Revision Checklist: Informational Writing
Revision is an essential part of the writing process in which we step back and re-envision the draft in order to improve a piece of writing. With this middle-school revision checklist, students will be guided to review their writing with a critical eye, focusing on their use of evidence, the overall structure, the use of language, and more. Students will use this checklist to evaluate their own informational writing draft. They will then exchange essays with a classmate for another review, and use the feedback to guide their next set of revisions.

View aligned standards
Peer Review Checklist
Janelle schwartz, english 201.
This is to give you an idea of the type of things you should be looking for and accomplishing in both your own paper and that of your peer(s). Use what follows as a kind of checklist for determining what is working effectively in a paper and what is not.
Introduction
Has the writer (either yourself or your classmate) clearly expressed the question (major claim, thesis) that he/she has selected to analyze? What is that question?
Is there any unnecessary information included in the introduction?
Having read the entire essay, suggest an alternate way to begin the essay.
Having read the entire essay, does the introduction fit the paper?
What are the main points that are being made in each paragraph? Briefly outline the point of each paragraph and sketch the evidence given in support for each.
How is the evidence linked to the main point of the paragraph? And to the main point of the essay?
Is there any unnecessary information throughout the body of the paper, such as plot summary, excessive quotation,
or unsupported claims?
Has the writer restated (not simply repeated) the major claim of the paper in light of its discussion throughout the paper? In other words, what should the reader have learned by the end of the argument?
What is your understanding of the initial question after reading the paper? Has this understanding been adequately expressed? And does it open up the major claim to the question of its implications? (Has this major claim ultimately been placed into a broader perspective or context?)
Suggest an alternate ending to the argument. General/Misc
Suggest an alternate title. Does it express “in a nutshell” the essay’s theme? Has it followed the proper “title: subtitle” format? [Note: This assumes the paper already has a title—thus, every paper must have a title!]
What confuses you about the draft? (For example, a certain word choice, the topic and/or its presentation, the explanation of something in particular.)
Does the flow of the essay break down at any point? In other words, does the essay become hard to read or lose its coherence? Where? And how might you fix it?
Does the essay remain within the chosen text(s)? If there are any generalizations, speculations, clichés, idiomatic expressions, or colloquialisms, underline them so that you can point them out to your peer(s).
What has the writer done well in his/her essay? Provide positive comments about the strength(s) of the essay.

Grammar / Vocabulary
Middle school writing instruction checklist.
- No Comments
I’ve been reflecting on what I would consider the non-negotiables of writing instruction at the middle school level. Over the years, I’ve shifted how I teach writing to students. Along the way, new instructional practices have been added while others have been left behind.
To the writing teacher reading this blog post and nodding your head but wondering how you can shift instruction within a school system that doesn’t allow you to, please know I see you, and this blog post is for you. Maybe you are part of a team that has common lessons, and you know it will be a tough sell to get other team members on board to make a change. You could be required to teach using a certain curriculum and feel uninspired and stuck. If you fall into one of these categories or a similar category, I’m including a free download that includes an instruction checklist. This checklist is meant to be used as an avenue for productive conversation with your curriculum coordinator, department chair, grade level content colleagues, PLC members, etc. Download the checklist by clicking on the image below.
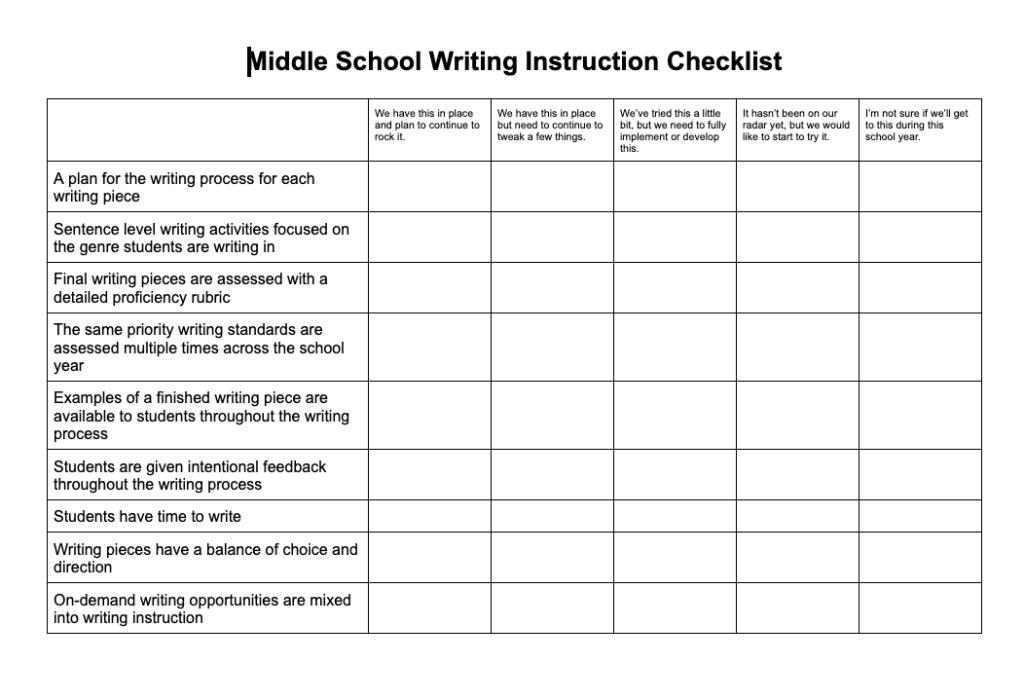
Non-Negotiable 1: A plan for the writing process
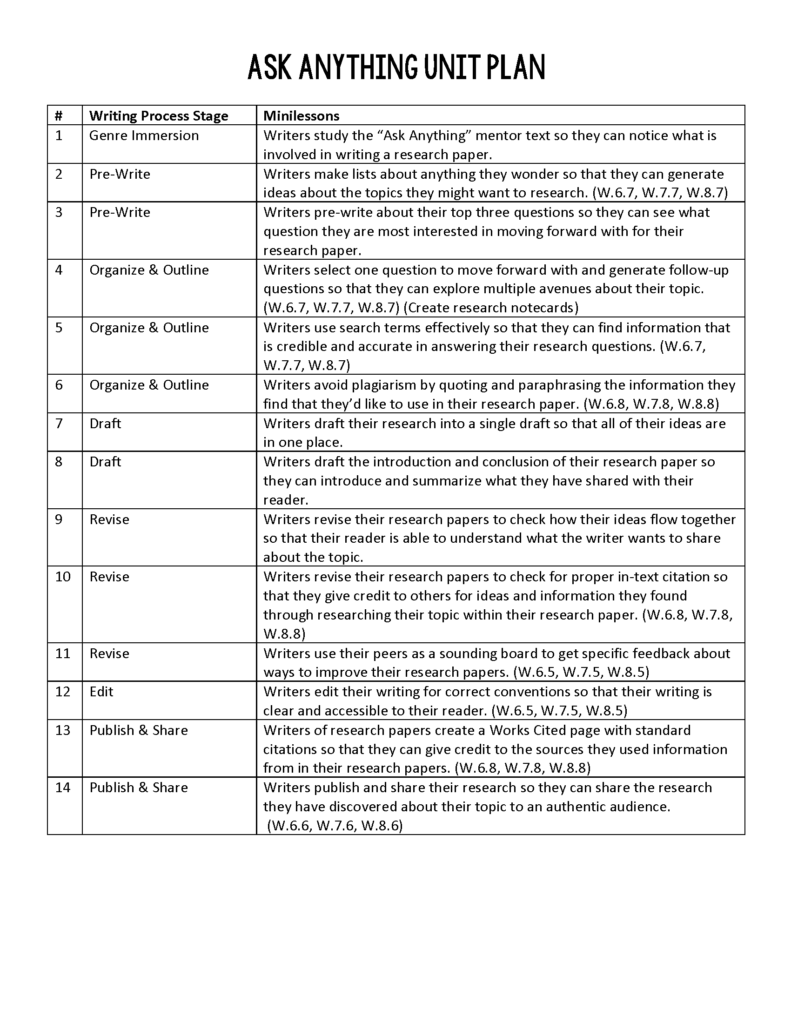
If students are going to produce a piece of writing, you should have a plan for how you’re going to get them from the beginning of the writing process to a published piece of writing. I have found the sweet spot of instructional time to spend on a single writing piece to be 2-3 weeks. I distribute the instructional days across the writing process and create a writing lesson for each day that will bring students from start to finish. The pieces of the writing process that I use are genre immersion, brainstorm & pre-write, organize & outline, draft, revise, edit, publish & share. Below is an example of a unit plan from my “ Ask Anything ” research writing unit that shows each writing lesson and what part of the writing process each writing lesson is in.
Non-Negotiable 2: Sentence level writing activities focused on the genre students are writing in.
It is clear students need sentence level writing activities. We must explicitly teach students how to write in complete sentences. Teaching grammar and writing conventions in isolation apart from students writing is not going to work. If we truly want to see the transfer of correct conventions into student writing, we must teach grammar through student writing.
I do sentence level writing activities as bellringers (do nows, class starters, etc.), focusing on a different types of sentences (complex, compound, sentence with an appositive, listing items in a series, sentence with two adjectives describing one noun) across the writing unit. As I teach about the different types of sentences, I model writing these types of sentences from the topic of our mentor text for the current writing unit. As students rehearse writing these types of sentences, they write the sentences with their topic for the current writing unit. Students don’t have to use the sentences they write in their final writing piece, but a lot of students do use the sentences they rehearse or variations of the sentences they try out. We rehearse the same types of sentences during each writing unit, but switch out the content we’re writing about to match our current writing unit topic.
Here are some examples below of what sentence level instruction and example sentences look like.

Non-Negotiable 3: Final writing pieces are assessed with a detailed proficiency rubric
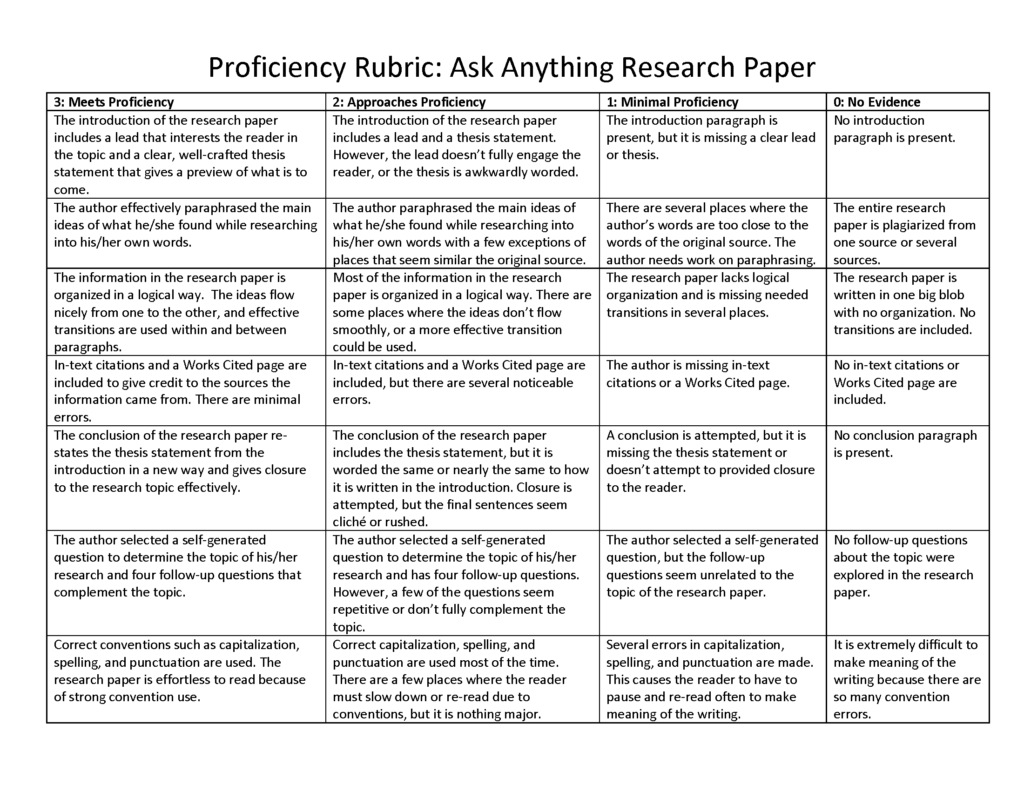
I’ve tried so many different types of rubrics over the years. Once my school made the shift to Standards Based Grading and Learning, I fell in love with proficiency rubrics. For teachers who work as a team and want to calibrate grading, proficiency rubrics are the way to go. Proficiency rubrics also save so much time on giving students feedback on their writing. If the proficiency rubric is written specifically for the writing piece it is assessing, then feedback is built into the rubric. Here is an example of the proficiency rubric that goes along with my “ Ask Anything ” writing unit.
Non-Negotiable 4: The same priority writing standards are assessed multiple times across the school year.
Standards ask us to have students write in different genres of writing: narrative, persuasive, explanatory/informative, research. However, we need to be clear on the common threads that will be taught and assessed during each unit, regardless of genre. Here are a few ideas: -Transitions/Sentence Fluency -Organization -Word Choice -Conventions (capitalization, spelling, punctuation) -Ideas meeting purpose of the genre
Non-Negotiable 5: Examples of a finished writing piece are available to students throughout the writing process
Students need to see what the end product is going to look like and sound like. I recommend always completing the writing piece you’re asking students to do. It’s great perspective to know what to teach for and how to encourage students throughout the writing process. Additionally, if you do through the writing process with students, you not only have a published piece to share with them, you also have your brainstorming, prewriting, outline, initial draft, revisions, edits, etc. Being able to model to students how to do each step of the writing process is so authentic and powerful.
Having published student pieces from prior school years is another great way to acquire mentor texts to share with students. The past work of students with have different voices and topics than we would write as adults. It will also potentially give students a more attainable mentor text to shoot for.

Non-Negotiable 6: Students are given intentional feedback throughout the writing process
When writing is a process that spans over several weeks, teachers need to be intentional about when and how feedback is going to happen. -Plan checkpoints on the unit plan of when you’re going to look over student writing and give feedback during the writing process. I really love Google Classroom for this because I have access to student work at any point in the writing process. It’s quick and easy for me to hop onto students’ drafts and look through how they’re going and leave comments. -Use peer feedback opportunities as a place for students to read their writing to each other and get verbal feedback. I’m not a huge fan of students swapping writing and doing correct-alls to each others’ writing because that’s where we lose what individual students know in the writing process. When students read their writing aloud and have conversations with other students as they seek and provide feedback to each other, great learning happens in that space. -Use the proficiency rubric to have students self-assess their writing at different points of the writing process. Proficiency rubrics are great for self-assessment and can be used piece-by-piece and not as an overwhelming whole.
Non-Negotiable 7: Students have time to write
Students need time and space during the class period to hear and see what writing is like. They need to feel creative energy and share to create a community of writers. During writing units, I always aim to give students 15 minutes or more of writing time daily.
Non-Negotiable 8: Writing pieces have a balance of choice and direction
As an adult, I enjoy making my own choices, but I also have times when I appreciate having a specific direction and goal. I think students are the same way and thrive when there is a balance of choice and direction. There is one extreme in writing instruction is so structured that students barely have choices in the words they use. Another extreme rests in this free-flowing writing instruction where students can write whatever they want, whenever they want.
I’m a believer that writing should be taught as writing units with clear starting and stopping points. The choice is in the topic and the direction comes from having an expected structure for the writing piece.
Non-Negotiable 9: On-demand writing opportunities are mixed into writing instruction
Writing is a process, but if we always teach writing as a 3-week process without the opportunity for students to write in on-demand formats, we run the risk of producing writers who are perfectionists. Students need to understand that not every piece of writing is going to go through days of revising and editing with feedback given every step of the way. Sometimes we need to produce writing in a single setting, get it done, and move on.
Using on-demand writing as a pre-assessment and/or a post-assessment in a writing unit is a great way to see what students learn and retain. In the “Ask Anything” writing unit I’ve been referring to throughout this post, an on-demand writing opportunity might look like giving students an article and asking them to respond to a research question answered in the article.
These are 9 ideas for what should be included in writing instruction at the middle school level. Don’t forget you can download the free checklist as a resource for yourself or your teaching team here .
Let's Be Teacher Friends
Let me make your life a little easier. Subscribe to receive teaching ideas, inspiration, and free resources.
Copyright 2020
Grab my FREE literature circle resource!
Bell Ringers
Teaching literary analysis in middle school.
My literary analysis resources have basically been seven or eight years in the making.
I don’t know about you, but when I first realized I needed to be teaching literary analysis to a bunch of twelve and thirteen year-olds, I didn’t even know where to begin.
I had been teaching upper elementary in the three years prior, and we had done some on-demand literary analysis reading responses, but really digging into a literary analysis essay overwhelmed me.
Truth be told, my teaching strengths at the time were primarily reading and math. I had always had to dig deep to find my writing teacher voice.
But, I was now a seventh and eighth grade ELA teacher who could no longer hope her students picked up some writing skills along the way.
So I did what any good teacher would do…. I Googled how to teach…
I think I Googled something like, “Examples of middle school literary analysis essays.”
Nothing showed up in Google.
Then I Googled, “How do you teach literary analysis essays?”
I was able to find an example of a college-level literary analysis essay…
… and that was about it.
Because I couldn’t really find what I was looking for, I began creating and practicing each step of the literary analysis essay before I taught it.
This also created a ton of exemplars for my students.

I broke down each area of a literary analysis essay into lessons, chunks, chart papers, reference materials, and writing examples.
In the beginning, it was to get my brain wrapped around things, but not surprisingly it was exactly what my students needed too.
I literally learned how to write a literary analysis essay in front of them.
I would type my rough drafts as they were working and I could stop them as I came to struggles.
My mini-lessons were based on challenges I was having and again, not surprisingly the same challenges they were having.
I could also make reference pages (like the ones in your freebie) as we went along in the unit, because I could see what terms and concepts they needed constant reminders and help with.
Want to know what happened?
My student’s ELA proficiency scores increased 45% in one year and almost 70% in just two years. Those are not typos.
>> CLICK HERE << to download the FREE Literary Analysis Reference Booklet.

- Read more about: Middle School Reading , Middle School Writing
You might also like...

Teach Students How to Effectively Conduct Research

How to Boost Reading Engagement with Book Clubs
4 Station Ideas for Middle School ELA Skills
Get your free middle school ela pacing guides with completed scopes and sequences for the school year..

My ELA scope and sequence guides break down every single middle school ELA standard and concept for reading, writing, and language in 6th, 7th, and 8th grade. Use the guides and resources exactly as is or as inspiration for you own!
Meet Martina

I’m a Middle School ELA teacher committed to helping you improve your teaching & implement systems that help you get everything done during the school day!
Let's Connect
Member login.
PRIVACY POLICY
TERMS OF USE
WEBSITE DISCLAIMERS
MEMBERSHIP AGREEEMENT
© The Hungry Teacher • Website by KristenDoyle.co • Contact Martina
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
The Beginner's Guide to Writing an Essay | Steps & Examples
An academic essay is a focused piece of writing that develops an idea or argument using evidence, analysis, and interpretation.
There are many types of essays you might write as a student. The content and length of an essay depends on your level, subject of study, and course requirements. However, most essays at university level are argumentative — they aim to persuade the reader of a particular position or perspective on a topic.
The essay writing process consists of three main stages:
- Preparation: Decide on your topic, do your research, and create an essay outline.
- Writing : Set out your argument in the introduction, develop it with evidence in the main body, and wrap it up with a conclusion.
- Revision: Check your essay on the content, organization, grammar, spelling, and formatting of your essay.

Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Essay writing process, preparation for writing an essay, writing the introduction, writing the main body, writing the conclusion, essay checklist, lecture slides, frequently asked questions about writing an essay.
The writing process of preparation, writing, and revisions applies to every essay or paper, but the time and effort spent on each stage depends on the type of essay .
For example, if you’ve been assigned a five-paragraph expository essay for a high school class, you’ll probably spend the most time on the writing stage; for a college-level argumentative essay , on the other hand, you’ll need to spend more time researching your topic and developing an original argument before you start writing.
| 1. Preparation | 2. Writing | 3. Revision |
|---|---|---|
| , organized into Write the | or use a for language errors |
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Before you start writing, you should make sure you have a clear idea of what you want to say and how you’re going to say it. There are a few key steps you can follow to make sure you’re prepared:
- Understand your assignment: What is the goal of this essay? What is the length and deadline of the assignment? Is there anything you need to clarify with your teacher or professor?
- Define a topic: If you’re allowed to choose your own topic , try to pick something that you already know a bit about and that will hold your interest.
- Do your research: Read primary and secondary sources and take notes to help you work out your position and angle on the topic. You’ll use these as evidence for your points.
- Come up with a thesis: The thesis is the central point or argument that you want to make. A clear thesis is essential for a focused essay—you should keep referring back to it as you write.
- Create an outline: Map out the rough structure of your essay in an outline . This makes it easier to start writing and keeps you on track as you go.
Once you’ve got a clear idea of what you want to discuss, in what order, and what evidence you’ll use, you’re ready to start writing.
The introduction sets the tone for your essay. It should grab the reader’s interest and inform them of what to expect. The introduction generally comprises 10–20% of the text.
1. Hook your reader
The first sentence of the introduction should pique your reader’s interest and curiosity. This sentence is sometimes called the hook. It might be an intriguing question, a surprising fact, or a bold statement emphasizing the relevance of the topic.
Let’s say we’re writing an essay about the development of Braille (the raised-dot reading and writing system used by visually impaired people). Our hook can make a strong statement about the topic:
The invention of Braille was a major turning point in the history of disability.
2. Provide background on your topic
Next, it’s important to give context that will help your reader understand your argument. This might involve providing background information, giving an overview of important academic work or debates on the topic, and explaining difficult terms. Don’t provide too much detail in the introduction—you can elaborate in the body of your essay.
3. Present the thesis statement
Next, you should formulate your thesis statement— the central argument you’re going to make. The thesis statement provides focus and signals your position on the topic. It is usually one or two sentences long. The thesis statement for our essay on Braille could look like this:
As the first writing system designed for blind people’s needs, Braille was a groundbreaking new accessibility tool. It not only provided practical benefits, but also helped change the cultural status of blindness.
4. Map the structure
In longer essays, you can end the introduction by briefly describing what will be covered in each part of the essay. This guides the reader through your structure and gives a preview of how your argument will develop.
The invention of Braille marked a major turning point in the history of disability. The writing system of raised dots used by blind and visually impaired people was developed by Louis Braille in nineteenth-century France. In a society that did not value disabled people in general, blindness was particularly stigmatized, and lack of access to reading and writing was a significant barrier to social participation. The idea of tactile reading was not entirely new, but existing methods based on sighted systems were difficult to learn and use. As the first writing system designed for blind people’s needs, Braille was a groundbreaking new accessibility tool. It not only provided practical benefits, but also helped change the cultural status of blindness. This essay begins by discussing the situation of blind people in nineteenth-century Europe. It then describes the invention of Braille and the gradual process of its acceptance within blind education. Subsequently, it explores the wide-ranging effects of this invention on blind people’s social and cultural lives.
Write your essay introduction
The body of your essay is where you make arguments supporting your thesis, provide evidence, and develop your ideas. Its purpose is to present, interpret, and analyze the information and sources you have gathered to support your argument.
Length of the body text
The length of the body depends on the type of essay. On average, the body comprises 60–80% of your essay. For a high school essay, this could be just three paragraphs, but for a graduate school essay of 6,000 words, the body could take up 8–10 pages.
Paragraph structure
To give your essay a clear structure , it is important to organize it into paragraphs . Each paragraph should be centered around one main point or idea.
That idea is introduced in a topic sentence . The topic sentence should generally lead on from the previous paragraph and introduce the point to be made in this paragraph. Transition words can be used to create clear connections between sentences.
After the topic sentence, present evidence such as data, examples, or quotes from relevant sources. Be sure to interpret and explain the evidence, and show how it helps develop your overall argument.
Lack of access to reading and writing put blind people at a serious disadvantage in nineteenth-century society. Text was one of the primary methods through which people engaged with culture, communicated with others, and accessed information; without a well-developed reading system that did not rely on sight, blind people were excluded from social participation (Weygand, 2009). While disabled people in general suffered from discrimination, blindness was widely viewed as the worst disability, and it was commonly believed that blind people were incapable of pursuing a profession or improving themselves through culture (Weygand, 2009). This demonstrates the importance of reading and writing to social status at the time: without access to text, it was considered impossible to fully participate in society. Blind people were excluded from the sighted world, but also entirely dependent on sighted people for information and education.
See the full essay example
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

The conclusion is the final paragraph of an essay. It should generally take up no more than 10–15% of the text . A strong essay conclusion :
- Returns to your thesis
- Ties together your main points
- Shows why your argument matters
A great conclusion should finish with a memorable or impactful sentence that leaves the reader with a strong final impression.
What not to include in a conclusion
To make your essay’s conclusion as strong as possible, there are a few things you should avoid. The most common mistakes are:
- Including new arguments or evidence
- Undermining your arguments (e.g. “This is just one approach of many”)
- Using concluding phrases like “To sum up…” or “In conclusion…”
Braille paved the way for dramatic cultural changes in the way blind people were treated and the opportunities available to them. Louis Braille’s innovation was to reimagine existing reading systems from a blind perspective, and the success of this invention required sighted teachers to adapt to their students’ reality instead of the other way around. In this sense, Braille helped drive broader social changes in the status of blindness. New accessibility tools provide practical advantages to those who need them, but they can also change the perspectives and attitudes of those who do not.
Write your essay conclusion
Checklist: Essay
My essay follows the requirements of the assignment (topic and length ).
My introduction sparks the reader’s interest and provides any necessary background information on the topic.
My introduction contains a thesis statement that states the focus and position of the essay.
I use paragraphs to structure the essay.
I use topic sentences to introduce each paragraph.
Each paragraph has a single focus and a clear connection to the thesis statement.
I make clear transitions between paragraphs and ideas.
My conclusion doesn’t just repeat my points, but draws connections between arguments.
I don’t introduce new arguments or evidence in the conclusion.
I have given an in-text citation for every quote or piece of information I got from another source.
I have included a reference page at the end of my essay, listing full details of all my sources.
My citations and references are correctly formatted according to the required citation style .
My essay has an interesting and informative title.
I have followed all formatting guidelines (e.g. font, page numbers, line spacing).
Your essay meets all the most important requirements. Our editors can give it a final check to help you submit with confidence.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
An essay is a focused piece of writing that explains, argues, describes, or narrates.
In high school, you may have to write many different types of essays to develop your writing skills.
Academic essays at college level are usually argumentative : you develop a clear thesis about your topic and make a case for your position using evidence, analysis and interpretation.
The structure of an essay is divided into an introduction that presents your topic and thesis statement , a body containing your in-depth analysis and arguments, and a conclusion wrapping up your ideas.
The structure of the body is flexible, but you should always spend some time thinking about how you can organize your essay to best serve your ideas.
Your essay introduction should include three main things, in this order:
- An opening hook to catch the reader’s attention.
- Relevant background information that the reader needs to know.
- A thesis statement that presents your main point or argument.
The length of each part depends on the length and complexity of your essay .
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . Everything else you write should relate to this key idea.
The thesis statement is essential in any academic essay or research paper for two main reasons:
- It gives your writing direction and focus.
- It gives the reader a concise summary of your main point.
Without a clear thesis statement, an essay can end up rambling and unfocused, leaving your reader unsure of exactly what you want to say.
A topic sentence is a sentence that expresses the main point of a paragraph . Everything else in the paragraph should relate to the topic sentence.
At college level, you must properly cite your sources in all essays , research papers , and other academic texts (except exams and in-class exercises).
Add a citation whenever you quote , paraphrase , or summarize information or ideas from a source. You should also give full source details in a bibliography or reference list at the end of your text.
The exact format of your citations depends on which citation style you are instructed to use. The most common styles are APA , MLA , and Chicago .
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked.
- How long is an essay? Guidelines for different types of essay
- How to write an essay introduction | 4 steps & examples
- How to conclude an essay | Interactive example
More interesting articles
- Checklist for academic essays | Is your essay ready to submit?
- Comparing and contrasting in an essay | Tips & examples
- Example of a great essay | Explanations, tips & tricks
- Generate topic ideas for an essay or paper | Tips & techniques
- How to revise an essay in 3 simple steps
- How to structure an essay: Templates and tips
- How to write a descriptive essay | Example & tips
- How to write a literary analysis essay | A step-by-step guide
- How to write a narrative essay | Example & tips
- How to write a rhetorical analysis | Key concepts & examples
- How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples
- How to write an argumentative essay | Examples & tips
- How to write an essay outline | Guidelines & examples
- How to write an expository essay
- How to write the body of an essay | Drafting & redrafting
- Kinds of argumentative academic essays and their purposes
- Organizational tips for academic essays
- The four main types of essay | Quick guide with examples
- Transition sentences | Tips & examples for clear writing
What is your plagiarism score?

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Essay Writing: Writer's Checklist Introduction: Is the main idea (i.e., the writer's opinion of the story title) stated clearly? Is the introductory paragraph interesting? Does it make the reader want to keep on reading? Body Paragraphs: Does each body paragraph have a clear topic sentence that is related to the main idea of the essay?
It is helpful to put the editing checklist on an overhead projector or document camera so all students can see the process. After the self-edit is complete, discuss the process with the students. Next, choose another student to serve as the peer editor for the piece that was just self-edited. Have the two students sit in the middle of the class ...
Microsoft Word - K12ELA6-5.3.3.1-Amy Kasten's-Argumentative-Essay-Revision-Checklist.docx. Argumentative Essay: Revision Checklist. REVISION CHECKLIST: Directions: Find, highlight, and revise these elements in your informational article. **If you don't have one of these things, ADD it!**. _____ The essay includes an attention-grabbing hook ...
4. Having the work published in school or town publications 5. Sending the work to other interested parties, companies, contests, newspapers, or literary magazines 6. Publishing pieces of writing in bound book form to be shared by other students in the school and community 7. Organizing a classroom or school read-a-thon day so that writers
Paragraph 5: Conclusion. -- It's time to wrap up your essay and tie it all together. Restate your thesis statement. Summarize your supporting points. Refer back to your attention-getting device in the introduction paragraph. REMEMBER: This is not the time to introduce new ideas or new quotes.
Good Argumentative Essay Topic Ideas (and Free, too!) With these 33 new argumentative essay topics for middle school students, you can help your students learn more about what makes a good argument and how to evaluate and decipher so-called "evidence.". As they explore topics like the ways in which schools handle bullying and whether or not ...
Peer-Editing Form for Argumentative Essay Directions: Check your partner's paper for the following items and write comments. Topic Comments Does the introduction engage the reader? Copy the thesis of the essay. What side is the writer on? What are two claims that the writer mentions from the other side? 1. 2. Does the writer refute these
Have your students use this editing checklist to make improvements on an essay they are working on. Then have them exchange essays and checklists with a peer for a second review! With an emphasis on grammar, mechanics, and style, this checklist is a great way to help middle-school writers hone their editing skills and gain familiarity with the ...
With this middle-school revision checklist, students will be guided to review their writing with a critical eye, focusing on their use of evidence, the overall structure, the use of language, and more. Students will use this checklist to evaluate their own informational writing draft. They will then exchange essays with a classmate for another ...
Peer Editing Form. Ask a classmate to read through what you have written, check off the box next to each question, and write a brief comment that will help improve your work. Underlining and changes are permitted if done in pencil.
With our Essay Editing Checklist - Middle School, giving your learners the guidelines to ensure that what they're currently working on is the best it can be is now easy peasy. With comprehensive points and a clean layout, the Essay Editing Checklist - Middle School is an easy-to-follow and intuitive-to-use checklist that features questions ...
The five paragraph essay is a staple of middle school writing. This essay format is an effective way to organize any assignment that requires a student to present, explain, examine, or discuss material. ... 5 Paragraph Essay Checklist Introduction Paragraph : Grabber 3 main points to support thesis Thesis
Janelle Schwartz, English 201. This is to give you an idea of the type of things you should be looking for and accomplishing in both your own paper and that of your peer (s). Use what follows as a kind of checklist for determining what is working effectively in a paper and what is not. Introduction. Has the writer (either yourself or your ...
This checklist is meant to be used as an avenue for productive conversation with your curriculum coordinator, department chair, grade level content colleagues, PLC members, etc. Download the checklist by clicking on the image below. Non-Negotiable 1: A plan for the writing process. If students are going to produce a piece of writing, you should ...
Peer Editing in Middle School. Middle school students are their own people. They're finding their way in life and thrive on social activity. Capitalize on this angle in your writing class by ...
FREE Middle/High School Digital Resources; Career, Technical, Agricultural Education; ... Keep in mind that each checklist is meant to be a broad overview of student expectations and not a comprehensive list—but they do include guidance for scoring based on the rubrics. Checklists may be consulted by the student in advance of writing (as a ...
Editing Checklist for Self- and Peer Editing Directions: Edit your written work using the Self-Edit columns, fixing any errors you notice. Then, have a peer complete the Peer Edit columns while you observe. Self-Edit Peer Edit Checklist Items After completing each step, place a check here. Checklist Items After completing each step, place a ...
Five-Paragraph Essay Writing Rubric. Thesis statement/topic idea sentence is clear, correctly placed, and restated in the closing sentence. Your three supporting ideas are briefly mentioned. Thesis statement/topic idea sentence is either unclear or incorrectly placed, and it's restated in the closing sentence.
My student's ELA proficiency scores increased 45% in one year and almost 70% in just two years. Those are not typos. >> CLICK HERE << to download the FREE Literary Analysis Reference Booklet. I broke down each area of teaching literary analysis in middle school into lessons, chunks, chart papers, reference materials, and examples.
Quick Revision Checklist Organization Organization fits the assignment and topic. Sentences and paragraphs are logically ordered. Writing uses transitions. The writing has a clear introduction, body, and conclusion. Ideas/Content Ideas are interesting, accurate, and appropriate. Ideas are clear.
Description. This checklist leads students through a series of revising and editing questions for an expository essay. It also has columns for self and peer editing check-offs, and a space for comments. Great for teaching students to think about their writing before they publish! Total Pages. 1 page.
Essay writing process. The writing process of preparation, writing, and revisions applies to every essay or paper, but the time and effort spent on each stage depends on the type of essay.. For example, if you've been assigned a five-paragraph expository essay for a high school class, you'll probably spend the most time on the writing stage; for a college-level argumentative essay, on the ...
This essay writing checklist is a wonderful tool that can be provided for students to help guide the essay writing process. ... Essay Writing Checklist - High School and Middle School. Rated 4.83 out of 5, based on 6 reviews. 6 Ratings. View Preview. Previous Next. Preview. A Teacher's Teacher. 164 Followers. Follow. Grade Levels. 7 th - 11 th ...