- Privacy Policy

Home » Table of Contents – Types, Formats, Examples

Table of Contents – Types, Formats, Examples
Table of Contents

Definition:
Table of contents (TOC) is a list of the headings or sections in a document or book, arranged in the order in which they appear. It serves as a roadmap or guide to the contents of the document, allowing readers to quickly find specific information they are looking for.
A typical table of contents includes chapter titles, section headings, subheadings, and their corresponding page numbers.
The table of contents is usually located at the beginning of the document or book, after the title page and any front matter, such as a preface or introduction.
Table of Contents in Research
In Research, A Table of Contents (TOC) is a structured list of the main sections or chapters of a research paper , Thesis and Dissertation . It provides readers with an overview of the organization and structure of the document, allowing them to quickly locate specific information and navigate through the document.
Importance of Table of Contents
Here are some reasons why a TOC is important:
- Navigation : It serves as a roadmap that helps readers navigate the document easily. By providing a clear and concise overview of the contents, readers can quickly locate the section they need to read without having to search through the entire document.
- Organization : A well-structured TOC reflects the organization of the document. It helps to organize the content logically and categorize it into easily digestible chunks, which makes it easier for readers to understand and follow.
- Clarity : It can help to clarify the document’s purpose, scope, and structure. It provides an overview of the document’s main topics and subtopics, which can help readers to understand the content’s overall message.
- Efficiency : This can save readers time and effort by allowing them to skip to the section they need to read, rather than having to go through the entire document.
- Professionalism : Including a Table of Contents in a document shows that the author has taken the time and effort to organize the content properly. It adds a level of professionalism and credibility to the document.
Types of Table of Contents
There are different types of table of contents depending on the purpose and structure of the document. Here are some examples:
Simple Table of Contents
This is a basic table of contents that lists the major sections or chapters of a document along with their corresponding page numbers.
Example: Table of Contents
I. Introduction …………………………………………. 1
II. Literature Review ………………………………… 3
III. Methodology ……………………………………… 6
IV. Results …………………………………………….. 9
V. Discussion …………………………………………. 12
VI. Conclusion ……………………………………….. 15
Expanded Table of Contents
This type of table of contents provides more detailed information about the contents of each section or chapter, including subsections and subheadings.
A. Background …………………………………….. 1
B. Problem Statement ………………………….. 2
C. Research Questions ……………………….. 3
II. Literature Review ………………………………… 5
A. Theoretical Framework …………………… 5
B. Previous Research ………………………….. 6
C. Gaps and Limitations ……………………… 8 I
II. Methodology ……………………………………… 11
A. Research Design ……………………………. 11
B. Data Collection …………………………….. 12
C. Data Analysis ……………………………….. 13
IV. Results …………………………………………….. 15
A. Descriptive Statistics ……………………… 15
B. Hypothesis Testing …………………………. 17
V. Discussion …………………………………………. 20
A. Interpretation of Findings ……………… 20
B. Implications for Practice ………………… 22
VI. Conclusion ……………………………………….. 25
A. Summary of Findings ……………………… 25
B. Contributions and Recommendations ….. 27
Graphic Table of Contents
This type of table of contents uses visual aids, such as icons or images, to represent the different sections or chapters of a document.
I. Introduction …………………………………………. [image of a light bulb]
II. Literature Review ………………………………… [image of a book]
III. Methodology ……………………………………… [image of a microscope]
IV. Results …………………………………………….. [image of a graph]
V. Discussion …………………………………………. [image of a conversation bubble]
Alphabetical Table of Contents
This type of table of contents lists the different topics or keywords in alphabetical order, along with their corresponding page numbers.
A. Abstract ……………………………………………… 1
B. Background …………………………………………. 3
C. Conclusion …………………………………………. 10
D. Data Analysis …………………………………….. 8
E. Ethics ……………………………………………….. 6
F. Findings ……………………………………………… 7
G. Introduction ……………………………………….. 1
H. Hypothesis ………………………………………….. 5
I. Literature Review ………………………………… 2
J. Methodology ……………………………………… 4
K. Limitations …………………………………………. 9
L. Results ………………………………………………… 7
M. Discussion …………………………………………. 10
Hierarchical Table of Contents
This type of table of contents displays the different levels of headings and subheadings in a hierarchical order, indicating the relative importance and relationship between the different sections.
A. Background …………………………………….. 2
B. Purpose of the Study ……………………….. 3
A. Theoretical Framework …………………… 5
1. Concept A ……………………………….. 6
a. Definition ………………………….. 6
b. Example ……………………………. 7
2. Concept B ……………………………….. 8
B. Previous Research ………………………….. 9
III. Methodology ……………………………………… 12
A. Research Design ……………………………. 12
1. Sample ……………………………………. 13
2. Procedure ………………………………. 14
B. Data Collection …………………………….. 15
1. Instrumentation ……………………….. 16
2. Validity and Reliability ………………. 17
C. Data Analysis ……………………………….. 18
1. Descriptive Statistics …………………… 19
2. Inferential Statistics ………………….. 20
IV. Result s …………………………………………….. 22
A. Overview of Findings ……………………… 22
B. Hypothesis Testing …………………………. 23
V. Discussion …………………………………………. 26
A. Interpretation of Findings ………………… 26
B. Implications for Practice ………………… 28
VI. Conclusion ……………………………………….. 31
A. Summary of Findings ……………………… 31
B. Contributions and Recommendations ….. 33
Table of Contents Format
Here’s an example format for a Table of Contents:
I. Introduction
C. Methodology
II. Background
A. Historical Context
B. Literature Review
III. Methodology
A. Research Design
B. Data Collection
C. Data Analysis
IV. Results
A. Descriptive Statistics
B. Inferential Statistics
C. Qualitative Findings
V. Discussion
A. Interpretation of Results
B. Implications for Practice
C. Limitations and Future Research
VI. Conclusion
A. Summary of Findings
B. Contributions to the Field
C. Final Remarks
VII. References
VIII. Appendices
Note : This is just an example format and can vary depending on the type of document or research paper you are writing.
When to use Table of Contents
A TOC can be particularly useful in the following cases:
- Lengthy documents : If the document is lengthy, with several sections and subsections, a Table of contents can help readers quickly navigate the document and find the relevant information.
- Complex documents: If the document is complex, with multiple topics or themes, a TOC can help readers understand the relationships between the different sections and how they are connected.
- Technical documents: If the document is technical, with a lot of jargon or specialized terminology, This can help readers understand the organization of the document and locate the information they need.
- Legal documents: If the document is a legal document, such as a contract or a legal brief, It helps readers quickly locate specific sections or provisions.
How to Make a Table of Contents
Here are the steps to create a table of contents:
- Organize your document: Before you start making a table of contents, organize your document into sections and subsections. Each section should have a clear and descriptive heading that summarizes the content.
- Add heading styles : Use the heading styles in your word processor to format the headings in your document. The heading styles are usually named Heading 1, Heading 2, Heading 3, and so on. Apply the appropriate heading style to each section heading in your document.
- Insert a table of contents: Once you’ve added headings to your document, you can insert a table of contents. In Microsoft Word, go to the References tab, click on Table of Contents, and choose a style from the list. The table of contents will be inserted into your document.
- Update the table of contents: If you make changes to your document, such as adding or deleting sections, you’ll need to update the table of contents. In Microsoft Word, right-click on the table of contents and select Update Field. Choose whether you want to update the page numbers or the entire table, and click OK.
Purpose of Table of Contents
A table of contents (TOC) serves several purposes, including:
- Marketing : It can be used as a marketing tool to entice readers to read a book or document. By highlighting the most interesting or compelling sections, a TOC can give readers a preview of what’s to come and encourage them to dive deeper into the content.
- Accessibility : A TOC can make a document or book more accessible to people with disabilities, such as those who use screen readers or other assistive technologies. By providing a clear and organized overview of the content, a TOC can help these readers navigate the material more easily.
- Collaboration : This can be used as a collaboration tool to help multiple authors or editors work together on a document or book. By providing a shared framework for organizing the content, a TOC can help ensure that everyone is on the same page and working towards the same goals.
- Reference : It can serve as a reference tool for readers who need to revisit specific sections of a document or book. By providing a clear overview of the content and organization, a TOC can help readers quickly locate the information they need, even if they don’t remember exactly where it was located.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Structure the Table of Contents for a Research Paper

4-minute read
- 16th July 2023
So you’ve made it to the important step of writing the table of contents for your paper. Congratulations on making it this far! Whether you’re writing a research paper or a dissertation , the table of contents not only provides the reader with guidance on where to find the sections of your paper, but it also signals that a quality piece of research is to follow. Here, we will provide detailed instructions on how to structure the table of contents for your research paper.
Steps to Create a Table of Contents
- Insert the table of contents after the title page.
Within the structure of your research paper , you should place the table of contents after the title page but before the introduction or the beginning of the content. If your research paper includes an abstract or an acknowledgements section , place the table of contents after it.
- List all the paper’s sections and subsections in chronological order.
Depending on the complexity of your paper, this list will include chapters (first-level headings), chapter sections (second-level headings), and perhaps subsections (third-level headings). If you have a chapter outline , it will come in handy during this step. You should include the bibliography and all appendices in your table of contents. If you have more than a few charts and figures (more often the case in a dissertation than in a research paper), you should add them to a separate list of charts and figures that immediately follows the table of contents. (Check out our FAQs below for additional guidance on items that should not be in your table of contents.)
- Paginate each section.
Label each section and subsection with the page number it begins on. Be sure to do a check after you’ve made your final edits to ensure that you don’t need to update the page numbers.
- Format your table of contents.
The way you format your table of contents will depend on the style guide you use for the rest of your paper. For example, there are table of contents formatting guidelines for Turabian/Chicago and MLA styles, and although the APA recommends checking with your instructor for formatting instructions (always a good rule of thumb), you can also create a table of contents for a research paper that follows APA style .
- Add hyperlinks if you like.
Depending on the word processing software you’re using, you may also be able to hyperlink the sections of your table of contents for easier navigation through your paper. (Instructions for this feature are available for both Microsoft Word and Google Docs .)
To summarize, the following steps will help you create a clear and concise table of contents to guide readers through your research paper:
1. Insert the table of contents after the title page.
2. List all the sections and subsections in chronological order.
3. Paginate each section.
4. Format the table of contents according to your style guide.
5. Add optional hyperlinks.
If you’d like help formatting and proofreading your research paper , check out some of our services. You can even submit a sample for free . Best of luck writing your research paper table of contents!
What is a table of contents?
A table of contents is a listing of each section of a document in chronological order, accompanied by the page number where the section begins. A table of contents gives the reader an overview of the contents of a document, as well as providing guidance on where to find each section.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
What should I include in my table of contents?
If your paper contains any of the following sections, they should be included in your table of contents:
● Chapters, chapter sections, and subsections
● Introduction
● Conclusion
● Appendices
● Bibliography
Although recommendations may differ among institutions, you generally should not include the following in your table of contents:
● Title page
● Abstract
● Acknowledgements
● Forward or preface
If you have several charts, figures, or tables, consider creating a separate list for them that will immediately follow the table of contents. Also, you don’t need to include the table of contents itself in your table of contents.
Is there more than one way to format a table of contents?
Yes! In addition to following any recommendations from your instructor or institution, you should follow the stipulations of your style guide .
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...
How to Ace Slack Messaging for Contractors and Freelancers
Effective professional communication is an important skill for contractors and freelancers navigating remote work environments....
3-minute read
How to Insert a Text Box in a Google Doc
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- Dissertation Table of Contents in Word | Instructions & Examples
Dissertation Table of Contents in Word | Instructions & Examples
Published on 15 May 2022 by Tegan George .
The table of contents is where you list the chapters and major sections of your thesis, dissertation, or research paper, alongside their page numbers. A clear and well-formatted table of contents is essential, as it demonstrates to your reader that a quality paper will follow.
The table of contents (TOC) should be placed between the abstract and the introduction. The maximum length should be two pages. Depending on the nature of your thesis, dissertation, or paper, there are a few formatting options you can choose from.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
What to include in your table of contents, what not to include in your table of contents, creating a table of contents in microsoft word, table of contents examples, updating a table of contents in microsoft word, other lists in your thesis, dissertation, or research paper, frequently asked questions about the table of contents.
Depending on the length of your document, you can choose between a single-level, subdivided, or multi-level table of contents.
- A single-level table of contents only includes ‘level 1’ headings, or chapters. This is the simplest option, but it may be too broad for a long document like a dissertation.
- A subdivided table of contents includes chapters as well as ‘level 2’ headings, or sections. These show your reader what each chapter contains.
- A multi-level table of contents also further divides sections into ‘level 3’ headings. This option can get messy quickly, so proceed with caution. Remember your table of contents should not be longer than 2 pages. A multi-level table is often a good choice for a shorter document like a research paper.
Examples of level 1 headings are Introduction, Literature Review, Methodology, and Bibliography. Subsections of each of these would be level 2 headings, further describing the contents of each chapter or large section. Any further subsections would be level 3.
In these introductory sections, less is often more. As you decide which sections to include, narrow it down to only the most essential.
Including appendices and tables
You should include all appendices in your table of contents. Whether or not you include tables and figures depends largely on how many there are in your document.
If there are more than three figures and tables, you might consider listing them on a separate page. Otherwise, you can include each one in the table of contents.
- Theses and dissertations often have a separate list of figures and tables.
- Research papers generally don’t have a separate list of figures and tables.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
All level 1 and level 2 headings should be included in your table of contents, with level 3 headings used very sparingly.
The following things should never be included in a table of contents:
- Your acknowledgements page
- Your abstract
- The table of contents itself
The acknowledgements and abstract always precede the table of contents, so there’s no need to include them. This goes for any sections that precede the table of contents.
To automatically insert a table of contents in Microsoft Word, be sure to first apply the correct heading styles throughout the document, as shown below.
- Choose which headings are heading 1 and which are heading 2 (or 3!
- For example, if all level 1 headings should be Times New Roman, 12-point font, and bold, add this formatting to the first level 1 heading.
- Highlight the level 1 heading.
- Right-click the style that says ‘Heading 1’.
- Select ‘Update Heading 1 to Match Selection’.
- Allocate the formatting for each heading throughout your document by highlighting the heading in question and clicking the style you wish to apply.
Once that’s all set, follow these steps:
- Add a title to your table of contents. Be sure to check if your citation style or university has guidelines for this.
- Place your cursor where you would like your table of contents to go.
- In the ‘References’ section at the top, locate the Table of Contents group.
- Here, you can select which levels of headings you would like to include. You can also make manual adjustments to each level by clicking the Modify button.
- When you are ready to insert the table of contents, click ‘OK’ and it will be automatically generated, as shown below.
The key features of a table of contents are:
- Clear headings and subheadings
- Corresponding page numbers
Check with your educational institution to see if they have any specific formatting or design requirements.
Write yourself a reminder to update your table of contents as one of your final tasks before submitting your dissertation or paper. It’s normal for your text to shift a bit as you input your final edits, and it’s crucial that your page numbers correspond correctly.
It’s easy to update your page numbers automatically in Microsoft Word. Simply right-click the table of contents and select ‘Update Field’. You can choose either to update page numbers only or to update all information in your table of contents.
In addition to a table of contents, you might also want to include a list of figures and tables, a list of abbreviations and a glossary in your thesis or dissertation. You can use the following guides to do so:
- List of figures and tables
- List of abbreviations
It is less common to include these lists in a research paper.
All level 1 and 2 headings should be included in your table of contents . That means the titles of your chapters and the main sections within them.
The contents should also include all appendices and the lists of tables and figures, if applicable, as well as your reference list .
Do not include the acknowledgements or abstract in the table of contents.
To automatically insert a table of contents in Microsoft Word, follow these steps:
- Apply heading styles throughout the document.
- In the references section in the ribbon, locate the Table of Contents group.
- Click the arrow next to the Table of Contents icon and select Custom Table of Contents.
- Select which levels of headings you would like to include in the table of contents.
Make sure to update your table of contents if you move text or change headings. To update, simply right click and select Update Field.
The table of contents in a thesis or dissertation always goes between your abstract and your introduction.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
George, T. (2022, May 15). Dissertation Table of Contents in Word | Instructions & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 27 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/contents-page/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, dissertation title page, how to write an abstract | steps & examples, thesis & dissertation acknowledgements | tips & examples.
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
A Table of Contents in APA Format
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Adah Chung is a fact checker, writer, researcher, and occupational therapist.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Adah-Chung-1000-df54540455394e3ab797f6fce238d785.jpg)
General Guidelines
- Table of Contents
APA style does not require a table of contents, but there are cases where you may need to include one. For example, your instructor may specify that your paper must be submitted with a table of contents. A table of contents can be particularly helpful in cases where your paper is lengthy or covers a lot of material, such as a thesis paper or dissertation. Research papers, in particular, may benefit from the addition of a table of contents.
APA style is the official publication style of the American Psychological Association. APA style is used in psychology courses as well as other social science classes including those in social science, behavioral sciences, and education.
The table of contents serves as a basic roadmap of your paper. It should list all of the major headings and subheadings within the body of your paper. For a standard psychology paper, it might include listings for the introduction, method, results, and discussion sections of your paper.
While the APA may not specify guidelines for a table of contents, you should use the basic APA format for formatting your table of contents:
- Use one-inch margins on all sides
- Use 12-point Times New Roman font
- Double-space
Since APA does not require a table of contents, you should always refer to your instructor’s guidelines when deciding whether or not to include one.
It is also important to note that the 7th edition of the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association was published in 2020, and included updated guidelines on many topics.
For example, while the previous edition of the style manual required a running head on each page of a paper, the 7th edition has eliminated that requirement on student papers unless your instructor specifies to include it. Always ask first.
If you are using a standard APA paper format, your table of contents should include the following sections:
- Introduction
The above format may work well for a standard lab report or research paper. However, your table of contents will look much different if you are writing something such as a critique, essay, or case study.
Notice, that the table of contents does not include the abstract or acknowledgments pages. When applicable, it should list the appendices and the lists of tables and figures.
The exact order of your paper depends largely on the type of paper you are writing. In general, your paper should be presented in the following order:
- Main Body of Paper
Table of Contents Format
Because there is no standard format for a table of contents in APA style, you should always defer to the provided guidelines for your assignment.
If your instructor does not have a preferred format, consider using the following:
- Title the page “Table of Contents” and center the title at the top of the page.
- Most papers should include at least two levels of headings, up to five levels.
- Level one headings will be for main topics, such as chapter titles like "Chapter One; Name of Chapter," or research sections like "Method," "Results," and "Discussion."
- All level-one headings should be flush-left and sub-headings should be indented five spaces deeper than the last.
- All heading levels should be in title case, capitalizing the first letter of each word. The font type, style, and size stay the same for each level.
- The page number for each heading is formatted flush-right. Include dot leaders between the headings and the page number to improve readability.
While you might not think that following APA format is important, it is one of those areas where students can lose points for making small errors. It pays to spend a little extra time and attention making sure that your paper is formatted in proper APA style.
- If you need help, you can get assistance from your school's writing lab.
- Getting your own copy of the latest edition of the APA publication manual can be very helpful.
- Always refer to any instructions or guidelines that were provided by your course instructor.
- There is a helpful feature in most word processors that you can use to pre-format your paper in APA style. It takes a little effort to set it up, but well worth it in the end, especially for longer documents. You can save the style to apply to your future papers saving you the effort next time.
For those writing a paper to submit for publication, check with the publisher for any specific formatting requirements that they may have.
American Psychological Association. Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (7th ed.) ; 2020.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
How to Write a Table of Contents for Different Formats With Examples
- Icon Calendar 18 May 2024
- Icon Page 984 words
- Icon Clock 6 min read
Rules that guide academic writing are specific to each paper format. However, some rules apply to all styles – APA, MLA, Chicago/Turabian, and Harvard. Basically, one of these rules is the inclusion of a Table of Contents (TOC) in an academic text, particularly long ones, like theses, dissertations, and research papers. When writing a TOC, students or researchers should observe some practices regardless of paper formats. Also, it includes writing the TOC on a new page after the title page, numbering the first-level and corresponding second-level headings, and indicating the page number of each entry. Hence, scholars need to learn how to write a table of contents in APA, MLA, Chicago/Turabian, and Harvard styles.
General Guidelines
When writing academic texts, such as theses, dissertations, and other research papers, students observe academic writing rules as applicable. Generally, the different paper formats – APA, MLA, Chicago/Turabian, and Harvard – have specific standards that students must follow in their writing. In this case, one of the rules is the inclusion of a Table of Contents (TOC) in the document. By definition, a TOC is a roadmap that scholars provide in their writing, outlining each portion of a paper. In other words, a TOC enables readers to locate specific information in documents or revisit favorite parts within written texts. Moreover, this part of academic papers provides readers with a preview of the paper’s contents.

Difference Between a Table of Contents and an Outline
In essence, a TOC is a description of first-level headings (topics) and second-level headings (subtopics) within the paper’s body. For a longer document, writers may also include third-level titles to make the text palatable to read. Ideally, the length of papers determines the depth that authors go into detailing their writing in TOCs. Basically, this feature means that shorter texts may not require third-level headings. In contrast, an essay outline is a summary of the paper’s main ideas with a hierarchical or logical structuring of the content. Unlike a TOC that only lists headings and subheadings, outlines capture these headings and then describe the content briefly under each one. As such, an outline provides a more in-depth summary of essay papers compared to a TOC.
How to Write a Table of Contents in APA
When writing a TOC in the APA format, writers should capture all the headings in the paper – first-level, second-level, and even third-level. Besides this information, they should also include an abstract, references, and appendices. Notably, while a TOC in the APA style has an abstract, this section is not necessary for the other formats, like MLA, Chicago/Turabian, and Harvard. Hence, an example of a Table of Contents written in the APA format is indicated below:
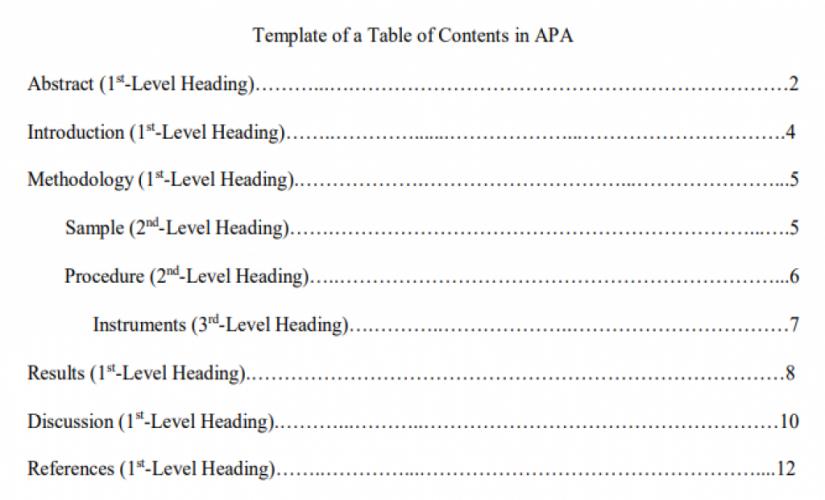
How to Write a Table of Contents in MLA
Unlike papers written in the APA style, MLA papers do not require a Table of Contents unless they are long enough. In this case, documents, like theses, dissertations, and books written in the MLA format should have a TOC. Even where a TOC is necessary, there is no specific method that a writer should use when writing it. In turn, the structure of the TOC is left to the writer’s discretion. However, when students have to include a TOC in their papers, the information they capture should be much more than what would appear in the APA paper. Hence, an example of writing a Table of Contents in MLA format is:

In the case of writing a research paper, an example of a Table of Contents should be:


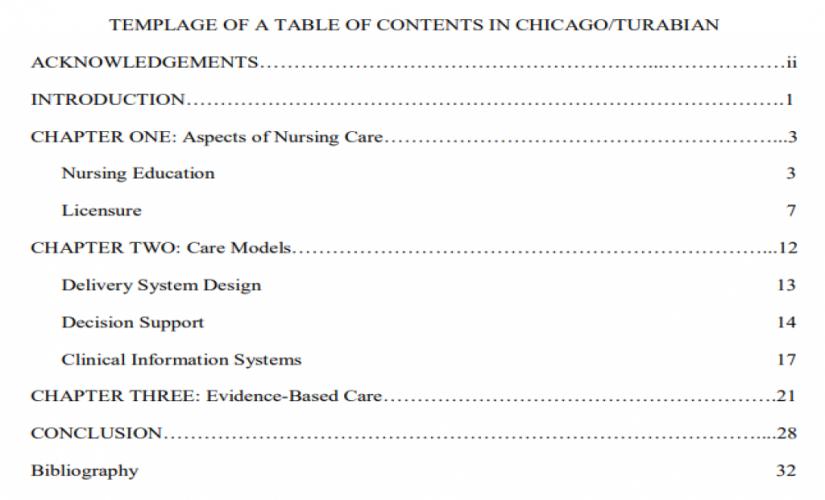
How to Write a Table of Contents in Chicago/Turabian
Like the MLA style, a Chicago/Turabian paper does not require writing a Table of Contents unless it is long enough. When a TOC is necessary, writers should capitalize on major headings. Additionally, authors do not need to add a row of periods (. . . . . . . .) between the heading entry and the page number. Moreover, the arrangement of the content should start with the first-level heading, then the second-level heading, and, finally, the third-level title, just like in the APA paper. In turn, all the information that precedes the introduction part should have lowercase Roman numerals. Also, the row of periods is only used for major headings. Hence, an example of writing a Table of Contents in a Chicago/Turabian paper is:
How to Write a Table of Contents in Harvard
Like in the other formats, writing a Table of Contents in the Harvard style is captured by having the title “Table of Contents” at the center of the page, in the first line. Basically, it comes after the title page and captures all the sections and subsections of Harvard papers. In other words, writers must indicate first-level headings in a numbered list. Also, scholars should align titles to the left side and capitalize them. In turn, if there is a need to show second-level headings, authors should list them under corresponding first-level headings by using bullet points. However, it is essential for students not to disrupt the numbering of first-level headings. Moreover, writers should align second-level headings to the left side and indent them by half an inch and capitalize on this content. Hence, an example of writing a Table of Contents in a Harvard paper should appear as below:
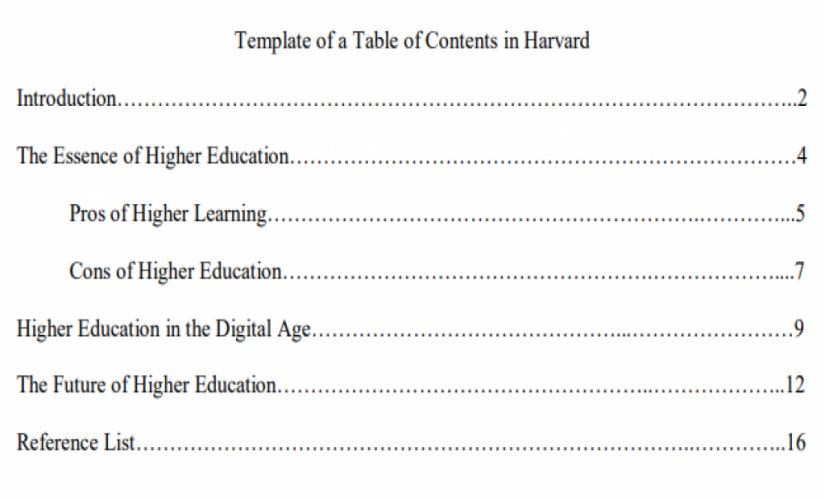
A Table of Content (TOC) is an essential component of an academic paper, particularly for long documents, like theses, dissertations, and research papers. When students are writing a TOC, they should be careful to follow the applicable format’s rules and standards. Regardless of the format, writers should master the following tips when writing a TOC:
- Write the TOC on a new page after the title page.
- Indicate first-level headings of the document in a numbered list.
- Indicate second-level headings under the corresponding first-level heading.
- If applicable, indicate third-level headings under the corresponding second-level heading.
- Write the page number for each heading.
- Put the content in a two-column table.
- Title the page with “Table of Contents.”
To Learn More, Read Relevant Articles

MIT Essay Prompts: Free Examples of Writing Assignments in 2024
- Icon Calendar 26 August 2020
- Icon Page 2576 words

How to Cite a Dictionary in MLA 9: Guidelines and Examples
- Icon Calendar 24 August 2020
- Icon Page 1342 words

The Plagiarism Checker Online For Your Academic Work
Start Plagiarism Check
Editing & Proofreading for Your Research Paper
Get it proofread now
Online Printing & Binding with Free Express Delivery
Configure binding now
- Academic essay overview
- The writing process
- Structuring academic essays
- Types of academic essays
- Academic writing overview
- Sentence structure
- Academic writing process
- Improving your academic writing
- Titles and headings
- APA style overview
- APA citation & referencing
- APA structure & sections
- Citation & referencing
- Structure and sections
- APA examples overview
- Commonly used citations
- Other examples
- British English vs. American English
- Chicago style overview
- Chicago citation & referencing
- Chicago structure & sections
- Chicago style examples
- Citing sources overview
- Citation format
- Citation examples
- College essay overview
- Application
- How to write a college essay
- Types of college essays
- Commonly confused words
- Definitions
- Dissertation overview
- Dissertation structure & sections
- Dissertation writing process
- Graduate school overview
- Application & admission
- Study abroad
- Master degree
- Harvard referencing overview
- Language rules overview
- Grammatical rules & structures
- Parts of speech
- Punctuation
- Methodology overview
- Analyzing data
- Experiments
- Observations
- Inductive vs. Deductive
- Qualitative vs. Quantitative
- Types of validity
- Types of reliability
- Sampling methods
- Theories & Concepts
- Types of research studies
- Types of variables
- MLA style overview
- MLA examples
- MLA citation & referencing
- MLA structure & sections
- Plagiarism overview
- Plagiarism checker
- Types of plagiarism
- Printing production overview
- Research bias overview
- Types of research bias
- Example sections
- Types of research papers
- Research process overview
- Problem statement
- Research proposal
- Research topic
- Statistics overview
- Levels of measurment
- Frequency distribution
- Measures of central tendency
- Measures of variability
- Hypothesis testing
- Parameters & test statistics
- Types of distributions
- Correlation
- Effect size
- Hypothesis testing assumptions
- Types of ANOVAs
- Types of chi-square
- Statistical data
- Statistical models
- Spelling mistakes
- Tips overview
- Academic writing tips
- Dissertation tips
- Sources tips
- Working with sources overview
- Evaluating sources
- Finding sources
- Including sources
- Types of sources
Your Step to Success
Plagiarism Check within 10min
Printing & Binding with 3D Live Preview
Table of Contents
How do you like this article cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
A guide to the table of contents page

Inhaltsverzeichnis
- 1 Definition: Table of Contents
- 3 Everything for Your Thesis
- 5 Create in Microsoft Word
- 6 In a Nutshell
Definition: Table of Contents
The table of contents is an organized listing of your document’s chapters, sections and, often, figures, clearly labelled by page number. Readers should be able to look at your table of contents page and understand immediately how your paper is organized, enabling them to skip to any relevant section or sub-section. The table of contents should list all front matter, main content and back matter, including the headings and page numbers of all chapters and the bibliography . A good table of contents should be easy to read, accurately formatted and completed last so that it is 100% accurate. Although you can complete a table of contents manually, many word processing tools like Microsoft Word enable you to format your table of contents automatically.
When adding the finishing touches to your dissertation, the table of contents is one of the most crucial elements. It helps the reader navigate (like a map) through your argument and topic points. Adding a table of contents is simple and it can be inserted easily after you have finished writing your paper. In this guide, we look at the do’s and don’ts of a table of contents; this will help you process and format your dissertation in a professional way.
When adding the finishing touches to your dissertation, the table of contents is one of the most crucial elements. It helps the reader navigate (like a map) through your argument and topic points. Adding a table of contents is simple and can be inserted easily after you have finished writing your paper. In this guide, we look at the do’s and don’ts of a table of contents; this will help you process and format your dissertation in a professional way.
- ✓ Post a picture on Instagram
- ✓ Get the most likes on your picture
- ✓ Receive up to $300 cash back
What is a table of contents?
A table of contents is a list, usually on a page at the beginning of a piece of academic writing , which outlines the chapters or sections names with their corresponding page numbers. In addition to chapter names, it includes bullet points of the sub-chapter headings or subsection headings. It usually comes right after the title page of a research paper.
How do you write a table of contents
To write a table of contents, you first write the title or chapter names of your research paper in chronological order. Secondly, you write the subheadings or subtitles, if you have them in your paper. After that, you write the page numbers for the corresponding headings and subheadings. You can also very easily set up a table of contents in Microsoft Word.
Where do you put a table of contents?
The table of contents is found on a page right at the beginning of an academic writing project. It comes specifically after the title page and acknowledgements, but before the introductory page of a writing project. This position at the beginning of an academic piece of writing is universal for all academic projects.
What to include in a table of contents?
A sample table of contents includes the title of the paper at the very top, followed by the chapter names and subtitles in chronological order. At the end of each line, is the page number of the corresponding headings. Examples of chapter names can be: executive summary, introduction, project description, marketing plan, summary and conclusion. The abstract and acknowledgments are usually not included in the table of contents, however this could depend on the formatting that is required by your institution. Scroll down to see some examples.
How important is a table of contents?
A table of contents is very important at the beginning of a writing project for two important reasons. Firstly, it helps the reader easily locate contents of particular topics itemized as chapters or subtitles. Secondly, it helps the writer arrange their work and organize their thoughts so that important sections of an academic project are not left out. This has the extra effect of helping to manage the reader’s expectation of any academic essay or thesis right from the beginning.
Everything for Your Thesis
A table of contents is a crucial component of an academic thesis. Whether you’re completing a Bachelor’s or a postgraduate degree, the table of contents is a requirement for dissertation submissions. As a rule of thumb, your table of contents will usually come after your title page , abstract, acknowledgement or preface. Although it’s not necessary to include a reference to this front matter in your table of contents, different universities have different policies and guidelines.
Although the table of contents is best completed after you have finished your thesis, it’s a good idea to draw up a mock table of contents in the early stages of writing. This allows you to formulate a structure and think through your topic and how you are going to research, answer and make your argument. Think of this as a form of “reverse engineering”. Knowing how your chapters are going to be ordered and what topics or research questions are included in each will help immensely when it comes to your writing.
The table of contents is not just an academic formality, it allows your examiner to quickly get a feel for your topic and understand how your dissertation will be presented. An unclear or sloppy table of contents may even have an adverse effect on your grade because the dissertation is difficult to follow.
Examiners are readers, after all, and a dissertation is an exercise in producing an argument. A clear table of contents will give both a good impression and provide an accurate roadmap to make the examiner’s job easier and your argument more persuasive.
Your table of contents section will come after your acknowledgements and before your introduction. It includes a list of all your headers and their respective pages and will also contain a sub-section listing your tables, figures or illustrations (if you are using them). In general, your thesis can be ordered like this:
1. Title Page 2. Copyright / Statement of Originality 3. Abstract 4. Acknowledgement, Dedication and Preface (optional) 5. Table of Contents 6. List of Figures/Tables/Illustrations 7. Chapters 8. Appendices 9. Endnotes (depending on your formatting) 10. Bibliography / References
The formatting of your table of contents will depend on your academic field and thesis length. Some disciplines, like the sciences, have a methodical structure which includes recommended subheadings on methodology, data results, discussion and conclusion. Humanities subjects, on the other hand, are far more varied. Whichever discipline you are working in, you need to create an organized list of all chapters in their order of appearance, with chapter subheadings clearly labelled.
Sample table of contents for a short dissertation:
Abstract ………………………………………………………………………………………………….. ii Acknowledgements ………………………………………………………………………………………………….. iii Dedication ………………………………………………………………………………………………….. iv List of Tables ………………………………………………………………………………………………….. x List of Figures ………………………………………………………………………………………………….. xi Chapter 1: Introduction ………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 1 Chapter 2: Literature Survey ………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 13 Chapter 3: Methodology ………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 42 Chapter 4: Analysis ………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 100 Chapter 5: Conclusion ………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 129 Appendices ………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 169 References ………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 172
When producing a more significant and longer dissertation, say for a Master’s degree or even a PhD, your chapter descriptions should contain all subheadings. These are listed with the chapter number, followed by a decimal point and the subheading number.
Sample table of contents for a PhD dissertation:
Chapter 1 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Literature Review 1.3 Data 1.4 Findings 1.5 Conclusion
Chapter 2, and so on.
The key to writing a good table of contents is consistency and accuracy. You cannot list subheadings for one chapter and forget them for another. Subheadings are not always required but they can be very helpful if you are dealing with a detailed topic. The page numbers in the table of contents must match with the respective pages in your thesis or manuscript.
What’s more, chapter titles and subheading titles must match their corresponding pages. If your first chapter is called “Chapter 1: The Beginning”, it must be written as such on both the table of contents and first chapter page. So long as you remain both accurate and consistent, your table of contents will be perfect.
Create in Microsoft Word
Fortunately, the days of manually writing a contents page are over. You can still produce a contents page manually with Microsoft Word, but consider using their automatic feature to guarantee accuracy and save time.
To produce an automatically-generated table of contents, you must first work with heading styles. These can be found in the home tab under “Styles”. Select top-level headings (your chapter titles) and apply the Heading 1 style. This ensures that they will be formatted as main headings. Second-level headings (subheadings) can be applied with the Heading 2 style. This will place them underneath and within each main heading.
Once you have worked with heading styles, simply click on the “References” tab and select “Table of Contents”. This option will allow you to automatically produce a page with accurate page links to your document. To customize the format and style applied to your table of contents, select “Custom Table of Contents” at the bottom of the tab. Remember to update your table of contents by selecting the table and choosing “Update” from the drop-down menu. This will ensure that your headings, sub-headings and page numbers all add up.

Thesis Printing & Binding
You are already done writing your thesis and need a high quality printing & binding service? Then you are right to choose BachelorPrint! Check out our 24-hour online printing service. For more information click the button below :
In a Nutshell
- The table of contents is a vital part of any academic thesis or extensive paper.
- It is an accurate map of your manuscript’s content – its headings, sub-headings and page numbers.
- It shows how you have divided your thesis into more manageable chunks through the use of chapters.
- By breaking apart your thesis into discrete sections, you make your argument both more persuasive and easier to follow.
- What’s more, your contents page should produce an accurate map of your thesis’ references, bibliography, illustrations and figures.
- It is an accurate map of the chapters, references, bibliography, illustrations and figures in your thesis.
We use cookies on our website. Some of them are essential, while others help us to improve this website and your experience.
- External Media
Individual Privacy Preferences
Cookie Details Privacy Policy Imprint
Here you will find an overview of all cookies used. You can give your consent to whole categories or display further information and select certain cookies.
Accept all Save
Essential cookies enable basic functions and are necessary for the proper function of the website.
Show Cookie Information Hide Cookie Information
Statistics cookies collect information anonymously. This information helps us to understand how our visitors use our website.
Content from video platforms and social media platforms is blocked by default. If External Media cookies are accepted, access to those contents no longer requires manual consent.
Privacy Policy Imprint

- Langson Library
- Science Library
- Grunigen Medical Library
- Law Library
- Connect From Off-Campus
- Accessibility
- Gateway Study Center

Email this link
Thesis / dissertation formatting manual (2024).
- Filing Fees and Student Status
- Submission Process Overview
- Electronic Thesis Submission
- Paper Thesis Submission
- Formatting Overview
- Fonts/Typeface
- Pagination, Margins, Spacing
- Paper Thesis Formatting
- Preliminary Pages Overview
- Copyright Page
- Dedication Page
Table of Contents
- List of Figures (etc.)
- Acknowledgements
- Text and References Overview
- Figures and Illustrations
- Using Your Own Previously Published Materials
- Using Copyrighted Materials by Another Author
- Open Access and Embargoes
- Copyright and Creative Commons
- Ordering Print (Bound) Copies
- Tutorials and Assistance
- FAQ This link opens in a new window
The Table of Contents should follow these guidelines:
- All sections of the manuscript are listed in the Table of Contents except the Title Page, the Copyright Page, the Dedication Page, and the Table of Contents.
- You may list subsections within chapters
- Creative works are not exempt from the requirement to include a Table of Contents
Table of Contents Example
Here is an example of a Table of Contents page from the Template. Please note that your table of contents may be longer than one page.

- << Previous: Dedication Page
- Next: List of Figures (etc.) >>
- Last Updated: Feb 20, 2024 2:09 PM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uci.edu/gradmanual
Off-campus? Please use the Software VPN and choose the group UCIFull to access licensed content. For more information, please Click here
Software VPN is not available for guests, so they may not have access to some content when connecting from off-campus.
- Dissertation & Thesis Guides
- Basics of Dissertation & Thesis Writing
- How to Create a Table of Contents for Dissertation, Thesis or Paper & Examples
- Speech Topics
- Basics of Essay Writing
- Essay Topics
- Other Essays
- Main Academic Essays
- Research Paper Topics
- Basics of Research Paper Writing
- Miscellaneous
- Chicago/ Turabian
- Data & Statistics
- Methodology
- Admission Writing Tips
- Admission Advice
- Other Guides
- Student Life
- Studying Tips
- Understanding Plagiarism
- Academic Writing Tips
- Essay Guides
- Research Paper Guides
- Formatting Guides
- Basics of Research Process
- Admission Guides
How to Create a Table of Contents for Dissertation, Thesis or Paper & Examples

Table of contents
Use our free Readability checker
A dissertation table of contents is a list of the chapters and sections included in a dissertation or thesis, along with their page numbers. It helps to navigate the document easily and locate specific information. Each chapter or section should be listed with its corresponding page number. The table of contents should be formatted according to the guidelines of the specific style guide being used, such as APA or MLA.
We would guess that students usually start working on the table of contents at the last minute. It is quite apparent and makes sense, as this is the list of chapters and sections with page locations. Do you think it's easy?
From our experience, it can be quite tricky to organize everything according to APA, Chicago, or any other academic writing style. In this blog, we will discuss how to write a table of contents for a research paper , thesis or dissertation in Microsoft Word. We will create it together to guide students through the process.
Also, here you will find examples of table of contents created by thesis writers at StudyCrumb . Let’s go!
What Is a Table of Contents: Definition
It is obvious that the table of contents (TOC) is an essential manuscript part you can’t skip. If you are dealing with a dissertation, thesis or research paper, you need to know how to build it in accordance with academic guidance. This is a detailed roadmap for your work and outlined structure you can follow for a research presentation.
In case you are working on an essay or report, you may not include the table of contents, as it is a short academic text. But for the research paper, thesis or dissertation, table of contents is essential and required. It is possible to say the same about any Master’s project. It should be located between the dissertation abstract and introduction chapter. In most cases, it is about 2-3 pages long.
Our expert dissertation writing service prepared a great template that can be used for your work. Make your research formatting easy with ready solutions!
Types of Table of Contents
How to choose which table of contents will fit your research paper, thesis, dissertation, or report best? Make a decision based on your work length. Some academic writing styles, such as APA paper format or MLA style , have specific formatting for this list.
However, we will outline the most commonly used typology:
- Single-level table of contents. At this type, we use only chapters. For instance, you will have an Introduction, Literature Review, methodology, and other chapters with page numbers. It can be used for shorter research work. For long writing forms like manuscripts, it can be too broad, and you will need to go into details.
- Subdivided table of contents. The most frequently used form to organize the contents table. It will include not only chapters but also sections — a level 2 subheading for each part. It will help to be more specific about what to expect in each part of your research work.
- Table of contents with multiple levels. This is a more divided structure, including subheadings with a level 3 for each section. Quite often, those subheadings can be rewritten or deleted during the last editing. It is essential to keep them in the right order.
Before you decide which type will work best for you, let us share with you some examples of each formatting style.
Example of Table of Contents With a Single Level
Introduction: The Misinformation Roots ………..…… 3 Literature Review .....................................….....………… 10 Research Methodology and Design ……................. 24 Results.............................................................................. 28 Discussion ....................................................................... 32
Sometimes, you will need to put an extra emphasis on subsections. Check this layout to see how your subheadings can be organized.
Example of Table of Contents Page with Subdivided Levels
Introduction: Information War ............……………….. 3 Background…………………………………….………..…… 4 Current State ……………………………………...…...…… 5 Defining Research Questions………………………. 9 Literature Review………………………...……………..……... 11 The Roots of Information Warfare ………....… 11 Information Wars …………………………….………..… 14 Cyber Wars Research ........................................ 17
If you are working on a lengthy, complex paper, this outline will suit your project most. It will help readers navigate through your document by breaking it down into smaller, more manageable sections.
Multi-Level Table of Contents Page Example
Introduction……………………………………………….......……….… 3 Emergence of Climate Change ………..……....….….. 3 Key Activist Groups in Climate Change .............. 5 Greenpeace International ………..…………......... 9 European Climate Foundation …….……………. 10 WWF ……………………………………….……….............. 11 Significant Movements ……………….………....……… 13 Literature Review ……………………………………......…………. 15
What Sections Should Be Included in a Table of Contents?
To start with, the scientific table of contents should include all chapters and its subheading. It is important to choose the formatting that will give your readers a full overview of your work from the very beginning. However, there are other chapters that you may miss constructing the 2-pager table. So, let's look at all you need to include:
- Dissertation introduction
- Literature review
- Research methodology
- Results section
- Dissertation discussion
- Conclusion of a thesis
- Reference list. Mention a number of a page where you start listing your sources.
- Appendices. For instance, if you have a data set, table or figure, include it in your research appendix .
This is how the ideal structured dissertation or research paper table of contents will look like. Remember that it still should take 2 pages. You need to choose the best formatting style to manage its length.
Tables, Figures, and Appendices in TOC
While creating a table of contents in a research paper, thesis or dissertation, you will need to include appendices in each case you have them. However, the formatting and adding tables and figures can vary based on the number and citation style. If you have more than 3 tables or figures, you may decide to have all of them at the end of your project. So, add them to the table of contents.
Figures, graphics, and diagrams in research papers, dissertations and theses should be numbered. If you use them from another source, ensure that you make a proper citation based on the chosen style guide.
Appendix in Table of Contents Example
Appendix A. Row Data Set…………………………………… 41 Appendix B. IBR Data………………………………………….… 43 Appendix C. SPSS Data………………………………………… 44
What Shouldn't Be Included in a Table of Contents?
When creating a dissertation table of contents, students want to include everything they have in a document. However, some components should not be on this page. Here is what we are talking about:
- Thesis acknowledgement
- Paper abstract
- The content list itself
Acknowledgement and abstract should be located before the content list, so there is no need to add them. You need to present a clear structure that will help your readers to navigate through the work and quickly find any requested information.
How to Create a Table of Contents for a Research Paper or Dissertation In Word?
It may look like working with this list can take a long. But we have one proposal for our users. Instead of writing a table of contents manually, create it automatically in Microsoft Word. You do not need any specific tech knowledge to do this. Let’s go through this process step-by-step and explain how to make a table of contents for a research paper or dissertation in a few clicks.
- Open Home tab and choose the style for your table of contents (ToC next).
- Apply heading 1 to your chapters, heading 2 to the subheading, and if needed heading 3 to the level 3 heading.
- Next, you are going to create a research paper or PhD dissertation table of contents. Open References and choose ToC.
- Choose the citation style for your work. For example, let’s choose APL for now. Meeting all style requirements (bold font, title formatting, numbers) is essential.
- Define the number of levels for your dissertation or thesis table of contents. In case you want to have 3 levels, choose Automatic Table 2.
- You are done! Click ok, and here is your page with listed chapters!
You see how easy it can be! Every time you make changes to your text or headings, it will be automatic.
Updating Your Table of Contents in MS Word
Table of contents of a research paper or dissertation is created, and you continue to edit your work until submission. It is common practice, and with MS Word, you can automate all the updates.
Let’s outline this process in our step-by-step guide!
- Right-click on your ToC in a document.
- Update field section is next.
- Choose “update ToC."
- Here, you can update your entire ToC — choose an option that works the best for you!
As you may see, working with automated solutions is much easier when you write a dissertation which has manifold subsections. That is why it is better to learn how to work on MS Word with the content list meaning be able to manage it effectively.
Table of Contents Examples
From our experience, students used to think that the content list was quite a complicated part of the work. Even with automated solutions, you must be clear about what to include and how to organize formatting. To solve the problem and answer all your questions, use our research paper or dissertation contents page example. Our paper writers designed a sample table of contents to illustrate the best practices and various styles in formatting the work.
Check our samples to find advanced options for organizing your own list.
Example of Table of Contents in Research Paper

As you can see, this contents page includes sections with different levels.
Thesis/Dissertation Table of Contents Example

Have a question about your specific case? Check samples first, as we are sure you can get almost all the answers in our guides and sample sets.
>> Read more: APA Format Table of Contents
Tips on Creating a Table of Contents
To finalize all that we shared on creating the table of contents page, let’s go through our tips list. We outline the best advice to help you with a dissertation table of contents.
- Use automated solutions for creating a list of chapters for your report, research papers, or dissertations — it will save you time in the future.
- Be clear with the formatting style you use for the research.
- Choose the best level type of list based on the paper length.
- Update a list after making changes to the text.
- Check the page list before submitting the work.
Bottom Line on Making Table of Contents for Dissertations/ Papers
To summarize, working with a research paper, thesis or dissertation table of contents can be challenging. This article outlines how to create a table of contents in Word and how to update it appropriately. You can learn what to include in the content list, how long it can be, and where to locate it. Write your work using more than one table of contents sample we prepared for students. It is often easy to check how the same list was made for other dissertations before finalizing yours. We encourage you to learn how to create a list with pages automatically and update it. It will definitely make your academic life easier.
Not sure if your work 's quality level is enough for getting a top-notch result? We’ve got you covered! Our team of skilled academic writers is always ready to help once you ask “ write my dissertation for me !" Just select your writer, send them your requirements and get a custom study tailored to your instructions.

Joe Eckel is an expert on Dissertations writing. He makes sure that each student gets precious insights on composing A-grade academic writing.
You may also like

This paper is in the following e-collection/theme issue:
Published on 27.5.2024 in Vol 8 (2024)
This is a member publication of University of Colorado Denver HARC
Lessons Learned From a Sequential Mixed-Mode Survey Design to Recruit and Collect Data From Case-Control Study Participants: Formative Evaluation
Authors of this article:

Original Paper
- Amanda D Tran 1 , MPH ;
- Alice E White 1 , MPH ;
- Michelle R Torok 1 , PhD ;
- Rachel H Jervis 2 , MPH ;
- Bernadette A Albanese 3 , MD, MPH ;
- Elaine J Scallan Walter 1 , MA, PhD
1 Department of Epidemiology, Colorado School of Public Health, University of Colorado, Aurora, CO, United States
2 Colorado Department of Public Health and Environment, Denver, CO, United States
3 Adams County Health Department, Brighton, CO, United States
Corresponding Author:
Elaine J Scallan Walter, MA, PhD
Department of Epidemiology
Colorado School of Public Health
University of Colorado
13001 East 17th Place
3rd Floor, Mail Stop B119
Aurora, CO, 80045
United States
Phone: 1 303 724 5162
Email: [email protected]
Background: Sequential mixed-mode surveys using both web-based surveys and telephone interviews are increasingly being used in observational studies and have been shown to have many benefits; however, the application of this survey design has not been evaluated in the context of epidemiological case-control studies.
Objective: In this paper, we discuss the challenges, benefits, and limitations of using a sequential mixed-mode survey design for a case-control study assessing risk factors during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Methods: Colorado adults testing positive for SARS-CoV-2 were randomly selected and matched to those with a negative SARS-CoV-2 test result from March to April 2021. Participants were first contacted by SMS text message to complete a self-administered web-based survey asking about community exposures and behaviors. Those who did not respond were contacted for a telephone interview. We evaluated the representativeness of survey participants to sample populations and compared sociodemographic characteristics, participant responses, and time and resource requirements by survey mode using descriptive statistics and logistic regression models.
Results: Of enrolled case and control participants, most were interviewed by telephone (308/537, 57.4% and 342/648, 52.8%, respectively), with overall enrollment more than doubling after interviewers called nonresponders. Participants identifying as female or White non-Hispanic, residing in urban areas, and not working outside the home were more likely to complete the web-based survey. Telephone participants were more likely than web-based participants to be aged 18-39 years or 60 years and older and reside in areas with lower levels of education, more linguistic isolation, lower income, and more people of color. While there were statistically significant sociodemographic differences noted between web-based and telephone case and control participants and their respective sample pools, participants were more similar to sample pools when web-based and telephone responses were combined. Web-based participants were less likely to report close contact with an individual with COVID-19 (odds ratio [OR] 0.70, 95% CI 0.53-0.94) but more likely to report community exposures, including visiting a grocery store or retail shop (OR 1.55, 95% CI 1.13-2.12), restaurant or cafe or coffee shop (OR 1.52, 95% CI 1.20-1.92), attending a gathering (OR 1.69, 95% CI 1.34-2.15), or sport or sporting event (OR 1.05, 95% CI 1.05-1.88). The web-based survey required an average of 0.03 (SD 0) person-hours per enrolled participant and US $920 in resources, whereas the telephone interview required an average of 5.11 person-hours per enrolled participant and US $70,000 in interviewer wages.
Conclusions: While we still encountered control recruitment challenges noted in other observational studies, the sequential mixed-mode design was an efficient method for recruiting a more representative group of participants for a case-control study with limited impact on data quality and should be considered during public health emergencies when timely and accurate exposure information is needed to inform control measures.
Introduction
Often used during disease outbreak investigations, case-control studies that retrospectively compare people who have a disease (case participants) with people who do not have the disease (control participants) are an efficient and relatively inexpensive method of identifying potential disease risk factors to guide control measures and interventions. Perhaps the most critical and challenging component of conducting a case-control study is the recruitment of appropriate control participants who are from the same source population as case participants [ 1 ]. Because control participants are not ill and may not be connected to the outbreak, they may be less motivated to complete a lengthy questionnaire that collects personal information and detailed exposure histories [ 2 - 4 ]. Moreover, with the increased use of mobile telephones and the routine use of caller ID, study participants contacted by traditional telephone-based survey methodologies may be less likely to answer the telephone [ 5 , 6 ], further reducing the opportunity for participant screening and recruitment.
Recruitment challenges are not unique to case-control studies, and other types of observational studies have shifted from traditional telephone interviews to web-based surveys with the goal of reaching larger groups of people more efficiently and at a lower cost [ 7 - 12 ]. While offering some advantages over traditional telephone interviews, web-based surveys often experience lower response rates and lower data quality [ 13 ], and some studies have found demographic differences between telephone and web-based survey participants, likely driven in part by disparities in internet connectivity and access [ 14 ]. For this reason, researchers have increasingly used both telephone interviews and web-based surveys in a sequential mixed-mode design, first contacting participants using a self-administered web-based survey, and then following up with nonresponders with an interviewer-administered telephone survey [ 15 ]. In other types of observational studies, this mixed-mode design has been shown to reduce selection bias, reduce costs, improve data quality, and result in higher response rates and faster participant recruitment [ 16 , 17 ], making it an appealing design choice for case-control studies.
In March 2020, the World Health Organization declared COVID-19 a global pandemic, and throughout many countries, public health or other governmental authorities implemented stay-at-home orders, travel restrictions, and other public health interventions to reduce disease transmission. In the absence of adequate data-driven evidence about community risk factors for COVID-19 transmission, we implemented a sequential mixed-mode case-control study design in Colorado to evaluate community exposures and behaviors associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection and inform public health control measures. While the benefits and limitations of sequential mixed-mode designs have been well-documented in other contexts [ 14 , 16 , 18 - 20 ], they have not been examined in the context of rapidly implemented epidemiological case-control studies. In this paper, we discuss the challenges, benefits, and limitations of using a sequential mixed-mode survey design using web-based surveys disseminated via SMS text message and telephone interviews for a case-control study assessing exposures during a public health emergency. Specific aims are (1) to compare the sociodemographic characteristics of web-based and telephone survey participants, (2) to evaluate the representativeness of survey participants to the sample population, (3) to assess the completeness of participant responses by survey mode, and (4) to estimate the time and resources required to recruit web-based and telephone survey participants.
Case-Control Study Design and Implementation
The case-control study was conducted among Colorado adults aged 18 years and older who had a positive (case) or negative (control) SARS-CoV-2 reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction test result in Colorado’s electronic laboratory reporting (ELR) system with a specimen collection date from March 16 to April 29, 2021 [ 21 ]. Eligible individuals testing positive with a completed routine public health interview in Colorado’s COVID-19 surveillance system were randomly selected and individually matched on age (±10 years), zip code (urban areas) or region (rural and frontier areas), and specimen collection date (±3 days) with up to 20 individuals with a negative test, with the goal of enrolling 2 matched controls per enrolled case.
Self-administered (web-based) and interviewer-administered (telephone) case and control surveys were developed in Research Electronic Data Capture (REDCap; Vanderbilt University). REDCap is a secure, web-based platform designed to support data capture for research studies [ 22 ]. The surveys asked about contact with a person with confirmed or suspected COVID-19, travel history, employment, mask use, and community exposure settings (bar or club; church, religious, or spiritual gathering; gathering; grocery or retail shopping; gym or fitness center; health care setting; restaurant, cafe, or coffee shop; salon, spa, or barber; social event; or sports or sporting events) during the 14 days before illness onset or specimen submission. The full survey questionnaire is available in Multimedia Appendix 1 . Demographic data were obtained from Colorado’s COVID-19 case surveillance system and the control survey. Web-based surveys were offered in English and Spanish and included clarifying language, prompts, skip logic, text piping, and progress bars. Interviewers used computer-assisted telephone interviewing in REDCap with scripting and language line services when needed. Questions and response options were identically worded in the web-based and telephone surveys, with the exception of a “refused” option for questions in the telephone survey.
Using the Twilio integration in REDCap, selected individuals were sent an SMS text message to the telephone number provided at the time of testing (which may include both landlines and mobile phones) 3 to 7 days after their specimen collection date, inviting them to complete the web-based survey. A team of trained interviewers began contacting nonresponders for telephone interviews approximately 3 hours after the initial SMS text message was sent, making 1 contact attempt for individuals testing positive for SARS-CoV-2 and up to 2 contact attempts for those testing negative. Interviewers only contacted as many controls by telephone as needed to enroll 2 matched controls per enrolled case. The web-based survey link was resent via SMS text message or sent via email when requested. When possible, voicemail messages were left encouraging SMS text message recipients to complete the web-based survey. As the goal of the case-control study was to assess the risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection from community exposures, we only included surveys that had responses to all 15 community exposure questions. Partial surveys that did not have complete community exposure data were excluded from analyses. Individuals were also excluded if they reported living in an institution, close contact with a household member with confirmed or suspected COVID-19, receiving ≥1 dose of a COVID-19 vaccine (which was not universally available in Colorado at the time of the study), symptom onset date >7 days from specimen collection (case participants), a prior positive COVID-19 result (control participants), or providing personal identifying information in the web-based survey that was inconsistent with information from the ELR system (control participants).
Evaluation of a Sequential Mixed-Mode Survey Design
We evaluated the impact of conducting the COVID-19 case-control study using a sequential mixed-mode design by (1) comparing the sociodemographic characteristics of web-based and telephone survey participants, (2) evaluating the representativeness of study participants to the sample population, (3) assessing the completeness of participant responses by survey mode, and (4) estimating the time and resources required to recruit web-based and telephone survey participants. All analyses were performed using SAS (version 9.4; SAS Institute).
Comparison of Web-Based and Telephone Survey Participants
Case and control participants were eligible individuals who completed the web-based or telephone survey. We compared the demographic characteristics (age, gender, race and ethnicity, geographic location, working outside the home, and socioeconomic factors) of case and control participants completing the web-based and telephone survey to each other using 2-tailed t tests, Pearson χ 2 , or Fisher exact tests. Socioeconomic factors, which are not routinely asked in surveillance and therefore not included in the survey, were evaluated by aggregating mean scores for 4 Colorado EnviroScreen indicators (less than high school education, linguistic isolation, low income, and people of color) based on the participant’s county of residence. Colorado EnviroScreen (version 1.0; Colorado State University and the Colorado Department of Public Health and Environment) is a publicly available environmental justice mapping tool developed by the Colorado Department of Public Health and Environment and Colorado State University that evaluates 35 distinct environmental, health, economic, and demographic indicators. Colorado EnviroScreen scores range from 0 to 100, with the highest score representing the highest burden of health injustice.
Representativeness of Study Participants
We compared the demographic characteristics (as described earlier) of case and control participants completing the web-based and telephone surveys (separately and combined) to the sample pool of all randomly selected individuals testing positive (case sample pool) or negative (control sample pool) for SARS-CoV-2 using 2-tailed t tests, Pearson χ 2 , or Fisher exact tests.
Participant Responses
We evaluated data completeness and differential responses between web-based and telephone survey modes by comparing responses to exposure and behavior questions we deemed prone to social desirability bias (close contact with individuals with confirmed or suspected COVID-19, community exposures, travel, and mask use). Two bivariate logistic regression models, the first adjusting for case-control status and the second adjusting for case-control status and sociodemographic variables shown to be associated with mode effects (age, gender, race and ethnicity, and geographic location), examined the association between survey mode and participant response. Question nonresponse, where data were missing or refused, was evaluated for these questions as well as for other questions with free-text or multiple-choice response options (industry, occupation, reasons for COVID-19 testing, and mask type).
Time and Resource Needs
The time spent by study personnel contacting potential participants by SMS text message and telephone was obtained from self-recorded data in timesheets and used to calculate the person-hours required per enrolled participant. Total expenditures for the web-based and telephone surveys were calculated using staff wages and Twilio texting costs (an average of US $0.008 for a 160-character SMS text message).
Ethical Considerations
The case-control study was deemed by the Colorado Multiple Institutional Review Board to be public health surveillance and not human participant research and was therefore exempt from full approval and requirements for informed consent (protocol 21-2973).
Case and Control Participant Enrollment
The case sample pool included 1323 individuals. Of these, 318 (24%) responded to the web-based survey, and 331 (25%) were interviewed by telephone ( Figure 1 ). A total of 537 (40.6%) case participants were enrolled after excluding 78 (5.9%) partial and 34 (2.6%) ineligible survey responses. Of the 10,898 individuals in the control sample pool, 1072 (9.8%) responded to the web-based survey, and 1268 (11.6%) were interviewed by telephone. A total of 648 (5.9%) control participants were enrolled after excluding 1565 (14.4%) partial and 127 (1.2%) ineligible surveys. Of the enrolled case and control participants, most were interviewed by telephone (308/537, 57.4% and 342/648, 52.8%, respectively).

Case participants completing the web-based and telephone surveys were similar in age (mean 37, SD 13.21 and 14.69 years, respectively), whereas web-based control participants were slightly older than those completing the telephone survey (mean 38, SD 12.44 vs mean 36, SD 12.62 years, respectively; Table 1 ). For both case and control participants, those aged 40-59 years were more likely to complete the web-based survey, whereas participants aged 18-39 years and 60 years and older were more likely to complete the telephone survey. Web-based case and control participants were more likely to identify as female, White, non-Hispanic, reside in urban areas, and be less likely to work outside the home. Compared to web-based case and control participants, telephone participants had higher EnviroScreen scores for all socioeconomic indicators, indicating they resided in counties with larger populations of individuals with less than high school education, linguistic isolation, low income, and people of color.
a Individuals with a positive SARS-CoV-2 test result.
b Individuals with a negative SARS-CoV-2 test result.
c P <.05; control participant web-based versus telephone.
d P <.01; survey mode (web-based, telephone, and web-based and telephone combined) versus sample pool.
e P <.05; case participant web-based versus telephone.
f P <.05; survey mode (web-based, telephone, and web-based and telephone combined) versus sample pool.
g Information on sex and working outside the home were not available from Colorado’s electronic laboratory reporting system for control participants.
h Not available.
i Colorado EnviroScreen is an environmental justice mapping tool. Scores are assigned at the county level, with a higher score indicating that an area is more likely to be affected by the indicated health injustice.
There were statistically significant sociodemographic differences noted between web-based and telephone case and control participants and their respective sample pools ( Table 1 ). More web-based case participants identified as female (134/228, 58.8%) than those in the case sample pool (642/1318, 48.7%). More web-based control participants identified as White, non-Hispanic (205/267, 76.8%) than those in the control sample pool (4467/7812, 57.2%) and more often resided in urban areas (247/306, 80.7%) than those in the control sample pool (7841/10,898, 71.9%). Case and control participants were more similar to their respective sample pools when evaluated as a single group (total enrolled).
In the model adjusting for case or control status only, web-based participants were less likely to report close contact with an individual with COVID-19 when compared to telephone participants (odds ratio [OR] 0.70, 95% CI 0.53-0.94) but more likely to report community exposures including visiting a grocery store or retail shop (OR 1.55, 95% CI 1.13-2.12), visiting a restaurant or cafe or coffee shop (OR 1.52, 95% CI 1.20-1.92), attending a gathering outside the home (OR 1.69, 95% CI 1.34-2.15), or attending or participating in a sport or sporting event (OR 1.05, 95% CI 1.05-1.88) in 14 days before symptom onset or specimen collection ( Table 2 ). When adjusted for case or control status, age, gender, race and ethnicity, and geographic location, the only associations that remained statistically significant were close contact (adjusted OR 0.65, 95% CI 0.48-0.88) and gatherings (adjusted OR 1.44, 95% CI 1.12-1.85).
a Full survey questions are available in Multimedia Appendix 1 .
b Adjusted for case or control status.
c OR: odds ratio.
d Adjusted for case or control status, age, gender, race and ethnicity, and geographic location.
e N/A: not applicable.
Question nonresponse was low across both modalities, with similar ranges of missingness between the web-based survey (0/535, 0% to 22/535, 4.1%) and telephone survey (2/650, 0.3% to 34/650, 5.2%). Nonresponse to industry, occupation, and masking questions was higher in the telephone survey (9/650, 1.4% to 34/650, 5.2%) than the web-based survey (1/535, 0.2% to 22/535, 4.1%; Table 2 ).
Over the course of the study, staff spent a cumulative 15 hours randomly selecting and texting potential participants for the web-based survey, averaging 0.03 person-hours per enrolled participant (15 person-hours per 535 web-based participants) and US $500 in staff wages. Twilio texting costs were US $420, amounting to US $920 in total expenditures for the web-based survey. Comparatively, 3319 hours were spent by interviewers attempting to contact nonresponders by telephone, for an average of 5.11 person-hours per enrolled participant (3319 person-hours per 650 telephone participants) and US $70,000 in interviewer wages.
Principal Findings
While the web-based survey was more time- and cost-efficient than the telephone interview, participant enrollment was low, and there were statistically significant sociodemographic differences between the web-based case and control participants and their respective sample pools. Adding the follow-up telephone interview increased participant enrollment and the representativeness of both the case and control participants to sample pools. Participant responses to exposure and behavior questions and data completeness were similar between the 2 survey modalities.
Enrollment more than doubled for case and control participants after interviewers called individuals who did not respond to the web-based survey to complete the survey by telephone. Case participant enrollment for our mixed-mode study was higher than those for other COVID-19 case-control studies using telephone only (40.6% vs 3%-25% case participant enrollment in other studies), but control participant enrollment was lower (5.9% vs 9%-13% control participant enrollment in other studies) [ 23 - 25 ]. However, control participant enrollment in our sequential mixed-mode study may not be comparable to telephone-only COVID-19 case-control studies for 2 reasons. First, we texted up to 20 potential controls for every enrolled case participant in anticipation of lower response rates for the web-based survey, inflating the number of contacted controls in our response rate calculations. Second, we did not follow up with all potential controls by telephone once our quota of 2 controls per case was reached. In contrast, telephone-only studies only call as many controls as needed to enroll the desired number of matched control participants, which is typically less than 20.
We found sociodemographic differences between participants completing the survey on the web and by telephone. Web-based respondents were more likely to be female, identify as White, non-Hispanic, have higher levels of education, and reside in urban areas, which was consistent with other studies evaluating survey mode effects [ 12 , 26 , 27 ]. Contrary to other studies that found higher web-based response rates among those younger than 35 years of age [ 14 ], participants aged 18-39 years in our case-control study were more likely to respond to the telephone survey, as were participants aged 60 years and older, participants working outside the home, and participants residing in areas with a higher burden of health injustices. Some of these differences may be attributable to the timing of when potential participants were contacted. While potential participants were texted a link to complete the web-based survey only in the morning, telephone interviews were administered throughout the day, including in the late afternoon and evening when more people may be at home and not working. In addition, older participants and participants in lower socioeconomic settings may experience more barriers to completing a web-based survey, such as limited internet access or less comfort using mobile platforms [ 15 ], making them more likely to complete a telephone interview.
While there were sociodemographic differences between web-based and telephone participants and between web-based and telephone case and control participants and their respective sample pools, the sociodemographic characteristics of combined web-based and telephone survey participants were broadly representative of the sample pools. This indicates that the sequential mixed-mode design allowed for the recruitment of more representative case and control participant groups than if we had used a telephone or web-based survey alone, and the use of this survey design can help reduce selection bias in case-control studies.
Telephone surveys conducted by trained interviewers have several advantages over other modes of administration. Most importantly, trained interviewers can answer participants’ questions, add clarifying questions, and probe interviewees for more complete responses, leading to better data completeness and quality. While increasing data quality, telephone surveys can lead to social desirability bias as participants may alter answers to questions to seem more favorable or socially acceptable to an interviewer [ 19 , 20 ]. An advantage of using a web-based survey is that the absence of an interviewer may provide participants with the opportunity to answer questions more candidly, potentially reducing social desirability bias [ 19 , 20 ]. While we found that web-based participants were more likely to report certain community exposures, most of the differential responses between web-based and telephone participants were no longer statistically significant after adjusting for variables shown to be associated with mode effects (age, gender, race, ethnicity, and geographic location). This suggests that demographic differences between web-based and telephone participants may be confounding variables and should be considered when analyzing and interpreting data for case-control studies.
Limitations
This project was subject to several limitations. First, cases were randomly selected from persons reported in Colorado’s COVID-19 surveillance system who had already completed an interview with public health, which may impact study findings. For example, this method of case-participant selection may account for the high enrollment rates we had for our case-control study, and these individuals may systematically differ from those testing positive for SARS-CoV-2 who did not complete an initial interview with public health. Second, sample pool data were obtained from the ELR system for control participants, which had incomplete demographic data. The sample pool characteristics presented in this paper may not be accurate because of these missing data and, in turn, affect our evaluations of sample representativeness. Third, the socioeconomic characteristics of participants may be subject to ecological fallacy as we used county-level Colorado EnviroScreen scores as a proxy for individual socioeconomic status. Fourth, it is unclear whether the systematic differences noted between web-based and telephone participants were due to the survey mode itself or due to the additional contact attempts made to enroll telephone participants. Finally, this sequential mixed-mode case-control study was implemented during the COVID-19 pandemic, a period marked by various political and social factors that could have influenced who responded to our survey and their responses. As such, findings from this paper may not be generalizable to case-control studies evaluating other diseases or outbreaks.
Conclusions
Telephone interviews conducted as part of an outbreak investigation are time-consuming and costly [ 8 ]. Given the limited resources and staff at many public health agencies, it is critical to find methods to increase efficiency and reduce the costs of outbreak investigations. Web-based surveys are more time- and cost-efficient than telephone interviews, greatly reducing the workload for health departments. However, web-based surveys may appeal to specific demographics, have lower enrollment rates, and may require a larger sample pool or a longer time to enroll participants, which may not be feasible for small outbreaks or ideal for public health emergencies when timely data collection is crucial.
By using a sequential mixed-mode design, we were able to efficiently recruit participants for a case-control study with limited impact on data quality. Moreover, using the sequential mixed-mode approach allowed for maximal sample representativeness compared to a web-based or telephone interview alone. This is critical during public health emergencies, when timely and accurate exposure information is needed to inform control measures and policy. While the sequential mixed-mode design allowed us to reach more potential control participants with fewer resources, we still encountered the same challenges recruiting control participants noted in other studies.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the following people for their contributions to the conception, design, or management of the case-control study: Nisha Alden, Andrea Buchwald, Nicole Comstock, Lauren Gunn-Sandell, Tye Harlow, Breanna Kawasaki, Emma Schmoll, RX Schwartz, Ginger Stringer, and Rachel K Herlihy. This project was supported by a financial assistance award from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and awarded to the Colorado Department of Public Health and Environment. The Colorado Department of Public Health and Environment contracted with EJSW at the Colorado School of Public Health. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily reflect the official views of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention or the Colorado Department of Public Health and Environment.
Data Availability
The data sets generated and analyzed during this study are not publicly available due to Colorado state statutes and regulations, which limit data release based on maintaining confidentiality for potentially identifiable person-level data, but are available from the Colorado Department of Public Health and Environment upon reasonable request.
Authors' Contributions
ADT contributed to the study’s conception, reviewed current research, performed statistical analyses, interpreted results, and was the primary author of the manuscript. AEW, MRT, and EJSW made significant contributions to the study’s conception and interpretation of results and critically revised the manuscript. RHJ and BAA substantively reviewed and revised the manuscript for its content. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
None declared.
Colorado COVID-19 case-control survey questionnaires.
- Schulz KF, Grimes DA. Case-control studies: research in reverse. Lancet. 2002;359(9304):431-434. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Mook P, McCormick J, Kanagarajah S, Adak GK, Cleary P, Elson R, et al. Online market research panel members as controls in case-control studies to investigate gastrointestinal disease outbreaks: early experiences and lessons learnt from the UK. Epidemiol Infect. 2018;146(4):458-464. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Waldram A, McKerr C, Gobin M, Adak G, Stuart JM, Cleary P. Control selection methods in recent case-control studies conducted as part of infectious disease outbreaks. Eur J Epidemiol. 2015;30(6):465-471. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Aigner A, Grittner U, Becher H. Bias due to differential participation in case-control studies and review of available approaches for adjustment. PLoS One. 2018;13(1):e0191327. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Czajka JL, Beyler A. Declining response rates in federal sureys: trends and implication. Mathematica Policy Research. 2016. URL: https://tinyurl.com/ycyte42a [accessed 2023-02-27]
- McClain C. Most Americans don't answer cellphone calls from unknown numbers. Pew Research Center. 2020. URL: https://tinyurl.com/3her7dc5 [accessed 2023-02-27]
- Yahata Y, Ohshima N, Odaira F, Nakamura N, Ichikawa H, Matsuno K, et al. Web survey-based selection of controls for epidemiological analyses of a multi-prefectural outbreak of enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157 in Japan associated with consumption of self-grilled beef hanging tender. Epidemiol Infect. 2018;146(4):450-457. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Ghosh TS, Patnaik JL, Alden NB, Vogt RL. Internet- versus telephone-based local outbreak investigations. Emerg Infect Dis. 2008;14(6):975-977. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Yasmin S, Pogreba-Brown K, Stewart J, Sunenshine R. Use of an online survey during an outbreak of Clostridium perfringens in a retirement community—Arizona, 2012. J Public Health Manag Pract. 2014;20(2):205-209. [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Srikantiah P, Bodager D, Toth B, Kass-Hout T, Hammond R, Stenzel S, et al. Web-based investigation of multistate salmonellosis outbreak. Emerg Infect Dis. 2005;11(4):610-612. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Taylor M, Galanis E. Online population control surveys: a new method for investigating foodborne outbreaks. Epidemiol Infect. 2020;148:e93. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Mauz E, Hoffmann R, Houben R, Krause L, Kamtsiuris P, Gößwald A. Mode equivalence of health indicators between data collection modes and mixed-mode survey designs in population-based health interview surveys for children and adolescents: methodological study. J Med Internet Res. 2018;20(3):e64. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Fan W, Yan Z. Factors affecting response rates of the web survey: a systematic review. Comput Hum Behav. 2010;26(2):132-139. [ CrossRef ]
- Hollier LP, Pettigrew S, Slevin T, Strickland M, Minto C. Comparing online and telephone survey results in the context of a skin cancer prevention campaign evaluation. J Public Health (Oxf). 2017;39(1):193-201. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- de Leeuw ED. To mix or not to mix data collection modes in surveys. J Off Stat. 2005;21(2):233-255. [ FREE Full text ]
- Braekman E, Drieskens S, Charafeddine R, Demarest S, Berete F, Gisle L, et al. Mixing mixed-mode designs in a national health interview survey: a pilot study to assess the impact on the self-administered questionnaire non-response. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2019;19(1):212. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Rivara FP, Koepsell TD, Wang J, Durbin D, Jaffe KM, Vavilala M, et al. Comparison of telephone with world wide web-based responses by parents and teens to a follow-up survey after injury. Health Serv Res. 2011;46(3):964-981. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Bowling A. Mode of questionnaire administration can have serious effects on data quality. J Public Health (Oxf). 2005;27(3):281-291. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Greene J, Speizer H, Wiitala W. Telephone and web: mixed-mode challenge. Health Serv Res. 2008;43(1 Pt 1):230-248. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Jones MK, Calzavara L, Allman D, Worthington CA, Tyndall M, Iveniuk J. A comparison of web and telephone responses from a national HIV and AIDS survey. JMIR Public Health Surveill. 2016;2(2):e37. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- White AE, Tran AD, Torok MR, Jervis RH, Albanese BA, Buchwald AG, et al. Community exposures among Colorado adults who tested positive for SARS-CoV-2—a case-control study, March-December 2021. PLoS One. 2023;18(3):e0282422. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Harris PA, Taylor R, Thielke R, Payne J, Gonzalez N, Conde JG. Research Electronic Data Capture (REDCap)—a metadata-driven methodology and workflow process for providing translational research informatics support. J Biomed Inform. 2009;42(2):377-381. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Andrejko KL, Pry JM, Myers JF, Fukui N, DeGuzman JL, Openshaw J, et al. Effectiveness of face mask or respirator use in indoor public settings for prevention of SARS-CoV-2 infection—California, February-December 2021. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2022;71(6):212-216. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Andrejko KL, Pry J, Myers JF, Jewell NP, Openshaw J, Watt J, et al. Prevention of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) by mRNA-based vaccines within the general population of California. Clin Infect Dis. 2022;74(8):1382-1389. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Fisher KA, Tenforde MW, Feldstein LR, Lindsell CJ, Shapiro NI, Files DC, et al. Community and close contact exposures associated with COVID-19 among symptomatic adults ≥18 years in 11 outpatient health care facilities—United States, July 2020. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2020;69(36):1258-1264. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Link MW, Mokdad AH. Alternative modes for health surveillance surveys: an experiment with web, mail, and telephone. Epidemiology. 2005;16(5):701-704. [ FREE Full text ] [ CrossRef ] [ Medline ]
- Roster CA, Rogers RD, Albaum G, Klein D. A comparison of response characteristics from web and telephone surveys. Int J Mark Res. 2018;46(3):359-373. [ CrossRef ]
Abbreviations
Edited by A Mavragani; submitted 19.01.24; peer-reviewed by M Couper, J Ziegenfuss; comments to author 13.02.24; revised version received 29.03.24; accepted 04.04.24; published 27.05.24.
©Amanda D Tran, Alice E White, Michelle R Torok, Rachel H Jervis, Bernadette A Albanese, Elaine J Scallan Walter. Originally published in JMIR Formative Research (https://formative.jmir.org), 27.05.2024.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work, first published in JMIR Formative Research, is properly cited. The complete bibliographic information, a link to the original publication on https://formative.jmir.org, as well as this copyright and license information must be included.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The table of contents is usually located at the beginning of the document or book, after the title page and any front matter, such as a preface or introduction. Table of Contents in Research. In Research, A Table of Contents (TOC) is a structured list of the main sections or chapters of a research paper, Thesis and Dissertation. It provides ...
Generating the table of contents. Now you can generate your table of contents. First write the title "Contents" (in the style of a level 1 heading). Then place your cursor two lines below this and go to the References tab. Click on Table of Contents and select Custom Table of Contents…. In the popup window, select how many levels of ...
Dissertation Table of Contents in Word | Instructions & Examples. Published on May 15, 2022 by Tegan George.Revised on July 18, 2023. The table of contents is where you list the chapters and major sections of your thesis, dissertation, or research paper, alongside their page numbers.A clear and well-formatted table of contents is essential, as it demonstrates to your reader that a quality ...
To summarize, the following steps will help you create a clear and concise table of contents to guide readers through your research paper: 1. Insert the table of contents after the title page. 2. List all the sections and subsections in chronological order. 3. Paginate each section. 4. Format the table of contents according to your style guide. 5.
The table of contents forms an essential part of any academic paper. Through the use of headings, sub-headings, and page numbers, we can construct an accurate road map to assist reviewers, evaluators, tutors, and general readers. The table of contents shows how effective the writer is at dividing the thesis into relevant and manageable sections.
A multi-level table of contents also further divides sections into 'level 3' headings. This option can get messy quickly, so proceed with caution. Remember your table of contents should not be longer than 2 pages. A multi-level table is often a good choice for a shorter document like a research paper.
A table of contents (TOC) is a list of a research paper's main sections and subsections, along with their page numbers. It serves as a roadmap for the reader, allowing them to find the information they need within the paper quickly. The table of contents for a research paper is usually placed at the beginning of the paper, after the title ...
For a standard psychology paper, it might include listings for the introduction, method, results, and discussion sections of your paper. While the APA may not specify guidelines for a table of contents, you should use the basic APA format for formatting your table of contents: Use one-inch margins on all sides. Use 12-point Times New Roman font.
Indent the first line of every paragraph of text 0.5 in. using the tab key or the paragraph-formatting function of your word-processing program. Page numbers: Put a page number in the top right corner of every page, including the title page or cover page, which is page 1. Student papers do not require a running head on any page.
Hence, an example of a Table of Contents written in the APA format is indicated below: How to Write a Table of Contents in MLA. Unlike papers written in the APA style, MLA papers do not require a Table of Contents unless they are long enough. In this case, documents, like theses, dissertations, and books written in the MLA format should have a TOC.
A table of contents is a list, usually on a page at the beginning of a piece of academic writing, which outlines the chapters or sections names with their corresponding page numbers. In addition to chapter names, it includes bullet points of the sub-chapter headings or subsection headings. It usually comes right after the title page of a ...
Here is an example of a Table of Contents page from the Template. Please note that your table of contents may be longer than one page. << Previous: Dedication Page
Open Home tab and choose the style for your table of contents (ToC next). Apply heading 1 to your chapters, heading 2 to the subheading, and if needed heading 3 to the level 3 heading. Next, you are going to create a research paper or PhD dissertation table of contents. Open References and choose ToC.
Formatting a Chicago paper. The main guidelines for writing a paper in Chicago style (also known as Turabian style) are: Use a standard font like 12 pt Times New Roman. Use 1 inch margins or larger. Apply double line spacing. Indent every new paragraph ½ inch. Place page numbers in the top right or bottom center.
Step 4: Click the arrow that is next to the TOC icon and select Custom Table of Contents. Here, select the level of heading that you would like to include in your table and also make the necessary adjustments to each level by clicking the modify button. Click on Custom table of contents.
The format of a table of contents varies depending upon the instructor and style guide. However, they all identify the chapters/sections within a paper and sequentially list them based on their order.
MS Word is equally as useful, but creating a table of contents in Google Docs is a really straightforward process. Choose your preferred location for your table of contents on the document. Click 'Insert' and choose 'Table of contents.'. Decide on your chosen table of contents format.
A decimal outline is similar in format to the alphanumeric outline, but with a different numbering system: 1, 1.1, 1.2, etc. Text is written as short notes rather than full sentences. Example: 1 Body paragraph one. 1.1 First point. 1.1.1 Sub-point of first point. 1.1.2 Sub-point of first point.
Table of Contents Sample for Research - Free download as Word Doc (.doc / .docx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. This document provides a table of contents for a research paper that examines the relationship between teaching styles and student learning. The paper includes chapters that introduce the topic, review related literature, describe the methodology, analyze ...
Table of Contents; Research - Free download as Word Doc (.doc / .docx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. This document contains an outline for a research study, including sections on the problem background, hypothesis, methodology, and results. The methodology section details that the research will use a quantitative design, describe the population and sampling, and ...
To do this, follow these steps: Navigate to the References tab, and click "Insert Caption," which you can find in the Captions group. Give your caption a name. In the Label list, you can select the label that best describes your figure or table, or make your own by selecting "New Label.". Next, you can insert the list of tables and ...
Background: Sequential mixed-mode surveys using both web-based surveys and telephone interviews are increasingly being used in observational studies and have been shown to have many benefits; however, the application of this survey design has not been evaluated in the context of epidemiological case-control studies. Objective: In this paper, we discuss the challenges, benefits, and limitations ...