How to Write a Discursive Essay: Awesome Guide and Template

The term "discursive" comes from the Latin word "discursus," meaning to move around or traverse. A discursive essay reflects this by exploring multiple viewpoints and offering a thorough discussion on a specific topic.
In this article, our term paper writing service will define what a discursive essay is, distinguish it from an argumentative essay, provide practical tips on how to write one effectively, and examine essay examples to illustrate its structure and approach.

What Is a Discursive Essay
A discursive essay is a type of essay where you discuss a topic from various viewpoints. The goal is to provide a balanced analysis by exploring different perspectives. Your essay should present arguments on the topic, showing both sides to give a comprehensive view.
Features of discursive essays typically include:
- Thesis Statement: Clearly states your position or argument on the topic.
- Discussion of Perspectives: Examines different viewpoints or aspects of the issue.
- Evidence and Examples: Supports arguments with relevant evidence and examples.
- Counterarguments: Addresses opposing viewpoints to strengthen your position.
- Logical Organization: Structured to present arguments coherently and persuasively.
Ready to Transform Your Essays?
From discursive writing to academic triumphs, let your words soar with our essay writing service!
How to Write a Discursive Essay
Writing a discursive essay involves examining a topic from different angles and presenting balanced viewpoints. Whether you're tackling a controversial issue or analyzing a complex subject, following these steps will help you craft a well-structured discursive essay.
.webp)
1. Understand the Topic
Before you start writing, make sure you grasp the topic thoroughly. Identify key terms and concepts to clarify what you need to discuss. Consider the different aspects and perspectives related to the topic that you will explore in your essay.
2. Research and Gather Evidence
Research is crucial for a discursive essay. Gather information from reliable sources such as books, academic journals, and reputable websites. Collect evidence that supports various viewpoints on the topic. Note down quotes, statistics, and examples that you can use to strengthen your arguments.
3. Plan Your Structure
Organize your essay effectively to ensure clarity and coherence. Start with an introduction that states your thesis or main argument. Outline the main points or perspectives you will discuss in the body paragraphs. Each paragraph should focus on a different aspect or viewpoint, supported by evidence. Consider including a paragraph that addresses counterarguments to strengthen your position.
4. Write the Introduction
Begin your essay with a compelling introduction that grabs the reader's attention. Start with a hook or an intriguing fact related to the topic. Clearly state your thesis statement, which outlines your position on the issue and previews the main points you will discuss. The introduction sets the tone for your essay and provides a roadmap for what follows.
5. Develop the Body Paragraphs
The body of your essay should present a balanced discussion of the topic. Each paragraph should focus on a different perspective or argument. Start each paragraph with a clear topic sentence that introduces the main idea. Support your points with evidence, examples, and quotes from your research. Ensure smooth transitions between paragraphs to maintain the flow of your argument.
6. Conclude Effectively
Wrap up your essay with a strong conclusion that summarizes the main points and reinforces your thesis statement. Avoid introducing new information in the conclusion. Instead, reflect on the significance of your arguments and how they contribute to the broader understanding of the topic. End with a thought-provoking statement or a call to action, encouraging readers to consider the complexities of the issue.
If you find this kind of writing challenging, simply say ' write my paper ', and professional writers will handle it for you.
Discursive Guide Checklist
| Aspect 📝 | Checklist ✅ |
|---|---|
| Understanding the Topic | Have I thoroughly understood the topic and its key terms? Have I identified the different perspectives or viewpoints related to the topic? |
| Research and Evidence | Have I conducted comprehensive research using reliable sources? Have I gathered sufficient evidence, including quotes, statistics, and to support each perspective? |
| Structuring the Essay | Have I planned a clear and logical structure for my essay? Does my introduction include a strong thesis statement that outlines my position? |
| Introduction | Does my introduction effectively grab the reader's attention? Have I clearly stated my thesis statement that previews the main arguments? |
| Body Paragraphs | Do my body paragraphs each focus on a different perspective or argument? Have I provided evidence and examples to support each argument? |
| Counterarguments | Have I addressed potential counterarguments to strengthen my position? Have I acknowledged and responded to opposing viewpoints where necessary? |
| Conclusion | Does my conclusion effectively summarize the main points discussed? Have I reinforced my thesis statement and the significance of my arguments? |
| Clarity and Coherence | Are my ideas presented in a clear and coherent manner? Do my paragraphs flow logically from one to the next? |
| Language and Style | Have I used clear and concise language throughout the essay? Is my writing style appropriate for the academic context, avoiding overly casual language? |
| Editing and Proofreading | Have I proofread my essay for grammar, punctuation, and spelling errors? Have I checked the overall structure and flow of my essay for coherence? |
Discursive Essay Examples
Here, let’s take a look at our samples and see how different topics are discussed from different viewpoints in real discursive essays.
If you found these examples helpful, you can order custom essay now and receive one on any topic you choose.
Discursive Essay Topics
Here are a range of topics that encourage exploration of different perspectives and critical analysis. Choose a topic that interests you and allows for a balanced analysis of arguments and evidence.
- Should governments impose higher taxes on sugary drinks to combat obesity?
- Is homeschooling beneficial for children's education?
- Should the use of drones for military purposes be restricted?
- Should the legal drinking age be lowered or raised?
- Is online education as effective as traditional classroom learning?
- Should parents be held legally responsible for their children's actions?
- Is artificial intelligence a threat to human employment?
- Are video games a positive or negative influence on young people?
- Should the voting age be lowered to 16?
- Should schools teach mindfulness and meditation techniques?
- Is cultural diversity in the workplace beneficial for companies?
- Should prisoners have the right to vote?
- Is social media addiction a real problem?
- Should plastic packaging be replaced with eco-friendly alternatives?
- Is it ethical to clone animals for agricultural purposes?
- Should the government provide subsidies for electric vehicles?
- Is privacy more important than national security?
- Should school uniforms be mandatory?
- Is renewable energy the future of our planet?
- Should parents have access to their children's social media accounts?
By the way, we also have a great collection of narrative essay topics to inspire your creativity.
What is the Difference Between a Discursive and Argumentative Essay
Discursive essays and argumentative essays share similarities but have distinct differences in their approach and purpose. While both essay types involve critical thinking and analysis, the main difference lies in the writer's approach to the topic and the overall goal of the essay—whether it aims to explore and discuss multiple perspectives (discursive) or to argue for a specific viewpoint (argumentative). Here’s a more detailed look at how they differ:
| Key Differences 📌 | Discursive Essay 📝 | Argumentative Essay 🗣️ |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose 🎯 | Provides a balanced discussion on a topic | Persuades the reader to agree with a specific viewpoint. |
| Approach 🔍 | Examines multiple perspectives without taking a definitive stance | Takes a clear position and argues for or against it throughout the essay. |
| Thesis Statement 📜 | Often states a general overview or acknowledges different viewpoints. | States a strong and specific thesis that outlines the writer's position clearly. |
| Argumentation 💬 | Presents arguments from various angles to provide a comprehensive view. | Presents arguments that support the writer's position and refute opposing views. |
Types of Discursive Essay
Before writing a discursive essay, keep in mind that they can be categorized into different types based on their specific purposes and structures. Here are some common types of discursive essays:
.webp)
Opinion Essays:
- Purpose: Expressing and supporting personal opinions on a given topic.
- Structure: The essay presents the writer's viewpoint and provides supporting evidence, examples, and arguments. It may also address counterarguments to strengthen the overall discussion.
Problem-Solution Essays:
- Purpose: Identifying a specific problem and proposing effective solutions.
- Structure: The essay introduces the problem, discusses its causes and effects, and presents possible solutions. It often concludes with a recommendation or call to action.
Compare and Contrast Essays:
- Purpose: Analyzing similarities and differences between two or more perspectives, ideas, or approaches.
- Structure: The essay outlines the key points of each perspective, highlighting similarities and differences. A balanced analysis is provided to give the reader a comprehensive understanding.
Cause and Effect Essays:
- Purpose: Exploring the causes and effects of a particular phenomenon or issue.
- Structure: The essay identifies the primary causes and examines their effects or vice versa. It may delve into the chain of events and their implications.
Argumentative Essays:
- Purpose: Presenting a strong argument in favor of a specific viewpoint.
- Structure: The essay establishes a clear thesis statement, provides evidence and reasoning to support the argument, and addresses opposing views. It aims to persuade the reader to adopt the writer's perspective.
Pro-Con Essays:
- Purpose: Evaluating the pros and cons of a given issue.
- Structure: The essay presents the positive aspects (pros) and negative aspects (cons) of the topic. It aims to provide a balanced assessment and may conclude with a recommendation or a summary of the most compelling points.
Exploratory Essays:
- Purpose: Investigating and discussing a topic without necessarily advocating for a specific position.
- Structure: The essay explores various aspects of the topic, presenting different perspectives and allowing the reader to form their own conclusions. It often reflects a process of inquiry and discovery.
These types of discursive essays offer different approaches to presenting information, and the choice of type depends on the specific goals of the essay and the preferences of the writer.
Discursive Essay Format
Writing a discursive essay needs careful planning to make sure it’s clear and flows well while presenting different viewpoints on a topic. Here’s how to structure your discursive essay:
Introduction
- Start with an interesting opening sentence to catch the reader's attention. Give some background information on the topic to show why it’s important.
- Clearly state your main argument or position on the topic, and mention that you’ll be discussing different viewpoints.
"Should genetically modified foods be more strictly regulated for consumer safety? This question sparks debates among scientists, policymakers, and consumers alike. This essay explores the different perspectives on genetically modified organisms (GMOs) to give a complete view of the issues."
Body Paragraphs
- Begin each paragraph with a sentence that introduces a key point or perspective about GMOs.
- Present arguments, evidence, and examples to support each perspective. Consider the benefits, risks, and ethical issues around GMOs.
- Address possible objections or opposing viewpoints to show a balanced analysis.
"Supporters of GMOs argue that genetically engineered crops can help solve global food shortages by increasing crop yields and resistance to pests. For example, studies have shown that GMOs like insect-resistant corn have reduced the need for chemical pesticides, which benefits both farmers and the environment."
Counterarguments
- Recognize the counterarguments or concerns raised by opponents of GMOs.
- Provide reasoned responses or rebuttals to these counterarguments, acknowledging the complexity of the issue.
"However, critics of GMOs worry about potential long-term health effects and environmental impacts. They argue that there isn’t enough research to ensure the safety of eating genetically modified foods over long periods."
- Summarize the main points discussed in the essay about GMOs.
- Reinforce your thesis statement while considering the different arguments presented.
- Finish with a thought-provoking statement or suggest what should be considered for future research or policy decisions related to GMOs.
"In conclusion, the debate over genetically modified foods highlights the need to balance scientific innovation with public health and environmental concerns. While GMOs offer potential benefits for global food security, ongoing research and transparent regulation are essential to address uncertainties and ensure consumer safety."
Formatting Tips
- Use clear and straightforward language throughout the essay.
- Ensure smooth transitions between paragraphs to maintain the flow of ideas.
- Use headings and subheadings if they help organize different perspectives.
- Properly cite sources when referencing research findings, quotes, or statistics.
Remember, besides writing compositions, you’ll also need to do math homework , something we can assist you with right away.
Yays and Nays of Writing Discourse Essays
In learning how to write a discursive essay, certain do's and don'ts serve as guiding principles throughout the writing process. By adhering to these guidelines, writers can navigate the complexities of presenting arguments, counterarguments, and nuanced analyses, ensuring the essay resonates with clarity and persuasiveness.
| Yays 👍 | Nays 👎 |
|---|---|
| Conduct thorough research to ensure a well-informed discussion. | Don’t express personal opinions in the body of the essay. Save personal commentary for the conclusion. |
| Explore various arguments and viewpoints on the issue. | Don't introduce new information or arguments in the conclusion. This section should summarize and reflect on existing content. |
| Maintain a balanced and neutral tone. Present arguments objectively without personal bias. | Don’t use overly emotional or subjective language. Maintain a professional and objective tone. |
| Structure your essay with a clear introduction, body, and conclusion. Use paragraphs to organize your ideas. | Ensure your arguments are supported by credible evidence. Don’t rely on personal opinions without sufficient research. |
| Include clear topic sentences at the beginning of each paragraph to guide the reader through your arguments. | Don’t have an ambiguous or unclear thesis statement. Clearly state the purpose of your essay in the introduction. |
| Use credible evidence from reputable sources to support your arguments. | Don’t ignore counterarguments. Address opposing viewpoints to strengthen your overall argument. |
| Ensure a smooth flow between paragraphs and ideas with transitional words and phrases. | Don’t use overly complex language if it doesn’t add to the clarity of your arguments. Aim for clarity and simplicity. |
| Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of different arguments and viewpoints. | Don’t present ideas in a disorganized manner. Ensure a logical flow between paragraphs and ideas. |
| Recap key points in the conclusion, summarizing the main arguments and perspectives discussed. | Don’t excessively repeat the same points. Present a variety of arguments and perspectives to keep the essay engaging. |
| Correct any grammar, spelling, or punctuation errors by proofreading your essay. | Don’t ignore the guidelines provided for your assignment. Follow any specific instructions or requirements given by your instructor or institution. |
Wrapping Up
Throughout this guide, you have acquired valuable insights into the art of crafting compelling arguments and presenting diverse perspectives. By delving into the nuances of topic selection, structuring, and incorporating evidence, you could hone your critical thinking skills and sharpen your ability to engage in informed discourse.
This guide serves as a roadmap, offering not just a set of rules but a toolkit to empower students in their academic journey. As you embark on future writing endeavors, armed with the knowledge gained here, you can confidently navigate the challenges of constructing well-reasoned, balanced discursive essays that contribute meaningfully to academic discourse and foster a deeper understanding of complex issues. If you want to continue your academic learning journey right now, we suggest that you read about the IEEE format next.
Overwhelmed by Essays?
Let professional writers be your writing wingman. No stress - just success!
What is a Discursive Example?
What is the difference between a discursive and argumentative essay, what are the 2 types of discursive writing.

Daniel Parker
is a seasoned educational writer focusing on scholarship guidance, research papers, and various forms of academic essays including reflective and narrative essays. His expertise also extends to detailed case studies. A scholar with a background in English Literature and Education, Daniel’s work on EssayPro blog aims to support students in achieving academic excellence and securing scholarships. His hobbies include reading classic literature and participating in academic forums.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.
- Updated old sections including definition, outline, writing guide.
- Added new topics, examples, checklist, FAQs.
- Discursive writing - Discursive Writing - Higher English Revision. (n.d.). BBC Bitesize. https://www.bbc.co.uk/bitesize/guides/zpdwwmn/revision/1
- Prepare for Exam Success: C1 Advanced self-access learning Writing Part 1 -the discursive essay Lesson summary. (n.d.). Retrieved June 28, 2024, from https://www.cambridgeenglish.org/Images/583526-c1-advanced-self-access-learning-writing-part-1-discursive-essay.pdf
- Tomeu. (n.d.). Advanced C1.1: How to write a DISCURSIVE ESSAY. Advanced C1.1. Retrieved June 28, 2024, from https://englishadvanced2.blogspot.com/2013/10/speakout-advanced-p-25-examples-of.html


26 Planning a Discursive Essay
Discursive essay – description.
A discursive essay is a form of critical essay that attempts to provide the reader with a balanced argument on a topic, supported by evidence. It requires critical thinking, as well as sound and valid arguments (see Chapter 25) that acknowledge and analyse arguments both for and against any given topic, plus discursive essay writing appeals to reason, not emotions or opinions. While it may draw some tentative conclusions, based on evidence, the main aim of a discursive essay is to inform the reader of the key arguments and allow them to arrive at their own conclusion.
The writer needs to research the topic thoroughly to present more than one perspective and should check their own biases and assumptions through critical reflection (see Chapter 30).
Unlike persuasive writing, the writer does not need to have knowledge of the audience, though should write using academic tone and language (see Chapter 20).
Choose Your Topic Carefully
A basic guide to choosing an assignment topic is available in Chapter 23, however choosing a topic for a discursive essay means considering more than one perspective. Not only do you need to find information about the topic via academic sources, you need to be able to construct a worthwhile discussion, moving from idea to idea. Therefore, more forward planning is required. The following are decisions that need to be considered when choosing a discursive essay topic:
- These will become the controlling ideas for your three body paragraphs (some essays may require more). Each controlling idea will need arguments both for and against.
- For example, if my topic is “renewable energy” and my three main (controlling) ideas are “cost”, “storage”, “environmental impact”, then I will need to consider arguments both for and against each of these three concepts. I will also need to have good academic sources with examples or evidence to support my claim and counter claim for each controlling idea (More about this in Chapter 27).
- Am I able to write a thesis statement about this topic based on the available research? In other words, do my own ideas align with the available research, or am I going to be struggling to support my own ideas due to a lack of academic sources or research? You need to be smart about your topic choice. Do not make it harder than it has to be. Writing a discursive essay is challenging enough without struggling to find appropriate sources.
- For example, perhaps I find a great academic journal article about the uptake of solar panel installation in suburban Australia and how this household decision is cost-effective long-term, locally stored, and has minimal, even beneficial environmental impact due to the lowering of carbon emissions. Seems too good to be true, yet it is perfect for my assignment. I would have to then find arguments AGAINST everything in the article that supports transitioning suburbs to solar power. I would have to challenge the cost-effectiveness, the storage, and the environmental impact study. Now, all of a sudden my task just became much more challenging.
- There may be vast numbers of journal articles written about your topic, but consider how relevant they may be to your tentative thesis statement. It takes a great deal of time to search for appropriate academic sources. Do you have a good internet connection at home or will you need to spend some quality time at the library? Setting time aside to complete your essay research is crucial for success.
It is only through complete forward planning about the shape and content of your essay that you may be able to choose the topic that best suits your interests, academic ability and time management. Consider how you will approach the overall project, not only the next step.
Research Your Topic
When completing a library search for online peer reviewed journal articles, do not forget to use Boolean Operators to refine or narrow your search field. Standard Boolean Operators are (capitalized) AND, OR and NOT. While using OR will expand your search, AND and NOT will reduce the scope of your search. For example, if I want information on ageism and care giving, but I only want it to relate to the elderly, I might use the following to search a database: ageism AND care NOT children. Remember to keep track of your search strings (like the one just used) and then you’ll know what worked and what didn’t as you come and go from your academic research.
The UQ Library provides an excellent step-by-step guide to searching databases:
Searching in databases – Library – University of Queensland (uq.edu.au)
Did you know that you can also link the UQ Library to Google Scholar? This link tells you how:
Google Scholar – Library – University of Queensland (uq.edu.au)
Write the Thesis Statement
The concept of a thesis statement was introduced in Chapter 21. The information below relates specifically to a discursive essay thesis statement.
As noted in the introduction to this chapter, the discursive essay should not take a stance and therefore the thesis statement must also impartially indicate more than one perspective. The goal is to present both sides of an argument equally and allow the reader to make an informed and well-reasoned choice after providing supporting evidence for each side of the argument.
Sample thesis statements: Solar energy is a cost -effective solution to burning fossil fuels for electricity , however lower income families cannot afford the installation costs .
Some studies indicate that teacher comments written in red may have no effect on students’ emotions , however other studies suggest that seeing red ink on papers could cause some students unnecessary stress. [1]
According to social justice principles, education should be available to all , yet historically, the intellectually and physically impaired may have been exempt from participation due to their supposed inability to learn. [2]
This is where your pros and cons list comes into play. For each pro, or positive statement you make, about your topic, create an equivalent con, or negative statement and this will enable you to arrive at two opposing assertions – the claim and counter claim.
While there may be multiple arguments or perspectives related to your essay topic, it is important that you match each claim with a counter-claim. This applies to the thesis statement and each supporting argument within the body paragraphs of the essay.
It is not just a matter of agreeing or disagreeing. A neutral tone is crucial. Do not include positive or negative leading statements, such as “It is undeniable that…” or “One should not accept the view that…”. You are NOT attempting to persuade the reader to choose one viewpoint over another.
Leading statements / language will be discussed further, in class, within term three of the Academic English course.
Thesis Structure:
- Note the two sides (indicated in green and orange)
- Note the use of tentative language: “Some studies”, “may have”, “could cause”, “some students”
- As the thesis is yet to be discussed in-depth, and you are not an expert in the field, do not use definitive language
- The statement is also one sentence, with a “pivot point” in the middle, with a comma and signposting to indicate a contradictory perspective (in black). Other examples include, nevertheless, though, although, regardless, yet, albeit. DO NOT use the word “but” as it lacks academic tone. Some signposts (e.g., although, though, while) may be placed at the start of the two clauses rather than in the middle – just remember the comma, for example, “While some studies suggest solar energy is cost-effective, other critical research questions its affordability.”
- Also note that it is based on preliminary research and not opinion: “some studies”, “other studies”, “according to social justice principles”, “critical research”.
Claims and Counter Claims
NOTE: Please do not confuse the words ‘claim’ and ‘counter-claim’ with moral or value judgements about right/wrong, good/bad, successful/unsuccessful, or the like. The term ‘claim’ simply refers to the first position or argument you put forward (whether for or against), and ‘counter-claim’ is the alternate position or argument.
In a discursive essay the goal is to present both sides equally and then draw some tentative conclusions based on the evidence presented.
- To formulate your claims and counter claims, write a list of pros and cons.
- For each pro there should be a corresponding con.
- Three sets of pros and cons will be required for your discursive essay. One set for each body paragraph. These become your claims and counter claims.
- For a longer essay, you would need further claims and counter claims.
- Some instructors prefer students to keep the pros and cons in the same order across the body paragraphs. Each paragraph would then have a pro followed by a con or else a con followed by a pro. The order should align with your thesis; if the thesis gives a pro view of the topic followed by a negative view (con) then the paragraphs should also start with the pro and follow with the con, or else vice versa. If not aligned and consistent, the reader may easily become confused as the argument proceeds. Ask your teacher if this is a requirement for your assessment.

Use previous chapters to explore your chosen topic through concept mapping (Chapter 18) and essay outlining (Chapter 19), with one variance; you must include your proposed claims and counter claims in your proposed paragraph structures. What follows is a generic model for a discursive essay. The following Chapter 27 will examine this in further details.
Sample Discursive Essay Outline
The paragraphs are continuous; the dot-points are only meant to indicate content.
Introduction
- Thesis statement
- Essay outline (including 3 controlling ideas)
Body Paragraphs X 3 (Elaboration and evidence will be more than one sentence, though the topic, claim and counter claim should be succinct)
- T opic sentence, including 1/3 controlling ideas (the topic remains the same throughout the entire essay; it is the controlling idea that changes)
- A claim/assertion about the controlling idea
- E laboration – more information about the claim
- E vidence -academic research (Don’t forget to tell the reader how / why the evidence supports the claim. Be explicit in your E valuation rather than assuming the connection is obvious to the reader)
- A counter claim (remember it must be COUNTER to the claim you made, not about something different)
- E laboration – more information about the counter claim
- E vidence – academic research (Don’t forget to tell the reader how / why the evidence supports the claim. Be explicit in your E valuation rather than assuming the connection is obvious to the reader)
- Concluding sentence – L inks back to the topic and/or the next controlling idea in the following paragraph
Mirror the introduction. The essay outline should have stated the plan for the essay – “This essay will discuss…”, therefore the conclusion should identify that this has been fulfilled, “This essay has discussed…”, plus summarise the controlling ideas and key arguments. ONLY draw tentative conclusions BOTH for and against, allowing the reader to make up their own mind about the topic. Also remember to re-state the thesis in the conclusion. If it is part of the marking criteria, you should also include a recommendation or prediction about the future use or cost/benefit of the chosen topic/concept.
A word of warning, many students fall into the generic realm of stating that there should be further research on their topic or in the field of study. This is a gross statement of the obvious as all academia is ongoing. Try to be more practical with your recommendations and also think about who would instigate them and where the funding might come from.
This chapter gives an overview of what a discursive essay is and a few things to consider when choosing your topic. It also provides a generic outline for a discursive essay structure. The following chapter examines the structure in further detail.
- Inez, S. M. (2018, September 10). What is a discursive essay, and how do you write a good one? Kibin. ↵
- Hale, A., & Basides, H. (2013). The keys to academic English. Palgrave ↵
researched, reliable, written by academics and published by reputable publishers; often, but not always peer reviewed
assertion, maintain as fact
The term ‘claim’ simply refers to the first position or argument you put forward (whether for or against), and ‘counter-claim’ is the alternate position or argument.
Academic Writing Skills Copyright © 2021 by Patricia Williamson is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
Verify originality of an essay
Get ideas for your paper
Cite sources with ease
How to write a discursive essay: step-by-step guideline
Updated 31 Jul 2024

Many students struggle with discursive writing as it can be tricky. It’s hard to manage different opinions and create a well-organized argument, leaving learners feeling unsure. In this article, we want to make creating discursive essays less confusing by giving helpful tips. If you grasp the essential information and follow our advice, you can tackle the challenges of this essay style and learn how to express convincing and well-thought-out ideas. Come with us as we explore the basic dos and don’ts for making successful writing.
What is a discursive essay?
This type of academic writing explores and presents various perspectives on a particular topic or issue. Unlike an argumentative essay, where the author takes a clear stance on the subject, discursive writing aims to provide a balanced and nuanced discussion of different viewpoints. What is the discursive essay meaning? The first word implies a conversation or discussion. So, the text encourages an exploration of diverse opinions and arguments.
This homework, commonly assigned in higher academia, serves various purposes:
- Students analyze diverse perspectives, fostering critical thinking as they weigh different viewpoints before forming a conclusion.
- Such essays involve thorough research, requiring students to synthesize information from various sources and present a comprehensive understanding of the topic.
- When struggling with how to write my essay for me, students develop their communication skills as they should express complex ideas clearly and coherently, creating smooth transitions between arguments.
- While not demanding a fixed stance, discursive papers require persuasive writing skills. The authors present each perspective convincingly, regardless of personal endorsement.
- Encouraging an appreciation for the issue’s complexity, the essays promote tolerance for diverse opinions.
In summary, these papers contribute to developing analytical, research, and communication skills, preparing students for nuanced engagement with complex topics in academic and professional settings.
What is the difference between discursive and argumentative essays?
While these documents may exhibit certain similarities, it’s crucial to underscore the notable distinctions that characterize them, delineating their unique objectives and methodologies.
Discursive essays
- Objective presentation: A five paragraph essay of this type aims to provide a comprehensive discussion on a particular topic without necessarily taking a clear stance.
- Multiple perspectives: Writers explore different viewpoints, neutrally presenting arguments and counterarguments.
- Complexity: These essays often deal with complex issues, encouraging a nuanced understanding of the subject.
- Balanced tone and language: Such writing allows for a more open expression of different ideas using objective and formal language.
- Flexible structure: These texts allow for a free-flowing topic analysis and may express numerous ideas in separate sections.
- Conclusion: While a discursive essay example may express the writer's opinion, it doesn’t necessarily require a firm conclusion or a call to action.
Argumentative essays
- Clear stance: This type involves taking a specific position and defending it with strong, persuasive arguments.
- Focused argumentation: The primary goal is to convince the reader of the writer's position, providing compelling evidence and logical reasoning.
- Counterarguments: While an argumentative essay acknowledges opposing views, the focus is on refuting them to strengthen the writer’s position.
- Assertive tone: This type aims to present ideas from the writer’s perspective and convict the reader using evidence and reasoning.
- Rigid structure: These texts come with a clear structure with a distinct introduction, thesis statement, body paragraphs with arguments and reasoning, and a conclusion that highlights the author’s stance.
- Call to action or conclusion: Such papers often conclude with a clear summary of the arguments and may include a call to action or a statement of the writer’s position.
The key distinction lies in the intent: discursive texts foster a broader understanding by presenting multiple perspectives. At the same time, argumentative papers aim to persuade the reader to adopt a specific viewpoint through strong, focused arguments.
Save your time! We can take care of your essay
- Proper editing and formatting
- Free revision, title page, and bibliography
- Flexible prices and money-back guarantee
Discursive writing types
When delving into discursive essay format, exploring three primary forms of writing is essential.
1. Opinion essay.
- In an opinion essay, your viewpoint on the discussed problem is crucial.
- State your opinion in the introduction, supported by examples and reasons.
- Present the opposing argument before the conclusion, explaining why you find it unconvincing.
- Summarize your important points in the conclusion.
2. Essay providing a solution to a problem.
- Focus on discussing an issue and proposing solutions.
- Introduce the issue at the beginning of the text.
- Detail possible solutions in separate body paragraphs.
- Summarize your opinion in the conclusion.
3. For and against essay.
- Write it as a debate with opposing opinions.
- Describe each viewpoint objectively, presenting facts.
- Set the stage for the problem in your discursive essay intro.
- Explore reasons, examples, and facts in the main body.
- Conclude with your opinion on the matter.
If you need professional writers' support when working on your homework, you may always pay for essay writing . Our experts can explain how to create different types of papers and suggest techniques to make them well-thought-out and compelling.
Discursive essay structure
Discover a concise outline that will help structure your thoughts and arguments, allowing for a comprehensive and articulate presentation of your ideas.
|
A. Hook or opening statement B. Background information on the topic C. Thesis statement (indicate the topic and your stance, if applicable)
(number of paragraphs can vary based on essay length) A. Presentation of perspective (1) 1. Statement of perspective (1) 2. Supporting evidence/examples 3. Analysis and discussion
B. Presentation of perspective (2) 1. Statement of perspective (2) 2. Supporting evidence/examples 3. Analysis and discussion
C. Presentation of perspective (3) (if applicable) 1. Statement of perspective (3) 2. Supporting evidence/examples 3. Analysis and discussion
D. Presentation of counterarguments 1. Acknowledge opposing views 2. Refute or counter opposing arguments 3. Provide evidence supporting your perspective
A. Summary of main points B. (if applicable) C. Closing thoughts or call to action (if applicable) |
The length of the discursive introduction example and the number of body paragraphs can vary based on the topic's complexity and the text's required length. Additionally, adjust the outline according to specific assignment guidelines or your personal preferences.
10 steps to create an essay
Many students wonder how to write a discursive essay. With the following guidelines, you can easily complete it as if you were one of the professional essay writers for hire . Look at these effective steps and create your outstanding text.
1. Choose an appropriate topic:
- Select a topic that sparks interest and is debatable. Ensure it is suitable for discursive examples with multiple viewpoints.
2. Brainstorm your ideas:
- Gather information from various sources to understand different perspectives on the chosen topic.
- Take notes on key arguments, evidence, and counterarguments.
3. Develop a clear thesis:
- Formulate a thesis statement that outlines your main idea. This could include your stance on the topic or a commitment to exploring various viewpoints.
4. Create a discursive essay outline:
- Structure your text with an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
- Outline the main points you want to cover in each section.
5. Write the introduction:
- Begin with a hook to grab the reader's attention.
- Provide background information on the topic.
- Clearly state your thesis or the purpose of the essay.
6. Create body paragraphs:
- Start each paragraph with a clear topic sentence.
- Present different perspectives on the topic in separate paragraphs.
- Support each perspective with relevant evidence and examples.
- Discuss the strengths and weaknesses of each viewpoint.
- Use smooth transitions between paragraphs.
7. Suggest counterarguments:
- Devote a section to acknowledging and addressing counterarguments.
- Refute or explain why you find certain counterarguments unconvincing.
8. Write the conclusion:
- Summarize the main points discussed in the body paragraphs.
- Restate your thesis or the overall purpose of the essay.
- Provide a concise discursive essay conclusion, highlighting the significance of the topic.
9. Proofread and revise:
- Review your work for clarity, coherence, and logical flow.
- Check for grammar, punctuation, and spelling errors.
- Ensure that your arguments are well-supported and effectively presented.
10. Finalize and submit:
- Make any necessary revisions based on feedback or additional insights.
- Ensure every discursive sentence in your paper meets specific requirements provided by your instructor.
- Submit your well-crafted document.
Following these steps will help you produce a well-organized and thought-provoking text that effectively explores and discusses the chosen topic.
Dos and don’ts when completing a discursive essay
If you want more useful writing tips, consider the dos and don’ts to create an impactful and compelling text.
- Thorough research: Do conduct extensive research on the topic to gather a diverse range of perspectives and solid evidence. It will strengthen your discursive thesis statement and demonstrate a comprehensive understanding of the subject.
- Clear structure: Do organize your essay with a clear introduction, body paragraphs that present different viewpoints, and a concise conclusion. Use a separate paragraph to introduce every point. This structure helps readers follow your argument effectively.
- Neutral tone: Do maintain a balanced tone and impersonal style throughout the essay. Avoid being overly emotional or biased, as the goal is to present a fair discussion of various perspectives.
- Critical analysis: Do critically analyze each perspective, highlighting strengths and weaknesses. Build your discursive thesis on trustworthy sources and make appropriate references following the rules of the required citation style. This showcases your critical thinking ability and contributes to a more nuanced discussion.
- Smooth transitions: Do use smooth transitions between paragraphs and arguments to create a cohesive flow. The use of linking phrases and words enhances the readability of your text and makes it easier for the reader to follow your line of reasoning.
Don’ts:
- Avoid biased language: Don’t use biased language or favor one perspective over another. Maintain an objective tone and present each viewpoint with equal consideration.
- Don’t oversimplify: Avoid oversimplifying complex issues. Acknowledge the nuances of the topic and provide a nuanced discussion that reflects a deep understanding of the subject matter.
- Steer clear of generalizations: Don’t make broad generalizations without supporting evidence. Ensure that relevant and credible sources back your arguments to strengthen your position.
- Don’t neglect counterarguments: Avoid neglecting counterarguments. Acknowledge opposing views and address them within your discursive essays. It adds credibility to your work and thoroughly examines the topic.
- Don’t be too personal : Avoid expressing your personal opinion too persistently, and don’t use examples from your individual experience.
- Refrain from unsupported claims: Don’t make claims without supporting them with evidence. Substantiate your arguments with reliable sources and statistics with proper referencing to enhance the credibility of your document.
By adhering to these dos and don’ts, you’ll be better equipped to navigate the complexities of writing a discursive text and present a well-rounded and convincing discussion.
Final thoughts
Mastering the art of writing a discursive essay is a valuable skill that equips students with critical thinking, research, and communication abilities. If your essay-writing journey is challenging, consider seeking assistance from EduBirdie, a trusted companion that guides students through the intricacies of these papers and helps them answer the question, “What is discursive writing?”. With our support, you can navigate the challenges of crafting a compelling and well-rounded discourse, ensuring success in your academic endeavors. Embrace the assistance of EduBirdie and elevate your writing experience to new heights.
Was this helpful?
Thanks for your feedback.

Written by Steven Robinson
Steven Robinson is an academic writing expert with a degree in English literature. His expertise, patient approach, and support empower students to express ideas clearly. On EduBirdie's blog, he provides valuable writing guides on essays, research papers, and other intriguing topics. Enjoys chess in free time.
Related Blog Posts
How to write winning scholarship essays: prompts, tips, and strategies.
What is a scholarship essay? Before we explore what to write in a scholarship essay, let’s specify the definition of this term. It is a written ...
How to Introduce Evidence in an Essay: Steps & Tips
Using evidence effectively in an essay is crucial for building a strong, compelling argument. If you create research, persuasive, or analytical wri...
Diversity essay: effective tips for expressing ideas
In today's interconnected and rapidly evolving world, the importance of diversity in all its forms cannot be overstated. From classrooms to workpla...
Join our 150K of happy users
- Get original papers written according to your instructions
- Save time for what matters most

- Business Intelligence Assignment Help
- Lab Report Writing Service
- Nursing Assignment Help
- Buy Response Essay
- CPM Homework Answers
- Do My Chemistry Homework
- Buy Argumentative Essay
- Do Your Homework
- Biology Essay Writers
- Business Development Assignment Help
- Best Macroeconomics Assignment Help
- Best Financial Accounting Assignment Help
- PHP Assignment Help
- Science Assignment Help
- Audit Assignment Help
- Perdisco Accounting Assignment Help
- Humanities Assignment Help
- Computer Network Assignment Help
- Arts and Architecture Assignment Help
- How it works
How to Write a Discursive Essay: Tips, Examples, and Structure
Calculate the price of your order:.

Mastering the Art of Writing a Discursive Essay
Table of contents.
Introduction
Understanding Discursive Essays
Discursive essay writing tips, discursive essay structure, examples of discursive essays, picking the right discursive essay topics, discursive essay format, crafting a strong discursive essay outline, writing an effective discursive essay introduction, nailing the discursive essay conclusion.
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on how to write a discursive essay effectively. If you’re unfamiliar with this type of essay or want to improve your skills, you’ve come to the right place! This guide will cover How to Write a Discursive Essay , examples, and strategies to help you craft a compelling discursive essay.
Are you ready to master this art of writing ? This article will explain a discursive essay and explore various aspects such as writing tips, structure, examples, and format. So, let’s dive right in and unveil the key elements of an impressive discursive essay.

Before we delve into the nitty-gritty of writing a discursive essay , let’s take a moment to understand its nature and purpose. A discursive essay presents a balanced argument on a particular topic by exploring different perspectives. It requires the writer to consider different viewpoints, present evidence, and critically analyze the subject matter.
Writing a discursive essay can be challenging, but you can excel in this art form with the right approach. Here are some valuable tips that will help you write a discursive essay effectively:
- Choose an Engaging Topic: Select a topic that is interesting and relevant to your audience. This will make the essay more engaging and enjoyable to read.
- Thorough Research: Gather extensive information from reliable sources to support your arguments and counterarguments.
- Plan and Outline: Take the time to plan and create an outline before diving into the writing process. This will help you organize your thoughts and arguments effectively.
- Clear Introduction: Start with a concise introduction that provides context and grabs the reader’s attention. Clearly state your thesis or main argument.
- Well-structured Paragraphs: Divide your essay into paragraphs that focus on specific points. Each paragraph should present a new idea or support a previous one.
- Logical Flow: Maintain a logical flow using transitional words and phrases that connect your ideas and paragraphs smoothly.
- Balance Your Arguments: Ensure a balance in presenting the pros and cons of each perspective. This will demonstrate your fairness and critical thinking skills.
- Support with Evidence: Provide evidence, facts, and examples to support your claims and make your arguments more persuasive.
- Use Clear Language: Avoid jargon and overly complex language. Opt for clear, concise, and precise language that is easy for readers to comprehend.
- Proofread and Edit: Always revise, proofread, and edit your essay to ensure clarity, coherence, and proper grammar usage.
Following these tips, you’ll be well-equipped to write an impressive discursive essay that effectively presents your arguments and engages your readers.
A well-structured discursive essay enhances readability and ensures that your arguments are coherent. Here’s a suggested structure that you can follow:
- Hook the reader with an attention-grabbing statement or anecdote.
- Introduce the topic and provide background information.
- Present your thesis statement or main argument.
- Start each paragraph with a topic sentence introducing a new argument or perspective.
- Provide evidence, examples, and supporting details to justify your claims.
- Address counterarguments and present rebuttals, showing your ability to consider different viewpoints.
- Use transitional words to maintain a smooth flow between paragraphs.
- Summarize the main points discussed in the essay.
- Restate your thesis statement while considering the arguments presented.
- End with a thought-provoking statement or call to action.
By adhering to this structure, your discursive essay will be well-organized and easy for readers to follow.
To gain a better understanding of how discursive essays are written, let’s explore a couple of examples:
Example 1: The Impact of Social Media
Introduction: The growing influence of social media in society.
Main Body: Discussing the positive and negative aspects of social media on communication, mental health, privacy, and relationships.
Conclusion: Weighing the overall impact of social media and proposing ways to harness its strengths and mitigate its drawbacks.
Example 2: The Pros and Cons of School Uniforms
Introduction: Introducing the debate on school uniforms.
Main Body: Exploring the arguments supporting school uniforms (such as fostering discipline and equality) and arguments against them (such as limiting self-expression).
Conclusion: Evaluating the advantages and disadvantages of school uniforms and suggesting potential compromises.
These examples illustrate how discursive essays analyze various perspectives on a topic while maintaining a balanced approach.
Choosing an engaging and relevant topic is crucial to capturing your readers’ attention. Here are some popular discursive essay topics to consider:
- Is social media beneficial or detrimental to society?
- Should the death penalty be abolished worldwide?
- Are genetically modified organisms (GMOs) safe for consumption?
- Should recreational marijuana use be legalized?
- Are video games responsible for the rise in violence among youth?
When selecting a topic, ensure it is captivating, allows for multiple viewpoints, and is backed by sufficient research material.
While there is flexibility in formatting a discursive essay, adhering to a standard format enhances clarity and readability. Consider following this general format:
- Font type and size: Times New Roman, Arial, or Calibri with a 12-point font size.
- Line spacing: Double-spaced throughout the essay.
- Page margins: 1-inch margins on all sides.
- Title page: Include the essay title, your name, course name, instructor’s name, and submission date (if applicable).
- Header: Insert a header with your last name and page number (top-right corner).
A consistent format will make your essay more professional and easier to navigate.

Before writing your discursive essay, creating an outline that organizes your thoughts and arguments effectively is essential. Here’s a sample outline to help you get started:
I. Introduction
B. Background information
C. Thesis statement
II. Main Body
A. Argument 1
1. Supporting evidence
2. Examples
B. Argument 2
C. Argument 3
1 . Supporting evidence
2 . Examples
III. Counterarguments and Rebuttals
A. Counterargument 1
1 . Rebuttal evidence
B. Counterargument 2
C . Counterargument 3
IV. Conclusion
A. Summary of main points
B . Restating the thesis statement
C. Call to action or thought-provoking statement
By structuring your ideas in an outline, you’ll have a clear roadmap for your essay, ensuring that your arguments flow logically.
The introduction of your discursive essay plays a vital role in capturing your reader’s attention and setting the tone for the essay. Here’s how you can make your introduction compelling:
Start With an Engaging Hook: Begin with a captivating opening sentence, such as a surprising statistic, an intriguing question, or a compelling anecdote related to your topic.
Provide Necessary Background Information: Briefly explain the topic and its relevance to the reader.
Present Your Thesis Statement: Clearly state your main argument or thesis, which will guide your essay’s direction and focus.
You’ll establish a strong foundation for your discursive essay by crafting an engaging and informative introduction.
The conclusion of your discursive essay should effectively summarize your main points and leave a lasting impression on your readers. Here’s how you can achieve this:
Summarize the Main Points: Briefly recap the key arguments and perspectives discussed in the essay.
Restate Your Thesis Statement: Reiterate your main argument while considering the various perspectives.
Call to Action or Thought-Provoking Statement: End your essay with a compelling statement or encourage readers to explore the topic further, sparking discussion and reflection.
By crafting a powerful conclusion, you’ll leave a lasting impact on your readers, ensuring they walk away with a clear understanding of your essay’s message.
Congratulations! You’ve now comprehensively understood how to write a discursive essay effectively. Remember to choose an engaging topic, conduct thorough research, create a clear structure, and present balanced arguments while considering different perspectives. Following these guidelines and incorporating our tips, you’ll be well-equipped to craft a compelling discursive essay.
So, start writing your discursive essay following our comprehensive guide. Unlock your writing potential and captivate your readers with an impressive discursive essay that showcases your analytical skills and ability to present compelling arguments. Happy writing!

Frequently Asked Questions About “How to Write a Discursive Essay Effectively”
What is a discursive essay, and how does it differ from other types of essays.
A discursive essay explores a particular topic by presenting different perspectives and arguments. It differs from other essays, emphasizing balanced, unbiased discussion rather than a single, strong stance.
How should I choose a topic for my discursive essay?
Select a topic that allows for multiple viewpoints and has room for discussion. Controversial issues or topics with various opinions work well, providing ample material for exploration.
What is the typical structure of a discursive essay?
A discursive essay typically has an introduction, several body paragraphs, and a conclusion. The introduction sets the stage, the body paragraphs present different viewpoints, and the conclusion summarizes the key points and your stance.
Is it necessary to choose a side in a discursive essay?
While you don’t have to take a definite side, you should present a balanced view. However, some essay prompts may ask you to argue for or against a particular position.
How do I start the introduction of a discursive essay?
Begin with a hook to capture the reader’s attention, provide background information, and clearly state the issue you will discuss. End the introduction with a thesis statement that outlines your approach.
Should I use formal language in a discursive essay?
Yes, maintain a formal and objective tone. Avoid using first-person pronouns and aim for clarity and precision in your language.
How many viewpoints should I include in the body paragraphs?
Include at least two or three well-developed viewpoints. Ensure that each paragraph focuses on a specific aspect or argument related to the topic.
How do I transition between paragraphs in a discursive essay?
Use transitional phrases to move smoothly from one idea to the next. This helps maintain a logical flow and coherence in your essay.
Can I include personal opinions in a discursive essay?
While you can present your opinions, remaining objective and supporting your views with evidence is crucial. The emphasis should be on presenting a well-rounded discussion rather than expressing personal bias.
How do I conclude a discursive essay effectively?
Summarize the main points discussed in the body paragraphs, restate your thesis nuancedly, and offer a closing thought or call to action. Avoid introducing new information in the conclusion.
Basic features
- Free title page and bibliography
- Unlimited revisions
- Plagiarism-free guarantee
- Money-back guarantee
- 24/7 support
On-demand options
- Writer's samples
- Part-by-part delivery
- Overnight delivery
- Copies of used sources
- Expert Proofreading
Paper format
- 275 words per page
- 12 pt Arial/Times New Roman
- Double line spacing
- Any citation style (APA, MLA, CHicago/Turabian, Havard)
Guaranteed originality
We guarantee 0% plagiarism! Our orders are custom made from scratch. Our team is dedicated to providing you academic papers with zero traces of plagiarism.
Affordable prices
We know how hard it is to pay the bills while being in college, which is why our rates are extremely affordable and within your budget. You will not find any other company that provides the same quality of work for such affordable prices.
Best experts
Our writer are the crème de la crème of the essay writing industry. They are highly qualified in their field of expertise and have extensive experience when it comes to research papers, term essays or any other academic assignment that you may be given!
Calculate the price of your order
Expert paper writers are just a few clicks away
Place an order in 3 easy steps. Takes less than 5 mins.
Reflective writing: Differences between discursive and reflective writing
- What is reflection? Why do it?
- What does reflection involve?
- Reflective questioning
- Reflective writing for academic assessment
- Types of reflective assignments
Differences between discursive and reflective writing
- Sources of evidence for reflective writing assignments
- Linking theory to experience
- Reflective essays
- Portfolios and learning journals, logs and diaries
- Examples of reflective writing
- Video summary
- Bibliography
On this page:
“Guidance for most academic writing emphasises the use of precise and objective language. Putting your reflection into words, in contrast, requires subjective language, since it is primarily your personal responses and views that are sought.” McMillan & Weyers, How to improve your critical thinking & reflective skills
Writing reflectively requires a personal style of writing that you may not be used to. Most assignments at university are discursive, using reason and evidence to present an argument. This style of writing is impersonal and is usually written in the third person. Reflective writing, however, in centred on first-person experiences, supplemented with references to the literature alongside personal thought. First person writing involves talking from a personal perspective (this involves the using the first-person singular pronoun "I" or the first person plural, "we"). The table below contrasts discursive and reflective writing:
|
|
|
| Based on broad reading of the subject area, uses to develop an | Examines personal to experiences, events, ideas and information |
| Impersonal style (written in the third person) | Personal style (written in the first person) |
| Examines the strengths and weaknesses of the theories, arguments and research of , compares and contrasts ideas and theories | Looks for meaning, analyses the significance of responses to opinions, experiences, events, thoughts and feelings |
| Limited to academic evidence | Not limited to academic evidence |
| Presents and justifies arguments | Looks for solutions to problems |
Reflective writing is very different from the discursive style that you may be used to. It is written in the first person, examines personal experiences and is not limited to academic evidence. Unless you have experience with reflective practice, your first attempt(s) at reflective writing may feel very uncomfortable. This is because it requires a very different style and approach to your usual writing. Stick with it...it gets much easier with time and practice.
- << Previous: Types of reflective assignments
- Next: Sources of evidence for reflective writing assignments >>
- Last Updated: Jan 19, 2024 10:56 AM
- URL: https://libguides.hull.ac.uk/reflectivewriting
- Login to LibApps
- Library websites Privacy Policy
- University of Hull privacy policy & cookies
- Website terms and conditions
- Accessibility
- Report a problem

Module C – Persuasive/Discursive Assessment w/Reflection
DOWNLOAD THE RESOURCE
Resource Description
Persuasive/discursive article (hybrid) with reflection, written for an assessment task. Techniques and ideas based on my prescribed texts: Noel Pearson’s speech “A Eulogy for Gough Whitlam”, Nam Le’s short story “Love and Honour and Pity and Pride and Compassion and Sacrifice”, and Siri Hustvedt’s discursive essay “Eight Days in a Corset”
Report a problem
Popular HSC Resources
- Speech on George Orwell ‘1984’ – Human Experiences
- How To Survive the HSC
- One Night the Moon – Analysis (Video)
- 2020 – Physics – PHS (Trial Paper)
- Business Studies Influences on HR (Quiz)
- Sci Ext – Portfolio Pack
- 2020 – Science Ext – Exam Choice (Trial Paper)
- Domino’s Marketing Case Study
Become a Hero
Easily become a resource hero by simply helping out HSC students. Just by donating your resources to our library!
What are you waiting for, lets Ace the HSC together!
Join our Email List
No account needed.
Get the latest HSC updates.
All you need is an email address.

Sussex Centre for Language Studies
| Analysing Your Essay Title Beginning the Research Process | Reading and Planning Producing a Sentence Outline | Writing a Draft Preparing for the final submission |
The Academic Writing Guide (AWG) is designed to familiarise you with the process of writing a discursive essay. A discursive essay is a genre of writing that requires you to investigate a topic; collect, generate, and evaluate evidence; and establish a position on the topic in a concise manner. Once you have decided on your position your writing will be an attempt to persuade your reader that it is a reasonable one to take. The pages in this guide will present information and activities designed to help you develop the skill of argumentation, which as well as being the main feature of discursive writing, underpins every aspect of university study.
Before you begin working through the AWG and using the examples and activities to help you research and write your own discursive essay watch the interview with James, one of our former Foundation Year students, who worked through the AWG and is reflecting on his progress. Some of what James says may not make sense to you yet, but come back to it occasionally as your own research skills develop and see if your experience resembles his. As you listen, notice what James says about how his perspective on the learning process changed during the course of the Foundation Year.
Academic writing does not aim simply to describe (although describing will be part of the process). An essay that is too descriptive will receive a very low mark at university level. Similarly, an essay that takes a ‘balanced’ view and does little more that weigh up the pros and cons of each side of an argument is rarely appropriate for university-level study.
Your aim in writing a discursive essay is to persuade your reader that your position (your argument) is a valid one. It makes a claim about a topic and defends this claim with evidence. A discursive essay must therefore begin with a thesis or claim that is debatable. In other words, the thesis must be something that people could reasonably have differing opinions on. If your thesis is something that is generally agreed upon or accepted as fact then there is no reason to try to persuade your reader of its merits.
Argumentation – mass noun
2. A reason or set of reasons that you use for persuading other people to support your views, opinions, etc.
His main argument is stated in the opening paragraph.
Discursive writing

| This thesis statement . Nobody would disagree with this statement as John le Carré’s background is public knowledge |
This is an example of a because reasonable people could disagree with it. Some people might think that his fictionalised settings and characters are not based in reality. Others might think that he is drawing heavily on his own experience when writing his novels. |
There is a lot of pre-writing work to do for a discursive essay. Before you can begin writing you need to:
Throughout the research and writing process you will submit a series of assessed tasks relating to this title. Each of the tasks is designed to support your writing development, and help you produce a well-argued discursive essay supported with appropriate academic evidence. Each submission carries a percentage of the overall marks for the portfolio, making it essential that you complete each one. The portfolio accounts for a large percentage of the overall marks for the two Academic Development modules (see module handbook).
At the start of each of the 3 Stages in the AWG you will be told what the aims and objectives are, as well as the different assessments you will have to complete for that Stage. You will also be told where to submit these assessments in Canvas (find details below and in the module handbook on your class Canvas site).

These voluntary, drop-in sessions offer you personalised support for your work with the Academic Writing Guide and all aspects of the Academic Development Module.
You don’t need an appointment for these sessions, just show up with any questions you have about the module or the AWG and the tutor will help you on a one-to-one basis. You are welcome to use the drop-in service as often as you like.
You can find information about the drop-in sessions on your Canvas site.
This resource will help you to develop your Academic Skills whilst at Sussex. It brings together all of the web resources, workshops and support that are available to you as a Sussex student. Academic Skills are essential to successful study; from time management and note making, all the way through to reference management and exam writing techniques. These skills will help you to fully engage with, and excel, in your studies. Use the navigation on the left side of the page to find the section you are after or use the search box in the header.
As you work through the Academic Writing Guide (AWG) you will create a range of documents that need to be saved as you go and then uploaded to an assessment point at the end of each stage.
As a Sussex student you can download Microsoft Office 365.
With Office 365 you can get Microsoft Office for your personally-owned computer and mobile device(s) at no cost, as well as access to online versions of Office products and 1TB of free cloud storage in OneDrive.
Remember you are not expected to have all these skills already - you will develop them throughout your time at Sussex.
Each Stage requires several hours of self-study to complete, and each Stage is assessed. You will have plenty of time to work through the 3 Stages, and at regular intervals will submit formal assessments that will be included in your assessed portfolio for the Academic Development module at the end of the year. After each submission your Academic Development tutor will give you feedback, which you will use to inform the process of developing your discursive essay further. Each assessed task carries a percentage of the overall marks for the portfolio, making it essential that you complete each one. The portfolio itself carries a large percentage of the overall marks for the Academic Development module.
You will find details about each of the assessments at relevant points in this Guide, and will need to pay close attention to them. Your Academic Development tutor will also be introducing and supporting the process in your Academic Development seminars.
The following is an overview:
| After completing all of the sections in this stage you will be assessed on your ability to: • Create a mind-map that shows how you intend to decode the essay question to support your continued research. • Produce a table with at least 5 sources with annotations showing the relevance of the sources to help inform the development of your essay. These sources will be written using either the MLA or Chicago referencing systems. • Write a short reflection on what you have learned about academic writing from completing this stage of the guide and how you can continue developing relevant academic skills to suit your context.
|
| After completing all of the sections in this stage you will be assessed on your ability to: • Produce an annotated bibliography for the 5 sources you will use in your essay (in addition to the core texts) that includes: • Produce a sentence outline/plan for your essay that includes: • Write a short reflection on what you have learned about academic writing from completing this stage of the Guide and how you can continue developing relevant academic skills to suit your context. |
| • Provide a Turnitin report of your draft • Write a short reflection on what you have learned about academic writing from completing this stage of the guide and how you can continue developing relevant academic skills to suit your context |
| More Assessment Criteria | Summative Assessment |
| Now you have read and understood what is required and what resources are available to you move on to |

How to Write a Band 6 Discursive Writing Piece for HSC English Module C

Just heard about the term discursive writing from HSC English for Module C?
Whether you’re an expert or beginner at discursive writing, we’re here to help secure a Band 6 for Module C! We’ll break down exactly what discursive writing involves and how to produce a Band 6 discursive writing piece.
Keen to know more? Then keep scrolling!
What is Discursive Writing? What’s in a HSC Discursive Writing Question? How to Write a Discursive Text How to Structure Your Discursive Writing Tips for Discursive Writing Features Should You Memorise Your Discursive Writing Piece for Module C? Discursive Writing Examples Discursive Writing Example Prompt

Click to download your own copy of our Discursive Writing guide!

What is Discursive Writing?
Discursive writing definition.
NESA defines discursive writing as including: Texts whose primary focus is to explore an idea or variety of topics. These texts involve the discussion of an idea(s) or opinion(s) without the direct intention of persuading the reader, listener or viewer to adopt any single point of view. Discursive texts can be humorous or serious in tone and can have a formal or informal register.
In this article, we’ll be giving you the lowdown on all types of discursive writing.
This encompasses forms such as creative non-fiction, travel blogs, discussion essays, speeches, personal essays and much more!
Discursive Writing for HSC
The purpose behind discursive writing is for you to engage in a deeply relatable, thought-provoking discussion by exploring multiple perspectives on a topic. It is not argumentative nor is it imaginative.
One style of writing you may not be so familiar with in HSC English Module C: The Craft of writing is discursive writing.
Common to both Advanced and Standard English, this module assesses a student’s ability to craft effective pieces of writing in relation to a given audience and purpose.
Unlike the other modules, the focus here is not as much on what you’ve written but more so a combination of what you’ve written and how you’ve written it.
The module takes up approximately 20 hours of course time. It will be assessed in one section in English Paper 2 in the HSC external examination block held in October, through one question containing up to two parts.
Discursive Writing is a new text type to appear on the syllabus in Module C. Let’s take a quick look at a part of the rubric for this module:

Excerpt of Module C in HSC English Syllabus from NESA
Modes of Writing
From this, we can see that within this module, you will be required to write in four different text types:
Imaginative: This type of writing often takes the form of a narrative and requires you to combine plot, setting and character to craft a short story.
Discursive: We’ll be diving into what exactly this style of writing entails in this guide!
Persuasive: This writing style aims for you to convince the reader of a particular argument or idea. It can be written in the form of an academic essay, personal essay or speech.
Informative: When writing an informative piece, you’ll be informing the reader of a particular topic — these are most commonly written as reports, explanations or descriptions.
For more on the different text types explored in Module C, check out our article !
What’s in a HSC Discursive Writing Question?
Here’s an example from NESA’s HSC English 2019 sample paper of a discursive writing question:

As you can see, Section III of the HSC exam paper focusses upon Module C: The Craft of Writing.
The question may ask you to write a persuasive, discursive or imaginative writing piece about a significant idea you have explored in your prescribed text whilst also using a stimulus.
Let’s take a look at another discursive writing question:

The exam question for this section may also be split into part (a) and part (b) — but don’t freak out!
Part (a) will require you to write an imaginative, discursive or persuasive writing piece using the stimulus provided, as well as one technique or stylistic feature used in your prescribed text.
Part (b) involves a reflective statement which will require you to explain how your prescribed text influenced your imaginative, discursive or persuasive writing piece in part (a).
In part (b) you may also be required to explain the literary or stylistic devices you employed in your writing.
Differences Between A Regular Persuasive Essay and Discursive Writing
Scratching your head at what you should do differently for your discursive writing, check out the key differences below!
| Discursive | Persuasive | |
|---|---|---|
| To engage in a thought-provoking discussion by exploring multiple perspectives on a topic. | To argue a single perspective. | |
| Includes an introduction, body and a conclusion. Varied number of paragraphs and paragraph length – you have a bit of freedom here. | Includes an introduction, body and a conclusion. Usually 3-4 body paragraphs, sometimes more. Body paragraphs typically follow a strict PEEL structure and paragraphs are of similar length. | |
| Try to strike a balance between formal and informal. You’re writing for an educated audience, yes, but you want your tone to also reflect who you are as a person – so hopefully something a little more friendly and open. | Formal, academic language. Don't write how you would talk. | |
| Go for it. | Generally avoided unless the question lends itself well to first person (e.g. something asking you to ). | |
| Include it, but you don’t need to conduct the literary analysis you would do in an essay. | Included throughout body paragraphs and analysed following a particular structure (PEEL). | |
| Welcomed. | Only include it if it’s part of a quote you’re analysing. |
Pros and Cons of Discursive Writing
To get some extra knowledge on the form, here is a good list of the pros and cons for discursive writing!
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| - Has the capacity to be incredibly personal; you can write and explore your own genuine thoughts, opinions and life experiences rather than those that simply look good in an essay. - The intended writing style is one that reflects your own personal voice - not as an author of a story or as an essayist, but your voice as a person. This means that you have the freedom to write both formally and informally, figuratively and factually. It’s up to you! - You can leave it open-ended. | - The amount of freedom you have in this text type can be intimidating. It’s hard to know whether or not you’re doing it right! - This text type is relatively new in the syllabus so you may not have had as much practice in writing it as you would have had with the other types. - I anticipate that, like imaginative writing, this one will also be marked rather subjectively. |
At Art of Smart Education our expert English Tutors can support you with Discursive Writing with tailored tutoring in your home or online.
How to Write a Discursive Text

While there is no single formula or “quick fix” to get a Band 6, there are certain steps you can take to increase your chances!
That said, you won’t jump from a Band 2 to a Band 6 overnight so be prepared to invest time and effort to achieve a Band 6-level result, or as close to it as you can get.
Discursive writing can be tricky. Our tutors here at Art of Smart can help you boost your marks with expert tips and tricks! Check out the K-12 English support we can provide in Parramatta , and all across Sydney!
Use the Discursive Writing Syllabus to Your Advantage
Let’s start by revisiting the marking criteria for Module C: The Craft of Writing:
- Craft language to address the demands of the question.
- Use language appropriate to audience, purpose and context to deliberately shape meaning.
So, how might these criteria apply to a discursive piece of writing?
| Criterion | How can I address this? |
|---|---|
| This requires you to use language in a way that addresses what the question is asking you to do, so a good place to start is by breaking down the question itself. Ensure you have read the question carefully. , underlining all key words. Only move on from reading over the question once you are 100% sure you understand it inside out. | |
| In a discursive piece of writing, you’ll be expected to write using your own personal voice – not your voice as the author of a story, or your voice as an essayist – your voice as a person. This is what your reader will be expecting and thus, this is what you should aim for to achieve. Momentarily forget everything you know about regular essay writing and let your own voice flow through onto the page, in a way that is authentically you. |

How to Start Your Discursive Piece
This will ultimately depend on the question so ensure you read it carefully.
Likely, you will be asked to explore a key idea or concern from one of your prescribed texts — either from Module C or another module.
You may take this literally, exploring the idea as it is presented in the prescribed text or instead, you can think laterally and consider how this idea applies to the real world, occasionally bringing in the text — or a related text — as examples.
Note that many of the key ideas and concerns encountered in your prescribed texts are quite broad and malleable , so you can twist them in any way you want.
Tip: Manipulate the Question As the focus here is on unleashing your own personal voice as a writer, it helps to be writing about something you a) are genuinely interested in and b) know a bit about. Manipulate the question as is necessary. Example You might decide to write about power — as it is a key concern in the prescribed text for the Common Module, Nineteen Eighty Four (Orwell) . Power lends itself quite easily to politics but what if you don’t want to talk about politics? Instead, you might write about the psychological power of manipulation or the importance of individual empowerment. As the marking criteria for Module C explicitly ask for language crafted to “address the demands of the question” , it is imperative that whatever you do end up writing about is something that can be related to the question — by both yourself and your marker.
Discursive Writing Examples
Here are some of our favourite pieces of discursive writing!
- Immigrating to English by Ocean Vuong
- Slouching Towards Bethelehem by Joan Didion
- Just Kids by Patti Smith
- Upstream by Mary Oliver
You can also trawl through newspapers, magazines and blogs for great examples of discursive writing:
- The Economist
- Time Magazine
- National Geographic
- The Conversation
- The Atlantic
Tip : Also check out TED talks , many of which take on a discursive style and all of which are available to view online for free . Most talks uploaded on TED’s official site also have a transcript so you can not only follow along, but also take note of how the speaker uses language to create meaning. Check out the 20 Most-Watched TED Talks !

How to Structure Your Discursive Writing
While discursive writing is not wedded to a formal structure, it helps to plan things out before you start writing. This can help to avoid confusion or a lack of clarity in your writing.
You’ll want to follow a logical, sequential structure:
Introduction – Catch your reader’s attention and introduce them to your topic – whether explicitly or implicitly.
Body – Several paragraphs in which you explore your topic in greater detail. These can be of varying lengths and the number of paragraphs is up to you.
Conclusion – Sum up your discussion and end on a reflective, thought-provoking note.
Planning your response beforehand — even if it’s some dot points crammed into the corner of the page — allows you to think deeply about how to best organise and present your ideas. For each paragraph, plan what its focus will be and which pieces of evidence you will include.
What Can You Include As Evidence in Discursive Writing?
Evidence is crucial in a discursive response as it adds legitimacy to your discussion and helps to build authenticity.
You may include, but are not limited to, the following types of evidence:
- Textual examples from prescribed texts
- Textual examples from related texts
- Personal anecdotes
- Historical events (careful not to write a history essay though!)
- References to popular culture
Do I Have to Analyse the Textual Evidence?
You can but you are not required to. This entirely depends on the nature of the question and how you prefer to answer it.
If you want your response to be focussed on texts, then some analysis may be helpful.
If you’re focussing on broader ideas or phenomena however, perhaps ease up on the techniques for now.

Tips for Discursive Writing Features
You might be thinking: Module C seems all a bit… unstructured ?
Ironically, if you think that, you’re on the right train of thought! You’ve actually understood the form excellently. It’s natural to find discursive writing a little unfamiliar, considering you’re much more used to writing in a highly-structured essay style.
Discursive writing is deliberately exploratory and personal in nature. Great discursive writer Annie Dillard sums up the form well, noting that discursive writing has “ a structure that arises from the materials and best contains them ”. The discursive writing style is highly personal and effectively you can dictate your own structure.
However, don’t let this freak you out! You can in fact use the vagueness of this form to your advantage.
Tip #1: Make your Personal Voice Engaging
Authors use literary techniques for a reason. They provide an interesting, more meaningful way of getting ideas across than just stating things outright.
Consider this example from our old mate, William Shakespeare:
“I will speak daggers to her but use none” (Hamlet, Hamlet , Act 3 Scene 2) Cool, right? Shakespeare uses a great metaphor of daggers to convey the sharp hostility Hamlet plans to convey in speaking to his mother. Can’t get enough of it. Let’s consider the same line without any techniques : I’ll speak rudely to her but I won’t actually do anything to physically harm her.
Look, it gets the meaning across and it’s nice and direct but let’s be real — it’s boring. The daggers metaphor captures our imagination and gets us thinking whereas the rewritten, metaphor-less line simply tells us what Hamlet is planning to do, no more.
Slightly random Hamlet analysis aside, techniques such as metaphors will help bring your writing voice to life — and will sure as heck engage your reader, if used correctly.
Tip #2: Use Good Techniques in Discursive Writing
When reading your prescribed texts, take note of techniques you personally find meaningful. Not just the techniques your teacher tells you to find meaningful but ones that you actually like yourself.
Experiment with these techniques in your own writing. Loved the dagger metaphor we learnt about from Hamlet just now? Have a go at writing your own metaphor to describe the way someone speaks to another . And so on, and so forth.
Don’t just focus on your prescribed texts either. If you’re keen on a Band 6 for HSC English, you should already be engaging in regular wide reading. As you do this, take note of any cool techniques you happen upon, and have a go at creating your own.
Here’s the absolute minimum set of techniques you should be including your discursive writing: Varying sentence structure: write like you’re a human, not a robot! Tone : depending on the formality or informality of the piece, the ultimate aim is to get them so immersed that they don’t feel like they’re reading at all! Nuance: Add in some information that goes against your argument, then disprove it — this actually makes the reader trust your opinion! Here are some fancier techniques you can include to secure that Band 6: A running symbol: especially in more creative pieces, this reminds the reader of your point of view. The symbol should evolve as your point of view evolves Hero’s Journey: to get your reader rooting for your side, implement the hero’s journey. Write your piece as if you’re telling a story: add a call to adventure, challenges and a transformation in your discursive writing! Imagery : Want your reader to feel like they’re not reading? Get them imagining the physical surroundings of your discursive text!
You’ll likely already be doing something similar to this in your classwork for Module C.
If you don’t know your techniques well, check out our handy dandy glossary !
Tip #3: Writing in First Person is Recommended
You can write in first or third person for discursive writing however first person is recommended as it allows you to craft a much more authentic and engaging personal voice.
Think of discursive writing almost as an extended, slightly-more-structured stream of consciousness. You’re exploring and bouncing between your thoughts on a particular topic, and doing so through a voice that is inherently and unashamedly yours.
While third person is not necessarily wrong , it runs the risk of your discursive writing reading more like a persuasive essay.
Tip #4: Get Personalised Feedback on Your Work
Even if you’re following the best advice on how to write a piece of discursive writing, it’s likely that you’ll struggle to accurately reflect on the quality of your work. You’ve probably heard this before: “HSC English is super subjective.” To a certain extent, this is true!
That’s why we recommend getting personalised guidance from an HSC English tutor who knows the syllabus inside and out. They can point you in the right direction and decipher your teacher’s feedback with you! That way, you’ll be able to move forward knowing that you’re doing the right things.
Should You Memorise Your Discursive Writing Piece for Module C?
In previous HSC exams, it was common practice for students to write and perfect a creative writing story, memorise that story word for word, and use it in the exam — adapting when necessary — in the hopes of a Band 6.
It seems to be heading this way with the imaginative writing component of Craft of Writing, with many students already writing and revising a story to be kept as their “safety net”.
While this can have benefits for imaginative writing, it might not play out so well for discursive writing.
The fluidity of discursive writing means that your structure and content are likely to depend almost entirely on what’s asked in the question. As you can’t predict the question, logically it is also difficult to pre-prepare a response.
Rather than rote-learning a discursive piece, it is much wiser to instead practise a range of different Module C questions using a discursive form. Have your teacher — or a tutor — read over your discursive writings and either rewrite them using their feedback, or write new responses, keeping the feedback in mind (or you can also do both).
After all, you might not even be asked to write discursively in the exam! All that time spent memorising for nothing… (same goes for imaginative writing, just sayin’…)
If you’ve already been on the lookout for practice questions, you can find a bunch in this article !
Discursive Writing Example Prompt
Now that you’re a little more familiar with discursive writing, here’s a practice question:
“I pay no attention to anybody’s praise or blame. I simply follow my own feelings” — Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart Use this quote as a stimulus for a piece of discursive writing that expresses your perspective about a significant concern or idea that you have engaged with in ONE of your prescribed texts from Module C.
Have a go at this question and get feedback from your HSC English teacher and/or tutor.
And in the meantime — you can have a look at our monster list of Module C practice questions so you can practise your discursive writing!
Looking for some extra help with discursive writing in Module C for HSC English?
We have an incredible team of hsc english tutors and mentors who are current hsc syllabus experts.
We can help you master discursive writing and ace your upcoming HSC English assessments with personalised lessons conducted one-on-one in your home, online or at one of our state of the art campuses in Hornsby or the Hills!
Feel confident tackling Module C with personalised tutoring support in Mosman or HSC English support in Hurstville !
We’ve supported over 8,000 students over the last 11 years , and on average our students score mark improvements of over 20%!
Looking for extra HSC English support in Wollongong? Get in touch with our team to secure your Wollongong English tutor today!
To find out more and get started with an inspirational HSC English tutor and mentor, get in touch today or give us a ring on 1300 267 888!
- Topics: ✏️ English , ✍️ Learn
Related Articles
The step-by-step guide to hsc english module c: the craft of writing, how to write a persuasive writing piece for module c: the craft of writing, how to integrate key ideas into your module c response, 45,861 students have a head start....
Get exclusive study content & advice from our team of experts delivered weekly to your inbox!

Looking for English Support?
Discover how we can help you!

We provide services in
How To Write The Best Module C Reflection

The final aspect of the English Paper 2 exam includes a reflection statement. This statement can range anywhere between 5 to 10 marks (out of 20), so it is crucial that students understand and complete this component to the best of their abilities. Reflection statements seek to provide analytical explanation behind students’ writing, and rationalise the creative choices made in conjunction with the exam stimulus. A reflection takes place after students complete their imaginative, discursive or persuasive writing.
Below are TutorTime’s essential components to writing a Band 6 reflection:
1. Rationale behind storyline and isolation of key techniques
Your reflection should begin with a brief explanation of why you chose the storyline of your piece. For example, if you complete an imaginative writing piece, your reflection could begin with: “I chose to write from the perspective of a teenage boy to interrogate the subconscious familial tensions that emerge when parents divorce”. However, do not spend too much time analysing your piece, and instead focus on the techniques that you included. For example, if your imaginative has a motif, you should mention this to the marker and explain why you chose to do so. Do not be afraid to quote your piece in your reflection.
2. Response to stimulus
Reflections must clearly outline how your writing piece thoroughly responds to the exam stimuli. For example, if the exam stimulus was a picture of a chessboard, you may want to write about how you used the technique of stichomythic dialogue to emulate the fast-moving discussion of a game of chess, or how the motif of ‘moves and countermoves’ was repeated throughout your writing. You must inform the marker that you have acknowledge and responded to the stimuli given. Do not be subtle in your inclusion of the stimulus.
3. Integration of Mod C text/s
Finally, your reflection should include the ways in which your writing has drawn from your Module C texts. For example, you may have been inspired by Nam Le’s conversational tone and use of flashbacks, or Margaret Atwood’s use of satire and intertextuality. Make it obvious to the marker that the ‘Craft of Writing’ prescribed texts have heavily influenced your own writing. Provide quotes and examples from your Mod C texts to substantiate this.
To learn more about how to write the perfect Mod C reflection, book a TutorTime tutor today!
More from TutorTime

Year 12 HSC Module C : The Craft of Writing Practice Questions
Looking for some HSC Module C questions to help you prepare? We have got you covered with 8 brand new questions! TutorTime would like to help you prepare for the HSC English…

Year 12 HSC Module B : Critical Study of Literature Practice Questions
Need help preparing for your HSC Module B exam? Here are 10 brand new questions for you! TutorTime would like to help you prepare for the HSC English Advanced Module B (paper…

Year 12 HSC Module A : Textual Conversations Practice Questions
Feeling stuck with your HSC Module A study? We have got you covered with 10 amazing new questions! TutorTime would like to help you prepare for the HSC English Advanced Module A…

Year 12 HSC Common Module: Texts and Human Experiences Practice Questions
Can’t find any helpful questions for HSC Module Text and Human Experience? Here are 10 brand new questions for you! TutorTime would like to help you prepare for the HSC English Common…

Best Tech For Primary And High School Kids
Teacher’s tips We spoke to Sophie Sparks, senior educator, CEO of TutorTime and founder of YOU CAN SIT WITH ME to get some educational tech tips. “We know that parents find apps really, really useful,” she…

Law Admissions Test at UNSW
The Law Admission Test (LAT) is a professionally designed and marked selection test developed to assess your critical thinking and analytical skills, problem-solving and ability to organise and express ideas. UNSW Law & Justice has always…
Book a tutor
Book a committed & reliable tutor with the TutorTime values instilled.
Become a tutor
Teach your passion on your terms, we'll look after the rest!
Have questions or need help?
Get in touch or give our team a call.
Our mission is to enable education anywhere for everyone with a community of trusted, expert tutors.

- © 2020 TutorTime
- ABN 57 618 909 336
- Essay Topic Generator
- Summary Generator
- Thesis Maker Academic
- Sentence Rephraser
- Read My Paper
- Hypothesis Generator
- Cover Page Generator
- Text Compactor
- Essay Scrambler
- Essay Plagiarism Checker
- Hook Generator
- AI Writing Checker
- Notes Maker
- Overnight Essay Writing
- Topic Ideas
- Writing Tips
- Essay Writing (by Genre)
- Essay Writing (by Topic)
Discursive Essay Writing – A Comprehensive Guide

Writing discursive essays is a common task that can be encountered in high school and college environments. Mastering the nuances of writing them will be a lot easier with this guide. Our team has prepared recommendations that cover the basics of discursive essays and their format. Additionally, you will find some helpful tips about improving your work. Let’s get started!
- 🧐 Definition & Purpose
✍️ Types of Discursive Writing
- 💡 Discursive Essay Topics
📝 Discursive Essay Format
💎 developing a discursive writing style, 📎 references, 🧐 discursive writing: definition & purpose.
Discursive essays are different from the argumentative and persuasive papers you might be used to. Discursive writing allows students to investigate various topics in depth and present different opinions on particular issues. Creating one involves gathering, reading, and assessing supportive evidence. As with other academic papers, discursive ones are built around a thesis statement that outlines the arguments.

Unlike other paper genres like persuasive essays , discursive essays are scarce on personal thoughts. They favor an unbiased look at the subject through the lens of facts and statistics. You can use them to discuss issues related to social norms, the economy, political movements, technology, and similar subjects. Whatever you write about, ensure you methodically cover every side of the issue.
Differences between Argumentative and Discursive Essays
Students often confuse these essay types, so we’ve decided to help you understand the difference. These descriptions will show you how to identify the purpose and tone of these papers and choose the appropriate one to match your writing goals.
| 🤔 Argumentative | 🧐 Discursive |
|---|---|
| present supporting evidence and disprove opposing claims. | serve as an analysis of the subject from different points of view. |
If your professor tasks you with this kind of assignment, you have a couple of ways to approach it. As we’ve mentioned before, there are several types of discursive essays. This segment of our article goes into some detail about each of them.

- For-and-against essay . These papers can be best described as a debate in written form. They provide opposing points of view on different topics. For example, such essays may be about the use of fossil fuels, the First Amendment, or the merits of capitalism. It’s vital to provide reasonable and objective arguments in both cases. Readers can come to their own conclusions after reading these discursive papers.
- Opinion essay . In these papers, you should present your opinion about particular issues. Use reason and evidence to back your arguments . Don’t forget to discuss the opposing opinion and explain why it lacks strength. These essays can discuss social, political, and economic topics.
- Problem-solution essay . This discursive essay type discusses a problem and suggests the best solutions for solving it, for example, helping combat the homelessness crisis, climate change, or other issues. Here, students establish the problem, its causes, and the consequences of not addressing them.
💡 Examples of Discursive Essay Topics
If you get to write a discursive essay on any subject you wish, this is the right segment for you. Here, we provide several pressing, engaging, and diverse topics for your work.
- Does social media affect people’s communication skills?
- Do people rely on technology too much?
- The environment is the prime factor in forming a person’s identity.
- Examine the history of vaccines and their effectiveness.
- What’s the best way to save the environment?
- Does technology make us lazier?
- Higher education is not for everybody.
- Should capital punishment be abolished?
- Therapy is the best way to deal with mental health issues.
- People should travel without borders.
- How much does culture influence a person’s upbringing?
- Is American education in dire need of change?
- Discuss how music provides stress relief.
- German is one of the most complex languages to learn.
- How to combat the drug crisis in America.
- Which book format is the best?
- Are TV shows oversaturated with violence?
- Discuss the link between poverty and crime.
- In modern media, censorship comes before facts.
- Approaches to addressing Higher English course challenges.
- Should special sports events be held for steroid users?
- Does alcohol harm the social fabric?
- Modern movies lack the creative touch.
- Is it OK to control the freedom of speech?
- Discuss if the government should regulate marital relationships.
- Have apps destroyed the dating market?
- The beauty industry wrecked the self-image of women.
- Does listening to heavy metal make a person more aggressive?
- The paradox of fast fashion: balancing trends and sustainability .
- Is religion underappreciated?
You may be tempted to write right away after choosing the appropriate topic for your discursive essay. However, before you do this, get acquainted with this paper’s format. Below, you’ll find a step-by-step guide for each section of the work.
How to Write a Discursive Essay Introduction
Crafting a compelling intro is the foundation of a successful discursive essay. This section outlines the essential elements and strategies to grab the audience’s attention. Read it to master the art of engaging intros.
- Conduct thorough research . Before writing the introductory part, look for reliable sources of information to draw from. Take the time to find supporting evidence, especially when working on an unknown topic.
- Start with a hook sentence . You can provide stats, pose a good question, or give a quote related to the topic. Since it’s the first impression you make, ensure it’s a memorable one.
- Follow with a compressed topic description in a couple of sentences . Your job is to show how the topic is relevant to the broader discourse. Pick your words carefully to leave a lasting impact.
- Introduce your thesis statement . In a sentence or two, describe the paper’s main idea and how you will disclose it later. Trim it down and edit until the statement perfectly encapsulates the core of your writing.
- Describe what the essay will be about . In a couple of sentences, explain what each part of the work will cover in its paragraphs.
- Finish with a transitional phrase or sentence. The last part of the introduction should also smoothly transition into the paper’s body paragraphs. It makes the writing more cohesive and forms a flowing narrative.

How to Write Discursive Essay Body Paragraphs
The body paragraphs offer a platform for in-depth analysis and presentation of multiple perspectives. The ones in discursive essays have distinctive characteristics that distinguish them from other papers.
- Fill each paragraph with evidence that supports your claims . Add facts, statistics, examples, and quotes. Analyze this content and show how it supports your statements.
- Aim to present a balanced discussion . Give each point of view fair consideration. Even if you have a strong personal opinion, it should not dominate the main arguments.
- Present an opposing point of view . Don’t forget to dedicate several sections for counter-arguments to make the paper more comprehensive. Provide supporting information to these claims and refute them later on.
- Use transitional phrases between perspectives . Smooth transitions between different viewpoints within the body paragraphs will help you maintain coherence and guide the reader through the diverse arguments.
- Work in a structure . The first paragraph produces an argument, while the second has an opposing one. Repeat this process throughout the essay to give your audience a bigger picture of the issue. Also, don’t forget to check your punctuation .
How to Write a Discursive Essay Conclusion
This section will show you how to restate your main points, complete your arguments, and leave a lasting impression .
- Return to the thesis statement . Don’t simply restate it. Instead, show how the paper helped expand upon it. Explain the importance of your work in the broader discussion.
- Remind about the critical points of the paper . Give a rundown of the main takeaways of your paper and why they matter. Stay brief and remember that the conclusion should be about one paragraph long.
- Demonstrate its importance . Tell the readers about the questions your paper raises and how they help understand the issue better. Offer practical suggestions for addressing the problem while relying on the provided data.
- Encourage future discussions . Your paper should make readers want to explore the topic on their own, and it should encourage further debates. Suggest other areas relating to your topic that could be investigated in the future.
You’re one step closer to writing your perfect essay. We recommend practicing to ensure that you triumph over these academic tasks. Follow our tips, and you will see the quality of your papers reach new heights.
| ✅ Be straightforward | Try using simple words and phrases whenever possible. This way, you’ll be less likely to make mistakes. It also helps people unfamiliar with the topic to understand it better. |
| ✅ Cut down on long sentences | When writing papers, stick to shorter sentence structures. If you see lengthy ones, cut them down into two or more. There’s no need to chop up every single one – do this when necessary. Practice and you’ll see better which sentences to separate or keep as they are. |
| ✅ Clear the clutter | Everybody sometimes writes words, phrases, or sentences that don’t add more information to the paper. Or they make the same remarks several times in the text. If the meaning doesn’t change with their removal, it’s best to exclude them. |
| ✅ Experiment with sentence structure | Sticking to the same sentence structure throughout the text makes it dull and uninteresting. If you want to impact readers, change things from time to time. |
| ✅ Rely on an active voice | Try writing in an , as it’s more direct and requires fewer words than its passive counterpart. This makes papers easier to follow and comprehend. You’ll also avoid wordiness. |
| ✅ Write in a formal tone | As essays are academic tasks, you should write in a formal tone. Avoid colloquialisms, slang, and other devices not associated with this style. Remember to write in the third person. |
| ✅ Stick to familiar vocabulary | When , you will come across new words and phrases. Never use them if you don’t fully comprehend their meaning. Instead, stick to the terms and phrases you’re sure of. |
We thank you for your attention. Hopefully, you’ve found the guide helpful. If you need any more ideas for your discursive essay, you can create one using our topic generator !
- How to Write a Good Argumentative Essay: Easy Step-by-Step Guide. – MasterClass
- Discursive/Expository Essays. – Universidad de Murcia
- Discursive Writing. – Fei-Yu Chuang, The University of Warwick
- Reflective Writing: Differences Between Discursive and Reflective Writing. – University of Hull
- Writing Styles: When and How You Should Use the 4 Main Types. – Jamie Birt, Indeed
- Discursive Writing. – BBC
- 8 Easy Ways to Improve Your Writing Style. – Oxford Royale Academy
Offer of the decade FLAT 20% off + sign up bonus of $20 Order Now
- [email protected]
- +14159918581
Files Missing!
Please upload all relevant files for quick & complete assistance.
How to Write a Discursive Essay ?
Home / Blog / How To Write A Discursive Essay ?

Introduction
It’s undoubtedly a crucial point when a student has been allotted with an assignment by the professor, and as soon he opens up the file, it’s a discursive essay task. The first thing that strikes the students’ mind is, what is a discursive essay & how can it be completed.
So without further ado, let’s dig deep into the facts and find out what it takes to write a discursive essay.
Discursive Essay Introduction: What Really Is The Ruckus About?
Discursive essay writing is the most common essay writing task given to the students when they are in their colleges. Like any other college assignment, for discursive essay writing, students also feel repugnance towards it.
However, if we keep all these dislikings at a distance and take a minute to think, discursive essay writing is not as bad as the generic perception goes by. Interestingly, writing a discursive essay involves a deep discussion on the given topic. Students need to figure out their argument based on the given topic, the supporting arguments surrounding it, counter-arguments to establish the supporting points, etc. so you see, it’s not really a cakewalk to search and present for and against reasons. It requires a lot of research on the internet, figuring out the best ones that permit both time and topic, hence an impactful presentation of discussing both sides of the viewpoints.
Discursive Essay Structure: Lets Figure Out Ways to Write It Proper
Before we go further, let’s figure out how to write is a discursive essay.
A discursive essay is divided into two types- Opinion Essay and For and Against Essay. However, the basic structure of putting all your thoughts in the conventional introduction-body-conclusion structure is the same, no matter what type you are writing on.
While writing an opinion essay is all about stating a personalized opinion about the given topic, students can start writing it by narrowing down the topic in order to find succinct augments and reasons to counter those. It’s simple, if you haven’t narrowed down your topic, you will simply puzzle yourself to find out arguments and to decide how many of those should be enough to put in your essay. Whatever they do, opinions and thoughts should be presented and followed by supporting data, examples, and statistics. The conclusion should incorporate the writer’s opinion in a gist.
On the other hand, as it comes to writing for and against essay, the readers should be provided with supporting and opposing arguments with details. The objective to write this type of essay is to present a well-balanced opinion of the writer, what he has in mind about the chosen topic. A balanced reflection on the topic should be stated again only in the conclusion.
Now, whatever the style you have got to write your essay in, the students should keep in mind that the writing style should pursue an impersonal tone. Yes, assignment writing is often synonymous with formal writing, but with the discursive essay, you can go with informal writing techniques. You have to think critically for more in-depth aspects when reviewing all viewpoints and aspects of discursive essay writing.
Now, how do a student who is writing a discursive essay for the first time, would structure it? Here is a guide:
Like all academic essay assignments, a discursive essay paper starts with an introduction and ends with a conclusion.
So how to start? Like always, give the readers a hook. Some interesting fact about the topic always interests the readers in reading on till the end. Declaring some problem and its causes is also a good way to start writing the introduction of the discursive essay. You can always provide a short explanation of the problem you have selected in the introduction. You may use quotations and rhetorical questions in the introduction. Show your readers both sides of the arguments and sum up.
Pro tip: start the introduction paragraph with an impactful issue sentence.
The next step of discursive essay writing is to compose the body paragraphs. Here are some pointers to remember while working on a discursive essay:
- The body of a discursive essay will comprise of multiple paragraphs. So, build your argumentation in a couple of paragraphs, and provide what you think of it in separate sections. This way, you will be able to state your reasons accurately, making each of the concerns distinct and comprehensible. Don’t forget to add data and statistics supporting your arguments.
- Some experts suggest writing the body of an essay in an alternate manner. Meaning, to grab the most attention of your readers; try putting one paragraph with the argument, and the second one with opposite reasons to it. What does it mean? Such a merger of supporting and opposing paragraphs will make your essay look self-evident and well researched.
- Do not try and put your opinion in the body paragraphs. Fill it with unprejudiced aspects and areas concerning the issue.
- Try and structure all the body paragraphs with evidence supporting your arguments. Writing a summary of the argument at the beginning lines help the reader understand the context.
Well, as you have almost done with writing the hardest part of your discursive essay, lets us focus on the concluding paragraphs. The conclusion is nothing fancy, except, it would have all your thoughts jotted down.
Also, do not forget the golden rule of drafting an essay conclusion . Add the summary of the main points, specifying in the body paragraphs. Try putting in findings backed up with data. Remember: it should be in line with your evidence stated in the body paragraphs. Don't repeat findings, just summarize them.
Keep the conclusion short. The length should not exceed more than a paragraph.
A Brief List Of Discursive Essay Topics For Your Disposal
Pick and choose any of the essay topics to practice how to write a discursive essay. Follow the structuring rules given above. Also, if you are looking for a discursive essay example, the internet is loaded with tons of samples. Do some research, and you will definitely be good to go. A little research on the internet will help you a long way.
- Is energy drinks pose health risks for people under 18?
- Food industry and GMO
- How many hours of sleep are needed for an adult to function properly?
- Does professional participation in sports impact children?
- Explain alcohol and its impact on the nervous system
- Write what you know and feel about domestic violence
- Effect of school bullying on children
- Music effects on human body and mind
- Earthquakes and potential dangers they bring
- Social media effect on young adults
- Poverty and its impact on growing youths
- Impact of drug use on the human body
- Telling lies: The cause and effect
- The causes of divorces
- Is the military’s use of drones an invasion of privacy?
Discursive essay templates, format , and samples are available on the internet. There are also a number of online academic help service providers who write essay papers on behalf of the students.
The Professionals of essayhack.io Can Help You Out In A Click
Contact essayhack.io, and you can get comprehensive assistance in writing a discursive essay here. The one-stop destination to curb your entire essay writing issues, we have housed PhD-qualified and extremely professional academic writers write assignments on your behalf.
The services we provide to the students include the following-
- We are extremely affordable and provide the students with a completely plagiarism-free write-up.
- 24*7 Customer Support
- Cashback And Freebies
- 100+ Students Support Executive to Listen to Students Requirement
- PhD-qualified Essay Writers
- Highest Grade Guarantee
- 250+ Completed Orders Per Day
- Years Of Experience in Academic Writing
- Round the Clock Support Service
Place an order at Essayhack.io, and pass with flying colors!
Do you want to share?
You might also like.

Top 100 Persuasive Essay Topics/Ideas for Students

Discursive Essay Topics for Students

How to Write an Essay Introduction?

How to Write a Law Essay: Writing Guide with Examples

How to Choose Ideal Argumentative Essay Topics to Work On

PEEL Paragraph a Guide to Write a Perfect Essay

100 Effective Persuasive Essay Topics

How to Write a Descriptive Essay?- Guide with Examples

Who Am I Essay : How to Write it?
Leave a reply, place order.
Want Impressive Essay Help?
Submit your requirements here

-->Admin --> Published On Oct 3, 2023 | Updated on Oct 4, 2023

-->Admin --> Published On Sep 30, 2023 | Updated on Sep 30, 2023

-->Admin --> Published On Sep 26, 2023 | Updated on Sep 26, 2023

-->Admin --> Published On Sep 22, 2023 | Updated on Sep 26, 2023

-->Admin --> Published On Sep 5, 2023 | Updated on Sep 11, 2023
Assignment Help
Dissertation
Research Paper

-->Admin --> Published On Apr 18, 2019 | Updated on Aug 10, 2023

-->Admin --> Published On Sep 22, 2018 | Updated on Sep 12, 2023

-->Admin --> Published On Feb 13, 2019 | Updated on Aug 10, 2023

-->Admin --> Published On Apr 5, 2023 | Updated on Aug 10, 2023

-->Admin --> Published On Jun 22, 2020 | Updated on Aug 10, 2023
Subscribe Newsletter
You can place your order for free now. Simply submit your order and see what our writers can Subscribe to get regular update!
Thank you for commenting.
Thank you for subscribed newsletter.
Thank You For Commenting.
Get acquainted with the top essay helpers in the country and glide smoothly towards your academic goals with the necessary essay writing help online from US’s top professionals.
Want quick $20? Share your details with us.
Thank you for subscribing our newsletter
Have any Query? Contact with us
Pardon Our Interruption
As you were browsing something about your browser made us think you were a bot. There are a few reasons this might happen:
- You've disabled JavaScript in your web browser.
- You're a power user moving through this website with super-human speed.
- You've disabled cookies in your web browser.
- A third-party browser plugin, such as Ghostery or NoScript, is preventing JavaScript from running. Additional information is available in this support article .
To regain access, please make sure that cookies and JavaScript are enabled before reloading the page.
How to Write a Discursive Essay: Tips to Succeed & Examples
So, you need to accomplish your discursive essay writing. The typical questions most students ask are: How do you write it? What is discursive essay?
A discursive essay is an academic paper that involves a discussion on a particular topic. It is usually assigned to college students. You may be required to write a paper wherein you have to do one of the following:
- argue for the issue or against it;
- present your points of view on both sides;
- provide your unprejudiced opinion on that matter.
Don’t panic!
Check out the tips from Custom-writing.org experts below. They will assist you in discursive writing and encourage you to examine essay examples. Moreover, in this article, you’ll also learn about different types of discursive essay, and its introduction, main body, and conclusion structure.
- ❓ What Is It?
- 🏁 Main Types
Introduction
- Basic Don’Ts
- ✏️ Frequent Questions
❓ What Is a Discursive Essay?
First of all, let’s figure out what the discursive essay is.
You may think it’s similar to the argumentative essay. Yes, but there’s a difference between them in the structure and purpose of these two types of assignments:
| Purpose | To provide a reliable and unbiased assessment of an issue. Nevertheless, your discursive writing does not have to be completely neutral. You should write it using the facts and research reports to present both sides of the issue. | To persuade the reader in your position, providing supporting evidence. This essay type relies on thorough research so that the author can both convince and educate the reader. However, the result should be less passionate and more concise than that of a . |
| Structure | Its style is more impersonal and formal in comparison with other assignment types: | Its style is general for essays as the reader should understand what you stand for |
We will take a detailed look at how to structure a discursive essay later, and now let’s find out what are the types of this assignment.
Keep reading!
🏁 Discursive Essay: Main Types
You have to think more critically and more in-depth when reviewing all viewpoints and aspects of discursive writing. Check these three main types of essay writing:
- Opinion Essay requires the author’s opinion on an issue which is stated in the introductory paragraph. It should be clearly presented and followed by reasons and supporting examples. Also, this essay paper should contain an opposing argument that comes before the conclusion. The writer must explain to readers why the mentioned argument is considered to be unconvincing. The writer’s opinion should be restated/summarized in the conclusion.
- For and Against Essay provides readers with a thorough debate on the topic with the help of opposing points of view. Each point should be discussed objectively and described in details. The introductory paragraph puts the issue under consideration. The main body of this essay paper should present examples, reasons, and arguments supported by justifications. The author’s own opinion with balanced reflections on the topic should be stated only in conclusion.
- Essay Suggesting Solution to a Problem discusses problems and finds the main solutions. The introduction paragraph explicitly declares a problem and analyses its causes and consequences. The main body of the essay should offer some suggestions for a possible solution to the problem and potential state consequences or expected results. In conclusion, author’s opinion should be distinctly summarized.
📑 How to Write a Discursive Essay
Well, it’s time to talk about the structure of a discursive essay. Like most of the assignments, a discursive paper starts with an introduction and ends with a conclusion:
The first question you may ask is how to start a discursive essay introduction. Simple!
- Give your readers a hook – something that would sound interesting to them.
- Provide a short explanation of the problem. You may use quotations, as well as rhetorical questions.
- Show your readers both sides of the arguments and sum up.
You may be wondering…
Is there something I should avoid in my discursive essay introduction?
Yes. No stereotypes and generalizations, please!
The next step under formal essay writing you should take is to compose the body.
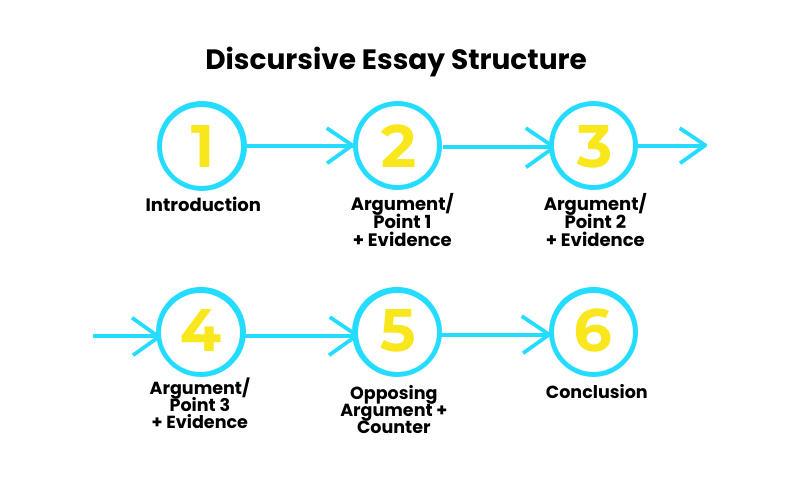
There are a few points you should remember:
- First and foremost: stay unprejudiced . Assess all of the aspects of an issue. Leave your feelings behind or for another essay type.
- Second: build your argumentation . If you have several arguments for your viewpoint—provide them in separate paragraphs. This will help you to keep your essay comprehensible and distinct. Don’t forget to submit supporting evidence.
- Third: write the body of an essay in an alternate manner. What does it mean? If your first paragraph supports the paper’s argument, then in the second paragraph you should write something in the opposite of it. Such a combination of supporting and opposite paragraphs will make your essay look apparent, and well researched. Besides, it will help you to remain neutral.
- Fourth: include topic sentences and evidence . Write a summary of the argument at the beginning of the paragraph. It will allow the reader to easier understand what the paragraph is about. Provide evidence to show that you’re not making the facts up.
Well, you’ve almost finished your writing. Now you should focus on the last section. Keep reading, and you will learn how to write a conclusion for a discursive essay.
- In the last section, you should summarize your article including the main points, specified in the body paragraphs.
- You may also logically express your opinion. Remember: it should resonate with your evidence stated in the body paragraphs.
- Don’t repeat findings, just summarize them.
Keep it short. Your conclusion length should not exceed one paragraph.
👍 Do’s and Don’ts
Do you want more discursive essay writing tips? Fine! Just check them below:
Basic Do’s of a Discursive Essay
- Write in formal, impersonal style.
- Introduce each point in a separate paragraph
- Use topic sentences for each paragraph
- Write well-developed paragraphs
- Give reasons and examples for each point
- Use sequencing
- Use linking words and phrases
- Make references to other sources and make sure that you follow proper citation style
- Identify used sources
Basic Don’Ts of a Discursive Essay
- Don’t use short forms, like I’ll, don’t, they’ve
- Don’t use informal/colloquial language, for example: old as the hills, ain’t, gonna, etc.
- Don’t use very emotional language, since it might make your discursive article look prejudiced
- Don’t use over-generalizations. Extending the features of some elements from a group more than it is reasonable will lead to generous and inaccurate conclusions.
- Don’t express your personal opinion too insistently
- Don’t refer to statistics without proper referencing (check our citation guides )
- Don’t use personal examples, leave it for a personal experience essay
Well, now you know what discursive essay means, what are its main types, and how to structure it.

Discursive Essay Topics
- Discussion of risk factors that impact human health.
- Discuss the necessity of understanding cultural heritage to provide efficient health care.
- Analyze different opinions on withdrawing patients’ treatment.
- Examine different views on the Civil War.
- Discuss what hostile emotional states are and how they impact human life.
- Discuss the meaning of metaphors used by Virgil in Aeneid .
- Describe different opinions on telehealth in nursing homes.
- The ethicality of stem cell technology.
- Explore the effectiveness of motivational interviewing.
- Discuss how people present themselves online .
- Discuss the reasons for Coca-Cola’s marketing success.
- Analyze the food safety issues and the ways to improve the situation.
- Examine the essential meaning of sleep for people’s physical and mental health.
- Explore various complications of working with groups.
- Discussion of the modern issues with virtue ethics.
- Describe different views on the definition of love.
- Give the for and against arguments considering food security technologies.
- Discuss how the concept of the American dream is presented in the film The Great Gatsby.
- Analyze the influence of family problems on children and suggest ways to improve the situation.
- Present the various points of view on the ethical concepts of Buddhism.
- Examine the attitudes towards the problem of homelessness and the suggested ways of its solution.
- Explore different opinions on the American revolution and its consequences.
- Discuss various policies and views around the globe on abortion.
- Discussion of the history of food foraging in different communities.
- Multiple thoughts on civility on the Internet .
- Analyze arguments on the effectiveness of hand sanitizers.
- Discuss the importance of visual aids in learning.
- Present and evaluate the theories of international development .
- Discuss how to prevent the spread of the West Nile Virus (WNV).
- Is embracing renewable energy sources beneficial for both environment and the global economy?
- Examine the correctness of the statement that the ideology of pleasure is the foundation of social activism.
- Discussion of the ethical dilemma of population control.
- Discuss the ethics of experimental studies .
- Analyze the topic of gun violence and gun control laws.
- Explore the reasons for opioid crises in the US.
- Give arguments for and against random drug testing.
- Discuss the problem of endangered species .
- Express your opinion on the necessity of parents to be included in children’s education .
- Present your attitude towards working in a bureaucratic organization.
- Discuss the issue of the nursing shortage and suggest a solution.
- Give different viewpoints on the definition of beauty .
- Analyze the problem of police misconduct.
- Discuss the description of violence of African people in literature.
- Examine the views on Gardner’s multiple intelligence theory.
- Describe the various opinions on mysticism and express your attitude towards it.
- Discuss the diverse standpoints on spirituality.
- Is nature protection an urgent problem?
- Analyze different ideas on physical privacy at work.
- Discussion on the Jewish heritage in nursing.
- Examine the views on the meaning of life.
Good luck with your discussions and discursive essays! Be sure to check out the articles on our blog for more academic wisdom. By the way, on the Custom-Writing website, you may find the best essay topics for your academic writing.
And don’t forget to share your opinion in the comments below.
You might also be interested in:
- Friendship Essay: Writing Guide & Topic Ideas about Friendship
- Teamwork Essay: Quick Guide on How to Write a Good Paper
- Compare and Contrast Essay Writing Tips and Examples
- Transportation Essay: Writing Tips and Brilliant Topics
✏️ Discursive Essay FAQ
There is no one definitely correct answer to this question. Like any other essay, the text should have a clear structure with an introduction, body, and conclusion. The most important thing is that the overall book needs to be cohesive, persuasive, and exciting to read.
An example of a step by step guide is:
1. Take a closer look at the topic, think about the points to cover.
2. Choose the most relevant points and compose the Body of the essay.
3. Add an appropriate Introduction and Conclusion.
To write a good conclusion, you need to have the rest of the essay finished. Does the body of your essay present well-structured points? Great, then see what you can conclude based on that. If possible, make a connection between the introduction and the conclusion.
To ensure that your essay has a perfect structure, start with creating an outline. Based on such a plan, you can present your points step by step. Your text should have a relevant introduction, several points in the main body (with examples), and a logical conclusion.
🔗 References
- Writing an Opinion Essay: Grace Fleming, ThoughtCo
- How to Write a Good Argumentative Essay: Easy Step-by-Step Guide: Master Class
- Ending the Essay: Conclusions: Harvard College Writing Center
- Academic Writing Style: University of Southern California
- Cite Your Sources: Library Guides at University of California, Santa Cruz
- Share to Facebook
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email

How to write a narrative essay? To do that, you need to know what a narrative essay is. It is an academic text usually written as a story and containing all the usual elements of a story. Narrative essays are often personal, experiential, and creative. Still, they should be made...
![discursive essay reflection College Essay Writing 101—the Comprehensive Guide [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/student-girl-making-notes-in-a-copybook-with-a-pencil-e1565634333206-284x153.png)
So, you can’t wait to get into college and join a fraternity, sorority, or student union. Well, we have some incredibly useful tips and helpful information for college admission essay writing! Remember: getting into college takes more than money. And outstanding essays get you great college scholarships!
![discursive essay reflection Americanism Essay: Examples, Tips & Topics [2024 Update]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/american-flag-284x153.jpg)
It’s not hard to see why Americanism is one of the most popular essay topics. The concept of Americanism is in the center of the US identity. Writing an essay about it is an excellent way to find out more about this great country. That being said: From this article,...

An art critique paper involves a comprehensive analysis and assessment of an artwork. Though this looks a bit complicated, the task doesn’t require a lot of time if you have sufficient critique writing skills. It’s an interesting assignment for students of art colleges as well as high schoolers. All you...

An article review is an academic assignment that invites you to study a piece of academic research closely. Then, you should present its summary and critically evaluate it using the knowledge you’ve gained in class and during your independent study. If you get such a task at college or university,...

When you hear the phrase “spiritual leadership,” you probably think it’s only associated with religion. But did you know that this form of leadership can also be found in business? The book Spiritual Leadership: Moving People on to God’s Agenda by Henry and Richard Blackaby is a good starting point...

High school and college students often face challenges when crafting a compare-and-contrast essay. A well-written paper of this kind needs to be structured appropriately to earn you good grades. Knowing how to organize your ideas allows you to present your ideas in a coherent and logical manner This article by...

“If a tree falls in the forest, does it make a sound?” is one of the most debatable philosophical questions regarding observation and perception. Many tried to answer it, including the English philosopher John Locke. Do you need to explore Locke’s perspective on this question in your essay? You are on the right...

The long-standing debate surrounding abortion has many opponents and advocates. Groups known as Pro-Choice and Pro-Life argue which approach is better, with no easy solution in sight. This ethical complexity is what makes abortion a popular topic for argumentative writing. As a student, you need to tackle it appropriately. If...

What is the most important part of any essay or research paper? Of course, it’s the thesis statement—a sentence that expresses the paper’s main idea and guides the readers through your arguments. But where do you place the thesis? You’ve probably answered, “in the introduction.” However, that’s not all of...

If you’re a student, you’ve heard about a formal essay: a factual, research-based paper written in 3rd person. Most students have to produce dozens of them during their educational career. Writing a formal essay may not be the easiest task. But fear not: our custom-writing team is here to guide...

Rhetorical analysis is never a simple task. This essay type requires you to analyze rhetorical devices in a text and review them from different perspectives. Such an assignment can be a part of an AP Lang exam or a college home task. Either way, you will need a solid outline...
It’s very helpful!
it’s a good site to learn from. However, it will be perfect if there is a small essay to clear the mess understanding from the advice
This was so helpful , thank you God bless you
Very good site,thank so much for your effort in writing the posts.
thank you my n word 👨🏿🦳
thank you so much!!!! is there any way to access an annotated example to help?
Thank you so much. That really helped me with writing my essay.
thanku so much for increasing my knowledge
Thank you. It was really helpful. It has answered all my questions.
‘In Pursuit’: The Power of Epistemic Humility
Elizabeth H. Bradley and Jonathon S. Kahn ask if the breakdown of dialogue on campus is in part a reflection of how we teach.
By Elizabeth H. Bradley and Jonathon S. Kahn
You have / 5 articles left. Sign up for a free account or log in.

Olena Zagoruyko/iStock/Getty Images Plus
A new academic year is set to begin after what was one of the most tumultuous years on college campuses since the Vietnam War–era protests. Depending on one’s perspective, higher education institutions have emerged as sites of protest against a disturbing foreign conflict rife with humanitarian crises; they have been dangerous hotbeds of radicalism threatening Jewish community members; or they have been testing grounds for the limits of free speech in the 21st century. From our vantage point, as the president and a faculty member at a small liberal arts college, all can be true, and it is precisely the legitimacy of multiple perspectives that has made life on campus this past year so difficult and demanding.
We can’t sugarcoat it, because we live it: The breakdown of dialogue on college campuses is real. The irony that liberal arts institutions of higher education are struggling to navigate diverse perspectives is not lost on us. Institutions of higher education insist that navigating differences is core to their work. Mission statements aplenty claim that being able to engage multiple viewpoints represents a central educational value. That so many colleges and universities are grappling with their most basic and central educational commitments should give pause.
It pushes us to ask a question that has largely gone unasked: Is a breakdown in how we now educate partially to blame for the current breakdown on campuses? In other words, is it us?
Most Popular
- Open-access expansion threatens academic publishing industry
- Stanford creative writing program laying off lecturers
- Colleges slam Ed Department's proposed attendance policy
Current tumult has obscured a crucial organizing tenet of higher education: to be always in pursuit of greater understanding. It is cliché, perhaps. But in these toughest of days, we found ourselves thinking about the deeper implications of being “in pursuit.” To pursue understanding is to conceive of knowledge building as requiring continuous seeking, revising and questioning. Such an approach to learning is desperately needed today not only because it fosters curiosity (which it does) but also because it staves off absolutist impulses to deride and silence others’ views, impulses we have seen firsthand.
Consider, for example, a tremendously difficult class one of us co-taught on the history of blackface performances and minstrel practices during the early part of the 20th century at what was then our all-women’s college. Since the course dealt with deeply racist practices, the understandable desire to singularly condemn the college’s history was palpable. Indeed, at the start of the class, many students, most of whom were white, described their motivations for taking the class primarily in terms of exposing the college’s racist past. “Critique” was the language they spoke, which they took to mean uncovering the college’s blameworthy history, denouncing the practices they were studying and confirming their own absolutes about race and hypocrisy at elite institutions more broadly. They described their attachment to the institution as tenuous. It was clear that, to their thinking, college was a place to have an educational experience and receive a degree, while the notion that they might develop a sense of fidelity or obligation to a college with a racist history, or develop a complex understanding of a condemned practice, was an anathema.
But something different happened. What unfolded over the course of the semester was an exercise in the pursuit of understanding. If the students began the course convinced about the racist motivations of their counterparts in the early 20th century, their research complicated those assumptions. They learned that all-women performances of blackface at that time were quite rare, and so what was happening on campus then represented something distinct. Their inquiries led them to consider the transition from 19th-century Victorian models of white womanhood to newer formulations in the early 20th century that came to be known as first-wave feminism. They began to ask: Is it possible that these blackface performances contributed to this transition? Did commitments to feminism and gender equality at that time actually reinforce persistent racial inequalities? How is it possible that these young women could have genuinely believed they were pursuing a form of self-liberation through racist tropes and performances?
Their answers to these questions went in many directions, and none of them excused the racism of this time. But instead of vilifying these earlier students and refusing to understand perspectives different from their own, our students began to see their predecessors as flawed and complicated with multiple motivations; these included a daring to do what men were doing in an attempt to articulate their own desires for equality. Again, our students did not excuse these practices or the women who participated in them as much as they began to understand their behavior as sitting in a complex network of forces, a condition that may very well mark the human experience. Crucially in the final sets of class meetings, the students began to wonder about themselves as similarly flawed and circumscribed by social forces of which they may not be fully aware.
The effects of this insight on the students’ relationships to the institution were significant. They began to see the college in the early 20th century as a context in which young white women, many of whom were from the middle classes, were struggling to craft a self during a tumultuous time of changing norms. The parallels became obvious. The students began to understand that they too sit in cross-pressured contexts in which they are haltingly and fallibly trying to make sense of themselves in their own turbulent times.
We do not want to overstate the effects of the class; however, the experience gave students a profound encounter with the power of epistemic humility, an acknowledgement of the necessity of curiosity, nuance, uncertainty and multiple perspectives needed for building knowledge. That encounter expanded the students’ capacity to understand—and even have empathy for—a broader range of experiences and perspectives, a necessary condition for engaging the pluralism possible on a college campus.
The question facing higher education today is how to build these types of experiences. The good news is that this doesn’t require fancy lab equipment or other expensive infrastructure. It does require three basic elements—instructors committed to giving their students an experience of novel inquiry, primary sources and time. When faculty make clear that the entire purpose of the class is for students to figure out what they think, students begin to understand the power of question asking. From there, any question—from the teacher, their classmates and themselves—feels exploratory and enticing.
Primary sources—original documents or images—are vital because they cry out for multiple interpretations, functioning like a ball-and-socket joint around which students’ thoughts, ideas and questions can begin to turn. Critically, all this takes time. Students need time to trust that the instructor genuinely wants them to go on a journey of their own. And the meanings of images and texts surface slowly, yielding only to the student’s patience and persistence to ask questions from multiple perspectives.
At the end of the 19th century, William James insisted that education required “the habit of always seeing an alternative, of not taking the usual for granted, of making conventionalities fluid again, of imagining foreign states of mind.” In the 20th century, W. E. B. Du Bois worried about the dangers of education reinforcing “the overwhelming sense of the I, and the consequent forgetting of the Thou.” And in the 21st century, the feminist literary theorist Rita Felski asks , “Why—even as we extol multiplicity, difference, hybridity … are we so hyperarticulate about our adversaries?”
Editors’ Picks
- ‘Red Wedding’: Storied Stanford Creative Writing Program Laying Off Lecturers
- Universities Hit Back Against Proposed Online Attendance Policy
- Re: Your Recent Email to Your Professor
All three circle around the same idea. To be always in the pursuit of greater understanding is to confess that we have more to learn. It is to conceive of education as a process of relationship building between our own perspectives and experiences not our own. Without this, our relationships with those with different experiences risk becoming brittle and unsustainable. Unable to contain a community’s multitudes, we resort to excising—canceling—those whom we cannot countenance. The pursuit of understanding requires the opposite.
Today’s campuses need to develop and be given greater latitude for this version of learning. We know from experience that this process is messy, and we need to allow for that messiness, knowing that exploration, mistakes and missteps are all part of learning. We must resist the temptation to drop the “in pursuit” and focus only on the “understanding,” as if learning amounts to nothing more than the dogmatic piling up of facts.
The pursuit of understanding emphasizes the dynamics of learning, which necessarily expands our abilities to comprehend a broad range of perspectives and experiences. Most importantly, the pursuit of understanding pushes us to ask what sort of human each of us wants to be in relation to others. Our future together relies on being forever in pursuit.
Elizabeth H. Bradley is the president of Vassar College and a professor of science, technology and society, and of political science. She is deeply engaged with research on the performance and quality of higher education institutions in the U.S. Jonathon S. Kahn is a professor of religion and the former director of engaged pluralism at Vassar College. He works at the intersection of race, religious ethics and politics.

Where Progressive Illiberalism Reigns
Litigation stemming from antisemitism on campuses shows that colleges must revive their commitments to freedom and to
Share This Article
More from views.

In Defense of the AAUP’s Statement on Boycotts
John K. Wilson opposes academic boycotts but supports the AAUP’s controversial new statement nevertheless.

A Model for Advancing Institutional Effectiveness via Undergraduate Research
To help scale traditional faculty/student models of undergraduate research engagement, institutional leaders can cons
- Become a Member
- Sign up for Newsletters
- Learning & Assessment
- Diversity & Equity
- Career Development
- Labor & Unionization
- Shared Governance
- Academic Freedom
- Books & Publishing
- Financial Aid
- Residential Life
- Free Speech
- Physical & Mental Health
- Race & Ethnicity
- Sex & Gender
- Socioeconomics
- Traditional-Age
- Adult & Post-Traditional
- Teaching & Learning
- Artificial Intelligence
- Digital Publishing
- Data Analytics
- Administrative Tech
- Alternative Credentials
- Financial Health
- Cost-Cutting
- Revenue Strategies
- Academic Programs
- Physical Campuses
- Mergers & Collaboration
- Fundraising
- Research Universities
- Regional Public Universities
- Community Colleges
- Private Nonprofit Colleges
- Minority-Serving Institutions
- Religious Colleges
- Women's Colleges
- Specialized Colleges
- For-Profit Colleges
- Executive Leadership
- Trustees & Regents
- State Oversight
- Accreditation
- Politics & Elections
- Supreme Court
- Student Aid Policy
- Science & Research Policy
- State Policy
- Colleges & Localities
- Employee Satisfaction
- Remote & Flexible Work
- Staff Issues
- Study Abroad
- International Students in U.S.
- U.S. Colleges in the World
- Intellectual Affairs
- Seeking a Faculty Job
- Advancing in the Faculty
- Seeking an Administrative Job
- Advancing as an Administrator
- Beyond Transfer
- Call to Action
- Confessions of a Community College Dean
- Higher Ed Gamma
- Higher Ed Policy
- Just Explain It to Me!
- Just Visiting
- Law, Policy—and IT?
- Leadership & StratEDgy
- Leadership in Higher Education
- Learning Innovation
- Online: Trending Now
- Resident Scholar
- University of Venus
- Student Voice
- Academic Life
- Health & Wellness
- The College Experience
- Life After College
- Academic Minute
- Weekly Wisdom
- Reports & Data
- Quick Takes
- Advertising & Marketing
- Consulting Services
- Data & Insights
- Hiring & Jobs
- Event Partnerships
4 /5 Articles remaining this month.
Sign up for a free account or log in.
- Sign Up, It’s FREE

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Pro-Con Essays: Purpose: Evaluating the pros and cons of a given issue. Structure: The essay presents the positive aspects (pros) and negative aspects (cons) of the topic. It aims to provide a balanced assessment and may conclude with a recommendation or a summary of the most compelling points. Exploratory Essays:
Nervous about the English Advanced Module C question? Not sure about how to respond to a creative task and a reflection? Don't worry in this post, we share a Matrix student's Band 6 response to a discursive essay and reflection task. Read the essay and then download the annotated essay and reflection statement.
A discursive essay is a form of critical essay that attempts to provide the reader with a balanced argument on a topic, supported by evidence. ... thoroughly to present more than one perspective and should check their own biases and assumptions through critical reflection (see Chapter 30). Unlike persuasive writing, the writer does not need to ...
3. For and against essay. Write it as a debate with opposing opinions. Describe each viewpoint objectively, presenting facts. Set the stage for the problem in your discursive essay intro. Explore reasons, examples, and facts in the main body. Conclude with your opinion on the matter.
Clear Introduction: Start with a concise introduction that provides context and grabs the reader's attention. Clearly state your thesis or main argument. Well-structured Paragraphs: Divide your essay into paragraphs that focus on specific points. Each paragraph should present a new idea or support a previous one.
The assessment task being written about. The level of English you're taking (Advanced or Extension) What your marking criteria says! Reflection statements will generally be between 300 and 800 words, likely hanging around the 400-word mark. However, for English Extension 2, your reflection statement is 1500 words long.
Reflective writing is very different from the discursive style that you may be used to. It is written in the first person, examines personal experiences and is not limited to academic evidence. Unless you have experience with reflective practice, your first attempt(s) at reflective writing may feel very uncomfortable.
Discursive (adj) [dis-ker-siv]: talking or writing about things that are not highly organized. moving from topic to topic without order. passing aimlessly from one topic to another. SYNONYMS: rambling, digressive, erratic, long-winded. Think of discursive as a BLEND of expository and argumentative because it uses elements from both:
Mod A - Plath and Hughes. Mod B - King Henry IV Part I. Discursive Mod C - 'Human Bookshelf. Discursive Reflection - Gwen Harwood's Father and Child. Discursive Reflection - Geraldine Brooks' A Home In Fiction. Mod C Imaginative - Cold Connotations. Imaginative Reflection - Name Le's Love and Honour and Pity and Pride and ...
topics in the course of a long discursive essay. (See Student Activity 1 based on the Merriam Webster Dictionary) So a discursive essay is not as much 'rambling' as it is 'graceful'; the 'rambling' is more about the exploratory nature of the form, meandering and 'touching on a few topics'. The twentieth century essayist Narayan ...
How To Write A Band 6 Module C Discursive Essay (New Syllabus) Don't know what a discursive essay is? Do you know what the differences between a discursive and persuasive essay are? Don't worry. In this article, we explain what discursive writing for Year 12 Module C: The Craft of Writing is and give you a step-by-step process for writing a ...
Resource Description. Persuasive/discursive article (hybrid) with reflection, written for an assessment task. Techniques and ideas based on my prescribed texts: Noel Pearson's speech "A Eulogy for Gough Whitlam", Nam Le's short story "Love and Honour and Pity and Pride and Compassion and Sacrifice", and Siri Hustvedt's discursive essay "Eight Days in a Corset"
The Academic Writing Guide (AWG) is designed to familiarise you with the process of writing a discursive essay. A discursive essay is a genre of writing that requires you to investigate a topic; collect, generate, and evaluate evidence; and establish a position on the topic in a concise manner. Once you have decided on your position your ...
Tip #4: Get Personalised Feedback on Your Work. Even if you're following the best advice on how to write a piece of discursive writing, it's likely that you'll struggle to accurately reflect on the quality of your work. You've probably heard this before: "HSC English is super subjective.".
A reflection takes place after students complete their imaginative, discursive or persuasive writing. Below are TutorTime's essential components to writing a Band 6 reflection: 1. Rationale behind storyline and isolation of key techniques. Your reflection should begin with a brief explanation of why you chose the storyline of your piece.
Pick your words carefully to leave a lasting impact. Introduce your thesis statement. In a sentence or two, describe the paper's main idea and how you will disclose it later. Trim it down and edit until the statement perfectly encapsulates the core of your writing. Describe what the essay will be about.
Everything students should know about writing discursive essays. Visit essayhack.io, and get comprehensive assistance in writing a discursive essay here. ... A balanced reflection on the topic should be stated again only in the conclusion. Now, whatever the style you have got to write your essay in, the students should keep in mind that the ...
A discursive essay presents both sides of an argument, then states your stance. The goal. The goal of a discursive essay is to present a balanced and objective analysis of both sides of the argument. (Keep in mind that, in some cases, you may need to examine three or more positions as topics may be more nuanced than basic for-or-against ...
Discursive essay + reflection. Discursive + reflection. Subject. Advanced English. 723 Documents. Students shared 723 documents in this course. Degree • Grade HSC • 12. School Sydney Secondary College. Academic year: 2023/2024. Uploaded by: Anonymous Student.
HOW TO WRITE A DISCURSIVE W/ REFLECTION DISCURSIVE Introduction 1. Rhetorical Questions that are used to convey a sense of speculation and mention both sides of the issue. 2. Some use of first-person narrative voice and some use of an inclusive second-person narrative voice to engage the responder. 3. A movement from reactions to a question towards a clarification of key ideas (from a ...
Start with an introduction to the topic. Discuss each essay question in a single paragraph. Begin each paragraph with a powerful issue sentence. Paragraphs with one point usually followed by a counterpoint paragraph. Its style is general for essays as the reader should understand what you stand for.
15 Found helpful • 2 Pages • Essays / Projects • Year: Pre-2021. This piece, titled 'Seclusion is a Swinging Pendulum', explores the idea of isolation and how it is seen in our world today. There is also a reflection segment where I relate the decisions I made to the Module C 'Craft of Writing' section of the English Advanced course.
Reflective essays are essays in which the writer looks back on, or reflects upon, his or her experiences and how they caused personal change. Reflective essays involve self-reflection. Typically ...
Elizabeth H. Bradley and Jonathon S. Kahn ask if the breakdown of dialogue on campus is in part a reflection of how we teach. A new academic year is set to begin after what was one of the most tumultuous years on college campuses since the Vietnam War-era protests. Depending on one's perspective, higher education institutions have emerged as sites of protest against a disturbing foreign ...