity to reach the closest version of a commercial product, while the business development team focuses on delivering a commercial final version of the business plan, sales and marketing strategy, IP strategy, regulatory planning, team formation and financial strategy to select the best commercial option with the highest probability of success and return on investment. In addition, if the university IP is used, the team must complete the technology transfer process. Moreover, according to the business model canvas template, this step must ensure that all nine blocks are validated with stakeholders in a way that leads to business growth and the commercial version of the MVP is refined accordingly. The next step is to finalize the IP submission and strategy, consisting of the final IP draft, valuation, and portfolio management, to obtain optimal legal protection and manage the IP effectively. IP valuation, calculated using either cost-based, income-based, or market-based methods, is useful for the entrepreneur to decide on a proper commercialization option and IP valuation for fundraising. Thus, it should be finalized before going to market. Even though IP services can be particularly expensive and time consuming for such early-stage endeavors, the benefit obtained from IP valuation and protection with a well-managed IP strategy generally increases company competitive advantages tremendously after successful exploitation.
The university technology transfer process is an intrinsic part of the technological innovation process. It is the process of conveying results stemming from scientific and technological research to the marketplace and to the wider society along with associated skills and procedures. To achieve a successful technological transfer, many factors must be considered. Souder et al. ( 1990 ) described seven best practices as analytical, facilities, pro-actions, people roles, conditions, technology quality, and organization. Meanwhile, Gorschek et al., ( 2006 ) recommended close cooperation and collaboration between researchers and practitioners. However, both entrepreneurs and tech transfer officers must discuss and plan each option carefully for the benefit of all stakeholders.
After completing the previous steps, it is time to decide on commercialization. Exploiting an innovation is not only about starting a new company, but there are also many other pathways to bring ideas to markets, such as licensing, joint ventures, and M&A (Schaufeld, 2015 ). Thus, to choose which option is suitable, the entrepreneur needs to consider factors such as market opportunity, IP protection, operation risk, time commitment, return on investment, and investment amount. A complete business plan should be developed and carefully verified, so that entrepreneurs can understand the business opportunities and risks in advance. Table 4 shows an example of an option comparison with a weight matrix between spin-offs and licenses. Briefly, the Option A spin-off scores higher than the Option B license, which means it is the more desirable commercial option to an entrepreneur.
Stage 5: scale-up. This activity focuses on collecting and analyzing the feedback obtained after launch, providing newer and better versions of commercial products or business plans using market feedback, and fully penetrating the target market. Several considerations can be analyzed. The first is to assess whether the product is performing according to pre-defined expectations in terms of technical and business aspects such as functionality, revenues, costs, profits, and so on. The second is to check customer satisfaction or anything that affects the company’s value chain, including purchasing raw material, selling the product, and delivering the goods to the customer. Finally, we examine the strengths and weaknesses of the entire NPD process to learn and improve.
Results and discussion
Case studies.
The case studies below highlight the importance of having an NPD framework that is adaptable to deep-tech within university research and emerging market contexts, yet extensive enough to cover all the essential components to transform deep-tech research into an innovation that has a high-fidelity MVP, an accomplished business and market strategy, a clear pathway towards implementation in the real world, and a complete IP strategy and technology transfer process from academia IP.
ReadMe is an artificial intelligence (AI) research project application that began in 2013 to perform Thai object character recognition (OCR) in any scene image, which often has high perspective and distortion error, uneven illumination, and different image resolutions. Additionally, the Thai character structure itself is very difficult to read automatically, particularly using software algorithms, because it consists of a syntactic structure of up to four layers and a strict relationship between words. The research team was conducting research and development internally and working with various industry partners. An e-commerce platform and a railway engineering company were contracted to help understand business demand as well as to improve and optimize the AI model for real-world applications. Nevertheless, after many years the technology remained a research project; early customers did not have purchase intent with a long-term commitment although the Thai OCR reading accuracy was high. Upon applying our Augmented Stage-Gate Framework to ReadMe in 2019, we successfully transformed the deep-tech research into a tech startup named Eikonnex AI ( https://www.eikonnex.ai/ ) that has now secured business deals for commercial use in private companies.
At the screening stage, the project’s potential for exploitation, validity, market feasibility, and technological feasibility was assessed and found to fulfill all the framework’s criteria. ReadMe, a national award-winning research project, was a deep-tech text reader that was in development for six years, had a research prototype proven well in the lab with a TRL of 4 and an IRL of 1, was the state-of-the-art Thai text reader that was more accurate than other better-known OCR technologies, and is a high-potential technology that could impact the business, medical, and transport industries.
Following their selection, the research team carried out innovation framework activities starting with continuous customer validation, that later helped them develop their market research and business plans. A large majority of their customers were banks, driven by the digital transformation trend and strong competition in the financial industry. One of the most challenging and high-volume applications is the personal loan approval credit scoring. Most were unable to automatically read Thai bank statements correctly due to statement template differences from different banks and Thai character challenges, increasing the time required for loan approval. The team saw this opportunity and pivoted their target customer and core technology to become an OCR with automatic template detection to read bank statements instead. After this decision, the team quickly redeveloped their MVP and carried out multiple user validations using the build–measure–learn process. In the meantime, the team worked closely with a network of mentors to adjust and validate the product idea and business plan.
After rigorously applying the framework’s validation activities, the technology underwent a complete transformation and reached commercial readiness. The technology now had a TRL of 7 and an IRL of 7, completed the IP strategy by obtaining a patent for their technique, concluded the technology transfer process, and set up a spin-off tech startup. Moreover, in early 2021 a few months after their establishment as a startup, the company received its first business deal from one of the biggest banks and completed the technology transfer process. Currently, the company is making its first sales by providing Thai document reader solution services either as an API or as a customized technology. They will continue to move towards digital transformation and expand into a coherent document digitization platform.
It is clear that with the support, guidance, and structure provided by the Augmented Stage-Gate Framework as explained in Table 5 , deep-tech research can be transformed into an innovative, high-impact, commercializable product and company in one to two years.
Chest X-ray AI reporter for COVID-19
Following the trend in the use of AI for healthcare, the chest X-ray reporter was an R&D project by physicians and computational researchers that aimed to create AI software that could classify and report abnormalities for physicians to consider as part of their diagnosis. Nonetheless, the technology remained a research project as it lacked a workforce to develop the complete application software and system integration and had no exit strategy.
With the application of our framework and the outbreak of the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic, the technology met the immediate needs of society by being able to detect COVID-19 and numerous other conditions from chest X-rays. As of the end of 2021, this innovation was used as a not-for-profit technology in the King Chulalongkorn Memorial Hospital, helping many patients in need.
The technology had a TRL of three and an IRL of one at the time of screening with an alpha version of the AI algorithm. As this project is led by physicians and computational researchers who are experts in the field, it is considered a deep technology with high potential for use in hospitals, especially rural government hospitals that sometimes lack healthcare personnel or technology to analyze chest X-rays efficiently. This innovation may also be adapted for use in other types of X-rays for other diseases and undoubtedly has large potential to improve the accuracy of medical diagnosis. Thus, this research is a good candidate for our Augmented Stage-Gate framework as explained in Table 6 .
Following the development and validation activities of our framework, the research team recruited more AI engineers to develop their algorithms and UX/UI to enable intuitive use of the technology. Here, the code and interface were continuously revised with frequent customer and domain expert validations to select the most relevant features and data for physicians. To protect intellectual property, the technique was kept a trade secret. After using the framework for only one year, the work reached a TRL level of 7 and an IRL level of 7 and gained acceptance for not-for-profit use in the hospital for preliminary screening of COVID-19 and other chest X-ray abnormalities. At present, the innovation is used at Chulalongkorn Hospital. We believe that, with its initial success, the technology can be implemented in other hospitals to help improve patients’ quality of life. The project team is now involved in the process of technology transfer and spin-off.
Progesterone test kit
The progesterone test kit for swine is a medical technology that began with a contracted research project between the Chulalongkorn University Faculty of Veterinary Medicine and a multinational science and technology company. The research team has in-depth knowledge and IP for developing a test kit that can easily test the progesterone level of animals from serum samples. In this research, the industry partner wanted to detect swine progesterone in the form of a strip test as it is a cheap and convenient method for mass adoption. The company promised to license the technology for sales and marketing purposes after the prototype showed promising results.
This research project has a potentially high impact on the local livestock industry. It is a new state-of-the-art technology and is an easy, effective, and low-cost solution that addresses many pain points faced by the swine farm industry. Moreover, we foresaw that the technology could be adapted to detect other hormones and health- or disease-related biomolecules in other livestock, increasing the market size and potential customers in the future. Finally, the initial readiness assessment revealed a TRL of 6 and an IRL of 1.
With our Augmented Stage-Gate framework, as explained in Table 7 , and business directions from the industry partner, the project established its market and business strategy and financial analysis. Moreover, the project team also brought in the qualified diagnostic development (QDD) center of Chulalongkorn University to support strip test design and small-scale manufacturing. Furthermore, with continuous iterations of customer validation, the researchers were able to fit the technology to the user’s needs and better understand the type of collaboration the industry was looking for. Thus, the team had business matching opportunities and discussed plausible deals with potential customers.
After more than 6 months of fine-tuning all aspects of the innovation, the project had a TRL of 7 and an IRL of 7 with a final prototype and licensed their technology to an international company that will use the kit for real-world applications. With the success of their first deal, the team has leverage to make future deals with other private companies.
The Augmented Stage-Gate Framework was used in these cases to validate the potential for exploitation, validity, market feasibility, and technological feasibility. All projects had low levels of investment readiness and different levels of technological readiness at the time of screening but were all considered deep technologies with high potential for use in their respective industries. The framework helped the teams carry out innovation framework activities, including continuous customer validation, market research, and business plans. All projects underwent a complete transformation after rigorously applying the framework’s validation activities, which included developing their MVP, carrying out multiple user validations, and adjusting their product idea and business plan with a network of mentors. In terms of commercial success, ReadMe successfully transformed into a tech startup named Eikonnex AI and secured business deals for commercial use in private companies. Chest X-ray AI Reporter for COVID-19 remained a not-for-profit technology used in King Chulalongkorn Memorial Hospital to detect COVID-19 and other chest X-ray abnormalities. Progesterone Test Kit licensed their technology to an international company. It is shown that the Augmented Stage-Gate Framework effectively transformed research projects into innovative, high-impact, commercialized products and companies.
Past literature has mentioned that traditional Stage-Gate models are not suitable for many of today’s businesses due to fast-changing user needs, uncertain market requirements (Cooper & Sommer, 2018 ), or industry complexity that requires highly iterative cycles and external collaboration (Sommer et al., 2015) and requires a more flexible and adaptive Stage-Gate model such as integrating agile process (Cocchi et al., 2021 ). Case studies leveraging these models were mostly conducted in corporates in developed economies. Directly adopting successful models from developed countries’ academic institutions require a well-established technology transfer office (Ravi & Janodia, 2022b ). Other studies that focus on the academic context in developing countries made suggestions in the policy level, recommending that the government encourage technology transfer by connecting industry and academia (Kirby & El Hadidi, 2019 ; Ravi & Janodia, 2022b ). None has given practical, step-by-step guideline model for technology initiated from academic institutions like ours.
Therefore, our work provides the first proved example of a new product development model that can be applied in similar contexts—commercializing university technology in an emerging economy. It solves the problems that persist in developing countries, Thailand especially, of lack of literature, lack of evaluation from key stakeholders, and a design-actuality gap (Abbasi et al., 2022 ; Heeks, 2002 ; Kalyanasundaram et al., 2021 ; Ravi & Janodia, 2022a ). However, we believe this model can also be applied to ecosystems with better infrastructure and maturity. Once research can be stably commercialized, building a strong infrastructure for technology transfer office like those in developed countries is a task recommended in the long run.
Lastly, even though the result from these case studies can confirm the validity of the proposed NPD model, it is not a hundred percent guarantee of successful exploitation. There might be other factors or circumstances that can affect the result such as market or technology that is highly regulated by local law, certain requirements of entrepreneur characteristics, appropriate timing for market or technology readiness, ecosystem or infrastructure that is required for research to commercial process, especially in emerging markets that might have no mature standard yet, etc. Those mentioned can be considered for future research.
Theoretical implications
This study develops a modified NPD framework that incorporates agile, lean startup, and design thinking to the Stage-Gate model for effective research to commercialization process generated from within the university in developing markets. Using the proposed Augmented Stage-Gate framework that has six stages (Innovation Ideation, Build Business Case, Development, Test and Validation, Launch, and Scale-up), we have presented three case studies from the Chulalongkorn University Technology Center. The approach is structural and based on critical thinking, which helps the technology incubator to accelerate the idea-to-launch process, decide the Go/No-Go of each innovation project stage to prioritize resource contribution, and reduce the risk of failure. Applying an open innovation concept can be beneficial during the NPD process of exchanging internal and external ideas. For example, introducing market demand to guide the direction of research, bringing in high-quality human resources from outside firms to accelerate the research and development, engaging users or customers to trial the product at an early stage, and co-creating the sandbox area to test and validate the innovation. Nevertheless, the project team must have an open mindset and absorptive capability to capture the value of this approach. In addition, university or business incubators should engage legal experts to supervise each activity to avoid conflicts of interest with external parties.
Managerial implications
The actual journey from idea to launch can be different from project to project. Engaging the Next-generation Stage-Gate’s Triple A System, (Adaptive, Agile and Accelerated) and Agile development to the NPD process is very important. Especially during early stages, each project team should focus on setting up a problem statement and then experimenting to learn and fail early, fast, and cheaply. Additionally, we summarized the key lessons learned during the first few batches of the UTC incubation program. First, the importance of the stage-gate committee role and organization as they are the gatekeepers in deciding the Go/No-Go of each project’s stage. The team needs to understand each project very well and be able to effectively track development progress and milestones. Project management software tools can be helpful in sharing ideas and tracking progress among teams, mentors, and committees whose roles must be considered carefully. Second, the incubator is usually responsible for providing NPD guidelines and mentoring for each stage; yet the incubator must also sometimes play a hands-on role solving issues by working closely with each team, especially for topics that they are unfamiliar with or that are at high risk such as regulatory and IP issues. Third, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic period, many activities were conducted online, such as business matching, mentoring, and customer meetings. Online activities lack many of the emotional and social aspects of work done in person. Therefore, the community manager had to work hard to build a supportive environment, maintain momentum and create positive team dynamics. Still, our experience suggests that it is possible to practice a hybrid onsite/online model while maintaining social distancing during the COVID-19 period. Fourth, legal considerations such as NDAs (Non-disclosure Agreements) and co-founder agreements should be considered as early as possible to avoid any conflicts that could cause project delay or failure. Finally, creating an environment where research, business partners, investors, and mentors can get to know each other is very important. These relationships can be developed informally and can lead to successful business deals. However, tech incubators should be able to identify, understand, and manage the expectations and relationships of each party before organizing networking events so that win–win situations can be realized.
Ideas for future research
Further research on the deep-tech NPD framework applied to specific technologies such as Med Tech that require extraordinary activities or have important limitations is needed. Case studies of successes and failures can be very useful. Challenges involving multiple stakeholders in different development journeys can lead to project failure due to miscommunication, lack of transparency, and a lack of legal knowledge. Thus, integrating legal perspectives and creating legal readiness levels in each NPD journey is essential. Finally, an analysis of co-founder characteristics, such as personality and working style, can suggest suitable ways of commercialization to maximize the probability of success.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
Artificial intelligence
Food and Drug Administration
Gross domestic product
Gross expenditure on R&D
Good manufacturing practice
- Intellectual property
Institutional review board
Investment readiness level
Minimal viable product
National Aeronautics and Space Administration
Non-disclosure agreement
- New product development
Object character recognition
Personal Data Protection Act
Politics, economics, social, technology, environment and legal
Qualified diagnostic development
Strength, weakness, opportunity, and threat
Technology acceptance model
Technology readiness level
Technology transfer office
User interface
Chulalongkorn University Technology Center
User experience
Abbasi, E., Amin, I., & Siddiqui, S. (2022). Towards developing innovation management framework (IMF) for ICT organizations at Pakistan. Journal of Innovation and Entrepreneurship . https://doi.org/10.1186/s13731-022-00231-6
Article Google Scholar
Aernoudt, R., San José, A., & Roure, J. (2007). Executive forum: Public support for the business angel market in Europe—a critical review. Venture Capital, 9 (1), 71–84. https://doi.org/10.1080/13691060600996723
Australia National Investment Council., & Marsden Jacob Associates. (1995). Financing growth : policy options to improve the flow of capital to Australia’s small and medium enterprises. 66. https://books.google.com/books/about/Financing_Growth.html?id=a_PkAAAACAAJ
Baldwin, C., & von Hippel, E. (2011). Modeling a Paradigm Shift: From producer innovation to user and open collaborative innovation. Organization Science, 22 (6), 1399–1417. https://doi.org/10.1287/ORSC.1100.0618
Barringer, B. R., & Ireland, R. D. (2012). Entrepreneurship: Successfully Launching New Ventures. In Zhurnal Eksperimental’noi i Teoreticheskoi Fiziki . Pearson Education.
Blank, S. (2014). How Investors Make Better Decisions: The Investment Readiness Level . https://steveblank.com/2014/07/01/how-investors-make-better-decisions-the-investment-readiness-level/
Brown, T. (2008). Design Thinking. Harvard Business Review , 84–92.
Cocchi, N., Dosi, C., & Vignoli, M. (2021). The Hybrid Model MatrixEnhancing Stage-Gate with Design Thinking, Lean Startup, and Agile. Research Technology Management . https://doi.org/10.1080/08956308.2021.1942645
Cooper, R. (2016). Agile-Stage-Gate Hybrids: The Next Stage for Product Development. Research-Technology Management .
Cooper, R. G., & Kleinschmidt, E. J. (2001). Stage-gate process for new product success. Innovation Management U , 3 .
Cooper, R. G., & Sommer, A. F. (2016). The Agile–Stage-Gate Hybrid Model: A promising new approach and a new research opportunity. Journal of Product Innovation Management . https://doi.org/10.1111/jpim.12314
Cooper, R. G., & Sommer, A. F. (2018). Agile–Stage-Gate for Manufacturers. Research-Technology Management, 61 (2), 17–26. https://doi.org/10.1080/08956308.2018.1421380
De la Tour, A., Soussan, P., Harlé, N., Chevalier, R., & Duportet, X. (2017). From tech to deep tech . Boston Consulting Group.
Google Scholar
European Commission. (2006). Investment readiness: Summary report of the workshop .
Fellnhofer, K. (2016). Literature review: Investment readiness level of small and medium sized companies. International Journal of Managerial and Financial Accounting, 7 (3–4), 268–284. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJMFA.2015.074904
Gorschek, T., Garre, P., Larsson, S., & Wohlin, C. (2006). A model for technology transfer in practice. IEEE Software, 23 (6), 88–95. https://doi.org/10.1109/MS.2006.147
Heeks, R. (2002). Information systems and developing countries: Failure, success, and local improvisations. Information Society . https://doi.org/10.1080/01972240290075039
Hicks, B., Larsson, A., Culley, S., & Larsson, T. (2009). A methodology for evaluating Technology Readiness during product development. DS 58-3: Proceedings of ICED 09, the 17th International Conference on Engineering Design , 3 .
Howard, L. W., Tang, T. L. P., & Jill Austin, M. (2015). Teaching critical thinking skills: Ability, motivation, intervention, and the Pygmalion effect. Journal of Business Ethics . https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-014-2084-0
Isaacson, W. (2011). Steve Jobs . Simon & Schuster.
Kalyanasundaram, G., Ramachandrula, S., & Mungila Hillemane, B. S. (2021). The life expectancy of tech start-ups in India: What attributes impact tech start-ups’ failures? International Journal of Entrepreneurial Behaviour and Research . https://doi.org/10.1108/IJEBR-01-2021-0025
Kirby, D. A., & El Hadidi, H. H. (2019). University technology transfer efficiency in a factor driven economy: The need for a coherent policy in Egypt. Journal of Technology Transfer . https://doi.org/10.1007/s10961-019-09737-w
Lee, Y., Kozar, K. A., & Larsen, K. R. T. (2003). The technology acceptance model: Past, present, and future. Communications of the Association for Information Systems . https://doi.org/10.17705/1cais.01250
Leydesdorff, L., & Etzkowitz, H. (1998). The Triple Helix as a model for innovation studies. Science and Public Policy, 25 (3), 195–203. https://doi.org/10.1093/SPP/25.3.195
Linden, A., & Fenn, J. (2003). Understanding Gartner’s Hype Cycles (Strategic Analysis Report No. R-20-1971) .
Mankins, J. C. (2009). Technology readiness assessments: A retrospective. Acta Astronautica . https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actaastro.2009.03.058
Mason, C., & Kwok, J. (2010). Investment readiness programmes and access to finance: A critical review of design issues. Local Economy . https://doi.org/10.1080/02690942.2010.504570
Office of National Higher Education Science Research and Innovation Policy Council. (2021). Results of survey on R&D expenditure and manpower in 2019 announced . https://www.nxpo.or.th/th/en/7981/
Osterwalder, A., Pigneur, Y., & Tucci, C. L. (2005). Clarifying business models: Origins, present, and future of the concept. Communications of the Association for Information Systems . https://doi.org/10.17705/1cais.01601
Ravi, R., & Janodia, M. D. (2022a). Factors Affecting Technology Transfer and Commercialization of University Research in India: A Cross-sectional Study. Journal of the Knowledge Economy . https://doi.org/10.1007/s13132-021-00747-4
Ravi, R., & Janodia, M. D. (2022b). University-Industry Technology Transfer in India: A Plausible Model Based on Success Stories from the USA, Japan, and Israel. Journal of the Knowledge Economy . https://doi.org/10.1007/s13132-022-00908-z
Ries, E. (2011). The lean startup (1st ed.). Crown Business.
Salvato, J. J., & Laplume, A. O. (2020). Agile Stage-Gate Management (ASGM) for physical products. R and D Management . https://doi.org/10.1111/radm.12426
Schaufeld, J. (2015). Commercializing innovation: Turning technology breakthroughs into products. In Commercializing Innovation: Turning Technology Breakthroughs into Products . https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4302-6353-1
Schumpeter, J. A. (1934). The theory of economic development. Harvard economic studies, Harvard Economic Studies , 34 .
Seferoglu, S. S., & Akbiyik, C. (2006). Teaching critical thinking [in Turkish]. Hacettepe University Journal of Education , 30 , 193–200. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/257655812_Seferoglu_S_S_Akbiyik_C_2006_Teaching_critical_thinking_in_Turkish_Hacettepe_University_Journal_of_Education_30_193-200
Souder, W. E., Nashar, A. S., & Padmanabhan, V. (1990). A guide to the best technology-transfer practices. The Journal of Technology Transfer . https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02377652
Thurman, B. A. (2009). Teaching of critical thinking skills in the English content area in South Dakota public high schools and colleges [University of South Dakota]. https://www.proquest.com/openview/8f7c02105eefefde326ae67612838bf2/1?pq-origsite=gscholar&cbl=18750
Tsai, C. H., Lin, C. F., & Liu, H. W. (2020). The diffusion of the sandbox approach to disruptive innovation and its limitations. Cornell International Law Journal . https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.3487175
Venkatesh, V., Morris, M. G., Davis, G. B., & Davis, F. D. (2003). User acceptance of information technology: Toward a unified view. MIS Quarterly Management Information Systems . https://doi.org/10.2307/30036540
von Hippel, E. (1976). The dominant role of users in the scientific instrument innovation process. Research Policy . https://doi.org/10.1016/0048-7333(76)90028-7
von Hippel, E. (1986). Lead users: A source of novel product concepts. Management Science, 32 (7), 791–805. https://doi.org/10.1287/mnsc.32.7.791
Walrave, B., Dolmans, S., Van Oorschot, K. E., Nuijten, A. L. P., Keil, M., & Van Hellemond, S. (2022). Dysfunctional agile-stage-gate hybrid development: keeping up appearances. International Journal of Innovation and Technology Management . https://doi.org/10.1142/S0219877022400041
Wuest, T., Liu, A., Lu, S. C. Y., & Thoben, K. D. (2014). Application of the stage gate model in production supporting quality management. Procedia CIRP . https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procir.2014.01.071
Yaldiz, N., & Bailey, M. (2019). The effect of critical thinking on making the right decisions in the new venture process. Procedia Computer Science . https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2019.09.053
Zasa, F. P., Patrucco, A., & Pellizzoni, E. (2020). Managing the hybrid organization: How can agile and traditional project management coexist? Research Technology Management . https://doi.org/10.1080/08956308.2021.1843331
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Eikonnex AI Co., Ltd., Chulalongkorn University Center for Artificial Intelligence in Medicine (CU-AIM), Chulalongkorn University Center of Excellence in Swine Reproduction, and Qualified Diagnostic Development (QDD) Center of Chulalongkorn University for assisting the required information and being used in the selected case studies. We would like to express our gratitude to the Second Century Fund (C2F) of Chulalongkorn University and the Program Management Unit for National Competitiveness Enhancement (PMU-C) of The Office of National Higher Education Science Research and Innovation Policy Council (NXPO) to support this research project. Lastly, we would like to thank the staffs of UTC, which now forms a research group called Ignite Innovation Lab.
Second Century Fund (C2F) of Chulalongkorn University and the Program Management Unit for National Competitiveness Enhancement (PMU-C) of The Office of National Higher Education Science Research and Innovation Policy Council (NXPO) to support this research project.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Graduate Affairs, Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, 10330, Thailand
Pravee Kruachottikul
University Technology Center (UTC), Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, 10330, Thailand
Faculty of Law, Chulalongkorn University, Debdvaravati Building 254 Soi Chula 42, Phayathai Road, Wangmai, Pathumwan, Bangkok, 10330, Thailand
Poomsiri Dumrongvute
Sasin School of Management, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, 10330, Thailand
Pinnaree Tea-makorn
Faculty of Accounting and Commerce, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, 10330, Thailand
Santhaya Kittikowit
Department of Psychiatry, Faculty of Medicine, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, 10330, Thailand
Arisara Amrapala
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
PK, PD, and SK conceived the concept of new product development and entrepreneurship for academic research and technology transfer. PT wrote the manuscript. AA collected data from each research team and the publication templating.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Poomsiri Dumrongvute .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Kruachottikul, P., Dumrongvute, P., Tea-makorn, P. et al. New product development process and case studies for deep-tech academic research to commercialization. J Innov Entrep 12 , 48 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13731-023-00311-1
Download citation
Received : 08 November 2022
Accepted : 16 June 2023
Published : 17 July 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s13731-023-00311-1
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Entrepreneurship
- Technopreneurship
- Research to commercialization
- Technology transfer

IMAGES
VIDEO