
Definition:
Problem Solving is the process of identifying, analyzing, and finding effective solutions to complex issues or challenges.
Key Steps in Problem Solving:
- Identification of the problem: Recognizing and clearly defining the issue that needs to be resolved.
- Analysis and research: Gathering relevant information, data, and facts to understand the problem in-depth.
- Formulating strategies: Developing various approaches and plans to tackle the problem effectively.
- Evaluation and selection: Assessing the viability and potential outcomes of the proposed solutions and selecting the most appropriate one.
- Implementation: Putting the chosen solution into action and executing the necessary steps to resolve the problem.
- Monitoring and feedback: Continuously evaluating the implemented solution and obtaining feedback to ensure its effectiveness.
- Adaptation and improvement: Modifying and refining the solution as needed to optimize results and prevent similar problems from arising in the future.
Skills and Qualities for Effective Problem Solving:
- Analytical thinking: The ability to break down complex problems into smaller, manageable components and analyze them thoroughly.
- Creativity: Thinking outside the box and generating innovative solutions.
- Decision making: Making logical and informed choices based on available data and critical thinking.
- Communication: Clearly conveying ideas, listening actively, and collaborating with others to solve problems as a team.
- Resilience: Maintaining a positive mindset, perseverance, and adaptability in the face of challenges.
- Resourcefulness: Utilizing available resources and seeking new approaches when confronted with obstacles.
- Time management: Effectively organizing and prioritizing tasks to optimize problem-solving efficiency.

Psychological Steps Involved in Problem Solving
A mental process or a phenomenon dedicated towards solving problems by discovering and analyzing the problem is referred to as problem-solving. It is a process dedicated to finding not just any solution, but the best solution to resolve any problems. There is no such thing as one best way to solve every kind of problem, since there are unique problems depending upon the situation there are unique solutions too.

In psychology, problem solving doesn’t necessarily refer to solving psychological/mental issues of the brain. The process simply refers to solving every kind of problems in life in a proper manner. The idea of including the subject in psychology is because psychology deals with the overall mental process. And, tactfully using our thought process is what leads to the solution of any problems.
There are number of rigid psychological steps involved in problem solving, which is also referred as problem-solving cycle. The steps are in sequential order, and solving any problem requires following them one after another. But, we tend to avoid following this rigid set of steps, which is why it often requires us to go through the same steps over and over again until a satisfactory solution is reached.
Here are the steps involved in problem solving, approved by expert psychologists.
1. Identifying the Problem
Identifying the problem seems like the obvious first stem, but it’s not exactly as simple as it sounds. People might identify the wrong source of a problem, which will render the steps thus carried on useless.
For instance , let’s say you’re having trouble with your studies. identifying the root of your failure is your first priority. The problem here could be that you haven’t been allocating enough time for your studies, or you haven’t tried the right techniques. But, if you make an assumption that the problem here is the subject being too hard, you won’t be able to solve the problem.
2. Defining/Understanding the Problem

It’s vital to properly define the problem once it’s been identified. Only by defining the problem, further steps can be taken to solve it. While at it, you also need to take into consideration different perspectives to understand any problem; this will also help you look for solutions with different perspectives.
Now, following up with the previous example . Let’s say you have identified the problem as not being able to allocate enough time for your studies. You need to sort out the reason behind it. Have you just been procrastinating? Have you been too busy with work? You need to understand the whole problem and reasons behind it, which is the second step in problem solving.
3. Forming a Strategy
Developing a strategy is the next step to finding a solution. Each different situation will require formulating different strategies, also depending on individual’s unique preferences.
Now, you have identified and studied your problem. You can’t just simply jump into trying to solve it. You can’t just quit work and start studying. You need to draw up a strategy to manage your time properly. Allocate less time for not-so-important works, and add them to your study time. Your strategy should be well thought, so that in theory at least, you are able to manage enough time to study properly and not fail in the exams.
4. Organizing Information

Organizing the available information is another crucial step to the process. You need to consider
- What do you know about the problem?
- What do you not know about the problem?
Accuracy of the solution for your problem will depend on the amount of information available.
The hypothetical strategy you formulate isn’t the all of it either. You need to now contemplate on the information available on the subject matter. Use the aforementioned questions to find out more about the problem. Proper organization of the information will force you to revise your strategy and refine it for best results.
5. Allocating Resources
Time, money and other resources aren’t unlimited. Deciding how high the priority is to solve your problem will help you determine the resources you’ll be using in your course to find the solution. If the problem is important, you can allocate more resources to solving it. However, if the problem isn’t as important, it’s not worth the time and money you might spend on it if not for proper planning.
For instance , let’s consider a different scenario where your business deal is stuck, but it’s few thousand miles away. Now, you need to analyze the problem and the resources you can afford to expend to solve the particular problem. If the deal isn’t really in your favor, you could just try solving it over the phone, however, more important deals might require you to fly to the location in order to solve the issue.
6. Monitoring Progress

You need to document your progress as you are finding a solution. Don’t rely on your memory, no matter how good your memory is. Effective problem-solvers have been known to monitor their progress regularly. And, if they’re not making as much progress as they’re supposed to, they will reevaluate their approach or look for new strategies.
Problem solving isn’t an overnight feat. You can’t just have a body like that of Brad Pitt after a single session in the gym. It takes time and patience. Likewise, you need to work towards solving any problem every day until you finally achieve the results. Looking back at the previous example , if everything’s according to plan, you will be allocating more and more time for your studies until finally you are confident that you’re improving. One way to make sure that you’re on a right path to solving a problem is by keeping track of the progress. To solve the problem illustrated in the first example, you can take self-tests every week or two and track your progress.
7. Evaluating the Results
Your job still isn’t done even if you’ve reached a solution. You need to evaluate the solution to find out if it’s the best possible solution to the problem. The evaluation might be immediate or might take a while. For instance , answer to a math problem can be checked then and there, however solution to your yearly tax issue might not be possible to be evaluated right there.
- Take time to identify the possible sources of the problem. It’s better to spend a substantial amount of time on something right, than on something completely opposite.
- Ask yourself questions like What, Why, How to figure out the causes of the problem. Only then can you move forward on solving it.
- Carefully outline the methods to tackle the problem. There might be different solutions to a problem, record them all.
- Gather all information about the problem and the approaches. More, the merrier.
- From the outlined methods, choose the ones that are viable to approach. Try discarding the ones that have unseen consequences.
- Track your progress as you go.
- Evaluate the outcome of the progress.
What are other people reading?

Divergent Thinking

Convergent Thinking

Convergent Vs Divergent Thinking
10 Best Problem-Solving Therapy Worksheets & Activities

Cognitive science tells us that we regularly face not only well-defined problems but, importantly, many that are ill defined (Eysenck & Keane, 2015).
Sometimes, we find ourselves unable to overcome our daily problems or the inevitable (though hopefully infrequent) life traumas we face.
Problem-Solving Therapy aims to reduce the incidence and impact of mental health disorders and improve wellbeing by helping clients face life’s difficulties (Dobson, 2011).
This article introduces Problem-Solving Therapy and offers techniques, activities, and worksheets that mental health professionals can use with clients.
Before you continue, we thought you might like to download our three Positive Psychology Exercises for free . These science-based exercises explore fundamental aspects of positive psychology, including strengths, values, and self-compassion, and will give you the tools to enhance the wellbeing of your clients, students, or employees.
This Article Contains:
What is problem-solving therapy, 14 steps for problem-solving therapy, 3 best interventions and techniques, 7 activities and worksheets for your session, fascinating books on the topic, resources from positivepsychology.com, a take-home message.
Problem-Solving Therapy assumes that mental disorders arise in response to ineffective or maladaptive coping. By adopting a more realistic and optimistic view of coping, individuals can understand the role of emotions and develop actions to reduce distress and maintain mental wellbeing (Nezu & Nezu, 2009).
“Problem-solving therapy (PST) is a psychosocial intervention, generally considered to be under a cognitive-behavioral umbrella” (Nezu, Nezu, & D’Zurilla, 2013, p. ix). It aims to encourage the client to cope better with day-to-day problems and traumatic events and reduce their impact on mental and physical wellbeing.
Clinical research, counseling, and health psychology have shown PST to be highly effective in clients of all ages, ranging from children to the elderly, across multiple clinical settings, including schizophrenia, stress, and anxiety disorders (Dobson, 2011).
Can it help with depression?
PST appears particularly helpful in treating clients with depression. A recent analysis of 30 studies found that PST was an effective treatment with a similar degree of success as other successful therapies targeting depression (Cuijpers, Wit, Kleiboer, Karyotaki, & Ebert, 2020).
Other studies confirm the value of PST and its effectiveness at treating depression in multiple age groups and its capacity to combine with other therapies, including drug treatments (Dobson, 2011).
The major concepts
Effective coping varies depending on the situation, and treatment typically focuses on improving the environment and reducing emotional distress (Dobson, 2011).
PST is based on two overlapping models:
Social problem-solving model
This model focuses on solving the problem “as it occurs in the natural social environment,” combined with a general coping strategy and a method of self-control (Dobson, 2011, p. 198).
The model includes three central concepts:
- Social problem-solving
- The problem
- The solution
The model is a “self-directed cognitive-behavioral process by which an individual, couple, or group attempts to identify or discover effective solutions for specific problems encountered in everyday living” (Dobson, 2011, p. 199).
Relational problem-solving model
The theory of PST is underpinned by a relational problem-solving model, whereby stress is viewed in terms of the relationships between three factors:
- Stressful life events
- Emotional distress and wellbeing
- Problem-solving coping
Therefore, when a significant adverse life event occurs, it may require “sweeping readjustments in a person’s life” (Dobson, 2011, p. 202).

- Enhance positive problem orientation
- Decrease negative orientation
- Foster ability to apply rational problem-solving skills
- Reduce the tendency to avoid problem-solving
- Minimize the tendency to be careless and impulsive
D’Zurilla’s and Nezu’s model includes (modified from Dobson, 2011):
- Initial structuring Establish a positive therapeutic relationship that encourages optimism and explains the PST approach.
- Assessment Formally and informally assess areas of stress in the client’s life and their problem-solving strengths and weaknesses.
- Obstacles to effective problem-solving Explore typically human challenges to problem-solving, such as multitasking and the negative impact of stress. Introduce tools that can help, such as making lists, visualization, and breaking complex problems down.
- Problem orientation – fostering self-efficacy Introduce the importance of a positive problem orientation, adopting tools, such as visualization, to promote self-efficacy.
- Problem orientation – recognizing problems Help clients recognize issues as they occur and use problem checklists to ‘normalize’ the experience.
- Problem orientation – seeing problems as challenges Encourage clients to break free of harmful and restricted ways of thinking while learning how to argue from another point of view.
- Problem orientation – use and control emotions Help clients understand the role of emotions in problem-solving, including using feelings to inform the process and managing disruptive emotions (such as cognitive reframing and relaxation exercises).
- Problem orientation – stop and think Teach clients how to reduce impulsive and avoidance tendencies (visualizing a stop sign or traffic light).
- Problem definition and formulation Encourage an understanding of the nature of problems and set realistic goals and objectives.
- Generation of alternatives Work with clients to help them recognize the wide range of potential solutions to each problem (for example, brainstorming).
- Decision-making Encourage better decision-making through an improved understanding of the consequences of decisions and the value and likelihood of different outcomes.
- Solution implementation and verification Foster the client’s ability to carry out a solution plan, monitor its outcome, evaluate its effectiveness, and use self-reinforcement to increase the chance of success.
- Guided practice Encourage the application of problem-solving skills across multiple domains and future stressful problems.
- Rapid problem-solving Teach clients how to apply problem-solving questions and guidelines quickly in any given situation.
Success in PST depends on the effectiveness of its implementation; using the right approach is crucial (Dobson, 2011).
Problem-solving therapy – Baycrest
The following interventions and techniques are helpful when implementing more effective problem-solving approaches in client’s lives.
First, it is essential to consider if PST is the best approach for the client, based on the problems they present.
Is PPT appropriate?
It is vital to consider whether PST is appropriate for the client’s situation. Therapists new to the approach may require additional guidance (Nezu et al., 2013).
Therapists should consider the following questions before beginning PST with a client (modified from Nezu et al., 2013):
- Has PST proven effective in the past for the problem? For example, research has shown success with depression, generalized anxiety, back pain, Alzheimer’s disease, cancer, and supporting caregivers (Nezu et al., 2013).
- Is PST acceptable to the client?
- Is the individual experiencing a significant mental or physical health problem?
All affirmative answers suggest that PST would be a helpful technique to apply in this instance.
Five problem-solving steps
The following five steps are valuable when working with clients to help them cope with and manage their environment (modified from Dobson, 2011).
Ask the client to consider the following points (forming the acronym ADAPT) when confronted by a problem:
- Attitude Aim to adopt a positive, optimistic attitude to the problem and problem-solving process.
- Define Obtain all required facts and details of potential obstacles to define the problem.
- Alternatives Identify various alternative solutions and actions to overcome the obstacle and achieve the problem-solving goal.
- Predict Predict each alternative’s positive and negative outcomes and choose the one most likely to achieve the goal and maximize the benefits.
- Try out Once selected, try out the solution and monitor its effectiveness while engaging in self-reinforcement.
If the client is not satisfied with their solution, they can return to step ‘A’ and find a more appropriate solution.

Download 3 Free Positive Psychology Exercises (PDF)
Enhance wellbeing with these free, science-based exercises that draw on the latest insights from positive psychology.
Download 3 Free Positive Psychology Tools Pack (PDF)
By filling out your name and email address below.
Positive self-statements
When dealing with clients facing negative self-beliefs, it can be helpful for them to use positive self-statements.
Use the following (or add new) self-statements to replace harmful, negative thinking (modified from Dobson, 2011):
- I can solve this problem; I’ve tackled similar ones before.
- I can cope with this.
- I just need to take a breath and relax.
- Once I start, it will be easier.
- It’s okay to look out for myself.
- I can get help if needed.
- Other people feel the same way I do.
- I’ll take one piece of the problem at a time.
- I can keep my fears in check.
- I don’t need to please everyone.

World’s Largest Positive Psychology Resource
The Positive Psychology Toolkit© is a groundbreaking practitioner resource containing over 500 science-based exercises , activities, interventions, questionnaires, and assessments created by experts using the latest positive psychology research.
Updated monthly. 100% Science-based.
“The best positive psychology resource out there!” — Emiliya Zhivotovskaya , Flourishing Center CEO
PST practitioners have many different techniques available to support clients as they learn to tackle day-to-day or one-off trauma.
5 Worksheets and workbooks
Problem-solving self-monitoring form.

Ask the client to complete the following:
- Describe the problem you are facing.
- What is your goal?
- What have you tried so far to solve the problem?
- What was the outcome?
Reactions to Stress
It can be helpful for the client to recognize their own experiences of stress. Do they react angrily, withdraw, or give up (Dobson, 2011)?
The Reactions to Stress worksheet can be given to the client as homework to capture stressful events and their reactions. By recording how they felt, behaved, and thought, they can recognize repeating patterns.
What Are Your Unique Triggers?
Helping clients capture triggers for their stressful reactions can encourage emotional regulation.
When clients can identify triggers that may lead to a negative response, they can stop the experience or slow down their emotional reaction (Dobson, 2011).
The What Are Your Unique Triggers ? worksheet helps the client identify their triggers (e.g., conflict, relationships, physical environment, etc.).
Problem-Solving worksheet
Imagining an existing or potential problem and working through how to resolve it can be a powerful exercise for the client.
Use the Problem-Solving worksheet to state a problem and goal and consider the obstacles in the way. Then explore options for achieving the goal, along with their pros and cons, to assess the best action plan.
Getting the Facts
Clients can become better equipped to tackle problems and choose the right course of action by recognizing facts versus assumptions and gathering all the necessary information (Dobson, 2011).
Use the Getting the Facts worksheet to answer the following questions clearly and unambiguously:
- Who is involved?
- What did or did not happen, and how did it bother you?
- Where did it happen?
- When did it happen?
- Why did it happen?
- How did you respond?
2 Helpful Group Activities
While therapists can use the worksheets above in group situations, the following two interventions work particularly well with more than one person.
Generating Alternative Solutions and Better Decision-Making
A group setting can provide an ideal opportunity to share a problem and identify potential solutions arising from multiple perspectives.
Use the Generating Alternative Solutions and Better Decision-Making worksheet and ask the client to explain the situation or problem to the group and the obstacles in the way.
Once the approaches are captured and reviewed, the individual can share their decision-making process with the group if they want further feedback.
Visualization
Visualization can be performed with individuals or in a group setting to help clients solve problems in multiple ways, including (Dobson, 2011):
- Clarifying the problem by looking at it from multiple perspectives
- Rehearsing a solution in the mind to improve and get more practice
- Visualizing a ‘safe place’ for relaxation, slowing down, and stress management
Guided imagery is particularly valuable for encouraging the group to take a ‘mental vacation’ and let go of stress.
Ask the group to begin with slow, deep breathing that fills the entire diaphragm. Then ask them to visualize a favorite scene (real or imagined) that makes them feel relaxed, perhaps beside a gently flowing river, a summer meadow, or at the beach.
The more the senses are engaged, the more real the experience. Ask the group to think about what they can hear, see, touch, smell, and even taste.
Encourage them to experience the situation as fully as possible, immersing themselves and enjoying their place of safety.
Such feelings of relaxation may be able to help clients fall asleep, relieve stress, and become more ready to solve problems.
We have included three of our favorite books on the subject of Problem-Solving Therapy below.
1. Problem-Solving Therapy: A Treatment Manual – Arthur Nezu, Christine Maguth Nezu, and Thomas D’Zurilla

This is an incredibly valuable book for anyone wishing to understand the principles and practice behind PST.
Written by the co-developers of PST, the manual provides powerful toolkits to overcome cognitive overload, emotional dysregulation, and the barriers to practical problem-solving.
Find the book on Amazon .
2. Emotion-Centered Problem-Solving Therapy: Treatment Guidelines – Arthur Nezu and Christine Maguth Nezu

Another, more recent, book from the creators of PST, this text includes important advances in neuroscience underpinning the role of emotion in behavioral treatment.
Along with clinical examples, the book also includes crucial toolkits that form part of a stepped model for the application of PST.
3. Handbook of Cognitive-Behavioral Therapies – Keith Dobson and David Dozois

This is the fourth edition of a hugely popular guide to Cognitive-Behavioral Therapies and includes a valuable and insightful section on Problem-Solving Therapy.
This is an important book for students and more experienced therapists wishing to form a high-level and in-depth understanding of the tools and techniques available to Cognitive-Behavioral Therapists.
For even more tools to help strengthen your clients’ problem-solving skills, check out the following free worksheets from our blog.
- Case Formulation Worksheet This worksheet presents a four-step framework to help therapists and their clients come to a shared understanding of the client’s presenting problem.
- Understanding Your Default Problem-Solving Approach This worksheet poses a series of questions helping clients reflect on their typical cognitive, emotional, and behavioral responses to problems.
- Social Problem Solving: Step by Step This worksheet presents a streamlined template to help clients define a problem, generate possible courses of action, and evaluate the effectiveness of an implemented solution.
If you’re looking for more science-based ways to help others enhance their wellbeing, check out this signature collection of 17 validated positive psychology tools for practitioners. Use them to help others flourish and thrive.

17 Top-Rated Positive Psychology Exercises for Practitioners
Expand your arsenal and impact with these 17 Positive Psychology Exercises [PDF] , scientifically designed to promote human flourishing, meaning, and wellbeing.
Created by Experts. 100% Science-based.
While we are born problem-solvers, facing an incredibly diverse set of challenges daily, we sometimes need support.
Problem-Solving Therapy aims to reduce stress and associated mental health disorders and improve wellbeing by improving our ability to cope. PST is valuable in diverse clinical settings, ranging from depression to schizophrenia, with research suggesting it as a highly effective treatment for teaching coping strategies and reducing emotional distress.
Many PST techniques are available to help improve clients’ positive outlook on obstacles while reducing avoidance of problem situations and the tendency to be careless and impulsive.
The PST model typically assesses the client’s strengths, weaknesses, and coping strategies when facing problems before encouraging a healthy experience of and relationship with problem-solving.
Why not use this article to explore the theory behind PST and try out some of our powerful tools and interventions with your clients to help them with their decision-making, coping, and problem-solving?
We hope you enjoyed reading this article. Don’t forget to download our three Positive Psychology Exercises for free .
- Cuijpers, P., Wit, L., Kleiboer, A., Karyotaki, E., & Ebert, D. (2020). Problem-solving therapy for adult depression: An updated meta-analysis. European P sychiatry , 48 (1), 27–37.
- Dobson, K. S. (2011). Handbook of cognitive-behavioral therapies (3rd ed.). Guilford Press.
- Dobson, K. S., & Dozois, D. J. A. (2021). Handbook of cognitive-behavioral therapies (4th ed.). Guilford Press.
- Eysenck, M. W., & Keane, M. T. (2015). Cognitive psychology: A student’s handbook . Psychology Press.
- Nezu, A. M., & Nezu, C. M. (2009). Problem-solving therapy DVD . Retrieved September 13, 2021, from https://www.apa.org/pubs/videos/4310852
- Nezu, A. M., & Nezu, C. M. (2018). Emotion-centered problem-solving therapy: Treatment guidelines. Springer.
- Nezu, A. M., Nezu, C. M., & D’Zurilla, T. J. (2013). Problem-solving therapy: A treatment manual . Springer.
Share this article:
Article feedback
What our readers think.
Thanks for your information given, it was helpful for me something new I learned
Let us know your thoughts Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Related articles

The Empty Chair Technique: How It Can Help Your Clients
Resolving ‘unfinished business’ is often an essential part of counseling. If left unresolved, it can contribute to depression, anxiety, and mental ill-health while damaging existing [...]

29 Best Group Therapy Activities for Supporting Adults
As humans, we are social creatures with personal histories based on the various groups that make up our lives. Childhood begins with a family of [...]

47 Free Therapy Resources to Help Kick-Start Your New Practice
Setting up a private practice in psychotherapy brings several challenges, including a considerable investment of time and money. You can reduce risks early on by [...]
Read other articles by their category
- Body & Brain (52)
- Coaching & Application (39)
- Compassion (23)
- Counseling (40)
- Emotional Intelligence (22)
- Gratitude (18)
- Grief & Bereavement (18)
- Happiness & SWB (40)
- Meaning & Values (26)
- Meditation (16)
- Mindfulness (40)
- Motivation & Goals (41)
- Optimism & Mindset (29)
- Positive CBT (28)
- Positive Communication (23)
- Positive Education (37)
- Positive Emotions (32)
- Positive Leadership (16)
- Positive Parenting (14)
- Positive Psychology (21)
- Positive Workplace (35)
- Productivity (16)
- Relationships (46)
- Resilience & Coping (39)
- Self Awareness (20)
- Self Esteem (37)
- Strengths & Virtues (29)
- Stress & Burnout Prevention (33)
- Theory & Books (42)
- Therapy Exercises (37)
- Types of Therapy (54)
7.3 Problem-Solving
Learning objectives.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Describe problem solving strategies
- Define algorithm and heuristic
- Explain some common roadblocks to effective problem solving
People face problems every day—usually, multiple problems throughout the day. Sometimes these problems are straightforward: To double a recipe for pizza dough, for example, all that is required is that each ingredient in the recipe be doubled. Sometimes, however, the problems we encounter are more complex. For example, say you have a work deadline, and you must mail a printed copy of a report to your supervisor by the end of the business day. The report is time-sensitive and must be sent overnight. You finished the report last night, but your printer will not work today. What should you do? First, you need to identify the problem and then apply a strategy for solving the problem.
The study of human and animal problem solving processes has provided much insight toward the understanding of our conscious experience and led to advancements in computer science and artificial intelligence. Essentially much of cognitive science today represents studies of how we consciously and unconsciously make decisions and solve problems. For instance, when encountered with a large amount of information, how do we go about making decisions about the most efficient way of sorting and analyzing all the information in order to find what you are looking for as in visual search paradigms in cognitive psychology. Or in a situation where a piece of machinery is not working properly, how do we go about organizing how to address the issue and understand what the cause of the problem might be. How do we sort the procedures that will be needed and focus attention on what is important in order to solve problems efficiently. Within this section we will discuss some of these issues and examine processes related to human, animal and computer problem solving.
PROBLEM-SOLVING STRATEGIES
When people are presented with a problem—whether it is a complex mathematical problem or a broken printer, how do you solve it? Before finding a solution to the problem, the problem must first be clearly identified. After that, one of many problem solving strategies can be applied, hopefully resulting in a solution.
Problems themselves can be classified into two different categories known as ill-defined and well-defined problems (Schacter, 2009). Ill-defined problems represent issues that do not have clear goals, solution paths, or expected solutions whereas well-defined problems have specific goals, clearly defined solutions, and clear expected solutions. Problem solving often incorporates pragmatics (logical reasoning) and semantics (interpretation of meanings behind the problem), and also in many cases require abstract thinking and creativity in order to find novel solutions. Within psychology, problem solving refers to a motivational drive for reading a definite “goal” from a present situation or condition that is either not moving toward that goal, is distant from it, or requires more complex logical analysis for finding a missing description of conditions or steps toward that goal. Processes relating to problem solving include problem finding also known as problem analysis, problem shaping where the organization of the problem occurs, generating alternative strategies, implementation of attempted solutions, and verification of the selected solution. Various methods of studying problem solving exist within the field of psychology including introspection, behavior analysis and behaviorism, simulation, computer modeling, and experimentation.
A problem-solving strategy is a plan of action used to find a solution. Different strategies have different action plans associated with them (table below). For example, a well-known strategy is trial and error. The old adage, “If at first you don’t succeed, try, try again” describes trial and error. In terms of your broken printer, you could try checking the ink levels, and if that doesn’t work, you could check to make sure the paper tray isn’t jammed. Or maybe the printer isn’t actually connected to your laptop. When using trial and error, you would continue to try different solutions until you solved your problem. Although trial and error is not typically one of the most time-efficient strategies, it is a commonly used one.
| Method | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Trial and error | Continue trying different solutions until problem is solved | Restarting phone, turning off WiFi, turning off bluetooth in order to determine why your phone is malfunctioning |
| Algorithm | Step-by-step problem-solving formula | Instruction manual for installing new software on your computer |
| Heuristic | General problem-solving framework | Working backwards; breaking a task into steps |
Another type of strategy is an algorithm. An algorithm is a problem-solving formula that provides you with step-by-step instructions used to achieve a desired outcome (Kahneman, 2011). You can think of an algorithm as a recipe with highly detailed instructions that produce the same result every time they are performed. Algorithms are used frequently in our everyday lives, especially in computer science. When you run a search on the Internet, search engines like Google use algorithms to decide which entries will appear first in your list of results. Facebook also uses algorithms to decide which posts to display on your newsfeed. Can you identify other situations in which algorithms are used?
A heuristic is another type of problem solving strategy. While an algorithm must be followed exactly to produce a correct result, a heuristic is a general problem-solving framework (Tversky & Kahneman, 1974). You can think of these as mental shortcuts that are used to solve problems. A “rule of thumb” is an example of a heuristic. Such a rule saves the person time and energy when making a decision, but despite its time-saving characteristics, it is not always the best method for making a rational decision. Different types of heuristics are used in different types of situations, but the impulse to use a heuristic occurs when one of five conditions is met (Pratkanis, 1989):
- When one is faced with too much information
- When the time to make a decision is limited
- When the decision to be made is unimportant
- When there is access to very little information to use in making the decision
- When an appropriate heuristic happens to come to mind in the same moment
Working backwards is a useful heuristic in which you begin solving the problem by focusing on the end result. Consider this example: You live in Washington, D.C. and have been invited to a wedding at 4 PM on Saturday in Philadelphia. Knowing that Interstate 95 tends to back up any day of the week, you need to plan your route and time your departure accordingly. If you want to be at the wedding service by 3:30 PM, and it takes 2.5 hours to get to Philadelphia without traffic, what time should you leave your house? You use the working backwards heuristic to plan the events of your day on a regular basis, probably without even thinking about it.
Another useful heuristic is the practice of accomplishing a large goal or task by breaking it into a series of smaller steps. Students often use this common method to complete a large research project or long essay for school. For example, students typically brainstorm, develop a thesis or main topic, research the chosen topic, organize their information into an outline, write a rough draft, revise and edit the rough draft, develop a final draft, organize the references list, and proofread their work before turning in the project. The large task becomes less overwhelming when it is broken down into a series of small steps.
Further problem solving strategies have been identified (listed below) that incorporate flexible and creative thinking in order to reach solutions efficiently.
Additional Problem Solving Strategies :
- Abstraction – refers to solving the problem within a model of the situation before applying it to reality.
- Analogy – is using a solution that solves a similar problem.
- Brainstorming – refers to collecting an analyzing a large amount of solutions, especially within a group of people, to combine the solutions and developing them until an optimal solution is reached.
- Divide and conquer – breaking down large complex problems into smaller more manageable problems.
- Hypothesis testing – method used in experimentation where an assumption about what would happen in response to manipulating an independent variable is made, and analysis of the affects of the manipulation are made and compared to the original hypothesis.
- Lateral thinking – approaching problems indirectly and creatively by viewing the problem in a new and unusual light.
- Means-ends analysis – choosing and analyzing an action at a series of smaller steps to move closer to the goal.
- Method of focal objects – putting seemingly non-matching characteristics of different procedures together to make something new that will get you closer to the goal.
- Morphological analysis – analyzing the outputs of and interactions of many pieces that together make up a whole system.
- Proof – trying to prove that a problem cannot be solved. Where the proof fails becomes the starting point or solving the problem.
- Reduction – adapting the problem to be as similar problems where a solution exists.
- Research – using existing knowledge or solutions to similar problems to solve the problem.
- Root cause analysis – trying to identify the cause of the problem.
The strategies listed above outline a short summary of methods we use in working toward solutions and also demonstrate how the mind works when being faced with barriers preventing goals to be reached.
One example of means-end analysis can be found by using the Tower of Hanoi paradigm . This paradigm can be modeled as a word problems as demonstrated by the Missionary-Cannibal Problem :
Missionary-Cannibal Problem
Three missionaries and three cannibals are on one side of a river and need to cross to the other side. The only means of crossing is a boat, and the boat can only hold two people at a time. Your goal is to devise a set of moves that will transport all six of the people across the river, being in mind the following constraint: The number of cannibals can never exceed the number of missionaries in any location. Remember that someone will have to also row that boat back across each time.
Hint : At one point in your solution, you will have to send more people back to the original side than you just sent to the destination.
The actual Tower of Hanoi problem consists of three rods sitting vertically on a base with a number of disks of different sizes that can slide onto any rod. The puzzle starts with the disks in a neat stack in ascending order of size on one rod, the smallest at the top making a conical shape. The objective of the puzzle is to move the entire stack to another rod obeying the following rules:
- 1. Only one disk can be moved at a time.
- 2. Each move consists of taking the upper disk from one of the stacks and placing it on top of another stack or on an empty rod.
- 3. No disc may be placed on top of a smaller disk.
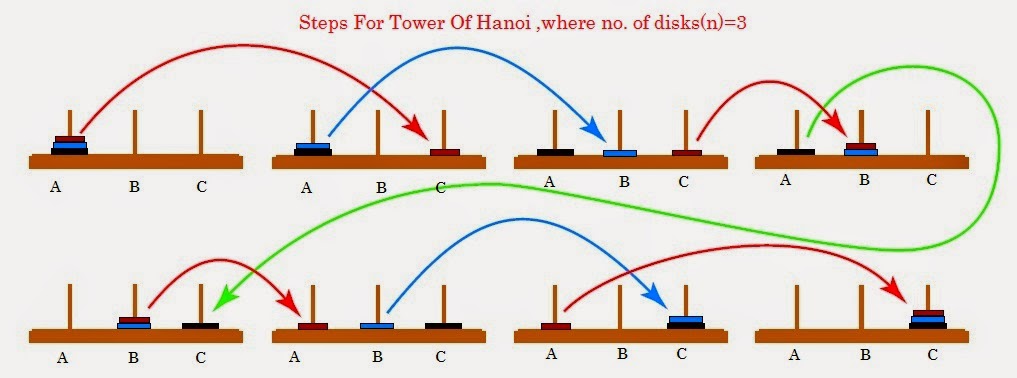
Figure 7.02. Steps for solving the Tower of Hanoi in the minimum number of moves when there are 3 disks.
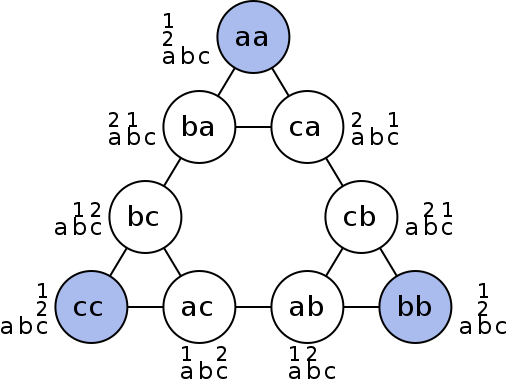
Figure 7.03. Graphical representation of nodes (circles) and moves (lines) of Tower of Hanoi.
The Tower of Hanoi is a frequently used psychological technique to study problem solving and procedure analysis. A variation of the Tower of Hanoi known as the Tower of London has been developed which has been an important tool in the neuropsychological diagnosis of executive function disorders and their treatment.
GESTALT PSYCHOLOGY AND PROBLEM SOLVING
As you may recall from the sensation and perception chapter, Gestalt psychology describes whole patterns, forms and configurations of perception and cognition such as closure, good continuation, and figure-ground. In addition to patterns of perception, Wolfgang Kohler, a German Gestalt psychologist traveled to the Spanish island of Tenerife in order to study animals behavior and problem solving in the anthropoid ape.
As an interesting side note to Kohler’s studies of chimp problem solving, Dr. Ronald Ley, professor of psychology at State University of New York provides evidence in his book A Whisper of Espionage (1990) suggesting that while collecting data for what would later be his book The Mentality of Apes (1925) on Tenerife in the Canary Islands between 1914 and 1920, Kohler was additionally an active spy for the German government alerting Germany to ships that were sailing around the Canary Islands. Ley suggests his investigations in England, Germany and elsewhere in Europe confirm that Kohler had served in the German military by building, maintaining and operating a concealed radio that contributed to Germany’s war effort acting as a strategic outpost in the Canary Islands that could monitor naval military activity approaching the north African coast.
While trapped on the island over the course of World War 1, Kohler applied Gestalt principles to animal perception in order to understand how they solve problems. He recognized that the apes on the islands also perceive relations between stimuli and the environment in Gestalt patterns and understand these patterns as wholes as opposed to pieces that make up a whole. Kohler based his theories of animal intelligence on the ability to understand relations between stimuli, and spent much of his time while trapped on the island investigation what he described as insight , the sudden perception of useful or proper relations. In order to study insight in animals, Kohler would present problems to chimpanzee’s by hanging some banana’s or some kind of food so it was suspended higher than the apes could reach. Within the room, Kohler would arrange a variety of boxes, sticks or other tools the chimpanzees could use by combining in patterns or organizing in a way that would allow them to obtain the food (Kohler & Winter, 1925).
While viewing the chimpanzee’s, Kohler noticed one chimp that was more efficient at solving problems than some of the others. The chimp, named Sultan, was able to use long poles to reach through bars and organize objects in specific patterns to obtain food or other desirables that were originally out of reach. In order to study insight within these chimps, Kohler would remove objects from the room to systematically make the food more difficult to obtain. As the story goes, after removing many of the objects Sultan was used to using to obtain the food, he sat down ad sulked for a while, and then suddenly got up going over to two poles lying on the ground. Without hesitation Sultan put one pole inside the end of the other creating a longer pole that he could use to obtain the food demonstrating an ideal example of what Kohler described as insight. In another situation, Sultan discovered how to stand on a box to reach a banana that was suspended from the rafters illustrating Sultan’s perception of relations and the importance of insight in problem solving.
Grande (another chimp in the group studied by Kohler) builds a three-box structure to reach the bananas, while Sultan watches from the ground. Insight , sometimes referred to as an “Ah-ha” experience, was the term Kohler used for the sudden perception of useful relations among objects during problem solving (Kohler, 1927; Radvansky & Ashcraft, 2013).
Solving puzzles.
Problem-solving abilities can improve with practice. Many people challenge themselves every day with puzzles and other mental exercises to sharpen their problem-solving skills. Sudoku puzzles appear daily in most newspapers. Typically, a sudoku puzzle is a 9×9 grid. The simple sudoku below (see figure) is a 4×4 grid. To solve the puzzle, fill in the empty boxes with a single digit: 1, 2, 3, or 4. Here are the rules: The numbers must total 10 in each bolded box, each row, and each column; however, each digit can only appear once in a bolded box, row, and column. Time yourself as you solve this puzzle and compare your time with a classmate.
How long did it take you to solve this sudoku puzzle? (You can see the answer at the end of this section.)
Here is another popular type of puzzle (figure below) that challenges your spatial reasoning skills. Connect all nine dots with four connecting straight lines without lifting your pencil from the paper:
Did you figure it out? (The answer is at the end of this section.) Once you understand how to crack this puzzle, you won’t forget.
Take a look at the “Puzzling Scales” logic puzzle below (figure below). Sam Loyd, a well-known puzzle master, created and refined countless puzzles throughout his lifetime (Cyclopedia of Puzzles, n.d.).

What steps did you take to solve this puzzle? You can read the solution at the end of this section.
Pitfalls to problem solving.
Not all problems are successfully solved, however. What challenges stop us from successfully solving a problem? Albert Einstein once said, “Insanity is doing the same thing over and over again and expecting a different result.” Imagine a person in a room that has four doorways. One doorway that has always been open in the past is now locked. The person, accustomed to exiting the room by that particular doorway, keeps trying to get out through the same doorway even though the other three doorways are open. The person is stuck—but she just needs to go to another doorway, instead of trying to get out through the locked doorway. A mental set is where you persist in approaching a problem in a way that has worked in the past but is clearly not working now.
Functional fixedness is a type of mental set where you cannot perceive an object being used for something other than what it was designed for. During the Apollo 13 mission to the moon, NASA engineers at Mission Control had to overcome functional fixedness to save the lives of the astronauts aboard the spacecraft. An explosion in a module of the spacecraft damaged multiple systems. The astronauts were in danger of being poisoned by rising levels of carbon dioxide because of problems with the carbon dioxide filters. The engineers found a way for the astronauts to use spare plastic bags, tape, and air hoses to create a makeshift air filter, which saved the lives of the astronauts.
Researchers have investigated whether functional fixedness is affected by culture. In one experiment, individuals from the Shuar group in Ecuador were asked to use an object for a purpose other than that for which the object was originally intended. For example, the participants were told a story about a bear and a rabbit that were separated by a river and asked to select among various objects, including a spoon, a cup, erasers, and so on, to help the animals. The spoon was the only object long enough to span the imaginary river, but if the spoon was presented in a way that reflected its normal usage, it took participants longer to choose the spoon to solve the problem. (German & Barrett, 2005). The researchers wanted to know if exposure to highly specialized tools, as occurs with individuals in industrialized nations, affects their ability to transcend functional fixedness. It was determined that functional fixedness is experienced in both industrialized and nonindustrialized cultures (German & Barrett, 2005).
In order to make good decisions, we use our knowledge and our reasoning. Often, this knowledge and reasoning is sound and solid. Sometimes, however, we are swayed by biases or by others manipulating a situation. For example, let’s say you and three friends wanted to rent a house and had a combined target budget of $1,600. The realtor shows you only very run-down houses for $1,600 and then shows you a very nice house for $2,000. Might you ask each person to pay more in rent to get the $2,000 home? Why would the realtor show you the run-down houses and the nice house? The realtor may be challenging your anchoring bias. An anchoring bias occurs when you focus on one piece of information when making a decision or solving a problem. In this case, you’re so focused on the amount of money you are willing to spend that you may not recognize what kinds of houses are available at that price point.
The confirmation bias is the tendency to focus on information that confirms your existing beliefs. For example, if you think that your professor is not very nice, you notice all of the instances of rude behavior exhibited by the professor while ignoring the countless pleasant interactions he is involved in on a daily basis. Hindsight bias leads you to believe that the event you just experienced was predictable, even though it really wasn’t. In other words, you knew all along that things would turn out the way they did. Representative bias describes a faulty way of thinking, in which you unintentionally stereotype someone or something; for example, you may assume that your professors spend their free time reading books and engaging in intellectual conversation, because the idea of them spending their time playing volleyball or visiting an amusement park does not fit in with your stereotypes of professors.
Finally, the availability heuristic is a heuristic in which you make a decision based on an example, information, or recent experience that is that readily available to you, even though it may not be the best example to inform your decision . Biases tend to “preserve that which is already established—to maintain our preexisting knowledge, beliefs, attitudes, and hypotheses” (Aronson, 1995; Kahneman, 2011). These biases are summarized in the table below.
| Bias | Description |
|---|---|
| Anchoring | Tendency to focus on one particular piece of information when making decisions or problem-solving |
| Confirmation | Focuses on information that confirms existing beliefs |
| Hindsight | Belief that the event just experienced was predictable |
| Representative | Unintentional stereotyping of someone or something |
| Availability | Decision is based upon either an available precedent or an example that may be faulty |
Were you able to determine how many marbles are needed to balance the scales in the figure below? You need nine. Were you able to solve the problems in the figures above? Here are the answers.

Many different strategies exist for solving problems. Typical strategies include trial and error, applying algorithms, and using heuristics. To solve a large, complicated problem, it often helps to break the problem into smaller steps that can be accomplished individually, leading to an overall solution. Roadblocks to problem solving include a mental set, functional fixedness, and various biases that can cloud decision making skills.
References:
Openstax Psychology text by Kathryn Dumper, William Jenkins, Arlene Lacombe, Marilyn Lovett and Marion Perlmutter licensed under CC BY v4.0. https://openstax.org/details/books/psychology
Review Questions:
1. A specific formula for solving a problem is called ________.
a. an algorithm
b. a heuristic
c. a mental set
d. trial and error
2. Solving the Tower of Hanoi problem tends to utilize a ________ strategy of problem solving.
a. divide and conquer
b. means-end analysis
d. experiment
3. A mental shortcut in the form of a general problem-solving framework is called ________.
4. Which type of bias involves becoming fixated on a single trait of a problem?
a. anchoring bias
b. confirmation bias
c. representative bias
d. availability bias
5. Which type of bias involves relying on a false stereotype to make a decision?
6. Wolfgang Kohler analyzed behavior of chimpanzees by applying Gestalt principles to describe ________.
a. social adjustment
b. student load payment options
c. emotional learning
d. insight learning
7. ________ is a type of mental set where you cannot perceive an object being used for something other than what it was designed for.
a. functional fixedness
c. working memory
Critical Thinking Questions:
1. What is functional fixedness and how can overcoming it help you solve problems?
2. How does an algorithm save you time and energy when solving a problem?
Personal Application Question:
1. Which type of bias do you recognize in your own decision making processes? How has this bias affected how you’ve made decisions in the past and how can you use your awareness of it to improve your decisions making skills in the future?
anchoring bias
availability heuristic
confirmation bias
functional fixedness
hindsight bias
problem-solving strategy
representative bias
trial and error
working backwards
Answers to Exercises
algorithm: problem-solving strategy characterized by a specific set of instructions
anchoring bias: faulty heuristic in which you fixate on a single aspect of a problem to find a solution
availability heuristic: faulty heuristic in which you make a decision based on information readily available to you
confirmation bias: faulty heuristic in which you focus on information that confirms your beliefs
functional fixedness: inability to see an object as useful for any other use other than the one for which it was intended
heuristic: mental shortcut that saves time when solving a problem
hindsight bias: belief that the event just experienced was predictable, even though it really wasn’t
mental set: continually using an old solution to a problem without results
problem-solving strategy: method for solving problems
representative bias: faulty heuristic in which you stereotype someone or something without a valid basis for your judgment
trial and error: problem-solving strategy in which multiple solutions are attempted until the correct one is found
working backwards: heuristic in which you begin to solve a problem by focusing on the end result

Share This Book
- Increase Font Size

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
9 Chapter 9. Problem-Solving

CHAPTER 9: PROBLEM SOLVING

How do we achieve our goals when the solution is not immediately obvious? What mental blocks are likely to get in our way, and how can we leverage our prior knowledge to solve novel problems?
CHAPTER 9 LICENSE AND ATTRIBUTION
Source: Multiple authors. Memory. In Cognitive Psychology and Cognitive Neuroscience. Wikibooks. Retrieved from https://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/ Cognitive_Psychology_and_Cognitive_Neuroscience
Wikibooks are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License.
Cognitive Psychology and Cognitive Neuroscience is licensed under the GNU Free Documentation License.
Condensed from original version. American spellings used. Content added or changed to reflect American perspective and references. Context and transitions added throughout. Substantially edited, adapted, and (in some parts) rewritten for clarity and course relevance.
Cover photo by Pixabay on Pexels.
Knut is sitting at his desk, staring at a blank paper in front of him, and nervously playing with a pen in his right hand. Just a few hours left to hand in his essay and he has not written a word. All of a sudden he smashes his fist on the table and cries out: “I need a plan!”
Knut is confronted with something every one of us encounters in his daily life: he has a problem, and he does not know how to solve it. But what exactly is a problem? Are there strategies to solve problems? These are just a few of the questions we want to answer in this chapter.
We begin our chapter by giving a short description of what psychologists regard as a problem. Afterward we will discuss different approaches towards problem solving, starting with gestalt psychologists and ending with modern search strategies connected to artificial intelligence. In addition we will also consider how experts solve problems.
The most basic definition of a problem is any given situation that differs from a desired goal. This definition is very useful for discussing problem solving in terms of evolutionary adaptation, as it allows us to understand every aspect of (human or animal) life as a problem. This includes issues like finding food in harsh winters, remembering where you left your provisions, making decisions about which way to go, learning, repeating and varying all kinds of complex movements, and so on. Though all of these problems were of crucial importance during the human evolutionary process, they are by no means solved exclusively by humans. We find an amazing variety of different solutions for these problems in nature (just consider, for example, the way a bat hunts its prey compared to a spider). We will mainly focus on problems that are not solved by animals or evolution; we will instead focus on abstract problems, such as playing chess. Furthermore, we will not consider problems that have an obvious solution. For example, imagine Knut decides to take a sip of coffee from the mug next to his right hand. He does not even have to think about how to do this. This is not because the situation itself is trivial (a robot capable of recognizing the mug, deciding whether it is full, then grabbing it and moving it to Knut’s mouth would be a highly complex machine) but because in the context of all possible situations it is so trivial that it no longer is a problem our consciousness needs to be bothered with. The problems we will discuss in the following all need some conscious effort, though some seem to be solved without us being able to say how exactly we got to the solution. We will often find that the strategies we use to solve these problems are applicable to more basic problems, too.
Non-trivial, abstract problems can be divided into two groups: well-defined problems and ill- defined problems.
WELL-DEFINED PROBLEMS
For many abstract problems, it is possible to find an algorithmic solution. We call problems well-defined if they can be properly formalized, which involves the following properties:
• The problem has a clearly defined given state. This might be the line-up of a chess game, a given formula you have to solve, or the set-up of the towers of Hanoi game (which we will discuss later).
• There is a finite set of operators, that is, rules you may apply to the given state. For the chess game, e.g., these would be the rules that tell you which piece you may move to which position.
• Finally, the problem has a clear goal state: The equations is resolved to x, all discs are moved to the right stack, or the other player is in checkmate.
A problem that fulfils these requirements can be implemented algorithmically. Therefore many well-defined problems can be very effectively solved by computers, like playing chess.
ILL-DEFINED PROBLEMS
Though many problems can be properly formalized, there are still others where this is not the case. Good examples for this are all kinds of tasks that involve creativity, and, generally speaking, all problems for which it is not possible to clearly define a given state and a goal state. Formalizing a problem such as “Please paint a beautiful picture” may be impossible.
Still, this is a problem most people would be able to approach in one way or the other, even if the result may be totally different from person to person. And while Knut might judge that picture X is gorgeous, you might completely disagree.
The line between well-defined and ill-defined problems is not always neat: ill-defined problems often involve sub-problems that can be perfectly well-defined. On the other hand, many everyday problems that seem to be completely well-defined involve — when examined in detail — a great amount of creativity and ambiguity. Consider Knut’s fairly ill-defined task of writing an essay: he will not be able to complete this task without first understanding the text he has to write about. This step is the first subgoal Knut has to solve. In this example, an ill-defined problem involves a well-defined sub-problem
RESTRUCTURING: THE GESTALTIST APPROACH
One dominant approach to problem solving originated from Gestalt psychologists in the 1920s. Their understanding of problem solving emphasizes behavior in situations requiring relatively novel means of attaining goals and suggests that problem solving involves a process called restructuring. With a Gestalt approach, two main questions have to be considered to understand the process of problem solving: 1) How is a problem represented in a person’s mind?, and 2) How does solving this problem involve a reorganization or restructuring of this representation?
HOW IS A PROBLEM REPRESENTED IN THE MIND?
In current research internal and external representations are distinguished: an internal representation is one held in memory, and which has to be retrieved by cognitive processes, while an external representation exists in the environment, such like physical objects or symbols whose information can be picked up and processed by the perceptual system.
Generally speaking, problem representations are models of the situation as experienced by the solver. Representing a problem means to analyze it and split it into separate components, including objects, predicates, state space, operators, and selection criteria.
The efficiency of problem solving depends on the underlying representations in a person’s mind, which usually also involves personal aspects. Re-analyzing the problem along different dimensions, or changing from one representation to another, can result in arriving at a new understanding of a problem. This is called restructuring . The following example illustrates this:
Two boys of different ages are playing badminton. The older one is a more skilled player, and therefore the outcome of matches between the two becomes predictable. After repeated defeats the younger boy finally loses interest in playing. The older boy now faces a problem, namely that he has no one to play with anymore. The usual options, according to M. Wertheimer (1945/82), range from “offering candy” and “playing a different game” to “not playing at full ability” and “shaming the younger boy into playing.” All of these strategies aim at making the younger boy stay.
The older boy instead comes up with a different solution: He proposes that they should try to keep the birdie in play as long as possible. Thus, they change from a game of competition to one of cooperation. The proposal is happily accepted, and the game is on again. The key in this story is that the older boy restructured the problem, having found that his attitude toward the game made it difficult to keep the younger boy playing. With the new type of game the problem is solved: the older boy is not bored, and the younger boy is not frustrated. In some cases, new representations can make a problem more difficult or much easier to solve. In the latter case insight – the sudden realization of a problem’s solution – may be the key to finding a solution.
There are two very different ways of approaching a goal-oriented situation . In one case an organism readily reproduces the response to the given problem from past experience. This is called reproductive thinking .
The second way requires something new and di fferent to achieve the goal—prior learning is of little help here. Such productive thinking is sometimes argued to involve insight . Gestalt psychologists state that insight problems are a separate category of problems in their own right.
Tasks that might involve insight usually have certain features: they require something new and non-obvious to be done, and in most cases they are difficult enough to predict that the initial solution attempt will be unsuccessful. When you solve a problem of this kind you often have a so called “aha” experience: the solution pops into mind all of a sudden. In one moment you have no idea how to answer the problem, and you feel you are not making any progress trying out different ideas, but in the next moment the problem is solved.
For readers who would like to experience such an effect, here is an example of an insight problem: Knut is given four pieces of a chain; each made up of three links. The task is to link it all up to a closed loop. To open a link costs 2 cents, and to close a link costs 3 cents. Knut has 15 cents to spend. What should Knut do?

If you want to know the correct solution, turn to the next page.
To show that solving insight problems involves restructuring , psychologists have created a number of problems that are more difficult to solve for participants with previous experiences, since it is harder for them to change the representation of the given situation.
For non-insight problems the opposite is the case. Solving arithmetical problems, for instance, requires schemas, through which one can get to the solution step by step.
Sometimes, previous experience or familiarity can even make problem solving more difficult. This is the case whenever habitual directions get in the way of finding new directions – an effect called fixation .
FUNCTIONAL FIXEDNESS
Functional fixedness concerns the solution of object use problems . The basic idea is that when the usual function an object is emphasized, it will be far more difficult for a person to use that object in a novel manner. An example for this effect is the candle problem : Imagine you are given a box of matches, some candles and tacks. On the wall of the room there is a cork-board. Your task is to fix the candle to the cork-board in such a way that no wax will drop on the floor when the candle is lit. Got an idea?

Here’s a clue: when people are confronted with a problem and given certain objects to solve it, it is difficult for them to figure out that they could use the objects in a different way. In this example, the box has to be recognized as a support rather than as a container— tack the matchbox to the wall, and place the candle upright in the box. The box will catch the falling wax.

A further example is the two-string problem : Knut is left in a room with a pair of pliers and given the task to bind two strings together that are hanging from the ceiling. The problem he faces is that he can never reach both strings at a time because they are just too far away from each other. What can Knut do?

Solution: Knut has to recognize he can use the pliers in a novel function: as weight for a pendulum. He can tie them to one of the strings, push it away, hold the other string and wait for the first one to swing toward him.
MENTAL FIXEDNESS
Functional fixedness as involved in the examples above illustrates a mental set: a person’s tendency to respond to a given task in a manner based on past experience. Because Knut maps an object to a particular function he has difficulty varying the way of use (i.e., pliers as pendulum’s weight).
One approach to studying fixation was to study wrong-answer verbal insight problems . In these probems, people tend to give an incorrect answer when failing to solve a problem rather than to give no answer at all.
A typical example: People are told that on a lake the area covered by water lilies doubles every 24 hours and that it takes 60 days to cover the whole lake. Then they are asked how many days it takes to cover half the lake. The typical response is “30 days” (whereas 59 days is correct).
These wrong solutions are due to an inaccurate interpretation , or representation , of the problem. This can happen because of sloppiness (a quick shallow reading of the problem and/or weak monitoring of their efforts made to come to a solution). In this case error feedback should help people to reconsider the problem features, note the inadequacy of their first answer, and find the correct solution. If, however, people are truly fixated on their incorrect representation, being told the answer is wrong does not help. In a study by P.I. Dallop and
R.L. Dominowski in 1992 these two possibilities were investigated. In approximately one third of the cases error feedback led to right answers, so only approximately one third of the wrong answers were due to inadequate monitoring.
Another approach is the study of examples with and without a preceding analogous task. In cases such like the water-jug task, analogous thinking indeed leads to a correct solution, but to take a different way might make the case much simpler:
Imagine Knut again, this time he is given three jugs with different capacities and is asked to measure the required amount of water. He is not allowed to use anything except the jugs and as much water as he likes. In the first case the sizes are: 127 cups, 21 cups and 3 cups. His goal is to measure 100 cups of water.
In the second case Knut is asked to measure 18 cups from jugs of 39, 15 and 3 cups capacity.
Participants who are given the 100 cup task first choose a complicated way to solve the second task. Participants who did not know about that complex task solved the 18 cup case by just adding three cups to 15.
SOLVING PROBLEMS BY ANALOGY
One special kind of restructuring is analogical problem solving. Here, to find a solution to one problem (i.e., the target problem) an analogous solution to another problem (i.e., the base problem) is presented.
An example for this kind of strategy is the radiation problem posed by K. Duncker in 1945:
As a doctor you have to treat a patient with a malignant, inoperable tumor, buried deep inside the body. There exists a special kind of ray which is harmless at a low intensity, but at sufficiently high intensity is able to destroy the tumor. At such high intensity, however, the ray will also destroy the healthy tissue it passes through on the way to the tumor. What can be done to destroy the tumor while preserving the healthy tissue?
When this question was asked to participants in an experiment, most of them couldn’t come up with the appropriate answer to the problem. Then they were told a story that went something like this:
A general wanted to capture his enemy’s fortress. He gathered a large army to launch a full- scale direct attack, but then learned that all the roads leading directly towards the fortress were blocked by landmines. These roadblocks were designed in such a way that it was possible for small groups of the fortress-owner’s men to pass over them safely, but a large group of men would set them off. The general devised the following plan: He divided his troops into several smaller groups and ordered each of them to march down a different road, timed in such a way that the entire army would reunite exactly when reaching the fortress and could hit with full strength.
Here, the story about the general is the source problem, and the radiation problem is the target problem. The fortress is analogous to the tumor and the big army corresponds to the highly intensive ray. Likewise, a small group of soldiers represents a ray at low intensity. The s olution to the problem is to split the ray up, as the general did with his army, and send the now harmless rays towards the tumor from different angles in such a way that they all meet when reaching it. No healthy tissue is damaged but the tumor itself gets destroyed by the ray at its full intensity.
M. Gick and K. Holyoak presented Duncker’s radiation problem to a group of participants in 1980 and 1983. 10 percent of participants were able to solve the problem right away, but 30 percent could solve it when they read the story of the general before. After being given an additional hint — to use the story as help — 75 percent of them solved the problem.
Following these results, Gick and Holyoak concluded that analogical problem solving consists of three steps:
1. Recognizing that an analogical connection exists between the source and the base problem.
2. Mapping corresponding parts of the two problems onto each other (fortress ® tumour, army ® ray, etc.)
3. Applying the mapping to generate a parallel solution to the target problem (using little groups of soldiers approaching from different directions ® sending several weaker rays from different directions)
Next, Gick and Holyoak started looking for factors that could help the recognizing and mapping processes.
The abstract concept that links the target problem with the base problem is called the problem schema. Gick and Holyoak facilitated the activation of a schema with their participants by giving them two stories and asking them to compare and summarize them. This activation of problem schemas is called “schema induction“.
The experimenters had participants read stories that presented problems and their solutions. One story was the above story about the general, and other stories required the same problem schema (i.e., if a heavy force coming from one direction is not suitable, use multiple smaller forces that simultaneously converge on the target). The experimenters manipulated how many of these stories the participants read before the participants were asked to solve the radiation problem. The experiment showed that in order to solve the target problem, reading two stories with analogical problems is more helpful than reading only one story. This evidence suggests that schema induction can be achieved by exposing people to multiple problems with the same problem schema.
HOW DO EXPERTS SOLVE PROBLEMS?
An expert is someone who devotes large amounts of their time and energy to one specific field of interest in which they, subsequently, reach a certain level of mastery. It should not be a surprise that experts tend to be better at solving problems in their field than novices (i.e., people who are beginners or not as well-trained in a field as experts) are. Experts are faster at coming up with solutions and have a higher rate of correct solutions. But what is the difference between the way experts and non-experts solve problems? Research on the nature of expertise has come up with the following conclusions:
1. Experts know more about their field,
2. their knowledge is organized differently, and
3. they spend more time analyzing the problem.
Expertise is domain specific— when it comes to problems that are outside the experts’ domain of expertise, their performance often does not differ from that of novices.
Knowledge: An experiment by Chase and Simon (1973) dealt with the question of how well experts and novices are able to reproduce positions of chess pieces on chess boards after a brief presentation. The results showed that experts were far better at reproducing actual game positions, but that their performance was comparable with that of novices when the chess pieces were arranged randomly on the board. Chase and Simon concluded that the superior performance on actual game positions was due to the ability to recognize familiar patterns: A chess expert has up to 50,000 patterns stored in his memory. In comparison, a good player might know about 1,000 patterns by heart and a novice only few to none at all. This very detailed knowledge is of crucial help when an expert is confronted with a new problem in his field. Still, it is not only the amount of knowledge that makes an expert more successful. Experts also organize their knowledge differently from novices.
Organization: In 1981 M. Chi and her co-workers took a set of 24 physics problems and presented them to a group of physics professors as well as to a group of students with only one semester of physics. The task was to group the problems based on their similarities. The students tended to group the problems based on their surface structure (i.e., similarities of objects used in the problem, such as sketches illustrating the problem), whereas the professors used their deep structure (i.e., the general physical principles that underlie the problems) as criteria. By recognizing the actual structure of a problem experts are able to connect the given task to the relevant knowledge they already have (e.g., another problem they solved earlier which required the same strategy).
Analysis: Experts often spend more time analyzing a problem before actually trying to solve it. This way of approaching a problem may often result in what appears to be a slow start, but in the long run this strategy is much more effective. A novice, on the other hand, might start working on the problem right away, but often reach dead ends as they chose a wrong path in the very beginning.
_________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Chase, W. G., & Simon, H. A. (1973). Perception in chess. Cognitive psychology, 4(1), 55-81.
Chi, M. T., Feltovich, P. J., & Glaser, R. (1981). Categorization and representation of physics problems by experts and novices. Cognitive science, 5(2), 121-152.
Duncker, K., & Lees, L. S. (1945). On problem-solving. Psychological monographs, 58(5).
Gick, M. L., & Holyoak, K. J. (1980). Analogical problem solving. Cognitive psychology, 12(3), 306-355. Gick, M. L., & Holyoak, K. J. (1983). Schema induction and analogical transfer. Cognitive psychology, 15(1), 1-38.
Goldstein, E.B. (2005). Cogntive Psychology. Connecting Mind, Research, and Everyday Experience. Belmont: Thomson Wadsworth.
R.L. Dominowski and P. Dallob, Insight and Problem Solving. In The Nature of Insight, R.J. Sternberg & J.E. Davidson (Eds). MIT Press: USA, pp.33-62 (1995).
Wertheimer, M., (1945). Productive thinking. New York: Harper.
ESSENTIALS OF COGNITIVE PSYCHOLOGY Copyright © 2023 by Christopher Klein is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book


The Process of Problem Solving
- Editor's Choice
- Experimental Psychology
- Problem Solving

In a 2013 article published in the Journal of Cognitive Psychology , Ngar Yin Louis Lee (Chinese University of Hong Kong) and APS William James Fellow Philip N. Johnson-Laird (Princeton University) examined the ways people develop strategies to solve related problems. In a series of three experiments, the researchers asked participants to solve series of matchstick problems.
In matchstick problems, participants are presented with an array of joined squares. Each square in the array is comprised of separate pieces. Participants are asked to remove a certain number of pieces from the array while still maintaining a specific number of intact squares. Matchstick problems are considered to be fairly sophisticated, as there is generally more than one solution, several different tactics can be used to complete the task, and the types of tactics that are appropriate can change depending on the configuration of the array.
Louis Lee and Johnson-Laird began by examining what influences the tactics people use when they are first confronted with the matchstick problem. They found that initial problem-solving tactics were constrained by perceptual features of the array, with participants solving symmetrical problems and problems with salient solutions faster. Participants frequently used tactics that involved symmetry and salience even when other solutions that did not involve these features existed.
To examine how problem solving develops over time, the researchers had participants solve a series of matchstick problems while verbalizing their problem-solving thought process. The findings from this second experiment showed that people tend to go through two different stages when solving a series of problems.
People begin their problem-solving process in a generative manner during which they explore various tactics — some successful and some not. Then they use their experience to narrow down their choices of tactics, focusing on those that are the most successful. The point at which people begin to rely on this newfound tactical knowledge to create their strategic moves indicates a shift into a more evaluative stage of problem solving.
In the third and last experiment, participants completed a set of matchstick problems that could be solved using similar tactics and then solved several problems that required the use of novel tactics. The researchers found that participants often had trouble leaving their set of successful tactics behind and shifting to new strategies.
From the three studies, the researchers concluded that when people tackle a problem, their initial moves may be constrained by perceptual components of the problem. As they try out different tactics, they hone in and settle on the ones that are most efficient; however, this deduced knowledge can in turn come to constrain players’ generation of moves — something that can make it difficult to switch to new tactics when required.
These findings help expand our understanding of the role of reasoning and deduction in problem solving and of the processes involved in the shift from less to more effective problem-solving strategies.
Reference Louis Lee, N. Y., Johnson-Laird, P. N. (2013). Strategic changes in problem solving. Journal of Cognitive Psychology, 25 , 165–173. doi: 10.1080/20445911.2012.719021
good work for other researcher
APS regularly opens certain online articles for discussion on our website. Effective February 2021, you must be a logged-in APS member to post comments. By posting a comment, you agree to our Community Guidelines and the display of your profile information, including your name and affiliation. Any opinions, findings, conclusions, or recommendations present in article comments are those of the writers and do not necessarily reflect the views of APS or the article’s author. For more information, please see our Community Guidelines .
Please login with your APS account to comment.

Careers Up Close: Joel Anderson on Gender and Sexual Prejudices, the Freedoms of Academic Research, and the Importance of Collaboration
Joel Anderson, a senior research fellow at both Australian Catholic University and La Trobe University, researches group processes, with a specific interest on prejudice, stigma, and stereotypes.

Experimental Methods Are Not Neutral Tools
Ana Sofia Morais and Ralph Hertwig explain how experimental psychologists have painted too negative a picture of human rationality, and how their pessimism is rooted in a seemingly mundane detail: methodological choices.
APS Fellows Elected to SEP
In addition, an APS Rising Star receives the society’s Early Investigator Award.
Privacy Overview
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| __cf_bm | 30 minutes | This cookie, set by Cloudflare, is used to support Cloudflare Bot Management. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| AWSELBCORS | 5 minutes | This cookie is used by Elastic Load Balancing from Amazon Web Services to effectively balance load on the servers. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| at-rand | never | AddThis sets this cookie to track page visits, sources of traffic and share counts. |
| CONSENT | 2 years | YouTube sets this cookie via embedded youtube-videos and registers anonymous statistical data. |
| uvc | 1 year 27 days | Set by addthis.com to determine the usage of addthis.com service. |
| _ga | 2 years | The _ga cookie, installed by Google Analytics, calculates visitor, session and campaign data and also keeps track of site usage for the site's analytics report. The cookie stores information anonymously and assigns a randomly generated number to recognize unique visitors. |
| _gat_gtag_UA_3507334_1 | 1 minute | Set by Google to distinguish users. |
| _gid | 1 day | Installed by Google Analytics, _gid cookie stores information on how visitors use a website, while also creating an analytics report of the website's performance. Some of the data that are collected include the number of visitors, their source, and the pages they visit anonymously. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| loc | 1 year 27 days | AddThis sets this geolocation cookie to help understand the location of users who share the information. |
| VISITOR_INFO1_LIVE | 5 months 27 days | A cookie set by YouTube to measure bandwidth that determines whether the user gets the new or old player interface. |
| YSC | session | YSC cookie is set by Youtube and is used to track the views of embedded videos on Youtube pages. |
| yt-remote-connected-devices | never | YouTube sets this cookie to store the video preferences of the user using embedded YouTube video. |
| yt-remote-device-id | never | YouTube sets this cookie to store the video preferences of the user using embedded YouTube video. |
| yt.innertube::nextId | never | This cookie, set by YouTube, registers a unique ID to store data on what videos from YouTube the user has seen. |
| yt.innertube::requests | never | This cookie, set by YouTube, registers a unique ID to store data on what videos from YouTube the user has seen. |
7.3 Problem Solving
Learning objectives.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Describe problem solving strategies
- Define algorithm and heuristic
- Explain some common roadblocks to effective problem solving and decision making
People face problems every day—usually, multiple problems throughout the day. Sometimes these problems are straightforward: To double a recipe for pizza dough, for example, all that is required is that each ingredient in the recipe be doubled. Sometimes, however, the problems we encounter are more complex. For example, say you have a work deadline, and you must mail a printed copy of a report to your supervisor by the end of the business day. The report is time-sensitive and must be sent overnight. You finished the report last night, but your printer will not work today. What should you do? First, you need to identify the problem and then apply a strategy for solving the problem.
Problem-Solving Strategies
When you are presented with a problem—whether it is a complex mathematical problem or a broken printer, how do you solve it? Before finding a solution to the problem, the problem must first be clearly identified. After that, one of many problem solving strategies can be applied, hopefully resulting in a solution.
A problem-solving strategy is a plan of action used to find a solution. Different strategies have different action plans associated with them ( Table 7.2 ). For example, a well-known strategy is trial and error . The old adage, “If at first you don’t succeed, try, try again” describes trial and error. In terms of your broken printer, you could try checking the ink levels, and if that doesn’t work, you could check to make sure the paper tray isn’t jammed. Or maybe the printer isn’t actually connected to your laptop. When using trial and error, you would continue to try different solutions until you solved your problem. Although trial and error is not typically one of the most time-efficient strategies, it is a commonly used one.
| Method | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Trial and error | Continue trying different solutions until problem is solved | Restarting phone, turning off WiFi, turning off bluetooth in order to determine why your phone is malfunctioning |
| Algorithm | Step-by-step problem-solving formula | Instructional video for installing new software on your computer |
| Heuristic | General problem-solving framework | Working backwards; breaking a task into steps |
Another type of strategy is an algorithm. An algorithm is a problem-solving formula that provides you with step-by-step instructions used to achieve a desired outcome (Kahneman, 2011). You can think of an algorithm as a recipe with highly detailed instructions that produce the same result every time they are performed. Algorithms are used frequently in our everyday lives, especially in computer science. When you run a search on the Internet, search engines like Google use algorithms to decide which entries will appear first in your list of results. Facebook also uses algorithms to decide which posts to display on your newsfeed. Can you identify other situations in which algorithms are used?
A heuristic is another type of problem solving strategy. While an algorithm must be followed exactly to produce a correct result, a heuristic is a general problem-solving framework (Tversky & Kahneman, 1974). You can think of these as mental shortcuts that are used to solve problems. A “rule of thumb” is an example of a heuristic. Such a rule saves the person time and energy when making a decision, but despite its time-saving characteristics, it is not always the best method for making a rational decision. Different types of heuristics are used in different types of situations, but the impulse to use a heuristic occurs when one of five conditions is met (Pratkanis, 1989):
- When one is faced with too much information
- When the time to make a decision is limited
- When the decision to be made is unimportant
- When there is access to very little information to use in making the decision
- When an appropriate heuristic happens to come to mind in the same moment
Working backwards is a useful heuristic in which you begin solving the problem by focusing on the end result. Consider this example: You live in Washington, D.C. and have been invited to a wedding at 4 PM on Saturday in Philadelphia. Knowing that Interstate 95 tends to back up any day of the week, you need to plan your route and time your departure accordingly. If you want to be at the wedding service by 3:30 PM, and it takes 2.5 hours to get to Philadelphia without traffic, what time should you leave your house? You use the working backwards heuristic to plan the events of your day on a regular basis, probably without even thinking about it.
Another useful heuristic is the practice of accomplishing a large goal or task by breaking it into a series of smaller steps. Students often use this common method to complete a large research project or long essay for school. For example, students typically brainstorm, develop a thesis or main topic, research the chosen topic, organize their information into an outline, write a rough draft, revise and edit the rough draft, develop a final draft, organize the references list, and proofread their work before turning in the project. The large task becomes less overwhelming when it is broken down into a series of small steps.
Everyday Connection
Solving puzzles.
Problem-solving abilities can improve with practice. Many people challenge themselves every day with puzzles and other mental exercises to sharpen their problem-solving skills. Sudoku puzzles appear daily in most newspapers. Typically, a sudoku puzzle is a 9×9 grid. The simple sudoku below ( Figure 7.7 ) is a 4×4 grid. To solve the puzzle, fill in the empty boxes with a single digit: 1, 2, 3, or 4. Here are the rules: The numbers must total 10 in each bolded box, each row, and each column; however, each digit can only appear once in a bolded box, row, and column. Time yourself as you solve this puzzle and compare your time with a classmate.
Here is another popular type of puzzle ( Figure 7.8 ) that challenges your spatial reasoning skills. Connect all nine dots with four connecting straight lines without lifting your pencil from the paper:
Take a look at the “Puzzling Scales” logic puzzle below ( Figure 7.9 ). Sam Loyd, a well-known puzzle master, created and refined countless puzzles throughout his lifetime (Cyclopedia of Puzzles, n.d.).
Pitfalls to Problem Solving
Not all problems are successfully solved, however. What challenges stop us from successfully solving a problem? Imagine a person in a room that has four doorways. One doorway that has always been open in the past is now locked. The person, accustomed to exiting the room by that particular doorway, keeps trying to get out through the same doorway even though the other three doorways are open. The person is stuck—but they just need to go to another doorway, instead of trying to get out through the locked doorway. A mental set is where you persist in approaching a problem in a way that has worked in the past but is clearly not working now.
Functional fixedness is a type of mental set where you cannot perceive an object being used for something other than what it was designed for. Duncker (1945) conducted foundational research on functional fixedness. He created an experiment in which participants were given a candle, a book of matches, and a box of thumbtacks. They were instructed to use those items to attach the candle to the wall so that it did not drip wax onto the table below. Participants had to use functional fixedness to overcome the problem ( Figure 7.10 ). During the Apollo 13 mission to the moon, NASA engineers at Mission Control had to overcome functional fixedness to save the lives of the astronauts aboard the spacecraft. An explosion in a module of the spacecraft damaged multiple systems. The astronauts were in danger of being poisoned by rising levels of carbon dioxide because of problems with the carbon dioxide filters. The engineers found a way for the astronauts to use spare plastic bags, tape, and air hoses to create a makeshift air filter, which saved the lives of the astronauts.
Link to Learning
Check out this Apollo 13 scene about NASA engineers overcoming functional fixedness to learn more.
Researchers have investigated whether functional fixedness is affected by culture. In one experiment, individuals from the Shuar group in Ecuador were asked to use an object for a purpose other than that for which the object was originally intended. For example, the participants were told a story about a bear and a rabbit that were separated by a river and asked to select among various objects, including a spoon, a cup, erasers, and so on, to help the animals. The spoon was the only object long enough to span the imaginary river, but if the spoon was presented in a way that reflected its normal usage, it took participants longer to choose the spoon to solve the problem. (German & Barrett, 2005). The researchers wanted to know if exposure to highly specialized tools, as occurs with individuals in industrialized nations, affects their ability to transcend functional fixedness. It was determined that functional fixedness is experienced in both industrialized and nonindustrialized cultures (German & Barrett, 2005).
In order to make good decisions, we use our knowledge and our reasoning. Often, this knowledge and reasoning is sound and solid. Sometimes, however, we are swayed by biases or by others manipulating a situation. For example, let’s say you and three friends wanted to rent a house and had a combined target budget of $1,600. The realtor shows you only very run-down houses for $1,600 and then shows you a very nice house for $2,000. Might you ask each person to pay more in rent to get the $2,000 home? Why would the realtor show you the run-down houses and the nice house? The realtor may be challenging your anchoring bias. An anchoring bias occurs when you focus on one piece of information when making a decision or solving a problem. In this case, you’re so focused on the amount of money you are willing to spend that you may not recognize what kinds of houses are available at that price point.
The confirmation bias is the tendency to focus on information that confirms your existing beliefs. For example, if you think that your professor is not very nice, you notice all of the instances of rude behavior exhibited by the professor while ignoring the countless pleasant interactions he is involved in on a daily basis. Hindsight bias leads you to believe that the event you just experienced was predictable, even though it really wasn’t. In other words, you knew all along that things would turn out the way they did. Representative bias describes a faulty way of thinking, in which you unintentionally stereotype someone or something; for example, you may assume that your professors spend their free time reading books and engaging in intellectual conversation, because the idea of them spending their time playing volleyball or visiting an amusement park does not fit in with your stereotypes of professors.
Finally, the availability heuristic is a heuristic in which you make a decision based on an example, information, or recent experience that is that readily available to you, even though it may not be the best example to inform your decision . Biases tend to “preserve that which is already established—to maintain our preexisting knowledge, beliefs, attitudes, and hypotheses” (Aronson, 1995; Kahneman, 2011). These biases are summarized in Table 7.3 .
| Bias | Description |
|---|---|
| Anchoring | Tendency to focus on one particular piece of information when making decisions or problem-solving |
| Confirmation | Focuses on information that confirms existing beliefs |
| Hindsight | Belief that the event just experienced was predictable |
| Representative | Unintentional stereotyping of someone or something |
| Availability | Decision is based upon either an available precedent or an example that may be faulty |
Watch this teacher-made music video about cognitive biases to learn more.
Were you able to determine how many marbles are needed to balance the scales in Figure 7.9 ? You need nine. Were you able to solve the problems in Figure 7.7 and Figure 7.8 ? Here are the answers ( Figure 7.11 ).
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Rose M. Spielman, William J. Jenkins, Marilyn D. Lovett
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Psychology 2e
- Publication date: Apr 22, 2020
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e/pages/7-3-problem-solving
© Jun 26, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
Our systems are now restored following recent technical disruption, and we’re working hard to catch up on publishing. We apologise for the inconvenience caused. Find out more: https://www.cambridge.org/universitypress/about-us/news-and-blogs/cambridge-university-press-publishing-update-following-technical-disruption
We use cookies to distinguish you from other users and to provide you with a better experience on our websites. Close this message to accept cookies or find out how to manage your cookie settings .
Login Alert
- < Back to search results
- The Psychology of Problem Solving
The Psychology of Problem Solving

- Get access Buy a print copy Check if you have access via personal or institutional login Log in Register
- Cited by 107

This Book has been cited by the following publications. This list is generated based on data provided by Crossref .
- Google Scholar
- Edited by Janet E. Davidson , Lewis and Clark College, Portland , Robert J. Sternberg , Yale University, Connecticut
- Export citation
- Buy a print copy
Book description
Problems are a central part of human life. The Psychology of Problem Solving organizes in one volume much of what psychologists know about problem solving and the factors that contribute to its success or failure. There are chapters by leading experts in this field, including Miriam Bassok, Randall Engle, Anders Ericsson, Arthur Graesser, Keith Stanovich, Norbert Schwarz, and Barry Zimmerman, among others. The Psychology of Problem Solving is divided into four parts. Following an introduction that reviews the nature of problems and the history and methods of the field, Part II focuses on individual differences in, and the influence of, the abilities and skills that humans bring to problem situations. Part III examines motivational and emotional states and cognitive strategies that influence problem solving performance, while Part IV summarizes and integrates the various views of problem solving proposed in the preceding chapters.
‘A good book on any subject should summarise the current state of knowledge, and point to the important areas where further work is needed, and this book does both. Overall, this is a very stimulating collection, which all researchers in problem solving will wish to consult.’
Source: Trends in Cognitive Sciences
- Aa Reduce text
- Aa Enlarge text
Refine List
Actions for selected content:.
- View selected items
- Save to my bookmarks
- Export citations
- Download PDF (zip)
- Save to Kindle
- Save to Dropbox
- Save to Google Drive
Save content to
To save content items to your account, please confirm that you agree to abide by our usage policies. If this is the first time you use this feature, you will be asked to authorise Cambridge Core to connect with your account. Find out more about saving content to .
To save content items to your Kindle, first ensure [email protected] is added to your Approved Personal Document E-mail List under your Personal Document Settings on the Manage Your Content and Devices page of your Amazon account. Then enter the ‘name’ part of your Kindle email address below. Find out more about saving to your Kindle .
Note you can select to save to either the @free.kindle.com or @kindle.com variations. ‘@free.kindle.com’ emails are free but can only be saved to your device when it is connected to wi-fi. ‘@kindle.com’ emails can be delivered even when you are not connected to wi-fi, but note that service fees apply.
Find out more about the Kindle Personal Document Service .
Save Search
You can save your searches here and later view and run them again in "My saved searches".
Frontmatter pp i-iv
- Get access Check if you have access via personal or institutional login Log in Register
Contents pp v-vi
Contributors pp vii-viii, preface pp ix-xii.
- By Janet E. Davidson , Associate Professor of Psychology, Lewis & Clark College, Robert J. Sternberg , IBM Professor of Psychology and Education, Yale University; Director, Yale Center for the Psychology of Abilities, Competencies and Expertise (PACE Center)
PART I - INTRODUCTION pp 1-2
1 - recognizing, defining, and representing problems pp 3-30.
- By Jean E. Pretz , Yale University, Adam J. Naples , Yale University, Robert J. Sternberg , Yale University
2 - The Acquisition of Expert Performance as Problem Solving: Construction and Modification of Mediating Mechanisms through Deliberate Practice pp 31-84
- By K. Anders Ericsson , Florida State University
PART II - RELEVANT ABILITIES AND SKILLS pp 85-86
3 - is success or failure at solving complex problems related to intellectual ability pp 87-126.
- By Dorit Wenke , Humboldt-University at Berlin, Peter A. Frensch , Humboldt-University at Berlin
4 - Creativity: A Source of Difficulty in Problem Solving pp 127-148
- By Todd I. Lubart , Université René Descartes, Paris, Christophe Mouchiroud , Université René Descartes, Paris
5 - Insights about Insightful Problem Solving pp 149-175
- By Janet E. Davidson , Associate Professor of Psychology, Lewis & Clark College
6 - The Role of Working Memory in Problem Solving pp 176-206
- By David Z. Hambrick , Michigan State University, Randall W. Engle , Georgia Institute of Technology
7 - Comprehension of Text in Problem Solving pp 207-230
- By Shannon Whitten , The University of Memphis, Arthur C. Graesser , The University of Memphis
PART III - STATES AND STRATEGIES pp 231-232
8 - motivating self-regulated problem solvers pp 233-262.
- By Barry J. Zimmerman , Graduate School and University Center, City University of New York, Magda Campillo , Graduate School and University Center, City University of New York
9 - Feeling and Thinking: Implications for Problem Solving pp 263-290
- By Norbert Schwarz , University of Michigan, Ian Skurnik , University of Michigan
10 - The Fundamental Computational Biases of Human Cognition: Heuristics That (Sometimes) Impair Decision Making and Problem Solving pp 291-342
- By Keith E. Stanovich , University of Toronto
11 - Analogical Transfer in Problem Solving pp 343-370
- By Miriam Bassok , University of Washington
PART IV - CONCLUSION AND INTEGRATION pp 371-372
12 - problem solving – large/small, hard/easy, conscious/nonconscious, problem-space/problem-solver: the issue of dichotomization pp 373-384.
- By Kenneth Kotovsky , Carnegie Mellon University
Index pp 385-394
Altmetric attention score, full text views.
Full text views reflects the number of PDF downloads, PDFs sent to Google Drive, Dropbox and Kindle and HTML full text views for chapters in this book.
Book summary page views
Book summary views reflect the number of visits to the book and chapter landing pages.
* Views captured on Cambridge Core between #date#. This data will be updated every 24 hours.
Usage data cannot currently be displayed.

Problem Solving: Understanding and Dealing with Challenges
The "three-legged-table" schema can help you spot problems..
Updated July 25, 2023 | Reviewed by Ray Parker
- What Is Therapy?
- Take our Do I Need Therapy?
- Find a therapist near me
- Problems can manifest in three ways: physical symptoms, negative thoughts, and maladaptive behaviours.
- Awareness of how your problems manifest and play out is essential for effective problem-solving.
- By identifying symptoms through the "three-legged table," you can effectively address your problems.
When life is going well, we think positively and we make healthy choices in our day-to-day lives. But when we are overwhelmed, struggling with negative, self-limiting thoughts or maladaptive habits or behaviors, life can seem unmanageable and out of control.
In my work as a clinical psychologist, I use this three-legged table to help my patients find clarity, support, and healing. There are times in our lives when it is critical that we pause, reflect, and try to understand what is going on in our bodies and minds. My three-legged table provides a means of doing just that. It has helped thousands of people understand their problems, and it can help you too. Here’s how it works.
Gaining an awareness of how problems manifest
Every problem we have in life manifests in three possible ways—physical symptoms, negative thoughts (cognitions), and maladaptive, negative behaviors. We can examine how our problems show up and play out in our lives by identifying our physical symptoms, and maladaptive thoughts and behaviors. With these insights and awareness, we can seek the support we need to address what’s happening and start to make positive changes.
A closer look at symptoms
Let’s start with physical symptoms—the first leg of our three-legged table. A number of physical symptoms are triggered by our emotions. Anxiety , for example, is often accompanied by a number of distressing physical symptoms , including headaches, gastrointestinal problems, muscle tension, fatigue, and a racing heart, to name a few. Insomnia , another troubling physical symptom, is also often tied to emotions.
Moving along to the second leg of our table, our problems also manifest as negative, unhealthy thoughts or cognitions. We internalize past hurts and ingrained negative beliefs about how the world works, and our sense of worth in the world.
In low self-esteem , we often develop negative thoughts, which lead to self-depreciation, feelings of hopelessness or worthlessness, and negative thoughts about our abilities, relationships, the world, and opportunities.
Onward to leg number three—maladaptive choices, patterns, and behaviors. Often, we distract or self-soothe with any number of unhealthy, maladaptive behaviors and habits —from eating too much, eating too little, sleeping too much or too little, relying on alcohol and drugs to numb physical symptoms or escape negative thoughts to angry outbursts, self-sabotage , procrastination , self-harm , inflicting or tolerating abuse, mismanaging money, gambling or shopping addictions, staying in a job we dislike, and many more unhealthy behaviors.
Putting the table to use
Whatever is troubling you, put your problem on the top of this three-legged table It can be used for work struggles, low self-esteem, becoming a caregiver to children or elderly parents, relationship troubles, inter-personal conflicts, anger , medical conditions, addictions (like food, alcohol, shopping, and gambling), chronic pain , money concerns, depression , anxiety: anything.
Mired in day-to-day physical symptoms, negative thoughts, and unhealthy patterns, we can feel overwhelmed and helpless. When we are stuck, awareness is the first step to creating positive change.
We can use the three-legged table to gain insight and awareness of the connections between our problems and symptoms, negative thoughts, and maladaptive behaviors. By identifying our symptoms in all three categories (legs), we can begin to address them effectively.
Seeking expert interventions
Most of us are comfortable seeking medical interventions for our physical symptoms, but less aware of what to do about our negative thoughts and maladaptive behaviors. Here, seeking therapy , and working with a mental health professional can be of great assistance in both healing and growth.
Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT), for example, is a solutions-based form of therapy that addresses maladaptive thoughts by challenging and reframing the cognitive distortions and thoughts we hold onto. It also facilitates positive changes by slowly shifting maladaptive behaviors, choices, and habits to healthier, more adaptive ones.

With a deeper understanding and awareness of how problems manifest and play out, we are better able to navigate life’s challenges. We owe it to ourselves to pay attention to our physical and mental health and to create positive change where change is needed.
The first step to positive change—and to addressing our physical symptoms and troublesome thoughts and behaviors—is awareness. With this awareness, we can begin to create positive changes that tackle our problems head-on.
Put your problems on the table
You can work on building awareness when you are struggling or feeling overwhelmed by:
- Listing your troubling physical/physiological symptoms, negative thoughts, and maladaptive behaviors, choices, and patterns
- Thinking about the areas of your life where you would like to create positive change
- Making a commitment to yourself to reach out and find the supports you need to address your physical symptoms, negative thoughts, and behaviors
- Bringing in the resources you need to address problematic thoughts and behaviors and address your physical symptoms
To find a therapist, please visit the Psychology Today Therapy Directory.

Monica Vermani, C. Psych., is a clinical psychologist specializing in the treatment of trauma, stress, mood and anxiety disorders, and the author of A Deeper Wellness .
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Self Tests NEW
- Therapy Center
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

It’s increasingly common for someone to be diagnosed with a condition such as ADHD or autism as an adult. A diagnosis often brings relief, but it can also come with as many questions as answers.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience

8 Effective Problem-Solving Strategies
Categories Cognition
If you need to solve a problem, there are a number of different problem-solving strategies that can help you come up with an accurate decision. Sometimes the best choice is to use a step-by-step approach that leads to the right solution, but other problems may require a trial-and-error approach.
Some helpful problem-solving strategies include: Brainstorming Step-by-step algorithms Trial-and-error Working backward Heuristics Insight Writing it down Getting some sleep
Table of Contents
Why Use Problem-Solving Strategies
While you can always make a wild guess or pick at random, that certainly isn’t the most accurate way to come up with a solution. Using a more structured approach allows you to:
- Understand the nature of the problem
- Determine how you will solve it
- Research different options
- Take steps to solve the problem and resolve the issue
There are many tools and strategies that can be used to solve problems, and some problems may require more than one of these methods in order to come up with a solution.
Problem-Solving Strategies
The problem-solving strategy that works best depends on the nature of the problem and how much time you have available to make a choice. Here are eight different techniques that can help you solve whatever type of problem you might face.
Brainstorming
Coming up with a lot of potential solutions can be beneficial, particularly early on in the process. You might brainstorm on your own, or enlist the help of others to get input that you might not have otherwise considered.
Step-by-Step
Also known as an algorithm, this approach involves following a predetermined formula that is guaranteed to produce the correct result. While this can be useful in some situations—such as solving a math problem—it is not always practical in every situation.
On the plus side, algorithms can be very accurate and reliable. Unfortunately, they can also be time-consuming.
And in some situations, you cannot follow this approach because you simply don’t have access to all of the information you would need to do so.
Trial-and-Error
This problem-solving strategy involves trying a number of different solutions in order to figure out which one works best. This requires testing steps or more options to solve the problem or pick the right solution.
For example, if you are trying to perfect a recipe, you might have to experiment with varying amounts of a certain ingredient before you figure out which one you prefer.
On the plus side, trial-and-error can be a great problem-solving strategy in situations that require an individualized solution. However, this approach can be very time-consuming and costly.
Working Backward
This problem-solving strategy involves looking at the end result and working your way back through the chain of events. It can be a useful tool when you are trying to figure out what might have led to a particular outcome.
It can also be a beneficial way to play out how you will complete a task. For example, if you know you need to have a project done by a certain date, working backward can help you figure out the steps you’ll need to complete in order to successfully finish the project.
Heuristics are mental shortcuts that allow you to come up with solutions quite quickly. They are often based on past experiences that are then applied to other situations. They are, essentially, a handy rule of thumb.
For example, imagine a student is trying to pick classes for the next term. While they aren’t sure which classes they’ll enjoy the most, they know that they tend to prefer subjects that involve a lot of creativity. They utilize this heuristic to pick classes that involve art and creative writing.
The benefit of a heuristic is that it is a fast way to make fairly accurate decisions. The trade-off is that you give up some accuracy in order to gain speed and efficiency.
Sometimes, the solution to a problem seems to come out of nowhere. You might suddenly envision a solution after struggling with the problem for a while. Or you might abruptly recognize the correct solution that you hadn’t seen before.
No matter the source, insight-based problem-solving relies on following your gut instincts. While this may not be as objective or accurate as some other problem-solving strategies, it can be a great way to come up with creative, novel solutions.
Write It Down
Sometimes putting the problem and possible solutions down in paper can be a useful way to visualize solutions. Jot down whatever might help you envision your options. Draw a picture, create a mind map, or just write some notes to clarify your thoughts.
Get Some Sleep
If you’re facing a big problem or trying to make an important decision, try getting a good night’s sleep before making a choice. Sleep plays an essential role in memory consolidation, so getting some rest may help you access the information or insight you need to make the best choice.
Other Considerations
Even with an arsenal of problem-solving strategies at your disposal, coming up with solutions isn’t always easy. Certain challenges can make the process more difficult. A few issues that might emerge include:
- Mental set : When people form a mental set, they only rely on things that have worked in the last. Sometimes this can be useful, but in other cases, it can severely hinder the problem-solving process.
- Cognitive biases : Unconscious cognitive biases can make it difficult to see situations clearly and objectively. As a result, you may not consider all of your options or ignore relevant information.
- Misinformation : Poorly sourced clues and irrelevant details can add more complications. Being able to sort out what’s relevant and what’s not is essential for solving problems accurately.
- Functional fixedness : Functional fixedness happens when people only think of customary solutions to problems. It can hinder out-of-the-box thinking and prevents insightful, creative solutions.
Important Problem-Solving Skills
Becoming a good problem solver can be useful in a variety of domains, from school to work to interpersonal relationships. Important problem-solving skills encompass being able to identify problems, coming up with effective solutions, and then implementing these solutions.
According to a 2023 survey by the National Association of Colleges and Employers, 61.4% of employers look for problem-solving skills on applicant resumes.
Some essential problem-solving skills include:
- Research skills
- Analytical abilities
- Decision-making skills
- Critical thinking
- Communication
- Time management
- Emotional intelligence
Solving a problem is complex and requires the ability to recognize the issue, collect and analyze relevant data, and make decisions about the best course of action. It can also involve asking others for input, communicating goals, and providing direction to others.
How to Become a Better Problem-Solver
If you’re ready to strengthen your problem-solving abilities, here are some steps you can take:
Identify the Problem
Before you can practice your problem-solving skills, you need to be able to recognize that there is a problem. When you spot a potential issue, ask questions about when it started and what caused it.
Do Your Research
Instead of jumping right in to finding solutions, do research to make sure you fully understand the problem and have all the background information you need. This helps ensure you don’t miss important details.
Hone Your Skills
Consider signing up for a class or workshop focused on problem-solving skill development. There are also books that focus on different methods and approaches.
The best way to strengthen problem-solving strategies is to give yourself plenty of opportunities to practice. Look for new challenges that allow you to think critically, analytically, and creatively.
Final Thoughts
If you have a problem to solve, there are plenty of strategies that can help you make the right choice. The key is to pick the right one, but also stay flexible and willing to shift gears.
In many cases, you might find that you need more than one strategy to make the choices that are right for your life.
Brunet, J. F., McNeil, J., Doucet, É., & Forest, G. (2020). The association between REM sleep and decision-making: Supporting evidences. Physiology & Behavior , 225, 113109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2020.113109
Chrysikou, E. G, Motyka, K., Nigro, C., Yang, S. I. , & Thompson-Schill, S. L. (2016). Functional fixedness in creative thinking tasks depends on stimulus modality. Psychol Aesthet Creat Arts , 10(4):425‐435. https://doi.org/10.1037/aca0000050
Sarathy, V. (2018). Real world problem-solving. Front Hum Neurosci , 12:261. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2018.00261
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Sweepstakes
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
What Is an Algorithm in Psychology?
Definition, Examples, and Uses
How Does an Algorithm Work?
Examples of algorithms.
- Reasons to Use Algorithms
- Potential Pitfalls
Algorithms vs. Heuristics
When solving a problem , choosing the right approach is often the key to arriving at the best solution. In psychology, one of these problem-solving approaches is known as an algorithm. While often thought of purely as a mathematical term, the same type of process can be followed in psychology to find the correct answer when solving a problem or making a decision.
An algorithm is a defined set of step-by-step procedures that provides the correct answer to a particular problem. By following the instructions correctly, you are guaranteed to arrive at the right answer.
At a Glance
Algorithms involve following specific steps in order to reach a solution to a problem. They can be a great tool when you need an accurate solution but tend to be more time-consuming than other methods.
This article discusses how algorithms are used as an approach to problem-solving. It also covers how psychologists compare this approach to other problem-solving methods.
An algorithm is often expressed in the form of a graph, where a square represents each step. Arrows then branch off from each step to point to possible directions that you may take to solve the problem.
In some cases, you must follow a particular set of steps to solve the problem. In other instances, you might be able to follow different paths that will all lead to the same solution.
Algorithms are essential step-by-step approaches to solving a problem. Rather than guessing or using trial-and-error, this approach is more likely to guarantee a specific solution.
Using an algorithm can help you solve day-to-day problems you face, but it can also help mental health professionals find ways to help people cope with mental health problems.
For example, a therapist might use an algorithm to treat a person experiencing something like anxiety. Because the therapist knows that a particular approach is likely to be effective, they would recommend a series of specific, focused steps as part of their intervention.
There are many different examples of how algorithms can be used in daily life. Some common ones include:
- A recipe for cooking a particular dish
- The method a search engine uses to find information on the internet
- Instructions for how to assemble a bicycle
- Instructions for how to solve a Rubik's cube
- A process to determine what type of treatment is most appropriate for certain types of mental health conditions
Doctors and mental health professionals often use algorithms to diagnose mental disorders . For example, they may use a step-by-step approach when they evaluate people.
This might involve asking the individual about their symptoms and their medical history. The doctor may also conduct lab tests, physical exams, or psychological assessments.
Using this information, they then utilize the "Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders" (DSM-5-TR) to make a diagnosis.
Reasons to Use Algorithms in Psychology
The upside of using an algorithm to solve a problem or make a decision is that yields the best possible answer every time. There are situations where using an algorithm can be the best approach:
When Accuracy Is Crucial
Algorithms can be particularly useful in situations when accuracy is critical. They are also a good choice when similar problems need to be frequently solved.
Computer programs can often be designed to speed up this process. Data then needs to be placed in the system so that the algorithm can be executed for the correct solution.
Artificial intelligence may also be a tool for making clinical assessments in healthcare situations.
When Each Decision Needs to Follow the Same Process
Such step-by-step approaches can be useful in situations where each decision must be made following the same process. Because the process follows a prescribed procedure, you can be sure that you will reach the correct answer each time.
Potential Pitfalls When Using Algorithms
The downside of using an algorithm to solve the problem is that this process tends to be very time-consuming.
So if you face a situation where a decision must be made very quickly, you might be better off using a different problem-solving strategy.
For example, an emergency room doctor making a decision about how to treat a patient could use an algorithm approach. However, this would be very time-consuming and treatment needs to be implemented quickly.
In this instance, the doctor would instead rely on their expertise and past experiences to very quickly choose what they feel is the right treatment approach.
Algorithms can sometimes be very complex and may only apply to specific situations. This can limit their use and make them less generalizable when working with larger populations.
Algorithms can be a great problem-solving choice when the answer needs to be 100% accurate or when each decision needs to follow the same process. A different approach might be needed if speed is the primary concern.
In psychology, algorithms are frequently contrasted with heuristics . Both can be useful when problem-solving, but it is important to understand the differences between them.
What Is a Heuristic?
A heuristic is a mental shortcut that allows people to quickly make judgments and solve problems.
These mental shortcuts are typically informed by our past experiences and allow us to act quickly. However, heuristics are really more of a rule-of-thumb; they don't always guarantee a correct solution.
So how do you determine when to use a heuristic and when to use an algorithm? When problem-solving, deciding which method to use depends on the need for either accuracy or speed.
When to Use an Algorithm
If complete accuracy is required, it is best to use an algorithm. By using an algorithm, accuracy is increased and potential mistakes are minimized.
If you are working in a situation where you absolutely need the correct or best possible answer, your best bet is to use an algorithm. When you are solving problems for your math homework, you don't want to risk your grade on a guess.
By following an algorithm, you can ensure that you will arrive at the correct answer to each problem.
When to Use a Heuristic
On the other hand, if time is an issue, then it may be best to use a heuristic. Mistakes may occur, but this approach allows for speedy decisions when time is of the essence.
Heuristics are more commonly used in everyday situations, such as figuring out the best route to get from point A to point B. While you could use an algorithm to map out every possible route and determine which one would be the fastest, that would be a very time-consuming process. Instead, your best option would be to use a route that you know has worked well in the past.
Psychologists who study problem-solving have described two main processes people utilize to reach conclusions: algorithms and heuristics. Knowing which approach to use is important because these two methods can vary in terms of speed and accuracy.
While each situation is unique, you may want to use an algorithm when being accurate is the primary concern. But if time is of the essence, then an algorithm is likely not the best choice.
Lang JM, Ford JD, Fitzgerald MM. An algorithm for determining use of trauma-focused cognitive-behavioral therapy . Psychotherapy (Chic) . 2010;47(4):554-69. doi:10.1037/a0021184
Stein DJ, Shoptaw SJ, Vigo DV, et al. Psychiatric diagnosis and treatment in the 21st century: paradigm shifts versus incremental integration . World Psychiatry . 2022;21(3):393-414. doi:10.1002/wps.20998
Bobadilla-Suarez S, Love BC. Fast or frugal, but not both: decision heuristics under time pressure . J Exp Psychol Learn Mem Cogn . 2018;44(1):24-33. doi:10.1037/xlm0000419
Giordano C, Brennan M, Mohamed B, Rashidi P, Modave F, Tighe P. Accessing artificial intelligence for clinical decision-making . Front Digit Health . 2021;3:645232. doi:10.3389/fdgth.2021.645232
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Problem-solving is a mental process that involves discovering, analyzing, and solving problems. The ultimate goal of problem-solving is to overcome obstacles and find a solution that best resolves the issue. The best strategy for solving a problem depends largely on the unique situation. In some cases, people are better off learning everything ...
In general, effective problem-solving strategies include the following steps: Define the problem. Come up with alternative solutions. Decide on a solution. Implement the solution. Problem-solving ...
Several mental processes are at work during problem-solving. Among them are: Perceptually recognizing the problem. Representing the problem in memory. Considering relevant information that applies to the problem. Identifying different aspects of the problem. Labeling and describing the problem.
Problem Solving is the process of identifying, analyzing, and finding effective solutions to complex issues or challenges. Key Steps in Problem Solving: Identification of the problem: Recognizing and clearly defining the issue that needs to be resolved. Analysis and research: Gathering relevant information, data, and facts to understand the ...
Here are the steps involved in problem solving, approved by expert psychologists. 1. Identifying the Problem. Identifying the problem seems like the obvious first stem, but it's not exactly as simple as it sounds. People might identify the wrong source of a problem, which will render the steps thus carried on useless.
14 Steps for Problem-Solving Therapy. Creators of PST D'Zurilla and Nezu suggest a 14-step approach to achieve the following problem-solving treatment goals (Dobson, 2011): Enhance positive problem orientation. Decrease negative orientation. Foster ability to apply rational problem-solving skills.
Steps for solving the Tower of Hanoi in the minimum number of moves when there are 3 disks. With 3 disks, the puzzle can be solved in 7 moves. The ... GESTALT PSYCHOLOGY AND PROBLEM SOLVING. As you may recall from the sensation and perception chapter, Gestalt psychology describes whole patterns, forms and configurations of perception and ...
Problem-solving is one technique used on the behavioral side of cognitive-behavioral therapy. The problem-solving technique is an iterative, five-step process that requires one to identify the ...
After being given an additional hint — to use the story as help — 75 percent of them solved the problem. Following these results, Gick and Holyoak concluded that analogical problem solving consists of three steps: 1. Recognizing that an analogical connection exists between the source and the base problem.
Here are three tips for executing step one like an expert. 1. Organize knowledge correctly. Often, novices have all the knowledge they need to solve the problem at hand. They just can't get to ...
The findings from this second experiment showed that people tend to go through two different stages when solving a series of problems. People begin their problem-solving process in a generative manner during which they explore various tactics — some successful and some not. Then they use their experience to narrow down their choices of ...
Cognitive—Problem solving occurs within the problem solver's cognitive system and can only be inferred indirectly from the problem solver's behavior (including biological changes, introspections, and actions during problem solving).. Process—Problem solving involves mental computations in which some operation is applied to a mental representation, sometimes resulting in the creation of ...
Problem-solving abilities can improve with practice. Many people challenge themselves every day with puzzles and other mental exercises to sharpen their problem-solving skills. Sudoku puzzles appear daily in most newspapers. Typically, a sudoku puzzle is a 9×9 grid. The simple sudoku below (Figure 7.7) is a 4×4 grid.
The Psychology of Problem Solving organizes in one volume much of what psychologists know about problem solving and the factors that contribute to its success or failure. There are chapters by leading experts in this field, including Miriam Bassok, Randall Engle, Anders Ericsson, Arthur Graesser, Keith Stanovich, Norbert Schwarz, and Barry ...
Problems can manifest in 3 ways: physical symptoms, negative thoughts, and maladaptive behaviours or habits. Awareness of how your problems manifest and play out is essential for effective problem ...
The Psychology of Problem Solving Problems are a central part of human life. The Psychology of Problem Solving organizes in one volume much of what psychologists know about problem solving and the factors that contribute to its success or failure. There are chapters by leading experts in this field, includ-
Problem-solving therapy is a brief intervention that provides people with the tools they need to identify and solve problems that arise from big and small life stressors. It aims to improve your overall quality of life and reduce the negative impact of psychological and physical illness. Problem-solving therapy can be used to treat depression ...
worksheet. Guide your clients and groups through the problem solving process with the help of the Problem Solving Packet. Each page covers one of five problem solving steps with a rationale, tips, and questions. The steps include defining the problem, generating solutions, choosing one solution, implementing the solution, and reviewing the process.
Problem recognition, also referred to as problem finding, is one of the earliest stages of problem solving. Getzels (1982) classified problems based on how they were "found.". According to Getzels, there are three kinds of problems: those that are presented, those that are discovered, and those that are created.
Problems can manifest in 3 ways: physical symptoms, negative thoughts, and maladaptive behaviours or habits. Awareness of how your problems manifest and play out is essential for effective problem ...
Important problem-solving skills encompass being able to identify problems, coming up with effective solutions, and then implementing these solutions. According to a 2023 survey by the National Association of Colleges and Employers, 61.4% of employers look for problem-solving skills on applicant resumes. Some essential problem-solving skills ...
In psychology, one of these problem-solving approaches is known as an algorithm. While often thought of purely as a mathematical term, the same type of process can be followed in psychology to find the correct answer when solving a problem or making a decision. An algorithm is a defined set of step-by-step procedures that provides the correct ...
1. Define the problem. Diagnose the situation so that your focus is on the problem, not just its symptoms. Helpful problem-solving techniques include using flowcharts to identify the expected steps of a process and cause-and-effect diagrams to define and analyze root causes.. The sections below help explain key problem-solving steps.