- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources

How to Make a Literature Review in Research (RRL Example)
What is an RRL in a research paper?
A relevant review of the literature (RRL) is an objective, concise, critical summary of published research literature relevant to a topic being researched in an article. In an RRL, you discuss knowledge and findings from existing literature relevant to your study topic. If there are conflicts or gaps in existing literature, you can also discuss these in your review, as well as how you will confront these missing elements or resolve these issues in your study.
To complete an RRL, you first need to collect relevant literature; this can include online and offline sources. Save all of your applicable resources as you will need to include them in your paper. When looking through these sources, take notes and identify concepts of each source to describe in the review of the literature.
A good RRL does NOT:
A literature review does not simply reference and list all of the material you have cited in your paper.
- Presenting material that is not directly relevant to your study will distract and frustrate the reader and make them lose sight of the purpose of your study.
- Starting a literature review with “A number of scholars have studied the relationship between X and Y” and simply listing who has studied the topic and what each scholar concluded is not going to strengthen your paper.
A good RRL DOES:
- Present a brief typology that orders articles and books into groups to help readers focus on unresolved debates, inconsistencies, tensions, and new questions about a research topic.
- Summarize the most relevant and important aspects of the scientific literature related to your area of research
- Synthesize what has been done in this area of research and by whom, highlight what previous research indicates about a topic, and identify potential gaps and areas of disagreement in the field
- Give the reader an understanding of the background of the field and show which studies are important—and highlight errors in previous studies
How long is a review of the literature for a research paper?
The length of a review of the literature depends on its purpose and target readership and can vary significantly in scope and depth. In a dissertation, thesis, or standalone review of literature, it is usually a full chapter of the text (at least 20 pages). Whereas, a standard research article or school assignment literature review section could only be a few paragraphs in the Introduction section .
Building Your Literature Review Bookshelf
One way to conceive of a literature review is to think about writing it as you would build a bookshelf. You don’t need to cut each piece by yourself from scratch. Rather, you can take the pieces that other researchers have cut out and put them together to build a framework on which to hang your own “books”—that is, your own study methods, results, and conclusions.
What Makes a Good Literature Review?
The contents of a literature review (RRL) are determined by many factors, including its precise purpose in the article, the degree of consensus with a given theory or tension between competing theories, the length of the article, the number of previous studies existing in the given field, etc. The following are some of the most important elements that a literature review provides.
Historical background for your research
Analyze what has been written about your field of research to highlight what is new and significant in your study—or how the analysis itself contributes to the understanding of this field, even in a small way. Providing a historical background also demonstrates to other researchers and journal editors your competency in discussing theoretical concepts. You should also make sure to understand how to paraphrase scientific literature to avoid plagiarism in your work.
The current context of your research
Discuss central (or peripheral) questions, issues, and debates in the field. Because a field is constantly being updated by new work, you can show where your research fits into this context and explain developments and trends in research.
A discussion of relevant theories and concepts
Theories and concepts should provide the foundation for your research. For example, if you are researching the relationship between ecological environments and human populations, provide models and theories that focus on specific aspects of this connection to contextualize your study. If your study asks a question concerning sustainability, mention a theory or model that underpins this concept. If it concerns invasive species, choose material that is focused in this direction.
Definitions of relevant terminology
In the natural sciences, the meaning of terms is relatively straightforward and consistent. But if you present a term that is obscure or context-specific, you should define the meaning of the term in the Introduction section (if you are introducing a study) or in the summary of the literature being reviewed.
Description of related relevant research
Include a description of related research that shows how your work expands or challenges earlier studies or fills in gaps in previous work. You can use your literature review as evidence of what works, what doesn’t, and what is missing in the field.
Supporting evidence for a practical problem or issue your research is addressing that demonstrates its importance: Referencing related research establishes your area of research as reputable and shows you are building upon previous work that other researchers have deemed significant.
Types of Literature Reviews
Literature reviews can differ in structure, length, amount, and breadth of content included. They can range from selective (a very narrow area of research or only a single work) to comprehensive (a larger amount or range of works). They can also be part of a larger work or stand on their own.
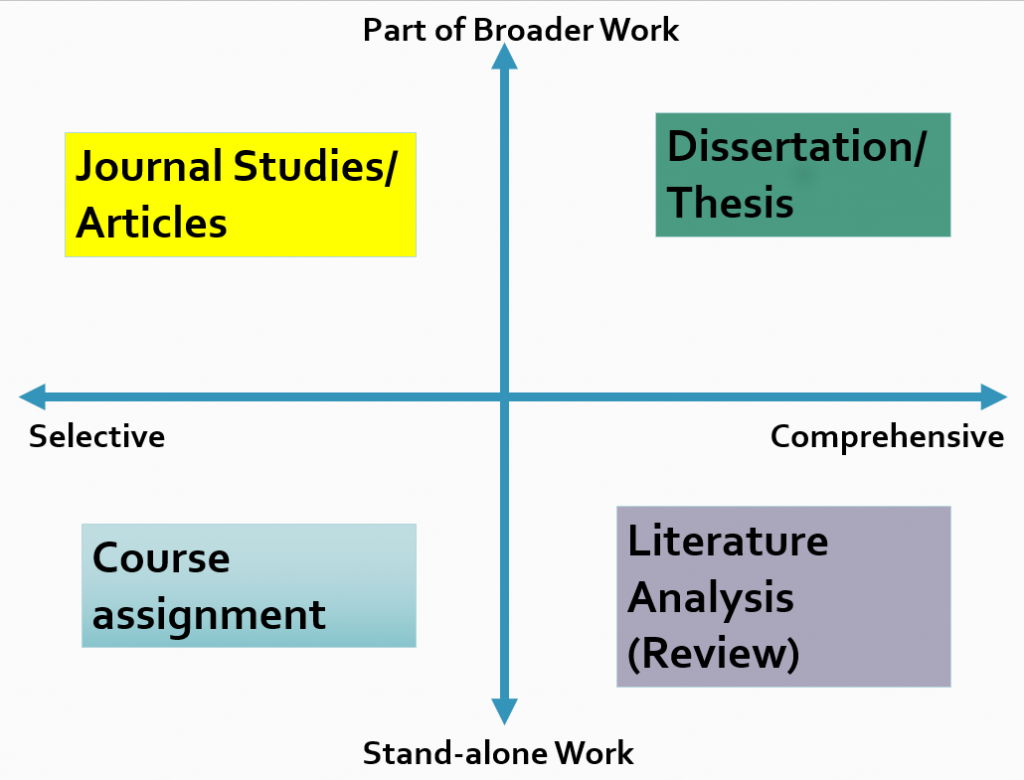
- A course assignment is an example of a selective, stand-alone work. It focuses on a small segment of the literature on a topic and makes up an entire work on its own.
- The literature review in a dissertation or thesis is both comprehensive and helps make up a larger work.
- A majority of journal articles start with a selective literature review to provide context for the research reported in the study; such a literature review is usually included in the Introduction section (but it can also follow the presentation of the results in the Discussion section ).
- Some literature reviews are both comprehensive and stand as a separate work—in this case, the entire article analyzes the literature on a given topic.
Literature Reviews Found in Academic Journals
The two types of literature reviews commonly found in journals are those introducing research articles (studies and surveys) and stand-alone literature analyses. They can differ in their scope, length, and specific purpose.
Literature reviews introducing research articles
The literature review found at the beginning of a journal article is used to introduce research related to the specific study and is found in the Introduction section, usually near the end. It is shorter than a stand-alone review because it must be limited to very specific studies and theories that are directly relevant to the current study. Its purpose is to set research precedence and provide support for the study’s theory, methods, results, and/or conclusions. Not all research articles contain an explicit review of the literature, but most do, whether it is a discrete section or indistinguishable from the rest of the Introduction.
How to structure a literature review for an article
When writing a literature review as part of an introduction to a study, simply follow the structure of the Introduction and move from the general to the specific—presenting the broadest background information about a topic first and then moving to specific studies that support your rationale , finally leading to your hypothesis statement. Such a literature review is often indistinguishable from the Introduction itself—the literature is INTRODUCING the background and defining the gaps your study aims to fill.
The stand-alone literature review
The literature review published as a stand-alone article presents and analyzes as many of the important publications in an area of study as possible to provide background information and context for a current area of research or a study. Stand-alone reviews are an excellent resource for researchers when they are first searching for the most relevant information on an area of study.
Such literature reviews are generally a bit broader in scope and can extend further back in time. This means that sometimes a scientific literature review can be highly theoretical, in addition to focusing on specific methods and outcomes of previous studies. In addition, all sections of such a “review article” refer to existing literature rather than describing the results of the authors’ own study.
In addition, this type of literature review is usually much longer than the literature review introducing a study. At the end of the review follows a conclusion that once again explicitly ties all of the cited works together to show how this analysis is itself a contribution to the literature. While not absolutely necessary, such articles often include the terms “Literature Review” or “Review of the Literature” in the title. Whether or not that is necessary or appropriate can also depend on the specific author instructions of the target journal. Have a look at this article for more input on how to compile a stand-alone review article that is insightful and helpful for other researchers in your field.

How to Write a Literature Review in 6 Steps
So how do authors turn a network of articles into a coherent review of relevant literature?
Writing a literature review is not usually a linear process—authors often go back and check the literature while reformulating their ideas or making adjustments to their study. Sometimes new findings are published before a study is completed and need to be incorporated into the current work. This also means you will not be writing the literature review at any one time, but constantly working on it before, during, and after your study is complete.
Here are some steps that will help you begin and follow through on your literature review.
Step 1: Choose a topic to write about—focus on and explore this topic.
Choose a topic that you are familiar with and highly interested in analyzing; a topic your intended readers and researchers will find interesting and useful; and a topic that is current, well-established in the field, and about which there has been sufficient research conducted for a review. This will help you find the “sweet spot” for what to focus on.
Step 2: Research and collect all the scholarly information on the topic that might be pertinent to your study.
This includes scholarly articles, books, conventions, conferences, dissertations, and theses—these and any other academic work related to your area of study is called “the literature.”
Step 3: Analyze the network of information that extends or responds to the major works in your area; select the material that is most useful.
Use thought maps and charts to identify intersections in the research and to outline important categories; select the material that will be most useful to your review.
Step 4: Describe and summarize each article—provide the essential information of the article that pertains to your study.
Determine 2-3 important concepts (depending on the length of your article) that are discussed in the literature; take notes about all of the important aspects of this study relevant to the topic being reviewed.
For example, in a given study, perhaps some of the main concepts are X, Y, and Z. Note these concepts and then write a brief summary about how the article incorporates them. In reviews that introduce a study, these can be relatively short. In stand-alone reviews, there may be significantly more texts and more concepts.
Step 5: Demonstrate how these concepts in the literature relate to what you discovered in your study or how the literature connects the concepts or topics being discussed.
In a literature review intro for an article, this information might include a summary of the results or methods of previous studies that correspond to and/or confirm those sections in your own study. For a stand-alone literature review, this may mean highlighting the concepts in each article and showing how they strengthen a hypothesis or show a pattern.
Discuss unaddressed issues in previous studies. These studies that are missing something you address are important to include in your literature review. In addition, those works whose theories and conclusions directly support your findings will be valuable to review here.
Step 6: Identify relationships in the literature and develop and connect your own ideas to them.
This is essentially the same as step 5 but focused on the connections between the literature and the current study or guiding concepts or arguments of the paper, not only on the connections between the works themselves.
Your hypothesis, argument, or guiding concept is the “golden thread” that will ultimately tie the works together and provide readers with specific insights they didn’t have before reading your literature review. Make sure you know where to put the research question , hypothesis, or statement of the problem in your research paper so that you guide your readers logically and naturally from your introduction of earlier work and evidence to the conclusions you want them to draw from the bigger picture.
Your literature review will not only cover publications on your topics but will include your own ideas and contributions. By following these steps you will be telling the specific story that sets the background and shows the significance of your research and you can turn a network of related works into a focused review of the literature.
Literature Review (RRL) Examples
Because creating sample literature reviews would take too long and not properly capture the nuances and detailed information needed for a good review, we have included some links to different types of literature reviews below. You can find links to more literature reviews in these categories by visiting the TUS Library’s website . Sample literature reviews as part of an article, dissertation, or thesis:
- Critical Thinking and Transferability: A Review of the Literature (Gwendolyn Reece)
- Building Customer Loyalty: A Customer Experience Based Approach in a Tourism Context (Martina Donnelly)
Sample stand-alone literature reviews
- Literature Review on Attitudes towards Disability (National Disability Authority)
- The Effects of Communication Styles on Marital Satisfaction (Hannah Yager)
Additional Literature Review Format Guidelines
In addition to the content guidelines above, authors also need to check which style guidelines to use ( APA , Chicago, MLA, etc.) and what specific rules the target journal might have for how to structure such articles or how many studies to include—such information can usually be found on the journals’ “Guide for Authors” pages. Additionally, use one of the four Wordvice citation generators below, choosing the citation style needed for your paper:
Wordvice Writing and Academic Editing Resources
Finally, after you have finished drafting your literature review, be sure to receive professional proofreading services , including paper editing for your academic work. A competent proofreader who understands academic writing conventions and the specific style guides used by academic journals will ensure that your paper is ready for publication in your target journal.
See our academic resources for further advice on references in your paper , how to write an abstract , how to write a research paper title, how to impress the editor of your target journal with a perfect cover letter , and dozens of other research writing and publication topics.
Review of Related Literature: Format, Example, & How to Make RRL
A review of related literature is a separate paper or a part of an article that collects and synthesizes discussion on a topic. Its purpose is to show the current state of research on the issue and highlight gaps in existing knowledge. A literature review can be included in a research paper or scholarly article, typically following the introduction and before the research methods section.

This article will clarify the definition, significance, and structure of a review of related literature. You’ll also learn how to organize your literature review and discover ideas for an RRL in different subjects.
🔤 What Is RRL?
- ❗ Significance of Literature Review
- 🔎 How to Search for Literature
- 🧩 Literature Review Structure
- 📋 Format of RRL — APA, MLA, & Others
- ✍️ How to Write an RRL
- 📚 Examples of RRL
🔗 References
A review of related literature (RRL) is a part of the research report that examines significant studies, theories, and concepts published in scholarly sources on a particular topic. An RRL includes 3 main components:
- A short overview and critique of the previous research.
- Similarities and differences between past studies and the current one.
- An explanation of the theoretical frameworks underpinning the research.
❗ Significance of Review of Related Literature
Although the goal of a review of related literature differs depending on the discipline and its intended use, its significance cannot be overstated. Here are some examples of how a review might be beneficial:
- It helps determine knowledge gaps .
- It saves from duplicating research that has already been conducted.
- It provides an overview of various research areas within the discipline.
- It demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with the topic.
🔎 How to Perform a Literature Search
Including a description of your search strategy in the literature review section can significantly increase your grade. You can search sources with the following steps:
🧩 Literature Review Structure Example
The majority of literature reviews follow a standard introduction-body-conclusion structure. Let’s look at the RRL structure in detail.
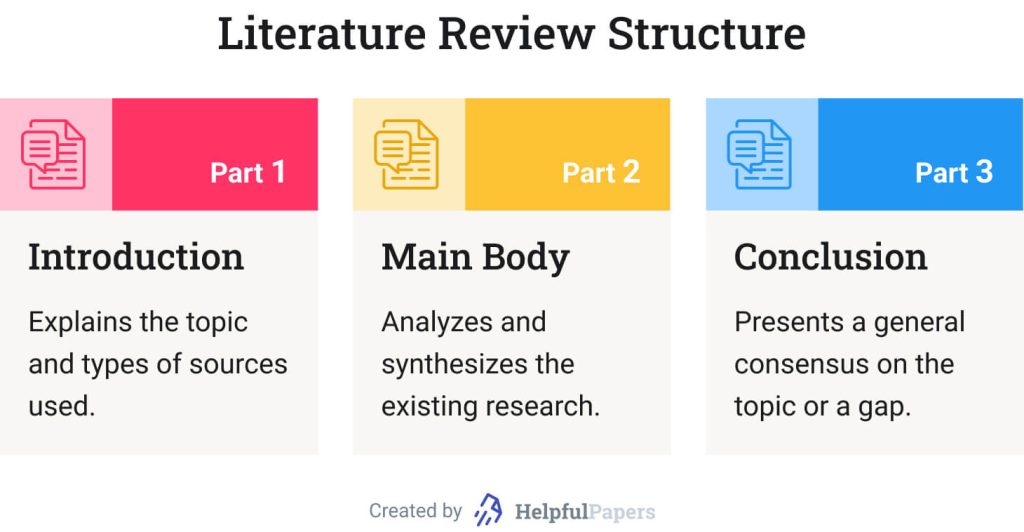
Introduction of Review of Related Literature: Sample
An introduction should clarify the study topic and the depth of the information to be delivered. It should also explain the types of sources used. If your lit. review is part of a larger research proposal or project, you can combine its introductory paragraph with the introduction of your paper.
Here is a sample introduction to an RRL about cyberbullying:
Bullying has troubled people since the beginning of time. However, with modern technological advancements, especially social media, bullying has evolved into cyberbullying. As a result, nowadays, teenagers and adults cannot flee their bullies, which makes them feel lonely and helpless. This literature review will examine recent studies on cyberbullying.
Sample Review of Related Literature Thesis
A thesis statement should include the central idea of your literature review and the primary supporting elements you discovered in the literature. Thesis statements are typically put at the end of the introductory paragraph.
Look at a sample thesis of a review of related literature:
This literature review shows that scholars have recently covered the issues of bullies’ motivation, the impact of bullying on victims and aggressors, common cyberbullying techniques, and victims’ coping strategies. However, there is still no agreement on the best practices to address cyberbullying.
Literature Review Body Paragraph Example
The main body of a literature review should provide an overview of the existing research on the issue. Body paragraphs should not just summarize each source but analyze them. You can organize your paragraphs with these 3 elements:
- Claim . Start with a topic sentence linked to your literature review purpose.
- Evidence . Cite relevant information from your chosen sources.
- Discussion . Explain how the cited data supports your claim.
Here’s a literature review body paragraph example:
Scholars have examined the link between the aggressor and the victim. Beran et al. (2007) state that students bullied online often become cyberbullies themselves. Faucher et al. (2014) confirm this with their findings: they discovered that male and female students began engaging in cyberbullying after being subject to bullying. Hence, one can conclude that being a victim of bullying increases one’s likelihood of becoming a cyberbully.
Review of Related Literature: Conclusion
A conclusion presents a general consensus on the topic. Depending on your literature review purpose, it might include the following:
- Introduction to further research . If you write a literature review as part of a larger research project, you can present your research question in your conclusion .
- Overview of theories . You can summarize critical theories and concepts to help your reader understand the topic better.
- Discussion of the gap . If you identified a research gap in the reviewed literature, your conclusion could explain why that gap is significant.
Check out a conclusion example that discusses a research gap:
There is extensive research into bullies’ motivation, the consequences of bullying for victims and aggressors, strategies for bullying, and coping with it. Yet, scholars still have not reached a consensus on what to consider the best practices to combat cyberbullying. This question is of great importance because of the significant adverse effects of cyberbullying on victims and bullies.
📋 Format of RRL — APA, MLA, & Others
In this section, we will discuss how to format an RRL according to the most common citation styles: APA, Chicago, MLA, and Harvard.
Writing a literature review using the APA7 style requires the following text formatting:
- When using APA in-text citations , include the author’s last name and the year of publication in parentheses.
- For direct quotations , you must also add the page number. If you use sources without page numbers, such as websites or e-books, include a paragraph number instead.
- When referring to the author’s name in a sentence , you do not need to repeat it at the end of the sentence. Instead, include the year of publication inside the parentheses after their name.
- The reference list should be included at the end of your literature review. It is always alphabetized by the last name of the author (from A to Z), and the lines are indented one-half inch from the left margin of your paper. Do not forget to invert authors’ names (the last name should come first) and include the full titles of journals instead of their abbreviations. If you use an online source, add its URL.
The RRL format in the Chicago style is as follows:
- Author-date . You place your citations in brackets within the text, indicating the name of the author and the year of publication.
- Notes and bibliography . You place your citations in numbered footnotes or endnotes to connect the citation back to the source in the bibliography.
- The reference list, or bibliography , in Chicago style, is at the end of a literature review. The sources are arranged alphabetically and single-spaced. Each bibliography entry begins with the author’s name and the source’s title, followed by publication information, such as the city of publication, the publisher, and the year of publication.
Writing a literature review using the MLA style requires the following text formatting:
- In the MLA format, you can cite a source in the text by indicating the author’s last name and the page number in parentheses at the end of the citation. If the cited information takes several pages, you need to include all the page numbers.
- The reference list in MLA style is titled “ Works Cited .” In this section, all sources used in the paper should be listed in alphabetical order. Each entry should contain the author, title of the source, title of the journal or a larger volume, other contributors, version, number, publisher, and publication date.
The Harvard style requires you to use the following text formatting for your RRL:
- In-text citations in the Harvard style include the author’s last name and the year of publication. If you are using a direct quote in your literature review, you need to add the page number as well.
- Arrange your list of references alphabetically. Each entry should contain the author’s last name, their initials, the year of publication, the title of the source, and other publication information, like the journal title and issue number or the publisher.
✍️ How to Write Review of Related Literature – Sample
Literature reviews can be organized in many ways depending on what you want to achieve with them. In this section, we will look at 3 examples of how you can write your RRL.

Thematic Literature Review
A thematic literature review is arranged around central themes or issues discussed in the sources. If you have identified some recurring themes in the literature, you can divide your RRL into sections that address various aspects of the topic. For example, if you examine studies on e-learning, you can distinguish such themes as the cost-effectiveness of online learning, the technologies used, and its effectiveness compared to traditional education.
Chronological Literature Review
A chronological literature review is a way to track the development of the topic over time. If you use this method, avoid merely listing and summarizing sources in chronological order. Instead, try to analyze the trends, turning moments, and critical debates that have shaped the field’s path. Also, you can give your interpretation of how and why specific advances occurred.
Methodological Literature Review
A methodological literature review differs from the preceding ones in that it usually doesn’t focus on the sources’ content. Instead, it is concerned with the research methods . So, if your references come from several disciplines or fields employing various research techniques, you can compare the findings and conclusions of different methodologies, for instance:
- empirical vs. theoretical studies;
- qualitative vs. quantitative research.
📚 Examples of Review of Related Literature and Studies
We have prepared a short example of RRL on climate change for you to see how everything works in practice!
Climate change is one of the most important issues nowadays. Based on a variety of facts, it is now clearer than ever that humans are altering the Earth's climate. The atmosphere and oceans have warmed, causing sea level rise, a significant loss of Arctic ice, and other climate-related changes. This literature review provides a thorough summary of research on climate change, focusing on climate change fingerprints and evidence of human influence on the Earth's climate system.
Physical Mechanisms and Evidence of Human Influence
Scientists are convinced that climate change is directly influenced by the emission of greenhouse gases. They have carefully analyzed various climate data and evidence, concluding that the majority of the observed global warming over the past 50 years cannot be explained by natural factors alone. Instead, there is compelling evidence pointing to a significant contribution of human activities, primarily the emission of greenhouse gases (Walker, 2014). For example, based on simple physics calculations, doubled carbon dioxide concentration in the atmosphere can lead to a global temperature increase of approximately 1 degree Celsius. (Elderfield, 2022). In order to determine the human influence on climate, scientists still have to analyze a lot of natural changes that affect temperature, precipitation, and other components of climate on timeframes ranging from days to decades and beyond.
Fingerprinting Climate Change
Fingerprinting climate change is a useful tool to identify the causes of global warming because different factors leave unique marks on climate records. This is evident when scientists look beyond overall temperature changes and examine how warming is distributed geographically and over time (Watson, 2022). By investigating these climate patterns, scientists can obtain a more complex understanding of the connections between natural climate variability and climate variability caused by human activity.
Modeling Climate Change and Feedback
To accurately predict the consequences of feedback mechanisms, the rate of warming, and regional climate change, scientists can employ sophisticated mathematical models of the atmosphere, ocean, land, and ice (the cryosphere). These models are grounded in well-established physical laws and incorporate the latest scientific understanding of climate-related processes (Shuckburgh, 2013). Although different climate models produce slightly varying projections for future warming, they all will agree that feedback mechanisms play a significant role in amplifying the initial warming caused by greenhouse gas emissions. (Meehl, 2019).
In conclusion, the literature on global warming indicates that there are well-understood physical processes that link variations in greenhouse gas concentrations to climate change. In addition, it covers the scientific proof that the rates of these gases in the atmosphere have increased and continue to rise fast. According to the sources, the majority of this recent change is almost definitely caused by greenhouse gas emissions produced by human activities. Citizens and governments can alter their energy production methods and consumption patterns to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and, thus, the magnitude of climate change. By acting now, society can prevent the worst consequences of climate change and build a more resilient and sustainable future for generations to come.
Have you ever struggled with finding the topic for an RRL in different subjects? Read the following paragraphs to get some ideas!
Nursing Literature Review Example
Many topics in the nursing field require research. For example, you can write a review of literature related to dengue fever . Give a general overview of dengue virus infections, including its clinical symptoms, diagnosis, prevention, and therapy.
Another good idea is to review related literature and studies about teenage pregnancy . This review can describe the effectiveness of specific programs for adolescent mothers and their children and summarize recommendations for preventing early pregnancy.
📝 Check out some more valuable examples below:
- Hospital Readmissions: Literature Review .
- Literature Review: Lower Sepsis Mortality Rates .
- Breast Cancer: Literature Review .
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases: Literature Review .
- PICO for Pressure Ulcers: Literature Review .
- COVID-19 Spread Prevention: Literature Review .
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Literature Review .
- Hypertension Treatment Adherence: Literature Review .
- Neonatal Sepsis Prevention: Literature Review .
- Healthcare-Associated Infections: Literature Review .
- Understaffing in Nursing: Literature Review .
Psychology Literature Review Example
If you look for an RRL topic in psychology , you can write a review of related literature about stress . Summarize scientific evidence about stress stages, side effects, types, or reduction strategies. Or you can write a review of related literature about computer game addiction . In this case, you may concentrate on the neural mechanisms underlying the internet gaming disorder, compare it to other addictions, or evaluate treatment strategies.
A review of related literature about cyberbullying is another interesting option. You can highlight the impact of cyberbullying on undergraduate students’ academic, social, and emotional development.
📝 Look at the examples that we have prepared for you to come up with some more ideas:
- Mindfulness in Counseling: A Literature Review .
- Team-Building Across Cultures: Literature Review .
- Anxiety and Decision Making: Literature Review .
- Literature Review on Depression .
- Literature Review on Narcissism .
- Effects of Depression Among Adolescents .
- Causes and Effects of Anxiety in Children .
Literature Review — Sociology Example
Sociological research poses critical questions about social structures and phenomena. For example, you can write a review of related literature about child labor , exploring cultural beliefs and social norms that normalize the exploitation of children. Or you can create a review of related literature about social media . It can investigate the impact of social media on relationships between adolescents or the role of social networks on immigrants’ acculturation .
📝 You can find some more ideas below!
- Single Mothers’ Experiences of Relationships with Their Adolescent Sons .
- Teachers and Students’ Gender-Based Interactions .
- Gender Identity: Biological Perspective and Social Cognitive Theory .
- Gender: Culturally-Prescribed Role or Biological Sex .
- The Influence of Opioid Misuse on Academic Achievement of Veteran Students .
- The Importance of Ethics in Research .
- The Role of Family and Social Network Support in Mental Health .
Education Literature Review Example
For your education studies , you can write a review of related literature about academic performance to determine factors that affect student achievement and highlight research gaps. One more idea is to create a review of related literature on study habits , considering their role in the student’s life and academic outcomes.
You can also evaluate a computerized grading system in a review of related literature to single out its advantages and barriers to implementation. Or you can complete a review of related literature on instructional materials to identify their most common types and effects on student achievement.
📝 Find some inspiration in the examples below:
- Literature Review on Online Learning Challenges From COVID-19 .
- Education, Leadership, and Management: Literature Review .
- Literature Review: Standardized Testing Bias .
- Bullying of Disabled Children in School .
- Interventions and Letter & Sound Recognition: A Literature Review .
- Social-Emotional Skills Program for Preschoolers .
- Effectiveness of Educational Leadership Management Skills .

Business Research Literature Review
If you’re a business student, you can focus on customer satisfaction in your review of related literature. Discuss specific customer satisfaction features and how it is affected by service quality and prices. You can also create a theoretical literature review about consumer buying behavior to evaluate theories that have significantly contributed to understanding how consumers make purchasing decisions.
📝 Look at the examples to get more exciting ideas:
- Leadership and Communication: Literature Review .
- Human Resource Development: Literature Review .
- Project Management. Literature Review .
- Strategic HRM: A Literature Review .
- Customer Relationship Management: Literature Review .
- Literature Review on International Financial Reporting Standards .
- Cultures of Management: Literature Review .
To conclude, a review of related literature is a significant genre of scholarly works that can be applied in various disciplines and for multiple goals. The sources examined in an RRL provide theoretical frameworks for future studies and help create original research questions and hypotheses.
When you finish your outstanding literature review, don’t forget to check whether it sounds logical and coherent. Our text-to-speech tool can help you with that!
- Literature Reviews | University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
- Writing a Literature Review | Purdue Online Writing Lab
- Learn How to Write a Review of Literature | University of Wisconsin-Madison
- The Literature Review: A Few Tips on Conducting It | University of Toronto
- Writing a Literature Review | UC San Diego
- Conduct a Literature Review | The University of Arizona
- Methods for Literature Reviews | National Library of Medicine
- Literature Reviews: 5. Write the Review | Georgia State University
How to Write an Animal Testing Essay: Tips for Argumentative & Persuasive Papers
Descriptive essay topics: examples, outline, & more.
Learn how to write a review of literature
What is a review of literature.
The format of a review of literature may vary from discipline to discipline and from assignment to assignment.
A review may be a self-contained unit — an end in itself — or a preface to and rationale for engaging in primary research. A review is a required part of grant and research proposals and often a chapter in theses and dissertations.
Generally, the purpose of a review is to analyze critically a segment of a published body of knowledge through summary, classification, and comparison of prior research studies, reviews of literature, and theoretical articles.
Writing the introduction
In the introduction, you should:
Define or identify the general topic, issue, or area of concern, thus providing an appropriate context for reviewing the literature.
Point out overall trends in what has been published about the topic; or conflicts in theory, methodology, evidence, and conclusions; or gaps in research and scholarship; or a single problem or new perspective of immediate interest.
Establish the writer’s reason (point of view) for reviewing the literature; explain the criteria to be used in analyzing and comparing literature and the organization of the review (sequence); and, when necessary, state why certain literature is or is not included (scope).
Writing the body
In the body, you should:
Group research studies and other types of literature (reviews, theoretical articles, case studies, etc.) according to common denominators such as qualitative versus quantitative approaches, conclusions of authors, specific purpose or objective, chronology, etc.
Summarize individual studies or articles with as much or as little detail as each merits according to its comparative importance in the literature, remembering that space (length) denotes significance.
Provide the reader with strong “umbrella” sentences at beginnings of paragraphs, “signposts” throughout, and brief “so what” summary sentences at intermediate points in the review to aid in understanding comparisons and analyses.
Writing the conclusion
In the conclusion, you should:
Summarize major contributions of significant studies and articles to the body of knowledge under review, maintaining the focus established in the introduction.
Evaluate the current “state of the art” for the body of knowledge reviewed, pointing out major methodological flaws or gaps in research, inconsistencies in theory and findings, and areas or issues pertinent to future study.
Conclude by providing some insight into the relationship between the central topic of the literature review and a larger area of study such as a discipline, a scientific endeavor, or a profession.
For further information see our handouts on Writing a Critical Review of a Nonfiction Book or Article or Reading a Book to Review It .
To learn more about literature reviews, take a look at our workshop on Writing Literature Reviews of Published Research.
Sample Literature Reviews
An important strategy for learning how to compose literature reviews in your field or within a specific genre is to locate and analyze representative examples. The following collection of annotated sample literature reviews written and co-written by colleagues associated with UW-Madison showcases how these reviews can do different kind of work for different purposes. Use these successful examples as a starting point for understanding how other writers have approached the challenging and important task of situating their idea in the context of established research.
- Sample 1 (PDF) A brief literature review within a political scientists’ National Science Foundation Graduate Research Fellowship grant
- Sample 2 (PDF) A several-page literature review at the beginning of a published, academic article about philosophy
- Sample 3 (PDF) A brief literature review at the beginning of a published, academic article about photochemistry

Academic and Professional Writing
This is an accordion element with a series of buttons that open and close related content panels.
Analysis Papers
Reading Poetry
A Short Guide to Close Reading for Literary Analysis
Using Literary Quotations
Play Reviews
Writing a Rhetorical Précis to Analyze Nonfiction Texts
Incorporating Interview Data
Grant Proposals
Planning and Writing a Grant Proposal: The Basics
Additional Resources for Grants and Proposal Writing
Job Materials and Application Essays
Writing Personal Statements for Ph.D. Programs
- Before you begin: useful tips for writing your essay
- Guided brainstorming exercises
- Get more help with your essay
- Frequently Asked Questions
Resume Writing Tips
CV Writing Tips
Cover Letters
Business Letters
Proposals and Dissertations
Resources for Proposal Writers
Resources for Dissertators
Research Papers
Planning and Writing Research Papers
Quoting and Paraphrasing
Writing Annotated Bibliographies
Creating Poster Presentations
Writing an Abstract for Your Research Paper
Thank-You Notes
Advice for Students Writing Thank-You Notes to Donors
Reading for a Review
Critical Reviews
Writing a Review of Literature
Scientific Reports
Scientific Report Format
Sample Lab Assignment
Writing for the Web
Writing an Effective Blog Post
Writing for Social Media: A Guide for Academics
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing a Literature Review

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels and plays). When we say “literature review” or refer to “the literature,” we are talking about the research ( scholarship ) in a given field. You will often see the terms “the research,” “the scholarship,” and “the literature” used mostly interchangeably.
Where, when, and why would I write a lit review?
There are a number of different situations where you might write a literature review, each with slightly different expectations; different disciplines, too, have field-specific expectations for what a literature review is and does. For instance, in the humanities, authors might include more overt argumentation and interpretation of source material in their literature reviews, whereas in the sciences, authors are more likely to report study designs and results in their literature reviews; these differences reflect these disciplines’ purposes and conventions in scholarship. You should always look at examples from your own discipline and talk to professors or mentors in your field to be sure you understand your discipline’s conventions, for literature reviews as well as for any other genre.
A literature review can be a part of a research paper or scholarly article, usually falling after the introduction and before the research methods sections. In these cases, the lit review just needs to cover scholarship that is important to the issue you are writing about; sometimes it will also cover key sources that informed your research methodology.
Lit reviews can also be standalone pieces, either as assignments in a class or as publications. In a class, a lit review may be assigned to help students familiarize themselves with a topic and with scholarship in their field, get an idea of the other researchers working on the topic they’re interested in, find gaps in existing research in order to propose new projects, and/or develop a theoretical framework and methodology for later research. As a publication, a lit review usually is meant to help make other scholars’ lives easier by collecting and summarizing, synthesizing, and analyzing existing research on a topic. This can be especially helpful for students or scholars getting into a new research area, or for directing an entire community of scholars toward questions that have not yet been answered.
What are the parts of a lit review?
Most lit reviews use a basic introduction-body-conclusion structure; if your lit review is part of a larger paper, the introduction and conclusion pieces may be just a few sentences while you focus most of your attention on the body. If your lit review is a standalone piece, the introduction and conclusion take up more space and give you a place to discuss your goals, research methods, and conclusions separately from where you discuss the literature itself.
Introduction:
- An introductory paragraph that explains what your working topic and thesis is
- A forecast of key topics or texts that will appear in the review
- Potentially, a description of how you found sources and how you analyzed them for inclusion and discussion in the review (more often found in published, standalone literature reviews than in lit review sections in an article or research paper)
- Summarize and synthesize: Give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: Don’t just paraphrase other researchers – add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically Evaluate: Mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: Use transition words and topic sentence to draw connections, comparisons, and contrasts.
Conclusion:
- Summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance
- Connect it back to your primary research question
How should I organize my lit review?
Lit reviews can take many different organizational patterns depending on what you are trying to accomplish with the review. Here are some examples:
- Chronological : The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time, which helps familiarize the audience with the topic (for instance if you are introducing something that is not commonly known in your field). If you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order. Try to analyze the patterns, turning points, and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred (as mentioned previously, this may not be appropriate in your discipline — check with a teacher or mentor if you’re unsure).
- Thematic : If you have found some recurring central themes that you will continue working with throughout your piece, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic. For example, if you are reviewing literature about women and religion, key themes can include the role of women in churches and the religious attitude towards women.
- Qualitative versus quantitative research
- Empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the research by sociological, historical, or cultural sources
- Theoretical : In many humanities articles, the literature review is the foundation for the theoretical framework. You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts. You can argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach or combine various theorical concepts to create a framework for your research.
What are some strategies or tips I can use while writing my lit review?
Any lit review is only as good as the research it discusses; make sure your sources are well-chosen and your research is thorough. Don’t be afraid to do more research if you discover a new thread as you’re writing. More info on the research process is available in our "Conducting Research" resources .
As you’re doing your research, create an annotated bibliography ( see our page on the this type of document ). Much of the information used in an annotated bibliography can be used also in a literature review, so you’ll be not only partially drafting your lit review as you research, but also developing your sense of the larger conversation going on among scholars, professionals, and any other stakeholders in your topic.
Usually you will need to synthesize research rather than just summarizing it. This means drawing connections between sources to create a picture of the scholarly conversation on a topic over time. Many student writers struggle to synthesize because they feel they don’t have anything to add to the scholars they are citing; here are some strategies to help you:
- It often helps to remember that the point of these kinds of syntheses is to show your readers how you understand your research, to help them read the rest of your paper.
- Writing teachers often say synthesis is like hosting a dinner party: imagine all your sources are together in a room, discussing your topic. What are they saying to each other?
- Look at the in-text citations in each paragraph. Are you citing just one source for each paragraph? This usually indicates summary only. When you have multiple sources cited in a paragraph, you are more likely to be synthesizing them (not always, but often
- Read more about synthesis here.
The most interesting literature reviews are often written as arguments (again, as mentioned at the beginning of the page, this is discipline-specific and doesn’t work for all situations). Often, the literature review is where you can establish your research as filling a particular gap or as relevant in a particular way. You have some chance to do this in your introduction in an article, but the literature review section gives a more extended opportunity to establish the conversation in the way you would like your readers to see it. You can choose the intellectual lineage you would like to be part of and whose definitions matter most to your thinking (mostly humanities-specific, but this goes for sciences as well). In addressing these points, you argue for your place in the conversation, which tends to make the lit review more compelling than a simple reporting of other sources.
What’s Included: Literature Review Template
This template is structure is based on the tried and trusted best-practice format for formal academic research projects such as dissertations and theses. The literature review template includes the following sections:
- Before you start – essential groundwork to ensure you’re ready
- The introduction section
- The core/body section
- The conclusion /summary
- Extra free resources
Each section is explained in plain, straightforward language , followed by an overview of the key elements that you need to cover. We’ve also included practical examples and links to more free videos and guides to help you understand exactly what’s required in each section.
The cleanly-formatted Google Doc can be downloaded as a fully editable MS Word Document (DOCX format), so you can use it as-is or convert it to LaTeX.
PS – if you’d like a high-level template for the entire thesis, you can we’ve got that too .
FAQs: Literature Review Template
What format is the template (doc, pdf, ppt, etc.).
The literature review chapter template is provided as a Google Doc. You can download it in MS Word format or make a copy to your Google Drive. You’re also welcome to convert it to whatever format works best for you, such as LaTeX or PDF.
What types of literature reviews can this template be used for?
The template follows the standard format for academic literature reviews, which means it will be suitable for the vast majority of academic research projects (especially those within the sciences), whether they are qualitative or quantitative in terms of design.
Keep in mind that the exact requirements for the literature review chapter will vary between universities and degree programs. These are typically minor, but it’s always a good idea to double-check your university’s requirements before you finalize your structure.
Is this template for an undergrad, Master or PhD-level thesis?
This template can be used for a literature review at any level of study. Doctoral-level projects typically require the literature review to be more extensive/comprehensive, but the structure will typically remain the same.
Can I modify the template to suit my topic/area?
Absolutely. While the template provides a general structure, you should adapt it to fit the specific requirements and focus of your literature review.
What structural style does this literature review template use?
The template assumes a thematic structure (as opposed to a chronological or methodological structure), as this is the most common approach. However, this is only one dimension of the template, so it will still be useful if you are adopting a different structure.
Does this template include the Excel literature catalog?
No, that is a separate template, which you can download for free here . This template is for the write-up of the actual literature review chapter, whereas the catalog is for use during the literature sourcing and sorting phase.
How long should the literature review chapter be?
This depends on your university’s specific requirements, so it’s best to check with them. As a general ballpark, literature reviews for Masters-level projects are usually 2,000 – 3,000 words in length, while Doctoral-level projects can reach multiples of this.
Can I include literature that contradicts my hypothesis?
Yes, it’s important to acknowledge and discuss literature that presents different viewpoints or contradicts your hypothesis. So, don’t shy away from existing research that takes an opposing view to yours.
How do I avoid plagiarism in my literature review?
Always cite your sources correctly and paraphrase ideas in your own words while maintaining the original meaning. You can always check our plagiarism score before submitting your work to help ease your mind.
Do you have an example of a populated template?
We provide a walkthrough of the template and review an example of a high-quality literature research chapter here .
Can I share this literature review template with my friends/colleagues?
Yes, you’re welcome to share this template in its original format (no editing allowed). If you want to post about it on your blog or social media, all we ask is that you reference this page as your source.
Do you have templates for the other dissertation/thesis chapters?
Yes, we do. You can find our full collection of templates here .
Can Grad Coach help me with my literature review?
Yes, you’re welcome to get in touch with us to discuss our private coaching services , where we can help you work through the literature review chapter (and any other chapters).


- University of Texas Libraries
- UT Libraries
Architecture
- Literature Reviews
- Databases, Journals, Websites
- Visual Resources
- GIS & Geospatial Data
- Archives & Primary Sources
- Codes and Standards
- Writing a Research Paper
- Evaluate Sources
- Case Studies
- Citations and Data
Literature Review
What is a Literature Review?
It is…. a systematic and critical analysis of the literature on a specific topic. It describes trends, quality, relationships, inconsistencies and gaps in the research; and it details how the works enhance your understanding of the topic at large.
It is NOT…. simply an annotated bibliography that summarizes and/or assesses each article. There is not one, correct way to approach and write a literature review. It can be a stand-alone paper or part of a thesis/dissertation. Format and requirements can vary between disciplines, purpose and intended audience.
A literature review is an overview of existing literature (books, articles, dissertations, conference proceedings, and other sources) in a particular scholarly area. With a lit review, you will:
- Gather information about your topic, including the sources used by others who have previously conducted research
- Find out if your specific research question has already been answered
- Find out what areas or perspectives have not yet been covered by others on your topic
- Analyze and evaluate existing information
The literature review will assist you in considering the validity and scope of your research question so that you can do the necessary revision and fine tuning to it. It provides the foundation to formulate and present strong arguments to justify your chosen research topic.
- How to Write a Literature Review (University of California, Santa Cruz)
Check out these books from the library for further guidance:
- Després, Carole. "The meaning of home: literature review and directions for future research and theoretical development." Journal of architectural and planning research 8, no.2, (Summer 1991): 96-155.
- Steiner, Frederick R. "Philadelphia, the holy experiment: A literature review and analysis." Ekistics , 49, (1982): 298-305.
Reckoning with Authorities
As you are developing your Lit Review, part of your objective is to identify the leading authorities within the field or who address your topic or theme. Some tips for identifying the scholars:
Old Fashioned Method:
- Keep notes on footnotes and names as you read articles, books, blogs, exhibition catalogs, etc. Are there names or works that everyone references? Use the catalog to track these reference down.
- Consider looking for state of the field articles often found either in a discipline's primary journal or in conference proceedings - keynote speakers.
- Look for book reviews.
Publication Metrics:
- These resources include information about the frequency of citations for an article/author.
- These resources are not specifically for Architecture or Planning. Remember therefore to be critical and careful about the assumptions you make with regard to the results!
The Web of Science platform currently also provides temporary access to several databases that are not part of the Core Collection, including Biosis Citation Index, Data Citation Index, and Zoological Record.
Use this link to access Google Scholar, and see our Google Scholar Guide for information on using this resource.
If you encounter a warning about the security certificate when using the FindIt@UT tool in Google Scholar, you can learn more about that using this guide .
- Last Updated: Oct 5, 2023 8:40 AM
- URL: https://guides.lib.utexas.edu/architecture

- University of Oregon Libraries
- Research Guides
How to Write a Literature Review
- 6. Synthesize
- Literature Reviews: A Recap
- Reading Journal Articles
- Does it Describe a Literature Review?
- 1. Identify the Question
- 2. Review Discipline Styles
- Searching Article Databases
- Finding Full-Text of an Article
- Citation Chaining
- When to Stop Searching
- 4. Manage Your References
- 5. Critically Analyze and Evaluate
Synthesis Visualization
Synthesis matrix example.
- 7. Write a Literature Review
- Synthesis Worksheet
About Synthesis
Approaches to synthesis.
You can sort the literature in various ways, for example:

How to Begin?
Read your sources carefully and find the main idea(s) of each source
Look for similarities in your sources – which sources are talking about the same main ideas? (for example, sources that discuss the historical background on your topic)
Use the worksheet (above) or synthesis matrix (below) to get organized
This work can be messy. Don't worry if you have to go through a few iterations of the worksheet or matrix as you work on your lit review!
Four Examples of Student Writing
In the four examples below, only ONE shows a good example of synthesis: the fourth column, or Student D . For a web accessible version, click the link below the image.

Long description of "Four Examples of Student Writing" for web accessibility
- Download a copy of the "Four Examples of Student Writing" chart

Click on the example to view the pdf.

From Jennifer Lim
- << Previous: 5. Critically Analyze and Evaluate
- Next: 7. Write a Literature Review >>
- Last Updated: May 3, 2024 5:17 PM
- URL: https://researchguides.uoregon.edu/litreview
Contact Us Library Accessibility UO Libraries Privacy Notices and Procedures

1501 Kincaid Street Eugene, OR 97403 P: 541-346-3053 F: 541-346-3485
- Visit us on Facebook
- Visit us on Twitter
- Visit us on Youtube
- Visit us on Instagram
- Report a Concern
- Nondiscrimination and Title IX
- Accessibility
- Privacy Policy
- Find People
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

CHAPTER 2 REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE AND STUDIES

Related Papers
Ana Liza Sigue
Motoky Hayakawa
Rene E Ofreneo
... Rene E. Ofreneo University of the Philippines School of Labor and Industrial Relations ... Erickson, Christopher L.; Kuruvilla, Sarosh ; Ofreneo, Rene E.; and Ortiz, Maria Asuncion , &quot;Recent Developments in Employment Relations in the Philippines&quot; (2001). ...
Lucita Lazo
This book begins by looking at the status of women in Filipino society and their place in the general socio-economic situation. It continues with sections on education and training in the Philippines and work and training. The next section reviews the constraints to women’s participation in training. In the summary the author gives a general overview of the situation of women and opportunities for work and training in the Philippines and offers some practical suggestions for the enhancement of women’s training and development.
EducationInvestor Global
Tony Mitchener
Rosalyn Eder
In this article, I examine the role of CHED and the Technical Panels (TPs) in the “production” of the globally competitive Filipina/o worker. For this paper, I draw on relevant literature on the topic and take nurse education, which is rooted in the colonial system established during the US-American occupation, as an example of how CHED and the TPs could be more linked to labor migration. I use the colonial difference - a space that offers critical insights and interpretation - to illustrate how coloniality remains hidden under the cloak of modernity. Link to the article: http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/00131946.2016.1214913
Asia Pacific Journal of Management and Sustainable Development ISSN 2782-8557(Print)
Ryan O Tayco , Pio Supat
This study aims to determine the employability of the Negros Oriental State University graduates from 2016 to 2020. Employability is measured using different dimensions-from the graduates' side including the perspectives of the employers. A total of 1, 056 NORSU graduates and 68 employers locally and abroad answered the questionnaire through online and offline survey methods. Basic statistics were used and simple linear regression was also used to estimate the relationship between manifestations of respondents in NORSU VMGOs and the job performance as perceived by the employers. Most of the respondents in the study are presently employed and work locally. Many of them stay and accept the job because of the salaries and benefits they received, a career challenge, and related to the course they have taken in college. The study shows that the curriculum used and competencies learned by the NORSU graduates are relevant to their job. Competencies such as communication skills, human relations skills, critical thinking skills, and problem-solving skills are found to be useful by the respondents. It is found that the manifestation of the respondents is very high and homogenous. The same can be said with job performance as perceived by employers in terms of attitudes and values, skills and competencies, and knowledge. Furthermore, job performance and the manifestation of NORSU VMGOs have a significant relationship. That is, those respondents who have higher job performance in terms of attitude and values, skills and competencies, and knowledge have higher manifestations of NORSU VMGOs.
Annals of Tropical Research
Pedro Armenia
Ezekiel Succor
RELATED PAPERS
Silvio Roberto Stefano
Environmental Evidence
María José Sanz
Alcohol Health and Research World
Diane Deitz
Pure and Applied Chemistry
Kunsang Yoon
Theoretical and Applied Mechanics
Stevan Pilipović
Romil Al-Adwan
THE 6TH BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING’S RECENT PROGRESS IN BIOMATERIALS, DRUGS DEVELOPMENT, AND MEDICAL DEVICES: Proceedings of the 6th International Symposium of Biomedical Engineering (ISBE) 2021
Ferry Gultom
Iranian Journal of Optimization
Mirpouya Mirmozaffari
购买princeton学位证书 普林斯顿大学毕业证学位证书范本GRE证书原版一模一样
Osinachi Okafor
Journal of Fatwa Management and Research
Manan Ismail
Suluh Pembangunan : Journal of Extension and Development
Muhammad Ibnu
IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing
Othmar Frey
Surgical Neurology
Marcel Rooze
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine
Graciela Reyes
Cadernos de Tradução
Andréa Cesco
Amc Acta medica colombiana
Revista Iberoamericana de Diagnóstico y Evaluación – e Avaliação Psicológica
jaqueline rodrigues
Historia Mexicana
Tomás Pérez Vejo
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A course assignment is an example of a selective, stand-alone work.It focuses on a small segment of the literature on a topic and makes up an entire work on its own. The literature review in a dissertation or thesis is both comprehensive and helps make up a larger work.; A majority of journal articles start with a selective literature review to provide context for the research reported in the ...
Sample Review of Related Literature Thesis. A thesis statement should include the central idea of your literature review and the primary supporting elements you discovered in the literature. Thesis statements are typically put at the end of the introductory paragraph. Look at a sample thesis of a review of related literature:
This puzzle leads to your research question and clarifies which literature(s) you should draw on at the beginning of your literature review. Theorize that tokens in the workplace experience isolation and obstacles to advancement. They attribute this to the the tokens low numbers and low status.
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
Demonstrate your knowledge of the research topic. Identify the gaps in the literature and show how your research links to these. Provide the foundation for your conceptual framework (if you have one) Inform your own methodology and research design. To achieve this, your literature review needs a well-thought-out structure.
Tips on how to write a review of related literature in research. Given that you will probably need to produce a number of these at some point, here are a few general tips on how to write an effective review of related literature 2. Define your topic, audience, and purpose: You will be spending a lot of time with this review, so choose a topic ...
A review may be a self-contained unit — an end in itself — or a preface to and rationale for engaging in primary research. A review is a required part of grant and research proposals and often a chapter in theses and dissertations. Generally, the purpose of a review is to analyze critically a segment of a published body of knowledge through ...
A review of the related literature (RRL) is an excellent way to provide an overview of current knowledge on the specific topic of your work. It brings to the fore the gaps in the knowledge of the topic you are addressing, allowing you to highlight how your study sets out to fill them. Your question is an interesting one.
Put simply, RRL is a thorough and in-depth analysis of existing literature related to the topic of your thesis or dissertation. In an RRL, you can include the concepts, methods, and results of the existing literature relevant to your topic; this will give you an overview of what has been done in your field of research, the methods adopted that ...
Conducting a review of related literature (RRL) is a crucial step in the process of writing an MBA dissertation. To perform a thorough RRL, start by identifying key themes and concepts relevant to your dissertation topic. Utilize academic databases and journals to search for scholarly articles, books, and other sources that provide insights ...
Okay - with the why out the way, let's move on to the how. As mentioned above, writing your literature review is a process, which I'll break down into three steps: Finding the most suitable literature. Understanding, distilling and organising the literature. Planning and writing up your literature review chapter.
objective, thesis or the problem / issue to be addressed. It is the scholarly core of the dissertation. ... sample in their study cons isted of 196 elementary school teachers in Shiraz, ...
Writing a Literature Review. A literature review is a document or section of a document that collects key sources on a topic and discusses those sources in conversation with each other (also called synthesis ). The lit review is an important genre in many disciplines, not just literature (i.e., the study of works of literature such as novels ...
This template is structure is based on the tried and trusted best-practice format for formal academic research projects such as dissertations and theses. The literature review template includes the following sections:. Before you start - essential groundwork to ensure you're ready; The introduction section; The core/body section; The conclusion/summary; Extra free resources
It can be a stand-alone paper or part of a thesis/dissertation. Format and requirements can vary between disciplines, purpose and intended audience. A literature review is an overview of existing literature (books, articles, dissertations, conference proceedings, and other sources) in a particular scholarly area. With a lit review, you will: ...
Chapter II. REVIEW OF RELATED LITERATURE AND STUDIES ¶. The literature and studies cited in this chapter tackle the different concept, understanding, and ideas, generalization or conclusions and different development related to study of the enrollment from the past up to the present and which serves as the researchers guide in developing the ...
study. Chapter 2 is divided into 4 parts, namely : (1) E-. Learning, (2) Conventional classroom learning, (3) English. Achievement; and (4) Synthesis. The first topic, E-Learning, is a discussion ...
Student A uses quotes from only ONE source and fails to use her own voice to make any arguments. Student B cherry picks quotes from THREE sources and uses block quotes instead of making his own point. Student C quotes from THREE sources but does not show how the sources interact or converse with one another and does not provide sources for their arguments in the final paragraph
To effectively structure and write a thematic literature review, follow these key steps: Define Your Research Question: Clearly define the overarching research question or topic you aim to explore thematically. When writing a thematic literature review, go through different literature review sections of published research work and understand ...
1984 •. Lucita Lazo. This book begins by looking at the status of women in Filipino society and their place in the general socio-economic situation. It continues with sections on education and training in the Philippines and work and training. The next section reviews the constraints to women's participation in training.
post test for whole sample 70 11 4.7 graphically compare the scores of the control and experimental groups in pre test and post test 71 . 9 CHAPTER I 1.0 CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORK 1.1 INTRODUCTION Education is the learning of knowledge, information and skills during the course of life .It is the action or process of being educated and is an integral ...
Chapter two RRL. RRL WRITING. Course. College of Education (Edu 102) 620 Documents. Students shared 620 documents in this course. University ... Sample of Detailed Lesson Plan in Mathematics IX. College of Education. Other. 100% (73) 5. Emcee Christmas Party Script. College of Education. Other. 99% (71) 4.
EXAMPLES OF RRL AND RRS. Subject. Social psychology. 118 Documents. Students shared 118 documents in this course. School Quezon National High School. Academic year: 2020/2021. Uploaded by: Anonymous Student. This document has been uploaded by a student, just like you, who decided to remain anonymous.
The promotion of effective teacher professional development (ETPD) is a critical issue in the field of teacher education. The present study investigated how ETPD is affected simultaneously by teacher- and school-level factors across the United States, China, Finland, and Singapore.