Poverty Essay for Students and Children
500+ words essay on poverty essay.
“Poverty is the worst form of violence”. – Mahatma Gandhi.


How Poverty is Measured?
For measuring poverty United nations have devised two measures of poverty – Absolute & relative poverty. Absolute poverty is used to measure poverty in developing countries like India. Relative poverty is used to measure poverty in developed countries like the USA. In absolute poverty, a line based on the minimum level of income has been created & is called a poverty line. If per day income of a family is below this level, then it is poor or below the poverty line. If per day income of a family is above this level, then it is non-poor or above the poverty line. In India, the new poverty line is Rs 32 in rural areas and Rs 47 in urban areas.
Get the huge list of more than 500 Essay Topics and Ideas
Causes of Poverty
According to the Noble prize winner South African leader, Nelson Mandela – “Poverty is not natural, it is manmade”. The above statement is true as the causes of poverty are generally man-made. There are various causes of poverty but the most important is population. Rising population is putting the burden on the resources & budget of countries. Governments are finding difficult to provide food, shelter & employment to the rising population.
The other causes are- lack of education, war, natural disaster, lack of employment, lack of infrastructure, political instability, etc. For instance- lack of employment opportunities makes a person jobless & he is not able to earn enough to fulfill the basic necessities of his family & becomes poor. Lack of education compels a person for less paying jobs & it makes him poorer. Lack of infrastructure means there are no industries, banks, etc. in a country resulting in lack of employment opportunities. Natural disasters like flood, earthquake also contribute to poverty.
In some countries, especially African countries like Somalia, a long period of civil war has made poverty widespread. This is because all the resources & money is being spent in war instead of public welfare. Countries like India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, etc. are prone to natural disasters like cyclone, etc. These disasters occur every year causing poverty to rise.
Ill Effects of Poverty
Poverty affects the life of a poor family. A poor person is not able to take proper food & nutrition &his capacity to work reduces. Reduced capacity to work further reduces his income, making him poorer. Children from poor family never get proper schooling & proper nutrition. They have to work to support their family & this destroys their childhood. Some of them may also involve in crimes like theft, murder, robbery, etc. A poor person remains uneducated & is forced to live under unhygienic conditions in slums. There are no proper sanitation & drinking water facility in slums & he falls ill often & his health deteriorates. A poor person generally dies an early death. So, all social evils are related to poverty.
Government Schemes to Remove Poverty
The government of India also took several measures to eradicate poverty from India. Some of them are – creating employment opportunities , controlling population, etc. In India, about 60% of the population is still dependent on agriculture for its livelihood. Government has taken certain measures to promote agriculture in India. The government constructed certain dams & canals in our country to provide easy availability of water for irrigation. Government has also taken steps for the cheap availability of seeds & farming equipment to promote agriculture. Government is also promoting farming of cash crops like cotton, instead of food crops. In cities, the government is promoting industrialization to create more jobs. Government has also opened ‘Ration shops’. Other measures include providing free & compulsory education for children up to 14 years of age, scholarship to deserving students from a poor background, providing subsidized houses to poor people, etc.
Poverty is a social evil, we can also contribute to control it. For example- we can simply donate old clothes to poor people, we can also sponsor the education of a poor child or we can utilize our free time by teaching poor students. Remember before wasting food, somebody is still sleeping hungry.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

- Travelling Essay
- Picnic Essay
- Our Country Essay
- My Parents Essay
- Essay on Favourite Personality
- Essay on Memorable Day of My Life
- Essay on Knowledge is Power
- Essay on Gurpurab
- Essay on My Favourite Season
- Essay on Types of Sports
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App


- History & Society
- Science & Tech
- Biographies
- Animals & Nature
- Geography & Travel
- Arts & Culture
- Games & Quizzes
- On This Day
- One Good Fact
- New Articles
- Lifestyles & Social Issues
- Philosophy & Religion
- Politics, Law & Government
- World History
- Health & Medicine
- Browse Biographies
- Birds, Reptiles & Other Vertebrates
- Bugs, Mollusks & Other Invertebrates
- Environment
- Fossils & Geologic Time
- Entertainment & Pop Culture
- Sports & Recreation
- Visual Arts
- Demystified
- Image Galleries
- Infographics
- Top Questions
- Britannica Kids
- Saving Earth
- Space Next 50
- Student Center
- Introduction
Cyclical poverty
Collective poverty, concentrated collective poverty, case poverty.

Our editors will review what you’ve submitted and determine whether to revise the article.
- Social Science LibreTexts - Poverty
- University of Minnesota Libraries - Open Textbooks - Explaining Poverty
- Pressbooks at Howard Community College - Introduction to Sociology: Understanding and Changing the Social World - Economic Inequality and Poverty in the United States
- CORE - Theories of Poverty: A Critical Review
- poverty - Student Encyclopedia (Ages 11 and up)
- Table Of Contents

poverty , the state of one who lacks a usual or socially acceptable amount of money or material possessions. Poverty is said to exist when people lack the means to satisfy their basic needs. In this context , the identification of poor people first requires a determination of what constitutes basic needs. These may be defined as narrowly as “those necessary for survival” or as broadly as “those reflecting the prevailing standard of living in the community.” The first criterion would cover only those people near the borderline of starvation or death from exposure; the second would extend to people whose nutrition, housing, and clothing, though adequate to preserve life, do not measure up to those of the population as a whole. The problem of definition is further compounded by the noneconomic connotations that the word poverty has acquired. Poverty has been associated, for example, with poor health, low levels of education or skills, an inability or an unwillingness to work, high rates of disruptive or disorderly behaviour, and improvidence. While these attributes have often been found to exist with poverty, their inclusion in a definition of poverty would tend to obscure the relation between them and the inability to provide for one’s basic needs. Whatever definition one uses, authorities and laypersons alike commonly assume that the effects of poverty are harmful to both individuals and society.
Although poverty is a phenomenon as old as human history, its significance has changed over time. Under traditional (i.e., nonindustrialized) modes of economic production, widespread poverty had been accepted as inevitable. The total output of goods and services, even if equally distributed, would still have been insufficient to give the entire population a comfortable standard of living by prevailing standards. With the economic productivity that resulted from industrialization , however, this ceased to be the case—especially in the world’s most industrialized countries , where national outputs were sufficient to raise the entire population to a comfortable level if the necessary redistribution could be arranged without adversely affecting output.

Several types of poverty may be distinguished depending on such factors as time or duration (long- or short-term or cyclical) and distribution (widespread, concentrated, individual).
(Read Indira Gandhi’s 1975 Britannica essay on global underprivilege.)
Cyclical poverty refers to poverty that may be widespread throughout a population, but the occurrence itself is of limited duration. In nonindustrial societies (present and past), this sort of inability to provide for one’s basic needs rests mainly upon temporary food shortages caused by natural phenomena or poor agricultural planning. Prices would rise because of scarcities of food, which brought widespread, albeit temporary, misery.
In industrialized societies the chief cyclical cause of poverty is fluctuations in the business cycle , with mass unemployment during periods of depression or serious recession . Throughout the 19th and early 20th centuries, the industrialized nations of the world experienced business panics and recessions that temporarily enlarged the numbers of the poor. The United States’ experience in the Great Depression of the 1930s, though unique in some of its features, exemplifies this kind of poverty. And until the Great Depression, poverty resulting from business fluctuations was accepted as an inevitable consequence of a natural process of market regulation . Relief was granted to the unemployed to tide them over until the business cycle again entered an upswing. The experiences of the Great Depression inspired a generation of economists such as John Maynard Keynes , who sought solutions to the problems caused by extreme swings in the business cycle. Since the Great Depression, governments in nearly all advanced industrial societies have adopted economic policies that attempt to limit the ill effects of economic fluctuation. In this sense, governments play an active role in poverty alleviation by increasing spending as a means of stimulating the economy. Part of this spending comes in the form of direct assistance to the unemployed, either through unemployment compensation , welfare, and other subsidies or by employment on public-works projects. Although business depressions affect all segments of society, the impact is most severe on people of the lowest socioeconomic strata because they have fewer marginal resources than those of a higher strata.

In contrast to cyclical poverty, which is temporary, widespread or “ collective ” poverty involves a relatively permanent insufficiency of means to secure basic needs—a condition that may be so general as to describe the average level of life in a society or that may be concentrated in relatively large groups in an otherwise prosperous society. Both generalized and concentrated collective poverty may be transmitted from generation to generation, parents passing their poverty on to their children.
Collective poverty is relatively general and lasting in parts of Asia, the Middle East , most of Africa, and parts of South America and Central America . Life for the bulk of the population in these regions is at a minimal level. Nutritional deficiencies cause disease seldom seen by doctors in the highly developed countries. Low life expectancy , high levels of infant mortality, and poor health characterize life in these societies.
Collective poverty is usually related to economic underdevelopment. The total resources of many developing nations in Africa, Asia, and South and Central America would be insufficient to support the population adequately even if they were equally divided among all of the citizens. Proposed remedies are twofold: (1) expansion of the gross national product (GNP) through improved agriculture or industrialization, or both, and (2) population limitation. Thus far, both population control and induced economic development in many countries have proved difficult, controversial, and at times inconclusive or disappointing in their results.
An increase of the GNP does not necessarily lead to an improved standard of living for the population at large, for a number of reasons. The most important reason is that, in many developing countries, the population grows even faster than the economy does, with no net reduction in poverty as a result. This increased population growth stems primarily from lowered infant mortality rates made possible by improved sanitary and disease-control measures. Unless such lowered rates eventually result in women bearing fewer children, the result is a sharp acceleration in population growth. To reduce birth rates, some developing countries have undertaken nationally administered family-planning programs, with varying results. Many developing nations are also characterized by a long-standing system of unequal distribution of wealth —a system likely to continue despite marked increases in the GNP. Some authorities have observed the tendency for a large portion of any increase to be siphoned off by persons who are already wealthy, while others claim that increases in GNP will always trickle down to the part of the population living at the subsistence level.
In many industrialized, relatively affluent countries, particular demographic groups are vulnerable to long-term poverty. In city ghettos , in regions bypassed or abandoned by industry, and in areas where agriculture or industry is inefficient and cannot compete profitably, there are found victims of concentrated collective poverty. These people, like those afflicted with generalized poverty, have higher mortality rates, poor health, low educational levels, and so forth when compared with the more affluent segments of society. Their chief economic traits are unemployment and underemployment, unskilled occupations, and job instability. Efforts at amelioration focus on ways to bring the deprived groups into the mainstream of economic life by attracting new industry, promoting small business, introducing improved agricultural methods, and raising the level of skills of the employable members of the society.
Similar to collective poverty in relative permanence but different from it in terms of distribution, case poverty refers to the inability of an individual or family to secure basic needs even in social surroundings of general prosperity. This inability is generally related to the lack of some basic attribute that would permit the individual to maintain himself or herself. Such persons may, for example, be blind, physically or emotionally disabled , or chronically ill. Physical and mental handicaps are usually regarded sympathetically, as being beyond the control of the people who suffer from them. Efforts to ameliorate poverty due to physical causes focus on education, sheltered employment, and, if needed, economic maintenance.
- Essay Topic Generator
- Essay Grader
- Reference Finder
- AI Outline Generator
- Paragraph Expander
- Essay Expander
- Literature Review Generator
- Thesis Generator
- Text Editing Tools
- AI Rewording Tool
- AI Sentence Rewriter
- AI Article Spinner
- AI Grammar Checker
- Spell Checker
- PDF Spell Check
- Paragraph Checker
- Free AI Essay Writer
- Paraphraser
- Grammar Checker
- Citation Generator
- Plagiarism Checker
- AI Detector
- AI Essay Checker
- Proofreading Service
- Editing Service
- AI Writing Guides
- AI Detection Guides
- Citation Guides
- Grammar Guides
- Paraphrasing Guides
- Plagiarism Guides
- Summary Writing Guides
- STEM Guides
- Humanities Guides
- Language Learning Guides
- Coding Guides
- Top Lists and Recommendations
- AI Detectors
- AI Writing Services
- Coding Homework Help
- Citation Generators
- Editing Websites
- Essay Writing Websites
- Language Learning Websites
- Math Solvers
- Paraphrasers
- Plagiarism Checkers
- Reference Finders
- Spell Checkers
- Summarizers
- Tutoring Websites
- Essay Checkers
- Essay Topic Finders
Most Popular
12 days ago
How To Write a Biography Essay
13 days ago
Dorm Overbooking And Transitional Housing: Problems Colleges Are Trying to Solve
Apu students get flexible on-campus working hours and other benefits.
11 days ago
New Program Drives More Latina Students to Colleges! What Problems Do They Face Daily?
10 days ago
How to Write a Profile Essay
Causes of poverty essay sample, example.

When analyzing such a global issue, one should consider historical and cultural factors. Nations that are among the poorest in the world were once colonies, or areas from which richer countries exported slaves; also, some of these territories were drained of resources. Rare exceptions like Canada or Australia do not deny the fact that, for example, almost the entire continent of Africa is a problematic area in terms of poverty and hunger. This happened due to the fact that colonialism contributed to the establishment of conditions where people living in former colonies cannot access capital or education. In addition, there exist several hot spots in the world where wars and political instability also cause a significant decrease in the quality of life: Syria, Egypt, Ukraine, and so on ( The Borgen Project ).
Perhaps the most direct causal link exists between poverty and the balance between a country’s population density and its agricultural capabilities. Although such countries as the Netherlands or Belgium have a high density of population, their agricultural industry is based on mechanized farming and high-tech solutions, so poverty and hunger have no chance there. The same refers to other technologically-advanced countries. In contrast, Bangladesh, which has one of the world’s largest population densities (2,791 persons in a square mile) exists on the edge of extreme poverty—mostly because the majority of population is involved in low-efficient manual farming. On the other hand, there are countries in Africa with only about 80 persons per square mile, but because of low soil fertility, and the use of manual labor, these countries cannot boost their productivity and development ( povertyhci.weebly.com ).
Along with objective poverty factors, it is also important to consider social factors—in particular, psychological traits that many poor people possess. In many developed countries, poor people do not try to improve their financial conditions, relying on welfare payments provided to them by governments (CliffsNotes). Due to the lack of education and skills (also caused by the inability to pay for them), they cannot work at well-paid jobs, although they can still become maids, cleaners, postal workers, couriers, and so on. Doing so would enable such people to earn more money necessary for education and personal development, but they prefer to keep the status quo.
Reasons of poverty are numerous, and it is difficult to analyze the entire complex of causes of such a global issue. However, some of them are obvious: a colonial background, wars and political instability, dense population combined with low agricultural capabilities, and certain psychological traits of poor people. These factors help keep poverty in the world’s list of the most urgent problems.
“Top 5 Causes of Poverty.” The Borgen Project. N.p., 25 June 2013. Web. 21 May 2015.
“Poverty at Large: A Dark Spot in Humanity.”Http://povertyhci.weebly.com/. N.p., n.d. Web. 21 May 2015.
“Causes and Effects of Poverty.” CliffNotes. N.p., n.d. Web. 21 May 2015.
Follow us on Reddit for more insights and updates.
Comments (0)
Welcome to A*Help comments!
We’re all about debate and discussion at A*Help.
We value the diverse opinions of users, so you may find points of view that you don’t agree with. And that’s cool. However, there are certain things we’re not OK with: attempts to manipulate our data in any way, for example, or the posting of discriminative, offensive, hateful, or disparaging material.
Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
More from Cause and Effect Essay Examples and Samples 2024

Jul 18 2023
How Your Childhood Affects Your Love Style Essay Sample Example

Apr 15 2019
How the Harry Potter Series Became So Popular Essay Sample, Example

Apr 05 2019
Why Our Ancestors Started to Walk on Two Feet Essay Sample, Example
Related writing guides, writing a cause and effect essay.
Remember Me
What is your profession ? Student Teacher Writer Other
Forgotten Password?
Username or Email
What Causes Poverty in the World Report (Assessment)
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
Poverty Rates in the World
Overpopulation and world poverty, culture and world poverty, global distribution of resources: historical injustices and poverty in nations, education and unemployment, environmental degradation, inflation and development approaches, works cited.
This essay discusses the causes of poverty in the world. Poverty and related social inequality are as old as human history. Over the years, people have postulated many causes of poverty and social inequality. The many causes of poverty not withstanding, many definitions of the phenomena have been established. Whichever the definition, poverty is associated with want, lack of or deprivation of necessities in life. According to World Bank, people are individuals who survive on less than a dollar per day.
Despite the fact that living below a dollar, especially in urban areas, is an indicator of being poor, this definition does not apply in given contexts. For people living in some rural areas, the value of what they use as per their market pricing is lower than a dollar. However, considering the quality of life they live, they are better off than many others who live on more than ten dollars a day in the big cities of the world. Therefore, poverty is a complex concept and highly relative in its application or misapplication.
The world of today has the many people living in better socio-economic conditions than a century ago. However, the divide between the rich has widened over the years with the poor in the world forming an overwhelming majority. Statistics indicate that Africa carries the bulk of the poor in the world.
However, even in highly developing nations like India and China, given regions are notably highly impoverished. The impoverished regions of the world are characterized by dilapidated housing, lack of access to education, health care, frequent famines and other humanitarian disasters and catastrophes.
Due to poor infrastructure, response to problems is not efficient and effective enough thus resultant high impacts of disasters that would otherwise be averted. To understand this point better, one has to consider how a natural disaster like a tsunami of say Katrina’s magnitude would affect a third world country. The effects would be high due to poor response unlike what actually happened in the USA.
One of the major factors that have contributed to poverty in given areas of the world is overpopulation (Jones 137). The condition of having many people with fewer available resources combined with little space inevitably results in poverty. Uncontrolled birth rates, in places like Africa, have resulted in a general population boom.
The population upsurge has continually exerted pressure on available resources in the world. The available resource in given countries can only support a given number of people (McCarthy 42). One of the critical resources that support mankind is farming. A majority of people around the world depend on farming or general agriculture for sustenance. Population upsurge and resultant splitting of land into smaller pieces has led to less food production.
Culture is one of the reasons why people remain glued to practices that perpetuate poverty. For example, in some developing countries the more children one has the higher he or she is regarded in society. Cultural practices in traditional rural communities usually sanction the ability of large members of the family (Baker 154).
The governments of most third world countries give little or no attention to family planning because it goes against the cultural assumptions of the people. People anticipating to have smaller families experience difficulty in realizing this as others consider them weird (Rohr 105). Surging population rates point to even higher poverty rates in developing countries (Rohr 149).
Some thinkers have attributed poverty in some parts of the world to unequal distribution of resources. The legacy of colonialism is largely blamed for unequal resource distribution in the world economy (Baker 1).
Most of the developing countries have put more efforts to develop and strengthen their economies with technology and industries but this has been unsuccessful. The inequality in world economy due to historical events has largely hampered poverty alleviation efforts in the world (Pogge 17). Colonialists, for example, left Africa with a very weak infrastructure i.e. transport systems, power generation and communication after bludgeoning the resources of the colonies.
These happenings have derailed all aspects of moving away from poverty because the infrastructure is critical in the development of industries and expansion of the economy (Pogge 123). In recent years, wealthier countries have been accused of neocolonialism i.e. economic based dominance. This influence has enabled the wealthier countries to acquire inexpensive resources such as oil, ores and mineral from poor countries (Fields 59).
Lack of educational opportunities hampers development especially of children from rural areas (Baker 26). For the educated, lack of employment opportunities denies them an opportunity for social mobility. The rural areas in most countries of the world have high rates of illiteracy.
Illiteracy has been more severe in developing countries especially Africa south of the Sahara. Governments of poor countries have faced the inability to provide good and efficient public schools thus not marching with developments in the developing countries. Without good and sound education people fail to find a meaningful income.
Most poor people, in rural areas, forego going to school to facilitate concentration on how to make a minimal living (Iceland 79). Developing countries provide minimal employment opportunities, especially for women, which dampens the youth’s morale of going to school. When people do not work, there is no money which is earned and thus this increases high unemployment rate which in turn increases the level of poverty (Gilbert 131).
Environmental degradation in many parts of the world has led to the increase of poverty in the world. The world natural resources, which support mankind and enable growth and development, are slowly getting depleted due to unsustainable usage.
The climatic conditions have been changing gradually and natural habitats have slowly but surely been severely changed (Fields 167). Water bodies, atmosphere, forests and soils have deteriorated and this is a major cause of increasing world poverty. Global environmental degradation has led to the phenomenon of global warming.
Weather conditions are no longer steady but rather erratic and unpredictable. Over use of fertilizers and other wrong use of land has highly affected crop yield. Intensive farming or land over use, for instance, has lead to soil infertility and decrease in crop production (Fields 218).
Pollution from industries such as power production, mining, automobiles, agricultural fertilizers and chemical production has adversely affected adequate food production, availability of clean water for drinking, and facilitated destruction of natural habitats especially for aquatic beings.
Deforestation has brought environmental effects especially in developing countries where some sections of the population depend entirely on forests as source of food and wood to power their activities. Their survival efforts have largely contributed to deforestation and its related effects (Fields 225). Forests absorb pollutant and offers catchment area for water. Without forests, the rain cycle is affected leading to increased famines in the world.
Poverty in the world is linked to economic trends. Developed countries, such as the United States in the 1950s, experienced high income growth (Dudley 167). Most families doubled their income within this period. However, in 1970s and early 1990s, inflation grew steadily hence raising the cost of living.
The economic recession of the 1980s adversely affected families; the young and less educated people could not get well paying jobs to support themselves. The change of labor market in most developed countries has also further aggravated the situation of poverty in the world today (Dudley 215).
The number of well paying jobs in the manufacturing industries has declined whereas in the service and technology industries, workers have significantly increased. Most people who cannot afford college education experiences hardship in securing a well paying work hence they are locked out of social mobility.
Moreover, in most wealthy countries, many people living in poverty have increased because of the rising inequality in the way resources are distributed. For instance in the United States, 20% of the poor have got smaller percentage of the total national income whereas the wealthy have increasingly earned much higher national income of 45%.
During this period, the middle and bottom income distribution has been progressively worse as the cost of living has gone up (Kendall 67). Demographic shifts have contributed to poverty especially among the children. In the US for example, family structures have been altered significantly increasing single parenting. This has increased poverty in the world (Kendall 73).
Poverty levels have been soaring around the world despite improved economic fortunes for a minority. The major causes of world poverty are improper policies and development approaches or plans undertaken in different nations. Economic imbalance or inequalities resulting from historical injustices also maintain a world order that does not sustain all. To alleviate world poverty, issues like overpopulation, environmental degradation among other factors have to be looked into more closely.
Baker, Judy, L. Poverty Reduction and Human Development in the Caribbean: a cross- country study, Parts 63-366 . Washington: World Bank Publication.1997
Fields, Gary, S. Poverty, Inequality, and Development . Florida: CUP Archive. 1980
Gilbert, Geoffrey. World poverty: a Reference handbook, Contemporary world issues. California: ABC-CLIO. 2004
Iceland, John. Poverty in America: a handbook . California: University of California Press. 2006
Jones, Philip, W. Education, Poverty and the World Bank . New Jersey: Sense Publishers. 2006
Kendall, Diana. Sociology in Our Times . Connecticut: Cengage Learning, 2007
McCarthy, Callaghan. The Causes of Poverty . East Yorkshire: P. S. King & Son, 1908
Pogge, Thomas, Winfried, Menko. World Poverty and Human Rights: Cosmopolitan Responsibilities and Reforms . Cambridge: Polity, 2008
- Rich and Poor Nations (Planet of Slums)
- Poverty in the Bronx: Negative Effects of Poverty
- The Impact of Overpopulation on the Global Environment
- How Overpopulation Affects Our Economy
- Overpopulation Challenges in China
- Justification for the title, ‘There are no children here’
- Poverty in Brazil
- Why Poverty Rates are Higher Among Single Black Mothers
- Urban Slum in the "City of God" (2002)
- Poverty and Its Impact on Global Health: Research Methodologies
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2018, July 10). What Causes Poverty in the World. https://ivypanda.com/essays/what-causes-poverty-in-the-world/
"What Causes Poverty in the World." IvyPanda , 10 July 2018, ivypanda.com/essays/what-causes-poverty-in-the-world/.
IvyPanda . (2018) 'What Causes Poverty in the World'. 10 July.
IvyPanda . 2018. "What Causes Poverty in the World." July 10, 2018. https://ivypanda.com/essays/what-causes-poverty-in-the-world/.
1. IvyPanda . "What Causes Poverty in the World." July 10, 2018. https://ivypanda.com/essays/what-causes-poverty-in-the-world/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "What Causes Poverty in the World." July 10, 2018. https://ivypanda.com/essays/what-causes-poverty-in-the-world/.
IvyPanda uses cookies and similar technologies to enhance your experience, enabling functionalities such as:
- Basic site functions
- Ensuring secure, safe transactions
- Secure account login
- Remembering account, browser, and regional preferences
- Remembering privacy and security settings
- Analyzing site traffic and usage
- Personalized search, content, and recommendations
- Displaying relevant, targeted ads on and off IvyPanda
Please refer to IvyPanda's Cookies Policy and Privacy Policy for detailed information.
Certain technologies we use are essential for critical functions such as security and site integrity, account authentication, security and privacy preferences, internal site usage and maintenance data, and ensuring the site operates correctly for browsing and transactions.
Cookies and similar technologies are used to enhance your experience by:
- Remembering general and regional preferences
- Personalizing content, search, recommendations, and offers
Some functions, such as personalized recommendations, account preferences, or localization, may not work correctly without these technologies. For more details, please refer to IvyPanda's Cookies Policy .
To enable personalized advertising (such as interest-based ads), we may share your data with our marketing and advertising partners using cookies and other technologies. These partners may have their own information collected about you. Turning off the personalized advertising setting won't stop you from seeing IvyPanda ads, but it may make the ads you see less relevant or more repetitive.
Personalized advertising may be considered a "sale" or "sharing" of the information under California and other state privacy laws, and you may have the right to opt out. Turning off personalized advertising allows you to exercise your right to opt out. Learn more in IvyPanda's Cookies Policy and Privacy Policy .

What is Poverty? The Causes, Facts, and Ways to Take Action
In 2022, the World Bank estimated that about 8% of the world’s population (which is almost 650 million people) lived on less than $2.15 per day. This state is known as “extreme poverty.” While extreme poverty is the most urgent issue, 47% of the world’s population is still struggling with less than $6.85 per day. What is poverty exactly?
In this article, we’ll provide a thorough definition alongside key facts everyone should know and the best ways to take action.
Poverty occurs when individuals and communities don’t have enough money or resources for a basic standard of living. That includes good housing, food, clean water, healthcare, and much more. COVID-19 stalled years of progress on ending poverty, which makes solutions like improved gender equity, universal health coverage, and taxes on the world’s richest all the more essential.
What is poverty?
Poverty happens when someone lacks the income and resources necessary to maintain a good standard of living. That includes safe housing, medical care, food, clean water, and so on. The UN emphasizes that it’s also “more than a lack of income.” There are varying socioeconomic factors at play such as race, sexuality, ethnicity, gender, the ability to access services, and opportunities for decent work. Poverty also drives many social issues like poor education, child labor, forced labor, poor health, violence, and more.
For years, extreme poverty – which affects the poorest people on Earth – referred to living on less than $1.90 a day. In 2022, the World Bank updated its line to $2.15. It was changed to reflect cost increases for basic food, clothing, and shelter in low-income countries between 2011 and 2017 relative to the rest of the world. $2.15 in 2017 prices is equal to $1.90 in 2011 prices. Before COVID-19, the world was doing a decent job reducing extreme poverty. According to the World Bank’s Poverty and Shared Prosperity report, 1 billion people escaped extreme poverty over 30 years. Then, COVID hit. In 2020, 70 million fell below the extreme poverty line. Based on estimates, about 7% of the world (most in Africa) will still be in extreme poverty by 2030. There’s also the matter of those vulnerable to poverty . These are people living on $2-$5 per day. There are 1.3 billion in this group. One financial setback like an illness, injury, job loss, or other crisis would be enough to push them into extreme poverty.
What causes poverty?
Many factors drive poverty, which is one of the reasons why it’s so difficult to eliminate. Here are five causes:
A lack of good education
Education is key to breaking long poverty cycles. Without a good education, it’s very difficult for people to get better-paying jobs that help them afford necessities and build wealth. A 2017 report from UNESCO and the Global Education Monitoring Report found that if all adults finished secondary school, the global poverty rate could be cut in half. Unfortunately, for those who are already in poverty, completing school is often difficult or impossible. Governments and NGOs need to step in to ensure students get as much education as possible.
Conflict and war
Conflict and poverty have a close, reinforcing relationship . Poverty fuels conflict. Conflict can then make poverty worse. The most obvious reason is that conflict disrupts people’s lives and destroys infrastructure. Those displaced by violence – especially women, children, disabled people, and the elderly – are much more likely to fall into poverty. Even when a conflict has ended, recovery can take a long time and fail to support the most harmed.
Environmental disasters and climate change
Like conflict, environmental disasters disrupt communities and destroy infrastructure. Climate change is quickly becoming a persistent source of disasters worldwide. While the world’s poorest contribute the least to climate change, they’re impacted the most. This is because poor people depend on agriculture, which climate change disrupts through floods, famines, hurricanes, and more. If significant changes aren’t made, climate change could push 130 million people into extreme poverty over the next decade.
Inaccessible healthcare
Poor healthcare is both a cause and a consequence of poverty. Cost is a big reason why. One expensive emergency can tip people into poverty and keep them there. Poverty also increases the risk of health issues that quickly drain a person’s wallet. There are issues beyond pure cost, however. Disenfranchised groups aren’t given equal access to information, services, nutritious food, and other resources necessary for good health. Even if healthcare were more affordable, there would be other steps needed to make it truly accessible.
Social injustice
There’s an established link between poverty and social injustices like racism and gender inequality. Take the United States. According to research from sociologist Regina Baker , Black populations living in southern states with a “strong historical racial regime” experience worse poverty. There’s also a wider poverty gap between Black and white populations in these states. Worldwide, gender inequality and poverty are deeply linked. If everyone received equal rights and opportunities, it would eliminate a lot of poverty.
What are the main facts about poverty?
There’s a lot to know about poverty, but here are three main facts everyone should remember:
#1. Around 1 billion children live in poverty
Children are deeply affected by poverty. According to UNICEF , 1 billion kids don’t have access to education, housing, nutrition, water, sanitation, or healthcare. Around 356 of those kids are living in extreme poverty. As a result, kids from the poorest households die at twice the rate of kids who aren’t as poor. The kids that do survive continue to face difficulties like poor nutrition, chronic disease, mental health problems, and hindered emotional development. Childhood poverty could even cause long-term effects on the brain , though environmental factors affect behavior, too.
#2. Poverty is concentrated in a few areas
According to data from the World Bank , South Sudan has the highest poverty rate at 82.30%. Equatorial Guinea is next at 76.80%. This is followed by Madagascar (70.70%), Guinea-Bissau (69.30%), and Eritrea (69.30%). In Burundi , which is a small country in East Africa with 12.1 million people, 70% of the population is poor. 52% of kids under 5 have stunted growth and high levels of malnutrition. In terms of GDP per capita, Burundi is the poorest country in the world.
#3. It’s not just poverty; it’s wealth inequality
Wealth inequality refers to differences in income, as well as the value of stocks, investments, houses, personal possessions, and so on. According to the World Bank Gini Index , South Africa has the highest rate of wealth inequality: 63%. That’s followed by Namibia (59.1%) and Suriname (57.9%). The United States, which has the largest economy in the world, also has issues. 2021 data showed that income at the top of the income distribution was 13.53 times higher than income at the bottom. Inequality is a global problem; in the past ten years, the world’s richest 1% have gotten almost 50% of all new wealth.
How can the world eliminate poverty?
The world was making great progress on ending poverty until COVID-19. Things need to improve quickly if we’re going to achieve SDG Goal #1 by 2030. Because poverty is such a complex, large-scale issue, it’s hard for individuals to make much of a difference on their own. However, people can educate themselves on the best solutions and pressure those in power to take action. Here are three solutions to learn more about:
#1. Focus on gender equity
As we mentioned before, poverty and gender inequality are deeply linked. It’s impossible to eliminate poverty without gender equality. According to the World Bank , about 2.4 billion women of working age aren’t getting equal economic opportunities. 95 countries don’t mandate equal pay for equal work. Improving equity would lift a huge number of women and their families out of poverty. What can individuals do to help? Support organizations that focus on women and children. Advocate for better policies at your workplace, like more paid family leave, more flexible hours, and an end to gender pay gaps.
#2. Advocate for universal health coverage
According to the WHO , universal healthcare is the assurance that everyone has “access to the full range of quality health services they need, when and where they need them, without financial hardship.” It’s a key part of eliminating poverty. While there was progress before COVID-19, 2 billion people are facing what the WHO calls “catastrophic or impoverishing health spending.” Individuals can support universal health coverage by donating to organizations and pressuring leaders to pass legislation.
#3. Tax the rich
According to an Oxfam report called Survival of the Richest , the fortunes of billionaires are rising by $2.7 billion a day. Meanwhile, 1.7 billion workers live in countries where inflation is rising faster than wages. In 2022, 95 food and energy corporations more than doubled their profits, which were passed on to billionaire shareholders. These massive corporate profits also drove half of the inflation in the US, UK, and Australia. If the world wants to end poverty, these excesses need to be addressed. According to the Oxfam report, a tax of up to 5% on the world’s richest could raise $1.7 trillion a year. That’s enough to help 2 billion people escape poverty.
You may also like

13 Facts about Child Labor

Environmental Racism 101: Definition, Examples, Ways to Take Action

11 Examples of Systemic Injustices in the US

Women’s Rights 101: History, Examples, Activists

What is Social Activism?

15 Inspiring Movies about Activism

15 Examples of Civil Disobedience

Academia in Times of Genocide: Why are Students Across the World Protesting?

Pinkwashing 101: Definition, History, Examples

15 Inspiring Quotes for Black History Month

10 Inspiring Ways Women Are Fighting for Equality

15 Trusted Charities Fighting for Clean Water
About the author, emmaline soken-huberty.
Emmaline Soken-Huberty is a freelance writer based in Portland, Oregon. She started to become interested in human rights while attending college, eventually getting a concentration in human rights and humanitarianism. LGBTQ+ rights, women’s rights, and climate change are of special concern to her. In her spare time, she can be found reading or enjoying Oregon’s natural beauty with her husband and dog.
Pardon Our Interruption
As you were browsing something about your browser made us think you were a bot. There are a few reasons this might happen:
- You've disabled JavaScript in your web browser.
- You're a power user moving through this website with super-human speed.
- You've disabled cookies in your web browser.
- A third-party browser plugin, such as Ghostery or NoScript, is preventing JavaScript from running. Additional information is available in this support article .
To regain access, please make sure that cookies and JavaScript are enabled before reloading the page.
About . Click to expand section.
- Our History
- Team & Board
- Transparency and Accountability
What We Do . Click to expand section.
- Cycle of Poverty
- Climate & Environment
- Emergencies & Refugees
- Health & Nutrition
- Livelihoods
- Gender Equality
- Where We Work
Take Action . Click to expand section.
- Attend an Event
- Partner With Us
- Fundraise for Concern
- Work With Us
- Leadership Giving
- Humanitarian Training
- Newsletter Sign-Up

Donate . Click to expand section.
- Give Monthly
- Donate in Honor or Memory
- Leave a Legacy
- DAFs, IRAs, Trusts, & Stocks
- Employee Giving
The top eleven causes of poverty around the world
Aug 23, 2024

Approximately 700 million people around the world live below the international poverty line. But why? Updated for 2024, we look at 11 of the top causes of poverty around the world.
For most of us, living on less than $2.15 a day seems far removed from reality. But it is the reality for roughly 700 million people around the globe (according to the latest World Bank data). That’s roughly 8.5% of the world’s population currently living in poverty.
We’ve made significant progress towards ending poverty in the last few decades — in 1990, the number of people living in poverty was 1.8 billion. However, in recent years we’ve also undone a lot of that progress. Climate change, conflict, and the continued impact of COVID-19 have led to an increase of nearly 100 million people experiencing poverty compared to 2019 figures. Let’s take a closer look at these, and eight other top causes of poverty.
1. Inequality
At Concern, our core understanding of poverty is that it’s a combination of inequality and risk. Inequality is easy enough to understand as a concept: It’s what happens when one group has fewer rights and resources based on an aspect of their identity (such as gender, caste, ethnicity, social status, age, ability).
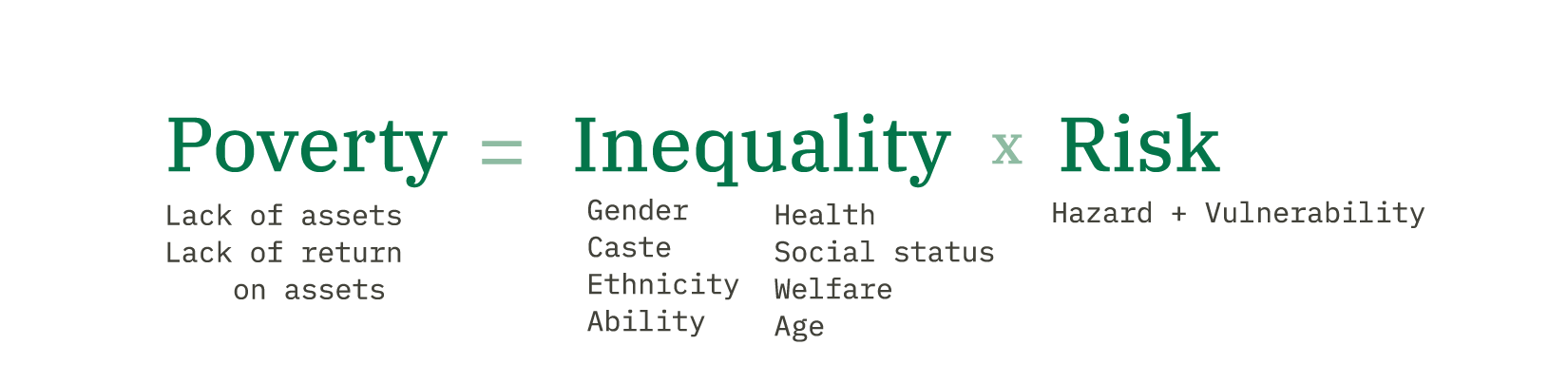
How inequality functions as a cause of poverty, however, is a bit more multifaceted. When people are given fewer rights or assets based on their ethnicity or tribal affiliation, that means they have fewer opportunities to move ahead in life. We see this often in gender inequalities that leave women with fewer economic and civic rights. In this case, it doesn't matter that someone has more rights than someone else. What matters is that there is someone else who doesn't have enough.
These inequalities become amplified when they’re combined with risk. For example: A widow raising a family of five may not have the same resources that would have been available to her husband based on her gender. If she also happens to be a refugee living in a camp, or in an area that’s especially vulnerable to climate change (or both), that puts even more pressure on the few resources she has. This is what fuels the cycle of poverty .
Let’s take a closer look at some of these risks…
Learn more about the causes of poverty — and how we're solving them
2. conflict.
Conflict is at the top of the list of risks that can send a person or family into poverty. Large-scale, protracted crises can grind an otherwise functioning economy to a halt. Prior to the conflict (and resulting humanitarian crisis) that began in 2011, as few as 10% of Syrians lived below the poverty line. Today, that number has been inverted, with UNHCR estimating over 90% of Syrians living below the poverty line at the end of 2023.
Conflict has become more localized over the last few decades, which has a huge impact on communities with fewer headlines in the international press. However, as we have also seen over the past two years with the escalated crisis in Ukraine , a major conflict in one part of the world can also have a ripple effect on economies in entirely different countries — and continents.

Poverty and conflict: How to break the cycle
Conflict is the single biggest driver of humanitarian needs today. Here, Dr. Caitriona Dowd looks at the links between poverty and conflict — and why we need to break the cycle.
3. Hunger and malnutrition
It’s a vicious cycle: poverty causes hunger , but hunger is also a key cause of poverty . If a person doesn’t get enough food, they’ll lack the strength and energy needed to work. Or their immune system will weaken from malnutrition and leave them more susceptible to illness that prevents them from getting to work. They may also go into further debt if they need to see a doctor or get ongoing care.
This can lead to a vicious cycle, especially for children. From womb to world, the first 1,000 days of a child’s life are critical for a lifetime of health. However, malnourished mothers are more likely to have malnourished children, and the costs of malnutrition can be felt over a lifetime. Adults who were stunted as children earn, on average, 22% less than those who weren't stunted. In Ethiopia, stunting contributes to GDP losses as high as 16%.

Poverty and hunger: A vicious cycle
There’s no way around it: If we want to end poverty, we have to end hunger. Here's how the two are connected.
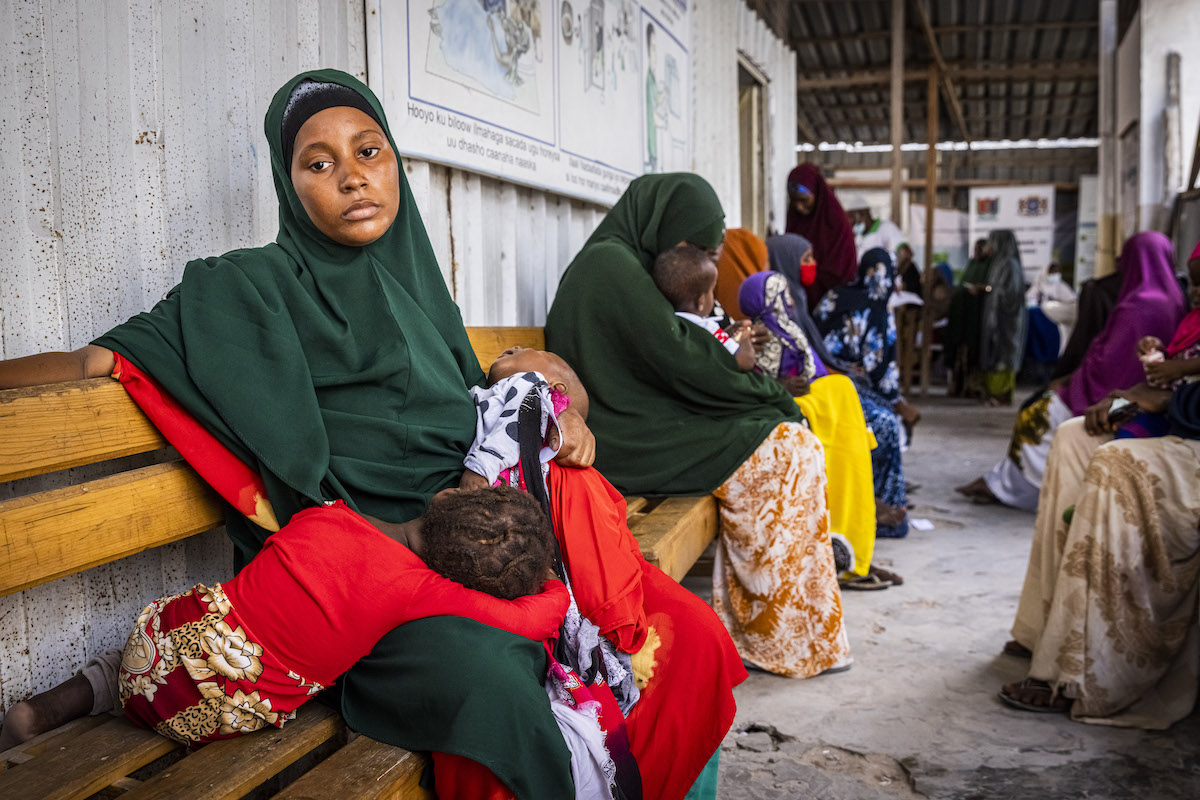
4. Poor healthcare systems — especially for mothers and children
As we saw above with the effects of hunger, extreme poverty and poor health go hand-in-hand. In countries with weakened health systems, easily-preventable and treatable illnesses like malaria, diarrhea, and respiratory infections can be fatal. Especially for young children.
When people must travel far distances to clinics or pay for medicine, it drains already vulnerable households of money and assets. This can tip a family from poverty into extreme poverty. For women in particular, pregnancy and childbirth can be a death sentence. Maternal health is often one of the most overlooked areas of healthcare in countries that are still built around patriarchal structures. New mothers and mothers-to-be are often barred from seeking care without their father's or husband's permission. Adolescent girls who are pregnant (especially out of wedlock) face even greater inequities and discrimination.

5. Public health crises and epidemics
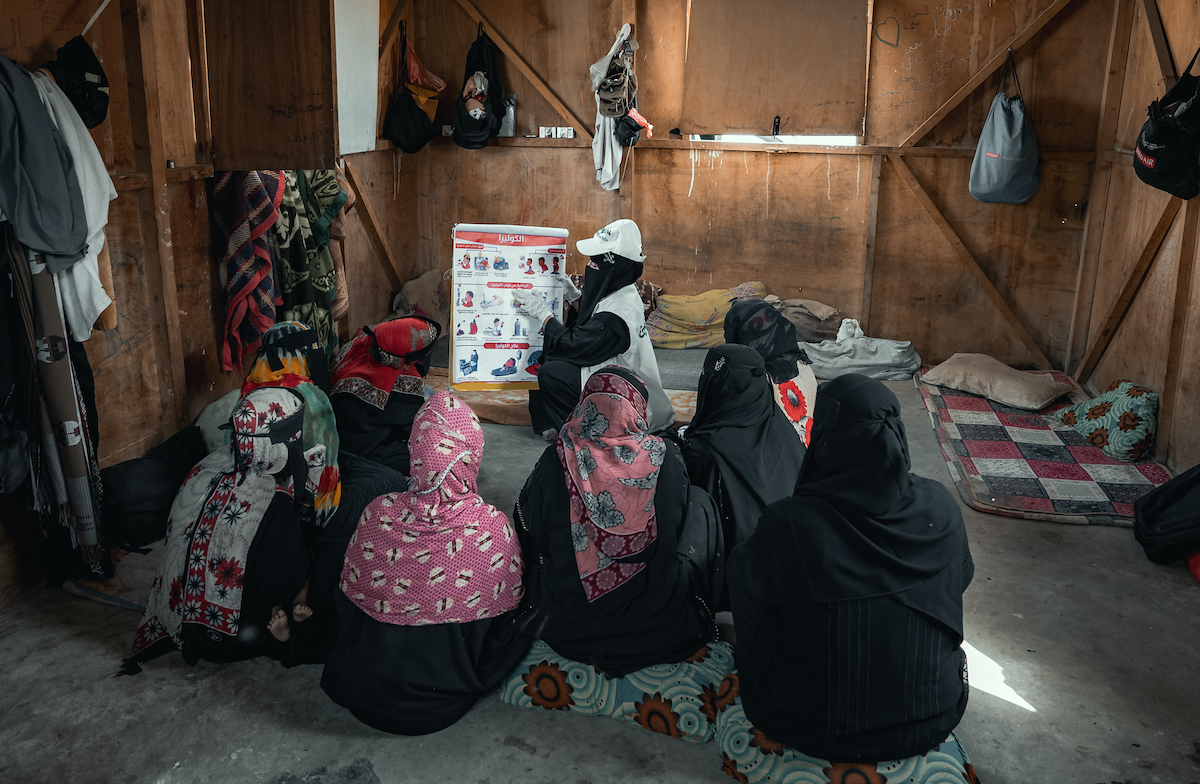
Living in a country without basic healthcare access is one thing, but what happens if a major epidemic or pandemic breaks out? The World Bank estimates that, during the first year of the West African Ebola epidemic , Liberia and Sierra Leone saw GDP losses of 3.4% and 3.3%, respectively. These losses (combined with a 2.1% loss in Guinea) totaled nearly $1.6 billion. A study from Johns Hopkins University estimates that cholera (another ongoing epidemic in many countries) costs Bangladesh $122 million per year.
In a community that’s experiencing an active outbreak, businesses, infrastructure, and governments can grind to a halt in order to manage current cases and prevent future spread. Shelter-in-place measures often prevent low-income people from getting to work as many jobs don’t have remote options. If a patient dies, especially if they were a parent or caregiver, other members of a family (including children) may need to step in to find work and make up for the lost income, which can mean a lifetime of working low-paying jobs.
As we saw with COVID-19, a public health crisis can also have an effect on countries that aren’t at the epicenter of contagion. Many countries in Africa experienced relatively low numbers of covid cases, however border closures and interruptions to trade and other key services mean that many families are still, four years later, recovering from the economic loss.

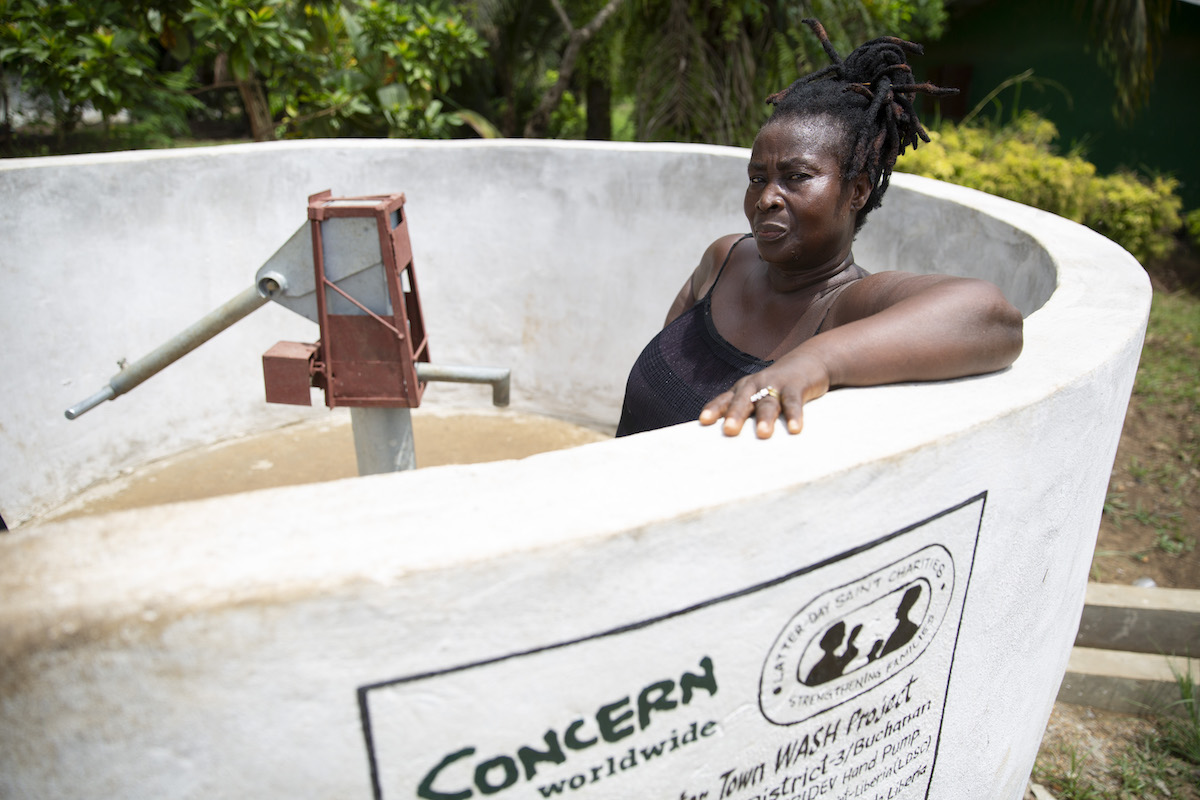
6. Little or no access to clean water, sanitation, and hygiene (WASH)
More than 2 billion people don’t have access to clean water at home. This presents another health issue that’s linked to poverty: Poor sanitation and hygiene means higher rates of disease transmission and even fatalities.
Beyond that, the global water crisis exacerbates many existing inequalities, broadening the poverty gap. When water points are far away, it’s usually the task of women and girls to collect it. UNICEF estimates that women and girls spend 200 million hours collecting water every day — time that could be better spent in school or working on other projects that can generate income for a family.
Investing in water can also be a key solution to poverty: The UN notes that every $1 invested in WASH initiatives brings a $4 return in costs (and then some).

7. Climate change
There’s no doubt in 2024 that climate change causes poverty and disproportionately affects low-income families and communities. And the problem is getting worse: In 2015, the World Bank estimated that the climate crisis would push more than 100 million people into poverty by 2030. In 2024, that estimate has gone up to more than 130 million people.
Many low-income countries are both on the frontlines of the climate crisis and rely heavily on agriculture and pastoralism for their economies. Malawi , as an example, is 80% agrarian. Farming families often have only just enough food and assets to last through the next season, and not enough reserves to fall back on in the event of a poor harvest. So when climate change or natural disasters (including the widespread droughts caused by El Niño ) leave millions of people without food, it pushes them further into poverty, and can make recovery even more difficult.

How climate change keeps people in poverty
By 2030, climate change could force over 130 million into extreme poverty. Here's how five effects of climate change keep communities trapped in poverty.
8. Lack of education
Not every person without an education is living in extreme poverty. But most adults living in extreme poverty did not receive a quality education . And, if they have children, they're likely passing that on to them.
But education is also called the great equalizer for a reason. It can open the door to jobs and other resources and skills that a family needs to not just survive, but thrive. UNESCO estimates that 171 million people could be lifted out of extreme poverty if they left school with basic reading skills. Poverty threatens education, but education can also help end poverty .
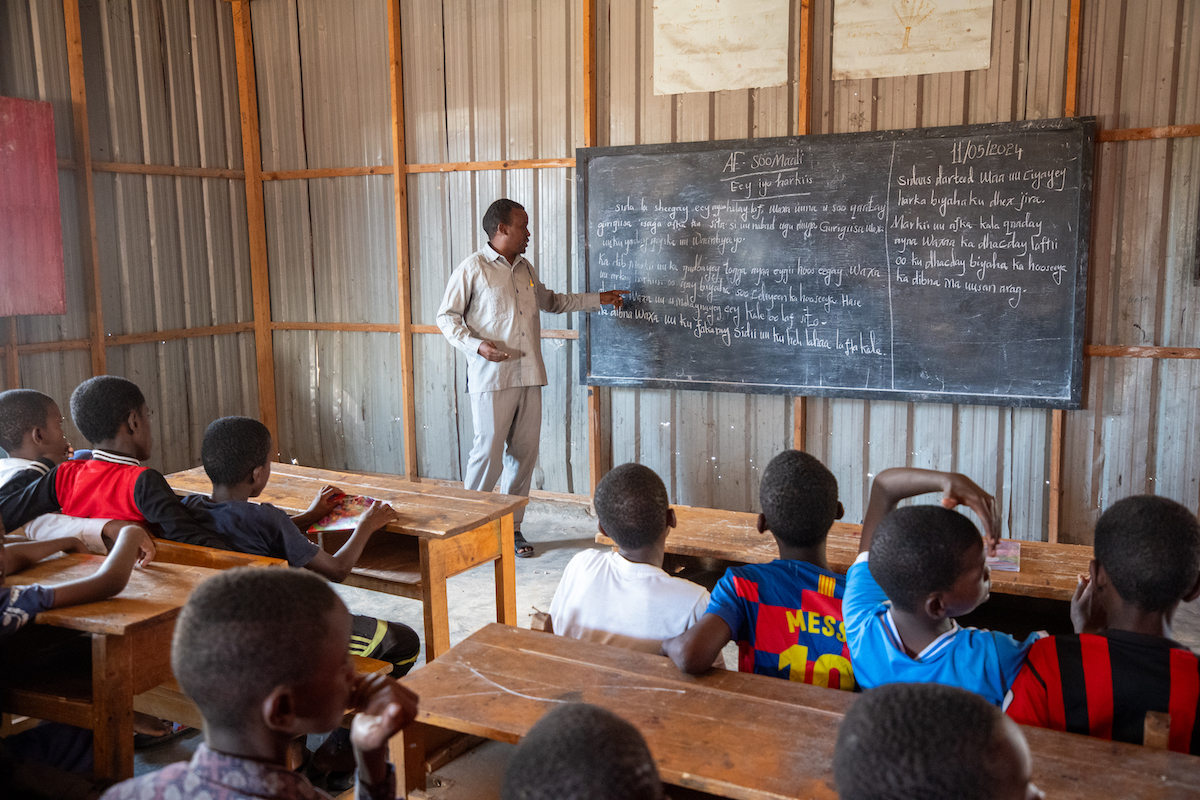

9. Poor public works and infrastructure
What if you have to go to work, but there are no roads to get you there? Or what if heavy rains have flooded your route and made it impossible to travel? We’re used to similar roadblocks (so to speak) in the United States. But usually we can rely on our local governments to step in.
A lack of infrastructure — from roads, bridges, and wells, to cables for light, cell phones, and internet — can isolate communities living in rural areas. Living off the grid often means living without the ability to go to school, work, or the market to buy and sell goods. Traveling further distances to access basic services not only takes time, it costs money, keeping families in poverty.
10. Lack of social support systems
In the United States, we’re familiar with social welfare programs that people can access if they need healthcare or food assistance. Many of us pay directly into unemployment insurance and our future retirement funds through our paychecks. These systems ensure that we have a safety net to fall back on if we lose our job or retire.
But not every government can provide this type of help to its citizens. Without that safety net, there’s nothing to stop vulnerable families from backsliding further into extreme poverty. This is especially true for countries facing conflict or other long-term crises that have also left people more vulnerable to natural and man-made disasters and less likely to receive the support they need when they need it.
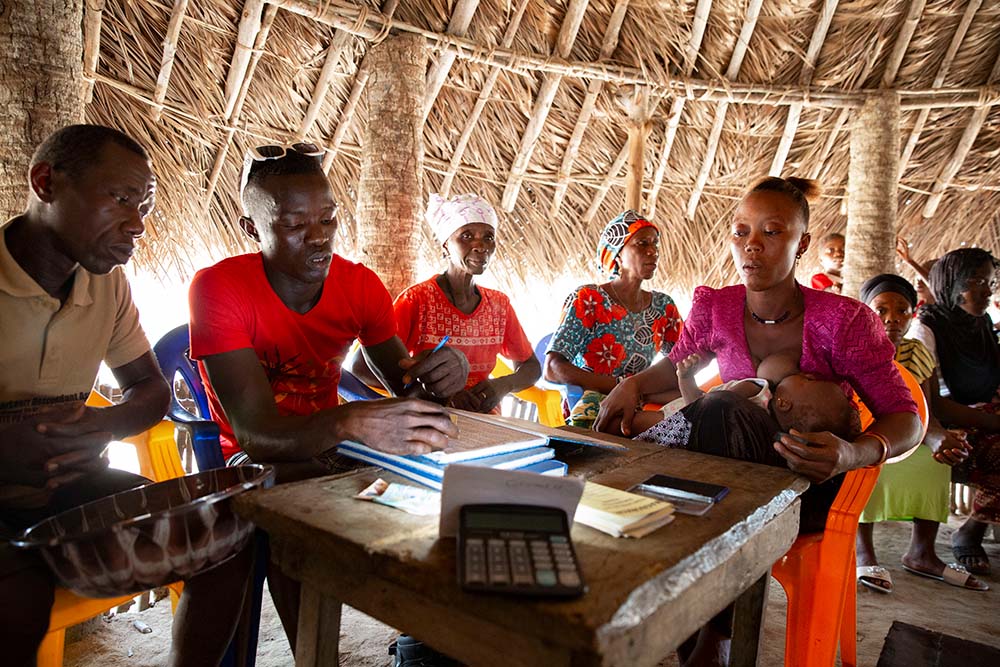

11. Lack of personal safety nets
If a family or community has reserves in place, they can weather some risk. They can fall back on savings accounts or even a low-interest loan in the case of a health scare or an unexpected layoff. Proper food storage systems can help stretch a previous harvest if a drought or natural disaster ruins the next one.
But people living in extreme poverty can’t rely on these safety nets. At its core, poverty is a lack of basic assets or a lack of return from what assets a person has. This leads to negative coping mechanisms, including pulling children out of school so that they can help support the family, and selling off assets to buy food. That can help them make it through one bad season, but not another. For communities constantly facing climate extremes or prolonged conflict, the repeated shocks can send a family reeling into extreme poverty and prevent them from ever recovering, let alone setting aside some funds for the next emergency.
Concern’s work to end poverty
At Concern, we work to sustainably end poverty by addressing inequality and risk, tailoring solutions that support the specific forms of inequality and vulnerabilities faced within each community.
Equality, particularly gender equality, is a pivotal part of all of our programs, and we work with community members and leaders to question and challenge the underlying assumptions that perpetuate equality gaps while designing solutions that accommodate people of all genders, levels of ability, ages, races, social status, and more. We aim for equality of outcomes, not equality of inputs.
From there, we look at the specific risks and conditions that cause poverty in a specific country, region, or community. Often our solutions to poverty work with families to build livelihoods that include more than one source of income. We mentor program participants and train them on business management, marketing, bookkeeping, and other essential skills. We also provide cash grants and help to establish local Village Savings and Loans Associations (and other similar committees) to help create community safety nets.
What we have found through more than 55 years of work is that the communities and individuals we work with already know what they want to do, they just need a few resources to make it happen. We provide those resources, along with some sustainable means of keeping them up long after we’re needed.
Support Concern's work
Causes of poverty, solved

How does education affect poverty? It can help end it.

How Village Savings and Loans Associations Are Beating Poverty Around the World

Solutions to poverty that actually work
Sign up for our newsletter.
Get emails with stories from around the world.
You can change your preferences at any time. By subscribing, you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy.

Why Poverty Persists in America
A Pulitzer Prize-winning sociologist offers a new explanation for an intractable problem.
A mother and son living in a Walmart parking lot in North Dakota in 2012. Credit... Eugene Richards
Supported by
- Share full article
By Matthew Desmond
- Published March 9, 2023 Updated April 3, 2023
In the past 50 years, scientists have mapped the entire human genome and eradicated smallpox. Here in the United States, infant-mortality rates and deaths from heart disease have fallen by roughly 70 percent, and the average American has gained almost a decade of life. Climate change was recognized as an existential threat. The internet was invented.
On the problem of poverty, though, there has been no real improvement — just a long stasis. As estimated by the federal government’s poverty line, 12.6 percent of the U.S. population was poor in 1970; two decades later, it was 13.5 percent; in 2010, it was 15.1 percent; and in 2019, it was 10.5 percent. To graph the share of Americans living in poverty over the past half-century amounts to drawing a line that resembles gently rolling hills. The line curves slightly up, then slightly down, then back up again over the years, staying steady through Democratic and Republican administrations, rising in recessions and falling in boom years.
What accounts for this lack of progress? It cannot be chalked up to how the poor are counted: Different measures spit out the same embarrassing result. When the government began reporting the Supplemental Poverty Measure in 2011, designed to overcome many of the flaws of the Official Poverty Measure, including not accounting for regional differences in costs of living and government benefits, the United States officially gained three million more poor people. Possible reductions in poverty from counting aid like food stamps and tax benefits were more than offset by recognizing how low-income people were burdened by rising housing and health care costs.
The American poor have access to cheap, mass-produced goods, as every American does. But that doesn’t mean they can access what matters most.
Any fair assessment of poverty must confront the breathtaking march of material progress. But the fact that standards of living have risen across the board doesn’t mean that poverty itself has fallen. Forty years ago, only the rich could afford cellphones. But cellphones have become more affordable over the past few decades, and now most Americans have one, including many poor people. This has led observers like Ron Haskins and Isabel Sawhill, senior fellows at the Brookings Institution, to assert that “access to certain consumer goods,” like TVs, microwave ovens and cellphones, shows that “the poor are not quite so poor after all.”
No, it doesn’t. You can’t eat a cellphone. A cellphone doesn’t grant you stable housing, affordable medical and dental care or adequate child care. In fact, as things like cellphones have become cheaper, the cost of the most necessary of life’s necessities, like health care and rent, has increased. From 2000 to 2022 in the average American city, the cost of fuel and utilities increased by 115 percent. The American poor, living as they do in the center of global capitalism, have access to cheap, mass-produced goods, as every American does. But that doesn’t mean they can access what matters most. As Michael Harrington put it 60 years ago: “It is much easier in the United States to be decently dressed than it is to be decently housed, fed or doctored.”
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .
Advertisement

Essay on Poverty

Updated February 18, 2023

Poverty is comparable to slavery when people cannot fulfill their desires. It has different expressions depending on who, where, and when you look at it. There are numerous ways to describe how someone feels or lives. Nobody wants to live in poverty, but some are bound to do so due to culture, the environment, natural disasters, or a lack of proper education. The person experiencing it usually wishes to flee. Poverty serves as a wake-up call for the poor to work hard and earn enough money to meet their basic needs, such as food, shelter, clothing, access to education, and safety from social and political violence. Let us now learn more about the essay on poverty.
Watch our Demo Courses and Videos
Valuation, Hadoop, Excel, Mobile Apps, Web Development & many more.
What is Poverty?
Poverty refers to a person or family not having enough money to meet even the most basic living standards. As a result, the poor cannot afford necessities such as housing, healthcare, and education due to insufficient support. Poverty can thus define as a lack of resources or, more broadly, as barriers to basic human needs. With the help of this poverty essay, students will learn what poverty is, the leading causes of poverty, and the steps taken to eradicate poverty in India.
The Poverty Line is the minimum spending (or income) required to meet a basic basket of goods and services. The number of people living below this line can use to calculate poverty. State governments use Below Poverty Line (BPL) censuses to collect data and measure it. While the methods for measuring poverty differ from country to country, the basic concept still needs to be. The poverty line remains the same: the consumption required to maintain the national minimum standard of living.
Causes of Poverty
A variety of factors cause poverty. The primary contributors are population growth, unemployment, illiteracy, and a lack of appropriate education and training. In addition, people cannot support themselves because they cannot find work. As a result, they cannot obtain essential services such as drinking water, sanitation, and healthcare. As a result, they are unable to feed their families and children. Additional causes of poverty include war, natural disasters, political instability, and other factors. For example, many nations were then affected by World War II and forced to live in poverty for an extended period. As a result, such nations found it difficult to return to their former states. Similarly, natural disasters severely impact some areas, resulting in poverty and hunger.
The problem is that, despite efforts to eradicate poverty worldwide, it has yet to declare a thing of the past. This issue impacts a person’s economy and daily life; a person’s nature and speech are also essential. Being poor in this world has become a curse. The poor lack access to education because having enough money to buy food is like breaking a curse.
Effects of Poverty
Numerous factors have contributed to it continuing for so long. As a result, freedom, physical and mental fitness, and a sense of unease remain. Therefore, the nation and the entire world must work together to ensure proper physical and mental health, complete education, a home for everyone, and other necessities for everyday life.
Poverty is a problem in today’s society that causes great suffering and despair for the poor. You must show a lack of many things due to a lack of money caused by poverty. Poverty children lead compelled lives. Parents will occasionally bring children’s books when forced to bake bread.
A person living in poverty cannot access necessities such as food twice a day, clean water, a home, clothes, a good education, and so on. Several factors cause poverty in India, and another factor is an unequal distribution of national income. Low-income people are significantly less wealthy than high-income people. Low-income children are never given a good education, adequate nutrition, or a fun environment to grow up in. The leading causes of poverty are income inequality, corruption, population growth, a weak agricultural sector, and illiteracy.
Government Initiatives towards Poverty
The Indian government also took several steps to end poverty in India. Some include population control, increased employment opportunities, and so on. Agriculture still provides a living for approximately 60% of India’s population. The government of India has implemented several policies to promote agriculture. The government constructed dams and canals to facilitate irrigation water access in our country. The government has also ensured that farming supplies such as seeds and equipment are affordable. Instead of growing food crops, the government promotes the cultivation of cash crops such as cotton. In addition, the government is encouraging urban industrialization to increase employment.
In addition, the government established “Ration shops.” Other measures include subsidized housing for the poor, free and compulsory education for children up to 14, scholarships for deserving students from low-income families, and so on.
Although poverty is a social ill, everyone can contribute to its reduction. For example, you could donate old clothes to the needy, sponsor a child’s education, or teach underprivileged students in your spare time. Before you waste food, consider that someone is still sleeping hungry.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Essay on Poverty” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information,
- Essay on Honesty is the Best Policy
- Essay on Artificial Intelligence
- Essay on Wonder of Science
- Essay on Health is Wealth
By signing up, you agree to our Terms of Use and Privacy Policy .

*Please provide your correct email id. Login details for this Free course will be emailed to you
Valuation, Hadoop, Excel, Web Development & many more.
Forgot Password?
This website or its third-party tools use cookies, which are necessary to its functioning and required to achieve the purposes illustrated in the cookie policy. By closing this banner, scrolling this page, clicking a link or continuing to browse otherwise, you agree to our Privacy Policy

Explore 1000+ varieties of Mock tests View more
Submit Next Question
Early-Bird Offer: ENROLL NOW

Mental health effects of poverty, hunger, and homelessness on children and teens

Rising inflation and an uncertain economy are deeply affecting the lives of millions of Americans, particularly those living in low-income communities. It may seem impossible for a family of four to survive on just over $27,000 per year or a single person on just over $15,000, but that’s what millions of people do everyday in the United States. Approximately 37.9 million Americans, or just under 12%, now live in poverty, according to the U.S. Census Bureau .
Additional data from the Bureau show that children are more likely to experience poverty than people over the age of 18. Approximately one in six kids, 16% of all children, live in families with incomes below the official poverty line.
Those who are poor face challenges beyond a lack of resources. They also experience mental and physical issues at a much higher rate than those living above the poverty line. Read on for a summary of the myriad effects of poverty, homelessness, and hunger on children and youth. And for more information on APA’s work on issues surrounding socioeconomic status, please see the Office of Socioeconomic Status .
Who is most affected?
Poverty rates are disproportionately higher among most non-White populations. Compared to 8.2% of White Americans living in poverty, 26.8% of American Indian and Alaska Natives, 19.5% of Blacks, 17% of Hispanics and 8.1% of Asians are currently living in poverty.
Similarly, Black, Hispanic, and Indigenous children are overrepresented among children living below the poverty line. More specifically, 35.5% of Black people living in poverty in the U.S. are below the age of 18. In addition, 40.7% of Hispanic people living below the poverty line in the U.S. are younger than age 18, and 29.1% of American Indian and Native American children lived in poverty in 2018. In contrast, approximately 21% of White people living in poverty in the U.S. are less than 18 years old.
Furthermore, families with a female head of household are more than twice as likely to live in poverty compared to families with a male head of household. Twenty-three percent of female-headed households live in poverty compared to 11.4% of male-headed households, according to the U.S. Census Bureau .
What are the effects of poverty on children and teens?
The impact of poverty on young children is significant and long lasting. Poverty is associated with substandard housing, hunger, homelessness, inadequate childcare, unsafe neighborhoods, and under-resourced schools. In addition, low-income children are at greater risk than higher-income children for a range of cognitive, emotional, and health-related problems, including detrimental effects on executive functioning, below average academic achievement, poor social emotional functioning, developmental delays, behavioral problems, asthma, inadequate nutrition, low birth weight, and higher rates of pneumonia.
Psychological research also shows that living in poverty is associated with differences in structural and functional brain development in children and adolescents in areas related to cognitive processes that are critical for learning, communication, and academic achievement, including social emotional processing, memory, language, and executive functioning.
Children and families living in poverty often attend under-resourced, overcrowded schools that lack educational opportunities, books, supplies, and appropriate technology due to local funding policies. In addition, families living below the poverty line often live in school districts without adequate equal learning experiences for both gifted and special needs students with learning differences and where high school dropout rates are high .
What are the effects of hunger on children and teens?
One in eight U.S. households with children, approximately 12.5%, could not buy enough food for their families in 2021 , considerably higher than the rate for households without children (9.4%). Black (19.8%) and Latinx (16.25%) households are disproportionately impacted by food insecurity, with food insecurity rates in 2021 triple and double the rate of White households (7%), respectively.
Research has found that hunger and undernutrition can have a host of negative effects on child development. For example, maternal undernutrition during pregnancy increases the risk of negative birth outcomes, including premature birth, low birth weight, smaller head size, and lower brain weight. In addition, children experiencing hunger are at least twice as likely to report being in fair or poor health and at least 1.4 times more likely to have asthma, compared to food-secure children.
The first three years of a child’s life are a period of rapid brain development. Too little energy, protein and nutrients during this sensitive period can lead to lasting deficits in cognitive, social and emotional development . School-age children who experience severe hunger are at increased risk for poor mental health and lower academic performance , and often lag behind their peers in social and emotional skills .
What are the effects of homelessness on children and teens?
Approximately 1.2 million public school students experienced homelessness during the 2019-2020 school year, according to the National Center for Homeless Education (PDF, 1.4MB) . The report also found that students of color experienced homelessness at higher proportions than expected based on the overall number of students. Hispanic and Latino students accounted for 28% of the overall student body but 38% of students experiencing homelessness, while Black students accounted for 15% of the overall student body but 27% of students experiencing homelessness. While White students accounted for 46% of all students enrolled in public schools, they represented 26% of students experiencing homelessness.
Homelessness can have a tremendous impact on children, from their education, physical and mental health, sense of safety, and overall development. Children experiencing homelessness frequently need to worry about where they will live, their pets, their belongings, and other family members. In addition, homeless children are less likely to have adequate access to medical and dental care, and may be affected by a variety of health challenges due to inadequate nutrition and access to food, education interruptions, trauma, and disruption in family dynamics.
In terms of academic achievement, students experiencing homelessness are more than twice as likely to be chronically absent than non-homeless students , with greater rates among Black and Native American or Alaska Native students. They are also more likely to change schools multiple times and to be suspended—especially students of color.
Further, research shows that students reporting homelessness have higher rates of victimization, including increased odds of being sexually and physically victimized, and bullied. Student homelessness correlates with other problems, even when controlling for other risks. They experienced significantly greater odds of suicidality, substance abuse, alcohol abuse, risky sexual behavior, and poor grades in school.
What can you do to help children and families experiencing poverty, hunger, and homelessness?
There are many ways that you can help fight poverty in America. You can:
- Volunteer your time with charities and organizations that provide assistance to low-income and homeless children and families.
- Donate money, food, and clothing to homeless shelters and other charities in your community.
- Donate school supplies and books to underresourced schools in your area.
- Improve access to physical, mental, and behavioral health care for low-income Americans by eliminating barriers such as limitations in health care coverage.
- Create a “safety net” for children and families that provides real protection against the harmful effects of economic insecurity.
- Increase the minimum wage, affordable housing and job skills training for low-income and homeless Americans.
- Intervene in early childhood to support the health and educational development of low-income children.
- Provide support for low-income and food insecure children such as Head Start , the National School Lunch Program , and Temporary Assistance for Needy Families (TANF) .
- Increase resources for public education and access to higher education.
- Support research on poverty and its relationship to health, education, and well-being.
- Resolution on Poverty and SES
- Pathways for addressing deep poverty
- APA Deep Poverty Initiative
Home — Essay Samples — Social Issues — Homelessness — Introduction to Poverty: Causes, Effects, and Management
Introduction to Poverty: Causes, Effects, and Management
- Categories: Homelessness Hunger Poverty in America
About this sample

Words: 2156 |
11 min read
Published: May 17, 2022
Words: 2156 | Pages: 5 | 11 min read
Table of contents
Introduction, global trends of poverty, causes of poverty, effects/impacts of poverty on the family, management and control, poverty in europe, poverty in africa, poverty in kenya, lack/poor education, feminization, low economic growth performance, divorce/separation, stress/depression, emotional and physical wellbeing of the children, the governments should come up with initiatives to alleviate poverty, educating the families and equipping them with technical skills.

Cite this Essay
To export a reference to this article please select a referencing style below:
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Verified writer
- Expert in: Social Issues

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
1 pages / 609 words
1 pages / 570 words
3 pages / 1403 words
3 pages / 1201 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Homelessness
Homelessness started to become a dilemma since the 1930s leaving millions of people without homes or jobs during The Great Depression. Homeless people face numerous challenges every day dealing with shelters and food in order to [...]
Homelessness is a complex and pressing issue that affects individuals and communities worldwide. It is a state of lacking stable and secure housing, often resulting in individuals living on the streets or in temporary shelters. [...]
Homelessness is a complex and deeply rooted issue that affects individuals and communities around the world. It is a problem that demands attention and action, as it not only poses a threat to the well-being of those [...]
Anthropologist and physician Seth Holmes takes readers on a journey through the experiences of migrant farmworkers in his book, Fresh Fruit, Broken Bodies. In his ethnographic account, Holmes sheds light on the harsh realities [...]
Canfield, J. (2014). The effects of homelessness on children. Journal of Family Issues, 36(2), 165-178.Chavkin, W., Kristal, A. R., Seabron, F., & Guigli, L. (1987). Reproductive experience of homeless women in welfare hotels in [...]
Homelessness is a multifaceted social issue that plagues societies around the world. By employing the social pathology model, we can delve into the intricate web of factors that contribute to homelessness and gain a deeper [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free

Miracle Foundation
Transform the lives of orphan children and change their story.
Stories: THE MIRACLE BLOG
The miracle blog, understanding the root causes of global poverty.

Marissa Ratton
On the marketing team at Miracle Foundation, and frequent blog contributor.
Publication Date: February 8, 2024
Overcoming poverty is a complex issue. By understanding and tackling the underlying reasons behind poverty, we can take strides toward creating a world where poverty is replaced with hope and opportunity.
Four Global Causes of Poverty:
- Structural Inequality: The first step is to recognize the impact of structural inequalities within societies. These inequalities create disparities in access to resources, opportunities, and decision-making power, and addressing them is essential for breaking the cycle of poverty.
- Limited Access to Education: Educational opportunities serve as a gateway out of poverty, yet millions encounter barriers such as inadequate infrastructure, gender-based discrimination, and economic constraints. Bridging the global education gap is vital for empowering communities and eliminating global poverty. We must ensure that every child goes to school and thrives in the educational environment. And actively commit to breaking down barriers and creating a pathway for a brighter future.
- Economic Injustice: Unfair economic systems contribute significantly to global poverty. Exploitative labor practices, unequal distribution of wealth, and limited access to credit and resources hinder the economic progress of vulnerable populations. Addressing these economic injustices is critical to a sustainable poverty solution.
- Social Discrimination and Exclusion: Marginalized social groups often bear the brunt of poverty’s weight disproportionately. In our pursuit of a world where everyone has an equal opportunity to thrive, combating social discrimination and fostering inclusivity becomes imperative. At the core of our mission lies the commitment to helping families thrive; we recognize that they are the heartbeat of flourishing communities.
The elimination of global poverty demands comprehensive and collaborative solutions. At Miracle Foundation, we approach our work strategically, guided by data-driven decisions, utilizing our Thrive Scale™ methodology . We strive to create a pathway for a brighter, more equitable future by connecting people with necessary resources and support. We are unwavering in our mission to contribute to the global effort of eradicating poverty and fostering thriving, empowered communities worldwide.
Want to stay connected? Sign up for our newsletter here.
- Our Beliefs
- Our Partners
- Miracle Foundation India
- See our Financials
- Our Global Work
- Our Local Work
- Sustainable Development Goals
- UN Rights of the Child
- Give a Gift
- Get Involved
- Join Miracle Village
- Host a Fundraiser
- Become a Corporate Partner
- Work with Us
- Be an Intern
- Watch our Videos
- Listen to Podcasts
- See our Press
- Read our Stories
- Life Skills Education
- Positive Parenting
- Psychosocial Support
- Case Management Toolkit
Sign up for our occasional newsletter below:
Subscribe to receive updates.
Join our mailing list to receive the latest news and updates from our team.
You have Successfully Subscribed!
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Poverty Essay for Students in English

Essay on Poverty
Poverty is a disease that has no cure. The deeper this disease is, the deeper its wound. By the way, man lives under compulsion. But usually one wants to avoid it. Poverty is a condition of extreme poverty for any person or human being. This is a situation when a person starts to lack important things in his life such as the roof, necessary food, clothes, medicines, etc. to continue his life.
The causes of poverty are excessive population, fatal and contagious diseases, natural disasters, low agricultural yields, unemployment, casteism, illiteracy, gender inequality, environmental problems, changing trends in the economy of the country, untouchability, little or limited access to people's rights, Problems such as political violence, sponsored crime, corruption, lack of encouragement, inaction, ancient social beliefs, etc. have to be faced.
Poverty has become a big problem of the world, efforts are being made across the world today to remove poverty, but the problem is that it does not take the name of ending. This problem affects a human's economic and daily life. Poverty teaches man to live like a slave in which he has to change the place over time, in this situation due to the lack of education of the poor, his nature and speech also make a difference. Living in a world of poor people has become a curse. Getting enough money to get food is like getting relief from a curse for the poor, that's why they do not have access to education.
Reasons of Poverty
There are many reasons that have continued with carrying it for a long time. Because of this, freedom, mental and physical fitness, and lack of security in a person remains. It is very important that in order to live a normal life, the country and the whole world will have to work together to bring proper physical and mental health, complete education, a home for everyone, and other important things.
In today's time, there is the problem of poverty which gives all the pain, pain, and despair to the poor. Due to the lack of money from poverty, I show the lack of many things. Poverty makes children spend life in compulsion. If forced to make bread, sometimes in bringing children's books. At that time he is also unable to raise children.
We can tell poverty in many ways like it has become a common thing in India. Most of the people here are unable to get the things they need. Here a vast section of the population is illiterate, hungry, and forced to live without clothes and a home. About half of India's population suffers from this epidemic of poverty.
A poor person lives his life without possession of basic things like food for two times, clean water, house, clothes, proper education, etc. There are many reasons for poverty in India. Incorrect distribution of national income is also a reason. People in the low-income group are much poorer than those in the high-income group. Children of poor families never get proper education, nutrition, and a happy childhood environment. The main cause of poverty is illiteracy, corruption, growing population, weak agriculture, the growing gap between rich and poverty, etc.
Measures to Control Poverty
Corruption has to be erased.
Unemployed will have to give proper employment
A growing population will have to be stopped
Farmers have to be given proper facilities for farming
Education should be provided to children for proper education
Poverty is not just a human problem but it is a national problem. It should be solved by implementing some effective methods on a quick basis. Every person should be united by ending corruption. A problem has been created in which he does not get even the basics. That is why at present, many measures are being taken to prevent poverty so that the standard of living of people around the world can be improved.
Short Essays on Poverty
Poverty is akin to being a slave, as a person cannot achieve anything he desires. It has various faces that alter depending on who you are, where you are, and when. It can be defined in various ways depending on how a person feels or experiences it.
Poverty is a state that no one wants to be in, but it must be removed owing to cultural norms, natural disasters, or a lack of adequate education. The individual who is experiencing it frequently wishes to flee. Poverty is a call for poor people to earn enough money to eat, have access to education, have adequate shelter, dress appropriately, and take steps to protect themselves from social and political violence.
It's a problem that goes unnoticed yet significantly impacts a person's social life. Poverty is an entirely avoidable problem, but there are various reasons why it has persisted in the past.
Poverty robs people of their freedom, mental health, physical well-being, and security. Everyone must strive to eradicate poverty from the country and the world, ensuring appropriate physical and mental health, full literacy, a home for all, and other necessities for living a simple life.
When a person cannot do anything according to his will, he is said to be in poverty. Many different faces alter depending on who you are, where you are, and time. It can be characterized in a variety of ways, depending on how the person feels or what they have achieved. Poverty is a circumstance that no one wants to be in, even if it is forced upon them due to a lack of experience, nature, natural disasters, or a lack of suitable education. Humans have won it, but they prefer to stay away from it. Poverty is a call for needed clothing and protection against social and political violence for the poor to earn enough money to buy food, receive an education, and find a suitable place to live.
This is an unseen problem that harms a person's social life. Even though numerous factors have contributed to its long-term persistence, poverty is a perfectly preventable problem. As a result, a person's freedom, mental and physical well-being, and sense of security are all compromised. It is critical to bring poverty and poverty from worldwide to work together to live everyday life, provide adequate physical and mental health, complete education, a home for everyone, and other essential things.

FAQs on Poverty Essay for Students in English
1. What are the Effects of Poverty?
When people are not able to afford their basic necessities. For example medications and hospital fees are impossible to afford for that means they choose crook ways of obtaining money i.e. stealing, robbery, etc.
2. What are the Possible Ways to Remove Poverty?
Since India is a developing country, eliminating poverty here is much tougher than in other countries but still some measures can be taken and government assistance would be much helpful in this step which requires some relevant planning and policies for those who fall under the poverty line. Another major factor of poverty is illiteracy and unemployment. Therefore education is the most efficient tool to confine the poverty line in the country.
3. What is the Poverty Line?
The Below Poverty Line (BPL) signifies the state of people who fall under poverty status. It also symbolizes an economic drawback. In addition, it is used for people who are in need of help and assistance from the government.
4. What are the causes of poverty?
Poverty has several causes, including a lack of access to essentials such as water, food, shelter, education, and healthcare. Poverty is also caused by inequities such as gender or ethnic discrimination, bad governance, conflict, exploitation, and domestic violence. These disparities not only cause a person or a society to fall into poverty, but they can also prevent people from receiving social assistance that could help them get out of it. Due to political upheaval, past or present conflict, corrupt authorities, and lousy infrastructure that restricts access to education, clean water, healthcare, and other essentials, children and communities in fragile states confront greater poverty rates.
5. What can we do to put an end to extreme poverty?
We can aid in the eradication of extreme poverty by determining what causes it in a particular community and then determining what needs to change. Because poverty manifests itself differently in different regions and is caused by different circumstances, the work to end extreme poverty differs depending on the situation. More economic resources are needed to assist people in increasing their income and better providing for themselves and their families. To ensure that poverty does not return, the work must be sustainable, regardless of the solution. As a result, the community must be involved at every stage.
6. What criteria are used to assess poverty?
Each country's government determines poverty levels by conducting home surveys of its citizens. The World Bank, for example, assists and may conduct their surveys, although data collecting is time-consuming and slow. New high-frequency surveys are being created and tested, leveraging estimations and mobile phone technologies. If you want to learn more about these topics, download the Vedantu App that has been specifically designed and curated for students by experts.
7. What is the poverty cycle?
Poverty can be a catch-22 situation. To escape poverty, a person requires access to possibilities such as education, clean water, local medical services, and financial means. Poverty creates a generational cycle if these critical factors are not there. If parents cannot afford to take their children to school, they will struggle to find work when they grow up. Even natural disasters and conflicts can exacerbate the poverty cycle by bringing more people.
8. What are the United Nations' Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)?
The Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) are a set of goals for countries worldwide to work together in a global partnership for the benefit of people, the environment, and prosperity. The Sustainable Development Goals aim to abolish extreme poverty for all people everywhere by 2030 and to reduce the proportion of people living in poverty in all forms by at least half. In September 2015, the United Nations member states accepted this objective as one of 17 to end extreme poverty.

Search form
- Our experts

The Causes of Poverty
This paper is an inquiry into the causes of poverty. By poverty we mean a circumstance of serious deprivation where a person lacks one or more basic need—as opposed to a condition of inequality. The question we wish to try to answer is this: Why do some people find themselves in a circumstance of serious deprivation and, more importantly, why are some able to escape poverty fairly easily while others endure persistent, long-term poverty?
This study’s working hypothesis is that there are two broad categories of the “initiating causes” of poverty—bad luck and bad choices. Bad luck means that we have no ability to avoid poverty. It is inevitable given the circumstance we find ourselves in. People caught in the middle of a war zone, people living through extreme weather events (droughts, floods, earthquakes, etc.), and people who live under maniacal autocracies where choice is severely limited or non-existent—all could be impoverished as a result of bad luck. In most western nations (which operate under a democratic system which has respect for basic rights and the rule of law) luck is less important as an explanation of poverty, but is still a factor. People born with inherited diseases or disabilities, people who face serious discrimination, and children who are raised by bad, abusive parents are all at higher risk of encountering poverty. However, while many are touched by poverty, only a small portion remain in poverty over the longer term, and their doing so depends both on the choices they make and the opportunities (or impediments) to upward mobility. This paper focuses attention on “choice” rather than luck as a more compelling explanation of poverty in modern democratic nations like Canada and the United States, and also focuses on the role that the state plays in enabling poverty.
None of us get to choose exactly where we end up in life. As we move out of childhood and begin to assume more autonomy over our own lives, we make thousands of decisions. These choices are always made without perfect information and with a variety of constraints and restrictions, most of which are inherent in the human condition. If we make enough good choices and avoid some really bad ones, we end up living in relative comfort and safety. By the time we enter adulthood, we recognize that making bad choices (“bad” as defined by the decisionmaker himself either at the time of the decision or subsequently) involves negative consequences. Those bad outcomes hurt. They make us worse off. But, in the process, they help us make better decisions in the future.
A third factor is important in explaining poverty, especially the kind of persistent, longer term poverty that is especially pernicious. We can say that poverty is “enabled” when systems and structures are in place to discourage the kinds of efforts that people would normally make to avoid poverty, i.e., find employment, find a partner (especially if children are present), improve one’s education and skill set, have a positive outlook, and take personal responsibility for your own actions. Ironically, it is government programs (welfare, in particular) that are intended to help the poor but end up actually enabling poverty.
This paper highlights a 2003 Brookings Institution study that identifies bad choices as the primary initiating cause of poverty in America. Specifically, the study shows that basic choices about education (at least finishing high school), work (acquiring a full-time job), and family (getting married or being in a committed relationship before having kids and only having the number of children you can afford), are critical to avoiding poverty. The Brookings study concludes that if these three basic societal norms are followed, your chance of falling into poverty is less than 3 percent. The Brookings authors, Isabel Sawhill and Ron Haskins, urge that anti-poverty efforts be directed toward encouraging people to follow these norms and to take responsibility for their own lives. Both authors would like to see an end to poverty and a more egalitarian society and they argue strongly that “playing by the rules” is the solution to poverty, not a welfare system that simply redistributes income.
In a follow-up policy paper, the Brookings Institution assembled a panel of experts representing various perspectives to outline the principal causes of and solutions to poverty. It lays out a plan of action that is broadly similar to the Sawhill-Haskins proposals and clearly implies that behavioural factors (i.e., choices) are the primary cause of poverty and that with the right policies and incentives as well as the expectation of personal responsibility, behaviours can change. Specifically, the experts suggest policies that promote cultural norms relating to parenthood and marriage, promote delayed, responsible childbearing, increase access to effective parenting education, improve skills and make work pay for the less educated, and increase public investments in early childhood education.
The Canadian evidence is similar to that presented for the United States. When social norms like finishing high school, getting a full-time job, and having children only after getting married are followed, poverty rates are extremely low (less than 1%) using 2015 data. Single-parent families, especially in those cases where the parent was never married, have among the highest incidence of poverty in Canada, as is the case in the US. Yet, single parent families where the parent is employed full-time reduce their risk of poverty more than four-fold.
Unless poverty is “enabled,” most people, regardless of their disadvantage, manage to escape poverty. So, bad choices and bad luck are not destiny. Enablement effectively reduces the cost of bad choices and makes them more likely. Bad choices can be enabled by ineffective and counterproductive policy. For example, the existing welfare system, undoubtedly developed with good intentions to help the poor, turns out to be the key enabler of poverty. In practice, a system that has no employment strategy for clients, has no requirements of them, and expects nothing from them, is simply unhelpful. It slowly traps some people, especially those with low self-esteem and little confidence, into a child-like state of dependency and permanent low income.
Anyone who cares about the poor and wants to eliminate this horrible predicament needs first to understand what causes poverty. This paper suggests that a useful framework for understanding poverty is to look at bad luck and bad choices as the proximate causes, and to enablement as the key explanation for persistent and enduring poverty. I have argued that bad choices are the dominant initiating cause of poverty in countries like Canada and the US, and that state policies like welfare are the critical enablers of poverty. I largely agree with the diverse Brookings Institution panel that the identification and promotion of beneficial personal life choices (such as those relating to education, work, and family) as well as the avoidance of counterproductive and harmful government policies are the obvious policy takeaways from this paper’s analysis.

More from this study
Subscribe to the Fraser Institute
Get the latest news from the Fraser Institute on the latest research studies, news and events.

COMMENTS
Understanding the causes and effects of poverty is crucial in developing effective strategies to combat it. This essay delves into the intricate causes and far-reaching effects of poverty, highlighting the interconnectedness of various factors that perpetuate this global issue.
These may include various addictions, insufficient level of education, a person's worldview, and other reasons. Structural factors include labor market conditions, demographic context, and other socio-economic circumstances. An example is the increase in poverty associated with the development of the COVID-19 pandemic.
In conclusion, poverty is a complex issue with various interrelated causes. Lack of education, unemployment, inadequate social welfare systems, gender inequality, and political instability all contribute to the perpetuation of poverty. Addressing these causes requires a comprehensive approach that involves investing in education, creating ...
We can define poverty as the condition where the basic needs of a family, like food, shelter, clothing, and education are not fulfilled. In this Essay on Poverty will discuss about causes and effects of Poverty.
Poverty, the state of one who lacks a usual or socially acceptable amount of money or material possessions. Poverty is said to exist when people lack the means to satisfy their basic needs. Learn more about types and causes of poverty in this article.
Looking for poverty essay ideas? Check our ultimate list of 390 poverty essay topics, research questions about poverty, and free essay examples.
What causes poverty in the first place? Here are ten root causes: #1. Lack of good jobs/job growth. This is the first reason a lot of people think about. When you don't have a good job, you aren't getting a good income. In many countries, traditional jobs like farming are disappearing. The Democratic Republic of Congo is a good example ...
The theory of poverty outlined in this paper suggests that a significant cause of poverty is people making bad choices—"bad" by the reckoning of the person him or herself either at the time or in hindsight. In this context, a bad choice is one that substantially increases a person's risk of falling into poverty.
Free cause and effect essay sample: Nations which are nowadays among the poorest in the world were once colonies, or areas from which richer countries exported slaves.
This essay discusses the causes of poverty in the world. Poverty and related social inequality are as old as human history. Over the years, people have postulated many causes of poverty and social inequality. The many causes of poverty not withstanding, many definitions of the phenomena have been established. Whichever the definition, poverty is associated with want, lack of or deprivation of ...
In this article, we'll provide a thorough definition alongside key facts everyone should know and the best ways to take action. Poverty occurs when individuals and communities don't have enough money or resources for a basic standard of living. That includes good housing, food, clean water, healthcare, and much more.
Causes and Effects of Poverty Any discussion of social class and mobility would be incomplete without a discussion of poverty, which is defined as the lack of the minimum food and shelter necessary for maintaining life. More specifically, this condition is known as absolute poverty.
Over 700 million people live in extreme poverty. But why? Updated for 2024, we look at 11 of the top causes of poverty around the world.
Poverty in the United States is a pervasive issue that continues to impact millions of individuals and families across the country. Despite being one of the wealthiest nations in the world, a significant portion of the population struggles to make ends meet, facing challenges such as inadequate access to education, healthcare, and affordable housing. This essay will explore the root causes of ...
Poverty can mean missed payments, which can ruin your credit. But just as troublesome as bad credit is having no credit score at all, which is the case for 26 million adults in the United States ...
Poverty can thus define as a lack of resources or, more broadly, as barriers to basic human needs. With the help of this poverty essay, students will learn what poverty is, the leading causes of poverty, and the steps taken to eradicate poverty in India.
Abstract—Poverty is a multi-facet phenomenon in today's globalised world. It is rooted in various causes and there are also multiple ways to do away with it. This paper begins with a review on the definitions and measurement of poverty and followed by discussing the various causes of poverty. This paper specifically identifies corruption, education, political instability, geographical ...
Learn about the effects of youth poverty on academic achievement, psychosocial outcomes and physical health, as well as the prevalence of child hunger in the U.S.
Poverty brings the poor to low levels of health and education, lack of clean water and sanitation, inadequate physical security, lack of voice, and insufficient capacity and opportunity to better one's life. To discuss the issue of poverty, this essay analyzes global trends, causes, effects, and management of poverty.
By understanding and tackling the underlying reasons behind poverty, we can take strides toward creating a world where poverty is replaced with hope and opportunity. Four Global Causes of Poverty: Structural Inequality: The first step is to recognize the impact of structural inequalities within societies. These inequalities create disparities ...
Learn about Poverty Essay Topic of English in detail explained by subject experts on vedantu.com. Register free for online tutoring session to clear your doubts.
The Causes of Poverty. This paper is an inquiry into the causes of poverty. By poverty we mean a circumstance of serious deprivation where a person lacks one or more basic need—as opposed to a condition of inequality. The question we wish to try to answer is this: Why do some people find themselves in a circumstance of serious deprivation and ...
The causes of poverty are innumerable, including overpopulation, lack of education, bad government, and countless more. People have a tendency to blame the poor for living in such state going back to the same causes time after time, but the global issue…. 751 Words.