
18 Moral Dilemma Examples

A moral dilemma is a situation in which an individual must choose between two moral options. Each option has advantages and disadvantages that contain significant consequences.
Choosing one option means violating the ethical considerations of the other option. So, no matter which option is selected, it both upholds and violates at least one moral principle.
When moral dilemmas are discussed formally, the individual that must make the decision is referred to as the agent .
Moral Dilemma Features
McConnell (2022) identifies the crucial features of a moral or ethical dilemma :
- The agent (person) is required to do one of two moral options
- The agent (person) is capable of doing each one
- The agent (person) cannot do both
McConnell explains that the agent should choose option A, but at the same time, the agent should choose option B. All things considered, both options are equivalently positive and negative, but in different aspects.
Thus, no matter which option is chosen, it will result in a moral failure.
Types of Moral Dilemmas
- Epistemic: This type of moral dilemma is when the person has no idea which option is the most morally acceptable. Although in many moral dilemmas it can be somewhat clear which option should take precedence, in the epistemic moral dilemma , the matter is ambiguous.
- Ontological: This is a moral dilemma in which the options available are equal in every respect. The person knows and has a clear understanding that both options are equivalent. Most experts on morality agree that ontological moral dilemmas are genuine dilemmas.
- Self-imposed: This is the type of moral dilemma that the person has created themselves. They have engaged in a wrongdoing of some kind and are then faced with resolving the matter.
- World-imposed: When the moral dilemma is brought about by others and the person must resolve the matter, it is referred to as a world-imposed moral dilemma, and is also often an example of a social dilemma . The person is in the situation, but not due to any wrongdoing or mistake they are responsible for.
- Obligation : Some moral dilemmas involve options in which the person feels they must enact each one. It is a sense of responsibility to engage both options that creates the moral dilemma. The tension arises because they can only choose one, but they are obligated to do both.
- Prohibition: A moral dilemma in which each option is reprehensible is called a prohibition dilemma . Each option would normally not be considered due to its unethical nature. However, the person must choose.
Moral Dilemma Examples
1. Exposing Your Best Friend: The person (aka the ‘agent’) is in a supervisory position but recently discovered that his best friend has been faking the numbers on several sales reports to boost his commissions.
Type: This is a self-imposed moral dilemma . The person has not done any wrongdoing, but they are in the position to decide whether to expose their friend’s unethical behavior .
2. Tricking a Loved One with Alzheimer’s: In this scenario, a loved one has been placed in a special residential center, which is expensive. Their children don’t have the funds to pay, but the loved one does. Unfortunately, the only way to access those funds is to trick the loved one into revealing their bank account information.
Type: This seems to be an obligation moral dilemma . The person feels they must take care of their loved one’s expenses, but they also feel a duty to respect their loved one’s autonomy and not deceive them.
3. Cheating on a Boyfriend: The person/agent cheated on their boyfriend while at a conference, which occurred right after a huge fight where they both said they wanted to break up. However, now that they’re back together, the question becomes: should the boyfriend be told?
Type: This is a self-imposed moral dilemma , as the person’s actions led to the situation where they must decide whether to confess their infidelity.
4. Selling a Used Car: The person has two close friends. One is considering buying a car from the other. They know the car has a serious problem with the engine, but their friend is not disclosing it.
Type: This can be seen as an ontological moral dilemma , as the person must choose between two equivalent actions: betraying the trust of one friend by revealing the car’s problems or betraying the trust of the other friend by staying silent.
5. Recalling a Faulty Product: The CEO of a large corporation has been informed that one of their products causes cancer in lab rats. The mortality rate is low and the company has spent millions on R&D and marketing. Recalling the product could mean bankruptcy and thousands of lost jobs.
Type: This could be a world-imposed moral dilemma as the person/agent didn’t personally contribute to the faulty product but must decide whether to recall the product or risk public health.
6. Global Supply Chains: The BOD knows that the rare Earth minerals they need for their electronics products are being mined by children. Not using that source means the company would be required to raise the price of its products considerably. And that means competitors will win huge market share.
Type: This is an obligation dilemma . The person feels obligated to both keep their products affordable (and their company competitive) and to avoid supporting unethical labor practices.
7. Admitting a Mistake: The person only analyzes part of the data involved in a pharmaceutical study so that the medication looks effective. A year later, the BOD is charged with a crime because the government learned that the medication causes a severe health issue in users.
Type: This is a self-imposed dilemma because the agent’s decision to only analyze part of the data led to the current situation.
8. In Child Protection Services: The ‘agent’ in this dilemma is a case worker. They know that charges against a parent were fabricated by a vengeful ex, but yet the rules state that charges must be filed and the children removed from the household, most likely for several months until a full investigation has been completed.
Type: This could be an epistemic dilemma because the person doesn’t know which action – following the protocol or not filing charges knowing they were fabricated – is the most morally correct.
9. Playground Accident at School: The agent’s co-teacher was looking at their phone on the playground when one of the students under their supervision fell off the equipment and broke their arm. If the person tells the truth, the co-teacher, who is supporting three children as a single parent, will be fired.
Type: This could be seen as an ontological dilemma , as the person must choose between two equally significant outcomes: telling the truth and potentially causing their co-teacher to lose their job, or staying silent and potentially putting the school and other students at risk.
10. In Geo-Politics: The president of a company knows that they are dependent on doing business with another country that has severe human rights violations. If they move out of that market it will mean huge losses. If they stay, it means putting money in the pockets of people that commit crimes against humanity.
Type: This might be classified as a prohibition dilemma , as both options – supporting a regime that violates human rights or causing significant financial loss to the company and its stakeholders – are morally objectionable.
11. Conflict of Professional Ethics: Imagine a journalist finds sensitive but vital information about a potential major scandal involving a beloved public figure who happens also to be the journalist’s dear friend.
Type: This represents a self-imposed dilemma , as the journalist must reconcile their professional obligation with their personal relationship.
12. Prioritizing Elder Care: Imagine a working individual struggling to balance work responsibilities with eldercare. On one hand, they want to provide proper care for their elderly parent but on the other hand, they fear losing their job.
Type: This could be classified as an obligation dilemma , as the individual is torn between two significant responsibilities.
13. Intellectual Property Misuse: A computer engineer discovers their colleague is misusing intellectual property from a previous employer to boost productivity at the current firm.
Type: This scenario represents an ontological moral dilemma , where the engineer must choose between reporting their colleague and protecting the workplace.
14. Revealing Confidential Information: An employee learns that their company’s financial health is more severe than communicated publicly. They fear that if they don’t warn their co-workers, they all risk losing their jobs without prior notice.
Type: This could be seen as a world-imposed moral dilemma , as the employee had no hand in creating the financial instability but must decide how to handle the information.
15. Exploitative Marketing: A marketing manager at a fast-food company is asked to develop campaigns targeting low-income neighborhoods, where obesity rates are already high.
Type: This represents an obligation dilemma , as the manager is expected to fulfill their job duty while battling against contributing to societies’ health problem.
16. Academic Dishonesty: A student discovers their friend plagiarizing an entire assignment. On one hand, they feel they should report the violation, but they also fear losing their friend.
Type: This is a self-imposed dilemma as the student’s action led to the situation where they must decide whether to uphold academic integrity or maintain their friendship.
17. Unethical Labor Practices: A manufacturing company explicitly doesn’t use sweatshop labor. It’s discovered that their major supplier uses such practices.
Type: This is an obligation dilemma , as the company feels a responsibility to its reputation and ethical standards, but severing ties with the major supplier could risk business operations.
18. Business Versus Environment: A construction company discovers an endangered species habitat in an area planned for building a lucrative housing project.
Type: This is an epistemic dilemma , as the company has to choose between its economic interests and environmental responsibilities not knowing which is the morally correct decision.
Applications of Moral Dilemmas
1. in nursing .
According to Arries (2005), among all of the professionals in healthcare, nurses have the most frequent interactions with patients.
As a result, they confront moral dilemmas on a regular basis, and often experience severe emotional distress.
They often must balance obligations regarding professional duties and personal convictions involving their values and beliefs.
In fact, nurses face a wide range of moral dilemmas. Rainer et al. (2018) conducted an integrative review of published research from 2000 – 2017 which dealt with ethical dilemmas faced by nurses.
The review identified several main categories or moral dilemmas: end-of-life issues, conflicts with physicians, conflicts with patient family members, patient privacy matters, and organizational constraints.
In a meta-analysis of nine studies in four countries, de Casterlé et al. (2008) examined the moral reasoning of nurses based on Kohlberg’s (1971) theory of moral development.
The study used an adapted version of the Ethical Behaviour Test (EBT) to measure nurses’ moral reasoning as it applies to practical nursing scenarios (de Casterle´ et al. 1997).
The results suggested that nurses tended to function at a conventional level of moral reasoning, rather than at a higher, postconventional level in Kohlberg’s stages.
2. In Journalism
Many people that enter the field of journalism do so out of noble goals to promote truth, help the public stay informed, and reveal unethical practices in society.
The very nature of those goals leads to journalists being immersed in moral dilemmas stemming from a variety of issues.
Sources Journalists must gather information from sources that can be reluctant to reveal their identity. This presents the moral dilemma of somehow establishing credibility for one’s information, but at the same time protecting the rights and wishes of an anonymous source.
Victim’s Rights Protecting victims’ rights to privacy can be in direct conflict with the public’s right to know. This produces an ethical quandary that nearly every journalist will face in their career. This can be particularly tricky when dealing with public figures, elected officials, or children.
Conflicts of Interest Conflicts of interest come into play in journalism in several situations. Journalists are supposed to be impartial and cover stories fairly and objectively. However, conflicts of interest can emerge when the story might impact an advertiser negatively or reflect poorly on the company’s ownership.
Accuracy Particularly troublesome in the era of new media news is the moral dilemma regarding the accuracy of information presented in coverage. On the one hand, journalists are obligated to provide the audience with information that is valid. That takes time. On the other hand, being first has always been a priority in the journalism profession. Accuracy is tied directly to credibility, but at the same time, being second to go public with news tarnishes the agency’s reputation.
Credibility Deuze and Yeshua (2001) point out that one core moral dilemma in journalism centers on how to establish credibility in the age of social media and the lightning speed of the Internet. New media journalists struggle to establish credibility in an environment crowded with gossip, amateur journalists, and fake news (Singer, 1996).
3. In Business
There are no shortage of moral dilemmas in the business world, no matter how large or small the company (Shaw & Barry, 2015).
A small sample of ethical issues are described below.
Product Quality vs. Profit Nearly every item made can be produced to a higher standard. That is not the problem. The problem is that those higher standards usually entail higher costs. So, the tradeoff becomes an issue of competing priorities : product quality or product profitability.
Outsourcing Labor This seems to be a decision that a lot of US corporations have already completed. Offshoring labor is usually cheaper. But, it comes at a cost to the homeland. Fewer jobs means a weaker economy and possibly an array of psychosocial dysfunctions. If you ask the various BODs however, they will tell you that they have to honor their fiduciary obligation to make the most profit for the company they run. Often, that means offshoring jobs.
Employee Social Media Behavior On the one hand, what people do in their personal time is supposed to be just that, personal. On the other hand, each employee represents the company and if they engage in behavior online that reflects poorly on the company, then that can justify terminating their contract.
Honest Marketing It can be easy to stretch the truth a little bit to make a product or service look its best. How far to stretch that line is where the moral dilemma forms. In cases that are basically inconsequential, like foods and such, a little gloss is relatively harmless. However, when it comes to products that are consequential such as pharmaceuticals and insurance policies, the moral dilemma is so serious that the government has legislated marketing rules and regulations that must be strictly followed.
Labor Practices Many countries have strict laws about labor practices that involve child labor and working conditions. But, many countries do not. Some of the labor practices in those countries are absolutely shocking. Companies in industrialized countries such as in the EU are supposed to monitor their supply chains carefully. They can be held accountable if found in violation of their home country’s regulations. The moral dilemma occurs when the company feels it must turn a blind-eye to circumstances if it wants to stay in business.
Environmental Protection So many companies today are aware of their environmental footprint. They must make a calculated decision as to how much environmental damage they can accept in balance with expectations of their customers and damage to the environment. That balance is getting harder to ignore as societies become more environmentally conscious and social media increasingly powerful.
A moral dilemma is when an individual, referred to as an agent , is confronted with a situation in which they must choose between two or more moral options.
Unfortunately, each option has its own ramifications that make the choice between one or the other difficult.
Moral dilemmas are prevalent in our personal and professional lives. Several professions are especially rife with moral dilemmas. For instance, those in the healthcare industry must make decisions that can have life-and-death consequences.
Journalists must grapple with a range of moral dilemmas that involve establishing credibility of their content, verifying the accuracy of their information, plus issues of impartiality.
Business leaders today also cannot escape moral dilemmas. They must make decisions that impact employees, customers, and unseen individuals that work throughout fast supply chains.
As the world has become so interconnected, it seems that the number and severity of moral dilemmas continues to grow.
Arries, E. (2005). Virtue ethics: An approach to moral dilemmas in nursing. Curationis , 28 (3), 64-72.
de Casterlé, B. D., Grypdonck, M., & Vuylsteke-Wauters, M. (1997). Development, reliability, and validity testing of the Ethical Behavior Test: a measure for nurses’ ethical behavior. Journal of Nursing Measurement , 5 (1), 87-112.
de Casterlé, B., Roelens, A., & Gastmans, C. (1998). An adjusted version of Kohlberg’s moral theory: Discussion of its validity for research in nursing ethics. Journal of Advanced Nursing , 27 (4), 829-835.
de Casterlé, B. D., Izumi, S., Godfrey, N. S., & Denhaerynck, K. (2008). Nurses’ responses to ethical dilemmas in nursing practice: meta‐analysis. Journal of Advanced Nursing , 63 (6), 540-549.
Deuze, M., & Yeshua, D. (2001). Online journalists face new ethical dilemmas: Lessons from the Netherlands. Journal of Mass Media Ethics , 16 (4), 273-292.
Kohlberg, L. (1971). Stages of moral development. Moral Education , 1 (51), 23-92.
McConnell, T. (2022 Fall edition). Moral Dilemmas. In Edward N. Zalta & Uri Nodelman (Eds.). The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy. Archived at https://plato.stanford.edu/archives/fall2022/entries/moral-dilemmas/
Rainer, J., Schneider, J. K., & Lorenz, R. A. (2018). Ethical dilemmas in nursing: An integrative review. Journal of Clinical Nursing, 27 (19-20), 3446–3461. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocn.14542
Sainsbury, M. (2009). Moral dilemmas. Think, 8 , 57 – 63. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1477175609000086
Shaw, W. H., & Barry, V. (2015). Moral issues in business . Cengage Learning.
Singer, J. B. (1996). Virtual anonymity: Online accountability and the virtuous virtual journalist. Journal of Mass Media Ethics, 11 , 95–106
Strauß, N. (2022). Covering sustainable finance: Role perceptions, journalistic practices and moral dilemmas. Journalism , 23 (6), 1194-1212.

Dave Cornell (PhD)
Dr. Cornell has worked in education for more than 20 years. His work has involved designing teacher certification for Trinity College in London and in-service training for state governments in the United States. He has trained kindergarten teachers in 8 countries and helped businessmen and women open baby centers and kindergartens in 3 countries.
- Dave Cornell (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/dave-cornell-phd/ 15 Theory of Planned Behavior Examples
- Dave Cornell (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/dave-cornell-phd/ 18 Adaptive Behavior Examples
- Dave Cornell (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/dave-cornell-phd/ 15 Cooperative Play Examples
- Dave Cornell (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/dave-cornell-phd/ 15 Parallel Play Examples

Chris Drew (PhD)
This article was peer-reviewed and edited by Chris Drew (PhD). The review process on Helpful Professor involves having a PhD level expert fact check, edit, and contribute to articles. Reviewers ensure all content reflects expert academic consensus and is backed up with reference to academic studies. Dr. Drew has published over 20 academic articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education and holds a PhD in Education from ACU.
- Chris Drew (PhD) #molongui-disabled-link 15 Theory of Planned Behavior Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) #molongui-disabled-link 18 Adaptive Behavior Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) #molongui-disabled-link 15 Cooperative Play Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) #molongui-disabled-link 15 Parallel Play Examples
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
203 Ethical Dilemma Topics & Moral Issues
If you are searching for the most interesting ethical dilemma essay topics, welcome to our base! An ethical dilemma essay requires you to study difficult choices involving conflicting moral principles, personal values, and societal norms. Our ethical dilemma topics will guide you through medical ethics, business dilemmas, technology ethics, and more.
🤔 TOP 7 Ethical Debate Topics
🏆 best ethical dilemma essay topics, ⚖️ contemporary moral issues essay topics, 👍 catchy ethical dilemma essay examples, 🎓 interesting ethical dilemma essay ideas, 📌 easy ethical debate topics, 💧 personal ethical dilemma essay examples, 💡 simple ethical dilemma topics, ❓ more ethical debate research questions.
- Ethical Dilemma and an Ethical Lapse Difference
- Lego Company’s Core Values and Ethical Dilemmas
- The Lifeboat Case as an Ethical Dilemma
- Ethical Dilemma in “Enron: The Smartest Guys in the Room”
- Ethical Dilemma in Homer’s “The Odyssey”
- Forensic Psychology Analysis: Ethical Dilemmas and Principles
- The Ethical Dilemmas in Law
- Apple Inc.: The Ethical Dilemmas Unfortunately, Apple falls short of effective ethical principles since there are some areas that need immediate attention.
- Personal Ethical Dilemma: Adidas Case Study Business ethics considers ethical and moral principles in the context of the business environment and governs the actions and behavior of individuals in an organization.
- Blue Bell Ethical Dilemma Case The Blue Bell ethical case was challenging as the president faced difficult choices since the company was top-selling in the ice cream industry.
- Ethical Dilemma in the Workplace This essay will explore how the process of ethical decision making can be used to handle the case of an employee who is underperforming hence causing undue burden to other workers.
- Ethical Dilemmas in Social Work Practice The society being the centerpiece of a civilization must have its own regulations and standards that create order and stability, governed by morals and obligations.
- Ethical Dilemmas in Nursing Practice Nurses face ethical dilemmas in the course of their duties, for they advocate for patients’ interest in spite of the imposing interests from doctors, relatives, and physicians.
- Aristotle, Mills, and Kant on Ethical Dilemmas Aristotle, Mill, and Kant provide their approaches to solving ethical dilemmas. The paper compares the three theories.
- Ethical Issues in Healthcare Essay: Ethical Dilemma This paper describes an ethical dilemma in healthcare, its specific characteristics, violated ethical principles, and existent barriers to ethical practice.
- Ethical Dilemmas in Psychology Forensic psychologists face numerous ethical dilemmas as they write reports and testimonies related to therapeutic interventions or evaluations in court proceedings.
- The Trolley Problem Scenarios & Ethical Dilemmas When faced with trolley problem scenarios, one’s decision will be significantly influenced by the ethical theory of utilitarianism.
- Ethical Dilemma of Privacy in Technology The paper argues legal and ethical implications of new technology necessitate new ethical guidelines regarding individuals’ privacy developments.
- BCBA Interview: Ethical Dilemmas and Cultural Challenges Identifying one’s biases towards other cultures and receiving training about handling a diverse client base may assist an ABA expert in becoming more culturally competent.
- Case: Evaluation of Ethical Dilemmas in Microsoft During Microsoft’s antitrust trial, Microsoft hired the Association for Competitive Technology to promote the new technology. Microsoft Corporation was the main financier of ACT.
- Ethical Dilemma: Consenting to Chemotherapy This paper explores the ethical dilemma of a minor child’s decision to undergo chemotherapy using the example of 17-year-old Kassandra.
- Ethical Dilemmas in Education Ethical dilemmas in education occur in many cases; one of the most common reasons for their generation is injustice.
- Hurricane Katrina: Government Ethical Dilemmas Hurricane Katrina is a prime example of government failure. That`s why the leadership and decision-making Issues are very important at every level: local, state and federal.
- Organizational Ethical Dilemmas, as Portrayed in “Snowden” Edward Snowden is portrayed in the 2016 film Snowden as a victim of multiple ethical issues. The problem of the whistleblower is the ethical difficulty.
- Parole Office’s Work Environment and Ethical Dilemma The parole officer has professionally entitled the right to disclose certain information as they regard potentially helpful in protecting and restoring the client’s health.
- Solving Ethical Dilemma of Discrimination This paper discusses one of the frequent ethical dilemmas in workplaces, which is discrimination, based on religion, gender, ethnicity, or nationality.
- Bias and Ethical Decision-Making in AI Systems.
- Ethical Considerations in Gene Editing Technologies.
- Privacy in the Digital Age: Balancing Surveillance and Individual Rights.
- Environmental Ethics and Climate Change.
- The Ethics of Animal Rights: Balancing Human Interests and Animal Welfare.
- The Ethical Dilemmas in Medical Decision-Making: End-of-Life Care and Assisted Suicide.
- What Is the Ethical Use of Personal Information Online?
- Income Inequality and Social Justice: Addressing Moral Concerns in Wealth Distribution.
- The Ethics of Immigration and Border Control: How to Integrate Humanitarian Concerns in National Security?
- The Moral Implications of Capital Punishment.
- How to Balance Scientific Advancements in Biomedical Research and Human Subjects’ Rights?
- Cybersecurity and Ethical Hacking.
- How Would Drug Legalization Impact the Society?
- The Ethics of Human Cloning – What Are the Moral Dimensions?
- Ethical Dilemmas in Artificial Reproductive Technologies.
- The Morality of Euthanasia: Considering the Right to Die and Medical Ethics.
- The Ethical Implications of Genetic Testing and Privacy Concerns.
- Ethical Considerations in the LGBTQ+ Movement.
- Ethical Issues in Humanitarian Aid.
- Ethical Challenges in Big Data and Data Analytics: User Privacy and Data Security.
- The Morality of Cultural Appropriation: Respect for Cultural Traditions and Expression.
- The Ethics of Autonomous Vehicles: Moral Decision-Making in Self-Driving Cars.
- What Are the Ethical Dimensions of Reproductive Rights?
- The Ethics of Animal Testing in Cosmetic and Medical Research.
- Ethical Concerns in Artificial Womb Technology: The Future of Reproductive Ethics.
- “Ethical Dilemmas in Nursing” by Rainer The ethical dilemmas that a nurse may face are varied, and understanding the core concepts behind them will help the nurse find solutions to these issues.
- Ethical Dilemma and Decision-Making Steps Social workers are often presented with ethical dilemmas in their duties that demand competence in the ethical decision-making processes.
- The Discussion and Solution of COVID-19 Ethical Dilemma The ethical issue during the COVID-19 pandemic is related to the duties of physicians and their rights, scarce resources management, and deficit of personal protective equipment.
- Abortion: An Ethical Dilemma There are many reasons as to why abortion poses an ethical dilemma for most women. Reasons such as religious beliefs, medical concerns are easily resolved by reason and need.
- Ethical Dilemma of Client Privacy Breach The case entails an ethical dilemma related to the appropriateness of a therapist’s breach of privacy and confidentiality when deciding the client’s best interest.
- Interpersonal Relations: One Cent Ethical Dilemma In the modern socio political environment, ethical guidelines might change over time. Therefore, it is vital to ensure that ethics training is relatable and based on current issues
- Ethical Dilemma in Palliative Care Nursing Modern changes necessitate the act of addressing ethical concerns that can match with the foundation of palliative medicine care practices.
- “A Modest Proposal” by Jonathan Swift: Ethical Dilemma “A Modest Proposal” is a film that unveils the poverty situation in Ireland. The movie’s setting was at a time when the population was increasing at a higher rate than the economy.
- Helping Others: Examining an Ethical Dilemma If you approach anyone on the street and ask them if helping others is a good thing to do, the answer would most likely be “Yes.”
- An Ethical Dilemma in Education This paper explores an ethical dilemma with a situation that opening an opportunity to engage in unethical behavior to reap the benefits of passing a midterm exam.
- An Ethical Dilemma of a Pregnant 16-Year-Old Girl The current ethical dilemma concerns a pregnant sixteen-year-old girl who is hesitant to tell her parents about her condition.
- Ethical Dilemmas, Kant’s Moral Theory, and Virtue Ethics Virtue ethics would not support the decision of breaking the contract on the grounds of loyalty. The concepts of holding to one’s word are at play here.
- Ethical Dilemma of Worldwide Gender Equality One of the most significant issues in the context of the 21st century, however, is the ethical dilemma of worldwide gender equality.
- Circumcision Ethical Dilemma and Nurse’s Role in It Circumcision is regarded as a cultural, traditional, or medical indicator. As a rule, the expediency of circumcision causes the most heated discussions.
- Ethical Dilemmas in Shakespeare’s “Hamlet” Hamlet is William Shakespeare’s tragedy play that was written in the late 14th century. The imagery in this play is both entertaining and creative.
- The Boeing Firm’s Ethical Dilemma Regarding the Airbus-Neo The Boeing 737-MAX airplane model was revealed nine months after the Airbus-NEO design. After the sales of the new model, two planes crashed in 2018 and 2019.
- Ethical Dilemma of Reporting Teacher Misconduct A teacher faces an ethical dilemma of whether to report her colleague on her conduct in relation to a student who has a mental disability.
- Drug Release: Ethical Dilemma in Pharmaceutics A moral issue has emerged as to whether a pharmaceutical company has to release a new drug or not. This drug is thought to be an effective treatment of depression.
- Ethical Dilemmas in Business: Plumpy’nut Controversy The paper is written against this background of business activities and ethical considerations. In this paper, a case study depicting a conventional ethical dilemma is illustrated.
- Ethical Dilemmas in Business The ethical dilemma is concerned with the issue of teamwork and could be described as ambiguity in managers’ attitudes towards a team of employees.
- Ethical Dilemma in Nursing An Ethical Nursing Practice is a decision-making challenge between two potential normative choices, neither of which is undoubtedly desirable to a nurse.
- Solving Ethical Dilemmas The main principles of responsible behavior with children are reflected in The NAEYC Code of Ethical Conduct. It sets the ground for solving the essential ethical dilemmas.
- Social Worker’s Ethical Dilemma of Confidentiality The patient’s family face communication difficulties after her brain injury. The social worker has no rights to talk about the patient’s case even to her relatives.
- Euthanasia as a Christian Ethical Dilemma The issue of euthanasia has been quite topical over the past few years. It is viewed as inadmissible from the Christian perspective.
- A Pig Heart Transplant for a Person: An Ethical Dilemma The David Bennett ethical dilemma resulted in a number of legal repercussions for the different groups of people that were involved in the xenotransplantation.
- Ethical Dilemmas in Healthcare Ethics codes exist to ensure ethical decisions are made and properly discussed, but unpredictable situations can arise that require original action methodologies.
- Analysis of the Situations Wherein Ethical Dilemma Is Encountered
- The Ethical Dilemma Surrounding the Second World War
- Ethical Dilemma Working With HIV Positive Client
- Analysis of the Ethical Dilemma of Forensic Psychiatric Expertise
- Ethical Dilemma and Medical Technology
- The Ethical Dilemma Associated With Vaccinations
- Inmates and Organ Transplants: An Ethical Dilemma
- Ethical Dilemma With the End of Life Decisions
- New Zealand’s Largest Ethical Dilemma
- Ethical Dilemma: Treatment and Jehovah’s Witnesses
- The Ethical Dilemma Faced by the Managers at the Law Firm
- Review of the Ethical Dilemma of Medical Institutions
- Money Over Mind: Ethical Dilemma in Schools
- Global Warming and Its Ethical Dilemma Assignment
- Personal Ethical Dilemma for Diverse Patients
- Ethical Dilemma Analysis: Consequentialist, Deontological, and Virtue Ethics Approach
- Review the Ethical Dilemma of Medical Errors
- Ethical Dilemma for Mental Health Professionals
- What Is the Ethical Dilemma of Forensic Psychologists?
- Ethical Dilemma Surrounding Nazi Human Experimentation
- Ethical Dilemmas as an Integral Part of Business Ethical dilemmas are ubiquitous and knowing how to make favorable decisions is critical in the contemporary business environment.
- Oil Extraction as an Ethical Dilemma Nowadays, oil extraction and exportation has become a significant factor for the wealth of the world community and the economic situation of a particular petroleum-exporting nation.
- Ethical Principles as Applied to an Ethical Dilemma (Medication Compliance) The paper discusses the four principles of nursing profession: the principle of beneficence, the principle of nonmaleficence, the principle of justice, and the principle of respect for autonomy.
- Ethical Dilemma of Circumcision: Nurse’s Role This paper discusses what is the role of the nurse in relations to an ethical dilemma involving circumcision, and is this a medical right or a human rights issue.
- Medical Gatekeeping and Related Ethical Dilemmas This paper discusses the ethical dilemmas in gatekeeping in managed healthcare systems and the lessons learned when it is included in other domains.
- Euthanasia as a Medical Ethical Dilemma The aim of the work is to analyze the ethical problem of medicine, such as euthanasia, and consider it as an example of a specific situation.
- Diversity at the Workplace: Ethical Dilemma Ethical dilemmas at the workplace involving racism must address the essence of diversity and God’s appreciation for the differences inherent amongst all people.
- Strategies to Cope with Ethical Dilemmas The navy can help individuals cope with ethical dilemmas they will encounter through cultural and historical training.
- Ethical Dilemmas in Software Engineering: Volkswagen Ethical Dilemma The Volkswagen controversy is a portrayal of how engineers have compromised the company, stakeholder satisfaction, and regulatory norms by engaging in unethical behavior.
- Ethical Dilemmas in Criminal Justice System It is appropriate to apply different penalties to people because of differences in age and prior offenses in the case at hand.
- Ethical Dilemma: Case Study of Harry and Dora The situation presented in the case study between Harry and Dora is a classic scenario between the letter and the spirit of the law.
- Ethical Dilemma of Patient’s Disease Awareness The ethical dilemma in the case study may be defined as a conflict between a professional algorithm and an ambiguous request from the patient’s family members.
- Sexual Abuse: Researching of Ethical Dilemma The ethical dilemma chosen revolves around the social worker dealing with a situation involving a 21-year-old female client who her father had sexually molested.
- Ethical Dilemma: Autonomy and End-of-Life Care The idea of providing someone with high-quality care involves the concept of respect and acceptance of the patient’s wishes.
- Researching of Ethical Dilemma in the Company Policies Moral dilemma is defined as a situation where the person is faced with multiple choices, all of which are undesirable as defined by the person.
- Ethical Dilemma Within a Clinical Organization This essay discusses in detail one of the most pressing problems of the current agenda, namely patient confidentiality as an object of health care delivery.
- Finding Solutions for Ethical Dilemma The ethical dilemma that Mr. Markham is currently facing is the necessity to choose between the two undesirable options.
- Lockdown Ethical Dilemma Lockdown measures are practiced in many regions. Whether lockdown is ethical is a matter of great concern, which has sparked great debate in most countries.
- Ethical Dilemma: Euthanasia The present paper compares the Christian worldview to own worldview assumptions of euthanasia.
- Medical Ethical Dilemmas at the End of Life The constitution prohibits anyone from taking his/her life. Society does not also allow people to commit suicide by any means.
- Current Ethical Dilemma: HIV and AIDS in Africa The New Hock Times newspaper published on May 14, 2010, was about the rising percentages of people suffering from Aids in South Africa.
- Ethical Dilemmas in Nursing Practice: Dealing With HIV & AIDS Patients When one is faced with an ethical dilemma, making decisions between two conflicting options should be done with care.
- Ethical Dilemma: Justifying a Right to Die This essay presents a discourse on the ethical dilemma of whether there are circumstances that justify one to have a right to die.
- Ethical Dilemmas in Public Health The public health sector must acquaint itself with the ethical principles that govern the public sector as well as the complexities that surround them.
- Ethical Dilemma: Should Gene Editing be Performed on Human Embryos? The compelling relevance of a new gene-editing technique, CRISPR has elicited debates on the modification of human genomes to eliminate genes that cause certain disorders.
- Ethical Dilemma: Eight Key Questions (8KQ) Ethics is one of the core components of human society as it regulates relations between individuals and protects them from undesired outcomes.
- A Decision to Report a Coworker’s Unethical Behavior at Work.
- Choosing Between Honesty and Protecting a Friend’s Secret.
- Deciding Whether to Speak up Against Discrimination or Harassment in the Workplace.
- An Ethical Dilemma Related to Academic Integrity and Cheating.
- A Conflict Between Personal Values and Professional Responsibilities.
- Balancing Family Obligations with Work Commitments.
- An Ethical Dilemma Concerning the Treatment of Animals and Animal Rights.
- Choosing Between Two Job Opportunities with Different Ethical Implications.
- A Decision about Whether to Donate a Substantial Portion of Income to Charity.
- A Personal Ethical Dilemma Related to Environmental Conservation and Sustainability.
- The Decision to Confront or Ignore a Friend’s Problematic Behavior.
- An Ethical Dilemma Involving Privacy and The Use of Social Media.
- Deciding Whether to Support a Controversial Political Movement.
- A Moral Dilemma Related to Medical Treatment Choices for Oneself or a Loved One.
- Choosing Between Personal Happiness and Societal Expectations.
- An Ethical Dilemma Concerning Cultural Appropriation and Respecting Other Cultures.
- Deciding Whether to Maintain a Friendship with Someone Who Holds Offensive Views.
- A Conflict Between Loyalty to Family and Individual Aspirations.
- Balancing the Need for Self-Care with Responsibilities to Others.
- An Ethical Dilemma Related to the Use of Personal Data by Technology Companies.
- Choosing Between the Truth and Protecting Someone from Getting Hurt.
- A Decision About Whether to Report a Crime Witnessed but Not Directly Involved in.
- A Personal Ethical Dilemma Involving a Financial Decision with Potential Consequences for Others.
- Deciding Whether to Intervene in a Situation of Bullying or Harassment.
- An Ethical Dilemma Related to the Disclosure of a Mental Health Condition in a Professional Setting.
- Choosing Between Personal Beliefs and Religious Expectations.
- A Conflict Between Personal Ambition and the Impact on Others.
- An Ethical Dilemma Involving the Use of Performance-Enhancing Drugs in Sports.
- Deciding Whether to Confront or Disengage from a Toxic Friendship or Relationship.
- A Personal Ethical Dilemma Related to the Treatment of Coworkers in a Leadership Position.
- “Leadership Styles of Nurse Managers in Ethical Dilemmas” by Zydziunaite This paper is a critique of the article, “Leadership styles of nurse managers in ethical dilemmas: Reasons and consequences,” whose authors are Zydziunaite and Suominen.
- Eggs and Salmonella as Ethical Dilemma in Community Eggs and the threat to get sick because of salmonella bacteria should make people think about the outcomes of their decisions and the possibilities to overcome negative results.
- Colorado Alternative Products and the Ethical Dilemma Working capital management is an essential contributor to the company’s growth and profitability, and resolving an ethical dilemma needs a careful assessment of both alternatives.
- Death With Dignity: Ethical Dilemma Brittany Maynard had an aggressive form of brain cancer, and to preserve her control over her life, she decided to move to the state that authorized the Death with Dignity Act.
- Ethical Dilemma: Regained Custody Through Legal Action The dilemma discussed in the present paper deals with a married couple addicted to drugs in the past and rehabilitated later.
- Nazi March Permission: The Ethical Dilemma The decision to deny the Nazis permission was informed by three key arguments. The Nazis do not deserve the permit to march in a particular neighborhood.
- Harry Truman’s Ethical Dilemma in Dropping the Second Atom Bomb on Japan The aim of Truman dropping the second bomb on Japan was to show them the need to surrender from fighting because if they did not stop they will face more deaths and suffering.
- Sale of Human Organs in the U.S: Ethical and Legal Dilemmas This essay examines the pros and cons of the issue of sale of human organs in the US through the legal, ethical, moral prisms and its interaction with individual freedoms to finally affirm the case for the motion.
- Ethical Dilemma: Handling a Request for No Further Cancer Treatment Modern technologies can prolong a person’s life and interrupt it, and this is a person’s choice of which decision to make.
- Ethical Dilemma: How to Make a Right Decision in Nursing? The ability to make the right decisions is a crucial component of the work of specialists in different conditions, including caring for distinctive categories of the population.
- Oncology and Ethical Dilemma Treatment of malignant tumors carried out most often with the use of physically and mentally traumatic means puts different ethical tasks before the doctor.
- Circumcision: Ethical Dilemma and Human Rights Circumcision is a complex phenomenon that can result in ethical dilemmas. To put it simply, circumcision consists of surgical operations on female and male genitals.
- Ethical Dilemma in Facing Death Situations The purpose of this essay is to answer the question: what is ethical in the situation where numerous people are facing death?
- Daily Ethical Dilemmas in Nursing Practice At some points in their careers, nurses may face serious ethical dilemmas in which there is a threat to them of losing their jobs or harming their patients.
- Ethical Dilemma Resolving: Dividing Ownership Shares Ethical issues are a common challenge related to entrepreneurial practice. This paper will address one of these problems – dividing ownership shares.
- Build & Imagine Company’s Ethical Dilemmas Apart from the need to maximize their profits, businesses face the need to be ethical. Build & Imagine, a toy-producing company, came across an ethical dilemma regarding their targeting.
- BP Company: Environmental-Based Ethical Dilemma In the last five years, the infamous deepwater horizon oil spill has generated heated debate across the globe on the sustainability of oil mining activities of the BP Company and other competitors.
- Nursing Challenges: Inexperience and Ethical Dilemmas To be a professional nurse means to face numerous challenges that arise from the nature of the given occupation.
- Ethical Dilemmas and Religious Beliefs in Healthcare For a patient, a blood transfusion is prescribed as emergent treatment. His parents do not accept the suggested treatment. So the ethical dilemma appears.
- Employee Conflicts Resolution and Ethical Dilemmas Any workplace is an environment in which many people have to interact with each other; as a result, there is a possibility of conflicts between employees.
- Medical Intervention: Ethical, Legal, and Moral Dilemmas The main ethical task of a nurse who knows about the patient’s plans to commit suicide is to prevent the realization of the client’s intentions.
- Ethical, Legal, and Moral Dilemmas in Nursing The nurse may be faced with challenge of deciding whether to respect the autonomy of patient or report to relevant authorities about the intention of patient to end own life.
- Ethical, Legal, Moral Dilemmas of Terminal Illness The moral behavior of nurses has often been described as grounded in commitment to, and receptivity for, the experience of patients, and directed towards alleviating suffering.
- Applying Ethical Frameworks: Solution of the Ethical Dilemma and Its Justification This paper attempt to provide a solution to the case study involving a work-based ethical dilemma and the justifications involved in coming up with the proposed solution.
- What Are the Sources of the Factors Which Created the Ethical Dilemma?
- How Do You Handle an Ethical Dilemma?
- What Is the Most Common Ethical Dilemma?
- How Do Ethical Dilemmas Arise and How Can They Be Solved?
- Why Is an Ethical Dilemma a Challenge in Decision-Making?
- What Causes an Ethical Dilemma in Conducting Business?
- Why Is It Important to Respond to Ethical Dilemmas?
- Is Cloning Animals Ethical Debate?
- How Do Ethical Dilemmas Arise in Healthcare?
- What Is the Impact of Ethical Dilemma?
- How to Handle Ethical Dilemmas in the Workplace?
- What Are the Characteristics of an Ethical Dilemma?
- Are There Approaches to Solving Ethical Dilemmas?
- What Are Different Types of Ethical Dilemmas That Could Occur in the Workplace?
- Is Time Management an Ethical Dilemma?
- What Are the Main Steps for Solving an Ethical Dilemma?
- How Are Ethical Debates Structured?
- What Is an Environmental Ethical Dilemma?
- Are There Ethical Debates of Cloning Today?
- What Are Some Key Ethical Dilemmas Facing Healthcare Leaders in Today’s Environment?
- How Has the Ethical Debate About Assisted Suicide Changed Over Time?
- What Are the Situations in Which an Accountant Might Face a Moral or Ethical Dilemma?
- How Does Same-Sex Marriage Ethical Debate Affect Society?
- Why Is Ethical Debate Important for Society?
- Has Ethical Debate on Face Transplantation Evolved Over Time?
Cite this post
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2022, January 16). 203 Ethical Dilemma Topics & Moral Issues. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/ethical-dilemma-essay-topics/
"203 Ethical Dilemma Topics & Moral Issues." StudyCorgi , 16 Jan. 2022, studycorgi.com/ideas/ethical-dilemma-essay-topics/.
StudyCorgi . (2022) '203 Ethical Dilemma Topics & Moral Issues'. 16 January.
1. StudyCorgi . "203 Ethical Dilemma Topics & Moral Issues." January 16, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/ethical-dilemma-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "203 Ethical Dilemma Topics & Moral Issues." January 16, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/ethical-dilemma-essay-topics/.
StudyCorgi . 2022. "203 Ethical Dilemma Topics & Moral Issues." January 16, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/ethical-dilemma-essay-topics/.
These essay examples and topics on Ethical Dilemma were carefully selected by the StudyCorgi editorial team. They meet our highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, and fact accuracy. Please ensure you properly reference the materials if you’re using them to write your assignment.
This essay topic collection was updated on January 22, 2024 .
12 Interesting Ethical Topics for Essay Papers
- Writing Essays
- Writing Research Papers
- English Grammar
- M.Ed., Education Administration, University of Georgia
- B.A., History, Armstrong State University
Writing a persuasive essay requires identifying interesting ethical topics, and these options might inspire you to create a powerful and engaging essay, position paper , or speech for your next assignment.
Should Teens Have Plastic Surgery?
Good looks are highly prized in society. You can see advertisements everywhere urging you to buy products that will supposedly enhance your appearance. While many products are topical, plastic surgery is probably the ultimate game-changer. Going under the knife to enhance your looks can be a quick fix and help you achieve the look you desire. It also carries risks and can have lifelong consequences. Consider whether you think teens—who are still developing into mature individuals—should have the right to make such a big decision at such a young age, or if their parents should be able to decide for them.
Would You Tell If You Saw a Popular Kid Bullying?
Bullying is a big problem in schools and even in society in general. But it can be difficult to show courage, step up—and step in—if you see a popular kid bullying someone at school. Would you report it if you saw this happening? Why or why not?
Would You Speak Up If Your Friend Abused an Animal?
Animal abuse by youngsters can foreshadow more violent acts as these individuals grow up. Speaking up might save the animal pain and suffering today, and it might steer that person away from more violent acts in the future. But would you have the courage to do so? Why or why not?
Would You Tell If You Saw a Friend Cheating on a Test?
Courage can come in subtle forms, and that can include reporting seeing someone cheat on a test. Cheating on a test might not seem like such a big deal; perhaps you've cheated on a test yourself. But it is against the policies of schools and universities worldwide. If you saw someone cheating, would you speak up and tell the teacher? What if it were your buddy cheating and telling might cost you a friendship? Explain your stance.
Should News Stories Slant Toward What People Want to Hear?
There is much debate over whether the news should be unbiased or allow commentary. Newspapers, radios, and news television stations are businesses, just as much as a grocery store or online retailers. They need customers to survive, and that means appealing to what their customers want to hear or see. Slanting reports toward popular opinions could increase ratings and readership, in turn saving newspapers and news shows, as well as jobs. But is this practice ethical? What do you think?
Would You Tell If Your Best Friend Had a Drink at the Prom?
Most schools have strict rules about drinking at the prom, but many students still engage in the practice. After all, they'll be graduating soon. If you saw a friend imbibing, would you tell or look the other way? Why?
Should Football Coaches Be Paid More Than Professors?
Football often brings in more money than any other single activity or program a school offers, including academic classes. In the corporate world, if a business is profitable, the CEO and those who contributed to the success are often rewarded handsomely. With that in mind, shouldn't it be the same in academia? Should top football coaches get paid more than top professors? Why or why not?
Should Politics and Church Be Separate?
Candidates often invoke religion when they're campaigning. It's generally a good way to attract votes. But should the practice be discouraged? The U.S. Constitution, after all, dictates that there should be a separation of church and state in this country. What do you think and why?
Would You Speak Up If You Heard an Ugly Ethnic Statement at a Party Filled With Popular Kids?
As in the previous examples, it can be hard to speak up, especially when an incident involves popular kids. Would you have the courage to say something and risk the ire of the "in" crowd? Who would you tell?
Should Assisted Suicides Be Allowed for Terminally Ill Patients?
Some countries, like the Netherlands, allow assisted suicides , as do some U.S. states. Should "mercy killing" be legal for terminally ill patients who are suffering from great physical pain? What about patients whose diseases will negatively impact their families? Why or why not?
Should a Student's Ethnicity Be a Consideration for College Acceptance?
There has been a long-standing debate about the role ethnicity should play in college acceptance. Proponents of affirmative action argue that underrepresented groups should be given a leg up. Opponents say that all college candidates should be judged on their merits alone. What do you think and why?
Should Companies Gather Information About Their Customers?
Information privacy is a big and growing issue. Every time you log onto the internet and visit an online retailer, news company, or social media site, companies gather information about you. Should they have the right to do so, or should the practice be banned? Why do you think so? Explain your answer.
- How to Ask and Answer Basic English Questions
- 100 Persuasive Speech Topics for Students
- 50 Argumentative Essay Topics
- 100 Persuasive Essay Topics
- 49 Opinion Writing Prompts for Students
- Fun March Writing Prompts for Journaling
- Engaging Writing Prompts for 3rd Graders
- 24 Journal Prompts for Creative Writing in the Elementary Classroom
- 9 Common Medical School Interview Questions and How to Answer Them
- Second Grade Writing Prompts
- May Writing Prompts
- Writing Prompts for 7th Grade
- January Writing Prompts
- October Writing Prompts
- April Writing Prompts
- 25 Essay Topics for American Government Classes
- Essay Guides
- Other Essays
- How to Write an Ethics Paper: Guide & Ethical Essay Examples
- Speech Topics
- Basics of Essay Writing
- Essay Topics
- Main Academic Essays
- Research Paper Topics
- Basics of Research Paper Writing
- Miscellaneous
- Chicago/ Turabian
- Data & Statistics
- Methodology
- Admission Writing Tips
- Admission Advice
- Other Guides
- Student Life
- Studying Tips
- Understanding Plagiarism
- Academic Writing Tips
- Basics of Dissertation & Thesis Writing
- Research Paper Guides
- Formatting Guides
- Basics of Research Process
- Admission Guides
- Dissertation & Thesis Guides
How to Write an Ethics Paper: Guide & Ethical Essay Examples

Table of contents
Use our free Readability checker
An ethics essay is a type of academic writing that explores ethical issues and dilemmas. Students should evaluates them in terms of moral principles and values. The purpose of an ethics essay is to examine the moral implications of a particular issue, and provide a reasoned argument in support of an ethical perspective.
Writing an essay about ethics is a tough task for most students. The process involves creating an outline to guide your arguments about a topic and planning your ideas to convince the reader of your feelings about a difficult issue. If you still need assistance putting together your thoughts in composing a good paper, you have come to the right place. We have provided a series of steps and tips to show how you can achieve success in writing. This guide will tell you how to write an ethics paper using ethical essay examples to understand every step it takes to be proficient. In case you don’t have time for writing, get in touch with our professional essay writers for hire . Our experts work hard to supply students with excellent essays.
What Is an Ethics Essay?
An ethics essay uses moral theories to build arguments on an issue. You describe a controversial problem and examine it to determine how it affects individuals or society. Ethics papers analyze arguments on both sides of a possible dilemma, focusing on right and wrong. The analysis gained can be used to solve real-life cases. Before embarking on writing an ethical essay, keep in mind that most individuals follow moral principles. From a social context perspective, these rules define how a human behaves or acts towards another. Therefore, your theme essay on ethics needs to demonstrate how a person feels about these moral principles. More specifically, your task is to show how significant that issue is and discuss if you value or discredit it.
Purpose of an Essay on Ethics
The primary purpose of an ethics essay is to initiate an argument on a moral issue using reasoning and critical evidence. Instead of providing general information about a problem, you present solid arguments about how you view the moral concern and how it affects you or society. When writing an ethical paper, you demonstrate philosophical competence, using appropriate moral perspectives and principles.
Things to Write an Essay About Ethics On
Before you start to write ethics essays, consider a topic you can easily address. In most cases, an ethical issues essay analyzes right and wrong. This includes discussing ethics and morals and how they contribute to the right behaviors. You can also talk about work ethic, code of conduct, and how employees promote or disregard the need for change. However, you can explore other areas by asking yourself what ethics mean to you. Think about how a recent game you watched with friends started a controversial argument. Or maybe a newspaper that highlighted a story you felt was misunderstood or blown out of proportion. This way, you can come up with an excellent topic that resonates with your personal ethics and beliefs.
Ethics Paper Outline
Sometimes, you will be asked to submit an outline before writing an ethics paper. Creating an outline for an ethics paper is an essential step in creating a good essay. You can use it to arrange your points and supporting evidence before writing. It also helps organize your thoughts, enabling you to fill any gaps in your ideas. The outline for an essay should contain short and numbered sentences to cover the format and outline. Each section is structured to enable you to plan your work and include all sources in writing an ethics paper. An ethics essay outline is as follows:
- Background information
- Thesis statement
- Restate thesis statement
- Summarize key points
- Final thoughts on the topic
Using this outline will improve clarity and focus throughout your writing process.
Ethical Essay Structure
Ethics essays are similar to other essays based on their format, outline, and structure. An ethical essay should have a well-defined introduction, body, and conclusion section as its structure. When planning your ideas, make sure that the introduction and conclusion are around 20 percent of the paper, leaving the rest to the body. We will take a detailed look at what each part entails and give examples that are going to help you understand them better. Refer to our essay structure examples to find a fitting way of organizing your writing.
Ethics Paper Introduction
An ethics essay introduction gives a synopsis of your main argument. One step on how to write an introduction for an ethics paper is telling about the topic and describing its background information. This paragraph should be brief and straight to the point. It informs readers what your position is on that issue. Start with an essay hook to generate interest from your audience. It can be a question you will address or a misunderstanding that leads up to your main argument. You can also add more perspectives to be discussed; this will inform readers on what to expect in the paper.
Ethics Essay Introduction Example
You can find many ethics essay introduction examples on the internet. In this guide, we have written an excellent extract to demonstrate how it should be structured. As you read, examine how it begins with a hook and then provides background information on an issue.
Imagine living in a world where people only lie, and honesty is becoming a scarce commodity. Indeed, modern society is facing this reality as truth and deception can no longer be separated. Technology has facilitated a quick transmission of voluminous information, whereas it's hard separating facts from opinions.
In this example, the first sentence of the introduction makes a claim or uses a question to hook the reader.
Ethics Essay Thesis Statement
An ethics paper must contain a thesis statement in the first paragraph. Learning how to write a thesis statement for an ethics paper is necessary as readers often look at it to gauge whether the essay is worth their time.
When you deviate away from the thesis, your whole paper loses meaning. In ethics essays, your thesis statement is a roadmap in writing, stressing your position on the problem and giving reasons for taking that stance. It should focus on a specific element of the issue being discussed. When writing a thesis statement, ensure that you can easily make arguments for or against its stance.
Ethical Paper Thesis Example
Look at this example of an ethics paper thesis statement and examine how well it has been written to state a position and provide reasons for doing so:
The moral implications of dishonesty are far-reaching as they undermine trust, integrity, and other foundations of society, damaging personal and professional relationships.
The above thesis statement example is clear and concise, indicating that this paper will highlight the effects of dishonesty in society. Moreover, it focuses on aspects of personal and professional relationships.
Ethics Essay Body
The body section is the heart of an ethics paper as it presents the author's main points. In an ethical essay, each body paragraph has several elements that should explain your main idea. These include:
- A topic sentence that is precise and reiterates your stance on the issue.
- Evidence supporting it.
- Examples that illustrate your argument.
- A thorough analysis showing how the evidence and examples relate to that issue.
- A transition sentence that connects one paragraph to another with the help of essay transitions .
When you write an ethics essay, adding relevant examples strengthens your main point and makes it easy for others to understand and comprehend your argument.
Body Paragraph for Ethics Paper Example
A good body paragraph must have a well-defined topic sentence that makes a claim and includes evidence and examples to support it. Look at part of an example of ethics essay body paragraph below and see how its idea has been developed:
Honesty is an essential component of professional integrity. In many fields, trust and credibility are crucial for professionals to build relationships and success. For example, a doctor who is dishonest about a potential side effect of a medication is not only acting unethically but also putting the health and well-being of their patients at risk. Similarly, a dishonest businessman could achieve short-term benefits but will lose their client’s trust.
Ethics Essay Conclusion
A concluding paragraph shares the summary and overview of the author's main arguments. Many students need clarification on what should be included in the essay conclusion and how best to get a reader's attention. When writing an ethics paper conclusion, consider the following:
- Restate the thesis statement to emphasize your position.
- Summarize its main points and evidence.
- Final thoughts on the issue and any other considerations.
You can also reflect on the topic or acknowledge any possible challenges or questions that have not been answered. A closing statement should present a call to action on the problem based on your position.
Sample Ethics Paper Conclusion
The conclusion paragraph restates the thesis statement and summarizes the arguments presented in that paper. The sample conclusion for an ethical essay example below demonstrates how you should write a concluding statement.
In conclusion, the implications of dishonesty and the importance of honesty in our lives cannot be overstated. Honesty builds solid relationships, effective communication, and better decision-making. This essay has explored how dishonesty impacts people and that we should value honesty. We hope this essay will help readers assess their behavior and work towards being more honest in their lives.
In the above extract, the writer gives final thoughts on the topic, urging readers to adopt honest behavior.
How to Write an Ethics Paper?
As you learn how to write an ethics essay, it is not advised to immediately choose a topic and begin writing. When you follow this method, you will get stuck or fail to present concrete ideas. A good writer understands the importance of planning. As a fact, you should organize your work and ensure it captures key elements that shed more light on your arguments. Hence, following the essay structure and creating an outline to guide your writing process is the best approach. In the following segment, we have highlighted step-by-step techniques on how to write a good ethics paper.
1. Pick a Topic
Before writing ethical papers, brainstorm to find ideal topics that can be easily debated. For starters, make a list, then select a title that presents a moral issue that may be explained and addressed from opposing sides. Make sure you choose one that interests you. Here are a few ideas to help you search for topics:
- Review current trends affecting people.
- Think about your personal experiences.
- Study different moral theories and principles.
- Examine classical moral dilemmas.
Once you find a suitable topic and are ready, start to write your ethics essay, conduct preliminary research, and ascertain that there are enough sources to support it.
2. Conduct In-Depth Research
Once you choose a topic for your essay, the next step is gathering sufficient information about it. Conducting in-depth research entails looking through scholarly journals to find credible material. Ensure you note down all sources you found helpful to assist you on how to write your ethics paper. Use the following steps to help you conduct your research:
- Clearly state and define a problem you want to discuss.
- This will guide your research process.
- Develop keywords that match the topic.
- Begin searching from a wide perspective. This will allow you to collect more information, then narrow it down by using the identified words above.
3. Develop an Ethics Essay Outline
An outline will ease up your writing process when developing an ethic essay. As you develop a paper on ethics, jot down factual ideas that will build your paragraphs for each section. Include the following steps in your process:
- Review the topic and information gathered to write a thesis statement.
- Identify the main arguments you want to discuss and include their evidence.
- Group them into sections, each presenting a new idea that supports the thesis.
- Write an outline.
- Review and refine it.
Examples can also be included to support your main arguments. The structure should be sequential, coherent, and with a good flow from beginning to end. When you follow all steps, you can create an engaging and organized outline that will help you write a good essay.
4. Write an Ethics Essay
Once you have selected a topic, conducted research, and outlined your main points, you can begin writing an essay . Ensure you adhere to the ethics paper format you have chosen. Start an ethics paper with an overview of your topic to capture the readers' attention. Build upon your paper by avoiding ambiguous arguments and using the outline to help you write your essay on ethics. Finish the introduction paragraph with a thesis statement that explains your main position. Expand on your thesis statement in all essay paragraphs. Each paragraph should start with a topic sentence and provide evidence plus an example to solidify your argument, strengthen the main point, and let readers see the reasoning behind your stance. Finally, conclude the essay by restating your thesis statement and summarizing all key ideas. Your conclusion should engage the reader, posing questions or urging them to reflect on the issue and how it will impact them.
5. Proofread Your Ethics Essay
Proofreading your essay is the last step as you countercheck any grammatical or structural errors in your essay. When writing your ethic paper, typical mistakes you could encounter include the following:
- Spelling errors: e.g., there, they’re, their.
- Homophone words: such as new vs. knew.
- Inconsistencies: like mixing British and American words, e.g., color vs. color.
- Formatting issues: e.g., double spacing, different font types.
While proofreading your ethical issue essay, read it aloud to detect lexical errors or ambiguous phrases that distort its meaning. Verify your information and ensure it is relevant and up-to-date. You can ask your fellow student to read the essay and give feedback on its structure and quality.
Ethics Essay Examples
Writing an essay is challenging without the right steps. There are so many ethics paper examples on the internet, however, we have provided a list of free ethics essay examples below that are well-structured and have a solid argument to help you write your paper. Click on them and see how each writing step has been integrated. Ethics essay example 1
Ethics essay example 2
Ethics essay example 3
Ethics essay example 4
College ethics essay example 5
Ethics Essay Writing Tips
When writing papers on ethics, here are several tips to help you complete an excellent essay:
- Choose a narrow topic and avoid broad subjects, as it is easy to cover the topic in detail.
- Ensure you have background information. A good understanding of a topic can make it easy to apply all necessary moral theories and principles in writing your paper.
- State your position clearly. It is important to be sure about your stance as it will allow you to draft your arguments accordingly.
- When writing ethics essays, be mindful of your audience. Provide arguments that they can understand.
- Integrate solid examples into your essay. Morality can be hard to understand; therefore, using them will help a reader grasp these concepts.
Bottom Line on Writing an Ethics Paper
Creating this essay is a common exercise in academics that allows students to build critical skills. When you begin writing, state your stance on an issue and provide arguments to support your position. This guide gives information on how to write an ethics essay as well as examples of ethics papers. Remember to follow these points in your writing:
- Create an outline highlighting your main points.
- Write an effective introduction and provide background information on an issue.
- Include a thesis statement.
- Develop concrete arguments and their counterarguments, and use examples.
- Sum up all your key points in your conclusion and restate your thesis statement.
Contact our academic writing platform and have your challenge solved. Here, you can order essays and papers on any topic and enjoy top quality.

Daniel Howard is an Essay Writing guru. He helps students create essays that will strike a chord with the readers.
You may also like


Moral Dilemmas
Moral dilemmas, at the very least, involve conflicts between moral requirements. Consider the cases given below.
1. Examples
2. the concept of moral dilemmas, 3. problems, 4. dilemmas and consistency, 5. responses to the arguments, 6. moral residue and dilemmas, 7. types of moral dilemmas, 8. conclusion, cited works, other worthwhile readings, other internet resources, related entries.
In Book I of Plato's Republic , Cephalus defines ‘justice’ as speaking the truth and paying one's debts. Socrates quickly refutes this account by suggesting that it would be wrong to repay certain debts — for example, to return a borrowed weapon to a friend who is not in his right mind. Socrates' point is not that repaying debts is without moral import; rather, he wants to show that it is not always right to repay one's debts, at least not exactly when the one to whom the debt is owed demands repayment. What we have here is a conflict between two moral norms: repaying one's debts and protecting others from harm. And in this case, Socrates maintains that protecting others from harm is the norm that takes priority.
Nearly twenty-four centuries later, Jean-Paul Sartre described a moral conflict the resolution of which was, to many, less obvious than the resolution to the Platonic conflict. Sartre [1957] tells of a student whose brother had been killed in the German offensive of 1940. The student wanted to avenge his brother and to fight forces that he regarded as evil. But the student's mother was living with him, and he was her one consolation in life. The student believed that he had conflicting obligations. Sartre describes him as being torn between two kinds of morality: one of limited scope but certain efficacy, personal devotion to his mother; the other of much wider scope but uncertain efficacy, attempting to contribute to the defeat of an unjust aggressor.
While the examples from Plato and Sartre are the ones most commonly cited, it should be clear that there are many others. If a person makes conflicting promises, she faces a moral conflict. Physicians and families who believe that human life should not be deliberately shortened and that unpreventable pain should not be tolerated face a conflict in deciding whether to withdraw life support from a dying patient.
What is common to the two well-known cases is conflict. In each case, an agent regards herself as having moral reasons to do each of two actions, but doing both actions is not possible. Ethicists have called situations like these moral dilemmas . The crucial features of a moral dilemma are these: the agent is required to do each of two (or more) actions; the agent can do each of the actions; but the agent cannot do both (or all) of the actions. The agent thus seems condemned to moral failure; no matter what she does, she will do something wrong (or fail to do something that she ought to do).
The Platonic case strikes many as too easy to be characterized as a genuine moral dilemma. For the agent's solution in that case is clear; it is more important to protect people from harm than to return a borrowed weapon. And in any case, the borrowed item can be returned later, when the owner no longer poses a threat to others. Thus in this case we can say that the requirement to protect others from serious harm overrides the requirement to repay one's debts by returning a borrowed item when its owner so demands. When one of the conflicting requirements overrides the other, we do not have a genuine moral dilemma. So in addition to the features mentioned above, in order to have a genuine moral dilemma it must also be true that neither of the conflicting requirements is overridden [Sinnott-Armstrong (1988), Chapter 1].
It is less obvious in Sartre's case that one of the requirements overrides the other. Why this is so, however, may not be so obvious. Some will say that our uncertainty about what to do in this case is simply the result of uncertainty about the consequences. If we were certain that the student could make a difference in defeating the Germans, the obligation to join the military would prevail. But if the student made little difference whatsoever in that cause, then his obligation to tend to his mother's needs would take precedence, since there he is virtually certain to be helpful. Others, though, will say that these obligations are equally weighty, and that uncertainty about the consequences is not at issue here.
Ethicists as diverse as Kant [1971/1797], Mill [1979/1861], and Ross [1930 and 1939] have assumed that an adequate moral theory should not allow for the possibility of genuine moral dilemmas. Only recently — in the last fifty years or so — have philosophers begun to challenge that assumption. And the challenge can take at least two different forms. Some will argue that it is not possible to preclude genuine moral dilemmas. Others will argue that even if it were possible, it is not desirable to do so.
To illustrate some of the debate that occurs regarding whether it is possible for any theory to eliminate genuine moral dilemmas, consider the following. The conflicts in Plato's case and in Sartre's case arose because there is more than one moral precept (using ‘precept’ to designate rules and principles), more than one precept sometimes applies to the same situation, and in some of these cases the precepts demand conflicting actions. One obvious solution here would be to arrange the precepts, however many there might be, hierarchically. By this scheme, the highest ordered precept always prevails, the second prevails unless it conflicts with the first, and so on. There are at least two glaring problems with this obvious solution, however. First, it just does not seem credible to hold that moral rules and principles should be hierarchically ordered. While the requirements to keep one's promises and to prevent harm to others clearly can conflict, it is far from clear that one of these requirements should always prevail over the other. In the Platonic case, the obligation to prevent harm is clearly stronger. But there can easily be cases where the harm that can be prevented is relatively mild and the promise that is to be kept is very important. And most other pairs of precepts are like this. This was a point made by Ross in The Right and the Good [1930, Chapter 2].
The second problem with this easy solution is deeper. Even if it were plausible to arrange moral precepts hierarchically, situations can arise in which the same precept gives rise to conflicting obligations. Perhaps the most widely discussed case of this sort is taken from William Styron's Sophie's Choice [1980] [Greenspan (1983)]. Sophie and her two children are at a Nazi concentration camp. A guard confronts Sophie and tells her that one of her children will be allowed to live and one will be killed. But it is Sophie who must decide which child will be killed. Sophie can prevent the death of either of her children, but only by condemning the other to be killed. The guard makes the situation even more excruciating by informing Sophie that if she chooses neither, then both will be killed. With this added factor, Sophie has a morally compelling reason to choose one of her children. But for each child, Sophie has an apparently equally strong reason to save him or her. Thus the same moral precept gives rise to conflicting obligations. Some have called such cases symmetrical [Sinnott-Armstrong (1988), Chapter 2].
We shall return to the issue of whether it is possible to preclude genuine moral dilemmas. But what about the desirability of doing so? Why have ethicists thought that their theories should preclude the possibility of dilemmas? At the intuitive level, the existence of moral dilemmas suggests some sort of inconsistency. An agent caught in a genuine dilemma is required to do each of two acts but cannot do both. And since he cannot do both, not doing one is a condition of doing the other. Thus, it seems that the same act is both required and forbidden. But exposing a logical inconsistency takes some work; for initial inspection reveals that the inconsistency intuitively felt is not present. Allowing OA to designate that the agent in question ought to do A (or is morally obligated to do A , or is morally required to do A ), that OA and OB are both true is not itself inconsistent, even if one adds that it is not possible for the agent to do both A and B . And even if the situation is appropriately described as OA and O ¬ A , that is not a contradiction; the contradictory of OA is ¬ OA . [See Marcus (1980).]
Similarly rules that generate moral dilemmas are not inconsistent, at least on the usual understanding of that term. Ruth Marcus suggests plausibly that we “define a set of rules as consistent if there is some possible world in which they are all obeyable in all circumstances in that world.” Thus, “rules are consistent if there are possible circumstances in which no conflict will emerge,” and “a set of rules is inconsistent if there are no circumstances, no possible world, in which all the rules are satisfiable” [Marcus (1980), p. 128 and p. 129]. I suspect that Kant, Mill, and Ross were aware that a dilemma-generating theory need not be inconsistent. Even so, they would be disturbed if their own theories allowed for such predicaments. If I am correct in this speculation, it suggests that Kant, Mill, Ross, and others thought that there is an important theoretical feature that dilemma-generating theories lack. And this is understandable. It is certainly no comfort to an agent facing a reputed moral dilemma to be told that at least the rules which generate this predicament are consistent. For a good practical example, consider the situation of the criminal defense attorney. She is said to have an obligation to hold in confidence the disclosures made by a client and to be required to conduct herself with candor before the court (where the latter requires that the attorney inform the court when her client commits perjury) [Freedman (1975), Chapter 3]. It is clear that in this world these two obligations often conflict. It is equally clear that in some possible world — for example, one in which clients do not commit perjury — that both obligations can be satisfied. Knowing this is of no assistance to defense attorneys who face a conflict between these two requirements in this world.
Ethicists who are concerned that their theories not allow for moral dilemmas have more than consistency in mind, I think. What is troubling is that theories that allow for dilemmas fail to be uniquely action-guiding . A theory can fail to be uniquely action-guiding in either of two ways: by not recommending any action in a situation that is moral or by recommending incompatible actions. Theories that generate genuine moral dilemmas fail to be uniquely action-guiding in the latter way. Since at least one of the main points of moral theories is to provide agents with guidance, that suggests that it is desirable for theories to eliminate dilemmas, at least if doing so is possible.
But failing to be uniquely action-guiding is not the only reason that the existence of moral dilemmas is thought to be troublesome. Just as important, the existence of dilemmas does lead to inconsistencies if one endorses certain widely held theses. Here we shall consider two different arguments, each of which shows that one cannot consistently acknowledge the reality of moral dilemmas while holding selected principles.
The first argument shows that two standard principles of deontic logic are, when conjoined, incompatible with the existence of moral dilemmas. The first of these is the principle of deontic consistency
Principle of Deontic Consistency ( PC ): OA → ¬ O ¬ A .
Intuitively this principle just says that the same action cannot be both obligatory and forbidden. Note that as initially described, the existence of dilemmas does not conflict with PC. For as described, dilemmas involve a situation in which an agent ought to do A , ought to do B , but cannot do both A and B . But if we add a principle of deontic logic, then we obtain a conflict with PC:
Principle of Deontic Logic ( PD ): □ ( A → B ) → ( OA → OB ).
Intuitively, PD just says that if doing A brings about B , and if A is obligatory (morally required), then B is obligatory (morally required). The first argument that generates inconsistency can now be stated. Premises (1), (2), and (3) represent the claim that moral dilemmas exist.
Line (10) directly conflicts with PC. And from PC and (1), we can conclude
(11) ¬ O ¬ A
And, of course, (9) and (11) are contradictory. So if we assume PC and PD, then the existence of dilemmas generates an inconsistency of the old-fashioned logical sort. [Note: In standard deontic logic, the ‘□’ in PD typically designates logical necessity. Here I take it to indicate physical necessity so that the appropriate connection with premise (3) can be made. And I take it that logical necessity is stronger than physical necessity.]
Two other principles accepted in most systems of deontic logic entail PC. So if PD holds, then one of these additional two principles must be jettisoned too. The first says that if an action is obligatory, it is also permissible. The second says that an action is permissible if and only if it is not forbidden. These principles may be stated as:
(OP): OA → PA ;
(D): PA ↔ ¬ O ¬ A .
The second argument that generates inconsistency, like the first, has as its first three premises a symbolic representation of a moral dilemma.
(1) OA (2) OB (3) ¬ C ( A & B )
And like the first, this second argument shows that the existence of dilemmas leads to a contradiction if we assume two other commonly accepted principles. The first of these principles is that ‘ought’ implies ‘can’. Intuitively this says that if an agent is morally required to do an action, it must be possible for the agent to do it. We may represent this as
(4) OA → CA (for all A )
The other principle, endorsed by most systems of deontic logic, says that if an agent is required to do each of two actions, she is required to do both. We may represent this as
(5) ( OA & OB ) → O ( A & B )
The argument then proceeds:
(6) O ( A & B ) → C ( A & B ) (an instance of 4) (7) OA & OB (from 1 and 2) (8) O ( A & B ) (from 5 and 7) (9) ¬ O ( A & B ) (from 3 and 6)
So if one assumes that ‘ought’ implies ‘can’ and if one assumes the principle represented in (5) — dubbed by some the agglomeration principle [Williams (1965)] — then again a contradiction can be derived.
Now obviously the inconsistency in the first argument can be avoided if one denies either PC or PD. And the inconsistency in the second argument can be averted if one gives up either the principle that ‘ought’ implies ‘can’ or the agglomeration principle. There is, of course, another way to avoid these inconsistencies: deny the possibility of genuine moral dilemmas. It is fair to say that much of the debate concerning moral dilemmas in the last fifty years has been about how to avoid the inconsistencies generated by the two arguments above.
Opponents of moral dilemmas have generally held that the crucial principles in the two arguments above are conceptually true, and therefore we must deny the possibility of genuine dilemmas. [See, for example, Conee (1982) and Zimmerman (1996).] Most of the debate, from all sides, has focused on the second argument. There is an oddity about this, however. When one examines the pertinent principles in each argument which, in combination with dilemmas, generates an inconsistency, there is little doubt that those in the first argument have a greater claim to being conceptually true than those in the second. Perhaps the focus on the second argument is due to the impact of Bernard Williams's influential essay [Williams (1965)]. But notice that the first argument shows that if there are genuine dilemmas, then either PC or PD must be relinquished. Even most supporters of dilemmas acknowledge that PC is quite basic. E.J. Lemmon, for example, notes that if PC does not hold in a system of deontic logic, then all that remains are truisms and paradoxes [Lemmon (1965), p. 51]. And giving up PC also requires denying either OP or D, each of which also seems basic. There has been much debate about PD — in particular, questions generated by the Good Samaritan paradox — but still it seems basic. So those who want to argue against dilemmas purely on conceptual grounds are better off focusing on the first of the two arguments above.
Some opponents of dilemmas also hold that the pertinent principles in the second argument — the principle that ‘ought’ implies ‘can’ and the agglomeration principle — are conceptually true. But foes of dilemmas need not say this. Even if they believe that a conceptual argument against dilemmas can be made by appealing to PC and PD, they have several options regarding the second argument. They may defend ‘ought’ implies ‘can’, but hold that it is a substantive normative principle, not a conceptual truth. Or they may even deny the truth of ‘ought’ implies ‘can’ or the agglomeration principle, though not because of moral dilemmas, of course.
Defenders of dilemmas need not deny all of the pertinent principles, of course. If one thinks that each of the principles at least has some initial plausibility, then one will be inclined to retain as many as possible. Among the earlier contributors to this debate, some took the existence of dilemmas as a counterexample to ‘ought’ implies ‘can’ [for example, Lemmon (1962) and Trigg (1971)]; others, as a refutation of the agglomeration principle [for example, Williams (1965) and van Fraassen (1973)]. The most common response to the first argument was to deny PD.
Friends and foes of dilemmas have a burden to bear in responding to the two arguments above. For there is at a prima facie plausibility to the claim that there are moral dilemmas and to the claim that the relevant principles in the two arguments are true. Thus each side must at least give reasons for denying the pertinent claims in question. Opponents of dilemmas must say something in response to the positive arguments that are given for the reality of such conflicts. One reason in support of dilemmas, as noted above, is simply pointing to examples. The case of Sartre's student and that from Sophie's Choice are good ones; and clearly these can be multiplied indefinitely. It will tempting for supporters of dilemmas to say to opponents, “If this is not a real dilemma, then tell me what the agent ought to do and why ?” It is obvious, however, that attempting to answer such questions is fruitless, and for at least two reasons. First, any answer given to the question is likely to be controversial, certainly not always convincing. And second, this is a game that will never end; example after example can be produced. The more appropriate response on the part of foes of dilemmas is to deny that they need to answer the question. Examples as such cannot establish the reality of dilemmas. Surely most will acknowledge that there are situations in which an agent does not know what he ought to do. This may be because of factual uncertainty, uncertainty about the consequences, uncertainty about what principles apply, or a host of other things. So for any given case, the mere fact that one does not know which of two (or more) conflicting obligations prevails does not show that none does.
Another reason in support of dilemmas to which opponents must respond is the point about symmetry. As the cases from Plato and Sartre show, moral rules can conflict. But opponents of dilemmas can argue that in such cases one rule overrides the other. Most will grant this in the Platonic case, and opponents of dilemmas will try to extend this point to all cases. But the hardest case for opponents is the symmetrical one, where the same precept generates the conflicting requirements. The case from Sophie's Choice is of this sort. It makes no sense to say that a rule or principle overrides itself. So what do opponents of dilemmas say here? They are apt to argue that the pertinent, all-things-considered requirement in such a case is disjunctive: Sophie should act to save one or the other of her children, since that is the best that she can do [for example, Zimmerman (1996), Chapter 7]. Such a move need not be ad hoc , since in many cases it is quite natural. If an agent can afford to make a meaningful contribution to only one charity, the fact that there are several worthwhile candidates does not prompt many to say that the agent will fail morally no matter what he does. Nearly all of us think that he should give to one or the other of the worthy candidates. Similarly, if two people are drowning and an agent is situated so that she can save either of the two but only one, few say that she is doing wrong no matter which she saves. Positing a disjunctive requirement in these cases seems perfectly natural, and so such a move is available to opponents of dilemmas as a response to symmetrical cases.
Supporters of dilemmas have a burden to bear too. They need to cast doubt on the adequacy of the pertinent principles in the two arguments that generate inconsistencies. And most importantly, they need to provide independent reasons for doubting whichever of the principles they reject. If they have no reason other than cases of putative dilemmas for denying the principles in question, then we have a mere standoff. Of the principles in question, the most commonly questioned on independent grounds are the principle that ‘ought’ implies ‘can’ and PD. Among supporters of dilemmas, Walter Sinnott-Armstrong [Sinnott-Armstrong (1988), Chapters 4 and 5] has gone to the greatest lengths to provide independent reasons for questioning some of the relevant principles.
One well-known argument for the reality of moral dilemmas has not been discussed yet. This argument might be called “phenomenological.” It appeals to the emotions that agents facing conflicts experience and our assessment of those emotions.
Return to the case of Sartre's student. Suppose that he joins the Free French forces. It is likely that he will experience remorse or guilt for having abandoned his mother. And not only will he experience these emotions, this moral residue, but it is appropriate that he does. Yet, had he stayed with his mother and not joined the Free French forces, he also would have appropriately experienced remorse or guilt. But either remorse or guilt is appropriate only if the agent properly believes that he has done something wrong (or failed to do something that he was all-things-considered required to do). Since no matter what the agent does he will appropriately experience remorse or guilt, then no matter what he does he will have done something wrong. Thus, the agent faces a genuine moral dilemma. [The best known proponents of arguments for dilemmas that appeal to moral residue are Williams (1965) and Marcus (1980).]
Many cases of moral conflict are similar to this example. Certainly the case from Sophie's Choice fits here. No matter which of her children Sophie saves, she will experience enormous guilt for the consequences of that choice. Indeed, if Sophie did not experience such guilt, we would think that there was something morally wrong with her. In these cases, proponents of the argument (for dilemmas) from moral residue must claim that four things are true: (1) when the agents acts, she experiences remorse or guilt; (2) that she experiences these emotions is appropriate and called for; (3) had the agent acted on the other of the conflicting requirements, she would also have experienced remorse or guilt; and (4) in the latter case these emotions would have been equally appropriate and called for [McConnell (1996), pp. 37-38]. In these situations, then, remorse or guilt will be appropriate no matter what the agent does and these emotions are appropriate only when the agent has done something wrong. Therefore, these situations are genuinely dilemmatic.
There is much to say about the moral emotions and situations of moral conflict; the positions are varied and intricate. Without pretending to resolve all of the issues here, it will be pointed out that opponents of dilemmas have raised two different objections to the argument from moral residue. The first objection, in effect, suggests that the argument is question-begging [McConnell (1978) and Conee (1982)]; the second objection challenges the assumption that remorse and guilt are appropriate only when the agent has done wrong.
To explain the first objection, note that it is uncontroversial that some bad feeling or other is called for when an agent is in a situation like that of Sartre's student or Sophie. But the negative moral emotions are not limited to remorse and guilt. Among these other emotions, consider regret. An agent can appropriately experience regret even when she does not believe that she has done something wrong. For example, a parent may appropriately regret that she must punish her child even though she correctly believes that the punishment is deserved. Her regret is appropriate because a bad state of affairs is brought into existence (say, the child's discomfort), even when bringing this state of affairs into existence is morally required. Regret can even be appropriate when one has no causal connection at all with the bad state of affairs. It is appropriate for me to regret the damage that a recent fire has caused to my neighbor's house, the pain that severe birth defects cause in infants, and the suffering that a starving animal experiences in the wilderness. Not only is it appropriate that I experience regret in these cases, but I would probably be regarded as morally lacking if I did not.
With remorse or guilt, at least two components are present: the experiential component, namely, the negative feeling that the agent has; and the cognitive component, namely, the belief that the agent has done something wrong and takes responsibility for it. Although this same cognitive component is not part of regret, the negative feeling is. And the experiential component alone cannot serve as a gauge to distinguish regret from remorse, for regret can range from mild to intense, and so can remorse. In part, what distinguishes the two is the cognitive component. But now when we examine the case of an alleged dilemma, such as that of Sartre's student, it is question-begging to assert that it is appropriate for him to experience remorse no matter what he does. No doubt, it is appropriate for him to experience some negative feeling. To say, however, that it is remorse that is called for is to assume that the agent appropriately believes that he has done something wrong. Since regret is warranted even in the absence of such a belief, to assume that remorse is appropriate is to assume , not argue, that the agent's situation is genuinely dilemmatic. Opponents of dilemmas can say that one of the requirements overrides the other, or that the agent faces a disjunctive requirement, and that regret is appropriate because even when he does what he ought to do, some bad will ensue. Either side, then, can account for the appropriateness of some negative moral emotion. To get more specific, however, requires more than is warranted by the present argument. This appeal to moral residue, then, does not establish the reality of moral dilemmas.
Matters are even more complicated, though, as the second objection to the argument from moral residue shows. The argument assumes that remorse or guilt is appropriate only if the agent believes that he has done something wrong. But this is questionable. Consider the case of a middle-aged man, Bill, and a seven-year-old boy, Johnny. It is set in a midwestern village on a snowy December day. Johnny and several of his friends are riding their sleds down a narrow, seldom used street, one that intersects with a busier, although still not heavily traveled, street. Johnny, in his enthusiasm for sledding, is not being very careful. During his final ride he skidded under an automobile passing through the intersection and was killed instantly. The car was driven by Bill. Bill was driving safely, had the right of way, and was not exceeding the speed limit. Moreover, given the physical arrangement, it would have been impossible for Bill to have seen Johnny coming. Bill was not at fault, legally or morally, for Johnny's death. Yet Bill experienced what can only be described as remorse or guilt about his role in this horrible event.
At one level, Bill's feelings of remorse or guilt are not warranted. Bill did nothing wrong. A friend might even recommend that Bill seek therapy. But this is not all there is to say. Most of us understand Bill's response. From Bill's point of view, the response is not inappropriate, not irrational, not uncalled-for. To see this, imagine that Bill had had a very different response. Suppose that Bill had said, “I regret Johnny's death. It is a terrible thing. But it certainly was not my fault. I have nothing to feel guilty about and I don't owe his parents any apologies.” Even if Bill is correct intellectually, it is hard to imagine someone being able to achieve this sort of objectivity about his own behavior. When human beings have caused great harm, it is natural for them to wonder if they are at fault, even if to outsiders it is obvious that they bear no moral responsibility for the damage. Human beings are not so finely tuned emotionally that when they have been causally responsible for harm, they can easily turn guilt on or off depending on their degree of moral responsibility. [See Zimmerman (1988), pp. 134-135.] And this is not a bad thing; for it likely makes agents more cautious about their actions, more sensitive about their responsibilities, and more empathetic regarding the plight of others.
All of this suggests that there are situations in which an agent's remorse or guilt is not inappropriate even though the agent has done nothing wrong. Because of this and because in any given situation the appropriate response may be regret and not remorse, opponents of dilemmas have a way to respond to the argument that appeals to the appropriateness of remorse.
It should be noted, however, that there is a complex array of issues concerning the relationship between ethical conflicts and the moral emotions, and the discussion here has been quite brief. [See Greenspan (1995).]
In the literature on moral dilemmas, it is common to draw distinctions among various types of dilemmas. Only some of these distinctions will be mentioned here. It is worth noting that both supporters and opponents of dilemmas tend to draw some, if not all, of these distinctions. And in most cases the motivation for doing so is clear. Supporters of dilemmas may draw a distinction between dilemmas of type V and W . The upshot is typically a message to opponents of dilemmas: “You think that all moral conflicts are resolvable. And that is understandable, because conflicts of type V are resolvable. But conflicts of type W are not resolvable. Thus, contrary to your view, there are some genuine moral dilemmas.” By the same token, opponents of dilemmas may draw a distinction between dilemmas of type X and Y . And their message to supporters of dilemmas is this: “You think that there are genuine moral dilemmas, and given certain facts, it is understandable why this appears to be the case. But if you draw a distinction between conflicts of types X and Y , you can see that appearances can be explained by the existence of type X alone, and type X conflicts are not genuine dilemmas.” With this in mind, let us note a few of the distinctions.
One distinction is between epistemic conflicts and ontological conflicts. The former involve conflicts between two (or more) moral requirements and the agent does not know which of the conflicting requirements takes precedence in her situation. Everyone concedes that there can be situations where one requirement does take priority over the other with which it conflicts, though at the time action is called for it is difficult for the agent to tell which requirement prevails. The latter are conflicts between two (or more) moral requirements, and neither is overridden. This is not simply because the agent does not know which requirement is stronger; neither is. Genuine moral dilemmas, if there are any, are ontological. Both opponents and supporters of dilemmas acknowledge that there are epistemic conflicts.
Another distinction is between self-imposed moral dilemmas and dilemmas imposed on an agent by the world , as it were. Conflicts of the former sort arise because of the agent's own wrongdoing [Aquinas; Donagan (1977 and 1984); and McConnell (1978)]. If an agent made two promises that he knew conflicted, then through his own actions he created a situation in which it is not possible for him to discharge both of his requirements. Dilemmas imposed on the agent by the world, by contrast, do not arise because of the agent's wrongdoing. The case of Sartre's student is an example, as is the case from Sophie's Choice . For supporters of dilemmas, this distinction is not all that important. But among opponents of dilemmas, there is a disagreement about whether the distinction is important. Some of these opponents hold that self-imposed dilemmas are possible, but that their existence does not point to any deep flaws in moral theory. Moral theory tells agents how they ought to behave; but if agents violate moral norms, of course things can go askew. Other opponents deny that even self-imposed dilemmas are possible. They argue that an adequate moral theory should tell agents what they ought to do in their current circumstances, regardless of how those circumstances arose. And given the prevalence of wrongdoing, if a moral theory did not issue uniquely action-guiding “contrary-to-duty imperatives,” it would be severely lacking.
Yet another distinction is between obligation dilemmas and prohibition dilemmas . The former are situations in which more than one feasible action is obligatory. The latter involve cases in which all feasible actions are forbidden. Some [especially, Valentyne (1987 and 1989)] argue that plausible principles of deontic logic may well render obligation dilemmas impossible; but they do not preclude the possibility of prohibition dilemmas. The case of Sartre's student, if genuinely dilemmatic, is an obligation dilemma; Sophie's case is a prohibition dilemma. There is another reason that friends of dilemmas emphasize this distinction. Some think that the “disjunctive solution” used by opponents of dilemmas — when equally strong precepts conflict, the agent is required to act on one or the other — is much more plausible when applied to obligation dilemmas than when applied to prohibition dilemmas.
As moral dilemmas are typically described, they involve a single agent . The agent ought, all things considered, to do A , ought, all things considered, to do B , and she cannot do both A and B . But we can distinguish multi-person dilemmas from single agent ones. The two-person case is representative of multi-person dilemmas. The situation is such that one agent, P1, ought to do A , a second agent, P2, ought to do B , and though each agent can do what he ought to do, it is not possible both for P1 to do A and P2 to do B . [See Marcus (1980), p. 122 and McConnell (1988).] Multi-person dilemmas have been called “interpersonal moral conflicts.” Such conflicts are most theoretically worrisome if the same moral system (or theory) generates the conflicting obligations for P1 and P2. A theory that precludes single-agent moral dilemmas remains uniquely action-guiding for each agent. But if that same theory does not preclude the possibility of interpersonal moral conflicts, not all agents will be able to succeed in discharging their obligations, no matter how well-motivated or how hard they try. For supporters of moral dilemmas, this distinction is not all that important. They no doubt welcome (theoretically) more types of dilemmas, since that may make their case more persuasive. But if they establish the reality of single-agent dilemmas, in one sense their work is done. For opponents of dilemmas, however, the distinction may be important. This is because at least some opponents believe that the conceptual argument against dilemmas applies principally to single-agent cases. It does so because the ought-to-do operator of deontic logic and the accompanying principles are properly understood to apply to entities about which decisions can be made. To be clear, this position does not preclude that collectives (such as businesses or nations) can have obligations. But a necessary condition for this being the case is that there is (or should be) a central deliberative standpoint from which decisions are made. This condition is not satisfied when two otherwise unrelated agents happen to have obligations both of which cannot be discharged. Put simply,while an individual act involving one agent can be the object of choice, a compound act involving multiple agents is difficult so to conceive. [See Smith (1986) and Thomason (1981).] To the extent that the possibility of interpersonal moral conflicts raises an intramural dispute among opponents of dilemmas, that dispute concerns how to understand the principles of deontic logic and what can reasonably be demanded of moral theories.
Debates about moral dilemmas have been extensive during the last five decades. These debates go to the heart of moral theory. Both supporters and opponents of moral dilemmas have major burdens to bear. Opponents of dilemmas must show why appearances are deceiving. Why are examples of apparent dilemmas misleading? Why are certain moral emotions appropriate if the agent has done no wrong? Supporters must show why several of many apparently plausible principles should be given up — principles such as PC, PD, OP, D, ‘ought’ implies ‘can’, and the agglomeration principle. Much progress has been made, but the debate is apt to continue.
Bibliography
- Aquinas, St. Thomas, 1964-1975, Summa Theologiae , Trans, Thomas Gilby et al, New York: McGraw-Hill.
- Donagan, Alan, 1977, The Theory of Morality , Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
- –––, 1984, “Consistency in Rationalist Moral Systems,” The Journal of Philosophy 81 : 291-309, [Reprinted in Gowans (1987): 271-290,]
- Freedman, Monroe, 1975, Lawyers' Ethics in an Adversary System , Indianapolis: Bobbs-Merrill.
- Gowans, Christopher W. (editor), 1987, Moral Dilemmas , New York: Oxford University Press.
- Greenspan, Patricia S., 1983, “Moral Dilemmas and Guilt,” Philosophical Studies 43 : 117-125,
- –––, 1995, Practical Guilt: Moral Dilemmas, Emotions, and Social Norms , New York: Oxford University Press.
- Kant, Immanuel, 1971/1797, The Doctrine of Virtue: Part II of the Metaphysics of Morals , Trans, Mary J. Gregor, Philadelphia: University of Pennsylvania Press.
- Lemmon, E.J., 1962, “Moral Dilemmas,” The Philosophical Review 70 : 139-158, [Reprinted in Gowans (1987): 101-114.
- –––, 1965, “Deontic Logic and the Logic of Imperatives,” Logique et Analyse 8 : 39-71.
- Marcus, Ruth Barcan, 1980, “Moral Dilemmas and Consistency,” The Journal of Philosophy 77 : 121-136, [Reprinted in Gowans (1987): 188-204,]
- Mason, H.E., (editor), 1996, Moral Dilemmas and Moral Theory , New York: Oxford University Press.
- McConnell, Terrance, 1978, “Moral Dilemmas and Consistency in Ethics,” Canadian Journal of Philosophy 8 : 269-287, [Reprinted in Gowans (1987): 154-173,]
- –––, 1988, “Interpersonal Moral Conflicts,” American Philosophical Quarterly 25 : 25-35.
- –––, 1996, “Moral Residue and Dilemmas,” in Mason (1996): 36-47.
- Mill, John Stuart, 1979/1861, Utilitarianism , Indianapolis: Hackett Publishing.
- Plato, The Republic , trans, Paul Shorey, in The Collected Dialogues of Plato , E. Hamilton and H. Cairns (eds.), Princeton: Princeton University Press.
- Ross, W.D., 1930, The Right and the Good , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- –––, 1939, The Foundations of Ethics , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Sartre, Jean-Paul, 1957/1946, “Existentialism is a Humanism,” Trans, Philip Mairet, in Walter Kaufmann (ed.), Existentialism from Dostoevsky to Sartre , New York: Meridian, 287-311,
- Sinnott-Armstrong, Walter, 1988, Moral Dilemmas , Oxford: Basil Blackwell.
- Smith, Holly M., 1986, “Moral Realism, Moral Conflict, and Compound Acts,” The Journal of Philosophy 83 : 341-345.
- Styron, William, 1980, Sophie's Choice , New York: Bantam Books.
- Thomason, Richmond, 1981, “Deontic Logic as Founded on Tense Logic,” in Risto Hilpinen (ed.), New Studies in Deontic Logic , Dordrecht: Reidel, 165-176.
- Trigg, Roger, 1971, “Moral Conflict,” Mind 80 : 41-55.
- Vallentyne, Peter, 1987, “Prohibition Dilemmas and Deontic Logic,” Logique et Analyse 30 : 113-122.
- –––, 1989, “Two Types of Moral Dilemmas,” Erkenntnis 30 : 301-318.
- Van Fraassen, Bas, 1973, “Values and the Heart's Command,” The Journal of Philosophy 70 : 5-19, [Reprinted in Gowans (1987): 138-153,]
- Williams, Bernard, 1965, “Ethical Consistency,” Proceedings of the Aristotelian Society , supp, vol. 39 : 103-124, [Reprinted in Gowans (1987): 115-137,]
- Zimmerman, Michael J., 1988, An Essay on Moral Responsibility , Totowa, NJ: Rowman and Littlefield.
- –––, 1996, The Concept of Moral Obligation , New York: Cambridge University Press.
- Anderson, Lyle V., 1985, “Moral Dilemmas, Deliberation, and Choice,” The Journal of Philosophy 82 : 139-162,
- Atkinson, R.F., 1965, “Consistency in Ethics,” Proceedings of the Aristotelian Society supp, vol. 39 : 125-138.
- Baumrin, Bernard H., and Peter Lupu, 1984, “A Common Occurrence: Conflicting Duties,” Metaphilosophy 15 : 77-90.
- Blackburn, Simon, 1996, “Dilemmas: Dithering, Plumping, and Grief,” in Mason (1996): 127-139.
- Bradley, F. H., 1927, Ethical Studies , 2 nd edition, Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Brink, David, 1989, Moral Realism and the Foundations of Ethics, New York: Cambridge University Press.
- –––, 1994, “Moral Conflict and Its Structure,” The Philosophical Review 103 : 215-247, [Reprinted in Mason (1996): 102-126,]
- Bronaugh, Richard, 1975, “Utilitarian Alternatives,” Ethics 85 : 175-178.
- Carey, Toni Vogel, 1985, “What Conflict of Duty is Not,” Pacific Philosophical Quarterly 66 : 204-215.
- Castañeda, Hector-Neri, 1974, The Structure of Morality , Springfield, IL: Charles C. Thomas.
- –––, 1978, “Conflicts of Duties and Morality,” Philosophy and Phenomenological Research 38 : 564-574.
- Chisholm, Roderick M., 1963, “Contrary-to-Duty Imperatives and Deontic Logic,” Analysis 24 : 33-36.
- Conee, Earl, 1982, “Against Moral Dilemmas,” The Philosophical Review 91 : 87-97, [Reprinted in Gowans (1987): 239-249,]
- –––, 1989, “Why Moral Dilemmas are Impossible,” American Philosophical Quarterly 26 : 133-141.
- Dahl, Norman O., 1974, “’Ought’ Implies ‘Can’” and Deontic Logic,“ Philosophia 4 : 485-511.
- –––, 1996, “Morality, Moral Dilemmas, and Moral Requirements,” in Mason(1996): 86-101.
- DeCew, Judith Wagner, 1990, “Moral Conflicts and Ethical Relativism,” Ethics 101 : 27-41.
- Donagan, Alan, 1996, “Moral Dilemmas, Genuine and Spurious: A Comparative Anatomy,” in Mason (1996): 11-22.
- Feldman, Fred, 1986, Doing the Best We Can , Dordrecht: D. Reidel Publishing Co.
- Foot, Philippa, 1983, “Moral Realism and Moral Dilemma,” The Journal of Philosophy 80 : 379-398, [Reprinted in Gowans (1987): 271-290,]
- Gewirth, Alan, 1978, Reason and Morality , Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
- Goldman, Holly Smith, 1976, “Dated Rightness and Moral Imperfection,” The Philosophical Review 85 : 449-487, [See also, Holly Smith ,]
- Gowans, Christopher W., 1989, “Moral Dilemmas and Prescriptivism,” American Philosophical Quarterly 26 : 187-197.
- –––, 1994, Innocence Lost: An Examination of Inescapable Wrongdoing , New York: Oxford University Press.
- –––, 1996, “Moral Theory, Moral Dilemmas, and Moral Responsibility,” in Mason (1996): 199-215.
- Griffin, James, 1977, “Are There Incommensurable Values?” Philosophy and Public Affairs 7 : 39-59.
- Guttenplan, Samuel, 1979-80, “Moral Realism and Moral Dilemma,” Proceedings of the Aristotelian Society 80 : 61-80.
- Hansson, Sven O., 1998, “Should We Avoid Moral Dilemmas?,” Journal of Value Inquiry , 32: 407-416.
- Hare, R.M., 1952, The Language of Morals , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- –––, 1963, Freedom and Reason , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- –––, 1981, Moral Thinking: Its Levels, Methods, and Point , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Hill, Thomas E., Jr, 1983, “Moral Purity and the Lesser Evil,” The Monist 66 : 213-232.
- –––, Jr, 1992, “A Kantian Perspective on Moral Rules,” Philosophical Perspectives 6 : 285-304.
- –––, Jr, “ Moral Dilemmas, Gaps, and Residues: A Kantian Perspective,” in Mason (1996): 167-198.
- Hoag, Robert W., 1983, “Mill on Conflicting Moral Obligations,” Analysis 43 : 49-54.
- Howard, Kenneth W., 1977, “Must Public Hands Be Dirty?” The Journal of Value Inquiry 11 : 29-40.
- Kant, Immanuel, 1965/1797, The Metaphysical Elements of Justice: Part I of the Metaphysics of Morals , Trans, John Ladd, Indianapolis: Bobbs-Merrill.
- Kolenda, Konstantin, 1975, “Moral Conflict and Universalizability,” Philosophy 50 : 460-465.
- Ladd, John, 1958, “Remarks on Conflict of Obligations,” The Journal of Philosophy 55 : 811-819.
- Lebus, Bruce, 1990, “Moral Dilemmas: Why They Are Hard to Solve,” Philosophical Investigations 13 : 110-125.
- MacIntyre, Alasdair, 1990, “Moral Dilemmas,” Philosophical and Phenomenological Research 50 : 367-382.
- Mallock, David, 1967, “Moral Dilemmas and Moral Failure,” Australasian Journal of Philosophy 45 : 159-178,
- Mann, William E., 1991, “Jephthah's Plight: Moral Dilemmas and Theism,” Philosophical Perspectives 5 : 617-647.
- Marcus, Ruth Barcan, 1996, “More about Moral Dilemmas,” in Mason (1996): 23-35.
- Marino, Patricia, 2001, “Moral Dilemmas, Collective Responsibility, and Moral Progress,” Philosophical Studies 104 : 203-225.
- Mason, H.E., 1996, “Responsibilities and Principles: Reflections on the Sources of Moral Dilemmas,” in Mason (1996): 216-235.
- McConnell, Terrance, 1976, “Moral Dilemmas and Requiring the Impossible,” Philosophical Studies 29 : 409-413.
- –––, 1981, “Moral Absolutism and the Problem of Hard Cases,” Journal of Religious Ethics 9 : 286-297.
- –––, 1981, “Moral Blackmail,” Ethics 91 : 544-567.
- –––, 1981, “Utilitarianism and Conflict Resolution,” Logique et Analyse 24 : 245-257.
- –––, 1986, “More on Moral Dilemmas,” The Journal of Philosophy 82 : 345-351.
- –––, 1993, “Dilemmas and Incommensurateness,” The Journal of Value Inquiry 27 : 247-252.
- McDonald, Julie M., 1995, “The Presumption in Favor of Requirement Conflicts,” Journal of Social Philosophy 26 : 49-58.
- Mothersill, Mary, 1996, “The Moral Dilemmas Debate,” in Mason (1996): 66-85.
- Nagel, Thomas, “War and Massacre,” Philosophy and Public Affairs 1 : 123-144.
- –––, 1979, “The Fragmentation of Value,” in Mortal Questions , New York: Cambridge University Press, [Reprinted in Gowans (1987): 174-187,]
- Nozick, Robert, 1968, “Moral Complications and Moral Structures,” Natural Law Forum 13 : 1-50.
- Paske, Gerald H., 1990, “Genuine Moral Dilemmas and the Containment of Incoherence,” The Journal of Value Inquiry 24 : 315-323.
- Pietroski, Paul, 1993, “Prima Facie Obligations, Ceteris Paribus Laws in Moral Theory,” Ethics 103 : 489-515.
- Price, Richard, 1974/1787, A Review of the Principal Questions of Morals , Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Prior, A.N., 1954, “The Paradoxes of Derived Obligation,” Mind 63 : 64-65.
- Quinn, Philip, 1978, Divine Commands and Moral Requirements , New York: Oxford University Press.
- –––, 1986, “Moral Obligation, Religious Demand, and Practical Conflict,” in Robert Audi and William Wainwright (eds.), Rationality, Religious Belief, and Moral Commitment , Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press, 195-212.
- Rabinowicz, Wlodzimierz, 1978, “Utilitarianism and Conflicting Obligations,” Theoria 44 : 1924.
- Rawls, John, 1971, A Theory of Justice , Cambridge: Harvard University Press.
- Railton, Peter, 1992, “Pluralism, Determinacy, and Dilemma,” Ethics 102 : 720-742.
- –––, 1996, “The Diversity of Moral Dilemma,” in Mason (1996): 140-166.
- Santurri, Edmund N., 1987, Perplexity in the Moral Life: Philosophical and Theological Considerations , Charlottesville, VA: University of Virginia Press.
- Sartorius, Rolf, 1975, Individual Conduct and Social Norms: A Utilitarian Account of Social Union and the Rule of Law , Encino, CA: Dickenson Publishing.
- Sayre-McCord, Geoffrey, 1986, “Deontic Logic and the Priority of Moral Theory,” Nous 20 : 179-197.
- Sinnott-Armstrong, Walter, 1984, “’Ought’ Conversationally Implies ‘Can’,” The Philosophical Review 93 : 249-261.
- –––, 1985, “Moral Dilemmas and Incomparability,” American Philosophical Quarterly 22 : 321-329.
- –––, 1987, “Moral Dilemmas and ‘Ought and Ought Not’,” Canadian Journal of Philosophy 17 : 127-139.
- –––, 1987, “Moral Realisms and Moral Dilemmas,” The Journal of Philosophy 84 : 263-276.
- –––, 1996, “Moral Dilemmas and Rights,” in Mason (1996): 48-65.
- Slote, Michael, 1985, “Utilitarianism, Moral Dilemmas, and Moral Cost,” American Philosophical Quarterly 22 : 161-168.
- Statman, Daniel, 1996, “Hard Cases and Moral Dilemmas,” Law and Philosophy 15 : 117-148.
- Steiner, Hillel, 1973, “Moral Conflict and Prescriptivism,” Mind 82 : 586-591.
- Stocker, Michael, 1971, “’Ought’ and ‘Can’,” Australasian Journal of Philosophy 49 : 303-316.
- –––, 1986, “Dirty Hands and Conflicts of Values and of Desires in Aristotle's Ethics,” Pacific Philosophical Quarterly 67 : 36-61.
- –––, 1987, “Moral Conflicts: What They Are and What They Show,” Pacific Philosophical Quarterly 68 : 104-123.
- –––, 1990, Plural and Conflicting Values , New York: Oxford University Press.
- Strasser, Mark, 1987, “Guilt, Regret, and Prima Facie Duties,” The Southern Journal of Philosophy 25 : 133-146.
- Swank, Casey, 1985, “Reasons, Dilemmas, and the Logic of ‘Ought’,” Analysis 45 : 111-116.
- Tannsjo, Torbjorn, 1985, “Moral Conflict and Moral Realism,” The Journal of Philosophy 82 : 113-117.
- Thomason, Richmond, 1981, “Deontic Logic and the Role of Freedom in Moral Deliberation,” in Risto Hilpinen (ed.), New Studies in Deontic Logic , Dordrecht: Reidel, 177-186.
- –––Vallentyne, Peter, 1992, “Moral Dilemmas and Comparative Conceptions of Morality,” The Southern Journal of Philosophy 30 : 117-124.
- Walzer, Michael, 1972, “Political Action: The Problem of Dirty Hands,” Philosophy and Public Affairs 2 : 160-180.
- Williams, Bernard, 1966, “Consistency and Realism,” Proceedings of the Aristotelian Society , supp, vol. 40 : 1-22.
- –––, 1972, Morality: An Introduction to Ethics , New York: Harper & Row.
- Zimmerman, Michael J., 1987, “Remote Obligation,” American Philosophical Quarterly 24 : 199-205.
- –––, 1988, “Lapses and Dilemmas,” Philosophical Papers 17 : 103-112.
- –––, 1990, “Where Did I Go Wrong?” Philosophical Studies 58 : 83-106.
- –––, 1992, “Cooperation and Doing the Best One Can,” Philosophical Studies 65 : 283-304.
- –––, 1995, “Prima Facie Obligation and Doing the Best One Can,” Philosophical Studies 78 : 87-123.
[Please contact the author with suggestions.]
-->Kant, Immanuel --> | logic: deontic | Mill, John Stuart | Plato | Sartre, Jean-Paul
Acknowledgments
I thank Michael Zimmerman for helpful comments on this essay.
Moral Dilemmas
- Open Access
- First Online: 11 April 2019
Cite this chapter
You have full access to this open access chapter

- Øyvind Kvalnes 2
278k Accesses
6 Citations
4 Altmetric
Moral dilemmas are situations in which the decision-maker must consider two or more moral values or duties but can only honor one of them; thus, the individual will violate at least one important moral concern, regardless of the decision. This chapter draws a distinction between real and false dilemmas. The former are situations in which the tension is between moral values or duties that are, more or less, on equal footing. In a real dilemma, the choice is between a wrong and another, roughly equal wrong. The latter are situations in which the decision-maker has a moral duty to act in one way but is tempted or pressured to act in another way. In a false dilemma, the choice is actually between a right and a wrong.
You have full access to this open access chapter, Download chapter PDF
- Moral dilemma
- Real dilemma
- False dilemma
Anne is the project manager for a large industrial project (run by a Nordic company) in a developing country. On a crucial day during the project, the entire plant’s electricity suddenly went out. Large quantities of cement were beginning to congeal in their mixers, and it was crucial to quickly reactivate them. More than one thousand employees were unable to do their work. Anne contacted the local authorities to solve the problem. A bureaucrat turned up at the plant and explained that he could turn the electricity back on very quickly—on the condition that he be allowed to bring ten of the company’s PCs back to the town hall, which had a desperate shortage of PCs that was preventing the bureaucrat and his colleagues from providing adequate service to the local community. Thus, he suggested a trade-off: PCs for electricity. In this manner, Anne and her company had the option to make a significant contribution to the local community.
Time was of the essence, and Anne had little time to dwell on the alternatives. There was no time to contact her supervisors in the firm’s home country for advice or instructions. She had to figure the situation out by herself. If the cement were to congeal, that would mean a considerable delay in the project, and several operations would have to be redone, at a high cost. That cost would be much higher than that of losing ten PCs, which could be easily replaced. Anne also had sympathy for the local bureaucrats and (the population they serve), who she believed would probably make very good use of the PCs. On the other hand, the demand was blackmail, and if she gave in this time, then it may happen again at other crucial stages of the project. Anne faced a difficult choice. What should she do?
Anne wanted to honor not just the moral value of finishing the project on time and within budget but also that of not giving in to blackmail and corruption. One of these values had to give way. There was no way in which Anne could act in a completely moral manner.
Moral dilemmas such as Anne’s are pervasive in working life. They occur in the public and private sectors and in organizations of all sizes. Any decision-maker can encounter them, whether at the executive level or below. In hectic working environments, people can become blind to their moral dilemmas, thus failing to see the moral dimensions of their choices. Understanding the nature of moral dilemmas is an important prerequisite to identifying them and finding ways in which to deal with them responsibly. Kidder ( 2005 ) suggested that, although there are myriad potential moral dilemmas, they tend to fall into four patterns: truth versus loyalty, individual versus community, short term versus long term, and justice versus virtue. Categorizing moral dilemmas in this manner can be a useful way to start addressing them.
Morality can be understood as a set of personal and shared beliefs about what is right and wrong in interpersonal interactions (Goodpaster, 1992 , p. 111). Over time, individuals and groups form moral convictions and beliefs about how they ought to behave toward others. The universe of beings that people have moral obligations toward can include other animals. The concepts of morality and ethics are understood to be synonymous in many contexts. Indeed, at the outset, the concepts had the same meaning. The term morality has Latin roots, whereas the term ethics stems from classical Greek, but both words originally referred to respectable behavior in a given society. Gradually, however, these concepts have become labels for different phenomena. As noted above, morality can be defined as a set of beliefs and convictions about right and wrong; this concept applies to interpersonal interactions, as well as to people’s obligations toward animals. Ethics, on the other hand, is the academic discipline of thinking systematically about right and wrong (Kvalnes & Øverenget, 2012 ). People learn morality and ethics in different ways. Moral beliefs and convictions are typically adopted through social interaction, whereas ethics is an academic discipline that must be learned by reading books, attending seminars, and such. There are ethics courses and exams, but there are no equivalent activities for morality; there are only moral tests, both in everyday life and in more extraordinary situations. A person’s actions on these tests determine whether that person is living in accordance with his or her moral convictions.
Morality and ethics play different roles in decision-making. The core difference can be outlined in the following manner:
A person facing a challenging situation can have a moral intuition about what would be the right choice, based on personal moral convictions, more or less shared in the community or culture. He or she can also engage in ethical analysis in order to clarify the issues at stake. (Kvalnes & Øverenget, 2012 , p. 5)
This distinction is similar to the one that Kahneman ( 2013 ) draws between fast and slow decision-making processes. Kahneman divided these processes into System 1 thinking, which is quick and impulsive, and System 2 thinking, which is slow and analytical. When a person faces a morally challenging situation, he or she can draw upon the resources of both systems. There may not be time for a full-scale analysis of the options at hand, however, and the person may have to rely on a gut feeling or moral impulse. Kahneman documented how people are prone to making mistakes when they rely solely on quick thinking and what their hearts tell them in the moment (Kahneman, 2013 ). People can reap great benefits from activating the slower System 2 processes when weighing alternatives. However, those who rely too heavily on analysis can become passive and immobile in situations that call for rapid responses. In some cases, by the time that an action has been thoroughly considered, it is too late to take the correct course.
People have both System 1 and System 2 resources in place to think about and respond to moral dilemmas. On the one hand are moral intuitions and gut feelings about what should be done; these are based on moral beliefs and convictions. On the other hand are opportunities to engage in ethical analysis so as to identify alternative courses of action and test whether those options are justified.
A dilemma, in the most general sense, is a situation that requires a choice between two options that are (or seem to be) equally undesirable or unsatisfactory. There are nonmoral dilemmas, in which the choice is between options that are undesirable or unsatisfactory for reasons other than morality. For instance, if a person seeks to buy both a book and a shirt but can only afford to purchase one of them, choosing one over the other will inevitably lead to disappointment, in that it will fulfill only one of the two desires. There need not be any moral dimension to this decision for it to be a dilemma.
A moral dilemma is a situation in which the decision-maker has to give priority to one moral value over another (Brinkmann, 2005 ; Maclagan, 2003 ; Toffler, 1986 ). Such dilemmas “arise when, faced with a difficult situation (e.g. fair treatment for some versus job security for others), two or more such values conflict in the perception of a decision-maker, or when one is assessing another’s moral choice” (Maclagan, 2003 , p. 22). A person who faces a dilemma must decide which moral duty to prioritize; “whichever action is taken … will offend an important moral value” (Maclagan, 2003 , p. 23).
In a moral dilemma, it is impossible to live up to all of one’s moral convictions and beliefs regarding how one should behave in that situation. In the opening example, Anne was morally committed to both keep the industrial project on track and reject the blackmail attempt. In that situation, one of these moral commitments had to give way at the expense of the other. She did not have a clear System 1 intuition, and even after initial System 2 reflection, the dilemma and tension remained. Her supervisors in the company’s home country were unavailable, so she had to respond to the bureaucrat’s offer on her own.
A moral dilemma can occur because of a prior personal mistake. This is called a self-inflicted dilemma. A classic example is the Bible story about King Herod. On Herod’s birthday, his stepdaughter Salome danced so well that he promised to give her whatever she wanted. Salome consulted her mother about what she should wish for, and she decided to ask for the head of John the Baptist on a platter. The king now had a choice between honoring the promise to his stepdaughter and honoring the life of John the Baptist. The king had inadvertently designed a moral trap for himself—a dilemma in which, whatever he decided, he would be acting immorally.
One contemporary and everyday instance of a self-inflicted moral dilemma involves double booking. Say that an individual makes separate and incompatible promises to two people she will be somewhere at 2:00. She cannot keep both promises and thus must choose which one to break. She may have good moral reasons to keep both promises, but she must choose between them.
In a narrow sense, a moral dilemma is a situation in which the moral values at stake are of equal importance. In this example, the two appointments have equally strong pull and significance. The individual’s moral reasons for keeping the two promises are thus equally strong. Neither choice is less wrong than the other. This situation is one in which moral wrongdoing is inescapable (Gowans, 1994 ).
In a wider sense, there can be moral dilemmas in which a person has strong moral reasons to act in one way, as well as notable—but not equally strong—moral reasons to act in another way. When considering the nature of two promises, it may be reasonable to conclude that it is better to fulfill one rather than the other. Deciding to keep the former promise and break the latter means a loss of some moral value, but it is not really a hard moral choice, as no one will have reason to challenge or cast doubt upon the rightness of the decision. The choice, in other words, is between a lesser wrong and a greater wrong. If an individual double-books, but one meeting has a higher priority than the other, the person whose meeting is canceled will be disappointed and irritated but will likely understand the decision based on the priority of keeping the other promise.
In the Herod case, there is an imbalance in the moral weight of the two options. Herod, in his exuberance, made a questionable promise to Salome, and in turn, she took advantage of the situation and made a horrific request. Herod had stronger moral reasons to spare the life of John the Baptist than he had to keep his word to his stepdaughter. He would give up some moral value either way, but one option was morally superior. This situation can still be called a moral dilemma—although not in the pure sense of representing a decision between moral values that are on equal footing.
False moral dilemmas are instances in which it is clear what ought to be done but in which there is temptation or pressure to act in another way. In business ethics, the distinction between true and false dilemmas has also been described as the distinction between dilemmas and temptations (Brinkmann, 2005 , p. 183; Kidder, 1995 , p. 7). Later in the book, I discuss professional ethics and how the handling of conflicts of interest are at the core of professionals’ moral responsibilities toward clients, customers, patients, students, and other users of professional services. For instance, lawyers and accountants can be tempted to prioritize self-interest over their clients’ interests. The knowledge gap between the professionals and the clients is such that the risk that clients will detect such choices is minimal. The professionals may claim that they are facing moral dilemmas when, for example, opportunities arise to overcharge clients. In the vocabulary of this book, the most appropriate term for such a situation is false dilemma . This situation may resemble a real dilemma in that the decision-maker must decide between two options that are both undesirable in some way, as cheating the client feels wrong, but so does turning down a chance to earn extra money. However, the former feeling has a moral component that is lacking in the latter. Thus, conflict-of-interest situations are generally false moral dilemmas with only superficial similarities to real dilemmas.
In connection with the dichotomy between real and false dilemmas, the continuum between them needs to be acknowledged, as Maclagan ( 2003 ) suggested. On one side of the spectrum, there are situations in which there is perfect balance between the opposing moral values. For example, being compassionate toward another person and being honest with that person can have equal moral weight. On the other side of the spectrum are situations in which one option is clearly morally right and the other is clearly morally wrong, as when a professional must choose between self-interest and clients’ interests. In some other cases that involve self-interest, however, the distinctions are not so clear-cut; for instance, pursuing self-interest on an organizational level can have some moral value. Concrete cases belong somewhere on the spectrum between purely real and purely false dilemmas.
Anne had to decide whether to get the plant’s electricity back by giving in to the blackmail from the local bureaucrat, or to stand firm and allow for a costly delay. How exactly should this situation be classified: as a real or false dilemma? This depends on the details of the case. The analysis that Anne had to make in preparation for her decision did not require her to precisely place the dilemma on this scale, but it did require her to acknowledge the nature of the situation in general. In Anne’s case, she decided on a two-step response. First, she handed over the PCs so that the bureaucrat would turn the electricity back on, thus getting the project on track again. Second, she invited the senior bureaucrats from the nearby town to a meeting in which she explained that the company wanted to contribute to the local community—but not in such a haphazard way. Instead, she proposed a systematic plan in which the company would help the town to modernize its electronic equipment. With this initiative, Anne came to be on better terms with the local administrators, thus avoiding further blackmail situations.
The following case from Kvalnes and Øverenget ( 2012 , p. 4) can serve to highlight how challenging a situation can be even when it is close to the false dilemma end of the spectrum:
Ben is the manager of a small private banking unit within a large financial services group. Results have slumped recently, mainly due to a bitter conflict between one employee and some of his colleagues. They complain that he is rude and difficult to cooperate with. Ben has attempted to mitigate, to no avail. National legislation prohibits the option of firing the quarrelsome employee, at least in the short run. Key members of Ben’s unit have become very upset by the situation and have started to look for work elsewhere. A recent turn of events is that the employee himself has applied for a job in a different part of the financial services group. Ben has agreed to serve as a reference person. He receives a phone call from the manager of the unit currently contemplating to hire the employee. She is particularly interested in the employee’s social skills. “Does he function well with his colleagues?” she asks. If Ben gives an honest answer, he is likely to be stuck with the employee for a long time. If he is vague about the employee’s social skills, he may get rid of a problem. He then runs the risk that his honesty will come up for questioning later. It also feels wrong to lie to another person in order to get rid of a problem at work. Lying in this case would be an attempt to transport one’s own problem over to someone else, instead of taking responsibility and deal with it in one’s own organization. How should Ben respond to the question about the employee’s social abilities?
In this example, Ben had to choose between being honest about an employee’s antisocial behavior and telling the truth, which would prevent the employee’s ability to move to another organization. Like Anne, Ben acknowledged that, regardless of what he decided to do, it would be wrong.
At first glance, this appears to be an obvious example of a false dilemma. Ben’s choice was between the moral value of being truthful to others and the selfish desire to get rid of a human resources problem. It was tempting for him to withhold information and thereby help the difficult employee move to a new job, but doing so would have violated Ben’s moral duty to be honest in business dealings. Ben could have reasoned that the employee deserved another chance in a new work environment. By this logic, if the employee were allowed to start anew in his career, he might be better able to fulfill his personal and professional potential. That is all very well, but that consideration is relatively weak and clearly is meant to camouflage a violation of the moral requirement to be straightforward and honest when acting as a reference person.
The extent to which Ben’s situation is a real or a false dilemma depends on the details of the case. I have used this case as a starting point when teaching ethics to both business managers and business-school students, as well as in research on moral psychology, the purpose of which was to map the extent that this situation creates moral dissonance, thus causing managers to engage in moral neutralization (Kvalnes, 2014 ). I return to this topic in Chap. 13 .
People’s responses to Ben’s dilemma reveal their moral convictions. When I ask for justifications regarding the choice of whether to be truthful, the participants in my ethics courses have come up with a wide variety of reasons, thus expressing their individual loyalties and preferences. People’s first responses are often based on their gut feelings, which cause one option to instantly feel right or wrong. These are from System 1, in which intuitions are dominant; my task as the facilitator is to introduce the participants to the slower System 2 type of reflection and analysis (Kahneman, 2013 ). Ethical reasoning involves slowing down to become aware of the moral issues at stake and progressing from a state of mismatching feelings to one in which the participants are able to recognize the ethical and moral foundations for their own choices.
Moral dilemmas are omnipresent in organizations. Situations on all parts of the scale, from acutely real dilemmas to false pseudo-dilemmas, constitute challenges that decision-makers should prepare for. The following four chapters describe analytical resources from moral philosophy and ethics. These principles and concepts can serve as tools for determining what one ought to do and for justifying one’s choices regarding moral dilemmas.
Brinkmann, J. (2005). Understanding insurance customer dishonesty: Outline of a situational approach. Journal of Business Ethics, 61 (2), 183–197.
Article Google Scholar
Goodpaster, K. E. (1992). Business ethics. In L. C. Becker & C. B. Becker (Eds.), Encyclopedia of ethics . New York: Garland Publishing.
Google Scholar
Gowans, C. (1994). Innocence lost . Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Kahneman, D. (2013). Thinking, fast and slow . New York: Farrar, Straus and Giroux.
Kidder, R. M. (1995). How good people make tough choices . New York: Morrow.
Kidder, R. M. (2005). Moral courage: Taking action when your values are put to the test . New York: William Morrow.
Kvalnes, Ø. (2014). Leadership and moral neutralisation. Leadership, 10 (4), 456–470.
Kvalnes, Ø., & Øverenget, E. (2012). Ethical navigation in leadership training. Etikk i praksis-Nordic Journal of Applied Ethics, 1 , 58–71.
Maclagan, P. (2003). Varieties of moral issue and dilemma: A framework for the analysis of case material in business ethics education. Journal of Business Ethics, 48 (1), 21–32.
Toffler, B. L. (1986). Tough choices: Managers talk ethics . New York: John Wiley and Sons.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Leadership and Organizational Development, BI Norwegian Business School, Oslo, Norway
Øyvind Kvalnes
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Rights and permissions
Open Access This chapter is licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license and indicate if changes were made.
The images or other third party material in this chapter are included in the chapter's Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the chapter's Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder.
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2019 The Author(s)
About this chapter
Kvalnes, Ø. (2019). Moral Dilemmas. In: Moral Reasoning at Work. Palgrave Pivot, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-15191-1_2
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-15191-1_2
Published : 11 April 2019
Publisher Name : Palgrave Pivot, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-030-15190-4
Online ISBN : 978-3-030-15191-1
eBook Packages : Business and Management Business and Management (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Home — Blog — Topic Ideas — 200 Ethical Topics & Questions to Debate in Essay
200 Ethical Topics & Questions to Debate in Essay
Ethical topics and questions are essential for stimulating thoughtful discussions and deepening our understanding of complex moral landscapes. Ethics, the study of what is right and wrong, underpins many aspects of human life and societal functioning. Whether you're crafting an essay or preparing for a debate, delving into ethical issues allows you to explore various perspectives and develop critical thinking skills.
Ethical issues encompass a wide range of dilemmas and conflicts where individuals or societies must choose between competing moral principles. Understanding what are ethical issues involves recognizing situations that challenge our values, behaviors, and decisions. This article provides a thorough guide to ethical topics, offering insights into current ethical issues, and presenting a detailed list of questions and topics to inspire your writing and debates.
Ethical Issues Definition
Ethical issues refer to situations where a decision, action, or policy conflicts with ethical principles or societal norms. These dilemmas often involve a choice between competing values or interests, such as fairness vs. efficiency, privacy vs. security, or individual rights vs. collective good. Ethical issues arise in various fields, including medicine, business, technology, and the environment. They challenge individuals and organizations to consider the moral implications of their actions and to seek solutions that align with ethical standards. Understanding ethical issues requires an analysis of both the potential benefits and the moral costs associated with different courses of action.
⭐ Top 10 Ethical Topics [2024]
- Climate Change Responsibility
- Data Privacy in the Digital Age
- Genetic Engineering
- Euthanasia and Assisted Suicide
- Corporate Social Responsibility
- AI and Automation
- Animal Rights
- Freedom of Speech vs. Hate Speech
- Healthcare Accessibility
- Human Rights in the Age of Globalization
Ethics Essay Writing Guide
Writing an ethics essay involves more than just presenting facts; it requires a thoughtful analysis of moral principles and their application to real-world scenarios. Understanding ethical topics and what constitutes ethical issues is essential for crafting a compelling essay. Here’s a guide to help you address current ethical issues effectively:
- Choose a Clear Topic: Select an ethical issue that is both interesting and relevant. Understanding the definition of ethical issues will help you narrow down your choices.
- Research Thoroughly: Gather information from credible sources to support your arguments. Knowing what ethical issues are and how they are defined can provide a solid foundation for your research.
- Present Multiple Perspectives: Show an understanding of different viewpoints on the issue. This will demonstrate your grasp of the complexity of current ethical issues.
- Use Real-world Examples: Illustrate your points with concrete examples. This not only strengthens your arguments but also helps to explain ethical topics in a relatable way.
- Structure Your Essay: Organize your essay with a clear introduction, body, and conclusion. A well-structured essay makes it easier to present your analysis of ethical issues.
- Provide a Balanced Argument: Weigh the pros and cons to offer a well-rounded discussion. Addressing various aspects of current ethical issues will make your essay more comprehensive.
- Conclude Thoughtfully: Summarize your findings and reflect on the broader implications of the issue. This is where you can discuss the impact of ethical issues on society and future considerations.
By following this guide, you will be able to write an ethics essay that not only presents facts but also offers a deep and nuanced analysis of ethical topics.
Selecting the Right Research Topic in Ethics
Choosing the right research topic in ethics can be challenging, but it is crucial for writing an engaging and insightful essay. Here are some tips:
- Relevance: Ensure the topic is relevant to current societal issues.
- Interest: Pick a topic that genuinely interests you.
- Scope: Choose a topic with enough scope for research and debate.
- Complexity: Aim for a topic that is complex enough to allow for in-depth analysis.
- Availability of Sources: Make sure there are enough resources available to support your research.
What Style Should an Ethics Essay Be Written In?
When writing an ethics essay, it is essential to adopt a formal and objective style. Clarity and conciseness are paramount, as the essay should avoid unnecessary jargon and overly complex sentences that might obscure the main points. Maintaining objectivity is crucial; presenting arguments without bias ensures that the discussion remains balanced and fair. Proper citations are vital to give credit to sources and uphold academic integrity.
Engaging the reader through a logical flow of ideas is important, as it helps sustain interest and facilitates a better understanding of the ethical topics being discussed. Additionally, the essay should be persuasive, making compelling arguments supported by evidence to effectively convey the analysis of moral issues. By following these guidelines, the essay will not only be informative but also impactful in its examination of ethical dilemmas.
List of Current Ethical Issues
- The impact of social media on privacy.
- Ethical considerations in genetic cloning.
- Balancing national security with individual rights.
- Privacy concerns in the digital age.
- The ethics of biohacking.
- Ethical considerations in space exploration.
- The ethics of surveillance and data collection by governments and corporations.
- Ethical issues in the use of facial recognition technology.
- The ethical implications of autonomous vehicles.
- The morality of animal testing in scientific research.
- Ethical concerns in the gig economy.
- The impact of climate change on ethical business practices.
- The ethics of consumer data usage by companies.
- Ethical dilemmas in end-of-life care and assisted suicide.
- The role of ethics in the development of renewable energy sources.
Ethical Issues in Psychology
- Confidentiality vs. duty to warn in therapy.
- Ethical dilemmas in psychological research.
- The use of placebo in psychological treatment.
- Ethical issues in the treatment of vulnerable populations.
- The ethics of involuntary commitment and treatment.
- Dual relationships and conflicts of interest in therapy.
- The use of deception in psychological experiments.
- The ethics of cognitive enhancement drugs.
- Ethical considerations in online therapy and telepsychology.
- Cultural competence and ethical practice in psychology.
- The ethics of forensic psychology and assessment.
- The impact of social media on mental health and ethical practice.
- The use of emerging technologies in psychological treatment.
- Ethical issues in the diagnosis and treatment of mental disorders.
- The role of ethics in psychological testing and assessment.
Ethical Debate Topics
- Is capital punishment morally justified?
- Should organ donation be mandatory?
- The ethics of artificial intelligence in warfare.
- Is euthanasia ethically permissible?
- Should human cloning be allowed?
- The morality of animal rights vs. human benefit.
- Is it ethical to use animals for entertainment?
- Should there be limits on free speech?
- The ethics of genetic modification in humans.
- Is it ethical to have mandatory vaccinations?
- The morality of government surveillance programs.
- Should assisted reproductive technologies be regulated?
- The ethics of using performance-enhancing drugs in sports.
- Should healthcare be considered a human right?
- The ethical implications of wealth inequality and redistribution.
Medical Ethics Topics
- Ariel Case Study: a Comprehensive Analysis
- The Case for and Against Daylight Saving Time
- Technological Advancements in Medical, Educational & Other Fields
- The Language of Medicine
- Medical Ethics: Beneficence and Non-maleficence
- Overview of What Sonography is
- The Use of Steroids and HGH in Sports
- Media and The Scientific Community Treat People Like Tools
- Informative Speech for Organ Donation
- Medicine in Our World
- The Origin of Medical Terminology
- Preserving Sight: My Journey to Becoming an Optometrist
- Case of Dr. Eric Poehlman's Ethical Violation
- Should The NHS Treat Patients with Self-Inflicted Illnesses
- My Education as a Medical Technologist
Ethics Essay Topics on Business
- Ethics Report on Panasonic Corporation
- Case Study on The ACS Code of Morals
- Differences in Business Ethics Among East Asian Countries
- Business Ethics in Sports
- Business Ethics in Different Countries, and Its Importance
- Selfless Service and Its Impact on Social Change
- Challenges in Doing Business Across The Border
- The Importance of Ethics in Advertising
- Ethical Issues that Businesses Face
- Profitability of Business Ethics
- The Law and Morality in Business
- How Ethnic Variances Effect Worldwide Business
- The Ethical Practices in The Business Sector in the Modern Economy
- Key Responsibilities and Code of Ethics in Engineering Profession
- Analysis of The Code of Ethics in Walmart
Ethics Essay Topics on Environment
- Understanding The Importance of Keeping Animals Safe
- The Importance of Treating Animals with Respect
- CWU and The Issue of Chimpanzee Captivity
- The Process of Suicidal Reproduction in the Animal World
- Analysis of The Egg Industry to Understand The Causes of The High Prices in Eggs
- The Dangers of Zoos
- Importance for Animals to Be Free from Harm by Humans
- Should Animals Be Killed for The Benefit of Humans
- Reasons Why Genetic Engineering Should Be Banned
- What I Learned in Ethics Class: Environmental Ethics
- Nanotechnology and Environment
- Review of The Environmental Protection Act
- How The Idea of Preservation of Nature Can Benefit from Environmental Ethics
- The Relation and Controversy Between American Diet and Environmental Ethics
- Green Technology
Work Ethics Essay Topics
- The impact of workplace surveillance on employee privacy.
- Ethical considerations in remote work.
- Discrimination in the workplace.
- An Examination of Addiction to Work in The Protestant Work Ethic
- The Work Ethic of The Millennials
- My Understanding of The Proper Environment in the Workplace
- Social Responsibility & Ethics Management Program in Business
- The Maternity Benefits Act, 1961
- The Issue of Stealing in The Workplace
- Chinese Work Management and Business Identity
- Ethical Issues of Using Social Media at the Workplace
- The Teleological Ethical Theories
- Learning Journal on Ethical Conflicts, Environmental Issues, and Social Responsibilities
- Social Media at Workplace: Ethics and Influence
- Ethical Issue of Employees Stealing and Whistleblowing
Ethics Essay Topics on Philosophy
- A Critical Analysis of Ethical Dilemmas in Education and Beyond
- Overview of What an Ethical Dilemma is
- The Implications of Exculpatory Language
- Ethical Dilemmas in End-of-life Decision Making
- What I Learned in Ethics Class: Integrating Ethics in Aviation
- Doing What is Right is not Always Popular: Philosophy of Ethics
- An Analysis of Public Trust and Corporate Ethics
- Ethical Concerns of Beauty Pageants
- Simone De Beauvoir’s Contribution to Philosophy and Ethics
- The Impact on Decision-making and Life Choices
- Importance and Improvement of Personal Ethics
- Personal Ethics and Integrity in Our Life
- Analysis of The Philosophical Concept of Virtue Ethics
- Understanding Moral Action
- How to Become a Gentleman
- A Call for Emphasis on Private Morality and Virtue Teaching
- A Positive Spin on Ethical Marketing in The Gambling Industry
- An Overview of The Ethical Dilemma in a Personal Case
- Bioethical Principles and Professional Responsibilities
- Ethical Considerations in Counseling Adolescents
- Ethical Dilemma in College Life
- Ethical Theories: Deontology and Utilitarianism
- Issues of Fraud, Ethics, and Regulation in Healthcare
- Navigating Ethical Dimensions in Education
- The Ethical Landscape of Advanced Technology
- Research Paper on The Ethical Issue of Publishing The Pentagon Papers
- The Trolley Problem: an Ethical Dilemma
- Analysis of "To The Bitter End" Case Study
- Ethical Theories: Virtue and Utilitarian Ethics
- Feminist Ethics: Deconstructing Gender and Morality
- Is Deadpool a Hero Research Paper
- My Moral and Ethical Stance
- The Concept of Ethics and The Pursuit of Happiness
- The Ethics of Graphic Photojournalism
- The Quintessence of Justice: a Critical Evaluation of Juror 11's Role
- The Wolf of Wall Street: Ethics of Greed
- The Importance of Ethics in Our Daily Life
- Analysis of The Envy Emotion and My Emotional Norms
- The Topic of Animal Rights in Relation to The Virtue Theory

Ethics Essay Topics on Science
- The Cause of Cancer as Illustrated in a Bioethics Study
- Bioethical Issues Related to Genetic Engineering
- Ethical Issues in Stem Cell Research
- The Role of Ethics Committees in Biomedical Research
- The Legal and Bioethical Aspects of Personalised Medicine Based on Genetic Composition
- The Ethics of Clinical Trials: Ensuring Informed Consent and Patient Safety
- Ethical Challenges in Neuroethics: Brain Privacy and Cognitive Liberty
- Gene Therapy: Ethical Dilemmas and Social Implications
- Overview of Bioethics The Trigger of Contentious Moral Topics
- The Progression of Bioethics and Its Importance
- The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Medical Ethics
- The Drawbacks of Free Healthcare: Economic, Quality, and Access Issues
- Bioethical Issues in My Sister’s Keeper: Having Your Autonomy Taken to Save Your Sibling
- The Ethics of Biotechnology in Agriculture: GMOs and Food Safety
- Ethical Considerations in Organ Donation and Transplantation
List of Ethical Questions for Students
Exploring ethical topics is crucial for students to develop critical thinking and moral reasoning. Here is a comprehensive list of ethical questions for students to discuss and debate. These topics cover a wide range of issues, encouraging thoughtful discussion and deeper understanding.
Good Ethical Questions for Discussion
- Is it ethical to eat meat?
- Should parents have the right to genetically modify their children?
- Is it ever acceptable to lie?
- Should schools monitor students' social media activity?
- Is it ethical to use animals in scientific research?
- Should companies be allowed to patent human genes?
- Is it right to impose cultural values on others?
- Should the government regulate internet content?
- Is it ethical to have designer babies?
- Should wealthy countries help poorer nations?
- Is it ethical to keep animals in zoos?
- Should there be limits to freedom of speech?
- Is it right to use artificial intelligence in decision-making?
- Should we prioritize privacy over security?
- Is it ethical to manipulate emotions through advertising?
Moral Questions to Debate
- Is genetic modification in humans ethical?
- Should vaccinations be mandatory?
- Is government surveillance justified?
- Is it ethical to use performance-enhancing drugs in sports?
- Is wealth inequality morally acceptable?
- Should education be free for everyone?
- Is it ethical to allow autonomous robots to make life-and-death decisions?
Ethical topics and questions are a rich field for exploration and discussion. Examining these issues, we can better understand the moral principles that guide our actions and decisions. Whether you're writing an essay or preparing for a debate, this comprehensive list of ethical topics and questions will help you engage with complex moral dilemmas and develop your critical thinking skills.

We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .

Ethical Dilemma
Ai generator.
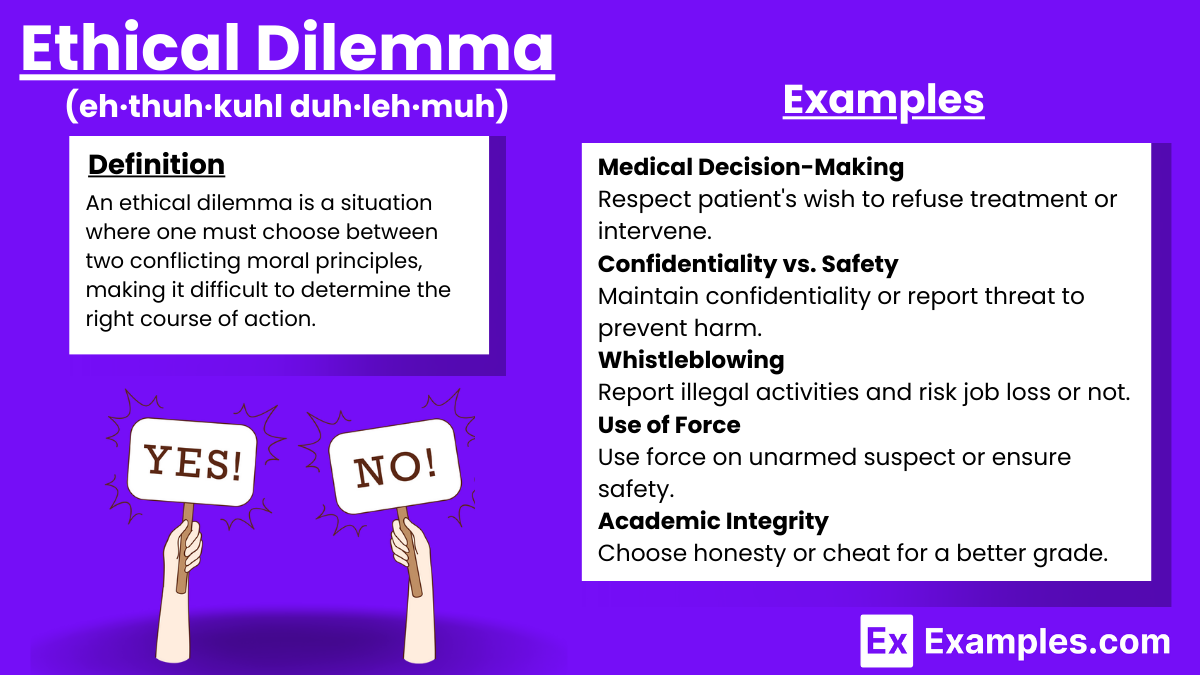
Ethical dilemmas present challenging situations where individuals must choose between conflicting moral principles. These scenarios often arise in various fields, from medicine to business, and compel individuals to weigh the consequences of their decisions. In an ethical dilemma, there is no clear right or wrong answer, making the resolution process complex and deeply personal. This article explores the nature of ethical dilemmas, examines notable examples, and provides frameworks for navigating these tough choices with integrity and thoughtfulness.
What is Ethical Dilemma? – Definition
An ethical dilemma is a problem that occurs in a person’s decision-making process, which has decisions that have large consequences for the people involved in the problem. These types of problems are often confusing and difficult to answer due to the complexity of the situation. The person has to take note and understand various elements , themes , and tones that contribute to the overall context of the ethical situation.
Ethical Dilemmas Examples

- Medical Decision-Making : A doctor must decide whether to respect a terminally ill patient’s wish to refuse treatment or to intervene to save their life.
- Confidentiality vs. Safety : A therapist learns that a client plans to harm someone but has sworn confidentiality.
- Whistleblowing : An employee discovers illegal activities within their company but fears losing their job if they report it.
- Use of Force : A police officer must decide whether to use force in a situation where a suspect appears threatening but unarmed.
- Academic Integrity : A student finds a way to cheat on an important exam and must choose between honesty and a better grade.
- Resource Allocation : A hospital must decide how to allocate limited resources like ventilators during a pandemic.
- Animal Testing : A researcher must balance the potential human benefits of their work against the ethical concerns of using animals for testing.
- Advertising Ethics : A marketing professional must decide whether to use potentially misleading claims to boost sales.
- Conflict of Interest : A journalist has a financial interest in a company they are assigned to cover.
- Environmental Responsibility : A company must choose between cost-saving measures that harm the environment and more expensive, eco-friendly alternatives.
- Cultural Sensitivity : A business must decide whether to respect local customs that conflict with its ethical standards.
- Data Privacy : A tech company must choose between collecting user data for profit and respecting users’ privacy rights.
- Euthanasia : A family must decide whether to support a terminally ill loved one’s wish for assisted suicide.
- Genetic Engineering : Scientists debate the ethical implications of editing human genes to prevent diseases.
- Charity Allocation : A nonprofit organization must decide which causes to fund with its limited resources.
- Freedom of Speech : A social media platform must balance the need for open discourse with the responsibility to prevent hate speech.
- End-of-Life Care : A family must decide whether to continue life support for a loved one in a vegetative state.
- Employee Surveillance : A company must decide whether to monitor employees’ activities to prevent theft or respect their privacy.
- Artificial Intelligence : Developers must consider the ethical implications of creating AI systems that could replace human jobs.
- Corporate Social Responsibility : A business must choose between maximizing profits and contributing to social causes.
- Journalistic Ethics : A reporter must decide whether to publish a story that could harm someone’s reputation but serves the public interest.
- Patient Autonomy : A doctor must decide whether to honor a patient’s request for an unproven treatment.
- Military Decisions : A soldier must choose between following orders and protecting innocent civilians.
- Privacy vs. Security : Governments must balance the need for surveillance to ensure national security with the right to individual privacy.
- Research Ethics : A scientist must decide whether to manipulate data to achieve desirable results.
- Corporate Governance : Board members must choose between actions that benefit shareholders and those that benefit employees and the community.
- Financial Reporting : An accountant must decide whether to report financial irregularities that could damage their company.
- Medical Research : Researchers must decide whether to continue a study that shows promising results but also serious side effects.
- Cultural Relativism : An international NGO must decide whether to intervene in local practices that violate human rights.
- Public Health vs. Individual Rights : Health officials must decide whether to impose quarantines to prevent disease spread, infringing on individual freedoms.
Real Life Examples of Ethical Dilemmas
- End-of-Life Care: A doctor might face an ethical dilemma when deciding whether to continue life-sustaining treatment for a terminally ill patient who is suffering and has little chance of recovery.
- Allocation of Resources: During a health crisis, such as a pandemic, healthcare professionals may need to decide who receives limited resources like ventilators or ICU beds.
- Whistleblowing: An employee discovers their company is engaging in illegal or unethical practices. They must decide whether to report it, potentially risking their job and personal well-being, or stay silent.
- Fair Labor Practices: A company must choose between outsourcing production to a country with cheaper labor but poor working conditions and keeping production local but at a higher cost.
- Defending the Guilty: A defense attorney knows their client is guilty but must still provide the best possible defense, as everyone has a right to legal representation.
- Sentencing: A judge must decide between a lenient sentence that might help rehabilitate a young offender and a harsher one that could serve as a deterrent to others.
- Development vs. Conservation: A community must decide whether to allow a new development project that could bring economic benefits but would harm the local environment and wildlife.
- Pollution: A company must choose between cheaper manufacturing processes that pollute the environment and more expensive, environmentally friendly options.
- Loyalty vs. Honesty: A friend discovers another friend’s spouse is cheating. They must decide whether to tell their friend, which could cause pain, or keep the secret to avoid hurting them.
- Family Obligations: An individual must choose between pursuing a career opportunity in another city or staying close to home to care for an aging parent.
- Data Privacy: A tech company must decide whether to sell user data to advertisers to generate revenue or protect users’ privacy at the expense of potential profits.
- AI and Automation: A company must choose between adopting automation, which could increase efficiency but lead to significant job losses, or maintaining current employment levels.
- Standardized Testing: An educator might face the dilemma of teaching to the test to ensure high scores, which can benefit the school and students’ futures, or providing a more well-rounded education that might not directly improve test scores.
- Grading Fairness: A teacher must decide whether to give a struggling student a passing grade out of sympathy or hold them to the same standards as other students.
Ethical Dilemma Examples for Students
- You studied hard for a math test, but your best friend, who didn’t study, asks to copy your answers during the test. Do you help them or not?
- You find a wallet with $50 on the school playground. Inside the wallet, there is also a student ID card. Do you keep the money or try to return it to the owner?
- You have a big project due tomorrow and you haven’t started it. You find a perfect essay online. Do you submit it as your own work?
- You see a popular student at your school posting mean comments about another student on social media. Do you report it, confront the bully, or ignore it?
- Your friend tells you that they are going to cheat on a major exam. If you tell a teacher, your friend might get into serious trouble. If you don’t, your friend’s actions could unfairly impact others. What do you do?
- Your friends pressure you to skip class and hang out at a local park. If you don’t go, they might stop inviting you to hang out with them. Do you go with them or attend your classes?
- At a party, someone offers you alcohol or drugs. You know it’s illegal and dangerous, but you don’t want to seem uncool. How do you handle the situation?
- You accidentally discover the password to a classmate’s social media account. Do you log in and snoop around, change the password to lock them out, or tell them about it?
- You notice that the school cafeteria uses a lot of single-use plastics. Do you organize a campaign to encourage more sustainable practices, or do you stay silent?
- In a group project, one member isn’t contributing at all, but they expect to get the same grade as everyone else. Do you talk to the teacher about it or let it slide?
- Your friend did something against school rules and the principal is investigating. Your friend asks you to lie to cover for them. Do you lie or tell the truth?
- Your group of friends decides to exclude a classmate who wants to join your lunch table. Do you stand up for the excluded student or go along with your friends?
- A friend confides in you about a personal problem, but you think they might need professional help. Do you keep their secret or tell an adult who can help?
- You have a big sports game on the same day as a family event. Your coach expects you to play, but your parents want you at the family event. How do you decide where to go?
- In a class discussion, a student expresses an opinion that you strongly disagree with. Do you challenge their opinion respectfully, ignore it, or get into an argument?
Ethical dilemma in business
An ethical dilemma in business occurs when a company or individual faces a situation where there are conflicting moral principles or ethical obligations, making it difficult to determine the right course of action. These dilemmas often involve decisions that can impact stakeholders such as employees, customers, shareholders, and the community. The challenge lies in balancing profitability and competitiveness with ethical considerations such as fairness, transparency, and social responsibility.
Examples of Ethical dilemma in business
Employee Privacy vs. Employer’s Right to Monitor
- Scenario : A company wants to monitor employees’ computer usage to ensure productivity and prevent misuse of company resources. However, employees feel this invades their privacy.
- Dilemma : Balancing the need for security and productivity with respecting employee privacy.
2. Product Safety vs. Profit
- Scenario : A company discovers that a product has a minor defect that could potentially harm a small percentage of users. The cost of recalling and fixing the product is substantial.
- Dilemma : Choosing between prioritizing customer safety and incurring significant financial losses.
3. Environmental Responsibility vs. Economic Gain
- Scenario : A manufacturing company can save costs by disposing of waste in a less environmentally friendly manner.
- Dilemma : Deciding between higher profits and committing to environmentally sustainable practices.
4. Transparency vs. Competitive Advantage
- Scenario : A company has developed a groundbreaking technology but keeping the details secret could give it a significant market advantage.
- Dilemma : Choosing between being transparent about practices and protecting competitive interests.
5. Fair Trade vs. Low Costs
- Scenario : Sourcing materials from suppliers that exploit cheap labor but keep costs low versus using fair trade suppliers that are more expensive.
- Dilemma : Balancing cost management with ethical sourcing practices.
6. Conflict of Interest
- Scenario : An executive has a significant financial interest in a supplier company that the business is considering for a major contract.
- Dilemma : Ensuring unbiased decision-making while managing personal financial interests.
7. Whistleblowing
- Scenario : An employee discovers that their company is engaging in illegal or unethical practices. Reporting this could lead to personal repercussions and harm the company’s reputation.
- Dilemma : Balancing the moral obligation to expose wrongdoing with the potential personal and professional risks.
8. Pricing Strategies
- Scenario : A pharmaceutical company has a life-saving drug and is debating how much to charge for it. Higher prices could make the drug unaffordable for many, but lower prices could limit the company’s ability to fund future research.
- Dilemma : Setting prices that balance profitability and accessibility.
9. Cultural Sensitivity vs. Market Expansion
- Scenario : A company wants to expand into a new international market but faces cultural practices that conflict with its ethical standards.
- Dilemma : Deciding whether to adapt to local customs that may be ethically questionable or maintaining company values, potentially losing business.
10. Advertising Ethics
- Scenario : A company considers using exaggerated claims in advertising to boost sales.
- Dilemma : Weighing the benefits of increased sales against the potential for misleading consumers and damaging trust.
Ethical Dilemma Examples in the Workplace
- You are involved in hiring a new team member, and one of the applicants is a close friend. Do you disclose this relationship and step back from the decision-making process, or do you keep it to yourself?
- You discover that your company is engaging in illegal activities, such as falsifying financial records. Do you report this to the authorities, risking your job, or stay silent to protect your position?
- Your manager shows obvious favoritism towards a colleague, giving them the best projects and promotions. Do you confront your manager, talk to HR, or accept the situation?
- You have limited resources and must decide between two projects: one that benefits the company’s profits and another that benefits employee welfare. Which do you prioritize?
- You make a mistake on a project that could have significant negative consequences. Do you own up to the mistake immediately or try to fix it quietly without informing anyone?
- You have an idea that could greatly benefit your company, but it wasn’t developed during work hours. Do you present it to your employer or keep it for a personal venture?
- You find out that a colleague is going through a personal crisis, which is affecting their performance. Do you inform your manager to explain the performance issues, or respect your colleague’s privacy?
- A vendor offers you an expensive gift during the holiday season. Accepting it could be seen as a bribe. Do you accept the gift, decline it, or report it?
- You have access to personal data of clients that could be useful for a side project you’re working on. Do you use the data, risking privacy breaches, or refrain from using it?
- You witness a colleague being harassed by another employee. Do you intervene directly, report it to HR, or stay out of it?
- A colleague frequently leaves work early or takes extended breaks without adjusting their timesheets. Do you report this behavior, confront them, or ignore it?
- You notice that your company’s hiring practices seem to overlook qualified candidates from diverse backgrounds. Do you bring this up with HR or assume it’s not your place?
- You notice a colleague frequently making errors that could jeopardize a project. Do you report their mistakes to a supervisor, discuss it with them first, or let it go?
- Your company is offered a lucrative contract from a client with a questionable reputation regarding environmental practices. Do you advise against taking the contract or go along with the company’s decision?
- You’re responsible for conducting performance reviews. A friend at work is underperforming. Do you give an honest review that could harm their career or a favorable one to maintain your friendship?
Ethical Dilemma in Nursing and healthcare
An ethical dilemma in nursing and healthcare arises when a healthcare professional encounters a situation where there are conflicting moral principles or ethical obligations, making it difficult to determine the right course of action. These dilemmas often involve situations where there is no clear right or wrong answer, and the decision can have significant consequences for patients, families, and healthcare providers.
Examples of Ethical Dilemmas in Nursing and Healthcare
- End-of-Life Care: A nurse must decide whether to honor a patient’s DNR order despite the family’s insistence on resuscitation.
- Informed Consent: A patient refuses a life-saving treatment, and the nurse must balance respecting the patient’s autonomy with the duty to advocate for their health.
- Resource Allocation: During a pandemic, nurses must decide which patients receive limited life-saving treatments like ventilators.
- Patient Privacy vs. Public Safety: A nurse must choose between maintaining patient confidentiality and informing public health authorities about a contagious disease.
- Mandatory Reporting: A nurse suspects child abuse but lacks concrete evidence and must decide whether to report it based on suspicion alone.
- Cultural Sensitivity: A nurse must respect a patient’s cultural beliefs that conflict with recommended medical treatments.
- Confidentiality vs. Family Involvement: A nurse must decide whether to share sensitive patient information with family members who are desperate for details.
- Pain Management: A nurse must decide whether to administer additional pain medication to a patient in severe pain despite potential addiction concerns.
- Vaccination Refusal: A nurse faces a dilemma when parents refuse to vaccinate their child, balancing respect for parental rights with public health concerns.
- Experimental Treatment: A nurse must decide whether to support a patient’s wish to try an unapproved experimental treatment.
- Healthcare Access: A nurse must decide how to provide the best care to uninsured patients with limited resources.
- Professional Boundaries: A nurse develops a close relationship with a patient and must navigate maintaining professional boundaries.
- Moral Distress: A nurse feels morally distressed when forced to participate in procedures that conflict with personal ethical beliefs.
- Conflict of Interest: A nurse must decide whether to recommend a particular treatment when aware of a potential financial benefit to the healthcare facility.
- Whistleblowing: A nurse discovers unethical practices in the workplace and must decide whether to report them, risking job security.
How to Solve Ethical Dilemma
Identify the problem.
- Clearly define the ethical issue.
- Determine who is affected by the dilemma.
2. Gather Information
- Collect all relevant facts.
- Understand the context and background of the dilemma.
- Identify the stakeholders involved.
3. Consider the Principles
- Reflect on ethical principles such as honesty, fairness, justice, and respect for others.
- Consider relevant laws and professional guidelines.
4. Evaluate the Options
- Generate a list of possible actions.
- Assess each option by considering the potential consequences for all stakeholders.
- Think about the long-term vs. short-term impact.
5. Seek Advice
- Consult with trusted colleagues, mentors, or ethical committees.
- Seek diverse perspectives to avoid personal bias.
6. Make a Decision
- Choose the option that aligns best with ethical principles and has the most favorable balance of outcomes.
- Ensure the decision is practical and feasible.
7. Implement the Decision
- Put the chosen course of action into practice.
- Communicate the decision clearly to all affected parties.
8. Reflect and Review
- After implementation, review the outcomes of the decision.
- Reflect on what was learned and how the process can be improved for future dilemmas.
Types of Ethical Dilemma
Here are some common types of ethical dilemmas
- Description : This occurs when a person or organization has multiple interests, and serving one interest might work against another. For example, a doctor who owns a stake in a pharmaceutical company might face a conflict between prescribing the best medication for a patient and promoting the company’s drugs.
- Example : A financial advisor who receives a commission for selling certain investment products may face a dilemma between recommending the best option for the client and promoting the product that earns them the highest commission.
- Description : This dilemma involves a conflict between telling the truth and being loyal to a person or organization. For instance, an employee might know about unethical practices in their company but feel loyal to their employer or colleagues.
- Example : An employee discovers that their close friend and coworker is falsifying expense reports. Reporting the friend would be truthful but could damage their relationship.
- Description : This type of dilemma arises when the needs or rights of an individual conflict with the needs or rights of a larger group. For example, quarantine measures during a pandemic protect public health but restrict individual freedoms.
- Example : A public health official must decide whether to disclose the identity of a person with a contagious disease to protect the community, potentially violating the individual’s privacy.
- Description : This dilemma involves making a choice between immediate benefits and long-term consequences. For instance, using non-renewable resources might provide short-term economic benefits but have negative long-term environmental impacts.
- Example : A company considers cutting costs by reducing its environmental safeguards, which would boost short-term profits but could lead to long-term environmental damage.
- Description : This dilemma occurs when there is a conflict between fairness and compassion. For example, a judge might face a decision between enforcing a strict punishment (justice) and showing leniency due to extenuating circumstances (mercy).
- Example : A manager must decide whether to terminate an underperforming employee who is struggling due to personal issues, balancing the need for workplace efficiency with compassion for the employee’s situation.
- Description : This dilemma arises when professional duties conflict with personal values or ethics. For example, a lawyer might have to defend a client they personally believe is guilty.
- Example : A journalist is assigned to cover a story that conflicts with their personal beliefs or values, challenging their professional responsibility to remain unbiased.
- Description : This type of dilemma involves balancing the right to privacy with the need for safety and security. For instance, surveillance measures can enhance security but may infringe on individuals’ privacy rights.
- Example : A government considers implementing widespread surveillance to prevent terrorist attacks, raising concerns about citizens’ privacy.
- Description : This dilemma arises when there is a conflict between respecting an individual’s autonomy and making decisions for their own good (paternalism). For instance, a doctor might face a decision between respecting a patient’s refusal of treatment and intervening to save their life.
- Example : A parent must decide whether to allow their teenager to make their own choices about school and career, respecting their autonomy, or to intervene to guide them toward what the parent believes is best.
How to Act and Answer an Ethical Dilemma in One’s Life
Ethical dilemmas sometimes appear in one’s life and cause the receiver to experience large amounts of stress the ethical dilemma creates. Not only that but the person will be at risk of cognitive dissonance when a person solves an ethical dilemma, which is highly dependent on the outcome conflicting with the person’s objectives , goals , ethics , and core values . If you want to learn more and understand various ethical dilemmas, you may use the various ethical dilemma examples in nursing, ethical dilemma examples in learning, and more on the links above.
Step 1: Analyze the Situation
Begin by analyzing the ethical dilemma. This means that you must try to deconstruct the dilemma you are in and take into account the various elements in play. You must determine if the dilemma is an ethical dilemma or a moral dilemma, as these have various observable connotations.
Step 2: List Out the Benefits and Consequences of Each Choice
If you have the time, you should try and list out the benefits and consequences each choice brings into play. This will help bring into perspective what each choice can bring to the table.
Step 3: Try to Create or Generate More Alternatives
If possible, you can brainstorm or conduct an introspective to try and generate or create more choices to answer the ethical dilemma. There might be possible alternatives that might not present themselves unless one thinks deeply about them.
Step 4a: Use the Value-Centered Approach
One of the best ways to answer an ethical dilemma is through the value-centered approach. This approach focuses more on the choice that creates the most value or benefits for the person making the said choice.
Step 4b: Choose the Choice that Brings the Least Amount of Consequences
Another way to answer an ethical dilemma is by choosing a choice that will bring the least amount of consequences to the people involved and affected by the ethical dilemma. This will require the person to weigh the benefits or consequences incurred by the choices.
Existence of ethical dilemmas
Ethical dilemmas are situations in which there is a conflict between two or more moral principles, making it challenging to decide on the right course of action. These dilemmas often arise in various aspects of life, including personal decisions, professional conduct, and societal issues. Here are a few examples illustrating the existence of ethical dilemmas:
- Medical Decisions : Healthcare professionals often face ethical dilemmas when deciding between treatments that might save a life but cause significant suffering, or when resources are limited and they must choose which patient to prioritize.
- Business Practices : Companies might encounter ethical dilemmas when balancing profit with social responsibility. For example, a business may need to decide whether to cut costs by outsourcing labor to countries with lower wages and poorer working conditions.
- Legal and Criminal Justice : Lawyers and judges may face ethical dilemmas in cases where the law conflicts with personal moral beliefs or when defending a client they know to be guilty.
- Environmental Issues : Ethical dilemmas arise when considering the trade-off between economic development and environmental conservation, such as deciding whether to support industries that provide jobs but also cause pollution.
- Personal Relationships : Individuals might encounter ethical dilemmas in their personal lives, such as choosing between telling the truth and sparing someone’s feelings or deciding whether to intervene in a friend’s harmful behavior.
What is an ethical dilemma?
An ethical dilemma is a situation where a person must choose between conflicting moral principles, making it challenging to determine the right course of action.
Why are ethical dilemmas significant?
Ethical dilemmas highlight the complexity of moral decision-making, helping individuals and organizations reflect on their values and responsibilities.
How do you resolve an ethical dilemma?
Resolving an ethical dilemma involves evaluating the consequences, considering ethical principles, and seeking advice from trusted sources.
Can ethical dilemmas be avoided?
Ethical dilemmas are often unavoidable but can be managed with clear guidelines, ethical training, and a strong moral framework.
What are common examples of ethical dilemmas?
How do ethical dilemmas impact businesses.
Ethical dilemmas can affect a business’s reputation, legal standing, and employee morale, highlighting the importance of ethical decision-making in corporate governance.
What role do personal values play in ethical dilemmas?
Personal values significantly influence how individuals perceive and resolve ethical dilemmas, shaping their ethical judgments and actions.
How do cultural differences influence ethical dilemmas?
Cultural differences can lead to varying interpretations of what constitutes an ethical dilemma, impacting decision-making processes in diverse environments.
Are there tools to help navigate ethical dilemmas?
Yes, tools like ethical frameworks, decision-making models, and professional guidelines can assist in navigating ethical dilemmas.
Why is it important to discuss ethical dilemmas?
Discussing ethical dilemmas fosters critical thinking, promotes ethical awareness, and prepares individuals to handle complex moral issues effectively.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
Home / Essay Samples / Life / Myself / Ethical Dilemma
Ethical Dilemma Essay Examples
The death penalty debate: weighing the pros and cons.
I chose the field of Law because I am interested in it. Law is my main topic because you can research many different things that have to do with our everyday lives. This is death penalty pros and cons essay in which I will briefly...
Death Penalty - Whether It's an Effective Sanction
The death penalty remains a highly debated topic within today’s society; albeit it presents itself as a sanction whose cons outweigh its pros, thus accentuating its unworthiness for reimplementation within Victoria. Though countries that maintain capital punishment for the most severe crimes have morphed into...
The Death Penalty Debate: an Argumentative Analysis
The topic of the death penalty or capital punishment has been one of controversy for a very long time now. The practice, which began many centuries ago, has seen various societies execute criminals for different capital offenses or crimes. In those countries where the death...
Ethical Dilemmas in Social Work - Personal Experience
This is one of the ethical dilemmas in social work essays where I will explore some ethical dilemmas I had during placement. I will be highlighting on a case that I dealt with as a form of my learning and development. I will be working...
The Heinz Dilemma: Moral Complexity in Everyday Life
The Heinz dilemma, is one where you have to question is stealing morally wrong? This is Heinz dilemma essay where I will give the answer to this question. Heinz’s wife was on her deathbed and the doctor informed him there was a drug that...
Ethical Dilemma: Ways to Solve It
To start ethical dilemma essay lets understand the terminology of this phrase. Ethical dilemma is a basically a problem in a decision-making process between possible options. These options can be approved from an ethical view, this can be extremely challenging for companies or employers. Ethical...
Endless Dilemma: Should Abortion Be Legal Or Illegal
One of the most debated topics in bioethics is abortion. This debate might not ever come to an agreement whether to legalize or illegalize abortion, but it’s very important that we, as a country, try. The problem with the debates in bioethics on abortion is...
A Fetus is not a Person: the Concept of Self-ownership
The United States was founded upon the notion that all persons are born with “inalienable rights.” However, even to this day, “life, liberty, and happiness” are not guaranteed to citizens of this nation, especially its women. America has allowed patriarchal and sexist influences to contaminate...
Abortion: the Role of Contraception and Religious Belief
Abortion ends a pregnancy before the fetus or the unborn child can live independently outside the mother. This issue happens approximately before 24 weeks of pregnancy. This essay considers that an abortion is a crime. Even if it is a fetus, it is still a...
Ethical Dilemma in Nursing: Chemically Impaired Nurses
Chemically impaired nurse on duty is the ethical dilemma in nursing that I will be writing about in the essay. It can be easy for a nurse to want to be chemically impaired due to stress of trying to keep someone alive and getting them...
Trying to find an excellent essay sample but no results?
Don’t waste your time and get a professional writer to help!
You may also like
- Humor Essays
- Self Reflection Essays
- Who Am I Essays
- Soul Essays
- Reputation Essays
- Belief Essays
- Maturity Essays
- Self Assessment Essays
- My Future Essays
- Coming of Age Essays
About Ethical Dilemma
An ethical dilemma describes a conflict between two morally correct courses of action, it takes place in a decision-making context where any of the available options requires the agent to violate or compromise on their ethical standards.
Truth vs loyalty, short-term vs long-term, individual vs community, and justice vs mercy.
samplius.com uses cookies to offer you the best service possible.By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .--> -->