From ANOVA to regression: 10 key statistical analysis methods explained
Last updated
24 October 2024
Reviewed by
Miroslav Damyanov
Every action we take generates data. When you stream a video, browse a website, or even make a purchase, valuable data is created. However, without statistical analysis, the potential of this information remains untapped.
Understanding how different statistical analysis methods work can help you make the right choice. Each is applicable to a certain situation, data type, and goal.
- What is statistical analysis?
Statistical analysis is the process of collecting, organizing, and interpreting data. The goal is to identify trends and relationships. These insights help analysts forecast outcomes and make strategic business decisions.
This type of analysis can apply to multiple business functions and industries, including the following:
Finance : helps companies assess investment risks and performance
Marketing : enables marketers to identify customer behavior patterns, segment markets, and measure the effectiveness of advertising campaigns
Operations: helps streamline process optimization and reduce waste
Human resources : helps track employee performance trends or analyze turnover rates
Product development : helps with feature prioritization, evaluating A/B test results, and improving product iterations based on user data
Scientific research: supports hypothesis testing, experiment validation, and the identification of significant relations in data
Government: informs public policy decisions, such as understanding population demographics or analyzing inflation
With high-quality statistical analysis, businesses can base their decisions on data-driven insights rather than assumptions. This helps build more effective strategies and ultimately improves the bottom line.
- Importance of statistical analysis
Statistical analysis is an integral part of working with data. Implementing it at different stages of operations or research helps you gain insights that prevent costly errors.
Here are the key benefits of statistical analysis:

Informed decision-making
Statistical analysis allows businesses to base their decisions on solid data rather than assumptions.
By collecting and interpreting data, decision-makers can evaluate the potential outcomes of their strategies before they implement them. This approach reduces risks and increases the chances of success.
Understanding relationships and trends
In many complex environments, the key to insights is understanding relationships between different variables. Statistical methods such as regression or factor analysis help uncover these relationships.
Uncovering correlations through statistical methods can pave the way for breakthroughs in fields like medicine, but the true impact lies in identifying and validating cause-effect relationships. By distinguishing between simple associations and meaningful patterns, statistical analysis helps guide critical decisions, such as developing potentially life-saving treatments.
Predicting future outcomes
Statistical analysis, particularly predictive analysis and time series analysis, provides businesses with tools to forecast events based on historical data.
These forecasts help organizations prepare for future challenges (such as fluctuations in demand, market trends, or operational bottlenecks). Being able to predict outcomes allows for better resource allocation and risk mitigation.
Improving efficiency and reducing waste
Using statistical analysis can lead to improved efficiency in areas where waste occurs. In operations, this can result in streamlining processes.
For example, manufacturers can use causal analysis to identify the factors contributing to defective products and then implement targeted improvements to eliminate the causes.
Enhancing accuracy in research
In scientific research, statistical methods ensure accurate results by validating hypotheses and analyzing experimental data.
Methods such as regression analysis and ANOVA (analysis of variance) allow researchers to draw conclusions from experiments by examining relationships between variables and identifying key factors that influence outcomes.
Without statistical analysis, research findings may not be reliable. This could result in teams drawing incorrect conclusions and forming strategies that cost more than they’re worth.
Validating business assumptions
When businesses make assumptions about customer preferences, market conditions, or operational outcomes, statistical analysis can validate them.
For example, hypothesis testing can provide a framework to either confirm or reject an assumption. With these results at hand, businesses reduce the likelihood of pursuing incorrect strategies and improve their overall performance.
- Types of statistical analysis
The two main types of statistical analysis are descriptive and inferential. However, there are also other types. Here’s a short breakdown:
Descriptive analysis
Descriptive analysis focuses on summarizing and presenting data in a clear and understandable way. You can do this with simple tools like graphs and charts.
This type of statistical analysis helps break down large datasets into smaller, digestible pieces. This is usually done by calculating averages, frequencies, and ranges. The goal is to present the data in an orderly fashion and answer the question, “What happened?”
Businesses can use descriptive analysis to evaluate customer demographics or sales trends. A visual breakdown of complex data is often useful enough for people to come to useful conclusions.
Diagnostic statistics
This analysis is used to determine the cause of a particular outcome or behavior by examining relationships between variables. It answers the question, “Why did this happen?”
This approach often involves identifying anomalies or trends in data to understand underlying issues.
Inferential analysis
Inferential analysis involves drawing conclusions about a larger population based on a sample of data. It helps predict trends and test hypotheses by accounting for uncertainty and potential errors in the data.
For example, a marketing team can arrive at a conclusion about their potential audience’s demographics by analyzing their existing customer base. Another example is vaccine trials, which allow researchers to come to conclusions about side effects based on how the trial group reacts.
Predictive analysis
Predictive analysis uses historical data to forecast future outcomes. It answers the question, “What might happen in the future?”
For example, a business owner can predict future customer behavior by analyzing their past interactions with the company. Meanwhile, marketers can anticipate which products are likely to succeed based on past sales data.
This type of analysis requires the implementation of complex techniques to ensure the expected results. These results are still educated guesses—not error-free conclusions.
Prescriptive analysis
Prescriptive analysis goes beyond predicting outcomes. It suggests actionable steps to achieve desired results.
This type of statistical analysis combines data, algorithms, and business rules to recommend actual strategies. It often uses optimization techniques to suggest the best course of action in a given scenario, answering the question, “What should we do next?”
For example, in supply chain management, prescriptive analysis helps optimize inventory levels by providing specific recommendations based on forecasts. A bank can use this analysis to predict loan defaults based on economic trends and adjust lending policies accordingly.
Exploratory data analysis
Exploratory data analysis (EDA) allows you to investigate datasets to discover patterns or anomalies without predefined hypotheses. This approach can summarize a dataset’s main characteristics, often using visual methods.
EDA is particularly useful for uncovering new insights that weren’t anticipated during initial data collection.
Causal analysis
Causal analysis seeks to identify cause-and-effect relationships between variables. It helps determine why certain events happen, often employing techniques such as experiments or quasi-experimental designs to establish causality.
Understanding the “why” of specific events can help design accurate proactive and reactive strategies.
For example, in marketing, causal analysis can be applied to understand the impact of a new advertising campaign on sales.
Bayesian statistics
This approach incorporates prior knowledge or beliefs into the statistical analysis. It involves updating the probability of a hypothesis as more evidence becomes available.
- Statistical analysis methods
Depending on your industry, needs, and budget, you can implement different statistical analysis methods. Here are some of the most common techniques:
A t-test helps determine if there’s a significant difference between the means of two groups. It works well when you want to compare the average performance of two groups under different conditions.
There are different types of t-tests, including independent or dependent.
T-tests are often used in research experiments and quality control processes. For example, they work well in drug testing when one group receives a real drug and another receives a placebo. If the group that received a real drug shows significant improvements, a t-test helps determine if the improvement is real or chance-related.
2. Chi-square tests
Chi-square tests examine the relationship between categorical variables. They compare observed results with expected results. The goal is to understand if the difference between the two is due to chance or the relationship between the variables.
For instance, a company might use a chi-square test to analyze whether customer preferences for a product differ by region.
It’s particularly useful in market research, where businesses analyze responses to surveys.
ANOVA, which stands for analysis of variance, compares the means of three or more groups to determine if there are statistically significant differences among them.
Unlike t-tests, which are limited to two groups, ANOVA is ideal when comparing multiple groups at once.
One-way ANOVA: analysis with one independent variable and one dependent variable
Two-way ANOVA: analysis with two independent variables
Multivariate ANOVA (MANOVA): analysis with more than two independent variables
Businesses often use ANOVA to compare product performance across different markets and evaluate customer satisfaction across various demographics. The method is also common in experimental research, where multiple groups are exposed to different conditions.
4. Regression analysis
Regression analysis examines the relationship between one dependent variable and one or more independent variables. It helps businesses and researchers predict outcomes and understand which factors influence results the most.
This method determines a best-fit line and allows the researcher to observe how the data is distributed around this line.
It helps economists with asset valuations and predictions. It can also help marketers determine how variables like advertising affect sales.
A company might use regression analysis to forecast future sales based on marketing spend, product price, and customer demographics.
6. Time series analysis
Time series analysis evaluates data points collected over time to identify trends. An analyst records data points at equal intervals over a certain period instead of doing it randomly.
This method can help businesses and researchers forecast future outcomes based on historical data. For example, retailers might use time series analysis to plan inventory around holiday shopping trends, while financial institutions rely on it to track stock market trends. An energy company can use it to evaluate consumption trends and streamline the production schedule.
7. Survival analysis
Survival analysis focuses on time-to-event data, such as the time it takes for a machine to break down or for a customer to churn. It looks at a variable with a start time and end time. The time between them is the focus of the analysis.
This method is highly useful in medical research—for example, when studying the time between the beginning of a patient’s cancer remission and relapse. It can help doctors understand which treatments have desired or unexpected effects.
This analysis also has important applications in business. For example, companies use survival analysis to predict customer retention, product lifespan, or time until product failure.
8. Factor analysis
Factor analysis (FA) reduces large sets of variables into fewer components. It’s useful when dealing with complex datasets because it helps identify underlying structures and simplify data interpretation. This analysis is great for extracting maximum common variance from all necessary variables and turning them into a single score.
For example, in market research, businesses use factor analysis to group customer responses into broad categories. This helps reveal hidden patterns in consumer behavior.
It’s also helpful in product development, where it can use survey data to identify which product features are most important to customers.
9. Cluster analysis
Cluster analysis groups objects or individuals based on their similarities. This technique works great for customer segmentation, where businesses group customers based on common factors (such as purchasing behavior, demographics, and location).
Distinct clusters help companies tailor marketing strategies and develop personalized services. In education, this analysis can help identify groups of students who require additional assistance based on their achievement data. In medicine, it can help identify patients with similar symptoms to create targeted treatment plans.
10. Principal component analysis
Principal component analysis (PCA) is a dimensionality-reduction technique that simplifies large datasets by converting them into fewer components. It helps remove similar data from the line of comparison without affecting the data’s quality.
PCA is widely used in fields like finance, marketing, and genetics because it helps handle large datasets with many variables. For example, marketers can use PCA to identify which factors most influence customer buying decisions.
- How to choose the right statistical analysis method
Since numerous statistical analysis methods exist, choosing the right one for your needs may be complicated. While all of them can be applicable to the same situation, understanding where to start can save time and money.
Define your objective
Before choosing any statistical method, clearly define the objective of your analysis. What do you want to find out? Are you looking to compare groups, predict outcomes, or identify relationships between variables?
For example, if your goal is to compare averages between two groups, you can use a t-test. If you want to understand the effect of multiple factors on a single outcome, regression analysis could be the right choice for you.
Identify your data type
Data can be categorical (like yes/no or product types) or numerical (like sales figures or temperature readings).
For example, if you’re analyzing the relationship between two categorical variables, you may need a chi-square test. If you’re working with numerical data and need to predict future outcomes, you could use a time series analysis.
Evaluate the number of variables
The number of variables involved in your analysis influences the method you should choose. If you’re working with one dependent variable and one or more independent variables, regression analysis or ANOVA may be appropriate.
If you’re handling multiple variables, factor analysis or PCA can help simplify your dataset.
Determine sample size and data availability
Consider the assumptions of each method.
Each statistical method has its own set of assumptions, such as the distribution of the data or the relationship between variables.
For example, ANOVA assumes that the groups being compared have similar variances, while regression assumes a linear relationship between independent and dependent variables.
Understand if observations are paired or unpaired
When choosing a statistical test, you need to figure out if the data is paired or unpaired.
Paired data : the same subjects are measured more than once, like before and after a treatment or when using different methods.
Unpaired data: each group has different subjects.
For example, if you’re comparing the average scores of two groups, use a paired t-test for paired data and an independent t-test for unpaired data.
- Making the most of key statistical analysis methods
Each statistical analysis method is designed to simplify the process of gaining insights from a specific dataset. Understanding which data you need to analyze and which results you want to see can help you choose the right method.
With a comprehensive approach to analytics, you can maximize the benefits of insights and streamline decision-making. This isn’t just applicable in research and science. Businesses across multiple industries can reap significant benefits from well-structured statistical analysis.
Should you be using a customer insights hub?
Do you want to discover previous research faster?
Do you share your research findings with others?
Do you analyze research data?
Start for free today, add your research, and get to key insights faster
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 24 October 2024
Last updated: 11 January 2024
Last updated: 17 January 2024
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 30 April 2024
Last updated: 4 July 2024
Last updated: 12 October 2023
Last updated: 5 March 2024
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 31 January 2024
Last updated: 23 January 2024
Last updated: 13 May 2024
Last updated: 20 December 2023
Latest articles
Related topics, decide what to build next, log in or sign up.
Get started for free
Coming November 13: Insight7 Launches as a Conversational Intelligence Platform. Learn more
Extract insights from interviews. at scale., analytical research methods explained with examples.
Home » Analytical Research Methods Explained with Examples
Analytical Research Techniques are fundamental tools that help researchers make sense of complex data. Imagine trying to decode insights from countless customer interactions without a systematic approach; the task would become overwhelming and inefficient. These techniques offer structured methods to analyze information, derive meaningful interpretations, and ultimately inform better decision-making in various fields.
Understanding these techniques is essential for effectively interpreting data and recognizing patterns. By employing analytical research methods, organizations can transform raw data into actionable insights. This not only fosters informed strategies but also enhances overall organizational performance. As we explore examples and applications, you'll gain insight into how these techniques can be effectively utilized in your research endeavors.
Types of Analytical Research Techniques
Analytical research techniques are essential tools for systematically gathering and interpreting data. Understanding these techniques allows researchers to derive meaningful insights and make informed decisions. Various methods exist, each serving specific purposes. For instance, qualitative techniques focus on understanding deeper motivations and attitudes, while quantitative techniques emphasize numerical data and statistical analysis.
The primary types of analytical research techniques include case studies, surveys, content analysis , and experimental research. Case studies provide in-depth investigations into specific instances, revealing complex dynamics. Surveys are effective for collecting broad data from target populations, enabling the identification of trends. Content analysis systematically evaluates existing materials, such as text or media, to uncover patterns. Experimental research, on the other hand, tests hypotheses through structured setups, providing causal insights.
By mastering these analytical research techniques, researchers can extract valuable insights that inform choices and strategies effectively. Understanding when to apply each technique is vital for optimizing research outcomes.
Quantitative Analytical Research Techniques
Quantitative analytical research techniques involve the systematic collection and analysis of numerical data to uncover patterns and draw conclusions. These methods allow researchers to quantify behaviors, opinions, and phenomena, enabling effective data-driven decision-making. Surveys and experiments are common approaches in this realm, as they allow for the collection of vast amounts of data in a structured manner.
Key techniques include descriptive statistics, which summarize data characteristics, and inferential statistics, which help make predictions or generalizations about a population based on sample data. Additionally, regression analysis can identify relationships between variables, while hypothesis testing provides a framework for validating theories. Collectively, these quantitative techniques form a robust foundation for analytical research methods, yielding actionable insights for various fields, from marketing to healthcare.
Qualitative Analytical Research Techniques
Qualitative analytical research techniques focus on understanding human behavior, emotions, and experiences. These methods gather rich, detailed data through various approaches, such as interviews, focus groups, and observations. Researchers often analyze this data to uncover patterns, themes, and insights that quantitative methods may overlook. By delving into participants' thoughts and feelings, qualitative methods offer a deeper comprehension of underlying motivations.
Several key techniques are commonly used in qualitative research . First, in-depth interviews provide personalized insights, allowing participants to share their stories and experiences openly. Second, focus groups facilitate dynamic discussions among participants, generating diverse perspectives on a topic. Finally, observational research enables researchers to witness behavior in natural settings, providing context to the data collected. Each technique plays a crucial role in shaping an understanding of the subject matter, ultimately enhancing the analytical research techniques available for interpretation and application.
Steps in Conducting Analytical Research
Conducting analytical research effectively involves a structured approach to gather and analyze data. First, define your research question. This step focuses on clarifying what you aim to uncover through research. An explicit question guides all subsequent steps by maintaining focus. Next, collect relevant data through various methods. This may include surveys, interviews, or secondary data sources, depending on the analytical research techniques you choose to utilize.
Once data is gathered, the next step is analysis. Employ statistical tools or qualitative methods to derive meaningful insights from the collected data. After analyzing, it's crucial to interpret the results. Consider how your findings relate to the initial research question. Finally, communicate your results plainly. Presenting your findings in a clear and actionable format ensures stakeholders can understand and apply the insights. Following these steps will enhance the effectiveness of your analytical research, leading to better-informed decisions.
Defining the Research Problem and Objectives
Defining a clear research problem is essential for any analytical study. It serves as the foundation upon which all elements of research are built. Initially, identifying the core issue helps researchers focus their inquiries and sets the direction for their analytical research techniques. Once the problem is articulated, specific objectives can be formulated that guide the research process and define the expected outcomes.
The objectives should align with the research problem and be measurable, allowing for a systematic approach to data collection and analysis. For instance, researchers might aim to assess user satisfaction, identify market trends, or understand consumer behavior. Establishing well-defined objectives not only clarifies the purpose of the research but also enhances the reliability of the findings. By understanding the problem and setting clear goals, researchers can utilize analytical methods more effectively, ensuring that their results generate meaningful insights.
Data Collection and Analysis Methods
Data collection and analysis methods are fundamental components of analytical research techniques. The process begins with identifying the research objectives, which guide what data needs to be collected. Researchers often employ qualitative methods like interviews or focus groups and quantitative methods such as surveys to gather valuable insights. Each method serves a different purpose, allowing researchers to explore in-depth nuances or identify broader trends.
Analysis follows data collection and typically includes coding qualitative data or employing statistical methods for quantitative data. Researchers can use various tools and techniques to extract meaningful patterns, trends, and anomalies. For instance, employing a matrix to pull specific insights from interviews can help pinpoint common pain points, as evidenced in the data trends discovered during the conversation analysis. Each step in this process is critical for achieving valid and actionable insights that inform decision-making.
Conclusion on Analytical Research Techniques
In conclusion, Analytical Research Techniques are essential for extracting valuable insights from various data sources. These techniques enable researchers to identify patterns and trends that inform decision-making processes across multiple disciplines. By employing these methods, organizations can create reports that convey pertinent findings to stakeholders effectively.
Furthermore, the application of these techniques promotes a deeper understanding of customer behavior and market dynamics. Analyzing data collaboratively improves content accuracy and enhances strategic planning. Ultimately, mastering analytical research techniques equips teams with the tools needed to navigate complex information and make informed decisions that drive success.
Turn conversations into actionable insights
On this Page
Top 12 Market Research Tools and Techniques for 2024
You may also like, deductive approach in qualitative research: a complete overview.
How to Apply Inductive Reasoning in Qualitative Research
Deductive vs inductive analysis: which is right for you.
Unlock Insights from Interviews 10x faster
- See a Live demo
- Start Analyzing Free
Odun Odubanjo, CEO of Insight7, announces new features that enables analysis of conversations across text, video, and audios formats, providing actionable insights for innovation.
Are you an agency specialized in UX, digital marketing, or growth? Join our Partner Program
Learn / Guides / Data analysis for marketers
Back to guides
How to use data analysis methods and techniques to create customer-centric marketing campaigns
Putting on your creativity cap to strategize a new marketing campaign is exciting—but what makes your hard work really feel worth it is when it resonates with your audience and performs well.
While some marketers might be lucky enough to find a winning formula on the first try, you need to use data analysis methods to guide your campaign strategy.
Last updated
Reading time.

Putting customers at the center of your decision-making through data analysis helps you create relevant campaigns that connect with your audience and hit KPI goals. This guide reviews five data analysis methods marketers need to make informed decisions .
The types of data analysis a marketer uses depend on what you want to learn and which data type you have. Marketers use quantitative data—like website traffic totals—and qualitative data—like customer interview transcripts—in data analysis. There are also times when you should combine quant and qual data.
Five data analysis methods marketers use include
Descriptive analytics to summarize quantitative data
Inferential analysis to create and test customer hypotheses
Regression analysis to compare the relationship between variables
Content analysis to quantify text-based insights
Predictive analysis to anticipate trends and learn about customer behavior
5 popular data analysis methods for marketers
Marketers use data analytics to review performance, prioritize campaign updates, and understand customers. As you’ll see in the data analysis techniques below, the method you choose depends on what you learn and the data you collect.
The types of data marketers most commonly use are:
Now that you know the different types of information marketers collect, use the methods below in your data analysis process to get the best results, prioritize product updates, and inform your business decisions.
1. Descriptive analysis
When you want to measure what happened in the past, use descriptive analytics . This data analysis method summarizes quantitative data results, like how many likes a social media post got or your newsletter sign-up rate . Popular descriptive analysis methods include average, median, mode, and simply comparing survey response rates of a multiple-choice question.
How marketers use descriptive analysis:
Benchmark organic traffic each month to understand the impact of content marketing
Compare campaign engagement and conversion results to quarterly goals
Use surveys to measure how prevalent a goal or problem is in your customer base
Benefits and challenges of descriptive analytics:
Many people have some experience with straightforward analysis methods like calculating an average or ranking percentage response, which makes this method quick to implement
Data collection becomes easy through existing web analytics or short surveys
Quantitative data is objective, which means there’s no room for differing interpretations
There are limitations to descriptive analytics:
The process measures an outcome but doesn’t describe why customers chose the response or behaved a certain way
You may lack context about a problem if you only look at one particular data point
You need enough data points to have statistical significance if you want to apply decisions to your entire audience confidently
❓ Pro tip: use premade survey questions to easily collect customer feedback.
Asking your audience questions with multiple-choice surveys is a great way to collect quantitative data—assuming you ask the right questions. Your research questions need to be specific enough to get relevant data but not so detailed that you accidentally lead customers to the answer you want to hear.
Use premade survey questions and leverage Hotjar AI to generate survey questions based on your goals to collect the right data.
Here are some survey questions marketers can use:
Where did you first hear about us?
Where else did you hear about us?
What do you use our product/service for?
Which industry does your company belong to?
How relevant is the content you found on our website?
What was your first impression of our product?
Browse 30+ ready-to-use survey templates .
Traffic attribution surveys reveal every channel customers hear about you through, instead of only seeing the referral source of your website analytics
2. Inferential analysis
Sometimes, you have a hunch but want to back up your ideas with data. Inferential analysis lets you hypothesize about your customers’ preferences and motivations by using a mix of multiple quantitative or qualitative data points . You create an inference by stacking insights observed at the same time.
For example, an Engagement Zone heatmap combines interaction data on a website page—like clicks and scrolling—to highlight the elements visitors engage with the most. If your heatmap reveals that a particular image or headline draws visitors in, you can use it in a future campaign to test if it drives engagement across other channels.

How marketers use inferential analysis:
Ask multiple questions in a customer interview and combine common themes to create a product narrative
Research customer preferences or priorities between item categories with surveys
Compare on-page customer feedback from different referral sources to learn about your audience coming from each traffic source
Benefits and challenges of inferential analysis:
Comparing customer responses across multiple questions or touchpoints gives you a fuller understanding of user behavior
Weighing customer responses based on specific conditions—like customer segments with the highest average order value—helps you prioritize which feedback and suggestions to implement
Creating hypotheses from actual customer interactions provides campaign ideas you may not have thought about before
There are drawbacks to inferential analysis:
Your hypothesis-building can be subjective, so look for multiple customer responses or data points that validate an assumption instead of relying on a single insight
You need to collect and manage multiple data sets, which can be time-consuming
An inference is an informed guess, so you still need to test your hypothesis with A/B testing
📹 Pro tip: follow up your A/B testing analysis with recordings.
Let’s say your A/B testing reveals that one campaign landing page far outperforms the other. Do you know why? Dig into why particular copy or design was so compelling using recordings —video playbacks of how visitors behaved on your site. Then, you can apply what you learned to future campaigns.
Hotjar Recordings lets you see what customers see

3. Regression analysis
Regression analysis is a powerful statistical analysis method that measures the relationship between data points, like comparing whether increased marketing spending is related to more revenue . The basic process of regression analysis involves plotting your two variables on a chart and then seeing how far those points stray from the regression line. There's a correlation if the data sits close to the line.
Since regression analysis includes multiple variables and some equations, it’s common to use a spreadsheet add-in or a tool like Tableau or The R Project .
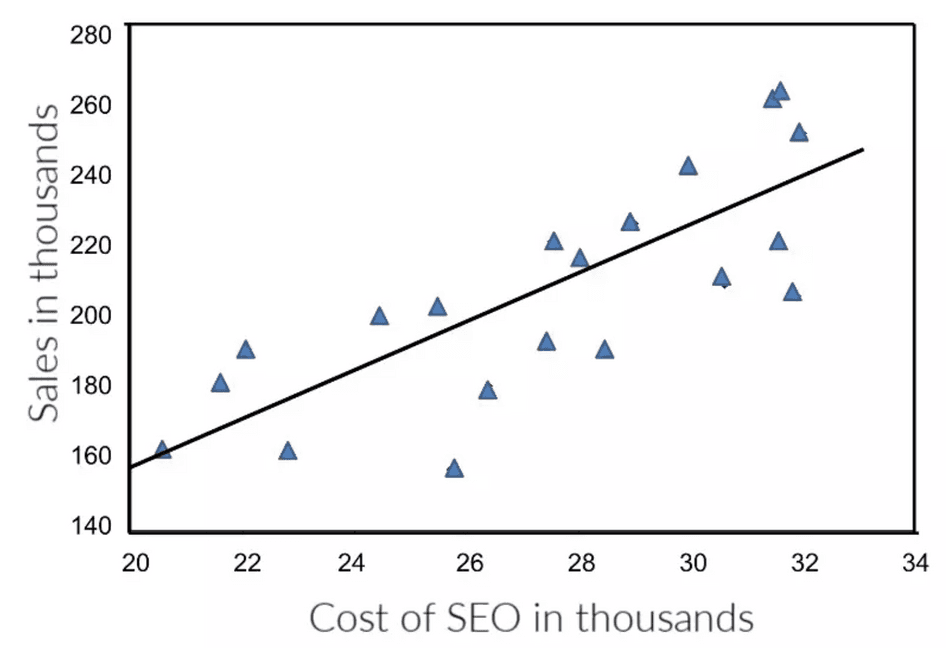
Linear regression analysis can help answer the question, ‘Does more SEO investment lead to more sales?’ Image via PracticalEcommerce
How marketers use regression analysis:
Discover which blogs shared on what social media channels resulted in the highest website traffic to update your social sharing strategy
Compare email engagement metrics to website sales to measure the potential impact of the channel
Learn which customer segment is happiest with your company and product through a survey to refine your targeting and messaging
Regression analysis benefits and challenges:
Measure how variables relate to one another to prove marketing impact
Evaluate what to do more of—for example, if you find a correlation between an investment or campaign and increased sales
Analyze large data sets using regression analysis tools and spreadsheets
There are downsides to regression analysis:
The process is a bit more complicated than simply checking your Google Analytics dashboard, so you’ll need a specialized tool or spreadsheet
Correlation isn’t causation, and you might not account for all potential variables that affect an outcome
A few outliers can easily skew results
4. Content analysis
Content analysis turns qualitative insights into quantifiable results to help you make conclusions about customer perspectives, perceptions, and motivations . For example, you can count how many open-ended survey question responses mentioned particular themes to rank their importance to your audience.
Pull content analysis data from open-ended surveys, recordings of real website interactions, interviews, reviews, testimonials, social comments, and brand mentions. You could even run a content analysis on competitor reviews to find what their customers dislike to position your brand against it.
How marketers use content analysis:
Compare repeating themes across customer interviews
Map the most common customer journey steps by watching recordings to learn how customers navigate your brand’s website before purchasing
Review testimonials to discover what stands out to customers to use in future campaigns
Benefits and challenges of content analysis:
You can pull from a wide range of data sources depending on what you already have access to and the time you have to research
Quantifying responses turns subjective responses into objective numbers
It’s easier to share customer response summaries with stakeholders than sharing multiple clips or large qualitative data sets
There are obstacles with content analysis:
Manual text analysis is slow, but there are tools like Lexalytics that help
There’s still some subjectivity involved since you decide how to group responses
Reducing long responses to simple ideas can leave valuable insights behind
🗂️ Pro tip: keep your insights organized with Hotjar.
Content analysis is time consuming (but impactful!) at the best of times, but you’ll quickly get confused without organization. Hotjar Highlights lets you save and share specific insights, like a high click rate on an image (from a heatmap) or a recording snippet from your newsletter page, to stay organized and collaborate with your team.
5. Predictive analysis
Predictive analytics anticipates future trends or analyzes customer behaviors with big data sets, predictive models, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning tools. In other words, it’s a bit advanced. However, marketers can unlock powerful insights, like when L’Oréal and Synthesio used AI to forecast beauty trends.
If you don’t want to work with a specialized agency or consultant, there are predictive analytics tools that help marketers without advanced data analysis skills pull insights from customer data.
How marketers use predictive analytics:
Uncover new customer segments based on small differentiating behaviors and psychographics
Find related products to recommend to customers based on past purchases for personalized experiences
Anticipate trends in your industry to create innovative campaigns
Benefits and challenges of predictive analytics:
You can review vast amounts of quantitative data faster than previously possible with technology like machine learning and AI
Nuanced customer insights and trend data give you a competitive advantage
Easily analyze customer behavior at scale, as opposed to manually reviewing a few interview transcripts
There are drawbacks to predictive analytics:
The output is only as good as the raw data input, so incomplete or inaccurate data within a large dataset can skew results
Collecting the volume and variety of data you need for predictive analytics can be time consuming
You’ll likely need to use a specialized tool or work with a data analyst
🚦 Pro tip: monitor customer behavior with Hotjar Trends.
Hotjar Trends lets you visualize your customer behavior metrics so you can spot trends easily.
For example, you can compare how customer segments interact with your pricing page to spot frustration or confusion that signals your marketing funnel needs an extra step. While trends don’t predict the future, continuous tracking gives you an early signal of wins or challenges.
Hotjar makes data visualization easy, with pie charts, line graphs, or bar graphs that give you a high-level understanding of user behavior
Combine data analysis with empathy to create effective campaigns
When you’re knee-deep in spreadsheets and up to your eyes in statistics, it’s easy to view customers as just numbers on the screen. Leading with empathy and curiosity will give you a new perspective on data analysis methods.
If you have a question, ask your customers in a survey. If you want to understand their motivations, chat with them in an interview. If you want to see how they move through your website’s marketing funnel, watch a recording of their behavior.
Your best strategies and campaigns come from a blend of data and humanity. Simply begin with a question or hypothesis and start investigating and analyzing.
Use customer-centric insights to drive your marketing campaigns
Hotjar’s tools give you a direct line to customers to learn about their goals, challenges, and preferences, so you create successful campaigns.
FAQs about data analysis methods for marketers
Why should marketers use data analytics.
Marketers use data analysis to review performance and understand customers, so they can create relevant campaigns.
What types of data do marketers use?
Marketers use numbers-based quantitative data, text-based qualitative data, or a combination of both for data analysis.
Which data analysis methods can marketers use?
Five data analysis methods marketers use are
Descriptive analytics
Inferential analysis
Regression analysis
Content analysis
Predictive analysis
Data analysis process
Previous chapter
Data analysis tools
Next chapter
- Technical Support
- Technical Papers
- Knowledge Base
- Question Library
Call our friendly, no-pressure support team.
Data Analytics in Marketing Research: Definition, Types, Process, and More
Data Analytics is a critical function affecting all aspects of the business. This article covers broad data analytic topics for those new to the area of data analytics. At Sawtooth Software, we focus on marketing research and primary data collection through survey research, so this article specifically calls out the use of data analytics in marketing sciences.
Before diving deep into the breadth of data analytics, let’s summarize key takeaways you will gain from this guide:
With that introduction, let’s dive deeper into the field of Data Analytics .
Table of Contents
What Is Data Analytics?
At its core, Data Analytics involves the computational analysis of data or statistics. Data can involve numeric values, text, graphics, video or audio files. The value of data analytics lies in its ability to transform vast amounts of raw, often unstructured data into actionable insights. These insights can then guide decision-making, optimize operations, and unveil opportunities for innovation.
Consider a retail business that leverages data analytics to understand customer purchasing patterns, preferences, and behaviors. By analyzing sales data, customer feedback, social media trends, along with primary survey data, the business can tailor its product offerings, improve customer service, predict future trends, and optimize products and pricing for new or existing products. This practical application underscores the transformative power of data analytics in driving business strategy and growth.
Data Analytics vs. Data Science
While often used interchangeably, Data Analytics and Data Science involve nuanced differences, with complementary roles within an organization. Data Analytics focuses on processing and performing statistical analysis on existing datasets. In contrast, Data Science typically involves heavier programming, developing algorithms, and model-building to derive additional insights to solve complex problems and predict future outcomes. Data scientists often leverage machine learning and AI (Artificial Intelligence) in building algorithms, models, and applications.
The impact of both fields on Decision-Making is important. Data analytics provides a more immediate, focused insight primarily aimed at enhancing operational efficiency and answering specific questions. Data Science, on the other hand, dives deeper into predictive analysis, machine learning, and AI to forecast future trends and behaviors.
Marketing Research Consulting
Need help with your research study? Contact our expert consulting team for help with survey design, fielding, and interpreting survey results.
Contact Our Consulting Team
Types of Data Analysis
Data Analysis can be broadly categorized into four main types, each serving a unique purpose in the data analytics landscape. Understanding these types helps you to apply the right analytical approach to your data to derive meaningful conclusions and strategies.
Descriptive Analytics
This type of analytics focuses on the “what” and is the most basic and commonly used. For market research surveys, descriptive analytics summarizes responses to demographic, psychographic, attitudinal, brand usage data, and the like. For historical data, it aims to provide a clear picture of what has happened in the past by summarizing such things as sales data, operations data, advertising data, and website click traffic. Descriptive analytics answers the "What happened?" question by analyzing key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics. For example, a business might use descriptive analytics to understand its sales trends, customer engagement levels, or production efficiencies over the past year.
Diagnostic Analytics
Moving beyond the “what” to understand the “why,” diagnostic analytics involves a deeper dive into data to examine patterns of association or correlation, with the hope to uncover root causes of attitudes, preference, events or trends. It employs techniques such as correlation analysis, t-tests, chi-square tests, key drivers analysis, and tree-based analysis (such as CART or random forests). For customer satisfaction research key drivers analysis tries to explain how overall customer satisfaction or loyalty can be improved by improving the features or elements of the product or service delivery. An organization might also leverage diagnostic analytics to identify why certain groups of respondents are more likely to be price sensitive or why customer churn increased in a specific period.
Predictive Analytics
This forward-looking analysis leverages data and models that can predict future outcomes. Conjoint analysis is a widely used predictive analytics approach for studying how changes to product features and prices affect demand. MaxDiff (best-worst scaling) is often used to assess which product claims will likely increase new product trial, or which side effects would most discourage patients from undergoing a cancer treatment therapy. Machine learning algorithms such as random forests can score a database to predict which customers are most likely to be receptive to an offer. As another example, a financial institution might use predictive analytics to assess the risk of loan default based on a customer's credit history, transaction data, and market conditions.
Prescriptive Analytics
An advanced form of analytics, prescriptive analytics, goes a step further by recommending actions you can take to affect desired outcomes. It not only predicts what will happen but also suggests various courses of action and the potential implications of each. This type of analytics is particularly valuable in complex decision-making environments. For example, a conjoint analysis market simulator leveraging optimization search routines can determine the right mix of product features and price to reach a particularly valuable market segment .
Each of these types of data analysis plays a critical role in an organization's data-driven decision-making process, enabling businesses to understand their past performance, diagnose issues, create successful products and services, predict future trends, and make informed choices that align with their strategic objectives.
Data Analytics Real-World Example
Consider the case of a data analyst working for an e-commerce platform. By analyzing customer purchase history, the analyst identifies a trend of increased sales in eco-friendly products ( descriptive analytics , the “what”). A survey is designed and conducted to dig deeper into which customers are preferring eco-friendly products, why they prefer them, and for which usage occasions ( diagnostic analytics , the “why”). Within another market research survey, a conjoint analysis or MaxDiff study is included for determining the right product claims, product features, and pricing, targeted to which market segments to develop new products for sales growth ( predictive and prescriptive analytics ).
The role of a data analyst is dynamic and impactful, bridging the gap between data and strategic decision-making. It's a role that requires not only technical skills but also curiosity, creativity, and a keen understanding of the business landscape.
The Data Analysis Process
Breaking down a data analytics process into systematic steps can demystify the journey, making it more approachable and manageable. The Data Analysis Process is a structured approach that guides data analysts from the initial phase of understanding the business problem to the final stage of delivering actionable insights.
Step 1: Defining the Question
The first and perhaps most critical step in the data analysis process is defining the question . This involves understanding the business objectives, the decisions that need to be supported by the data, and the specific questions that the analysis aims to answer. A well-defined question not only provides direction for the analysis but also ensures that the outcomes are relevant and actionable.
Step 2: Collecting Clean Data
Data collection is the next step, where data analysts gather the necessary data from various sources. This could include internal databases, secondary sources of data, customer surveys, and more. Ensuring the cleanliness of the data is paramount at this stage; hence, data cleaning and preprocessing become essential tasks. This involves removing inaccuracies, inconsistencies, handling missing values, and trimming outliers to ensure the data is reliable and accurate for analysis. For market research surveys, this also involves identifying unreliable respondents, fraudulent respondents, and records completed by survey bots.
Step 3: Data Analysis and Interpretation
With clean data in hand, analysts proceed to the heart of the process: data analysis and interpretation . This involves applying statistical methods and analytical models to the data to identify patterns, trends, and correlations. The choice of techniques varies depending on the data and the questions at hand, ranging from simple descriptive statistics to complex predictive models.
Step 4: Data Visualization and Sharing Findings
Data visualization plays a crucial role in this phase, as it transforms complex data sets into visual representations that are easier to understand and interpret. Tools like charts, graphs, and dashboards are used to illustrate the findings compellingly and intuitively.
Finally, sharing the findings with stakeholders is an integral part of the data analysis process. This involves not just presenting the data, but also providing insights, recommendations, and potential implications in a clear and persuasive manner. Effective communication is key here, as the ultimate goal is to inform decision-making and drive action based on the data insights.
For product optimization and pricing research, market simulators from conjoint analysis can be even more useful to a decision-maker than charts and graphs. They allow the manager to test thousands of potential product formulations and prices, to find the right products to best reach target market segments.
Example Scenario
Imagine a data analyst working for a healthcare provider, tasked with reducing patient wait times. By following the data analysis process, the analyst:
- Defines the question: What factors contribute to increased wait times?
- Collects and cleans data from patient records, appointment systems, and feedback surveys.
- Analyzes the data to identify patterns, such as peak times for appointments and common delays in the patient check-in process.
- Visualizes the findings using graphs that highlight peak congestion times and the factors causing delays.
- Shares the insights with the healthcare management team, recommending adjustments to appointment scheduling and check-in processes to reduce wait times.
This systematic approach not only provides actionable insights but also showcases the power of data analytics in solving real-world problems.
Understanding the data analysis process is foundational for anyone looking to delve into data analytics, providing a roadmap for transforming data into insights that can drive informed decision-making.
Tools and Techniques
The field of Data Analytics is supported by a variety of tools and techniques designed to extract, analyze, and interpret data. Market research surveys are often a key source of data. The choice of the right analytics tools and the application of specific analytical techniques can significantly impact the quality of the insights generated. In this section, we will explore some of the key data analytics techniques and highlight commonly used tools, especially for primary survey research, providing tips on how to choose the right ones for specific projects.
Key Data Analytics Techniques
Statistical Testing: When summarizing data using means (for continuous data) or percent of observations falling into different categories (for categorical or nominal data), we often want to know whether the differences we’re observing between groups of respondents, branches of a company, or time periods are statistically meaningful (that they were unlikely to occur by chance).
Correlation Analysis : A statistical approach that examines whether there is a positive, negative, or no correlation between two continuous variables. The square of the correlation coefficient indicates the percent of variance in one variable that is explained by the other.
Regression Analysis : A statistical method used to examine the relationship between dependent (outcome) and independent (predictor) variables. There are regression techniques for predicting continuous variables (ordinary least squares) as well as for categorical outcomes (logistic regression). Regression analysis is particularly useful for identifying relationships between variables, making predictions, and forecasting.
Tree-Based Analysis : These techniques are used for finding which variables tend to predict or explain some outcome, such as purchase of a product, or diagnosis with a disease. Common examples are Classification and Regression Trees (CART) and Random Forests, a combination of multiple trees that can be ensembled for a more accurate consensus prediction.
Time-Series Analysis : Focused on analyzing data points collected or recorded at specific time intervals. This technique is crucial for trend analysis, seasonal pattern identification, and forecasting.
Cluster Analysis : A family of methods used to group a set of objects (such as respondents) in such a way that objects in the same group (called a cluster) are more similar to each other than to those in other groups. It’s extensively used in market segmentation and targeting strategies. Common approaches include k-means clustering, latent class clustering, and ensemble approaches that leverage multiple techniques to achieve a more robust consensus solution.
Conjoint Analysis and MaxDiff: Discrete choice methods often used in market research and economics for assessing the importance of features, measuring price sensitivity , and predicting demand for products or services.
Quick and Intuitive Conjoint Analysis Software
Need to launch a conjoint analysis study? Get access to our free conjoint analysis tool. In just a few minutes, you can create full conjoint analysis exercises with just a few clicks of our easy-to-use interface.
Conjoint Analysis Software Tool or Request a Product Tour
Commonly Used Data Analytics Tools
Excel : A versatile tool for basic data analysis, familiar to most professionals, capable of handling various data analysis functions including pivot tables, basic statistical functions, and data visualization.
SQL : Essential for data extraction, especially from relational databases. SQL allows analysts to query specific data from large databases efficiently.
Python/R : Both are powerful programming languages favored in data analytics for their libraries and packages that support data manipulation, statistical analysis, and machine learning.
Tableau/Power BI : These tools are leaders in data visualization, providing robust platforms for creating dynamic and interactive dashboards and reports.
Sawtooth Software : Provides tools, support services, and consulting services for designing and fielding market research surveys, as well as conducting conjoint analysis, MaxDiff, and cluster analysis.
Free Survey Maker Tool
Get access to our free and intuitive survey maker. In just a few minutes, you can create powerful surveys with its easy-to-use interface.
Try our Free Survey Maker or Request a Product Tour
Choosing the Right Tools and Techniques
Selecting the appropriate tools and techniques depends on several factors:
Project Requirements : The nature of the data and the specific questions you are trying to answer will guide your choice. For instance, Python might be preferred for its machine learning capabilities, while Tableau is chosen for sophisticated visualizations.
Data Size and Complexity : Large datasets and complex analyses might require more advanced tools like Python or R, whereas Excel (limited to around 1 million rows and 16 thousand columns) could suffice for smaller, simpler datasets.
Skill Set : The proficiency of the data analyst in using these tools also plays a significant role. It’s essential to balance the choice of tool with the analyst's comfort level and expertise.
Budget and Resources : Some tools require significant investment, both in terms of licenses and training. Open-source options like Python and R offer powerful functionalities at no cost.
Example Application
Consider a retail company looking to optimize its inventory levels based on historical sales data. The data analyst might use:
- SQL to extract sales data from the company's database.
- Python for conducting time-series analysis to identify sales trends and predict future demand.
- Tableau to create visualizations that illustrate these trends and forecasts, facilitating strategic discussions on inventory management.
Through the strategic application of these tools and techniques, data analysts can uncover valuable insights that drive informed decision-making and strategic planning within organizations.
The exploration of tools and techniques underscores the versatility and power of data analytics. Whether through statistical analysis, predictive modeling, or insightful visualizations, these tools empower analysts to turn data into strategic assets.
Importance and Uses of Data Analytics
Data analytics has become a pivotal element of business strategy, influencing decisions across all levels of an organization. Its importance cannot be overstated, as it provides the insights needed for businesses to innovate, stay competitive, and improve operational efficiency. This section explores the significance of data analytics across various domains, including healthcare, product optimization and pricing, and its relevance for small enterprises and startups.
Embracing data analytics allows organizations to move from intuition-based decisions to informed strategies. As we advance, the integration of data analytics into every aspect of business operations and strategy will become more pronounced, highlighting its critical role in shaping the future of industries worldwide.
Transforming Business Success
Data analytics empowers businesses to make informed decisions by providing a deep understanding of customer behavior, market trends, and operational performance. It enables companies to:
- Optimize Operations : By analyzing data, businesses can identify inefficiencies in their operations and find ways to reduce costs and improve productivity.
- Enhance Customer Experience : Data analytics allows businesses to understand their customers' preferences and behaviors, leading to improved revenues, customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Product Innovation/Optimization and Pricing : Survey research methods such as conjoint analysis and MaxDiff are especially useful for optimizing features for and pricing products/services, keeping companies at the forefront of innovation and competitiveness.
In healthcare, data analytics plays a critical role in improving patient outcomes and operational efficiency. By analyzing patient data, healthcare providers can:
- Predict Outbreaks : Data analytics can help in predicting disease outbreaks, enabling healthcare systems to prepare and respond effectively.
- Personalize Treatment : Analytics (including MaxDiff and conjoint analysis) can elicit real-time preferences from patients that can lead to better personalized treatment plans, improving patient care and outcomes. Several groups of physicians and academic researchers have presented research at Sawtooth Software conferences on using these tools for facilitating better communication between patients and doctors and selecting treatment plans for diseases such as cancer to result in improved outcomes.
- Improve Operational Efficiency : Data analytics can optimize hospital operations, reducing wait times and improving patient flow.
Product Optimization and Pricing
Repositioning existing products, developing new products, and setting effective pricing strategies are vital to most any business. By using gold standard tools for survey research such as conjoint analysis and MaxDiff, businesses can:
- Find Optimal Sets of Features : Conjoint analysis can within a single survey research project evaluate 1000s of potential feature configurations, determining which feature sets will compete best relative to specific competitors.
- Identify Profitable Target Segments : Conjoint analysis or MaxDiff are excellent techniques for identifying and sizing market segments that have specific needs and are associated with different levels of price sensitivity.
- Measure Price Elasticity: Choice-Based Conjoint (CBC) analysis is particularly valuable for estimating price elasticity of demand for the firm’s brand(s), as well as assessing how changes to competitor’s prices affect quantity demanded for the firm’s brand(s) ( cross-elasticity ).
Relevance for Small Enterprises and Startups
For small enterprises and startups, data analytics offers a competitive edge, enabling them to:
- Make Informed Decisions : Even with limited resources, small businesses can use data analytics to make strategic decisions based on market trends and customer feedback.
- Identify Opportunities : Analytics can reveal market gaps and customer needs, providing startups with insights to innovate and capture new markets.
The Role of a Data Analyst
In the heart of data-driven organizations lies the Data Analyst , a professional whose responsibilities are as varied as they are critical. Understanding the role of a data analyst not only highlights the importance of data analytics in modern business but also sheds light on the skills and perspectives needed to excel in this field.
Responsibilities and Tasks
A data analyst's journey often begins with problem formulation and developing hypotheses and strategies for solving a business or organizational problem. Next often follows data collection, ensuring the quality and accuracy of the data sourced from various channels, including survey research. This foundational step is critical, as the integrity of the data directly impacts the insights derived from it. The analyst then proceeds to clean and preprocess the data, preparing it for analysis. This involves handling missing values, removing duplicates, trimming outliers, and ensuring the data is in a format suitable for analysis.
The core of a data analyst's role involves statistical analysis and data modeling to interpret the data. They employ a range of techniques, from simple descriptive statistics to more complex predictive models, to unearth trends, patterns, and correlations within the data.
However, the role extends beyond just analyzing data. Data visualization and reporting are equally important, as these allow the analyst to communicate their findings in a clear, compelling manner. Whether through dashboards, reports, or presentations, the ability to present data in an accessible way is crucial for informing decision-making processes within an organization.
Professional Insights
From the perspective of a seasoned data analyst, the job is not just about numbers and algorithms; it's about solving challenging business and organizational problems and storytelling with data. It involves translating complex datasets into actionable insights that can drive strategy and impact. An effective data analyst combines analytical skills with business acumen, understanding the broader context in which the data exists.
Career Opportunities in Data Analytics
The field of data analytics offers a dynamic career landscape, characterized by a high demand for skilled professionals capable of turning data into actionable insights. As businesses across industries continue to recognize the value of data-driven decision-making, the demand for data analysts has surged, creating a wealth of opportunities for those equipped with the right skills and knowledge. This section will explore career prospects, including job growth, and discuss the relevance of degrees and certifications in data analytics.
Job Growth and Demand
The demand for data analysts is projected to grow significantly in the coming years. According to industry reports and labor statistics, the job market for data analysts is expected to grow much faster than the average for all occupations. This growth is driven by the increasing volume of data generated by businesses and the need to analyze this data to make informed decisions.
- Projected Job Growth : Data analytics roles are expected to see one of the highest rates of job growth across all sectors.
- Industries Hiring : While technology and finance traditionally lead in hiring data analysts, healthcare, marketing, and retail are rapidly catching up, reflecting the broad applicability of data analytics skills.
Salary Ranges
Salaries for data analysts can vary widely based on experience, location, and industry. However, data analysts typically command competitive salaries, reflecting the high demand and specialized skill set required for the role.
- Entry-Level Positions : Even at entry levels, data analysts can expect salaries that are competitive, with potential for rapid growth as experience and skills develop.
- Senior Roles : Experienced data analysts, especially those with specialized skills or leadership roles, can command significantly higher salaries.
Degrees and Certifications
While a degree in data science, statistics, computer science, or a related field can provide a strong foundation, the field of data analytics also values practical experience and specialized skills.
- Relevant Degrees : Bachelors and masters degrees in relevant fields are highly valued, but not always required.
- Certifications : Certifications can supplement academic degrees and provide evidence of specialized skills in data analytics tools and methodologies. Popular certifications include Certified Analytics Professional (CAP), Google Data Analytics Professional Certificate, and various platform-specific certifications (e.g., Tableau, SAS).
Making It in Data Analytics
Success in a data analytics career is not solely determined by technical skills. Employers also value problem-solving abilities, business acumen, and the capacity to communicate complex findings in a clear and actionable manner. Continuous learning and adaptation to new tools, technologies, and methodologies are essential in this rapidly evolving field.
Get Started with Your Survey Research Today!
Ready for your next research study? Get access to our free survey research tool. In just a few minutes, you can create powerful surveys with our easy-to-use interface.
Start Survey Research for Free or Request a Product Tour
Data analytics is not just a tool but a strategic asset that can drive significant business value, enhance operational efficiency, and foster innovation across various sectors. From improving healthcare outcomes to enabling small businesses to compete more effectively, the applications of data analytics are vast and varied.
As we embrace the future, the importance of data analytics in driving business success and societal improvement will only continue to grow. For those considering a career in data analytics or looking to implement data-driven strategies in their operations, the potential is limitless. The benefits of data-driven decision-making underscore the transformative power of data analytics, making it an indispensable part of modern business and governance.
Whether you are a budding data analyst, a business leader, or simply curious about the potential of data analytics, the journey into this field is not only rewarding but essential for those looking to make an impact in the digital age.
Sawtooth Software
3210 N Canyon Rd Ste 202
Provo UT 84604-6508
United States of America
Support: [email protected]
Consulting: [email protected]
Sales: [email protected]
Products & Services
Support & Resources

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Data analysis is, put simply, the process of discovering useful information by evaluating data. This is done through a process of inspecting, cleaning, transforming, and modeling data using analytical …
An energy company can use it to evaluate consumption trends and streamline the production schedule. 7. Survival analysis. Survival analysis focuses on time-to-event data, …
Analytical research techniques are essential tools for systematically gathering and interpreting data. Understanding these techniques allows researchers to derive meaningful insights and …
Marketing analytics is a diverse field, with both academic researchers and practitioners coming from a range of backgrounds including marketing, expert systems, …
Explore various data analysis methods, techniques, and types to gain valuable insights into consumer behavior and refine your marketing strategies.
Discover how data analytics transforms raw data into actionable insights, impacts decision-making, and opens career opportunities. Perfect for beginners eager to explore and …