How to master communication in problem solving
May 11, 2023 The path from problem to solution is not linear. In fast-moving, complex times, decision-makers can’t effectively act alone when it comes to solving complicated workplace problems; diverse perspectives and rigorous debate are crucial to determining the best steps to take. What’s missing in many companies is the use of “contributory dissent,” or the capabilities required to engage in healthy if divergent discussions about critical business problems, write Ben Fletcher , Chris Hartley , Rupert Hoskin , and Dana Maor in a recent article . Contributory dissent allows individuals and groups to air their differences in a way that moves the discussion toward a positive outcome and doesn’t undermine leadership or group cohesion. Check out these insights to learn how to establish cultures and structures where individuals and teams feel free to bring innovative—and often better—alternative solutions to the table, and dive into the best ways to master communication in problem solving.
Into all problem-solving, a little dissent must fall
Capturing the value of ‘one firm’
Bias Busters: A better way to brainstorm
Psychological safety and the critical role of leadership development
The next competitive advantage in talent: Continuous employee listening
Author Talks: Fred Dust on making conversations count
What is an effective meeting?
Bias Busters: Getting both sides of the story
Fear factor: Overcoming human barriers to innovation
Listen with your head and heart: How Mars anchors on principles and people


Search Utah State University:
Effective communication skills: resolving conflicts .
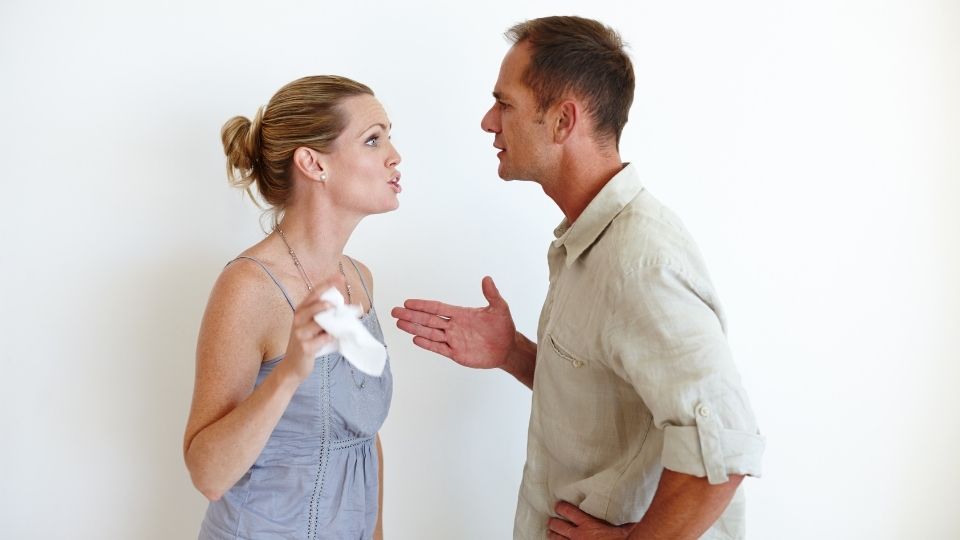

Even the happiest of relationships experience conflicts and problems (Markman, Stanley, Blumberg, Jenkins & Whiteley, 2004). If handled well, issues provide opportunities for personal and relationship growth. There are many skills that can help individuals seeking to resolve conflicts in a healthy way. One of the greatest skills that aids in conflict resolution is effective communication.
Common Conflicts
Issues, or conflicts, in relationships consist of any situation, event or experience that is of concern or importance to those involved. A variety of factors lead to conflict, some of which include topics such as money, children, and in-laws, personal issues such as selfesteem, values, expectations, or goals, or relational issues such as the amount of together time versus alone time, support versus control, affection, and communication (Miller & Miller, 1997). While there are seemingly endless reasons for conflicts, they generally surround the underlying needs of all humans including physical, intellectual, emotional, social, and spiritual (Miller & Miller, 1997; Townsend, 2010). Most importantly, how we approach and communicate about these issues often determines the outcome.
Conflicts in Communication
Most people know that in order to resolve conflicts, we need to communicate about the issue; but negative patterns of communication can often lead to greater frustration and escalation of conflict. Consider the following communication challenges:
Body Language/Tone of Voice
Communication is more than the words we choose to use. In fact, our body language and tone of voice often speak louder than our words. For example, shouting “I’m not angry” is not a very convincing message! When we give an incongruent message where our tone of voice and body language does not match our message, confusion and frustration often follow (Gottman & DeClaire, 2001). In order to overcome this communication challenge, we need to be aware of what messages our body language and tone of voice may be sending others. Speak calmly, give eye contact, smile when appropriate, and maintain an open and relaxed posture (Paterson, 2000).
Differences in Style
Each of us has a unique way of communicating, often based on our family experiences, culture, gender and many other factors (Markman et al., 2004; Miller & Miller, 1997). For example, we may tend to be more loud, outgoing, or emotional when compared to our partner. While there is no right or wrong style, our past experiences often lead to expectations that are not usually verbally communicated with others, which can cause tension and misunderstandings in relationships. For example, if we came from a large family that tended to shout in order to be heard, we may think that speaking loudly is normal. But if our partner came from a calmer family environment, he/she may be uncomfortable or even frightened by a raised voice (Markman et al., 2004).
Discussing our backgrounds and perceptions can help to clarify expectations to ourselves and others and can also help our partner to understand our point of view. Knowing this information can often help in the problem solving process.
Communication Roadblocks
Communication roadblocks occur when two people talk in such a way that neither one feels understood. Research has found four particularly negative styles of communication, often referred to as the “four horsemen of the apocalypse,” (Gottman, 1999, p.27) because if left unchecked, these styles of interaction can eventually become lethal to relationships. These styles are criticism, contempt, defensiveness, and stonewalling (Gottman, 1999).
- Criticism attacks the character or personality of another. While it is normal to have complaints about another’s specific actions, it is very different to put them down as a person because of those actions. For example, a complaint might be, “I felt worried when you did not call to tell me that you were going to be home late.” A criticism in the same situation would be expressed as “You are so inconsiderate, you never call me when you are going to be late.” Critiques focus on certain behaviors; criticism negatively focuses on the person’s intentions and character.
- Contempt portrays disgust and a lack of respect for the other person through body language, such as eye rolling or sneering, or by name calling, sarcasm and cutting remarks.
- Defensiveness is a seemingly understandable reaction that individuals take to criticism and contempt; however, it often escalates the conflict. When we are defensive, we tend to stop listening to the other’s viewpoint and communication is shut down.
- Stonewalling is withdrawing from communication and refusing to engage in discussion. In other words, it is the adult version of the “silent treatment” that young children utilize when they are upset. Conflict resolution is impossible without communication!
Some additional examples of communication roadblocks include (Miller & Miller, 1997):
- Ordering (“Stop complaining!”)
- Warning (“If you do that, you’ll be sorry.”)
- Preaching (“You shouldn’t act like that.”)
- Advising (“Just wait a couple of years before deciding.”)
- Lecturing (“If you do this now, you won’t grow up to be a responsible adult.”)
- Agreeing, just to keep the peace (“I think you’re right.”)
- Ridiculing (“OK, little baby.”)
- Interpreting (“You don’t really believe that.”)
- Sympathizing (“Don’t worry, it’ll all work out.”)
- Questioning (“Who put that idea into your head?”)
- Diverting (“Let’s talk about something more pleasant.”)
Communication roadblocks are very common; however, they do not promote healthy conflict resolution and often lead to escalation of the conflict. Recognizing these roadblocks and making efforts to effectively communicate can help individuals overcome roadblocks.
Tips to Resolve Conflict
Soften the startup.
One of the skills to overcome communication roadblocks includes a soft startup to the conversation by starting with something positive, expressing appreciation, focusing on problems one at a time and taking responsibility for thoughts and feelings (Gottman, 1999; Gottman & Declaire, 2001; Patterson, 2000). In addition, when expressing the problem, starting the message with “I” instead of “You” can decrease defensiveness and promote positive interactions with others (Darrington & Brower, 2012). For example, “I want to stay more involved in making decisions about money” rather than “You never include me in financial decisions.”
Make and Receive Repair Attempts.
Another important skill in overcoming communication roadblocks is learning to make and receive repair attempts (Gottman, 1999). Repair attempts are efforts to keep an increasingly negative interaction from going any further by taking a break or making efforts to calm the situation. This is important because when conflicts arise, we often experience intense emotional and physical stress that can impact our ability to think and reason, which can lead to communication roadblocks (Gottman & DeClaire, 2001). Taking time away from the conflict (at least 20 minutes) to calm down can help us be more prepared to discuss the issue (Gottman, 1999; Gottman & DeClaire, 2001; Markman et al, 2004).
Effective Speaking and Listening Skills
Overcoming communication roadblocks requires effective speaking and listening skills. Markman, Stanley and Blumberg (2010) share what they call the “speaker-listener” technique to help individuals more effectively communicate. Each partner takes turns being the speaker and the listener.
The rules for the speaker include (Markman et al., 2004; Markman, Stanley & Blumberg, 2010):
- The speaker should share his/her own thoughts, feelings and concerns—not what he/she thinks the listener’s concerns are.
- Use “I” statements when speaking to accurately express thoughts and feelings.
- Keep statements short, to ensure the listener does not get overwhelmed with information.
- Stop after each short statement so that the listener can paraphrase, or repeat back in his/her own words, what was said to ensure he/she understands. If the paraphrase is not quite right, gently rephrase the statement again to help the listener understand.
The rules for the listener include:
- Paraphrase what the speaker is saying. If unclear, ask for clarification. Continue until the speaker indicates the message was received correctly.
- Don’t argue or give opinion about what the speaker says—wait to do this until you are the speaker, and then do so in a respectful manner.
- While the speaker is talking, the listener should not talk or interrupt except to paraphrase after the speaker.
The speaker and listener should take turns in each role so that each has a chance to express his/her thoughts and feelings. Either can call for a time out at any time. The goal of this activity is not to solve a particular problem, but rather to have a safe and meaningful discussion and to understand each other’s point of view. While we may not always agree with the other’s point of view, understanding and validating other’s thoughts and feelings can improve relationships and help us build on common ground, which may lead to more effective negotiation and problem resolution (Gottman, 1999).
Dealing with conflict can take varying amounts of mental, emotional, and physical energy (Miller & Miller, 1997). It can be work! However, learning and implementing a few simple communication skills can increase positive interactions with others. The opportunities for personal and relationship growth are well worth the effort.
For more information or for classes and workshops:
- Go to http://strongermarriage.org for tips, articles, and to find relationship education classes near you.
- Check out your local Extension office for relationship education classes and events.
- Darrington, J., & Brower, N. (2012). Effective communication skills: “I” messages and beyond. Utah State University Extension. https://extension.usu.edu/htm/publications/publi cation=14541
- Gottman, J. M., & DeClaire, J. (2001). The relationship cure: A 5 step guide to strengthening your marriage, family, and friendships. New York, NY: Three Rivers Press.
- Gottman, J. M., & Silver, N. (1999). The seven principles for making marriage work. New York, NY: Three Rivers Press.
- Markman, H. J., Stanley, S. M., & Blumberg, S. L. (2010). Fighting for your marriage. San Francisco: Jossey Bass.
- Markman, H. J, Stanley, S. M., Blumberg, S. L., Jenkins, N. H., & Whiteley, C. (2004). 12 hours to a great marriage: A step-by-step guide for making love last. San Francisco: Jossey Bass.
- Miller, S., & Miller, P. A. (1997). Core communication: Skills and processes. Evergreen, Co: Interpersonal Communication Programs, Inc.
- Paterson, R. J. (2000). The assertiveness workbook: How to express your ideas and stand up for yourself at work and in relationships. Oakland, CA: New Harbinger, Inc.
- Townsend, M. (2010). Starved stuff: Feeding the 7 basic needs of healthy relationships. Townsend Relationship Center.
Naomi Brower, MFHD, CFLE, Extension Assistant Professor; Jana Darrington, MS, Extension Assistant Professor

Naomi Brower
Extension Professor | Couple and Family Relationships | Weber County Director
Home and Community Department
Related Research

Building a Better Marriage
If you have been struggling with your marital relationship, or if you would like to improve the quality of your relationship, you are not alone. Just as Jenny and Michael want to strengthen their marria

Effective Communication Skills: Resolving Conflicts
Even the happiest of relationships experience conflicts and problems (Markman, Stanley, Blumberg, Jenkins & Whiteley, 2004). If handled well, issues provide opportunities for personal and relationship growth.

Effective Communication Skills: “I” Messages and Beyond
Communication is something we do on a regular basis. As young children we initially learn ways to communicate as we observe our parent, sibling, and family interactions. Throughout our lives our communication patterns evolve and are reinforced by our expe

Effects of Pornography on Relationships
Pornography is not a new issue in relationships; however, the expansion of the Internet appears to have increased pornography viewing and exacerbated pre-existing tendencies (Cooper, Boies, Maheu & Greenfield, 1999; Young, 2008). One key factor in this in

From Time to Quality Time: Making Every Moment Count
Couples and families often look for ways to find more time together and to make better use of that time. Most people struggle to find enough time in their day for everything. In fact, according to Dr. William Doherty (2001), those that care about each oth

Have Fun! The Importance of Play in Couple Relationships
Boring, drab, lifeless, stale, dull, tedious. These are probably not the words you hope to use to describe your relationships. How about well planned, frugal, precise, productive, serious, busy? Though these can be characteristics of a strong, healthy rel

Healthy Conflict Management
Conflicts are a natural part of human interaction. Whenever two or more people are in the same environment for a long enough period of time, it is inevitable that conflict will occur. However, the conflict itself is not the problem, but rather how they ch

Honey, I’m Home: Strengthening Your Marriage Ten Minutes at a Time
Strengthen your marriage relationship by making the first ten minutes of your interactions together a positive experience. Learn how to have stress-reducing conversation, emotionally support each other, and sooth self and partner in positive communication

Keys for Strong Commitment in Marriage
Having commitment means being dedicated to a cause. Commitment comes in all different shapes and sizes, but the most important type of commitment, for many, is a commitment to your marriage. Often couples start their marriage with commitment, but they don

Making Media Work for Your Marriage
Increased options for instant connection can have positive and negative impacts on relationships. While online resources can help us stay connected to those we love and increase relationship satisfaction Pettigrew, 2009; Sidelinger, Avash, Godorhazy, & T

Making the Most of Marriage Therapy
All relationships experience change over time (Larson, 2003). Even the strongest relationships can often benefit from a skilled a marriage counselor to help to smooth over the rough patches in their relationship. While the needs of relationships vary, som

Marriage Principles from a National Extension Model
Through this fact sheet, you will learn about these seven principles—Choose, Care for Self, Know, Care, Share, Manage, and Connect—and how to apply them in your life.

Supporting Others Coping with Infertility
It is likely that you know an individual or couple who is impacted by infertility. The natural human response is to want to comfort them, but it can be difficult to know what to say or do, especially if you have not experienced infertility yourself.

Technology Tips and Traps in Your Relationship
This fact sheet will help you be aware of some of the positive and negative effects of technology and how to protect your marriage from being swamped by it.

Tips to Strengthen Relationships Today
Research conducted by Dr. Sonja Lyubomirsky shows that happier people tend to have larger circles of friends, experience strong social support, and are more likely to be a support for others. But this research also shows that the connection between happin
Body Language and Nonverbal Communication
Improving emotional intelligence (eq), conflict resolution skills.
- Empathy: How to Feel and Respond to the Emotions of Others
Anger Management: Help for Anger Issues
Managing conflict with humor.
- The 5 Love Languages and Their Influence on Relationships
- Gaslighting: Turning Off the Gas on Your Gaslighter
- Online Therapy: Is it Right for You?
- Mental Health
- Health & Wellness
- Children & Family
- Relationships
Are you or someone you know in crisis?
- Bipolar Disorder
- Eating Disorders
- Grief & Loss
- Personality Disorders
- PTSD & Trauma
- Schizophrenia
- Therapy & Medication
- Exercise & Fitness
- Healthy Eating
- Well-being & Happiness
- Weight Loss
- Work & Career
- Illness & Disability
- Heart Health
- Childhood Issues
- Learning Disabilities
- Family Caregiving
- Teen Issues
- Communication
- Emotional Intelligence
- Love & Friendship
- Domestic Abuse
- Healthy Aging
- Aging Issues
- Alzheimer’s Disease & Dementia
- Senior Housing
- End of Life
- Meet Our Team
What is effective communication?
Tips for improving your communication skills.
- Tip 1: Understand the barriers to effective communication
Tip 2: Become an engaged listener
Tip 3: pay attention to nonverbal signals, tip 4: keep stress in check, tip 5: assert yourself, effective communication improving your interpersonal skills.
Want better communication skills? These tips will help you avoid misunderstandings, grasp the real meaning of what’s being communicated, and greatly improve your work and personal relationships.

Effective communication is about more than just exchanging information. It’s about understanding the emotion and intentions behind the information. As well as being able to clearly convey a message, you need to also listen in a way that gains the full meaning of what’s being said and makes the other person feel heard and understood.
Effective communication sounds like it should be instinctive. But all too often, when we try to communicate with others something goes astray. We say one thing, the other person hears something else, and misunderstandings, frustration, and conflicts ensue. This can cause problems in your home, school, and work relationships.
But by learning effective communication skills, you can deepen your connections to others, build greater trust and respect, and improve teamwork, problem solving, and your overall social and emotional health
Whether you’re trying to improve communication with your romantic partner, kids, boss, or coworkers, learning the following communication skills can help strengthen your interpersonal relationships.
Tip 1: Understand what’s stopping you from communicating well
Common barriers to effective communication include:
Stress and out-of-control emotion. When you’re stressed or emotionally overwhelmed, you’re more likely to misread other people, send confusing or off-putting nonverbal signals, and lapse into unhealthy knee-jerk patterns of behavior. To avoid conflict and misunderstandings, you can learn how to quickly calm down before continuing a conversation.
Lack of focus. You can’t communicate effectively when you’re multitasking. If you’re checking your phone , planning what you’re going to say next, or daydreaming, you’re almost certain to miss nonverbal cues in the conversation. To communicate effectively, you need to avoid distractions and stay focused.
Inconsistent body language. Nonverbal communication should reinforce what is being said, not contradict it. If you say one thing, but your body language says something else, your listener will likely feel that you’re being dishonest. For example, you can’t say “yes” while shaking your head no.
[Read: Nonverbal Communication and Body Language]
Negative body language. If you disagree with or dislike what’s being said, you might use negative body language to rebuff the other person’s message, such as crossing your arms, avoiding eye contact, or tapping your feet. You don’t have to agree with, or even like what’s being said, but to communicate effectively and not put the other person on the defensive, it’s important to avoid sending negative signals.
When communicating with others, we often focus on what we should say. However, effective communication is less about talking and more about listening. Listening well means not just understanding the words or the information being communicated, but also understanding the emotions the speaker is trying to convey.
There’s a big difference between engaged listening and simply hearing. When you really listen—when you’re engaged with what’s being said—you’ll hear the subtle intonations in someone’s voice that tell you how that person is feeling and the emotions they’re trying to communicate. When you’re an engaged listener, not only will you better understand the other person, you’ll also make that person feel heard and understood, which can help build a stronger, deeper connection between you.
By communicating in this way, you’ll also experience a process that lowers stress and supports physical and emotional well-being. If the person you’re talking to is calm, for example, listening in an engaged way will help to calm you, too. Similarly, if the person is agitated, you can help calm them by listening in an attentive way and making the person feel understood.
If your goal is to fully understand and connect with the other person, listening in an engaged way will often come naturally. If it doesn’t, try the following tips. The more you practice them, the more satisfying and rewarding your interactions with others will become.
Tips for becoming an engaged listener
Focus fully on the speaker. You can’t listen in an engaged way if you’re constantly checking your phone or thinking about something else. You need to stay focused on the moment-to-moment experience in order to pick up the subtle nuances and important nonverbal cues in a conversation. If you find it hard to concentrate on some speakers, try repeating their words over in your head—it’ll reinforce their message and help you stay focused.
Favor your right ear. As strange as it sounds, the left side of the brain contains the primary processing centers for both speech comprehension and emotions. Since the left side of the brain is connected to the right side of the body, favoring your right ear can help you better detect the emotional nuances of what someone is saying.
Avoid interrupting or trying to redirect the conversation to your concerns. By saying something like, “If you think that’s bad, let me tell you what happened to me.” Listening is not the same as waiting for your turn to talk. You can’t concentrate on what someone’s saying if you’re forming what you’re going to say next. Often, the speaker can read your facial expressions and know that your mind’s elsewhere.
Show your interest in what’s being said. Nod occasionally, smile at the person, and make sure your posture is open and inviting. Encourage the speaker to continue with small verbal comments like “yes” or “uh huh.”
Try to set aside judgment. In order to communicate effectively with someone, you don’t have to like them or agree with their ideas, values, or opinions. However, you do need to set aside your judgment and withhold blame and criticism in order to fully understand them. The most difficult communication, when successfully executed, can often lead to an unlikely connection with someone.
[Read: Improving Emotional Intelligence (EQ)]
Provide feedback. If there seems to be a disconnect, reflect what has been said by paraphrasing. “What I’m hearing is,” or “Sounds like you are saying,” are great ways to reflect back. Don’t simply repeat what the speaker has said verbatim, though—you’ll sound insincere or unintelligent. Instead, express what the speaker’s words mean to you. Ask questions to clarify certain points: “What do you mean when you say…” or “Is this what you mean?”
Hear the emotion behind the words . It’s the higher frequencies of human speech that impart emotion. You can become more attuned to these frequencies—and thus better able to understand what others are really saying—by exercising the tiny muscles of your middle ear (the smallest in the body). You can do this by singing, playing a wind instrument, or listening to certain types of high-frequency music (a Mozart symphony or violin concerto, for example, rather than low-frequency rock, pop, or hip-hop).
The way you look, listen, move, and react to another person tells them more about how you’re feeling than words alone ever can. Nonverbal communication, or body language, includes facial expressions, body movement and gestures, eye contact, posture, the tone of your voice, and even your muscle tension and breathing.
Developing the ability to understand and use nonverbal communication can help you connect with others, express what you really mean, navigate challenging situations, and build better relationships at home and work.
- You can enhance effective communication by using open body language—arms uncrossed, standing with an open stance or sitting on the edge of your seat, and maintaining eye contact with the person you’re talking to.
- You can also use body language to emphasize or enhance your verbal message—patting a friend on the back while complimenting him on his success, for example, or pounding your fists to underline your message.
Improve how you read nonverbal communication
Be aware of individual differences. People from different countries and cultures tend to use different nonverbal communication gestures, so it’s important to take age, culture, religion, gender, and emotional state into account when reading body language signals. An American teen, a grieving widow, and an Asian businessman, for example, are likely to use nonverbal signals differently.
Look at nonverbal communication signals as a group. Don’t read too much into a single gesture or nonverbal cue. Consider all of the nonverbal signals you receive, from eye contact to tone of voice to body language. Anyone can slip up occasionally and let eye contact go, for example, or briefly cross their arms without meaning to. Consider the signals as a whole to get a better “read” on a person.
Improve how you deliver nonverbal communication
Use nonverbal signals that match up with your words rather than contradict them. If you say one thing, but your body language says something else, your listener will feel confused or suspect that you’re being dishonest. For example, sitting with your arms crossed and shaking your head doesn’t match words telling the other person that you agree with what they’re saying.
Adjust your nonverbal signals according to the context. The tone of your voice, for example, should be different when you’re addressing a child than when you’re addressing a group of adults. Similarly, take into account the emotional state and cultural background of the person you’re interacting with.
Avoid negative body language. Instead, use body language to convey positive feelings, even when you’re not actually experiencing them. If you’re nervous about a situation—a job interview, important presentation, or first date, for example—you can use positive body language to signal confidence, even though you’re not feeling it. Instead of tentatively entering a room with your head down, eyes averted, and sliding into a chair, try standing tall with your shoulders back, smiling and maintaining eye contact, and delivering a firm handshake. It will make you feel more self-confident and help to put the other person at ease.
How many times have you felt stressed during a disagreement with your spouse, kids, boss, friends, or coworkers and then said or done something you later regretted? If you can quickly relieve stress and return to a calm state, you’ll not only avoid such regrets, but in many cases you’ll also help to calm the other person as well. It’s only when you’re in a calm, relaxed state that you’ll be able to know whether the situation requires a response, or whether the other person’s signals indicate it would be better to remain silent.
In situations such as a job interview, business presentation, high-pressure meeting, or introduction to a loved one’s family, for example, it’s important to manage your emotions, think on your feet, and effectively communicate under pressure.
Communicate effectively by staying calm under pressure
Use stalling tactics to give yourself time to think. Ask for a question to be repeated or for clarification of a statement before you respond.
Pause to collect your thoughts. Silence isn’t necessarily a bad thing—pausing can make you seem more in control than rushing your response.
Make one point and provide an example or supporting piece of information. If your response is too long or you waffle about a number of points, you risk losing the listener’s interest. Follow one point with an example and then gauge the listener’s reaction to tell if you should make a second point.
Deliver your words clearly. In many cases, how you say something can be as important as what you say. Speak clearly, maintain an even tone, and make eye contact. Keep your body language relaxed and open.
Wrap up with a summary and then stop. Summarize your response and then stop talking, even if it leaves a silence in the room. You don’t have to fill the silence by continuing to talk.
Quick stress relief for effective communication
When a conversation starts to get heated, you need something quick and immediate to bring down the emotional intensity. By learning to quickly reduce stress in the moment, you can safely take stock of any strong emotions you’re experiencing, regulate your feelings, and behave appropriately.
Recognize when you’re becoming stressed. Your body will let you know if you’re stressed as you communicate. Are your muscles or stomach tight? Are your hands clenched? Is your breath shallow? Are you “forgetting” to breathe?
Take a moment to calm down before deciding to continue a conversation or postpone it.
Bring your senses to the rescue. The best way to rapidly and reliably relieve stress is through the senses—sight, sound, touch, taste, smell—or movement. For example, you could pop a peppermint in your mouth, squeeze a stress ball in your pocket, take a few deep breaths, clench and relax your muscles, or simply recall a soothing, sensory-rich image. Each person responds differently to sensory input, so you need to find a coping mechanism that is soothing to you.
[Read: Quick Stress Relief]
Look for humor in the situation. When used appropriately, humor is a great way to relieve stress when communicating . When you or those around you start taking things too seriously, find a way to lighten the mood by sharing a joke or an amusing story.
Be willing to compromise. Sometimes, if you can both bend a little, you’ll be able to find a happy middle ground that reduces the stress levels for everyone concerned. If you realize that the other person cares much more about an issue than you do, compromise may be easier for you and a good investment for the future of the relationship.
Agree to disagree, if necessary, and take time away from the situation so everyone can calm down. Go for a stroll outside if possible, or spend a few minutes meditating. Physical movement or finding a quiet place to regain your balance can quickly reduce stress.
Find your space for healing and growth
Regain is an online couples counseling service. Whether you’re facing problems with communication, intimacy, or trust, Regain’s licensed, accredited therapists can help you improve your relationship.
Direct, assertive expression makes for clear communication and can help boost your self-esteem and decision-making skills. Being assertive means expressing your thoughts, feelings, and needs in an open and honest way, while standing up for yourself and respecting others. It does NOT mean being hostile, aggressive, or demanding. Effective communication is always about understanding the other person, not about winning an argument or forcing your opinions on others.
To improve your assertiveness
Value yourself and your options. They are as important as anyone else’s.
Know your needs and wants. Learn to express them without infringing on the rights of others.
Express negative thoughts in a positive way. It’s okay to be angry , but you must remain respectful as well.
Receive feedback positively. Accept compliments graciously, learn from your mistakes, ask for help when needed.
Learn to say “no.” Know your limits and don’t let others take advantage of you. Look for alternatives so everyone feels good about the outcome.
Developing assertive communication techniques
Empathetic assertion conveys sensitivity to the other person. First, recognize the other person’s situation or feelings, then state your needs or opinion. “I know you’ve been very busy at work, but I want you to make time for us as well.”
Escalating assertion can be employed when your first attempts are not successful. You become increasingly firm as time progresses, which may include outlining consequences if your needs are not met. For example, “If you don’t abide by the contract, I’ll be forced to pursue legal action.”
Practice assertiveness in lower risk situations to help build up your confidence. Or ask friends or family if you can practice assertiveness techniques on them first.
More Information
- Effective Communication: Improving Your Social Skills - Communicate more effectively, improve your conversation skills, and become more assertive. (AnxietyCanada)
- Core Listening Skills - How to be a better listener. (SucceedSocially.com)
- Effective Communication - How to communicate in groups using nonverbal communication and active listening techniques. (University of Maine)
- Some Common Communication Mistakes - And how to avoid them. (SucceedSocially.com)
- 3aPPa3 – When cognitive demand increases, does the right ear have an advantage? – Danielle Sacchinell | Acoustics.org . (n.d.). Retrieved May 22, 2022, from Link
- How to Behave More Assertively . (n.d.). 10. Weger, H., Castle Bell, G., Minei, E. M., & Robinson, M. C. (2014). The Relative Effectiveness of Active Listening in Initial Interactions. International Journal of Listening , 28(1), 13–31. Link
More in Communication
How to read body language to build better relationships at home and work

Boost your EQ to help find happiness and success

Tips for handling conflicts, arguments, and disagreements

How to feel and respond to the emotions of others

Tips and techniques for getting anger under control

Using laughter and play to resolve disagreements

The 5 Love Languages
What they are and how they influence relationships

Turning Off the Gas on Your Gaslighter
5 ways to deal with gaslighting

Professional therapy, done online
BetterHelp makes starting therapy easy. Take the assessment and get matched with a professional, licensed therapist.
Help us help others
Millions of readers rely on HelpGuide.org for free, evidence-based resources to understand and navigate mental health challenges. Please donate today to help us save, support, and change lives.
49 Communication Activities, Exercises & Games

Read on to learn about how important communication is in a relationship and how you can work on improving your communication skills.
Before you continue, we thought you might like to download our three Positive Communication Exercises (PDF) for free . These science-based tools will help you and those you work with build better social skills and better connect with others.
This Article Contains:
What are communication activities, exercises, and games, the role of communication in a relationship, how can we develop better communication skills, 18 communication games and activities for adults, 17 exercises to help improve communication in a relationship, the importance of communication in the family unit, 14 family therapy activities for communication, a take-home message.
The resources in this piece include tips, techniques, exercises, games, and other activities that give you the opportunity to learn more about effective communication, help guide your interactions with others, and improve your communication skills.
Some might feel like a chore you need to cross off your to-do list while others may make you forget you’re not just having fun with your family , but actually boosting vital life skills; however, they all have one thing in common: they will help you become a better, more effective, and more positive communicator with those who mean the most to you.
But what’s the deal with these activities, exercises, and therapy games ? Are they really that important or impactful? Do we really need to work on communicating when it seems like we’re pretty good at it already?

Check out this quote from Stephen R. Covey and take a minute to think about how vital communication really is.
The most important ingredient we put into any relationship is not what we say or what we do, but what we are. And if our words and our actions come from superficial human relations techniques rather than from our own inner core, others will sense that duplicity. We simply won’t be able to create and sustain the foundation necessary for effective interdependence.
Stephen R. Covey
As Covey notes, communication is the foundation of all of our relationships , forming the basis of our interactions and feelings about one another.
According to Australia’s Better Health Channel, communication is “ the transfer of information from one place to another ” and within relationships, it “ allows you to explain to someone else what you are experiencing and what your needs are ” (Victoria Department of Health & Human Services, n.d.).
When communication is good, we feel good about our relationships. Dr. Susan Heitler (2010) puts it this way:
When people say, ‘We have a great relationship,’ what they often mean is how they feel when they talk with one another. They mean, ‘I feel positive toward that person when we interact. I send and I receive positive vibes with them.’
Besides making our relationships easier, there are also relationship-boosting benefits to good communication:
- Effective communication shows respect and value of the other person.
- It helps us to better understand each other; not all communication is about understanding—some are intended to fight, dismiss, invalidate, undermine, etc.—but it should be!
- It makes us feel more comfortable with each other and encourages even more healthy and effective communication (Abass, n.d.).

Download 3 Communication Exercises (PDF)
These detailed, science-based exercises will equip you or your clients with tools to improve communication skills and enjoy more positive social interactions with others.
Download 3 Free Communication Tools Pack (PDF)
By filling out your name and email address below.
- Email Address *
- Your Expertise * Your expertise Therapy Coaching Education Counseling Business Healthcare Other
- Phone This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Fortunately, all it takes to develop better communication skills is a commitment to do so and a little bit of effort.
These tips from Australia’s Better Health Channel can help guide you toward better communication with your partner or spouse (these tips can also apply to any other relationship in your life with a little tweaking):
- Set aside time to talk without interruption from other people or distractions like phones, computers or television.
- Think about what you want to say.
- Be clear about what you want to communicate.
- Make your message clear, so that your partner hears it accurately and understands what you mean.
- Talk about what is happening and how it affects you.
- Talk about what you want, need and feel – use ‘I’ statements such as ‘I need’, ‘I want’ and ‘I feel’.
- Accept responsibility for your own feelings.
- Listen to your partner. Put aside your own thoughts for the time being and try to understand their intentions, feelings, needs and wants (this is called empathy ).
- Share positive feelings with your partner, such as what you appreciate and admire about them, and how important they are to you.
- Be aware of your tone of voice.
- Negotiate and remember that you don’t have to be right all the time. If the issue you are having is not that important, sometimes let the issue go, or agree to disagree (Victoria Department of Health & Human Services, n.d.).
If you’re experiencing high levels of conflict in your relationship(s), the Better Health Channel has some specific recommendations for you:
- Avoid using the silent treatment.
- Don’t jump to conclusions. Find out all the facts rather than guessing at motives.
- Discuss what actually happened. Don’t judge.
- Learn to understand each other, not to defeat each other.
- Talk using the future and present tense, not the past tense.
- Concentrate on the major problem, and don’t get distracted by other minor problems.
- Talk about the problems that hurt your or your partner’s feelings, then move on to problems about differences in opinions.
- Use ‘I feel’ statements, not ‘You are’ statements (Victoria Department of Health & Human Services, n.d.).
8 Tips on How to Teach Communication Skills

This useful framework comes from Alice Stott at Edutopia (2018):
- Physical: How a speaker uses their body language, facial expressions, and voice.
- Linguistic: The speaker’s use of language, including their understanding of formality and rhetorical devices.
- Cognitive: The content of what a speaker says and their ability to build on, challenge, question, and summarize others’ ideas.
- Social and emotional : How well a speaker listens, includes others, and responds to their audience (Stott, 2018).
Once you have a good framework for understanding communication, try these 8 ways to foster effective communication in your children or students:
- Teach your kids empathy so they can get a sense of what the other person is thinking and feeling.
- Teach your kids conversation skills with techniques like puppets and video modeling, which they can then apply in exercises and activities.
- Establish listening and speaking procedures in the classroom or at home (e.g., Dr. Allen Mendler’s SLANT strategy : Sit up straight, Listen, Answer and ask questions, Nod to show interest, Track the speaker; Mendler, 2013).
- Teach respectful vocabulary and remind students that being “cold” (passive) or “hot” (angry) will probably result in less understanding and more conflict.
- Teach the power of pausing (e.g., encourage them to pause, think, and ask questions like “What do you mean by that?” and “Why?”).
- Have your kids practice speaking and listening in natural settings (e.g., outside of the home and classroom).
- Encourage introspection in your children; it will help them understand themselves better as well as those around them.
- Practice taking turns with a talking stick or a ball, teaching your children that they can speak when they have the object but they are expected to listen when others are talking (Stanfield, 2017).
One of the most effective ways to avoid unnecessary disputes is to practice non-violent communication (NVC). According to Rosenberg (1999), non-violent communication methods can serve us in three ways:
- It can increase your ability to live with choice, meaning, and connection
- It helps connect empathically with yourself and others to have more satisfying relationships
- It shares resources so everyone is able to benefit
In an effort to exemplify the various forms that communication can take, we want to share some key differences between passive, assertive, and aggressive communication styles.
- Specifically, a passive communicator prioritizes the needs of others, even at their own expense. This often leads to being taken advantage of and having their own needs disregarded by others as well.
- An assertive communicator mirrors the values of NVC, which is what we should aim for. This communication style emphasizes the importance of all parties’ needs and is defined by confidence and the willingness to compromise
- Aggressive communication, also referred to as violent communication, disregards any other parties involved and consists of constant disrespect, interrupting, and domination.
Now that you are familiar with these types of communication styles, it’s time to analyze how you convey your thoughts to others (and if there is any room for improvement).

If you’re looking for some concrete ways to build communication skills in adults, you’ve come to the right place. Below are 18 games, activities, and exercises that you can use to help adults develop more effective listening and communication skills.
5 Communication Activities for Adults
To get started improving your (or your team’s, or your student’s) communication skills, give these 5 activities a try.
1. Card Pieces
This exercise from the team at MindTools is a good way to help participants develop more empathy, consider other perspectives, build their communication and negotiation skills.
First, make sure you have enough people for at least three teams of two, enough playing cards to give out between 4 and 6 cards to each person, and 15 minutes to spare.
Here’s how the activity works:
- Cut each playing card into half diagonally, then in half diagonally again, so you have four triangular pieces for each card.
- Mix all the pieces together and put equal numbers of cards into as many envelopes as you have teams.
- Divide people up into teams of three or four. You need at least three teams. If you’re short of people, teams of two will work just as well.
- Give each team an envelope of playing card pieces.
- Each team has three minutes to sort its pieces, determine which ones it needs to make complete cards, and develop a bargaining strategy.
- After three minutes, allow the teams to start bartering for pieces. People can barter on their own or collectively with their team. Give the teams eight minutes to barter.
- When the time is up, count each team’s completed cards. Whichever team has the most cards wins the round.
Afterward, you can use these questions to guide discussion on the exercise:
- Which negotiation strategies worked? Which didn’t?
- What could they have done better?
- What other skills, such as active listening or empathy, did they need to use?
2. Listen and Draw
This game is easy to play but not so easy to “win.” It requires participants’ full attention and active listening.
Gather your group of participants together and hand out a piece of paper and a pen or pencil to each player. Tell them you will give them verbal instructions on drawing an object, one step at a time.
For example, you might give them instructions like:
- Draw a square, measuring 5 inches on each side.
- Draw a circle within the square, such that it fits exactly in the middle of the square.
- Intersect 2 lines through the circle, dividing the circle into 4 equal parts.
As the exercise continues, it will get progressively harder; one misstep could mean that every following instruction is misinterpreted or misapplied. Participants will need to listen carefully to ensure their drawing comes out accurately. Once the instructions have all been read, compare drawings and decide who won.
For added engagement, decide in advance on what the finished product is supposed to represent (e.g., a spiderweb, a tree).
3. Communication Origami
This is a great exercise to help people understand that we all hear and interpret things differently, even if we are given the exact same information.
Here’s how it works:
- Give one sheet of standard-sized paper (8.5 x 11 inches) to each participant.
- Tell your participants that you will be giving them step-by-step instructions on how to fold their piece of paper into an origami shape.
- Inform your participants that they must keep their eyes and mouths closed as they follow instructions; they are not allowed to look at the paper or ask any clarifying questions.
- Give the group your instructions on how to fold the paper into the origami shape of your choice.
- Once the instructions have all been given, have everyone open their eyes and compare their shape with the intended shape.
You will likely find that each shape is a little bit different! To hit the point home, refer to these discussion points and questions:
- Make the point that each paper looks different even though you have given the same instructions to everybody. What does this mean?
- Ask the group if you think the results would have been better if they kept their eyes open or were allowed to ask questions.
- Communicating clearly is not easy, we all interpret the information we get differently that’s why it’s very important to ask questions and confirm understanding to ensure the communicated message is not distorted.
4. Guess the Emotion
Another useful exercise from the Training Course Material website is called “ Guess the Emotion .” As you might expect, it involves acting out and guessing emotions. This helps all participants practice empathy and better understand their coworkers or group members’ reactions.
Follow these instructions to play this engaging game:
- Divide the group into two teams.
- Place on a table (or put in a box) a packet of cards, each of which has a particular emotion typed on it
- Have a participant from Group A take the top card from the table and act out (pantomime) the emotion for his/her group. This is to be done in a fixed time limit (such as a minute or two).
- If the emotion is guessed correctly by Group A, they receive ten points.
- Now have a participant from Group B act out an emotion; award points as appropriate.
- Rotate the acting opportunities between the two groups.
- After 20 to 30 minutes of acting and guessing, call time and announce the winning team based on its point total.
If you have a particularly competitive group, consider giving a prize to the winning team!
5. The Guessing Game
Finally, another fun and engaging game that can boost communication skills: “ The Guessing Game. ” You will probably recognize this game, as it’s similar to what many people know as “ Twenty Questions ,” except there is no hard limit on the number of questions you can ask.
To start, separate the group into two teams of equal (or roughly equal) size. Instruct one player from each team to leave the room for one minute and come up with a common object that can be found in most offices (e.g., a stapler, a printer, a whiteboard).
When this person returns, their teammates will try to guess what the object is by asking only “Yes or No” questions (i.e., questions that can only be answered with “yes” or “no”). The team can ask as many questions as they need to figure it out, but remind them that they’re in competition with the other team. If there’s time, you can have multiple rounds for added competition between the teams.
Take the last 10 minutes or so to discuss and debrief. Use the following points and questions to guide it:
- Tell the group that obviously it took a long time and effort for us to find out the object in each round, but what if we didn’t have time and only had one question to ask to find out the object, what would that question be?
- The question would be “What is the object?” which is an open-ended question.
- Open-ended questions are an excellent way to save time and energy and help you get to the information you need fast, however, closed questions can also be very useful in some instances to confirm your understanding or to help you control the conversation with an overly talkative person/customer.
5 Listening Activities for Adults
If you’re intent on improving listening skills, in particular, you have lots of options; give these 5 activities a try.
1. Telephone Exercise
This classic exercise from Becky Norman (2018) at Sift’s Training Zone illustrates why listening is such an important skill, and why we shouldn’t ignore any opportunities to improve it.
Split your group into two even lines. At opposite ends of each line, whisper a phrase or short sentence to the person on the end and tell them to pass it on using only whispers, one person at a time. They can only repeat the phrase or sentence once.
While participants are busy passing the message along to the next person in line, play music or engage them in conversation to create some white noise. This will make it a bit more difficult but it will mimic real-life conditions, where distractions abound.
When the messages have made it to the end of each line, have the last person to receive the message in each line report out on what they heard. Next, have the first person to receive the message in each line report the original message and compare it to the final message received.
2. Stop Listening Exercise
This exercise , also from Becky Norman’s piece (2018), will show participants the emotional consequences of not listening and—hopefully—encourage them to practice better listening skills.
Split your group into two smaller groups of equal size and take one group outside the room. Tell them that they are instructed to stop listening to their partner after about 30 seconds, and to be open in showing their disinterest. Tell the other group to think of something that they are passionate about and be prepared to tell their soon-to-be partner a meaningful or personally relevant story about this topic.
Bring the other group back in, put all the participants into pairs, and tell them to get started. Observe the behavior from the listeners and the reactions from the speakers until you’re sure each speaker has picked up on what’s happening. Stop the conversations at this point and explain the instructions that were given to each group.
Facilitate a group discussion on the importance of listening, how to use active listening, and what indicates that someone is truly listening.
3. Listener and Talker Activity
The “Listener and Talker” activity is another good activity for showing the importance of active listening and giving participants a chance to practice their skills.
Divide your group into pairs, with one partner assigned to the talker role and the other assigned to the listener role. The talker’s job is to describe what he or she wants from a vacation without specifying a destination. The listener’s job is to listen attentively to what is being said (and what is not being said) and to demonstrate their listening through their behavior.
After a few minutes of active listening, the listener should summarize the three or main criteria the talker is considering when it comes to enjoying their vacation. Finally, the listener should try to sell the talker on a destination for their vacation. After a quick debrief on how well the listener listened, the two should switch roles and try the exercise again.
This exercise gives each participant a chance to practice talking about their wants and needs, as well as an opportunity to engage in active listening and use the knowledge they gained to understand and relate to the speaker.
4. Memory Test Activity
This great activity from TrainingCourseMaterial.com is called the “Memory Test” activity.
- Tell participants that you are going to read them a list of words to test their memory.
- Instruct them to listen carefully, as they cannot write down any of the words. Tell them you will test them later to see how many of the words they can remember.
- When you finish reading the list of words, distract your participants by talking about something else for at least one full minute.
- Once you have finished talking, have each participant write down as many words as they can remember from the list.
You (and your participants) will find that it’s pretty difficult to remember a list of somewhat-random words, especially when there is a break in time and another discussion in between hearing them and recalling them! Relate this to real-life listening by emphasizing the importance of paying attention to people when they are speaking to you, especially if it’s an important conversation.
5. Just Listen Activity
This activity comes from the folks at MindTools.com and offers participants a chance to communicate their feelings and provide a recap or rephrasing of another person’s feelings on a subject.
To get started, you will need an even number of people to pair off (or prepare to partner with one yourself) and eight index cards per pair. These index cards should have one topic written on each card; try to make sure the topics are interesting but not too controversial, as you don’t want listeners to dislike the speakers if they disagree with their viewpoint (e.g., you should probably avoid politics and religion).
Use these instructions to conduct the activity:
- Have the team members sit down in their pairs.
- Give each pair eight of the index cards.
- Instruct one partner to choose a random card and then speak for three minutes on how he or she feels about the topic.
- Instruct the other partner to stay quiet while the first partner talks, just listening instead of speaking.
- After the three minutes is up, the listener has one minute to recap what the speaker said (not agree, disagree, or debate, just recap).
- Have each pair switch roles and repeat the exercise so both partners get a chance to speak and to listen.
After each participant has played both roles, end the activity and guide a discussion with the following questions:
- How did speakers feel about their partners’ ability to listen with an open mind? Did their partners’ body language communicate how they felt about what was being said?
- How did listeners feel about not being able to speak about their own views on the topic? How well were they able to keep an open mind? How well did they listen?
- How well did the listening partners summarize the speakers’ opinions? Did they get better as the exercise progressed?
- How can they use the lessons from this exercise at work?
You will find this activity at this link , exercise #4.
6 Nonverbal Communication Activities for Adults

Nonverbal communication is just as important as verbal communication, if not more so!
Use these 6 activities to practice reading and “speaking” effective nonverbal messages.
1. Power of Body Language
This activity from TrainingCourseMaterial.com will help your participants work on their body language skills.
- Tell the participants that you are going to give them a series of instructions and you want them to follow them as fast as they can.
- Put your hand to your nose.
- Clap your hands.
- Touch your shoulder.
- Stamp your foot.
- Cross your arms.
- Put your hand to your mouth (but while saying this one, put your hand to your nose).
- Observe how many participants copied what you did instead of what you said.
Share this observation with your group and lead a discussion on how body language can influence our understanding and our reactions. It can reinforce what we hear or it can interfere with the verbal communication we receive. The more aware we are of this possibility, the better communicators we become. It’s vital to keep your own body language in mind, just as it’s vital to notice and understand others’ body language.
2. Clap and Follow
The “Clap and Follow” activity is a great way to practice using your body in conjunction with verbal communication.
It works like this:
- Tell your group that this is a game that requires their full concentration.
- When they hear one clap from the leader (you), tell them this means they should stand up.
- When they hear two claps from the leader, they should hop once in place.
- When they hear three claps, they should rub their belly.
- When they hear four claps, they should do a 360-degree turn on the spot.
- When they hear five claps, they should pat their head.
- Begin the activity! Start with one clap, then two claps, and so on until you have given the group each instruction once.
- Now, mix it up! Switch between the five different instructions and begin to pick up the pace. This is when the eliminations begin.
- Each time a participant engages in the wrong activity, eliminate them from the game. Continue until there is one clear winner.
If you have a competitive group, you may want to bring a prize to ensure active engagement with the exercise. It will give participants a chance to practice nonverbal communication in a fun context.
3. Wordless Acting
This activity from Grace Fleming (2018) at ThoughtCo will show your participants how much we “speak” with our body language and facial expressions.
Here are the instructions:
- Separate your group into pairs.
- Assign one participant in each pair to be Partner A and the other to be Partner B.
- Give each participant a copy of the script (copied below).
- Instruct Participant A to read his or her lines out loud, but instruct Participant B to communicate his or her lines in a nonverbal way.
- Provide Participant B with a secret emotional distraction written on a piece of paper (e.g., Participant B is in a rush, is really bored, or is feeling guilty).
- Have each pair work through the script.
- After each pair has finished working through the script, have the “A” participants guess what emotion their partner was feeling.
This is the script you will give each participant:
A: Have you seen my book? I can’t remember where I put it. B: Which one? A: The murder mystery. The one you borrowed. B: Is this it? A: No. It’s the one you borrowed. B: I did not! A: Maybe it’s under the chair. Can you look? B: Okay—just give me a minute. A: How long are you going to be? B: Geez, why so impatient? I hate when you get bossy. A: Forget it. I’ll find it myself. B: Wait—I found it!
After the activity, guide a discussion on how much information we can pick up from nonverbal communication and how important it is to regulate our bodies and our facial expressions when communicating, even if we’re also using verbal communication.
4. We Have to Move Now!
Another great exercise from Grace Fleming (2018) is called “We Have to Move Now!” and it will help your participants learn how to express and detect several different emotions.
These are the instructions for this activity:
- Cut several strips of paper.
- On each strip of paper, write down a mood, feeling, or disposition, like guilty, happy, suspicious, paranoid, insulted, or insecure.
- Fold the strips of paper so you can’t see what is written on it and place them in a bowl or jar. These are your prompts.
- Have each participant take a prompt from the bowl or jar and read the exact same sentence to the class, but with the emotion the prompt specifies.
- The sentence everybody will read is: “We all need to gather our possessions and move to another building as soon as possible.”
- Have the participants guess the emotion of each reader by writing down what they think the speaker is feeling (or what they are supposed to be feeling).
After each participant has had a chance to read the sentence based on one of the prompts, run through the emotions displayed and see how many each participant guessed correctly. Finally, lead a debriefing discussion on how things like tone and body language can impact the way a message is received.
5. Stack the Deck
All you’ll need for this exercise is a deck of playing cards, a blindfold for each participant, and some space to move around.
Here’s how “Stack the Deck” works:
- Shuffle the deck of cards and hand one out to each participant.
- Instruct the participants to keep their cards a secret; no one should see the suit or color of another participant’s card.
- Tell the participants that they will not be allowed to talk at all during this exercise.
- Instruct your participants to assemble into four groups according to their suit (hearts, clubs, diamonds, spades), but using only nonverbal communication.
- If you have the time and your participants have the inclination, try blindfolding each participant and giving the same instructions—it makes it much more difficult and more time-consuming!
- Once participants have all gathered into one of the four groups, have them line up according to their rank (Ace is the lowest, King is the highest); again, they cannot speak or show their cards to anyone during this part of the exercise.
- The group that lines up in the right order first wins!
As always, you can offer a prize to the winning team to motivate your participants.
This exercise will show how difficult it is to communicate without words, but it will also show your participants that it is not only possible, it gets easier as they start to pick up on one another’s nonverbal cues.
You can find this exercise at this link (Activity #3).
6. Silent Movie
Finally, facilitate this activity to really drive home the importance of effective nonverbal communication.
Divide your participants into two groups. For the first half of the activity, one group will be screenwriters and the other group will be actors. In the second half, the two groups will switch roles.
Instruct the screenwriters to write a silent movie, but to keep these things in mind:
- Silent movies tell a story without words. It’s important to start the scene with the actor doing an obvious task, like cleaning the house or rowing a boat.
- The scene must be interrupted when a second actor (or several actors) enter the scene, and their arrival should have a big impact. The character(s) could be anyone (or anything), including burglars, salesmen, children, or even animals.
- A physical commotion must occur.
- The problem that is caused by the commotion must be resolved by the end of the scene.
Give the screenwriters time to write out their script, then have the actors perform the script. Once the scene is finished, have the groups switch roles.
The communication game – Asgar Hussain
2 Communication Group Activities
Other great activities for group communication include the “Square Talk” and “Follow All Instructions” activities.
1. Square Talk Activity
For this activity , you will need one blindfold for each participant, one long piece of rope for each team (teams should be composed of around 5 participants each), and 25 minutes.
Follow these steps to give this activity a try:
- Divide your group of participants into groups of about 5 each.
- Clear the room so you have as much space as possible.
- Blindfold each participant and tell them their objective: to make a square from a rope (i.e., stand in the shape of a square with their team).
- Disorientate each participant by moving them a bit, spinning them around, etc.
- All team members are blindfolded and must remain so for the duration of the activity.
- The rope you are holding is approximately ___ feet in length.
- The role you are holding is knotted together to form a circle; it must not be undone.
- You must not let go of the rope.
- You will be told when you have 5 minutes remaining.
- Allow the teams to work on the activity and inform them when they have 5 minutes left.
Once the teams have given this activity their best shot, use these 5 discussion questions to review the importance of good group communication:
- Do you feel as a group you communicated effectively?
- During the Activity, what communication skills did you use effectively?
- During the activity, what communication skills could you have used to improve performance?
- How important is communication in the workplace? Why?
- What key points have you learned about communication from this activity, that you wish to apply in the workplace?
2. Follow All Instructions Activity
This activity from TrainingCourseMaterial.com is a great one for young people, but it can be used with participants of all ages. All you’ll need is a set of instructions for each participant.
- Write all of your teams initials at the top right-hand corner of this sheet.
- Write your first name on your sheet of paper.
- Write the total of 3 + 16 + 32 + 64 here: __________________
- Underline instruction 1 above.
- Check the time by your watch with that of one of your neighbor’s.
- Write down the difference in time between the two watches at the foot of this page.
- Draw three circles in the left-hand margin.
- Put a tick in each of the circles mentioned in 6.
- Sign your signature at the foot of the page.
- On the back of the page, divide 50 by 12.5.
- When you get to this point in the test, stand up, then sit down and continue with the next item.
- If you have carefully followed all these instructions, call out ‘I have’.
- On the reverse of this page, draw quickly what you think an upright bicycle looks like from overhead.
- Check your answer to Item 9, multiply it by 5 and write the result in the left-hand margin opposite this item.
- Write the 5th, 10th, 9th and 20th letters of the alphabet here: ___________________
- Punch three holes with your pen here: o o o
- If you think you are the first person to get this far, call out ‘I’m in the lead’.
- Underline all the even digits on the left-hand side of the page.
- Draw triangles around the holes you punched in Item 15.
- Now you’ve finished reading all the instructions, obey only 1, 2, 20 & 21.
- Stand up and say, “We’re the greatest team in the World!”
As you can see, the instructions include lots of silly directives (e.g., “When you get to this point in the test, stand up, then sit down and continue with the next item.”) that will identify who is following the directions and who is not—but the person that stands is actually the one not following directions!
The first and only verbal instruction you will give participants is to read all the written instructions first before engaging in any of the directives. The first person to complete the list will be declared the winner of the activity. You can offer a prize to the winner if you think the group would be motivated by it.
This exercise is a fun way to see who is paying attention and who is skipping the most vital instruction—to read everything before acting.

7 Communication Games for Couples
Defeating Divorce shares the following three games aimed at improving communication in a romantic relationship.
This game is goal-directed, meaning the couple is working towards a common goal, and that goal requires effective communication.
- The couple sits back to back with an identical set of building blocks in front of each of them.
- One partner uses their blocks to create some sort of building or structure.
- The builder partner then relays a series of instructions to the other partner to help him or her build the exact same structure.
- The listener partner must try to build the same structure based on the speaker partner’s instructions.
This game takes some serious teamwork and good communication, and it can be repeated as needed to help a couple build their skills.
2. Minefield
“Minefield” is a physical game that will not only get both partners up and moving, but it will also require a great deal of trust and communication to complete the challenge.
You will need a blindfold for one partner, some space to navigate, and some objects with which you can create a minefield or obstacle course. Once the course is ready to go, blindfold one partner and bring them into the room.
The challenge here is for the non-blindfolded partner to guide the blindfolded partner through the obstacle course using only verbal communication. The couple will only succeed if the blindfolded partner has trust in their partner and the non-blindfolded partner is an effective verbal communicator.
Feelings of frustration are common in this game, but it can be a great way to highlight issues in communication or, alternately, highlight the couple’s communication strengths.
3. Give Me a Hand
This game is another one that can be frustrating for the couple but ultimately provides a great opportunity to build effective communication skills and unite the two in a common goal.
In this game, the couple will be given a seemingly easy task to complete, such as buttoning a shirt or tying a shoe, but with a catch—each partner will have one arm tied behind their back. The couple will find that the lack of one arm makes the task much more difficult than they might expect!
To complete the task, the couple will need to communicate effectively and coordinate their movements. It will be tough, but immensely satisfying to successfully complete this challenge!
4. Twenty Questions Times Two
If you remember the game “Twenty Questions”, you’ll recognize this game. It can be used to help couples communicate, share important details, and strengthen their connection.
Here’s how:
- The couple should schedule some time alone, without distractions.
- Before playing the game, each partner should come up with a list of 20 detailed personal questions to ask the other partner. The couple should feel free to get creative here!
- Both partners take turns asking each other one question at a time.
- When they’ve finished asking each other their questions, they should reverse them! Instead of asking questions like, “What is your favorite color?” each partner will ask, “What is my favorite color?”
This fun twist on a familiar game will result in greater knowledge and understanding of your spouse and, hopefully, better communication skills.
5. Eye-to-Eye
This game is a good way for couples to work on communicating and improving their connection, and all you need is your eyes!
Here’s how to do it:
- The couple sits facing each other, close enough to hold hands.
- Each partner looks directly into the other partner’s eyes.
- Each partner should take a minute to notice the feelings they are experiencing at this point.
- One partner begins talking about something simple and easy to discuss, like what happened that day, what they had for lunch, or something they are grateful for.
- The other partner reciprocates with a similar conversation, all while holding eye contact.
- The couple continues sharing things one at a time until each partner has shared at least three or four times.
- The couple discusses what the experience was like.
Many people find this game uncomfortable at first, but with practice, it can greatly enhance your sense of intimacy with your partner.
6. The Top Three
Similar to the “three good things” exercise, this game’s aim is to boost a couple’s gratitude for one another and give them both a chance to practice expressing it. Couples should schedule a time for this game every day, but the good news is that it doesn’t take long—just a few minutes will do.
To play “The Top Three”, couples should follow these instructions:
- At the end of each day, take some time to reflect on your day. Think about what your partner has done for you today.
- Take turns sharing those three things with your partner and tell them what each thing meant to you.
- Don’t forget to say “thank you” or otherwise verbally express your gratitude to your partner!
This game gets couples to practice vocalizing their appreciation and expressing gratitude, two things that are not necessarily in everyone’s daily communications but can have a big impact on a relationship.
7. Make a Playdate
Playdates are not just for kids or puppies—they are a great idea for couples as well! A play date is not your average, regularly scheduled programming sort of date, but something that is different, spontaneous, unique, and/or just plain fun!
Here are the three ground rules for the playdate:
- It has to be something for just the couple to do and they cannot include the kids or discuss mundane things like chores or bills.
- It has to be something that requires both partners to be present in the moment; think sailing, rock climbing, or dance lessons rather than seeing a movie or going out to dinner.
- The couple should take turns picking the activity and try to surprise their partner with something new.
Planning this date will not only make it easier to feel connected and closer to one another, but it also provides couples with an opportunity to communicate their love for one another through their actions. Depending on the date activity, it can also provide some much-needed time for the couple to talk.
5 Exercises and Activities for Married Couples
These exercises , also from Defeating Divorce, are not just for married couples, but for anyone in a committed relationship.
1. Fireside Chats
This communication exercise is based on President Franklin D. Roosevelt’s “fireside chats,” in which he addressed the American people with the intention of making it feel as if he was speaking directly into their living room, carrying on a calm and rational discussion of important issues.
The intention of this exercise for couples is similar: to make the couple feel more connected, more aware of what is going on in each other’s lives, and to maintain a pulse on how the relationship is going.
The two partners should schedule a 15 to 30-minute “fireside chat” each week to practice their ability to speak calmly, respectfully, and effectively about important and relevant issues. They should minimize the chances of distraction (turn off the TV, put their phones on silent, etc.) and focus only on one another for these chats.
What the couple discusses is up to them, but if there are salient relationship issues, this is a good time to talk about them. If the issues are very serious, it may be a good idea to start out this exercise talking about less intense, less emotional topics before moving on to the problem areas.
2. High-Low Activity
The high-low activity also aims to help couples feel more connected and in touch with one another, which requires measured and thoughtful communication. Engaging in this exercise daily will give the couple a chance to practice their communication skills on a regular basis, as well as their active listening skills.
Here’s how the exercise works:
- Wait until the end of the day (e.g., at the end of dinner, around bedtime) to put it into practice.
- The couple will then “check-in” with each other about the other’s day.
- Each partner will ask the other to share their “high” of the day or the best part of their day.
- Next, each partner will ask the other to share their “low” of the day or the worst or most disappointing part of their day.
- As one partner is sharing, the other should practice active listening techniques, conveying their empathy and understanding to their partner.
This simple activity will result in a more intimate and understanding relationship between the two partners, all for just a few minutes a day.
3. Listening Without Words
If a couple wants to practice both their verbal and nonverbal communication, this is a great way to do it. The “Listening Without Words” activity allows each partner to apply both verbal and nonverbal communication skills, as it involves switching between only speaking and only listening.
This is how to practice it:
- The couple will schedule some time for themselves without kids, work, or other responsibilities interrupting them.
- They set a timer for somewhere between 3 to 5 minutes.
- Until the timer goes off, one partner acts as the speaker and the other acts as the listener. The speaker will talk about any subject they’d like to talk about.
- While the speaker talks, the listener will attempt to show the speaker compassion, empathy, and understanding through nonverbal communication only (e.g., smiling, nodding, taking their partner’s hand).
- When the timer goes off, the partners will have a chance to process what they experienced and discuss any thoughts or feelings that came up.
- Finally, the partners switch roles and repeat the exercise.
This exercise is a great way to boost your bond and your skills at the same time.
4. Eye See You
Similar to a previous exercise (“Eye-to-Eye”), this exercise relies heavily on eye contact; however, unlike the previous exercise, this one does not allow talking until the end.
Here’s how to give it a try:
- The couple should be in a quiet and relaxing environment, with as few distractions as possible.
- They sit in two chairs facing one another, near to one another but not touching.
- The couple sets a timer for five minutes and settles in their respective seats, making and holding eye contact with one another. They will hold eye contact but refrain from speaking or touching until the timer goes off.
- Both partners should be encouraged to note any thoughts, feelings, or sensations that come bubbling up during these five minutes.
- Once the timer goes off, the two should try to guess what the other person was thinking and feeling during the five minutes. Once they have a chance to guess, they should discuss these things that bubbled to the surface as they maintained eye contact.
It might surprise some people to hear what their partner was thinking and feeling during the activity, but a strong relationship depends on understanding and empathizing with one another, making communication like this a necessity.
5. Send Me a Postcard
Although we’ve mostly focused on verbal communication and communications via body language, facial expressions, and touch, there is another form that we haven’t mentioned: written communication. This activity guides the couple in developing more effective written communication skills.
Both partners should have two blank postcards and something to write with for this exercise. On one postcard, each partner will write down a message to the other partner communicating a frustration, a feeling, or a desire. They should take a few minutes to create a thoughtful message to their partner.
Once they have their postcard ready to “mail” each partner will deliver their message to their partner without any verbal communication. They will both read their partner’s message and take a few moments to process. When they feel ready, they will use their remaining blank postcard to craft a response to their partner’s message.
When both partners have finished writing their response, they will deliver those messages to one another as well. After they have both read the response postcards, the couple can debrief and discuss their messages to one another.
5 Communication Exercises for Couples Therapy
If you’re hungry for more couples’ communication exercises, maybe these five exercises will hit the spot!
1. Active Listening
Active listening is not the easiest skill to master, but it is an important one to develop. This exercise from marriage counseling expert Racheal Tasker will give you a chance to practice it with the person closest to you.
The next time you and your partner are talking about something important or sensitive, put these tips and techniques into practice:
- The speaker should remain focused on a single thought or idea.
- The listener should listen attentively to the speaker, concentrating on understanding their perspective and attempting to gain new insights into their thoughts and feelings.
- The speaker and listener should switch roles after a while to allow each to practice both types of communication.
- Both partners should practice speaking and listening with patience and love, allowing their feelings for their partner to guide them toward true understanding rather than just reacting (Tasker, n.d.).
2. Sharing Emotions Freely
It can be tough to be truly open with our emotions, but it’s vital for effective communication and a healthy relationship. Try this exercise to work on this skill.
The couple should agree to try this exercise together and follow these instructions:
- Decide on a specific time and place to put this exercise into practice.
- Let your partner know what you need to feel safe sharing your feelings, and listen to what your partner needs to feel safe sharing his or her feelings.
- Be sure to also ask your partner what would make him or her feel more comfortable as you share your feelings, as it can be just as difficult to hear as it is to share.
- Share with your partner! If it helps, use a timer to limit how much sharing can occur and to ensure equal time to share feelings.
- Listen to what your partner tells you and discuss what, if any, concrete steps you can take based on the information you’ve both shared. Commit to using the information you gained to improve your communication skills and your relationship in general (Tasker, n.d.).
3. Use Positive Language
Another great exercise from Racheal Tasker is focused on using positive language with one another. It can be surprisingly easy to slide into a pattern of mostly neutral or even negative language with your partner, but you can use this exercise to counter that tendency.
Here’s what to do:
- Commit to using positive language when you communicate with your partner.
- Ask your partner to make the same commitment to positive language.
- Avoid being overly critical or negative when communicating with your partner.
- Use a positive and encouraging tone when you speak to your partner.
- Keep an eye on the words you use; try to incorporate words like “love”, “feel”, “appreciate”, and ditch words like “fault”, “never”, and “hate” (e.g., “I hate it when you do X!”).
As partners continue to practice this exercise on a regular basis, they will find that their communication style grows more positive with less effort, and their relationship will flourish (Tasker, n.d.).
4. Take a Trip Together
There’s nothing like traveling with someone to work on your communication skills! Making a trip successful requires tons of communication, coordination, and clear expectations, but it can also open you up to fun new experiences and relaxation. To practice communicating with your partner, try planning and taking a trip together.
Plan your trip with a focus on doing things you both like, going to a place you’d both like to visit, and trying new food, activities, and other experiences together. Getting out of your routine and into a novel environment can do wonders for your communication—not to mention your overall mood.
Use some of the other tips and techniques mentioned in this article when you are planning your trip and while you are enjoying your trip; you’re sure to see some improvements to your communication with your partner (Tasker, n.d.).
You can find this exercise at this link , second exercise from the bottom.
5. I Feel (Blank)
The final exercise from Tasker is called “I Feel _____” and it’s a simple one.
We often have trouble sharing our feelings, even (or especially) with those we are closest to. A great way to work on communicating your feelings more often—and more effectively—is to practice saying “I feel (blank).”
The next time you are experiencing strong emotions or discussing a sensitive or difficult subject with your partner, try beginning your sentences with “I feel…” and continue from there. So, if you’re upset with your partner for forgetting about an important appointment or canceling plans at the last minute, instead of saying “You don’t respect my time,” try “I feel like you don’t respect my time.”
Framing your discussion in this manner—as a statement of your feelings rather than a personal attack or blaming session—is not only conducive to greater understanding, it also shows your partner that you care about having a constructive conversation and that your intentions are not to hurt them but to help them see from your perspective.

According to researchers Peterson and Green (2009), family communication is so important because:
“…it enables members to express their needs, wants, and concerns to each other. Open and honest communication creates an atmosphere that allows family members to express their differences as well as love and admiration for one another.”
The benefits of high-quality communication make spending time on improving the way family members relate to one another a task that is well worth the time spent on it. If you’re interested in working on your communication skills as a family, give the following activities and exercises a try.
These 14 activities are great tools to use in family therapy, but you can also try them at home.
4 Group Exercises for the Family
These four group exercises are a great introduction to communication skill-building as a family. They’re fun, engaging, and good for all ages!
1. What If?
The best time to work on communication skills is when families take the time to just sit and relax together. This simple game is a great way to do that, allowing families to improve how they communicate with one another while laughing together and putting their imagination to good use.
You will need strips of paper, a pencil or pen for each family member, and two bowls.
- Get two slips of paper and something to write with for each family member.
- On the first slip, have each family member write a question off the top of his or her head; it can be silly, serious, or anywhere in between. Put all the questions in one of the bowls and give them a good mix.
- On the second slip of paper, have each family member write an answer to the question they came up with. Place these slips in the second bowl and mix them up.
- Pass each bowl around the room and have each family member take one question slip and one answer slip.
- Have each family member read the question and the answer that they have in their hand. The questions and answers might fit well together or they may result in absurd combinations!
- Continue the game with two more slips of blank paper. It may take a few rounds for everyone to get the hang of the game, but family members will get more comfortable with the game and enjoy it more as they go along.
Use the following questions to guide your discussion as a family:
- Did the activity spark your imagination?
- Why did the questions and answers get funnier after several rounds?
2. Expressing Individuality
Although families usually share values, norms, and beliefs, that doesn’t mean all family members will see things the same way. It can be hard for some family members to communicate their thoughts and feelings when they feel like the odd one out or a “black sheep” in the family.
To make sure your family is a safe space for everyone to share their thoughts and feelings, give the “Expressing Individuality” activity a try. It will help each family member understand that they are a valuable part of the family and that they are always free to share their unique perspective.
You’ll need about an hour for this activity, 15 minutes to make the dough and 45 minutes for the activity itself. Use one of the recipes below to make your own play dough as a family.
If you want to make reusable play dough, mix together:
- 1 cup flour
- 1 cup water (add food coloring to water if you want colored clay)
- 1 teaspoon cream of tartar
- 1 tablespoon oil
After mixing these ingredients together, put over low heat and stir slowly. When the dough has formed into a small ball, remove it from the heat and knead while still warm. Store the clay in a sealed container.
If you plan on baking your designs at the end of this activity to preserve them, mix together:
- ½ cup water
- Food coloring (if desired—you can also paint the figures after you bake them)
Follow these instructions to encourage each family member to express their individuality:
- If you love Boy Scouts, you may want to mold the image of a person sitting on a log by a campfire.
- If you received an award as the “Employee of the Month,” you may want to mold the image of something that represents hard work, or dependability.
- If friendliness is a personal characteristic that you value, you may want to mold a face with a pleasant smile, or if you have a great love for animals, you may want to mold several of your favorite animals.
- After creating your unique design, you can preserve it by placing it on a cookie sheet and baking it in the oven on warm for several hours (until hard). This will harden the clay hard so that it maintains its shape. If you did not use food coloring to color the clay, or if you like to paint, you could paint the hardened figure. Once everyone has completed a mold, display these molds in the home.
To continue working on communicating your individuality as a family, ask these questions and discuss your answers together:
- Why did you choose to make what you did?
- What does it mean to you?
If the idea of creating a figure out of play dough doesn’t appeal to you, you can also try these two alternatives:
- You could draw pictures using plain white paper and colored pencils/crayons. Drawing may allow you to express more ideas than if you use clay. Make sure that you do not place an emphasis on artistic abilities. It is okay to draw simple stick figures that represent people or other objects.
- You could cut pictures out of old magazines and paste them on a poster board. After each person has completed a mold, picture, or collage, allow each family member to explain how their collage, picture or mold represents them.
3. Hints of Anger
Anger is a normal human emotion, and we will all get angry at some point. Instead of trying to avoid or deny anger, it’s vital that families learn how to manage their anger and communicate it to others in a healthy way. This activity will help family members identify their anger cues (the signs that indicate they are getting angry) and help them regulate their emotions to ensure they don’t say or do something they will regret.
Here’s how to do this activity as a family:
- Tell family members to think about a time when they were angry or upset, and consider how they felt.
- Were your hands relaxed or clenched in a fist?
- Was your heart rate normal or beating fast?
- Were your muscles relaxed or tight with tension?
- What kind of thoughts was going through your head?
- As a family, discuss any discrepancies between what you think about your anger cues and what other family members think.
- How did your body feel during this period of time?
- In which scenario did you feel more comfortable, angry, or happy?
- Discuss the importance of knowing when you are getting upset and might need to take a break and think.
After the activity, discuss these questions as a family:
- Why is it important to recognize the signs that you are angry?
- Why is it important to control your anger?
- What do you feel like specifically, when you are upset?
- What are the things you are going to do to manage your anger so it does not hurt your family relationships?
- Can recognizing anger cues help in managing your anger?
4. Family Meetings
Family meetings are a good idea for a lot of reasons, but yet another benefit of these get-togethers is the potential for building and developing better communication skills as a family. Regular family meetings can help family members learn how to:
- Make joint decisions
- Plan together
- Accept responsibility
- Show concern for others
- Spend some quality time together
Pick one night of the week when your family can consistently get together for a weekly family meeting that lasts 30 to 60 minutes, and make sure it’s scheduled on everyone’s calendar.
Here’s how to conduct good family meetings:
- Set a regular time. Setting a regular time and place gives the family council a position of importance and results in it becoming a permanent part of family operations. If everyone knows that the family is meeting together regularly, they find that most problems can wait a few days to be discussed. For this reason, some families like weekly meetings.
- Use an agenda. Post a paper during the week where family members can list concerns they want brought up (possibly, the message center). Discuss things in the order listed. This also reduces problems between meetings when parents can say, “List it on the agenda and we’ll discuss it at the meeting.”
- Attendance is voluntary . All members of the family are invited to attend — but attendance is voluntary. However, if a member is not present, he/she is still expected to abide by any decisions made by the family council.
- Each person has an equal voice . Everyone should be encouraged to contribute ideas and suggestions. All members must be treated the same, regardless of age. Using the steps of negotiation to (1) introduce the problem, (2) discuss solutions, and (3) vote on a solution. This gives everyone a chance to be involved. Councils do not always run smoothly. Teenagers are often suspicious that the new program is just another way for parents to gain compliance with their demands. In the first council meetings, rebelliousness may be exhibited to deliberately test whether parents are sincere about including them in family decision-making.
- Use rules of order . If participation is to be equal, then some type of order must be maintained. If a person has the right to express himself, then he also has the right to be heard — which implies that others have the obligation to listen. Rules of order help this situation.
- Rotate chairmanship . If the same person conducts all meetings, that person eventually begins to assume an air of superiority. To help maintain a feeling of equality, family members should take turns conducting the councils. This allows each person to experience the privileges and the responsibilities of this position.
- Accentuate solutions . Family council should not be “just a gripe session” — a time to get together and complain. In order to prevent this, you may decide that the person presenting a problem must also suggest one possible solution. Family members could then discuss alternate solutions or modify the one presented. In practice, some solutions do not work as well as anticipated. As family members begin to live with a decision, they may decide it needs to be changed. This change, however, must wait until the next regular meeting. Children soon recognize a need for better solutions and they learn by experience to make wiser choices. When family council is held regularly, each member learns to project ahead and anticipate problems. When this occurs, the emphasis at council meetings shifts from problem-solving to problem prevention and planning. Family council can also be a time to plan fun things like vacations or family outings. Families can talk about different places to visit and how they want to spend the time available.
- Decide on the authority level . The family council can be the final authority for the family, or a family can have a modified version of decision making. For it to be effective, however, most decisions made by the council need to be binding. If parents always overrule the council, children will soon lose interest.
- Keep a record . There sometimes develops a difference of opinions as to who conducted the last meeting, what matters were discussed, and what plans were agreed upon. For this reason, a secretary to record minutes is most helpful. The secretary can rotate with each meeting.
After your first family meeting, discuss these questions as a family:
- How did your first family meeting go?
- What about the meeting was good? What was bad?
- What do you want to incorporate in future meetings?
4 Active Listening Exercises
Active listening is a vital part of communication and can greatly improve relationships between family members. These four active listening exercises are a great way to boost your skills.
1. Precision Communication
Another activity that can help your family build and continue to develop good communication skills is called “Precision Communication.” It’s focused on active listening, which is a vital part of communication and conducive to better understanding and stronger, healthier relationships.
Here’s how to put this activity into practice:
- Set up a maze in your home using furniture, such as kitchen chairs or other pieces of furniture that can act as a barrier.
- Tie string or yarn between the furniture to create a clear path through the maze.
- Select a family member that will try to walk through the maze blindfolded. This person must not see the maze prior to being blindfolded.
- Have someone give voice instructions so the family member can be directed through the maze.
This activity’s aim is to see if the family member giving instructions can help the blindfolded family member get through the maze without bumping into the furniture, walls, or string. This means that not only must the speaking family member communicate clear and detailed instructions, but the blindfolded family member must also use their active listening skills to receive the instructions and implement them effectively.
Use these discussion questions to debrief and maximize this learning opportunity:
- Why was clear detailed communication necessary for this exercise?
- How important was it to listen carefully to the one giving instructions? Why?
- What were some of the difficulties associated with helping a family member complete this exercise?
- Using some of the ideas from this exercise, how can you, as a family, improve your communication skills?
If you want more from this activity, try this follow-up:
Draw a simple picture or pattern on a piece of paper. Without letting family members see the diagram, tell them what they need to do to make a copy of your picture that matches as closely as possible. After giving detailed instructions, see how accurately the pictures match up.
2. End of the Word—Beginning of the Next
This is a fun game on the Encourage Play website that can keep your kids actively engaged in building their listening skills.
Here’s how to play:
- One person (probably an adult) starts the game by giving out one word—it can be any word, it just needs to be one that every family member knows how to spell.
- The next family member must listen to the word the previous person said, then come up with a word that starts with the letter the last word ended with.
This is an easy game to play since you don’t need any materials, just a few minutes and the ability to hear one another! That makes it a great game for car rides, waiting in restaurants, or standing in a long line. To make it more challenging, give it a bit of complexity by limiting the words to a category, like animals or cities.
3. Red Light Green Light
Another exercise from the Encourage Play website is a familiar one. It’s based on the classic “Red Light, Green Light” game in which the leader gives instructions by color: saying “red light” means stop and saying “green light” means go.
To make the game a bit more challenging and really emphasize the importance of active listening, incorporate these three variations to the game:
- Different colors refer to different types of movement; for example, yellow light could mean skipping, purple light could mean crab walking, and blue light could mean hopping.
- Pretend to be a different animal for different colors (yellow = lion, green = bunny, purple = frog, etc.).
- Use words that rhyme with red or green to see if the players catch the difference (e.g., “Bread Light! Teen Light!”).
4. Tell a Group Story
Group stories are a great way to practice active listening with the whole family. It also gives kids a chance to be creative and silly, which helps to keep them engaged in the activity.
- The first person (probably an adult) starts a story with just one sentence (e.g., “Once upon a time, there was a very curious brown bunny”).
- The next person adds onto the story with just one sentence as well (e.g., “This bunny lived with her mother and father in a cozy little burrow under a willow tree”).
- The story continues until everyone has contributed at least a couple of sentences to the story.
This activity boosts active listening skills because it requires careful and attentive listening to what has already been said in order to make a good contribution to the story.
3 Assertive Communication Exercises
One of the best skills to teach your kids is how to be assertive instead of aggressive or passive (or passive-aggressive). Use these three assertive communication activities to help them learn this important skill.
1. Assertive Communication Worksheet
This worksheet is a great way to help older kids understand the difference between types of communication and to learn how to communicate assertively.
The worksheet first provides a good working definition of assertive communication:
“A communication style in which a person stands up for their own needs and wants, while also taking into consideration the needs and wants of others, without behaving passively or aggressively.”
It also outlines the traits of people who are assertive communicators, including:
- Clearly state needs and wants
- Eye contact
- Listens to others without interruption
- Appropriate speaking volume
- Steady tone of voice
- Confident body language
Next, it shares four tips on communicating assertively:
- Respect yourself—your wants and needs are as important as everyone else’s.
- Express your thought and feelings calmly rather than using the silent treatment or yelling and threatening.
- Plan out what you’re going to say before you say it.
- Say “no” when you need to, say it clearly, and do it without lying.
After some examples of assertive communication, we get to the active part of the worksheet. It’s geared toward adults, but the scenarios can be tweaked to fit kids as well.
There are four situations presented and space to write out your own assertive response to each. These situations are:
- Your partner says, “ I know you have plans for the weekend, but I really need you to watch the kids. I have a friend coming to town, and we made plans .”
- Situation: You’ve just received your food at a restaurant, and it was prepared incorrectly. Your sandwich seems to have extra mayo, instead of no mayo.
- Your friend says, “ Hey, can I borrow some money? I want to buy these shoes, but I left my wallet at home. I’ll pay you back soon, I swear. It won’t be like last time .”
- Situation: Your neighbor is adding an expansion to their house, and the crew starts working, very loudly, at 5 am. It has woken you up every day for a week.
Working through these scenarios as a family can help your kids see what healthy assertive communication looks like and show them that it’s okay to say “no” sometimes.
2. The Aggressive Alligator
The Aggressive Alligator is a great tool from Kristina Marcelli-Sargent, for teaching assertiveness over-aggressiveness or passiveness. It makes what can be a dry and boring subject more interesting and engaging.
Start by giving simple definitions to the terms “passive,” “aggressive,” and “assertive.” Next, show them a list of animals or a bin of small stuffed animals and allow them to choose an animal that they feel represents each definition. The aggressive animal doesn’t need to be an alligator, it can be anything that makes sense to your children.
After your kids have chosen an animal for each term, describe some social situations and instruct your kids to act them out with their animals. Each animal should act according to the definition it represents (e.g., the aggressive alligator should act aggressively, the passive panda should act passively, and the assertive anteater should act assertively).
Once all scenarios have been acted out, talk to your kids about how the outcomes differed between the three animals. Point out which one(s) resulted in a positive outcome and which one(s) should probably be avoided. In the future, you can refer back to the assertive anteater to remind your kids to be assertive instead of passive or aggressive (Sargent, 2015).
3. Keeping Cool
A great lesson for kids to learn is that assertive communication is about being firm and direct without being angry or upset. This activity will help you teach healthy assertiveness to your kids or students.
Here’s how to go about it:
- First, ask your kids how people might feel when they are bullied. If they have trouble coming up with answers, talk about how people might feel angry, scared, sad, upset, embarrassed, or confused.
- Next, ask your kids what kinds of things people want to do when they feel this way. If they can’t think of things people might do when they feel upset, angry, or sad, mention that they might yell, throw something, hit something, hide, cry, or do something else to make another person feel as bad as they feel.
- Ask your kids if they think these are good or helpful things to do. Explain how everyone has strong, negative feelings like this sometimes, and that it’s okay to feel them. These feelings have a purpose; they tell us that something is wrong or that something needs to be fixed, but they can also encourage us to do the wrong thing unless we learn how to keep a cool head.
- Close your eyes and take several slow deep breaths
- Count to ten
- Relax the muscles in your face and body
- Talk silently to yourself and repeat a soothing phrase, such as “Keep calm” or “I control my feelings”
- Get a drink of water
- Go sit by a person you trust
Discuss these options with the whole group and decide together on what the best techniques are, then practice using them together.
Click here to read about this exercise from the Education Development Center’s Bullying Prevention program.
3 Nonverbal Communication Exercises
Finally, although verbal communication is generally the focus of skill-building exercises and activities, nonverbal communication is also a vital skill to develop.
Use these 3 exercises to help your kids build their nonverbal skills.
1. Understanding Non-Verbal Communication
Things like tone of voice, facial expressions, body posture, and hand gestures are all non-verbal, but they are hugely important in our communication with others. If we say one thing with our words and another with our face or body, we can end up giving mixed messages and confusing others.
To make sure we are saying what we want to say with our words and our face, body, and tone, help your kids learn how to understand and “speak” non-verbal communications.
Here’s s description of this activity:
“As a family, make a list of different non-verbal actions. For example, folding your arms, snorting, frowning, etc… Select a TV program or a segment of a video. Watch about 5 to 7 minutes of the program with the volume off. While watching the program without volume, identify the different non-verbal messages, especially the feelings that are expressed. After 5 to 7 minutes, turn off the TV and discuss what you observed. You could even carry on the discussion as the program continues.”
To get the discussion started, use questions like:
- What were the non-verbal messages that you observed?
- How important do you think the non-verbal messages are in helping you to enjoy the movie and understand what was going on in the movie?
- Did you observe any confusing non-verbal messages?
- What feelings were expressed through non-verbal communication?
- What were some of the difficulties of this activity?
- What can you do to be more aware of non-verbal messages?
- Did everyone think the non-verbal message meant the same thing?
- Are non-verbal messages always obvious in real life?
If you want more from this exercise, try this follow-up activity. Seat two family members away from each other and have them carry on a conversation about giving directions to somewhere or explaining how to do something. As they talk, they should focus on trying to understand the other person’s feelings.
After doing this for a few minutes, the two should turn around, face each other, and continue the discussion—they will likely find it much easier!
Use the following questions to guide your discussion after the follow-up:
- When you had your backs to each other, did a lack of non-verbal communication affect your ability to communicate with the other person? If so, how?
- What feelings did you experience as you communicated with your back to the other person?
- When you spoke to the other person face-to-face, did this improve your ability to communicate and understand the other person’s feelings? If so, how?
- Did face-to-face communication improve your ability to understand the other person’s feelings?
- How can you increase your awareness of non-verbal messages you do not mean to be sending?
- How can you be aware of how we may misinterpret someone else’s non-verbal messages?”
2. Charades
Charades is a popular game with kids since it’s fun, easy to play, and can result in some seriously silly situations.
Here’s what you need to do:
- Animals: Monkey, dog, cat, rabbit, kangaroo, snake
- Activities: brushing teeth, playing cards, shining a flashlight, fishing, playing frisbee
- Emotions: scared, sad, bored, angry, happy, wary, proud
Acting out these prompts will give kids an opportunity to practice communicating non-verbally, a skill that they can easily build over time (Simmons, n.d.).
This nonverbal communication activity is available from Sue Simmons at Equinox Family Consulting.
3. Silent Snack
Finally, another activity from Sue Simmons is called “ Silent Snack ” and it gives young children a chance to have fun while building their nonverbal communication skills.
Follow these instructions to give it a try:
- Put out a few different snacks in individual bowls.
- Tell everyone it’s “Silent Snack Time,” meaning there’s no talking allowed!
- Offer each person a taste of each snack.
- Each player should take turns sharing their opinion on each snack. They can use indicators like thumbs up and thumbs down or facial expressions to communicate their opinions.
It’s a simple activity, but an effective one! Give it a try at your next snack time.

World’s Largest Positive Psychology Resource
The Positive Psychology Toolkit© is a groundbreaking practitioner resource containing over 500 science-based exercises , activities, interventions, questionnaires, and assessments created by experts using the latest positive psychology research.
Updated monthly. 100% Science-based.
“The best positive psychology resource out there!” — Emiliya Zhivotovskaya , Flourishing Center CEO
I hope you leave this piece with a treasure trove of new resources you can use to improve your own life or the lives of your clients.
Communication skills are one of the most important skills a person can have, making it well worth your while to devote some time and energy to develop them.
What are your favorite ways to work on communicating with your spouse? Do you schedule a time to talk about how your relationship is doing or do you just let it flow naturally? What do you think are the best ways to build, enhance, and maintain your communication skills? Let us know in the comments section.
We hope you enjoyed reading this article. Don’t forget to download our three Positive Communication Exercises (PDF) for free .
- Abass, S. (n.d.). 3 benefits of effective communication in a relationship. Lifehack. Retrieved from https://www.lifehack.org/509189/3-benefits-effective-communication-relationship
- https://defeatingdivorce.com/communication-exercises-for-couples/
- Fleming, G. (2018). 4 helpful nonverbal communication activities. ThoughtCo. Retrieved from https://www.thoughtco.com/nonverbal-communication-activities-1857230
- Heitler, S. (2010). What does communication have to do with a good relationship? GoodTherapy. Retrieved from https://www.goodtherapy.org/blog/what-does-communication-have-to-do-with-good-relationship
- Lee, T. R., & Pyfer, T. (n.d.). Helping youth succeed: Strengthening family ties: A workbook of activities designed to strengthen family relationships . Utah State University Extension. Retrieved from https://www.families-first.net/uploads/userfiles/files/FL_Youth_02.pdf
- Mendler, A. (2013). Teaching your students how to have a conversation. Edutopia. Retrieved from https://www.edutopia.org/blog/teaching-your-students-conversation-allen-mendler
- Norman, B. (2018). Trainers’ tips: Active listening exercises. Training Zone . Retrieved from https://www.trainingzone.co.uk/develop/cpd/trainers-tips-active-listening-exercises
- Peterson, R., & Green, S. (2009). Helping Youth Succeed: Keys to successful family functioning: Communication . Virginia Cooperative Extension. Retrieved from https://www.pubs.ext.vt.edu/content/dam/pubs_ext_vt_edu/350/350-092/350-092_pdf.pdf
- Reichmann, D. (n.d.). 5 communication games guaranteed to bring you closer. Engaged Marriage . Retrieved from https://www.engagedmarriage.com/5-communication-games/
- Rosenberg, M. B. (1999). Nonviolent communication: A language of compassion. Del Mar.
- Sargent, K. M. (2015). The aggressive alligator: Fun ways to teach assertiveness to children. Art of Social Work . Retrieved from https://kristinamarcelli.wordpress.com/2015/10/21/the-aggressive-alligator-fun-ways-to-teach-assertiveness-to-children/
- Simmons, S. (n.d.). Nonverbal games: 10 simple activities . Equinox Family Consulting, Ltd. Retrieved from https://equinoxfamilyconsulting.com/communication/nonverbal-games-10-simple-activities/
- Stanfield, J. (2017). 8 tips to teach effective communication skills. James Stanfield. Retrieved from https://stanfield.com/blog/2017/11/8-tips-teach-effective-communication-skills/
- Sott, A. (2018). Teaching communication skills. Edutopia. Retrieved from https://www.edutopia.org/article/teaching-communication-skills
- Tasker, R. (n.d.). 6 amazing couples therapy exercises for improving communication . GuideDoc . Retrieved from https://guidedoc.com/couples-therapy-exercises-for-improving-communication
- Victoria Department of Health & Human Services. (n.d.). Relationships and communications . Better Health Channel. Retrieved from https://www.betterhealth.vic.gov.au/health/healthyliving/relationships-and-communication
Share this article:
Article feedback
What our readers think.
Very good exercises. Thanks for sharing.
Let us know your thoughts Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Related articles

How to Say No & Master the Art of Personal Freedom
In a world that often values compliance over authenticity, the notion of personal freedom becomes not just a luxury but a necessity for our wellbeing [...]

Conflict Resolution Training: 18 Best Courses and Master’s Degrees
All humans have some things in common. We all need air to breathe and water to stay alive. We are all social beings, and if [...]

How to Foster Positive Communication: 9 Effective Techniques
Can you recall a really good conversation you’ve had? What was memorable about it? Was it the topic, the words, or just a feeling it [...]
Read other articles by their category
- Body & Brain (49)
- Coaching & Application (58)
- Compassion (25)
- Counseling (51)
- Emotional Intelligence (23)
- Gratitude (18)
- Grief & Bereavement (21)
- Happiness & SWB (40)
- Meaning & Values (26)
- Meditation (20)
- Mindfulness (44)
- Motivation & Goals (45)
- Optimism & Mindset (34)
- Positive CBT (30)
- Positive Communication (22)
- Positive Education (47)
- Positive Emotions (32)
- Positive Leadership (19)
- Positive Parenting (16)
- Positive Psychology (34)
- Positive Workplace (37)
- Productivity (18)
- Relationships (43)
- Resilience & Coping (38)
- Self Awareness (21)
- Self Esteem (38)
- Strengths & Virtues (32)
- Stress & Burnout Prevention (34)
- Theory & Books (46)
- Therapy Exercises (37)
- Types of Therapy (64)

- Name This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.

- Onsite training
3,000,000+ delegates
15,000+ clients
1,000+ locations
- KnowledgePass
- Log a ticket
01344203999 Available 24/7
What are Communication Skills? A Comprehensive Guide
Great Communication Skills act as a pillar in your success story. This comprehensive blog will explain to you what Communication Skills are and how you can improve your Communication Skills. Read till the end to gain insights into how to communicate effectively and why it is important to pay attention to body language.

Exclusive 40% OFF
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Share this Resource
- Effective Communication Skills
- English Speaking Course
- Assertiveness Skills Training
- Executive Communication Training
- Interpersonal Skills Training Course

Your Communcation Skills act as your advocate, they represent who you are and add personality to your voice. And just like in court, you would like to have a good advocate to win your case and set you on the path to success.
This blog will help you understand what Communication Skills are and how you can work on them efficiently. Read till the end to gain insights into the Communication Skills you will need in a job interview. So, grab your briefcase and get ready to build your own advocate.
Table of Contents
1) What are Communication Skills?
2) How to improve your Communication Skills?
3) Why do you require Communication Skills?
4) Examples of Communication Skills
5) Communication Skills in job interviews
6) Conclusion
What are Communication Skills?
Communication Skills involve the methods used in conveying, receiving and processing information through verbal and non-verbal means. It includes speaking and listening effectively, interpreting gestures, body language, and emotions and being able to use the right communication on the right occasion. Communication Skills broadly refers to a person’s ability to establish rapport, work in teams, negotiate, quit and effectively deliver messages.
Effective Communication Skills encompass a variety of methods, such as written text, oral presentations, and digital platforms like email and social media. By enhancing these skills, you can swiftly mobilise your team, facilitating the swift and efficient achievement of your business objectives.
For instance, when discussing a particular issue or a subject, you want to be convincing and create a statement. It is crucial to involve people in the project and keep them informed about everything that goes on to guarantee accountability. It is also good to be able to describe how one feels and do so in a professional manner to maintain satisfactory working conditions.
Points to consider:
a) Business communication isn't limited to face-to-face or phone conversations.
b) Being comfortable with digital tools like Social Media and Email is essential for effective remote collaboration and networking.
c) Good business communication involves active listening, observing, and understanding others. It builds trust, improves teamwork, and leads to successful negotiations.

How to improve your Communication Skills?
The following tips will tell you all about How to Improve Your Communication Skills.
Consider your audience
Effective Communication begins with understanding your audience. Take the time to assess who you are communicating with. Consider their background, expertise, interests, and expectations. Whether you are speaking to a colleague, a client, or a group of employees, tailoring your message to align with their needs and preferences is crucial. By doing so, you can ensure that your message resonates more effectively and is more likely to be well-received.
Think about the most effective way to convey your message
Communication is not one-size-fits-all. One cannot overemphasise the fact that different circumstances require the adoption of different measures. Consider the message which you have to share and the environment where you need to dispatch it. Email, face-to-face meeting, or phone call – which is the best approach to address your conflict situations?
Take into account the subject matter of the message, the level of emergency and the audience’s propensity to read lengthy messages. Picking the right media and tonality improves the likelihood of your message being received and responded to.
Encourage participation
Effective communication is a dialogue, not a monologue. Promote engagement through cultivating an environment that welcomes all members. Encourage them to ask questions and to give us back their feedback and thoughts.
Listen to the things they say with interest, try to understand what they want to explain to you. If more people are willing to get involved into what is being said then they will consider it worthwhile to listen to what you have to say and even participate actively in the process. This participatory approach makes it easier to solve conflicts and early involvement of the workers should be encouraged.
Leverage face-to-face contact
Although instant and efficient, digital communication lacks a certain level of intimacy, especially when it comes to communicating in confidence, negotiating, and sharing sensitive information.
Generally, prefer face to face communication specially when the topic is serious or sensitive. At least, you are there and, in a position, to sense signals such as gestures, intonation, and looks, which may give one vital information or make a big difference.
Make eye contact
Interpersonal eye contact is a significant aspect of the non-verbal communication process. By increasing eye contact to an appropriate level, you make sure that the other person perceives you as interested, attentive, and receptive. It is affectionate and warm and enables a rapport to be built.
But do not overdo it because staring in a very intense manner or for an extended period of time takes people off guard or makes them feel uneasy. And there we have it; the whole idea is all about striking the perfect balance that will make the end result appealing to a broad range of people.
Recognise non-verbal cues
Communication is not only the use of words but also the meaning and having proper practices. When observing people’s communicative behaviour, focus on kinaesthetic, vocal, and ocular modes of communication. It is the unspoken communication or hidden messages that may help to understand people's feelings and responses.
Noting these cues enables a person to actively modify the conversational pattern in the ongoing interaction. For example, if the employee looks lost, you can help him/her by providing more information; or if they seem stressed, using reassuring and calming language.
Reduce interruptions
It is also important to reduce interferences during communication so that messages get to the intended recipient with ease. Focus entirely on what you are doing while talking to a partner. This not only does show respect of their time and ideas but also helps in focusing the communication and information exchange on a particular track.
If you’re working in front of a computer, minimise all the unnecessary windows, shut the chat programs and apps, make yourself comfortable, and be ready to have a meaningful Communication. In this way, you can make sure that people have an environment that can support idea sharing and no interruption.
Why do you require Communication Skills?
Communication Skills are necessary because they help us effectively share information, understand others, and build connections. Let’s dive deeper to know why Communication Skills are so important:
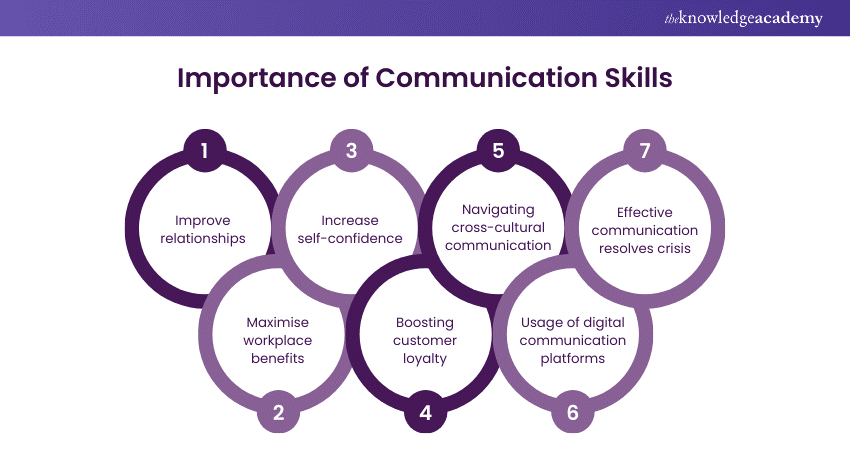
Improve relationships
When you work on your Communication Skills, you can share your ideas, emotions and needs, therefore developing better inter-personal relation. They resolve conflicts, establish trust, and improve relationships Therefore they improve relationships. Similar to Conflict Solving, Effective Communication also leads to better relations, empathy, active listening, and better means of responding.
Effective Communication is essential at all forms of the industry to ensure good working relations with other employees, customers, and investors. It helps to work together, establish rapport and foster, cooperation hence resulting in better performance and results in the organisation.
Master the art of effective communication with our Effective Communication Skills - Sign up now!
Maximise workplace benefits
Interpersonal communication is regarded as an essential component of business organisations. Communication enables the formulation of proper instructions, efficiency of the flow of information, and proper coordination in a particular team or organisation.
It is very effective in preventing misinterpretation and communication gaps that lead to conflict and sometimes costly mistakes. Also, the flow of information encourages a healthy workplace climate and increases the motivation and retention levels of workers.
Increase self-confidence
Practical Communication Skills in business can increase self-confidence by enabling individuals to express themselves, deliver impactful speeches, assert their needs, build professional relationships, and confidently handle challenging situations. Excellent Communication Skills enhance self-confidence, professional networking, and career advancement opportunities. They enable individuals to convey ideas, influence others, and showcase expertise, leading to greater recognition and success.
Boosting customer loyalty
Effective Communication Skills play an essential role in building and maintaining strong customer relationships. Businesses can enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty by actively listening to customer needs, addressing their concerns promptly, and providing clear and empathetic communication. This improves business relations, positive word-of-mouth referrals, and long-term success.
Navigating cross-cultural communication
In today's global business landscape, cross-cultural Communication Skills are increasingly valuable. Understanding cultural gaps, adapting communication styles, and respecting diverse perspectives are essential for successful international collaborations and negotiations. Businesses prioritising cross-cultural Communication Skills gain a competitive edge in the global marketplace.

Usage of digital communication platforms
Technology is advancing day by day hence a proper understanding and usage of digital media is highly important. Today, Business Communication Skills is not only limited to face-to-face and telephone communication. They also utilise platforms like e-mailing, Facebook, X (formally known as twitter), video conferencing and other virtual collaborating tools.
These channels can be mastered for facilitating, remote communication, virtual teams, and market expansion at a global level. Knowing how to use them effectively can work wonders to boost your business.
Effective communication resolves crisis
In the course of disasters or when the market situation is volatile, it is necessary to disseminate information widely to foster trust and confidence. Crisis management communication refers to the timely release of information. The compassionate approach of addressing stakeholders’ concerns and the active management of the stakeholder concerns during a particular crisis.
Hence, it is possible to sum up that only with appropriate, clear, and empathetic management of crises, companies are able to manage to avoid losses to their reputation and protect the trust of stakeholders with great care.
Master the art of Effective Communication with our Effective Communication Skills Course .Sign up now!
Examples of Communication Skills
When applying for a job, showcasing the Communication Skills that recruiters value in your cover letter and resume is essential. These skills are also crucial to demonstrate during your job interview. Here are some examples of Communication Skills and what they include:
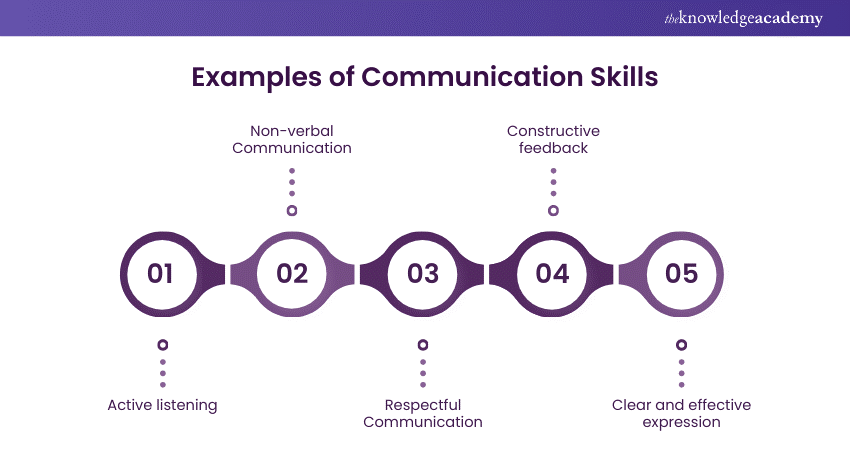
Active listening
Active listening means focusing entirely on and understanding what others say. It involves giving your undivided attention, asking clarifying questions, and providing verbal and non-verbal feedback to show you are engaged. For example, during a team meeting, actively listening would involve maintaining eye contact, nodding in agreement, and paraphrasing what others have said to demonstrate understanding.
Non-verbal Communication
Non-verbal Communication refers to the messages conveyed through gestures, facial expressions, and body language. It plays a vital role in how others perceive and interpret your communication. For example, maintaining an open and confident posture, smiling, and using appropriate hand gestures can enhance communication effectiveness.
Respectful Communication
Respectful Communication include s treating others with dignity, courtesy, and consideration. It involves valuing diverse perspectives and opinions, even when they differ from your own. Respecting others' ideas creates a positive and inclusive work environment. During an interview or in your cover letter, emphasising your ability to actively listen, appreciate differing viewpoints, and provide constructive feedback demonstrates respectful communication.
Learn how to implement effective strategies to improve cross-cultural Communication Skills with our Cross-Cultural Communications Training - Join today!
Constructive feedback
Giving and taking constructive feedback is crucial for personal and professional growth. It involves providing specific and actionable suggestions to help others improve. Being open to feedback and responding positively also showcases your willingness to learn and grow. In an interview, you can highlight instances where you have given or received constructive feedback, emphasising its generated positive outcomes.
Clear and effective expression
Clear communication is essential for accurately conveying ideas and information. It involves articulating thoughts clearly, using appropriate language and tone, and structuring your message concisely and organised. In your cover letter, resume, and interview responses, focus on showcasing your ability to express yourself effectively, using simple and concise language that is easy to understand.
Communication Skills for job interviews
In a job interview, make sure to actively listen to the person speaking to you. Make sure to sit straight and make eye contact with the interviewers whenever you are speaking. Remember to speak confidently, be positive, make eye contact and smile.
Almost everything you do, both in terms of the job interview as well as in life, can be seen as a form of communication. By correctly identifying and assessing your strengths and weaknesses and practising good communication habits, you can enhance your Communication Skills to a great extent.
Conclusion
To sum it up, e ffective Communication Skills are the key to building connections, fostering collaboration, and achieving success. Effective Communication promotes teamwork, collaboration, and problem-solving, improving productivity and positive outcomes. Improving your Communication Skills for personal and professional growth will help you explore better employment prospects and career options.
Learn real-world Communication Skills that can be applied in the organisation by registering for our Communication Skills Training . Register now!
Frequently Asked Questions
Effective communication is vital for career success as it fosters clarity and reduces the chance of misunderstandings. Good communication helps you create a collaborative environment that helps build teamwork and get work done.
Cultural awareness enhances communication by fostering respect for diverse perspectives, avoiding misunderstandings, and promoting inclusivity. Recognising and adapting to cultural differences strengthens relationships, boosts collaboration, and creates a harmonious environment.
The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs , videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA .
The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass , a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
The Knowledge Academy offers various Communication skills Courses including Negotiation skills and Negotiation techniques. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into Negotiation methodologies.
Our blogs on Business skills covers a range of topics related to communication skills along with negotiation techniques and examples, offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your Communication skills, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming Business Skills Resources Batches & Dates
Fri 28th Jun 2024
Fri 9th Aug 2024
Fri 25th Oct 2024
Fri 27th Dec 2024
Get A Quote
WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
My employer
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry
- Business Analysis
- Lean Six Sigma Certification
Share this course
Our biggest spring sale.

We cannot process your enquiry without contacting you, please tick to confirm your consent to us for contacting you about your enquiry.
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry.
We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Or select from our popular topics
- ITIL® Certification
- Scrum Certification
- Change Management Certification
- Business Analysis Courses
- Microsoft Azure Certification
- Microsoft Excel Courses
- Microsoft Project
- Explore more courses
Press esc to close
Fill out your contact details below and our training experts will be in touch.
Fill out your contact details below
Thank you for your enquiry!
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go over your training requirements.
Back to Course Information
Fill out your contact details below so we can get in touch with you regarding your training requirements.
* WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
Preferred Contact Method
No preference
Back to course information
Fill out your training details below
Fill out your training details below so we have a better idea of what your training requirements are.
HOW MANY DELEGATES NEED TRAINING?
HOW DO YOU WANT THE COURSE DELIVERED?
Online Instructor-led
Online Self-paced
WHEN WOULD YOU LIKE TO TAKE THIS COURSE?
Next 2 - 4 months
WHAT IS YOUR REASON FOR ENQUIRING?
Looking for some information
Looking for a discount
I want to book but have questions
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go overy your training requirements.
Your privacy & cookies!
Like many websites we use cookies. We care about your data and experience, so to give you the best possible experience using our site, we store a very limited amount of your data. Continuing to use this site or clicking “Accept & close” means that you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about our privacy policy and cookie policy cookie policy .
We use cookies that are essential for our site to work. Please visit our cookie policy for more information. To accept all cookies click 'Accept & close'.
Whole Farm > Human Resources > Human Relationships
Updated November, 2022 File C6-56
Good communication can help solve problems.
When organizing and operating a value-added business, disagreements can arise among committee members or project managers over how to solve problems facing the project or business. Using good communication skills can help the group find solutions. Practice the suggestions below to improve your communication skills during problem solving discussions.
The following communication rules can improve problem solving:
- State your problem and interests. Acknowledge others' problems and interests. Avoid name calling and answering a complaint with another complaint.
- Listen to the other parties and know their interests. Ask “why,” “why not” and “what if” questions to better understand. Use silence to demonstrate you are willing to listen or to help move the other side into a position to listen more effectively to you.
- Offer an apology when appropriate.
- Stay in the present and the future. The past has already been lived.
- Stick to the present topic.
- Look for areas of agreement.
- Set the time for the next discussion and take a time out if the discussion deteriorates.
- Use mutual restating until a party who continues to feel misunderstood feels understood appropriately.
- State requests for change in behavioral terms. Don’t ask for changes in attitude or feeling just to be different.
- Consistently express verbal and body messages. If negative feelings must be expressed, only use words. Show confidence in the process, relax, use good eye contact and show interest.
Nonverbal communication is important. The persuasiveness of a message depends on:
- Nonverbal communication - includes facial expression, movement and gestures.
- Voice communication - includes the tone with which the message is conveyed such as confidence, desperation, anger or condescension.
- Data communication - includes the actual meaning of words and any supporting information.
You can listen to each other and still have differences. These characteristics apply:
- Listen to understand.
- Accept that what the other person is saying is true for him/her. Respect the others’ feelings.
- Repeat for clarification.
- Find a point of agreement.
- State or restate your own opinion.
- Acknowledge another’s statements and state, “I will give it serious consideration before I take further action.”
When you receive feedback:
- Listen carefully and repeat what you heard.
- Ask to fully understand.
- Say thank you and state that you will consider their comments before taking further action.
- Seriously reflect on what you heard before taking further action.
When you give feedback:
- Separate the behavior from the person. Be specific and factual about behaviors. Avoid value judgments and demands for a change in attitude or emotion.
- Describe how you feel.
- Describe how this affected you.
- Be sensitive and respectful. Present this feedback as a gift, then leave it behind.
Mary Holz-Clause, former co-director, Ag Marketing Resource Center , former associate vice president for ISU Extension and Outreach
Mary Holz-Clause
Former co-director, ag marketing resource center former associate vice president for isu extension and outreach view more from this author.
Advertisement
Communication, Critical Thinking, Problem Solving: A Suggested Course for All High School Students in the 21st Century
- Published: 05 December 2013
- Volume 44 , pages 63–81, ( 2013 )
Cite this article

- Terresa Carlgren 1
3895 Accesses
23 Citations
Explore all metrics
The skills of communication, critical thinking, and problem solving are essential to thriving as a citizen in the 21st century. These skills are required in order to contribute as a member of society, operate effectively in post-secondary institutions, and be competitive in the global market. Unfortunately they are not always intuitive or simple in nature. Instead these skills require both effort and time be devoted to identifying, learning, exploring, synthesizing, and applying them to different contexts and problems. This article argues that current high school students are hindered in their learning of communication, critical thinking, and problem solving by three factors: the structure of the current western education system, the complexity of the skills themselves, and the competence of the teachers to teach these skills in conjunction with their course material. The article will further advocate that all current high school students need the opportunity to develop these skills. Finally, it will posit that a course be offered to explicitly teach students these skills within a slightly modified western model of education.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others
Assessing early writing: a six-factor model to inform assessment and teaching

Creating a Motivating Classroom Environment

21st Century Skills
A model of education as organized from western countries such as Canada, Great Britain, the United States, and some European nations by way of organizational structure (identified curricular outcomes, assessment strategies, hierarchical administrative levels).
Immersion in terms of critical thinking instruction refers to “deep, thoughtful, well understood subject-matter instruction in which the students are encouraged to think critically in the subject … but in which general critical thinking principles are not made explicit” (Ennis 1989 , p. 5).
Infusion as it refers to critical thinking involves the explicit instruction of critical thinking principles and strategies in conjunction with the subject material (Ennis 1989 , p. 5).
5 credit course as per government of Alberta standards (Alberta, Canada), http://education.alberta.ca/media/6719891/guidetoed2012.pdf , p. 42.
See basic structure of Alberta Education curriculum. Example from Science 10; http://education.alberta.ca/media/654833/science10.pdf .
Note: the curricular framework for this course is modelled after that of some curriculum in Alberta (Alberta Education 2005 ).
Alberta Education. (2005). Science 10 . Retrieved from http://education.alberta.ca/media/654833/science10.pdf .
Alberta Education. (2008). Mathematics grades 10–12 . Retrieved from http://education.alberta.ca/media/655889/math10to12.pdf .
Alberta Education. (2012). Guide to education: ECS to grade 12 . Retrieved from http://educaiton.alberta.ca/media/6719891/guidetoed2012.pdf .
Alliance for Excellent Education. (2011). A time for deeper learning: Preparing students for a changing world. Education Digest, 77 (4), 43–49. Retrieved from http://web.ebscohost.com.ezproxy.lib.ucalgary.ca/ehost/pdfviewer/pdfviewer?vid=5&hid=12&sid=9695cbbb-ab96-496a-941e-35fa2bee2852%40sessionmgr4 .
Berger, E. B., & Starbird, M. (2012). The 5 elements of effective thinking . Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
Google Scholar
Brookfield, S. D. (1995). Becoming a critically reflective teacher . San Francisco: Jossey-Bass Inc.
Conley, D. T., & McGaughy, C. (2012). College and career readiness: Same or different? Educational Leadership, 69 (7), 28–34. Retrieved from http://web.ebscohost.com.ezproxy.lib.ucalgary.ca/ehost/pdfviewer/pdfviewer?vid=4&hid=12&sid=9695cbbb-ab96-496a-941e-35fa2bee2852%40sessionmgr4 .
Covey, S. (2004). The 7 habits of highly effective people: Restoring the character ethic . New York: Simon & Schuster.
Crenshaw, P., Hale, E., & Harper, S. L. (2011). Producing intellectual labour in the classroom: The utilization of a critical thinking model to help students take command of their thinking. Journal of College Teaching & Learning, 8 (7), 13–26. Retrieved from http://web.ebscohost.com.ezproxy.lib.ucalgary.ca/ehost/pdfviewer/pdfviewer?vid=3&sid=333f52c4-101e-4d9f-89e7-1088c51b14e7%40sessionmgr15&hid=19 .
Dobozy, E. (2012). Failed innovation implementation in teacher education: A case analysis. Problems of Education in the 21st Century, 40 , 35–44. Retrieved from http://web.ebscohost.com.ezproxy.lib.ucalgary.ca/ehost/pdfviewer/pdfviewer?vid=4&sid=333f52c4-101e-4d9f-89e7-1088c51b14e7%40sessionmgr15&hid=19 .
Ennis, R. H. (1989). Critical thinking and subject specificity: Clarification and needed research. Educational Researcher, 18 (3), 4–10. Retrieved from http://www.jstor.org.ezproxy.lib.ucalgary.ca/stable/pdfplus/1174885.pdf?acceptTC=true .
Ennis, R. H., & Millman, J. (1985). Cornell critical thinking test level x . Pacific Grove, CA: Midwest Publications.
Greenstein, L. (2012). Assessing 21st century skills: A guide to evaluating mastery and authentic learning . Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin.
Holloway-Libell, J., Amrein-Beardsley, A., & Collins, C. (2012). All hat & no cattle. Educational Leadership, 70 (3), 65–68. Retrieved from http://web.ebscohost.com.ezproxy.lib.ucalgary.ca/ehost/pdfviewer/pdfviewer?sid=ec665c98-aef1-44e8-8737-016b87157907%40sessionmgr13&vid=5&hid=1 .
Johanson, J. (2010). Cultivating critical thinking: An interview with Stephen Brookfield. Journal of Developmental Education, 33 (3), 26–30. Retrieved from http://web.ebscohost.com.ezproxy.lib.ucalgary.ca/ehost/pdfviewer/pdfviewer?vid=14&sid=333f52c4-101e-4d9f-89e7-1088c51b14e7%40sessionmgr15&hid=19 .
Jonassen, D. H. (2011). Learning to solve problems: A handbook for designing problem-solving learning environments . New York: Routledge.
Jonassen, D. H. (2012). Designing for decision making. Educational Technology Research and Development, 60 (2), 341–359. doi: 10.1007/s11423-011-9230-5 .
Article Google Scholar
Kassim, H., & Fatimah, A. (2010). English communicative events and skills needed at the workplace: Feedback from the industry. English for Specific Purposes, 29 (3), 168–182. Retrieved from http://www.sciencedirect.com.ezproxy.lib.ucalgary.ca/science/article/pii/S0889490609000635 .
Kirikkaya, E. B., & Bozurt, E. (2011). The effects of using newspapers in science and technology course activities on students’ critical thinking skills. Eurasian Journal of Educational Research, 44 , 149–166. Retrieved from http://web.ebscohost.com.ezproxy.lib.ucalgary.ca/ehost/pdfviewer/pdfviewer?vid=3&sid=2e1f2c2a-6199-4516-a3d0-5114f7c35314%40sessionmgr15&hid=19 .
Paige, M. (2012). Using VAM in high stakes employment decisions. Phi Delta Kappan, 94 (3), 29–32.
Passini, S. (2013). A binge-consuming culture: The effect of consumerism on social interaction in western societies. Culture & Psychology, 19 (3), 369–393. doi: 10.1177/1354067x13489317 .
Patterson, K., Grenny, J., & McMillan, R. (2011). Crucial conversations: Tools for talking when stakes are high (2nd ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Paul, R., & Elder, L. (2008). The miniature guide to critical thinking concepts and tools (5th ed.). Dillon Beach, CA: The Foundation for Critical Thinking.
Raybould, J., & Sheedy, V. (2005). Are graduates equipped with the right skills in the employability stakes? Industrial and Commercial Training, 37(4/5), 259–263. Retrieved from http://search.proquest.com.ezproxy.lib.ucalgary.ca/docview/214105484/fulltextPDF/13C3AF7848A26CBC442/26?accountid=9838 .
Richardson, J. (2011). Tune into what the new generation of teachers can do. Phi Delta Kappan, 92 (4), 14–19.
Robinson, K. (2011). Out of our minds . Chichester, West Sussex: Capstone Publishing Ltd.
Rosefsky, S., & Opfer, D. (2012). Learning 21st-century skills requires 21st-century teaching. Phi Delta Kappan, 94 (2), 8–13.
Sahlberg, P. (2006). Education reform for raising economic competitiveness. Journal of Educational Change, 7 , 259–287. doi: 10.1007/s10833-005-4884-6 .
Schleicher, A. (Ed.) (2012). Preparing teachers and developing school leaders for the 21st century: Lessons from around the world . Retrieved from http://site.ebrary.com.ezproxy.lib.ucalgary.ca/lib/ucalgary/docDetail.action?docID=10589565 .
Sherblom, P. (2010). Creating critically thinking educational leaders with courage, knowledge and skills to lead tomorrow’s schools today. Journal of Practical Leadership, 5 , 81–90. Retrieved from http://web.ebscohost.com.ezproxy.lib.ucalgary.ca/ehost/pdfviewer/pdfviewer?vid=11&hid=12&sid=9695cbbb-ab96-496a-941e-35fa2bee2852%40sessionmgr4 .
Spencer, J. T. (2013). I’m a better teacher when students aren’t tested. Phi Delta Kappan, 94 (5), 72–73.
Tsang, K. L. (2012). Development of communication skills using an embedded approach for the evolving professional. The International Journal of Learning, 18 (3), 203–221. Retrieved from http://web.ebscohost.com.ezproxy.lib.ucalgary.ca/ehost/pdfviewer/pdfviewer?vid=3&sid=924c3e4d-4fa2-4f95-a769-cbd05ada6724%40sessionmgr4&hid=28 .
Williamson, P. K. (2011). The creative problem solving skills of arts and science students—The two cultures debate revisited. Thinking Skills and Creativity, 6 , 31–43. doi: 10.1016/j.tsc.2010.08.001 .
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
University of Calgary, Calgary, AB, Canada
Terresa Carlgren
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Terresa Carlgren .
Course Syllabus and Outline
Title: Communication, Critical Thinking, and Problem Solving (an introduction)
Course Components
No exclusionary, discriminatory, or derogatory material will be taught in this course, nor will the content in this course be deemed controversial in any way.
Philosophy and Rationale
Much of our thinking, left to itself, is biased, distorted, partial, uniformed or down-right prejudiced. Yet the quality of our life and that of what we produce, make, or build depends precisely on the quality of our thought. Shoddy thinking is costly, both in money and in quality of life. Excellence in thought, however, must be systematically cultivated (Paul and Elder 2008 , p. 2).
The skills required of today’s youth are more pronounced than that of the past. Students are required to have basic knowledge of content in areas of Science, Math, and English; as well as technological skills, problem solving skills, critical thinking skills, and the ability to communicate (Sahlberg 2006 ). However, with the time constraints placed on teachers, knowledge outcomes taking priority on learning due to the high stakes standardized achievement tests, and an understanding that the particular skills of communication, critical thinking, and problem solving require explicit instruction (Rosefsky and Opfer 2012 ); students are not mastering these skills to an acceptable standard.
In order for students to acquire and master the skills necessary to compete and be successful in the work force, post secondary education, and life; students must have the opportunity to engage by learning these skills through practice, application, and devoted explicit attention. Furthermore, students must explore these skills without fear of failure but rather with hope that they can improve and move forward from the learning experience. In this way, learning these skills as a secondary item within the context of another content based course will not do the students justice.
Historically, the skills of sewing, cooking, woodworking, and mechanics where offered in high school as application based courses that required hands on and explorative learning with teacher guidance. More recently computer courses, and digital citizenship are taking hold in schools to teach students these skills. There is no reason why the skills of communication, critical thinking, and problem solving should be treated any differently.
Without the structure and organization of education making drastic changes to mandate these skills be made more of a priority in the classroom, it is feared that the teaching and learning of these skills will remain an oversight. It is unfortunate that the students; citizens, economic and market contributors of our future, will be underserved. It is with these reasons that this course offering takes place; such that an opportunity within the current educational structure can provide students the opportunity to guard themselves with new foundational skills for the future.
General Learner Expectations
By the end of this course, it is expected learners will have developed and ascertained explicit knowledge of communication, critical thinking and problem solving. More importantly, students will have acquired the skills of communication, critical thinking, and problem solving through application, exploration, and trial and error, such that they can utilize these skills in different contexts of their lives in preparation for the work force or post-secondary education.
Specific Learner Expectations
The following is a list of specific learner expectations for the course. Please note that the units identified for this course are titled ‘Skill-sets’ for a reason as they are not discrete topics to be taught in isolation, but rather guides toward the encompassing theme of acquiring these skills. This course is in no way designed as a check the outcome box course, nor is it organized in order by skill or outcome number. Rather, the outcomes and skill-sets must be taught in conjunction with each other through the duration of the course with trust being given to the fact that through student exploration and leadership; along side teacher guidance and facilitation, students will improve on their existing skill-set for these skills.
Skill Set A: Critical Thinking Skills Footnote 6
Knowledge Outcomes: (Students will be able to)
A.K.1 Define the difference between fact and inference.
A.K.2 Derive criteria for which to judge a problem or predicament.
A.K.3 List the elements of thought associated with critical thinking as per one critical thinking model (Paul and Elder, Rusten and Schuman).
A.K.4 Identify inherent and hidden bias in an argument.
A.K.5 Identify faults in thinking due to oversimplifying or over generalizing issues or problems.
A.K.6 Identify and state the purpose of thinking.
Skill Outcomes: (Students will be able to)
A.S.1 Utilize background knowledge to solve a problem or predicament.
A.S.2 Apply evidence to solve a problem or predicament.
A.S.3 Express an argument that is logical, clear, and concise.
A.S.4 Derive and model a process by which to critically analyze, think, and solve a problem or predicament that involves a reasonable, logical, and relevant thinking strategy.
A.S.5 Explore alternative options and methods before drawing a conclusion.
A.S.6 Illustrate and explore the consequences and implications following the solution of a problem or issue.
A.S.7 Model, display, or perform the ability to think critically through verbal, written, and physical means.
Attitudes Outcomes: (Students will)
A.A.1 Believe that it is possible for themselves to solve problems with a reasonable level of confidence.
A.A.2 Have confidence that they are able to ascertain information needed to help themselves think critically about a problem or issue.
A.A.3 Respect the diverse nature of thinking and problem solving that allows for others’ opinions and arguments to be taken into account without discrimination.
Skill Set B: Problem Solving Skills
B.K.1 Define convergent and divergent thinking.
B.K.2 State that for any given problem there is more than one problem solving strategy.
B.K.3 List possible problem solving strategies that exist.
B.K.4 State that problem solving strategies are used in context and explore the types of contexts that might exist.
B.K.5 Identify that for any problem solving strategy there must be an evaluative component and an ability to modify the strategy to fit a new context or problem.
B.S.1 Derive and model, illustrate, or describe a problem solving strategy that is context specific.
B.S.2 Derive and model a personal problem solving strategy to solve a personal problem.
B.S.3 Solve problems using mathematical reasoning.
B.S.4 Solve problems using technological means or supports.
B.S.5 Solve problems by modeling existing economic structures.
B.S.6 Solve problems by modeling existing political structures.
B.A.1 Have improved self-confidence in attempting to solve problems in a number of different contexts.
B.A.2 Be proud of the problem solving ability they have acquired.
B.A.3 Feel empowered to attempt new problem solving methods that are logical and relevant without fear of failure.
Skill Set C: Decision Making Skills
C.K.1 Identify that decision making is a process toward problem solving.
C.K.2 Identify personal bias in an argument.
C.K.3 State the difference between dialectic and rhetorical arguments.
C.K.4 Illustrate the types of decisions expected in personal, professional, and civic lives.
C.K.5 Describe the difference between rational and emotional expressions.
C.K.6 State and explain the difference between normative and naturalistic decision making.
C.K.7 Define the term dilemma.
C.K.8 State that the primary purpose of decision making is to decide on the best option, or provide maximum utility.
C.K.9 State that decision making can be made based on what is most consistent with personal beliefs or past experiences.
C.K.10 Identify that there is uncertainty and risk associated with every decision.
C.S.1 Construct a decision making process that includes identification, evidence, evaluation and modification of a problem.
C.S.2 Construct and apply a method of decision making to solve personal problems.
C.S.3 Construct and apply a method of decision making to solve professional problems.
C.S.4 Construct and apply a method of decision making to solve civic problems.
C.S.5 Examine positive and negative methods of modifying and changing decisions after they have been made.
C.S.6 Examine circumstances by which to modify, change, or renegotiate a decision.
Attitude Outcomes: (Students will)
C.A.1 Acknowledge that a commitment needs to be made upon making a decision.
C.A.2 Take ownership of decisions made using the decision making skills.
C.A.3 Understand that decisions require a course of action that is intended to yield results that are satisfying for special individuals.
C.A.4 Reflect on decisions made in their life and decide if they were appropriate or not.
Skill Set D: Communication Skills
Knowledge outcomes: (students will be able to).
D.K.1 Identify factors affecting communication.
D.K.2 State that communication involves more than one person.
D.K.3 Identify and explore the roles of speaker and listener in any conversation.
D.K.4 List and explore different environments involving communication (i.e.; formal language vs. slang, workplace vs. home life).
D.K.5 Describe the difference between teamwork and collaboration.
D.K.6 Describe what effective and ineffective communication looks, sounds, and feels like.
D.K.7 Explain the role of respect, honesty, fairness, and reason in any communication interaction.
D.S.1 Model and illustrate different conflict resolution strategies.
D.S.2 Identify and illustrate factors affecting teamwork.
D.S.3 Communicate effectively with peers while working collaboratively as a team.
D.S.4 Communicate effectively with teachers and parents regarding conflicts and successes.
D.S.5 Communicate clearly, logically, and precisely in verbal and written modes.
D.S.6 Ask and accept help in communicating when needed.
D.A.1 Feel empowered to communicate with peers.
D.A.2 Have confidence in the skill of communicating to discuss difficult issues with parents, teachers, and employers.
D.A.3 Feel empowered to ask and accept help by communicating in an appropriate fashion without fear of rejection or judgment.
Course Assessment
The assessment for this course is by way of individual student improvement in conjunction with final skill aptitude of the above stated skill sets by course end. This improvement and aptitude can be measured through a number of different means and will depend on the structure of the course as arranged and organized by the teacher. Outlined below are some classroom activities and possible assessments that might be of benefit to teachers planning this course.
Activities:
A pre and post written statement of the intention for being in the course and the problems and skills a student would like to solve and understand.
Assessed formatively (both pre and post) for critical thinking skills such as clarity of work, logic, reasoning, and evidence provided.
Pre and post formative assessments then evaluated for level of improvement.
Debate as a form of argument, decision making, communication and problem solving.
Following and respecting debate rules and roles of speaker/listener.
Utilizing rubrics for argument, decision making, communication and problem solving.
Market modeling—modeling the course as a competitive market with students given roles based on an application from them on their expertise and motivation toward the given problem. The roles would dictate a level of income for the student as well as a level of responsibility and leadership for them.
Assessed by way of improvement and movement ‘up the market ladder’—i.e.—what by way of promotion, what conflict resolution strategies or problems needed to be overcome, how long did it take to resolve or solve the problem?
Take into account rationale for why students have chosen their particular role (provided this rationale is given in a clear, appropriate, relevant, and significant manner)—i.e. standard of living, other priorities at the time etc.
Socratic Seminar on issue at hand to interpret and illustrate improvement in speaking and communicating an argument.
Assessed by way of quality and strength of participation and argument.
Resume of students skills ascertained and improved on through the course.
Cross curricular problems and projects modeling real life i.e. effects of globalization, and marketization on students by multinational companies. Projects to be displayed and presented to the class.
Assessed by way of rubrics (teacher and peer).
Likert scale survey for teacher and student on level of improvement of outcomes throughout the course.
Utilization of pre-existing rubrics i.e. Decision Making (Jonassen 2012 ).
Cornell CT Test level X for critical thinking as a pre and post test? (a quantitative assessment ordered from http://www.criticalthinking.com/getProductDetails.do?code=c&id=05501 ) (Ennis and Millman 1985 ).
Assessment strategies as well as possible outcomes for skill-sets can be found in Greenstein’s ( 2012 ), Assessing 21st Century Skills: A guide to evaluating mastery and authentic learning .
It is expected that all students will learn skill-set outcomes through the duration of the course. The question is how much will be learned? The answer depends on the individual student as well as their incoming skill level in each given area. In this case equal does not mean equitable and the goal of assessment for this course is to ascertain what improvement as well as final level of understanding an individual student has.
It should be stated that the nature of the course is student-centered and driven by the student. The teacher, however, is responsible for setting up the course and providing students an opportunity to explore this learning. Therefore, the teacher must come up with valid, rich, open activities for students to work within while at the same time ideally allowing the students to come up with the problems, scenarios, and arguments with which to discuss and solve. Explicit instruction may be necessary but should be severely limited allowing students ample opportunity for application and practice.
It is highly recommended that students work the duration of this course in groups (and differing groups) as it is here that communication, collaboration, and teamwork skills will be developed. It is further recommended that students be a part of the assessment process in deciding on the nature of the assessments, the criteria for the assessment, and in self and peer assessment. Allowing students to direct and lead requires trust and openness on the part of the teacher but is in fact part of the learning process.
Learning Resources
Since the premise of this course is for the teacher to be a ‘guide on the side’ and not a ‘sage on the stage’, there are no required learning resources for this course. However, it is recommended that teachers undertake professional development in the skill-set areas to ensure they have developed the necessary skills to pass on. Books such as: Becoming a Critically Reflective Teacher by Brookfield, Learning to Solve Problems: A Handbook for Designing Problem - Solving Learning Environments by Jonassen, 7 Habits of Highly Effective People , Crucial Conversations, and The 5 Elements of Effective Thinking would be an introduction. Journal articles and professional publications regarding 21st century skills and the development of these would be helpful. Finally, professional development seminars or sessions by leading experts such as Richard Paul from The Foundation for Critical Thinking would be almost necessary.
From this learning, the teacher will need to develop a tool kit of resources at their disposal in which to best help their students. The nature of the course being student-centered will require a teacher to be flexible in the work that is undertaken. The teacher will also have to be reactive to issues, problems, and learning scenarios that take place in the classroom. However, as this is a course in allowing the students to ascertain skills in problem solving, critical thinking, and communication, it must be mentioned that it is the students who are doing the brunt of the work and actually doing the problem solving and critical thinking themselves. For instance, it would not be sufficient for a question to be: What book should we read to learn critical thinking? And have the answer to the problem be: go ask the teacher and he/she will tell us. Rather the answer should be: let us go to the library or use the internet and find out which book is the best book. What options are available? What type of critical thinking are we looking at? What is critical thinking? Who are the leading experts in the field? What bias do they have? Where can I actually find or order these books? What cost and what is my budget? In the end, a seemingly simple question—is wrought with learning experiences by the student provided the teacher take a backburner to the work and allow the student to take the reins.
Course Evaluation
The open nature of this course allows for a teacher at any time to make changes to the structure, organization, and assessment of the course due to evaluation and reflection. The evaluation and reflection of this course should therefore be ongoing by the student and teacher immersed in the learning environment. The teacher is responsible for periodically seeking feedback from students regarding the nature of the course, as well as professionally reflecting themselves on the presentation of the course to their students.
The teacher is also responsible for keeping records of the course, as well as feedback collected that identifies the (a) strengths and weaknesses of the course as it is being facilitated, (b) activities and assessments being implemented in the course, and (c) improvements to the course for a later date. The teacher should ideally create a long range plan (or running calendar) that becomes more descriptive as the course proceeds, about the level of difficulty, quality of problems, activities, resources, feedback, and assessments being utilized in the course to reference at a later date. Finally, the teacher should be able to provide evidence to the local school authority at any time in order for the authority to monitor, evaluate, and report progress should it be required.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Carlgren, T. Communication, Critical Thinking, Problem Solving: A Suggested Course for All High School Students in the 21st Century. Interchange 44 , 63–81 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10780-013-9197-8
Download citation
Received : 19 April 2013
Accepted : 21 November 2013
Published : 05 December 2013
Issue Date : December 2013
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s10780-013-9197-8
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Communication
- Critical thinking
- Global market
- High school course
- Problem solving
- Western model of education
- 21st Century
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- AI Essentials for Business
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading Change and Organizational Renewal
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
Why Problem-Solving Skills Are Essential for Leaders in Any Industry

- 17 Jan 2023
Any organization offering a product or service is in the business of solving problems.
Whether providing medical care to address health issues or quick convenience to those hungry for dinner, a business’s purpose is to satisfy customer needs .
In addition to solving customers’ problems, you’ll undoubtedly encounter challenges within your organization as it evolves to meet customer needs. You’re likely to experience growing pains in the form of missed targets, unattained goals, and team disagreements.
Yet, the ubiquity of problems doesn’t have to be discouraging; with the right frameworks and tools, you can build the skills to solve consumers' and your organization’s most challenging issues.
Here’s a primer on problem-solving in business, why it’s important, the skills you need, and how to build them.
Access your free e-book today.
What Is Problem-Solving in Business?
Problem-solving is the process of systematically removing barriers that prevent you or others from reaching goals.
Your business removes obstacles in customers’ lives through its products or services, just as you can remove obstacles that keep your team from achieving business goals.
Design Thinking
Design thinking , as described by Harvard Business School Dean Srikant Datar in the online course Design Thinking and Innovation , is a human-centered , solutions-based approach to problem-solving and innovation. Originally created for product design, design thinking’s use case has evolved . It’s now used to solve internal business problems, too.
The design thinking process has four stages :

- Clarify: Clarify a problem through research and feedback from those impacted.
- Ideate: Armed with new insights, generate as many solutions as possible.
- Develop: Combine and cull your ideas into a short list of viable, feasible, and desirable options before building prototypes (if making physical products) and creating a plan of action (if solving an intangible problem).
- Implement: Execute the strongest idea, ensuring clear communication with all stakeholders about its potential value and deliberate reasoning.
Using this framework, you can generate innovative ideas that wouldn’t have surfaced otherwise.
Creative Problem-Solving
Another, less structured approach to challenges is creative problem-solving , which employs a series of exercises to explore open-ended solutions and develop new perspectives. This is especially useful when a problem’s root cause has yet to be defined.
You can use creative problem-solving tools in design thinking’s “ideate” stage, which include:
- Brainstorming: Instruct everyone to develop as many ideas as possible in an allotted time frame without passing judgment.
- Divergent thinking exercises: Rather than arriving at the same conclusion (convergent thinking), instruct everyone to come up with a unique idea for a given prompt (divergent thinking). This type of exercise helps avoid the tendency to agree with others’ ideas without considering alternatives.
- Alternate worlds: Ask your team to consider how various personas would manage the problem. For instance, how would a pilot approach it? What about a young child? What about a seasoned engineer?
It can be tempting to fall back on how problems have been solved before, especially if they worked well. However, if you’re striving for innovation, relying on existing systems can stunt your company’s growth.
Related: How to Be a More Creative Problem-Solver at Work: 8 Tips
Why Is Problem-Solving Important for Leaders?
While obstacles’ specifics vary between industries, strong problem-solving skills are crucial for leaders in any field.
Whether building a new product or dealing with internal issues, you’re bound to come up against challenges. Having frameworks and tools at your disposal when they arise can turn issues into opportunities.
As a leader, it’s rarely your responsibility to solve a problem single-handedly, so it’s crucial to know how to empower employees to work together to find the best solution.
Your job is to guide them through each step of the framework and set the parameters and prompts within which they can be creative. Then, you can develop a list of ideas together, test the best ones, and implement the chosen solution.
Related: 5 Design Thinking Skills for Business Professionals
4 Problem-Solving Skills All Leaders Need
1. problem framing.
One key skill for any leader is framing problems in a way that makes sense for their organization. Problem framing is defined in Design Thinking and Innovation as determining the scope, context, and perspective of the problem you’re trying to solve.
“Before you begin to generate solutions for your problem, you must always think hard about how you’re going to frame that problem,” Datar says in the course.
For instance, imagine you work for a company that sells children’s sneakers, and sales have plummeted. When framing the problem, consider:
- What is the children’s sneaker market like right now?
- Should we improve the quality of our sneakers?
- Should we assess all children’s footwear?
- Is this a marketing issue for children’s sneakers specifically?
- Is this a bigger issue that impacts how we should market or produce all footwear?
While there’s no one right way to frame a problem, how you do can impact the solutions you generate. It’s imperative to accurately frame problems to align with organizational priorities and ensure your team generates useful ideas for your firm.
To solve a problem, you need to empathize with those impacted by it. Empathy is the ability to understand others’ emotions and experiences. While many believe empathy is a fixed trait, it’s a skill you can strengthen through practice.
When confronted with a problem, consider whom it impacts. Returning to the children’s sneaker example, think of who’s affected:
- Your organization’s employees, because sales are down
- The customers who typically buy your sneakers
- The children who typically wear your sneakers
Empathy is required to get to the problem’s root and consider each group’s perspective. Assuming someone’s perspective often isn’t accurate, so the best way to get that information is by collecting user feedback.
For instance, if you asked customers who typically buy your children’s sneakers why they’ve stopped, they could say, “A new brand of children’s sneakers came onto the market that have soles with more traction. I want my child to be as safe as possible, so I bought those instead.”
When someone shares their feelings and experiences, you have an opportunity to empathize with them. This can yield solutions to their problem that directly address its root and shows you care. In this case, you may design a new line of children’s sneakers with extremely grippy soles for added safety, knowing that’s what your customers care most about.
Related: 3 Effective Methods for Assessing Customer Needs
3. Breaking Cognitive Fixedness
Cognitive fixedness is a state of mind in which you examine situations through the lens of past experiences. This locks you into one mindset rather than allowing you to consider alternative possibilities.
For instance, your cognitive fixedness may make you think rubber is the only material for sneaker treads. What else could you use? Is there a grippier alternative you haven’t considered?
Problem-solving is all about overcoming cognitive fixedness. You not only need to foster this skill in yourself but among your team.
4. Creating a Psychologically Safe Environment
As a leader, it’s your job to create an environment conducive to problem-solving. In a psychologically safe environment, all team members feel comfortable bringing ideas to the table, which are likely influenced by their personal opinions and experiences.
If employees are penalized for “bad” ideas or chastised for questioning long-held procedures and systems, innovation has no place to take root.
By employing the design thinking framework and creative problem-solving exercises, you can foster a setting in which your team feels comfortable sharing ideas and new, innovative solutions can grow.

How to Build Problem-Solving Skills
The most obvious answer to how to build your problem-solving skills is perhaps the most intimidating: You must practice.
Again and again, you’ll encounter challenges, use creative problem-solving tools and design thinking frameworks, and assess results to learn what to do differently next time.
While most of your practice will occur within your organization, you can learn in a lower-stakes setting by taking an online course, such as Design Thinking and Innovation . Datar guides you through each tool and framework, presenting real-world business examples to help you envision how you would approach the same types of problems in your organization.
Are you interested in uncovering innovative solutions for your organization’s business problems? Explore Design Thinking and Innovation —one of our online entrepreneurship and innovation courses —to learn how to leverage proven frameworks and tools to solve challenges. Not sure which course is right for you? Download our free flowchart .

About the Author
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Int J Environ Res Public Health

Communication Skills, Problem-Solving Ability, Understanding of Patients’ Conditions, and Nurse’s Perception of Professionalism among Clinical Nurses: A Structural Equation Model Analysis
This study was intended to confirm the structural relationship between clinical nurse communication skills, problem-solving ability, understanding of patients’ conditions, and nurse’s perception of professionalism. Due to changes in the healthcare environment, it is becoming difficult to meet the needs of patients, and it is becoming very important to improve the ability to perform professional nursing jobs to meet expectations. In this study method, structural model analysis was applied to identify factors influencing the perception of professionalism in nurses. The subjects of this study were 171 nurses working at general hospitals in city of Se, Ga, and Geu. Data analysis included frequency analysis, identification factor analysis, reliability analysis, measurement model analysis, model fit, and intervention effects. In the results of the study, nurse’s perception of professionalism was influenced by factors of communication skills and understanding of the patient’s condition, but not by their ability to solve problems. Understanding of patient’s condition had a mediating effect on communication skills and nursing awareness. Communication skills and understanding of the patient’s condition greatly influenced the nurse’s perception of professionalism. To improve the professionalism of clinical nurses, nursing managers need to emphasize communication skills and understanding of the patient’s condition. The purpose of this study was to provide a rationale for developing a program to improve job skills by strengthening the awareness of professional positions of clinical nurses to develop nursing quality of community.
1. Introduction
Changes in the environment related to climate and pollution are causing health problems and various diseases such as respiratory and circulatory problems, metabolic disorders, and chronic diseases. Moreover, access to modern healthcare facilities has created greater expectations among patients receiving personalized healthcare and high-quality healthcare. As the difficulty of satisfying the demands of patients increases, enhancing nursing capabilities has become increasingly important [ 1 ]. To improve this, hospitals are making efforts to change the internal and external environments so as to increase the number of nurses, reduce the length of hospital stays, and enable efficient nursing practice. Despite these efforts, the workloads of nurses and the demand for clinical nurses are continuously increasing [ 2 , 3 ]. As a result, nurses are developing negative attitudes and prejudices toward patients, as well as negative perceptions of professionalism. To address this, the cultivation and strengthening of nursing professionals’ capabilities is essential.
Nurses’ perception of professionalism is an important element influencing their ability to perform independent nursing, and a good perception of their profession results in a positive approach to solving patients’ problems [ 4 , 5 ]. In addition, the characteristics and abilities of individual nurses can influence the level of care and enable them to understand patients, solve problems, and provide holistic care, which is the ultimate goal of the nursing process [ 6 , 7 ]. Thus, patients expect nurses to not only have medical knowledge of the disease but to also be able to comprehensively assess the patient’s problems and be independent and creative in nursing [ 8 ]. This attitude can have a major impact on the quality of nursing services and can inspire pride in the nursing occupation and professional achievement. These findings can also be used by nurses to prevent burnout and maintain professionalism [ 9 , 10 ].
To respond to the increasing demands for diverse qualitative and quantitative nursing services and to strengthen the capabilities of nursing professionals, efforts have been made to move nursing education toward scientific and creative education. However, in point-of-care environments, not only are nurses prevented from making independent decisions regarding nursing, but also the diverse personal capabilities necessary for such independent behavior are not sufficiently developed [ 11 ]. Therefore, it is important to enhance clinical nurses’ perceptions of the nursing profession; maintain a balance of nursing capabilities; provide novel, high-quality nursing services; and identify assistive nursing education methods and obstructive environmental factors [ 10 ].
Communication skills involve a person’s ability to accurately understand (through both verbal and non-verbal indications) another person, and sufficiently deliver what the person desires [ 12 , 13 ]. Good communication skills are a primary requirement for providing professional nursing services because they enable an in-depth understanding of patients, solving of complicated problems, and reasonable and logical analysis of situations [ 14 , 15 , 16 ]. When effective communication takes place, nurses’ problem-solving abilities and perceived professionalism strengthen [ 17 , 18 ].
According to Park [ 19 ], nurses have difficulties in interpersonal relationships when social tension and interaction skills are low and communication is poor. In addition, these factors are negatively affected not only in the work of the nurse but also in the perception of the profession. Communication skills are associated with both the formation of relationships with patients and the ability to perform holistic nursing [ 20 ]. In order to improve and develop the overall nursing function of a clinical nurse like this, it is important to complement the relevant integrated nursing abilities [ 21 , 22 ].
Previous studies have investigated the importance of communication skills for nurses, and the relationships between nurses’ problem-solving ability and their understanding of the patients’ conditions. Nonetheless, data that can comprehensively explain the structural relationships between these qualities and how they affect the job perception of nurses remains insufficient.
Therefore, the present study aims to identify the structural model for the relationships between nurses’ communication skills, problem-solving ability, understanding of patients’ conditions, and nurse’s perception of professionalism. Additionally, the study provides basic data necessary for developing programs for improving nursing abilities.
The purpose of this study is to construct a theoretical model that explains the structural relationships among nurses’ communication skills, problem-solving ability, understanding of patients’ conditions, and nurse’s perception of professionalism. In addition, the study aimed to verify this model using empirical data.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. study design.
To create and analyze the structural model for clinical nurses’ communication skills, problem-solving ability, understanding of patients’ conditions, and nurse’s perception of professionalism, the theoretical relationships among the variables were developed based on related theories.
In this study, communication skills were set as the exogenous variables, whereas problem-solving ability, understanding of patients’ conditions, and perception of the nursing occupation were set as the endogenous variables. In addition, communication skills were set as the independent variables and nursing job perceptions as the dependent variable. This is because the ability of communication helps to maintain an intimate relationship with the patient and to assess the patient’s condition through each other’s relationship and to solve problems and develop correct understanding. Communication skills, problem-solving ability, and understanding of patients’ conditions were set as the parameters for determining causality. The research model is shown in Figure 1 .

Study model.
2.2. Study Participants
The structural equation model has less than 12 measurement variables. The sample size usually requires 200 to 400 participants [ 23 ]. A total of 250 participants were selected for the study. In line with ethical standards and practices, participants received a full explanation on the purpose of the study. They were briefed that the information collected would be used for research purposes only. Furthermore, they were informed that they could withdraw from the study at any time.
2.3. Data Collection Method
Data collection for this study was performed by two researchers unrelated to the hospital from April 20 to May 1, 2019. A questionnaire was used to collect data from clinical nurses working in five hospitals in Seoul, Gyeonggi, and Gangwon provinces. Of the 250 questionnaires disseminated, we received 225 completed returns. However, 54 were considered inaccurate, inconsistent, or unsatisfactory for coding purposes. Thus, 171 fully completed valid questionnaires comprised the final dataset for analysis.
2.4. Research Instruments
2.4.1. communication skills.
In this study, the communication skill instrument developed by Lee and Jang [ 24 ] was used. Its contents were modified and supplemented to clearly understand the communication skills of nurses. Our questionnaire comprised 20 questions with five questions each concerning “interpretation ability,” “self-reveal,” “leading communication,” and “understanding others’ perspectives.” The answers were rated on a five-point Likert scale ranging from 0 = “strongly disagree” to 4 = “strongly agree.” For this study, the Cronbach’s alpha value was 0.81.
2.4.2. Problem-Solving Ability
The tool developed by Lee [ 25 ] was used to measure the problem-solving ability of clinical nurses. The survey comprised 25 questions, with five questions each concerning “problem recognition,” “information-gathering,” “divergent thinking,” “planning power,” and “evaluation.” Items were scored on a five-point Likert scale ranging from 0 = “strongly disagree” to 4 = “strongly agree.” The internal consistency confidence value Cronbach’s alpha was 0.79.
2.4.3. Understanding Patients’ Condition
To measure nurses’ understanding of patients’ conditions, we developed 10 questions by revising and supplementing items from an existing understanding-measurement tool [ 26 ]. With a total of ten questions, we measured “diagnostic name,” “patient-treatment planning,” and “nursing intervention processes.” Items were scored using a five-point Likert scale ranging from 0 = “strongly disagree” to 4 = “strongly agree.” The internal consistency confidence value Cronbach’s alpha was 0.81.
2.4.4. Nurse’s Perception of Professionalism
Nurse’s perception of professionalism was measured using a tool developed by revising the 25 questions created by Kang et al. [ 1 ]. With a total of ten questions, we measured “vocation” and “autonomy.” Items were scored using a five-point Likert scale. The internal consistency confidence value Cronbach’s alpha was 0.81.
2.5. Data Analysis
To identify the relationships among the set variables, the data were computed statistically using the program included in IBM SPSS 24.0 and AMOS 23.0. (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA). The analysis methods were as follows:
- Frequency analysis was conducted to identify the subjects’ demographic and general characteristics.
- The reliability of the questionnaire was verified using Cronbach’s α coefficients.
- Confirmatory factor analysis (CFA) was performed to verify the convergent validity of the selected measurement tool.
- The normality of the data was determined through analyzing the skewness and kurtosis of the measurement variables.
- The fitness of the model was verified using structural equation modeling (SEM).
- Bootstrapping was utilized to verify the mediating effect in the set study model, as well as the mediating effects of the nurses’ problem-solving ability and understanding of patients’ conditions.
3.1. Demographic Characteristics
The demographic and general characteristics of the study subjects are shown in Table 1 . Overall, 71 respondents were aged 25–29 years (41.5%), representing the most numerous age group. University graduates comprised 113 (66.1%) of the sample, while 50 (29.2%) held graduate degrees, with eight (4.7%) holding master’s degrees. Fifty-three respondents (31.0%) had over seven years of clinical experience, 43 (25.1%) had two to three years of experience, 42 (24.6%) had four to six years of experience, and 33 (19.3%) had less than two years of experience. Additionally, 121 respondents (70.8%) worked at secondary hospitals, while 50 (29.2%) worked at tertiary hospitals; 159 respondents (93.0%) reported that they were general nurses.
Participants’ general characteristics ( N = 171, %).
3.2. Technical Metrics of the Measurement Variables
The multivariate normality of the findings related to the factors of the latent variables was verified through standard deviations, skewness, and kurtosis. The present study meets the criteria for the skewness and kurtosis values mentioned by Hu and Bentler [ 27 ].
All sub-factors of the latent variables secured normality.
In this study, a normal distribution was obtained for each of the four sub-factors of communication skills, five sub-factors of problem-solving ability, three sub-factors for understanding the patient’s condition, and two sub-factors of the nurse’s perception of professionalism as shown in Table 2 .
Technical metrics of the measurement variables ( N = 171).
3.3. Correlations between the Measured Variables
The correlations between the measurement variables were analyzed using Pearson’s product–moment correlation coefficient analysis ( Table 3 ). The correlations among all individual measurement variables were found to show a positive correlation.
Correlations between the observed variables.
3.4. Confirmatory Factor Analysis of the Measurement Model
This study examined how well the measurement variables represented the latent variables in the measurement model. Each set path coefficient was evaluated using non-standardization factors, standardization factors, and standard errors. The path coefficients refer to the factor loadings in CFA. The standardization factors of the individual paths were shown to be at least 0.50 (except for vocation: 0.36), and the critical ratio (CR) was at least 1.96. This indicated that the measurement tool had good convergent validity ( Table 4 ).
Confirmatory factor analysis of the measurement model.
*** p < 0.001; CR: critical ratio.
3.5. Verification of the Structural Model
The structural model for relationships among clinical nurses’ communication skills, problem-solving ability, understanding of patients’ condition, and nurse’s perception of professionalism that would be suitable for predicting the influencing relationships was verified. Since the fitness index of the modified model was shown to be higher than that of the initial model, the final model for this study was set as shown in Figure 2 .

Final model. * χ 2 = 124.074 (df = 61, p <0.001), GFI(Goodness of Fit Index)= 0.90, RMSEA(Root Mean Square Error Approximation)=0.07, NFI(Normed Fit Index)=0.87, IFI(Incremental Fit Index)= 0.93, TLI(Tucker-Lewis Index)= 0.91, CFI(Comparative Fit Index)= 0.92.
3.6. Influencing Relationships between Variables of the Study Model
The standardization factors and CR values of the final model were examined to determine whether there were direct relationships between communication skills, problem-solving ability, understanding of patients’ conditions, and nurse’s perception of professionalism. The results are shown
For the relationship between communication ski in Table 5 .lls and problem-solving ability, the standardization factor was 0.85 and the CR value was 7.37; communication skills showed a statistically significant effect. Consequently. The relationship between communication skills and understanding of patients’ conditions also showed a statistically significant effect. Consequently, Hypothesis 1 was supported.
The relationships between the human effects of the measurement model.
* p < 0.05, *** p < 0.001; CR: critical ratio.
For the relationship between communication skills and nurse’s perception of professionalism, the standardization factor was 0.54, and the CR value was 2.02. Communication skills showed a statistically significant effect. Consequently. For the relationship between problem-solving ability and nurse’s perception of professionalism, the standardization factor was −0.056, and the CR value was −0.39. Problem-solving ability had no statistically significant effect. Consequently.
The relationship between nurses’ understanding of patients’ conditions and nurse’s perception of professionalism had a statistically significant effect. Consequently Figure 2 shows the influencing relationships between the study variables of the final study model, considering non-standardization and standardization factors of the relationships between the study variables.
3.7. Direct and Indirect Effects of the Variables
To grasp the significance of the mediating effect in the final study model, the direct and indirect effects of each variable were examined. To examine the mediating effect of the problem-solving ability and understanding of patients’ conditions variables, the bootstrapping method provided by the AMOS 23.0 program included in IBM was utilized. The results are shown in Table 6 .
Mediating effect analysis.
* p < 0.05, *** p < 0.001
The indirect effect of communication skills on nurse’s perception of professionalism through nurses’ understanding of patients’ conditions was statistically significant. That is, clinical nurses’ communication skills have an indirect positive effect on their nurse’s perception of professionalism, with nurses’ understanding of patients’ conditions acting as a parameter. We also found that the effect of communication skills on nurse’s perception of professionalism was statistically significant. Therefore, communication skills have a partially mediated effect on nurse’s perception of professionalism, with understanding of patients’ conditions acting as a parameter. However, communication skills were found to have no indirect positive effect on nurse’s perception of professionalism when problem-solving ability was set as a parameter.
4. Discussion
In this study, we developed and analyzed a hypothetical model regarding clinical nurses’ communication skills, problem-solving ability, and understanding of patients’ conditions, and how these factors influence their nurse’s perception of professionalism.
4.1. Effect of Communication Skills on Nurses’ Perception of Professionalism
Communication skills were found to have statistically significant effects on their relationship with nurses’ problem-solving ability, understanding of patients’ conditions, and nurse’s perception of professionalism. Nurses’ communication skills not only affected their problem-solving ability but also their understanding of patients’ conditions and nurse’s perception of professionalism. Good communication among nurses can reduce uncomfortable situations and improve interactions with patients, which can consequently enhance problem-solving [ 28 ]. Supporting our findings, Ancel [ 17 ] reported that communication skills afford the maintenance of amicable cooperative relationships with patients across diverse medical classes, thereby enhancing the efficiency of nursing-related problem-solving.
Nurses’ communication is also closely related to their understanding of patients’ conditions, particularly regarding the treatment processes. Nurses frequently experience difficulties as a result of poor communication with not only patients and their family members but also other medical personnel. Further, poor delivery of explanations and questions affects nurses’ understanding of patients’ situations and problems, and patients can also feel concern regarding whether nurses accurately understand their problems [ 29 ]. Nurses frequently experience psychological abuse when communicating with patients and develop stress or discomfort [ 30 ]; this can lead to distrustful relationships with and inhibited understanding of patients [ 31 , 32 ]. Vermeir et al. [ 18 ] reported that scientific approaches are required to understand patients in-depth. To accurately understand both oneself and others, the most important method is successful communication. Such findings support the present study’s indication that nurses’ communication is a basic means of solving nursing problems, with both actions being interrelated.
Our finding that nurses’ communication skills are structurally related to their nurse’s perception of professionalism supports the findings of many previous studies. Regarding nurse’s perception of professionalism, Adams et al. [ 33 ] as well as Lee and Kim [ 34 ] explained that a good perception leads to higher-level capabilities, fostering high-level nursing of patients and the development of autonomous vocation. The above studies reported that, since nurses’ communication skills are related to their nurse’s perception of professionalism, communication skills should be considered a predictor of success. Further, McGlynn et al. [ 35 ] recommended positively reinforcing communication skills to improve nurse’s perception of professionalism. This supports the findings of the present study, indicating that communication and nursing professional perception are interrelated.
Thus, communication skills are important for nursing patients. They enable nurses to accurately understand patients’ problems, serve (by forming patient trust) an important function in the process of administering nursing interventions, and positively affect nurses’ perception of their profession. As such, each concept is important. However, nurses working in the clinic are critically aware of their professionalism. In order to reinforce this, communication skills are required, and the emphasis is placed on strengthening the nurses’ ability to solve problems as well as assess and understand patients. As a result, communication skills play an important role in helping nurses understand patients’ problems accurately, build patient trust in nursing interventions, and create structural relationships that have a positive impact on the perception of nursing occupations. Therefore, efforts to improve nurses’ communication skills not only improve their problem-solving abilities and understanding of patients’ conditions but also improve their nurse’s perception of professionalism. To maintain the professionalism of nurses, “competency development programs” would be helpful, thereby emphasizing the need for their application in nursing colleges and clinical practice.
4.2. Relationship between Nurses’ Problem-Solving Ability and Nurse’s Perception of Professionalism
We found clinical nurses’ problem-solving ability to have no positive effect on their perception of professionalism. This contrasts with previous studies, which reported that problem-solving ability is helpful for such perception of professionalism [ 36 ]. We also found that problem-solving ability does not affect nursing professional perception through a mediating effect.
The present findings indicate that the distinctiveness of the fields of nursing should not be overlooked. In nursing organizations that have a culture of discouraging diversity, when negative results are obtained from attempts to solve nursing problems, confusion regarding the identity of nursing professionals means perception of the profession is not reinforced; in many cases, the opposite perception is formed. Furthermore, for those in lower-level positions, nurse’s perception of professionalism is thought to be low because they cannot voice their opinions and have difficulties such as excessive workloads. Although few previous studies have directly examined this, Vermeir et al. [ 18 ] explained that, as the role expectation for nurses increases, factors for job turnover increase as a result of a sense of confusion regarding the nurses’ role and increases in stress. These findings indicate that factors that degrade nurses’ problem-solving ability induce skepticism regarding nursing and possibly career change, thereby supporting the findings of this study.
However, in the present study, positive results with low levels of relevancy in the structural model but high correlations were found. It is expected that, if nurses’ environmental conditions are improved and their nursing capabilities are developed so that they can solve nursing problems with confidence, their nursing professional perception will improve.
4.3. Relationship between Nurses’ Understanding of Patients’ Conditions and Nurse’s Perception of Professionalism
Our findings indicated that the relationship between nurses’ understanding of patients’ conditions and nurse’s perception of professionalism was statistically significant. This supports Nilsson et al. [ 21 ] and Philip et al. [ 29 ], who reported that, in the fields of nursing, when patients accurately understand nurses’ instructions or explanations and health information, they can participate in, independently adjust, and engage in creative decision-making related to self-nursing.
McGlynn et al. [ 35 ] suggested that understanding patient problems is an important element in resolving negative situations; meanwhile, Heo and Lim [ 37 ] indicated that clinical nurses provide high-quality nursing services and develop self-efficacy when they apply professional knowledge and a desire to understand patients’ problems. These study findings accord with our own findings.
The aforementioned findings suggest that the development and application of programs that can enhance nurses’ understanding of patients’ conditions should be emphasized, and that studies of various patient types, the characteristics of patients by age group and hospital areas, as well as the introduction of simulation education programs to improve nurses’ understanding of patients’ conditions should be continuously implemented.
5. Conclusions
This study aimed to verify the structural relationships between clinical nurses’ communication skills and their problem-solving ability, understanding of patients’ conditions, and nurse’s perception of professionalism. We also aimed to identify, through a structural model, the mediating effects of nurses’ problem-solving ability and understanding of patients’ conditions in the relationship between communication skills and nurse’s perception of professionalism.
The findings of this study are as follows (all significance levels = 0.05). In the relationship between communication skills and problem-solving ability, the value of the standardization factor was 0.85 and the CR value was 7.37, indicating that communication skills had a statistically significant effect. In the relationship between nurses’ communication skills and understanding of patients’ conditions, the value of the standardization factor was 0.61 and the CR value was 6.35, indicating that communication skills had a statistically significant effect. In the relationship between communication skills and nurse’s perception of professionalism, the value of the standardization factor was 0.54 and the CR value was 2.02, indicating that communication skills had a statistically significant effect. However, in the relationship between problem-solving ability and nurse’s perception of professionalism, the value of the standardization factor was −0.05 and the CR value was −0.39, indicating that problem-solving ability has no statistically significant effect. Finally, in the relationship between nurses’ understanding of patients’ conditions and nurse’s perception of professionalism, the value of the standardization factor was 0.56, and the CR value was 2.14, indicating that nurses’ understanding of patients’ conditions has a statistically significant effect.
There are some limitations to this study. First, as we only examined nurses at secondary and tertiary university hospitals, our findings may not be generalizable to all clinical nurses. Replication studies examining a range of levels of medical institutions and associated workers are necessary. Second, the structural relationship between problem-solving ability and the nurse’s perception of professionalism turned out to be insignificant or mediated. Subsequent studies on the various approaches to revisit this structural relationship should be performed. Third, theories should be systematically developed to establish the values of the nursing profession, and additional studies are necessary to explore other variables.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the staff nurses who participated in the survey and took the time to complete the initial assessment.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.Y.K. and I.O.S.; methodology, A.Y.K.; software, I.O.S.; validation, A.Y.K. and I.O.S.; formal analysis, A.Y.K. and I.O.S.; investigation, A.Y.K.; resources, A.Y.K.; data curation, A.Y.K.; writing—original draft preparation, A.Y.K.; writing—review and editing, A.Y.K. and I.O.S.; visualization, A.Y.K. and I.O.S.; supervision, I.O.S.; project administration, I.O.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- My Account Login
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Review Article
- Open access
- Published: 11 January 2023
The effectiveness of collaborative problem solving in promoting students’ critical thinking: A meta-analysis based on empirical literature
- Enwei Xu ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-6424-8169 1 ,
- Wei Wang 1 &
- Qingxia Wang 1
Humanities and Social Sciences Communications volume 10 , Article number: 16 ( 2023 ) Cite this article
16k Accesses
16 Citations
3 Altmetric
Metrics details
- Science, technology and society
Collaborative problem-solving has been widely embraced in the classroom instruction of critical thinking, which is regarded as the core of curriculum reform based on key competencies in the field of education as well as a key competence for learners in the 21st century. However, the effectiveness of collaborative problem-solving in promoting students’ critical thinking remains uncertain. This current research presents the major findings of a meta-analysis of 36 pieces of the literature revealed in worldwide educational periodicals during the 21st century to identify the effectiveness of collaborative problem-solving in promoting students’ critical thinking and to determine, based on evidence, whether and to what extent collaborative problem solving can result in a rise or decrease in critical thinking. The findings show that (1) collaborative problem solving is an effective teaching approach to foster students’ critical thinking, with a significant overall effect size (ES = 0.82, z = 12.78, P < 0.01, 95% CI [0.69, 0.95]); (2) in respect to the dimensions of critical thinking, collaborative problem solving can significantly and successfully enhance students’ attitudinal tendencies (ES = 1.17, z = 7.62, P < 0.01, 95% CI[0.87, 1.47]); nevertheless, it falls short in terms of improving students’ cognitive skills, having only an upper-middle impact (ES = 0.70, z = 11.55, P < 0.01, 95% CI[0.58, 0.82]); and (3) the teaching type (chi 2 = 7.20, P < 0.05), intervention duration (chi 2 = 12.18, P < 0.01), subject area (chi 2 = 13.36, P < 0.05), group size (chi 2 = 8.77, P < 0.05), and learning scaffold (chi 2 = 9.03, P < 0.01) all have an impact on critical thinking, and they can be viewed as important moderating factors that affect how critical thinking develops. On the basis of these results, recommendations are made for further study and instruction to better support students’ critical thinking in the context of collaborative problem-solving.
Similar content being viewed by others
Fostering twenty-first century skills among primary school students through math project-based learning
A meta-analysis to gauge the impact of pedagogies employed in mixed-ability high school biology classrooms

A guide to critical thinking: implications for dental education
Introduction.
Although critical thinking has a long history in research, the concept of critical thinking, which is regarded as an essential competence for learners in the 21st century, has recently attracted more attention from researchers and teaching practitioners (National Research Council, 2012 ). Critical thinking should be the core of curriculum reform based on key competencies in the field of education (Peng and Deng, 2017 ) because students with critical thinking can not only understand the meaning of knowledge but also effectively solve practical problems in real life even after knowledge is forgotten (Kek and Huijser, 2011 ). The definition of critical thinking is not universal (Ennis, 1989 ; Castle, 2009 ; Niu et al., 2013 ). In general, the definition of critical thinking is a self-aware and self-regulated thought process (Facione, 1990 ; Niu et al., 2013 ). It refers to the cognitive skills needed to interpret, analyze, synthesize, reason, and evaluate information as well as the attitudinal tendency to apply these abilities (Halpern, 2001 ). The view that critical thinking can be taught and learned through curriculum teaching has been widely supported by many researchers (e.g., Kuncel, 2011 ; Leng and Lu, 2020 ), leading to educators’ efforts to foster it among students. In the field of teaching practice, there are three types of courses for teaching critical thinking (Ennis, 1989 ). The first is an independent curriculum in which critical thinking is taught and cultivated without involving the knowledge of specific disciplines; the second is an integrated curriculum in which critical thinking is integrated into the teaching of other disciplines as a clear teaching goal; and the third is a mixed curriculum in which critical thinking is taught in parallel to the teaching of other disciplines for mixed teaching training. Furthermore, numerous measuring tools have been developed by researchers and educators to measure critical thinking in the context of teaching practice. These include standardized measurement tools, such as WGCTA, CCTST, CCTT, and CCTDI, which have been verified by repeated experiments and are considered effective and reliable by international scholars (Facione and Facione, 1992 ). In short, descriptions of critical thinking, including its two dimensions of attitudinal tendency and cognitive skills, different types of teaching courses, and standardized measurement tools provide a complex normative framework for understanding, teaching, and evaluating critical thinking.
Cultivating critical thinking in curriculum teaching can start with a problem, and one of the most popular critical thinking instructional approaches is problem-based learning (Liu et al., 2020 ). Duch et al. ( 2001 ) noted that problem-based learning in group collaboration is progressive active learning, which can improve students’ critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Collaborative problem-solving is the organic integration of collaborative learning and problem-based learning, which takes learners as the center of the learning process and uses problems with poor structure in real-world situations as the starting point for the learning process (Liang et al., 2017 ). Students learn the knowledge needed to solve problems in a collaborative group, reach a consensus on problems in the field, and form solutions through social cooperation methods, such as dialogue, interpretation, questioning, debate, negotiation, and reflection, thus promoting the development of learners’ domain knowledge and critical thinking (Cindy, 2004 ; Liang et al., 2017 ).
Collaborative problem-solving has been widely used in the teaching practice of critical thinking, and several studies have attempted to conduct a systematic review and meta-analysis of the empirical literature on critical thinking from various perspectives. However, little attention has been paid to the impact of collaborative problem-solving on critical thinking. Therefore, the best approach for developing and enhancing critical thinking throughout collaborative problem-solving is to examine how to implement critical thinking instruction; however, this issue is still unexplored, which means that many teachers are incapable of better instructing critical thinking (Leng and Lu, 2020 ; Niu et al., 2013 ). For example, Huber ( 2016 ) provided the meta-analysis findings of 71 publications on gaining critical thinking over various time frames in college with the aim of determining whether critical thinking was truly teachable. These authors found that learners significantly improve their critical thinking while in college and that critical thinking differs with factors such as teaching strategies, intervention duration, subject area, and teaching type. The usefulness of collaborative problem-solving in fostering students’ critical thinking, however, was not determined by this study, nor did it reveal whether there existed significant variations among the different elements. A meta-analysis of 31 pieces of educational literature was conducted by Liu et al. ( 2020 ) to assess the impact of problem-solving on college students’ critical thinking. These authors found that problem-solving could promote the development of critical thinking among college students and proposed establishing a reasonable group structure for problem-solving in a follow-up study to improve students’ critical thinking. Additionally, previous empirical studies have reached inconclusive and even contradictory conclusions about whether and to what extent collaborative problem-solving increases or decreases critical thinking levels. As an illustration, Yang et al. ( 2008 ) carried out an experiment on the integrated curriculum teaching of college students based on a web bulletin board with the goal of fostering participants’ critical thinking in the context of collaborative problem-solving. These authors’ research revealed that through sharing, debating, examining, and reflecting on various experiences and ideas, collaborative problem-solving can considerably enhance students’ critical thinking in real-life problem situations. In contrast, collaborative problem-solving had a positive impact on learners’ interaction and could improve learning interest and motivation but could not significantly improve students’ critical thinking when compared to traditional classroom teaching, according to research by Naber and Wyatt ( 2014 ) and Sendag and Odabasi ( 2009 ) on undergraduate and high school students, respectively.
The above studies show that there is inconsistency regarding the effectiveness of collaborative problem-solving in promoting students’ critical thinking. Therefore, it is essential to conduct a thorough and trustworthy review to detect and decide whether and to what degree collaborative problem-solving can result in a rise or decrease in critical thinking. Meta-analysis is a quantitative analysis approach that is utilized to examine quantitative data from various separate studies that are all focused on the same research topic. This approach characterizes the effectiveness of its impact by averaging the effect sizes of numerous qualitative studies in an effort to reduce the uncertainty brought on by independent research and produce more conclusive findings (Lipsey and Wilson, 2001 ).
This paper used a meta-analytic approach and carried out a meta-analysis to examine the effectiveness of collaborative problem-solving in promoting students’ critical thinking in order to make a contribution to both research and practice. The following research questions were addressed by this meta-analysis:
What is the overall effect size of collaborative problem-solving in promoting students’ critical thinking and its impact on the two dimensions of critical thinking (i.e., attitudinal tendency and cognitive skills)?
How are the disparities between the study conclusions impacted by various moderating variables if the impacts of various experimental designs in the included studies are heterogeneous?
This research followed the strict procedures (e.g., database searching, identification, screening, eligibility, merging, duplicate removal, and analysis of included studies) of Cooper’s ( 2010 ) proposed meta-analysis approach for examining quantitative data from various separate studies that are all focused on the same research topic. The relevant empirical research that appeared in worldwide educational periodicals within the 21st century was subjected to this meta-analysis using Rev-Man 5.4. The consistency of the data extracted separately by two researchers was tested using Cohen’s kappa coefficient, and a publication bias test and a heterogeneity test were run on the sample data to ascertain the quality of this meta-analysis.
Data sources and search strategies
There were three stages to the data collection process for this meta-analysis, as shown in Fig. 1 , which shows the number of articles included and eliminated during the selection process based on the statement and study eligibility criteria.
This flowchart shows the number of records identified, included and excluded in the article.
First, the databases used to systematically search for relevant articles were the journal papers of the Web of Science Core Collection and the Chinese Core source journal, as well as the Chinese Social Science Citation Index (CSSCI) source journal papers included in CNKI. These databases were selected because they are credible platforms that are sources of scholarly and peer-reviewed information with advanced search tools and contain literature relevant to the subject of our topic from reliable researchers and experts. The search string with the Boolean operator used in the Web of Science was “TS = (((“critical thinking” or “ct” and “pretest” or “posttest”) or (“critical thinking” or “ct” and “control group” or “quasi experiment” or “experiment”)) and (“collaboration” or “collaborative learning” or “CSCL”) and (“problem solving” or “problem-based learning” or “PBL”))”. The research area was “Education Educational Research”, and the search period was “January 1, 2000, to December 30, 2021”. A total of 412 papers were obtained. The search string with the Boolean operator used in the CNKI was “SU = (‘critical thinking’*‘collaboration’ + ‘critical thinking’*‘collaborative learning’ + ‘critical thinking’*‘CSCL’ + ‘critical thinking’*‘problem solving’ + ‘critical thinking’*‘problem-based learning’ + ‘critical thinking’*‘PBL’ + ‘critical thinking’*‘problem oriented’) AND FT = (‘experiment’ + ‘quasi experiment’ + ‘pretest’ + ‘posttest’ + ‘empirical study’)” (translated into Chinese when searching). A total of 56 studies were found throughout the search period of “January 2000 to December 2021”. From the databases, all duplicates and retractions were eliminated before exporting the references into Endnote, a program for managing bibliographic references. In all, 466 studies were found.
Second, the studies that matched the inclusion and exclusion criteria for the meta-analysis were chosen by two researchers after they had reviewed the abstracts and titles of the gathered articles, yielding a total of 126 studies.
Third, two researchers thoroughly reviewed each included article’s whole text in accordance with the inclusion and exclusion criteria. Meanwhile, a snowball search was performed using the references and citations of the included articles to ensure complete coverage of the articles. Ultimately, 36 articles were kept.
Two researchers worked together to carry out this entire process, and a consensus rate of almost 94.7% was reached after discussion and negotiation to clarify any emerging differences.
Eligibility criteria
Since not all the retrieved studies matched the criteria for this meta-analysis, eligibility criteria for both inclusion and exclusion were developed as follows:
The publication language of the included studies was limited to English and Chinese, and the full text could be obtained. Articles that did not meet the publication language and articles not published between 2000 and 2021 were excluded.
The research design of the included studies must be empirical and quantitative studies that can assess the effect of collaborative problem-solving on the development of critical thinking. Articles that could not identify the causal mechanisms by which collaborative problem-solving affects critical thinking, such as review articles and theoretical articles, were excluded.
The research method of the included studies must feature a randomized control experiment or a quasi-experiment, or a natural experiment, which have a higher degree of internal validity with strong experimental designs and can all plausibly provide evidence that critical thinking and collaborative problem-solving are causally related. Articles with non-experimental research methods, such as purely correlational or observational studies, were excluded.
The participants of the included studies were only students in school, including K-12 students and college students. Articles in which the participants were non-school students, such as social workers or adult learners, were excluded.
The research results of the included studies must mention definite signs that may be utilized to gauge critical thinking’s impact (e.g., sample size, mean value, or standard deviation). Articles that lacked specific measurement indicators for critical thinking and could not calculate the effect size were excluded.
Data coding design
In order to perform a meta-analysis, it is necessary to collect the most important information from the articles, codify that information’s properties, and convert descriptive data into quantitative data. Therefore, this study designed a data coding template (see Table 1 ). Ultimately, 16 coding fields were retained.
The designed data-coding template consisted of three pieces of information. Basic information about the papers was included in the descriptive information: the publishing year, author, serial number, and title of the paper.
The variable information for the experimental design had three variables: the independent variable (instruction method), the dependent variable (critical thinking), and the moderating variable (learning stage, teaching type, intervention duration, learning scaffold, group size, measuring tool, and subject area). Depending on the topic of this study, the intervention strategy, as the independent variable, was coded into collaborative and non-collaborative problem-solving. The dependent variable, critical thinking, was coded as a cognitive skill and an attitudinal tendency. And seven moderating variables were created by grouping and combining the experimental design variables discovered within the 36 studies (see Table 1 ), where learning stages were encoded as higher education, high school, middle school, and primary school or lower; teaching types were encoded as mixed courses, integrated courses, and independent courses; intervention durations were encoded as 0–1 weeks, 1–4 weeks, 4–12 weeks, and more than 12 weeks; group sizes were encoded as 2–3 persons, 4–6 persons, 7–10 persons, and more than 10 persons; learning scaffolds were encoded as teacher-supported learning scaffold, technique-supported learning scaffold, and resource-supported learning scaffold; measuring tools were encoded as standardized measurement tools (e.g., WGCTA, CCTT, CCTST, and CCTDI) and self-adapting measurement tools (e.g., modified or made by researchers); and subject areas were encoded according to the specific subjects used in the 36 included studies.
The data information contained three metrics for measuring critical thinking: sample size, average value, and standard deviation. It is vital to remember that studies with various experimental designs frequently adopt various formulas to determine the effect size. And this paper used Morris’ proposed standardized mean difference (SMD) calculation formula ( 2008 , p. 369; see Supplementary Table S3 ).
Procedure for extracting and coding data
According to the data coding template (see Table 1 ), the 36 papers’ information was retrieved by two researchers, who then entered them into Excel (see Supplementary Table S1 ). The results of each study were extracted separately in the data extraction procedure if an article contained numerous studies on critical thinking, or if a study assessed different critical thinking dimensions. For instance, Tiwari et al. ( 2010 ) used four time points, which were viewed as numerous different studies, to examine the outcomes of critical thinking, and Chen ( 2013 ) included the two outcome variables of attitudinal tendency and cognitive skills, which were regarded as two studies. After discussion and negotiation during data extraction, the two researchers’ consistency test coefficients were roughly 93.27%. Supplementary Table S2 details the key characteristics of the 36 included articles with 79 effect quantities, including descriptive information (e.g., the publishing year, author, serial number, and title of the paper), variable information (e.g., independent variables, dependent variables, and moderating variables), and data information (e.g., mean values, standard deviations, and sample size). Following that, testing for publication bias and heterogeneity was done on the sample data using the Rev-Man 5.4 software, and then the test results were used to conduct a meta-analysis.
Publication bias test
When the sample of studies included in a meta-analysis does not accurately reflect the general status of research on the relevant subject, publication bias is said to be exhibited in this research. The reliability and accuracy of the meta-analysis may be impacted by publication bias. Due to this, the meta-analysis needs to check the sample data for publication bias (Stewart et al., 2006 ). A popular method to check for publication bias is the funnel plot; and it is unlikely that there will be publishing bias when the data are equally dispersed on either side of the average effect size and targeted within the higher region. The data are equally dispersed within the higher portion of the efficient zone, consistent with the funnel plot connected with this analysis (see Fig. 2 ), indicating that publication bias is unlikely in this situation.
This funnel plot shows the result of publication bias of 79 effect quantities across 36 studies.
Heterogeneity test
To select the appropriate effect models for the meta-analysis, one might use the results of a heterogeneity test on the data effect sizes. In a meta-analysis, it is common practice to gauge the degree of data heterogeneity using the I 2 value, and I 2 ≥ 50% is typically understood to denote medium-high heterogeneity, which calls for the adoption of a random effect model; if not, a fixed effect model ought to be applied (Lipsey and Wilson, 2001 ). The findings of the heterogeneity test in this paper (see Table 2 ) revealed that I 2 was 86% and displayed significant heterogeneity ( P < 0.01). To ensure accuracy and reliability, the overall effect size ought to be calculated utilizing the random effect model.
The analysis of the overall effect size
This meta-analysis utilized a random effect model to examine 79 effect quantities from 36 studies after eliminating heterogeneity. In accordance with Cohen’s criterion (Cohen, 1992 ), it is abundantly clear from the analysis results, which are shown in the forest plot of the overall effect (see Fig. 3 ), that the cumulative impact size of cooperative problem-solving is 0.82, which is statistically significant ( z = 12.78, P < 0.01, 95% CI [0.69, 0.95]), and can encourage learners to practice critical thinking.
This forest plot shows the analysis result of the overall effect size across 36 studies.
In addition, this study examined two distinct dimensions of critical thinking to better understand the precise contributions that collaborative problem-solving makes to the growth of critical thinking. The findings (see Table 3 ) indicate that collaborative problem-solving improves cognitive skills (ES = 0.70) and attitudinal tendency (ES = 1.17), with significant intergroup differences (chi 2 = 7.95, P < 0.01). Although collaborative problem-solving improves both dimensions of critical thinking, it is essential to point out that the improvements in students’ attitudinal tendency are much more pronounced and have a significant comprehensive effect (ES = 1.17, z = 7.62, P < 0.01, 95% CI [0.87, 1.47]), whereas gains in learners’ cognitive skill are slightly improved and are just above average. (ES = 0.70, z = 11.55, P < 0.01, 95% CI [0.58, 0.82]).
The analysis of moderator effect size
The whole forest plot’s 79 effect quantities underwent a two-tailed test, which revealed significant heterogeneity ( I 2 = 86%, z = 12.78, P < 0.01), indicating differences between various effect sizes that may have been influenced by moderating factors other than sampling error. Therefore, exploring possible moderating factors that might produce considerable heterogeneity was done using subgroup analysis, such as the learning stage, learning scaffold, teaching type, group size, duration of the intervention, measuring tool, and the subject area included in the 36 experimental designs, in order to further explore the key factors that influence critical thinking. The findings (see Table 4 ) indicate that various moderating factors have advantageous effects on critical thinking. In this situation, the subject area (chi 2 = 13.36, P < 0.05), group size (chi 2 = 8.77, P < 0.05), intervention duration (chi 2 = 12.18, P < 0.01), learning scaffold (chi 2 = 9.03, P < 0.01), and teaching type (chi 2 = 7.20, P < 0.05) are all significant moderators that can be applied to support the cultivation of critical thinking. However, since the learning stage and the measuring tools did not significantly differ among intergroup (chi 2 = 3.15, P = 0.21 > 0.05, and chi 2 = 0.08, P = 0.78 > 0.05), we are unable to explain why these two factors are crucial in supporting the cultivation of critical thinking in the context of collaborative problem-solving. These are the precise outcomes, as follows:
Various learning stages influenced critical thinking positively, without significant intergroup differences (chi 2 = 3.15, P = 0.21 > 0.05). High school was first on the list of effect sizes (ES = 1.36, P < 0.01), then higher education (ES = 0.78, P < 0.01), and middle school (ES = 0.73, P < 0.01). These results show that, despite the learning stage’s beneficial influence on cultivating learners’ critical thinking, we are unable to explain why it is essential for cultivating critical thinking in the context of collaborative problem-solving.
Different teaching types had varying degrees of positive impact on critical thinking, with significant intergroup differences (chi 2 = 7.20, P < 0.05). The effect size was ranked as follows: mixed courses (ES = 1.34, P < 0.01), integrated courses (ES = 0.81, P < 0.01), and independent courses (ES = 0.27, P < 0.01). These results indicate that the most effective approach to cultivate critical thinking utilizing collaborative problem solving is through the teaching type of mixed courses.
Various intervention durations significantly improved critical thinking, and there were significant intergroup differences (chi 2 = 12.18, P < 0.01). The effect sizes related to this variable showed a tendency to increase with longer intervention durations. The improvement in critical thinking reached a significant level (ES = 0.85, P < 0.01) after more than 12 weeks of training. These findings indicate that the intervention duration and critical thinking’s impact are positively correlated, with a longer intervention duration having a greater effect.
Different learning scaffolds influenced critical thinking positively, with significant intergroup differences (chi 2 = 9.03, P < 0.01). The resource-supported learning scaffold (ES = 0.69, P < 0.01) acquired a medium-to-higher level of impact, the technique-supported learning scaffold (ES = 0.63, P < 0.01) also attained a medium-to-higher level of impact, and the teacher-supported learning scaffold (ES = 0.92, P < 0.01) displayed a high level of significant impact. These results show that the learning scaffold with teacher support has the greatest impact on cultivating critical thinking.
Various group sizes influenced critical thinking positively, and the intergroup differences were statistically significant (chi 2 = 8.77, P < 0.05). Critical thinking showed a general declining trend with increasing group size. The overall effect size of 2–3 people in this situation was the biggest (ES = 0.99, P < 0.01), and when the group size was greater than 7 people, the improvement in critical thinking was at the lower-middle level (ES < 0.5, P < 0.01). These results show that the impact on critical thinking is positively connected with group size, and as group size grows, so does the overall impact.
Various measuring tools influenced critical thinking positively, with significant intergroup differences (chi 2 = 0.08, P = 0.78 > 0.05). In this situation, the self-adapting measurement tools obtained an upper-medium level of effect (ES = 0.78), whereas the complete effect size of the standardized measurement tools was the largest, achieving a significant level of effect (ES = 0.84, P < 0.01). These results show that, despite the beneficial influence of the measuring tool on cultivating critical thinking, we are unable to explain why it is crucial in fostering the growth of critical thinking by utilizing the approach of collaborative problem-solving.
Different subject areas had a greater impact on critical thinking, and the intergroup differences were statistically significant (chi 2 = 13.36, P < 0.05). Mathematics had the greatest overall impact, achieving a significant level of effect (ES = 1.68, P < 0.01), followed by science (ES = 1.25, P < 0.01) and medical science (ES = 0.87, P < 0.01), both of which also achieved a significant level of effect. Programming technology was the least effective (ES = 0.39, P < 0.01), only having a medium-low degree of effect compared to education (ES = 0.72, P < 0.01) and other fields (such as language, art, and social sciences) (ES = 0.58, P < 0.01). These results suggest that scientific fields (e.g., mathematics, science) may be the most effective subject areas for cultivating critical thinking utilizing the approach of collaborative problem-solving.
The effectiveness of collaborative problem solving with regard to teaching critical thinking
According to this meta-analysis, using collaborative problem-solving as an intervention strategy in critical thinking teaching has a considerable amount of impact on cultivating learners’ critical thinking as a whole and has a favorable promotional effect on the two dimensions of critical thinking. According to certain studies, collaborative problem solving, the most frequently used critical thinking teaching strategy in curriculum instruction can considerably enhance students’ critical thinking (e.g., Liang et al., 2017 ; Liu et al., 2020 ; Cindy, 2004 ). This meta-analysis provides convergent data support for the above research views. Thus, the findings of this meta-analysis not only effectively address the first research query regarding the overall effect of cultivating critical thinking and its impact on the two dimensions of critical thinking (i.e., attitudinal tendency and cognitive skills) utilizing the approach of collaborative problem-solving, but also enhance our confidence in cultivating critical thinking by using collaborative problem-solving intervention approach in the context of classroom teaching.
Furthermore, the associated improvements in attitudinal tendency are much stronger, but the corresponding improvements in cognitive skill are only marginally better. According to certain studies, cognitive skill differs from the attitudinal tendency in classroom instruction; the cultivation and development of the former as a key ability is a process of gradual accumulation, while the latter as an attitude is affected by the context of the teaching situation (e.g., a novel and exciting teaching approach, challenging and rewarding tasks) (Halpern, 2001 ; Wei and Hong, 2022 ). Collaborative problem-solving as a teaching approach is exciting and interesting, as well as rewarding and challenging; because it takes the learners as the focus and examines problems with poor structure in real situations, and it can inspire students to fully realize their potential for problem-solving, which will significantly improve their attitudinal tendency toward solving problems (Liu et al., 2020 ). Similar to how collaborative problem-solving influences attitudinal tendency, attitudinal tendency impacts cognitive skill when attempting to solve a problem (Liu et al., 2020 ; Zhang et al., 2022 ), and stronger attitudinal tendencies are associated with improved learning achievement and cognitive ability in students (Sison, 2008 ; Zhang et al., 2022 ). It can be seen that the two specific dimensions of critical thinking as well as critical thinking as a whole are affected by collaborative problem-solving, and this study illuminates the nuanced links between cognitive skills and attitudinal tendencies with regard to these two dimensions of critical thinking. To fully develop students’ capacity for critical thinking, future empirical research should pay closer attention to cognitive skills.
The moderating effects of collaborative problem solving with regard to teaching critical thinking
In order to further explore the key factors that influence critical thinking, exploring possible moderating effects that might produce considerable heterogeneity was done using subgroup analysis. The findings show that the moderating factors, such as the teaching type, learning stage, group size, learning scaffold, duration of the intervention, measuring tool, and the subject area included in the 36 experimental designs, could all support the cultivation of collaborative problem-solving in critical thinking. Among them, the effect size differences between the learning stage and measuring tool are not significant, which does not explain why these two factors are crucial in supporting the cultivation of critical thinking utilizing the approach of collaborative problem-solving.
In terms of the learning stage, various learning stages influenced critical thinking positively without significant intergroup differences, indicating that we are unable to explain why it is crucial in fostering the growth of critical thinking.
Although high education accounts for 70.89% of all empirical studies performed by researchers, high school may be the appropriate learning stage to foster students’ critical thinking by utilizing the approach of collaborative problem-solving since it has the largest overall effect size. This phenomenon may be related to student’s cognitive development, which needs to be further studied in follow-up research.
With regard to teaching type, mixed course teaching may be the best teaching method to cultivate students’ critical thinking. Relevant studies have shown that in the actual teaching process if students are trained in thinking methods alone, the methods they learn are isolated and divorced from subject knowledge, which is not conducive to their transfer of thinking methods; therefore, if students’ thinking is trained only in subject teaching without systematic method training, it is challenging to apply to real-world circumstances (Ruggiero, 2012 ; Hu and Liu, 2015 ). Teaching critical thinking as mixed course teaching in parallel to other subject teachings can achieve the best effect on learners’ critical thinking, and explicit critical thinking instruction is more effective than less explicit critical thinking instruction (Bensley and Spero, 2014 ).
In terms of the intervention duration, with longer intervention times, the overall effect size shows an upward tendency. Thus, the intervention duration and critical thinking’s impact are positively correlated. Critical thinking, as a key competency for students in the 21st century, is difficult to get a meaningful improvement in a brief intervention duration. Instead, it could be developed over a lengthy period of time through consistent teaching and the progressive accumulation of knowledge (Halpern, 2001 ; Hu and Liu, 2015 ). Therefore, future empirical studies ought to take these restrictions into account throughout a longer period of critical thinking instruction.
With regard to group size, a group size of 2–3 persons has the highest effect size, and the comprehensive effect size decreases with increasing group size in general. This outcome is in line with some research findings; as an example, a group composed of two to four members is most appropriate for collaborative learning (Schellens and Valcke, 2006 ). However, the meta-analysis results also indicate that once the group size exceeds 7 people, small groups cannot produce better interaction and performance than large groups. This may be because the learning scaffolds of technique support, resource support, and teacher support improve the frequency and effectiveness of interaction among group members, and a collaborative group with more members may increase the diversity of views, which is helpful to cultivate critical thinking utilizing the approach of collaborative problem-solving.
With regard to the learning scaffold, the three different kinds of learning scaffolds can all enhance critical thinking. Among them, the teacher-supported learning scaffold has the largest overall effect size, demonstrating the interdependence of effective learning scaffolds and collaborative problem-solving. This outcome is in line with some research findings; as an example, a successful strategy is to encourage learners to collaborate, come up with solutions, and develop critical thinking skills by using learning scaffolds (Reiser, 2004 ; Xu et al., 2022 ); learning scaffolds can lower task complexity and unpleasant feelings while also enticing students to engage in learning activities (Wood et al., 2006 ); learning scaffolds are designed to assist students in using learning approaches more successfully to adapt the collaborative problem-solving process, and the teacher-supported learning scaffolds have the greatest influence on critical thinking in this process because they are more targeted, informative, and timely (Xu et al., 2022 ).
With respect to the measuring tool, despite the fact that standardized measurement tools (such as the WGCTA, CCTT, and CCTST) have been acknowledged as trustworthy and effective by worldwide experts, only 54.43% of the research included in this meta-analysis adopted them for assessment, and the results indicated no intergroup differences. These results suggest that not all teaching circumstances are appropriate for measuring critical thinking using standardized measurement tools. “The measuring tools for measuring thinking ability have limits in assessing learners in educational situations and should be adapted appropriately to accurately assess the changes in learners’ critical thinking.”, according to Simpson and Courtney ( 2002 , p. 91). As a result, in order to more fully and precisely gauge how learners’ critical thinking has evolved, we must properly modify standardized measuring tools based on collaborative problem-solving learning contexts.
With regard to the subject area, the comprehensive effect size of science departments (e.g., mathematics, science, medical science) is larger than that of language arts and social sciences. Some recent international education reforms have noted that critical thinking is a basic part of scientific literacy. Students with scientific literacy can prove the rationality of their judgment according to accurate evidence and reasonable standards when they face challenges or poorly structured problems (Kyndt et al., 2013 ), which makes critical thinking crucial for developing scientific understanding and applying this understanding to practical problem solving for problems related to science, technology, and society (Yore et al., 2007 ).
Suggestions for critical thinking teaching
Other than those stated in the discussion above, the following suggestions are offered for critical thinking instruction utilizing the approach of collaborative problem-solving.
First, teachers should put a special emphasis on the two core elements, which are collaboration and problem-solving, to design real problems based on collaborative situations. This meta-analysis provides evidence to support the view that collaborative problem-solving has a strong synergistic effect on promoting students’ critical thinking. Asking questions about real situations and allowing learners to take part in critical discussions on real problems during class instruction are key ways to teach critical thinking rather than simply reading speculative articles without practice (Mulnix, 2012 ). Furthermore, the improvement of students’ critical thinking is realized through cognitive conflict with other learners in the problem situation (Yang et al., 2008 ). Consequently, it is essential for teachers to put a special emphasis on the two core elements, which are collaboration and problem-solving, and design real problems and encourage students to discuss, negotiate, and argue based on collaborative problem-solving situations.
Second, teachers should design and implement mixed courses to cultivate learners’ critical thinking, utilizing the approach of collaborative problem-solving. Critical thinking can be taught through curriculum instruction (Kuncel, 2011 ; Leng and Lu, 2020 ), with the goal of cultivating learners’ critical thinking for flexible transfer and application in real problem-solving situations. This meta-analysis shows that mixed course teaching has a highly substantial impact on the cultivation and promotion of learners’ critical thinking. Therefore, teachers should design and implement mixed course teaching with real collaborative problem-solving situations in combination with the knowledge content of specific disciplines in conventional teaching, teach methods and strategies of critical thinking based on poorly structured problems to help students master critical thinking, and provide practical activities in which students can interact with each other to develop knowledge construction and critical thinking utilizing the approach of collaborative problem-solving.
Third, teachers should be more trained in critical thinking, particularly preservice teachers, and they also should be conscious of the ways in which teachers’ support for learning scaffolds can promote critical thinking. The learning scaffold supported by teachers had the greatest impact on learners’ critical thinking, in addition to being more directive, targeted, and timely (Wood et al., 2006 ). Critical thinking can only be effectively taught when teachers recognize the significance of critical thinking for students’ growth and use the proper approaches while designing instructional activities (Forawi, 2016 ). Therefore, with the intention of enabling teachers to create learning scaffolds to cultivate learners’ critical thinking utilizing the approach of collaborative problem solving, it is essential to concentrate on the teacher-supported learning scaffolds and enhance the instruction for teaching critical thinking to teachers, especially preservice teachers.
Implications and limitations
There are certain limitations in this meta-analysis, but future research can correct them. First, the search languages were restricted to English and Chinese, so it is possible that pertinent studies that were written in other languages were overlooked, resulting in an inadequate number of articles for review. Second, these data provided by the included studies are partially missing, such as whether teachers were trained in the theory and practice of critical thinking, the average age and gender of learners, and the differences in critical thinking among learners of various ages and genders. Third, as is typical for review articles, more studies were released while this meta-analysis was being done; therefore, it had a time limit. With the development of relevant research, future studies focusing on these issues are highly relevant and needed.
Conclusions
The subject of the magnitude of collaborative problem-solving’s impact on fostering students’ critical thinking, which received scant attention from other studies, was successfully addressed by this study. The question of the effectiveness of collaborative problem-solving in promoting students’ critical thinking was addressed in this study, which addressed a topic that had gotten little attention in earlier research. The following conclusions can be made:
Regarding the results obtained, collaborative problem solving is an effective teaching approach to foster learners’ critical thinking, with a significant overall effect size (ES = 0.82, z = 12.78, P < 0.01, 95% CI [0.69, 0.95]). With respect to the dimensions of critical thinking, collaborative problem-solving can significantly and effectively improve students’ attitudinal tendency, and the comprehensive effect is significant (ES = 1.17, z = 7.62, P < 0.01, 95% CI [0.87, 1.47]); nevertheless, it falls short in terms of improving students’ cognitive skills, having only an upper-middle impact (ES = 0.70, z = 11.55, P < 0.01, 95% CI [0.58, 0.82]).
As demonstrated by both the results and the discussion, there are varying degrees of beneficial effects on students’ critical thinking from all seven moderating factors, which were found across 36 studies. In this context, the teaching type (chi 2 = 7.20, P < 0.05), intervention duration (chi 2 = 12.18, P < 0.01), subject area (chi 2 = 13.36, P < 0.05), group size (chi 2 = 8.77, P < 0.05), and learning scaffold (chi 2 = 9.03, P < 0.01) all have a positive impact on critical thinking, and they can be viewed as important moderating factors that affect how critical thinking develops. Since the learning stage (chi 2 = 3.15, P = 0.21 > 0.05) and measuring tools (chi 2 = 0.08, P = 0.78 > 0.05) did not demonstrate any significant intergroup differences, we are unable to explain why these two factors are crucial in supporting the cultivation of critical thinking in the context of collaborative problem-solving.
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included within the article and its supplementary information files, and the supplementary information files are available in the Dataverse repository: https://doi.org/10.7910/DVN/IPFJO6 .
Bensley DA, Spero RA (2014) Improving critical thinking skills and meta-cognitive monitoring through direct infusion. Think Skills Creat 12:55–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsc.2014.02.001
Article Google Scholar
Castle A (2009) Defining and assessing critical thinking skills for student radiographers. Radiography 15(1):70–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.radi.2007.10.007
Chen XD (2013) An empirical study on the influence of PBL teaching model on critical thinking ability of non-English majors. J PLA Foreign Lang College 36 (04):68–72
Google Scholar
Cohen A (1992) Antecedents of organizational commitment across occupational groups: a meta-analysis. J Organ Behav. https://doi.org/10.1002/job.4030130602
Cooper H (2010) Research synthesis and meta-analysis: a step-by-step approach, 4th edn. Sage, London, England
Cindy HS (2004) Problem-based learning: what and how do students learn? Educ Psychol Rev 51(1):31–39
Duch BJ, Gron SD, Allen DE (2001) The power of problem-based learning: a practical “how to” for teaching undergraduate courses in any discipline. Stylus Educ Sci 2:190–198
Ennis RH (1989) Critical thinking and subject specificity: clarification and needed research. Educ Res 18(3):4–10. https://doi.org/10.3102/0013189x018003004
Facione PA (1990) Critical thinking: a statement of expert consensus for purposes of educational assessment and instruction. Research findings and recommendations. Eric document reproduction service. https://eric.ed.gov/?id=ed315423
Facione PA, Facione NC (1992) The California Critical Thinking Dispositions Inventory (CCTDI) and the CCTDI test manual. California Academic Press, Millbrae, CA
Forawi SA (2016) Standard-based science education and critical thinking. Think Skills Creat 20:52–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsc.2016.02.005
Halpern DF (2001) Assessing the effectiveness of critical thinking instruction. J Gen Educ 50(4):270–286. https://doi.org/10.2307/27797889
Hu WP, Liu J (2015) Cultivation of pupils’ thinking ability: a five-year follow-up study. Psychol Behav Res 13(05):648–654. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1672-0628.2015.05.010
Huber K (2016) Does college teach critical thinking? A meta-analysis. Rev Educ Res 86(2):431–468. https://doi.org/10.3102/0034654315605917
Kek MYCA, Huijser H (2011) The power of problem-based learning in developing critical thinking skills: preparing students for tomorrow’s digital futures in today’s classrooms. High Educ Res Dev 30(3):329–341. https://doi.org/10.1080/07294360.2010.501074
Kuncel NR (2011) Measurement and meaning of critical thinking (Research report for the NRC 21st Century Skills Workshop). National Research Council, Washington, DC
Kyndt E, Raes E, Lismont B, Timmers F, Cascallar E, Dochy F (2013) A meta-analysis of the effects of face-to-face cooperative learning. Do recent studies falsify or verify earlier findings? Educ Res Rev 10(2):133–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.edurev.2013.02.002
Leng J, Lu XX (2020) Is critical thinking really teachable?—A meta-analysis based on 79 experimental or quasi experimental studies. Open Educ Res 26(06):110–118. https://doi.org/10.13966/j.cnki.kfjyyj.2020.06.011
Liang YZ, Zhu K, Zhao CL (2017) An empirical study on the depth of interaction promoted by collaborative problem solving learning activities. J E-educ Res 38(10):87–92. https://doi.org/10.13811/j.cnki.eer.2017.10.014
Lipsey M, Wilson D (2001) Practical meta-analysis. International Educational and Professional, London, pp. 92–160
Liu Z, Wu W, Jiang Q (2020) A study on the influence of problem based learning on college students’ critical thinking-based on a meta-analysis of 31 studies. Explor High Educ 03:43–49
Morris SB (2008) Estimating effect sizes from pretest-posttest-control group designs. Organ Res Methods 11(2):364–386. https://doi.org/10.1177/1094428106291059
Article ADS Google Scholar
Mulnix JW (2012) Thinking critically about critical thinking. Educ Philos Theory 44(5):464–479. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-5812.2010.00673.x
Naber J, Wyatt TH (2014) The effect of reflective writing interventions on the critical thinking skills and dispositions of baccalaureate nursing students. Nurse Educ Today 34(1):67–72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nedt.2013.04.002
National Research Council (2012) Education for life and work: developing transferable knowledge and skills in the 21st century. The National Academies Press, Washington, DC
Niu L, Behar HLS, Garvan CW (2013) Do instructional interventions influence college students’ critical thinking skills? A meta-analysis. Educ Res Rev 9(12):114–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.edurev.2012.12.002
Peng ZM, Deng L (2017) Towards the core of education reform: cultivating critical thinking skills as the core of skills in the 21st century. Res Educ Dev 24:57–63. https://doi.org/10.14121/j.cnki.1008-3855.2017.24.011
Reiser BJ (2004) Scaffolding complex learning: the mechanisms of structuring and problematizing student work. J Learn Sci 13(3):273–304. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15327809jls1303_2
Ruggiero VR (2012) The art of thinking: a guide to critical and creative thought, 4th edn. Harper Collins College Publishers, New York
Schellens T, Valcke M (2006) Fostering knowledge construction in university students through asynchronous discussion groups. Comput Educ 46(4):349–370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2004.07.010
Sendag S, Odabasi HF (2009) Effects of an online problem based learning course on content knowledge acquisition and critical thinking skills. Comput Educ 53(1):132–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2009.01.008
Sison R (2008) Investigating Pair Programming in a Software Engineering Course in an Asian Setting. 2008 15th Asia-Pacific Software Engineering Conference, pp. 325–331. https://doi.org/10.1109/APSEC.2008.61
Simpson E, Courtney M (2002) Critical thinking in nursing education: literature review. Mary Courtney 8(2):89–98
Stewart L, Tierney J, Burdett S (2006) Do systematic reviews based on individual patient data offer a means of circumventing biases associated with trial publications? Publication bias in meta-analysis. John Wiley and Sons Inc, New York, pp. 261–286
Tiwari A, Lai P, So M, Yuen K (2010) A comparison of the effects of problem-based learning and lecturing on the development of students’ critical thinking. Med Educ 40(6):547–554. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2929.2006.02481.x
Wood D, Bruner JS, Ross G (2006) The role of tutoring in problem solving. J Child Psychol Psychiatry 17(2):89–100. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-7610.1976.tb00381.x
Wei T, Hong S (2022) The meaning and realization of teachable critical thinking. Educ Theory Practice 10:51–57
Xu EW, Wang W, Wang QX (2022) A meta-analysis of the effectiveness of programming teaching in promoting K-12 students’ computational thinking. Educ Inf Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-022-11445-2
Yang YC, Newby T, Bill R (2008) Facilitating interactions through structured web-based bulletin boards: a quasi-experimental study on promoting learners’ critical thinking skills. Comput Educ 50(4):1572–1585. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2007.04.006
Yore LD, Pimm D, Tuan HL (2007) The literacy component of mathematical and scientific literacy. Int J Sci Math Educ 5(4):559–589. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10763-007-9089-4
Zhang T, Zhang S, Gao QQ, Wang JH (2022) Research on the development of learners’ critical thinking in online peer review. Audio Visual Educ Res 6:53–60. https://doi.org/10.13811/j.cnki.eer.2022.06.08
Download references
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the graduate scientific research and innovation project of Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region named “Research on in-depth learning of high school information technology courses for the cultivation of computing thinking” (No. XJ2022G190) and the independent innovation fund project for doctoral students of the College of Educational Science of Xinjiang Normal University named “Research on project-based teaching of high school information technology courses from the perspective of discipline core literacy” (No. XJNUJKYA2003).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
College of Educational Science, Xinjiang Normal University, 830017, Urumqi, Xinjiang, China
Enwei Xu, Wei Wang & Qingxia Wang
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding authors
Correspondence to Enwei Xu or Wei Wang .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Additional information.
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary tables, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Xu, E., Wang, W. & Wang, Q. The effectiveness of collaborative problem solving in promoting students’ critical thinking: A meta-analysis based on empirical literature. Humanit Soc Sci Commun 10 , 16 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-023-01508-1
Download citation
Received : 07 August 2022
Accepted : 04 January 2023
Published : 11 January 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-023-01508-1
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
This article is cited by
Impacts of online collaborative learning on students’ intercultural communication apprehension and intercultural communicative competence.
- Hoa Thi Hoang Chau
- Hung Phu Bui
- Quynh Thi Huong Dinh
Education and Information Technologies (2024)
Exploring the effects of digital technology on deep learning: a meta-analysis
Sustainable electricity generation and farm-grid utilization from photovoltaic aquaculture: a bibliometric analysis.
- A. A. Amusa
- M. Alhassan
International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology (2024)
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies

Team Building Problem-Solving Activities Drive Performance
T eam building activities are essential for fostering a collaborative and cohesive work environment. Among the various types of team-building exercises, problem-solving activities stand out as particularly effective. They not only enhance critical thinking and creativity but also improve communication and build trust among team members.
Executed effectively, engaging team activities can have a dramatic impact on business performance, culture, and job satisfaction. In this blog post, we'll explore the numerous benefits of team-building problem-solving activities, highlighting several examples, including the increasingly popular escape rooms.
Why Team Building Problem-Solving Activities Matter
Enhances critical thinking and creativity.
Problem-solving activities require team members to think critically and come up with innovative solutions. This stimulates the brain and encourages out-of-the-box thinking, which can translate to more creative problem-solving in the workplace.
Improves Communication
Effective communication is the backbone of any successful team. Problem-solving activities force team members to communicate their ideas clearly and listen to others. This practice helps in breaking down communication barriers and enhances overall team interaction.
Builds Trust and Collaboration
Trust is built when team members rely on each other to overcome challenges. Dynamic team-building events and activities require collaboration, where each member's input is valued. This mutual dependence fosters a sense of trust and strengthens team bonds.
Develops Leadership Skills
These activities often present opportunities for team members to step up and lead. It helps identify potential leaders and allows them to develop their leadership skills in a supportive environment.
Boosts Morale and Engagement
Engaging in fun and challenging activities outside the regular work routine can boost team morale. It provides a refreshing break and can reignite enthusiasm and motivation among team members.
Examples of Effective Problem-Solving Activities
1. escape rooms.
Escape rooms have become a popular choice for team-building activities. In an escape room, a team is locked in a themed room and must solve a series of puzzles and riddles to "escape" within a set time limit. The immersive and high-pressure environment encourages teamwork, sharpens problem-solving skills, and enhances communication.
Benefits of Escape Rooms:
- Enhanced Cooperation: Teams must work together to solve puzzles, ensuring everyone's input is considered.
- Improved Time Management: With a ticking clock, teams learn to prioritize tasks and manage their time effectively.
- Increased Engagement: The thrilling and immersive experience keeps team members engaged and invested in the outcome.
2. Treasure/Scavenger Hunts
Treasure hunts involve teams following clues to find a hidden "treasure." This activity can be conducted indoors or outdoors and requires strategic planning and teamwork.
Benefits of Treasure/Scavenger Hunts:
- Strategic Thinking: Teams must plan their route and approach to find the treasure efficiently.
- Collaboration: Clues often require combined knowledge and skills, promoting teamwork.
- Fun and Physical Activity: It combines mental and physical challenges, making it a well-rounded activity.
3. Problem-Solving Workshops
Workshops focused on specific problem-solving techniques can be highly beneficial. These workshops often involve case studies, role-playing, and group discussions to tackle real-world problems.
Benefits of Problem-Solving Workshops:
- Skill Development: Team members learn new problem-solving techniques and strategies.
- Real-World Application: Workshops often address actual workplace issues, providing immediate value.
- Knowledge Sharing: Participants share their experiences and insights, fostering a collaborative learning environment.
4. Puzzle Challenges
Puzzle challenges can range from jigsaw puzzles to more complex logic puzzles. Teams must work together to complete the puzzle within a time limit.
Benefits of Puzzle Challenges:
- Enhanced Focus: Solving puzzles requires concentration and attention to detail.
- Patience and Persistence: Team members learn the value of persistence and patience in overcoming challenges.
- Team Synergy: Successful completion often requires understanding each team member's strengths and leveraging them effectively.
5. Simulation Games
Simulation games create realistic scenarios where teams must solve problems or make decisions under pressure. These can range from business simulations to survival scenarios.
Benefits of Simulation Games:
- Realistic Experience: Teams face realistic challenges, making the learning experience more impactful.
- Decision-Making Skills: Participants must make quick, informed decisions, improving their decision-making abilities.
- Crisis Management: Teams learn to manage stress and work efficiently under pressure.
A Powerful Tool to Drive Performance in Modern Business
Team-building problem-solving activities are a powerful tool for enhancing team dynamics and fostering a positive work environment. Whether it's the excitement of an escape room or the strategic planning of a treasure hunt, these activities offer numerous benefits that translate to improved performance and collaboration in the workplace. By investing in such activities, organizations can build stronger, more cohesive teams ready to tackle any challenge that comes their way.

- Request Info

- About Antioch University
- Core Attributes of an Antioch Education
- Equity, Diversity, Inclusion, and Belonging
- Why Antioch University?
- Common Thread
- Antioch Works for Democracy
- Executive Leadership
- Board of Governors
- Office of the Chancellor
Administrative Resources
- Accreditation
- University Policies
Discover Our Campuses
- Antioch Los Angeles
- Antioch New England
- Antioch Online
- Antioch Santa Barbara
- Antioch Seattle
- Graduate School of Leadership & Change
Academic Focus Areas
- Creative Writing & Communication
- Counseling & Therapy
- Environmental Studies & Sustainability
- Individualized Studies
- Leadership & Management
- Undergraduate Studies
Programs by Type
- Master’s
- Bachelor’s
- Certificates
- Credentials & Endorsements
- Continuing Education
Programs by Modality
- Low-Residency
Programs by Campus
- Los Angeles
- New England
- Santa Barbara
Academic Resources
- Academic Calendars
- Academic Catalog
- Disability Support Services
- Faculty Directory
- Writing Centers
- Admissions Overview
- Unofficial Transcript Evaluation
- Upcoming Admissions Events
- What to Expect
Information for
- International Students
- Transfer & Degree Completion Students
- Veterans & Military-Connected Students
Dates & Deadlines
Tuition & fees.
- GSLC Tuition & Fees
- AULA Tuition & Fees
- AUNE Tuition & Fees
- AUO Tuition & Fees
- AUSB Tuition & Fees
- AUS Tuition & Fees
Financial Aid
- Financial Aid Overview
- Financial Aid Forms
- Scholarships & Grants
- Types of Aid
- Work-Study Opportunities
- Discover GSLC
- Department & Office Directory
- The Antiochian Leader (Newsletter)
- Discover AULA
- Department & Office Directory
- Location & Contact Info
- Discover AUNE
- Location & Contact Info
- Discover AU Online
- Online Learning @AU
- Discover AUSB
- Location & Contact Information
- Discover AUS
- Department and Office Directory
- Advancement
- Grants and Foundation Relations
- Information Technology
- Institutional Effectiveness
- Strategic Partnerships
- Student Accounts
- Academic Assessment
- Consumer Information
- Licensure Information
- Resource List
- Student Policies
- Alumni Magazine
- Chancellor’s Communications
- Common Thread (University News)
- Event Calendar
Program Coordinator II (Remote)
- Posted 2 days ago

Antioch University
Department: Distance & Extended Education Classification: Staff, Full-Time, Non-Exempt Reports to: Dean, Distance & Extended Education Location: Remote Compensation: $26.00 – $27.00/Hour
Position Overview
The primary responsibility of this position is to provide support to the programs within Antioch University Distance and Extended Education. Duties require excellent communication and problem-solving skills; the ability to work independently and coordinate multiple tasks.
Essential Job Functions
- Provide administrative support to the Dean in the administration of all programs and activities in Distance and Extended Education, including monitoring budgets
- Coordinate with Continuing Education Directors to manage the University’s CE websites and storefront to assure up-to-date information and accurate linking to Elevate (CE platform)
- Assist Continuing Education Directors with course building/data entry in Elevate (CE platform)
- Assist with hosting/problem solving for virtual meetings.
- Identify and coordinate database needs for DEE and collaborate with Institutional Technology and Office of Institutional Effectiveness staff.
- Provide support to CE participants and visiting students, answering questions about CE programs or referring to the appropriate University personnel for assistance
- Coordinate with other University departments where programs overlap and provide assistance (e.g. development of Articulation Agreements)
- Enter data and assist in the development of reports and other documents.
- Provide information to AU Human Resources to verify, distribute, and support all HR functions in DEE, including the processing of contracts for CE facilitators.
- Oversee purchasing as needed and process appropriate payment requests according to Antioch University protocol.
- Collaborate with Strategic Initiative team and contribute to the development of partnership initiatives.
- Collaborate on revisions to written and video handbooks, manuals and forms; make updates as assigned.
- Attend department meetings
- Participate in planning of special events (e.g. Commencement) and attend as assigned.
- Participate in cross-training in order to provide back-up support for other DEE staff members.
- Perform other duties as assigned
Minimum Requirements
- Bachelor’s degree or higher preferred.
- Three years of experience in a program support role
Knowledge,Skills and Abilities
- Must exercise professional judgment regarding highly confidential budget and student matters.
- Ability to get along with others and to be a positive member of the Antioch community.
- Ability to work independently, organize, handle detail, follow-through on tasks and problem solve with minimal supervision, in a complex administrative environment.
- Excellent oral and written communication skills.
- Strong critical and analytical thinking skills.
- Ability to use computer applications to access data, maintain records, review, and generate reports.
- Proficiency in the Microsoft and/or Google suite of office applications, and related web tools required. Willingness to learn new software applications. Adobe Acrobat, Constant Contact, and Canva are a plus.
- Experience in an academic institution preferred.
- Experience in an online learning environment preferred.
Hours of Employment
This is a full-time non-exempt position serving a national university. The work schedule will be established in consultation with supervisor. Evenings and/or weekend hours may be required. The typical work week is Monday through Friday, 40 hours per week.
Work Location
This is a remote position working from a home office. Some travel may be required.
Physical Requirements
The essential functions represent the basic job duties that an employee must be able to perform, with or without a reasonable accommodation. Reasonable accommodations may be made to enable individuals with disabilities to perform the essential functions.
Antioch University reserves the right to change the duties of the job at any time.
Benefits Summary
Voluntary Health, dental and vision plan and flexible spending account options; employer retirement plan contribution of 6%; voluntary salary deduction to a pre-tax or post-tax retirement account; employer paid life insurance and short term disability; voluntary supplemental life insurance, long-term disability, accidental death/dismemberment, critical illness, and accident coverage plans; vacation accrues monthly (3 weeks from 0 – 5 years; 4 weeks after 6 years; carry-over allowed up to 3.75 days 0 – 5 years; up to 5 days, after 6 years and up); 12 days per year sick leave (carry-over up to 65 days); 15 paid holidays; tuition remission for employees and dependents at Antioch University campuses; and employee paid options with AFLAC, LegalShield, and Liberty Mutual. (This list is meant to be an informal summary of benefits. Plan benefits and eligibility requirements are governed by the plan documents and University policies which will be made available upon request).
Coalition for the Common Good (CCG) EEO Statement
The Coalition for the Common Good provides equal employment opportunity to all employees and applicants and prohibits discrimination on the basis of race, color, religion, age, sex, sexual orientation, gender identity, gender expression, pregnancy, national origin, disability status, genetics, protected veteran status, or any other characteristic or class protected by federal, state or local laws in matters affecting employment or in providing access to programs. This policy applies to all terms and conditions of employment, including recruitment, hiring, placement, promotion, termination, layoff, recall, transfer, leaves of absence, compensation, benefits, and training. The CCG complies with all state and federal laws that prohibit discrimination, including Title VII of the Civil Rights Act, Title IX, Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act, the Americans with Disabilities Act, the Equal Pay Act and the Age Discrimination in Employment Act. Inquiries should be addressed to the Office of Human Resources or the Office of the General Counsel.
To Apply: Qualified applicants must submit a cover letter, resume/CV, and three business references with contact information at the time of application.
Click Here To Apply
NOTE: The successful candidate for this position will be subject to a pre-employment background check
To apply for this job please visit ats.applicantone.com .
Back to Job Listings
Coordinator of Administration and Communication
Duke memorial united methodist church.
POSITION OVERVIEW This position provides organizational, administrative, and communication support to Duke Memorial UMC. This position requires a person who possesses flexibility, creativity and problem-solving skills as well as a pleasant and helpful manner in working with the church, its members, the community, laity, and staff.
EMPLOYMENT STATUS Full-time (40 hours/week), non-exempt position
SKILLS AND COMPETENCIES REQUIRED ● Friendly, professional demeanor ● Ability to manage multiple projects and tasks ● Ability to create systems to increase office efficiency ● Well-developed skills with Microsoft Office software (especially Word, Publisher, and Excel) ● Ability to utilize email and the Internet to facilitate communication and workflow ● Working knowledge of office equipment (computer, telephone, printer, copiers, fax machine, postage meter, etc.) ● General computer and network troubleshooting skills ● Ability to maintain and update a website using Weebly or other web design software ● Creative, with the ability to work on several tasks at one time ● Knowledgeable of print graphic design, layout and digital communication (Mailchimp, Adobe InDesign) ● Desire to serve God and the church, and to contribute to the mission and vision of Duke Memorial UMC ● Committed to team-based ministry—working with lay teams and a staff team—to enable the Church to achieve its mission.
ESSENTIAL DUTIES AND RESPONSIBILITIES ● Provide Administrative Support ● Complete Charge Conference reports, UMC Tables, and other online data collection tools required by NCCUMC as directed by Lead Pastor ● Provide administrative support to Lead Pastor as needed ● Oversee Church calendar for all ongoing activities; coordinate facility reservation requests ● Offer hospitality and assistance to groups using church facilities ● Work with the Lead Pastor and the Financial Administrator to make sure that bills are paid in a timely manner ● Manage office equipment lease agreements and office supply inventory ● Coordinate office systems with building tenants (mail, building use) ● Provide a presence in the church office and monitor doors and phones. Manage access control for exterior doors ● Supervise office volunteers ● Manage Digital and Print Communications and Records ● Create and distribute email communications regularly (weekly) and as needed ● Manage all aspects of Duke Memorial United Methodist Church website ● Proactively work to make sure Duke Memorial maintains an effective presence on the internet including style/presence, search engines, advertising events, and new technology ● Create and maintain social media presence ● Maintain database records for members and visitors ● Create, format and publish the bulletin for each Sunday Service and all Special/Holiday services ● Create slides for livestream of Sunday and special worship services. ● Design and format publications (e.g. flyers, brochures, directories, program books, stationery, letterhead, forms, etc.) as needed ● Design print materials (i.e. devotional books, stewardship campaign materials, small group brochures, ministry brochures, stationery, special offering materials, ads and posters) as needed ● Design indoor and outdoor banners for various seasons (Advent, Lent, Pride) ● Ensure that communication is accessible (managing Streamtext caption software and paying attention to the language we use) ● Provide Support to Ministry Areas ● Provide consultation in overall communications strategy for the church and its ministries ● Work with staff and laity to continuously improve systems of communications ● Partner with ministry areas to plan, coordinate and implement marketing and information materials for various programs, ministries and church events ● Capture critical stories that share God’s work inside of Duke Memorial UMC and beyond ● Gain and maintain knowledge of all church ministries, their activities and their relationships to one another ● Work with the relevant ministry areas to develop strategies to market and promote teaching series, big events, etc. Provide IT Technical Support ● Troubleshoot minor problems (e.g. email not working, network not responding, paper jams, minor electrical problems, etc.) in a timely manner ● Maintain computers (e.g. regular maintenance, desktop clean-up, etc.) ● Administer user accounts (such as Google Workspace, Microsoft Admin, JumpCloud, etc.) to manage computer devices. ● Coordinate additional IT support when needed.
Support of Trustees ● Is the designated liaison for tenants for daily building or infrastructure problems ● Sets up and supports Google Drive storage system for Trustees’ documents, such as tenant contracts, recurring contracts, office equipment, and facilities ● Maintain facility vendor list ● Invoice and track the receipt of special events payments from tenants and building users ● Follow up with tenants whose rental payments are past due, under the guidance and support of Trustees and Lead Pastor.
Human Resources ● Manage orientation of new employees: employment paperwork, handbook, keys, accounts, procedures, background checks, etc. ● Support the work of Search Teams as needed and in consultation with the Lead Pastor.
ACCOUNTABILITY - The Office Administrator will: ● In collaboration with the Lead Pastor, set and share goals for ministry including targets for growth of the various ministries ● Be accountable to and evaluated by the Senior Pastor on an annual basis.
ABOUT DUKE MEMORIAL UMC - Duke Memorial United Methodist Church is a historic urban congregation in downtown Durham, NC. Mission: Sharing the love of Christ from the heart of Durham. Welcome Statement: As our Lord Jesus Christ calls us to love and accept every person, Duke Memorial United Methodist Church welcomes into our life together those of every age, race, ethnic background, nationality, gender identity, sexual orientation, family or socioeconomic status, educational background, and physical or mental ability. In our commitment to the reconciliation of all persons as beloved children of God, we celebrate our diversity and recognize the sacred worth and dignity of all. We invite you to join us in our faith journey toward discipleship in Christ with mutual respect, understanding, and love.
- Admissions & Aid Overview
- How to Apply
- Funding Your Education Overview
- Scholarships & Fellowships
- Black Church Studies and Latinx Studies Fellowships
- Thriving Communities Fellowship
- Lipe Leadership Fellowship
- External Scholarships
- Tuition and Estimated Expenses
- Which Degree Is Right for Me?
- Supporting Our Students
- Overview of Student Life
- Student Council & Organizations
- The Women’s Center
- Office of the Chaplain
- Office of Student Life
- Admissions Staff & Contact Info
- Overview of Resources for Admitted Students
- New Student Orientation & Checklist
- Paying Your Deposit
- Registering for Courses
- Housing and Local Resources
- RISE Academic Workshop
- Divinity Bulletin and Conduct Covenant
- Duke and Durham
- Statement of Diversity in Admissions
- Academics Overview
- Overview of Master's Degrees
- Master of Divinity (M.Div.)
- Hybrid Master of Divinity (M.Div.)
- Master of Arts in Christian Practice (M.A.)
- Master of Theological Studies (M.T.S.)
- Master of Theology (Th.M.)
- Overview of Doctoral Degrees
- Doctor of Theology (Th.D.)
- Doctor of Ministry (D.Min.)
- Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.)
- Hybrid Online Degrees and Programs
- Overview of Dual Degrees & Programs
- Master of Divinity/Master of Public Policy (M.Div./M.P.P.)
- Master of Divinity/Master of Social Work (M.Div./M.S.W.)
- Master of Theological Studies/Juris Doctorate (M.T.S./J.D.)
- Master of Theological Studies/Master of Public Policy (M.T.S./M.P.P.)
- Overview of Standalone Certificates
- Certificate in Theology and Health Care
- Overview of Degree-Based Certificates
- Certificate in Anglican Studies
- Certificate in Baptist Studies
- Certificate in Black Church Studies
- Certificate in Catholic Studies
- Certificate in Chaplaincy
- Certificate in Christian Education
- Certificate in Faith, Food, and Environmental Justice
- Certificate in Faith-based Organizing, Advocacy, and Social Transformation
- Certificate in Gender, Sexuality, Theology, and Ministry
- Certificate in Latinx Studies
- Certificate in Methodist/Wesleyan Studies
- Certificate in Missional Innovation
- Certificate in Preaching
- Certificate in Prison Studies
- Certificate in Reflective and Faithful Teaching
- Certificate in Theology and the Arts
- Certificate in Theology, Medicine, and Culture
- Certificate in Worship
- Other Duke University Certificates
- Overview of Field Education
- Clinical Pastoral Education (CPE)
- Communities of Learning
- International Field Education
- Supervisors
- Forms & Policies
- Office of Field Education
- Study Abroad
- Academic Calendar & Course Schedules
- Center for Writing and Academic Support
- Divinity Library
- Accreditation
- Educational Effectiveness
- Houses of Study Overview
- Anglican Episcopal House of Studies
- Asian House of Studies
- Baptist House of Studies
- Hispanic House of Studies
- Methodist House of Studies
- Office of Black Church Studies
- Presbyterian/Reformed House of Studies
- Initiatives Overview
- Center for Reconciliation
- Clergy Health Initiative
- Duke Initiatives in Theology and the Arts
- Fons Vitae Catholic Initiative
- Leadership Education at Duke Divinity
- Ormond Center
- Racial Justice and Cultural Competency
- Theology, Medicine, and Culture
- Thriving Rural Communities
- Traditioned Innovation Project
- Wesleyan Initiatives & Programs
- Faculty Overview
- Faculty Directory
- Faculty Books
- Faculty Experts
- Faculty in the Media
- About the School
- Dean's Welcome
- Directions & Parking
- Divinity School Jobs
- Department Directory
- Faculty & Staff Directory
- Continuing Education Overview
- All Guided Learning Programs
- All Self-Paced Learning Programs
- Formation Overview
- Spiritual Formation
- Vocational Formation
- Global and Intercultural Formation
- News Overview
- Divinity Magazine
- Divinity Medium Channel
- Faith & Leadership
- Video and Podcasts Archive
- News & Features Archive
- Sign up for Our Newsletter
- Events Overview
- All Upcoming Events
- Alumni Overview
- Update Contact Info & Class Notes
- Alumni Council & Board of Visitors
- Office of External Relations Staff
- The Shepherd's Fund for Alumni in Need
- Jobs and Internships
- Transcript Requests

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Into all problem-solving, a little dissent must fall. Capturing the value of 'one firm'. Bias Busters: A better way to brainstorm. Psychological safety and the critical role of leadership development. The next competitive advantage in talent: Continuous employee listening. Author Talks: Fred Dust on making conversations count.
Even the happiest of relationships experience conflicts and problems (Markman, Stanley, Blumberg, Jenkins & Whiteley, 2004). If handled well, issues provide opportunities for personal and relationship growth. There are many skills that can help individuals seeking to resolve conflicts in a healthy way. One of the greatest skills that aids in conflict resolution is effective communication.
Although problem-solving is a skill in its own right, a subset of seven skills can help make the process of problem-solving easier. These include analysis, communication, emotional intelligence, resilience, creativity, adaptability, and teamwork. 1. Analysis. As a manager, you'll solve each problem by assessing the situation first.
Problem-solving skills defined. Problem-solving skills are skills that allow individuals to efficiently and effectively find solutions to issues. This attribute is a primary skill that employers look for in job candidates and is essential in a variety of careers. This skill is considered to be a soft skill, or an individual strength, as opposed ...
Communication skills in the workplace include a mix of verbal and non-verbal abilities. Learn more about the importance of communication skills and how you can improve yours. ... Communication, coupled with problem-solving skills and time management, are the top three qualities hiring managers look for, according to TopResume ...
Let's now look at three free worksheets and tools you can use to help develop your clients' perspective taking, self-awareness, and empathy when communicating. Active Listening Reflection Worksheet. This worksheet provides a useful summary of the techniques involved in active listening.
This can cause problems in your home, school, and work relationships. But by learning effective communication skills, you can deepen your connections to others, build greater trust and respect, and improve teamwork, problem solving, and your overall social and emotional health. Tips for improving your communication skills
Communication is a key skill for employee relations, especially when you need to solve problems with your colleagues, managers, or clients. Effective communication can help you avoid ...
Improving additional workplace skills like problem-solving, collaboration, and time management can also enhance your communication efforts. These skills require listening, patience, and organization, which all play a role in sound communication. 13. Get rid of conversation fillers.
A 2006 study found that people with better communication skills had greater relationship satisfaction, even after controlling for other variables such as attachment style and problem-solving skills (Eğeci & Gençöz, 2006). Unsurprisingly, negative communication has been shown to decrease a couple's ability to handle conflicts which leads to ...
To get started improving your (or your team's, or your student's) communication skills, give these 5 activities a try. 1. Card Pieces. This exercise from the team at MindTools is a good way to help participants develop more empathy, consider other perspectives, build their communication and negotiation skills.
This blog will help you discover the power of Communication Skills, improve your skills, and excel in your career with practical examples. 01344203999 ... collaboration, and problem-solving, improving productivity and positive outcomes. Improving your Communication Skills for personal and professional growth will help you explore better ...
Essential Communication Skills for Leaders 1. Ability to Adapt Your Communication Style. ... Just acknowledging mistakes can encourage experimentation and create a safe space for active problem-solving. Every individual should understand the role they play in the company's success. The more transparent leaders are, the easier it is for ...
The following communication rules can improve problem solving: State your problem and interests. Acknowledge others' problems and interests. Avoid name calling and answering a complaint with another complaint. Listen to the other parties and know their interests. Ask "why," "why not" and "what if" questions to better understand.
The skills of communication, critical thinking, and problem solving are essential to thriving as a citizen in the 21st century. These skills are required in order to contribute as a member of society, operate effectively in post-secondary institutions, and be competitive in the global market. Unfortunately they are not always intuitive or simple in nature. Instead these skills require both ...
Such details can be effective in communicating emotions and offer your audience insights into how others interpret your message. 7. Empathy. Having empathy means that you can not only understand but also share in the emotions of others. This communication skill is important in both team and one-on-one settings.
4 Problem-Solving Skills All Leaders Need. 1. Problem Framing. One key skill for any leader is framing problems in a way that makes sense for their organization. Problem framing is defined in Design Thinking and Innovation as determining the scope, context, and perspective of the problem you're trying to solve.
Active listening. Analysis. Research. Creativity. Communication. Decision-making. Team-building. Problem-solving skills are important in every career at every level. As a result, effective problem-solving may also require industry or job-specific technical skills.
Effective communication skills are foundational to any good personal or professional relationship. Learning successful strategies in communication can impact your ability to motivate others, have more engaging conversations, share information, and practice more efficient problem-solving.
Problem-solving skills are vital at all levels in many careers, and effective problem-solving may also require job- or industry-specific technical skills. For instance, a registered nurse will need active listening and communication skills when interacting with patients but will also need effective technical knowledge related to diseases and ...
Nurses' communication skills not only affected their problem-solving ability but also their understanding of patients' conditions and nurse's perception of professionalism. Good communication among nurses can reduce uncomfortable situations and improve interactions with patients, which can consequently enhance problem-solving [ 28 ].
MMODULEODULE T TWOHREE • supporting recovery from a mental or substance use disorder • communication and problem-solving skills • supporting recovery from a mental or substance use disorder • communication and problem-solving skills MODULEMODULE T HREETWO 2 • how you can help • toolkit for families • www.heretohelp.bc.ca • • how you can help • toolkit for families • www ...
Clear communication is the linchpin of effective problem-solving. Whether it's through written reports, presentations, or casual discussions, ensure that your communication is concise, structured ...
Duch et al. noted that problem-based learning in group collaboration is progressive active learning, which can improve students' critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Collaborative ...
Examples of Effective Problem-Solving Activities 1. Escape Rooms ... The immersive and high-pressure environment encourages teamwork, sharpens problem-solving skills, and enhances communication.
Duties require excellent communication and problem-solving skills; the ability to work. Department: Distance & Extended Education Classification: Staff, Full-Time, Non-Exempt Reports to: Dean, Distance & Extended Education Location: Remote Compensation: $26.00 - $27.00/Hour Position Overview The primary responsibility of this position is to ...
POSITION OVERVIEW This position provides organizational, administrative, and communication support to Duke Memorial UMC. This position requires a person who possesses flexibility, creativity and problem-solving skills as well as a pleasant and helpful manner in working with the church, its members, the community, laity, and staff. EMPLOYMENT STATUS Full-time (40 hours/week), non-exempt position
These include skills like communication, teamwork and problem-solving. On the other hand, hard skills are more technical, industry-specific skills that you learn through education or on-the-job training, such as knowledge of accounting software, basic maths abilities and understanding of invoice processing. Accounts payable clerk soft skills